5 Key Causes of World War I
Illustration by Hugo Lin. ThoughtCo.
- M.A., History, University of Florida
- B.A., History, University of Florida
World War I, known as the "war to end all wars," occurred between July 1914 and November 11, 1918. By the end of the war, over 17 million people had been killed, including over 100,000 American troops. While the causes of the war are infinitely more complicated than a simple timeline of events, and are still debated and discussed to this day, the list below provides an overview of the most frequently-cited events that led to war.

Watch Now: 5 Causes of World War I
Mutual defense alliances.
Countries throughout the world have always made mutual defense agreements with their neighbors, treaties that could pull them into battle. These treaties meant that if one country was attacked, the allied countries were bound to defend them. Before World War 1 began, the following alliances existed:
- Russia and Serbia
- Germany and Austria-Hungary
- France and Russia
- Britain and France and Belgium
- Japan and Britain
When Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia, Russia got involved to defend Serbia. Germany, seeing that Russia was mobilizing, declared war on Russia. France was then drawn in against Germany and Austria-Hungary. Germany attacked France by marching through Belgium pulling Britain into war. Then Japan entered the war to support its British allies. Later, Italy and the United States would enter on the side of the Allies (Britain, France, Russia, etc.).
Imperialism
Imperialism is when a country increases their power and wealth by bringing additional territories under their control, usually without outright colonizing or resettling them. Before World War I, several European countries had made competing imperialistic claims in Africa and parts of Asia, making them points of contention. Because of the raw materials these areas could provide, tensions around which country had the right to exploit these areas ran high. The increasing competition and desire for greater empires led to an increase in confrontation that helped push the world into World War I.
As the world entered the 20th century, an arms race had begun, primarily over the number of each country's warships, and the increasing size of their armies—countries began training more and more of their young men to be prepared for battle. The warships themselves increased in size, number of guns, speed, method of propulsion, and quality armor, beginning in 1906 with Britain's HMS Dreadnought . Dreadnought was soon out-classed as the Royal Navy and Kaiserliche Marine quickly expanded their ranks with increasingly modern and powerful warships.
By 1914, Germany had nearly 100 warships and two million trained soldiers. Great Britain and Germany both greatly increased their navies in this time period. Further, in Germany and Russia particularly, the military establishment began to have a greater influence on public policy. This increase in militarism helped push the countries involved into war.
Nationalism
Much of the origin of the war was based on the desire of the Slavic peoples in Bosnia and Herzegovina to no longer be part of Austria-Hungary but instead be part of Serbia. This specific essentially nationalistic and ethnic revolt led directly to the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand , which was the event that tipped the scales to war.
But more generally, nationalism in many of the countries throughout Europe contributed not only to the beginning but to the extension of the war across Europe and into Asia. As each country tried to prove their dominance and power, the war became more complicated and prolonged.
Immediate Cause: Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
The immediate cause of World War I that made the aforementioned items come into play (alliances, imperialism, militarism, and nationalism) was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary. In June 1914, a Serbian-nationalist terrorist group called the Black Hand sent groups to assassinate the Archduke. Their first attempt failed when a driver avoided a grenade thrown at their car. However, later that day a Serbian nationalist named Gavrilo Princip shot the Archduke and his wife while they were driving through Sarajevo, Bosnia which was part of Austria-Hungary. They died of their wounds.
The assassination was in protest to Austria-Hungary having control of this region: Serbia wanted to take over Bosnia and Herzegovina. The assassination of Ferdinand led to Austria-Hungary declaring war on Serbia. When Russia began to mobilize to defend its alliance with Serbia, Germany declared war on Russia. Thus began the expansion of the war to include all those involved in the mutual defense alliances.
The War to End All Wars
World War I saw a change in warfare, from the hand-to-hand style of older wars to the inclusion of weapons that used technology and removed the individual from close combat. The war had extremely high casualties over 15 million dead and 20 million injured. The face of warfare would never be the same again.
- Causes of World War I and the Rise of Germany
- The Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, 1914
- World War I Timeline From 1914 to 1919
- Biography of Franz Ferdinand, Archduke of Austria
- The Causes and War Aims of World War One
- World War I Timeline: 1914, The War Begins
- World War I Introduction and Overview
- World War 1: A Short Timeline Pre-1914
- The Major Alliances of World War I
- World War I: Opening Campaigns
- The First Battle of the Marne
- The Fourteen Points of Woodrow Wilson's Plan for Peace
- Key Historical Figures of World War I
- The Black Hand: Serbian Terrorists Spark WWI
- The Consequences of World War I
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
World War I
By: History.com Editors
Updated: August 11, 2023 | Original: October 29, 2009

World War I, also known as the Great War, started in 1914 after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria. His murder catapulted into a war across Europe that lasted until 1918. During the four-year conflict, Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire (the Central Powers) fought against Great Britain, France, Russia, Italy, Romania, Canada, Japan and the United States (the Allied Powers). Thanks to new military technologies and the horrors of trench warfare, World War I saw unprecedented levels of carnage and destruction. By the time the war was over and the Allied Powers had won, more than 16 million people—soldiers and civilians alike—were dead.
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Tensions had been brewing throughout Europe—especially in the troubled Balkan region of southeast Europe—for years before World War I actually broke out.
A number of alliances involving European powers, the Ottoman Empire , Russia and other parties had existed for years, but political instability in the Balkans (particularly Bosnia, Serbia and Herzegovina) threatened to destroy these agreements.
The spark that ignited World War I was struck in Sarajevo, Bosnia, where Archduke Franz Ferdinand —heir to the Austro-Hungarian Empire—was shot to death along with his wife, Sophie, by the Serbian nationalist Gavrilo Princip on June 28, 1914. Princip and other nationalists were struggling to end Austro-Hungarian rule over Bosnia and Herzegovina.
The assassination of Franz Ferdinand set off a rapidly escalating chain of events: Austria-Hungary , like many countries around the world, blamed the Serbian government for the attack and hoped to use the incident as justification for settling the question of Serbian nationalism once and for all.
Kaiser Wilhelm II
Because mighty Russia supported Serbia, Austria-Hungary waited to declare war until its leaders received assurance from German leader Kaiser Wilhelm II that Germany would support their cause. Austro-Hungarian leaders feared that a Russian intervention would involve Russia’s ally, France, and possibly Great Britain as well.
On July 5, Kaiser Wilhelm secretly pledged his support, giving Austria-Hungary a so-called carte blanche, or “blank check” assurance of Germany’s backing in the case of war. The Dual Monarchy of Austria-Hungary then sent an ultimatum to Serbia, with such harsh terms as to make it almost impossible to accept.
World War I Begins
Convinced that Austria-Hungary was readying for war, the Serbian government ordered the Serbian army to mobilize and appealed to Russia for assistance. On July 28, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia, and the tenuous peace between Europe’s great powers quickly collapsed.
Within a week, Russia, Belgium, France, Great Britain and Serbia had lined up against Austria-Hungary and Germany, and World War I had begun.
The Western Front
According to an aggressive military strategy known as the Schlieffen Plan (named for its mastermind, German Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen ), Germany began fighting World War I on two fronts, invading France through neutral Belgium in the west and confronting Russia in the east.
On August 4, 1914, German troops crossed the border into Belgium. In the first battle of World War I, the Germans assaulted the heavily fortified city of Liege , using the most powerful weapons in their arsenal—enormous siege cannons—to capture the city by August 15. The Germans left death and destruction in their wake as they advanced through Belgium toward France, shooting civilians and executing a Belgian priest they had accused of inciting civilian resistance.
First Battle of the Marne
In the First Battle of the Marne , fought from September 6-9, 1914, French and British forces confronted the invading German army, which had by then penetrated deep into northeastern France, within 30 miles of Paris. The Allied troops checked the German advance and mounted a successful counterattack, driving the Germans back to the north of the Aisne River.
The defeat meant the end of German plans for a quick victory in France. Both sides dug into trenches , and the Western Front was the setting for a hellish war of attrition that would last more than three years.
Particularly long and costly battles in this campaign were fought at Verdun (February-December 1916) and the Battle of the Somme (July-November 1916). German and French troops suffered close to a million casualties in the Battle of Verdun alone.

HISTORY Vault: World War I Documentaries
Stream World War I videos commercial-free in HISTORY Vault.
World War I Books and Art
The bloodshed on the battlefields of the Western Front, and the difficulties its soldiers had for years after the fighting had ended, inspired such works of art as “ All Quiet on the Western Front ” by Erich Maria Remarque and “ In Flanders Fields ” by Canadian doctor Lieutenant-Colonel John McCrae . In the latter poem, McCrae writes from the perspective of the fallen soldiers:
Published in 1915, the poem inspired the use of the poppy as a symbol of remembrance.
Visual artists like Otto Dix of Germany and British painters Wyndham Lewis, Paul Nash and David Bomberg used their firsthand experience as soldiers in World War I to create their art, capturing the anguish of trench warfare and exploring the themes of technology, violence and landscapes decimated by war.
The Eastern Front
On the Eastern Front of World War I, Russian forces invaded the German-held regions of East Prussia and Poland but were stopped short by German and Austrian forces at the Battle of Tannenberg in late August 1914.
Despite that victory, Russia’s assault forced Germany to move two corps from the Western Front to the Eastern, contributing to the German loss in the Battle of the Marne.
Combined with the fierce Allied resistance in France, the ability of Russia’s huge war machine to mobilize relatively quickly in the east ensured a longer, more grueling conflict instead of the quick victory Germany had hoped to win under the Schlieffen Plan .
Russian Revolution
From 1914 to 1916, Russia’s army mounted several offensives on World War I’s Eastern Front but was unable to break through German lines.
Defeat on the battlefield, combined with economic instability and the scarcity of food and other essentials, led to mounting discontent among the bulk of Russia’s population, especially the poverty-stricken workers and peasants. This increased hostility was directed toward the imperial regime of Czar Nicholas II and his unpopular German-born wife, Alexandra.
Russia’s simmering instability exploded in the Russian Revolution of 1917, spearheaded by Vladimir Lenin and the Bolsheviks , which ended czarist rule and brought a halt to Russian participation in World War I.
Russia reached an armistice with the Central Powers in early December 1917, freeing German troops to face the remaining Allies on the Western Front.
America Enters World War I
At the outbreak of fighting in 1914, the United States remained on the sidelines of World War I, adopting the policy of neutrality favored by President Woodrow Wilson while continuing to engage in commerce and shipping with European countries on both sides of the conflict.
Neutrality, however, it was increasingly difficult to maintain in the face of Germany’s unchecked submarine aggression against neutral ships, including those carrying passengers. In 1915, Germany declared the waters surrounding the British Isles to be a war zone, and German U-boats sunk several commercial and passenger vessels, including some U.S. ships.
Widespread protest over the sinking by U-boat of the British ocean liner Lusitania —traveling from New York to Liverpool, England with hundreds of American passengers onboard—in May 1915 helped turn the tide of American public opinion against Germany. In February 1917, Congress passed a $250 million arms appropriations bill intended to make the United States ready for war.
Germany sunk four more U.S. merchant ships the following month, and on April 2 Woodrow Wilson appeared before Congress and called for a declaration of war against Germany.
Gallipoli Campaign
With World War I having effectively settled into a stalemate in Europe, the Allies attempted to score a victory against the Ottoman Empire, which entered the conflict on the side of the Central Powers in late 1914.
After a failed attack on the Dardanelles (the strait linking the Sea of Marmara with the Aegean Sea), Allied forces led by Britain launched a large-scale land invasion of the Gallipoli Peninsula in April 1915. The invasion also proved a dismal failure, and in January 1916 Allied forces staged a full retreat from the shores of the peninsula after suffering 250,000 casualties.
Did you know? The young Winston Churchill, then first lord of the British Admiralty, resigned his command after the failed Gallipoli campaign in 1916, accepting a commission with an infantry battalion in France.
British-led forces also combated the Ottoman Turks in Egypt and Mesopotamia , while in northern Italy, Austrian and Italian troops faced off in a series of 12 battles along the Isonzo River, located at the border between the two nations.
Battle of the Isonzo
The First Battle of the Isonzo took place in the late spring of 1915, soon after Italy’s entrance into the war on the Allied side. In the Twelfth Battle of the Isonzo, also known as the Battle of Caporetto (October 1917), German reinforcements helped Austria-Hungary win a decisive victory.
After Caporetto, Italy’s allies jumped in to offer increased assistance. British and French—and later, American—troops arrived in the region, and the Allies began to take back the Italian Front.
World War I at Sea
In the years before World War I, the superiority of Britain’s Royal Navy was unchallenged by any other nation’s fleet, but the Imperial German Navy had made substantial strides in closing the gap between the two naval powers. Germany’s strength on the high seas was also aided by its lethal fleet of U-boat submarines.
After the Battle of Dogger Bank in January 1915, in which the British mounted a surprise attack on German ships in the North Sea, the German navy chose not to confront Britain’s mighty Royal Navy in a major battle for more than a year, preferring to rest the bulk of its naval strategy on its U-boats.
The biggest naval engagement of World War I, the Battle of Jutland (May 1916) left British naval superiority on the North Sea intact, and Germany would make no further attempts to break an Allied naval blockade for the remainder of the war.
World War I Planes
World War I was the first major conflict to harness the power of planes. Though not as impactful as the British Royal Navy or Germany’s U-boats, the use of planes in World War I presaged their later, pivotal role in military conflicts around the globe.
At the dawn of World War I, aviation was a relatively new field; the Wright brothers took their first sustained flight just eleven years before, in 1903. Aircraft were initially used primarily for reconnaissance missions. During the First Battle of the Marne, information passed from pilots allowed the allies to exploit weak spots in the German lines, helping the Allies to push Germany out of France.
The first machine guns were successfully mounted on planes in June of 1912 in the United States, but were imperfect; if timed incorrectly, a bullet could easily destroy the propeller of the plane it came from. The Morane-Saulnier L, a French plane, provided a solution: The propeller was armored with deflector wedges that prevented bullets from hitting it. The Morane-Saulnier Type L was used by the French, the British Royal Flying Corps (part of the Army), the British Royal Navy Air Service and the Imperial Russian Air Service. The British Bristol Type 22 was another popular model used for both reconnaissance work and as a fighter plane.
Dutch inventor Anthony Fokker improved upon the French deflector system in 1915. His “interrupter” synchronized the firing of the guns with the plane’s propeller to avoid collisions. Though his most popular plane during WWI was the single-seat Fokker Eindecker, Fokker created over 40 kinds of airplanes for the Germans.
The Allies debuted the Handley-Page HP O/400, the first two-engine bomber, in 1915. As aerial technology progressed, long-range heavy bombers like Germany’s Gotha G.V. (first introduced in 1917) were used to strike cities like London. Their speed and maneuverability proved to be far deadlier than Germany’s earlier Zeppelin raids.
By the war’s end, the Allies were producing five times more aircraft than the Germans. On April 1, 1918, the British created the Royal Air Force, or RAF, the first air force to be a separate military branch independent from the navy or army.
Second Battle of the Marne
With Germany able to build up its strength on the Western Front after the armistice with Russia, Allied troops struggled to hold off another German offensive until promised reinforcements from the United States were able to arrive.
On July 15, 1918, German troops launched what would become the last German offensive of the war, attacking French forces (joined by 85,000 American troops as well as some of the British Expeditionary Force) in the Second Battle of the Marne . The Allies successfully pushed back the German offensive and launched their own counteroffensive just three days later.
After suffering massive casualties, Germany was forced to call off a planned offensive further north, in the Flanders region stretching between France and Belgium, which was envisioned as Germany’s best hope of victory.
The Second Battle of the Marne turned the tide of war decisively towards the Allies, who were able to regain much of France and Belgium in the months that followed.
The Harlem Hellfighters and Other All-Black Regiments
By the time World War I began, there were four all-Black regiments in the U.S. military: the 24th and 25th Infantry and the 9th and 10th Cavalry. All four regiments comprised of celebrated soldiers who fought in the Spanish-American War and American-Indian Wars , and served in the American territories. But they were not deployed for overseas combat in World War I.
Blacks serving alongside white soldiers on the front lines in Europe was inconceivable to the U.S. military. Instead, the first African American troops sent overseas served in segregated labor battalions, restricted to menial roles in the Army and Navy, and shutout of the Marines, entirely. Their duties mostly included unloading ships, transporting materials from train depots, bases and ports, digging trenches, cooking and maintenance, removing barbed wire and inoperable equipment, and burying soldiers.
Facing criticism from the Black community and civil rights organizations for its quotas and treatment of African American soldiers in the war effort, the military formed two Black combat units in 1917, the 92nd and 93rd Divisions . Trained separately and inadequately in the United States, the divisions fared differently in the war. The 92nd faced criticism for their performance in the Meuse-Argonne campaign in September 1918. The 93rd Division, however, had more success.
With dwindling armies, France asked America for reinforcements, and General John Pershing , commander of the American Expeditionary Forces, sent regiments in the 93 Division to over, since France had experience fighting alongside Black soldiers from their Senegalese French Colonial army. The 93 Division’s 369 regiment, nicknamed the Harlem Hellfighters , fought so gallantly, with a total of 191 days on the front lines, longer than any AEF regiment, that France awarded them the Croix de Guerre for their heroism. More than 350,000 African American soldiers would serve in World War I in various capacities.
Toward Armistice
By the fall of 1918, the Central Powers were unraveling on all fronts.
Despite the Turkish victory at Gallipoli, later defeats by invading forces and an Arab revolt that destroyed the Ottoman economy and devastated its land, and the Turks signed a treaty with the Allies in late October 1918.
Austria-Hungary, dissolving from within due to growing nationalist movements among its diverse population, reached an armistice on November 4. Facing dwindling resources on the battlefield, discontent on the homefront and the surrender of its allies, Germany was finally forced to seek an armistice on November 11, 1918, ending World War I.
Treaty of Versailles
At the Paris Peace Conference in 1919, Allied leaders stated their desire to build a post-war world that would safeguard itself against future conflicts of such a devastating scale.
Some hopeful participants had even begun calling World War I “the War to End All Wars.” But the Treaty of Versailles , signed on June 28, 1919, would not achieve that lofty goal.
Saddled with war guilt, heavy reparations and denied entrance into the League of Nations , Germany felt tricked into signing the treaty, having believed any peace would be a “peace without victory,” as put forward by President Wilson in his famous Fourteen Points speech of January 1918.
As the years passed, hatred of the Versailles treaty and its authors settled into a smoldering resentment in Germany that would, two decades later, be counted among the causes of World War II .
World War I Casualties
World War I took the lives of more than 9 million soldiers; 21 million more were wounded. Civilian casualties numbered close to 10 million. The two nations most affected were Germany and France, each of which sent some 80 percent of their male populations between the ages of 15 and 49 into battle.
The political disruption surrounding World War I also contributed to the fall of four venerable imperial dynasties: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Russia and Turkey.
Legacy of World War I
World War I brought about massive social upheaval, as millions of women entered the workforce to replace men who went to war and those who never came back. The first global war also helped to spread one of the world’s deadliest global pandemics, the Spanish flu epidemic of 1918, which killed an estimated 20 to 50 million people.
World War I has also been referred to as “the first modern war.” Many of the technologies now associated with military conflict—machine guns, tanks , aerial combat and radio communications—were introduced on a massive scale during World War I.
The severe effects that chemical weapons such as mustard gas and phosgene had on soldiers and civilians during World War I galvanized public and military attitudes against their continued use. The Geneva Convention agreements, signed in 1925, restricted the use of chemical and biological agents in warfare and remain in effect today.
Photo Galleries

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

- Modern History
The four MAIN causes of World War I explained

The First World War was the first conflict that occurred on a staggering scale. World War I (WWI) was unprecedented in its global impact and the extent of its industrialization.
However, the reason why the war originally began is incredibly complex. To try and explain the causes of the war, historians have tried to simplify it down to four main causes.
They create the acronym: MAIN.
Imperialism
Nationalism.
This simplified acronym is a useful way to remember the four MAIN causes of the war.
However, we will explain each of these concepts out of order below.
One of the most commonly discussed causes of WWI was the system of alliances that existed by 1914, the year the war started.
An 'alliance' is an agreement made between two countries, where each side promises to help the other if required.
Most of the time, this involves military or financial assistance. When an alliance is created, the countries involved are known as 'allies'.
By the dawn of the First World War, most European countries had entered into one or more alliances with other countries.
What made this an important cause of WWI, was that many of these alliances were military in nature: that if one country attacked or was attacked, all of their allies had promised to get involved as well.
This meant, that if just one country attacked another, most of Europe would immediately be at war, as each country jumped in to help out their friends.
Imperialism, as a concept, has been around for a very long time in human history. Imperialism is the desire to build an empire for your country.
This usually involves invading and taking land owned by someone else and adding it to your empire.
By the 19th century, many European countries had been involved in imperialism by conquering less advanced nations in Asia, the Americas or Africa.
By 1900, the British Empire was the largest imperial power in the world. It controlled parts of five different continents and owned about a quarter of all land in the world.
France was also a large empire, with control over parts of south-east Asia and Africa.
By 1910, Germany had been trying to build its own empire to rival that of Britain and France and was interested in expanding its colonial holdings.
This meant that when an opportunity for a war of conquest became available, Germany was very keen to take advantage of it.
Militarism is the belief that a country's army and navy (since air forces didn't exist at the start of WWI) were the primary means that nations resolved disagreement between each other.
As a result, countries like to boast about the power of their armed forces.
Some countries spent money improving their land armies, while others spent money on their navies.
Some countries tried to gain the advantage by having the most number of men in their armies, while others focused more on having the most advanced technology in their forces.
Regardless of how they approached it, countries used militarism as a way of gaining an edge on their opponents.
An example of this competition for a military edge can be seen in the race between Britain and Germany to have the most powerful navy.
Britain had recently developed a special ship known as a 'dreadnought’. The Germans were so impressed by this, that they increased their government spending so that they also had some dreadnoughts.
The final of the four causes is 'nationalism'. Nationalism is the idea that people should have a deep love for their country, even to the extent that they are willing to die for it.
Throughout the 19th century, most countries had developed their own form of nationalism, where they encouraged a love of the nation in their citizens through the process of creating national flags and writing national anthems.
Children at schools were taught that their country was the best in the world and that should it ever be threatened, that they should be willing to take up arms to defend it.
The growing nationalist movements created strong animosity between countries that had a history of armed conflict.
A good example of this is the deep anger that existed between Germany and France.
These two countries had a recent history of war and struggling over a small region between the two, called Alsace-Lorraine.
Germany had seized control of it after the Franco-Prussian War in 1871, which the French were deeply upset by.
As a result, France believed that they should be willing to fight and die to take it back.
Conflicts and Crises
In the two decades before WWI started in 1914, there were a number of smaller conflicts and crises that had already threatened to turn into global conflicts.
While these didn't eventually start the global war, it does show the four causes mentioned above and how they interacted in the real world.
The Moroccan Crisis
In 1904, Britain recognized France's sphere of influence over Morocco in North Africa in exchange for France recognizing Britain's sphere of influence in Egypt.
However, the Moroccans had a growing sense of nationalism and wanted their independence.
In 1905, Germany announced that they would support Morocco if they wanted to fight for their freedom.
To avoid war, a conference was held which allowed France to keep Morocco. Then, in 1911, the Germans again argued for Morocco to fight against France.
To again avoid war. Germany received territorial compensation in the French Congo in exchange for recognizing French control over Morocco.
The Bosnian Crisis
In 1908, the nation of Austria-Hungary had been administrating the Turkish regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina since 1878, but they formally annexed it in 1908, which caused the crisis.
The country of Serbia was outraged, because they felt that it should have been given to them. As a result, Serbia threatened to attack Austria-Hungary.
To support them, Russia, who was allied to Serbia, prepared its armed forces. Germany, however, who was allied to Austria-Hungary, also prepared its army and threaten to attack Russia.
Luckily, war was avoided because Russia backed down. However, there was some regional fighting during 1911 and 1912, as Turkey lost control of the region.
Despite this, Serbia and Austria-Hungary were still angry with each other as they both wanted to expand into these newly liberated countries.
Further reading
What do you need help with, download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email

Sign Up Today
Start your 14 day free trial today

The History Hit Miscellany of Facts, Figures and Fascinating Finds
- 20th Century
The 4 M-A-I-N Causes of World War One

Alex Browne
28 sep 2021.
It’s possibly the single most pondered question in history – what caused World War One? It wasn’t, like in World War Two, a case of a single belligerent pushing others to take a military stand. It didn’t have the moral vindication of resisting a tyrant.
Rather, a delicate but toxic balance of structural forces created a dry tinder that was lit by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo . That event precipitated the July Crisis, which saw the major European powers hurtle toward open conflict.
The M-A-I-N acronym – militarism, alliances, imperialism and nationalism – is often used to analyse the war, and each of these reasons are cited to be the 4 main causes of World War One. It’s simplistic but provides a useful framework.
The late nineteenth century was an era of military competition, particularly between the major European powers. The policy of building a stronger military was judged relative to neighbours, creating a culture of paranoia that heightened the search for alliances. It was fed by the cultural belief that war is good for nations.
Germany in particular looked to expand its navy. However, the ‘naval race’ was never a real contest – the British always s maintained naval superiority. But the British obsession with naval dominance was strong. Government rhetoric exaggerated military expansionism. A simple naivety in the potential scale and bloodshed of a European war prevented several governments from checking their aggression.

A web of alliances developed in Europe between 1870 and 1914 , effectively creating two camps bound by commitments to maintain sovereignty or intervene militarily – the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance.
- The Triple Alliance of 1882 linked Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy.
- The Triple Entente of 1907 linked France, Britain and Russia.
A historic point of conflict between Austria Hungary and Russia was over their incompatible Balkan interests, and France had a deep suspicion of Germany rooted in their defeat in the 1870 war.
The alliance system primarily came about because after 1870 Germany, under Bismarck, set a precedent by playing its neighbours’ imperial endeavours off one another, in order to maintain a balance of power within Europe
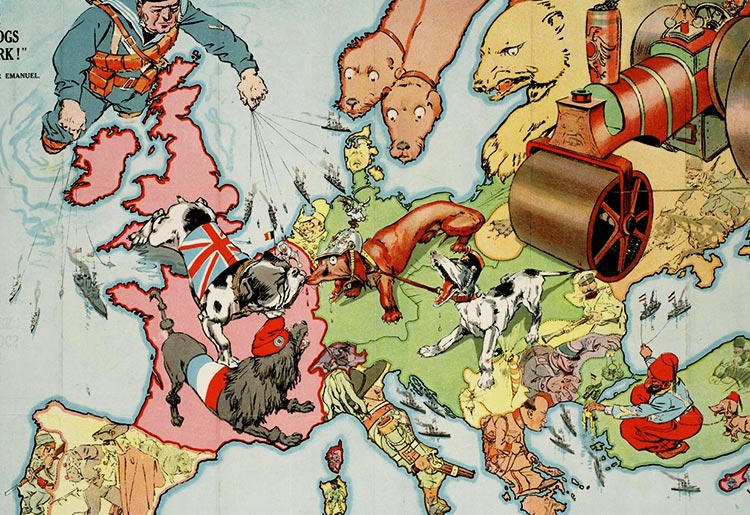
‘Hark! hark! the dogs do bark!’, satirical map of Europe. 1914
Image Credit: Paul K, CC BY 2.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
Imperialism
Imperial competition also pushed the countries towards adopting alliances. Colonies were units of exchange that could be bargained without significantly affecting the metro-pole. They also brought nations who would otherwise not interact into conflict and agreement. For example, the Russo-Japanese War (1905) over aspirations in China, helped bring the Triple Entente into being.
It has been suggested that Germany was motivated by imperial ambitions to invade Belgium and France. Certainly the expansion of the British and French empires, fired by the rise of industrialism and the pursuit of new markets, caused some resentment in Germany, and the pursuit of a short, aborted imperial policy in the late nineteenth century.
However the suggestion that Germany wanted to create a European empire in 1914 is not supported by the pre-war rhetoric and strategy.
Nationalism
Nationalism was also a new and powerful source of tension in Europe. It was tied to militarism, and clashed with the interests of the imperial powers in Europe. Nationalism created new areas of interest over which nations could compete.

For example, The Habsburg empire was tottering agglomeration of 11 different nationalities, with large slavic populations in Galicia and the Balkans whose nationalist aspirations ran counter to imperial cohesion. Nationalism in the Balkan’s also piqued Russia’s historic interest in the region.
Indeed, Serbian nationalism created the trigger cause of the conflict – the assassination of the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
The spark: the assassination
Ferdinand and his wife were murdered in Sarajevo by Gavrilo Princip, a member of the Bosnian Serbian nationalist terrorist organization the ‘Black Hand Gang.’ Ferdinand’s death, which was interpreted as a product of official Serbian policy, created the July Crisis – a month of diplomatic and governmental miscalculations that saw a domino effect of war declarations initiated.
The historical dialogue on this issue is vast and distorted by substantial biases. Vague and undefined schemes of reckless expansion were imputed to the German leadership in the immediate aftermath of the war with the ‘war-guilt’ clause. The notion that Germany was bursting with newfound strength, proud of her abilities and eager to showcase them, was overplayed.
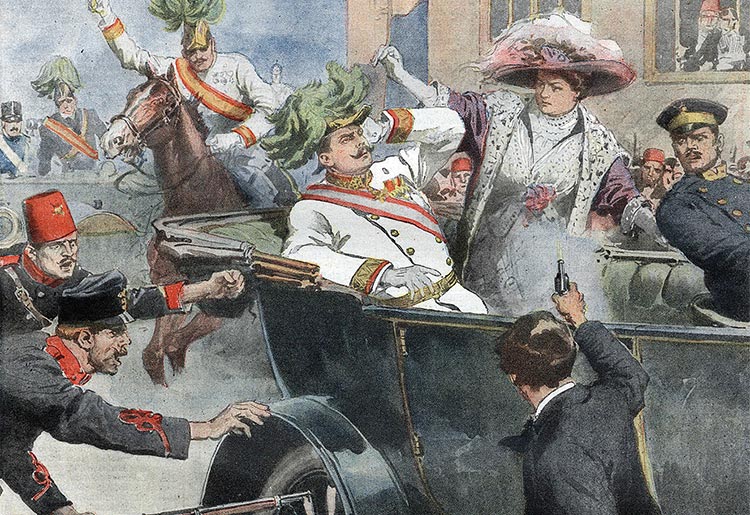
The first page of the edition of the ‘Domenica del Corriere’, an Italian paper, with a drawing by Achille Beltrame depicting Gavrilo Princip killing Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in Sarajevo
Image Credit: Achille Beltrame, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The almost laughable rationalization of British imperial power as ‘necessary’ or ‘civilizing’ didn’t translate to German imperialism, which was ‘aggressive’ and ‘expansionist.’ There is an on-going historical discussion on who if anyone was most culpable.
Blame has been directed at every single combatant at one point or another, and some have said that all the major governments considered a golden opportunity for increasing popularity at home.
The Schlieffen plan could be blamed for bringing Britain into the war, the scale of the war could be blamed on Russia as the first big country to mobilise, inherent rivalries between imperialism and capitalism could be blamed for polarising the combatants. AJP Taylor’s ‘timetable theory’ emphasises the delicate, highly complex plans involved in mobilization which prompted ostensibly aggressive military preparations.
Every point has some merit, but in the end what proved most devastating was the combination of an alliance network with the widespread, misguided belief that war is good for nations, and that the best way to fight a modern war was to attack. That the war was inevitable is questionable, but certainly the notion of glorious war, of war as a good for nation-building, was strong pre-1914. By the end of the war, it was dead.

You May Also Like

Mac and Cheese in 1736? The Stories of Kensington Palace’s Servants

The Peasants’ Revolt: Rise of the Rebels

10 Myths About Winston Churchill

Medusa: What Was a Gorgon?

10 Facts About the Battle of Shrewsbury

5 of Our Top Podcasts About the Norman Conquest of 1066

How Did 3 People Seemingly Escape From Alcatraz?

5 of Our Top Documentaries About the Norman Conquest of 1066

1848: The Year of Revolutions

What Prompted the Boston Tea Party?

15 Quotes by Nelson Mandela

The History of Advent
World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started) Essay
Introduction, causes of world war 1.
Bibliography
Since time immemorial the world has witnessed wars between different groups, states, countries, and allies. Initially, the motive behind wars was survival. Ancient people fought in order to usurp land for cultivation. Gradually, as the world population grew, the motives behind wars became multifarious.
Different groups and countries started fighting with each other in order to gain control of areas where there were natural resources such as gold. Another reason for war was to gain access to routes generally used for movement of commodities from the starting place to the consumption areas.
It is understood that after a war, one group prospered at the cost of another. Religion also has been an instigating factor for many wars. However, in all the wars, the motive was to gain advantage of some sort.
During the past years, when countries came together as allies, there have been instances when allies of a particular group had to go to war just because they wanted to safeguard themselves from the disadvantages of not participating in the war. In this paper, we shall discuss the reasons that led to World War 1. “World War 1 began in eastern Europe. The war started when Serbia, Austria-Hungary, Russia, and Germany decided that war or the risk of war was an acceptable policy option [1] ”.
General Causes
1879 onwards, the world witnessed formation of alliances between nations having similar interests. Following are some of the major alliances that took place:
- The Dual Alliance: Germany and Austria-Hungary entered into an alliance in 1879 in order to defend against Russia.
- Austro-Serbian Alliance: Austria-Hungary and Serbia entered into an alliance in 1881 in order to prevent Russia from asserting power in Serbia.
- The Triple Alliance: Germany and Austria-Hungary entered into an alliance with Italy in 1882 so that the latter could not favor Russia’s moves.
- Franco-Russian Alliance: Russia and France entered into an alliance in 1894 in order to protect their countries from the Dual Alliance of Germany and Austria-Hungary.
- Entente Cordiale: France and Britain entered into a formal agreement in 1904 in order to protect each other’s interests.
- Anglo-Russian Entente: Britain and Russia entered into a formal agreement in 1907 in order to protect each other’s interests.
- Triple Entente: Russia, France and Britain entered into an alliance to counteract Germany’s growing threats. Later, in 1914 and under the same alliance, all the three countries concurred that they will not sign any peace treaty without mutual consent.
All these alliances (from 1879 to 1914) forced some countries to go to war just because they were in some alliance.
Imperialism
Imperialism is a term used for instances where any country usurps any other country’s land and asserts its supremacy and power. Due to the incessant progress of industrialization, countries felt the need of venturing into fresh marketplaces.
By the year 1900, Britain had extended its empire in five continents and France controlled major parts of Africa. The increase of both these countries’ power did not go well with Germany; Germany had only small areas under its rule. Following is a map that depicts the colonies of these three major European players in 1914.
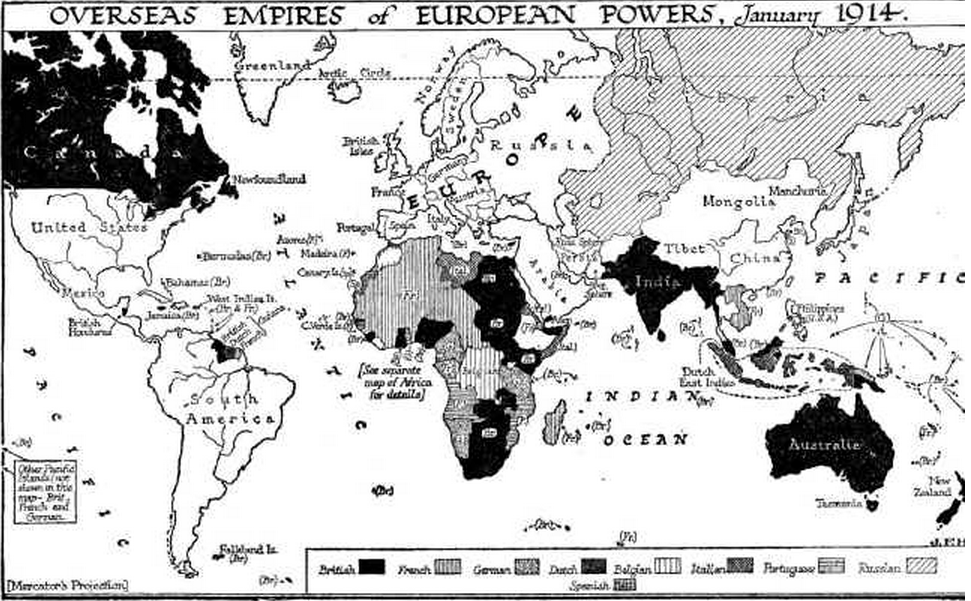
Source: Web.
William Anthony Hay claims that according to McMeekin, a tutor of international relations, “The war’s real catalyst lay in Russia’s ambition to supplant the waning Ottoman Empire in the Near East and to control the Turkish straits – the Bosphorus and Dardanelles – linking the Black Sea and the Mediterranean [2] ”.
But Richard Evans contradicts this opinion by stating that “In the end it was the Austro-Hungarian invasion of Serbia that set off the process that ended in the outbreak of World War 1, not Russian ambitions in the Straits [3] . But if we think logically, no country will enter into a war without personal interests.
Alliances were also made to serve individual interests. So it is wrong to say that Russia did not have any interest or ambitions in the Straits. Russia was an industrialized nation and needed to sell its products to people in other nations. For this purpose, it needed a safe passage and new markets.
When any country gives preference to its army, it is said to be following militarism. The growing alliances among various nations prompted nations to empower their army with more arms and ammunitions. France and Germany doubled the strengths of their respective armies.
Britain and Germany seemed to be in a competition of better sea control. In 1906, Britain launched the ‘Dreadnought’, considered to be a very efficient battleship. Following the footsteps, Germany also launched its own version of impressive battleships. The following illustration shows how Germany planned to attack France in case Russia attacked Germany; France and Russia were allies. So due to the alliance, Russia was bound to retaliate when one of its allies was attacked.
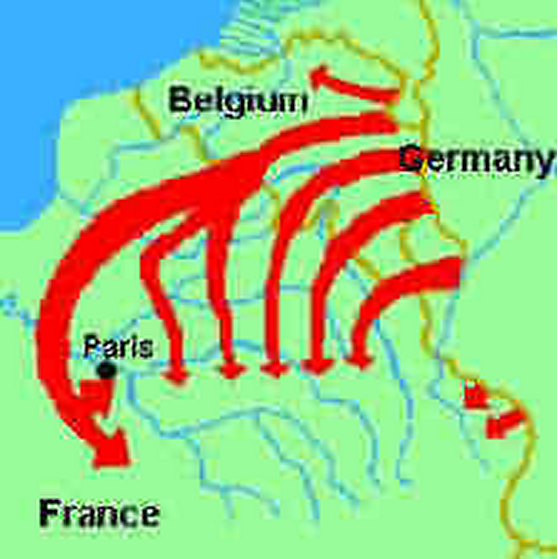
“A military revolution occurred in the seventeenth century. The most important of the many changes was a considerable growth in the size of the armies. Those large forces could no longer live off the land: steal supplies from the populace [4] ”.
Nationalism
We all have love for our respective countries. So did the people of that period. Austria-Hungary and Serbia had different radical groups trying to free their states from foreign involvement. Both Italy and Germany were divided. People of these countries wanted unification. “Along with the history of imperial machinations, however, World War 1 should be understood in the context of the popular imagination and the growth of nationalist sentiment in Europe [5] ”.
Moroccan Crisis
As part of an understanding, Britain gave control of Morocco to France in 1904. The Moroccan people wanted freedom. Germany, in order to take an advantage of the situation, proclaimed its support for the freedom of Morocco. A conference was held that allowed France to continue its control over Morocco and a war was averted. Again, in 1911, Germany started pronouncing its support for the Moroccan independence but again it was persuaded to compromise its stand on the issue.
Bosnian Crisis
Bosnia (a Turkish province) was taken over by Austria-Hungary in 1908. This action of Austria-Hungary did not go well with the Serbians. The Serbians thought Bosnia was under them. As such, a conflict aroused. Serbia proclaimed war over Austria-Hungary. Russia supported Serbia and Germany supported Austria-Hungary. A war was about to start but at the nick of the time Russia backed off and the war was averted.
But tensions were still mounting up between Serbia and Austria-Hungary. “It is true that during July the German decision makers sometimes expressed the hope that the conflict would be localized: in other words that Austria would be able to vanquish Serbia without Russian Intervention [6] ”. Dale Copeland argues that “Germany actively sought war in July 1914 and that German leaders by the end of July preferred world war to a negotiated peace, even to one that gave Austria most of what it wanted [7] ”.
The Immediate Trigger
World War 1 started in the year 1914. The assassination of Austria’s Archduke, Franz Ferdinand, acted as a trigger to World War 1. Franz Ferdinand and his wife were murdered in 1914 by Gavrilo Princip, member of a Bosnian radical group. “The crumbling Austro-Hungarian Empire decided, after the assassination on 28 June, to take action against Serbia, which was suspected of being behind the murder [8] ”.
This was considered to be an immediate reason for the war but the real reasons seem to be more complex and are still topics of debate among various historians. According to William Anthony Hay, “Germany bears responsibility for the war, in this view, because its leaders deliberately turned a regional clash between Austria-Hungary and Serbia into an existential Struggle of rival alliances [9] ”.
Hay is right in his opinion because history reveals that there were other options with Germany that could have averted the war. But since Germany wanted to gain on its own interests, it forced other countries to plunge into a war that they did not intend. “The size and wealth of the conquered Eastern territories easily outweighed what would have been lost had the Germans withdrawn from Belgium and France. Had they done so, France might have made peace and the anti-German coalition collapsed [10] ”.
All these instances make us to believe that Germany was behind waging the World War 1. In its ambitions to usurp power, Germany was thought to have instigated the war. But it is to be understood that down the years, historians put an end to the controversy as to which country was responsible for the World War 1.
Historians from the two main countries (Germany and France) came to an understanding that none of their countries should be blamed for instigating World War 1. It was the policies of militarization of each of the participating countries that led to the war.
But certain facts still point the finger towards Germany. After the war started, some confidential documents were discovered that suggested that the German government had vast plans of extending its territory due to the economic requirements.
Copeland, Dale. The Origins of Major War. New York: Cornell University Press, 2001.
Evans, Richard. “ The Road to Slaughter. ” New Republic . 2011. Web.
Fergusan, Niall. “Germany and the origins of the First World War: New Perspectives.” The Historical Journal 35, no. 3 (1992): 725-752.
Hamilton, Richard and Holger Herwig. The Origins of World War 1. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003.
Hay, William. “ Ambition in the East .” The Wall Street Journal . 2011. Web.
Merriman, John. “The Origins of World War 1.” Yale University . 2013. Web.
Sheffield, Gary. “ The Origins of World War One. ” BBC. 2011. Web.
Williamson, Samuel. “The Origins of World War 1.” Journal of Interdisciplinary History 18, no. 4 (1988): 795-818.
- Samuel Williamson, “The Origins of World War 1,” Journal of Interdisciplinary History 18, no. 4 (1988): 795.
- William Anthony Hay, “Ambition in the East,” The Wall Street Journal , 2011.
- Richard Evans, “The Road to Slaughter,” 2011.
- Richard Hamilton and Holger Herwig, The Origins of World War 1 (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003), 5.
- John Merriman, “The Origins of World War 1,” Yale University , 2013.
- Niall Fergusan, “Germany and the origins of the First World War: New Perspectives”, Historical Journal 35, no. 3 (1992): 731.
- Dale Copeland, The Origins of Major War (New York: Cornell University Press , 2001), 79.
- Gary Sheffield, “The Origins of World War One,” BBC , 2011.
- William Anthony Hay, “Ambition in the East” in The Wall Street Journal
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 14). World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started). https://ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/
"World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)." IvyPanda , 14 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)'. 14 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)." February 14, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/.
1. IvyPanda . "World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)." February 14, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/.
IvyPanda . "World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)." February 14, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/.
- World War I Causes by Ethnic Problems in Austro-Hungary
- The Causes and Effects of World War I
- World War I, Its Origin and Allies
- The First World War's Long- and Short-Term Causes
- MTV Pop Culture: The Lyrics by Dire Straits
- First World War Issues and Causes
- The Central Powers in the First World War
- Hay Criteria in Job Grading
- Why Europe Went to War
- World War 1 and Technological Improvement
- The World War I
- Outbreak of War in Europe in 1914
- Importance of Accountability: World War I
- Events Leading Up to WWI
- Experiences That Make a Soldier More Human
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Connection — Unveiling the Causes and Consequences of World War I
Unveiling The Causes and Consequences of World War I
- Categories: Connection Contract Monarchy
About this sample

Words: 557 |
Published: Mar 1, 2019
Words: 557 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology Law, Crime & Punishment Government & Politics

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 954 words
2 pages / 757 words
1 pages / 319 words
2 pages / 1024 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Connection
Qualities of strong relationships are the foundation upon which enduring connections are built. This essay delves into the essential characteristics that contribute to the strength and resilience of relationships. By exploring [...]
In Cynthia Rylant's novella, "Stray," readers are taken on a journey that explores themes of loss, redemption, and the power of human connection. Through the story of Doris, a middle-aged woman who finds solace in adopting a [...]
Television has a unique ability to capture the essence of human experiences and transport viewers into different worlds. Among the myriad narratives that television explores, there's a particular fascination with tales of chance [...]
Remember by Joy Harjo is a powerful and thought-provoking poem that explores themes of identity, memory, and connection to the natural world. Through the use of vivid imagery, symbolism, and a unique narrative structure, Harjo [...]
Love can hold us captive, chain us down and make us slaves to its cruel ways, blinding us from all judgement. The human condition of love can be expressed as a strong affection for another arising out of kinship, enthusiasm, or [...]
In the ever-evolving tapestry of human existence, two contrasting outlooks often guide our perceptions and actions: realism and optimism. Realism encourages us to confront life's challenges with a clear-eyed view of the world, [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
Advertisement
Iran’s Attacks Bring Long Shadow War With Israel Into the Open
The volley of drones and missiles was the first time that Tehran directly attacked Israel from its own territory, one expert said.
- Share full article

By Cassandra Vinograd
- Published April 14, 2024 Updated April 18, 2024
Follow live updates on Israeli military strikes in Iran.
For decades, Israel and Iran have fought a shadow war across the Middle East , trading attacks by land, sea, air and in cyberspace. The barrage of drones and missiles Iran launched at Israel on Saturday — though nearly all were shot down or intercepted — represented a watershed in the conflict.
It was the first time that Iran directly attacked Israel from its own territory, according to Ahron Bregman, a political scientist and expert in Middle East security issues at King’s College in London, who called it a “historic event.”
Iran has largely used foreign proxies such as Lebanon’s Hezbollah militia to strike Israeli interests, while targeted assassinations of Iranian military leaders and nuclear scientists have been a key part of Israel’s strategy. Here is a recent history of the conflict:
August 2019: An Israeli airstrike killed two Iranian-trained militants in Syria, a drone set off a blast near a Hezbollah office in Lebanon and an airstrike in Qaim, Iraq, killed a commander of an Iran-backed Iraqi militia. Israel accused Iran at the time of trying to establish an overland arms-supply line through Iraq and northern Syria to Lebanon, and analysts said the strikes were aimed at stopping Iran and signaling to its proxies that Israel would not tolerate a fleet of smart missiles on its borders.
January 2020: Israel greeted with satisfaction the assassination of Maj. Gen. Qassim Suleimani , the commander of the foreign-facing arm of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps, in an American drone strike in Baghdad.
Iran hit back by attacking two bases in Iraq that housed American troops with a barrage of missiles, wounding about 100 U.S. military personnel .
2021-22: In July 2021, an oil tanker managed by an Israeli-owned shipping company was attacked off the coast of Oman, killing two crew members, according to the company and three Israeli officials. Two of the officials said that the attack appeared to have been carried out by Iranian drones.
Iran did not explicitly claim or deny responsibility, but a state-owned television channel described the episode as a response to an Israeli strike in Syria.
In November 2021, Israel killed Iran’s top nuclear scientist, Mohsen Fakhrizadeh , and followed up with the assassination of a Revolutionary Guards commander, Col. Sayad Khodayee , in May 2022.
December 2023: After Israel’s bombardment of Gaza began in response to the Oct. 7 Hamas-led assault, Iranian-backed militias stepped up their own attacks . And late last year, Iran accused Israel of killing a high-level military figure, Brig. Gen. Sayyed Razi Mousavi , in a missile strike in Syria.
A senior adviser to the Revolutionary Guards, General Mousavi was described as having been a close associate of General Suleimani and was said to have helped oversee the shipment of arms to Hezbollah. Israel, adopting its customary stance, declined to comment directly on whether it was behind General Mousavi’s death.
January 2024: An explosion in a suburb of Beirut, Lebanon, killed Saleh al-Arouri , a Hamas leader, along with two commanders from that group’s armed wing, the first assassination of a top Hamas official outside the West Bank and Gaza in recent years. Officials from Hamas, Lebanon and the United States ascribed the blast to Israel , which did not publicly confirm involvement.
Hezbollah, which receives major support from Iran, stepped up its assaults on Israel after Mr. al-Arouri’s death. Israel’s military hit back at Hezbollah in Lebanon, killing several of the group’s commanders .
March and April: An Israeli drone strike hit a car in southern Lebanon, killing at least one person. Israel’s military said it had killed the deputy commander of Hezbollah’s rocket and missile unit. Hezbollah acknowledged the death of a man, Ali Abdulhassan Naim, but did not provide further details.
The same day, airstrikes killed soldiers near Aleppo, northern Syria, in what appeared to be one of the heaviest Israeli attacks in the country in years. The strikes killed 36 Syrian soldiers, seven Hezbollah fighters and a Syrian from a pro-Iran militia, according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, a British-based group that tracks Syria’s civil war.
Israel’s military did not claim responsibility. But the country’s defense minister, Yoav Gallant, wrote on social media, “We will pursue Hezbollah every place it operates and we will expand the pressure and the pace of the attacks.”
Three days later, strikes on an Iranian Embassy building in Damascus killed three top Iranian commanders and four officers, an attack Iran blamed on Israel.
Matthew Mpoke Bigg contributed reporting.
- International

Trump hush money trial

Israel-Hamas war

Columbia University protests
April 14, 2024 - Iran's attack on Israel
By Jerome Taylor, Heather Chen , James Legge, Sophie Tanno, Emma Tucker , Kaanita Iyer , Paul LeBlanc , Catherine Nicholls, Maureen Chowdhury , Antoinette Radford and Eve Rothenberg, CNN
Our live coverage of Iran's attack on Israel has moved here .
India calls on Iran to release 17 Indian crew members on board seized container ship
From CNN's Sandi Sidhu in Hong Kong
India has called on Iran to release 17 Indian crew members on board a container ship seized by Iran on Saturday.
Indian External Affairs Minister Subrahmanyam Jaishankar said that he spoke to his Iranian counterpart Iranian Foreign Minister Hossein Amir Abdollahian and "took up the release of 17 Indian crew members of MSC Aries."
Four Filipino seamen were also on board the ship, according to the Philippine Department of Migrant Workers.
The department said it was working with its government, the ship owner, and the operator to release the captured seafarers.
On Saturday, Iran’s Revolutionary Guards seized an Israeli-linked container ship in a helicopter operation near the Strait of Hormuz, state news agency IRNA reported.
Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC) said there were 25 crew members on board.
Japanese prime minister condemns Iran's attack on Israel
From CNN's Junko Ogura in Tokyo
Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida on Sunday said he "strongly condemns" Iran's missile and drone attack on Israel.
"(The attack) further aggravates the current situation in the Middle East. We are deeply concerned and strongly condemn such an escalation," Kishida told reporters.
Kishida said Japan would continue diplomatic efforts to "prevent the situation from worsening and to calm the situation down," and "respond in cooperation with other countries."
Blinken calls British and German counterparts following Iran's attack on Israel
From CNN's Philip Wang
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken spoke with his counterparts from the United Kingdom and Germany on Sunday following Iran's attack on Israel, according to readouts from the State Department.
All parties agreed "the importance of condemning Iran's attack in the strongest possible terms and preventing further escalation," the readout said.
Blinken earlier held phone calls with his counterparts from Turkey, Egypt, Jordan and Saudi Arabia , in which he emphasized the importance of avoiding escalation in the Middle East and of "a coordinated diplomatic response."
US forces destroyed more than 80 attack drones from Iran and Yemen, Central Command says
From CNN's Philip Wang
US forces intercepted more than 80 one-way attack drones and at least six ballistic missiles from Iran and Yemen during its attack on Israel, according to a statement from the Central Command.
The operation included destroying a ballistic missile on its launcher vehicle and seven drones on the ground in Iranian-backed Houthi-controlled areas of Yemen, CENTCOM said.
"Iran's continued unprecedented, malign, and reckless behavior endangers regional stability and the safety of U.S. and coalition forces," the statement added.
Israeli and Iranian ambassadors trade accusations during UN Security Council session
From Abel Alvarado in Atlanta
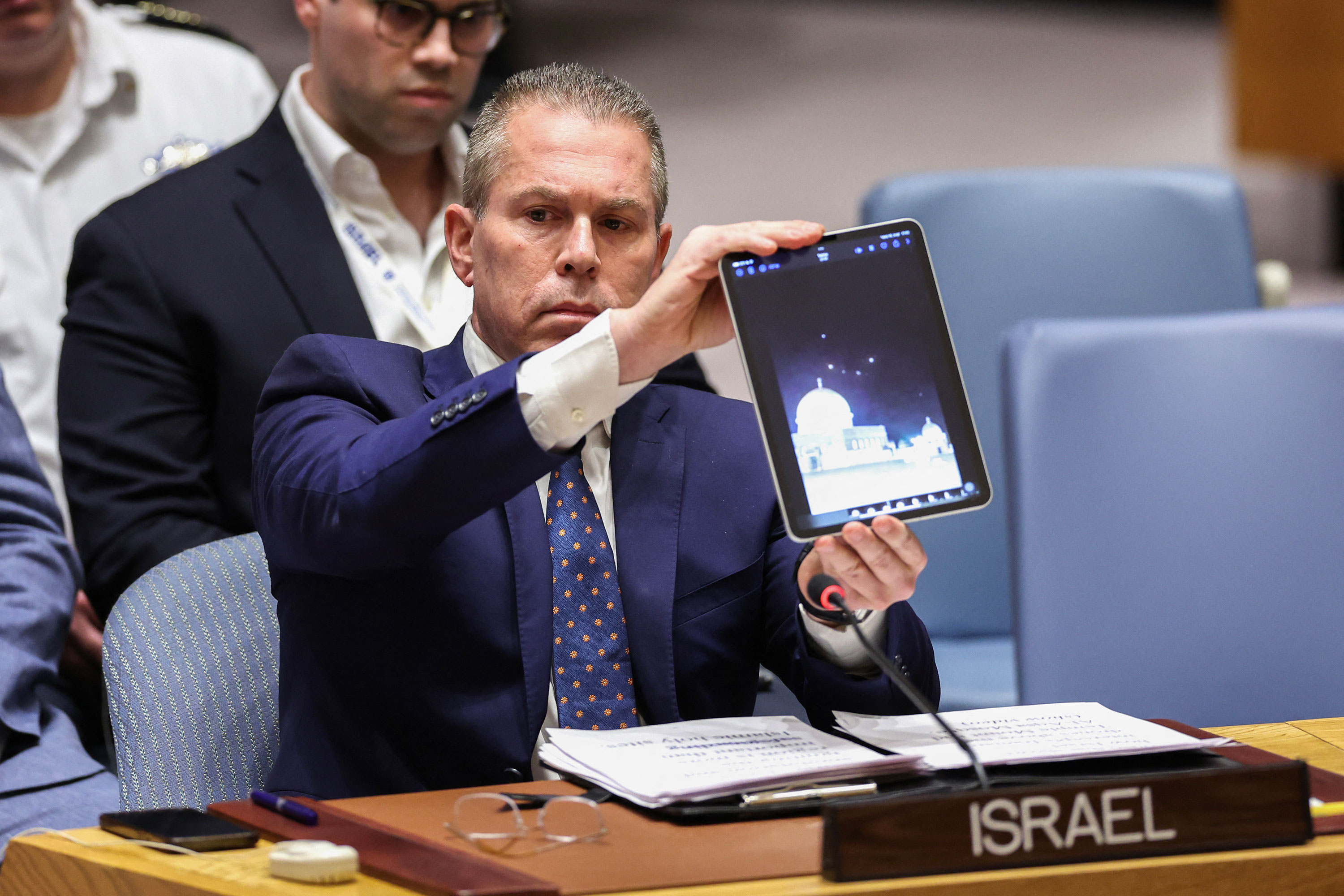

Israel and Iran’s United Nations ambassadors condemned each other’s actions during Sunday’s UN Security Council emergency session called to address Iran’s attack on Israel.
Israel’s UN ambassador Gilad Erdan said Iran "must be stopped before it drives the world to a point of no return, to a regional war that can escalate to a world war." Erdan accused Iran of seeking world domination and that its attack proved that Tehran "cares nothing, nothing for Islam or Muslims" before pulling out a tablet to show a video of Israel intercepting Iranian drones above Jerusalem’s Al-Aqsa Mosque.
Erdan called on the UN Security Council to designate the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) as a terror organization.
“Action must be taken now, not for Israel's sake, not for the region's sake, but for the world's sake. Stop Iran today."
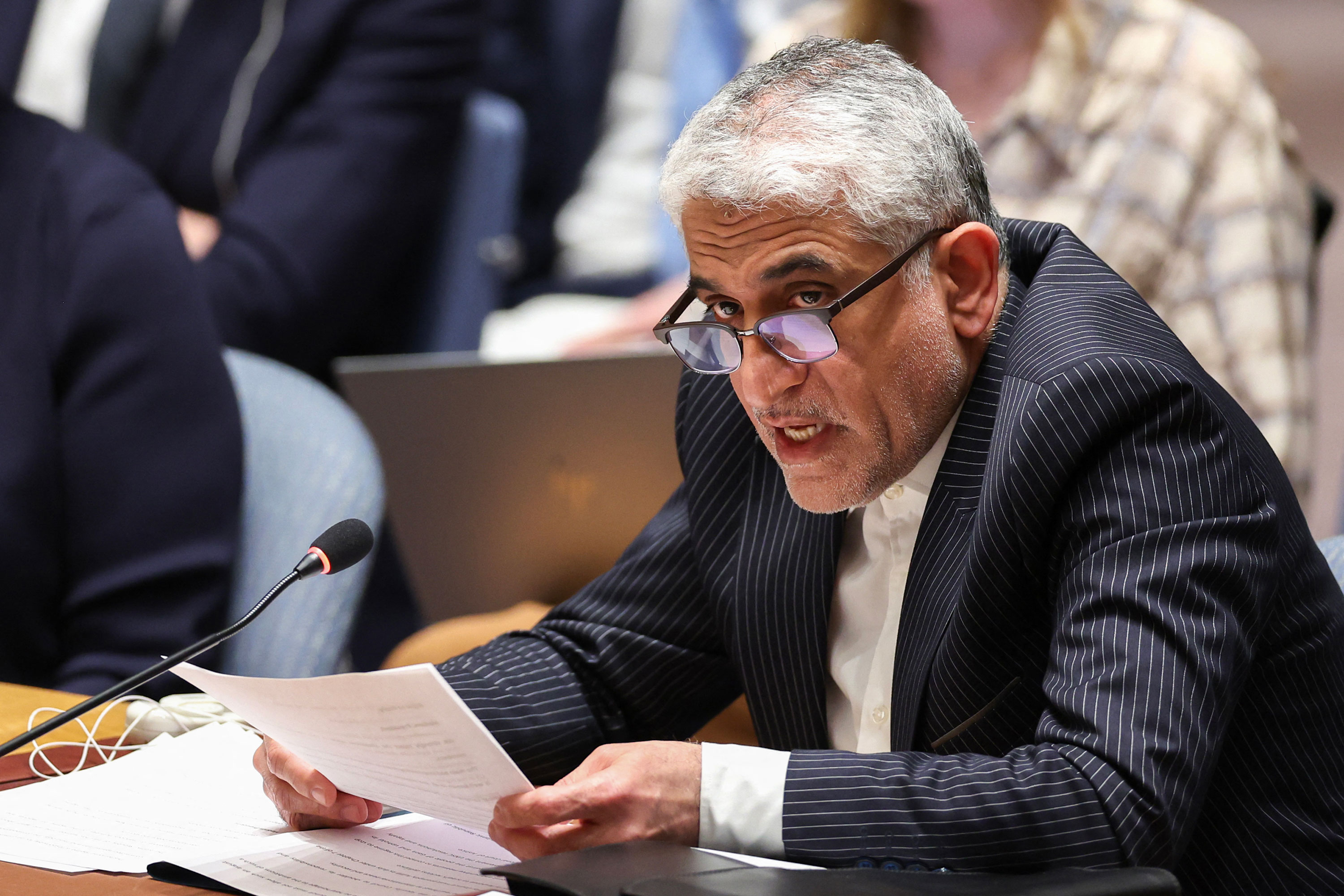
Iran’s UN Ambassador Amir Saeid Iravani said his country’s operation was "entirely in the exercise of Iran’s inherent right to self-defense, as outlined in Article 51 of the Charter of the United Nations and recognized by international law."
Iravani said:
"This concluded action was necessary and proportionate," adding that the operation was “precise and only targeted military objectives” to reduce the potential of escalation and to prevent civilian harm. “Iran is never seeking to contribute to the spillover of the conflict in the region, nor does it to escalate or spread the tension to the entire region," he said.

Tehran’s attack had been anticipated since a suspected Israeli strike on an Iranian diplomatic complex in Syria earlier this month.
Iravani added Iran has “no intention of engaging in conflict with the US in the region” but warned Iran will use its “inherent right to respond proportionately” should the US initiate a military operation against “Iran, its citizens or its security.”
Israeli war cabinet says it's ready to respond to Iran's attack but delays immediate action. Here's the latest
From CNN staff
The hours-long Israeli war cabinet meeting ended Sunday night without a decision on how Israel will respond to Iran’s missile and drone attack , an Israeli official said.
The cabinet is determined to respond — but has yet to decide on the timing and scope and the official said the military has been tasked with coming up with additional options for a response.
Separately, a senior Biden administration official told reporters that an Israeli official told the United States that it's not looking to significantly escalate the showdown with Iran.
CNN analyst Barak Ravid said Israeli ministers Benny Gantz and Gadi Eisenkot advocated for swift action, but US President Joe Biden's phone call with Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu led to a decision to delay the response until the next day.
Here are the latest headlines:
- Retaliation is over, Iran told US: Iran privately messaged the United States that its retaliation against Israel had concluded, echoing what Tehran said publicly, according to a senior administration official. Late Saturday, Iran said its attack on Israel is a response to Israel's strike on the Iranian consulate in Damascus, and "the matter can be deemed concluded." However, President Ebrahim Raisi said any “new aggression against the interests of the Iranian nation will be met with a heavier and regrettable response,” according to Iran’s state news channel IRIB.
- United Nations response: UN Secretary-General António Guterres called for a de-escalation of violence after Iran’s attack. Guterres said the United Nations and member countries have a “shared responsibility” to engage “all parties concerned to prevent further escalation.” He also called for a ceasefire in the Israel-Gaza conflict. “Neither the region nor the world can afford more war,” he said.
- G7 and others: Amid a flurry of diplomatic activity in response to Iran's attack, the G7 nations said they would work together to "stabilize the situation" in the Middle East, according to a statement from Biden. Also, Jordan summoned Iran's ambassador in Amman on Sunday after it intercepted Iranian drones over the country.
- Meanwhile in Gaza: As thousands of Palestinians were turned away from returning to their homes in northern Gaza on Sunday, a 5-year-old girl was shot in the head by Israeli soldiers, her mother said. Video showed a man carrying a 5-year-old girl named Sally Abu Laila, who was bleeding from her head, with people crowding around her in panic trying to cover her wound.
Also on Sunday:
- Israel decided to lift its restrictions on large gatherings and to reopen schools on Monday.
- The US Department of Homeland Security has not identified any “specific or credible threats” to the US since Iran attacked Israel.
Blinken calls Turkish, Egyptian, Jordanian and Saudi counterparts following Iran's attack
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken on Sunday spoke with his counterparts in Turkey, Egypt, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia following Iran's attacks in Israel, according to readouts from the State Department.
During his phone calls, Blinken emphasized the importance of avoiding escalation in the region and the importance of "a coordinated diplomatic response."
In his conversation with Jordan and Egypt, Blinken also underlined the significance of achieving an "enduring end to the crisis in Gaza."
Iran will be held responsible if any action is taken against the US or Israel, deputy ambassador warns
From CNN’s Abel Alvarado
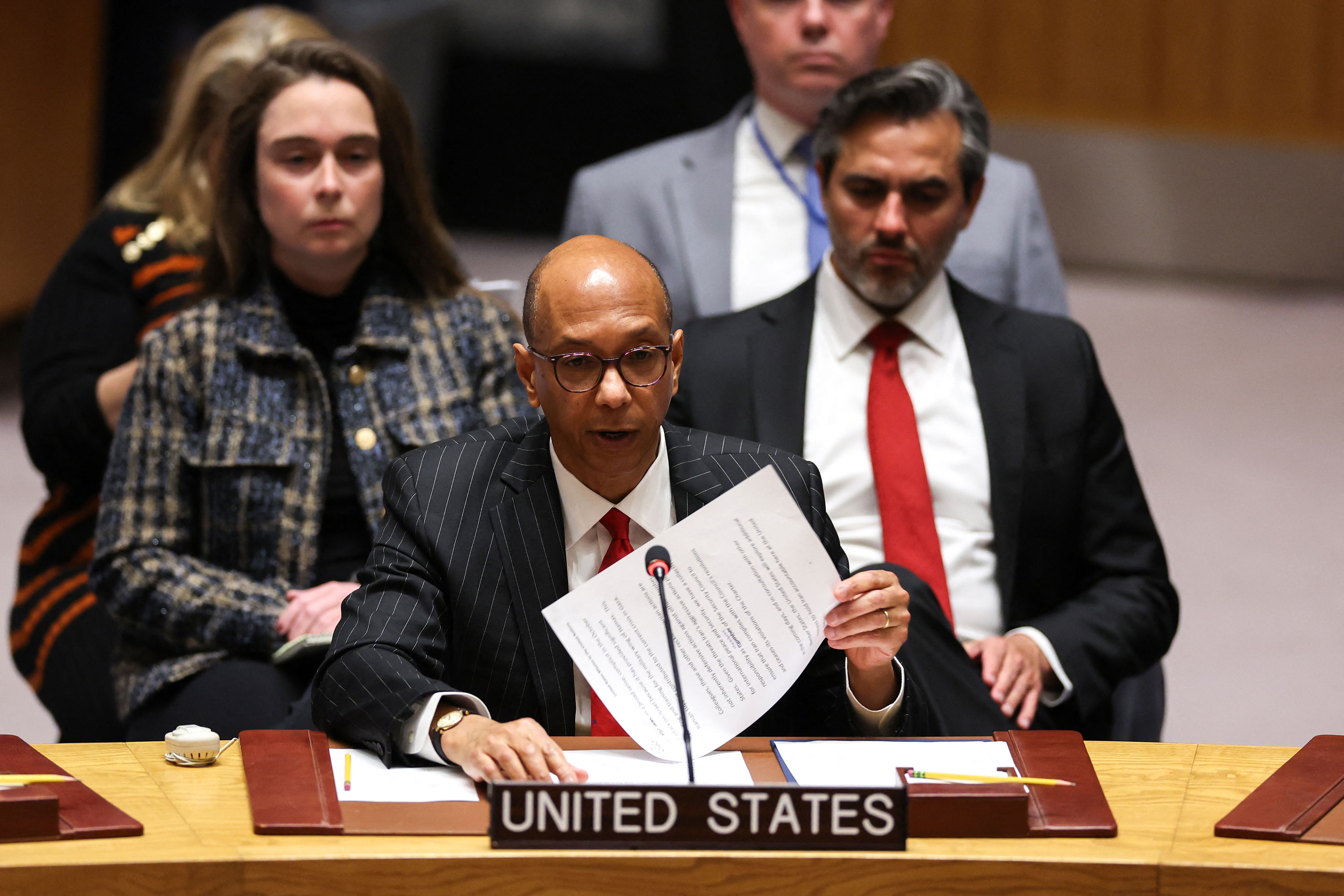

The United States warned Iran against taking any action against the US or Israel during the UN Security Council emergency session over Iran’s attack on Israel.
“Let me be clear, if Iran or its proxies take actions against the US or further action against Israel, Iran will be held responsible,” US Deputy Ambassador to the UN Robert Wood said Sunday.
The United States is “not seeking escalation, our actions have been purely defensive in nature,” adding that the “best way to prevent such escalation is an unambiguous condemnation of the council of Iran’s unprecedented large-scale attack,” he said.
The envoy reiterated US support for Israel and condemned Iran’s attack. “Iran’s intent was to cause significant damage and death in Israel,” Wood said.
Wood also said the UN Security Council had an “obligation to not let Iran’s actions go unanswered.”
“For far too long, Iran has flagrantly violated its international legal obligations,” he said before listing occasions Iran has violated UN Security Council resolutions and international law.
Wood accused Iran of being in a “broad sense complicit” of the October 7 attack on Israel by providing “significant funding and training for the military wing of Hamas.”
He added the US will explore "additional measures to hold Iran accountable here in the UN.”
Please enable JavaScript for a better experience.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Yellen says Iran’s actions could cause global economic spillovers as White House vows new sanctions
U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen attends a press conference in Beijing, China, Monday, April 8, 2024. Ever since she ate mushrooms that can have psychedelic effects in Beijing last July, Americans and Chinese have been united in their interest in what Janet Yellen will eat next. (AP Photo/Tatan Syuflana)

- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen warned Tuesday of potential global economic damage from rising tensions in the Middle East as the Biden administration said it was readying new sanctions in response to Iran’s malevolent activity in the region.
Yellen spoke out against Iran’s “malign and destabilizing activity” in remarks ahead of this week’s spring meetings of the International Monetary Fund and World Bank, saying Iran’s weekend missile and drone attack on Israel “underscores the importance of Treasury’s work to use our economic tools to counter Iran’s malign activity.”
She added: “From this weekend’s attack to the Houthi attacks in the Red Sea, Iran’s actions threaten the region’s stability and could cause economic spillovers.”
Iran’s attack on Israel early Sunday came in response to what it says was an Israeli strike on Iran’s consulate in Syria earlier this month. Israel’s military chief said Monday that his country will respond to the attack, while world leaders caution against retaliation, trying to avoid a spiral of violence.
As the IMF and its fellow lending agency, the World Bank, hold their spring meetings this week , high on the agenda are the fast-rising tensions between Iran and Israel and what escalation could spell for the global economy.
Meanwhile, White House national security adviser Jake Sullivan also said Tuesday that coming U.S. sanctions would target Iran’s missile and drone program and entities supporting the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps and Iran’s Defense Ministry.
“We anticipate that our allies and partners will soon be following with their own sanctions,” Sullivan said in a statement. “In addition, we continue to work through the Department of Defense and U.S. Central Command to further strengthen and expand the successful integration of air and missile defense and early warning systems across the Middle East to further erode the effectiveness of Iran’s missile and UAV capabilities.”
Israel and Iran have been on a collision course throughout Israel’s six-month war against Hamas militants in Gaza. The war erupted after two militant groups backed by Iran led an attack on Oct. 7 that killed 1,200 people in Israel and kidnapped 250 others. An Israeli offensive in Gaza has caused widespread devastation and killed over 33,000 people, according to local health officials.
“We’ve targeted over 500 individuals and entities connected to terrorism and terrorist financing by the Iranian regime and its proxies since the start of the Administration,” Yellen said, citing sanctions against Iran’s drone and missile programs, militant groups Hamas, the Houthis, Hezbollah, and other Iraqi militia groups.
Yellen said she expected the additional sanctions to be announced in the coming days.
The annual gathering will take place as other ongoing conflicts, including Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, threaten global financial stability.
Yellen in February offered her strongest public support yet for the idea of liquidating roughly $300 billion in frozen Russian Central Bank assets and using them for Ukraine’s long-term reconstruction.
She said Tuesday that the U.S. is “continuing to work with our international partners to unlock the economic value of immobilized Russian sovereign assets and ensure that Russia pays for the damage it has caused.” Yellen added that she will meet with Group of Seven finance leaders Wednesday to continue discussions on the topic and will look at “a series of possibilities, ranging from actually seizing the assets to using them as collateral.”
Another major issue for this year’s meetings on the U.S. side, Yellen said, will be ongoing conversations about Chinese industrial policy that poses a threat to U.S. jobs and the global economy. She traveled to Guangzhou and Beijing earlier this month, to hold “difficult conversations” with counterparts over what she describes as China’s overcapacity in its wave of low-priced Chinese green tech exports that could overwhelm factories in the U.S. and make it impossible to compete.
Yellen said she plans to meet later this week with her Chinese counterparts for a fourth meeting of the U.S.-China Economic and Financial Working Groups, “to share information, identify potential areas of cooperation, and, when we disagree, frankly communicate concerns.”
U.S. Treasury and China’s Ministry of Finance launched the economic working groups in an effort to ease tensions and deepen ties between the nations.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Germany and Austria-Hungary. France and Russia. Britain and France and Belgium. Japan and Britain. When Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia, Russia got involved to defend Serbia. Germany, seeing that Russia was mobilizing, declared war on Russia. France was then drawn in against Germany and Austria-Hungary.
The essay explores the causes of World War 1, which took place from 1914 to 1918. It begins with a brief overview of the war's timeline and the major countries involved, including the United Kingdom, France, Russia, Italy, Romania, Japan, the United States of America, Germany, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire.
World War I was one of the great watersheds of 20th-century geopolitical history. It led to the fall of four great imperial dynasties (in Germany, Russia, Austria-Hungary, and Turkey), resulted in the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia, and, in its destabilization of European society, laid the groundwork for World War II.. The last surviving veterans of World War I were American serviceman Frank ...
World War I started in 1914, after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, and ended in 1918. During the conflict, the countries of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire ...
Effects. As many as 8.5 million soldiers and some 13 million civilians died during World War I. Four imperial dynasties collapsed as a result of the war: the Habsburgs of Austria-Hungary, the Hohenzollerns of Germany, the sultanate of the Ottoman Empire, and the Romanovs of Russia. The mass movement of soldiers and refugees helped spread one of ...
Origins of World War I. To understand the origins of World War I, let's first go back to the early 1800s. For centuries, a competing patchwork of European empires and kingdoms had waged near-constant war with each other. These conflicts were generally fought over land, colonies, religion, resources, and dynastic rivalries.
European diplomatic alignments shortly before the war. The Ottomans joined the Central Powers shortly after the war started, with Bulgaria joining the following year. Italy remained neutral in 1914 and joined the Allies in 1915. Map of the world with the participants in World War I c. 1917.Allied Powers in blue, Central Powers in orange, and the neutral countries are in grey.
Alliances. One of the most commonly discussed causes of WWI was the system of alliances that existed by 1914, the year the war started. An 'alliance' is an agreement made between two countries, where each side promises to help the other if required. Most of the time, this involves military or financial assistance.
Killing the archduke then was like killing the crown prince of Britain right now. Also, the assassination was not the only reason for war. the naval arms race and the scramble for africa are also reasons for the world war. basically, everybody wanted war. the killing of the archduke is what instigated it, thats all.
Political clashes in Germany were a reason for the country's government to resort to the military conflict as a way of "averting civil unrest" (Levinson, 2014). Another factor that caused World War I was the desire of France to revenge a military defeat in the Franco-Prussian War of 1871 (Levinson, 2014).
In the short term, this was indeed one of the spurs for British involvement but the underlying reasons for war stretched back over many years. Wars occur when the aims and ambitions or the ...
M-A-I-N. The M-A-I-N acronym - militarism, alliances, imperialism and nationalism - is often used to analyse the war, and each of these reasons are cited to be the 4 main causes of World War One. It's simplistic but provides a useful framework.
In conclusion, the First World War led to the loss of many lives. These included soldiers and innocent citizens of the countries at war. The First World War also led to extensive destruction of property. The infrastructure and buildings in many towns crumbled. It contributed to displacement of people from their homes.
1 . What is trench warfare, and why was so much of World War I dominated by this method of fighting? Consider such elements as technology, strategy, attitudes of leaders, and any other factors you can think of. How did trench warfare affect the duration of the war? 2 . After the war, Germany was punished much more severely than were the ...
The Immediate Trigger. World War 1 started in the year 1914. The assassination of Austria's Archduke, Franz Ferdinand, acted as a trigger to World War 1. Franz Ferdinand and his wife were murdered in 1914 by Gavrilo Princip, member of a Bosnian radical group.
Published: Mar 1, 2019. A war erupted between countries from 1914 to 1918 which is known as World War 1 which was between major powers of Europe. During the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th-century countries were in nonstop conflict. Tensions between the major powers and Germany were quickly advancing and always on an edge of a hill.
as the root causes of World War 1. 1. Mutual Defense Alliances Over time, countries throughout Europe made mutual defense agreements that would pull them into battle. These treaties meant that if one country was attacked, allied countries were bound to defend them. Before World War 1, the following alliances existed: Russia and Serbia Germany ...
10 Lines on World War 1 Essay in English. 1. The First World War was instigated in 1914 by Serbia. 2. The cause of the war was a competition between countries to acquire weapons and build military powers. 3. In 1914, Serbia aroused anger by assassinating Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the heir of Austria-Hungary throne. 4.
Militarism was one of the main causes of the First World War. Increase in military control of the civilian government after 1907, there was an increase in military influence on policy making. This could be reflected particularly in Germany and Russia. The German Army at this period was called a "State within the State".
Another cause of World War 1 is imperialism. Imperialism is when a larger country or government is becoming stronger by taking on poorer or weaker, resourceful countries. Imperialism is one of the main causes of World War 1 because there was a major competition between gaining empires as well as raw substances.
What Were The Causes Of World War 1 Essay. World War I was one of the biggest events in history caused by many factors and ended with some of the most significant immediate and long-term effects in history. Many aspects lead to the beginning of World War I. Before this Great War began, Europe was divided into two alliances (Doc A).
What Was The Causes Of World War 1 Essay. Causes of World War I There were many factors that lead to World War I. In 1914 to 1918, European countries go to war. The start of the war was the assassination of Austria-Hungary's archduke, who was killed by Serbian nationalist.
Iran's massive missile and drone attack on Israel, which began in the late hours of April 13, pushed the conflict between the two countries into a potentially explosive new phase. For decades ...
Demonstrators protesting the ongoing war in Gaza, block southbound traffic on Interstate 880 in Oakland, Calif., on Monday, April 15, 2024. Traffic in the San Francisco Bay Area was also snarled for hours Monday morning as pro-Palestinian demonstrators shut down both directions of the Golden Gate Bridge and stalled a 17-mile (27-kilometer) stretch of Interstate 880 in Oakland.
It was one of the victims of the First World War, defeated and torn apart by the end of the conflict. But in 1914, the Habsburg family had ruled this empire for almost four centuries. It was a huge, multi-ethnic empire located in the middle of Europe. Franz Ferdinand's uncle, the emperor, ruled over its many ethnic communities with difficulty.
Iran's Attacks Bring Long Shadow War With Israel Into the Open. The volley of drones and missiles was the first time that Tehran directly attacked Israel from its own territory, one expert said.
Israel's war cabinet meeting ended Sunday without a decision on how Israel will respond to Iran's attack, an Israeli official said. The cabinet is determined to respond -- but has yet to decide on ...
As the IMF and its fellow lending agency, the World Bank, hold their spring meetings this week, high on the agenda are the fast-rising tensions between Iran and Israel and what escalation could spell for the global economy.. Meanwhile, White House national security adviser Jake Sullivan also said Tuesday that coming U.S. sanctions would target Iran's missile and drone program and entities ...
A year's worth of rain unleashed immense flash flooding in Dubai Tuesday as roads turned into rivers and rushing water inundated homes and businesses. Shocking video showed the tarmac of Dubai ...
Chaos ensued in the United Arab Emirates after the country witnessed the heaviest rainfall in 75 years, with some areas recording more than 250 mm of precipitation in fewer than 24 hours, the ...