What can we do to slow or stop global warming?
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to stopping or slowing global warming, and each individual, business, municipal, state, tribal, and federal entity must weigh their options in light of their own unique set of circumstances. Experts say it is likely many strategies working together will be needed. Generally speaking, here are some examples of mitigation strategies we can use to slow or stop the human-caused global warming ( learn more ):
- Where possible, we can switch to renewable sources of energy (such as solar and wind energy) to power our homes and buildings, thus emitting far less heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere.
- Where feasible, we can drive electric vehicles instead of those that burn fossil fuels; or we can use mass transit instead of driving our own cars.
- Where affordable, we can conserve energy by better insulating our homes and buildings, and by replacing old, failing appliances with more energy-efficient models.
- Where practicable, we can counterbalance our annual carbon dioxide emissions by investing in commercial services that draw down an equal amount of carbon out of the atmosphere, such as through planting trees or carbon capture and storage techniques.
- Where practical, we can support more local businesses that use and promote sustainable, climate-smart practices such as those listed above.
- We can consider placing an upper limit on the amount of carbon dioxide we will allow ourselves to emit into the atmosphere within a given timeframe.
Note that NOAA doesn’t advocate for or against particular climate policies. Instead, NOAA’s role is to provide data and scientific information about climate, including how it has changed and is likely to change in the future depending on different climate policies or actions society may or may not take. More guidance on courses of action can be found in the National Academy of Sciences' 2010 report, titled Informing an Effective Response to Climate Change . Also learn more here, here, and here .
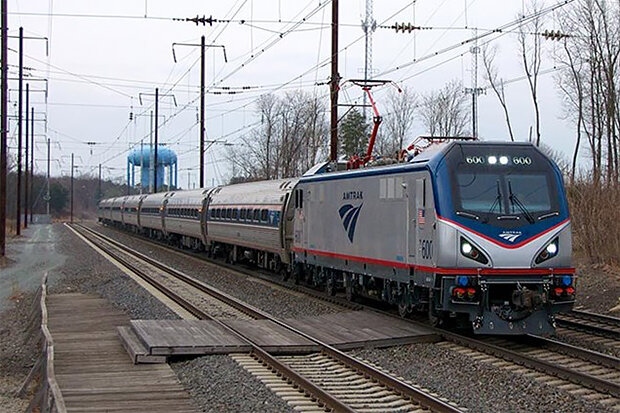

Thanks to low friction between train wheels and tracks, and level train tracks with gradual turns, trains have high energy efficiency. Photo from National Park Service Amtrak Trails and Rails .
Stabilizing global temperature near its current level requires eliminating all emissions of heat-trapping gases or, equivalently, achieving a carbon-neutral society in which people remove as much carbon from the atmosphere as they emit. Achieving this goal will require substantial societal changes in energy technologies and infrastructure that go beyond the collective actions of individuals and households to reduce emissions.

We value your feedback
Help us improve our content
Related Content
News & features, after sandy: changes and choices, national climate assessment: states and cities are already reducing carbon emissions to save lives and dollars, improving models for wind energy, maps & data, land - terrestrial climate variables, climate forcing, precipitation - 1991-2020 monthly average, teaching climate, toolbox for teaching climate & energy, climate youth engagement, young voices for the planet film series, climate resilience toolkit, climate science for water professionals, carbon balance, alaska and the arctic.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Global Warming
- Updated on
- Nov 23, 2023

Being able to write an essay is an integral part of mastering any language. Essays form an integral part of many academic and scholastic exams like the SAT , and UPSC amongst many others. It is a crucial evaluative part of English proficiency tests as well like IELTS , TOEFL , etc. Major essays are meant to emphasize public issues of concern that can have significant consequences on the world. To understand the concept of Global Warming and its causes and effects, we must first examine the many factors that influence the planet’s temperature and what this implies for the world’s future. Here’s an unbiased look at the essay on Global Warming and other essential related topics.
This Blog Includes:
Short essay on global warming and climate change, what are the causes of global warming, solutions for global warming, effects of global warming, essay on global warming paragraph in 100 – 150 words, essay on global warming in 250 words, essay on global warming in 500 words, essay on global warming upsc, climate change and global warming essay, tips to write an essay.
Since the industrial and scientific revolutions, Earth’s resources have been gradually depleted. Furthermore, the start of the world’s population’s exponential expansion is particularly hard on the environment. Simply put, as the population’s need for consumption grows, so does the use of natural resources , as well as the waste generated by that consumption.
Climate change has been one of the most significant long-term consequences of this. Climate change is more than just the rise or fall of global temperatures; it also affects rain cycles, wind patterns, cyclone frequencies, sea levels, and other factors. It has an impact on all major life groupings on the planet.
Also Read: World Population Day
What is Global Warming?
Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth’s average surface temperature over the past century, primarily due to the greenhouse gases released by people burning fossil fuels . The greenhouse gases consist of methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and chlorofluorocarbons. The weather prediction has been becoming more complex with every passing year, with seasons more indistinguishable, and the general temperatures hotter. The number of hurricanes, cyclones, droughts, floods, etc., has risen steadily since the onset of the 21st century. The supervillain behind all these changes is Global Warming. The name is quite self-explanatory; it means the rise in the temperature of the Earth.
Also Read: What is a Natural Disaster?
According to recent studies, many scientists believe the following are the primary four causes of global warming:
- Deforestation
- Greenhouse emissions
- Carbon emissions per capita
Extreme global warming is causing natural disasters , which can be seen all around us. One of the causes of global warming is the extreme release of greenhouse gases that become trapped on the earth’s surface, causing the temperature to rise. Similarly, volcanoes contribute to global warming by spewing excessive CO2 into the atmosphere.
The increase in population is one of the major causes of Global Warming. This increase in population also leads to increased air pollution . Automobiles emit a lot of CO2, which remains in the atmosphere. This increase in population is also causing deforestation, which contributes to global warming.
The earth’s surface emits energy into the atmosphere in the form of heat, keeping the balance with the incoming energy. Global warming depletes the ozone layer, bringing about the end of the world. There is a clear indication that increased global warming will result in the extinction of all life on Earth’s surface.
Also Read: Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation, and Wildlife Resources
Of course, industries and multinational conglomerates emit more carbon than the average citizen. Nonetheless, activism and community effort are the only viable ways to slow the worsening effects of global warming. Furthermore, at the state or government level, world leaders must develop concrete plans and step-by-step programmes to ensure that no further harm is done to the environment in general.
Although we are almost too late to slow the rate of global warming, finding the right solution is critical. Everyone, from individuals to governments, must work together to find a solution to Global Warming. Some of the factors to consider are pollution control, population growth, and the use of natural resources.
One very important contribution you can make is to reduce your use of plastic. Plastic is the primary cause of global warming, and recycling it takes years. Another factor to consider is deforestation, which will aid in the control of global warming. More tree planting should be encouraged to green the environment. Certain rules should also govern industrialization. Building industries in green zones that affect plants and species should be prohibited.
Also Read: Essay on Pollution
Global warming is a real problem that many people want to disprove to gain political advantage. However, as global citizens, we must ensure that only the truth is presented in the media.
This decade has seen a significant impact from global warming. The two most common phenomena observed are glacier retreat and arctic shrinkage. Glaciers are rapidly melting. These are clear manifestations of climate change.
Another significant effect of global warming is the rise in sea level. Flooding is occurring in low-lying areas as a result of sea-level rise. Many countries have experienced extreme weather conditions. Every year, we have unusually heavy rain, extreme heat and cold, wildfires, and other natural disasters.
Similarly, as global warming continues, marine life is being severely impacted. This is causing the extinction of marine species as well as other problems. Furthermore, changes are expected in coral reefs, which will face extinction in the coming years. These effects will intensify in the coming years, effectively halting species expansion. Furthermore, humans will eventually feel the negative effects of Global Warming.
Also Read: Concept of Sustainable Development
Sample Essays on Global Warming
Here are some sample essays on Global Warming:
Global Warming is caused by the increase of carbon dioxide levels in the earth’s atmosphere and is a result of human activities that have been causing harm to our environment for the past few centuries now. Global Warming is something that can’t be ignored and steps have to be taken to tackle the situation globally. The average temperature is constantly rising by 1.5 degrees Celsius over the last few years. The best method to prevent future damage to the earth, cutting down more forests should be banned and Afforestation should be encouraged. Start by planting trees near your homes and offices, participate in events, and teach the importance of planting trees. It is impossible to undo the damage but it is possible to stop further harm.
Also Read: Social Forestry
Over a long period, it is observed that the temperature of the earth is increasing. This affected wildlife , animals, humans, and every living organism on earth. Glaciers have been melting, and many countries have started water shortages, flooding, and erosion and all this is because of global warming. No one can be blamed for global warming except for humans. Human activities such as gases released from power plants, transportation, and deforestation have increased gases such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere. The main question is how can we control the current situation and build a better world for future generations. It starts with little steps by every individual. Start using cloth bags made from sustainable materials for all shopping purposes, instead of using high-watt lights use energy-efficient bulbs, switch off the electricity, don’t waste water, abolish deforestation and encourage planting more trees. Shift the use of energy from petroleum or other fossil fuels to wind and solar energy. Instead of throwing out the old clothes donate them to someone so that it is recycled. Donate old books, don’t waste paper. Above all, spread awareness about global warming. Every little thing a person does towards saving the earth will contribute in big or small amounts. We must learn that 1% effort is better than no effort. Pledge to take care of Mother Nature and speak up about global warming.
Also Read: Types of Water Pollution
Global warming isn’t a prediction, it is happening! A person denying it or unaware of it is in the most simple terms complicit. Do we have another planet to live on? Unfortunately, we have been bestowed with this one planet only that can sustain life yet over the years we have turned a blind eye to the plight it is in. Global warming is not an abstract concept but a global phenomenon occurring ever so slowly even at this moment. Global Warming is a phenomenon that is occurring every minute resulting in a gradual increase in the Earth’s overall climate. Brought about by greenhouse gases that trap the solar radiation in the atmosphere, global warming can change the entire map of the earth, displacing areas, flooding many countries, and destroying multiple lifeforms. Extreme weather is a direct consequence of global warming but it is not an exhaustive consequence. There are virtually limitless effects of global warming which are all harmful to life on earth. The sea level is increasing by 0.12 inches per year worldwide. This is happening because of the melting of polar ice caps because of global warming. This has increased the frequency of floods in many lowland areas and has caused damage to coral reefs. The Arctic is one of the worst-hit areas affected by global warming. Air quality has been adversely affected and the acidity of the seawater has also increased causing severe damage to marine life forms. Severe natural disasters are brought about by global warming which has had dire effects on life and property. As long as mankind produces greenhouse gases, global warming will continue to accelerate. The consequences are felt at a much smaller scale which will increase to become drastic shortly. The power to save the day lies in the hands of humans, the need is to seize the day. Energy consumption should be reduced on an individual basis. Fuel-efficient cars and other electronics should be encouraged to reduce the wastage of energy sources. This will also improve air quality and reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Global warming is an evil that can only be defeated when fought together. It is better late than never. If we all take steps today, we will have a much brighter future tomorrow. Global warming is the bane of our existence and various policies have come up worldwide to fight it but that is not enough. The actual difference is made when we work at an individual level to fight it. Understanding its import now is crucial before it becomes an irrevocable mistake. Exterminating global warming is of utmost importance and each one of us is as responsible for it as the next.
Always hear about global warming everywhere, but do we know what it is? The evil of the worst form, global warming is a phenomenon that can affect life more fatally. Global warming refers to the increase in the earth’s temperature as a result of various human activities. The planet is gradually getting hotter and threatening the existence of lifeforms on it. Despite being relentlessly studied and researched, global warming for the majority of the population remains an abstract concept of science. It is this concept that over the years has culminated in making global warming a stark reality and not a concept covered in books. Global warming is not caused by one sole reason that can be curbed. There are multifarious factors that cause global warming most of which are a part of an individual’s daily existence. Burning of fuels for cooking, in vehicles, and for other conventional uses, a large amount of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, and methane amongst many others is produced which accelerates global warming. Rampant deforestation also results in global warming as lesser green cover results in an increased presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which is a greenhouse gas. Finding a solution to global warming is of immediate importance. Global warming is a phenomenon that has to be fought unitedly. Planting more trees can be the first step that can be taken toward warding off the severe consequences of global warming. Increasing the green cover will result in regulating the carbon cycle. There should be a shift from using nonrenewable energy to renewable energy such as wind or solar energy which causes less pollution and thereby hinder the acceleration of global warming. Reducing energy needs at an individual level and not wasting energy in any form is the most important step to be taken against global warming. The warning bells are tolling to awaken us from the deep slumber of complacency we have slipped into. Humans can fight against nature and it is high time we acknowledged that. With all our scientific progress and technological inventions, fighting off the negative effects of global warming is implausible. We have to remember that we do not inherit the earth from our ancestors but borrow it from our future generations and the responsibility lies on our shoulders to bequeath them a healthy planet for life to exist.
Also Read: Essay on Disaster Management
One good action in a day is to combat the heat.
Global Warming and Climate Change are two sides of the same coin. Both are interrelated with each other and are two issues of major concern worldwide. Greenhouse gases released such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere cause Global Warming which leads to climate change. Black holes have started to form in the ozone layer that protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays. Human activities have created climate change and global warming. Industrial waste and fumes are the major contributors to global warming. Another factor affecting is the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation and also one of the reasons for climate change. Global warming has resulted in shrinking mountain glaciers in Antarctica, Greenland, and the Arctic and causing climate change. Switching from the use of fossil fuels to energy sources like wind and solar. When buying any electronic appliance buy the best quality with energy savings stars. Don’t waste water and encourage rainwater harvesting in your community.
Also Read: Essay on Air Pollution
Writing an effective essay needs skills that few people possess and even fewer know how to implement. While writing an essay can be an assiduous task that can be unnerving at times, some key pointers can be inculcated to draft a successful essay. These involve focusing on the structure of the essay, planning it out well, and emphasizing crucial details. Mentioned below are some pointers that can help you write better structure and more thoughtful essays that will get across to your readers:
- Prepare an outline for the essay to ensure continuity and relevance and no break in the structure of the essay
- Decide on a thesis statement that will form the basis of your essay. It will be the point of your essay and help readers understand your contention
- Follow the structure of an introduction, a detailed body followed by a conclusion so that the readers can comprehend the essay in a particular manner without any dissonance.
- Make your beginning catchy and include solutions in your conclusion to make the essay insightful and lucrative to read
- Reread before putting it out and add your flair to the essay to make it more personal and thereby unique and intriguing for readers
Relevant Blogs
Ans. Both natural and man-made factors contribute to global warming. The natural one also contains methane gas, volcanic eruptions, and greenhouse gases. Deforestation , mining , livestock raising, burning fossil fuels, and other man-made causes are next.
Ans. The government and the general public can work together to stop global warming. Trees must be planted more often, and deforestation must be prohibited. Auto usage needs to be curbed, and recycling needs to be promoted.
Ans. Switching to renewable energy sources , adopting sustainable farming, transportation, and energy methods, and conserving water and other natural resources.
We hope this blog gave you an idea about how to write and present an essay on global warming that puts forth your opinions. The skill of writing an essay comes in handy when appearing for standardized language tests . Thinking of taking one soon? Leverage Edu provides the best online test prep for the same via Leverage Live . Register today to know more!
Digvijay Singh
Having 2+ years of experience in educational content writing, withholding a Bachelor's in Physical Education and Sports Science and a strong interest in writing educational content for students enrolled in domestic and foreign study abroad programmes. I believe in offering a distinct viewpoint to the table, to help students deal with the complexities of both domestic and foreign educational systems. Through engaging storytelling and insightful analysis, I aim to inspire my readers to embark on their educational journeys, whether abroad or at home, and to make the most of every learning opportunity that comes their way.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
This was really a good essay on global warming… There has been used many unic words..and I really liked it!!!Seriously I had been looking for a essay about Global warming just like this…
Thank you for the comment!
I want to learn how to write essay writing so I joined this page.This page is very useful for everyone.
Hi, we are glad that we could help you to write essays. We have a beginner’s guide to write essays ( https://leverageedu.com/blog/essay-writing/ ) and we think this might help you.
It is not good , to have global warming in our earth .So we all have to afforestation program on all the world.
thank you so much
Very educative , helpful and it is really going to strength my English knowledge to structure my essay in future
Thank you for the comment, please follow our newsletter to get more insights on studying abroad and exams!
Global warming is the increase in 𝓽𝓱𝓮 ᴀᴠᴇʀᴀɢᴇ ᴛᴇᴍᴘᴇʀᴀᴛᴜʀᴇs ᴏғ ᴇᴀʀᴛʜ🌎 ᴀᴛᴍᴏsᴘʜᴇʀᴇ

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Prevention of Global Warming Essay

Essay on Prevention of Global Warming
Global warming is an extremely serious concern and we humans must take immediate measures to control it as soon as possible. Industrialization has led to the fast growth of technology, health, and economy but has been ruining planet Earth for the last few centuries. The monumental increase in the accumulation of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere has raised an alarm. It will cause a chaotic change that we humans will not be able to survive. This effect also endangers the rest of the species existing harmonically with nature.
Global warming is a serious environmental issue that we need to concentrate on and solve immediately. It all starts with the identification of its causes. It has become a very threatening man-made disaster for the entire planet. We need to immediately act on the causes and stop them so that we can save our planet.
What Causes Global Warming?
Man-Made activities such as running industries, using appliances emitting CFCs, have contributed to a humongous increase in the accumulation of global warming gasses. These glasses have an innate physical property to trap heat and cause the average temperature of the earth to increase. The accumulation of these gasses creates an invisible blanket in the earth’s atmosphere. This blanket lets the sun rays enter and heat up the earth’s surface. When the earth’s surface emits heat, this blanket does not allow it to pass through and traps it leading to the elevation of the average temperature of the earth.
It has been found that these gasses tend to accumulate more on the polar ice caps. It has a direct influence on the melting of ice caps causing the global sea level to rise. This is resulting in an increase in the average temperature of marine water and hampering its ecosystem. On the other hand, the coral reefs are getting extremely damaged from the rise in temperature too. Marine animals, as well as, freshwater animals are unable to adjust to such drastic changes and are suffering from the threats of extinction.
The rise in average atmospheric temperature will also cause the islands to drown. Many archipelagos of geographical significance will be underwater within a decade. In fact, the coastal lines are also receding causing turmoil in many countries. Scientists across the world have come to the conclusion that we have only 7 years left in our hands to make a change or this global warming will become irreversible causing a catastrophic change in the entire planet.
What can we do as Responsible Human Beings to Control Climate Change?
Small changes will have a great impact and will help us to fight against global warming. For instance, if we use LED bulbs instead of light bulbs and CFLs, we can contribute to the cause. We can spread awareness regarding the emission of different global warming gasses from factory chimneys and domestic appliances. These glasses should be treated before they are released into the atmosphere. We can also pledge to use eco-friendly products that show immense responsibility towards our planet’s crises.
We can also stop deforestation and do our part by planting more trees. We need to restrict the use of fossil fuels and seek alternative renewable sources of energy. Our lifestyle should become eco-friendlier and more responsible for Mother Earth. Now is the time to act and make everyone aware. Start small but make it big by including everyone you know to protect our planet. We live in a big harmonious ecosystem. Disturbing its balance with manmade disasters like global warming will not leave a chance to survive if not checked. It is time to act accordingly and do every bit on our part to stop this catastrophe.
Some Facts about Global Warming
Global warming is defined as an increase in the average surface temperature of the Earth as a result of greenhouse gasses that accumulate in the atmosphere like a blanket that traps the sun's heat which causes the globe to warm.
Greenhouse gasses trap heat at the surface of the planet, making it habitable for people and animals. Global warming, on the other hand, is mostly due to an excess of these gasses and fossil fuels (natural oil, gasoline, coal).
The industry started growing in the 1700s, as a result, people began to use more fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas to power our automobiles, trucks, and factories. You will save money on petrol and help to avert global warming by driving a "smarter" automobile.
Today's atmosphere contains more carbon dioxide than at any time in the past 800,000 years.
Global sea levels have risen by around 8 inches since 1870.
The planet has already been affected by climate change. Glaciers have been shrinking constantly for years now, ice on rivers and lakes has broken up earlier, plant and animal ranges have altered, and trees have begun to bloom earlier.
Heatwaves brought on by global warming increase the risk of heat-related disease and mortality, especially for diabetics who are elderly or very young.
As the water heats, scientists fear that coral reefs may be unable to adapt rapidly enough to the consequent shifting circumstances, leading to an increase in bleaching incidents and illnesses.

FAQs on Prevention of Global Warming Essay
1. What is Global Warming?
Too much carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) in the atmosphere behaves as a blanket, trapping heat and warming the earth, resulting in global warming. Carbon accumulates over time and overloads our atmosphere as we burn fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas for electricity or cut down and burn forests to construct pastures and plantations. Other strong global warming gasses, such as methane and nitrous oxide, are released by certain waste management and agricultural methods, worsening the situation.
2. What Effects are being Witnessed due to Global Warming?
There has been a drastic change in the climatic conditions over a few decades. Due to heavy industrialization and uncontrolled emission of greenhouse gases, the average temperature of land and water is increasing. It has harmed the survival of many aquatic and terrestrial animals. If a pillar of an ecosystem is affected, the rest will be affected too. It will trigger a chain reaction causing the human species and other animals to go extinct. Marine life is highly affected. Coral reefs are extremely damaged due to an increase in water temperature. The storms and rainfall have become much stronger. These are a few effects of global warming that scientists have concluded.
3. What can We do to Control Global Warming?
We need to plant more trees, stop the emission of greenhouse gasses as soon as possible, and make people aware of the problem. It is our smallest initiative that will make a huge change in the forthcoming years. We need to stop using any product that contributes to this problem. All we have to remember is that we do not have a spare planet to live on.
4. What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect describes how "greenhouse gasses" trap heat at the Earth's surface. The gasses are like a blanket wrapped over the earth which traps the heat, keeping it warmer than it would be otherwise. Carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides are examples of greenhouse gasses. Carbon dioxide's warming impact, according to scientists, aids in the stabilization of the Earth's atmosphere. The terrestrial greenhouse effect would be destroyed if carbon dioxide was removed. The Earth's surface would be 33 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit) colder without carbon dioxide.
5. What is the difference between global warming and climate change?
Although the phrases "global warming" and "climate change" are frequently interchanged, "global warming" is simply one facet of climate change.
Global warming refers to the planet's long-term warming. Since the early 20th century, and especially since the late 1970s, global temperatures have been steadily rising. In comparison to the mid-20th century, the average surface temperature has risen roughly 1 °C (nearly 2 °F) globally since 1880. (of 1951-1980). This comes on top of an extra 0.15 degrees Celsius of warming between 1750 and 1880.
"Climate change" refers to a larger spectrum of changes that are taking place on our planet than just global warming. Sea levels are also rising day by day, mountain glaciers are decreasing constantly, ice melt in Greenland, Antarctica, and the Arctic is increasing, and flower/plant blooming periods are shifting. All of these are results of global warming, which is mostly caused by humans burning fossil fuels and emitting heat-trapping gasses.
6. Is it too late to prevent climate change?
Humans have already triggered massive climatic changes, and we are on the verge of causing many more. But, if we immediately stopped generating greenhouse gasses, the rise in global temperatures would begin to level out within a few years. Temperatures would subsequently reach a plateau but would stay substantially above normal for several centuries. Although there is a lag between what we do and how we feel, it is less than a decade.
While the consequences of human actions on Earth's climate to date are irreversible on the timeframe of today's people, every amount of prevented future temperature increases results in less warming that would otherwise endure indefinitely. Reduced greenhouse gas emissions provide advantages in the same period as the political actions that result in such reductions.
7. Where can I find notes and questions on Global Warming?
Vedantu provides students with notes and questions on global warming. This contains topics such as what is global warming, the effects of global warming, solutions to global warming, climate change, and much more. Vedantu's content is created by teachers who are experts in their fields. Furthermore, the data is organized in a way that makes it easier for students to understand and remember the principles. Vedantu also offers study materials and a variety of competitive exams to students in grades 1 through 12. The content includes notes, important topics and questions, revision notes, and other things. All of these resources are available for free on Vedantu. To access any of these resources, students must first register on the Vedantu website. You may also join up using the Vedantu smartphone app.
UN climate report: It’s ‘now or never’ to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees

Facebook Twitter Print Email
A new flagship UN report on climate change out Monday indicating that harmful carbon emissions from 2010-2019 have never been higher in human history, is proof that the world is on a “fast track” to disaster, António Guterres has warned , with scientists arguing that it’s ‘now or never’ to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees.
Reacting to the latest findings of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change ( IPCC ), the UN Secretary-General insisted that unless governments everywhere reassess their energy policies, the world will be uninhabitable.
#LIVE NOW the press conference to present the #IPCC’s latest #ClimateReport, #ClimateChange 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change, the Working Group III contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report. Including a Q&A session with registered media. https://t.co/iIl81zXev7 IPCC IPCC_CH
His comments reflected the IPCC’s insistence that all countries must reduce their fossil fuel use substantially, extend access to electricity, improve energy efficiency and increase the use of alternative fuels, such as hydrogen.
Unless action is taken soon, some major cities will be under water, Mr. Guterres said in a video message, which also forecast “unprecedented heatwaves, terrifying storms, widespread water shortages and the extinction of a million species of plants and animals”.
Horror story
The UN chief added: “This is not fiction or exaggeration. It is what science tells us will result from our current energy policies. We are on a pathway to global warming of more than double the 1.5-degree (Celsius, or 2.7-degrees Fahreinheit) limit ” that was agreed in Paris in 2015.
Providing the scientific proof to back up that damning assessment, the IPCC report – written by hundreds of leading scientists and agreed by 195 countries - noted that greenhouse gas emissions generated by human activity, have increased since 2010 “across all major sectors globally”.
In an op-ed article penned for the Washington Post, Mr. Guterres described the latest IPCC report as "a litany of broken climate promises ", which revealed a "yawning gap between climate pledges, and reality."
He wrote that high-emitting governments and corporations, were not just turning a blind eye, "they are adding fuel to the flames by continuing to invest in climate-choking industries. Scientists warn that we are already perilously close to tipping points that could lead to cascading and irreversible climate effects."
Urban issue
An increasing share of emissions can be attributed to towns and cities , the report’s authors continued, adding just as worryingly, that emissions reductions clawed back in the last decade or so “have been less than emissions increases, from rising global activity levels in industry, energy supply, transport, agriculture and buildings”.
Striking a more positive note - and insisting that it is still possible to halve emissions by 2030 - the IPCC urged governments to ramp up action to curb emissions.
The UN body also welcomed the significant decrease in the cost of renewable energy sources since 2010, by as much as 85 per cent for solar and wind energy, and batteries.
You might also like
- ‘Lifeline’ of renewable energy can steer world out of climate crisis
- 8 reasons not to give up hope - and take climate action
Encouraging climate action
“We are at a crossroads. The decisions we make now can secure a liveable future,” said IPCC Chair Hoesung Lee. “ I am encouraged by climate action being taken in many countries . There are policies, regulations and market instruments that are proving effective. If these are scaled up and applied more widely and equitably, they can support deep emissions reductions and stimulate innovation.”
To limit global warming to around 1.5C (2.7°F), the IPCC report insisted that global greenhouse gas emissions would have to peak “before 2025 at the latest, and be reduced by 43 per cent by 2030”.
Methane would also need to be reduced by about a third, the report’s authors continued, adding that even if this was achieved, it was “almost inevitable that we will temporarily exceed this temperature threshold”, although the world “could return to below it by the end of the century”.
Now or never
“ It’s now or never, if we want to limit global warming to 1.5°C (2.7°F); without immediate and deep emissions reductions across all sectors, it will be impossible ,” said Jim Skea, Co-Chair of IPCC Working Group III, which released the latest report.
Global temperatures will stabilise when carbon dioxide emissions reach net zero. For 1.5C (2.7F), this means achieving net zero carbon dioxide emissions globally in the early 2050s; for 2C (3.6°F), it is in the early 2070s, the IPCC report states.
“This assessment shows that limiting warming to around 2C (3.6F) still requires global greenhouse gas emissions to peak before 2025 at the latest, and be reduced by a quarter by 2030.”

Policy base
A great deal of importance is attached to IPCC assessments because they provide governments with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies.
They also play a key role in international negotiations to tackle climate change.
Among the sustainable and emissions-busting solutions that are available to governments, the IPCC report emphasised that rethinking how cities and other urban areas function in future could help significantly in mitigating the worst effects of climate change.
“These (reductions) can be achieved through lower energy consumption (such as by creating compact, walkable cities), electrification of transport in combination with low-emission energy sources, and enhanced carbon uptake and storage using nature,” the report suggested. “There are options for established, rapidly growing and new cities,” it said.
Echoing that message, IPCC Working Group III Co-Chair, Priyadarshi Shukla, insisted that “the right policies, infrastructure and technology…to enable changes to our lifestyles and behaviour, can result in a 40 to 70 per cent reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. “The evidence also shows that these lifestyle changes can improve our health and wellbeing.”

- climate action
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
Global Warming 101
Everything you wanted to know about our changing climate but were too afraid to ask.

Temperatures in Beijing rose above 104 degrees Fahrenheit on July 6, 2023.
Jia Tianyong/China News Service/VCG via Getty Images

- Share this page block
What is global warming?
What causes global warming, how is global warming linked to extreme weather, what are the other effects of global warming, where does the united states stand in terms of global-warming contributors, is the united states doing anything to prevent global warming, is global warming too big a problem for me to help tackle.
A: Since the Industrial Revolution, the global annual temperature has increased in total by a little more than 1 degree Celsius, or about 2 degrees Fahrenheit. Between 1880—the year that accurate recordkeeping began—and 1980, it rose on average by 0.07 degrees Celsius (0.13 degrees Fahrenheit) every 10 years. Since 1981, however, the rate of increase has more than doubled: For the last 40 years, we’ve seen the global annual temperature rise by 0.18 degrees Celsius, or 0.32 degrees Fahrenheit, per decade.
The result? A planet that has never been hotter . Nine of the 10 warmest years since 1880 have occurred since 2005—and the 5 warmest years on record have all occurred since 2015. Climate change deniers have argued that there has been a “pause” or a “slowdown” in rising global temperatures, but numerous studies, including a 2018 paper published in the journal Environmental Research Letters , have disproved this claim. The impacts of global warming are already harming people around the world.
Now climate scientists have concluded that we must limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2040 if we are to avoid a future in which everyday life around the world is marked by its worst, most devastating effects: the extreme droughts, wildfires, floods, tropical storms, and other disasters that we refer to collectively as climate change . These effects are felt by all people in one way or another but are experienced most acutely by the underprivileged, the economically marginalized, and people of color, for whom climate change is often a key driver of poverty, displacement, hunger, and social unrest.
A: Global warming occurs when carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and other air pollutants collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight and solar radiation that have bounced off the earth’s surface. Normally this radiation would escape into space, but these pollutants, which can last for years to centuries in the atmosphere, trap the heat and cause the planet to get hotter. These heat-trapping pollutants—specifically carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and synthetic fluorinated gases—are known as greenhouse gases, and their impact is called the greenhouse effect .
Though natural cycles and fluctuations have caused the earth’s climate to change several times over the last 800,000 years, our current era of global warming is directly attributable to human activity—specifically to our burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, gasoline, and natural gas, which results in the greenhouse effect. In the United States, the largest source of greenhouse gases is transportation (29 percent), followed closely by electricity production (28 percent) and industrial activity (22 percent). Learn about the natural and human causes of climate change .
Curbing dangerous climate change requires very deep cuts in emissions, as well as the use of alternatives to fossil fuels worldwide. The good news is that countries around the globe have formally committed—as part of the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement —to lower their emissions by setting new standards and crafting new policies to meet or even exceed those standards. The not-so-good news is that we’re not working fast enough. To avoid the worst impacts of climate change, scientists tell us that we need to reduce global carbon emissions by as much as 40 percent by 2030. For that to happen, the global community must take immediate, concrete steps: to decarbonize electricity generation by equitably transitioning from fossil fuel–based production to renewable energy sources like wind and solar; to electrify our cars and trucks; and to maximize energy efficiency in our buildings, appliances, and industries.
A: Scientists agree that the earth’s rising temperatures are fueling longer and hotter heat waves, more frequent droughts, heavier rainfall, and more powerful hurricanes .
In 2015, for example, scientists concluded that a lengthy drought in California—the state’s worst water shortage in 1,200 years —had been intensified by 15 to 20 percent by global warming. They also said the odds of similar droughts happening in the future had roughly doubled over the past century. And in 2016, the National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine announced that we can now confidently attribute some extreme weather events, like heat waves, droughts, and heavy precipitation, directly to climate change.
The earth’s ocean temperatures are getting warmer, too—which means that tropical storms can pick up more energy. In other words, global warming has the ability to turn a category 3 storm into a more dangerous category 4 storm. In fact, scientists have found that the frequency of North Atlantic hurricanes has increased since the early 1980s, as has the number of storms that reach categories 4 and 5. The 2020 Atlantic hurricane season included a record-breaking 30 tropical storms, 6 major hurricanes, and 13 hurricanes altogether. With increased intensity come increased damage and death. The United States saw an unprecedented 22 weather and climate disasters that caused at least a billion dollars’ worth of damage in 2020, but 2017 was the costliest on record and among the deadliest as well: Taken together, that year's tropical storms (including Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria) caused nearly $300 billion in damage and led to more than 3,300 fatalities.
The impacts of global warming are being felt everywhere. Extreme heat waves have caused tens of thousands of deaths around the world in recent years. And in an alarming sign of events to come, Antarctica has lost nearly four trillion metric tons of ice since the 1990s. The rate of loss could speed up if we keep burning fossil fuels at our current pace, some experts say, causing sea levels to rise several meters in the next 50 to 150 years and wreaking havoc on coastal communities worldwide.
A: Each year scientists learn more about the consequences of global warming , and each year we also gain new evidence of its devastating impact on people and the planet. As the heat waves, droughts, and floods associated with climate change become more frequent and more intense, communities suffer and death tolls rise. If we’re unable to reduce our emissions, scientists believe that climate change could lead to the deaths of more than 250,000 people around the globe every year and force 100 million people into poverty by 2030.
Global warming is already taking a toll on the United States. And if we aren’t able to get a handle on our emissions, here’s just a smattering of what we can look forward to:
- Disappearing glaciers , early snowmelt, and severe droughts will cause more dramatic water shortages and continue to increase the risk of wildfires in the American West.
- Rising sea levels will lead to even more coastal flooding on the Eastern Seaboard, especially in Florida, and in other areas such as the Gulf of Mexico.
- Forests, farms, and cities will face troublesome new pests , heat waves, heavy downpours, and increased flooding . All of these can damage or destroy agriculture and fisheries.
- Disruption of habitats such as coral reefs and alpine meadows could drive many plant and animal species to extinction.
- Allergies, asthma, and infectious disease outbreaks will become more common due to increased growth of pollen-producing ragweed , higher levels of air pollution , and the spread of conditions favorable to pathogens and mosquitoes.
Though everyone is affected by climate change, not everyone is affected equally. Indigenous people, people of color, and the economically marginalized are typically hit the hardest . Inequities built into our housing , health care , and labor systems make these communities more vulnerable to the worst impacts of climate change—even though these same communities have done the least to contribute to it.
A: In recent years, China has taken the lead in global-warming pollution , producing about 26 percent of all CO2 emissions. The United States comes in second. Despite making up just 4 percent of the world’s population, our nation produces a sobering 13 percent of all global CO2 emissions—nearly as much as the European Union and India (third and fourth place) combined. And America is still number one, by far, in cumulative emissions over the past 150 years. As a top contributor to global warming, the United States has an obligation to help propel the world to a cleaner, safer, and more equitable future. Our responsibility matters to other countries, and it should matter to us, too.
A: We’ve started. But in order to avoid the worsening effects of climate change, we need to do a lot more—together with other countries—to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and transition to clean energy sources.
Under the administration of President Donald Trump (a man who falsely referred to global warming as a “hoax”), the United States withdrew from the Paris Climate Agreement, rolled back or eliminated dozens of clean-air protections, and opened up federally managed lands, including culturally sacred national monuments , to fossil fuel development. Although President Biden has pledged to get the country back on track, years of inaction during and before the Trump administration—and our increased understanding of global warming’s serious impacts—mean we must accelerate our efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Despite the lack of cooperation from the Trump administration, local and state governments made great strides during this period through efforts like the American Cities Climate Challenge and ongoing collaborations like the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative . Meanwhile, industry and business leaders have been working with the public sector, creating and adopting new clean-energy technologies and increasing energy efficiency in buildings, appliances, and industrial processes. Today the American automotive industry is finding new ways to produce cars and trucks that are more fuel efficient and is committing itself to putting more and more zero-emission electric vehicles on the road. Developers, cities, and community advocates are coming together to make sure that new affordable housing is built with efficiency in mind , reducing energy consumption and lowering electric and heating bills for residents. And renewable energy continues to surge as the costs associated with its production and distribution keep falling. In 2020 renewable energy sources such as wind and solar provided more electricity than coal for the very first time in U.S. history.
President Biden has made action on global warming a high priority. On his first day in office, he recommitted the United States to the Paris Climate Agreement, sending the world community a strong signal that we were determined to join other nations in cutting our carbon pollution to support the shared goal of preventing the average global temperature from rising more than 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels. (Scientists say we must stay below a 2-degree increase to avoid catastrophic climate impacts.) And significantly, the president has assembled a climate team of experts and advocates who have been tasked with pursuing action both abroad and at home while furthering the cause of environmental justice and investing in nature-based solutions.
A: No! While we can’t win the fight without large-scale government action at the national level , we also can’t do it without the help of individuals who are willing to use their voices, hold government and industry leaders to account, and make changes in their daily habits.
Wondering how you can be a part of the fight against global warming? Reduce your own carbon footprint by taking a few easy steps: Make conserving energy a part of your daily routine and your decisions as a consumer. When you shop for new appliances like refrigerators, washers, and dryers, look for products with the government’s ENERGY STAR ® label; they meet a higher standard for energy efficiency than the minimum federal requirements. When you buy a car, look for one with the highest gas mileage and lowest emissions. You can also reduce your emissions by taking public transportation or carpooling when possible.
And while new federal and state standards are a step in the right direction, much more needs to be done. Voice your support of climate-friendly and climate change preparedness policies, and tell your representatives that equitably transitioning from dirty fossil fuels to clean power should be a top priority—because it’s vital to building healthy, more secure communities.
You don’t have to go it alone, either. Movements across the country are showing how climate action can build community , be led by those on the front lines of its impacts, and create a future that’s equitable and just for all .
This story was originally published on March 11, 2016 and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
Related Stories

Liquefied Natural Gas 101

What’s the Most Energy-Efficient Water Heater?

What Do “Better” Batteries Look Like?
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
How Do We Reduce Greenhouse Gases?
To stop climate change , we need to stop the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, from increasing. For the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, which naturally pull carbon dioxide out of the air, has caused greenhouse gas levels to increase. There are two main ways to stop the amount of greenhouse gases from increasing: we can stop adding them to the air, and we can increase the Earth’s ability to pull them out of the air.
This is called climate mitigation . There is not one single way to mitigate climate change. Instead, we will have to piece together many different solutions to stop the climate from warming. Below are descriptions of the main methods that we can use.
Many of these solutions are already being implemented in places around the world. Some can be tackled by individuals, such as using less energy, riding a bike instead of driving, driving an electric car, and switching to renewable energy. Other actions to mitigate climate change involve communities, regions, or nations working together to make changes, such as switching power plants from burning coal or gas to renewable energy and growing public transit.
Use less electricity.
Taking steps to use less electricity, especially when it comes from burning coal or gas, can take a big bite out of greenhouse gas emissions. Worldwide, electricity use is responsible for a quarter of all emissions.
Some steps that you can take to use less electricity are simple and save money, like replacing incandescent light bulbs with LED bulbs that use less electricity, adding insulation to your home, and setting the thermostat lower in the winter and higher in the summer, especially when no one is home. There are also new technologies that help keep buildings energy efficient, such as glass that reflects heat, low-flow water fixtures, smart thermostats, and new air conditioning technology with refrigerants that don’t cause warming. In urban and suburban environments, green or cool roofs can limit the amount of heat that gets into buildings during hot days and help decrease the urban heat island effect .

Green roof on the Walter Reed Community Center in Arlington, VA, US Credit: Arlington County on Flickr/CC BY-SA 2.0
Generate electricity without emissions.
Renewable energy sources include solar energy, geothermal energy, wind turbines, ocean wave and tidal energy, waste and biomass energy, and hydropower. Because they do not burn fossil fuels, these renewable energy sources do not release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere as they generate electricity. Nuclear energy also creates no greenhouse gas emissions, so it can be thought of as a solution to climate change. However, it does generate radioactive waste that needs long-term, secure storage.
Today, the amount of electricity that comes from renewable energy is growing. A few countries, such as Iceland and Costa Rica, now get nearly all of their electricity from renewable energy. In many other countries, the percentage of electricity from renewable sources is currently small (5 - 10%) but growing.

Wind turbines can be on land or in the ocean, where high winds are common. Credit: Nicholas Doherty on Unsplash
Shrink the footprint of food.
Today, about a fifth of global carbon emissions come from raising farm animals for meat. For example, as cattle digest food they burp, releasing methane, a powerful greenhouse gas, and their manure releases the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide. And forests, which take carbon dioxide out of the air, are often cut down so that cattle have space to graze.
Eating a diet that is mostly or entirely plant-based (such as vegetables, bread, rice, and beans) lowers emissions. According to the Drawdown Project , if half the population worldwide adopts a plant-rich diet by 2050, 65 gigatons of carbon dioxide would be kept out of the atmosphere over about 30 years. (For a sense of scale, 65 gigatons of carbon dioxide is nearly two-years-worth of recent emissions from fossil fuels and industry.) Reducing food waste can make an even larger impact, saving about 90 gigatons of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere over 30 years.

Eating a plant-rich diet lowers greenhouse gas emissions. Credit: Victoria Shes on Unsplash
Travel without making greenhouse gases.
Most of the ways we have to get from place to place currently rely on fossil fuels: gasoline for vehicles and jet fuel for planes. Burning fossil fuels for transportation adds up to 14% of global greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. We can reduce emissions by shifting to alternative technologies that either don’t need gasoline (like bicycles and electric cars) or don’t need as much (like hybrid cars). Using public transportation, carpooling, biking, and walking leads to fewer vehicles on the road and less greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Cities and towns can make it easier for people to lower greenhouse gas emissions by adding bus routes, bike paths, and sidewalks.

Electric bicycles can be a way to get around without burning gasoline. Credit: Karlis Dambrans/CC BY 2.0
Reduce household waste.
Waste we put in landfills releases greenhouse gases. Almost half the gas released by landfill waste is methane, which is an especially potent greenhouse gas. Landfills are, in fact, the third largest source of methane emissions in the U.S., behind natural gas/petroleum use and animals raised for food production (and their manure). In the U.S., each member of a household produces an average of 2 kg (4.4 lbs) of trash per day. That's 726 kg (1660 lbs) of trash per person per year! Conscious choices, including avoiding unnecessary purchases, buying secondhand, eliminating reliance on single-use containers, switching to reusable bags, bottles, and beverage cups, reducing paper subscriptions and mail in favor of digital options, recycling, and composting, can all help reduce household waste.
Reduce emissions from industry.
Manufacturing, mining for raw materials, and dealing with the waste all take energy. Most of the products that we buy — everything from phones and TVs to clothing and shoes — are created in factories, which produce up to about 20% of the greenhouse gases emitted worldwide.
There are ways to decrease emissions from manufacturing. Using materials that aren’t made from fossil fuels and don’t release greenhouse gases is a good start. For example, cement releases carbon dioxide as it hardens, but there are alternative products that don’t create greenhouse gases. Similarly, bioplastics made from plants are an alternative to plastics that come from fossil fuels. Companies can also use renewable energy sources to power factories and ship the products that they create in fuel-saving cargo ships.
Take carbon dioxide out of the air.
Along with reducing the amount of carbon dioxide that we add to the air, we can also take action to increase the amount of carbon dioxide we take out of the air. The places where carbon dioxide is pulled out of the air are called carbon sinks. For example, planting trees, bamboo, and other plants increases the number of carbon sinks. Conserving forests, grasslands, peatlands, and wetlands, where carbon is held in plants and soils, protects existing carbon sinks. Farming methods such as planting cover crops and crop rotation keep soils healthy so that they are effective carbon sinks. There are also carbon dioxide removal technologies, which may be able to pull large amounts of greenhouse gases out of the atmosphere.

As the trees and other plants in a forest use sunlight to create the food they need, they are also pulling carbon dioxide out of the air. Credit: B NW on Unsplash
© 2020 UCAR
- Solving Climate Change
- Why Earth Is Warming
- The Greenhouse Effect
- What's Your Carbon Footprint?
- Classroom Activity: Mitigation or Adaptation?
- Classroom Activity: Solving the Carbon Dioxide Problem
- Stabilization Wedges (Activity and Resources)

- ENVIRONMENT
How global warming is disrupting life on Earth
The signs of global warming are everywhere, and are more complex than just climbing temperatures.
Our planet is getting hotter. Since the Industrial Revolution—an event that spurred the use of fossil fuels in everything from power plants to transportation—Earth has warmed by 1 degree Celsius, about 2 degrees Fahrenheit.
That may sound insignificant, but 2023 was the hottest year on record , and all 10 of the hottest years on record have occurred in the past decade.
Global warming and climate change are often used interchangeably as synonyms, but scientists prefer to use “climate change” when describing the complex shifts now affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems.
Climate change encompasses not only rising average temperatures but also natural disasters, shifting wildlife habitats, rising seas , and a range of other impacts. All of these changes are emerging as humans continue to add heat-trapping greenhouse gases , like carbon dioxide and methane, to the atmosphere.
What causes global warming?
When fossil fuel emissions are pumped into the atmosphere, they change the chemistry of our atmosphere, allowing sunlight to reach the Earth but preventing heat from being released into space. This keeps Earth warm, like a greenhouse, and this warming is known as the greenhouse effect .
Carbon dioxide is the most commonly found greenhouse gas and about 75 percent of all the climate warming pollution in the atmosphere. This gas is a product of producing and burning oil, gas, and coal. About a quarter of Carbon dioxide also results from land cleared for timber or agriculture.
Methane is another common greenhouse gas. Although it makes up only about 16 percent of emissions, it's roughly 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide and dissipates more quickly. That means methane can cause a large spark in warming, but ending methane pollution can also quickly limit the amount of atmospheric warming. Sources of this gas include agriculture (mostly livestock), leaks from oil and gas production, and waste from landfills.
What are the effects of global warming?
One of the most concerning impacts of global warming is the effect warmer temperatures will have on Earth's polar regions and mountain glaciers. The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the planet. This warming reduces critical ice habitat and it disrupts the flow of the jet stream, creating more unpredictable weather patterns around the globe.
( Learn more about the jet stream. )
A warmer planet doesn't just raise temperatures. Precipitation is becoming more extreme as the planet heats. For every degree your thermometer rises, the air holds about seven percent more moisture. This increase in moisture in the atmosphere can produce flash floods, more destructive hurricanes, and even paradoxically, stronger snow storms.
The world's leading scientists regularly gather to review the latest research on how the planet is changing. The results of this review is synthesized in regularly published reports known as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports.
A recent report outlines how disruptive a global rise in temperature can be:
- Coral reefs are now a highly endangered ecosystem. When corals face environmental stress, such as high heat, they expel their colorful algae and turn a ghostly white, an effect known as coral bleaching . In this weakened state, they more easily die.
- Trees are increasingly dying from drought , and this mass mortality is reshaping forest ecosystems.
- Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are making wildfires more common and more widespread. Research shows they're even moving into the eastern U.S. where fires have historically been less common.
- Hurricanes are growing more destructive and dumping more rain, an effect that will result in more damage. Some scientists say we even need to be preparing for Cat 6 storms . (The current ranking system ends at Cat 5.)
How can we limit global warming?
Limiting the rising in global warming is theoretically achievable, but politically, socially, and economically difficult.
Those same sources of greenhouse gas emissions must be limited to reduce warming. For example, oil and gas used to generate electricity or power industrial manufacturing will need to be replaced by net zero emission technology like wind and solar power. Transportation, another major source of emissions, will need to integrate more electric vehicles, public transportation, and innovative urban design, such as safe bike lanes and walkable cities.
( Learn more about solutions to limit global warming. )
One global warming solution that was once considered far fetched is now being taken more seriously: geoengineering. This type of technology relies on manipulating the Earth's atmosphere to physically block the warming rays of the sun or by sucking carbon dioxide straight out of the sky.
Restoring nature may also help limit warming. Trees, oceans, wetlands, and other ecosystems help absorb excess carbon—but when they're lost, so too is their potential to fight climate change.
Ultimately, we'll need to adapt to warming temperatures, building homes to withstand sea level rise for example, or more efficiently cooling homes during heat waves.
LIMITED TIME OFFER
Get a FREE tote featuring 1 of 7 ICONIC PLACES OF THE WORLD
Related Topics
- CLIMATE CHANGE
- ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION
- POLAR REGIONS
You May Also Like

Why all life on Earth depends on trees

Life probably exists beyond Earth. So how do we find it?

For Antarctica’s emperor penguins, ‘there is no time left’
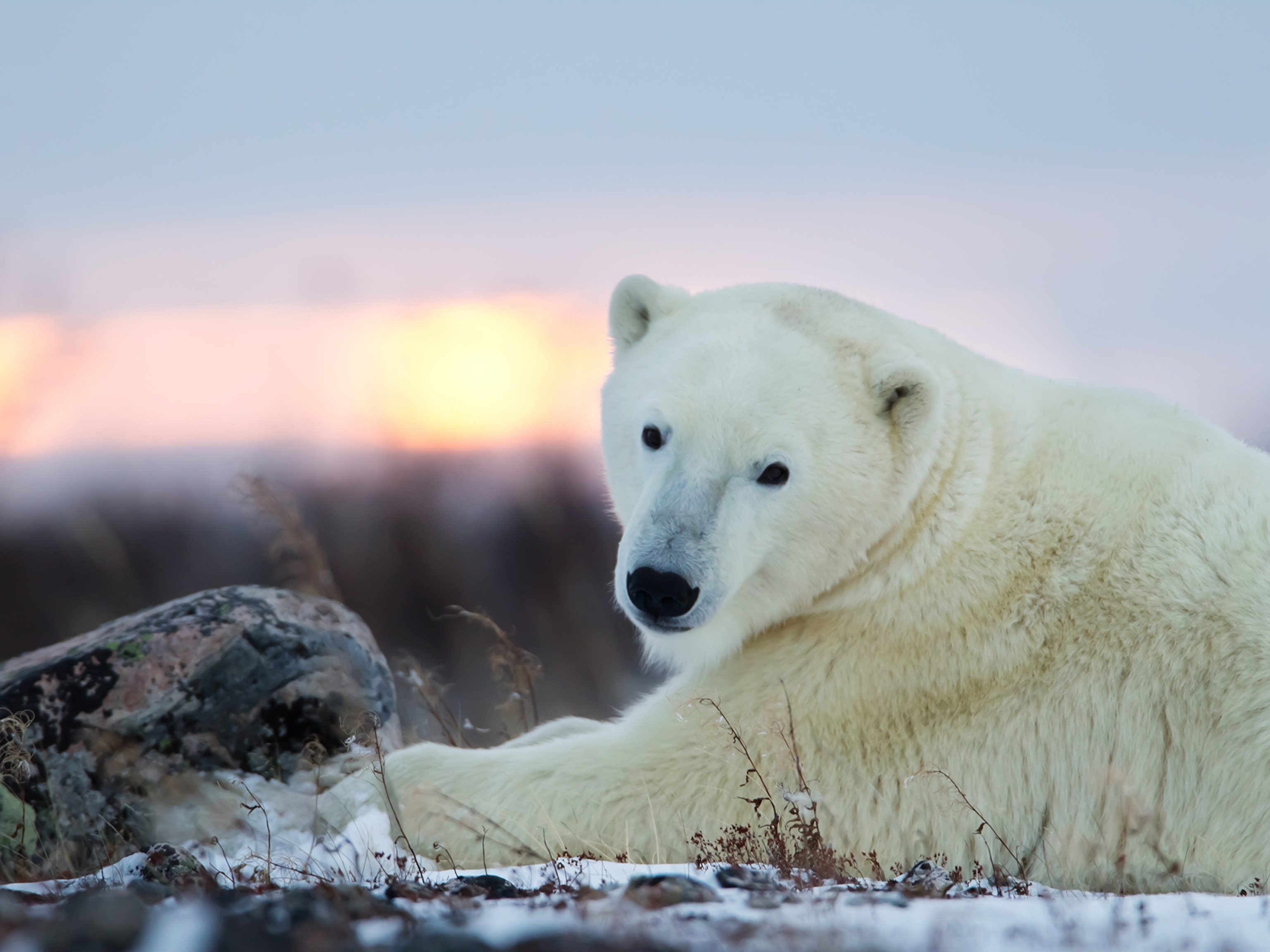

Polar bears are trying to adapt to a warming Arctic. It’s not working.

A photographic eulogy for Greenland's departing icebergs
- Paid Content
- Environment
History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Women of Impact
- History & Culture
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Destination Guide
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

Greenpeace UK
- Email signup
- Donate/Join
What are the solutions to climate change?
Climate change is already an urgent threat to millions of lives – but there are solutions. From changing how we get our energy to limiting deforestation, here are some of the key solutions to climate change.
Climate change is happening now, and it’s the most serious threat to life on our planet. Luckily, there are plenty of solutions to climate change and they are well-understood.
In 2015, world leaders signed a major treaty called the Paris agreement to put these solutions into practice.
Core to all climate change solutions is reducing greenhouse gas emissions , which must get to zero as soon as possible.
Because both forests and oceans play vitally important roles in regulating our climate, increasing the natural ability of forests and oceans to absorb carbon dioxide can also help stop global warming.
The main ways to stop climate change are to pressure government and business to:
- Keep fossil fuels in the ground . Fossil fuels include coal, oil and gas – and the more that are extracted and burned, the worse climate change will get. All countries need to move their economies away from fossil fuels as soon as possible.
- Invest in renewable energy . Changing our main energy sources to clean and renewable energy is the best way to stop using fossil fuels. These include technologies like solar, wind, wave, tidal and geothermal power.
- Switch to sustainable transport . Petrol and diesel vehicles, planes and ships use fossil fuels. Reducing car use, switching to electric vehicles and minimising plane travel will not only help stop climate change, it will reduce air pollution too.
- Help us keep our homes cosy . Homes shouldn’t be draughty and cold – it’s a waste of money, and miserable in the winter. The government can help households heat our homes in a green way – such as by insulating walls and roofs and switching away from oil or gas boilers to heat pumps .
- Improve farming and encourage vegan diets . One of the best ways for individuals to help stop climate change is by reducing their meat and dairy consumption, or by going fully vegan. Businesses and food retailers can improve farming practices and provide more plant-based products to help people make the shift.
- Restore nature to absorb more carbon . The natural world is very good at cleaning up our emissions, but we need to look after it. Planting trees in the right places or giving land back to nature through ‘rewilding’ schemes is a good place to start. This is because photosynthesising plants draw down carbon dioxide as they grow, locking it away in soils.
- Protect forests like the Amazon . Forests are crucial in the fight against climate change, and protecting them is an important climate solution. Cutting down forests on an industrial scale destroys giant trees which could be sucking up huge amounts of carbon. Yet companies destroy forests to make way for animal farming, soya or palm oil plantations. Governments can stop them by making better laws.
- Protect the oceans . Oceans also absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which helps to keep our climate stable. But many are overfished , used for oil and gas drilling or threatened by deep sea mining. Protecting oceans and the life in them is ultimately a way to protect ourselves from climate change.
- Reduce how much people consume . Our transport, fashion, food and other lifestyle choices all have different impacts on the climate. This is often by design – fashion and technology companies, for example, will release far more products than are realistically needed. But while reducing consumption of these products might be hard, it’s most certainly worth it. Reducing overall consumption in more wealthy countries can help put less strain on the planet.
- Reduce plastic . Plastic is made from oil, and the process of extracting, refining and turning oil into plastic (or even polyester, for clothing) is surprisingly carbon-intense . It doesn’t break down quickly in nature so a lot of plastic is burned, which contributes to emissions. Demand for plastic is rising so quickly that creating and disposing of plastics will account for 17% of the global carbon budget by 2050 (this is the emissions count we need to stay within according to the Paris agreement ).
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed, and to feel that climate change is too big to solve. But we already have the answers, now it’s a question of making them happen. To work, all of these solutions need strong international cooperation between governments and businesses, including the most polluting sectors.
Individuals can also play a part by making better choices about where they get their energy, how they travel, and what food they eat. But the best way for anyone to help stop climate change is to take collective action. This means pressuring governments and corporations to change their policies and business practices.
Governments want to be re-elected. And businesses can’t survive without customers. Demanding action from them is a powerful way to make change happen.
Take action
For seven years, a government ban has blocked new onshore wind farms in England – the cheapest, cleanest energy going. With a global energy crisis and sky-high energy bills, now's the time for change. Add your name to tell Rishi Sunak to end the ban on new onshore wind projects in England.
Please fill out all required fields
Thanks for signing
If you can, please chip in to help make this campaign a success.
You don’t have to leave your email address or phone number, but if you do, we’ll use these to keep you updated on how you can get involved through petitions, campaigning, volunteering and donating. You can opt out at any time . We take the security of your data seriously. Your information is safe and secure with us – read our privacy policy
The fossil fuel industry is blocking climate change action
Major oil and gas companies including BP, Exxon and Shell have spent hundreds of millions of pounds trying to delay or stop government policies that would have helped tackle the climate crisis.
Despite the effects of climate change becoming more and more obvious, big polluting corporations – the ones responsible for the majority of carbon emissions – continue to carry on drilling for and burning fossil fuels.
Industries including banks, car and energy companies also make profits from fossil fuels. These industries are knowingly putting money over the future of our planet and the safety of its people.

What are world leaders doing to stop climate change?
With such a huge crisis facing the entire planet, the international response should be swift and decisive. Yet progress by world governments has been achingly slow. Many commitments to reduce carbon emissions have been set, but few are binding and targets are often missed.
In Paris in 2015, world leaders from 197 countries pledged to put people first and reduce their countries’ greenhouse gas emissions. The Paris agreement has the aim of limiting global warming to well below 2ºC and ideally to 1.5°C.
If governments act swiftly on the promises they made in the Paris climate agreement, and implement the solutions now, there’s still hope of avoiding the worst consequences of climate change .
World leaders and climate negotiators meet at annual COPs – which stands for Conference of the Parties (the countries that signed the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, or UNFCCC).
At COPs and other climate talks, nations take stock of their ability to meet their commitments to reduce emissions.
Recently, talks have focused on climate finance – money to help poorer countries adapt to climate change and reduce emissions. Rich countries have pledged $100 billion in annual funding to help developing countries reduce emissions and manage the impacts of climate change. This is yet to materialise, and much more money is needed.
As the impacts of climate change are increasing, important talks have also started on “loss and damage” funding. This is money needed by worst-impacted countries to deal with extreme weather and other climate change impacts.
Global climate change activism
Around the world, millions of us are taking steps to defend our climate. People of all ages and from all walks of life are desperately demanding solutions to the climate emergency.
Over the years, Greenpeace has challenged oil companies chasing new fossil fuels to extract and burn. We’ve also called out the governments for their failure to act fast enough on the climate emergency. Greenpeace activists are ordinary people taking extraordinary action, to push the solutions to climate change.
Indigenous Peoples are most severely affected by both the causes and effects of climate change . They are often on the front lines, facing down deforestation or kicking out fossil fuel industries polluting their water supplies.
Communities in the Pacific Islands are facing sea level rises and more extreme weather. But they are using their strength and resilience to demand world leaders take quicker climate action.
For many of these communities, the fight against climate change is a fight for life itself.
Even in the UK, climate change is impacting people more severely. As a country with the wealth and power to really tackle climate change, it’s never been more important to demand action.
Keep exploring

What can I do to stop climate change?
Individuals can make changes to their lives to reduce their personal carbon footprint. But it’s more important to persuade decision-makers in governments and businesses to drive emissions reductions on a much larger scale. This is the best way to stop climate change getting worse.

What is the UK doing about climate change?
All countries need to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to global warming. So how’s the UK doing?

Renewable energy: a beginner's guide
Clean renewable energy is a vital tool for tackling climate change. Discover how it works and understand the advantages of wind, solar and water power.

Environmental justice, explained
The environmental crisis doesn't affect everyone equally. Often the worst impacts fall on those who are already most exploited by people in power. The fight for environmental justice is about addressing this unfairness, and making sure green solutions don't add to the problem.
Things You Can Do to Reduce Global Warming
Larry West is an award-winning environmental journalist and writer. He won the Edward J. Meeman Award for Environmental Reporting.
- University of Washington
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Betsy-Petrick-4x5-70cf94b5a1934c9199bddce1f2457f37.jpg)
- Ohio Wesleyan University
- Brandeis University
- Northeastern University
Treehugger / Hugo Lin
- Planet Earth
- Climate Crisis
- Recycling & Waste
- Natural Disasters
- Transportation
Burning fossil fuels such as natural gas, coal, oil, and gasoline raises the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, and carbon dioxide is a major contributor to the greenhouse effect and global warming. Global climate change is certainly one of the top environmental issues today.
You can help to reduce the demand for fossil fuels, which in turn reduces global warming, by using energy more wisely. Here are 10 simple actions you can take to help reduce global warming.
Watch Now: 10 Easy Ways to Help Save the Environment
Reduce, reuse, recycle.
Do your part to reduce waste by choosing reusable products instead of disposables -- get a reusable water bottle , for example. Buying products with minimal packaging (including the economy size when that makes sense for you) will help to reduce waste. And whenever you can, recycle paper , plastic, newspaper, glass, and aluminum cans . If there isn't a recycling program at your workplace, school, or in your community, ask about starting one. By recycling half of your household waste, you can save 2,400 pounds of carbon dioxide annually.
Use Less Heat and Air Conditioning
Adding insulation to your walls and attic, and installing weather stripping or caulking around doors and windows can lower your heating costs by 15 percent or more, by reducing the amount of energy you need to heat and cool your home.
Turn down the heat while you're sleeping at night or away during the day, and keep temperatures moderate at all times. Setting your thermostat just 2 degrees lower in winter and higher in summer could save about 2,000 pounds of carbon dioxide each year.
Change a Light Bulb
Wherever practical, use LED bulbs to replace regular light bulbs; they are even better than compact fluorescent light (CFL). ENERGY STAR-qualified LEDs use 20 percent - 25 percent of the energy and last up to 25 times longer than the traditional incandescent bulbs they replace.
Drive Less and Drive Smart
Less driving means fewer emissions. Besides saving gasoline, walking and biking are practical forms of exercise. Explore your community mass transit system, and check out options for carpooling to work or school. Even vacations can provide opportunities to reduce your carbon footprint.
When you do drive, make sure your car is running efficiently. For example, keeping your tires properly inflated can improve your gas mileage by more than 3 percent. Every gallon of gas you save not only helps your budget, it also keeps 20 pounds of carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere.
Buy Energy-Efficient Products
When it's time to buy a new car, choose one that offers good gas mileage. Home appliances now come in a range of energy-efficient models, and LED bulbs are designed to provide more natural-looking light while using far less energy than standard light bulbs. Look into your state's energy efficiency programs ; you might find some help.
Avoid products that come with excess packaging, especially molded plastic and packaging that can't be recycled. If you reduce your household garbage by 10 percent, you can save 1,200 pounds of carbon dioxide annually.
Use Less Hot Water
Set your water heater at 120 degrees to save energy, and wrap it in an insulating blanket if it is more than 5 years old. Buy low-flow showerheads to save hot water and about 350 pounds of carbon dioxide yearly. Wash your clothes in warm or cold water to reduce your use of hot water and the energy required to produce it. That change alone can save at least 500 pounds of carbon dioxide annually in most households. Use the energy-saving settings on your dishwasher and let the dishes air-dry.
Use the "Off" Switch
Save electricity and reduce global warming by turning off lights when you leave a room, and using only as much light as you need. And remember to turn off your television, video player, stereo, and computer when you're not using them.
It's also a good idea to turn off the water when you're not using it. While brushing your teeth, shampooing the dog or washing your car, turn off the water until you actually need it for rinsing. You'll reduce your water bill and help to conserve a vital resource.
Plant a Tree
If you have the means to plant a tree, start digging. During photosynthesis, trees and other plants absorb carbon dioxide and give off oxygen. They are an integral part of the natural atmospheric exchange cycle here on Earth, but there are too few of them to fully counter the increases in carbon dioxide caused by automobile traffic, manufacturing, and other human activities. Help mitigate climate change: a single tree will absorb approximately one ton of carbon dioxide during its lifetime.
Get a Report Card from Your Utility Company
Many utility companies provide free home energy audits to help consumers identify areas in their homes that may not be energy efficient. In addition, many utility companies offer rebate programs to help pay for the cost of energy-efficient upgrades.
Encourage Others to Conserve
Share information about recycling and energy conservation with your friends, neighbors, and co-workers, and take opportunities to encourage public officials to establish programs and policies that are good for the environment.
These steps will take you a long way toward reducing your energy use and your monthly budget. And less energy use means less dependence on the fossil fuels that create greenhouse gasses and contribute to global warming.
Edited by Frederic Beaudry
“ Fossil Fuels .” Environmental and Energy Study Institute .
“ Reduce Your Carbon Footprint .” Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection .
“ Home Envelope: An Energy Guide To Help You Keep The Outside Out And The Inside In .” North Dakota State University .
“ Lighting Choices To Save You Money .” U.S. Department of Energy.
“ What’s My Carbon Footprint ?.” Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control.
“ Savings Project: Lower Water Heating Temperature .” U.S. Department of Energy .
“ Savings Project: Insulate Your Water Heater Tank .” U.S. Department of Energy.
“ Planting 1.2 Trillion Trees Could Cancel Out a Decade of CO2 Emissions, Scientists Find .” Yale School of Environment .
- 5 Effortless Ways to Save Energy at Home
- What Is a Smart Home? Overview and Sustainability
- 15 Things You Can Do at Home to Help Solve Climate Change
- 22 Sustainable Swaps to Make at Home
- Earth Month Challenge: 30 Easy Actions for Every Day of April
- Three Types of Global Warming Solutions and Their Economic Benefits
- How to Go Green: Commuting
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Eco Tech
- 13 Eco-Conscious Ways to Save Money on Gas
- Eco-Friendly Home Guide
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Eco Decor
- Built-In Dishwashers Versus Hand-Washing: Which Is Greener?
- The Benefits of Aluminum Recycling
- Energy Efficiency Isn’t Enough Anymore
- How to Go Green: Gadgets
- 20 Ways for Renters to Stay Cool and Save Money This Summer
Read our research on: TikTok | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
In response to climate change, citizens in advanced economies are willing to alter how they live and work, many doubt success of international efforts to reduce global warming.

This analysis focuses on attitudes toward global climate change around the world. For this report, we conducted nationally representative Pew Research Center surveys of 16,254 adults from March 12 to May 26, 2021, in 16 advanced economies. All surveys were conducted over the phone with adults in Canada, Belgium, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden, the UK, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, Singapore, South Korea and Taiwan.
In the United States, we surveyed 2,596 U.S. adults from Feb. 1 to 7, 2021. Everyone who took part in the U.S. survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories.
This study was conducted in countries where nationally representative telephone surveys are feasible. Due to the coronavirus outbreak, face-to-face interviewing is not currently possible in many parts of the world.
Here are the questions used for the report, along with responses. See our methodology database for more information about the survey methods outside the U.S. For respondents in the U.S., read more about the ATP’s methodology .
A new Pew Research Center survey in 17 advanced economies spanning North America, Europe and the Asia-Pacific region finds widespread concern about the personal impact of global climate change. Most citizens say they are willing to change how they live and work at least some to combat the effects of global warming, but whether their efforts will make an impact is unclear.
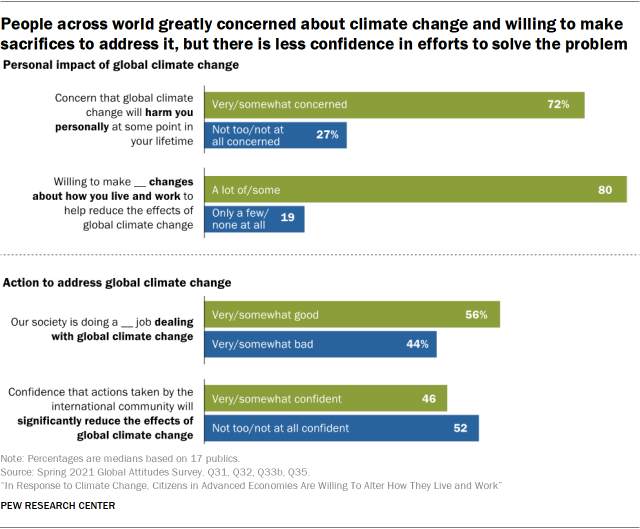
Citizens offer mixed reviews of how their societies have responded to climate change, and many question the efficacy of international efforts to stave off a global environmental crisis.
Conducted this past spring, before the summer season ushered in new wildfires , droughts , floods and stronger-than-usual storms , the study reveals a growing sense of personal threat from climate change among many of the publics polled. In Germany, for instance, the share that is “very concerned” about the personal ramifications of global warming has increased 19 percentage points since 2015 (from 18% to 37%).
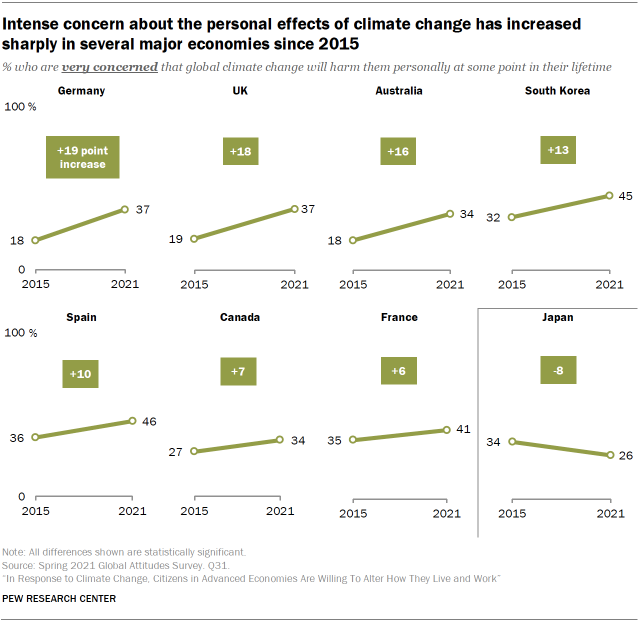
In the study, only Japan (-8 points) saw a significant decline in the share of citizens deeply concerned about climate change. In the United States, views did not change significantly since 2015.
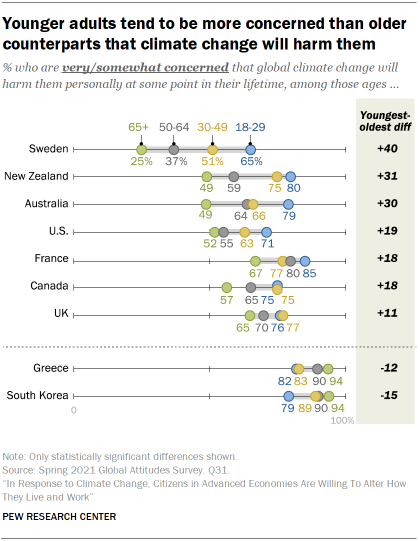
Young adults, who have been at the forefront of some of the most prominent climate change protests in recent years, are more concerned than their older counterparts about the personal impact of a warming planet in many publics surveyed. The widest age gap is found in Sweden, where 65% of 18- to 29-year-olds are at least somewhat concerned about the personal impacts of climate change in their lifetime, compared with just 25% of those 65 and older. Sizable age differences are also found in New Zealand, Australia, the U.S., France and Canada.
Public concern about climate change appears alongside a willingness to reduce its effects by taking personal steps. Majorities in each of the advanced economies surveyed say they are willing to make at least some changes in how they live and work to address the threat posed by global warming. And across all 17 publics polled, a median of 34% are willing to consider “a lot of changes” to daily life as a response to climate change.
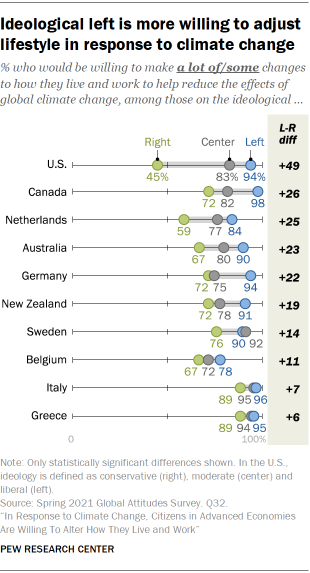
Generally, those on the left of the political spectrum are more open than those on the right to taking personal steps to help reduce the effects of climate change. This is particularly true in the U.S., where citizens who identify with the ideological left are more than twice as willing as those on the ideological right (94% vs. 45%) to modify how they live and work for this reason. Other countries where those on the left and right are divided over whether to alter their lives and work in response to global warming include Canada, the Netherlands, Australia and Germany.
Beyond individual actions, the study reveals mixed views on the broader, collective response to climate change. In 12 of the 17 publics polled, half or more think their own society has done a good job dealing with global climate change. But only in Singapore (32%), Sweden (14%), Germany (14%), New Zealand (14%) and the United Kingdom (13%) do more than one-in-ten describe such efforts as “very good.” Meanwhile, fewer than half in Japan (49%), Italy (48%), the U.S. (47%), South Korea (46%) and Taiwan (45%) give their society’s climate response favorable marks.
Abroad, the U.S. response to climate change is generally seen as wanting. Among the 16 other advanced economies surveyed, only Singaporeans are slightly positive in their assessment of American efforts (53% say the U.S. is doing a “good job” of addressing climate change). Elsewhere judgments are harsher, with six-in-ten or more across Australia, New Zealand and many of the European publics polled saying the U.S. is doing a “bad job” of dealing with global warming. However, China fares substantially worse in terms of international public opinion: A median of 78% across 17 publics describe China’s handling of climate change as “bad,” including 45% who describe the Chinese response as “very bad.” That compares with a cumulative median of 61% who judge the American response as “bad.”
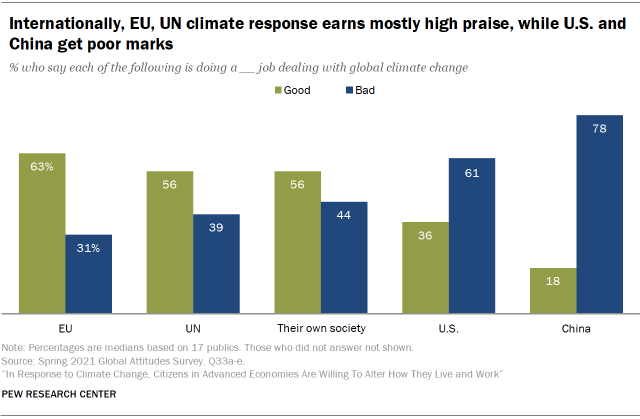
At the cross-national level, the European Union’s response to climate change is viewed favorably by majorities in each of the advanced economies surveyed, except Germany where opinion is split (49% good job; 47% bad job). However, there is still room for improvement, as only a median of 7% across the publics polled describe the EU’s efforts as “very good.” The United Nations’ actions to address global warming are also generally seen in a favorable light: A median of 56% say the multilateral organization is doing a good job. But again, the reviews are tempered, with just 5% describing the UN’s response to climate change as “very good.”
Publics in the advanced economies surveyed are divided as to whether actions by the international community can successfully reduce the effects of global warming. Overall, a median of 52% lack confidence that a multilateral response will succeed, compared with 46% who remain optimistic that nations can respond to the impact of climate change by working together. Skepticism of multilateral efforts is most pronounced in France (65%), Sweden (61%) and Belgium (60%), while optimism is most robust in South Korea (68%) and Singapore (66%).
These are among the findings of a new Pew Research Center survey, conducted from Feb. 1 to May 26, 2021, among 18,850 adults in 17 advanced economies.
People concerned climate change will harm them during their lifetimes
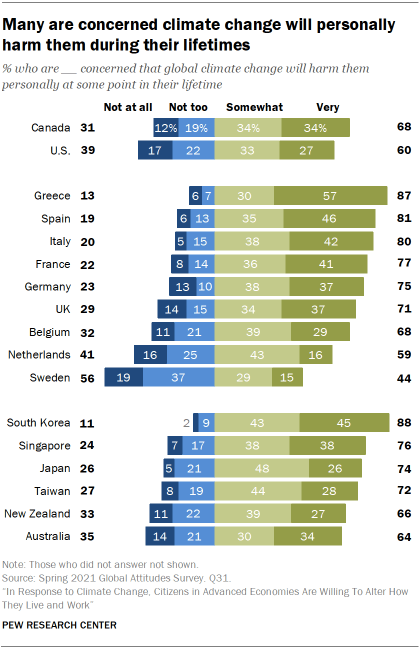
Many people across 17 advanced economies are concerned that global climate change will harm them personally at some point in their lifetime. A median of 72% express at least some concern that they will be personally harmed by climate change in their lifetimes, compared with medians of 19% and 11% who say they are not too or not at all concerned, respectively. The share who say they are very concerned climate change will harm them personally ranges from 15% in Sweden to 57% in Greece.
Roughly two-thirds of Canadians and six-in-ten Americans are worried climate change will harm them in their lifetimes. Only 12% of Canadians and 17% of Americans are not at all concerned about the personal impact of global climate change.
Publics in Europe express various degrees of concern for potential harm caused by climate change. Three-quarters or more of those in Greece, Spain, Italy, France and Germany say they are concerned that climate change will harm them at some point during their lives. Only in Sweden does less than a majority of adults express concern about climate change harming them. Indeed, 56% of Swedes are not concerned about personal harm related to climate change.
In general, Asia-Pacific publics express more worry about climate change causing them personal harm than not. The shares who express concern range from 64% in Australia to 88% in South Korea. About one-third or more in South Korea, Singapore and Australia say they are very concerned climate change will harm them personally.

The share who are very concerned climate change will harm them personally at some point during their lives has increased significantly since 2015 in nearly every country where trend data is available. In Germany, for example, the share who say they are very concerned has increased 19 percentage points over the past six years. Double-digit changes are also present in the UK (+18 points), Australia (+16), South Korea (+13) and Spain (+10). The only public where concern for the harm from climate change has decreased significantly since 2015 is Japan (-8 points).
While many worry climate change will harm them personally in the future, there is widespread sentiment that climate change is already affecting the world around them. In Pew Research Center surveys conducted in 2019 and 2020, a median of 70% across 20 publics surveyed said climate change is affecting where they live a great deal or some amount. And majorities in most countries included as part of a 26-nation survey in 2018 thought global climate change was a major threat to their own country (the same was true across all 14 countries surveyed in 2020 ).
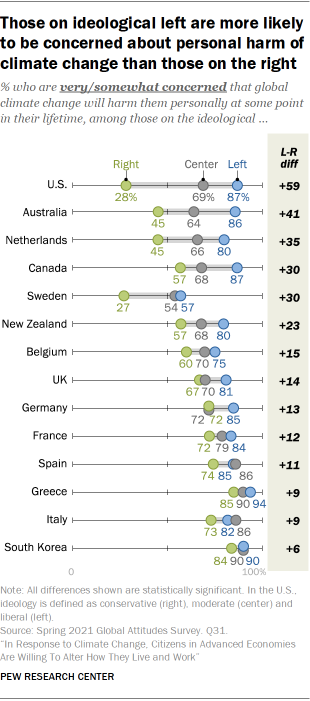
Those who place themselves on the left of the ideological spectrum are more likely than those who place themselves on the right to be concerned global climate change will harm them personally during their lifetime. This pattern is present across all 14 nations where ideology is measured. In 10 of these 14, though, majorities across the ideological left, center and right are concerned climate change will harm them personally.
The difference is starkest in the U.S.: Liberals are 59 percentage points more likely than conservatives to express concern for this possibility (87% vs. 28%, respectively). However, large ideological differences are also present in Australia (with liberals 41 points more likely to say this), the Netherlands (+35), Canada (+30), Sweden (+30) and New Zealand (+23).
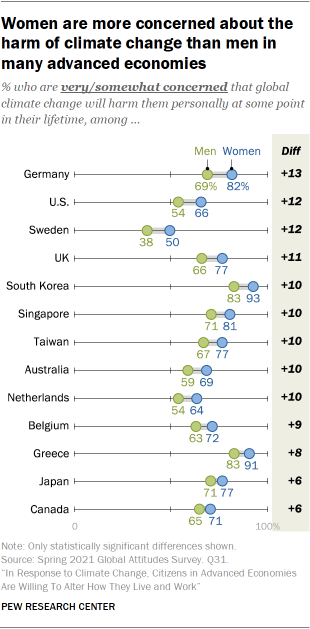
Women are more concerned than men that climate change will harm them personally in many of the publics polled. In Germany, women are 13 points more likely than men to be concerned that climate change will cause them harm (82% vs 69%, respectively). Double-digit differences are also present across several publics, including the U.S., Sweden, the UK, South Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, Australia and the Netherlands.
When this question was first asked in 2015 , women were also more likely to express concern than their male counterparts that climate change will harm them in the U.S., Germany, Canada, Japan, Spain and Australia.
Young people have been at the forefront of past protests seeking government action on climate change. In eight places surveyed, young adults ages 18 to 29 are more likely than those 65 and older to be concerned climate change will harm them during their lifetime. The difference is greatest in Sweden, home of youth climate activist Greta Thunberg . Young Swedes are 40 points more likely than their older counterparts to say they are concerned about harm from climate change. Large age gaps are also present in New Zealand (with younger adults 31 points more likely to say this), Australia (+30) and Singapore (+20). And young Americans, French, Canadians and Brits are also more likely to say that climate change will personally harm them in their lifetimes.
While large majorities across every age group in Greece and South Korea are concerned climate change will harm them personally, those ages 65 and older are more likely to hold this sentiment than those younger than 30.
Many across the world willing to change how they live and work to reduce effects of climate change
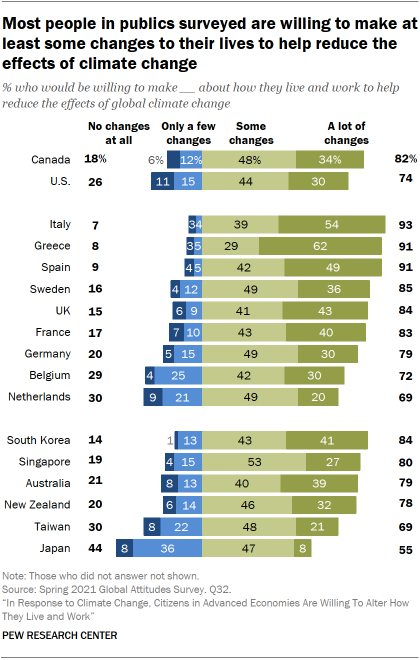
Many across the publics surveyed say they are willing to make at least some changes to the way they live and work to reduce the effects of climate change. A median of 80% across 17 publics say they would make at least some changes to their lives to reduce the effects of climate change, compared with a median of 19% who say they would make a few changes or no changes at all. The share willing to make a lot of changes ranges from 8% in Japan to 62% in Greece.
In North America, about three-quarters or more of both Canadians and Americans say they are willing to make changes to reduce the effects of climate change.
Large majorities across each of the European publics surveyed say they are willing to change personal behavior to address climate change, but the share who say they are willing to make a lot of changes varies considerably. About half or more in Greece, Italy and Spain say they would make a lot of changes, while fewer than a third in Belgium, Germany and the Netherlands say the same.
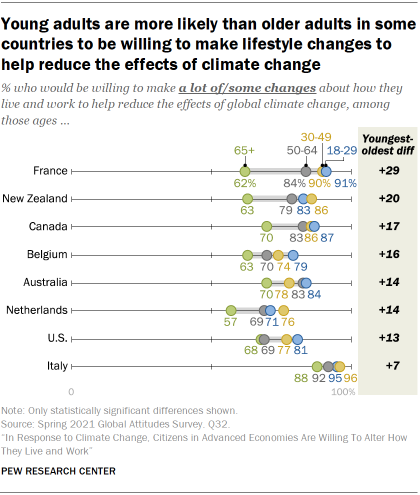
Majorities in each of the Asia-Pacific publics polled say they would make some or a lot of changes to how they live and work to combat the effects of climate change, including more than three-quarters in South Korea, Singapore, Australia and New Zealand. But in Japan, fully 44% say they are willing to make few or no changes to how they live and work to address climate change, the largest share of any public surveyed.
In eight countries surveyed, those ages 18 to 29 are more likely than those 65 and older to say they are willing to make at least some changes to how they live and work to help reduce the effects of climate change. In France, for example, about nine-in-ten of those younger than 30 are willing to make changes in response to climate change, compared with 62% of those 65 and older.
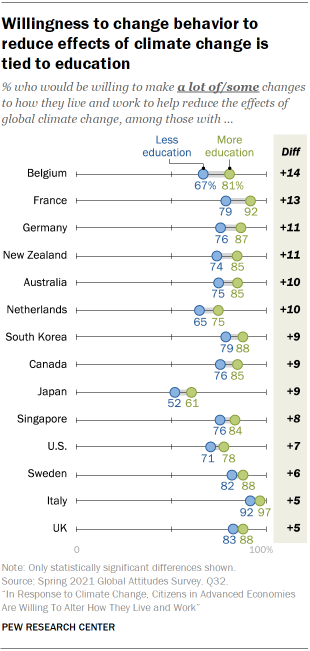
Ideologically, those on the left are more likely than those on the right to express willingness to change their behavior to help reduce the effects of global climate change. The ideological divide is widest in the U.S., where 94% of liberals say they are willing to make at least some changes to how they live and work to help reduce the effects of climate change, compared with 45% of conservatives. Large ideological differences are also present between those on the left and the right in Canada (a difference of 26 percentage points), the Netherlands (25 points), Australia (23 points) and Germany (22 points).
In most publics, those with more education are more likely than those with less education to say they are willing to adjust their lifestyles in response to the impact of climate change. 1 In Belgium, for example, those with a postsecondary degree or higher are 14 points more likely than those with a secondary education or below to say they are willing to make changes to the way they live. Double-digit differences are also present between those with more education and less education in France, Germany, New Zealand, the Netherlands and Australia.
And in most places surveyed, those with a higher-than-median income are more likely than those with a lower income to express willingness to make at least some changes to reduce the effects of climate change. For example, in Belgium, about three-quarters (76%) of those with a higher income say they would make changes to their lives, compared with 66% of those with a lower income.
Many are generally positive about how their society is handling climate change
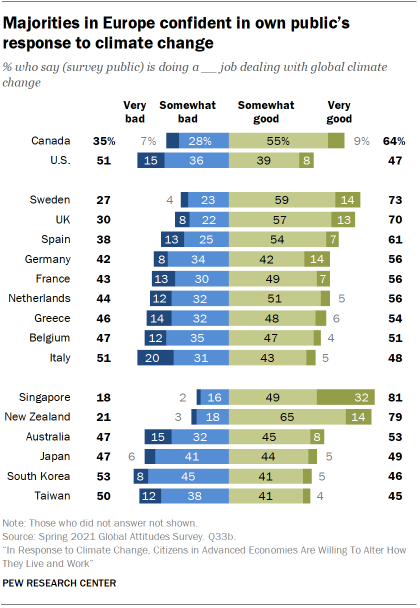
Respondents give mostly positive responses when asked to reflect on how their own society is handling climate change. Around half or more in most places say they their society is doing at least a somewhat good job, with a median of 56% saying this across the 17 advanced economies.
Roughly two-thirds (64%) of Canadians say their country is doing a good job, while nearly half of Americans say the same.
In most of the European publics surveyed, majorities believe their nation’s climate change response is at least somewhat good. Those in Sweden and the UK are especially optimistic, with around seven-in-ten saying their society is doing a good job dealing with climate change. In Europe, Italians are the most critical of their country’s performance: 20% say their society is doing a very bad job, the largest share among all publics surveyed.
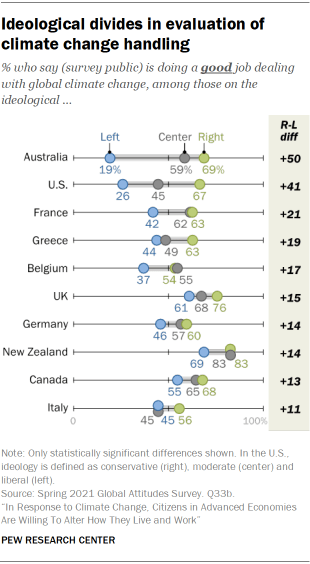
Around eight-in-ten in Singapore and New Zealand say their publics are doing a good job – the highest levels among all societies surveyed. This includes around a third (32%) in Singapore who say they are doing a very good job. Adults in the other Asia-Pacific publics surveyed are more circumspect; about half or fewer say their society is doing a good job.
Political ideology plays a role in how people evaluate their own public’s handling of climate change. For adults in 10 countries, those on the right tend to rate their country’s performance with regard to climate change more positively. The difference is most stark in Australia: 69% of those on the right say Australia is handling climate change well, compared with just 19% of those on the left – a 50-point difference. A striking difference also appears in the U.S., where conservatives are 41 points more likely than liberals to say the U.S. is doing a good job dealing with climate change.
Evaluations are also tied to how people view governing parties. In 10 of 17 publics surveyed, people who see the governing party positively are more likely than those with a negative view of the party to think climate change is being handled well. The opposite is true in the U.S., where only 33% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say the U.S. is handling climate change well, compared with 61% of those who do not support the Democratic Party.
Mixed views on whether action by the international community can reduce the effects of climate change
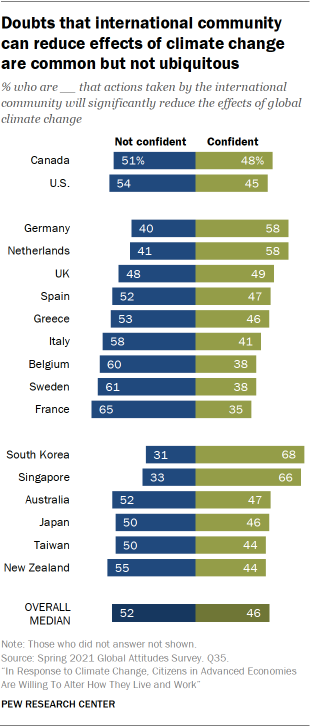
Only a median of 46% across the publics polled are confident that actions taken by the international community will significantly reduce the effects of climate change. A median of 52% are not confident these actions will reduce the effects of climate change.
Canadians are generally divided on whether international climate action can reduce the impact of climate change. And 54% of Americans are not confident in the international community’s response to the climate crisis.
In Europe, majorities in Germany and the Netherlands express confidence that international climate action can significantly address climate change. However, majorities in France, Sweden, Belgium and Italy are not confident in climate actions taken by the international community.
South Koreans and Singaporeans say they are confident in international climate action, but elsewhere in the Asia-Pacific region, public opinion is either divided or leans toward pessimism about international efforts.
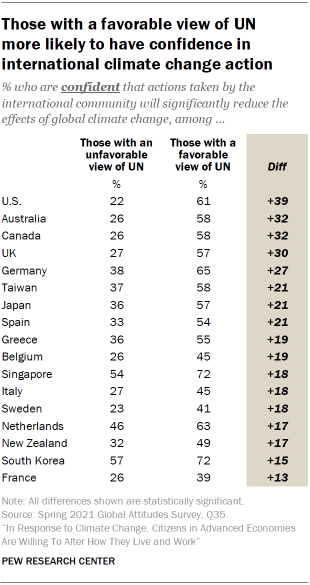
Opinion of international organizations, like the United Nations, is linked to confidence that actions taken by the international community will significantly reduce the effects of global climate change. Those with a favorable view of the UN are more confident that actions taken by the international community will significantly reduce the effects of climate change than those with an unfavorable view of the UN. This difference is largest in the U.S., where 61% with a favorable view of the UN say international action will reduce the effects of climate change, compared with just 22% of those with an unfavorable view of the organization. Double-digit differences are present in every public polled.
Similarly, in every EU member state included in the survey, those with favorable views of the bloc are more likely to have confidence in international efforts to combat climate change than those with unfavorable views.
Little consensus on whether international climate action will harm or benefit domestic economies
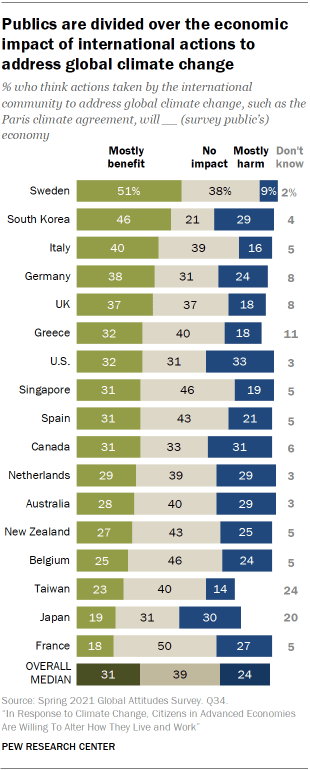
Relatively few in the advanced economies surveyed think actions taken by the international community to address climate change, such as the Paris climate agreement, will mostly benefit or harm their own economy. A median of 31% across 17 publics say these actions will be good for their economy, while a median of 24% believe such actions will mostly harm their economy. A median of 39% say actions like the Paris climate agreement will have no economic impact.
In Sweden, about half (51%) feel international climate actions will mostly benefit their economy. On the other hand, only 18% in France say their public will benefit economically from international climate agreements.
In no public do more than a third say international action on climate change will harm their economy. But in the U.S., which pulled out of the Paris climate agreement under former President Donald Trump and has just recently rejoined the accord under President Joe Biden, a third say international climate agreements will harm the economy. (For more on how international publics view Biden’s international policy actions, see “ America’s Image Abroad Rebounds With Transition From Trump to Biden .”)
The more widespread sentiment among those surveyed is that climate actions will have no impact on domestic economies. In eight publics, four-in-ten or more hold this opinion, including half in France. And in two places – Japan and Taiwan – one-in-five or more offer no opinion.
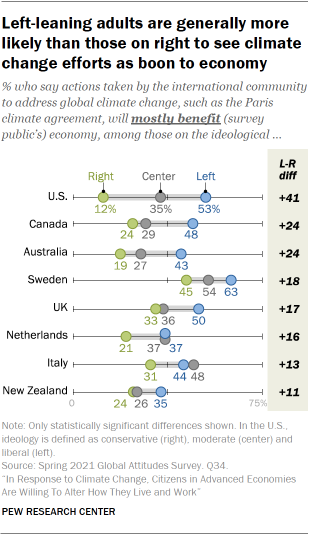
Those on the left of the ideological spectrum are more likely than those on the right to say international action to address climate change – such as the Paris Agreement – will mostly benefit their economies. U.S. respondents are particularly divided by ideology. Roughly half (53%) of liberals feel international actions related to climate change will benefit the U.S. economy, compared with just 12% of conservatives. The next largest difference is in Canada, where those on the left are 24 percentage points more likely than those on the right to think this type of international action will benefit their economy.
Those on the right in many publics are, in turn, more likely than those on the left to think international actions such as the Paris Agreement will mostly harm their economies. Here again, ideological divisions in the U.S. are much larger than those in other publics: 65% of conservatives say international climate change actions will harm the American economy, compared with 12% of liberals who say the same.
In several advanced economies, those who say their current economic situation is good are more likely to say that actions taken by the international community to address climate change will mostly benefit their economies than those who say the economic situation is bad. In Sweden, for example, a majority (55%) of those who say the current economic situation is good also believe international action like the Paris Agreement will benefit the Swedish economy, compared with 31% who are more negative about the state of the economy.
Evaluating the climate change response from the EU, UN, U.S. and China
In addition to reflecting on their own public, respondents were asked to evaluate how four international organizations or countries are handling global climate change. Of the entities asked about, the European Union receives the best ratings, with a median of 63% across the 17 publics surveyed saying the EU is doing a good job handling climate change. A median of 56% say the same for the United Nations. Far fewer believe the U.S. or China – the two leading nations in carbon dioxide emissions – are doing a good job.
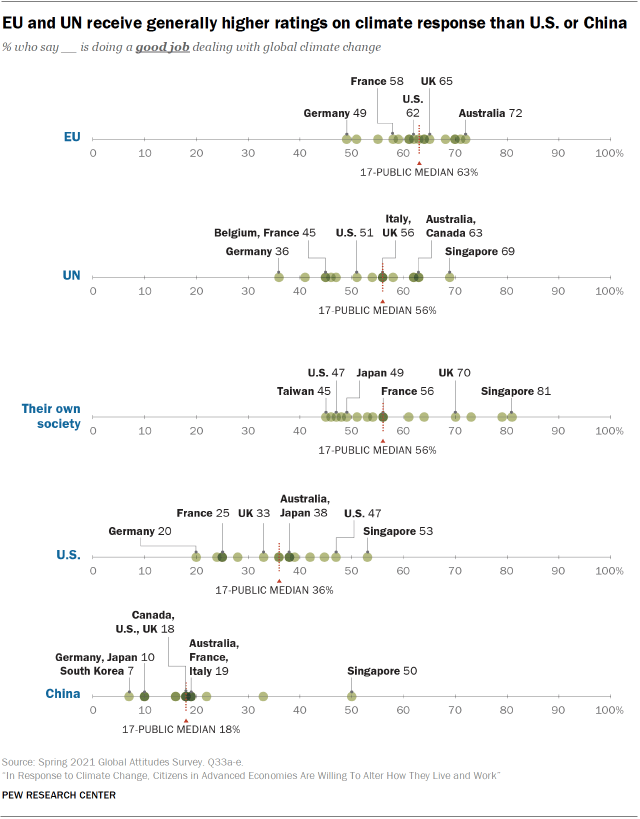
EU handling of climate change receives high marks in and outside of Europe
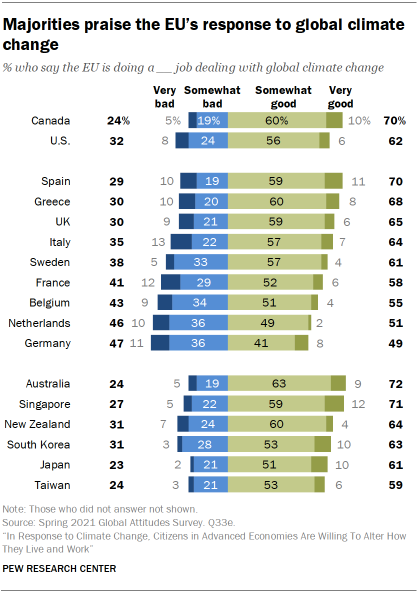
Majorities in all but two of the publics surveyed think the EU is doing a good job addressing climate change. However, this positivity is tempered, with most respondents saying the EU’s effort is somewhat good, but few saying it is very good.
Praise for the bloc’s response to climate change is common among the European countries surveyed. In Spain and Greece, around seven-in-ten say the EU is doing at least a somewhat good job, and about six-in-ten or more in the UK, Italy, Sweden and France agree. The Dutch and Germans have more mixed feelings about how the EU is responding to climate change. Notably, only about one-in-ten say the EU is doing a very bad job handling climate change in every European country surveyed but Sweden, where only 5% say so.
Seven-in-ten Canadians believe the EU is doing a good job dealing with climate change, and 62% in the U.S. express the same view.
The Asia-Pacific publics surveyed report similarly positive attitudes on the EU’s climate plans. Around seven-in-ten Australians and Singaporeans consider the EU’s response to climate change at least somewhat good. About six-in-ten or more in New Zealand, South Korea, Japan and Taiwan echo this sentiment.
Climate change actions by UN seen positively among most surveyed
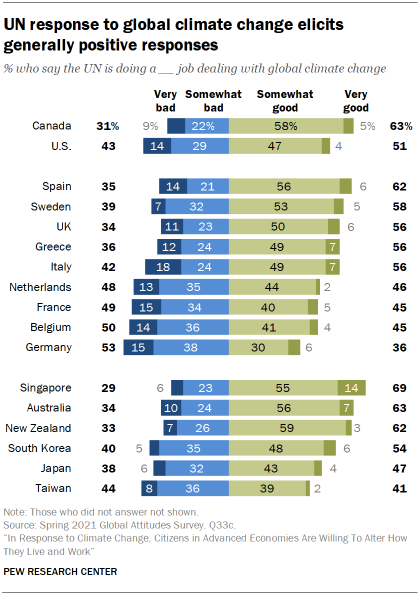
Majorities in most publics also consider the UN response to climate change to be good. A median of 49% across all publics surveyed say that the UN’s actions are somewhat good, and a median of 5% say the actions are very good.
Canadians evaluate the UN’s performance on climate more positively than Americans do. In Canada, roughly six-in-ten say the multilateral organization is doing at least a somewhat good job handling climate change. About half of those in the U.S. agree with that evaluation, with 43% of Americans saying the UN is doing a bad job of dealing with climate change.
In Europe, majorities in Spain, Sweden, the UK, Greece and Italy approve of how the UN is dealing with climate change. Fewer than half of adults in the Netherlands, France and Belgium agree with this evaluation, and only about a third in Germany say the same.
Singaporeans stand out as the greatest share of adults among those surveyed who see the UN’s handling of climate change as good. This includes 14% who say the UN response is very good, which is at least double the share in all other societies surveyed. Majorities in Australia and New Zealand similarly say that the UN is doing a good job.
Many critical of U.S. approach to climate change
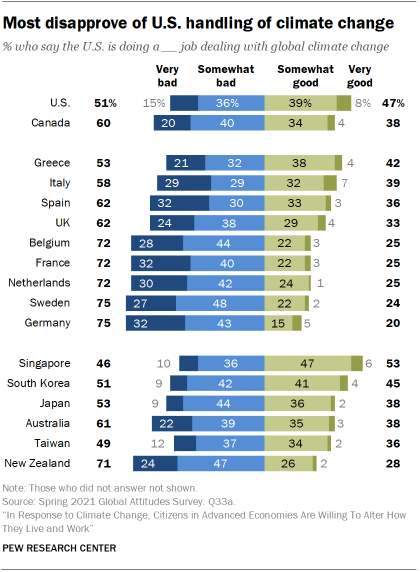
In most publics surveyed, adults who say the U.S. is doing a good job of handling climate change are in the minority. A median of 33% say the U.S. is doing a somewhat good job, and a median of just 3% believe the U.S. is doing a very good job.
About half of Americans say their own country is doing a good job in dealing with global climate change, but six-in-ten Canadians say their southern neighbor is doing a bad job.
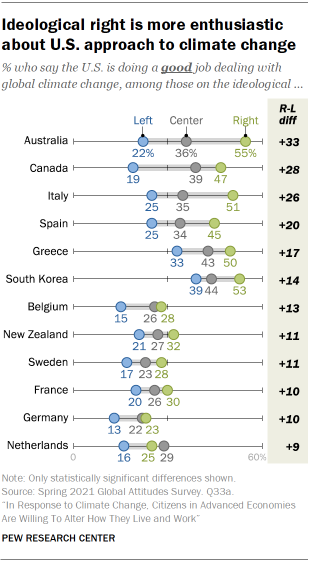
Across Europe, most think the U.S. is doing a bad job of addressing climate change, including 75% of Germans and Swedes. And at least a quarter in all European nations surveyed except the UK and Greece say the U.S. is doing a very bad job.
Singaporeans offer the U.S. approach to climate change the most praise in the Asia-Pacific region and across all publics surveyed; around half say they see the U.S. strategy positively. New Zealanders are the most critical in the Asia-Pacific region: Only about a quarter say the U.S. is doing at least a somewhat good job.
Political ideology is linked to evaluations of the U.S. climate strategy. In 12 countries, those on the right of the political spectrum are significantly more likely than those on the left to say the U.S. is doing a good job dealing with global climate change. The difference is greatest in Australia, Canada and Italy.
Few give China positive marks for handling of climate change
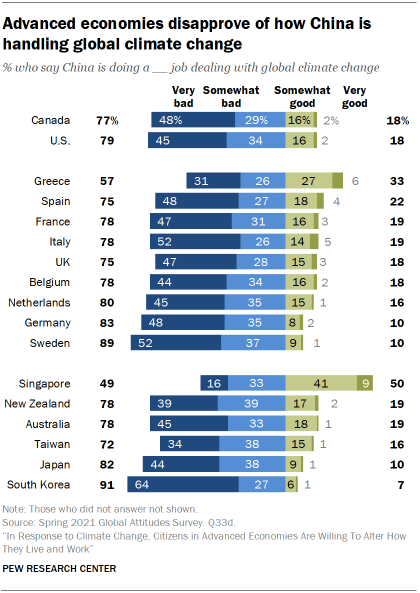
The publics surveyed are unenthusiastic about how China is dealing with climate change. A median of 18% across the publics say China is doing a good job, compared with a median of 78% who say the opposite. Notably, a median of 45% say that China is doing a very bad job handling climate change.
Just 18% of Americans and Canadians believe China is doing a good job handling climate change.
Similarly, few in Europe think China is dealing effectively with climate change. In fact, more than four-in-ten in nearly all European countries polled say China is doing a very bad job with regards to climate change. Criticism is less common in Greece, where a third give China positive marks for its climate change action.
Adults in the Asia-Pacific region also generally give China poor ratings for dealing with climate change. South Koreans are exceptionally critical; about two-thirds say China is doing a very bad job, the highest share in all publics surveyed. About four-in-ten or more in New Zealand, Japan and Australia concur. Singaporeans stand out, as half say China is doing a good job, nearly 20 percentage points higher than the next highest public.
In nine countries surveyed, those with less education are more positive toward China’s response to climate change than those with more education. Likewise, those with lower incomes are more inclined to provide positive evaluations of China’s climate change response. Those with less education or lower incomes are also less likely to provide a response in several publics.
CORRECTION (Oct. 13, 2021): In the chart “Publics are divided over the economic impact of international actions to address global climate change,” the “Don’t Know” column has been edited to reflect updated percentages to correct for a data tabulation error. These changes did not affect the report’s substantive findings.
- For the purpose of comparing educational groups across publics, education levels are standardized based on the UN’s International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED). The “less education” category is secondary education or below and the “more education” category is postsecondary or above in Australia, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Singapore, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Taiwan, UK and U.S. ↩
Add Pew Research Center to your Alexa
Say “Alexa, enable the Pew Research Center flash briefing”
Report Materials
Table of contents, many people globally see united nations in a positive light, including its handling of climate change, americans are less concerned – but more divided – on climate change than people elsewhere, many globally are as concerned about climate change as about the spread of infectious diseases, despite pandemic, many europeans still see climate change as greatest threat to their countries, a look at how people around the world view climate change, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

Search the United Nations
- What Is Climate Change
- Myth Busters
- Renewable Energy
- Finance & Justice
- Initiatives
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Paris Agreement
- Climate Ambition Summit 2023
- Climate Conferences
- Press Material
- Communications Tips

Renewable energy – powering a safer future
Energy is at the heart of the climate challenge – and key to the solution.
A large chunk of the greenhouse gases that blanket the Earth and trap the sun’s heat are generated through energy production, by burning fossil fuels to generate electricity and heat.
Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and gas, are by far the largest contributor to global climate change , accounting for over 75 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 percent of all carbon dioxide emissions.
The science is clear: to avoid the worst impacts of climate change, emissions need to be reduced by almost half by 2030 and reach net-zero by 2050.
To achieve this, we need to end our reliance on fossil fuels and invest in alternative sources of energy that are clean, accessible, affordable, sustainable, and reliable.
Renewable energy sources – which are available in abundance all around us, provided by the sun, wind, water, waste, and heat from the Earth – are replenished by nature and emit little to no greenhouse gases or pollutants into the air.
Fossil fuels still account for more than 80 percent of global energy production , but cleaner sources of energy are gaining ground. About 29 percent of electricity currently comes from renewable sources.
Here are five reasons why accelerating the transition to clean energy is the pathway to a healthy, livable planet today and for generations to come.
1. Renewable energy sources are all around us
About 80 percent of the global population lives in countries that are net-importers of fossil fuels -- that’s about 6 billion people who are dependent on fossil fuels from other countries, which makes them vulnerable to geopolitical shocks and crises.
In contrast, renewable energy sources are available in all countries, and their potential is yet to be fully harnessed. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) estimates that 90 percent of the world’s electricity can and should come from renewable energy by 2050.
Renewables offer a way out of import dependency, allowing countries to diversify their economies and protect them from the unpredictable price swings of fossil fuels, while driving inclusive economic growth, new jobs, and poverty alleviation.
2. Renewable energy is cheaper
Renewable energy actually is the cheapest power option in most parts of the world today. Prices for renewable energy technologies are dropping rapidly. The cost of electricity from solar power fell by 85 percent between 2010 and 2020. Costs of onshore and offshore wind energy fell by 56 percent and 48 percent respectively.
Falling prices make renewable energy more attractive all around – including to low- and middle-income countries, where most of the additional demand for new electricity will come from. With falling costs, there is a real opportunity for much of the new power supply over the coming years to be provided by low-carbon sources.
Cheap electricity from renewable sources could provide 65 percent of the world’s total electricity supply by 2030. It could decarbonize 90 percent of the power sector by 2050, massively cutting carbon emissions and helping to mitigate climate change.
Although solar and wind power costs are expected to remain higher in 2022 and 2023 then pre-pandemic levels due to general elevated commodity and freight prices, their competitiveness actually improves due to much sharper increases in gas and coal prices, says the International Energy Agency (IEA).
3. Renewable energy is healthier
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 99 percent of people in the world breathe air that exceeds air quality limits and threatens their health, and more than 13 million deaths around the world each year are due to avoidable environmental causes, including air pollution.
The unhealthy levels of fine particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide originate mainly from the burning of fossil fuels. In 2018, air pollution from fossil fuels caused $2.9 trillion in health and economic costs , about $8 billion a day.
Switching to clean sources of energy, such as wind and solar, thus helps address not only climate change but also air pollution and health.
4. Renewable energy creates jobs
Every dollar of investment in renewables creates three times more jobs than in the fossil fuel industry. The IEA estimates that the transition towards net-zero emissions will lead to an overall increase in energy sector jobs : while about 5 million jobs in fossil fuel production could be lost by 2030, an estimated 14 million new jobs would be created in clean energy, resulting in a net gain of 9 million jobs.
In addition, energy-related industries would require a further 16 million workers, for instance to take on new roles in manufacturing of electric vehicles and hyper-efficient appliances or in innovative technologies such as hydrogen. This means that a total of more than 30 million jobs could be created in clean energy, efficiency, and low-emissions technologies by 2030.
Ensuring a just transition , placing the needs and rights of people at the heart of the energy transition, will be paramount to make sure no one is left behind.
5. Renewable energy makes economic sense
About $7 trillion was spent on subsidizing the fossil fuel industry in 2022, including through explicit subsidies, tax breaks, and health and environmental damages that were not priced into the cost of fossil fuels.
In comparison, about $4 trillion a year needs to be invested in renewable energy until 2030 – including investments in technology and infrastructure – to allow us to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
The upfront cost can be daunting for many countries with limited resources, and many will need financial and technical support to make the transition. But investments in renewable energy will pay off. The reduction of pollution and climate impacts alone could save the world up to $4.2 trillion per year by 2030.
Moreover, efficient, reliable renewable technologies can create a system less prone to market shocks and improve resilience and energy security by diversifying power supply options.
Learn more about how many communities and countries are realizing the economic, societal, and environmental benefits of renewable energy.
Will developing countries benefit from the renewables boom? Learn more here .

What is renewable energy?
Derived from natural resources that are abundant and continuously replenished, renewable energy is key to a safer, cleaner, and sustainable world. Explore common sources of renewable energy here.
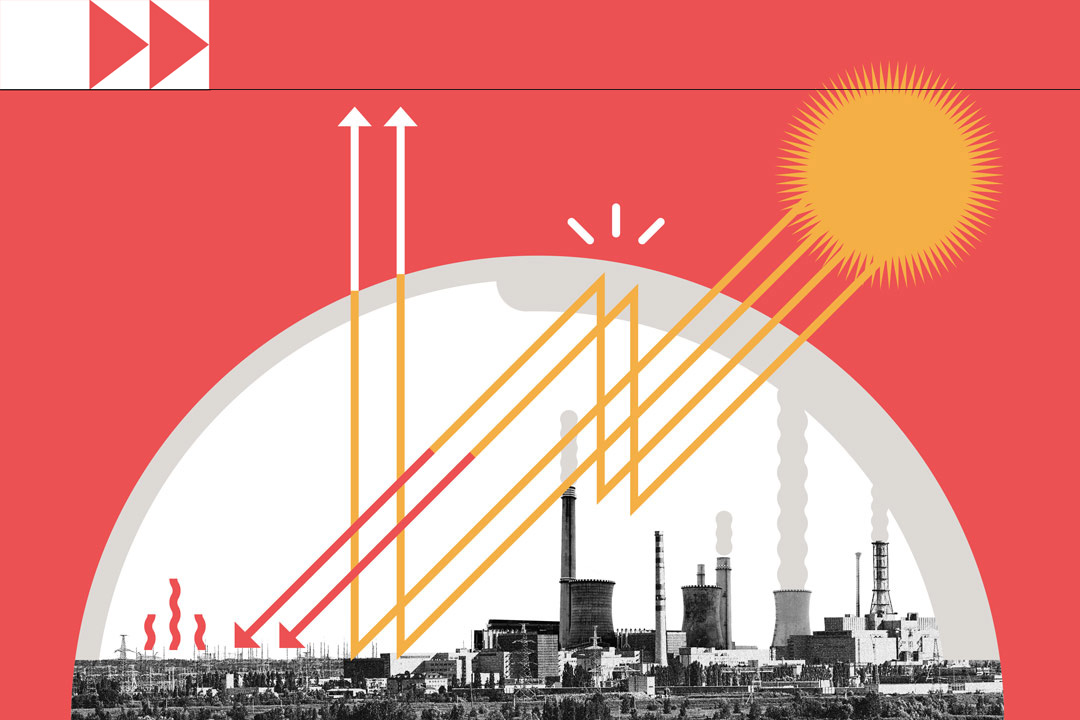

Why invest in renewable energy?
Learn more about the differences between fossil fuels and renewables, the benefits of renewable energy, and how we can act now.

Five ways to jump-start the renewable energy transition now
UN Secretary-General outlines five critical actions the world needs to prioritize now to speed up the global shift to renewable energy.

What is net zero? Why is it important? Our net-zero page explains why we need steep emissions cuts now and what efforts are underway.
- What is climate change?
Our climate 101 offers a quick take on the how and why of climate change. Read more.

How will the world foot the bill? We explain the issues and the value of financing climate action.

Climate issues
Learn more about how climate change impacts are felt across different sectors and ecosystems.
It’s time to stop burning our planet, and start investing in the abundant renewable energy all around us." ANTÓNIO GUTERRES , United Nations Secretary-General

Facts and figures
- Causes and effects
- Myth busters
Cutting emissions
- Explaining net zero
- High-level expert group on net zero
- Checklists for credibility of net-zero pledges
- Greenwashing
- What you can do
Clean energy
- Renewable energy – key to a safer future
- What is renewable energy
- Five ways to speed up the energy transition
- Why invest in renewable energy
- Clean energy stories
- A just transition
Adapting to climate change
- Climate adaptation
- Early warnings for all
- Youth voices
Financing climate action
- Finance and justice
- Loss and damage
- $100 billion commitment
- Why finance climate action
- Biodiversity
- Human Security
International cooperation
- What are Nationally Determined Contributions
- Acceleration Agenda
- Climate Ambition Summit
- Climate conferences (COPs)
- Youth Advisory Group
- Action initiatives
- Secretary-General’s speeches
- Press material
- Fact sheets
- Communications tips
Facilities Management, Northwestern University
10 ways to stop global warming, want to help stop global warming here are 10 simple things you can do and how much carbon dioxide you'll save doing them..
Change a light Replacing one regular light bulb with a compact fluorescent light bulb will save 150 pounds of carbon dioxide a year.
Drive less Walk, bike, carpool or take mass transit more often. You'll save one pound of carbon dioxide for every mile you don't drive!
Recycle more You can save 2,400 pounds of carbon dioxide per year by recycling just half of your household waste.
Check your tires Keeping your tires inflated properly can improve your gas mileage by more than 3 percent. Every gallon of gasoline saved keeps 20 pounds of carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere.
Use less hot water It takes a lot of energy to heat water. Use less hot water by taking shorter and cooler showers and washing your clothes in cold or warm instead of hot water (more than 500 pounds of carbon dioxide saved per year).
Avoid products with a lot of packaging You can save 1,200 pounds of carbon dioxide if you reduce your garbage by 10 percent.
Adjust your thermostat Moving your thermostat down just 2 degrees in winter and up 2 degrees in summer could save about 2,000 pounds of carbon dioxide a year.
Plant a tree A single tree will absorb one ton of carbon dioxide over its lifetime.
Turn off electronic devices Simply turning off your television, DVD player, stereo, and computer, when you're not using them, will save you thousands of pounds of carbon dioxide a year.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Subscriber-only Newsletter
David Wallace-Wells
When we see the climate more clearly, what will we do.

By David Wallace-Wells
Opinion Writer
This month MethaneSAT, an $88 million, 770-pound surveillance satellite conceived by the Environmental Defense Fund and designed at Harvard to precisely track the human sources of methane being released so promiscuously into the atmosphere, was launched by SpaceX, to great fanfare.
Methane, a somewhat less notorious greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide, is produced by industrial and natural processes — leaking oil and gas infrastructure, decomposing melted permafrost, the belching of cows and the microbial activity of wetlands. We’ve known that methane is producing a lot of warming and that there is a lot more of it in the atmosphere now , but we didn’t have the full picture. Beginning next year, MethaneSAT will begin beaming down everything picked up by its spectrometer, providing a publicly available quick-turnaround methane-monitoring system that has filled the hearts of climate advocates and data nerds with anticipation. What will it see?
The hope is that it will see a map of climate malfeasance that doubles as a global to-do list. MethaneSAT is not the first effort to track emissions from space, but its launch has been accompanied by a wave of can-do climate optimism for four big reasons.
The first is that methane really matters. By some accounts , it explains about one-third of warming since the Industrial Revolution, with estimates steadily growing in recent years, along with the astonishing rise of its concentration in the atmosphere. The second is that actually doing something about the emissions from fossil-fuel infrastructure shouldn’t be that hard or that expensive. Human activities are responsible for about 60 percent of all methane emissions, and according to the International Energy Agency, 40 percent of industrial emissions are avoidable at no net cost, with the balance of the industrial problem solvable for the price of just 5 percent of last year’s fossil-fuel profits. The third is that those benefits would arrive quickly. Methane, unlike carbon dioxide, dissipates quickly, whereas you have to wait for centuries or even millenniums to get the full temperature benefit of zeroing out carbon dioxide, so we can clear the atmosphere of human-produced methane in about a decade. And the fourth is that all of the pretty granular MethaneSAT data will be publicly available, scrollable and shame-able for anyone who cares to scan its website for burps or flares of planet-heating gas from at least 80 percent of the world’s fossil-fuel facilities.
This probably sounds like progress, which it is, on balance. But the satellite will probably bring some bad news, too. One of the scientists who developed it described the launch as “like looking over the edge of the cliff,” and almost invariably, whenever we get a better look at methane emissions, the problem appears bigger than we’d thought. The latest example is a revelatory paper , published in Nature last week, which surveyed U.S. oil and gas infrastructure and found that the country’s fossil-fuel industry is producing three times as much methane as previously estimated by the E.P.A.
The figure is both shocking and predictable. Previous Environmental Defense Fund research suggested that annual methane emissions from oil and gas were 60 percent higher than the E.P.A. had estimated. Last year, work published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences suggested it was 70 percent higher . Globally, the International Energy Agency estimates , only about 5 percent of methane emissions were reported to the United Nations by the companies responsible. Reporting by countries was a bit better but still covered less than half of the total estimated by the agency. The Guardian documented more than a thousand superemitter events around the world in 2022. Leaks from just two fossil-fuel fields in Turkmenistan that year warmed the planet more than all the carbon emissions produced that year by Britain.
At least at first, this will probably be the message of MethaneSAT: In most parts of the world, we are doing worse than we had hoped. This should be reason to act, especially because methane is perhaps the lowest hanging fruit of the green transition.
But one of the unfortunate lessons of recent years is that such knowledge of the problem alone is rarely sufficient to drive us to solve it. Since 2021, more than 155 countries have pledged to reduce methane emissions by 30 percent from 2020 levels by 2030, in what was widely hailed as a major breakthrough for climate diplomacy and perhaps the most significant new global warming agreement since the landmark Paris Agreement of 2015. In the years since, new pledges have been extended ; if all promised cuts are made, methane emissions from fossil fuels will be cut in half by the end of the decade — a radical goal requiring a precipitous and immediate decline.
In order to keep the world in contact with its most ambitious warming targets, cuts of 75 percent would be required this decade . But methane from fossil-fuel infrastructure climbed again last year, the International Energy Agency reported last Wednesday, after climbing in 2021 and 2022. The organization believes a decline may be right around the corner, and there is considerably more global momentum for tackling methane now than in even the quite recent past. But the agency’s report noted that large leaks of the kind documented by The Guardian in 2022 grew last year by more than 50 percent. One such leak in Kazakhstan spewed gas for more than 200 days.
Though most of the attention paid to methane emissions these days focuses on that leaky industrial infrastructure and the climate risks of new liquid natural gas facilities, what worries me most is how much of it seems to be coming from natural sources, which may be responsible for 40 percent of the annual total — and the share may be growing, thanks to the effects of warming on emissions from wetlands, in particular, where higher temperatures promote more microbial activities that generate methane.
In 2020 the Covid pandemic suppressed industrial activity and reduced emissions of methane, but additional emissions from wetlands, researchers found , might have offset that industrial decline five times over. Last year a group of scientists published research documenting the exceptional surge from wetlands, which exceeded average projections from even the most pessimistic warming scenarios drawn up by the U.N.’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. From 2007 to 2021, wetlands emissions were already outpacing those extreme scenarios, and beginning in 2020, the rate of release roughly doubled the rate from 2000 to 2006.
This is not good. It is also another sign that over the past few years, we have somewhat left behind what the statistician Erica Thompson memorably called “model land” and begun to enter — or crash up against — a much messier climate reality.
In some ways, the news has been encouraging. As I wrote previously, perhaps the single most significant climate story of the past half-decade is the realization that extreme warming long considered the business-as-usual base line for our future is now looking much less likely.
But along other dimensions the reality has been more dispiriting than the models predicted. At the beginning of last year, it seemed unlikely that the planet would set a record for global average temperature, but by December, we had not just broken but shattered the record . Carbon concentrations in the atmosphere are increasing at eye-popping rates . An annual review by the World Meteorological Organization published this week declared, “The state of the climate in 2023 gave ominous new significance to the phrase ‘off the charts.’” And off-the-charts exceptional heat across the world’s oceans continues to perplex and worry an awful lot of climate scientists . The earth’s energy imbalance, which is about the best measure of the greenhouse effect over time, roughly doubled from 2005 to 2019 (though by some measures, it recently peaked ).
This, ultimately, is what MethaneSAT will see, circling the planet 15 times daily and keeping a watchful eye on human activities: that down here on the surface we are continuing to run a climatological experiment at a geologically unprecedented pace and scale. The world is warming faster than it had in tens of millions of years, and the rate of warming is accelerating. We’re adding carbon to the atmosphere at record levels, and the stuff we’ve put up there weighs more than the total of everything we’ve built on the earth’s surface. Because carbon dioxide dissipates so slowly, it will probably last much longer, too, making that planet-heating blanket of CO2 perhaps the largest monument to human civilization we’ve managed yet. In theory, we could get rid of the blanket of methane much more quickly. But will we? And if not, what does that tell us about the harder parts of the problem?

Is it too late to prevent climate change?
Humans have caused major climate changes to happen already, and we have set in motion more changes still. However, if we stopped emitting greenhouse gases today, the rise in global temperatures would begin to flatten within a few years. Temperatures would then plateau but remain well-elevated for many, many centuries. There is a time lag between what we do and when we feel it, but that lag is less than a decade.
While the effects of human activities on Earth's climate to date are irreversible on the timescale of humans alive today, every little bit of avoided future temperature increases results in less warming that would otherwise persist for essentially forever. The benefits of reduced greenhouse gas emissions occur on the same timescale as the political decisions that lead to those reductions.
Without major action to reduce emissions, global temperature is on track to rise by 2.5 ° C to 4.5 ° C (4.5 ° F to 8 ° F) by 2100, according to the latest estimates.
But it may not be too late to avoid or limit some of the worst effects of climate change. Responding to climate change will involve a two-tier approach:

- “Mitigation” – reducing the flow of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere
- “Adaptation” – learning to live with, and adapt to, the climate change that has already been set in motion. The key question is, what will our emissions of carbon dioxide and other pollutants be in the years to come?
Read more about NASA's efforts to address climate change at https://climate.nasa.gov/solutions/resources/ .
- An unrecognizable Arctic
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore Earth Science

Earth Science in Action

Earth Science Data
Facts About Earth

India has millions of dairy farmers. It’s creating a methane problem that’s tricky to solve

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Abinaya Tamilarasu said her four cows are part of the family. She has a degree in commerce from a local college, but prefers being home milking cows and tending to her family’s land.
“Our family cannot let farming go, it’s a way of life for us,” said the 28-year-old, who lives on her family farm in India’s southern Tamil Nadu state. Even when she could be making more money elsewhere, she said she’s “still happy we have our cows.”
India is the world’s largest milk producer, and is home to 80 million dairy farmers who made 231 million tons of milk last year. Many farmers, like Tamilarasu, only have a few cows, but the industry as a whole has 303 million bovine cattle like cows and buffalo, making it the largest contributor to planet-warming methane emissions in the country. The federal government has made some positive steps to reduce methane, but wants to focus emissions cuts elsewhere, like by moving to renewable energy , saying most methane emissions are a fact of life. But experts say the industry can and should make more reductions that can quickly limit warming .
India is the third largest emitter of methane in the world, according to figures published earlier this month by the International Energy Agency, and livestock are responsible for about 48% of all methane emissions in India, the vast majority from cattle. Methane is a potent planet-warming gas that can trap more than 80 times more heat in the atmosphere in the short term than carbon dioxide.
The Indian government has not joined any global pledges to cut methane emissions, which many see as low-hanging fruit for climate solutions , as methane emissions only last in the atmosphere for about a dozen years, compared to CO2 that can linger for a couple of hundred years.
But there’s some work on methane reduction in agriculture on the national level: The government’s National Dairy Development Board, which works with over 17 million farmers across the country, is looking into genetic improvement programs to provide more nutritious feed to livestock which would make cows more productive, meaning each farmer would need fewer cows to produce the same amount of milk. Studies by the NDDB show that emissions are reduced by as much as 15% when a balanced diet is provided to the animals.
The board is also looking into reducing crop burning, a high-emitting practice that some farmers use to clear their lands, by feeding those crops to cows.
“Climate-smart dairying is the need of the hour,” said Meenesh Shah, the board’s chairman.
Vineet Kumar, from the New Delhi-based Centre for Science and Environment, agreed that good quality feed can help lower emissions. He also said encouraging more local breeds that emit less can help. “These solutions can be a win-win for everyone,” he said.
But Thanammal Ravichandran, a veterinarian based in the southern Indian city of Coimbatore, noted that there’s currently a shortage of feed in India, so farmers give their cattle whatever they can, which is mostly lower quality and higher emitting.
“Farmers are also not able to invest in better quality feed for their cattle,” she said. To get better, and more affordable feed, dairy farmers need more government support, she said.
Whatever measures are taken to reduce methane emissions, experts note that it should have minimal impact on farmers’ livelihoods, and should account for the ways people raise their livestock.
“Livestock have been closely integrated within the Indian farming system,” said Kumar, meaning any drastic changes to farming methods would have severe effects on farmers. He added that efforts to reduce emissions shouldn’t reduce the use of cow manure as fertilizer on India’s farms, as chemical fertilizers emit nitrous oxide, an even more potent greenhouse gas.
But looking at India’s methane emissions as a whole could provide some more obvious solutions to slashing the gas, said Bandish Patel, an energy analyst at the climate thinktank Ember. Focusing on the energy sector is an easy win for targeted reduction of methane emissions, he said.
“You look at agriculture, those emissions are very dispersed in nature, whereas, with oil, gas and coal mining, there are very pointed sources from which you can basically reduce methane going forward,” he said.
Shah from the NDDB added that India’s high agricultural emissions must be considered in the context of the country being home to the world’s largest cattle population, the largest producer of milk, and the largest rice exporter, as rice production also produces significant methane emissions.
“In this light, India’s agriculture sector emissions must be considered significantly low,” Shah said. Because of its large population, India’s per capita emissions are well below average.
For dairy farmers like Tamilarasu, better welfare for her cows and programs for farmers to have better practices are welcome, but she won’t be leaving her cows for the climate any time soon. She plans to continue dairy farming for the foreseeable future.
“The way we see it, our cows and us support each other. If we can make their lives better, they will make ours better too,” she said.
Follow Sibi Arasu on X at @sibi123
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org .
Top headlines by email, weekday mornings
Get top headlines from the Union-Tribune in your inbox weekday mornings, including top news, local, sports, business, entertainment and opinion.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the San Diego Union-Tribune.
More in this section

Nation-World
Deadly attack on Moscow concert hall shakes Russian capital and sows doubts about security
Shocked Russians are bringing flowers and teddy bears to the Crocus City concert hall on the outskirts of Moscow to pay their respects to more than 100 people who died in a grisly attack claimed by the Islamic State group

Russia’s Foreign Ministry says Spanish reporter denied a visa was invited to stay
Russia’s Foreign Ministry says it issued the necessary documents for a Spanish journalist to stay in the country although the reporter claims he was forced to leave because his visa was not renewed

Biden signs $1.2 trillion funding package after Senate’s early-morning passage ended shutdown threat
President Joe Biden has signed a $1.2 trillion package of spending bills that Congress just passed, ending the threat of a potential partial government shutdown

Rain helps contain still-burning wildfires in Virginia’s Shenandoah Valley; state sending more aid
Officials say crews battling still-burning wildfires in Virginia’s Shenandoah Valley are getting an assist from rain and from the state government, which has deployed new resources to the area

Thunderstorms delay flights at Miami airport, suspend music festival and disrupt tennis tournament
Severe thunderstorms in South Florida delayed departures at the Miami International Airport during the busy spring break season, suspended a popular electronic music festival and disrupted matches at a high-profile tennis tournament
The Moscow concert hall attack wasn’t the first during Putin’s 25-year rule
The attack on a Moscow concert hall in which armed men opened fire and set the building ablaze, killing at least 133 people, was the latest in a long series of bombings and sieges that have unsettled and outraged Russians during Vladimir Putin’s nearly quarter-century as either prime minister or president

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Experts say it is likely many strategies working together will be needed. Generally speaking, here are some examples of mitigation strategies we can use to slow or stop the human-caused global warming ( learn more ): Where possible, we can switch to renewable sources of energy (such as solar and wind energy) to power our homes and buildings ...
1. Spread the word. Encourage your friends, family and co-workers to reduce their carbon pollution. Join a global movement like Count Us In, which aims to inspire 1 billion people to take practical steps and challenge their leaders to act more boldly on climate.
5. Reduce water waste. Saving water reduces carbon pollution, too. That's because it takes a lot of energy to pump, heat, and treat your water. So take shorter showers, turn off the tap while ...
Effect of Global Warming Short Essay. Since hundreds of years ago, greenhouse gases have remained in the atmosphere for several years. Global warming, on the other hand, would have disastrous consequences for the planet. If global warming persists, a slew of negative consequences will emerge. Melting polar ice caps, economic effects, warming ...
The earth's surface emits energy into the atmosphere in the form of heat, keeping the balance with the incoming energy. Global warming depletes the ozone layer, bringing about the end of the world. There is a clear indication that increased global warming will result in the extinction of all life on Earth's surface.
Yes. Humans have the solutions to fight a global environmental crisis. Do we have the will? The evidence that humans are causing climate change, with drastic consequences for life on the planet ...
Modern global warming is the result of an increase in magnitude of the so-called greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and other greenhouse gases. In 2014 the IPCC first reported that concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and ...
Global warming is defined as an increase in the average surface temperature of the Earth as a result of greenhouse gasses that accumulate in the atmosphere like a blanket that traps the sun's heat which causes the globe to warm. Greenhouse gasses trap heat at the surface of the planet, making it habitable for people and animals.
This shows that trees have a large role in reducing the impact of global warming. Plants or plants can function to eliminate air pollution due to a large amount of smoke from vehicles or motorbikes as well as smoke from industrial sites. Planting trees does not have to have a lot of lands. Nowadays, land for planting trees is very rare because ...
If these are scaled up and applied more widely and equitably, they can support deep emissions reductions and stimulate innovation." To limit global warming to around 1.5C (2.7°F), the IPCC report insisted that global greenhouse gas emissions would have to peak "before 2025 at the latest, and be reduced by 43 per cent by 2030".
A: Global warming occurs when carbon dioxide (CO 2) and other air pollutants collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight and solar radiation that have bounced off the earth's surface. Normally ...
This essay explores the causes, effects of global warming and takes a look at potential solutions to the current environmental issues leading to global warming on an unprecedented scale. ... To reduce global warming we can do to reduce the contribution of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. Therefore, the solutions that we can reduce global ...
To stop climate change, we need to stop the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, from increasing.For the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, which naturally pull carbon dioxide out of the air, has caused greenhouse gas levels to increase. There are two main ways to stop the amount of greenhouse gases from increasing: we can stop adding them to the air ...
Average global temperatures have increased by 2.2 degrees Fahrenheit, or 1.2 degrees Celsius, since 1880, with the greatest changes happening in the late 20th century. Land areas have warmed more ...
What are the effects of global warming? One of the most concerning impacts of global warming is the effect warmer temperatures will have on Earth's polar regions and mountain glaciers. The Arctic ...
Because both forests and oceans play vitally important roles in regulating our climate, increasing the natural ability of forests and oceans to absorb carbon dioxide can also help stop global warming. The main ways to stop climate change are to pressure government and business to: Keep fossil fuels in the ground. Fossil fuels include coal, oil ...
Wash your clothes in warm or cold water to reduce your use of hot water and the energy required to produce it. That change alone can save at least 500 pounds of carbon dioxide annually in most ...
Publics in the advanced economies surveyed are divided as to whether actions by the international community can successfully reduce the effects of global warming. Overall, a median of 52% lack confidence that a multilateral response will succeed, compared with 46% who remain optimistic that nations can respond to the impact of climate change by ...
In conclusion, climate change is the most significant problem facing the world. Global warming is increasing day by day. If we cannot prevent it as soon as possible, our world will face undesirable consequences. Artificial intelligence and machine learning, which have been quite advanced recently, is our immense weapon in the fight against ...
A rise in global temperatures can lead to additional changes in the environment, such as rising sea levels. Since an increase in the temperature causes the glaciers and icebergs to melt at a rapid pace, it causes the sea levels to rise. On the Weather: Global Warming causes intense heat waves by significantly increasing the temperature which ...
Renewable energy - powering a safer future. Energy is at the heart of the climate challenge - and key to the solution. A large chunk of the greenhouse gases that blanket the Earth and trap the ...
Use less hot water. It takes a lot of energy to heat water. Use less hot water by taking shorter and cooler showers and washing your clothes in cold or warm instead of hot water (more than 500 pounds of carbon dioxide saved per year). Avoid products with a lot of packaging. You can save 1,200 pounds of carbon dioxide if you reduce your garbage ...
The world is warming faster than it had in tens of millions of years, and the rate of warming is accelerating. We're adding carbon to the atmosphere at record levels, and the stuff we've put ...
Humans have caused major climate changes to happen already, and we have set in motion more changes still. However, if we stopped emitting greenhouse gases today, the rise in global temperatures would begin to flatten within a few years. Temperatures would then plateau but remain well-elevated for many, many centuries.
The federal government has made some positive steps to reduce methane, but wants to focus emissions cuts elsewhere, like by moving to renewable energy, saying most methane emissions are a fact of ...