

How to Write a Startup Business Plan (10 Effective Steps)
Learn how to create an effective business plan in 10 easy steps and discover the transformative power of mentorship to elevate your startup's strategy.

Robin Waite
5 minute read

Short answer
What should an effective business plan include?
An effective business plan should include the following elements:
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Your products or services
- Marketing and sales strategies
- Organization and management
- Financial projections
- Funding requirements
- Risk assessment
- Conclusion and Call to Action
You need a strategic business plan to successfully navigate the startup world
Diving into the startup world without a clear plan is like setting sail without a compass ; you might drift aimlessly or even crash.
A solid business plan isn't just a piece of paper—it's your roadmap to success. It attracts the right investors, guides your decisions, and sets you on a clear path to victory.
In this article, I’ll walk you through 10 essential steps to craft that perfect plan. Plus, I’ll touch on the invaluable insights a business mentor can offer.
So, if you want to avoid common pitfalls and boost your chances of success, keep reading. Your startup's future might just depend on it.
Step 1: Executive summary
Think of the executive summary as the elevator pitch for your startup. It's a quick snapshot that captures the heart of your business idea, mission, and goals.
In this brief section, make sure to highlight who your target audience is, what sets you apart in the market, and your unique selling points.
And don't forget to give a glimpse of your financial outlook and any funding needs—it sets the stage for the details that follow.
Here's an example of an executive summary slide:

Step 2: Company description
Here's where you tell your startup's story. It's not just a list of facts or a timeline. It's about painting a picture that connects with your readers.
Clearly outline your vision, mission, and the values that drive you. Share key milestones you've hit and where you currently stand in your business journey. This section gives depth to your startup, showing both where you've been and where you're headed.
Here's an example of a company introduction slide:

Step 3: Market analysis
To thrive, you've got to know the lay of the land. That's where market analysis comes in. Start by zeroing in on your target audience and truly understanding what they're looking for.
Dive deep into industry trends, the overall market size, and where it's headed. And don't just know your competitors—understand what makes you stand out from the crowd.
Here's what a market analysis slide should look like:

Step 4: Products or services
Here's your chance to shine a spotlight on what you're offering. What problems are your products or services solving? What makes them special? Whether it's a unique feature, a patent, or some groundbreaking tech, make it clear why your offerings are game-changers.
Here's an example of a solution slide:

Step 5: Marketing and sales strategies
In today's crowded market, standing out is crucial. This step is all about your game plan to grab attention and win customers. Detail how you'll sell, where you'll promote, and how you'll get your products or services into the hands of those who need them.
Here's what a go-to-market slide should look like:

Step 6: Organization and management
Behind every great startup is a team of passionate people. Here, introduce your squad. Highlight their expertise, define their roles, and show the structure that keeps everything running smoothly.
If you've got advisors or partners in your corner, mention them—it shows you're serious about growing in every direction.
Here’s a full guide on how to create the perfect team slide for your startup . And here's a great example of one:

Step 7: Financial projections
Numbers don't lie, and in this step, they sketch out your startup's potential future. Dive into the financials, projecting where you see your revenue, expenses, and profits heading over the next few years.
By breaking down your initial costs and where you expect to get your funding, you give a clear view of how you're setting up for success.
Here's an example of a financials slide:

Step 8: Funding requirements
Every startup needs fuel to get off the ground, and that fuel is capital. Here, be clear about how much you need to launch and keep things running.
Break down where every dollar will go, whether that's marketing, product development, or daily operations.
If you've already got some backers or have your eye on potential investors, mention them—it adds weight to your pitch.
Here's what a use of funds slide should look like:

Step 9: Risk assessment
Every venture has its bumps in the road. Here, show that you're not just aware of potential challenges but that you've got a plan to tackle them. In assessing risks, it's crucial to choose the right business structure at the beginning. For examples, the formation of an LLC as a strategic measure not only protects your personal assets from business liabilities but also mitigates financial risks for stakeholders. By laying out your strategies for handling risks, you prove you're not just optimistic—you're realistic and ready.
Here's an example of a risk assessment slide:

Step 10: Conclusion and Call to Action
Time to wrap it up and rally your readers. Summarize the key points of your plan, driving home why your startup is a solid bet.
But remember, this isn't just a conclusion—it's a launchpad. Encourage readers to get involved, whether that's investing, partnering, or simply supporting your vision. Let's get this journey started!
And, if you need more information, check out our comprehensive guide on how to write a business plan .
Here's an example of a next step slide:

Seek guidance from a business mentor
While a solid business plan is your startup's compass, adding guidance from a business mentor to your journey is like having a seasoned captain on board.
They bring a treasure trove of insights, lessons from past experiences, and a network of industry contacts. Their tailored advice doesn't just polish your plan—it also boosts your confidence and resilience, two must-haves for the unpredictable startup seas.
By embracing mentorship, you're signaling that you're all in on growth, ready to soak up wisdom and accelerate your path to success.
Why is a business plan crucial for startups?
Think of a business plan as your startup's GPS. It helps you navigate the twists and turns, pointing out both the challenges and the golden opportunities ahead. It's your master blueprint, detailing everything from your big-picture goals to your financial forecasts .
What role does a business mentor play in this process?
A business mentor serves as a seasoned guide in the startup journey. Drawing from their wealth of experience, they offer invaluable insights, helping startups navigate challenges and optimize their strategies. Their guidance is instrumental in making informed, strategic decisions.
How can a mentor enhance my market analysis?
Mentors have their finger on the pulse of the industry. They can help you get a clearer picture of market trends, spot who you're really up against, and gauge where the opportunities lie. With their insights, your market analysis won't just be good—it'll be top-notch.
Can a mentor assist in financial projections?
Absolutely. If your mentor has a financial background, they can be a goldmine. They'll help you craft projections that are both ambitious and grounded in reality. From revenue estimates to potential expenses, they'll ensure your numbers make sense.
How can you incorporate mentorship into the business plan?
Consider adding a dedicated section in your business plan to highlight the mentorship aspect. By detailing the insights and guidance you've received, or intend to seek, you underscore your commitment to informed growth. This proactive approach can resonate well with potential investors and stakeholders.
Business plan templates
Starting your business plan can feel like staring at a blank canvas—it's full of potential, but where do you begin? That's where interactive business plan templates come into play.
These templates serve as a structured guide, ensuring you don't miss any crucial details while allowing for flexibility and customization. They're designed to streamline the process, making it easier to organize your thoughts and present your vision in a coherent manner.
Ready to dive in? Grab a template from the library below and give your business plan a head start.

Robin Waite is a business coach based in the UK, bestselling author, and also regular business speaker. Robin's Fearless Business Accelerator covers pricing, productising services, and sales for coaches, consultants, and freelancers. Robin's passion is content marketing and blogging and he enjoys finding creative ways to make complex business topics simple for his readers.

Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.
Create your best business plan to date
Try Storydoc interactive presentation maker for 14 days free (keep any presentation you make forever!)
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Executive summary.

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Overview and Business Objectives
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Company Description
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Define Your Target Market
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis
Competitive analysis.
In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
Organization and Management Team
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered
Marketing and sales strategy.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Logistics and Operations Plan
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Financial Projections Plan
In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Income Statement
The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Cash Flow Statement
| Section | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Summary | Brief overview of the business plan | Overview of EcoTech and its mission |
| Overview & Objectives | Outline of company's goals and strategies | Market leadership in sustainable technology |
| Company Description | Detailed explanation of the company and its unique selling proposition | EcoTech's history, mission, and vision |
| Target Market | Description of ideal customers and their needs | Environmentally conscious consumers and businesses |
| Market Analysis | Examination of industry trends, customer needs, and competitors | Trends in eco-friendly technology market |
| SWOT Analysis | Evaluation of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats | Strengths and weaknesses of EcoTech |
| Competitive Analysis | In-depth analysis of competitors and their strategies | Analysis of GreenTech and EarthSolutions |
| Organization & Management | Overview of the company's structure and management team | Key roles and team members at EcoTech |
| Products & Services | Description of offerings and their unique features | Energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers |
| Marketing & Sales | Outline of marketing channels and sales strategies | Digital advertising, content marketing, influencer partnerships |
| Logistics & Operations | Details about daily operations, supply chain, inventory, and quality control | Partnerships with manufacturers, quality control |
| Financial Projections | Forecast of revenue, expenses, and profit for the next 3-5 years | Projected growth in revenue and net profit |
| Income Statement | Summary of company's revenues and expenses over a specified period | Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold, Gross Profit, Net Income |
| Cash Flow Statement | Overview of cash inflows and outflows within the business | Net Cash from Operating Activities, Investing Activities, Financing Activities |
Tips on Writing a Business Plan
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
What is a Business Plan?
Why you should write a business plan, what are the different types of business plans.
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
| Type of Business Plan | Purpose | Key Components | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Startup Business Plan | Outlines the company's mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. | Mission Statement, Company Description, Market Analysis, Competitive Analysis, Organizational Structure, Marketing and Sales Strategy, Financial Projections. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Internal Business Plan | Serves as a management tool for guiding the company's growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. | Strategies, Milestones, Deadlines, Resource Allocation. | Internal Team Members |
| Strategic Business Plan | Outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them. | SWOT Analysis, Market Research, Competitive Analysis, Long-Term Goals. | Executives, Managers, Investors |
| Feasibility Business Plan | Assesses the viability of a business idea. | Market Demand, Competition, Financial Projections, Potential Obstacles. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Growth Business Plan | Focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. | Market Analysis, New Product/Service Offerings, Financial Projections. | Business Owners, Investors |
| Operational Business Plan | Outlines the company's day-to-day operations. | Processes, Procedures, Organizational Structure. | Managers, Employees |
| Lean Business Plan | A simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements. | Value Proposition, Customer Segments, Revenue Streams, Cost Structure. | Entrepreneurs, Startups |
| One-Page Business Plan | A concise summary of your company's key objectives, strategies, and milestones. | Key Objectives, Strategies, Milestones. | Entrepreneurs, Investors, Partners |
| Nonprofit Business Plan | Outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation for nonprofit organizations. | Mission Statement, Goals, Target Audience, Fundraising Strategies, Budget. | Nonprofit Leaders, Board Members, Donors |
| Franchise Business Plan | Focuses on the franchisor's requirements, as well as the franchisee's goals, strategies, and financial projections. | Franchise Agreement, Brand Standards, Marketing Efforts, Operational Procedures, Financial Projections. | Franchisors, Franchisees, Investors |
Using Business Plan Software
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
| Software | Key Features | User Interface | Additional Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| LivePlan | Over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking against KPIs | User-friendly, visually appealing | Allows creation of professional-looking business plans |
| Upmetrics | Customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, collaboration capabilities | Simple and intuitive | Provides a resource library for business planning |
| Bizplan | Drag-and-drop builder, modular sections, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking | Simple, visually engaging | Designed to simplify the business planning process |
| Enloop | Industry-specific templates, financial forecasting tools, automatic business plan generation, unique performance score | Robust, user-friendly | Offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget |
| Tarkenton GoSmallBiz | Guided business plan builder, customizable templates, financial projection tools | User-friendly | Offers CRM tools, legal document templates, and additional resources for small businesses |
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan, what are the 3 main purposes of a business plan, can i write a business plan by myself.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
How long should a business plan be, what is a business plan outline, what are the 5 most common business plan mistakes, what questions should be asked in a business plan.
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
How is business planning for a nonprofit different.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Feature Updates Startup Business Plans 101: Your Path to Success
Startup Business Plans 101: Your Path to Success
Written by: Jay Nair Jul 24, 2023

It’s time — you’ve got a promising idea and you’re now prepared to invest the necessary effort to turn it into reality. Startup business plans are vital hack tools that will guide you through your entrepreneurial journey and a business venture with clarity and purpose.
Though vital, business planning doesn’t have to be a chore. Business plans for lean startups and solopreneurs can simply outline the business concept, sales proposition, target customers and sketch out a plan of action to bring the product or service to market. These plans will serve as strategic documents outlining your company’s vision, mission statements, business objectives, target market, financial forecasts and growth strategies.
To simplify the creation of a robust business plan as an entrepreneur, you can harness the power of a business plan maker . This invaluable tool streamlines the process and ensures a polished and well-organized presentation. Startup business plan templates provide pre-designed frameworks that can be customized to suit your specific industry needs, saving valuable time and effort while preserving the essential structure of a comprehensive business plan.
Ready to begin? Let’s go!

Just so you know, some of our business plan templates are free to use and some require a small monthly fee. Sign-up is always free, as is access to Venngage’s online drag-and-drop editor.
Click to jump ahead:
- Laying the foundation of your startup business plan
- Business plan executive summary
- Writing your business description
- Marketing & sales strategies
- Startup operational plans
- Financial plans – forecasting and projections
- Team and management
- Appendix and supporting documents
FAQs on startup business plans
- Use Venngage to create your startup business plan
Preparation and research: 6 steps to laying the foundation of your startup business plan
- What problem does your product or service solve?
- Who are your target customers?
- What differentiates your offering from existing solutions in the market?
This self-reflection will help you establish a clear direction for your startup.
- Next, conduct market research to gather valuable insights about your target market , including demographics, preferences, and purchasing behavior . This data will enable you to tailor your product or service to meet the specific needs of your customers. Identify trends, industry growth projections, and any potential barriers or challenges you may encounter.
- Competitive analysis is another critical aspect of preparation and research. Study your competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and strategies. Analyze their pricing, marketing tactics, customer experience, and product/service features. This analysis will allow you to identify gaps in the market and position your startup to offer a unique value proposition .
- Financial research is equally important during this phase. Calculate the costs associated with starting and operating your business , including overhead expenses, production costs, marketing expenses, and employee salaries. Assess potential revenue streams and estimate your expected sales. This financial analysis will help you determine the feasibility of your business idea and outline a realistic financial plan.
- Additionally, gather information about legal and regulatory requirements that apply to your industry and location . Understand the necessary permits, licenses, and certifications you need to operate legally. Complying with these regulations from the outset will prevent potential setbacks or legal issues in the future.
- Finally, organize your findings and insights into a coherent business plan. Create your business plan outline , list your business plan goals, strategies, target market, competitive analysis, marketing plan, financial projections and any other relevant information. This compilation will serve as a roadmap for your startup, guiding your decisions and actions moving forward.
You’ve just encountered a wealth of information and are well on your way to becoming a seasoned business owner! This can sometimes feel overwhelming. But don’t worry, take a moment to breathe deeply and remember how far you’ve come. You’ve got this!
To help you condense and organize your essential points, I have brilliant one-page samples of business plan layouts and templates that will capture everything in a concise format.

Knowing when to use a one-page business plan versus a more comprehensive plan depends on various factors. A one-page business plan is ideal for providing a quick overview, saving time, and internal planning. However, it may not suffice for detailed information, complex business models, or meeting external stakeholders’ expectations.
Ultimately, consider the purpose, audience, and complexity of your business when deciding whether to utilize a one-page business plan or opt for a more detailed approach.
Executive Summary: Your Startup’s Elevator Pitch
First impressions are crucial, and a concise yet comprehensive executive summary is your chance to grab potential investors’ attention.
To create a compelling elevator pitch, consider the following key elements:
Problem Statement : Clearly articulate the problem or pain point that your startup addresses. Emphasize the significance of the problem and the potential market size
Solution : Concisely describe your innovative solution or product that solves the identified problem. Highlight its unique features or benefits that differentiate it from existing alternatives.
Target Market : Define your ideal customer segment and outline the market potential. Demonstrate a deep understanding of your target audience’s needs, preferences, and behavior.
Competitive Advantage : Showcase the competitive edge that sets your startup apart from competitors. This could include intellectual property, strategic partnerships, cost advantages, or disruptive technology.
Business Model : Briefly explain how your startup generates revenue and sustains profitability. Outline your monetization strategy, pricing model, and any recurring revenue streams .
Traction and Milestones : Highlight any significant achievements or milestones reached by your startup. This could include customer acquisitions, partnerships, product development progress, or market validation.
Team : Showcase the expertise and qualifications of your founding team or business partners. Highlight key members and their relevant experiences demonstrating their ability to execute the business plan.
I can sense your eagerness to dive right in! To expedite your progress, I’m excited to present you with a collection of meticulously crafted executive summary templates. These templates have been thoughtfully designed and structured by Venngage designers, ensuring seamless integration into your thorough business plan. All you need to do is infuse them with your brilliant startup ideas, and you’ll be well on your way to success!

Now, remember that there’s still a ton of work to be done. Let’s take a moment to regroup and ensure we’re on the right track. Before diving into the process of writing your business plan , it’s imperative to gather a wealth of essential information. Conducting comprehensive research is key, and it should encompass the following aspects:
How to assess your target audience
To gain comprehensive insights into your potential user base, creating a user persona report is invaluable. This persona guide report will help you develop a detailed understanding of various user profiles, enabling you to tailor your products or services to meet their specific needs and preferences.
Understanding Your Market and Competition
Analyze your market and any trends relevant to your startup. Research your competitors, their strengths and weaknesses, and identify what differentiates your offering from the competition.
Developing a Unique Value Proposition
A business Unique Value Proposition (UVP) is a concise statement that communicates the unique advantage a product or service offers over competitors, addressing a specific problem or need. It highlights the distinctive value and benefits customers can expect, helping businesses attract and retain customers by differentiating themselves in the market.
Your unique value proposition (UVP) is the cornerstone of your startup, defining what sets you apart from your competitors. A strong UVP focuses on the specific benefits and solutions your startup offers to customers.
Company Description: Painting the Picture
Your company description allows you to showcase your startup’s unique features and provide more in-depth details about your business. This section should include:
The Purpose of the Company Description
Clarify the purpose of your business, your goals and how your startup is uniquely positioned to achieve them.
Essential Information to Include
Include details such as your company’s legal structure, location and a brief history of any founders or key personnel.
Showcase Your Company’s Unique Features
Emphasize the unique aspects of your startup, explaining how these features translate into a competitive advantage.
Allow me to provide you with a dash of inspiration to ignite the momentum for your startup business plan:
When it comes to showcasing your company’s unique features, keep in mind that it is essential to emphasize and highlight the distinctive aspects of your startup . Clearly articulate how these features set your company apart from competitors and translate into a tangible competitive advantage .
Whether it’s through cutting-edge technology, innovative business models, exceptional customer service, or a combination of factors, conveying the value and impact of these unique features is crucial. By effectively communicating the benefits they bring to customers, investors, and partners, you can demonstrate the significance of your offerings and differentiate yourself in the market.
Product/Service Line: What You’re Bringing to the Table
This section highlights the finer details of your product or service offerings:
Detailing Your Product/Service Offerings
Provide a thorough description of your products/services, highlighting key features and their intended use.
Highlighting Features, Benefits, and Solutions
Demonstrate how your startup’s offerings solve specific problems or address customer needs through an analysis of product features and associated benefits.
Defining Your Pricing and Revenue Model
Outline your startup’s pricing strategy and how it aligns with the overall business model. Detail any plans for scaling or expanding your revenue sources in the future.
Presenting Your Market Research Findings
Share insights from your market research, including target customer demographics, market size, and growth potential.
Identifying Market Trends and Opportunities
Discuss current trends, emerging opportunities, and how your startup will capitalize on these developments.
Marketing and Sales Strategies: Spreading the Word
Developing a robust marketing and sales strategy plan aligns with your overall business strategy and ensures steady growth. Marketing planning will be an essential part of your journey once you’ve got your business plan tight-knit! Also, creating a marketing strategy can be the most fun part of your business plan!
Developing a Comprehensive Marketing Strategy & Plan
- Outline Specific Marketing Goals : Clearly define your marketing objectives, whether it’s increasing brand awareness, driving website traffic, generating leads, or boosting sales . Set measurable targets to track progress.
- Identify Target Audience : Conduct thorough market research to identify your ideal customer profiles. Understand their demographics, behaviors, preferences, and pain points. Tailor your marketing messages to resonate with their needs.
- Select Effective Marketing Channels : Consider both digital and traditional channels that align with your target audience and marketing goals. This may include online advertising, social media marketing, content marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), email campaigns, print media, events, or partnerships.
- Craft Compelling Messages : Develop persuasive and consistent messaging that highlights the unique value proposition of your products or services. Clearly communicate how your offerings solve customer problems or improve their lives.
5 Tips for Effective Sales Techniques and Growth Strategies + free templates
- Define Your Sales Strategy : Outline the approach and tactics your sales team will use to reach and convert customers. This may involve direct sales, channel partnerships, online sales, or a combination of strategies. Specify your sales process, including lead generation, qualification, nurturing, and closing.
- Expand Your Customer Base : Identify opportunities to expand your customer reach. Consider targeting new customer segments, entering new geographic markets, or exploring untapped market niches. Develop strategies to attract and engage these potential customers.
- Penetrate New Markets : Assess the feasibility of expanding into new markets or verticals. Market research will help you understand the dynamics, competition, and customer needs in these markets. Adapt your marketing and sales strategies accordingly to effectively penetrate and capture market share.
- Innovate Products/Services : Continuously evaluate and enhance your product or service offerings to meet evolving customer demands. Identify areas for innovation or improvement and develop a roadmap for launching new features, versions, or complementary offerings.
- Perform a SWOT analysis : By conducting a sales SWOT analysis , you will gather valuable insights to enhance your department’s performance. This analysis involves evaluating your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, enabling you to identify areas for improvement and capitalize on advantageous factors in the market.
Here’s a hack to get you organized – Get right into it with the help of these growth strategy templates and strategic planning templates :

Operational Plan: How Your Startup Will Run
Define an efficient and scalable operational plan, keeping in mind the following points:
Defining an Efficient and Scalable Plan
Outline the day-to-day operations, including processes, timelines, and necessary resources.
Legal Considerations for Your Startup Business
Identify any legal requirements or considerations, such as licenses, permits, or regulations that may apply to your startup.
Key Elements of Supply Chain Management and Logistics
Discuss supply chain and logistical aspects relevant to your business. Include details on how you plan to manage and scale these processes.
Here’s a kickstart on how you can structure your operating plans:
Financial Projections: Crunching the Numbers
A startup’s financial projections are vital in securing investor buy-in. This section should address:
The Importance of Financial Forecasting and Budgeting
Explain the significance of accurate financial forecasting, budgeting, and the assumptions made in your projections.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Highlight the KPIs used to gauge your business’s financial health and growth trajectory.
Outlining Funding Requirements
Detail the amount and type of funding your startup requires , including how the funds will be allocated and how this investment positions the company for growth.
Team and Management Structure: Building Your Dream Team
Your startup’s success depends on the people behind it. This section should cover:
Tips for Building the Right Team
Share your strategy for assembling a skilled team that supports your startup’s vision and growth trajectory.
Founders’ Background and Roles
Provide an overview of the founders’ backgrounds, their roles within the company, and how their skills contribute to the startup’s success.
Organizational Structure and Key Management Personnel
Outline your startup’s organizational structure, including any key management personnel who play a pivotal role in day-to-day operations.
Appendices and Supporting Documents: Backing Up Your Plan
Include any other relevant supporting documents, such as:
- Research data, market analysis, or competitor analyses.
- Financial statements, budgeting or forecasting data, and other financial documentation.
- Legal documents, agreements or contracts, and any patent or trademark information.
Finally, remember to review and update your business plan regularly as the industry, market, and competitive landscape evolve!
1. Why is a business plan essential for a startup?
A startup business plan is crucial for a startup because it provides a framework for strategic decision-making, facilitates financial planning, helps assess risks, aligns teams, communicates your vision, and ensures effective resource allocation.
2. What should a startup business plan include?
A startup business plan should include:
- Vision and Direction : Set clear goals and objectives, and outline strategies to achieve them. With a well-defined plan, you will stay focused, make informed decisions, and ensure alignment with your vision.
- Market Analysis : A business plan necessitates thorough market research to understand your target market, identify competition, and assess product/service demand. These insights enable you to tailor offerings, meet customer needs, and gain a competitive edge.
- Financial Planning : By constructing a financial roadmap through projected statements such as income, cash flow, and balance sheets, a business plan unveils the expected revenues, expenses, and profitability. This comprehensive planning not only anticipates challenges and sets realistic goals but also serves as a magnet for attracting investors and securing funding.
- Risk Assessment : Devise strategies for risk mitigation and contingency planning. By proactively doing this, you can significantly enhance the likelihood of success by anticipating and effectively addressing potential obstacles.
- Communication and Team Alignment : From fostering effective communication with both internal and external stakeholders to aligning team members and showcasing your startup’s unique value proposition, a business plan plays a crucial role. It enables you to articulate target market insights, competitive advantages, and growth strategies to potential investors, partners, and employees.
- Resource Allocation : A business plan helps you identify the resources required to launch and operate your startup successfully. It includes an assessment of your human resources, technology needs, infrastructure requirements, and other key resources. By understanding your resource needs, you can allocate them effectively, ensuring that you have the necessary assets to execute your business strategy.
- Adaptability and Flexibility : Your business plan should be flexible enough to accommodate changes and adapt to new circumstances. Startups operate in dynamic environments, and a well-designed plan allows you to monitor progress, evaluate outcomes, and make adjustments as needed. This agility enables you to seize new opportunities and navigate challenges effectively.
3. What is the ideal length for a startup business plan?
The optimal length for a startup business plan typically depends on the specific requirements and intended audience, but a concise and focused plan of around 20 to 30 pages is often recommended.
4. How to write a good startup business plan?
To write a good and effective startup plan, include an executive summary, company description, market analysis, detailed products/services description and a clear marketing and sales strategy. Also incorporate a comprehensive financial plan, outline your organizational structure, and demonstrates your team’s expertise and capabilities. Your plan should be well-researched, concise, and compelling, with a focus on your company’s unique value proposition and market opportunity, making it attractive to investors and stakeholders.
Utilizing Venngage templates & other tools for success
A visually appealing and professional business plan needn’t be a daunting task. Leverage tools like Venngage Business Plan Maker for effective templates that cater to various industries and streamline the process.
- Leveraging Venngage for Visually Appealing and Professional Business Plans
Venngage offers a range of templates designed specifically for business plans, allowing you to craft a polished and visually engaging plan without any design experience. Simply choose a template, customize it to suit your startup’s branding, and populate it with your content.
- Exploring Additional Resources and Tools for Entrepreneurs. In addition to Venngage, several other resources and tools can assist entrepreneurs in crafting the perfect business plan. Examples include:
- Small Business Administration (SBA) – Offers guidance on writing business plans and provides templates and resources for each section.
- SCORE – A nonprofit organization providing mentorship, workshops, and other resources for entrepreneurs.
- Industry-specific resources – Research relevant professional organizations, industry publications, and blogs to stay up to date on industry trends and insights.
Embarking on the entrepreneurial path may present formidable challenges, yet it offers abundant rewards in various aspects. Embrace the art of continuous learning, delving not only into the essence of your business idea but also immersing yourself in the vast world that surrounds it. Cultivate a genuine passion for understanding every facet of your enterprise, for it is through this journey of exploration that you will uncover invaluable insights and experience the true fulfillment of entrepreneurship.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples
By Joe Weller | May 6, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up a variety of the top, professionally designed startup business plan templates, all of which are free to download in PDF, Word, and Excel formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find a one-page startup business plan template , a business plan outline template for startups , a startup business planning template with a timeline , and a sample startup business plan .
Startup Business Plan Template

Download Startup Business Plan Template - Word
Word | Smartsheet
This startup business plan template contains the essential components you need to convey your business idea and strategy to investors and stakeholders, but you can customize this template to fit your needs. The template provides room to include an executive summary, a financial overview, a marketing strategy, details on product or service offerings, and more.
One-Page Startup Business Plan Template
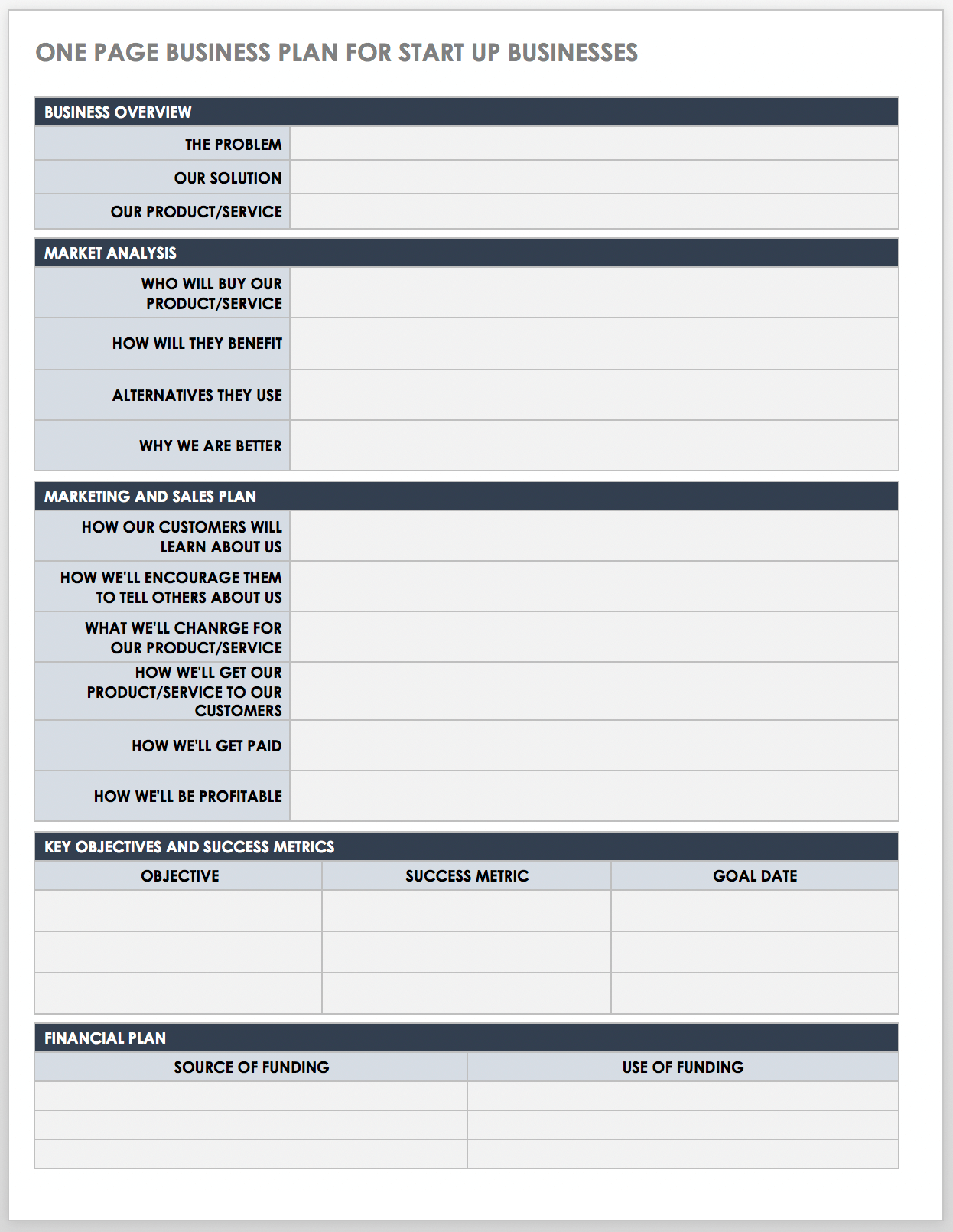
Download One-Page Startup Business Plan Template
Excel | Word | PDF
This one-page business plan is ideal for startup companies that want to document and organize key business concepts. The template offers an easy-to-scan layout that’s ideal for investors and stakeholders. Use this plan to create a high-level view of your business idea and as a reference as you flesh out a more detailed roadmap for your business.
For additional resources, visit " Free One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
Simple Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Template for Startups
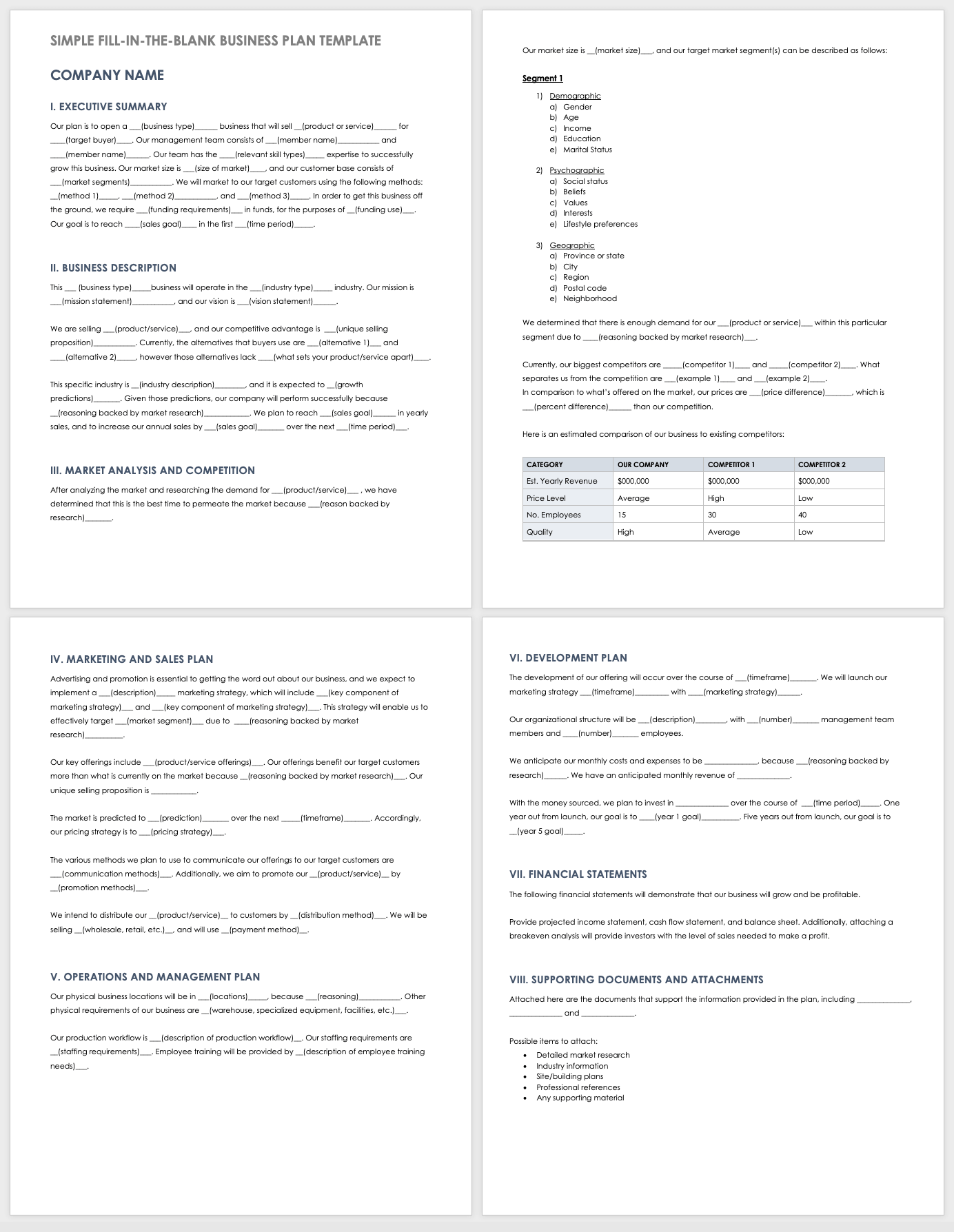
Download Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template for Startups
This comprehensive fill-in-the-blank business plan template is designed to guide entrepreneurs through the process of building a startup business plan. This template comes with a customizable cover page and table of contents, and each section includes sample content that you can modify to fit the needs of your business. For more fill-in business templates, read our "Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates" article.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
This Lean business plan template takes a traditional business plan outline and extracts the most essential elements. Use this template to outline your company and industry overview, convey the problem you are solving, identify customer segments, highlight key performance metrics, and list a timeline of key activities.
Business Plan Outline Template for Startups

Download Business Plan Outline Template for Startups
You can use this business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains all the elements of a traditional business plan, including a title page, a table of contents, and information on what to include in each section. Simplify or expand this outline based on the size and needs of your startup business.
Startup Business Planning Template with Timeline
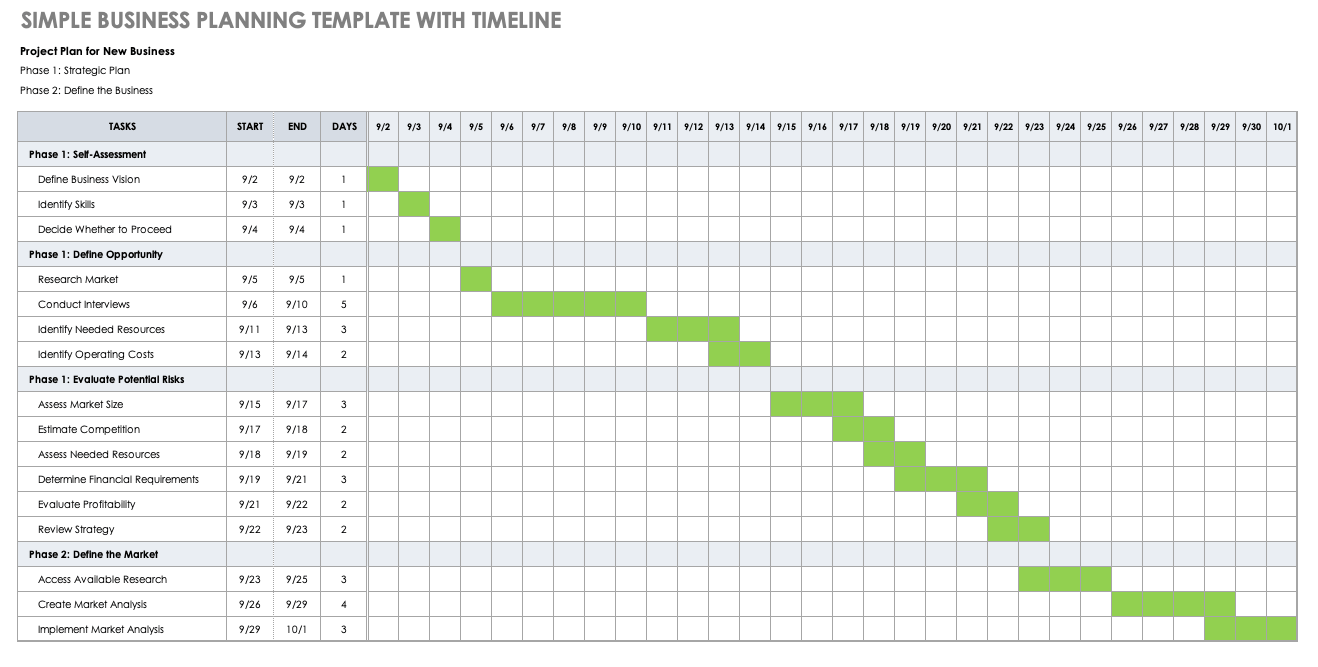
Download Startup Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
As you create your business plan, this business planning template doubles as a schedule and timeline to track the progress of key activities. This template enables you to break down your plan into phases and provides space to include key tasks and dates for each task. For a visual timeline, shade in the cells according to each task’s start and end dates. The timeline ensures that your plan stays on track.
Business Plan Rubric Template for Startups
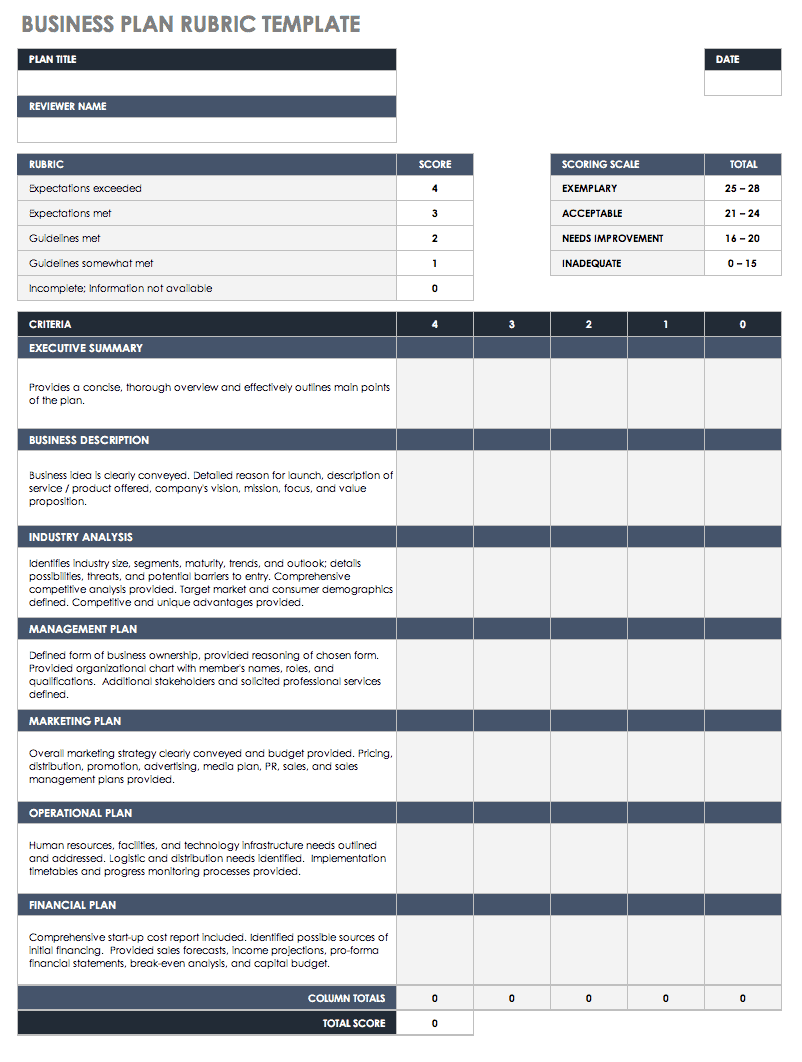
Download Business Plan Rubric Template for Startups
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
If you’re starting a business and want to keep all your ducks in a row, use this rubric to evaluate and score each aspect of your startup business plan. You can tailor this template to the needs of your specific business, and can also highlight areas of your plan that require improvement or expansion. Use this template as a tool to make sure your plan is clear, articulate, and organized. A sharp, insightful, well thought-out plan will definitely get the attention of potential investors and partners.
For additional resources to help support your business planning efforts, check out “Free Startup Plan, Budget, and Cost Templates.”
What’s the Best Business Plan Template for Startups?
The template you choose for your startup business depends on a number of factors, including the size and specific needs of your company. Moreover, as your business grows and your objectives change, you will need to adjust your plan (and possibly your choice of template) accordingly.
Some entrepreneurs find it useful to use a Lean business plan template design in order to jot down a business concept and see if it’s feasible before pursuing it further. Typically one to three pages, a Lean business plan template encourages you to highlight core ideas and strategic activities and remain focused on key points.
Other entrepreneurs prefer a template with a more traditional business plan design, which allows you to go into greater detail and ensure you include every detail. A traditional plan can range from 10 to 100 pages and cover both the high-level and granular particulars of your overall concept, objectives, and strategy.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution, but the following section outlines the minimum that your business plan template should include in order to gain buy-in from potential investors.
What to Include in a Startup Business Plan
Whether you choose to use a template to develop your startup business plan or decide to write one from scratch, you need to include the following elements:
- An overview of your company and the industry in which it operates
- The problem you are solving and the proposed solution
- A description of your product or service offerings, including key features
- The existing alternatives that customers use and your competitive advantage
- The target customer segments and the channels you will use to reach them
- The cost structure and revenue streams associated with your business
- A financial plan, including sales and revenue projections (ideally 3-5 years)
- If applicable, the financial requirements to get your business running, including how you will source and allocate funds
Each of the following sections provides an example of a business plan that you can use for reference as you develop your own.
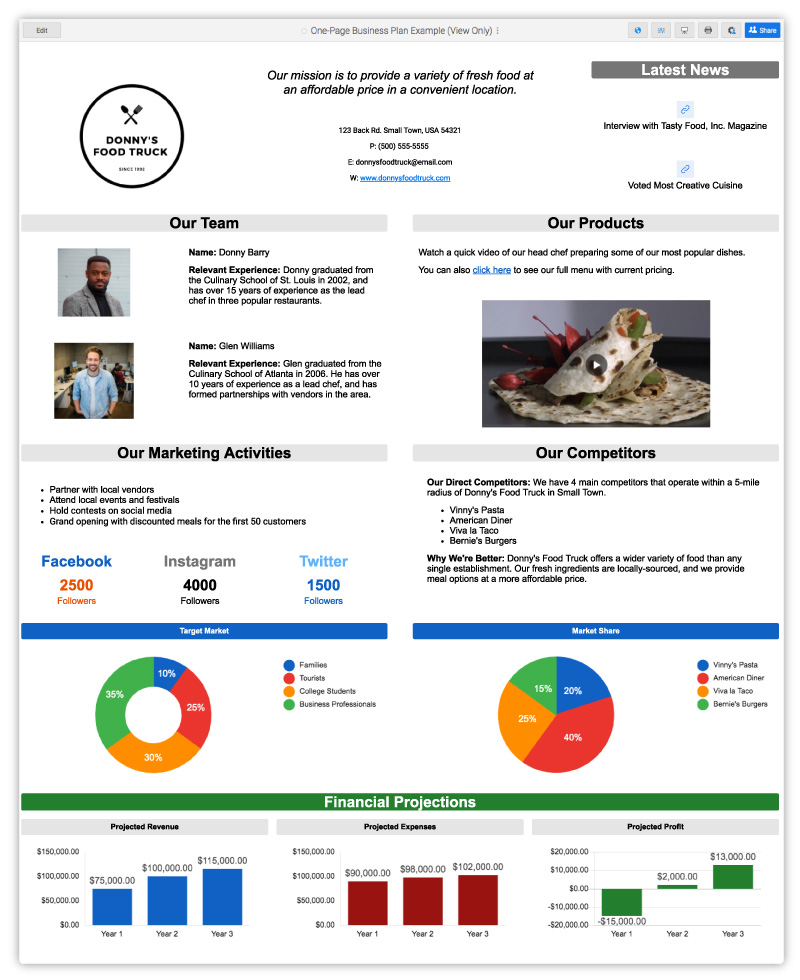
One-Page Lean Business Plan Example
This Lean business plan example displays a visually appealing and scannable one-page illustration of a business plan. It conveys the key strategies you need to meet your main objectives. Each element of this concise plan provides stakeholders and potential investors with links to resources that support and expand upon the plan’s details, and it can also serve as an investor pitch deck.
Startup Business Plan Sample
This business plan sample contains all the aspects of a standard business plan. Using a fictional food truck business as the basis for a startup business plan, this sample will give you all the ideas you need to make your plan outstanding.
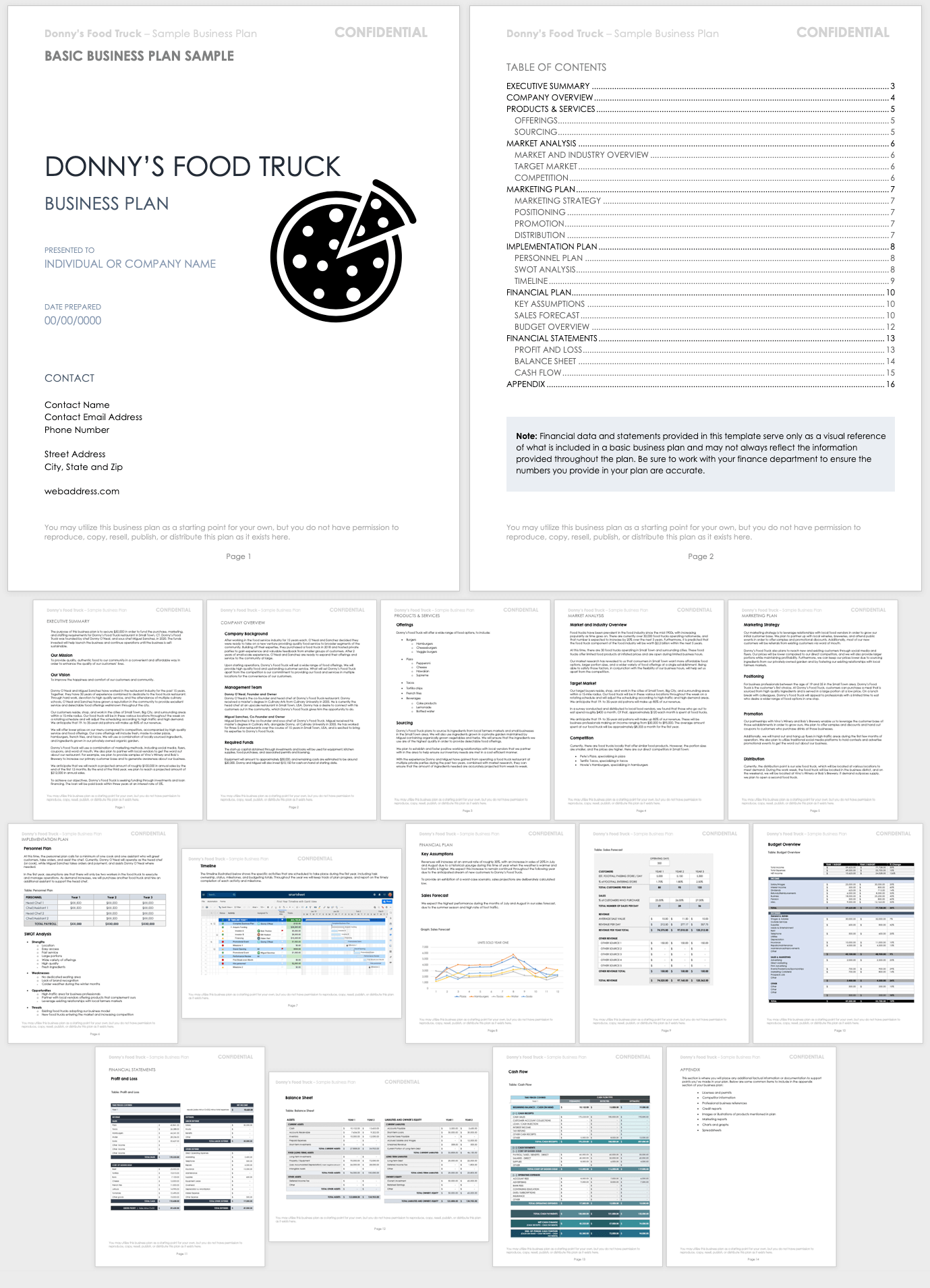
Download Startup Business Plan Sample - PDF
When the time comes that you need more space to lay out your goals and strategies, choose from our variety of free simple business plan templates . You can learn how to write a successful simple business plan here .
Visit this free non-profit business plan template roundup or of you are looking for a business plan template by file type, visit our pages dedicated specifically to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates. Read our articles offering free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options.
Top 10 Tips to Create a Startup Business Plan
Putting together a business plan can be overwhelming and time consuming, especially if you aren’t sure where to begin. Below, we share tips you can use to help simplify the process of developing a startup business plan of your own.
- Use a business plan template, or begin with a business plan outline that provides all the elements of a standard plan to get your ideas down on paper in a structured manner. (You can choose from the selection of templates above.)
- Remove sections from your outline that aren’t relevant or that aren’t necessary to launch and operate your business.
- Compile the data you have gathered on your business and industry, including research on your target market and product or service offerings, details on the competitive landscape, and a financial plan that anticipates the next three to five years. Use that information to fill in the sections of your plan outline.
- Get input and feedback from team members (e.g., finance, marketing, sales) and subject matter experts to ensure that the information you’ve included in the plan is accurate.
- Make certain that the objectives of your plan align with marketing, sales, and financial goals to ensure that all team members are moving in the same direction.
- Although this section of the plan comes first, write the executive summary last to provide an overview of the key points in your business plan.
- Prepare a pitch deck for potential clients, partners, or investors with whom you plan to meet in order to share vital information about your business, including what sets you apart and the direction you are headed.
- Who are the founders and management executives, and what relevant experience do they bring to the table?
- What is the problem you are solving, and how is your solution better than what currently exists?
- What’s the size of the market, and how much market share do you plan to capture?
- What are the trends in your market, and how are you applying them to your business?
- Who are your direct competitors, and what is your competitive advantage?
- What are the key features of your product or service that set it apart from alternative offerings, and what features do you plan to add in the future?
- What are the potential risks associated with your business, and how do you plan to address them?
- How much money do you need to get your business running, and how do you plan to source it?
- With the money you source, how do you plan to use it to scale your business?
- What are the key performance metrics associated with your business, and how will you know when you’re successful?
- Revisit and modify your plan on a regular basis as your goals and strategies evolve.
- Use a work collaboration tool that keeps key information across teams in one place, allows you to track plan progress, and captures updates in real time.
Successfully Implement Your Startup Business Plan with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
How to make a business plan
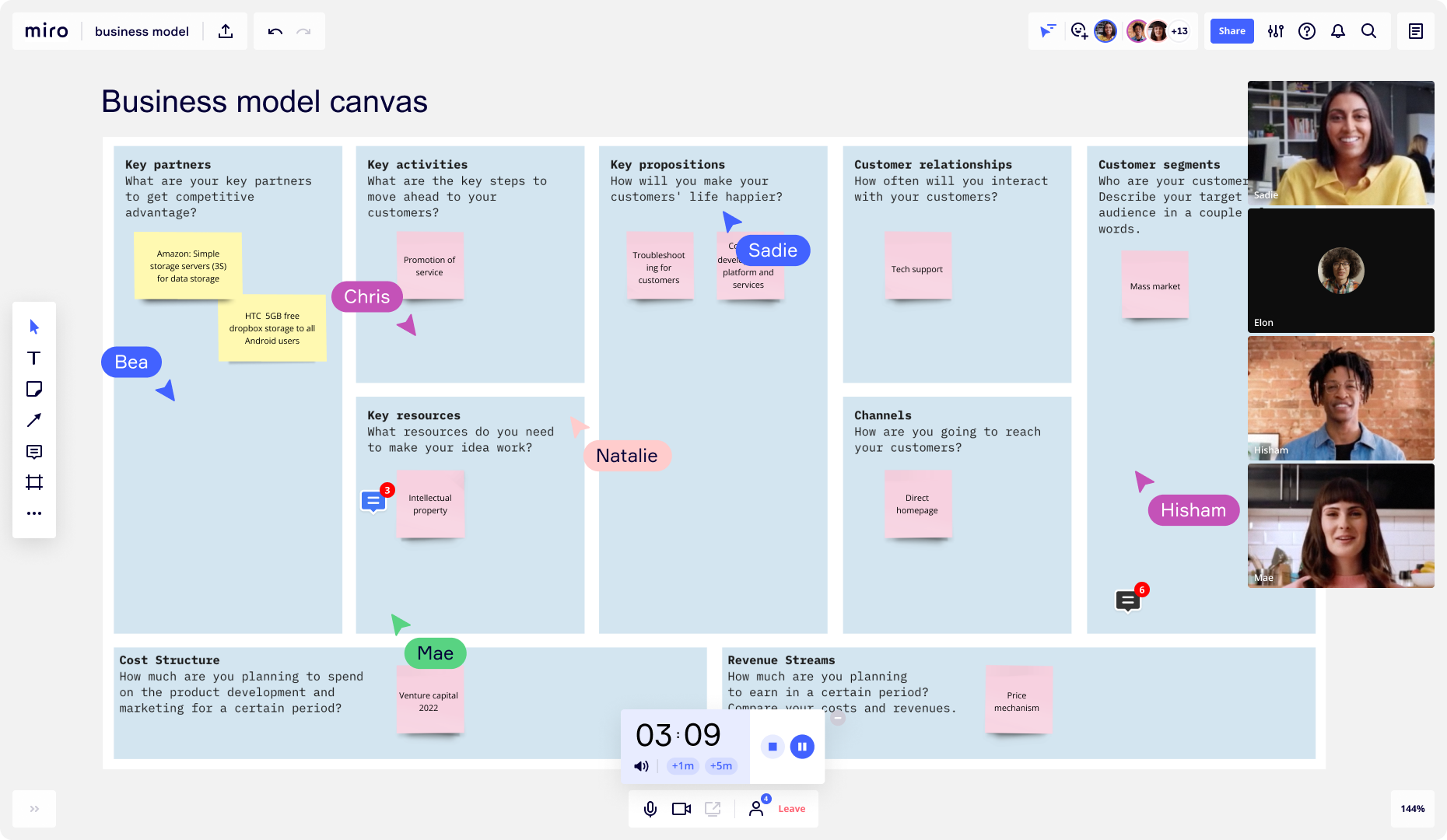
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Strategic planning |
- Business plan
Business plan template
If you’re looking for a way to start your business off on the right foot, a business plan template can help you establish the foundation for your strategy. Get started in a few clicks with Asana’s free business plan template.
Sign up to use this template.
INTEGRATED FEATURES
Recommended apps.
You’re pumped—you just thought of the greatest business idea ever. You want to get started, but you don’t have a plan laid out. You need a loan to get your idea off the ground, and the bank wants to see an in-depth business plan. We’re here to help.
What is a business plan template?
A business plan template is a framework that helps you solidify your ideas in an organized format. Our free business plan template walks you through how to create a new business from scratch, or re-imagine your existing business in a new market.
What components are included in a business plan template?
Our business plan template covers what an organization wants to achieve within three to five years. By using our template, you’ll have a place to capture all of the major information you need in order to complete your business plan. That includes:
Company description : Information like your executive summary , your company’s mission statement and vision, and your founder’s bio.
Product and services: A high-level overview of what your company provides, including core products or services. This may also include how your product is developed, any potential screenshots or prototypes of your product, and pricing plans.
Marketing plan: How you plan to bring your product into market at a high level. You can add information like a SWOT analysis , target market research, and brand positioning in this section.
Financial plan: Important financial information such as balance sheets, a break-even analysis, and your cash flow projections.
Management and organization information: Information on your company’s founders, executive team, and the board of directors.
How to use our free business plan template
Using Asana’s free business plan template is simple. Start by creating a new project with our free template. From there, add relevant information for your specific business plan in the sections provided in our template. If there’s more information you want to include in your business plan, you’re free to add sections, custom fields, or additional tasks to make this template fit your needs.
Integrated features
Goals . Goals in Asana directly connect to the work you’re doing to hit them, making it easy for team members to see what they’re working towards. More often than not, our goals live separate from the work that goes into achieving them. By connecting your team and company goals to the work that supports them, team members have real-time insight and clarity into how their work directly contributes to your team—and company—success. As a result, team members can make better decisions. If necessary, they can identify the projects that support the company’s strategy and prioritize work that delivers measurable results.
Reporting . Reporting in Asana translates project data into visual charts and digestible graphs. By reporting on work where work lives, you can reduce duplicative work and cut down on unnecessary app switching. And, because all of your team’s work is already in Asana, you can pull data from any project or team to get an accurate picture of what’s happening in one place.
Milestones . Milestones represent important project checkpoints. By setting milestones throughout your project, you can let your team members and project stakeholders know how you’re pacing towards your goal. Use milestones as a chance to celebrate the little wins on the path towards the big project goal.
Project Overview . Project Overview is your one-stop-shop for all important project context. Give your team a bird’s-eye view of the what, why, and how of your project work. Add a project description to set the tone for how you’ll work together in Asana. Then, share any important resources and context—like meeting details, communication channels, and project briefs—in one place.
Microsoft Teams . With the Microsoft Teams + Asana integration, you can search for and share the information you need without leaving Teams. Easily connect your Teams conversations to actionable items in Asana. Plus, create, assign, and view tasks during a Teams Meeting without needing to switch to your browser.
Slack . Turn ideas, work requests, and action items from Slack into trackable tasks and comments in Asana. Go from quick questions and action items to tasks with assignees and due dates. Easily capture work so requests and to-dos don’t get lost in Slack.
Google Workplace . Attach files directly to tasks in Asana with the Google Workplace file chooser, which is built into the Asana task pane. Easily attach any My Drive file with just a few clicks.
Gmail . With the Asana for Gmail integration, you can create Asana tasks directly from your Gmail inbox. Any tasks you create from Gmail will automatically include the context from your email, so you never miss a beat. Need to refer to an Asana task while composing an email? Instead of opening Asana, use the Asana for Gmail add-on to simply search for that task directly from your Gmail inbox.
How do I create a business plan template? .css-i4fobf{-webkit-transition:-webkit-transform 200ms ease-in-out;transition:transform 200ms ease-in-out;-webkit-transform:rotateZ(0);-moz-transform:rotateZ(0);-ms-transform:rotateZ(0);transform:rotateZ(0);}
Instead of taking the time to create a business plan from scratch, start the process off with Asana’s free template.To further customize your template, add evergreen information about your specific business, such as your business model, company name, address, mission statement, value proposition, or target audience. Adding these details to your template lets you avoid documenting this information from scratch every time you create a new business plan.
What components should I include in a business plan template?
Business plan templates typically contain five main sections: a company description, products and services, a marketing plan, basic management and organization information, and your current financial plan.
How long should my business plan be?
Short answer—as long as you need it to be. The long answer is that your business plan should have the answers to specific questions on how your business is run, from the perspective of an investor. The goal of a business plan is to highlight your business strategy for the next three to five years. This means any important operational, financial, and strategic information should be included.
Related templates
Action plan template
Taking action has never been easier. Learn how to create a reusable action plan template in Asana to take the guesswork out of strategic planning.

Marketing strategy
A marketing strategy template is a useful tool that helps your marketing team achieve their goals. Learn how to create your marketing strategy with Asana.

PEST analysis
A PEST analysis template helps compile info on the external environment affecting your business. Learn how to prevent risk with a PEST analysis template.
Objectives and key results (OKR) template
Learn how to create an OKR template in Asana so you can standardize the goal-setting process for everyone.
Cost benefit analysis template
Digital cost benefit analysis templates are a useful framework to see if a new project or idea is viable. Learn how to create your own in a few simple steps, with Asana.
Nonprofit business plan template
Success doesn’t just happen—it’s planned. Stay focused on your most crucial work with a custom nonprofit business plan template.
Contingency plan
Using a contingency plan template will help you create well-developed strategies to help you protect your business from potential risk. Learn how Asana can help.

Requirements traceability matrix
A requirements traceability matrix template is a tool to help organize project requirements in a concise manner. Learn how to create one for your team.
Creating a digital punch list template can help streamline the final bits of a project for your team. Here’s how to create one.
Go-to-market strategy template
Simplify your GTM strategy with a go-to-market strategy template that aligns teams and keeps work on track. Learn how in Asana.
Project closure template
Endings are important. Create a project closure template to help your team tie up loose ends and finish their projects with confidence.
Project reporting
Stay on top of your project’s performance. Keep everyone on the same page about what’s been completed and where your project is headed.
![business plan model startup [Templates] Product Roadmap (Card image)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/2728edf4-eb35-4dd5-8d03-25ba8cbe5864/TG23-web-thumbnail-028-scrumban-feature-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Product roadmap
What if you could create, share, and update your product roadmap in one place? Everyone could see you’re tackling the right priorities. Start planning your product roadmap with this template.

Program roadmap
Create a program roadmap template and know the exact structure of each program, how they operate, and their future plans—company-wide.

Operational plan template
Learn how Asana’s operations team uses standardized processes to streamline strategic planning—no matter how many stakeholders are involved.
Strategic planning template
When you’re launching a new product, team, or even a new business, strategic planning templates keep you laser-focused and on task.

Annual planning template
Set clear goals and streamline your planning process—so every level of your company is aligned on what’s important.
Competitive analysis template
The more you know about your competitors, the better your strategy will be. Competitive analysis templates use a data-driven approach to see exactly how your business, products, and features compare to your competition.

Crisis management plan
Does your team know what to do during a crisis? Using a crisis management plan template can help keep all your employees on the same page.
SIPOC template
Use your SIPOC template to ensure that the processes outlined in your SIPOC diagrams are consistent and up to your standards.
Small business, big goals
Coming up with your business strategy can be daunting, but Asana helps businesses of all sizes track and hit their goals. See how with a free trial.
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)

Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles

698 Endearing Daycare Names (2024)

How to Start a Home Business (in 9 Steps)

Opening a Gas Station: The Ultimate Guide (2024)
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

7 Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own (2024)
Need support creating your business plan? Check out these business plan examples for inspiration.

Any aspiring entrepreneur researching how to start a business will likely be advised to write a business plan. But few resources provide business plan examples to really guide you through writing one of your own.
Here are some real-world and illustrative business plan examples to help you craft your business plan .
7 business plan examples: section by section
The business plan examples in this article follow this template:
- Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business.
- Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists.
- Market analysis. Research-based information about the industry and your target market.
- Products and services. What you plan to offer in exchange for money.
- Marketing plan. The promotional strategy to introduce your business to the world and drive sales.
- Logistics and operations plan. Everything that happens in the background to make your business function properly.
- Financial plan. A breakdown of your numbers to show what you need to get started as well as to prove viability of profitability.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary is a page that gives a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. It’s easiest to save this section for last.
In this free business plan template , the executive summary is four paragraphs and takes a little over half a page:

- Company description
You might repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, social media profile pages, or other properties that require a boilerplate description of your small business.
Soap brand ORRIS has a blurb on its About page that could easily be repurposed for the company description section of its business plan.

You can also go more in-depth with your company overview and include the following sections, like in the example for Paw Print Post:
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your business —as an LLC , sole proprietorship, corporation, or other business type . “Paw Print Post will operate as a sole proprietorship run by the owner, Jane Matthews.”
- Nature of the business. “Paw Print Post sells unique, one-of-a-kind digitally printed cards that are customized with a pet’s unique paw prints.”
- Industry. “Paw Print Post operates primarily in the pet industry and sells goods that could also be categorized as part of the greeting card industry.”
- Background information. “Jane Matthews, the founder of Paw Print Post, has a long history in the pet industry and working with animals, and was recently trained as a graphic designer. She’s combining those two loves to capture a niche in the market: unique greeting cards customized with a pet’s paw prints, without needing to resort to the traditional (and messy) options of casting your pet’s prints in plaster or using pet-safe ink to have them stamp their ‘signature.’”
- Business objectives. “Jane will have Paw Print Post ready to launch at the Big Important Pet Expo in Toronto to get the word out among industry players and consumers alike. After two years in business, Jane aims to drive $150,000 in annual revenue from the sale of Paw Print Post’s signature greeting cards and have expanded into two new product categories.”
- Team. “Jane Matthews is the sole full-time employee of Paw Print Post but hires contractors as needed to support her workflow and fill gaps in her skill set. Notably, Paw Print Post has a standing contract for five hours a week of virtual assistant support with Virtual Assistants Pro.”
Your mission statement may also make an appearance here. Passionfruit shares its mission statement on its company website, and it would also work well in its example business plan.
- Market analysis
The market analysis consists of research about supply and demand, your target demographics, industry trends, and the competitive landscape. You might run a SWOT analysis and include that in your business plan.
Here’s an example SWOT analysis for an online tailored-shirt business:
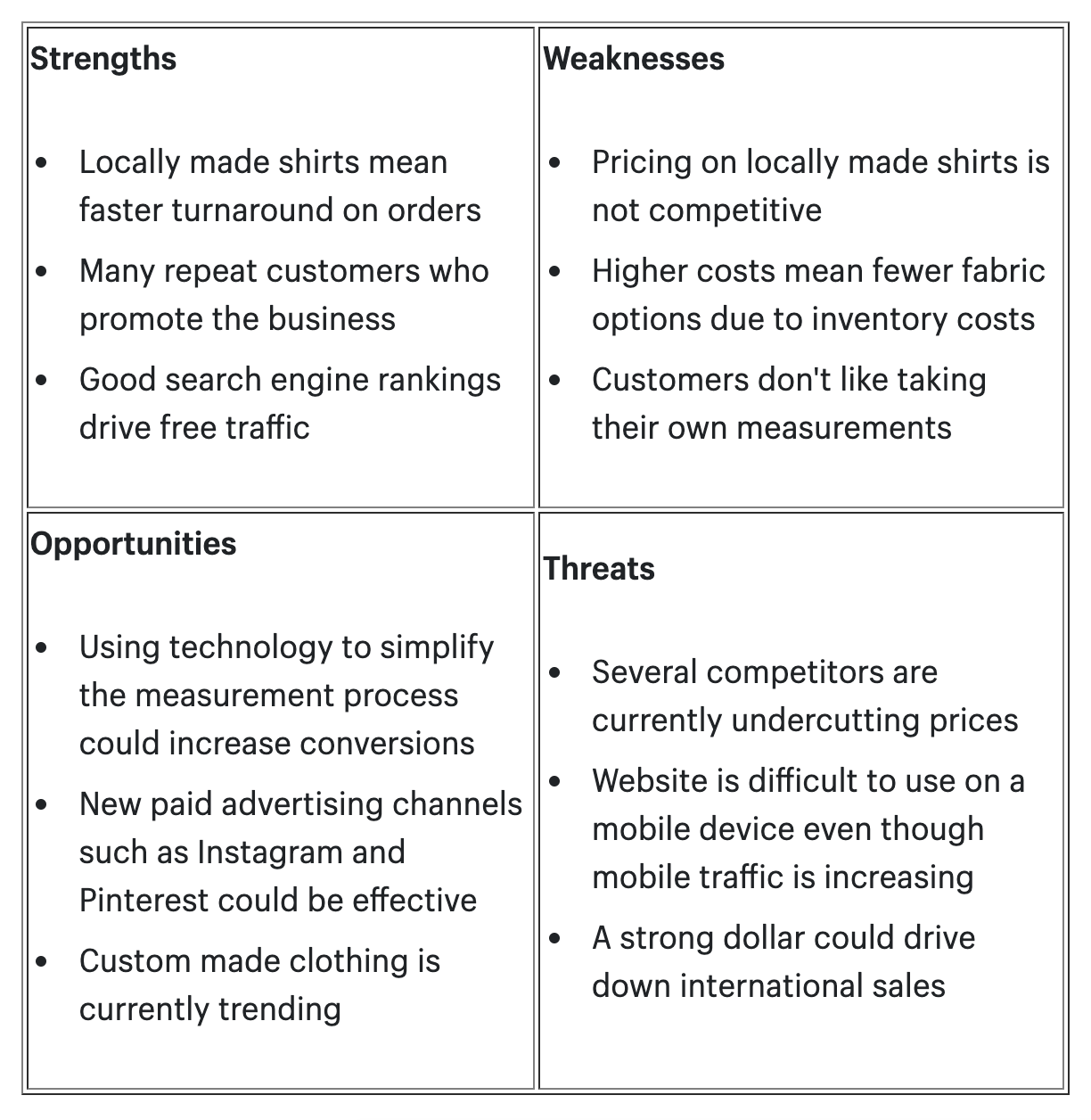
You’ll also want to do a competitive analysis as part of the market research component of your business plan. This will tell you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to differentiate your brand. A broad competitive analysis might include:
- Target customers
- Unique value add or what sets their products apart
- Sales pitch
- Price points for products
- Shipping policy
- Products and services
This section of your business plan describes your offerings—which products and services do you sell to your customers? Here’s an example for Paw Print Post:

- Marketing plan
It’s always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you’ll get the word out about your business, and it’s an essential component of your business plan as well.
The Paw Print Post focuses on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. However, you can take a different approach with your marketing plan. Maybe you can pull from your existing marketing strategy , or maybe you break it down by the different marketing channels. Whatever approach you take, your marketing plan should describe how you intend to promote your business and offerings to potential customers.
- Logistics and operations plan
The Paw Print Post example considered suppliers, production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan provides a breakdown of sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and other relevant financial metrics related to funding and profiting from your business.
Ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy’s financial plan breaks down predicted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
It then dives deeper into the financials to include:
- Funding needs
- Projected profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Projected cash-flow statement
You can use this financial plan spreadsheet to build your own financial statements, including income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement.
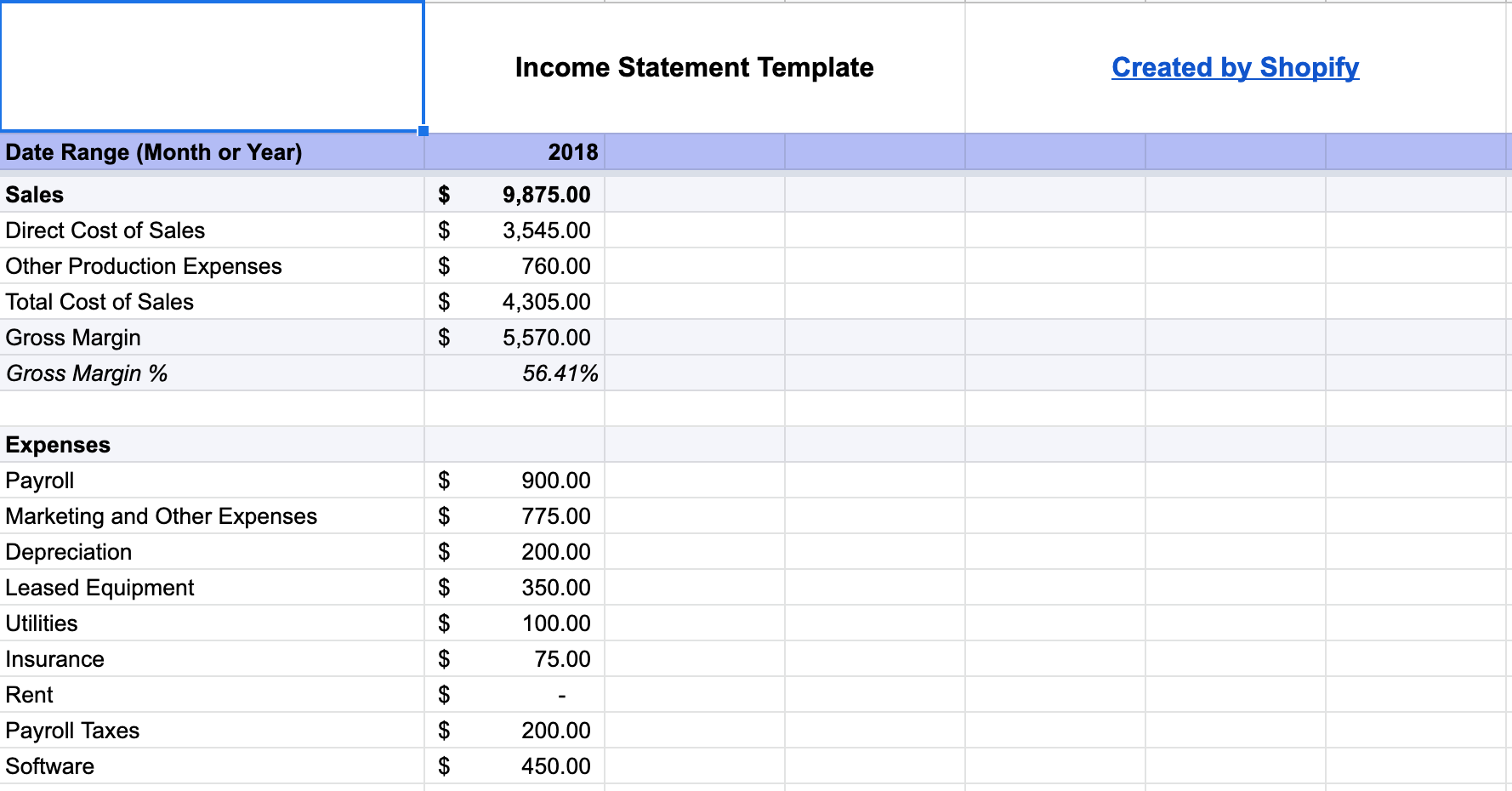
Types of business plans, and what to include for each
A one-page business plan is meant to be high level and easy to understand at a glance. You’ll want to include all of the sections, but make sure they’re truncated and summarized:
- Executive summary: truncated
- Market analysis: summarized
- Products and services: summarized
- Marketing plan: summarized
- Logistics and operations plan: summarized
- Financials: summarized
A startup business plan is for a new business. Typically, these plans are developed and shared to secure outside funding . As such, there’s a bigger focus on the financials, as well as on other sections that determine viability of your business idea—market research, for example.
- Market analysis: in-depth
- Financials: in-depth
Your internal business plan is meant to keep your team on the same page and aligned toward the same goal.
A strategic, or growth, business plan is a bigger picture, more-long-term look at your business. As such, the forecasts tend to look further into the future, and growth and revenue goals may be higher. Essentially, you want to use all the sections you would in a normal business plan and build upon each.
- Market analysis: comprehensive outlook
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Marketing plan: comprehensive outlook
- Logistics and operations plan: comprehensive outlook
- Financials: comprehensive outlook
Feasibility
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it’s worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it’s mostly centered around research.
Set yourself up for success as a business owner
Building a good business plan serves as a roadmap you can use for your ecommerce business at launch and as you reach each of your business goals. Business plans create accountability for entrepreneurs and synergy among teams, regardless of your business model .
Kickstart your ecommerce business and set yourself up for success with an intentional business planning process—and with the sample business plans above to guide your own path.
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The 13 Best Dropshipping Suppliers in 2024
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- 25+ Ideas for Online Businesses To Start Now (2024)
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Build a Business Website for Beginners
- 7 Inspiring Marketing Plan Examples (and How You Can Implement Them)
- 10 Ways to Write Product Descriptions That Persuade (2024)
- Get Guidance- 6 Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
- Business Valuation- Learn the Value of Your Business
Business plan examples FAQ
How do i write a simple business plan, what is the best format to write a business plan, what are the 4 key elements of a business plan.
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the company's mission, goals, target audience, and financial objectives.
- Business description: A description of the company's purpose, operations, products and services, target markets, and competitive landscape.
- Market analysis: An analysis of the industry, market trends, potential customers, and competitors.
- Financial plan: A detailed description of the company's financial forecasts and strategies.
What are the 3 main points of a business plan?
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business and provide an overall summary of what you intend to accomplish.
- Contents: Your content should include details about the products and services you provide, your target market, and your competition.
- Cashflow: Your cash flow section should include information about your expected cash inflows and outflows, such as capital investments, operating costs, and revenue projections.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Jun 21, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.

550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily we have a round-up of real-world pitch deck examples used by successful startups that you can review and reference as you build your pitch.
For more resources, check out our full Business Pitch Guide .
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Sample Business Plans
Startup Business Plan
Starting a business is an exciting and overwhelming prospect at the same time. Having a business gives you autonomy but comes with a lot of responsibility at the same time.
But you don’t need to worry! If you plan your business down to the last detail, all the overwhelming aspects of your business can become easier to manage.
Proper business planning also helps you get the maximum out of your business efforts and writing a business plan is the first step for any business planning.
A well-written business plan helps you grow your business rapidly and optimally. To make the business plan writing process easy and faster, we have created this startup business plan.
First, let’s understand an important question.
What is Business Plan Template?
A business plan template is a guide that consists of an outline of all the required sections of a perfect business plan. It also includes step-by-step instructions on how to write each section of the business plan.
A good business plan usually consists of an executive summary, business overview, market analysis, operations plan, and so on.
Now that you know what a business plan template is, let’s move on to understand why you need one.
Why do you need a business plan for your startup?
If you’ve recently set up your startup business, it’s understandable why you might be dumbstruck. There’s a lot that needs to be done and it’s not always obvious why. Fortunately, we can help you create a business plan. Some of the reasons why you need a business plan are:
- Getting started: Getting a business up and running may seem chaotic. You may be unsure of where to begin, and here’s when a business plan can help you set things straight. It helps prioritize and organize your business activities.
- Predict challenges: Creating a startup business plan helps determine the risks and obstacles that your startup is likely to face in the future. This helps you stay prepared with suitable tactics to overcome these challenges.
- Funding: Attracting investors to score funding is essential for startups. Whether you’re applying for a loan or seeking investors, a business plan helps gain their trust. Having a business plan conveys that you are serious about your business and are trustworthy.
- Goals and milestones: A business plan helps you create measurable goals . It further helps induce focus and track your progress. Witnessing the progress motivates you and your team to perform better and achieve more milestones.
- Finances: Finances are one of the trickiest aspects of a business, especially for a startup. Every decision you make has a financial implication. Hence, it is vital to consider every aspect in decision-making. A business plan helps you manage, track, and predict your finances.
- Revising strategies: When you’re just setting up your business, you’re bound to make the wrong assumptions. A business plan helps you identify your mistakes and revamp your strategies to get back on track.
Types of Business Plan Template
Moreover, business plan templates come in different forms and you can select the one that fits your needs the best.
Here are the two most common ones:
Simple Business Plan
Traditional business plan.
Let’s understand what’s the difference between these business plans and which one is best for you.
A simple business plan template is super handy to write a quick and concise business plan.
It helps you cover all the pointers necessary to attract investors as well as for creating a well-rounded plan.
A lean business plan is not only easy to write but it is also written in a way that helps you take action to solve business problems as well as to introduce product and service-based solutions in the market.
Here are the 9 sections of a simple or lean business plan:
- Problem: This section consists of a brief description of the market problem you are trying to solve with your product or service.
- Solution: This section would consist of how you’ll solve the concerned market problem, and how is your solution different from the already existing ones.
- Key Metrics: Include all your data including sales target, break-even analysis, funding requirements, and so on in this section.
- Unique Proposition: In this section, you’ll describe the USP of your product and the data to support your claim. It can either be in the form of surveys or customer and competitive analysis.
- Unfair Advantage: This section will help you take note of all the unfair advantages of your competitors and how you’ll prevent them from using the same.
- Channels: In this section list down mediums through which you can market and distribute your product or service.
- Target Audience: Through this section, you’ll describe the key attributes of your ideal customer or draw out your customer persona .
- Cost Structure: This section would consist of the cost structure and describe its feasibility.
- Revenue Streams: In this section list out your revenue stream and when you plan on starting it.
In conclusion, a lean business plan is a great tool if you are just starting and don’t want to get into the hassle of writing a 30-page-long business plan. Moreover, it can also serve as a pitch for investors.
But despite all of its advantages, a lean business plan might not be your cup of tea. Or if you plan on growing your business you might need a more detailed and elaborate plan.
And for that, a traditional business plan is a very handy tool. It might seem tedious to write, but it acts as a guide at every step of your business.
And here’s what you’ll include in a traditional business plan.
A traditional business plan is a living document that grows alongside your business. It helps you grab opportunities unforeseen by unplanned businesses and helps you tackle obstacles smartly and smoothly. A business plan is one of the best investments of time that you can put into your business.
Here are a few major sections of a traditional business plan:
- Business Overview
- Mission Statement
- Product/Service Summary
- Market Opportunity Summary
- Traction Summary
- Vision Statement
- Capital Request
- Problem Analysis
- Market Size & Growth
- Market Trends
- Market Segments
- Industry Success Stories
- Market position
- Unique selling position
- Pricing strategy
- Value to customer
- Revenue Channels
- Critical Costs
- Cost Maturation & Milestones
- Investment Costs
- Operating Efficiencies
- Competitor 1
- Competitor 2
- Similarities & Differences
- Customer Definition
- Channel Cost Assumptions
- SWOT – internal and external forces
- Launch Strategy and Budget
- Distribution Channels
- Product Development
- Manufacturing/Distribution
- Early Customers & Revenue
- Testimonials & Social Proof
- Partnerships
- Intellectual Property
- Press Mentions
- Organization Chart
- Hiring Plan
- Funding Goal
- Use of Funds
- Why Invest? / Conclusion
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Break-Even Analysis
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Why Choose a Traditional Business Plan?
Startups are very different from established businesses. The most obvious reason is that startups don’t have any previous data on how to run their business. This is precisely why a traditional business plan will work for any startup.
There are some vital differences between a traditional business plan and a simple business plan. These differences exist due to several reasons:
- Lack of a definite business model In the early stages, it’s difficult to state the structure of your business model because your business idea and its execution are still in the testing phase. Only after a certain period of trial and error, you would be able to describe your business model.
- No performance history While creating financial projections, an established company examines its credit history, past sales, revenue, expenditure, and growth rate. In contrast, a startup needs to begin with assumptions. You have to predict sales, costs, expenses, growth rate, etc. To increase the accuracy of your predictions, you need to gather reliable factual data to back your predictions.
- Increased risk Startups have an increased risk factor compared to established businesses. This is because startups lack a loyal customer base, an expert team, brand recognition, etc. Devise strategies to overcome the potential risks and challenges that may come your way in the future.
These are the reasons why you need a dedicated business plan for your startup that helps focus on the essential elements while setting up your business.
Before you start writing your business plan, go through the below checkpoints to make sure you are ready for it.
Tips to Create a Business Plan for Your Startup
Writing your first business plan can be overwhelming and confusing. However daunting it may seem, it is still something you can’t avoid.
- Use a startup business plan template: It can be hard to start from scratch, especially when you are unsure of where to begin. A business plan template helps you get started quickly. You can use it to navigate and structure your plan according to your standards
- Tailor your plan: After choosing a template, it is essential to customize it to your business requirements. Remove sections that are irrelevant and create your business plan based on the purpose you need it for. For instance, if you are building a business plan to get funding, the financial section of your business plan needs more emphasis.
- Research thoroughly: Every section of your business plan needs extensive research. Collect data about your market, industry, and competitors. Study their pricing strategies and market trends. Run surveys and talk to your potential customers to understand their needs and problems.
- Compose according to your objectives: It can be easy to lose sight of your objectives and get lost in the process of writing your business plan. To avoid that, make sure that your marketing strategies, operations, and financial goals are aligning with your business objectives.
- Ask for feedback: Once you finish creating a business plan, get your team and various experts to provide your feedback. This helps you revise and make adjustments to your plan before presenting it to an investor or client.
- Be prepared to answer questions: Before you present your startup business plan, it is crucial to prepare yourself to answer any questions related to your plan. It can be because the reader of your business plan may not understand a specific topic or want to test your knowledge. Regardless, keep yourselves informed and ready.
Download a sample startup business plan
Need help writing your business plan from scratch? Here you go; download our free startup business plan pdf to start.
It’s a modern business plan template specifically designed for your house-flipping business. Use the example business plan as a guide for writing your own.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
In conclusion, a business plan is an extremely handy device to get the best out of your efforts if you use it the right way. Planning your business involves consideration of several aspects that make up your business like the type of your industry, the stage of your business, the number of competitors, market size, etc.
Nonetheless, business planning always acts as a plus while tackling the challenges your business will face. It provides you with a proper structure to deal with your business problems head-on.
So, are you thinking of starting your own business? Then go ahead and start planning!
After getting started with Upmetrics , you can copy this startup business plan template into your business plan, modify the required information, and download your startup business plan pdf or doc file. It’s the fastest and easiest way to start writing a business plan for your new startup.
Related Articles On Business Plan Writing
- How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
- Deciding the Ideal Length of Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Your Business Plan
- Browse Through 400+ Free Business Plan Examples
- How to Design a Detailed Table of Contents for Your Business Plan
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Original text

Do you want to increase the odds that your business startup will be a success? Download this step-by-step business plan template to lay the groundwork for your new business.
Writing a business plan allows you to carefully think through every step of starting your company so you can better prepare and handle any challenges. While a thorough business plan is essential in the financing process, it's helpful even if you don’t need outside financing.
Creating a business plan can:
- Help you discover any weaknesses in your business idea so you can address them before you open for business
- Identify business opportunities you may not have considered and plan how to take advantage of them
- Analyze the market and competition to strengthen your idea
- Give you a chance to plan strategies for dealing with potential challenges so they don’t derail your startup
- Convince potential partners, customers, and key employees that you’re serious about your idea and persuade them to work with you
- Force you to calculate when your business will make a profit and how much money you need to reach that point so that you can be prepared with adequate startup capital
- Determine your target market and how to reach them
A detailed, step-by-step plan gives you a blueprint you can refer to during the startup process and helps you maintain momentum.
What this business plan template includes
Writing a business plan for a startup can sometimes seem overwhelming. To make the process easier and more manageable, this template will guide you step-by-step. The template includes easy-to-follow instructions for completing each business plan section, questions to help you think through each aspect, and corresponding fillable worksheet/s for critical sections.
After you complete the 11 worksheets, you will have a working business plan for your startup to show your SCORE mentor .
Business plan sections covered in this template:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Products and Services
- Marketing Plan
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organization
- Startup Expenses and Capitalization
- Financial Plan
The Appendices include documents that supplement information in the body of the plan. These might be contracts, leases, purchase orders, intellectual property, key managers’ resumes, market research data or anything that supports assumptions or statements made in the plan.
The last section of the template, “Refining Your Plan,” explains ways to modify your plan for specific purposes, such as getting a bank loan, or for specific industries, such as retail or manufacturing.
Complete the Business Plan Template for a Startup Business to create a working business plan for your startup.
Then, contact a SCORE mentor to review and refine your plan online or in person.
Quick Start Business Plan The aim of this module is to give you the tools, direction and ideas you need to build a business plan. If you're starting a business then a business plan is essential, because it forces you to think through your ideas and options.
10 Business Planning Tips for Starting a Business In this webinar, you'll learn 10 business planning tips to help you start your entrepreneurial journey on the right path.
Business Plan 101: Sales & Marketing The sales and marketing section of your business plan describes how you intend to sell your product. Learn what you should include in this section.
Copyright © 2024 SCORE Association, SCORE.org
Funded, in part, through a Cooperative Agreement with the U.S. Small Business Administration. All opinions, and/or recommendations expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the SBA.
Case Studies
Resource Hub
Featured post
What is a Pitch Deck? Tips, Examples, & Effective Templates

Explore our latest posts
Pitch Deck Funding Stages: How to Personalize Your Pitch Deck by the Stage

Building a Resilient Startup Culture in a Hybrid Work Environment

Innovative Revenue Models for Startups: Exploring New Ways to Monetize

Business Model Breakdown: Guide to Forming Startup Framework
Learn how to create a successful business model with our complete guide. Conduct market research, choose the right pricing model, and incorporate customer feedback for a sustainable and profitable business.
December 14, 2023
Starting your own business can be exciting, but also terrifying. You might have a great idea, but not know how to turn it into a profitable venture. This is where a business model comes in.
Introduction: Getting Started with a Startup Idea & Why You Need a Business Model?
A business model can help you define your ideas regarding who will purchase your product, how they will pay for it, and what features they desire. Additionally, it can assist you in estimating the amount of money required for starting up and determining if the company is worth the investment. This section will provide you with all the necessary information about what a business model is and how to create one for your validated startup idea .
What is a Business Model?
A business model is a set of systematic ways to create, deliver, and capture value. It is a blueprint for how your company will make money. A startup business model describes how a company earns income and profits from its operations. Startups mostly go for highly scalable business models that allow them to operate with few assets, zero heavy investments, and cheap capital expenditures.
In the digital age, the number of businesses that have a clear and well-tested business model is on the decline. This may be because it seems like you don't need one as long as you have an idea that has gone viral, or because people think they can create anything without having to worry about making money.
Importance of a Business Model
According to statistics, 90% of startups fail , with 10% failing within the first year and only 50% of businesses making it to their fifth year . A properly designed business model can help avoid these issues. A business model aids in targeting a company's consumer base and helps in the development of marketing plans, as well as income and expense projections, taking into account the various business models and clienteles. In order to learn about the potential accessible targets in the market, a business model should be designed. Understanding and choosing the appropriate business model allows companies to better understand the financial contributions they can make in the initial stage of their business. By evaluating a company's business model, a person can learn more about its products, as well as the business tactics it can use to grow and sustain future prospects. The other benefits of business models include the following:
- A good business model gives a company a competitive advantage and helps them understand their own operations better.
- A powerful business model gives the company a good reputation in the market and enables the owner to carve out a space for the company.
- Making a good business model from the outset leads to a well-established finance plan, which results in increased cash flows and rapid profit growth.
- A pre-developed startup business plan enhances the organization's financial stability.

Types of Business Models
In the market, startups are categorized into different types based on the business models they choose to pursue. However, not all of these models are necessarily profitable. Some of the most common business models used today are low-risk startup models.
Low Risk/High Reward Model
A low-risk model is one where there is minimal risk involved in starting up the company. These businesses require little capital to get started, have fewer obstacles to entry than other company models, and have high-profit potential, making them an excellent alternative for people who wish to start their own business without risking everything. For example, a company may sell its product with no upfront costs to them or their customers. This can include selling consultancy services, freelancing (selling skills), and much more. This type of model works great for people who want to sell products that they think will sell well in the market with very little investment on their part.
High Risk/High Reward Model
The most common business model is the high risk/high reward model, where the entrepreneur invests a lot of time and energy to build something that they hope will be successful. To achieve such a high degree of accomplishment, these people had to take significant risks. Successful entrepreneurship is inextricably linked to taking risks. Regardless of how strong your cash flow is or how much effort or time you put in, the end result might be positive or negative. You must be prepared for the physical, financial, and psychological stress that comes with establishing a business and keep believing in yourself and working hard to see the fruit of your efforts. This is what you typically see with startups like Facebook or Microsoft. These tech giants undertook high risks and invested their time and resources in creating exceptionally unique and highly demanded platforms. Taking risks surely leads to miraculous evolutions in the history of the business world.

Best Startup Models
There are two different types of best startup models:
- Bootstrapping is when an entrepreneur starts a business with their own time, skills, and resources. This self-funded business does not rely on the support of common financing methods, such as crowdfunding, investment, or loans from banks.
- Scaling up is when an entrepreneur starts with a small business and then invests in making it bigger. To scale a business means opening the door to more work duties and creating opportunities while remaining cost-effective and meeting your company's demands without suffering or overstretching. It's all about adjusting to the increasing workload, clients, or users, and then delivering.
Perks of Choosing Bootstrap Business Model
- Retaining Full Ownership: This business model allows the owner to fully own their business with zero shares in equity. When anyone starts a business based on investors' funding, they often ask for a huge share in equity and have a say in decision making. This is why Bootstrap is ideal in the longer run. You have control, and you get to do whatever you want.
- Gets Rid of Unnecessary Burden: When you start a business through a loan or investment, there is a burden on your shoulders to return it. Instead of designing a complete and long-term lasting business model, you focus on earning revenue even if that disturbs the essence of your business. However, with the bootstrap business model, you feel a sense of freedom. You focus on maintaining the essence of your business and strategically develop ways to increase cash flows.
- Empowers Business Owner: Starting a business on your own empowers a person. Building it from scratch highly motivates a person to keep going and gain success. We recommend following our checklist for starting a business .
Perks of Using a Scaling Business Model
- Creates Efficiency: When a business is ready to expand at the right time, it efficiently brings in more profit for the corporation. They are able to deal with different circumstances while still remaining rigorous.
- Creates Growth Consistency: When the business has grown into a stable state, the owner makes sure to scale it to keep the growth factor consistent. Though it seems like staying in the same state is safe, businesses don't last long if they aren't growing. Scaling a business ensures that growth is gradually increasing with time. The owner makes sure never to stop at some level; they keep taking new steps on the ladder while ensuring they don't trip at any step.
- Adaptable to Tough Situations: Creating flexibility ensures that the business is able to adapt to tough situations and thrive nonetheless. Businesses not only scale for growth but also to create new opportunities for income generation. The market is ever-changing, and one cannot entirely depend on a single business to maintain sustainability. Scaling your business to another aspect makes your corporation more adaptable to unplanned events. If a part of your business is disturbed by a change in the market, you can smoothly earn from another domain of your business.

Sizes of Companies and Their Typical Business Models
Different types of companies operate at varying scales in different industries. Some start-ups operate in the early stages of their life cycle, for example, operating small brick-and-mortar shops but not yet an online store. Others begin with an online store and later expand to include physical stores, while some might take the opposite approach. There are also companies that do not have either brick-and-mortar or online stores, and instead focus on other channels like social media. A start-up can be of various types, but the most common categories are:
- Technology-based
- Business-to-business or B2B
- Business-to-consumer or B2C
Technology-Based Start-ups
Technology start-ups focus on developing a new product or service with the aim of disrupting an existing market. Since technology is in popular demand nowadays, tech start-ups are now focusing more on innovativeness, scalability, and growth.
Business-to-Business (B2B)
Market research for startups is crucial in identifying potential customers and understanding their needs. A business-to-business start-up offers a product or service for sale to other businesses. Some B2B firms produce a component of a final product and sell it to distributors, who then sell it to their own customers. Moreover, a business-to-business deal can also occur when a company produces a product used as a component in another company's product. For example, Intel sells Apple processors for use in the Macbook Pro.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
Business-to-consumer (B2C) refers to the process of selling products and services directly to customers who are the end-users of the company's products or services. Consumer start-ups sell products and services directly to consumers. Some early-stage start-ups will have an initial product or service that they offer for free. They do this to acquire customers and improve the product before taking it live. They may also offer their customers other products and services in addition to their core offerings in order to generate revenue while they build up their main offering.
How to Choose the Perfect Business Model for Your Start-up?
Choosing the right business model is not easy. That is why there are tools available to help you with this choice. One such tool is the Business Model Canvas, which is a diagram used to create a visual representation of a start-up's business model. A blank canvas can be found online and needs to be filled in with five important components: value proposition, customer segments, key activities, channels, and revenue streams. Another tool is the St. Gallen Business Model Navigator, which can help you select the best model for your business needs and provide templates for all models you might need when starting your own company. If you want to start raising money, you should know how to make the most out of your pre-seed funding round.

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Developing a Business Model
Developing a business model can be tricky, especially for first-time entrepreneurs. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when developing a business model:
1. Failing to Understand Your Target Market
One of the biggest mistakes entrepreneurs make when developing a business model is failing to understand their target market. It's important to conduct market research and gather data about your target audience's needs and preferences before developing your business model. Without this information, you risk developing a product or service that no one wants or needs.
2. Focusing Too Much on Features and Not Enough on Benefits
Another common mistake entrepreneurs make is focusing too much on the features of their product or service and not enough on the benefits. Features describe the characteristics of your product or service, while benefits describe how those characteristics will help your target audience. By focusing on benefits, you can create a more compelling value proposition and increase the chances of success for your business. It is important to consider these benefits when conducting startup financial modelling and projecting your revenue streams.
3. Not Validating Your Business Model
Many entrepreneurs make the mistake of assuming that their business model will work without testing it first. It's important to validate your business model by conducting market research and getting feedback from potential customers. This can help you identify any flaws in your business model and make adjustments before launching your business.
4. Failing to Plan for the Future
Another common mistake entrepreneurs make is failing to plan for the future. It's important to consider how your business model will evolve over time and make plans for growth and expansion. This can help you stay ahead of the competition and ensure the long-term success of your business.
5. Ignoring Financial Projections
Financial projections are an important part of developing a business model. They help you estimate how much money you will need to start and grow your business, as well as how much revenue you can expect to generate. Failing to consider financial projections can lead to a lack of funding or an inability to sustain your business over time.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can develop a strong and effective business model that will help you achieve your goals and succeed in the market.

How to Test and Validate Your Business Model
Before launching your business, it is important to ensure that your business model is viable and will be successful in the market. Here are some steps to test and validate your business model:
1. Conduct Market Research
Market research is crucial in validating your business model. It involves gathering and analyzing data about the market, potential customers, and competitors. By conducting market research, you can gain valuable insights into the needs and preferences of your target audience, as well as identify gaps in the market that your business can fill.
2. Build a Prototype
Building a prototype allows you to test your product or service in the market and get feedback from potential customers. This can help you identify any issues or areas for improvement before launching your business.
3. Conduct User Testing
User testing involves getting feedback from potential customers on your product or service. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of market research. By understanding what your customers want and need, you can develop a product or service that will meet their needs and stand out in the market.
4. Analyze Your Financial Projections
Analyzing your financial projections is crucial in validating your business model. This involves creating a financial plan that outlines your expected revenue and expenses, and then comparing it to industry benchmarks and competitors. By doing so, you can identify any potential issues and adjust your business model accordingly.
5. Seek Feedback
Seeking feedback from mentors, investors, and other business owners can be invaluable in validating your business model. They can provide valuable insights and advice based on their own experiences, which can help you identify potential issues and adjust your business model accordingly.
By following these steps, you can test and validate your business model to ensure that it is viable and will be successful in the market.

Tips for Creating a Successful Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is a popular tool for creating a visual representation of a start-up's business model. Here are some tips for creating a successful Business Model Canvas:
1. Start with a Value Proposition
The first component of the Business Model Canvas is the value proposition. This describes the unique value that your product or service provides to your customers. It's important to start with a clear and concise value proposition that communicates your product or service's benefits in a compelling way.
2. Identify Your Customer Segments
The next step is to identify your customer segments. This involves understanding who your target customers are and what their needs and preferences are. By doing so, you can tailor your product or service to meet their specific needs and develop targeted marketing strategies to reach them.
3. Define Your Key Activities
The key activities component of the Business Model Canvas describes the activities that are necessary to deliver your product or service to your customers. This includes everything from product design and development to marketing and sales. It's important to identify the key activities that are essential to your business and focus on optimizing them for maximum efficiency.
4. Choose Your Channels
The channels component of the Business Model Canvas describes how you will reach your customers. This includes everything from traditional marketing channels like advertising and public relations to digital channels like social media and email marketing. It's important to choose the channels that are most effective for reaching your target customers and focus on optimizing them for maximum effectiveness.
5. Determine Your Revenue Streams
The revenue streams component of the Business Model Canvas describes how your business will make money. This includes everything from product sales to advertising revenue. It's important to identify the revenue streams that are most important to your business and focus on optimizing them for maximum profitability.
6. Consider Your Cost Structure
The cost structure component of the Business Model Canvas describes the costs associated with running your business. This includes everything from product development and marketing to overhead costs like rent and salaries. It's important to identify the costs that are most important to your business and focus on optimizing them for maximum efficiency.
7. Keep it Simple and Clear
Finally, it's important to keep your Business Model Canvas simple and clear. Avoid using jargon or technical language that may confuse your audience. Instead, focus on communicating your business model in a way that is easy to understand and compelling to your target customers.
By following these tips, you can create a successful Business Model Canvas that effectively communicates your business model and helps you achieve your goals.

The Role of Market Research in Developing a Business Model
Market research is a crucial step in developing a successful business model. It involves gathering and analyzing data about the market, potential customers, and competitors. By conducting market research, you can gain valuable insights into the needs and preferences of your target audience, as well as identify gaps in the market that your business can fill.
Market Analysis
The first step in market research is to conduct a market analysis. This involves gathering data about the overall market size, growth trends, and key players in the industry. By understanding the broader market landscape, you can identify opportunities and potential challenges for your business.
Customer Research
Once you have a good understanding of the market, the next step is to conduct customer research. This can involve surveys, focus groups, or other forms of market research to gather information about the needs and preferences of your target audience. By understanding what your customers want and need, you can develop a product or service that will meet their needs and stand out in the market.
Competitive Analysis
In addition to understanding the broader market landscape and the needs of your target audience, it's also important to conduct a competitive analysis. This involves gathering data about your competitors, including their strengths and weaknesses, pricing strategies, and marketing tactics. By understanding your competitors, you can identify ways to differentiate your business and develop a unique value proposition.
Iterative Process
Market research is an iterative process, meaning it requires ongoing analysis and adaptation. As your business grows and evolves, it's important to continue gathering data and refining your business model. By staying up-to-date with market trends and customer needs, you can ensure that your business remains competitive and successful.
In conclusion, market research is a critical step in developing a successful business model. By conducting a market analysis, customer research, and competitive analysis, you can gain valuable insights into the needs and preferences of your target audience, as well as identify opportunities and potential challenges for your business. By making market research an ongoing process, you can ensure that your business remains competitive and successful in the long run.

How to Pivot Your Business Model When Things Aren't Working Out
Sometimes, even the best-laid business plans don't work out as expected. In these situations, it may be necessary to pivot your business model in order to adapt to changing market conditions or customer needs. Here's how to do it:
1. Identify the Problem
The first step in pivoting your business model is to identify the problem. What is not working in your current business model? Is it a lack of demand for your product or service? Are you not generating enough revenue to sustain your business? Are there new competitors in the market that are taking away your customers?
2. Brainstorm Solutions
Once you've identified the problem, it's time to brainstorm solutions. What changes can you make to your business model to address the issue? Can you change your target market or customer segments? Can you offer new products or services that better meet customer needs? Can you change your pricing model to better reflect the value of your offerings?
3. Test Your Ideas
Before making any major changes to your business model, it's important to test your ideas. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of market research. Determine what your customers want and need, and test different ideas to see what works best.
4. Implement the Changes
Once you've tested your ideas and determined what works best, it's time to implement the changes. This may involve rebranding your company, changing your product offerings, or targeting a new customer segment. It's important to communicate these changes to your customers and stakeholders so that they understand why you are making them.
5. Monitor the Results
After implementing the changes, it's important to monitor the results. Are you generating more revenue? Are you attracting new customers? Are you meeting your business goals? If not, it may be necessary to pivot again or make further adjustments to your business model.
Remember, pivoting your business model is not a sign of failure. It's a necessary step in adapting to changing market conditions and customer needs. By identifying problems, brainstorming solutions, testing your ideas, implementing changes, and monitoring the results, you can successfully pivot your business model and ensure the long-term success of your company.

The Importance of Flexibility in Your Business Model
Flexibility is an essential aspect of any successful business model. In today's ever-changing market, it is crucial to be able to adapt quickly to new technologies, customer needs, and market trends. A flexible business model will allow you to pivot your strategy when needed and take advantage of new opportunities as they arise.
One of the most significant benefits of a flexible business model is the ability to respond to customer feedback. By listening to your customers and their needs, you can adjust your product or service offerings to better meet their demands. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
A flexible business model can also help you stay ahead of the competition. By continually innovating and adapting to new technologies and trends, you can differentiate yourself from other businesses in your industry. This can give you a competitive edge and help you attract new customers.
In addition to responding to customer needs, a flexible business model can also help you navigate economic downturns and other unexpected events. By being able to pivot your strategy and adjust your offerings, you can better position your business for success even in challenging times.
Overall, building flexibility into your business model is essential for long-term success. By being willing to adapt and change as needed, you can stay ahead of the competition and better meet the needs of your customers.

Examples of Successful Business Models in Different Industries
The following are some examples of successful business models in different industries that have been able to grow and sustain in today's competitive market.
Subscription Box Model
Subscription boxes are becoming increasingly popular in the e-commerce industry. This business model involves sending customers a box of products on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly, for a set price. The products in the box are curated according to the customer's preferences. Birchbox, a beauty subscription box, and Dollar Shave Club, a grooming subscription box, are two examples of companies that have successfully implemented this business model.
Freemium Model
The freemium business model offers customers a basic version of the product or service for free, with the option to upgrade to a premium version for a fee. This model is commonly used in the digital industry, particularly with mobile apps and online tools. Dropbox, a cloud storage service, and Spotify, a music streaming platform, are two examples of companies that have successfully used this business model.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Model
The DTC business model involves companies selling their products or services directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels. This model has become increasingly popular in the fashion industry, with companies like Warby Parker, an eyewear company, and Everlane, a clothing company, successfully implementing this approach.
Platform Model
The platform business model involves creating a platform that connects buyers and sellers, earning revenue through transaction fees or advertising. Airbnb, a home-sharing platform, and Uber, a ride-sharing platform, are two examples of companies that have successfully implemented this business model.
Membership Model
The membership business model involves charging customers a fee to gain access to exclusive content, products, or services. Amazon Prime, a membership program that offers free shipping and access to streaming services, and LinkedIn Premium, a subscription service that offers additional features for job seekers, are two examples of companies that have successfully implemented this business model.
Razor-Blade Model
The razor-blade business model involves selling a product at a low cost, then making a profit on the consumable products required to use the product. This model is commonly used in the printer and shaving industries. Gillette, a shaving company, and HP, a printer company, are two examples of companies that have successfully used this business model.
Crowdfunding Model
The crowdfunding business model involves raising funds from a large number of people, typically through an online platform, to finance a project or product. Kickstarter, an online crowdfunding platform, and Indiegogo, a similar platform, are two examples of companies that have successfully implemented this business model.
Pay-What-You-Can Model
The pay-what-you-can business model allows customers to pay what they can afford for a product or service. This model is commonly used in the restaurant industry, with some restaurants allowing customers to pay what they can for a meal. Panera Bread, a bakery-cafe chain, has implemented this model through its Panera Cares program.
These are just a few examples of successful business models in different industries. By understanding these models and how they have been implemented, entrepreneurs can learn how to create a sustainable and profitable business model for their own venture.
How to Choose the Right Pricing Model for Your Business
Choosing the right pricing model for your business depends on several factors, including your target audience, industry, and business goals. Here are some tips to help you choose the best pricing model for your product or service:
- Know your target audience : Understand your target audience's willingness to pay and what they value in your product or service.
- Research the competition : Analyze your competitors' pricing strategies and determine how you can differentiate yourself in the market.
- Consider your business goals : Determine what your revenue targets are and which pricing model will help you achieve them.
- Test and iterate : Don't be afraid to experiment with different pricing models and adjust as necessary based on customer feedback and market conditions.
Different Pricing Models
There are several pricing models that you can use to monetize your product or service, including:
- Cost-plus pricing : This model involves adding a markup to the cost of producing your product or service to determine the selling price. It is a straightforward approach that ensures you cover your costs and make a profit.
- Value-based pricing : This model involves setting a price based on the perceived value of your product or service to the customer. It requires a deep understanding of your target audience and their willingness to pay.
- Subscription pricing : This model involves charging customers a recurring fee for access to your product or service. It is a popular model for software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies and other businesses that offer ongoing services.
- Freemium pricing : This model involves offering a basic version of your product or service for free while charging for premium features or services. It is a common model for mobile apps and online tools.
- Dynamic pricing : This model involves setting prices based on current market conditions, demand, and other factors. It is commonly used in the airline and hotel industries.

How to Monetize Your Product or Service with Your Business Model
Creating a successful business model requires not only defining your value proposition and target customer segments but also determining how you will generate revenue. In this section, we will explore various ways of monetizing your product or service and how to choose the right pricing model for your business.
Once you have chosen the right pricing model for your business, it's time to start monetizing your product or service. Here are some ways to generate revenue:
- Direct sales : Sell your product or service directly to customers through a website, online marketplace, or physical store.
- Affiliate marketing : Partner with other businesses and earn a commission for promoting their products or services to your audience.
- Licensing : License your product or service to other businesses for a fee.
- Advertising : Sell advertising space on your website, mobile app, or other digital platform.
- Sponsorship : Partner with other businesses to sponsor your product or service in exchange for exposure to your audience.
Monetizing your product or service is a crucial aspect of creating a successful business model. By understanding your target audience, researching the competition, and choosing the right pricing model, you can generate revenue and build a sustainable business.
The Role of Customer Feedback in Developing a Business Model
Customer feedback is a critical component of any successful business model. It provides valuable insights into how customers perceive your product or service, what they like and dislike, and what changes they would like to see. Incorporating customer feedback into the development of your business model can help ensure that you are meeting the needs of your target audience and delivering a product or service that they truly value.
One effective way to gather customer feedback is through surveys. Surveys can be conducted online or in-person and can provide valuable information about customer preferences, pain points, and satisfaction levels. Another method is to engage with customers through social media or email and encourage them to share their thoughts and opinions.
Once you have gathered customer feedback, it is important to analyze and interpret the data. Look for patterns and trends in the feedback to identify common themes and areas for improvement. Use this information to make informed decisions about how to adjust your business model to better meet the needs of your customers.
It is also important to continue gathering feedback and making adjustments over time. The needs and preferences of your customers may change, and your business model should be adaptable to these changes. By staying attuned to customer feedback and making adjustments as needed, you can ensure that your business remains relevant and successful in the long term.

Developing a successful business model requires careful consideration of several key factors. Conducting market research, understanding your target audience, choosing the right pricing model, and incorporating customer feedback are all essential components of creating a sustainable and profitable business. By following the tips and examples outlined in this guide, entrepreneurs can develop a strong and effective business model that will help them achieve their goals and succeed in the market.
Key Takeaways
A successful business model starts with a clear and concise value proposition that communicates your product or service's benefits in a compelling way.
Identifying your target audience and tailoring your product or service to meet their specific needs is crucial for success.
It's important to choose the channels that are most effective for reaching your target customers and focus on optimizing them for maximum effectiveness.
Choosing the right pricing model for your business depends on several factors, including your target audience, industry, and business goals.
Customer feedback is a critical component of any successful business model. It provides valuable insights into how customers perceive your product or service, what they like and dislike, and what changes they would like to see.
.webp)
Table Of Content
Explore Our Services

Explore our top-notch pitch deck service
We help discerning startups and growing businesses create powerful pitch decks that attract investors and secure big deals.

Subscribe to our newsletter and keep in touch with us
An error has occurred somewhere and it is not possible to submit the form. Please try again later.
Only available to newsletter subscribers!
Answers, To The Most Asked Questions
What is a business model canvas, what is market research, and why is it important for developing a business model, what are some common pricing models for monetizing a product or service, how important is customer feedback for developing a successful business model, how can a business model be adapted over time to better meet the needs of customers, you may like.

10 Best Cyber Security Startup Ideas
Discover the most promising cybersecurity startup ideas for 2023. Drive innovation, meet market demands, and elevate digital safety. Start your journey now!
Read Article

10 Best Software Startup Ideas
Discover the hottest software startup ideas for 2023. Dive into trends, market potentials, and launch strategies to kickstart your entrepreneurial journey!

10 Pros and Cons of Venture Capital You Should Know
Explore the dynamics of venture capital. Dive into its benefits, potential pitfalls, and learn how it can shape startup trajectories. Make informed decisions with our guide.

10 Unique Clothing Business Ideas
Discover groundbreaking fashion business concepts for 2023! From sustainability to tech trends, master the art of differentiating your brand. Dive in now!
discover the menu
Get Ready For Funding
Pitch Deck Service
Pitch Training
Financial Modeling
Investor Outreach
Fundraising Consultant
We normally respond within 24 hours
View all our blog articles
- Best Countries for a Business
- How to Do Market Research
- Define Your Target Market
- How to Write a Business Plan
- Key Elements of a Business Plan
- How to Buy a Business
- What is a Pitch Deck?
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Best Business Opportunities
- Best Small Business Ideas
- Lucrative Online Business Ideas
- Side Ideas for Women
- Small Scale Business Ideas
- Best Tech Startup Ideas
- App Ideas for Start-Ups
- Small Business Ideas in India
- Business Tycoons to Learn From
- Most Innovative Entrepreneurs
- Successful Women Entrepreneurs
- Best Business Books of All Time
- Startup Pitch Deck Examples
- Successful Social Entrepreneurs
- Top Entrepreneurs of India
- Best Online Legal Services
- Small Business Software
- Apps for Daily Operations
- Business Name Generators
- Mission Statement Generators
- Privacy Policy Generators
- Start a Profitable Online Store
- Start a Dropshipping Business
- Start a Consulting Business
- Start a Podcast: 10-Step Tutorial
- Create a Successful Online Course
- How to Sell on Etsy
The 15 Minute Business Plan: Business Model Canvas for Validating Your Startup Idea Fast
If you have ever thought of starting a new business or working on a tech startup idea , then you must definitely have come up with some sort of a plan.
At least in your mind, you may be thinking of a way to execute your idea and achieve the goal you are looking for from your business.
But how should you plan and how much should you plan? After all, with so much uncertainty and ambiguity what if your plan really doesn’t materialize?
Don’t worry, we are here to help you.
If you are brainstorming about the key aspects of your business and don’t know where to begin or if you are an existing manager who needs a better view of your current business, then you must read this article.
Instead of coming up with a 500 page document, articulating each and every aspect of your business plan, there is a wonderful standard template that applies wonderfully to all different kinds of businesses.
Be it an online business like blogging or ecommerce, or a manufacturing based business, retail or aviation, all types of businesses can use the elegant ‘Business Model Canvas’.
A Business Model Canvas will not only save you the time or hassle of complicated planning, but also provide you a brilliant single page look of your business that you can then use to analyse various aspects of it.
But what is Business Model Canvas?
Let’s dive straight in.
What’s the Business Model Canvas?
“ A Business Model Canvas is a tool used to visualize all the building blocks when you want to start a business, including customers, route to market, value proposition and finance. “ – eship.ox.ac.uk
In fact, a Business Model Canvas divides all the key activities, internal processes and stakeholders of a business into 9 building blocks , each representing an important area or aspect of business.
Following are the nine building blocks and the key questions they answer.
- Customer Segments : Who are the key customers of your business? And what are their key characteristics and needs?
- Value Propositions: Why do customers buy your product or service? What is the key benefit that your business offers?
- Channels : How are these benefits communicated to your customers and how is the product or service sold or delivered and why?
- Customer Relationships : What are the key touch points between you and your customers? And how do you connect with them throughout their journey?
- Revenue Streams: How does business actually earn money from various value propositions?
- Key Activities: What are the key things that your business strategically does to deliver this proposition?
- Key resources : What are the assets that business requires in order to stay competitive and create value?
- Key Partnerships: What are the external entities or stakeholders that are key to delivering the product and service to your customer? What are some of the partners to whom you have outsourced certain activities to focus more on your core work?
- Cost Drivers: What are the major cost drivers for your business and how are they linked to your revenue?
Here is an example of a simple Business Model Canvas for an ice cream vendor.

These 9 blocks are essential in order to create, capture and deliver value to your customers and affect each other in various ways.
In fact, a change in one of these building blocks may affect other areas and thus looking at them together will give you a sense of what happens in one area if you change another.
For example, say you are in an ecommerce business selling physical products. Today you manufacture your products yourself, but considering the scale you want to achieve you want to outsource manufacturing to an external vendor.
This may affect your key partnerships, cost structure, key resources and key activities. You can then clearly visualize all the changes that such a decision would require.
Well, this gives you a basic idea of what a Business Model Canvas is and its basic template.
But why should you really use a Business Model Canvas and not some other method? And how will it fit in what you want to do?
Why You Should Use the Business Model Canvas. And Not a Business Plan.
A business plan is like a blueprint of the business with detailed business models and financial projections, typically running into hundreds of pages.
On the other hand a Business Model Canvas is like a single page template with 9 building blocks that are key to delivering value to your customers.
So which one should you use and why?
If you are just starting a business or have started one already and are in a growth phase or an environment that is dynamic, we would recommend using a Business Model Canvas and not a business plan .
In fact, today Business Model Canvas is being used for a variety of reasons. And almost 36% of people who use it, do it for an entirely new business.

Here are a few reasons why using a business model makes better sense than using a business plan.
1. Business Model Canvas is Built for Handling Change
A Business Model Canvas represents all the key aspects of your business in a very simple fashion on a one page model.
If there is any change that happens in any one part of the model then you can easily visualize the trickling effect and understand what other blocks will be affected.
This way you can easily change and adjust everything in one place . This is important because when you are starting out or working on a new problem in your existing business, there is great deal of uncertainty.
Modern day business work in an iterative manner. That is, they start with certain assumptions and then as things become clearer they keep on adjusting according to the changing environment.
A business plan on the other hand requires you to put in a lot of work upfront and come up with projections that may or may not turn out to be true.
Adjusting the whole business plan is also tough as various parts are present in different sections of a lengthy document. It is also possible that you may miss out on understanding how a change in part affects the other.
2. Business Model Canvas is a Simple and Commonly Understood and Proven Template
Do you know, companies like Microsoft and Mastercard actually use Business Model Canvas.
Not only that it has proved to be an important tool for startups as well.
The key point here is that this template is not only simple but also well understood by a lot of people hence it facilitates great discussion .
If you want to discuss some key points to strategize or propose some business model to your colleagues then it surely makes a lot of sense to use the Business Model Canvas.
The issue with a 400+ page document is that you tend to lose focus in skimming through such a heavy file.
And also, there are so many different templates of business plans available and some sections of those may not really make sense for your business.
On the contrary, all the 9 blocks of a Business Model Canvas are inherent and applicable to almost all business models.
This leads to much better collaboration and understanding, better teamwork and a structured conversation.
In fact, according to a research , with a score of 3.5/4 better strategizing and sharing a common language were the top two areas that people believed following a Business Model Canvas helped them in.

3. Business Model Canvas Reduces Risk of Failure
When you look at all aspects of your business in a structured manner in a single page template, you are much better able to understand the bonds or pillars that keep your business stable.
Running a successful business involves both strategic planning and efficient implementation.
In order for both these to work, different departments, areas, resources and customers have to be considered and a balance has to be created.
To avoid the risks of failure, it makes a lot of sense to have a robust Business Model Canvas.
For example, consider that you want to shift your business from offline to online in light of the recent pandemic and your long term vision.
Just cataloging your products and building a website will not make your existing and new customers come to your business.
You may have to revisit your customer segments who now have to be digitally savvy and your channels. Your touch points with your customer or the Customer Relationship block will also evolve.
Since, you can see all these aspects you are now better prepared to execute the plan and make sure that all necessary factors are taken care of while evolving your model.
Now, that you understand the importance and usage of a Business Model Canvas, you need to understand how to really create a Business Model Canvas, and how each of the 9 building blocks can be thought of and filled for best results.
It is important to give careful thought to each of these. Don’t worry we will help you out.
Proceed to the next section of the article.
Practical Business Model Canvas Walk-through
Step 1: customer segments.
Arguably, the most important stakeholders for your business are your customers.
Irrespective of whether you start an online business to earn money , or a business with a physical presence, knowing your customers comes first.
And rightly so, the process of building your Business Model Canvas begins with identifying your customers.
The first step in this exercise is dividing your prospective customers into groups with similar features known as segments .
This is necessary because different groups or segments may have very different needs and hence the product/service that would be most relevant for them may be very different.
Not just for the design of the product or service, but segments are also important when you plan about your marketing communication.
For example, say someone who buys your product in small packs very often may be targeted differently than someone who buys high volumes of your product infrequently.
So, how to go about segmentation.
Deciding between B2C or B2B model
You have to first identify, whether you are going to be in the Business to Business (B2B) or a Business to Consumer (B2C) model .
Typically in a B2B business your customers are other businesses, while in B2C your customers are individual consumers .
The behavior and characteristics of these two types of customers are very different.
B2B customers follow a much more stringent and rational approach towards buying than individual customers and B2B buying is almost never based on impulse.
There are usually clear requirements regarding what a B2B customer is looking for in the product.
On the other hand, a B2C business is mostly driven by brand awareness and the decision making cycle for buying is also much shorter.
In terms of the number of buyers, you may be able to run a very profitable business with a handful of customers in B2B, but you will require a larger base when it comes to B2C.
| B2C | B2B | |
|---|---|---|
| Customer type | Individuals | Business entity |
| Sales Cycle | Short | Long |
| Key Drivers | Brand Awareness | Expertise, recommendations for similar work, product fit |
| Revenue per user | Low | High |
| Examples | Retail, consumer blogs, ecommerce | Enterprise Software, Consulting |
If you are already an expert in a particular field or have come up with a SaaS product that enterprise can use, you can be in B2B, but if you want to play on brand awareness and individual engagement, then B2C may be a fit for you.
The segmentation strategy will differ according to whether you are in B2B or B2C business. To segment your prospective customers you will need something called a segmentation variable.
Segmentation variables are the basis on which you will divide your customers.
Choosing a Customer Segmentation Variable
Broadly, there are two ways in which you can divide your audience.
Demographics
Psychographics
The number and characteristics of people who live in a particular area or form a particular group, especially in relation to their age, how much money they have and what they spend it on. – Definition of Demographics by Cambridge University
Demographics will help you understand the basic features or characteristics of your customers and are typically easy to understand and collect.
For example, you can source demographic data from the US Census Bureau and the Pew Research .
Alternatively, you can collect this data through primary research, surveys and questionnaires by asking your customers to fill up forms .
If you are in an online business and want to improve your SEO or find out what are the demographics of users who are searching for relevant keywords, we recommend a tool called Demographics.io .
For example, say you own a website that publishes content related to writing blogs. A search for the keyword ‘blog’ on this site tells you that around 27% of people searching for this keyword are between the age group 25-34 and more than 54% are females.

For a B2B business your segments may be something like Industry type, turnover, geography, number of employees etc.
While demographics are an important indicator of some things, for a deeper understanding of your customers you would need a more nuanced understanding of their motivations and behavior.
Market research or statistics classifying population groups according to psychological variables (such as attitudes, values, or fears) – Definition of Psychographics by Merriam-Webster
Here are some of the questions that psychographics can answer for you.
- How do your customers spend most of their time?
- What do they do on weekends?
- What are their hobbies and interests?
- What are their religious inclinations?
- Are they heavy users or light users of your products?
Psychographics are extremely important in order to add value to your customers.
For instance, the same product or service may mean different things for different people and the motivations behind using them may vary.
For example, some people may eat healthy food in order to feel energetic throughout the day, others may be doing it to support their gym routine while some others may just want glowing skin.
Understanding your customers this way will not only help you tailor your products or service according to their specific needs but also help you to create your communication in a way that is the most effective.

Now after this exercise you need to understand your target segments.
Choosing your target customer segments
Two extremely important things that would determine whether you earn money from your customers or not are:
- Ability to pay
- Willingness to pay
Ability to pay depends on the income of individuals or businesses that you want to engage with and can be more or less determined from the demographics data.
On the other hand willingness to pay can be estimated on the basis of the psychographics and whether your product or service has a major value add for the lives of your customers.
Some other factors to consider are:
- High audience revenue potential : The market size for your chosen segment should be high.
- Expected growth rate over time: The growth rate of usage and market over time.
- Customer loyalty: The current loyalty levels of customers to available products.
- Attainable Market Share: What amount of market share is achievable for you?
- Market Profitability: Is there enough margin that you can obtain from customers that justifies your cost and goals?
In a nutshell, you would ideally want to be in a market that has substantial demand, which is expected to grow and you can make the existing customers switch to your product because you serve their needs better, at the same time earning profit.
One important thing to understand is that it is possible that you target different segments, this is especially true if you operate a multi sided platform .
For example, say you own a marketplace platform where you earn through your customers by charging them a subscription fee and charge a fixed price from your sellers for advertisements.
Here both end consumers and sellers become your customer. In order for the platform to succeed, you would need to pay close attention to both these stakeholders.
We would recommend, if you are just starting out, to keep your focus on one particular segment.
For instance, say you want to start a blogging business and are deciding on the niche , it is always better to cater to particular segments. This will increase your chances to earn money and your customers are more likely to draw value and become loyal.

Possibly you would be certain about your target customer segments by now, so you can fill out these details clearly in your Business Model Canvas.
For instance, say you are opening a romantic restaurant targeted at young couples and the theme of the restaurant is adventure and will be situated in California, then your target segment could be…
“Young men and women aged between 25-40, who reside in California and are fond of adventure”.
Step 2: Value Propositions
A value proposition is like a simple statement of benefits that your target customers get from your products or services.
This is extremely important because your customers use your products or service depending on how strong your value proposition is.
If you are starting a new business then this becomes even more important because you would want your customers to switch from your competitors to you.
Only if you meet their needs better and they find more value in what they pay you than your competitors will they think about switching.
So, how do you begin?
Understand Customer Problems and Competition
First thing is to understand the problems faced by your customers .
The idea is to answer and resolve the most pressing issues faced by your customers effectively.
Once you narrow down on the key problems and needs of the customer, study your competition to understand what needs or problems they are solving well and where the gap lies.
For example, say you are starting an ecommerce business and want to sell physical products like portable bluetooth speakers.
One great place to understand the demands of your customers and the performance of your competitors is Amazon.com .
You could develop a good understanding of your competition from the reviews section.
In the image, you can clearly see where your prospective competition is good and where customers expect better.
The number of reviews also give you an indication of how much demand already exists for the product.

In fact, it can provide you information on a lot of categories all the way from electronics to baby care and from automotive parts to groceries.
All you have to do is search for the product you want to research on and study the results.
Here is the list of top product categories on Amazon.com.

Another way to research demand and competition is through keywords .
Estimating Consumer Demand and Competition Through Keywords
The internet today gives you a lot of information about what people are searching.
Do you know, around 48% of online shoppers begin their online journeys through search.
Thus, understanding what keywords are being searched for the most and the competition for advertisements and seo for those keywords is a great first step to estimate demand.
One tool we recommend is SEMRush.com .
This tool not only gives you an idea of the total volume of search, but also of how much competition exists for the keyword.
For instance, searching for the keyword ‘bluetooth speakers’ clearly gives the exact volume of search.
The ‘keyword difficulty’ and ‘Com.’ metrics tell you how difficult it would be for you to rank in the first page of Google search if you are new to business.
In our case keyword difficulty level is 92% which is on the higher side.

Now that you know the key questions your customers are asking and what is required in order to beat the competition, next is to decide how you are going to differentiate yourself.
Building a Strategy to Make Your Customer Switch to Your Product/Service

To make the customers switch to your products you can choose one of the four quadrants from the above matrix.
A narrow focus means that you concentrate on a particular segment or niche rather than a mass market.
If you are just starting out, it is better to focus on a narrow approach because you will be able to meet the needs of a particular segment better.
The other option you have to choose from is whether you want to beat your competition on price or by offering a better product .
You can make the customers switch to your product by selling the available product in the market at a lesser price. But to follow this strategy you would either need scale or a way to produce your goods and services at a lesser cost than the competitor.
Hence, we would suggest to first differentiate your product and give benefits and features that are not provided in the market by your competitors.
Writing a Value Proposition Statement
Now that you have a fair idea of what your consumer needs and how you will beat the competition.
You have to come up with clear value proposition statements .
If you are catering to multiple target customer segments, then you should have a clear and simple value proposition mapped to each of these customer segments in your Business Model Canvas.

For instance, say you start a blog that offers tips on making regular food healthy.
The typical target customer segments you have are the people who want to build muscles and stay at home moms.
Now these are two very different segments and your value proposition would be very different.
A good value proposition statement would look like this:
We help stay-at-home moms lose 14 pounds of fat in 45 days without having a jojo-effect .
We help muscle building enthusiasts reduce fat by 5 percent in 60 days without lowering energy .
Now you just have to enter these in the value proposition segment of your business model canvas.
Here is a quick checklist to validate if your value proposition is good or not.
- Are the benefits explicit and clearly stated?
- Is the target customer segment clearly identified?
- Is the value proposition clear and simple?
- Is the value proposition supported by evidence of demand?
- Is the value proposition viable in light of competition?
Step 3: Channels
The third building block of the business model canvas is ‘channels’.
Channels refer to the touch points through which the company delivers value to its customers .
The primary functions of a channel are:
- Educate the prospects regarding services and products that a company offers
- Provide an opportunity to prospects to try these services/products
- Facilitate the purchase of products or services for the customers
- Helping the customers realize and benefit from the value proposition
- Providing the after sales services for the clients
But how do you go about planning your channels and what are the factors to be considered. Don’t worry we have you covered.
First let us classify the channels to be decided.
Broadly we can divide the channels into two types:
- Acquisition Channels : These are the channels that help you acquire your customers and bring to the point of sale.
- Delivery Channels : These are channels through which the product or service is actually delivered to your customers
Let us see how to go about deciding each of these.
Acquisition Channels
Your acquisition channels help you generate more leads that eventually become paying customers.
This part consists of deciding how you will advertise and communicate about your products to the customers and guide them into buying your products .
You can choose to advertise on billboards, television, radio and other physical areas to make a large number of people aware about your offering. However, these channels help you reach a large audience but are also extremely expensive.
Today the internet offers you various avenues where you can get these leads in a very cost effective manner.
If you want to make money online and are in a digital business, it makes even more sense to try digital channels for advertising and generating leads.
Your methods of traffic acquisition could be either organic , which means natural growth and acquisition of your customers without paying. Or inorganic , which includes paid media and channels online.
The main way to acquire traffic online in an organic manner is through SEO .
Search engine optimization or SEO involves making your content search friendly and relevant so as to feature in the top results when someone searches for a product/service you offer.
With most online journeys beginning with search, SEO is the one of most effective ways for long term victory online.

Only downside is that it may take a while before you build your SEO to promising levels.
The next option you have is to advertise on social media channels like Facebook , Instagram, Youtube, Pinterest etc.
The great advantage that these channels offer is that they have sophisticated ways to target customers and you can customize who you want to target based on a variety of factors like demographics, geography and interests.
But how to decide between these channels?
First you have to make sure that the kind of traffic or leads you are looking for are actually logging into these sides.
For instance, if you are in a B2B business then advertising on LinkedIn would be more relevant, given that most decision makers from corporates actually spend time on it or have their profiles there.
While for B2C other channels may make more sense.

It is best to start with multiple channels and then invest more money into the ones which give you better results .
For example, say you invest $50 each on Facebook and Youtube. From Youtube you get 100 leads but only 20 from Facebook.
20 of the 100 leads from Youtube become paying customers and only 5 from Facebook eventually purchase.
Clearly Youtube is offering you better return on investment. Hence it makes sense to pump in more dollars into this channel.
Distribution Channels
Next comes distribution channels. These channels enable the delivery of goods or services to a customer.
For example, if you are in a business of selling clothes. Then how do these clothes reach the end customers? Is it through a retail outlet, or can they purchase online?
All these questions are answered by what channels you choose to distribute your products.
Broadly speaking there are two different types of channels:
- Direct Channels
- Indirect Channels
Direct channels are those wherein you as a company directly interact and sell to your end consumers.
For example, say you own a website which sells physical products. Your customers ‘directly’ purchase from you online.
Similarly, if you own the brick and mortar retail stores where your customers come and get your products then also you are directly interacting with your consumers.
On the other hand if you sell to some middlemen and they in turn reach your consumers then it counts as an indirect channel.

While you have more control over your margins in a direct channel approach, indirect channels usually offer less margins.
But the flip side is that indirect channels usually buy in bulk and hence are good for volumes.
To choose a particular channel you should consider these factors.
- Number of consumer segments and types of market you are targeting : You want to be selling at a place where your target customers are most likely to visit. For instance, notice how Coke and Pepsi sell their soft drinks at fast food outlets like McDonalds or Burger King.
- Total cost for each channel: There is an associated cost for each channel that you wish to set up . For example, the cost of setting up an ecommerce website or leasing or building your own retail channel could result in higher costs than simply selling your products to a wholesaler.
- Type of product being sold and the consumer's awareness about it: If the product you are selling is fairly standard then you may need much explanation to be given to customers. But a complicated product may require the company to be in direct contact with customers to explain the offering.
- Amount of control required over experience: Channels owned directly offer more chances of making the experience in line with the brand and product, while indirect channels will offer a similar experience for you and competitor products.
- Duration of partnership: How long you intend to sell through the same customers also has a bearing on which channel you would choose. Hence, it is important to negotiate your terms in case you employ indirect distributors for your products.
Once you are sure of which channels to choose you can simply write them in the block. Make sure it is extremely convenient to find and buy your products for all your target customer segments.
Remember, the easier it is for customers to get the products, the more you will sell .
Step 4: Customer Relationships
This is an important block of the Business Model Canvas and helps you engage with customers in one or several ways .
Customer relationships block mentions all the ways in which a company chooses to maintain relationships with the customers.
Customer relationships are maintained with a primary motive of selling more to the customers while keeping the customer satisfied.
The goal of customer relationship management is to assist the customer in three stages of his journey with the company.
Customer Acquisition
Customer retention.
Your first task here is to guide a prospect to become a customer .
Typically this happens through different steps in a customer journey.
Let us see how each step in this journey may require different efforts on your part for customer relationship management.
Your customers mainly follow four broad steps before they become paying customers.
These stages are awareness , desire , interest and action .
The first step is to make your target customer segment aware about your offering. This includes letting your customers know that you have a potential solution to a problem that affects them.
Based on the type of business this may be done either in an automated or a manual way.
For instance, if you are in a B2B business you may choose to send over a sales representative or a solution expert to a customer.
Or wait for leads to show up themselves after you publish about your expertise in places like magazines or blogs where these prospective customers find you themselves.

Mostly awareness is built through advertising, SEO and word of mouth for a B2C business .
For instance, to build awareness about your offering you may choose to show a video ad to users who see a music video regarding your online music course.
While many users may become aware about your business, some of them may actually be convinced of its value or at least become curious about your product or service.
Consider that you showed an ad which generated 10,000 impressions or 10,000 users saw the ad. Now say 2,000 of them clicked and visited your website to read about your offering.
These 2,000 have now moved up the funnel by showing interest to buy the product.
At this stage, you may choose to save their email addresses for a more personalized conversation. You may even assign a sales rep to contact them if they choose to leave their details.
All these touch points become part of your customer relationship management strategy.
Now say that the person from your company who contacted the user showing interest manages to explain the value proposition you offer to around 500 of these users who now desire to buy your product.
The next step is to seal the deal with an action on the prospect’s part. The action of purchase by which they become your paying customers.
The goal of CRM (Customer Relationship Management) here is to make this journey as smooth as possible and convert the maximum number of prospects into paying customers.
There are certain goods and services that provide continuous value to customers and so customers keep buying them.
This stage deals with creating loyal customers who stick to your brand .
For instance, say you run an ecommerce website selling gifts. You realize that on an average a person buys gifts for someone at least once every two months. You would ideally want your customers to keep coming back for more orders every second month.
To do this your customer relationship program will have to make sure that you keep communicating with the users, apprising them of latest offers and products.
These are the few ways in which you can increase the chances of customer retention:
- Create a brand image that your customers associate with.
- Deliver the quality you promise.
- Always solve problems and reduce friction for your customers.
- Incentivize them for buying regularly from you with points or freebies.
- Promptly resolve all their complaints.
Your sales will increase by either getting new customers or selling more to the existing customers.
Upselling deals with making your existing customers buy more from you. You can do this by increasing their usage of the existing products or by selling different kinds of products to them.
For example, if you have an online business that helps people find relevant jobs and you charge a subscription fee for sending them relevant openings. You can add more value to them by offering resume making services and earn more for yourself as well.
In a B2B setup, your engagement manager can actively look for opportunities to sell more.
If you are an independent consultant, then you can offer more services to your customers if you have some expertise.
Maintaining Customer Relations through Touchpoints
Now that you understand the main objectives that you can accomplish with this block, you may want to know how to maintain relationships with your customers for different touch points.
There are broadly six ways of engagement:
- Personal Assistance : In this method you personally contact the customers through a human touch. These contacts may be made through call center agents or other employees.
- Dedicated Personal Assistance: For buyers who are very valuable, for example, take people with high net worth for a bank who deposit millions of dollars. A bank may have a dedicated person to maintain the relationship.
- Self Service: The ‘do it yourself’ method works great for reducing cost, but isn’t as strong as a human touch. This can be accomplished through videos explaining a process or an FAQ section on the website.
- Automated: These include all the automated methods like an IVR or a chatbot that interacts to solve problems for your customers.
- Communities: You may create communities and forums with your best customers playing a key role to solve problems for other customers. For example, there are tech groups that help all the users related to a particular technology.
- Co-creation: There are products and services where you engage with your customers to co-create services that suit them. In this method the customer actively participates in the process to add value to himself/herself. For instance, an interior designing service which actively asks customers to define their taste and be involved in the designing process.
You have to focus on the cost of each of these methods and whether the value that the customer brings to you justifies it or not.
For instance, you may not want to have a dedicated person who you pay $1,000 a month for a customer who only gives you $100 business a month.
All you have to do now is enter your chosen ways maintaining customer relations and put it in the block. Remember you should have touchpoints mapped to each of the customer segments.
So for example, if you have an SaaS (software as a service) online business wherein you charge for monthly usage of the product and have individual users as well as enterprise users.
You can map ‘automated’ service of individual users and ‘dedicated’ personnel for enterprise.
Step 5: Revenue Streams
The revenue streams block covers the various ways in which you monetize your business and earn money from your customers.
There are multiple ways of earning money. Some these are:
- Sale of Assets : You can completely transfer the goods or property for a price to a buyer. For example, a hotel chain selling one of the hotels to raise some cash.
- Usage : Payment collected for each usage of a product or service.
- Subscription: When payment is made for a repeated use of a service over a particular period. For instance, Netflix, Amazon Prime etc.
- Leasing/Renting: Renting out an asset for use for a fixed period. For example, renting an apartment for a fixed period.
- Licensing: Allowing the use of your intellectual property for usage by another company or person.
- Brokerage Fees: Acting as an intermediary between two parties and earning a commission as a result. For instance, stock brokers who earn a commission by enabling sale and purchase of equity shares.
- Advertising: Allowing your medium to be used as an advertising platform for other companies. For example, Google, Facebook and other platforms that earn money for allowing other companies to advertise on their platform.
Which method and price will work for you, depends on what kind of business you are in.
Pricing your product or service
The basic rule is that your customers pay you when the ‘perceived value’ they get from your product/service is more than what they pay.
From your perspective, you have to sell higher than the cost on an average so you earn money for yourself.

While this is the basic rule, other things to consider is the price at which competition offers similar products and the supply and demand for the kind of product/service you offer.
If your value proposition is very strong, then you can charge a higher price than your competition. Otherwise to make the customers switch you will have to keep your prices lower.
It is possible that you don’t get your pricing right the first time. You can start with some assumptions and planning, and adjust your prices as you go forward. It is important to have a learning mindset.
Here is a quick snapshot of various pricing strategies that can help you.

One you decide on the price of the service, then next is to choose one of the methods of charging.
Method of charging customers for your product/service
- Transaction Revenue : Charging for each transaction that customer does. For example, each time a user buys an item from your website you charge a fixed amount.
- Recurring Revenue : Similar to a subscription based service where the revenue is collected automatically every month (or any fixed period) depending on usage. For example, your electricity service that charges every month based on usage.
Onboarding customers to services where the charges are recurring is tougher than transactional method because the customer is worried about committing for a longer duration to a service which is new for him/her.
Hence, you see companies offering a free trial before asking the customers to pay.
This way they try to reduce the ‘cost of trial’ for the customer.
You can decide which method will work for you based on the usage of your offering. For example, if you offer a product that is used only once in a long time, then a subscription based charging may not be the best for you.
Thinking long term with pricing
Most businesses exist to earn profit. So, remember no matter what pricing method you choose it should result in a positive cash flow for your business.
It should also be sustainable and should lead to long term success of your business.
With a dynamically evolving environment, various new offerings may be released in the market and you may get new competitors from time to time. Hence, it is possible that you may have to revisit your pricing strategy from time to time.
The important thing is that you keep the customer at the core of your decisions and be extremely clear about the value that you are adding.
If your customer is also convinced of the value, then it will be easy to make them pay.
Managing multiple revenue streams
Different customer segments may contribute to your revenue in different ways.
Take the example of Microsoft, they sell licenses for softwares like Windows, Microsoft Office for individual customers and also earn from enterprises by offering bulk deals or enterprise services through cloud.
You should be aware about what percentage of revenue is contributed by which customer segment, basis the value proposition.
For example, if you are in an ecommerce business, you may have a corporate gifting option specifically for office going people which contributes 10% of revenue .
This is important for you to understand which part of business contributes the most amount of cash for you.
Step 6: Key Activities
This block consists of all the activities that are key to delivering your value proposition to your customers .
The span of control and how you handle the key activities will vary depending on what kind of business you are in.
Some parts of your activities may be outsourced while some may be controlled internally.
To understand the key activities carried out by your business you should focus on the value chain of your business.

Following are the key activities and how to decide if they are key to your competitive advantage. While these activities may differ depending on your business model, the basic flow and idea will remain similar.
Let’s dive.
Research and Development
The value of R&D is particularly high in technology based companies and big companies spend billions of dollars on it.
Here are the top 10 spenders on R&D (values in million dollars)

Nevertheless, to stay relevant and innovative you always need to research and improve your products.
There are three basic things for which you will use R&D.
- New Product Development : For growth, one of the ways to increase revenue is by offering more products in the market. Imagine a company like Apple, which first came up with iPods, then iPhones and iPads, and then Airpods. With each of these products it was able to grow its revenues multifold.
- Modifications to Existing Product: With the needs of the users changing and improvement in other areas you may choose to make modifications to your existing product. The goal of this exercise may be to reduce cost, earn more revenue, stay relevant or a combination of these factors. For instance, Android comes up with a new version of their operating system with added functionalities and increased efficiencies.
- Radical Innovation: Radical innovation gives you an opportunity to completely disrupt the current ways of working. This innovation may be to develop a product or a process that completely changes the status quo.
Though the chances of success are less in this scenario the gains may be very high. Consider how Uber and Airbnb changed the world, or the invention of smartphones revolutionized the mobile phone industry. If you manage to get a patent, then you can monetize it even better.
This part deals with manufacturing or procuring the end product that your customers may use.
There are three basic models that you can use:
- Producing everything in house: You may choose to produce everything in your factories or facilities by procuring raw materials. The benefit here is that you are able to control the quality of your product extremely well and if you have some specialized technology this can become your competitive edge. The downside is that it is usually very capital intensive and scaling your business may also be difficult using this approach.
- Outsourcing production: The next option you have is to completely outsource production and procure the end product through manufacturing partners. This reduces your overheads, allows you to scale quickly while also covering your risks. The only reason to not follow this approach is when you have some proprietary technology you don’t want to share or when the product is so different that it is difficult to find manufacturing partners.
- Outsourcing a part of the production process: You can also follow a mixed approach where you can outsource a part of the production process. In this case you procure some part of the product and then process it to make the final product. For example, say you manufacture smartphones. You can procure all the parts from outside and just assemble them in house.

This part of the activity will also include handling logistics and inventory.
Logistics include all the transportation including bringing in the raw materials to your facilities, moving the unfinished products between factories (if required), moving the finished products to inventory and then finally delivering to the end customer.
Inventory includes the storage of your products in warehouses that is needed to fulfil demand of the customers. You will have to estimate demand and then plan your inventory to avoid stock outs.
Remember, managing inventory is essential as it is a major cost and you may want to minimize wastage while also maximizing sales.
Sales and Marketing
The key activities that will be performed by this function range from designing the strategy to enabling the last mile fulfillment.
- Strategy : This includes the overall planning for what the company is trying to achieve from the marketing perspective and how it will go about doing it. For instance, say you are targeting a million dollars in revenue in a year, then the strategy would include everything from what products you will sell, how it will be advertised and so on.
- Product Development: The marketing team works together with R&D or product development team to validate consumer demand for the new products being developed and help them design features that are most relevant to customers.
- Communications and Advertising : All the communication to the customers and messaging about the company and product offerings are controlled by marketing. This includes the events that will be arranged for activations of products like exhibitions etc.
- After Sales Support: These set of activities include helping your customers in the post purchase journey. Your customer support departments, automated chatbots and other ways in which you help your customers maximize the value from products they have bought and solve the required problems are covered here.
These sets of activities are just indicative. It is possible that some of them may not be relevant to your business model.
For example, if you are in a blogging business then production may not apply to you like a manufacturing process. Instead it would mean the development of content, which again you can choose to do by yourself or by hiring external help.
Similarly if you are in an ecommerce retail business then you may or may not own inventory depending on your model. In that scenario, partner management would become your key activity.
Step 7: Key Resources
This building block comprises the assets that help you unlock and create value for your customers. Key resources deal with the operational aspects of your business and are responsible for bringing the value proposition to life for your customers.
There are various kinds of key resources that act as enablers for your business.
These key resources should be well differentiated from your customers in order to be better than them
Types of Key Resources
Broadly there are four different kinds of key resources.
Physical Resources
Physical resources, like equipment, machinery, buildings etc, are tangible resources which are used to create the products and services for the customers.
While these may not be extremely vital for an online business, they have great importance when it comes to businesses which have to deal with the physical world.
For example, Amazon will need to have large warehouses, where the products are sorted and stored. Similarly, a giant like Apple would need labs to experiment on its devices and manufacturing facilities to deliver value.
A telecom company would need towers, switching centers and servers to ensure continuity of services. A cloud company like Oracle will need data centers to meet the demands of the customers.
Depending on the type of industry, these assets may comprise a large portion of the capital required for setting up business.
Intellectual Resources
Intellectual resources are powerful intangible tools that enable a company to maintain its edge over competitors.
Do you know, Coke has a secret formula for producing the syrup that eventually translates into the beverage. Similarly, Google has its proprietary page rank algorithm that retrieves the most relevant search results for you.
In the world of pharmaceuticals, this is even more important when producing medicines which have been patented.
Another intellectual resource that an online business has is the data that it collects over a period of time. With analytics and machine learning uncovering insights and patterns, data can unlock great opportunities. This also includes the customer lists or emails that you collect over a period of time.
In fact, intellectual resources are a great way to get a competitive advantage . No wonder the number of patents granted in the US is increasing year on year.

Human Resources
Employees are the key enablers of value in an organization. In fact, hardly any company can run successfully without its employees.
Imagine, would the big machines in so many industries function without any operators or maintenance staff? Would Dominos be able to deliver pizzas without delivery guys?
In service industries the role of employees is even more profound. The quality of work delivered by consulting organizations like McKinsey, BCG, Bain or the Big4 is highly dependent on the quality of consultants they have (no wonder they hire the best of people).
Hence, this block should include the key human resources that are important to your business.
In online business, content creators or people who write code for you are very important. Google may not have been the giant that it is, if it did not have expert coders.
This will also give you an idea of what kind of hiring your business would need to deliver the key products.
Financial Resources
Financial resources include the capital , the sources of debt (or line of credit) and the stock owned by a company. The requirement of this kind of resource will vary depending on the kind of business that you choose to do.
For example, the capital requirements of a bank may be completely different from that of a business that makes money through online sale of educational courses.
If you are just starting a business, you may choose to raise funds from friends and family in the beginning. Once it gets established you may turn to investors and venture capitalists.
If your business has massive requirements of advertising or needs rapid expansion to various geographies then financial resources will be the key to your success.
Another important consideration here is working capital . Working capital is the money required to meet your day to day operations like paying your vendors and buying inventory etc to keep your business running.
Which resources are most important?
To decide which resources are the most important for you, you will need to evaluate the resources without which you cannot continue your business and those which contribute greatly to your success.
Hence, employees may be more important than machinery when it comes to consulting business. Similarly, power generation will have a major dependence on plants that produce electricity.
Step 8: Key Partnerships
This block consists of entities which are not internal to your business but are extremely important in delivering value .
Consider the supplier of goods for your business, or the manufacturer to whom you have outsourced business, or the investor who has promised to back your venture.
All these are important partners for your business and are critical to the success of your model.
In fact, with the rise of outsourcing partnerships have become even more important.

Would Kindle be a successful product if book writers don’t agree to publishing their content in the format? Or would the Apple iPod be successful without the music producers selling their music on the platform.
Hence, these outside partners are equally important and this justifies their place in the Business Model Canvas.
There are four broad types of partnerships that you will have:
- Strategic Alliances : These are partnerships between non competitors that benefit both the parties. For example, an automobile manufacturer may give exclusive rights to a partner in one country to distribute its products.
- Coopetition : These are alliances between competitors for mutual gain. For example, two video content creators may collaborate for an even greater share of audience, leading to increase in popularity of both influencers.
- Buyer-Seller Relationships: You may procure raw materials or sometimes finished products from outside. These types of relationships or partnerships are referred to as Buyer-Seller relationships. Sometimes, these relationships can also become a great source of competitive edge. For example, say you have exclusive rights to buying a superior quality of coffee in a particular region with a seller. Outsourcing relationships with partners also fall under this category.
- Joint Ventures: Joint ventures are partnerships between two separate companies when they have some sort of a mutual gain in working together. This could include sharing of resources, sharing of technology or if they produce complementary products. For instance, a data storage company may partner with an enterprise software firm to offer an end to end solution to the customer.
Key questions to ask before getting into partnerships
- Have I researched my partner well? The first thing to do is to research your partner well. This includes the history of the company, financial stability, integrity and the quality of products delivered.
- Is it a win win agreement? The partnership should be mutually beneficial. A good long term relationship cannot be built if one loses and the other wins. Therefore, there should be enough money to be made for both the parties.
- How long should the partnership be? Your contract duration should be negotiated on the basis of length of the relationship required to make your business successful.
- Are the key expectations and deliverables well defined? You should be clear about the terms of agreement and they should specifically contain what is to be expected from the partnership.
- Is the process being outsourced part of my core activity? As long as possible you should have direct control of the most key core activity of your business.
- Are my financial resources enough to cover the cost of partnership? You will need to pay your vendors on time to stay in business. Hence, be sure that the rate being negotiated is something you can easily pay for.
- Do I have quality checks in place? Getting work done from partners may require strict levels of quality control. Hence, make sure you have dedicated employees to validate quality.
Why Should You Choose Partners for Some Activities?
We should remember that some types of outsourcing in business process are more common, and there are specific reasons why companies choose to delegate some work to partners.

The major reasons are reducing costs and focussing on core activities.
For instance, you may choose to focus on the core activities that generate value and outsource the ones that can be easily done by others.
Do you know, Coke mostly focuses on its marketing activities and outsources bottling to another company?
Some other reasons are improving quality , conserving capital and increasing speed to market .
Step 9: Cost Structure
This brings us to the last building block – the block for cost structures.
Cost structures include the major sources from which your business incurs cost.
The first step is to understand what are the costs contributed by each of the key activities and key partners. In order to be cash positive you should collect your revenues on time and have cost under control.
Now, different business models will have different kinds of costs attached to it. While some business businesses will be capital intensive, that is, they will require a large amount of capital in order to function (e.g. telecom) while others may not require a lot of capital to begin with (e.g. software development).
There are two major kinds of costs associated with a business:
Fixed Costs
Variable costs.

Fixed costs are costs which are paid upfront and do not vary with the number of customers served by a business.
For example, consider the money that the airlines pay to the airports. There is usually a fixed component to it known as the yearly fee. No matter how many customers fly, this cost will always exist.
Another example is rent. Consider a restaurant which pays monthly rent for the building it operates in. No matter how many customers come to dine in, this cost always remains the same.
Now, fixed cost doesn’t always have to remain fixed, it only means that it remains fixed for a particular period of time.
Example of fixed costs:
- Advertising and marketing expenses
- Depreciation
Contrary to fixed cost, variable cost varies with the number of customers served. For example, sales commissions paid for each dollar of sales or shipping charges per item delivered to the customers.
The biggest portion of variable costs in most businesses are the raw materials and utility bills.
Examples of variable costs:
- Raw material cost
- Labor costs
- Shipping costs
- Packing supplies
- Utility bills like electricity

Your business model will decide whether you have a larger proportion of fixed costs or variable costs.
For example, consider a brick and mortar apparel business and an ecommerce based apparel business.
A brick and mortar based business will have rent as the major fixed cost while the cost of operations is the major driver of cost in an ecommerce business.
Another way to classify costs is categorizing them as Capital Expense (CAPEX) or Operational Expense (OPEX). Capital expenses are costs which are spent in order to acquire an asset.
Operational costs are costs which are expensed. Consider a company buying stationery, this will be counted as an operational expense. On the other hand the expenditure done to buy a big server to support operations will be classified as a capital expense since the acquired server becomes an asset.
Ideally, the margin that you obtain from your revenue over variable costs should be enough to cover your fixed costs in order to generate positive cash for you.
This can be done in two ways:
- Economies of Scale : Economies of scale occur when you sell enough quantities of an item such that the cost of serving each customer reduces. This happens due to multiple reasons. A first that operates on scale is able to negotiate better prices with the vendors. This is because they get volume discounts. Since, the scale is big, fixed costs are much better covered.
- Economies of Scope: Economies of scope occur when the same fixed costs are covered by different products and services. For example, consider a firm that operates its own logistics network. If it enters multiple product categories then the same trucks can now transport these multiple products sharing the cost for each of them.
How conservative should you be with costs?
This will depend on whether you consider yourself as a cost driven business or a value driven business .
A cost driven business focuses more on reducing cost. For example, consider ‘Ryanair’, the airline is based on removing all the frills and just offering the basic airline services in order to cut costs.
On the other hand a luxurious hotel business will focus less on cost and more on providing the best of comfort and facilities to its guests.
Usually luxury products are focused more on value and basic products that have less differentiation focus more on cost.
Once you decide your major cost heads, jot them down in the cost driver block and see them in conjunction with revenue from various sources.
It is important to validate whether your business model will be successful in generating cash and what level of scale you will require to make it work and whether it is doable or not.
Business Model Canvas FAQ
A business model canvas is a one page visual template that covers the key aspects required to make a business work. It consists of 9 building blocks which should work in conjunction with each other in order to deliver the key value proposition of business to the target customer segments.
A business model canvas has 9 building blocks. These are: 1. Customer Segments: Who are the key customers of your business? And what are their key characteristics and needs? 2 . Value Propositions: Why do customers buy your product or service? What is the key benefit that your business offers? 3 . Channels : How are these benefits communicated to your customers and how is the product or service sold or delivered and why? 4 . Customer Relationships : What are the key touch points between you and your customers? And how do you connect with them throughout their journey? 5 . Revenue Streams: How does business actually earn money from various value propositions? 6 . Key Activities: What are the key things that your business strategically does to deliver this proposition? 7 . Key resources : What are the assets that business requires in order to stay competitive and create value? 8 . Key Partnerships: What are the external entities or stakeholders that are key to delivering the product and service to your customer? What are some of the partners to whom you have outsourced certain activities to focus more on your core work? 9 . Cost Drivers: What are the major cost drivers for your business and how are they linked to your revenue?
Instead of coming up with a 500 page document that describes your business model, you should start with a quick business model canvas. This will give you an idea of the key parts that are required to make your business work. Start with a business model and come up with an initial version of your business model canvas. Then test your key hypothesis through experiments and take the learning from those experiments to adjust your business model canvas. Use this as an iterative process for learning and keep adjusting your business model canvas till it becomes perfect. Business model canvas is better for testing model assumptions because it is easy to change. It is also a standard template and is well understood by all. Many companies have successfully used it especially in dynamic environments.
There are various kinds of business models depending on what method of monetization you use and how charge your customers for your value proposition. Here are a few of them you can adopt if you don’t have a completely new business model. 1. Brokerage : Bring together buyers and suppliers and charge a commission for the transaction. 2 . Bundling: Offer a few products or services together as one package (eg. iPod and iTunes) 3 . Crowdsourcing : Raise funds from a group of people who are interested in supporting your offering 4 . Disintermediation : Sell directly by cutting out the middlemen 5 . Freemium: Charge a few customers for specialized service and offer a free version with limited functionality 6 . Auction: Sell products through an auction rather than a fixed price (Eg. eBay) 7 . Subscription: Charge for a fixed period of time for unlimited usage of service (Eg. Netflix) 8 . Leasing: Lease or rent an asset for a fixed period of time for money 9 . Usage : A simple model where you charge per transaction or usage of product/service 10. Advertising : Charge other businesses for advertising on your platform. 11. Affiliate: Earn a commission by selling someone else’s products. This list is just indicative, you can have a lot of business models based on one or many of these ideas.
Business model canvas was invented by Alexander Osterwalder. He is a Swiss theorist, author, consultant, speaker and entrepreneur.

A lean canvas is just an adapted version of the business model canvas which is more suited for startups. It was created because there are some blocks of the business model canvas which are difficult for a startup to know when it starts doing business. This is because by definition a startup tries to do something that no one has done before making the whole model extremely uncertain. Here is a complete list of differences between the two.
| Element | Business Model Canvas | Lean Canvas |
|---|---|---|
| Target | New and existing businesses | Startup businesses purely |
| Focus | Customers, Investors, Entrepreneurs, Consultants, Advisors | Entrepreneurs purely |
| Customers | Lays emphasis on customer segments, channels and customer relationships for all businesses | Does not lay much emphasis on customer segments because startups have no known or tested products to sell |
| Approach | It lays down the infrastructure, lists the nature and sources of financing and the anticipated revenue streams of the business | It begins with the problem, a proposed solution, the channels to achieving the solution, costs involved and the anticipated revenue streams |
| Competition | It focuses on value proposition in quantitative and qualitative terms as way to stay smart in the market | It assesses whether the business has an unfair advantage over the rest and how to capitalize on it for better grounding |
| Application | It fosters candid understanding, creativity, discussion and constructive analysis | It is a simple problem-solution oriented approach which enables the entrepreneur to develop step-by-step |
Source: canvanizer.com
Ready to Launch Your Startup using the Business Model Canvas?
Having read this article in detail, you must now be well versed with a business model canvas and how to create a quick one for your business.
If you are looking to start a side business to earn some money online or any full time business then this template is going to be very useful for you.
A lot of learning about your business and whether your assumptions are true or not will become clear only when you start your venture.
The important thing is to think like an entrepreneur and have a learning mindset and you will definitely succeed.
If you are short on money you can apply the business model canvas to earn money from a blogging business with less than a $100 investment or you can choose any business model that suits you.
The important thing is to take the dive and begin, and if you follow all the tips and tricks shared here, you will definitely succeed.
Was This Article Helpful?
Anastasia belyh.
Anastasia has been a professional blogger and researcher since 2014. She loves to perform in-depth software reviews to help software buyers make informed decisions when choosing project management software, CRM tools, website builders, and everything around growing a startup business.
Anastasia worked in management consulting and tech startups, so she has lots of experience in helping professionals choosing the right business software.
How to Start a Business: A Startup Guide for Entrepreneurs [Template]
Published: February 15, 2024
I started a local HVAC business in the summer of 2020, and since then, I’ve learned a lot about which steps are most important for getting a business venture off the ground. To help you make your business idea a reality, I've put together a complete guide that walks you through the steps of starting a business.

The guide covers every step I’ve discovered you need to start a business, from the paperwork and finances to creating your business plan and growing your business online. At the bottom, you’ll find a library of the best free tools and resources to start selling and marketing your products and services.
Use the links below to navigate to each section of the guide:
- What do you need to start a business?
How to Start a Business
How to make a business plan, how to decide on a company name.
- How to Choose a Business Structure
How to Register Your Business
How to comply with legal requirements, how to find funding for your new business, how to create a brand identity for your new business, tips for starting a business, resources to start a business, how to start a business online.
Let's get started.
Every budding entrepreneur wants more visitors, more qualified leads, and more revenue. But starting a business isn’t one of those “if you build it, they will come” situations. So much of getting a startup off the ground has to do with timing, planning, and the market, so consider if the economic conditions are right to start a company and whether you can successfully penetrate the market with your solution.
In order to build and run a successful company , you’ll also need to create and fine-tune a business plan, assess your finances, complete all the legal paperwork, pick your partners, research apps for startup growth, choose the best tools and systems to help you get your marketing and sales off the ground … and a whole lot more.
When I first started my business, I felt overwhelmed by the sheer magnitude of requirements, which is why I’ve summed up the process to make it easier for you.
In brief, the requirements for starting a business are:
- A business plan.
- A business name.
- An ownership or business structure.
- A business registration certificate.
- A legal license or seller’s permit (as well as other legal documents).
- A source of funding.
- A brand identity.
Without these elements in place, you unnecessarily risk your new business’s future. Now let’s go over these basic steps for starting a business.
- Write a business plan.
- Choose a business name.
- Choose an ownership structure.
- Register your business.
- Review and comply with legal requirements.
- Apply for funding.
- Create a brand identity.
Having a great business idea is only part of the journey. In order to be successful, you’ll need to take a few steps to get it off the ground. In order to refine your business idea and set yourself up for success, consider doing the following:
1. Write a business plan.
Your business plan maps out the details of your business, including how it’s structured, what product or service you’ll sell, and how you’ll be selling it. Creating a business plan will help you find any obstacles on the horizon before you jump into running a business.
Pro tip: Remember that part of a business plan is telling investors or funders which specific items you need funding for. Be sure to list what you need to be funded, the reasoning behind items, and how long you will need funding.
Recommended Reading:
- What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
- How to Build a Detailed Business Plan That Stands Out
- How to Write an Ecommerce Business Plan
- How to Become an Entrepreneur With No Money or Experience
70 Small Business Ideas for Anyone Who Wants to Run Their Own Business
Jump to: How to Start a Business Plan →
Featured Resource: Free Business Plan Template

Below are the key elements in a business plan template, details about what goes into each of them, and example sections at the bottom. You’ll also learn tips for writing a business plan .
1. Use a business plan template .

The executive summary should be about a page long. It should cover:
- Overview . Briefly explain what the company is, where you’ll be located, what you’ll sell, and who you’ll sell to.
- Company profile. Briefly explain the business structure, who owns it, what prior experience/skills they’ll bring to the table, and who the first hires might be.
- Products or services . Briefly explain what you’ll sell.
- The market. Briefly explain your main findings from your market analysis and product market fit .
- Financial considerations . Briefly explain how you plan to fund the business and what your financial projections are.
Featured Resource: Executive Summary Template

On the marketing side, you’ll want to cover answers to questions like:
- How do you plan to penetrate the market?
- How will you grow your business?
- Which channels will you focus on for distribution?
- How will you communicate with your customers?
Pro tip: Marketing trends change year after year, so be sure to keep up on the latest trends by subscribing to the Hubspot Marketing blog .
On the sales side, you’ll need to cover answers to questions like:
- What’s your sales strategy ?
- What will your sales team look like, and how do you plan to grow it over time?
- How do you plan to scale for growth ?
- How many sales calls will you need to make to make a sale?
- What’s the average price per sale?
Speaking of average price per sale, you’ll want to go into your pricing strategy as well.
Featured Resource: Marketing & Sales Alignment Template
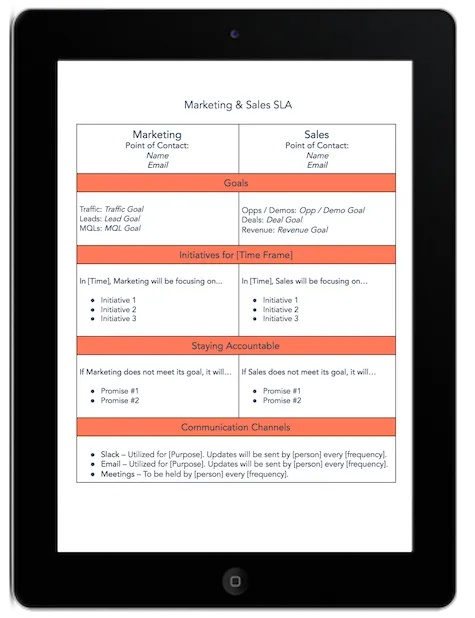
More importantly, it typically doesn’t entail giving partial ownership of the business away. Instead, it’s a way of getting funding not from potential co-owners, but from potential fans and customers who want to support the business idea, but not necessarily own it.
What you give donors in exchange is entirely up to you — and typically, people will come away with early access to a product, or a special version of a product, or a meet-and-greet with the founders.
Pro tip: Choose the right platform for your crowdfunding campaign type. Some platforms are more geared towards traditional investors, while others are for donations. Learn more about crowdfunding here .
5. Venture Capital Financing
Only a very small percentage of businesses are either fit for venture capital or have access to it. All the other methods described earlier are available to the vast majority of new businesses.
If you’re looking for a significant amount of money to start your company and can prove you can quickly grow its value, then venture capital financing is probably the right move for you.
Venture capital financing usually means one or more venture capital firms make large investments in your company in exchange for preferred stock of the company — but, in addition to getting that preferred return as they would in series seed financing, venture capital investors also usually get governance rights, like a seat on the Board of Directors or approval rights on certain transactions.
VC financing typically occurs when a company can demonstrate a significant business opportunity to quickly grow the value of the company but requires significant capital to do so.
Pro tip: A lot of venture capital financing is simply being in the right room with the right people. Make sure to network extensively if this is your approach to financing.
When you’re first starting a business, you’ll need to build the foundation for a strong brand identity. Your brand identity is about your values, how you communicate concepts, and which emotions you want your customers to feel when they interact with your business. Having a consistent brand identity to promote your business will make you look more professional and help you attract new customers.
Here’s what you need to do to develop your brand identity:
1. Design a logo.
Creating the right logo for your business requires careful thought and consideration. It should be representative of your brand’s purpose and target audience, while also being memorable and distinct from competitors.
To start, you need a deep understanding of your business’s mission, values, and target audience. Think beyond what your company does and truly examine why you do what you do and who you do it for. This knowledge will serve as the foundation for your logo.
Conducting market research and identifying current logo trends can help you understand what works well for others and strategize on how to stand out. Then, start brainstorming design ideas that showcase what makes your business unique.
For instance, you could try writing out a list of words that best describe your business and what makes it special and then use those words as inspiration to start sketching ideas and concepts.
Once you have some sketches created, pick which ones you think are the best and share them with stakeholders, colleagues, and buyer personas to gather feedback and refine your design. After narrowing down a design, you’ll want to test its versatility and scalability to ensure it works well in different sizes and formats.
Pro tip: Check out this blog on designing your logo, and then try out different logo design features in Canva’s logo maker .
2. Develop a visual identity.
Your brand’s visual identity doesn’t stop at creating a logo — you’ll also need to establish guidelines for typography, color palette, imagery, and other graphic elements. The more consistent your brand is with its visuals, the more consumers will be able to recognize and trust it.
To get started, consider creating a brand mood board. Ask yourself: What kind of emotions do you want your brand to evoke? Is there a specific visual aesthetic that you want to emulate? This can help you gather visual inspiration that resonates with your brand.
Choose your color palette and typography wisely. Spend some time researching color theory , as color can have a major impact on how people perceive your brand. Make sure your typography is readable and looks good across different sizes and formats.
Additionally, you should create other visual assets such as patterns, shapes, illustrations, and icons that pair well with your color palette and typography.
Pro tip: If design and color palettes aren’t your thing, consider hiring a freelance graphic designer on LinkedIn or Fiverr to help you create your visual identity and incorporate it into your logo and overall design.
3. Craft a tagline.
In just a few words, your tagline should encapsulate your brand’s essence and communicate its value. Think of it as a written or verbal version of your logo. Both elements are created to immediately capture the attention of your audience. Even if consumers don’t remember anything about your product or service, they will remember a catchy tagline.
When crafting your tagline, keep it simple. You want your tagline to be memorable, so aim for a short phrase and focus on key benefits or unique aspects of your brand. Also consider using techniques like alliteration, rhyme, or play on words to make your tagline stand out — just make sure it aligns with the rest of your brand’s voice and tone.
Pro tip: This is another element of starting a business that could benefit from someone with experience. A marketing consultant or a content writer could help you establish a compelling tagline with the next step of developing your voice and tone.
4. Develop your voice and tone.
Your brand voice refers to the personality that your brand adopts in its communication with its audience. It provides direction on what to say and how to say it, allowing you to differentiate yourself and cut through the noise.
A well-defined brand voice helps create a distinct and memorable identity for your brand, allowing you to connect with your target audience on a deeper and more meaningful level.
When determining the appropriate voice and tone for your brand, remember that consistency is key. Ensure that your brand voice and tone align with your brand’s values, mission, and positioning. Alignment between your brand’s personality and its communication style is crucial for building trust and authenticity.
Pro tip: Adapt your voice and tone to suit the preferences and understanding of your audience. Additionally, use emotion and storytelling techniques to engage your audience and resonate with them.
5. Create brand guidelines.
Once you determine all of the previously mentioned brand elements, establish a set of brand guidelines that communicate how to appropriately use them. Having these rules and standards set in place ensures consistent and cohesive messaging and representation for your brand.
Get started by defining the rules for using your brand elements across different channels and applications, such as digital and print media, social media profiles, web design, packaging, and any other relevant materials.
Show practical examples of correct and incorrect usage scenarios to demonstrate the do’s and don’ts of brand representation. This helps stakeholders and users understand the guidelines and their application. You can also offer your team templates or mock-ups to ensure correct implementation.
Once the brand guidelines are set, distribute them to internal stakeholders and relevant external partners. To make sure everyone’s on the same page, take the time to review the guidelines with everyone and consider conducting training sessions if necessary.
As your brand evolves, so should your brand guidelines. Continuously review and update them to reflect any changes or refinements. Keep the guidelines easily accessible and communicate any updates effectively.
Pro tip: A writing style guide is a great place to start when creating brand guidelines. Check out this blog on brand style guide examples.
.webp)
Starting a business online is a little different from starting a traditional business. Here are some important steps for starting and scaling your business online.
1. Determine your niche and business idea.
Your business niche is the target focus area for your product or service. It’s important to choose a niche because customers like brands and businesses that specifically cater to their needs. Most customers are more likely to purchase products or services from a brand that provides personalized experiences.
When determining your niche and business idea, first identify your target audience and specify everything from their age to their interests. Then, use that information to figure out their principal need. If your product doesn’t resolve a specific need, your business will fail to get off the ground.
Pro tip: You should have a good idea of the market at this point. Use that knowledge to position yourself in a way that differentiates you from your competitors.
2. Conduct market research.
Conduct market research to understand what product or service you should offer, whom you should serve, and where you face the stiffest competition. From physical goods to digital downloads, understanding your target market and competitors will help you determine how to best position your product.
Your research should help you create a strong selling proposition . In other words, what makes your business unique? Why should someone buy from you?
Pro tip: Sometimes, market research is as easy as calling around to competitors and getting a quote on services. Make sure your pricing is competitive but not so low as to be unsustainable.
3. Learn online business laws.
While online businesses may require fewer licenses and permits than traditional businesses, there are still legal requirements that you will need to adhere to. Be sure to check:
- What kind of business license (if any) do you need to start operations?
- What legal structure makes the most sense for your company?
- Are there any permits that you need to obtain?
- Are there any inspections that you need to pass?
- Do you need a sales tax license?
- Are there any specific regulations applicable to online businesses only?
- What are the laws regarding hiring contractors and hiring employees?
Pro tip: Check out this article for more information on starting an online business and navigating online laws.
4 . Make sure your business is insured.
Depending on your business type, you may be required by state law to be both licensed and insured. HVAC businesses have a lot of liability as they involve both plumbing and electricity. I spoke with several insurance agents before deciding on the best insurance for my business needs.
There are also many different business insurance types, such as:
- Liability insurance.
- Worker’s comp.
- Property insurance (think your business location, tools, and equipment you use).
- And more. Be sure to research these different insurance types and purchase the necessary ones.
Pro tip: Check out this article on small business insurance.
5. Create a website.
After handling the research, taking care of legalities, and honing your products or services, it is time to create your website . When creating your website, you will need to choose a strong ecommerce platform that will allow you to sell products online.
Pro tip: Check out Hubspot’s free CMS tool for website building here.
6. Set up shop.
Once your website is complete, it’s time to add products or services to your store. When adding your products, pay attention to product images and descriptions. Having a crisp image and a detailed but concise description will help your audience maneuver your website smoothly.
After you have finished setting up your store, it’s critical to ensure you offer a seamless shipping or delivery experience to your buyers. For example, you can use HubSpot to manage quality control before you ship products out.
Finally, you want to make sure everything is working before you hit the live button on your website. Make sure that everything is clickable and that all pages look good across all devices and browsers. Once you’ve checked that, you are ready to go live.
Pro tip: If you take credit card information on your website, you will need to abide by compliance laws that ensure the safety of sensitive data. Read more on credit card compliance .
7. Create a marketing plan.
You’ve created an awesome product, and now it’s time to get the word out. In other words, it’s time to grow your audience. There are numerous ways to reach your target customer, including:
- Social media : Use hashtags and paid ads to expand your reach.
- Influencer marketing : Send free samples to “celebrities” in your niche.
- Facebook groups : Connect with your target market on this platform.
- Google advertising : Put your products in front of people all over the web.
- Content marketing : Publish blog posts to bring organic traffic to your site.
- Word-of-mouth : Encourage customers to spread the word.
- YouTube videos : Start a channel to showcase your products.
Pro Tip: Google ads and LinkedIn ads regularly offer discounts or free ad money; consider using these promos to try online advertisements out.
8 . Grow your business.
You’ve heard it said that in business, you’re either growing or you’re dying. Here are a couple of tips for growing your business online:
- Reduce the amount of time it takes online viewers to receive value from you and your brand.
- Answer the questions no one in your industry is answering — for example, a lot of companies won’t talk about pricing, forcing customers to keep looking for someone who will.
- Create a dynamic website that changes with the times. Update your images and writing to reflect what’s happening with your business now, and ensure your website isn’t dating you.
- Invest in content and SEO . They aren’t cheap, but they are really important for being found online, organically.
Pro tip: Check out this blog on how to become an SEO expert, according to HubSpot’s SEO team.
9. Watch your income and expenditures closely.
The first year of your business is an essential set point for discovering your overhead and your profit. Have a date in mind of when you want your business to start turning a profit and a solid plan for if you aren’t meeting that goal. Read further on potential exit strategies below.
Pro tip: Use a free business budget template to monitor your finances.
10. Plan for an exit strategy.
If you’re like me, you didn’t consider an exit strategy when thinking up your business. You probably assumed you’d run your business for the foreseeable future. However, economic uncertainty or unexpected success can both impact the end of your business. In fact, 90% of startups fail , which makes it a wise choice to know under what circumstances you would close down your business.
You could also experience unexpected buzz and success and be offered a buyout. A good exit strategy will plan for this as well. What amount of money would make selling worth it? Consider also how long you would have to run your business before considering offers. Some want to sell high and fast, whereas other business owners want to see where things go during a set amount of time.
An exit strategy could also include who you want to inherit your business, maybe family or an employee.
Pro tip: Check out this blog on the importance of having an exit strategy.
Next Steps: Getting Ready to Launch Your Business
I know from experience that being a small business owner isn’t easy, but with the right plan, you can set up your business for success. Be sure to check and know your requirements, have a solid business plan, and submit your legal paperwork before you take your business live. Once you have a solid business plan and the financing to execute your goals, you’ll be well on the path to launching a successful enterprise.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in August 2019 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![business plan model startup How to Write a Business Proposal [Examples + Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-to-write-business-proposal%20%281%29.webp)
How to Write a Business Proposal [Examples + Template]

Amazon Affiliate Program: How to Become an Amazon Associate to Boost Income

A Complete Guide to Successful Brand Positioning

Door-to-Door Sales: The Complete Guide

Product Differentiation and What it Means for Your Brand

The 25 Best PayPal Alternatives of 2023

The First-Mover Advantage, Explained

Intrapreneurship vs. Entrepreneurship: What's the Difference?

What Are Current Assets? Definition + Examples
9 templates to help you brainstorm a business name, develop your business plan, and pitch your idea to investors.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
How To Start A Business In 11 Steps (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 7, 2024, 1:44pm

Table of Contents
Before you begin: get in the right mindset, 1. determine your business concept, 2. research your competitors and market, 3. create your business plan, 4. choose your business structure, 5. register your business and get licenses, 6. get your finances in order, 7. fund your business, 8. apply for business insurance, 9. get the right business tools, 10. market your business, 11. scale your business, what are the best states to start a business, bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Starting a business is one of the most exciting and rewarding experiences you can have. But where do you begin? There are several ways to approach creating a business, along with many important considerations. To help take the guesswork out of the process and improve your chances of success, follow our comprehensive guide on how to start a business. We’ll walk you through each step of the process, from defining your business idea to registering, launching and growing your business .
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
The public often hears about overnight successes because they make for a great headline. However, it’s rarely that simple—they don’t see the years of dreaming, building and positioning before a big public launch. For this reason, remember to focus on your business journey and don’t measure your success against someone else’s.
Consistency Is Key
New business owners tend to feed off their motivation initially but get frustrated when that motivation wanes. This is why it’s essential to create habits and follow routines that power you through when motivation goes away.
Take the Next Step
Some business owners dive in headfirst without looking and make things up as they go along. Then, there are business owners who stay stuck in analysis paralysis and never start. Perhaps you’re a mixture of the two—and that’s right where you need to be. The best way to accomplish any business or personal goal is to write out every possible step it takes to achieve the goal. Then, order those steps by what needs to happen first. Some steps may take minutes while others take a long time. The point is to always take the next step.
Most business advice tells you to monetize what you love, but it misses two other very important elements: it needs to be profitable and something you’re good at. For example, you may love music, but how viable is your business idea if you’re not a great singer or songwriter? Maybe you love making soap and want to open a soap shop in your small town that already has three close by—it won’t be easy to corner the market when you’re creating the same product as other nearby stores.
If you don’t have a firm idea of what your business will entail, ask yourself the following questions:
- What do you love to do?
- What do you hate to do?
- Can you think of something that would make those things easier?
- What are you good at?
- What do others come to you for advice about?
- If you were given ten minutes to give a five-minute speech on any topic, what would it be?
- What’s something you’ve always wanted to do, but lacked resources for?
These questions can lead you to an idea for your business. If you already have an idea, they might help you expand it. Once you have your idea, measure it against whether you’re good at it and if it’s profitable.
Your business idea also doesn’t have to be the next Scrub Daddy or Squatty Potty. Instead, you can take an existing product and improve upon it. You can also sell a digital product so there’s little overhead.
What Kind of Business Should You Start?
Before you choose the type of business to start, there are some key things to consider:
- What type of funding do you have?
- How much time do you have to invest in your business?
- Do you prefer to work from home or at an office or workshop?
- What interests and passions do you have?
- Can you sell information (such as a course), rather than a product?
- What skills or expertise do you have?
- How fast do you need to scale your business?
- What kind of support do you have to start your business?
- Are you partnering with someone else?
- Does the franchise model make more sense to you?
Consider Popular Business Ideas
Not sure what business to start? Consider one of these popular business ideas:
- Start a Franchise
- Start a Blog
- Start an Online Store
- Start a Dropshipping Business
- Start a Cleaning Business
- Start a Bookkeeping Business
- Start a Clothing Business
- Start a Landscaping Business
- Start a Consulting Business
- Start a Photography Business
- Start a Vending Machine Business
Most entrepreneurs spend more time on their products than they do getting to know the competition. If you ever apply for outside funding, the potential lender or partner wants to know: what sets you (or your business idea) apart? If market analysis indicates your product or service is saturated in your area, see if you can think of a different approach. Take housekeeping, for example—rather than general cleaning services, you might specialize in homes with pets or focus on garage cleanups.
Primary Research
The first stage of any competition study is primary research, which entails obtaining data directly from potential customers rather than basing your conclusions on past data. You can use questionnaires, surveys and interviews to learn what consumers want. Surveying friends and family isn’t recommended unless they’re your target market. People who say they’d buy something and people who do are very different. The last thing you want is to take so much stock in what they say, create the product and flop when you try to sell it because all of the people who said they’d buy it don’t because the product isn’t something they’d buy.
Secondary Research
Utilize existing sources of information, such as census data, to gather information when you do secondary research. The current data may be studied, compiled and analyzed in various ways that are appropriate for your needs but it may not be as detailed as primary research.
Conduct a SWOT Analysis
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Conducting a SWOT analysis allows you to look at the facts about how your product or idea might perform if taken to market, and it can also help you make decisions about the direction of your idea. Your business idea might have some weaknesses that you hadn’t considered or there may be some opportunities to improve on a competitor’s product.

Asking pertinent questions during a SWOT analysis can help you identify and address weaknesses before they tank your new business.
A business plan is a dynamic document that serves as a roadmap for establishing a new business. This document makes it simple for potential investors, financial institutions and company management to understand and absorb. Even if you intend to self-finance, a business plan can help you flesh out your idea and spot potential problems. When writing a well-rounded business plan, include the following sections:
- Executive summary: The executive summary should be the first item in the business plan, but it should be written last. It describes the proposed new business and highlights the goals of the company and the methods to achieve them.
- Company description: The company description covers what problems your product or service solves and why your business or idea is best. For example, maybe your background is in molecular engineering, and you’ve used that background to create a new type of athletic wear—you have the proper credentials to make the best material.
- Market analysis: This section of the business plan analyzes how well a company is positioned against its competitors. The market analysis should include target market, segmentation analysis, market size, growth rate, trends and a competitive environment assessment.
- Organization and structure: Write about the type of business organization you expect, what risk management strategies you propose and who will staff the management team. What are their qualifications? Will your business be a single-member limited liability company (LLC) or a corporation ?
- Mission and goals: This section should contain a brief mission statement and detail what the business wishes to accomplish and the steps to get there. These goals should be SMART (specific, measurable, action-orientated, realistic and time-bound).
- Products or services: This section describes how your business will operate. It includes what products you’ll offer to consumers at the beginning of the business, how they compare to existing competitors, how much your products cost, who will be responsible for creating the products, how you’ll source materials and how much they cost to make.
- Background summary: This portion of the business plan is the most time-consuming to write. Compile and summarize any data, articles and research studies on trends that could positively and negatively affect your business or industry.
- Marketing plan: The marketing plan identifies the characteristics of your product or service, summarizes the SWOT analysis and analyzes competitors. It also discusses how you’ll promote your business, how much money will be spent on marketing and how long the campaign is expected to last.
- Financial plan: The financial plan is perhaps the core of the business plan because, without money, the business will not move forward. Include a proposed budget in your financial plan along with projected financial statements, such as an income statement, a balance sheet and a statement of cash flows. Usually, five years of projected financial statements are acceptable. This section is also where you should include your funding request if you’re looking for outside funding.
Learn more: Download our free simple business plan template .
Come Up With an Exit Strategy
An exit strategy is important for any business that is seeking funding because it outlines how you’ll sell the company or transfer ownership if you decide to retire or move on to other projects. An exit strategy also allows you to get the most value out of your business when it’s time to sell. There are a few different options for exiting a business, and the best option for you depends on your goals and circumstances.
The most common exit strategies are:
- Selling the business to another party
- Passing the business down to family members
- Liquidating the business assets
- Closing the doors and walking away
Develop a Scalable Business Model
As your small business grows, it’s important to have a scalable business model so that you can accommodate additional customers without incurring additional costs. A scalable business model is one that can be replicated easily to serve more customers without a significant increase in expenses.
Some common scalable business models are:
- Subscription-based businesses
- Businesses that sell digital products
- Franchise businesses
- Network marketing businesses
Start Planning for Taxes
One of the most important things to do when starting a small business is to start planning for taxes. Taxes can be complex, and there are several different types of taxes you may be liable for, including income tax, self-employment tax, sales tax and property tax. Depending on the type of business you’re operating, you may also be required to pay other taxes, such as payroll tax or unemployment tax.
Start A Limited Liability Company Online Today with ZenBusiness
Click to get started.
When structuring your business, it’s essential to consider how each structure impacts the amount of taxes you owe, daily operations and whether your personal assets are at risk.
An LLC limits your personal liability for business debts. LLCs can be owned by one or more people or companies and must include a registered agent . These owners are referred to as members.
- LLCs offer liability protection for the owners
- They’re one of the easiest business entities to set up
- You can have a single-member LLC
- You may be required to file additional paperwork with your state on a regular basis
- LLCs can’t issue stock
- You’ll need to pay annual filing fees to your state
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
An LLP is similar to an LLC but is typically used for licensed business professionals such as an attorney or accountant. These arrangements require a partnership agreement.
- Partners have limited liability for the debts and actions of the LLP
- LLPs are easy to form and don’t require much paperwork
- There’s no limit to the number of partners in an LLP
- Partners are required to actively take part in the business
- LLPs can’t issue stock
- All partners are personally liable for any malpractice claims against the business
Sole Proprietorship
If you start a solo business, you might consider a sole proprietorship . The company and the owner, for legal and tax purposes, are considered the same. The business owner assumes liability for the business. So, if the business fails, the owner is personally and financially responsible for all business debts.
- Sole proprietorships are easy to form
- There’s no need to file additional paperwork with your state
- You’re in complete control of the business
- You’re personally liable for all business debts
- It can be difficult to raise money for a sole proprietorship
- The business may have a limited lifespan
Corporation
A corporation limits your personal liability for business debts just as an LLC does. A corporation can be taxed as a C corporation (C-corp) or an S corporation (S-corp). S-corp status offers pass-through taxation to small corporations that meet certain IRS requirements. Larger companies and startups hoping to attract venture capital are usually taxed as C-corps.
- Corporations offer liability protection for the owners
- The life span of a corporation is not limited
- A corporation can have an unlimited number of shareholders
- Corporations are subject to double taxation
- They’re more expensive and complicated to set up than other business structures
- The shareholders may have limited liability
Before you decide on a business structure, discuss your situation with a small business accountant and possibly an attorney, as each business type has different tax treatments that could affect your bottom line.
Helpful Resources
- How To Set Up an LLC in 7 Steps
- How To Start a Sole Proprietorship
- How To Start a Corporation
- How To Start a Nonprofit
- How To Start a 501(c)(3)
There are several legal issues to address when starting a business after choosing the business structure. The following is a good checklist of items to consider when establishing your business:
Choose Your Business Name
Make it memorable but not too difficult. Choose the same domain name, if available, to establish your internet presence. A business name cannot be the same as another registered company in your state, nor can it infringe on another trademark or service mark that is already registered with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
Business Name vs. DBA
There are business names, and then there are fictitious business names known as “Doing Business As” or DBA. You may need to file a DBA if you’re operating under a name that’s different from the legal name of your business. For example, “Mike’s Bike Shop” is doing business as “Mike’s Bikes.” The legal name of the business is “Mike’s Bike Shop,” and “Mike’s Bikes” is the DBA.
You may need to file a DBA with your state, county or city government offices. The benefits of a DBA include:
- It can help you open a business bank account under your business name
- A DBA can be used as a “trade name” to brand your products or services
- A DBA can be used to get a business license
Register Your Business and Obtain an EIN
You’ll officially create a corporation, LLC or other business entity by filing forms with your state’s business agency―usually the Secretary of State. As part of this process, you’ll need to choose a registered agent to accept legal documents on behalf of your business. You’ll also pay a filing fee. The state will send you a certificate that you can use to apply for licenses, a tax identification number (TIN) and business bank accounts.
Next, apply for an employer identification number (EIN) . All businesses, other than sole proprietorships with no employees, must have a federal employer identification number. Submit your application to the IRS and you’ll typically receive your number in minutes.
Get Appropriate Licenses and Permits
Legal requirements are determined by your industry and jurisdiction. Most businesses need a mixture of local, state and federal licenses to operate. Check with your local government office (and even an attorney) for licensing information tailored to your area.
- Best LLC Services
- How To Register a Business Name
- How To Register a DBA
- How To Get an EIN for an LLC
- How To Get a Business License
Start an LLC Online Today With ZenBusiness
Click on the state below to get started.
Open a Business Bank Account
Keep your business and personal finances separate. Here’s how to choose a business checking account —and why separate business accounts are essential. When you open a business bank account, you’ll need to provide your business name and your business tax identification number (EIN). This business bank account can be used for your business transactions, such as paying suppliers or invoicing customers. Most times, a bank will require a separate business bank account to issue a business loan or line of credit.
Hire a Bookkeeper or Get Accounting Software
If you sell a product, you need an inventory function in your accounting software to manage and track inventory. The software should have ledger and journal entries and the ability to generate financial statements.
Some software programs double as bookkeeping tools. These often include features such as check writing and managing receivables and payables. You can also use this software to track your income and expenses, generate invoices, run reports and calculate taxes.
There are many bookkeeping services available that can do all of this for you, and more. These services can be accessed online from any computer or mobile device and often include features such as bank reconciliation and invoicing. Check out the best accounting software for small business, or see if you want to handle the bookkeeping yourself.
Determine Your Break-Even Point
Before you fund your business, you must get an idea of your startup costs. To determine these, make a list of all the physical supplies you need, estimate the cost of any professional services you will require, determine the price of any licenses or permits required to operate and calculate the cost of office space or other real estate. Add in the costs of payroll and benefits, if applicable.
Businesses can take years to turn a profit, so it’s better to overestimate the startup costs and have too much money than too little. Many experts recommend having enough cash on hand to cover six months of operating expenses.
When you know how much you need to get started with your business, you need to know the point at which your business makes money. This figure is your break-even point.
In contrast, the contribution margin = total sales revenue – cost to make product
For example, let’s say you’re starting a small business that sells miniature birdhouses for fairy gardens. You have determined that it will cost you $500 in startup costs. Your variable costs are $0.40 per birdhouse produced, and you sell them for $1.50 each.
Let’s write these out so it’s easy to follow:


































.png)
.jpg)
-min.webp)


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process.
10 steps to start your business; Plan your business. Market research and competitive analysis; Write your business plan; Calculate your startup costs ... You can search the web to find free templates to build your business plan. We discuss nine components of a model business plan here: Key partnerships. Note the other businesses or services you ...
Create a Company Description. After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you'll need to ...
Step 1: Executive summary. Think of the executive summary as the elevator pitch for your startup. It's a quick snapshot that captures the heart of your business idea, mission, and goals. In this brief section, make sure to highlight who your target audience is, what sets you apart in the market, and your unique selling points.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
Business Model: Briefly explain how your startup generates revenue and sustains profitability. Outline your monetization strategy, pricing model, ... The optimal length for a startup business plan typically depends on the specific requirements and intended audience, but a concise and focused plan of around 20 to 30 pages is often recommended. ...
Download Startup Business Plan Template - Word. Word | Smartsheet. This startup business plan template contains the essential components you need to convey your business idea and strategy to investors and stakeholders, but you can customize this template to fit your needs. The template provides room to include an executive summary, a financial ...
1. Investors Are Short On Time. If your chief goal is using your business plan to secure funding, then it means you intend on getting it in front of an investor. And if there's one thing investors are, it's busy. So keep this in mind throughout writing a business plan.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
1. Executive Summary. While your executive summary is the first page of your business plan, it's the section you'll write last. That's because it summarizes your entire business plan into a succinct one-pager. Begin with an executive summary that introduces the reader to your business and gives them an overview of what's inside the ...
This section of your simple business plan template explores how to structure and operate your business. Details include the type of business organization your startup will take, roles and ...
This is why crafting a business plan is an essential step in the entrepreneurial process. In this post, we'll walk you through the process of filling out your business plan template, like this free, editable version: Download a free, editable one-page business plan template. We know that when looking at a blank page on a laptop screen, the idea ...
Instead of taking the time to create a business plan from scratch, start the process off with Asana's free template.To further customize your template, add evergreen information about your specific business, such as your business model, company name, address, mission statement, value proposition, or target audience.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements. No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let's dig deeper into each.
7 business plan examples: section by section. The business plan examples in this article follow this template: Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business. Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists. Market analysis.
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
A business plan template is a guide that consists of an outline of all the required sections of a perfect business plan. It also includes step-by-step instructions on how to write each section of the business plan. A good business plan usually consists of an executive summary, business overview, market analysis, operations plan, and so on.
A business plan is a document that helps small business owners determine the viability of their business idea. Combining market research and financial analysis, a professional business plan helps startup CEOs and potential investors determine if the company can compete in the target market. Typically, a good business plan consists of the following:
Complete the Business Plan Template for a Startup Business to create a working business plan for your startup. Then, contact a SCORE mentor to review and refine your plan online or in person. To increase your odds of a successful business startup, download this step-by-step business plan template you can use to plan for your new business.
A pre-developed startup business plan enhances the organization's financial stability. Infographic: Business Model: The Complete Guide to a Startup Business Model ... One such tool is the Business Model Canvas, which is a diagram used to create a visual representation of a start-up's business model. A blank canvas can be found online and needs ...
Here are a few reasons why using a business model makes better sense than using a business plan. 1. Business Model Canvas is Built for Handling Change. ... Instead of coming up with a 500 page document that describes your business model, you should start with a quick business model canvas. This will give you an idea of the key parts that are ...
7. Create a brand identity. Once you have the first six steps squared away, you can focus on developing a unique brand identity for your business. Key components include your brand personality and experience, as well as visual elements like your logo, color palette, typography, imagery, graphic elements, and more.
The type of insurance you need depends on your business model and what risks you face. ... To rank the best states to start a business in 2024, Forbes Advisor analyzed 18 key metrics across five ...
6. Create a Business Plan. Writing a business plan might feel old-school and outdated, but it has a few data-backed benefits for businesses, including: Higher average annual growth; Greater chances of success; Improved business performance; Get out a pencil and some notepad and get to work. A business plan will keep you on track and ensure you ...
Starting a clothing business: 4 key considerations. The retail clothing industry provides business models of all shapes and sizes. Choosing between options like dropshipping, print on demand, or wholesale is crucial for minimizing startup and operational costs. So before you go all-in on your business plan, consider: Your niche.
There are a number of government services available to help you plan, start or grow your business. These services can provide general advice, workshops, seminars and networking events, and can even match you with a mentor or business coach. Get expert help from a business adviser in your area. 5. Review your plan regularly
The Business Plan is a crucial step in starting your own business because it represents the goals you want to achieve and outlines how they will be accomplished. USE BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE 7. Sequoia Capital Pitch Deck ... Industry: Ed-tech startup; Business Model: Freemium, SaaS, Partnerships;
Step 2. Plan your business. As you start to plan your business, you may notice a fine line between getting strategic and getting stuck! The planning process should help you: Get clarity. Crystalize the core elements of your business model so you know your purpose and direction.
We understand this massive transformation and simplification of the portfolio and our business model has raised many questions and concerns as you continue to evaluate how to maximize value from your VMware software investments. We are proactively working with the sales teams and channel partners to help customers make this transition and ...
Tags: U.S. news, Business, Technology FILE - Hoan Ton-That, CEO of Clearview AI, demonstrates the company's facial recognition software using a photo of himself in New York on Tuesday, Feb. 22, 2022.