

Essay on Conflicts Between Friends
Students are often asked to write an essay on Conflicts Between Friends in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Conflicts Between Friends
Understanding conflicts.
When friends argue, it’s called a conflict. This happens because people have different ideas and feelings. Just like when you want pizza and your friend wants a burger. It’s normal and can happen to anyone.
Reasons for Arguments
Friends might fight for many reasons. Maybe someone didn’t share, or they broke a promise. Sometimes, one friend might feel left out or jealous. These are common issues that can lead to a disagreement.
Solving the Problem
To fix a fight, friends need to talk and listen to each other. It’s important to say sorry if you hurt your friend’s feelings. By understanding each other, friends can make up and become closer.
Learning from Fights
After a fight, friends can learn how to act better next time. They learn about forgiveness and respect. Remember, making mistakes is okay, but fixing them and moving on is what really counts.
250 Words Essay on Conflicts Between Friends
What are conflicts between friends.
When friends disagree or fight, we call it a conflict. It’s like when two people want different things and can’t agree. Imagine two friends who both want to play with the same toy, but there’s only one toy. That could start a conflict.
Why Do These Conflicts Happen?
Conflicts can happen for many reasons. Maybe friends don’t share well, or they get jealous of each other. Sometimes, one friend might feel left out or hurt by what the other said. It’s normal because everyone is different and has their own ideas and feelings.
Can Conflicts Be Good?
Yes, conflicts can be good if friends learn from them. They can talk about what made them upset and understand each other better. This can make their friendship stronger. But, it’s important to fix the conflict by talking and listening, not by yelling or being mean.
How to Fix Conflicts
To fix a conflict, friends should talk to each other calmly. They should say how they feel and listen to what the other has to say. It’s also good to say sorry if you hurt your friend. Sometimes, you might need a break to cool down before talking.
Conflicts between friends are common and can be fixed if handled well. It’s all about understanding and respecting each other. Remember, it’s okay to disagree, but it’s not okay to hurt each other. Friends who work through conflicts can have even stronger friendships.
500 Words Essay on Conflicts Between Friends
When we talk about conflicts between friends, we mean times when friends disagree or get upset with each other. Just like how sometimes you might not want to share your toy with your sibling, friends can also have moments when they don’t see eye to eye. It could be about small things like who gets to use the soccer ball first, or bigger issues like feeling left out of a group.
Why Do Conflicts Happen?
Conflicts can happen for many reasons. Sometimes, friends might misunderstand each other. For example, if your friend didn’t wave back to you at the park, you might think they are mad at you. But maybe they just didn’t see you! Other times, friends might want different things. If you want to play video games and your friend wants to play basketball, you both might feel a little upset.
Feelings in Conflicts
When friends fight, they can feel many emotions. You might feel angry if you think your friend was being unfair. Or you might feel sad if you miss playing with them. It’s normal to have these feelings, but it’s important to handle them in a good way.
Talking It Out
One of the best ways to solve a conflict is to talk about it. This means sitting down with your friend and telling them how you feel. It’s important to listen to them, too. They might have feelings that you didn’t know about. When both friends share and listen, they can often find a way to make things better.
Apologizing and Forgiving
Sometimes, saying sorry is needed to fix a friendship. If you did something that hurt your friend, a sincere apology can show them you care. It’s just as important to forgive, too. If your friend says sorry, try to let go of the anger and move on. This doesn’t mean you forget what happened, but you choose not to stay upset about it.
Learning From Conflicts
Believe it or not, conflicts can actually help friendships grow stronger. When you work through a problem with a friend, you learn more about each other. You also learn how to solve problems, which is a skill you’ll use your whole life.
When to Get Help
Sometimes, a fight might be too big to handle on your own. If you and your friend can’t stop fighting, it might be time to talk to someone like a teacher or a parent. They can help you understand the problem better and find a way to make peace.
Conflicts between friends are a normal part of life. They can make you feel upset, but they can also be a chance to make your friendship even better. By talking, apologizing, and forgiving, you can solve most problems. And remember, it’s okay to ask for help if you need it. In the end, working through conflicts can teach you important lessons about friendship and about yourself.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Contemporary Art
- Essay on Leadership Experience As A Student
- Essay on Leadership Experience
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

We’re here for you.
What are you facing today.
Can’t find your issue? Talk to us. It’s confidential.

Resolving Conflict in Friendships
The other day I had a bit of a falling out with my good friend Alissa. I told a guy she liked about a conversation we shared, not knowing she would be so offended by it. After my disagreement with Alissa, I realized that I had some decisions to make as to how I was going to deal with this conflict.
Yes, I had overstepped my boundaries. No, I didn’t want to lose my three-year friendship with Alissa over a comment I made to the guy she liked. So now what? In my mind, the options were to let her go in hopes the problem would go away or to try to talk it out with her. I decided to attempt the confrontation.
Conflict. It’s a fact of life. It’s a fact in friendships. You develop a friendship with someone, and conflict is sure to occur .
Many superficial friendships end up being shelved after an argument because there isn’t enough depth to warrant all the trouble it takes to smooth over the disagreement. Unfortunately, even when the friendship reaches a deeper level, conflict continues to happen and can break apart a relationship.
First and foremost, talk the situation over soon after it occurs. And do it quickly! From my experience, people begin to talk about what happened while it is still fresh in their minds. Good, step in the right direction, right? Well, not always… particularly when the talking isn’t with the person involved, but with other friends or acquaintances.
People begin to pick sides. The gossip circulates and all of a sudden, friends become enemies. Suddenly everyone is mad at everyone else. So, be sure to talk with the person with whom you are upset without the interference of people who aren’t really involved.
Resolve it the day it happens. One rule my parents follow in their marriage is that they don’t go to bed angry with each other. They always attempt to resolve things the day it happens so that in the morning, it’s a fresh start with no past grudges. I’ve found I need a short cool down period of a couple of minutes so that I don’t act in anger, and can instead act with a more rational mind. For some, counting to one hundred before saying anything may be an option. Whatever you do, don’t let things ride for too long. Even when you don’t see eye to eye, agree to disagree. Tell them that while you may not agree with what they’re saying, you still value their friendship.
Try to see the other person’s perspective. Sometimes if you sit down and talk things over, you begin to see where the other person is coming from. Realize that everyone has been created differently with various talents, abilities, and personality traits. For example, you might be a leader while your friend is more of a follower. You may be frustrated with him or her for not being very decisive. Yet it is important to understand that no matter what your quirks, each person is still unique and needs to be appreciated.
Here’s a tough one – initiate resolution. Be the first person in a fight to say sorry for your part. Even when you think the other person is wrong, it’s not a bad thing to say “I’m sorry you feel that way” or “I’m sorry if I offended you in that way.” If you’re honest, genuine, and gentle in delivering your words, there’s a good chance your friend will reciprocate positively. Use feeling words since no one can argue with your feelings. For example, “When you do this, you make me feel silly.”
Focus on the bigger picture. Successfully facing and working through the discomfort of conflict in a friendship has a worthwhile reward: a deeper relationship.
Don’t accuse by using the word, “you.”
Be sensitive. Try to offer solutions when appropriate, but know when to listen. Don’t underestimate the importance of a listening ear.
Most important, be loving in what you do. Don’t go out to “get” the other person, but try to focus on peacefully resolving the disagreement.
Resolving conflict in any friendship is not the most pleasant task, but it is worth the hassle because the result on the other end is a deeper friendship.
Reprinted with permission from Iamnext.com
This article was written by: Kristin Feenstra
You don't have to journey alone. Fill in the form below and one of our mentors will respond as soon as possible. It's confidential and always free.
Our mentors are not counsellors. They are ordinary people willing to join people on their journey in a compassionate and respectful manner.
All fields are required unless otherwise indicated.
We ask for gender and age to assign you the appropriate mentor. Terms of Service & Privacy Policy .
Depression: Hello Darkness My Old Friend
I get trapped in this dark place where there’s nothing to do but sleep or cry until my head pounds. On those days, just getting out of bed is a
Dating the Wrong Guy: It Felt So Right
I felt truly pretty for the first time in my life. Sunshine covered my world. Being with him made me feel great. But then things changed.
How to Handle Friendship Conflicts Like an Adult

Friends are the best. Having people who are there for you, support you, inspire you, and send you relatable memes (“lol it’s us”) is one of life’s greatest treasures. But that doesn’t mean you’ll never experience some tension (or, worse, a full-blown fight) with your friends. And that can be a major stressor in our lives, especially since most of us aren't experts at how to handle conflicts in our friendships .
If you’d rather stick your hand in an ant hill than bring up a conflict with a friend, we get it. Our culture tends to emphasize being “cool” and letting things slide. But that’s probably not helping your bond.
“When we turn toward avoidance, we turn away from healthier connections,” says Miriam Kirmayer, PhD , clinical psychologist and friendship expert. “The healthiest, closest friendships are ones where people will say, ‘Yeah, we have had disagreements, we've had arguments, and we've been able to work through those together.’”
Not to mention that addressing and resolving friendship issues is great practice for other areas of your life too. Navigating sticky friend situations can help you develop the skills to get through relationship issues with partners, colleagues, and even children, says Dr. Kirmayer.
But addressing problems with friends maturely and calmly takes practice, and you might feel a little (or a lot) uncomfortable at first. Take a deep breath, be brave, and try one of these techniques.
What to do if: You don’t feel like your friendship is being prioritized.
As with most beefs, you don’t want to assume you have all the information or that you know exactly what your friend is going through. One technique that therapist Chase Cassine, LCSW , recommends for these conversations: “Name the situation, say how you're feeling, and explain how you want to resolve it,” he says.
In the case of feeling like your friend isn’t showing up for you, that might look like: “Last week we had plans to hang out and you canceled. That’s happened a few times recently, and I’m feeling hurt. Can we talk about it?”
If this is a problem that’s been bothering you for a while, it might be worth getting a little more vulnerable about how it’s affecting your view of the friendship. Dr. Kirmayer recommends a phrase like, “The story I’m telling myself is…”
For example: “The story I’m telling myself is that you don’t want to see me.” This allows space for you to share what you’re feeling, while also admitting that your truth is only half of the story. This way, you’re inviting them to respond just as honestly without judgment.
What to do if: The friendship feels competitive.
If you both enjoy a little competition, then no biggie. Maybe they’re the Paris Geller to your Rory Gilmore and it just works. But if not, Dr. Kirmayer says to start with a little self-reflection. Again, it helps to hone in on the story you’re telling yourself, she says. Is there actual evidence that you two are competing in some way? Or are you maybe comparing yourself to your friend more than you should? You might just need to work on your own self-talk rather than confronting your person.
But if it does feel like an interpersonal issue—your friend can’t seem to hear your good news without trying to one-up it with her own accomplishments—address the problem as a dynamic rather than blaming your friend. “Frame it as something that's co-constructed,” Dr. Kirmayer explains. For example, you might say: “I've noticed that some of our conversations can take on a layer of competitiveness. Have you noticed that? Or does it surprise you that I’m saying it?” Your next move will depend on how your friend responds. For example, maybe your friend might explain that they’re not trying to compete with you at all—they’re super, truly, and genuinely happy for you, and they brag about how amazing you are all the time. Hopefully that helps you reframe the crummy feelings you’ve been having about it, so next time it feels less like competition and more like mutual sharing. Or maybe they explain what’s happening on their end, and you find that you’ve been playing into the dynamic too (whoops). In that case, you can brainstorm possible solutions together, like making an effort to give words of affirmation or congratulations before diving into your own good news.
What to do if: Your friend’s comments feel judgemental or harsh lately.
First, avoid generalizing, which is a really easy thing to do when feeling hurt. Generalizing looks like, “You’ve been really mean to me lately,” or, “You’re always saying negative stuff.” Instead, get specific and try to keep your tone calm , Cassine says.
He recommends something like, “I want to talk to you about something that’s been bothering me. Last time we hung out, you said X. You may have meant it as a joke, but it really affected me.” The goal isn’t to punish your friend but to give concrete examples rather than being vague or passive-aggressive, Cassine says. Your friend might have questions or want to explain what they meant. To avoid a constant back-and-forth of you-said-no-you-said, try to keep the conversation geared toward the future rather than rehashing the past more than once. After you’ve both said your peace, how can you avoid these kinds of comments (or misunderstandings!) in future convos? Maybe you agree to skip sharing feedback on something that you feel a little insecure about—or you just avoid that topic altogether.
What to do if: Your interests and opinions kinda conflict sometimes.
Hey, friends don’t always agree on everything. Maybe it’s about what you like to do for fun (the party friend and the introvert friend), where you enjoy living (the city friend and the suburb friend), or how you approach finances (the friend who drops thousands on concert tickets and the friend who…doesn’t). When you have mismatched interests in these areas, it can be awkward to work out, and you might both end up feeling like the other one is criticizing your choices whenever they don’t align.
Dr. Kirmayer’s recommendation: Don’t take their preferences personally, and remember that neither of you is wrong—or, rather, you’re both right. “Whatever tension arises isn't something that the other person is doing to you, it's something that they're doing for themselves,” Dr. Kirmayer says. Next comes compromise—but don’t freak out. Most people assume that compromise means one person totally loses out on what they’re looking for, says Dr. Kirmayer. But that’s a bad deal. Instead, compromise should be about brainstorming ways you can both get as much of what you want as possible.
Let’s imagine you’re on vacation and you want to spend all your time at the beach while your BFF wants a museum buddy. There are lots of ways to solve for this that involve both of you winning. Maybe you split your time evenly, or maybe you come up with a third idea that hadn’t been on either of your radar—like a guided walk that gets you out in the sun and your friend immersed in culture. Or you can try to look at the history of the friendship and see whose “turn” it might be to pick the plan. “The important thing is that you talk about not just what the solution is but how you're coming to that solution together,” Dr. Kirmayer explains.
What to do if: You fundamentally disagree on something major.
You probably have some friends that feel like they’re an extension of you walking around with a copy-and-paste of your exact brain. And then there are friends that you love and appreciate despite not being on the same page about some big things—like politics, religion, science, whatever. It’s absolutely possible to have friends with different viewpoints on these subjects, but if those viewpoints or actions feel discriminatory or unsafe for you or your loved ones, that can be a lot harder to work around.
Depending on how extreme the situation is, you might be able to preserve the friendship by upping your boundaries . This might look like agreeing to avoid a certain topic, or it might mean deprioritizing the friendship so that you’re only seeing each other in larger group settings and keeping conversations more surface-level, says Dr. Kirmayer.
But friendship should feel chosen, reminds Dr. Kirmayer, who offers a few key indicators that it might be time to choose to step away: “When the friendship comes at the expense of your well-being, when it’s a clash in values that leads you to feel chronically unsafe or unseen, [and] when you have done all you feel you can do and there doesn’t seem to be a change.” If that sounds like your situation, it might be time to let the friendship go . We’ll be blunt here: These conversations are rarely easy. Dr. Kirmayer recommends explaining what feels broken about the friendship and why the subject of this disagreement is important to you. Remember, the goal isn’t to convince the other person that your viewpoint is correct. You’re offering your perspective, acknowledging that they may have a different one, and expressing how you feel about the state of your friendship in those circumstances.
What to do if: You’re caught in the middle between friends.
Social media and buddy comedies might make big friend groups look ideal, but they come with their own set of issues. Like… if two of those friends are fighting, and you’re having to hear all about it.
The good news? It’s a great time to practice boundaries, Dr. Kirmayer says. First, you’ll want to figure out what’s making you uncomfortable. Are they asking for advice? Are they forcing you to (or implying that you should) pick sides? Is it that they’re sharing information not meant for you? Is it that you just don’t feel comfortable hearing about it at all?
Once you figure that out, it’s time to tell your friends—probably separately. Be sure to remind them that you support them both and are neutral in this matter. Then explain what you are and aren’t comfortable with. For example,“I know you’re going through a hard time right now, but I’m not comfortable giving advice about our mutual friend.” Or you might say, “I love you both and I’m really not comfortable being in the middle, so I’d prefer we didn’t talk about what’s going on between you two.”
Your friends might have follow-up questions, and together you can navigate what is and isn’t on the table. For example, one friend might want to know if they can talk more generally about the falling out (like that they’re feeling betrayed or isolated or lonely, but not giving you a play-by-play), and you’ll have to decide whether you’re OK with that.
You might have to remind your friends a few times what you are and aren’t comfortable with before it sinks in, and that’s OK, Dr. Kirmayer says. “Set and reset” boundaries, she says. “The truth is it often takes people a few times to not just hear something but really listen and be able to follow.”
Wondermind does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Any information published on this website or by this brand is not intended as a replacement for medical advice. Always consult a qualified health or mental health professional with any questions or concerns about your mental health.

Sign up for our newsletter to get expert advice and candid convos delivered right to your inbox

- Frequently Asked Questions
- Helpful Free Resources
- Happiness & Fun
- Healthy Habits
- Love & Relationships
- Mental Health
- Mindfulness & Peace
- Purpose & Passion
- Fun & Inspiring
- Submit a Post
- Books & Things
- Tiny Buddha’s Breaking Barriers to Self-Care

“Treat your friends like you do your best pictures; place them in the best light.” ~Unknown
I recently had a disagreement with a close friend.
There was a good deal of uncontrolled emotion on my side. I wasn’t expressing myself well and I knew it. I became more and more frustrated and less effective at explaining my feelings.
I found myself laying unwarranted blame on my friend rather than admitting openly that something was hurting me and I was feeling vulnerable.
Ultimately, he said the words I was having trouble finding for me, and that resolved the situation.
I was embarrassed and grateful, but I realized I needed to evaluate a few of my shortcomings to avoid making the same mistake again.
I also realized that what I was feeling wasn’t the problem.
It was my inability to effectively convey what was in my heart and on my mind that led to hurt feelings and further misunderstanding.
After much self examination, I’ve come up with a few tips to communicate effectively during a conflict.
1. Think about whether this needs to be said right now, in this moment.
Sometimes the opportunity will be missed if not.
In my case, I felt I needed to bring the subject up right then or I might not have gotten the nerve again. I went for it, but it could have gone better if I’d waited to form a well organized idea of what I wanted to say.
2. Think about the other person’s state of mind.
Is he/she tired, under other stress, or not in an ideal place right now to have a heartfelt talk?
3. Consider if you have a good handle on your emotions.
Also, consider if you have the proper perspective to deal with the potential consequences.
Email, texts, and cell phone calls are not an ideal way to introduce the need to talk about something substantial.
4. Hold off on the confrontation if you feel the time is not right.
There is a marked difference in avoiding a hard topic and thoughtfully planning the ideal time to have a potentially difficult conversation.
5. Focus on breathing to help control your emotions.
If you begin a difficult conversation starting from a place of controlled emotion and grace, the path will be smoother.
6. Keep your perspective broad and realistic.
Don’t place too much importance on a single talk. Most of the progress in relationships comes from a series of discussions as they unravel naturally. Try and stay in the moment and minimize added drama by bringing up old or irrelevant issues.
7. Listen more than you talk.
It’s fine to be heard, but if you are not listening to the other’s response, the discussion is pointless.
8. Avoid adding unnecessary drama.
These things never help to fix a problem and ultimately bring more hurt to all involved. These include ultimatums, yelling, threatening to cut off the friendship, name calling, and personal attacks.
If it comes to that, walk away. Breathe, step back, and allow some time before you try again.
9. Focus on what the person is trying to communicate.
I’m often reminded as a parent to listen to my children’s words and not necessarily the emotion behind them. Emotions are fleeting, and rarely final. They are simply a temporary reaction to the current situation.
My three-year-old sometimes throws temper tantrums when she’s frustrated, but if I listen and respond to her words, it often diffuses her anger. Many times she is telling me she is not feeling heard as the youngest member of our family. I focus on the simple phrase, “Mommy! Listen to me!” Not her screaming voice and kicking feet.
10. Acknowledge the feelings.
If you acknowledge that someone is angry or hurt, you can better understand the sharp or harsh words that may be coming from them. You can choose to help them deal with their emotions or let them regain their composure to talk another time.
11. Take a realistic assessment of your true feelings in the moment.
I tend to distort and add unintended nuances to the words that others say when I am upset. This has caused me a great deal of distress in past conflicts. I am not on the wrong page, but in the wrong book sometimes metaphorically speaking.
After such experiences, I find the other person saying “How did you come to that conclusion from what I said?”
This is a classic example of our ability to inflict the worst hurts upon ourselves.
If I realize that I am upset and try to hear the words being said to me as they are, without my running mental commentary, things come across much clearer.
12. Clear the emotional fog enough to receive the message.
If you need to ask for clarification or even repeat what you think the other person is trying to say, so be it.
13. Know that most well established relationships can weather the occasional conflict just fine.
It can even be an opportunity to grow and evolve as you turn a new corner of understanding one another.
The friend I argued with is the best kind. He challenges me to broaden my perspective. He is relentless in keeping me from settling and expecting too little from life. He pushes me out of the nest over and over when I get too comfortable.
Don’t avoid expressing how you feel for the sake of preserving a friendship.
The foundation of all relationships is grounded on honesty and trust. It’s okay to show weakness, to be wrong, or to just plain melt down from time to time. Each person has something to give and something to learn. Conflict might be considered the way to pass along such knowledge.
I am fortunate my friend knew me well and was willing to give me space and offer forgiveness. The next time I have something to say, I will try to remember this and be more straightforward.
Every challenge with another is a chance to better our response. They give us the chance to practice patience, respect for others, detachment, and compassion. The added benefit is strengthening our relationships and our ability to communicate.
About Nicole Franco
Nicole Franco is an emerging freelance fiction writer seeking representation for her first novel. She enjoys family, horses, travel, reading, photography, and making others laugh. To read more of her writing or hire her for freelance work, visit francowrites.com .
Did you enjoy this post? Please share the wisdom :)
Related posts:

Free Download: Buddha Desktop Wallpaper

Recent Forum Topics
- Don’t enjoy my best friend anymore, one of my only
- Struggling to settle in new role
- Selfish husband
- Working on stuff
- Past Hurts & Present Concerns: Advice Needed for a Stronger Bond
- Fake friend….or a jealous friend
- Why sometime it takes years to miss some one

True Love Is When…
GET MORE FUN & INSPIRING IMAGES & VIDEOS .
Latest Posts

The Big Impact We Don’t Realize We Make Every Day

When It’s Time Tell Your Story: How to Step Out of Hiding and Into Healing

How to Make a Big Change by Embracing Love and Confronting Fear

How to Free Yourself from Your Constant Desires

Submit Your Quote for Tiny Buddha’s 2026 Calendar
This site is not intended to provide and does not constitute medical, legal, or other professional advice. The content on Tiny Buddha is designed to support, not replace, medical or psychiatric treatment. Please seek professional care if you believe you may have a condition.
Tiny Buddha, LLC may earn affiliate income from qualifying purchases, including from the Amazon Associate Program.
Before using the site, please read our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
Click to opt-out of Google Analytics tracking.
Who Runs Tiny Buddha?

Get More Tiny Buddha
- Youtube
- RSS Feed
Credits & Copyright
- Back to Top
Essays About Conflict in Life: Top 5 Examples and Prompts
Conflict is a broad and gripping topic, but most struggle to write about it. See our top essays about conflict in life examples and prompts to start your piece.
Conflict occurs when two people with different opinions, feelings, and behaviours disagree. It’s a common occurrence that we can observe wherever and whenever we are. Although conflicts usually imply negative aspects, they also have benefits such as stronger relationships and better communication.
To aid you in your paper, here are five examples to familiarize you with the subject:
1. Useful Notes On 4 Major Types Of Conflicts (Motivational Conflict) By Raghavendra Pras
2. encountering conflict by julius gregory, 3. complete guide to understanding conflict and conflict resolution by prasanna, 4. analysis of personal conflict experience by anonymous on gradesfixer, 5. personal conflict resolving skills essay by anonymous on ivypanda, 1. conflict: what is and how to avoid it, 2. conflicts in our everyday lives, 3. review on movies or books about conflicts, 4. actions and conflicts , 5. conflicts at home, 6. conflicts that changed my life, 7. my personal experience in covert conflict, 8. cascading conflicts, 9. how does conflict in life benefit you, 10. the importance of conflict management.
“Conflict… results when two or more motives drive behaviour towards incompatible goals.”
Pras regards conflict as a source of frustration with four types. Experimental psychologists identified them as approach-approach, avoidance-avoidance, approach-avoidance, and multiple approach-avoidance. He discusses each through his essay and uses theoretical analysis with real-life examples to make it easier for the readers to understand.
“The nature of conflict shows that conflict can either push people away or bring them into having a closer, more comfortable relationship.”
The main points of Gregory’s essay are the typical causes and effects of conflicts. He talks about how people should not avoid conflicts in their life and instead solve them to learn and grow. However, he’s also aware that no matter if a dispute is big or small, it can lead to severe consequences when it’s wrongly dealt with. He also cites real-life events to prove his points. At the end of the essay, he acknowledges that one can’t wholly avoid conflict because it’s part of human nature.
“…it is important to remember that regardless of the situation, it is always possible to resolve a conflict in some constructive or meaningful way.”
To help the reader understand conflict and resolutions, Prasanna includes the types, causes, difficulties, and people’s reactions to it. She shows how broad conflict is by detailing each section. From simple misunderstandings to bad faith, the conflict has varying results that ultimately depend on the individuals involved in the situation. Prasanna ends the essay by saying that conflict is a part of life that everyone will have to go through, no matter the relationship they have with others.
“I also now understand that trying to keep someone’s feelings from getting hurt might not always be the best option during a conflict.”
To analyze how conflict impacts lives, the author shares his personal experience. He refers to an ex-friend, Luke, as someone who most of their circle doesn’t like because of his personality. The author shares their arguments, such as when Luke wasn’t invited to a party and how they tried to protect his feelings by not telling Luke people didn’t want him to be there. Instead, they caved, and Luke was allowed to the gathering. However, Luke realized he wasn’t accepted at the party, and many were uncomfortable around him.
The essay further narrates that it was a mistake not to be honest from the beginning. Ultimately, the writer states that he would immediately tell someone the truth rather than make matters worse.
“To me if life did not have challenges and difficult circumstances we were never going to know the strength that we have in us.”
The essay delves into the writer’s conflicts concerning their personal feelings and professional boundaries. The author narrates how they initially had a good relationship with a senior until they filed for a leave. Naturally, they didn’t expect the coworker to lie and bring the situation to their committee. However, the author handled it instead of showing anger by respecting their relationship with the senior, controlling their emotion, and communicating properly.
10 Helpful Prompts On Essays About Conflict in Life
Below are easy writing prompts to use for your essay:
Define what constitutes a conflict and present cases to make it easier for the readers to imagine. To further engage your audience, give them imaginary situations where they can choose how to react and include the results of these reactions.
If writing this prompt sounds like a lot of work, make it simple. Write a 5-paragraph essay instead.
There are several types of conflict that a person experiences throughout their life. First, discuss simple conflicts you observe around you. For example, the cashier misunderstands an order, your mom forgets to buy groceries, or you have clashing class schedules.
Pick a movie or book and summarize its plot. Share your thoughts regarding how the piece tackles the conflicts and if you agree with the characters’ decisions. Try the 1985 movie The Heavenly Kid , directed by Cary Medoway, or Where the Conflict Really Lies: Science, Religion, and Naturalism by philosopher Alvin Plantinga.
In this essay, describe how actions can lead to conflict and how specific actions can make a conflict worse. Make your essay interesting by presenting various characters and letting them react differently to a particular conflict.
For example, Character A responds by being angry and making the situation worse. Meanwhile, Character B immediately solves the discord by respectfully asking others for their reasons. Through your essay, you’ll help your readers realize how actions significantly affect conflicts. You’ll also be able to clearly explain what conflicts are.

Your home is where you first learn how to handle conflicts, making it easier for your readers to relate to you. In your essay, tell a story of when you quarreled with a relative and how you worked it out. For instance, you may have a petty fight with your sibling because you don’t want to share a toy. Then, share what your parents asked you to do and what you learned from your dispute.
If there are simple conflicts with no serious consequences, there are also severe ones that can impact individuals in the long run. Talk about it through your essay if you’re comfortable sharing a personal experience. For example, if your parents’ conflict ended in divorce, recount what it made you feel and how it affected your life.
Covert conflict occurs when two individuals have differences but do not openly discuss them. Have you experienced living or being with someone who avoids expressing their genuine feelings and emotions towards you or something? Write about it, what happened, and how the both of you resolved it.
Some results of cascading conflict are wars and revolutions. The underlying issues stem from a problem with a simple solution but will affect many aspects of the culture or community. For this prompt, pick a relevant historical happening. For instance, you can talk about King Henry VIII’s demand to divorce his first wife and how it changed the course of England’s royal bloodline and nobles.
People avoid conflict as much as possible because of its harmful effects, such as stress and fights. In this prompt, focus on its positive side. Discuss the pros of engaging in disputes, such as having better communication and developing your listening and people skills.
Explain what conflict management is and expound on its critical uses. Start by relaying a situation and then applying conflict resolution techniques. For example, you can talk about a team with difficulties making a united decision. To solve this conflict, the members should share their ideas and ensure everyone is allowed to speak and be heard.
Here are more essay writing tips to help you with your essay.

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts

- Online Services
- Get Signed Up
- Access Client Portal
- Book and DVD
- Atlanta, GA
- Charlotte, NC
- Chicago, IL
- Columbus, OH
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York City, NY
- Palo Alto, CA
- Philadelphia, PA
- Phoenix, AZ
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- San Jose, CA

Ways to Resolve Conflict with a Friend
Friendship is a precious bond that can bring joy, laughter, and support to our lives. However, like any relationship, friendships can also experience conflicts and disagreements. Conflict is a natural part of human interaction, and it’s important to learn how to resolve conflicts in a healthy and constructive manner, especially when it involves a close friend. In this blog, we will explore some effective ways to resolve conflicts with a friend, including the benefits of social skills training with SocialSkillsCenter.com.
- Open and Honest Communication: Communication is key to resolving conflicts with a friend. It’s important to express your thoughts and feelings in a calm and respectful manner. Avoid using accusatory language or attacking your friend, as this can escalate the conflict further. Instead, use “I” statements to express how you feel, such as “I feel hurt when you don’t include me in your plans” or “I’m frustrated because I feel like you’re not listening to me.” This allows your friend to understand your perspective without feeling attacked, and it can create a safe space for open and honest communication.
- Active Listening: Listening is an essential part of effective communication. When your friend is expressing their thoughts and feelings, make sure to give them your full attention. Avoid interrupting or thinking about your response while they speak. Instead, focus on understanding their perspective and validating their feelings. Repeat what they’ve said to ensure that you’ve understood them correctly. This shows respect and empathy toward your friend’s point of view, which can help defuse the conflict.
- Find Common Ground: In the midst of a conflict, it’s easy to get caught up in our differences and disagreements. However, finding common ground can be a powerful way to resolve conflicts with a friend. Look for areas where you both agree, and build upon them. This can create a sense of shared understanding and help you find a solution that benefits both parties. For example, if you’re arguing about where to go for dinner, focus on the types of cuisine you both enjoy and try to find a restaurant that offers those options.
- Practice Empathy: Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. It’s a crucial social skill for resolving conflicts. Try to see the situation from your friend’s perspective. Consider their emotions, experiences, and background. This can help you understand why they might be feeling or reacting the way they are, and it can create a sense of understanding and compassion. When you express empathy toward your friend, it can help validate their feelings and build a bridge to resolution.
- Take Responsibility: Conflict often arises from misunderstandings or miscommunication. It’s important to take responsibility for your actions and acknowledge any ways you’ve contributed to the conflict. This doesn’t mean taking all the blame, but rather recognizing your part in the conflict and being willing to make amends. Apologize sincerely if you’ve hurt your friend’s feelings, and express your willingness to work toward a resolution. Taking responsibility for your actions can show maturity and accountability, and it can pave the way for a resolution.
- Seek a Neutral Mediator: If you find it difficult to resolve the conflict on your own, consider seeking the help of a neutral mediator. A mediator is a third party who can facilitate communication and help you find a solution that satisfies both parties. This can be a trusted mutual friend, a counselor, or a professional mediator. Mediators are trained to remain impartial and provide guidance and support in resolving conflicts. They can help create a safe space for communication and provide strategies for finding common ground and resolving the conflict in a constructive manner.
- Take a Break to Cool Off: In the heat of the moment, it’s easy to say things we don’t mean or to act impulsively. If you find that the conflict is escalating and emotions are running high, it’s okay to take a break and give yourself and your friend some time to cool off. Stepping away from the situation can allow you to gain perspective and come back with a calmer mindset. During the break, try to engage in self-care activities that help you relax and destress, such as going for a walk, meditating, or talking to a trusted confidant. When you and your friend are both in a more relaxed state, it can be easier to approach the conflict with a clear mind and a willingness to resolve it.
- Brainstorm Solutions Together: Conflict resolution is about finding a solution that works for both parties. Once you’ve communicated openly, listened to each other’s perspectives, and found common ground, it’s time to brainstorm potential solutions together. Be open to each other’s ideas and suggestions for creative solutions that meet both of your needs. Avoid being rigid or stubborn, and be willing to compromise. Remember that the goal is not to “win” the argument but to find a resolution that preserves the friendship and promotes a healthy relationship.
- Follow Up and Follow Through: Resolving a conflict doesn’t end with a single conversation. It’s important to follow up and follow through on the solutions and agreements that you’ve reached with your friend. Check-in with each other after some time to see how things are going and if any adjustments need to be made. Hold each other accountable for the commitments that you’ve made toward resolving the conflict. This shows that you’re invested in maintaining the friendship and that you’re committed to working through any issues that may arise in the future.
Benefits of Social Skills Training with the Social Skills Center
In addition to the strategies mentioned above, social skills training can be a valuable resource in resolving conflicts with friends. The Social Skills Center is an online platform that offers comprehensive social skills training programs for individuals of all ages, including adolescents in high school. Here are some benefits of social skills training in the context of resolving conflicts with friends:
- Improved Communication Skills: Effective communication is crucial in resolving conflicts, and social skills training can help individuals develop better communication Through social skills training, individuals can learn how to express themselves clearly, listen actively, and use respectful language, which can enhance their ability to communicate and resolve conflicts in a healthy and constructive manner.
- Increased Empathy and Perspective-Taking: Social skills training often includes exercises and activities that promote empathy and perspective-taking. These skills can help individuals understand and appreciate different perspectives, which can be valuable in resolving conflicts with friends. Being able to see the situation from the other person’s point of view and showing empathy toward their feelings and experiences can create a more conducive environment for conflict resolution.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: Conflict resolution often requires creative problem-solving. Social skills training can provide individuals with strategies and techniques to effectively identify problems, generate solutions, and evaluate the pros and cons of different options. These problem-solving skills can be applied to conflicts with friends, helping individuals find solutions that meet all parties’ needs and result in a win-win outcome.
- Increased Self-Awareness: Social skills training can also promote self-awareness, which is essential in resolving conflicts. Through self-reflection and self-assessment exercises, individuals can gain a better understanding of their own thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, as well as their impact on others. This self-awareness can help individuals to identify any triggers or patterns that contribute to conflicts and to take steps to manage them effectively.
- Strengthened Relationships: Social skills training can ultimately lead to strengthened relationships, including friendships. When individuals develop better communication skills, empathy, perspective-taking, problem-solving skills, and self-awareness through social skills training, they are better equipped to navigate conflicts and resolve them in a healthy and constructive manner. This can lead to stronger and more resilient friendships; conflicts are inevitable in any relationship, but how we handle them can make all the difference in maintaining a healthy and positive connection with our friends.
The Social Skills Center is an excellent resource for individuals looking to improve their social skills and enhance their conflict resolution abilities. Their comprehensive social skills training programs are designed to cater to the unique needs of adolescents in high school, providing them with the necessary tools and techniques to navigate various social situations, including conflicts with friends. The online platform offers a user-friendly interface, interactive activities, and practical strategies that can be applied in real-life situations.
Conflicts with friends are a normal part of human relationships, and they can be resolved in a healthy and constructive manner with effective communication, active listening, empathy, perspective-taking, problem-solving skills, and self-awareness. By following the strategies outlined in this blog and considering social skills training with the Social Skills Center, individuals can develop the necessary skills to navigate conflicts and maintain healthy friendships. Remember that conflict can be an opportunity for growth, understanding, and strengthening relationships. With open-mindedness, patience, and a willingness to work through differences, conflicts can be resolved, and friendships can flourish. So, the next time you find yourself in a conflict with a friend, take a step back, reflect on these strategies, and approach the situation with a positive and proactive mindset. Happy resolving!
Interested in one of our group social skill groups ? Get started today!
127 Friendship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
When you have a good friendship topic, essay writing becomes as easy as it gets. We have some for you!
📝 Friendship Essay Structure
🏆 best friendship topic ideas & essay examples, 💡 good essay topics on friendship, 🎓 simple & easy friendship essay titles, 📌 most interesting friendship topics to write about, ❓ research questions about friendship.
Describing a friend, talking about your relationship and life experiences can be quite fun! So, take a look at our topics on friendship in the list below. Our experts have gathered numerous ideas that can be extremely helpful for you. And don’t forget to check our friendship essay examples via the links.
Writing a friendship essay is an excellent way to reflect on your relationships with other people, show your appreciation for your friends, and explore what friendship means to you. What you include in your paper is entirely up to you, but this doesn’t mean that you shouldn’t structure it properly. Here is our advice on structuring an essay on friendship:
- Begin by selecting the right topic. It should be focused and creative so that you can earn a high mark. Think about what friendship means to you and write down your thoughts. Reflect on your relationship with your best friend and see if you can write an essay that incorporates these themes. If these steps didn’t help – don’t worry! Fortunately, there are many web resources that can help you choose. Browse samples of friendship essays online to see if there are any topics that interest you.
- Create a title that reflects your focus. Paper titles are important because they grasp the reader’s attention and make them want to read further. However, many people find it challenging to name their work, so you can search for friendship essay titles online if you need to.
- Once you get the first two steps right, you can start developing the structure of your essay. An outline is a great tool because it presents your ideas in a clear and concise manner and ensures that there are no gaps or irrelevant points. The most basic essay outline has three components: introduction, body, and conclusion. Type these out and move to the next step. Compose an introduction. Your introduction should include a hook, some background information, and a thesis. A friendship essay hook is the first sentence in the introduction, where you draw the reader’s attention. For instance, if you are creating an essay on value of friendship, include a brief description of a situation where your friends helped you or something else that comes to mind. A hook should make the reader want to read the rest of the essay. After the hook, include some background information on your chosen theme and write down a thesis. A thesis statement is the final sentence of the first paragraph that consists of your main argument.
- Write well-structured body paragraphs. Each body paragraph should start with one key point, which is then developed through examples, references to resources, or other content. Make sure that each of the key points relates to your thesis. It might be useful to write out all of your key points first before you write the main body of the paper. This will help you to see if any of them are irrelevant or need to be swapped to establish a logical sequence. If you are composing an essay on the importance of friendship, each point should show how a good friend can make life better and more enjoyable. End each paragraph with a concluding sentence that links it to the next part of the paper.
- Finally, compose a conclusion. A friendship essay conclusion should tie together all your points and show how they support your thesis. For this purpose, you should restate your thesis statement at the beginning of the final paragraph. This will offer your reader a nice, well-balanced closure, leaving a good impression of your work.
We hope that this post has assisted you in understanding the basic structure of a friendship paper. Don’t forget to browse our website for sample papers, essay titles, and other resources!
- Friendship of Amir and Hassan in The Kite Runner The idea of friendship in The Kite Runner is considered to be one of the most important, particularly in terms of how friendship is appreciated by boys of different classes, how close the concepts of […]
- Classification of Friendship Best friends An acquaintance is someone whose name you know, who you see every now and then, who you probably have something in common with and who you feel comfortable around.
- Friendship as a Personal Relationship Friends should be people who are sources of happiness to one another and will not forsake each other even when everybody around is against them.
- Gilgamesh and Enkidu Friendship Essay The role of friendship in the Epic of Gilgamesh is vital. This essay unfolds the theme of friendship between Gilgamesh and Enkidu that develops in the course of the story.
- Friendship and Friend’s Support It is the ability to find the right words for a friend, help in a difficult moment, and find a way out together.
- The Theme of Friendship in the “Arranged” Film As can be seen, friendship becomes the source of improved emotional and mental well-being, encouraging Rochel and Nasira to remain loyal to their values and beliefs.
- The Confessions of St. Augustine on Friendship: Term Paper Augustine of Hippo believes that the only real source of friendship is God, and he adds that it is only through this God-man relationship that people can understand the ideal meaning of friendship.
- Defining of True Friendship This is the same devotion that my friends and I have toward each other. Another thing that best defines friends is the sacrifices that they are willing to make for each other.
- The Importance of Friendship in “The Epic of Gilgamesh” At the beginning of the story, Gilgamesh, the king of the Sumerian city of Uruk, despite achievements in the development of the town, causes the dislike of his subjects.
- Effect of Friendship on Students’ Emotional Health The study discovered a significant positive correlation between the quality of new friendships and adjustment to university; this association is more robust for students living in residence than those commuting to university. Friday and Adkins […]
- Friendship in The Old Man and The Sea The book was the last published during the author’s lifetime, and some critics believe that it was his reflection on the topics of death and the meaning of life.
- Friendship in the ‘Because of Winn Dixie’ by Kate Dicamillo In the book “Because of Winn Dixie”, Kate DiCamillo focuses on a ten-year-old girl India Opal Buloni and her friend, a dog named Winn Dixie.
- Greek and Roman Perspectives on Male Friendship in Mythology The reason for such attitude can be found in the patriarchal culture and the dominant role of free adult males in the Greek and Roman social life. However, this was not the only, and probably […]
- Gender and Cultural Studies: Intimacy, Love and Friendship Regardless of the driving force, intimacy and sexual connections are common in many happy relationships. Of significance is monogamy whose definition among the heterosexuals and lesbians remains a challenge.
- Friendship’s Philosophical Description In order for a friendship to exist, the two parties must demonstrate first and foremost a willingness to ensure that only the best occurs to their counterpart.
- Friendship as Moral Experience One of the things I have realized over the course of the last few years is that while it is possible to experience friendship and have a deep, spiritual connection with another person, it is […]
- Friendship Type – Companionship Relationship A friendship is ideally not an obsession since the latter involves a craving for another person that might even lead to violence just to be in site of the other party.
- Analysis of Internet Friendship Issues Despite the correlation that develops on the internet, the question of whether social media can facilitate and guarantee the establishment of a real friend has remained a key area of discussion.
- “Feminism and Modern Friendship” by Marilyn Friedman Individualism denies that the identity and nature of human beings as individuals is a product of the roles of communities as well as social relationships.
- Childhood Friendship and Psychology Based on their research, they have founded a theory, according to which it is assumed that the children consider close relationship, appraisals, and sharing common interests as something very important to them and on the […]
- Friendship and Peer Networking in Middle Childhood Peer networking and friendship have a great impact on the development of a child and their overall well-being. Students in elementary need an opportunity to play and network with their peers.
- Friendship in “The Song of Roland” This phrase sums up Roland’s predicament in the book as it relates to his reluctance to sound the Oliphant horn. In the final horn-blowing episode, Roland is aggressively persuaded to blow the horn for Charlemagne’s […]
- True Friendship from Personal Perspective The perfect understanding of another person’s character and visions is one of the first characteristics of a true friendship. In such a way, true friendship is an inexhaustible source of positive emotions needed for everyone […]
- Trust Aspect of Friendship: Qualitative Study Given the previous research on preserving close communication and terminating it, the authors seek to examine the basics of productive friendship and the circumstances that contribute to the end of the interaction.
- Educator-Student Relationships: Friendship or Authority? Ford and Sassi present the view that the combination of authority and the establishment of interpersonal relations should become the way to improve the performance of learners.
- Friendship in the Film “The Breakfast Club” The main themes which can be identified in the storyline are crisis as a cause and catalyst of friendship, friendship and belonging, and disclosure and intimacy in friendship.
- Friendship Police Department Organizational Change The one that is going to challenge the efforts, which will be aimed at rectifying the situation, is the lack of trust that the employees have for the new leader who they expect to become […]
- Friendship in the Analects and Zhuangzi Texts The author of “The Analects of Confucius” uses the word friend in the first section of the text to emphasize the importance of friendship.
- How to Develop a Friendship: Strategies to Meet New Friends Maintaining a connection with old friends and finding time to share life updates with them is a good strategy not to lose ties a person already has. A person should work hard to form healthy […]
- Is There Friendship Between Women? In conclusion, comparing my idea of women’s friendship discussed in my proposal to the theoretic materials of the course I came to a conclusion that strong friendship between women exists, and this is proved in […]
- Online Friendship Formationby in Mesch’s View The modern world tends to the situation when people develop the greatest empathy towards their online friends because it seems that the ratio and the deepness of these relationships can be controlled; written and posted […]
- Canadian-American Diefenbaker-Eisenhower Friendship In particular, the paper investigates the Mandatory Oil Import Program and the exemption of Canada from this initiative as well as the historical treaty that was officially appended by the two leaders in regard to […]
- Friendship from a Sociological Perspective For example Brazilians studying in Europe and United States were met with the stereotypes that Brazilians are warm people and are easy to establish friendships.
- Friendship Influencing Decisions When on Duty The main stakeholders are the local community, the judge, and the offenders. The right of the society is to receive objective and impartial treatment of its members.
- Friendship: To Stay or to Leave Each member of the group found out who really is a friend and who is not. This implies that the level of trust is high between Eddie and Vic.
- “Understanding Others, and Individual Differences in Friendship Interaction in Young Children”: Article Analysis The aspect of socio-cognitive abilities of small children in the process of interaction was disclosed with the help of psychological theories.
- Friendship: Sociological Term Review But one is not aware of that type of friendship; it is necessary to study it. Friendship is a matter of consciousness; love is absolutely unconscious.
- The Significance of Friendship in Yeonam The paper examines the depth and extent to which Yeonam was ready to go and if he was bound by the norms of the human friendship and association of his era.
- Cicero and Plutarch’s Views on Friendship He believed that befriending a man for sensual pleasures is the ideal of brute beasts; that is weak and uncertain with caprice as its foundation than wisdom. It is this that makes such carelessness in […]
- Friendship: The Meaning and Relevance Although the basic definition of a friendship falls under the category of somebody whom we feel a level of affection and trust for or perhaps a favored companion, the truth of the matter is that […]
- “Is True Friendship Dying Away?” and “The Price We Pay” Then Purpose of the essay is to depict the way social media such as Facebook and Twitter have influenced the lifestyles of every person in the world.
- Social Media Communication and Friendship According to Maria Konnikova, social media have altered the authenticity of relationships: the world where virtual interactions are predominant is likely to change the next generation in terms of the ability to develop full social […]
- Fate of Friendship and Contemporary Ethics Is friendship possible in the modern world dominated by pragmatism and will it exist in the future? For instance, Cicero takes the point of view of the social entity, in other words, he defines friendship […]
- Feminism and Modern Friendship While criticizing these individuals, Marilyn asserts that the omission of sex and gender implies that these individuals wanted to affirm that social attachment such as societies, families, and nationalities contribute to identity rather than sex […]
- Creating a Friendship Culture This family will ensure every church member and youth is part of the youth ministry. I will always help every newcomer in the ministry.
- Friendship is in Everyone’s Life Though, different books were written in different times, the descriptions of a friendship have the same essence and estimate that one cannot be completely satisfied with his/her life if one does not have a friend.
- Intimacy, Love and Friendship and how they translate to employability The use of love and its conventions in the NAB campaigns is an illustration of how love as a concept can be used to translate to employability.
- Intimacy, Love and Friendship In the past, women in Australia led a life characterized by a lot of hardships because of the harsh traditions that they were supposed to follow.
- Contemporary Understanding of Intimacy and Friendship The Social Network film discusses how Facebook was developed and the challenges of developing the giant social site. Many people are of the view that Facebook has the effect of enslaving them by making their […]
- Friendship’s meaning around the world Globally it’s very ludicrous today for people to claim that they are in a friendship yet they do not even know the true meaning of friendship.
- Interpretation of Friendship among Confucian and Neo-Confucian writers In his article “The Fifth Relationship; Dangerous Friendships in the Confucian Context”, Norman Kutcher explores the friendship as outlined under the Confucian system. The above writers have different interpretations of friendship of the under the […]
- Why International Students Find It Hard to Make Friends On the other hand, in societies that promote a high power distance, less powerful individuals accept their position in the chain of command and acknowledge the strengths of their superiors in the hierarchy.
- Gender Stereotyping and Friendship: Women Relationships The most interesting about this article is its ending which states that” the core of a friendship has to have more in-person interactions and experience”.
- The Impact of Friendship in the Epic of Gilgamesh The elusive coalition between Enkidu and Gilgamesh, their fateful destinies and eventual epiphanies broaden the societal apprehension of the elements/value of friendship as expounded in the next discussion.
- Woman Intimacy and Friendship with the Appearance of Social Media The anonymity provided by the social media makes this medium very appealing to both women and men as they are able to “reconstruct” themselves to a level they deem “cool” enough to garner more desired […]
- Faux Friendship and Social Networking The modern-day relationships have dissolved the meaning of the word friendship; as aromatic lovers refer to each other as friends, parents want their children to think of them as friends, teachers, clergymen and bosses have […]
- Aristotle’s Ideas on Civic Relationships: Happiness, the Virtues, Deliberation, Justice, and Friendship On building trust at work, employers are required to give minimum supervision to the employees in an effort to make the latter feel a sense of belonging and responsibility.
- Gender Role Development and Friendship As far as the conflict goes, the boy’s main problem is that he is unwilling to change his behavior towards a socially accepted one under the pretext that girls are more beautiful and, therefore, it […]
- Article Study on the Friendship Concept In the critical review article, the views of Norman Kutcher on the formation of friendships are discussed in detail. In this article, the views of other scholars are discussed in order to strengthen the works […]
- Henry Thoreau: The Concept of the Friendship Not every person is able to understand the essence of nature, its uniqueness, and importance. To my mind, his close connection to nature and a kind of isolation from people helped him to understand deeper […]
- Why Honesty Is Important In A Friendship
- The Truth and Friendship in the Movie Camelot
- A Discussion About the Value of Friendship as Portrayed in Damon and Pythias
- What Is the Meaning of True Friendship
- A Literary Analysis of Friendship in Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare
- Factors Contributing to the Ups and Downs of Friendship in Knowles’ A Separate Peace
- Friendship and Love in the Little Prince
- Confidantes, Marriage, and Friendship in Pride and Prejudice
- What Makes A Successful Friendship
- Understanding Friendship Through The Staircase Model
- An Analysis of Friendship and Rejection in The Heart is a Lonely Hunter by Carson McCullers
- A Discussion on the Different Types of Friendship
- An Analysis of Friendship in Lord of the Flies by William Golding
- A Literary Analysis of Friendship in a Separate Peace by John Knowles
- An Analysis of the Concept of Friendship in A Separate Piece by John Knowles
- A Separate Peace and Of Mice and Men – Real Friendship
- The Theme of True Friendship in the Book of Mice and Men by John Steinbeck
- The Value of Friendship in Great Expectations
- What Makes A Good Friendship
- The Theme of Friendship in Separate Ways by Higuchi Ichiyo and Uncanny Stories by SongLing
- Virtual Friendship and the New Narcissism
- The Waltz Of Sociability : Intimacy, Dislocation And Friendship
- The True Meaning of the Word Friendship
- A Description of Impartiality, Beneficence and Friendship According to Lawrence Blum
- Aristotle ‘s Views On Friendship
- Friendship and Courage in The Old Man and the Sea by Ernest Hemingway
- An Analysis of Friendship and Loyalty in the Film The Deer Hunter
- Turning Away from True Friendship
- Different Types of Friendship and The Need for Friends
- An Analysis of the Dangers of Friendship
- The Victorian Female Friendship and Homosexual References in Emily Dickinson’s Work
- What Is Friendship And How Is God Man ‘s Best Friend?
- The Venerable Kassapa Thera: A Living Symbol of Dedication, Courage, Altruism and Intimate Friendship
- “The Undoing Project: A Friendship that Changed Our Minds” by Michael Lewis
- Building from Happiness to Friendship
- What Do You Think Steinbeck Says About the Theme of Friendship in of Mice and Men
- Distributive Justice and the Problem of Friendship
- How Does Shakespeare Demonstrate That Love and Friendship Can Overcome Greed in the Merchant of Venice?
- Does Borrowing Money From Friends Harm Friendship?
- Can Friendship Be Defined by Any Scientific Criteria?
- How Can Enduring Happiness Arise From Friendship?
- Does Campus Diversity Promote Friendship Diversity?
- Is There Any Objection to the Teacher Establishing a Friendship Relationship With the Students?
- How Do Children Cope With Friendship and Death After Reading Charlottes Web?
- Does Ragging Develop Friendship?
- How Does Shakespeare Create Friendship?
- Should Becoming Friends With Benefits Ruin Your Friendship?
- How Does the Nature of Children’s Friendship Change With Age?
- Do Friendships Vary Across Countries?
- What Are Friends for and How Can a Friendship Be Tested?
- How Does the Theme of Loneliness Affect the Friendship and Relationships in “Of Mice and Men”?
- What Are the Elements That Build a Strong Friendship?
- How Does Friendship Help Students Succeed in the University?
- What Does Friendship Mean?
- How Does Friendship Help With Your Mental Health?
- What Does True Friendship Require?
- How Do Friendship Network Characteristics Influence Subjective Well-Being?
- What Was Aristotle’s Thought on Friendship?
- How Do Friendship Networks Work in Online P2P Lending Markets?
- Why Is Friendship Important?
- How Has Friendship Changed Because of the Spread of Social Networking?
- Why Does Friendship End?
- How Do Society and Culture Affect Friendship?
- Can Everything Be Bought for Money?
- How Do Gamers Take the Gaming Experience, Elements Such as Friendships Outside the Game Context?
- Do Friends Generally Have Similar Educational Interests?
- What Individual and Country-Level Factors Might Interact With Friendship Importance to Predict Health and Well-Being?
- Adulthood Titles
- Social Norms Essay Ideas
- Communication Research Ideas
- Respect Essay Topics
- Self Esteem Research Ideas
- Victimology Research Ideas
- Social Development Essay Topics
- Conflict Resolution Essay Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 24). 127 Friendship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/friendship-essay-examples/
"127 Friendship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 24 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/friendship-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '127 Friendship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 24 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "127 Friendship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/friendship-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "127 Friendship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/friendship-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "127 Friendship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/friendship-essay-examples/.
Every item on this page was chosen by a Shondaland editor. We may earn commission on some of the items you choose to buy.
The Art of Friendship: How to Address and Respond to Conflict
Learn the best methods for navigating disagreements with friends, whether you’re bringing up or responding to hurt feelings.
Friendships are love stories too. In the Shondaland series The Art of Friendship , we explore and appreciate the beauty and complexities of friendship, as well as what makes it so powerful. From expert tips on how to navigate conflicts and deepen your friendships to uplifting stories of reconnections and advice on making new friends, these stories are reminders of the joy, value, and meaning that companionship brings to our lives.
Taylor Lamb is friends with five women who have known one another for the better part of the last seven years. Following their college years at the University of Virginia, the group became more intentional about maintaining their bond when proximity no longer bound them together. They revved up a group chat, held virtual hangouts around the holidays, and committed to always celebrating birthdays in person — even if it meant jumping on a train or a plane.
After a few years, each of the women ended up in the mid-Atlantic region for work, medical school, or law school. While they were physically close again, they began experiencing splinters in their seven-year friendship for the first time when some members of the group started backing out of planned gatherings at the last minute.
“I feel like people were feeling unheard and wanting more support,” Lamb says of the rift. The 25-year-old community engagement associate recognized that navigating the pandemic made communication even more difficult. “It just seemed like we all just needed to get in a room and talk.”
Lamb reached out to each friend individually and gauged their willingness for a group conversation; they all agreed to have one. In early May, they gathered in person (with one friend tuning in virtually) to have an open discussion with Lamb as their facilitator. With conversational guidelines painted onto a poster as a North Star, the ground rules were set. The gentle reminders encouraged the women to release any spirit of defensiveness, refrain from interrupting others, assume best intent — but mind impact — pause and take a deep breath if needed, and partake in other helpful actions.

To start, Lamb acknowledged that conflict is hard, especially for those who did not grow up encouraged to talk about their feelings or were unable to do so in a safe space. “I feel like acknowledging that made people not want to be reactive,” she says. Her goal wasn’t to come with an agenda but to “hold the space” for her friends to feel like they could share their thoughts safely. She opened the floor by asking who wanted to speak first, and each individual shared how they were feeling.
“The conclusions we came to,” Lamb says, “were that people had expectations of what they needed to be cared for, but they never said those.” She adds that bell hooks’ All About Love inspired how she approaches her relationships. “Me personally being an abolitionist and wanting to build a new world, we have to be willing to talk about our issues. And expecting other people to know how we feel is not what love really is.”
William Morrow & Company All About Love: New Visions

Before the exchange concluded, they each took turns expressing what makes them feel cared for, sharing their love language and coming up with specific communication guidelines to use moving forward. It dawned on Lamb that these women didn’t only want to be in one another’s lives for the good times, but that they cared about and valued one another enough to stick it out through the hard ones too. “I feel really happy that we’re all committed to our friendship in this way,” she says. “I feel closer to them.”
There’s a glaring absence of dialogue today on how to work through conflict with friends. The popular belief that a friendship shouldn’t make you uncomfortable and that you should cut someone off at the first sign of tension or disappointment has seeped into the collective consciousness, but relationship experts agree: That’s not real friendship.
Platonic: How the Science of Attachment Can Help You Make — and Keep — Friends

Conflict is not an automatic sign that a friendship will end; addressing it can be a signal that both parties are committed to the relationship. Many people talk themselves out of bringing up an issue because they don’t want to seem as if they’re the problem, but withholding discomfort can manifest itself in another way, whether through withdrawal or resentment. “Think of it as something that will help not hurt,” says female friendship coach and educator Danielle Bayard Jackson .
Why should you address conflict with friends?
Honing your ability to work through conflict in a long-term platonic relationship is no different than learning to do so in a committed romantic partnership. Many withhold their feelings out of the fear that they will be perceived as dramatic or difficult or that it will tear the friendship apart, but with a real friend, that’s not the case. A 2012 paper found that open, non-blaming conversations lead to deeper intimacy between people, as opposed to not having those conversations at all.
Psychoanalyst Virginia Goldner came up with a concept for the illusion of closeness without conflict: flaccid safety versus dynamic safety . Flaccid safety is the sense of stability within a relationship when we pretend that nothing is bothering us. Dynamic safety is a more robust, deeper level of intimacy that is achieved when there’s rupture and repair, or in Goldner’s words, a cycle of “risk-taking and resolution” or “separation and reunion.” There is trust in the knowledge that issues will less easily come between friends and authentic comfort in the shared history that you are willing to work through hard emotions together.
“That closeness that you want with the friend where you feel like you can be yourself and you can say anything that we all dreamily speak of — to achieve that, sometimes you have to go through the awkwardness of bringing up something that makes you feel uncomfortable,” says Jackson. “It gives her a chance to demonstrate: I love you. I care about you. I hear you. We might get into it. We might disagree. All those things. But once we work it out, I’m going to feel more connected to you than I did before. That is not possible without having a difficult moment.”
When the challenge arises, don’t run from the chance to deepen your bond. Here’s how to address conflict with a friend, whether you’re bringing up the issue or responding to your loved one’s concern.
How to Address Conflict
Examine the problem
Coping with conflict is the goal, but that doesn’t mean you have to confront your friend every single time they do something that bothers or annoys you. A helpful way to assess if it’s worth going to them about it is if it is a recurring issue or a situation that has continued to affect how you perceive your friend and how you show up in your friendship.
“Anger is a signal that there might be some conflict to address, because anger tends to be a signal that there’s an injustice that’s happening,” Franco says. While this is true, Franco notes that we can acknowledge our anger without it being the emotion that guides the conversation.
Assess the relationship
Your level of closeness to the person is a factor worth considering when deciding whether to bring up an issue with your friend. Franco suggests, “If it’s not a friend that you’re particularly close to or if it’s a newer friend and you already find yourself getting into conflict, ask yourself: Is this a sign that this is maybe not a good friendship for me?”
Franco adds, “Generally, I say that if it’s a friend you’ve had for a long time, and you have each other’s best interests at heart, it’s always worth it to address it.” Conflict isn’t automatically an indicator of incompatibility; it may simply be the sign of differing preferences that can be bridged with communication.


Define timing
As the saying goes — timing is everything. “Ask yourself, ‘If this goes wrong, do I really have the capacity to tolerate that?’ You will hopefully say yes to that question,” Franco says. Emotional regulation is key to an effective conversation, and we are better at regulating our emotions when we’ve slept well , exercised, meditated, and are in a physically good space in addition to our mental one.
While you shouldn’t continually use personal struggles as an excuse to keep putting off the discussion, it is important to consider if you have the immediate capacity for it. Carve out an entire afternoon — or day, if you need it — so that you aren’t rushing through your chat and have time to process any emotions you may feel afterward.

Provide a warning
When it comes to conflict resolution, don’t surprise your friend with the topic. If you’ve given yourself a chance to prepare for the conversation, you should also extend the same courtesy to your friend. “If their pet just died or they’re going through a breakup,” Franco says, “they might just not have the capacity to do conflict well.”
Consider if they are in a space where they can actually receive and process your feelings. If not, it’s likely that they will go into fight-or-flight mode, and the discussion could be doomed from the start. While it’s important to be thoughtful, don’t make assumptions about whether your friend is in a good or bad space. Trust in their ability to decide for themselves, and ask gently ahead of time.
“I like to text an introduction to the conflict,” Franco says. You don’t have to be specific, but you can let them know that you have something on your mind you want to work through together and ask if they’d be up for talking about it.
Lean into vulnerability
If you feel nervous about bringing your feelings up, that may be a signal that it’s worth sharing. You don’t have to wait until you’re feeling confident about it; use those authentic feelings as leverage.
Jackson encourages resolution-seekers to acknowledge their messy emotions rather than shy away from them. “A lot of us feel anxious or vulnerable bringing it up,” she says, “but it can actually work in our favor.” Start the conversation by being honest about your nerves. (Jackson provides a few scripts: “I’m hesitant to bring this up because the last thing I want is for it to be awkward” or “I’m nervous, but I want to be open with you, and I hope you’d do the same for me.”)
If a friend sees that you have been thoughtful and considerate, it may ease their nerves as well and expand their ability to receive your emotions. “Being that transparent about your internal dilemma sometimes works for you,” Jackson notes, “in bringing down their walls.”
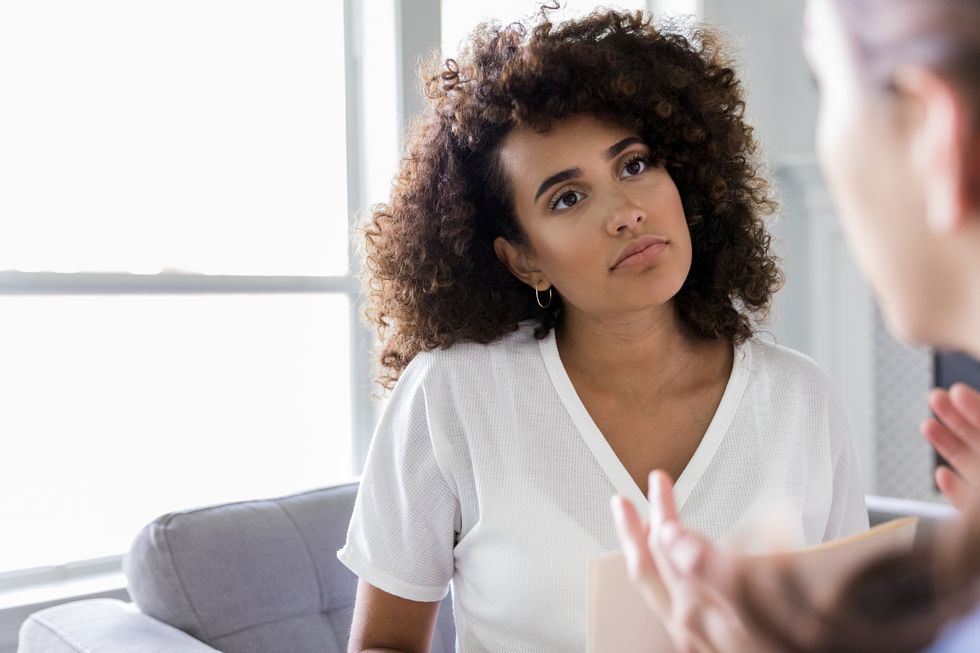

Use inviting language
When it comes to conflict, how you start the conversation influences the mood, tone, and direction of the talk more than you know. Franco calls this framing, or using verbiage that welcomes your friend in rather than alienates them. She gives an example of a positive framing script: “Hey, our friendship is really important to me, so I want to make sure we talk through things so that they don’t get between us. I was wondering if we can talk about something that’s been on my mind.”
It’s a warm way to remind your friend — and yourself — that you’re on the same team, not opposing sides. “You’re telling them how to interpret this,” Franco says. “That this is an act of love and a sign of your investment in the friendship, so the framing line is really important.”
Speak to your reality, not theirs
Addressing conflict isn’t about right or wrong; it’s about coming to a sense of mutual understanding. When sharing your dilemma, keep the focus of your words on you and how you feel by using “I” statements. Start by expressing how it made you feel when your friend did what they did. Don’t blame them, project assumptions onto them, or attack their character or ability to be a friend overall.
Think of it as a moment to share how it made you feel. Remember: Feelings are information, not fact. You have every right to feel let down that a friend bailed on you at the last minute, for example, but it doesn’t mean that your friend plotted to let you down.
Ask about their experience
After sharing your hurt, put on your listening ears, and listen to where your friend was coming from. Franco recommends asking about what was going on for them at that time, and what might have gotten in the way for them. “What you’re trying to do in a larger way is to embrace something called mutuality, which means you’re considering their experience and your experience at the same time instead of only thinking about yourself or thinking about them.” Franco says true mutuality is not about right or wrong but about finding balance and understanding. You don’t need to kowtow to their reasoning, but you should hear them out.
How to Respond to Conflict
View it as an act of love
If you have been approached by a friend about how you’ve hurt them, remember that they care enough to bring it to you and are willing to be their vulnerable self with you, which is not easy for most people.
While it may be uncomfortable, it might be even more unpleasant to think what might happen if they didn’t come to you. There is a chance they may have withdrawn from the friendship and let you go entirely. “Remind yourself that this is an act of love that is there to heal us and bring us together,” Franco says, “and that this is your friend showing that they’re invested in you enough to want to work through this issue.”
Protect yourself from fight or flight
Whatever you do, do not take notes from dramatic TV show scenes where two best friends are shouting what they hate about each other from across the room and one person stomps out.
“When you’re in fight or flight, you’re not able to engage in mutuality. You’re only thinking about your reality,” Franco says. Do what you need to do to refrain from sending emotions into overdrive — even if that means you need to take a break during the actual conversation. “If you have the capacity to de-escalate, always do,” Franco says. “For me, I think about the idea of splitting into two selves. … I see the part of me that wants to escalate this, and I have this other part of me that is going to try to access my higher self for this conversation.”
If the dialogue grows heated, verbalize that you need a moment instead of shutting down. Franco provides another script: “Hey, that’s kind of hurtful. I hope that we can have this conversation in a way that we’re not going to be labeling each other or putting each other down. And maybe that means we take a moment here.”

Ask for time
In the heat of the moment, it’s hard to remember that we are real people and not characters we see on TV. The witty, speedy, perfectly curated dialogue on-screen is not always a reality. In fact, quippy back-and-forth dialogue can promote defensiveness and regrettable statements.
If your friend surprises you with their concern, you are allowed to ask for some time to process this new information. “No one wants to hear that what they’re doing is not good enough,” Jackson says.
To keep from providing a knee-jerk reaction or justifying your actions, take a pause, ask for a moment, and call back later, or even take a day or two. It will help your relationship in the long run and give you space to be receptive rather than reactive. “I think you’ll find it very liberating,” Jackson adds, “because the first thing you want to say is often not the route you end up really wanting to have taken.”
Depersonalize it
Whatever your friend might tell you, rather than spiraling out of control about how you may be a bad friend, succumbing to the imaginary conclusion that they hate you, or convincing yourself that may be too [insert negative adjective here], frame it as information instead.
“At the risk of oversimplifying this, I wonder how much we’d be able to salvage our friendships if we took a breath and said, ‘Okay. That’s not mean. This is data,’” Jackson says. If a friend conjures up the courage to tell you they don’t like how you spoke to them or that a joke hurt their feelings, remember that it is simply their preference. A certain word or action may trigger them, but it might not trigger you, and vice versa. It’s simply about respecting and honoring your friend’s request next time.
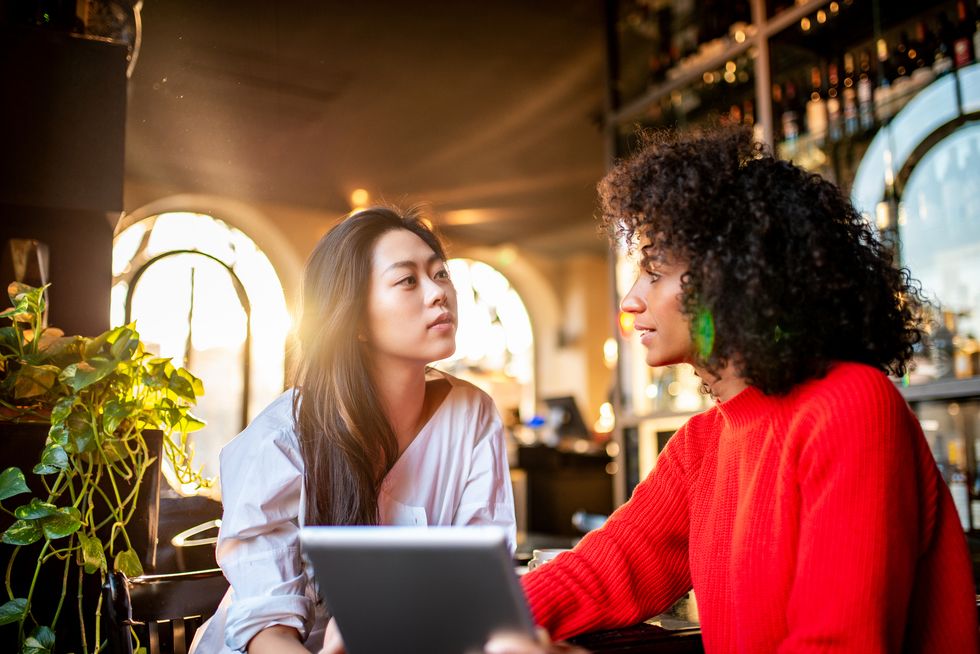

Listen to understand
Don’t be afraid to ask questions to fully understand where your friend is coming from. Whatever information you need, take this as an opportunity to learn more about your friend and your friendship. Before the conversation ends, let your friend know that you hear them. Confirm what has upset them, and verbalize that you care and understand where they’re coming from — no ifs, ands, or buts. If you would like to avoid hurting them in the future, express how you will go about it next time.
Mia Brabham is a staff writer at Shondaland. Follow her on Twitter at @hotmessmia .

Relationships & Family

55 Fun Valentine's Day Trivia Facts

64 Valentine’s Day Gifts for Every Loved One

I Liberated Myself From My Mother’s Hoarding

My Daughter Helped Me Grow a Backbone

I Challenged Myself to Stop Talking About Myself

My Neighbor Looks Exactly Like My Ex

Why Do People Laugh at Bad News?

I Helped My Mother Reconnect With Nature

How to Be Antifragile

Please Don’t Text Me “Good Morning”

What It Took to Find Friendship
- Dissertation
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Book Report/Review
- Research Proposal
- Math Problems
- Proofreading
- Movie Review
- Cover Letter Writing
- Personal Statement
- Nursing Paper
- Argumentative Essay
- Research Paper
- Discussion Board Post
Mastering The Art Of Writing A Great Conflict Essay

Table of Contents

… But how to write a conflict essay?
This task can become a real stone of stumbling for many students, especially when they write admissions essays.
The practice shows that students tend to describe conflicts in the one-dimensional narrative, where one side of the conflict is depicted as a knight in shining armor and the other side is a complete villain.
Of course, it is the simplest way to manage conflicts (as anyone sees clearly, who is right), however, this approach highlight the inability to give an unbiased assessment of both sides of the conflict.
Here we will cover the essentials of writing such essays and how to avoid the most common mistakes in the conflict papers.
Studying the basics of the conflict essay
What is conflict, and what are its causes? Is it possible to avoid it, and how to solve it? Who are the participants, and is there a possibility for them to have a peaceful order? Here are the main points that should be covered in your text.
But what are you going to write about?
Different vocabularies give so many different definitions of this term that it is so easy to be bamboozled by all these meanings.
- A war of a fight.
- A mental struggle.
- An opposition of persons or forces.
- Anything that sets the character back from achieving a specific goal (in fiction).
That is why it is crucial to read and understand the task before you start writing.
Writing guideline for the essays about conflict
Your journey to the perfect paper should start with the proper investigation:
- What is the type of conflict you are writing about?
- What are its reasons?
- What are the consequences?
- How to solve it?
Taking into consideration all mentioned above, it becomes clear that the disagreement between two people does not limit the type of conflict. It also may cover a conflict between a man and society or nature, or even a fight against self.
And do not forget about the key players: the protagonist and antagonist of the conflict.
As soon as you have defined the central conflicts and leading players, it is time to gather facts that prove this point of view. Arm yourself with a pen and start searching for the evidence of conflict in the literary work, if your task is to cover the conflict depicted in a novel or a poem.
You may use many sources for data collection; however, make sure that they are reliable and relevant. And do not forget to jot down the information about the source for proper referencing; otherwise, using materials without appropriate arrangement will be considered plagiarism.
Carefully analyze gathered material and single out a precise thesis statement that will be the basis of the paper. Later it will become the last sentence of the introduction, but now it is the basis of the outline for your essay on conflict. The basic outline template for such paper will look like this:
- A hook sentence – an interesting fact, question, quote, or anecdote.
- Introduction part that makes readers aware of the conflict.
- Thesis statement.
- 3 body paragraphs , each with one issue of the conflict and several proofs.
- Address whether the conflict was resolved or not.
- You may also discuss the ways of avoiding or solving the conflict.
- The conclusion should cover the main points of the paper with the rephrasing of a thesis.
Breaking down a personal conflict essay
Two types of conflict can be covered in the essay – personal and internal. Personal, on its turn, can be divided into a conflict between people, or a person and organization, or a person and a state (especially in the countries of the totalitarian regime).
Usually, students prefer to describe their own conflict experience, for example, with parents or peers. In this case, one has to define the purpose of writing as thereon hangs the tone of the text. For example, the aim is to show that there are no right or wrong, but two legitimate points of view.
Then the tone of the paper will be empathic as the writer has the insight into the opposite point of view and there are two sides of every story.
What about an internal conflict essay?
Such essays deal with the psychological conflicts inside one person. Thus, they discuss what happens when we have to do something that is against ethical standards or values, or the clash of logical and emotional response to something.
Here much prominence should be given to the ways of overcoming this conflict and as a result, becoming a better person.
And in both cases, it is necessary to follow these guidelines to improve the quality of the text:
- Pay attention to the task requirements: do not exceed the word limit , arrange the quotes according to the chosen referencing style, format the paper properly.
- Make sure that the paper is plagiarism-free .
- Edit and proofread the text.
Take advantage of a well-written conflict essay example
As they say, seeing once is better than hearing twice. When you look through a top-notch paper written by a professional writer, everything clicks into place.
What is more, you can use such paper as a template for your own paper and as a source of inspiration.
…What’s not to love?
Can’t complete such task in time? Entrust it to the professionals! Save time and energy, while your flawless paper will be ready for you in no time!

Descriptive Essay About a Person
100 proposal topics ideas for your assignment, an ultimate guide on how to write a research paper for a+.
- Browse Topics
- Executive Committee
- Affiliated Faculty
- Harvard Negotiation Project
- Great Negotiator
- American Secretaries of State Project
- Awards, Grants, and Fellowships
- Negotiation Programs
- Mediation Programs
- One-Day Programs
- In-House Training – Inquiry Form
- In-Person Programs
- Online Programs
- Advanced Materials Search
- Contact Information
- The Teaching Negotiation Resource Center Policies
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Negotiation Journal
- Harvard Negotiation Law Review
- Working Conference on AI, Technology, and Negotiation
- 40th Anniversary Symposium
- Free Reports and Program Guides
Free Videos
- Upcoming Events
- Past Events
- Event Series
- Our Mission
- Keyword Index
PON – Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School - https://www.pon.harvard.edu
Team-Building Strategies: Building a Winning Team for Your Organization

Discover how to build a winning team and boost your business negotiation results in this free special report, Team Building Strategies for Your Organization, from Harvard Law School.
- How Conflict Examples Can Teach Us to Listen
Listening deeply to our counterparts is a critical negotiation skill. Here, we look at how conflict examples can help us transform unproductive conflict into opportunities to listen and learn.
By Katie Shonk — on June 3rd, 2024 / Conflict Resolution
Listening is perhaps the clearest path to understanding others and resolving conflict, but it can be difficult to practice. The desire to disagree, prove we’re “right,” and engage in hardball tactics often get in the way. Here, we consider how transformative listening can be, then study how deep listening plays out in conflict examples.
Learning When Forced to Listen
In the 1980s, Jessie Daniels entered the sociology PhD program at the University of Texas with a lot of assumptions about the world, as she writes in a new anthology of personal essays by sociologists, Between Us: Healing Ourselves and Changing the World Through Sociology . Some of those assumptions were profoundly shaken when she secured a research position with Dr. Joe Feagin.
Feagin assigned Daniels the task of transcribing interviews with middle-class Black Americans about their experience with racism. At the time, Daniels, who is white, naively assumed that because the Civil Rights Act had made racial discrimination illegal in the United States, the interviewees might be “overly sensitive, looking for discrimination where there was none,” she recalls.
In fact, she soon found, the interviewees were slow to complain. When they did share stories of possible discrimination, they agonized over how to interpret them. One woman, for instance, described being seated at the back of a restaurant, near the kitchen. “Oh, come on,” Daniels thought. “ That could happen to anyone .” But as Daniels noted, the woman on the tape “couldn’t hear me, and I couldn’t actually interrupt her, so I just kept typing.”
In her interview, the woman expressed how confusing the incident was: “It could be discrimination, or it could not be, but now I’ve got to spend my energy to try and figure this out, because you know, I don’t want to be one of those complaining types.” She concluded, “It’s an exhausting way to go through life.” From nearly every interviewee, Daniels heard similar stories of “internal calculation in response to discrimination.”
By listening closely to the interviewees—with no opportunity to question or rebut them—Daniels gained a deeper understanding of systemic racism and the pain and confusion it causes. “By the end of transcribing those interviews, something fundamental in me had shifted,” she writes. “Instead of arguing or disagreeing with the Black people I’d spent time listening to, I was in solidarity with them.”
Daniels’ story illustrates how listening deeply to other people can challenge our preconceived beliefs. Listening can be especially beneficial in bringing disputing parties together, as the following conflict examples suggest.
Transforming Your Listening Skills
In her book Transformative Negotiation: Strategies for Everyday Change and Equitable Futures , Sarah Federman explores real-world conflict examples to illustrate how negotiation can help those in financial precarity achieve greater stability. While teaching negotiation at the University of Baltimore, she learned to adapt traditional negotiation training to the lives of her students, who were coping with problems such as negotiating car insurance claims and adapting to life after incarceration.
Teaching active listening skills in negotiation was core to this training. In particular, Federman encourages her students to “ ask five information-seeking questions with no agenda ” of others in their lives. “This means they can only ask questions to better understand the person’s world, not to lead the person toward or away from a particular solution,” she writes.
One student asked the following five questions of his brother, who had been diagnosed with paranoid schizophrenia and recently discharged from the hospital:
- How do you feel?
- How do you like the new medication?
- How do we make sure you stay on the medication and go for quarterly checkups?
- Would you talk to me whenever you feel like the drugs are not working?
- Do you need anything?
By asking these questions and listening carefully, the student gained a new understanding of how much his brother had suffered and of his past behavior. As Federman writes, “Good listening can reduce household and workplace tension, preventing conflict and making negotiations easier when they occur.”
Listening Is Contagious
Turning to conflict examples in a galaxy far, far away, mediator and coach Danielle Blumenberg describes the power of listening in negotiation in an essay for the new anthology Star Wars and Conflict Resolution II: My Negotiations Will Not Fail , which gleans conflict-resolution strategies from the Star Wars universe. In the film The Force Awakens, Blumenberg describes encounters between the self-reliant scavenger Rey, hero Luke Skywalker, and dark side warrior Kylo Ren.
In one scene, Rey tries telling Luke about the “darkness she feels calling to her,” Blumenberg writes, but “Luke doesn’t listen well—instead, he reacts with fear and shuts her down.” In a later encounter with Kylo, Rey “mirrors Luke’s approach, casting accusations at Kylo and not seeking information.” Clearly, poor listening can become a vicious cycle.
But rather than shutting her down, as Luke did, Kylo “responds with curiosity”; he ignores her insults and begins asking questions. The next time they connect, Rey reciprocates by asking Kylo questions and seeking to understand his behavior. “Their mutual listening begins to move them past their conflict,” writes Blumenberg. The key to this breakthrough was Kylo’s ability to move beyond accusation and respond by listening closely—a negotiation strategy we can all adopt.
What have you learned from recent conflict examples in your life?
Related Posts
- Business Conflict Management
- Conflict Resolution Examples in History: Learning from Nuclear Disarmament
- Strategies to Resolve Conflict over Deeply Held Values
- How to Handle Conflict in Teams: Lessons from Scientific Collaborations
- 5 Conflict Resolution Strategies
Click here to cancel reply.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Negotiation and Leadership
- Learn More about Negotiation and Leadership

NEGOTIATION MASTER CLASS
- Learn More about Harvard Negotiation Master Class

Negotiation Essentials Online
- Learn More about Negotiation Essentials Online

Beyond the Back Table: Working with People and Organizations to Get to Yes
- Learn More about Beyond the Back Table

Select Your Free Special Report
- Negotiation Master Class November 2024 Program Guide
- Beyond the Back Table September 2024 and February 2025 Program Guide
- Negotiation and Leadership Fall 2024 Program Guide
- Negotiation Essentials Online (NEO) Spring 2024 Program Guide
- Negotiation and Leadership Spring 2024 Program Guide
- Make the Most of Online Negotiations
- Managing Multiparty Negotiations
- Getting the Deal Done
- Salary Negotiation: How to Negotiate Salary: Learn the Best Techniques to Help You Manage the Most Difficult Salary Negotiations and What You Need to Know When Asking for a Raise
- Overcoming Cultural Barriers in Negotiation: Cross Cultural Communication Techniques and Negotiation Skills From International Business and Diplomacy
Teaching Negotiation Resource Center
- Teaching Materials and Publications
Stay Connected to PON
Preparing for negotiation.
Understanding how to arrange the meeting space is a key aspect of preparing for negotiation. In this video, Professor Guhan Subramanian discusses a real world example of how seating arrangements can influence a negotiator’s success. This discussion was held at the 3 day executive education workshop for senior executives at the Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School.
Guhan Subramanian is the Professor of Law and Business at the Harvard Law School and Professor of Business Law at the Harvard Business School.
Articles & Insights
- Managing Difficult Negotiators
- Learning from BATNA Examples in Negotiation
- Power and Negotiation: Advice on First Offers
- 10 Hard-Bargaining Tactics to Watch Out for in a Negotiation
- The Good Cop, Bad Cop Negotiation Strategy
- How to Set Negotiation Goals as a Manager
- Signing Bonus Negotiation 101
- Top 10 Notable Negotiations of 2022
- Framing in Negotiation
- Negotiation Tactics, BATNA and Examples for Creating Value in Business Negotiations
- AI Negotiation in the News
- Crisis Negotiation Skills: The Hostage Negotiator’s Drill
- Police Negotiation Techniques from the NYPD Crisis Negotiations Team
- Famous Negotiations Cases – NBA and the Power of Deadlines at the Bargaining Table
- Negotiating Change During the Covid-19 Pandemic
- Dealing with Difficult People and Negotiation: When Should You Give Up the Fight?
- Managing Difficult Employees: Listening to Learn
- Dealing with Hardball Tactics in Negotiation
- Dealing with Difficult People: Coping with an Insulting Offer in Contract Negotiations
- When Dealing with Difficult People, Look Inward
- Negotiating Skills: Learn How to Build Trust at the Negotiation Table
- What is Distributive Negotiation and Five Proven Strategies
- Dear Negotiation Coach: How Should I Handle an Early Offer Negotiation?
- Managing a Multiparty Negotiation
- MESO Negotiation: The Benefits of Making Multiple Equivalent Simultaneous Offers in Business Negotiations
- In Contract Negotiations, Agree on How You’ll Disagree
- Union Strikes and Dispute Resolution Strategies
- The Importance of Power in Negotiations: Taylor Swift Shakes it Off
- Settling Out of Court: Negotiating in the Shadow of the Law
- How to Negotiate with Friends and Family
- Cross Cultural Communication: Translation and Negotiation
- Famous Negotiators: Tony Blair’s 10 Principles to Guide Diplomats in International Conflict Resolution
- What is the Multi-Door Courthouse Concept
- Famous Negotiators: Angela Merkel and Vladimir Putin
- The Importance of Relationship Building in China
- Moral Leadership: Do Women Negotiate More Ethically than Men?
- What Is Facilitative Leadership?
- What Is Collective Leadership?
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Leadership Styles: Uncovering Bias and Generating Mutual Gains
- Leadership and Decision-Making: Empowering Better Decisions
- Employee Mediation Techniques – Resolve Disputes and Manage Conflict with These Mediation Skills
- How Mediation Works When Both Parties Agree They Need Help Resolving the Dispute
- Negotiations and Logrolling: Discover Opportunities to Generate Mutual Gains
- Using E-Mediation and Online Mediation Techniques for Conflict Resolution
- Undecided on Your Dispute Resolution Process? Combine Mediation and Arbitration, Known as Med-Arb
- Six Guidelines for “Getting to Yes”
- When a Job Offer is “Nonnegotiable”
- Emotional Intelligence as a Negotiating Skill
- Principled Negotiation: Focus on Interests to Create Value
- Power in Negotiation: The Impact on Negotiators and the Negotiation Process
- 3-D Negotiation Strategy
- Use a Negotiation Preparation Worksheet for Continuous Improvement
- The Importance of a Relationship in Negotiation
- Collaborative Negotiation Examples: Tenants and Landlords
- Ethics and Negotiation: 5 Principles of Negotiation to Boost Your Bargaining Skills in Business Situations
- Are Salary Negotiation Skills Different for Men and Women?
- How to Ask for a Salary Increase
- How to Negotiate Salary: 3 Winning Strategies
- How to Negotiate a Higher Salary
- Setting Standards in Negotiations
- Teaching Mediation: Exercises to Help Students Acquire Mediation Skills
- Teach Your Students to Negotiate a Management Crisis
- Teaching with Multi-Round Simulations: Balancing Internal and External Negotiations
- Asynchronous Learning: Negotiation Exercises to Keep Students Engaged Outside the Classroom
- Redevelopment Negotiation: The Challenges of Rebuilding the World Trade Center
- 5 Win-Win Negotiation Strategies
- What is a Win-Win Negotiation?
- Win-Win Negotiation: Managing Your Counterpart’s Satisfaction
- Win-Lose Negotiation Examples
- How to Negotiate Mutually Beneficial Noncompete Agreements
PON Publications
- Negotiation Data Repository (NDR)
- New Frontiers, New Roleplays: Next Generation Teaching and Training
- Negotiating Transboundary Water Agreements
- Learning from Practice to Teach for Practice—Reflections From a Novel Training Series for International Climate Negotiators
- Insights From PON’s Great Negotiators and the American Secretaries of State Program
- Gender and Privilege in Negotiation
Remember Me This setting should only be used on your home or work computer.
Lost your password? Create a new password of your choice.
Copyright © 2024 Negotiation Daily. All rights reserved.
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets and Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Services
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
Communicating Through Conflict: How to Get Along with Anyone
In this episode, Amy Gallo shares how disagreements, if reframed, can lead to more productive outcomes.
May 29, 2024
Many of us would rank getting along with colleagues as an important aspect of work, but, as Amy Gallo explains, relationships devoid of disagreement can actually be less productive.
“While our natural human instinct is to avoid conflict, I believe that conflicts are not only an inevitable part of interacting with other humans, but they’re a necessary part.”
Gallo is a workplace expert, host of HBR’s Women at Work podcast, and the author of Getting Along: How to Work With Anyone . Across her work, Gallo demonstrates that the key to transforming conflicts into something productive is to understand their root causes and learn how to reframe them.
“Even at the base of those unhealthy conflicts or those unproductive conflicts is something that needs to be resolved,” she says.
In her conversation with host and strategic communications lecturer Matt Abrahams, Gallo provides useful frameworks and new concepts on how we can approach conflicts at work.
Listen & Subscribe
Think Fast, Talk Smart is a podcast produced by Stanford Graduate School of Business. Each episode provides concrete, easy-to-implement tools and techniques to help you hone and enhance your communication skills.
Full Transcript
Note: Transcripts are generated by machine and lightly edited by humans. They may contain errors.
Matt Abrahams: Many of us seek to keep conflict out of our work, but counterintuitively conflict can actually help us be better at work. My name is Matt Abrahams and I teach Strategic Communication at Stanford Graduate School of Business. Welcome to Think Fast Talk Smart, the podcast . Today I look forward to speaking with Amy Gallo. Amy is a workplace expert who writes and speaks about gender, interpersonal dynamics, difficult conversations, feedback, and effective communication. She’s the author of Getting Along: How to Work with Anyone, even Difficult People , and the HBR Guide to Dealing With Conflict , and she co-hosts HBR’s popular Women at Work podcast. Amy, thanks for being here.
Amy Gallo: Thanks for having me. I feel like we’re going to have a lot to talk about.
Matt Abrahams: Oh, I agree, and I’m so excited to get started. Are you ready?
Amy Gallo: I’m Ready.
[01:00] Matt Abrahams: Many of us see conflict as bad as something that we should avoid. Can you give us your thoughts on conflict and its importance in relationships, teams and organizations?
Amy Gallo: Yeah, it’s funny you’d think that I would be brought in to situations, organizations, teams where people are having too much conflict, but it’s actually quite the reverse. I’m often brought in because there’s not enough disagreement happening, there’s not enough feedback, not enough tension or friction, and I am a big believer that while our natural human instinct is to avoid conflict, because of course we are hardwired for likability and we see conflict as a potential rupture in our relationship or possibly damaging to our reputation, I actually believe that conflicts are not only inevitable part of interacting with other humans, but they’re a necessary part. There’s lots of research that shows that conflict leads to better work outcomes, stronger relationships, and of course that depends on navigating the conflict in a professional, productive, relational way with compassion and caring. But when done well, conflict has a whole host of good outcomes, both for our relationships, most certainly for teams, and as well for organizations. And I think we actually should be spending more time not trying to eliminate conflict, but trying to create the right kinds of conflict.
Matt Abrahams: Wow, I love that you’re brought in to talk about how to actually facilitate effective conflict. What are some of the things we can do to bring around what you call the right type of conflict? How do we do that?
[02:39] Amy Gallo: Well, one, I think we have to normalize conflict, right? So I’m sure you’ve been in this situation where you’re in a team meeting and someone disagrees with someone, someone says, or maybe is a slightly dismissive or just something starts to happen and the whole room just gets tense, right? And everyone feels like, oh gosh, well, how are we going to deal with this? And some people may immediately try to smooth it over. It might devolve quickly. The reality is we don’t make conflict normal. We don’t say we’re going to disagree. We’re not going to see eye to eye all the time. We should be debating ideas. And that’s the first step I think for teams and organizations. We want leaders who say, conflict’s going to happen. That’s good. We want the tensions. We want people to disagree about the best way to roll out this project or the right way to design a feature for our customers.
We want that disagreement and we want it to be about the ideas, not about the people. And I think that’s the key part is that when conflicts happen, we immediately think, oh, Matt and Amy aren’t getting along. Oh, there’s going to be a fight. What’s going to happen here? And we immediately think it’s you versus me as opposed to, oh wow, Matt really cares about speed. Matt is always the one who really puts the pedal to the metal, wants us to get there fast, whereas Amy is pressing on the brakes saying No highest quality product possible. Those are good tensions to have. We’re glad Matt and Amy are debating this because we’ll figure out the right way to proceed if we keep it on that level of ideas. The other thing I think is really key is I go back always to Amy Edmondson or at Harvard Business Schools work around psychological safety. You really need to have psychological safety on your team in order to have these disagreements, right? We talk about admitting mistakes, speaking up without fear of retribution or fear of negative consequences. If people are going to feel comfortable enough to say, you know what, Matt, I’m not sure I see that the same way. Let’s talk it through. That is a potential risk to our relationship, so it’s going to cause a disruption, but we have to normalize those disruptions and give people permission to raise them.
[04:45] Matt Abrahams: So there’s a lot that we can do to set up in our relationships, be they in our personal life or in our work life, to actually facilitate conflict that is actually productive. So establishing psychological safety makes a lot of sense. Amy was a guest on the podcast, and I encourage everybody to listen in to the specifics of how we can do that. We have to feel comfortable disagreeing, and then it sounds like those in power, the leaders of a group can acknowledge that conflict is good and recognize it when it’s happening. I like that example you gave where you say, Hey, these two people are in conflict and we need that conflict to help us stay of the course. And then clearly it’s really important that we focus on the problem or the issue and not the people, because once it becomes personal, the emotions can certainly change. So I really appreciate you helping us understand how we can set up an environment for positive conflict. Now, I’d like to have you help us when that conflict we’re having is not so positive. Can you share a framework or two for helping us navigate conflict that might not be the kind of conflict we really want to have?
Amy Gallo: Yeah, and the idea is not to eliminate conflict even if we feel like it’s unhealthy, but it’s to try to transform it into something more productive. Because usually even at the base of those unhealthy conflicts or those unproductive conflicts is something that needs to be resolved. So one framework I’ll share, and this is from my first book, the HBR Guide to Dealing with Conflict, is really thinking about before you even have a difficult conversation, say you have a conflict where you and the other person have been disrespecting each other, maybe there was a snarky email that got sent with lots of people CC’d on it, and you need to actually have a conversation before you do that. I recommend taking four steps, and these also, by the way, can be used as a coaching tool. So perhaps you’re a leader and someone comes to you and says, I’m having a conflict with so-and-So you can use these four steps to help that person think through the conflict as well.
[06:42]: The first step is to think about the other person. So when we are under stress or when we have a threat, conflict is often seen as a threat, as a threat to our identity, to our resources, to the sense of harmony we have. When that happens, we become naturally narcissistic and we become focused on what do I want to say? What do I want to do? We don’t think about the other person, not out of generosity, but the very first step is to think strategically what’s going on with that other person? What’s motivating them? What do they care about? What would be a rational reason that they’re behaving this way? And that’s going to give you some cues as to how to navigate this not so healthy conflict. Put yourself in their shoes just for a few minutes. Then you want to think about what are we actually disagreeing about?
[07:27]: Because sometimes we take these shortcuts, like the snarky email goes out and we’re like, oh, Matt and I have never gotten along. We have this total personality clash attributed to the person, or we make it bigger than it really is, and you have to really think what is at issue here, right? Are we disagreeing about the goal of this project? Are we disagreeing about status? Who actually gets to make the call? What do we actually disagree about? Really try to understand. Then the third step is to think about your goal. What is it that I actually want to achieve? You might be tempted to have a short-term goal. I just want to prove I’m right and he’s wrong, not helpful. What’s your long-term goal? What is it you? Is it that you need to get this project done on time? Is it that you want to preserve your relationship with the other person because you need to work closely together for the next six months?
[08:14]: Whatever it is, focus on that and with that information, what you know about the other person, what you’re disagreeing about, what your goal is, you then make a decision about how to proceed. It has to be really thoughtful. I think we often act rashly because we’re sort of activated from the conflict, but you have to really be thoughtful. Does it make sense to sit down and talk this through? Who else might need to be in the room? Should I have a phone call if we’re remote, should I do a zoom meeting? Whatever it is, think through what’s the best way to set up this conversation for success. So that four step framework is something I always use whenever I’m trying to coach someone who’s really uncomfortable in thinking, I don’t want to have this conversation, or I just want to tell them they’re wrong and have them fix it. So those four steps can help you be much more thoughtful about preparing and being ready for the conversation.
[09:06] Matt Abrahams: One of the things I appreciate so much about your work is the frameworks that you provide, and I think frameworks are wonderful to help. Give us a moment to step back and reflect on what it is in terms of the best approach to managing these situations. I love that we first start by being other focused. It is so easy to get focused on our needs and what we want in that moment, and then to really look at what’s the source? What’s causing this conflict? What is it I want to achieve for me and perhaps for the other person or the organization. And then to really create a plan for how to proceed and then to think about when I actually do have the conversation, what’s the best way to do it in terms of timing, in terms of who else needs to be present and in terms of which is the best channel through which to have that communication really, really matters. I know for myself, when I’m in conflictual situations, I just want it to be over. I want to make sure that I get my way and I just want to move on. Having a framework like yours can really help slow me down and make me other focused, which I think will really help in resolving these conflicts.
Amy Gallo: Can I just make a comment? Having it my way is so normal, it’s so relatable. I mean, I’m thinking about a conflict I had yesterday and I was like, how can I set this up and truthfully, how can I manipulate this situation so it just goes my way? And then I was like, wait a second, I’m going to put this person completely on the defensive. This is all going to devolve, and then I’m going to have to have five more conversations instead of one in which I’m actually collaborative instead of manipulative. And so I think we really, that’s an important part is I often get asked, well, how can I make them do this? I was like, you cannot make them do anything, but what you can do is lay the groundwork for a collaborative discussion in which hopefully you both will get what you want or at least part of what you want. It’s rare to have a zero sum situation where you can’t sort of find something where you both can win a little.
[11:09] Matt Abrahams: People can’t see that I’m smiling broadly because it does my heart well to know that an expert in conflict management still falls into some of the traps that I do. Something there that you said that I think is really critical that I want to call out is that the goal of these conversations is invitation rather than getting the person to be defensive, that you want to invite the person to work with you to solve the problem. It’s a collaborative effort rather than a manipulative effort where you’re just trying to work around the other person. And one of the biggest payoffs beyond collaboration is it ultimately saves you time because as you implied, if you just try to manipulate the situation, you then have to spend so much time cleaning up that mess. So there’s an incentive just in terms of efficiency, I think, in all of this.
Amy Gallo: Absolutely.
[11:56] Matt Abrahams: Now, we’ve talked a lot about conflict and people that are difficult. I’d like to switch gears and look at the other side of the coin. In your book getting along, you share the benefits of having friends at work and actually seeking out those friendships. Can you shed some light on the benefits of having colleagues and friends at work, and what are some of your principles for how we can get along with anyone that we work with?
[12:22] Amy Gallo: I love this question because I think we could spend all day talking through the patterns of behavior that drive us up a wall, but the reality is when you look at all of the stats, most people have a majority of positive relationships at work, or at least neutral. The problem is those negative relationships take up an outsized portion of our energy and emotion, and so we’re really thinking a lot about the difficult people when in reality we should be spending most of our time focusing on the more positive relationships because there’s lots and lots of research that shows that those positive relationships have such a huge benefit, not only emotionally on us, right? Of course, it feels good to have a best friend on work, but also creatively in terms of efficiency. One of my favorite pieces of research I found in working on the book was a group of researchers at Rutgers University found that people who reported having a best friend at work had higher performance ratings.
[13:20] I think we often think about relationships as a bonus, right? Like, oh, I like the people I work with. Oh, how lucky you are. But the reality is it affects how we actually do our jobs. It’s not the icing on the cake. It is the cake. Now, that doesn’t mean that everyone at work has to be your best friends. You don’t have to go out for drinks. You don’t have to invite each other over for cookouts on the weekend. It just means you have to care about one another and be invested in one another’s success. That sort of warmth and benevolence between people really can make a big difference in how we experience work, but also in how we carry out and do the work.
[13:58] Matt Abrahams: But I’m hearing you say as your friends help you lighten your load. That’s right. That’s amazing. I know I made a mistake early in my managerial career where my whole goal was to be liked. I just wanted people to like me to be my friends, and I over-indexed on that so much so that people would take advantage of me. I’d love for you to share some advice about how to actually foster friendships at work without going to the extreme as I did and actually end up not making friends and actually making life a little bit worse for those who are reporting to me.
[14:29] Amy Gallo: So many people have been in your shoes, myself included, of if I’m liked, that is the gold. Every manager just wants to be everyone’s favorite manager. Why wouldn’t you want that? But if you think back to the managers you had, they weren’t necessarily my favorite managers. Sometimes it was actually the person who I didn’t have the warmest relationship with, but I respect it and I learned a lot and they pushed me. So I think really mentally thinking, focus on respect over likability. The other key piece is boundaries, and I think the issue there is you’re managing people, you’re becoming friends, and then you either feel taken advantage of, people start to perceive favoritism, all of those things that can happen, and that’s where you really need boundaries. In fact, I actually reported at one point in my career to someone who was a very good friend from college, and when we began our working relationship, we were very clear.
[15:22] We’re like, we got to keep this separate for the perception of others. We don’t want us to be perceived as playing favorites or giving one another advantages, but also because we don’t want it to impact our friendship. If she called me, I would say I’d pick up and say, friend call or work call, and I think it was really clear, and when there were potential conflicts of interest, which there were sometimes we were very clear about, okay, how are we going to navigate this? And I think that has to be true even if your friend is your peer, right, have a conversation. It doesn’t have to be sort of this in depth define the relationship conversation, but it could be helpful to say, sometimes I’m going to have information that you’re not going to be privy to. Sometimes I’m going to have to make a decision that I know is not going to be something you’re going to be super happy with, but how do we want to handle that? When that comes up, how do we want to make sure our friendship stays intact and not impact the work relationships? So I think boundaries are really important.
[16:16] Matt Abrahams: That is so helpful, and the notion of boundary setting is critical to those relationships, and you might set different boundaries with different colleagues, but having an overt, explicit conversation about the boundaries I think is critical, and certainly your advice to focus on being respected versus being liked is what I ultimately came to that conclusion, but it certainly had some, there were negative consequences before I learned that lesson, and in fact, the advice I give all new managers is focus on building trust, focus on building respect and liking often comes from that.
Amy Gallo: That’s right.
Matt Abrahams: Amy, this has been fantastic. I’ve enjoyed listening to all of your advice and guidance and it is so applicable in my daily life and I’m sure in the lives of the listeners we have. Before we end, I’d like to ask you three questions. One, I’m going to create just for you, and the other two are consistent across all of our guests. Are you up for answering?
Amy Gallo: Absolutely
[17:12] Matt Abrahams: Great. I’d like for you to think back to a challenging or conflictual situation you’ve had and what are you most proud of in terms of how you handled it?
[17:23] Amy Gallo: I have a 17-year-old daughter, and we talk about conflict a lot. What I’m realizing and what I’m most proud of in negotiating conflicts with her is being able to in the moment say, here are the various things that I’m struggling with. I want to be a good mom. I want to appear as a good mom. I want to care for you, and I also need my needs met, and to be able to talk through the conflicts of interest that have, it’s not always easy. Sometimes I’m just at level 10 and losing my mind, but when I can sort of take it down a few levels and actually be present enough to say, Hey, this is what’s going on, she’s so much more responsive because instead of being that know it all mom who’s just telling her what to do instead, I’m a real person who’s struggling saying, I don’t know what the best answer is, and this is why I’m doing what I’m doing.
[18:16] Matt Abrahams: I think that is wonderful that you can do that, and I strive to do that. It can help in any interaction, not just with our kids to say, here are the things I’m struggling with in this moment, sounding real, and maybe even getting some advice and guidance to be more collaborative. Question number two, who is a communicator that you admire and why?
Amy Gallo: I have maybe a slightly strange answer, but there’s a comedian named TIG Nataro. She’s an interesting communicator. She speaks very slowly. She’s very dry, sense of humor. The other thing I like about the way she communicates, it’s delightful. She doesn’t always say what you expect, the element of surprise, not in a bad way because you can also really feel the authenticity and the intention behind what she says, and so the way that she sort of surprises you by reacting in a certain way or just sort of laying a joke that’s very relatable, very human. I always appreciate what TIG has to say.
Matt Abrahams: So it sounds like the conversational and surprising nature of the communication is what really attracts you to it. I think those are two criteria that can draw all of us into communication. We often can be very scripted and purposeful in everything we say, and sometimes having a little bit of surprise can be helpful. Final question for you, what are the first three ingredients that go into a successful communication recipe?
Amy Gallo: First, I would say empathy. I think ultimately communication is about balancing your needs and someone else’s needs. I would say assertiveness, actually knowing what you want to say and saying it confidently, and then curiosity. I really always try to lead with what do I not know that I want to know, and how do I communicate in a way that will help me get that
[20:01] Matt Abrahams: Empathy, curiosity, and assertiveness. Great communication recipe. Start with what the others need, understand their perspective. Be curious about how you can connect and collaborate and then be clear and assertive in what you want. Amy, thank you so much for your time and for your guidance. I certainly have benefited personally in dealing with challenging situations. I appreciate your time and your information. Thank you so much.
Amy Gallo: Thank you, Matt. This has been really fun.
[20:34] Matt Abrahams: Thanks for joining us for another episode of Think Fast Talk Smart, the podcast from Stanford Graduate School of Business. This episode was produced by Jenny Luna, Michael Reilly, and me Matt Abrahams. For more information and episodes, visit gsb.stanford.edu or subscribe to our show wherever you get your podcasts. Finally, find us on social media at StanfordGSB.
For media inquiries, visit the Newsroom .
Explore More
Power, culture, persuasion, and the self: communication insights from stanford gsb faculty, when words aren’t enough: how to excel at nonverbal communication, navigating the nuance: the art of disagreeing without conflict, editor’s picks.

April 15, 2024 Embracing Failure: How to Make Mistakes That Work In this podcast episode, Amy C. Edmonson outlines how leaders can foster an environment where failure is viewed as a success.
- Priorities for the GSB's Future
- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Business Transformation
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2024 Awardees
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships and Prizes
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Get Involved
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- GMAT & GRE
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Letters of Recommendation
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Entering Class Profile
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- Career Advancement
- Career Change
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- Information for Recommenders
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- After You’re Admitted
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Education & CV
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- Videos, Code & Data
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Reading Materials
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Conflict
Conflicts Essay Example
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Conflict , Management , Workplace , Leadership , Society , Organization , Employee , Teamwork
Words: 1250
Published: 03/16/2021
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Arguably, not every society in the world can avoid conflict. In fact, conflict is part of human nature. Conflict among organizations and individuals is an unavoidable aspect of daily life. Many scholars assert that conflict is inevitable. Perhaps, understanding how it escalates and starts entails progressive strategy in using it to the advantage of those concerned. Conflict refers to a situation in which groups and people think, or have incompatible goals and objectives. Conflict is a wide concept, but many people belief only violence and war is conflict. However, conflict takes place in all levels of society and in all situations. Generally, organizations, individuals and people experience various types of conflicts every day (Philips, 2007).
As a matter of fact, conflict escalation is a steady regression from immature and mature level of various emotional developments. Certainly, the psychological course develops from one step to another. Conflict escalates in various stages, and each stage has various characteristics. Some conflict escalates for a good course; good relationship face at times conflict. In most case, parties look for solutions cooperatively and objectively. Furthermore, ways that conflict escalates include complaints, passive resistance, active resistance, assaultive, as well as use of lethal force (Wandberg, 2005).
Undeniably, the organization of society is in a way that it has both root causes and factors that may escalate conflicts. Unjust and unequal treatment of individuals in the community could lead to conflicting situations. For example, if leadership and opportunities in the nation do not represent the members of the entire society (Philips, 2007). Other scholars assert that, conflict is as a result of arithmetical progression of resource supply and geometrical progression in population increase. Due to imbalance in population and resource allocation, individuals will struggle to survive leading to conflict.
Conversably, individual differences in society cause conflict. As a matter of fact, people in society are different in nature and have variation on issues such as ideas, aspirations, attitudes, as well as interest. Therefore, this difference puts them in a situation that they cannot accommodate each other, leading to conflict. Additionally, cultural issues could tremendous cause conflicting situations (O’Rourke & Collins, 2008). Culture differ from one community to another, this variation sometimes causes tension. Among these communities, there are various interests among individuals, making conflict inevitable.
Social change is part of societal growth and progress. Nevertheless, the rate in which social change escalates may lead to the uprising of conflict. In the 21st century, there are various conflicting scenarios between the old norms and the new generations. Conflict expresses a state of social disequilibrium among the parties. Other core causes of conflict include, political discrimination, identity and ethnic affiliation, economic issues, as well, as modernization.
Addressing conflict in society is very important. In fact, addressing conflict is crucial in achieving enhancing productivity, as well as organizational effectiveness. In society, most individuals and organizations suffer from chronic patters of conflicts that have never been resolved. This may cause dysfunction among the conflicting parties. Hence, addressing conflicts resolves issues and ensure that there is normal functioning in the society. Generally, addressing conflict is crucial because it increases productivity, reduces costs, increase collaboration, as well as bringing satisfaction (Wandberg, 2005).
The existence of conflict in an organization, among individuals, and in the government is not a bad thing. Certainly, when conflict is resolved effectively it leads to development and growth at professional and personal level. Nevertheless, effective resolution of conflict creates a difference between negative and positive outcomes. When conflict is resolved effectively, it leads to positive impacts; hence, it justifies on the occurrence of the conflict (Philips, 2007). Effective conflict resolution leads to unbelievable benefits such as increased understanding, group cohesion, and improvement in self-knowledge. The strategies used to effectively resolve conflict, expands the awareness of people on issues, strengthening of bonds, prevent fights, as well as providing them with insights on how to achieve cooperate and personal objectives.
Whether your inquiries are ' write my essay free ' or i wanna 'edit my paper', please address WowEssays and we will help!
However, poor handling of conflict could lead to a negative outcome. In fact, conflicting objectives may promptly turn to be organizational and personal dislikes. The teamwork among the parties is broken, talent wasted, as well as tremendous decrease in production. Individuals in society should understand and appreciate the existence of competition, and uniqueness. Perhaps, these will lead to collaboration, accommodation and compromising of situation (O’Rourke & Collins, 2008).
In society today, there are various incidences of conflict. In fact, the incident objectively observed demonstrated various aspects of conflict, which include causes, parties’ reactions, as well as strategies to resolve it. The incident took place between management and the employees over working conditions and remunerations. The situation in the workplace was very critical. As a matter of fact, there were few conflict cowards in the group. Every individual wanted his or her views to be heard and considered. The entire group of employees were united in airing their views; many of them were furious because they had addressed their problem to the management team, but their problems were not solved.
The conflicts in the workplace were caused by various reasons. The management team and the employees differed in addressing priorities; the management placed higher priorities to the progress of the company more than the priorities of the m employees. Additionally, the methods of promotions and awarding process in the company were not equally carried out. Therefore, it developed a lot of tension among the employees and the management team. Moreover, the conflicting groups complained of various organizational issues, which in one way or another escalated conflicts. The organizational factors included budget, management, long working hours, leadership. Adherence to core values, disagreements, as well as financial problems. Other core issues that were observable were poor communications, differences in interests, and personality clashes (Wandberg, 2005).
The main parties on the workplace conflict focused in resolving the conflict through communication. The management team elaborated on improving various organizational practices. Perhaps, they established the cause of the problem and established subordinate goals, minimized authorities of management as well as improving policies. The tension among the parties was very high, but the few individuals who were against negative conflicts acted and tried to make the parties reach a consensus. Furthermore, the organization made changes on human resource department that will focus on analyzing internal problems. Ultimately, the remuneration agreement was arrived at.
Undeniably, the deals made during conflict resolution process eased the tension, and the parties came to a compromising position. Despite the efforts, others were still emotional and could not accept some terms. As a matter of fact, it is very difficult to convince everyone in a conflict situation. The employees and management have different priorities, personalities as well as interests O’Rourke, J & Collins, S. (2008). The ultimate decision that was focused on was to involve the employees in setting the appropriate remuneration percentage, which will affect the company and employees equally. The most important strategy in making the entire decisions was to reduce tension and encourage communication. The cost of conflict should not outweigh the entire progress of the organization; hence, management team should focus on preventing conflict to escalate further. Conflict is part of human life and should always be handled with great care.
O’Rourke, J & Collins, S. (2008). Managing Conflict and Workplace Relationship. London: John Wiley & Sons.
Philips, G. (2007). The Conflict. New Jersey: Echo Press. Wandberg, R. (2005). Conflict Resolution: Communication, Cooperation, Compromise. New York: Wadsworth.

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 782
This paper is created by writer with
ID 286534807
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Probation argumentative essays, tokyo term papers, igor stravinsky term papers, adam and eve term papers, procrastination term papers, open source software term papers, social engineering term papers, sierra leone term papers, heroism term papers, traffic congestion term papers, david hume term papers, neurology term papers, postmodernism in bloody jack essay examples, persuasive essay sample, free serious games essay example, the travels of a t shirt in the global economy report, free essay on modern masters exhibit, example of obama health care bill essay, the vision of islam by sachiko murata and william c chittick book reviews example, good research paper on wuthering heights, reintegration of prisoners research papers examples, abortion research paper sample, example of research paper on comparison and contrast of architecture flow between united states of america and, good research paper on mechanical engineering major, good example of how do the two acolytes in tanizaki junichirs the two acolytes represent essay, others report, diagram responses and summary term paper samples, good example of essay on a study of the morality of zoos, good example of specialty courts report, good essay about as an alternative to the conventional closed narrative in which loose ends, classical argument essay sample, wikipedia project essays examples, good obesity essay example, appian essays, englewood essays, dutton essays, gigi essays, juvenile offenders essays, progressive movement essays, sex discrimination act essays, gender issues essays, inventory system essays, product strategy essays.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
The Best Ways to Resolve Conflicts Between Students

- Share article
It’s not unusual for students to have conflicts with their classmates. What are the best ways teachers can create the conditional to stop them before they occur and respond once they have begun?
This series will explore possible actions educators can take.
Today, Vickie Gomez, Danny Woo, Kevin Parr, Jessica Torres, Rosalind Wiseman, and Dr. Bryan Harris contribute their ideas. You can listen to a 10-minute conversation I had with Danny, Kevin, and Jessica on my BAM! Radio Show . You can also find a list of, and links to, previous shows here .
Our school is very lucky because we have a very relational culture focused on restorative practices, and campus monitors who are experienced in conflict resolution.
For years, any time any of my students have had conflicts, I’ve texted Vickie Gomez, a campus monitor who is assigned to our “Small Learning Community.” Except for the very few times those conflicts had escalated into physical fights before I had called her in, she has mediated every dispute and it’s been resolved by the next class. I know that many other teachers in our school have had had similar experiences.
Last week, I asked Vickie to describe what she does:
I first talk with each student individually to find out what happened in class and to also find out what else has happened in that student’s day. Often the problem has nothing to do with the other student—something else took place earlier and it just boiled over. I try to get each student to put themselves into the other student’s position and how they might see things. I ask each student what ideas they have for resolving the problem. I take in this information, especially their ideas on how to resolve the problem, and take the two of them on a “walk and talk” together. I explain that I have to kick things up to administration—and to their parents—if they can’t resolve things. The vast majority of time, students work it out.
Students—and school staff—have an enormous amount of respect and affection for Vickie!
Response From Danny Woo
Danny Woo is a middle school science teacher at San Jose Charter Academy in West Covina, Calif. He centers his class on the implications science has on social, economic, and environmental justice:
The way adults handle student conflicts can go a long way in setting the tone of your classroom learning environment. If educators wish to establish a culture that values a sense of community, conflicts between students will be approached with reconciliation as the goal. This is the hallmark of the restorative justice model and nonviolent communication (NVC) where community building is achieved by focusing on strengthening and repairing relationships. This approach is most effective when it is a shared value among school leadership and is embedded in school wide practice. That said, if your school leans toward a traditional approach to discipline, you can still exercise restorative practices within your own classroom.
Before responding to student conflicts, we need to keep in mind Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs. Every student is looking for a sense of security, belonging, acknowledgment, and independence. And in the case of pre-teens and adolescents, these needs are heightened. In most cases, conflict arises when one of these needs are threatened.
My first steps in helping students resolve their conflict is to speak to both parties separately. This is a fact finding session to get a clearer picture of what each student involved is thinking. I ask the students for their point of view, establishing that I am reserving judgment. I make a point of being transparent and let each party know that I will be having this same conversation with the other student(s) but will not render an opinion. I make it clear that my goal is to eventually help them reconnect.
When I’ve had a chance to speak with all involved, we set up a time to meet together with me as the mediator. Prior to the meeting, I ask the students to think about what feelings are alive inside of them. Sometimes you will have to provide them with the language to describe their feelings. Next I ask them to think about what they need from the other party. This is the framework we use in our group session:
- What is your perspective of the situation? Describe and share your point of view.
- What are your feelings? What is alive inside of you? Name them.
- What do you need from the person(s) who you have conflict with?
In the group session I have each party share their perspective on the situation. No one is allowed to interrupt or interject while the other person is sharing. Each party will have a turn to share their perspective and what feelings they harbor. I encourage them to be as explicit as possible in identifying and describing how they feel.
The last phase of this process is for each party to express their requests in the spirit of healing and reconciliation. In my 17 years of teaching, I have yet to meet children who are not amenable to finding solutions to an issue, especially if there is a history of friendship between the two parties. In the majority of cases I have dealt with, I found that conflicts arise due to a deficit in language to identify and express their feelings and needs. Children need to be given a framework that honors their thoughts and authentic self, as well as provides the opportunity to hear one another.
Response From Kevin Parr
Kevin Parr is a 4th grade teacher from Wenatchee, Wash., and an ASCD Emerging Leader:
Student Conflicts: Teachable Moments
Conflicts between students are a natural part of life inside a classroom or school and should be treated as such. In fact, helping students respond to and resolve conflicts with peers is an important part of their learning. Here are a few ways teachers can treat student-student conflicts as teachable moments:
Listen: At times, teachers try to quickly extinguish conflicts by resolving the problem for students rather than help students resolve conflicts themselves. In doing so, teachers deny students the opportunity to develop the skills and mindsets they will need to resolve interpersonal conflicts throughout their personal and professional lives. It may seem overly simplistic but a teacher’s primary role in helping kids resolve conflicts is to listen. Listening not only empowers students to take ownership of the conflict, it also models the important skill for them.
Avoid jumping to conclusions: When listening to student’s perspectives on a conflict it is easy for teachers to place blame on a particular student has been involved in similar conflicts before. Whereas reputations can exist for a reason a few things are wrong with this approach. First, if the goal is for students to learn to resolve their own conflicts, placing blame robs students of their ownership of the conflict. Second, it demonstrates to kids that their past mistakes will follow them forever even if their decisions and actions change. If our focus is on learning, every child deserves another chance.
Everyone has a role: Usually, there is more than one person at fault in student conflicts. Multiple kids generally have a role in creating the situation and/or making it worse. Rather than seeking to find a singular “guilty party” teachers should help all students see their role in the conflict and discover ways to act or react differently in the future.
You are not alone: It is important that teachers let students know that conflicts are normal and all people, including adults, have conflicts with others. Kids should also know that their current conflict will not be their last conflict so the skills they are learning and practicing will help them throughout their life. Furthermore, teachers can use personal stories to reinforce the notion that the skills students are building are life-long skills.
Understanding that student conflicts are natural can help teachers use them as teachable moments. Teachers should expect and embrace these conflicts as part of a child’s learning.
Response From Jessica Torres
Jessica Torres is a first year elementary assistant principal at Brook Avenue Elementary school in Waco, Texas. She formerly served as an instructional coach and a public Montessori elementary teacher. Torres is a current doctoral student in Tarleton State’s Educational Leadership Program. She obtained her Masters in Educational Administration through Concordia University, and her Bachelor degree from Stephen F. Austin. Known widely as @owl_b_torresedu by her Twitter PLN, Mrs. Torres is a staunch supporter of public education, personalized professional development and connecting with others who are passionate about education and students:
Conflict—Is it a Bad Word?
Responding to disputes between students is a skill often overlooked during many teacher preparation programs. Many new teachers walk into the classroom with the belief that a well-managed classroom will alleviate any scuffles or disagreements among students—this could not be further from the truth. Even the best teacher will have students who experience conflict with one another. Conflict is not always negative. Conflict can bring about change, different perspectives and allow various types of growth. The methods we use to prepare our students to deal with conflict effectively ultimately can determine whether or not students are prepared to step into the world as productive, peaceful citizens. Experiencing conflict in the classroom should not be viewed as a disruption to be removed or halted, but instead as an opportunity to teach students missing skills.
Responding to the Conflict
When responding to conflict, it is important to ensure safety first. If students have a physical conflict, ensure that they are separated and provided their areas in which to calm down. In a nonbiased tone, ask each student to describe what happened during the incident either verbally or in writing, whichever the student is most comfortable using to communicate. There are many behavior “think sheets” available online for students to complete during times of conflict. Once each student has shared their version of the incident discuss with them the effects their behavior had on the students around them, the teacher, and their learning.
Students often fail to realize that the conflict is not a contained event. Their actions impact more than just those involved directly. During this time coaching should come into play. Reminding students of the strategies that they can use when they feel themselves become angry, for example, breathing techniques, visiting a calm-down corner, or even reading a book with a character going through a similar situation. Supporting students as they feel emotions is critical to showing them appropriate ways to manage their feelings. Students must understand that everyone is allowed to feel angry or upset, the difference is in whether we react physically or inappropriately with words as opposed to rationally and calmly.
Restorative practices encourage the students to discuss with each other how they felt before, during and after the conflict. After acknowledging each other’s feelings, ask both students what can be done to fix the situation. Students often surprise me during this stage with their compassion and willingness to forgive each other. If students can come to a reasonable solution allow them to shake hands and continue with their day without receiving a punitive consequence. Through this process, students will begin moving away from expecting results, but instead working towards peace and restoring relationships.
Response From Rosalind Wiseman
Rosalind Wiseman is a teacher and bestselling author of Queen Bees & Wannabees , the book that inspired the hit movie Mean Girls, Masterminds & Wingmen , as well as Owning Up: Empowering Adolescents to Confront Social Cruelty, Bullying, and Injustice , a new curriculum for middle and high school students. She is the founder of Cultures of Dignity and lives in Colorado with her husband and two children. Follow her on Twitter at @cultureodignity :
This situation is harder than it looks. Were these students friends in the past and now they aren’t? Have they never gotten along? Is one child targeted for a specific reason like their ethnicity, race, disability, gender, socioeconomic class, or some other perceived inherent trait? If this dynamic exists then this situation should be defined as bullying instead of a conflict.
So first, take a step back and just watch your students to see if you notice a pattern in the students’ interaction. Are there consistent times of the day when the conflict seems to flare? Are other kids exacerbating the tension?
Once you’ve done the research, it’s time to reach out to each student—and that also requires consideration. In most cases, it’s more effective to meet with the students individually instead of meeting with the group where the dynamics within the relationship it can sabotage any hope for a positive outcome. So say something like, “Can we set up a time to talk? You’re not in trouble. I just want to check in with you about something that may be important.” Then meet with each student during a time of day and in a location that feels private and comfortable to the student.
Start the meeting by communicating the following: “Thanks for meeting with me, I want to talk about something that is important that has come to my attention.” Then explain the situation as it has been shared with you and/or what you observed. Ask the student how accurate they think your information is and listen to their anwer. If the child is willing to tell you what’s going on, give them the space to unload. If they are reluctant or deny it, respond with “I can probably understand why you may not want to tell me but I don’t want to make assumptions. So can you tell me why you don’t want to tell me? I think that’s probably really important for me to know. “
For all students it’s critical to communicate the following (in your own words): “It’s common for people to get into conflicts but it’s not ok if that conflict is making you or anyone else feel unsafe or that don’t want to come to class (or the school). As your teacher, it’s my responsibility to do whatever I need to do whatever support you and every student in my class. So I’m going to ask you a few questions and together we will figure out next steps.”
Then ask the student to answer the following questions
- Why do they think the conflict is happening?
- Why is the conflict making them feel bad/angry/anxious?
- If this conflict involves a group of people, ask the student how they think the group is influencing the conflict.
- What do they want to change? Even if that change seems small or obvious, what would it be?
- What do they want out of the relationship with the person they are now in a conflict with? Do they want to be completely separated from this person? If they were friends before, do they still want a friendship?
- What is one action, no matter how small, that they can take to make the situation better—where they feel good about how they’ve handled it.
While the child is talking the you can write down what they’re saying. After their done, read it back to them and ask them if you got it right or if they need to make any changes. The purpose is to help the student put their feelings to words and identify what they need. Remember in these situations, some students are trying to figure out how much you know so they can shut you down, others are relieved that an adult has brought it up. If the child is not feeling safe, then the teacher and student need to decide who in the school they can go to to tell and take additional steps. All to say when you’re having this talk, it’s really important to pay attention to the student body language, their tone, and the nature of their responses.
At the end of the conversation it’s time to reinforce your expectations; which should include some combination of “Every student in my class has the right to feel worthy and included. As your teacher, that looks like X to me. This situation is difficult and I really appreciate that you trusted me to tell me even a little of what’s going on. You can always come back and tell me more things you’re thinking or feeling. But for right now, you’ve done a lot. You’ve said what you don’t like and what you want. You’ve identified one thing you can do that will make you proud. So let’s check in tomorrow and see how you’re feeling.”
Response From Dr. Bryan Harris
Dr. Bryan Harris serves as the Director of Professional Development for the Casa Grande Elementary School District in Arizona. He is the author of five books on topics ranging from classroom management to student engagement. For more information his trainings and workshops, he can be reached at www.bryan-harris.com:
I am convinced of this one very important truth: the world would be a much better place if we all accepted the fact that conflict is a natural and unavoidable part of life. The world would also be a better place if people took more naps and someone invented zero-calorie cheesecake (but that’s a topic for another time).
When helping students work through conflict, we first need to understand the nature of it; as educators, we must have a solid grasp of what conflict is, how it is likely to manifest itself in the classroom, and effective ways to build conflict resolutions skills in our students. In order to do that, we need to briefly dig into some definitions and truths about conflict.
If you have no conflict in your life, one of two things is true: you’re dead or you’re not paying attention to the people around you. Since you are reading this, let’s start with the latter. Whenever you interact with the people around you—whether they be family members, co-workers, friends, or a stranger at the store there is the possibility (or the likelihood) that conflict will arise. If you look up dictionary definitions you’ll find phrases like struggle for power, strong disagreement, and an opposition of forces. None of those are pleasant so it’s no wonder people strive to avoid conflict. However, conflict is simply a by-product of being around other people. That is one of the first things I want students to understand—conflict simply is. It exists because I interact with other people. Its existence does not make me a bad person nor does it necessarily mean that I am doing something wrong (although my responses can often make the situation much, much worse). Too often we assign blame, place guilt upon ourselves, or ignore conflict when it arises. None of those are healthy responses.
So, what exactly is conflict and where does it come from? When working with students, we want to provide straightforward, honest, and simple answers even though the concepts are deep and complicated. In terms of external conflict with other people, I want students to understand that conflict typically comes from one of three situations: blocked goals or expectations, opposing beliefs or points of view, or miscommunication. In the simplest terms, someone has something I want = conflict. Someone is in my way = conflict. Someone thinks or says something I don’t like = conflict. Someone communicates in a way I don’t understand or appreciate = bingo, conflict!
Before we attempt to help mediate conflict among students, we first need to understand what we are dealing with. That, and we need to have a good handle on our own understanding of conflict. In summary, here are some big truths about conflict:
- It is— As I mentioned before, conflict is just a natural part of the human existence. Its presence in my life merely means that I am interacting with other flawed, imperfect people.
- It is unavoidable, expect it— I should not be surprised, flabbergasted, or stunned when I find myself in conflict with someone. Nor should I be overly frustrated. As educators, we should not be surprised or upset when our students are in conflict with each other. The fact is that many of our students are not learning effective conflict resolution skills at home and there aren’t a ton of excellent examples of conflict resolution models in the media, sports, entertainment, or politics.
- It can be a good thing— The right kind of conflict can serve as a catalyst for personal growth. Don’t get me wrong, I don’t love conflict but when it is handled correctly, I learn a lot about myself and the people around me.
- Our goal is to empower others— As educators, we should always be seeking ways to build skills in our students. We certainly adopt that belief when it comes to core academic skills and “soft” skills such as perseverance, attention to detail, and patience. We need to adopt this belief about building conflict resolution skills as well. Quite simply, the ability to understand and learn from conflict is a life skill. If students don’t learn it and create effective habits, life is going to be tough... regardless of their scores on achievement tests.
To answer the question directly, “How do we respond when students are having conflict with each other?” consider the following principles:
- Don’t take it personally—Someone once shared the following acronym with me: QTIP (Quite Taking It Personally). Other peoples’ behavior typically says more about them then it does about me. When students act in inappropriate ways, it is not usually about the teacher (unless, of course, it is about the teacher because there is a level of disrespect, disorganization, or outright cruel behavior. The good news is that most teachers are positive role models who love their students.) As educators, we need to remember that students need patient, loving guidance from an adult who doesn’t take offense at every transgression.
- Don’t catastrophize, exaggerate, or trivialize—When helping others work through their struggles, we need to remain tactful and neutral. Although we may think that their conflict is silly, we can make it worse if we go to extremes to show our disdain.
- Avoid pronouns—When we use terms like I, they, us, we, and them we automatically pit people and groups against each other. It is best to stick to the facts when describing a situation that needs to be addressed. Although students may use lots of pronouns as they describe their conflict, we can help lower the stress levels if we remain neutral in our language.
- Avoid sarcasm—Sarcasm will always make the situation worse.
- Respond rather than react—Remember that conflict is a natural result of people spending time together. Classrooms are unique places... lots of people crammed together in a confined space for long periods of time. That’s practically a recipe for conflict. So, it’s not a matter of if there will be problems, it’s a matter of when and how often. As teachers and leaders, our job is to respond with a thoughtful plan.
- Embody respect—In some cases (perhaps in many cases) we are the best role models our students have. As a result, we must always embody respect, show empathy, and express appreciation for all our students. Quite simply, our students will not develop appropriate conflict resolution skills unless we model it for them. Think about the message we are sending to kids if get easily offended, outright mad, start yelling, or demean those around us. When helping others, we need to be aware of our own emotions, body language, and frustrations.
- Teach—Use role-plays, scenarios, current events, and other real-life situations to teach students the appropriate ways to handle conflict. Our students need and deserve to learn these skills. However, we cannot wait until “the heat of the moment” to try to talk kids through the process. Again, it’s not a matter of if there will be conflict in your classroom, it’s a matter of when. So get ahead of the curve and incorporate teaching opportunities throughout the school year.
The principles described above are reminders for us, the adults, as we direct and guide students. However, each of the principles can and should be taught to students. Of course, the age and maturity level of your students will dictate how you teach the principles but they should be made a priority.
Thanks to Vickie, Danny, Kevin, Jessica, Rosalind, and Bryan for their contributions!
(This is the first post in a two-part series)
The new question-of-the-week is:
When two or more students are having a conflict, what are the most effective ways teachers can respond to the situation?
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Anyone whose question is selected for this weekly column can choose one free book from a number of education publishers.
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder—you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email . And, if you missed any of the highlights from the first six years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below. They don’t include ones from this current year.
This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
Classroom Management Advice
Race & Gender Challenges
Implementing The Common Core
Best Ways To Begin The School Year
Best Ways To End The School Year
Student Motivation & Social Emotional Learning
Teaching Social Studies
Project-Based Learning
Using Tech In The Classroom
Parent Engagement In Schools
Teaching English Language Learners
Student Assessment
Brain-Based Learning
Reading Instruction
Writing Instruction
Education Policy Issues
Differentiating Instruction
Math Instruction
Science Instruction
Advice For New Teachers
Author Interviews
Entering The Teaching Profession
Administrator Leadership
Teacher Leadership
Relationships In Schools
Professional Development
Instructional Strategies
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
Look for Part Two in a few days.
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update

- Relationships
What's Your Fighting Style?
Understanding how people argue can help you resolve conflicts in a useful way..
Posted May 30, 2024 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader
- Why Relationships Matter
- Find a therapist to strengthen relationships
- People in conflict with others tend to behave in several discrete ways.
- The four main types of conflict style are appeasement, avoidance, aggression, and alliance.
- Understanding the conflict style of someone close to you can help you resolve arguments more productively.

You’ve probably heard all about the five love languages (Chapman, 2015) and you may even know the five types of attraction . But if it’s possible to count the ways in which people show love for each other, perhaps it’s also possible to understand conflict—the ways in which people clash—in the same manner. In other words, is there a small, knowable number of styles that people resort to when they argue? The question has been studied in a number of ways, from popular to experimental to psychoanalytic . You won’t have any trouble finding a variety of answers with Google: People have divided the most common “fighting styles”—not to be confused with the 16 basic types of martial arts—into four, or five, or six, or even more. These patterns of behavior, however, come down to four main responses to interpersonal challenge: aggression , avoidance, appeasement, and alliance.
1. Aggression. I’ll start with the aggressor, whom you’ll recognize as a person whose first instinct is to argue—the one with a very short fuse, who immediately fights back and ratchets up the stakes. Aggressors come to be seen as hot-headed, sensitive, or easily triggered to anger. In the best-case scenario, they’re competitive and assertive, although they don’t easily cooperate. An aggressor may speak up impulsively and quickly resort to anger—in a frightening way, sometimes—or may even try so hard to win a fight that they’ll dispense with fairness and say things they do not mean. What an aggressor says in the heat of the moment may cause long-term damage to the bonds between friends or family. Inside, though, aggressive people may be terrified. Even if they want an argument resolved, they still must struggle with an upwelling of inner feelings that they can’t easily express. They may be exquisitely aware of their own vulnerability; they may believe, at some level, that if they do not win an argument then their internal fragility will be revealed. This creates a chronic sense of anxiety and a quick, defensive response to a perceived threat. Aggressors believe they can only win when you lose, so they try very hard to tilt any game in their direction—which gives the impression that they value their own private needs over those of a relationship.
2. Avoidance. Other people are prone to retreating at the first hint of an argument. They prefer to ignore problems, hoping they’ll go away, rather than to manage them openly; this habit may lead them to dodge potentially productive conversations. As such, they will often be seen as something less than assertive, and they can give the impression of not caring about a given issue (or the people involved). Avoiders sometimes come across to others as emotionally cold, distant, or silent. The disagreements in which they find themselves embroiled may go own simmering for years without bursting into open conflict. Avoidant people tend to project an attitude of not caring about the personal needs of others, or even about their own; continually avoiding conflicts generally results in a lose-lose outcome, in which nobody ever wins and progress is never made.
- 2a. A prominent subtype of avoidance is intellectualization —the perceived need to look for “rational” answers, or to make efforts to solve problems using “logic.” Even when winning a debate like this will deepen a conflict, intellectualizers may continue to press their points; in addition, people who insist on intellectualizing their conflicts will likely completely ignore the feelings of the people with whom they argue. Consequently, their personal style may come across as not only cold, but also arrogant.
- 2b. Another type of avoider has been called the “defector”—a person who physically disappears when conflict rears its head. They’re so non-confrontational that they prefer to leave the room entirely, or even depart from a relationship, rather than to communicate dissent. Outside, they’ll seem blank or cold as they stonewall you, fall silent, or decline to engage; inside, they may be churning with discomfort that they do not know how to express.
3. Appeasement. Not everyone made physically uncomfortable by conflict is likely to vanish at the mere hint of it; others will try to resolve conflicts as quickly as possible, even if such a resolution is premature or superficial. Appeasers do their best to accommodate anyone who challenges them, and in “rolling over” this way, may even make a significant sacrifice of their own needs in favor of promptly ending an argument. Argue with an appeaser and you will undoubtedly “win” at their expense, which may not feel terribly satisfying: Their self-sabotage can convey a lack of assertiveness or even a sense of martyrdom. Solutions reached this way may be frivolous or inappropriate, and can ultimately lead to resentment, which often produces long-term negative consequences for a relationship.
- 3a. A more useful subtype here is the compromiser —a person who seeks to resolve an issue by finding a quick and mutually acceptable solution. If everyone is partially satisfied, they seem to believe, no one really has to lose. Compromisers value your goals as much as they appear to value their own, and they will make concessions in an effort to reach results. However, in their efforts to end the conflict quickly, the adjustments made may fall short of full satisfaction. This type of participation in a conflict may well save time and will preserve the harmony in a relationship, but an outcome produced this way will fully satisfy no one.
4. Alliance. The last style of conflict tends to be the most effective. Some people prefer to find ways to cooperate rather than to reach a zero-sum solution, in order to keep their relationships healthy. These people may be able to manage their own emotional discomfort so as to avoid becoming defensive in the midst of an argument, and they can often muster their empathy at difficult times in order to see past such heated moments. Negotiating with unusually assertive, strategic, and moderate people like this means that everyone may have a chance to “win” simultaneously, even if the outcome is not realized quickly. With this type of solution, long-term relationships are prioritized, while momentary victories are not seen as important.
If you recognize your personal style of argument here, and you don’t particularly like what you see, you should remember that styles of conflict can change. With insight and patience, you can choose to modify your behavior patterns to keep your relationships healthy. And just as you can learn the “love language” of your partner, you can begin to better understand their “fighting style” as well: Perhaps you don’t have to take seriously the things they say when an argument is at its peak, or maybe you can allow your partner to spend a few minutes alone when a conversation runs the risk of becoming unproductive. No matter what, though, please remember that arguing with your partner is not unusual or abnormal, and always remember to ask yourself if it is really more important to be “right” than to be happy.
Benoliel, B. (n.d.) What’s your conflict management style? Retrieved from https://www.waldenu.edu/news-and-events/walden-news/2017/0530-whats-your-conflict-management-style
Chapman, G. (2015). The 5 love languages: The secret to love that lasts (Reprint ed.). Northfield.
Martin, M. S. (2021). What's your conflict style? Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/brave-talk/202103/whats-your-conflict-style
Rossler, K. (n.d.). The art of arguing: The 4 argument styles. Retrieved from https://katierossler.com/the-art-of-arguing-the-4-argument-styles
Sherman, J.E. (2022, August 9). What is your argument style? Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/ambigamy/202208/what-is-your-argument-style
The University of Texas. (n.d.) Understanding conflict handling styles. Retrieved from https://www.utsystem.edu/offices/human-resources/current-employees/manager-resources/employee-relations/understanding-conflict-handling-styles

Loren Soeiro, Ph.D., ABPP , is a psychologist in private practice in New York City, specializing in helping people find success, fulfillment, and peace in their relationships and their work.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Home — Essay Samples — Business — Conflict — The Tell-Tale Heart: Conflict and Psychological Turmoil
The Tell-tale Heart: Conflict and Psychological Turmoil
- Categories: Conflict The Tell Tale Heart
About this sample

Words: 738 |
Published: Jun 6, 2024
Words: 738 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Internal conflict: the narrator's descent into madness, external conflict: the narrator versus the old man, the interplay of internal and external conflicts.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Business Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1331 words
1 pages / 673 words
3 pages / 1174 words
4 pages / 1996 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Conflict
In Edgar Allan Poe's short story, "The Tell-Tale Heart," the conflict between the narrator and his own sanity serves as a central theme that drives the plot forward. The narrator's descent into madness and his inability to [...]
One of the main sources of conflict between John Proctor and Abigail Williams is their past romantic relationship. Abigail, who is still in love with John, becomes jealous when she realizes that he is no longer interested in [...]
Conflict is an inevitable part of human existence, manifesting in various forms and settings, from personal relationships to global political arenas. It is defined as a serious disagreement or argument, typically a protracted [...]
In the classic novel Lord of the Flies by William Golding, two main characters, Ralph and Jack, are used to represent contrasting ideas and themes. Ralph, the protagonist, is a symbol of order, civilization, and democracy, while [...]
The Thirty Years” War (1618-1648) first began with when the Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II of Bohemia tried to reduce the religious activities of his subjects, provoked rebellion among Protestants. The war involved the [...]
When the Europeans began to migrate to the New World, problems began almost immediately. These problems consisted of land use, religion, and disease. Owning land was extremely important to the European settlers. In England, and [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
America’s Military Is Not Prepared for War — or Peace

By Roger Wicker
Mr. Wicker, a Republican, is the ranking member of the U.S. Senate Armed Services Committee.
“To be prepared for war,” George Washington said, “is one of the most effectual means of preserving peace.” President Ronald Reagan agreed with his forebear’s words, and peace through strength became a theme of his administration. In the past four decades, the American arsenal helped secure that peace, but political neglect has led to its atrophy as other nations’ war machines have kicked into high gear. Most Americans do not realize the specter of great power conflict has risen again.
It is far past time to rebuild America’s military. We can avoid war by preparing for it.
When America’s senior military leaders testify before my colleagues and me on the U.S. Senate Armed Services Committee behind closed doors, they have said that we face some of the most dangerous global threat environments since World War II. Then, they darken that already unsettling picture by explaining that our armed forces are at risk of being underequipped and outgunned. We struggle to build and maintain ships, our fighter jet fleet is dangerously small, and our military infrastructure is outdated. Meanwhile, America’s adversaries are growing their militaries and getting more aggressive.
In China, the country’s leader, Xi Jinping, has orchestrated a historic military modernization intended to exploit the U.S. military’s weaknesses. He has overtaken the U.S. Navy in fleet size, built one of the world’s largest missile stockpiles and made big advances in space. President Vladimir Putin of Russia has thrown Europe into war and mobilized his society for long-term conflict. Iran and its proxy groups have escalated their shadow war against Israel and increased attacks on U.S. ships and soldiers. And North Korea has disregarded efforts toward arms control negotiations and moved toward wartime readiness.
Worse yet, these governments are materially helping one another, cooperating in new ways to prevent an American-led 21st century. Iran has provided Russia with battlefield drones, and China is sending technical and logistical help to aid Mr. Putin’s war. They are also helping one another prepare for future fights by increasing weapons transfers and to evade sanctions. Their unprecedented coordination makes new global conflict increasingly possible.
That theoretical future could come faster than most Americans think. We may find ourselves in a state of extreme vulnerability in a matter of a few years, according to a growing consensus of experts. Our military readiness could be at its lowest point in decades just as China’s military in particular hits its stride. The U.S. Indo-Pacific commander released what I believe to be the largest list of unfunded items ever for services and combatant commands for next year’s budget, amounting to $11 billion. It requested funding for a raft of infrastructure, missile defense and targeting programs that would prove vital in a Pacific fight. China, on the other hand, has no such problems, as it accumulates the world’s leading hypersonic arsenal with a mix of other lethal cruise and attack missiles.
Our military leaders are being forced to make impossible choices. The Navy is struggling to adequately fund new ships, routine maintenance and munition procurement; it is unable to effectively address all three. We recently signed a deal to sell submarines to Australia, but we’ve failed to sufficiently fund our own submarine industrial base, leaving an aging fleet unprepared to respond to threats. Two of the three most important nuclear modernization programs are underfunded and are at risk of delays. The military faces a backlog of at least $180 billion for basic maintenance, from barracks to training ranges. This projects weakness to our adversaries as we send service members abroad with diminished ability to respond to crises.
Fortunately, we can change course. We can avoid that extreme vulnerability and resurrect American military might.
On Wednesday I am publishing a plan that includes a series of detailed proposals to address this reality head-on. We have been living off the Reagan military buildup for too long; it is time for updates and upgrades. My plan outlines why and how the United States should aim to spend an additional $55 billion on the military in the 2025 fiscal year and grow military spending from a projected 2.9 percent of our national gross domestic product this year to 5 percent over the next five to seven years.
It would be a significant investment that would start a reckoning over our nation’s spending priorities. There will be conversations ahead about all manner of budget questions. We do not need to spend this much indefinitely — but we do need a short-term generational investment to help us prevent another world war.
My blueprint would grow the Navy to 357 ships by 2035 and halt our shrinking Air Force fleet by producing at least 340 additional fighters in five years. This will help patch near-term holes and put each fleet on a sustainable trajectory. The plan would also replenish the Air Force tanker and training fleets, accelerate the modernization of the Army and Marine Corps, and invest in joint capabilities that are all too often forgotten, including logistics and munitions.
The proposal would build on the $3.3 billion in submarine industrial base funding included in the national security supplemental passed in April, so we can bolster our defense and that of our allies. It would also rapidly equip service members all over the world with innovative technologies at scale, from the seabed to the stars.
We should pair increased investment with wiser spending. Combining this crucial investment with fiscal responsibility would funnel resources to the most strategic ends. Emerging technology must play an essential role, and we can build and deploy much of it in less than five years. My road map would also help make improvements to the military procurement system and increase accountability for bureaucrats and companies that fail to perform on vital national security projects.
This whole endeavor would shake our status quo but be far less disruptive and expensive than the alternative. Should China decide to wage war with the United States, the global economy could immediately fall into a depression. Americans have grown far too comfortable under the decades-old presumption of overwhelming military superiority. And that false sense of security has led us to ignore necessary maintenance and made us vulnerable.
Our ability to deter our adversaries can be regained because we have done it before. At the 50th anniversary of Pearl Harbor, in the twilight of the Soviet Union, George H.W. Bush reflected on the lessons of Pearl Harbor. Though the conflict was long gone, it taught him an enduring lesson: “When it comes to national defense,” he said, “finishing second means finishing last.”
Regaining American strength will be expensive. But fighting a war — and worse, losing one — is far more costly. We need to begin a national conversation today on how we achieve a peaceful, prosperous and American-led 21st century. The first step is a generational investment in the U.S. military.
Roger Wicker is the senior U.S. senator from Mississippi and the ranking member of the Senate Armed Services Committee.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Conflicts can happen for many reasons. Sometimes, friends might misunderstand each other. For example, if your friend didn't wave back to you at the park, you might think they are mad at you. But maybe they just didn't see you! Other times, friends might want different things. If you want to play video games and your friend wants to play ...
Essay About Conflict Between Friends. Maria, Rosa and I are long-time friends, Maria had a birthday party for Rosa, I told them that I was not going to be going to the party because I will be out of town. But at the time that I told them, they was talking to each other about what was needed for the party and not paying any attention to me.
Let your friend know that you would like to have a discussion about the relationship. No one likes having this kind of conversation "sprung on them," so give your friend some advance notice ...
Don't accuse by using the word, "you.". Be sensitive. Try to offer solutions when appropriate, but know when to listen. Don't underestimate the importance of a listening ear. Most important, be loving in what you do. Don't go out to "get" the other person, but try to focus on peacefully resolving the disagreement.
Experience of Interpersonal Conflicts Essay. Exclusively available on IvyPanda®. Interpersonal conflicts are inseparable elements of living in human society and building relations with other people. Even though their scope varies, there are some universal strategies, which can be deployed to solve them, referred to as communication theories.
He recommends something like, "I want to talk to you about something that's been bothering me. Last time we hung out, you said X. You may have meant it as a joke, but it really affected me.". The goal isn't to punish your friend but to give concrete examples rather than being vague or passive-aggressive, Cassine says.
There are many reasons that conflict may arise between you and your friend. Common examples are jealousy, poor communication skills, lack of consideration and/or respect, different principles or outlooks on life and one friend contributing more to the relationship than the other. Arguments or conflict may result from experiencing a bad day or ...
Conflict is a clash between two parties, often because of religious, social, or political disagreements. The ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine began in early 2014 and is an example of armed conflict. It affects the citizens, economy, tourism, and other sectors of the two countries, with impacts reaching other areas of the world.
Not her screaming voice and kicking feet. 10. Acknowledge the feelings. If you acknowledge that someone is angry or hurt, you can better understand the sharp or harsh words that may be coming from them. You can choose to help them deal with their emotions or let them regain their composure to talk another time. 11.
There are several types of conflict that a person experiences throughout their life. First, discuss simple conflicts you observe around you. For example, the cashier misunderstands an order, your mom forgets to buy groceries, or you have clashing class schedules. 3. Review On Movies Or Books About Conflicts.
Open and Honest Communication: Communication is key to resolving conflicts with a friend. It's important to express your thoughts and feelings in a calm and respectful manner. Avoid using accusatory language or attacking your friend, as this can escalate the conflict further.
Aristotle's Ideas on Civic Relationships: Happiness, the Virtues, Deliberation, Justice, and Friendship. On building trust at work, employers are required to give minimum supervision to the employees in an effort to make the latter feel a sense of belonging and responsibility. Gender Role Development and Friendship.
Here is an excellent selection of ten multi-genre conflict stories for students in middle and high school from CommonLit! " We Have Been Friends Together " by Caroline Elizabeth Sarah Norton (6th Grade) In this poem, the speaker describes a conflict that arises in a friendship. The speaker talks about the relationship, which began when both ...
Published: Feb 12, 2024. Conflicts are a common occurrence in various relationships, whether it be between friends, family members, colleagues, or even strangers. Some conflicts require resolution, while others are best to be avoided altogether. I have personally experienced both outcomes - a broken friendship due to conflicting interests ...
Start Writing. Once you've found your examples and written your thesis, write your first draft. Remember to start your essay with a "hook" - a question, a quote, or a statistic, for example that will introduce the conflict you'll be analyzing. Start each body paragraph with a topic sentence that states a main point, and then support ...
Speak to your reality, not theirs. Addressing conflict isn't about right or wrong; it's about coming to a sense of mutual understanding. When sharing your dilemma, keep the focus of your words on you and how you feel by using "I" statements. Start by expressing how it made you feel when your friend did what they did.
14. What Have Your Friends Taught You About Life? iStock/Getty Images. "My friends taught me different perspectives on life.". "My friends have taught me to not care what other people think ...
A hook sentence - an interesting fact, question, quote, or anecdote. Introduction part that makes readers aware of the conflict. Thesis statement. 3 body paragraphs, each with one issue of the conflict and several proofs. Address whether the conflict was resolved or not. You may also discuss the ways of avoiding or solving the conflict.
Introduction to Conflict. Conflict is an inevitable part of human existence, manifesting in various forms and settings, from personal relationships to global political arenas. It is defined as a serious disagreement or argument, typically a protracted one, that can vary in intensity and duration. Understanding conflict is crucial for developing ...
Here, we look at how conflict examples can help us transform unproductive conflict into opportunities to listen and learn. Listening is perhaps the clearest path to understanding others and resolving conflict, but it can be difficult to practice. The desire to disagree, prove we're "right," and engage in hardball tactics often get in the way.
Having solid friendships is important for two main reasons. First, they make life more enjoyable. We get to share the beautiful aspects of life with people who we love, which can enrich our ...
The following 3 short stories express this dilemma in their own unique ways. My first story of 490 words and titled " In Quest of Friendship " indicates the difficulty of turning away someone voicing a crucial need for contact and companionship. My second story of 535 words and titled " Learning From a Book On My Head " refers to a ...
In this episode, Amy Gallo shares how disagreements, if reframed, can lead to more productive outcomes. Many of us would rank getting along with colleagues as an important aspect of work, but, as Amy Gallo explains, relationships devoid of disagreement can actually be less productive. "While our natural human instinct is to avoid conflict, I ...
Conflict refers to a situation in which groups and people think, or have incompatible goals and objectives. Conflict is a wide concept, but many people belief only violence and war is conflict. However, conflict takes place in all levels of society and in all situations. Generally, organizations, individuals and people experience various types ...
My first steps in helping students resolve their conflict is to speak to both parties separately. This is a fact finding session to get a clearer picture of what each student involved is thinking ...
People in conflict with others tend to behave in several discrete ways. The four main types of conflict style are appeasement, avoidance, aggression, and alliance. Understanding the conflict style ...
This essay will explore the primary conflicts in "The Tell-Tale Heart," including the internal conflict within the narrator and the external conflict between the narrator and the old man. The seamless intertwining of these conflicts not only heightens the reader's sense of suspense but also provides profound insights into the complexities of ...
1850. By Ruth Whippman. Ms. Whippman is the author of "Boymom: Reimagining Boyhood in the Age of Impossible Masculinity.". The 20-year-old college student and gamer I met in Cedar City, Utah ...
America's Military Is Not Prepared for War — or Peace. Mr. Wicker, a Republican, is the ranking member of the U.S. Senate Armed Services Committee. "To be prepared for war," George ...