
105 Best Words To Start A Paragraph
The first words of a paragraph are crucial as they set the tone and inform the reader about the content that follows.
Known as the ‘topic’ sentence, the first sentence of the paragraph should clearly convey the paragraph’s main idea.
This article presents a comprehensive list of the best words to start a paragraph, be it the first, second, third, or concluding paragraph.
Words to Start an Introduction Paragraph
The words you choose for starting an essay should establish the context, importance, or conflict of your topic.
The purpose of an introduction is to provide the reader with a clear understanding of the topic, its significance, and the structure of the ensuing discussion or argument.
Students often struggle to think of ways to start introductions because they may feel overwhelmed by the need to effectively summarize and contextualize their topic, capture the reader’s interest, and provide a roadmap for the rest of the paper, all while trying to create a strong first impression.
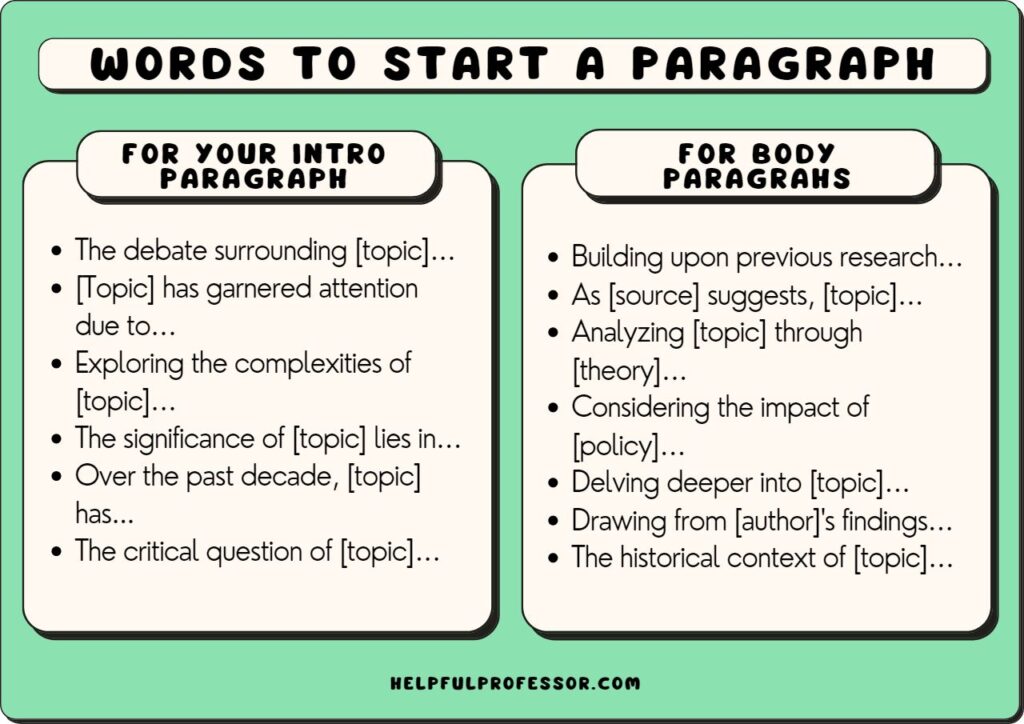
Choose one of these example words to start an introduction to get yourself started:
- The debate surrounding [topic]…
- [Topic] has garnered attention due to…
- Exploring the complexities of [topic]…
- The significance of [topic] lies in…
- Over the past decade, [topic] has…
- The critical question of [topic]…
- As society grapples with [topic]…
- The rapidly evolving landscape of [topic]…
- A closer examination of [topic] reveals…
- The ongoing conversation around [topic]…
Don’t Miss my Article: 33 Words to Avoid in an Essay
Words to Start a Body Paragraph
The purpose of a body paragraph in an essay is to develop and support the main argument, presenting evidence, examples, and analysis that contribute to the overall thesis.
Students may struggle to think of ways to start body paragraphs because they need to find appropriate transition words or phrases that seamlessly connect the paragraphs, while also introducing a new idea or evidence that builds on the previous points.
This can be challenging, as students must carefully balance the need for continuity and logical flow with the introduction of fresh perspectives.
Try some of these paragraph starters if you’re stuck:
- Building upon previous research…
- As [source] suggests, [topic]…
- Analyzing [topic] through [theory]…
- Considering the impact of [policy]…
- Delving deeper into [topic]…
- Drawing from [author]’s findings…
- [Topic] intersects with [related topic]…
- Contrary to popular belief, [topic]…
- The historical context of [topic]…
- Addressing the challenges of [topic]…
Words to Start a Conclusion Paragraph
The conclusion paragraph wraps up your essay and leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
It should convincingly summarize your thesis and main points. For more tips on writing a compelling conclusion, consider the following examples of ways to say “in conclusion”:
- In summary, [topic] demonstrates…
- The evidence overwhelmingly suggests…
- Taking all factors into account…
- In light of the analysis, [topic]…
- Ultimately, [topic] plays a crucial role…
- In light of these findings…
- Weighing the pros and cons of [topic]…
- By synthesizing the key points…
- The interplay of factors in [topic]…
- [Topic] leaves us with important implications…
Complete List of Transition Words
Above, I’ve provided 30 different examples of phrases you can copy and paste to get started on your paragraphs.
Let’s finish strong with a comprehensive list of transition words you can mix and match to start any paragraph you want:
- Secondly, …
- In addition, …
- Furthermore, …
- Moreover, …
- On the other hand, …
- In contrast, …
- Conversely, …
- Despite this, …
- Nevertheless, …
- Although, …
- As a result, …
- Consequently, …
- Therefore, …
- Additionally, …
- Simultaneously, …
- Meanwhile, …
- In comparison, …
- Comparatively, …
- As previously mentioned, …
- For instance, …
- For example, …
- Specifically, …
- In particular, …
- Significantly, …
- Interestingly, …
- Surprisingly, …
- Importantly, …
- According to [source], …
- As [source] states, …
- As [source] suggests, …
- In the context of, …
- In light of, …
- Taking into consideration, …
- Given that, …
- Considering the fact that, …
- Bearing in mind, …
- To illustrate, …
- To demonstrate, …
- To clarify, …
- To put it simply, …
- In other words, …
- To reiterate, …
- As a matter of fact, …
- Undoubtedly, …
- Unquestionably, …
- Without a doubt, …
- It is worth noting that, …
- One could argue that, …
- It is essential to highlight, …
- It is important to emphasize, …
- It is crucial to mention, …
- When examining, …
- In terms of, …
- With regards to, …
- In relation to, …
- As a consequence, …
- As an illustration, …
- As evidence, …
- Based on [source], …
- Building upon, …
- By the same token, …
- In the same vein, …
- In support of this, …
- In line with, …
- To further support, …
- To substantiate, …
- To provide context, …
- To put this into perspective, …
Tip: Use Right-Branching Sentences to Start your Paragraphs
Sentences should have the key information front-loaded. This makes them easier to read. So, start your sentence with the key information!
To understand this, you need to understand two contrasting types of sentences:
- Left-branching sentences , also known as front-loaded sentences, begin with the main subject and verb, followed by modifiers, additional information, or clauses.
- Right-branching sentences , or back-loaded sentences, start with modifiers, introductory phrases, or clauses, leading to the main subject and verb later in the sentence.
In academic writing, left-branching or front-loaded sentences are generally considered easier to read and more authoritative.
This is because they present the core information—the subject and the verb—at the beginning, making it easier for readers to understand the main point of the sentence.
Front-loading also creates a clear and straightforward sentence structure, which is preferred in academic writing for its clarity and conciseness.
Right-branching or back-loaded sentences, with their more complex and sometimes convoluted structure, can be more challenging for readers to follow and may lead to confusion or misinterpretation.
Take these examples where I’ve highlighted the subject of the sentence in bold. Note that in the right-branching sentences, the topic is front-loaded.
- Right Branching: Researchers found a strong correlation between sleep and cognitive function after analyzing the data from various studies.
- Left-Branching: After analyzing the data from various studies, a strong correlation between sleep and cognitive function was found by researchers.
- The novel was filled with vivid imagery and thought-provoking themes , which captivated the audience from the very first chapter.
- Captivating the audience from the very first chapter, the novel was filled with vivid imagery and thought-provoking themes.
The words you choose to start a paragraph are crucial for setting the tone, establishing context, and ensuring a smooth flow throughout your essay.
By carefully selecting the best words for each type of paragraph, you can create a coherent, engaging, and persuasive piece of writing.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- ALL ARTICLES
- How To Study Effectively
- Motivation & Stress
- Smarter Study Habits
- Memorise Faster
- Ace The Exam
- Write Better Essays
- Easiest AP Classes Ranked
- Outsmart Your Exams
- Outsmart Your Studies
- Recommended Reads
- For Your Students: Revision Workshops
- For Your Teaching Staff: Memory Science CPD
- Our Research: The Revision Census
- All Courses & Resources
- For School Students and Their Parents
- For University Students
- For Professionals Taking Exams
- Study Smarter Network
- Testimonials

How To Start A Paragraph: 200+ Important Words And Phrases
by Kerri-Anne Edinburgh | Aug 3, 2022
There’s a lot to get right when you’re writing an essay. And a particularly important skill is knowing how to start a paragraph effectively. That first sentence counts!
Luckily for you, we’ve compiled HEAPS of advice, example phrases and top connective words to help you transition between paragraphs and guide your reader with ease.
So read on for a pick ’n’ mix of how to start a paragraph examples!
Paragraphs: the lowdown
So why exactly are paragraphs such an important tool for writing effectively ? Well:
- They’re an important part of keeping your reader captivated
- They help your reader to follow your argument or narrative
- And they keep your writing in easily digestible chunks of information!
And an important part of all that is nailing the start of your paragraphs . Honestly!
Start off strong and your reader will know exactly what you’re going to do next and how your information interrelates. Top marks here you come – and for the low, low cost of some clever vocab!
Start your paragraphs off weakly however, without setting up effective signposting and transitions , and they’ll get lost and ( horror !) might have to re-read your essay to make sense of it. Ugh.

What should your paragraphs contain?
If you’re writing an academic essay, there are a lot of popular conventions and guides about what a paragraph should include.
Academic writing guides favour well-developed paragraphs that are unified, coherent, contain a topic sentence, and provide adequate development of your idea. They should be long enough to fully discuss and analyse your idea and evidence.
And remember – you should ALWAYS start a new paragraph for each new idea or point .
You can read more about paragraph break guidelines in our helpful what is a paragraph article! If you’re wondering how long your paragraphs should be , check out our guideline article.
Paragraph structure (the PEEL method)
Academic paragraphs often follow a common structure , designed to guide your reader through your argument – although not all the time ! It goes like this:
- Start with a “topic sentence”
- Give 1-2 sentences of supporting evidence for (or against) your argument
- Next, write a sentence analysing this evidence with respect to your argument or topic sentence
- Finally, conclude by explaining the significance of this stance, or providing a transition to the next paragraph
(A quick definition: A “topic sentence” introduces the idea your paragraph will focus upon and makes summarising easy. It can occur anywhere but placing it at the start increases readability for your audience. )
One popular acronym for creating well-developed academic paragraphs is PEEL . This stands for Point, Evidence, Explanation, Link . Using this method makes it easy to remember what your paragraph should include.
- I.e. your point (the topic sentence), some evidence and analysis of how it supports your point, and a transitional link back to your essay question or forwards to your next paragraph.
NOTE : You shouldn’t start all your paragraphs the same way OR start every sentence in your paragraph with the same word – it’s distracting and won’t earn you good marks from your reader.
Free: Exam Success Cheat Sheet
My Top 6 Strategies To Study Smarter and Ace Your Exams
Privacy protected because life’s too short for spam. Unsubcribe anytime.
How to create clarity for your readers
Paragraphs are awesome tools for increasing clarity and readability in your writing. They provide visual markers for our eyes and box written content into easily digestible chunks.
But you still need to start them off strongly . Do this job well, and you can seamlessly guide your readers through the narrative or argument of your writing.
The first sentence of your paragraph is an important tool for creating that clarity . You can create links with the surrounding paragraphs and signal the purpose of this paragraph for your reader.
- Transitions show the links and relationships between the ideas you’re presenting: addition, contrast, sequential, conclusion, emphasis, example/citation
- Connective words help you to join together multiple paragraphs in a sequence
- Note: there is quite a lot of overlap in vocabulary! Some transitions are also great signposts etc.
Tip : Don’t overuse them! These techniques can make your writing sounds more professional and less like spoken language by smoothing over jarring jumps between topics. But using too many will make your writing stilted.
A common term that encompasses these three tools is “ sentence starter ”. They are typically set apart from the body of your sentence by a comma.
You can learn more about these key skills in our two helpful articles linked above – or explore a range of other writing skills advice, such as how to start an essay , structure an essay , and proofread an essay effectively!
Picking the right tone
It is important that the paragraph-starting phrases and connective words you choose complement the style of your writing and the conventions of the subject you are writing for .
For example, scientific papers usually have much clearer and expected structure and signposting conventions than arts and humanities papers.
If you’re unsure, it’s best to check some of the sources you’ve researched for your essay, explore the relevant academic style guide, or get help from a teacher – ask them for some examples!
Getting your grammar right
Grammatical conventions can be a minefield, but they’re worth remembering if you want to get top marks!
If you’re looking to increase the clarity of your writing and paragraphs, make sure you pick the right spot for your commas and colons .
For example, when you’re starting a new paragraph, many of the common signposting words and phrases require a comma. These include: however, therefore, moreover, what’s more, firstly, secondly, finally, likewise, for example, in general … (and more!).
These phrases should always be followed by a comma if it’s at the start of a sentence, or separated with a comma before and after like this if placed mid-sentence:
However, we cannot say for sure what happened here. We know, for example, that X claims to have lost the icon.
A word about “ this ” (a tip for really great writing)
As you start writing your paragraphs (and even sentences), you might be tempted to kick off with the word “ this” – as in the classic “ this shows that … ”.
But that’s not a great idea.
Why ? Academic essays aim should aim for maximum clarity, and “ this ” is just vague !
What’s important is that the connections that are clear to you , the writer (who is – hopefully – intimately familiar with your argument), are ALSO clear to your reader , who has probably never read your essay before.
Just imagine, your reader might be muttering “this what??” as they read, and then having to re-read the paragraph and the paragraph before to check … which is not ideal for getting good marks.
In complex documents (especially essays and theses) where a lot of information is presented at once, the points you’re referencing might be spread across several paragraphs of evidence and argument-building. So, unless your sentence/paragraph-starting “this” follows on immediately from the point it references, it’s best to try a different phrase.
And all it really takes is a little signposting and clarification to avoid the vagueness of “ this shows that ”. Ask yourself “ this WHAT shows that? ” And just point out what you’re referencing – and be obvious !
Here’s some examples:

You can also do a similar exercise with “ they ” and other demonstrative pronouns (that, these, those).
Specifying what your pronouns refer to will great help to increase the clarity of your (topic) sentences . And as an added bonus, your writing will also sound more sophisticated!
What type of paragraph are you starting?
When it comes to essay writing, there’s usually an expected structure: introduction, body (evidence and analysis) and conclusion .
With other genres of writing your paragraphs might not conform to such
Consider the structure of your paragraph. What do you want it to do? What is the topic? Do you want to open with your topic sentence?
How to start an introductory paragraph
Nailing the introduction of your essay is simultaneously one of the most important and hardest sections to write . A great introduction should set up your topic and explain why it’s significant.
One of the primary goals of an effective introduction is to clearly state your “ thesis statement ” (what your essay is about, and what you are setting out to achieve with your argument).
A popular (and easy) technique to start an introduction is to begin your first paragraph by immediately stating your thesis statement .
Here’s some examples of how to start a paragraph with your thesis statement:
- This paper discusses …
- In this paper, you will find …
- This essay argues that …
- This thesis will evaluate …
- This article will explore the complex socio-political factors that contributed to the decline of the Roman Empire between the reign of Constantine (312-337AD) and the fall of Rome in 476AD .
However, starting your introductory paragraph effectively is not all about immediately stating your thesis!
So head over to our great article on how to start an essay , for lots of more advice and examples on how to kick off your introductions and capture your reader’s attention with style!

How to start a body paragraph
Unless you’re writing an introduction or conclusion, you’ll be writing a “body paragraph”. Body paragraphs make up the majority of your essay, and should include all of your main points, data, evidence, analysis, deductions and arguments.
Each paragraph should have a particular purpose and be centred around one idea . Your body paragraphs might be analytical, evidential, persuasive, descriptive etc.
To help your reader make sense of the body of your essay, it’s important to guide them with signposts and transitions. These usually occur at the start of your paragraphs to demonstrate their relationship to preceding information.
However, that means there are LOTS of different techniques for starting your body paragraphs! So for 200+ words and phrases for effectively starting a body paragraph, simply keep reading!
How to start a concluding paragraph
Concluding paragraphs are a little different to other paragraphs because they shouldn’t be presenting new evidence or arguments . Instead, you’re aiming to draw your arguments together neatly, and tie up loose ends.
You might find them as part of a smaller sub-section within a longer academic dissertation or thesis. Or as part of the conclusion of your essay.
When starting your conclusion it’s always a great idea to let your reader know they’ve arrived by signposting its purpose . This is especially true if your essay doesn’t contain any headers!
Here are some examples of how to kick off your concluding paragraph:
- In conclusion, this paper has shown that …
- In summary, we have found that …
- A review of these analyses indicates that …
- To conclude, this essay has demonstrated that we must act immediately if we want to halt the drastic dwindling of our global bee population.
How to start a paragraph: 200+ top words and phrases for a winning first sentence
Choosing the best start for your paragraph is all about understanding the purpose of this paragraph within the wider context of the preceding (and following) paragraphs and your essay as a whole.
Where does it fit into the structure of your essay? Is it:
- Opening a new topic or theme?
- Providing explanations or descriptions?
- Continuing a list or sequence?
- Providing evidence?
- Presenting a different opinion or counter-argument?
- Beginning an analysis?
- Highlighting consequences?
- Drawing a conclusion?
It’s important to be direct in how you start each paragraph – especially if you’re struggling to get your point across!
The best way to craft a killer first sentence is to be clear on what you want it to do . We’ve covered 12 options below, packed with vocab and examples to get you started …
And don’t forget to consider when you should start a new paragraph , and how long you want your paragraphs to be . Where you place your paragraph breaks will have a big effect on the kind of starting sentence you need !
Finally – remember that the best time to craft effective opening sentences is after you’ve written your first draft and decided on your paragraph breaks! You should already have all your ideas arranged into a logical order.
Showing structure and presenting concepts
This first type of paragraphs are commonly found throughout your essay, whether you’re introducing your ideas, providing evidence and data, or presenting results.
There a lots of useful types of connective words and phrases to help you kick off your paragraphs with clarity:

Most notable are the sequential signposting words , which you can use throughout your essay to guide your reader through the steps of your argument, or a list of related evidence, for example.
If you’re looking for something a little more specific, read on for four sets of example academic phrases to use to start a paragraph!
1. Starting or continuing a sequence
One of the most important types of transitional phrases to help you start a paragraph is a sequential transition . These signposting transitions are great for academic arguments because they help you to present your points in order, without the reader getting lost along the way.
Sequential connectives and transitions create order within your narrative by highlighting the temporal relationship between your paragraphs. Think lists of events or evidence , or setting out the steps in your narrative .
You’ll often find them in combination with other paragraph-starting phrases ( have a look at the examples below to spot them !)
Why not try out some of these examples to help guide the readers of your essay?
- Before considering X, it is important to note that …
- Following on from Y, we should also consider …
- The first notion to discuss is …
- The next point to consider is …
- Thirdly, we know that Y is also an important feature of …
- As outlined in the previous paragraph, the next steps are to …
- Having considered X, it is also necessary to explore Y …
2. Providing evidence, examples or citations
Once you’ve made your claims or set out your ideas, it’s important to properly back them up. You’ll probably need to give evidence, quote experts and provide references throughout your essay .
If you’ve got more than one piece of evidence, it’s best to separate them out into individual paragraphs . Sequential signposting can be a helpful tool to help you and your reader keep track of your examples.
If your paragraph is all about giving evidence for a preceding statement, why not start with one of these phrases:
- For example, X often …
- This stance is clearly illustrated by …
- Consider the example of Y, which …
- This concept is well supported by …
If you want to quote or paraphrase a source or expert, a great way to start your paragraph is by introducing their views. You can also use phrases like these to help you clearly show their role in your essay:
- [Author], in particular, has argued that …
- According to [source], Y is heavily influenced by …
- [Source] for example, demonstrates the validity of this assertion by …
- This [counter-] argument is supported by evidence from X, which shows that …
Always remember to provide references for your sources in the manner most appropriate for your field ( i.e. footnotes, and author-date methods ).
3. Giving emphasis to your point
Not all points and paragraphs in an essay are made equal. It’s natural you’ll want to highlight ideas and evidence for your reader to make sure they’re persuaded by your argument !
So, if you want to give emphasis to what you’re about to discuss, be obvious ! In fact, you may need to be more direct than you think:
- This detail is significant because …
- Undoubtedly, this experience was …
- Certainly, there are ramifications for …
- The last chapters, in particular, are revealing of X …
4. Acknowledging uncertainty
In academia it’s common to find a little uncertainty in your evidence or results, or within the knowledge of your field . That’s true whether you’re a historian exploring artefacts from Ancient Greece, or a social scientist whose questionnaire results haven’t produced a clear answer.
Don’t hide from this uncertainty – it’s a great way to point ahead to future research that needs to be done. In fact, you might be doing it in your essay!
Why not try one of these examples to highlight the gaps in your academic field or experiment?
- Whether X is actually the case remains a matter of debate, as current explorations cannot …
- Although not proven, it is commonly understood that X …
- Whilst the likelihood of X is debateable …
- Given the age of the artifacts, it is impossible to say with accuracy whether Y …
- Although we cannot know for sure, the findings above suggest that …
- Untangling the causes of X is a complex matter and it is impossible to say for sure whether …
Showing the relationships between your points
As your essay progresses you will need to guide your reader through a succession of points, ideas and arguments by creating a narrative for them to follow. And important part of this task is the use of signposting to demonstrate the relationship between your paragraphs . Do they support each other? Do they present opposite sides of a debate?
Luckily there are lots of agreement , opposition and contextual connectives to help you increase your clarity:

Read on for four more sets of example academic phrases to help you present your ideas!
5. Making a new point
If there’s no connection between your new paragraph and the preceding material, you’re probably starting a new topic, point or idea.
That means it’s less likely ( although not impossible ) that you’ll need transitional phrases . However, it’s still important to signpost the purpose and position of this new paragraph clearly for your reader.
- We know that X …
- This section of the essay discusses …
- We should now turn to an exploration of Y …
- We should begin with an overview of the situation for X …
- Before exploring the two sides of the debate, it is important to consider …
You can find some great ideas and examples for starting a new topic in our how to start an essay article. Whilst they’re definitely applicable to introductions, these strategies can also work well for kicking off any new idea!
6. Presenting accepted concepts
If you’re aiming to take a new stance or question an accepted understanding with your essay, a great way to start a paragraph is by clearly setting out the concepts you want to challenge .
These phrases are also an effective way to establish the context of your essay within your field:
- It is commonly believed that …
- The accepted interpretation of X is …
- Until recently, it was thought that …
- Historically, X has been treated as a case of …
- Over the past two decades, scholars have approached X as an example of …
- The most common interpretation of Y is …
7. Adding similar points
Agreement connectives are an important tool in your arsenal for clearly indicating the continuation or positive relationship between similar ideas or evidence you’re presenting.
If you’re looking to continue your essay with a similar point, why not try one of these examples:
- Another aspect of X is …
- Another important point is …
- By the same token, Y should be explored with equal retrospection for …
- Moreover, an equally significant factor of X is …
- We should also consider …
- Proponents of Y frequently also suggested that …
8. Demonstrating contrast
In contrast, if you’re looking to present a counter-argument, opposite side of a debate, or critique of the ideas, evidence or results in your preceding paragraph(s), you’ll need to turn to contradiction and opposition connectives.
These phrases will help you to clearly link your paragraphs whilst setting them in contrast within your narrative:
- A contrary explanation is that …
- On the other side of this debate, X suggests that …
- Given this understanding of X, it is surprising that Y …
- On the other hand, critics of X point to …
- Despite these criticisms, proponents of X continue to …
- Whilst the discussion in the previous paragraph suggests X to be true, it fails to take into consideration Y …
Note : some paragraph-opening sentences can be modified using connective words to show either agreement or contrast! Here are some examples:
- It could also be said that X does [not] …
- It is [also] important to note that X … OR It is important, however, to note that X …
- There is [also/however], a further point to be considered …
Presenting analyses, arguments and results
An important stage of any essay is the analysis – that’s when you bring your own arguments to the table, based on your data and results.
Signalling this clearly, therefore, is pretty important! Happily, there are plenty of connective words and phrases that can help you out:

Read on for four sets of example academic phrases to use to start your analysis, results and summary paragraphs!
9. Conducting an analysis and constructing your argument
Once you’ve set out your evidence or data, it’s time to point out the connections within them. Or to analyse how they support the argument you want to make.
With humanities essays it is common to analyse the impact of your evidence as you present it. In contrast, sciences essays often contain a dedicated analysis section after the data has been presented.
You’ll probably need several analytical paragraphs to address each of your points. So, a great way to get started is to dive straight in by signposting the connections you want to make in each one:
- Each of these arguments make an important contribution to X because …
- In order to fully understand Y, we need to analyse the findings from …
- Each model of X and Y changed throughout the experiment because …
- Exploring this dataset reveals that, in fact, X is not as common as hypothesised …
- Notwithstanding such limitations, this data still shows that …
- Of central concern to Y, therefore, is the evidence that …
- This interpretation of X is …
- This critique implies that …
- This approach is similar to that of Y, who, as we have seen above, argues that …
- The resulting graphs suggest that …
- Whilst conducting the survey, it was discovered that …
10. Presenting results
Having completed your analyses of any evidence (and hopefully persuaded your reader of your argument), you may need to present your results. This is especially relevant for essays that examine a specific dataset after a survey or experiment .
If you want to signpost this section of your essay clearly, start your paragraph with a phrase like these:
- The arguments presented above show that …
- In this last analysis, we can see that X has shown …
- As we have seen, the data gathered demonstrates that …
- As demonstrated above, our understanding of X primarily stems from …
11. Demonstrating cause and effect
When writing an academic essay you may often need to demonstrate the cause and effect relationship between your evidence or data, and your theories or results . Choosing the right connective phrases can be important for showing this relationship clearly to your reader.
Try one of these phrases to start your paragraph to clearly explain the consequences:
- As a consequence, X cannot be said to …
- Therefore, we can posit that …
- Provided that X is indeed true, it has been shown that Y …
- As such, it is necessary to note that …
- For this reason, the decision was made to …
- The evidence show that the primary cause of X was …
- As a result of Y, it was found that …
12. Summarising a topic or analysis
In general, summary paragraphs should not present any new evidence or arguments. Instead, they act as a reminder of the path your essay has taken so far.
Of course, these concluding paragraphs commonly occur at the end of an essay as part of your conclusion. However, they are also used to draw one point or stage of your argument to a close before the next begins .
Within a larger essay or dissertation, these interludes can be useful reminders for your reader as you transition between providing context, giving evidence, suggesting new approaches etc.
It’s worth noting that concluding your topic or analysis isn’t always the same as presenting results, although there can be some similarities in vocabulary.
Connect your arguments into summaries with clear linking phrases such as:
- Altogether, these arguments demonstrate that …
- Each of these arguments make an important contribution to our understanding of X …
- From this overview of X and Y, we can conclude that …
- We can therefore see that …
- It was hypothesised that X, however, as we have seen …
- Therefore, we can [clearly] see that …
Time to get writing your paragraphs!
And that’s it! You should now have a much-improved understanding of how to start a paragraph.
Whether you we’re worried about how to start your introductions or conclusions, or were wondering about specific types of body paragraphs, hopefully you’ve found what you need in the examples above .
If you need more writing advice to help you nail top marks for your essay, we’ve got a whole series of articles designed to improve your writing skills – perfect ! Have a read for top tips to for capturing easy marks 😊
You can learn:
- how to create effective paragraphs
- about the ideal length(s) for your paragraphs
- how to start an essay AND how to structure an essay
- the 70+ top connective words and phrases to improve your writing
- how to signpost your essay for top marks
- about improving clarity with easy proofreading tricks
Good luck completing your essay!
The Science Of Studying Smart
Download my free exam success cheat sheet: all my #1 must-know strategies to supercharge your learning today.
Your privacy protected. No spam. Unsubscribe any time.
- Latest Posts
- [2024] Are AP US Government & Politics and AP Comparative Government and Politics Hard or Easy? Difficulty Rated ‘Quite Easy’ (Real Student Reviews + Pass Data) - 5 Jan 2024
- [2024] Is AP Human Geography Hard or Easy? Difficulty Rated ‘Quite Easy’ (Real Student Reviews + Pass Data) - 5 Jan 2024
- [2024] Is AP Microeconomics Hard or Easy? Difficulty Rated ‘Quite Easy’ (Real Student Reviews + Pass Data) - 5 Jan 2024
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Read My Test-Taking Technique Book For More Marks In Exams

Top Picks: Recommended Reading From The Blog
How To Study Effectively : Ultimate Guide [READER FAVOURITE]
Exam Memorization Secrets
Inspirational Exam Quotes
Finding The Perfect Study Routine
Pomodoro Method : 9-Step Guide
Best Books About Studying
Listen To The Podcast

Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument . Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”

35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Sentence Starters: Ultimate List to Improve Your Essays and Writing

Ashley Shaw

This blog post is going to be about … No. Too boring.
Today, I am going to talk to you about ... No. Too specific.
This is a blog post for all writers ... Nope. Too generic.
Has this ever been you while writing? I get it. Writing a good sentence can be hard, and when you have to string a whole lot of them together, the task can become daunting. So what do you do?
From the first sentence you write to the very last, you want each one to show your style and motivate your reader to keep reading. In this post, we are going to think about how you start your sentences.

What Is a Good Sentence Starter for an Essay Introduction?
What is a good sentence starter for a body paragraph, 25 useful transitions, can i repeat a sentence starter, how can i rephrase "in conclusion".
The first paragraph of a paper can make or break your grade. It is what gets your audience into the topic and sets the whole stage. Because of this, it is important to get your readers hooked early.
The first sentence of a paper is often called the hook. It shouldn’t be anything ordinary. It should have strong language and be a little surprising, with an interesting fact, story, statistic, or quote on the topic.
Because it is designed to pull the reader in and surprise them a little, it is often good to avoid pre-written sentence starter examples when writing your hook. Just get into it here, and worry about the flow later.
Here are some examples:
Spider webs were once used as bandages.
I taught myself to read when I was three. At least, that’s the story my parents tell.
Recent studies suggest that the average person lies at least once in every conversation.
“The world is bleeding and humans wield the knife,” or so says environmental scientist So Andso.
(P.S. Except for example 1, which is true, I just made all of these up to demonstrate my point. So, please don’t quote me on these!)
Once you jump right in with your hook, it is time to start working on ways to move sentences along. Here is where you may need some sentence starter examples.
In your first paragraph, you basically want to connect your hook to your thesis. You’ll do this with a few sentences setting up the stage for your topic and the claim you will make about it. To do that, follow the tips found in the next section on body paragraphs and general sentence starter tips.
Many of the tips I am about to discuss can be used anywhere in a paper, but they are especially helpful when writing body paragraphs.
Let’s start with one of the most important types of sentence starter in essay writing: transition words.
How Do I Use Transitions in an Essay?

If you want to start writing terrific sentences (and improve your essay structure ), the first thing you should do is start using transition words.
Transition words are those words or phrases that help connect thoughts and ideas. They move one sentence or paragraph into another, and they make things feel less abrupt.
The good thing about transition words is that you probably know a lot of them already and currently use them in your speech. Now, you just need to transition them into your writing. (See what I did there?)
Before we get into examples of what a good transition word is, let’s look at a paragraph without any transitions:
I went to the store. I bought bacon and eggs. I saw someone I knew. I said hello. I went to the cashier. They checked me out. I paid. I got my groceries. I went to my car. I returned home.
Yikes! That is some boring writing. It was painful to write, and I am sure it is even worse to read. There are two reasons for this:
- I start every sentence with the same word (more on this later)
- There are no signposts showing me how the ideas in the paragraph connect.
In an essay, you need to show how each of your ideas relate to each other to build your argument. If you just make a series of statements one after the other, you’re not showing your instructor that you actually understand those statements, or your topic.
How do we fix this? Transition words. Roughly 25% of your sentences should start with a transition word. If you can hit that number in your essay, you’ll know that you’ve made meaningful steps towards demonstrating your understanding.
Of course, hitting that number isn’t enough—those transitions need to be meaningful. Let’s look at the different types of transitions and how you can use them.
What Are Words Like First , Next , and Last Called?
You probably already use some transitions in your essays. For example, if you start a paragraph with firstly , you’ve used a transition word. But transitions can do so much more!
Here are 25 common transitional words and phrases that you could use in your essay:
- Additionally / In Addition
- Alternatively / Conversely
- As a result of
- At this time
- Consequently
- Contrary to
- First(ly), Second(ly), etc.
- In contrast
- Nonetheless
- On the other hand
- Particularly / In particular
- In other words

This list isn’t exhaustive, but it is a good start.
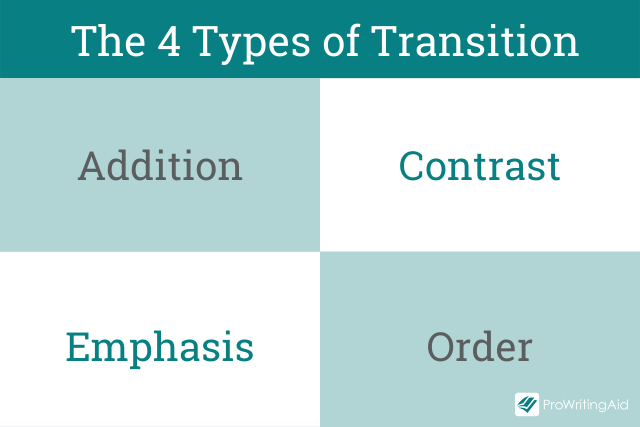
These words show different types of relationships between ideas. These relationships fall into four main categories: Emphasis , Contrast , Addition , and Order .
What Are Emphasis Transition Words?
These phrases are used when you want to highlight a point. Examples from my above list include clearly , particularly , and indeed . Want to see some more? Follow my bolded transitions: Undoubtedly , you understand now. It should be noted that you don’t need to worry.
How Do You Use Addition Transitions?
These words add on to what you just said. These are words like along with , moreover , and also . Here are some more: Not only are you going to be great at transitions after this, but you will also be good at writing sentences. Furthermore , everyone is excited to see what you have to say.
How Can I Use Transitions to Contrast Ideas?
This is the opposite of addition, and you use it when you want to show an alternative view or to compare things. Examples from my list include words like nonetheless , contrary to , and besides .
Here are some more: Unlike people who haven’t read this article, you are going to be really prepared to write great sentences. Even so , there is still a lot more about writing to learn.
How Do I Order Ideas in My Essay?
A good first step is using order transition words.
This set of transitions helps mark the passage of time or gives an order to events. From the list, think of things like first and finally . Now for some extras: At this time yesterday , you were worried about starting sentences. Following this , though, you will be an expert.
Now that you get the concept of transitions, let’s go back to that poorly written paragraph above and add some in to see what happens:
This morning , I went to the store. While I was there, I bought bacon and eggs. Then I saw someone I knew. So I said hello. After that , I went to the cashier. At that time , they checked me out. First , I paid. Next , I got my groceries. Following that , I went to my car. Finally , I returned home.
(Notice the use of commas after most of these transitions!)
This isn’t the best paragraph I’ve ever written. It still needs a lot of work. However, notice what a difference just adding transitions makes. This is something simple but effective you can start doing to make your sentences better today.
If you want to check your transition usage, try ProWritingAid’s Transitions report . You’ll see how many of each type of transition word you've used so you can pin-point where you might be losing your reader.
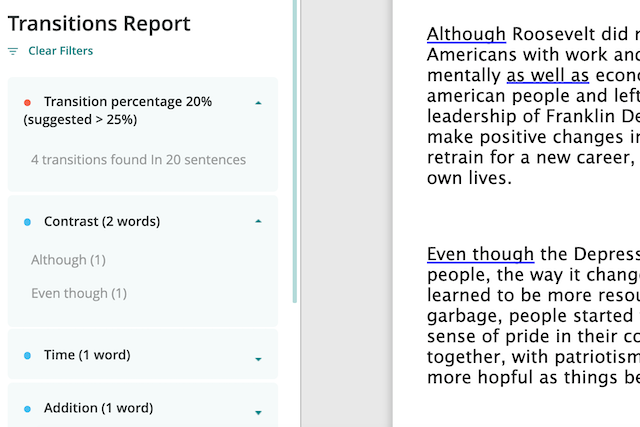
Sign up for a free ProWritingAid account to try it out.
What Are Some Linking Phrases I Can Use in My Essay?
As well as individual words, you can also use short phrases at the beginning of your sentences to transition between ideas. I just did it there— "As well as individual words" shows you how this section of the article is related to the last.
Here are some more phrases like this:
As shown in the example,
As a result of this,
After the meeting,
While this may be true,
Though researchers suggest X,
Before the war began,
Until we answer this question,
Since we cannot assume this to be true,
While some may claim Y,
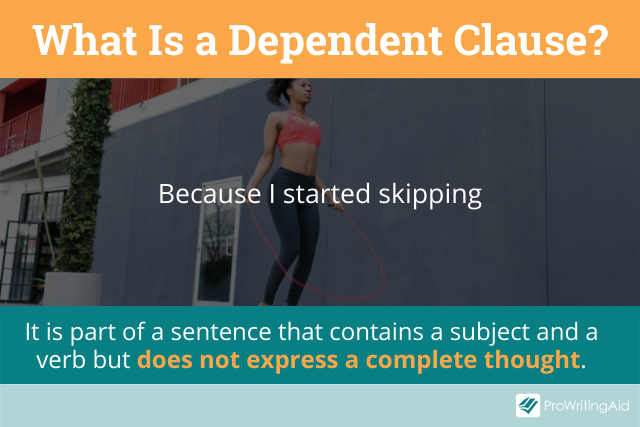
Because we know that Z is true,
These short phrases are called dependent clauses . See how they all end with a comma? That's because they need you to add more information to make them into complete sentences.
- While some may claim that chocolate is bad for you, data from a recent study suggests that it may have untapped health benefits .
- Since we cannot assume that test conditions were consistent, it is impossible to reach a solid conclusion via this experiment .
- As a result of this, critics disagree as to the symbolism of the yellow car in The Great Gatsby .
The bolded text in each example could stand on its own as a complete sentence. However, if we take away the first part of each sentence, we lose our connection to the other ideas in the essay.
These phrases are called dependent clauses : they depend on you adding another statement to the sentence to complete them. When you use a sentence starter phrase like the ones above in your writing, you signal that the new idea you have introduced completes (or disrupts) the idea before it.
Note: While some very short dependent clauses don’t need a comma, most do. Since it is not wrong to use one on even short ones (depending on the style guide being used), it is a good idea to include one every time.
Along with missing transitions and repeating sentence structure, another thing that stops sentences from being great is too much repetition. Keep your sentences sharp and poignant by mixing up word choices to start your sentences.
You might start your sentence with a great word, but then you use that same word 17 sentences in a row. After the first couple, your sentences don’t sound as great. So, whether it is varying the transitional phrases you use or just mixing up the sentence openers in general, putting in some variety will only improve your sentences.
ProWritingAid lets you know if you’ve used the same word repeatedly at the start of your sentences so you can change it.
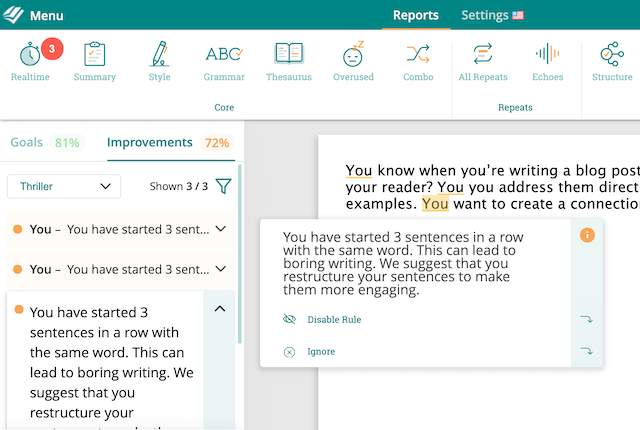
The Repeats Report also shows you all of the repeats in your document. If you've used a sentence starter and then repeated it a couple of paragraphs down, the report will highlight it for you.
Try the Repeats Report with a free ProWritingAid account.
Now that you have your introduction sentences and body sentences taken care of, let’s talk a little about conclusion sentences. While you will still use transitions and clauses as in the body, there are some special considerations here.
Your conclusion is what people will remember most after they finish reading your paper. So, you want to make it stand out. Don’t just repeat yourself; tell them what they should do with what you just told them!
Use the tips from above, but also remember the following:
Be unique. Not only should you vary the words you use to start different sentences, but you should also think outside of the box. If you use the same conclusion sentence starter everyone else is using, your ideas will blend in too.
Be natural. Some of the best writing out there is writing that sounds natural. This goes for academic writing, too. While you won’t use phrases like "at the end of the day" in essay writing, stilted phrases like "in conclusion" can disrupt the flow you’ve created earlier on.
Here are some alternatives to "in conclusion" you could use in an essay:
- To review, ... (best for scientific papers where you need to restate your key points before making your final statement)
- As has been shown, ...
- In the final analysis, ...
- Taking everything into account, ...
- On the whole, ...
- Generally speaking, ...
If you’re looking for more ways to rephrase "in conclusion," take a look at our complete list of synonyms you can use.

There may not be a set word or words that you can use to make your sentences perfect. However, when you start using these tips, you’ll start to see noticeable improvement in your writing.
If you’ve ever heard people talk about pacing and flow in academic writing, and you have no idea what they mean or how to improve yours, then this is your answer. These tips will help your writing sound more natural, which is how you help your ideas flow.
Take your writing to the next level:

20 Editing Tips from Professional Writers
Whether you are writing a novel, essay, article, or email, good writing is an essential part of communicating your ideas., this guide contains the 20 most important writing tips and techniques from a wide range of professional writers..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Ashley Shaw is a former editor and marketer/current PhD student and teacher. When she isn't studying con artists for her dissertation, she's thinking of new ways to help college students better understand and love the writing process.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Boost Your English Writing with These Top Transition Words to Start a Paragraph
By: Author ESLBUZZ
Posted on Last updated: March 22, 2024
Sharing is caring!
If you’re learning English or trying to improve your writing skills, understanding how to use transition words is essential. Transition words can help you to write more clearly and effectively, making it easier for your reader to follow your ideas. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about transition words to start a paragraph, from their definition to their usage, and we’ll provide plenty of examples to help you master this important writing skill.
Transition Words to Start a Paragraph

Understanding Transition Words
What are transition words.
Transition words are words or phrases that indicate the relationship between sentences or ideas. They help readers follow your writing, making it more coherent and organized. Transition words can be used to show a contrast, addition, conclusion, comparison, time, and many other relationships between ideas.
Why are Transition Words Important?
Transition words are important because they help your writing flow smoothly. They make it easier for the reader to understand your ideas and follow your argument. Without transition words, your writing can sound choppy and disjointed, making it difficult to read and understand.
Examples of Transition Words
Here are some examples of transition words you can use to start a new paragraph:
Here are some example sentences that use transition words:
- Additionally, I would like to point out that…
- However, there are some drawbacks to this approach.
- In conclusion, it is clear that…
- Similarly, we can see that…
- Meanwhile, let’s take a closer look at…
Importance of Transition Words in Writing
Purpose of transition words.
The purpose of transition words is to guide the reader through your writing. They help the reader understand the relationship between ideas and how they are connected. Without transition words, your writing may seem disjointed and difficult to follow. By using transition words, you can create a clear and logical progression of ideas that makes your writing easier to understand.
Flow of Writing
Transition words are essential for maintaining the flow of your writing. They help you move smoothly from one idea to the next without abrupt changes or interruptions. When you use transition words, your writing becomes more cohesive and easier to read. This is particularly important when writing longer pieces, such as essays or research papers, where the reader needs to follow a complex argument.
Connecting Sentences and Paragraphs
Transition words are also useful for connecting sentences and paragraphs. They help you link one idea to the next, creating a seamless transition between different parts of your writing. This is particularly important when writing persuasive or argumentative pieces, where you need to build a strong case for your point of view.
Starting a paragraph can be challenging, especially when you’re trying to connect it to the previous one. That’s where transition words come in handy.
First Paragraph
When you’re writing the first paragraph of an essay or article, you need to introduce your topic and grab the reader’s attention. Here are some transition words that can help you achieve that:
For example:
- Firstly, let’s discuss the importance of exercise for a healthy lifestyle.
- To begin with, we need to understand the history of the conflict.
- In the first place, the government needs to address the issue of poverty.
- Initially, we need to gather all the necessary information.
- At the outset, it’s important to establish the goals of the project.
Introducing a New Point
When you’re introducing a new point or idea in your writing, you need to use transition words that show the relationship between the previous and the new sentence. Here are some transition words that can help you achieve that:
- Additionally, we need to consider the environmental impact of our actions.
- Furthermore, the study found that the new treatment was more effective.
- Moreover, the company has seen a significant increase in profits.
- In addition, we need to take into account the cultural differences.
- Also, it’s important to note that the study had a small sample size.
Contrasting Ideas
When you’re presenting contrasting ideas in your writing, you need to use transition words that show the difference between the two ideas. Here are some transition words that can help you achieve that:
- However, some experts disagree with this approach.
- Nevertheless, the study found some positive results.
- On the other hand, some argue that the benefits outweigh the risks.
- In contrast, the previous study found no significant difference.
- Nonetheless, the company decided to proceed with the project.
Sequential Transition Words
When writing an essay or a report, it is important to use transition words to help guide the reader through your ideas. Sequential transition words are especially useful when you want to show a sequence of events or ideas.
The word “next” is often used to show that something is going to happen after something else. Here are some examples:
- I finished my homework. Next, I went to bed.
- We need to buy some milk. Next, we can go to the park.
“Secondly” is a more formal way of saying “next”. It is often used when you want to show that there are two or more points you want to make. Here are some examples:
- Firstly, we need to make sure we have all the ingredients. Secondly, we need to preheat the oven.
- There are two main reasons why I want to go on vacation. Firstly, I need a break from work. Secondly, I want to spend time with my family.
“Third” is used to show that something is happening after two other things. Here are some examples:
- First, we need to make a plan. Second, we need to gather our materials. Third, we can start building.
- There are three things I need to do today. First, I need to go to the bank. Second, I need to buy groceries. Third, I need to do laundry.
Subsequently
“Subsequently” is a more formal way of saying “afterward”. It is often used to show that something happened as a result of something else. Here are some examples:
- I missed my bus. Subsequently, I was late for work.
- The company lost a lot of money. Subsequently, many employees were laid off.
“Sequential” is an adjective that means “in sequence”. Here are some examples:
- We need to follow a sequential process to complete this project.
- The chapters in this book are arranged in sequential order.
Cause and Effect Transition Words
What are cause and effect transition words.
Cause and effect transition words are used to show the relationship between a cause and its effect. They are used to indicate why something happened (cause) and what happened as a result (effect). Some common cause and effect transition words include:
- Cause: because, since, as, due to, for this reason
- Effect: consequently, as a result, hence, therefore, thus
Examples of Cause and Effect Transition Words
Here are some examples of how cause and effect transition words can be used in a sentence:
- Due to the heavy rain, the streets were flooded. (Cause: heavy rain, Effect: flooded streets)
- Because the company invested in new technology, productivity increased. (Cause: investment in technology, Effect: increased productivity)
- As a result of the pandemic, many businesses closed down. (Cause: pandemic, Effect: business closures)
- The traffic was heavy, hence I was late for the meeting. (Cause: heavy traffic, Effect: late for meeting)
List of Cause and Effect Transition Words
Here is a list of cause and effect transition words that you can use in your writing:
Tips for Using Cause and Effect Transition Words
When using cause and effect transition words in your writing, it is important to remember the following tips:
- Use them sparingly: While transition words are important, using too many can make your writing sound unnatural.
- Use them correctly: Make sure you are using the correct transition word to show the relationship between cause and effect.
- Vary your language: Try to use a variety of transition words to keep your writing interesting.
Contrast and Comparison Transition Words
When writing a paragraph, it is important to use transition words to help the reader understand the relationship between the ideas presented. One common type of transition word is the contrast and comparison transition word. These words are used to show the differences and similarities between two or more ideas. Here are some examples and meanings of contrast and comparison transition words:
Example Sentences:
- However , the new policy has not been well received by employees.
- Although the company has experienced some setbacks, it remains profitable.
- The weather was bad, though we still managed to have a good time.
- We should invest in renewable energy. On the other hand , fossil fuels are becoming increasingly scarce.
- The company’s profits have increased. Conversely , its stock price has decreased.
- Despite the fact that he was tired, he went to the gym.
- The company’s sales have been declining, whereas its competitors’ sales have been increasing.
- The first book was boring. In contrast , the second book was exciting.
- Notwithstanding the challenges, we were able to complete the project on time.
Using contrast and comparison transition words can help make your writing more clear and concise. They allow the reader to easily understand the relationship between ideas, and can make your writing more interesting to read.
Emphasis and Addition Transition Words
Emphasis transition words.
Emphasis transition words are used to highlight the importance of a particular point. These words help you to draw the reader’s attention to a specific idea or argument. Some of the commonly used emphasis transition words are:
- Above all , it is important to prioritize your health.
- Equally important , we need to consider the environmental impact of our actions.
- Indeed , the research shows that regular exercise can improve mental health.
- In fact , studies have found that social media can have a negative impact on mental health.
- Not only does smoking affect your health, but also it harms the environment.
- We need to reduce our carbon footprint, but also we need to find ways to reduce plastic waste.
Addition Transition Words
Addition transition words are used to add more information to your writing. These words help you to connect your ideas and to make your writing more cohesive. Some of the commonly used addition transition words are:
- Regular exercise can improve mental health. Moreover , it can also reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Social media can have a negative impact on mental health. Furthermore , it can also affect sleep patterns.
- We need to reduce our carbon footprint. Additionally , we need to find ways to reduce plastic waste.
- Likewise , we need to consider the impact of our actions on future generations.
- The research shows that smoking is harmful to health. Further , it can also harm the health of those around you.
Conclusion and Summarization Transition Words
In Conclusion
This phrase is commonly used to signal the final remarks in a piece of writing. It helps summarize the main points or findings that have been discussed throughout the text.
Example: In conclusion , it is clear that the benefits of exercise outweigh the risks.
This word is used to indicate a logical conclusion or result. It is often used to summarize the main argument of a piece of writing.
Example: Therefore , it is important to take steps to reduce carbon emissions to prevent climate change .
Example: Thus , it can be concluded that the research supports the hypothesis.
This word is used to indicate the outcome of a particular action or event. It is often used to summarize the main findings of a study or experiment.
Example: The result of the study showed that there was a significant improvement in the students’ test scores.
This word is used to indicate a brief summary of the main points or findings of a piece of writing.
Example: To summarize , the study found that there was a positive correlation between exercise and mental health.
This phrase is used to indicate a brief summary of the main points or findings of a piece of writing.
Example: In sum , the research supports the hypothesis that there is a link between stress and illness.
Example: In short , the study found that there was a significant improvement in the students’ reading comprehension.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some effective transition words for starting a new paragraph?
Some effective transition words for starting a new paragraph include “firstly,” “secondly,” “furthermore,” “moreover,” “in addition,” and “however.” These words help to connect ideas and make your writing more cohesive.
How can I use transition words to improve my writing?
Using transition words can improve your writing by making it more organized and easier to follow. They help to signal changes in thought and guide the reader through your writing. Make sure to use them appropriately and sparingly, as overusing them can make your writing sound forced or choppy.
What are some common transition words used in English writing?
Some common transition words used in English writing include “therefore,” “consequently,” “nevertheless,” “meanwhile,” and “likewise.” These words help to show relationships between ideas and make your writing more coherent.
Can transition words be used at the beginning of a sentence?
Yes, transition words can be used at the beginning of a sentence. However, be careful not to overuse them, as this can make your writing sound repetitive or formulaic.
What are some examples of transitional phrases?
Some examples of transitional phrases include “in conclusion,” “on the other hand,” “as a result,” “in summary,” and “for instance.” These phrases help to signal changes in thought and guide the reader through your writing.
Some effective transition words for starting a new paragraph include \"firstly,\" \"secondly,\" \"furthermore,\" \"moreover,\" \"in addition,\" and \"however.\" These words help to connect ideas and make your writing more cohesive.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"How can I use transition words to improve my writing?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some common transition words used in English writing?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Some common transition words used in English writing include \"therefore,\" \"consequently,\" \"nevertheless,\" \"meanwhile,\" and \"likewise.\" These words help to show relationships between ideas and make your writing more coherent.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Can transition words be used at the beginning of a sentence?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some examples of transitional phrases?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Some examples of transitional phrases include \"in conclusion,\" \"on the other hand,\" \"as a result,\" \"in summary,\" and \"for instance.\" These phrases help to signal changes in thought and guide the reader through your writing.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"How can I make my writing flow better using transition words?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
To make your writing flow better using transition words, try to use them sparingly and only when necessary. Make sure that they are used appropriately and that they help to connect your ideas in a logical and coherent manner. Additionally, try to vary your sentence structure and avoid using the same transition words repeatedly.
Here is a table of some common transition words with their meanings:
- Recent Posts
- Ed Words: Expand Your Vocabulary and Improve Your Writing! - April 15, 2024
- List of Ethnicities and Their Cultures from Around the World - April 2, 2024
- Mastering English Writing: Essential Transitional Words for Body Paragraphs - March 25, 2024
Related posts:
- Amazing Words that Start With A: Expand Your English Vocabulary Today!
- Brilliant Words that Start with B to Broaden Your Vocabulary
- Words that Start with D: Expand Your English Vocabulary Today!
- Words that Start with E in English
Some experts argue that focusing on individual actions to combat climate change takes the focus away from the collective action required to keep carbon levels from rising. Change will not be effected, say some others, unless individual actions raise the necessary awareness.
While a reader can see the connection between the sentences above, it’s not immediately clear that the second sentence is providing a counterargument to the first. In the example below, key “old information” is repeated in the second sentence to help readers quickly see the connection. This makes the sequence of ideas easier to follow.
Sentence pair #2: Effective Transition
Some experts argue that focusing on individual actions to combat climate change takes the focus away from the collective action required to keep carbon levels from rising. Other experts argue that individual actions are key to raising the awareness necessary to effect change.
You can use this same technique to create clear transitions between paragraphs. Here’s an example:
Some experts argue that focusing on individual actions to combat climate change takes the focus away from the collective action required to keep carbon levels from rising. Other experts argue that individual actions are key to raising the awareness necessary to effect change. According to Annie Lowery, individual actions are important to making social change because when individuals take action, they can change values, which can lead to more people becoming invested in fighting climate change. She writes, “Researchers believe that these kinds of household-led trends can help avert climate catastrophe, even if government and corporate actions are far more important” (Lowery).
So, what’s an individual household supposed to do?
The repetition of the word “household” in the new paragraph helps readers see the connection between what has come before (a discussion of whether household actions matter) and what is about to come (a proposal for what types of actions households can take to combat climate change).
Sometimes, transitional words can help readers see how ideas are connected. But it’s not enough to just include a “therefore,” “moreover,” “also,” or “in addition.” You should choose these words carefully to show your readers what kind of connection you are making between your ideas.
To decide which transitional word to use, start by identifying the relationship between your ideas. For example, you might be
- making a comparison or showing a contrast Transitional words that compare and contrast include also, in the same way, similarly, in contrast, yet, on the one hand, on the other hand. But before you signal comparison, ask these questions: Do your readers need another example of the same thing? Is there a new nuance in this next point that distinguishes it from the previous example? For those relationships between ideas, you might try this type of transition: While x may appear the same, it actually raises a new question in a slightly different way.
- expressing agreement or disagreement When you are making an argument, you need to signal to readers where you stand in relation to other scholars and critics. You may agree with another person’s claim, you may want to concede some part of the argument even if you don’t agree with everything, or you may disagree. Transitional words that signal agreement, concession, and disagreement include however, nevertheless, actually, still, despite, admittedly, still, on the contrary, nonetheless .
- showing cause and effect Transitional phrases that show cause and effect include therefore, hence, consequently, thus, so. Before you choose one of these words, make sure that what you are about to illustrate is really a causal link. Novice writers tend to add therefore and hence when they aren’t sure how to transition; you should reserve these words for when they accurately signal the progression of your ideas.
- explaining or elaborating Transitions can signal to readers that you are going to expand on a point that you have just made or explain something further. Transitional words that signal explanation or elaboration include in other words, for example, for instance, in particular, that is, to illustrate, moreover .
- drawing conclusions You can use transitions to signal to readers that you are moving from the body of your argument to your conclusions. Before you use transitional words to signal conclusions, consider whether you can write a stronger conclusion by creating a transition that shows the relationship between your ideas rather than by flagging the paragraph simply as a conclusion. Transitional words that signal a conclusion include in conclusion , as a result, ultimately, overall— but strong conclusions do not necessarily have to include those phrases.
If you’re not sure which transitional words to use—or whether to use one at all—see if you can explain the connection between your paragraphs or sentence either out loud or in the margins of your draft.
For example, if you write a paragraph in which you summarize physician Atul Gawande’s argument about the value of incremental care, and then you move on to a paragraph that challenges those ideas, you might write down something like this next to the first paragraph: “In this paragraph I summarize Gawande’s main claim.” Then, next to the second paragraph, you might write, “In this paragraph I present a challenge to Gawande’s main claim.” Now that you have identified the relationship between those two paragraphs, you can choose the most effective transition between them. Since the second paragraph in this example challenges the ideas in the first, you might begin with something like “but,” or “however,” to signal that shift for your readers.
- picture_as_pdf Transitions
How To Write An Essay
Transition Words For Essays

Transition Words for Essays - An Ultimate List
12 min read
Published on: Jan 1, 2021
Last updated on: Jan 30, 2024

People also read
How To Write An Essay - "The Secret To Craft an A+ Essay"
Learn How to Title an Essay Like a Professional Writer
How to Write an Essay Outline Like a Pro
Essay Format - An Easy Guide & Examples
What is a Thesis Statement, and How is it Written? - Know Here
Arguable and Strong Thesis Statement Examples for Your Essay
200+ Creative Hook Examples: Ready, Set, Hook
A Guide to Writing a 1000 Word Essay for School or College
All You Need to Know About a 500-word Essay
Different Types of Essay: Definition With Best Examples
Writing an Essay Introduction - Step by Step Guide
Jumpstart Your Writing with These Proven Strategies on How to Start an Essay
Learn How to Write a Topic Sentence that Stands Out
A Guide to Crafting an Impactful Conclusion for Your Essay
Amazing Essay Topics & Ideas for Your Next Project (2024)
Explore the Different Types of Sentences with Examples
Share this article
Are you tired of reading essays that feel disjointed and difficult to follow? Do you find yourself struggling to connect your ideas smoothly and effectively?
If so, then you're in luck, because today we're going to take a closer look at the magic of transition words.
In this blog, we'll cover different types of transition words and their precise usage, and how they can elevate your writing. By the end, you'll have the tools to captivate your readers and leave a lasting impression.
Let's dive in!
On This Page On This Page -->
What are Transition Words?
Transition words are linking words used to connect sentences and ideas in the content. They help the audience move from one idea to another, building a coherent relationship within the document.
When writing an essay , it is essential to make sure that the information provided is readable and understandable by the readers. For this purpose, explicit language, transition words, and phrases are used.
Moreover, these words set a base for the idea that is going to be discussed next.
Transition words can either make or break the entire essay. It is mandatory to keep in view that not every sentence in your essay needs a transitional phrase.
Types of Transitions
Generally, there are three types of transitions that are used while drafting a piece of document. Depending on the length, complexity, and kind of text, transitions can take the following form:
- Transition Between Sections - When your document is lengthy, transition paragraphs are used to summarize a particular section for the readers. In addition to this, it also links the information that is to be shared next.
For example:
"In the following section..." "Moving on to..." "Now, let's explore..." "Turning our attention to..." "To delve deeper, we will now examine..."
- Transition Between Paragraphs - The transition between paragraphs is when you logically connect the two paragraphs. This connection summarizes the paragraphâs primary concern and links it to the next idea of the other paragraph.
"Furthermore..." "On the other hand..." "Similarly..." "In contrast..." "Moreover..." "Additionally..." "In addition to..." "Conversely..." "Likewise..." "In a similar vein...
- Transition Within Paragraphs - They act as cues for the readers to prepare them for what is coming next. They are usually single words or small phrases.
"For instance..." "In particular..." "To illustrate..." "Additionally..." "Moreover..." "Furthermore..." "On the contrary..." "However..." "In contrast..." "In other words..."

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Types of Transition Words
Here's a table showcasing different types of transition words and their corresponding functions:
Transition Words For Different Types of Essays
Transitional words depend on the relationship you want to convey to the audience about the ideas and paragraphs. Below is a list of words and phrases that can be used to link different sentences, paragraphs, and sections.
Identify which transition expression you want to share for your logical relationship.
Transition Words for Argumentative Essay
- In the same way
- Equally important
- Furthermore
- Comparatively
- Additionally
- In addition
- Not only...but also
Transition Words for Compare and Contrast Essay
- In contrast
- Different from
- On the contrary
- In spite of
Transition Words for Informative Essay
- Provided that
- With this in mind
- For the purpose of
- In the hope that
- In order to
- With this intention
Transition Words for College Essays
- In other words
- By all means
- To demonstrate
- As in illustration
- To put it another way
Transition Words for Cause and Effect Essay
- As a result
- For this reason
- Because the
- Under those circumstances
- Accordingly
- Consequently
Transition Words for Expository Essay
- Not long after that
- Specifically
- To begin with
- Without doubt
- Undoubtedly
- Due to circumstances
- In similar fashion
Transition Words for Different Parts of Essay
Here's a table listing transition words for different parts of an essay:
How Transitions work
Transitions work by creating a bridge between ideas, sentences, paragraphs, or sections in your essay. They help to establish logical connections and guide the reader through the flow of your writing.
Here's how transitions work:
- Coherence : Transitions create smooth connections between ideas, ensuring a coherent flow in your writing.
- Signal Relationships: Transitions clarify how ideas are related, such as cause and effect, comparison, contrast, or sequence.
- Guide the Reader: It acts as signpost, guiding readers through your essay and indicating the direction of your thoughts.
- Enhance Clarity: Transitions improve clarity by organizing ideas and helping readers understand logical progression.
- Improve Flow: It ensures a seamless flow between sentences, paragraphs, and sections, preventing choppiness.
- Emphasize Key Points: Transitions can be used strategically to highlight important ideas and make them more impactful.
Let's consider an example:
In the above example, transitions like " one such source " connect the idea of solar power to renewable energy sources. " Similarly " then introduces the concept of wind power, creating a logical progression. These transitions help readers follow the flow of ideas and understand the relationships between different energy sources.
Tips to Use Transition Words in your Essay
Here are some tips to effectively use transition words in your essay:
- Understand the Purpose: Familiarize yourself with the different types and functions of transition words, phrases, or sentences. Recognize how they connect ideas, provide structure, and indicate relationships between different parts of your essay.
- Plan your Essay Structure: Before you start writing, outline the main sections, paragraphs, and points you want to cover. Consider where transition words can be used to improve the flow and coherence of your essay.
- Use Transition Words Appropriately: Ensure that the transition word you choose accurately reflects the relationship between ideas. Don't force a transition where it doesn't fit naturally.
- Vary Transition Words: Avoid repetitive or excessive use of the same transition word throughout your essay. Use a variety of transition words to maintain reader interest and enhance overall readability.
- Pay Attention to Placement: Place transition words at the beginning, middle, or end of sentences, depending on the desired effect. Consider the logical flow of your ideas and choose the appropriate placement for each transition word.
- Use Transitional Phrases: Instead of using single transition words, consider incorporating transitional phrases or clauses. These can provide more context and clarity, strengthening the connection between ideas.
- Revise and Edit: After completing your essay, review it for the effectiveness and smoothness of transitions. Ensure that they serve their purpose in guiding the reader and enhancing the overall coherence of your writing.
- Seek Feedback: Share your essay with others and ask for feedback, specifically on the use of transition words. Others' perspectives can help you identify any areas that need improvement or where transitions could be strengthened.
To sum it up! While mastering transition words may require time and practice, it is a skill well worth developing. These words are crucial for creating coherence and flow in your essays. Throughout this blog, we have explored various transition words and phrases that can greatly enhance your writing.
Remember, practice makes perfect, so don't hesitate to apply these newfound skills in your future essays. You can utilize an AI essay writer to enhance and refine your writing skills.
If you still need assistance or have further inquiries, our team at CollegeEssay.org is available to provide legit essay writing service .
Contact us today, and let us be a part of your journey toward academic excellence!
Barbara P (Literature, Marketing)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
On Paragraphs

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is a paragraph?
A paragraph is a collection of related sentences dealing with a single topic. Learning to write good paragraphs will help you as a writer stay on track during your drafting and revision stages. Good paragraphing also greatly assists your readers in following a piece of writing. You can have fantastic ideas, but if those ideas aren't presented in an organized fashion, you will lose your readers (and fail to achieve your goals in writing).
The Basic Rule: Keep one idea to one paragraph
The basic rule of thumb with paragraphing is to keep one idea to one paragraph. If you begin to transition into a new idea, it belongs in a new paragraph. There are some simple ways to tell if you are on the same topic or a new one. You can have one idea and several bits of supporting evidence within a single paragraph. You can also have several points in a single paragraph as long as they relate to the overall topic of the paragraph. If the single points start to get long, then perhaps elaborating on each of them and placing them in their own paragraphs is the route to go.
Elements of a paragraph
To be as effective as possible, a paragraph should contain each of the following: Unity, Coherence, A Topic Sentence, and Adequate Development. As you will see, all of these traits overlap. Using and adapting them to your individual purposes will help you construct effective paragraphs.
The entire paragraph should concern itself with a single focus. If it begins with one focus or major point of discussion, it should not end with another or wander within different ideas.
Coherence is the trait that makes the paragraph easily understandable to a reader. You can help create coherence in your paragraphs by creating logical bridges and verbal bridges.
Logical bridges
- The same idea of a topic is carried over from sentence to sentence
- Successive sentences can be constructed in parallel form
Verbal bridges
- Key words can be repeated in several sentences
- Synonymous words can be repeated in several sentences
- Pronouns can refer to nouns in previous sentences
- Transition words can be used to link ideas from different sentences
A topic sentence
A topic sentence is a sentence that indicates in a general way what idea or thesis the paragraph is going to deal with. Although not all paragraphs have clear-cut topic sentences, and despite the fact that topic sentences can occur anywhere in the paragraph (as the first sentence, the last sentence, or somewhere in the middle), an easy way to make sure your reader understands the topic of the paragraph is to put your topic sentence near the beginning of the paragraph. (This is a good general rule for less experienced writers, although it is not the only way to do it). Regardless of whether you include an explicit topic sentence or not, you should be able to easily summarize what the paragraph is about.
Adequate development
The topic (which is introduced by the topic sentence) should be discussed fully and adequately. Again, this varies from paragraph to paragraph, depending on the author's purpose, but writers should be wary of paragraphs that only have two or three sentences. It's a pretty good bet that the paragraph is not fully developed if it is that short.
Some methods to make sure your paragraph is well-developed:
- Use examples and illustrations
- Cite data (facts, statistics, evidence, details, and others)
- Examine testimony (what other people say such as quotes and paraphrases)
- Use an anecdote or story
- Define terms in the paragraph
- Compare and contrast
- Evaluate causes and reasons
- Examine effects and consequences
- Analyze the topic
- Describe the topic
- Offer a chronology of an event (time segments)
How do I know when to start a new paragraph?
You should start a new paragraph when:
- When you begin a new idea or point. New ideas should always start in new paragraphs. If you have an extended idea that spans multiple paragraphs, each new point within that idea should have its own paragraph.
- To contrast information or ideas. Separate paragraphs can serve to contrast sides in a debate, different points in an argument, or any other difference.
- When your readers need a pause. Breaks between paragraphs function as a short "break" for your readers—adding these in will help your writing be more readable. You would create a break if the paragraph becomes too long or the material is complex.
- When you are ending your introduction or starting your conclusion. Your introductory and concluding material should always be in a new paragraph. Many introductions and conclusions have multiple paragraphs depending on their content, length, and the writer's purpose.
Transitions and signposts
Two very important elements of paragraphing are signposts and transitions. Signposts are internal aids to assist readers; they usually consist of several sentences or a paragraph outlining what the article has covered and where the article will be going.
Transitions are usually one or several sentences that "transition" from one idea to the next. Transitions can be used at the end of most paragraphs to help the paragraphs flow one into the next.
- Pay for essays
- Essay submission
Home > Essay writing and study advice
- How to begin a new paragraph. Useful linking words and phrases.
It is a good idea to occasionally use linking words and phrases at the start of a new paragraph. They can help to link what you have said in the previous paragraph to what you are about to say in your new paragraph.
These link words and phrases are often referred to as signposts. This is because they help to indicate to the reader when one point ends and other begins, as well as the relationship between each point.
Used with care, they can help to guide examiners and tutors through your essay. As well as bolster the impression of a coherent, flowing and logical piece of work.
Useful linking words and phrases that can be used at the start of new paragraphs:
A contrary explanation is that, …
Although, …
As a consequence, …
As a result, …
As we have seen, …
At the same time, …
Accordingly, …
An equally significant aspect of…
Another, significant factor in…
Before considering X it is important to note Y
By the same token, …
But we should also consider, …
Despite these criticisms, …it’s popularity remains high.
Certainly, there is no shortage of disagreement within…
Consequently, …
Correspondingly, …
Conversely, …
Chaytor, … in particular, has focused on the
Despite this, …
Despite these criticisms, … the popularity of X remains largely undiminished.
Each of these theoretical positions make an important contribution to our understanding of, …
Evidence for in support of this position, can be found in…,
For this reason, …
For these reasons, …
Furthermore, …
Given, the current high profile debate with regard to, …it is quite surprising that …
Given, the advantages of … outlined in the previous paragraph, …it is quite predictable that …
Having considered X, it is also reasonable to look at …
In addition to, …
In contrast, …
In this way, …
In this manner, …
In the final analysis, …
In short, …
It can be seen from the above analysis that, …
It could also be said that, …
It is however, important to note the limitations of…
It is important to note however, that …
It is important however not to assume the applicability of, …in all cases.
It is important however not to overemphasis the strengths of …
In the face of such criticism, proponents of, …have responded in a number of ways.
Moreover, …
Notwithstanding such criticism, ….it’s popularity remains largely undiminished.
Notwithstanding these limitations, ….it worth remains in a number of situations.
Noting the compelling nature of this new evidence, …has suggested that.
Nevertheless, …remains a growing problem.
Nonetheless, the number of, …has continued to expand at an exponential rate.
On the other hand, critics of, …point to its blindness, with respect to.
Of central concern therefore to, …sociologists is explaining how societal processes and institutions…
Proponents of…, have also suggested that…
Subsequently, …
Similarly, …
The sentiment expressed in the quotation, embodies the view that, …
This interpretation of, … has not been without it’s detractors however.
This approach is similar to the, …. position
This critique, unfortunately, implies a singular cause of, …
This point is also sustained by the work of, …
This counter argument is supported by evidence from, …
The use of the term, …
Therefore, …
There appears then to be an acceleration in the growth of
There is also, however, a further point to be considered.
These technological developments have greatly increased the growth in, …
To be able to understand, …
Undoubtedly, …
While such failures must not be discounted, … there were in comparison small, when compared
Whilst the discussion in the preceding paragraph, …
Whether crime rates were actually lower at this time continues to be a matter of debate. Evidence from…
There are an almost limitless number of linking phrases and words one can use. What is important is that they complement the style of your writing.
Use these examples to arouse your creativity.
Remember that you don’t have to use them all the time. Using words like, ‘therefore’ ‘subsequently’ ‘moreover’ etc. for every new paragraph would probably become repetitive and detract from the key component of most academic work – critical analysis.
Finally, remember to succinctly, identify the key paragraphs and/or sections of your essay during your introductory paragraph. Then restate them along side an unambiguous position in your concluding paragraph. Again this will help to communicate a clear and understandable progression and structure, to those who read or mark your essay.
Best wishes. S J Tonge.
144 Responses to “How to begin a new paragraph. Useful linking words and phrases.”
It’s fine but describe it a little better with examples and stuff like that.
Thank you for your kind message. You’re very welcome 🙂
I couldn’t be more thankful! This particular link has helped me on a number of occasions! I actually have it bookmarked on my laptop! Thank you for taking the time to do this for us! For those of you who felt the need to leave a negative comment, STOP BEING SO IGNORANT! Think outside the box and make them work or continue to look for other resources!
Although I’m sure this will help me for future essays, I am looking for ways to start a paragraph instead. Thanks anyway, I will keep this in mind when composing the body of the essay 🙂
thanks so much. i think this will help me to improve my writing skill !
thankyou for this,really helped me alot.
This help Thx love dis!
this thing sucks. im looking for the begining of a paragraph not middle of end. Stupid site!!!!!!!!!
Righting my first high school paper and want to make a big impression this page saved me thanx 🙂
really helpful
Harvey, harvey, harvey, harvey DEarman. i use this site all then time for my personal pleasure
Hello my nam3e is Jeppy Dickdearman and i use this site a lot while writing essays. irt is very useful. daimon barrow also uses it
There are always frustrated guys that believe that formulating destructive criticisms is the way to be perceived as a sort of an illuminated and important being… If they knew…
Please, don’t pay attention to those as… You have done an excellent job!! THANKS!!!!!!!!
By the way.. another word you may use to link paragraphs is “additionally…”
Enjoy time and life and waive the morons… their opinion is useless…
This really gave me a central idea how to start a paragraph with a strong start. So THANK YOU SOOOOOO….. MUCH
Great this is chiken soup for my academic wrting.
this is good. anyone criticizing this is a dumbass and should get a life.
Thank you!!! This article helped me a lot to make my paper flow.
Nice job! It must have taken such a long time for you to do this. It was very helpful.
What are these haters looking for on this page in the first place??
THANK YOU so much. I am going to print this and use it as a mini manual.
Thank you so much for the useful list. I am currently working on my research paper and i definitely needed this! 😉
Thank you soooo much . We are doing a 6th grade debate and I had no idea how to start it. you help me so much
this is the best dont listen to all the dummies!
this helped me so much! thank uuuuuuuuuuuuuuu!!!!!!!!
I find this very helpful and brilliant words for my essay, thanks a lot
thank you so much, this is a useful site which people shouldn’t miss, it has improved my writing skills.
thank you once more and be blessed 🙂
Not so sure these are *all* ways to start a Paragraph, nevertheless the words that aren’t really paragraph openers are stilll great transitional words and phrases. Great work.
Hey bro, this does not suck and it is in fact a great help. you are the one who sucks here, swagalishis. And also, your name sucks as well.
Very useful, brilliant phrases, helped a lot! Many thanks
Thankss!! This helped me a lot! I got a good grade on my essay because of all these words 🙂 P.S Don’t listen to these idiots, they just hating on you because they cant come up with anything better..
If you have nothing positive to say just do not say it at all, or at least try to be polite if you dislike something. Show some kind of maturity.
This actually has helped me a lot . Thanks
Bookmarking this! Thank you so much! Brilliant!
good site had the most fun writing my essay with such tool loved it <3
I will be using some of these on the FCAT writes thank you so much
I don’t think this helped because most of the paragraph starters are ways of linking the new paragraph to the previous paragraph. What if you want a clever way to start a new topic in a new paragraph?
thanks u helped alot
Me again!!!!!
Thanks again for the help!!! Used the list again and got a great grade because of this!!!!
Thank you sooooooo much!!!!
A Nanny Mouse 😀
i was only joking promise this helped me a lot hopefully it will help me in my essay 2morrow
listen to this u dont even help anyone i need sentences not words anyway this helped me
this helped me so much thank you very much
Thank you, ignore any bad comments this is brilliantly clever 🙂
im trying to write a thesis statement for my research paper and this kind of help me thankssss.
thanks this site have helped me a lot with the things that I didn’t know
Sucks!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
To the chump before me, you need to get a life because this saved me thank you so much.
You suck!!!!!!!!! It says for words to start a paragraph not words for in the middle of the paragraph. Can you people read!!!!!!!!!!!
Please, leave a comment
Name (optional)
Join essayzone
Download quality essays written by UK students for only £4.99
Registration is fast and easy
Welcome back
- Degree Level Essays
- A-Level Essays
- GCSE Coursework
- International Baccalaureate
- UCAS Personal Statements
- How do I gain access?
- Essay writing and study advice
Essay writing help
- How to write the introduction to an essay
- 10 things to remember when using paragraphs within your essay
- The use of the apostrophe: avoid using contractions within your essay
- On the importance of taking a critical approach in your essay writing
- Help with understanding essay questions: 21 terms and phrases explained
- Essay questions: terms & phrases
- Critical essay writing: a step by step approach
- The use of the apostrophe: it’s versus its
- How writing is different from talking
- Editing your essay. To keep earlier drafts or to discard them?
- How to write a dissertation: free online resources
How to write your UCAS personal statement
- The first part of your UCAS personal statement: Your choice of subject.
- The second part of your UCAS personal statement: your academic experience, subject knowledge and abilities
- The third part of your UCAS personal statement: extracurricular interests and achievements
- Anatomy of the UCAS personal statement: what a successful UCAS personal statement should consist of.
- What should be included in your UCAS personal statement. A concise reminder.
- Your UCAS Personal Statement: The 70 Essential Questions
- 21 UCAS Personal Statement Mistakes
Study skills
- 26 Essential study skills
- 26 Essential study skills...continued
- How to skim read a book
- How to speed read a book
- 12 positive things about exams
- How to work with other students without cheating
- Why are English words difficult to spell?
- What is plagiarism? Why avoid it?
- How can plagiarism happen by accident?
- How to prepare for a viva
- How to get the most out of university lectures
- How to take lecture notes quickly. Common abbreviations and symbols for students
- Think positively and you may be able to help your self
Time management
- Steal a few minutes
- Ten time saving suggestions
33 Transition Words and Phrases
Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one.
Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that “this follows logically from the preceding” include accordingly, therefore, and consequently . Words that mean “in addition to” include moreover, besides, and further . Words that mean “contrary to what was just stated” include however, nevertheless , and nonetheless .
as a result : THEREFORE : CONSEQUENTLY
The executive’s flight was delayed and they accordingly arrived late.
in or by way of addition : FURTHERMORE
The mountain has many marked hiking trails; additionally, there are several unmarked trails that lead to the summit.
at a later or succeeding time : SUBSEQUENTLY, THEREAFTER
Afterward, she got a promotion.
even though : ALTHOUGH
She appeared as a guest star on the show, albeit briefly.
in spite of the fact that : even though —used when making a statement that differs from or contrasts with a statement you have just made
They are good friends, although they don't see each other very often.
in addition to what has been said : MOREOVER, FURTHERMORE
I can't go, and besides, I wouldn't go if I could.
as a result : in view of the foregoing : ACCORDINGLY
The words are often confused and are consequently misused.
in a contrasting or opposite way —used to introduce a statement that contrasts with a previous statement or presents a differing interpretation or possibility
Large objects appear to be closer. Conversely, small objects seem farther away.
used to introduce a statement that is somehow different from what has just been said
These problems are not as bad as they were. Even so, there is much more work to be done.
used as a stronger way to say "though" or "although"
I'm planning to go even though it may rain.
in addition : MOREOVER
I had some money to invest, and, further, I realized that the risk was small.
in addition to what precedes : BESIDES —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
These findings seem plausible. Furthermore, several studies have confirmed them.
because of a preceding fact or premise : for this reason : THEREFORE
He was a newcomer and hence had no close friends here.
from this point on : starting now
She announced that henceforth she would be running the company.
in spite of that : on the other hand —used when you are saying something that is different from or contrasts with a previous statement
I'd like to go; however, I'd better not.
as something more : BESIDES —used for adding information to a statement
The city has the largest population in the country and in addition is a major shipping port.
all things considered : as a matter of fact —used when making a statement that adds to or strengthens a previous statement
He likes to have things his own way; indeed, he can be very stubborn.
for fear that —often used after an expression denoting fear or apprehension
He was concerned lest anyone think that he was guilty.
in addition : ALSO —often used to introduce a statement that adds to and is related to a previous statement
She is an acclaimed painter who is likewise a sculptor.
at or during the same time : in the meantime
You can set the table. Meanwhile, I'll start making dinner.
BESIDES, FURTHER : in addition to what has been said —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
It probably wouldn't work. Moreover, it would be very expensive to try it.
in spite of that : HOWEVER
It was a predictable, but nevertheless funny, story.
in spite of what has just been said : NEVERTHELESS
The hike was difficult, but fun nonetheless.
without being prevented by (something) : despite—used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
Notwithstanding their youth and inexperience, the team won the championship.
if not : or else
Finish your dinner. Otherwise, you won't get any dessert.
more correctly speaking —used to introduce a statement that corrects what you have just said
We can take the car, or rather, the van.
in spite of that —used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
I tried again and still I failed.
by that : by that means
He signed the contract, thereby forfeiting his right to the property.
for that reason : because of that
This tablet is thin and light and therefore very convenient to carry around.
immediately after that
The committee reviewed the documents and thereupon decided to accept the proposal.
because of this or that : HENCE, CONSEQUENTLY
This detergent is highly concentrated and thus you will need to dilute it.
while on the contrary —used to make a statement that describes how two people, groups, etc., are different
Some of these species have flourished, whereas others have struggled.
NEVERTHELESS, HOWEVER —used to introduce a statement that adds something to a previous statement and usually contrasts with it in some way
It was pouring rain out, yet his clothes didn’t seem very wet.
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Usage Notes
Prepositions, ending a sentence with, hypercorrections: are you making these 6 common mistakes, a comprehensive guide to forming compounds, can ‘criteria’ ever be singular, singular nonbinary ‘they’: is it ‘they are’ or ‘they is’, grammar & usage, a list of most commonly confused words, more commonly misspelled words, 10 words you see but don't hear, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), 9 other words for beautiful, rare and amusing insults, volume 2, etymologies for every day of the week, the words of the week - apr. 19, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version).
Advertisement
Shadow War Between Iran and Israel: A Timeline
A recent round of strikes has brought the conflict more clearly into the open and raised fears of a broader war.
- Share full article

By Cassandra Vinograd
- April 19, 2024
For decades, Israel and Iran have fought a shadow war across the Middle East , trading attacks by land, sea, air and in cyberspace. A recent round of strikes — mainly an aerial barrage by Iran against Israel last weekend — has brought the conflict more clearly into the open and raised fears of a broader war.
A retaliatory Israeli strike on an Iranian air base on Friday, however, appeared limited in scope, and analysts said it suggested an effort to pull back from the dangerous cycle and potentially move the war back into the shadows.
Here is a recent history of the conflict:
August 2019: An Israeli airstrike killed two Iranian-trained militants in Syria, a drone set off a blast near a Hezbollah office in Lebanon and an airstrike in Qaim, Iraq, killed a commander of an Iran-backed Iraqi militia. Israel accused Iran at the time of trying to establish an overland arms-supply line through Iraq and northern Syria to Lebanon, and analysts said the strikes were aimed at stopping Iran and signaling to its proxies that Israel would not tolerate a fleet of smart missiles on its borders.
January 2020: Israel greeted with satisfaction the assassination of Maj. Gen. Qassim Suleimani , the commander of the foreign-facing arm of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps, in an American drone strike in Baghdad.
Iran hit back by attacking two bases in Iraq that housed American troops with a barrage of missiles, wounding about 100 U.S. military personnel .
2021-22: In July 2021, an oil tanker managed by an Israeli-owned shipping company was attacked off the coast of Oman, killing two crew members, according to the company and three Israeli officials. Two of the officials said that the attack appeared to have been carried out by Iranian drones.
Iran did not explicitly claim or deny responsibility, but a state-owned television channel described the episode as a response to an Israeli strike in Syria.
In November 2021, Israel killed Iran’s top nuclear scientist, Mohsen Fakhrizadeh , and followed up with the assassination of a Revolutionary Guards commander, Col. Sayad Khodayee , in May 2022.
December 2023: After Israel’s bombardment of Gaza began in response to the Oct. 7 Hamas-led assault, Iranian-backed militias stepped up their own attacks . And late last year, Iran accused Israel of killing a high-level military figure, Brig. Gen. Sayyed Razi Mousavi , in a missile strike in Syria.
A senior adviser to the Revolutionary Guards, General Mousavi was described as having been a close associate of General Suleimani and was said to have helped oversee the shipment of arms to Hezbollah. Israel, adopting its customary stance, declined to comment directly on whether it was behind General Mousavi’s death.
January 2024: An explosion in a suburb of Beirut, Lebanon, killed Saleh al-Arouri , a Hamas leader, along with two commanders from that group’s armed wing, the first assassination of a top Hamas official outside the West Bank and Gaza in recent years. Officials from Hamas, Lebanon and the United States ascribed the blast to Israel , which did not publicly confirm involvement.
Hezbollah, which receives major support from Iran, stepped up its assaults on Israel after Mr. al-Arouri’s death. Israel’s military hit back at Hezbollah in Lebanon, killing several of the group’s commanders .
March: An Israeli drone strike hit a car in southern Lebanon, killing at least one person. Israel’s military said it had killed the deputy commander of Hezbollah’s rocket and missile unit. Hezbollah acknowledged the death of a man, Ali Abdulhassan Naim, but did not provide further details.
The same day, airstrikes killed soldiers near Aleppo, northern Syria, in what appeared to be one of the heaviest Israeli attacks in the country in years. The strikes killed 36 Syrian soldiers, seven Hezbollah fighters and a Syrian from a pro-Iran militia, according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, a British-based group that tracks Syria’s civil war.
Israel’s military did not claim responsibility. But the country’s defense minister, Yoav Gallant, wrote on social media, “We will pursue Hezbollah every place it operates and we will expand the pressure and the pace of the attacks.”
April: A strike on an Iranian Embassy building in Damascus on April 1 killed three top Iranian commanders and four officers. Iran blamed Israel and vowed to hit back forcefully.
Two weeks later, Tehran launched a barrage of more than 300 drones and missiles at Israel, an unexpectedly large-scale attack , although nearly all the weapons were shot down by Israel and allies. Israel said for days it would respond, before a strike on Friday hit a military air base near the central Iranian city of Isfahan.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Words to Start an Introduction Paragraph. The words you choose for starting an essay should establish the context, importance, or conflict of your topic. The purpose of an introduction is to provide the reader with a clear understanding of the topic, its significance, and the structure of the ensuing discussion or argument.
Start with a "topic sentence". Give 1-2 sentences of supporting evidence for (or against) your argument. Next, write a sentence analysing this evidence with respect to your argument or topic sentence. Finally, conclude by explaining the significance of this stance, or providing a transition to the next paragraph.
Transition words commonly appear at the start of a new sentence or clause ... Transition sentences are used to start a new paragraph or section in an essay. They help the reader understand connections between ideas. ... Use topic sentences to structure your ideas and keep your paragraphs focused. 1120. Scribbr. Our editors; Jobs;
A sentence starter is simply a word or a phrase that will help you to get your sentence going when you feel stuck, and it can be helpful in many different situations. A good sentence starter can help you better transition from one paragraph to another or connect two ideas. If not started correctly, your sentence will likely sound choppy, and ...
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
If you want to start writing terrific sentences (and improve your essay structure ), the first thing you should do is start using transition words. Transition words are those words or phrases that help connect thoughts and ideas. They move one sentence or paragraph into another, and they make things feel less abrupt.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Starting a body paragraph is very different than starting an essay. The body paragraphs are the ''meat'' of the essay, and each paragraph usually covers a certain sub-topic or supporting detail ...
Tips for Using Transition Words and Phrases. 1. Use a variety of transition words, not the same one. 2. Put a comma after the transition word. 3. Put the subject of the sentence after the comma. Choosing the right word to start, end, and transition topics can make or break an essay.
Words to start a paragraph are transitions that provide direction for the reader as to where you are going with an argument, analysis, explanation or narrative. These include words and phrases that introduce comparisons, contrasts, evidence, themes, conclusions, stories or explanations. The following are common words that can be used to start ...
Key takeaways. You should start a new paragraph with a natural transition from the previous one. Paragraphs should have a clear topic sentence. A topic sentence should identify the subject and purpose of the paragraph. Clarify any ambiguous terms that you will use in the rest of the paper.
Transition Words to Start a Paragraph. Starting a paragraph can be challenging, especially when you're trying to connect it to the previous one. That's where transition words come in handy. First Paragraph. When you're writing the first paragraph of an essay or article, you need to introduce your topic and grab the reader's attention.
Transitions. Transitions help your readers move between ideas within a paragraph, between paragraphs, or between sections of your argument. When you are deciding how to transition from one idea to the next, your goal should be to help readers see how your ideas are connected—and how those ideas connect to the big picture.
This blog lists transition words for all essay types, ensuring smooth transitions & improved readability. Order. ... Transition Words/Phrases: Starting a Paragraph: Firstly, To begin with, Initially, In the first place: First Body Paragraph: Firstly, To start, To begin with, Initially:
A paragraph is a collection of related sentences dealing with a single topic. Learning to write good paragraphs will help you as a writer stay on track during your drafting and revision stages. Good paragraphing also greatly assists your readers in following a piece of writing. You can have fantastic ideas, but if those ideas aren't presented ...
Using words like, 'therefore' 'subsequently' 'moreover' etc. for every new paragraph would probably become repetitive and detract from the key component of most academic work - critical analysis. Finally, remember to succinctly, identify the key paragraphs and/or sections of your essay during your introductory paragraph.
33 Transition Words and Phrases. 'Besides,' 'furthermore,' 'although,' and other words to help you jump from one idea to the next. Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one. Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that ...
If you're looking for good conclusion starters to finish your piece strongly, look no further. Find examples of great ways to begin your conclusion here.
April 19, 2024. For decades, Israel and Iran have fought a shadow war across the Middle East, trading attacks by land, sea, air and in cyberspace. A recent round of strikes — mainly an aerial ...