- Open access
- Published: 06 July 2023

Pros & cons: impacts of social media on mental health
- Ágnes Zsila 1 , 2 &
- Marc Eric S. Reyes ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5280-1315 3
BMC Psychology volume 11 , Article number: 201 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
469k Accesses
17 Citations
119 Altmetric
Metrics details
The use of social media significantly impacts mental health. It can enhance connection, increase self-esteem, and improve a sense of belonging. But it can also lead to tremendous stress, pressure to compare oneself to others, and increased sadness and isolation. Mindful use is essential to social media consumption.
Social media has become integral to our daily routines: we interact with family members and friends, accept invitations to public events, and join online communities to meet people who share similar preferences using these platforms. Social media has opened a new avenue for social experiences since the early 2000s, extending the possibilities for communication. According to recent research [ 1 ], people spend 2.3 h daily on social media. YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, and Snapchat have become increasingly popular among youth in 2022, and one-third think they spend too much time on these platforms [ 2 ]. The considerable time people spend on social media worldwide has directed researchers’ attention toward the potential benefits and risks. Research shows excessive use is mainly associated with lower psychological well-being [ 3 ]. However, findings also suggest that the quality rather than the quantity of social media use can determine whether the experience will enhance or deteriorate the user’s mental health [ 4 ]. In this collection, we will explore the impact of social media use on mental health by providing comprehensive research perspectives on positive and negative effects.
Social media can provide opportunities to enhance the mental health of users by facilitating social connections and peer support [ 5 ]. Indeed, online communities can provide a space for discussions regarding health conditions, adverse life events, or everyday challenges, which may decrease the sense of stigmatization and increase belongingness and perceived emotional support. Mutual friendships, rewarding social interactions, and humor on social media also reduced stress during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 4 ].
On the other hand, several studies have pointed out the potentially detrimental effects of social media use on mental health. Concerns have been raised that social media may lead to body image dissatisfaction [ 6 ], increase the risk of addiction and cyberbullying involvement [ 5 ], contribute to phubbing behaviors [ 7 ], and negatively affects mood [ 8 ]. Excessive use has increased loneliness, fear of missing out, and decreased subjective well-being and life satisfaction [ 8 ]. Users at risk of social media addiction often report depressive symptoms and lower self-esteem [ 9 ].
Overall, findings regarding the impact of social media on mental health pointed out some essential resources for psychological well-being through rewarding online social interactions. However, there is a need to raise awareness about the possible risks associated with excessive use, which can negatively affect mental health and everyday functioning [ 9 ]. There is neither a negative nor positive consensus regarding the effects of social media on people. However, by teaching people social media literacy, we can maximize their chances of having balanced, safe, and meaningful experiences on these platforms [ 10 ].
We encourage researchers to submit their research articles and contribute to a more differentiated overview of the impact of social media on mental health. BMC Psychology welcomes submissions to its new collection, which promises to present the latest findings in the emerging field of social media research. We seek research papers using qualitative and quantitative methods, focusing on social media users’ positive and negative aspects. We believe this collection will provide a more comprehensive picture of social media’s positive and negative effects on users’ mental health.
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Statista. (2022). Time spent on social media [Chart]. Accessed June 14, 2023, from https://www.statista.com/chart/18983/time-spent-on-social-media/ .
Pew Research Center. (2023). Teens and social media: Key findings from Pew Research Center surveys. Retrieved June 14, 2023, from https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/04/24/teens-and-social-media-key-findings-from-pew-research-center-surveys/ .
Boer, M., Van Den Eijnden, R. J., Boniel-Nissim, M., Wong, S. L., Inchley, J. C.,Badura, P.,… Stevens, G. W. (2020). Adolescents’ intense and problematic social media use and their well-being in 29 countries. Journal of Adolescent Health , 66(6), S89-S99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.02.011.
Marciano L, Ostroumova M, Schulz PJ, Camerini AL. Digital media use and adolescents’ mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health. 2022;9:2208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.641831 .
Article Google Scholar
Naslund JA, Bondre A, Torous J, Aschbrenner KA. Social media and mental health: benefits, risks, and opportunities for research and practice. J Technol Behav Sci. 2020;5:245–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00094-8 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Harriger JA, Thompson JK, Tiggemann M. TikTok, TikTok, the time is now: future directions in social media and body image. Body Image. 2023;44:222–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2021.12.005 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chi LC, Tang TC, Tang E. The phubbing phenomenon: a cross-sectional study on the relationships among social media addiction, fear of missing out, personality traits, and phubbing behavior. Curr Psychol. 2022;41(2):1112–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-0135-4 .
Valkenburg PM. Social media use and well-being: what we know and what we need to know. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022;45:101294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.101294 .
Bányai F, Zsila Á, Király O, Maraz A, Elekes Z, Griffiths MD, Urbán R, Farkas J, Rigó P Jr, Demetrovics Z. Problematic social media use: results from a large-scale nationally representative adolescent sample. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(1):e0169839. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169839 .
American Psychological Association. (2023). APA panel issues recommendations for adolescent social media use. Retrieved from https://apa-panel-issues-recommendations-for-adolescent-social-media-use-774560.html .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Ágnes Zsila was supported by the ÚNKP-22-4 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Culture and Innovation from the source of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Psychology, Pázmány Péter Catholic University, Budapest, Hungary
Ágnes Zsila
Institute of Psychology, ELTE Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary
Department of Psychology, College of Science, University of Santo Tomas, Manila, 1008, Philippines
Marc Eric S. Reyes
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AZ conceived and drafted the Editorial. MESR wrote the abstract and revised the Editorial. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Marc Eric S. Reyes .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors have no competing interests to declare relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zsila, Á., Reyes, M.E.S. Pros & cons: impacts of social media on mental health. BMC Psychol 11 , 201 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01243-x
Download citation
Received : 15 June 2023
Accepted : 03 July 2023
Published : 06 July 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01243-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Social media
- Mental health
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Sign into My Research
- Create My Research Account
- Company Website
- Our Products
- About Dissertations
- Español (España)
- Support Center
Select language
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Português (Brasil)
- Português (Portugal)
Welcome to My Research!
You may have access to the free features available through My Research. You can save searches, save documents, create alerts and more. Please log in through your library or institution to check if you have access.

Translate this article into 20 different languages!
If you log in through your library or institution you might have access to this article in multiple languages.

Get access to 20+ different citations styles
Styles include MLA, APA, Chicago and many more. This feature may be available for free if you log in through your library or institution.

Looking for a PDF of this document?
You may have access to it for free by logging in through your library or institution.

Want to save this document?
You may have access to different export options including Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive and citation management tools like RefWorks and EasyBib. Try logging in through your library or institution to get access to these tools.

- More like this
- Preview Available
- Dissertation or Thesis

Positive and Negative Effects of Social Media on Adolescent Well-Being
No items selected.
Please select one or more items.
Document Section options
- Current view Preview - PDF
- Abstract/Details
It appears you don't have support to open PDFs in this web browser. To view this file, Open with your PDF reader
Suggested sources
- About ProQuest
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Effects of social media use on psychological well-being: a mediated model.

- 1 School of Finance and Economics, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
- 2 Research Unit of Governance, Competitiveness, and Public Policies (GOVCOPP), Center for Economics and Finance (cef.up), School of Economics and Management, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal
- 3 Department of Business Administration, Sukkur Institute of Business Administration (IBA) University, Sukkur, Pakistan
- 4 CETYS Universidad, Tijuana, Mexico
- 5 Department of Business Administration, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Israel
- 6 Business School, Shandong University, Weihai, China
The growth in social media use has given rise to concerns about the impacts it may have on users' psychological well-being. This paper's main objective is to shed light on the effect of social media use on psychological well-being. Building on contributions from various fields in the literature, it provides a more comprehensive study of the phenomenon by considering a set of mediators, including social capital types (i.e., bonding social capital and bridging social capital), social isolation, and smartphone addiction. The paper includes a quantitative study of 940 social media users from Mexico, using structural equation modeling (SEM) to test the proposed hypotheses. The findings point to an overall positive indirect impact of social media usage on psychological well-being, mainly due to the positive effect of bonding and bridging social capital. The empirical model's explanatory power is 45.1%. This paper provides empirical evidence and robust statistical analysis that demonstrates both positive and negative effects coexist, helping to reconcile the inconsistencies found so far in the literature.
Introduction
The use of social media has grown substantially in recent years ( Leong et al., 2019 ; Kemp, 2020 ). Social media refers to “the websites and online tools that facilitate interactions between users by providing them opportunities to share information, opinions, and interest” ( Swar and Hameed, 2017 , p. 141). Individuals use social media for many reasons, including entertainment, communication, and searching for information. Notably, adolescents and young adults are spending an increasing amount of time on online networking sites, e-games, texting, and other social media ( Twenge and Campbell, 2019 ). In fact, some authors (e.g., Dhir et al., 2018 ; Tateno et al., 2019 ) have suggested that social media has altered the forms of group interaction and its users' individual and collective behavior around the world.
Consequently, there are increased concerns regarding the possible negative impacts associated with social media usage addiction ( Swar and Hameed, 2017 ; Kircaburun et al., 2020 ), particularly on psychological well-being ( Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas, 2016 ; Jiao et al., 2017 ; Choi and Noh, 2019 ; Chatterjee, 2020 ). Smartphones sometimes distract their users from relationships and social interaction ( Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas, 2016 ; Li et al., 2020a ), and several authors have stressed that the excessive use of social media may lead to smartphone addiction ( Swar and Hameed, 2017 ; Leong et al., 2019 ), primarily because of the fear of missing out ( Reer et al., 2019 ; Roberts and David, 2020 ). Social media usage has been associated with anxiety, loneliness, and depression ( Dhir et al., 2018 ; Reer et al., 2019 ), social isolation ( Van Den Eijnden et al., 2016 ; Whaite et al., 2018 ), and “phubbing,” which refers to the extent to which an individual uses, or is distracted by, their smartphone during face-to-face communication with others ( Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas, 2016 ; Jiao et al., 2017 ; Choi and Noh, 2019 ; Chatterjee, 2020 ).
However, social media use also contributes to building a sense of connectedness with relevant others ( Twenge and Campbell, 2019 ), which may reduce social isolation. Indeed, social media provides several ways to interact both with close ties, such as family, friends, and relatives, and weak ties, including coworkers, acquaintances, and strangers ( Chen and Li, 2017 ), and plays a key role among people of all ages as they exploit their sense of belonging in different communities ( Roberts and David, 2020 ). Consequently, despite the fears regarding the possible negative impacts of social media usage on well-being, there is also an increasing number of studies highlighting social media as a new communication channel ( Twenge and Campbell, 2019 ; Barbosa et al., 2020 ), stressing that it can play a crucial role in developing one's presence, identity, and reputation, thus facilitating social interaction, forming and maintaining relationships, and sharing ideas ( Carlson et al., 2016 ), which consequently may be significantly correlated to social support ( Chen and Li, 2017 ; Holliman et al., 2021 ). Interestingly, recent studies (e.g., David et al., 2018 ; Bano et al., 2019 ; Barbosa et al., 2020 ) have suggested that the impact of smartphone usage on psychological well-being depends on the time spent on each type of application and the activities that users engage in.
Hence, the literature provides contradictory cues regarding the impacts of social media on users' well-being, highlighting both the possible negative impacts and the social enhancement it can potentially provide. In line with views on the need to further investigate social media usage ( Karikari et al., 2017 ), particularly regarding its societal implications ( Jiao et al., 2017 ), this paper argues that there is an urgent need to further understand the impact of the time spent on social media on users' psychological well-being, namely by considering other variables that mediate and further explain this effect.
One of the relevant perspectives worth considering is that provided by social capital theory, which is adopted in this paper. Social capital theory has previously been used to study how social media usage affects psychological well-being (e.g., Bano et al., 2019 ). However, extant literature has so far presented only partial models of associations that, although statistically acceptable and contributing to the understanding of the scope of social networks, do not provide as comprehensive a vision of the phenomenon as that proposed within this paper. Furthermore, the contradictory views, suggesting both negative (e.g., Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas, 2016 ; Van Den Eijnden et al., 2016 ; Jiao et al., 2017 ; Whaite et al., 2018 ; Choi and Noh, 2019 ; Chatterjee, 2020 ) and positive impacts ( Carlson et al., 2016 ; Chen and Li, 2017 ; Twenge and Campbell, 2019 ) of social media on psychological well-being, have not been adequately explored.
Given this research gap, this paper's main objective is to shed light on the effect of social media use on psychological well-being. As explained in detail in the next section, this paper explores the mediating effect of bonding and bridging social capital. To provide a broad view of the phenomenon, it also considers several variables highlighted in the literature as affecting the relationship between social media usage and psychological well-being, namely smartphone addiction, social isolation, and phubbing. The paper utilizes a quantitative study conducted in Mexico, comprising 940 social media users, and uses structural equation modeling (SEM) to test a set of research hypotheses.
This article provides several contributions. First, it adds to existing literature regarding the effect of social media use on psychological well-being and explores the contradictory indications provided by different approaches. Second, it proposes a conceptual model that integrates complementary perspectives on the direct and indirect effects of social media use. Third, it offers empirical evidence and robust statistical analysis that demonstrates that both positive and negative effects coexist, helping resolve the inconsistencies found so far in the literature. Finally, this paper provides insights on how to help reduce the potential negative effects of social media use, as it demonstrates that, through bridging and bonding social capital, social media usage positively impacts psychological well-being. Overall, the article offers valuable insights for academics, practitioners, and society in general.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section Literature Review presents a literature review focusing on the factors that explain the impact of social media usage on psychological well-being. Based on the literature review, a set of hypotheses are defined, resulting in the proposed conceptual model, which includes both the direct and indirect effects of social media usage on psychological well-being. Section Research Methodology explains the methodological procedures of the research, followed by the presentation and discussion of the study's results in section Results. Section Discussion is dedicated to the conclusions and includes implications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
Literature Review
Putnam (1995 , p. 664–665) defined social capital as “features of social life – networks, norms, and trust – that enable participants to act together more effectively to pursue shared objectives.” Li and Chen (2014 , p. 117) further explained that social capital encompasses “resources embedded in one's social network, which can be assessed and used for instrumental or expressive returns such as mutual support, reciprocity, and cooperation.”
Putnam (1995 , 2000) conceptualized social capital as comprising two dimensions, bridging and bonding, considering the different norms and networks in which they occur. Bridging social capital refers to the inclusive nature of social interaction and occurs when individuals from different origins establish connections through social networks. Hence, bridging social capital is typically provided by heterogeneous weak ties ( Li and Chen, 2014 ). This dimension widens individual social horizons and perspectives and provides extended access to resources and information. Bonding social capital refers to the social and emotional support each individual receives from his or her social networks, particularly from close ties (e.g., family and friends).
Overall, social capital is expected to be positively associated with psychological well-being ( Bano et al., 2019 ). Indeed, Williams (2006) stressed that interaction generates affective connections, resulting in positive impacts, such as emotional support. The following sub-sections use the lens of social capital theory to explore further the relationship between the use of social media and psychological well-being.
Social Media Use, Social Capital, and Psychological Well-Being
The effects of social media usage on social capital have gained increasing scholarly attention, and recent studies have highlighted a positive relationship between social media use and social capital ( Brown and Michinov, 2019 ; Tefertiller et al., 2020 ). Li and Chen (2014) hypothesized that the intensity of Facebook use by Chinese international students in the United States was positively related to social capital forms. A longitudinal survey based on the quota sampling approach illustrated the positive effects of social media use on the two social capital dimensions ( Chen and Li, 2017 ). Abbas and Mesch (2018) argued that, as Facebook usage increases, it will also increase users' social capital. Karikari et al. (2017) also found positive effects of social media use on social capital. Similarly, Pang (2018) studied Chinese students residing in Germany and found positive effects of social networking sites' use on social capital, which, in turn, was positively associated with psychological well-being. Bano et al. (2019) analyzed the 266 students' data and found positive effects of WhatsApp use on social capital forms and the positive effect of social capital on psychological well-being, emphasizing the role of social integration in mediating this positive effect.
Kim and Kim (2017) stressed the importance of having a heterogeneous network of contacts, which ultimately enhances the potential social capital. Overall, the manifest and social relations between people from close social circles (bonding social capital) and from distant social circles (bridging social capital) are strengthened when they promote communication, social support, and the sharing of interests, knowledge, and skills, which are shared with other members. This is linked to positive effects on interactions, such as acceptance, trust, and reciprocity, which are related to the individuals' health and psychological well-being ( Bekalu et al., 2019 ), including when social media helps to maintain social capital between social circles that exist outside of virtual communities ( Ellison et al., 2007 ).
Grounded on the above literature, this study proposes the following hypotheses:
H1a: Social media use is positively associated with bonding social capital.
H1b: Bonding social capital is positively associated with psychological well-being.
H2a: Social media use is positively associated with bridging social capital.
H2b: Bridging social capital is positively associated with psychological well-being.
Social Media Use, Social Isolation, and Psychological Well-Being
Social isolation is defined as “a deficit of personal relationships or being excluded from social networks” ( Choi and Noh, 2019 , p. 4). The state that occurs when an individual lacks true engagement with others, a sense of social belonging, and a satisfying relationship is related to increased mortality and morbidity ( Primack et al., 2017 ). Those who experience social isolation are deprived of social relationships and lack contact with others or involvement in social activities ( Schinka et al., 2012 ). Social media usage has been associated with anxiety, loneliness, and depression ( Dhir et al., 2018 ; Reer et al., 2019 ), and social isolation ( Van Den Eijnden et al., 2016 ; Whaite et al., 2018 ). However, some recent studies have argued that social media use decreases social isolation ( Primack et al., 2017 ; Meshi et al., 2020 ). Indeed, the increased use of social media platforms such as Facebook, WhatsApp, Instagram, and Twitter, among others, may provide opportunities for decreasing social isolation. For instance, the improved interpersonal connectivity achieved via videos and images on social media helps users evidence intimacy, attenuating social isolation ( Whaite et al., 2018 ).
Chappell and Badger (1989) stated that social isolation leads to decreased psychological well-being, while Choi and Noh (2019) concluded that greater social isolation is linked to increased suicide risk. Schinka et al. (2012) further argued that, when individuals experience social isolation from siblings, friends, family, or society, their psychological well-being tends to decrease. Thus, based on the literature cited above, this study proposes the following hypotheses:
H3a: Social media use is significantly associated with social isolation.
H3b: Social isolation is negatively associated with psychological well-being.
Social Media Use, Smartphone Addiction, Phubbing, and Psychological Well-Being
Smartphone addiction refers to “an individuals' excessive use of a smartphone and its negative effects on his/her life as a result of his/her inability to control his behavior” ( Gökçearslan et al., 2018 , p. 48). Regardless of its form, smartphone addiction results in social, medical, and psychological harm to people by limiting their ability to make their own choices ( Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas, 2016 ). The rapid advancement of information and communication technologies has led to the concept of social media, e-games, and also to smartphone addiction ( Chatterjee, 2020 ). The excessive use of smartphones for social media use, entertainment (watching videos, listening to music), and playing e-games is more common amongst people addicted to smartphones ( Jeong et al., 2016 ). In fact, previous studies have evidenced the relationship between social use and smartphone addiction ( Salehan and Negahban, 2013 ; Jeong et al., 2016 ; Swar and Hameed, 2017 ). In line with this, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H4a: Social media use is positively associated with smartphone addiction.
H4b: Smartphone addiction is negatively associated with psychological well-being.
While smartphones are bringing individuals closer, they are also, to some extent, pulling people apart ( Tonacci et al., 2019 ). For instance, they can lead to individuals ignoring others with whom they have close ties or physical interactions; this situation normally occurs due to extreme smartphone use (i.e., at the dinner table, in meetings, at get-togethers and parties, and in other daily activities). This act of ignoring others is called phubbing and is considered a common phenomenon in communication activities ( Guazzini et al., 2019 ; Chatterjee, 2020 ). Phubbing is also referred to as an act of snubbing others ( Chatterjee, 2020 ). This term was initially used in May 2012 by an Australian advertising agency to describe the “growing phenomenon of individuals ignoring their families and friends who were called phubbee (a person who is a recipients of phubbing behavior) victim of phubber (a person who start phubbing her or his companion)” ( Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas, 2018 ). Smartphone addiction has been found to be a determinant of phubbing ( Kim et al., 2018 ). Other recent studies have also evidenced the association between smartphones and phubbing ( Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas, 2016 ; Guazzini et al., 2019 ; Tonacci et al., 2019 ; Chatterjee, 2020 ). Vallespín et al. (2017 ) argued that phubbing behavior has a negative influence on psychological well-being and satisfaction. Furthermore, smartphone addiction is considered responsible for the development of new technologies. It may also negatively influence individual's psychological proximity ( Chatterjee, 2020 ). Therefore, based on the above discussion and calls for the association between phubbing and psychological well-being to be further explored, this study proposes the following hypotheses:
H5: Smartphone addiction is positively associated with phubbing.
H6: Phubbing is negatively associated with psychological well-being.
Indirect Relationship Between Social Media Use and Psychological Well-Being
Beyond the direct hypotheses proposed above, this study investigates the indirect effects of social media use on psychological well-being mediated by social capital forms, social isolation, and phubbing. As described above, most prior studies have focused on the direct influence of social media use on social capital forms, social isolation, smartphone addiction, and phubbing, as well as the direct impact of social capital forms, social isolation, smartphone addiction, and phubbing on psychological well-being. Very few studies, however, have focused on and evidenced the mediating role of social capital forms, social isolation, smartphone addiction, and phubbing derived from social media use in improving psychological well-being ( Chen and Li, 2017 ; Pang, 2018 ; Bano et al., 2019 ; Choi and Noh, 2019 ). Moreover, little is known about smartphone addiction's mediating role between social media use and psychological well-being. Therefore, this study aims to fill this gap in the existing literature by investigating the mediation of social capital forms, social isolation, and smartphone addiction. Further, examining the mediating influence will contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of social media use on psychological well-being via the mediating associations of smartphone addiction and psychological factors. Therefore, based on the above, we propose the following hypotheses (the conceptual model is presented in Figure 1 ):
H7: (a) Bonding social capital; (b) bridging social capital; (c) social isolation; and (d) smartphone addiction mediate the relationship between social media use and psychological well-being.
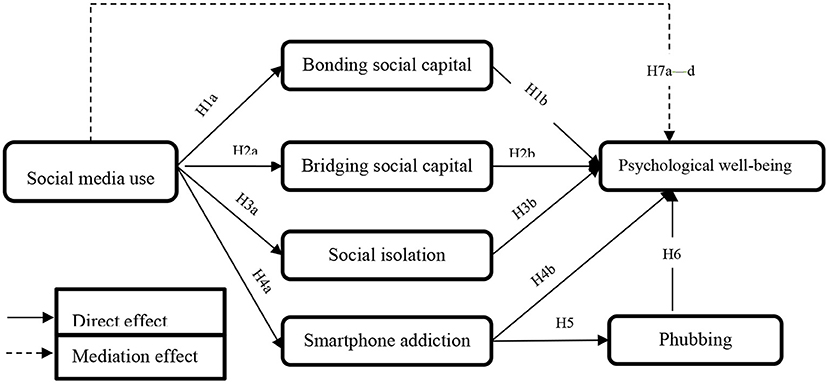
Figure 1 . Conceptual model.
Research Methodology
Sample procedure and online survey.
This study randomly selected students from universities in Mexico. We chose University students for the following reasons. First, students are considered the most appropriate sample for e-commerce studies, particularly in the social media context ( Oghazi et al., 2018 ; Shi et al., 2018 ). Second, University students are considered to be frequent users and addicted to smartphones ( Mou et al., 2017 ; Stouthuysen et al., 2018 ). Third, this study ensured that respondents were experienced, well-educated, and possessed sufficient knowledge of the drawbacks of social media and the extreme use of smartphones. A total sample size of 940 University students was ultimately achieved from the 1,500 students contacted, using a convenience random sampling approach, due both to the COVID-19 pandemic and budget and time constraints. Additionally, in order to test the model, a quantitative empirical study was conducted, using an online survey method to collect data. This study used a web-based survey distributed via social media platforms for two reasons: the COVID-19 pandemic; and to reach a large number of respondents ( Qalati et al., 2021 ). Furthermore, online surveys are considered a powerful and authenticated tool for new research ( Fan et al., 2021 ), while also representing a fast, simple, and less costly approach to collecting data ( Dutot and Bergeron, 2016 ).
Data Collection Procedures and Respondent's Information
Data were collected by disseminating a link to the survey by e-mail and social network sites. Before presenting the closed-ended questionnaire, respondents were assured that their participation would remain voluntary, confidential, and anonymous. Data collection occurred from July 2020 to December 2020 (during the pandemic). It should be noted that, because data were collected during the pandemic, this may have had an influence on the results of the study. The reason for choosing a six-month lag time was to mitigate common method bias (CMB) ( Li et al., 2020b ). In the present study, 1,500 students were contacted via University e-mail and social applications (Facebook, WhatsApp, and Instagram). We sent a reminder every month for 6 months (a total of six reminders), resulting in 940 valid responses. Thus, 940 (62.6% response rate) responses were used for hypotheses testing.
Table 1 reveals that, of the 940 participants, three-quarters were female (76.4%, n = 719) and nearly one-quarter (23.6%, n = 221) were male. Nearly half of the participants (48.8%, n = 459) were aged between 26 and 35 years, followed by 36 to 35 years (21.9%, n = 206), <26 (20.3%, n = 191), and over 45 (8.9%, n = 84). Approximately two-thirds (65%, n = 611) had a bachelor's degree or above, while one-third had up to 12 years of education. Regarding the daily frequency of using the Internet, nearly half (48.6%, n = 457) of the respondents reported between 5 and 8 h a day, and over one-quarter (27.2%) 9–12 h a day. Regarding the social media platforms used, over 38.5 and 39.6% reported Facebook and WhatsApp, respectively. Of the 940 respondents, only 22.1% reported Instagram (12.8%) and Twitter (9.2%). It should be noted, however, that the sample is predominantly female and well-educated.
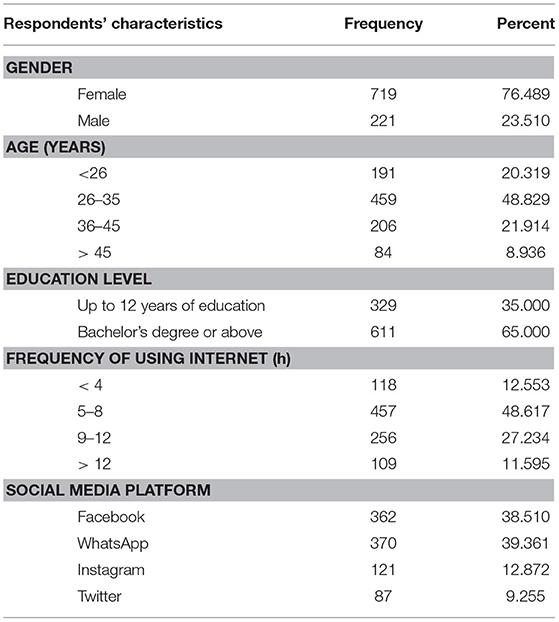
Table 1 . Respondents' characteristics.
Measurement Items
The study used five-point Likert scales (1 = “strongly disagree;” 5 = “strongly agree”) to record responses.
Social Media Use
Social media use was assessed using four items adapted from Karikari et al. (2017) . Sample items include “Social media is part of my everyday activity,” “Social media has become part of my daily life,” “I would be sorry if social media shut down,” and “I feel out of touch, when I have not logged onto social media for a while.” The adapted items had robust reliability and validity (CA = 783, CR = 0.857, AVE = 0.600).
Social Capital
Social capital was measured using a total of eight items, representing bonding social capital (four items) and bridging social capital (four items) adapted from Chan (2015) . Sample construct items include: bonging social capital (“I am willing to spend time to support general community activities,” “I interact with people who are quite different from me”) and bridging social capital (“My social media community is a good place to be,” “Interacting with people on social media makes me want to try new things”). The adapted items had robust reliability and validity [bonding social capital (CA = 0.785, CR = 0.861, AVE = 0.608) and bridging social capital (CA = 0.834, CR = 0.883, AVE = 0.601)].
Social Isolation
Social isolation was assessed using three items from Choi and Noh (2019) . Sample items include “I do not have anyone to play with,” “I feel alone from people,” and “I have no one I can trust.” This adapted scale had substantial reliability and validity (CA = 0.890, CR = 0.928, AVE = 0.811).
Smartphone Addiction
Smartphone addiction was assessed using five items taken from Salehan and Negahban (2013) . Sample items include “I am always preoccupied with my mobile,” “Using my mobile phone keeps me relaxed,” and “I am not able to control myself from frequent use of mobile phones.” Again, these adapted items showed substantial reliability and validity (CA = 903, CR = 0.928, AVE = 0.809).
Phubbing was assessed using four items from Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas (2018) . Sample items include: “I have conflicts with others because I am using my phone” and “I would rather pay attention to my phone than talk to others.” This construct also demonstrated significant reliability and validity (CA = 770, CR = 0.894, AVE = 0.809).
Psychological Well-Being
Psychological well-being was assessed using five items from Jiao et al. (2017) . Sample items include “I lead a purposeful and meaningful life with the help of others,” “My social relationships are supportive and rewarding in social media,” and “I am engaged and interested in my daily on social media.” This study evidenced that this adapted scale had substantial reliability and validity (CA = 0.886, CR = 0.917, AVE = 0.688).
Data Analysis
Based on the complexity of the association between the proposed construct and the widespread use and acceptance of SmartPLS 3.0 in several fields ( Hair et al., 2019 ), we utilized SEM, using SmartPLS 3.0, to examine the relationships between constructs. Structural equation modeling is a multivariate statistical analysis technique that is used to investigate relationships. Further, it is a combination of factor and multivariate regression analysis, and is employed to explore the relationship between observed and latent constructs.
SmartPLS 3.0 “is a more comprehensive software program with an intuitive graphical user interface to run partial least square SEM analysis, certainly has had a massive impact” ( Sarstedt and Cheah, 2019 ). According to Ringle et al. (2015) , this commercial software offers a wide range of algorithmic and modeling options, improved usability, and user-friendly and professional support. Furthermore, Sarstedt and Cheah (2019) suggested that structural equation models enable the specification of complex interrelationships between observed and latent constructs. Hair et al. (2019) argued that, in recent years, the number of articles published using partial least squares SEM has increased significantly in contrast to covariance-based SEM. In addition, partial least squares SEM using SmartPLS is more appealing for several scholars as it enables them to predict more complex models with several variables, indicator constructs, and structural paths, instead of imposing distributional assumptions on the data ( Hair et al., 2019 ). Therefore, this study utilized the partial least squares SEM approach using SmartPLS 3.0.
Common Method Bias (CMB) Test
This study used the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) test to measure the sampling adequacy and ensure data suitability. The KMO test result was 0.874, which is greater than an acceptable threshold of 0.50 ( Ali Qalati et al., 2021 ; Shrestha, 2021 ), and hence considered suitable for explanatory factor analysis. Moreover, Bartlett's test results demonstrated a significance level of 0.001, which is considered good as it is below the accepted threshold of 0.05.
The term CMB is associated with Campbell and Fiske (1959) , who highlighted the importance of CMB and identified that a portion of variance in the research may be due to the methods employed. It occurs when all scales of the study are measured at the same time using a single questionnaire survey ( Podsakoff and Organ, 1986 ); subsequently, estimates of the relationship among the variables might be distorted by the impacts of CMB. It is considered a serious issue that has a potential to “jeopardize” the validity of the study findings ( Tehseen et al., 2017 ). There are several reasons for CMB: (1) it mainly occurs due to response “tendencies that raters can apply uniformity across the measures;” and (2) it also occurs due to similarities in the wording and structure of the survey items that produce similar results ( Jordan and Troth, 2019 ). Harman's single factor test and a full collinearity approach were employed to ensure that the data was free from CMB ( Tehseen et al., 2017 ; Jordan and Troth, 2019 ; Ali Qalati et al., 2021 ). Harman's single factor test showed a single factor explained only 22.8% of the total variance, which is far below the 50.0% acceptable threshold ( Podsakoff et al., 2003 ).
Additionally, the variance inflation factor (VIF) was used, which is a measure of the amount of multicollinearity in a set of multiple regression constructs and also considered a way of detecting CMB ( Hair et al., 2019 ). Hair et al. (2019) suggested that the acceptable threshold for the VIF is 3.0; as the computed VIFs for the present study ranged from 1.189 to 1.626, CMB is not a key concern (see Table 2 ). Bagozzi et al. (1991) suggested a correlation-matrix procedure to detect CMB. Common method bias is evident if correlation among the principle constructs is >0.9 ( Tehseen et al., 2020 ); however, no values >0.9 were found in this study (see section Assessment of Measurement Model). This study used a two-step approach to evaluate the measurement model and the structural model.

Table 2 . Common method bias (full collinearity VIF).
Assessment of Measurement Model
Before conducting the SEM analysis, the measurement model was assessed to examine individual item reliability, internal consistency, and convergent and discriminant validity. Table 3 exhibits the values of outer loading used to measure an individual item's reliability ( Hair et al., 2012 ). Hair et al. (2017) proposed that the value for each outer loading should be ≥0.7; following this principle, two items of phubbing (PHUB3—I get irritated if others ask me to get off my phone and talk to them; PHUB4—I use my phone even though I know it irritated others) were removed from the analysis Hair et al. (2019) . According to Nunnally (1978) , Cronbach's alpha values should exceed 0.7. The threshold values of constructs in this study ranged from 0.77 to 0.903. Regarding internal consistency, Bagozzi and Yi (1988) suggested that composite reliability (CR) should be ≥0.7. The coefficient value for CR in this study was between 0.857 and 0.928. Regarding convergent validity, Fornell and Larcker (1981) suggested that the average variance extracted (AVE) should be ≥0.5. Average variance extracted values in this study were between 0.60 and 0.811. Finally, regarding discriminant validity, according to Fornell and Larcker (1981) , the square root of the AVE for each construct should exceed the inter-correlations of the construct with other model constructs. That was the case in this study, as shown in Table 4 .
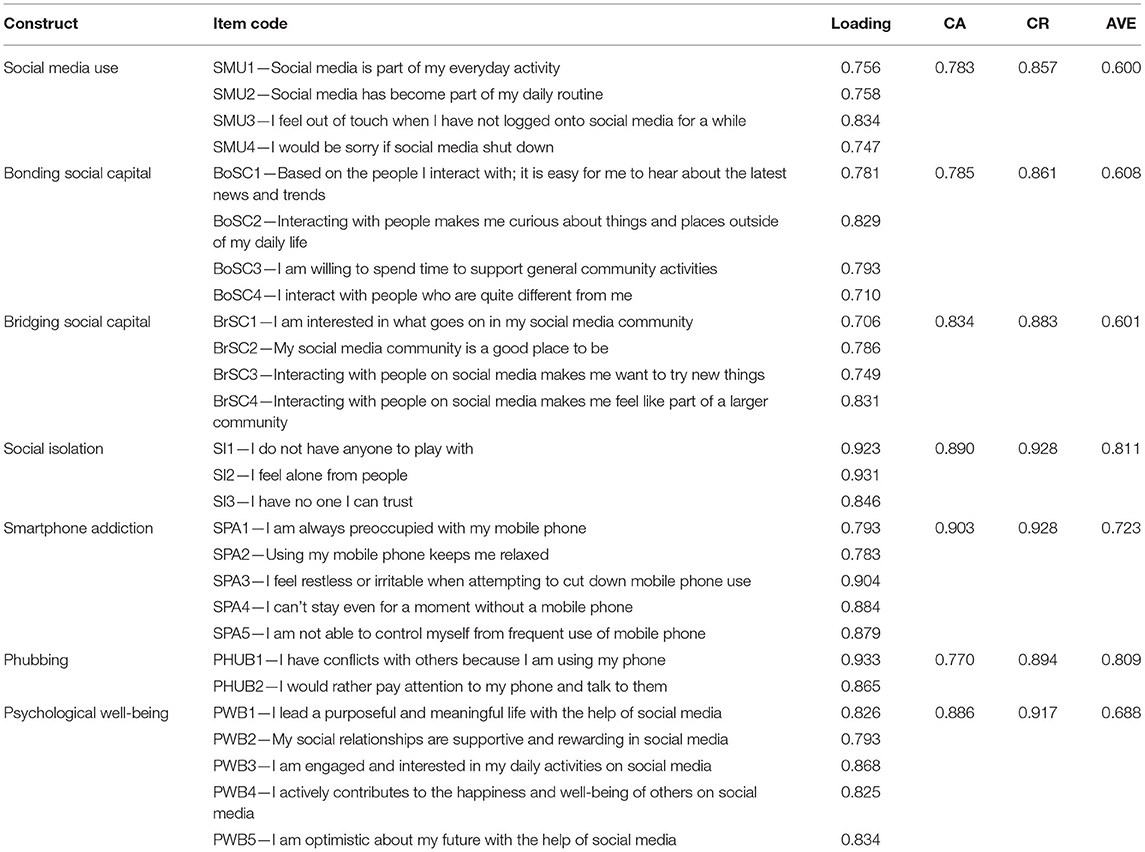
Table 3 . Study measures, factor loading, and the constructs' reliability and convergent validity.
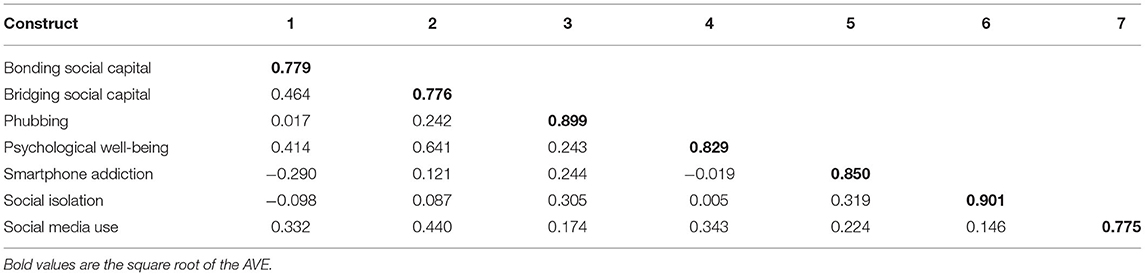
Table 4 . Discriminant validity and correlation.
Hence, by analyzing the results of the measurement model, it can be concluded that the data are adequate for structural equation estimation.
Assessment of the Structural Model
This study used the PLS algorithm and a bootstrapping technique with 5,000 bootstraps as proposed by Hair et al. (2019) to generate the path coefficient values and their level of significance. The coefficient of determination ( R 2 ) is an important measure to assess the structural model and its explanatory power ( Henseler et al., 2009 ; Hair et al., 2019 ). Table 5 and Figure 2 reveal that the R 2 value in the present study was 0.451 for psychological well-being, which means that 45.1% of changes in psychological well-being occurred due to social media use, social capital forms (i.e., bonding and bridging), social isolation, smartphone addiction, and phubbing. Cohen (1998) proposed that R 2 values of 0.60, 0.33, and 0.19 are considered substantial, moderate, and weak. Following Cohen's (1998) threshold values, this research demonstrates a moderate predicting power for psychological well-being among Mexican respondents ( Table 6 ).
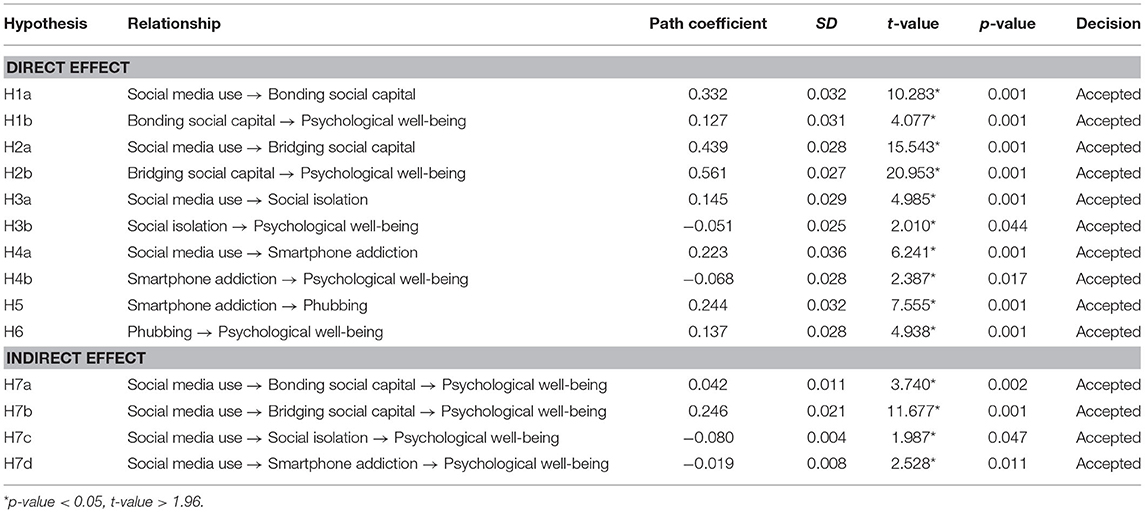
Table 5 . Summary of path coefficients and hypothesis testing.
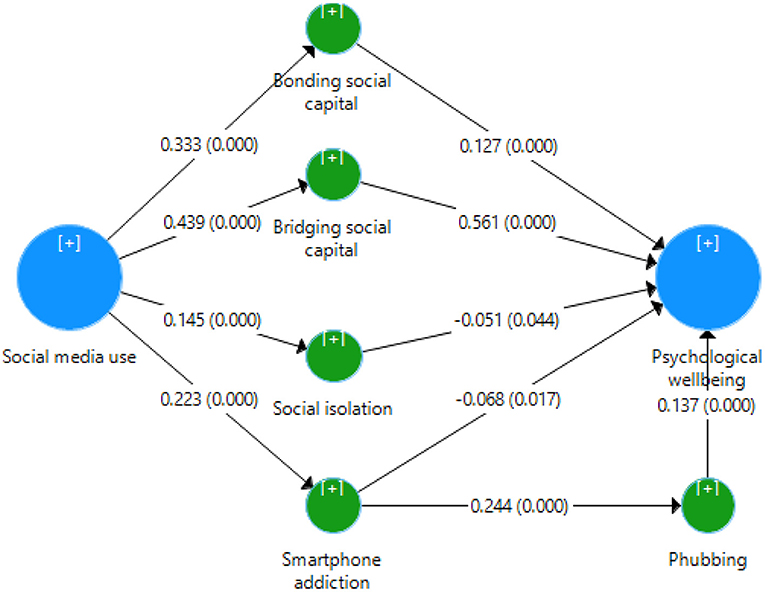
Figure 2 . Structural model.

Table 6 . Strength of the model (Predictive relevance, coefficient of determination, and model fit indices).
Apart from the R 2 measure, the present study also used cross-validated redundancy measures, or effect sizes ( q 2 ), to assess the proposed model and validate the results ( Ringle et al., 2012 ). Hair et al. (2019) suggested that a model exhibiting an effect size q 2 > 0 has predictive relevance ( Table 6 ). This study's results evidenced that it has a 0.15 <0.29 <0.35 (medium) predictive relevance, as 0.02, 0.15, and 0.35 are considered small, medium, and large, respectively ( Cohen, 1998 ). Regarding the goodness-of-fit indices, Hair et al. (2019) suggested the standardized root mean square residual (SRMR) to evaluate the goodness of fit. Standardized root mean square is an absolute measure of fit: a value of zero indicates perfect fit and a value <0.08 is considered good fit ( Hair et al., 2019 ). This study exhibits an adequate model fitness level with an SRMR value of 0.063 ( Table 6 ).
Table 5 reveals that all hypotheses of the study were accepted base on the criterion ( p -value < 0.05). H1a (β = 0.332, t = 10.283, p = 0.001) was confirmed, with the second most robust positive and significant relationship (between social media use and bonding social capital). In addition, this study evidenced a positive and significant relationship between bonding social capital and psychological well-being (β = 0.127, t = 4.077, p = 0.001); therefore, H1b was accepted. Regarding social media use and bridging social capital, the present study found the most robust positive and significant impact (β = 0.439, t = 15.543, p = 0.001); therefore, H2a was accepted. The study also evidenced a positive and significant association between bridging social capital and psychological well-being (β = 0.561, t = 20.953, p = 0.001); thus, H2b was accepted. The present study evidenced a significant effect of social media use on social isolation (β = 0.145, t = 4.985, p = 0.001); thus, H3a was accepted. In addition, this study accepted H3b (β = −0.051, t = 2.01, p = 0.044). Furthermore, this study evidenced a positive and significant effect of social media use on smartphone addiction (β = 0.223, t = 6.241, p = 0.001); therefore, H4a was accepted. Furthermore, the present study found that smartphone addiction has a negative significant influence on psychological well-being (β = −0.068, t = 2.387, p = 0.017); therefore, H4b was accepted. Regarding the relationship between smartphone addiction and phubbing, this study found a positive and significant effect of smartphone addiction on phubbing (β = 0.244, t = 7.555, p = 0.001); therefore, H5 was accepted. Furthermore, the present research evidenced a positive and significant influence of phubbing on psychological well-being (β = 0.137, t = 4.938, p = 0.001); therefore, H6 was accepted. Finally, the study provides interesting findings on the indirect effect of social media use on psychological well-being ( t -value > 1.96 and p -value < 0.05); therefore, H7a–d were accepted.
Furthermore, to test the mediating analysis, Preacher and Hayes's (2008) approach was used. The key characteristic of an indirect relationship is that it involves a third construct, which plays a mediating role in the relationship between the independent and dependent constructs. Logically, the effect of A (independent construct) on C (the dependent construct) is mediated by B (a third variable). Preacher and Hayes (2008) suggested the following: B is a construct acting as a mediator if A significantly influences B, A significantly accounts for variability in C, B significantly influences C when controlling for A, and the influence of A on C decreases significantly when B is added simultaneously with A as a predictor of C. According to Matthews et al. (2018) , if the indirect effect is significant while the direct insignificant, full mediation has occurred, while if both direct and indirect effects are substantial, partial mediation has occurred. This study evidenced that there is partial mediation in the proposed construct ( Table 5 ). Following Preacher and Hayes (2008) this study evidenced that there is partial mediation in the proposed construct, because the relationship between independent variable (social media use) and dependent variable (psychological well-being) is significant ( p -value < 0.05) and indirect effect among them after introducing mediator (bonding social capital, bridging social capital, social isolation, and smartphone addiction) is also significant ( p -value < 0.05), therefore it is evidenced that when there is a significant effect both direct and indirect it's called partial mediation.
The present study reveals that the social and psychological impacts of social media use among University students is becoming more complex as there is continuing advancement in technology, offering a range of affordable interaction opportunities. Based on the 940 valid responses collected, all the hypotheses were accepted ( p < 0.05).
H1a finding suggests that social media use is a significant influencing factor of bonding social capital. This implies that, during a pandemic, social media use enables students to continue their close relationships with family members, friends, and those with whom they have close ties. This finding is in line with prior work of Chan (2015) and Ellison et al. (2007) , who evidenced that social bonding capital is predicted by Facebook use and having a mobile phone. H1b findings suggest that, when individuals believe that social communication can help overcome obstacles to interaction and encourage more virtual self-disclosure, social media use can improve trust and promote the establishment of social associations, thereby enhancing well-being. These findings are in line with those of Gong et al. (2021) , who also witnessed the significant effect of bonding social capital on immigrants' psychological well-being, subsequently calling for the further evidence to confirm the proposed relationship.
The findings of the present study related to H2a suggest that students are more likely to use social media platforms to receive more emotional support, increase their ability to mobilize others, and to build social networks, which leads to social belongingness. Furthermore, the findings suggest that social media platforms enable students to accumulate and maintain bridging social capital; further, online classes can benefit students who feel shy when participating in offline classes. This study supports the previous findings of Chan (2015) and Karikari et al. (2017) . Notably, the present study is not limited to a single social networking platform, taking instead a holistic view of social media. The H2b findings are consistent with those of Bano et al. (2019) , who also confirmed the link between bonding social capital and psychological well-being among University students using WhatsApp as social media platform, as well as those of Chen and Li (2017) .
The H3a findings suggest that, during the COVID-19 pandemic when most people around the world have had limited offline or face-to-face interaction and have used social media to connect with families, friends, and social communities, they have often been unable to connect with them. This is due to many individuals avoiding using social media because of fake news, financial constraints, and a lack of trust in social media; thus, the lack both of offline and online interaction, coupled with negative experiences on social media use, enhances the level of social isolation ( Hajek and König, 2021 ). These findings are consistent with those of Adnan and Anwar (2020) . The H3b suggests that higher levels of social isolation have a negative impact on psychological well-being. These result indicating that, consistent with Choi and Noh (2019) , social isolation is negatively and significantly related to psychological well-being.
The H4a results suggests that substantial use of social media use leads to an increase in smartphone addiction. These findings are in line with those of Jeong et al. (2016) , who stated that the excessive use of smartphones for social media, entertainment (watching videos, listening to music), and playing e-games was more likely to lead to smartphone addiction. These findings also confirm the previous work of Jeong et al. (2016) , Salehan and Negahban (2013) , and Swar and Hameed (2017) . The H4b results revealed that a single unit increase in smartphone addiction results in a 6.8% decrease in psychological well-being. These findings are in line with those of Tangmunkongvorakul et al. (2019) , who showed that students with higher levels of smartphone addiction had lower psychological well-being scores. These findings also support those of Shoukat (2019) , who showed that smartphone addiction inversely influences individuals' mental health.
This suggests that the greater the smartphone addiction, the greater the phubbing. The H5 findings are in line with those of Chatterjee (2020) , Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas (2016) , Guazzini et al. (2019) , and Tonacci et al. (2019) , who also evidenced a significant impact of smartphone addiction and phubbing. Similarly, Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas (2018) corroborated that smartphone addiction is the main predictor of phubbing behavior. However, these findings are inconsistent with those of Vallespín et al. (2017 ), who found a negative influence of phubbing.
The H6 results suggests that phubbing is one of the significant predictors of psychological well-being. Furthermore, these findings suggest that, when phubbers use a cellphone during interaction with someone, especially during the current pandemic, and they are connected with many family members, friends, and relatives; therefore, this kind of action gives them more satisfaction, which simultaneously results in increased relaxation and decreased depression ( Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas, 2018 ). These findings support those of Davey et al. (2018) , who evidenced that phubbing has a significant influence on adolescents and social health students in India.
The findings showed a significant and positive effect of social media use on psychological well-being both through bridging and bonding social capital. However, a significant and negative effect of social media use on psychological well-being through smartphone addiction and through social isolation was also found. Hence, this study provides evidence that could shed light on the contradictory contributions in the literature suggesting both positive (e.g., Chen and Li, 2017 ; Twenge and Campbell, 2019 ; Roberts and David, 2020 ) and negative (e.g., Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas, 2016 ; Jiao et al., 2017 ; Choi and Noh, 2019 ; Chatterjee, 2020 ) effects of social media use on psychological well-being. This study concludes that the overall impact is positive, despite some degree of negative indirect impact.
Theoretical Contributions
This study's findings contribute to the current literature, both by providing empirical evidence for the relationships suggested by extant literature and by demonstrating the relevance of adopting a more complex approach that considers, in particular, the indirect effect of social media on psychological well-being. As such, this study constitutes a basis for future research ( Van Den Eijnden et al., 2016 ; Whaite et al., 2018 ) aiming to understand the impacts of social media use and to find ways to reduce its possible negative impacts.
In line with Kim and Kim (2017) , who stressed the importance of heterogeneous social networks in improving social capital, this paper suggests that, to positively impact psychological well-being, social media usage should be associated both with strong and weak ties, as both are important in building social capital, and hence associated with its bonding and bridging facets. Interestingly, though, bridging capital was shown as having the greatest impact on psychological well-being. Thus, the importance of wider social horizons, the inclusion in different groups, and establishing new connections ( Putnam, 1995 , 2000 ) with heterogeneous weak ties ( Li and Chen, 2014 ) are highlighted in this paper.
Practical Contributions
These findings are significant for practitioners, particularly those interested in dealing with the possible negative impacts of social media use on psychological well-being. Although social media use is associated with factors that negatively impact psychological well-being, particularly smartphone addiction and social isolation, these negative impacts can be lessened if the connections with both strong and weak ties are facilitated and featured by social media. Indeed, social media platforms offer several features, from facilitating communication with family, friends, and acquaintances, to identifying and offering access to other people with shared interests. However, it is important to access heterogeneous weak ties ( Li and Chen, 2014 ) so that social media offers access to wider sources of information and new resources, hence enhancing bridging social capital.
Limitations and Directions for Future Studies
This study is not without limitations. For example, this study used a convenience sampling approach to reach to a large number of respondents. Further, this study was conducted in Mexico only, limiting the generalizability of the results; future research should therefore use a cross-cultural approach to investigate the impacts of social media use on psychological well-being and the mediating role of proposed constructs (e.g., bonding and bridging social capital, social isolation, and smartphone addiction). The sample distribution may also be regarded as a limitation of the study because respondents were mainly well-educated and female. Moreover, although Internet channels represent a particularly suitable way to approach social media users, the fact that this study adopted an online survey does not guarantee a representative sample of the population. Hence, extrapolating the results requires caution, and study replication is recommended, particularly with social media users from other countries and cultures. The present study was conducted in the context of mainly University students, primarily well-educated females, via an online survey on in Mexico; therefore, the findings represent a snapshot at a particular time. Notably, however, the effect of social media use is increasing due to COVID-19 around the globe and is volatile over time.
Two of the proposed hypotheses of this study, namely the expected negative impacts of social media use on social isolation and of phubbing on psychological well-being, should be further explored. One possible approach is to consider the type of connections (i.e., weak and strong ties) to explain further the impact of social media usage on social isolation. Apparently, the prevalence of weak ties, although facilitating bridging social capital, may have an adverse impact in terms of social isolation. Regarding phubbing, the fact that the findings point to a possible positive impact on psychological well-being should be carefully addressed, specifically by psychology theorists and scholars, in order to identify factors that may help further understand this phenomenon. Other suggestions for future research include using mixed-method approaches, as qualitative studies could help further validate the results and provide complementary perspectives on the relationships between the considered variables.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.

Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Jiangsu University. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
This study is supported by the National Statistics Research Project of China (2016LY96).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbas, R., and Mesch, G. (2018). Do rich teens get richer? Facebook use and the link between offline and online social capital among Palestinian youth in Israel. Inf. Commun. Soc. 21, 63–79. doi: 10.1080/1369118X.2016.1261168
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Adnan, M., and Anwar, K. (2020). Online learning amid the COVID-19 pandemic: students' perspectives. J. Pedagog. Sociol. Psychol. 2, 45–51. doi: 10.33902/JPSP.2020261309
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ali Qalati, S., Li, W., Ahmed, N., Ali Mirani, M., and Khan, A. (2021). Examining the factors affecting SME performance: the mediating role of social media adoption. Sustainability 13:75. doi: 10.3390/su13010075
Bagozzi, R. P., and Yi, Y. (1988). On the evaluation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 16, 74–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02723327
Bagozzi, R. P., Yi, Y., and Phillips, L. W. (1991). Assessing construct validity in organizational research. Admin. Sci. Q. 36, 421–458. doi: 10.2307/2393203
Bano, S., Cisheng, W., Khan, A. N., and Khan, N. A. (2019). WhatsApp use and student's psychological well-being: role of social capital and social integration. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 103, 200–208. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2019.06.002
Barbosa, B., Chkoniya, V., Simoes, D., Filipe, S., and Santos, C. A. (2020). Always connected: generation Y smartphone use and social capital. Rev. Ibérica Sist. Tecnol. Inf. E 35, 152–166.
Google Scholar
Bekalu, M. A., McCloud, R. F., and Viswanath, K. (2019). Association of social media use with social well-being, positive mental health, and self-rated health: disentangling routine use from emotional connection to use. Health Educ. Behav. 46(2 Suppl), 69S−80S. doi: 10.1177/1090198119863768
Brown, G., and Michinov, N. (2019). Measuring latent ties on Facebook: a novel approach to studying their prevalence and relationship with bridging social capital. Technol. Soc. 59:101176. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2019.101176
Campbell, D. T., and Fiske, D. W. (1959). Convergent and discriminant validation by the multitrait-multimethod matrix. Psychol. Bull. 56, 81–105. doi: 10.1037/h0046016
Carlson, J. R., Zivnuska, S., Harris, R. B., Harris, K. J., and Carlson, D. S. (2016). Social media use in the workplace: a study of dual effects. J. Org. End User Comput. 28, 15–31. doi: 10.4018/JOEUC.2016010102
Chan, M. (2015). Mobile phones and the good life: examining the relationships among mobile use, social capital and subjective well-being. New Media Soc. 17, 96–113. doi: 10.1177/1461444813516836
Chappell, N. L., and Badger, M. (1989). Social isolation and well-being. J. Gerontol. 44, S169–S176. doi: 10.1093/geronj/44.5.s169
Chatterjee, S. (2020). Antecedents of phubbing: from technological and psychological perspectives. J. Syst. Inf. Technol. 22, 161–118. doi: 10.1108/JSIT-05-2019-0089
Chen, H.-T., and Li, X. (2017). The contribution of mobile social media to social capital and psychological well-being: examining the role of communicative use, friending and self-disclosure. Comput. Hum. Behav. 75, 958–965. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.06.011
Choi, D.-H., and Noh, G.-Y. (2019). The influence of social media use on attitude toward suicide through psychological well-being, social isolation, and social support. Inf. Commun. Soc. 23, 1–17. doi: 10.1080/1369118X.2019.1574860
Chotpitayasunondh, V., and Douglas, K. M. (2016). How “phubbing” becomes the norm: the antecedents and consequences of snubbing via smartphone. Comput. Hum. Behav. 63, 9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.018
Chotpitayasunondh, V., and Douglas, K. M. (2018). The effects of “phubbing” on social interaction. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 48, 304–316. doi: 10.1111/jasp.12506
Cohen, J. (1998). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences . Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Davey, S., Davey, A., Raghav, S. K., Singh, J. V., Singh, N., Blachnio, A., et al. (2018). Predictors and consequences of “phubbing” among adolescents and youth in India: an impact evaluation study. J. Fam. Community Med. 25, 35–42. doi: 10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_71_17
David, M. E., Roberts, J. A., and Christenson, B. (2018). Too much of a good thing: investigating the association between actual smartphone use and individual well-being. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 34, 265–275. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2017.1349250
Dhir, A., Yossatorn, Y., Kaur, P., and Chen, S. (2018). Online social media fatigue and psychological wellbeing—a study of compulsive use, fear of missing out, fatigue, anxiety and depression. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 40, 141–152. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.01.012
Dutot, V., and Bergeron, F. (2016). From strategic orientation to social media orientation: improving SMEs' performance on social media. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 23, 1165–1190. doi: 10.1108/JSBED-11-2015-0160
Ellison, N. B., Steinfield, C., and Lampe, C. (2007). The benefits of Facebook “friends:” Social capital and college students' use of online social network sites. J. Comput. Mediat. Commun. 12, 1143–1168. doi: 10.1111/j.1083-6101.2007.00367.x
Fan, M., Huang, Y., Qalati, S. A., Shah, S. M. M., Ostic, D., and Pu, Z. (2021). Effects of information overload, communication overload, and inequality on digital distrust: a cyber-violence behavior mechanism. Front. Psychol. 12:643981. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.643981
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Market. Res. 18, 39–50. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104
Gökçearslan, S., Uluyol, Ç., and Sahin, S. (2018). Smartphone addiction, cyberloafing, stress and social support among University students: a path analysis. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 91, 47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2018.05.036
Gong, S., Xu, P., and Wang, S. (2021). Social capital and psychological well-being of Chinese immigrants in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:547. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18020547
Guazzini, A., Duradoni, M., Capelli, A., and Meringolo, P. (2019). An explorative model to assess individuals' phubbing risk. Fut. Internet 11:21. doi: 10.3390/fi11010021
Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., and Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 31, 2–24. doi: 10.1108/EBR-11-2018-0203
Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Pieper, T. M., and Ringle, C. M. (2012). The use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in strategic management research: a review of past practices and recommendations for future applications. Long Range Plann. 45, 320–340. doi: 10.1016/j.lrp.2012.09.008
Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., and Gudergan, S. P. (2017). Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Hajek, A., and König, H.-H. (2021). Social isolation and loneliness of older adults in times of the CoViD-19 pandemic: can use of online social media sites and video chats assist in mitigating social isolation and loneliness? Gerontology 67, 121–123. doi: 10.1159/000512793
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sinkovics, R. R. (2009). “The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing,” in New Challenges to International Marketing , Vol. 20, eds R.R. Sinkovics and P.N. Ghauri (Bigley: Emerald), 277–319.
Holliman, A. J., Waldeck, D., Jay, B., Murphy, S., Atkinson, E., Collie, R. J., et al. (2021). Adaptability and social support: examining links with psychological wellbeing among UK students and non-students. Fron. Psychol. 12:636520. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.636520
Jeong, S.-H., Kim, H., Yum, J.-Y., and Hwang, Y. (2016). What type of content are smartphone users addicted to? SNS vs. games. Comput. Hum. Behav. 54, 10–17. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.035
Jiao, Y., Jo, M.-S., and Sarigöllü, E. (2017). Social value and content value in social media: two paths to psychological well-being. J. Org. Comput. Electr. Commer. 27, 3–24. doi: 10.1080/10919392.2016.1264762
Jordan, P. J., and Troth, A. C. (2019). Common method bias in applied settings: the dilemma of researching in organizations. Austr. J. Manag. 45, 3–14. doi: 10.1177/0312896219871976
Karikari, S., Osei-Frimpong, K., and Owusu-Frimpong, N. (2017). Evaluating individual level antecedents and consequences of social media use in Ghana. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 123, 68–79. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2017.06.023
Kemp, S. (January 30, 2020). Digital 2020: 3.8 billion people use social media. We Are Social . Available online at: https://wearesocial.com/blog/2020/01/digital-2020-3-8-billion-people-use-social-media .
Kim, B., and Kim, Y. (2017). College students' social media use and communication network heterogeneity: implications for social capital and subjective well-being. Comput. Hum. Behav. 73, 620–628. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.03.033
Kim, K., Milne, G. R., and Bahl, S. (2018). Smart phone addiction and mindfulness: an intergenerational comparison. Int. J. Pharmaceut. Healthcare Market. 12, 25–43. doi: 10.1108/IJPHM-08-2016-0044
Kircaburun, K., Alhabash, S., Tosuntaş, S. B., and Griffiths, M. D. (2020). Uses and gratifications of problematic social media use among University students: a simultaneous examination of the big five of personality traits, social media platforms, and social media use motives. Int. J. Mental Health Addict. 18, 525–547. doi: 10.1007/s11469-018-9940-6
Leong, L.-Y., Hew, T.-S., Ooi, K.-B., Lee, V.-H., and Hew, J.-J. (2019). A hybrid SEM-neural network analysis of social media addiction. Expert Syst. Appl. 133, 296–316. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.05.024
Li, L., Griffiths, M. D., Mei, S., and Niu, Z. (2020a). Fear of missing out and smartphone addiction mediates the relationship between positive and negative affect and sleep quality among Chinese University students. Front. Psychiatr. 11:877. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00877
Li, W., Qalati, S. A., Khan, M. A. S., Kwabena, G. Y., Erusalkina, D., and Anwar, F. (2020b). Value co-creation and growth of social enterprises in developing countries: moderating role of environmental dynamics. Entrep. Res. J. 2020:20190359. doi: 10.1515/erj-2019-0359
Li, X., and Chen, W. (2014). Facebook or Renren? A comparative study of social networking site use and social capital among Chinese international students in the United States. Comput. Hum. Behav . 35, 116–123. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.02.012
Matthews, L., Hair, J. F., and Matthews, R. (2018). PLS-SEM: the holy grail for advanced analysis. Mark. Manag. J. 28, 1–13.
Meshi, D., Cotten, S. R., and Bender, A. R. (2020). Problematic social media use and perceived social isolation in older adults: a cross-sectional study. Gerontology 66, 160–168. doi: 10.1159/000502577
Mou, J., Shin, D.-H., and Cohen, J. (2017). Understanding trust and perceived usefulness in the consumer acceptance of an e-service: a longitudinal investigation. Behav. Inf. Technol. 36, 125–139. doi: 10.1080/0144929X.2016.1203024
Nunnally, J. (1978). Psychometric Methods . New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Oghazi, P., Karlsson, S., Hellström, D., and Hjort, K. (2018). Online purchase return policy leniency and purchase decision: mediating role of consumer trust. J. Retail. Consumer Serv. 41, 190–200.
Pang, H. (2018). Exploring the beneficial effects of social networking site use on Chinese students' perceptions of social capital and psychological well-being in Germany. Int. J. Intercult. Relat. 67, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijintrel.2018.08.002
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J.-Y., and Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 88, 879–903. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Podsakoff, P. M., and Organ, D. W. (1986). Self-reports in organizational research: problems and prospects. J. Manag. 12, 531–544. doi: 10.1177/014920638601200408
Preacher, K. J., and Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res. Methods 40, 879–891. doi: 10.3758/brm.40.3.879
Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Sidani, J. E., Whaite, E. O., yi Lin, L., Rosen, D., et al. (2017). Social media use and perceived social isolation among young adults in the US. Am. J. Prev. Med. 53, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2017.01.010
Putnam, R. D. (1995). Tuning in, tuning out: the strange disappearance of social capital in America. Polit. Sci. Polit. 28, 664–684. doi: 10.2307/420517
Putnam, R. D. (2000). Bowling Alone: The Collapse and Revival of American Community . New York, NY: Simon and Schuster.
Qalati, S. A., Ostic, D., Fan, M., Dakhan, S. A., Vela, E. G., Zufar, Z., et al. (2021). The general public knowledge, attitude, and practices regarding COVID-19 during the lockdown in Asian developing countries. Int. Q. Commun. Health Educ. 2021:272684X211004945. doi: 10.1177/0272684X211004945
Reer, F., Tang, W. Y., and Quandt, T. (2019). Psychosocial well-being and social media engagement: the mediating roles of social comparison orientation and fear of missing out. New Media Soc. 21, 1486–1505. doi: 10.1177/1461444818823719
Ringle, C., Wende, S., and Becker, J. (2015). SmartPLS 3 [software] . Bönningstedt: SmartPLS.
Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., and Straub, D. (2012). A critical look at the use of PLS-SEM in “MIS Quarterly.” MIS Q . 36, iii–xiv. doi: 10.2307/41410402
Roberts, J. A., and David, M. E. (2020). The social media party: fear of missing out (FoMO), social media intensity, connection, and well-being. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 36, 386–392. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2019.1646517
Salehan, M., and Negahban, A. (2013). Social networking on smartphones: when mobile phones become addictive. Comput. Hum. Behav. 29, 2632–2639. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2013.07.003
Sarstedt, M., and Cheah, J.-H. (2019). Partial least squares structural equation modeling using SmartPLS: a software review. J. Mark. Anal. 7, 196–202. doi: 10.1057/s41270-019-00058-3
Schinka, K. C., VanDulmen, M. H., Bossarte, R., and Swahn, M. (2012). Association between loneliness and suicidality during middle childhood and adolescence: longitudinal effects and the role of demographic characteristics. J. Psychol. Interdiscipl. Appl. 146, 105–118. doi: 10.1080/00223980.2011.584084
Shi, S., Mu, R., Lin, L., Chen, Y., Kou, G., and Chen, X.-J. (2018). The impact of perceived online service quality on swift guanxi. Internet Res. 28, 432–455. doi: 10.1108/IntR-12-2016-0389
Shoukat, S. (2019). Cell phone addiction and psychological and physiological health in adolescents. EXCLI J. 18, 47–50. doi: 10.17179/excli2018-2006
Shrestha, N. (2021). Factor analysis as a tool for survey analysis. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 9, 4–11. doi: 10.12691/ajams-9-1-2
Stouthuysen, K., Teunis, I., Reusen, E., and Slabbinck, H. (2018). Initial trust and intentions to buy: The effect of vendor-specific guarantees, customer reviews and the role of online shopping experience. Electr. Commer. Res. Appl. 27, 23–38. doi: 10.1016/j.elerap.2017.11.002
Swar, B., and Hameed, T. (2017). “Fear of missing out, social media engagement, smartphone addiction and distraction: moderating role of self-help mobile apps-based interventions in the youth ,” Paper presented at the 10th International Conference on Health Informatics (Porto).
Tangmunkongvorakul, A., Musumari, P. M., Thongpibul, K., Srithanaviboonchai, K., Techasrivichien, T., Suguimoto, S. P., et al. (2019). Association of excessive smartphone use with psychological well-being among University students in Chiang Mai, Thailand. PLoS ONE 14:e0210294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210294
Tateno, M., Teo, A. R., Ukai, W., Kanazawa, J., Katsuki, R., Kubo, H., et al. (2019). Internet addiction, smartphone addiction, and hikikomori trait in Japanese young adult: social isolation and social network. Front. Psychiatry 10:455. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00455
Tefertiller, A. C., Maxwell, L. C., and Morris, D. L. (2020). Social media goes to the movies: fear of missing out, social capital, and social motivations of cinema attendance. Mass Commun. Soc. 23, 378–399. doi: 10.1080/15205436.2019.1653468
Tehseen, S., Qureshi, Z. H., Johara, F., and Ramayah, T. (2020). Assessing dimensions of entrepreneurial competencies: a type II (reflective-formative) measurement approach using PLS-SEM. J. Sustain. Sci. Manage. 15, 108–145.
Tehseen, S., Ramayah, T., and Sajilan, S. (2017). Testing and controlling for common method variance: a review of available methods. J. Manag. Sci. 4, 146–165. doi: 10.20547/jms.2014.1704202
Tonacci, A., Billeci, L., Sansone, F., Masci, A., Pala, A. P., Domenici, C., et al. (2019). An innovative, unobtrusive approach to investigate smartphone interaction in nonaddicted subjects based on wearable sensors: a pilot study. Medicina (Kaunas) 55:37. doi: 10.3390/medicina55020037
Twenge, J. M., and Campbell, W. K. (2019). Media use is linked to lower psychological well-being: evidence from three datasets. Psychiatr. Q. 90, 311–331. doi: 10.1007/s11126-019-09630-7
Vallespín, M., Molinillo, S., and Muñoz-Leiva, F. (2017). Segmentation and explanation of smartphone use for travel planning based on socio-demographic and behavioral variables. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 117, 605–619. doi: 10.1108/IMDS-03-2016-0089
Van Den Eijnden, R. J., Lemmens, J. S., and Valkenburg, P. M. (2016). The social media disorder scale. Comput. Hum. Behav. 61, 478–487. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.03.038
Whaite, E. O., Shensa, A., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., and Primack, B. A. (2018). Social media use, personality characteristics, and social isolation among young adults in the United States. Pers. Indiv. Differ. 124, 45–50. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2017.10.030
Williams, D. (2006). On and off the'net: scales for social capital in an online era. J. Comput. Mediat. Commun. 11, 593–628. doi: 10.1016/j.1083-6101.2006.00029.x
Keywords: smartphone addiction, social isolation, bonding social capital, bridging social capital, phubbing, social media use
Citation: Ostic D, Qalati SA, Barbosa B, Shah SMM, Galvan Vela E, Herzallah AM and Liu F (2021) Effects of Social Media Use on Psychological Well-Being: A Mediated Model. Front. Psychol. 12:678766. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.678766
Received: 10 March 2021; Accepted: 25 May 2021; Published: 21 June 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Ostic, Qalati, Barbosa, Shah, Galvan Vela, Herzallah and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sikandar Ali Qalati, sidqalati@gmail.com ; 5103180243@stmail.ujs.edu.cn ; Esthela Galvan Vela, esthela.galvan@cetys.mx
† ORCID: Dragana Ostic orcid.org/0000-0002-0469-1342 Sikandar Ali Qalati orcid.org/0000-0001-7235-6098 Belem Barbosa orcid.org/0000-0002-4057-360X Esthela Galvan Vela orcid.org/0000-0002-8778-3989 Feng Liu orcid.org/0000-0001-9367-049X
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Virtual Commons - Bridgewater State University
- < Previous
Home > Honors Program > theses > 530
Honors Program Theses and Projects
The negative effects of social media sites on adolescents and the benefits of evoking empathy through reading.
Lindsay Everson , Bridgewater State University
Document Type
This thesis describes the rise in narcissistic behaviors, cyberbullying, and mental health issues in adolescents ages 13-19 due to frequent social media usage on sites such as TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook. The rise in narcissistic behavior, cyberbullying, and mental health issues among teens places prominence on the need for adolescents to engage in activities that evoke empathy. To combat the issues that come with an adolescent’s frequent social media usage this paper reveals the benefits of reading when it comes to evoking empathy in teens. The paper concludes that evoking empathy in adolescents through reading encourages them to contribute to the greater good of society as they learn how to be socially and culturally aware.
Thesis Comittee
Lisa M. Litterio, PhD., Thesis Advisor Jessica Birthisel, PhD., Committee Member Lee Torda, PhD., Committee Member
Recommended Citation
Everson, Lindsay. (2022). The Negative Effects of Social Media Sites on Adolescents and the Benefits of Evoking Empathy Through Reading. In BSU Honors Program Theses and Projects. Item 530. Available at: https://vc.bridgew.edu/honors_proj/530
Copyright © 2022 Lindsay Everson
Since August 18, 2022
Included in
Developmental Psychology Commons
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
- Disciplines
- Author FAQs
- Honors Program
- Maxwell Library
- Bridgewater State University
- BSU Faculty Profiles
This collection is part of the Undergraduate Research Commons
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Social Media — Social Media: Thesis Statement
Social Media: Thesis Statement
- Categories: Journalism Social Media
About this sample

Words: 562 |
Published: Mar 16, 2024
Words: 562 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Positive effects, negative effects, positive social change.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1260 words
6 pages / 2596 words
2 pages / 844 words
5 pages / 2086 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Social Media
Clarke, Roger. 'Dataveillance by Governments: The Technique of Computer Matching.' In Information Systems and Dataveillance, edited by Roger Clarke and Richard Wright, 129-142. Sydney, Australia: Australian Computer Society, [...]
Fake news has become an alarming and pervasive issue in today's digital age, particularly within the realm of social media. The spread of misinformation and false narratives through online platforms has raised concerns about its [...]
Bulmer, J. G., McLeod, J. M., & Rice, R. E. (2009). Television and Political Life: Studies in Six European Countries. Springer Science & Business Media.Fulcher, J., & Scott, J. (2011). Sociology. Oxford University Press.Kitts, [...]
ABC News. (2011). Twitter: The Political Sex Scandal Response Tool of the 21st Century. Retrieved from [...]
Ever since social media was introduced as such a necessary and almost vital part of our lives, several concerns have risen about the boundaries at which we must draw in terms of our privacy. The mass of information users pour [...]
Additionally, this study can serve as a contribution to managers a more in-depth understanding of not just personal branding but also personally branded professionals. This research can also provide a contribution to marketers, [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Social Media’s Impact on Physical Body Dissatisfaction and Objectified Body Consciousness: Investigating Miami’s Adolescent Self-Perception from Exposure to TikTok
- Amaya Garcia Academy for Advanced Academics
This paper examines the variables that led to the highest levels of objectified body consciousness (OBC) and physical body dissatisfaction (PBD) among adolescents aged 13-19 who were exposed to TikTok and attended school in Miami-Dade County after the COVID-19 pandemic. TikTok is used at high frequencies by various adolescent age ranges; however, previous studies identified that constant exposure leads to negative body image issues, ultimately resulting in long-term detrimental health effects. Factor analysis identified the correlation among variables collected through the distribution of a questionnaire in which adolescents shared their feelings about their body images from exposure to TikTok. The strongest variables identifying PBD and OBC among adolescents were the exposure before and after one’s reported TikTok experience and the belief that one’s TikTok experience affects an adolescent’s perception of their physical appearance and the answer to this question, respectively. This study identified that users who engaged in higher frequencies of TikTok usage were more likely to rate themselves with a higher overall body satisfaction due to pre-established conditioning of harmful exposure from TikTok, regardless of one’s gender. Conclusions drawn were that social media applications such as TikTok directly impact an adolescent’s feeling of OBC and PBD, and increased exposure will only lead to lower PBD levels and higher OBC levels, altering one’s self-perception.
Copyright (c) 2024 Intersect: The Stanford Journal of Science, Technology, and Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access ).
Information
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians

- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Terms of Use
- Emergency Info
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 . Copyright Complaints
Essay Service Examples Sociology Effects of Social Media
Negative Effects Of Social Media Essay
Introduction
- Proper editing and formatting
- Free revision, title page, and bibliography
- Flexible prices and money-back guarantee

Works Cited
- Ascharya, Kat. “What Facebook Is Doing to Your Brain Is Kind of Shocking.” Latterell, pp. 131-36.
- Latterell, Catherine G., editor. Remix. 3rd ed., Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2017.
- The Onion. “New Facebook Notifications Alert Users When They Are Not Currently Looking at Facebook.” Latterell, pp. 129-30.
Our writers will provide you with an essay sample written from scratch: any topic, any deadline, any instructions.
Cite this paper
Related essay topics.
Get your paper done in as fast as 3 hours, 24/7.
Related articles

Most popular essays
- Career Choice
- Effects of Social Media
In the current job economy, there are thousands of jobs that can be occupied if the right...
- Social Media
Social media has become an integral part of our lives, revolutionizing the way we communicate,...
Facebook is a social media platform which allows users to connect with friends colleagues or...
Facebook, Twitter, and other social media sites are part of our daily life. Social media...
- Human Behavior
The internet and its continually progressive nature have shaped society in ways that have...
- Multitasking
Social media has become an integral aspect of individuals’ lives including young adults. With the...
- Child Behavior
Social media is everywhere around us but are we truly aware of the consequences it may bring when...
The rising acceptance of social media devices has contributed to a rapid rise in screen time...
Students and adolescents all over the world use YouTube as a form of entertainment, and learning....
Join our 150k of happy users
- Get original paper written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Fair Use Policy
EduBirdie considers academic integrity to be the essential part of the learning process and does not support any violation of the academic standards. Should you have any questions regarding our Fair Use Policy or become aware of any violations, please do not hesitate to contact us via [email protected].
We are here 24/7 to write your paper in as fast as 3 hours.
Provide your email, and we'll send you this sample!
By providing your email, you agree to our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
Say goodbye to copy-pasting!
Get custom-crafted papers for you.
Enter your email, and we'll promptly send you the full essay. No need to copy piece by piece. It's in your inbox!

Social Media
The dark side of social media, a new study finds spending less time on social media leads to greater well-being..
Posted June 21, 2024 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- A new study finds social media use is linked to increased anxiety and depression in teens.
- Social media can make teens feel worse about themselves.
- Researchers find teens who cut their social media use in half experienced less anxiety, depression, and FOMO.
In a previous post , my team and I explored how social media use can negatively impact body image in youth. As young people are on their phones more and more, constant exposure to unrealistic beauty standards can leave them particularly vulnerable to low self-esteem and unfavorable social comparisons. However, evidence suggests that poor body image is not the only impact of social media on youth.
As rates of anxiety and depression in teens have been growing alongside an increase in social media usage, we have to wonder how closely the two are connected. In 2021, Statistics Canada reported that 36% of youth experience clinically concerning symptoms of depression, and 23% experience elevated levels of anxiety. At the same time, 81.3% of Canadian youth reported spending more than two hours on social media daily, and 96% reported regular use of at least one social media platform, rates that are similar or higher among teens in the US. Multiple studies have found a correlation between social media use and poor mental health, and it makes sense why.
We all know that people tend to share just the highlights of their lives on social media, rarely sharing the challenges or low points they may be experiencing. Scrolling through social media, it seems like everyone is going on a beach holiday, showing off their perfectly airbrushed bodies, or sharing the great news of their newest accomplishments. We can't help but compare ourselves to these seemingly “perfect” lives, even when we know they are fabricated. This constant comparison can make a young person feel inadequate or worthless, leading to feelings of depression and anxiety. On top of this, the more we scroll, the more we see all the things we are missing out on. Imagine going on Instagram and noticing pictures of all your friends at a party you weren’t invited to. It hurts, right? And yet, we keep wanting to check for updates. Who is at the party? Are they having fun without me? This unhealthy cycle of fear of missing out (FoMO) can impact your self-esteem, trigger your anxiety, and make you feel incredibly alone.
In addition to negative social comparisons, displacement theory provides another answer as to why screen time and social media have a negative impact on health and mental health. The theory posits that spending large amounts of time on social media allows an individual less time to spend on other mental-health-promoting activities like sleep, physical activity, recreational and social activities with friends, and pursuing pleasurable hobbies.
Although a correlational relationship has already been established, our study is the first to examine a causal relationship between social media use and mental health in youth experiencing emotional distress. Among 220 youth experiencing symptoms of anxiety or depression, we found that reducing social media by half, to a maximum of one hour per day, led to greater reductions in anxiety, depression, the experience of FoMO, and increases in sleep compared to a placebo group that had unrestricted access. Our findings support the “displacement theory” of screen time, suggesting that spending less time on things that make people truly happy makes people more likely to experience poor mental health. Although our findings did not demonstrate that reduced social media improved mental health due to reduced negative social comparisons, it is too early to throw “the baby out with the bathwater,” as correlational studies have found this link.
While it makes sense to think that reducing social media usage would make people feel even more isolated or left out, our study indicated that the opposite was true. Although initial reduction time in social media may increase FoMO, this typically only lasts a few days, and our findings support that FoMO will go down with continued reduced use. In fact, reduced social media use may lead to increased social connection and positive mental health behaviors as people are forced to adapt and meet their social needs in healthier ways.
The study also indicated that reduced social media use led to earlier bedtimes and longer sleep. As the displacement theory suggests, less time on social media means more time to get some well-needed rest. On top of this, reduced feelings of anxiety and depression likely helped people fall asleep easier, or perhaps the increased sleep resulting from less social media use reduced anxiety and depression symptoms. Further research is needed to make the direction of these findings more clear.
The results of the study beg the question: why do we torture ourselves? Sure, social media has many benefits. It helps us connect with long-lost friends, plan our social lives, and share our successes with people we care about. But when our life becomes a constant competition , and we feel like we just don't measure up, and when we know social media takes time away from sleep and in-person social and recreational activities that make us feel good, why do we continue to use it so much?
Important takeaways from our study suggest reducing your usage of social media will help you get more sleep and boost your mood. Instead of scrolling on Instagram, try taking your dog for a walk, reading a book, or catching up with a friend. As parents, we suggest implementing rules to reduce screen time during meals or social activities to promote better attachment and connection with friends and family. We also recommend implementing a “no-phone” rule 30 minutes before bedtime and no-phones in children's and youth’s bedrooms overnight. Lastly, parents are the most important role models for their children, and there is a relationship between parent screen and social media use and their children’s mental health. This means parents should also try to reduce their own social media use and engage in non-screen health-promoting alternative activities, as well as support their children in doing the same. This will help your child promote better sleep, lead to more efficient learning at school, and improve their mental health.
Davis, C. G., & Goldfield, G. S. (2024). Limiting social media use decreases depression, anxiety, and fear of missing out in youth with emotional distress: A randomized controlled trial. Psychology of Popular Media . https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000536

Gary Goldfield, PhD., C. Psych., is a Senior Scientist with the Healthy Active Living & Obesity (HALO) Research Group at the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute in Ottawa, Canada.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
The effect of social media on the development of students’ affective variables
1 Science and Technology Department, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, China
2 School of Marxism, Hohai University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
3 Government Enterprise Customer Center, China Mobile Group Jiangsu Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China
The use of social media is incomparably on the rise among students, influenced by the globalized forms of communication and the post-pandemic rush to use multiple social media platforms for education in different fields of study. Though social media has created tremendous chances for sharing ideas and emotions, the kind of social support it provides might fail to meet students’ emotional needs, or the alleged positive effects might be short-lasting. In recent years, several studies have been conducted to explore the potential effects of social media on students’ affective traits, such as stress, anxiety, depression, and so on. The present paper reviews the findings of the exemplary published works of research to shed light on the positive and negative potential effects of the massive use of social media on students’ emotional well-being. This review can be insightful for teachers who tend to take the potential psychological effects of social media for granted. They may want to know more about the actual effects of the over-reliance on and the excessive (and actually obsessive) use of social media on students’ developing certain images of self and certain emotions which are not necessarily positive. There will be implications for pre- and in-service teacher training and professional development programs and all those involved in student affairs.
Introduction
Social media has turned into an essential element of individuals’ lives including students in today’s world of communication. Its use is growing significantly more than ever before especially in the post-pandemic era, marked by a great revolution happening to the educational systems. Recent investigations of using social media show that approximately 3 billion individuals worldwide are now communicating via social media ( Iwamoto and Chun, 2020 ). This growing population of social media users is spending more and more time on social network groupings, as facts and figures show that individuals spend 2 h a day, on average, on a variety of social media applications, exchanging pictures and messages, updating status, tweeting, favoring, and commenting on many updated socially shared information ( Abbott, 2017 ).
Researchers have begun to investigate the psychological effects of using social media on students’ lives. Chukwuere and Chukwuere (2017) maintained that social media platforms can be considered the most important source of changing individuals’ mood, because when someone is passively using a social media platform seemingly with no special purpose, s/he can finally feel that his/her mood has changed as a function of the nature of content overviewed. Therefore, positive and negative moods can easily be transferred among the population using social media networks ( Chukwuere and Chukwuere, 2017 ). This may become increasingly important as students are seen to be using social media platforms more than before and social networking is becoming an integral aspect of their lives. As described by Iwamoto and Chun (2020) , when students are affected by social media posts, especially due to the increasing reliance on social media use in life, they may be encouraged to begin comparing themselves to others or develop great unrealistic expectations of themselves or others, which can have several affective consequences.
Considering the increasing influence of social media on education, the present paper aims to focus on the affective variables such as depression, stress, and anxiety, and how social media can possibly increase or decrease these emotions in student life. The exemplary works of research on this topic in recent years will be reviewed here, hoping to shed light on the positive and negative effects of these ever-growing influential platforms on the psychology of students.
Significance of the study
Though social media, as the name suggests, is expected to keep people connected, probably this social connection is only superficial, and not adequately deep and meaningful to help individuals feel emotionally attached to others. The psychological effects of social media on student life need to be studied in more depth to see whether social media really acts as a social support for students and whether students can use social media to cope with negative emotions and develop positive feelings or not. In other words, knowledge of the potential effects of the growing use of social media on students’ emotional well-being can bridge the gap between the alleged promises of social media and what it actually has to offer to students in terms of self-concept, self-respect, social role, and coping strategies (for stress, anxiety, etc.).
Exemplary general literature on psychological effects of social media
Before getting down to the effects of social media on students’ emotional well-being, some exemplary works of research in recent years on the topic among general populations are reviewed. For one, Aalbers et al. (2018) reported that individuals who spent more time passively working with social media suffered from more intense levels of hopelessness, loneliness, depression, and perceived inferiority. For another, Tang et al. (2013) observed that the procedures of sharing information, commenting, showing likes and dislikes, posting messages, and doing other common activities on social media are correlated with higher stress. Similarly, Ley et al. (2014) described that people who spend 2 h, on average, on social media applications will face many tragic news, posts, and stories which can raise the total intensity of their stress. This stress-provoking effect of social media has been also pinpointed by Weng and Menczer (2015) , who contended that social media becomes a main source of stress because people often share all kinds of posts, comments, and stories ranging from politics and economics, to personal and social affairs. According to Iwamoto and Chun (2020) , anxiety and depression are the negative emotions that an individual may develop when some source of stress is present. In other words, when social media sources become stress-inducing, there are high chances that anxiety and depression also develop.
Charoensukmongkol (2018) reckoned that the mental health and well-being of the global population can be at a great risk through the uncontrolled massive use of social media. These researchers also showed that social media sources can exert negative affective impacts on teenagers, as they can induce more envy and social comparison. According to Fleck and Johnson-Migalski (2015) , though social media, at first, plays the role of a stress-coping strategy, when individuals continue to see stressful conditions (probably experienced and shared by others in media), they begin to develop stress through the passage of time. Chukwuere and Chukwuere (2017) maintained that social media platforms continue to be the major source of changing mood among general populations. For example, someone might be passively using a social media sphere, and s/he may finally find him/herself with a changed mood depending on the nature of the content faced. Then, this good or bad mood is easily shared with others in a flash through the social media. Finally, as Alahmar (2016) described, social media exposes people especially the young generation to new exciting activities and events that may attract them and keep them engaged in different media contexts for hours just passing their time. It usually leads to reduced productivity, reduced academic achievement, and addiction to constant media use ( Alahmar, 2016 ).
The number of studies on the potential psychological effects of social media on people in general is higher than those selectively addressed here. For further insights into this issue, some other suggested works of research include Chang (2012) , Sriwilai and Charoensukmongkol (2016) , and Zareen et al. (2016) . Now, we move to the studies that more specifically explored the effects of social media on students’ affective states.
Review of the affective influences of social media on students
Vygotsky’s mediational theory (see Fernyhough, 2008 ) can be regarded as a main theoretical background for the support of social media on learners’ affective states. Based on this theory, social media can play the role of a mediational means between learners and the real environment. Learners’ understanding of this environment can be mediated by the image shaped via social media. This image can be either close to or different from the reality. In the case of the former, learners can develop their self-image and self-esteem. In the case of the latter, learners might develop unrealistic expectations of themselves by comparing themselves to others. As it will be reviewed below among the affective variables increased or decreased in students under the influence of the massive use of social media are anxiety, stress, depression, distress, rumination, and self-esteem. These effects have been explored more among school students in the age range of 13–18 than university students (above 18), but some studies were investigated among college students as well. Exemplary works of research on these affective variables are reviewed here.
In a cross-sectional study, O’Dea and Campbell (2011) explored the impact of online interactions of social networks on the psychological distress of adolescent students. These researchers found a negative correlation between the time spent on social networking and mental distress. Dumitrache et al. (2012) explored the relations between depression and the identity associated with the use of the popular social media, the Facebook. This study showed significant associations between depression and the number of identity-related information pieces shared on this social network. Neira and Barber (2014) explored the relationship between students’ social media use and depressed mood at teenage. No significant correlation was found between these two variables. In the same year, Tsitsika et al. (2014) explored the associations between excessive use of social media and internalizing emotions. These researchers found a positive correlation between more than 2-h a day use of social media and anxiety and depression.
Hanprathet et al. (2015) reported a statistically significant positive correlation between addiction to Facebook and depression among about a thousand high school students in wealthy populations of Thailand and warned against this psychological threat. Sampasa-Kanyinga and Lewis (2015) examined the relationship between social media use and psychological distress. These researchers found that the use of social media for more than 2 h a day was correlated with a higher intensity of psychological distress. Banjanin et al. (2015) tested the relationship between too much use of social networking and depression, yet found no statistically significant correlation between these two variables. Frison and Eggermont (2016) examined the relationships between different forms of Facebook use, perceived social support of social media, and male and female students’ depressed mood. These researchers found a positive association between the passive use of the Facebook and depression and also between the active use of the social media and depression. Furthermore, the perceived social support of the social media was found to mediate this association. Besides, gender was found as the other factor to mediate this relationship.
Vernon et al. (2017) explored change in negative investment in social networking in relation to change in depression and externalizing behavior. These researchers found that increased investment in social media predicted higher depression in adolescent students, which was a function of the effect of higher levels of disrupted sleep. Barry et al. (2017) explored the associations between the use of social media by adolescents and their psychosocial adjustment. Social media activity showed to be positively and moderately associated with depression and anxiety. Another investigation was focused on secondary school students in China conducted by Li et al. (2017) . The findings showed a mediating role of insomnia on the significant correlation between depression and addiction to social media. In the same year, Yan et al. (2017) aimed to explore the time spent on social networks and its correlation with anxiety among middle school students. They found a significant positive correlation between more than 2-h use of social networks and the intensity of anxiety.
Also in China, Wang et al. (2018) showed that addiction to social networking sites was correlated positively with depression, and this correlation was mediated by rumination. These researchers also found that this mediating effect was moderated by self-esteem. It means that the effect of addiction on depression was compounded by low self-esteem through rumination. In another work of research, Drouin et al. (2018) showed that though social media is expected to act as a form of social support for the majority of university students, it can adversely affect students’ mental well-being, especially for those who already have high levels of anxiety and depression. In their research, the social media resources were found to be stress-inducing for half of the participants, all university students. The higher education population was also studied by Iwamoto and Chun (2020) . These researchers investigated the emotional effects of social media in higher education and found that the socially supportive role of social media was overshadowed in the long run in university students’ lives and, instead, fed into their perceived depression, anxiety, and stress.
Keles et al. (2020) provided a systematic review of the effect of social media on young and teenage students’ depression, psychological distress, and anxiety. They found that depression acted as the most frequent affective variable measured. The most salient risk factors of psychological distress, anxiety, and depression based on the systematic review were activities such as repeated checking for messages, personal investment, the time spent on social media, and problematic or addictive use. Similarly, Mathewson (2020) investigated the effect of using social media on college students’ mental health. The participants stated the experience of anxiety, depression, and suicidality (thoughts of suicide or attempts to suicide). The findings showed that the types and frequency of using social media and the students’ perceived mental health were significantly correlated with each other.
The body of research on the effect of social media on students’ affective and emotional states has led to mixed results. The existing literature shows that there are some positive and some negative affective impacts. Yet, it seems that the latter is pre-dominant. Mathewson (2020) attributed these divergent positive and negative effects to the different theoretical frameworks adopted in different studies and also the different contexts (different countries with whole different educational systems). According to Fredrickson’s broaden-and-build theory of positive emotions ( Fredrickson, 2001 ), the mental repertoires of learners can be built and broadened by how they feel. For instance, some external stimuli might provoke negative emotions such as anxiety and depression in learners. Having experienced these negative emotions, students might repeatedly check their messages on social media or get addicted to them. As a result, their cognitive repertoire and mental capacity might become limited and they might lose their concentration during their learning process. On the other hand, it should be noted that by feeling positive, learners might take full advantage of the affordances of the social media and; thus, be able to follow their learning goals strategically. This point should be highlighted that the link between the use of social media and affective states is bi-directional. Therefore, strategic use of social media or its addictive use by students can direct them toward either positive experiences like enjoyment or negative ones such as anxiety and depression. Also, these mixed positive and negative effects are similar to the findings of several other relevant studies on general populations’ psychological and emotional health. A number of studies (with general research populations not necessarily students) showed that social networks have facilitated the way of staying in touch with family and friends living far away as well as an increased social support ( Zhang, 2017 ). Given the positive and negative emotional effects of social media, social media can either scaffold the emotional repertoire of students, which can develop positive emotions in learners, or induce negative provokers in them, based on which learners might feel negative emotions such as anxiety and depression. However, admittedly, social media has also generated a domain that encourages the act of comparing lives, and striving for approval; therefore, it establishes and internalizes unrealistic perceptions ( Virden et al., 2014 ; Radovic et al., 2017 ).
It should be mentioned that the susceptibility of affective variables to social media should be interpreted from a dynamic lens. This means that the ecology of the social media can make changes in the emotional experiences of learners. More specifically, students’ affective variables might self-organize into different states under the influence of social media. As for the positive correlation found in many studies between the use of social media and such negative effects as anxiety, depression, and stress, it can be hypothesized that this correlation is induced by the continuous comparison the individual makes and the perception that others are doing better than him/her influenced by the posts that appear on social media. Using social media can play a major role in university students’ psychological well-being than expected. Though most of these studies were correlational, and correlation is not the same as causation, as the studies show that the number of participants experiencing these negative emotions under the influence of social media is significantly high, more extensive research is highly suggested to explore causal effects ( Mathewson, 2020 ).
As the review of exemplary studies showed, some believed that social media increased comparisons that students made between themselves and others. This finding ratifies the relevance of the Interpretation Comparison Model ( Stapel and Koomen, 2000 ; Stapel, 2007 ) and Festinger’s (1954) Social Comparison Theory. Concerning the negative effects of social media on students’ psychology, it can be argued that individuals may fail to understand that the content presented in social media is usually changed to only represent the attractive aspects of people’s lives, showing an unrealistic image of things. We can add that this argument also supports the relevance of the Social Comparison Theory and the Interpretation Comparison Model ( Stapel and Koomen, 2000 ; Stapel, 2007 ), because social media sets standards that students think they should compare themselves with. A constant observation of how other students or peers are showing their instances of achievement leads to higher self-evaluation ( Stapel and Koomen, 2000 ). It is conjectured that the ubiquitous role of social media in student life establishes unrealistic expectations and promotes continuous comparison as also pinpointed in the Interpretation Comparison Model ( Stapel and Koomen, 2000 ; Stapel, 2007 ).
Implications of the study
The use of social media is ever increasing among students, both at school and university, which is partly because of the promises of technological advances in communication services and partly because of the increased use of social networks for educational purposes in recent years after the pandemic. This consistent use of social media is not expected to leave students’ psychological, affective and emotional states untouched. Thus, it is necessary to know how the growing usage of social networks is associated with students’ affective health on different aspects. Therefore, we found it useful to summarize the research findings in recent years in this respect. If those somehow in charge of student affairs in educational settings are aware of the potential positive or negative effects of social media usage on students, they can better understand the complexities of students’ needs and are better capable of meeting them.
Psychological counseling programs can be initiated at schools or universities to check upon the latest state of students’ mental and emotional health influenced by the pervasive use of social media. The counselors can be made aware of the potential adverse effects of social networking and can adapt the content of their inquiries accordingly. Knowledge of the potential reasons for student anxiety, depression, and stress can help school or university counselors to find individualized coping strategies when they diagnose any symptom of distress in students influenced by an excessive use of social networking.
Admittedly, it is neither possible to discard the use of social media in today’s academic life, nor to keep students’ use of social networks fully controlled. Certainly, the educational space in today’s world cannot do without the social media, which has turned into an integral part of everybody’s life. Yet, probably students need to be instructed on how to take advantage of the media and to be the least affected negatively by its occasional superficial and unrepresentative content. Compensatory programs might be needed at schools or universities to encourage students to avoid making unrealistic and impartial comparisons of themselves and the flamboyant images of others displayed on social media. Students can be taught to develop self-appreciation and self-care while continuing to use the media to their benefit.
The teachers’ role as well as the curriculum developers’ role are becoming more important than ever, as they can significantly help to moderate the adverse effects of the pervasive social media use on students’ mental and emotional health. The kind of groupings formed for instructional purposes, for example, in social media can be done with greater care by teachers to make sure that the members of the groups are homogeneous and the tasks and activities shared in the groups are quite relevant and realistic. The teachers cannot always be in a full control of students’ use of social media, and the other fact is that students do not always and only use social media for educational purposes. They spend more time on social media for communicating with friends or strangers or possibly they just passively receive the content produced out of any educational scope just for entertainment. This uncontrolled and unrealistic content may give them a false image of life events and can threaten their mental and emotional health. Thus, teachers can try to make students aware of the potential hazards of investing too much of their time on following pages or people that publish false and misleading information about their personal or social identities. As students, logically expected, spend more time with their teachers than counselors, they may be better and more receptive to the advice given by the former than the latter.
Teachers may not be in full control of their students’ use of social media, but they have always played an active role in motivating or demotivating students to take particular measures in their academic lives. If teachers are informed of the recent research findings about the potential effects of massively using social media on students, they may find ways to reduce students’ distraction or confusion in class due to the excessive or over-reliant use of these networks. Educators may more often be mesmerized by the promises of technology-, computer- and mobile-assisted learning. They may tend to encourage the use of social media hoping to benefit students’ social and interpersonal skills, self-confidence, stress-managing and the like. Yet, they may be unaware of the potential adverse effects on students’ emotional well-being and, thus, may find the review of the recent relevant research findings insightful. Also, teachers can mediate between learners and social media to manipulate the time learners spend on social media. Research has mainly indicated that students’ emotional experiences are mainly dependent on teachers’ pedagogical approach. They should refrain learners from excessive use of, or overreliance on, social media. Raising learners’ awareness of this fact that individuals should develop their own path of development for learning, and not build their development based on unrealistic comparison of their competences with those of others, can help them consider positive values for their activities on social media and, thus, experience positive emotions.
At higher education, students’ needs are more life-like. For example, their employment-seeking spirits might lead them to create accounts in many social networks, hoping for a better future. However, membership in many of these networks may end in the mere waste of the time that could otherwise be spent on actual on-campus cooperative projects. Universities can provide more on-campus resources both for research and work experience purposes from which the students can benefit more than the cyberspace that can be tricky on many occasions. Two main theories underlying some negative emotions like boredom and anxiety are over-stimulation and under-stimulation. Thus, what learners feel out of their involvement in social media might be directed toward negative emotions due to the stimulating environment of social media. This stimulating environment makes learners rely too much, and spend too much time, on social media or use them obsessively. As a result, they might feel anxious or depressed. Given the ubiquity of social media, these negative emotions can be replaced with positive emotions if learners become aware of the psychological effects of social media. Regarding the affordances of social media for learners, they can take advantage of the potential affordances of these media such as improving their literacy, broadening their communication skills, or enhancing their distance learning opportunities.
A review of the research findings on the relationship between social media and students’ affective traits revealed both positive and negative findings. Yet, the instances of the latter were more salient and the negative psychological symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and stress have been far from negligible. These findings were discussed in relation to some more relevant theories such as the social comparison theory, which predicted that most of the potential issues with the young generation’s excessive use of social media were induced by the unfair comparisons they made between their own lives and the unrealistic portrayal of others’ on social media. Teachers, education policymakers, curriculum developers, and all those in charge of the student affairs at schools and universities should be made aware of the psychological effects of the pervasive use of social media on students, and the potential threats.
It should be reminded that the alleged socially supportive and communicative promises of the prevalent use of social networking in student life might not be fully realized in practice. Students may lose self-appreciation and gratitude when they compare their current state of life with the snapshots of others’ or peers’. A depressed or stressed-out mood can follow. Students at schools or universities need to learn self-worth to resist the adverse effects of the superficial support they receive from social media. Along this way, they should be assisted by the family and those in charge at schools or universities, most importantly the teachers. As already suggested, counseling programs might help with raising students’ awareness of the potential psychological threats of social media to their health. Considering the ubiquity of social media in everybody’ life including student life worldwide, it seems that more coping and compensatory strategies should be contrived to moderate the adverse psychological effects of the pervasive use of social media on students. Also, the affective influences of social media should not be generalized but they need to be interpreted from an ecological or contextual perspective. This means that learners might have different emotions at different times or different contexts while being involved in social media. More specifically, given the stative approach to learners’ emotions, what learners emotionally experience in their application of social media can be bound to their intra-personal and interpersonal experiences. This means that the same learner at different time points might go through different emotions Also, learners’ emotional states as a result of their engagement in social media cannot be necessarily generalized to all learners in a class.
As the majority of studies on the psychological effects of social media on student life have been conducted on school students than in higher education, it seems it is too soon to make any conclusive remark on this population exclusively. Probably, in future, further studies of the psychological complexities of students at higher education and a better knowledge of their needs can pave the way for making more insightful conclusions about the effects of social media on their affective states.
Suggestions for further research
The majority of studies on the potential effects of social media usage on students’ psychological well-being are either quantitative or qualitative in type, each with many limitations. Presumably, mixed approaches in near future can better provide a comprehensive assessment of these potential associations. Moreover, most studies on this topic have been cross-sectional in type. There is a significant dearth of longitudinal investigation on the effect of social media on developing positive or negative emotions in students. This seems to be essential as different affective factors such as anxiety, stress, self-esteem, and the like have a developmental nature. Traditional research methods with single-shot designs for data collection fail to capture the nuances of changes in these affective variables. It can be expected that more longitudinal studies in future can show how the continuous use of social media can affect the fluctuations of any of these affective variables during the different academic courses students pass at school or university.
As already raised in some works of research reviewed, the different patterns of impacts of social media on student life depend largely on the educational context. Thus, the same research designs with the same academic grade students and even the same age groups can lead to different findings concerning the effects of social media on student psychology in different countries. In other words, the potential positive and negative effects of popular social media like Facebook, Snapchat, Twitter, etc., on students’ affective conditions can differ across different educational settings in different host countries. Thus, significantly more research is needed in different contexts and cultures to compare the results.
There is also a need for further research on the higher education students and how their affective conditions are positively and negatively affected by the prevalent use of social media. University students’ psychological needs might be different from other academic grades and, thus, the patterns of changes that the overall use of social networking can create in their emotions can be also different. Their main reasons for using social media might be different from school students as well, which need to be investigated more thoroughly. The sorts of interventions needed to moderate the potential negative effects of social networking on them can be different too, all requiring a new line of research in education domain.
Finally, there are hopes that considering the ever-increasing popularity of social networking in education, the potential psychological effects of social media on teachers be explored as well. Though teacher psychology has only recently been considered for research, the literature has provided profound insights into teachers developing stress, motivation, self-esteem, and many other emotions. In today’s world driven by global communications in the cyberspace, teachers like everyone else are affecting and being affected by social networking. The comparison theory can hold true for teachers too. Thus, similar threats (of social media) to self-esteem and self-worth can be there for teachers too besides students, which are worth investigating qualitatively and quantitatively.
Probably a new line of research can be initiated to explore the co-development of teacher and learner psychological traits under the influence of social media use in longitudinal studies. These will certainly entail sophisticated research methods to be capable of unraveling the nuances of variation in these traits and their mutual effects, for example, stress, motivation, and self-esteem. If these are incorporated within mixed-approach works of research, more comprehensive and better insightful findings can be expected to emerge. Correlational studies need to be followed by causal studies in educational settings. As many conditions of the educational settings do not allow for having control groups or randomization, probably, experimental studies do not help with this. Innovative research methods, case studies or else, can be used to further explore the causal relations among the different features of social media use and the development of different affective variables in teachers or learners. Examples of such innovative research methods can be process tracing, qualitative comparative analysis, and longitudinal latent factor modeling (for a more comprehensive view, see Hiver and Al-Hoorie, 2019 ).
Author contributions
Both authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
This study was sponsored by Wuxi Philosophy and Social Sciences bidding project—“Special Project for Safeguarding the Rights and Interests of Workers in the New Form of Employment” (Grant No. WXSK22-GH-13). This study was sponsored by the Key Project of Party Building and Ideological and Political Education Research of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications—“Research on the Guidance and Countermeasures of Network Public Opinion in Colleges and Universities in the Modern Times” (Grant No. XC 2021002).
Conflict of interest
Author XX was employed by China Mobile Group Jiangsu Co., Ltd. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Aalbers G., McNally R. J., Heeren A., de Wit S., Fried E. I. (2018). Social media and depression symptoms: A network perspective. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 148 1454–1462. 10.1037/xge0000528 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Abbott J. (2017). Introduction: Assessing the social and political impact of the internet and new social media in Asia. J. Contemp. Asia 43 579–590. 10.1080/00472336.2013.785698 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alahmar A. T. (2016). The impact of social media on the academic performance of second year medical students at College of Medicine, University of Babylon, Iraq. J. Med. Allied Sci. 6 77–83. 10.5455/jmas.236927 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Banjanin N., Banjanin N., Dimitrijevic I., Pantic I. (2015). Relationship between internet use and depression: Focus on physiological mood oscillations, social networking and online addictive behavior. Comp. Hum. Behav. 43 308–312. 10.1016/j.chb.2014.11.013 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barry C. T., Sidoti C. L., Briggs S. M., Reiter S. R., Lindsey R. A. (2017). Adolescent social media use and mental health from adolescent and parent perspectives. J. Adolesc. 61 1–11. 10.1016/j.adolescence.2017.08.005 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang Y. (2012). The relationship between maladaptive perfectionism with burnout: Testing mediating effect of emotion-focused coping. Pers. Individ. Differ. 53 635–639. 10.1016/j.paid.2012.05.002 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Charoensukmongkol P. (2018). The impact of social media on social comparison and envy in teenagers: The moderating role of the parent comparing children and in-group competition among friends. J. Child Fam. Stud. 27 69–79. 10.1007/s10826-017-0872-8 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chukwuere J. E., Chukwuere P. C. (2017). The impact of social media on social lifestyle: A case study of university female students. Gender Behav. 15 9966–9981. [ Google Scholar ]
- Drouin M., Reining L., Flanagan M., Carpenter M., Toscos T. (2018). College students in distress: Can social media be a source of social support? Coll. Stud. J. 52 494–504. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dumitrache S. D., Mitrofan L., Petrov Z. (2012). Self-image and depressive tendencies among adolescent Facebook users. Rev. Psihol. 58 285–295. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fernyhough C. (2008). Getting Vygotskian about theory of mind: Mediation, dialogue, and the development of social understanding. Dev. Rev. 28 225–262. 10.1016/j.dr.2007.03.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Festinger L. (1954). A Theory of social comparison processes. Hum. Relat. 7 117–140. 10.1177/001872675400700202 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fleck J., Johnson-Migalski L. (2015). The impact of social media on personal and professional lives: An Adlerian perspective. J. Individ. Psychol. 71 135–142. 10.1353/jip.2015.0013 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fredrickson B. L. (2001). The role of positive emotions in positive psychology: The broaden-and-build theory of positive emotions. Am. Psychol. 56 218–226. 10.1037/0003-066X.56.3.218 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Frison E., Eggermont S. (2016). Exploring the relationships between different types of Facebook use, perceived online social support, and adolescents’ depressed mood. Soc. Sci. Compu. Rev. 34 153–171. 10.1177/0894439314567449 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hanprathet N., Manwong M., Khumsri J., Yingyeun R., Phanasathit M. (2015). Facebook addiction and its relationship with mental health among Thai high school students. J. Med. Assoc. Thailand 98 S81–S90. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hiver P., Al-Hoorie A. H. (2019). Research Methods for Complexity Theory in Applied Linguistics. Bristol: Multilingual Matters. 10.21832/HIVER5747 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Iwamoto D., Chun H. (2020). The emotional impact of social media in higher education. Int. J. High. Educ. 9 239–247. 10.5430/ijhe.v9n2p239 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Keles B., McCrae N., Grealish A. (2020). A systematic review: The influence of social media on depression, anxiety and psychological distress in adolescents. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 25 79–93. 10.1080/02673843.2019.1590851 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ley B., Ogonowski C., Hess J., Reichling T., Wan L., Wulf V. (2014). Impacts of new technologies on media usage and social behavior in domestic environments. Behav. Inform. Technol. 33 815–828. 10.1080/0144929X.2013.832383 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li J.-B., Lau J. T. F., Mo P. K. H., Su X.-F., Tang J., Qin Z.-G., et al. (2017). Insomnia partially mediated the association between problematic Internet use and depression among secondary school students in China. J. Behav. Addict. 6 554–563. 10.1556/2006.6.2017.085 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mathewson M. (2020). The impact of social media usage on students’ mental health. J. Stud. Affairs 29 146–160. [ Google Scholar ]
- Neira B. C. J., Barber B. L. (2014). Social networking site use: Linked to adolescents’ social self-concept, self-esteem, and depressed mood. Aus. J. Psychol. 66 56–64. 10.1111/ajpy.12034 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- O’Dea B., Campbell A. (2011). Online social networking amongst teens: Friend or foe? Ann. Rev. CyberTher. Telemed. 9 108–112. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Radovic A., Gmelin T., Stein B. D., Miller E. (2017). Depressed adolescents positive and negative use of social media. J. Adolesc. 55 5–15. 10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.12.002 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sampasa-Kanyinga H., Lewis R. F. (2015). Frequent use of social networking sites is associated with poor psychological functioning among children and adolescents. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Network. 18 380–385. 10.1089/cyber.2015.0055 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sriwilai K., Charoensukmongkol P. (2016). Face it, don’t Facebook it: Impacts of social media addiction on mindfulness, coping strategies and the consequence on emotional exhaustion. Stress Health 32 427–434. 10.1002/smi.2637 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stapel D. A. (2007). “ In the mind of the beholder: The interpretation comparison model of accessibility effects ,” in Assimilation and Contrast in Social Psychology , eds Stapel D. A., Suls J. (London: Psychology Press; ), 143–164. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stapel D. A., Koomen W. (2000). Distinctiveness of others, mutability of selves: Their impact on self-evaluations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 79 1068–1087. 10.1037//0022-3514.79.6.1068 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tang F., Wang X., Norman C. S. (2013). An investigation of the impact of media capabilities and extraversion on social presence and user satisfaction. Behav. Inform. Technol. 32 1060–1073. 10.1080/0144929X.2013.830335 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tsitsika A. K., Tzavela E. C., Janikian M., Ólafsson K., Iordache A., Schoenmakers T. M., et al. (2014). Online social networking in adolescence: Patterns of use in six European countries and links with psychosocial functioning. J. Adolesc. Health 55 141–147. 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.11.010 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vernon L., Modecki K. L., Barber B. L. (2017). Tracking effects of problematic social networking on adolescent psychopathology: The mediating role of sleep disruptions. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 46 269–283. 10.1080/15374416.2016.1188702 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Virden A., Trujillo A., Predeger E. (2014). Young adult females’ perceptions of high-risk social media behaviors: A focus-group approach. J. Commun. Health Nurs. 31 133–144. 10.1080/07370016.2014.926677 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang P., Wang X., Wu Y., Xie X., Wang X., Zhao F., et al. (2018). Social networking sites addiction and adolescent depression: A moderated mediation model of rumination and self-esteem. Pers. Individ. Differ. 127 162–167. 10.1016/j.paid.2018.02.008 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weng L., Menczer F. (2015). Topicality and impact in social media: Diverse messages, focused messengers. PLoS One 10 : e0118410 . 10.1371/journal.pone.0118410 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yan H., Zhang R., Oniffrey T. M., Chen G., Wang Y., Wu Y., et al. (2017). Associations among screen time and unhealthy behaviors, academic performance, and well-being in Chinese adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 14 : 596 . 10.3390/ijerph14060596 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zareen N., Karim N., Khan U. A. (2016). Psycho-emotional impact of social media emojis. ISRA Med. J. 8 257–262. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang R. (2017). The stress-buffering effect of self-disclosure on Facebook: An examination of stressful life events, social support, and mental health among college students. Comp. Hum. Behav. 75 527–537. 10.1016/j.chb.2017.05.043 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

- The Star ePaper
- Subscriptions
- Manage Profile
- Change Password
- Manage Logins
- Manage Subscription
- Transaction History
- Manage Billing Info
- Manage For You
- Manage Bookmarks
- Package & Pricing
Establish legal framework to control social media platform operators, say experts
Tuesday, 02 Jul 2024
Related News

MCMC probing 'Bola Tribe' over sensitive social media posts, says Fahmi
China’s social media companies pledge to clamp down on anti-japanese posts after a fatal stabbing attack last week, social media platforms themselves remove content, not just on govt's request, says teo.
KUALA LUMPUR: The use of social media does have many benefits, but there is also a dark side when it is misused, bringing negative effects to users, including financial losses.
Through social media platforms, many have fallen victim to online fraud, cyberbullying, misuse of personal information, violation of privacy and sexual grooming involving children as well as activities like prostitution and the sale of pornographic content. Mohammad Ezaly Iman Ramli, a cyber security analyst at the Malaysian Digital Foundation, said that laws to regulate social media platform operators like Facebook, TikTok, X, Telegram and WhatsApp should be established to ensure that content and posts veering towards criminal aspects such as fraud, cyberbullying and child grooming can be controlled.
He said that in its bid to regulate social media operators, the government must identify the legal responsibilities of these entities, such as requiring them to reject or block any advertisement promoting illegal activities like online gambling and non-existent investment schemes.
"This move can save many social media users from falling victim to online crimes, in addition to creating a safe social media ecosystem that people of all ages can use,” he told Bernama.
It is learnt that regulatory frameworks for online platform providers, especially social media, have been introduced in countries like Australia, Indonesia, the European Union, Singapore and the United Kingdom.
Meanwhile, Assoc Prof Dr M. Selvakumar, a cyber security expert from Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM), believes that laws to regulate social media platforms should have been established years ago following the increased use of social media in daily life.
"Social media companies, most of which are based in the United States, have philosophies and principles that are different from those in Malaysia, so we need laws to ensure that the content uploaded is in line with the culture and norms of our people,” he said.
Elaborating, he said the time has come for the government to be firm with social media platforms and make them share the responsibility of filtering uploaded content so that it does not violate the laws of the country.
"Currently, illegal content is only taken down if there is a complaint or request from the authorities. The advancement of artificial intelligence technology over the past two years can be used to filter content,” he said.
Malaysia Cyber Consumer Association president Siraj Jalil concurs and said that the Communications and Multimedia Act 1998 and the Cyber Security Act 2024 could be amended if necessary and be used as a reference in the regulatory framework for social media platform operators.
"These operators should be held accountable to ensure they provide sufficient operational and technological resources to enable them to detect content that could be harmful to users,” he said.
Siraj said that regulatory methods for social media platform operators should follow local governance, culture and practices, without referring to foreign countries, as Malaysia has its own identity.
He explained that currently there are no specific laws for social media platform operators other than cooperation and discretion to remove content that violates Malaysian laws.
He said that with the regulatory framework on social media platform providers, the government could make it compulsory for them to introduce an effective monitoring system to ensure children below 13 are not allowed to create social media accounts.
He added that the regulatory framework could also make it compulsory for platform providers to immediately block and report any sexual grooming activities occurring on their platforms to the authorities.
"Establishing regulatory methods against social media platform operators will not affect users but rather protect them from becoming victims of online crime,” he said.
Based on the Royal Malaysia Police records, through the Bukit Aman Commercial Crime Investigation Department, an average of 92 commercial crime cases are received daily based on the 14,051 commercial crime cases investigated as of week 22 of this year, which is June 2, with a total loss of RM959,041,692.
Meanwhile, Bukit Aman Criminal Investigation Department’s Sexual, Women and Child Investigation Division (D11) principal assistant director SAC Siti Kamsiah Hassan said rape cases involving underage girls had shown a significant increase in the last three years and most of it began from grooming via social media, including messaging applications like WhatsApp.
She said police statistics recorded a total of 1,590 underage rape cases throughout 2023, an increase compared to 1,388 cases in 2022 and 1,299 cases in 2021. She added that, based on investigations, most victims told police that they got to know the perpetrators through social media platforms. - Bernama
Tags / Keywords: Social Media , Cybersecurity , Fraud , Laws , Regulatory
Found a mistake in this article?
Report it to us.
Thank you for your report!

Flexible options to pursue UK university studies
Next in nation.

Trending in News
Air pollutant index, highest api readings, select state and location to view the latest api reading.
- Select Location
Source: Department of Environment, Malaysia
Others Also Read
Best viewed on Chrome browsers.

We would love to keep you posted on the latest promotion. Kindly fill the form below
Thank you for downloading.
We hope you enjoy this feature!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Positive and Negative Effects of Social Media on Adolescent Well-Being. Katie Kennedy Minnesota State University, Mankato ... This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Graduate Theses, Dissertations, and Other Capstone Projects at Cornerstone: A Collection of Scholarly and Creative Works for Minnesota State University ...
negative emotions seem to indicate that addictive behaviors are on the rise and are closely related. to overuse of social media. On the other side of the coin, social media use also produces positive effects on. emotional well-being such as happiness, Mudita, humor, support, validation, and a more frequent.
A THESIS . Presented to the Department of Psychology . and the Robert D. Clark Honors College . ... 5.2 Moderators of Negative Effects of Social Media and Social Networking Site Usage 17 5.3 Limitations 18 5.4 Future Directions 18 Bibliography 20. v List of Figures . Figure 1. Most Often Used Social Networking Sites, Lenhart (2015)
examine the relationship between adolescents' social media use and their psychosocial well-being. I conducted a survey and social browsing experiment (n=588), followed by semi-structured interviews with a purposeful sub-sample of youth (n=28). In Study 1, I present an architecture of emotional life infused with social technologies.
depression due to a sense of social capital. Yet, there is ample evidence to suggest that. social media is associated with depression and other problems, such as classroom. disruption, sleeping disturbances, anxiety, jealousy, and low self-esteem in young adults.
cortisol, from heavy social media usage, over time causes damage to your gastrointestinal tract. (gut), which opens the door to an immuno-inflammatory response in the body and brain, leading. to depression anxiety.7 Another side effect of social media leading to depression is the experience of false.
Impact on mental health. Mental health is defined as a state of well-being in which people understand their abilities, solve everyday life problems, work well, and make a significant contribution to the lives of their communities [].There is debated presently going on regarding the benefits and negative impacts of social media on mental health [9,10].
Benefits. The use of social media significantly impacts mental health. It can enhance connection, increase self-esteem, and improve a sense of belonging. But it can also lead to tremendous stress, pressure to compare oneself to others, and increased sadness and isolation. Mindful use is essential to social media consumption.
Many researchers have postulated that worsening mental health attributed to social media use may be because social media replaces face-to-face interactions for young people (Twenge & Campbell, 2018), and may contribute to greater loneliness (Bucci et al., 2019), and negative effects on other aspects of health and wellbeing (Woods & Scott, 2016).
Positive and Negative Effects of Social Media on Adolescent Well-Being. Kennedy, Katie. Minnesota State University, Mankato ProQuest Dissertations & Theses, 2019. 13884786. Explore millions of resources from scholarly journals, books, newspapers, videos and more, on the ProQuest Platform.
Notably, however, the effect of social media use is increasing due to COVID-19 around the globe and is volatile over time. Two of the proposed hypotheses of this study, namely the expected negative impacts of social media use on social isolation and of phubbing on psychological well-being, should be further explored.
Despite mounting evidence of social media's negative effects on adolescent mental health, there is still a scarcity of empirical research on how teens comprehend social media, particularly as a body of wisdom, or how they might employ wider modern media discourses to express themselves. Youth use cell phones and other forms of media in large ...
The assumption is that using social media has both positive and negative impacts. Among the expected positive impacts are increased social networking and providing different study tools for students. Another positive impact is the access to quick communication. The biggest negative impact should be addiction to social media and wasting time.
Depression, anxiety, catfishing, bullying, terro rism, and. criminal activities are some of the negative side s of social media on societies. Generall y, when peoples use social. media for ...
Title of Bachelor´s thesis: Impacts of Social Media on Mental Health . Supervisor: Ilkka Mikkonen . Term and year of completion: Autumn 2018 Number of pages: 36 . Social media has become an integral part of human beings in the present era. It has influenced them in many ways. On the one hand, numerous benefits of social media such as online ...
negative social media behaviors can cause isolation, depression, and mood changes based on negative content users see while scrolling (Belluomini, 2015). With an increase in the use of social media over the last decade, it is important to assess any impact social media might have on mental health. There
urther investigation of how adolescents' varied digital media experiences relate to well-being.Indeed, ado. escents' social media experiences are influenced by the nature of their networked interactions. Elevated Facebook-related appearance exposure, though not overall Facebook use, is correlated with weight dis.
This thesis describes the rise in narcissistic behaviors, cyberbullying, and mental health issues in adolescents ages 13-19 due to frequent social media usage on sites such as TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook. The rise in narcissistic behavior, cyberbullying, and mental health issues among teens places prominence on the need for adolescents to engage in activities that evoke empathy. To combat ...
With the rise of platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, social media has transformed the way we connect with others and consume content. This essay will explore the impact of social media on society, focusing on the thesis statement that social media has both positive and negative effects on individuals and communities.
This paper examines the variables that led to the highest levels of objectified body consciousness (OBC) and physical body dissatisfaction (PBD) among adolescents aged 13-19 who were exposed to TikTok and attended school in Miami-Dade County after the COVID-19 pandemic. TikTok is used at high frequencies by various adolescent age ranges; however, previous studies identified that constant ...
1.1. Definition of social identity from the perspective of social work. The thinker Alex Mitchell considered that identity is an integrated system of physical, psychological, moral and social data involving a pattern of cognitive integration processes (Mitchell et al., 2016, pp12-16).It is characterized by its unity, which is embodied in the inner spirit, and has the characteristic of the ...
The lack of social skills, perception of an idealized reality and increase in isolation are the adverse effects of social media. In an era where technology is all around, it is no surprise that there is a noticeable difference in the social skills of many generations. The delay in response time on social media allows people to be reactive ...
At the same time, 81.3% of Canadian youth reported spending more than two hours on social media daily, and 96% reported regular use of at least one social media platform, rates that are similar or ...
I have real concerns about the negative effects of social media." In an opinion piece published in the New York Times, the Surgeon General, Vivek Murthy, expressed similar concerns when he called for warning labels to be added on to social media sites , especially for teenagers and their parents, detailing the mental health dangers behind ...
Social media engagement. With the increasing importance of social media in students' lives, HEIs today turn more frequently to those channels for relationship marketing purposes (Clark et al., Citation 2017).As active communicators, users react to brand communication via social media with different behaviors (Piehler et al., Citation 2019).Schivinski et al. (Citation 2016) speak of consumer ...
When US Surgeon General Dr. Vivek Murthy pushed last week for a tobacco-style warning on social media, he called the mental health crisis in young people an emergency that demanded action without ...
Health professionals warn of social media's negative effects. More for You. Morgan Stanley's explosive call on interest rates if Trump wins. 60 Years Ago, the Most Influential Sci-Fi Show Aired ...
In recent years, several studies have been conducted to explore the potential effects of social media on students' affective traits, such as stress, anxiety, depression, and so on. The present paper reviews the findings of the exemplary published works of research to shed light on the positive and negative potential effects of the massive use ...
KUALA LUMPUR: The use of social media does have many benefits, but there is also a dark side when it is misused, bringing negative effects to users, including financial losses.
"Social media is a big negative (to the mental well-being of sports players today)" Said Pienaar. "There are a lot of positives with it but there are negatives too.