- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

How Great Leaders Communicate
- Carmine Gallo

Four strategies to motivate and inspire your team.
Transformational leaders are exceptional communicators. In this piece, the author outlines four communication strategies to help motivate and inspire your team: 1) Use short words to talk about hard things. 2) Choose sticky metaphors to reinforce key concepts. 3) Humanize data to create value. 4). Make mission your mantra to align teams.
In the age of knowledge, ideas are the foundation of success in almost every field. You can have the greatest idea in the world, but if you can’t persuade anyone else to follow your vision, your influence and impact will be greatly diminished. And that’s why communication is no longer considered a “soft skill” among the world’s top business leaders. Leaders who reach the top do not simply pay lip service to the importance of effective communication. Instead, they study the art in all its forms — writing, speaking, presenting — and constantly strive to improve on those skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Communication →

- 16 Feb 2024
- Research & Ideas
Is Your Workplace Biased Against Introverts?
Extroverts are more likely to express their passion outwardly, giving them a leg up when it comes to raises and promotions, according to research by Jon Jachimowicz. Introverts are just as motivated and excited about their work, but show it differently. How can managers challenge their assumptions?

- 06 Nov 2023
Did You Hear What I Said? How to Listen Better
People who seem like they're paying attention often aren't—even when they're smiling and nodding toward the speaker. Research by Alison Wood Brooks, Hanne Collins, and colleagues reveals just how prone the mind is to wandering, and sheds light on ways to stay tuned in to the conversation.
.jpg)
- 31 Oct 2023
Checking Your Ethics: Would You Speak Up in These 3 Sticky Situations?
Would you complain about a client who verbally abuses their staff? Would you admit to cutting corners on your work? The answers aren't always clear, says David Fubini, who tackles tricky scenarios in a series of case studies and offers his advice from the field.

- 24 Jul 2023
Part-Time Employees Want More Hours. Can Companies Tap This ‘Hidden’ Talent Pool?
Businesses need more staff and employees need more work, so what's standing in the way? A report by Joseph Fuller and colleagues shows how algorithms and inflexibility prevent companies from accessing valuable talent in a long-term shortage.

- 23 Jun 2023
This Company Lets Employees Take Charge—Even with Life and Death Decisions
Dutch home health care organization Buurtzorg avoids middle management positions and instead empowers its nurses to care for patients as they see fit. Tatiana Sandino and Ethan Bernstein explore how removing organizational layers and allowing employees to make decisions can boost performance.

- 24 Jan 2023
Passion at Work Is a Good Thing—But Only If Bosses Know How to Manage It
Does showing passion mean doing whatever it takes to get the job done? Employees and managers often disagree, says research by Jon Jachimowicz. He offers four pieces of advice for leaders who yearn for more spirit and intensity at their companies.

- 10 Jan 2023
How to Live Happier in 2023: Diversify Your Social Circle
People need all kinds of relationships to thrive: partners, acquaintances, colleagues, and family. Research by Michael Norton and Alison Wood Brooks offers new reasons to pick up the phone and reconnect with that old friend from home.

- 15 Nov 2022
Why TikTok Is Beating YouTube for Eyeball Time (It’s Not Just the Dance Videos)
Quirky amateur video clips might draw people to TikTok, but its algorithm keeps them watching. John Deighton and Leora Kornfeld explore the factors that helped propel TikTok ahead of established social platforms, and where it might go next.

- 03 Nov 2022
Feeling Separation Anxiety at Your Startup? 5 Tips to Soothe These Growing Pains
As startups mature and introduce more managers, early employees may lose the easy closeness they once had with founders. However, with transparency and healthy boundaries, entrepreneurs can help employees weather this transition and build trust, says Julia Austin.

- 15 Sep 2022
Looking For a Job? Some LinkedIn Connections Matter More Than Others
Debating whether to connect on LinkedIn with that more senior executive you met at that conference? You should, says new research about professional networks by Iavor Bojinov and colleagues. That person just might help you land your next job.

- 08 Sep 2022
Gen Xers and Millennials, It’s Time To Lead. Are You Ready?
Generation X and Millennials—eagerly waiting to succeed Baby Boom leaders—have the opportunity to bring more collaboration and purpose to business. In the book True North: Emerging Leader Edition, Bill George offers advice for the next wave of CEOs.

- 05 Aug 2022
Why People Crave Feedback—and Why We’re Afraid to Give It
How am I doing? Research by Francesca Gino and colleagues shows just how badly employees want to know. Is it time for managers to get over their discomfort and get the conversation going at work?

- 23 Jun 2022
All Those Zoom Meetings May Boost Connection and Curb Loneliness
Zoom fatigue became a thing during the height of the pandemic, but research by Amit Goldenberg shows how virtual interactions can provide a salve for isolation. What does this mean for remote and hybrid workplaces?

- 13 Jun 2022
Extroverts, Your Colleagues Wish You Would Just Shut Up and Listen
Extroverts may be the life of the party, but at work, they're often viewed as phony and self-centered, says research by Julian Zlatev and colleagues. Here's how extroverts can show others that they're listening, without muting themselves.

- 24 May 2022
Career Advice for Minorities and Women: Sharing Your Identity Can Open Doors
Women and people of color tend to minimize their identities in professional situations, but highlighting who they are often forces others to check their own biases. Research by Edward Chang and colleagues.

- 12 May 2022
Why Digital Is a State of Mind, Not Just a Skill Set
You don't have to be a machine learning expert to manage a successful digital transformation. In fact, you only need 30 percent fluency in a handful of technical topics, say Tsedal Neeley and Paul Leonardi in their book, The Digital Mindset.

- 08 Feb 2022
Silos That Work: How the Pandemic Changed the Way We Collaborate
A study of 360 billion emails shows how remote work isolated teams, but also led to more intense communication within siloed groups. Will these shifts outlast the pandemic? Research by Tiona Zuzul and colleagues. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- Cold Call Podcast
What’s Next for Nigerian Production Studio EbonyLife Media?
After more than 20 years in the media industry in the UK and Nigeria, EbonyLife Media CEO Mo Abudu is considering several strategic changes for her media company’s future. Will her mission to tell authentic African stories to the world be advanced by distributing films and TV shows direct to customers? Or should EbonyLife instead distribute its content through third-party streaming services, like Netflix? Assistant Professor Andy Wu discusses Abudu’s plans for her company in his case, EbonyLife Media. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
.jpg)
- 11 Jan 2022
Feeling Seen: What to Say When Your Employees Are Not OK
Pandemic life continues to take its toll. Managers who let down their guard and acknowledge their employees' emotions can ease distress and build trust, says research by Julian Zlatev and colleagues. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 04 Jan 2022
Scrap the Big New Year's Resolutions. Make 6 Simple Changes Instead.
Self-improvement doesn't need to be painful, especially during a pandemic. Rather than set yet another gym goal, look inward, retrain your brain, and get outside, says Hirotaka Takeuchi. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
Communication Studies: Effective Communication Leads to Effective Leadership
Affiliation.
- 1 University of Kansas.
- PMID: 32187871
- DOI: 10.1002/yd.20371
This chapter explores how communication studies focuses on human communication among people in groups, teams, and organizations. While persuasive communication has long been at the heart of leadership development, the discipline's contributions to effective leadership also range from advancing our understanding of organizational communicative systems to the development of skills for deliberative democracy and civic engagement.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Publication types
- Communication*
- Education, Professional*
- Leadership*
- Universities*
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Effective Communication in the Workplace

Source: https://pixabay.com/vectors/social-media-connections-networking-3846597/ is in the Public Domain at Pixabay.com. Retrieved 07.05.2022.
Effective workplace communication helps maintain the quality of working relationships and positively affects employees' well-being. This article discusses the benefits of practicing effective communication in the workplace and provides strategies for workers and organizational leaders to improve communication effectiveness.
Workplace Communication Matters
Effective workplace communication benefits employees' job satisfaction, organizational productivity, and customer service (Adu-Oppong & Agyin-Birikorang, 2014). We summarized Bosworth's (2016) and Adu-Oppong and Agyin-Birikorang's (2014) works below related to the benefits of practicing effective communication in the workplace.
- Reduces work-related conflicts
- Enhances interpersonal relationships
- Increases workers' performance and supervisors' expectations
- Increases workforce productivity through constructive feedback
- Increases employee engagement and job satisfaction
- Builds organizational loyalty and trust
- Reduces employees' turnover rate
- Facilitates the proper utilization of resources
- Uncovers new employees' talents
Strategies to Improve Communication Effectiveness
Effective communication is a two-way process that requires both sender and receiver efforts. We summarized research works and guidelines for good communication in the workplace proposed by Cheney (2011), Keyton (2011), Tourish (2010), and Lunenburg (2010).
Sender's strategies for communication planning
- Clearly define the idea of your message before sharing it.
- Identify the purpose of the message (obtain information, initiate action, or change another person's attitude)
- Be aware of the physical and emotional environment in which you communicate your message. Consider the tone you want to use, the configuration of the space, and the context.
- Consult with others when you do not feel confident or comfortable communicating your message.
- Be mindful of the primary content of the message.
- Follow-up previous communications to verify the information.
- Communicate on time, avoid postponing hard conversations, and be consistent.
- Be aware that your actions support your messages and be coherent in your verbal and behavioral communication style.
- Be a good listener, even when you are the primary sender.
Receiver's strategies during a conversation
- Show interest and attitude to listen.
- Listen more than talk.
- Pay attention to the talker and the message, avoiding distractions.
- Be patient and allow the talker time to transmit the message.
- Be respectful and avoid interrupting a talker.
- Hold your temper. An angry person takes the wrong meaning from words
- Go easy on argument and criticism.
- Engage in the conversation by asking questions. This attitude helps develop key points and keep a fluid conversation.
Effective communication practices are essential for any successful team and organization. Organizational communication helps to disseminate important information to employees and builds relationships of trust and commitment.
Key points to improve communication in the workplace
- Set clear goals and expectations
- Ask clarifying questions
- Schedule regular one-on-one meetings
- Praise in public, criticize in private
- Assume positive intent
- Repeat important messages
- Raise your words, not your voice
- Hold town hall meetings and cross-functional check-ins.
Adu-Oppong, A. A., & Agyin-Birikorang, E. (2014). Communication in the Workplace: Guidelines for improving effectiveness. Global journal of commerce & management perspective , 3 (5), 208–213.
Bosworth, P. (2021, May 19). The power of good communication in the workplace . Leadership Choice. Retrieved May 18, 2022.
Cheney, G. (2011). Organizational communication in an age of globalization: Issues, reflections, practices . Waveland Press.
Keyton, J. (2011). Communication and organizational culture: A key to understanding work experience . Sage.
Tourish, D. (2010). Auditing organizational communication: A handbook of research, theory, and practice . Routledge
Lunenburg, F. C. (2010). Communication: The process, barriers, and improving effectiveness. Schooling , 1 (1), 1-10.

- Adult leadership
- Volunteerism
- Volunteer management
You may also be interested in ...

Diferencias culturales en el ambiente laboral

Consejos Para Desarrollar una Filosofía Personal de Liderazgo

How to Become a Community Leader

Importance of Incorporating Local Culture into Community Development

Conducting Effective Surveys - 'Rules of the Road'

Conflict Styles, Outcomes, and Handling Strategies

Employee Disengagement and the Impact of Leadership

Dealing with Conflict

Developing Self-Leadership Competencies

Diversity Training in the Workplace
Personalize your experience with penn state extension and stay informed of the latest in agriculture..
Nonverbal Communication and Body Language
Improving emotional intelligence (eq), conflict resolution skills.
- Empathy: How to Feel and Respond to the Emotions of Others
Anger Management
Managing conflict with humor.
- Gaslighting: Turning Off the Gas on Your Gaslighter
Setting Healthy Boundaries in Relationships
- Online Therapy: Is it Right for You?
- Mental Health
- Health & Wellness
- Children & Family
- Relationships
Are you or someone you know in crisis?
- Bipolar Disorder
- Eating Disorders
- Grief & Loss
- Personality Disorders
- PTSD & Trauma
- Schizophrenia
- Therapy & Medication
- Exercise & Fitness
- Healthy Eating
- Well-being & Happiness
- Weight Loss
- Work & Career
- Illness & Disability
- Heart Health
- Childhood Issues
- Learning Disabilities
- Family Caregiving
- Teen Issues
- Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Love & Friendship
- Domestic Abuse
- Healthy Aging
- Aging Issues
- Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia
- Senior Housing
- End of Life
- Meet Our Team
What is effective communication?
Effective communication skill 1: become an engaged listener, skill 2: pay attention to nonverbal signals, skill 3: keep stress in check, skill 4: assert yourself, effective communication.
Want to communicate better? These tips will help you avoid misunderstandings, grasp the real meaning of what’s being communicated, and greatly improve your work and personal relationships.

Effective communication is about more than just exchanging information. It’s about understanding the emotion and intentions behind the information. As well as being able to clearly convey a message, you need to also listen in a way that gains the full meaning of what’s being said and makes the other person feel heard and understood.
Effective communication sounds like it should be instinctive. But all too often, when we try to communicate with others something goes astray. We say one thing, the other person hears something else, and misunderstandings, frustration, and conflicts ensue. This can cause problems in your home, school, and work relationships.
For many of us, communicating more clearly and effectively requires learning some important skills. Whether you’re trying to improve communication with your spouse, kids, boss, or coworkers, learning these skills can deepen your connections to others, build greater trust and respect, and improve teamwork, problem solving, and your overall social and emotional health.
What’s stopping you from communicating effectively?
Common barriers to effective communication include:
Stress and out-of-control emotion. When you’re stressed or emotionally overwhelmed, you’re more likely to misread other people, send confusing or off-putting nonverbal signals, and lapse into unhealthy knee-jerk patterns of behavior. To avoid conflict and misunderstandings, you can learn how to quickly calm down before continuing a conversation.
Lack of focus. You can’t communicate effectively when you’re multitasking. If you’re checking your phone , planning what you’re going to say next, or daydreaming, you’re almost certain to miss nonverbal cues in the conversation. To communicate effectively, you need to avoid distractions and stay focused.
Inconsistent body language. Nonverbal communication should reinforce what is being said, not contradict it. If you say one thing, but your body language says something else, your listener will likely feel that you’re being dishonest. For example, you can’t say “yes” while shaking your head no.
[Read: Nonverbal Communication and Body Language]
Negative body language. If you disagree with or dislike what’s being said, you might use negative body language to rebuff the other person’s message, such as crossing your arms, avoiding eye contact, or tapping your feet. You don’t have to agree with, or even like what’s being said, but to communicate effectively and not put the other person on the defensive, it’s important to avoid sending negative signals.
When communicating with others, we often focus on what we should say. However, effective communication is less about talking and more about listening. Listening well means not just understanding the words or the information being communicated, but also understanding the emotions the speaker is trying to convey.
There’s a big difference between engaged listening and simply hearing. When you really listen—when you’re engaged with what’s being said—you’ll hear the subtle intonations in someone’s voice that tell you how that person is feeling and the emotions they’re trying to communicate. When you’re an engaged listener, not only will you better understand the other person, you’ll also make that person feel heard and understood, which can help build a stronger, deeper connection between you.
By communicating in this way, you’ll also experience a process that lowers stress and supports physical and emotional well-being. If the person you’re talking to is calm, for example, listening in an engaged way will help to calm you, too. Similarly, if the person is agitated, you can help calm them by listening in an attentive way and making the person feel understood.
If your goal is to fully understand and connect with the other person, listening in an engaged way will often come naturally. If it doesn’t, try the following tips. The more you practice them, the more satisfying and rewarding your interactions with others will become.
Tips for becoming an engaged listener
Focus fully on the speaker. You can’t listen in an engaged way if you’re constantly checking your phone or thinking about something else. You need to stay focused on the moment-to-moment experience in order to pick up the subtle nuances and important nonverbal cues in a conversation. If you find it hard to concentrate on some speakers, try repeating their words over in your head—it’ll reinforce their message and help you stay focused.
Favor your right ear. As strange as it sounds, the left side of the brain contains the primary processing centers for both speech comprehension and emotions. Since the left side of the brain is connected to the right side of the body, favoring your right ear can help you better detect the emotional nuances of what someone is saying.
Avoid interrupting or trying to redirect the conversation to your concerns. By saying something like, “If you think that’s bad, let me tell you what happened to me.” Listening is not the same as waiting for your turn to talk. You can’t concentrate on what someone’s saying if you’re forming what you’re going to say next. Often, the speaker can read your facial expressions and know that your mind’s elsewhere.
Show your interest in what’s being said. Nod occasionally, smile at the person, and make sure your posture is open and inviting. Encourage the speaker to continue with small verbal comments like “yes” or “uh huh.”
Try to set aside judgment. In order to communicate effectively with someone, you don’t have to like them or agree with their ideas, values, or opinions. However, you do need to set aside your judgment and withhold blame and criticism in order to fully understand them. The most difficult communication, when successfully executed, can often lead to an unlikely connection with someone.
[Read: Improving Emotional Intelligence (EQ)]
Provide feedback. If there seems to be a disconnect, reflect what has been said by paraphrasing. “What I’m hearing is,” or “Sounds like you are saying,” are great ways to reflect back. Don’t simply repeat what the speaker has said verbatim, though—you’ll sound insincere or unintelligent. Instead, express what the speaker’s words mean to you. Ask questions to clarify certain points: “What do you mean when you say…” or “Is this what you mean?”
Hear the emotion behind the words . It’s the higher frequencies of human speech that impart emotion. You can become more attuned to these frequencies—and thus better able to understand what others are really saying—by exercising the tiny muscles of your middle ear (the smallest in the body). You can do this by singing, playing a wind instrument, or listening to certain types of high-frequency music (a Mozart symphony or violin concerto, for example, rather than low-frequency rock, pop, or hip-hop).
The way you look, listen, move, and react to another person tells them more about how you’re feeling than words alone ever can. Nonverbal communication, or body language, includes facial expressions, body movement and gestures, eye contact, posture, the tone of your voice, and even your muscle tension and breathing.
Developing the ability to understand and use nonverbal communication can help you connect with others, express what you really mean, navigate challenging situations, and build better relationships at home and work.
- You can enhance effective communication by using open body language—arms uncrossed, standing with an open stance or sitting on the edge of your seat, and maintaining eye contact with the person you’re talking to.
- You can also use body language to emphasize or enhance your verbal message—patting a friend on the back while complimenting him on his success, for example, or pounding your fists to underline your message.
Improve how you read nonverbal communication
Be aware of individual differences. People from different countries and cultures tend to use different nonverbal communication gestures, so it’s important to take age, culture, religion, gender, and emotional state into account when reading body language signals. An American teen, a grieving widow, and an Asian businessman, for example, are likely to use nonverbal signals differently.
Look at nonverbal communication signals as a group. Don’t read too much into a single gesture or nonverbal cue. Consider all of the nonverbal signals you receive, from eye contact to tone of voice to body language. Anyone can slip up occasionally and let eye contact go, for example, or briefly cross their arms without meaning to. Consider the signals as a whole to get a better “read” on a person.
Improve how you deliver nonverbal communication
Use nonverbal signals that match up with your words rather than contradict them. If you say one thing, but your body language says something else, your listener will feel confused or suspect that you’re being dishonest. For example, sitting with your arms crossed and shaking your head doesn’t match words telling the other person that you agree with what they’re saying.
Adjust your nonverbal signals according to the context. The tone of your voice, for example, should be different when you’re addressing a child than when you’re addressing a group of adults. Similarly, take into account the emotional state and cultural background of the person you’re interacting with.
Avoid negative body language. Instead, use body language to convey positive feelings, even when you’re not actually experiencing them. If you’re nervous about a situation—a job interview, important presentation, or first date, for example—you can use positive body language to signal confidence, even though you’re not feeling it. Instead of tentatively entering a room with your head down, eyes averted, and sliding into a chair, try standing tall with your shoulders back, smiling and maintaining eye contact, and delivering a firm handshake. It will make you feel more self-confident and help to put the other person at ease.
How many times have you felt stressed during a disagreement with your spouse, kids, boss, friends, or coworkers and then said or done something you later regretted? If you can quickly relieve stress and return to a calm state, you’ll not only avoid such regrets, but in many cases you’ll also help to calm the other person as well. It’s only when you’re in a calm, relaxed state that you’ll be able to know whether the situation requires a response, or whether the other person’s signals indicate it would be better to remain silent.
In situations such as a job interview, business presentation, high-pressure meeting, or introduction to a loved one’s family, for example, it’s important to manage your emotions, think on your feet, and effectively communicate under pressure.
Communicate effectively by staying calm under pressure
Use stalling tactics to give yourself time to think. Ask for a question to be repeated or for clarification of a statement before you respond.
Pause to collect your thoughts. Silence isn’t necessarily a bad thing—pausing can make you seem more in control than rushing your response.
Make one point and provide an example or supporting piece of information. If your response is too long or you waffle about a number of points, you risk losing the listener’s interest. Follow one point with an example and then gauge the listener’s reaction to tell if you should make a second point.
Deliver your words clearly. In many cases, how you say something can be as important as what you say. Speak clearly, maintain an even tone, and make eye contact. Keep your body language relaxed and open.
Wrap up with a summary and then stop. Summarize your response and then stop talking, even if it leaves a silence in the room. You don’t have to fill the silence by continuing to talk.
Quick stress relief for effective communication
When a conversation starts to get heated, you need something quick and immediate to bring down the emotional intensity. By learning to quickly reduce stress in the moment, you can safely take stock of any strong emotions you’re experiencing, regulate your feelings, and behave appropriately.
Recognize when you’re becoming stressed. Your body will let you know if you’re stressed as you communicate. Are your muscles or stomach tight? Are your hands clenched? Is your breath shallow? Are you “forgetting” to breathe?
Take a moment to calm down before deciding to continue a conversation or postpone it.
Bring your senses to the rescue. The best way to rapidly and reliably relieve stress is through the senses—sight, sound, touch, taste, smell—or movement. For example, you could pop a peppermint in your mouth, squeeze a stress ball in your pocket, take a few deep breaths, clench and relax your muscles, or simply recall a soothing, sensory-rich image. Each person responds differently to sensory input, so you need to find a coping mechanism that is soothing to you.
[Read: Quick Stress Relief]
Look for humor in the situation. When used appropriately, humor is a great way to relieve stress when communicating . When you or those around you start taking things too seriously, find a way to lighten the mood by sharing a joke or an amusing story.
Be willing to compromise. Sometimes, if you can both bend a little, you’ll be able to find a happy middle ground that reduces the stress levels for everyone concerned. If you realize that the other person cares much more about an issue than you do, compromise may be easier for you and a good investment for the future of the relationship.
Agree to disagree, if necessary, and take time away from the situation so everyone can calm down. Go for a stroll outside if possible, or spend a few minutes meditating. Physical movement or finding a quiet place to regain your balance can quickly reduce stress.
Find your space for healing and growth
Regain is an online couples counseling service. Whether you’re facing problems with communication, intimacy, or trust, Regain’s licensed, accredited therapists can help you improve your relationship.
Direct, assertive expression makes for clear communication and can help boost your self-esteem and decision-making skills. Being assertive means expressing your thoughts, feelings, and needs in an open and honest way, while standing up for yourself and respecting others. It does NOT mean being hostile, aggressive, or demanding. Effective communication is always about understanding the other person, not about winning an argument or forcing your opinions on others.
To improve your assertiveness
Value yourself and your options. They are as important as anyone else’s.
Know your needs and wants. Learn to express them without infringing on the rights of others.
Express negative thoughts in a positive way. It’s okay to be angry , but you must remain respectful as well.
Receive feedback positively. Accept compliments graciously, learn from your mistakes, ask for help when needed.
Learn to say “no.” Know your limits and don’t let others take advantage of you. Look for alternatives so everyone feels good about the outcome.
Developing assertive communication techniques
Empathetic assertion conveys sensitivity to the other person. First, recognize the other person’s situation or feelings, then state your needs or opinion. “I know you’ve been very busy at work, but I want you to make time for us as well.”
Escalating assertion can be employed when your first attempts are not successful. You become increasingly firm as time progresses, which may include outlining consequences if your needs are not met. For example, “If you don’t abide by the contract, I’ll be forced to pursue legal action.”
Practice assertiveness in lower risk situations to help build up your confidence. Or ask friends or family if you can practice assertiveness techniques on them first.
More Information
- Effective Communication: Improving Your Social Skills - Communicate more effectively, improve your conversation skills, and become more assertive. (AnxietyCanada)
- Core Listening Skills - How to be a better listener. (SucceedSocially.com)
- Effective Communication - How to communicate in groups using nonverbal communication and active listening techniques. (University of Maine)
- Some Common Communication Mistakes - And how to avoid them. (SucceedSocially.com)
- 3aPPa3 – When cognitive demand increases, does the right ear have an advantage? – Danielle Sacchinell | Acoustics.org . (n.d.). Retrieved May 22, 2022, from Link
- How to Behave More Assertively . (n.d.). 10. Weger, H., Castle Bell, G., Minei, E. M., & Robinson, M. C. (2014). The Relative Effectiveness of Active Listening in Initial Interactions. International Journal of Listening , 28(1), 13–31. Link
More in Communication
How to read body language to build better relationships at home and work

Boost your emotional intelligence to help you be happy and successful

Tips for handling conflicts, arguments, and disagreements

How to feel and respond to the emotions of others

Tips and techniques for getting anger under control

Using laughter and play to resolve disagreements

Turning Off the Gas on Your Gaslighter
5 ways to deal with gaslighting

Strengthen your connections and improve your self-esteem

Professional therapy, done online
BetterHelp makes starting therapy easy. Take the assessment and get matched with a professional, licensed therapist.
Help us help others
Millions of readers rely on HelpGuide.org for free, evidence-based resources to understand and navigate mental health challenges. Please donate today to help us save, support, and change lives.
- News & Highlights
- Publications and Documents
- Postgraduate Education
- Browse Our Courses
- C/T Research Academy
- K12 Investigator Training
- Translational Innovator
- SMART IRB Reliance Request
- Biostatistics Consulting
- Regulatory Support
- Pilot Funding
- Informatics Program
- Community Engagement
- Diversity Inclusion
- Research Enrollment and Diversity
- Harvard Catalyst Profiles

Effectively Communicating Research
Intensive course designed to provide researchers with the skills necessary to express their science clearly to diverse audiences
For more information:
Course goals.
- Understand how and why to effectively communicate your research through a variety of platforms.
- Understand the structure of content that is appropriate and how to achieve the highest quality for each mode of scientific communication.
- Learn how to make written and graphic content more accessible and engaging.
- Know how to deliver oral presentations effectively with diverse audiences and settings.
- Learn approaches to request and respond to feedback from mentors, colleagues, and external reviewers.
How do you effectively draft your scientific message so that it has the optimal chance to be accepted for publication? How do you communicate your science in an oral presentation? How much text is appropriate for a poster? What are some guidelines and tips for dealing with the media? Communication is an essential part of your research and a crucial component for a successful career as a researcher.
Effectively Communicating Research is a two-day, intensive course offered by Harvard Catalyst. The course is designed to provide fellows and junior faculty with the skills necessary to express their science clearly to diverse audiences; to prepare abstracts, manuscripts, and posters, and to speak effectively.
With the guidance and expertise of the course faculty, including journal editors and leading scientists, participants will acquire the tools necessary to convey their science effectively.
Session dates
November 14 & 16, 2022
Time commitment
Participants accepted into the course must commit to fully participate in two days of the course.
As long as public health conditions permit, we will be running this event in-person , on the Harvard Medical School campus. Participants will be required to follow all Covid-19 guidelines outlined by Harvard Medical School.
Fellows and junior faculty who are in the process of writing for publication or creating communication materials for scientific oral or poster presentations.
We believe that the research community is strengthened by understanding how a number of factors including gender identity, sexual orientation, race and ethnicity, socioeconomic status, culture, religion, national origin, language, disability, and age shape the environment in which we live and work, affect each of our personal identities, and impacts all areas of human health.
Eligibility
- MD and/or PhD (or equivalent) involved in medical research
- Fellows and Junior Faculty
Free for Harvard-affiliated schools and institutions.
Accreditation statement
The Harvard Catalyst Education Program is accredited by the Massachusetts Medical Society to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Harvard Catalyst Education Program’s policy requires full attendance and the completion of all activity surveys to be eligible for CME credit; no partial credit is allowed.
Harvard Catalyst Postgraduate Education is dedicated to addressing equity and intersectionality in medicine. Race, ethnicity, age, and sex can impact how different people respond to the same intervention. Diversity of thought and perspectives through the lens of a participant’s background contributes to an enhanced course experience, improved research and development, and overall better medical devices. The benefits of bringing more seats to the table extends far beyond this course. With this in mind, ECR is intentionally reserving space for applicants from historically excluded communities to attend the course.
The application process is closed. Please check back for future opportunities.

Search Utah State University:
Effective communication skills: resolving conflicts .

Even the happiest of relationships experience conflicts and problems (Markman, Stanley, Blumberg, Jenkins & Whiteley, 2004). If handled well, issues provide opportunities for personal and relationship growth. There are many skills that can help individuals seeking to resolve conflicts in a healthy way. One of the greatest skills that aids in conflict resolution is effective communication.
Common Conflicts
Issues, or conflicts, in relationships consist of any situation, event or experience that is of concern or importance to those involved. A variety of factors lead to conflict, some of which include topics such as money, children, and in-laws, personal issues such as selfesteem, values, expectations, or goals, or relational issues such as the amount of together time versus alone time, support versus control, affection, and communication (Miller & Miller, 1997). While there are seemingly endless reasons for conflicts, they generally surround the underlying needs of all humans including physical, intellectual, emotional, social, and spiritual (Miller & Miller, 1997; Townsend, 2010). Most importantly, how we approach and communicate about these issues often determines the outcome.
Conflicts in Communication
Most people know that in order to resolve conflicts, we need to communicate about the issue; but negative patterns of communication can often lead to greater frustration and escalation of conflict. Consider the following communication challenges:
Body Language/Tone of Voice
Communication is more than the words we choose to use. In fact, our body language and tone of voice often speak louder than our words. For example, shouting “I’m not angry” is not a very convincing message! When we give an incongruent message where our tone of voice and body language does not match our message, confusion and frustration often follow (Gottman & DeClaire, 2001). In order to overcome this communication challenge, we need to be aware of what messages our body language and tone of voice may be sending others. Speak calmly, give eye contact, smile when appropriate, and maintain an open and relaxed posture (Paterson, 2000).
Differences in Style
Each of us has a unique way of communicating, often based on our family experiences, culture, gender and many other factors (Markman et al., 2004; Miller & Miller, 1997). For example, we may tend to be more loud, outgoing, or emotional when compared to our partner. While there is no right or wrong style, our past experiences often lead to expectations that are not usually verbally communicated with others, which can cause tension and misunderstandings in relationships. For example, if we came from a large family that tended to shout in order to be heard, we may think that speaking loudly is normal. But if our partner came from a calmer family environment, he/she may be uncomfortable or even frightened by a raised voice (Markman et al., 2004).
Discussing our backgrounds and perceptions can help to clarify expectations to ourselves and others and can also help our partner to understand our point of view. Knowing this information can often help in the problem solving process.
Communication Roadblocks
Communication roadblocks occur when two people talk in such a way that neither one feels understood. Research has found four particularly negative styles of communication, often referred to as the “four horsemen of the apocalypse,” (Gottman, 1999, p.27) because if left unchecked, these styles of interaction can eventually become lethal to relationships. These styles are criticism, contempt, defensiveness, and stonewalling (Gottman, 1999).
- Criticism attacks the character or personality of another. While it is normal to have complaints about another’s specific actions, it is very different to put them down as a person because of those actions. For example, a complaint might be, “I felt worried when you did not call to tell me that you were going to be home late.” A criticism in the same situation would be expressed as “You are so inconsiderate, you never call me when you are going to be late.” Critiques focus on certain behaviors; criticism negatively focuses on the person’s intentions and character.
- Contempt portrays disgust and a lack of respect for the other person through body language, such as eye rolling or sneering, or by name calling, sarcasm and cutting remarks.
- Defensiveness is a seemingly understandable reaction that individuals take to criticism and contempt; however, it often escalates the conflict. When we are defensive, we tend to stop listening to the other’s viewpoint and communication is shut down.
- Stonewalling is withdrawing from communication and refusing to engage in discussion. In other words, it is the adult version of the “silent treatment” that young children utilize when they are upset. Conflict resolution is impossible without communication!
Some additional examples of communication roadblocks include (Miller & Miller, 1997):
- Ordering (“Stop complaining!”)
- Warning (“If you do that, you’ll be sorry.”)
- Preaching (“You shouldn’t act like that.”)
- Advising (“Just wait a couple of years before deciding.”)
- Lecturing (“If you do this now, you won’t grow up to be a responsible adult.”)
- Agreeing, just to keep the peace (“I think you’re right.”)
- Ridiculing (“OK, little baby.”)
- Interpreting (“You don’t really believe that.”)
- Sympathizing (“Don’t worry, it’ll all work out.”)
- Questioning (“Who put that idea into your head?”)
- Diverting (“Let’s talk about something more pleasant.”)
Communication roadblocks are very common; however, they do not promote healthy conflict resolution and often lead to escalation of the conflict. Recognizing these roadblocks and making efforts to effectively communicate can help individuals overcome roadblocks.

Tips to Resolve Conflict
Soften the startup.
One of the skills to overcome communication roadblocks includes a soft startup to the conversation by starting with something positive, expressing appreciation, focusing on problems one at a time and taking responsibility for thoughts and feelings (Gottman, 1999; Gottman & Declaire, 2001; Patterson, 2000). In addition, when expressing the problem, starting the message with “I” instead of “You” can decrease defensiveness and promote positive interactions with others (Darrington & Brower, 2012). For example, “I want to stay more involved in making decisions about money” rather than “You never include me in financial decisions.”
Make and Receive Repair Attempts.
Another important skill in overcoming communication roadblocks is learning to make and receive repair attempts (Gottman, 1999). Repair attempts are efforts to keep an increasingly negative interaction from going any further by taking a break or making efforts to calm the situation. This is important because when conflicts arise, we often experience intense emotional and physical stress that can impact our ability to think and reason, which can lead to communication roadblocks (Gottman & DeClaire, 2001). Taking time away from the conflict (at least 20 minutes) to calm down can help us be more prepared to discuss the issue (Gottman, 1999; Gottman & DeClaire, 2001; Markman et al, 2004).
Effective Speaking and Listening Skills
Overcoming communication roadblocks requires effective speaking and listening skills. Markman, Stanley and Blumberg (2010) share what they call the “speaker-listener” technique to help individuals more effectively communicate. Each partner takes turns being the speaker and the listener.
The rules for the speaker include (Markman et al., 2004; Markman, Stanley & Blumberg, 2010):
- The speaker should share his/her own thoughts, feelings and concerns—not what he/she thinks the listener’s concerns are.
- Use “I” statements when speaking to accurately express thoughts and feelings.
- Keep statements short, to ensure the listener does not get overwhelmed with information.
- Stop after each short statement so that the listener can paraphrase, or repeat back in his/her own words, what was said to ensure he/she understands. If the paraphrase is not quite right, gently rephrase the statement again to help the listener understand.
The rules for the listener include:
- Paraphrase what the speaker is saying. If unclear, ask for clarification. Continue until the speaker indicates the message was received correctly.
- Don’t argue or give opinion about what the speaker says—wait to do this until you are the speaker, and then do so in a respectful manner.
- While the speaker is talking, the listener should not talk or interrupt except to paraphrase after the speaker.
The speaker and listener should take turns in each role so that each has a chance to express his/her thoughts and feelings. Either can call for a time out at any time. The goal of this activity is not to solve a particular problem, but rather to have a safe and meaningful discussion and to understand each other’s point of view. While we may not always agree with the other’s point of view, understanding and validating other’s thoughts and feelings can improve relationships and help us build on common ground, which may lead to more effective negotiation and problem resolution (Gottman, 1999).
Dealing with conflict can take varying amounts of mental, emotional, and physical energy (Miller & Miller, 1997). It can be work! However, learning and implementing a few simple communication skills can increase positive interactions with others. The opportunities for personal and relationship growth are well worth the effort.
For more information or for classes and workshops:
- Go to http://strongermarriage.org for tips, articles, and to find relationship education classes near you.
- Check out your local Extension office for relationship education classes and events.
- Darrington, J., & Brower, N. (2012). Effective communication skills: “I” messages and beyond. Utah State University Extension. https://extension.usu.edu/htm/publications/publi cation=14541
- Gottman, J. M., & DeClaire, J. (2001). The relationship cure: A 5 step guide to strengthening your marriage, family, and friendships. New York, NY: Three Rivers Press.
- Gottman, J. M., & Silver, N. (1999). The seven principles for making marriage work. New York, NY: Three Rivers Press.
- Markman, H. J., Stanley, S. M., & Blumberg, S. L. (2010). Fighting for your marriage. San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
- Markman, H. J, Stanley, S. M., Blumberg, S. L., Jenkins, N. H., & Whiteley, C. (2004). 12 hours to a great marriage: A step-by-step guide for making love last. San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
- Miller, S., & Miller, P. A. (1997). Core communication: Skills and processes. Evergreen, Co: Interpersonal Communication Programs, Inc.
- Paterson, R. J. (2000). The assertiveness workbook: How to express your ideas and stand up for yourself at work and in relationships. Oakland, CA: New Harbinger, Inc.
- Townsend, M. (2010). Starved stuff: Feeding the 7 basic needs of healthy relationships. Townsend Relationship Center.
Naomi Brower, MFHD, CFLE, Extension Assistant Professor; Jana Darrington, MS, Extension Assistant Professor

Naomi Brower
Extension Professor | Couple and Family Relationships | Weber County Director
Home and Community Department
Related Research

Building a Better Marriage
If you have been struggling with your marital relationship, or if you would like to improve the quality of your relationship, you are not alone. Just as Jenny and Michael want to strengthen their marria

Effective Communication Skills: Resolving Conflicts
Even the happiest of relationships experience conflicts and problems (Markman, Stanley, Blumberg, Jenkins & Whiteley, 2004). If handled well, issues provide opportunities for personal and relationship growth.

Effective Communication Skills: “I” Messages and Beyond
Communication is something we do on a regular basis. As young children we initially learn ways to communicate as we observe our parent, sibling, and family interactions. Throughout our lives our communication patterns evolve and are reinforced by our expe

Effects of Pornography on Relationships
Pornography is not a new issue in relationships; however, the expansion of the Internet appears to have increased pornography viewing and exacerbated pre-existing tendencies (Cooper, Boies, Maheu & Greenfield, 1999; Young, 2008). One key factor in this in

From Time to Quality Time: Making Every Moment Count
Couples and families often look for ways to find more time together and to make better use of that time. Most people struggle to find enough time in their day for everything. In fact, according to Dr. William Doherty (2001), those that care about each oth

Have Fun! The Importance of Play in Couple Relationships
Boring, drab, lifeless, stale, dull, tedious. These are probably not the words you hope to use to describe your relationships. How about well planned, frugal, precise, productive, serious, busy? Though these can be characteristics of a strong, healthy rel

Healthy Conflict Management
Conflicts are a natural part of human interaction. Whenever two or more people are in the same environment for a long enough period of time, it is inevitable that conflict will occur. However, the conflict itself is not the problem, but rather how they ch

Honey, I’m Home: Strengthening Your Marriage Ten Minutes at a Time
Strengthen your marriage relationship by making the first ten minutes of your interactions together a positive experience. Learn how to have stress-reducing conversation, emotionally support each other, and sooth self and partner in positive communication

Keys for Strong Commitment in Marriage
Having commitment means being dedicated to a cause. Commitment comes in all different shapes and sizes, but the most important type of commitment, for many, is a commitment to your marriage. Often couples start their marriage with commitment, but they don

Making Media Work for Your Marriage
Increased options for instant connection can have positive and negative impacts on relationships. While online resources can help us stay connected to those we love and increase relationship satisfaction Pettigrew, 2009; Sidelinger, Avash, Godorhazy, & T

Making the Most of Marriage Therapy
All relationships experience change over time (Larson, 2003). Even the strongest relationships can often benefit from a skilled a marriage counselor to help to smooth over the rough patches in their relationship. While the needs of relationships vary, som

Marriage Principles from a National Extension Model
Through this fact sheet, you will learn about these seven principles—Choose, Care for Self, Know, Care, Share, Manage, and Connect—and how to apply them in your life.

Supporting Others Coping with Infertility
It is likely that you know an individual or couple who is impacted by infertility. The natural human response is to want to comfort them, but it can be difficult to know what to say or do, especially if you have not experienced infertility yourself.

Technology Tips and Traps in Your Relationship
This fact sheet will help you be aware of some of the positive and negative effects of technology and how to protect your marriage from being swamped by it.

Tips to Strengthen Relationships Today
Research conducted by Dr. Sonja Lyubomirsky shows that happier people tend to have larger circles of friends, experience strong social support, and are more likely to be a support for others. But this research also shows that the connection between happin
- Getting Published
- Open Research
- Communicating Research
- Life in Research
- For Editors
- For Peer Reviewers
- Research Integrity
How to communicate your research more effectively
Author: guest contributor.

by Angie Voyles Askham, Content Marketing Intern
"Scientists need to excite the public about their work in part because the public is paying for it, and in part because science has very important things to say about some of the biggest problems society faces."
Stephen S. Hall has been reporting and writing about science for decades. For the past ten years, he's also been helping researchers at New York University improve their writing skills through the school's unique Science Communication Workshops . In our interview below, he explains why the public deserves good science communication and offers some tips for how researchers can make their writing clear and engaging.
How would you descr ibe your role as a science journalist?
I’ve always made a distinction between "science writer" and a writer who happens to be interested in science. That may sound like wordplay, but I think it captures what we aspire to do. Even as specialists, science journalists wear several hats: we explain, we report, we investigate, we step back and provide historical context to scientific developments to help people understand what’s new, why something is controversial, who drove a major innovation. And like any writer, we look for interesting, provocative, and deeply reported ways to tell these stories.
I know you from the science communication workshop that’s offered to NYU graduate students. One of the most important things that I got out of the workshop, at least initially, was training myself out of the stuffy academic voice that I think a lot researchers fall into when writing academic papers. Why do you think scientists fall into this particular trap, and how do you help them get out of it?
Scientists are trained—and rightly so—to describe their work in neutral, objective terms, qualifying all observations and openly acknowledging experimental limitations. Those qualities play very well in scientific papers and talks, but are terrible for effective communication to the general public. In our Science Communication workshops at NYU, we typically see that scientists tend to communicate in dense, formal and cautious language; they tell their audiences too much; they mimic the scientific literature’s affinity for passive voice; and they slip into jargon and what I call “jargonish,” defensive language. Over ten years of conducting workshops, we’ve learned to attack these problems on two fronts: pattern recognition (training people to recognize bad writing/speaking habits and fixing them) and psychological "deprogramming" (it’s okay to leave some details and qualifications out!). And a key ingredient to successful communication is understanding your audience; there is no such thing as the "general public," but rather a bunch of different potential audiences, with different needs and different levels of expertise. We try to educate scientists to recognize the exact audience they're trying to reach—what they need to know and, just as important, what they don't need to know.
What are some other common mistakes that you see researchers making when they’re trying to communicate about their work, either with each other or with the public?
We see the same tendencies over and over again: vocabulary (not simply jargon, but common expressions—such as gene “expression”—that are second-hand within a field, but not clear to non-experts); abstract, complicated explanations rather than using everyday language; sentences that are too long; and “optics” (paragraphs that are too long and appear monolithic to readers). We’ve found that workshops are the perfect setting to play out the process of using everyday language to explain something without sacrificing scientific accuracy.
Why is it important for researchers to be better communicators?
Scientists need to learn to tell their own stories, first and foremost, because society needs their expertise, their perspective, their evidence-based problem solving skills for the future. But the lay public, especially in an era where every fact seems up for grabs, needs to be reminded of what the scientific method is: using critical thinking and rigorous analysis of facts to reach evidence-based conclusions. Scientists need to excite the public about their work in part because the public is paying for it, and in part because science has very important things to say about some of the biggest problems society faces—climate change, medical care, advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, among many other issues. As climate scientist Michael Mann said in a celebrated 2014 New York Times OpEd, scientists can no longer stay on the sidelines in these important public debates.
As a science journalist, part of your job is to hunt for interesting stories to tell. How can scientists make their work more accessible to people like you—or to other people outside of their specific area of research—so that their stories are told more widely?
The key word in your question is “stories.” Think like a writer. What’s the story behind your discovery? What were the ups and downs on the way to the finding? Where does this fit into a larger history of science narrative? Was there a funny incident or episode in the work (humor is a great way to draw and sustain public interest)? Was there a conflict or competition that makes the work even more interesting? Is there a compelling historical or contemporary figure involved that will help you humanize the science? It's been our-longstanding belief that scientists have a great intuitive feel for good storytelling (we incorporate narrative training in our workshops), but just don’t think about it when it comes to describing their own work. The other key thing is to explain why your research matters.
One of the ways that many researchers try to share their work is through Twitter, but I noticed that on the NYU website it says you’re a Twitter conscientious objector. Why is that? What effect do you think Twitter has had on science communication and journalism in general?
I actually think Twitter can be a great tool for science communication, and many of my colleagues use it deftly. I tend to gravitate toward stories that everyone is not talking about, so Twitter doesn’t help much in that regard. The larger reason I’m a Twitter “refusenik,” as my colleague Dan Fagin sometimes calls me, is that I think the technology has been widely abused to disseminate misinformation, intimidate enemies, and subvert democratic norms; I don’t use it primarily for those reasons.
Are there any other tips that you can offer researchers who want to be better communicators and just aren’t sure where to start?
One first step might be to see if your institution offers any communication training and to take advantage of those programs; if not, think about how you might establish a program. We’ve posted a few of the things we’ve learned at NYU on our website ; we’ve also established a publishing platform for science communicators at NYU called the Cooper Square Review , which is a good way for scientists to get experience publishing their own work and reaching a larger public.
Stephen S. Hall has been reporting and writing about science for nearly 30 years. In addition to numerous cover stories in the New York Times Magazine, where he also served as a Story Editor and Contributing Writer, his work has appeared in The New Yorker, The Atlantic Monthly, and a number of other outlets. He is also the author of six non-fiction books about contemporary science. In addition to teaching the Science Communication Workshops at NYU, he also teaches for NYU's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program (SHERP) and has taught graduate seminars in science writing and explanatory journalism at Columbia University.
Click here to learn how Springer Nature continues to support the needs of Early Career Researchers.
Guest Contributors include Springer Nature staff and authors, industry experts, society partners, and many others. If you are interested in being a Guest Contributor, please contact us via email: [email protected] .
- early career researchers
- research communication
- Open research
- Tools & Services
- Account Development
- Sales and account contacts
- Professional
- Press office
- Locations & Contact
We are a world leading research, educational and professional publisher. Visit our main website for more information.
- © 2023 Springer Nature
- General terms and conditions
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Your Privacy Choices / Manage Cookies
- Accessibility
- Legal notice
- Help us to improve this site, send feedback.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- Subscribers For Subscribers
- ELN Write for Entrepreneur
- Store Entrepreneur Store
- Spotlight Spotlight
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Working With a Third-Party Logistics Provider? Here Are 3 Key Steps to Ensure a Seamless and Successful Partnership. Effective communication, strategic partnerships and technology adoption are vital for successful collaborations between brands and their 3PLs.
By Mark Ang • Mar 27, 2024
Key Takeaways
- Establishing transparent and regular communication with third-party logistics (3PL) providers is crucial for long-term success.
- Brands should treat their 3PL as an integral part of their team to avoid inefficiencies and missed opportunities. This also leads to smoother operations and better customer experiences.
- Leveraging technology offered by 3PLs can provide real-time insights and drive efficiency in operations.
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
Brands spend major dollars making positive connections with customers. They seek out touch points to build awareness, create personalized experiences and establish emotional links that drive greater engagement, sales and loyalty. And they are well aware that every interaction counts.
Yet, amid this flurry of activity, there's one vital relationship brands may be overlooking that can make or break their entire customer connection: It's the partnership with their third-party logistics (3PL) provider.
Much like any successful relationship, this connection thrives on clear communication, mutual trust, compatibility and a deep understanding of each other's needs and objectives. It's not just up to a 3PL to make the relationship work — it's a collaborative path that leads to its success.
Going well beyond contractual agreements, here are the three essential strategies brands can employ to nurture a thriving 3PL partnership and enhance their customer experience:
Related: The 4 Key Tenets of Every Successful Partnership
1. Communicate openly and often
When a brand engages with a 3PL, establishing transparent and consistent communication is key to its long-term success. It starts during the evaluation phase when brands lay out their requirements and leads into the proposal phase when 3PLs share their core competencies. Before a partnership decision is even made, 3PLs should have their implementation plan mapped out, accounting for a brand's system integrations, inventory management, packing details and carrier preferences, among other leading factors.
Open communication shouldn't end with a service agreement. For a truly successful partnership, brands can't take a set-it-and-forget-it approach with their 3PL. They can make warehouse site visits, establish channels for communication and share vital information regularly. The same goes for 3PLs. They cannot simply take over warehousing, inventory management, picking and packing, shipping and delivery without understanding all the nuances of a brand's business, from a brand's identity and SOPs to its specific compliance requirements for order fulfillment. Each partner must be willing to go all in on communicating transparently, frequently sharing forecasting and sales data, providing visibility into inventory levels and discussing any issues, performance metrics and customer feedback that arise.
By fostering a strong collaborative relationship with their 3PL, brands can achieve efficient operations, transparent pricing aligned with expectations, and effective communication tailored to its unique needs. This alignment cultivates a positive customer experience, characterized by predictability and reliability.
2. Treat your 3PL as an extension of your brand
A successful 3PL-brand partnership goes beyond mere transactions. In the most successful partnerships , brands view their 3PL as a true extension of their team. This is an intentional process that takes more than simple collaboration. It requires a willingness from both brands and their 3PLs to integrate themselves into each other's business.
3PLs aren't typically experts in retail, but they are experts in getting products to shoppers. By relegating a 3PL to just operational tasks without integrating them into the broader strategic framework, brands can encounter inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
Take sales and promotions as an example. Say a brand has invested significant time and resources into launching a new product with a splashy ad campaign but didn't inform their 3PL partner of the expected upswing in inventory and sales. This will result in staffing shortages, fulfillment delays and disappointed shoppers. By leaving their 3PL in the dark, and not giving them the opportunity to prepare, the brand didn't support a successful partnership.
Communicating variances, whether it's new SKUs or expected volume fluctuations, is a simple way to bring the 3PL along for the journey. Brands and 3PLs can take it further by establishing a point of contact who regularly shares updates, discusses KPIs like dock-to-stock metrics or inventory and picking accuracy, and aligns their customer support programs to quickly resolve shopper issues.
Operating as an integral part of a brand's team gives 3PLs the flexibility needed to adapt their operation to address partner needs instead of imposing rigid, one-size-fits-all solutions.
Related: These are the Do's and Don'ts of Working With a Third Party Service Provider
3. Embrace 3PL technology and the visibility it provides
As retailers look for methods to improve their customer experience , 3PLs embracing technology are rising to the occasion to meet their needs.
It's not enough just to partner with tech-forward 3PLs, though. Brands need to go all in on the technology offered to stay competitive and meet the ever-evolving demands of their customers.
Various technology platforms, such as Order Management Systems (OMS), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS), offer brands real-time insights into their 3PL, fulfillment and delivery operations, drive efficiency and offer visibility throughout their entire operation. What's more, a 3PL's automation, robotics and AI tools can boost productivity, reduce costs and enhance workforce experiences — leading to happier warehouse and delivery associates who perform better for brand partners.
Embracing technology and the 3PLs that adopt it, enhances operational efficiency and provides brands with the visibility they need to make informed decisions and proactively address customer needs, ultimately leading to a more seamless and satisfying shopping experience.
Related: How To Get the Most Out of External Partners
Maintaining open lines of communication, viewing 3PLs as a strategic partner rather than a service provider and embracing their technology are all key to forming successful partnerships.
With a strong 3PL relationship, brands can elevate their customer experience to drive brand loyalty and stay ahead of the curve in the increasingly competitive retail environment.
Entrepreneur Leadership Network® Contributor
CEO and Co-founder of GoBolt
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- 'The IRS is Coming in Hot': Jason Tartick Says All Business Owners Should Do This 1 Thing Before Filing Taxes — Or Risk a Potentially Pricey Audit
- Lock What Is a 'Dry Promotion' — and Has It Happened to You? Employees in This Specific Group May Be the Most Likely Victims .
- I Was a 25-Year-Old Nurse When I Started a Side Hustle to Combat Anxiety. It Made $1 Million in 7 Months — Then Sold for a Life-Changing Amount.
- Lock 2 Phrases I Learned From a Senior CIA Officer That Changed My Leadership Style
- The U.S. Justice Department Is Suing Apple in a Groundbreaking iPhone Monopoly Lawsuit — Here's Why
- Lock I Built My Company to 23 Profitable Stores. Here's My Advice to Small Business Owners Who Want to Grow Their Retail Presence.
Most Popular Red Arrow
Why dei still matters for small businesses and startups.
DEI shouldn't be just a buzzword.
Mark Zuckerberg Told Meta Engineers to 'Figure Out' Snapchat's Privacy Protections: 'We Have No Analytics on Them'
Recently unsealed court documents detail "Project Ghostbusters," Meta's project to work around Snapchat's end-to-end encryption to intercept data.
Save $240 on a Lifetime Subscription That Provides More Than 1,500 Book Summaries
With Headway Premium, you can gain knowledge at a rapid rate.
Sam Bankman-Fried Sentenced to 25 Years in Prison for Multibillion-Dollar Crypto Fraud
Southern District of New York Judge Lewis Kaplan said that the loss amount to the victims of Bankman-Fried's crimes surpassed $550 million.
The Brand Whiz Behind Sun Bum Is Famous For Making Boring Products Fun. Then, This One Stumped Him.
Everything Tom Rinks touched turned to gold until he took on a brand launch at Target that fizzled. Then, he found a creepy doll on Ebay, and he saw a way forward.
How To Improve Your Soft Skills and Emotional Intelligence in 7 Easy Steps
Using these simple but effective approaches will help a person in their business, life and relationships.
Successfully copied link
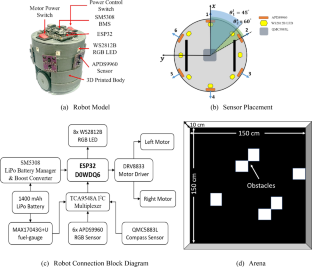
Decentralised Coordination in Swarm Robots Through XGBoost-Enhanced Colour Light Communication
- Research Article-Electrical Engineering
- Published: 27 March 2024
Cite this article
- Abhishek Kaushal ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4870-8545 1 ,
- Anuj Kumar Sharma 1 &
- Krishna Gupta 2
11 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Inspired by natural swarm systems, robotic swarms aim to solve complicated problems through the emergent behaviour of coordinating robots (agents). Communication among the robots is of paramount importance for their effective coordination, cooperation, and overall performance. This research presents a colour light-based communication system for miniature mobile swarm robots, on which a pre-trained supervised machine learning model runs and is responsible for effective colour recognition, enhancing inter-robot local communication. The performance of various supervised machine learning techniques was examined, and XGBoost performed best overall, with a classification accuracy of 96.66%, an execution time of 0.403 ms, an average sensing distance of 87.38 cm, and an acceptable size of 402.1 kilobytes while running on a 32-bit embedded microcontroller. The current work also demonstrates various swarming behaviours, utilising the developed communication as proof of concept.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Lukeman, R.; Li, Y.-X.; Edelstein-Keshet, L.: Inferring individual rules from collective behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107 (28), 12576–12580 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1001763107
Article Google Scholar
Dorigo, M., et al.: Evolving self-organizing behaviors for a swarm-bot. Auton. Robots 17 (2/3), 223–245 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AURO.0000033973.24945.f3
Tan, Y.; Zheng, Z.: Research advance in swarm robotics. Defence Technol. 9 (1), 18–39 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2013.03.001
Dorigo, M.; Theraulaz, G.; Trianni, V.: Swarm robotics: past, present, and future. Proc. IEEE 109 (7), 1152–1165 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2021.3072740
Tang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.: Dynamic target searching and tracking with swarm robots based on stigmergy mechanism. Rob Auton Syst 120 , 103251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2019.103251
Benavidez, P.; et al.: Multi-domain robotic swarm communication system. In: 2008 IEEE international conference on system of systems engineering, SoSE 2008. https://doi.org/10.1109/SYSOSE.2008.4724189 .
Chamanbaz, M., et al.: Swarm-enabling technology for multi-robot systems. Front. Robot. AI 4 (APR), 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2017.00012
Zeng, T.; Mozaffari, M.; Semiari, O.; Saad, W.; Bennis, M.; Debbah, M.: Wireless communications and control for swarms of cellular-connected UAVs. In: Conf Rec Asilomar Conf Signals Syst Comput , vol. 2018-Octob, pp. 719–723 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACSSC.2018.8645472 .
Gielis, J.; Shankar, A.; Prorok, A.: A critical review of communications in multi-robot systems. Curr. Robot. Rep. 3 (4), 213–225 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43154-022-00090-9
Mjaid, A.Y.; Prasad, V.; Jonker, M.; Van Der Horst, C.; De Groot, L.; Narayana, S.: AI-based simultaneous audio localization and communication for robots. In: ACM International Conference Proceeding Series . Association for Computing Machinery, pp. 172–183 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1145/3576842.3582373
Trenkwalder, S.M.; Esnaola, I.; Kaszubowski Lopes, Y.; Kolling, A.; Groß, R.: SwarmCom: an infra-red-based mobile ad-hoc network for severely constrained robots. Auton. Robots 44 (1), 93–114 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-019-09873-0
Patil, D.; Shah, K.; Patadia, U.; Sheth, N.; Solanki, R.; Singh, A.: Swarm robots in a closed loop visual odometry system by using visible light communication. Adv. Signal Process. Intell. Recognit. Syst. 1 , 201–212 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67934-1_18
Sun, X.; Liu, T.; Hu, C.; Fu, Q.; Yue, S.: ColCOS Φ: a multiple pheromone communication system for swarm robotics and social insects research. In: 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), pp. 59–66. IEEE (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICARM.2019.8833989 .
Na, S., et al.: Bio-inspired artificial pheromone system for swarm robotics applications. Adapt. Behav.Behav. 29 (4), 395–415 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/1059712320918936
Liu, T.; Sun, X.; Hu, C.; Fu, Q.; Yue, S.: A versatile vision-pheromone-communication platform for swarm robotics. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) , pp. 7261–7266. IEEE (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA48506.2021.9561911 .
Garzón Ramos, D.; Salman, M.; Ubeda Arriaza, K.; Hasselmann, K.; Birattari, M.: MoCA : a modular RGB color arena for swarm robotics experiments. 2022. Technical report number TR/IRIDIA/2022-014
Ramos, D.G.; Birattari, M.: Automatic design of collective behaviors for robots that can display and perceive colors. Appl. Sci. (Switzerland) (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134654
Maxseiner, A.B.; Lofaro, D.M.; Sofge, D.A.: Visible light communications with inherent agent localization and simultaneous message receiving capabilities for robotic swarms. In: 2021 18th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots, UR 2021, pp. 633–639 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/UR52253.2021.9494636
Kaushal, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, G.K.: Color-coded light signals based communication for swarming behaviors in mobile robotic system. J Sens 2023 , 1–15 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/8660847
Eloquentarduino, “Micromlgen,” Github.com. Accessed: 25, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://github.com/eloquentarduino/micromlgen
Shah, K.; Patel, H.; Sanghvi, D.; Shah, M.: A comparative analysis of logistic regression, random forest and KNN models for the text classification. Augmented Human Res. 5 (1), 12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41133-020-00032-0
Duan, K.B.; Keerthi, S.S.: Which is the best multiclass SVM method? An empirical study. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci.Comput. Sci. 3541 , 278–285 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/11494683_28
Kotsiantis, S.B.: Decision trees: a recent overview. Artif. Intell. Rev.. Intell. Rev. 39 (4), 261–283 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-011-9272-4
Speiser, J.L.; Miller, M.E.; Tooze, J.; Ip, E.: A comparison of random forest variable selection methods for classification prediction modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 134 , 93–101 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.05.028
Chen, T.; Guestrin, C.: XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 785–794. ACM, New York (2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Advanced Studies, Lucknow, India
Abhishek Kaushal & Anuj Kumar Sharma
Dr. Shakuntala Misra National Rehabilitation University, Lucknow, India
Krishna Gupta
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Abhishek Kaushal .
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kaushal, A., Sharma, A.K. & Gupta, K. Decentralised Coordination in Swarm Robots Through XGBoost-Enhanced Colour Light Communication. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-08923-9
Download citation
Received : 04 October 2023
Accepted : 29 February 2024
Published : 27 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-08923-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Decentralised control
- Swarm robots
- Visible light communication
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Clin Transl Sci
- v.4(3); 2020 Jun

Communicating and disseminating research findings to study participants: Formative assessment of participant and researcher expectations and preferences
Cathy l. melvin.
1 College of Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
Jillian Harvey
2 College of Health Professions/Healthcare Leadership & Management, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
Tara Pittman
3 South Carolina Clinical & Translational Research Institute (CTSA), Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
Stephanie Gentilin
Dana burshell.
4 SOGI-SES Add Health Study Carolina Population Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Teresa Kelechi
5 College of Nursing, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
Introduction:
Translating research findings into practice requires understanding how to meet communication and dissemination needs and preferences of intended audiences including past research participants (PSPs) who want, but seldom receive, information on research findings during or after participating in research studies. Most researchers want to let others, including PSP, know about their findings but lack knowledge about how to effectively communicate findings to a lay audience.
We designed a two-phase, mixed methods pilot study to understand experiences, expectations, concerns, preferences, and capacities of researchers and PSP in two age groups (adolescents/young adults (AYA) or older adults) and to test communication prototypes for sharing, receiving, and using information on research study findings.
Principal Results:
PSP and researchers agreed that sharing study findings should happen and that doing so could improve participant recruitment and enrollment, use of research findings to improve health and health-care delivery, and build community support for research. Some differences and similarities in communication preferences and message format were identified between PSP groups, reinforcing the best practice of customizing communication channel and messaging. Researchers wanted specific training and/or time and resources to help them prepare messages in formats to meet PSP needs and preferences but were unaware of resources to help them do so.
Conclusions:
Our findings offer insight into how to engage both PSP and researchers in the design and use of strategies to share research findings and highlight the need to develop services and support for researchers as they aim to bridge this translational barrier.
Introduction
Since 2006, the National Institutes of Health Clinical and Translational Science Awards (CTSA) have aimed to advance science and translate knowledge into evidence that, if implemented, helps patients and providers make more informed decisions with the potential to improve health care and health outcomes [ 1 , 2 ]. This aim responded to calls by leaders in the fields of comparative effectiveness research, clinical trials, research ethics, and community engagement to assure that results of clinical trials were made available to participants and suggesting that providing participants with results both positive and negative should be the “ethical norm” [ 1 , 3 ]. Others noted that
on the surface, the concept of providing clinical trial results might seem straightforward but putting such a plan into action will be much more complicated. Communication with patients following participation in a clinical trial represents an important and often overlooked aspect of the patient-physician relationship. Careful exploration of this issue, both from the patient and clinician-researcher perspective, is warranted [ 4 ].
Authors also noted that no systematic approach to operationalizing this “ethical norm” existed and that evidence was lacking to describe either positive or negative outcomes of sharing clinical trial results with study participants and the community [ 4 ]. It was generally assumed, but not supported by research, that sharing would result in better patient–physician/researcher communication, improvement in patient care and satisfaction with care, better patient/participant understanding of clinical trials, and enhanced clinical trial accrual [ 4 ].
More recent literature informs these processes but also raises unresolved concerns about the communication and dissemination of research results. A 2008 narrative review of available data on the effects of communicating aggregate and individual research showed that
- research participants want aggregate and clinically significant individual study results made available to them despite the transient distress that communication of results sometimes elicits [ 3 , 5 ]. While differing in their preferences for specific channels of communication, they indicated that not sharing results fostered lack of participant trust in the health-care system, providers, and researchers [ 6 ] and an adverse impact on trial participation [ 5 ];
- investigators recognized their ethical obligation to at least offer to share research findings with recipients and the nonacademic community but differed on whether they should proactively re-contact participants, the type of results to be offered to participants, the need for clinical relevance before disclosure, and the stage at which research results should be offered [ 5 ]. They also reported not being well versed in communication and dissemination strategies known to be effective and not having funding sources to implement proven strategies for sharing with specific audiences [ 5 ];
- members of the research enterprise noted that while public opinion regarding participation in clinical trials is positive, clinical trial accrual remains low and that the failure to provide information about study results may be one of many factors negatively affecting accrual. They also called for better understanding of physician–researcher and patient attitudes and preferences and posit that development of effective mechanisms to share trial results with study participants should enhance patient–physician communication and improve clinical care and research processes [ 5 ].
A 2010 survey of CTSAs found that while professional and scientific audiences are currently the primary focus for communicating and disseminating research findings, it is equally vital to develop approaches for sharing research findings with other audiences, including individuals who participate in clinical trials [ 1 , 5 ]. Effective communication and dissemination strategies are documented in the literature [ 6 , 7 ], but most are designed to promote adoption of evidence-based interventions and lack of applicability to participants overall, especially to participants who are members of special populations and underrepresented minorities who have fewer opportunities to participate in research and whose preferences for receiving research findings are unknown [ 7 ].
Researchers often have limited exposure to methods that offer them guidance in communicating and disseminating study findings in ways likely to improve awareness, adoption, and use of their findings [ 7 ]. Researchers also lack expertise in using communication channels such as traditional journalism platforms, live or face-to-face events such as public festivals, lectures, and panels, and online interactions [ 8 ]. Few strategies provide guidance for researchers about how to develop communications that are patient-centered, contain plain language, create awareness of the influence of findings on participant or population health, and increase the likelihood of enrollment in future studies.
Consequently, researchers often rely on traditional methods (e.g., presentations at scientific meetings and publication of study findings in peer-reviewed journals) despite evidence suggesting their limited reach and/or impact among professional/scientific and/or lay audiences [ 9 , 10 ].
Input from stakeholders can enhance our understanding of how to assure that participants will receive understandable, useful information about research findings and, as appropriate, interpret and use this information to inform their decisions about changing health behaviors, interacting with their health-care providers, enrolling in future research studies, sharing their study experiences with others, or recommending to others that they participate in studies.
Purpose and Goal
This pilot project was undertaken to address issues cited above and in response to expressed concerns of community members in our area about not receiving information on research studies in which they participated. The project design, a two-phase, mixed methods pilot study, was informed by their subsequent participation in a committee of community-academic representatives to determine possible options for improving the communication and dissemination of study results to both study participants and the community at large.
Our goals were to understand the experiences, expectations, concerns, preferences, and capacities of researchers and past research participants (PSP) in two age groups (adolescents/young adults (AYA) aged 15–25 years and older adults aged 50 years or older) and to test communication prototypes for sharing, receiving, and using information on research study findings. Our long-term objectives are to stimulate new, interdisciplinary collaborative research and to develop resources to meet PSP and researcher needs.
This study was conducted in an academic medical center located in south-eastern South Carolina. Phase one consisted of surveying PSP and researchers. In phase two, in-person focus groups were conducted among PSP completing the survey and one-on-one interviews were conducted among researchers. Participants in either the interviews or focus groups responded to a set of questions from a discussion guide developed by the study team and reviewed three prototypes for communicating and disseminating study results developed by the study team in response to PSP and researcher survey responses: a study results letter, a study results email, and a web-based communication – Mail Chimp (Figs. 1 – 3 ).

Prototype 1: study results email prototype. MUSC, Medical University of South Carolina.

Prototype 3: study results MailChimp prototypes 1 and 2. MUSC, Medical University of South Carolina.

Prototype 2: study results letter prototype.
PSP and researcher surveys
A 42-item survey questionnaire representing seven domains was developed by a multidisciplinary team of clinicians, researchers, and PSP that evaluated the questions for content, ease of understanding, usefulness, and comprehensiveness [ 11 ]. Project principal investigators reviewed questions for content and clarity [ 11 ]. The PSP and researcher surveys contained screening and demographic questions to determine participant eligibility and participant characteristics. The PSP survey assessed prior experience with research, receipt of study information from the research team, intention to participate in future research, and preferences and opinions about receipt of information about study findings and next steps. Specific questions for PSP elicited their preferences for communication channels such as phone call, email, social or mass media, and public forum and included channels unique to South Carolina, such as billboards. PSP were asked to rank their preferences and experiences regarding receipt of study results using a Likert scale with the following measurements: “not at all interested” (0), “not very interested” (1), “neutral” (3), “somewhat interested” (3), and “very interested” (4).
The researcher survey contained questions about researcher decisions, plans, and actions regarding communication and dissemination of research results for a recently completed study. Items included knowledge and opinions about how to communicate and disseminate research findings, resources used and needed to develop communication strategies, and awareness and use of dissemination channels, message development, and presentation format.
A research team member administered the survey to PSP and researchers either in person or via phone. Researchers could also complete the survey online through Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap©).
Focus groups and discussion guide content
The PSP focus group discussion guide contained questions to assess participants’ past experiences with receiving information about research findings; identify participant preferences for receiving research findings whether negative, positive, or equivocal; gather information to improve communication of research results back to participants; assess participant intention to enroll in future research studies, to share their study experiences with others, and to refer others to our institution for study participation; and provide comments and suggestions on prototypes developed for communication and dissemination of study results. Five AYA participated in one focus group, and 11 older adults participated in one focus group. Focus groups were conducted in an off-campus location with convenient parking and at times convenient for participants. Snacks and beverages were provided.
The researcher interview guide was designed to understand researchers’ perspectives on communicating and disseminating research findings to participants; explore past experiences, if any, of researchers with communication and dissemination of research findings to study participants; document any approaches researchers may have used or intend to use to communicate and disseminate research findings to study participants; assess researcher expectations of benefits associated with sharing findings with participants, as well as, perceived and actual barriers to sharing findings; and provide comments and suggestions on prototypes developed for communication and dissemination of study results.
Prototype materials
Three prototypes were presented to focus group participants and included (1) a formal letter on hospital letterhead designed to be delivered by standard mail, describing the purpose and findings of a fictional study and thanking the individual for his/her participation, (2) a text-only email including a brief thank you and a summary of major findings with a link to a study website for more information, and (3) an email formatted like a newsletter with detailed information on study purpose, method, and findings with graphics to help convey results. A mock study website was shown and included information about study background, purpose, methods, results, as well as, links to other research and health resources. Prototypes were presented either in paper or PowerPoint format during the focus groups and explained by a study team member who then elicited participant input using the focus group guide. Researchers also reviewed and commented on prototype content and format in one-on-one interviews with a study team member.
Protection of Human Subjects
The study protocol (No. Pro00067659) was submitted to and approved by the Institutional Review Board at the Medical University of South Carolina in 2017. PSP (or the caretakers for PSP under age 18), and researchers provided verbal informed consent prior to completing the survey or participating in either a focus group or interview. Participants received a verbal introduction prior to participating in each phase.
Recruitment and Interview Procedures
Past study participants.
A study team member reviewed study participant logs from five recently completed studies at our institution involving AYA or older adults to identify individuals who provided consent for contact regarding future studies. Subsequent PSP recruitment efforts based on these searches were consistent with previous contact preferences recorded in each study participant’s consent indicating desire to be re-contacted. The primary modes of contact were phone/SMS and email.
Efforts to recruit other PSP were made through placement of flyers in frequented public locations such as coffee shops, recreation complexes, and college campuses and through social media, Yammer, and newsletters. ResearchMatch, a web-based recruitment tool, was used to alert its subscribers about the study. Potential participants reached by these methods contacted our study team to learn more about the study, and if interested and pre-screened eligible, volunteered and were consented for the study. PSP completing the survey indicated willingness to share experiences with the study team in a focus group and were re-contacted to participate in focus groups.
Researcher recruitment
Researchers were identified through informal outreach by study investigators and staff, a flyer distributed on campus, use of Yammer and other institutional social media platforms, and internal electronic newsletters. Researchers responding to these recruitment efforts were invited to participate in the researcher survey and/or interview.
Incentives for participation
Researchers and PSP received a $25 gift card for completing the survey and $75 for completing the interview (researcher) or focus group (PSP) (up to $100 per researcher or PSP).
Data tables displaying demographic and other data from the PSP surveys (Table (Table1) 1 ) were prepared from the REDCap© database and responses reported as number and percent of respondents choosing each response option.
Post study participant (PSP) characteristics by Adolescents/Young Adults (AYA), Older Adults, and ALL (All participants regardless of age)
Age mean (SD) = 49.7 (18.6).
Focus group and researcher interview data were recorded (either via audio recording and/or notes taken by research staff) and analyzed via a general inductive qualitative approach, a method appropriate for program evaluation studies and aimed at condensing large amounts of textual data into frameworks that describe the underlying process and experiences under study [ 12 ]. Data were analyzed by our team’s qualitative expert who read the textual data multiple times, developed a coding scheme to identify themes in the textual data, and used group consensus methods with other team members to identify unique, key themes.
Sixty-one of sixty-five PSP who volunteered to participate in the PSP survey were screened eligible, fifty were consented, and forty-eight completed the survey questionnaire. Of the 48 PSP completing the survey, 15 (32%) were AYA and 33 (68%) older adults. The mean age of survey respondents was 49.7 years, 23.5 for AYA, and 61.6 for older adults. Survey respondents were predominantly White, non-Hispanic/Latino, female, and with some college or a college degree (Table (Table1). 1 ). The percentage of participants in each group never or rarely needing any help with reading/interpreting written materials was above 93% in both groups.
Over 90% of PSP responded that they would participate in another research study, and more than 75% of PSP indicated that study participants should know about study results. Most (68.8%) respondents indicated that they did not receive any communications from study staff after they finished a study .
PSP preferences for communication channel are summarized in Table Table2 2 and based on responses to the question “How do you want to receive information?.” Both AYA and older adults agree or completely agree that they prefer email to other communication channels and that billboards did not apply to them. Older adult preferences for communication channels as indicated by agreeing or completely agreeing were in ranked order of highest to lowest: use of mailed letters/postcards, newsletter, and phone. A majority (over 50%) of older adults completely disagreed or disagreed on texting and social media as options and had only slight preference for mass media, public forum, and wellness fairs or expos.
Communication preference by group: AYA * , older adult ** , and ALL ( n = 48)
ALL, total per column.
While AYA preferred email over all other options, they completely disagreed/disagreed with mailed letters/postcards, social media, and mass media options.
When communication formats were ranked overall by each group and by both groups combined, the ranking from most to least preferred was written materials, opportunities to interact with study teams and ask questions, visual charts, graphs, pictures, and videos, audios, and podcasts.
PSP Focus Groups
PSP want to receive and share information on study findings for studies in which he/she participated. Furthermore, participants stated their desire to share study results across social networks and highlighted opportunities to share communicated study results with their health-care providers, family members, friends, and other acquaintances with similar medical conditions.
Because of the things I was in a study for, it’s a condition I knew three other people who had the same condition, so as soon as it worked for me, I put the word out, this is great stuff. I would forward the email with the link, this is where you can go to also get in on this study, or I’d also tell them, you know, for me, like the medication. Here’s the medication. Here’s the name of it. Tell your doctor. I would definitely share. I’d just tell everyone without a doubt. Right when I get home, as soon as I walk in the door, and say Renee-that’s my daughter-I’ve got to tell you this.
Communication of study information could happen through several channels including social media, verbal communication, sharing of written documents, and forwarding emails containing a range of content in a range of formats (e.g., reports and pamphlets).
Word of mouth and I have no shame in saying I had head to toe psoriasis, and I used the drug being studied, and so I would just go to people, hey, look. So, if you had it in paper form, like a pamphlet or something, yeah I’d pass it on to them.
PSP prefer clear, simple messaging and highlighted multiple, preferred communication modalities for receiving information on study findings including emails, letters, newsletters, social media, and websites.
The wording is really simple, which I like. It’s to the point and clear. I really like the bullet points, because it’s quick and to the point. I think the [long] paragraphs-you get lost, especially when you are reading on your phone.
They indicated a clear preference for colorful, simple, easy to read communication. PSP also expressed some concern about difficulty opening emails with pictures and dislike lengthy written text. “I don’t read long emails. I tend to delete them”
PSP indicated some confusion about common research language. For example, one participant indicated that using the word “estimate” indicates the research findings were an approximation, “When I hear those words, I just think you’re guessing, estimate, you know? It sounds like an estimate, not a definite answer.”
Researcher Survey
Twenty-three of thirty-two researchers volunteered to participate in the researcher survey, were screened eligible, and two declined to participate, resulting in 19 who provided consent to participate and completed the survey. The mean age of survey respondents was 51.8 years. Respondents were predominantly White, non-Hispanic/Latino, and female, and all were holders of either a professional school degree or a doctoral degree. When asked if it is important to inform study participants of study results, 94.8% of responding researchers agreed that it was extremely important or important. Most researchers have disseminated findings to study participants or plan to disseminate findings.
Researchers listed a variety of reasons for their rating of the importance of informing study participants of study results including “to promote feelings of inclusion by participants and other community members”, “maintaining participant interest and engagement in the subject study and in research generally”, “allowing participants to benefit somewhat from their participation in research and especially if personal health data are collected”, “increasing transparency and opportunities for learning”, and “helping in understanding the impact of the research on the health issue under study”.
Some researchers view sharing study findings as an “ethical responsibility and/or a tenet of volunteerism for a research study”. For example, “if we (researchers) are obligated to inform participants about anything that comes up during the conduct of the study, we should feel compelled to equally give the results at the end of the study”.
One researcher “thought it a good idea to ask participants if they would like an overview of findings at the end of the study that they could share with others who would like to see the information”.
Two researchers said that sharing research results “depends on the study” and that providing “general findings to the participants” might be “sufficient for a treatment outcome study”.
Researchers indicated that despite their willingness to share study results, they face resource challenges such as a lack of funding and/or staff to support communication and dissemination activities and need assistance in developing these materials. One researcher remarked “I would really like to learn what are (sic) the best ways to share research findings. I am truly ignorant about this other than what I have casually observed. I would enjoy attending a workshop on the topic with suggested templates and communication strategies that work best” and that this survey “reminds me how important this is and it is promising that our CTSA seems to plan to take this on and help researchers with this important study element.”
Another researcher commented on a list of potential types of assistance that could be made available to assist with communicating and disseminating results, that “Training on developing lay friendly messaging is especially critically important and would translate across so many different aspects of what we do, not just dissemination of findings. But I’ve noticed that it is a skill that very few people have, and some people never can seem to develop. For that reason, I find as a principal investigator that I am spending a lot of my time working on these types of materials when I’d really prefer research assistant level folks having the ability to get me 99% of the way there.”
Most researchers indicated that they provide participants with personal tests or assessments taken from the study (60% n = 6) and final study results (72.7%, n = 8) but no other information such as recruitment and retention updates, interim updates or results, information on the impact of the study on either the health topic of the study or the community, information on other studies or provide tips and resources related to the health topic and self-help. Sixty percent ( n = 6) of researcher respondents indicated sharing planned next steps for the study team and information on how the study results would be used.
When asked about how they communicated results, phone calls were mentioned most frequently followed by newsletters, email, webpages, public forums, journal article, mailed letter or postcard, mass media, wellness fairs/expos, texting, or social media.
Researchers used a variety of communication formats to communicate with study participants. Written descriptions of study findings were most frequently reported followed by visual depictions, opportunities to interact with study staff and ask questions or provide feedback, and videos/audio/podcasts.
Seventy-three percent of researchers reported that they made efforts to make study findings information available to those with low levels of literacy, health literacy, or other possible limitations such as non-English-speaking populations.
In open-ended responses, most researchers reported wanting to increase their awareness and use of on-campus training and other resources to support communication and dissemination of study results, including how to get resources and budgets to support their use.
Researcher Interviews
One-on-one interviews with researchers identified two themes.
Researchers may struggle to see the utility of communicating small findings
Some researchers indicated hesitancy in communicating preliminary findings, findings from small studies, or highly summarized information. In addition, in comparison to research participants, researchers seemed to place a higher value on specific details of the study.
“I probably wouldn’t put it up [on social media] until the actual manuscript was out with the graphs and the figures, because I think that’s what people ultimately would be interested in.”
Researchers face resource and time limitations in communication and dissemination of study findings
Researchers expressed interest in communicating research results to study participants. However, they highlighted several challenges including difficulties in tracking current email and physical addresses for participants; compliance with literacy and visual impairment regulations; and the number of products already required in research that consume a considerable amount of a research team’s time. Researchers expressed a desire to have additional resources and templates to facilitate sharing study findings. According to one respondent, “For every grant there is (sic) 4-10 papers and 3-5 presentations, already doing 10-20 products.” Researchers do not want to “reinvent the wheel” and would like to pull from existing papers and presentations on how to share with participants and have boilerplate, writing templates, and other logistical information available for their use.
Researchers would also like training in the form of lunch-n-learns, podcasts, or easily accessible online tools on how to develop materials and approaches. Researchers are interested in understanding the “do’s and don’ts” of communicating and disseminating study findings and any regulatory requirements that should be considered when communicating with research participants following a completed study. For example, one researcher asked, “From beginning to end – the do’s and don’ts – are stamps allowed as a direct cost? or can indirect costs include paper for printing newsletters, how about designing a website, a checklist for pulling together a newsletter?”
The purpose of this pilot study was to explore the current experiences, expectations, concerns, preferences, and capacities of PSP including youth/young adult and older adult populations and researchers for sharing, receiving, and using information on research study findings. PSP and researchers agreed, as shown in earlier work [ 3 , 5 ], that sharing information upon study completion with participants was something that should be done and that had value for both PSP and researchers. As in prior studies [ 3 , 5 ], both groups also agreed that sharing study findings could improve ancillary outcomes such as participant recruitment and enrollment, use of research findings to improve health and health-care delivery, and build overall community support for research. In addition, communicating results acknowledges study participants’ contributions to research, a principle firmly rooted in respect for treating participants as not merely a means to further scientific investigation [ 5 ].
The majority of PSP indicated that they did not receive research findings from studies they participated in, that they would like to receive such information, and that they preferred specific communication methods for receipt of this information such as email and phone calls. While our sample was small, we did identify preferences for communication channels and for message format. Some differences and similarities in preferences for communication channels and message format were identified between AYA and older adults, thus reinforcing the best practice of customizing communication channel and messaging to each specific group. However, the preference for email and the similar rank ordering of messaging formats suggest that there are some overall communication preferences that may apply to most populations of PSP. It remains unclear whether participants prefer individual or aggregate results of study findings and depends on the type of study, for example, individual results of genotypes versus aggregate results of epidemiological studies [ 13 ]. A study by Miller et al suggests that the impact of receiving aggregate results, whether clinically relevant or not, may equal that of receiving individual results [ 14 ]. Further investigation warrants evaluation of whether, when, and how researchers should communicate types of results to study participants, considering multiple demographics of the populations such as age and ethnicity on preferences.
While researchers acknowledged that PSP would like to hear from them regarding research results and that they wanted to meet this expectation, they indicated needing specific training and/or time and resources to provide this information to PSP in a way that meets PSP needs and preferences. Costs associated with producing reports of findings were a concern of researchers in our study, similar to findings from a study conducted by Di Blasi and colleagues in which 15% (8 of 53 investigators) indicated that they wanted to avoid extra costs associated with the conduct of their studies and extra administrative work [ 15 ]. In this same study, the major reason for not informing participants about study results was that forty percent of investigators never considered this option. Researchers were unaware of resources available on existing platforms at their home institution or elsewhere to help them with communication and dissemination efforts [ 10 ].
Addressing Barriers to Implementation
Information from academic and other organizations on how to best communicate research findings in plain language is available and could be shared with researchers and their teams. The Cochrane Collaborative [ 16 ], the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [ 17 ], and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute [ 18 ] have resources to help researchers develop plain language summaries using proven approaches to overcome literacy and other issues that limit participant access to study findings. Some academic institutions have electronic systems in place to confidentially share templated laboratory and other personal study information with participants and, if appropriate, with their health-care providers.
Limitations
Findings from the study are limited by several study and respondent characteristics. The sample was drawn from research records at one university engaging in research in a relatively defined geographic area and among two special populations: AYA and older adults. As such, participants were not representative of either the general population in the area, the population of PSP or researchers available in the area, or the racial and ethnic diversity of potential and/or actual participants in the geographic area. The small number of researcher participants did not represent the pool of researchers at the university, and the research studies from which participants were drawn were not representative of the broad range of clinical and translational research undertaken by our institution or within the geographic community it serves. The number of survey and focus group participants was insufficient to allow robust analysis of findings specific to participants’ race, ethnicity, gender, or membership in the target age groups of AYA or older adult. However, these data will inform a future trial with adequate representations from underrepresented and special population groups.
Since all PSP had participated in research, they may have been biased in favor of wanting to know more about study results and/or supportive/nonsupportive of the method of communication/dissemination they were exposed to through their participation in these studies.
Conclusions
Our findings provide information from PSP and researchers on their expectations about sharing study findings, preferences for how to communicate and disseminate study findings, and need for greater assistance in removing roadblocks to using proven communication and dissemination approaches. This information illustrates the potential to engage both PSP and researchers in the design and use of communication and dissemination strategies and materials to share research findings, engage in efforts to more broadly disseminate research findings, and inform our understanding of how to interpret and communicate research findings for members of special population groups. While several initial prototypes were developed in response to this feedback and shared for review by participants in this study, future research will focus on finalizing and testing specific communication and dissemination prototypes aimed at these special population groups.
Findings from our study support a major goal of the National Center for Advancing Translational Science Recruitment Innovation Center to engage and collaborate with patients and their communities to advance translation science. In response to the increased awareness of the importance of sharing results with study participants or the general public, a template for dissemination of research results is available in the Recruitment and Retention Toolbox through the CTSA Trial Innovation Network (TIN: trialinnovationnetwork.org ). We believe that our findings will inform resources for use in special populations through collaborations within the TIN.
Acknowledgment
This pilot project was supported, in part, by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the NIH under Grant Number UL1 TR001450. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Approval
This study was reviewed, approved, and continuously overseen by the IRB at the Medical University of South Carolina (ID: Pro00067659). All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Find out about insurance programs, pay types, leave options, and retirement planning.
Discover resources to have a balanced career at NIH.
Resources for training to develop your leadership and professional skills.
Access your personnel information and process HR actions through these systems.
Information for managers to support staff including engagement, recognition, and performance.
Discover what’s next at the NIH.
Check Out the Upcoming 2024 DDM Seminars
The Deputy Director for Management (DDM) Seminar Series offers the NIH community engaging presentations to provide meaningful insights into leadership and management concepts, challenges, and solutions. January’s DDM seminar, “ Intentional Workplace Culture ,” featured Jessica Kriegel, who leads groundbreaking research, strategy, and innovation on workplace culture. The March seminar, “ Effective Communication from Leaders ,” featured Lynn Perry Wooten, who specializes in crisis leadership, diversity and inclusion, and positive leadership. These videocasts are available for viewing on the DDM Past Seminars website.
Please join us for the remaining two DDM seminars in FY24. For details and to register, visit the DDM Seminar Series website. Registration for DDM Seminars opens approximately 1-2 weeks before the session date.

May 16, 2024, 11 a.m.–12:30 p.m. Laura Vanderkam – “The New Corner Office” Laura Vanderkam is an expert on time management who shares her techniques for getting the most out of each day with audiences of busy people everywhere. She draws on 18 years of working from home to share strategies for productivity, creativity, and health in the new corner office, post-pandemic and beyond. Her work has appeared in publications including: The New York Times , The Wall Street Journal , USA Today , City Journal , Fortune , and Fast Company .

July 11, 2024, 11 a.m.–12:30 p.m. John Amaechi – “Building Effective Teams” John Amaechi is a respected organizational psychologist, an OBE (Order of the British Empire), Chartered Scientist, elected Fellow of the Royal Society for Public Health, bestselling New York Times author, Research Fellow at the University of East London, and Founder of APS Intelligence. Mr. Amaechi uses his deep psychological insight combined with real life experience to provide a touchstone for people and companies who want to thrive, achieve, and align their beliefs, values, and ethics.
⇒ Consider proposing a speaker for next year’s DDM Seminar Series! ⇐
It is never too early to start considering speakers for the FY25 DDM Seminar Series. Nomination submissions will be open on the DDM Seminar Series website July 1-31.
Please contact [email protected] with questions or comments.
Back to Newsletter
In This Issue
The Emerging Talent Program Kicks Off
Don’t Wait to Get Your Recertification CLPs!
New Classes at the NIH Training Center in Q3
Soft Skills September is now Soft Skills Summer
Brush Up on Your Budget, Data, and Purchase Card Skills!
Training for Your IC Employees
Questions about Planning for Retirement? Find a Workshop That’s Right for You!
LMS Reports Corner
Stay Informed with Training Insights
Communities Corner
Send Us Feedback
Read Past Issues
Training Locations
NIH Training Center Headquarters White Flint III 11601 Landsdown Street North Bethesda, MD 20852
Natcher (Building 45) 45 Center Drive Bethesda, MD 20892 Phone: (301) 496-6211 [email protected]
Contact us to ask a question, provide feedback, or report a problem.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Be an Active Listener. The starting place for effective communication is effective listening. "Active listening is listening with all of one's senses," says physician communication expert Kenneth H. Cohn, MD, MBA, FACS. "It's listening with one's eyes as well as one's years. Only 8% of communication is related to content—the rest ...
Effective communication with the leader requires employees to feel greater involvement and to experience a higher level of satisfaction. ... Omilion-Hodges L. M., Ptacek J. K., & Zerilli D. H. (2016). A comprehensive review and communication research agenda of the contextualized workgroup: The evolution and future of leader-member exchange ...
Effective communication is the process of exchanging ideas, thoughts, opinions, knowledge, and data so that the message is received and understood with clarity and purpose. When we communicate effectively, both the sender and receiver feel satisfied. Communication occurs in many forms, including verbal and non-verbal, written, visual, and ...
Summary. Transformational leaders are exceptional communicators. In this piece, the author outlines four communication strategies to help motivate and inspire your team: 1) Use short words to talk ...
by Michael Blanding. People who seem like they're paying attention often aren't—even when they're smiling and nodding toward the speaker. Research by Alison Wood Brooks, Hanne Collins, and colleagues reveals just how prone the mind is to wandering, and sheds light on ways to stay tuned in to the conversation. 31 Oct 2023. HBS Case.
Communication Research (CR), peer-reviewed and published bi-monthly, has provided researchers and practitioners with the most up-to-date, comprehensive and important research on communication and its related fields.It publishes articles that explore the processes, antecedents, and consequences of communication in a broad range of societal systems.
This chapter explores how communication studies focuses on human communication among people in groups, teams, and organizations. While persuasive communication has long been at the heart of leadership development, the discipline's contributions to effective leadership also range from advancing our understanding of organizational communicative systems to the development of skills for ...
Strategies to Improve Communication Effectiveness. Effective communication is a two-way process that requires both sender and receiver efforts. We summarized research works and guidelines for good communication in the workplace proposed by Cheney (2011), Keyton (2011), Tourish (2010), and Lunenburg (2010). Sender's strategies for communication ...
University of Education, Winneba. Communication is the process of transmitting information and common understanding from one person to another. Communication in the workplace is critical to ...
Purpose: This article presents a systematic review of research into the teaching and learning of communication skills in social work education.Methods: We conducted a systematic review, adhering to the Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews for Interventions and PRISMA reporting guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses.Results: Sixteen records reporting on fifteen studies met the ...
Human communication is a specific way of interaction, information exchange relationship between the partners and also a process in which they understand and influence each other. Communication is ...
Communication is the vehicle for effective management of man environment (Spero-Jack, 2000). Malik (2018) suggests eight indicators that promote organizational communication success and been ...
Effective communication among research sites is crucial and can considerably impact the success of a study. Field updates on the project status should be frequent so that potential problems are identified and quickly resolved. The adoption of the Internet as a medium for real-time communication is important and provides significant support for ...
Effective communication skill 1: Become an engaged listener. When communicating with others, we often focus on what we should say. However, effective communication is less about talking and more about listening. Listening well means not just understanding the words or the information being communicated, but also understanding the emotions the ...
Communication is an essential part of your research and a crucial component for a successful career as a researcher. Effectively Communicating Research is a two-day, intensive course offered by Harvard Catalyst. The course is designed to provide fellows and junior faculty with the skills necessary to express their science clearly to diverse ...
Even the happiest of relationships experience conflicts and problems (Markman, Stanley, Blumberg, Jenkins & Whiteley, 2004). If handled well, issues provide opportunities for personal and relationship growth. There are many skills that can help individuals seeking to resolve conflicts in a healthy way. One of the greatest skills that aids in conflict resolution is effective communication.
Whether you're giving a conference talk, writing a grant, or explaining your work to a family member, the ability to effectively communicate about your research is an essential skill for an Early Career Researcher (ECR) to develop. Read on for our interview with science writer Stephen S. Hall to learn how he helps researchers improve their ...
Abstract. Effective communication is critical for leaders to influence and create an impact within and outside organizations. Despite this, questions are raised regarding the efficacy & effectiveness of organizational leaders in conducting meaningful communication & conversations with their teams. Often, organizations are unsure of the specific ...
Effective communication is a cornerstone of quality healthcare. Communication helps providers bond with patients, forming therapeutic relationships that benefit patient-centred outcomes. ... Research has shown that combining a machine learning tool and a single reviewer can significantly reduce the risk of missing relevant records .
Research has shown that effective communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential for the provision of patient care and recovery [5-8]. Madula et al. [ 6 ], in a study on maternal care in Malawi, noted that patients reported being happy when the nurses and midwives communicated well and treated them with warmth, empathy ...
Much of the recent research in this area has focused on whether empathic and positive communication are beneficial, 6,7 and whether empathic communication can be taught (it seems that it can). 8 A 2001 systematic review found that empathy and positive communication might also improve patient outcomes. 9 However, the evidence has moved on significantly, with numerous randomised trials having ...
2. Treat your 3PL as an extension of your brand. A successful 3PL-brand partnership goes beyond mere transactions. In the most successful partnerships, brands view their 3PL as a true extension of ...
Inspired by natural swarm systems, robotic swarms aim to solve complicated problems through the emergent behaviour of coordinating robots (agents). Communication among the robots is of paramount importance for their effective coordination, cooperation, and overall performance. This research presents a colour light-based communication system for miniature mobile swarm robots, on which a pre ...
Effective communication and dissemination strategies are documented in the literature [6,7], but most are designed to promote adoption of evidence-based interventions and lack of applicability to participants overall, especially to participants who are members of special populations and underrepresented minorities who have fewer opportunities ...
Effective communication is crucial in all service contexts, but especially in clinical healthcare, given its high (sometimes life-or-death) stakes. ... they also highlight the need for our review. As can be seen, verbal communication research typically does not consider nonverbal communication or listening, and research on the latter two ...
July 11, 2024, 11 a.m.-12:30 p.m. John Amaechi - "Building Effective Teams" John Amaechi is a respected organizational psychologist, an OBE (Order of the British Empire), Chartered Scientist, elected Fellow of the Royal Society for Public Health, bestselling New York Times author, Research Fellow at the University of East London, and Founder of APS Intelligence.