Target Market Examples
Elon Glucklich
7 min. read
Updated April 24, 2024
Imagine your dream is to own a diner.
You have restaurant experience and a great location in mind – you just need the bank to approve your loan to get started.
But the bank has questions. A big one it wants answered is: who is your target market?
It might be tempting just to say, “hungry diners.” But you’ll need to dig deeper to truly define your target market .
In this article, we’ll use this diner scenario to walk through the market research process and illustrate what the final result could look like.
- Questions about your target market
Before you even set foot in the bank, you should already have asked – and taken steps to answer – several key questions about your target market.
Let’s call our example business the Bplans Diner. Where is that perfect location you’ve found for the diner? Is it in a densely populated urban area, suburban neighborhood, or rural?
What are your hours of operation? Some diners cater to a breakfast crowd, while others might offer 24-hour dining to be a favorite among night owls. When you expect your peak hours could help determine whether you should expect to sell more omelets or hamburgers.
What’s the area’s median income, and what types of businesses or institutions are nearby? This information will help you determine pricing and marketing strategies for your diner. For instance, if your diner is located in a business district, you may want to offer lunch specials. But if it’s near a college or university, you might want to offer student discounts.
This is what a thorough target market analysis looks like, providing key insights and data to pinpoint the specific groups of customers most likely to patronize your diner. Gathering all of this information may sound intimidating, but it’s really just a matter of doing research. If you need help and guidance, check out our complete guide to conducting market research for your business .
Let’s look at an example of a target market analysis for this diner. Then, we’ll break it down and discuss each element in detail.
- Example of a target market analysis

As you can see, the target market analysis follows the basic market segmentation process of splitting out potential customers into their demographic, geographic, psychographic and behavioral traits.
Next, let’s take a look at each in more detail. Afterward, we’ll look at how you can harness your target market analysis into actual business strategies.
- Demographic
You may have noticed that the demographic analysis in our example is very broad – 18 to 65 years old, including students, workers, and some seniors.
Finding your target market isn’t always about identifying a narrow demographic to cater to. In the case of a restaurant, it makes sense to focus on the geographic location and who currently frequents the area (more on that in the next section).
A different approach may be needed for a technology product that’s sold online. In that case, narrowing the demographic focus to specific age ranges or needs would be much more important than where the business is located.
In the case of the diner, we reached our decision by conducting a demographic analysis, examining the age ranges, occupations, and other concrete data points about potential customers near the proposed location (Reminder: we didn’t do this for the Bplans Diner, we’re just providing an example).
There are several ways to go about collecting this information for your business. The most straightforward is to get out in the neighborhood, take a look around and talk to people. Are you mostly seeing students, or families? Are there a lot of office workers in the area?
You can also look up data from the U.S. Census Bureau , which includes population, age, income and other useful information, often down to the neighborhood level.
After conducting this research, one valuable step is to create a detailed customer persona that represents the typical customer you expect for your business (we provide an example of a customer persona for the diner further down in this article).
While the demographic analysis considers the type of people who might frequent your business, the geographic analysis considers the characteristics of the neighborhood itself.
Our target market analysis for Bplans Diner noted that we plan to operate in an urban area near a university with heavy foot traffic and expect a fair amount of late-night diners.
A key reason for examining the geographic makeup of your businesses is to size up your competition. If there’s already a popular diner in the area you plan to target, getting customers could be a major challenge. But if there’s a lack of dining options or no one is serving diner-style food, you’re more likely to be successful. Determining the size of your market will help you create reasonable revenue projections.
We also mentioned the plan for Bplans Diner to cater to a late-night crowd. Examining the geographic makeup of the neighborhood will help you determine if there are the kinds of businesses – bars, music venues, or businesses such as hospitals where people are working all hours – to justify targeting this group.
- Psychographic
You know the demographics and geographic characteristics of your market. Now it’s time to consider the attitudes and values of your potential customers.
The psychographic analysis helps to understand the lifestyle of potential customers and how that might affect their preferences as consumers. If many of your potential customers are health-conscious, for instance, you’ll want to ensure your diner provides options like salads or gluten-free menu items. But if most customers are families looking for a place to bring their children, it may be important to keep classic items like hamburgers and french fries on the menu.
The best way to understand your potential customers’ attitudes is to get out and talk to them. Customer interviews are among the most powerful methods of validating a business idea , since you’ll get honest, real-time feedback from the kinds of people your business would depend on.
Finally, the behavioral analysis expands on customer psychographics by examining what customers do, given their values. This is another place where it’s worth considering the broad demographics of the diner’s target market – 18 to 65 years old, split among students, workers, and seniors.
They may all want the diner’s food, but their behaviors will vary widely. College students might be looking for a late-night study spot, or a place to meet up with friends for dinner before a concert or sporting event. But workers and seniors might be more interested in breakfast or lunch specials.
Each of these behaviors gives a business owner valuable information to target individual segments of their target audience. For instance, you might want to play popular music in the evenings to get young diners ready for a night out on the town. But you’ll want a quieter ambiance at the time of day when seniors are most likely to come in. The environment can be adjusted based on when certain customers frequent the business.
Addressing behavioral aspects like buying motivations and concerns of your potential customers will also help you effectively market your diner. For example, you could create marketing campaigns based on student discounts, late-night specials, or a family-friendly atmosphere, depending on your customers’ behaviors.
- Connecting a target market analysis to business strategy
So far, we’ve touched on each of the components of a target market analysis for a diner: customer demographics, geographics, psychographics, and behaviors. (It’s also important to conduct an industry analysis to understand competitive and macroeconomic forces affecting your planning.)
With the target market analysis complete, you’re better equipped to demonstrate a thorough understanding of your customers to a lender.
Here are a few insights a business owner could use for the Bplans Diner, developed through the above analysis.
- Bplans Diner Competitive Analysis
Market Trends: Growing demand for late-night food options, increasing preference for healthy dining options.
Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses:
Competitor A: Strong brand but limited menu options.
Competitor B: Wide variety of options but lacking in ambiance.
- Bplans Diner Marketing Strategy
Product Differentiation: Offering a diverse menu that caters to various preferences, including healthy options.
Positioning: Establishing Bplans Diner as a reliable, quality, 24-hour dining option in the region.
Promotion: Utilizing social media to announce special night-time deals and promotions.
- Get started with your business plan template
A target market analysis is a key part of any business plan. But it’s just one piece. At Bplans, we take some of the pain out of business planning. We’ve developed a free business planning template to help reduce entrepreneurs’ time to create a full, lender-ready business plan. Bplans has also collected over 550 free sample business plans across numerous industries. Find a plan in your industry to get inspiration for your plan.
Brought to you by

Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Elon is a marketing specialist at Palo Alto Software, working with consultants, accountants, business instructors and others who use LivePlan at scale. He has a bachelor's degree in journalism and an MBA from the University of Oregon.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

4 Min. Read
How to Define Your Target Market

8 Min. Read
How to Conduct an Industry Analysis

10 Min. Read
How to Create a Detailed User or Buyer Persona

9 Min. Read
How to Write a Customer Analysis
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write a Business Plan: Target Market Analysis
The Business Plan and the Importance of Defining Your Target Market
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Conducting a Market Analysis
Polling your target market, writing the market analysis, online tools for market research, u.s. online market research sources, canadian online market research, local sources of market research, doing your own market research.
Creative Commons CC0
The market analysis is basically the target market section of your business plan . It is a thorough examination of the ideal people to whom you intend to sell your products or services.
Even if you intend on selling a product or service only in your community, you won't be selling that service to everyone who lives there. Knowing exactly what type(s) of people might be interested in buying your product or service and how many of them reside in your projected area or region is fundamental in creating your market analysis.
Once target market data has been established, you'll also work on sales projections within specific time frames, as well as how prospective sales might be affected by trends and policies.
Research is key and cornerstone of any solid business plan .
Don't Skip This Step!
Don't skip market research; otherwise, you could end up starting a business that doesn't have a paying market.
Use these general terms as linchpins in research data for the market analysis section of your business plan, and to identify your target market:
| What age range are you catering products/services to? Kids? Adults? Seniors? Gen X? Millennials? | |
| Are you targeting men, women, or both sexes? | |
| Are your target customers married or single, or divorced? | |
| What is their family structure (number of children, extended family, etc.)? | |
| Where do they live? Are you selling locally? Regionally, nationally, or internationally? | |
| How much education do they have? | |
| What is their income? | |
| What do they do for a living? | |
| Are they members of a particular religious group? | |
| Are they members of a particular language group? | |
| What is their lifestyle like? | |
| What motivates them? | |
| What is the size of the target market? |
But don't stop here. To succinctly define your target market, poll or survey members of your prospective clients or customers to ask specific questions directly related to your products or services. For instance, if you plan to sell computer-related services, ask questions relating to the number of computing devices your prospective customers own and how often they require servicing. If you plan on selling garden furniture and accessories, ask what kinds of garden furniture or accessories your potential customers have bought in the past, how often, and what they expect to buy within the next one, three, and five years.
Answers to these and other questions related to your market are to help you understand your market potential.
The goal of the information you collect is to help you project how much of your product or service you'll be able to sell. Review these important questions you need to try to answer using the data you collect:
- What proportion of your target market has used a product similar to yours before?
- How much of your product or service might your target market buy? (Estimate this in gross sales and/or in units of product/service sold.)
- What proportion of your target market might be repeat customers?
- How might your target market be affected by demographic shifts?
- How might your target market be affected by economic events (e.g. a local mill closing or a big-box retailer opening locally)?
- How might your target market be affected by larger socio-economic trends?
- How might your target market be affected by government policies (e.g. new bylaws or changes in taxes)?
One purpose of the market analysis is to ensure you have a viable business idea.
Find Your Buying Market
Use your market research to make sure people don't just like your business idea, but they're also willing to pay for it.
If you have information suggesting that you have a large enough market to sustain your business goals, write the market analysis in the form of several short paragraphs using appropriate headings for each. If you have several target markets, you may want to number each.
Sections of your market analysis should include:
- Industry Description and Outlook
- Target Market
- Market Research Results
- Competitive Analysis
Remember to properly cite your sources of information within the body of your market analysis as you write it. You and other readers of your business plan, such as potential investors, will need to know the sources of the statistics or opinions that you've gathered.
There are several online resources to learn if your business idea is something worth pursing, including:
- Keyword searches can give you an overall sense of potential demand for your product or service based on the number of searches.
- Google Trends analysis can tell you how the number of searches has changed over time.
- Social media campaigns can give you an indication of the potential customer interest in your business idea.
The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) has information on doing your market research and analysis , as well as a list of free small business data and trends resources you can use to conduct your research. Consider these sources for data collection:
- SBA Business Data and Statistics
- The U.S. Census Bureau maintains a huge database of demographic information that is searchable by state, county, city/town, or zip code using its census data tool . Community, housing, economic, and population surveys are also available.
- The U.S. Department of Commerce Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) has extensive statistics on the economy including consumer income/spending/consumption, business activity, GDP, and more, all of which are searchable by location.
The Government of Canada offers a guide on doing market research and tips for understanding the data you collect. Canadian data resources include:
- Statistics Canada offers demographic and economic data.
- The Business Development Bank of Canada (BDC) offers market research and consulting with industry experts.
- The Canada Business Network provides business information to entrepreneurs by province/territory, including market research data.
There are also a great many local resources for building target market information to explore, including:
- Local library
- Local Chamber of Commerce
- Board of Trade
- Economic Development Centre
- Local government agent's office
- Provincial business ministry
- Local phone book
All of these will have information helpful in defining your target market and providing insights into trends.
The above resources are secondary sources of information, in which others have collected and compiled the data. To get specific information about your business, consider conducting your own market research . For instance, you might want to design a questionnaire and survey your target market to learn more about their habits and preferences relating to your product or service.
Market research is time-consuming but is an important step in affording your business plan validity. If you don't have the time or the research skills to thoroughly define your target market yourself, hiring a person or firm to do the research for you can be a wise investment.
Small Business Administration. " Market Research and Competitive Analysis. " Accessed Jan. 13, 2020.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A lot of preparation goes into starting a business before you can open your doors to the public or launch your online store. One of your first steps should be to write a business plan . A business plan will serve as your roadmap when building your business.
Within your business plan, there’s an important section you should pay careful attention to: your market analysis. Your market analysis helps you understand your target market and how you can thrive within it.
Simply put, your market analysis shows that you’ve done your research. It also contributes to your marketing strategy by defining your target customer and researching their buying habits. Overall, a market analysis will yield invaluable data if you have limited knowledge about your market, the market has fierce competition, and if you require a business loan. In this guide, we'll explore how to conduct your own market analysis.
How to conduct a market analysis: A step-by-step guide
In your market analysis, you can expect to cover the following:
Industry outlook
Target market
Market value
Competition
Barriers to entry
Let’s dive into an in-depth look into each section:
Step 1: Define your objective
Before you begin your market analysis, it’s important to define your objective for writing a market analysis. Are you writing it for internal purposes or for external purposes?
If you were doing a market analysis for internal purposes, you might be brainstorming new products to launch or adjusting your marketing tactics. An example of an external purpose might be that you need a market analysis to get approved for a business loan .
The comprehensiveness of your market analysis will depend on your objective. If you’re preparing for a new product launch, you might focus more heavily on researching the competition. A market analysis for a loan approval would require heavy data and research into market size and growth, share potential, and pricing.
Step 2: Provide an industry outlook
An industry outlook is a general direction of where your industry is heading. Lenders want to know whether you’re targeting a growing industry or declining industry. For example, if you’re looking to sell VCRs in 2020, it’s unlikely that your business will succeed.
Starting your market analysis with an industry outlook offers a preliminary view of the market and what to expect in your market analysis. When writing this section, you'll want to include:
Market size
Are you chasing big markets or are you targeting very niche markets? If you’re targeting a niche market, are there enough customers to support your business and buy your product?
Product life cycle
If you develop a product, what will its life cycle look like? Lenders want an overview of how your product will come into fruition after it’s developed and launched. In this section, you can discuss your product’s:
Research and development
Projected growth
How do you see your company performing over time? Calculating your year-over-year growth will help you and lenders see how your business has grown thus far. Calculating your projected growth shows how your business will fare in future projected market conditions.
Step 3: Determine your target market
This section of your market analysis is dedicated to your potential customer. Who is your ideal target customer? How can you cater your product to serve them specifically?
Don’t make the mistake of wanting to sell your product to everybody. Your target customer should be specific. For example, if you’re selling mittens, you wouldn’t want to market to warmer climates like Hawaii. You should target customers who live in colder regions. The more nuanced your target market is, the more information you’ll have to inform your business and marketing strategy.
With that in mind, your target market section should include the following points:
Demographics
This is where you leave nothing to mystery about your ideal customer. You want to know every aspect of your customer so you can best serve them. Dedicate time to researching the following demographics:
Income level
Create a customer persona
Creating a customer persona can help you better understand your customer. It can be easier to market to a person than data on paper. You can give this persona a name, background, and job. Mold this persona into your target customer.
What are your customer’s pain points? How do these pain points influence how they buy products? What matters most to them? Why do they choose one brand over another?
Research and supporting material
Information without data are just claims. To add credibility to your market analysis, you need to include data. Some methods for collecting data include:
Target group surveys
Focus groups
Reading reviews
Feedback surveys
You can also consult resources online. For example, the U.S. Census Bureau can help you find demographics in calculating your market share. The U.S. Department of Commerce and the U.S. Small Business Administration also offer general data that can help you research your target industry.
Step 4: Calculate market value
You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value.
A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the two. It requires for you to calculate the entire market and then estimate how much of a share you expect your business to get. For example, let’s assume your target market consists of 100,000 people. If you’re optimistic and manage to get 1% of that market, you can expect to make 1,000 sales.
A bottom-up analysis is more data-driven and requires more research. You calculate the individual factors of your business and then estimate how high you can scale them to arrive at a projected market share. Some factors to consider when doing a bottom-up analysis include:
Where products are sold
Who your competition is
The price per unit
How many consumers you expect to reach
The average amount a customer would buy over time
While a bottom-up analysis requires more data than a top-down analysis, you can usually arrive at a more accurate calculation.
Step 5: Get to know your competition
Before you start a business, you need to research the level of competition within your market. Are there certain companies getting the lion’s share of the market? How can you position yourself to stand out from the competition?
There are two types of competitors that you should be aware of: direct competitors and indirect competitors.
Direct competitors are other businesses who sell the same product as you. If you and the company across town both sell apples, you are direct competitors.
An indirect competitor sells a different but similar product to yours. If that company across town sells oranges instead, they are an indirect competitor. Apples and oranges are different but they still target a similar market: people who eat fruits.
Also, here are some questions you want to answer when writing this section of your market analysis:
What are your competitor’s strengths?
What are your competitor’s weaknesses?
How can you cover your competitor’s weaknesses in your own business?
How can you solve the same problems better or differently than your competitors?
How can you leverage technology to better serve your customers?
How big of a threat are your competitors if you open your business?
Step 6: Identify your barriers
Writing a market analysis can help you identify some glaring barriers to starting your business. Researching these barriers will help you avoid any costly legal or business mistakes down the line. Some entry barriers to address in your marketing analysis include:
Technology: How rapid is technology advancing and can it render your product obsolete within the next five years?
Branding: You need to establish your brand identity to stand out in a saturated market.
Cost of entry: Startup costs, like renting a space and hiring employees, are expensive. Also, specialty equipment often comes with hefty price tags. (Consider researching equipment financing to help finance these purchases.)
Location: You need to secure a prime location if you’re opening a physical store.
Competition: A market with fierce competition can be a steep uphill battle (like attempting to go toe-to-toe with Apple or Amazon).
Step 7: Know the regulations
When starting a business, it’s your responsibility to research governmental and state business regulations within your market. Some regulations to keep in mind include (but aren’t limited to):
Employment and labor laws
Advertising
Environmental regulations
If you’re a newer entrepreneur and this is your first business, this part can be daunting so you might want to consult with a business attorney. A legal professional will help you identify the legal requirements specific to your business. You can also check online legal help sites like LegalZoom or Rocket Lawyer.
Tips when writing your market analysis
We wouldn’t be surprised if you feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information needed in a market analysis. Keep in mind, though, this research is key to launching a successful business. You don’t want to cut corners, but here are a few tips to help you out when writing your market analysis:
Use visual aids
Nobody likes 30 pages of nothing but text. Using visual aids can break up those text blocks, making your market analysis more visually appealing. When discussing statistics and metrics, charts and graphs will help you better communicate your data.
Include a summary
If you’ve ever read an article from an academic journal, you’ll notice that writers include an abstract that offers the reader a preview.
Use this same tactic when writing your market analysis. It will prime the reader of your market highlights before they dive into the hard data.
Get to the point
It’s better to keep your market analysis concise than to stuff it with fluff and repetition. You’ll want to present your data, analyze it, and then tie it back into how your business can thrive within your target market.
Revisit your market analysis regularly
Markets are always changing and it's important that your business changes with your target market. Revisiting your market analysis ensures that your business operations align with changing market conditions. The best businesses are the ones that can adapt.
Why should you write a market analysis?
Your market analysis helps you look at factors within your market to determine if it’s a good fit for your business model. A market analysis will help you:
1. Learn how to analyze the market need
Markets are always shifting and it’s a good idea to identify current and projected market conditions. These trends will help you understand the size of your market and whether there are paying customers waiting for you. Doing a market analysis helps you confirm that your target market is a lucrative market.
2. Learn about your customers
The best way to serve your customer is to understand them. A market analysis will examine your customer’s buying habits, pain points, and desires. This information will aid you in developing a business that addresses those points.
3. Get approved for a business loan
Starting a business, especially if it’s your first one, requires startup funding. A good first step is to apply for a business loan with your bank or other financial institution.
A thorough market analysis shows that you’re professional, prepared, and worth the investment from lenders. This preparation inspires confidence within the lender that you can build a business and repay the loan.
4. Beat the competition
Your research will offer valuable insight and certain advantages that the competition might not have. For example, thoroughly understanding your customer’s pain points and desires will help you develop a superior product or service than your competitors. If your business is already up and running, an updated market analysis can upgrade your marketing strategy or help you launch a new product.
Final thoughts
There is a saying that the first step to cutting down a tree is to sharpen an axe. In other words, preparation is the key to success. In business, preparation increases the chances that your business will succeed, even in a competitive market.
The market analysis section of your business plan separates the entrepreneurs who have done their homework from those who haven’t. Now that you’ve learned how to write a market analysis, it’s time for you to sharpen your axe and grow a successful business. And keep in mind, if you need help crafting your business plan, you can always turn to business plan software or a free template to help you stay organized.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

Small Business Trends
What is a target market and how to pick one (examples and template included).
In this guide, we’ll explore what a target market is, how to define one, and why it’s so important. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What is Target Marketing?

Before you start a business, it’s also important to write a business plan that includes a personal brand statement and a vision statement to clearly define your goals and objectives.
How to Define Your Target Market
1. conduct market research, 2. define your unique selling proposition (usp).
Your USP is what differentiates your product or service from competitors and should be tailored to meet the needs of your target market. By clearly defining your USP, you can create a compelling marketing message that resonates with potential customers.
3. Analyze Your Competition
4. segment your market, 5. determine personas, 6. refine your strategy.
Based on the insights you have gathered in Steps 1-5, refine your overall marketing strategy to best cater to each segment of customers. Things you can refine include messaging, promotions and pricing, content, and channels of distribution.
Defining Your Target Market Template
Target market template:, why knowing your target market is so important for your marketing strategy.
Without a proper understanding of the needs and wants of your target audience, it’s nearly impossible to craft a message that will resonate and result in sales.
Target Market Segmentation
Take, for example, a clothing brand using psychographic segmentation to target fashion-forward young adults who prioritize sustainability. This approach enabled them to craft a resonant marketing message.
Psychographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation, geographic target market.
A geographic target market is defined by the consumer’s location. This type of target market focuses on reaching consumers in a specific geographic area.
Firmographic Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation, types of target markets.
B2B (Business-to-Business) is an industry term used to describe companies that sell products or services to other businesses rather than individual consumers.
Niche Markets
Knowing your niche market can help you create more targeted ads and better understand the specific needs and wants of potential customers within that group.
How Big Should a Target Market be?
Target market examples, starbucks target market.
They focus on providing a convenient and comfortable experience for their customers, with a wide variety of coffee and food options.
Nike Target Market
Tesla target market, disney target market.
| Company | Target Market | Focus | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starbucks | Busy professionals, college students, and older adults | Providing a convenient and comfortable experience with a wide variety of coffee and food options | - Consumers who frequent high-traffic areas - Willing to pay a premium for high-quality coffee and an inviting atmosphere |
| Nike | Consumers who value fitness and healthy living, including serious athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and casual athletes | Providing high-performance athletic apparel and footwear for a wide range of sports and activities | - Youth and urban culture - Interested in collaborations with popular athletes and fashion designers |
| Tesla | Environmentally conscious consumers who value innovation and technology | Providing sustainable and efficient electric vehicles and energy solutions | - Early adopters of technology - Looking for an alternative to traditional gasoline vehicles - Willing to pay a premium for high-performance electric cars |
| Disney | Families and children, including grandparents and adults who are young at heart | Creating magical experiences through theme parks, cruises, movies, and TV shows | - Willing to pay for the Disney brand experience and for the memories that come with it |
Target Marketing Strategies
Developing effective target marketing strategies can help you reach the right customers and increase your return on investment. Here are five target marketing strategies to consider:
| Strategy | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segmenting the Market | Dividing the market into smaller groups of customers with similar characteristics | - Allows for more specific, tailored marketing strategies - Higher chances of reaching the right customers - Can help increase customer engagement and conversion rates | - Requires comprehensive market research - Can be time-consuming and expensive - Difficulties might arise in correctly identifying and defining segments |
| Creating Buyer Personas | Creating a fictional representation of the ideal customer | - Helps to understand customer needs, wants, and pain points - Can aid in tailoring marketing messages - Enables more personal and relatable marketing | - Risk of oversimplification or stereotype - Requires comprehensive and ongoing customer research - Real customers might not perfectly align with created personas |
| Developing a Unique Value Proposition (UVP) | Creating a statement that communicates the unique benefits of the product or service | - Helps to differentiate from competition - Clearly communicates value to potential customers - Can drive targeted customer attraction | - Difficulty in finding truly unique benefits - Requires in-depth understanding of the market and competitors - Needs constant revision to remain relevant |
| Using Data and Analytics | Using data analysis to understand the target market and develop effective marketing strategies | - Provides quantitative basis for decision making - Helps in identifying customer behaviors and trends - Can lead to more efficient and targeted marketing | - Requires skills and tools to collect, analyze, and interpret data - Can be expensive, especially for smaller businesses - Issues related to privacy and data security |
| Test and Optimize | Testing and refining marketing strategies based on results | - Helps to improve effectiveness of marketing strategies - Allows for constant refinement and learning - Can improve ROI of marketing efforts | - Can be time-consuming - Requires resources for ongoing testing and analysis - May lead to short-term failures as part of the learning process |
What is a target market?
Can you have multiple target markets, how do i answer the question ‘what is your target market’.
This could include demographic information such as age, gender, income level, and geographic location, and/or psychographic information such as values, interests, lifestyle choices, or preferences.
What are the 3 common target markets?
How detailed should a target market be what is the purpose of a target market, what is the difference between target market and target audience.
The difference between a target market and a target audience is that a target market is the group of potential customers that your company is aiming to reach, while a target audience is the people who are most likely to purchase your product or service.
What Is a Target Market (And How to Find Yours)
The better you understand your target market, the more you’ll be able to focus your ads and reach the audience most likely to convert into customers.

Table of Contents
Your target market sets the tone for your entire marketing strategy — from how you develop and name your products or services right through to the marketing channels you use to promote them.
Here’s a hint before we dig in: Your target market is not “everyone” ( unless you’re Google ). Your task in defining your target market is to identify and understand a smaller, relevant niche so you can dominate it. It’s all about narrowing your focus while expanding your reach.
In this guide, we’ll help you learn who’s already interacting with your business and your competitors, then use that information to develop a clear target market as you build your brand .
Bonus: Get the free template to easily craft a detailed profile of your ideal customer and/or target audience.
What is a target market?
A target market is the specific group of people you want to reach with your marketing message . They are the people who are most likely to buy your products or services, and they are united by some common characteristics, like demographics and behaviors.
The more clearly you define your target market, the better you can understand how and where to reach your ideal potential customers. You can start with broad categories like millennials or single dads, but you need to get much more detailed than that to achieve the best possible conversion rates.
Don’t be afraid to get highly specific. This is all about targeting your marketing efforts effectively, not stopping people from buying your product.
People who are not included in your targeted marketing can still buy from you—they’re just not your top focus when crafting your marketing strategy. You can’t target everyone, but you can sell to everyone.
Your target market should be based on research, not a gut feeling . You need to go after the people who really want to buy from you, even if they’re not the customers you originally set out to reach.
What is target market segmentation?
Target market segmentation is the process of dividing your target market into smaller, more specific groups. It allows you to create a more relevant marketing message for each group.
Remember — you can’t be all things to all people. But you can be different things to different groups of people.
For example, as a vegetarian, I’ve eaten plenty of Impossible Burgers. I’m definitely a target customer. But vegetarians are a surprisingly small target market segment for Impossible Foods: only 10% of their customer base.
That’s why Impossible Foods’ first national advertising campaign was definitely not targeted at me:
https://www.facebook.com/ImpossibleFoods/videos/158779836141556
The target market segment for this ad campaign was “meat eaters who haven’t yet tried Impossible products.”
Vegetarians and meat eaters have different reasons for eating plant-based burgers and want different things from the experience. Target market segmentation ensures the company reaches the right audience with the right message.
How to define your target market
Step 1. compile data on your current customers.
A great first step in figuring out who most wants to buy from you is to identify who is already using your products or services. Once you understand the defining characteristics of your existing customer base, you can go after more people like that.
Depending on how someone connects with your business, you might have only a little information about them, or a lot.
This doesn’t mean you should add a lot of questions to your order or opt-in process just for audience research purposes — this can annoy customers and result in abandoned shopping carts.
But do be sure to use the information you naturally acquire to understand trends and averages .
Your CRM is a goldmine here. UTM parameters combined with Google Analytics can also provide useful information about your customers.
Some data points you might want to consider are:
- Age: You don’t need to get too specific here. It won’t likely make a difference whether your average customer is 24 or 27. But knowing which decade of life your customers are in can be very useful.
- Location (and time zone): Where in the world do your existing customers live? In addition to understanding which geographic areas to target, this helps you figure out what hours are most important for your customer service and sales reps to be online, and what time you should schedule your social ads and posts to ensure best visibility.
- Language: Don’t assume your customers speak the same language you do. And don’t assume they speak the dominant language of their (or your) current physical location.
- Spending power and patterns: How much money do your current customers have to spend? How do they approach purchases in your price category?
- Interests: What do your customers like to do, besides using your products or services? What TV shows do they watch? What other businesses do they interact with?
- Challenges: What pain points are your customers facing? Do you understand how your product or service helps them address those challenges?
- Stage of life: Are your customers likely to be college students? New parents? Parents of teens? Retirees?
If you’re selling B2B products, your categories will look a little different. You might want to collect information about the size of businesses that buy from you, and information about the titles of the people who tend to make the buying decisions. Are you marketing to the CEO? The CTO? The social marketing manager?
Step 2. Incorporate social data
Social media analytics can be a great way of filling out the picture of your target market. They help you understand who’s interacting with your social accounts, even if those people are not yet customers.
These people are interested in your brand. Social analytics can provide a lot of information that might help you understand why. You’ll also learn about potential market segments you may not have thought to target before.
You can also use social listening to help identify the people who are talking about you and your product on social media, even if they don’t follow you.
If you want to reach your target market with social ads, lookalike audiences are an easy way to reach more people who share characteristics with your best customers.
Step 3. Check out the competition
Now that you know who’s already interacting with your business and buying your products or services, it’s time to see who’s engaging with the competition.
Knowing what your competitors are up to can help you answer some key questions:
- Are your competitors going after the same target market segments as you are?
- Are they reaching segments you hadn’t thought to consider?
- How are they positioning themselves?
Our guide on how to do competitor research on social media walks you through the best ways to use social tools to gather competitor insights.
You won’t be able to get detailed audience information about the people interacting with your competitors, but you’ll be able to get a general sense of the approach they’re taking and whether it’s allowing them to create engagement online.
This analysis will help you understand which markets competitors are targeting and whether their efforts appear to be effective for those segments.
Step 4. Clarify the value of your product or service
This comes down to the key distinction all marketers must understand between features and benefits. You can list the features of your product all day long, but no one will be convinced to buy from you unless you can explain the benefits .
Features are what your product is or does. The benefits are the results. How does your product make someone’s life easier, or better, or just more interesting?
If you don’t already have a clear list of the benefits of your product, it’s time to start brainstorming now. As you create your benefit statements, you’ll also by default be stating some basic information about your target audience.
For example, if your service helps people find someone to look after their pets while they’re away, you can be pretty confident that your market will have two main segments: (1) pet owners and (2) existing or potential pet-sitters.
If you’re not sure exactly how customers benefit from using your products, why not ask them in a survey, or even a social media poll ?
You might find that people use your products or services for purposes you haven’t even thought of. That might, in turn, change how you perceive your target market for future sales.
Step 5. Create a target market statement
Now it’s time to boil everything you’ve discovered so far into one simple statement that defines your target market. This is actually the first step in creating a brand positioning statement , but that’s a project for another day. For now, let’s stick to creating a statement that clearly defines your target market.
For example, here’s Zipcar’s brand positioning statement, as cited in the classic marketing text Kellogg on Marketing . We’re interested in the first part of the statement, which defines the target market:
“To urban-dwelling, educated, techno-savvy consumers who worry about the environment that future generations will inherit, Zipcar is the car-sharing service that lets you save money and reduce your carbon footprint, making you feel you’ve made a smart, responsible choice that demonstrates your commitment to protecting the environment.”
Zipcar is not targeting all residents of a particular city. They’re not even targeting all the people in a given city who don’t own a car. They’re specifically targeting people who:
- live in an urban area
- have a certain degree of education
- are comfortable with technology
- are concerned about the environment
These are all interests and behaviors that Zipcar can specifically target using social content and social ads .
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Zipcar (@zipcar)
They also help to guide the company’s overall approach to its service, as evidenced by the rest of the positioning statement.
When crafting your target market statement, try to incorporate the most important demographic and behavior characteristics you’ve identified. For example:
Our target market is [gender(s)] aged [age range], who live in [place or type of place], and like to [activity].
Don’t feel like you need to stick to these particular identifiers. Maybe gender is irrelevant for your market, but you have three or four key behaviors to incorporate in your statement.
If you offer multiple products or services, you might need to create a target market statement for each market segment. In this case, it’s useful to define buyer personas .
Target market examples
Nike target market.
Despite its current market domination, Nike actually provides a great example of what can go wrong when you try to target too general of an audience.
Nike started out as a running shoe company. In the 1980s, they tried to expand their target market beyond runners to include anyone who wanted comfortable shoes. They launched a line of casual shoes, and it flopped.
Here’s the thing: Non-runners were already buying Nike shoes to walk to work, or for other casual purposes. Nike spotted this as an opportunity to expand. Instead, they diluted their brand promise, and the company actually started losing money.
The lesson, according to company founder Phil Knight?
“Ultimately, we determined that we wanted Nike to be the world’s best sports and fitness company and the Nike brand to represent sports and fitness activities. Once you say that, you have focus.”
While Nike would certainly not stop casual users from buying its shoes, the company refocused everything from product development to marketing on its target market: athletes of all levels, from pro to beer league.
In fact, understanding the importance of focus led Nike into a highly effective strategy of target market segmentation. The brand has multiple target markets for its various product lines.
On social, that means they use multiple accounts to reach their different target market groups. No one account tries to be all things to all customers.
The post below from Nike’s general Instagram account targets the segment of their audience interested in fashion and lifestyle products.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Nike Basketball (@nikebasketball)
But the company also has channels dedicated to specific sports. Here’s an example of the content they create for runners:
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Nike Running (@nikerunning)
And that means … the brand has been able to return to marketing its products specifically for casual wear. It just reaches the casual target market through different channels than it uses for its athletic markets. It’s a different target market segment, and a different marketing message
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Nike Sportswear (@nikesportswear)
Like Nike, you might have one target market, or many, depending on the size of your brand. Remember that you can only speak effectively to one target market segment at a time.
Takasa target market
Takasa is a Canadian retail homewares company that specializes in organic, fair trade bedding and bath linens.
Here’s their target market as defined by founders Ruby and Kuljit Rakhra:
“ Our target market is the LOHAS segment, which means Family Lifestyles of Health and Sustainability. This group of people is already living, or striving to live, a green lifestyle … We know our target demo is very conscious about what their families consume, as well as the impact this consumption has on the environment.”
In their social content, they clearly identify the product features most important to their target market: organic materials and fair labor practices.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Organic + Fairtrade Home Goods (@takasa.co)
The City of Port Alberni’s target market
Why does a city need a target market? In Port Alberni’s case, the city is working to “attract investment, business opportunities and new residents.” To that end, they launched a rebranding and marketing campaign.
And a marketing campaign, of course, needs a target market. Here’s how the city defined it:
“ Our target market is young people and young families 25 to 45 years of age who are entrepreneurial-minded, family oriented, adventurous, enjoy an active lifestyle, desire an opportunity to contribute to growth, well-educated and skilled professionals or tradespeople.”
In their social content, they highlight recreational opportunities aimed at those active and adventurous young families, even using the handle @PlayinPA.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by City of Port Alberni (@playinpa)
White House Black Market target market
White House Black Market is a women’s fashion brand. Here’s how they describe their target customer on their website :
“Our customer … is strong yet subtle, modern yet timeless, hard-working yet easy-going.”
That’s a fine description when talking directly to customers. But the marketing department needs a target market definition with a few more specifics. Here’s the detailed target market as described by the company’s former president:
“ Our target market is women [with a] median age of about 45 … at a stage in her life where she’s very busy, primarily a working woman. She’s probably got one or two kids left at home [or] … her children may be out of the house and on their way to college.”
With their hashtag #WHBMPowerhouse, they focus on this key demographic of women in their 40s with busy home lives and careers.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by White House Black Market (@whbm)
Use Hootsuite to better target your audience on social media. Create, schedule, and publish posts to every network, get demographic data, performance reports, and more. Try it free today.
Start your free 30-day trial
Do it better with Hootsuite , the all-in-one social media tool. Stay on top of things, grow, and beat the competition.
Become a better social marketer.
Get expert social media advice delivered straight to your inbox.
Christina Newberry is an award-winning writer and editor whose greatest passions include food, travel, urban gardening, and the Oxford comma—not necessarily in that order.
Related Articles

How To Create Better Buyer Personas [Free Template]
A well-defined buyer persona—also called a customer persona, audience persona, or marketing persona—will help you target your ideal customer.

How to Create a Social Media Marketing Strategy in 9 Easy Steps [Free Template]
Creating your social media marketing strategy doesn’t need to be painful. Create an effective plan for your business in 9 simple steps.

How to Create a Social Media Report [Free Template Included]
A comprehensive social media report proves the value of your social marketing plan. It shows what you’ve accomplished, backed up by data.

21 of the Best Social Media Analytics Tools for 2024
Are you a social media marketer who wants to better focus your time, effort, and budget? It’s time for some new social media analytics tools!
BUSINESS STRATEGIES
What is a target market and how to define yours
- Rebecca Strehlow
- Dec 7, 2023
- 11 min read

One of the first steps in starting a business is determining your target market. This step alone can be the basis for what products you create, how you brand your business and ultimately who you market to.
With that in mind, you’ll need to develop assets that resonate with your target market. Start by creating a business website that represents your business and uses language and visuals relatable to your audience. Consider what niche you can fit into and what separates your business from the competition. From there you can create messaging, branding and advertising designed for your target market and convert more leads into customers.
Keep reading to learn more about defining your target market and gain expert tips on how to implement this targeting throughout your business strategy.
What is a target market?
Your target market is your product’s primary consumer. Once you know who this is, you can tailor your branding and marketing efforts toward them.
A target market can be composed of a broad group, such as married men over 40 in the US, or it can be quite narrow, such as urban, health-conscious, vegetarian women in Texas. Your market will depend on the particular consumer needs your product addresses.
The three key aspects of a target market include:
Demographics: Age, gender, income, education or employment status.
Geographics: Primary location of your market.
Personality traits: What they like and dislike, as well as where they shop and their favorite brands.
To pinpoint your target market, you’ll need to analyze data about your product niche, your customers and your competitors. You'll also need to understand more about the specific types of target markets in more detail.
What are the types of target markets?
In general there are several ways business owners can categorize target markets. For the most part target markets are divided into the following four main types: demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral.
Demographic
This type of target market is defined by a number of demographic variables such as age, gender, income, education, and family size. Companies might target specific demographic groups based on their buying habits and purchasing power.
Geographic target markets are defined, as the name suggests, by geographic variables such as region, state, city and population density.
Psychographic
Psychographic variables such as lifestyle, values, personality, and social class make up the definition of this target market.
This type of target market is defined by consumer behavior, such as the benefits sought, usage rate, and customer loyalty.
It's important to note that a business may choose to target one or multiple types of target markets, depending on their specific business objectives and marketing strategies.
Why are target markets important?
Understanding your target market is a crucial aspect of developing a successful business. Below we explore the main reasons why understanding your target market is so important in order to ensure a profitable business.
Better customer segmentation : Understanding your target market allows you to segment your customers more effectively, which in turn helps you tailor your marketing messages and products to meet their specific needs and preferences.
Increased focus and efficiency: Focusing on a specific target market allows you to be more efficient with marketing resources while avoiding wasting time and money on efforts that are not likely to reach or resonate with your target audience.
Improved brand reputation: Understanding your target market can help you establish and maintain a positive brand reputation by allowing you to align your brand with the values and interests of your market.
Increased customer loyalty : By understanding your target market and delivering products and services that meet their needs and expectations, you will foster a loyal customer base that is more likely to recommend your brand to others.
Better decision making: Understanding your target market provides valuable insights that can inform important business decisions, such as product development, pricing strategies and distribution channels for marketing efforts.
Target market vs. target audience?
Often used interchangeably, target market and target audience are not the same thing. Your target market is the end consumer while your target audience is to whom your company advertises. While your target market might fall into your target audience, who you advertise to may not, in the end, be the one who consumes the product.
To clarify, let’s look at an example: Kids toys, for example, have a very clear target market: children. In addition, toys are often marketed toward children who identify with a specific gender category. Nevertheless, kids don’t purchase their toys, their parents do. So toy companies must focus their advertising strategies on parents (the target audience) to sell toys for their kids (the target market).
For example, Generation Alpha , kids born between 2010 and 2025 with millennial parents, play with much different toys than their parents did because millennials have different consumer preferences than their Baby Boomer parents. Rather than shopping in big-box stores for brightly-colored toy packages, millennial parents are more likely to purchase clean, minimalistic, and gender-inclusive toys from Instagram ads or Amazon. Therefore, toy companies are using Millennial preferences (the target audience) to sell toys to their Generation Alpha kids (the target market).

How to determine your target market
Gather consumer data
Know your product’s benefits
Investigate your competitors
Segment your audience
Write a target market statement
Refine your research
01. Gather consumer data
The first step in defining your target market is to learn more about your customers. Even if you’ve just started an online store and don’t have many customers yet, these practices will come in handy further down the line.
Start by gathering information about current and past buyers and try to identify characteristics that they have in common. This data will help you market your product to people with similar interests. If you are still in the early stages of your business and haven’t started selling your product, look at competitor markets and use that information to determine your target market.
Using website analytics tools, social media and email marketing analytics platforms, here are some data points you’ll want to consider:
Age: Do your customers share a common decade or generation? Are they millennials, older adults, or something in between?
Location: Where in the world do most of your customers live? Consider the different cities, countries, and regions.
Language: Which languages do your customers speak? Remember that your customers’ language isn’t necessarily the dominant language of their country.
Spending power: Consider socioeconomic factors that may be affecting your customers. How much money are they willing or able to spend?
Hobbies and career: What do your customers enjoy doing? What are their professions, and what do they do in their spare time?
Stage of life: Where are your customers in life? Are they college students? New parents? Retirees?
If your company is B2B rather than B2C , you’ll want to look for characteristics of companies, rather than individual consumers. These traits include:
Business size: Are the businesses that buy from you small, medium, or large?
Location: Where are these businesses physically located?
Vertical: Which industries are most of these businesses in?
Budget: How have these businesses raised money ? Consider how much they’d be willing or able to spend on products like yours.
Be sure to track this information in an orderly manner so that you can keep your findings organized and easily identify trends. Analyzing these trends will allow you to identify shared characteristics within your customer base. These characteristics will inform your inbound marketing efforts and steer your strategy toward your target audience.
02. Know your product benefits
The next step is to understand your consumers’ motivation behind purchasing your product, rather than a competitor. You can learn this information by speaking to your customers directly, asking for testimonials, and by doing in depth competitor research to understand the difference between your product and theirs.
Get to know the benefits—and not just the features—of your product or service. The features are your product’s characteristics. For example, if your business sells suitcases, you might describe your product as being small, compact and having multiple compartments. Your product’s benefits, on the other hand, are the advantages it brings to your customers. Think about how your product makes someone’s life better or easier. The compact, multi-compartment suitcase offers the benefits of being easy to carry and pack as a carry-on.
It’s vital to understanding how your product fulfills its target market’s specific needs. For the suitcase company discussed above, for instance, the target market would be people who benefit from a lightweight, carry-on suitcase—such as business travelers who take short, frequent trips.
03. Investigate your competitors
Hone in on your target market even further by taking a look at which your competitors are targeting. Of course you won't have access to their customer analytics data, but you can understand their customers with a SWOT analysis .
Take a deep dive into competitor websites, blogs and social channels. Consider who their target market is based on their website content, content marketing strategy, and social media branding. You’ll likely be able to infer details about their audience based on their brand language and tone. You can also check for comments on their social media pages to see which types of people are engaging with their posts.
Take an especially close look at their most successful social media and blog posts. Do these pieces of content have anything in common in terms of their offering or branding? Which interests or needs do they address? Use this information to consider what kinds of qualities or advantages appeal most to consumers within your industry.
04. Segment your audience
At this point, you’ve gathered some information about the characteristics and interests of your target audience. Now, it’s time to use that information to clearly define your customer types. This is going to form the basis of your target market.
The best way to do this is through market segmentation. This involves dividing your customers into different groups, or segments, based on their shared qualities.
You can divide your customers based on:
Geography: Physical location, whether it’s your own city or a different part of the world. Note that if your customers are located around the world, you may need to create a multilingual website, as well as localized ads and marketing materials.
Demographics: Characteristics such as age, gender, race or ethnicity, income level, or marital status.
Psychographics: Inner qualities such as personality, lifestyle, or personal values. These are often a product of geographic and demographic factors such as location, generation, or stage of life.
Behavior: Perceived qualities based on online behavior, such as buyer readiness or frequency of use.
If you’re a B2B company, use similar characteristics but apply them to business. Consider firm demographics—known as firmographics—such as industry, location, customer size, business structure, and performance.
To gain a deeper understanding of your segments, you can also create buyer personas. Also called user personas, buyer personas are imaginary characters with traits and behaviors similar to those of typical customers. Ultimately, these fictional characters represent your target market, helping you gain insights into the needs, desires, and lifestyles of your actual customers.
05. Write a target market statement
Now that you’ve determined the defining features of your audience, it’s time to put your findings on paper. Write a target market statement that focuses on the most important audience characteristics you’ve identified in your research. Your statement should include:
Demographic information about your target market, such as gender and age.
Geographic location of your target market.
Key interests of your target market.
Then, sum it up in a single sentence. For example:
“Our target market is women in their 30s and 40s who live in the United States and enjoy casual, comfortable fashion.”
Doing this will keep your brand identity and marketing efforts consistent. It will also come in useful as you adapt your company’s mission statement to be as relevant as possible for your audience.
06. Refine your research
Defining your target market is based on thorough research, but that doesn’t mean it’s going to be perfect the first time around. Even after you identify your market, you’ll still need to continually test and experiment to get an increasingly precise picture of your customers. Staying on top of your market research can also help you keep up with the times, as consumer interests change over the years with technological developments, generational attitudes and passing trends.
To narrow in on your audience, you’ll need to assess your business success and test your targeting efforts. Take a look at who is actually buying from you and which specific products or services they are purchasing. Try to understand how you can adapt future product development or modify your branding or marketing efforts to better fit your customer base.
Utilize A/B testing with your marketing efforts to test the same ad on different audiences and see which version performs better. Alternatively, you can develop two different creatives, each with their own look and language and compare your audience’s responses. Based on the results, you might need to either adjust your business strategy or revise your target market statement. The bottom line is to build a brand that resonates strongly with your audience. Remember, the more targeted your content, the more effective your lead generation strategies—and the more customers you’ll bring to your brand.
What are examples of a target market?
These website examples clearly cater to their target markets. Take note of the phrases and visuals these websites use.
01. Amanda Darby
Let’s take a look at how nutritionist Amanda Darby appeals to her target market. She aims to address people looking to make healthier food and dieting choices. To do this, she’s created a website that fosters a sense of joy and personal empowerment around food. The light and airy background, coupled with the cheerful images of cooking and eating, instantly makes it clear that she targets people looking for a healthy lifestyle.
She also hones in on her audience even further, using phrases that directly appeal to middle-aged women. In the section of her homepage that discusses her nutrition coaching: “You will be the mom who loves food, her body, and knows life isn't perfect, but is perfectly happy living the life she has vs. waiting for the life she will have when she reaches her goal weight.” By directly addressing the concerns of her target market, Amanda helps her audience feel heard and understood. This strengthens their trust in her brand and persuades them that she is the right coach for their needs.

02. Curtinsmith Guitars
From the very first image that appears across the top of this website, it’s clear that Curtinsmith Guitars is crafting something unique. By displaying photographs of their workshop and describing their guitars as “custom” and “handmade,” they directly single out a target market of those looking for unique, one-of-a-kind guitars. This target market is likely musical, appreciative of craftsmanship and not afraid to spend their money on their passions.
The About Us section of the site confirms this targeting. The owner, Paul, writes, “I find it quite profound to create something which, in itself, will continue to create. It is an absolute joy crafting these instruments and it is my prayer that they continue to be a joy for those who play them and listen to them, for many generations.”
In this statement, the brand makes it clear that it targets musicians who value the creative process. They also allude to the quality of their product, portraying them as long-lasting heirlooms with sentimental value.

03. Lima Cakes
Sona Karapetyan uses her artistic vision to create showstopping celebratory cakes. The About section on her website says that Sona “was always experimenting with graphic art & design” and, “When Sona decided to embark on the cake art journey, she experimented with different textures, shapes and architectural elements to create a unique design language.” It also states that she never creates the same cake twice so each cake is unique to each client.
Her neutral-colored web design and sophisticated copy narrow her target market down to mature individuals who appreciate art. Her website also features images of her cakes, clearly displaying her skills to her potential customers. The prices of her custom-made cakes will reflect the effort that goes into each one. These details show that she likely targets an educated, older, affluent crowd with an appreciation for modern art and design.

What are market segments?
Market segments are subgroups within a larger market that share specific characteristics and needs. These characteristics can include demographics, lifestyle, interests, behavior and purchasing patterns. By identifying and understanding these segments, businesses can tailor their marketing messages, products and services to better resonate with each group. This allows for more targeted and effective marketing efforts.
Target market FAQ
How detailed should a target market be.
The level of detail for a target market depends on your specific business and goals. However, it should be defined enough to create targeted marketing campaigns and avoid wasting resources. Consider including demographic information (age, gender, income, etc.), psychographics (lifestyle, values, interests), and behavioral factors (purchasing habits, media consumption). While details are important, avoid over-segmentation, as it can limit your reach and marketing effectiveness.
What is an example of a target market?
What is the purpose of a target market, what is the best target market, related posts.
How to start a dog walking business in 7 steps
How to price dropshipping products without shortchanging yourself
How to start an eyelash business in 7 steps
Was this article helpful?
Plan Projections
ideas to numbers .. simple financial projections
Home > Business Plan > Target Market in a Business Plan

Target Market in a Business Plan
… we are targeting this part of the market …
What is the Target Market?

Target Market Segments
Your product will not be of equal interest to all potential customers, as they do not all have the same needs and characteristics. This section of the business plan deals with the analysis of the target market into different groups of customers (customer or target market segments) each having distinct characteristics and needs from the product.
The target market segmentation strategy depends on the business and the product, but generally segmentation falls into the following customer characteristics groups.
Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation splits up a sales market of a business based on such things as the social class, lifestyle choices, personality traits, tastes, attitudes, and the opinions of its customers.
Psychographic market segmentation examples include the promotion of products such as cars as these often reflect a customers lifestyle, and leisure activities. For example, a car business might identify customers who are interested in keeping the environment green and promote hybrid cars to them, or a business involved in activity holidays will seek to market to customers who show a preference for an active lifestyle.
Demographic segmentation
- Social class
- Size of family
- Nationality
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation is the process of splitting up a sales market of a business based on the geographical location of the customers. It is a particularly important marketing tool when the business is a multinational, worldwide business, but is also used by businesses to split their markets into region, county, state, city, neighborhood, or postal code.
A geographic segmentation example would be seasonal clothing items such as coats and swimwear. In contrast, in a colder climate coats would be marketed and sold all year round whereas swimwear would be highly seasonal during the holiday period. In a hot climate swimwear would be the all year round product and winter coats might not be sold at all.
Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral segmentation is the process of splitting up the sales market based on brand loyalty, usage, benefits required.
Target Market Presentation in the Business Plan
The business plan target market section can be presented in a number of formats, but a listing of the major customer segments together with a pie chart will show the investor where the main potential for the product lies. In the example below, the market is split into four main segments both in terms of number of customers and percentage of the total target market.

The average customer spend is also included, to reconcile the total target market back to the served available market (SAM) in monetary terms. Finally, a brief statement about the growth prospects for the market is included to show the investor the potential for growth in your chosen customer segments.
When identifying the target-market segments, it is important to be as specific as possible about the customer characteristics which make up each segment. In choosing which segments to concentrate on, take into account the size and potential for growth of each segment, and identify clearly what benefits, both emotional and financial, the product provides for the customer.
This is part of the financial projections and Contents of a Business Plan Guide , a series of posts on what each section of a simple business plan should include. The next post in this series is about the analysis of the competition for the target-market.
About the Author
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
You May Also Like
Target Markets: Why They Aren't Just for Marketers [A Quick Guide]
Published: August 08, 2022
Sales teams and entrepreneurs need to know their target market. You can get there by asking yourself, "Who is the ideal fit for my offering? What are their interests and priorities?"

Answering these questions can help you prioritize the deals you're most likely to win. But how can you really understand the ins-and-outs of your target market?
Let's take a closer look at what a target market is, go over how to conduct a target market analysis, see some helpful examples, review target market segmentation, and look into how sales teams can leverage target markets.
![what is the target market in a business plan → Download Now: Market Research Templates [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/6ba52ce7-bb69-4b63-965b-4ea21ba905da.png)
Table of Contents
How to analyze your target market, target market analysis example, target market examples, target market segmentation.
How Sales Teams Can Leverage Target Markets
What Is a Target Market?
A target market is a group of customers for which your products and services are aimed. First defined by an industry (i.e., healthcare, travel, technology, etc.), it represents a specific subset of the broader market the industry covers. It's usually based on factors like behavioral tendencies, geographic location, and demographic characteristics.
Let's say you've created a B2B software product that helps remote construction teams. In that case (and to state the obvious), you'd probably focus on companies within the construction industry. But defining your target market doesn't stop there.
You know your industry, but there's no one-size-fits-all mold for the businesses within it. If you were pinning down a target market for your product, you'd have to start with business characteristics — for instance, scale would be a good place to begin.
Your product will suit certain companies better than others, and selling to a Fortune 1000 company isn't the same as a small construction business with less than 100 employees.
In this case, you'd want to pin down the size of your ideal customer's business — and this number would be the start of a target market analysis.
Let's take a closer look at what that process looks like.
- Analyze your product or service.
- Check out the competition.
- Choose criteria to segment by.
- Perform research.
- Track and evaluate your results.
As the name implies, target market analysis is the basis for identifying your target market. Here are the five steps you can take to do one of your own.
1. Analyze your product or service.
Take a look at what you're selling to understand which consumers would get value from your product. The questions below will help with the brainstorming process:
- "What need does your product or service fill?"
- "Are there any problems or pain points it solves for?"
- "Who would benefit most from your product or service?"
Once you've answered these questions, you might want to consider getting feedback from current customers. Conduct a focus group or ask your service department about their common problems.
Analyzing your product or service in this way will help you better understand your target market. In fact, you might learn that your current customers aren't the people you're trying to target. If you notice a disconnect in this process, you'll want to better align your target market with your actual marketing goals so you can realign.
2. Check out the competition.
Perform an analysis of your competitors to see who they're targeting. Take a look at their customer base, and see if you can find an area of the market you could focus on that they might be missing.
The best way to do this is to conduct a competitive analysis . This entails researching who your competitors are, what they offer, and even review their sales tactics.
Looking at your competitors will even help you identify target market gaps that you can fill. Are there any target markets they do not focusing on?
This could lead you to expand into new markets geographically or develop new products to target a different market.
3. Choose criteria to segment by.
A target market can be segmented by a few different variables. Consumers can be split by demographic, geographic, and behavioral factors.
This is essentially the process of creating a buyer persona . You'll divide your target market into several target customers — also known as (you guessed it) buyer personas.
For example, perhaps your target market is midsized companies looking to purchase marketing automation software. You could divide your target customers into several groups, including marketing department leaders, sales leaders, founders, or CEOs.
Here are some of the most common ways to segment a target market:
4. Perform research.
As you begin narrowing your market, the research phase doesn't end there. What marketing strategies should you use to reach your potential target market? Is the target market large enough for your product or service? Market research will help you learn more about your target market.
Picking the right target market can tell you a great deal about your business. Are you looking to become a true velocity business, or do you see yourself as a steadier flow of pipeline with enterprises and consumers?
5. Track and evaluate your results.
Target market analysis should never be static — you don't just conduct one, be immediately content with the results, and stop there. It's an ongoing process. You need to continuously track your results, evaluate what you see, and iterate on the conception of your target market to more effectively appeal to it.
Let's imagine a company that sells inexpensive, "function-over-form" athletic footwear that stresses comfort and arch support instead of trendy aesthetics.
1. Analyze the product or service.
When conducting its target market analysis, the business in question would have to start by taking a thorough, objective look at its product to get a solid grip on its value and differentiating factors.
The company would likely find that its shoes are better suited for day-to-day wear instead of legitimate athletic competition, lack trendy appeal, and can help with sore feet while standing.
This initial insight can help shape the personas that the company will ultimately target. It would have a better picture of how to construct its value proposition. In this case, the business might find that suburban men over 50 who don't exercise regularly appear to be the most likely to buy its shoes.
Next, the company would dig into its competitor's products, how they were selling them, and any noticeable gaps in their potential target markets. After conducting a competitive analysis, the company might find that its competition was ignoring some geographical trends embedded in its target markets.
Let's say its competitors' retail locations and store placements were primarily in cities — ignoring locations like suburban strip malls and local "mom and pop" retail stores. With that information in mind, the company in question could have a starting point for appealing to a target market its competition is ignoring.
Here, the company would begin to string more detailed personas together. Again, it would base its segmentation criteria on its product analysis and refine it according to its competitive analysis.
In this case, a significant portion of the criteria would revolve around age, social class, location, and interests — making one of its personas older, working class, suburban consumers who prioritize function over form.
After creating its target persona, the company would conduct a market analysis, survey consumers that fit its target market bill, potentially employ more direct tactics like hosting focus groups, and take any other strides it sees fit to ensure that it has a thorough understanding of its target consumers.
From there, it can shape a thoughtful value proposition that will guide its sales messaging, outreach strategies, pricing structure, and other crucial sales-related factors that influence how it reaches consumers.
5. Track and evaluate results.
Once the other steps have been covered, the company would continue to monitor how its efforts resonate with its target persona. If sales aren't where they need to be — or it appears the company might have other personas it can cater to — it might restart this process and shift gears on its messaging, strategies, or target market as a whole.
Let's look at some of the best-in-class companies — both B2C and B2B — to see how they set up their target markets.
1. Atlassian Target Market
Atlassian offers a suite of collaboration tools designed to help developers and product leaders take their projects from concept to completion.
Like most larger companies, Atlassian uses target market segmentation to look at different markets and break up its unique value propositions, terminology, and values.
By diving into one segment, like retail, we see they're working with several large companies — especially with their support-related products.
This tells us that while Atlassian can work with almost anyone doing software development, it recognizes how its value proposition changes depending on the market segment in question.
Even the same product for two different customer types creates different levels of value.
2. Nike Target Market
Nike offers products to athletes and other consumers who want to exercise regularly. They offer apparel, equipment, shoes, and accessories.
They work with athletes and a fitness-minded audience, but we know a good target market definition can't be that broad. Let's break two of their segments down:
- Young athletes — Kids who get frequent exercise and play sports growing up are a huge, growing category for Nike. Nike engages with this market through sports leagues and associations and with endorsements from popular sports stars like LeBron James.
- Runners — With a focus on new types of shoes, Nike shows it targets consumers based on both demographic information and lifestyle. Nike launches shoes and apparel designed to help the avid runner stay on the road a bit longer.
3. Starbucks Target Market
Next time you're sipping your cold foam Cascara cold brew, ponder the target market of the top coffee destination in town: Starbucks .
Many of their locations have been remodeled and offer a hip, contemporary look. Not that surprising since about half of their customers are between the ages of 25 and 40.
If you spend more than five minutes sitting and drinking your coffee, you'll probably hear a barista shout, "mobile order!" The mobile process now accounts for 24% of Starbucks' transactions which shows they're catering to a tech-savvy crowd.
The next clue we have on their target market is the location of their shops. By positioning its locations in heavily urban areas, Starbucks is attracting on-the-go professionals. To recap, here are a few of Starbucks' target markets:
- 25 - 40-year-olds — Remodeled locations accommodate their largest demographic base.
- Tech-savvy adults — Their mobile app has caught on and lends itself to a forward-thinking crowd.
- Working professionals — Their urban focus tells us the type of lifestyle they're catering to.

4. Apple Target Market
What about a company that occupies both the B2B and B2C spaces? How can it develop a target market with such a broad set of customers? Apple is the textbook case for innovation and product design.
But how does that apply to finding a target market? With its wide array of product offerings, Apple has a little something for everyone. Here are two of their target markets:
- Tech enthusiasts — A customer category that launched Apple's brand decades ago, technology enthusiasts still get attention from the company. With launches of new tech categories (including wearables, Apple TVs, and HomePods), Apple has shown it's still creating value for this segment. There is also a tremendous ecosystem where owning a suite of Apple products enables better interoperability among your tech.
- Healthcare — One market Apple has its eyes on is healthcare. By focusing on the appeal of having information right at your fingertips with mobile and the iPad, they've positioned healthcare workers to more conveniently communicate with patients.
Apple doesn't seem to exclude many people from its target market and has positioned itself to benefit both consumers and businesses — even with the same products like the iPad.
Its success has been more about understanding the value of its different segments rather than excluding people from them.
5. McDonald's Target Market
McDonald's target market is broad and encompasses a wide variety of customer personas. Younger professionals represent one of the chain's more prominent target market segments — and that trend is reflected in many of the company's location remodels. Several McDonald's franchises have been revamped to look sleeker, more modern, and better suited for millennials.

Image Source: Community Impact
"Full nest" families with children over six represent another key base for the chain. The franchise takes many strides to appeal to this specific segment, primarily reflected in its Happy Meal options.
But there's another factor that underscores virtually every target market McDonald's tries to appeal to — social class. The chain makes a conscious effort to resonate with lower, working, and middle-class patrons.
Pricing is the basis of McDonald's value proposition. It tries to bill itself as an affordable alternative to more expensive options in the spaces it attempts to sell in. For instance, when promoting its McCafe line, the chain stressed the brand's particularly low price points as a major selling point.

Image Source: McDonald's
Ultimately, the franchise's target market isn't singular and clear-cut in terms of most demographics — but it is specific in terms of its various personas' economic circumstances. Its value proposition fundamentally rests on the fact that its food is inexpensive.
Target Customers
A target customer is an individual that's most likely to buy your product. And it's a subset of the broader target market. For example, if your target market is female athletes between the ages of 13 to 25, a target customer could be female athletes in the specific age range of 13 to 16.
You need to have a firm grasp of your target customers if you're going to develop pointed, effective value propositions. The success and viability of your sales messaging, prospecting efforts, and broader sales process rests on your knowledge of who's buying your product or service and the mindset that makes them do it.
That starts with target market segmentation.
Target market segmentation is the process of partitioning your target audience into more focused, identifiable, and approachable groups (or segments). It's a broad concept that can take on a lot of forms, including:
- Geographic segmentation — Dividing your target market based on geographical boundaries
- Firmographic segmentation — A practice specific to B2B sales where firms are divided based on characteristics like company size or number of employees
- Behavioral segmentation — Dividing your target market based on behavioral tendencies and decision-making patterns
- Demographic segmentation — Dividing your target market based on factors like income, education, race, gender, or occupation
- Psychographic segmentation — Dividing your target market-based elements like personality traits, values, and opinions
How you elect to segment your target market will be specific to your company's needs and interests. In many — if not most — cases, you'll employ more than one of the segmentation methods listed above when defining a target market.
When you identify the customers you want to serve — and the ones you don't — ask:
- "Do my target customers have different problems they're solving with my product?"
- "Do my target customers get different value from my product?"
- "Are either of these things related to demographic, geographic, or lifestyle components?"
In order to segment effectively, you must have a decent way of measuring the value you provide to the market. Then, identify if certain groups are getting more value than others.
This will power the positioning of your product. Suddenly, you can pinpoint pain for your customers while speaking their language.
This helps you refine your position in the market and connect on a deeper level with your customer. Having a target market (or target customer) is all about relevancy and relating to the person on the other side of the cash register.
How Sales Teams Can Leverage Target Markets + Segmentation
Segmentation poses several benefits for sales teams. If you know who will be most receptive to your product or service, you get a leg up when conducting most steps of your sales process.
For one, effective segmentation can be a major asset in prospecting. If your SDRs have a solid picture of the types of customers that show an interest in your offering, cold leads can become a little warmer — letting those reps make more thoughtfully guided use of your sales messaging when connecting with prospects.
Beyond that, segmentation can also help with lead qualification. Knowing whether a lead fits the bill of a class of high-converting customers gives reps a head start during that stage.
You need to have some kind of criteria that can immediately distinguish a prospect who needs your product or service from one that lacks the decision-making tendencies, location, or economic circumstances to actually get something out of it. Target market segmentation gets you there.
Finally, target markets provide sales teams with the necessary information to breach new markets and sell to them effectively. If you're not on top of any emerging markets that might need your product or service, you could hit a wall with your sales potential and lose out on incredibly lucrative business opportunities.
Ultimately, knowing your target markets inside and out is one of the most fundamental tenets of successful sales efforts. If you're not actively analyzing, pursuing, and refining your understanding of your target markets, you're losing out on sales and painting yourself into a corner with your business potential.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in July 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

8 Seaweed Startups Riding the $18.4B Green Wave

10 Best Etsy Alternatives to Sell Your Crafts

4 Opportunities in The $884B Home Improvement Business

How Dylan Jacob Scaled BrüMate to $100m+ in 5 Years

7 Opportunities to Make Life Easier for New Moms (and Make Money)

Digital Scent: A $1.2B Market Primed for Innovation

Entrepreneurial Competency: What it Is & Why it Matters

3 Ways to Cash In on Golf's Takeover by Millennials and Gen Z

This YouTuber Makes $300k A Year Teaching People How to Sew

The $6.8B Sewing Boom Is Here to Stay — 3 Ways to Take Your Cut
Free Guide & Templates to Help Your Market Research
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Brand Experience
Market Segmentation
- Target Market
Try Qualtrics for free
Target market: definition, purpose, examples, & best practices.
11 min read Aiming for your target market with a highly focused marketing strategy is now easier than ever with the support of insights from data and machine learning. Read our in-depth guide to learn how to successfully reach your target market.
What is a target market?
A target market is a subset of the audience you’re aiming to reach (your market). It is made up of a group of customers that have one or more commonalities between them and are most likely to be interested in your products.
These commonalities might be:
- Demographic targeting : They all have common features, such as age, income level, family status, level of disposable income, and marital status
- Psychographic segmentation : They all hold common interests, values, wants, goals, political leanings or lifestyle choices
- Behavioral patterns: They all have common behaviors, such as when they purchase a product or how often they buy
- Geographic segmentation : They are all located in the same region or local area
There are other factors that might group your target market’s members together, and, more often than not, there might be a blend of multiple factors. Keep in mind that there’s also a slight variation if you are looking for B2B customers, as this might include:
- Firmographics: The details about the businesses you’re targeting, such as industry, company size, global or regional spread
- Buying style: The businesses’ buying policies, budgets or stakeholder involvement
- Company behavior: How much they purchase and when, their appetite for risk
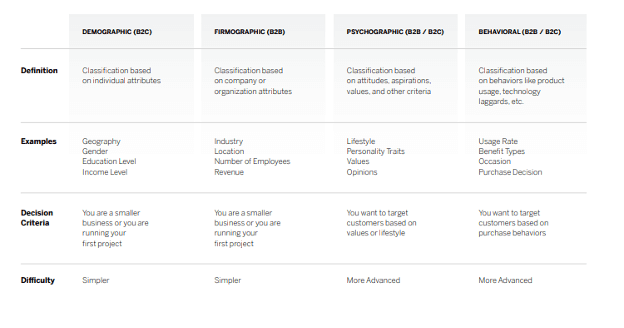
Free eBook: 2024 global market research trends report
What is target marketing?
Target marketing is the process of reaching out to particular market segments of your potential customers or your existing audience. This target market is defined by their commonality as mentioned above, usually within a range, such as consumers aged 25-45 or those working in the hospitality industry.
Your marketing strategy will be tailored to that particular niche market, and will encompass all the channels that the target audience might use. Your marketing should be based on market research and take into account the needs and wants of that specific group. Ideally, this means that you have data-led insights about your target market to allow you to create digital marketing or offline marketing strategies that work effectively.
What is consumer targeting?
Where your target market is the broader group of individuals that have a feature in common, your target consumers are the individuals you believe are most likely to purchase your product or service. Your marketing efforts for consumer targeting will be aimed at a more specific audience, such as 35-year-olds or hotel managers.
Consumer targeting vs market segmentation
Consumer targeting is the process of marketing to the specific audience you think will potentially buy your products, based on data-led insights on prior sales data and more.
Market segmentation is a broader process, being the general division of your entire potential audience into target markets, based on the features they share or the products and services they’d be interested in.
Both are necessary processes to narrow down the focus of your marketing efforts for the best results.
Why should you create a target marketing strategy?
Creating a marketing strategy for a specific target market has several advantages over a more general approach.
- You’re more likely to reach an audience interested in your products or services. Having a clear idea of who would be most interested in your offering means you don’t waste time marketing to those who are less likely to buy.
- You can create a more appealing and effective marketing strategy. Knowing your target audiences’ distinct features means you can create a marketing approach that will be more appealing to them.
- You’ll stand out from the competition. By honing in on your target customers and adapting your strategy accordingly, you’ll be ahead of the 76% of marketing executives that don’t use behavioral data to target their marketing efforts .
- You’re able to target and retarget your audience for better outcomes. Comscore found that retargeting customers led to a 1046% uplift in searches for the advertised brand.
- You can discover which customers are more likely to pay a premium for your product. Increase profitability and revenue by targeting the target audience with the highest ROI.
How to target market segments
Step 1: finding your target markets.
Whether you’re planning on exploring target markets for a new or an established business, market research will be vital to discover the most fertile areas for growth. Here are a few ideas on how to define your target market:
Study your current customers
Your current customers have a wealth of information that can help you create a marketing plan for your ideal target market. By gathering data, either through customer feedback channels such as surveys or focus groups, or by examining operations data such as customer purchase patterns, you can develop a persona that describes your ideal customer. What common characteristics do your biggest spenders have? Start by sending a survey with open-ended questions to a small representative sample of customers, perhaps 300 or more, to understand their values in their own words.

Examine the competition
Your competitors are likely targeting the same audiences as you. Analyze how they promote their product or service, and see how their ideal customer responds. What are they providing that you don’t, and what can you give customers that isn’t currently on the market?
Understand the motivations for purchase
Your customers are often telling you in their own words how they feel about your offering and why they have chosen your brand—you just need to listen. Use sophisticated listening tools, such as conversation analytics, to understand things such as customer intent, emotion, effort, and motivation. This will help you build a more solid picture of what your ideal target market looks like, and what challenges your offering solves for them.
Identify groups of customers
Your target markets will be made up of groups of ideal customers. What key characteristics link them together? Build a list of target markets, all defined by distinct features that you can target with your marketing efforts.
Create personas
Developing a persona, or a fictional character that embodies the type of customer you’d like to pinpoint, means you can better reach your target audience. Identify their roles, goals, and pain points and understand how they like to communicate. By helping them reach goals, fulfill role requirements and solving their pain points, you can better hone your marketing efforts.
Judge near-term vs longer-term opportunities
Not all your target markets will be worth targeting in the near term, perhaps because of the time of year, their growth projections and other factors. It’s a good idea to consider which target market is right for immediate targeting, and which segments are better kept for the longer term.
Evaluate product-market fit and positioning
Where will your value proposition have the most impact? Your product market fit will not be the same for every target market you identify, and sometimes you can position your product more effectively for one market than another. Evaluate which target markets will provide the greatest ROI and focus efforts there first.
Understand how to reach your target audience
Your target market will have preferences for how they want to engage with your brand. Learning how they interact with you by examining internal data and analyzing customer behavior will help you to speak to your target market on the platforms they prefer.
Step 2: Create an effective targeting strategy
There is the option of engaging in mass marketing, creating marketing campaigns designed to reach as many people as possible. However, for an effective strategy, you should forgo the entire market and target only the markets and customers you believe will be responsive.
Consider which marketing strategy will be most effective
Mass marketing is a one-size-fits-all approach that won’t have the same impact as targeting a specific audience. Here are some alternatives:
Differentiated marketing: This marketing strategy develops different marketing campaigns for each target market’s preferences. This helps to demonstrate your value proposition for each target audience, rather than marketing generally about your products and services. This may require more initial budget, as various marketing campaigns will be needed, but is more likely to have a greater impact on each individual target market.
Niche marketing: Through your market research, you may have identified a particular market where a small target audience has needs that are not being met by the offerings of your competitors. Creating a highly targeted marketing campaign for this specific audience can be lucrative if the gap in the market is not being served and if the potential purchases by this audience will be high in value.
Micromarketing: Even more targeted than niche marketing is micro marketing. Taking a small segment of your already-small niche market, you divide the audience into further characteristics that unite them, such as geographic location. Again, focusing on this hyper-specific target market can pay dividends if their potential spend outweighs the cost of serving them such a specific marketing campaign.
Create an omnichannel strategy with customer preferences in mind
Your market research should have uncovered how your target audience prefers to communicate. Frequently, the purpose of the engagement—to buy a product, resolve a query, find an answer—dictates how customers want to be reached. As a result, it’s best to create an omnichannel marketing strategy that can guide audiences on a personalized customer journey.
Step 4. Implement and learn
Once you’ve established your target market and understand how to reach them, it’s time to test your marketing campaigns and targeted advertising, and then learn from the response. Evaluations to consider include:
- What drives customers to purchase, and what has less of an effect on buying behaviors?
- Which target markets are the most lucrative, and why?
- What new market segments could be targeted with similar strategies?
- How measurable are the results of your strategies?
- How accessible are your strategies to all of your target customers?

Improve your customer targeting with Qualtrics
Enable more accurate customer targeting with in-depth research supported by Qualtrics’ range of business tools. The CoreXM platform allows you to collect and collate data for unrivaled insights into your target market for highly effective marketing.
Use AI-powered analytics and embedded machine learning to evaluate structured and unstructured data. Best of all, access all your data and insights that make an impact all on one platform.
Related resources
User personas 14 min read.
Analysis & Reporting
Data Saturation In Qualitative Research 8 min read
How to determine sample size 12 min read.
Focus Groups
Focus Groups 15 min read
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, thematic analysis 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Marketing Plan?
Understanding marketing plans, how to write a marketing plan, marketing plan vs. business plan.
- Marketing Plan FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
James Chen, CMT is an expert trader, investment adviser, and global market strategist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/photo__james_chen-5bfc26144cedfd0026c00af8.jpeg)
Pete Rathburn is a copy editor and fact-checker with expertise in economics and personal finance and over twenty years of experience in the classroom.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/E7F37E3D-4C78-4BDA-9393-6F3C581602EB-2c2c94499d514e079e915307db536454.jpeg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Investopedia / Zoe Hansen
A marketing plan is an operational document that outlines an advertising strategy that an organization will implement to generate leads and reach its target market . A marketing plan details the outreach and PR campaigns to be undertaken over a period, including how the company will measure the effect of these initiatives. The functions and components of a marketing plan include the following:
- Market research to support pricing decisions and new market entries
- Tailored messaging that targets certain demographics and geographic areas
- Platform selection for product and service promotion: digital, radio, Internet, trade magazines, and the mix of those platforms for each campaign
- Metrics that measure the results of marketing efforts and their reporting timelines
A marketing plan is based on a company’s overall marketing strategy.
Key Takeaways
- The marketing plan details the strategy that a company will use to market its products to customers.
- The plan identifies the target market, the value proposition of the brand or the product, the campaigns to be initiated, and the metrics to be used to assess the effectiveness of marketing initiatives.
- The marketing plan should be adjusted on an ongoing basis based on the findings from the metrics that show which efforts are having an impact and which are not.
- Digital marketing shows results in near real-time, whereas TV ads require rotation to realize any level of market penetration.
- A marketing plan is part of a business plan, which describes all of the important aspects of a business, such as its goals, values, mission statement, budget, and strategies.
The terms marketing plan and marketing strategy are often used interchangeably because a marketing plan is developed based on an overarching strategic framework. In some cases, the strategy and the plan may be incorporated into one document, particularly for smaller companies that may only run one or two major campaigns in a year. The plan outlines marketing activities on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis while the marketing strategy outlines the overall value proposition.
Types of Marketing Plans
There are a variety of different marketing plans that suit different businesses and different business needs.
New Product Launch: This is a marketing plan that outlines how a new product will enter the market, who it will target, and in what way advertising will be done.
Social Media: A social media marketing plan focuses on the advertising strategies on different social media platforms and how to engage with the users on these platforms.
Time-Based: Time-based marketing plans, such as those that are executed quarterly or annually, focus on the time of the year, the current condition of the business, and the best strategies in that period.
Mission and Value Proposition
A marketing plan considers the value proposition of a business. The value proposition is the overall promise of value to be delivered to the customer and is a statement that appears front and center of the company website or any branding materials.
The value proposition should state how a product or brand solves the customer's problem, the benefits of the product or brand, and why the customer should buy from this company and not another. The marketing plan is based on this value proposition to the customer.
Establishing your key performance indicators (KPIs) will allow you to measure the success of your marketing plan in relation to your company's value proposition . For example, if your goal is to engage with a certain demographic in a certain region, you can track social media and website visits.
The most effective digital marketing techniques in 2020 according to marketers are content marketing and marketing automation.
Identify Your Target Market
The marketing plan identifies the target market for a product or brand. Market research is often the basis for a target market and marketing channel decisions. For example, whether the company will advertise on the radio, on social media, through online ads, or on regional TV.
Knowing who you want to sell to and why is an extremely critical component of any business plan. It allows you to focus your business and measure its success. Different demographics have different tastes and needs, knowing what your target market is will help you market to them.
Strategy and Execution
The marketing plan includes the rationale for these decisions. The plan should focus on the creation, timing, scheduling, and placement of specific campaigns. The plan will include the metrics that will measure the outcomes of your marketing efforts. For example, will you advertise on the radio or on social media? What time will you air advertisements if they are on the radio or TV? The strategy may include flighting scheduling , which includes the times when you can make the most of your advertising dollars.
Set Your Budget
A marketing plan costs money. Knowing your budget for a marketing plan will allow you to create a suitable plan within that context, stick to it, and prevent runaway costs. It will also help you allocate to different areas of your marketing plan.
Adjust Your Plan
A marketing plan can be adjusted at any point based on the results from the metrics. If digital ads are performing better than expected, for example, the budget for a campaign can be adjusted to fund a higher-performing platform or the company can initiate a new budget. The challenge for marketing leaders is to ensure that every platform has sufficient time to show results.
Without the correct metrics to assess the impact of outreach and marketing efforts, an organization will not know which campaigns to repeat and which ones to drop; maintaining ineffective initiatives will unnecessarily increase marketing costs.
Digital marketing shows results in near real-time, whereas TV ads require rotation to realize any level of market penetration. In the traditional marketing mix model, a marketing plan would fall under the category of "promotion," which is one of the four Ps , a term coined by Neil Borden to describe the marketing mix of product, price, promotion, and place.
A business plan details how a business will operate and function in its entirety. A business plan is a roadmap for a business. It will cover the goals, missions , values, financials, and strategies that the business will use in day-to-day operations and in the achievement of its objectives.
A business plan will include an executive summary, the products and services sold, a marketing analysis, a marketing strategy, financial planning, and a budget , to name but a few items.
As mentioned, a business plan will include a marketing plan, which focuses on creating a marketing strategy on how to bring awareness to the public of the company's product or service, how to reach the target market, and generate sales.
Example of a Marketing Plan
John came up with a new business idea that he believes is a niche offering in the market. He decides to start a business and his first step is creating a business plan that outlines all of the objectives, goals, values, pitfalls, and finances of his company.
John is able to raise enough capital from friends and family to get started, hires a few employees, and eventually creates his product. He now has to start selling his product and generate sales to keep his business operating.
To achieve this, John, with the help of a marketing company, creates a marketing plan. The marketing plan consists of market research that details the target market for John's product, which is recently retired men.
The marketing plan then comes up with the best methods of reaching this target market. The marketing plan stresses radio and television as opposed to social media as older, retired men use social media less than traditional forms of media, according to the market research that was conducted.
The ads are tailored to the target market, showing how John's product will benefit their lives, particularly when compared to market alternatives. Once the marketing plan has been executed, the marketing team analyzes how the efforts translate into sales.
What Is a Marketing Plan Template?
A marketing plan template is a document that an individual can use to create a marketing plan. The marketing plan template will contain all the important elements and the various needed language with blank sections. A user can insert their own information related to their business in the blank sections to ultimately create their own marketing plan.
What Is an Executive Summary in a Marketing Plan?
The executive summary of a marketing plan provides a brief overview of the entire marketing plan. The executive summary will contain the key findings of the market research, the company's objectives, marketing goals, an overview of the marketing trends, the description of the product or service being marketed, information on the target market, and how to financially plan for the marketing plan.
What Is a Top-Down Marketing Strategy?
A top-down marketing strategy is a traditional marketing strategy. This is where a business determines who it should sell to and how, and the customer base is largely passive and spurred to take action once they hear the advertisement. For example, a top-down marketing strategy would include ads on radio or television. Top-down marketing strategies are usually determined by the executives of a firm. It usually consists of what a firm desires to do and then determining a way to do it.
What Is a Bottom-Up Marketing Strategy?
A bottom-up marketing strategy focuses on discovering a workable strategy and then building on that strategy to create an impactful advertising campaign. Today's consumer wants to relate to a product or service in a meaningful way and a bottom-up marketing strategy is better suited to this. A bottom-up marketing strategy should focus on the target market and how better to create value for them.
How Much Does a Marketing Plan Cost?
The cost of a marketing plan will vary based on the company, the complexity, and the length of the overall strategy. The cost can range anywhere from $10,000 to $40,000.
A marketing plan is the advertising strategy that a business will implement to sell its product or service. The marketing plan will help determine who the target market is, how best to reach them, at what price point the product or service should be sold, and how the company will measure its efforts.
Constantly monitoring and adjusting a market plan is an important part of running a business as it shows what are the best and worst ways to generate sales. Without a successful marketing plan, a business may not be able to continue operating for very long.
Statista. " Most Effective Digital Marketing Techniques According to Marketers Worldwide in 2020 ."
Laire. " How Much Does a Marketing Plan Cost? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Marketing-Strategy-20dd671d870c4f1db1c9166de9e44e27.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Build your business
Business Tools
- Profit Margin Calculator
- Business Name Generator
- Slogan Generator
- Traffic Calculator
- Ecommerce Statistics
- Ecommerce Wiki
Free business tools
Start a business and design the life you want – all in one place.
- © 2015-2024 Oberlo

The 7 Best Business Plan Examples (2024)
As an aspiring entrepreneur gearing up to start your own business , you likely know the importance of drafting a business plan. However, you might not be entirely sure where to begin or what specific details to include. That’s where examining business plan examples can be beneficial. Sample business plans serve as real-world templates to help you craft your own plan with confidence. They also provide insight into the key sections that make up a business plan, as well as demonstrate how to structure and present your ideas effectively.
Example business plan
To understand how to write a business plan, let’s study an example structured using a seven-part template. Here’s a quick overview of those parts:
- Executive summary: A quick overview of your business and the contents of your business plan.
- Company description: More info about your company, its goals and mission, and why you started it in the first place.
- Market analysis: Research about the market and industry your business will operate in, including a competitive analysis about the companies you’ll be up against.
- Products and services: A detailed description of what you’ll be selling to your customers.
- Marketing plan: A strategic outline of how you plan to market and promote your business before, during, and after your company launches into the market.
- Logistics and operations plan: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools that are needed to run your business in the background.
- Financial plan: A map of your short-term (and even long-term) financial goals and the costs to run the business. If you’re looking for funding, this is the place to discuss your request and needs.
7 business plan examples (section by section)
In this section, you’ll find hypothetical and real-world examples of each aspect of a business plan to show you how the whole thing comes together.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary offers a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. You’ll want to include a brief description of your company, market research, competitor analysis, and financial information.
In this free business plan template, the executive summary is three paragraphs and occupies nearly half the page:
- Company description
You might go more in-depth with your company description and include the following sections:
- Nature of the business. Mention the general category of business you fall under. Are you a manufacturer, wholesaler, or retailer of your products?
- Background information. Talk about your past experiences and skills, and how you’ve combined them to fill in the market.
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your company —as a corporation, sole proprietorship, LLC, or other business type.
- Industry. Which business sector do you operate in? The answer might be technology, merchandising, or another industry.
- Team. Whether you’re the sole full-time employee of your business or you have contractors to support your daily workflow, this is your chance to put them under the spotlight.
You can also repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, Instagram page, or other properties that ask for a boilerplate description of your business. Hair extensions brand Luxy Hair has a blurb on it’s About page that could easily be repurposed as a company description for its business plan.
- Market analysis
Market analysis comprises research on product supply and demand, your target market, the competitive landscape, and industry trends. You might do a SWOT analysis to learn where you stand and identify market gaps that you could exploit to establish your footing. Here’s an example of a SWOT analysis for a hypothetical ecommerce business:
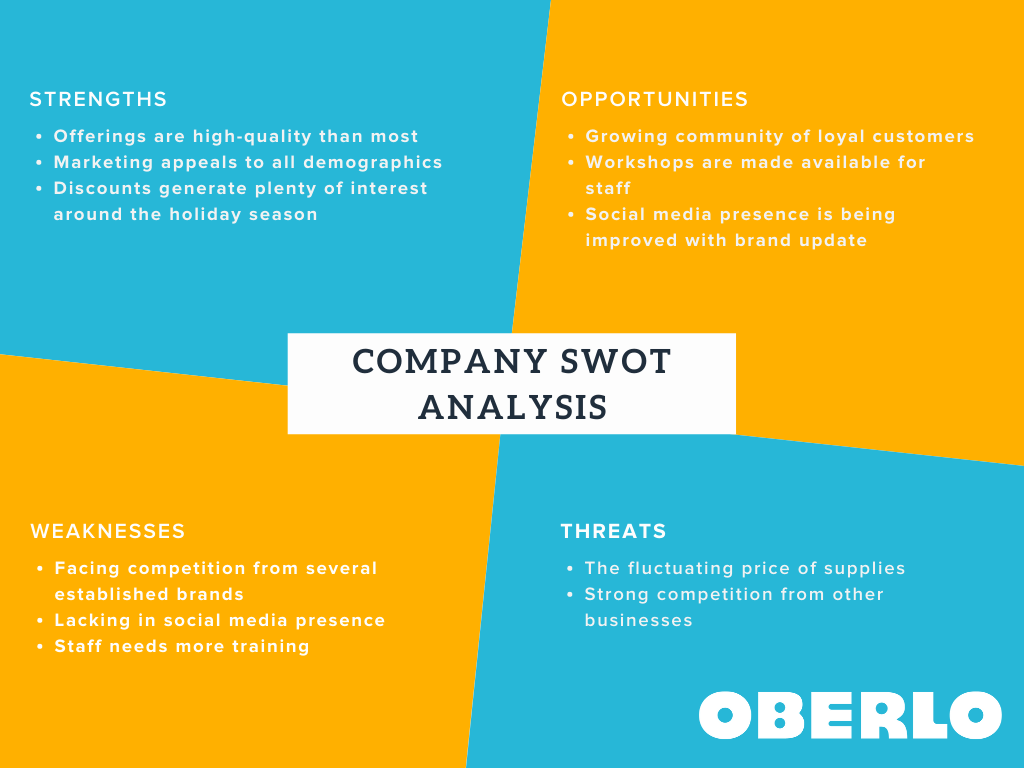
You’ll also want to run a competitive analysis as part of the market analysis component of your business plan. This will show you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to gain an edge over the competition.
- Products and services
This part of your business plan describes your product or service, how it will be priced, and the ways it will compete against similar offerings in the market. Don’t go into too much detail here—a few lines are enough to introduce your item to the reader.
- Marketing plan
Potential investors will want to know how you’ll get the word out about your business. So it’s essential to build a marketing plan that highlights the promotion and customer acquisition strategies you’re planning to adopt.
Most marketing plans focus on the four Ps: product, price, place, and promotion. However, it’s easier when you break it down by the different marketing channels . Mention how you intend to promote your business using blogs, email, social media, and word-of-mouth marketing.
Here’s an example of a hypothetical marketing plan for a real estate website:

Logistics and operations
This section of your business plan provides information about your production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan (a.k.a. financial statement) offers a breakdown of your sales, revenue, expenses, profit, and other financial metrics. You’ll want to include all the numbers and concrete data to project your current and projected financial state.
In this business plan example, the financial statement for ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy includes forecasted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
It then goes deeper into the financials, citing:
- Funding needs
- Project cash-flow statement
- Project profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
You can use Shopify’s financial plan template to create your own income statement, cash-flow statement, and balance sheet.
Types of business plans (and what to write for each)
A one-page business plan is a pared down version of a standard business plan that’s easy for potential investors and partners to understand. You’ll want to include all of these sections, but make sure they’re abbreviated and summarized:
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financials
A startup business plan is meant to secure outside funding for a new business. Typically, there’s a big focus on the financials, as well as other sections that help determine the viability of your business idea—market analysis, for example. Shopify has a great business plan template for startups that include all the below points:
- Market research: in depth
- Financials: in depth
Your internal business plan acts as the enforcer of your company’s vision. It reminds your team of the long-term objective and keeps them strategically aligned toward the same goal. Be sure to include:
- Market research
Feasibility
A feasibility business plan is essentially a feasibility study that helps you evaluate whether your product or idea is worthy of a full business plan. Include the following sections:
A strategic (or growth) business plan lays out your long-term vision and goals. This means your predictions stretch further into the future, and you aim for greater growth and revenue. While crafting this document, you use all the parts of a usual business plan but add more to each one:
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Market analysis: detailed analysis
- Marketing plan: detailed strategy
- Logistics and operations plan: detailed plan
- Financials: detailed projections
Free business plan templates
Now that you’re familiar with what’s included and how to format a business plan, let’s go over a few templates you can fill out or draw inspiration from.
Bplans’ free business plan template

Bplans’ free business plan template focuses a lot on the financial side of running a business. It has many pages just for your financial plan and statements. Once you fill it out, you’ll see exactly where your business stands financially and what you need to do to keep it on track or make it better.
PandaDoc’s free business plan template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is detailed and guides you through every section, so you don’t have to figure everything out on your own. Filling it out, you’ll grasp the ins and outs of your business and how each part fits together. It’s also handy because it connects to PandaDoc’s e-signature for easy signing, ideal for businesses with partners or a board.
Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template

Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template helps you map out the essentials of your business, like partnerships, core activities, and what makes you different. It’s a collaborative tool for you and your team to learn how everything in your business is linked.
Better business planning equals better business outcomes
Building a business plan is key to establishing a clear direction and strategy for your venture. With a solid plan in hand, you’ll know what steps to take for achieving each of your business goals. Kickstart your business planning and set yourself up for success with a defined roadmap—utilizing the sample business plans above to inform your approach.
Business plan FAQ
What are the 3 main points of a business plan.
- Concept. Explain what your business does and the main idea behind it. This is where you tell people what you plan to achieve with your business.
- Contents. Explain what you’re selling or offering. Point out who you’re selling to and who else is selling something similar. This part concerns your products or services, who will buy them, and who you’re up against.
- Cash flow. Explain how money will move in and out of your business. Discuss the money you need to start and keep the business going, the costs of running your business, and how much money you expect to make.
How do I write a simple business plan?
To create a simple business plan, start with an executive summary that details your business vision and objectives. Follow this with a concise description of your company’s structure, your market analysis, and information about your products or services. Conclude your plan with financial projections that outline your expected revenue, expenses, and profitability.
What is the best format to write a business plan?
The optimal format for a business plan arranges your plan in a clear and structured way, helping potential investors get a quick grasp of what your business is about and what you aim to achieve. Always start with a summary of your plan and finish with the financial details or any extra information at the end.
Want to learn more?
- Question: Are You a Business Owner or an Entrepreneur?
- Bootstrapping a Business: 10 Tips to Help You Succeed
- Entrepreneurial Mindset: 20 Ways to Think Like an Entrepreneur
- 101+ Best Small Business Software Programs
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

Free Business Plan Template for Small Businesses (2024)
Use this free business plan template to write your business plan quickly and efficiently.
A good business plan is essential to successfully starting your business — and the easiest way to simplify the work of writing a business plan is to start with a business plan template.
You’re already investing time and energy in refining your business model and planning your launch—there’s no need to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing a business plan. Instead, to help build a complete and effective plan, lean on time-tested structures created by other entrepreneurs and startups.
Ahead, learn what it takes to create a solid business plan and download Shopify's free business plan template to get started on your dream today.
What this free business plan template includes
- Executive summary
- Company overview
- Products or services offered
- Market analysis
- Marketing plan
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financial plan
This business plan outline is designed to ensure you’re thinking through all of the important facets of starting a new business. It’s intended to help new business owners and entrepreneurs consider the full scope of running a business and identify functional areas they may not have considered or where they may need to level up their skills as they grow.
That said, it may not include the specific details or structure preferred by a potential investor or lender. If your goal with a business plan is to secure funding , check with your target organizations—typically banks or investors—to see if they have business plan templates you can follow to maximize your chances of success.
Our free business plan template includes seven key elements typically found in the traditional business plan format:
1. Executive summary
This is a one-page summary of your whole plan, typically written after the rest of the plan is completed. The description section of your executive summary will also cover your management team, business objectives and strategy, and other background information about the brand.
2. Company overview
This section of your business plan will answer two fundamental questions: “Who are you?” and “What do you plan to do?” Answering these questions clarifies why your company exists, what sets it apart from others, and why it’s a good investment opportunity. This section will detail the reasons for your business’s existence, its goals, and its guiding principles.
3. Products or services offered
What you sell and the most important features of your products or services. It also includes any plans for intellectual property, like patent filings or copyright. If you do market research for new product lines, it will show up in this section of your business plan.
4. Market analysis
This section includes everything from estimated market size to your target markets and competitive advantage. It’ll include a competitive analysis of your industry to address competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. Market research is an important part of ensuring you have a viable idea.
5. Marketing plan
How you intend to get the word out about your business, and what strategic decisions you’ve made about things like your pricing strategy. It also covers potential customers’ demographics, your sales plan, and your metrics and milestones for success.
6. Logistics and operations plan
Everything that needs to happen to turn your raw materials into products and get them into the hands of your customers.
7. Financial plan
It’s important to include a look at your financial projections, including both revenue and expense projections. This section includes templates for three key financial statements: an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash-flow statement . You can also include whether or not you need a business loan and how much you’ll need.
Business plan examples
What do financial projections look like on paper? How do you write an executive summary? What should your company description include? Business plan examples can help answer some of these questions and transform your business idea into an actionable plan.
Professional business plan example
Inside our template, we’ve filled out a sample business plan featuring a fictional ecommerce business .
The sample is set up to help you get a sense of each section and understand how they apply to the planning and evaluation stages of a business plan. If you’re looking for funding, this example won’t be a complete or formal look at business plans, but it will give you a great place to start and notes about where to expand.

Lean business plan example
A lean business plan format is a shortened version of your more detailed business plan. It’s helpful when modifying your plan for a specific audience, like investors or new hires.
Also known as a one-page business plan, it includes only the most important, need-to-know information, such as:
- Company description
- Key members of your team
- Customer segments
💡 Tip: For a step-by-step guide to creating a lean business plan (including a sample business plan), read our guide on how to create a lean business plan .

Benefits of writing a solid business plan
It’s tempting to dive right into execution when you’re excited about a new business or side project, but taking the time to write a thorough business plan and get your thoughts on paper allows you to do a number of beneficial things:
- Test the viability of your business idea. Whether you’ve got one business idea or many, business plans can make an idea more tangible, helping you see if it’s truly viable and ensure you’ve found a target market.
- Plan for your next phase. Whether your goal is to start a new business or scale an existing business to the next level, a business plan can help you understand what needs to happen and identify gaps to address.
- Clarify marketing strategy, goals, and tactics. Writing a business plan can show you the actionable next steps to take on a big, abstract idea. It can also help you narrow your strategy and identify clear-cut tactics that will support it.
- Scope the necessary work. Without a concrete plan, cost overruns and delays are all but certain. A business plan can help you see the full scope of work to be done and adjust your investment of time and money accordingly.
- Hire and build partnerships. When you need buy-in from potential employees and business partners, especially in the early stages of your business, a clearly written business plan is one of the best tools at your disposal. A business plan provides a refined look at your goals for the business, letting partners judge for themselves whether or not they agree with your vision.
- Secure funds. Seeking financing for your business—whether from venture capital, financial institutions, or Shopify Capital —is one of the most common reasons to create a business plan.
Why you should you use a template for a business plan
A business plan can be as informal or formal as your situation calls for, but even if you’re a fan of the back-of-the-napkin approach to planning, there are some key benefits to starting your plan from an existing outline or simple business plan template.
No blank-page paralysis
A blank page can be intimidating to even the most seasoned writers. Using an established business planning process and template can help you get past the inertia of starting your business plan, and it allows you to skip the work of building an outline from scratch. You can always adjust a template to suit your needs.
Guidance on what to include in each section
If you’ve never sat through a business class, you might never have created a SWOT analysis or financial projections. Templates that offer guidance—in plain language—about how to fill in each section can help you navigate sometimes-daunting business jargon and create a complete and effective plan.
Knowing you’ve considered every section
In some cases, you may not need to complete every section of a startup business plan template, but its initial structure shows you you’re choosing to omit a section as opposed to forgetting to include it in the first place.
Tips for creating a successful business plan
There are some high-level strategic guidelines beyond the advice included in this free business plan template that can help you write an effective, complete plan while minimizing busywork.
Understand the audience for your plan
If you’re writing a business plan for yourself in order to get clarity on your ideas and your industry as a whole, you may not need to include the same level of detail or polish you would with a business plan you want to send to potential investors. Knowing who will read your plan will help you decide how much time to spend on it.
Know your goals
Understanding the goals of your plan can help you set the right scope. If your goal is to use the plan as a roadmap for growth, you may invest more time in it than if your goal is to understand the competitive landscape of a new industry.
Take it step by step
Writing a 10- to 15-page document can feel daunting, so try to tackle one section at a time. Select a couple of sections you feel most confident writing and start there—you can start on the next few sections once those are complete. Jot down bullet-point notes in each section before you start writing to organize your thoughts and streamline the writing process.
Maximize your business planning efforts
Planning is key to the financial success of any type of business , whether you’re a startup, non-profit, or corporation.
To make sure your efforts are focused on the highest-value parts of your own business planning, like clarifying your goals, setting a strategy, and understanding the target market and competitive landscape, lean on a business plan outline to handle the structure and format for you. Even if you eventually omit sections, you’ll save yourself time and energy by starting with a framework already in place.
- How to Start an Online Boutique- A Complete Playbook
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- 6 Creative Ways to Start a Business With No Money in 2024
- What is Shopify and How Does it Work?
- What Is Affiliate Marketing and How to Get Started
- How to Price Your Products in 3 Simple Steps
- 10 Common Small Business Mistakes to Avoid
- How to Turn a Hobby into a Business in 8 Steps
Business plan template FAQ
What is the purpose of a business plan.
The purpose of your business plan is to describe a new business opportunity or an existing one. It clarifies the business strategy, marketing plan, financial forecasts, potential providers, and more information about the company.
How do I write a simple business plan?
- Choose a business plan format, such as a traditional or a one-page business plan.
- Find a business plan template.
- Read through a business plan sample.
- Fill in the sections of your business plan.
What is the best business plan template?
If you need help writing a business plan, Shopify’s template is one of the most beginner-friendly options you’ll find. It’s comprehensive, well-written, and helps you fill out every section.
What are the 5 essential parts of a business plan?
The five essential parts of a traditional business plan include:
- Executive summary: This is a brief overview of the business plan, summarizing the key points and highlighting the main points of the plan.
- Business description: This section outlines the business concept and how it will be executed.
- Market analysis: This section provides an in-depth look at the target market and how the business will compete in the marketplace.
- Financial plan: This section details the financial projections for the business, including sales forecasts, capital requirements, and a break-even analysis.
- Management and organization: This section describes the management team and the organizational structure of the business.
Are there any free business plan templates?
There are several free templates for business plans for small business owners available online, including Shopify’s own version. Download a copy for your business.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Jun 11, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
How To Start A Business In 11 Steps (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 7, 2024, 1:44pm

Table of Contents
Before you begin: get in the right mindset, 1. determine your business concept, 2. research your competitors and market, 3. create your business plan, 4. choose your business structure, 5. register your business and get licenses, 6. get your finances in order, 7. fund your business, 8. apply for business insurance, 9. get the right business tools, 10. market your business, 11. scale your business, what are the best states to start a business, bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Starting a business is one of the most exciting and rewarding experiences you can have. But where do you begin? There are several ways to approach creating a business, along with many important considerations. To help take the guesswork out of the process and improve your chances of success, follow our comprehensive guide on how to start a business. We’ll walk you through each step of the process, from defining your business idea to registering, launching and growing your business.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
The public often hears about overnight successes because they make for a great headline. However, it’s rarely that simple—they don’t see the years of dreaming, building and positioning before a big public launch. For this reason, remember to focus on your business journey and don’t measure your success against someone else’s.
Consistency Is Key
New business owners tend to feed off their motivation initially but get frustrated when that motivation wanes. This is why it’s essential to create habits and follow routines that power you through when motivation goes away.
Take the Next Step
Some business owners dive in headfirst without looking and make things up as they go along. Then, there are business owners who stay stuck in analysis paralysis and never start. Perhaps you’re a mixture of the two—and that’s right where you need to be. The best way to accomplish any business or personal goal is to write out every possible step it takes to achieve the goal. Then, order those steps by what needs to happen first. Some steps may take minutes while others take a long time. The point is to always take the next step.
Most business advice tells you to monetize what you love, but it misses two other very important elements: it needs to be profitable and something you’re good at. For example, you may love music, but how viable is your business idea if you’re not a great singer or songwriter? Maybe you love making soap and want to open a soap shop in your small town that already has three close by—it won’t be easy to corner the market when you’re creating the same product as other nearby stores.
If you don’t have a firm idea of what your business will entail, ask yourself the following questions:
- What do you love to do?
- What do you hate to do?
- Can you think of something that would make those things easier?
- What are you good at?
- What do others come to you for advice about?
- If you were given ten minutes to give a five-minute speech on any topic, what would it be?
- What’s something you’ve always wanted to do, but lacked resources for?
These questions can lead you to an idea for your business. If you already have an idea, they might help you expand it. Once you have your idea, measure it against whether you’re good at it and if it’s profitable.
Your business idea also doesn’t have to be the next Scrub Daddy or Squatty Potty. Instead, you can take an existing product and improve upon it. You can also sell a digital product so there’s little overhead.
What Kind of Business Should You Start?
Before you choose the type of business to start, there are some key things to consider:
- What type of funding do you have?
- How much time do you have to invest in your business?
- Do you prefer to work from home or at an office or workshop?
- What interests and passions do you have?
- Can you sell information (such as a course), rather than a product?
- What skills or expertise do you have?
- How fast do you need to scale your business?
- What kind of support do you have to start your business?
- Are you partnering with someone else?
- Does the franchise model make more sense to you?
Consider Popular Business Ideas
Not sure what business to start? Consider one of these popular business ideas:
- Start a Franchise
- Start a Blog
- Start an Online Store
- Start a Dropshipping Business
- Start a Cleaning Business
- Start a Bookkeeping Business
- Start a Clothing Business
- Start a Landscaping Business
- Start a Consulting Business
- Start a Photography Business
- Start a Vending Machine Business
Most entrepreneurs spend more time on their products than they do getting to know the competition. If you ever apply for outside funding, the potential lender or partner wants to know: what sets you (or your business idea) apart? If market analysis indicates your product or service is saturated in your area, see if you can think of a different approach. Take housekeeping, for example—rather than general cleaning services, you might specialize in homes with pets or focus on garage cleanups.
Primary Research
The first stage of any competition study is primary research, which entails obtaining data directly from potential customers rather than basing your conclusions on past data. You can use questionnaires, surveys and interviews to learn what consumers want. Surveying friends and family isn’t recommended unless they’re your target market. People who say they’d buy something and people who do are very different. The last thing you want is to take so much stock in what they say, create the product and flop when you try to sell it because all of the people who said they’d buy it don’t because the product isn’t something they’d buy.
Secondary Research
Utilize existing sources of information, such as census data, to gather information when you do secondary research. The current data may be studied, compiled and analyzed in various ways that are appropriate for your needs but it may not be as detailed as primary research.
Conduct a SWOT Analysis
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Conducting a SWOT analysis allows you to look at the facts about how your product or idea might perform if taken to market, and it can also help you make decisions about the direction of your idea. Your business idea might have some weaknesses that you hadn’t considered or there may be some opportunities to improve on a competitor’s product.

Asking pertinent questions during a SWOT analysis can help you identify and address weaknesses before they tank your new business.
A business plan is a dynamic document that serves as a roadmap for establishing a new business. This document makes it simple for potential investors, financial institutions and company management to understand and absorb. Even if you intend to self-finance, a business plan can help you flesh out your idea and spot potential problems. When writing a well-rounded business plan, include the following sections:
- Executive summary: The executive summary should be the first item in the business plan, but it should be written last. It describes the proposed new business and highlights the goals of the company and the methods to achieve them.
- Company description: The company description covers what problems your product or service solves and why your business or idea is best. For example, maybe your background is in molecular engineering, and you’ve used that background to create a new type of athletic wear—you have the proper credentials to make the best material.
- Market analysis: This section of the business plan analyzes how well a company is positioned against its competitors. The market analysis should include target market, segmentation analysis, market size, growth rate, trends and a competitive environment assessment.
- Organization and structure: Write about the type of business organization you expect, what risk management strategies you propose and who will staff the management team. What are their qualifications? Will your business be a single-member limited liability company (LLC) or a corporation ?
- Mission and goals: This section should contain a brief mission statement and detail what the business wishes to accomplish and the steps to get there. These goals should be SMART (specific, measurable, action-orientated, realistic and time-bound).
- Products or services: This section describes how your business will operate. It includes what products you’ll offer to consumers at the beginning of the business, how they compare to existing competitors, how much your products cost, who will be responsible for creating the products, how you’ll source materials and how much they cost to make.
- Background summary: This portion of the business plan is the most time-consuming to write. Compile and summarize any data, articles and research studies on trends that could positively and negatively affect your business or industry.
- Marketing plan: The marketing plan identifies the characteristics of your product or service, summarizes the SWOT analysis and analyzes competitors. It also discusses how you’ll promote your business, how much money will be spent on marketing and how long the campaign is expected to last.
- Financial plan: The financial plan is perhaps the core of the business plan because, without money, the business will not move forward. Include a proposed budget in your financial plan along with projected financial statements, such as an income statement, a balance sheet and a statement of cash flows. Usually, five years of projected financial statements are acceptable. This section is also where you should include your funding request if you’re looking for outside funding.
Learn more: Download our free simple business plan template .
Come Up With an Exit Strategy
An exit strategy is important for any business that is seeking funding because it outlines how you’ll sell the company or transfer ownership if you decide to retire or move on to other projects. An exit strategy also allows you to get the most value out of your business when it’s time to sell. There are a few different options for exiting a business, and the best option for you depends on your goals and circumstances.
The most common exit strategies are:
- Selling the business to another party
- Passing the business down to family members
- Liquidating the business assets
- Closing the doors and walking away
Develop a Scalable Business Model
As your small business grows, it’s important to have a scalable business model so that you can accommodate additional customers without incurring additional costs. A scalable business model is one that can be replicated easily to serve more customers without a significant increase in expenses.
Some common scalable business models are:
- Subscription-based businesses
- Businesses that sell digital products
- Franchise businesses
- Network marketing businesses
Start Planning for Taxes
One of the most important things to do when starting a small business is to start planning for taxes. Taxes can be complex, and there are several different types of taxes you may be liable for, including income tax, self-employment tax, sales tax and property tax. Depending on the type of business you’re operating, you may also be required to pay other taxes, such as payroll tax or unemployment tax.
Start A Limited Liability Company Online Today with ZenBusiness
Click to get started.
When structuring your business, it’s essential to consider how each structure impacts the amount of taxes you owe, daily operations and whether your personal assets are at risk.
An LLC limits your personal liability for business debts. LLCs can be owned by one or more people or companies and must include a registered agent . These owners are referred to as members.
- LLCs offer liability protection for the owners
- They’re one of the easiest business entities to set up
- You can have a single-member LLC
- You may be required to file additional paperwork with your state on a regular basis
- LLCs can’t issue stock
- You’ll need to pay annual filing fees to your state
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
An LLP is similar to an LLC but is typically used for licensed business professionals such as an attorney or accountant. These arrangements require a partnership agreement.
- Partners have limited liability for the debts and actions of the LLP
- LLPs are easy to form and don’t require much paperwork
- There’s no limit to the number of partners in an LLP
- Partners are required to actively take part in the business
- LLPs can’t issue stock
- All partners are personally liable for any malpractice claims against the business
Sole Proprietorship
If you start a solo business, you might consider a sole proprietorship . The company and the owner, for legal and tax purposes, are considered the same. The business owner assumes liability for the business. So, if the business fails, the owner is personally and financially responsible for all business debts.
- Sole proprietorships are easy to form
- There’s no need to file additional paperwork with your state
- You’re in complete control of the business
- You’re personally liable for all business debts
- It can be difficult to raise money for a sole proprietorship
- The business may have a limited lifespan
Corporation
A corporation limits your personal liability for business debts just as an LLC does. A corporation can be taxed as a C corporation (C-corp) or an S corporation (S-corp). S-corp status offers pass-through taxation to small corporations that meet certain IRS requirements. Larger companies and startups hoping to attract venture capital are usually taxed as C-corps.
- Corporations offer liability protection for the owners
- The life span of a corporation is not limited
- A corporation can have an unlimited number of shareholders
- Corporations are subject to double taxation
- They’re more expensive and complicated to set up than other business structures
- The shareholders may have limited liability
Before you decide on a business structure, discuss your situation with a small business accountant and possibly an attorney, as each business type has different tax treatments that could affect your bottom line.
Helpful Resources
- How To Set Up an LLC in 7 Steps
- How To Start a Sole Proprietorship
- How To Start a Corporation
- How To Start a Nonprofit
- How To Start a 501(c)(3)
There are several legal issues to address when starting a business after choosing the business structure. The following is a good checklist of items to consider when establishing your business:
Choose Your Business Name
Make it memorable but not too difficult. Choose the same domain name, if available, to establish your internet presence. A business name cannot be the same as another registered company in your state, nor can it infringe on another trademark or service mark that is already registered with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
Business Name vs. DBA
There are business names, and then there are fictitious business names known as “Doing Business As” or DBA. You may need to file a DBA if you’re operating under a name that’s different from the legal name of your business. For example, “Mike’s Bike Shop” is doing business as “Mike’s Bikes.” The legal name of the business is “Mike’s Bike Shop,” and “Mike’s Bikes” is the DBA.
You may need to file a DBA with your state, county or city government offices. The benefits of a DBA include:
- It can help you open a business bank account under your business name
- A DBA can be used as a “trade name” to brand your products or services
- A DBA can be used to get a business license
Register Your Business and Obtain an EIN
You’ll officially create a corporation, LLC or other business entity by filing forms with your state’s business agency―usually the Secretary of State. As part of this process, you’ll need to choose a registered agent to accept legal documents on behalf of your business. You’ll also pay a filing fee. The state will send you a certificate that you can use to apply for licenses, a tax identification number (TIN) and business bank accounts.
Next, apply for an employer identification number (EIN) . All businesses, other than sole proprietorships with no employees, must have a federal employer identification number. Submit your application to the IRS and you’ll typically receive your number in minutes.
Get Appropriate Licenses and Permits
Legal requirements are determined by your industry and jurisdiction. Most businesses need a mixture of local, state and federal licenses to operate. Check with your local government office (and even an attorney) for licensing information tailored to your area.
- Best LLC Services
- How To Register a Business Name
- How To Register a DBA
- How To Get an EIN for an LLC
- How To Get a Business License
Start an LLC Online Today With ZenBusiness
Click on the state below to get started.
Open a Business Bank Account
Keep your business and personal finances separate. Here’s how to choose a business checking account —and why separate business accounts are essential. When you open a business bank account, you’ll need to provide your business name and your business tax identification number (EIN). This business bank account can be used for your business transactions, such as paying suppliers or invoicing customers. Most times, a bank will require a separate business bank account to issue a business loan or line of credit.
Hire a Bookkeeper or Get Accounting Software
If you sell a product, you need an inventory function in your accounting software to manage and track inventory. The software should have ledger and journal entries and the ability to generate financial statements.
Some software programs double as bookkeeping tools. These often include features such as check writing and managing receivables and payables. You can also use this software to track your income and expenses, generate invoices, run reports and calculate taxes.
There are many bookkeeping services available that can do all of this for you, and more. These services can be accessed online from any computer or mobile device and often include features such as bank reconciliation and invoicing. Check out the best accounting software for small business, or see if you want to handle the bookkeeping yourself.
Determine Your Break-Even Point
Before you fund your business, you must get an idea of your startup costs. To determine these, make a list of all the physical supplies you need, estimate the cost of any professional services you will require, determine the price of any licenses or permits required to operate and calculate the cost of office space or other real estate. Add in the costs of payroll and benefits, if applicable.
Businesses can take years to turn a profit, so it’s better to overestimate the startup costs and have too much money than too little. Many experts recommend having enough cash on hand to cover six months of operating expenses.
When you know how much you need to get started with your business, you need to know the point at which your business makes money. This figure is your break-even point.
In contrast, the contribution margin = total sales revenue – cost to make product
For example, let’s say you’re starting a small business that sells miniature birdhouses for fairy gardens. You have determined that it will cost you $500 in startup costs. Your variable costs are $0.40 per birdhouse produced, and you sell them for $1.50 each.
Let’s write these out so it’s easy to follow:





















IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Get started with your business plan template. A target market analysis is a key part of any business plan. But it's just one piece. At Bplans, we take some of the pain out of business planning. We've developed a free business planning template to help reduce entrepreneurs' time to create a full, lender-ready business plan.
Sections of your market analysis should include: Industry Description and Outlook. Target Market. Market Research Results. Competitive Analysis. Remember to properly cite your sources of information within the body of your market analysis as you write it. You and other readers of your business plan, such as potential investors, will need to ...
Step 4: Calculate market value. You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value. A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the ...
Creating a marketing strategy for your business begins with defining your primary target market. Knowing who your ideal customer is and understanding their needs and wants is essential for creating an effective plan. Here's how to define your target market in six simple steps: 1. Conduct Market Research.
A target market is a specific group of people with shared characteristics that a business markets its products or services to. Companies use target markets to thoroughly understand their potential customers and craft marketing strategies that help them meet their business and marketing objectives. Identifying a target market is an integral part ...
Target Market: A target market is the market a company wants to sell its products and services to, and it includes a targeted set of customers for whom it directs its marketing efforts ...
Target market segmentation ensures the company reaches the right audience with the right message. How to define your target market. Step 1. Compile data on your current customers. A great first step in figuring out who most wants to buy from you is to identify who is already using your products or services.
A business will promote its product or service to the target market from which the organization may generate the greatest profitable action, thus achieving the goal of marketing.. While B2C businesses may focus most on audience-specific characteristics to define their target markets, B2B businesses typically consider industries, niches, and verticals as the primary characteristics to describe ...
This type of target market is defined by consumer behavior, such as the benefits sought, usage rate, and customer loyalty. It's important to note that a business may choose to target one or multiple types of target markets, depending on their specific business objectives and marketing strategies.
Plan several rounds of edits or have someone else review it. Keep everything in the context of your business. Make sure all the statistics and data you use in your market analysis relate back to your business. Your focus should be on how you are uniquely positioned to meet the needs of the target market.
These chosen segments become your target markets. Developing a Winning Business Plan. Incorporating the insights gained from market research and target market analysis, a well-crafted business plan becomes a powerful roadmap for your company's success. Axiom Business Strategy specializes in creating detailed, investor-ready business plans that ...
Target Market Presentation in the Business Plan. The business plan target market section can be presented in a number of formats, but a listing of the major customer segments together with a pie chart will show the investor where the main potential for the product lies. In the example below, the market is split into four main segments both in ...
As the name implies, target market analysis is the basis for identifying your target market. Here are the five steps you can take to do one of your own. 1. Analyze your product or service. Take a look at what you're selling to understand which consumers would get value from your product.
This target market is defined by their commonality as mentioned above, usually within a range, such as consumers aged 25-45 or those working in the hospitality industry. Your marketing strategy will be tailored to that particular niche market, and will encompass all the channels that the target audience might use.
You will know: how to tailor your marketing to motivate them to buy your product or service. 1. Research your market. To define your target market effectively you'll need to do some research. Gathering statistics and other market research data helps you to understand your potential customers and their needs and make better marketing decisions.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
A target market strategy is a business plan focused on growing sales and brand awareness within a specific group of consumers. To do this, businesses strategize based on demographics that make up a market, which is an area or group specified for product sales. Target markets represent the opportunity for new business and increased sales.
Marketing Plan: A marketing plan is a business's operational document for advertising campaigns designed to reach its target market . A marketing plan pulls together all the campaigns that will be ...
Our durable business model is designed to stand the test of time and differentiate us in the marketplace. Over the years, we've built a foundation that serves our current and future guests, team members, vendors, communities and shareholders well — and delivers strong results — no matter how the environment around us evolves.It's the framework that guides us as we live out Target's ...
Marketing plan: A strategic outline of how you plan to market and promote your business before, during, and after your company launches into the market. Logistics and operations plan: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools that are needed to run your business in the background. Financial plan: A map of your short-term (and even ...
If you do market research for new product lines, it will show up in this section of your business plan. 4. Market analysis. ... Market analysis: This section provides an in-depth look at the target market and how the business will compete in the marketplace. Financial plan: This section details the financial projections for the business, ...
Market analysis: This section of the business plan analyzes how well a company is positioned against its competitors. The market analysis should include target market, segmentation analysis ...
Identifying a target market is an integral part of any new business undertaking, whether at a Fortune 500 company or a soon-to-be-launched small business. Knowing your target market sets you up for success. This article will cover why target markets matter, examples of them in action, how they are defined through segmentation, and the range of ...
Our template steps you through the process of developing a succession plan with links to extra information if you need it. You may want to check our tips below before you start. 1. Analyse your market. 2. Set your goals and objectives. 3. Outline your marketing strategies. 4.
The four Ps are a "marketing mix" comprised of four key elements—product, price, place, and promotion—used when marketing a product or service. Typically, successful marketers and businesses consider the four Ps when creating marketing plans and strategies to effectively market to their target audience. Although there are many other ...
Marketing Plan Example (Filled Out) Here's a fake content marketing plan example for a fictitious shoe company. Marketing Plan Template: [Project Zeus Running Collection] Marketing Goal. Drive $200,000 in sales for the new Zeus running collection within the first 4 months of launch day. Target Audience.
Goldman Sachs rates Apple at "Buy" with a $238 price target. Citi: 'Best WWDC ever' "We believe Apple's WWDC was the best WWDC conference in a long time as it introduced 'AI for the rest of the ...