14 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan

10 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
There’s no question that starting and running a business is hard work. But it’s also incredibly rewarding. And, one of the most important things you can do to increase your chances of success is to have a business plan.
A business plan is a foundational document that is essential for any company, no matter the size or age. From attracting potential investors to keeping your business on track—a business plan helps you achieve important milestones and grow in the right direction.

A business plan isn’t just a document you put together once when starting your business. It’s a living, breathing guide for existing businesses – one that business owners should revisit and update regularly.
Unfortunately, writing a business plan is often a daunting task for potential entrepreneurs. So, do you really need a business plan? Is it really worth the investment of time and resources? Can’t you just wing it and skip the whole planning process?
Good questions. Here’s every reason why you need a business plan.
- 1. Business planning is proven to help you grow 30 percent faster
Writing a business plan isn’t about producing a document that accurately predicts the future of your company. The process of writing your plan is what’s important. Writing your plan and reviewing it regularly gives you a better window into what you need to do to achieve your goals and succeed.
You don’t have to just take our word for it. Studies have proven that companies that plan and review their results regularly grow 30 percent faster. Beyond faster growth, research also shows that companies that plan actually perform better. They’re less likely to become one of those woeful failure statistics, or experience cash flow crises that threaten to close them down.
- 2. Planning is a necessary part of the fundraising process
One of the top reasons to have a business plan is to make it easier to raise money for your business. Without a business plan, it’s difficult to know how much money you need to raise, how you will spend the money once you raise it, and what your budget should be.
Investors want to know that you have a solid plan in place – that your business is headed in the right direction and that there is long-term potential in your venture.
A business plan shows that your business is serious and that there are clearly defined steps on how it aims to become successful. It also demonstrates that you have the necessary competence to make that vision a reality.
Investors, partners, and creditors will want to see detailed financial forecasts for your business that shows how you plan to grow and how you plan on spending their money.
- 3. Having a business plan minimizes your risk
When you’re just starting out, there’s so much you don’t know—about your customers, your competition, and even about operations.
As a business owner, you signed up for some of that uncertainty when you started your business, but there’s a lot you can do to reduce your risk . Creating and reviewing your business plan regularly is a great way to uncover your weak spots—the flaws, gaps, and assumptions you’ve made—and develop contingency plans.
Your business plan will also help you define budgets and revenue goals. And, if you’re not meeting your goals, you can quickly adjust spending plans and create more realistic budgets to keep your business healthy.
Brought to you by

Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- 4. Crafts a roadmap to achieve important milestones
A business plan is like a roadmap for your business. It helps you set, track and reach business milestones.
For your plan to function in this way, your business plan should first outline your company’s short- and long-term goals. You can then fill in the specific steps necessary to reach those goals. This ensures that you measure your progress (or lack thereof) and make necessary adjustments along the way to stay on track while avoiding costly detours.
In fact, one of the top reasons why new businesses fail is due to bad business planning. Combine this with inflexibility and you have a recipe for disaster.
And planning is not just for startups. Established businesses benefit greatly from revisiting their business plan. It keeps them on track, even when the global market rapidly shifts as we’ve seen in recent years.
- 5. A plan helps you figure out if your idea can become a business
To turn your idea into reality, you need to accurately assess the feasibility of your business idea.
You need to verify:
- If there is a market for your product or service
- Who your target audience is
- How you will gain an edge over the current competition
- If your business can run profitably
A business plan forces you to take a step back and look at your business objectively, which makes it far easier to make tough decisions down the road. Additionally, a business plan helps you to identify risks and opportunities early on, providing you with the necessary time to come up with strategies to address them properly.
Finally, a business plan helps you work through the nuts and bolts of how your business will work financially and if it can become sustainable over time.
6. You’ll make big spending decisions with confidence
As your business grows, you’ll have to figure out when to hire new employees, when to expand to a new location, or whether you can afford a major purchase.
These are always major spending decisions, and if you’re regularly reviewing the forecasts you mapped out in your business plan, you’re going to have better information to use to make your decisions.
7. You’re more likely to catch critical cash flow challenges early
The other side of those major spending decisions is understanding and monitoring your business’s cash flow. Your cash flow statement is one of the three key financial statements you’ll put together for your business plan. (The other two are your balance sheet and your income statement (P&L).
Reviewing your cash flow statement regularly as part of your regular business plan review will help you see potential cash flow challenges earlier so you can take action to avoid a cash crisis where you can’t pay your bills.
- 8. Position your brand against the competition
Competitors are one of the factors that you need to take into account when starting a business. Luckily, competitive research is an integral part of writing a business plan. It encourages you to ask questions like:
- What is your competition doing well? What are they doing poorly?
- What can you do to set yourself apart?
- What can you learn from them?
- How can you make your business stand out?
- What key business areas can you outcompete?
- How can you identify your target market?
Finding answers to these questions helps you solidify a strategic market position and identify ways to differentiate yourself. It also proves to potential investors that you’ve done your homework and understand how to compete.
- 9. Determines financial needs and revenue models
A vital part of starting a business is understanding what your expenses will be and how you will generate revenue to cover those expenses. Creating a business plan helps you do just that while also defining ongoing financial needs to keep in mind.
Without a business model, it’s difficult to know whether your business idea will generate revenue. By detailing how you plan to make money, you can effectively assess the viability and scalability of your business.
Understanding this early on can help you avoid unnecessary risks and start with the confidence that your business is set up to succeed.
- 10. Helps you think through your marketing strategy
A business plan is a great way to document your marketing plan. This will ensure that all of your marketing activities are aligned with your overall goals. After all, a business can’t grow without customers and you’ll need a strategy for acquiring those customers.
Your business plan should include information about your target market, your marketing strategy, and your marketing budget. Detail things like how you plan to attract and retain customers, acquire new leads, how the digital marketing funnel will work, etc.
Having a documented marketing plan will help you to automate business operations, stay on track and ensure that you’re making the most of your marketing dollars.
- 11. Clarifies your vision and ensures everyone is on the same page
In order to create a successful business, you need a clear vision and a plan for how you’re going to achieve it. This is all detailed with your mission statement, which defines the purpose of your business, and your personnel plan, which outlines the roles and responsibilities of current and future employees. Together, they establish the long-term vision you have in mind and who will need to be involved to get there.
Additionally, your business plan is a great tool for getting your team in sync. Through consistent plan reviews, you can easily get everyone in your company on the same page and direct your workforce toward tasks that truly move the needle.
- 12. Future-proof your business
A business plan helps you to evaluate your current situation and make realistic projections for the future.
This is an essential step in growing your business, and it’s one that’s often overlooked. When you have a business plan in place, it’s easier to identify opportunities and make informed decisions based on data.
Therefore, it requires you to outline goals, strategies, and tactics to help the organization stay focused on what’s important.
By regularly revisiting your business plan, especially when the global market changes, you’ll be better equipped to handle whatever challenges come your way, and pivot faster.
You’ll also be in a better position to seize opportunities as they arise.
- 13. Tracks your progress and measures success
An often overlooked purpose of a business plan is as a tool to define success metrics. A key part of writing your plan involves pulling together a viable financial plan. This includes financial statements such as your profit and loss, cash flow, balance sheet, and sales forecast.
By housing these financial metrics within your business plan, you suddenly have an easy way to relate your strategy to actual performance. You can track progress, measure results, and follow up on how the company is progressing. Without a plan, it’s almost impossible to gauge whether you’re on track or not.
Additionally, by evaluating your successes and failures, you learn what works and what doesn’t and you can make necessary changes to your plan. In short, having a business plan gives you a framework for measuring your success. It also helps with building up a “lessons learned” knowledge database to avoid costly mistakes in the future.
- 14. Your business plan is an asset if you ever want to sell
Down the road, you might decide that you want to sell your business or position yourself for acquisition. Having a solid business plan is going to help you make the case for a higher valuation. Your business is likely to be worth more to a buyer if it’s easy for them to understand your business model, your target market, and your overall potential to grow and scale.

Free business plan template
Join over 1-million businesses and make planning easy with our simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template.
Download Template
- Writing your business plan
By taking the time to create a business plan, you ensure that your business is heading in the right direction and that you have a roadmap to get there. We hope that this post has shown you just how important and valuable a business plan can be. While it may still seem daunting, the benefits far outweigh the time investment and learning curve for writing one.
Luckily, you can write a plan in as little as 30 minutes. And there are plenty of excellent planning tools and business plan templates out there if you’re looking for more step-by-step guidance. Whatever it takes, write your plan and you’ll quickly see how useful it can be.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- 6. You’ll make big spending decisions with confidence
- 7. You’re more likely to catch critical cash flow challenges early
Related Articles

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes

10 Min. Read
When Should You Write a Business Plan?

3 Min. Read
How Long Should a Business Plan Be?

5 Min. Read
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Sign up for our newsletter for product updates, new blog posts, and the chance to be featured in our Small Business Spotlight!

The importance of a business plan
Business plans are like road maps: it’s possible to travel without one, but that will only increase the odds of getting lost along the way.
Owners with a business plan see growth 30% faster than those without one, and 71% of the fast-growing companies have business plans . Before we get into the thick of it, let’s define and go over what a business plan actually is.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a 15-20 page document that outlines how you will achieve your business objectives and includes information about your product, marketing strategies, and finances. You should create one when you’re starting a new business and keep updating it as your business grows.
Rather than putting yourself in a position where you may have to stop and ask for directions or even circle back and start over, small business owners often use business plans to help guide them. That’s because they help them see the bigger picture, plan ahead, make important decisions, and improve the overall likelihood of success.
Why is a business plan important?
A well-written business plan is an important tool because it gives entrepreneurs and small business owners, as well as their employees, the ability to lay out their goals and track their progress as their business begins to grow. Business planning should be the first thing done when starting a new business. Business plans are also important for attracting investors so they can determine if your business is on the right path and worth putting money into.
Business plans typically include detailed information that can help improve your business’s chances of success, like:
- A market analysis : gathering information about factors and conditions that affect your industry
- Competitive analysis : evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors
- Customer segmentation : divide your customers into different groups based on specific characteristics to improve your marketing
- Marketing: using your research to advertise your business
- Logistics and operations plans : planning and executing the most efficient production process
- Cash flow projection : being prepared for how much money is going into and out of your business
- An overall path to long-term growth
10 reasons why you need a business plan
I know what you’re thinking: “Do I really need a business plan? It sounds like a lot of work, plus I heard they’re outdated and I like figuring things out as I go...”.
The answer is: yes, you really do need a business plan! As entrepreneur Kevin J. Donaldson said, “Going into business without a business plan is like going on a mountain trek without a map or GPS support—you’ll eventually get lost and starve! Though it may sound tedious and time-consuming, business plans are critical to starting your business and setting yourself up for success.
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business.
1. To help you with critical decisions
The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and crisis management. Sitting down and considering all the ramifications of any given decision is a luxury that small businesses can’t always afford. That’s where a business plan comes in.
Building a business plan allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time.
Creating a robust business plan is a forcing function—you have to sit down and think about major components of your business before you get started, like your marketing strategy and what products you’ll sell. You answer many tough questions before they arise. And thinking deeply about your core strategies can also help you understand how those decisions will impact your broader strategy.
*While subscribed to Wave’s Pro Plan, get 2.9% + $0 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0 (Amex) per transaction for unlimited transactions during the offer period. After the offer ends: over 10 transactions per month at 2.9% + $0.60 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0.60 (Amex) per transaction. Discover processing is only available to US customers. See full terms and conditions.
See Terms of Service for more information.
Send invoices, get paid, track expenses, pay your team, and balance your books with our financial management software.
2. To iron out the kinks
Putting together a business plan requires entrepreneurs to ask themselves a lot of hard questions and take the time to come up with well-researched and insightful answers. Even if the document itself were to disappear as soon as it’s completed, the practice of writing it helps to articulate your vision in realistic terms and better determine if there are any gaps in your strategy.
3. To avoid the big mistakes
Only about half of small businesses are still around to celebrate their fifth birthday . While there are many reasons why small businesses fail, many of the most common are purposefully addressed in business plans.
According to data from CB Insights , some of the most common reasons businesses fail include:
- No market need : No one wants what you’re selling.
- Lack of capital : Cash flow issues or businesses simply run out of money.
- Inadequate team : This underscores the importance of hiring the right people to help you run your business.
- Stiff competition : It’s tough to generate a steady profit when you have a lot of competitors in your space.
- Pricing : Some entrepreneurs price their products or services too high or too low—both scenarios can be a recipe for disaster.
The exercise of creating a business plan can help you avoid these major mistakes. Whether it’s cash flow forecasts or a product-market fit analysis , every piece of a business plan can help spot some of those potentially critical mistakes before they arise. For example, don’t be afraid to scrap an idea you really loved if it turns out there’s no market need. Be honest with yourself!
Get a jumpstart on your business plan by creating your own cash flow projection .
4. To prove the viability of the business
Many businesses are created out of passion, and while passion can be a great motivator, it’s not a great proof point.
Planning out exactly how you’re going to turn that vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between concept and reality. Business plans can help you confirm that your grand idea makes sound business sense.

A critical component of your business plan is the market research section. Market research can offer deep insight into your customers, your competitors, and your chosen industry. Not only can it enlighten entrepreneurs who are starting up a new business, but it can also better inform existing businesses on activities like marketing, advertising, and releasing new products or services.
Want to prove there’s a market gap? Here’s how you can get started with market research.
5. To set better objectives and benchmarks
Without a business plan, objectives often become arbitrary, without much rhyme or reason behind them. Having a business plan can help make those benchmarks more intentional and consequential. They can also help keep you accountable to your long-term vision and strategy, and gain insights into how your strategy is (or isn’t) coming together over time.
6. To communicate objectives and benchmarks
Whether you’re managing a team of 100 or a team of two, you can’t always be there to make every decision yourself. Think of the business plan like a substitute teacher, ready to answer questions any time there’s an absence. Let your staff know that when in doubt, they can always consult the business plan to understand the next steps in the event that they can’t get an answer from you directly.
Sharing your business plan with team members also helps ensure that all members are aligned with what you’re doing, why, and share the same understanding of long-term objectives.
7. To provide a guide for service providers
Small businesses typically employ contractors , freelancers, and other professionals to help them with tasks like accounting , marketing, legal assistance, and as consultants. Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, while ensuring everyone is on the same page.
8. To secure financing
Did you know you’re 2.5x more likely to get funded if you have a business plan?If you’re planning on pitching to venture capitalists, borrowing from a bank, or are considering selling your company in the future, you’re likely going to need a business plan. After all, anyone that’s interested in putting money into your company is going to want to know it’s in good hands and that it’s viable in the long run. Business plans are the most effective ways of proving that and are typically a requirement for anyone seeking outside financing.
Learn what you need to get a small business loan.
9. To better understand the broader landscape
No business is an island, and while you might have a strong handle on everything happening under your own roof, it’s equally important to understand the market terrain as well. Writing a business plan can go a long way in helping you better understand your competition and the market you’re operating in more broadly, illuminate consumer trends and preferences, potential disruptions and other insights that aren’t always plainly visible.
10. To reduce risk
Entrepreneurship is a risky business, but that risk becomes significantly more manageable once tested against a well-crafted business plan. Drawing up revenue and expense projections, devising logistics and operational plans, and understanding the market and competitive landscape can all help reduce the risk factor from an inherently precarious way to make a living. Having a business plan allows you to leave less up to chance, make better decisions, and enjoy the clearest possible view of the future of your company.
Understanding the importance of a business plan
Now that you have a solid grasp on the “why” behind business plans, you can confidently move forward with creating your own.
Remember that a business plan will grow and evolve along with your business, so it’s an important part of your whole journey—not just the beginning.
Related Posts
Now that you’ve read up on the purpose of a business plan, check out our guide to help you get started.

The information and tips shared on this blog are meant to be used as learning and personal development tools as you launch, run and grow your business. While a good place to start, these articles should not take the place of personalized advice from professionals. As our lawyers would say: “All content on Wave’s blog is intended for informational purposes only. It should not be considered legal or financial advice.” Additionally, Wave is the legal copyright holder of all materials on the blog, and others cannot re-use or publish it without our written consent.

Do you REALLY need a business plan?
The top three questions that I get asked most frequently as a professional business plan writer will probably not surprise you:
- What is the purpose of a business plan – why is it really required?
- How is it going to benefit my business if I write a business plan?
- Is a business plan really that important – how can I actually use it?
Keep reading to get my take on what the most essential advantages of preparing a business plan are—and why you may (not) need to prepare one.
The importance, purpose and benefit of a business plan is in that it enables you to validate a business idea, secure funding, set strategic goals – and then take organized action on those goals by making decisions, managing resources, risk and change, while effectively communicating with stakeholders.
Let’s take a closer look at how each of the important business planning benefits can catapult your business forward:
1. Validate Your Business Idea
The process of writing your business plan will force you to ask the difficult questions about the major components of your business, including:
- External: industry, target market of prospective customers, competitive landscape
- Internal: business model, unique selling proposition, operations, marketing, finance
Business planning connects the dots to draw a big picture of the entire business.
And imagine how much time and money you would save if working through a business plan revealed that your business idea is untenable. You would be surprised how often that happens – an idea that once sounded so very promising may easily fall apart after you actually write down all the facts, details and numbers.
While you may be tempted to jump directly into start-up mode, writing a business plan is an essential first step to check the feasibility of a business before investing too much time and money into it. Business plans help to confirm that the idea you are so passionate and convinced about is solid from business point of view.
Take the time to do the necessary research and work through a proper business plan. The more you know, the higher the likelihood that your business will succeed.
2. Set and Track Goals
Successful businesses are dynamic and continuously evolve. And so are good business plans that allow you to:
- Priorities: Regularly set goals, targets (e.g., sales revenues reached), milestones (e.g. number of employees hired), performance indicators and metrics for short, mid and long term
- Accountability: Track your progress toward goals and benchmarks
- Course-correction: make changes to your business as you learn more about your market and what works and what does not
- Mission: Refer to a clear set of values to help steer your business through any times of trouble
Essentially, business plan is a blueprint and an important strategic tool that keeps you focused, motivated and accountable to keep your business on track. When used properly and consulted regularly, it can help you measure and manage what you are working so hard to create – your long-term vision.
As humans, we work better when we have clear goals we can work towards. The everyday business hustle makes it challenging to keep an eye on the strategic priorities. The business planning process serves as a useful reminder.
3. Take Action
A business plan is also a plan of action . At its core, your plan identifies where you are now, where you want your business to go, and how you will get there.
Planning out exactly how you are going to turn your vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between an idea and reality. Success comes not only from having a vision but working towards that vision in a systematic and organized way.
A good business plan clearly outlines specific steps necessary to turn the business objectives into reality. Think of it as a roadmap to success. The strategy and tactics need to be in alignment to make sure that your day-to-day activities lead to the achievement of your business goals.
4. Manage Resources
A business plan also provides insight on how resources required for achieving your business goals will be structured and allocated according to their strategic priority. For example:
Large Spending Decisions
- Assets: When and in what amount will the business commit resources to buy/lease new assets, such as computers or vehicles.
- Human Resources: Objectives for hiring new employees, including not only their pay but how they will help the business grow and flourish.
- Business Space: Information on costs of renting/buying space for offices, retail, manufacturing or other operations, for example when expanding to a new location.
Cash Flow It is essential that a business carefully plans and manages cash flows to ensure that there are optimal levels of cash in the bank at all times and avoid situations where the business could run out of cash and could not afford to pay its bills.
Revenues v. Expenses In addition, your business plan will compare your revenue forecasts to the budgeted costs to make sure that your financials are healthy and the business is set up for success.
5. Make Decisions
Whether you are starting a small business or expanding an existing one, a business plan is an important tool to help guide your decisions:
Sound decisions Gathering information for the business plan boosts your knowledge across many important areas of the business:
- Industry, market, customers and competitors
- Financial projections (e.g., revenue, expenses, assets, cash flow)
- Operations, technology and logistics
- Human resources (management and staff)
- Creating value for your customer through products and services
Decision-making skills The business planning process involves thorough research and critical thinking about many intertwined and complex business issues. As a result, it solidifies the decision-making skills of the business owner and builds a solid foundation for strategic planning , prioritization and sound decision making in your business. The more you understand, the better your decisions will be.
Planning Thorough planning allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time , prepare for anticipate problems before they arise, and ensure that any tactical solutions are in line with the overall strategy and goals.
If you do not take time to plan, you risk becoming overwhelmed by countless options and conflicting directions because you are not unclear about the mission , vision and strategy for your business.
6. Manage Risk
Some level of uncertainty is inherent in every business, but there is a lot you can do to reduce and manage the risk, starting with a business plan to uncover your weak spots.
You will need to take a realistic and pragmatic look at the hard facts and identify:
- Major risks , challenges and obstacles that you can expect on the way – so you can prepare to deal with them.
- Weaknesses in your business idea, business model and strategy – so you can fix them.
- Critical mistakes before they arise – so you can avoid them.
Essentially, the business plan is your safety net . Naturally, business plan cannot entirely eliminate risk, but it can significantly reduce it and prepare you for any challenges you may encounter.
7. Communicate Internally
Attract talent For a business to succeed, attracting talented workers and partners is of vital importance.
A business plan can be used as a communication tool to attract the right talent at all levels, from skilled staff to executive management, to work for your business by explaining the direction and growth potential of the business in a presentable format.
Align performance Sharing your business plan with all team members helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page when it comes to the long-term vision and strategy.
You need their buy-in from the beginning, because aligning your team with your priorities will increase the efficiency of your business as everyone is working towards a common goal .
If everyone on your team understands that their piece of work matters and how it fits into the big picture, they are more invested in achieving the objectives of the business.
It also makes it easier to track and communicate on your progress.
Share and explain business objectives with your management team, employees and new hires. Make selected portions of your business plan part of your new employee training.
8. Communicate Externally
Alliances If you are interested in partnerships or joint ventures, you may share selected sections of your plan with the potential business partners in order to develop new alliances.
Suppliers A business plan can play a part in attracting reliable suppliers and getting approved for business credit from suppliers. Suppliers who feel confident that your business will succeed (e.g., sales projections) will be much more likely to extend credit.
In addition, suppliers may want to ensure their products are being represented in the right way .
Professional Services Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, including attorneys, accountants, and other professional consultants as needed, to make sure that everyone is on the same page.
Advisors Share the plan with experts and professionals who are in a position to give you valuable advice.
Landlord Some landlords and property managers require businesses to submit a business plan to be considered for a lease to prove that your business will have sufficient cash flows to pay the rent.
Customers The business plan may also function as a prospectus for potential customers, especially when it comes to large corporate accounts and exclusive customer relationships.
9. Secure Funding
If you intend to seek outside financing for your business, you are likely going to need a business plan.
Whether you are seeking debt financing (e.g. loan or credit line) from a lender (e.g., bank or financial institution) or equity capital financing from investors (e.g., venture or angel capital), a business plan can make the difference between whether or not – and how much – someone decides to invest.
Investors and financiers are always looking at the risk of default and the earning potential based on facts and figures. Understandably, anyone who is interested in supporting your business will want to check that you know what you are doing, that their money is in good hands, and that the venture is viable in the long run.
Business plans tend to be the most effective ways of proving that. A presentation may pique their interest , but they will most probably request a well-written document they can study in detail before they will be prepared to make any financial commitment.
That is why a business plan can often be the single most important document you can present to potential investors/financiers that will provide the structure and confidence that they need to make decisions about funding and supporting your company.
Be prepared to have your business plan scrutinized . Investors and financiers will conduct extensive checks and analyses to be certain that what is written in your business plan faithful representation of the truth.
10. Grow and Change
It is a very common misconception that a business plan is a static document that a new business prepares once in the start-up phase and then happily forgets about.
But businesses are not static. And neither are business plans. The business plan for any business will change over time as the company evolves and expands .
In the growth phase, an updated business plan is particularly useful for:
Raising additional capital for expansion
- Seeking financing for new assets , such as equipment or property
- Securing financing to support steady cash flows (e.g., seasonality, market downturns, timing of sale/purchase invoices)
- Forecasting to allocate resources according to strategic priority and operational needs
- Valuation (e.g., mergers & acquisitions, tax issues, transactions related to divorce, inheritance, estate planning)
Keeping the business plan updated gives established businesses better chance of getting the money they need to grow or even keep operating.
Business plan is also an excellent tool for planning an exit as it would include the strategy and timelines for a transfer to new ownership or dissolution of the company.
Also, if you ever make the decision to sell your business or position yourself for a merger or an acquisition , a strong business plan in hand is going to help you to maximize the business valuation.
Valuation is the process of establishing the worth of a business by a valuation expert who will draw on professional experience as well as a business plan that will outline what you have, what it’s worth now and how much will it likely produce in the future.
Your business is likely to be worth more to a buyer if they clearly understand your business model, your market, your assets and your overall potential to grow and scale .
Related Questions
Business plan purpose: what is the purpose of a business plan.
The purpose of a business plan is to articulate a strategy for starting a new business or growing an existing one by identifying where the business is going and how it will get there to test the viability of a business idea and maximize the chances of securing funding and achieving business goals and success.
Business Plan Benefits: What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan benefits businesses by serving as a strategic tool outlining the steps and resources required to achieve goals and make business ideas succeed, as well as a communication tool allowing businesses to articulate their strategy to stakeholders that support the business.
Business Plan Importance: Why is business plan important?
The importance of a business plan lies in it being a roadmap that guides the decisions of a business on the road to success, providing clarity on all aspects of its operations. This blueprint outlines the goals of the business and what exactly is needed to achieve them through effective management.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
The Undeniable Importance of a Business Plan
We often hear about business plans in the context of early-stage companies; however, constructing excellent business plans is difficult and time-consuming, so many entrepreneurs avoid them. But, is this a mistake?
While most people may be aware of the “soft” arguments for and against writing a business plan, in this article, a Toptal Finance Expert takes a data-driven approach to addressing the debate. In it, he finds strong evidence to support the notion that writing an excellent business plan is time well spent.
By Sean Heberling
Sean has analyzed 10,000+ companies, built complex models, and helped facilitate $1+ billion in investment transactions.
PREVIOUSLY AT
Executive Summary
- Individuals who write business plans are 2.5x as likely to start businesses.
- Business planning improves corporate executive satisfaction with corporate strategy development.
- Angels and venture capitalists value business plans and their [financial models](https://www.toptal.com/finance/tutorials/what-is-a-financial-model).
- Companies who complete business plans are 2.5x as likely to get funded.
- Even if a small-scale early-stage venture seeking just $250,000 in capital spent almost $40,000 on business planning and another almost $40,000 on capital raising, it should still expect to "break even" on a probability-weighted basis.
- Larger early-stage ventures enjoy extraordinary probability-weighted returns on investment from business planning. Because the target net capital so greatly exceeds the money spent on business planning, the prospective ROI is huge.
- Company Overview: An explanation of why your company is relevant and the need you are addressing.
- Market Overview: A description of the state of your market and its important trends, a detailed description of your customers, and a description of your current competitors and their advantages.
- Product/Service Overview: A description of your product(s), how they compete with other brands, why they are needed, and why customers will pay a fair economic value for it.
- Financial Projections: Three thorough financial plans with conservative, moderate, and optimistic assumptions.
- The process of writing forces the author to ask introspectively how they reached their conclusions and each of the sub-conclusions along the way because they must explain their logic to a cynical reader.
- The written author needs to support all conclusions with facts and logic to prove that they are not "making it up" or relying upon popular "myths."
- Outlined reports and outlined business plans are not generally subject to the same level of reader scrutiny.
We often hear about business plans in the context of early-stage companies , but constructing excellent business plans is difficult and time-consuming, so many entrepreneurs avoid them. That’s a mistake, as there is strong evidence demonstrating that business plans generate positive returns on time and money invested .
The business world has long debated the importance of business plans, and most involved understand the “soft” arguments. However, this article delves into the data to conclude that writing an excellent business plan is time well spent. I developed a similar view over my 20+ year financial career , during which I have analyzed well over 10,000 different types of companies. I have noticed that while a business plan may not be required for a venture to become successful, having one does seem to greatly improve the probability of successful outcomes.
Expert Opinions Support the Value of Business Planning
Expert opinions support the four following conclusions:
- Angels and venture capitalists value business plans and their financial models.
Individuals Who Write Business Plans Are 2.5x More Likely to Become Entrepreneurs
Many people have business ideas over the course of their careers, but often, these ideas never come to fruition, or they get lost amidst our daily obligations. Interestingly, studies support the notion that those who write business plans are far more likely to launch their companies. Data from the Panal Study of Entrepreneurial Dynamics in fact suggests that business planners were 2.5x as likely to get into business . The study, which surveyed more than 800 people across the United States who were in the process of starting businesses, therefore concluded that “writing a plan greatly increased the chances that a person would actually go into business.”
Of course, causation of this phenomenon is hard to pin down. There are several different possible reasons why this correlation between writing business plans and actually starting a business may exist. But William Gartner, Clemson University Entrepreneurship Professor and author of the Panal Study, believes that “‘research shows that business plans are all about walking the walk. People who write business plans also do more stuff.’ And doing more stuff, such as researching markets and preparing projections, increases the chances an entrepreneur will follow through.”
Research shows that business plans are all about walking the walk. People who write business plans also do more stuff. And doing more stuff, such as researching markets and preparing projections, increases the chances an entrepreneur will follow through.
William Bygrave, a professor emeritus at Babson College, reached a similar conclusion despite having previously shown “that entrepreneurs who began with formal plans had no greater success than those who started without them.” Bygrave does admit, however, that “40% of Babson students who have taken the college’s business plan writing course go on to start businesses after graduation, twice the rate of those who didn’t study plan writing.”
Business Planning Improves Corporate Executive Satisfaction
Another important way in which business plans can provide tangible help is by aligning everyone in an organization with the vision and strategy going forward. And this, in turn, has important ramifications on corporate executive satisfaction. A study by McKinsey & Company which surveyed nearly 800 corporate executives across a range of industries confirms this conclusion. In it, McKinsey found that “formal strategic-planning processes play an important role in improving overall satisfaction with strategy development. That role can be seen in the responses of the 79 percent of managers who claimed that the formal planning process played a significant role in developing strategies and were satisfied with the approach of their companies, compared with only 21 percent of the respondents who felt that the process did not play a significant role. Looked at another way, 51% of the respondents whose companies had no formal process were dissatisfied with their approach to the development of strategy, against only 20% of those at companies with a formal process.”
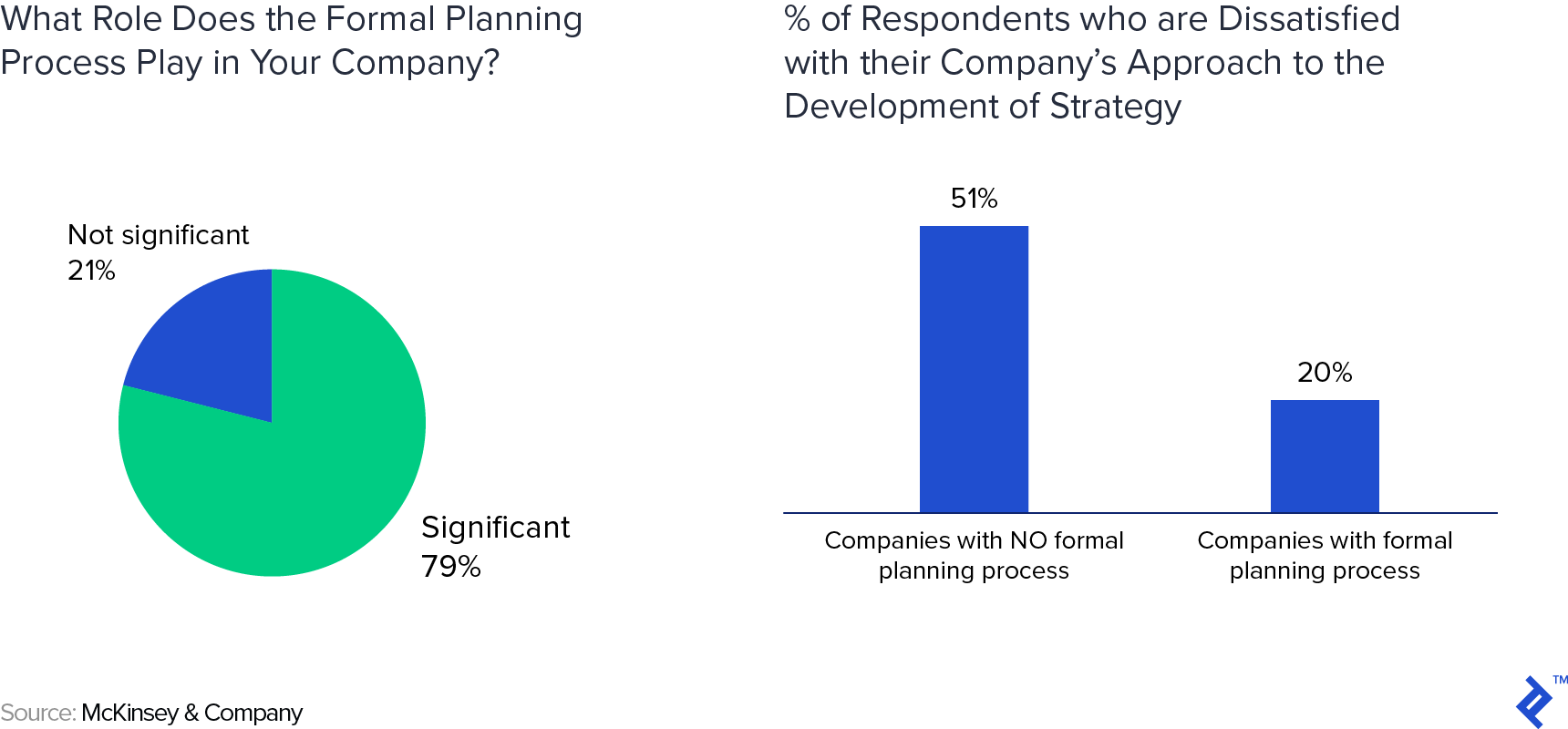
Of course, not all planning is equal. Planning just for the sake of planning doesn’t have the desired effects. As McKinsey itself noted in their study, “Just 45% of the respondents said they were satisfied with the strategic planning process. Moreover, only 23% indicated that major strategic decisions were made within its confines. Given these results, managers might well be tempted to jettison the planning process altogether.” As such, entrepreneurs and business managers should take the time and effort required to put together a well-written and well-researched business plan. Later in the article, I outline some of the elements of a well-written plan.
Business Plans and Their Financial Models Are Valuable to Angels and Venture Capitalists
Many entrepreneurs will eventually need to raise outside capital to grow and develop their businesses. In my experience, a business plan is a crucial tool in maximizing the chances of raising money from external investors. A well-written plan not only helps investors understand your business and your vision, but also shows them that you’ve taken the time to carefully assess and think through the issues your business will face, as well as the more detailed questions surrounding the economics and fundamentals of your business model.
Nathan Beckford, CFA, is the CEO of FounderSuite, the funding stack used by startups in Y Combinator, TechStars, 500s, and more to raise over $750 million. Nathan illustrates the above point nicely in an email he wrote to me recently: “Prior to starting Foundersuite.com, I ran a startup consulting business called VentureArchetypes.com. For the first few years, our primary business was cranking out bold, bullish, beautifully-written business plans for startups to present to investors. Around the mid-2000s, business plans started to go out of favor as the ‘Lean Startup’ methodology became popular. Instead of a written plan, we saw a huge uptick in demand for detailed financial models. Bottom line, I still see value in taking time to be contemplative and strategic before launching a startup. Does that need to be in the form of a 40-page written document? No. But if that’s the format that best works for you, and it can help you model scenarios and ‘see around the corner’ then that’s valuable.”
Nathan and I have frequently interacted, as I maintain a subscription to FounderSuite, software I use when running capital campaigns for early-stage companies on whose boards I sit, or when raising capital for my own firm’s investment projects. Nathan’s feedback is helpful, as he frequently interacts with thousands of entrepreneurs simultaneously running capital campaigns, providing him with a great perspective on which approaches work and which don’t. Clearly, he sees that financial models and business plans in some form help entrepreneurs raise capital.
Companies Who Complete Business Plans Are 2.5x as Likely to Get Funded
Following the section above, naturally, if business plans are useful to outside investors, these are therefore likely to also increase one’s chances of successfully raising capital. A study by Palo Alto Software confirms this hypothesis. The study showed that although 65% of entrepreneurs had NOT completed business plans, the ones who had were twice as likely to have secured funding for their businesses.
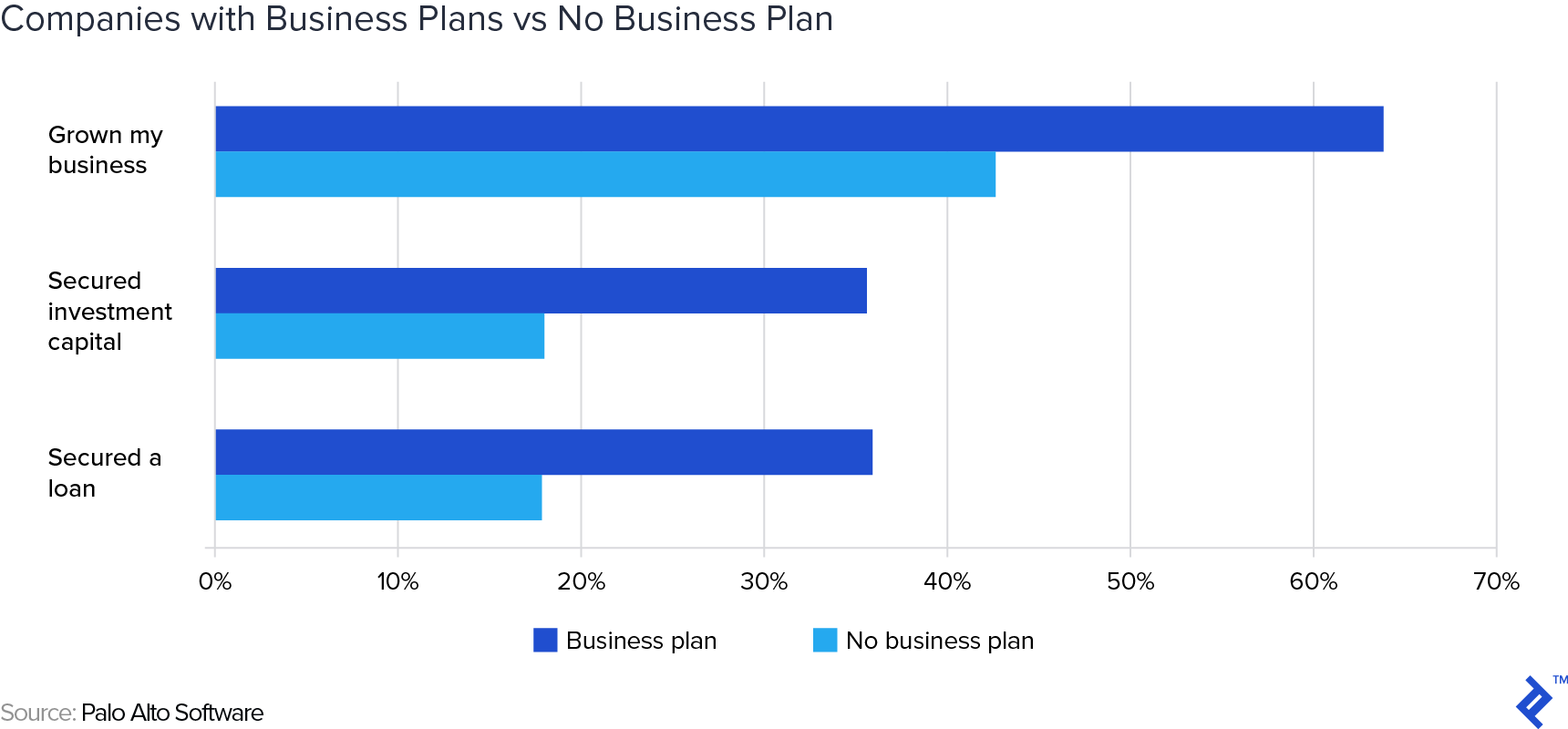
This study surveyed 2,877 entrepreneurs. Of those, 995 had completed business plans, with 297 of them (30%) having secured loans, 280 of them (28%) having secured investment capital, and 499 of them (50%) having grown their businesses. Contrast these percentages with the results for the 1,882 entrepreneurs who had not completed business plans, where just 222 of them (12%) had secured loans, 219 of them (12%) had secured investment capital, and 501 of them (27%) had grown their businesses. (Note that the percentages among the business plan population sum to over 100% because of some overlap between each of the sub-categories.) These results led the study authors to conclude that “Except in a small number of cases, business planning appeared to be positively correlated with business success as measured by our variables. While our analysis cannot say that completing a business plan will lead to success, it does indicate that the type of entrepreneur who completes a business plan is also more likely to run a successful business.”
Calculating the Return on Investment for Business Planning
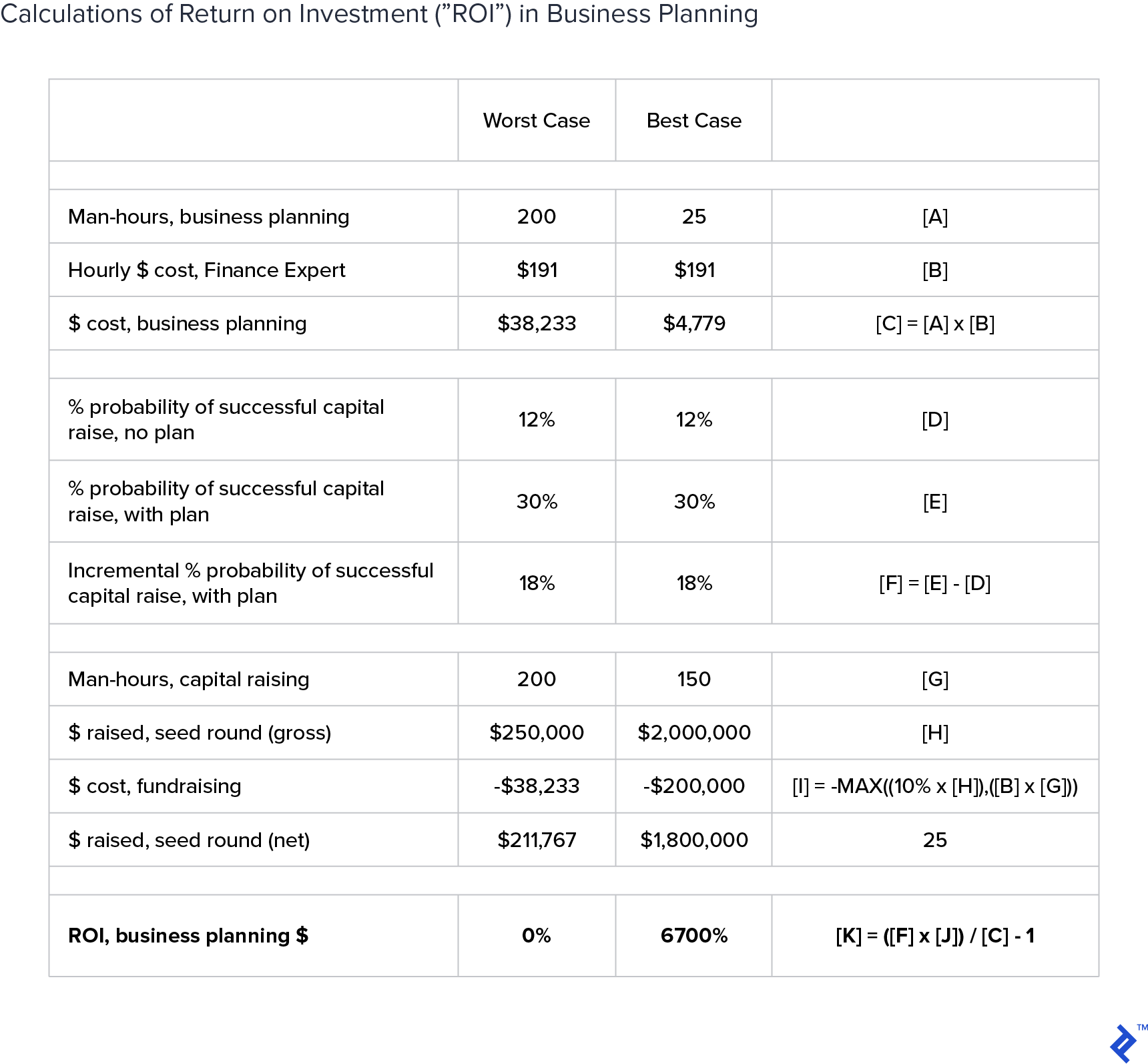
The data and studies outlined above all serve to prove something that I have come to understand very clearly throughout my career. Nevertheless, I still often find that startups struggle with the idea of having to put together a business plan, and in particular with the option of hiring an outside professional to help them do that. As such, I quantified the ROI of such an activity, using data and numbers based on my many years of business consulting. The results of the exercise are summarized in the table at the end of the section, but there are two overarching conclusions:
- Even a small-scale early-stage company can “afford” to pay a finance expert $191 per hour both to create a business plan and to guide the capital raising process, at worst “breaking even” on the investment.
- Larger early-stage companies can expect significant returns on investments in business planning, perhaps as much as 6,700% (67x the amount of money invested).
Diving into the analysis, my inputs included:
- My professional experience with writing business plans. I have spent 25 - 200 hours apiece creating business plans I feel comfortable sharing with founders, advisors, and investors.
- Data from the Palo Alto study discussed earlier in this article. This study showed that 30% of early-stage ventures with business plans had secured funding, 2.5x as great as the 12% of early-stage ventures without business plans who managed to secure funding despite the absence of such plans.
- The hourly rate for a finance expert x (150 to 200 hours) for one round of financing, OR
- 10% of the amount of capital targeted
My analysis illustrates the following:
- Early-stage companies should expect to spend $4,000 - $40,000 on business planning, including the financial modeling associated with it.
- Early-stage companies should expect to spend $30,000 - $200,000 for an initial round of financing between $250,000 and $2 million in size, resulting in net financing of $200,000 - $1.8 million.
- Even if a small-scale early-stage venture seeking just $250,000 in capital spent almost $40,000 on business planning and another almost $40,000 on capital raising, it should still expect to “break even” on a probability-weighted basis. In other words, because the odds of success with a professional business plan are 2.5x greater than without one, small-scale early-stage ventures can justify such a significant investment. This also assumes NO additional odds for success from engaging a professional to coordinate the fundraising effort. I suspect that doing so may push the odds of success from 12% without a business plan and 30% with a business plan to above 50%. It is also likely that a smaller-scale venture may require significantly fewer hours for business planning and capital raising that what is outlined in the “worst case” below.
- Larger early-stage ventures enjoy extraordinary probability-weighted returns on investment from business planning. Because the target net capital so greatly exceeds the money spent on business planning, the prospective ROI is huge, and this analysis just assumes ONE round of equity financing. Most successful startups will experience several rounds of financing.
Thoughts on Writing an Excellent Business Plan
An extensive overview of how to write an excellent business plan is beyond the scope of this article. However, here are two key thoughts that have emerged from my years of experience with startups.
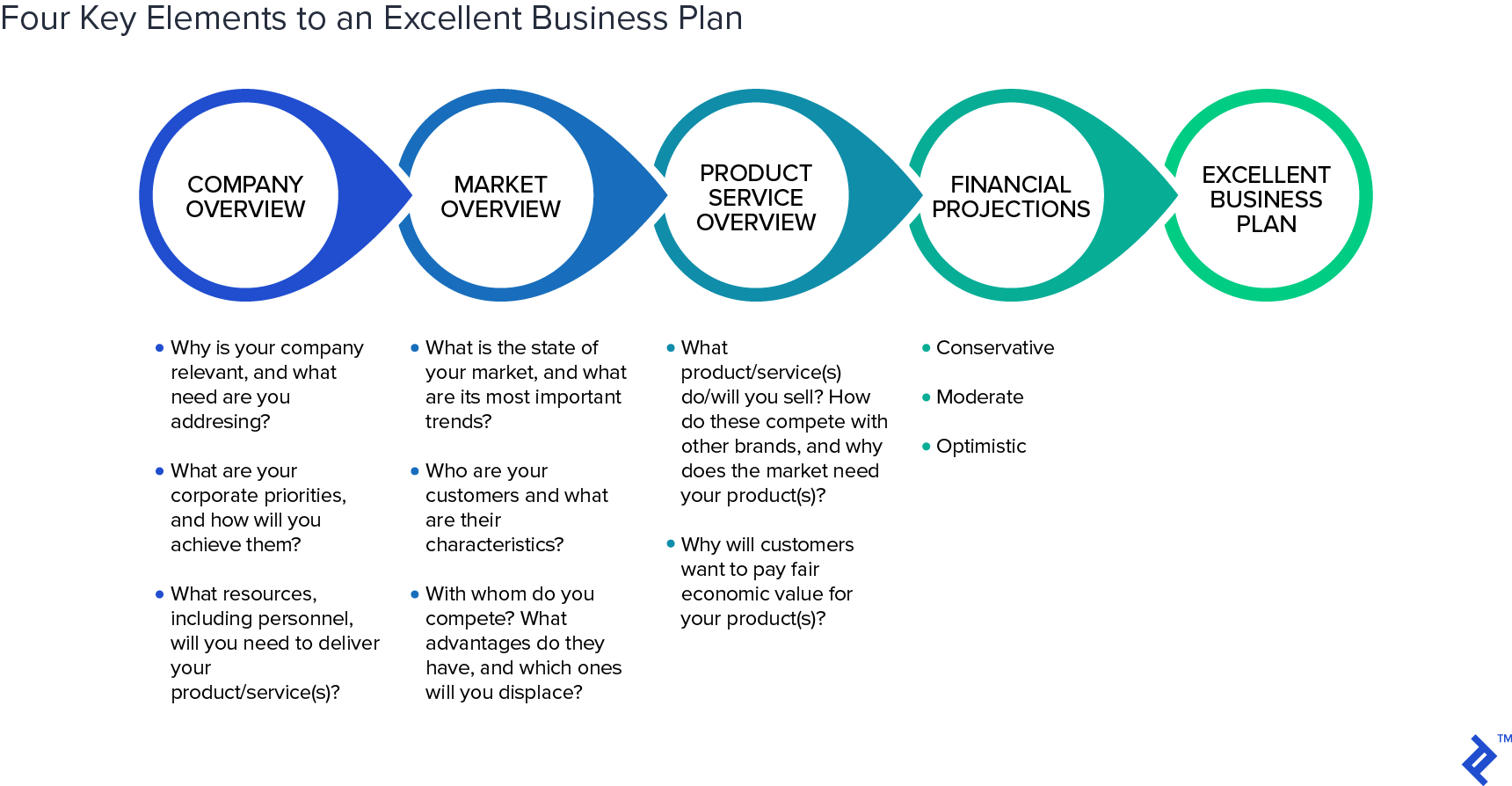
First, there are four common elements to an excellent business plan. In Alan Hall’s Forbes article, “ How to Build a Billion Dollar Business Plan: 10 Top Points ,” he interviews Thomas Harrison, Chairman of Diversified Agency Services, an Omnicom division that has purchased “a vast number of firms,” to share his views on the key elements of a great business plan. Although each of these ten elements is essential, I reorganized the list into four broad categories:
1. Company Overview
- An explanation of why your company is relevant and the need are you addressing
- A description of corporate priorities and the processes to achieve them.
- An overview of the various resources, including the people that will be needed, to deliver what’s expected by the customer.
2. Market Overview
- A description of the state of your market and its important trends.
- A detailed description of your customers.
- A description of your current competitors and their advantages. Which ones will you displace?
3. Product/Service Overview
- A description of your products, how they compete with other brands, and why they are needed.
- An explanation of why customers will pay a fair economic value for your product or service. This element is conspicuously absent from some of today’s most expensive unicorns. Companies such as Uber and Tesla are losing massive amounts of money on rapidly growing sales because these companies may not be selling their services/products for fair economic value. Of course, sales grow rapidly when customers can buy your services/products for far less than their fair economic values!
4. Financial Projections
- Conservative
- Each scenario should have realistic and achievable sales, margins, expenses, and profits on monthly, quarterly, and annual bases. Again, these elements appear to be conspicuously absent from some of today’s most expensive unicorns.
Second, written business plans are superior to those just “outlined.” As an adjunct professor of finance for Villanova University, I require my students to write research reports prior to developing slide decks to present their findings from a full semester of industry research. The process of writing forces the authors to ask themselves how they reached their conclusions and each of the sub-conclusions along the way because they must explain their logic to cynical readers. The written authors need to support their conclusions with facts and logic to prove that they are not “making it up” or relying upon popular “myths.” Outlined reports and outlined business plans are not generally subject to the same level of reader scrutiny. Therefore, written business plans are superior to those just “outlined.” Outlined plans are often kept on 10-12 slide decks, and the slide deck is an important tool in the capital raising process, but the written business plan that stands behind it will differentiate an entrepreneur from their seemingly infinite competition.
Parting Thoughts
Some argue that many public multi-billion-dollar companies such as Apple or Google never had formal business plans before they started, but this argument is flawed because most of these companies likely developed business plans either during the solicitation of venture capital or during the process of going public. Apple and Google were both funded with venture capital, and soliciting venture capital involves business planning. The founders of Apple and Google likely created financial projections and outlined strategic paths.
Moreover, Apple and Google are both public companies, and going public involves business planning. Underwriters employ research analysts creating financial forecasts based on business plans projected by management at the companies going public. Buy-side firms purchasing and holding shares in newly public companies create forecasts based upon the business plans projected by public company management teams.
Admittedly, you don’t need a written business plan to have a successful company. You may not even need a business plan at all to have a successful company. However, the probability of success without a business plan is much lower. Angels and venture capitalists like to know about your business plan, and public companies need to project business plans to persuade underwriters and investors to purchase their securities.
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
- Creating a Narrative from Numbers
- Business Plan Consultants: Who They Are and How They Create Value
- Building a Business Continuity Plan
- Building the Next Big Thing: A Guide to Business Idea Development
- Mission Statements: How Effectively Used Intangible Assets Create Corporate Value
Understanding the basics
Why it is important to have a business plan.
Expert opinions and numerous studies show that business plans improve corporate satisfaction, are useful for angel investors and venture capitalists, and increase a company’s chances of raising capital by 2.5x.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
Individuals who write business plans are 2.5x as likely to start businesses. Moreover, business planning improves corporate executive satisfaction with corporate strategy development. Finally, investors value business plans, making the chances of raising capital 2.5x greater.
What does an investor look for in a business plan?
The four key sections of a business plan are: the company overview, a market overview, your product/service overview, and the financial projections.
- BusinessPlan
Sean Heberling
Bryn Mawr, PA, United States
Member since October 18, 2017
About the author
World-class articles, delivered weekly.
Subscription implies consent to our privacy policy
Toptal Finance Experts
- Blockchain Consultants
- Business Management Consultants
- Business Plan Consultants
- Business Process Optimization Consultants
- Certified Public Accountants (CPA)
- Economic Development Consultants
- Equity Research Analysts
- Excel Experts
- Financial Benchmarking Consultants
- Financial Forecasting Experts
- Financial Modeling Consultants
- Financial Writers
- Fintech Consultants
- FP&A Consultants
- Fractional CFOs
- Fundraising Consultants
- FX Consultants
- Growth Strategy Consultants
- Integrated Business Planning Consultants
- Interim CFOs
- Investment Managers
- Investment Thesis Consultants
- Investor Relations Consultants
- M&A Consultants
- Market Sizing Experts
- Pitch Deck Consultants
- Private Equity Consultants
- Procurement Consultants
- Profitability Analysis Experts
- Real Estate Experts
- Restructuring Consultants
- Risk Management Consultants
- Small Business Consultants
- Supply Chain Management Consultants
- Valuation Specialists
- Venture Capital Consultants
- Virtual CFOs
- Xero Experts
- View More Freelance Finance Experts
Join the Toptal ® community.
Just in Time for Spring 🌻 50% Off for 3 Months. BUY NOW & SAVE
50% Off for 3 Months Buy Now & Save
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Automatically track your mileage and never miss a mileage deduction again
Time-saving all-in-one bookkeeping that your business can count on
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Organized and professional, helping you stand out and win new clients
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
Pay your employees and keep accurate books with Payroll software integrations
- Team Management
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Freelancers
- Self-Employed Professionals
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Marketing & Agencies
- Construction & Trades
- IT & Technology
- Business & Prof. Services
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs QuickBooks
- FreshBooks vs HoneyBook
- FreshBooks vs Harvest
- FreshBooks vs Wave
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Free Invoice Generator
- Invoice Templates
- Accounting Templates
- Business Name Generator
- Estimate Templates
- Help Center
- Business Loan Calculator
- Mark Up Calculator
Call Toll Free: 1.866.303.6061
1-888-674-3175
- All Articles
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Bookkeeping
Resources for Your Growing Business
The importance of business plan: 5 key reasons.
A key part of any business is its business plan. They can help define the goals of your business and help it reach success. A good business plan can also help you develop an adequate marketing strategy. There are a number of reasons all business owners need business plans, keep reading to learn more!
Here’s What We’ll Cover:
What Is a Business Plan?
5 reasons you need a well-written business plan, how do i make a business plan, key takeaways.
A business plan contains detailed information that can help determine its success. Some of this information can include the following:
- Market analysis
- Cash flow projection
- Competitive analysis
- Financial statements and financial projections
- An operating plan
A solid business plan is a good way to attract potential investors. It can also help you display to business partners that you have a successful business growing. In a competitive landscape, a formal business plan is your key to success.

Check out all of the biggest reasons you need a good business plan below.
1. To Secure Funding
Whether you’re seeking funding from a venture capitalist or a bank, you’ll need a business plan. Business plans are the foundation of a business. They tell the parties that you’re seeking funding from whether or not you’re worth investing in. If you need any sort of outside financing, you’ll need a good business plan to secure it.
2. Set and Communicate Goals
A business plan gives you a tangible way of reviewing your business goals. Business plans revolve around the present and the future. When you establish your goals and put them in writing, you’re more likely to reach them. A strong business plan includes these goals, and allows you to communicate them to investors and employees alike.
3. Prove Viability in the Market
While many businesses are born from passion, not many will last without an effective business plan. While a business concept may seem sound, things may change once the specifics are written down. Often, people who attempt to start a business without a plan will fail. This is because they don’t take into account all of the planning and funds needed to get a business off of the ground.
Market research is a large part of the business planning process. It lets you review your potential customers, as well as the competition, in your field. By understanding both you can set price points for products or services. Sometimes, it may not make sense to start a business based on the existing competition. Other times, market research can guide you to effective marketing strategies that others lack. To have a successful business, it has to be viable. A business plan will help you determine that.
4. They Help Owners Avoid Failure
Far too often, small businesses fail. Many times, this is due to the lack of a strong business plan. There are many reasons that small businesses fail, most of which can be avoided by developing a business plan. Some of them are listed below, which can be avoided by having a business plan:
- The market doesn’t need the business’s product or service
- The business didn’t take into account the amount of capital needed
- The market is oversaturated
- The prices set by the business are too high, pushing potential customers away
Any good business plan includes information to help business owners avoid these issues.

5. Business Plans Reduce Risk
Related to the last reason, business plans help reduce risk. A well-thought-out business plan helps reduce risky decisions. They help business owners make informed decisions based on the research they conduct. Any business owner can tell you that the most important part of their job is making critical decisions. A business plan that factors in all possible situations helps make those decisions.
Luckily, there are plenty of tools available to help you create a business plan. A simple search can lead you to helpful tools, like a business plan template . These are helpful, as they let you fill in the information as you go. Many of them provide basic instructions on how to create the business plan, as well.
If you plan on starting a business, you’ll need a business plan. They’re good for a vast number of things. Business plans help owners make informed decisions, as well as set goals and secure funding. Don’t put off putting together your business plan!
If you’re in the planning stages of your business, be sure to check out our resource hub . We have plenty of valuable resources and articles for you when you’re just getting started. Check it out today!
RELATED ARTICLES

Save Time Billing and Get Paid 2x Faster With FreshBooks
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
Get more great content in your Inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive communications from FreshBooks and acknowledge and agree to FreshBook’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time by contacting us at [email protected].
👋 Welcome to FreshBooks
To see our product designed specifically for your country, please visit the United States site.

- Entrepreneurship
- Starting a Business
- My #1 Online Biz
- Business Planning
- Advertising
- Content Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Public Relations
- Business Model
- Financial Forecasting
- Market Research
- Risk Management
- Business Plan
- Conferences
- Online Communities
- Professional Associations
- Social Media
- Human Resource
- Productivity
- Legal Requirements
- Business Structure
- Mission Statement
- Financial Plan
- Market Analysis
- Operational Plan
- SWOT Analysis
- Target Market
- Competitor Analysis
- Customer Profiling
- Market Trends
- Pricing Strategies
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Cooperative
- Corporation
- Limited Liability
The Importance Of Business Planning: A Beginner’s Guide
by Mike Vestil
Business planning is the process of determining the goals and objectives of a business and developing a roadmap to achieve them.
It involves the analysis of current and future market conditions, operational capabilities, financial resources, and other factors that impact business success.
Effective business planning helps entrepreneurs and organizations navigate the complexities of the market and make strategic decisions that increase profitability and longevity.
Whether you are starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a well-crafted business plan is critical to your success.
In this article, we will explore the key components of business planning and provide insights on how to create a plan that meets your specific needs.
Introduction To Business Planning
What is business planning.
A business plan can be described as a document that outlines and describes the goals of a business and the strategies that will be employed to achieve these goals.
It typically includes detailed information about the company, such as the products, services, and customers that it intends to target, as well as an analysis of the market and the competition.
A business plan also describes the financial projections and resources needed to achieve these goals, such as the amount of money that will be invested, the sales projections, and the operational costs.
The purpose of a business plan is to provide a roadmap for the business owner and all stakeholders, including investors, employees, and management teams.
The importance of a business plan cannot be overstated as it serves as a guide to identify and address potential challenges that a business owner may encounter along the way.
Starting and running a business can be a daunting task, but having a well-crafted business plan can help alleviate some of the stress associated with the unknowns of business ownership.
A business plan helps to define and communicate the vision of the business, which can be invaluable to gaining traction with potential investors or partners who can assist in the growth and development of the company.
It also serves as a tool for measuring success as it provides specific goals and objectives that can be compared to actual results.
In conclusion, a well-written business plan is essential to the overall success of a business.
It provides a clear road map of what the business hopes to achieve and how it intends to do so. It serves as a guide for all stakeholders and helps to communicate the vision of the business to potential investors, employees, and partners.
Ultimately, a business plan helps to mitigate potential risks and set the business up for success.
Importance Of Business Planning
Business planning is an essential activity that every organization must engage in irrespective of its nature or size. It helps organizations in setting goals, staying focused, and measuring progress.
There are several reasons why business planning is of great importance, such as guiding decision-making, allocating resources, and identifying potential risks and opportunities.
First and foremost, business planning helps organizations in setting realistic goals and determining the best strategies to achieve them. It provides a roadmap for the future that enables executives and managers to make informed decisions based on available data and market trends.
Additionally, business planning is a critical tool for allocating resources and ensuring that they are used efficiently.
By analyzing financial data and identifying areas of potential wastage, organizations can reduce costs and increase profitability.
Furthermore, business planning is an effective means of identifying potential risks and opportunities that an organization may face.
By conducting a thorough analysis of internal and external factors that may impact the business, organizations can develop contingency plans to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
Another essential aspect of business planning is that it enables organizations to monitor and measure their progress.
Through the use of key performance indicators (KPIs), organizations can track their performance against set objectives and make adjustments where necessary.
This helps to ensure that the organization is on track towards achieving its goals and that everyone within the organization is working towards the same objectives.
Moreover, business planning is a critical tool for securing external funding. Investors and lenders are more likely to invest in organizations that have a well-defined strategy and a clear understanding of their market and industry.
In conclusion, business planning is a critical activity for any organization that wants to thrive in a competitive marketplace.
It provides a framework for decision-making, resource allocation, risk management, and measuring progress. Without a solid business plan, organizations are likely to struggle to achieve their goals, make efficient use of their resources, and identify potential risks and opportunities.
Therefore, it is crucial for organizations to invest time and resources into developing a comprehensive and realistic business plan that reflects their unique strengths, weaknesses, and objectives.
Purpose Of Business Planning
Business planning is a critical aspect of establishing a successful business. The purpose of business planning is to outline the objectives, strategies, and steps necessary to achieve those objectives.
This process involves creating a roadmap for the future of the business, identifying potential obstacles and opportunities, and developing tactics to overcome or leverage them.
Business planning is essential for potential investors, as it provides an overview of the company’s goals and how they plan to achieve them. It also allows for more effective decision-making, as it provides a framework for assessing whether or not certain decisions align with the company’s overall goals.
Similarly, business planning is critical for internal stakeholders, as it helps to establish a shared vision and objective for the company, as well as the roadmap for achieving it.
Ultimately, business planning is a vital tool for any business owner or entrepreneur looking to establish a thriving enterprise in today’s complex and competitive market.
Key Elements Of Business Planning
Executive summary.
The executive summary is a critical component of any business plan, providing a concise yet comprehensive summary of the key elements of the plan.
It should provide a clear and compelling overview of the business, highlighting its unique value proposition, target market, competitive advantages, and key strategies for success.
Key financial projections should also be included, providing investors and other stakeholders with a clear understanding of the anticipated risks and rewards associated with the venture.
The executive summary should be written in a clear and concise manner, using language that is both easy to understand and engaging to the reader.
It should be designed to capture the attention of potential investors, lenders, or other stakeholders, providing them with a clear understanding of the business and its potential for success.
Market Analysis Of Business Planning
The Market Analysis section of a business plan is a crucial component that provides a thorough analysis of the target market, industry trends, competition, and customer base.
This subsection should focus on the target market’s size, demographics, and psychographics, including their purchasing habits, preferences, and behaviors.
The assessment of industry trends involves investigating the direction of the market, identifying opportunities, and assessing the impact of external factors such as economic conditions and government regulations.
The section on competition analysis must provide a detailed analysis of direct and indirect competitors, including their strengths, weaknesses, and market share.
This information can be obtained through the use of surveys, online research, and networking. The subsection should also assess the customer base, including market segmentation, potential growth, and loyalty.
Moreover, the subsection should include a SWOT analysis that examines the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the company.
The analysis should focus on the potential challenges faced by the company as well as the opportunities that can be leveraged to achieve success.
This analysis provides an insight into the company’s competitive position and helps identify areas where the company can improve.
Overall, the Market Analysis section is critical for any business plan as it provides a well-rounded understanding of the target market, industry trends, and competitive landscape.
The information provided in this section can be used to develop a sound business strategy and make informed decisions that drive the company’s success.
Company Description Of A Business Plan
The Company Description subsection of a business plan provides an overview of the company and its history, current status, and future prospects.
It should detail what the company does, what sets it apart from competitors, and how it intends to achieve success. A well-crafted company description should also communicate the company’s core values, mission statement, and vision for the future.
It is important to include any relevant company history and milestones as well as any notable achievements, partnerships, or industry awards.
Additionally, a clear explanation of the management team’s experience and qualifications, including their education, certifications, and industry experience, is essential to demonstrate the company’s capacity to succeed.
Furthermore, the products or services offered by the company and how they meet the needs and desires of customers should also be emphasized.
Overall, a concise and compelling company description sets the foundation for the rest of the business plan and conveys a sense of confidence and expertise to potential investors and stakeholders.
Organization And Management
The Organization and Management subsection is crucial in any business plan as it highlights the structure, roles, and responsibilities of the key personnel who will be at the helm of the organization.
The success of any business is largely dependent on the capabilities of the people managing it.
Therefore, it is essential to outline the experience and expertise of each member of the management team. This subsection should also provide clear information on the ownership structure of the organization, including the distribution of shares or ownership percentages.
It is important to highlight any legal or regulatory requirements that the management needs to fulfill to operate the business effectively.
Additionally, the subsection should explain the key operational and administrative functions, as well as any external professional services that will be necessary to ensure the smooth running of the business.
Service Or Product Line
Service or Product Line is a crucial section of a business plan that outlines the products or services a company intends to offer.
This section must describe the key attributes of the product or service, including its unique features, the target market, and what sets it apart from competitors.
Additionally, this section must touch on the production process and costs, as well as the pricing strategy the company will use to ensure that the product or service is profitable.
A successful business plan must ensure that its offerings add value to the target market and adapt accordingly by conducting market research, understanding the competition, and leveraging innovation to create new and improved products.
Marketing And Sales Of A Business Plan
The Marketing and Sales subsection of a business planning document is designed to outline the strategies that will be used to promote and sell a company’s product or service.
This section should include a market analysis and an explanation of how the company plans to differentiate itself from competitors. The marketing plan should identify target customers, their needs, and the benefits that the product or service will provide.
The sales plan should identify the distribution channels that will be used, as well as the pricing model and the sales team structure.
Additionally, this section should identify any marketing and sales metrics that will be used to measure success, such as conversion rates and lead generation.
It is crucial for companies to have a comprehensive marketing and sales plan in place to ensure that they are able to effectively reach their target audience and drive revenue growth.
Funding Request Of A Business Plan
The Funding Request subsection of a business plan is where the entrepreneur explains their financial needs to potential investors or lenders. This section starts with the amount of money required and how it will be utilized, such as for inventory, facilities, or equipment.
The business owner must provide an accurate estimate of the total costs involved, including monthly expenses and projected revenues.
It is also essential to explain how the funding request will affect the company’s financial position and how it will help achieve the specified goals.
Sometimes, entrepreneurs may need to explain their willingness to give up a portion of their company’s ownership to secure financing.
The funding request should be provided with detailed financial statements and projections to support the proposal.
Moreover, entrepreneurs should also specify the repayment schedule and interest rates if they are looking for loans.
The objective is to persuade potential investors or lenders that the proposed investment is feasible, and the revenue from the company is likely to provide a satisfactory return on investment within an acceptable time frame.
A well-written and researched funding request inspires confidence in potential investors or lenders and increases the entrepreneur’s chance of securing the necessary funds.
Importance Of Financial Projections In Business Plan
The subsection Financial Projections is a crucial aspect of any business plan. It entails forecasting the financial outcomes of the proposed business operations.
Financial projections encompass several critical elements, including income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets.
Accurately projecting financial outcomes is vital for securing funding from investors and financial institutions.
Furthermore, it is a critical tool for managing resources, making critical financial decisions, and monitoring day-to-day financial activities.
When preparing financial projections, it is essential to consider various factors that might influence the outcomes, such as market trends, competition, industry regulations, and other economic indicators.
One critical element that should not be overlooked is setting realistic goals and timelines for achieving the forecasted outcomes.
Additionally, it is essential to prepare alternative scenarios to gauge the impact of unforeseen events on the business’s financial health.
Overall, the Financial Projection subsection provides insights into the potential financial performance of the business and enables entrepreneurs to develop a well-informed roadmap for success.
Appendix Section In A Business Plan
The Appendix section is an optional section that can be included in a business plan. This section provides space to include any additional information that investors or lenders may find useful in evaluating the business plan.
The Appendix can be used to include resumes of key personnel, product or service brochures, legal documents, and any other relevant information that supports the business plan.
It is important to remember that the Appendix should not be used to include information that should be in other sections, but rather to include supplementary information that adds value to the overall plan.
Steps In Business Planning
Step 1: research and analysis.
A crucial step in creating a successful business plan is conducting thorough research and analysis. This step involves collecting and analyzing relevant data from various sources, such as industry reports, customer surveys, and competitor analysis.
The purpose of this research is to gain a deep understanding of the market, identify potential customers, and evaluate market trends and changes.
Analyzing the data collected enables entrepreneurs to identify opportunities and potential threats that their business may face.
Additionally, this step involves evaluating the resources required to establish and run the business, including understanding the costs associated with acquiring and retaining customers, product development, and distribution.
One of the essential factors to consider during the research and analysis stage is the target market. It is important to identify the audience who would be interested in the product or service offered by the business.
Identifying the target market helps entrepreneurs to evaluate the size of the market, the preferences of their potential customers, and the most effective marketing strategies.
Moreover, research provides entrepreneurs with an understanding of customer spending habits and the overall demand for the product.
This knowledge enables entrepreneurs to tailor their business plan to meet the needs of the target market and increase the likelihood of success.
Another critical aspect of the research and analysis stage is evaluating the competition. An analysis of the existing businesses in the industry helps entrepreneurs identify potential rivals.
It also provides insights into the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, their marketing strategies, and the types of products or services they offer.
This information empowers entrepreneurs to develop unique value propositions and competitive advantages that will differentiate their business from others in the market.In summary, research and analysis are the foundation of a successful business plan.
It provides entrepreneurs with a clear understanding of the market, target audience, and competition.
This information enables entrepreneurs to create a comprehensive plan that outlines the steps required to establish and run a profitable business.
Conducting thorough research and analysis is essential to increase the chances of success and minimize the risks associated with starting a new business.
Step 2: Develop A Strategic Plan
The second step in the business planning process is to develop a strategic plan. This is a critical step that involves identifying goals and objectives for the company, as well as the strategies and tactics that will be used to achieve them.
A strategic plan should include a detailed analysis of the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This information can be obtained through market research, customer surveys, and other methods.
Once this analysis is complete, the company can begin to develop a plan for achieving its goals. This should include a detailed description of the company’s products or services, its target market, and its competitors.
It should also include a plan for marketing and sales, as well as financial projections for the next few years.
An important component of the strategic plan is the identification of key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure the success of the plan.
These KPIs should be specific and measurable, and should be reviewed regularly to ensure that the plan is on track.
The strategic plan should also consider the company’s resources, including its human capital, financial resources, and technological infrastructure. It should identify any gaps in these resources and make recommendations for how they can be filled.
Ultimately, the strategic plan should be a living document that is reviewed and updated regularly. As the company grows and changes, the plan should be adjusted accordingly to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Step 3: Create A Business Plan
Step 4: implement the plan.
The actual implementation of a business plan involves executing each step of the strategy. The effectiveness of the plan heavily relies on the satisfaction of the plan’s objectives, the use of realistic timelines, and the deployment of adequate resources.
The business’ management will need to generate functional plans to ensure that resources are allocated optimally. Timelines must also be established for every step of the process to monitor progress and adjust the plan if necessary.
Good communication with all stakeholders is essential to successful implementation. The plan must be communicated to all employees, contractors, and vendors.
The resources, including personnel and funding, must be aligned with the plan. Efficient coordination is necessary to ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal.
Performance measurement is crucial, as adjustment to the plan may be necessary to achieve the intended outcomes.
Technology and software may also be necessary in executing specific strategies, which should be included in the plan.
Addressing challenges and roadblocks along the way may also require flexible thinking and adapting the plan accordingly.
Therefore, the process of implementing a business plan involves evaluating the plan’s success and adaption of the plan to current business operations.
By successfully implementing the plan, the business can achieve its desired outcome and ultimately achieve its end goal.
Step 5: Monitor And Review
After implementing a business plan, monitoring and reviewing are crucial steps to ensure success. This stage is vital because it allows a business owner to determine if their strategies are working effectively or if changes need to be made.
It is an opportunity to observe the strengths and weaknesses of a business, discover any financial or operational problems, and measure progress toward established goals.
Monitoring includes tracking financial performance, sales figures, production levels, and customer satisfaction rates.
Reviewing involves analyzing the data gathered from monitoring activities and implementing changes to improve the business.
Monitoring and reviewing also help with business planning, providing entrepreneurs with a basis for decision-making.
Ongoing tracking and analysis can identify potential areas of growth, new opportunities, and potential risks.
Keeping current with industry trends, competitive analysis, and customer feedback can be included in the monitoring and review process.
By identifying and addressing challenges, a business can stay ahead of the competition and improve operations, products, and services.
Regular reviews act as a preventative measure for changes in the market or industry. Real-time optimization can be applied to marketing campaigns, cost structures, sales techniques, and more.
By consistently monitoring and reviewing, a business owner can take immediate corrective action instead of waiting until it’s too late.
Additionally, reviewing allows for continual improvement by providing insight into potential opportunities for growth and increased profitability.
A monitoring and review system should be established as part of the overall plan. This should include setting benchmarks and metrics, as well as scheduling regular reviews of progress toward established goals.
Once the system is in place, the focus should shift towards utilizing data gathered from monitoring and review activities.
This data should be analyzed, identifying areas that require changes and taking action to implement those changes.
In conclusion, monitoring and reviewing are important elements to ensure the continued success of a business.
Through monitoring and reviewing activities, entrepreneurs can gain a better understanding of their business operations and optimize accordingly.
By utilizing data and implementing changes, businesses can ensure long-term profitability and sustainable growth.
Types Of Business Plans
Startup business plan.
A startup business plan is an essential document that outlines the road map for a new business venture.
It is a comprehensive document that typically includes an executive summary, market analysis, company description, product or service offerings, marketing and sales strategies, financials, and a timeline.
The purpose of the business plan is to help entrepreneurs map out their goals and objectives, identify potential roadblocks, and develop strategies to overcome them.
By creating a startup business plan, entrepreneurs can gain a better understanding of their customers, competitors, and market trends.
In addition, they can use the plan to secure funding from investors or financial institutions, to communicate their vision to potential employees, and to develop a clear and concise strategy for scaling the business.
A well-crafted startup business plan is a crucial component of launching a successful new business venture.
Internal Business Plan
The Internal Business Plan is a critical component of the overall business plan. It outlines the internal strategies and tactics that a company will use to achieve its objectives.
This plan is developed by the management team and guides the day-to-day operations of the company. The Internal Business Plan addresses the company’s marketing, operations, financial, and human resources objectives.
A key part of the plan is developing a clear understanding of the company’s competitive advantage and how it will use this advantage to successfully compete within the marketplace.
The Internal Business Plan is also used to assess the company’s progress toward its goals and to make adjustments to the plan as needed.
This plan is different from the Strategic Business Plan which addresses the direction and overall vision of the company, while the Internal Business Plan is focused on the day-to-day operations.
A successful Internal Business Plan is critical to any start-up business as it provides a roadmap for the company to follow and helps create a culture of accountability and focus on achieving the company’s objectives.
Strategic Business Plan
A strategic business plan is a vital component of any successful business. It outlines a company’s overall direction, goals, and objectives over the long term.
A strategic business plan is not just a document, but rather a roadmap that guides a company’s decision-making processes.
It involves conducting a thorough analysis of a company’s market, competition, resources, and capabilities to create a unique value proposition.
The strategic business plan enables a company to position itself in the market and differentiate itself from competitors. The plan should also outline specific actions that need to be taken to achieve the desired objectives.
The strategic business plan typically includes the mission statement, which defines the company’s purpose, values, and culture.
It should also identify the target market and customer segments, as well as the channels and strategies used to reach them.
The plan should also analyze the competitive landscape, identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) to the business.
One of the critical components of a strategic business plan is setting clear and measurable goals and objectives over the long term.
These should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). The goals and objectives should align with the company’s mission statement and vision, and support the overall strategy.
The strategic plan should also outline the tactics and actions that will be taken to achieve these goals, as well as the timeline and resources required.
Another important element of a strategic business plan is the financial plan. This should include a detailed budget, sales forecast, cost of goods sold, cash flow projection, and profit and loss statement.
The financial plan should also consider contingencies and risk management strategies.
A well-executed strategic business plan can significantly benefit a company’s growth and success.
It provides a clear roadmap for decision-making, enabling a company to make informed and strategic choices.
It also helps to align all stakeholders around a common vision and direction, which can improve employee engagement and motivation.
Finally, a strategic business plan enhances a company’s credibility and reputation, which can attract investors, customers, and partners.
Operations Business Plan
The Operations Business Plan is a crucial component of any business plan, as it details the necessary steps to achieve operational efficiency and success.
This subsection focuses on the day-to-day running of the business, outlining the processes and procedures that will be followed, including production, logistics, inventory management, customer service, and more.
A well-crafted Operations Business Plan should provide clear guidance on how the company will meet its goals, reduce costs, and optimize processes.
One of the key elements of an Operations Business Plan is the production plan, which outlines the processes and resources needed to manufacture products or deliver services to customers.
This plan should include production schedules, quality control measures, and contingency plans in case of unexpected delays or problems.
Additionally, inventory management is crucial to ensure that the business has the appropriate amount of goods on hand, minimizing waste and avoiding shortages.
Another important aspect of an Operations Business Plan is logistics, covering the transport of goods and services from the company to the customers.
Logistics might include shipping, delivery, or other transportation-related activities that can affect the efficiency and effectiveness of the business.
Customer service is also a critical component, ensuring that customers feel valued and satisfied with their interactions with the company.
Efficient operation requires effective management, and an Operations Business Plan should outline the organizational structure of the company, including roles and responsibilities of staff members.
Clear communication and collaboration among team members are essential to ensuring that the business runs smoothly and effectively.
Overall, a well-conceived Operations Business Plan is a fundamental component of an effective business plan.
By addressing the day-to-day operations and processes needed for a business to function, this plan helps ensure that the company can operate effectively, minimize waste, and achieve its goals.
Feasibility Business Plan
One of the most critical components of a successful business launch is creating a feasibility business plan.
This type of plan focuses on determining whether a business idea is practical and worth pursuing.
At its core, a feasibility plan looks at the market demand for a product or service, analyzes the competition, examines potential revenue streams, and evaluates the resources required to bring the idea to fruition.
The plan should also outline the risks and challenges associated with the business, as well as any legal and regulatory considerations that may impact its viability.
During the feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs should identify their target audience and understand their behavior and needs.
This analysis is crucial in determining the market demand for the product or service. At the same time, businesses must determine how they will differentiate themselves from the competition.
It’s important to analyze your competition’s strengths and weaknesses, identify opportunities, and determine how to leverage them to create a competitive advantage.
Another critical aspect of the feasibility analysis is identifying potential revenue streams. Businesses need to consider the various ways they can generate income and determine which ones are the most viable.
They should also consider potential expenses, such as marketing and advertising, rent, utilities, and employee salaries.
Once revenue and expenses have been identified, businesses can create financial projections to determine their profitability and whether their business idea is economically sound.
Resource allocation is another essential consideration in a feasibility business plan. Entrepreneurs need to determine what resources they will require to launch and sustain their business.
This includes financial resources, such as startup capital and ongoing funding, as well as human resources, such as employees and contractors.
Businesses must also consider the resources required for production, such as equipment, raw materials, and supplies.
Finally, it’s essential to identify and understand the risks and challenges associated with launching and running a business.
This includes legal and regulatory concerns, such as permits and licenses, as well as other challenges, such as technological advancements or changes in the market.
By identifying and evaluating these risks, businesses can create contingency plans and ensure they have the resources and expertise needed to overcome potential obstacles.
In conclusion, creating a feasibility business plan is an essential first step in launching a successful business.
It provides a comprehensive overview of the business idea, evaluating its potential and risks, and determines whether it is a sound investment.
By conducting a thorough analysis of the market demand, competition, potential revenue streams, resource allocation, and risk and challenges, entrepreneurs can make an informed decision and pursue their business idea with a greater level of confidence and success.
Growth Business Plan
Growth Business Plan is a vital component for businesses that have survived their initial stages and are looking to scale up their operations.
This type of plan focuses on strategies that can be implemented to facilitate growth and increased profitability.
One of the primary concerns of a Growth Business Plan is identifying new areas for expansion, such as new products, markets, or services.
It also involves assessing current operations to determine how they can be optimized and scaled efficiently.
The first step to creating a Growth Business Plan is conducting a market analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of industry trends, consumer demands, and emerging opportunities.
This involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources such as industry reports, competitor analysis, and consumer feedback.
The goal is to identify untapped markets, potential partnerships, and new revenue streams that can be leveraged to facilitate growth.
The second step is to assess the existing organizational structure to determine if changes need to be made to support growth.
This includes hiring additional staff, expanding the physical infrastructure, or investing in new technology.
A comprehensive growth strategy must also address potential risks and challenges that may arise during the scaling process, such as changes in consumer behavior, supply chain disruptions, or regulatory changes.
Another critical aspect of a Growth Business Plan is financial planning. This involves conducting a financial analysis of the company’s operations to identify areas where cost savings can be realized and new revenue streams can be generated.
The plan must also include a detailed financial forecast that outlines revenue projections, cash flow forecasts, and budgets for capital expenditures.
Ultimately, a successful Growth Business Plan must articulate a clear and comprehensive strategy that establishes a roadmap for scaling up operations while maintaining profitability.
The plan must be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the market, consumer behavior, or the regulatory environment while also being prudent in managing risks associated with growth.
Clear communication of the plan to all the stakeholders of the business is necessary for flawless execution of the expansion efforts.
Exit Business Plan
One important aspect of business planning that is often overlooked is the Exit Business Plan. This subsection of a business plan outlines the steps that the company will take in the event that it needs to close down or be sold.
This can be an important consideration for investors and stakeholders, as it can help them understand the potential risks and rewards associated with their investment.
The Exit Business Plan should include a thorough analysis of the company’s financials, including any outstanding debts or liabilities, as well as projections for future revenue and expenses.
It should also outline the company’s strategy for selling its assets or winding down its operations, including any legal or regulatory considerations that may come into play.
Another important aspect of the Exit Business Plan is succession planning. This involves identifying key personnel who will be responsible for ensuring a smooth transition in the event of an exit, and outlining their roles and responsibilities.
It may also involve identifying potential buyers or partners who could take over the company, and developing a strategy for negotiating a sale or merger.
Ultimately, the purpose of the Exit Business Plan is to minimize risk and maximize value for all stakeholders involved.
By planning for the possibility of an exit from the outset, companies can be better prepared to handle unforeseen circumstances and minimize the potential impact on their investors and employees.
Summary Of Business Planning
Business planning is an essential component of any successful enterprise. It serves as a roadmap for achieving business objectives, providing a framework for decision-making, and establishing accountability.
Through the process of business planning, a company can identify its strengths and weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate risks.
When developing a business plan, it is essential to consider a variety of factors, such as market trends, competitive analysis, financial projections, and growth strategies.
Although it can be challenging to predict the future, a comprehensive business plan can help a company navigate the uncertainties of the marketplace, establish credibility with stakeholders, and secure funding.
The process of creating a business plan can also reveal gaps in knowledge or resources, providing an opportunity for further research or collaboration.
As businesses continue to evolve and adapt to changing market conditions, a robust business plan can serve as a foundation for future growth and success.
Future Outlook Of Business Planning
The future of business planning is promising and exciting. As technology continues to advance, businesses are able to gather more data and better understand their customers, which can inform their strategic planning.
With the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning, businesses can gather insights faster and with greater accuracy. This allows for more precise forecasting and strategic decision-making.
Another relevant trend is the growing popularity of sustainability-focused business planning. Many companies are recognizing the importance of sustainability, given the impact of climate change and the increasing demand for sustainable products and services.
This approach to planning involves looking beyond short-term profits and considering the long-term impact of a business’s actions on the environment and society.
Moreover, the trend toward remote work and decentralized teams is changing how businesses approach planning. Virtual collaboration tools, such as video conferencing and online project management platforms, have made it easier for teams to work effectively from anywhere in the world.
This allows businesses to tap into talent pools globally, which can lead to more diverse and innovative ideas.
Finally, the future of business planning involves adapting to the changing needs of customers, who are increasingly looking for personalized and convenient experiences. Businesses that can offer this are likely to thrive, while those that fail to adapt may fall behind.
This means incorporating customer feedback into planning and investing in technologies, such as chatbots and personalization engines, that can help businesses provide more targeted and relevant experiences to their customers.
Implementing Recommendations
After conducting a thorough examination of Business Planning, it is clear that several recommendations must be made to ensure successful implementation of a business plan.
Firstly, businesses must ensure that every employee is included in the planning process. All departments within the company must have clear communication channels, as collaboration is essential to the success of the plan.
Secondly, businesses should regularly collect and analyze data relevant to their operations. This data can be used to improve and adjust plans as necessary.
Thirdly, businesses must regularly review their business plans and make necessary alterations to keep their plan relevant and up-to-date.
Finally, businesses should always have contingency plans in place. This will help them prepare for unexpected circumstances and better navigate potential risks.
In conclusion, businesses must remain flexible and adaptable in their planning to achieve success, and implementation of the above recommendations will enable them to do so.
Business Planning: FAQs
1. what is business planning.
Business Planning is the process of creating a roadmap for a business’s future. It comprises various steps, including identifying company objectives, conducting a market analysis, determining financial projections, and outlining strategies to achieve goals.
2. Who Needs A Business Plan?
Business planning is essential for any business, irrespective of its size, stage of operations, or industry. Entrepreneurs, startups, and established businesses that want to scale their operations and increase their profitability require a comprehensive and well-structured business plan.
3. Why Is Business Planning Important?
It ensures that a business has a clear direction and vision, helps identify potential opportunities, mitigates challenges, and reduces risks. Furthermore, it plays a crucial role in securing financing, attracting investors, and keeping the organization focused and accountable for its actions.
4. What Should My Business Plan Include?
A comprehensive business plan should include an executive summary, company overview, market analysis, products and services description, marketing and sales strategy, financial projections, organization structure, and operational plan.
5. How Often Should I Update My Business Plan?
Business plans aren’t static documents and should be updated regularly to reflect changes in the market, business evolution, and goals. A business plan should be reviewed annually and updated as needed to ensure that it remains effective and relevant.
6. Can I Write My Own Business Plan?
Yes, although it may be challenging to develop a comprehensive and effective business plan without prior experience. However, there are several resources and tools available, including templates, guides, software, or seeking the services of a business consultant.

Learn how to make passive income online
I've put together a free training on *How We Used The Brand New "Silver Lining Method" To Make $3k-$10k/mo (profit) With Just A Smart Phone In As Little As 8 Weeks …
About the author
Mike Vestil
Mike Vestil is an author, investor, and speaker known for building a business from zero to $1.5 million in 12 months while traveling the world.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
Why is a business plan important and what should it include?

Posted: Tue 12th Mar 2019
How do you go from a bright idea to a successful business? Planning. It's easy to imagine successful entrepreneurs played it by ear and got lucky. People often change direction but planning's a crucial part of testing a start-up idea and building a business.
This guide examines why you should write a business plan, what it needs to include and how to use it. We've also highlighted additional resources that can help you go through the process.
Why write a business plan?
Business plans provide accountability. They allow business owners to sense-check what they're doing and why. They provide an opportunity to get ideas out of your head and start working on them.
"Not having to report to anyone is attractive when you start up. As you grow it can be tricky not to have a sounding board. A business plan can be useful for that," said Jonathan Bareham , co-founder of accountancy firm Raeden.
He highlights the role of goal setting in the planning process. Why are you starting a business? Is it because you want a good work-life balance? Do you want to make an environmental impact? It's likely a combination of factors. Writing down your motivation provides a reference for big decisions and makes sure you don't lose focus.
Business plans help explain what you're doing to other people. The process of writing everything down makes sure you can answer key questions about what you're doing.
Hiring people, opening a premise or buying equipment requires significant investment. Planning and justifying what you're going to spend is important. Sharing them externally helps reassure partners, whether you're looking to borrow money or win over a mentor.
What basic things should a business plan include?
Whatever format and length you decide on there are several common topics to cover in a business plan. Bareham outlines five points to include:
A summary of what you're going to do
Details of the market you're going into
What you have that other businesses don't (your unfair advantage)
A cash-flow forecast
Personnel needed
Business owners need to think about the strengths and weaknesses they have, he added. Be honest and make sure you identify where you will need help.
Your cash-flow forecast is crucial. It shows the money coming into your business from customers and what you're spending. This includes costs like buying raw materials, office space, marketing and paying employees. This plan will evolve into a document you look at regularly when the business is up and running.
Enterprise Nation founder Emma Jones compares having a business plan to a route map and uses the acronym 'I'm off' as a memory aid on what to include:
Operations: What kit do you need?
Friends: A support network
You can tailor your business plans to specific audiences and we'll go into the main formats in the next section.
Watch this detailed video with Enterprise Nation adviser and accountant Jonathan Bareham sharing tips on business plans, cash flow, accounts and more.
What business plan format should I use?
There are several formats you can use to create a business plan. It's important to pick the one that's right for your situation. The key considerations are what you know so far and how you're going to use the plan.
You'll generally cover the sections we outlined in the section above but the amount of detail can vary.
If the plan's for the benefit of the business owner you need to think about how much you can know at this point. There are lots of assumptions around sales and costs that you won't know until they're tested. This will limit the level of detail you can include.
The audience is important too. You could write a five-page summary if the business plans just for you. If the business plan's for raising investment or applying for a loan it's going to require more detail and might be 15-20 pages long.
Organisations like the Prince's Trust and Start Up Loans , which offer start-up funding, have templates that they prefer or require applicants to fill out.
David Abrahamovitch, founder and CEO of London café-bar and restaurant company GRIND, told Enterprise Nation that his founding team didn't create a business plan until they needed to borrow money. He believes a formal business plan doesn't provide much value at the concept stage.
"Business plans absolutely have their place but I see people who are spending months writing a business plan. They're worried about who's going to copy their idea about trademarks. All of these things are important, but at the moment you don't have a business. You don't have a brand to protect. You're worried about the wrong things. "You have to get to the minimum viable form of that business as quickly as possible and just test it."
Abrahamovitch added that things like pop-up stores and online tools mean the barriers to entry are lower than ever, reducing the risk of testing an idea.
What a traditional business plan looks like
What we're calling 'traditional business plans' are A4 documents that cover the key elements of your business. These include five main elements:
The executive summary: Summarise the main points of your business plan. Showcase what you're doing and sell your vision to the reader.
Opportunity analysis: Describe the business opportunity. Look at the size of the market, customer segments, competitors and the key trends.
Marketing: Highlight the key messages you want to communicate to customers and detail the channels you will use to reach them (telemarketing, social media etc.). Provide an idea of cost for this activity and, if possible, the level of business you expect to generate.
Logistics: Plan where and how you are going to operate your business. Include plans for manufacturing, transportation, office costs, staff needed etc.
Finance: Make sure that you detail all your associated costs - both your estimated start-up costs as well as your running costs. Include a cash-flow forecast that shows how your business will become sustainable.
Additional information like the founders' CVs can be included in your appendix. This often depends on what evidence your audience requires and may not be relevant for a document that's used internally.
Presentation is important because it provides credibility. Think about adding company logos, a cover page and other touches that make the document look professional.
Abrahamovitch said writing a business plan is useful to examine what's working, how much energy things take up and the margin of different products when you've tested ideas.
"Distill that down into its simplest form and put that in a business plan," he said. "Talk about how you're going to scale it. That's where it really adds value."
The lean canvas model
The length of traditional business plans can be intimidating. You may also lack the information to complete the document if you haven't started trading yet.
Lean canvas and business model canvas allow you to create a business plan on a single page. The structure examines whether a business idea is viable. The nine boxes capture entrepreneurs' key assumptions, covering topics like metrics and marketing channels.
Lean canvas is designed to provide a snapshot of your idea and challenge the assumptions you've made. It's not meant to be perfect. The inventor of lean canvas model suggests taking 20 minutes to fill everything out.
Test your assumptions through research
Launching and growing a small business is really exciting because you don't know what's going to happen. However, writing a business plan can be daunting as there are so many things you don't know yet.
Make phone calls and search the internet to strengthen your assumptions. It's possible to find information on standard services like accountants, renting desks or buying raw materials.
There are other aspects that are more difficult to predict. Projecting sales, for example, is one of the trickiest parts of forecasting. You love your product but will customers flock to the business?
One opportunity to solve this problem is to do a small amount of test trading. Paying for a market stall may cost you a thousand pounds after you pay for the stock and a location. But the investment may pay dividends if it gives you a reality check on what customers are willing to pay and how popular your offering is. What's the least you can spend to learn the most?
Research competitors offerings too. What are people paying for related products?
Service-based business can have the opportunity to trial their offering part-time. Perhaps you can take on a client while still working your day job.
Make sure you justify any forecasts in your business plan and provide a logical explanation of how you came to your conclusions.
Will a business plan guarantee success?
No. But business plans will help crystallise your goals and test your assumptions. The framework is really useful to develop ideas, particularly if they've been rattling around in your head for some time.
Make sure you return to your business plan regularly. Reinforcing your original goals will help keep you on track. Forecasting is a skill. Check your projections against performance and try to figure out what assumptions were correct and where there were issues.
The way you use business plans will evolve over time. Filling in a lean canvas might work if you have an idea and haven't started working on it yet. Eventually, you might need to create a business plan to land investment or it can provide an opportunity to reassess what you do.

Access support to start your business
Visit the StartUp UK hub for resources that give you the education and inspiration to get started on your entrepreneurial journey.
You might also like…

Get business support right to your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive business tips, learn about new funding programmes, join upcoming events, take e-learning courses, and more.
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Interested in joining the WSI family?
We'd love to chat further to see if there's a mutual fit.
Request More Info

We're a Unique Franchise Network
Ask any of our zees, and they'll tell you, "WSI is more than a network...it's a family!"
Reasons Why a Business Plan Is Important for Entrepreneurs

Editor's Note: This post was originally published in September 2018 and has been updated with new content that highlights the importance of proper business planning in 2021's economy.
What is a business plan? For people who are just starting out and forming their own company, whether it's a small freelance business at home or a new venture with an office and a starting pool of employees, there's a lot of importance to a business plan. It is a road map, an outline, a document that explains what your business is, what the goals of the enterprise are, and how exactly it will set about achieving those goals. So beyond being a document that identifies your business, what else does such a plan do for you?
1. Target Your Problems

2. Get Better Advice
The importance of a business plan to entrepreneurship can also be in the way it crystallizes just what kind of help you need. Merely telling a friend or potential business mentor you're aiming to start with ten employees, for example, is not an exceptionally detailed statement. Showing a business plan that outlines the exact duties, salaries, and expectations you have for employees gives far more information for people to provide advice about.
3. Organize Your Resources
A business plan is also essential as the primary guide for how you will structure and allocate your resources. It's here that you will see just how feasible it is to open an office, hire employees, and look at operating costs. The business plan can quickly show you whether you will be making a profit or running at a loss, and it shows how much those losses may be every month.
4. Approach Investors
For some, this may be critical. Investors want to know that you know what you’re doing. A business plan can often be the single most important document you can present to your investors that will provide the structure and confidence that they need to make decisions about funding and supporting your company.
5. Create Milestones
A business plan is also a plan of action. By laying out milestones, you now have targets to shoot for in the short, mid and long term. These goals also mean that you can "course correct" with greater agility if you have targets and realize that you may need to make some changes in order to meet them.
The importance of a business plan can be critical for entrepreneurs. Business may have some artistry to it, but real success comes from having a vision and being organized in the way you strive towards that vision. A business plan will help you immensely and in so many ways!
Template for a Business Plan for Entrepreneurs
To determine whether you have a solid business idea, you will need to do thorough research and create a business plan to see if your idea is feasible. Here is a simple business plan template that is broken into sections that include the key elements for what goes into each step of the process to help get you started.
Section 1: Executive Summary
Write an executive summary. The purpose of the executive summary is to give readers a high-level view of the company and the market before delving into the details. It appears first but is written last and provides a snapshot of your company explaining who you are, what you do, and why. The executive summary provides a short, concise, and optimistic overview of your business to capture the reader's attention and create a need to learn more.
Section 2: Business/Industry Overview
Describe your company and business model by summarizing what your company does, your mission statement, location details, business structure and business owner details, the marketplace needs that your business is trying to meet, and how your products/services meet those needs. Define your business's purpose (mission) and a statement based on your perception of the company's growth potential (vision). Include specific business goals and objectives. Provide background information about the company, including a brief history of the business and a list of fundamental company principles.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
Analyze your market's conditions. The market will ultimately determine how successful your business will be. You will need to demonstrate that you have thoroughly analyzed your target market and have a high-enough demand for your products/services to make your business viable. The competitive analysis should include a comprehensive assessment of your competition and how your business will compete in the sector. Describe the industry within which your business will operate, identify and provide a general profile of your target market, and describe what share of the market you currently have or anticipate. Include both an analysis of research done by others, along with primary research you have collected yourself — whether via customer surveys, interviews, or other methods. Outline the strengths and weaknesses of potential competitors and strategies that will give you a competitive advantage.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
Design a marketing and sales strategy. Here is where you can plan out your comprehensive marketing and sales strategies to cover how you plan on selling your product. Before working on your marketing and sales plan, you will need to have your market analysis completely fleshed out and choose your target client personas, i.e., your ideal customers. Talk about the competitive landscape. Describe how you intend to entice customers to buy your products or services, including advertising and promotion, sales and distribution, pricing strategy, and post-sales support.
Section 5: Ownership and Management Plan
Outline all operations and management roles. This section describes the ownership, legal structure, and your business's management and staffing requirements. Use this section to outline your company's unique organizational and management structure. Describe how your company is organized, including its legal structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation); identify any special licenses or permits your business operates with; provide a brief bio of key managers within your company; include an organization chart.
Section 6: Operating Plan
The operating plan outlines your business's physical requirements, such as office, warehouse, retail space, equipment, inventory and supplies, and labor. For a one-person, home-based consulting firm, the operating plan may be short and straightforward. However, for businesses such as restaurants or manufacturers that require custom facilities, supply chains, multiple employees, and specialized equipment, the operating plan may need to be very detailed.
Section 7: Financial Plan
This section is the most crucial part of the business plan, especially if you need debt financing or want to attract investors. The financial plan must demonstrate your business' growth and profitability potential. To do this, you will need to provide projected income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. For new businesses, these are forecasts. A golden rule of thumb is to underestimate revenues and overestimate expenses. Outline your financial model, including your business costs, revenue projections, and a funding request if you pitch to investors. Your start-up cost refers to the resources you will need to get your business up and running — and an estimate of how much each of those resources will cost.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
Summarize the above with an appendix. The appendices and exhibits section should contain any detailed information needed to support other areas of the plan, including company brochures, resumes of key employees, a list of business equipment, copies of press articles and advertisements, pictures of your business location and products, any applicable information about your industry or products, key business agreements such as lease, and contracts.
Who Needs a Business Plan?
Start-up Businesses : The most classic business planning scenario is for a start-up, for which the plan helps the founders break down uncertainty into meaningful pieces, like the sales projection, expense budget, milestones, and tasks. When you realize you do not know how much money you need or when you need it without first laying out projected sales, costs, expenses, and payment timing, the need becomes apparent. And that is for all start-ups, whether they need to convince investors, banks, or family and friends to part with their money and fund the new venture. Existing Businesses : Established businesses use business plans to manage and steer their business strategies to address changes in their markets and take advantage of new opportunities. They often use plans to reinforce strategy, establish metrics, track results, manage responsibilities and goals, plan and manage critical resources such as cash flow, and set regular review and revision schedules. Business plans can be a powerful driver of growth for existing businesses.
Finding the Right Plan for You
Considering that business plans serve diverse purposes, it is no surprise that they come in various forms. But before you even start writing your business plan, you need to think about who the audience is and your plan's goals. While there are standard components found in almost every business plan, such as sales forecasts and marketing strategy, business plan formats can differ depending on the audience and business type. For example, if you are building a biotech firm plan, your plan will detail government approval processes. If you are writing a restaurant plan, details about location and renovations might be critical factors. The language you would use in the biotech firm's business plan would be much more technical than the language you would use in the restaurant plan. Plans can also differ significantly in length, detail, and presentation. Those that never leave the office and are used only for internal strategic planning and management may often use more casual language and might not have much visual polish. On the other end of the spectrum, a plan destined for a top venture capitalist's desk will have a high polish and focus on the business' high-growth aspects and the experienced team to deliver desirable results.
Elements of a Business Plan
While the plans may vary by type, certain key elements appear in virtually all business plans. These components include the review schedule, strategy summary, milestones, responsibilities, metrics (numerical goals that can be tracked), and basic projections. The projections include sales, costs, expenses, and cash flow. These core elements grow organically for the actual purpose needed for the business.
Developing a High Power Business Plan
The business plan development process described here can provide the guidance entrepreneurs require for developing a business plan best suited for their needs; a high power business plan.
The Stages of Development
There are six stages involved in developing a high-power business plan.
Essential Initial Research
This stage requires you to analyze the environment in which you anticipate operating at each of the societal, market, industry, and firm levels of analysis. In this planning stage, the essential initial research is a necessary first step for better understanding the trends that affect their business and their decisions to lay the groundwork for and improve their potential for success.
Business Model
Inherent to any business plan is a description of the entrepreneur's chosen business model that will best ensure success. Based upon your essential initial research of the setting in which you anticipate starting your business (your analysis from stage one), you should determine how each element of your business model might fit together to improve the potential success of your business venture. These elements include their revenue streams, cost structure, customer segments, value propositions, key activities, and key partners.
Initial Business Plan Draft
This stage involves taking the knowledge and ideas developed during the first two stages and integrating them into a business plan format. A suggested approach is to create a complete draft of the business plan with all the sections, including the front part with the business description, values, vision, mission, value proposition statement, a preliminary set of goals, table of contents, and lists of tables and figures set up using the software features enabling their automatic generation. Writing all the operations, human resources, marketing, and financial plans as part of the first draft ensures that all these necessary parts can be appropriately integrated. The business plan should tell the story of a planned business start-up in two ways: using primarily words, along with charts and graphs in the operations, human resources, and marketing plans, and through the financial plan. Both approaches must tell the same story.
Making Business Plan Realistic
The first draft of a business plan will seldom be realistic. As you write the plan, it will naturally change as new information is gathered. Another factor that commonly renders the first draft unrealistic is the difficulty in ensuring that the written section—in the front part of the plan and the operations, human resources, and marketing plans—tells the same story as the financial part does. This working stage involves making the necessary adjustments to the plan to make it as realistic as possible.
Making Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
A business plan can be realistic without appealing to potential investors or other external stakeholders, such as suppliers, employees, and needed business partners. It may also be realistic and possibly appealing to stakeholders without necessarily being desirable to the entrepreneur. During this stage, try to keep it as realistic as possible when adjusting the plan to appeal to potential investors and yourself.
Finishing the Business Plan
The final stage involves putting all the essential finishing touches on the business plan so it will present well to potential investors and alike. This step involves ensuring that the math and links between the written and financial sections are accurate. It also involves ensuring that all the needed corrections are made to the formatting, spelling, and grammar. The ultimate set of goals should be written to appeal to targeted readers and reflect what the business plan specifies. An executive summary should be written and included as the final step.
FAQs about Business Plans
What are the 4 types of business plans.
1. Mini-plan : A mini-plan may comprise one to 10 pages and include at least cursory attention to such critical matters as business concepts, financing needs, marketing plans, and financial statements, especially cash flow, balance sheet, and income projections. It is a great way to quickly test a business concept or measure the interest of a potential partner or minor investor. It could also serve as a valuable prelude to a full-length plan later on.
2. Working Plan : A working plan is a tool to operate your business. It should be lengthy in detail but may be short on presentation. As with a mini-plan, you can probably afford a somewhat higher degree of candor and informality when preparing a working plan.
3. Presentation Plan : If you take a working plan, with its low stress on cosmetic appeal and impression, and twist the lever to boost the amount of attention paid to its visual appearance, you will end up with a presentation plan. This plan is suitable for showing to financiers, investors, stakeholders, and others outside the company.
4. Electronic Plan : Most business plans are composed on a computer, then printed out and presented in hard copy. However, more and more business information transferred between parties only on paper can now be sent electronically, so you may find it convenient to have an electronic version of your plan available. An electronic plan can be useful for presentations to groups using a computer-driven overhead projector, for instance, or for satisfying the demands of discriminating investors who want to delve deeply into the underpinnings of complex spreadsheets.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
1. Establish a business focus : The primary purpose of a business plan is to establish your plans for your business's future. These plans should include goals and milestones alongside detailed steps on how the business will reach each step. Creating a roadmap to your goals will help determine your business focus and pursue growth.
2. Secure funding : One of the first things private investors, banks, and other lenders look for before investing in your business is a well-researched business plan. Investors and stakeholders want to know how you operate your business, revenue and expense projections, and how they will receive a return on their investment.
3. Attract executives : As your business grows, you will likely need to add executives to your team. The business plan helps you attract executive talent and determine whether they are a good fit for your company.
What are the 5 elements of a business plan?
1. Business concept : Describes the business, its products/services, and the market it will serve. It should point out exactly what will be sold, to whom, and why your business will hold a competitive advantage.
2. Financial features : Highlights the important financial points of the company, including sales, cash flows, profits, and return on investment.
3. Financial requirements : Clearly state the capital needed to start the business and expand. It should detail how capital will be used and the equity that will be provided for funding. If the loan for initial capital is based on security instead of equity, also specify the source of collateral.
4. Current business position : Furnishes relevant information about the business, its legal form of operation, the principal owners, when it was formed, and key personnel.
5. Major achievements : Details of any developments within the company essential to the business's success. Major achievements include patents, prototypes, location of a facility, any binding contracts that need to be in place for product development, or any test marketing results.
Take your first step to becoming an entrepreneur by downloading our special guide for entrepreneurs.

About The Author
Daniel plays a fundamental role in WSI’s global franchise expansion and development. He has since overseen WSI’s franchise development process, and he is personally associated with the recruitment of 600+ global franchisees.
Featuring the Best in Career Advice, Digital Marketing and Franchising
The WSI Franchise Blog is your ideal place to get career advice and best practices for digital marketing from WSI experts!
Don't Stop The Learning Now!
Here are some other blog posts you may be interested in.

How to Create Work-Life Balance as a Franchisee
Are you looking for a better work-life balance? Inside this guide, you will discover how WSI franchisee, Taylor Russell, gets it right!

6 Time Management Tips For The Entrepreneurial Mind

Get Your E2 Visa and Move to the USA
830 Dixon Road, Etobicoke, ON Canada M9W 6Y8
Local: 905.678.7588 US Toll-Free: 888.678.7588 UK Toll-Free: 08.08.234.6105 Fax: 905.678.7242 Email: [email protected]
- The WSI Story
- Culture and Values
- WSI in the Community
- Contact WSI Head Office
- Request a Consultation
- Become a WSI Consultant
- Competitive Analysis
- Buyer Persona Development
- Landing Page Optimization
- Web Design and Development
- Content Marketing
- Inbound Marketing
- Social Media Marketing
- Social Selling Mastery Course
- Paid Search Advertising
- Adaptive Search Engine Optimization
- Marketing Automation
- Email Marketing
- Mobile Marketing
- Video Marketing
- Analytics and Reporting
- Making a Difference
- Case Studies
- Testimonials
- Leveraging Global Expertise
- Delivering Local Results
- Speak to an Expert
- Book a Digital Marketing Speaker
- Visit the Blog
- Subscribe Now
© 2024 WSI. All rights reserved. WSI ICE and WSI IM are registered trademarks of RAM. Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy . Sitemap . Each WSI Franchise is an independently owned and operated business.
Do You Really Need a Business Plan?
The art of storytelling, from net margin to sales.
Why is a business plan important?
- Who will the reader be?
- What do you want their response to be?
Four Reasons to Write a Business Plan
1. To raise money for your business
2. To make sound decisions
3. To help you identify any potential weaknesses
4. To communicate your ideas with stakeholders

More by this contributor:
- Challenges Become Opportunities
- Discontinuing Healthy Workplace Consultancy
- Financial Planning for the Pandemic
Comments (0)
You may like.
How to Write a Business Plan for Your Small Business
Table of Contents
What is a business plan, the advantages of having a business plan, the types of business plans, the key elements of a business plan, best business plan software, common challenges of writing a business plan, become an expert business planner, business planning: it’s importance, types and key elements.

Every year, thousands of new businesses see the light of the day. One look at the World Bank's Entrepreneurship Survey and database shows the mind-boggling rate of new business registrations. However, sadly, only a tiny percentage of them have a chance of survival.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 20% of small businesses fail in their first year, about 50% in their fifth year.
Research from the University of Tennessee found that 44% of businesses fail within the first three years. Among those that operate within specific sectors, like information (which includes most tech firms), 63% shut shop within three years.
Several other statistics expose the abysmal rates of business failure. But why are so many businesses bound to fail? Most studies mention "lack of business planning" as one of the reasons.
This isn’t surprising at all.
Running a business without a plan is like riding a motorcycle up a craggy cliff blindfolded. Yet, way too many firms ( a whopping 67%) don't have a formal business plan in place.
It doesn't matter if you're a startup with a great idea or a business with an excellent product. You can only go so far without a roadmap — a business plan. Only, a business plan is so much more than just a roadmap. A solid plan allows a business to weather market challenges and pivot quickly in the face of crisis, like the one global businesses are struggling with right now, in the post-pandemic world.
But before you can go ahead and develop a great business plan, you need to know the basics. In this article, we'll discuss the fundamentals of business planning to help you plan effectively for 2021.
Now before we begin with the details of business planning, let us understand what it is.
No two businesses have an identical business plan, even if they operate within the same industry. So one business plan can look entirely different from another one. Still, for the sake of simplicity, a business plan can be defined as a guide for a company to operate and achieve its goals.
More specifically, it's a document in writing that outlines the goals, objectives, and purpose of a business while laying out the blueprint for its day-to-day operations and key functions such as marketing, finance, and expansion.
A good business plan can be a game-changer for startups that are looking to raise funds to grow and scale. It convinces prospective investors that the venture will be profitable and provides a realistic outlook on how much profit is on the cards and by when it will be attained.
However, it's not only new businesses that greatly benefit from a business plan. Well-established companies and large conglomerates also need to tweak their business plans to adapt to new business environments and unpredictable market changes.
Before getting into learning more about business planning, let us learn the advantages of having one.
Since a detailed business plan offers a birds-eye view of the entire framework of an establishment, it has several benefits that make it an important part of any organization. Here are few ways a business plan can offer significant competitive edge.
- Sets objectives and benchmarks: Proper planning helps a business set realistic objectives and assign stipulated time for those goals to be met. This results in long-term profitability. It also lets a company set benchmarks and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) necessary to reach its goals.
- Maximizes resource allocation: A good business plan helps to effectively organize and allocate the company’s resources. It provides an understanding of the result of actions, such as, opening new offices, recruiting fresh staff, change in production, and so on. It also helps the business estimate the financial impact of such actions.
- Enhances viability: A plan greatly contributes towards turning concepts into reality. Though business plans vary from company to company, the blueprints of successful companies often serve as an excellent guide for nascent-stage start-ups and new entrepreneurs. It also helps existing firms to market, advertise, and promote new products and services into the market.
- Aids in decision making: Running a business involves a lot of decision making: where to pitch, where to locate, what to sell, what to charge — the list goes on. A well thought-out business plan provides an organization the ability to anticipate the curveballs that the future could throw at them. It allows them to come up with answers and solutions to these issues well in advance.
- Fix past mistakes: When businesses create plans keeping in mind the flaws and failures of the past and what worked for them and what didn’t, it can help them save time, money, and resources. Such plans that reflects the lessons learnt from the past offers businesses an opportunity to avoid future pitfalls.
- Attracts investors: A business plan gives investors an in-depth idea about the objectives, structure, and validity of a firm. It helps to secure their confidence and encourages them to invest.
Now let's look at the various types involved in business planning.
Become a Business and Leadership Professional
- Top 10 skills in demand Business Analysis As A Skill In 2020
- 14% Growth in Jobs Of Business Analysis Profile By 2028
Business Analyst
- Industry-recognized certifications from IBM and Simplilearn
- Masterclasses from IBM experts
Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis
- Certificate from Simplilearn in collaboration with Purdue University
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Assistant Consultant at Tata Consultancy Services , Tata Consultancy Services
My experience with Simplilearn has been great till now. They have good materials to start with, and a wide range of courses. I have signed up for two courses with Simplilearn over the past 6 months, Data Scientist and Agile and Scrum. My experience with both is good. One unique feature I liked about Simplilearn is that they give pre-requisites that you should complete, before a live class, so that you go there fully prepared. Secondly, there support staff is superb. I believe there are two teams, to cater to the Indian and US time zones. Simplilearn gives you the most methodical and easy way to up-skill yourself. Also, when you compare the data analytics courses across the market that offer web-based tutorials, Simplilearn, scores over the rest in my opinion. Great job, Simplilearn!
I was keenly looking for a change in my domain from business consultancy to IT(Business Analytics). This Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis course helped me achieve the same. I am proficient in business analysis now and am looking for job profiles that suit my skill set.
Business plans are formulated according to the needs of a business. It can be a simple one-page document or an elaborate 40-page affair, or anything in between. While there’s no rule set in stone as to what exactly a business plan can or can’t contain, there are a few common types of business plan that nearly all businesses in existence use.
Here’s an overview of a few fundamental types of business plans.
- Start-up plan: As the name suggests, this is a documentation of the plans, structure, and objections of a new business establishments. It describes the products and services that are to be produced by the firm, the staff management, and market analysis of their production. Often, a detailed finance spreadsheet is also attached to this document for investors to determine the viability of the new business set-up.
- Feasibility plan: A feasibility plan evaluates the prospective customers of the products or services that are to be produced by a company. It also estimates the possibility of a profit or a loss of a venture. It helps to forecast how well a product will sell at the market, the duration it will require to yield results, and the profit margin that it will secure on investments.
- Expansion Plan: This kind of plan is primarily framed when a company decided to expand in terms of production or structure. It lays down the fundamental steps and guidelines with regards to internal or external growth. It helps the firm to analyze the activities like resource allocation for increased production, financial investments, employment of extra staff, and much more.
- Operations Plan: An operational plan is also called an annual plan. This details the day-to-day activities and strategies that a business needs to follow in order to materialize its targets. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the managing body, the various departments, and the company’s employees for the holistic success of the firm.
- Strategic Plan: This document caters to the internal strategies of the company and is a part of the foundational grounds of the establishments. It can be accurately drafted with the help of a SWOT analysis through which the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats can be categorized and evaluated so that to develop means for optimizing profits.
There is some preliminary work that’s required before you actually sit down to write a plan for your business. Knowing what goes into a business plan is one of them.
Here are the key elements of a good business plan:
- Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers’ first impression of your business. As such, it could define the opinions of customers and investors from the get-go.
- Business Description: A thorough business description removes room for any ambiguity from your processes. An excellent business description will explain the size and structure of the firm as well as its position in the market. It also describes the kind of products and services that the company offers. It even states as to whether the company is old and established or new and aspiring. Most importantly, it highlights the USP of the products or services as compared to your competitors in the market.
- Market Analysis: A systematic market analysis helps to determine the current position of a business and analyzes its scope for future expansions. This can help in evaluating investments, promotions, marketing, and distribution of products. In-depth market understanding also helps a business combat competition and make plans for long-term success.
- Operations and Management: Much like a statement of purpose, this allows an enterprise to explain its uniqueness to its readers and customers. It showcases the ways in which the firm can deliver greater and superior products at cheaper rates and in relatively less time.
- Financial Plan: This is the most important element of a business plan and is primarily addressed to investors and sponsors. It requires a firm to reveal its financial policies and market analysis. At times, a 5-year financial report is also required to be included to show past performances and profits. The financial plan draws out the current business strategies, future projections, and the total estimated worth of the firm.
The importance of business planning is it simplifies the planning of your company's finances to present this information to a bank or investors. Here are the best business plan software providers available right now:
- Business Sorter
The importance of business planning cannot be emphasized enough, but it can be challenging to write a business plan. Here are a few issues to consider before you start your business planning:
- Create a business plan to determine your company's direction, obtain financing, and attract investors.
- Identifying financial, demographic, and achievable goals is a common challenge when writing a business plan.
- Some entrepreneurs struggle to write a business plan that is concise, interesting, and informative enough to demonstrate the viability of their business idea.
- You can streamline your business planning process by conducting research, speaking with experts and peers, and working with a business consultant.
Whether you’re running your own business or in-charge of ensuring strategic performance and growth for your employer or clients, knowing the ins and outs of business planning can set you up for success.
Be it the launch of a new and exciting product or an expansion of operations, business planning is the necessity of all large and small companies. Which is why the need for professionals with superior business planning skills will never die out. In fact, their demand is on the rise with global firms putting emphasis on business analysis and planning to cope with cut-throat competition and market uncertainties.
While some are natural-born planners, most people have to work to develop this important skill. Plus, business planning requires you to understand the fundamentals of business management and be familiar with business analysis techniques . It also requires you to have a working knowledge of data visualization, project management, and monitoring tools commonly used by businesses today.
Simpliearn’s Executive Certificate Program in General Management will help you develop and hone the required skills to become an extraordinary business planner. This comprehensive general management program by IIM Indore can serve as a career catalyst, equipping professionals with a competitive edge in the ever-evolving business environment.
What Is Meant by Business Planning?
Business planning is developing a company's mission or goals and defining the strategies you will use to achieve those goals or tasks. The process can be extensive, encompassing all aspects of the operation, or it can be concrete, focusing on specific functions within the overall corporate structure.
What Are the 4 Types of Business Plans?
The following are the four types of business plans:
Operational Planning
This type of planning typically describes the company's day-to-day operations. Single-use plans are developed for events and activities that occur only once (such as a single marketing campaign). Ongoing plans include problem-solving policies, rules for specific regulations, and procedures for a step-by-step process for achieving particular goals.
Strategic Planning
Strategic plans are all about why things must occur. A high-level overview of the entire business is included in strategic planning. It is the organization's foundation and will dictate long-term decisions.
Tactical Planning
Tactical plans are about what will happen. Strategic planning is aided by tactical planning. It outlines the tactics the organization intends to employ to achieve the goals outlined in the strategic plan.
Contingency Planning
When something unexpected occurs or something needs to be changed, contingency plans are created. In situations where a change is required, contingency planning can be beneficial.
What Are the 7 Steps of a Business Plan?
The following are the seven steps required for a business plan:
Conduct Research
If your company is to run a viable business plan and attract investors, your information must be of the highest quality.
Have a Goal
The goal must be unambiguous. You will waste your time if you don't know why you're writing a business plan. Knowing also implies having a target audience for when the plan is expected to get completed.
Create a Company Profile
Some refer to it as a company profile, while others refer to it as a snapshot. It's designed to be mentally quick and digestible because it needs to stick in the reader's mind quickly since more information is provided later in the plan.
Describe the Company in Detail
Explain the company's current situation, both good and bad. Details should also include patents, licenses, copyrights, and unique strengths that no one else has.
Create a marketing plan ahead of time.
A strategic marketing plan is required because it outlines how your product or service will be communicated, delivered, and sold to customers.
Be Willing to Change Your Plan for the Sake of Your Audience
Another standard error is that people only write one business plan. Startups have several versions, just as candidates have numerous resumes for various potential employers.
Incorporate Your Motivation
Your motivation must be a compelling reason for people to believe your company will succeed in all circumstances. A mission should drive a business, not just selling, to make money. That mission is defined by your motivation as specified in your business plan.
What Are the Basic Steps in Business Planning?
These are the basic steps in business planning:
Summary and Objectives
Briefly describe your company, its objectives, and your plan to keep it running.
Services and Products
Add specifics to your detailed description of the product or service you intend to offer. Where, why, and how much you plan to sell your product or service and any special offers.
Conduct research on your industry and the ideal customers to whom you want to sell. Identify the issues you want to solve for your customers.
Operations are the process of running your business, including the people, skills, and experience required to make it successful.
How are you going to reach your target audience? How you intend to sell to them may include positioning, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
Consider funding costs, operating expenses, and projected income. Include your financial objectives and a breakdown of what it takes to make your company profitable. With proper business planning through the help of support, system, and mentorship, it is easy to start a business.
Our Business And Leadership Courses Duration And Fees
Business And Leadership Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Business and Leadership
Business Analysis Basics

Data Science & Business Analytics
Business Intelligence Fundamentals
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
From Concept to Market - How to Excel at Product Management in 2024 with SP Jain Program
Ascend the Product Management Career Ladder in 2024 with UC San Diego
Career Information Session: Find Out How to Become a Business Analyst with IIT Roorkee
Recommended Reads
Business Intelligence Career Guide: Your Complete Guide to Becoming a Business Analyst
Corporate Succession Planning: How to Create Leaders According to the Business Need
Top Business Analyst Skills
Business Analytics Basics: A Beginner’s Guide
Financial Planning for Businesses Across the Globe
How to Become a Business Analyst
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

20 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan in 2024
Written by Dave Lavinsky

What is the Purpose of a Business Plan?
The purpose of a business plan is to provide a clear roadmap for the company’s future. It outlines the vision, goals, and strategies of the business, guiding entrepreneurs and stakeholders in understanding its operations and objectives. A business plan template helps attract investors and funding by showcasing the potential for profitability and growth.
Top 20 Reasons Why you Need a Business Plan
1. to prove that you’re serious about your business.
A formal business plan is necessary to show all interested parties — employees, investors, partners and yourself — that you are committed to building the business. Creating your plan forces you to think through and select the strategies that will propel your growth.
2. To Establish Business Milestones
The business plan should clearly lay out the long-term milestones that are most important to the success of your business. To paraphrase Guy Kawasaki, a milestone is something significant enough to come home and tell your spouse about (without boring him or her to death). Would you tell your spouse that you tweaked the company brochure? Probably not. But you’d certainly share the news that you launched your new website or reached $1M in annual revenues.
3. To Better Understand Your Competition
Creating the business plan forces you to analyze the competition. All companies have competition in the form of either direct or indirect competitors, and it is critical to understand your company’s competitive advantages. And if you don’t currently have competitive advantages, to figure out what you must do to gain them.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
Quickly & easily complete your business plan: Download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template and finish your business plan & financial model in hours.
4. To Better Understand Your Customer
Why do they buy when they buy? Why don’t they when they don’t? An in-depth customer analysis is essential to an effective business plan and to a successful business. Understanding your customers will not only allow you to create better products and services for them, but will allow you to more cost-effectively reach them via advertising and promotions.
5. To Enunciate Previously Unstated Assumptions
The process of actually writing the business plan helps to bring previously “hidden” assumptions to the foreground. By writing them down and assessing them, you can test them and analyze their validity. For example, you might have assumed that local retailers would carry your product; in your business plan, you could assess the results of the scenario in which this didn’t occur.
6. To Assess the Feasibility of Your Venture
How good is this opportunity? The business plan process involves researching your target market, as well as the competitive landscape, and serves as a feasibility study for the success of your venture. In some cases, the result of your planning will be to table the venture. And it might be to go forward with a different venture that may have a better chance of success.
7. To Document Your Revenue Model
How exactly will your business make money? This is a critical question to answer in writing, for yourself and your investors. Documenting the revenue model helps to address challenges and assumptions associated with the model. And upon reading your plan, others may suggest additional revenue streams to consider.
8. To Determine Your Financial Needs
Does your business need to raise capital? How much? One of the purposes of a business plan is to help you to determine exactly how much capital you need and what you will use it for. This process is essential for raising capital for business and for effectively employing the capital. It will also enable you to plan ahead, particularly if you need to raise additional funding in the future.
9. To Attract Investors
A formal business plan is the basis for financing proposals. The business plan answers investors’ questions such as: Is there a need for this product/service? What are the financial projections? What is the company’s exit strategy? While investors will generally want to meet you in person before writing you a check, in nearly all cases, they will also thoroughly review your business plan.
10. To Reduce the Risk of Pursuing the Wrong Opportunity
The process of creating the business plan helps to minimize opportunity costs. Writing the business plan helps you assess the attractiveness of this particular opportunity, versus other opportunities. So you make the best decisions.
11. To Force You to Research and Really Know Your Market
What are the most important trends in your industry? What are the greatest threats to your industry? Is the market growing or shrinking? What is the size of the target market for your product/service? Creating the business plan will help you to gain a wider, deeper, and more nuanced understanding of your marketplace. And it will allow you to use this knowledge to make decisions to improve your company’s success.
12. To Attract Employees and a Management Team
To attract and retain top quality talent, a business plan is necessary. The business plan inspires employees and management that the idea is sound and that the business is poised to achieve its strategic goals. Importantly, as you grow your company, your employees and not you will do most of the work. So getting them aligned and motivated will be key to your success.
13. To Plot Your Course and Focus Your Efforts
The business plan provides a roadmap from which to operate, and to look to for direction in times of doubt. Without a business plan, you may shift your short-term strategies constantly without a view to your long-term milestones. You wouldn’t go on a long driving trip without a map; think of your business plan as your map.
14. To attract partners
Partners also want to see a business plan, in order to determine whether it is worth partnering with your business. Establishing partnerships often requires time and capital, and companies will be more likely to partner with your venture if they can read a detailed explanation of your company.
15. To Position Your Brand
Creating the business plan helps to define your company’s role in the marketplace. This definition allows you to succinctly describe the business and position the brand to customers, investors, and partners. With the industry, customer and competitive insight you gain during the business planning process, you can best determine how to position your brand.
16. To Judge the Success of Your Business
A formal business plan allows you to compare actual operational results versus the business plan itself. In this way, it allows you to clearly see whether you have achieved your strategic, financing, and operational goals (and why you have or have not).
17. To Reposition Your Business to Deal with Changing Conditions
For example, during difficult economic conditions, if your current sales and operational models aren’t working, you can rewrite your business plan to define, try, and validate new ideas and strategies.
18. To Document Your Marketing Plan
How are you going to reach your customers? How will you retain them? What is your advertising budget? What price will you charge? A well-documented marketing plan is essential to the growth of a business. And the marketing strategies and tactics you use will evolve each year, so revisiting your marketing plan at least annually is critical.
19. To Understand and Forecast Your Company’s Staffing Needs
After completing your business plan, you will not be surprised when you are suddenly short-handed. Rather, your business plan provides a roadmap for your staffing needs, and thus helps to ensure smoother expansion. Importantly your plan can not only help you understand your staffing needs, but ensure your timing is right as it takes time to recruit and train great employees.
20. To Uncover New Opportunities
Through the process of brainstorming, white-boarding and creative interviewing, you will likely see your business in a different light. As a result, you will often come up with new ideas for marketing your product/service and running your business. It’s coming up with these ideas and executing on them which is often the difference between a business that fails or just survives and one that thrives.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a business plan.
A business plan is a document that details your business concept and strategy for growth.
A business plan helps guide your company's efforts and, if applicable, gives investors and lenders the information they need to decide whether or not to fund your company. A business plan template helps you to most easily complete your plan.
Why Do You Need a Business Plan?
A business plan provides details about your company, competition, customers and industry so that you make the best possible decisions to grow your company.
What is the Importance of a Business Plan?
The 3 most important purposes of a business plan are 1) to create an effective strategy for growth, 2) to determine your future financial needs, and 3) to attract investors (including angel investors and VC funding ) and lenders.
Why is a Business Plan Important to an Entrepreneur?
Business plans help entrepreneurs take their visions and turn them into tangible action plans for success.
Need help with your business plan?
- Speak with a professional business plan consultant from our team.
- Use our simple business plan template .
- Check out our business plan examples .
- Or, if you’re creating your own PPM, you can save time and money with Growthink’s private placement memorandum template .
- Learn more about us via our Growthink Business Plan Review page
The World’s #1 Business Plan Template
Would you like to know the quickest and easiest way to create a winning business plan?
And how to use it to raise funding, improve your strategy, or both?
Well, we’ve developed the ultimate business plan template to help you do this. Simply click below to learn more.

Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


What is Business Plan? Importance, Setting Goals & Objective, Process, Format, Fails
- Post last modified: 14 March 2024
- Reading time: 27 mins read
- Post category: Entrepreneurship

What is Business Plan?
A business plan is an operating document that describes the dream of an entrepreneur with the objectives and plans to achieve them. A business plan shows the viability of the business idea from every aspect. A business plan is a crucial document that is utilized by both the company’s external and internal audiences.
A business plan seeks investment and it is reviewed and revised regularly to see whether goals are accomplished. A fresh business plan is sometimes written for an existing company that has opted to take a different path.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Business Plan?
- 2 Importance of Business Plan
- 3.1 Business Goals Vs. Business Objectives
- 3.2 How to Set Short-term Business Goals?
- 4.1.1 Determine Your Strategic Position
- 4.1.2 Prioritise Objectives
- 4.1.3 Develop a Plan
- 4.1.4 Execute and Manage the Plan
- 4.1.5 Review and Revise the Plan
- 5.1 Section 1: Executive Summary
- 5.2 Section 2: Industry Overview
- 5.3 Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- 5.4 Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- 5.5 Section 5: Management Plan
- 5.6 Section 6: Operating Plan
- 5.7 Section 7: Financial Plan
- 5.8 Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- 6.1 Lack of planning
- 6.2 Leadership failure
- 6.3 No differentiation
- 6.4 Ignoring customer needs
- 6.5 Inability to learn from failure
- 6.6 Poor management
- 6.7 Lack of capital
- 6.8 Premature scaling
- 6.9 Poor location
- 6.10 Lack of profit
Importance of Business Plan
Let us discuss the importance of a business plan.
- It explains the vision and goals of the founder.
- It acts as a guide for the new entrepreneur.
- It serves as a blueprint for a company’s overall operation. Sales, expenditures, periods, and strategic direction can all be used to gauge a company’s success and progress.
- It may also assist an entrepreneur or management in identifying and focusing on possible areas both inside and outside the organization. Proposed remedies and contingency plans can be integrated into the company’s strategy once potentially difficult areas have been identified.
- It covers the marketing opportunities and future funding requirements, which demand managerial attention.
- In certain cases when an entrepreneur decides to transform a cherished pastime into a home-based business, the business plan can be as short as a one- or two-page document. A company’s proposal with substantial intricacy and financial ramifications, on the other hand, should have a far more detailed plan.
Setting Goals and Objectives
Business objectives are an important component of creating priorities and positioning an organization for long-term success. Setting company goals and developing separate targets to assist in achieving each goal will considerably improve the capacity to attain those goals. Here, we look at how to define company goals, the distinction between business goals and objectives, and examples of short- and long-term business goals.
Business objectives may be defined for a whole organization as well as specific departments, employees, managers, and clients. Goals are usually used to symbolize a company’s wider purpose and provide an end goal for personnel to work toward. Business objectives may not need to be precise or have well-defined activities. Business objectives, on the other hand, are broad results that a company aims to attain.
Business objectives are measures taken to achieve a company’s larger goals that are clearly stated and quantifiable. Objectives are particular and they are simple to establish and track. To fulfill their business objectives, companies must set objectives.
Business Goals Vs. Business Objectives
The distinction between business goals and business objectives is as follows:
- Business objectives establish the “how” of a company’s purpose, whereas business goals define the “what.”
- Business objectives specify concrete tasks, whereas business goals often merely give a broad direction for a firm to pursue.
- Business objectives are usually measurable, whereas business goals are not.
- Business objectives are more detailed, whereas business goals are more wide and inclusive.
- Business objectives are usually time-bound, whereas business goals are not.
How to Set Short-term Business Goals?
Short-term business objectives are those that you wish to attain in the next few weeks or months for a firm. When it comes to short-term business goals, you may take the following steps:
- Recognize the Short-term Business Goals of the Company for A Set period : In this step, short-term objectives of the company are established so that the set objective can be accomplished in a specific time frame. Many short-term goals are secondary to the fulfillment of long-term objectives. Consider your long-term objectives as well as what you want to achieve in the coming weeks or months and turn them into short-term objectives that will help your company grow.
- Break Goals Into Actionable Business Objectives: Here, management breaks the goals into specific targets. These goals should be represented by the measures an organization will take to achieve them. For example, the target for Kalyani is to convert 5 leads and get 5 new customers for the business within the next 2 months, objectives will be the job or work done for getting 5 customers’ such as placing a new advertisement in the newspaper, social media and posting three times a week on YouTube and Instagram.
- Objectives Should Be Measurable: The established business goals should be quantifiable or measurable. For example, if an employee has the short-term goal of posting an advertisement or banner on social media then, do not assign responsibility to him/her by just saying “post more and more on social media”. Instead, give him/her a per-day target to make it quantifiable or measurable. For example “Post on Instagram three times a week and Facebook two times a week for eight weeks,”.
- Goal-related Tasks Must Be Assigned to Employees: Once the objectives for each short-term goal have been determined, assign each one to an individual or team of employees who will see it through to completion.
- Check and Keep a Record of Performance regularly: Measure your short-term goals’ progress regularly to verify you are on pace to fulfill them within the timeframe you set. Measure any additional customer/potential customer contact you receive as a result of increasing your social media postings to three times a week as part of a business objective. Keep track of progress and, if necessary, change your targets to better fulfill your objectives.
Process of Writing the Business Plan
Every company should have a strategic plan, but you might be surprised by the number of companies that try to function without one (or at least one that is well expressed). According to Strategy research, 86 percent of executive teams spend less than one hour per month discussing strategy, while 95 percent of the average worker has no idea what their company’s strategy is. Because so many firms fail in these areas, strategic planning can help you get ahead of the game.
The strategic planning process is more comprehensive; it aids in the creation of a roadmap for which strategic objectives you should focus on and which projects will be less beneficial to the company. The phases of the strategic planning process are listed below.
Strategic Planning Process
Determine your strategic position.
This phase of preparation sets the tone for the rest of the project. To figure out where you need to go and how you will get there, you must first figure out where you are. Include the appropriate stakeholders from the start, taking into account both the internal and the external sources.
Identify significant strategic concerns by speaking with corporate management, gathering consumer feedback, and gathering industry and market data to acquire a comprehensive picture of your position in the market and the thoughts of your customers.
It is better to write a good idea, purpose, and vision statement for the company to get a clear picture of what success looks like. Additionally, you should analyze your firm’s basic principles to remind yourself of how your organization will achieve these goals.
To begin, identify the challenges that need to be solved using industry and market data, including consumer insights and current/future requests. Create a list of your company’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external possibilities (ways your company may develop to meet requirements that the market doesn’t currently meet) and threats (your competition).
Use a SWOT diagram as a foundation for your initial analysis. You may easily classify your results as Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats or SWOT to define your present position with input from executives, customers, and external market data.
Political, Economic, Socio-cultural, and Technological or PEST is a strategic technique for identifying dangers and possibilities for your company.
Prioritise Objectives
After you have determined your present market position, you will need to set targets to assist you reach your objectives. Your goals should be in sync with the mission and vision of your firm.
Ask important questions to help you prioritize your goals, such as:
- Which of these measures will have the biggest impact on attaining our company’s mission/vision and strengthening our market position?
- What are the most critical sorts of effects (e.g., client acquisition vs. revenue)?
- What will the competition’s response be?
- Which projects are the most critical?
- What will we have to do to achieve our objectives?
- How will we track our progress and see if we have met our objectives?
To assist you in achieving your long-term strategic goals and activities stated in step one, objectives should be unique and quantifiable. Updated website content, improved email open rates and new leads in the pipeline are all possible goals.
SMART goals may help you set a schedule and identify the resources you will need to reach your objectives, as well as track your progress with key performance indicators or KPIs.
Develop a Plan
Now is the time to develop a strategic strategy for achieving your objectives. This phase entails deciding the techniques required to achieve your goals, as well as establishing a timeframe and communicating responsibilities.
Strategy maps, which work from the top down, make it straightforward to see company processes and find areas for development.
True strategic decisions generally entail a cost-of-opportunity trade-off. For example, your organization could opt to spend less money on customer service to put more money into producing an intuitive user experience. Prepare to say “no” to efforts that will not improve your long-term strategic position, based on your values, mission statement, and defined priorities.
Execute and Manage the Plan
You are now ready to put your strategy into action. To begin, share necessary material with the organization to convey the plan. After that, the real job begins. By mapping your processes, you can turn your overall strategy into a tangible plan.
To communicate team roles, use KPI dashboards. The completion process and ownership for each stage of the journey are depicted in this detailed method. Establish frequent evaluations with individual contributors and their supervisors, as well as check-in points, to ensure you stay on track.
Review and Revise the Plan
The plan’s last step, review, and revision, allows you to examine your goals and make course corrections based on past successes and failures. Determine the KPIs your team has met and how you can continue to fulfill them every quarter, changing your plan as needed.
It is critical to assess your goals and strategic position every year to ensure that you stay on course for long-term success. Balanced scorecards can help you keep track of your progress and achieve strategic goals by giving you a complete picture of your company’s performance.
Your goal and vision may need to evolve; an annual assessment is an excellent time to examine such changes, draft a new strategy, and re-implement it.
Typical Business Plan Format and Content
Here is a simple template that any company may use to create a business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Give an overview of the company’s mission.
- Describe the product and/or service offerings of the firm.
- Give a brief overview of the target market’s demographics.
- Explain how the firm will gain a piece of the available market by summarising the industry competition.
- Provide an overview of the operations strategy, including inventory, office and labor requirements, and equipment needs.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s industry position.
- Describe the industry’s current competitiveness and significant players.
- Provide details on the industry in which the company will operate, projected revenues, industry trends, government influences, and the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their requirements, and their location.
- Describe the market’s size, the number of units of the company’s products that potential consumers might buy, and any market changes that might occur as a result of broader economic developments.
- Give a summary of the projected sales volume in comparison to what your rivals sell.
- Give an outline of how the firm intends to compete with current competitors to achieve and maintain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the company’s items for sale as well as its unique selling proposition.
- List the many advertising outlets that the company will utilize to communicate with clients.
- Describe how the company intends to price its items so that it can earn a profit.
- Give specifics on how the company’s items will be delivered and shipped to the target market.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the company’s organizational structure.
- Make a list of the company’s owners and their ownership percentages.
- Make a list of the top executives, their responsibilities, and their pay.
- List any internal and external professionals the organization intends to recruit, as well as their salaries.
- If available, include a list of the advisory board members.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the business’s location, including the need for an office and a warehouse.
- Describe the company’s workforce requirements. Outline the number of employees the firm need, their jobs, the skills training that will be required, and the length of time that each person will be with the organization (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process and how long one unit of a product will take to make.
- Describe equipment and machinery requirements, as well as whether the firm will lease or buy the equipment and machinery, as well as the estimated expenses.
- Provide a list of raw material needs, as well as how they will be procured and the primary vendors that will provide the necessary inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Include the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and projected balance sheet projection in your description of the company’s financial predictions.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Lease quotes for buildings and machinery
- Plan for offices and warehouses that has been proposed
- An overview of the target market and market research
- The owners’ credit information
- Product and/or service list
Understand Why Business Plans Fail
The saddest aspect of a failing firm is that the owner is frequently completely oblivious to what is going on until it is too late. It makes sense because if the entrepreneur had truly understood what he/she was doing incorrectly, he/she may have been able to rescue the company.
The following is a list of some of the most common causes:
Lack of planning
Businesses fail due to a lack of both short- and long-term planning. The business strategy should address where a company will be in the coming months and years. Quantifiable objectives and outcomes and specific to-do lists with dates and deadlines will be included in the correct plan. Your business will suffer if you do not plan.
Leadership failure
Businesses collapse as a result of poor leadership. Leadership must be capable of making correct judgments the majority of the time. Leadership failures will affect all parts of your firm, from financial management to staff management. To develop their leadership qualities, the most successful entrepreneurs learn, research, and seek out mentors.
No differentiation
Having a fantastic product is not enough. You must also create a distinct value offer; otherwise, you will become lost in the crowd. What distinguishes your company from the competition? What distinguishes your company? Understanding what your rivals do better than you is critical. You won’t be able to develop a brand if you do not separate yourself.
Ignoring customer needs
Every company will tell you that a customer is number one, but only a small fraction of them do so. Failure causes businesses to lose contact with their customers. Keep an eye on your clients’ changing values. Check to see if they still enjoy your products. Are they looking for new features? Therefore, what exactly are they saying? Are you paying attention?
Inability to learn from failure
While we all know that failure is typically a terrible thing, businesses seldom learn from it. Realistically, businesses fail for a variety of reasons. Entrepreneurs are frequently blind to their errors. It is tough to learn from mistakes.
Poor management
Inability to listen, micro-managing – often known as a lack of trust – operating without standards or processes, poor communication, and a lack of feedback are all examples of poor management.
Lack of capital
This might prevent you from attracting investors. A lack of capital is a red flag. It indicates that a company may be unable to pay its payments, loans, and other financial obligations. Lack of finance makes it harder to expand the firm and puts day-to-day operations in jeopardy.
Premature scaling
Scaling is beneficial if done at the appropriate time. To put it another way, if you grow your firm too quickly, it will fail. You may, for example, be recruiting too many staff too rapidly or overspending on marketing. Do not expand your company unless you are ready.
Pets.com collapsed because it attempted to expand too quickly. They opened too many warehouses across the country too soon and it bankrupted them. Even their strong brand equity wasn’t enough to save them. Their stock dropped from $11 to $0.19 in a matter of months.
Poor location
Inconvenient location is a disadvantage that may be difficult to overcome. If your business relies on foot traffic, choosing the right location is crucial. Your client acquisition expenses may be excessively high due to a bad location.
Lack of profit
Revenue is not the same as profit. As an entrepreneur, you must always keep profitability in mind. Profit permits expansion. Only 40% of small firms are successful, 30% are breaking even and 30% are losing money, according to Small Business Trends.
- Pednekar, A. (2010). Entrepreneurship management. Himalaya Pub. House.
- Stutely, R. (2012). The definitive business plan. Pearson.
Marketing Management
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
Sales Management
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO) ?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
Marketing Essentials
- What i s Marketing?
- What i s A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M'S Of Advertising
- What i s Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What i s Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What i s International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
Consumer Behaviour
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
Business Communication
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal C ommunication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
Business Law
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
Brand Management
- What is Brand Management?
- 4 Steps of Strategic Brand Management Process
- Customer Based Brand Equity
- What is Brand Equity?
You Might Also Like
What is social entrepreneurship ecological, sustainable, micro, small and medium enterprises (msme), family business and entrepreneurship, successful entrepreneurs, development of entrepreneurship, raising funding: business valuation, early-stage funding, sources, entrepreneurial proces, innovation and ideas, entrepreneurial venture, what is intellectual property rights copyright, patents, trademark, what is rural entrepreneurship need, types, challenges, importance, what is women entrepreneurship definition, concept, problems, what is an entrepreneur definition, types, qualities, characteristics, entrepreneurship, nature, importance, types, how to become, role, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal growth.

Development
Small Business Trends
How to create a farm business plan.

If you buy something through our links, we may earn money from our affiliate partners. Learn more .
Crafting a comprehensive farm business plan is a crucial step towards transforming your agricultural visions into tangible realities. This plan serves as a blueprint, enabling you to formally articulate your thoughts, ideas, and aspirations. Engaging in this process can lead to profound insights, illuminating the path to a thriving agricultural enterprise.
Even though the term ‘farm business plan’ might evoke a sense of formal rigidity, it’s important to remember that this document is, in fact, a living, evolving entity. Just like a seedling that sprouts, grows, and changes with the seasons, your business plan is not meant to be static.
It’s something you nurture, revise, and expand as circumstances dictate and as your farm business matures. Feeling pressure to perfect your business plan from the outset could be paralyzing. Instead, we suggest you view this document as a foundation that can be continuously built upon.

To get you started, we offer a detailed farm business plan template. This invaluable resource can be tailored and expanded to suit your unique agricultural venture, whether you’re cultivating a sprawling wheat field or nurturing a boutique organic herb garden.
The most effective business plans are those that exhibit flexibility and resilience, characteristics that are at the heart of any successful farm business. Agriculture, by its very nature, is a domain subject to the whims of Mother Nature. From unpredictable weather patterns to seasonal variations, farmers of all kinds grapple with an array of external factors.
Therefore, your farm business plan should not only anticipate these challenges but also prescribe adaptive measures to navigate through them. It’s this inherent adaptability that transforms a good farm business plan into a great one.
Writing a Farm Business Plan Template: 15+ Things Entrepreneurs Should Include

A farm business plan, like any strategic document, should be comprehensive, encompassing all aspects of your operation, be it agricultural (crops) or product-based. Utilize these 15 key sections to shape your farm business plan template.
Do bear in mind that while these sections are integral, they are by no means exhaustive. Your farm business plan may necessitate additional topics based on your specific farming operations.
Creating a robust business plan is of paramount importance, whether you’re kickstarting a farm venture or acquiring an existing one. Our farm business plan template starts off with an executive summary.
Executive Summary
The executive summary provides an essential overview of your farm business. It helps to streamline communication and understanding between various stakeholders, such as internal team members, potential lenders, business partners, and customers. When drafting your executive summary, consider the following key components:
- Business Profile : Provide a snapshot of your farm business, describing its nature and scope. Are you into crop cultivation, livestock rearing, or any specialized farming practices?
- Products : Clearly outline what product or products your farm will produce. These could range from dairy products to specific crops or even services like agrotourism.
- Production Methodology : Describe how you plan to achieve your production goals. This could involve discussing your farming techniques, usage of technology, or unique methodologies.
- Target Audience : Identify the individuals or groups who will be interested in your farm products or services. These might be local consumers, restaurants, farmers’ markets, or even online customers.
- Key Strategies : Highlight the strategies you plan to implement to run and grow your business. This could cover marketing techniques, sustainability practices, or partnerships.
- Mission and Vision : Briefly outline the mission and vision of your farm business. This helps to convey your long-term objectives and core values.
Remember, your executive summary is essentially the first impression of your business plan. Making it comprehensive, clear, and compelling will help attract interest and support from stakeholders.
Goals and Objectives
A well-crafted business plan should encapsulate both personal and economic goals and objectives. Many successful farm business plans also address environmental stewardship and community outreach. You may want to include goals around preserving farm resources for future generations, ensuring that both the operational and stewardship aspects remain within the family.
Introduction
Your introduction should provide information about the business owners, including their backgrounds and levels of industry experience.
Mission Statement and Values of Your Farming Business Plan

This section enables you to express the core values that led you to the farming business, whether it’s an urban farming venture or a homemade product-based farm. Your mission statement should reflect these values. Sustainable practices and conservation are often key motivations that draw people to farming, so don’t be shy to share your commitment to such principles.
Industry History
Understanding your place within the wider agricultural landscape is key. Be sure to research farms that have historically dominated your region, whether they specialize in vineyards, urban farming, or livestock rearing. Use this research to make educated projections about the future.
Company Background and History
Share the history of your farm if it has been a long-standing family venture or the journey leading up to your purchase if it wasn’t. If your farm business is a startup, focus on the business experience and backgrounds of the involved parties.
Competitor Analysis
Understanding your competition is crucial. In the agricultural sector, farmers often share resources, such as a high-tech corn planter , or cooperate in marketing endeavors. Factor in such synergies when analyzing competitors.
Target Market
Clearly define your target market. This can include area groceries, farmers’ markets, or online customers. If you’ll be relying on online sales, ensure your website is professionally designed, keyword optimized, and easily discoverable.
Products and Services
Describe each product or service offered by your farm, highlighting those features most appealing to your target market.
Organization, Human Resources, and Management Plans
These interconnected elements cover your farm’s day-to-day operations, employee roles and responsibilities (including their job descriptions ), and overarching management plans.
SWOT Analysis
Conduct a SWOT analysis to identify your farm’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This will help you strategize on how to leverage your strengths, mitigate your weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and neutralize threats.
Your vision is the roadmap for your farm’s future. It should express not just your financial aspirations but also your plans for the farm operation in the long run.
Growth Strategy
A comprehensive growth strategy should outline your plans for debt reduction, savings, and business expansion. Keeping detailed farm production records is key to evaluating the effectiveness of your growth strategy.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include elements like balance sheets, income statements, projected cash flows, loan repayment schedules, and depreciation factors.
Marketing Strategy
A robust marketing strategy is essential for your farm’s success. Look into brochures, advertisements, and joining co-op groups. Resources from institutions like the University of Minnesota and Cornell University offer comprehensive insights into effective marketing strategies for farm businesses.
Establishing a Farming Business Entity
Discuss the legal structure of your farm business. Will it be a sole proprietorship, a partnership, an LLC, or a corporation? Outline the pros and cons of each and why the chosen structure is the best fit for your farm business.
Detailed Description of Farm Operations
Include a section that provides an in-depth look at your day-to-day farm operations. This can cover everything from crop rotation plans, livestock breeding programs, to the use of technology and machinery in your farming activities.
Risk Management Strategies
Address potential risks and challenges your farm might face, such as natural disasters, market fluctuations, or pest infestations. Discuss the strategies you plan to implement to mitigate these risks, like insurance coverage, diversification, and emergency response plans.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Highlight your farm’s approach to sustainability and its impact on the environment. Discuss practices like organic farming, conservation techniques, and renewable energy usage, which demonstrate your commitment to environmental stewardship.
Community Involvement and Social Responsibility
Describe how your farm business plans to engage with and contribute to the local community. This could include hosting educational farm tours, participating in farmers’ markets, or supporting local food programs.
Supply Chain and Vendor Relationships
Detail your farm’s supply chain and vendor relationships. Explain how you plan to source inputs like seeds, feed, or equipment, and any partnerships with local suppliers or distributors.
Technology and Innovation
Discuss the role of technology and innovation in your farm business. This could include the use of precision agriculture, innovative irrigation systems, or the adoption of farm management software to enhance efficiency and productivity.
Training and Development Plans
Explain how you intend to train and develop your staff. Include plans for ongoing education, skill development, and potentially, leadership training for future farm managers.
Expansion and Diversification
Outline your long-term plans for expansion and diversification. This could involve adding new crops, branching into agrotourism, or exploring value-added products like farm-produced jams or cheeses.
Exit Strategy
Consider including an exit strategy for your farming business. This could be a plan for succession, selling the business, or transitioning to a different type of agricultural operation.
Wrap up your business plan with a conclusion that reiterates your farm’s core mission and vision, and express your enthusiasm and commitment to making your farm business a success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Include a FAQ section at the end of your business plan to address common questions potential investors or partners may have about your farm business. This can include queries about your business model, funding needs, or market potential.
Provide an addendum for additional documents that support your business plan. This can include resumes of key team members, detailed financial projections, market research data, or letters of support from future customers or partners.
Do I Need a Business Plan for My Farm?
Even if you’re knee-deep in the dirt, tending to your crops or livestock, every farming enterprise has the core elements of a business at its heart. These include aspects such as operations, marketing, human resources, and finances. When you embark on developing a farm business plan, it might astonish you to see where the journey takes you. You could end up discovering facets of your farm business that you hadn’t previously considered.
One of the many advantages of constructing your business plan is the opportunity it affords to involve others. Employees, family members, even your loyal farm dog might have innovative small farm business ideas that could significantly enhance your farm’s productivity and marketability. A different perspective can often yield solutions for issues you might not have even been aware of. Therefore, encourage an open exchange of thoughts and ideas. Who knows, the next great idea could be lying right under your hay bale!

More than just a document outlining your farm’s structure, your farm business plan should serve as a valuable decision-making tool. With it, you can confidently navigate the varied terrain of farm management, from daily operations to larger strategic initiatives. When you’ve got a meticulously crafted, robust farm business plan, it doesn’t just narrate your farm’s story, but also provides you with a roadmap to future growth and success.
Beyond this, a top-notch farm business plan can also be a lever that helps you access critical financing. Lenders and investors are more likely to support your venture when they see a well-structured, thoughtful business plan that articulates your vision, illustrates your understanding of the market, and demonstrates your commitment to fiscal responsibility.
So, where to begin? Let’s dive into our fundamental guide to crafting a farm business plan using our adaptable template. This resource has been designed to help you capture every aspect of your agricultural venture, laying a strong foundation for a bountiful future.
How Do I Write a Small Farm Business Plan?

Don’t sit down to write the whole thing. Chip away, one section at a time. Keep in mind that the plan doesn’t have to be the definitive last word. You can make adaptations.
How do you start a farm business plan?
Start with one piece of the business plan. One of the hardest sections of a business plan to write is the Mission Statement . If you get bogged down there, continue and come back to it later.
How much do farm owners make a year?
As you can imagine, the net income varies greatly by type of farm business.
The bottom line after expenses may not be high. Farmers need to consider net worth as assets grow and the farm property increases in value.
How much does it cost to start a small farm?
Getting set up to raise 100 beef cattle costs lots more than getting set up to raise 100 rabbits.
Things like property acquisition, soil preparation, equipment and machinery and the key costs. Other costs may be i rrigation systems , packaging and trucking.
What is the most profitable farming business?
Poultry farming is currently the most profitable – and common – farm business in the world. It includes chicken, turkey, quail, ducks and goose, that are being raised for meat or eggs.
It’s also one of the most expensive businesses to start, requiring significant capital investment. The industry is very labor-intensive and labor costs are high.
Image: Depositphotos

Comments are closed.
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
Content Search
Consultancy to develop business plan for nature-based initiative - bee keeping enterprise.
- International Fund for Animal Welfare
The objective of the assignment
The objective of this consultancy service is to develop a comprehensive business plan for beekeeping initiatives targeting the local beekeeping groups and members of the Taita Taveta Wildlife Conservancies Association. The business plan should outline strategies for establishing and operating successful beekeeping enterprises within the conservancies/ranches and the county at large while integrating principles of sustainability, community engagement, and conservation
Scope of Work:
This assignment will be undertaken in the larger Tsavo Conservation area (Taita Taveta County) specific target of 35 ranches. However, the scoping for the market is not limited to the geography under consideration. The consultancy work will include, but not be limited to, the following tasks:
Conduct a situational analysis of the beekeeping sector within the Taita Taveta county including market dynamics, existing initiatives, and potential challenges and opportunities.
Reviewing existing beekeeping practices within the TTWCA membership and identifying areas for improvement.
Assess the feasibility of beekeeping as a nature-based enterprise for TTWCA members and local beekeeping groups considering factors such as resource availability, market demand, and regulatory frameworks.
Identify suitable beekeeping techniques and technologies that are appropriate for the local context and align with conservation practices.
Develop a detailed business model for beekeeping enterprises, including production processes, marketing strategies, financial projections, and risk management plans.
Explore the current value chain of beekeeping and resultant products with the aim of improving it under different investment scenarios.
Propose new marketing procedures or potential markets that would guarantee farmers value for the bee products.
Outline capacity-building needs for TTWCA members and local groups interested in engaging in beekeeping activities, including training requirements and support services.
Propose mechanisms for monitoring and evaluating the success of beekeeping initiatives in achieving conservation and livelihood objectives.
Expected Deliverables:
The consultancy will deliver the following key outputs:
Situational analysis report on the beekeeping sector within Taita Taveta County.
Feasibility study report assessing the viability of beekeeping as a nature-based enterprise for TTWCA members and the local community.
Comprehensive business plan for beekeeping initiatives, including all required components as outlined in the scope of work.
Training materials and capacity-building recommendations for TTWCA members and local communities interested in beekeeping.
Final consultancy report summarizing the methodology, findings, and recommendations
The consultant is expected to complete the work within 60 days from the commencement date.
Required Skills, Experience, and Competencies
The consultancy team should possess the following qualifications and expertise: Demonstrated 7 years of experience in developing business plans for naturebased enterprises, preferably in the conservation or natural resource management sectors. animal health, Natural resource management, and/or related field. At least 6 years experience in beekeeping and knowledge of best practices in apiculture. A deep understanding of nature-based enterprises, including sustainable resource management, eco-friendly practices, and the integration of nature conservation into business models Proven experience in designing and delivering training programs and workshops, with the ability to engage diverse audiences and create interactive learning experiences.
How to apply
Interested candidates should send their technical and financial proposals (not exceeding 15 pages), CVs (demonstrating their qualification, competency, and experience in undertaking similar assignments), company profile, two recent references, and their availability to [email protected] and [email protected] CC: [email protected] with the subject as BUSINESS PLAN FOR NATURE BASED INITIATIVE BEEKEEPING ENTERPRISE FOR TAITA TAVETA WILDLIFE CONSERVANCIES not later than CoB Friday, 3 rd May 2024
Related Content
Identifying and measuring the effectiveness of socio-technical innovation bundles on empowerment and resilience in kenya: a baseline report, climate information and kenya’s women smallholder farmers: a needs assessment (jan 2023), under the scorching sun kenyan farmers find new ways to beat climate change, why land rights are important for climate action.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

UPDATED 13:11 EDT / APRIL 16 2024

Google Cloud develops strategic AI plan for enterprise success
by Brian Njuguna
As artificial intelligence reshapes our world with groundbreaking innovations, it’s clear that conventional strategies won’t suffice. Organizations need a visionary AI plan — one that embraces bold, unconventional ideas to harness the full potential of these technologies for superior results.
Spinning things up with AI continues to take center stage in the enterprise world because it acts as the stepping stone toward better decision-making, demonstrating that a specific AI plan is required now more than ever, according to Bobby Allen (pictured), cloud therapist at Google LLC.
“Customers obviously want to talk AI all the time,” Allen said. “They’ve got to come up with an AI plan. Are you talking of a plan for AI-assisted development? You want to create AI workloads? You want AI-infused insights on your platform? You want AI-assisted collaboration? Yes. They want all of those things, and so we have to kind of break down exactly what [they’re] looking for at the time. AI is not the thing; AI is the thing that makes the thing better.”
Allen spoke with theCUBE analysts John Furrier , Savannah Peterson and Dustin Kirkland at Google Cloud Next 2024 , during an exclusive broadcast on theCUBE, SiliconANGLE Media’s livestreaming studio. They discussed why jumping on the AI bandwagon is a necessity, and how Google’s Cloud Run platform is essential for deploying AI-driven applications quickly and securely. (* Disclosure below.)
Streamlining AI deployment for strategic advantage
By using easy-to-deploy features that do not forfeit enterprise-grade visibility or security, Google’s Cloud Run application canvas should be seen as an ideal starting point in the AI journey, according to Allen. This is because it’s a fully managed platform that is designed to generate, modify and deploy Cloud Run applications.
“We did three demos in that one session alone [at Google Cloud Next],” Allen said. “The first one was on what we call Cloud Run application canvas. The cool thing about it is you’re literally using AI to create AI. Cloud Run is already the simplest way to deploy your code to a container. Literally, and I’m not exaggerating, in five minutes, you can get an application running. You can say, ‘I want a gen AI application that looks like this, and it’ll build it.’”
Google Cloud is accelerating the AI narrative through cutting-edge features. For instance, Gemini Cloud Assist enables teams to optimize, operate and design their application lifecycle because innovation happens at the intersection of where the model lives and where the app runs, Allen pointed out.
“The second demo was what we call Gemini Cloud Assist … where you’re using AI to help you operate and optimize existing workloads in a platform like GKE,” Allen said. “The third demo was Security Posture, because unfortunately our pace of innovation is increasing, but the bad actors are still doing the bad acting. They’re still doing their thing … we’ve got tools.”
Here’s the complete video interview, part of SiliconANGLE’s and theCUBE Research’s coverage of Google Cloud Next 2024 :
(* Disclosure: TheCUBE is a paid media partner for Google Cloud Next 2024. Neither Google LLC, the primary sponsor for theCUBE’s event coverage, nor other sponsors have editorial control over content on theCUBE or SiliconANGLE.)
Photo: SiliconANGLE
A message from john furrier, co-founder of siliconangle:, your vote of support is important to us and it helps us keep the content free., one click below supports our mission to provide free, deep, and relevant content. , join our community on youtube, join the community that includes more than 15,000 #cubealumni experts, including amazon.com ceo andy jassy, dell technologies founder and ceo michael dell, intel ceo pat gelsinger, and many more luminaries and experts..
Like Free Content? Subscribe to follow.
LATEST STORIES

Landmark UK law would criminalize making sexualized deepfakes even if they aren't shared

Linux Foundation, Intel and others promote open-source data stacks for enterprise generative AI

AMD and Nvidia unveil new processors for AI PCs

EY launches blockchain-based business contract management solution on Ethereum

UnitedHealth investigating reported leak of data from its Change Healthcare unit
Rivos raises $250M+ to develop chips for AI and analytics workloads
POLICY - BY JAMES FARRELL . 24 MINS AGO
AI - BY MIKE WHEATLEY . 50 MINS AGO
INFRA - BY MIKE WHEATLEY . 2 HOURS AGO
BLOCKCHAIN - BY KYT DOTSON . 3 HOURS AGO
SECURITY - BY MARIA DEUTSCHER . 4 HOURS AGO
AI - BY MARIA DEUTSCHER . 6 HOURS AGO
Our use of cookies
We use necessary cookies to make our site work (for example, to manage your session). We’d also like to use some non-essential cookies (including third-party cookies) to help us improve the site. By clicking ‘Accept recommended settings’ on this banner, you accept our use of optional cookies.
Necessary cookies
Necessary cookies enable core functionality on our website such as security, network management, and accessibility. You may disable these by changing your browser settings, but this may affect how the website functions.
Analytics cookies
We use analytics cookies so we can keep track of the number of visitors to various parts of the site and understand how our website is used. For more information on how these cookies work please see our Cookie policy .
Prudential Regulation Authority Business Plan 2024/25
Related links related links.
- PRA annual reports and business plans
- CP4/24 – Regulated fees and levies: Rates proposals 2024/25
Maintain and build on the safety and soundness of the banking and insurance sectors, and ensure continuing resilience
Be at the forefront of identifying new and emerging risks, and developing international policy
Support competitive and dynamic markets, alongside facilitating international competitiveness and growth, in the sectors that we regulate, run an inclusive, efficient, and modern regulator within the central bank, the pra’s strategy.
Our strategy for 2024/25 will be delivered through our strategic goals, extracts of which are below. For the full detail of our workplan against each strategic priorities, see pages 10 to 41 of this Business Plan .
Foreword by Chief Executive Sam Woods
Sam Woods Deputy Governor, Prudential Regulation Chief Executive of the PRA
First, this will be our first full year operating under the Financial Services and Markets Act (FSMA 2023), which established a new, post-Brexit regulatory framework for the UK. FSMA 2023 expanded our rulemaking responsibilities and gave us a new secondary objective to support the competitiveness and growth of the United Kingdom.
Competitiveness and growth have always been important considerations for the PRA. Nonetheless, this new objective represents a significant change, and embedding it into our approach has been a major priority for the organisation as a whole, and for me personally as CEO. That effort will continue this year.
Our business plan includes a range of initiatives aimed squarely at promoting the UK’s competitiveness and growth. Some of the most significant are:
- Our ‘Strong and Simple’ project, which aims to simplify regulatory requirements for smaller banks, thus reducing compliance burdens without compromising on strong standards.
- The ‘Solvency UK’ reforms of insurance capital standards, which will reduce bureaucracy in the regulatory regime, while also allowing insurers to invest in a wider range of productive assets.
- The Banking Data Review, which aims to reduce burdens on firms by focusing our data collection on the most useful and relevant information.
- Improvements to our authorisation processes – we have made significant progress in improving the speed and efficiency of authorisations without sacrificing the robustness of our controls; maintaining this progress will be a key focus for next year.
- Reforms to ring-fencing, following the independent review led by Sir Keith Skeoch.
The second point I want to highlight is our ongoing programme of work to maintain the resilience of the UK’s banking and insurance sectors, which is at the heart of our role. The events of 2023 (including the high-profile failures of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) and Credit Suisse (CS)) demonstrate the importance of a focus on resilience – and while I am encouraged by how the UK banking and insurance sectors have remained stable through a stressful period, we cannot take this for granted.
A major priority this year will be the implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards, which will complete the long process of post-financial crisis regulatory reform. While I expect the capital impact of these reforms to be limited for UK banks, they will nonetheless play a vital role in maintaining sufficient consistency in risk measurement across firms and jurisdictions – which is the cornerstone of the bank capital regime.
Another major priority this year will be ensuring firms have adequate standards of operational and cyber resilience. Following FSMA 2023, we have new powers to oversee the services provided to regulated firms by so-called ‘critical third parties’, and we will be implementing that regime over the coming year. And in March 2025 we will reach an important milestone with the full implementation of our wider operational resilience policy.
The day-to-day work of supervision will continue alongside these reforms. As always, our supervisory teams continue to work with PRA-regulated firms to ensure high standards of financial and operational resilience, governance, risk management, and controls. Stress testing remains a key element of our approach to resilience, and alongside colleagues from the wider Bank of England we will deliver a desk-based stress test of banks, and a system-wide exploratory scenario, in 2024. We will also work towards the next round of insurance stress tests in 2025.
I have really only scratched the surface of the work we are doing this year, as you can see from a glance at this document’s contents page. In order to deliver this work, we will need to run an efficient and effective regulator, and I am particularly excited by the potential of our data and analytics agenda to create new opportunities to improve how we work. And if past years are anything to go by, we will continue to engage with innovation in many forms across the industry, whether in the form of new entrants or new approaches to doing business in areas like digital money.
I am very much looking forward to the challenges that the next year will bring, and to working together with a team of very committed colleagues at the PRA to deliver on this business plan.
11 April 2024
Overview of responsibilities and approach
The PRA has two primary objectives: a general objective to promote the safety and soundness of PRA-authorised persons, and an objective specific to insurance firms for the protection of policyholders.
The PRA has two secondary objectives:
- the competition objective, which is focused on facilitating effective competition in the markets for services provided by PRA-authorised persons in carrying on regulated activities; and
- the competitiveness and growth objective, which is focused on facilitating, subject to alignment with relevant international standards, (a) the international competitiveness of the economy of the UK (including, in particular, the financial services sector through the contribution of PRA-authorised persons), and (b) its growth in the medium to long term.
In its December 2022 recommendations letter to the Prudential Regulation Committee (PRC), HM Treasury (HMT) set out aspects of the Government’s economic policy to which the PRA must have regard, while building on the important themes of openness, competitiveness, competition, and innovation, as well as delivering energy security and net zero.
In December 2023, the PRA published a consultation paper (CP)27/23 – The Prudential Regulation Authority’s approach to policy , which sets out the PRA’s approach to policymaking as it takes on expanded rule-making powers introduced through FSMA 2023. These expanded powers will enable the PRA to replace relevant assimilated law (previously known as retained EU law) with PRA rules and other policy material, and move towards a more British system of regulation, with most of the technical rules made by independent UK regulators within a framework set by Parliament. In addition, FSMA 2023 introduces new accountability measures that require the PRA to keep its rules under review , and to establish a Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) Panel composed of external members, which will scrutinise and provide input into the PRA’s CBA framework. These measures should enable the PRA to deliver policies that are well suited to the UK’s financial sector. In addition:
- In December 2023, the PRA took a significant step towards implementing the remaining Basel III standards in the UK by publishing the first of two near-final sets of rules with policy statement (PS)17/23 – Implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards near-final part 1 , which takes account of responses received to CP16/22 . The near-final rules aim to promote the safety and soundness of PRA-regulated firms and support their international competitiveness by making capital ratios more consistent, comparable, and aligned with international standards. The PRA will publish its second near-final policy statement in 2024 Q2 on the remaining aspects of the Basel 3.1 package, which include credit risk, the output floor, reporting, and disclosure requirements. The PRA plans to implement the Basel 3.1 standards over a 4.5-year transitional period beginning on 1 July 2025 and ending on 1 January 2030. Among other things, the PRA will also continue to support international efforts to monitor and promote the implementation of Basel 3.1.
- In December 2023, the PRA published PS15/23 – The Strong and Simple Framework: Scope Criteria, Liquidity and Disclosure Requirements , taking account of feedback to CP4/23 . The policy addresses liquidity and disclosure requirements for Simpler-regime Firms and Pillar 3 remuneration disclosure. The PRA will move further towards finalising and implementing the Strong and Simple prudential framework for Small Domestic Deposit Takers (SDDTs) during 2024. footnote [1]
- Following the publication of discussion paper (DP)3/22 – Operational resilience: Critical third parties to the UK financial sector , in December 2023, the PRA published CP26/23 , jointly with the Bank of England (‘the Bank’) and FCA (‘the supervisory authorities’). CP26/23 sets out the supervisory authorities’ proposed requirements for critical third parties (CTPs), footnote [2] including the mechanism for identifying potential CTPs, recommending them for designation by HMT, incident notification triggers and requirements, and proposed CTP Fundamental Rules. In 2024, the PRA will continue to work with the supervisory and other authorities to develop the final policy and oversight approach.
- In September 2023, the PRA published CP19/23 – Review of Solvency II: Reform of the Matching Adjustment , which marks a significant milestone in the PRA's reforms to the Solvency II regime for the UK insurance market. Following the publication of PS2/24 – Review of Solvency II: Adapting to the UK insurance market and PS3/24 – Review of Solvency II: Reporting and disclosure phase 2 near-final , the PRA will publish its final rules, subject to alignment with anticipated legislation, in 2024.
The PRA’s objectives and priorities are delivered through regulation and supervision, and by developing standards and policies that set out expectations of firms. The PRA’s approach to supervision is forward-looking, judgement-based, and focused on the issues and firms that pose the greatest risk to the stability of the UK financial system and policyholders. This approach is set out in the PRA’s approach to supervision of the banking and insurance sectors .
The PRA’s regulatory focus is primarily at the individual firm and sector level, with the most important decisions taken by the PRC, which works with the Bank’s other areas of remit, including its role as supervisor of Financial Market Infrastructures (FMIs), the UK’s Resolution Authority, and its committees, including the Financial Policy Committee (FPC), which has responsibility for the stability of the entire UK financial system. The PRA also works closely with the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), including through the Chief Executive of the PRA being a member of the FCA Board and the Chief Executive of the FCA being a member of the PRC.
The PRA regulates 1,330 firms and groups. footnote [3] These consist of 730 deposit-takers (banks, building societies, credit unions, and designated investment firms footnote [4] (DIFs)), and 600 insurers of all types (general insurers, life insurers, friendly societies, mutuals, the London market, and insurance special purpose vehicles (ISPVs)).
Chart 1: PRA supervised deposit-takers, as at January 2024
Chart 2: pra supervised insurers, as at january 2024, the pra’s strategy, shaping the pra’s strategy.
Each year, the PRA is required by law footnote [5] to review and, if necessary, revise its strategy in line with its statutory objectives:
- the general primary objective to promote the safety and soundness of PRA-authorised firms;
- specifically for insurance firms, a primary objective to contribute to the securing of an appropriate degree of protection for those who are or may become policyholders;
- a secondary objective to act, so far as is reasonably possible, in a way that facilitates effective competition in the markets for services provided by PRA-authorised firms; and
- a new secondary objective to act, so far as reasonably possible, in a way that facilitates the UK economy’s international competitiveness and its growth over the medium to long term, subject to alignment with international standards.
In addition to the statutory objectives, the PRA’s strategy is shaped by other responsibilities, such as the requirement to implement legislation and other changes necessary to meet international standards, and to continue to adapt to market changes in areas such as financial technology (FinTech), climate change, and digitalisation.
When considering how to advance its objectives, there are a set of regulatory principles to which the PRA must also have regard. This includes regulatory principles from FSMA 2000, and considerations from HMT’s December 2022 letter to the PRC on the Government’s economic policy, the Equality Act 2010, the Legislative and Regulatory Reform Act 2006, and the Natural Environment and Rural Communities Act 2006. In its pursuit of its objectives, the PRA will review all the regulatory principles, identify which are significant to the proposed policy, and judge the extent to which they should influence the outcome being sought.
Furthermore, as part of the Bank, the PRA contributes to the delivery of the Bank’s wider financial stability and monetary policy objectives, for example by:
- maintaining and, where appropriate, strengthening or updating prudential standards;
- being at the forefront of identifying new and emerging risks, and developing international policy; and
- ensuring that banks and other financial institutions can continue to provide essential services.
Strategic priorities for 2024/25
This year’s business plan continues to be structured around the PRA’s four strategic priorities, as set out in its 2023/24 Business Plan . The PRA’s strategic priorities for 2024/25 will remain unchanged because the PRA updated its priorities in 2023 to take account of its new powers, new secondary objective, and expanded role brought about by FSMA 2023. The strategic priorities for 2024/25 are to:
- maintain and build on the safety and soundness of the banking and insurance sectors, and ensure continuing resilience;
- be at the forefront of identifying new and emerging risks, and developing international policy;
- support competitive and dynamic markets, alongside facilitating international competitiveness and growth, in the sectors that we regulate; and
- run an inclusive, efficient, and modern regulator within the central bank.
PRA Business Plan 2024/25
Maintain and build on the safety and soundness of the banking and insurance sectors and ensure continuing resilience.
During the decade following the financial crisis of 2007-09, the PRA designed and implemented extensive reforms that materially improved the safety and soundness of firms, insurance policyholder protection, and financial stability. Since then, the robust regulatory standards that the PRA has implemented and its strong international collaboration have played a key role in maintaining the resilience of the banking and insurance sectors, consistent with its objectives and those of the FPC. The PRA will continue to ensure that the firms it regulates remain adequately capitalised and have sufficient liquidity and stable funding profiles, with appropriately defined impact tolerances for disruption to their business services. The PRA’s regulatory framework encourages PRA-regulated firms to take a holistic approach to managing risks by identifying, monitoring, and taking action to remove or reduce systemic risks.
The PRA’s role as a rulemaker was further expanded following the introduction of FSMA 2023. Under the new regulatory framework , the PRA will continue to be a strong, accountable, responsive, and accessible policymaker, and make rules to meet its regulatory obligations, while adopting a risk-based approach, as set out in CP27/23 , in a way that is tailored to the specific features of financial services in the UK. Among other things, the PRA will continue to faithfully implement agreed international standards and reforms in a way that best serves the UK. For example, in 2024 the PRA will publish its final rules on the implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards and on replacing relevant and/or remaining firm-facing Solvency II requirements from assimilated law with the PRA’s own rules, which will become part of the PRA’s Rulebook and other policy materials. In addition, the PRA will move further towards finalising and implementing the Strong and Simple prudential framework , which provides a simpler but robust set of prudential rules for non-systemic, domestic-focused banks and building societies in the UK.
The PRA will also continue to pay particular attention to the business opportunities and threats that are posed by changes in the economic environment, both in the UK and other jurisdictions, that could pose risks to the UK.
The PRA will continue to promote a strong risk culture among regulated firms, including a conscious and controlled approach to risk taking activities, and ensure that this is supported by adequate financial and non-financial resources. At the same time, the PRA will maintain a robust regulatory regime that is able to respond to the external factors that pose the greatest risk to firms’ safety and soundness.
Risk factors also include global geopolitical risks, which have intensified over the past year. The PRA will continue to ensure that PRA-regulated firms are resilient to such risks by liaising with both domestic and international regulatory counterparts and continuing to monitor and engage with affected firms. Effective international collaboration remains central to addressing global risks and maintaining UK financial stability as well as the safety and soundness of internationally active firms.
The PRA will monitor and assess firms’ ability to manage cyber threats through the ongoing use of threat-led penetration testing ( CBEST and STAR-FS ) and the cyber questionnaire ( CQUEST ). In collaboration with the FCA, including in response to known technology, cyber and third-party incidents, the PRA will continue to monitor and engage with firms on their execution of large and complex IT change programmes. Furthermore, the FPC’s cyber stress testing has broadened the PRA’s understanding of how operational disruptions such as cyberattacks may affect financial stability.
The PRA will continue to engage in collective action to develop a view on sector-wide risks, support the building of firm- and sector-level resilience, and enhance the sector’s ability to respond to system-wide disruption. This will include ongoing sector engagement through the Cross-Market Operational Resilience Group (CMORG), which delivers industry guidance, response capabilities, and technical solutions, and through cross-jurisdictional coordination via the G7 Cyber Experts Group (CEG). Through CMORG, the PRA will deliver a sector-wide simulation exercise (SIMEX24) to assess the sector’s resilience to major operational disruption. The PRA will continue to develop its ability to respond to operational incidents in the sector through its authorities ( Authorities Response Framework ) and sector ( Cross Market Business Continuity Group ) response mechanisms.
Financial resilience – banking
Implementation of the basel 3.1 standards.
In March 2023, the PRA concluded its consultation on proposals published in November 2022 about the parts of the Basel III standards that remain to be implemented in the UK (‘Basel 3.1’). In September 2023, the PRA announced that it would split the publication of the near-final Basel 3.1 rules in two, moving implementation back by six months to 1 July 2025 to reduce the transitional period to 4.5 years and ensure full implementation by 1 January 2030, in line with the proposals set out in CP16/22. The first near-final PS17/23 – Implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards near-final part 1 , covering market risk, credit valuation adjustment risk, counterparty credit risk, and operational risk, was published in December 2023. The PRA will publish the second near-final PS, covering the remaining elements of credit risk, the output floor, as well as Pillar 3 disclosure and reporting requirements, in due course.
The near-final rules from the two PSs will be made final once Parliament has revoked the relevant parts of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR). The PRA expects this to happen later in 2024. In addition to finalising Basel 3.1 rules, the PRA will continue to increase its supervisory focus on firms’ implementation plans.
Bank stress testing
The concurrent stress testing of firms is one of the key tools used by the PRA and the Bank to support their microprudential and macroprudential objectives. Banking stress tests examine the potential impact of a hypothetical scenario on the major UK banks and building societies that make up the banking system, and on the system as a whole. The PRA normally runs two types of banking stress test – the annual cyclical scenario and other exploratory scenarios.
In 2024, the PRA will support the Bank in taking stock of and updating its framework for concurrent bank stress testing. The stocktake will draw on lessons from the first decade of concurrent stress testing, and so ensure that the framework continues to support the FPC and PRC in meeting its objectives. The PRA will also contribute to supporting the Bank’s desk-based stress test in 2024, which is being conducted in place of an ACS. The desk-based exercise will make use of the PRA’s risk expertise along with models developed in the PRA and elsewhere in the Bank to test the financial resilience of the UK banking system under more than one adverse macroeconomic scenario. Stress testing exercises involving firm submissions of stressed projections are currently expected to resume in 2025.
In addition, the Bank is conducting a system-wide exploratory scenario (SWES), working closely with and with the full support of the PRA, FCA, and TPR (The Pensions Regulator). The exercise was launched in June 2023 and aims to improve the understanding of the behaviours of banks and non-bank financial institutions (NBFI) in stressed financial market conditions. The participating firms in this exercise are representative of markets that are core to UK financial stability.
Private equity and credit
The evolving macro environment is expected to challenge firms’ approach to risk management, increasing the need for robust governance, risk management, and controls. One area of focus for the PRA will be exposures to NBFI, particularly any challenges that may manifest around the trend toward illiquid private equity financing and private credit. The PRA will continue to closely monitor private asset financing and the way that firms consider the risks they could face from these activities. In particular, the PRA will look for further improvements in firms’ ability to identify and assess correlations across financing activities with multiple clients.
Replacing assimilated law
HMT has prioritised the CRR as one of the initial areas of focus in the process of transferring assimilated law into the supervisory authorities’ rules and legislation following the enactment of FSMA 2023. The latter granted the PRA expanded rulemaking powers to replace assimilated law with PRA rules, thereby moving towards a more British system of regulation. In 2024/25, the PRA will consult on proposed rules to replace, with modifications where appropriate, the relevant firm-facing provisions in Part Two of the CRR.
Model risk management (MRM) and internal ratings-based approach/hybrid models
Banks’ use of and reliance on models and scenario analysis to assess future risks has increased significantly over the past decade. The introduction of new, sophisticated modelling techniques – including the potential use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) – has highlighted the need for sound model governance and effective model risk management practices.
In 2023, the PRA published a supervisory statement (SS)1/23 – Model risk management principles for banks , which applies to firms with internal model (IM) approval to calculate regulatory capital requirements. It is structured around five high-level principles that set out the core disciplines necessary for a robust model risk management framework to manage model risk effectively across all model and risk types. The adoption of these principles will help banks to develop good practices of model risk management, raising prudential standards at banks operating in the UK. The new policy comes into effect on 17 May 2024. Banks within the scope of the policy are expected to conduct an initial self-assessment against these principles, and, where relevant, prepare remediation plans to address any identified shortcomings.
During 2024, the PRA will focus on how banks are embedding and implementing the expectations set out in SS1/23. In particular, the PRA will seek to understand the extent to which banks’ management teams are adopting the principles and promoting the management of model risk as a risk discipline in its own right across their firms.
The PRA has published a range of policy statements on changes to the internal ratings-based (IRB) approach to credit risk over recent years. footnote [6] The PRA will continue to work with firms as they progress their model approval and review submissions in line with these requirements and expectations. The PRA will focus on the ‘hybrid’ approach to mortgage modelling, and the IRB repair programme, both carried forward from previous years.
Where appropriate, firms are holding post-model adjustments (PMAs) in the form of risk-weighted asset (RWA) add-ons, helping to mitigate potential capital underestimation while they develop their new models. During 2024, the PRA will continue to assess the adequacy of the PMAs to ensure any potential capital underestimation is addressed.
Liquidity risk management
The events of 2023 brought a further focus on the liquidity and funding risks faced by deposit takers, in particular the deposit outflows experienced by CS and SVB leading up to their acquisition and resolution, respectively.
The PRA will continue its close supervision of firms’ liquidity and funding risks in light of recent stresses. Through its ongoing supervision of banks and building societies, the PRA will follow up on how firms are taking account of the lessons they learnt from the events at CS and SVB. The PRA will continue to use its regular programme of Liquidity Supervisory Review and Evaluation Processes (L-SREPs) across PRA-authorised firms to assess their liquidity and funding risks, in quantitative and qualitative terms, and to ensure appropriate financial and non-financial resources are in place to manage and mitigate these risks.
The PRA will also continue to engage with firms and within the wider Bank on PRA-authorised firms’ access to the Bank’s Sterling Monetary Framework .
The PRA will also monitor closely how firms consider changes in depositor behaviour in the current funding environment and proactively take into consideration forthcoming changes in bank funding and liquidity conditions. footnote [7]
Credit risk management
The PRA is closely monitoring firms’ credit risk management practices given the uncertain credit risk outlook across key markets. The PRA’s assessment will include a focus on how credit risk management practices have evolved – in particular, how they can remain robust and adaptable to changing conditions, whether there is appropriate consideration of downside and contagion risks, as well as firms’ monitoring and planning for the impacts of customer refinancing. The PRA will undertake a thematic review of smaller firms’ credit risk management frameworks during 2024/25.
The PRA will monitor changes to firms’ business mix and credit exposures, and continue to monitor vulnerable segments, including cyclical sectors and key international portfolios, as well as traditionally higher-risk portfolios such as buy-to-let, credit cards, unsecured personal loans, small to medium-sized enterprises, leveraged lending, and commercial real estate. In addition, counterparty credit risk will remain a key area of supervisory focus through 2024, especially exposures to NBFI across certain business lines.
Separately, in 2024, the PRA will continue to progress its review of regulatory policies to assess whether the policy framework for trading book risk management, controls, and culture is adequate, robust, and accessible.
The UK banking system is well capitalised. However, the overall operating and risk environment remains challenging, and firms must manage their financial resilience to ensure that the financial sector can continue to support businesses and households. The PRA will continue to assess firms’ capital positions and planning, including firms’ use of forward-looking capital indicators, stress testing, and contingency plans.
The PRA intends to review its Pillar 2A methodologies (see section ‘Review of the Pillar 2 framework’ of PS17/23 ) for banks after the rules on Basel 3.1 are finalised, with a view to consulting on any proposed changes in 2025.
Securitisation regulation
HMT has prioritised the Securitisation Regulation as one of the initial areas of focus in the process of transferring assimilated law into regulatory rules and legislation following the enactment of FSMA 2023. The PRA will publish its final policy (simultaneously with the FCA) on final rules to replace or modify the relevant firm-facing provisions in the Securitisation Regulation and related Technical Standards in 2024-25.
The PRA also intends to consult on draft PRA rules to replace firm-facing requirements, subject to HMT making the necessary legislation. The PRA has gathered views and evidence from firms through DP3/23 – Securitisation: capital requirements , which will inform its approach to capital requirements for securitisation.
Financial resilience – insurers
Solvency uk implementation.
In June 2024, the PRA will publish its final policy on the matching adjustment (MA) reforms set out in CP19/23 – Review of Solvency II: Reform of the Matching Adjustment . The majority of these reforms will take effect from end-June to allow PRA-authorised firms to take immediate advantage of new investment opportunities. The remaining Solvency II reforms consulted upon in CP12/23 – Review of Solvency II: Adapting to the UK insurance market will take effect on 31 December 2024.
To facilitate implementation of the reforms consulted on in CP12/23 and CP19/23, the PRA will streamline the application processes for new internal model permissions and variations of existing permissions. There will be similar proposals for MA permissions, if the final policy is the same as set out in the CP. The PRA remains committed to assessing and providing decisions on applications for permissions as quickly as possible and aims to do this within the timescales published in the associated statements of policy. This will be supported by the establishment of dedicated, specialised teams for reviewing applications.
In practice, delivering timely decisions will in part depend on good engagement between firms and the PRA during the application process, and on the preparation of high-quality and complete applications by firms. To facilitate this, the PRA will publish templates for use by firms , including templates for reporting the updated Matching Adjustment Asset and Liability Information Return (MALIR) and the Analysis of Change (AoC) and Quarterly Model Change (QMC) for internal models. These measures are intended to assist with a smooth transition to the Solvency UK regime.
A variety of proposals were made in responses to CP19/23 to further reform the MA in the form of so-called ‘sandboxes’, which would allow an element of self-certification of eligibility, or a route to further expand eligibility in response to innovations in primary financing markets. In 2024, the PRA will explore these proposals with industry with the goal of determining whether they can be developed into schemes that further advance the objectives of the Solvency II review.
Solvency II reporting reforms
To deliver the regulatory reporting and disclosure reforms consulted on in CP14/22 and CP12/23 , the PRA published PS3/24 – Review of Solvency II: Reporting and disclosure phase 2 near-final , including finalised templates and instruction files. The PRA will also publish a finalised single taxonomy package in 2024 Q2, which encompasses proposals in CP14/22 and CP12/23 , and deletions published in PS29/21 . The PRA will engage with firms, including through industry roundtables, to prepare them in meeting the new reporting requirements coming into force from 31 December 2024.
Solvency II transfer
The PRA will publish a CP in 2024 H1 that will set out how it will transfer the remaining Solvency II requirements from assimilated law into the PRA Rulebook and other policy material such as supervisory statements or statements of policy (‘the UK framework’).
This will provide a more comprehensive Rulebook and will make it easier for firms to access and navigate the rules that apply to them.
Insurance stress testing
Stress testing forms an important part of the PRA’s supervisory approach and risk assessment of insurance firms, helping to assess and identify the vulnerabilities of life and general insurance sectors to a range of risks in different scenarios.
Major life insurers participate in regular and concurrent stress testing prescribed by the PRA, and the next test will take place in 2025. For the first time, the PRA will publish the individual results of the largest annuity-writing firms to help inform stakeholders about the level of firms’ resilience in the scenarios set out, and thereby strengthen market discipline.
The PRA will continue to engage with the industry on the technical, operational, and communication aspects of the stress test, and will publish an approach document for the life insurance stress test 2025. The 2025 test will for the first time include an exploratory scenario to assess exposure to the recapture of funded reinsurance contracts.
For general insurers, the PRA has previously conducted four general insurance stress test exercises between 2015 and 2022. In 2025, the PRA will run its first dynamic stress test . The objectives of the exercise will be to:
- assess the industry’s solvency and liquidity resilience to a specific adverse scenario;
- assess the effectiveness of insurers’ risk management and management actions following an adverse scenario; and
- inform the PRA’s supervisory response following a market-wide adverse scenario.
The dynamic nature of the 2025 exercise represents a significant change from previous exercises and will involve simulating a sequential set of adverse events over a short period of time. The PRA has begun engaging with industry trade bodies and will provide more details of this exercise (including participation, design, and timelines) during 2024. Results of this exercise will be disclosed at an aggregate industry level.
Cyber underwriting risk
As the scope of technology continues to expand globally, cyber underwriting risk has become increasingly relevant, as reflected in the actual and planned growth of cyber insurance within the UK sector. As well as being inherently volatile and systemic in nature, cyber underwriting risk is diverse in how it can manifest in different lines of business.
Given the uncertainty of this risk, robust risk management, risk appetite-setting, and stress testing will be important factors in ensuring that capital and exposure management capabilities reflect firms’ actual exposures.
Monitoring and assessing cyber underwriting risk will be at the core of the PRA’s supervisory focus, particularly for firms with material exposures. The PRA will share the aggregate findings of its recent thematic project focused on cyber underwriting risk with industry, and continue to monitor the risk landscape and market dynamics to identify and assess potential risk drivers, including areas such as contract (un)certainty risk.
Model drift
The PRA will continue its scrutiny of internal models used by insurers to calculate capital requirements and aid risk management, to identify potential trends in the strength of firms’ calibrations, and as an indicator of the effectiveness of firms’ risk management.
In its 2023 model drift analysis , the PRA identified a number of findings across firms using internal models within the non-life sector. These are related to levels of allowances for inflation uncertainty, potential optimism in expected underwriting profits, potential optimism in the cost and benefit of reinsurance, and the limited allowance for economic and geopolitical uncertainties.
In 2024, the PRA will address perceived systemic trends that may weaken the robustness of models used across the market as a whole. The PRA will also focus on specific model drift within individual firms, with an emphasis on improving the effectiveness of internal model validation, so that firms can develop the capability to self-identify and address potential challenges.
Funded reinsurance
In 2024, the PRA will continue to pay close attention to the rapidly increasing use of funded reinsurance transactions in the UK life insurance market, and the risks that the growth in their use may pose to policyholder protection and UK financial stability. The PRA is particularly focused on the risk of an erosion in standards for assets used as collateral in these transactions, and individual and sectoral concentrated exposures to correlated, credit-focused counterparties.
As well as preparing to examine exposures to the recapture of funded reinsurance in the 2025 life insurance stress test, in 2024. The PRA will also, subject to responses to CP24/23 – Funded reinsurance , finalise and implement its policy expectations for UK life insurers that use funded reinsurance arrangements. As stated in the PRA’s letter on ‘ Insurance supervision: 2024 priorities ’, these policy expectations will cover how firms should manage risks associated with funded reinsurance at both individual transaction and at aggregate level. This will include the expectation that firms place limits on their activities to ensure sound risk management.
Impact on general and claims inflation
Claims inflation continues to be a significant risk for general insurers. Following a thematic review, the PRA published a Dear Chief Actuary letter in June 2023 setting out its findings that, while reserves have increased, there remains material uncertainty and the potential for excessive optimism with respect to reserving, pricing, and capital and reinsurance planning.
The PRA expects a continued lag in the emergence of claims inflation in the data, which insurers should be alert to. The PRA will continue to monitor the ongoing impact through the regulatory data collected and supervisory activities throughout 2024. Should the PRA’s assessment of this risk change, further focused work may be considered.
Market-wide stresses in March 2020 and September 2022 highlighted gaps in insurers’ liquidity risk management frameworks and, consequently, the importance of having comparable, accurate, and timely information on insurers’ liquidity. The PRA will build on the existing liquidity framework, currently based on risk management expectations set out in SS5/19 – Liquidity risk management for insurers , and develop liquidity reporting requirements for insurance firms most exposed to liquidity risk. The information collected will be used to supervise firms’ liquidity positions more effectively and produce meaningful peer comparisons. The PRA will work closely with firms to inform them about its development of these requirements and explore the necessity of a minimum liquidity requirement as part of a future policy consultation.
In addition, the Bank has signalled its intention to develop a new lending tool for eligible NBFIs to help tackle future episodes of severe dysfunction in core markets that threaten UK financial stability. The development of the PRA’s approach to supervising liquidity will therefore inform the design of the lending tool as it relates to insurers.
The reforms to Solvency II offer life insurers opportunities to expand the range of credit risk assets that are used to back their annuity liabilities, and enable them to meet their commitment to invest in assets that contribute to the productivity of the economy and the transition to net zero. These opportunities require sophisticated credit risk management, and insurers’ capabilities will remain a key focus. Increased activity in the bulk purchase annuity (BPA) market is expected to lead to further growth in firms’ exposure to credit risk, and potentially to concentrations in exposure to internally valued and rated assets.
The PRA will continue to focus on the effectiveness of firms’ credit risk management capabilities and seek further assurance that firms’ internal credit assessments appropriately reflect the risk profile of their asset holdings. The PRA will assess how firms’ credit risk management frameworks are evolving in line with its supervisory expectations, and also review the suitability of firms’ current and forward-looking internal credit assessment validation plans and approaches. In both cases, the PRA will seek to provide feedback on a firm-specific or thematic basis as appropriate.
Regulatory reforms
Operational risk and resilience (including the implementation of the critical third-party regime).
Operational disruption can impact financial stability, threaten the safety and soundness of individual firms and financial market infrastructures, or cause harm to consumers, policyholders, and other parts of the financial system. The PRA defines operational resilience as the ability of firms and the financial sector to prevent, respond to, recover, and learn from operational disruptions, including cyber threats.
The FCA, Bank, and PRA’s operational resilience policies came into force in March 2022 . Firms have now identified their most important business services, set impact tolerances, and commenced a programme of scenario testing. The PRA will continue to work closely with the FCA to assess firms’ progress, with a particular focus on the ability of firms to deliver important business services within defined impact tolerances during severe but plausible scenarios over a reasonable time frame, and no later than March 2025.
The PRA will also continue to monitor threats to firms’ resilience, including their growing dependency on third parties, while respecting the principle of proportionality.
Critical third parties to the UK financial sector
Section 312L of FSMA 2023 gave HMT the power to designate certain third-party service providers as ‘critical’ if they provide services to the financial sector, which, if disrupted or subject to failure, could cause financial stability concerns or risks to the confidence in the UK’s financial system. Prior to designating these parties, HMT must consult with the Bank, PRA, and FCA (the authorities the Act appoints as Regulators of the new regime). FSMA 2023 also gives the Regulators new powers to oversee the services provided by critical third parties (CTPs) to regulated firms. In December 2023, the PRA, Bank, and FCA jointly published CP26/23 – Operational resilience: Critical third parties to the UK financial sector , proposing how these powers could be used to assess and strengthen the resilience of services provided by CTPs to firms and FMIs, thereby reducing the risk of systemic disruption. The PRA will continue to work with other authorities to develop the final policy and oversight approach in 2024.
Additionally, the PRA is developing regulatory expectations on incident reporting, aligned with its operational resilience expectations.
Review of enforcement policies
Enforcement supports and supplements the PRA’s regulatory and supervisory tools by ensuring that it has credible mechanisms for holding regulated firms to account when they do not meet requirements and expectations. Enforcement policies also provide a wider deterrent effect. The PRA is therefore committed to holding individuals to account and, when appropriate, taking regulatory and/or enforcement action against those individuals that breach its standards. The PRA clearly sets out, for the benefit of the whole regulated community, the actions and standards of behaviour that are considered unacceptable ( The Bank of England’s approach to enforcement ).
In January 2024, following a review of its policies and public consultation, the PRA published PS1/24 – The Bank of England's approach to enforcement , which sets out the revised approach to enforcement across the Bank’s full remit (including when acting as the PRA).
The PRA is committed to conducting any enforcement investigations as promptly and efficiently as possible. In line with that aim, PS1/24 introduced a new Early Account Scheme (EAS or ‘the Scheme’), which provides for a new path for early cooperation and greater incentives for early admissions with the aim of reaching outcomes more quickly in specific cases.
Diversity and inclusion in PRA-regulated firms
Enhancing diversity and inclusion (D&I) can support better governance, decision-making, and risk management in firms by reducing groupthink and promoting a culture that allows employees to feel able to speak up and challenge the status quo.
In September 2023, the PRA published CP18/23 – Diversity and inclusion in PRA-regulated firms . Under the proposals, all in-scope firms would need to understand their D&I position, develop appropriate strategies to make meaningful progress, and monitor and report on progress. The proposals are flexible and carefully tailored to recognise that firms are at different stages of their work on D&I, and, most importantly, are best placed to develop their own D&I solutions.
The PRA also outlined that the proposals in CP18/23 contribute towards its secondary objectives of ensuring effective competition and facilitating competitiveness and growth, because enhanced D&I can help support greater innovation and make firms more attractive in the labour market.
In 2024, the PRA will continue its industry engagement, assess responses to CP18/23, and provide a further update in due course.
The PRA maintains flexibility to adapt and respond to changes in the external environment, economic and market developments, and any other risks that may affect its statutory objectives or priorities. The PRA has continued to use its horizon-scanning programme to achieve the following aims:
- identify emerging external risks, regulatory arbitrage, and potentially dangerous practices;
- highlight features of the regulatory regime that are not yet delivering the desired results; and
- allocate supervisory and policy resources to tackling the highest-priority risks in a timely manner.
Consistent with its mission, the PRA will continue to contribute to lessons learned internationally, policy/standards evaluation, and, in particular, internationally agreed standards with the aim of promoting the safety and soundness of the firms it regulates. For example, in 2024/25, the PRA will continue to focus on identifying and addressing emerging risks internationally, working closely with the BCBS on its response to consultations launched in 2023 (including on cryptoassets; disclosure for climate-related financial risks; and the Basel Core Principles and other outstanding work in support of its 2023/24 work programme and strategic priorities ). The PRA will also continue to work closely with the International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS) on its finalisation of the Insurance Capital Standard (ICS), Insurance Core Principles on valuation (ICP 14) and capital adequacy (ICP17) .
In addition, the PRA will continue to monitor the potential for capital and profit erosion in firms that are slower to adopt new technologies, as well as firms’ involvement in new technologies, and changes in the profile of cyber-risks they face.
International engagement and influencing regulatory standards
The PRA plays a leading role in influencing international regulatory standards and will continue to participate actively in global standard-setting bodies, such as the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) , the IAIS, and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) .
Building on the BCBS’s report on the 2023 banking turmoil , the PRA will work with international stakeholders and the BCBS to strengthen supervisory effectiveness and identify issues that could merit additional guidance at a global level. The PRA will work with BCBS to pursue additional follow-up analytical work based on empirical evidence to assess whether specific features of the Basel Framework have performed as intended, such as liquidity risk and interest rate risk in the banking book, and assess the need to explore policy options over the medium term, alongside supporting the BCBS in pursuing its medium-term programme on evaluating the impact and efficacy of Basel III, and in light of lessons drawn from the Covid-19 pandemic.
In addition, the PRA pursues international collaboration through less formal mechanisms, for example through regular bilateral and trilateral engagements, ensuring close collaboration on a number of supervision, risk, and policy topics of joint interest. The PRA also collaborates internationally on joint global thematic reviews with other regulatory authorities, for example, to address a joint interest in banks’ exposures to NBFIs and the use of critical third parties.
The PRA will also continue to support international efforts to monitor and promote consistent implementation of Basel 3.1, as well as the implementation and monitoring of the ICS.
Supervisory co-operation
Effective international collaboration remains crucial to addressing global risks, and is central to maintaining UK financial stability, the safety and soundness of internationally active firms, and reducing regulatory arbitrage.
The PRA will continue to promote international collaboration through supervisory colleges and set out clear expectations for firms wanting to branch into the UK. The PRA will also maintain its existing memoranda of understanding (MoUs) and, if needed, expand the number of jurisdictions with which it has an MoU to facilitate the supervision of international groups and therefore enhance the safety and openness of the UK for financial services activities.
The PRA will continue to support HMT via its international collaboration activities (eg The Berne Financial Services Agreement ) and with assessments of other jurisdictions to facilitate safe access to overseas markets for UK firms, among other benefits.
Overseas bank branches
The PRA will consult on targeted refinements to its approach to banks branching into the UK, reflecting lessons from the failure of SVB to ensure the PRA’s framework for assessing branches captures activities of potential concern. The PRA is committed to the UK remaining a responsibly open jurisdiction for branches, and expects the vast majority of branch business to be unaffected by any changes. The PRA also intends to consult on clarifying expectations for group entity senior manager functions (SMFs) footnote [8] and expectations of booking arrangements.
Operational and cyber resilience
The PRA engages internationally on operational and cyber resilience, in support of its supervision objectives and to raise international standards. The PRA co-chairs the G7 Cyber Expert Group (CEG), which works to coordinate cyber resilience strategy and management across G7 jurisdictions. The PRA also co-chairs the European Systemic Cyber Group (ESCG), which helps European authorities develop systemic capabilities to prevent and mitigate risks to the financial system that might emanate from cyber incidents. The PRA has also led work at the Financial Stability Board (FSB) on cyber incident reporting. In 2024, the PRA will continue to engage with standard-setting bodies and bilaterally with other jurisdictions on third-party risk management and CTPs.
Managing the financial risks arising from climate change
Climate change presents a source of material and increasing financial risk to firms and the financial system. Managing the risks to firms’ safety and soundness from climate change requires action and remains a key priority for the PRA. The Bank first set out expectations around enhancing banks’ and insurers’ approaches to managing the financial risks emanating from climate change in April 2019 via SS3/19 – Enhancing banks’ and insurers’ approaches to managing the financial risks from climate change . The PRA has since provided further guidance via two Dear CEO letters, footnote [9] incorporating observations from supervisory processes and the 2022 Climate Biennial Exploratory Scenario exercise , as well as by providing thematic feedback via Dear CFO letters footnote [10] to promote high-quality and consistent accounting for climate change .
As noted in its 2024 priorities letter to firms, the PRA expects firms to make further progress and demonstrate how they are responding to the PRA’s expectations, and to set out the steps they are taking to address barriers to progress. The PRA will continue to assess firms’ progress in managing climate-related financial risks. In 2024, the PRA will commence work to update SS3/19 and publish thematic findings on banks’ processes to quantify the impact of climate risks on expected credit losses.
The PRA, alongside the FCA, will continue to work with industry through the Climate Financial Risk Forum to produce practical guides and tools that help financial firms embed the financial risks from climate change into their operations. The PRA will also continue to engage with domestic and international partners, including international standard-setters, to contribute to the development of international frameworks in support of managing climate-related risks.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Following the publication of a feedback statement (FS)2/23 – Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning , the PRA and FCA intends to conduct the third edition of the joint survey on machine learning in UK financial services , in 2024 Q2. Responses to the survey will allow the PRA and FCA to further explore how best to address the issues/risks posed by AI/ML in a way that is aligned with the PRA’s and FCA’s statutory objectives. The PRA will also continue to monitor firms’ compliance of its expectations, as set out in SS1/23 , and will seek to explore further updates where necessary.
International policy on digitalisation and managing associated risks
The PRA aims to be at the forefront of identifying and responding to opportunities and risks faced by PRA-authorised firms as they seek to use technology in innovative ways to attract and retain customers, reduce costs, and increase efficiencies.
External context and business risk are important facets of the PRA’s approach to supervision. Developments are monitored, with specialist input from the Bank’s Fintech Hub , to identify risks such as fragmentation of the value chain, novel outsourcing arrangements, and concentration risks across and within firms.
In order to take a responsive and responsibly open approach, the PRA will continue to consider policy proposals to respond to digitalisation and adapt its supervisory approach accordingly. Through the New Bank Start-up and Insurer Start-Up Units, the PRA will continue to engage with applicant firms that have novel uses of technology. The PRA will continue to work closely with domestic and international partners, and through engagement with industry and stakeholders, to take a pro-active approach to digital innovations within the financial sector.
The PRA is a significant contributor to discussions on digitalisation in international standard-setting fora, and will continue to support the BCBS’s work on the developments in the digitalisation of finance and the implications for banks and supervisors . The PRA will also continue be an active part of the IAIS Fintech Forum.
Digital money and innovation
In February 2023, HMT published a consultation and Call for Evidence on the future financial services regulatory regime for cryptoassets , focused on enhancing market integrity, custody requirements, and transparency. The consultation closed in October 2023 with the publication of an update on the government’s plans for its legislative approach to the regulation of stablecoins. HMT confirmed that tokenised deposits would continue to be regulated as deposits. The PRA will continue to work with HMT and the FCA to ensure that the regulatory perimeter and the boundaries between different activities are clearly and robustly delineated.
In November 2023, the Bank, PRA, and FCA published a cross-authority package on innovations in money and payments . As part of this, the PRA published a Dear CEO letter to provide clarity on the PRA’s expectation on how deposit-takers should address risks arising from the emergence of multiple forms of digital money and money-like instruments. footnote [11] It published the letter alongside the Bank’s proposed regime for systemic payment systems using stablecoins and related service providers , and the FCA’s proposed regime for stablecoin issuers, custodians, and the use of stablecoins as a means of payment. A roadmap paper was also published to explain how these regimes fit together.
The PRA will continue to contribute to the Bank’s broader work on innovation in money and payments, which in 2024 will include work on wholesale payments and settlements – and their interaction with retail payments.
In 2024, the PRA will continue to work within the global regulatory community to finalise a set of amendments made to the international standard on the treatment of banks’ cryptoassets exposures. These amendments were published for consultation by the Basel Committee in December 2023, following the finalisation of the standard in 2022.
Once the amendments are finalised, the PRA will implement the standard within the UK, following the PRA’s policymaking process. Alongside this, the PRA will continue to engage with international partners, including the BCBS, to assess bank-related developments in cryptoassets markets, the role of banks as issuers of stablecoins and tokenised deposits, custodians of cryptoassets, and potential channels of interconnections with the cryptoassets ecosystem.
The PRA advances its primary and secondary objectives by making rules that support competitive and dynamic markets in the sectors that it regulates. The PRA will go further in developing proportionate and efficient prudential requirements, thereby reducing the burden on firms where appropriate, and pursuing its secondary objectives. The PRA also remains committed to playing an active role in international standard-setting, given the important role of global rules in safeguarding the UK’s open economy through ensuring safe financial markets.
Regulatory change – embedding the PRA’s approach to rule-making
FSMA 2023 has significantly changed the powers and responsibilities of the PRA, allowing it to ensure the UK financial services framework is fit for the future, reflecting the UK’s position outside of the EU. FSMA 2023 also introduces enhanced objectives and accountability requirements that support the PRA’s transparency and accountability to Parliament.
FSMA 2023 provides a framework to repeal and replace assimilated law relating to financial services. Most technical rules will now be made by operationally independent regulators within a framework set by Parliament, enabling the PRA to deliver policies better suited to the UK financial sector. The PRA’s responsibility, in cooperation with HMT and FCA, is to ensure that the new rules are made in accordance with the PRA’s remit and statutory objectives, including the new secondary competitiveness and growth objective.
The PRA has worked closely with HMT and FCA on the sequencing of the repeal and the replacement of the files of assimilated law. Once the replacement material is in PRA rules, the PRA will have the power to evaluate these rules, amend them if needed, and/or create new rules when required.
The PRA has already made good progress with respect to the files that HMT has prioritised into the first two ‘tranches’, including key files such as Solvency II, Securitisation, CRR, among others. The PRA has consulted on significant parts of tranches 1 and 2 in 2023 and will continue this work throughout 2024 and 2025. The completion of the repeal and replacement of Solvency II and Securities Regulation files is expected by the end of 2024, and the last of the PRA's tranche 1 and 2 files is planned for implementation in 2026. Work on the remaining files that were not included in tranches 1 and 2 will begin in 2024.
The PRA is consulting its stakeholders as it develops its approach to policymaking in light of the new requirements. In December 2023, the PRA published CP27/23 , setting out the proposed approach to policy under the regulatory framework as amended by FSMA 2023, and building on the previously published DP4/22 – The Prudential Regulation Authority’s future approach to policy . CP27/23 outlines the PRA's planned approach to maintain robust prudential standards, which are the cornerstone of UK financial stability and long-term economic growth, while addressing risks and opportunities in a responsive manner, appropriately adapted to the circumstances of the UK. Responses to CP27/23 will inform the PRA’s finalised approach document to be published in 2024 H2.
Secondary competitiveness and growth objective (SCGO)
FSMA 2023 gave the PRA a new secondary objective which requires the PRA to act, so far as reasonably possible, to facilitate the UK economy’s international competitiveness (including in particular the financial services sector through the contribution of PRA-authorised persons) and its growth over the medium to long term, subject to alignment with international standards. FSMA 2023 maintained the PRA’s other objectives without change.
In addition to specific policy measures, the PRA has taken practical steps to embed the SCGO in its operations, including through internal changes, and the launch of a research programme to deepen its understanding of the ways prudential requirements can affect the international competitiveness and growth of the UK economy.
The PRA will continue to look for ways in which it can facilitate the UK’s competitiveness and growth when discharging its general functions. The approach focuses on strengthening the three regulatory foundations that were set out in CP27/23, specifically:
- Maintaining trust among domestic and foreign firms in the PRA and UK prudential framework via a range of policies, including those that promote strong prudential standards appropriately calibrated for the UK, and the alignment of said policies with international standards.
- Adopting effective regulatory processes and engagement, including providing for the efficient handling of regulatory processes, such as authorisations and data collections, as well as facilitating the accessibility of the PRA Rulebook to reduce the operating costs of firms.
- Taking a responsive and responsibly open approach to UK risks and opportunities, including making rules that account more effectively for the needs of the UK. This approach means responding faster to emerging risks and opportunities in the UK financial sector, for example, by using regulatory tools to support innovation safely. To this end, in 2024, the PRA will hold a pilot roundtable to gather stakeholders’ views on how the PRA can help to reduce the barriers to innovation that the industry faces.
The policy initiatives discussed in the rest of this section provide examples of how the PRA will advance its secondary objectives in 2024/25.
Furthermore, the Bank’s Independent Evaluation Office (IEO) is evaluating the PRA’s approach to its new secondary objective. Both the outcome of the IEO’s evaluation and the PRA’s response to it will be included in the PRA’s – ‘Secondary Objectives Report’ to be published alongside the PRA’s Annual Report 2023/24. The Secondary Objectives Report will also give an overview of all the PRA’s policy initiatives that have advanced the SCO and the SCGO .
Strong and Simple framework
In 2021, the PRA published FS1/21 – A strong and simple prudential framework for non-systemic banks and building societies , that set out a vision to simplify prudential requirements for smaller, domestic-focused banks and building societies, while maintaining those firms’ resilience.
As outlined in the PRA 2023/24 Business Plan , the PRA will continue its planned programme of work on creating a simpler but equally resilient prudential framework for smaller, domestically focused banks and building societies, known as the Strong and Simple framework. This framework is designed to maintain the financial resilience of banks and building societies operating in the UK, while reducing costs associated with prudential requirements for non-systemic banks and building societies. In 2023/24, the PRA published its final policy on scope criteria and simplified liquidity and disclosure requirements for SDDTs in PS15/23.
In December 2023, the PRA published PS16/23 – The Strong and Simple Framework: Scope criteria, liquidity and disclosure requirements , which finalises the scope of the framework. The PS builds on the first layer of the Strong and Simple framework, which focused on the smallest firms and is known as the SDDT regime. The overall aim of the framework is to maintain the financial resilience of banks and building societies operating in the UK, while addressing the ‘complexity problem,’ under which the same prudential requirements are applied to all firms, regardless of size, even though the costs of interpreting and operationalising those requirements are higher for small firms, relative to the associated public policy benefits.
In 2024/25, the PRA will move further towards finalising and implementing the Strong and Simple prudential framework for SDDTs. A key step will be to implement the simplifications to liquidity requirements that were introduced in Phase 1. The PRA will also finalise the rules for the Interim Capital Regime, which will allow firms eligible to be SDDTs to stay under capital rules equivalent to those currently in place until the simplified capital regime for SDDTs is implemented. The PRA plans to consult on a simplified capital regime for SDDTs in 2024 Q2.
Insurance Special Purpose Vehicles regime
In 2017, the PRA introduced a framework for the authorisation and supervision of ISPVs to provide guidance for parties wishing to obtain authorisation as an ISPV, or for insurers and reinsurers seeking to use UK ISPVs as risk mitigation in accordance with Solvency II.
The UK ISPV regime has not seen as much activity as originally envisaged. While new issuances of insurance-linked securitisations (ILS) transactions in the UK over the last two years have exceeded USD400 million, there are steps to be taken which can improve the regime and increase its usage.
The PRA has been in discussion with industry on this matter with the aim of understanding the key areas of the regime in which market participants would recommend changes.
The PRA expects to consult on a package of reforms to the UK ISPV regime. These reforms are intended to:
- allow a wider range of transaction structures in the UK regime;
- improve the speed of the application process, and thereby also reduce costs for applicants; and
- clarify the PRA’s expectations of UK insurers who cede risks to ISPVs, wherever they are established.
Remuneration reforms
The PRA’s remuneration rules ensure that key decision-makers and material risk-takers at PRA-regulated firms have the right incentives and can be held accountable. In 2023, following consultation, the PRA removed the bonus cap and made changes to its rules to enhance proportionality for small firms .
In advancing its primary and secondary objectives, the PRA is considering further changes to the remuneration regime that is better suited to the UK’s financial sector, while maintaining the remuneration regime’s overall structure and objectives, which are based on internationally agreed FSB principles and standards . The PRA intends to consult on any changes in 2024 H2.
Implementing changes to the Senior Managers & Certification Regime (SM&CR)
In March 2023, the PRA and FCA jointly published DP1/23 – Review of the Senior Managers and Certification Regime (SM&CR) , with a particular focus on gathering views about the regime’s effectiveness, scope, and proportionality. HMT in parallel launched a Call for Evidence covering the legislative aspects of the SM&CR. The period for sending responses to the discussion paper ended on 1 June 2023.
The PRA received over 90 responses relevant to its work as a prudential regulator, reflecting the significant level of stakeholder interest in the regime. The PRA, working closely with the FCA and HMT, is considering potential policy options for reform in response to the comments received and intends to consult on proposed changes to the regime in 2024 H1.
Complete the establishment of the Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) Panel
The PRA is continuing to make progress under the new framework provided by FSMA 2023, setting out CBA as an integral part of developing the best possible policy approach, and the results will help shape the PRA’s policymaking. CBAs inform and refine the policy approach to identified issues, helping to design approaches that offer the greatest benefits.
One of the key elements of enhancing the PRA’s scrutiny and accountability mechanisms relates to its approach to CBA and the establishment of a new CBA panel. The role of the CBA Panel is to support increased transparency and scrutiny of the PRA’s policymaking by providing regular, independent input into the PRA’s CBAs relating to PRA rules and the PRA’s statement of policy in relation to CBAs . The Panel will review how the PRA is performing more generally in carrying out its duties with regard to CBA and may provide recommendations to the PRA.
The PRA has completed an open, competitive, and rigorous recruitment process for identifying and appointing a diverse range of expert individuals to constitute the CBA Panel. The PRA will finalise the set-up of the Panel and then start consulting it on the PRA’s statement of policy in relation to CBAs and on the preparation of CBAs. The appointments, including that of the Chair, will be announced in due course.
In 2024, the PRA will consult on its CBA framework, which will set out how the PRA intends to continue to conduct a robust CBA and how it engages with the CBA panel.
PRA Rulebook
The new regulatory framework set out in FSMA 2023 enables the PRA to develop a more coherent and easily accessible Rulebook. The aim is to improve the efficiency and accessibility of the PRA Rulebook by reducing the number of policy document formats currently in use to three: rules, supervisory statements, and statements of policy. In order to achieve this, the PRA’s specialist teams will begin the process of reviewing the EU Guidelines, European Supervisory Authorities (ESA) Q&As, and UK technical standards (UKTS) that are relevant to PRA rules, to determine what should be incorporated into those rules or related supervisory statements and statements of policy. Once the review of these documents is completed, references to the EU Guidelines, ESA Q&As, and UKTSs will be removed.
The PRA is also looking at grouping the elements in the Rulebook to make it easier for users to access relevant information. To support usability and clarity, the PRA will take a consistent approach to the structure of, and language in its policies.
The speed at which the PRA will achieve many of its ambitions for the Rulebook will partly depend on the Government’s approach to the repeal of relevant assimilated law and its replacement in PRA rules and other policy materials. However, the PRA will move ahead with the proposed reforms as quickly as possible to help users more easily navigate the new regulatory landscape.
Banking Data Review
The Banking Data Review BDR, launched in 2023-24, will be delivered as an integral part of the Transforming Data Collection TDC programme. The work will enable the PRA’s banking regulatory data collections to be better aligned with the day-to-day needs of supervisors, ensure the PRA has good-quality data to carry out its new policymaking responsibilities in line with the post-Brexit regulatory framework, and reduce burdens on firms by better integrating and streamlining data collections.
The PRA will consult on the first of three phases of reforms under the BDR in 2024 H2. The consultation will focus on streamlining of the existing regulatory reporting estate, removing reporting templates that may no longer be needed or which contain information that can be gathered at lower cost elsewhere, reviewing collections of counterparty credit information, and incorporating lessons from recent market events.
In parallel, the PRA will continue to work on plans for future phases of reform, focused on credit risk in the second phase, and with all remaining areas covered in a third phase. Engagement with industry participants will be done under the newly appointed TDC Advisory Board, which will be responsible for setting industry working groups on key topics relating to TDC. The TDC’s main industry forum in this area is the Data Standards Committee (DSC), which led the work on the recommendations underpinning the jointly published response by the Bank and the FCA, entitled Transforming data collection – Data Standards Review with recommendations and Bank of England and FCA response . A further working group is the BDR Industry Consultative Forum that is open to all PRA-regulated banks.
Supporting and authorising new market entrants via new ‘mobilisation’ regime
The PRA will continue to support potential market entrants in navigating the authorisation process. This includes providing clear online guidance and industry engagement to build awareness of expectations and seek feedback on firms’ experience of the process. The PRA offers potential applicants the opportunity to meet with staff through a structured pre-application stage, allowing firms to iterate and develop their proposition to support a better-quality application.
The PRA will continue to make use of the mobilisation stage for newly authorised banks, where appropriate, to allow them to operate with restrictions while they complete their set-up before starting to trade fully.
In line with PS2/24 – Review of Solvency II: Adapting to the UK insurance market , the PRA will introduce a new ‘mobilisation’ regime to facilitate entry and expansion for new insurers from 31 December 2024, similar to the mobilisation stage for new banks. Mobilisation will help to facilitate competition, and the international competitiveness and growth of the UK insurance sector, with the aim of benefiting firms who are contemplating applying for authorisation as an insurer in the UK now or in the future.
Newly authorised insurers in mobilisation could be offered the option of using a set period of extra time to build up systems and resources while operating with business restrictions, proportionate regulatory requirements, and lower minimum capital requirements. New insurers could be suitable for mobilisation when they have a shortlist of activities to complete before they can meet full regulatory requirements.
Ease of exit
Improving how firms can leave regulated markets in an orderly way is a vital corollary to greater ease of entry into those markets. It enables a dynamic and competitive market which entrants can join and leave with minimal impact on the wider market and the PRA’s statutory objectives. The PRA has published the first of two planned policy in this topic, (eg, PS5/24 – Solvent exit planning for non-systemic banks and building societies ). A further PS on solvent exit planning for insurers is expected in 2024 H2, following the completion of the market consultation initiated by CP2/24 – Solvent exit planning for insurers . Both of these form part of the PRA’s strategic focus on increasing the ease of exit.
Ring-fencing regime
The Bank and PRA continue to work closely with HMT on implementing the recommendations made in March 2022 by the Independent Review of Ring-fencing and Proprietary Trading , led by Sir Keith Skeoch. On 28 September 2023, both HMT and the PRA published consultations with the aim of giving effect to recommendations of that review.
HMT consulted on removing the blanket restriction which prevents ring-fenced bodies (RFBs) operating in countries outside the EEA. The PRA consulted on introducing a new rule and updating SS8/16 – Ring-fenced bodies (RFBs) , to align with HMT’s proposed legislative changes. These changes aim to implement certain safeguards to ensure that RFBs are not exposed to material risks through the business of their overseas subsidiaries or branches. The PRA will publish its policy and a rule Instrument once the legislative changes are brought into force. Simultaneously, the PRA will update SS8/16 to reflect the changes.
FSMA requires the PRA to conduct a review of its ring-fencing rules and provide a report to HMT every five years. The first such review was completed on 12 December 2023 and the resulting report was laid before Parliament on 25 January 2024 and published on the Bank’s website.
The PRA intends to consult on potential changes to the ring-fencing regime identified by the Rule Review once a fuller exploration of costs and benefits has been undertaken. The Bank and PRA will continue to support HMT with technical advice to enable HMT to finalise its legislative changes, and to consider responses to its Call for Evidence on longer-term reforms.
Effective authorisation processes
The PRA handles over 1,800 regulatory transactions a year, ranging from new firm authorisations to variations of permission for existing firms and cancellations of permission for firms leaving the market. Over the coming year, the PRA will continue to handle these transactions in more streamlined, efficient, transparent, and accessible way while maintaining strong risk controls to ensure the UK’s success as a global financial centre.
In parallel to consulting on reforms to the SM&CR, the PRA will continue to enhance and streamline internal processes on SM&CR applications and other transactions to drive further improvements in operational effectiveness, as measured through the quarterly publication of metrics on timeliness of decisions. This will include close collaboration with the FCA to ensure an efficient and coordinated review of cases, as well as improvements to case handling and recording technology platforms. The PRA will extend existing industry engagement on New Bank Start-ups to also cover new insurers and SM&CR applications in order to promote transparency and spread best practice in support of efficient case handling. In addition, the Wholesale Insurance Accelerated Authorisation Pathway, developed jointly by the PRA and FCA, will continue to provide an accelerated route for the authorisation of a sub-set of London market wholesale applicants.
The PRA’s operation within the Bank plays a critical role in maintaining the stability and integrity of the UK’s financial system. In pursuit of its objectives and work programme, the PRA ensures that its regulatory framework is inclusive, considering the diverse landscape of financial institutions. It aims to create a level playing field, while recognising and planning for the potential impact of the changes in the environment in which we are operating.
In line with its mission, the PRA continually adapts regulations to address emerging risks and opportunities, fostering inclusivity to enhance trust, transparency, and accountability in the financial sector. As a prudential regulator, the PRA maintains and strives for operational efficiency in its regulatory processes, technology, and its workforce. This involves streamlining procedures, driving inclusive recruitment, and leveraging technology to enhance effectiveness – noting that efficient regulation benefits both regulated entities and the broader economy by reducing unnecessary burdens and facilitating smoother interactions between financial institutions and the regulator.
Data and technology
The PRA will continue its programme of work to strengthen and transform its data-related capabilities. The PRA will also continue to play a leading role in international collaboration on the regulatory use of data and technology, liaising closely with other regulators, central banks, academic institutions, and industry. The PRA intends to run a multi-day innovation-focused event for PRA colleagues to support learning and increase awareness about the impact of technological advances and initiatives across the financial sector.
Transforming Data Collection by building on digital regulatory reporting
The PRA will continue to work towards achieving the objectives of the TDC programme for 2026:
- Goal 1: the PRA has the data and tools it needs to rapidly identify and probe emerging issues, risk, and policy questions, including integration into a single customisable supervisory dashboard; and
- Goal 2: the PRA only collects data that it needs from firms, thereby reducing unnecessary burdens on firms.
Regarding Goal 1, the PRA will continue to improve existing and deliver new priority data visualisation and analysis tools to support supervision, covering financial and operational data for PRA-regulated firms. The PRA will also make use of speech-to-text technology to support day-to-day work for staff, and to contribute to the Bank’s wider work on the appropriate use of artificial intelligence to support its objectives, including large third-party language models. This will be underpinned by ongoing support for PRA staff undertaking renewed digital skills training alongside individual and group coaching for some staff cohorts, and planning for those programmes in future years.
Regarding Goal 2, the PRA will continue to work with the FCA and the wider Bank on the TDC programme , which envisions that ‘regulators are able to get the data they need to fulfil their mission at the lowest possible cost to industry’ through improvements to the integration of reporting, reporting instructions, and data standards. Over the coming years, TDC therefore aims to deliver a new target operating model for all of the Bank’s regulatory, statistical, and stress-testing data collections.
Diversity, equity and inclusion at the PRA
The PRA continues to take action to strengthen its culture and working environment. The Bank’s Court review into ethnic diversity and inclusion reported its findings in July 2021. The PRA, alongside the rest of the Bank, is implementing the recommendations of this review and has made considerable progress in terms of embedding inclusive recruitment, investing in talent development, and advancing a psychologically safe culture to promote employees’ ability to voice their opinions via the ‘speak my mind’ initiative. There is also increased accountability for senior leaders to advance a diverse and inclusive Bank.
The PRA recognises the importance of all staff feeling valued and being able to thrive. Key focus areas for 2024/25 include progressing initiatives to improve psychological safety, ethnic and gender representation, and disability disclosure. The PRA continues to benefit from the Bank’s excellent employee networks that cater to diverse groups such as disability, LGBTQ+, social mobility, gender, age, carers, different ethnicities, and many more.
PRA Agenda for Research
The PRA plans to build on its research efforts in 2024/25, including through improving central coordination and capacity-building projects.
Research priorities are captured in the PRA Research agenda 2023+ below (Table 1). The PRA will continue to deliver on those, while making sure that a timely delivery of high-quality research, expertise, and critical evaluation is given to PRC, FPC, and other senior decision-making activities. These deliverables are captured in the research metrics and the PRA Research Annual. The metrics track the quantity, quality, and impact of the PRA’s research, while the PRA Research Annual provides further details on how timely and effective the research advisory (inside and outside the institution) has been. New for this business year is that the PRA will additionally produce impact cases, with the purpose of tracking the lifespan of key research projects and evaluating their total policy/social impact.
To ensure that the organisation has the right capacity and skills, the PRA will initiate new capacity-building projects on models, tools, and data, while reinforcing external collaborations on those. It will also continue efforts to disseminate this work and foster strategic cooperations with research departments at other central banks, regulatory authorities, research institutes, or universities.
Table 1: PRA Research agenda 2023+
Risks to delivery of business plan.
Operating in a complex and fast-moving environment gives rise to risks to the delivery of this business plan. The PRA monitors, manages, actively mitigates (where possible), and reports these risks to the PRC and relevant Bank fora on a regular basis.
Over the course of 2023/24, attrition levels reduced and there was an improvement in recruitment into key roles. Looking ahead to 2024/25, headcount required to deliver this Business Plan is forecast to remain broadly flat.
The PRA will continue to impose discipline on how it deploys its budget to ensure resources are allocated appropriately. The PRA will also need to reprioritise during the year in response to changes in the external environment, as it routinely does. The PRA will continue to focus on managing operational risks and strengthening horizon-scanning capabilities so that it can respond quickly to changes in risk and drive decisions on prioritisation, business planning, and resourcing.
Having access to the right technology and data remains a key area of focus in 2024/25 as part of a multi-year investment across the PRA and the Bank to ensure that the PRA’s technology capabilities support its strategic priorities. This focus will take account of developments in regulatory technology, reduce inefficiencies, and leverage the benefits of being a regulator within the UK’s central bank. There is a risk that the PRA may be unable to deliver its intended technology ambition given the congested change agenda across the Bank. This challenge is being managed through careful prioritisation and scoping of key projects, including delaying some lower-priority activities.
Dependencies
Given the interconnected nature of the global financial system, dependencies on external parties, such as the FCA, HMT, and overseas regulators, could present a risk for the PRA. Policy development, authorisation processes, and supervision activities are contingent on maintaining relationships and co-operation with these parties. The PRA fosters its domestic relationships to ensure effective regulation and supervision across the UK financial sector. The PRA also works closely with international regulators to address cross-border risks for firms operating internationally. The PRA continues to foster these important relationships at all levels of the organisation through several channels, including international committees, supervisory colleges, joint reviews, information-sharing, and joint publications.
PRA Budget 2024/25
The PRA’s provisional budget for 2024/25, which is subject to finalisation of pension costs and year-end adjustments, is estimated at £353.0 million. This is an increase of £34.0 million (11%) on the 2023/24 budget. To reduce the impact to firms in 2024/25, the PRA has taken two measures, as set out in CP4/24 , to limit the increase in fees paid by firms to 7%. This increase follows a 1% reduction to fees in 2023/24 compared with 2022/23.
The PRA is constraining the increase in its own direct costs to 2%, which means a real-terms cut to the budget that will be managed by increasing efficiency in the PRA’s supervisory approach, end-to-end policymaking process, and operations. Alongside this, the PRA needs to fund inflation-driven increases in support services provided to the PRA by the Bank and the PRA’s share of tackling obsolescence in the Bank’s technology estate on which the PRA relies.
Budgeted headcount is forecast to remain broadly flat for 2024/25 ending the year at 1,541 (this compares closely to the actual year-end headcount position for 2023/24 of 1,537). The budgeted headcount reflects the PRA’s need to invest in key areas, including increasing the capacity to approve the efficiency of the IRB model review process, the implementation and supervision of CTPs, investment in the BDR, and implementing lessons learned from the failure of SVB and CS.
Details on how the PRA proposes to fund its budget can be found in CP4/24 – Regulated fees and levies: Rates proposals 2024/25 . It includes proposals for allocating costs of the PRA’s 2024/25 ongoing regulatory activities across PRA fee payers.
Abbreviations
ACS – Annual Cyclical Scenario
AI/ML – Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning
AoC – Analysis of Change
Bank – Bank of England
BCBS – Basel Committee on Banking Supervision
BDR – Banking Data Review
CBA – Cost Benefit Analysis
CEG – Cyber Expert Group
CEO – Chief Executive Officer
CMORG – Cross Market Operational Resilience Group
CP – Consultation Paper
CRR – Capital Requirements Regulation
CTP – Critical Third Party
DEI – Diversity, equity, and inclusion
DP – Discussion paper
DSC – Data Standards Committee
D&I – Diversity and inclusion
EAS – Early Account Scheme
EU – European Union
ESA – European Securities and Markets Authority
ESCG – European Systemic Cyber group
FCA – Financial Conduct Authority
FinTech – Financial Technology
FMI – Financial Market Intermediary
FMIs – Financial Market Infrastructures
FPC – Financial Policy Committee
FRF – Future Regulatory Framework
FSB – Financial Stability Board
FSMA – Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (as amended)
HMT – His Majesty's Treasury
IAIS – International Association of Insurance Supervisors
ICS – Insurance Capital Standard
ILS – insurance-linked securitisations
IRB – internal ratings-based
IRRBB – interest rate risk in the banking book
ISPV – Insurance special purpose vehicle
L-SREPs – Liquidity Supervisory Review and Evaluation Processes
MA – Matching adjustment
MALIR – Matching Adjustment Asset and Liability Information Return
MDA - Maximum distributable amount
MoU – Memorandum of Understanding
MRM – Model Risk Management
NBFI – Non-Bank Financial Institution
PMA – Post Model Adjustment
PRA – Prudential Regulation Authority
PRC – Prudential Regulation Committee
PS – Policy statement
QMC – Quarterly Model Change
RFB – Ring-fenced bodies
RWA – Risk-weighted asset
SCGO – Secondary Competitiveness and Growth Objective
SCO – Secondary Competition Objective
SDDT – Small domestic deposit takers
SMCR – Senior Managers and Certification Regime
SME – Small and medium-sized enterprise
SMF – Senior management function
SS – Supervisory statement
SVB – Silicon Valley Bank
SWES – System-wide exploratory scenario
TDC – Transforming Data Collection
TFSME – Term Funding Scheme with additional incentives for SMEs
TPR – The Pension Regulator
UKTS – UK Technical Standards
Contacting the Bank of England and the PRA
Please send any enquiries related to this publication to [email protected] .
In PS15/23, the PRA set out its rationale to rename Simpler-regime firms to Small Domestic Deposit Takers (SDDTs), and Simpler-regime consolidation entities to SDDT consolidation entities. To avoid confusion, throughout the rest of this document, the PRA will refer to SDDTs, SDDT consolidation entities, the Small Domestic Deposit Takers regime or SDDT regime, and SDDT criteria, rather than Simpler-regime firm, Simpler-regime consolidation entities, simpler regime, and Simpler-regime criteria, even when referring to past consultations.
A CTP is an entity that will be designated by HMT by a regulation made in exercise of the power in section 312L(1) of 2000, as amended by the FSMA 2023.
As at 1 January 2024.
Strictly speaking, DIFs do not accept deposits and are included under the category of deposit-takers for presentational purposes only.
Section 2E of FSMA.
SS11/13 – Internal Ratings Based (IRB) approaches .
As set out in the 2024 priorities letter on UK deposit takers .
SMFs are a type of controlled function carried out by ‘approved persons’, ie individuals who have to be approved. SMFs are the most senior people in a firm with the greatest potential to cause harm or impact upon market integrity.
Managing climate-related financial risk – thematic feedback from the PRA’s review of firms’ SS3/19 plans and clarifications of expectations and Thematic feedback on the PRA’s supervision of climate-related financial risk and the Bank of England’s Climate Biennial Exploratory Scenario exercise .
Thematic feedback from the 2021/2022 round of written auditor reporting and Thematic feedback from the 2022/2023 round of written auditor reporting.
‘Digital money’ refers to claims on deposit-takers or other financial institutions, which exist only in electronic form and whose value is preserved through a combination of strict regulation and issuers’ access to central bank deposits. ‘Digital money-like instruments’ refers to other assets that exist only in electronic form and are used for payments. Some of these are regulated to support a stable value, but their issuers do not have access to central bank deposits and are subject to lighter regulation.
Back to top

Best Cruise Insurance Plans of April 2024
Find a Qualified Financial Advisor
Finding a qualified financial advisor doesn't have to be hard. Datalign's free tool matches you with financial advisors in your area in as little as 3 minutes. All firms have been vetted by Datalign and all advisors are registered with the SEC. Get started with achieving your financial goals!
The offers and details on this page may have updated or changed since the time of publication. See our article on Business Insider for current information.
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate insurance products to write unbiased product reviews.
A cruise vacation can take much of the stress out of planning a vacation. With a pre-set itinerary on the high seas, you don't have to worry about how you're getting to your destination and what you're going to do there. However, an unexpected emergency can take the wind out of your sails and money out of your travel budget. So you'll want to ensure you have the best cruise insurance plan that won't leave you high and dry in an emergency.
Best Cruise Insurance Companies
Best Overall: Nationwide Travel Insurance
Best for affordability: AXA Assistance USA
Best for seniors: Seven Corners Travel Insurance
Best for expensive trips: HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance
Best for exotic locations: World Nomads Travel Insurance
Best overall: Nationwide
Nationwide Travel Insurance is a long-standing and reputable brand within the insurance marketplace that offers cruise insurance plans with solid coverage and reasonable rates.
It has three cruise insurance options: Universal, Choice, and Luxury. The Nationwide Choice plan, for example, offers $100,000 in emergency medical coverage and $500,000 in emergency medical evacuation coverage.
The right plan for you depends on your budget and coverage needs. But each plan offers cruise-specific coverages like ship-based mechanical breakdowns, coverage for missed prepaid excursions if your cruise itinerary changes, and covered service disruptions aboard the cruise ship.
Read our Nationwide Travel Insurance review here.
Best for affordability: AXA
AXA Assistance USA offers three comprehensive coverage plans: Gold, Silver, and Platinum. Each of these plans offers coverage for issues like missed flights, medical emergencies, lost luggage, and more.
The highest-tier Platinum plan provides $250,000 in medical emergency coverage and $1 million in medical evacuation coverage. The baggage loss coverage is $3,000 per person, and their missed connection coverage is $1,500 per person for cruises and tours.
In addition, travelers can take advantage of AXA's concierge service, which provides an extensive network of international service providers. They'll be able to assist you with things like restaurant reservations and referrals, golf course information, and more. This service could come in handy if you're stopping at a variety of unfamiliar destinations during your cruise.
The coverage limits on AXA's policies are on the higher end compared to other providers. And you can buy coverage for a little as 4% of your trip cost depending on your age, travel destination, and state of residence.
Read our AXA Travel Insurance review here.
Best for seniors: Seven Corners
Seven Corners Travel Insurance lets cruisers enjoy traveling in their golden years with the knowledge they're covered in the event of an accident or emergency. While other providers do offer coverage to those 80+ years old, Seven Corners is known for its affordable premiums while offering above-average medical expenses and medical evacuation coverage limits — two areas of travel insurance coverage that are even more important as we get older.
Seven Corners also offers the option of a preexisting conditions waiver and CFAR insurance at an additional cost, plus "Trip Interruption for Any Reason" coverage, which you won't find on many policies.
You can choose between the Trip Protection Basic or Trip Protection Choice plans, with the higher-tier Choice plan costing more but providing more coverage.
Read our Seven Corners Travel Insurance review here.
Best for expensive trips: HTH Worldwide
HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance offers three levels of trip protection: TripProtector Economy, Classic, and Preferred. The higher the tier, the more coverage you'll get for things like baggage delays, trip delays & cancellations, and medical expenses. But their premiums remain reasonable even at the highest tier of coverage.
Not only does the HTH Worldwide Trip Protector Preferred plan offer higher-than-average medical emergency and evacuation coverage limits ($500,000 and $1 million, respectively), but you'll also get a baggage loss coverage limit of $2,000 per person and coverage for trip interruption of up to 200% of the trip cost. You also have the option to add CFAR coverage for an additional cost.
Read our HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance review here.
Best for exotic locations: World Nomads
World Nomads Travel Insurance has been a top choice for comprehensive travel insurance for many years now. And it's a great option when it comes to cruise coverage, too.
Even the most basic Standard Plan comes with $100,000 in medical emergency coverage and $300,000 in emergency evacuation coverage. And you'll get higher coverage limits with their Premium Plan. Plus, unlike many other providers, World Nomads trip cancellation and emergency medical coverage include COVID-19-related issues.
What sets World Nomads apart from many other insurance companies is that its policies cover 200+ adventure sports. This can be important for adventurous cruisers who plan to take part in activities like jet skiing, scuba diving, or parasailing during their cruise.
Read our World Nomads Travel Insurance review here.
Introduction to Cruise Insurance
Cruise insurance may offer unique coverage like missed port of call and medical evacuation coverage. You might not need the flight protections of a regular travel insurance plan if you're catching a cruise at a port near you, but medical and cancel for any reason coverage could be critical. The best travel insurance plans will provide flexibility to add coverage options to fit your travels needs.
Understanding the Basics of Cruise Insurance
At its core, cruise insurance is your financial lifeboat, designed to protect you from unforeseen events that could disrupt your sea voyage. Whether it's a sudden illness, adverse weather, or other unexpected occurrences, having the right insurance can make a world of difference.
Why Cruise Insurance is Important
Picture this: You're all set for your dream cruise, but a sudden family emergency means you can't set sail. Or worse, you fall ill in the middle of the ocean. Without cruise insurance, you're not just missing out on an adventure, but also facing potentially huge financial losses. That's why securing cruise insurance isn't just recommended; it's a crucial part of your cruise planning.
Types of Cruise Insurance Coverage
Cruise insurance isn't a one-size-fits-all life jacket. There are various types of coverage, each tailored to protect different aspects of your cruise experience.
Trip Cancellation and Interruption Coverage
This coverage is like your safety net, catching you financially if you need to cancel your trip last minute or cut it short due to emergencies, be it due to personal, health-related, or even certain work conflicts.
Medical Coverage
Being on a cruise shouldn't mean being adrift from medical care. Medical coverage ensures that if you fall ill or get injured, your medical expenses won't sink your finances.
Emergency Evacuation Coverage
In the rare case that you need to be evacuated from the ship due to a medical emergency or severe weather, this coverage ensures you're not left adrift in a sea of expenses.
Baggage and Personal Effects Coverage
Imagine reaching your dream destination only to find your luggage lost at sea. This coverage ensures that lost, stolen, or damaged baggage doesn't dampen your cruise experience.
Buying Cruise Insurance
Securing the best cruise insurance isn't just about finding the best price; it's about ensuring it covers all your potential needs.
When to Purchase Cruise Insurance
Timing is everything. Purchasing your insurance soon after booking your cruise can often provide additional benefits and ensure you're covered for any early surprises. As you get closer to your trip your coverage options may get more expensive, and certain providers may not be able to offer you coverage.
How to Find the Best Deals on Cruise Insurance
Keep a lookout for deals, but remember, the cheapest option isn't always the best. Balance cost with coverage, and ensure you're getting the protection you need at a price that doesn't rock your financial boat. A travel insurance comparison site like SquareMouth is a good place to compare multiple quotes from all of the major carriers at once.
How we reviewed cruise insurance plans
When comparing cruise travel insurance providers, we evaluated them based on the following criteria to come up with our list of top picks:
Customer Satisfaction
We look at ratings from JD Power and other industry giants to see where a company ranks in customer satisfaction. We also look at customer review sites like Trustpilot and SquareMouth.
Policy Types
We look at policy types and offerings, from standard travel protections to adventure sports coverage. We look at the amount of insurance offered
Average Premiums
We compare average premiums per trip. Some companies also offer annual plans, and we compare policies accordingly.
Claims Paid
How frequently do companies pay claims easily and quickly? We check customer reviews and other resources to see which companies honor policies most effectively.
We look at the company's overall behavior. Is it operating ethically? Companies can earn additional points for such behaviors.
You can read more about how Business Insider rates insurance here.
How much does insurance cost for a cruise?
As a rule of thumb, you can expect to pay between 5% and 10% of your prepaid, nonrefundable trip expenses for cruise insurance coverage. The price will vary depending on factors like your age, your travel destination, and whether you require additional coverage.
When is the best time to buy cruise insurance?
If you're booking a cruise, we recommend purchasing travel insurance when you make your first trip payment. That could be for the cruise itself or an expense like airfare to get you to your cruising destination. This way, if you have to cancel your trip, you'll have the most extended coverage period possible.
Can I buy my own cruise insurance?
You can buy your own cruise insurance that isn't offered directly through the cruise line operator. In fact, this could be a better option if you want coverage for your travel to the cruise's departure point, not just for the cruise itself.
What is the difference between travel insurance and cruise insurance?
The difference between traditional travel insurance and cruise insurance is that cruise insurance offers more specialized coverage, for situations such as missing a departure port and more coverage for medical evacuations, since it's more expensive to evacuate someone at sea than on land.
Can I claim for missed ports on a cruise?
Most cruise insurance includes coverage for missing a departure port, so you should be able to claim for a missed port. Just make sure you check the details of your policy before you file a claim, and before you travel so you know what compensation you're entitled to.
If you enjoyed this story, be sure to follow Business Insider on Microsoft Start.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Road Trips: How to Plan an Accessible Getaway

By Syren Nagakyrie
Planning an accessible road trip is getting a little easier for people with disabilities. There are more resources created by and for the disability community, and the tourism industry is starting to recognize the value of accessible travel. As a disabled, chronically ill, neurodivergent person, I take road trips every year and have learned some tips and tricks along the way.
Renting a vehicle
Most major car companies offer adaptive driving devices for their vehicles at no additional cost. Enterprise , for example, offers hand controls, left foot accelerators, pedal extenders and spinner knobs to facilitate steering. Budget can provide hand controls, spinner knobs, a panoramic mirror, swivel seats and transfer boards. Be prepared to request adaptive devices at least three business days in advance.
For a wheelchair-accessible van with a ramp or a lift, rent from a mobility company like BraunAbility , one of the largest builders of wheelchair-accessible vans in the country, with rentals at many locations. MobilityWorks , an accessible-vehicle and adaptive-equipment dealer, has rental locations in 34 states. AccessibleGO , which offers a one-stop shop for adapted rental cars and wheelchair-accessible vans, has agreements with 100 wheelchair van rental locations nationwide; request a quote on their website. For accessibleGO’s rental cars, you can request hand controls and a spinner knob at checkout.
Route planning
You can use Google Maps, Waze and MapQuest for initial accessibility research using photos and street view. Google Maps provides directions for some wheelchair-accessible pedestrian and transit routes.
Sites such as Roadtrippers and Furkot can plot an entire itinerary. While these websites are not disability specific, they are invaluable tools. (Roadtrippers does have a wheelchair-accessible check box in the search function.) You can filter by types of destinations such as national parks or museums, and search for hotels and campgrounds. Furkot allows you to input how long you want to drive each day, whether you want to travel on Interstate highways or take more scenic roads. The app will determine the best route and length of time between stops, and suggest where to stay overnight.
Finding lodging
While hotels and other accommodations are required to comply with the Americans With Disabilities Act, many hotels do not meet all accessibility needs. Most of the booking sites list hotels with accessible rooms for those with mobility, hearing and vision needs, but this information is not always verified. Do additional research on review sites and look for photos. Hyatt, Marriott, Hilton and Fairmont hotels offer allergy-friendly and scent-free rooms in some locations. Call the hotel to verify accessibility and to make sure a specific room is reserved for you.
Vacation rentals are typically not required to be A.D.A. compliant, but some do provide accessibility information. Airbnb recently rolled out an adapted category with accessibility search features and homes that have been scanned for accessibility. Review photos and contact the host for more information. Some hosts will make accommodations, such as changing the cleaning supplies or shifting furniture, but document your request using the in-app messaging system so that customer service can help if you run into issues.
Wheel the World is an accessible travel agency offering bookings at over 3,000 verified accessible hotels in the United States. The hotels have been reviewed in person by trained assessors; only those that meet the criteria are listed. Sign up as a disabled traveler or a companion and complete a personal profile that includes options for a variety of disabilities and accessibility needs. The site will provide listings that match your profile with partial, adequate and outstanding match options.
Food and medication
There are a variety of options to keep food or medication cold while traveling. Electric coolers can plug into your vehicle’s 12-volt outlet, but pay attention to the type of cooling mechanism — the less expensive versions are usually thermoelectric and will cool only to about 30 degrees below ambient temperature (if it is 70 degrees in the car, it will cool to 40 degrees). Compressor coolers are more expensive but maintain normal refrigerated temperatures.
Many hotels provide mini-refrigerators. When you know you will be stopping somewhere with a fridge almost every night, layer large ice packs and supplies in a cooler, then top them with another insulating layer like a cooling bag. This keeps everything cold for a couple of days at a time.
It’s also a good idea to travel with a single-burner cooktop — electric to use inside, or propane to use at rest areas and campgrounds — and a camp mess kit so that you can safely cook meals.
Some of the best apps to find food, restaurants and grocery stores that accommodate dietary needs are Fig for allergy-specific options, Happy Cow for vegan-friendly options and Find Me Gluten Free for celiac-safe spots. Add your favorite options to the route-planning app so that you know where to stop.
Finding activities
In addition to the apps mentioned in the route-planning section, state and local tourism organizations are good sources for accessible destinations.
National parks and monuments, which are required to meet federal accessibility guidelines, typically have visitor centers and recreation sites with accessible features. Each park website has information, as well as programs and services within the park. While accessibility varies, you can usually find information on wheelchair-accessible trails and campsites, tactile and audio features, assistive listening devices, and American Sign Language interpreters.
At state parks, accessibility features may not be consistent, but you can usually find some information on each park’s website.
Apps like AllTrails list wheelchair-friendly trails across the country, but the information may not be verified, so contact the park or land manager for verification. Among the parks with notable accessible trails are Redwood National and State Parks, North Cascades National Park, Badlands National Park, and Great Smoky Mountains National Park .
Syren Nagakyrie, the founder of the nonprofit Disabled Hikers and the author of “The Disabled Hiker’s Guide to Western Washington and Oregon” and “The Disabled Hiker’s Guide to Northern California,” among other guidebooks, leads group hikes and conducts assessments throughout the United States.
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
Mumbai: Spend 36 hours in this fast-changing Indian city by exploring ancient caves, catching a concert in a former textile mill and feasting on mangoes.
Kyoto: The Japanese city’s dry gardens offer spots for quiet contemplation in an increasingly overtouristed destination.
Iceland: The country markets itself as a destination to see the northern lights. But they can be elusive, as one writer recently found .
Texas: Canoeing the Rio Grande near Big Bend National Park can be magical. But as the river dries, it’s getting harder to find where a boat will actually float .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business plan is essential as an entrepreneur. It helps you set clear goals and guidelines for how you will manage your business. A business plan may also be needed to set employee goals, obtain funding or even to sell your business one day. In this article, we discuss the importance of a business plan for entrepreneurs, as well as a few main ...
Here's every reason why you need a business plan. 1. Business planning is proven to help you grow 30 percent faster. Writing a business plan isn't about producing a document that accurately predicts the future of your company. The process of writing your plan is what's important. Writing your plan and reviewing it regularly gives you a ...
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business. 1. To help you with critical decisions. The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and ...
Let's take a closer look at how each of the important business planning benefits can catapult your business forward: 1. Validate Your Business Idea. The process of writing your business plan will force you to ask the difficult questions about the major components of your business, including: External: industry, target market of prospective ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Expert opinions support the four following conclusions: Individuals who write business plans are 2.5x as likely to start businesses. Business planning improves corporate executive satisfaction with corporate strategy development. Angels and venture capitalists value business plans and their financial models.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success. Why You Should Write a Business Plan. Understanding the importance of a business plan in today's competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five ...
A business plan contains detailed information that can help determine its success. Some of this information can include the following: Market analysis. Cash flow projection. Competitive analysis. Financial statements and financial projections. An operating plan. A solid business plan is a good way to attract potential investors.
A business plan is an effective way of communicating with potential investors, and the level of expertise and time used in preparing a business plan also gives professional credibility to entrepreneurs. It analyzes and predicts the chances of success for the investor and helps to raise capital. Features of a Good Business Plan 1. Executive Summary
The importance of a business plan cannot be overstated as it serves as a guide to identify and address potential challenges that a business owner may encounter along the way. ... Business planning is an essential component of any successful enterprise. It serves as a roadmap for achieving business objectives, providing a framework for decision ...
Creating a business plan is an indispensable part of any business. The main purpose of creating such a document is to attract prospective investors to provide capital to the enterprise. Therefore, the plan should cover all the important perspectives of a business - financial, operational, personnel, competition, etc.
This plan will evolve into a document you look at regularly when the business is up and running. Enterprise Nation founder Emma Jones compares having a business plan to a route map and uses the acronym 'I'm off' as a memory aid ... There are several formats you can use to create a business plan. It's important to pick the one that's right for ...
Create a Brief Business Plan. Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business.
The importance of a business plan can be critical for entrepreneurs. Take your first step to becoming an entrepreneur with our special guide. ... there's a lot of importance to a business plan. It is a road map, an outline, a document that explains what your business is, what the goals of the enterprise are, and how exactly it will set about ...
A business plan is a communication tool that you can use to secure investment capital from financial institutions or lenders. You can also use it to convince people to work for your enterprise, secure credit from suppliers, and to attract potential customers. Creating a business plan involves a lot of thought. You need to consider what you want ...
Financial Plan: This is the most important element of a business plan and is primarily addressed to investors and sponsors. It requires a firm to reveal its financial policies and market analysis. At times, a 5-year financial report is also required to be included to show past performances and profits.
1. To Prove That You're Serious About Your Business. A formal business plan is necessary to show all interested parties — employees, investors, partners and yourself — that you are committed to building the business. Creating your plan forces you to think through and select the strategies that will propel your growth. 2.
Planning shouldn't happen once a year; it should happen all year long. The questions one attempts to answer in strategic planning should be asked and answered as often as you have new information.
Business plan key takeaways and best practices. Remember: Creating a business plan is crucial when starting a business. You can use this document to guide your decisions and actions and even seek funding from lenders and investors. Keep these best practices in mind: Your business plan should evolve as your business grows.
Published Aug 14, 2023. A business plan is essential as an entrepreneur. It helps you set clear goals and guidelines for how you will manage your business. A business plan may also be needed to ...
I. Developmental Importance of the "Business Plan" While a business plan is best-known as the blueprint for starting a business or seeking financing for a ... enterprise will pay back the initial investment and then determine if this is an acceptable period of time to wait. To apply this method, first calculate projected future income from the ...
A business plan is an operating document that describes the dream of an entrepreneur with the objectives and plans to achieve them. A business plan shows the viability of the business idea from every aspect. A business plan is a crucial document that is utilized by both the company's external and internal audiences.
Creating a robust business plan is of paramount importance, whether you're kickstarting a farm venture or acquiring an existing one. Our farm business plan template starts off with an executive summary. ... every farming enterprise has the core elements of a business at its heart. These include aspects such as operations, marketing, human ...
The new rule defines a DBE as follows: "Disadvantaged Business Enterprise or DBE means a for-profit small business concern— (1) That is at least 51% owned by one or more individuals who are both socially and economically disadvantaged; and (2) Whose management and daily business operations are controlled by one or more of the socially and ...
The consultancy team should possess the following qualifications and expertise: Demonstrated 7 years of experience in developing business plans for naturebased enterprises, preferably in the ...
Organizations need a visionary AI plan — one that embraces bold, Discover the essential role of an AI plan in unlocking AI potential and enterprise innovation with Google Cloud's strategic approach.
This year's business plan continues to be structured around the PRA's four strategic priorities, as set out in its 2023/24 Business Plan. The PRA's strategic priorities for 2024/25 will remain unchanged because the PRA updated its priorities in 2023 to take account of its new powers, new secondary objective, and expanded role brought ...
Read our Nationwide Travel Insurance review here.. Best for affordability: AXA AXA Assistance USA offers three comprehensive coverage plans: Gold, Silver, and Platinum.Each of these plans offers ...
Enterprise, for example, offers hand controls, left foot accelerators, pedal extenders and spinner knobs to facilitate steering. Budget can provide hand controls, spinner knobs, a panoramic mirror ...