

GED Essay Writing Guide
What is the ged rla “extended response” question.
The Reasoning Through Language Arts (RLA) section of the GED includes an Extended Response essay question. You will only have 45 minutes to complete this essay, so it is important to familiarize yourself with the nature of the prompt. Read through this guide to become more familiar with the prompt and how to write the best response possible.
If you follow the strategies and the template provided in this guide, you’ll be able to produce a high-scoring essay in the time allotted! 😀
GED Essay Overview
Since the GED Exam is administered on a computer, you will type your essay into a text box. You will first be presented with two Stimulus Passages and then you will be given an essay prompt. The Stimulus Passages will each have 4–5 short paragraphs that introduce an issue and take a stance on that issue, with one passage opposing the other. You will then be given the following prompt:
➤ Pro Tip: Remember that the 45 minutes includes the time you take to read the Stimulus Passages. Read the passages thoroughly, but quickly, and make note of any specific points that stand out to you so that you can easily reference them as you formulate your argument.
GED Essay Strategy
In order to maximize your 45 minutes, it’s important to decide ahead of time how much time you will spend on each step. We recommend following the guide below, but you should write some practice responses with a timer nearby to get a good understanding of how our guide can best serve you. Make sure you do not hand-write your practice essays, as it is always best to recreate test conditions as closely as possible when preparing.
Follow this strategy when writing your GED Essay:
Step 1 ► Read and Analyze the Stimulus Passages (5 Minutes).
Start by reading both of the passages. Make sure you understand the issue and the position that each passage is taking. Try to ignore your own personal feelings on the topic as you read. Ultimately, your job is to explain why one of the sides is better supported ; it is fine to completely disagree with the side you defend, so long as you adequately support your stance. You are not writing about who you agree with, you are writing about who supports their argument best .
Step 2 ► Select Your Position and Outline Your Ideas (5 Minutes).
Ask yourself: which side seems like it has more supporting details and/or examples? Your task with this essay is similar to that of a teacher grading an essay. It doesn’t matter if you agree with the position; it matters that the writer supported their position well.
Remember, “better-supported” does not necessarily mean “right.” You are not required to argue in favor of one of the positions; you only need to explain why one position is better-supported than the other position.
Passage 1 : argues that school lunches should be 100% vegetarian in order to improve the health of students and to tackle the obesity epidemic in schools. This passage provides:
- statistics showing that vegetables are good for children.
Passage 2 : argues that animal protein is crucial for superior athletic performance and sustained energy levels in children. This passage provides:
- quotes from a doctor who says that protein from meat keeps children alert in classes after lunchtime.
- scientific research that supports this claim.
- statistics from counties that switched to vegetarian lunches which show that test scores dropped after adopting vegetarian lunches.
Which side is “best supported?” Which side should you choose for your essay? If you said, Passage 2, you are correct. Even if you are a vegetarian, you should be able to see that there is more supporting evidence in the passages for the “pro-meat” side. You will not receive a bad score if you choose to support the side that has less evidence, but it makes your task harder.
You should spend approximately 5 minutes deciding your position and outlining your essay. You can simply type your outline at the top of the text box (and delete it after you finish your essay). We will discuss more specifics about how to outline our essay in the “Template” below!
Step 3 ► Write your Essay (30 Minutes).
At this point, approximately 10 minutes will have gone by. You have read the passages and outlined your position. Now, simply start with paragraph 1, and follow the outline you created. Remember to stop periodically and refer back to your outline at the top. Most GED Extended Response essays are between 4–7 paragraphs and each paragraph is composed of 3–7 sentences. We suggest that you aim for 5 paragraphs; doing so ensures that your argument is complete.
As you will see in the Template below, it’s okay if some paragraphs are shorter than others! Don’t feel like you have to write sentences to fill up space; always write with purpose. Once you’ve made your point in a given paragraph, add a concluding sentence and move on. You should spend approximately 30 minutes on your essay.
Step 4 ► Read Everything Over At Least Once (5 Minutes).
Proofreading can make a good essay great, and a great essay stellar, so don’t forget that you will need at least 5 minutes at the end to thoroughly read through what you have written. Go back to the outline and review your notes. Does the essay you wrote follow the outline? Is it well-organized? If you’re happy that you didn’t stray from your plan, delete your outline notes. This is very important! If you do not delete your notes, scorers will think it is part of your response and take points off.
If you have extra time, look for spelling and grammar errors. Do your verb tenses agree? Did you accidentally leave off the “s” on a plural noun? How are the transitions between paragraphs? Does the essay “flow?” Remember, you can re-type any sentences you dislike, and you can add additional sentences for clarity. This is a timed response, so it does not have to be perfect, but if you have the time to fix mistakes you’ll only be helping your chances.
GED Essay Template
In the four-part strategy above, you read about the importance of planning and making an outline for the position you selected. Your outline should follow this general format:
- Paragraph 1 — Introduction
- Paragraph 2 — Body Paragraph
- Paragraph 3 — Body Paragraph
- Paragraph 4 — Body Paragraph
- Paragraph 5 — Conclusion
★ Paragraph 1 — Introduction
The introduction and conclusion are short paragraphs that “bookend” your essay. Your introduction should:
- introduce the topic from the passage,
- explain both sides of the issue (showing that you understood what you read),
- and make a claim that one side is better-supported and thus, more convincing (this should be the final sentence of the introduction).
Below is a possible template for the introductory paragraph. When you are writing your essay, you can write a very similar introductory paragraph while replacing the underlined portions to fit the prompt that you are answering:
★ Paragraphs 2–4 — Body Paragraphs
The real strength of your essay lies in your body paragraphs. Each body paragraph must introduce and describe one reason why the position you chose is better-supported. There will be 3 reasons in total (if you follow the 5-paragraph format). Look for some of these common ready-made arguments when reviewing the passages:
Authority figure — Does the passage quote a reputable figure with specialized knowledge, such as a doctor, scientist, or other expert? Does the reference lend credibility to the overall argument?
History — Does the passage explain a historical event or a precedent to back up its claim?
Statistics — Does the passage provide any numbers or data? Does the data help the author’s position?
Logical reasoning — Is there a strong element of logic or “common-sense” to the argument, and is it presented in a clear, cohesive manner?
Ethics — Is a moral argument made? Does the author insist his or her position is correct because it is the “morally right” thing to do?
Emotion — Does the author appeal to the reader’s feelings? Does the argument evoke an emotional response?
Reasonable Assumptions — Does the author rely on assumptions to draw any conclusions? Are the assumptions reasonable?
Forceful Vocabulary — Does the author’s word choice add weight and importance to the argument?
Not all of these will be present in every passage, but you will only need 3, and it is likely that at least 2–3 of these will be used in each argument. If the passage you choose only has 2 of the above supports, consider writing more than one paragraph about each, using different support. Let’s look at how we can “plug” three of these examples into our thesis from above:
When you outline your GED Essay, pre-write your thesis and decide on which three forms of support you will discuss to prove that your passage is better-supported. This will help you organize of the rest of your essay. Now that we have chosen our three examples, we can make a more specific outline:
- Paragraph 1 — Introduction (why Position X is better-supported)
- Paragraph 2 — Emotional Appeal
- Paragraph 3 — Authority Figure’s Opinion
- Paragraph 4 — Forceful Vocabulary
- Paragraph 5 — Conclusion (why Position Y is not well supported)
Let’s look at how we can “plug” some of these ready-made arguments into a body paragraph:
Notice how this body paragraph introduces the example in the first sentence (“logical reasoning”), and then cites 3 specific examples from the passage that employ this logical reasoning. The final sentence reiterates and emphasizes the overall idea of the paragraph. This paragraph is only 5 sentences (if you include a quote), yet it does a great job (1) introducing the superiority of the argued position, (2) giving examples from the passage to support a specific idea, and (3) concluding the paragraph.
In each body paragraph, you must defend your assertion that ONE position is better-supported with at least one specific reference showing this support. If you choose, “authority figures” as an example, but there is only 1 authority figure mentioned in the passage, it’s okay to spend the entire body paragraph discussing that one figure. You do not need to make up anything that is not in the passage—in fact, you shouldn’t!
★ Paragraph 5 — Conclusion
Finally, let’s look at how we can structure the conclusion:
GED Essay Scoring
Three separate scorers will grade your response based on each of the three traits of your essay: (1) Analysis of Arguments and Use of Evidence, (2) Development of Ideas and Structure, and (3) Clarity and Command of Standard English. Notice that if you follow the strategy and template provided above, all of these traits will be accounted for, and you won’t have to worry about them on Test Day! 😀
GED Essay Practice
Now you’re ready to write a practice essay. Try our GED Essay Practice Question .
Best Practices 5 Steps for Great Extended Constructed Responses

Rob Fleisher
In this post, teacher Cara Popecki gives tips to make writing effective, collaborative, and fun.
It’s on every major college readiness and state exam, and it also elicits the most groans from students and teachers alike: the dreaded extended constructed response. Students are generally asked to read and answer questions about two passages that share a common theme, and then they must write an essay that incorporates evidence and analysis from both texts.
On-demand writing, especially writing that requires students to understand multiple texts, can be really stressful and challenging for students. On this high school Smarter Balanced test , students must read two articles about mandatory financial literacy classes before writing an argumentative essay. Building these types of assignments is also challenging for teachers — where do you find all those paired texts?
At CommonLit, we have tried to make this as easy as possible! Use these five steps to create rigorous, high-interest cross-textual assignments that can be implemented all year long.
STEP 1: Pick Two Interesting Texts that Share a Common Theme and Genre
Extended constructed responses offer a great opportunity to expose students to high-interest fiction and informational texts.
We’ve made finding two texts that share a common theme and genre extremely easy. First, go to Commonlit.org and select the library . Use the search filters to narrow the library to the particular grade level that you teach. You can also use the search filters to narrow your search by genre.
Once you’ve found a text that will pique your students’ interest, navigate to the “Paired Texts” tab to find a list of related texts. For example, the informational article “Fear Prompts Teens to Act Impulsively” (1090L) comes with a host of great paired text suggestions.
One example is the informational text “Raising Elephants” (1020L). The text explains the social interactions that teenage male elephants must navigate in order to make the transition to adulthood. Students reading both texts will have fun uncovering the similarities and differences between the behaviors of teenage elephants and teenage humans.
Once you’ve selected your pair of high-interest texts, you’re ready to write the essay prompt.
STEP 2: Write an Aligned, Extended-Response Prompt
To write an aligned, extended-response prompt, start by reading an example extended-response prompt from a released state test. Here is a sample prompt from a 7th grade Smarter Balanced assessment:
Your Assignment: Now that you have completed research on the topic of sleep, the journalism club advisor has asked you to write an explanatory article about sleep and naps for the next issue of the school newspaper. The audience for your article will be other students, teachers, and parents.
Next, read the CommonLit suggested pairing prompt for the two articles you have chosen for inspiration.
Finally, craft a writing prompt that mirrors the style of the state assessment:
Your Assignment: Now that you have completed your research on the topic of social interactions during adolescence, the director of the zoo where you work has asked you to write an explanatory article comparing and contrasting the adolescent phase of humans and elephants for the next issue of the zoo’s newsletter. The audience for your article will be other students and adults who are thinking about visiting the zoo.
STEP 3: Create a Student-Friendly Rubric
Especially if your students are new to extended constructed responses, they will likely get overwhelmed by a traditional teacher-centric rubric. Our recommendation is to introduce students to a student-friendly rubric and focus your lessons on helping students master one rubric row at a time.
CommonLit provides a rubric for short-answer responses that you can edit. You can also create your own student-friendly rubric based on the SAT, ACT, or your state test.
If you are showing students a rubric for the first time, don’t just hand them a complex rubric. Make time to go over each section using an actual essay as a model.
STEP 4: Help Students Internalize What Success Looks Like
If students are going to be successful, they need to develop a vision of mastery that is similar to the teacher’s. Letting students read and score sample student essays (both good and bad) by using the rubric is a wonderful way for students to internalize the goal. For each rubric row, ask students to explain why they gave the score they gave.
You can find sample essays either from your own students’ work (keeping them anonymous), from the college readiness exams (SAT or ACT), or from your state assessments (PARCC, Smarter Balance, FSA, STAAR, etc.).
Do this activity multiple times throughout the year to really drive it home.
STEP 5: Involve Students Through a Peer Revision Process
Especially if you have loads of students, it’s nearly impossible to give students thorough feedback on their drafts before grading their work. One great strategy to address this is through peer revision as a way to help students become more proficient writers.
To kickoff peer revision, first model some essential revision strategies through a think-aloud:
Give specific praise 3–4 times
- I like the way you…
- This [word/sentence] is really…
Write 1–2 specific suggestions for improvement
- I recommend that you…
- Have you tried…
Summarize your feedback
- To sum it all up…
Doing regular peer revision will help students understand that writing is a process, not just a product. Many students struggle with writing because they think they only need to attempt it once without revisiting their own work. It’s tough, but if you build the habit with peer revisions, students will become more self-sufficient over time.
These strategies are not just for test prep. The best way for students to build confidence as writers is not to just practice but to receive clear expectations, feedback, and assignments that compel them to think analytically.
If you are an administrator looking to leverage CommonLit in your school or district, our partnerships team can help. We offer benchmark assessments, professional learning, and more!
Chat with CommonLit
CommonLit’s team will reach out with more information on our school and district partnerships.

GED Extended Response Essay Prompts & Examples
A quick guide to writing an extended response for the ged language arts test.
GED® Reading & Writing Practice Test ( 25 Questions )
GED® Reading & Writing Practice ( Tons Questions )
GED® Reading and Writing Lessons ( 10 Lessons )
Check out our other Free GED© Practice Test
Many students fear the writing part of the GED test. And we understand. After all, it takes effort and time to organize your ideas, fix sentence structures, and ensure that grammar, punctuation, capitalization, and spelling are correct. With only 45 minutes to complete your essay, how will you be able to finish your piece? Thankfully, there are ways to make this part easy for you. You don’t have to be a gifted writer to write succeed in writing a winning essay for the Extended Response portion of the GED writing test. There are tips to succeed in writing your essay.
Start reviewing with our helpful contents: GED Reasoning Through Language Arts Guide
What’s in the GED Writing Extended Response Portion of the Test?

This test will check how well you create arguments and use evidence. Also, it would also test your clarity and command of Standard English language.
Quick Tips to Remember When Writing Your Essay:

- Take a deep breath. Nervous about the test? Ease anxiety by taking deep breaths before writing your essay. Being stressed while writing might keep your focus away from the task and affect the quality of your essay.
- Read the two passages carefully . Make sure you understand each passage before choosing your position.
- Make an outline . Don’t write right away. Create an outline first. Choose a position that you can easily defend based on what you’ve read, then list down the main points to support this position.
- Your essay should have:
- 1. An introduction that states your main argument 2. At least 3 paragraphs with your supporting evidence 3. A conclusion that restates your main argument and main points.
- Focus on the first and last paragraphs first . This will help you stick to your argument and main points.
- Be clear . The paragraphs in between your first and last paragraphs should clearly explain your main points. Start each paragraph by stating the main point that you want to talk about.
- Proofread your work . Check your work for grammar and spelling errors. Improve sentence structures with the time that’s left.
Keep in mind that the saying, “practice makes perfect” applies here. Mastering essay writing takes a lot of practice and reading. Begin practicing your writing as well improving your comprehension skills with our Free GED Practice Tests for Language Arts. We also recommend reading high-quality newspapers, publications, and literary pieces to help build your English writing skills.
Related Topics:
- 7 Top Jobs For GED Graduates: Earn Six Figure Income Without A College Degree
- GED Reading Practice Test
- Reasoning Through Language Arts
- GED Reasoning through Language Arts
- GED Reasoning through Language Art PRACTICE TEST
- GED Math Practice Questions | Fractions
- GED® Reasoning Through Language Arts Practice Tests
- GED Science Practice Questions | GED Study Guide
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Utilizing Extended Response Items to Enhance Student Learning
- An Introduction to Teaching
- Tips & Strategies
- Policies & Discipline
- Community Involvement
- School Administration
- Technology in the Classroom
- Teaching Adult Learners
- Issues In Education
- Teaching Resources
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.Ed., Educational Administration, Northeastern State University
- B.Ed., Elementary Education, Oklahoma State University
"Extended response items" have traditionally been called "essay questions." An extended response item is an open-ended question that begins with some type of prompt. These questions allow students to write a response that arrives at a conclusion based on their specific knowledge of the topic. An extended response item takes considerable time and thought. It requires students not only to give an answer but also to explain the answer with as much in-depth detail as possible. In some cases, students not only have to give an answer and explain the answer, but they also have to show how they arrived at that answer.
Teachers love extended response items because they require students to construct an in-depth response that proves mastery or lack thereof. Teachers can then utilize this information to reteach gap concepts or build upon individual student strengths. Extended response items require students to demonstrate a higher depth of knowledge than they would need on a multiple choice item. Guessing is almost completely eliminated with an extended response item. A student either knows the information well enough to write about it or they do not. Extended response items also are a great way to assess and teach students grammar and writing. Students must be strong writers as an extended response item also tests a student's ability to write coherently and grammatically correct.
Extended response items require essential critical thinking skills. An essay, in a sense, is a riddle that students can solve using prior knowledge, making connections, and drawing conclusions. This is an invaluable skill for any student to have. Those who can master it have a better chance of being successful academically. Any student who can successfully solve problems and craft well-written explanations of their solutions will be at the top of their class.
Extended response items do have their shortcomings. They are not teacher friendly in that they are difficult to construct and score. Extended response items take a lot of valuable time to develop and grade. Additionally, they are difficult to score accurately. It can become difficult for teachers to remain objective when scoring an extended response item. Each student has a completely different response, and teachers must read the entire response looking for evidence that proves mastery. For this reason, teachers must develop an accurate rubric and follow it when scoring any extended response item.
An extended response assessment takes more time for students to complete than a multiple choice assessment . Students must first organize the information and construct a plan before they can actually begin responding to the item. This time-consuming process can take multiple class periods to complete depending on the specific nature of the item itself.
Extended response items can be constructed in more than one way. It can be passage-based, meaning that students are provided with one or more passages on a specific topic. This information can help them formulate a more thoughtful response. The student must utilize evidence from the passages to formulate and validate their response on the extended response item. The more traditional method is a straightforward, open-ended question on a topic or unit that has been covered in class. Students are not given a passage to assist them in constructing a response but instead must draw from memory their direct knowledge on the topic.
Teachers must remember that formulating a well written extended response is a skill in itself. Though they can be a great assessment tool, teachers must be prepared to spend the time to teach students how to write a formidable essay . This is not a skill that comes without hard work. Teachers must provide students with the multiple skills that are required to write successfully including sentence and paragraph structure, using proper grammar, pre-writing activities, editing, and revising. Teaching these skills must become part of the expected classroom routine for students to become proficient writers.
- Questions for Each Level of Bloom's Taxonomy
- Creating and Scoring Essay Tests
- Bloom's Taxonomy in the Classroom
- An Overview of the Common Core Assessments
- The Study Island Program: An In-Depth Review
- 3 Surveys for Student Feedback to Improve Instruction
- T.E.S.T. Season for Grades 7-12
- Tips to Create Effective Matching Questions for Assessments
- Reading Comprehension Practice Questions
- Authentic Ways to Develop Performance-Based Activities
- 5 Free Assessment Apps for Teachers
- GMAT Exam Structure, Timing, and Scoring
- Inference: A Critical Assumption
- Methods for Presenting Subject Matter
- Topics for a Lesson Plan Template
- How Depth of Knowledge Drives Learning and Assessment

- How to Write an Extended Response in High School

It’s your first day in high school and your teacher has given you an extended response to write. But what is an extended response anyway?
We’re here for you! In this article, we will help you understand what an extended response is and how to write an amazing one to ace your assessments!
Plus, we’ve added in a downloadable scaffold sheet for you!
So, let’s dive right in!
What is an Extended Response in High School? Types of Extended Responses for High School How Long is a High School Extended Response? How to Start Your Extended Response How to Structure an Extended Response in High School Extended Responses VS Essay: What’s the Difference?
What is an Extended Response in High School?
In short, an extended response is any piece of writing that is longer than one paragraph .
Research , analysis and planning are important when writing an extended response. However, answering the question is key to excelling your extended response.
To answer the question, avoid jotting down everything you know about the topic. Instead, focus on the ‘key words’ in the questions.
Tip : A good way to remember your ‘keywords’ is to circle or highlight them before you start planning your extended response .
An example of a key word would be an ‘action word’ , such as ‘describe, ‘explain’ and ‘evaluate’. This will give you an idea of how you should be answering the question.
If the words ‘extended response’ sound scary, don’t worry ! In Year 5 or 6, you’ve already started to write longer answers to challenging questions.
In high school, you’ll work further on these same skills , so you’ll step up to the next level!
Also writing a feature article for high school English? Check out our ultimate guide and structure to writing a feature article here !
Types of Extended Responses for High School
In most subjects, your high school teacher can ask you to write an extended response. This means that the type and structure of extended response can be different depending on the subject !
The good news is, your teacher can help you plan your subject-specific extended responses by providing detailed, up-to-date instructions .
T his way, you understand exactly what you need to do! To give you an idea of what types of extended responses that you may be asked to write, here is a list :
For discussions, you will explore two sides of the argument, otherwise known as “for” and “against” .
To contrast these arguments, you will learn how to use words such as “ however ”, “ nonetheless ” and “ in contrast ”.
Critical Analysis

For a critical analysis, you will need to show that you understand the text inside and out .
Oftentimes, this type of extended response is longer than the others . This is because you will need to write more than one paragraph per point .
Add some variety and spice to your critical analysis extended response and use our essential list of language features here !
Exposition or Persuasive

For expositions and/or persuasive pieces, you will need to make a strong argument to persuade your reader to side with you.
Looking for strong and convincing words in your exposition and persuasive writing? Read our extensive list of high modality words here !
Compare and Contrast

For this type of extended response, you will need to write about the similarities and differences between two texts .
It is important that you show how the two text are similar and different, rather than story-telling the text.
Check out our breakdown and guide to using persuasive techniques here !
How Long is a High School Extended Response?
So, how long should an extended response be? 100, 200 or 500 words?
According to NESA , an extended response for high school should have an intro , at least 3 body paragraphs and a conclusion .
This means that your extended response will have at least 5 paragraphs in total with 3 to 7 sentences per paragraph , adding up to 300 to 500 words!
However, you can choose to write an additional body paragraph or two if you have more points to make to answer your question more effectively!
How to Start Your Extended Response
Most students make the mistake of jumping right into writing without thinking about what they want to write.
Instead, it is important to start an extended response by planning it out first !
You can start by asking yourself, “ What is the question asking me to do? ”.
A great tip is to circle or highlight the keywords in the question and define them . This helps to make sure you understand the question and in doing so, you’re able to decide on a key idea to answer the question directly.
Next, you would want to create a list of ideas or facts that address the question . A mind map i s a great way to put your ideas on paper and make sense of it!
After this, you should find examples from your text that answer the question. These examples can be events, facts or quotes from your text which you may use to support your points.
Tip : A good trick is to try writing these notes down in your own words, to avoid copying other people’s work.
Finally, plan the structure of your extended response! You can do this by arranging your points in a logical order so the ideas link well together.
How to Structure an Extended Response in High School
Not sure how to structure your extended response in high school?
It’s as simple as ABC! An extended response has the same basic structure as an essay — with an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Here’s a breakdown on how an extended response should be structured:
Access our comprehensive guide to our High School Extended Responses structure and template here!
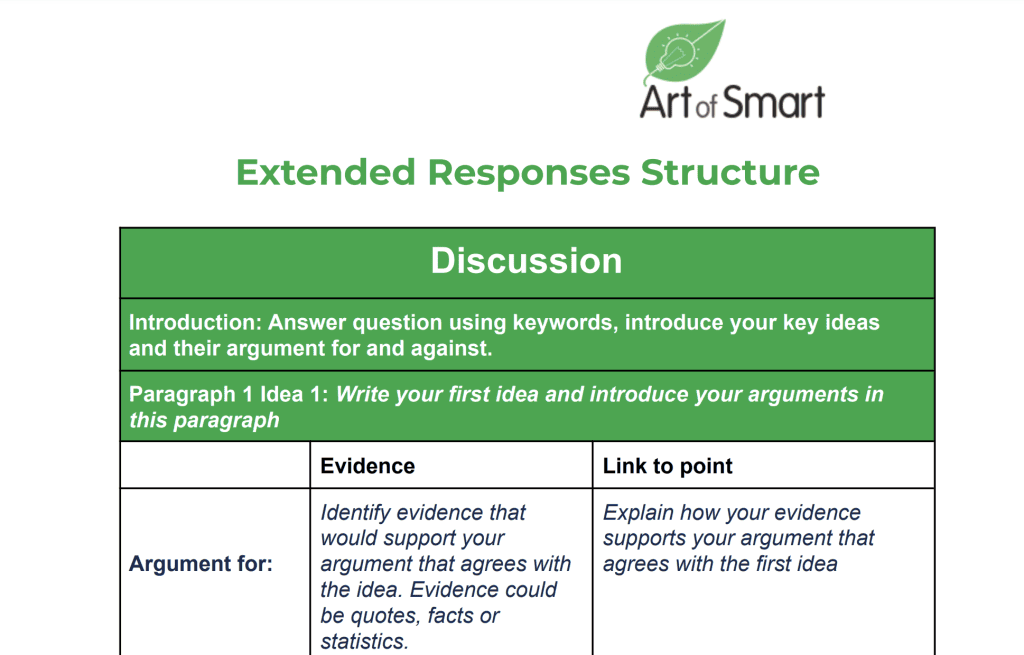
Introduction
In the introduction, you will need to answer the question directly and introduce the points that you will make in your body paragraphs.
Body Paragraph
NESA recommends that you have at least 3 body paragraphs in your extended response.
At times, more complex ideas will need more than one paragraph and that is totally ok!
However, try to separate your points into their own paragraphs , rather than mixing them all up in one paragraph. This is to make sure that your points are loud and clear for your teacher to understand!
Remember to back up your point in each paragraph with enough evidence — c heck out how to find and use quotes here !
Conclusion
At the end of your high-school extended response, you will write a conclusion which summarises the main points you have talked about in your extended response.
It is important to not mention new points here!
And don’t forget to reference your resources at the end of each assignment!
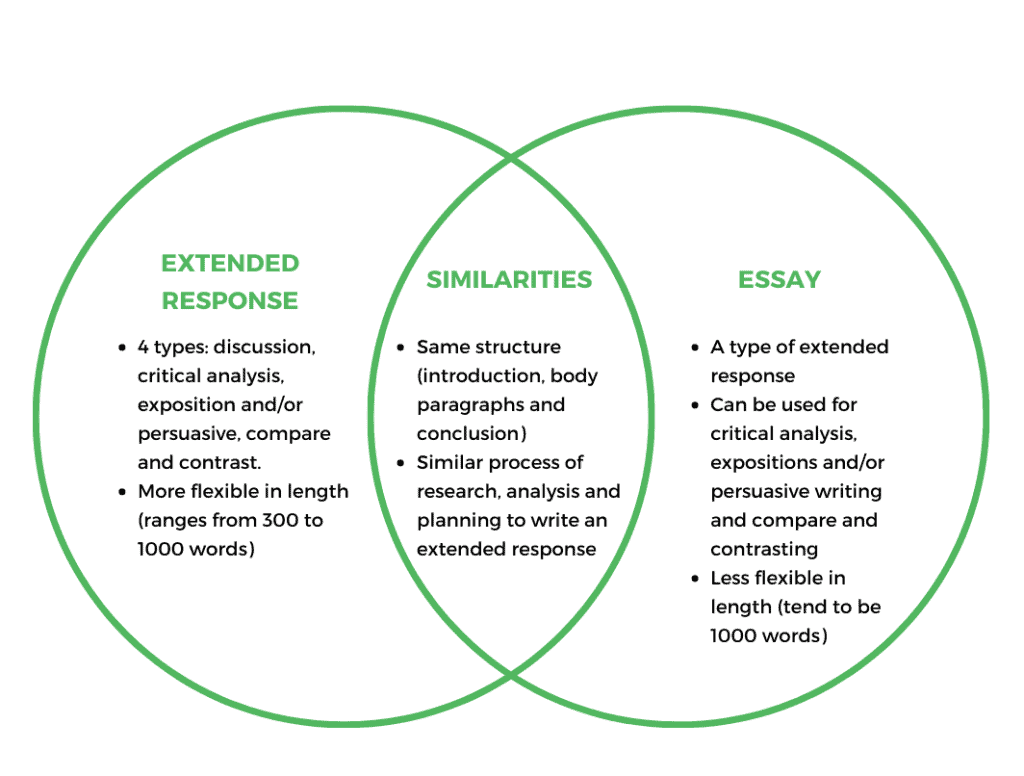
Extended responses VS Essay: What’s the Difference?
Wait, isn’t an extended response and an essay the same thing?
Well, not really. An extended response and an essay share the same structure — with its introduction, body paragraphs and conclusions.
The process of writing an extended response is also similar to writing an essay , with its research, analysis and planning.
So, what makes them different?
Think of extended response as a category , and this category is separated into its 4 types (ie. discussion, critical analysis, exposition/persuasive and compare and contrast).
Also writing an essay for high school English? Check out our tips to writing a STEEL paragraph and acing your essay writing here !
Meanwhile, essays are a type of extended response that encompasses critical analysis, persuasive writing and at times, compare and contrast.
Additionally, extended responses are also more flexible in terms of its length , as it may vary from 300 to 1000 words, depending on how many points and paragraphs you have to make.
On the other hand, essays tend to be 1000 words long .
And, That’s It!
Don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter so you can receive free scaffolds for all 4 types of extended responses: discussion, critical analysis, exposition/persuasive and compare and contrast!
Want to improve your analytical skills for English? Check out why you should keep a reading journal for English here !
On the hunt for other useful resources?
Have another writing assignment? Here are our other writing guides:
The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Feature Article
- The Ultimate Guide to Using Persuasive Techniques for English
- The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Recount in Primary School
- The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Persuasive Text
The Essential List of High Modality Words for Persuasive Writing
Are you looking for some extra help with writing your extended responses for high school.
We have an incredible team of tutors and mentors!
We can help you master your extended response writing and ace your upcoming assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or online! We also have knowledgeable tutors in Western Sydney who can support you.
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years , and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Kate Lynn Law graduated in 2017 with an all rounders HSC award and an ATAR of 97.65. Passionate about mentoring, she enjoys working with high school students to improve their academic, work and life skills in preparation for the HSC and what comes next. An avid blogger, Kate had administered a creative writing page for over 2000 people since 2013, writing to an international audience since her early teenage years.
- Topics: ✏️ English , ✍️ Learn
Related Articles
How to keep a reading journal for english and improve your analytical skills, 45,861 students have a head start....
Get exclusive study content & advice from our team of experts delivered weekly to your inbox!

Looking for English Support?
Discover how we can help you!

We provide services in

GED Essay: Everything You Need To Know In 2024
Learn all you need to know about the GED essay, its structure sample, topics, tips, and how it is scored in this post.
January 1, 2022
The GED essay is intimidating to many people. Writing an entire essay from scratch in 45 minutes or less may seem difficult, but it does not have to be. This GED essay writing overview will help you prepare for and learn about the written section of the exam . In this post, Get-TestPrep will show everything you need to know about GED essays , including their structure, sample topics, tips, and how they are stored .
What Is The GED Essay?

The GED exam consists of four subjects : Mathematical Reasoning, Social Studies, Science, and Language Arts Reasoning (RLA ). The GED extended response , sometimes known as the GED essay, is one of the two portions of the RLA subject test. You’ll have 45 minutes to finish the essay to your best capacity. Don’t worry if you don’t finish on time! Because the essay accounts for just 20% of your ultimate RLA score, you can still pass the test even if you don’t receive a high essay score.
The GED extended response can cover a wide range of topics, but it will always be formatted in the same way. You will be assigned two articles on the same topic, which will typically be argumentative essays with a firm position. You’ll be asked to assess the two arguments and create your own argumentative essay based on which article delivered the more compelling argument. The essay should be three to five paragraphs long, with each paragraph including three to seven sentences.
GED Essay Structure
An introduction, a body, and a conclusion are included in every well-written GED essay. You have to write an argument or an argumentative essay. Keep in mind that you are not expressing your own view on the subject. You’re analyzing two of the author’s points of view and determining which one is more compelling. Keep in mind that the Extended Response (GED Essay) is graded by machine intelligence that has been designed to detect the right responses. So, instead of trying to be creative, simply be accurate. Also:
- Make sure you’re using proper grammar and sentence structure.
- Practice writing a 300-500 word essay.
Let’s take a look at the format of a GED Essay : an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
- The introduction outlines your claim or thesis statement and explains the topic you’re writing about. Maintain your position.
- The body of the essay includes facts and arguments to back up your claim. This section of the response should be at least two paragraphs long.
- The concluding paragraph restates your claim and summarises your important points.
GED Essay Topic Examples
Here are a few GED Essay Topics to get you started:
Topic 1: An Analysis of Daylight-Saving Time
The article presents arguments from proponents and opponents of Daylight Saving Time, who disagree on the practice’s impact on energy consumption and safety.
Topic 2: Should the Penny Stay in Circulation?
Analyze the arguments offered and pick which one has the most support.
Topic 3: Is Golf a Sport?
Golf , according to proponents, satisfies the criteria of “sport.” Opponents argue that golf more closely resembles a “game” than a “sport.” Analyze both points of view to see which one has the most support.
Visit our website for more topics as well as full articles on each topic and take our free latest FREE GED practice test 2024 to get ready for your exam!
GED Essay Examples
Getting to know the GED essay sample can assist you in planning your essay and determining which elements are most vital.
When reading the essay topic, you should truly take your time to collect your views. You will be able to articulate your views better on paper if you organize your thoughts properly. Concentrate on the standards that you learned in English class before you begin writing.
Pay attention to how you use the English language (grammar); you must use proper punctuation and capitalization, and you must use appropriate word solutions.
Tips For Writing Your GED Essay
Make sure you carefully read the stimulus and prompt.
Putting this into practice is an excellent idea. Examine each question carefully and set aside some time to determine the topic and the type of response that will be requested. It is critical to read the questions thoroughly. Students frequently skip past the stimulus and prompt and get right into writing, assuming that they will save time this way.
This is, by far, the most uninteresting thing to do. Take a few moments to attempt to fully comprehend the questions so that you can reply accurately. If you like, underline the important words and phrases in the stimulus so you can go over it again later to make sure you’re on track.
Make a rough outline for the GED language arts essay
In general, planning your essay will only take a few minutes, but it is critical that you spend that time. Make an outline of the essay and follow it as soon as you have a complete understanding of the questions and have scribbled down some early ideas.
Make an outline for your introduction, body, and conclusion. Following this procedure will save you a lot of time and aid in the development of a logical thought process.
Keep your focus on the topic
To describe your evidence, each paragraph in the body of your response should explain why a piece of evidence supports your claim or disputes the opposing claim. You have the option of describing or restarting it. This demonstrates that you know exactly what it means and how it applies to your claim. Refer to the specifics or facts of a certain issue that you’ve discussed and tie them to your claim.
Include evidence from both passages in your response, and explain why strong evidence supports one thesis and why flawed evidence undermines the other.
Revision and proofreading
By the time you’ve finished writing your essay, you should go back to the beginning and reread it attentively, since you may easily have missed a comma or misspelled a term while doing so.
Pay great attention when rereading your essay to see if it has well-targeted arguments, is arranged properly, contains particular information and facts, has good sentence construction, and has no grammatical or spelling mistakes.
Learn more about how to practice GED essays as well as the whole Language Arts section in GED Language Arts Study Guide
How To Write a GED Essay?
When writing the GED essay, you should allocate the time as follows:
- 3 minutes to read the directions and the topic
- 5 minutes of prewriting (freewriting, brainstorming , grouping, mapping, etc.)
- 3 minutes to organize (create a thesis statement or controlling idea, and summarize important points)
- 20 minutes to draft (write the essay)
- 8 minutes to revise (go over the essay and make adjustments to concepts)
- 6 minutes to edit (check for grammatical and spelling errors).
How Your GED Essay Is Scored?
Smart machines that are designed to detect the right answers score your GED essay. So don’t try to be creative; just be accurate.
They will evaluate your essay based on five factors.
- Organization : did you give a well-thought-out approach to writing your essay and were you clear on the main idea?
- Clear and swift response: Did you deal with the matter appropriately, without straying from one emphasis point to another, with a clear and quick response?
- Progress and specifics: instead of utilizing lists or repeating the same material, did you use relevant instances and particular details to expound on your initial notions or arguments?
- Grammar Rules of English: Did you apply proper writing strategies such as sentence structure, spelling, punctuation, syntax, and grammar, and did you shape and revise your essay after you finished the initial draft?
- Word choice : How well did you pick and use appropriate phrases to express your points of view?
Your 45 minutes will fly by, so focus on these key elements to get the best score possible. What is more important is to state unequivocally which side is more popular. Check that your phrases are clear and that your paragraphs are organized logically.
Each of the four modules (independent subtests) in Mathematical Reasoning (Math), Reasoning via Language Arts, Science, and Social Studies can be taken independently. To pass the subtest(s) for which you registered, you must study thoroughly and be efficient on test day. Consider taking our GED Language Arts Practice Test for the Language Arts section.
GED essay writing can be difficult, but you can keep a list of everything you need to know and switch to proper essay writing approaches before the exam. Simply practice a lot and you’ll notice that it gets better over time. So you’ve learned everything there is to know about writing the GED Essay .
How to write an essay for the GED?
- Read through all of the instructions.
- Create an outline.
- Make a list of all the evidence.
- Last, write your introduction.
- Write first, then edit.
- Make use of formal language.
- Don’t look at the time.
Is there an essay portion on the GED test?
How is the ged essay graded.
The essay is graded on a four-point scale by two certified GED essay readers. The scores of the two GED readers are averaged. If the essay achieves a score of 2 or above, it is merged with the language arts multiple-choice score to generate a composite result.
Final Words
In conclusion, this guide on the GED essay provides valuable insights and strategies to help you excel in the GED essay section. By understanding the structure of the GED essay , practicing effective writing techniques, and familiarizing yourself with the scoring rubric, you can approach the GED essay with confidence and achieve a successful outcome. Remember to plan your essay, organize your thoughts, and support your ideas with relevant examples and evidence. Additionally, refining your grammar and punctuation skills will enhance the overall quality of your writing. With consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the expectations for the GED essay, you can showcase your writing abilities and earn a strong score on the GED essay.
Eligibility Requirements For GED In District of Columbia
November 25, 2022

Eligibility Requirements For GED In New York

Eligibility Requirements For GED In Wyoming
You may learn more about how to obtain a GED in Wyoming by reading the answers to the questions related to GED requirements in Wyoming we receive below.
September 19, 2022

- Gradehacker
- Meet the Team
- Essay Writing
- Degree Accelerator
- Entire Class Bundle
- Learning Center
- Gradehacker TV
How To Write The GED Essay 2024 (Extended Response)
Santiago mallea.
- Career Planning , Non-Traditional Students , Writing Tips

Chief of Content At Gradehacker
- Updated on May, 2024
How to Write The GED Essay
The best strategy for writing the GED essay is:
- Read the passages (5 minutes)
- Analyze the data and create an outline (5 minutes)
- Write your extended response (30 minutes)
- Reread and edit your writing (5 minutes)
If you want a clear example of what your GED essay should like like, later in this blog you’ll find a sample.

Struggling with GED prep? We’re here!
Book a free call for personalized support and a strategic plan to excel in your GED essay and studies.
If you are planning on taking the GED test , you’ll eventually have to pass the GED essay .
Also known as the extended response, this assignment tests your evidence-based writing skills, and it’s where many students get stuck. However, writing the GED essay is easier than most people make it out to be .
It just takes practice and patience . And with these tips, you’ll be able to ace the test in no time!
Here at Gradehacker, we are the non-traditional adult student’s most trusted resource. Earning a GED diploma is necessary to enroll in college or access better job opportunities. We want you to be capable of writing an entire essay that will clearly show that you are up to the task .
This guide will teach you how to write a GED essay and share the best tips to make your text stand out and meet the passing score.
What Is The GED Essay?
The GED test consists of four sections:
- Mathematics
- Social Studies
- English Language Arts
The Reasoning Through Language Arts exam mainly consists of multiple-choice questions but also includes the Extended Response assignment, where you have to write an essay from scratch from two passages they give you.
You’ll have 45 minutes to analyze these two texts, choose which argument presents strong evidence, and explain why each piece of evidence supports your point.
While this part only represents 20% of your Reasoning Through Language Arts exam score (meaning that you can pass the Language Arts writing test even if you perform poorly in this section), it’s key that you know how to create a well-written GED essay.
Since they are testing your analysis of arguments and writing skills, it’s your opportunity to prove that you have mastered the core elements of the entire Language Arts section.
Plus, if you are planning on pursuing a college degree, where knowing how to analyze texts and write an essay response is important, passing the GED extended response is key.

GED Essay Prompt
To pass the essay portion, you’ll have to read two different passages that talk about the same issue but take an opposite stance about it. Your task is to determine which position presented is better supported.
It doesn’t matter if you disagree with that position; you must defend and explain your decision using multiple pieces of evidence from the texts.
Regarding length, the essay prompt suggests that your response should be approximately four to seven paragraphs of three to seven sentences each , which should be a 300-500 word essay.
While there is no essay length requirement regarding the number of words, we recommend writing between 400 and 500 .
GED Essay Sentence Structure
So, how do you write a GED extended response? Well, It has a structure similar to an argumentative essay.
- Introductory paragraph:
This should be a primary and short thesis statement where you clearly address which of the two passages is better supported.
- Body paragraphs:
Consist of three or four body paragraphs where you formulate your thesis using the text’s information as your source.
- Conclusion paragraph:
As a final step, briefly summarize your argument and reiterate its importance. If this is not your forte, there are many conclusion tips that can help you!
How to Pass The GED Essay
Now that you understand the GED Extended Response and what you need to do, here is our essay writing guide.
You’ll find multiple tips throughout it, but essentially, to write a cohesive, well-constructed essay, you’ll have to follow this four-part strategy:
- Read the passages
- Analyze the data and create an outline
- Write your extended response essay
- Reread and edit your writing

Write a Winning GED Essay
Fear poor writing no more. Book a free coaching call for expert advice and a strategic study plan.
Read the two passages (5 min)
The first step is to read both body passages thoroughly but quickly.
You need to understand what the topic is about, and while you read the text, highlight the statistics and factual data each author uses as support.
Remember that you can have differing views on your chosen side. Recognize which stance has better sources to defend your point, and explain why in your essay.
Analyze the data and create an outline (5 min)
Once you are done reading both texts and already highlighted all the essential information the authors use, you’ll need to analyze the evidence!
While ideally, you should recognize who supports their point better in the previous step , doing it in this part will be easier as you have all the factual data on sig ht.
Usually, the text with more information highlighted will be the one that defends its stance the best .
So, the next thing you need to do is make an outline and write down your ideas. This way, you’ll have all the information organized to begin the most crucial part of the writing process.
Write your extended response essay (30 min)
And now, with evidence highlighted and an outline created, you are ready to start writing!
If you are going for the minimum and writing a 5-paragraph essay, you’ll need at least three major ideas to develop individually in separate paragraphs.
Stick to one idea per paragraph , and include one or two of your selected pieces of evidence from the texts to organize the information better and keep a good flow.
Remember to use connectors! However, nevertheless, furthermore, additionally, and more! These vital elements will help you introduce the reason for your argument at the beginning of each paragraph.
And just like with any essay, you must use formal and academic language , but remember to be concise and straightforward. It’s the content of what you write that’s important here, so choose your words wisely to show your English language knowledge.
Plus, remember that there’s no specific word count you need to meet.
Our own pro-tip here is to write the introductory paragraph last.
Because many students struggle and waste valuable minutes when trying to begin with the introduction, you can save extra time by explaining and defending your arguments first and writing the intro once you are done.
You’ll see how easy it will be to summarize the main issue and thesis statement once you’ve already developed your points.
Since the GED essay works very similarly to an argumentative paper, there are many more pro-tips you can learn in our guide on how to write an argumentative essay . So be sure to check it out!

Reread and edit your writing (5 min)
Before submitting your essay, you must read what you wrote, check for spelling errors, and ensure that your ideas are clearly understood .
Not editing your essay can be one of your most critical mistakes!
Remember they are testing your understanding of the English language and writing skills; handing in an essay with spelling mistakes, flawed evidence, or poorly structured text can make you lose valuable points.
For this part, it’s crucial you know the most common essay mistakes so you can avoid them!

Transform your adult college journey
Book a 30-min coaching call for free and find the personalized support and mentorship you deserve!
GED Essay Sample
Follow all of these tips, and you are guaranteed to pass the GED essay!
However, here you have a GED Testing Service’s essay example that perfectly explains how this assignment should be completed:

Mastering the GED Essay
Now you know how to write the GED essay!
Remember to follow our essay-writing strategy to pass the Language Arts section by demonstrating mastery of your writing skills.
You are more than capable of completing the GED test with the highest score and then applying to the best colleges to continue your educational journey .
Once you make it happen, don’t forget that if you ever need assistance with your essays or classes , Gradehacker is always here to help!
And if you need more tips on how to improve your writing skills , check out these related blog posts:

EssayPro Honest Review | How Their Editing Service Work

Best AI to Write Essays

How Much Does It Cost for Help with My Entire Class?

Best Apps For Writing 2024 | Boost Your Writing Skills

How to Write a Research Paper | The Ultimate Step-by-Step Guide

How Much Does it Cost to Write My Essay?

Write an Essay From Scratch With Chat GPT: Step-by-Step Tutorial

Santiago Mallea is a curious and creative journalist who first helped many college students as a Gradehacker consultant in subjects like literature, communications, ethics, and business. Now, as a Content Creator in our blog, YouTube channel, and TikTok, he assists non-traditional students improve their college experience by sharing the best tips. You can find him on LinkedIn .
- Best Apps and Tools
- Writing Tips
- Financial Tips and Scholarships
- Career Planning
- Non-Traditional Students
- Student Wellness
- Cost & Pricing

- 2525 Ponce de Leon Blvd Suite 300 Coral Gables, FL 33134 USA
- Phone: (786) 991-9293
- Gradehacker 2525 Ponce de Leon Blvd Suite 300 Coral Gables, FL 33134 USA
About Gradehacker
Business hours.
Mon - Fri: 10:00 am - 7 pm ET Sat - Sun: 10 am - 3 pm ET
© 2024 Gradehacker LLC All Rights Reserved.
Tips for writing a killer extended response

Sam Di Sano
Teacher and School Enablement Leader at Atomi

So, what makes a good extended response? Glad you asked. Be honest, how many times has your teacher pulled the old PEEL card trick out and you’ve just been sitting there in class thinking ‘wtf is this old guy going on about?’
Well I’ve gotta say - your teacher has a point. PEEL is the way to go if you want to write a solid extended response, with all the analysis, evidence and links that you need to get those top marks.
Let’s break it down
What is this PEEL concept all about? Pretty much it’s about breaking down your 4-6 sentence paragraphs into smaller chunks, which will help you write really concise statements that actually answer the question. To do this you need to include your P oint or topic sentence, a little E vidence with an E xplanation of that evidence and then finally a L ink sentence.
Let’s break these down some more:
Point or Topic Sentence
This is your opening statement where in one sentence you essentially answer the question (so address that key term, i.e. 'explain', 'discuss', 'analyse') by using the words of the question and by stating your position and formulating your own argument or thesis. This can then be followed by another sentence or two giving a little more information for those people who are still a little confused and need it to be explained a bit more.
This is where you start to bring in the proof you need to cement your position. Remember, you’re trying to argue your perspective so you have to be able to back up what you’re saying with actual evidence from the text or stimulus you’ve been given. Here you get the opportunity to bring in all those quotes or key dates you’ve spent the last 3 weeks trying to memorise. It’s also a good chance to show the marker that you’ve analysed the stimulus and have a good understanding of these.
Explanation
Your next couple of sentences now need to explain how that evidence is actually proving your point. This is your chance to really bring in those critical thinking and analysis skills that you’ve been practising. It’s also the perfect time to bring in any techniques that can also help you prove your point. Whether it’s the use of analogy in English, or the context of the source given in a History exam, these details can really bulk up your explanations and show the marker that you know what you’re talking about and are able to put together a really solid argument.
Like any good piece of writing, it’s all about structure. So, now it’s time to wrap it all up and bring it back to where you started. A little like public speaking I guess, you draw your audience back to the question and your point or topic. No, this does not mean you get to just restate your first sentence exactly. It’s all about summing up how every point you just made in that paragraph answers the question and reconfirms your point of view.
But it doesn’t stop there. Repeat these steps a couple of times per paragraph and that’s when you’ll get some really quality paragraphs starting to come together.
Why mine is better than yours
So if it is that simple, what makes one paragraph better than another? There are two things that will make your work stand out over the person next to you;
- The level of sophistication you put into the language you use.
- The level of sophistication you put into the techniques you use and facts you quote.
That’s where you can really develop an edge. Remember, you don’t want your extended responses to go over the word limit or be so long that you can't get the whole thing down in an exam, so make an effort to keep your writing really tight and succinct. You can't waste any time fluffing around with your words so choose every one of them carefully. Same with your evidence. Be well read and use a body of work to prove your point wisely. You don’t have to prove a theory is right - you need to prove your particular perspective is plausible and you do that by using sources of evidence that think the same way you do.
If it’s your first time writing out a paragraph using the PEEL method, a really good way to keep track of everything is to use different coloured pens or a different colour highlighter for each of your PEEL sentences. The more you do this, the easier it’ll become and before you know it you’ll be writing paragraphs that fit the structure without even trying.
See - it’s really not that hard to write a good extended response, but it does take heaps of practice to really sharpen and polish your work. The more you practice, the more sophisticated your writing will become. I see you band 6 👀!
Published on
July 18, 2018
Recommended reads

Strategies for using retrieval

The syllabus: your key to smashing your studies

Techniques to smash procrastination
What's atomi.
Engaging, curriculum-specific videos and interactive lessons backed by research, so you can study smarter, not harder.
With tens of thousands of practice questions and revision sessions, you won’t just think you’re ready. You’ll know you are!
Study skills strategies and tips, AI-powered revision recommendations and progress insights help you stay on track.
Short, curriculum-specific videos and interactive content that’s easy to understand and backed by the latest research.
Active recall quizzes, topic-based tests and exam practice enable students to build their skills and get immediate feedback.
Our AI understands each student's progress and makes intelligent recommendations based on their strengths and weaknesses.
GED Essay-Topics, Samples, And Tips
Last Updated on May 16, 2024.
This language Arts lesson is part of this website’s free online GED classes a nd practice tests, generously provided by the accredited comprehensive GED prep course created by Onsego.
Pass the GED Test in 2 Months
Learn just 1 hour a day . it doesn’t matter when you left school..
Our free support is a great way to start with your GED prep, and if you like these free practice tests and video lessons, you may easily switch to Onsego GED Prep’s full-scope, accredited course to earn your GED fast!
One part of the GED Reasoning through Language Arts (RLA) test is writing a GED Essay, also known as the Extended Response. You have 45 minutes to create your essay. The GED essay is an argumentative essay.
A common method for writing this type of essay is the five-paragraph approach.
Writing your GED Essay is not about writing an opinion on the topic at hand. Your opinion is irrelevant. You are asked to determine and explain which of the arguments is better.
This lesson is provided by Onsego GED Prep.
Online GED Classes – Fast and Easy
Prepare Quickly To Pass The GED Test. Get Your Diploma in 2 Months .
Table of Contents
- 0.1 Video Transcription
- 1 GED Essay Structure
- 2 GED Essay Topics
- 3 GED Essay Samples
- 4 Tips for Writing your GED Essay
- 5 How your GED Essay is Scored
Video Transcription
After reading the stimulus with two different arguments about a subject, your task is to explain why one of these arguments is better.
Remember, when writing your GED Essay, you are NOT writing your opinion on the topic. That’s irrelevant. You must write about why one argument is better than the other.
You are writing an analysis of the author’s two positions and explaining which argument is stronger. These two arguments are presented in the stimulus, so you don’t need to create any own examples.
So again, you only need to decide what argument is stronger and claim it and prove it. It is NOT about your opinion.
Since in your essay, you need to determine which argument is best supported, your claim should clearly state which of the two positions is stronger.
You will be provided with the stimulus material and a prompt.
The stimulus is a text that provides 2 opposing opinions about a certain subject. The prompt provides instructions and tells you what you need to do.
I’ll say it again because so many students make mistakes here, it’s NOT about your opinion on the topic but the subject that matters!
You need to analyze the arguments and determine which opinion is best supported throughout the text.
You are NOT asked which argument you agree with more, and you should NEVER respond with a personal opinion.
So, don’t use the word “I” such as “I think that…” “I agree because…” “In my opinion…”.
The GED essay is graded on a machine that uses algorithms to figure out your score.
So, no teacher will decide about the score in any way.
It’s very important that you remember this!
Let’s take a look at the structure, topics, and format of the GED Essay.
GED Essay Structure
Ged essay topics.
- GED Essay Sample
- GED Essay Scoring
- GED Essay Writing Tips
Remember: you need to analyze which of the presented arguments is better and explain why it’s better.
Likewise, make sure your reasons come from the text – you aren’t making up your examples; you’re talking about the ones in the passages.
How should you prove that one argument is stronger? – Look at the evidence in the text.
Did the author use a relevant statistic from a reliable source, or did he/she assume something with a hypothetical anecdote?
Once you know which is better supported, you’re on your way.
Keep in mind: Don’t Summarize!
It’s easy to substitute a simpler task (summarize each side) for the more complex task of evaluating arguments. But if all you do is summarize, your response will be considered off-topic and likely will not receive any points.
The GED Essay should contain:
- 4-7 paragraphs of 3 to 7 sentences each and 300-500 words in total.
- An essay (or response) that is significantly shorter could put you in danger of scoring a 0 just for not showing enough of your writing skills.
- As you read the stimulus material (text), think carefully about the argumentation presented in the passage(s). “Argumentation” refers to the assumptions, claims, support, reasoning, and credibility on which a position is based.
- Pay close attention to how the author(s) use these strategies to convey his or her position.
Every well-written GED essay has an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
Your response will be an argument or an argumentative essay. Remember that you are NOT writing your opinion on the topic.
You are writing an analysis of two of the author’s positions and explaining which argument is stronger.
Things to keep in mind: the Extended Response (GED Essay) is scored by smart machines that are programmed to recognize correct answers. So, don’t try to be creative; just be correct. Also:
- Use proper grammar and sentence structure.
- Practice writing a 300 to 500-word essay.
Let’s look at the GED Essay structure: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
- The Introduction introduces the topic you are writing about and states your claim or thesis statement. Stand your position.
- The Body of the essay presents reasoning and evidence to support your claim. This is the longest part of the response and should be at least two paragraphs.
- The concluding paragraph sums up your main points and restates your claim.
Here are a few examples of GED Essay Topics. Click on the title to read a full stimulus and a prompt.
An Analysis of Daylight-Saving Time
The article presents arguments from both supporters and critics of Daylight-Saving Time who disagree about the practice’s impact on energy consumption and safety. Check here to read the full article.
Should the Penny Stay in Circulation?
Analyze the presented arguments and decide which one is better supported. Check here to read the full article.
Is Golf a Sport?
Proponents say that golf meets the definition of “sport.” Opponents say that golf better meets the definition of “game” than “sport. Analyze both opinions and determine which one is better supported. Check here to read the full article.
GED Essay Samples
Click here to access a sample of a GED essay with an explanation of the structure. Getting familiar with GED essay samples will help you plan your essay and understand what elements are important.
When reading the essay subject, you really should take the time to pull together your thoughts. By arranging your ideas rationally, you will be able to express your thoughts far better on paper. When you start writing, concentrate on the guidelines that you came to understand in English class.
Pay attention to English language usage (grammar); you must use the right punctuation and capitalization and decide on suitable word solutions.
Check here to read a GED Essay Sample with our comments.
Tips for Writing your GED Essay
1. Make sure you read the stimulus and prompt cautiously
It’s good to practice this carefully. Check out each question carefully and take a little time to figure out the topic and what kind of answer will be expected.
It is important to read the questions meticulously.
Usually, students simply run over stimulus and prompt and begin to write immediately, believing that they will save time this way.
Well, this actually the most undesirable thing to do. Take a short while and try to understand the questions completely in order to respond to them appropriately. If you wish, highlight the essential words and phrases in the stimulus to be able to look at it from time to time to be certain you stick to the topic.
2. Sketch an outline for the essay
In general, you will only need a few minutes to plan your essay, and it is imperative to take that time. As soon as you grasp the questions entirely, and once you have scribbled down some initial ideas, make an outline of the essay and follow that.
Plan an introduction, body, and conclusion. Following this process is going to save you a lot of time and it helps establish a rational development of thoughts.
3. Stick to the subject
Each paragraph in the body of your response should explain why a piece of evidence supports your claim or disputes the opposing claim to explain your evidence.
You can describe or restate it. This shows that you understand precisely what it means and how it relates to your claim.
Cite the mentioned details or facts of a specific point and relate them to your claim.
Your response should include evidence from both passages and explain what strong evidence supports one argument and why faulty evidence weakens the other argument.
4. Proofreading and Revision
By the time you completed writing your essay, you should go back to the beginning and read your essay carefully again, as you quite easily could have forgotten a comma or have misspelled a word while writing your essay. See also this post -> Is the GED Language Arts Test Hard?
While rereading your essay, pay close attention to whether your essay provides well-targeted points, is organized clearly, presents specific information and facts, comes with proper sentence construction, and has no grammar or spelling mistakes.
How your GED Essay is Scored
Your GED essay is scored by smart machines that are programmed to recognize correct answers. So don’t try to be creative; just be correct.
They will be using five criteria to assess your essay.
- Organization: were you clear about the essential idea, and did you present a well-thought strategy for composing your essay?
- Clear and swift response: did you deal with the subject adequately, without shifting from one focal point to another?
- Progress and details: did you apply relevant examples and specific details to elaborate on your original concepts or arguments, as opposed to using lists or repeating identical information?
- Grammar Rules of English: did you use decent writing techniques like sentence structure, spelling, punctuation, syntax, and grammar, and did you shape and edit your essay after you penned the first draft?
- Word choice: how far did you choose and employ suitable words to indicate your points of view?
Your 45 minutes will go quickly, so focus on these important points to get the best score.
What’s important is to make a clear statement about which position is better supported. Write clear sentences and arrange paragraphs in a logical order.
GED testing includes four modules (independent subtests) in Mathematical Reasoning (Math), Reasoning through Language Arts, Science, and Social Studies that can be taken separately. You should study very well, be effective on test day, and pass the subtest(s) you registered for.
GED writing for essays may be a bit tricky, but you can store all this information for proper learning on a list and change to proper write essay techniques before test day has arrived. Just practice a lot, and you’ll see that it’ll be getting better and better. So now you know all about writing the GED Essay.

- Extended Response
How to do an extended response exam

In an extended response question, you will be given a topic or a question and be given specific instructions on how to respond.
Knowing what the question is asking for, and knowing how to structure your response, is crucial to obtaining the best results.
Understand the question
Read the question carefully to find the key word or phrase in regard to what you need to do.
The most common key words and phrases are listed below with a brief explanation of what you need to do:
| Key Word or Phrase | Explanation |
| Account for | Give reasons why |
| Analyse | Examine to explain meaning, relationships, similarities or differences |
| Argue | Give reasons for or against |
| Assess | Determine the value or |
| What things led to or the historical event? | |
| What was different as a of this event or person? | |
| Compare | Examine and note similarities |
| What happened as a of the historical event or person | |
| Consider | Judge and come to an opinion |
| What , or ? | |
| Contrast | Emphasise the differences |
| Discuss | Examine by argument, considering for and against |
| Explain | Offer reasons for |
| How | Explain the process, steps or key events |
| The for their actions | |
| Why is it important? | |
| To what extent | Quantify the importance (to a great extent? to a limited extent?) |
| Why | Explain the , reasons or |
Extended Response Structure
Your Extended Response paragraph should follow the same paragraph structure as an analytical essay body paragraph. Parts of a good body paragraph :
1. Topic sentence : The very first sentence that clearly states what you are going to be arguing in the paragraph.
2. Explanation sentence: provides a detailed explanation of what your topic sentence means, or the main points that your sources will focus on. This usually means provided details about a historical person, location or event.
3. Evidence from your sources : Incorporate a number of good pieces (usually 3-4) of evidence from sources that prove your point for this paragraph. A typical evidence sentence has the following structure:
[Source name] says that [direct/indirect quote] which shows that [explanation] (in-text reference).
For example:
Smith says that "Romans were cruel soldiers", which shows that Roman legionaries had a reputation for excessive violence (1977, 186).
As you incorporate your quotes, ensure you provide analysis and evaluation of your sources. For examples for how to do this, proceed to this section of the History Skills website.
4. Clincher : Make a clear statement about how all the evidence you provided helps prove what you had stated in your Topic Sentence.
Example Extended Response
Example Extended Response Question:
How did the differences in Caesar’s and Pompey’s attitudes towards their defeated enemies effect how the Roman people reacted to the two leaders?
Example Extended Response Answer:
The difference between Caesar’s clemency and Pompey’s harsh punishments polarised the Roman populace, causing them to love one but hate the other. On one hand, Caesar spared the lives of the defeated Pompeian soldiers who had fought against him. His clemency was promoted throughout Italy, which increased popular opinion in Caesar’s favour. Caesar himself was reported have said to Cicero, a close political ally, that such a strategy was intended to “willingly win the support of all and gain a permanent victory…grow[ing] strong through pity and generosity” (Cicero, Atticus , VII.11). It must be noted that Cicero demonstrated a favourable opinion towards the future dictator at that point in time, so the senator may have produced this notion on behalf of Caesar. However, the indication is that the stratagem worked and Caesar gained substantial popularity in Italy as a result. In contrast to Caesar’s generosity, Pompey and the optimates were reputedly very harsh towards their enemies. They had announced that those who remained in Rome were to be regarded as enemies (Kamm, 2006, 106). This is confirmed by Goldsworthy, when he notes that after the victory at Dyrrachium, Pompey’s commanders were allowed to mock and execute imprisoned troops in front of Caesar’s army (2006, 421). The news of both Caesar’s and Pompey’s differing attitudes towards defeated enemies had a powerful effect on the Romans. The sharp contrast between the two policies of the two civil war generals impressed the Italians in Caesar’s favour and, as a result, Pompey lost most of his popular support on the peninsula.
What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
--> Read more » -->