Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., ai + human expertise – a paradigm shift..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai....
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 1:27 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Literature Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Introduction
OK. You’ve got to write a literature review. You dust off a novel and a book of poetry, settle down in your chair, and get ready to issue a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” as you leaf through the pages. “Literature review” done. Right?
Wrong! The “literature” of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. “Literature” could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL. And a review does not necessarily mean that your reader wants you to give your personal opinion on whether or not you liked these sources.
What is a literature review, then?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Who writes these things, anyway?
Literature reviews are written occasionally in the humanities, but mostly in the sciences and social sciences; in experiment and lab reports, they constitute a section of the paper. Sometimes a literature review is written as a paper in itself.
Let’s get to it! What should I do before writing the literature review?
If your assignment is not very specific, seek clarification from your instructor:
- Roughly how many sources should you include?
- What types of sources (books, journal articles, websites)?
- Should you summarize, synthesize, or critique your sources by discussing a common theme or issue?
- Should you evaluate your sources?
- Should you provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history?
Find models
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word “review” in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you’ve already read are also excellent entry points into your own research.
Narrow your topic
There are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books on most areas of study. The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good survey of the material. Your instructor will probably not expect you to read everything that’s out there on the topic, but you’ll make your job easier if you first limit your scope.
Keep in mind that UNC Libraries have research guides and to databases relevant to many fields of study. You can reach out to the subject librarian for a consultation: https://library.unc.edu/support/consultations/ .
And don’t forget to tap into your professor’s (or other professors’) knowledge in the field. Ask your professor questions such as: “If you had to read only one book from the 90’s on topic X, what would it be?” Questions such as this help you to find and determine quickly the most seminal pieces in the field.
Consider whether your sources are current
Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Information even two years old could be obsolete. However, if you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be what is needed, because what is important is how perspectives have changed through the years or within a certain time period. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine. More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews also must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Begin composing
Once you’ve settled on a general pattern of organization, you’re ready to write each section. There are a few guidelines you should follow during the writing stage as well. Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion:
However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990). Hamilton (1988) asked students to complete sentences that required them to fill in pronouns that agreed with gender-neutral antecedents such as “writer,” “pedestrian,” and “persons.” The students were asked to describe any image they had when writing the sentence. Hamilton found that people imagined 3.3 men to each woman in the masculine “generic” condition and 1.5 men per woman in the unbiased condition. Thus, while ambient sexism accounted for some of the masculine bias, sexist language amplified the effect. (Source: Erika Falk and Jordan Mills, “Why Sexist Language Affects Persuasion: The Role of Homophily, Intended Audience, and Offense,” Women and Language19:2).
Use evidence
In the example above, the writers refer to several other sources when making their point. A literature review in this sense is just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence to show that what you are saying is valid.
Be selective
Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the review’s focus, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological.
Use quotes sparingly
Falk and Mills do not use any direct quotes. That is because the survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. Some short quotes here and there are okay, though, if you want to emphasize a point, or if what the author said just cannot be rewritten in your own words. Notice that Falk and Mills do quote certain terms that were coined by the author, not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. But if you find yourself wanting to put in more quotes, check with your instructor.
Summarize and synthesize
Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each paragraph as well as throughout the review. The authors here recapitulate important features of Hamilton’s study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study’s significance and relating it to their own work.
Keep your own voice
While the literature review presents others’ ideas, your voice (the writer’s) should remain front and center. Notice that Falk and Mills weave references to other sources into their own text, but they still maintain their own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with their own ideas and their own words. The sources support what Falk and Mills are saying.
Use caution when paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. In the preceding example, Falk and Mills either directly refer in the text to the author of their source, such as Hamilton, or they provide ample notation in the text when the ideas they are mentioning are not their own, for example, Gastil’s. For more information, please see our handout on plagiarism .
Revise, revise, revise
Draft in hand? Now you’re ready to revise. Spending a lot of time revising is a wise idea, because your main objective is to present the material, not the argument. So check over your review again to make sure it follows the assignment and/or your outline. Then, just as you would for most other academic forms of writing, rewrite or rework the language of your review so that you’ve presented your information in the most concise manner possible. Be sure to use terminology familiar to your audience; get rid of unnecessary jargon or slang. Finally, double check that you’ve documented your sources and formatted the review appropriately for your discipline. For tips on the revising and editing process, see our handout on revising drafts .
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Jones, Robert, Patrick Bizzaro, and Cynthia Selfe. 1997. The Harcourt Brace Guide to Writing in the Disciplines . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
Troyka, Lynn Quittman, and Doug Hesse. 2016. Simon and Schuster Handbook for Writers , 11th ed. London: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
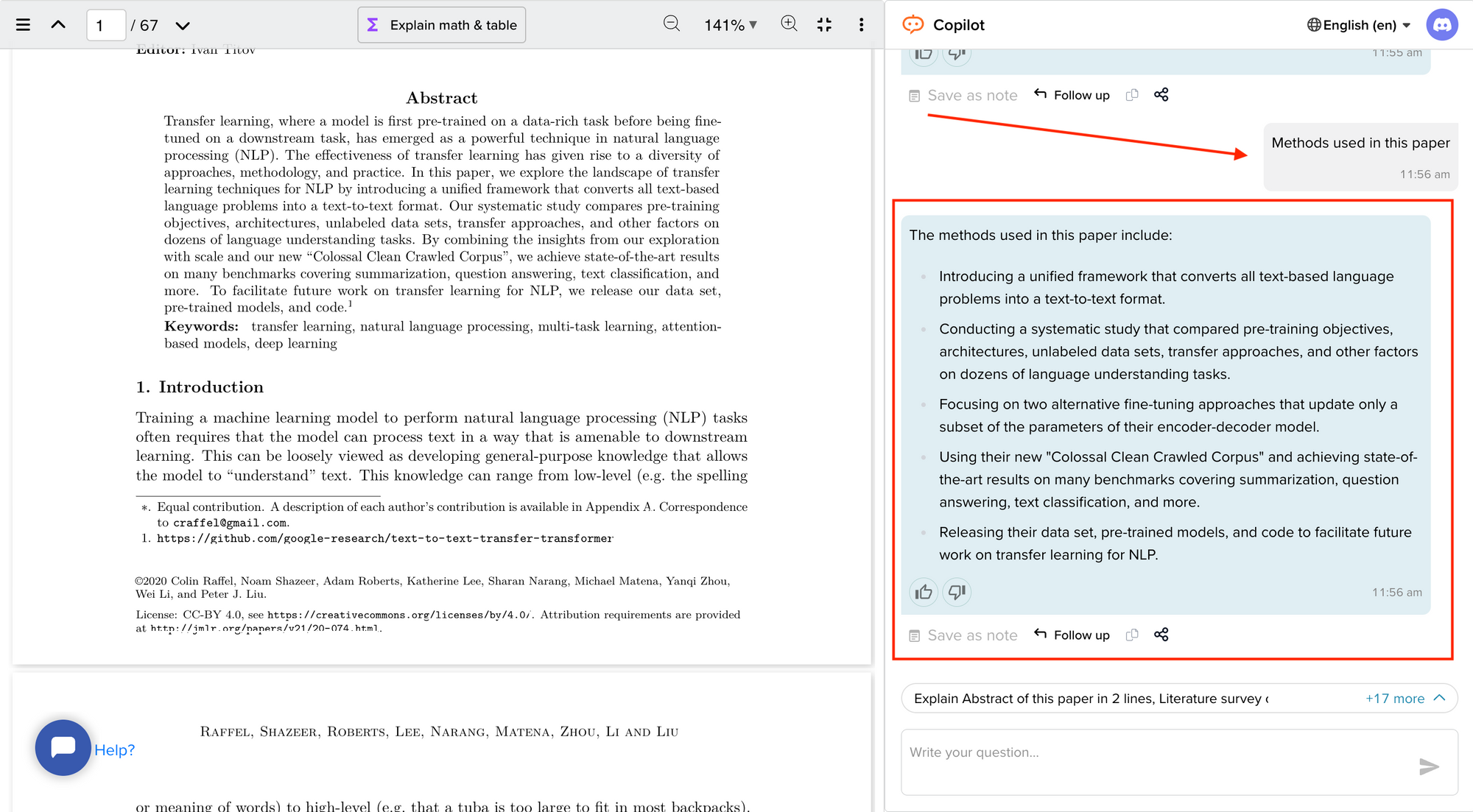
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.

APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Literature Review
Definition:
A literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It involves identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant literature, including scholarly articles, books, and other sources, to provide a summary and critical assessment of what is known about the topic.
Types of Literature Review
Types of Literature Review are as follows:
- Narrative literature review : This type of review involves a comprehensive summary and critical analysis of the available literature on a particular topic or research question. It is often used as an introductory section of a research paper.
- Systematic literature review: This is a rigorous and structured review that follows a pre-defined protocol to identify, evaluate, and synthesize all relevant studies on a specific research question. It is often used in evidence-based practice and systematic reviews.
- Meta-analysis: This is a quantitative review that uses statistical methods to combine data from multiple studies to derive a summary effect size. It provides a more precise estimate of the overall effect than any individual study.
- Scoping review: This is a preliminary review that aims to map the existing literature on a broad topic area to identify research gaps and areas for further investigation.
- Critical literature review : This type of review evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a critical analysis of the literature and identify areas where further research is needed.
- Conceptual literature review: This review synthesizes and integrates theories and concepts from multiple sources to provide a new perspective on a particular topic. It aims to provide a theoretical framework for understanding a particular research question.
- Rapid literature review: This is a quick review that provides a snapshot of the current state of knowledge on a specific research question or topic. It is often used when time and resources are limited.
- Thematic literature review : This review identifies and analyzes common themes and patterns across a body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the literature and identify key themes and concepts.
- Realist literature review: This review is often used in social science research and aims to identify how and why certain interventions work in certain contexts. It takes into account the context and complexities of real-world situations.
- State-of-the-art literature review : This type of review provides an overview of the current state of knowledge in a particular field, highlighting the most recent and relevant research. It is often used in fields where knowledge is rapidly evolving, such as technology or medicine.
- Integrative literature review: This type of review synthesizes and integrates findings from multiple studies on a particular topic to identify patterns, themes, and gaps in the literature. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Umbrella literature review : This review is used to provide a broad overview of a large and diverse body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to identify common themes and patterns across different areas of research.
- Historical literature review: This type of review examines the historical development of research on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a historical context for understanding the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Problem-oriented literature review : This review focuses on a specific problem or issue and examines the literature to identify potential solutions or interventions. It aims to provide practical recommendations for addressing a particular problem or issue.
- Mixed-methods literature review : This type of review combines quantitative and qualitative methods to synthesize and analyze the available literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research question by combining different types of evidence.
Parts of Literature Review
Parts of a literature review are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction of a literature review typically provides background information on the research topic and why it is important. It outlines the objectives of the review, the research question or hypothesis, and the scope of the review.
Literature Search
This section outlines the search strategy and databases used to identify relevant literature. The search terms used, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and any limitations of the search are described.
Literature Analysis
The literature analysis is the main body of the literature review. This section summarizes and synthesizes the literature that is relevant to the research question or hypothesis. The review should be organized thematically, chronologically, or by methodology, depending on the research objectives.
Critical Evaluation
Critical evaluation involves assessing the quality and validity of the literature. This includes evaluating the reliability and validity of the studies reviewed, the methodology used, and the strength of the evidence.
The conclusion of the literature review should summarize the main findings, identify any gaps in the literature, and suggest areas for future research. It should also reiterate the importance of the research question or hypothesis and the contribution of the literature review to the overall research project.
The references list includes all the sources cited in the literature review, and follows a specific referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, Harvard).
How to write Literature Review
Here are some steps to follow when writing a literature review:
- Define your research question or topic : Before starting your literature review, it is essential to define your research question or topic. This will help you identify relevant literature and determine the scope of your review.
- Conduct a comprehensive search: Use databases and search engines to find relevant literature. Look for peer-reviewed articles, books, and other academic sources that are relevant to your research question or topic.
- Evaluate the sources: Once you have found potential sources, evaluate them critically to determine their relevance, credibility, and quality. Look for recent publications, reputable authors, and reliable sources of data and evidence.
- Organize your sources: Group the sources by theme, method, or research question. This will help you identify similarities and differences among the literature, and provide a structure for your literature review.
- Analyze and synthesize the literature : Analyze each source in depth, identifying the key findings, methodologies, and conclusions. Then, synthesize the information from the sources, identifying patterns and themes in the literature.
- Write the literature review : Start with an introduction that provides an overview of the topic and the purpose of the literature review. Then, organize the literature according to your chosen structure, and analyze and synthesize the sources. Finally, provide a conclusion that summarizes the key findings of the literature review, identifies gaps in knowledge, and suggests areas for future research.
- Edit and proofread: Once you have written your literature review, edit and proofread it carefully to ensure that it is well-organized, clear, and concise.
Examples of Literature Review
Here’s an example of how a literature review can be conducted for a thesis on the topic of “ The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers’ Mental Health”:
- Start by identifying the key terms related to your research topic. In this case, the key terms are “social media,” “teenagers,” and “mental health.”
- Use academic databases like Google Scholar, JSTOR, or PubMed to search for relevant articles, books, and other publications. Use these keywords in your search to narrow down your results.
- Evaluate the sources you find to determine if they are relevant to your research question. You may want to consider the publication date, author’s credentials, and the journal or book publisher.
- Begin reading and taking notes on each source, paying attention to key findings, methodologies used, and any gaps in the research.
- Organize your findings into themes or categories. For example, you might categorize your sources into those that examine the impact of social media on self-esteem, those that explore the effects of cyberbullying, and those that investigate the relationship between social media use and depression.
- Synthesize your findings by summarizing the key themes and highlighting any gaps or inconsistencies in the research. Identify areas where further research is needed.
- Use your literature review to inform your research questions and hypotheses for your thesis.
For example, after conducting a literature review on the impact of social media on teenagers’ mental health, a thesis might look like this:
“Using a mixed-methods approach, this study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes in teenagers. Specifically, the study will examine the effects of cyberbullying, social comparison, and excessive social media use on self-esteem, anxiety, and depression. Through an analysis of survey data and qualitative interviews with teenagers, the study will provide insight into the complex relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes, and identify strategies for promoting positive mental health outcomes in young people.”
Reference: Smith, J., Jones, M., & Lee, S. (2019). The effects of social media use on adolescent mental health: A systematic review. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65(2), 154-165. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2019.03.024
Reference Example: Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range. doi:0000000/000000000000 or URL
Applications of Literature Review
some applications of literature review in different fields:
- Social Sciences: In social sciences, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing research, to develop research questions, and to provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as sociology, psychology, anthropology, and political science.
- Natural Sciences: In natural sciences, literature reviews are used to summarize and evaluate the current state of knowledge in a particular field or subfield. Literature reviews can help researchers identify areas where more research is needed and provide insights into the latest developments in a particular field. Fields such as biology, chemistry, and physics commonly use literature reviews.
- Health Sciences: In health sciences, literature reviews are used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, identify best practices, and determine areas where more research is needed. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as medicine, nursing, and public health.
- Humanities: In humanities, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing knowledge, develop new interpretations of texts or cultural artifacts, and provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as history, literary studies, and philosophy.
Role of Literature Review in Research
Here are some applications of literature review in research:
- Identifying Research Gaps : Literature review helps researchers identify gaps in existing research and literature related to their research question. This allows them to develop new research questions and hypotheses to fill those gaps.
- Developing Theoretical Framework: Literature review helps researchers develop a theoretical framework for their research. By analyzing and synthesizing existing literature, researchers can identify the key concepts, theories, and models that are relevant to their research.
- Selecting Research Methods : Literature review helps researchers select appropriate research methods and techniques based on previous research. It also helps researchers to identify potential biases or limitations of certain methods and techniques.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Literature review helps researchers in data collection and analysis by providing a foundation for the development of data collection instruments and methods. It also helps researchers to identify relevant data sources and identify potential data analysis techniques.
- Communicating Results: Literature review helps researchers to communicate their results effectively by providing a context for their research. It also helps to justify the significance of their findings in relation to existing research and literature.
Purpose of Literature Review
Some of the specific purposes of a literature review are as follows:
- To provide context: A literature review helps to provide context for your research by situating it within the broader body of literature on the topic.
- To identify gaps and inconsistencies: A literature review helps to identify areas where further research is needed or where there are inconsistencies in the existing literature.
- To synthesize information: A literature review helps to synthesize the information from multiple sources and present a coherent and comprehensive picture of the current state of knowledge on the topic.
- To identify key concepts and theories : A literature review helps to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to your research question and provide a theoretical framework for your study.
- To inform research design: A literature review can inform the design of your research study by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
Characteristics of Literature Review
Some Characteristics of Literature Review are as follows:
- Identifying gaps in knowledge: A literature review helps to identify gaps in the existing knowledge and research on a specific topic or research question. By analyzing and synthesizing the literature, you can identify areas where further research is needed and where new insights can be gained.
- Establishing the significance of your research: A literature review helps to establish the significance of your own research by placing it in the context of existing research. By demonstrating the relevance of your research to the existing literature, you can establish its importance and value.
- Informing research design and methodology : A literature review helps to inform research design and methodology by identifying the most appropriate research methods, techniques, and instruments. By reviewing the literature, you can identify the strengths and limitations of different research methods and techniques, and select the most appropriate ones for your own research.
- Supporting arguments and claims: A literature review provides evidence to support arguments and claims made in academic writing. By citing and analyzing the literature, you can provide a solid foundation for your own arguments and claims.
- I dentifying potential collaborators and mentors: A literature review can help identify potential collaborators and mentors by identifying researchers and practitioners who are working on related topics or using similar methods. By building relationships with these individuals, you can gain valuable insights and support for your own research and practice.
- Keeping up-to-date with the latest research : A literature review helps to keep you up-to-date with the latest research on a specific topic or research question. By regularly reviewing the literature, you can stay informed about the latest findings and developments in your field.
Advantages of Literature Review
There are several advantages to conducting a literature review as part of a research project, including:
- Establishing the significance of the research : A literature review helps to establish the significance of the research by demonstrating the gap or problem in the existing literature that the study aims to address.
- Identifying key concepts and theories: A literature review can help to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to the research question, and provide a theoretical framework for the study.
- Supporting the research methodology : A literature review can inform the research methodology by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
- Providing a comprehensive overview of the literature : A literature review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge on a topic, allowing the researcher to identify key themes, debates, and areas of agreement or disagreement.
- Identifying potential research questions: A literature review can help to identify potential research questions and areas for further investigation.
- Avoiding duplication of research: A literature review can help to avoid duplication of research by identifying what has already been done on a topic, and what remains to be done.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research : A literature review helps to enhance the credibility of the research by demonstrating the researcher’s knowledge of the existing literature and their ability to situate their research within a broader context.
Limitations of Literature Review
Limitations of Literature Review are as follows:
- Limited scope : Literature reviews can only cover the existing literature on a particular topic, which may be limited in scope or depth.
- Publication bias : Literature reviews may be influenced by publication bias, which occurs when researchers are more likely to publish positive results than negative ones. This can lead to an incomplete or biased picture of the literature.
- Quality of sources : The quality of the literature reviewed can vary widely, and not all sources may be reliable or valid.
- Time-limited: Literature reviews can become quickly outdated as new research is published, making it difficult to keep up with the latest developments in a field.
- Subjective interpretation : Literature reviews can be subjective, and the interpretation of the findings can vary depending on the researcher’s perspective or bias.
- Lack of original data : Literature reviews do not generate new data, but rather rely on the analysis of existing studies.
- Risk of plagiarism: It is important to ensure that literature reviews do not inadvertently contain plagiarism, which can occur when researchers use the work of others without proper attribution.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Strategies to Find Sources
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Strategies to Find Sources
- Getting Started
- Introduction
- How to Pick a Topic
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
The Research Process
![how to identify the literature review of a research paper Interative Litearture Review Research Process image (Planning, Searching, Organizing, Analyzing and Writing [repeat at necessary]](https://libapps.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/64450/images/ResearchProcess.jpg)
Planning : Before searching for articles or books, brainstorm to develop keywords that better describe your research question.
Searching : While searching, take note of what other keywords are used to describe your topic, and use them to conduct additional searches
♠ Most articles include a keyword section
♠ Key concepts may change names throughout time so make sure to check for variations
Organizing : Start organizing your results by categories/key concepts or any organizing principle that make sense for you . This will help you later when you are ready to analyze your findings
Analyzing : While reading, start making notes of key concepts and commonalities and disagreement among the research articles you find.
♠ Create a spreadsheet to record what articles you are finding useful and why.
♠ Create fields to write summaries of articles or quotes for future citing and paraphrasing .
Writing : Synthesize your findings. Use your own voice to explain to your readers what you learned about the literature on your topic. What are its weaknesses and strengths? What is missing or ignored?
Repeat : At any given time of the process, you can go back to a previous step as necessary.
Advanced Searching
All databases have Help pages that explain the best way to search their product. When doing literature reviews, you will want to take advantage of these features since they can facilitate not only finding the articles that you really need but also controlling the number of results and how relevant they are for your search. The most common features available in the advanced search option of databases and library online catalogs are:
- Boolean Searching (AND, OR, NOT): Allows you to connect search terms in a way that can either limit or expand your search results
- Proximity Searching (N/# or W/#): Allows you to search for two or more words that occur within a specified number of words (or fewer) of each other in the database
- Limiters/Filters : These are options that let you control what type of document you want to search: article type, date, language, publication, etc.
- Question mark (?) or a pound sign (#) for wildcard: Used for retrieving alternate spellings of a word: colo?r will retrieve both the American spelling "color" as well as the British spelling "colour."
- Asterisk (*) for truncation: Used for retrieving multiple forms of a word: comput* retrieves computer, computers, computing, etc.
Want to keep track of updates to your searches? Create an account in the database to receive an alert when a new article is published that meets your search parameters!
- EBSCOhost Advanced Search Tutorial Tips for searching a platform that hosts many library databases
- Library's General Search Tips Check the Search tips to better used our library catalog and articles search system
- ProQuest Database Search Tips Tips for searching another platform that hosts library databases
There is no magic number regarding how many sources you are going to need for your literature review; it all depends on the topic and what type of the literature review you are doing:
► Are you working on an emerging topic? You are not likely to find many sources, which is good because you are trying to prove that this is a topic that needs more research. But, it is not enough to say that you found few or no articles on your topic in your field. You need to look broadly to other disciplines (also known as triangulation ) to see if your research topic has been studied from other perspectives as a way to validate the uniqueness of your research question.
► Are you working on something that has been studied extensively? Then you are going to find many sources and you will want to limit how far back you want to look. Use limiters to eliminate research that may be dated and opt to search for resources published within the last 5-10 years.
- << Previous: How to Pick a Topic
- Next: Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 1. Identify the Question
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
Identify the question
Developing a research question.
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write a Literature Review
From Topic to Question (Infographic)
This graphic emphasizes how reading various sources can play a role in defining your research topic.
( Click to Enlarge Image )

Text description of "From Topic to Question" for web accessibility

In some cases, such as for a course assignment or a research project you're working on with a faculty mentor, your research question will be determined by your professor. If that's the case, you can move on to the next step . Otherwise, you may need to explore questions on your own.
A few suggestions

Photo Credit: UO Libraries
According to The Craft of Research (2003) , a research question is more than a practical problem or something with a yes/no answer. A research question helps you learn more about something you don't already know and it needs to be significant enough to interest your readers.
Your Curiosity + Significance to Others = Research Question
How to get started.
In a research paper, you develop a unique question and then synthesize scholarly and primary sources into a paper that supports your argument about the topic.
- Identify your Topic (This is the starting place from where you develop a research question.)
- Refine by Searching (find background information) (Before you can start to develop a research question, you may need to do some preliminary background research to see (1) what has already been done on the topic and (2) what are the issues surrounding the topic.) HINT: Find background information in Google and Books.
- Refine by Narrowing (Once you begin to understand the topic and the issues surrounding it, you can start to narrow your topic and develop a research question. Do this by asking the 6 journalistic question words.
Ask yourself these 6 questions
These 6 journalistic question words can help you narrow your focus from a broad topic to a specific question.
Who : Are you interested in a specific group of people? Can your topic be narrowed by gender, sex, age, ethnicity, socio-economic status or something else? Are there any key figures related to your topic?
What : What are the issues surrounding your topic? Are there subtopics? In looking at background information, did you notice any gaps or questions that seemed unanswered?
Where : Can your topic be narrowed down to a geographic location? Warning: Don't get too narrow here. You might not be able to find enough information on a town or state.
When : Is your topic current or historical? Is it confined to a specific time period? Was there a causative event that led your topic to become an area of study?
Why : Why are you interested in this topic? Why should others be interested?
How : What kinds of information do you need? Primary sources, statistics? What is your methodology?
Detailed description of, "Developing a Research Question" for web accessibility
- << Previous: Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- Next: 2. Review Discipline Styles >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 9 methods for literature reviews.
Guy Paré and Spyros Kitsiou .
9.1. Introduction
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and synthesizing the contents of many empirical and conceptual papers. Among other methods, literature reviews are essential for: (a) identifying what has been written on a subject or topic; (b) determining the extent to which a specific research area reveals any interpretable trends or patterns; (c) aggregating empirical findings related to a narrow research question to support evidence-based practice; (d) generating new frameworks and theories; and (e) identifying topics or questions requiring more investigation ( Paré, Trudel, Jaana, & Kitsiou, 2015 ).
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the “literature review” or “background” section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses ( Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013 ). It may also provide a theoretical foundation for the proposed study, substantiate the presence of the research problem, justify the research as one that contributes something new to the cumulated knowledge, or validate the methods and approaches for the proposed study ( Hart, 1998 ; Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Rather than providing a base for a researcher’s own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow, 1987 ). The so-called “review article” is a journal-length paper which has an overarching purpose to synthesize the literature in a field, without collecting or analyzing any primary data ( Green, Johnson, & Adams, 2006 ).
When appropriately conducted, review articles represent powerful information sources for practitioners looking for state-of-the art evidence to guide their decision-making and work practices ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, high-quality reviews become frequently cited pieces of work which researchers seek out as a first clear outline of the literature when undertaking empirical studies ( Cooper, 1988 ; Rowe, 2014 ). Scholars who track and gauge the impact of articles have found that review papers are cited and downloaded more often than any other type of published article ( Cronin, Ryan, & Coughlan, 2008 ; Montori, Wilczynski, Morgan, Haynes, & Hedges, 2003 ; Patsopoulos, Analatos, & Ioannidis, 2005 ). The reason for their popularity may be the fact that reading the review enables one to have an overview, if not a detailed knowledge of the area in question, as well as references to the most useful primary sources ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Although they are not easy to conduct, the commitment to complete a review article provides a tremendous service to one’s academic community ( Paré et al., 2015 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Most, if not all, peer-reviewed journals in the fields of medical informatics publish review articles of some type.
The main objectives of this chapter are fourfold: (a) to provide an overview of the major steps and activities involved in conducting a stand-alone literature review; (b) to describe and contrast the different types of review articles that can contribute to the eHealth knowledge base; (c) to illustrate each review type with one or two examples from the eHealth literature; and (d) to provide a series of recommendations for prospective authors of review articles in this domain.
9.2. Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
As explained in Templier and Paré (2015) , there are six generic steps involved in conducting a review article:
- formulating the research question(s) and objective(s),
- searching the extant literature,
- screening for inclusion,
- assessing the quality of primary studies,
- extracting data, and
- analyzing data.
Although these steps are presented here in sequential order, one must keep in mind that the review process can be iterative and that many activities can be initiated during the planning stage and later refined during subsequent phases ( Finfgeld-Connett & Johnson, 2013 ; Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ).
Formulating the research question(s) and objective(s): As a first step, members of the review team must appropriately justify the need for the review itself ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ), identify the review’s main objective(s) ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ), and define the concepts or variables at the heart of their synthesis ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ; Webster & Watson, 2002 ). Importantly, they also need to articulate the research question(s) they propose to investigate ( Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ). In this regard, we concur with Jesson, Matheson, and Lacey (2011) that clearly articulated research questions are key ingredients that guide the entire review methodology; they underscore the type of information that is needed, inform the search for and selection of relevant literature, and guide or orient the subsequent analysis. Searching the extant literature: The next step consists of searching the literature and making decisions about the suitability of material to be considered in the review ( Cooper, 1988 ). There exist three main coverage strategies. First, exhaustive coverage means an effort is made to be as comprehensive as possible in order to ensure that all relevant studies, published and unpublished, are included in the review and, thus, conclusions are based on this all-inclusive knowledge base. The second type of coverage consists of presenting materials that are representative of most other works in a given field or area. Often authors who adopt this strategy will search for relevant articles in a small number of top-tier journals in a field ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In the third strategy, the review team concentrates on prior works that have been central or pivotal to a particular topic. This may include empirical studies or conceptual papers that initiated a line of investigation, changed how problems or questions were framed, introduced new methods or concepts, or engendered important debate ( Cooper, 1988 ). Screening for inclusion: The following step consists of evaluating the applicability of the material identified in the preceding step ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ; vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). Once a group of potential studies has been identified, members of the review team must screen them to determine their relevance ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). A set of predetermined rules provides a basis for including or excluding certain studies. This exercise requires a significant investment on the part of researchers, who must ensure enhanced objectivity and avoid biases or mistakes. As discussed later in this chapter, for certain types of reviews there must be at least two independent reviewers involved in the screening process and a procedure to resolve disagreements must also be in place ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Shea et al., 2009 ). Assessing the quality of primary studies: In addition to screening material for inclusion, members of the review team may need to assess the scientific quality of the selected studies, that is, appraise the rigour of the research design and methods. Such formal assessment, which is usually conducted independently by at least two coders, helps members of the review team refine which studies to include in the final sample, determine whether or not the differences in quality may affect their conclusions, or guide how they analyze the data and interpret the findings ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Ascribing quality scores to each primary study or considering through domain-based evaluations which study components have or have not been designed and executed appropriately makes it possible to reflect on the extent to which the selected study addresses possible biases and maximizes validity ( Shea et al., 2009 ). Extracting data: The following step involves gathering or extracting applicable information from each primary study included in the sample and deciding what is relevant to the problem of interest ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Indeed, the type of data that should be recorded mainly depends on the initial research questions ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ). However, important information may also be gathered about how, when, where and by whom the primary study was conducted, the research design and methods, or qualitative/quantitative results ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Analyzing and synthesizing data : As a final step, members of the review team must collate, summarize, aggregate, organize, and compare the evidence extracted from the included studies. The extracted data must be presented in a meaningful way that suggests a new contribution to the extant literature ( Jesson et al., 2011 ). Webster and Watson (2002) warn researchers that literature reviews should be much more than lists of papers and should provide a coherent lens to make sense of extant knowledge on a given topic. There exist several methods and techniques for synthesizing quantitative (e.g., frequency analysis, meta-analysis) and qualitative (e.g., grounded theory, narrative analysis, meta-ethnography) evidence ( Dixon-Woods, Agarwal, Jones, Young, & Sutton, 2005 ; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic. Our classification scheme is largely inspired from Paré and colleagues’ (2015) typology. Below we present and illustrate those review types that we feel are central to the growth and development of the eHealth domain.
9.3.1. Narrative Reviews
The narrative review is the “traditional” way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative knowledge from what is reviewed ( Davies, 2000 ; Green et al., 2006 ). Instead, the review team often undertakes the task of accumulating and synthesizing the literature to demonstrate the value of a particular point of view ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ). As such, reviewers may selectively ignore or limit the attention paid to certain studies in order to make a point. In this rather unsystematic approach, the selection of information from primary articles is subjective, lacks explicit criteria for inclusion and can lead to biased interpretations or inferences ( Green et al., 2006 ). There are several narrative reviews in the particular eHealth domain, as in all fields, which follow such an unstructured approach ( Silva et al., 2015 ; Paul et al., 2015 ).
Despite these criticisms, this type of review can be very useful in gathering together a volume of literature in a specific subject area and synthesizing it. As mentioned above, its primary purpose is to provide the reader with a comprehensive background for understanding current knowledge and highlighting the significance of new research ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Faculty like to use narrative reviews in the classroom because they are often more up to date than textbooks, provide a single source for students to reference, and expose students to peer-reviewed literature ( Green et al., 2006 ). For researchers, narrative reviews can inspire research ideas by identifying gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge, thus helping researchers to determine research questions or formulate hypotheses. Importantly, narrative reviews can also be used as educational articles to bring practitioners up to date with certain topics of issues ( Green et al., 2006 ).
Recently, there have been several efforts to introduce more rigour in narrative reviews that will elucidate common pitfalls and bring changes into their publication standards. Information systems researchers, among others, have contributed to advancing knowledge on how to structure a “traditional” review. For instance, Levy and Ellis (2006) proposed a generic framework for conducting such reviews. Their model follows the systematic data processing approach comprised of three steps, namely: (a) literature search and screening; (b) data extraction and analysis; and (c) writing the literature review. They provide detailed and very helpful instructions on how to conduct each step of the review process. As another methodological contribution, vom Brocke et al. (2009) offered a series of guidelines for conducting literature reviews, with a particular focus on how to search and extract the relevant body of knowledge. Last, Bandara, Miskon, and Fielt (2011) proposed a structured, predefined and tool-supported method to identify primary studies within a feasible scope, extract relevant content from identified articles, synthesize and analyze the findings, and effectively write and present the results of the literature review. We highly recommend that prospective authors of narrative reviews consult these useful sources before embarking on their work.
Darlow and Wen (2015) provide a good example of a highly structured narrative review in the eHealth field. These authors synthesized published articles that describe the development process of mobile health ( m-health ) interventions for patients’ cancer care self-management. As in most narrative reviews, the scope of the research questions being investigated is broad: (a) how development of these systems are carried out; (b) which methods are used to investigate these systems; and (c) what conclusions can be drawn as a result of the development of these systems. To provide clear answers to these questions, a literature search was conducted on six electronic databases and Google Scholar . The search was performed using several terms and free text words, combining them in an appropriate manner. Four inclusion and three exclusion criteria were utilized during the screening process. Both authors independently reviewed each of the identified articles to determine eligibility and extract study information. A flow diagram shows the number of studies identified, screened, and included or excluded at each stage of study selection. In terms of contributions, this review provides a series of practical recommendations for m-health intervention development.
9.3.2. Descriptive or Mapping Reviews
The primary goal of a descriptive review is to determine the extent to which a body of knowledge in a particular research topic reveals any interpretable pattern or trend with respect to pre-existing propositions, theories, methodologies or findings ( King & He, 2005 ; Paré et al., 2015 ). In contrast with narrative reviews, descriptive reviews follow a systematic and transparent procedure, including searching, screening and classifying studies ( Petersen, Vakkalanka, & Kuzniarz, 2015 ). Indeed, structured search methods are used to form a representative sample of a larger group of published works ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, authors of descriptive reviews extract from each study certain characteristics of interest, such as publication year, research methods, data collection techniques, and direction or strength of research outcomes (e.g., positive, negative, or non-significant) in the form of frequency analysis to produce quantitative results ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). In essence, each study included in a descriptive review is treated as the unit of analysis and the published literature as a whole provides a database from which the authors attempt to identify any interpretable trends or draw overall conclusions about the merits of existing conceptualizations, propositions, methods or findings ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In doing so, a descriptive review may claim that its findings represent the state of the art in a particular domain ( King & He, 2005 ).
In the fields of health sciences and medical informatics, reviews that focus on examining the range, nature and evolution of a topic area are described by Anderson, Allen, Peckham, and Goodwin (2008) as mapping reviews . Like descriptive reviews, the research questions are generic and usually relate to publication patterns and trends. There is no preconceived plan to systematically review all of the literature although this can be done. Instead, researchers often present studies that are representative of most works published in a particular area and they consider a specific time frame to be mapped.
An example of this approach in the eHealth domain is offered by DeShazo, Lavallie, and Wolf (2009). The purpose of this descriptive or mapping review was to characterize publication trends in the medical informatics literature over a 20-year period (1987 to 2006). To achieve this ambitious objective, the authors performed a bibliometric analysis of medical informatics citations indexed in medline using publication trends, journal frequencies, impact factors, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) term frequencies, and characteristics of citations. Findings revealed that there were over 77,000 medical informatics articles published during the covered period in numerous journals and that the average annual growth rate was 12%. The MeSH term analysis also suggested a strong interdisciplinary trend. Finally, average impact scores increased over time with two notable growth periods. Overall, patterns in research outputs that seem to characterize the historic trends and current components of the field of medical informatics suggest it may be a maturing discipline (DeShazo et al., 2009).
9.3.3. Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews attempt to provide an initial indication of the potential size and nature of the extant literature on an emergent topic (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Daudt, van Mossel, & Scott, 2013 ; Levac, Colquhoun, & O’Brien, 2010). A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the presentation of a detailed research agenda for future works along with potential implications for both practice and research.
Unlike narrative and descriptive reviews, the whole point of scoping the field is to be as comprehensive as possible, including grey literature (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005). Inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to help researchers eliminate studies that are not aligned with the research questions. It is also recommended that at least two independent coders review abstracts yielded from the search strategy and then the full articles for study selection ( Daudt et al., 2013 ). The synthesized evidence from content or thematic analysis is relatively easy to present in tabular form (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
One of the most highly cited scoping reviews in the eHealth domain was published by Archer, Fevrier-Thomas, Lokker, McKibbon, and Straus (2011) . These authors reviewed the existing literature on personal health record ( phr ) systems including design, functionality, implementation, applications, outcomes, and benefits. Seven databases were searched from 1985 to March 2010. Several search terms relating to phr s were used during this process. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts to determine inclusion status. A second screen of full-text articles, again by two independent members of the research team, ensured that the studies described phr s. All in all, 130 articles met the criteria and their data were extracted manually into a database. The authors concluded that although there is a large amount of survey, observational, cohort/panel, and anecdotal evidence of phr benefits and satisfaction for patients, more research is needed to evaluate the results of phr implementations. Their in-depth analysis of the literature signalled that there is little solid evidence from randomized controlled trials or other studies through the use of phr s. Hence, they suggested that more research is needed that addresses the current lack of understanding of optimal functionality and usability of these systems, and how they can play a beneficial role in supporting patient self-management ( Archer et al., 2011 ).
9.3.4. Forms of Aggregative Reviews
Healthcare providers, practitioners, and policy-makers are nowadays overwhelmed with large volumes of information, including research-based evidence from numerous clinical trials and evaluation studies, assessing the effectiveness of health information technologies and interventions ( Ammenwerth & de Keizer, 2004 ; Deshazo et al., 2009 ). It is unrealistic to expect that all these disparate actors will have the time, skills, and necessary resources to identify the available evidence in the area of their expertise and consider it when making decisions. Systematic reviews that involve the rigorous application of scientific strategies aimed at limiting subjectivity and bias (i.e., systematic and random errors) can respond to this challenge.
Systematic reviews attempt to aggregate, appraise, and synthesize in a single source all empirical evidence that meet a set of previously specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a clearly formulated and often narrow research question on a particular topic of interest to support evidence-based practice ( Liberati et al., 2009 ). They adhere closely to explicit scientific principles ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) and rigorous methodological guidelines (Higgins & Green, 2008) aimed at reducing random and systematic errors that can lead to deviations from the truth in results or inferences. The use of explicit methods allows systematic reviews to aggregate a large body of research evidence, assess whether effects or relationships are in the same direction and of the same general magnitude, explain possible inconsistencies between study results, and determine the strength of the overall evidence for every outcome of interest based on the quality of included studies and the general consistency among them ( Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ). The main procedures of a systematic review involve:
- Formulating a review question and developing a search strategy based on explicit inclusion criteria for the identification of eligible studies (usually described in the context of a detailed review protocol).
- Searching for eligible studies using multiple databases and information sources, including grey literature sources, without any language restrictions.
- Selecting studies, extracting data, and assessing risk of bias in a duplicate manner using two independent reviewers to avoid random or systematic errors in the process.
- Analyzing data using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Presenting results in summary of findings tables.
- Interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Many systematic reviews, but not all, use statistical methods to combine the results of independent studies into a single quantitative estimate or summary effect size. Known as meta-analyses , these reviews use specific data extraction and statistical techniques (e.g., network, frequentist, or Bayesian meta-analyses) to calculate from each study by outcome of interest an effect size along with a confidence interval that reflects the degree of uncertainty behind the point estimate of effect ( Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009 ; Deeks, Higgins, & Altman, 2008 ). Subsequently, they use fixed or random-effects analysis models to combine the results of the included studies, assess statistical heterogeneity, and calculate a weighted average of the effect estimates from the different studies, taking into account their sample sizes. The summary effect size is a value that reflects the average magnitude of the intervention effect for a particular outcome of interest or, more generally, the strength of a relationship between two variables across all studies included in the systematic review. By statistically combining data from multiple studies, meta-analyses can create more precise and reliable estimates of intervention effects than those derived from individual studies alone, when these are examined independently as discrete sources of information.
The review by Gurol-Urganci, de Jongh, Vodopivec-Jamsek, Atun, and Car (2013) on the effects of mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments is an illustrative example of a high-quality systematic review with meta-analysis. Missed appointments are a major cause of inefficiency in healthcare delivery with substantial monetary costs to health systems. These authors sought to assess whether mobile phone-based appointment reminders delivered through Short Message Service ( sms ) or Multimedia Messaging Service ( mms ) are effective in improving rates of patient attendance and reducing overall costs. To this end, they conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases using highly sensitive search strategies without language or publication-type restrictions to identify all rct s that are eligible for inclusion. In order to minimize the risk of omitting eligible studies not captured by the original search, they supplemented all electronic searches with manual screening of trial registers and references contained in the included studies. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments were performed independently by two coders using standardized methods to ensure consistency and to eliminate potential errors. Findings from eight rct s involving 6,615 participants were pooled into meta-analyses to calculate the magnitude of effects that mobile text message reminders have on the rate of attendance at healthcare appointments compared to no reminders and phone call reminders.
Meta-analyses are regarded as powerful tools for deriving meaningful conclusions. However, there are situations in which it is neither reasonable nor appropriate to pool studies together using meta-analytic methods simply because there is extensive clinical heterogeneity between the included studies or variation in measurement tools, comparisons, or outcomes of interest. In these cases, systematic reviews can use qualitative synthesis methods such as vote counting, content analysis, classification schemes and tabulations, as an alternative approach to narratively synthesize the results of the independent studies included in the review. This form of review is known as qualitative systematic review.
A rigorous example of one such review in the eHealth domain is presented by Mickan, Atherton, Roberts, Heneghan, and Tilson (2014) on the use of handheld computers by healthcare professionals and their impact on access to information and clinical decision-making. In line with the methodological guidelines for systematic reviews, these authors: (a) developed and registered with prospero ( www.crd.york.ac.uk/ prospero / ) an a priori review protocol; (b) conducted comprehensive searches for eligible studies using multiple databases and other supplementary strategies (e.g., forward searches); and (c) subsequently carried out study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments in a duplicate manner to eliminate potential errors in the review process. Heterogeneity between the included studies in terms of reported outcomes and measures precluded the use of meta-analytic methods. To this end, the authors resorted to using narrative analysis and synthesis to describe the effectiveness of handheld computers on accessing information for clinical knowledge, adherence to safety and clinical quality guidelines, and diagnostic decision-making.
In recent years, the number of systematic reviews in the field of health informatics has increased considerably. Systematic reviews with discordant findings can cause great confusion and make it difficult for decision-makers to interpret the review-level evidence ( Moher, 2013 ). Therefore, there is a growing need for appraisal and synthesis of prior systematic reviews to ensure that decision-making is constantly informed by the best available accumulated evidence. Umbrella reviews , also known as overviews of systematic reviews, are tertiary types of evidence synthesis that aim to accomplish this; that is, they aim to compare and contrast findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Umbrella reviews generally adhere to the same principles and rigorous methodological guidelines used in systematic reviews. However, the unit of analysis in umbrella reviews is the systematic review rather than the primary study ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Unlike systematic reviews that have a narrow focus of inquiry, umbrella reviews focus on broader research topics for which there are several potential interventions ( Smith, Devane, Begley, & Clarke, 2011 ). A recent umbrella review on the effects of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with heart failure critically appraised, compared, and synthesized evidence from 15 systematic reviews to investigate which types of home telemonitoring technologies and forms of interventions are more effective in reducing mortality and hospital admissions ( Kitsiou, Paré, & Jaana, 2015 ).
9.3.5. Realist Reviews
Realist reviews are theory-driven interpretative reviews developed to inform, enhance, or supplement conventional systematic reviews by making sense of heterogeneous evidence about complex interventions applied in diverse contexts in a way that informs policy decision-making ( Greenhalgh, Wong, Westhorp, & Pawson, 2011 ). They originated from criticisms of positivist systematic reviews which centre on their “simplistic” underlying assumptions ( Oates, 2011 ). As explained above, systematic reviews seek to identify causation. Such logic is appropriate for fields like medicine and education where findings of randomized controlled trials can be aggregated to see whether a new treatment or intervention does improve outcomes. However, many argue that it is not possible to establish such direct causal links between interventions and outcomes in fields such as social policy, management, and information systems where for any intervention there is unlikely to be a regular or consistent outcome ( Oates, 2011 ; Pawson, 2006 ; Rousseau, Manning, & Denyer, 2008 ).
To circumvent these limitations, Pawson, Greenhalgh, Harvey, and Walshe (2005) have proposed a new approach for synthesizing knowledge that seeks to unpack the mechanism of how “complex interventions” work in particular contexts. The basic research question — what works? — which is usually associated with systematic reviews changes to: what is it about this intervention that works, for whom, in what circumstances, in what respects and why? Realist reviews have no particular preference for either quantitative or qualitative evidence. As a theory-building approach, a realist review usually starts by articulating likely underlying mechanisms and then scrutinizes available evidence to find out whether and where these mechanisms are applicable ( Shepperd et al., 2009 ). Primary studies found in the extant literature are viewed as case studies which can test and modify the initial theories ( Rousseau et al., 2008 ).
The main objective pursued in the realist review conducted by Otte-Trojel, de Bont, Rundall, and van de Klundert (2014) was to examine how patient portals contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The specific goals were to investigate how outcomes are produced and, most importantly, how variations in outcomes can be explained. The research team started with an exploratory review of background documents and research studies to identify ways in which patient portals may contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The authors identified six main ways which represent “educated guesses” to be tested against the data in the evaluation studies. These studies were identified through a formal and systematic search in four databases between 2003 and 2013. Two members of the research team selected the articles using a pre-established list of inclusion and exclusion criteria and following a two-step procedure. The authors then extracted data from the selected articles and created several tables, one for each outcome category. They organized information to bring forward those mechanisms where patient portals contribute to outcomes and the variation in outcomes across different contexts.
9.3.6. Critical Reviews
Lastly, critical reviews aim to provide a critical evaluation and interpretive analysis of existing literature on a particular topic of interest to reveal strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, controversies, inconsistencies, and/or other important issues with respect to theories, hypotheses, research methods or results ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ; Kirkevold, 1997 ). Unlike other review types, critical reviews attempt to take a reflective account of the research that has been done in a particular area of interest, and assess its credibility by using appraisal instruments or critical interpretive methods. In this way, critical reviews attempt to constructively inform other scholars about the weaknesses of prior research and strengthen knowledge development by giving focus and direction to studies for further improvement ( Kirkevold, 1997 ).
Kitsiou, Paré, and Jaana (2013) provide an example of a critical review that assessed the methodological quality of prior systematic reviews of home telemonitoring studies for chronic patients. The authors conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases to identify eligible reviews and subsequently used a validated instrument to conduct an in-depth quality appraisal. Results indicate that the majority of systematic reviews in this particular area suffer from important methodological flaws and biases that impair their internal validity and limit their usefulness for clinical and decision-making purposes. To this end, they provide a number of recommendations to strengthen knowledge development towards improving the design and execution of future reviews on home telemonitoring.
9.4. Summary
Table 9.1 outlines the main types of literature reviews that were described in the previous sub-sections and summarizes the main characteristics that distinguish one review type from another. It also includes key references to methodological guidelines and useful sources that can be used by eHealth scholars and researchers for planning and developing reviews.
Typology of Literature Reviews (adapted from Paré et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 9.1 , each review type addresses different kinds of research questions or objectives, which subsequently define and dictate the methods and approaches that need to be used to achieve the overarching goal(s) of the review. For example, in the case of narrative reviews, there is greater flexibility in searching and synthesizing articles ( Green et al., 2006 ). Researchers are often relatively free to use a diversity of approaches to search, identify, and select relevant scientific articles, describe their operational characteristics, present how the individual studies fit together, and formulate conclusions. On the other hand, systematic reviews are characterized by their high level of systematicity, rigour, and use of explicit methods, based on an “a priori” review plan that aims to minimize bias in the analysis and synthesis process (Higgins & Green, 2008). Some reviews are exploratory in nature (e.g., scoping/mapping reviews), whereas others may be conducted to discover patterns (e.g., descriptive reviews) or involve a synthesis approach that may include the critical analysis of prior research ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Hence, in order to select the most appropriate type of review, it is critical to know before embarking on a review project, why the research synthesis is conducted and what type of methods are best aligned with the pursued goals.
9.5. Concluding Remarks
In light of the increased use of evidence-based practice and research generating stronger evidence ( Grady et al., 2011 ; Lyden et al., 2013 ), review articles have become essential tools for summarizing, synthesizing, integrating or critically appraising prior knowledge in the eHealth field. As mentioned earlier, when rigorously conducted review articles represent powerful information sources for eHealth scholars and practitioners looking for state-of-the-art evidence. The typology of literature reviews we used herein will allow eHealth researchers, graduate students and practitioners to gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between review types.
We must stress that this classification scheme does not privilege any specific type of review as being of higher quality than another ( Paré et al., 2015 ). As explained above, each type of review has its own strengths and limitations. Having said that, we realize that the methodological rigour of any review — be it qualitative, quantitative or mixed — is a critical aspect that should be considered seriously by prospective authors. In the present context, the notion of rigour refers to the reliability and validity of the review process described in section 9.2. For one thing, reliability is related to the reproducibility of the review process and steps, which is facilitated by a comprehensive documentation of the literature search process, extraction, coding and analysis performed in the review. Whether the search is comprehensive or not, whether it involves a methodical approach for data extraction and synthesis or not, it is important that the review documents in an explicit and transparent manner the steps and approach that were used in the process of its development. Next, validity characterizes the degree to which the review process was conducted appropriately. It goes beyond documentation and reflects decisions related to the selection of the sources, the search terms used, the period of time covered, the articles selected in the search, and the application of backward and forward searches ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). In short, the rigour of any review article is reflected by the explicitness of its methods (i.e., transparency) and the soundness of the approach used. We refer those interested in the concepts of rigour and quality to the work of Templier and Paré (2015) which offers a detailed set of methodological guidelines for conducting and evaluating various types of review articles.
To conclude, our main objective in this chapter was to demystify the various types of literature reviews that are central to the continuous development of the eHealth field. It is our hope that our descriptive account will serve as a valuable source for those conducting, evaluating or using reviews in this important and growing domain.
- Ammenwerth E., de Keizer N. An inventory of evaluation studies of information technology in health care. Trends in evaluation research, 1982-2002. International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004; 44 (1):44–56. [ PubMed : 15778794 ]
- Anderson S., Allen P., Peckham S., Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008; 6 (7):1–12. [ PMC free article : PMC2500008 ] [ PubMed : 18613961 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Archer N., Fevrier-Thomas U., Lokker C., McKibbon K. A., Straus S.E. Personal health records: a scoping review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2011; 18 (4):515–522. [ PMC free article : PMC3128401 ] [ PubMed : 21672914 ]
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2005; 8 (1):19–32.
- A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2011); June 9 to 11; Helsinki, Finland. 2011.
- Baumeister R. F., Leary M.R. Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology. 1997; 1 (3):311–320.
- Becker L. A., Oxman A.D. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Overviews of reviews; pp. 607–631.
- Borenstein M., Hedges L., Higgins J., Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2009.
- Cook D. J., Mulrow C. D., Haynes B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 (5):376–380. [ PubMed : 9054282 ]
- Cooper H., Hedges L.V. In: The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C., editors. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. Research synthesis as a scientific process; pp. 3–17.
- Cooper H. M. Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society. 1988; 1 (1):104–126.
- Cronin P., Ryan F., Coughlan M. Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008; 17 (1):38–43. [ PubMed : 18399395 ]
- Darlow S., Wen K.Y. Development testing of mobile health interventions for cancer patient self-management: A review. Health Informatics Journal. 2015 (online before print). [ PubMed : 25916831 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daudt H. M., van Mossel C., Scott S.J. Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13 :48. [ PMC free article : PMC3614526 ] [ PubMed : 23522333 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Davies P. The relevance of systematic reviews to educational policy and practice. Oxford Review of Education. 2000; 26 (3-4):365–378.
- Deeks J. J., Higgins J. P. T., Altman D.G. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 243–296.
- Deshazo J. P., Lavallie D. L., Wolf F.M. Publication trends in the medical informatics literature: 20 years of “Medical Informatics” in mesh . bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2009; 9 :7. [ PMC free article : PMC2652453 ] [ PubMed : 19159472 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Agarwal S., Jones D., Young B., Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Services Research and Policy. 2005; 10 (1):45–53. [ PubMed : 15667704 ]
- Finfgeld-Connett D., Johnson E.D. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69 (1):194–204. [ PMC free article : PMC3424349 ] [ PubMed : 22591030 ]
- Grady B., Myers K. M., Nelson E. L., Belz N., Bennett L., Carnahan L. … Guidelines Working Group. Evidence-based practice for telemental health. Telemedicine Journal and E Health. 2011; 17 (2):131–148. [ PubMed : 21385026 ]
- Green B. N., Johnson C. D., Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2006; 5 (3):101–117. [ PMC free article : PMC2647067 ] [ PubMed : 19674681 ]
- Greenhalgh T., Wong G., Westhorp G., Pawson R. Protocol–realist and meta-narrative evidence synthesis: evolving standards ( rameses ). bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 :115. [ PMC free article : PMC3173389 ] [ PubMed : 21843376 ]
- Gurol-Urganci I., de Jongh T., Vodopivec-Jamsek V., Atun R., Car J. Mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments. Cochrane Database System Review. 2013; 12 cd 007458. [ PMC free article : PMC6485985 ] [ PubMed : 24310741 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart C. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE Publications; 1998.
- Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. Hoboken, nj : Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Jesson J., Matheson L., Lacey F.M. Doing your literature review: traditional and systematic techniques. Los Angeles & London: SAGE Publications; 2011.
- King W. R., He J. Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2005; 16 :1.
- Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977–984. [ PubMed : 9147203 ]
- Kitchenham B., Charters S. ebse Technical Report Version 2.3. Keele & Durham. uk : Keele University & University of Durham; 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering.
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013; 15 (7):e150. [ PMC free article : PMC3785977 ] [ PubMed : 23880072 ]
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Effects of home telemonitoring interventions on patients with chronic heart failure: an overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2015; 17 (3):e63. [ PMC free article : PMC4376138 ] [ PubMed : 25768664 ]
- Levac D., Colquhoun H., O’Brien K. K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (1):69. [ PMC free article : PMC2954944 ] [ PubMed : 20854677 ]
- Levy Y., Ellis T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science. 2006; 9 :181–211.
- Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A. et al. Moher D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009; 151 (4):W-65. [ PubMed : 19622512 ]
- Lyden J. R., Zickmund S. L., Bhargava T. D., Bryce C. L., Conroy M. B., Fischer G. S. et al. McTigue K. M. Implementing health information technology in a patient-centered manner: Patient experiences with an online evidence-based lifestyle intervention. Journal for Healthcare Quality. 2013; 35 (5):47–57. [ PubMed : 24004039 ]
- Mickan S., Atherton H., Roberts N. W., Heneghan C., Tilson J.K. Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: a systematic review. bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2014; 14 :56. [ PMC free article : PMC4099138 ] [ PubMed : 24998515 ]
- Moher D. The problem of duplicate systematic reviews. British Medical Journal. 2013; 347 (5040) [ PubMed : 23945367 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Montori V. M., Wilczynski N. L., Morgan D., Haynes R. B., Hedges T. Systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of location and citation counts. bmc Medicine. 2003; 1 :2. [ PMC free article : PMC281591 ] [ PubMed : 14633274 ]
- Mulrow C. D. The medical review article: state of the science. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987; 106 (3):485–488. [ PubMed : 3813259 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Evidence-based information systems: A decade later. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems ; 2011. Retrieved from http://aisel .aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent .cgi?article =1221&context =ecis2011 .
- Okoli C., Schabram K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. ssrn Electronic Journal. 2010
- Otte-Trojel T., de Bont A., Rundall T. G., van de Klundert J. How outcomes are achieved through patient portals: a realist review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2014; 21 (4):751–757. [ PMC free article : PMC4078283 ] [ PubMed : 24503882 ]
- Paré G., Trudel M.-C., Jaana M., Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: A typology of literature reviews. Information & Management. 2015; 52 (2):183–199.
- Patsopoulos N. A., Analatos A. A., Ioannidis J.P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293 (19):2362–2366. [ PubMed : 15900006 ]
- Paul M. M., Greene C. M., Newton-Dame R., Thorpe L. E., Perlman S. E., McVeigh K. H., Gourevitch M.N. The state of population health surveillance using electronic health records: A narrative review. Population Health Management. 2015; 18 (3):209–216. [ PubMed : 25608033 ]
- Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: a realist perspective. London: SAGE Publications; 2006.
- Pawson R., Greenhalgh T., Harvey G., Walshe K. Realist review—a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):21–34. [ PubMed : 16053581 ]
- Petersen K., Vakkalanka S., Kuzniarz L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Information and Software Technology. 2015; 64 :1–18.
- Petticrew M., Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Malden, ma : Blackwell Publishing Co; 2006.
- Rousseau D. M., Manning J., Denyer D. Evidence in management and organizational science: Assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. The Academy of Management Annals. 2008; 2 (1):475–515.
- Rowe F. What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems. 2014; 23 (3):241–255.
- Shea B. J., Hamel C., Wells G. A., Bouter L. M., Kristjansson E., Grimshaw J. et al. Boers M. amstar is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62 (10):1013–1020. [ PubMed : 19230606 ]
- Shepperd S., Lewin S., Straus S., Clarke M., Eccles M. P., Fitzpatrick R. et al. Sheikh A. Can we systematically review studies that evaluate complex interventions? PLoS Medicine. 2009; 6 (8):e1000086. [ PMC free article : PMC2717209 ] [ PubMed : 19668360 ]
- Silva B. M., Rodrigues J. J., de la Torre Díez I., López-Coronado M., Saleem K. Mobile-health: A review of current state in 2015. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2015; 56 :265–272. [ PubMed : 26071682 ]
- Smith V., Devane D., Begley C., Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 (1):15. [ PMC free article : PMC3039637 ] [ PubMed : 21291558 ]
- Sylvester A., Tate M., Johnstone D. Beyond synthesis: re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2013; 32 (12):1199–1215.
- Templier M., Paré G. A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2015; 37 (6):112–137.
- Thomas J., Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2008; 8 (1):45. [ PMC free article : PMC2478656 ] [ PubMed : 18616818 ]
- Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2009); Verona, Italy. 2009.
- Webster J., Watson R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Management Information Systems Quarterly. 2002; 26 (2):11.
- Whitlock E. P., Lin J. S., Chou R., Shekelle P., Robinson K.A. Using existing systematic reviews in complex systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (10):776–782. [ PubMed : 18490690 ]
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Paré G, Kitsiou S. Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
- Disable Glossary Links
In this Page
- Introduction
- Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
- Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
- Concluding Remarks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Ev... Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 24, Issue 2
- Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0157-5319 Ahtisham Younas 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7839-8130 Parveen Ali 3 , 4
- 1 Memorial University of Newfoundland , St John's , Newfoundland , Canada
- 2 Swat College of Nursing , Pakistan
- 3 School of Nursing and Midwifery , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , South Yorkshire , UK
- 4 Sheffield University Interpersonal Violence Research Group , Sheffield University , Sheffield , UK
- Correspondence to Ahtisham Younas, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; ay6133{at}mun.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research. 1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis in reviews, the use of literature summary tables is of utmost importance. A literature summary table provides a synopsis of an included article. It succinctly presents its purpose, methods, findings and other relevant information pertinent to the review. The aim of developing these literature summary tables is to provide the reader with the information at one glance. Since there are multiple types of reviews (eg, systematic, integrative, scoping, critical and mixed methods) with distinct purposes and techniques, 2 there could be various approaches for developing literature summary tables making it a complex task specialty for the novice researchers or reviewers. Here, we offer five tips for authors of the review articles, relevant to all types of reviews, for creating useful and relevant literature summary tables. We also provide examples from our published reviews to illustrate how useful literature summary tables can be developed and what sort of information should be provided.
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Tabular literature summaries from a scoping review. Source: Rasheed et al . 3
The provision of information about conceptual and theoretical frameworks and methods is useful for several reasons. First, in quantitative (reviews synthesising the results of quantitative studies) and mixed reviews (reviews synthesising the results of both qualitative and quantitative studies to address a mixed review question), it allows the readers to assess the congruence of the core findings and methods with the adapted framework and tested assumptions. In qualitative reviews (reviews synthesising results of qualitative studies), this information is beneficial for readers to recognise the underlying philosophical and paradigmatic stance of the authors of the included articles. For example, imagine the authors of an article, included in a review, used phenomenological inquiry for their research. In that case, the review authors and the readers of the review need to know what kind of (transcendental or hermeneutic) philosophical stance guided the inquiry. Review authors should, therefore, include the philosophical stance in their literature summary for the particular article. Second, information about frameworks and methods enables review authors and readers to judge the quality of the research, which allows for discerning the strengths and limitations of the article. For example, if authors of an included article intended to develop a new scale and test its psychometric properties. To achieve this aim, they used a convenience sample of 150 participants and performed exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the same sample. Such an approach would indicate a flawed methodology because EFA and CFA should not be conducted on the same sample. The review authors must include this information in their summary table. Omitting this information from a summary could lead to the inclusion of a flawed article in the review, thereby jeopardising the review’s rigour.
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for each article
Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using various templates for critical appraisal, authors often do not provide detailed information about each reviewed article’s strengths and limitations. Merely noting the quality score based on standardised critical appraisal templates is not adequate because the readers should be able to identify the reasons for assigning a weak or moderate rating. Many recent critical appraisal checklists (eg, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool) discourage review authors from assigning a quality score and recommend noting the main strengths and limitations of included studies. It is also vital that methodological and conceptual limitations and strengths of the articles included in the review are provided because not all review articles include empirical research papers. Rather some review synthesises the theoretical aspects of articles. Providing information about conceptual limitations is also important for readers to judge the quality of foundations of the research. For example, if you included a mixed-methods study in the review, reporting the methodological and conceptual limitations about ‘integration’ is critical for evaluating the study’s strength. Suppose the authors only collected qualitative and quantitative data and did not state the intent and timing of integration. In that case, the strength of the study is weak. Integration only occurred at the levels of data collection. However, integration may not have occurred at the analysis, interpretation and reporting levels.
Tip 3: write conceptual contribution of each reviewed article
While reading and evaluating review papers, we have observed that many review authors only provide core results of the article included in a review and do not explain the conceptual contribution offered by the included article. We refer to conceptual contribution as a description of how the article’s key results contribute towards the development of potential codes, themes or subthemes, or emerging patterns that are reported as the review findings. For example, the authors of a review article noted that one of the research articles included in their review demonstrated the usefulness of case studies and reflective logs as strategies for fostering compassion in nursing students. The conceptual contribution of this research article could be that experiential learning is one way to teach compassion to nursing students, as supported by case studies and reflective logs. This conceptual contribution of the article should be mentioned in the literature summary table. Delineating each reviewed article’s conceptual contribution is particularly beneficial in qualitative reviews, mixed-methods reviews, and critical reviews that often focus on developing models and describing or explaining various phenomena. Figure 2 offers an example of a literature summary table. 4
Tabular literature summaries from a critical review. Source: Younas and Maddigan. 4
Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing
While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review. Such an approach prevents the review authors from understanding the article’s conceptual contribution, developing rigorous synthesis and drawing reasonable interpretations of results from an individual article. Ultimately, it affects the generation of novel review findings. For example, one of the articles about women’s healthcare-seeking behaviours in developing countries reported a theme ‘social-cultural determinants of health as precursors of delays’. Instead of using this theme as one of the review findings, the reviewers should read and interpret beyond the given description in an article, compare and contrast themes, findings from one article with findings and themes from another article to find similarities and differences and to understand and explain bigger picture for their readers. Therefore, while developing literature summary tables, think twice before using the predeveloped themes. Including your themes in the summary tables (see figure 1 ) demonstrates to the readers that a robust method of data extraction and synthesis has been followed.
Tip 5: create your personalised template for literature summaries
Often templates are available for data extraction and development of literature summary tables. The available templates may be in the form of a table, chart or a structured framework that extracts some essential information about every article. The commonly used information may include authors, purpose, methods, key results and quality scores. While extracting all relevant information is important, such templates should be tailored to meet the needs of the individuals’ review. For example, for a review about the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, a literature summary table must include information about the intervention, its type, content timing, duration, setting, effectiveness, negative consequences, and receivers and implementers’ experiences of its usage. Similarly, literature summary tables for articles included in a meta-synthesis must include information about the participants’ characteristics, research context and conceptual contribution of each reviewed article so as to help the reader make an informed decision about the usefulness or lack of usefulness of the individual article in the review and the whole review.
In conclusion, narrative or systematic reviews are almost always conducted as a part of any educational project (thesis or dissertation) or academic or clinical research. Literature reviews are the foundation of research on a given topic. Robust and high-quality reviews play an instrumental role in guiding research, practice and policymaking. However, the quality of reviews is also contingent on rigorous data extraction and synthesis, which require developing literature summaries. We have outlined five tips that could enhance the quality of the data extraction and synthesis process by developing useful literature summaries.
- Aromataris E ,
- Rasheed SP ,
Twitter @Ahtisham04, @parveenazamali
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 08 April 2024
A systematic review and multivariate meta-analysis of the physical and mental health benefits of touch interventions
- Julian Packheiser ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9805-6755 2 na1 nAff1 ,
- Helena Hartmann 2 , 3 , 4 na1 ,
- Kelly Fredriksen 2 ,
- Valeria Gazzola ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0324-0619 2 ,
- Christian Keysers ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2845-5467 2 &
- Frédéric Michon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1289-2133 2
Nature Human Behaviour ( 2024 ) Cite this article
18k Accesses
1838 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Human behaviour
- Paediatric research
- Randomized controlled trials
Receiving touch is of critical importance, as many studies have shown that touch promotes mental and physical well-being. We conducted a pre-registered (PROSPERO: CRD42022304281) systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis encompassing 137 studies in the meta-analysis and 75 additional studies in the systematic review ( n = 12,966 individuals, search via Google Scholar, PubMed and Web of Science until 1 October 2022) to identify critical factors moderating touch intervention efficacy. Included studies always featured a touch versus no touch control intervention with diverse health outcomes as dependent variables. Risk of bias was assessed via small study, randomization, sequencing, performance and attrition bias. Touch interventions were especially effective in regulating cortisol levels (Hedges’ g = 0.78, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.24 to 1.31) and increasing weight (0.65, 95% CI 0.37 to 0.94) in newborns as well as in reducing pain (0.69, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.89), feelings of depression (0.59, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.78) and state (0.64, 95% CI 0.44 to 0.84) or trait anxiety (0.59, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.77) for adults. Comparing touch interventions involving objects or robots resulted in similar physical (0.56, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.88 versus 0.51, 95% CI 0.38 to 0.64) but lower mental health benefits (0.34, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.49 versus 0.58, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.73). Adult clinical cohorts profited more strongly in mental health domains compared with healthy individuals (0.63, 95% CI 0.46 to 0.80 versus 0.37, 95% CI 0.20 to 0.55). We found no difference in health benefits in adults when comparing touch applied by a familiar person or a health care professional (0.51, 95% CI 0.29 to 0.73 versus 0.50, 95% CI 0.38 to 0.61), but parental touch was more beneficial in newborns (0.69, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.88 versus 0.39, 95% CI 0.18 to 0.61). Small but significant small study bias and the impossibility to blind experimental conditions need to be considered. Leveraging factors that influence touch intervention efficacy will help maximize the benefits of future interventions and focus research in this field.
Similar content being viewed by others

Touching the social robot PARO reduces pain perception and salivary oxytocin levels
Nirit Geva, Florina Uzefovsky & Shelly Levy-Tzedek
The impact of mindfulness apps on psychological processes of change: a systematic review
Natalia Macrynikola, Zareen Mir, … John Torous
The why, who and how of social touch
Juulia T. Suvilehto, Asta Cekaite & India Morrison
The sense of touch has immense importance for many aspects of our life. It is the first of all the senses to develop in newborns 1 and the most direct experience of contact with our physical and social environment 2 . Complementing our own touch experience, we also regularly receive touch from others around us, for example, through consensual hugs, kisses or massages 3 .
The recent coronavirus pandemic has raised awareness regarding the need to better understand the effects that touch—and its reduction during social distancing—can have on our mental and physical well-being. The most common touch interventions, for example, massage for adults or kangaroo care for newborns, have been shown to have a wide range of both mental and physical health benefits, from facilitating growth and development to buffering against anxiety and stress, over the lifespan of humans and animals alike 4 . Despite the substantial weight this literature gives to support the benefits of touch, it is also characterized by a large variability in, for example, studied cohorts (adults, children, newborns and animals), type and duration of applied touch (for example, one-time hug versus repeated 60-min massages), measured health outcomes (ranging from physical health outcomes such as sleep and blood pressure to mental health outcomes such as depression or mood) and who actually applies the touch (for example, partner versus stranger).
A meaningful tool to make sense of this vast amount of research is through meta-analysis. While previous meta-analyses on this topic exist, they were limited in scope, focusing only on particular types of touch, cohorts or specific health outcomes (for example, refs. 5 , 6 ). Furthermore, despite best efforts, meaningful variables that moderate the efficacy of touch interventions could not yet be identified. However, understanding these variables is critical to tailor touch interventions and guide future research to navigate this diverse field with the ultimate aim of promoting well-being in the population.
In this Article, we describe a pre-registered, large-scale systematic review and multilevel, multivariate meta-analysis to address this need with quantitative evidence for (1) the effect of touch interventions on physical and mental health and (2) which moderators influence the efficacy of the intervention. In particular, we ask whether and how strongly health outcomes depend on the dynamics of the touching dyad (for example, humans or robots/objects, familiarity and touch directionality), demographics (for example, clinical status, age or sex), delivery means (for example, type of touch intervention or touched body part) and procedure (for example, duration or number of sessions). We did so separately for newborns and for children and adults, as the health outcomes in newborns differed substantially from those in the other age groups. Despite the focus of the analysis being on humans, it is widely known that many animal species benefit from touch interactions and that engaging in touch promotes their well-being as well 7 . Since animal models are essential for the investigation of the mechanisms underlying biological processes and for the development of therapeutic approaches, we accordingly included health benefits of touch interventions in non-human animals as part of our systematic review. However, this search yielded only a small number of studies, suggesting a lack of research in this domain, and as such, was insufficient to be included in the meta-analysis. We evaluate the identified animal studies and their findings in the discussion.
Touch interventions have a medium-sized effect
The pre-registration can be found at ref. 8 . The flowchart for data collection and extraction is depicted in Fig. 1 .
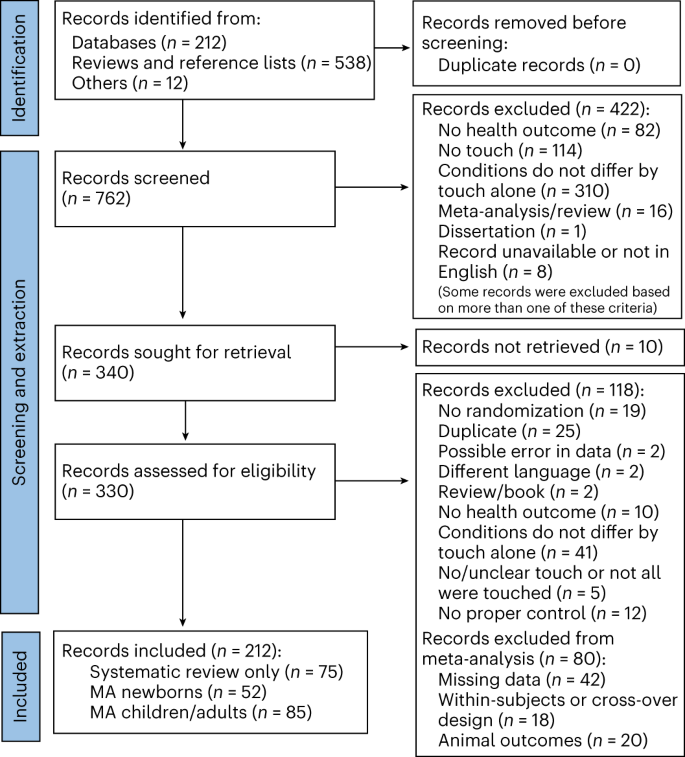
Animal outcomes refer to outcomes measured in non-human species that were solely considered as part of a systematic review. Included languages were French, Dutch, German and English, but our search did not identify any articles in French, Dutch or German. MA, meta-analysis.
For adults, a total of n = 2,841 and n = 2,556 individuals in the touch and control groups, respectively, across 85 studies and 103 cohorts were included. The effect of touch overall was medium-sized ( t (102) = 9.74, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.52, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.42 to 0.63; Fig. 2a ). For newborns, we could include 63 cohorts across 52 studies comprising a total of n = 2,134 and n = 2,086 newborns in the touch and control groups, respectively, with an overall effect almost identical to the older age group ( t (62) = 7.53, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.56, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.71; Fig. 2b ), suggesting that, despite distinct health outcomes, touch interventions show comparable effects across newborns and adults. Using these overall effect estimates, we conducted a power sensitivity analysis of all the included primary studies to investigate whether such effects could be reliably detected 9 . Sufficient power to detect such effect sizes was rare in individual studies, as investigated by firepower plots 10 (Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2 ). No individual effect size from either meta-analysis was overly influential (Cook’s D < 0.06). The benefits were similar for mental and physical outcomes (mental versus physical; adults: t (101) = 0.79, P = 0.432, Hedges’ g difference of −0.05, 95% CI −0.16 to 0.07, Fig. 2c ; newborns: t (61) = 1.08, P = 0.284, Hedges’ g difference of −0.19, 95% CI −0.53 to 0.16, Fig. 2d ).
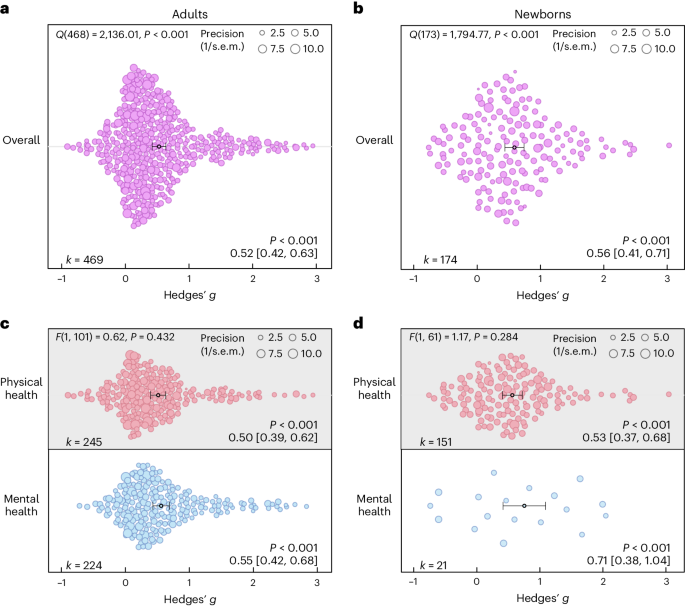
a , Orchard plot illustrating the overall benefits across all health outcomes for adults/children across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. b , The same as a but for newborns across 174 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. c , The same as a but separating the results for physical versus mental health benefits across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. d , The same as b but separating the results for physical versus mental health benefits across 172 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. Each dot reflects a measured effect, and the number of effects ( k ) included in the analysis is depicted in the bottom left. Mean effects and 95% CIs are presented in the bottom right and are indicated by the central black dot (mean effect) and its error bars (95% CI). The heterogeneity Q statistic is presented in the top left. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). Note that the P values above the mean effects indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. The dot size reflects the precision of each individual effect (larger indicates higher precision). Small-study bias for the overall effect was significant ( F test, two-sided test) in the adult meta-analysis ( F (1, 101) = 21.24, P < 0.001; Supplementary Fig. 3 ) as well as in the newborn meta-analysis ( F (1, 61) = 5.25, P = 0.025; Supplementary Fig. 4 ).
Source data
On the basis of the overall effect of both meta-analyses as well as their median sample sizes, the minimum number of studies necessary for subgroup analyses to achieve 80% power was k = 9 effects for adults and k = 8 effects for newborns (Supplementary Figs. 5 and 6 ). Assessing specific health outcomes with sufficient power in more detail in adults (Fig. 3a ) revealed smaller benefits to sleep and heart rate parameters, moderate benefits to positive and negative affect, diastolic blood and systolic blood pressure, mobility and reductions of the stress hormone cortisol and larger benefits to trait and state anxiety, depression, fatigue and pain. Post hoc tests revealed stronger benefits for pain, state anxiety, depression and trait anxiety compared with respiratory, sleep and heart rate parameters (see Fig. 3 for all post hoc comparisons). Reductions in pain and state anxiety were increased compared with reductions in negative affect ( t (83) = 2.54, P = 0.013, Hedges’ g difference of 0.31, 95% CI 0.07 to 0.55; t (83) = 2.31, P = 0.024, Hedges’ g difference of 0.27, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.51). Benefits to pain symptoms were higher compared with benefits to positive affect ( t (83) = 2.22, P = 0.030, Hedges’ g difference of 0.29, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.54). Finally, touch resulted in larger benefits to cortisol release compared with heart rate parameters ( t (83) = 2.30, P = 0.024, Hedges’ g difference of 0.26, 95% CI 0.04–0.48).
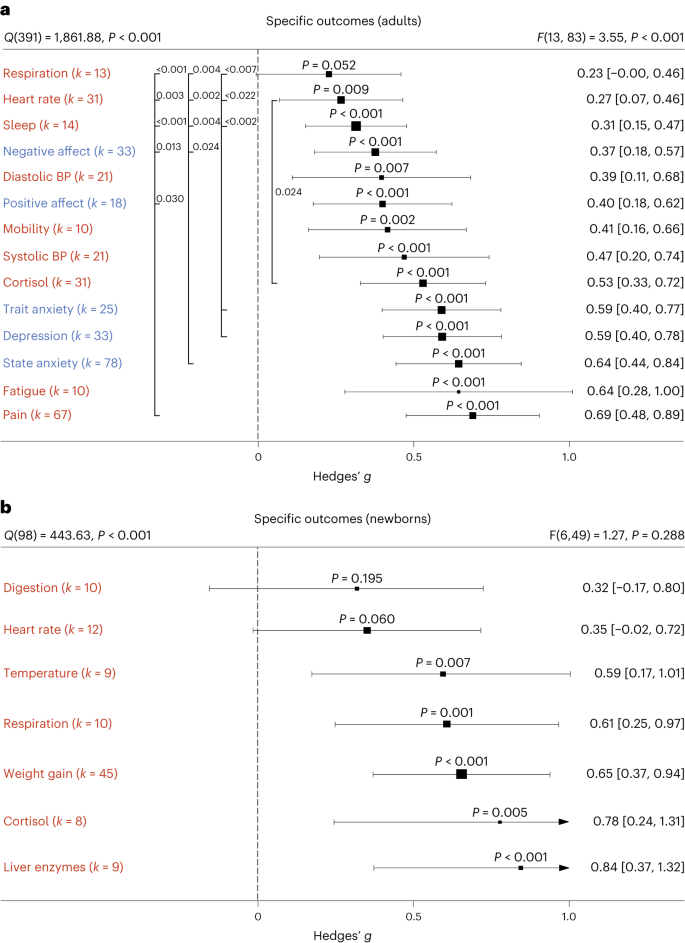
a , b , Health outcomes in adults analysed across 405 in part dependent effect sizes from 79 studies and 97 cohorts ( a ) and in newborns analysed across 105 in part dependent effect sizes from 46 studies and 56 cohorts ( b ). The type of health outcomes measured differed between adults and newborns and were thus analysed separately. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents the heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
In newborns, only physical health effects offered sufficient data for further analysis. We found no benefits for digestion and heart rate parameters. All other health outcomes (cortisol, liver enzymes, respiration, temperature regulation and weight gain) showed medium to large effects (Fig. 3b ). We found no significant differences among any specific health outcomes.
Non-human touch and skin-to-skin contact
In some situations, a fellow human is not readily available to provide affective touch, raising the question of the efficacy of touch delivered by objects and robots 11 . Overall, we found humans engaging in touch with other humans or objects to have medium-sized health benefits in adults, without significant differences ( t (99) = 1.05, P = 0.295, Hedges’ g difference of 0.12, 95% CI −0.11 to 0.35; Fig. 4a ). However, differentiating physical versus mental health benefits revealed similar benefits for human and object touch on physical health outcomes, but larger benefits on mental outcomes when humans were touched by humans ( t (97) = 2.32, P = 0.022, Hedges’ g difference of 0.24, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.44; Fig. 4b ). It must be noted that touching with an object still showed a significant effect (see Supplementary Fig. 7 for the corresponding orchard plot).
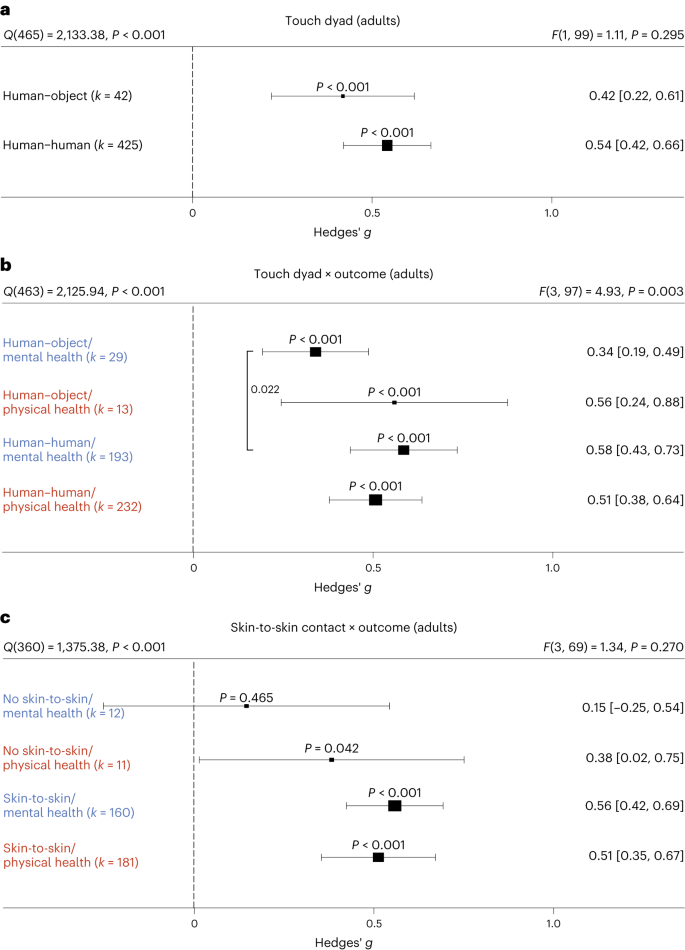
a , Forest plot comparing humans versus objects touching a human on health outcomes overall across 467 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 101 cohorts. b , The same as a but separately for mental versus physical health outcomes across 467 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 101 cohorts. c , Results with the removal of all object studies, leaving 406 in part dependent effect sizes from 71 studies and 88 cohorts to identify whether missing skin-to-skin contact is the relevant mediator of higher mental health effects in human–human interactions. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents the heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
We considered the possibility that this effect was due to missing skin-to-skin contact in human–object interactions. Thus, we investigated human–human interactions with and without skin-to-skin contact (Fig. 4c ). In line with the hypothesis that skin-to-skin contact is highly relevant, we again found stronger mental health benefits in the presence of skin-to-skin contact that however did not achieve nominal significance ( t (69) = 1.95, P = 0.055, Hedges’ g difference of 0.41, 95% CI −0.00 to 0.82), possibly because skin-to-skin contact was rarely absent in human–human interactions, leading to a decrease in power of this analysis. Results for skin-to-skin contact as an overall moderator can be found in Supplementary Fig. 8 .
Influences of type of touch
The large majority of touch interventions comprised massage therapy in adults and kangaroo care in newborns (see Supplementary Table 1 for a complete list of interventions across studies). However, comparing the different types of touch explored across studies did not reveal significant differences in effect sizes based on touch type, be it on overall health benefits (adults: t (101) = 0.11, P = 0.916, Hedges’ g difference of 0.02, 95% CI −0.32 to 0.29; Fig. 5a ) or comparing different forms of touch separately for physical (massage therapy versus other forms: t (99) = 0.99, P = 0.325, Hedges’ g difference 0.16, 95% CI −0.15 to 0.47) or for mental health benefits (massage therapy versus other forms: t (99) = 0.75, P = 0.458, Hedges’ g difference of 0.13, 95% CI −0.22 to 0.48) in adults (Fig. 5c ; see Supplementary Fig. 9 for the corresponding orchard plot). A similar picture emerged for physical health effects in newborns (massage therapy versus kangaroo care: t (58) = 0.94, P = 0.353, Hedges’ g difference of 0.15, 95% CI −0.17 to 0.47; massage therapy versus other forms: t (58) = 0.56, P = 0.577, Hedges’ g difference of 0.13, 95% CI −0.34 to 0.60; kangaroo care versus other forms: t (58) = 0.07, P = 0.947, Hedges’ g difference of 0.02, 95% CI −0.46 to 0.50; Fig. 5d ; see also Supplementary Fig. 10 for the corresponding orchard plot). This suggests that touch types may be flexibly adapted to the setting of every touch intervention.
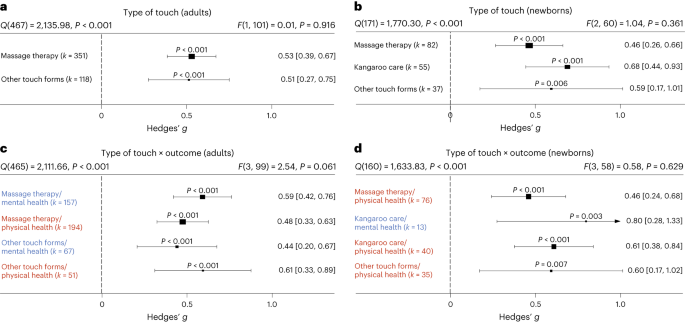
a , Forest plot of health benefits comparing massage therapy versus other forms of touch in adult cohorts across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. b , Forest plot of health benefits comparing massage therapy, kangaroo care and other forms of touch for newborns across 174 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. c , The same as a but separating mental and physical health benefits across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. d , The same as b but separating mental and physical health outcomes where possible across 164 in part dependent effect sizes from 51 studies and 62 cohorts. Note that an insufficient number of studies assessed mental health benefits of massage therapy or other forms of touch to be included. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
The role of clinical status
Most research on touch interventions has focused on clinical samples, but are benefits restricted to clinical cohorts? We found health benefits to be significant in clinical and healthy populations (Fig. 6 ), whether all outcomes are considered (Fig. 6a,b ) or physical and mental health outcomes are separated (Fig. 6c,d , see Supplementary Figs. 11 and 12 for the corresponding orchard plots). In adults, however, we found higher mental health benefits for clinical populations compared with healthy ones (Fig. 6c ; t (99) = 2.11, P = 0.037, Hedges’ g difference of 0.25, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.49).
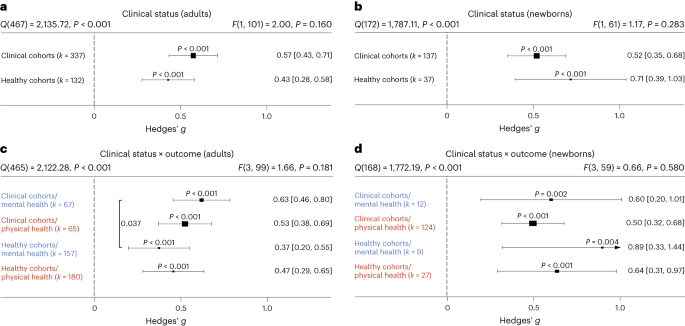
a , Health benefits for clinical cohorts of adults versus healthy cohorts of adults across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. b , The same as a but for newborn cohorts across 174 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. c , The same as a but separating mental versus physical health benefits across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. d , The same as b but separating mental versus physical health benefits across 172 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test).The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents the heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
A more detailed analysis of specific clinical conditions in adults revealed positive mental and physical health benefits for almost all assessed clinical disorders. Differences between disorders were not found, with the exception of increased effectiveness of touch interventions in neurological disorders (Supplementary Fig. 13 ).
Familiarity in the touching dyad and intervention location
Touch interventions can be performed either by familiar touchers (partners, family members or friends) or by unfamiliar touchers (health care professionals). In adults, we did not find an impact of familiarity of the toucher ( t (99) = 0.12, P = 0.905, Hedges’ g difference of 0.02, 95% CI −0.27 to 0.24; Fig. 7a ; see Supplementary Fig. 14 for the corresponding orchard plot). Similarly, investigating the impact on mental and physical health benefits specifically, no significant differences could be detected, suggesting that familiarity is irrelevant in adults. In contrast, touch applied to newborns by their parents (almost all studies only included touch by the mother) was significantly more beneficial compared with unfamiliar touch ( t (60) = 2.09, P = 0.041, Hedges’ g difference of 0.30, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.59) (Fig. 7b ; see Supplementary Fig. 15 for the corresponding orchard plot). Investigating mental and physical health benefits specifically revealed no significant differences. Familiarity with the location in which the touch was applied (familiar being, for example, the participants’ home) did not influence the efficacy of touch interventions (Supplementary Fig. 16 ).
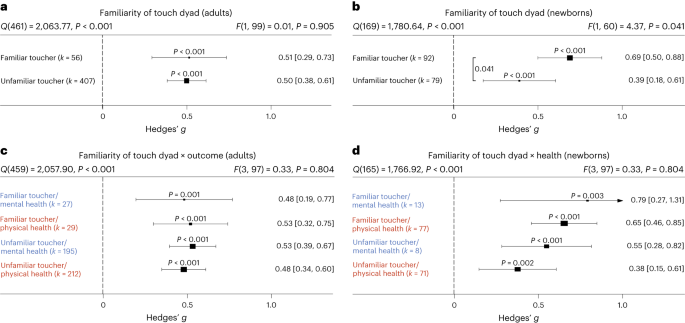
a , Health benefits for being touched by a familiar (for example, partner, family member or friend) versus unfamiliar toucher (health care professional) across 463 in part dependent effect sizes from 83 studies and 101 cohorts. b , The same as a but for newborn cohorts across 171 in part dependent effect sizes from 51 studies and 62 cohorts. c , The same as a but separating mental versus physical health benefits across 463 in part dependent effect sizes from 83 studies and 101 cohorts. d , The same as b but separating mental versus physical health benefits across 169 in part dependent effect sizes from 51 studies and 62 cohorts. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents the heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
Frequency and duration of touch interventions
How often and for how long should touch be delivered? For adults, the median touch duration across studies was 20 min and the median number of touch interventions was four sessions with an average time interval of 2.3 days between each session. For newborns, the median touch duration across studies was 17.5 min and the median number of touch interventions was seven sessions with an average time interval of 1.3 days between each session.
Delivering more touch sessions increased benefits in adults, whether overall ( t (101) = 4.90, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.02, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.03), physical ( t (81) = 3.07, P = 0.003, Hedges’ g = 0.02, 95% CI 0.01–0.03) or mental benefits ( t (72) = 5.43, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.02, 95% CI 0.01–0.03) were measured (Fig. 8a ). A closer look at specific outcomes for which sufficient data were available revealed that positive associations between the number of sessions and outcomes were found for trait anxiety ( t (12) = 7.90, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.03, 95% CI 0.02–0.04), depression ( t (20) = 10.69, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.03, 95% CI 0.03–0.04) and pain ( t (37) = 3.65, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.03, 95% CI 0.02–0.05), indicating a need for repeated sessions to improve these adverse health outcomes. Neither increasing the number of sessions for newborns nor increasing the duration of touch per session in adults or newborns increased health benefits, be they physical or mental (Fig. 8b–d ). For continuous moderators in adults, we also looked at specific health outcomes as sufficient data were generally available for further analysis. Surprisingly, we found significant negative associations between touch duration and reductions of cortisol ( t (24) = 2.71, P = 0.012, Hedges’ g = −0.01, 95% CI −0.01 to −0.00) and heart rate parameters ( t (21) = 2.35, P = 0.029, Hedges’ g = −0.01, 95% CI −0.02 to −0.00).
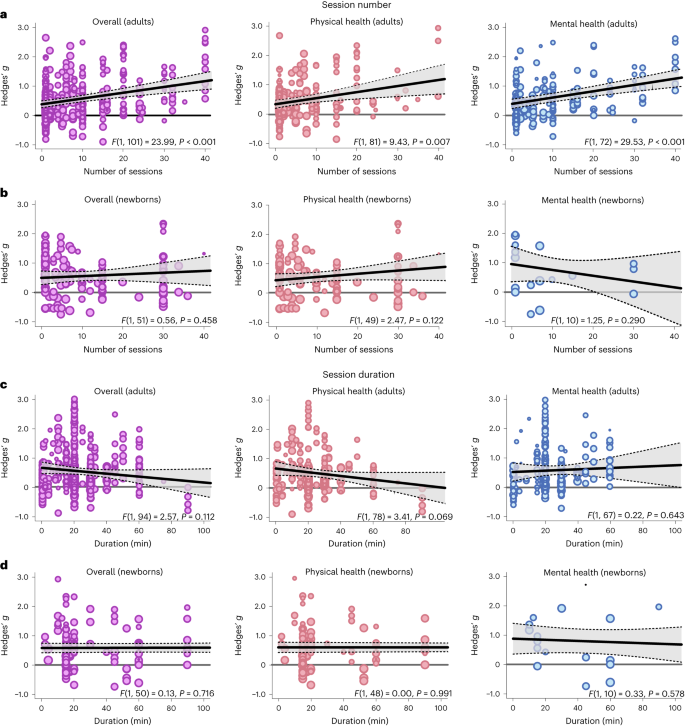
a , Meta-regression analysis examining the association between the number of sessions applied and the effect size in adults, either on overall health benefits (left, 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts) or for physical (middle, 245 in part dependent effect sizes from 69 studies and 83 cohorts) or mental benefits (right, 224 in part dependent effect sizes from 60 studies and 74 cohorts) separately. b , The same as a for newborns (overall: 150 in part dependent effect sizes from 46 studies and 53 cohorts; physical health: 127 in part dependent effect sizes from 44 studies and 51 cohorts; mental health: 21 in part dependent effect sizes from 11 studies and 12 cohorts). c , d the same as a ( c ) and b ( d ) but for the duration of the individual sessions. For adults, 449 in part dependent effect sizes across 80 studies and 96 cohorts were included in the overall analysis. The analysis of physical health benefits included 240 in part dependent effect sizes across 67 studies and 80 cohorts, and the analysis of mental health benefits included 209 in part dependent effect sizes from 56 studies and 69 cohorts. For newborns, 145 in part dependent effect sizes across 45 studies and 52 cohorts were included in the overall analysis. The analysis of physical health benefits included 122 in part dependent effect sizes across 43 studies and 50 cohorts, and the analysis of mental health benefits included 21 in part dependent effect sizes from 11 studies and 12 cohorts. Each dot represents an effect size. Its size indicates the precision of the study (larger indicates better). Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test (two-sided test). The P values in each panel represent the result of a regression analysis testing the hypothesis that the slope of the relationship is equal to zero. P values are not corrected for multiple testing. The shaded area around the regression line represents the 95% CI.
Demographic influences of sex and age
We used the ratio between women and men in the single-study samples as a proxy for sex-specific effects. Sex ratios were heavily skewed towards larger numbers of women in each cohort (median 83% women), and we could not find significant associations between sex ratio and overall ( t (62) = 0.08, P = 0.935, Hedges’ g = 0.00, 95% CI −0.00 to 0.01), mental ( t (43) = 0.55, P = 0.588, Hedges’ g = 0.00, 95% CI −0.00 to 0.01) or physical health benefits ( t (51) = 0.15, P = 0.882, Hedges’ g = −0.00, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.01). For specific outcomes that could be further analysed, we found a significant positive association of sex ratio with reductions in cortisol secretion ( t (18) = 2.31, P = 0.033, Hedges’ g = 0.01, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.01) suggesting stronger benefits in women. In contrast to adults, sex ratios were balanced in samples of newborns (median 53% girls). For newborns, there was no significant association with overall ( t (36) = 0.77, P = 0.447, Hedges’ g = −0.01, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.01) and physical health benefits of touch ( t (35) = 0.93, P = 0.359, Hedges’ g = −0.01, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.01). Mental health benefits did not provide sufficient data for further analysis.
The median age in the adult meta-analysis was 42.6 years (s.d. 21.16 years, range 4.5–88.4 years). There was no association between age and the overall ( t (73) = 0.35, P = 0.727, Hedges’ g = 0.00, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.01), mental ( t (53) = 0.94, P = 0.353, Hedges’ g = 0.01, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.02) and physical health benefits of touch ( t (60) = 0.16, P = 0.870, Hedges’ g = 0.00, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.01). Looking at specific health outcomes, we found significant positive associations between mean age and improved positive affect ( t (10) = 2.54, P = 0.030, Hedges’ g = 0.01, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.02) as well as systolic blood pressure ( t (11) = 2.39, P = 0.036, Hedges’ g = 0.02, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.04).
A list of touched body parts can be found in Supplementary Table 1 . For the touched body part, we found significantly higher health benefits for head touch compared with arm touch ( t (40) = 2.14, P = 0.039, Hedges’ g difference of 0.78, 95% CI 0.07 to 1.49) and torso touch ( t (40) = 2.23, P = 0.031; Hedges’ g difference of 0.84, 95% CI 0.10 to 1.58; Supplementary Fig. 17 ). Touching the arm resulted in lower mental health compared with physical health benefits ( t (37) = 2.29, P = 0.028, Hedges’ g difference of −0.35, 95% CI −0.65 to −0.05). Furthermore, we found a significantly increased physical health benefit when the head was touched as opposed to the torso ( t (37) = 2.10, P = 0.043, Hedges’ g difference of 0.96, 95% CI 0.06 to 1.86). Thus, head touch such as a face or scalp massage could be especially beneficial.
Directionality
In adults, we tested whether a uni- or bidirectional application of touch mattered. The large majority of touch was applied unidirectionally ( k = 442 of 469 effects). Unidirectional touch had higher health benefits ( t (101) = 2.17, P = 0.032, Hedges’ g difference of 0.30, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.58) than bidirectional touch. Specifically, mental health benefits were higher in unidirectional touch ( t (99) = 2.33, P = 0.022, Hedges’ g difference of 0.46, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.66).
Study location
For adults, we found significantly stronger health benefits of touch in South American compared with North American cohorts ( t (95) = 2.03, P = 0.046, Hedges’ g difference of 0.37, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.73) and European cohorts ( t (95) = 2.22, P = 0.029, Hedges’ g difference of 0.36, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.68). For newborns, we found weaker effects in North American cohorts compared to Asian ( t (55) = 2.28, P = 0.026, Hedges’ g difference of −0.37, 95% CI −0.69 to −0.05) and European cohorts ( t (55) = 2.36, P = 0.022, Hedges’ g difference of −0.40, 95% CI −0.74 to −0.06). Investigating the interaction with mental and physical health benefits did not reveal any effects of study location in both meta-analyses (Supplementary Fig. 18 ).
Systematic review of studies without effect sizes
All studies where effect size data could not be obtained or that did not meet the meta-analysis inclusion criteria can be found on the OSF project 12 in the file ‘Study_lists_final_revised.xlsx’ (sheet ‘Studies_without_effect_sizes’). Specific reasons for exclusion are furthermore documented in Supplementary Table 2 . For human health outcomes assessed across 56 studies and n = 2,438 individuals, interventions mostly comprised massage therapy ( k = 86 health outcomes) and kangaroo care ( k = 33 health outcomes). For datasets where no effect size could be computed, 90.0% of mental health and 84.3% of physical health parameters were positively impacted by touch. Positive impact of touch did not differ between types of touch interventions. These results match well with the observations of the meta-analysis of a highly positive benefit of touch overall, irrespective of whether a massage or any other intervention is applied.
We also assessed health outcomes in animals across 19 studies and n = 911 subjects. Most research was conducted in rodents. Animals that received touch were rats (ten studies, k = 16 health outcomes), mice (four studies, k = 7 health outcomes), macaques (two studies, k = 3 health outcomes), cats (one study, k = 3 health outcomes), lambs (one study, k = 2 health outcomes) and coral reef fish (one study, k = 1 health outcome). Touch interventions mostly comprised stroking ( k = 13 health outcomes) and tickling ( k = 10 health outcomes). For animal studies, 71.4% of effects showed benefits to mental health-like parameters and 81.8% showed positive physical health effects. We thus found strong evidence that touch interventions, which were mostly conducted by humans (16 studies with human touch versus 3 studies with object touch), had positive health effects in animal species as well.
The key aim of the present study was twofold: (1) to provide an estimate of the effect size of touch interventions and (2) to disambiguate moderating factors to potentially tailor future interventions more precisely. Overall, touch interventions were beneficial for both physical and mental health, with a medium effect size. Our work illustrates that touch interventions are best suited for reducing pain, depression and anxiety in adults and children as well as for increasing weight gain in newborns. These findings are in line with previous meta-analyses on this topic, supporting their conclusions and their robustness to the addition of more datasets. One limitation of previous meta-analyses is that they focused on specific health outcomes or populations, despite primary studies often reporting effects on multiple health parameters simultaneously (for example, ref. 13 focusing on neck and shoulder pain and ref. 14 focusing on massage therapy in preterms). To our knowledge, only ref. 5 provides a multivariate picture for a large number of dependent variables. However, this study analysed their data in separate random effects models that did not account for multivariate reporting nor for the multilevel structure of the data, as such approaches have only become available recently. Thus, in addition to adding a substantial amount of new data, our statistical approach provides a more accurate depiction of effect size estimates. Additionally, our study investigated a variety of moderating effects that did not reach significance (for example, sex ratio, mean age or intervention duration) or were not considered (for example, the benefits of robot or object touch) in previous meta-analyses in relation to touch intervention efficacy 5 , probably because of the small number of studies with information on these moderators in the past. Owing to our large-scale approach, we reached high statistical power for many moderator analyses. Finally, previous meta-analyses on this topic exclusively focused on massage therapy in adults or kangaroo care in newborns 15 , leaving out a large number of interventions that are being carried out in research as well as in everyday life to improve well-being. Incorporating these studies into our study, we found that, in general, both massages and other types of touch, such as gentle touch, stroking or kangaroo care, showed similar health benefits.
While it seems to be less critical which touch intervention is applied, the frequency of interventions seems to matter. More sessions were positively associated with the improvement of trait outcomes such as depression and anxiety but also pain reductions in adults. In contrast to session number, increasing the duration of individual sessions did not improve health effects. In fact, we found some indications of negative relationships in adults for cortisol and blood pressure. This could be due to habituating effects of touch on the sympathetic nervous system and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, ultimately resulting in diminished effects with longer exposure, or decreased pleasantness ratings of affective touch with increasing duration 16 . For newborns, we could not support previous notions that the duration of the touch intervention is linked to benefits in weight gain 17 . Thus, an ideal intervention protocol does not seem to have to be excessively long. It should be noted that very few interventions lasted less than 5 min, and it therefore remains unclear whether very short interventions have the same effect.
A critical issue highlighted in the pandemic was the lack of touch due to social restrictions 18 . To accommodate the need for touch in individuals with small social networks (for example, institutionalized or isolated individuals), touch interventions using objects/robots have been explored in the past (for a review, see ref. 11 ). We show here that touch interactions outside of the human–human domain are beneficial for mental and physical health outcomes. Importantly, object/robot touch was not as effective in improving mental health as human-applied touch. A sub-analysis of missing skin-to-skin contact among humans indicated that mental health effects of touch might be mediated by the presence of skin-to-skin contact. Thus, it seems profitable to include skin-to-skin contact in future touch interventions, in line with previous findings in newborns 19 . In robots, recent advancements in synthetic skin 20 should be investigated further in this regard. It should be noted that, although we did not observe significant differences in physical health benefits between human–human and human–object touch, the variability of effect sizes was higher in human–object touch. The conditions enabling object or robot interactions to improve well-being should therefore be explored in more detail in the future.
Touch was beneficial for both healthy and clinical cohorts. These data are critical as most previous meta-analytic research has focused on individuals diagnosed with clinical disorders (for example, ref. 6 ). For mental health outcomes, we found larger effects in clinical cohorts. A possible reason could relate to increased touch wanting 21 in patients. For example, loneliness often co-occurs with chronic illnesses 22 , which are linked to depressed mood and feelings of anxiety 23 . Touch can be used to counteract this negative development 24 , 25 . In adults and children, knowing the toucher did not influence health benefits. In contrast, familiarity affected overall health benefits in newborns, with parental touch being more beneficial than touch applied by medical staff. Previous studies have suggested that early skin-to-skin contact and exposure to maternal odour is critical for a newborn’s ability to adapt to a new environment 26 , supporting the notion that parental care is difficult to substitute in this time period.
With respect to age-related effects, our data further suggest that increasing age was associated with a higher benefit through touch for systolic blood pressure. These findings could potentially be attributed to higher basal blood pressure 27 with increasing age, allowing for a stronger modulation of this parameter. For sex differences, our study provides some evidence that there are differences between women and men with respect to health benefits of touch. Overall, research on sex differences in touch processing is relatively sparse (but see refs. 28 , 29 ). Our results suggest that buffering effects against physiological stress are stronger in women. This is in line with increased buffering effects of hugs in women compared with men 30 . The female-biased primary research in adults, however, begs for more research in men or non-binary individuals. Unfortunately, our study could not dive deeper into this topic as health benefits broken down by sex or gender were almost never provided. Recent research has demonstrated that sensory pleasantness is affected by sex and that this also interacts with the familiarity of the other person in the touching dyad 29 , 31 . In general, contextual factors such as sex and gender or the relationship of the touching dyad, differences in cultural background or internal states such as stress have been demonstrated to be highly influential in the perception of affective touch and are thus relevant to maximizing the pleasantness and ultimately the health benefits of touch interactions 32 , 33 , 34 . As a positive personal relationship within the touching dyad is paramount to induce positive health effects, future research applying robot touch to promote well-being should therefore not only explore synthetic skin options but also focus on improving robots as social agents that form a close relationship with the person receiving the touch 35 .
As part of the systematic review, we also assessed the effects of touch interventions in non-human animals. Mimicking the results of the meta-analysis in humans, beneficial effects of touch in animals were comparably strong for mental health-like and physical health outcomes. This may inform interventions to promote animal welfare in the context of animal experiments 36 , farming 37 and pets 38 . While most studies investigated effects in rodents, which are mostly used as laboratory animals, these results probably transfer to livestock and common pets as well. Indeed, touch was beneficial in lambs, fish and cats 39 , 40 , 41 . The positive impact of human touch in rodents also allows for future mechanistic studies in animal models to investigate how interventions such as tickling or stroking modulate hormonal and neuronal responses to touch in the brain. Furthermore, the commonly proposed oxytocin hypothesis can be causally investigated in these animal models through, for example, optogenetic or chemogenetic techniques 42 . We believe that such translational approaches will further help in optimizing future interventions in humans by uncovering the underlying mechanisms and brain circuits involved in touch.
Our results offer many promising avenues to improve future touch interventions, but they also need to be discussed in light of their limitations. While the majority of findings showed robust health benefits of touch interventions across moderators when compared with a null effect, post hoc tests of, for example, familiarity effects in newborns or mental health benefit differences between human and object touch only barely reached significance. Since we computed a large number of statistical tests in the present study, there is a risk that these results are false positives. We hope that researchers in this field are stimulated by these intriguing results and target these questions by primary research through controlled experimental designs within a well-powered study. Furthermore, the presence of small-study bias in both meta-analyses is indicative that the effect size estimates presented here might be overestimated as null results are often unpublished. We want to stress however that this bias is probably reduced by the multivariate reporting of primary studies. Most studies that reported on multiple health outcomes only showed significant findings for one or two among many. Thus, the multivariate nature of primary research in this field allowed us to include many non-significant findings in the present study. Another limitation pertains to the fact that we only included articles in languages mostly spoken in Western countries. As a large body of evidence comes from Asian countries, it could be that primary research was published in languages other than specified in the inclusion criteria. Thus, despite the large and inclusive nature of our study, some studies could have been missed regardless. Another factor that could not be accounted for in our meta-analysis was that an important prerequisite for touch to be beneficial is its perceived pleasantness. The level of pleasantness associated with being touched is modulated by several parameters 34 including cultural acceptability 43 , perceived humanness 44 or a need for touch 45 , which could explain the observed differences for certain moderators, such as human–human versus robot–human interaction. Moreover, the fact that secondary categorical moderators could not be investigated with respect to specific health outcomes, owing to the lack of data points, limits the specificity of our conclusions in this regard. It thus remains unclear whether, for example, a decreased mental health benefit in the absence of skin-to-skin contact is linked mostly to decreased anxiolytic effects, changes in positive/negative affect or something else. Since these health outcomes are however highly correlated 46 , it is likely that such effects are driven by multiple health outcomes. Similarly, it is important to note that our conclusions mainly refer to outcomes measured close to the touch intervention as we did not include long-term outcomes. Finally, it needs to be noted that blinding towards the experimental condition is essentially impossible in touch interventions. Although we compared the touch intervention with other interventions, such as relaxation therapy, as control whenever possible, contributions of placebo effects cannot be ruled out.
In conclusion, we show clear evidence that touch interventions are beneficial across a large number of both physical and mental health outcomes, for both healthy and clinical cohorts, and for all ages. These benefits, while influenced in their magnitude by study cohorts and intervention characteristics, were robustly present, promoting the conclusion that touch interventions can be systematically employed across the population to preserve and improve our health.
Open science practices
All data and code are accessible in the corresponding OSF project 12 . The systematic review was registered on PROSPERO (CRD42022304281) before the start of data collection. We deviated from the pre-registered plan as follows:
Deviation 1: During our initial screening for the systematic review, we were confronted with a large number of potential health outcomes to look at. This observation of multivariate outcomes led us to register an amendment during data collection (but before any effect size or moderator screening). In doing so, we aimed to additionally extract meta-analytic effects for a more quantitative assessment of our review question that can account for multivariate data reporting and dependencies of effects within the same study. Furthermore, as we noted a severe lack of studies with respect to health outcomes for animals during the inclusion assessment for the systematic review, we decided that the meta-analysis would only focus on outcomes that could be meaningfully analysed on the meta-analytic level and therefore only included health outcomes of human participants.
Deviation 2: In the pre-registration, we did not explicitly exclude non-randomized trials. Since an explicit use of non-randomization for group allocation significantly increases the risk of bias, we decided to exclude them a posteriori from data analysis.
Deviation 3: In the pre-registration, we outlined a tertiary moderator level, namely benefits of touch application versus touch reception. This level was ignored since no included study specifically investigated the benefits of touch application by itself.
Deviation 4: In the pre-registration, we suggested using the RoBMA function 47 to provide a Bayesian framework that allows for a more accurate assessment of publication bias beyond small-study bias. Unfortunately, neither multilevel nor multivariate data structures are supported by the RoBMA function, to our knowledge. For this reason, we did not further pursue this analysis, as the hierarchical nature of the data would not be accounted for.
Deviation 5: Beyond the pre-registered inclusion and exclusion criteria, we also excluded dissertations owing to their lack of peer review.
Deviation 6: In the pre-registration, we stated to investigate the impact of sex of the person applying the touch. This moderator was not further analysed, as this information was rarely given and the individuals applying the touch were almost exclusively women (7 males, 24 mixed and 85 females in studies on adults/children; 3 males, 17 mixed and 80 females in studied on newborns).
Deviation 7: The time span of the touch intervention as assessed by subtracting the final day of the intervention from the first day was not investigated further owing to its very high correlation with the number of sessions ( r (461) = 0.81 in the adult meta-analysis, r (145) = 0.84 in the newborn meta-analysis).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
To be included in the systematic review, studies had to investigate the relationship between at least one health outcome (physical and/or mental) in humans or animals and a touch intervention, include explicit physical touch by another human, animal or object as part of an intervention and include an experimental and control condition/group that are differentiated by touch alone. Of note, as a result of this selection process, no animal-to-animal touch intervention study was included, as they never featured a proper no-touch control. Human touch was always explicit touch by a human (that is, no brushes or other tools), either with or without skin-to-skin contact. Regarding the included health outcomes, we aimed to be as broad as possible but excluded parameters such as neurophysiological responses or pleasantness ratings after touch application as they do not reflect health outcomes. All included studies in the meta-analysis and systematic review 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 , 102 , 103 , 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 108 , 109 , 110 , 111 , 112 , 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 117 , 118 , 119 , 120 , 121 , 122 , 123 , 124 , 125 , 126 , 127 , 128 , 129 , 130 , 131 , 132 , 133 , 134 , 135 , 136 , 137 , 138 , 139 , 140 , 141 , 142 , 143 , 144 , 145 , 146 , 147 , 148 , 149 , 150 , 151 , 152 , 153 , 154 , 155 , 156 , 157 , 158 , 159 , 160 , 161 , 162 , 163 , 164 , 165 , 166 , 167 , 168 , 169 , 170 , 171 , 172 , 173 , 174 , 175 , 176 , 177 , 178 , 179 , 180 , 181 , 182 , 183 , 184 , 185 , 186 , 187 , 188 , 189 , 190 , 191 , 192 , 193 , 194 , 195 , 196 , 197 , 198 , 199 , 200 , 201 , 202 , 203 , 204 , 205 , 206 , 207 , 208 , 209 , 210 , 211 , 212 , 213 , 214 , 215 , 216 , 217 , 218 , 219 , 220 , 221 , 222 , 223 , 224 , 225 , 226 , 227 , 228 , 229 , 230 , 231 , 232 , 233 , 234 , 235 , 236 , 237 , 238 , 239 , 240 , 241 , 242 , 243 , 244 , 245 , 246 , 247 , 248 , 249 , 250 , 251 , 252 , 253 , 254 , 255 , 256 , 257 , 258 , 259 , 260 , 261 , 262 , 263 are listed in Supplementary Table 2 . All excluded studies are listed in Supplementary Table 3 , together with a reason for exclusion. We then applied a two-step process: First, we identified all potential health outcomes and extracted qualitative information on those outcomes (for example, direction of effect). Second, we extracted quantitative information from all possible outcomes (for example, effect sizes). The meta-analysis additionally required a between-subjects design (to clearly distinguish touch from no-touch effects and owing to missing information about the correlation between repeated measurements 264 ). Studies that explicitly did not apply a randomized protocol were excluded before further analysis to reduce risk of bias. The full study lists for excluded and included studies can be found in the OSF project 12 in the file ‘Study_lists_final_revised.xlsx’. In terms of the time frame, we conducted an open-start search of studies until 2022 and identified studies conducted between 1965 and 2022.
Data collection
We used Google Scholar, PubMed and Web of Science for our literature search, with no limitations regarding the publication date and using pre-specified search queries (see Supplementary Information for the exact keywords used). All procedures were in accordance with the updated Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines 265 . Articles were assessed in French, Dutch, German or English. The above databases were searched from 2 December 2021 until 1 October 2022. Two independent coders evaluated each paper against the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inconsistencies between coders were checked and resolved by J.P. and H.H. Studies excluded/included for the review and meta-analysis can be found on the OSF project.
Search queries
We used the following keywords to search the chosen databases. Agents (human versus animal versus object versus robot) and touch outcome (physical versus mental) were searched separately together with keywords searching for touch.
TOUCH: Touch OR Social OR Affective OR Contact OR Tactile interaction OR Hug OR Massage OR Embrace OR Kiss OR Cradling OR Stroking OR Haptic interaction OR tickling
AGENT: Object OR Robot OR human OR animal OR rodent OR primate
MENTAL OUTCOME: Health OR mood OR Depression OR Loneliness OR happiness OR life satisfaction OR Mental Disorder OR well-being OR welfare OR dementia OR psychological OR psychiatric OR anxiety OR Distress
PHYSICAL OUTCOME: Health OR Stress OR Pain OR cardiovascular health OR infection risk OR immune response OR blood pressure OR heart rate
Data extraction and preparation
Data extraction began on 10 October 2022 and was concluded on 25 February 2023. J.P. and H.H. oversaw the data collection process, and checked and resolved all inconsistencies between coders.
Health benefits of touch were always coded by positive summary effects, whereas adverse health effects of touch were represented by negative summary effects. If multiple time points were measured for the same outcome on the same day after a single touch intervention, we extracted the peak effect size (in either the positive or negative direction). If the touch intervention occurred multiple times and health outcomes were assessed for each time point, we extracted data points separately. However, we only extracted immediate effects, as long-term effects not controlled through the experimental conditions could be due to influences other than the initial touch intervention. Measurements assessing long-term effects without explicit touch sessions in the breaks were excluded for the same reason. Common control groups for touch interventions comprised active (for example, relaxation therapy) as well as passive control groups (for example, standard medical care). In the case of multiple control groups, we always contrasted the touch group to the group that most closely matched the touch condition (for example, relaxation therapy was preferred over standard medical care). We extracted information from all moderators listed in the pre-registration (Supplementary Table 4 ). A list of included and excluded health outcomes is presented in Supplementary Table 5 . Authors of studies with possible effects but missing information to calculate those effects were contacted via email and asked to provide the missing data (response rate 35.7%).
After finalizing the list of included studies for the systematic review, we added columns for moderators and the coding schema for our meta-analysis per our updated registration. Then, each study was assessed for its eligibility in the meta-analysis by two independent coders (J.P., H.H., K.F. or F.M.). To this end, all coders followed an a priori specified procedure: First, the PDF was skimmed for possible effects to extract, and the study was excluded if no PDF was available or the study was in a language different from the ones specified in ‘ Data collection ’. Effects from studies that met the inclusion criteria were extracted from all studies listing descriptive values or statistical parameters to calculate effect sizes. A website 266 was used to convert descriptive and statistical values available in the included studies (means and standard deviations/standard errors/confidence intervals, sample sizes, F values, t values, t test P values or frequencies) into Cohen’s d , which were then converted in Hedges’ g . If only P value thresholds were reported (for example, P < 0.01), we used this, most conservative, value as the P value to calculate the effect size (for example, P = 0.01). If only the total sample size was given but that number was even and the participants were randomly assigned to each group, we assumed equal sample sizes for each group. If delta change scores (for example, pre- to post-touch intervention) were reported, we used those over post-touch only scores. In case frequencies were 0 when frequency tables were used to determine effect sizes, we used a value of 0.5 as a substitute to calculate the effect (the default setting in the ‘metafor’ function 267 ). From these data, Hedges’ g and its variance could be derived. Effect sizes were always computed between the experimental and the control group.
Statistical analysis and risk of bias assessment
Owing to the lack of identified studies, health benefits to animals were not included as part of the statistical analysis. One meta-analysis was performed for adults, adolescents and children, as outcomes were highly comparable. We refer to this meta-analysis as the adult meta-analysis, as children/adolescent cohorts were only targeted in a minority of studies. A separate meta-analysis was performed for newborns, as their health outcomes differed substantially from any other age group.
Data were analysed using R (version 4.2.2) with the ‘rma.mv’ function from the ‘metafor’ package 267 in a multistep, multivariate and multilevel fashion.
We calculated an overall effect of touch interventions across all studies, cohorts and health outcomes. To account for the hierarchical structure of the data, we used a multilevel structure with random effects at the study, cohort and effects level. Furthermore, we calculated the variance–covariance matrix of all data points to account for the dependencies of measured effects within each individual cohort and study. The variance–covariance matrix was calculated by default with an assumed correlation of effect sizes within each cohort of ρ = 0.6. As ρ needed to be assumed, sensitivity analyses for all computed effect estimates were conducted using correlations between effects of 0, 0.2, 0.4 and 0.8. The results of these sensitivity analyses can be found in ref. 12 . No conclusion drawn in the present manuscript was altered by changing the level of ρ . The sensitivity analyses, however, showed that higher assumed correlations lead to more conservative effect size estimates (see Supplementary Figs. 19 and 20 for the adult and newborn meta-analyses, respectively), reducing the type I error risk in general 268 . In addition to these procedures, we used robust variance estimation with cluster-robust inference at the cohort level. This step is recommended to more accurately determine the confidence intervals in complex multivariate models 269 . The data distribution was assumed to be normal, but this was not formally tested.
To determine whether individual effects had a strong influence on our results, we calculated Cook’s distance D . Here, a threshold of D > 0.5 was used to qualify a study as influential 270 . Heterogeneity in the present study was assessed using Cochran’s Q , which determines whether the extracted effect sizes estimate a common population effect size. Although the Q statistic in the ‘rma.mv’ function accounts for the hierarchical nature of the data, we also quantified the heterogeneity estimator σ ² for each random-effects level to provide a comprehensive overview of heterogeneity indicators. These indicators for all models can be found on the OSF project 12 in the Table ‘Model estimates’. To assess small study bias, we visually inspected the funnel plot and used the standard error as a moderator in the overarching meta-analyses.
Before any sub-group analysis, the overall effect size was used as input for power calculations. While such post hoc power calculations might be limited, we believe that a minimum number of effects to be included in subgroup analyses was necessary to allow for meaningful conclusions. Such medium effect sizes would also probably be the minimum effect sizes of interest for researchers as well as clinical practitioners. Power calculation for random-effects models further requires a sample size for each individual effect as well as an approximation of the expected heterogeneity between studies. For the sample size input, we used the median sample size in each of our studies. For heterogeneity, we assumed a value between medium and high levels of heterogeneity ( I ² = 62.5% 271 ), as moderator analyses typically aim at reducing heterogeneity overall. Subgroups were only further investigated if the number of observed effects achieved ~80% power under these circumstances, to allow for a more robust interpretation of the observed effects (see Supplementary Figs. 5 and 6 for the adult and newborn meta-analysis, respectively). In a next step, we investigated all pre-registered moderators for which sufficient power was detected. We first looked at our primary moderators (mental versus physical health) and how the effect sizes systematically varied as a function of our secondary moderators (for example, human–human or human–object touch, duration, skin-to-skin presence, etc.). We always included random slopes to allow for our moderators to vary with the random effects at our clustering variable, which is recommended in multilevel models to reduce false positives 272 . All statistical tests were performed two-sided. Significance of moderators was determined using omnibus F tests. Effect size differences between moderator levels and their confidence intervals were assessed via t tests.
Post hoc t tests were performed comparing mental and physical health benefits within each interacting moderator (for example, mental versus physical health benefits in cancer patients) and mental or physical health benefits across levels of the interacting moderator (for example, mental health benefits in cancer versus pain patients). The post hoc tests were not pre-registered. Data were visualized using forest plots and orchard plots 273 for categorical moderators and scatter plots for continuous moderators.
For a broad overview of prior work and their biases, risk of bias was assessed for all studies included in both meta-analyses and the systematic review. We assessed the risk of bias for the following parameters:
Bias from randomization, including whether a randomization procedure was performed, whether it was a between- or within-participant design and whether there were any baseline differences for demographic or dependent variables.
Sequence bias resulting from a lack of counterbalancing in within-subject designs.
Performance bias resulting from the participants or experiments not being blinded to the experimental conditions.
Attrition bias resulting from different dropout rates between experimental groups.
Note that four studies in the adult meta-analysis did not explicitly mention randomization as part of their protocol. However, since these studies never showed any baseline differences in all relevant variables (see ‘Risk of Bias’ table on the OSF project ) , we assumed that randomization was performed but not mentioned. Sequence bias was of no concern for studies for the meta-analysis since cross-over designs were excluded. It was, however, assessed for studies within the scope of the systematic review. Importantly, performance bias was always high in the adult/children meta-analysis, as blinding of the participants and experimenters to the experimental conditions was not possible owing to the nature of the intervention (touch versus no touch). For studies with newborns and animals, we assessed the performance bias as medium since neither newborns or animals are likely to be aware of being part of an experiment or specific group. An overview of the results is presented in Supplementary Fig. 21 , and the precise assessment for each study can be found on the OSF project 12 in the ‘Risk of Bias’ table.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
All data are available via Open Science Framework at https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/C8RVW (ref. 12 ). Source data are provided with this paper.
Code availability
All code is available via Open Science Framework at https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/C8RVW (ref. 12 ).
Fulkerson, M. The First Sense: a Philosophical Study of Human Touch (MIT Press, 2013).
Farroni, T., Della Longa, L. & Valori, I. The self-regulatory affective touch: a speculative framework for the development of executive functioning. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 43 , 167–173 (2022).
Article Google Scholar
Ocklenburg, S. et al. Hugs and kisses—the role of motor preferences and emotional lateralization for hemispheric asymmetries in human social touch. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 95 , 353–360 (2018).
Ardiel, E. L. & Rankin, C. H. The importance of touch in development. Paediatr. Child Health 15 , 153–156 (2010).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Moyer, C. A., Rounds, J. & Hannum, J. W. A meta-analysis of massage therapy research. Psychol. Bull. 130 , 3–18 (2004).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lee, S. H., Kim, J. Y., Yeo, S., Kim, S. H. & Lim, S. Meta-analysis of massage therapy on cancer pain. Integr. Cancer Ther. 14 , 297–304 (2015).
LaFollette, M. R., O’Haire, M. E., Cloutier, S. & Gaskill, B. N. A happier rat pack: the impacts of tickling pet store rats on human–animal interactions and rat welfare. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 203 , 92–102 (2018).
Packheiser, J., Michon, F. Eva, C., Fredriksen, K. & Hartmann H. The physical and mental health benefits of social touch: a comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. PROSPERO https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42022304281 (2023).
Lakens, D. Sample size justification. Collabra. Psychol. 8 , 33267 (2022).
Quintana, D. S. A guide for calculating study-level statistical power for meta-analyses. Adv. Meth. Pract. Psychol. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1177/25152459221147260 (2023).
Eckstein, M., Mamaev, I., Ditzen, B. & Sailer, U. Calming effects of touch in human, animal, and robotic interaction—scientific state-of-the-art and technical advances. Front. Psychiatry 11 , 555058 (2020).
Packheiser, J. et al. The physical and mental health benefits of affective touch: a comparative systematic review and multivariate meta-analysis. Open Science Framework https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/C8RVW (2023).
Kong, L. J. et al. Massage therapy for neck and shoulder pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013 , 613279 (2013).
Wang, L., He, J. L. & Zhang, X. H. The efficacy of massage on preterm infants: a meta-analysis. Am. J. Perinatol. 30 , 731–738 (2013).
Field, T. Massage therapy research review. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 24 , 19–31 (2016).
Bendas, J., Ree, A., Pabel, L., Sailer, U. & Croy, I. Dynamics of affective habituation to touch differ on the group and individual level. Neuroscience 464 , 44–52 (2021).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Charpak, N., Montealegre‐Pomar, A. & Bohorquez, A. Systematic review and meta‐analysis suggest that the duration of Kangaroo mother care has a direct impact on neonatal growth. Acta Paediatr. 110 , 45–59 (2021).
Packheiser, J. et al. A comparison of hugging frequency and its association with momentary mood before and during COVID-19 using ecological momentary assessment. Health Commun. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2023.2198058 (2023).
Whitelaw, A., Heisterkamp, G., Sleath, K., Acolet, D. & Richards, M. Skin to skin contact for very low birthweight infants and their mothers. Arch. Dis. Child. 63 , 1377–1381 (1988).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yogeswaran, N. et al. New materials and advances in making electronic skin for interactive robots. Adv. Robot. 29 , 1359–1373 (2015).
Durkin, J., Jackson, D. & Usher, K. Touch in times of COVID‐19: touch hunger hurts. J. Clin. Nurs. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.15488 (2021).
Rokach, A., Lechcier-Kimel, R. & Safarov, A. Loneliness of people with physical disabilities. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 34 , 681–700 (2006).
Palgi, Y. et al. The loneliness pandemic: loneliness and other concomitants of depression, anxiety and their comorbidity during the COVID-19 outbreak. J. Affect. Disord. 275 , 109–111 (2020).
Heatley-Tejada, A., Dunbar, R. I. M. & Montero, M. Physical contact and loneliness: being touched reduces perceptions of loneliness. Adapt. Hum. Behav. Physiol. 6 , 292–306 (2020).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Packheiser, J. et al. The association of embracing with daily mood and general life satisfaction: an ecological momentary assessment study. J. Nonverbal Behav. 46 , 519–536 (2022).
Porter, R. The biological significance of skin-to-skin contact and maternal odours. Acta Paediatr. 93 , 1560–1562 (2007).
Hawkley, L. C., Masi, C. M., Berry, J. D. & Cacioppo, J. T. Loneliness is a unique predictor of age-related differences in systolic blood pressure. Psychol. Aging 21 , 152–164 (2006).
Russo, V., Ottaviani, C. & Spitoni, G. F. Affective touch: a meta-analysis on sex differences. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 108 , 445–452 (2020).
Schirmer, A. et al. Understanding sex differences in affective touch: sensory pleasantness, social comfort, and precursive experiences. Physiol. Behav. 250 , 113797 (2022).
Berretz, G. et al. Romantic partner embraces reduce cortisol release after acute stress induction in women but not in men. PLoS ONE 17 , e0266887 (2022).
Gazzola, V. et al. Primary somatosensory cortex discriminates affective significance in social touch. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109 , E1657–E1666 (2012).
Sorokowska, A. et al. Affective interpersonal touch in close relationships: a cross-cultural perspective. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 47 , 1705–1721 (2021).
Ravaja, N., Harjunen, V., Ahmed, I., Jacucci, G. & Spapé, M. M. Feeling touched: emotional modulation of somatosensory potentials to interpersonal touch. Sci. Rep. 7 , 40504 (2017).
Saarinen, A., Harjunen, V., Jasinskaja-Lahti, I., Jääskeläinen, I. P. & Ravaja, N. Social touch experience in different contexts: a review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 131 , 360–372 (2021).
Huisman, G. Social touch technology: a survey of haptic technology for social touch. IEEE Trans. Haptics 10 , 391–408 (2017).
Lewejohann, L., Schwabe, K., Häger, C. & Jirkof, P. Impulse for animal welfare outside the experiment. Lab. Anim. https://doi.org/10.17169/REFUBIUM-26765 (2020).
Sørensen, J. T., Sandøe, P. & Halberg, N. Animal welfare as one among several values to be considered at farm level: the idea of an ethical account for livestock farming. Acta Agric. Scand. A 51 , 11–16 (2001).
Google Scholar
Verga, M. & Michelazzi, M. Companion animal welfare and possible implications on the human–pet relationship. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 8 , 231–240 (2009).
Coulon, M. et al. Do lambs perceive regular human stroking as pleasant? Behavior and heart rate variability analyses. PLoS ONE 10 , e0118617 (2015).
Soares, M. C., Oliveira, R. F., Ros, A. F. H., Grutter, A. S. & Bshary, R. Tactile stimulation lowers stress in fish. Nat. Commun. 2 , 534 (2011).
Gourkow, N., Hamon, S. C. & Phillips, C. J. C. Effect of gentle stroking and vocalization on behaviour, mucosal immunity and upper respiratory disease in anxious shelter cats. Prev. Vet. Med. 117 , 266–275 (2014).
Oliveira, V. E. et al. Oxytocin and vasopressin within the ventral and dorsal lateral septum modulate aggression in female rats. Nat. Commun. 12 , 2900 (2021).
Burleson, M. H., Roberts, N. A., Coon, D. W. & Soto, J. A. Perceived cultural acceptability and comfort with affectionate touch: differences between Mexican Americans and European Americans. J. Soc. Personal. Relatsh. 36 , 1000–1022 (2019).
Wijaya, M. et al. The human ‘feel’ of touch contributes to its perceived pleasantness. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 46 , 155–171 (2020).
Golaya, S. Touch-hunger: an unexplored consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 43 , 362–363 (2021).
Ng, T. W. H., Sorensen, K. L., Zhang, Y. & Yim, F. H. K. Anger, anxiety, depression, and negative affect: convergent or divergent? J. Vocat. Behav. 110 , 186–202 (2019).
Maier, M., Bartoš, F. & Wagenmakers, E.-J. Robust Bayesian meta-analysis: addressing publication bias with model-averaging. Psychol. Methods 28 , 107–122 (2022).
Ahles, T. A. et al. Massage therapy for patients undergoing autologous bone marrow transplantation. J. Pain. Symptom Manag. 18 , 157–163 (1999).
Albert, N. M. et al. A randomized trial of massage therapy after heart surgery. Heart Lung 38 , 480–490 (2009).
Ang, J. Y. et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of massage therapy on the immune system of preterm infants. Pediatrics 130 , e1549–e1558 (2012).
Arditi, H., Feldman, R. & Eidelman, A. I. Effects of human contact and vagal regulation on pain reactivity and visual attention in newborns. Dev. Psychobiol. 48 , 561–573 (2006).
Arora, J., Kumar, A. & Ramji, S. Effect of oil massage on growth and neurobehavior in very low birth weight preterm neonates. Indian Pediatr. 42 , 1092–1100 (2005).
PubMed Google Scholar
Asadollahi, M., Jabraeili, M., Mahallei, M., Asgari Jafarabadi, M. & Ebrahimi, S. Effects of gentle human touch and field massage on urine cortisol level in premature infants: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J. Caring Sci. 5 , 187–194 (2016).
Basiri-Moghadam, M., Basiri-Moghadam, K., Kianmehr, M. & Jani, S. The effect of massage on neonatal jaundice in stable preterm newborn infants: a randomized controlled trial. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 65 , 602–606 (2015).
Bauer, B. A. et al. Effect of massage therapy on pain, anxiety, and tension after cardiac surgery: a randomized study. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 16 , 70–75 (2010).
Beijers, R., Cillessen, L. & Zijlmans, M. A. C. An experimental study on mother-infant skin-to-skin contact in full-terms. Infant Behav. Dev. 43 , 58–65 (2016).
Bennett, S. et al. Acute effects of traditional Thai massage on cortisol levels, arterial blood pressure and stress perception in academic stress condition: a single blind randomised controlled trial. J. Bodyw. Mov. Therapies 20 , 286–292 (2016).
Bergman, N., Linley, L. & Fawcus, S. Randomized controlled trial of skin-to-skin contact from birth versus conventional incubator for physiological stabilization in 1200- to 2199-gram newborns. Acta Paediatr. 93 , 779–785 (2004).
Bigelow, A., Power, M., MacLellan‐Peters, J., Alex, M. & McDonald, C. Effect of mother/infant skin‐to‐skin contact on postpartum depressive symptoms and maternal physiological stress. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 41 , 369–382 (2012).
Billhult, A., Bergbom, I. & Stener-Victorin, E. Massage relieves nausea in women with breast cancer who are undergoing chemotherapy. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 13 , 53–57 (2007).
Billhult, A., Lindholm, C., Gunnarsson, R. & Stener-Victorin, E. The effect of massage on cellular immunity, endocrine and psychological factors in women with breast cancer—a randomized controlled clinical trial. Auton. Neurosci. 140 , 88–95 (2008).
Braun, L. A. et al. Massage therapy for cardiac surgery patients—a randomized trial. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 144 , 1453–1459 (2012).
Cabibihan, J.-J. & Chauhan, S. S. Physiological responses to affective tele-touch during induced emotional stimuli. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 8 , 108–118 (2017).
Campeau, M.-P. et al. Impact of massage therapy on anxiety levels in patients undergoing radiation therapy: randomized controlled trial. J. Soc. Integr. Oncol. 5 , 133–138 (2007).
Can, Ş. & Kaya, H. The effects of yakson or gentle human touch training given to mothers with preterm babies on attachment levels and the responses of the baby: a randomized controlled trial. Health Care Women Int. 43 , 479–498 (2021).
Carfoot, S., Williamson, P. & Dickson, R. A randomised controlled trial in the north of England examining the effects of skin-to-skin care on breast feeding. Midwifery 21 , 71–79 (2005).
Castral, T. C., Warnock, F., Leite, A. M., Haas, V. J. & Scochi, C. G. S. The effects of skin-to-skin contact during acute pain in preterm newborns. Eur. J. Pain. 12 , 464–471 (2008).
Cattaneo, A. et al. Kangaroo mother care for low birthweight infants: a randomized controlled trial in different settings. Acta Paediatr. 87 , 976–985 (1998).
Charpak, N., Ruiz-Peláez, J. G. & Charpak, Y. Rey-Martinez kangaroo mother program: an alternative way of caring for low birth weight infants? One year mortality in a two cohort study. Pediatrics 94 , 804–810 (1994).
Chermont, A. G., Falcão, L. F. M., de Souza Silva, E. H. L., de Cássia Xavier Balda, R. & Guinsburg, R. Skin-to-skin contact and/or oral 25% dextrose for procedural pain relief for term newborn infants. Pediatrics 124 , e1101–e1107 (2009).
Chi Luong, K., Long Nguyen, T., Huynh Thi, D. H., Carrara, H. P. O. & Bergman, N. J. Newly born low birthweight infants stabilise better in skin-to-skin contact than when separated from their mothers: a randomised controlled trial. Acta Paediatr. 105 , 381–390 (2016).
Cho, E.-S. et al. The effects of kangaroo care in the neonatal intensive care unit on the physiological functions of preterm infants, maternal–infant attachment, and maternal stress. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 31 , 430–438 (2016).
Choi, H. et al. The effects of massage therapy on physical growth and gastrointestinal function in premature infants: a pilot study. J. Child Health Care 20 , 394–404 (2016).
Choudhary, M. et al. To study the effect of Kangaroo mother care on pain response in preterm neonates and to determine the behavioral and physiological responses to painful stimuli in preterm neonates: a study from western Rajasthan. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 29 , 826–831 (2016).
Christensson, K. et al. Temperature, metabolic adaptation and crying in healthy full-term newborns cared for skin-to-skin or in a cot. Acta Paediatr. 81 , 488–493 (1992).
Cloutier, S. & Newberry, R. C. Use of a conditioning technique to reduce stress associated with repeated intra-peritoneal injections in laboratory rats. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 112 , 158–173 (2008).
Cloutier, S., Wahl, K., Baker, C. & Newberry, R. C. The social buffering effect of playful handling on responses to repeated intraperitoneal injections in laboratory rats. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 53 , 168–173 (2014).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cloutier, S., Wahl, K. L., Panksepp, J. & Newberry, R. C. Playful handling of laboratory rats is more beneficial when applied before than after routine injections. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 164 , 81–90 (2015).
Cong, X. et al. Effects of skin-to-skin contact on autonomic pain responses in preterm infants. J. Pain. 13 , 636–645 (2012).
Cong, X., Ludington-Hoe, S. M., McCain, G. & Fu, P. Kangaroo care modifies preterm infant heart rate variability in response to heel stick pain: pilot study. Early Hum. Dev. 85 , 561–567 (2009).
Cong, X., Ludington-Hoe, S. M. & Walsh, S. Randomized crossover trial of kangaroo care to reduce biobehavioral pain responses in preterm infants: a pilot study. Biol. Res. Nurs. 13 , 204–216 (2011).
Costa, R. et al. Tactile stimulation of adult rats modulates hormonal responses, depression-like behaviors, and memory impairment induced by chronic mild stress: role of angiotensin II. Behav. Brain Res. 379 , 112250 (2020).
Cutshall, S. M. et al. Effect of massage therapy on pain, anxiety, and tension in cardiac surgical patients: a pilot study. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 16 , 92–95 (2010).
Dalili, H., Sheikhi, S., Shariat, M. & Haghnazarian, E. Effects of baby massage on neonatal jaundice in healthy Iranian infants: a pilot study. Infant Behav. Dev. 42 , 22–26 (2016).
Diego, M. A., Field, T. & Hernandez-Reif, M. Vagal activity, gastric motility, and weight gain in massaged preterm neonates. J. Pediatr. 147 , 50–55 (2005).
Diego, M. A., Field, T. & Hernandez-Reif, M. Temperature increases in preterm infants during massage therapy. Infant Behav. Dev. 31 , 149–152 (2008).
Diego, M. A. et al. Preterm infant massage elicits consistent increases in vagal activity and gastric motility that are associated with greater weight gain. Acta Paediatr. 96 , 1588–1591 (2007).
Diego, M. A. et al. Spinal cord patients benefit from massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 112 , 133–142 (2002).
Diego, M. A. et al. Aggressive adolescents benefit from massage therapy. Adolescence 37 , 597–607 (2002).
Diego, M. A. et al. HIV adolescents show improved immune function following massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 106 , 35–45 (2001).
Dieter, J. N. I., Field, T., Hernandez-Reif, M., Emory, E. K. & Redzepi, M. Stable preterm infants gain more weight and sleep less after five days of massage therapy. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 28 , 403–411 (2003).
Ditzen, B. et al. Effects of different kinds of couple interaction on cortisol and heart rate responses to stress in women. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32 , 565–574 (2007).
Dreisoerner, A. et al. Self-soothing touch and being hugged reduce cortisol responses to stress: a randomized controlled trial on stress, physical touch, and social identity. Compr. Psychoneuroendocrinol. 8 , 100091 (2021).
Eaton, M., Mitchell-Bonair, I. L. & Friedmann, E. The effect of touch on nutritional intake of chronic organic brain syndrome patients. J. Gerontol. 41 , 611–616 (1986).
Edens, J. L., Larkin, K. T. & Abel, J. L. The effect of social support and physical touch on cardiovascular reactions to mental stress. J. Psychosom. Res. 36 , 371–382 (1992).
El-Farrash, R. A. et al. Longer duration of kangaroo care improves neurobehavioral performance and feeding in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Res. 87 , 683–688 (2020).
Erlandsson, K., Dsilna, A., Fagerberg, I. & Christensson, K. Skin-to-skin care with the father after cesarean birth and its effect on newborn crying and prefeeding behavior. Birth 34 , 105–114 (2007).
Escalona, A., Field, T., Singer-Strunck, R., Cullen, C. & Hartshorn, K. Brief report: improvements in the behavior of children with autism following massage therapy. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 31 , 513–516 (2001).
Fattah, M. A. & Hamdy, B. Pulmonary functions of children with asthma improve following massage therapy. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 17 , 1065–1068 (2011).
Feldman, R. & Eidelman, A. I. Skin-to-skin contact (kangaroo care) accelerates autonomic and neurobehavioural maturation in preterm infants. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 45 , 274–281 (2003).
Feldman, R., Eidelman, A. I., Sirota, L. & Weller, A. Comparison of skin-to-skin (kangaroo) and traditional care: parenting outcomes and preterm infant development. Pediatrics 110 , 16–26 (2002).
Feldman, R., Singer, M. & Zagoory, O. Touch attenuates infants’ physiological reactivity to stress. Dev. Sci. 13 , 271–278 (2010).
Feldman, R., Weller, A., Sirota, L. & Eidelman, A. I. Testing a family intervention hypothesis: the contribution of mother–infant skin-to-skin contact (kangaroo care) to family interaction, proximity, and touch. J. Fam. Psychol. 17 , 94–107 (2003).
Ferber, S. G. et al. Massage therapy by mothers and trained professionals enhances weight gain in preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 67 , 37–45 (2002).
Ferber, S. G. & Makhoul, I. R. The effect of skin-to-skin contact (kangaroo care) shortly after birth on the neurobehavioral responses of the term newborn: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 113 , 858–865 (2004).
Ferreira, A. M. & Bergamasco, N. H. P. Behavioral analysis of preterm neonates included in a tactile and kinesthetic stimulation program during hospitalization. Rev. Bras. Fisioter. 14 , 141–148 (2010).
Fidanza, F., Polimeni, E., Pierangeli, V. & Martini, M. A better touch: C-tactile fibers related activity is associated to pain reduction during temporal summation of second pain. J. Pain. 22 , 567–576 (2021).
Field, T. et al. Leukemia immune changes following massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 5 , 271–274 (2001).
Field, T. et al. Benefits of combining massage therapy with group interpersonal psychotherapy in prenatally depressed women. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 13 , 297–303 (2009).
Field, T., Delage, J. & Hernandez-Reif, M. Movement and massage therapy reduce fibromyalgia pain. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 7 , 49–52 (2003).
Field, T. et al. Fibromyalgia pain and substance P decrease and sleep improves after massage therapy. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 8 , 72–76 (2002).
Field, T., Diego, M., Gonzalez, G. & Funk, C. G. Neck arthritis pain is reduced and range of motion is increased by massage therapy. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 20 , 219–223 (2014).
Field, T., Diego, M., Hernandez-Reif, M., Deeds, O. & Figueiredo, B. Pregnancy massage reduces prematurity, low birthweight and postpartum depression. Infant Behav. Dev. 32 , 454–460 (2009).
Field, T. et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 increased in preterm neonates following massage therapy. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 29 , 463–466 (2008).
Field, T. et al. Yoga and massage therapy reduce prenatal depression and prematurity. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 16 , 204–209 (2012).
Field, T., Diego, M., Hernandez-Reif, M., Schanberg, S. & Kuhn, C. Massage therapy effects on depressed pregnant women. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 25 , 115–122 (2004).
Field, T., Diego, M., Hernandez-Reif, M. & Shea, J. Hand arthritis pain is reduced by massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 11 , 21–24 (2007).
Field, T., Gonzalez, G., Diego, M. & Mindell, J. Mothers massaging their newborns with lotion versus no lotion enhances mothers’ and newborns’ sleep. Infant Behav. Dev. 45 , 31–37 (2016).
Field, T. et al. Children with asthma have improved pulmonary functions after massage therapy. J. Pediatr. 132 , 854–858 (1998).
Field, T., Hernandez-Reif, M., Diego, M. & Fraser, M. Lower back pain and sleep disturbance are reduced following massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 11 , 141–145 (2007).
Field, T. et al. Effects of sexual abuse are lessened by massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 1 , 65–69 (1997).
Field, T. et al. Pregnant women benefit from massage therapy. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 20 , 31–38 (1999).
Field, T. et al. Juvenilerheumatoid arthritis: benefits from massage therapy. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 22 , 607–617 (1997).
Field, T., Hernandez-Reif, M., Taylor, S., Quintino, O. & Burman, I. Labor pain is reduced by massage therapy. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 18 , 286–291 (1997).
Field, T. et al. Massage therapy reduces anxiety and enhances EEG pattern of alertness and math computations. Int. J. Neurosci. 86 , 197–205 (1996).
Field, T. et al. Brief report: autistic children’s attentiveness and responsivity improve after touch therapy. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 27 , 333–338 (1997).
Field, T. M. et al. Tactile/kinesthetic stimulation effects on preterm neonates. Pediatrics 77 , 654–658 (1986).
Field, T. et al. Massage reduces anxiety in child and adolescent psychiatric patients. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 31 , 125–131 (1992).
Field, T. et al. Burn injuries benefit from massage therapy. J. Burn Care Res. 19 , 241–244 (1998).
Filho, F. L. et al. Effect of maternal skin-to-skin contact on decolonization of methicillin-oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus in neonatal intensive care units: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0496-1 (2015).
Forward, J. B., Greuter, N. E., Crisall, S. J. & Lester, H. F. Effect of structured touch and guided imagery for pain and anxiety in elective joint replacement patients—a randomized controlled trial: M-TIJRP. Perm. J. 19 , 18–28 (2015).
Fraser, J. & Ross Kerr, J. Psychophysiological effects of back massage on elderly institutionalized patients. J. Adv. Nurs. 18 , 238–245 (1993).
Frey Law, L. A. et al. Massage reduces pain perception and hyperalgesia in experimental muscle pain: a randomized, controlled trial. J. Pain. 9 , 714–721 (2008).
Gao, H. et al. Effect of repeated kangaroo mother care on repeated procedural pain in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 52 , 1157–1165 (2015).
Garner, B. et al. Pilot study evaluating the effect of massage therapy on stress, anxiety and aggression in a young adult psychiatric inpatient unit. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 42 , 414–422 (2008).
Gathwala, G., Singh, B. & Singh, J. Effect of kangaroo mother care on physical growth, breastfeeding and its acceptability. Trop. Dr. 40 , 199–202 (2010).
Geva, N., Uzefovsky, F. & Levy-Tzedek, S. Touching the social robot PARO reduces pain perception and salivary oxytocin levels. Sci. Rep. 10 , 9814 (2020).
Gitau, R. et al. Acute effects of maternal skin-to-skin contact and massage on saliva cortisol in preterm babies. J. Reprod. Infant Psychol. 20 , 83–88 (2002).
Givi, M. Durability of effect of massage therapy on blood pressure. Int. J. Prev. Med. 4 , 511–516 (2013).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Glover, V., Onozawa, K. & Hodgkinson, A. Benefits of infant massage for mothers with postnatal depression. Semin. Neonatol. 7 , 495–500 (2002).
Gonzalez, A. et al. Weight gain in preterm infants following parent-administered vimala massage: a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Perinatol. 26 , 247–252 (2009).
Gray, L., Watt, L. & Blass, E. M. Skin-to-skin contact is analgesic in healthy newborns. Pediatrics 105 , e14 (2000).
Grewen, K. M., Anderson, B. J., Girdler, S. S. & Light, K. C. Warm partner contact is related to lower cardiovascular reactivity. Behav. Med. 29 , 123–130 (2003).
Groër, M. W., Hill, J., Wilkinson, J. E. & Stuart, A. Effects of separation and separation with supplemental stroking in BALB/c infant mice. Biol. Res. Nurs. 3 , 119–131 (2002).
Gürol, A. P., Polat, S. & Nuran Akçay, M. Itching, pain, and anxiety levels are reduced with massage therapy in burned adolescents. J. Burn Care Res. 31 , 429–432 (2010).
Haley, S. et al. Tactile/kinesthetic stimulation (TKS) increases tibial speed of sound and urinary osteocalcin (U-MidOC and unOC) in premature infants (29–32 weeks PMA). Bone 51 , 661–666 (2012).
Harris, M., Richards, K. C. & Grando, V. T. The effects of slow-stroke back massage on minutes of nighttime sleep in persons with dementia and sleep disturbances in the nursing home: a pilot study. J. Holist. Nurs. 30 , 255–263 (2012).
Hart, S. et al. Anorexia nervosa symptoms are reduced by massage therapy. Eat. Disord. 9 , 289–299 (2001).
Hattan, J., King, L. & Griffiths, P. The impact of foot massage and guided relaxation following cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Issues Innov. Nurs. Pract. 37 , 199–207 (2002).
Haynes, A. C. et al. A calming hug: design and validation of a tactile aid to ease anxiety. PLoS ONE 17 , e0259838 (2022).
Henricson, M., Ersson, A., Määttä, S., Segesten, K. & Berglund, A.-L. The outcome of tactile touch on stress parameters in intensive care: a randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 14 , 244–254 (2008).
Hernandez-Reif, M., Diego, M. & Field, T. Preterm infants show reduced stress behaviors and activity after 5 days of massage therapy. Infant Behav. Dev. 30 , 557–561 (2007).
Hernandez-Reif, M., Dieter, J. N. I., Field, T., Swerdlow, B. & Diego, M. Migraine headaches are reduced by massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 96 , 1–11 (1998).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. Natural killer cells and lymphocytes increase in women with breast cancer following massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 115 , 495–510 (2005).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. Children with cystic fibrosis benefit from massage therapy. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 24 , 175–181 (1999).
Hernandez-Reif, M., Field, T., Krasnegor, J. & Theakston, H. Lower back pain is reduced and range of motion increased after massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 106 , 131–145 (2001).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. High blood pressure and associated symptoms were reduced by massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 4 , 31–38 (2000).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. Parkinson’s disease symptoms are differentially affected by massage therapy vs. progressive muscle relaxation: a pilot study. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 6 , 177–182 (2002).
Hernandez-Reif, M., Field, T. & Theakston, H. Multiple sclerosis patients benefit from massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2 , 168–174 (1998).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. Breast cancer patients have improved immune and neuroendocrine functions following massage therapy. J. Psychosom. Res. 57 , 45–52 (2004).
Hertenstein, M. J. & Campos, J. J. Emotion regulation via maternal touch. Infancy 2 , 549–566 (2001).
Hinchcliffe, J. K., Mendl, M. & Robinson, E. S. J. Rat 50 kHz calls reflect graded tickling-induced positive emotion. Curr. Biol. 30 , R1034–R1035 (2020).
Hodgson, N. A. & Andersen, S. The clinical efficacy of reflexology in nursing home residents with dementia. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 14 , 269–275 (2008).
Hoffmann, L. & Krämer, N. C. The persuasive power of robot touch. Behavioral and evaluative consequences of non-functional touch from a robot. PLoS ONE 16 , e0249554 (2021).
Holst, S., Lund, I., Petersson, M. & Uvnäs-Moberg, K. Massage-like stroking influences plasma levels of gastrointestinal hormones, including insulin, and increases weight gain in male rats. Auton. Neurosci. 120 , 73–79 (2005).
Hori, M. et al. Tickling during adolescence alters fear-related and cognitive behaviors in rats after prolonged isolation. Physiol. Behav. 131 , 62–67 (2014).
Hori, M. et al. Effects of repeated tickling on conditioned fear and hormonal responses in socially isolated rats. Neurosci. Lett. 536 , 85–89 (2013).
Hucklenbruch-Rother, E. et al. Delivery room skin-to-skin contact in preterm infants affects long-term expression of stress response genes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 122 , 104883 (2020).
Im, H. & Kim, E. Effect of yakson and gentle human touch versus usual care on urine stress hormones and behaviors in preterm infants: a quasi-experimental study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 46 , 450–458 (2009).
Jain, S., Kumar, P. & McMillan, D. D. Prior leg massage decreases pain responses to heel stick in preterm babies. J. Paediatr. Child Health 42 , 505–508 (2006).
Jane, S.-W. et al. Effects of massage on pain, mood status, relaxation, and sleep in Taiwanese patients with metastatic bone pain: a randomized clinical trial. Pain 152 , 2432–2442 (2011).
Johnston, C. C. et al. Kangaroo mother care diminishes pain from heel lance in very preterm neonates: a crossover trial. BMC Pediatr. 8 , 13 (2008).
Johnston, C. C. et al. Kangaroo care is effective in diminishing pain response in preterm neonates. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 157 , 1084–1088 (2003).
Jung, M. J., Shin, B.-C., Kim, Y.-S., Shin, Y.-I. & Lee, M. S. Is there any difference in the effects of QI therapy (external QIGONG) with and without touching? a pilot study. Int. J. Neurosci. 116 , 1055–1064 (2006).
Kapoor, Y. & Orr, R. Effect of therapeutic massage on pain in patients with dementia. Dementia 16 , 119–125 (2017).
Karagozoglu, S. & Kahve, E. Effects of back massage on chemotherapy-related fatigue and anxiety: supportive care and therapeutic touch in cancer nursing. Appl. Nurs. Res. 26 , 210–217 (2013).
Karbasi, S. A., Golestan, M., Fallah, R., Golshan, M. & Dehghan, Z. Effect of body massage on increase of low birth weight neonates growth parameters: a randomized clinical trial. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 11 , 583–588 (2013).
Kashaninia, Z., Sajedi, F., Rahgozar, M. & Noghabi, F. A. The effect of kangaroo care on behavioral responses to pain of an intramuscular injection in neonates . J. Pediatr. Nurs. 3 , 275–280 (2008).
Kelling, C., Pitaro, D. & Rantala, J. Good vibes: The impact of haptic patterns on stress levels. In Proc. 20th International Academic Mindtrek Conference 130–136 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2016).
Khilnani, S., Field, T., Hernandez-Reif, M. & Schanberg, S. Massage therapy improves mood and behavior of students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Adolescence 38 , 623–638 (2003).
Kianmehr, M. et al. The effect of massage on serum bilirubin levels in term neonates with hyperbilirubinemia undergoing phototherapy. Nautilus 128 , 36–41 (2014).
Kim, I.-H., Kim, T.-Y. & Ko, Y.-W. The effect of a scalp massage on stress hormone, blood pressure, and heart rate of healthy female. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 28 , 2703–2707 (2016).
Kim, M. A., Kim, S.-J. & Cho, H. Effects of tactile stimulation by fathers on physiological responses and paternal attachment in infants in the NICU: a pilot study. J. Child Health Care 21 , 36–45 (2017).
Kim, M. S., Sook Cho, K., Woo, H.-M. & Kim, J. H. Effects of hand massage on anxiety in cataract surgery using local anesthesia. J. Cataract Refr. Surg. 27 , 884–890 (2001).
Koole, S. L., Tjew A Sin, M. & Schneider, I. K. Embodied terror management: interpersonal touch alleviates existential concerns among individuals with low self-esteem. Psychol. Sci. 25 , 30–37 (2014).
Krohn, M. et al. Depression, mood, stress, and Th1/Th2 immune balance in primary breast cancer patients undergoing classical massage therapy. Support. Care Cancer 19 , 1303–1311 (2011).
Kuhn, C. et al. Tactile-kinesthetic stimulation effects sympathetic and adrenocortical function in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 119 , 434–440 (1991).
Kumar, J. et al. Effect of oil massage on growth in preterm neonates less than 1800 g: a randomized control trial. Indian J. Pediatr. 80 , 465–469 (2013).
Lee, H.-K. The effects of infant massage on weight, height, and mother–infant interaction. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 36 , 1331–1339 (2006).
Leivadi, S. et al. Massage therapy and relaxation effects on university dance students. J. Dance Med. Sci. 3 , 108–112 (1999).
Lindgren, L. et al. Touch massage: a pilot study of a complex intervention. Nurs. Crit. Care 18 , 269–277 (2013).
Lindgren, L. et al. Physiological responses to touch massage in healthy volunteers. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 158 , 105–110 (2010).
Listing, M. et al. Massage therapy reduces physical discomfort and improves mood disturbances in women with breast cancer. Psycho-Oncol. 18 , 1290–1299 (2009).
Ludington-Hoe, S. M., Cranston Anderson, G., Swinth, J. Y., Thompson, C. & Hadeed, A. J. Randomized controlled trial of kangaroo care: cardiorespiratory and thermal effects on healthy preterm infants. Neonatal Netw. 23 , 39–48 (2004).
Lund, I. et al. Corticotropin releasing factor in urine—a possible biochemical marker of fibromyalgia. Neurosci. Lett. 403 , 166–171 (2006).
Ma, Y.-K. et al. Lack of social touch alters anxiety-like and social behaviors in male mice. Stress 25 , 134–144 (2022).
Massaro, A. N., Hammad, T. A., Jazzo, B. & Aly, H. Massage with kinesthetic stimulation improves weight gain in preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 29 , 352–357 (2009).
Mathai, S., Fernandez, A., Mondkar, J. & Kanbur, W. Effects of tactile-kinesthetic stimulation in preterms–a controlled trial. Indian Pediatr. 38 , 1091–1098 (2001).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Matsunaga, M. et al. Profiling of serum proteins influenced by warm partner contact in healthy couples. Neuroenocrinol. Lett. 30 , 227–236 (2009).
CAS Google Scholar
Mendes, E. W. & Procianoy, R. S. Massage therapy reduces hospital stay and occurrence of late-onset sepsis in very preterm neonates. J. Perinatol. 28 , 815–820 (2008).
Mirnia, K., Arshadi Bostanabad, M., Asadollahi, M. & Hamid Razzaghi, M. Paternal skin-to-skin care and its effect on cortisol levels of the infants. Iran. J. Pediatrics 27 , e8151 (2017).
Mitchell, A. J., Yates, C., Williams, K. & Hall, R. W. Effects of daily kangaroo care on cardiorespiratory parameters in preterm infants. J. Neonatal-Perinat. Med. 6 , 243–249 (2013).
Mitchinson, A. R. et al. Acute postoperative pain management using massage as an adjuvant therapy: a randomized trial. Arch. Surg. 142 , 1158–1167 (2007).
Modrcin-Talbott, M. A., Harrison, L. L., Groer, M. W. & Younger, M. S. The biobehavioral effects of gentle human touch on preterm infants. Nurs. Sci. Q. 16 , 60–67 (2003).
Mok, E. & Pang Woo, C. The effects of slow-stroke back massage on anxiety and shoulder pain in elderly stroke patients. Complement. Ther. Nurs. Midwifery 10 , 209–216 (2004).
Mokaberian, M., Noripour, S., Sheikh, M. & Mills, P. J. Examining the effectiveness of body massage on physical status of premature neonates and their mothers’ psychological status. Early Child Dev. Care 192 , 2311–2325 (2021).
Mori, H. et al. Effect of massage on blood flow and muscle fatigue following isometric lumbar exercise. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 10 , CR173–CR178 (2004).
Moyer-Mileur, L. J., Haley, S., Slater, H., Beachy, J. & Smith, S. L. Massage improves growth quality by decreasing body fat deposition in male preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 162 , 490–495 (2013).
Moyle, W. et al. Foot massage and physiological stress in people with dementia: a randomized controlled trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 20 , 305–311 (2014).
Muntsant, A., Shrivastava, K., Recasens, M. & Giménez-Llort, L. Severe perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury induces long-term sensorimotor deficits, anxiety-like behaviors and cognitive impairment in a sex-, age- and task-selective manner in C57BL/6 mice but can be modulated by neonatal handling. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 13 , 7 (2019).
Negahban, H., Rezaie, S. & Goharpey, S. Massage therapy and exercise therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis: a randomized controlled pilot study. Clin. Rehabil. 27 , 1126–1136 (2013).
Nelson, D., Heitman, R. & Jennings, C. Effects of tactile stimulation on premature infant weight gain. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 15 , 262–267 (1986).
Griffin, J. W. Calculating statistical power for meta-analysis using metapower. Quant. Meth. Psychol . 17 , 24–39 (2021).
Nunes, G. S. et al. Massage therapy decreases pain and perceived fatigue after long-distance Ironman triathlon: a randomised trial. J. Physiother. 62 , 83–87 (2016).
Ohgi, S. et al. Comparison of kangaroo care and standard care: behavioral organization, development, and temperament in healthy, low-birth-weight infants through 1 year. J. Perinatol. 22 , 374–379 (2002).
O′Higgins, M., St. James Roberts, I. & Glover, V. Postnatal depression and mother and infant outcomes after infant massage. J. Affect. Disord. 109 , 189–192 (2008).
Okan, F., Ozdil, A., Bulbul, A., Yapici, Z. & Nuhoglu, A. Analgesic effects of skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding in procedural pain in healthy term neonates. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 30 , 119–128 (2010).
Oliveira, D. S., Hachul, H., Goto, V., Tufik, S. & Bittencourt, L. R. A. Effect of therapeutic massage on insomnia and climacteric symptoms in postmenopausal women. Climacteric 15 , 21–29 (2012).
Olsson, E., Ahlsén, G. & Eriksson, M. Skin-to-skin contact reduces near-infrared spectroscopy pain responses in premature infants during blood sampling. Acta Paediatr. 105 , 376–380 (2016).
Pauk, J., Kuhn, C. M., Field, T. M. & Schanberg, S. M. Positive effects of tactile versus kinesthetic or vestibular stimulation on neuroendocrine and ODC activity in maternally-deprived rat pups. Life Sci. 39 , 2081–2087 (1986).
Pinazo, D., Arahuete, L. & Correas, N. Hugging as a buffer against distal fear of death. Calid. Vida Salud 13 , 11–20 (2020).
Pope, M. H. et al. A prospective randomized three-week trial of spinal manipulation, transcutaneous muscle stimulation, massage and corset in the treatment of subacute low back pain. Spine 19 , 2571–2577 (1994).
Preyde, M. Effectiveness of massage therapy for subacute low-back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 162 , 1815–1820 (2000).
Ramanathan, K., Paul, V. K., Deorari, A. K., Taneja, U. & George, G. Kangaroo mother care in very low birth weight infants. Indian J. Pediatr. 68 , 1019–1023 (2001).
Reddan, M. C., Young, H., Falkner, J., López-Solà, M. & Wager, T. D. Touch and social support influence interpersonal synchrony and pain. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 15 , 1064–1075 (2020).
Rodríguez-Mansilla, J. et al. The effects of ear acupressure, massage therapy and no therapy on symptoms of dementia: a randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 29 , 683–693 (2015).
Rose, S. A., Schmidt, K., Riese, M. L. & Bridger, W. H. Effects of prematurity and early intervention on responsivity to tactual stimuli: a comparison of preterm and full-term infants. Child Dev. 51 , 416–425 (1980).
Scafidi, F. A. et al. Massage stimulates growth in preterm infants: a replication. Infant Behav. Dev. 13 , 167–188 (1990).
Scafidi, F. A. et al. Effects of tactile/kinesthetic stimulation on the clinical course and sleep/wake behavior of preterm neonates. Infant Behav. Dev. 9 , 91–105 (1986).
Scafidi, F. & Field, T. Massage therapy improves behavior in neonates born to HIV-positive mothers. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 21 , 889–897 (1996).
Scarr-Salapatek, S. & Williams, M. L. A stimulation program for low birth weight infants. Am. J. Public Health 62 , 662–667 (1972).
Serrano, B., Baños, R. M. & Botella, C. Virtual reality and stimulation of touch and smell for inducing relaxation: a randomized controlled trial. Comput. Hum. Behav. 55 , 1–8 (2016).
Seyyedrasooli, A., Valizadeh, L., Hosseini, M. B., Asgari Jafarabadi, M. & Mohammadzad, M. Effect of vimala massage on physiological jaundice in infants: a randomized controlled trial. J. Caring Sci. 3 , 165–173 (2014).
Sharpe, P. A., Williams, H. G., Granner, M. L. & Hussey, J. R. A randomised study of the effects of massage therapy compared to guided relaxation on well-being and stress perception among older adults. Complement. Therap. Med. 15 , 157–163 (2007).
Sherman, K. J., Cherkin, D. C., Hawkes, R. J., Miglioretti, D. L. & Deyo, R. A. Randomized trial of therapeutic massage for chronic neck pain. Clin. J. Pain. 25 , 233–238 (2009).
Shiloh, S., Sorek, G. & Terkel, J. Reduction of state-anxiety by petting animals in a controlled laboratory experiment. Anxiety, Stress Coping 16 , 387–395 (2003).
Shor-Posner, G. et al. Impact of a massage therapy clinical trial on immune status in young Dominican children infected with HIV-1. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 12 , 511–516 (2006).
Simpson, E. A. et al. Social touch alters newborn monkey behavior. Infant Behav. Dev. 57 , 101368 (2019).
Smith, S. L., Haley, S., Slater, H. & Moyer-Mileur, L. J. Heart rate variability during caregiving and sleep after massage therapy in preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 89 , 525–529 (2013).
Smith, S. L. et al. The effect of massage on heart rate variability in preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 33 , 59–64 (2013).
Solkoff, N. & Matuszak, D. Tactile stimulation and behavioral development among low-birthweight infants. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 6 , 3337 (1975).
Srivastava, S., Gupta, A., Bhatnagar, A. & Dutta, S. Effect of very early skin to skin contact on success at breastfeeding and preventing early hypothermia in neonates. Indian J. Public Health 58 , 22–26 (2014).
Stringer, J., Swindell, R. & Dennis, M. Massage in patients undergoing intensive chemotherapy reduces serum cortisol and prolactin: massage in oncology patients reduces serum cortisol. Psycho-Oncol. 17 , 1024–1031 (2008).
Suman Rao, P. N., Udani, R. & Nanavati, R. Kangaroo mother care for low birth weight infants: a randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatr. 45 , 17–23 (2008).
Sumioka, H. et al. A huggable device can reduce the stress of calling an unfamiliar person on the phone for individuals with ASD. PLoS ONE 16 , e0254675 (2021).
Sumioka, H., Nakae, A., Kanai, R. & Ishiguro, H. Huggable communication medium decreases cortisol levels. Sci. Rep. 3 , 3034 (2013).
Suzuki, M. et al. Physical and psychological effects of 6-week tactile massage on elderly patients with severe dementia. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 25 , 680–686 (2010).
Thomson, L. J. M., Ander, E. E., Menon, U., Lanceley, A. & Chatterjee, H. J. Quantitative evidence for wellbeing benefits from a heritage-in-health intervention with hospital patients. Int. J. Art. Ther. 17 , 63–79 (2012).
Triplett, J. L. & Arneson, S. W. The use of verbal and tactile comfort to alleviate distress in young hospitalized children. Res. Nurs. Health 2 , 17–23 (1979).
Walach, H., Güthlin, C. & König, M. Efficacy of massage therapy in chronic pain: a pragmatic randomized trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 9 , 837–846 (2003).
Walker, S. C. et al. C‐low threshold mechanoafferent targeted dynamic touch modulates stress resilience in rats exposed to chronic mild stress. Eur. J. Neurosci. 55 , 2925–2938 (2022).
Weinrich, S. P. & Weinrich, M. C. The effect of massage on pain in cancer patients. Appl. Nurs. Res. 3 , 140–145 (1990).
Wheeden, A. et al. Massage effects on cocaine-exposed preterm neonates. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 14 , 318–322 (1993).
White, J. L. & Labarba, R. C. The effects of tactile and kinesthetic stimulation on neonatal development in the premature infant. Dev. Psychobiol. 9 , 569–577 (1976).
Wilkie, D. J. et al. Effects of massage on pain intensity, analgesics and quality of life in patients with cancer pain: a pilot study of a randomized clinical trial conducted within hospice care delivery. Hosp. J. 15 , 31–53 (2000).
Willemse, C. J. A. M., Toet, A. & van Erp, J. B. F. Affective and behavioral responses to robot-initiated social touch: toward understanding the opportunities and limitations of physical contact in human–robot interaction. Front. ICT 4 , 12 (2017).
Willemse, C. J. A. M. & van Erp, J. B. F. Social touch in human–robot interaction: robot-initiated touches can induce positive responses without extensive prior bonding. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 11 , 285–304 (2019).
Woods, D. L., Beck, C. & Sinha, K. The effect of therapeutic touch on behavioral symptoms and cortisol in persons with dementia. Res. Complement. Med. 16 , 181–189 (2009).
Yamaguchi, M., Sekine, T. & Shetty, V. A salivary cytokine panel discriminates moods states following a touch massage intervention. Int. J. Affect. Eng. 19 , 189–198 (2020).
Yamazaki, R. et al. Intimacy in phone conversations: anxiety reduction for Danish seniors with hugvie. Front. Psychol. 7 , 537 (2016).
Yang, M.-H. et al. Comparison of the efficacy of aroma-acupressure and aromatherapy for the treatment of dementia-associated agitation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 15 , 93 (2015).
Yates, C. C. et al. The effects of massage therapy to induce sleep in infants born preterm. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 26 , 405–410 (2014).
Yu, H. et al. Social touch-like tactile stimulation activates a tachykinin 1-oxytocin pathway to promote social interactions. Neuron 110 , 1051–1067 (2022).
Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: a practical primer for t -tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 4 , 863 (2013).
Page, M. J., et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4 (2021).
Wilson, D. B. Practical meta-analysis effect size calculator (Version 2023.11.27). https://campbellcollaboration.org/research-resources/effect-size-calculator.html (2023).
Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v036.i03 (2010).
Scammacca, N., Roberts, G. & Stuebing, K. K. Meta-analysis with complex research designs: dealing with dependence from multiple measures and multiple group comparisons. Rev. Educ. Res. 84 , 328–364 (2014).
Pustejovsky, J. E. & Tipton, E. Meta-analysis with robust variance estimation: expanding the range of working models. Prev. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Prev. Res. 23 , 425–438 (2022).
Cook, R. D. in International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science (ed. M. Lovric) S. 301–302 (Springer, 2011).
Higgins, J. P. T., Thompson, S. & Deeks, J. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557 (2003).
Oberauer, K. The importance of random slopes in mixed models for Bayesian hypothesis testing. Psychol. Sci. 33 , 648–665 (2022).
Nakagawa, S. et al. The orchard plot: cultivating a forest plot for use in ecology, evolution, and beyond. Res. Synth. Methods 12 , 4–12 (2021).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Frick and E. Chris for supporting the initial literature search and coding. We also thank A. Dreisoerner, T. Field, S. Koole, C. Kuhn, M. Henricson, L. Frey Law, J. Fraser, M. Cumella Reddan, and J. Stringer, who kindly responded to our data requests and provided additional information or data with respect to single studies. J.P. was supported by the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (LPDS 2021-05). H.H. was supported by the Marietta-Blau scholarship of the Austrian Agency for Education and Internationalisation (OeAD) and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation, project ID 422744262 – TRR 289). C.K. received funding from OCENW.XL21.XL21.069 and V.G. from the European Research Council (ERC) under European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme, grant ‘HelpUS’ (758703) and from the Dutch Research Council (NWO) grant OCENW.XL21.XL21.069. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Open access funding provided by Ruhr-Universität Bochum.
Author information
Julian Packheiser
Present address: Social Neuroscience, Faculty of Medicine, Ruhr University Bochum, Bochum, Germany
These authors contributed equally: Julian Packheiser, Helena Hartmann.
Authors and Affiliations
Social Brain Lab, Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, Royal Netherlands Academy of Art and Sciences, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
Julian Packheiser, Helena Hartmann, Kelly Fredriksen, Valeria Gazzola, Christian Keysers & Frédéric Michon
Center for Translational and Behavioral Neuroscience, University Hospital Essen, Essen, Germany
Helena Hartmann
Clinical Neurosciences, Department for Neurology, University Hospital Essen, Essen, Germany
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
J.P. contributed to conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing the original draft, review and editing, visualization, supervision and project administration. HH contributed to conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing the original draft, review and editing, visualization, supervision and project administration. K.F. contributed to investigation, data curation, and review and editing. C.K. and V.G. contributed to conceptualization, and review and editing. F.M. contributed to conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing the original draft, and review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Julian Packheiser .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Human Behaviour thanks Ville Harjunen, Rebecca Boehme and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Supplementary Figs. 1–21 and Tables 1–4.
Reporting Summary
Peer review file, supplementary table 1.
List of studies included in and excluded from the meta-analyses/review.
Supplementary Table 2
PRISMA checklist, manuscript.
Supplementary Table 3
PRISMA checklist, abstract.
Source Data Fig. 2
Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) information for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 3 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (column ‘Outcome’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 4 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (columns ‘dyad_type’ and ‘skin_to_skin’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 5 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (column ‘touch_type’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 6 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (column ‘clin_sample’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 7 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (column ‘familiarity’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 7 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (columns ‘touch_duration’ and ‘sessions’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Packheiser, J., Hartmann, H., Fredriksen, K. et al. A systematic review and multivariate meta-analysis of the physical and mental health benefits of touch interventions. Nat Hum Behav (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-024-01841-8
Download citation
Received : 16 August 2023
Accepted : 29 January 2024
Published : 08 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-024-01841-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, analyzing the relationship between consumers’ and entrepreneurs’ food waste and sustainable development using a bibliometric approach.

- 1 Department of Economics and Sustainable Development, School of Environment, Geography and Applied Economics, Harokopio University of Athens, Kallithea, Greece
- 2 Department of Public and Community Health, University of West Attica, Athens, Greece
The present study investigates the relationship between food waste and sustainable development, aiming to reveal contextual insights and present novel findings regarding the pivotal importance of waste and environmental strategies toward a circular economy. This research represents an effort to delineate methodological and thematic contributions, thoroughly analyze key themes, examine co-citation patterns, assess collaboration among countries, and identify current knowledge gaps in the literature. As waste management takes precedence within the framework of sustainable development goals, policymakers, and academia will better understand how effective food waste management can contribute to environmental sustainability. Methodologically, we employ systematic review, employing the PRISMA approach, analyzing 761 final papers, and investigating the relationship between food waste and sustainable development. We delve deeper to reveal contextual insights and present empirical findings that underscore the critical role of food waste in the economy and environment. Furthermore, guided by the identified knowledge gaps, we illuminate potential future research avenues that hold immense promise for advancing our understanding of food waste and its impact on sustainable development.
1 Introduction
Sustainable Development Goals centered on food security, environmental preservation, and optimizing material and energy usage are significant motivators for effectively managing the overuse of food waste ( Kaur et al., 2021 ). Food waste is a pressing global issue that squanders valuable resources and exacerbates challenges related to food security, environmental sustainability, and economic efficiency. Food waste, as defined by the Waste and Resources Action Programme, 1 “ is any food and inedible parts sent to a specified list of food waste destinations, where “food” is defined as any substance that was at some point intended for human consumption.”
A critical issue facing our global food system is the enormous amounts of food wasted yearly, leaving millions hungry. In order to resolve this contradiction, it is essential to comprehend the complex relationship between food waste and consumption patterns. This comprehensive investigation explores the different ways that consuming habits, from meal preparation and disposal to planning and purchasing, contribute to the creation of food waste. By looking at these relationships, we hope to pinpoint important intervention areas and create plans to encourage ethical and sustainable food consumption habits, ultimately reducing waste and guaranteeing everyone fair access to wholesome food. Approximately one-third of the food produced for human consumption goes to waste ( Schanes et al., 2018 ). This phenomenon leads to several environmental issues, such as soil erosion, deforestation, water and air pollution, and the release of greenhouse gases during various stages of food production ( Mourad, 2016 ). Thus, most developed countries have witnessed growing awareness and concern regarding the magnitude of food waste within their borders in recent years. Understanding food waste’s intricate parameters and dynamics becomes paramount as we strive to become more environmentally conscious and sustainable.
The current study broadly examines the available literature and discusses the interdisciplinary nature of food waste and its role in sustainable development ( Buczacki et al., 2021 ). Our investigation seeks to unravel the main findings of the current research on sustainable development and SDGs. In doing so, we aim to shed light on the extent of the problem, the societal, economic, and environmental repercussions, and the potential strategies and interventions that can be adopted to mitigate food waste. The world, characterized by its cultural diversity, varying consumption patterns, and dynamic economies, presents a unique and complex landscape for studying food waste. Our investigation extends academic discussion on the association between food waste and sustainability.
More specifically, this study highlights the countries, the authors, and the sources that decidedly investigate the relationship between food waste and sustainable development. By analyzing the successes and challenges faced in the region, we aim to provide valuable insights that can underline possible scientific gaps, inform policy development, and encourage cross-border collaboration in the fight against food waste. In conclusion, this research contributes to the growing knowledge surrounding food waste. By examining the shape of food waste dynamics, we hope to provide food of thought for a foundation for evidence-based policies and practices to minimize food waste’s detrimental impact on society, the environment, and the economy. Pursuing a more sustainable and food-secure future for Europe necessitates a deeper understanding of food waste, making this study an essential step toward that goal.
In sum, the main contribution of this systematic literature review is twofold. Firstly, it serves as a tool for pinpointing areas where scholarly evidence remains insufficient, highlighting the need for further research to expand our understanding of food waste behavior. Secondly, it establishes a knowledge repository that can offer valuable insights for evidence-based decision-making and policy formulation. This, in turn, can enhance the quality and efficacy of policy measures and technological innovations to reduce food waste. However, several objectives and research questions should be addressed and responded to achieve these goals. The main objectives are as follows:
• To investigate the relationship between food waste and sustainable development through a bibliometric analysis.
• To identify key themes, trends, and knowledge gaps in the existing research on food waste and its connection to sustainability within the framework of a circular economy and
• To provide valuable insights for policymakers, academics, and stakeholders working toward reducing food waste and achieving sustainable development goals.
After that, the research questions that are necessary to be addressed and be able to achieve the objectives of the current research are as follows:
• RQ1: What are the dominant themes and research trends in the literature on food waste and sustainable development within a circular economy framework, as revealed by a bibliometric analysis?
• RQ2: What key methodological approaches are employed in the existing research on food waste and sustainable development?
• RQ3: What are the prominent countries, institutions, and authors contributing to the field, and how do they collaborate on research related to food waste and sustainable development?
• RQ4: What are the critical knowledge gaps and potential future research avenues identified in the current body of literature on food waste and sustainable development?
By addressing these research questions, this study aims to offer a comprehensive and data-driven understanding of the current knowledge surrounding food waste and its connection to achieving sustainable development within a circular economy. This understanding can inform future research efforts and guide the development of effective strategies to address this pressing global challenge.
The remaining components are organized as follows: Section 2 summarizes the research methodology and data selection. Section 3 delves into the empirical findings, exploring their connections to the article’s conceptual, intellectual, and social framework. Section 4 presents the conclusion and implications for policy.
2 Scheme of the research and empirical methodology
2.1 bibliometric data.
The bibliometrics approach assesses information trends to emphasize the contributions of both individuals and research groups. We also utilize review processes to synthesize content and generate innovative policy recommendations concerning the relationship between food waste and sustainable development. For the subsequent procedures, we exclusively rely on the Scopus database, which is recognized as one of the most reliable and comprehensive sources. We used “ food waste ” and “ sustainable development ” to pinpoint publications. After that, we eliminated non-relevant publications to exclude irrelevant studies ( Shahbaz et al., 2021 ) following the PRISMA methodology ( Page et al., 2021 ).
In particular, a comprehensive search string in Scopus combined relevant keywords related to food waste and sustainable development. The exclusion criteria were as follows: duplicates were removed, non-English language articles were excluded, and conference materials, editorials, and letters to maintain focus on in-depth research were also removed. Following data extraction using a standardized form, we employed a multifaceted approach. Bibliometric software like VOSviewer and bibliometrix facilitated co-citation analysis, keyword clustering, and citation network visualization are also employed. Additionally, text analysis techniques complemented our understanding of key themes and emerging trends within the selected publications. This process narrows our selection to a final set of 761 studies from 214 sources for further examination.
A compilation of 1,480 research publications published between 2003 and 2023 is the outcome of our first search. We chose this time frame with significant consideration for the reasons listed below. First, we want to highlight some recent developments. There has been much advancement in food waste and its relationship to sustainable development in recent years. With an emphasis on studies released after 2003, we sought to encompass the most recent findings and patterns in this quickly developing subject. Second, it is critical to comprehend the most recent research findings and their implications for current policy and practice as the urgency of tackling food waste and reaching sustainable development goals increases.
2.2 Bibliometric analysis
Researchers can use quantitative and qualitative methodologies to identify gaps in the scientific literature by using the bibliometrics methodology to track trends in academic research ( Siddiqui et al., 2023 ). We have used bibliometric tools like VOSviewer, the R-package, and Biblioshiny to analyze publications about food waste ( Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017 ). The VOSviewer is a tool that uses a two-dimensional map to show the relationships between co-citation data, geographic locations, research journals, and keywords. Their proximity shows the degree of link or similarity between nodes in this visualization. More specifically, this software is excellent at producing two-dimensional maps showing the connections between various items in a dataset. The most popular keywords and how they gathered together are shown in the visualization, which sheds light on the recurring themes in food waste. In addition, VOSviewer assists us in recognizing significant research and schools of thinking that have shaped our current comprehension of food waste and its relationship to sustainability.
On the other hand, R-package and Biblioshiny utilize a diverse set of bibliometric tools that serve as visualization functions for conducting information analysis and generating scientific maps related to the intersection of food waste and sustainability ( da Silva Duarte et al., 2021 ; Srinivas, 2022 ). The package facilitates efficient data processing and transformation, ensuring the accuracy and consistency of the analysis. Biblioshiny provides advanced functions for constructing and analyzing bibliographic networks, allowing us to explore the intricate relationships between different entities within the food waste literature.
3 Empirical results
3.1 publication output and citation growth.
Figure 1 presents a per annum publication and citation growth trend since 2003, with an average of 75.6 citations per document. Notably, interdisciplinary research on food waste has received significant attention recently ( Dhir et al., 2020 ). There has been an exponential increase in publications in recent years, with 2023 having the highest number of publications (146 articles).
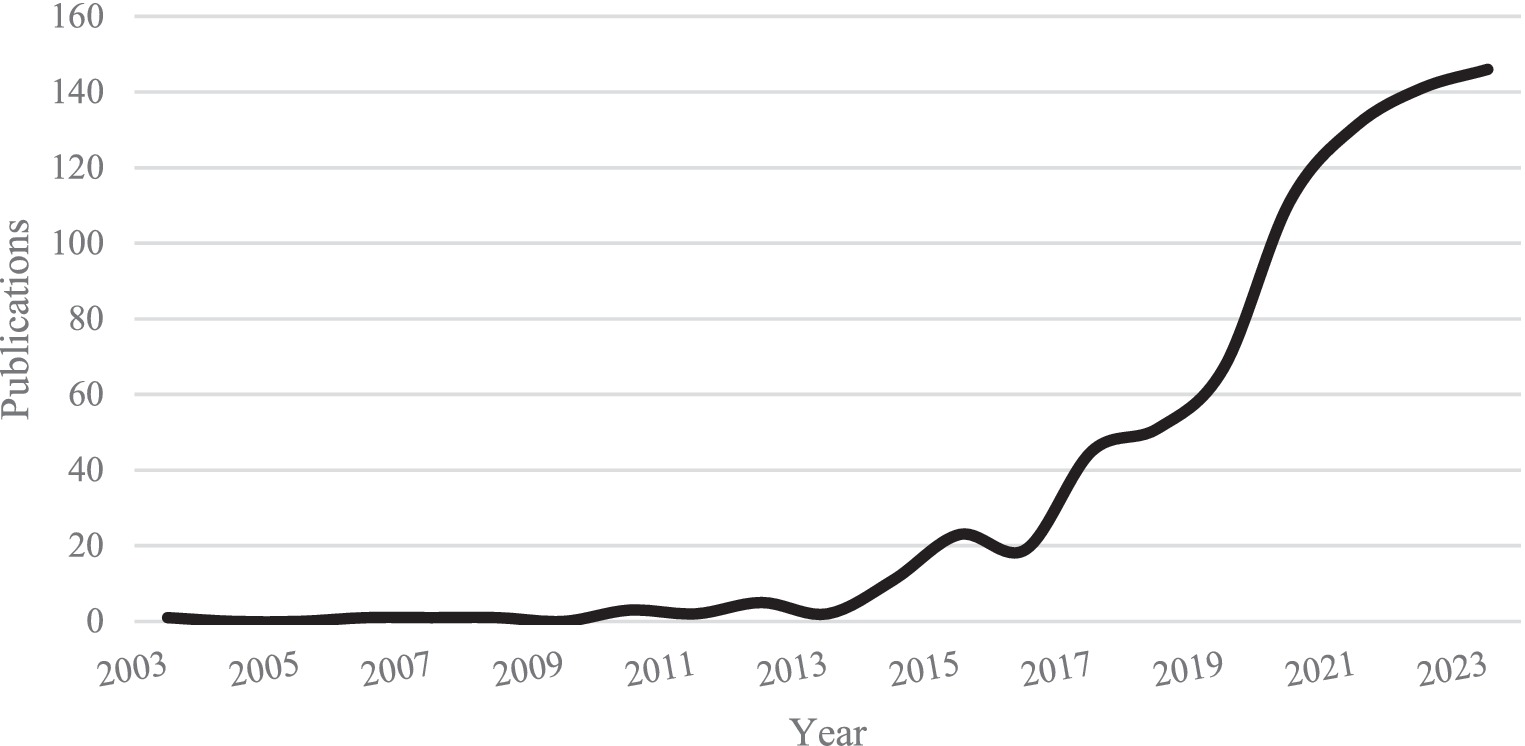
Figure 1 . Publication output.
Document-citation analysis was also performed using the “document” unit from the downloaded publications to create a table based on citation data by selecting the first ten documents as a threshold. For each of the ten documents, the number of citations and doi number are presented in the following Table 1 . For brevity, most citations reported by Papargyropoulou et al. (2014) (910 citations) have investigated the factors that increase food waste through several channels of the food supply chain and propose a framework for appropriately managing food waste. Guo et al. (2010) (636 citations) focused their interest on agricultural production and the degradation of the natural environment due to the energy crisis. Authors propose hydrogen as one of the most promising substitutes for fossil fuels. After that, a group of authors with around 300 citations consists of Notarnicola et al. (2017) , who has a total of 383 citations; Williams et al. (2012) , with 360 citations, and Xue et al. (2017) , who has 359 citations. Next, Alexander et al. (2017) , Mourad, Garrone et al. (2014) , Sharma P. et al. (2020) , and Sharma S. et al. (2020) papers have more than 200 citations, but less than 300 completed the first ten high-cited documents.
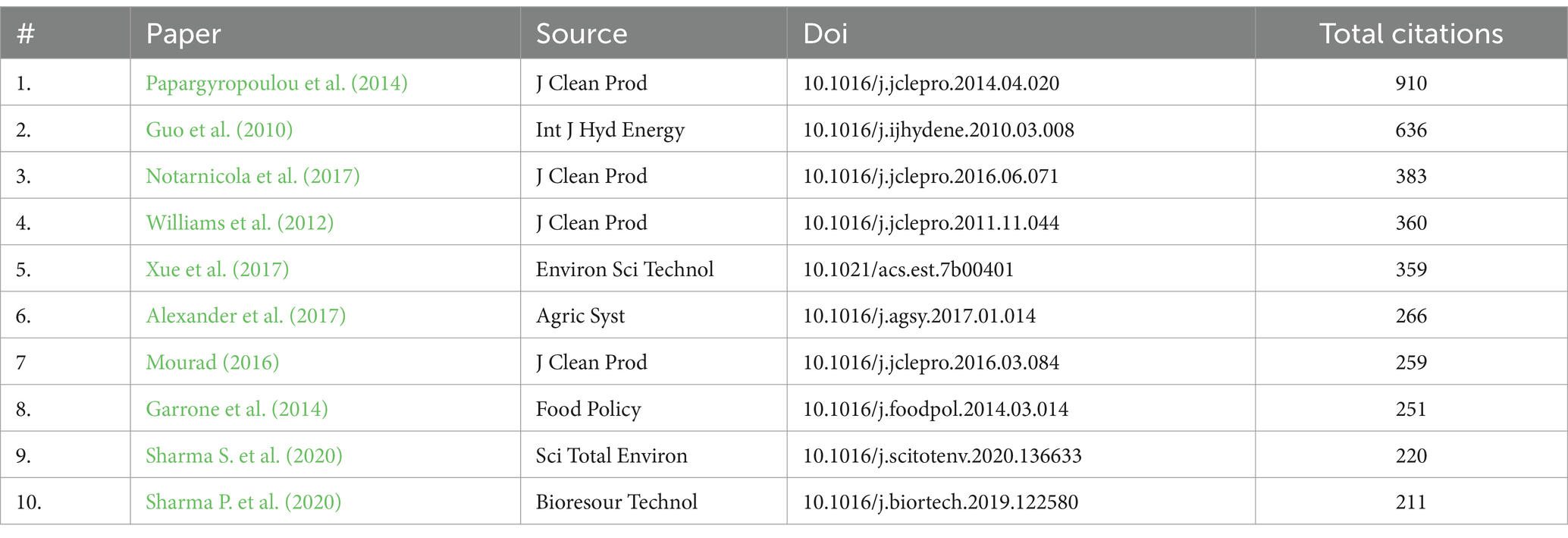
Table 1 . Top 10 most cited documents.
3.2 Countries’ collaboration networks
Next, Figures 2 , 3 visually represent global research collaboration among countries, displaying the collaboration network and the volume of publications contributed by each country.
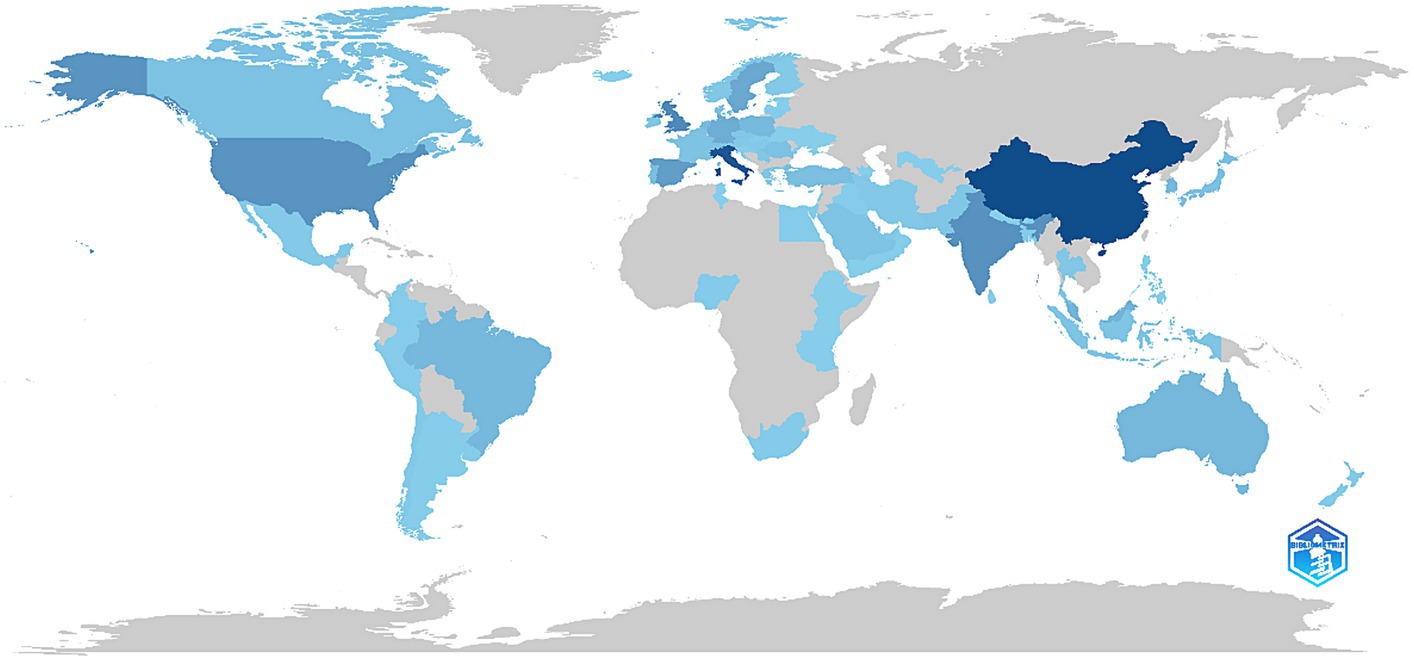
Figure 2 . Country scientific production.
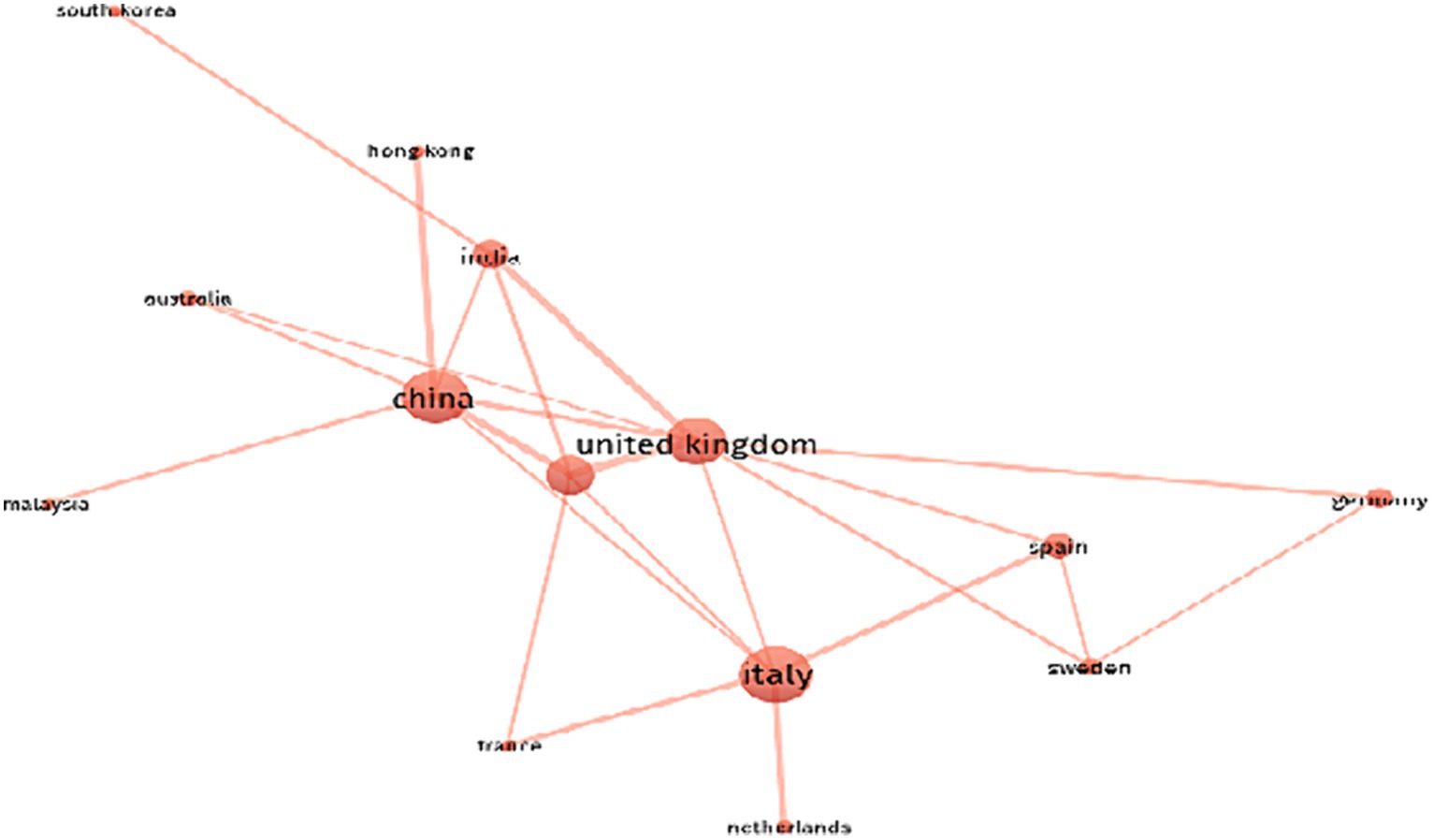
Figure 3 . Countries’ collaboration network.
In Figure 2 , the research output is presented with varying shades of color, wherein the darker colors represent the regions with the highest frequency of publications. Notably, China is the global leader in research publications, with an impressive count of 481, showcasing its substantial contribution to the academic landscape. Following closely behind are other key players in the research arena, with Italy contributing 442 publications, the United Kingdom with 246, India with 215, and the United States with 208, all demonstrating their significant presence in the global research community. Additionally, several other highly productive economies, such as Spain, Sweden, Germany, Malaysia, and Australia, are notable contributors, further enriching the global research output landscape.
Moving on to Figure 3 , it describes the collaborative aspect of research on a global scale, shedding light on the interconnections and partnerships between various countries in the pursuit of knowledge and academic advancement.
A compelling pattern emerges when examining collaborations between authors and countries in food waste. Notably, China, Italy, and the United Kingdom substantially collaborate. This outcome highlights their proactive stance in fostering international partnerships to tackle food waste and sustainability nexus. Following closely behind are the United States and Spain, both of which also participate actively in collaborative initiatives. These findings underscore the global significance of addressing food waste and the willingness of these nations to join forces in addressing this critical challenge.
3.3 Keywords, authors, and key countries framework
The upcoming section aims to reveal how researchers have documented various research streams across different countries. To achieve this, we employ the CAK framework to introduce innovative visualizations that portray the amalgamation of authors, research themes, and countries.
It is evident from Figure 4 that Italy, China, and the UK are the most prominent geographical locations. Likewise, the most dominant research themes are food waste, sustainable development, waste management, and waste disposal. It is worth noting that the smaller size of countries with limited contributions suggests that the current state of research is in its early stages. Additional research, mainly from European economies with substantial food demands, should shed light on recent research developments and explore new avenues of inquiry.
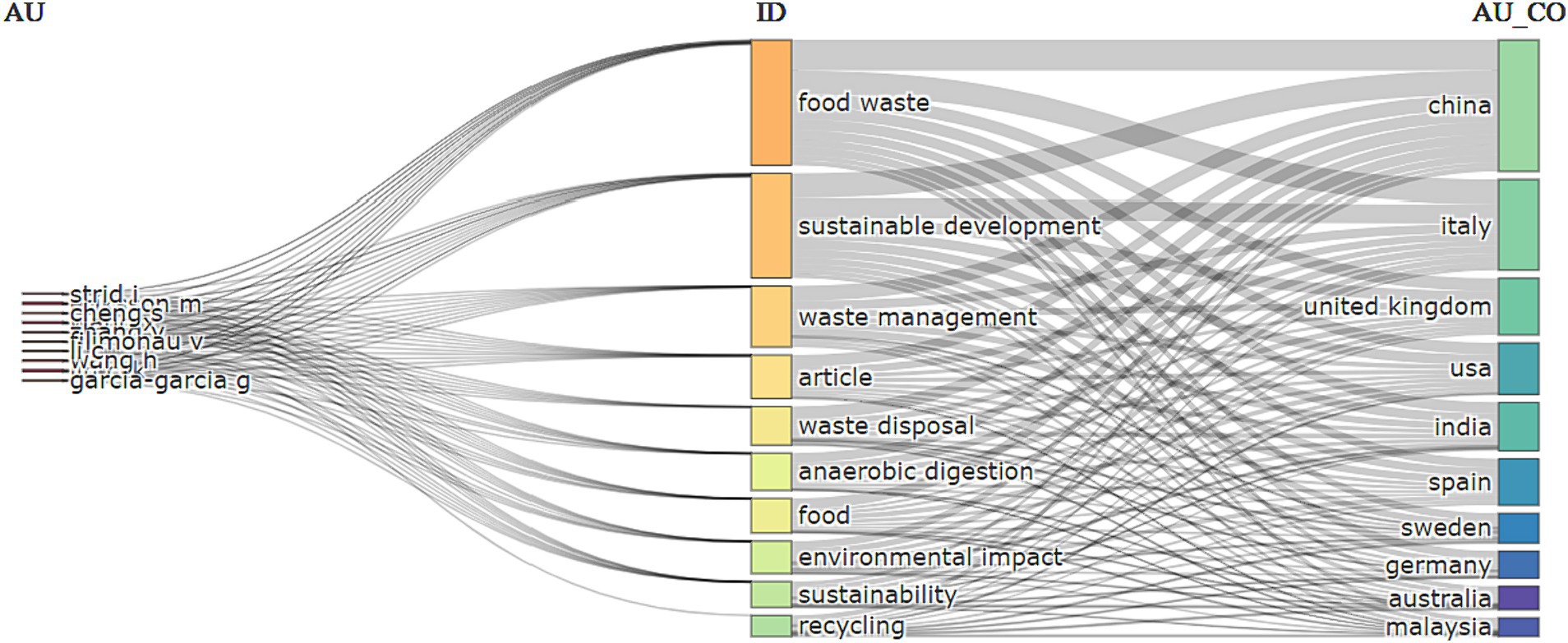
Figure 4 . CAK framework. Authors, keywords, countries.
Figure 5 , depicted as a tree diagram, visually represents the keywords extensively employed in the array of previously studied records. A closer examination of the results illuminates the prominent themes authors have chosen to emphasize in their works.
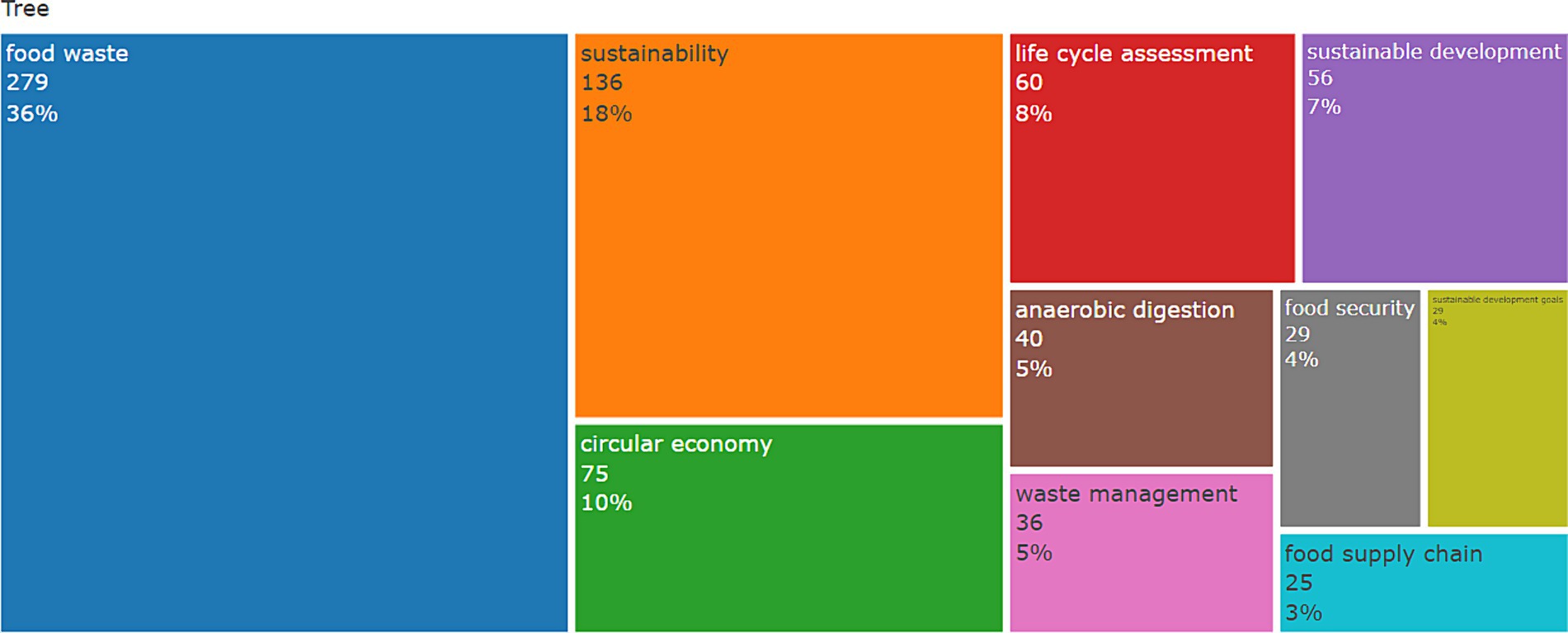
Figure 5 . Keywords tree-map.
Notably, “food waste” takes the lead, featuring in approximately 36% of the articles. This underscores the paramount significance of addressing food waste within the scope of the research, signifying its pervasive relevance in current academic discourse. Sustainability is another crucial focus in 18% of the articles, highlighting the shared commitment to promoting sustainable practices and environmental responsibility within food waste management. Furthermore, the concept of a “circular economy” garners notable attention, being employed as a keyword in 10% of the publications, reflecting the growing interest in developing circular and resource-efficient systems to combat food waste. The utilization of “life cycle assessment” as a keyword in 8% of the articles underscores the methodological approach many authors took, emphasizing the importance of assessing environmental impacts across the entire life cycle of food products. Finally, the notion of “sustainable development” is reflected in 7% of the works, signifying the broader context in which food waste mitigation is situated, emphasizing the pursuit of development that satisfies current requirements without jeopardizing those of coming generations. This breakdown of prevalent keywords offers valuable insights into the thematic and methodological orientations of the scholarly discourse surrounding food waste. It underscores the critical areas of focus within this research domain.
3.4 Co-citation analysis of authors – intellectual structure
Afterward, we utilize co-citation analysis to understand better how literature has evolved in recent decades. The extent to which studies reference one another indicates the interrelatedness within the scientific literature. Co-citation analysis is a constantly changing metric that aids in recognizing emerging paradigms within a selected body of academic literature ( Buczacki et al., 2021 ). In our present study, we refer to Figure 6 (co-citation analysis), where the number of citations is represented, and the relatedness of topics is indicated by the distance between these nodes, shedding light on academic discourse. The visualization in Figure 6 reveals two distinct clusters.
Figure 6 . Co-citations analysis of authors.
The first group of publications delves into the importance of food waste as a critical element in developing a sustainable food system ( Quested et al., 2011 ). They also attempt to identify the losses occurring along the entire food chain and identify the causes of food losses and possible ways of preventing them ( Quested et al., 2011 ; Falasconi et al., 2015 ; Eriksson et al., 2020 ). Conversely, a second cluster examines food issues in a more global scale analysis linked to sustainable development goals ( Liu et al., 2022 ) introducing, for instance, the effects of international food trade on the food system ( Wang et al., 2022 ). Smaller groups use a more quantitative analysis highlighting possible environmental and socio-economic impacts of food waste ( Albizzati et al., 2021 ) and policies at a micro level ( Lassen et al., 2019 ).
3.5 Conceptual structure of the publications
Recently, keyword co-occurrence networks have become increasingly popular in systematic review-based studies, offering a means to harness knowledge mapping and uncover associations among research themes in research management ( Bashir et al., 2021 ). This approach empowers researchers to comprehensively understand a specific field within the amassed knowledge, harnessing the associations between keywords to reveal insights in economic literature. In our current research, we utilize a keyword co-occurrence network approach, setting a threshold of at least five occurrences for a word to be included. Consequently, out of a total of 1,136 keywords, 113 satisfied this requirement (see Figures 7 , 8 ).
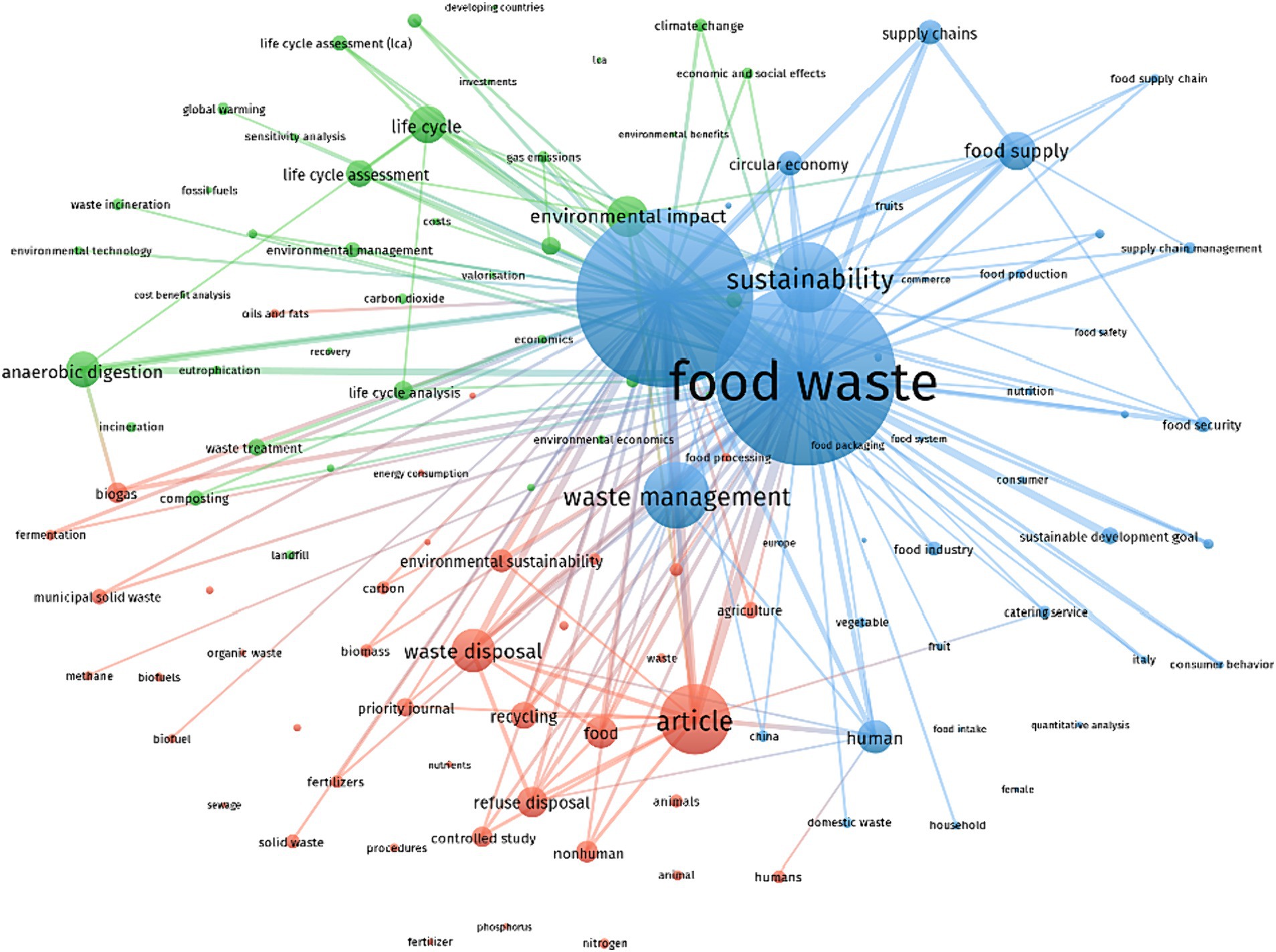
Figure 7 . Keywords co-occurrence network.
Figure 8 . Keywords co-occurrence network.
Notably, keywords like “food waste,” “sustainability,” “waste management,” “environmental impact,” and “waste disposable” are the most frequently occurring. Furthermore, as depicted in Figure 7 , three separate groups of keywords are evident (green, red, and blue). Looking at the blue cluster, the keywords “sustainability,” “food supply,” “food security,” “nutrition” and “supply chain” exhibit close associations. As far as the red cluster is concerned, the keywords “article,” “waste disposal,” “fertilizer,” “biogas,” and “nitrogen” indicate a group of research that investigates the concept of food waste from a different perspective. An interesting observation is that keywords (green cluster) such as “life cycle assessment,” “gas emissions,” “anaerobic digestion,” “municipal waste,” and “climate change” have small node sizes but remain interconnected in terms of links.
After that, we expanded the keywords’ co-occurrence network by exploring its time evolution. The connection between food waste and sustainability is relatively recent, with most publications emerging after 2019. Even more recently, authors have also incorporated into their analysis the “circular economy,” “sustainable development goals,” “waste management,” and “food supply.” These keywords provide more information on the trend already in process around the relationship between food waste management and sustainability in the future. A notable trend is observed, with most publications centered around food waste, sustainability, environmental impact assessment, food supply, and climate change.
We further employ Figure 9 to explore thematic mapping from the perspective of four distinct subdivisions, which aids in comprehending the diversity and significance of sub-components within the scientific literature ( Buczacki et al., 2021 ). We have established the maximum number of keywords at 119 and the minimum cluster frequency at 3.
Figure 9 . Thematic map.
The upper right section encompasses “motor themes,” representing research topics with the highest density and centrality, such as “food waste,” “sustainability,” “circular economy,” “life cycle assessment,” and “waste management.” In the lower-right quadrant, we find “food security” characterized by low density, discussing topics like “recycling,” “climate change,” “food waste management,” and “food supply chain.” These transversal themes hold significant importance in the research, contributing to discussions on various research directions. Lastly, “declining or emerging themes” and “niche themes” encompass research topics related to “household food waste” and “co-digestion.” In summary, Figure 9 serves as a valuable tool for understanding the current academic discourse and the potential role of food waste in future waste management policies.
4 Discussion
The present work aims to offer researchers and policymakers a toolbox of organized ideas to tackle food waste. Simultaneously, to achieve the objectives outlined in the Sustainable Development Goals, the target of reducing food waste and adopting a comprehensive strategy incorporating various measures is domineering. These efforts rectify informational gaps already highlighted by previous systematic literature review works ( Schanes et al., 2018 ).
Besides, similar to previous studies ( Principato et al., 2021 ) our research sheds light on the complex sides of the food waste phenomenon, highlighting the trend of research on this topic ( Zhang et al., 2018 ; Vásquez Neyra et al., 2022 ; D'Adamo et al., 2023 ). More specifically, our study provides an essential segment of information presenting the issues around food waste that are denoted as the motor themes with a critical role of food waste in future food waste management and policies, such as the concept of circular economy ( de Oliveira et al., 2021 ; Nikolaou and Tsagarakis, 2021 ; Santagata et al., 2021 ). In this direction, the European Food Safety Authority (2020) highlights that circular economy initiatives are increasing attention to food waste as a food and feed source.
Furthermore, our review, concentrating on strategies to reduce food waste and promote sustainability, dovetails with the Green Deal’s priorities, such as resource efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable consumption. By positioning the study within the broader context of global sustainability challenges, it becomes evident that addressing food waste is integral to achieving the Green Deal’s ambitious targets. In this direction, according to FAO (2021) one of the ways toward more sustainable agriculture and food production is to manage food production systems sustainably through significant reductions in food loss and waste.
5 Concluding remarks and policy implications
The central objective of our research is to investigate the relationship between food waste and sustainability through a review of academic literature. Our study thoroughly examines all pertinent publications on the nexus between food waste and sustainable development. Given the pivotal role of food waste in the context of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), it becomes crucial for policymaking institutions to evaluate socio-economic and policy variables.
This evaluation is essential for harmonizing food consumption and environmental sustainability via several policy implications. For instance, policymakers should prioritize integrating food waste reduction strategies into the broader framework of SDGs. This approach ensures a more holistic and sustainable approach to addressing food waste while advancing the global sustainability agenda. Also, at a microeconomic level, governments must focus on socio-economic and policy factors that directly influence food waste. By designing policies that incentivize food waste reduction at the individual, household, and industrial levels, they can contribute to achieving both economic and environmental goals. On a more global-scale and macroeconomic level, collaboration among countries, mainly focusing on emerging economies, is essential to address the multifaceted challenges posed by food waste. Policymakers should explore international partnerships to facilitate knowledge sharing, best practices, and innovative strategies in mitigating food waste.
In a more specific and focused aspect, our analysis identifies key themes and research areas related to food waste and sustainability. European and national policy measures should emphasize the need to integrate specific food waste reduction strategies into national SDG goals such as Goal 2 (zero hunger) and Goal 12 (responsible consumption and production). Moreover, governments and policymakers can identify specific socio-economic and policy factors that significantly influence food waste at individual, household, and industrial levels. These policy interventions could include consumer awareness campaigns, incentivizing food waste reduction within entrepreneurs, exploring policies like tax breaks for businesses implementing waste reduction strategies, or introducing waste disposal fees based on waste generation. Financially, the public sector could also encourage policies that facilitate the redistribution of surplus food to those in need, reducing waste and promoting social welfare. That can be done by promoting the establishment of international funding mechanisms to support emerging economies in implementing effective food waste reduction strategies.
However, it is noteworthy that conducting country-specific analyses can offer valuable insights and potentially address limitations associated with quantitative data and analysis. Understanding the specific dynamics of food waste in different nations is crucial for tailoring effective policies and interventions. In addition, we urge future research to delve into the role of addressing food waste issues, particularly in emerging economies. Such research endeavors have the potential to yield diverse policy insights. By examining the unique challenges and opportunities food waste presents in these regions, policymakers can better understand the evolving issues in developing and developed nations. This knowledge is invaluable for shaping effective strategies to reduce food waste and promote sustainable practices worldwide.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
IK: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SP: Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GM: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. ^ https://wrap.org.uk/
Albizzati, P. F., Tonini, D., and Astrup, T. F. (2021). High-value products from food waste: an environmental and socio-economic assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 755:142466. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142466
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Alexander, P., Brown, C., Arneth, A., Finnigan, J., Moran, D., and Rounsevell, M. D. (2017). Losses, inefficiencies and waste in the global food system. Agric. Syst. 153, 190–200. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2017.01.014
Aria, M., and Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics , 11, 959–975. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Bashir, M. F., Ma, B., Qin, Y., and Bashir, M. A. (2021). Evaluation of one belt one road publications: a bibliometric and literature review analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 37016–37030. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14621-y
Buczacki, A., Gładysz, B., and Palmer, E. (2021). HoReCa food waste and sustainable development goals—a systemic view. Sustain. For. 13:5510. doi: 10.3390/su13105510
D'Adamo, I., Desideri, S., Gastaldi, M., and Tsagarakis, K. P. (2023). Sustainable food waste management in supermarkets. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 43, 204–216. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2023.11.005
de Oliveira, M. M., Lago, A., and Dal’Magro, G. P. (2021). Food loss and waste in the context of the circular economy: a systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 294:126284. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126284
da Silva Duarte, K. S., Lima, T. A. C., Alves, L. R., Rios, P. A. P., and Motta, W. H. (2021). The circular economy approach for reducing food waste: a systematic review. Revista Produção e desenvolvimento 7. doi: 10.32358/rpd.2021.v7.572
Dhir, A., Talwar, S., Kaur, P., and Malibari, A. (2020). Food waste in hospitality and food services: A systematic literature review and framework development approach. Journal of Cleaner Production , 270, 122861. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122861
Eriksson, M., Malefors, C., Bergström, P., Eriksson, E., and Persson Osowski, C. (2020). Quantities and quantification methodologies of food waste in Swedish hospitals. Sustain. For. 12:3116. doi: 10.3390/su12083116
European Food Safety AuthorityMaggiore, A., Afonso, A., Barrucci, F., and Sanctis, G. D. (2020). Climate change as a driver of emerging risks for food and feed safety, plant, animal health and nutritional quality. EFSA Support. Publ. 17:1881E. doi: 10.2903/sp.efsa.2020.EN-1881
Falasconi, L., Vittuari, M., Politano, A., and Segrè, A. (2015). Food waste in school catering: an Italian case study. Sustain. For. 7, 14745–14760. doi: 10.3390/su71114745
FAO. (2021) In Brief to The State of Food and Agriculture “ Making agrifood systems more resilient to shocks and stresses .” Rome, FAO.
Google Scholar
Garrone, P., Melacini, M., and Perego, A. (2014). Opening the black box of food waste reduction. Food Policy 46, 129–139. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2014.03.014
Guo, X. M., Trably, E., Latrille, E., Carrère, H., and Steyer, J. (2010). Hydrogen production from agricultural waste by dark fermentation: a review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 35, 10660–10673. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.03.008
Kaur, G., Lasaridi, K., and Wong, J. (2021). “Sustainable food waste management: an introduction” in Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering (Elsevier), 1–10.
Lassen, A. D., Christensen, L. M., Spooner, M. P., and Trolle, E. (2019). Characteristics of canteens at elementary schools, upper secondary schools and workplaces that comply with food service guidelines and have a greater focus on food waste. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16:1115. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16071115
Liu, Y., Tan, Q., Chen, J., Pan, T., Penuelas, J., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). Dietary transition determining the tradeoff between global food security and sustainable development goals varied in regions. Earth's Future 10:e2021EF002354 doi: 10.1029/2021EF002354
Mourad, M. (2016). Recycling, recovering and preventing “food waste”: competing solutions for food systems sustainability in the United States and France. J. Clean. Prod. 126, 461–477. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.03.084
Nikolaou, I. E., and Tsagarakis, K. P. (2021). An introduction to circular economy and sustainability: some existing lessons and future directions. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 28, 600–609. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2021.06.017
Notarnicola, B., Sala, S., Anton, A., McLaren, S. J., Saouter, E., and Sonesson, U. (2017). The role of life cycle assessment in supporting sustainable Agri-food systems: a review of the challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 140, 399–409. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.071
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology , 134, 178–89. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33789819
Papargyropoulou, E., Lozano, R., Steinberger, J. K., Wright, N., and bin Ujang, Z. (2014). The food waste hierarchy as a framework for the management of food surplus and food waste. J. Clean. Prod. 76, 106–115. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.04.020
Principato, L., Mattia, G., Di Leo, A., and Pratesi, C. A. (2021). The household wasteful behaviour framework: a systematic review of consumer food waste. Ind. Mark. Manag. 93, 641–649. doi: 10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.07.010
Quested, T. E., Parry, A. D., Easteal, S., and Swannell, R. (2011). Food and drink waste from households in the UK , vol. 36, 460–467.
Santagata, R., Ripa, M., Genovese, A., and Ulgiati, S. (2021). Food waste recovery pathways: challenges and opportunities for an emerging bio-based circular economy. A systematic review and an assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 286:125490 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125490
Schanes, K., Dobernig, K., and Gözet, B. (2018). Food waste matters-a systematic review of household food waste practices and their policy implications. J. Clean. Prod. 182, 978–991. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.030
Siddiqui, A., Altekar, S., Kautish, P., Fulzele, S., Kulkarni, N., Siddiqui, M., et al. (2023). Review of measurement of sustainable development goals: A comprehensive bibliometric and visualized analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research , 30, 91761–91779. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-28887-x
Shahbaz, M., Bashir, M. F., Bashir, M. A., and Shahzad, L. (2021). A bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review of tourism-environmental degradation nexus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 58241–58257. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14798-2
Sharma, S., Basu, S., Shetti, N. P., and Aminabhavi, T. M. (2020). Waste-to-energy nexus for circular economy and environmental protection: recent trends in hydrogen energy. Sci. Total Environ. 713:136633. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136633
Sharma, P., Gaur, V. K., Kim, S., and Pandey, A. (2020). Microbial strategies for bio-transforming food waste into resources. Bioresour. Technol. 299:122580. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122580
Srinivas, H. (2022). “Nexus in green economics for Asian countries” in Progress in green economics , 1–16.
Vásquez Neyra, J. M., Cequea, M. M., Gomes Haensel Schmitt, V., and Ferasso, M. (2022). Food consumption and food waste behaviour in households in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Br. Food J. 124, 4477–4495. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-07-2021-0798
Wang, J. M., Liu, Q., Hou, Y., Qin, W., Bai, Z. H., Zhang, F. S., et al. (2022). Impacts of international food and feed trade on nitrogen balances and nitrogen use efficiencies of food systems. Sci. Total Environ. 838:156151. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156151
Williams, H., Wikström, F., Otterbring, T., Löfgren, M., and Gustafsson, A. (2012). Reasons for household food waste with special attention to packaging. J. Clean. Prod. 24, 141–148. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.11.044
Xue, L., Liu, G., Parfitt, J., Liu, X., Van Herpen, E., Stenmarck, Å., et al. (2017). Missing food, missing data? A critical review of global food losses and food waste data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 6618–6633. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b00401
Zhang, M., Gao, M., Yue, S., Zheng, T., Gao, Z., Ma, X., et al. (2018). Global trends and future prospects of food waste research: a bibliometric analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 24600–24610. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2598-6
Keywords: food waste, sustainability, behavior, bibliometric analysis, VOSviewer, bibliometrix
Citation: Kostakis I, Papadaki S and Malindretos G (2024) Analyzing the relationship between consumers’ and entrepreneurs’ food waste and sustainable development using a bibliometric approach. Front. Sustain . 5:1373802. doi: 10.3389/frsus.2024.1373802
Received: 20 January 2024; Accepted: 15 March 2024; Published: 04 April 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Kostakis, Papadaki and Malindretos. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ioannis Kostakis, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Innovation in Sustainable Food

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies ("sleeping beauties" )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
The main purpose of the review is to introduce the readers to the need for conducting the said research. A literature review should begin with a thorough literature search using the main keywords in relevant online databases such as Google Scholar, PubMed, etc. Once all the relevant literature has been gathered, it should be organized as ...
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
A literature review is a surveys scholarly articles, books and other sources relevant to a particular. issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, providing a description, summary, and ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic; Identify a problem in a field of research ; Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology, 1(3), 311-320. What kinds of sources require a Literature Review? A research paper assigned in a course; A thesis or ...
Literature search. Fink has defined research literature review as a "systematic, explicit and reproducible method for identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing the existing body of completed and recorded work produced by researchers, scholars and practitioners."[]Review of research literature can be summarized into a seven step process: (i) Selecting research questions/purpose of the ...
In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions. ... A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the ...
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
This paper discusses literature review as a methodology for conducting research and offers an overview of different types of reviews, as well as some guidelines to how to both conduct and evaluate a literature review paper. It also discusses common pitfalls and how to get literature reviews published. Previous. Next.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
This article is organized as follows: The next section presents the methodology adopted by this research, followed by a section that discusses the typology of literature reviews and provides empirical examples; the subsequent section summarizes the process of literature review; and the last section concludes the paper with suggestions on how to improve the quality and rigor of literature ...
Types of Literature Review are as follows: Narrative literature review: This type of review involves a comprehensive summary and critical analysis of the available literature on a particular topic or research question. It is often used as an introductory section of a research paper. Systematic literature review: This is a rigorous and ...
Finding sources (scholarly articles, research books, dissertations, etc.) for your literature review is part of the research process. This process is iterative, meaning you repeat and modify searches until you have gathered enough sources for your project. The main steps in this research process are:
A literature review should: be organized around and related directly to the thesis or research question you are developing. synthesize results into a summary of what is and is not known. identify areas of controversy in the literature. formulate questions that need further research.
How to Write a Literature Review; 1. Identify the Question; Search this Guide Search. ... In a research paper, you develop a unique question and then synthesize scholarly and primary sources into a paper that supports your argument about the topic. Identify your Topic (This is the starting place from where you develop a research question.) ...
A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature (Paré et al., 2015). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the ...
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
This pre-registered systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis examined the effects of receiving touch for promoting mental and physical well-being, quantifying the efficacy of touch ...
Contribution. Yigitbasioglu et al. (Citation 2023) and Jackson et al. (Citation 2023) review the need for broadening the research literature on technology and its impact on student employability skills.To address this issue, this study makes the following important contributions to the existing knowledge. Firstly, it explores what topics should be incorporated into the management accounting ...
A systematic literature review was conducted by reviewing twenty-eight (28) relevant papers published until March 2024 in the Scopus and Web of Science databases. The VOS viewer software (version 1.6.11) was used to perform a co-occurrence analysis of keywords to identify new and popular study areas in the field.
The present study investigates the relationship between food waste and sustainable development, aiming to reveal contextual insights and present novel findings regarding the pivotal importance of waste and environmental strategies toward a circular economy. This research represents an effort to delineate methodological and thematic contributions, thoroughly analyze key themes, examine co ...
The literature search was performed using PubMed and Embase to identify articles on the use of cryoanalgesia in children. It excluded editorials, reviews, meta-analyses, and non-English articles. The analysis focused on the study methods, data analysis, patient selection, and patient follow-up. This review includes a total of 25 articles.
Currently, no review has been done to comprehensively reveal the trend of maize research in Hungary, as well as key players such as institutions, universities, industry and researchers. Hence, this bibliographic review was conducted to: i) identify the major research institutions and their contribution towards maize research in Hungary; ii ...