Essay on the Positive and Negative Effects of Technology
How it works
The advent and evolution of technology have brought about profound changes in society, impacting almost every aspect of modern life. While technology has yielded numerous benefits, it has also introduced several challenges and concerns. This essay explores both the positive and negative effects of technology on various facets of human life.
On the positive side, technology has revolutionized communication, making it easier, faster, and more efficient. With the advent of the internet, social media, and mobile communication, people can connect with others across the globe instantly.
This has facilitated not just personal communication but also broadened the scope for global business and educational opportunities. Additionally, technology has significantly advanced healthcare, leading to improved diagnostics, treatments, and increased life expectancy. The accessibility of information and digital resources has also enhanced education and learning processes, making knowledge more accessible to a wider audience.
Another positive impact of technology is seen in the realm of productivity and efficiency. Automation and digital tools have streamlined various processes in industries, reducing manual labor and enhancing precision. This has led to increased productivity and innovation, contributing to economic growth and development. Moreover, technology has played a critical role in advancing research and development across various fields, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and innovations.
However, the negative effects of technology are equally significant. One of the primary concerns is the impact on mental health and well-being. The overuse of digital devices and social media has been linked to issues like anxiety, depression, and social isolation, especially among younger populations. Additionally, the digital divide and access to technology remain significant challenges, leading to disparities in information access and technological benefits.
Another downside of technology is the threat to privacy and security. With the increasing amount of personal data being shared online, individuals are more susceptible to privacy breaches, identity theft, and cybercrimes. Furthermore, the reliance on technology has led to concerns over job displacement due to automation, raising questions about the future of work and employment stability.
Environmental concerns are also associated with technology. The production and disposal of electronic devices contribute to environmental degradation and e-waste, posing challenges for sustainable development. Additionally, the energy consumption required to power digital infrastructures has implications for global energy resources and climate change.
In conclusion, technology has a dual impact on society, offering numerous benefits in terms of communication, healthcare, education, and productivity, while also presenting challenges related to mental health, privacy, job security, and environmental sustainability. Balancing these positive and negative aspects is crucial for harnessing the potential of technology in a way that benefits society as a whole.

Cite this page
Essay On The Positive And Negative Effects Of Technology. (2023, Nov 14). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/essay-on-the-positive-and-negative-effects-of-technology/
"Essay On The Positive And Negative Effects Of Technology." PapersOwl.com , 14 Nov 2023, https://papersowl.com/examples/essay-on-the-positive-and-negative-effects-of-technology/
PapersOwl.com. (2023). Essay On The Positive And Negative Effects Of Technology . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/essay-on-the-positive-and-negative-effects-of-technology/ [Accessed: 28 Aug. 2024]
"Essay On The Positive And Negative Effects Of Technology." PapersOwl.com, Nov 14, 2023. Accessed August 28, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/essay-on-the-positive-and-negative-effects-of-technology/
"Essay On The Positive And Negative Effects Of Technology," PapersOwl.com , 14-Nov-2023. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/essay-on-the-positive-and-negative-effects-of-technology/. [Accessed: 28-Aug-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2023). Essay On The Positive And Negative Effects Of Technology . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/essay-on-the-positive-and-negative-effects-of-technology/ [Accessed: 28-Aug-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
#prosvscons

The Pros and Cons of Technology in Today's World
Exploring the benefits and drawbacks of modern technology.
In today's modern world, technology plays a crucial role in almost every aspect of our lives. From communication to transportation, and from healthcare to entertainment, technology has revolutionized the way we live and work. However, along with its numerous benefits, technology also brings about certain drawbacks and challenges. In this article, we'll explore the advantages and disadvantages of technology, providing a balanced view of its impact on our society and individual lives.
As we delve into the realm of technology, it's important to consider its positive and negative effects on various aspects of life. From increased efficiency and productivity to concerns about privacy and security, technology has a multifaceted influence. By examining both the pros and cons, we can gain a deeper understanding of how to harness the benefits of technology while addressing its limitations and potential risks.
The rapid advancement of technology has significantly transformed our world, bringing forth a multitude of benefits and opportunities. Let's dive into the various advantages that technology offers and how they have improved our daily lives and global society.
Missing a pro?
While technology offers numerous advantages, it also presents a range of challenges and drawbacks that have sparked debates and concerns. It's essential to examine the potential pitfalls and limitations of technology to ensure responsible usage and address emerging issues.
Missing a con?
Technology is undeniably a powerful force that has reshaped our world, bringing about transformative changes and opportunities. While its numerous advantages have propelled progress and innovation, acknowledging the associated disadvantages is crucial for fostering responsible and sustainable technological integration. By balancing the benefits with the drawbacks, we can navigate the evolving landscape of technology with awareness and conscientious decision-making.
You might also like 👇

#PROSVSCONS
Essay on Technology – A Boon or Bane for Students
500+ words essay on technology for students.
In this essay on technology, we are going to discuss what technology is, what are its uses, and also what technology can do? First of all, technology refers to the use of technical and scientific knowledge to create, monitor, and design machinery. Also, technology helps in making other goods that aid mankind.
Essay on Technology – A Boon or Bane?
Experts are debating on this topic for years. Also, the technology covered a long way to make human life easier but the negative aspect of it can’t be ignored. Over the years technological advancement has caused a severe rise in pollution . Also, pollution has become a major cause of many health issues. Besides, it has cut off people from society rather than connecting them. Above all, it has taken away many jobs from the workers class.

Familiarity between Technology and Science
As they are completely different fields but they are interdependent on each other. Also, it is due to science contribution we can create new innovation and build new technological tools. Apart from that, the research conducted in laboratories contributes a lot to the development of technologies. On the other hand, technology extends the agenda of science.
Vital Part of our Life
Regularly evolving technology has become an important part of our lives. Also, newer technologies are taking the market by storm and the people are getting used to them in no time. Above all, technological advancement has led to the growth and development of nations.
Negative Aspect of Technology
Although technology is a good thing, everything has two sides. Technology also has two sides one is good and the other is bad. Here are some negative aspects of technology that we are going to discuss.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
With new technology the industrialization increases which give birth to many pollutions like air, water, soil, and noise. Also, they cause many health-related issues in animals, birds, and human beings.
Exhaustion of Natural Resources
New technology requires new resources for which the balance is disturbed. Eventually, this will lead to over-exploitation of natural resources which ultimately disturbs the balance of nature.
Unemployment
A single machine can replace many workers. Also, machines can do work at a constant pace for several hours or days without stopping. Due to this, many workers lost their job which ultimately increases unemployment .
Types of Technology
Generally, we judge technology on the same scale but in reality, technology is divided into various types. This includes information technology, industrial technology , architectural technology, creative technology and many more. Let’s discuss these technologies in brief.
Industrial Technology
This technology organizes engineering and manufacturing technology for the manufacturing of machines. Also, this makes the production process easier and convenient.
Creative Technology
This process includes art, advertising, and product design which are made with the help of software. Also, it comprises of 3D printers , virtual reality, computer graphics, and other wearable technologies.
Information Technology
This technology involves the use of telecommunication and computer to send, receive and store information. Internet is the best example of Information technology.

FAQs on Essay on Technology
Q.1 What is Information technology?
A – It is a form of technology that uses telecommunication and computer systems for study. Also, they send, retrieve, and store data.
Q.2 Is technology harmful to humans?
A – No, technology is not harmful to human beings until it is used properly. But, misuses of technology can be harmful and deadly.
Download Toppr – Best Learning App for Class 5 to 12
Toppr provides free study materials, last 10 years of question papers, 1000+ hours of video lectures, live 24/7 doubts solving, and much more for FREE! Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Technology pros and cons: is technology good or bad for society?

Find out what are the main the pros and cons of technology. We discuss the history, importance and role of technology, as well as its impact on society. Is technological progress good or is it becoming a threat to us? Vote in our poll and debate (see below)
Is technology good for society? A brief history
The impact of technology on society is undeniable. Technology and science have played a central role in human history and help shape entire civilizations. Technological progress was key for the emergence and downfall of empires. The development of hunting and farming tools allowed our ancestors to dominate other hominid species. The invention of the wheel and writing, as well as the introduction of metal tools and weapons were other landmarks in the history of technology . Many successive civilizations have contributed to the world's advancement. Often the development of technology also helped these societies to dominate militarily , politically, and economically their neighbors, as well as increase the welfare of their citizens.
The Egyptians invented many farming, medical and construction technologies. The Mesopotamians are credited for introducing irrigation and drainage systems, as well as sophisticated mud-brick and stone architecture techniques. Greeks were responsible for many inventions, such as the watermill, and the improvement on many existing technologies. Still today Greek mathematicians, engeneers and philosophers are recognised as fundamental to the history of human thought and technology. The Romans brought technology to a new level, and their monumental amphitheatres, aqueducts, bridges, harbours, dams and public baths help them dominate the Western world for centuries. Ancient Indian civilizations are credited for developing good understanding of seafaring, sanitation and hydrological technologies. Chinese discoveries include paper, matches, the cross-bow, seismological detectors, the wheelbarrow, the suspension bridge and the compass, among others.
During the Middle Ages architecture, navigation, papermaking and military technologies were developed. The Arab conquest of the Iberian Peninsula helped to introduce Europe to many technological advances developed in the east. The Renaissance and the Age of Explorations also demonstrated how innovation shaped societies. Research and inventions were put into practice. The use of artillery, new cranes and medical techniques marked a beginning of a scientific revolution. The Portuguese and Spanish discoveries, were enabled by technological progress but also help connecting different civilization which accelerated the spread of innovation. The industrial revolution brought the steam engine and developments in mining, metalurgy, manufacturing and transport. Since the 19th century, science and technology have evolved even faster. The 20th century brought the expansion of electrification and communication technologies, mass industrial production, electronic computing, nuclear technology and space exploration among others. It also demonstrated the devastating power of some of the technologies developed by humans. The weapons developed during that century, including the weapons of mass destruction, caused the deaths of millions.
The 21st century seems to have accelerated even faster these processes and intensified the impact of technology on society. Technology colleges such as MIT and Stanford have help accelerate scientific discovery. Genetic engineering, nanotechnology, 3D printing, wireless powered devices, augmented reality, articifical intelligence, drones , quantum computers and superconductivity are among the many new technologies we are witnessing today. But what come next? Can technology continue to help our lives or is it becoming a real threat to us? Can we keep scientific progress under control or will technology control our lives? Let's discuss the advantages and disadvantages or technology.
Pros and cons of technology
Pros of technological progress
- Thanks to technological progress humans live longer and much more comfortable lives. The medical advancements have helped us develop vaccines and treatment for diseases which were previously lethal. Giving birth is not as dangerous as it used to be. Technological progress has allowed develop new techniques for diagnosis and mitigation of diseases and other conditions. Scientific research has improved our understanding of nutrition and contributed to healthier lifestyles.
- Technology has allowed humans to travel faster and trade goods all over the world. Crossing the Atlantic was historically an adventure that would take weeks. Now in just a few hours you can travel from New York to London or Paris . Thanks to technology we can have holidays in remote locations and capture these moments through pictures. We can now buy and consume goods produced far away. In the same supermarket you can find French cheeses, South African wines, Spanish olive oils, Brazilian coffees, and Japanese fish.
- Without technology we would still be nomads hunting and gathering fruits and vegetables. Industrial societies heavily rely on technological progress. We can feed a fast growing world population thanks to the continuous innovation in production techniques. New inventions help foster the production, storage, treatment and transportation of goods. Societies which invest in research and development have a competitive edge and thrive. The people in technologically advanced societies live more comfortable lives.
- Genetically modified foods (GMO) may help fight hunger and ensure that world population continues to be fed. Genetic modification techniques contribute to produce more food and to maintain agricultural production at affordable prices.
- The Internet, computers and mobile phones illustrate the role of technology in improving society. Efficiency has skyrocketed thanks to these inventions. Our work and social lives have been transformed. People can now work from home and collaborate with teams located in other towns, countries or even continents. We can keep a fluid communication and relationship with friends and family living abroad. News of events cross the globe in seconds. Social netwoks such as facebook and twitter are extremely useful. Thanks to technology grandparents get to see and chat with their grandchildren much more often. People today get to meet others sharing similar hobbies or interests.
- Thanks to new technologies, alternative forms of entertainment and art have developed during the last century. Photography, radio, movies, television shows, music and video games occupy a central spot in people's lives. There are new forms of entertainment at our doorstep, such as virtual reality . Additionally, IT is facilitating the work of creators and help increase the quality of entertainment.
- The importance of technology in the delopment of renewable energies is evident. Without technological progress it would be difficult to envisage a green future in which the problem of climate change could be kept under control. Scientific advancements are making electric cars more affordable and enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of solar and eolic energy, as well as that hydropower .
Cons and risks of technology
- Technology is altering our lifestyle and will alter the cognitive and social development of current and future generations. There are many different ways in which the evolution of technology and society are connected. Technological innovation has changed our lives. Computers , smartphones and the internet have strongly affected how we interact with other people. Many claim that they are dehumanizing our lives and making us more solitary people. Technology may be also facilitating cultural colonialism and reducing diversity. Today, children play less with other children and spend much of their time watching videos in their tablets and playing video games. People are doing less physical exercise than their ancestors. We are becoming increasingly detached from nature and attached to technological gadgets.
- Human cloning technology is a reality and in addition to some obvious advantages, human cloning brings some risks. For instance it could create worrisome divides in society between those genetically divided to be smarter or physically more attractive and the rest. Human cloning will be difficult to regulate and will bring concerns regarding its interference with nature and religious beliefs.
- Weaponization of viruses . For instance, viruses such as Ebola or AIDS could be transformed into a virus that could be transmitted through the air. This could endanger or even cause the extinction of the the human race . Lifeforms can be created through genetic manipulation. With techonological progress the techniques to create or manipulate lifeforms will be increasingly accessible to us. Potentially even high school children will be able to create life in science experiments. Genomes of infectious diseases will be available to download from the internet. Terrorists, psychopaths and other criminals will have the capacity to use genetic manipulation to harm or threaten others.
- Similarly, scientific experimentation might create enormous dangers for society. Risky experiments may go wrong . Researchers are currently mutating microorganism in order to find cures to diseases. By accident these diseases could escape the laboratory and spread. Experiments with particle accelerators, such as the Large Hadron Collider , entail some serious risks. Some scientists even claimed that humans could create a black hole that could destroy Earth.
- Enrichment of uranium is becoming an increasingly cheaper process. Traditionally the infrastructure required to produce nuclear power and build nuclear bombs was extremely expensive. Thanks to technological progress and the use of laser beams to separate U-235 and U-238, in the not so distant future, people might be able to enrich uranium home. Nuclear weapons in the hands of the wrong organizations or individuals could create enormous unrest in the world population and a serious security threat.
- Technological progress is to be blamed for the negative effects of global warming and climate change . The role of technology fostering economic progress is difficult to deny. However, at the same time the generation of enegy necessary to the increased production and transportation of goods, for instance through combustion engines and thermoelectric generators, has produced an increased in the emission and concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Technology can be also used as an undesirable tool of control . For instance, scientists are working to develop brain scanning machines which could allow read a person's thoughts. This would have great benefits as could allow people with disabilities or people having suffered brain damage to communicate. Moreover if through a magnetic resoncance we could enquire criminals and terrorist we could also prevent harm for society. Similarly, thanks to advanced IT, it is possible to analyse the communications of millions of people and identify potential crimes and wrongdoers. Unfortunately, there is a very real possibility that technology will end up used by some governments in a draconian way. A dystopian future where people are constantly inquisitorially surveilled by a Big Brother as in Orwell's science fiction classic 1984.
What do you think, is technology good or bad? Is technological progress out of control? Will the rest of the 21st century see the importance of technology reduced?
Vote to see result and collect 1 XP. Your vote is anonymous. If you change your mind, you can change your vote simply by clicking on another option.
Voting results
New to netivist?
Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free. You will not receive any promotional materials from third parties.
Or sign in with your favourite Social Network:
Join the debate
In order to join the debate you must be logged in.
Already have an account on netivist? Just login . New to netivist? Create your account for free .
Report Abuse and Offensive language
Was there any kind of offensive or inappropriate language used in this comment.
If you feel this user's conduct is unappropriate, please report this comment and our moderaters will review its content and deal with this matter as soon as possible.
NOTE: Your account might be penalized should we not find any wrongdoing by this user. Only use this feature if you are certain this user has infringed netivist's Terms of Service .
Our moderators will now review this comment and act accordingly. If it contains abusive or inappropriate language its author will be penalized.
Posting Comment
Your comment is being posted. This might take a few seconds, please wait.
Error Posting Comment
error.
We are having trouble saving your comment. Please try again .
Most Voted Debates
| Rank | |
|---|---|
Start a Debate
Would you like to create a debate and share it with the netivist community? We will help you do it!
Found a technical issue?

Are you experiencing any technical problem with netivist? Please let us know!
Help netivist
Help netivist continue running free!
Please consider making a small donation today. This will allow us to keep netivist alive and available to a wide audience and to keep on introducing new debates and features to improve your experience.

- What is netivist?
- Entertainment
- Top Debates
- Top Campaigns
- Provide Feedback

Follow us on social media:

Share by Email
There was an error...
Email successfully sent to:

Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free You will not recive any promotional materials from third parties
Join netivist
Already have a netivist account?
If you already created your netivist account, please log in using the button below.
If you are new to netivist, please create your account for free and start collecting your netivist points!
You just leveled up!
Congrats you just reached a new level on Netivist. Keep up the good work.

Together we can make a difference
Follow us and don't miss out on the latest debates!
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Information Science and Technology Impact of Technology
The Positive and Negative Impact of Technology on Society
Table of contents, introduction, positive impacts of technology on society, negative impacts of technology on society, striking a balance, works cited, enhanced communication, medical advancements, accessibility of information, economic growth and job creation, privacy concerns, mental health issues, environmental degradation, social disconnection, job displacement due to automation.
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Class Reflection
- Air Conditioner
- Cryptography
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.

Essay on Pros and Cons of Technology
Students are often asked to write an essay on Pros and Cons of Technology in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Pros and Cons of Technology
Introduction.
Technology has become a vital part of our lives. It has its advantages, making tasks easier, but it also has downsides.
Pros of Technology
Technology helps us in many ways. It makes communication easy, helps in learning, and saves time by making tasks quicker.
Cons of Technology
However, technology also has negatives. It can lead to addiction, may reduce physical activity, and sometimes, it invades our privacy.
In conclusion, technology has both pros and cons. It’s important to use it wisely to enjoy the benefits and avoid the drawbacks.
250 Words Essay on Pros and Cons of Technology
The first benefit of technology is efficiency. It has automated complex tasks, reducing the time taken to complete them and boosting productivity. For instance, AI and robotics have revolutionized industries, undertaking tasks with precision and speed.
Moreover, technology has enhanced communication and connectivity. The advent of the internet, smartphones, and social media platforms have made it easier to connect with people globally, fostering cultural exchange and global understanding.
Despite its advantages, technology also has its drawbacks. The most prominent is the issue of privacy. With the rise of digital platforms, personal data is often at risk, leading to potential misuse.
Another downside is the impact on job security. Automation and AI have replaced human labor in certain sectors, creating job insecurity. Additionally, the over-reliance on technology has led to a decline in human interaction and increased screen time, affecting mental and physical health.
In conclusion, technology is a double-edged sword. While it brings numerous benefits such as efficiency and connectivity, it also poses challenges like privacy concerns and job insecurity. Therefore, it’s crucial to use technology responsibly and implement policies that mitigate its negative impacts.
500 Words Essay on Pros and Cons of Technology
Efficiency and productivity.
Technology has significantly increased efficiency and productivity across various sectors. Automation and artificial intelligence have streamlined operations in industries, reducing human error and increasing output. In the education sector, e-learning platforms have made knowledge accessible to anyone with an internet connection, breaking geographical barriers.
Communication and Connectivity
The advent of the internet and smartphones has revolutionized communication. Social media platforms, emails, and video conferencing have made it possible to connect with anyone, anywhere, at any time. This has fostered global collaboration, enabling the exchange of ideas and cultures.
Healthcare Improvements
Dependency and laziness.
While technology has made life easier, it has also led to increased dependency. Many people find it difficult to perform simple tasks without the aid of technology. This over-reliance may lead to laziness and a decrease in critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Privacy and Security Concerns
The digital age has brought about serious concerns regarding privacy and security. Cybercrimes, such as hacking and identity theft, are on the rise. Furthermore, the collection and use of personal data by corporations and governments have raised questions about privacy rights.
Job Displacement
Technology, with its myriad benefits and challenges, is a double-edged sword. It has the potential to enhance our lives, but it also presents significant risks. As we continue to innovate and explore new technological frontiers, it is crucial to consider these pros and cons. By doing so, we can ensure that technology serves humanity’s best interests, rather than becoming a tool for its own downfall.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Popular Topics
- youtube tips
- youtube marketing tools
- youtube marketing strategy
- youtube marketing
- YouTube Channel
Trending Now View All

The Benefits of Selling Your Property Online: Speed, Efficiency, and Reach
In today’s digital age, selling property online has become a popular choice for

Navigating the Job Market with AI Resume and Cover Letter Tools
Nowadays, making a strong first impression is crucial as the unemployment rate

Benefits of Multi-Drop Delivery Services for Food Businesses
The food industry is very competitive and this has led to various players in the

Why Funder Advisory is Essential for Construction Project Financing
Securing financing for construction projects is a critical aspect that can
The Impact of Technology on Education: Positive and Negative Effects

Technology has graced our learning institutions for centuries now. Right from the use of radios to incorporation of modern computers, our classrooms will never be the same. Assignments that took hours to grind have been reduced to minutes using edtech such as laptops, spreadsheets, online calculators, integrated apps, etc. Access to learning materials have also improved significantly as colleges embrace cloud storage. Not to mention that lecturers can now deliver lectures from anywhere in the world, reducing geographic limitations.
While this should be good news to educators and learners, it comes with some drawbacks. In fact, stakeholders in the education sector have remained firmly embroiled in heated debates about the effects of technology on education . Whereas it’s hard to determine the side with more credible arguments, it’s undeniable that edtech has changed the way knowledge is imparted and acquired. And with such massive changes come both positives and negatives. In this short article, we’ll explore the impact of technology on education, covering both the positive and negative outcomes. Read on to learn more.
Impact of Technology on Education: The Digital Divide
Edtech has done better than bad to our education system. In fact, some people firmly believe that the challenges we’re facing with it today are just bad teething problems. Yet, it’s undeniable that it has magnified the digital divide, exacerbating existing inequalities. This is a major problem in a world where the top one percent own more than 60 percent of the global population combined. So, only a select few fully benefit from edtech. Disparities are based on learners’ socioeconomic background, geographic location, and access to technology. This is worth noting, as it hinders some students’ academic progress and future opportunities. It’s a cruel reality, an impact of technology on education that many fear confronting.
The Positive Effects of Technology on Education
Even if you’re against edtech, you must, at the very least, acknowledge the positive impact it has had on our education system. There’s just so much to talk about. However, we’ve listed the main advantages below:
Enhanced information access
Some of us started schooling when textbooks were the only access to information. Even so, they were quite rare and only children from privileged families had them. We spent weekends at neighboring estates, sharing a few copies to complete assignments. In fact, some students walked several kilometers to find copies of textbooks. In other cases, we had to stay back at school until quite late, copying the assignments. Colleges filled their libraries with old, irrelevant books, forcing students to fight for the few relevant ones. It was never easy. Then came technology. With just a few clicks, students can now explore a wide range of resources, such as online libraries, journals, educational websites, and multimedia content from any location on earth. All you need is an internet connection and an access device. How cooler can it get!
Improved collaboration
Collaboration is critical to learning, which explains why most curricula have incorporated activities and exercises for it. Unfortunately, it has never been easy in traditional learning setups. The limited time in school and the many subjects to cover hindered teachers from instituting adequate collaborative activities. The pressure reduced most educators into syllabus covering machines.
One of the positive effects of technology on education today is that it has changed things for the better. It has expanded the breadth and width of collaboration among stakeholders, i.e., students, teachers, guardians, and parents. They can instantly and seamlessly connect with each other via online platforms, video conferencing tools, and educational apps. You’re no longer alone when stuck with a difficult assignment because you easily reach your tutors, lecturers, and instructors to explain things out. If no one is available, you can collaborate with an expert team of essay writers at CustomWritings that professionally help students with academic writing issues online.
Personalized learning
Have you had the honor of watching the film Slumdog Millionaire 2008 ? If you haven’t, you’re certainly missing out. A masterpiece. A marvelous work of art and entertainment that highlights the struggles of many people who schooled a few decades ago. Forget about India’s high population and poor living standards, most students of the early 1980s confronted crowded and poorly ventilated classes. Teachers never delivered education to suit each student. Instead, they expected each learner to fit, a one system fits all approach. Thanks to edtech, things have gotten better. Adaptive learning software has allowed personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs. A slow learner can go at their own pace as they receive customized learning paths and immediate feedback.
Improved learning experiences for all
Malik Jamal thrived in the crowded Mumbai classrooms, but others didn’t. Well, we were referring to the film Slumdog Millionaire, again! Many kids struggled. While the case may seem extreme for the US and other western nations, especially in this age, it shows just how our experiences in the classroom can differ. This is especially true for people with disabilities and mental illnesses. Edtech has improved not only their access to education but also learning experiences. Assistive technologies , such as screen readers, speech recognition software, and tactile interfaces, have enabled such students to participate fully in educational activities.
Improved classroom engagement
Can you imagine keeping young learners in a crowded classroom engaged for just one hour? It’s almost impossible, right? Now, that’s what some teachers confront every day! With few teaching aids, making students engaged is a complete nightmare. This is where technology comes in. Most teachers have stopped relying solely on traditional teaching methods and integrated edtech such as multimedia presentations, virtual reality simulations, video games, interactive puzzle games and quizzes to make learning more enjoyable. As a result, some studies have reported increased motivation and deeper understanding and retention of concepts. A win -win situation.
WorkBot AI chatbot can be a game-changer for higher education . Imagine having an intelligent assistant that can answer student queries 24/7, from course details to enrollment processes. It can streamline administrative tasks, freeing up professors to focus on teaching. Additionally, WorkBot can provide personalized learning experiences by adapting to individual student needs. This technology can potentially enhance student engagement and success while increasing efficiency within educational institutions.
The Negative Effects of Technology on Education
Now that we’ve discussed the pros, it’s time to explore the negative effects of technology on education. There’s always a downside to any tech. Below are a few ones derailing the education sector:
Distraction
The presence of tech devices such as laptops, smartphones, tablets, and computers in the classroom can derail some students. Not all learners are equal or the same. So, you’ll always find the ones hooked to social media and online games rather than classwork. They’d rather chat than write their essays.
Erosion of social skills
As we go increasingly online, we limit opportunities for face-to-face interaction. This is the case with edtech. Students are finding it easier and more comfortable chatting online than having face-to-face conversations, which undermines interpersonal skills development. If you can’t communicate well in person, you’re heading in the wrong direction.
Information overload
The internet has opened the door to a whole new world of information that’s hard to process and verify. Even fools can open websites, blogs, and social media pages where they share misinformation. These can be exceedingly difficult for students to discern, leading to confusion and potentially inaccurate learning.
Health implications
Well, too much of anything is dangerous. Having technology in class could lead students into dependency, using their gadgets in all other aspects of life. The consequences could be far-reaching. For instance, studies have linked excessive screen time and poor ergonomic practices to various health implications, including eye strain, musculoskeletal problems, and sedentary behavior.
Academic dishonesty
This is the elephant in the room right now. New technological inventions, especially AI, have had a significant negative impact on academic honesty. Most students no longer do their research. Instead, they rely on ChatGPT, Textero, and other language-based techs to write their papers. This has proven quite problematic for educators.
The Future is EdTech but with a Lease!
Technology has undoubtedly revolutionized our education system for the better. Our children have avoided some many troubles and we were confronted with very little benefits. Edtech is here and it’s going nowhere. We should embrace it and enjoy its benefits. At the same time, we should have measures to minimize, if not eliminate, its disadvantages. As it is said, where there is a will, there is a way.
The content published on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, health or other professional advice.
- Academic Collaboration
- Digital Divide
- Negative Effects of Technology
- Online Learning
- Positive Effects of Technology
- Technology in Education

B2C Ecommerce: 5 Strategies You Can Adopt To Drive More Leads
Do you know that as a B2C ecommerce company, you stand a better chance at

6 Strategies for Getting Your Store Ready for Surges in Customer Traffic
Seeing your customer base grow is a good sign for your physical retail business
You May Also Like

Implementing Headless SFCC: Best Practices and Strategies
Interest in headless commerce has been steadily growing for the last seven

Is the Managed IT Services Cost Justifiable for Small Businesses
In today’s digital age, small businesses are increasingly reliant on

How to Save Money on Business Courier Services
The opening move for economizing business courier service expenses is to

What to Study If You Want to Help People: 10 Fields to Consider
In today’s world, more and more individuals are drawn to professions that
Home — Essay Samples — Information Science and Technology — Impact of Technology — Positive And Negative Effects Of Technology On Society
Positive and Negative Effects of Technology on Society
- Categories: Impact of Technology Negative Impact of Technology
About this sample

Words: 939 |
Published: Feb 8, 2022
Words: 939 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read
Works Cited:
- Ali, A. (2017). 10 Mysterious Places That Science Cannot Explain. ScoopWhoop.
- Amusing Planet. (n.d.). The Moeraki Boulders of New Zealand.
- Atlas Obscura. (n.d.). Magnetic Hill.
- Discovery. (n.d.). Blood Falls, Antarctica.
- Fernandez, M. (2020). Surtsey: The Birth of an Island. Geology In. https://www.geologyin.com/2020/06/surtsey-birth-of-island.html
- Fradkin, P. L. (2009). Daylight comes to Longyearbyen. Polar Research, 28(2), 338–347.
- National Park Service. (n.d.). Old Faithful. Yellowstone National Park.
- Owlcation. (2020). The Mystery of Moving Rocks on Racetrack Playa, Death Valley. Owlcation. https://owlcation.com/stem/The-Mystery-of-Moving-Rocks-on-Racetrack-Playa-Death-Valley
- Tours by Locals. (n.d.). Pamukkale: The Travertine Terraces of Turkey. https://www.toursbylocals.com/Pamukkale-Turkey-Tours
- Wojtal, A. Z. (2022). Eternal Flame Falls. Atlas Obscura.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Information Science and Technology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1166 words
4 pages / 2045 words
4 pages / 2022 words
6 pages / 2869 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Impact of Technology
A Digital Revolution: Enter the era of smartphones, AI, and the Internet of Things, where technology is the driving force. Join me as we explore how technology has transformed our lives and the profound impact it has [...]
Technology has transformed the way we live, work and communicate. The advancements in technology have brought about numerous benefits, but they have also raised concerns regarding the effects on different aspects of our lives. [...]
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, have been a topic of great interest and debate in recent years due to their potential to revolutionize the way we travel. These vehicles have the ability to navigate roads [...]
In the digital age, the pervasive use of technology has raised concerns about its impact on attention spans. This essay presents findings from a survey conducted among Generation Z individuals to draw inductive conclusions [...]
The amount of time that children spend on screens (i.e., televisions, computers, IPads, and phones) has become a concern amongst many parents and people who work with children, such as teachers. There has been controversy on [...]
There has been lot of improvements in the field of technology and communication. Texting is one of them. This is something that you don’t need verbal speaking and is very short. Basically, young generations are more influenced [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
The Positive and Negative Effects of Technology on Your Life

Your changes have been saved
Email is sent
Email has already been sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
7 Things We Love About the Wellness Coach App
How to use strava’s goals feature to stay motivated, how to use strava’s beacon feature to share your location while exercising.
Technology is around us everywhere, from simple devices like our smartphones, laptop, and TV to background tech that we don't even notice. It isn't going anywhere anytime soon, meaning we have to get accustomed to it. Once we get the hang of using tech the right way, it can improve our lives.
On the other hand, tech can also make our lives harder. Whether tech has a positive or negative effect on our lives, it all depends on how we use it. So, let's look at some of the positive and negative aspects of technology in our lives, shall we?
Positives of Technology in Our Lives
Technology has, without a doubt, made all our lives easier over the past two decades. From connecting with people across the globe from the comfort of your home to running a full-fledged business without a physical space, technology has impacted our lives positively in several ways. So, read on below:
1. Technology Boosts Business

Many new tech advancements and innovations are made by and for businesses. Why? Because companies are always looking to upgrade their products and services for profit.
New technology continues to come out faster than we can keep up with. The purpose is to boost business and make the daily management of enterprises more systematic, structured, and successful.
Tech has boosted businesses by improving the hiring process, error-free collection and analysis of business data, and better communication with clients and partners.
Additionally, tech has also changed the way we work remotely for the better. It is now commonplace for people to work from home. However, certain tech, like the cloud, has made it easier than ever to work whether you're at the office or not.
What's more, tech has made it effortless to communicate remotely too. Businesses now typically use tools like Slack and Zoom on a regular basis.
2. Technology Makes Shopping Online Possible
Advancements in tech have made it easier for more people to access the internet, resulting in online shopping being more popular now than ever.
Currently, most people prefer to shop online without leaving the house because of its sheer convenience. Instead of wasting hours in the shopping mall, tech makes shopping simple.
A few of the benefits of online shopping include cheaper products, saved time, fuel, and energy, easier-to-find items, a wider variety online, and no added pressure.
Amazon is a great website to do basically all of your online shopping. It's one of the most popular online shopping platforms because you can practically find everything you're looking for, from groceries to clothing.
Generous discounts, cheap shipping, and a massive selection of products are just some of the other excellent benefits of shopping online using Amazon. What's more, there is an Amazon Shopping mobile app that you can download and use for free. If Amazon isn't available to you there are plenty of alternatives to Amazon for your online shopping .
Download: Amazon Shopping for iOS | Android
3. Technology Has Advanced Education
One of the most downplayed areas of technology that has dramatically improved over the past few years is education. Technology has definitely been beneficial for those in the business world, but it has impacted education in a big way.
A few examples include the availability of online courses, accessibility of web seminars, and unlimited online resources for research. Before tech, you'd have to physically go to class, attend a meeting or go to the library to do research.
Now, education is easier for everyone, no matter where you live. Online classes have made it possible for all students to enroll without leaving their homes.
Today, you can find several great sites for free college courses online , such as Udemy—a fantastic website that offers thousands of free and paid-for courses to choose from. Whether you want to create virtual reality games or become a yoga instructor, Udemy has a course that's perfect for you.
In terms of technology, Udemy also offers a wide variety of great tech-related online courses. The categories available range from IT hardware and software to operating systems and network and security. So tech can help you master your chosen path and possibly broaden your career opportunities.
4. Technology Makes Everyday Life Better
Most technology these days is created to improve businesses and generate profit. However, tech can also make our daily lives so much better.
Tech has made an immensely positive impact on the daily lives of everyday people. Some positive examples include improvements in the transportation system.
The Bullet Train is an amazing piece of tech that can travel six times faster than a regular train. Think about the introduction of self-driving cars, too: they were unheard of a few years ago, and now they're a reality.
A fair amount of people drive Teslas, and they are well-known for having state-of-the-art self-driving capabilities. Some other companies that support autonomous driving capabilities besides Tesla are Mercedes-Benz and Volvo.
Besides transportation, technology has also had a positive influence on household items. For example, smart homes are now commonplace. Smart hubs allow households to connect their devices and appliances, making life a lot easier.
Negatives of Technology in Our Lives
As much as we appreciate technology for the convenience it brought to our lives, several aspects of it have impacted our society negatively in more ways than one.
1. Technology Causes Health Problems
As technology advances, we are connected now more than ever, and it has become a huge part of our lives. That's why it's possible for technology to impact our physical health negatively.
These physical health problems can be severe. Nevertheless, you can avoid most of them by creating healthy tech habits instead of bad ones.
Apart from creating unhealthy sleeping patterns, electronic devices can cause digital eye strain, poor posture, and increased inactivity, leading to health problems like obesity.
Taking regular breaks from these devices can help you avoid these health problems. You can find a range of apps that remind you to take frequent breaks.
One popular app to use is called Focus Keeper. This app will help you reduce your digital eye strain, take regular breaks, and prevent tech burnout.
Using the Focus Keeper app is easy. All you have to do is pick the time you want to focus on something and hit the play button to start the session. When the session is over there is a quick break and then the next session begins.
In addition, you can customize the settings under Options to change the sessions per round, daily focus goal, and timer sounds.
Download: Focus Keeper for Android | iOS (Free, in-app purchases available)
2. Technology Creates Job Insecurity
Job loss and downsizing are two significant adverse effects of technology. Because of advances in the tech field such as AI integration, automating and accomplishing tasks have become easy.
In this day and age, most companies need to stay up to date with the latest technology, but in the process, low-skilled employees, like factory workers and cashiers, will be replaced.
Machines can now carry out tasks that only humans could do so far, which creates a massive shortage of jobs. The bottom line is that people aren't necessarily needed for work tasks anymore because of how efficient tech has become.
3. Tech Products Lack Longevity
Technology grows incredibly quickly, so the digital devices and gadgets that we use have a short lifespan and become outdated in a matter of months.
Since these devices are so important in our daily lives, we need to maintain and upgrade them regularly. Besides maintenance and upgrades, these pieces of tech may just become outdated and pushed aside by newer, more advanced versions.
Tech products lack longevity, so they can be costly and lead to unnecessary e-waste. Instead of throwing your older devices away or tossing them in the cupboard, use a website like Decluttr . This site makes it easy to buy and sell your used tech online.
You can sell your old tech on the Decluttr website, whether you want to get rid of your outdated phone, wearable, or console.
When you've found the correct category and product, tap Sell Now and the website gives you an instant price based on its carrier and condition. Moreover, Decluttr is also available as a free iOS or Android app to help you declutter your life .
4. Technology Spawns Misinformation and Fake News
The spread of misinformation and fake news online is nothing new. In fact, it has been going on for many years. However, with all the developments that happen so frequently in technology, it has become harder to define what's true and what's not.
Since so many people cannot tell what information is factual and what isn't, it creates a lot of skepticism and misunderstanding about important topics. This can be especially harmful when it comes to political issues and trusting the media.
One example of how tech advancements are negatively affecting us is the use of deepfakes. Several negative deepfake incidents have surfaced, and it's getting harder and harder to spot them.
These incidents can warn us about the possible risk of tech in the future. If you're finding it difficult to spot fake news and misinformation , an online platform like Credder is a great tool to use.
Credder will help you avoid fake news and misinformation because it only follows news and information provided by trustworthy sources.
Technology Is a Boon and Bane to Society
Overall, tech is amazing, and it has changed the world for the better, from improving our daily lives to building better businesses. The majority of the adverse effects of technology stem from its misuse.
The way we choose to utilize tech can help or harm ourselves and others. Instead of blaming the tool, we need to use technology in a healthy, more disciplined way. By doing this, technology can continue to benefit our lives.
- Electronics
- Tuesday, August 27, 2024
Future Educators
Helping America's Future Teachers
Pros and Cons of Technology in the Classroom
Student learning is an area with enormous potential to benefit from information technology. Information dissemination is, after all, a core strength of today’s technologies. And digital technology offers versatile platforms to streamline classroom teaching.
While technology unlocks innovation opportunities, blended teaching and learning are not without disadvantages. What are the downsides that come with the powers and benefits of technology?
Debate is still going on concerning potential harm from integrating technology into the classroom. Let’s look at both sides by discussing the advantages and disadvantages of students accessing computers and digital information.

Advantages of Technology in Education
By offering digital tools and learning platforms, technology offers great advantages in school education. Students have more information at their fingertips and build technology skills. Tech can do some tasks equally or better than teachers, including administration, data gathering and supporting self-direct learning. Here are the top five pros to technology in the classroom.
1. Access high-quality, current information

Modern technology is fantastic when it comes to making information available to everyone. In a classroom setting, getting the most up-to-date data helps ensure the best educational experience. Teachers are also able to use or direct students towards trusted sources to ensure accurate information.
Students are also able to assimilate information more efficiently with the interactive presentation that digital technology allows. Instead of reading through text sequentially, the teacher or student can navigate information on a topic using hyperlinks, tabs, accordions, etc. References can be checked immediately as well.
Classroom technology definitely beats paper textbooks for accessing relevant information quickly. The trick is to place structure around activities to maintain focus and ensure the class is covering the same material. The need to keep everyone on the same page so to speak is a limiting factor in the use of technology for gaining information.
2. Gather student performance metrics easily
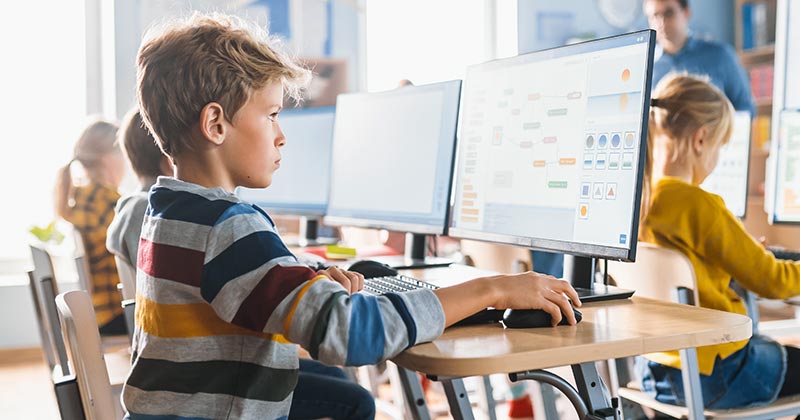

A clear and powerful advantage of using technology in education is that it allows teachers to perform their job better. The automatic collection of data in digital testing and learning environments has the benefits of: allowing more student performance data to be collected, freeing teachers from repetitive grading exercises, and providing instant feedback to students.
Platforms that yield data analytics can pinpoint the areas where each student is having most difficulty. Performance information allows instructors to quickly adjust teaching strategies and the syllabus according to the data gathered and analyzed.
When a given learning goal can be achieved with technology or traditional methods with about equal effectiveness, the technology-based approach may be preferred just because of the data advantages. Once in this digital environment, the technology and instructional content may be improved over time, leaving traditional instruction techniques further and further behind.
3. Students learn technology skills

Using technology in the classroom naturally increases opportunities for students to learn technology skills. While it’s possible to take all but the simplest IT skills out of a lesson, keeping some technical challenges in there is healthy for student development. After all, we live in a digital world and have things like virtual offices and working online from home .
Children are fast learners when it comes to most things but especially with technology. Given the chance, they’ll quickly build computer operation skills and digital literacy. Examples of skills they’ll learn include keyboard awareness, logging in and password protection, navigating apps, setting preferences, online document sharing, and using standard software such as text editors and spreadsheet workbooks.
Teachers can offer exercises that give pupils the opportunity to test and expand their capabilities. For example, you can give students freedom in how they present project results. The smart ones, who could perhaps become IT professionals in the future, will find and deploy internet resources, such as graphics or charting software, to enhance the presentation.
4. Improved student participation and engagement

Students generally love technology and introducing it is a way to boost engagement. Mixing up traditional instruction styles with technology makes the class less predictable and the learning environment more dynamic.
Examples of how teachers can inject technology are to: direct students to online resources, present short videos, use interactive software, make digital presentations, and ask students to create digital content themselves.
Online platforms are often flexible in allowing you to exercise your creativity. You can, for instance, customize quizzes to make them more engaging and competitive. Any good resources you find online might be useful additions to the lesson. The possibilities are limitless.
You can also apply technology to get more information from reserved students. If you need to ask the opinion of everyone regarding a topic or even a simple question, why not use an online polling platform? This way, even quiet students who normally wouldn’t want to speak in the classroom will participate.
5. Automate repetitive tasks

Teaching can include tedious tasks such as keeping track of attendance, recording quiz scores and noting tasks completed. With the present technology available, such tasks can now be partially or fully automated. This can unlock time teachers are able to divert to substantive teaching endeavors.
Existing technology can be used to help teachers in several areas: planning lessons, assessing students, grading homework, giving feedback and administrative paperwork. Jill Barshay
Implementing technology is not a costless exercise however and the effectiveness depends on how well software is programmed and made easy to use. But, over time, we can expect the work of teachers to become more streamlined. Instructors will have fewer administrative tasks and more time to capitalize on human strengths, such as making connections, inspiring students and creating a sense of shared purpose.
Disadvantages to Technology in the Classroom
The recency of many innovations means we’re still grappling with how best to incorporate technology in schools. Educators may lack the time and knowledge to implement tech effectively. Using technology without sufficient care can produce poorer learning outcomes and cause students to miss out on social interaction. These are key cons of technology in the classroom and online education.
1. Faster but less memorable learning

While the lightning pace with which technology operates may seem like a clear benefit, experienced educators are actually wary of this aspect. Devices and learning apps are able to function faster than the corresponding learning speed of the human mind. Students may gloss over material, missing texture and depth along the way.
Proper and coherent cognitive thought takes time. Otherwise, engagement can be drastically reduced. It’s for this reason experts are suggesting we modify media use, such as how videos are presented , to slow down and allow for more rumination and contemplation.
The simple act of writing something by hand has slowing, stimulatory effects that brain research has shown to aid both learning and memorization. Although efficient, typing is repetitive as each keystroke is almost the same action. Writing by hand is more challenging, intricate and slower, allowing your brain to form more “hooks” to imprint thoughts.
2. Technology can be distracting

Devices such as laptops and tablets in the classroom are bound to become sources of distraction to students. This is especially true if the software doesn’t prevent access to apps unrelated to lessons, quizzes and other educational activities.
A need exists for appropriate restrictive measures on gadgets in education to ensure they further learning goals and aren’t used, for example, to play games or use social media for pure entertainment. You can be sure that some badly behaved students will always try to use technology for fun instead of the intended purpose.
A problem here is that high school students may be more tech savvy than their teachers. One technique students use to access out-of-bounds sites is to go to a proxy site that delivers content from other sites without the student technically visiting those sites. Another method to bypass a school firewall is to use a virtual private network (VPN ) to encrypt browsing data so the student’s internet activities can’t be monitored.
3. Less direct social interaction

The apparent way in which technology excises social interaction is another cause for concern. Students have less need to verbally communicate and interact with their teachers and one another when using technology. Online teaching and learning excludes face-to-face interaction altogether.
To address this, classroom teachers should ensure activities such as oral presentations, recitations and group work happen regularly. There needs to be a mindfulness that we’re trying to prepare well-rounded people for adulthood.
For students addicted to gaming or social media, school might actually be a place where they get some downtime from tech. It’s up to teachers to identify when students are spending too much time with their heads buried in devices. When technology isn’t being used, students should be encouraged or pressed to show some life and interact.
4. Integrating tech is often time consuming

While technology could make the job of a teacher very easy in the future, we are not there yet . Devising effective lessons using digital technology rather than traditional methods can be challenging and time consuming. That’s why it’s important for educators to share their insights on how to effectively teach kids when there is technology in the classroom.
Showing up to your class and teaching by talking and interacting with students doesn’t require special preparation. But when you make extensive use of technology during the lesson, you’re normally going to have to prepare for that. Teachers taking advantage of technology have the same amount of face-to-face instruction time but may need to do more planning, placing an extra strain on their workload.
Online learning when classes are held remotely have shown the limitations of tech. Just trying to corral students, to ensure they’re all logged in and paying attention, is a challenge in itself. The quality of lessons suffers as educators grapple with tech while trying to meet the practical learning needs of students.
6 Tips on How To Engage With Students
31 thoughts on “ pros and cons of technology in the classroom ”.
This was helpfull
Upvote!!!!!!!!
My child has been influenced due to the bad technology. He was a nice 9 year old kid before he found out about the thug shaker from technology. He keeps saying “Im bout to blow.” Technology has effected our society. And the thug shaker is a prime example.
OKAY BOOMER!
This comment section be crazy yall.
i think ur over exaggerating
gangsta rap
The amount of privilege in this paragraph is nothing short of nauseating. “Teachers can offer exercises that give pupils the opportunity to test and expand their capabilities. For example, you can give students freedom in how they present project results. The smart ones, who could perhaps become IT professionals in the future, will find and deploy internet resources, such as graphics or charting software, to enhance the presentation.” Oh wow, just wow… “The smart ones”, you mean the ones that sit still, eyes on you, have stable households, technology access at home, maybe even only from this country… Do better future educators, do better….
Everyone in a classroom should be expected to pay attention, no matter their background. You don’t have to be privileged to do it. And every child should be given the opportunity to reach their potential – no ceilings.
chat gpt cookin
Some of us knew how to write before Chat GPT came along.
im a 12 year old sacred heart student and im reading your comments for a debate thank you so much 12\10\2023
Technology is very bad. Technology reminds me of the turbunence, strapping down your seatbelts, thug shaker, and people getting addicted to their phones, whenever i go in public people start doing turbulence, and always yelling out stuff and it influenced our society very big.
Stop being rude.
Travis Scott in da building
Technology can be a distraction for students, making it difficult for them to focus on learning. For example, students may be more interested in checking social media on their devices than paying attention to the lesson. Also when students rely too heavily on technology, they may become less capable of solving problems or completing tasks without it. This can hinder their ability to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
no you are wrong
i think that it is not that it is not that bad to have a phone
Maybe so. However, the use of technology and electronic devices can have negative effects on concentration and the ability to write well-structured sentences. Everyone, including educators, need to find a balance and limit the use of technology to enhance academic performance.
pluh using ai
Technology needs to be included to a certain degree but if we use it in every aspect of learning, you will see more and more children suffering with ADHD, ADD, and other learning issues. I see it now with children as young as 8 years old walking around with smartphones!
The good news is there is no evidence in this study or anything else I’ve read that cell phone use would create ADHD
There are pros and cons to everything, that’s why everything should be used in a controlled way. This is true nothing can replace the conventional method of teaching, but we can make it more interesting and better for students with a little use of tech. Like the use of animation, quiz polls, etc. So everything is cool until it is used in a particular way.
I would like to point out that you’re contradicting yourself on the Pro#4 with the interaction of a student via tech, and with the Con #3, that a student needs to interact with oral participation. The Pro #4 would discourage oral participation, which I believe is huge asset for all students. A student should be encouraged and helped with speaking out on different discussions. Teaches would call on me, even though they knew I didn’t like it, but it helped me get over my shyness. I hated speech in high school, but I did it and thank God for it. It has helped me tremendously.
That’s a good point Billiam. We shouldn’t lose the art of conversation and talking in person. Using technology to engage students is a balancing act.
I think it’s imperative that kids learn technology. Just don’t abandon everything. For example, we don’t use quills and inkpots (or fountain pens for that matter), but we should still teach kids to write with pens and pencils. That includes cursive, which is proven to help kids’ learning. There are grey areas though. One of them is calculators. We don’t teach kids how to use slide rules, but should we abandon calculators for certain situations? Then there are things that have completely been abandoned, but for no good reason. Why can’t kids tell time with non-digital clocks?
I can agree on most of your points. My question would be, when do we introduce students to technology? Call me old fashioned, but I believe that the task of learning simple math (1-3 digit computations), parts of speech, and sentence structure should be taught without the use of any type of technology. As students progress, I think technology is a great thing to interject into education. I do believe, however, this should be minimalized until about fifth grade. Students taking assessment test need to know how to write instead of just clicking on an answer. Calculators were never allowed in school until junior high when I attended. There are many students, in the school where I work, that will not write because they do not know how to form the letters on paper. Many times the students who do know how to write, have horrible handwriting because they do not write every day. Yes, technology is wonderful, but at what age should it be introduced in order for students to be able to succeed before technology is used?
This is how I see technology in the classroom: you have to use a hybrid model because there is no escaping how ingrained technology is in our lives and even more in the students’ lives. I would argue that in some cases the students are ahead of their teachers when it comes to being tech-savvy and understanding where things are headed. However, there are traditional skills that are overlooked far too much including reading from books, writing (printing and cursive), and doing research without a computer. Add these items to your article and I can’t think of any better description of the pros and cons of using technology in classrooms.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Related Posts
5 letter word with most vowels (wordle words), how to use videos in the classroom, 21 ways of teaching soft skills to students.

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
Children and Technology: Positive and Negative Effects
January 18, 2022
Tables of Contents
Evolution of Children’s Use of Technology
Positive and negative effects of technology on children, technology and children statistics, technology and social interaction in children, ensuring safe and nurturing digital environments for children.
Imagine spending a year or more of your childhood almost entirely at home: no time in a classroom, no chance to join friends on the playground, and very few opportunities to enjoy favorite pastimes and experience new places, people, and activities.
The worldwide lockdowns that helped limit the spread of the coronavirus created a kind of twilight zone for children that put much of their environment off-limits and kept them separated from everyone but their immediate families. However, not all was lost. What vestiges of their pre-COVID life children were able to maintain were made possible by a range of technologies that kept them learning, interacting with friends, and entertained.
The growing presence of technology in children’s lives, from their first year through their teens, is a double-edged sword. While technologies are neutral, how they are applied and how children are exposed to them can be either positive or negative.
The impact of children and technology becomes increasingly difficult to gauge as the pace of technological innovation speeds up. This guide presents a snapshot of the many roles that technology products and services play in the lives of children. It balances the pluses and minuses of the effects of technology use by children on their development, social interactions, and prospects for the future.
Learn how people develop physically, emotionally and socially within the context of family and society
The online BA in human development and family studies from Maryville University prepares you with knowledge and skills related to child development, family dynamics and interpersonal relationships. No SAT or ACT scores required.
- Benefit from a curriculum that follows the 10 content areas of the National Council on Family Relations (NCFR).
- Engage in a range of relevant course topics, from interpersonal relationships to medical terminology.
From the earliest electric model trains in the early 20th century through the first home video game systems and remote-controlled toys, children’s introduction to technology has been through their toys. What were marvels of technology three, two, or even one generation ago seem almost quaint by today’s standards. However, the progress from Pong to Oculus virtual reality games occurred in a relatively brief period of time.
Early Examples of Children and Technology
Children have been interacting with digital technology since the earliest days of the PC revolution . One of the first electronic educational toys was Texas Instruments’ Speak & Spell, which was released in the late 1970s. This relatively simple device was a precursor to the first PCs designed for children in the 1980s. It also presaged the growth of computer-assisted instruction hardware and software in the pre-World Wide Web era.
- The first Speak & Spell toys debuted in 1978 to teach children ages 7 and older how to pronounce and spell 200 commonly misspelled words. It relied on electronic speech synthesis and bubble memory (a precursor to RAM) and was the first such product to use solid-state circuitry to replace all moving parts.
- While Magnavox’s Odyssey was the first gaming console upon its release in 1972, the device was soon eclipsed by the home version of Atari’s Pong arcade video game, which began shipping in 1975. This was followed by the Atari 2600 game console in 1977 and similar devices from Nintendo, Mattel, and Coleco, among other vendors. Sega and Nintendo came to dominate the home video market through the 1980s, along with Commodore, Atari, and Sony’s PlayStation, which was released in 1994.
Evolution of Technology Designed to Educate and Entertain Children
The arrival of the World Wide Web in the mid-1990s changed that nature of tech toys and education hardware and software. Smart Toy Lab , an Intel and Mattel joint venture launched in 1998, developed the first web-connected interactive toys, or “smart toys.” Among the first toys the lab developed were the QX3 Microscope, which featured a built-in video camera that sent images to a PC via a USB link, and the Me2Cam, which let children play interactive games using gestures to move “objects” on the screen.
Some early internet-connected toys and educational devices were criticized for violating children’s privacy by collecting personal information without parental consent. For example, Hello Barbie was released in 2015 and featured a built-in microphone and voice recognition software, as well as a Wi-Fi connection. The doll’s call-and-response function was a precursor to Amazon’s Alexa/Echo and Apple’s Siri voice assistants. However, hackers soon figured out how to break into the toy’s system and access users’ private information.
Today many children — from toddlers to teenagers — regularly use tablets, smartphones, and virtual environments for entertainment and educational purposes. Pandemic-related restrictions have increased children’s reliance on these and other technologies to connect with the outside world. With increased use of these products comes heightened prospects of damage and abuse:
- A recent study published in Children and Youth Services Review identified problematic smartphone use (present in 16.4% of high school students surveyed), daytime sleepiness (20.2%), and symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (6.9%) as spiking during pandemic lockdowns.
- A study published in the Italian Journal of Pediatrics found that 66.3% of the children and adolescents surveyed used their smartphone for more than four hours a day during the pandemic, compared with 16.3% who did so before the pandemic. In addition, 56% of the children and adolescents surveyed used their smartphone after midnight at least three times each week, compared with 30.4% before the pandemic.
Back To Top
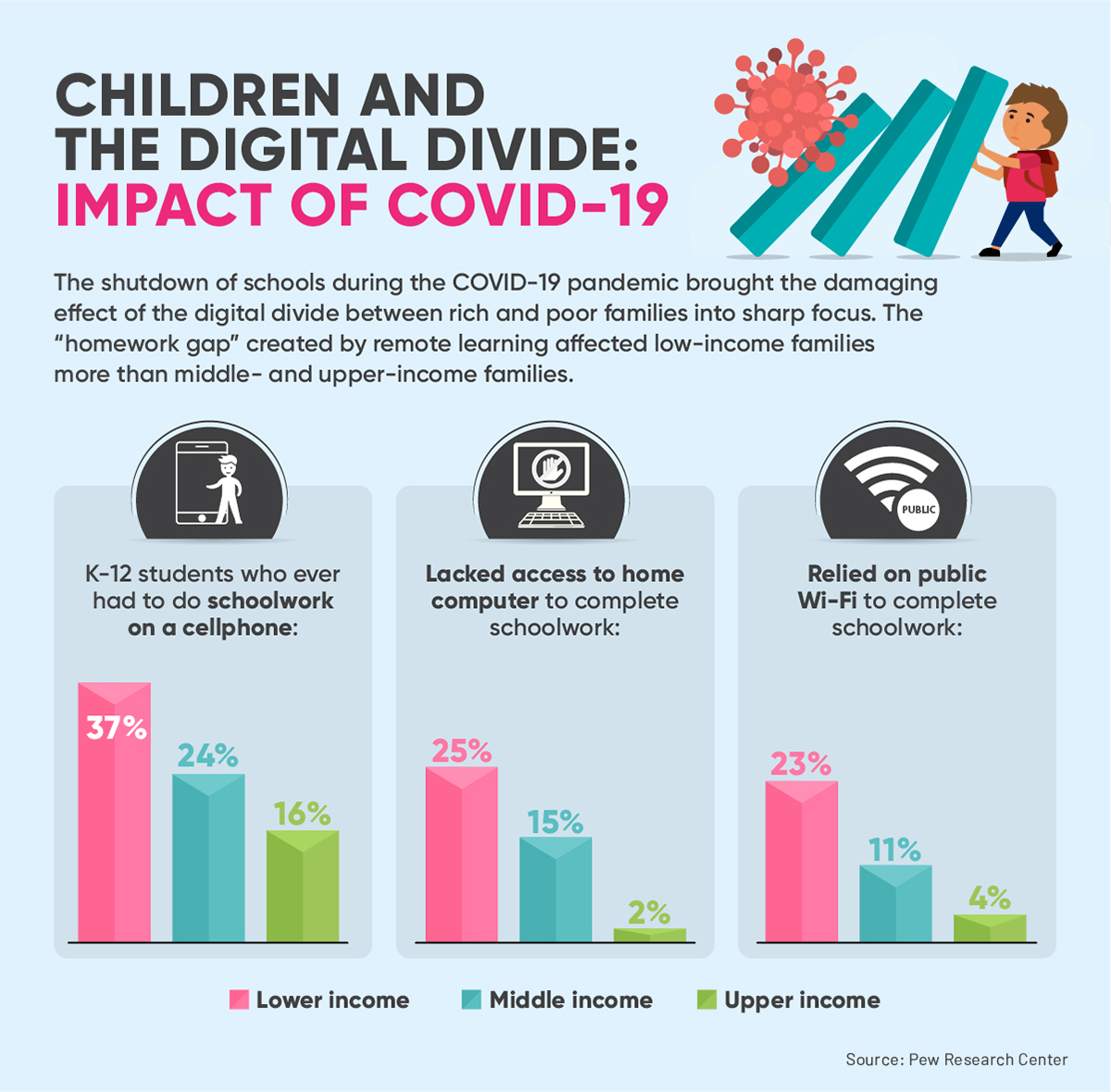
The shutdown of schools during the COVID-19 pandemic brought the damaging effect of the digital divide between rich and poor families into sharp focus. Pew Research Center data shows that the “homework gap” created by remote learning affected low-income families more than middle- and upper-income families. K-12 students who ever had to do schoolwork on a cellphone: lower income: 37%; middle income: 24%; upper income: 16%. K-12 students who ever lacked access to a home computer to complete schoolwork: lower income: 25%; middle income: 15%; upper income: 2%. K-12 students who ever relied on public Wi-Fi to complete schoolwork: lower income: 23%; middle income: 11%; upper income: 4%.
Children can benefit from technology by gaining new learning opportunities; it’s especially important for children who are physically or developmentally challenged. However, technology use has also been found to contribute to poor self-esteem and isolation in some children. As digital technologies become more ubiquitous, parents struggle to find the optimum amount of technology for their children’s lives.
Positive Effects of Technology on Children
All the “rules” about children’s access to computers and the internet were rewritten by the COVID-19 pandemic , according to parenting expert Anya Kamenetz. Technology provides children with easy access to information and boosts their creativity. Tech hardware and software helps children develop social skills and introduces them to various arts and sciences.
These are among the less obvious positive effects of technology on children:
- Technology allows children to connect with their family, friends, and others in ways that enrich their relationships, especially when using video chat and other real-time interactions.
- Parents and caregivers are learning to slow down and tone down the applications, games, and other content children use to avoid overloading their senses. This teaches children how to moderate their own use of technology.
- Rather than trying to eliminate all risk to children when using technology, the goal should be reducing the risk and adapting when problems arise, such as preventing children from accessing devices at specific times of the day.
Many parents hesitate to allow their preschool-age children to use technology products and services due to concerns about how it’ll impact their well-being and development. However, the children are surrounded by technology, much of which offers them significant benefits , as BSD Education explains:
- Technology helps children become independent learners more quickly. Once they learn how to access digital information sources safely, they’re able to explore the topics that interest them on their own.
- Children learn the importance of building communities and how to interact with people in social situations. When circumstances prevent children from establishing physical bonds with family members, friends, and others, they’re able to use technology to create “virtual bonds.”
- Early access to technology teaches the digital literacy skills that children will need for their future success in school and as adults.
- Many technology products promote hand-eye coordination in young children, while others focus on developing their language and problem-solving skills.
Negative Effects of Technology on Children
Children are especially susceptible to technology overuse. The American Psychological Association (APA) recommends limiting the use of technology to one hour per day of high-quality programming for children ages 2 to 5. For children ages 6 and up, it’s most important to set consistent limits on various types of media, such as gaming devices and smartphones.
APA suggests that parents focus on the content on children’s screens and how the children are interacting with it. A survey of research on the possible negative effects of technology on children establishes a connection between the level of a child’s use of technology and various developmental and behavior problems.
- Lack of attention, aggressive behaviors, obesity, physical inactivity, sleep problems
- Musculoskeletal problems related to a sedentary lifestyle
- Greater risk of lifetime obesity and cardiovascular disease
- Sleep disturbances and poor-quality sleep for children who overuse social media or keep mobile devices in their bedroom
These are among the negative effects of technology on children:
- Exposure to harmful online content and sexual exploitation: A study by Irish researchers found that children of all ages are able to bypass the age verification systems of social media apps, such as Snapchat, TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook. This can bring children into direct contact with potential predators and other dangers.
- Cyber bullying: The Cyberbullying Research Center reports that incidents of cyber bullying are most prevalent at ages 12 to 15. A recent survey by the center of 13- to 17-year-olds found that 23.7% of girls, 21.9% of boys, and 35.4% of transgender teens had experienced being bullied.
- Low self-esteem and increased anxiety: CNN reports that teens and adolescents are using image filters on Instagram to enhance their appearance even though the result looks nothing like them. “Self-esteem addiction” can make young people feel inadequate. As children spend more time on social media, they may become withdrawn or find themselves obsessively checking their social media feeds.
Resources on Ways Children Are Affected by Technology
- The Register, “Technology Does Widen the Education Divide. But Not Always in the Way You Expect” — One educator found that upon returning from online education during lockdown, children had turned away from technology, preferring real books and nontech activities because tech is no longer seen as “fun.”
- Edutopia, “Helping Parents Feel More Comfortable with Tech” — Advice for teachers about how to convince parents to support technology in the classroom.
- UNICEF, “Harnessing the Power of Technology and Digital Innovation for Children” — A report describing the initiatives and successes of the Digital UNICEF 2020 program, which is intended to extend the reach of UNICEF’s aid efforts.
When it comes to children’s access to technology, the digital divide between rich and poor persists. The increased reliance of children on technology for remote schooling during the COVID-19 pandemic adds a new and dangerous dimension to the problem, which some analysts refer to as the “ homework gap .”
- A survey by Common Sense Media found that 49% of 8- to 18-year-olds in the U.S. had attended classes fully or partially online since the start of the pandemic.
- Hispanic/Latinx students (48%) and Black students (39%) were much more likely than their white counterparts (20%) to attend school fully online.
- Similarly, students from low-income families (42%) were more likely to rely completely on online instruction than those from middle-income and high-income families (31% and 27%, respectively).
- While 92% of white students had a computer at home, only 87% of Hispanic/Latinx students and 78% of Black students did.
- Broadband access at home was available to 90% of students from families with high incomes, compared with 80% for middle-income families and 61% for lower-income families.
- In addition, 88% of white families had broadband access at home, while 76% of Black families and 68% of Hispanic/Latinx families had broadband access at home.
Common Sense Media estimates that closing the digital divide for K-12 public school students will cost between $6 billion and $11 billion in the first year, and between $4 billion and $8 billion annually in subsequent years. An additional $1 billion will be required to upgrade the remote access technologies that teachers use.
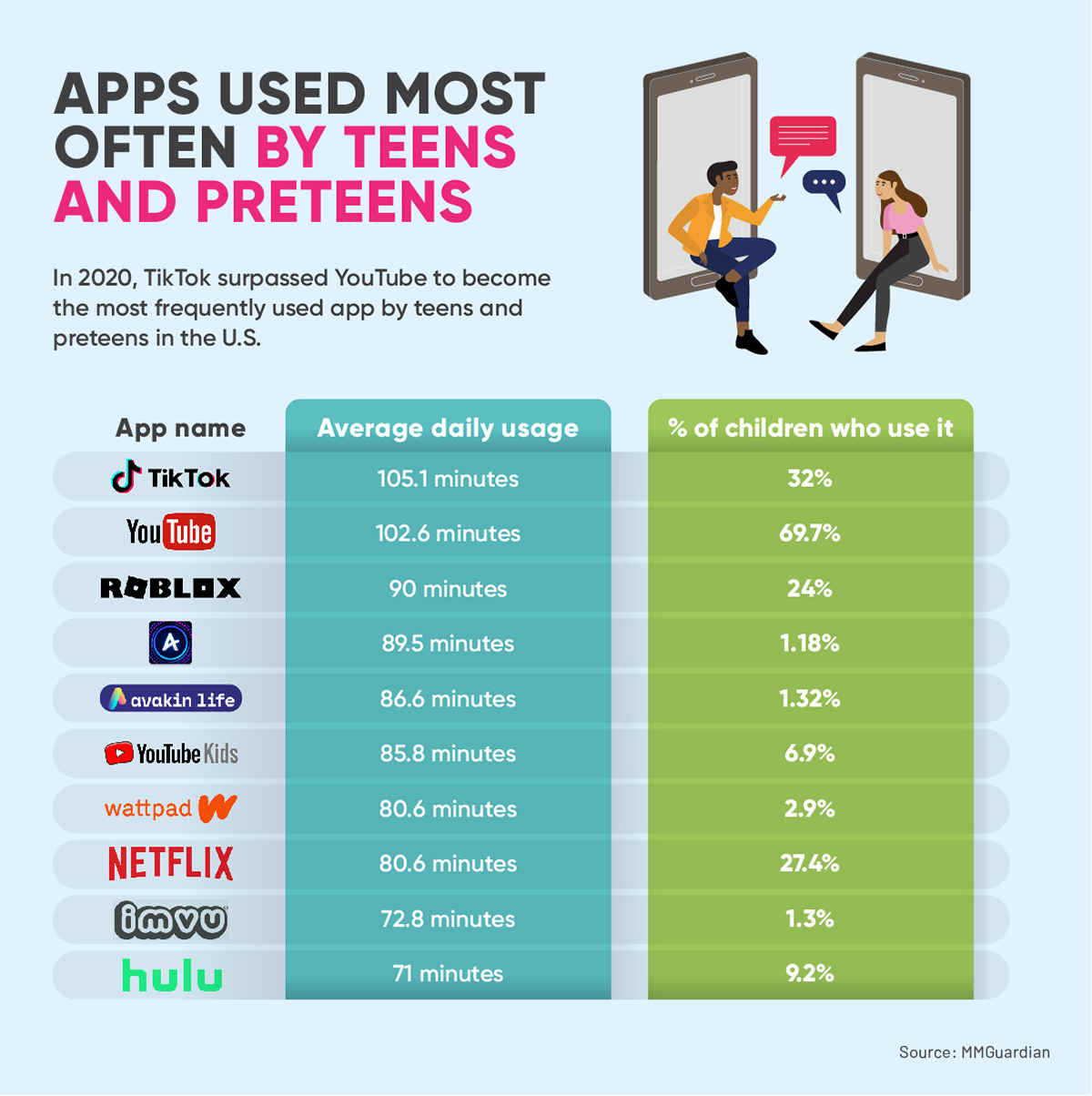
In 2020, TikTok surpassed YouTube to become the most frequently used app by teens and preteens in the U.S., according to MMGuardian. 1. TikTok: average daily usage, 105.1 minutes; % of children who use it, 32%. 2. YouTube: average daily usage, 102.6 minutes; % of children who use it, 69.7%. 3. Roblox: average daily usage, 90 minutes; % of children who use it, 24%. 4. Amino: average daily usage, 89.5 minutes; % of children who use it, 1.18%. 5. Avakin Life: average daily usage, 86.6 minutes; % of children who use it, 1.32%. 6. YouTube Kids: average daily usage, 85.8 minutes; % of children who use it, 6.9%. 7. Wattpad: average daily usage, 80.6 minutes; % of children who use it, 2.9%. 8. Netflix: average daily usage, 80.6 minutes; % of children who use it, 27.4%. 9. IMVU: average daily usage, 72.8 minutes; % of children who use it, 1.3%. 10. Hulu: average daily usage, 71 minutes; % of children who use it, 9.2%.
Statistics on Children’s Online Activities
The most common activity for children online is accessing software, audio, and video content (44% of children had done so between March 2020 and April 2021). The next most popular activities are using internet-based communications (22%); playing video games (14%); accessing online stores, banks, or payment systems (13%); and reading news media (4%).
A study by the National Institute for Early Education Research (NIEER) on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on children’s learning and development determined that children lost learning opportunities at home and in preschool programs. This resulted in “unusually high” rates of socio-emotional and mental health problems in children as reported by their parents.
- Twenty-two percent of 4- to 7-year-olds had high levels of conduct problems in the fall of 2020, compared with 11% who did so in a survey conducted before the pandemic.
- Higher levels of hyperactivity (15% vs. 10%), peer problems (17% vs. 9%), lack of prosocial behavior (20% vs. 8%), and total difficulties (15% vs. 8%) were also recorded among 4- to 7-year-olds during the pandemic.
How Children’s Screen Time Correlates to Their Mental and Physical Health
A primary concern among parents about their children’s use of technology is the amount of time children spend in front of a television, computer, smartphone, or another screen. Researchers have established a link between the amount of time adolescents spend in front of a screen , their level of moderate or vigorous physical activity (MVPA), and the amount of sleep they get.
- Screen time involves sedentary activities that detract from MVPA and delay bedtime and that interrupt sleep with digital notifications.
- The result is an increased risk of children becoming overweight or obese, as well as more sleepiness during the day and lower academic achievement.
- While most of the 13- and 14-year-olds in the study met the recommendations for total screen time (less than two hours per day) and MVPA (at least one hour per day), only half met the recommendation for sleep (8.5 hours per night). Meeting the recommendation for screen time and one of the other two factors led to better academic outcomes.
Some research into the connection between children’s screen time and their psychological well-being has been brought into question because of discrepancies between actual and reported use of digital media by children. A recent meta-analysis of research on the impact of screen time on children found either no significant impact or only a moderate impact. More indicative of potential psychological or developmental problems in children than overall screen time is the type of content that children view and interact with.
However, studies have established a link between excessive screen time and children’s levels of attention deficit symptoms; impaired emotional and social intelligence; social isolation; phantom vibration syndrome; and diagnosable mental illnesses, such as depression, anxiety, and technology addiction.
Finding the Right Amount of Time Online for Children
Many activities that benefit children can become dangerous if used too much. During the pandemic, the time that adolescents spent in front of a screen nearly doubled, according to a study published in JAMA Pediatrics . Adolescents were spending an average of 7.7 hours a day in front of a screen early in the pandemic, compared with 3.8 hours per day before the pandemic. Indications are that the elevated level of screen time will persist.
Determining the optimal amount of screen time for children has become challenging for parents because of the potential problems arising related to children’s vision, posture, and other physical development concerns. While the standard recommendation of experts remains that children under the age of 8 spend less than two hours per day in front of a screen, many factors must be considered when setting a limit for children:
- Allow more screen time for positive educational activities.
- Encourage children to take breaks from the screen that involve outdoor activities.
- Avoid using screens as “babysitters” that keep children occupied. Find other nonscreen activities, such as creative toys, coloring books, and storybooks.
- Don’t let children’s use of electronics cut into their sleep time.
- Make sure that children take short breaks from the screen every 20 minutes or so to protect their vision.
- Check the area of the screen activity to ensure that the lighting is neither too dark nor too bright.
Tech Companies’ Growing Impact on Children
After pressure from government regulators, Facebook shelved its plans to develop a version of Instagram called Instagram Kids that targeted children under the age of 13, as The New York Times reports. In 2019, YouTube paid $170 million to settle claims that it targeted children under the age of 13 in its advertising and collected personal information about them.
These are just two of the many examples of giant tech companies targeting children to meet their need for continuous growth. In the absence of federal privacy laws, companies such as Google (which owns YouTube), Facebook (now known as Meta), Amazon, and TikTok are left to self-regulate their privacy and other policies.
- The Verge reports that Facebook is exploring the use of playdates to spur children to use its Messenger Kids application.
- According to Reuters, attorneys general of several states are investigating Instagram for its attempts to attract young children in violation of consumer protection laws.
- YouTube is being sued in the U.K. over alleged violations of children’s privacy and data rights, according to Tech Monitor.
- A recent survey by Accountable Tech found that 74% of parents believe that Facebook cares more about profits than about keeping their children safe on the site.
Parents, educators, and regulators are also concerned about the safety of educational technology platforms that use machine learning and other artificial intelligence technologies to harvest massive amounts of data about children. Many fear that ubiquitous surveillance will lead to behavioral control and potentially a total loss of privacy for children. They’re calling for more accountability from such platforms, as well as legislation that guarantees children’s “right to future tense.”
Resources Providing Statistics on Children and Technology
- International Central Institute for Youth and Educational Television, International Data Youth and Media 2021 — Statistics on the types of technologies that children use in countries around the world, as well as daily use of media by children in various age groups.
- Family Online Safety Institute, “Healthy Screen Time: Mobile Technology’s Relationship with Children’s Exercise” — A study reporting a sharp decrease in the amount of time children spend playing outdoors and the growing reliance on applications that entail physical activity, such as Nintendo’s Wii console.
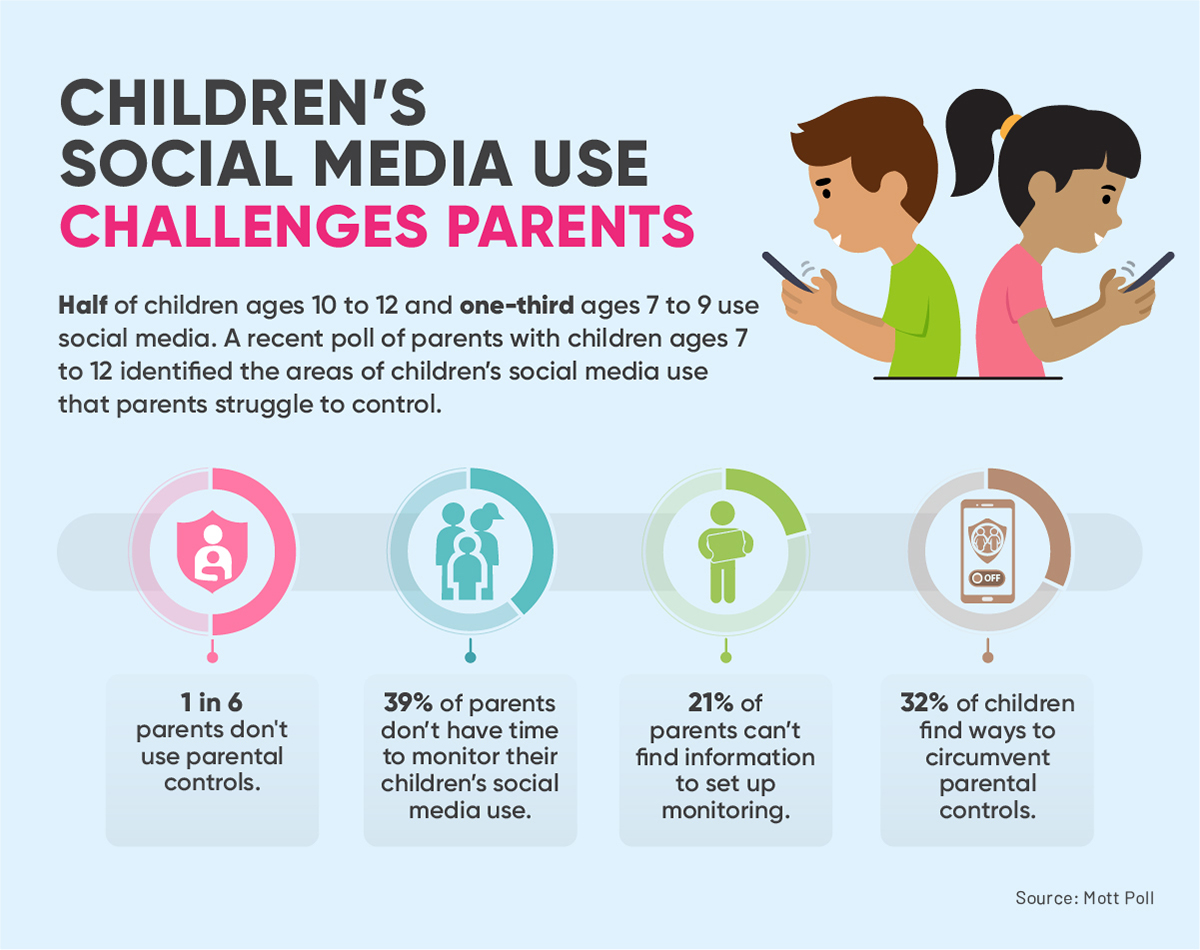
Half of children ages 10 to 12 and one-third ages 7 to 9 use social media, according to a recent Mott poll of parents with children ages 7 to 12. Parents identified the areas of children’s social media use that they struggle to control; for instance, one in six parents don’t use parental controls. Additionally, 39% of parents don’t have time to monitor their children’s social media use, 21% of parents can’t find information to set up monitoring, and 32% of children find ways to circumvent parental controls.
The lockdowns deprived young children of opportunities to develop social skills by interacting with other children. As a result, educators report that some children returning to school are struggling with classroom routine. However, the pandemic has disrupted the lives of many families of students and teachers.
- Some children are experiencing anxiety in the classroom that may relate to separation anxiety after spending a prolonged period with family.
- While most students readjust quickly to their school routine, those who’ve experienced trauma at home are most likely to struggle in school. This is especially true for children in kindergarten and first grade.
- Children are showing their resilience in adapting quickly to masking and social distancing requirements.
Research presented at a recent conference of the Society of Neuroscience indicates that isolation in adolescents can change the development of the brain systems related to fear, risk and reward, and social recognition. This may make it more difficult for them to distinguish friendly behavior from threatening behavior in their peers, for example.
A good way to break feelings of social isolation that developed as a result of the pandemic is to increase the amount of school time devoted to physical activities.
Child Development and Technology
Researchers are studying how the way young children play with technology compares with the way they play with real-world toys. They’ve found that all the types of play in the nondigital environment are present in the digital realm as well.
- Digital play develops a range of abilities in children, including subject knowledge and understanding; digital skills; and skills related to social, emotional, cognitive, and creative development.
- Because digital and physical play are intermixed in children’s lives, it’s more appropriate to look at play holistically.
Most research on children and technology relates to children ages 9 to 16, but interactions with technology may have a greater impact on the development of children ages 3 to 8. Digital education for young children increasingly takes the form of applications running on tablets and smartphones, language development applications, and physical coordination from manipulating game controls and videos that teach dancing and other activities.
Since the advent of Apple’s iPad in 2010, computer use by young children has skyrocketed , especially as teaching philosophies focus on play activities over traditional classes and formal teaching. Some schools now test each child’s digital skills and teach children digital competence, such as knowing when and why digital tools are used.
One approach to understanding the complexity of technology’s impact on children is the domestication theory that compares the introduction of digital tools into society to the process of taming a wild animal. The four phases of the domestication process render the tools nonthreatening and also make them useful, important, and meaningful.
- Appropriation is the reason for acquiring the digital tool.
- Objectification of the digital tool instills a personal meaning for the tool in the child using it.
- Incorporation describes how the digital tool becomes a part of the child’s life. It also explains appropriate and inappropriate uses of the tool.
- Conversion occurs when the digital tool has redefined the child’s worldview and relations with others.
Resources on the Impact of Technology on Children’s Development and Social Interactions
- Early Childhood Education Journal, “Investigating Young Children’s Interactions During Digital Play” — Research into children’s social behaviors within digital play environments found that adding a social dimension increased a child’s engagement in the activity.
- OECD iLibrary, “Children and Digital Technologies: Trends and Outcomes” — Topics include use of social robots to help treat children with chronic diseases and the impact of digital technologies on children’s physical health.
Technological advances happen so quickly that parents and educators don’t have much opportunity to consider how children’s growth and well-being may be improved or impaired by the types of technologies they interact with and the ways in which those interactions occur. However, technology continues to play a more important part of the lives of most children when they’re in school, at home, and at play. The judicious application of technology will enhance a child’s education and other aspects of life.
Infographic Sources
Associated Press, “TikTok Is Now the Most-Used App by Teens and Pre-teens in the U.S.”
Mott Poll Report, “Sharing too Soon? Children and Social Media Apps”
Pew Research Center, “The Internet and the Pandemic”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.
Is technology good or bad for learning?
Subscribe to the brown center on education policy newsletter, saro mohammed, ph.d. smp saro mohammed, ph.d. partner - the learning accelerator.
May 8, 2019
I’ll bet you’ve read something about technology and learning recently. You may have read that device use enhances learning outcomes . Or perhaps you’ve read that screen time is not good for kids . Maybe you’ve read that there’s no link between adolescents’ screen time and their well-being . Or that college students’ learning declines the more devices are present in their classrooms .
If ever there were a case to be made that more research can cloud rather than clarify an issue, technology use and learning seems to fit the bill. This piece covers what the research actually says, some outstanding questions, and how to approach the use of technology in learning environments to maximize opportunities for learning and minimize the risk of doing harm to students.
In my recent posts , I have frequently cited the mixed evidence about blended learning, which strategically integrates in-person learning with technology to enable real-time data use, personalized instruction, and mastery-based progression. One thing that this nascent evidence base does show is that technology can be linked to improved learning . When technology is integrated into lessons in ways that are aligned with good in-person teaching pedagogy, learning can be better than without technology.
A 2018 meta-analysis of dozens of rigorous studies of ed tech , along with the executive summary of a forthcoming update (126 rigorous experiments), indicated that when education technology is used to individualize students’ pace of learning, the results overall show “ enormous promise .” In other words, ed tech can improve learning when used to personalize instruction to each student’s pace.
Further, this same meta-analysis, along with other large but correlational studies (e.g., OECD 2015 ), also found that increased access to technology in school was associated with improved proficiency with, and increased use of, technology overall. This is important in light of the fact that access to technology outside of learning environments is still very unevenly distributed across ethnic, socio-economic, and geographic lines. Technology for learning, when deployed to all students, ensures that no student experiences a “21st-century skills and opportunity” gap.
More practically, technology has been shown to scale and sustain instructional practices that would be too resource-intensive to work in exclusively in-person learning environments, especially those with the highest needs. In multiple , large-scale studies where technology has been incorporated into the learning experiences of hundreds of students across multiple schools and school systems, they have been associated with better academic outcomes than comparable classrooms that did not include technology. Added to these larger bodies of research are dozens, if not hundreds, of smaller , more localized examples of technology being used successfully to improve students’ learning experiences. Further, meta-analyses and syntheses of the research show that blended learning can produce greater learning than exclusively in-person learning.
All of the above suggest that technology, used well, can drive equity in learning opportunities. We are seeing that students and families from privileged backgrounds are able to make choices about technology use that maximize its benefits and minimize its risks , while students and families from marginalized backgrounds do not have opportunities to make the same informed choices. Intentional, thoughtful inclusion of technology in public learning environments can ensure that all students, regardless of their ethnicity, socioeconomic status, language status, special education status, or other characteristics, have the opportunity to experience learning and develop skills that allow them to fully realize their potential.
On the other hand, the evidence is decidedly mixed on the neurological impact of technology use. In November 2016, the American Association of Pediatrics updated their screen time guidelines for parents, generally relaxing restrictions and increasing the recommended maximum amount of time that children in different age groups spend interacting with screens. These guidelines were revised not because of any new research, but for two far more practical reasons. First, the nuance of the existing evidence–especially the ways in which recommendations change as children get older–was not adequately captured in the previous guidelines. Second, the proliferation of technology in our lives had made the previous guidelines almost impossible to follow.
The truth is that infants, in particular, learn by interacting with our physical world and with other humans, and it is likely that very early (passive) interactions with devices–rather than humans–can disrupt or misinform neural development . As we grow older, time spent on devices often replaces time spent engaging in physical activity or socially with other people, and it can even become a substitute for emotional regulation, which is detrimental to physical, social, and emotional development.
In adolescence and young adulthood, the presence of technology in learning environments has also been associated with (but has not been shown to be the cause of) negative variables such as attention deficits or hyperactivity , feeling lonely , and lower grades . Multitasking is not something our brains can do while learning , and technology often represents not just one more “task” to have to attend to in a learning environment, but multiple additional tasks due to the variety of apps and programs installed on and producing notifications through a single device.
The pragmatic
The current takeaway from the research is that there are potential benefits and risks to deploying technology in learning environments. While we can’t wrap this topic up with a bow just yet–there are still more questions than answers–there is evidence that technology can amplify effective teaching and learning when in the hands of good teachers. The best we can do today is understand how technology can be a valuable tool for educators to do the complex, human work that is teaching by capitalizing on the benefits while remaining fully mindful of the risks as we currently understand them.
We must continue to build our understanding of both the risks and benefits as we proceed. With that in mind, here are some “Dos” and “Don’ts” for using technology in learning environments:
| Do use technology: | Don’t use technology: |
| ● To enhance or extend social interactions ● To provide access to learning environments (like advanced courses, simulations, etc) that otherwise would not be available ● To facilitate and generate learning experiences that are meaningfully aligned with in-person learning experiences ● To personalize, individualize, and/or differentiate learning to each student’s pace, path, abilities, and interests ● To provide students with choice, agency, and ownership of their learning ● To ensure equitable access to technology and its supporting infrastructure itself, as well as the opportunity to develop skills associated with technology use | ● For many or unlimited hours each day ● To remove students from learning experiences that their peers have access to ● To implement, scale, or sustain effective in-person instructional strategies ● To track or stream students into rigid or long-term, standardized learning groups ● To automate or make decisions about learning without input from teachers and students ● With the assumption that students intuitively know how to use it (or have access to it), especially for learning |
Related Content
Saro Mohammed, Ph.D.
November 3, 2017
June 16, 2017
September 27, 2017
Education Technology K-12 Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Zachary Billot, Annie Vong, Nicole Dias Del Valle, Emily Markovich Morris
August 26, 2024
Brian A. Jacob, Cristina Stanojevich
Christine Apiot Okudi, Atenea Rosado-Viurques, Jennifer L. O’Donoghue
August 23, 2024
- Essay Editor
The Impact of Technology on Modern Society
1. introduction.
The role of technology in our society is important. In the past few decades, advancements in technology have pushed the boundaries of what is possible. It has altered the way humans interact and makes significant changes in the ways we communicate, work, and play, so as to change the way we live. The changes brought about to our society have been both positive and negative. Without doubt, the conversation must begin with the history of technology. From the dark ages to the age of pandemic, through eras of industrialization and now in the era of information and globalization, technology has reshaped our environment to meet the demands of the people in it. More importantly, people have embraced technology like never before. From the moment people wake to the time they sleep, they live surrounded by technology, embracing it willingly. The significance of this research will allow a further understanding of the value of technology to modern society. Additionally, there are many sides to the argument, and the research being conducted is not free from bias. Thus, it would be interesting to acknowledge both sides of the argument and to investigate how and if technology should integrate further into the societal institution. Most importantly, the valuable findings from this research can be translated into a practical perspective. Whether we wish to minimize the negative impact of technology or maximize the benefits from innovation, it is important to understand how the interaction between technology and society works and what determines technological progress.
2. Historical Evolution of Technology
The historical evolution of technology presents a very curious and complex picture. According to common knowledge, technology is giving us greater and greater control. It reveals itself to us today not primarily as a set of complicated tools or intricate chains of mechanical or electronic devices, but rather as a body of catholic abstract understanding, a way of perceiving and ordering. Yet the sheer list of inventions and discoveries shows up technology as something that grows in the manner of a chain letter, or some compound interest, money function. With its continued growth, technology begins not only to preserve but also to turn on its creator, man, and involve him and even threaten him. Among the most intelligent, it creates the concentrated stupidity of much that goes by the name of science. Primitive man was as dependent on tools as modern man is, though using different holdings. But the expanded functions and products of the modern world have added more complexity and coherence to technology and have led to the complexities and intensities of human involvement in technology that we now witness. The striking contrast between how things were once done and how they are done now has shaken whenever he has managed to emerge, the stable picture of man in the world which supported the abstracting and symboling individuality of animate civilization. And, evidently, on at least one occasion quite profound changes in the level of technology ended the group. On another occasion, the same profound changes seemingly separated forever one group of men from their neighbors.
3. Technological Advancements in Various Sectors
Technological advancements in various fields are the most transforming events in human civilization. Over time, technology has been responsible for creating amazing resources, which literally put the human right at our fingertips. Major technological inventions come in various fields which modernize different sectors up to a great extent and lead to the ultimate economic growth. Serious technological advancements truly began in the late 19th and the early 20th century which has improved our living standards many folds. Improvement in agriculture, infrastructure, industrialization are some of the initial steps in the transformation of traditional to modern society. Major Advancements Due to Technology The main advancements due to technology are listed in the following fields: Defense Technology: The defense technology that includes battle tanks, small arms, rockets, jet aircraft; the nuclear weaponry was made during the World War II to defend the other production sectors. Also, it is noted that about 70% of the technology commercialized by the civil sector has been also produced by the defense research centers or laboratories. As a consequence, technology is described as a system that allows enterprises to keep, trade, use complex information to create a system and solve problems from the use of available knowledge and resources. Thanks to these decades of technology, the defense technology has been so sophisticated in order to be classified as high tech which is often produced with or derived from the other technologies.
3.1. Healthcare
It is nearly impossible to talk about the impact of technology on modern society without acknowledging the wealth of knowledge and information gained through the lessons learned in the healthcare field, particularly in the last few decades. The advancements in medical technology through the years, for example, can largely be attributed not only to the resulting impact on research, diagnosis, and treatment protocols, but interdisciplinary knowledge from fields such as engineering and computing has also brought, and is continuously bringing, about an impressive change in lifestyle and consequently in human behavior. Society has been influenced in such a way by the overcoming of technological challenges. This influence, in turn, produces effects that affect the public, namely through health and education (for example, by training experts). It is also difficult to sum up the results in a few words. However, in testing questionnaires on the Brazilian public about the possibilities of using Computer-Assisted Education (CAI) and the use of computers in the evaluation of students, it could be observed, from the responses given to the questions and the debates conducted with the conclusions of these responses, that the expectations of the individuals about the results of the implementation of the two indicated medical domains are not only justified by the relevance that these issues present, but can be expected to have an incidence of effects corresponding to the healthcare reality of the modern man, and therefore well-received by everyone.
3.2. Education
When we consider the various elements of the current educational environment, often referred to as the 'information age', we immediately see that we have to do with a paradox in the eulogies addressed to education. In our society, education is described as a universal remedy and is highly praised by all, but in actual fact, there is something unpleasant about education which people continually want to evade. Education certainly is an extremely sensitive instrument and that, precisely, is the problem. The precisely directed, specific, focused functioning of education and information is suspect: it is confronted with the insuperable fact that it has incomplete choice between the uses to which its instruments are put. We have invented the concept of education without ever having asked what it really is and what it can really do. One of the most important functions of present-day schools, which is largely ignored, is that they have continuously to break the 'news' of technology and cultural productions to learners, presenting these as already existing information packages. This function is more important than the function of transmitting acquired cultural heritage, for this task has already been successfully carried out elsewhere and no longer falls exclusively to the school. The shaping of attitudes and the development of value systems adapt to the direction of the society which forms these attitudes. Not only do educators offer plans for action which may not be realized or used, but by doing so, they also indicate a way of feeling and valuing, governing the fundamental orientation of the modern world.
3.3. Communication
In the first communication revolution, many feared that the cinema, radio, and telephone would destroy real-life human communication, but they soon became incorporated into the communicative microworld of its users. The development of computer-assisted communication, from word processing to bulletin boards, teletex, videotex, and electronic mail, has taken place alongside the remote action and enaction capabilities of computers, from games and card cataloguing to industrial robots and tele-existence. Word processing, in particular, has transformed written text into an endlessly malleable and reproducible substance, and as a result, the computer may eventually displace printing, although pen or pencil still possesses advantages for original composition. Printing has transformed the growth, dissemination, and social importance of written text, and as a cultural medium, it is likely to survive the change from a mechanical to an electronic basis. Tele-existence uses sensory feedback to enable the user's body to function interactively in a remote environment. The operating surgeon, anthropologist, military telepresence user, or female telephone sex worker experiences seeing, hearing, and touching (the last through an artificial hand rather than the genitals) the sensate world of the remote environment.
4. Ethical and Social Implications of Technology
In what follows, I will take up the major objections to technology as mechanisms for establishing and maintaining power in a society. As the problems are subtle, so too will be the solutions, and indeed nary a solution will be offered. Instead, it will be a call for greater understanding of the implications of technology and a united effort on the part of industry, government, and society to recognize and adjust the same. Military applications of technology were published briefly. Philosophical problems related to those of technology have been discussed long ago by the early Greeks. These are not problems of technology, but problems related to technology, primarily as the result of science. Now a lot is known about these problems, and many who study the early Greeks believe that they might have been solved using the tools available to them. Their material views were primitive, at best, as is demonstrated by the breaking point of a soul. The mere perception of learning, or of knowledge, was viewed then with fear and superstition. For knowledge, to be animistic beliefs that animate the trivial fairy tales of those Greeks—Aristotle's missing cousin spoke out for art's own sake! Moreover, what may sound like subjective knowledge: how to recognize an apple, the way its surface feels to the touch, are distinctly not the characteristics of the apple; it is an object of an ontological class. Fascism only comes with an orchestrated effort to become something not persuasive, but overwhelming a society. Recently the etymology of fascism has undergone another instantaneous programmation. Schools are then doubly dangerous: they lure the ability of millions to make a better world. No further criticism shall be passed over in silence.
5. Future Trends and Innovations
While the development of technology has typically had significant benefits associated with it, such developments also come at a significant cost to the rest of human society. The three main areas where future trends are likely to have the greatest impact are information technology, measurement technology, including nondestructive testing, and alternative energy technology, including new energy-producing systems and new energy-saving devices. Other areas of future research could include medical and several technologies for the prediction of catastrophic natural events. The pace of change will speed up and multidisciplinary teams will increase. The objective of such teams should be to improve the quality of life and to provide environments that are beneficial to people both in their working and in their living activities. We have to face the fact that in the next 10 to 15 years, the human population of the planet will have surpassed the amount of resources that our technology can provide for a decent life to all people. People from advanced societies also have to recognize that they have passed through this crisis a long time ago and that the per capita resources that they take for granted cannot be extended to all people of the world. But the conflict between the wealthy and the poor is increasing. Shortsightedness only exacerbates that conflict. Small arms and money can hold for only so long; it is imperative that goodwill efforts change our human attitudes to each other.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, it is impossible to deny the effect of technology on today's society. Nevertheless, technology has its drawbacks. It is also true that many people are using technology to deal with family and interpersonal relationships as well as for accessing corporate affiliation. Taking all these contributions of technology to society, we should not overlook the adverse circumstances as well. The examples of the enslavement caused by technological development are abundant. Therefore, we should carefully develop technology keeping the full spectrum of human emotions in mind. We hope it will go without saying that humans are not puppets of technology. Technology should reflect our principles for the realization of society. Certainly, we often ignore any limitations and fear of technology. Some people describe technology in the following expressions: promising things ahead, a splendid but fickle toy, and a Pandora's box. If technology goes too far, where is the room for human beings, that is, who is to serve whom? Indeed, technology, especially electronics, is deeply connected with our lives these days. However, our attitudes towards it vary and give rise to a variety of challenges and issues. We have to notice limitations and fear of this technology. Otherwise, we humans will become totally dependent on technology. We have to take care that that does not happen.
Related articles
The impact of electronic communication on social interactions.
1. Introduction The internet is the decisive technology of the Information Age, and with the explosion of wireless communication in the early twenty-first century, we can say that humankind is now almost entirely connected, albeit with great levels of inequality in terms of access, use, and effectiveness. On the one hand, the internet is an open network with complex global governance and distributive mechanisms. Additionally, the development of the internet has enabled social networks within cy ...
La influencia de las tecnologías antiguas y actuales en la sociedad moderna
1. Introducción a la tecnología y su impacto en la sociedad La tecnología es un concepto que proviene del término latín "technologia" que deriva de "tecne" (técnica) o arte y "logia" (ciencia o estudio). Cuando hablamos de algún hecho, conducta o pensamiento que se desvanece del acontecer natural y que es provocado por el hombre, se le está dando el atributo de tecnológico. Por último, la técnica es la expresión más concreta de un problema que estudia la comunidad científica. Toda técnica se or ...
1. Introduction Impact of technology on modern society Like any society, modern society is a product of history. And this self-identity is not determined by its material culture or indeed by the artifacts it has produced, but by the attitude of its members to these artifacts. And the impact of these novel technological artifacts, it is contended, is sufficient to effect a modest social revolution. The thesis of this paper is that any concept of technology is loaded to some extent with at least ...
La complejidad de las relaciones interpersonales en la sociedad moderna
1. Introducción a la temática de las relaciones interpersonales en la sociedad moderna La sociedad moderna se caracteriza por la nada despreciable complejidad de actividades que componen el tejido social, en donde el ser humano es cada vez más hábil y capaz para desarrollarse y autorealizarse. La riqueza intelectual de una comunidad y la capacidad técnica del ser humano moderno nunca han sido tan completas y autosuficientes. Sin embargo, todas estas realidades urbanas se fundan en el apriorismo ...
The Impact of Social Media on Modern Communication
1. Introduction Social media has become more than an entertainment channel through the years. It actually includes some of the most popular communication channels people all around the world use to keep in touch. From social media users' opinions and decisions to the visibility an institution can get, all the way to the political interferences made in different countries, social networks have been silently influencing many aspects of today's societies. With a big amount of information produced ...
La importancia de preservar la naturaleza en el siglo XXI
1. Introducción El mundo y sus constantes cambios han evolucionado desde la aparición del hombre. Este hecho ha figurado una alteración en los mecanismos de autorregulación del planeta que ha modificado sus formas ecológicas de vida. La naturaleza ha experimentado y experimenta a día de hoy diferentes avatares. Estos no sólo son explicados por su propia biología evolutiva sino que al igualar el planeta hay que añadir cambios y alteraciones por parte de la comunidad de sistemas vivos entre los q ...
The Impact of Technological Change on Cultural Values
1. Introduction As with markets, governments, and other workaday institutions, culture is changing. It is changing rapidly and in some unexpected ways. The changes come from many sources, including a growing world population; increased production and consumption of information and culture across the globe; the emergence of a global youth culture, which is pioneered by Western and Japanese producers of cultural products; the spread of new communication technologies; the rise of a global popular ...
La Importancia de la Autoevaluación en el Desarrollo Personal y Profesional
1. Introducción a la Autoevaluación La autoevaluación es el proceso de captar información en forma de retroalimentación (feedback) sobre las estrategias de aprendizaje, y en general, sobre el desarrollo personal y profesional de las propias actividades y experiencias. Esta práctica tiene una gran importancia en la medida en que favorece el adecuado desarrollo de las competencias necesarias para el logro de los objetivos de la enseñanza y aprendizaje, además de ser una competencia fundamental en ...
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
What Makes Technology Good or Bad for Us?
Everyone’s worried about smartphones. Headlines like “ Have smartphones destroyed a generation? ” and “ Smartphone addiction could be changing your brain ” paint a bleak picture of our smartphone addiction and its long-term consequences. This isn’t a new lament—public opinion at the advent of the newspaper worried that people would forego the stimulating pleasures of early-morning conversation in favor of reading the daily .
Is the story of technology really that bad? Certainly there’s some reason to worry. Smartphone use has been linked to serious issues, such as dwindling attention spans , crippling depression , and even increased incidence of brain cancer . Ultimately, though, the same concern comes up again and again: Smartphones can’t be good for us, because they’re replacing the real human connection of the good old days.
Everyone’s heard how today’s teens just sit together in a room, texting, instead of actually talking to each other. But could those teenagers actually be getting something meaningful and real out of all that texting?
The science of connection

A quick glance at the research on technology-mediated interaction reveals an ambivalent literature. Some studies show that time spent socializing online can decrease loneliness , increase well-being , and help the socially anxious learn how to connect to others. Other studies suggest that time spent socializing online can cause loneliness , decrease well-being , and foster a crippling dependence on technology-mediated interaction to the point that users prefer it to face-to-face conversation.
It’s tempting to say that some of these studies must be right and others wrong, but the body of evidence on both sides is a little too robust to be swept under the rug. Instead, the impact of social technology is more complicated. Sometimes, superficially similar behaviors have fundamentally different consequences. Sometimes online socialization is good for you, sometimes it’s bad, and the devil is entirely in the details.
This isn’t a novel proposition; after all, conflicting results started appearing within the first few studies into the internet’s social implications, back in the 1990s. Many people have suggested that to understand the consequences of online socialization, we need to dig deeper into situational factors and circumstances. But what we still have to do is move beyond recognition of the problem to provide an answer: When, how, and why are some online interactions great, while others are dangerous?
The interpersonal connection behaviors framework
As a scientist of close relationships, I can’t help but see online interactions differently from thinkers in other fields. People build relationships by demonstrating their understanding of each other’s needs and perspectives, a cyclical process that brings them closer together. If I tell you my secrets, and you respond supportively, I’m much more likely to confide in you again—and you, in turn, are much more likely to confide in me.
This means that every time two people talk to each other, an opportunity for relationship growth is unfolding. Many times, that opportunity isn’t taken; we aren’t about to have an in-depth conversation with the barista who asks for our order. But connection is always theoretically possible, and that’s true whether we’re interacting online or face-to-face.
Close relationships are the bread and butter of happiness—and even health. Being socially isolated is a stronger predictor of mortality than is smoking multiple cigarettes a day . If we want to understand the role technology plays in our well-being, we need to start with the role it plays in our relationships.
And it turns out that the kind of technology-mediated interactions that lead to positive outcomes are exactly those that are likely to build stronger relationships. Spending your time online by scheduling interactions with people you see day in and day out seems to pay dividends in increased social integration . Using the internet to compensate for being lonely just makes you lonelier; using the internet to actively seek out connection has the opposite effect .
“The kind of technology-mediated interactions that lead to positive outcomes are exactly those that are likely to build stronger relationships”
On the other hand, technology-mediated interactions that don’t really address our close relationships don’t seem to do us any good—and might, in fact, do us harm. Passively scrolling through your Facebook feed without interacting with people has been linked to decreased well-being and increased depression post-Facebook use.
That kind of passive usage is a good example of “ social snacking .” Like eating junk food, social snacking can temporarily satisfy you, but it’s lacking in nutritional content. Looking at your friends’ posts without ever responding might make you feel more connected to them, but it doesn’t build intimacy.
Passive engagement has a second downside, as well: social comparison . When we compare our messy lived experiences to others’ curated self-presentations, we are likely to suffer from lowered self-esteem , happiness, and well-being. This effect is only exacerbated when we consume people’s digital lives without interacting with them, making it all too easy to miss the less photogenic moments of their lives.
Moving forward
The interpersonal connection behaviors framework doesn’t explain everything that might influence our well-being after spending time on social media. The internet poses plenty of other dangers—for two examples, the sense of wasting time or emotional contagion from negative news. However, a focus on meaningful social interaction can help explain decades of contradictory findings. And even if the framework itself is challenged by future work, its central concept is bound to be upheld: We have to study the details of how people are spending their time online if we want to understand its likely effects.
In the meantime, this framework has some practical implications for those worried about their own online time. If you make sure you’re using social media for genuinely social purposes, with conscious thought about how it can improve your life and your relationships, you’ll be far more likely to enjoy your digital existence.
This article was originally published on the Behavioral Scientist . Read the original article .
About the Author

Jenna Clark
Jenna Clark, Ph.D. , is a senior behavioral researcher at Duke University's Center for Advanced Hindsight, where she works to help people make healthy decisions in spite of themselves. She's also interested in how technology contributes to our well-being through its effect on our close personal relationships.
You May Also Enjoy

Are Smartphones Bad for Teen Mental Health?

How Smartphones Are Killing Conversation

How to Keep Your Smartphone from Hurting Your Relationships

Five Ways to Build Caring Community on Social Media

How to Stop Your Smartphone From Hurting Your Health

Does Technology Cut Us Off from Other People?
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Environ Res Public Health

Positive Effects of Digital Technology Use by Adolescents: A Scoping Review of the Literature
Aaron haddock.
1 Frances L. Hiatt School of Psychology, Mosakowski Institute for Public Enterprise, Clark University, Worcester, MA 01610, USA
2 School of Education, University of California, Riverside, Riverside, CA 92521, USA
Nicole O’Dea
Associated data.
The data presented in the study is available upon request from the first author.
This study examines the research literature published from 2012 to 2022 on the relationship between increases in adolescent consumption of digital technologies and its impact on multiple areas of development, with a focus on how adolescent immersion in an increasingly ubiquitous digital world engenders positive outcomes in terms of brain, cognitive, and social-emotional development. The literature search yielded 131 articles, 53 of which were empirical studies of the relationship between increases in consumption of digital technology and brain development, cognitive development, or social-emotional development among adolescents. Overall, these studies identify positive outcomes for adolescents who use different types of digital tech, including the internet, social media, and video games.
1. Introduction
Today’s youth are growing up in a world in which digital technology is ubiquitous and integrated into nearly every aspect of life. Basic human activities, including those related to education, socialization, and recreation, increasingly take place on digital platforms which have spawned new modes of engagement (e.g., socialization via social media, recreation, and learning via video gameplay). According to a recent research report based on a nationally representative survey among a random sample of tweens (8- to 12-year-olds) and teens (13- to 18-year-olds) in the United States, digital media use among teens, which varies across multiple demographic variables (e.g., gender, race/ethnicity, and household income), is on the rise, up nearly 17 percent since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic [ 1 ]. It is estimated that, on average, adolescents today spend roughly eight and a half hours a day engaged with digital media, not including their use of digital technology for schoolwork [ 1 ]. The largest increases in digital media use have been in watching online videos, using social media, and browsing websites. Of these activities, both tweens (8- to 12-year-olds) and teens (13- to 18-year-olds) report that watching videos on YouTube is their favorite form of digital media activity, followed in order of preference by Snapchat, TikTok, Instagram, Discord, Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, Reddit, and Tumblr [ 1 ]. On average, teens spend close to an hour and a half a day on social media [ 1 ]. Around a quarter of teens play video games on a console or computer daily, but nearly half report playing mobile games daily [ 1 ]. In terms of time spent, teens spend the most time watching videos, followed by gaming on various platforms, social media, and browsing websites. In terms of gender differences, boys use more screen media than girls and enjoy video games more; girls enjoy social media more than boys do. In a nationally representative sample of 743 teens in the United States, 97 percent of boys said they play video games compared to 83 percent of girls [ 2 ]. About 20 percent of teens regularly listen to podcasts. In the 21st century, digital engagement via various technological devices, platforms, and tools has become necessary for youth to accomplish key developmental tasks.
The saturation of the environment with digital media has prompted adjustments to established theoretical paradigms and birthed the field of media ecology, which examines how interactions with technology in the media environment shape, affect, facilitate, and impede human development. Importantly for this review, media ecology looks specifically at the impact on adolescent development when key developmental activities and interactions are mediated by digital technologies [ 3 , 4 ]. To accomplish this, media ecology draws on research in developmental psychology and Bronfenbrenner’s bioecological model of human development, a foundational paradigm for the fields of developmental psychology, applied psychology, pediatrics and childhood studies [ 5 , 6 ].
The bioecological model of human development views individuals as biosocial beings placed at the center of nested systems that reciprocally interact to inform developmental outcomes [ 6 , 7 ]. At the core of this theory is the focus on proximal processes, or the reciprocal interactions between the developing individual and persons, objects or symbols within the immediate ecological context [ 8 , 9 ]. Human development is thus characterized as a product of the transactional relationship between the developing individual as an active agent and drivers of development across ecological contexts [ 10 ]. Bronfenbrenner’s bioecological model consists of five nested systems. The microsystem is the immediate environment in which the youth lives and includes any immediate relationships or organizations they interact with (i.e., caregivers, other immediate family members, school, or other places of care). Surrounding the microsystem is the mesosystem, which is essentially the different parts of the microsystem working together for the sake of the youth. For example, the mesosystem captures the interrelationships between the technologies youth engage with across home and school contexts. The exosystem includes other individuals and places that youth may not interact with directly but still influence development, including caregivers’ workplaces, extended family members, and the larger community context. Further, the macrosystem or outermost system of this model embodies sociocultural factors and ideologies that inform the ways in which youth development is supported across contexts [ 10 ]. This might include perceptions of tech engagement and misconceptions about influence that in turn dictate the extent to which youth engage with tech in the first place. Finally, the outermost system, or the chronosystem, captures the historical development of each system and the developing youth over time. This system is particularly important to consider given the historical advances in tech and the shifting discourse on digital tech effects on youth development.
Scholars are now updating the original bio-ecological framework to reflect how digital technology’s deep impingement into the microsystem and mesosystem impacts human development [ 11 , 12 ]. For example, Johnson and Puplampu [ 13 ] introduced the concept of the ecological techno-subsystem (see Figure 1 ). As a feature of the microsystem, this subsystem accounts for different types of technology and the interactions they support between the developing individual and others in their system (i.e., family, peers, teachers). This theoretical shift utilizes an ecological perspective to hone in on youth development while drawing from media ecology [ 14 ]. Media ecology focuses on the ways in which all types of media shape the psychosocial characteristics of individuals, recognizing the environment that media technologies provide for interaction and identity development [ 12 , 14 ]. Like the intent of this scoping review, a major question stemming from media ecology is how and why various forms of digital engagement facilitate or impede processes of development and in turn, developmental outcomes. Focusing on media ecology as part of the innermost nested subsystem of influence, the role of technology use in development becomes a critical element of consideration that warrants holistic exploration [ 12 ].

Ecological Techno-Subsystem.
As a generation known as “digital natives”, [ 12 , 15 ] youth have choice and control in the type and frequency of which they engage with technology across ecological contexts that is unparalleled. The need to account for an additional zone that “mediates [the] bidirectional interaction between the child and the microsystem” in the most immediate developmental context underscores the profound influence of digital technology on child development in the 21st century.
The Current Study
There is a growing body of research literature that identifies positive outcomes for youth who use different types of digital technologies, including the internet, social media, and video games. This study provides a scoping review of the extant literature examining adolescent consumption of digital technology and its impact on brain, cognitive, and social-emotional development, with a particular focus on how their immersion in an increasingly ubiquitous digital world engenders positive outcomes across these outcomes of interest.
2. Materials and Methods
In keeping with the research literature on digital engagement and media effects, this literature review employs the concept of digital media as a superordinate term that encompasses the broad category of types of digital technologies, applications, devices, platforms, and tools. Information and communication technologies (ICT) is another term frequently found in the literature that is synonymous with digital media. Similarly, Crone and Konijn [ 16 ] simply use the term media to describe the “media-saturated world, where media is used not only for entertainment purposes, such as listening to music or watching movies, but is also used increasingly for communicating with peers via WhatsApp, Instagram, SnapChat, Facebook, etc”. (p. 1).
This literature review employs the term digital engagement to capture youth’s “quotidian digital and online activity” and “the digital world”. Like digital media, digital engagement is “a broad concept of digital participation, which is not dependent on a specific technological device, platform, or tool” [ 17 ] (p. 102). An important aspect of adolescents’ and young adults’ digital engagement is captured by the concept of socio-digital participation (SDP) [ 18 ], which refers to participation in socio-digital activities via socio-digital technologies, defined as “the integrated systems of novel technological tools, social media, and the internet that enable constant and intensive online interaction with information, people, and artifacts” [ 19 ] (p. 16). Importantly, social-digital engagement is conceptualized as a participatory social practice reflective of adolescents’ lived experiences—and not merely acts of technology usage [ 19 , 20 , 21 ]. Typically, adolescents’ digital engagement activities are friendship-driven, interest-driven, or a combination of these digital engagement practices [ 21 ].
Search Strategies
PRISMA is an evidence-based minimum set of items for reporting in scoping reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses. In alignment with the PRISMA guidelines [ 22 ], the authors conducted a scoping review to source all literature with relevance to technology engagement and youth development. Articles were identified for possible inclusion from five relevant databases PsycINFO, PubMed, Google Scholar, PLoS, and PsychARTICLES; additional searches were conducted using Academic Search Premier, a large database that includes 8500 journals that cut across a range of scientific disciplines. Search terms included: Adolescen*, brain development, cognitive development, college and career readiness, communication skills, digital media, digital technolog*, learning, neuroplasticity, social development, social emotional, technology, youth. All searches included one search term related to technology (i.e., digital technolog*, digital media, technology) and a term related to a developmental outcome of interest (e.g., brain development, cognitive development). Terms were combined using AND when searches were intended to be inclusive of all terms (i.e., adolescen* AND digital technolog* AND cognitive development), while terms that can be interchanged were combined using OR (e.g., adolescen* OR youth). Results were limited to articles that were peer- reviewed and published between 2012–2022.
The authors conducted an initial screening of all identified articles using the following inclusion criteria: (a) empirical study or review of the literature, (b) examines the effects of the use of digital technologies (i.e., internet, social media, video games) on at least one developmental domain of interest (i.e., brain development, cognitive development, social-emotional development, mental health/well-being). The initial search yielded 131 articles, of which 73 were excluded due to the criteria described above (see Figure 2 ). Fifty-three articles were fully reviewed between three of the authors. Inclusion decisions were made using a consensus approach where each article was discussed between at least three authors in a group format and then determined by the group to be included or not. Table 1 provides a summative overview of the selected articles organized by developmental domains of interest.

PRISMA Flow Diagram for Scoping Review.
Overview of Selected Articles.
| Developmental Domain | Articles(N = 53) | Tech Types | Major Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | 6 | Video games |
|
| Cognitive | 11 | Video games, Internet use |
|
| Social-Emotional | 22 | Video games, Internet use, Social Media |
|
| Mental health and well-being | 14 | Video games |
|
4. Findings
The discourse on the impact of digital media on youth is an extension of an age-old cultural concern and debate over the impact of new forms of technology on youth [ 23 ]. As Orben [ 24 ] has traced, concern and, at times even panic, over the influence of technology on youth has a long history. For example, in the Phaedrus, written circa 370 BCE, Plato recorded Socrates’ concern that the invention of writing and reading would ruin young people’s ability to use their memory and make them seem well educated and wise when in fact they were ignorant and unwise. In more recent centuries, tech fears have ranged from the novel giving rise to reading addiction, reading mania, and risky, immoral behavior in the 18th century to concerns about the negative influence of radio, television, smartphones, video games, and social media in the 20th and 21st centuries.
Although research on media effects has established that youth’s engagement with digital media can drive both positive and negative outcomes [ 3 , 25 , 26 ], the public perspective has focused more on its potential harm than benefits. Despite the focus on the negative impacts of technology on child development, the evidence linking digital engagement and negative outcomes is frequently overstated, focused on extreme users, and supported by studies lacking requisite nuance and complexity to discern specific effects [ 27 , 28 ]. Since the literature is largely based on correlational self-report data instead of sophisticated experimental designs, the direction of effects between digital media use and negative outcomes remains unclear [ 29 , 30 ]. When factors such as the type and quality of digital engagement, the social and developmental context, age, and individual differences are taken into consideration, digital engagement can function as a resource or a demand [ 31 ]. While it is a commonly held belief that digital engagement displaces important alternate activities, like sleep, interacting with friends and family, reading, and physical activity, the extant research has not substantiated this concern [ 27 , 32 , 33 , 34 ]. Conversely, the empirical evidence indicates that digital media facilitates peer communication, connection, and closeness (e.g., Davis [ 35 ]) and that engagement with tech at moderate levels is likely not deleterious [ 26 , 36 , 37 ] and may be promotive in a digital world (e.g., Giovanelli et al. [ 38 ]). For example, Lenhart et al. [ 39 ] found that social media use and collaborative gaming can facilitate friendships, social engagement, positive peer relations, and the provision of social support.
Digital media use is, according to Giedd [ 23 ], “in fact exquisitely aligned with the biology of the teen brain and our evolutionary heritage” (p. 128). Grounded in research on the neurobiological changes occurring during adolescence, Giedd clarifies how teens’ digital engagement is driven by changes in the brain’s reward system during puberty (dopamine, serotonin, GABA), teens’ efforts to accomplish key developmental tasks (e.g., Borca et al. [ 40 ]), and core features of the developing brain. fMRI studies on the adolescent brain demonstrate that, during adolescence, forming social connections becomes particularly salient and highly rewarding, which is reflected in their sensitized socio-affective brain circuits (Somerville, 2013). Given humans’ evolutionary history and the importance of strong connections with others, teens experience an existential drive for human connection, acceptance, and identification with groups (e.g., Crone & Dahl [ 41 ]; Blakemore & Mills [ 42 ]). Similarly, our evolutionary psychology predisposes humans to explore the environment, seek out adventure, and master threats—especially during the adolescent years when all social mammals exhibit increases in sensation seeking and risk taking. Adolescents also find experiences that enhance their affective development, or their emotional capacity to experience, recognize, and express a range of emotions and respond to others’ emotional cues, particularly reinforcing [ 41 ]. Developing the skills and aptitudes needed to transition to adulthood is highly motivating and rewarding for teens; whether these experiences take place in environments that are real or simulated matters little to the teen mind (e.g., Przybylski et al. [ 43 ]). Teens also exhibit a strong desire for information driven by evolutionary survival pressures and the human brain’s need for massive amounts of data from the environment for maturation (i.e., brain plasticity) and improved decision making. Thus, when it comes to digital technologies, what adolescents seek and find especially rewarding are opportunities to (1) face and overcome challenges, (2) connect and identify with a group, (3) grow emotionally, and (4) gain immediate access to actionable information.
4.1. Digital Tech & the Brain
While the research linking technology use and changes in the brain is still in its infancy, studies are emerging that indicate that digital engagement may positively (and negatively) influence human brains and behavior. For instance, studies utilizing brain imaging techniques have documented how intensive digital engagement can lead to changes in the brains of children and adolescents and affect brain functions, such as cognition, language, and visual perception (e.g., Firth et al. [ 44 ]; Hutton et al. [ 45 ]; Winnick & Zolna [ 46 ]).
4.1.1. Video Games
Several studies have examined the connection between playing video games and brain structure using structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI). In one such study involving 152 adolescent participants in Germany, Kühn et al. [ 47 ] found a positive association between the reported amount of time spent playing video games (of any type) and cortical thickness in the prefrontal areas of the left hemisphere (i.e., dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and frontal eye field). They concluded that the thickness of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex was related to executive control and the thickness of the front eye field was related visual-spatial attention and visual-motor integration.
Additionally, some studies have employed functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to examine the connection between playing video games and brain activity. For example, Mosaila et al. [ 48 ] used fMRI scans to compare the performance of 167 adolescents and young adults in Finland, who varied in terms of how frequently they played video games, on a task with selective attention and working memory demands. Results showed that those who reported playing video games more frequently displayed enhanced working memory functioning and task-difficulty-dependent modulation in a network of frontal and parietal brain areas in both hemispheres.
4.1.2. Social Media/Internet
Studies have also documented specific brain regions engaged to build and maintain online social networks that are different from those used for offline social networks along with changes in the cortical volume of the brain stemming from engagement with peers via social media. Kanai et al. [ 49 ] found that, among participants in England, variation in online social network size strongly predicted gray matter volume and density in particular regions of the brain associated with social cognition, including navigating social networks and maintaining positive peer relationships, but not areas associated with understanding others’ actions, intentions, and perspectives. Kanai et al. [ 49 ] also found that online social network size was associated with areas of the brain responsible for remembering name-face associations. While this study was unable to determine the direction of the relationship between brain structure and participation in online social networks and whether friendships drive observed brain changes, scholars have pointed to these findings as evidence of adolescents’ and emerging adults’ sensitivity to the interpersonal dynamics involved when engaging with peers on social media.
4.2. Digital Tech & Cognitive Development
Cognitive development is best defined as the processes through which individuals acquire and organize new information or knowledge in order to apply it to novel situations [ 50 ]. Youth cognitive development is a salient domain when considering technology engagement. Often, engaging with technology like video games involves developing and sustaining problem-solving skills [ 51 ] and honing in on skills that enhance spatial recognition [ 52 ]. Below, we summarize findings that emphasize a positive relationship between tech engagement and both problem- solving and spatial skill development.
4.2.1. Social Media/Internet
Fitton and colleagues [ 53 ] examined the relationship between internet use and cognitive and psychosocial development among a cohort of adolescents in the United States (N = 128). Authors conducted semi-structured interviews to gather insight on youths’ use of technology, level of comfort engaging with it, and how they feel it influences their own development. Overall, technology was perceived by youth as an integral part of their daily lives and a positive influence on their development. Specifically, they emphasized noticeable increases in skills and competencies related to recognizing information that they need and finding it on their own. With that, they recognized enhanced abilities in acquiring knowledge and creative thinking.
4.2.2. Video Games
Uttal and colleagues [ 52 ] conducted a meta-analysis of studies that focused on trainings that aimed to improve spatial skills. Spatial skills of interest included: (1) spatial perception, or the ability to determine spatial relationships in relation to an individual’s own location even with distraction; (2) mental rotation, or the ability to visualize the movement of an object without any physical movement in order to make judgements; and (3): spatial visualization, or the ability to carry out a series of manipulations of stimuli that is spatially present [ 52 ]. Upon close examination of 217 studies involving diverse youth, authors concluded playing video games can be an effective training intervention to enhance spatial skills, where video game players across studies performed significantly better in tasks that require spatial attention and skill. Authors note, however, that the effectiveness of video game play as a spatial training intervention is based on personal characteristics, type of video game, and the duration and frequency of training sessions.
Kühn and colleagues [ 47 ] took a closer look at spatial skills by conducting a randomized comparative effectiveness trial with a sample of young adults in Germany (N = 48). The intervention arm, or video game training group, received instructions to complete various spatial tasks whereas the control group was instructed to freely explore during play. The training group engaged in video game training for at least 30 min a day for a span of two months using Super Mario 64, a widely known platformer game. Brain scans were conducted for both groups after the two- month training period. Results demonstrated significant differences between groups in brain imaging, showing an increase in gray matter in areas of the brain that are important for spatial navigation, strategic planning, and working memory. Overall, results supported the notion that video game training can be used to augment gray matter in the brain that are responsible for cognitive abilities.
4.3. Digital Tech & Social-Emotional Development
Social-emotional development is characterized by learning how to understand, manage, and express emotions in the context of learning about and building relationships with others [ 54 ]. Engaging with technology often involves a social context. Building on the social-emotional development literature, the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) [ 55 ] has provided the most widely utilized definition of social and emotional learning (SEL): “SEL is the process through which all young people and adults acquire and apply the knowledge, skills, and attitudes to develop healthy identities, manage emotions and achieve personal and collective goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain supportive relationships, and make responsible and caring decisions”. Studies outlined below emphasize aspects of social-emotional development that are enhanced by tech engagement. For a research-based review of potential ways technology can be leveraged to support SEL (see Slovák & Fitzpatrick [ 56 ]).
4.3.1. Digital Media
Przybylski and Weinstein [ 26 ] studied links between digital screen time (i.e., video games, computers, smartphones, films and other media) and mental well-being (i.e., happiness, life satisfaction, psychological functioning, and social functioning) in a sample of 120,115 15-year-olds in the United Kingdom. Female participants reported more engagement with smartphones, computers, and the internet, whereas male participants reported significantly more engagement with video games. Results indicated that moderate digital engagement (e.g., on a weekday, spending less than 1 h and 40 min playing video games or less than 1 h and 57 min using a smartphone) across device types is positively associated with mental well-being and does not appear to displace other activities that foster mental well-being. As the authors conclude, the study results suggest that, when used in moderation, digital technologies may “afford measurable advantages to adolescents” (p. 213), including providing opportunities for communication, creativity, and development.
It should be noted that the relationship between digital engagement and well-being among adolescents is still unclear and appears to vary by individual differences and the quantity and quality of digital media use. Studies have documented a variety of associations, including small, negative associations [ 28 , 57 , 58 ], no association [ 59 ], positive associations [ 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 ], and mixed results [ 64 , 65 , 66 ].
4.3.2. Social Media/Internet
Studies have documented how adolescents’ social media use enhance social development and enhance relationships and social connections. For example, Reid et al. [ 67 ] found that social media platforms facilitate teens’ access to and interactions with others different from themselves, which increases understanding and empathy. In a study of 200 adolescents and emerging adults in Israel, Ziv and Kiasi [ 68 ] found that Facebook use provided users with a positive community that supported their psychological well-being; these effects were particularly pronounced for users with lower social skills who may have struggled more with in-person interactions. In a quantitative 7-day diary study of 162 adolescent Facebook users in Germany, Wenninger et al. [ 63 ] documented the positive association between targeted communication activities on social media that evoke reciprocity, like chatting and exchanging feedback via comments and likes, and positive emotions. As previously noted, this is in part because the adolescent brain is particularly sensitive to forming and maintaining social connections and developing an identity in relation to others.
4.3.3. Video Games
Przybylski [ 69 ] examined the relationship between video game engagement and psychosocial adjustment (i.e., prosocial behavior, life satisfaction, and internalizing and externalizing problems) in a sample of 4899 10–15-year-olds from England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales. Analyses found small (<1.6% of variance) yet statistically significant positive associations between low levels of video game play and psychosocial adjustment. When compared to non-video game players, light video game play (i.e., less than one hour per day) was associated with positive psychosocial adjustment, including higher life satisfaction and prosocial behavior and lower levels of problems with peers, conduct problems, and emotional symptoms. No significant differences were detected for moderate levels of video game engagement (i.e., 1–3 h per day) when compared with nonplaying peers. However, heavy video game play (over 3 h daily) was associated with more negative psychosocial adjustment—indicating a possible dosage effect. Results suggest that playing video games responsibly provides youth with opportunities for socialization, identity development, and cognitive challenges that are facilitative of social-emotional development in a manner similar to more traditional forms of play.
In 2017, Adachi and Willoughby [ 70 ] reviewed the literature on the link between playing video games and positive youth outcomes, such as well-being, intrinsic motivation, learning, optimal functioning, and positive peer relationships. The review focuses on studies that apply self-determination theory (SDT) to explain how video games may create contexts that satisfy basic psychological needs (i.e., competence, autonomy, and relatedness) and, in turn, effectuate positive outcomes. Citing numerous studies published between 2000 and 2016, the authors argue convincingly that playing video games afford experiences of independence, interdependence, cooperation, exploration, and challenge that in turn foster enhanced autonomy, competence, human relatedness, and well-being. The review also establishes a link between playing video games and developing problem-solving skills (e.g., identify the problem, generate and evaluate possible solutions) that hold the potential to not only improve adolescents’ game play but also their peer relationships. This link is further buttressed by research on how playing online video games cooperatively with diverse youth enhances intergroup relations and feelings of social connection.
EmoTIC is an example of a game-based social-emotional program with demonstrated impact on adolescent social and emotional development [ 71 ]. The intervention has a science-fiction theme and is delivered via a digital app. Users participate in four classroom group sessions and complete twelve individual home activities focused on acquiring foundational SEL concepts (e.g., emotional skills, social skills, enhancing self-knowledge and self-esteem, and assessing growth. Results showed that adolescents in Madrid, Spain between the ages of 11 and 15 ( n = 119) who completed the program improved on several measures, including self-esteem, feelings of well-being, emotion regulation, and prosocial behavior.
4.4. Digital Tech & Mental Health/Well-Being
Youth mental health and well-being is an all-encompassing term that represents a balance of emotional, psychological, and social wellness [ 72 ]. It involves the ways in which youth handle stress, practice healthy habits, and maintain social engagement. Mental health and well-being are particularly important for youth as they are at the cusp of developmental milestones that heavily rely on mental, social, and emotional wellness.
4.4.1. Video Games
Video games possess the unique ability to enable adolescents to experiment with and “try on” different identities and experiences not available in their current life situation or developmental phase. In a study of emerging adults (nationality not provided) by Przybylski et al. [ 43 ], researchers found that when games facilitated alignment between players’ ideal-self characteristics and game-self characteristics, players experienced higher levels of intrinsic motivation and well-being. These results suggest that digital engagement experiences that enable adolescents and young adults to simulate and experience ideal aspects of themselves (e.g., helping others, graduating from college, having a desirable career) may enhance motivation to engage in the experience while offering virtual exposure experiences that promote self-exploration and goal identification and adoption.
Barr & Copeland-Stewart [ 73 ] examined video game play and youths’ overall well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic. Using an online survey with closed and open-ended questions, authors measured game play habits and aspects of mental health and well-being among a large sample of youth (N = 781) during the pandemic. Results indicated that youth engaged in more frequent game play for longer segments of time, describing their extended engagement as an “escape from the pandemic”. This finding correlated with increased socialization during the lockdown advisory and decreased anxiety and depression. Further, respondents reported feeling as though engaging in video game play provided more feelings of control and agency during a particularly challenging time. Overall, this article emphasizes that video game play can provide support and relief that contributes to improved mental, social, and emotional wellness.
4.4.2. Social Media/Internet
Multiple studies have demonstrated that most people use social media to support, maintain, and enhance offline social relationships [ 74 , 75 , 76 ]. For instance, in a nationally representative survey of teens in the United States (743 youth between the ages of 13 and 17) by the Pew Research Center, 31 percent of teens said that social media has had a mostly positive impact, especially when it comes to connecting and staying in touch with friends and family [ 2 , 77 ]. Respondents also emphasized how their use of social media enabled them to meet and connect with others with similar interests, explore their identity and express themselves, garner peer support, and learn new things. Eighty one percent said social media makes them feel more connected to their friends; 69 percent said it helps them interact with a more diverse group of people; and 68 percent said it makes them feel as if they have people who will support them through tough times. Overall, teens associated social media use with positive emotions, including feelings of inclusion and confidence [ 2 ].
Kanai et al. [ 49 ] found that variability in the size of users’ offline social networks was correlated with variability in the size of users’ online networks. Building on this finding, Davis [ 61 ] examined the impact of digital media use and online peer communication on friendship quality in 2079 adolescents in Bermuda. Analyses revealed a positive association between more frequent online communications with friends and friendship quality. In discussing the findings, Davis noted that studies support the view that, despite the negative public perception, the existing evidence suggests that online peer communication is largely positive and serves to enhance peer relationships.
In a systematic review of the literature, which included large numbers of adolescents and emerging adults, Erfani and Abedin [ 78 ] found social media use led to increased well-being and had positive effects on users’ social support, communication, and connectedness. Meta-analyses have also found that connecting with others via social media enhances both social support and users’ perceived social resources [ 79 , 80 ].
There are some potential limitations concerning the results of this study. It is possible that the search terms used were not inclusive of all possible variants and the databases searched were not inclusive of all relevant journals, thus resulting in the exclusion of relevant studies. However, it is important to note that scoping reviews are not intended to be exhaustive [ 81 ]. In addition, it is possible that the synthesis literature included in this review suffers from the prevalent issue of non-independence of observations (i.e., overlap among primary-level studies). However, non-independence “may be fairly minimal” in reviews that draw from a broader body of literature that includes sources representing many different disciplines [ 82 ].
4.5. Conclusions
In sum, this scoping review of the empirical research literature on the relationship between digital engagement and positive youth development found evidence of specific positive effects on adolescent brain development, cognitive development, social-emotional development, and mental health and well-being. These included improvements in executive control, visual-spatial attention, visual motor integration, problem solving, working memory, strategic planning, and information gathering; increases in social-emotional learning, intrinsic motivation, socialization, social support, social connection, and creativity; and enhancements to autonomy, competence, communication skills, and well-being.
4.6. Recommendations for Leveraging Digital Tech Use to Promote Positive Outcomes for Adolescents
Given the documented impact of digital engagement on adolescent development, tech-based interventions demonstrate promising potential across domains of youth development. There is clearly a unique opportunity to leverage technology in a manner that will positively engage teens and intervene with them to help them learn about themselves, advocate for themselves, and explore careers. However, as evidenced by the scoping review, there is a limited number of articles that focus primarily on positive outcomes. The following recommendations are based on the findings of the scoping review, behavior change design principles, and insights from startup product development.
4.6.1. Employ an Intervention Design Process
When developing tech-based interventions, begin by carefully defining the problem to be solved, the outcomes of interest, the target users, and the target users’ relevant contexts. Then, explore a variety of potential solutions. When exploring solutions, consider (a) possible intervention designs and (b) possible tech-based delivery methods. The findings of this literature review are particularly pertinent to this phase of the design process and will help clarify which types of solutions are likely to be most effective. This can be visually represented in an outcome logic map or logic model. Program evaluators employ logic models to define the specific outcomes an intervention is intended to achieve, the activities (i.e., mechanisms of action) that will facilitate achievement of the targeted outcomes, and how the intervention’s results will be measured. When applied to tech-enabled interventions, it is especially important to clarify how the intervention will be implemented and used.
Employ a customer discovery approach to determine how best to meet potential users’ needs [ 83 ]. Interview target users to understand their perspective, motivations, priorities, values, goals, and identities. Explore their reasons for engaging with the intervention being developed. Ask them what tech product features and intervention components they think will help them achieve the target outcomes (e.g., increased self-knowledge, career exploration). If the intervention aims to change behavior, consider using the Behavior Change Wheel as a product design framework. Based on in-depth research on 19 behavior change frameworks, the Behavior Change Wheel helps product designers identify solutions that enhance users’ capability, opportunity, and motivation to change or engage in a particular behavior. See Michie, Atkins, & West’s practical guide to intervention design, The Behaviour Change Wheel: A Guide to Designing Interventions [ 84 ] and Bucher’s Engaged: Designing for Behavior Change [ 85 ].
4.6.2. Convene a Youth Advisory Board
If teens are the target users, engage teens at every phase of the design process to create a teen-centric intervention that connects their motivations with the target outcomes. Convene a diverse and inclusive teen advisory board to get their perspectives and solicit their guidance on what teens need, want, and will use. Once a beta version of the intervention is ready, relentlessly collect feedback from teens on what works and what needs to be changed.
Have the teen advisory board work closely with subject matter experts and technologists to ensure the interventions and experiences integrate into their lives and use language they will respond to. Like other popular forms of digital engagement, interventions will work best if they meet youth where they are at in familiar and fun ways.
Highlight teens involvement with the creation of the intervention and provide opportunities for teens to promote it.
4.6.3. Create Authentic and Engaging Digital Experiences
Youth are particularly sensitive and responsive to authentic social media messaging. Social media campaigns and initiatives will be most effective if developed and deployed by youth with the support of subject matter experts. Rallying authentic youth engagement (e.g., “likes”, “retweets”, etc.) and promotion of the campaign or message is key. For example, a social media campaign aimed at inspiring youth to consider pursuing a technical career as a possible alternative to college could begin by convening a teen advisory board charged with discovering, for example, teens’ questions about the decision to pursue a technical career. The youth advisory board’s process of gathering this information (e.g., through social media queries, focus groups, surveys, interviews, etc.) could be shared in creative social media posts, videos, and photos and serve to promote the campaign and create a community around the initiative online. This will build trust and buy-in.
Digital interventions that leverage social media should take into consideration the social norms of the platform. There is evidence to suggest that teens are increasingly reluctant to explore, experiment with, and express their identity or emerging identities on mainstream social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram, but continue to do so on YouTube and fanfiction sites and in microblogging communities [ 86 ]. Therefore, interventions that aim to facilitate identity exploration and development in the service of greater self-awareness and self-knowledge should keep this in mind and create online spaces where teens feel understood, experience camaraderie, and can be genuine and engage in authentic self-exploration [ 61 , 87 ]. Ideally, an online social network will engender positive growth, provide teens with social support, and connect them with the peers, experts, and professionals that will help them achieve their goals and the intervention’s target outcomes.
Tech-based interventions to facilitate self-knowledge, self-awareness, and identity development should provide youth with opportunities to explore different identities, including idealized versions of themselves, and contexts that are not currently accessible. For instance, a video game or virtual reality experience could enable users to try out different careers in a variety of roles (e.g., programmer, team leader, copywriter, marketing director). An app could help teens imagine their future self in college or a career coupled with an opportunity to set short- and long-term goals and create a detailed action plan aligned with their values. The app-based action plan could guide and support users as they take concrete steps toward their goals, offer timely tips and encouraging feedback, and celebrate and reward users when they reach important milestones on their journey.
If the digital intervention leverages a social component, provide users with choice. The research is clear that online social support can be beneficial for teens; however, not all users want to engage in a social aspect or have their activities be made public. Nevertheless, provide all users with the option to witness the social engagement of others, even if they do not participate. Research has shown that witnessing the online social engagement of others can be nearly as beneficial as active participation [ 85 ].
4.6.4. Leverage the Best Features and Most Popular Forms of Digital Engagement
Teens range freely across digital media platforms and tools. Design tech-enabled interventions that leverage the best features of gaming, social media, online videos, streaming, and digital content creation devices. Take teens’ favorite forms of digital media activity into consideration; among teens in the U.S., research indicates watching videos on YouTube is their favorite form of digital media activity, followed in order of preference by Snapchat, TikTok, Instagram, Discord, Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, Reddit, and Tumblr [ 1 ].
Leverage technological innovations to support SEL. For example, use mobile devices to provide youth with just-in-time prompts (e.g., to label emotions and practice emotion regulation skills when high levels of stress are detected by physiological sensors), reminders (e.g., to engage in activities that promote well-being or facilitate social connection), and scaffolding and support (e.g., how to use problem solving skills; prompts to track experiences to facilitate self-reflection and/or discussions at a later time). Use social media sites to support reflection, sharing of experiences, and social-emotional self-awareness. Online social networks can also be used for online support groups that provide, for instance, information on and support around college and career exploration or mental health. Natural language understanding technology is already being used by mental health professionals to monitor therapy sessions and glean evidence-based insights; a similar approach could be applied in everyday life to foster social-emotional development and communication skills.
While virtual reality’s (VR) ability to create powerfully immersive experiences continues to hold incredible promise for SEL, skill building, and mental health promotion and treatment [ 88 ], currently less than 20 percent of youth have access to VR headsets [ 1 ].
4.6.5. Use Video Games to Build Community, Provide Exposure Experiences, Explore Identity, and Enhance Perspective Taking
Video game play among youth is particularly high and thus provides a unique opportunity to engage their interests in a way that promotes development and engages them within the community. Offering opportunities for youth to engage in game play within the community, for example, in-person or virtual tournaments, provides youth with a platform that not only supports their cognitive development and psychosocial wellness, but also maintains social connection during the extended pandemic period. There is also evidence to suggest that interactive media experiences can facilitate perspective taking, communication skills, and collaboration.
When designing video game-based interventions, provide the player with enough challenge to make the game engaging, but not so challenging that the player feels the task is insurmountable. Game-based interventions that provide players with novel opportunities to embody and experience ideal aspects of themselves (i.e., how they would like to experience themselves) will enhance intrinsic motivation to play the game along with enjoyment [ 43 ].
4.6.6. Understand the Environment in Which Digital Interventions Are Implemented
Considering how technology now mediates interactions between the developing individual and others in their microsystem (i.e., family, peers, teachers), when designing tech-based interventions it is important to consider the role it will play in teens’ techno-subsystem. For example, how will this intervention integrate with what teens are already doing in their daily lives? How may the reciprocal interactions with other important individuals in the teens’ microsystem facilitate or impede intervention effectiveness? How might influential peers, parents, and mentors be recruited to support and amplify the aims of an intervention? Tech-based interventions that easily integrate with existing influential relationships in the youth’s microsystem will be most engaging and effective.
In light of changes in the brain occurring during adolescence, the most naturally engaging and effective digital interventions will: (a) be fun, engaging, and social; (b) foster emotional growth; (c) give teens agency over their education; (d) enable identity exploration and experimentation; (e) engage other influential people in teens’ developmental context; (f) help teens draw connections between their core values, priorities, and short- and long-term goals, (g) empower exploration and mastery of their environment; (h) facilitate achievement of key developmental tasks; and (i) provide immediate access to actionable information.
Funding Statement
This research was funded by American Student Assistance (ASA).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.H., N.W., R.Y. and N.O.; methodology, A.H., N.W., R.Y. and N.O.; formal analysis, A.H., R.Y. and N.O.; investigation, A.H., N.W., R.Y. and N.O.; writing—original draft preparation, A.H., N.W., R.Y. and N.O.; writing—review and editing, A.H., N.W., R.Y. and N.O.; visualization, R.Y. and N.O.; supervision, A.H. and N.W.; project administration, A.H. and N.W.; funding acquisition, N.W. and A.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
What is WRAP and how can it help train AI more efficiently?
Web rephrase augmented pre-training (WRAP) could be key for helping businesses shape existing content to better suit AI training
Generative AI is booming, though developers are quickly running into obstacles, from the high energy demands of AI compute to the complex infrastructure required to train systems.
For the latter, data is of the utmost importance. Stockpiles of clear, quality data are vital for those companies looking to train and build their own AI models. Getting data pools in order is a key part of the early development process.
One novel theory for making this process easier is web rephrase augmented pre-training (WRAP), a technique put forward by researchers at Apple and Carnegie Mellon University in a paper published earlier this year .
In it, the researchers noted that many large language models (LLMs) are trained on data scraped from the web that is often “ unstructured , noisy, and poorly phrased,” making it harder to use for training.
While synthetic data can be used to get around this problem, it can fall victim to bias. While the alternative practice of data curation to remove lower-quality data can be effective, the researchers put forward their own solution.
Get the ITPro. daily newsletter
Receive our latest news, industry updates, featured resources and more. Sign up today to receive our FREE report on AI cyber crime & security - newly updated for 2024.
Rather than creating synthetic data, WRAP uses an “off-the-shelf instruction-tuned model prompted to paraphrase documents on the web in specific styles such as ‘like Wikipedia’ or in ‘question-answer format’ to jointly pre-train LLMs on real and synthetic rephrases.”
According to the report, WRAP sped up pretraining by about three times when used on a “naturally noisy” dataset.
How does WRAP work?
In the paper, researchers use the rephrasing process on ‘The Pile,’ a collection of datasets commonly used in AI according to senior research and development manager of data science at Synopsys, Dr Andrew Bolster.
“Some datasets are used as benchmarks to compare architectures and scales. One such collection of datasets is known as ‘The Pile,’” Bolster tells ITPro.
This is an 825GB collection of web scraped data, Bolster goes on, featuring content from a range of sites including PubMed, Github, Stack Exchange, HackerNews, and YouTube subtitles.
The researchers augment ‘The Pile’ by rephrasing large portions of it before combining these rephrased portions with the original dataset to train an LLM which answers questions, Bolster says. This LLM is then evalued for its zero-shot accuracy – meaning its capacity to answer questions not rooted in its training data.
“This is a form of ‘synthetic data augmentation’, where in any modeling system, there may not be sufficient ‘real’ input/training data to accurately converge a model’s behavior,” Bolster says.
“Data Scientists may simply ‘repeat’ the training data over and over again, hoping for the best, but over the past decade, this has largely been replaced with synthetic data generation involving the training of intermediate models to generate more data that ‘looks like’ the provided training set,” he adds.
The LLM trained on the rephrased data within the paper reportedly “outperforms other techniques” that fulfill the same need. There is a “small but clear improvement,” Bolster says.
WRAP appears to beat other natural language augmentation techniques such as synonym replacement and random word deletion, though Bolster is careful to point out that there are some evident downsides.
The pros and the cons of WRAP
For any businesses or developers looking to WRAP as a method of driving efficiency during AI model training, there are some key advantages and disadvantages to consider, particularly regarding proprietary data.
WRAP could work best for in-house AI training , says Stefan Leichenauer, vice president of engineering at SandboxAQ, but there may be “limited effectiveness out-of-the-box” when the method is applied to proprietary data .
“In-house training data may not be as naturally messy as what we find on the public internet,” Leichenauer tells ITPro . To fix this, he suggests businesses should convert their data into “something that is more in line with the end application we are interested in.”
“So, for example, if you are interested in training a customer service chatbot , then you should try transforming your internal documentation into a question-answer format before training the AI,” he says.
Messy data has always been a problem, Leichenauer adds, noting that WRAP is one of many tools developers can use to perform “initial data transformations” for more effective training.
On the other hand, Bolster notes that WRAP could cut the up-front costs of creating enterprise-grade LLMs, which is generally eaten up in the “establishment of curated / domain specific data”. In this sense, WRAP could have its advantages.
“This rephrase capability might be a valid method for making the most of limited data to train against,” Bolster says.
Having said that, WRAP has a “significant upfront cost” of its own – the generation of synthetic data. At present, there arealso sensitivities to rephrasing “styles” and model selection which could cause issues.
It’s clear that as WRAP matures, it could have a big impact on the way that companies pursue their own LLMs and refine their data to ensure the best ROI on their AI investments . Whether it will become as pivotal a development as the likes of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has yet to be seen, but businesses will be keenly investigating its benefits and drawbacks.
George Fitzmaurice is a staff writer at ITPro , C hannelPro , and CloudPro , with a particular interest in AI regulation, data legislation, and market development. After graduating from the University of Oxford with a degree in English Language and Literature, he undertook an internship at the New Statesman before starting at ITPro. Outside of the office, George is both an aspiring musician and an avid reader.
UK firms are stuck in an “AI pilot purgatory” – here’s how they can drive success
Microsoft Copilot could have serious vulnerabilities after researchers reveal data leak issues in RAG systems
Civil service hopes to attract best and brightest cyber talent with new graduate scheme
Most Popular
AI Code security report: Organizations must change their approach

Gen AI buyer’s guide

A CISO's guide to safely unleashing the power of GenAI

Giving your people the tools to stay productive, wherever they spend their working day
- 2 Eric Schmidt’s car crash Stanford interview showed big tech’s true colors on remote work
- 3 StayLinked names Brandon Black as new CEO
- 4 AI and data protection: What businesses need to know
- 5 Hackers could dupe Slack's AI features to expose private channel messages

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Disadvantages of Modern Technology. Despite its advantages, modern technology also has its downsides. One of the main disadvantages is the issue of privacy and security. With the increasing amount of data being shared online, there is a growing concern about data breaches, identity theft, and cybercrime. Another disadvantage is the impact on ...
While technology has yielded numerous benefits, it has also introduced several challenges and concerns. This essay explores both the positive and negative effects of technology on various facets of human life. On the positive side, technology has revolutionized communication, making it easier, faster, and more efficient.
Conclusion. In conclusion, the pros and cons of technology are complex and multifaceted, requiring a nuanced understanding of its impact on society. While technology has the power to improve efficiency, connectivity, and innovation, it also raises important ethical and social considerations that must be addressed.
687 Words. 3 Pages. Open Document. People very often debate whether technology is good or bad. Many people believe that technology can only cause harm to their lives and society, while many others strongly defend the technologies which have made their lives much more leisurely and enriching than it could have been several hundred years ago.
While technology facilitates communication, its overreliance can lead to social disconnection, reduced interpersonal skills, and a growing dependency on digital interactions. Excessive screen time and social media use have been linked to social isolation and decreased face-to-face interactions. -2.
FAQs on Essay on Technology. Q.1 What is Information technology? A - It is a form of technology that uses telecommunication and computer systems for study. Also, they send, retrieve, and store data. Q.2 Is technology harmful to humans? A - No, technology is not harmful to human beings until it is used properly.
The impact of technology on society is undeniable. Technology and science have played a central role in human history and help shape entire civilizations. Technological progress was key for the emergence and downfall of empires. The development of hunting and farming tools allowed our ancestors to dominate other hominid species.
Technology plays a crucial role in today's society. Wherever you go, there is a dependent use of technology at home, in the public, etc. Technology has had both positive and negative impacts on my life. One common positive side of the use of technology is that it makes our lives easier such as transportation, kitchen technology, getting work ...
This essay aims to provide a balanced view of the positive and negative impacts of technology on society. Positive Impacts of Technology on Society Enhanced Communication. Technology has revolutionized the way we communicate with each other.
250 Words Essay on Pros and Cons of Technology Introduction. Technology has become an integral part of our lives, driving significant changes in various sectors such as healthcare, education, and business. However, like any other phenomenon, it has both advantages and disadvantages. Pros of Technology. The first benefit of technology is efficiency.
And with such massive changes come both positives and negatives. In this short article, we'll explore the impact of technology on education, covering both the positive and negative outcomes. Read on to learn more. Impact of Technology on Education: The Digital Divide . Edtech has done better than bad to our education system.
People are easily communicating through a screen, but struggling to hold or even start a conversation face to face. Using technology causes social tension between people. Lack of social interaction can also be alarming to a person's well being, causing feelings of isolation.
Certainly, some technological developments might cause populaces to be distracted, too worried, and gradually out-of-the-way also many people may be tangled in many numbers of societies with the technologies today however; the property of these relationships might make people feeling qualitatively empty. Clearly, technology has had a reflective ...
4. Technology Spawns Misinformation and Fake News. The spread of misinformation and fake news online is nothing new. In fact, it has been going on for many years. However, with all the developments that happen so frequently in technology, it has become harder to define what's true and what's not.
Students have more information at their fingertips and build technology skills. Tech can do some tasks equally or better than teachers, including administration, data gathering and supporting self-direct learning. Here are the top five pros to technology in the classroom. 1. Access high-quality, current information.
Sleep problems. Technology in the bedroom can interfere with sleep in a number of ways. A 2015 study demonstrated that exposure to the blue light that devices emit can suppress melatonin and ...
Positive Effects of Technology on Children. All the "rules" about children's access to computers and the internet were rewritten by the COVID-19 pandemic open_in_new, according to parenting expert Anya Kamenetz. Technology provides children with easy access to information and boosts their creativity.
Positive Effects Of Technology Essay. 1923 Words8 Pages. Intro. In the present globalized world, we are living in the era of advanced technology. Every part of our daily life is related to technology in one or other way. When compared with olden days, we are having better facilities and even better luxuries with the help of increased technology.
When technology is integrated into lessons in ways that are aligned with good in-person teaching pedagogy, learning can be better than without technology. A 2018 meta-analysis of dozens of ...
1. Introduction The role of technology in our society is important. In the past few decades, advancements in technology have pushed the boundaries of what is possible. It has altered the way humans interact and makes significant changes in the ways we communicate, work, and play, so as to change the way we live. The changes brought about to our society have been both positive and negative ...
A quick glance at the research on technology-mediated interaction reveals an ambivalent literature. Some studies show that time spent socializing online can decrease loneliness, increase well-being, and help the socially anxious learn how to connect to others. Other studies suggest that time spent socializing online can cause loneliness ...
While this raises many questions for skeptics of AI tools, perhaps the biggest question is: In what ways will it have a positive or negative impact? Discover the pros and cons of AI in higher education, and learn how advancements in AI will likely continue to change the educational landscape. Pro: AI Increases Accessibility to Knowledge and Skills
Conclusions. In sum, this scoping review of the empirical research literature on the relationship between digital engagement and positive youth development found evidence of specific positive effects on adolescent brain development, cognitive development, social-emotional development, and mental health and well-being.
There is increasing interest in the use of technology in education. In April 2019, the UK government announced a £10 m investment in education technology for England. ... the direction of the effect (positive, negative or no change) and the strength of the evidence (i.e. how secure the finding is). Where the papers report the means and the ...
The pros and the cons of WRAP. For any businesses or developers looking to WRAP as a method of driving efficiency during AI model training, there are some key advantages and disadvantages to consider, particularly regarding proprietary data.