How to Write Your Math IA
Aug 19, 2021 | IB subjects

1. What Exactly is the Math IA?
1.1 about the math ia.
The Math IA is an internal assessment that makes up 20% of your final grade. Also known as the mathematical exploration component, students are expected to create a 6-12 page research paper with a topic of their choice.
Although the IB Mathematics curriculum includes two subjects, Analysis & Approaches (AA) and Applications & Interpretations (AI), the IA itself is the same for both of them. For SL students, the content is based on what you have learned in class. On the other hand, HL students will be expected to write something that is not from the IB syllabus.
1.2 Distribution of Marks
The criteria for both Math AA and AI are the same. The distribution of marks is also the same for both SL and HL students. The criteria includes the following five components: Presentation, Mathematical Communication, Personal Engagement, Reflection, and Use of Mathematics.
| Presentation | Mathematical Communication | Personal Engagement | Reflection | Use of Mathematics |
| 4 marks | 4 marks | 3 marks | 3 marks | 6 marks |
As you can see, the IA puts a lot of focus on the Use of Mathematics as it makes up 6 marks of your entire IA (20 marks in total) . So don’t forget the importance of this component!
1.3 The Process
Here is the process of crafting your IA:
- Deciding the topic
- Doing the calculations
- Analysing the results
- Constructing the IA
The Math IA is mainly researched based unlike the Science IA.
After deciding your topic, you will have to conduct some research on the formulas and concepts that you would like to use and see if they can be applied to real life situations. When you managed to fully understand the use of the formulas, use them to do your calculations. Your aim is to find a solution to your investigation through this process.
The next step of this is to analyse your process of calculations and gain feedback from your teachers. Finally, construct your IA using all the information mentioned above.
It is said that the process of deciding the topic is the hardest part of the Math IA . Your IA directly links to your final score for maths, so having a good understanding of how to structure your IA is very important . Don’t worry! In this article, you will find tons of advices for writing your IA!
2. How to Decide Your Math IA Topic
2.1 show the examiner how math can be applied to our everyday lives.
Many students have trouble deciding what to write for the IA. As a result, many would try to see if they can link their hobbies such as music and geography to mathematical concepts. However, it is actually better to choose a mathematical concept first and then think about how you can apply that to our everyday lives .
In simple words, your Math IA should be something that can show the examiner how mathematical concepts can be used in the real world. So, without doubt, the main spice is the use of mathematical formulas and concepts .
If you choose your topic through your hobbies first, then there is a possibility that your focus might go off the road. As a result, you might end up talking more about your hobby instead of math . However, if you choose your topic through the mathematical concepts first, you will most likely end up going into the right direction.
Therefore, it is recommended that you make a list of mathematical formulas and concepts first . Then, think about which ones are suitable for applying to real life.
2.2 How Difficult Should the Math be?
The next question that many of you might ask is, “how difficult should the math be?”. The truth is, it doesn’t have to be more difficult than the curriculum itself . For SL students, choose something that is the same level as the curriculum. The same goes for HL students.
SL students shouldn’t be too worried as you can choose anything from the syllabus. However, for HL students, many of you might be quite frustrated as you can’t choose something that is from the curriculum. It is also difficult to judge how hard a mathematical concept is. For those of you who are struggling, here are some links that can give you some inspiration!
- 50 IB Math IA Topic Ideas
https://www.lanternaeducation.com/ib-blog/50-ib-maths-ia-topic-ideas/
- 20 Math Internal Assessment Topic Ideas for IB Standard Level
https://writersperhour.com/blog/20-math-internal-assessment-topic-ideas-for-ib-standard-level
- IB HL Math IA Topics
https://coggle.it/diagram/WQCrik-6SAABUsF1/t/ib-hl-math-ia-topics
3. How Should You Write Your Math IA?
As mentioned above, the IA is based on five components. So how can you score high on these components?
3.1 Understanding the Components
<Presentation>
The way you present the data and the formulas will be evaluated. Your research content and results should also be effectively communicated throughout the IA.
Things that you should consider
- Make your IA easy to read
- Use the same font for all the mathematical formulas
- Colour your graphs and tables
- Number your graphs and figures (refer back to the numbers when talking about them)
- Don’t go over the page limit
- Show your IA to a third person (your family or friends) to see if it is easy to read
<Mathematical Communication>
Your use of mathematical symbols and equations will be evaluated. You should also define the mathematical terms when necessary.
- Use mathematical equations for your explanations
(or use tools such as screenshots of your graphing calculator, data, or graphs)
- Define terms that you haven’t learned in class
<Personal Engagement>
The personal engagement component is where you should show your personal interest in the topic as well as originality.
- Talk about your personal experience and explain why you chose to research on the topic
- Talk about the challenges that you have faced and how you have solved them
- Show how your IA has led to your personal growth
- Use first person pronouns when explaining your thoughts and personal experiences
- Explain your feelings when faced with challenges
(ex. I thought of _______, therefore I tried to __________)
<Reflection>
This component evaluates whether students have effectively reflected on their research.
- Explain anomalies and give future solutions for the problems
- If you have conducted your research in a wrong manner and managed to fix it in the end, explain how you have corrected your mistakes.
<Use of Mathematics>
This component is used to see whether the math you have used matches the level of your course.
- The most important thing is to show whether you have fully understood the topic rather than how difficult your topic is
- Choose a simple topic, but dive deep into the topic and analyse it thoroughly
3.2 The Structure
There isn’t a specific answer to how you should structure your Math IA. There are IAs that score high without having labels for the Introduction and the Conclusion.
However, as you have seen in the “Presentation” section, the effectiveness of your presentation is one of the important points that you should consider while writing your IA. Therefore, it is recommended that you divide your IA into different sections . Again, there isn’t a rule for this so as long as it is easy to read, it should be fine!
Here is one of the ways that you can structure your IA:
- Introduction
- Background Information
- Calculation
So how should you write each section? Read the section below to find out more!
3.3 How Should You Write Each Section?
<Introduction>
Your introduction should talk about what the IA is about , why you chose that particular topic , and the purpose of your IA . Remember to write the following in your introduction!
- Research question
Describe what you are investigating in a brief manner.
Write about why you chose the topic and how you are going to conduct your research . Remember to include your personal experiences when explaining because this will help you score better in the Personal Engagement component!
Be explicit about what you are trying to find out through this research.
<Background Information>
In this section, you should talk about what kind of knowledge (mathematical concepts, formulas, ways of researching) is needed in order to conduct an investigation on your research question.
The most important thing is to make your IA understandable to someone who has 0 knowledge about the mathematical concepts . Therefore, explain the mathematical concepts, ways of researching & collecting data, and all the steps involved clearly.
<Calculation>
This is the practical part of your IA where you have to give an answer to your research question . It is the place where you should use the mathematical concepts explained in you background information to further explore the topic.
The ways of your investigation depends on your topic. However, you are most likely going to collect data and do calculations based on it. The Mathematical Communication component is based on this section so use the mathematical formulas to explain your processes rather than using words.
Because there will be a lot of information in this section, the key is to make sure that everything is presented neatly and concisely . If you have collected a set of data, use visuals representations such as graphs to present it. That way, you can also gain points int he Presentation component too.
In order to make everything easy to understand, you should also include every single mathematical formula regardless of how simple it is .
<Conclusion>
For the conclusion, you should reflect on your entire IA instead of simply stating what happened. Here are some things that you should keep in mind when writing the IA.
- Evaluation of results
By now, you have probably answered the research question through your calculations. Using this answer, refer back to your rationale. Reflect about why you chose that topic, whether you have managed to find out what you wanted to know, and whether the answer was the same as your hypothesis .
- Limitation and challenges faced
Write about the strengths and weaknesses of your research. Again, the most important thing is your reflection. Reflect on the strengths and weaknesses. Then, explain why it went well or why it didn’t go well . Also mention your solution to certain problems that you faced during your research .
- Improvements and further exploration
State improvements that you will make in the future if you were to conduct this research again . Also talk about how you research can lead to other possible research topics . Writing about how your IA leads to the future can help you conclude it perfectly.
<Citations>
Include all citations with the correct style and format.
4. What You Should Remember
After looking at how you should write your IA, you probably have a good grasp of how everything goes now. Lastly, this article will introduce some important points that you should never forget while writing your IA!
4.1 What’s the Point of Your Research?
The main point of your research is the fact that it is a piece of research conducted by students, rather than it being a full explanation about the logic behind a mathematical concept. The examiner wants to know how the student has thought about the research process and how he/ she has analysed the results .
There is a page limit so always remember to include your own thoughts into your IA rather than a whole bunch of explanations.
4.2 Know the Importance of Your Teacher’s Feedback
Your math teacher is going to be your IA examiner so the IB limits the amount of time your teacher help you in order to protect your originality.
As a result, your feedback time is limited to only once or twice . Use this time wisely and give your best shot. Your draft should be a completed IA so that your teacher can give you advice on how to bring it to a higher level.
4.3 Handy Softwares That You Can Use
There are several softwares that can help draw graphs and figures. It is important to have clear graphical representations or tables in your IA so here are some handy softwares that you can use!
This can be used for geometry, algebra, statistics and calculus application.
- Microsoft Excel
This software can help you with collecting data and making graphs from your data.
- Microsoft Word
You can insert mathematical formulas using this software.
- IB subjects
- Intro to IB
Recent Posts
- 21 IB Graduates Share Tips to Overcome IB Struggles
- 5 Things to Consider When IB Students Choose University
- 5 Tips for Supporting IB Students as a Parent
- 50 IB CAS Ideas by IB Graduates
- 6 Examples and Tips for IB Physics IA
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
Avoid These 11 Common Mistakes in Your IB Math IA Paper
Table of contents
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay
IB Maths Resources from Intermathematics
IB Maths Resources: 300 IB Maths Exploration ideas, video tutorials and Exploration Guides
Maths IA – 300 Maths Exploration Topics
Maths ia – 300 maths exploration topics:.
Scroll down this page to find over 300 examples of maths IA exploration topics and ideas for IB mathematics students doing their internal assessment (IA) coursework. Topics include Algebra and Number (proof), Geometry, Calculus, Statistics and Probability, Physics, and links with other subjects. Suitable for Applications and Interpretations students (SL and HL) and also Analysis and Approaches students (SL and HL).
New online Maths IA Course!
I have just made a comprehensive online course: Getting a 7 in IB Maths Coursework .
Gain the inside track on what makes a good coursework piece from an IB Maths Examiner as you learn all the skills necessary to produce something outstanding. This course is written for current IB Mathematics students. There is more than 240 minutes of video tutorial content as well as a number of multiple choice quizzes to aid understanding. There are also a number of pdf downloads to support the lesson content. I think this will be really useful – check it out!
Modelling allows us to predict real world events using mathematical functions.
Why is this topic a good idea?
This topic is a nice combination of graphical skills, regression and potentially calculus. It easily links to the real world and so is easy to find engaging ideas.
Some suggested ideas:

Calculus and Physics
Calculus allows us to understand rates of change and therefore motion over time. It’s one of the most powerful tools ever invented.
This topic allows a nice demonstration of calculus skills, often links with graphical ideas and is easy to create real world links.

Data and Probability
The modern currency of the internet is data – and data collection and data interpretation skills are essential.
This topic if done well can bring in ideas of probability, statistics and other branches of mathematics.

Statistics and data analysis are important skills in business and science. There are many different tests which help us understand the significance of results
This topic if done well can allow students to do some experiments and investigations

Geometry connects us with mathematics done for over 2000 years by the likes of Euclid done with compasses and rulers.
This topic is a nice combination of graphical skills and the ability to apply to new situations.

Pure Mathematics
Pure mathematics allows us to experience ideas of proof and gets us closer to what “real” mathematicians do.
This topic is a nice chance to explore ideas in proof, number theory and complex numbers.

Matrices and computing
Here are some more interesting topic ideas spanning a variety of mathematical fields – linking to matrices and computational ideas

Using matrices to make fractals

Google page rank – billion dollar maths!
Further ideas
If the ideas above aren’t enough I’ve also added even more ideas and links below. Please explore!

1) Modular arithmetic – This technique is used throughout Number Theory. For example, Mod 3 means the remainder when dividing by 3.
2) Goldbach’s conjecture: “Every even number greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two primes.” One of the great unsolved problems in mathematics.
3) Probabilistic number theory
4) Applications of complex numbers : The stunning graphics of Mandelbrot and Julia Sets are generated by complex numbers.
5) Diophantine equations : These are polynomials which have integer solutions. Fermat’s Last Theorem is one of the most famous such equations.
6) Continued fractions : These are fractions which continue to infinity. The great Indian mathematician Ramanujan discovered some amazing examples of these.
7) Patterns in Pascal’s triangle : There are a large number of patterns to discover – including the Fibonacci sequence.
8) Finding prime numbers : The search for prime numbers and the twin prime conjecture are some of the most important problems in mathematics. There is a $1 million prize for solving the Riemann Hypothesis and $250,000 available for anyone who discovers a new, really big prime number.
9) Random numbers
10) Pythagorean triples : A great introduction into number theory – investigating the solutions of Pythagoras’ Theorem which are integers (eg. 3,4,5 triangle).
11) Mersenne primes : These are primes that can be written as 2^n -1.
12) Magic squares and cubes : Investigate magic tricks that use mathematics. Why do magic squares work?
13) Loci and complex numbers
14) Egyptian fractions : Egyptian fractions can only have a numerator of 1 – which leads to some interesting patterns. 2/3 could be written as 1/6 + 1/2. Can all fractions with a numerator of 2 be written as 2 Egyptian fractions?
15) Complex numbers and transformations
16) Euler’s identity: An equation that has been voted the most beautiful equation of all time, Euler’s identity links together 5 of the most important numbers in mathematics.
17) Chinese remainder theorem . This is a puzzle that was posed over 1500 years ago by a Chinese mathematician. It involves understanding the modulo operation.
18) Fermat’s last theorem : A problem that puzzled mathematicians for centuries – and one that has only recently been solved.
19) Natural logarithms of complex numbers
20) Twin primes problem : The question as to whether there are patterns in the primes has fascinated mathematicians for centuries. The twin prime conjecture states that there are infinitely many consecutive primes ( eg. 5 and 7 are consecutive primes). There has been a recent breakthrough in this problem.
21) Hypercomplex numbers
22) Diophantine application: Cole numbers
23) Perfect Numbers: Perfect numbers are the sum of their factors (apart from the last factor). ie 6 is a perfect number because 1 + 2 + 3 = 6.
24) Euclidean algorithm for GCF
25) Palindrome numbers: Palindrome numbers are the same backwards as forwards.
26) Fermat’s little theorem : If p is a prime number then a^p – a is a multiple of p.
27) Prime number sieves
28) Recurrence expressions for phi (golden ratio): Phi appears with remarkable consistency in nature and appears to shape our understanding of beauty and symmetry.
29) The Riemann Hypothesis – one of the greatest unsolved problems in mathematics – worth $1million to anyone who solves it (not for the faint hearted!)
30) Time travel to the future : Investigate how traveling close to the speed of light allows people to travel “forward” in time relative to someone on Earth. Why does the twin paradox work?
31) Graham’s Number – a number so big that thinking about it could literally collapse your brain into a black hole.
32) RSA code – the most important code in the world? How all our digital communications are kept safe through the properties of primes.
33) The Chinese Remainder Theorem : This is a method developed by a Chinese mathematician Sun Zi over 1500 years ago to solve a numerical puzzle. An interesting insight into the mathematical field of Number Theory.
34) Cesaro Summation: Does 1 – 1 + 1 – 1 … = 1/2? . A post which looks at the maths behind this particularly troublesome series.
35) Fermat’s Theorem on the sum of 2 squares – An example of how to use mathematical proof to solve problems in number theory.
36) Can we prove that 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 …. = -1/12 ? How strange things happen when we start to manipulate divergent series.
37) Mathematical proof and paradox – a good opportunity to explore some methods of proof and to show how logical errors occur.
38) Friendly numbers, Solitary numbers, perfect numbers. Investigate what makes a number happy or sad, or sociable! Can you find the loop of infinite sadness?
39) Zeno’s Paradox – Achilles and the Tortoise – A look at the classic paradox from ancient Greece – the philosopher “proved” a runner could never catch a tortoise – no matter how fast he ran.
40) Stellar Numbers – This is an excellent example of a pattern sequence investigation. Choose your own pattern investigation for the exploration.
41) Arithmetic number puzzle – It could be interesting to do an exploration where you solve number problems – like this one.
42) Normal Numbers – and random number generators – what is a normal number – and how are they connected to random number generators?
43) Narcissistic Numbers – what makes a number narcissistic – and how can we find them all?
44) Modelling Chaos – how we can use grahical software to understand the behavior of sequences
45) The Mordell Equation . What is the Mordell equation and how does it help us solve mathematical problems in number theory?
46) Ramanujan’s Taxi Cab and the Sum of 2 Cubes . Explore this famous number theory puzzle.
47) Hollow cubes and hypercubes investigation. Explore number theory in higher dimensions!
48) When do 2 squares equal 2 cubes? A classic problem in number theory which can be solved through computational power.
49) Rational approximations to irrational numbers. How accurately can be approximate irrationals?
50) Square triangular numbers. When do we have a square number which is also a triangular number?
51) Complex numbers as matrices – Euler’s identity. We can use a matrix representation of complex numbers to test whether Euler’s identity still holds.
52) Have you got a Super Brain? How many different ways can we use to solve a number theory problem?

1a) Non-Euclidean geometries: This allows us to “break” the rules of conventional geometry – for example, angles in a triangle no longer add up to 180 degrees. In some geometries triangles add up to more than 180 degrees, in others less than 180 degrees.
1b) The shape of the universe – non-Euclidean Geometry is at the heart of Einstein’s theories on General Relativity and essential to understanding the shape and behavior of the universe.
2) Hexaflexagons: These are origami style shapes that through folding can reveal extra faces.
3) Minimal surfaces and soap bubbles : Soap bubbles assume the minimum possible surface area to contain a given volume.
4) Tesseract – a 4D cube : How we can use maths to imagine higher dimensions.
5) Stacking cannon balls: An investigation into the patterns formed from stacking canon balls in different ways.
6) Mandelbrot set and fractal shapes : Explore the world of infinitely generated pictures and fractional dimensions.
7) Sierpinksi triangle : a fractal design that continues forever.
8) Squaring the circle : This is a puzzle from ancient times – which was to find out whether a square could be created that had the same area as a given circle. It is now used as a saying to represent something impossible.
9) Polyominoes : These are shapes made from squares. The challenge is to see how many different shapes can be made with a given number of squares – and how can they fit together?
10) Tangrams: Investigate how many different ways different size shapes can be fitted together.
11) Understanding the fourth dimension: How we can use mathematics to imagine (and test for) extra dimensions.
12) The Riemann Sphere – an exploration of some non-Euclidean geometry. Straight lines are not straight, parallel lines meet and angles in a triangle don’t add up to 180 degrees.
13) Graphically understanding complex roots – have you ever wondered what the complex root of a quadratic actually means graphically? Find out!
14) Circular inversion – what does it mean to reflect in a circle? A great introduction to some of the ideas behind non-euclidean geometry.
15) Julia Sets and Mandelbrot Sets – We can use complex numbers to create beautiful patterns of infinitely repeating fractals. Find out how!
16) Graphing polygons investigation. Can we find a function that plots a square? Are there functions which plot any polygons? Use computer graphing to investigate.
17) Graphing Stewie from Family Guy. How to use graphic software to make art from equations.
18) Hyperbolic geometry – how we can map the infinite hyperbolic plane onto the unit circle, and how this inspired the art of Escher.
19) Elliptical Curves – how this class of curves have importance in solving Fermat’s Last Theorem and in cryptography.
20) The Coastline Paradox – how we can measure the lengths of coastlines, and uses the idea of fractals to arrive at fractional dimensions.
21) Projective geometry – the development of geometric proofs based on points at infinity.
22) The Folium of Descartes . This is a nice way to link some maths history with studying an interesting function.
23) Measuring the Distance to the Stars . Maths is closely connected with astronomy – see how we can work out the distance to the stars.
24) A geometric proof for the arithmetic and geometric mean . Proof doesn’t always have to be algebraic. Here is a geometric proof.
25) Euler’s 9 Point Circle . This is a lovely construction using just compasses and a ruler.
26) Plotting the Mandelbrot Set – using Geogebra to graphically generate the Mandelbrot Set.
27) Volume optimization of a cuboid – how to use calculus and graphical solutions to optimize the volume of a cuboid.
28) Ford Circles – how to generate Ford circles and their links with fractions.
29) Classical Geometry Puzzle: Finding the Radius . This is a nice geometry puzzle solved using a variety of methods.
30) Can you solve Oxford University’s Interview Question? . Try to plot the locus of a sliding ladder.
31) The Shoelace Algorithm to find areas of polygons . How can we find the area of any polygon?
32) Soap Bubbles, Wormholes and Catenoids . What is the geometric shape of soap bubbles?
33) Can you solve an Oxford entrance question? This problem asks you to explore a sliding ladder.
34) The Tusi circle – how to create a circle rolling inside another circle using parametric equations.
35) Sphere packing – how to fit spheres into a package to minimize waste.
36) Sierpinski triangle – an infinitely repeating fractal pattern generated by code.
37) Generating e through probability and hypercubes . This amazing result can generate e through considering hyper-dimensional shapes.
38) Find the average distance between 2 points on a square . If any points are chosen at random in a square what is the expected distance between them?
39) Finding the average distance between 2 points on a hypercube . Can we extend our investigation above to a multi-dimensional cube?
40) Finding focus with Archimedes. The Greeks used a very different approach to understanding quadratics – and as a result had a deeper understanding of their physical properties linked to light and reflection.
41) Chaos and strange Attractors: Henon’s map . Gain a deeper understanding of chaos theory with this investigation.
Calculus/analysis and functions

1) The harmonic series: Investigate the relationship between fractions and music, or investigate whether this series converges.
2) Torus – solid of revolution : A torus is a donut shape which introduces some interesting topological ideas.
3) Projectile motion: Studying the motion of projectiles like cannon balls is an essential part of the mathematics of war. You can also model everything from Angry Birds to stunt bike jumping. A good use of your calculus skills.
4) Why e is base of natural logarithm function: A chance to investigate the amazing number e.
5) Fourier Transforms – the most important tool in mathematics? Fourier transforms have an essential part to play in modern life – and are one of the keys to understanding the world around us. This mathematical equation has been described as the most important in all of physics. Find out more! (This topic is only suitable for IB HL students).
6) Batman and Superman maths – how to use Wolfram Alpha to plot graphs of the Batman and Superman logo
7) Explore the Si(x) function – a special function in calculus that can’t be integrated into an elementary function.
8) The Remarkable Dirac Delta Function . This is a function which is used in Quantum mechanics – it describes a peak of zero width but with area 1.
9) Optimization of area – an investigation . This is an nice example of how you can investigation optimization of the area of different polygons.
10) Envelope of projectile motion . This investigates a generalized version of projectile motion – discover what shape is created.
11) Projectile Motion Investigation II . This takes the usual projectile motion ideas and generalises them to investigate equations of ellipses formed.
12) Projectile Motion III: Varying gravity . What would projectile motion look like on different planets?
13) The Tusi couple – A circle rolling inside a circle . This is a lovely result which uses parametric functions to create a beautiful example of mathematical art.
14) Galileo’s Inclined Planes . How did Galileo achieve his breakthrough understanding of gravity? Follow in the footsteps of a genius!
Statistics and modelling 1 [topics could be studied in-depth]

1) Traffic flow : How maths can model traffic on the roads.
2) Logistic function and constrained growth
3) Benford’s Law – using statistics to catch criminals by making use of a surprising distribution.
4) Bad maths in court – how a misuse of statistics in the courtroom can lead to devastating miscarriages of justice.
5) The mathematics of cons – how con artists use pyramid schemes to get rich quick.
6) Impact Earth – what would happen if an asteroid or meteorite hit the Earth?
7) Black Swan events – how usefully can mathematics predict small probability high impact events?
8) Modelling happiness – how understanding utility value can make you happier.
9) Does finger length predict mathematical ability? Investigate the surprising correlation between finger ratios and all sorts of abilities and traits.
10) Modelling epidemics/spread of a virus
11) The Monty Hall problem – this video will show why statistics often lead you to unintuitive results.
12) Monte Carlo simulations
13) Lotteries
14) Bayes’ theorem : How understanding probability is essential to our legal system.
15) Birthday paradox: The birthday paradox shows how intuitive ideas on probability can often be wrong. How many people need to be in a room for it to be at least 50% likely that two people will share the same birthday? Find out!
16) Are we living in a computer simulation? Look at the Bayesian logic behind the argument that we are living in a computer simulation.
17) Does sacking a football manager affect results ? A chance to look at some statistics with surprising results.
18) Which times tables do students find most difficult? A good example of how to conduct a statistical investigation in mathematics.
19) Introduction to Modelling. This is a fantastic 70 page booklet explaining different modelling methods from Moody’s Mega Maths Challenge.
20) Modelling infectious diseases – how we can use mathematics to predict how diseases like measles will spread through a population
21) Using Chi Squared to crack codes – Chi squared can be used to crack Vigenere codes which for hundreds of years were thought to be unbreakable. Unleash your inner spy!
22) Modelling Zombies – How do zombies spread? What is your best way of surviving the zombie apocalypse? Surprisingly maths can help!
23) Modelling music with sine waves – how we can understand different notes by sine waves of different frequencies. Listen to the sounds that different sine waves make.
24) Are you psychic? Use the binomial distribution to test your ESP abilities.
25) Reaction times – are you above or below average? Model your data using a normal distribution.
26) Modelling volcanoes – look at how the Poisson distribution can predict volcanic eruptions, and perhaps explore some more advanced statistical tests.
27) Could Trump win the next election ? How the normal distribution is used to predict elections.
28) How to avoid a Troll – an example of a problem solving based investigation
29) The Gini Coefficient – How to model economic inequality
30) Maths of Global Warming – Modeling Climate Change – Using Desmos to model the change in atmospheric Carbon Dioxide.
31) Modelling radioactive decay – the mathematics behind radioactivity decay, used extensively in science.
32) Circular Motion: Modelling a Ferris wheel . Use Tracker software to create a Sine wave.
33) Spotting Asset Bubbles . How to use modeling to predict booms and busts.
34) The Rise of Bitcoin . Is Bitcoin going to keep rising or crash?
35) Fun with Functions! . Some nice examples of using polar coordinates to create interesting designs.
36) Predicting the UK election using linear regression . The use of regression in polling predictions.
37) Modelling a Nuclear War . What would happen to the climate in the event of a nuclear war?
38) Modelling a football season . We can use a Poisson model and some Excel expertise to predict the outcome of sports matches – a technique used by gambling firms.
39) Modeling hours of daylight – using Desmos to plot the changing hours of daylight in different countries.
40) Modelling the spread of Coronavirus (COVID-19) . Using the SIR model to understand epidemics.
41) Finding the volume of a rugby ball (or American football) . Use modeling and volume of revolutions.
42) The Martingale system paradox. Explore a curious betting system still used in currency trading today.
Statistics and modelling 2 [more simplistic topics: correlation, normal, Chi squared]

1) Is there a correlation between hours of sleep and exam grades? Studies have shown that a good night’s sleep raises academic attainment.
2) Is there a correlation between height and weight? (pdf). The NHS use a chart to decide what someone should weigh depending on their height. Does this mean that height is a good indicator of weight?
3) Is there a correlation between arm span and foot height? This is also a potential opportunity to discuss the Golden Ratio in nature.
4) Is there a correlation between smoking and lung capacity?
5) Is there a correlation between GDP and life expectancy? Run the Gapminder graph to show the changing relationship between GDP and life expectancy over the past few decades.
7) Is there a correlation between numbers of yellow cards a game and league position? Use the Guardian Stats data to find out if teams which commit the most fouls also do the best in the league.
8) Is there a correlation between Olympic 100m sprint times and Olympic 15000m times? Use the Olympic database to find out if the 1500m times have got faster in the same way the 100m times have got quicker over the past few decades.
9) Is there a correlation between time taken getting to school and the distance a student lives from school?
10) Does eating breakfast affect your grades?
11) Is there a correlation between stock prices of different companies? Use Google Finance to collect data on company share prices.
12) Is there a correlation between blood alcohol laws and traffic accidents ?
13) Is there a correlation between height and basketball ability? Look at some stats for NBA players to find out.
14) Is there a correlation between stress and blood pressure ?
15) Is there a correlation between Premier League wages and league positions ?
16) Are a sample of student heights normally distributed? We know that adult population heights are normally distributed – what about student heights?
17) Are a sample of flower heights normally distributed?
18) Are a sample of student weights normally distributed?
19) Are the IB maths test scores normally distributed? (pdf). IB test scores are designed to fit a bell curve. Investigate how the scores from different IB subjects compare.
20) Are the weights of “1kg” bags of sugar normally distributed?
21) Does gender affect hours playing sport? A UK study showed that primary school girls play much less sport than boys.
22) Investigation into the distribution of word lengths in different languages . The English language has an average word length of 5.1 words. How does that compare with other languages?
23) Do bilingual students have a greater memory recall than non-bilingual students? Studies have shown that bilingual students have better “working memory” – does this include memory recall?
Games and game theory

1) The prisoner’s dilemma : The use of game theory in psychology and economics.
3) Gambler’s fallacy: A good chance to investigate misconceptions in probability and probabilities in gambling. Why does the house always win?
4) Bluffing in Poker: How probability and game theory can be used to explore the the best strategies for bluffing in poker.
5) Knight’s tour in chess: This chess puzzle asks how many moves a knight must make to visit all squares on a chess board.
6) Billiards and snooker
7) Zero sum games
8) How to “Solve” Noughts and Crossess (Tic Tac Toe) – using game theory. This topics provides a fascinating introduction to both combinatorial Game Theory and Group Theory.
9) Maths and football – Do managerial sackings really lead to an improvement in results? We can analyse the data to find out. Also look at the finances behind Premier league teams
10) Is there a correlation between Premier League wages and league position? Also look at how the Championship compares to the Premier League.
11) The One Time Pad – an uncrackable code? Explore the maths behind code making and breaking.
12) How to win at Rock Paper Scissors . Look at some of the maths (and psychology behind winning this game.
13) The Watson Selection Task – a puzzle which tests logical reasoning. Are maths students better than history students?
Topology and networks

2) Steiner problem
3) Chinese postman problem – This is a problem from graph theory – how can a postman deliver letters to every house on his streets in the shortest time possible?
4) Travelling salesman problem
5) Königsberg bridge problem : The use of networks to solve problems. This particular problem was solved by Euler.
6) Handshake problem : With n people in a room, how many handshakes are required so that everyone shakes hands with everyone else?
7) Möbius strip : An amazing shape which is a loop with only 1 side and 1 edge.
8) Klein bottle
9) Logic and sets
10) Codes and ciphers : ISBN codes and credit card codes are just some examples of how codes are essential to modern life. Maths can be used to both make these codes and break them.
11) Zeno’s paradox of Achilles and the tortoise : How can a running Achilles ever catch the tortoise if in the time taken to halve the distance, the tortoise has moved yet further away?
12) Four colour map theorem – a puzzle that requires that a map can be coloured in so that every neighbouring country is in a different colour. What is the minimum number of colours needed for any map?
13) Telephone Numbers – these are numbers with special properties which grow very large very quickly. This topic links to graph theory.
14) The Poincare Conjecture and Grigori Perelman – Learn about the reclusive Russian mathematician who turned down $1 million for solving one of the world’s most difficult maths problems.
Mathematics and Physics

1) The Monkey and the Hunter – How to Shoot a Monkey – Using Newtonian mathematics to decide where to aim when shooting a monkey in a tree.
2) How to Design a Parachute – looking at the physics behind parachute design to ensure a safe landing!
3) Galileo: Throwing cannonballs off The Leaning Tower of Pisa – Recreating Galileo’s classic experiment, and using maths to understand the surprising result.
4) Rocket Science and Lagrange Points – how clever mathematics is used to keep satellites in just the right place.
5) Fourier Transforms – the most important tool in mathematics? – An essential component of JPEG, DNA analysis, WIFI signals, MRI scans, guitar amps – find out about the maths behind these essential technologies.
6) Bullet projectile motion experiment – using Tracker software to model the motion of a bullet.
7) Quantum Mechanics – a statistical universe? Look at the inherent probabilistic nature of the universe with some quantum mechanics.
8) Log Graphs to Plot Planetary Patterns . The planets follow a surprising pattern when measuring their distances.
9) Modeling with springs and weights . Some classic physics – which generates some nice mathematical graphs.
10) Is Intergalactic space travel possible? Using the physics of travel near the speed of light to see how we could travel to other stars.
Maths and computing

1) The Van Eck Sequence – The Van Eck Sequence is a sequence that we still don’t fully understand – we can use programing to help!
2) Solving maths problems using computers – computers are really useful in solving mathematical problems. Here are some examples solved using Python.
3) Stacking cannonballs – solving maths with code – how to stack cannonballs in different configurations.
4) What’s so special about 277777788888899? – Playing around with multiplicative persistence – can you break the world record?
5) Project Euler: Coding to Solve Maths Problems . A nice starting point for students good at coding – who want to put these skills to the test mathematically.
6) Square Triangular Numbers . Can we use a mixture of pure maths and computing to solve this problem?
7) When do 2 squares equal 2 cubes? Can we use a mixture of pure maths and computing to solve this problem?
8) Hollow Cubes and Hypercubes investigation . More computing led investigations
9) Coding Hailstone Numbers . How can we use computers to gain a deeper understanding of sequences?
Further ideas:

1) Radiocarbon dating – understanding radioactive decay allows scientists and historians to accurately work out something’s age – whether it be from thousands or even millions of years ago.
2) Gravity, orbits and escape velocity – Escape velocity is the speed required to break free from a body’s gravitational pull. Essential knowledge for future astronauts.
3) Mathematical methods in economics – maths is essential in both business and economics – explore some economics based maths problems.
4) Genetics – Look at the mathematics behind genetic inheritance and natural selection.
5) Elliptical orbits – Planets and comets have elliptical orbits as they are influenced by the gravitational pull of other bodies in space. Investigate some rocket science!
6) Logarithmic scales – Decibel, Richter, etc. are examples of log scales – investigate how these scales are used and what they mean.
7) Fibonacci sequence and spirals in nature – There are lots of examples of the Fibonacci sequence in real life – from pine cones to petals to modelling populations and the stock market.
8) Change in a person’s BMI over time – There are lots of examples of BMI stats investigations online – see if you can think of an interesting twist.
9) Designing bridges – Mathematics is essential for engineers such as bridge builders – investigate how to design structures that carry weight without collapse.
10) Mathematical card tricks – investigate some maths magic.
11) Flatland by Edwin Abbott – This famous book helps understand how to imagine extra dimension. You can watch a short video on it here
12) Towers of Hanoi puzzle – This famous puzzle requires logic and patience. Can you find the pattern behind it?
13) Different number systems – Learn how to add, subtract, multiply and divide in Binary. Investigate how binary is used – link to codes and computing.
14) Methods for solving differential equations – Differential equations are amazingly powerful at modelling real life – from population growth to to pendulum motion. Investigate how to solve them.
15) Modelling epidemics/spread of a virus – what is the mathematics behind understanding how epidemics occur? Look at how infectious Ebola really is .
16) Hyperbolic functions – These are linked to the normal trigonometric functions but with notable differences. They are useful for modelling more complex shapes.
17) Medical data mining – Explore the use and misuse of statistics in medicine and science.
18) Waging war with maths: Hollow squares . How mathematical formations were used to fight wars.
19) The Barnsley Fern: Mathematical Art – how can we use iterative processes to create mathematical art?
Share this:
39 thoughts on “ maths ia – 300 maths exploration topics ”.
this website is a real reference for me, thanks!
Very interesting topics for the students who whish to go beyond the curriculum
My name is Eden and this is so good resource. Much learn of math over up in here!! $$$ E.B.D.
Dis resources halp meh al0t
Very very good thanks
I need some good quality feedback on my exploration paper! Please contact me if you can help me out!
orayt rock n roll
Hi my name is Layal and I really like this Hong does too
it really good topics in math and i really like it and its new in math.
Awesome, thx. <3
amazing thank you
It help so much when i see math topic for studie and i use experiment to expand ideas among mathmatical world for further education. I was feared zombies so i did equation to predicatate
Thank you! Good resources for ideas
Hi would investigating the formula 1 racing strategy using game theory and monte carlo simulation be a good enough topic for hl?
Thanx for great ideas
very very useful 🙂
i tried to copy the name “i tried to copy the name but it was too long” but it was too long.
very good really useful.
+ first comment in 2 years
Powered by WordPress.com .

IB Maths IA: 60 Examples and Guidance
Charles Whitehouse
The International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme offers a variety of assessments for students, including Internal Assessments (IAs), which are pieces of coursework marked by students’ teachers. The Mathematics Internal Assessment follows the same assessment criteria across Mathematics Analysis and Approaches (AA) and Mathematics Application and Interpretation (AI). It forms 20% of a student’s Mathematics grade.
In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about the IB Mathematics IA, including the structure, assessment criteria, and some tips for success.
What is the Mathematics IA?
The Maths IA is an individual exploration of an area of mathematics, based on the student’s own work with guidance from their teacher. Mathematical communication is an important part of the IA, which should be demonstrated through both effective written communication and use of formulae, diagrams, tables, and graphs. The exploration should be 12 to 20 pages long and students will spend 10 to 15 hours on the work.
Even A-Level Maths tutors and A-Level Further Maths tutors have found the concept of an IA-like component in IB Maths to be both challenging and rewarding, enriching the learning experience.
To learn more about the IB Maths Internal Assessment, you can have a look at the IB Maths AA resources as well as the IB Maths AI resources :
- IB Maths AA Past Papers
- IB Maths AI Past Papers
What are the assessment criteria?
Like most IB IAs, the IB Maths IA is marked on a group of 5 criteria which add up to 20 marks. Online Maths tutors recommend to look through these carefully before and during your investigation, to ensure that you are hitting the criteria to maximise your mark.
Source : IB Mathematics Applications and Interpretation Guide
Criterion A: Communication (4 marks) – This refers to the organisation and coherence of your work, and the clarity of your explanations. The investigation should be coherent, well-organized, and concise.
Criterion B: Mathematical Presentation (4 marks) – This refers to how well you use mathematical language, including notation, symbols and terminology. Your notation should be accurate, sophisticated, and consistent. Define your key terms and present your data in a varied but proper way (including labelling those graphs).
Criterion C: Personal Engagement (3 marks) – There should be evidence of outstanding personal engagement in the IA. This is primarily demonstrated through showing unique thinking, not just repeating analysis found in textbooks. This can be evidenced through analysing independently or creatively, presenting mathematical ideas in their own way, exploring the topic from different perspectives, making and testing predictions.
Criterion D: Reflection (3 marks) – This refers to how you evaluate both your sources and the strengths and weaknesses of any methodology you use. There should be “substantial evidence of critical reflection”. This could be demonstrated by considering what another stage of investigation could be, discussing implications of results, discussing strengths and weaknesses of approaches, and considering different perspectives.
Criterion E: Use of Mathematics (6 marks ) –
Note that only 6 marks are available for the actual use of mathematics! The focus of the investigation is on explaining well and analysing with genuine, personal curiosity. The level of mathematics expected also depends on the level the subject is studied at: Standard Level students’ maths is expected to be “correct”, while Higher Level students’ maths is expected to be “precise” and demonstrate “sophistication and rigour”.
Examiners are primarily looking for thorough understanding, which also requires clear communication of the principles behind the mathematics used - not just coming to the right answer.
Have a look at our comprehensive set resources for IB Maths developed by expert IB teachers and examiners!
- IB Maths AI SL Study Notes
- IB Maths AI HL Study Notes
- IB Maths AA SL Study Notes
- IB Maths AA HL Study Notes
What are some example research questions?
Students should choose a research area that they are interested in and have a comprehensive understanding of. Often, student may choose to consult with an expert IB Maths tutor to help them decide a good question. It should have a link to something of personal interest, as indicated by Criterion C. Popular topics include Calculus, Algebra and Number (proof), Geometry, Statistics, and Probability, or Physics. Some students make links between Math and other subjects – a good way to combine knowledge from your other IB courses!
Here are examples with details of potential research questions that could inspire your Mathematics IA:
1 - Investigating the properties of fractals and their relationship to chaos theory.
Use computer software or mathematical equations to generate and analyze fractals. Explore the patterns and properties of the fractals, such as self-similarity and complexity. Investigate how changes in the initial conditions or parameters affect the resulting fractals. Analyze the relationship between fractals and chaos theory, and how fractals can be used to model chaotic systems. Present findings through visual representations and data analysis.
2 - Analyzing the behavior of recursive sequences and their applications in computer science and cryptography.
Use mathematical formulas to generate recursive sequences and analyze their behavior. This could involve plotting the sequences and observing patterns, finding closed-form expressions for the sequences, and exploring their applications in computer science and cryptography. For example, recursive sequences can be used in algorithms for sorting and searching data, and in encryption methods such as the Fibonacci cipher. The results of the analysis could be presented in a research paper or presentation.
3 - Exploring the properties of different types of differential equations and their applications in physics and engineering.
Conduct research on the different types of differential equations and their applications in physics and engineering. This could involve studying examples of differential equations used in fields such as fluid dynamics, electromagnetism, and quantum mechanics. The properties of each type of differential equation could be analyzed, such as their order, linearity, and homogeneity. The applications of each type of differential equation could also be explored, such as how they are used to model physical systems and solve engineering problems. The findings could be presented in a report or presentation.
4 - Investigating the properties of chaotic dynamical systems and their applications in physics and biology.
Use computer simulations to model chaotic dynamical systems and explore their behavior. This could involve studying the Lorenz attractor, the logistic map, or other well-known examples of chaotic systems. The simulations could be used to investigate the sensitivity of the systems to initial conditions, the presence of strange attractors, and other key features of chaotic dynamics. The results could then be applied to real-world systems in physics and biology, such as weather patterns, population dynamics, or chemical reactions.
5 - Designing an optimized route for a delivery service to minimize travel time and fuel costs.
Use a computer program or algorithm to analyze data on the locations of delivery destinations and the most efficient routes to reach them. The program would need to take into account factors such as traffic patterns, road conditions, and the size and weight of the packages being delivered. The output would be a map or list of optimized delivery routes that minimize travel time and fuel costs. This could be used to improve the efficiency and profitability of the delivery service.
6 - Developing a model to predict the spread of infectious diseases in a population.
Collect data on the population size, infection rate, and transmission rate of the disease in question. Use this data to create a mathematical model that simulates the spread of the disease over time. The model should take into account factors such as population density, age distribution, and vaccination rates. The accuracy of the model can be tested by comparing its predictions to real-world data on the spread of the disease. The model can be used to explore different scenarios, such as the impact of different vaccination strategies or the effectiveness of quarantine measures.
7 - Investigating the relationship between different geometric shapes and their properties.
Conduct a series of experiments in which different geometric shapes are tested for various properties such as volume, surface area, and weight. The data collected could then be analyzed to determine if there is a relationship between the shape of an object and its properties. This could involve creating 3D models of the shapes using computer software, or physically measuring the shapes using laboratory equipment. The results could be presented in a graph or chart to illustrate any trends or patterns that emerge.
8 - Analyzing the behavior of projectile motion and its applications in physics.
Conduct experiments in which a projectile is launched at different angles and velocities, and its trajectory is tracked using high-speed cameras or other measurement devices. The data collected can be used to analyze the motion of the projectile and determine its velocity, acceleration, and other physical properties. This information can then be applied to real-world scenarios, such as designing rockets or calculating the trajectory of a ball in sports. Additionally, the behavior of projectile motion can be studied in different environments, such as in the presence of air resistance or in a vacuum, to better understand its applications in physics.
9 - Developing a model to predict the path of a planet based on gravitational forces.
Collect data on the mass, position, and velocity of the planet at a given time. Use the law of gravitation to calculate the gravitational forces acting on the planet from other celestial bodies in the system. Use this information to predict the path of the planet over time, taking into account any changes in velocity or direction caused by gravitational forces. The accuracy of the model could be tested by comparing its predictions to observations of the planet's actual path.
10 - Investigating the properties of conic sections and their applications in geometry and physics.
Use mathematical equations to explore the properties of conic sections such as circles, ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas. Investigate their applications in geometry, such as in the construction of satellite dishes and reflectors, and in physics, such as in the orbits of planets and comets. Develop models and simulations to demonstrate these applications and their impact on real-world scenarios.
Get expert help with IB Maths
The world's leading online IB Maths tutoring provider trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
4.92 /5 based on 480 reviews
11 - Modeling the spread of a virus through a population and analyzing the effectiveness of different intervention strategies.
Develop a mathematical model that simulates the spread of the virus through a population. The model would need to take into account factors such as the infectiousness of the virus, the rate of transmission between individuals, and the effectiveness of different intervention strategies such as social distancing or vaccination. The model could then be used to analyze the effectiveness of different intervention strategies and predict the potential impact of future outbreaks. The output of the model would be a set of data and visualizations that show the predicted spread of the virus and the effectiveness of different intervention strategies.
12 - Modeling the spread of a rumor or disease through a network and analyzing the impact of network topology.
Develop a mathematical model that simulates the spread of the rumor or disease through a network. The model should take into account factors such as the probability of transmission between individuals, the rate of recovery or decay of the rumor or disease, and the structure of the network. The impact of network topology could be analyzed by comparing the spread of the rumor or disease in different types of networks, such as random, scale-free, or small-world networks. The results of the simulation could be visualized using graphs or heat maps to show the spread of the rumor or disease over time.
13 - Developing a model to predict the growth of a population over time.
Collect data on the current population size and growth rate of the population over a period of time. Use this data to develop a mathematical model that predicts the population growth rate over time. The model could be tested by comparing its predictions to actual population growth data from previous years. The model could also be used to predict future population growth and to identify factors that may affect the population's growth rate.
14 - Investigating the properties of exponential functions and their applications in finance and economics.
Develop a mathematical model for an exponential function, including its domain and range, growth/decay rate, and asymptotes. Use this model to analyze real-world scenarios in finance and economics, such as compound interest, population growth, or stock market trends. Graph the function and interpret the results in terms of the original problem.
15 - Developing a model to predict the outcomes of a sporting event based on historical data and team statistics.
Collect historical data on the two teams playing in the sporting event, including their win-loss records, player statistics, and any relevant trends or patterns. Use this data to develop a statistical model that predicts the outcome of the game based on these factors. The model can then be tested and refined using additional data and feedback from experts in the field. The final output would be a prediction of the outcome of the game, along with a measure of the model's accuracy and any potential limitations or uncertainties.
16 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of sequences and their convergence or divergence.
Use mathematical models and computer simulations to analyze the behavior of different types of sequences. This would involve testing various sequences for convergence or divergence, and comparing their behavior under different conditions. The results of these simulations could be used to develop new mathematical theories and algorithms for analyzing sequences, and could have applications in fields such as computer science, physics, and engineering.
17 -Investigating the properties of different types of angles and their relationship to geometry and trigonometry.
Conduct a study of different types of angles, including acute, obtuse, right, and straight angles. Explore their properties, such as their degree measurements, relationships to other angles, and their use in geometry and trigonometry. This could involve creating visual aids, such as diagrams or graphs, to illustrate the concepts being studied. The results of the study could be presented in a report or presentation format, highlighting the key findings and insights gained from the investigation.
18 - Developing a model to predict the outcomes of a game based on probability theory.
Collect data on the outcomes of previous games, including the teams playing, the score, and any relevant factors such as weather conditions or injuries. Use this data to calculate the probability of each team winning based on various factors. Develop a model that takes into account these probabilities and predicts the outcome of future games. The model would need to be tested and refined using additional data and statistical analysis. The final output would be a reliable model for predicting the outcomes of games based on probability theory.
19 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of inequalities and their applications in algebra and calculus.
Create a graph to visually represent the behavior of different types of inequalities, such as linear, quadratic, and exponential inequalities. Use examples to demonstrate how these inequalities can be applied in algebra and calculus, such as finding the maximum or minimum value of a function subject to certain constraints. Additionally, provide real-world applications of these concepts, such as optimizing production processes or predicting population growth.
20 - Investigating the properties of different types of graphs and their applications in computer science and social science.
Conduct a literature review to identify the different types of graphs and their applications in computer science and social science. Develop a set of criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of different types of graphs in conveying information and insights. Use these criteria to analyze and compare several examples of graphs from each field. Based on the analysis, identify the most effective types of graphs for different types of data and research questions in each field. Develop guidelines for selecting and creating effective graphs in computer science and social science research.
21 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of matrices and their applications in linear algebra and quantum mechanics.
Conduct experiments to test the behavior of different types of matrices in linear algebra and quantum mechanics. For example, in linear algebra, the inverse of a matrix can be calculated and used to solve systems of linear equations. In quantum mechanics, matrices are used to represent quantum states and operators. The behavior of these matrices can be analyzed by performing matrix operations and observing the resulting changes in the system. The applications of these matrices in various fields can also be explored and analyzed.
22 - Developing a model to predict the outcomes of a business investment based on market trends and financial data.
Collect and analyze market trends and financial data relevant to the business investment. This could include factors such as industry growth rates, consumer demand, and financial statements of similar companies. Using this data, develop a predictive model that takes into account various variables and their potential impact on the investment. The model could be tested and refined using historical data and adjusted as new information becomes available. The output would be a prediction of the potential outcomes of the investment based on the model's calculations.
23 - Modeling the spread of a forest fire and analyzing the effectiveness of different containment strategies.
Develop a computer model of the forest fire spread using data on wind direction, temperature, humidity, and fuel load. The model could be calibrated using historical data on past forest fires to ensure its accuracy. Different containment strategies could then be simulated in the model, such as creating fire breaks or using water or fire retardant chemicals to slow the spread of the fire. The effectiveness of each strategy could be evaluated by comparing the simulated fire spread with and without the strategy in place.
24 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of optimization problems and their applications in engineering and computer science.
Conduct a literature review to identify different types of optimization problems and their applications in engineering and computer science. Develop a framework for analyzing the behavior of these problems, taking into account factors such as the size of the problem, the complexity of the solution space, and the type of optimization algorithm used. Apply this framework to a set of case studies, comparing the performance of different optimization algorithms and identifying best practices for solving different types of optimization problems.
25 - Investigating the properties of different types of geometric transformations and their applications in computer graphics and animation.
Conduct a literature review to gather information on the properties of different geometric transformations and their applications in computer graphics and animation. This could include translations, rotations, scaling, and shearing. Develop a set of test cases to demonstrate the use of these transformations in creating different types of graphics and animations. The results of these tests could be used to compare the effectiveness of different types of transformations for different applications. Additionally, the limitations and challenges associated with each transformation could be identified and discussed.
26 - Developing a model to predict the outcomes of an election based on polling data.
Collect polling data from a representative sample of the population and analyze it using statistical methods such as regression analysis or machine learning algorithms. The model would need to be trained on historical election data to ensure its accuracy. The output of the model would be a prediction of the likely outcome of the election based on the polling data and the historical trends. The model could also be used to identify key factors that are driving voter behavior and to test different scenarios, such as changes in voter turnout or shifts in public opinion.
27 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of integrals and their applications in calculus and physics.
Conduct a series of experiments to analyze the behavior of different types of integrals, such as definite and indefinite integrals, and their applications in calculus and physics. For example, one experiment could involve calculating the area under a curve using both definite and indefinite integrals and comparing the results. Another experiment could involve analyzing the motion of an object using calculus and determining its velocity and acceleration at different points in time. The results of these experiments could be used to develop a deeper understanding of the behavior of integrals and their applications in various fields.
28 - Studying the properties of different types of probability distributions and their applications in statistics and finance.
Conduct a literature review to gather information on different types of probability distributions and their applications in statistics and finance. Develop a theoretical framework to analyze the properties of these distributions and their relevance in different contexts. Use statistical software to simulate data and test the theoretical framework. Analyze the results and draw conclusions about the usefulness of different probability distributions in various applications.
29 - Developing a model to predict the outcomes of a marketing campaign based on consumer data.
Collect consumer data such as demographics, purchasing habits, and social media activity. Use this data to identify patterns and trends that can be used to develop a predictive model. The model would need to be trained using historical data on marketing campaigns and their outcomes. Once the model is trained, it can be used to predict the outcomes of future marketing campaigns based on the input data. The accuracy of the model can be tested by comparing its predictions to the actual outcomes of the campaigns.
30 - Investigating the properties of different types of symmetry and their relationship to geometry and physics.
Conduct a study of different types of symmetry, such as bilateral, radial, and rotational symmetry. This could involve creating models or diagrams of different symmetrical shapes and analyzing their properties, such as the number of axes of symmetry and the angles of rotation. The relationship between symmetry and geometry could be explored by examining how different symmetrical shapes can be used to create geometric patterns. The relationship between symmetry and physics could be investigated by exploring how symmetrical structures are used in physics, such as in the design of crystals or the study of particle physics.
31 - Modeling the spread of a rumor or news story through a population and analyzing its impact.
Develop a mathematical model that simulates the spread of the rumor or news story through a population. This model could take into account factors such as the initial number of people who hear the rumor, the rate at which they share it with others, and the likelihood that each person will believe and share the rumor. The impact of the rumor could be analyzed by looking at factors such as changes in people's behavior or attitudes, or the spread of related rumors or misinformation. The model could be refined and tested using data from real-world examples of rumor or news story propagation.
32 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of exponential growth and decay functions and their applications in science and engineering.
Use mathematical models to analyze the behavior of exponential growth and decay functions. This could involve studying the equations that describe these functions, graphing them to visualize their behavior, and analyzing how they are used in various fields such as biology, economics, and physics. Applications could include modeling population growth, decay of radioactive materials, and the spread of diseases. The results of this analysis could be used to inform decision-making in these fields and to develop more accurate models for predicting future trends.
33 - Modeling the spread of a pandemic through a population and analyzing the effectiveness of different intervention strategies.
Develop a mathematical model that simulates the spread of the pandemic through a population, taking into account factors such as the transmission rate, incubation period, and recovery rate. The model could be used to predict the number of cases over time and the effectiveness of different intervention strategies, such as social distancing, mask-wearing, and vaccination. The model would need to be validated using real-world data and adjusted as new information becomes available. The results of the analysis could be used to inform public health policies and interventions to control the spread of the pandemic.
34 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of functions and their applications in science and engineering.
Conduct a study of different types of functions, such as linear, quadratic, exponential, and logarithmic functions, and their applications in science and engineering. This could involve analyzing real-world data sets and modeling them using different types of functions to determine which function best fits the data. The study could also explore the use of functions in fields such as physics, chemistry, and economics, and how they are used to make predictions and solve problems. The results of the study could be presented in a report or presentation, highlighting the importance of understanding the behavior of different types of functions in various fields.
35 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of numerical methods for solving differential equations and their applications in science and engineering.
Conduct a series of simulations using different numerical methods for solving differential equations, such as Euler's method, Runge-Kutta methods, and finite difference methods. The simulations could involve modeling physical phenomena such as fluid flow, heat transfer, or chemical reactions. The accuracy and efficiency of each method could be compared by analyzing the error and computational time for each simulation. The results could be applied to optimize numerical methods for solving differential equations in various scientific and engineering applications.
36 - Developing a model to predict the outcomes of a medical treatment based on patient data and medical history.
Collect patient data and medical history, including demographic information, medical conditions, medications, and treatment outcomes. Use statistical analysis and machine learning algorithms to develop a predictive model that can accurately predict the outcomes of a medical treatment based on patient data and medical history. The model would need to be validated using a separate set of patient data to ensure its accuracy and reliability. The model could then be used to inform medical decision-making and improve patient outcomes.
37 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of linear regression models and their applications in analyzing trends in public opinion polls.
Collect data from public opinion polls on a particular topic of interest, such as political preferences or social attitudes. Use different types of linear regression models, such as simple linear regression, multiple linear regression, and logistic regression, to analyze the data and identify trends and patterns. Compare the performance of the different models and determine which one is most appropriate for the specific data set and research question. The results of the analysis could be used to make predictions or inform policy decisions.
38 - Developing a model to predict the growth of a startup company based on market trends and financial data.
Collect market trend data and financial data for a range of startup companies. Use statistical analysis to identify patterns and correlations between the data. Develop a predictive model based on these patterns and correlations, taking into account factors such as industry trends, competition, funding, and management. The model could be tested and refined using data from existing startups, and could be used to make predictions about the growth potential of new startups based on their characteristics and market conditions.
39 - Studying the properties of different types of statistical distributions and their applications in analyzing public health data.
Analyze public health data using different statistical distributions such as normal, Poisson, and binomial distributions. This would involve understanding the properties and characteristics of each distribution and selecting the appropriate one based on the nature of the data being analyzed. The data could then be plotted and analyzed using statistical software to identify trends and patterns, and to draw conclusions about the health outcomes being studied. The results could be presented in the form of graphs, tables, and statistical summaries.
40 - Investigating the properties of different types of series and their convergence or divergence.
Conduct a series of tests on different types of series, such as geometric, arithmetic, and harmonic series. Use mathematical formulas and calculations to determine their convergence or divergence. Graphs and charts could be used to visually represent the data and make comparisons between the different types of series. The results of the tests could be analyzed to draw conclusions about the properties of each type of series and their behavior under different conditions.
41 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of functions and their limits.
Graph the different types of functions and analyze their behavior as the input values approach certain limits. This could involve finding the asymptotes, determining if the function is continuous or discontinuous at certain points, and identifying any points of inflection. The results could be presented in a report or presentation, highlighting the similarities and differences between the different types of functions and their limits.
42 - Investigating the properties of different types of sets and their relationships in set theory.
Conduct a comparative analysis of different types of sets, such as finite and infinite sets, empty sets, and subsets. Investigate their properties, such as cardinality, intersection, union, and complement. Use diagrams and examples to illustrate the relationships between the different types of sets. This analysis could be used to develop a deeper understanding of set theory and its applications in various fields.
43 - Exploring the properties of different types of number systems, such as real, complex, or p-adic numbers.
Conduct a literature review of the properties of different number systems and compile a list of key characteristics and equations. Then, design a series of mathematical problems that test these properties for each type of number system. These problems could include solving equations, graphing functions, and analyzing patterns. The results of these problems could be used to compare and contrast the properties of each number system.
44 - Developing a model to predict the behavior of a physical system using calculus of variations.
Collect data on the physical system being studied, such as its initial state and any external factors that may affect its behavior. Use the calculus of variations to develop a mathematical model that predicts the system's behavior over time. The model can then be tested against real-world observations to determine its accuracy and refine the model as needed. The final output would be a reliable model that accurately predicts the behavior of the physical system.
45 - Investigating the properties of different types of topological spaces and their relationships in topology.
Conduct a study of the different types of topological spaces, including Euclidean spaces, metric spaces, and topological manifolds. Analyze their properties, such as compactness, connectedness, and continuity, and explore how they are related to each other. This could involve creating visual representations of the spaces, such as diagrams or models, and using mathematical tools to analyze their properties. The results of the study could be used to better understand the fundamental principles of topology and their applications in various fields.
46 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of integrals, such as line integrals or surface integrals, and their applications in physics and engineering.
Conduct a literature review on the different types of integrals and their applications in physics and engineering. This could include researching the use of line integrals in calculating work done by a force field or the use of surface integrals in calculating flux through a surface. Based on the findings, develop a research question or hypothesis related to the behavior of a specific type of integral and its application in a particular field. Design and conduct an experiment or simulation to test the hypothesis and analyze the results to draw conclusions about the behavior of the integral and its practical applications.
47 - Developing a model to predict the behavior of a chemical reaction using chemical kinetics.
Collect data on the initial concentrations of reactants, temperature, and other relevant factors for the chemical reaction being studied. Use this data to develop a mathematical model that predicts the behavior of the reaction over time. The model could be tested by comparing its predictions to actual experimental data collected during the reaction. Adjustments could be made to the model as needed to improve its accuracy. The final model could be used to predict the behavior of the reaction under different conditions or to optimize reaction conditions for maximum efficiency.
48 - Investigating the properties of different types of algebraic structures, such as groups, rings, or fields.
Conduct a thorough literature review to gather information on the properties of different algebraic structures. Develop a clear research question or hypothesis to guide the investigation. Choose a specific algebraic structure to focus on and collect data by performing calculations and analyzing examples. Compare and contrast the properties of the chosen algebraic structure with other types of algebraic structures to draw conclusions about their similarities and differences. Present findings in a clear and organized manner, using appropriate mathematical language and notation.
49 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of functions, such as trigonometric, logarithmic, or hyperbolic functions, and their applications in science and engineering.
Conduct a study of the behavior of different types of functions, such as trigonometric, logarithmic, or hyperbolic functions, and their applications in science and engineering. This study could involve analyzing real-world data sets and identifying which type of function best fits the data. The study could also involve creating models using different types of functions to predict future outcomes or behavior. The results of this study could be used to inform decision-making in fields such as engineering, finance, or physics.
50 - Developing a model to predict the behavior of a financial market using mathematical finance.
Collect data on the financial market, such as stock prices, interest rates, and economic indicators. Use mathematical models, such as stochastic calculus and differential equations, to analyze the data and develop a predictive model. The model could be tested and refined using historical data and validated using real-time data. The output would be a model that can be used to predict the behavior of the financial market and inform investment decisions.
51 - Investigating the properties of different types of complex systems and their behavior, such as network dynamics, agent-based models, or game theory.
Develop a simulation model for each type of complex system being investigated. The model would need to incorporate the relevant variables and interactions between agents or components of the system. The behavior of the system could then be observed and analyzed under different conditions or scenarios. This would allow for a better understanding of the properties and dynamics of each type of complex system and how they may behave in real-world situations.
52 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of partial differential equations and their applications in physics and engineering.
Conduct a literature review to identify different types of partial differential equations and their applications in physics and engineering. Develop mathematical models to simulate the behavior of these equations and analyze their solutions using numerical methods. The results of the analysis could be used to gain insights into the behavior of physical systems and to develop new technologies or improve existing ones. Examples of applications could include fluid dynamics, heat transfer, and electromagnetic fields.
53 - Developing a model to predict the behavior of a fluid using fluid dynamics.
Use computational fluid dynamics software to create a model of the fluid system being studied. The software would simulate the behavior of the fluid under different conditions, such as changes in flow rate or temperature. The model could be validated by comparing its predictions to experimental data. Once validated, the model could be used to predict the behavior of the fluid under different conditions, such as changes in the geometry of the system or the addition of different chemicals. These predictions could be used to optimize the design and operation of the fluid system.
54 - Investigating the properties of different types of geometric objects, such as manifolds or curves, and their applications in geometry and physics.
Conduct a literature review to gather information on the properties of different geometric objects and their applications in geometry and physics. This could involve researching existing theories and models, as well as conducting experiments or simulations to test these theories. The findings could then be analyzed and synthesized to draw conclusions about the properties of different geometric objects and their potential applications in various fields. This could also involve developing new theories or models based on the findings.
55 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of stochastic processes, such as random walks or Markov chains, and their applications in probability theory and statistics.
Conduct simulations of different stochastic processes using software such as R or Python. Analyze the behavior of the simulations and compare them to theoretical predictions. Use the results to draw conclusions about the properties of the different stochastic processes and their applications in probability theory and statistics. Additionally, explore real-world examples of stochastic processes, such as stock prices or weather patterns, and analyze their behavior using the concepts learned from the simulations.
56 - Developing a model to predict the behavior of a biological system using mathematical biology, such as population dynamics, epidemiology, or ecology.
Collect data on the biological system being studied, such as population size, birth and death rates, and environmental factors. Use this data to develop a mathematical model that can predict the behavior of the system over time. The model can be tested and refined using additional data and compared to real-world observations to ensure its accuracy. This model could be used to make predictions about the future behavior of the system, such as the spread of a disease or the impact of environmental changes on a population.
57 - Investigating the properties of different types of wave phenomena, such as sound waves or electromagnetic waves, and their applications in physics and engineering.
Conduct experiments to study the properties of different types of wave phenomena, such as frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. These experiments could involve using instruments such as oscilloscopes, microphones, and antennas to measure and analyze the waves. Applications of these wave phenomena could include designing communication systems, medical imaging technologies, and musical instruments. The results of these experiments could be presented in a report or presentation, highlighting the key findings and their significance in physics and engineering.
58 - Analyzing the behavior of different types of optimization problems in dynamic environments, such as optimal control or dynamic programming.
Conduct simulations of different optimization algorithms in dynamic environments, using various scenarios and parameters to test their performance. The results could be analyzed to determine which algorithms are most effective in different types of dynamic environments and under what conditions. This information could be used to develop more efficient and effective optimization strategies for real-world applications.
59 - Developing a model to predict the behavior of a social network using social network analysis, such as centrality measures, community detection, or opinion dynamics.
Collect data on the social network, such as the number of connections between individuals, the frequency and content of interactions, and any changes in the network over time. Use social network analysis techniques to identify patterns and trends in the data, such as the most influential individuals, the formation of subgroups or communities, and the spread of opinions or behaviors. Develop a model based on these findings that can predict future behavior or changes in the network. The model could be tested and refined using additional data or by comparing its predictions to real-world outcomes.
60 - Investigating the properties of different types of algebraic curves and surfaces, such as elliptic curves or algebraic varieties, and their applications in algebraic geometry.
Conduct a literature review to gather information on the properties of different types of algebraic curves and surfaces. Use mathematical software to generate and analyze examples of these curves and surfaces. Explore their applications in algebraic geometry, such as in cryptography or coding theory. Present findings in a research paper or presentation.
How can I score highly?
Scoring highly in the mathematics internal assessment in the IB requires a combination of a thorough understanding of mathematical concepts and techniques, effective problem-solving skills, and clear and effective communication.
To achieve a high score, students should start by choosing a topic that interests them and that they can explore in depth. They should also take the time to plan and organize their report, making sure to include a clear introduction, a thorough development, and a thoughtful conclusion. The introduction in particular should demonstrate students’ genuine personal engagement with the topics.
Students should pay attention to the formal presentation and mathematical communication, making sure to use proper mathematical notation, correct grammar and spelling, and appropriate use of headings and subheadings.
Finally, students should make sure to engage with the problem and reflect on their own learning, and also make connections between different mathematical concepts and techniques. If they feel difficulty in these, then taking the help of an IB tutor can prove to be quite beneficial.
By following these steps, students can increase their chances of scoring highly on their mathematics internal assessment and contribute positively to their overall grade in the IB Mathematics course.
Need help from an expert?
The world’s top online tutoring provider trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
Study and Practice for Free
Trusted by 100,000+ Students Worldwide
Achieve Top Grades in your Exams with our Free Resources.
Practice Questions, Study Notes, and Past Exam Papers for all Subjects!
Need Expert Help?
If you’re looking for assistance with IB Maths, get in touch with the TutorChase team and we’ll be able to provide you with an expert IB Maths tutor . We’ll be there every step of the way!

Professional tutor and Cambridge University researcher

Written by: Charles Whitehouse
Charles scored 45/45 on the International Baccalaureate and has six years' experience tutoring IB and IGCSE students and advising them with their university applications. He studied a double integrated Masters at Magdalen College Oxford and has worked as a research scientist and strategy consultant.
Related Posts

Is IB Maths Hard?

IB Chemistry IA: 60 Examples and Guidance

IB Physics IA: 60 Examples and Guidance

Hire a tutor
Please fill out the form and we'll find a tutor for you
- Select your country
- Afghanistan
- Åland Islands
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bouvet Island
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- Brunei Darussalam
- Burkina Faso
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Congo, The Democratic Republic of the
- Cook Islands
- Cote D'Ivoire
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands (Malvinas)
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern Territories
- Guinea-Bissau
- Heard Island and Mcdonald Islands
- Holy See (Vatican City State)
- Iran, Islamic Republic Of
- Isle of Man
- Korea, Democratic People'S Republic of
- Korea, Republic of
- Lao People'S Democratic Republic
- Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- Liechtenstein
- Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia, Federated States of
- Moldova, Republic of
- Netherlands
- Netherlands Antilles
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territory, Occupied
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- Russian Federation
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Serbia and Montenegro
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
- Switzerland
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Taiwan, Province of China
- Tanzania, United Republic of
- Timor-Leste
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Virgin Islands, British
- Virgin Islands, U.S.
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara

Still have questions? Let’s get in touch.
IB Math IA Guide - Math IA Shenanigans That No One Will Tell Yeh!
Ace Your IB Math IA with our ultimate guide for 2023! Get top marks and ace your IA with ease. Discover proven tips, tricks and strategies to nail your Math IA today!

Table of content
Criterion a - mathematical presentation: (levels- 0, 1, 2, 3, 4), criterion b - mathematical communication: (levels- 0, 1, 2, 3, 4), criterion c - personal engagement: (levels - 0, 1, 2, 3), criterion d - reflection: (levels - 0, 1, 2, 3), criterion e - use of mathematics: (levels - 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), introduction, body of your exploration.
IB Math students will tell you how they’re always on the edge of their seats for some help, but IB Math IA takes that anxiety to an entirely different level. The reality is far from frightening; nonetheless, IB Math IA can be handled well with a unique IB Math IA topic in hand and lots of coffee!
But does that guarantee a dependable 7?
It takes more than just a perfect IB Math IA topic to ace.
How’s that, you’d ask.
From researching several IB Math IA examples to planning the mathematical working of your exploration, your IB Math IA structure will get you into trouble if you don’t give it the time it demands. With all the varied content available in bulk online, the process is bound to become anything but easy.
But worry not!
You are at the right place - The Ultimate Guide to IB Math IA!
This article covers IB Math IA rubrics, process key pointers, the structure of the investigation, and interesting IB Math IA topics that will stimulate your mind and help you begin your exploration!
You should also know about the updated course structure of IB Mathematics. Students are allowed to opt for any one of the following four courses in Math:
- Analysis and Approaches ( AA HL ) - Higher Level
- Analysis and Approaches (AA SL) - Standard Level
- Applications and Interpretation (AI HL) - Higher Level
- Applications and Interpretation (AI SL) - Standard Level
For more information about choosing your course, check out our latest article: Confused about IB Math AA & IB Math AI?
Also, here’s a great surprise for all students!
Patrick Jones , the creator of PatrickJMT Math Videos, acknowledged as the best Math teacher globally with over 1.2 million subscribers on YouTube, has gotten on board with our team at Nail IB! How great is that! He is already working on creating an entire Nail IB video course, and it will prove to be a wholesome guide for you as you tread on your IB Math journey! You should check out his excellent, world-renowned content here !
Before moving any further, we insist you check out our Free IB Resources for IB Mathematics SL and IB Mathematics HL. These are specially assembled for your benefit and will surely assist you on your IB Math journey!
For an absolute hold on IB Math, check out our premium notes designed and curated specially for you, be it IB Mathematics SL or IB Mathematics HL . These bundles are not just limited to messages but offer past year papers and How-to Guides for Extended Essays, Internal Assessments, and more; examples included! You’re in for a smooth ride with these by your side;)
You can also stream our webinar on How to Write an IB Math Internal Assessment in under 30 minutes and hear directly from a recent IB graduate to understand the fundamental pointers and some fantastic hacks to lay the foundation of your IB Math IA. Getting the proper guidance ensures you a 7 in the subject you have feared for too long. Click here to watch it now!
First things first, let’s understand the criteria. Unless we acknowledge the requirements against which our exploration is scored, it’ll be equivalent to a shot in the dark. The conditions, irrespective of whether you opt for SL, HL (AA or AI), are as follows:
Assessment is done on the conciseness, brevity, and clarity/coherence of your investigation. The proper structure must be given to your IA. As per IB guidelines,
a coherent exploration is,
- Logically developed
- Easy to follow and,
- Meets the Aim.
Also, a well-organized exploration,
- Includes Introduction
- Describes the Aim of the investigation and
- Has a Conclusion
Assessment is done on the appropriateness of the mathematical terminology, notation, and symbols used to progress the exploration. Marks and notes should be correctly used as are used in IB textbooks. For example, x2 should not be written as x^2.
If used, different mathematical representation tools such as tables, graphs, and diagrams must be relevant to the working and be commented on/explained well. Avoid inconsistent use of Mathematical terminology. Applying ICT Tools(for example- GeoGebra and Desmos ) should be made wisely. For Calculations, Graphic Display Calculators can also be used, but that doesn't outdo math formulas' importance.
Assessment is done on the personal involvement shown. The sure shot way to ensure Engagement is, first and foremost, by going ahead with a topic that interests you (something unique or that affects real-life situations). Personal Engagement is seen throughout the exploration by:
- Independent thinking and creativity showed by the student
- Making the Math Idea your own
- Investigating the idea from varied perspectives
- Exploring different possibilities
Avoid portraying superficial interest. Opportunities for demonstration of personal Engagement should be noticed.
Assessment is done on the evaluation and analysis of the investigation. Mentioning the significance of your exploration results, discussing possible limitations, and justifying why you chose the procedure you did can portray a fair reflection of the IA. Merely explaining your results will get you only a score of 1 out of 3. According to IB guidelines, a review should be meaningful and critical.
A meaningful reflection includes
- Considering limitations in the work
- Comparing different Mathematical Approaches
- Linking to the Aim
- Commenting on the Learning
A critical reflection entails,
- Considering What Next
- Discussing the implications of the results
- Discussing the strengths and weaknesses of the approaches
- Considering different perspectives
Reflection is an analysis of the student's work, seen throughout the exploration, not just the Conclusion.
Assessment is done on the implementation of Mathematics in the IA. It is essential to understand that the Math used should be on par with the course, nothing too simple and nothing you need help understanding. Also, the Mathematics used should be fully understood and engrained by you. Unfamiliar Mathematics, if used, should be explained well by giving personal examples. As per IB guidelines, students are expected to produce work that is,
- Commensurate with the level of the course(should either be part of the syllabus at a similar level or slightly beyond)
- Relevant Mathematics used means Math which supports the development of the exploration towards the completion of its Aim
To score higher levels in Criterion E, it is crucial to understand the meaning of the following terms:
- Precise Mathematics is error-free and uses an appropriate level of accuracy at all times
- Sophistication means the Math should be commensurate with the HL syllabus
- Rigour involves clarity of logic and language when making Mathematical arguments and calculations.
Here is a fully annotated sample IB Math IA, going through which you can gain a lot of insight (Read the annotations properly).
Another example, the Breaking the Code investigation(fully annotated)- is given here for IB Mathematics HL. The IA explores encryption and decryption in the context of Mathematics.
- Going through the report, we see that the document needs more structure in the beginning since the Introduction does not mention the Rationale or Aim. You don't want to be committing such a blunder.
- Moving further, we see that the body encompasses Math, which is well explained, thereby excelling on criterion E when graded on the SL scale. To excel in HL, the math should have been more rigorous than descriptive.
- Toward the end, the report needs to include a Reflection on the results obtained, which doesn't fare well for the IA. Potential implications of the topic need to be included, and the Conclusion seems bland.
Another interesting annotated sample- for IB Mathematics SL- Regularisation of Irregular Verbs: When can I use the words swimming and know correctly? is given for reference here . Understand which key points have been missed and which have been taken care of. The more you go through sample IAs, the better your chances of preparing an investigation that'll be scored well.
Like any other exploration, your IB Math IA expects you to give it a fair shot of effort and interest. If you see it as a burden, it will undoubtedly become one. Equally important is to draw an analogy between the topic of your choice and the math involved. Taking care of these points in general, let's understand all that goes into making one's IB Math IA (a brief outline):
- It can have a personal story attached; mention it in your Introduction. If not, explain how the topic underhand impacts real-world situations and motivates you to land on it. Your passion for the IA idea shows in your work, and you don't want to be doing your investigation just for the sake of it.
- f you're curious about Fibonacci numbers, the Golden ratio , and nature alike, try looking for relationships among them on the Internet. This will entail going through many research papers, publications, and journals and finally settling on mathematical findings and proofs that will help you investigate that particular something you wish to explore. For example, if you want to study how Traffic Jams have math running in the background , research it in detail since Traffic snarls are an imminent pain for us all. Only you will have to pick up parts you think are relevant and understandable to you.
- The cycle of Inquiry, Action, and Reflection in learning is vital. Learning the implication of Plagiarism, Collusion, and Duplication of Work is essential to keep one's IA transparent and impressive.
- Besides citing references in the bibliography section, ensure you include it in the body as a footnote or in the exploration itself. Citing credible sources shows how transparent your work is and helps examiners cross-check for correctness. Acknowledging the author's work is essential to the IA-making process.
With this, let's discuss the Structure/Layout of the Investigation. There are numerous guidelines available all over the Internet. Regarding the IA length, though you should keep 6 -12 pages as the prescribed length, your focus should be on including all that pertains to your idea and ruling out everything that's not. So don't set out with a mindset to refrain from exceeding six pages; set out to include everything you know needs to be. Similarly, it is advised to make sure the Math used is suitable for SL and HL levels.
Without any further adieu, let's highlight what the layout of the IA should look like:
- Sets the background of your exploration and gives an argument for your topic choice. Your Rationale tells why you chose so and so topic.
- This is where you define your investigation's objective and tell what you wish to achieve with this idea.
- Let's say, for instance, you have opted for Math HL; for a simple mathematical investigation that scores six on the Math SL grade scale, you might end up with a mere four on the HL. The difficulty of your opted Math subject should reflect in your Internal Assessment. It would help if you also outlined the areas of mathematics you will cover in your investigation.
- Elaborate on the method you used for the exploration and justify why you chose to proceed with that particular method.
- Use relevant mathematical tools like labelled graphs, charts, etc., for your mathematical work and explain them in the IA context.
- State your results relating them to the Aim of your Internal Assessment. The significance and impact of these results should be highlighted, as well. In addition, briefly tell how the exploration was helpful to you and all you have gained from it. Possibilities of extension should be mentioned. The bibliography is for you to cite the sources used by you in the making of the IA. We suggest you use the Citation Machine for additional guidance in the bibliography.
Now that we're comfortable with the IB Math IA structure let's look at some interesting IB Math IA topics that will get your creative juices flowing and help kickstart your Math IA journey today!
- Simulating models to study and forecast weather patterns. (You could come up with a personal account that led you to land on something like this)
- Exploring the different probabilities associated with a game of your choice; for example, Solitaire(if you're a game buff).
- Investigating the Math associated with the Global Positioning System(GPS) and the intricacies of the technology involved.
- Exploring Fermat's little theorem or Goldbach's conjecture (one of the most significant unsolved problems in Mathematics).
- Finding the volume and surface area of an egg, apple, mango or any other real-world object using Calculus's power (Simulation could be used). A good IA on modelling manages to score an easy 15-16 marks out of 20.
- Investigating the structural designs of bridges that prevent collapse under loading.
- Studying complex roots graphically.
- Exploring how guitar frets are arranged in Pythagoras Ratios.
- Comparing which will prove beneficial: lump-sum payment of a lottery prize or fee done in instalments?
- Understanding how ISBN codes and Credit Card Codes can be cracked.
And that's a wrap!
Just like any other IA, IB Mathematics IA needs to be started early so that you don't end up compiling just anything at the last minute!
Give it the time it needs, and it will surely pay off. It might seem heavy, but once you decide to pursue an idea of your liking, there will be no turning back! Keep in mind the essential pointers and win the battle courageously!
Want some A-quality guidance? Look no further; at Nail IB, we have assembled premium content for you to ace your IBs, and you should check out our resources for a smooth IB experience. Click here for top-notch IB resources or to assess how your prep is going! Our exclusive Nail IB course, created by Patrick Jones, will be out soon too, so stay tuned, as there is no way you would want to miss the holy grail every Math IB student wants!!
This article will serve as a solid foundation for your Math IB Internal Assessment.
IB Resources you will love!
Ibia Writing Service
Ace your grades this summer, get a free originality report, math ia topics.
Welcome to the ultimate guide to Math IB IA topics! This guide is designed to help readers understand what International Baccalaureate (IB) math Internal Assessment is and how to develop the most successful project. Understanding Math IB IA topics is essential for any student interested in pursuing the IB diploma program.
Our comprehensive guide will provide an introduction to understanding Math IB IA topics, provide an overview of math courses required for the IB diploma program, examples of past math IA topics, helpful tips on writing a math IA, strategies for selecting a good topic, and more.
The International Baccalaureate Diploma Program is recognized internationally and is a challenging program that covers a broad range of topics. The internal assessment portion of the program not only tests students’ knowledge, but their ability to apply their knowledge to real-world problems. As such, an effective and well-organized math IA is a necessity for success in the program.
By the end of this guide, readers will have a strong understanding of the importance of math IB IA topics and the necessary steps needed to compose a winning project. So let’s get started!

What is International Baccalaureate?
The International Baccaluareate (IB) Diploma Program is an internationally recognised program that requires students to complete a set of core courses. To obtain the full diploma, students must study six core classes and three electives. IB courses focus on knowledge, skills and attitudes that will help the students become lifelong learners.
IB offers different levels of diploma programs. Each program covers different topics, has different prerequisites, and has different assessments. The three levels are Primary Years Program (PYP), Middle Years Program (MYP), and Diploma Program (DP).
The Primary Years Program (PYP) is for students aged 3-11 years old. It focuses on helping young students to become inquisitive and enthusiastic life-long learners. This program consists of six core themes: Who We Are, Where We Are in Place and Time, How We Express Ourselves, How the World Works, How We Organize Ourselves, and Sharing the Planet.
The Middle Years Program (MYP) is for students aged 11-16 years old. It focuses on developing academic skills such as inquiry, communication, and critical thinking. This program consists of eight subject groups: Language and Literature, Language Acquisition, Individuals and Societies, Sciences, Mathematics, Arts, Physical and Health Education, and Design.
The Diploma Program (DP) is for students aged 16-19 years old. It is the most comprehensive level of IB instruction. This program focuses on global awareness and critical thinking. To earn the diploma, students must take six core classes, including a Theory of Knowledge class, three higher level classes, and three standard level classes. They must also complete the Creativity, Action, Service (CAS) program, designed to develop students’ physical, creative, and social skills.
Overview of Mathematics in IB
When you are participating in an International Baccalaureate (IB) program, mathematics is a core subject you must complete and pass in order to gain your diploma. The math courses offered in an IB program consist of Higher Level Maths and Standard Level Maths, with each course having its own corresponding syllabus covering the topics within it.
The Higher Level Maths course is more comprehensive and covers a wider range of topics than the Standard Level Maths course. Some of the topics included in the Higher Level Maths syllabus are Algebra & Functions, Trigonometry, Calculus, Statistics & Probability, Sequences & Series and Vectors. For the Standard Level Maths syllabus, some of the topics covered are Number, Algebra & Functions, Geometry, Statistics & Probability and Discrete Mathematics.
In addition to course topics, the IB program also outlines certain expectations for the assignments and assessment criteria that students must meet in order to be successful in their math courses. For the math Internal Assessment, students are required to complete a research project and write a report on the specific topic, usually by collecting and analyzing data. The assessment criteria for math Internal Assessments include criteria such as understanding, application, communication, and accuracy.
Upon successful completion of the IB math program, there are various educational opportunities available for students. These include college degree programs and job/career paths that require a solid understanding of mathematics. With the skills and knowledge gained from the IB math program, students will be able to apply them to further their education and career advancement.
Crafting a Winning Math IB IA
For the Math IB IA, the journey starts with selecting a topic. You should aim to pick a topic that interests you and is suitable to the syllabus. It’s important to do your research here, so that you really know what you’re talking about! After you’ve narrowed down the topic, you’ll need to draw up a research plan to guide you in your investigation.
Once you have your plan, it’s time to start doing the research and collecting data. This may require conducting interviews, surveys, or experiments. Record your observations as you go, so that you can remember them later. All of this data and information forms the basis for your IA paper.
Now comes the tricky bit – writing your paper. Be sure to use your research plan to structure the paper, and make sure to include all of your findings in the main body. Then, write the introduction, which explains what the paper is about and why it matters. Lastly, conclude your paper by summarizing the main points and emphasizing the practical implications of your research.
You should also be aware of any external sources you used in your paper, such as textbooks, journals, or websites. Be sure to cite them correctly, using an agreed-upon style such as APA or MLA. Lastly, make sure that you adhere to any formatting and layout guidelines given to you by your school.
A successful Math IB IA requires careful planning and hard work. But if you follow each step of the process, from selecting a topic to citing sources correctly, you will be well on your way to crafting a winning paper!
Examples of Math IA Topics
When it comes to Internal Assessments (IAs) in mathematics, it can be challenging to come up with a good topic. It’s important to select a topic that is interesting, relevant and within the scope of the IB mathematics curriculum.
Below we’ll provide several examples of past math IA topics and discuss suggestions from IB coordinators, teachers and students to help you come up with your own unique topic.
One example of an IA topic for Mathematics HL is a comparison of the Standard Deviation and Variance for two data sets. This could involve using different methods such as graphical analysis or direct calculations to compare the two values.
Another idea for a Math IA topic is the investigation of the relationship between two exponential functions. This could involve exploring the properties of the two functions, investigating the behavior of their respective graphs, or performing calculations to compare and contrast the two.
A third example of a Math IA topic is a study of the evolution of numerical patterns based on a given set of input numbers. This could involve analyzing the evolution of the sequence by looking at the output numbers, or calculating the difference between successive output numbers to gain insight into the pattern.
Finally, an investigation into the properties of geometric figures can also make for an interesting Math IA topic. This could involve exploring the properties of shapes such as triangles and circles, or investigating the relationships between different figures.
These are just a few ideas to get your creative juices flowing when it comes to selecting a topic for your Math IA. Remember, you can always talk to your teacher or IB coordinator for more ideas and advice on selecting the best topic for you.
Tips on Writing a Math IB IA
Strong introduction, solid research methods, effective analysis techniques, writing & presentation tips, strategies for choosing an effective math ia topic.
When deciding on the perfect math Internal Assessment (IA) topic, it’s important to pick something that is interesting, focused, and manageable. IB math topics range from Algebra, Calculus, Statistics & Probability, to Geometry and Trigonometry, so make sure that you select a topic that best fits your strengths and interests.
There are some key strategies that can help you choose an effective Math IA topic. Firstly, review all of the possible IA topics your teacher has suggested and make sure they fit the necessary criteria. Secondly, narrow down your selection by choosing a specific area from each topic that appeals to you. Thirdly, research each potential topic thoroughly to make sure there will be enough information available for a complete IA project.
In addition, it’s important to avoid topics that are too broad or too narrow. A topic that is too broad can make it difficult to focus the research, while a topic that is too narrow can limit the project and make it difficult to find sufficient resources. Once you have identified a potential topic, look into books, articles, and websites that discuss the topic in more detail to ensure there will be enough information available.
Lastly, don’t be afraid to come up with fresh ideas or topics that may not have been suggested by your teacher. A good idea is to brainstorm with your friends, teachers, or parents to generate some new ideas.
Following these strategies can help you choose an effective Math IA topic that will be interesting and within the scope of the IB criteria. With your research, you can develop a great Internal Assessment project and earn the grade you deserve.
Completing a math IB IA project, is an important and valuable part of the International Baccalaureate Diploma. It helps to develop key research and analytical thinking skills, which are important for success in any type of higher learning. Doing a thorough and effective project can be challenging but it provides the opportunity for students to use their knowledge and creativity to create a product that demonstrates their learning and understanding of the topic.
This guide has provided an overview of the IB IA program and has explored the various topics and strategies that students can use to create a successful math IB IA project. It is important for students to remember to be creative and take time to carefully choose a relevant and interesting topic, do thorough research and ask for help if needed. If the IA is done effectively, it can provide a great opportunity to gain insight into their chosen topic while also showcasing the student’s knowledge.
In summary, the International Baccalaureate IA program is a great way for students to explore a topic of their choice, develop key research and analytical thinking skills and further their knowledge and understanding of the topic. With this guide, readers can have the necessary tools to create an effective and engaging math IB IA project.

Emily Chen is a highly experienced education professional who has dedicated her career to helping students all over the world achieve their academic goals. With over seven years of experience in the education niche, Emily specializes in helping students navigate the IB Diploma program. Through her blog, Emily writes articles and provides valuable resources for IB students, covering a range of topics including study tips, exam strategies, college admissions, and career advice. Her passion for education and her desire to help students succeed has led her to become a trusted resource for IB students around the world. As a former IB Diploma Program Coordinator and teacher, Emily's knowledge and expertise are invaluable to those seeking guidance in the IB community.

How to write Music IB IA
Succeed on your Music IB Internal Assessment with detailed guidance on what to include in your project and how to complete it successfully. Learn tips for formulating a clear thesis statement, organizing and writing your paper, and proofreading your work.


Visual Arts IA Topics
Create an effective Visual Arts IB Internal Assessment with this guide! Learn about the components, research tools, and other strategies outlined in this comprehensive guide.

Design Technology IA Topics
Get all the details about Design Technology Internal Assessments. Learn about different types and topics, find inspiration and ideas, and prepare for examinations with our helpful guide. Act now and start the journey!

Physics IA Topics
Learn more about Physics IA topics with this definitive resource for students. Find out about selecting a topic, researching methods and scoring criteria. Get the right advice and get the highest score. Take action now!

From core math courses to preparing a research plan, learn everything you need to know about creating an effective Math IB IA project. Discover strategies for selecting an effective topic and writing tips to help you succeed.
Revision Policy
Money back policy, privacy policy, cookie policy, terms & conditions.
Copyright © 2023. All Rights Reserved

- Sep 20, 2023
Ultimate Guide to IB Math IA: Tips, Tricks, and Expert Support
Updated: May 20

Navigating the world of the International Baccalaureate (IB) Math Internal Assessment (IA) can be challenging. This guide is designed to provide you with essential tips and tricks to excel in your IA and introduce you to expert support that can make a significant difference in your academic journey.
Understanding the IB Math IA
The IB Math IA is a cornerstone of the IB program, allowing students to delve deep into a mathematical concept of their choice. Whether you're enrolled in Mathematics Analysis and Approaches (Math AA) or Mathematics Applications and Interpretation (Math AI), the IA is a pivotal component of your grade. It's not just about understanding mathematical concepts; it's about meticulous planning, structure, and application.
Key Elements of a Strong Math IA Structure:
Introduction: Engage the reader with real-world scenarios and provide a clear focus on your chosen topic.
Mathematical Background: Offer a concise overview of the mathematical concepts and techniques you'll be using.
Exploration: Demonstrate your ability to apply mathematical tools to real-world problems, showcasing your calculations and reasoning.
Conclusion: Summarize your findings, reflect on any limitations, and suggest potential areas for further research.
References: Cite all sources you've used, ensuring academic integrity.
Crafting Your Math IA: Tips and Tricks
Choose an Engaging Topic: Select a topic that resonates with you. Your passion will shine through in your work.
Diversify Your Sources: Use a mix of textbooks, academic journals, and reputable websites to showcase a well-researched IA.
Show Your Work: Detail your thought process, calculations, and reasoning. Visual aids like graphs and diagrams can be invaluable.
Incorporate Real-World Examples: Connect mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios to make your IA more relatable and engaging.
Seek Feedback: Regularly consult with peers, teachers, or experts to refine your IA.
Expert IB Math IA Support with Rajat Sir
If you're seeking specialized "IB Math IA help", Rajat Sir offers tailored "IB Maths IA support" to guide you through the process.
Personalized Feedback on IAs:
Rajat Sir has a proven track record of helping students secure perfect 7s on their Math IAs. The unique approach includes:
Detailed Review: Send your IA/EE/TOK Essay, and Rajat Sir will provide comments and suggestions.
Interactive Sessions: Engage in voice or Zoom calls to discuss feedback and areas of improvement.
Iterative Process: Work on the suggestions and repeat the process until your IA reaches its highest potential.
If you're at the initial stages or struggling with writing, Rajat Sir can assist in topic selection and the writing phase.
Online Personal Tutoring:
Rajat Sir provides the best IB Math IA teacher support through online personal tutoring sessions. With firsthand experience of the IB process, Rajat Sir focuses on ensuring students grasp the core concepts and develop the skills needed to excel in their exams.
Tutoring Offered For:
Physics HL / SL
Math (all levels)
The IB Math IA journey can be demanding, but with the right strategies and expert support, success is within reach. Whether you're starting your IA or refining it, this guide and Rajat Sir's expertise can be your roadmap to achieving a perfect score.
Information Related to IB Tutoring By Rajat Sir
IB tutor in India
Best IB Online Tutoring Classes
Best IB Physics Tutor
Best IB Tutors Online for Maths and Physics
Best Digital SAT Online Classes
Best Online AMC 10 Tutors
AMC Math Online Classes for class 8 to 12
AMC tutor online for class 8 to 12
AP Calculus Tutor Online
Online AP Physics Tutor
Calculus AB and BC
IB Maths Physics tutor
AMC IMO Maths Online Tutor
Digital sat online tutor
Ap Calculus Tutor
A level Tutor
TMUA STEP MAT Tutor
TMUA MAT STEP Tutor
Expert IB tutor in India
Digital SAT
Physics Olympiads
IB Maths tutors Online
IB Maths Group Classes
AP Calculus AB and BC
A level tutor in India
Recent Posts
Experimental Design FRQs on AP Physics
Ultimate Guide to a stellar IB Physics Extended Essay (EE): Tips, Tricks and Expert Guidance!
10 Hardest DIGITAL SAT Math Questions
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
IB Math SL Internal Assessment (IA) Example Topics
What’s covered:, what is the ib internal assessment (ia), ib math ia examples and ideas, how is the ib math ia scored, how does the ib math ia affect my admissions chances.
The International Baccalaureate Diploma Program , or IBDP for short, is the most common alternative to an upper-level highschool education to an AP class. It is not only challenging, but also highly recognized for college admissions around the world, making its rigor and academic difficulty worthwhile.
One of the best parts about the IBDP is that the program takes a holistic approach to schooling, as opposed to a system solely based on examinations. An important component of this is the internal assessment (IA). An IA is any component of IB that is internally graded (i.e not graded by IB). Usually the biggest one of these is a research-based essay, often called an investigation at most schools, that will allow students to take concepts learned in their 6 classes, and write a university-level paper to showcase their extents to learn above the required amount. In this blog, we will be talking about the IA for IB Math SL, one of IB’s most popular courses.
The IA is more simple than it sounds. Any piece of work that is internally graded at your school, be it oral, a presentation, or any form for media, is considered an IA. An externally graded assessment such as the official examinations at the end of the two-year program, is an external assessment. Understanding this difference is important to better prepare for your numerous IAs.
Most schools will require students to submit research papers for an IA on top of presentations and other mediums, with this research paper constituting a bulk of the IA portion of the total grade. This research paper is often intended to be investigative in nature, allowing the student to question a concept and use this curiosity to show higher-level thinking.
In the case of IB Math SL , most students will take concepts taught in class and find practical ways to use these concepts in real life. This allows students to prove understanding of a concept and its uses.
You might be struggling with getting started on your IB Math IA, but don’t worry because this is very common. Most students struggle to come up with original ideas that are interesting and enjoyable to do. Hopefully the following ideas can provide some inspiration for your IAs.
IA Idea 1 – Birthday Paradox
The idea tackles the paradoxical concept of how probability dictates that those in a room full of people are very likely to share a birthday.
This idea uses concepts from probability and data coursework in Math SL. While solving the paradox would be nothing new, perhaps taking the information and applying it into other mathematical concepts, or testing the data with a sample population of people would be an interesting direction to take. Presentation of the data is as important too – powerpoints are the go to method, so try something new! Maybe you could develop a simple application to showcase the paradox in the form of a game. The possibilities are endless, and just goes to show how creative you can be with the IA.
IA Idea 2 – Modeling Statistics
Modeling IAs can generally refer to any project where a certain change in statistics is being presented in a visual manner. One example is modeling the radioactive decay of chernobyl, and determining if conditions are suitable for living. Another example can be modeling the population of a country and determining the time left until the area is deemed overpopulated.
Modeling is in itself an easy task but trying to make the information digestible and interesting is the hard part.
IA Idea 3 – Analyzing the Math of Monopoly
A fun IA idea could be analyzing the probability and statistics behind the game Monopoly! Is there a certain strategy to win or is the game luck-based? Try collecting data on how the game behaves based on numerous trials, conveniently collected through playing the game with friends! Maybe you find that the game isn’t so based on luck, and probability shows a consistent and reliable tactic to win? This concept can be done with almost any board game, making the application of the idea boundless!
This IA idea brings the fun into Mathematics SL, and would be as fun to write a report on!
The IA is internally scored, meaning the IB isn’t responsible for any grade associated with your IA assignments. Your teachers however, are heavily associated with the process of creating your IAs for all your classes. They are the ones responsible for your IA grades, so it’s always best to refer to your teacher and request any sort of rubric that you could work with!
Each class will require a different method of grading IAs. For example, a practical science like Chemistry HL would need a more investigative approach in an IA through the scientific method as compared to an IA in Spanish SL. This means you must face each IA with a different mindset!
The IAs in Math SL make a little more than 10% of the total grade, which is a sizable chunk! You should aim to take advantage of this, because the IAs are definitely scored more leniently than the examinations and other external assessments. This 10% can be the difference between a 6 and 7 in the final grade of the class!
Don’t Overdo It
While the IAs are important, they are not intended to be as massive of a research project as the extended essay (EE), the most important piece of research work you’ll be doing as an IB student. If you find that an IA takes up time from working on your EE, you should change the IA topic to make it easier. The EE is worth much more than the IA, to the point where failing the EE immediately disqualifies a student from gaining the diploma!
Save a Great Idea
If you notice your IA idea is too difficult for the scope of an IA, then maybe it could make a great EE idea. Perhaps with more fleshing out, you could create a great EE topic, which would be beneficial in making it easier to get the diploma!
Make it Interesting
The IAs are a great opportunity to be more fun and creative compared to other projects that require more serious tones and formats. Create media and forms of presentations that are enjoyable and fun!
The IAs have no direct effects on your chances of admissions, but they do help you become a more holistic student, a quality that schools find attractive. Amongst holistic mindsets, there are numerous other factors admissions officers seek out when accepting students into their schools. To get a better understanding of your shots into a university, try CollegeVine’s admission calculator ! This intuitive tool accounts for many factors, from GPA to extracurriculars, and tells you your shots of getting into your dream school!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

50 IB Maths IA Topic Ideas
IB Maths is a struggle for most people going through their diploma. To make matters worse, on top of just doing the dreaded maths exam, we’re also expected to write a Maths IA exploration into a topic of our choice! Where do you even begin such a task? How do you even choose a topic? To make things easier, we have plenty of free Maths resources! Firstly though, we’ve compiled 50 common Maths IA topics that may spark some creative juices and set you on your way to conquering one of the hardest assignments of the diploma!
Once you have chosen your topic, you may want to check out our other posts on how to structure and format your Maths IA or how to write your IA .
NOTE: These topics are purely meant as inspiration and are not to be chosen blindly. Even though many of these topics led to high scores for some of our graduates in the past, it is important that you listen to the advice of your subject teacher before choosing any topic!
- Pascal’s triangle : Discovering patterns within this famous array of numbers
- Pythagorean triples : Can you find patterns in what numbers form a pythagorean triple?
- Monty Hall problem : How does Bayesian probability work in this real-life example, and can you add a layer of complexity to it?
- The Chinese Remainder Theorem : An insight into the mathematics of number theory
- Sum of all positive integers is -1/12? Explore this fascinating physics phenomenon through the world of sequences and series
- Birthday paradox : Why is it that in a room of people probability dictates that people are very likely to share a birthday?
- Harmonic series : Explore why certain notes/chords in music sound dissonant, and others consonant, by looking at the ratios of frequencies between the notes.
- Optimizing areas : Optimizing the area of a rectangle is easy, but can you find a way to do it for any polygon?
- Optimizing volumes : Explore the mathematics of finding a maximum volume of a cuboid subject to some constraint
- Flow of traffic : How does mathematics feed into our traffic jams that we endure every morning?
- Football statistics : Does spending a lot of cash during the transfer window translate to more points the following year? Or is there a better predictor of a team’s success like wages, historic performance, or player valuation?
- Football statistics #2 : How does a manager sacking affect results?
- Gini coefficient : Can you use integration to derive the gini coefficient for a few countries, allowing you to accurately compare their levels of economic inequality?
- Linear regressions : Run linear regressions using OLS to predict and estimate the effect of one variable on another.
- The Prisoner’s Dilemma : Use game theory in order to deduce the optimal strategy in this famous situation
- Tic Tac Toe : What is the optimal strategy in this legendary game? Will my probability of winning drastically increase by some move that I can make?
- Monopoly : Is there a strategy that dominates all others? Which properties should I be most excited to land on?
- Rock Paper Scissors : If I played and won with rock already, should I make sure to change what I play this time? Or is it better to switch?
- The Toast problem : If there is a room of some number of people, how many toasts are necessary for everyone to have toasted with everyone?
- Cracking a Password : How long would it take to be able to correctly guess a password? How much safer does a password get by adding symbols or numbers?
- Stacking Balls : Suppose you want to place balls in a cardboard box, what is the optimal way to do this to use your space most effectively?
- The Wobbly Table : Many tables are wobbly because of uneven ground, but is there a way to orient the tables to make sure they are always stable?
- The Stable Marriage Problem : Is there a matching algorithm that ensures each person in society ends up with their one true love? What is the next best alternative if this is not viable?
- Mathematical Card Tricks : Look at the probabilities at play in the famous 3 card monte scam.
- Modelling the Spread of a Virus : How long would it take for us all to be wiped out if a deadly influenza spreads throughout the population?
- The Tragedy of the Common s : Our population of fish is dwindling, but how much do we need to reduce our production by in order to ensure the fish can replenish faster than we kill?
- The Risk of Insurance : An investigation into asymmetric information and how being unsure about the future state of the world may lead us to be risk-averse
- Gabriel’s Horn : This figure has an infinite surface area but a finite volume, can you p rove this?
- Modelling the Shape of an Egg : Although it may sound easy, finding the surface area or volume of this common shape requires some in-depth mathematical investigation
- Voting Systems : What voting system ensures that the largest amount of people get the official that they would prefer? With 2 candidates this is logical, but what if they have more than 2?
- Probability : Are Oxford and Cambridge biased against state-school applicants?
- Statistics : With Tokyo 2020 around the corner, how aboutmodelling change in record performances for a particular discipline?
- Analysing Data : In the 200 meter dash, is there an advantage to a particular lane in track?
- Coverage : Calculation of rate of deforestation, and afforestation. How long will our forests last?
- Friendly numbers, Solitary numbers, perfect numbers : Investigate what changes the condition of numbers
- Force : Calculating the intensity of a climber’s fall based upon their distance above where they last clamped in
- Königsberg bridge problem : Using networks to solve problems.
- Handshake problem : How many handshakes are required so that everyone shakes hands with all the other people in the room?
- The mathematics of deceit : How con artists use pyramid schemes to get rich quick!
- Modelling radioactive decay : The maths of Chernobyl – when will it be safe to live there?
- Mathematics and photography : Exploring the relationship between the aperture of a camera and a geometric sequence
- Normal Distribution : Using distributions to examine the 2008 financial crisis
- Mechanics : Body Proportions for Track and Field events
- Modelling : How does a cup of Tea cool?
- Relationships : Do BMI ratings and country wealth share a significant relationship?
- Modelling : Can we mathematically model musical chords and concepts like dissonance?
- Evaluating limits : Exploring L’Hôpital’s rule
- Chinese postman problem : How do we calculate shortest possible routes?
- Maths and Time : Exploring ideas regarding time dilation
- Plotting Planets : Using log functions to track planets!
So there we have it: 50 IB Maths IA topic ideas to give you a head-start for attacking this piece of IB coursework ! We also have similar ideas for Biology , Chemistry , Economics , History , Physics , TOK … and many many more tips and tricks on securing those top marks on our free resources page – just click the ‘Maths resources’ button!
Still feeling confused, or want some personalised help? We offer online private tuition from experienced IB graduates who got top marks in their Maths IA.
Share article links
Related Articles

- Most Popular
30 IB Biology IA Topic Ideas!
Are you struggling with choosing your topic for your IB Biology IA? Don’t worry, we’ve all been there. Finding a topic is one of the – if not THE – most important part of writing your IA, so we want to make sure that you get it right! Luckily, there are so many great topics […]
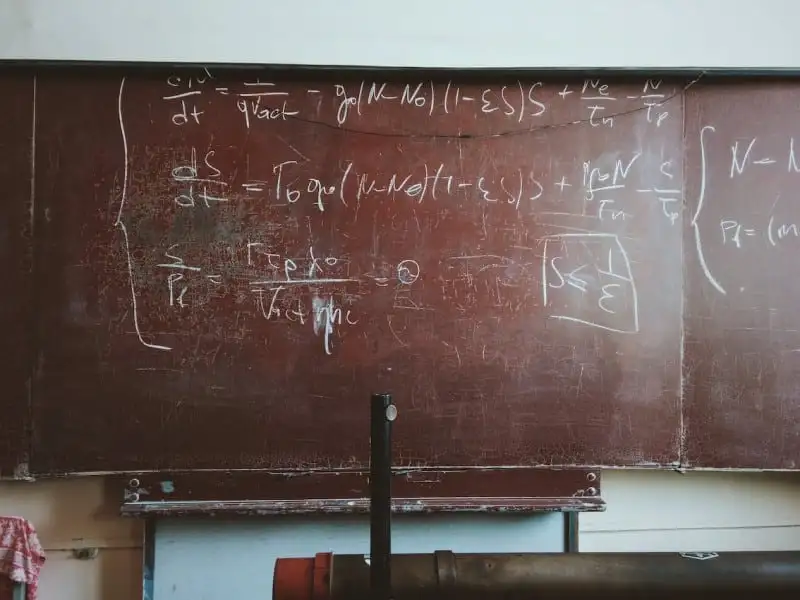
20 IB Physics IA Topic Ideas!
Choosing where to start with an IA can be the hardest part, and this is definitely true for the Physics IA. We know that our topic has to be somewhat related to the syllabus, but where should we focus? Thankfully, we’ve asked some of our favourite IB graduates for some of the ideas they pursued! […]
25 History IA Topic Ideas!
Are you about to start your History internal assessment? We know the struggle. One of the most difficult parts about the task is finding a good History IA topic because it feels like you can just write about anything. The IB breaks it down into 7 main different types of topics that you can choose, […]

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
The Definitive Guide to Choosing the Best IB Mathematics IA Topics
by Antony W
August 19, 2022

Imagine you were fascinated by the shape of nuclear reactor chimneys, called Natural Draft Cooling Towers. What an odd shape, you think (a hyperboloid, if you’re wondering). But how would you find out why they are so shaped? As it turns out, mathematics is a beautiful, fascinating language you can use to describe something like that. And when you explore such a personally fascinating subject within certain regulations of the IB, you will be writing your mathematics internal assessment.
As you can deduce, the IB math internal assessment is all about exploring mathematically a subject of personal interest. How well you do that and present your process determines how many marks out of the total 20 you will receive. However, most students live in mortal fear or both the IB math exam and the internal assessment.
If you are one such student, fear not. This detailed guide will teach you how you need to approach the math assessment by choosing the right topics, as well as how to make a top-grade essay. You can also get further IB guides in full detail here on our blog.
The team at Help for Assessments is also ready to give more than just passive “how to” assistance. Let us take the IB internal assessment nightmare away from you and write the essay for you. Our highly skilled and experienced team assures you of top-notch work, original and flawless in research and quality. All these at the best rates, so don’t hesitate to give us your order. We will even give you 25% off your first order to get you started.
Do you still want to push on? This article will give you all you need to choose suitable topics for your maths IA, explore what the test is about, and finish with some fresh sample idea topics for the math IA.
Struggling to pick your Math IA or AA topic?
What the IB Maths Internal Assessment Topics All About
The mathematics internal assessment is about exploring the math behind a topic of interest, then presenting the whole thing in the form of a short thorough report. Ideally, the topic should be completely original and serve to prove that you have a firm grasp of mathematical concepts, principals, and knowledge.
According to the IA mathematics rubric, the IBO is looking for the following in a good essay:
- Communication : Communication measures how well you organize and explain your exploration. It must be logically developed and coherent. The essay generally should have three parts: an introduction, the rationale or explanation, and a conclusion.
- Mathematical presentation: You need to use appropriate mathematical languages, with the right formulae, diagrams, tables, charts, models, and other figures as needed.
- Personal engagement: This is a measure of the level to which the student interacts with the subject matter on a personal level. It is more than being original or authentic with the idea - it has to stem from some experience in your life or one you have direct links with.
- Reflection: This criterion assesses how the student reviews and analyzes the problem and its solution in the exploration.
- Use of mathematics: This is self-explanatory - how well does the student use the concepts, knowledge, and skills gained in their respective mathematical level so far?
Thus, the maths IA is about displaying your ability to apply abstract concepts and knowledge in math to a real-world situation and communicating clearly to your audience. In this case, the audience is your instructor/professor, and writing a good IA essay starts from picking the right topic.
Not sure whether to order Math IA or AA? Click below to see our latest samples!
What Makes a Good Math IA Topic
A good topic for the IB mathematics internal assessment is one that allows you to fulfill all the above requirements. It will help you explore an area of interest deeply and exhaustively, while at the same time providing an avenue for you to put your acquired mathematical skills into good use.
If you are to be successful in these goals, your essay should have certain important qualities. These are the same qualities your topic should have:
- Simple and clear language: The rule of thumb is that everyone in your age group (your classmates) must be able to understand your essay. Thus, your topic needs to be simple. A complex subject will be hard for you to write, tough to break down into manageable bites, and ultimately cost you valuable marks.
- Concise and well-focused: The essay will be 6-12 pages in length, so you need to have a topic that can be exhaustively examined in that range. As is said in other IB assessments, the topic should be specific but not too narrow that it restrains or limits you. For example, our chosen problem of the nuclear reactor exhaust steam funnels could be confined to modeling the hyperboloid shape of the cooling towers and start from there.
- Interesting : The chosen topic needs to be exciting enough to elicit not only your interest but that of your audience. It needs to be one that is naturally intriguing to warrant a 12-page study into its underlying mathematical principles.
- Fresh : By fresh, we mean a relatively unexplored topic. Too many students do game theory, but that topic has been gone through by thousands of students in decades of consecutive years. Don't do that - go for something fresh, or seek to add an extra twist to something that already exists.
- Has clear connections with one or more mathematical fields: Your chosen topic should be based on a given mathematical area, or rely on a few of them. Drawing connections between different areas, e.g. Calculus and geometry will impress your instructor. However, always keep it within your attained academic level.
With the goal in mind, it's time to look into the process that precedes choosing a perfect math IA topic.
How to Choose a Mathematics IA Topic
Most math gurus insist that math is not just an abstract subject. It has real and effective links to the real world, and that is what the whole point of the internal assessment is.
To choose the topic, start with the real-life experiences to help you pinpoint an area of math you want to explore.
The following steps will help you:
- Brainstorm: The first hurdle is to find a general area of interest, which ideally should be related or founded on your interests. For example, if you love medicine and want to study it in the future, you can start with a certain field that fascinates you. Future lawyers, businessmen, engineers, and IT enthusiasts can all find something intriguing to pursue.
- Narrow down: With the first few ideas, the next step is to find a topic that has a lot of mathematical potential. You will find that reading lots of journals, watching videos, and talking with friends gives you lots of seed ideas for this stage.
- Evaluate: Evaluate each of the ideas you have on the strength of the qualities above. Is it relevant? Simple enough for your level? Exciting? Will it be useful to you in your career or your life?
- General research: General research into the mathematics involved in your chosen topic will help you determine what you need to learn and determine how feasible your topic is. The point here is to find out if the topic is right for you, and whether you can find the right material to base your exploration on.
- Come up with a working research question: Every IA needs to have a research question to streamline the exploration and provide direction to the essay. As with the topic, the research question needs to be specific but just wide enough to give you enough material to fill the said 6-12 pages.
Or the other hand, perhaps this topic would be better suited to the Physics IA? It’s up to you!
Do you need help with your Math IA or AA?
30+ Math IA Topics for SL and HL Levels
We’ve been writing IB Math IA assignments for over 5 years. From a professional academic writing assistance point of view, the number one challenge that many IB learners have is topic selection.
On the surface, Math IA is about investigating concepts within a topic of interest and presenting your findings in a 2,200-word report.
In practice, coming up with an original topic, which you can investigate to prove that you have a strong grip of mathematical concepts and principles can be somewhat challenging.
In this section, we put together a list of 20+ IB Math IA topic for SL and HL to help you understand what good topic looks like based on the selection criteria that we’ve shared in this guide.
- How accurate are mathematical predictions for events with a low likelihood but huge impact?
- Considering the risks involved in making decisions based on incomplete or conflicting information might make us more cautious.
- How do normal numbers fare when compared to random number generators?
- Create a virtual version of the disaster at Chernobyl and its subsequent effects on Japan.
- Do the numbers that make up a Pythagorean triple follow any kind of regularity?
- Does a high degree of association exist between BMI and GDP per capita?
- What kinds of character combinations are best for online safety in light of brute force attacks?
- To what extent does Bayesian probability work in a real-life setting and is it possible to add complexity to it?
- How do those involved in pyramid schemes or other forms of fast-paced fraud use mathematics to amass huge fortunes so quickly?
- Determine the climber's fall severity by measuring the distance from the final point of connection.
- Is it feasible to forecast the outcome of athletic events using a Poisson model and some familiarity with Excel?
- How long would it take someone to try to guess someone else’s password? What's the deal with adding symbols and digits to a password?
- How can we identify individual tones using sine waves of different frequencies?
- Is there a way to utilize arithmetic to predict how contagious diseases like measles will move across a population?
- Do large transfer window expenditures result in a higher victory percentage a sports season?
- With what method of voting can the most people be certain that their preferred candidate will win the election?
- A study of the geometric sequence's connection to the camera's aperture
- How well do you think integration would work to determine the gini coefficient for a sample of nations, allowing you to make reliable comparisons of the economic inequality between them?
- Find out if there's a correlation between music and fractions, or see if this series converges.
- If a fatal flu virus were to sweep the globe, how long do you think it would take humanity to perish?
- Examine the ratios of frequencies between notes to see why some do not sound good together while others do.
- What kinds of numbers have the most bearing on a basketball team's success?
- A look at how uncertainty about the future might make people more risk-averse and how asymmetric information plays a role in this phenomenon.
- The ideal amount of force and launch angle for a javelin or shot put world record throw.
- The gravitational attraction of other things in space causes the orbits of planets and comets to be elliptical. Look into the field of space exploration!
- Study the numbers behind the processes of heredity and natural selection.
- How can we utilize computers to learn more about sequences?
- Is it possible to employ computational methods in addition to pure mathematics to find an answer?
- Applying the mechanics of fast-moving spacecraft to the problem of interstellar travel
- Applying quantum mechanics, we may examine the universe's innate probabilistic character.
- If it takes the tortoise twice as long to cover the same distance as a runner, then there's no way the runner can catch up to it no matter how fast he runs.
- Using tools from probability and game theory, researchers investigate the most effective bluffing techniques for poker.
- Does the time it takes a kid to arrive to school depend on how far they live from the school?
- Check out the Guardian Stats to see if the top teams in the league are also the ones that commit the most fouls.
Tips to Help You Write the Best Math IA Assignment
The following tips can help you write a more comprehensive IB Math IA assignment:
1. Choose a Topic You’re Interested In
Since you will be working on your Math IA for a few months, it would be preferable if you choose a topic that genuinely interests you, rather than one that is simply required.
2. Use a Simple Language
Ensure that language is exact, clear, and succinct. Write your IA in a way that anybody of your age can read and understand.
Choosing a complicated topic may result in a disorganized and difficult-to-understand IA, so try to avoid doing so. Also, avoid writing lengthy accounts of your own experiences. This is the requirement for "Communication" on the math IA.
3. Use Appropriate Terms
Use appropriate mathematical notation and symbols throughout your IA report.
To properly format all mathematical symbols, use MathType or a comparable program for mathematical expressions. Doing so will enhance clarity and will get you easy points for "Mathematical Presentation"
IB also requires you to reflect on your findings in the report as part of your IA. Comment (thoughtfully), but avoid paraphrasing the results.
Describe some of the insights you've acquired from the IA mathematical conclusion. The greater the depth of your contemplation, the more points you will receive for the "Reflection" criterion.
Do You Need Help With Your IB Math Internal Assessment?
The mathematics internal assessment requires an astute mind to complete, and choosing the topic is the least of your worries. Many students are scared stiff on its account, but you don’t have to be. Help for Assessment is here to help you pass the internal assessment in maths, and not just because of this guide. The team here is made up of top IB experts who will do the internal assessment for you upon request. All you have to do is leave us your order here , and we guarantee you top grades and 100% original, impeccably researched, and fully proofed work. Of course, confidentiality is guaranteed, no matter where you come from.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I need help finding a math ia topic related to cars as its my interest but i am very confused and need some guidance
Hello Muhannad.
Thanks for reaching out. We’re happy to help. One of our representatives will get back to you via e-mail shortly. Thank you.
I need help in deciding a viable topic for my math is. I am very interested in cryptocurrency, the stock market, cricket, exercise, video games. Anything, but guidance would be highly appreciated.
Thanks for reaching out. We’re happy to help. One of our representatives will get back to you via your email for further assistance
Hi there, can you provide some help regarding math IA topics? I am a bit interested in the billiards topic and the math behind billiards, is the mathematics in billiards hard? or else I would like to use your help to choose a topic that has easy maths as I am an application student standard level, thank you for your coordination.
Hi, I stuck in choosing the best topic inline with the 3D shapes, for my exploration . Would you please assist me?
I am not really sure where to start for this IA. I am interested in the piano and music, however there have been past IAs on that. I don't know what else to think of.
I need help finding a math ia topic related to medicine and business
hi i need to find a topic and a research question that I am interested in. i have a few ideas but it is hard to narrow it down
Hey, I'm in need of some help finding an IA topic related to cars and I'm not sure where to start or what to do
Hi, I am Dina I need help in deciding my IA topic. I'm more concerned with the medical field and pharmacokinetics of medicines.
Hi, I would like to engage Mr. Anthony W for IB IA topic for Math AA HL for my son. Appreciate if you can get in touch wtih me at the earliest.
Hi, I need help in finding a topic about my math IA, I'm interested in the statistics and probabilities of winning a sneaker raffle. But I don't know how to do the maths of it.
Good day, I am currently struggling to come up with a math IA. I would like to do my exploration around medicine or something relating to careers. I currently have a few ideas about what I want to do, but I am in need of some assistance.
I need help finding a math IA HL topic related need some guidance.Please help me
I need help finding a math analysis and approach IA HL topic related need some guidance. Please help me
I need help in Maths IA for HL maths. How to go about to seek help?
I need a math IA topic that is related to statistics and could include something that is easy to find data for. I was thinking traffic flow, yet I don't know where to get the data from.
Hey, I have an research question for maths, but I not sure how to start it. Will someone be able to help me out?
I need to find my IA topic based on an example of how mathematics apply to real life
Hi! I need some assistance in finding an IA topic and the math. I am thinking of how essential immigrant workers are to the community and how without them especially during the pandemic, affects the food industry. I am not sure what kind of math I would have to be doing. Can you please help me?
Please help me choose an IA topic !!
Kindly read this guide carefully again. It should help you choose an IA topic for your next assignment.
i clearly don't know what to choose for my IA I don't really have some favorite stuff but I play basketball by myself not within a team or I thought if I can do an IA about coffee because I drink a lot of different types of coffee but in the same time I want a great IA that interests the person that is gonna read it
i need a ia topic and writing it
I need help finding a math ia topic related to keyboards or computers related. I was wondering if you can reach back to me immediately and we can talk about it? Thank you
Hello, I want to write a maths IA about Scouts because I was a scout and I am interested in scouts. I am finding it difficult to relate to maths and to find a research question. Do you have any suggestions for me?
hello! im currently struggling on finding my math IA topics and the due date is already getting near. can you please help me and give some guidance?
hi i need help choosing a math ia topic, anything easy and simple will be good please and thank you
i need help in find a IA for math AI HL I'm interested in exercise, dance, business, food
IA idea check
I need help in finding my internal assessment topic, which will be on modeling
I AM FINDING DIFFICUTLY IN SEARCHING IA HL MATH TOPIC. PLZ.HELP
Hello, I want help in math aa IA. I am interested in cooking so please tell me something related to it.
Hello, I am not sure what to choose as a topic for my math IA. I am a standard level student and math is not my strength so something where knowledge of simple maths is enough would be perfect. I am very interested in medicine so something in this area would suit my interest but I don't exactly know how to combine it with maths. Also, maybe math behind billiards but I don't know if this is too complicated for me.
I want to do a AA math IA in Statistics or logarithms but I don't know what topics to do or where to start.
Hey, I need help in finding a maths IA topic. I am interested in cars, technology, and cricket. Could you please help me
Hi I need help with finding a math IA topic. I'm interested in something along the lines of differentiation or volume of revolution. I'm also really interested on the knitting idea mentioned above but could not see how IB math would relate to that. Can you help me out? Thanks.
hey i need help for my math ia
i need help picking a maths IA topic related to zeno's paradox and infinite geometric sequences, I need an example that differs Achilles and the Tortoise. Otherwise a topic in medicine would also be really interesting.
We’ve updated the guide to include example topics to help you get started.
Hello Everyone,
We've updated this guide with 30+ topic ideas in Math IA for SL and HL levels for inspiration. We hope this guide continues to be helpful.
Hi, I really like chess. Do you think I could cerate an IA topic linking chess and math ? Could you help me pls?
Hi, I need help to know which theories or mathematics I could use to know what would be the number and shape necessary to cover a surface with various mosaics and (if possible) without having to break any.

Writing Your Thesis
The thesis should be the heart of your graduate school career. It will certainly be the most involved and difficult thing you do while in grad school.
Of course, before writing the thesis, one needs to have research to report. To make things easier on yourself, it’s a good idea to record your results as you work. Don’t rely on your memory to save you when you need to write everything down in your thesis! While you needn’t have everything written in final draft, having a detailed account of your research progress is a great idea. When you start your research, you and your advisor should try to establish a goal for your thesis as soon as possible. Performing research without a goal can be very difficult and even more frustrating.
When one does mathematical research, one rarely knows exactly where they are going. Gaining mathematical intuition comes from lots of hard work, not simply being very smart. A tried and true method for doing research is to do lots of examples, and make simplifying assumptions when needed. Before you can prove a theorem, you need a conjecture; these aren’t going to just fall in your lap! The idea is that after seeing enough examples, one can make a general conjecture and then hopefully prove it.
It’s a good idea to find out who else in the community (both in and out of the department) thinks about your field. You may find it useful to contact these people from time to time. This serves multiple purposes: you’ll lessen the chance of duplicating someone else’s research; you’ll find multiple sources of advice. While your advisor will likely be the single biggest source of help in writing your thesis, they needn’t be your only source. Talking to many people about your work will give you several different perspectives on the same thing. Seeing the same thing in different ways can be invaluable in understanding something.
When you have enough results such that you and your advisor are satisfied, you need to organize your work into one coherent document. This can be a highly non-trivial task! Make sure that your problem is stated clearly, along with why it is important, and how you solved it. Your thesis shouldn’t simply be a list of definitions, theorems, and proofs; there should be quite a bit of prose to explain the mathematical ambiance of your work. What is the motivation for even thinking about this problem? The more people that find your research interesting, the better.
Please refer to this manual for guidelines on formatting your thesis: http://grad.ucsd.edu/_files/academics/BlueBook%202017-18%20updated%204.13.18.pdf
Defending Your Thesis
Setting a time to defend your dissertation can be frustrating. Contact your committee members well in advance in order to check availability and schedule a date/time.
You would think that finding a time for 6 people to meet would be an easy task. However, it can be exceedingly difficult. You may need to be very flexible and accommodating in order to make things work. You may also need to be persistent about asking if you have a non-responsive committee member.
Please carefully review these guidelines regarding committee attendance:
Department Policy on Graduate Examination Format:
Effective Fall 2022, the default format of a graduate examination in the Mathematics Department is in person , i.e., all the committee members and the student are physically present in the same room for a scheduled examination . (This is set by the Division of GEPA.) However, when an unexpected situation arises and affects a committee member’s ability to participate in the examination synchronously, and when the student agrees, a remote or hybrid examination is allowed and can be decided by the committee chair or co-chairs. The following guidelines should be followed to arrange a remote or hybrid, synchronous examination:
- In forming the committee, the student needs to provide different examination options, in person, remote, or hybrid, to potential faculty committee members, and based on the conversation, the student can decide whether or not they want the faculty member on their committee. If such conversation did not take place, and if an unexpected situation arises, the faculty committee member can request remote examination, and can be released from the committee duty should the student refuse the request.
- In general, the graduate student is not allowed to opt for a remote examination unless there are extenuating circumstances, such as illness, travel difficulties related to visa problems, or a graduation deadline. Under such circumstances, the committee chair can decide to reschedule an in-person examination, or have a remote or hybrid examination.
- According to the Division of GEPA, there must be sufficient expertise among present members to examine the student. If a committee member must be absent for the scheduled exam, it is permissible for one absent committee member to examine the candidate on a separate date. The committee chair, or one co-chair, must participate synchronously in the scheduled exam.
Make sure to inform the PhD staff advisor in advance if any of your committee members will not be physically present.
During this scheduling phase, you also want to schedule your “Preliminary Appointment” with Graduate Division: https://gradforms.ucsd.edu/calendar/index.php – this appointment is optional but highly recommended! The purpose of this appointment is for them to check the margins and the formatting of your dissertation. While the above information should get you through this part without any problem, sometimes there are minor issues that arise and must be confronted (for example, published work that shows up in your dissertation has some extra requirements associated to it). The meeting should last about 30 minutes and you’ll receive a couple questionnaires to complete before your final appointment. You will also be required to schedule a Final Appointment with Graduate Division – allow at least a few days between your defense and your final appointment in order to finalize department paperwork.
In addition, the following information is critical to you completing your thesis, defending it, and completing your PhD:
- The university requires that your committee members each have a good readable draft of your dissertation at least FOUR WEEKS before your final defense.
- It is your responsibility to make arrangements with each committee member for the date and time of your defense. Room reservations should be made at the Front Desk (in person or email to [email protected])
- The Final Report form must have the original signatures of all members of the doctoral committee; the Final Report must also be signed by the program chair. (The Final Report form is initiated by the graduate coordinator and signatures are obtained from each faculty member through DocuSign.). Proxy signatures are not accepted.
- After your examination, committee chair emails PhD staff advisor confirming the passing of the defense. PhD staff advisor prepares Final Report through DocuSign.
- The final version of the thesis must conform to procedures outlined in the " Preparation and Submission Manual for Doctoral Dissertations and Master's Theses "
- The student submits the final approved dissertation to the Graduate Division at the final document review (the Final Report form is routed electronically from the program’s graduate coordinator via DocuSign). Final approval and acceptance of the dissertation by the Dean of the Graduate Division (on behalf of the University Archivist and Graduate Council) represents the final step in the completion of all requirements for the doctoral degree.
A few other suggestions:
About a week before you defend, you should send an email to your committee to remind them that your defense is coming, and you might even want to send a day-before or day-of reminder.
You should discuss the details of your defense with your advisor, but it’s basically a 50-minute talk where you highlight the main results of your dissertation. The audience is usually your committee plus a few graduate students.
Once Graduate Division has signed off on your thesis, it is time to submit your thesis online to Proquest/UMI. When you do this, they give you an option to purchase bound copies of your thesis from them. This is not particularly appealing for three reasons:
- They are rather pricey, about $40-$60 per copy
- They will print it exactly as you submitted it, according to Graduate Division standards: double-spaced, 8.5×11, etc, which doesn’t make for an attractive book. (How many of the math books on your shelf are 8.5×11 double-spaced?)
Fortunately, another option is available: self-publishing services. Originally these were intended for authors who had written a book, but couldn’t find a publisher for it, so they’d have it printed at their own expense. Nowadays, there are online sites filling this market, where you submit your manuscript and design the book yourself through their site. They can print on demand, so there is no minimum number of copies to order, and they can be quite inexpensive. A former graduate student, Nate Eldredge, chose to go with Lulu, so this article will describe that service.
You can begin by creating an account on Lulu’s site, which is pretty self-explanatory. They have several different book types available. I decided to go with a 6×9 “casewrap hardcover”, which is a pretty standard size and style for a book. If you have a yellow Springer book on your shelf, that’s a pretty good facsimile of what we’re talking about here.
The main issue, then, is reformatting the thesis into a 6×9 format. Fortunately, LaTeX makes this pretty easy. Pretty much, you just need to swich from the UCSD thesis class to the standard LaTeX book class and make a few other changes. Here is a modified version of the UCSD thesis template, modified to fit this format. Nate put comments in various places indicating the relevant changes and choices he made. In several places he took advantage of the fact that he no longer had to conform to OGS’s awkward requirements to make the thesis more “book-like” and remove some things that wouldn’t appear in a book. It shouldn’t take you more than an hour or two to convert your thesis file, depending how fastidious you are. (If you don’t want to go to this trouble, Lulu will also print 8.5×11 books. You could use your existing PDF without change. It may not look as pretty, but it will still be cheaper than UMI.)
Note that you should check carefully for overfull \hbox’es when you compile the thesis, because changing the paper size may have caused things to run outside the margins or off the page. You may have to manually break up long equations or reword paragraphs. Also, the book class will insert several apparently blank pages; these relate to the fact that the book will be printed double-sided, and guarantee that certain things always appear on the left- or right-hand side of a spread. If you want a book-like effect, you should not try to defeat this.
Once you’ve generated an appropriate 6×9 PDF file and uploaded it to Lulu, you can design a cover for it. They have a couple of different interfaces. For his thesis, Nate created a pretty simple cover with a UCSDish blue color scheme, and the abstract and a graduation photo on the back cover.
When you are all finished, Lulu creates a page where you or anyone else can buy copies of the book. (You have the option of keeping this private, so that only people you share it with can find it.) Then you can buy as many copies as you want to keep or give away, and you can also send the link to your parents if they want to buy lots of copies for all the relatives. (In this case, Lulu’s “revenue” option may be useful, where you select an amount to add to the price of the book, which Lulu passes along to you after each sale. The page remains up indefinitely if you want more copies later.
If you want to see what a finished product looks like, Nate Eldredge’s thesis Lulu page is located at http://www.lulu.com/content/7559872.
The book turned out quite nice looking, with quality and appearance comparable to commercially published math books. And they were only $15.46 per copy (plus tax and shipping). Overall that is a vast improvement over UMI.
Also, Nate uploaded the template as a Lulu project. It can be found at http://www.lulu.com/content/7686303.

9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, CA 92093-0112
(858) 534-3590
Graduate College
Analysis on geometric singularities.
Mathematics
Doctor of philosophy in mathematics, get your phd in mathematics.
The PhD program places a strong emphasis on preparation for research and teaching.
Students must earn at least 72 semester hours of graduate credit and spend at least three years in residence at a graduate college, including at least one year at the University of Iowa.
They must complete specific courses designated as preparatory for the PhD qualifying examinations; pass the qualifying and comprehensive exams; and write a PhD thesis.
For a complete description of these requirements see the graduate student handbook .
Graduate student resources
- For students enrolled fall of 2020 and later
- For students enrolled prior to fall of 2020
- Teaching assistant handbook
- Graduate policies
- PhD qualifying and MS comprehensive exam archives
- Absence form
Create your academic path
You'll find degree overviews, requirements, course lists, academic plans, and more to help you plan your education and explore your possibilities.
Current course list
The MyUI Schedule displays registered courses for a particular session and is available to enrolled students. The list view includes course instructors, time and location, and features to drop courses or change sections.
Senior Thesis
This page is for Undergraduate Senior Theses. For Ph.D. Theses, see here .
A senior thesis is required by the Mathematics concentration to be a candidate for graduation with the distinction of High or Highest honors in Mathematics. See the document ‘ Honors in Mathematics ’ for more information about honors recommendations and about finding a topic and advisor for your thesis. With regards to topics and advisors: The document ‘ Faculty research areas ’ lists the research interests of current members of the Math Department.
So that Math Department senior theses can more easily benefit other undergraduate, we would like to exhibit more senior theses online (while all theses are available through Harvard University Archives, it would be more convenient to have them online). It is absolutely voluntary, but if you decide to give us your permission, please send an electronic version of your thesis to cindy@math. The format can be in order of preference: DVI, PS, PDF. In the case of submitting a DVI format, make sure to include all EPS figures. You can also submit Latex or MS word source files.
If you are looking for information and advice from students and faculty about writing a senior thesis, look at this document. It was compiled from comments of students and faculty in preparation for, and during, an information session. Let Wes Cain ([email protected]) know if you have any questions not addressed in the document.

UKnowledge > College of Arts & Sciences > Mathematics > Theses & Dissertations
Theses and Dissertations--Mathematics
Theses/dissertations from 2024 2024.
Adams operations on the Burnside ring from power operations , Lewis Dominguez
Solid Angle Measure Approximation Methods for Polyhedral Cones , Allison Fitisone
Pairs of Quadratic Forms over p-Adic Fields , John Hall
Properties of Skew-Polynomial Rings and Skew-Cyclic Codes , Kathryn Hechtel
Computational Methods for OI-Modules , Michael Morrow
SLₖ-Tilings and Paths in ℤᵏ , Zachery T. Peterson
Dirichlet Problems in Perforated Domains , Robert Righi
A Multiple-Case Study on the Impact of an Introductory Real Analysis Course on Undergraduate Students' Understanding of Function Continuity , Ryan Joseph Rogers
Uniform Regularity Estimates for the Stokes System in Perforated Domains , Jamison R. Wallace
Bicategorical Character Theory , Travis Wheeler
Theses/Dissertations from 2023 2023
Bicategorical Traces and Cotraces , Justin Barhite
Geometric and Combinatorial Properties of Lattice Polytopes Defined from Graphs , Kaitlin Bruegge
Toric Bundles as Mori Dream Spaces , Courtney George
Lattice minors and Eulerian posets , William Gustafson
Surjectivity of the Wahl Map on Cubic Graphs , Angela C. Hanson
q-Polymatroids and their application to rank-metric codes. , Benjamin Jany
Asymptotic behaviour of hyperbolic partial differential equations , Shi-Zhuo Looi
Normalization Techniques for Sequential and Graphical Data , Cole Pospisil
Geometry of Pipe Dream Complexes , Benjamin Reese
A Scattering Result for the Fifth-order KP-II Equation , Camille Schuetz
Slices of C_2, Klein-4, and Quaternionic Eilenberg-Mac Lane Spectra , Carissa Slone
Methods of Computing Graph Gonalities , Noah Speeter
Novel Architectures and Optimization Algorithms for Training Neural Networks and Applications , Vasily I. Zadorozhnyy
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Tropical Geometry of T-Varieties with Applications to Algebraic Statistics , Joseph Cummings
Inverse Boundary Value Problems for Polyharmonic Operators With Non-Smooth Coefficients , Landon Gauthier
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
Browse by Author
- Collections
- Disciplines
Author Corner
- Submit Research
New Title Here
Below. --> connect.
- Law Library
- Special Collections
- Copyright Resource Center
- Graduate School
- Scholars@UK

- We’d like your feedback
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
University of Kentucky ®
An Equal Opportunity University Accreditation Directory Email Privacy Policy Accessibility Disclosures
- Directories
Search form
You are here.
- Autumn 2024
MATH 700 A: Master's Thesis
- News Feed
- Alumni Update
- Mailing List

COMMENTS
IA Idea 1 - Modeling Statistics. Modeling statistics is a pretty broad concept for an IA, but it can refer to any project where a change in statistics is presented in a visually effective manner. An example of modeling is presenting the rate at which a country's population changes relative to external factors.
1. What Exactly is the Math IA? 1.1 About the Math IA. The Math IA is an internal assessment that makes up 20% of your final grade. Also known as the mathematical exploration component, students are expected to create a 6-12 page research paper with a topic of their choice.. Although the IB Mathematics curriculum includes two subjects, Analysis & Approaches (AA) and Applications ...
8. Inadequate explanations and interpretations. The IB Math IA paper assesses students' ability to analyze and interpret the data and make informed conclusions. However, failing to provide adequate explanations and interpretations of the findings can lead to a mark deduction.
Maths IA - 300 Maths Exploration Topics: Scroll down this page to find over 300 examples of maths IA exploration topics and ideas for IB mathematics students doing their internal assessment (IA) coursework. Topics include Algebra and Number (proof), Geometry, Calculus, Statistics and Probability, Physics, and links with other subjects.
Source: IB Mathematics Applications and Interpretation Guide. Criterion A: Communication (4 marks) - This refers to the organisation and coherence of your work, and the clarity of your explanations. The investigation should be coherent, well-organized, and concise. Criterion B: Mathematical Presentation (4 marks) - This refers to how well you use mathematical language, including notation ...
This article covers IB Math IA rubrics, process key pointers, the structure of the investigation, and interesting IB Math IA topics that will stimulate your mind and help you begin your exploration! You should also know about the updated course structure of IB Mathematics. Students are allowed to opt for any one of the following four courses in ...
The first criterion is about the presentation, with the aim of assessing the general organization and coherence of your IA. Although students tend to focus on the complexity of math that their exploration demonstrates, a full 4 points are rewarded for the clarity of your explanations and structure. In order to score in the top range here, make ...
Math AI IA ideas . IBDP candidates: Here you could use statistical analysis to plot the number of IB Diploma Program students over a range of years, and use that to model the future growth of IB.. Infant mortality rate: In this one, you could use statistical analysis to explore how the infant mortality rate is related to the GDP per capita of a country and can compare these values across ...
A math IA is an important part of the International Baccalaureate Diploma Program, and it is essential to understand how to write and present one. Writing a math IA can be a daunting task, but with the right steps and some helpful tips, you can craft a successful math IA with ease. ... Learn tips for formulating a clear thesis statement ...
Crafting Your Math IA: Tips and Tricks. Choose an Engaging Topic: Select a topic that resonates with you. Your passion will shine through in your work. Diversify Your Sources: Use a mix of textbooks, academic journals, and reputable websites to showcase a well-researched IA. Show Your Work: Detail your thought process, calculations, and reasoning.
IA Maths SL 7. High scoring IB Maths Internal Assessment examples. See what past students did and make your Maths IA perfect by learning from examiner commented examples!
Each class will require a different method of grading IAs. For example, a practical science like Chemistry HL would need a more investigative approach in an IA through the scientific method as compared to an IA in Spanish SL. This means you must face each IA with a different mindset! The IAs in Math SL make a little more than 10% of the total ...
Maths and Time: Exploring ideas regarding time dilation. Plotting Planets: Using log functions to track planets! So there we have it: 50 IB Maths IA topic ideas to give you a head-start for attacking this piece of IB coursework! We also have similar ideas for Biology, Chemistry, Economics, History, Physics, TOK… and many many more tips and ...
Mathematics: applications and interpretation guide 1. The Diploma Programme is a rigorous pre-university course of study designed for students in the 16-19 age range. It is a broad-based two-year course that aims to encourage students to be knowledgable and
Write your IA in a way that anybody of your age can read and understand. Choosing a complicated topic may result in a disorganized and difficult-to-understand IA, so try to avoid doing so. Also, avoid writing lengthy accounts of your own experiences. This is the requirement for "Communication" on the math IA. 3.
finite sets. The findings will hopefully be used to figure out how to use math to improve chess skills. The goal of this thesis is to ultimately present a way to understand the world's greatest board game via mathematics. Hopefully, the findings will answer the research question: Can math be used to perfect a player's chess skills?
IA. Math AI - HL. May 2023. 6 (Breakdown) Examiner's summary. Criterion A [3/4]:The student's exploration is well-structured, with clear sections including an introduction, body, and conclusion. The body of the work is further divided into phases of the exploration, which are clearly indicated. The topic of the exploration is stated clearly in ...
Defending Your Thesis. Setting a time to defend your dissertation can be frustrating. Contact your committee members well in advance in order to check availability and schedule a date/time. You would think that finding a time for 6 people to meet would be an easy task. However, it can be exceedingly difficult.
Thesis and Dissertation. New! The Author Deposit Agreement; Formatting Your Thesis ... Mathematics. Chair(s) Hao Fang. The University of Iowa. Graduate College. Office of the Dean 201 Gilmore Hall 319-335-2143 Office of Academic Affairs 205 Gilmore Hall 319-335-2144 Iowa City, IA 52242-1320 Contact Us Website Feedback. Social Media. Instagram ...
Get your PhD in Mathematics The PhD program places a strong emphasis on preparation for research and teaching. ... and write a PhD thesis. For a complete description of these requirements see the graduate student handbook. Graduate student resources. Graduate student handbook: ... Iowa City, IA 52242-1419. 319-335-0714 319-335-0627 mathematics ...
advice about writing any mathematics paper, not just a thesis, is provided in [3], and also [2, 4, 5].) 1. Basic requirements Your thesis must make a contribution to some eld of mathematics, and also report what was previously known about the topic. A Ph.D. thesis is expected to have a signi cant amount of original mathematical research.
A senior thesis is required by the Mathematics concentration to be a candidate for graduation with the distinction of High or Highest honors in Mathematics. See the document ' Honors in Mathematics ' for more information about honors recommendations and about finding a topic and advisor for your thesis. With regards to topics and advisors ...
Theses/Dissertations from 2024. Adams operations on the Burnside ring from power operations, Lewis Dominguez. Solid Angle Measure Approximation Methods for Polyhedral Cones, Allison Fitisone. Pairs of Quadratic Forms over p-Adic Fields, John Hall. Properties of Skew-Polynomial Rings and Skew-Cyclic Codes, Kathryn Hechtel.
MATH 700 A: Master's Thesis. Autumn 2024; View in MyPlan. View in Time Schedule. Meeting Time: to be arranged. Location: * * SLN: 18536. Credits: 1.0 - 10.0. Status: Active. ... Department of Mathematics University of Washington Administrative Office C-138 Padelford Box 354350 Seattle, WA 98195-4350 Phone: (206) 543-1150