

Business Exit Strategy Planning
Written by Dave Lavinsky

This guide to planning your exit strategy is the result of Growthink’s 20+ years of experience helping companies develop successful exit plans.
The guide starts by explaining what a business exit strategy is. It then explains the types of exit strategies available to your business.
It then discusses the key takeaways to successful exit strategy planning. In this section, we spend a significant amount of time going through the 20 ways to maximize the value of your company to realize a successful exit.
Finally, this guide provides helpful tips regarding how to create an exit strategy business plan for your organization.
What is a Business Exit Strategy?
A business exit strategy is a plan that an owner or executive creates and follows to liquidate their stake in a business, ideally at a substantial profit.
A successful business exit strategy requires careful planning and should be periodically revised to best reflect the current business conditions.
Types of Common Exit Strategies
To ultimately build an effective exit plan it’s important to understand the ways you can exit a business and which type of exit aligns with your business goals and values.
For example, if your end goal is generating money and personal wealth, then selling your business to a competitor or a private equity group might be a viable exit plan. However, if you are more attached to your business’ legacy and wish to see it operational even after your exit, then selling to current skilled employees or family member succession planning might be business exit strategies worth exploring.
Below are the six core types of exit strategies, organized into two core categories: Selling Your Business and Other Business Exit Strategies.
Selling Your Business
There are three main audiences to consider when selling your business: another business, a financial group, and employees. When evaluating the sale, gauge the attractiveness of your business from the perspective of potential buyers or other investors.
A solid reputation, customer base, and track record of growth are some factors that make a business appealing to buyers. Other factors could include strong cash flow, patented intellectual property, or niche expertise. Note that these factors are discussed in the “Keys to Successful Exit Strategy Planning” section later in this guide.
Another Business (or a Strategic Buyer) : Businesses acquire other businesses for a variety of reasons. From a buyer’s perspective, a strategic acquisition is often the quickest way to grow and/or diversify a business. It is also a surefire way to eliminate competition. For these reasons, valuations in strategic acquisitions are often highest. The drawback to this path is that most companies do not have an active mandate to acquire another business. A business owner may first need to be convinced of the idea of an acquisition exit strategy generally before entertaining the specific opportunity to purchase your business. He or she may then need to obtain financing to complete a transaction. Both of these elements can slow your exit process.
Therefore, when exploring this path it is important to plan ahead and identify firms that could be potential acquirers by keeping up with transaction activity in the same industry. Keep a lookout for firms that are actively buying other businesses and position your business in a way that appeals most to them. This will maximize your chances of receiving an enviable acquisition offer from a larger business that is prepared to buy.
Financial Buyer : A financial buyer refers to an individual or group, like a private equity firm, who is primarily interested in the cash flows your business can generate post-acquisition. Financial buyers’ sole activity is the buying and selling of businesses, so these buyers are prepared to efficiently and effectively evaluate a business and have capital in place to quickly execute a transaction. Given their valuation approach and goal of future cash flows, financial buyers are typically looking for relatively high historical operating profits ($3 million at a minimum). Typically private equity groups value a company based largely, if not exclusively, on a multiple of past operating profits. These multiples may or may not take into consideration the growth opportunities you see for your business and so you may not see the same valuation as a strategic buyer.
Your Employees : Selling the business to employees is another business exit strategy to consider. The advantage of this employee or management buyout strategy is that you are transitioning to people who are well-versed in the business and have a vested interest to see it thrive. If you are structured as a corporation, you can create an Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP), which allows employees to vest ownership in your business. When you are ready to exit, the larger business then purchases your shares from you and redistributes them to the remaining employees. A similar option is establishing a worker-owned cooperative. In this scenario, employees invest personal capital into shares of the cooperative. For this to work, it is essential that you foster a participatory culture in your organization and be mentally prepared to stay on until the transition is complete.
Other Business Exit Strategies
If you do not plan to sell your business, the following are other exit strategies to consider.
Family Succession : This business exit strategy involves transferring the mantle of leadership to the next generation in your family. This common exit strategy is popular with owners who wish to see their legacy continue. The advantages of family succession include the ability to choose a successor of your choice and groom them. It also allows for the sole business owner to remain involved. The success of this exit strategy often hinges on the personal attributes and professional skills of the new successor. Their commitment to the family business and the quality of their relationships with other employees are also critical factors.
Asset Sale : This business exit strategy involves shutting down the entire business and selling some or all its assets. For this exit strategy to be profitable the business needs to have certain value-adding assets it can sell, such as land, building(s), or equipment.
Compared to a stock sale, asset sales typically involve limited negotiations. You also do not have to worry about the transfer and transition of the business ownership. The negative obviously is the loss of the business you built.
Taking Your Business Public : Another company exit strategy you may consider is an Initial Public Offering (IPO). We mention this last since it’s only relevant to a tiny portion of companies. An IPO involves selling your business in public markets like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). IPOs receive wide media coverage but are not very common. This is because they are very expensive and laborious to undertake. Every IPO requires thorough financial, operational, and staffing reports among others which can be very costly to produce. Incurring such costs is not feasible for small to medium-sized businesses; hence this exit strategy is not practical for many organizations. If you do manage an IPO then the pros are instant popularity as IPOs are usually quite a hyped event. You might even get lucky and have your business valued highly on the stock market leading to your stock value appreciating exponentially.
What’s the Best Exit Strategy?
There is no single best or preferred exit strategy. The ideal choice for your business depends on your unique circumstances.
Your Business Goals : You need to assess how ready you are to give up control of the business and when you want to exit. This is a personal decision but consider this: if you have been running the business solo or with a very small team, then an initial public offering (IPO) or selling to a larger business may not be the best option.
Your Business Size and Structure : Another key consideration is your company size and structure. If you are a small business, then an asset sale or family member succession might be the more feasible option for you. On the other hand, if you are a corporation with tens or hundreds of employees, then going public is a more viable option.
Your Business Age and Stage : The next thing you need to consider is your company’s age and stage. If your business is young and growing, then you might want to consider an IPO as your exit strategy. However, if your business is in its maturity stage or even in decline, then an asset sale or family succession might be more suitable.
The Bottom Line
No one can tell you what the best exit strategy is for your business. The key is to weigh all the options and make a decision that aligns with your personal and professional goals for a successful future.
Keys to Successful Exit Strategy Planning
The key to successful business exit planning involves just two steps: 1) determining how strategic or financial buyers will value your business, and 2) maximizing that value.
Determining How Your Business Will/Might Be Valued
As discussed above, if you seek a financial buyer, they will value your business based on your company’s financials, cash flow, and future growth prospects.
Strategic buyers, which nearly always pay more money than financial buyers, and thus should generally be your focus, will value your business differently.
The best way to identify how they will value your business is to:
- Research acquisitions in your market (via trade journals, Google searches, etc.)
- Determine exactly what metrics will you be primarily valued on? Ideally in your searches, you will see what attributes were mentioned in articles discussing the acquisitions. Did they mention the acquired company’s revenues, # of subscribers/customers, market share, EBITDA? Whatever metrics are mentioned will be key-value drives.
- Identify factors multiple strategic buyers would value, such as new products, a distribution network, intellectual property (IP), unique location(s), financial savings, better systems/processes, permits, etc. These factors are discussed in more detail in the next section.
Maximize the Value of Your Business
To help in your business exit planning, we have identified 20 ways to build and maximize the value of your business. Each of these concepts is discussed in detail below.
1. Build Synergistic Value
Synergistic value is when you and an acquiring company together have more value than the two separate companies.
So how might you create synergy? Perhaps your products or services could be sold to the acquiring company’s large customer base?
For example, maybe the acquiring business sells parts to bicycle stores and you have a new part that is also sold to bicycle stores. But perhaps they sell to 5,000 bicycle stores and you only sell to 500.
By getting your part into the additional 4,500 stores, they may be able to increase your sales tenfold. That’s huge synergy.
There are many other areas of potential synergy. Perhaps you have a unique core competency that can be leveraged by the acquiring business. Maybe you’re an incredible Internet marketer and the company that wants to acquire you is not great at internet marketing. And by leveraging your unique marketing skills they could dramatically grow their business.
So think through the synergy fit. Think through what companies might want to buy you at some point and what synergistic value you could bring to that organization.
2. Diversify & Lock Down Your Customer Base
The next thing you can do to maximize the value of your business is to diversify and lock down your customer base.
There’s a threat to your company’s value when you have a concentrated customer base, which is few customers or customers representing 5%, 10%, or more of your sales. That is risky because if one of your bigger customers or multiple big customers leave, your sales and profits could drop precipitously.
Another big risk is when customers have personal relations with the owner because you (the owner) would be lost after the acquisition. Or if customers have personal relationships that are too strong with a salesperson and that salesperson leaves your business and the customer leaves us with them.
So what are the solutions to these threats?
First, diversify your customer base. You need to be thinking about diversifying your customer base so that you don’t have the risk of a big customer or more leaving.
Secondly, if possible, secure contractual sale agreements such as long-term contracts and licenses to ensure ongoing sales from customers. The idea here (and lowest risk to buyers) is contractually recurring revenues.
3. Diversify Vendors
The third thing you want to do to maximize the value of your business is to diversify your vendors. Consider what would happen if a key vendor raises its prices or goes out of business. Would your business be in trouble?
Acquirers are going to ask what happens if something happens to one of your vendors. Likewise, you need to be asking this question of your business right now.
So what are the solutions?
Finding and using multiple vendors. Importantly, you’re probably not going to generate more revenue tomorrow because you spend hours looking for multiple vendors. But it’s going to make your business stronger. It’s going to remove risk from your business and make it more valuable to acquirers.
4. Put “Successor” Clauses in Customer (and Partner, Vendor/Supplier, etc.) Contracts
The next way to maximize your value is to put successor clauses in your customer, partner, and vendor contracts.
Successor clauses ensure that your key contracts survive significant changes in ownership so the buyer receives full value from them. Many contracts become void if your business transfers ownership and you obviously don’t want that. So when you sign contracts with customers, vendors, partners, etc., make sure you have clauses that the contract survives the acquisition of your company. If not, this could significantly reduce the value of your business.
5. Bolster Your Senior Management Team
The next way to maximize the value of your business is to bolster your senior management. You need to make sure your business can run without you because then there’s less risk to the buyer.
Doing this also means that you might need to stay with the business for less time after you sell it. To bolster your senior team, and make sure that you’ve hired and trained quality people that can run the business for you.
6. Bolster Your Middle Management Team
The next thing to boost value is to bolster your middle management team. Once again, you need more trained people so the business can run without you. This lessens the risk to a buyer.
Having trained middle management will help ensure a smooth transition to the new owner. There’s always going to be a transition period where you’re integrating your business with the acquirers. The more trained staff you have makes it much easier for the acquirer to buy your business and have the business run as usual from the get-go.
7. Build Management Team Solidarity
The next value-building strategy is to build management team solidarity on a day-to-day basis. To succeed with the day-to-day business operations, your team must have the same business vision and financial goals as you.
During the sales process to an acquirer, the same holds true. This is because buyers will interview your team members individually during the due diligence phase to make sure there is a cohesive vision/direction among your key employees.
8. Improve the Quality of Your Team
Will acquiring your team add significant value to the buyer? How unique is your team? And do you have unique talents?
As you can imagine from these questions, your team can add a lot of value to your company.
To begin, if your team has unique technical capabilities, great customer service people, etc., it could have great value to an acquirer. Likewise, it’s extremely valuable if your team have a track record or ability to do things really well on an ongoing basis, such as:
- Conduct R&D to come up with new products
- Bring new products to market
- Provide exceptional customer service
So, think about what your team is great at, and work to make them even better.
9. Build Brand Value
The next way to maximize the value of your company is to build your brand. The value of your brand and your reputation can be considerable. A well-known brand results in recognition which often equals sales for the foreseeable future.
So building your brand gives you a lot of recognition, which has a lot of value. Building your brand also gives you trust. This is why a lot of brands are acquired.
So think about the value of your brand. How can you build your brand to make it more well-known?
10. Build Intellectual Property
Intellectual Property (IP) can provide significant value. IP includes your patents, processes, copyrights, trademarks and service marks, and trade secrets.
Sometimes your IP value can represent the entire purchase price of your business.
Think about intellectual property and how you use that IP to create real value for your company. And ideally how it can provide even more value to an acquirer.
11. Improve Your Culture
The next way to build value is through your culture.
Zappos is a great example of a company that built a great culture. And as a result, Amazon acquired it for over a billion dollars.
So you think about how you can build a great company culture that allows you to build a solid company and be acquired for a lot of money. Importantly, Zappos’ culture became a threat to Amazon and Amazon purchased the company because of this threat.
So consider this question: can your culture positively “infect” the culture of an acquirer?
It’s one thing to build a great culture but think about if you can create a great culture that when acquired, is so great and strong that you can “infect” the larger company that buys you with it. That’s a great way to build value.
12. Build Back-Office Infrastructure
You can also build value through your back-office infrastructure.
Your back-office infrastructure includes all the departments that support your revenue-generating areas, such as IT, human resources, accounting, legal, etc. A solid back-office ensures your business continues to run smoothly without you and after an acquisition.
This is really important to financial buyers because financial buyers want to see your business grow as a standalone business. They’re looking to acquire your business, grow it for four to eight years, and then sell it.
A strong back-office infrastructure can also be important for strategic buyers. They will care if you have a strategic or competitive advantage in any of these back-office areas. If not, they’re going to dissolve or integrate your back office into their own departments.
13. Build Revenues, Subscribers/Customers &/or EBITDA
Building revenue streams, subscribers, customers, and/or EBITDA is an obvious way to really build value in your company.
Subscribers and customers are assets that are highly valued and bring future sales and maximize profits.
And revenue and EBITDA are key financial measures that show your success and can be used to estimate the price at which acquirers might purchase your company.
14. Acquire Great Locations
Another way to maximize your value. Is by making sure your location(s) is/are very strong.
By locking up the right locations, you can add a lot of value to your organization.
For example, Rosetta Stone has kiosk lease agreements at airports throughout the world. That’s really valuable…if an acquirer wanted to buy Rosetta Stone, they would instantly gain visibility in airports throughout the world.
Likewise, when FedEx purchased Kinko’s, it instantly gained hundreds of well-placed retail locations.
15. Build Your Distribution Network
Another way to maximize value is through your distribution network.
Distributors, resellers, and/or affiliates are individuals and organizations that sell their products and services for you. That’s a huge asset that can maximize your revenues and profits, and which could do the same for your acquirer.
So, the question to ask yourself is: what can you do to gain a large distribution network that will increase your revenues and make you a more attractive acquisition target?
16. Improve Your Product/Service Portfolio
The next way to really build value in your business is to focus on your product and service portfolio.
Think about the products and services you currently offer. Are they unique? Can they be leveraged by an acquirer? Do they represent a threat to an acquirer’s business?
Think about what new products and or services you can build to develop value. More products generally equal more revenues, more customers, more intellectual property, and less vulnerability.
The more products you have, the more you could cross-sell your current customers, upsell them, and the less vulnerable you’d be to a competitor who launches a similar product to yours.
17. Show Financial Savings
The next way to maximize value is through financial savings. Do you have economies of scale in certain areas? Do you do things so often that you’re able to get your costs down on a per-unit basis? If so, such cost savings could be valuable to an acquirer.
18. Create Systems & Processes
Likewise, do you have any processes, systems and ways and ways of doing business that save money? These will all be valuable to your current business and to acquirers.
Likewise, systems and processes can add tremendous value to your business right away. And quality systems and processes are valuable assets. They allow you to perform with precision and consistency. They allow you to perform at lower costs and gain efficiencies and allows you to quickly and easily train and integrate new team members.
So focus on building quality systems and processes.
19. Create a Great Website
Your website can also be a source of value maximization too.
Not only might your website, based on your brand, attract visitors. But, if you’ve invested in SEO or search engine optimization, you might organically rank for many keywords. If your site is SEO optimized, an acquirer might be able to use it to rank for additional keywords that have significant value to them.
So it’s worth building a great website and optimizing it for search engines.
20. Achieving Government Hurdles
Achieving/overcoming government hurdles can add significant value to your business. Getting permits, zoning approval licenses, regulatory approvals, and certifications can be extremely valuable in the short-term to your business, but also really valuable to an acquirer.
Doubling the Value of Your Company
Doing everything listed above can exponentially increase the value of your business. In addition, you can literally double the value/purchase price of your company by expertly executing the sales transaction:
- Presentation : how you position your company and support your valuation
- Professional sales process : getting more buyers, revealing information at the right times, etc.
- Negotiating and closing skills : getting the right deal done
Creating Your Exit Strategy Business Plan
The process of creating your exit strategy business plan includes the following:
1. Create a List of Potential Acquirers
If you are interested in being acquired at some point in the future, identify companies you think would be ideal.
2. Determine How You Will/Might Be Valued
Go through the 20 value maximization concepts presented above and identify which of them would be most valuable to each potential acquirer.
3. Create Your Strategic Plan
In your strategic plan, identify each of the ways you will build value (e.g., develop new systems).
Document the timeline for creating each new asset along with the financial requirements and the staff members who will lead each initiative.
How Growthink Can Help
These concepts should help you think about how your brand can be more valuable to potential acquirers. The goal is not only to attract them but also to convert casual visitors into sales. Achieving these goals will make it easier for you to get out of the rat race and finally achieve success as an entrepreneur or business owner. If this all sounds complicated and overwhelming, we’re here to help!
You can get started today on your exit strategy using our Ultimate Business Plan Template to help you create a business plan if you are seeking funding. If you don’t need outside funding to execute your exit plan, use our Ultimate Strategic Plan Template .
Our team of experts is also ready to help! At Growthink, we specialize in helping entrepreneurs grow their businesses through expert advice on business models, business plans & strategy, financial planning, and exit strategy and valuation services. Contact us today to learn more.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Exit Strategies - All You Need to Know about Business Exit Planning

Kison Patel is the Founder and CEO of DealRoom, a Chicago-based diligence management software that uses Agile principles to innovate and modernize the finance industry. As a former M&A advisor with over a decade of experience, Kison developed DealRoom after seeing first hand a number of deep-seated, industry-wide structural issues and inefficiencies.

The question, “What is your exit plan?” tends to draw blank expressions when asked to business owners.
A survey of business owners conducted by the Exit Planning Institute shows that a startling 2 out of 10 businesses that are listed for sale eventually close a transaction, and of these, around a half end up closing only after significant concessions have been made by the seller.
Business owners need to think about exit planning before searching for potential buyers. The tools provided by DealRoom can be a valuable asset to any business owner looking to develop an exit strategy.
By working with a team of professional advisors, accountants, lawyers, and brokers, you can ensure the right documents are in place for a business exit whenever the time comes.
In this article, we talk about creating a business exit plan and how to make one for your business.
What is a Business Exit Strategy?
A business exit strategy outlines the steps that a business owner needs to take to generate maximum value from selling their company. A well-designed business exit strategy should be flexible enough to allow for unforeseen contingencies and account for the fact that business owners don’t always decide on their own terms when to exit. By creating a strategy in advance, owners can ensure that they can at least maximize value in the event of an unplanned exit from the business.

Investor exit strategy
An investor exit strategy is similar to that of a business exit strategy. However, investors look for a financial return on their exit from a company, so bequeathing is never one of the options considered. An investor will often have a list of potential acquirers in mind, as well as a timeframe, as soon as their investment is made. In this type of scenario, there is often an exit multiple in mind (i.e. a multiple of EBITDA or a multiple of the original investment made in the business).
Venture capital exit strategy
Another business exit strategy option is a venture capital exit strategy. As our article on venture capital outlines, if a company is venture funded then consider that your investor will have a pre-planned exit. As an early stage company, this is a natural part of taking investments. Usually, with a VC investment, the aim is for an exit after five years, either through an industry sale or an IPO, where they can liquidate their original equity investment.
Motives for Developing Exit Strategies
Technically, it is important for equity owners to have a broad outline of what an exit would look like. For example, the image below represents various motives ranging from financial gain to mitigating environmental risk.

Some of the common motives for business exit include the following:
Retirement - Arguably the most common reason of all motives is retirement. Business owners will inevitably retire at some stage, and it’s best that they have an exit strategy in place before doing so.
Investment return - A business exit strategy as part of a wider investment strategy - for example, the VC company planning to go to IPO after five years - makes the exit valuation part a component of the initial investment in the business.
Loss limit -A business exit is ultimately a kind of real option for a business. If the business is hemorrhaging money, the best option may be to exit immediately - ‘cutting your losses’ on the business, a sit was.
Force majeure - Like the examples of Covid-19 and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, sometimes an investor or owner doesn’t really have a choice: The circumstances dictate that they have to exit.
Types of Exit Strategies
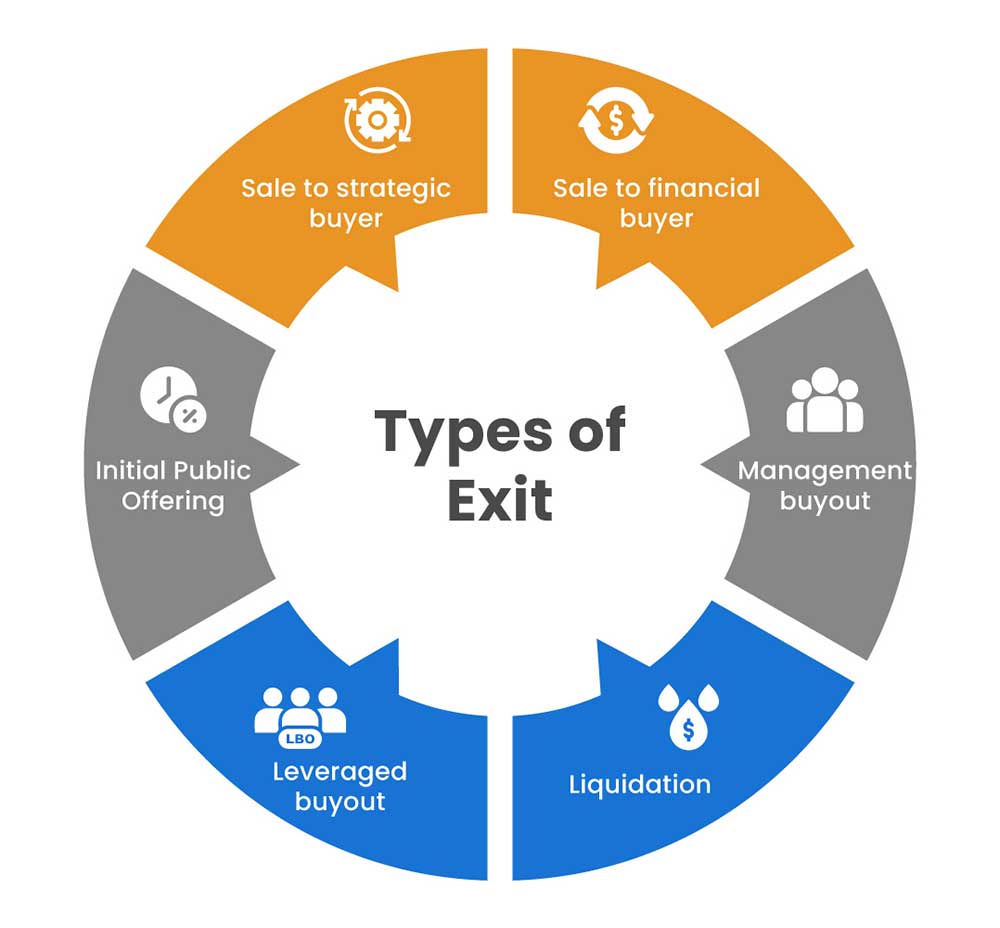
Sale to a strategic buyer
Strategic buyers are usually in the same industry as the company whose owner is looking to exit. And in other cases, the buyer can be in an adjacent market looking to compliment their products in an existing market, or expansion of their products into a market.
Sale to a financial buyer
Financial buyers are solely looking for a financial return from their investment in a business and the exit is the primary means of achieving this return. Examples include venture capital and private equity investors.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
This form of exit, far more common with startups than mature companies, enables company owners to exit by selling their equity to investors in public equity markets.
Management buyout (MBO)
An exit through MBO would occur when the owner sells the company to its current management team, whose familiarity with the business technically should make them the best candidates to achieve value from an acquisition.
Leveraged buyout (LBO)
A leveraged buyout occurs when a buyer takes a loan or debt to purchase another company. The buyer also uses a combination of their assets and the acquired company's assets as collateral. Financial models can be used for multiple scenarios and simulations of when an LBO is an effective choice.
Liquidation
Liquidation can be used by a business owner to exit if they feel like the liquidation would yield cash faster or that the individual assets (i.e. property, plant, and equipment) of the business were more liquid than the business as a going entity.
Exit Strategy for Startups
Startups looking for VC investment can include an exit strategy as part of their initial pitch. It is not mandatory. Sometimes this can work when well, for example, when a startup founder is well versed in the industry and has a credible 5-year forecast.
Startup exit strategies depend on a few different factors:
Market timing
How have IPOs for startups performed in the past 12-18 months? If public markets are showing enthusiasm for companies like the one being pitched, it makes it easier to show how an exit can occur.
Comparable transactions
Similar to IPOs, companies can use comparable transactions (industry or private equity sales) to show investors their route to an exit. The comparable firms should be operating in the same or close to the same competitive space.
How to Put Together a Business Exit Plan
Remember that the purpose of the plan is to make the new business owner transition as straightforward as possible.
Although the steps which follow are general, nobody knows a business better than its owner, so take whatever steps are necessary to make your business as marketable to potential buyers as possible.
These steps also assume that you, the owner of a business, have weighed up the options elsewhere. Personal finances, family situations, and other career options are beyond the scope of this article.
Rather, the intention of the points below is to ensure that a business will be ready to sell in the fastest possible time at a fair price.
Business exit plan
- Know the business
- Ensure that finances are in order
- Pay off creditors
- Remove yourself from the business
- Create a set of standard operating procedures
- Establish (and train) the management team
- Draw up a list of potential buyers
1. Know the business
This sounds obvious but a business can lose focus quickly in the aim of diversification, to the extent that it becomes ‘everything to every man.’
This may be useful in the short-term for revenue streams, but just be sure that your business has focus. It will help you find the right buyers when the time comes and to be able to communicate which part of the market your business occupies.
2. Ensure that finances are in order
This should be a priority regardless of any future business plans.
But if you intend to sell your business at short notice, it's best to have a clean, well-maintained set of financial statements going back at least three years.
3. Pay off creditors
The less debt that a business holds on its balance sheet, the more attractive it will be to potential buyers.
A common theme among small business owners in the US is thousands of dollars of credit card debt. This can be a red flag to many buyers and should be paid off as soon as possible.
4. Remove yourself from the business
How important are you to the day-to-day operations? If your business would lose more than 10% of its revenue were you to leave, the answer is “too important.”
If revenues are tied to the owner, buyers are not going to want to buy the business if the owner is going to leave right after.
Although it can be a challenge, seek to minimize your direct impact on the business, in turn making it more marketable.
5. Create a set of standard operating procedures
Closely related to the above point, ensure that your business has a set of standard operating procedures (SOPs), ideally in written form, that would allow any owner to maintain the business in working order merely by following a set of instructions.
6. Establish (and train) the management team
Are the existing managers capable of taking over the business and running it as is? If you leave the business for a vacation and one of your managers calls you several times, the answer to this question may be ‘no’.
They may need more training, or you may need a different set of managers. In either case, having a capable team in place will be valuable whether you decide to exit your business or not.
7. Draw up a list of potential buyers
A list of buyers should be made and refreshed on a reasonably regular basis. Ideally, you would know their criteria for buying a business, but this is not always practical.
Keeping a long list of buyers means that you can reach out to them at short notice if it is required at some point in the future.
This list is likely to include at least some of your managers or suppliers.
Importance of Exit Strategy
Many owners make the mistake of thinking that a business exit plan means the same thing as a ‘retirement plan’, believing that they can start thinking about putting one together as soon as they hit 55 years of age.
This is an error. Not because your departure is impending, but because it doesn’t give you the flexibility.
Instead of looking at a business exit plan as a retirement plan, rethink it as a divestment option.
An alternative way of thinking about this is, what happens to the business owner that doesn’t have an exit strategy? Think of the value destruction that occurs to the business if something unexpected happens and the owner has to make an unplanned sale, at a discount, in unattractive market circumstances, or even at a time of personal loss.
Instead of thinking about the business exit as something that will happen in the future, rethink it as something that could happen at any moment.
Exercising critical thinking to write a business exit strategy can be exciting as well as enlightening. Thinking of an exit as an end state is not the best approach since this limits businesses to a strict definition. Rather, consider how the process can be supportive of a business' growth strategy. Take these top three considerations:
- Financial considerations: If the exit strategy has a target revenue number in 5 years then how will the business get there? What financial dashboards are needed to properly run the company? How will expenses be managed so a business does not outspend against earnings?
- Supply chain considerations: What products will need to be in your catalog to maximize margins? What inventory turns ratio are you aiming for on a monthly basis?
- People considerations: Who do I hire to grow the company exponentially? What benefits do I offer to attract the best talent but don't cause complications at the exit? How do I write the force majeure so I protect the company and employees?
A business's primary goal is long-term value generation to its customers, itself, and its stakeholders. Having a thoughtful exit strategy shows the maturity of a business's Leadership towards longevity and value creation. There are many facets of the journey from owner motivation to financial strategies.
At DealRoom we help the owners of businesses of all sizes prepare for this eventuality. Our Professional Services team is ready to help businesses think through these details. It is important that an exit strategy be a journey throughout the growth stages.
Talk to us about how our tools can be an asset for you in your exit plan.

Build your exit plan with our Program Exit Criteria Template!

About DealRoom

- Pipeline management
- Diligence management
- Integration management
- Divestiture management
Get your M&A process in order. Use DealRoom as a single source of truth and align your team.

Get weekly updates about M&A Science upcoming webinars, podcasts and events!

Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, ready to move on how to create an exit plan for your business.
Exit plans are necessary to secure a business owner’s financial future, but many don’t think to establish one until they’re ready to leave.

An exit strategy is an important consideration for business owners, but it’s often overlooked until significant changes are necessary. Without planning an exit strategy that informs business direction, entrepreneurs risk limiting their future options. To ensure the best for your business, plan your exit strategy before it’s time to leave.
What is an exit strategy?
An exit strategy is often thought of as the way to end a business — which it can be — but in best practice, it’s a plan that moves a business toward long-term goals and allows a smooth transition to a new phase, whether that involves re-imagining business direction or leadership, keeping financially sustainable or pivoting for challenges.
A fully formed exit strategy takes all business stakeholders, finances and operations into account and details all actions necessary to sell or close. Exit strategies vary by business type and size, but strong plans recognize the true value of a business and provide a foundation for future goals and new direction.
If a business is doing well, an exit strategy should maximize profits; and if it is struggling, an exit strategy should minimize losses. Having a good exit strategy in practice will ensure business value is not undermined, providing more opportunities to optimize business outcomes.
[Read more: What Is a Business Valuation and How Do You Calculate It? ]
Benefits of an exit strategy
Planning a complete exit strategy well before its execution does more than prepare for unexpected circumstances; it builds purposeful business practices and focuses on goals.
Even though a plan may not be used for years or decades, developing one benefits business owners in the following ways:
- Making business decisions with direction . With the next stage of your business in mind, you will be more likely to set goals with strategic decisions that make progress toward your anticipated business outcomes.
- Remaining committed to the value of your business . Developing an exit strategy requires an in-depth analysis of finances. This gives a measurable value to inform the best selling situation for your business.
- Making your business more attractive to buyers . Potential buyers will place value in businesses with planned exit strategies because it demonstrates a commitment to business vision and goals.
- Guaranteeing a smooth transition . Exit strategies detail all roles within a business and how responsibilities contribute to operations. With every employee and stakeholder well-informed, transitions will be clear and expected.
- Seeing through business — and personal — goals after exit . Executing an exit strategy that’s right for your business’s value and potential can prevent unwanted consequences of exit, like bankruptcy.
Because leaving your business can be emotional and overwhelming, planning a proper exit strategy requires diligence in time and care.
Weighing your options: closing vs. selling
There are two strategies to consider for your exit plan.
Sell to a new owner
Selling your business to a trusted buyer, such as a current employee or family member, is an easy way to transition out of the day-to-day operations of your business. Ideally, the buyer will already share your passion and continue your legacy.
In a typical seller financing agreement, the seller will allow the buyer to pay for the business over time. This is a win-win for both parties, because:
- The seller will continue to make money while the buyer can start running the show without a huge upfront investment;
- The seller may also remain involved as a mentor to the buyer, to guide the overall business direction; and
- The transition for your employees and customers will be a smooth one since the buyer likely already has a stake in the business.
However, there are downsides to selling your business to someone you know. Your relationship with the buyer may tempt you to compromise on value and sell the business for less than what it’s worth. Passing the business to a relative can also potentially cause familial tensions that spill into the workplace.
Instead, you may choose to target a larger company to acquire your business. This approach often means making more money, especially when there is a strong strategic fit between you and your target.
The challenge with this option is the merging of two cultures and systems, which often causes imbalance and the potential that some or many of your current employees may be laid off in the transition.
[Read more: 5 Things to Know When Selling Your Small Business ]
Liquidate and close the business
It’s hard to shut down the business you worked so hard to build, but it may be the best option to repay investors and still make money.
Liquidating your business over time, also known as a “lifestyle business,” works by paying yourself until your business funds run dry and then closing up shop.
The benefit of this method is that you will still get a paycheck to maintain your lifestyle. However, you will probably upset your investors (and employees). This method also stunts your business’s growth, making it less valuable on the market should you change your mind and decide to sell.
The second option is to close up shop and sell assets as quickly as possible. While this method is simple and can happen very quickly, the money you make only comes from the assets you are able to sell. These may include real estate, inventory and equipment. Additionally, if you have any creditors, the money you generate must pay them before you can pay yourself.
Whichever way you decide to liquidate, before closing your business for good, these important steps must be taken:
- File your business dissolution documents.
- Cancel all business expenses that you no longer need, like registrations, licenses and your business name.
- Make sure your employee payment during closing is in compliance with federal and state labor laws.
- File final taxes for your business and keep tax records for the legally advised amount of time, typically three to seven years.
Steps to developing your exit plan
To plan an exit strategy that provides maximum value for your business, consider the six following steps:
- Prepare your finances . The first step to developing an exit plan is to prepare an accurate account of your finances, both personally and professionally. Having a sound understanding of expenses, assets and business performance will help you seek out and negotiate for an offer that’s aligned with your business’s real value.
- Consider your options . Once you have a complete picture of your finances, consider several different exit strategies to determine your best option. What you choose depends on how you envision your life after your exit — and how your business fits into it (or doesn’t). If you have trouble making a decision, it may be helpful to speak with your business lawyer or a financial professional.
- Speak with your investors . Approach your investors and stakeholders to share your intent to exit the business. Create a strategy that advises the investors on how they will be repaid. A detailed understanding of your finances will be useful for this, since investors will look for evidence to support your plans.
- Choose new leadership . Once you’ve decided to exit your business, start transferring some of your responsibilities to new leadership while you finalize your plans. If you already have documented operations in practice in your business strategy, transitioning new responsibilities to others will be less challenging.
- Tell your employees . When your succession plans are in place, share the news with your employees and be prepared to answer their questions. Be empathetic and transparent.
- Inform your customers . Finally, tell your clients and customers. If your business will continue with a new owner, introduce them to your clients. If you are closing your business for good, give your customers alternative options.
The best exit strategy for your business is the one that best fits your goals and expectations. If you want your legacy to continue after you leave, selling it to an employee, customer or family member is your best bet. Alternatively, if your goal is to exit quickly while receiving the best purchase price, targeting an acquisition or liquidating the company are the optimal routes to consider.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .

Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
How to file an insurance claim for your business, how small businesses can create strong community partnerships, how to partner with a university as a small business.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
It’s Not the End: Why Creating an Exit Strategy Sets Your Business Up for Long-Term Success

While there is a lot of content around how to successfully get your business off the ground, there isn’t much talk about creating an exit strategy to successfully quit a business. After all, who would want to think about leaving when you have likely spent years, if not decades, establishing your empire? Many businesses think of an exit strategy as a sort of “doom and gloom” outlook. In reality, it’s a good safety net to have, especially when you understand what it is and what it means for your business.
What is an exit strategy in business?
An exit strategy is a proactive plan to shift out of or liquidate an investment position, business transaction or venture. “An exit plan provides a roadmap for how businesses or investors will exit after realizing gains from their investment,” notes Carey Smith, senior vice president and chief operating officer of Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota. “Having a plan to exit helps manage risk by reducing exposure to potential downsides if conditions change and is especially important for startups or high-risk investments that face higher levels of uncertainty.”
Just as important as the strategy that initiated the business is the one that guides the “how” and “when” to exit. In an ideal situation, this plan is detailed along with triggers, measures and even events that could signal the right time to exit and move to the next thing.
“Being deliberate in defining the exit triggers is important because they may not be recognizable when they arise, if there hasn’t been proactive thought as to what they may be,” Smith adds. Also, business models, strategies and market conditions frequently change and evolve as the business progresses, so it is important to revisit them periodically. While not all exit triggers might need drastic action, defining them helps the business understand when to persevere and when to move on.
“Remaining flexible is important. In our case at Plurilock, we went public very early during the pandemic, as that was an option available to us then,” says Ian Paterson, CEO and founder of Plurilock, a leading AI cybersecurity company. “However, if we wanted to do the same thing right now, it would have been very difficult to accomplish that.”
Plan your business with the end in mind
As creators and entrepreneurs, starting with the end in mind is not an easy mindset to have and certainly requires a shift in perspective. Be aware of business environments and world factors that could influence or impact your decision, and make that a point of focus while building the strategy.
When thinking about the “how to” of exit strategies, Paterson recommends thinking of it like a car trip.
- Start with the end in mind . Know who you’re going to sell to and what they value.
- Plan a route . Know what milestones you need to hit at various stages along the journey.
- Ask for directions . Engage with service providers like bankers and accountants frequently.
- Don’t run out of gas . Make sure when you go to sell the company you don’t run out of money and negotiating power.
- Pace yourself . It’s a long ride.
And contrary to popular belief, an exit strategy does in fact align interests, incentives and goals regarding growth and profitability because it defines targets aimed toward business growth. “A well-defined exit strategy allows both businesses and investors to set expectations, manage risks, provide motivation and unlock the value created in an investment,” Smith notes.
Are there different types of exit strategies?
Key types of exit strategies available to businesses include sale of ownership, initial public offering (IPO), liquidation, recapitalization, debt restructuring or refinancing, ownership transfer, merger or buyback.
To determine which strategy might work best for you, a good place to start is to look at industry models applicable to similar businesses. Paterson advises that if the exit strategy is acquired by a competitor, certain aspects of the company, like corporate finances and internal controls, are more important than if the goal was to take the company public.
If the goal is to get acquired by a venture capital, intellectual property, personnel and other assets might be more valuable. “With my company Plurilock, where we are acquiring regional cybersecurity providers, we are looking for strong sales and marketing teams with strong contracts,” he adds. “We value the strength of those relationships, and it is a strong component of our value process.”
Exit strategy models to emulate
When looking at industry models to emulate, both Smith and Paterson share examples of both successes and failures. Smith notes that Facebook’s acquisition of Instagram ($1 billion), Oculus ($2 billion) and WhatsApp ($19 billion) provided significant returns for its investors.
Likewise, Walt Disney Company’s acquisitions of Pixar and Marvel provided significant revenue and strategic market positioning. Perhaps one of the most notable is Google’s acquisition of Android, “which has successfully positioned Google as the market leader in smartphone operating systems, allowing significant control and access to consumer data,” Smith shares.
“Twitter is an interesting case study because it played out on the public stage,” Paterson notes. “Like many exits, at some points during the process, it looked like the deal would not go through, but eventually it closed roughly as expected.”
For all the successful exits, there are an equal or greater number of failed exits that didn’t get the expected results. “Yahoo is one of the best examples of failing to acquire other exiting companies and failing to maximize on their own exit,” Smith recalls. “Yahoo refused to buy Google for $1 billion in 1998 and again refused $5 billion in 2002. In 2023, Google has a market cap of $1.7 trillion. And sadly, in 2008 Yahoo turned down an offer to be acquired by Microsoft for $44.6 billion and instead sold themselves to Verizon in 2016 for only $4.6 billion.”
How to create an exit strategy
When building a successful exit strategy, Smith suggests a checklist to help you get started:
- Document all the potential situations that would call for an exit, like market considerations, industry challenges and business model economics.
- Allow for flexibility to support changes in priorities and space for new ideas, alternatives and changes in market conditions.
- Define success metrics and articulate the outcome objectives and the value they will generate.
- Note investor expectations to ensure alignment with the achievable value expected.
- Create a roadmap with an exit timeline and expected targeted returns.
The choice of business model and industry influences the selection of an appropriate exit strategy. Startups take time to build an attractive valuation and therefore require patient investors with long-term exit plans such as venture capital firms. High-growth businesses require large capital investments, so they typically prefer acquisition exits in order to scale.
High capital-intensive businesses have exit plans that require mergers where value is created through combined scale. Business models that generate value from intellectual property (IP) typically have exit plans that involve acquisition or revenue sharing and licensing deals that provide royalty.
Plan B: Less conventional options
If none of these types of exit strategies work, the good news is that there are a few less conventional exit strategies to consider. Employee stock ownership plans (ESOPs) give employees a more vested interest in the company, thereby allowing the original investor or owners to step back. Joint ventures (JVs) are co-owned partnerships where external parties are brought into the company fold.
“Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC) is a newer exit strategy that is growing in popularity, where a merger takes place with external SPAC providing capital investment opportunities that allow it to go public (IPO) at a much higher valuation,” Smith advises. Lastly, earnouts are contingent payments that can be based on future company performance.
Creating an exit strategy is a smart business decision from the get-go and shows a forward-thinking approach to any business. For one to be successful, it is important to research and think about all factors that would impact the how , why and what of an exit strategy.
“The most helpful thing to do would be to talk to a specialist, such as an investment banker and business broker to talk through strategies,” Paterson suggests. Smith adds, “Aligning the exit strategy with the vision and entrepreneurial motivations allows achieving value while also serving goals beyond just an immediate financial return.”
Photo by Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock.com
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply

Do you have the world's best boss? Enter them to win two tickets to Sandals!
Why Every Business Owner Needs an Exit Strategy

Table of Contents
You wrote a business plan to launch your company. To say goodbye to it, you need an exit plan to get the maximum possible return and to limit any future exposure to what happens to the company after your departure. But years of experience teach you that nothing in business is predictable — and that’s why you need two exit plans.
Why every business owner needs an exit strategy
Today, most business brokers and advisors recommend incorporating a thorough exit strategy into your business planning from the very start. While it may seem counterintuitive to plan on starting or buying a business and simultaneously plan how you’re going to sell or remove yourself from it, this is the smartest move you can make in today’s fast-paced economy.
Here are some of the benefits of developing an exit strategy.
Gives you an end goal
If you don’t know where you’re going, you’ll never know when you get there. An exit strategy helps define what success is for you and provides you with a timetable complete with milestones toward your exit.
Informs strategic decision-making
Without a plan, it’s easy to get caught up working “for” the business, and resolving day-to-day issues. With a firm end game in mind, you have the vision to work “on” the business instead, planning and executing the strategies you need to achieve the ultimate end goal you’ve set for yourself.
Enhances the value of the business
If you don’t have an exit plan, your business will have some inherent value when you look to change ownership, but this is often the baseline value. With an exit strategy where you have a clear end goal in mind, your business is worth more to potential buyers or investors. You’ve grown it, locked its profitability, trained a strong management team, established a customer base, cemented meaningful supplier relationships and, most importantly, structured the business to operate independently of your personal involvement. That is valuable.
Provides a flexible template
At some point, you will likely need to make adjustments to your exit strategy. Sometimes, that will be for business reasons. Other times, something unexpected and unwanted like a sudden death, divorce, major health problem or required relocation may force you to change course. It’s easier to revise and tweak a plan that already exists with clear objectives and milestones than to come up with one suddenly to cope with a sudden change.
Having a preexisting strategy makes managing unforeseen events simpler. That’s because you already have a way of making decisions for growth — one that’s got you to where you are. You can strengthen this by involving outside professional advisors like a business broker, attorney and accountant to help you course correct when necessary and to monitor progress against your goals.
Why you need 2 exit strategies
Creating one exit strategy may seem daunting enough, but to cover your bases, you should craft two different plans: one for a voluntary exit and one for an involuntary exit.
With a voluntary exit strategy, you’ll know the following:
- When you want to leave: Maybe it’s in five years, 10 years or when revenue hits $10 million.
- Who you want to take over the business: It could be a brand-new owner, your current management or a family member.
- How much money you want to leave with: Perhaps you’d like a lump-sum payment, a share of profits every month for the rest of your life or a mixture of both.
- What to do if you’re approached by a potential buyer: How will you react if you’re contacted out of the blue? More business owners today are receiving unsolicited buyout offers than in years past.
But things don’t always go the way you expect them to, so you need a plan for that as well. With an involuntary exit strategy, you’ll know what to do in the following situations:
- You fall ill and you’re not able to work in the way you used to (or at all): You need to know who’ll take the reins and make decisions and you need to train them now so the business is ready.
- Your business begins to fail financially: You need to know which employees and assets you can jettison so you can stay solvent and in business.
- You burn out and just can’t take it anymore: If it’s all getting to be too much, you need to look after yourself. Do you hang in there, appoint a successor for day-to-day overall management or look to sell up? A well-defined involuntary exit strategy can lead the way.
The best way to plan for leaving your business for good is to prepare as if you have to leave it involuntarily. That might sound strange, but the situations that lead to voluntary and involuntary exits have a lot in common. For example, in either scenario, you need to do the following:
- Train people to run the company in your absence: If you want to sell up, the person who wants to buy it probably won’t want to run the company day to day. If they know your business is not owner-reliant, this is a massive selling point. Meanwhile, if you fall ill or burn out, it’s a big comfort knowing your staff can keep the business operational so it can continue flourishing.
- Know which assets and staff to cut to survive: This is not only a way for you to reduce costs when business is suffering. It’s also a road map for a new owner looking to streamline operations and make more money from their investment.
- Sell off nonvital assets quickly for cash: A new owner will want to know they can sell certain assets to offset some of the amount they paid you to take over the business. If you’re managing a crisis and need cash, you need to know which assets you can sell (or refinance) to bring money into your account.
With two exit plans in place, you have more bases covered, and you can carry out strategies that benefit both you and the new ownership.
Don’t think of an exit strategy as something for the short term. It might take five or 10 years for a successful exit strategy to reach its end. This is all about being ready to leave your business on your terms whenever the time comes.
What an exit strategy involves
Developing a well-rounded exit strategy entails the following.
Knowing when you want to leave
For your voluntary exit strategy, set yourself a date in the future by which you want to achieve your ultimate goals. These milestones could be based on metrics like company revenue and profitability. Decide on whether you’ll still proceed with a sale if you’re not successful in hitting those targets.
When you have a fixed date of departure in mind, your approach to running the business changes. You now think long-term as well as short-term because you’ll constantly be looking for ways to not only improve profitability but also build more value in your business to make it as attractive as possible to potential buyers.
Discovering who your most likely buyers are
Try to come up with “buyer personas” — documents that detail the type of person or company that would want to buy your business and why. (These are similar to customer personas , which are developed to identify your ideal customer.) To get your wheels turning, look below at potential buyers for four very different types of businesses.
Think about what specific aspects of your business will be valuable to buyers. Consider how you’ll develop and showcase those assets to increase the appeal and value of your company at the point of exit.
Developing assets that are valuable to other businesses
Sometimes, your company’s real value may be hidden behind your North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) Code. Don’t limit your company’s selloff potential by only considering buyers in your specific field.
Consider this example: You’re an e-commerce retailer and you’ve developed custom software that places your products in prominent search positions on third-party sales platforms. That, of course, would have great value for a purchaser from your sector. But it may have much greater value to a technology company and you could make a lot more money selling or licensing that software than doing a traditional sale to a competitor. Another benefit is that you could sell or license this software to raise cash if your company falls on hard times and needs money quickly.
Improving performance in your business
Keep finding areas of improvement across your business. If you have developed custom software, as mentioned above, continue to develop it with your own needs in mind first but also consider what other companies would need to make them want to rent from you.
Look at new ways to get more people to your website or your premises every month with each visit costing you less. For instance, consider changing suppliers if you’re offered a similar quality product or service that does the job for a lower price. Ask yourself what you need to do to get that package to your customer in three days instead of four.
Another great way to build value is to do a competitor analysis. Investigate the competition in your market. Where are they doing better than you and how can you match or beat them?
Chasing profitable growth
Be experimental and creative in your advertising and keep tweaking every campaign to find wins like a drop in cost per sale or conversion. If you can prove to a potential buyer that by spending $1 on this campaign, you get $10 in revenue back and that’s been the case for years, that has tremendous value.
Promote deals to customers through email marketing campaigns and short message service messaging and aim to make as much money as you can on each sale. Think of your future buyer when pricing up and chasing new business.
Doing everything you can to keep customers loyal
Don’t use the client email addresses and phone numbers you’ve collected just to move inventory; use them to grow customer loyalty .
Let customers know about a new product before it goes live on your website and give them the first opportunity to buy it. Send emails asking repeat clients to recommend you in online reviews. When someone does, give them a shoutout on social media and offer them a present as a thank you. [Learn the importance of social media for small businesses .]
Use customer tracking tools to work out the annual and lifetime value of each customer. Buyers look for those types of numbers. They also like companies with lots of clients who have given permission to receive emails and texts.
Customer loyalty is also key in any involuntary exit plan. If a crisis arises, you can attract regular clients and raise money quickly with a one-time sale. For example, if you sell subscription services, offer a special annual deal to existing customers to generate an influx of cash.
According to Bain & Company , customers spend 67 percent more in their 31st to 36th months as a loyal patron than in the first six months. Customer relationship management software can help you nurture these relationships. See our review of the Freshworks CRM for an example.
Handing over responsibilities to employees
The hardest types of businesses to sell are mom-and-pop shops and one-man bands. To a buyer, it’s like buying a job, not a company. It’s also really hard to sell businesses where there are 10 to 20 employees but success is still the responsibility of the owner. That’s because it’s like buying the job of a senior manager.
Delegate an increasing number of responsibilities to your employees over time. Train them and trust them to take on key tasks. If they make a mistake, be there to help them fix it and build up their confidence. If you don’t delegate, you’re training helplessness instead of anything valuable.
If a buyer asks, “Have you spent time away from the business?” you want to be able to confidently and truthfully say something like, “I spent three months in Hawaii and got one update email from the team a week. Everything ran like clockwork.”
For an involuntary exit plan, knowing you can step away for a while and still draw money thanks to your responsible staff gives comfort if you’re suffering from ill health or burnout.
Paying down company debt
You should try to pay down as much company debt as possible. That’s because when one company takes over another, things like business equipment loans and factoring service agreements cannot be novated.
In other words, they have to be settled in full on “completion day” (the day you sell your business). Normally, whatever you owe creditors is subtracted from the agreed-upon price you sell your company for, so you want to have less debt to subtract. Paying down debt also reduces your monthly servicing bills, meaning more profit in the meantime.
Reducing debt should be part of your involuntary exit plan too. You can sell unneeded or unwanted assets to pay down outstanding bills.
Starting to save money
Selling your business costs a lot of money. There are lawyers’ fees, accountant fees, professional service fees, a commission to your broker and more. For a business with $1 million in annual revenue, expect to pay up to $150,000 for a successful sale. If a deal is agreed to but falls through, you’ll still have to pay your team of outside advisors and experts.
If your business is struggling financially, having a decent amount of money saved up gives you more time to delegate day-to-day tasks to staff and raise cash by selling assets. If you also shrink your payroll and look for other savings, this will buy you even more time, financially speaking.
Exit strategies for startups vs. established businesses
There are dozens of ways for owners and investors to exit their businesses; however, the path chosen often depends on the age and size of the company.
Exit strategies for startups
- Initial public offerings (IPOs): IPOs are the favored way for many startup business owners to divest themselves, especially tech businesses that have already gone through a few rounds of funding. When you opt for an IPO, your business becomes a publicly traded and you and your investors should all make substantial returns. Bear in mind there are many regulation and governance hurdles to jump in preparation for an IPO.
- Strategic acquisitions: Most times, startup business owners end up selling their companies to larger competitors in the same or a related industry. You sell the shares in the business to your acquirer and this results in a complete transfer of ownership. Quite often, startups are bought for some aspect of their business that is unique and valuable, not necessarily due to their levels of profitability or market share.
- Management buyouts (MBOs) : In an MBO, a team consisting primarily of your current management raises the money to buy you out. Returns for owners on MBOs can be good but are generally not as high as a strategic acquisition. Still, MBOs are an excellent way of ensuring the company remains in capable hands.
Exit strategies for established businesses
- Merger or acquisition: For established businesses with good profitability and an impressive market share, you can merge with or be acquired by another company. Businesses are often valued at multiples of annual profit and the higher your turnover and profitability, the greater the multiple you’re likely to receive. If you want to stay involved with your business after a merger, you can make it a condition of the sale that you stay on the board of the business you’re selling and/or have a seat on the board of the merged company.
- Liquidation: If you wish to exit the business on a faster timeline than it takes to find a buyer, liquidation is an option. You sell all your assets and settle all your existing debts, allowing you to extract the remaining residual value from your business as income. While quick, it’s much less lucrative than a sale or merger in most cases.
- Bankruptcy: If your business is facing insurmountable debts, you have two choices. First, there’s Chapter 11 bankruptcy, which keeps your doors open while you restructure your debt. Second, there’s Chapter 7 bankruptcy, which allows you to settle company debts by selling off your assets. This is a tough decision to make, but bankruptcy can relieve many financial burdens your company is suffering, giving it a chance to do business again in the future. There are a few specialist venture capitalist and private equity firms that specialize in purchasing bankrupt or near-bankrupt companies too.
- Spin-offs: If your business has several operating divisions, whether distinguished by geography, activity or both, you could spin them off into separate entities and sell them to realize their value. This way, you receive a payout and reduce the size of the operations you’re responsible for.
Word of caution
Beware of earn-outs. With an earn-out, you receive part of the agreed price for your company now and the remainder in tranches over a period of time based on the business’s continued performance.
It is perfectly normal not to receive your asking price in one go. However, if you agree that what you’re paid will be linked to the performance of the business once you’re no longer in control of it, you’ll be putting yourself in grave danger of not getting all the money you’re expecting.
Tips for executing an exit strategy
Now that you know what creating an exit strategy involves and how exits can differ for startups versus established businesses, follow these tips when executing your plans.
1. Bring in outside expertise.
You need to build your own professional team for the sales process because your buyer will almost certainly have one. You want to level the field as much as possible, but you also want people on your side who know the intricacies of selling companies.
Consider hiring part-time chief financial officers or fractional chief marketing officers well before you put your company on the market. Bring experienced, proven talent with wider connections in the business world to your C-suite to help you improve the organization first. They’ll be invaluable in helping you carry out your exit strategy when a deal is on the table.
These same professionals will have proven themselves adept at crisis management in their careers too. They’ll be able to help you get out of awkward financial situations and train your workers to handle management responsibilities.
2. Keep your accounts up to date and your accountants close.
Inform your accountants that you want to be in a permanent state of readiness in case you receive a purchase offer out of the blue or decide to put your company on the market. Once you’ve identified the financial areas of greatest interest to your buyer type, make sure your accountant updates the company’s finance reports on a weekly or monthly basis and keeps historical records of them. The best accounting software will come in handy. [Related article: How to Hire the Right Accountant for Your Business ]
3. Hire a corporate lawyer.
Retain a lawyer, preferably one with mergers and acquisitions (M&A) experience. Your buyer’s corporate lawyers will vigorously defend their interests and try to use the information you provide about your business during the due diligence process to bring down the selling price. You need someone on your team to advocate on your behalf.
4. Hire a business broker and M&A advisor.
Opinions differ on the effectiveness of business brokers and M&A advisors for companies with an annual revenue of less than $1 million. If you’re confident enough, it might be worth forgoing an advisor and handling the process yourself.
But what does a broker do? They market your business in many ways, often on websites like businessesforsale.com. They also handle initial inquiries, verify potential buyers have the required funds to purchase your company and sit in on the negotiations over price. Many try to engineer a bidding situation where two or more interested buyers make offers at the same time to try to drive up the price.
Brokers often also intervene during the due diligence stage. During due diligence, the buyer’s professional team of lawyers and accountants will ask for lots of detailed information about your company, often over a period of between three and six months. Their job is to help the buyer understand exactly what it is they’re buying. Tempers often become fraught during due diligence for a variety of reasons. When this happens, the brokers often act as go-betweens to smooth relations and keep the deal on track.
5. Create your own data room.
In years past, a buyer’s lawyer would enter a private room at your lawyer’s office called a “data room.” Here, they’d inspect financial and employment records, as well as documentation regarding intellectual property ownership and previous and ongoing legal disputes. Most data rooms are now virtual and the professional teams acting for the buyer and the seller usually email documentation to each other.
Create your own online data room as soon as you can and ask your accountants, lawyers and managers to submit updated reports every month. Delays in providing information can upset buyers — something you want to keep to a minimum.
You don’t need to cure all the imperfections in your company before putting it on the market. A common myth among sellers is that buyers want spotless, perfectly run businesses. They don’t. All they want is a company they can add value to and they expect a certain degree of imperfection.
Running your business like nothing else is happening
Once you’ve settled on an exit strategy for your business, don’t spend any more than 30 minutes per day on it, even if you have a deal on the table and it’s going through due diligence. Concentrate on running your business as well as possible to retain and build on the value you’ve already created. Buyers will expect this and they’ll be able to monitor if you’re protecting their interests from the updated information in the data room. Proceeding with business as usual while simultaneously preparing for the future is the best way to be ready for a voluntary or involuntary exit.
Bruce Hakutizwi contributed to this article.
Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!
Business Owners’ Special Series #11

Mergers & Acquisitions – They say selling a business is an art – we’ve turned it into a science
Get started today. At Morgan & Westfield, there are never any long-term contracts.
Morgan & Westfield is a leading M&A firm. Here are some of the people who make it happen.
Our goal is to help you successfully exit your business. Here are answers to some of our most commonly asked questions.
Selling a business is complicated. We make it simple.
Morgan & Westfield offers transparent a-la-carte pricing—no hidden fees, no long-term contracts.
Real stories from real clients who have sold their businesses through Morgan & Westfield.
Morgan & Westfield sold in 100+ industries. Whatever your business, we’ve got you covered.
Morgan & Westfield has completed transactions in 100+ industries globally, representing business owners and buyers in North America, Central America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
If you’re thinking of selling but not quite ready yet, browse our free resources.
Morgan & Westfield is committed to making the process of buying a business as simple as possible. Browse our businesses for sale now.
Here is an overview of the process of buying a business, presented in concise summaries from our experts.
From processing and manufacturing to production and distribution, we’ll give you the advice you need to maximize the value of your company when it comes time to sell.
Business services firms differ in the services they offer, so we customize our solutions to meet and exceed clients’ service goals.
Morgan & Westfield serves as a trusted partner to plumbing and HVAC businesses, mechanical and commercial contractors, and other home service enterprises looking to sell.
Comprehensive articles on every step of the process of buying or selling a business in the M&A industry.
The Art of the Exit, A Beginner’s Guide to Business Valuation, The Exit Strategy Handbook, Closing the Deal, Acquired, and Food and Beverage M&A
Priceless advice for entrepreneurs of middle-market businesses with revenues up to $100 million.
M&A Talk is the #1 podcast on mergers & acquisitions. We talk to the most experienced professionals in the industry to uncover their secrets.
Food & Beverage Talk is the #1 podcast exclusively focused on the food and beverage industry. We offer interviews with the top experts in the food & beverage industry.
Don’t be confused or intimidated by any terms or abbreviations in the M&A world. You’ll find answers here.
Downloadable templates for seamless deal success.
At Morgan & Westfield, we employ consistent strategies to help ensure your transaction remains confidential from beginning to end.
If you would like to speak with us about buying, selling, or valuing a business.
Need a quote for your M&A article or segment? Contact us today for media resources and appearances.
At Morgan & Westfield, we’re always looking for talented deal makers, agents, analysts, professionals, office owners, and associates to join our remote team.

Business Exit Plan & Strategy Checklist | A Complete Guide

It’s not enough to merely hand over the keys at the closing. You need a strategy. An exit strategy.
An exit strategy, as the term implies, is a plan to assist you in exiting your business. All exit plans will vary, but they all contain common elements.
The three common elements that all business exit strategies should contain are:
- A valuation of your company. The process of valuing your company involves three steps, the first being an assessment of the current value of your business. Once this value is calculated, you should plan how to both preserve and increase that value.
- Your exit options. After you have determined a range of values for your company and developed plans for preserving and increasing this value, you can begin exploring your potential exit options. These can be broken down into inside, outside, and involuntary exit options.
- Your team. Finally, you should form a team to help you prepare and execute your exit plan. Your team can consist of an M&A advisor, attorney, accountant, financial planner, and business coach.
If you are considering selling your business in the near future, planning for the sale is imperative if you want to maximize the price and ensure a successful transaction. This article will give you a solid understanding of these elements and how you can put them together to orchestrate a smooth exit from your business.
Business Exit Plan Strategy Component #1: Valuation
Your exit strategy should begin with a valuation, or appraisal, of your company. The process of valuing your company involves three steps, the first being an assessment of the current value of your business. Once this value is calculated, you should then plan how to both preserve and increase the value of your business.
Let’s explore each of these components — assess, preserve, increase — in more depth.
Assess the Value
The first step in any exit plan is to assess the current value of your business.
Here are questions to address before beginning a valuation of your company:
- Who will value your company?
- What methods will that person use to value your company?
- What form will the valuation take?
Who: Ideally, whoever values your company should have real-world experience buying and selling companies , whether through business brokerage, M&A, or investment banking experience. They should also have experience selling companies comparable to yours in size and complexity. Specific industry experience related to your business is helpful, but not essential, in our opinion. There are loads of professionals out there who possess the academic qualifications to appraise your business but who have never sold a company in their lives. These individuals can include accountants or CPAs, your financial advisor, or business appraisers. It is essential that your appraiser have real-world M&A experience. Without hands-on experience buying and selling companies comparable to yours, an appraiser will be unprepared to address the myriad nuances of the report or field the dozens of questions that will arise after preparing the valuation.
Action Step: Ask whoever is valuing your business how many companies they have sold and what percentage of their professional practice is devoted to buying and selling businesses versus other activities.
What Methods: Most business appraisers perform business valuations for legal purposes such as divorce, bankruptcy, tax planning, and so forth. These types of appraisals differ from an appraisal prepared for the purpose of selling your business. The methods used are different , and the values will altogether be different as well. By hiring someone who has real-world experience selling businesses, as opposed to theoretical knowledge regarding buying and selling businesses, you will work with someone who will know how to perform an appraisal that will stand the test of buyers in the real world.
Form: Your M&A business valuation can take one of two forms:
- Verbal Opinion of Value: This typically involves the professional spending several hours reviewing your financial statements and business, then verbally communicating an opinion of their assessment to you.
- Written Report: A written report can take the form of either a “calculation of value” or a “full report.” A calculation of value cannot be used for legal purposes such as divorce, tax planning, or bankruptcy, but for the purpose of selling a business, either type is acceptable.
Is a verbal or written report preferable? It depends. A verbal opinion of value can be quite useful if you are the sole owner and you do not need to have anyone else review the valuation.
The limitations of a verbal opinion of value are:
- If there are multiple owners, there may be confusion or disagreement regarding an essential element of the valuation. If a disagreement does arise, supporting documentation for each side will be necessary to resolve the disagreement.
- You will not have a detailed written report to share with other professionals on your team, such as attorneys , your accountant, financial advisor, and insurance advisor.
- The lack of such a detailed report makes it difficult to seek a second opinion, as the new appraiser will have to start from scratch, adding time and money to your process.
For the reasons above, we often recommend a written report, particularly if you are not planning to sell your business immediately.
We have been involved in situations in which CPA firms have valued a business but had little documentation (one to two pages in many cases) to substantiate the basis of the valuation.
In one example, the CPA firm’s measure of cash flow was not even defined; it was simply listed as “‘cash flow.” This is a misnomer as there are few agreements regarding the technical definition of this term. As a result, any assumption we might have made would have led to a 20% to 25% error at minimum in the valuation of the company. By having a written report in which the appraiser’s assumptions are documented, it is simple to have these assumptions reviewed or discussed.
Note: When hiring someone to value your company, you are paying for a professional’s opinion but keep in mind that this opinion may differ from a prospective buyer’s opinion. Some companies have a narrow range of value (perhaps 10% to 20%), while other companies’ valuations can vary wildly based on who the buyer is, often by up to 100% to 200%. By having a valuation performed, you will be able to understand the wide range of values that your company may attain. As an example, business appraisers’ valuations often contain a final, exact figure, such as $2,638,290. Such precision is misleading in a valuation for the purpose of a sale. We prefer valuations that result in a more realistic price range, such as $2,200,000 to $2,800,000. An experienced M&A professional can explain where you will likely fall within that range and why.
Preserve the Value
Once you have established the range of values for your company, you should develop a plan to “preserve” this value. Note that preserving value is different from increasing value. Preserving value primarily involves preventing a loss in value.
Your plan should contain clear strategies to prevent catastrophic losses in the following categories:
- Litigation: Litigation can destroy the value of your company. You and your team should prepare a plan to mitigate the damaging effects of litigation. Have your attorney perform a legal audit of your company to identify any concerns or discrepancies that need to be addressed.
- Losses you can mitigate through insurance: Meet with your CPA, attorney, financial advisor, and insurance advisor to discuss potential losses that can be minimized through intelligent insurance planning. Examples include your permanent disability, a fire at your business, a flood, or other natural disasters, and the like.
- Taxes: You should also meet with your CPA, attorney, financial advisor, and tax planner to mitigate potential tax liabilities.
Important: The particulars of your plan to preserve the value of your company also depend on your exit options, which we will discuss below. Many elements of your exit plan are interdependent. This interdependency increases the complexity of the planning process and underscores the importance of a team when planning your exit.
Only after you have taken steps to preserve the value of your company should you begin actively taking steps to increase the value of your company.
Increase the Value
There is no simple method or formula for increasing the value of any business. This step must be customized for your company.
This plan begins with an in-depth analysis of your company, its risk factors, and its growth opportunities. It is also crucial to determine who the likely buyer of your business will be . Your broker or M&A advisor will be able to advise you regarding what buyers in the marketplace are looking for.
Here are some steps you can take to increase the value of your business:
- Avoid excessive customer concentration
- Avoid excessive employee dependency
- Avoid excessive supplier dependency
- Increase recurring revenue
- Increase the size of your repeat-customer base
- Document and streamline operations
- Build and incentivize your management team
- Physically tidy up the business
- Replace worn or old equipment
- Pay off equipment leases
- Reduce employee turnover
- Differentiate your products or services
- Document your intellectual property
- Create additional product or service lines
- Develop repeatable processes that allow your business to scale more quickly
- Increase EBITDA or SDE
- Build barriers to entry
Note: A professional advisor can help you ascertain and prioritize the best actions for your unique situation to increase the value of your business. Unfortunately, we have seen owners of businesses spend three months to a year on initiatives to increase the value of their business, only to discover that the initiatives they worked on were unlikely to yield any value to a buyer.
Business Exit Strategy Component #2: Exit Options
After you have determined a range of values for your company and developed plans for preserving and increasing this value, you can begin exploring your potential exit options.
Note: These steps are interdependent. You can’t determine your exit options until you have a baseline valuation for your company, but you can’t prepare a valuation for your business until you have explored your exit options. A professional can help you determine the best order to explore these steps, or if the two components should be explored simultaneously. This is why real-world experience is critical.
All exit options can be broadly categorized into three groups:
- Inside: Buyer comes from within your company or family
- Outside: Buyer comes from outside of your company or family
- Involuntary: Includes involuntary situations such as death, divorce, or disability
Inside Exit Options
Inside options include:
- Selling to your children or other family members
- Selling to your business to your employees
- Selling to a co-owner
Inside exits require a professional who has experience dealing with family businesses, as they often involve emotional elements that must be navigated and addressed discreetly, gracefully, and without bias. Inside exit options also greatly benefit from tax planning because if the money used to buy the company is generated from the business, it may be taxed twice. Lastly, inside exits also tend to realize a much lower valuation than outside exits. Due to these complexities, most business owners avoid inside exits and choose outside options. Fortunately, most M&A advisors specialize in outside exit options.
Outside Exit Options
Outside exit options include:
- Selling to a private individual
- Selling to another company or competitor
- Selling to a financial buyer, such as a private equity group
Outside exits tend to realize the most value. This is also the area where business brokers, M&A advisors, and investment bankers specialize.
Involuntary Exit Options
Involuntary exits can result from death, disability, or divorce. Your plan should anticipate such occurrences, however unlikely they may seem, and include steps to avoid or mitigate potential adverse effects.
Business Exit Strategy Component #3: Team
Team members.
Finally, you should form a team to help you plan and execute your exit plan. Many of these steps are interdependent — they are not always performed sequentially, and some steps may be performed at the same time. Forming a team will help you navigate the options and the sequence.
Your team should involve the following:
- M&A Advisor/Investment Banker/Business Broker: If you are considering an outside exit.
- Estate planning
- Financial planning
- Tax planning, employee incentives, and benefits
- Family business
- Accountant/CPA: Your accountant should have experience in many of the same areas as your attorney, along with audit experience and retirement planning. Again, it is unlikely that your CPA possesses all of the skills you need. If further expertise is needed, the CPA should be able to access the skills you need, either through colleagues at their firm or by referral to another accountant.
- Financial Planner/Insurance Advisor: This team member is critical. We were once in the late stages of a sale when the owner suddenly realized that, after deducting taxes, his estimated proceeds from the sale would not be enough to retire on. An experienced financial planner can help with matters like these. They should have estate and business continuity planning experience, as well as experience with benefits and retirement plans.
- Business Coach: A business consultant or coach may be necessary to help implement many of the changes needed to increase the value of your business, such as building infrastructure and establishing a strong, cohesive management team. Doing this often requires someone who can point out your blind spots. A coach can help you take these important steps.
Where to find professionals for your team
The best way to find professionals for your team is through referrals from trusted friends and colleagues who have personally worked with the professional in question. Don’t ignore your intuition, however. It’s important that you and your team members have good chemistry.
The Annual Audit
We recommend that you assemble your professional advisors for an annual meeting to perform an audit of your business. The goal of this audit is to prevent and discover problems early on and resolve them. As the saying goes, “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.”
Your advisors are a valuable source of information. This annual meeting is an opportunity to ensure that they’re all on the same page and that there are no conflicts among your legal, financial, operational, and other plans. An in-person or virtual group meeting enables you to accomplish this quickly and efficiently.
A sample agenda might include a review of the following:
- Your operating documents
- New forms of liability your business has assumed
- Any increase in value in your business and changes that need to be made, such as increases in insurance or tax planning
- Capital needs
- Insurance requirements and audit, and review of existing coverages to ensure these are adequate
- Tax planning — both personal and corporate
- Estate planning — includes an assessment of your net worth and business value, and any needed adjustments
- Personal financial planning
If you are contemplating selling your business, creating an exit plan will answer these critical questions:
- How much is my business worth? To whom?
- How much can I get for my business? In what market?
- How much do I need to make from the sale of my business to meet my goals?
Taking the strategic steps discussed in this article — assembling a stellar professional team and optimizing the team’s collective experience — will get you well on your way toward successfully selling your business and turning confidently toward your next adventure.
Schedule a Consultation
Selling your business is a big deal.
You’ve invested your blood, sweat, and tears into an enterprise that has provided for you, your family and your employees. The moment has finally come for you to start a new chapter in your life. Explore your options now.

Download Your FREE PDF Copy: Food and Beverage M&A
" * " indicates required fields
Download Your FREE PDF Copy: The Art of the Exit
Download your free pdf copy: acquired.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write a Business Exit Plan
Create a profitable plan from the start
All good business planning documents have a clear business exit plan that outlines your most likely exit strategy from day one.
It may seem odd to develop a business exit plan this soon, to anticipate the day you'll leave your business, but potential investors will want to know your long-term plans. Your exit plans need to be clear in your mind because they will dictate how you operate the company.
For example, if you plan to get listed on the stock market, you’ll want to follow certain accounting regulations from day one that'd otherwise be non-essential and potentially cost prohibitive if your ambitions are to quickly sell the company to a more established competitor in your industry. If you plan to pass the business to your children, you’ll need to start training them at a certain point and get them invested in the company from an early age.
Here’s a look at some of the available strategies for entrepreneurs who want to build a business exit plan into their early planning process:
Long-Term Involvement
- Let It Run Dry: This can work especially well in small businesses like sole proprietorships . In the years before you plan to exit, increase your personal salary and pay yourself bonuses. Make sure you are on track to settle any remaining debt, and then you can simply close the doors and liquidate any remaining assets. With the larger income, naturally, comes a larger tax liability, but this business exit plan is one of the easiest to execute.
- Sell Your Shares: This works particularly well in partnerships such as law and medical practices. When you are ready to retire, you can sell your equity to the existing partners, or to a new employee who is eligible for partnership. You leave the firm cleanly, plus you gain the earnings from the sale.
- Liquidate: Sell everything at market value and use the revenue to pay off any remaining debt. It is a simple approach, but also likely to reap the least revenue as a business exit plan. Since you are simply matching your assets with buyers, you probably will be eager to sell and therefore at a disadvantage when negotiating.

Short-Term Involvement
- Go Public: The dot-com boom and bust reminded everyone of the potential hazards of the stock market. While you may be sitting on the next Google, IPOs take much time to prepare and can cost anywhere from several hundred thousand to several million dollars, depending on the exchange and the size of the offering. However, the costs can often be covered by intermediate funding rounds. Keep in mind, that the likelihood of your company ever going public is very low, as you'll likely need to reach into the tens of millions of dollars in annual revenue before you're an attractive IPO candidate.
- Merge: Sometimes, two businesses can create more value as one company. If you believe such an opportunity exists for your firm as a business exit plan, then a merger may be your ticket. If you’re looking to leave entirely, then the merger would likely call for the head of the other involved company to stay on and take over your company's activities. If you don’t want to relinquish all involvement, consider staying on in an advisory role.
- Be Acquired: Other companies might want to acquire your business and keep its value for themselves. Make sure the offered sale price meshes with your business valuation. You may even seek to cultivate potential acquirers by courting companies you think would benefit from such a deal. If you choose your acquirer wisely, the value of your business can far exceed what you might otherwise earn in a sale.
- Sell: Selling outright can also allow for an easy exit. If you wish, you can take the money from the sale and sever yourself from the company. You may also negotiate for equity in the buying company, allowing you to earn dividends afterward — it is in your interest to ensure your firm is a good fit for the buyer and therefore more likely to prosper.
Your business exit strategy in 9 steps
You’ll leave your business some day, so how do you make sure it’s on the best possible terms?

What is a business exit strategy?
An exit strategy is a plan for wrapping up your involvement in a business. For most people, that means readying the business for a change of owner. Executing a well thought-out exit strategy can increase your sale price, while ensuring the business continues to thrive after you’ve left. This can also be called succession planning. What does it involve?
Succession planning definition and goals
The aim is to leave your business in the best possible shape for a new owner. That means it should be operating at peak profitability, the books should be spick and span, and all your processes will be written down so a stranger can come in and run the place. Oh, and the business won’t need you anymore – no matter how important you once were.
It takes years to do all this. That’s why it’s never too soon to start on your succession plan, or exit strategy.
How to sell a business
Business advisors and brokers recommend these nine steps to help get a succession plan in place.
1. Pick a target buyer
There will be different priorities depending on who you're selling to. If it's family, take pains to make everything transparent and fair. You don’t want the transaction to cause tension or conflict between children. If you’re selling to employees, be prepared for staggered payments. They’ll probably start with a deposit and pay you the rest from business income. If you sell to the highest bidder, then get all your records in order as otherwise they won’t have any idea how you operate, or what sort of money you make.
2. Decide how fast you’ll want out
Some buyers, such as family or employees, won’t have the cash to buy you out straight away. You might have to keep an interest in the business and stay involved to protect your investment. If that’s the case, you’ll need to negotiate consulting fees. If you want a clean break, you’ll probably be better off selling on the open market. That may not work if you have a client services business, however. Buyers of those types of businesses will expect you to stay around to help ensure clients don't leave.
3. Get your accounting sorted
Smart buyers will ask to see at least two years worth of clean and dependable financial records. If your bookkeeping isn't all it could be, get it fixed now. And if there’s something you can do to improve profitability, do it as soon as possible. You want that upswing to show in your accounts as a sustainable trend rather than as a recent spike. Use our balance sheet template to help get things in order.
4. Make yourself redundant
No one’s going to buy your business if it can’t survive without you. If you have employees, give them the training and authority they need to succeed. Scale back your involvement. Be less available to customers and clients. Delegate big decisions. Go into work less often.
5. Ensure your business is a well-oiled machine
Ensure you have formal (and efficient) processes for getting work done. Who does what, when, and how? Make sure there are protocols to guide all this. Potential buyers will be impressed if some things in your business happen automatically.
6. Write down how everything happens in your business
Write a “how to” manual for your business, so that a stranger could pick up the reins and run everything tomorrow. Record every process, including admin. Make a note of the steps you follow for each of these tasks. While you’re at it, write formal job descriptions for employees. And create templates for tasks that are repeated in your business.
7. Figure out how to drive up the valuation of your small business
What are the things that make your business great? Do you have a really outstanding product? Loyal customers? Amazing intellectual property? Find the strengths in your business and grow them, so that they become even more valuable. Similarly, figure out the biggest holdbacks and fix them. You’ll need someone from outside the business to provide this assessment. Get your accountant involved. If they don’t have the particular skills you need, they may be able to recommend someone who does.
8. Get a guideline business valuation
You won’t know what you’ll get for your business until the day it’s sold, but you can get a rough estimate. Ask for a professional opinion. Your accountant should be able to introduce you to someone, or you could search for a local business broker. A guideline valuation will help satisfy your curiosity and set realistic expectations. If they predict a lower price than you’d hoped, you might delay your exit, and spend some time building value in the business.
9. Work on a sales pitch
Buyers need to be excited by your business, so come up with an elevator pitch that captures the essentials. Craft a story that explains why you got started, how you’ve grown, and what you’ve achieved. Paint a positive picture of the future, too, but keep it real. Incorporate stats and facts to support what you’re saying.
Exits happen
Exiting your business is inevitable. It will happen whether you’re in control of it or not. So make a plan now and start getting your business ready for the next owner. It’ll help you command a better price, and increase the chance that your business survives. Learn more about selling your business.
And remember that anything you do to benefit your future buyer, will also benefit you. You’ll have a more efficient, profitable and easier to manage business.
It’s never too soon to build a business exit strategy. Speak to your accountant or business advisor today. If you don’t have an accountant, look for one in the Xero advisor directory .
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.
Start using Xero for free
Access Xero features for 30 days, then decide which plan best suits your business.
- Included Safe and secure
- Included Cancel any time
- Included 24/7 online support
Or compare all plans

- Business Exit Strategies

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on February 23, 2024
Get Any Financial Question Answered
Table of contents, exit strategy overview.
Exit strategies are crucial for business owners to ensure a smooth transition of ownership or dissolution of their business. Planning for an exit strategy is vital as it helps owners to maximize the value of their business, minimize taxes, and achieve their personal and financial goals .
The choice of an exit strategy depends on various factors, including the business's size, industry, financial performance, and the owner's personal objectives.
Read Taylor's Story

Taylor Kovar, CFP®
CEO & Founder
(936) 899 - 5629
[email protected]
I'm Taylor Kovar, a Certified Financial Planner (CFP), specializing in helping business owners with strategic financial planning.
A few years back, I guided a retiring tech firm owner through a staggered exit, initially selling a minority stake to inject fresh resources and innovation. This strategic move not only ensured a smooth leadership transition but also expanded market reach and operational stability, significantly enhancing the firm's valuation. By maintaining cultural integrity and showcasing long-term viability, we attracted competitive bids, turning a potential concern into a lucrative exit and preserving the owner's legacy.
Contact me at (936) 899 - 5629 or [email protected] to discuss how we can achieve your financial objectives.
WHY WE RECOMMEND:
Fee-Only Financial Advisor Show explanation
Certified financial planner™, 3x investopedia top 100 advisor, author of the 5 money personalities & keynote speaker.
IDEAL CLIENTS:
Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals
Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation
Types of Business Exit Strategies
Liquidation.
Liquidation refers to the process of selling off a business's assets and using the proceeds to pay off its debts and liabilities . This strategy is often considered when a business is struggling financially or when the owner wants to retire or move on to another venture.
The following table shows the pros and cons including the suitability of liquidation as an exit strategy.

Selling the Business
Selling a business involves transferring its ownership to a new party in exchange for monetary compensation. The sale can take various forms, such as an asset sale, stock sale, or merger/acquisition.

Types of Sale
An asset sale involves selling individual assets of a business, such as equipment, inventory, and intellectual property.
A stock sale involves transferring the ownership of the business's shares to a new owner.
Merger or Acquisition
In a merger or acquisition , the business is combined with another company, typically a larger one, and the owner may receive cash, shares, or a combination of both.
Finding the Right Buyer
To find the right buyer, business owners should consider the following factors:
Compatibility with the business's values and culture
Financial capability
Reputation and track record
Management Buyout (MBO)
An MBO occurs when a company's management team purchases the business from its current owner. This strategy is suitable when the owner wishes to retire or pursue other opportunities, and the management team is capable of running the business.
The table below shows the pros and cons of MBO including the factors to consider when choosing this strategy.

Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP)
An Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) is a strategy that involves transferring ownership of a business to its employees through a trust. This allows employees to acquire shares in the company, and the owner gradually exits the business.
The table below shows the pros and cons of ESOP including the factors to consider in this strategy.

Initial Public Offering (IPO)
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the process of offering a company's shares to the public for the first time. This strategy is suitable for businesses with strong financial performance and growth potential.
The table below shows the pros and cons of IPO including the suitable scenarios for such strategy.

Family Succession
Family succession involves transferring the ownership and management of a business to family members, typically the next generation.
The table below shows the pros and cons of family succession including the factors to consider in this strategy.
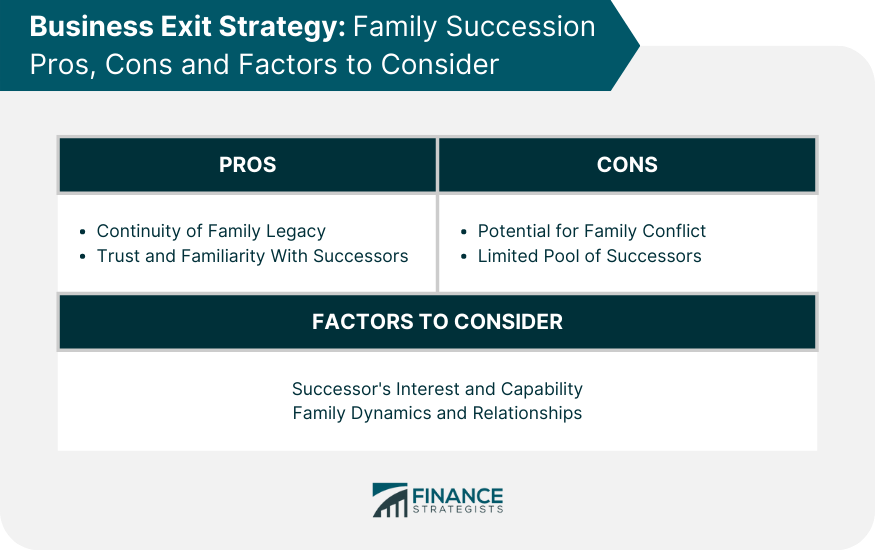
Preparing for an Exit Strategy
Timing considerations.
Choosing the right time to exit a business is crucial for maximizing its value and ensuring a smooth transition. Factors to consider include:
Market conditions
Business performance
Personal goals and readiness
Business Valuation
A proper business valuation is essential to determine the fair market value of a company. Various methods can be used, such as:
Asset-based approach
Income-based approach
Market-based approach
Legal and Financial Preparations
Preparing for an exit strategy involves addressing legal and financial aspects, such as:
Ensuring compliance with regulations
Resolving outstanding liabilities
Updating financial records
Enhancing Business Attractiveness
To maximize the value of a business, owners should focus on enhancing its attractiveness to potential buyers, including:
Streamlining operations
Increasing profitability
Building a strong management team
Developing a Transition Plan
A well-crafted transition plan is essential to ensure a smooth transfer of ownership and minimize disruptions. Key components of a transition plan include:
Timeline for the exit process
Roles and responsibilities of stakeholders
Training and support for the new owner or management team
Execution of the Exit Strategy
Engaging professional advisors.
Working with professional advisors can help navigate the complexities of the exit process. Key advisors include:
Accountants
Business brokers
Investment bankers
Negotiating Terms and Conditions
Negotiating favorable terms and conditions is crucial for maximizing the value of the exit. Key aspects to consider include:
Payment terms
Non-compete agreements
Warranties and indemnities
Due Diligence Process
The due diligence process allows potential buyers to verify the accuracy of the information provided by the seller. Key aspects of due diligence include:
Financial review
Legal review
Operational review
Closing the Deal
Closing the deal involves finalizing the terms and conditions, signing legal documents, and transferring ownership. Key steps include:
Reviewing and approving final documents
Ensuring all conditions are met
Receiving payment and transferring ownership
Post-Exit Considerations
Taxes and financial planning.
Exiting a business may have tax implications, and proper financial planning is essential to minimize the tax burden and maximize the owner's financial well-being.
Non-Compete Agreements
Non-compete agreements can be part of the exit strategy to protect the new owner and ensure a smooth transition. The terms of such agreements should be clear and reasonable.
Business Owner's Role Post-Exit
The exiting owner may continue to play a role in the business after the exit, such as serving as a consultant or board member. This should be clearly defined and agreed upon with the new owner.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Exiting a business can have emotional and psychological effects on the owner. It is essential to prepare for this transition and seek support from friends, family, or professional counselors.

A well-planned exit strategy is essential for business owners seeking a smooth transition and maximum value from their business.
Key points to emphasize include considering factors such as financial performance, personal goals, and industry conditions when choosing the right exit strategy.
Some business exit strategies to consider are liquidation, selling the business, management buyouts, employee stock ownership, IPOs,. and family succession.
Preparation involves timing, valuation, legal and financial preparations, enhancing business attractiveness, and developing a transition plan.
Execution requires engaging professional advisors, negotiating terms, conducting due diligence, and closing the deal.
Post-exit considerations include tax and financial planning, non-compete agreements, defining the owner's role, and addressing emotional and psychological impacts.
By carefully considering these key points and implementing a comprehensive exit strategy, business owners can secure their legacy and achieve their personal and financial goals.
Business Exit Strategies FAQs
What are business exit strategies.
Business exit strategies are plans put in place to help business owners leave their companies, either by transferring ownership or dissolving the business.
What are some common business exit strategies?
Some common business exit strategies include selling the company to another party, transferring ownership to family members or employees, going public through an initial public offering (IPO), or liquidating assets and closing the business.
Why is it important to have a business exit strategy?
Having a business exit strategy is important because it provides a clear path for the owner to exit the business on their own terms, while also ensuring the future success of the company.
When should you start planning your business exit strategy?
It is recommended that business owners start planning their exit strategy at least 3-5 years before they plan to exit the business. This allows for ample time to prepare the business for a successful transfer of ownership.
How can a professional help with business exit strategies?
A professional, such as a business broker, lawyer, or financial advisor, can provide valuable expertise and guidance in developing and implementing a successful business exit strategy. They can also help navigate legal and financial considerations associated with the exit process.
About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
- Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- Capital Planning
- Change-In-Control Agreements
- Corporate Giving Programs
- Corporate Philanthropy
- Cross-Purchase Agreements
- Crowdfunding Platforms
- Employee Retention and Compensation Planning
- Employee Volunteer Programs (EVPs)
- Endorsement & Sponsorship Management
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Entity-Purchase Agreements
- Equity Crowdfunding
- Family Business Continuity
- Family Business Governance
- Family Business Transition Planning
- Family Limited Partnerships (FLPs) and Buy-Sell Agreements
- Human Resource Planning (HRP)
- Jumpstart Our Business Startups (JOBS) Act
- Request for Information (RFI)
- Request for Proposal (RFP)
- Revenue Sharing
- SEC Regulation D
- Sale of Business Contract
- Security Token Offerings (STOs)
- Shareholder Engagement and Proxy Voting
- Social Engagements
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Meet top certified financial advisors near you, find advisor near you, our recommended advisors.

Claudia Valladares
Bilingual in english / spanish, founder of wisedollarmom.com, quoted in gobanking rates, yahoo finance & forbes.
Retirees, Immigrants & Sudden Wealth / Inheritance
Retirement Planning, Personal finance, Goals-based Planning & Community Impact
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
How to Create an Exit Strategy Plan

In order to capture and share the critical information regarding your exit plan in an organized and easy-to-reference format, I recommend an approach like the one used by the increasingly popular business model canvas (BMC).
The BMC is a lean startup template. It depicts in a simple, yet highly informative visual layout the nine essential building blocks of a business model: customer segments , value propositions, channels , customer relationships , revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships and cost structure. This brings us to what I call the exit strategy canvas (ESC) as a template for your exit plan.
The main goal of the ESC is to document the essential building blocks of your exit strategy and create a shared language for communicating and iterating on your exit plan. I recommend that you lay out the ESC on one page to focus on what is absolutely critical and essential.
I recommend that you include the following essential building blocks in your ESC.
6 Essential Building Blocks of an Exist Strategy
- Success definition : What would a successful exit look like?
- Core hypotheses : What do you have to believe to be true for a successful exit to happen?
- Strategic opportunities : What are key areas for value creation through partnerships?
- Key acquirers : Who are your potential acquirers, and what are your selection criteria?
- Risks and challenges : What can jeopardize a successful sale to an acquirer?
- Key mitigants : What can you do to improve your chances of a successful sale?
Success Definition
The entire exit strategy is worthless unless it is crystal clear to all involved what specific outcome an exit is intended to achieve. Once everyone understands the destination, then they can support the journey.
For many entrepreneurs, a successful exit is one that ensures the survival of their startup. And this survival is all about the continuation of what lies at the heart of a startup’s core values and what the founding team considers to be a part of their personal legacy. That may consist of taking its products from a regional offering to the national or global level, creating new distribution channels, or enabling new features that can make it appealing to wholly new customer segments.
As you consider breathing life into your dream scenario, make sure your definition of success answers the following:
- How would an exit best manifest the values of your startup?
- How could an exit best promote the mission of your startup?
- What would be the ideal time frame for an exit transaction?
Core Hypotheses
The next task is to make explicit what you would have to believe to be true for that outcome to manifest. Explicitly stating your assumptions helps you and other team members to discuss and gain clarity about what are the necessary conditions for success, and use them to gauge your future progress.
For example, if a successful exit for you would entail providing growth opportunities for your employees, then at the time of the acquisition you have to believe that your employees have sufficient skills and expertise of value to an acquirer. Thus, stating the hypothesis allows you and your team to reflect on whether this holds true for the current state of affairs, and if not, what you can do to make that a reality going forward.
To adopt a more quantitative approach, especially if your definition of success has a valuation threshold, you need to investigate and make explicit what it would take to justify your valuation goal based on either other comparable transactions or public market valuation benchmarks. Your desired valuation will likely necessitate achieving a certain set of financial (e.g., revenues, margin, profitability profile, or unit economics) or user (e.g., customer size, growth rate) metrics. A specific valuation goal makes it much more efficient for you to screen and filter acquisition opportunities as they arise.
More Built in Book Excerpts Why Salesforce’s Biggest Customer Hated Our Product
Strategic Opportunities
In its simplest form, strategic opportunities are the key areas for value creation with your acquirer. They are the areas of complementarity between your strengths and those of the acquirer.
As such, to identify areas of strategic opportunity you have to start with a good sense of the strengths and weaknesses of your startup. Then, you need to consider the strengths and weaknesses of potential acquirers and how your strengths can fill in the missing piece for their weaknesses and vice versa. This is what is referred to as “synergy.”

If you have a prohibitively high cost of customer acquisition that prevents you from profitably growing and acquiring new customers at scale, you would have a strategic opportunity to partner with a company that has already figured out a way to acquire those customers at scale profitably but is looking for additional products to sell to those customers.
Think of companies in your ecosystem for whom you could fill a strategic need, such as adding revenue, adding profits, staving off a competitive threat, accelerating time to market for a product or service, or improving their market share.
As you enter into discussions with potential strategic partners, you will want to validate and revise your assumptions around areas of synergy and strategic opportunities and be on the lookout to uncover new areas to add to your list.
Enjoying the Excerpt? Check Out the Book! Exit Path: How to Win the Startup End Game
Key Acquirers
This is your wish list of potential acquirers. It will also serve as the list of potential strategic partners whom you will be building a business relationship with over the course of the coming months and years. Be as aspirational as possible. You are not looking for who could be an acquirer of your startup today; instead, you are looking for whom you would be thrilled to join forces with long-term.
For most cases, you could simply state the category or type of company. For a startup serving small businesses, you could refer to “domain registrars,” “website creation platforms,” “e-commerce tool providers” as potential acquirers.
Keep in mind that at this stage your goal is to provide directional guidance as to what are critically important criteria for assessing strategic partners and what the universe of those potential partners looks like.
Risks and Challenges
When considering your exit path, there are in general three types of risks that most businesses have to contend with: execution risk, market risk, and competitive risk.
Execution Risk
Execution risk is a reflection of your core competencies, external relationships, reputation, and capitalization structure, all of which can make or break a successful exit. Weakness in your core competencies (such as an inability to manage the mergers and acquisitions process effectively, leadership gaps or a lack of a scalable business model) can stop many acquirers in their tracks. That is why building a strong business is table stakes for a successful exit.
Another often-overlooked risk factor in selling one’s startup is its capitalization structure: you increase your exit risk as you raise more money at higher valuations as well as when you grant voting rights to financial and strategic investors , as it reduces the founding team’s control and increases the possibility for others to block a transaction. It’s important that you understand the implication of those increasingly lofty valuations which at some point may render you “too expensive” for many acquirers.
More on Startups 4 Strategies for Growing a Company Without VC Funding
Market Risk
As those of us who have tried to sell a company during a market crash know, market risk is always around the corner, and changes in macroeconomic conditions can very much impact the appetite of potential acquirers without forewarning. Because market risk is always present, the more desperate you are to sell, the higher the impact of market risk will be on your startup, so it is ideal not to time a potential exit around a time when you think you will be running out of cash.
Competitive Risk
No matter how unique your startup’s offering is, there is always competition in the market. And thus there exists the competitive risk that your ideal potential acquirers snatch up your competitor instead. Be sure to identify and list your largest competitive threats as an important strategic reminder for your organization.
Key Mitigants
For each risk and challenge you identify, call out a clear and specific set of mitigants.
Mitigating execution risks and competitive risks will generally involve building the requisite capabilities and creating strong relationships with your potential acquirers. The best way to mitigate against market risks, in my opinion, is to increase your operating runway so that you can live through short-term market fluctuations.
Remember that the ESC is a tool intended to efficiently capture and communicate your exit plan. As you create your ESC, feel free to customize it to your own needs, modifying what is captured in each block or adding new blocks that you may find to be particularly well-suited for your startup’s unique set of values, challenges, and opportunities.
Excerpted from the book Exit Path: How to Win the Startup End Game by Touraj Parang, pages 44-53. Copyright © 2022 by Touraj Parang. Published by McGraw Hill, August 2022.

Serve Robotics
Built In’s expert contributor network publishes thoughtful, solutions-oriented stories written by innovative tech professionals. It is the tech industry’s definitive destination for sharing compelling, first-person accounts of problem-solving on the road to innovation.
Great Companies Need Great People. That's Where We Come In.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is an Exit Strategy?
Understanding exit strategies, who needs an exit plan, why is it important to have an exit plan, exit strategies for startups, exit strategies for established businesses, exit strategies for investors, why is it important to have an exit plan, what are common exit strategies used by startups, what are common exit strategies used by established companies, what exit strategies can investors use, the bottom line.
- Investing Basics
Exit Strategy Definition for an Investment or Business
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Gordon Scott has been an active investor and technical analyst or 20+ years. He is a Chartered Market Technician (CMT).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/gordonscottphoto-5bfc26c446e0fb00265b0ed4.jpg)
An exit strategy is a contingency plan executed by an investor , venture capitalist , or business owner to liquidate a position in a financial asset or dispose of tangible business assets once predetermined criteria have been met or exceeded.
An exit strategy may be executed to exit a nonperforming investment or close an unprofitable business. In this case, the purpose of the exit strategy is to limit losses.
An exit strategy may also be executed when an investment or business venture has met its profit objective. For instance, an angel investor in a startup company may plan an exit strategy through an initial public offering (IPO) .
Other reasons for executing an exit strategy may include a significant change in market conditions due to a catastrophic event; legal reasons, such as estate planning , liability lawsuits, or a divorce; or even because the business owner/investor is retiring and wants to cash out.
Key Takeaways
- An exit strategy is a conscious plan to dispose of an investment in a business venture or financial asset.
- An exit strategy helps to minimize losses and maximize profits on investments.
- Startup exit strategies include initial public offerings (IPOs), acquisitions, or buyouts but may also include liquidation or bankruptcy to exit a failing company.
- Established business exit plans include mergers and acquisitions as well as liquidation and bankruptcy for insolvent companies.
- Exit strategies for investors include the 1% rule, a percentage-based exit, a time-based exit, or selling a stake in a business.
An effective exit strategy should be planned for every positive and negative contingency regardless of the investment type or business venture. This planning should be integral to determining the risk associated with the investment or business venture.
An exit strategy is a business owner’s strategic plan to sell ownership in a company to investors or another company. It outlines a process to reduce or liquidate ownership in a business and, if the business is successful, make a substantial profit.
If the business is not successful, an exit strategy (or exit plan) enables the owner to limit losses. An exit strategy may also be used by an investor, such as a venture capitalist, to prepare for a cash-out of an investment.
For investors, exit strategies and other money management techniques can greatly help remove emotion and reduce risk . Before entering an investment, investors should set a point at which they will sell for a loss and a point at which they will sell for a gain.
Business owners of both small and large companies need to create and maintain plans to control what happens to their business when they want to exit. An entrepreneur of a startup may exit their business through an IPO, a strategic acquisition, or a management buyout, while the CEO of a larger company may turn to mergers and acquisitions as an exit strategy.
Investors, such as venture capitalists or angel investors, need an exit plan to reduce or eliminate exposure to underperforming investments so they can capitalize on other opportunities. A well-thought-out exit strategy also provides guidance on when to book profits on unrealized gains.
Businesses and investors should have a clearly defined exit plan to minimize potential losses and maximize profits on their investments. Here are several specific reasons why it’s important to have an exit plan.
Removes emotions : An exit plan removes emotions from the decision-making process. Having a predetermined level at which to exit an investment or sell a business helps avoid panic selling or making rushed decisions when emotions are high, which could accentuate a loss or not fully realize a profit.
Goal setting : Having an exit plan with specific goals helps answer important questions and guides future strategic decision making. For example, a startup’s exit plan might include a future buyout price that it would accept based on revenue turnover. That figure would help make strategic decisions about how big to grow the company to reach predetermined sales targets.
Unexpected events : Unexpected events are a part of life. Therefore, it’s essential to have an exit strategy for what happens when things don’t go to plan. For instance, what happens to a business if the owner faces an unexpected illness? What happens if the company loses a key supplier or customer? These situations need planning in advance to minimize potential losses and capitalize on gains.
Succession planning : An exit plan specifies what happens to the business when key personnel leave. For example, an exit strategy might stipulate through a succession plan that the company passes to another family member or that the business sells a stake to other owners or founders. Carefully detailed succession planning of an exit strategy can help avoid potential conflict when a business owner wants to or has to depart.
In the case of a startup business, successful entrepreneurs plan for a comprehensive exit strategy to prepare for business operations not meeting predetermined milestones.
If cash flow draws down to a point where business operations are no longer sustainable, and an external capital infusion is no longer feasible to maintain operations, then a planned termination of operations and a liquidation of all assets are sometimes the best options to limit further losses.
Most venture capitalists insist that a carefully planned exit strategy be included in a business plan before committing any capital. Business owners or investors may also choose to exit if a lucrative offer for the business is tendered by another party.
Ideally, an entrepreneur will develop an exit strategy in their initial business plan before launching the business. The choice of exit plan will influence business development decisions. Common types of exit strategies include IPOs, strategic acquisitions , and management buyouts (MBOs).
The exit strategy that an entrepreneur chooses depends on many factors, such as how much control or involvement they want to retain in the business, whether they want the company to continue being operated in the same way, or if they are willing to see it change going forward. The entrepreneur will want to be paid a fair price for their ownership share.
A strategic acquisition, for example, will relieve the founder of their ownership responsibilities but will also mean giving up control. IPOs are often considered the ultimate exit strategy since they are associated with prestige and high payoffs. Contrastingly, bankruptcy is seen as the least desirable way to exit a startup.
A key aspect of an exit strategy is business valuation , and there are specialists who can help business owners (and buyers) examine a company’s financial statements to determine a fair value. There are also transition managers whose role is to assist sellers with their business exit strategies.
In the case of an established business, successful CEOs develop a comprehensive exit strategy as part of their contingency planning for the company.
Larger businesses often favor a merger or acquisition as an exit strategy, as it can be a lucrative way to remunerate owners and/or shareholders. Rival companies often pay a premium to buy out a company that allows them to increase market share , acquire intellectual property, or eliminate competition. This raises the prospects of other rivals also placing a bid for the company, ultimately rewarding the sellers of the business.
However, a merger-and-acquisition-focused exit strategy should factor in the time and costs to organize large deals as well as regulatory considerations, such as antitrust laws .
Established companies also plan for how to exit a failing business, which usually involves liquidation or bankruptcy. Liquidation consists of closing down the business and selling off all its assets , with any leftover cash going toward paying off debts and distributing among shareholders .
As mentioned above, most businesses see bankruptcy as a last-resort exit; however, it sometimes becomes the only viable option. Under this scenario, a company’s assets are seized, and it receives relief from its debts. However, declaring bankruptcy could prevent business owners from borrowing credit or starting another company in the future.
Investors can use several different exit strategies to prudently manage their investments. Below, we look at several strategies that help minimize losses and maximize gains.
Selling equity stake : Investors with shares in a startup or small company could exit by selling their equity stake in the business to other investors or a family member. Selling an equity stake may form part of a succession plan agreed upon by founders when starting a business. If selling a startup stake to a family member, it’s important that they understand any conditions tied to the investment.
The 1% rule : Investors apply this rule by exiting an investment if the maximum loss equals 1% of their liquid net worth . For example, if Olivia has a liquid net worth of $2 million, she would cut an investment if it generates a loss of $20,000 ((1 ÷ 100) × 2,000,000). The 1% rule helps investors take a systematic approach to protect their capital.
Percentage exit : Using this strategy, investors exit an investment when it has gained or fallen by a certain percentage from its purchase price. For instance, Ethan, an angel investor, may decide to sell his share in a startup if it achieves a 300% return on investment (ROI) . Conversely, Amelia, a venture capitalist, may decide to sell her share in a startup if it drops 20% in value.
Time-based exit : Investors apply this strategy by exiting their investment after a specific amount of time has passed. For example, Noah may decide to sell his stake in a business after 18 months if it has not generated a positive return. A time-based exit helps free up capital from underperforming investments that could be used for other opportunities.
Businesses should have a clearly defined exit plan to help manage risk and capitalize on opportunities. Specifically, an exit plan helps remove emotion from decision making, assists with strategic direction, helps to plan for unexpected events, and provides details about an actionable succession plan.
Exit strategies used by early-stage companies include initial public offerings (IPOs), strategic acquisitions, and management buyouts (MBOs). Entrepreneurs typically select an exit plan before launching a business that fits their longer-term business development decisions and goals. The exit strategy that an entrepreneur chooses depends on factors such as how much involvement they want to retain in the business and its future long-term potential.
More established companies favor mergers and acquisitions as an exit strategy because it often leads to a favorable deal for shareholders, particularly if a rival company wants to increase its market share or acquire intellectual property. Larger companies may exit a loss-making business by liquidating their assets or declaring bankruptcy.
Investors can capitalize on gains and reduce risk by using exit strategies such as the 1% rule, a percentage-based exit, a time-based exit, or selling their equity stake in a business to other investors or family members. Investors typically set an exit strategy before entering into an investment, as it helps to manage emotions and determine if there is a favorable risk-return tradeoff .
Exit strategy refers to how a business owner or investor will liquidate an asset once predetermined conditions have been met. An exit plan helps to minimize potential losses and maximize profits by keeping emotions in check and setting quantifiable goals.
Common exit strategies for startups include IPOs, strategic acquisitions, and MBOs. More established companies often favor a merger or acquisition as an exit strategy but may also choose to go into liquidation or file for bankruptcy if becoming insolvent . Meanwhile, investors can exit investments using strategies such as the 1% rule, a percentage-based exit, a time-based exit, or selling their equity stake in a business.
Selling My Business. “ The Importance of Having an Exit Plan .”
AllBusiness.com, via Internet Archive. “ 10 Reasons Why Your Exit Strategy Is as Important as Your Business Plan .”
Ansarada. “ Different Business Exit Strategies, Their Pros and Cons .”
Experian. “ What Is an Exit Strategy for Investing? ”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/thinkstockphotos_80410231-5bfc2b97c9e77c0026b4fb20.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
1-800-488-6040
- My Career or Business
- My Health & Vitality
- My Mental Health
- My Finances & Building Wealth
- My Relationship
- My Leadership Skills
- My Productivity
- Growth Solutions
- About Tony Robbins
- The Science of Tony Robbins
- Contribution
- Company Culture
- Get Involved
- Success Stories
- Case Studies
- Events Calendar
- Unleash the Power Within
- Business Mastery
- Date With Destiny
- Life Mastery Virtual
- Wealth Mastery Virtual
- Life & Wealth Mastery Fiji
- Leadership Academy
- Inner Circle Community
- Pinnacle Enterprise
- Platinum Partnership
- Unleash Her Power Within
- Business Coaching
- Results Coaching
- Business Results Training
- Life Coaching
- Health Coaching
- Meet Tony’s Coaches
- All Products
- Nutraceuticals
- Life Force Book
- Tony Robbins Books
- Training Systems
- Breakthrough App
- Netflix Documentary
- Free Tools & Quizzes
Home » The Tony Robbins Blog » Career & Business » What is an exit strategy in business?
What is an exit strategy in business?
4 examples of business exit strategies – and how to achieve them.

After a seven -year journey through space, Cassini went into orbit around Saturn and stayed there for 13 years. It explored Saturn’s rings and atmosphere, and the information it sent to NASA broadened our understanding of what kind of life might exist on worlds beyond Earth. A 20-year job is no joke, especially in today’s economy.
After 20 years of service, Cassini didn’t come back to Earth for retirement. No one ever wondered “ What is an exit strategy for this mission?” It had one job, and it ended its service being crushed and vaporized as it crashed into Saturn on September 15, 2017. This is how Cassini shows the real difference between having a job and having a business . You can’t leave a job behind, but you can leave a business – if you have an exit strategy.
Will you leverage your business into future success? Or will you crash and burn like Cassini? Watch the video from Tony Robbins below on how to tell the difference between a job and a business, and what life without an exit strategy looks like.
What is an exit strategy?
Exit strategy; noun: a pre-planned means of extricating oneself from a situation that has become difficult or unpleasant in a way that limits overall losses.
A business exit strategy does not have to be unpleasant, though. It can simply mean you have accomplished all you’ve set to do with your company and are ready to move on to the next phase of your life. Your goal could be that your business achieves a certain amount of growth. Another common goal is that your business becomes both sufficiently established and marketable so that you can sell it. Regardless, your business has reached a point that it is appropriate for you to move away from it, and it is now time to act on your exit strategy. Your exit strategy business plan needs to benefit you financially and emotionally and fit in with your desired legacy .
Why do I need a business exit strategy ?
Think about why you started your company in the first place. Was it so you could sit behind a desk all day issuing orders and signing contracts? Probably not. You likely envisioned how having financial freedom could make your life better. If you didn’t have to worry about money, you could travel more. You could spend more time with your family. You could pursue the interests that fulfill your soul, perhaps by giving back or learning new skills.
Your business exit strategy allows you to begin to take a step back from your day-to-day operations. It allows you to start creating a money machine that can sustain you without you setting foot in the office. And eventually, it allows you to sell your business or pass on something profitable to the next generation.
No one wants to purchase a small, unprofitable business, nor do they want to pass this type of business on. Your potential buyer wants to see a thriving company, one that has returned your investment and continues to expand. If you want to eventually sell your business and use the money to fulfill your dreams , you need to create something you can sell. That means knowing from the start that you want to sell it and knowing what a potential buyer would desire . If you don’t plan on selling it, instead leaving it to your children or passing it on in some other way, you need a business exit strategy that plans for this.
Creating an exit strategy can also help you grow your business faster and be more successful. If you are ultra-focused on selling your company, then you will set goals and make choices that will lead to the growth of your business , rather than stagnation.
Who needs an exit strategy ?
In short, everyone.
But if you don’t have an exit strategy just yet, you’re not alone. Many business owners build their companies from the ground up – and then stop. They set out to create a product or offer a service to make their business talkably different , but don’t think ahead any further than that. Why would they? Running a business is tiring work. For many business owners, the thought of leaving their business is unsettling. Because of this resistance, some business owners may never have pondered, “What is an exit strategy?” and “Should I have an exit strategy business plan?” Business owners such as these are likely driven by fear: fear of letting go, fear of failing at a new business venture, fear of retirement – the potential list goes on and on.

For many business owners, the thought of leaving their business is unsettling. Because of this resistance, some may never have pondered, “ What is an exit strategy ?” and “ Do I need a business exit strategy ?” Business owners such as these are likely driven by fear: fear of letting go, fear of failing at a new business venture, fear of retirement – the list goes on.
Just as fear can be detrimental in other life situations , the same is true in this situation. Like Cassini, these business owners keep going and going, only to find that when they want to turn around and go back to Earth – or recoup their investment and put it toward what they want to do – they have no ability to do so. Their business might provide them income, but they can hardly walk away from it.
Sounds like a job, doesn’t it? If you want to be a true business owner, not just an operator, you need an exit strategy.
Types of exit strategies
There are two main types of exit strategies: a business exit strategy , for owners who want to move on or retire, and an employee exit strategy, for when employees leave the company. Both have an impact on how your business is perceived and ultimately how profitable it will become.
Business exit strategy
What is an exit strategy in business ? It’s your strategy for transitioning your business to its next stage of ownership. At first, it may sound counterintuitive, especially if you are still at the beginning stages of the business. You’re pouring all you have into this new venture; making plans to exit it – seemingly abandoning it – seems like a terrible mindset for a new business owner to take.
On the contrary: While a business exit strategy isn’t like mapping out a plan for your company , it’s a critical component to your success. Most business owners have strategies to scale, to increase market share and to become profitable , but do not have a strategy to make their exit.
Employee exit strategy
Just as you need a business exit strategy when you’re ready to move on, you also need an employee exit strategy to deal with team members who resign from your company. Whether they leave because they are unhappy at work or to take on a new position that provides them the fulfillment they need, handling their exit sends an important message to your team and can help you retain or even strengthen the loyalty of your other employees.
The key to a successful employee exit strategy is to remain calm and professional, to ensure knowledge gets transferred from the employee who is leaving to whomever will take their role. An exit interview with the employee leaving, as well as interviews with those remaining in their department who are directly affected by the person’s departure, are excellent employee exit strategy tools. When you ask the right questions of both your exiting employee and those they worked with, you can use the departure as a way to improve your organizational culture .

Key elements of a business exit strategy
Your exit strategy is more than a few thoughts you had one night or a quick discussion with your business partner . It’s a written plan of action that accounts for the following:
- The date you plan to enact the exit strategy
- The business valuation you will reach before exiting
- SMART goals and an actionable plan for reaching that valuation
- All viable options for exiting the business (such as the four examples below)
- Potential buyers for your business
If you’re creating an exit strategy years in advance, know that things may change. Business triggers like changes in the economy and in your life will happen. Your exit strategy can actually help you stay on track by providing a clear path to follow – and you can always update it.
Examples of business exit strategies
To fully answer the question, “ What is an exit strategy ?” take a look at these four common plans and the pros and cons of each.
Exit strategy #1: Lifestyle company strategy
The lifestyle company strategy involves taking the biggest salary you can, rewarding yourself with bonuses and issuing special shares that produce very high dividends. The reasoning behind this business exit strategy is to take whatever you can from the business while it’s thriving and leaving nothing to sell once you’re ready to exit.
You can live a pretty good lifestyle and you don’t have to worry about putting a lot of thought into developing a massive action plan for growth.
You may be taxed for money you pull out and you’ll have no big pay-out when you’re ready to leave the business . You’ll also be leaving your team high and dry as your business will close when you leave.
Exit strategy #2: Liquidation
If you’re ready to call it quits and don’t owe money, you can simply close your doors and be done with the business. Liquidation is often what happens when a business fails to anticipate problems , does not have an exit strategy business plan or when things don’t go as planned, but it can be something you choose.
It’s easy and there is no need to transfer anything to new owners.
Your business ends up having no value in the end and your reputation and business relationships could suffer. Just as with a lifestyle exit strategy, your employees will be out of a job with this strategy.
Exit strategy #3: Selling to a friendly buyer
If you’ve created a business based on meaning and purpose , it’s likely that others believe in what you’re doing. When you’re ready to put an exit strategy in place, these like-minded individuals could be willing to buy it from you and continue your vision. Often, these buyers are employees, family members or colleagues. You can finance the sale over time to give them the opportunity to pay a fair market value while giving you the freedom to leave the business as they pay off the loan.
You already know the buyers and therefore less background checking is needed. You also can see your business continue to fulfill your vision.
You may end up selling it for less than it’s worth because you want to help out a friend or family member. You could also do major damage to your family or friendship if problems occur with the business and the buyer blames you.
Exit strategy #4: Acquisition
Acquisition is the most common form of exit strategy and involves finding another company to buy yours. If you seek out a strategic fit and are able to convince them of your value, you could make a tidy profit off your business.
You could get much more than what your company is actually worth, and you don’t have to worry about maintaining personal relationships with those who buy the business. Because this is the most common business exit strategy, you can find a number of professionals to help you complete the process.
Acquisitions and the subsequent transitions can be messy and uncomfortable and you may have to watch your valued employees being laid off. They can also come with non-competes or other stipulations that could make it difficult for you to start another company.
What are my next steps?
Now that you’ve reviewed the different business exit strategies, it’s time to be clear with yourself. Take the advice of business guru and marketing mogul Jay Abraham. The first thing you need to do is review your goals and priorities . Your goals for your business exit strategy may be different depending on your stage of life. Whatever your priorities may be, make sure your exit strategy is leading you toward the life you want.
Another bit of advice from Jay Abraham: Don’t value your business yourself. Instead, hire a professional to evaluate your business and all its assets to get a clear picture of its worth. This process will also help you understand which parts of your business are ripe for improvement. If you’re fortunate, you might be able to make a few minor adjustments based on the evaluation to add real value to your business before you take the next step in your exit strategy.
If your business is not as valuable as you think it could be, it might be wise to set aside six months or a year for potential adjustment. Using Jay Abraham’s internal exponential growth factors , you can potentially add real value to your business in a short time.
Now that you’ve got a clear sense of value, decide which of the exit strategies above best suits your needs. Remember, as you proceed with any deal, exercise full disclosure to potential buyers. If you withhold information, it’s possible the entire deal may fall through.
When you answer “ What is an exit strategy in business ?” and “Which exit strategies are the best fit for me?” you can be proactive in moving toward another stage of growth as you build your business.
Team Tony cultivates, curates and shares Tony Robbins’ stories and core principles, to help others achieve an extraordinary life.
featured collections

Career & Business

Love & Relationships

Mind & Meaning
Related posts, elevate your impact: 10 leadership qualities of remarkable leaders, achieve more with smart goals.
Get Tony Robbins' articles, podcasts and videos in your inbox, biweekly.
Join Our Newsletter!
© 2024 Robbins Research International, Inc. All rights reserved.
- Small Business
- Ways to Bank
- More Scotiabank Sites
- English selected
- Scotia OnLine Mobile
- ScotiaConnect
- Cash & Coin Service
- Advice Centre
Using advisors to plan your exit strategy
Advisors are a valuable asset when planning to leave your business.

It’s never too early to start planning for the sale of your business. What you don’t want is to leave it too late.
Whether your company is brand new or well-seasoned, right now could be the best time for you to consider how you will exit it. Early planning means you and your advisors can develop a strategy that ensures the best outcome.
Exit options
There are many ways to transition ownership of your business. You may want to sell to a large corporation or you may plan to pass control to a family member. What’s important is planning the process carefully.
Start by considering why you want to sell your business. Your plan might be to:
- Take money out of your company
- Reap the rewards of the time and money investment you have made
- Retire completely and pursue personal passions
- Reduce your working hours
- Leave a legacy to your family or community
- Start another business
- Become an angel investor
It’s also important to know when you want to sell your business and what you want from the result.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do you want to sell within a couple of years or a couple of decades?
- What do you financially need or want from your company?
- Do you want to continue working in the company or consulting with it after the sale?
- Will you start a company in a similar or completely different industry?
There are no right or wrong answers to these questions. Every business owner will different priorities, and it’s important you figure out what yours are.
Assemble your team of advisors
Professional advisors will help you consider your alternatives and make decisions. It’s important to work with advisors because an effective ownership transition plan is complex.
You’ll need tax and legal counsel, personal financial planning, and business valuation expertise.
Scotia is always here to help. Get in touch with a Small Business Advisor today to find out how we can assist your plans.
We can also draw on our industry contacts to help you assemble your advisory team.
Create a financial plan
For business owners, identifying the most tax efficient methods to receive income from a business starts early and continues right up to the date the business is sold.
The expertise of advisors, such as financial planners, accountants, lawyers, and wealth management experts, can have a significant impact on the financial results you achieve personally over your lifetime.
Your financial plan should also address estate planning, insurance, and tax issues such as:
- Creating a will
- Establishing appropriate powers of attorney
- Income and pension splitting
- Trust solutions and holding companies
- Charitable and legacy objectives
Related articles
Boost your business value quickly.
Ideas on how you can create value over time.
Buyer’s market: who will buy your business?
If you’re planning to sell your business in the near future, it may pay to profile potential buyers now.
Saving for retirement as a business owner
Create a plan for the retirement you deserve.
Unilever Global Change location
Unilever to accelerate Growth Action Plan through separation of Ice Cream and launch of productivity programme
Published: 19 March 2024
Average read time: 5 minutes

Unilever today announced steps to accelerate its Growth Action Plan (GAP) through the separation of Ice Cream and the launch of a major productivity programme.
The Board believes that Unilever should be increasingly focused on a portfolio of unmissably superior brands with strong positions in highly attractive categories that have complementary operating models. This is where the company can most effectively apply its innovation, marketing and go-to-market capabilities. Ice Cream has a very different operating model, and as a result the Board has decided that the separation of Ice Cream best serves the future growth of both Ice Cream and Unilever.
Following separation, Unilever will become a simpler, more focused company, operating four Business Groups across Beauty & Wellbeing, Personal Care, Home Care and Nutrition. These Business Groups have complementary routes to market, and/or R&D, manufacturing and distribution systems, across both developed markets and Unilever’s extensive emerging markets footprint.
The separation of Ice Cream will assist Unilever’s management to accelerate the implementation of its GAP, announced in October 2023, which is focused on doing fewer things, better, with greater impact to drive consistent and stronger topline growth, enhance productivity and simplicity, and step up Unilever’s performance culture. In addition, Unilever will continue to optimise its portfolio within the four Business Groups towards higher growth spaces and through brands with global reach or significant potential to scale.
Separation of Ice Cream
The Unilever Board is confident that the future growth potential of Ice Cream will be better delivered under a different ownership structure. Ice Cream has distinct characteristics compared with Unilever’s other operating businesses. These include a supply chain and point of sale that support frozen goods, a different channel landscape, more seasonality, and greater capital intensity.
The separation of Ice Cream will create a world-leading business, operating in a highly attractive category, with brands that together delivered turnover of €7.9 billion in 2023. The business has five of the top 10 selling global ice cream brands including Wall’s, Magnum and Ben & Jerry’s, with exposure in both the in-home and out-of-home segments across a global footprint.
Under new leadership, Ice Cream is already making significant operational changes at pace that are expected to drive stronger performance. These include improved productivity and efficiencies, product rationalisation, and investment behind significant innovations.
As a standalone, more focused business, Ice Cream’s management team will have operational and financial flexibility to grow its business, allocate capital and resources in support of the company’s distinct strategy, including further optimising its manufacturing and logistics network, and developing wide-reaching, flexible, distribution channels over and above the changes that are currently under way in the business.
A demerger of Ice Cream is the most likely separation route, and in that case we expect the company to operate with a capital structure in line with comparable listed companies. Other options for separation will be considered to maximise returns for shareholders. The costs and operational dis-synergies relating to the separation of Ice Cream will be determined by the precise transaction structure chosen.
Separation activity will begin immediately, with full separation expected by the end of 2025. Further information will be provided in due course.
Launch of productivity programme
Building on the early momentum of GAP we have identified additional efficiencies that can now be accelerated. In addition to the portfolio changes, Unilever intends to launch a comprehensive productivity programme, driving focus and faster growth through a leaner and more accountable organisation, enabled by investment in technology.
The productivity programme is anticipated to deliver total cost savings of around €800 million over the next three years, more than offsetting estimated operational dis-synergies from the separation of Ice Cream. Incremental net savings from the programme beyond dis-synergies will provide flexibility for accelerated growth investments behind our brands and R&D, and support margin improvement over time. The programme will further reduce complexity and duplication through technology-led interventions, process standardisation and operational centres of excellence to drive efficiencies.
The proposed changes are expected to impact around 7,500 predominantly office-based roles globally, with total restructuring costs now anticipated to be around 1.2% of Group turnover for the next three years (up from the around 1% of Group turnover previously communicated). These proposals will be subject to consultation.
Enhanced medium-term guidance
The separation of Unilever and Ice Cream in combination with the productivity programme will ensure that Unilever’s financial and management resources are focused on its strongest, global or scalable brands. These will have the capability to drive category expansion and deliver accelerated, sustainable levels of growth and improved profitability. After separating Ice Cream and implementing the productivity programme, Unilever will have a structurally higher margin. Post separation, Unilever aims to deliver mid-single digit underlying sales growth and modest margin improvement.
Ian Meakins, Chair of Unilever said: “The Board is determined to transform Unilever into a higher-growth, higher-margin business that will deliver consistently for all stakeholders. Improving our performance and sharpening our portfolio are key to delivering the improved results we believe Unilever can achieve.
“The separation of Ice Cream and the delivery of the productivity programme will help create a simpler, more focused, and higher performing Unilever. It will also create a world-leading ice cream business, with strong growth prospects and an exciting future as a standalone business.”
Hein Schumacher, CEO of Unilever said: “Under the Growth Action Plan we have committed to do fewer things, better, and with greater impact. The changes we are announcing today will help us accelerate that plan, focusing our business and our resources on global or scalable brands where we can apply our leading innovation, technology and go-to-market capabilities across complementary operating models.
“Simplifying our portfolio and driving greater productivity will allow us to further unlock the potential of this business, supporting our ambition to position Unilever as a world-leading consumer goods company delivering strong, sustainable growth and enhanced profitability.
“We are committed to carrying out our productivity programme in consultation with employee representatives, and with respect and care for those of our people who are impacted.”
Unilever to spin off ice cream business, cut 7,500 jobs for cost savings
- About 5.9% of global workforce to be cut to slash costs
- Ice cream unit to be spun off into standalone company
- Spinoff to yield modest sales growth, margin improvement

VOLATILE BUSINESS
Get U.S. personal finance tips and insight straight to your inbox with the Reuters On the Money newsletter. Sign up here.
Reporting by Eva Mathews in Bengaluru and Richa Naidu in London; Editing by Louise Heavens, Kirsten Donovan, Bernadette Baum and Susan Fenton
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
London-based reporter covering retail and consumer goods, analysing trends including coverage of supply chains, advertising strategies, corporate governance, sustainability, politics and regulation. Previously wrote about U.S. based retailers, major financial institutions and covered the Tokyo 2020 Olympic Games.

Southwest Gas Holdings unit Centuri Holdings plans to go public in the United States, the infrastructure services company said in a filing on Friday, as the IPO market gradually recovers from a nearly two-year lull.

S&P 500 ends near flat but index posts biggest weekly gain of year
The S&P 500 ended little changed on Friday, but the index registered its biggest weekly percentage gain of 2024 after the Federal Reserve this week stuck with projections for three interest rate cuts by year's end.

Top Goldman Sachs exec Stephanie Cohen explains why she's leaving Wall Street for tech
- Stephanie Cohen, one of the highest-profile women on Wall Street, is leaving Goldman Sachs.
- Cohen is joining the tech company Cloudflare as its first chief strategy officer.
- Cohen's exit comes after a monthslong leave and a retreat from the consumer business, which she led.
One of Goldman's most visible female leaders is leaving the bank and Wall Street altogether.
Stephanie Cohen , one of the few women in Goldman's history to run a major division at the firm, went on a personal leave last June to focus on her family. During her sabbatical, she said, she considered her career — she'd increasingly been drawn toward the most tech-oriented parts of the organization, most recently serving as the head of platform solutions.
"I just got to this place where it was, 'I want to do this for real,'" Cohen told Business Insider in an interview. "This is what I want to do. I don't want technology to be just a part of it; I want it to be what I do."
Cohen, 46, will join Cloudflare, a San Francisco technology company aimed at helping businesses improve their internet security and performance. Cohen will be its first chief strategy officer, based in Utah. It will be a familiar role, as she served as Goldman's strategy chief from 2018 to 2020.
"One of the things that happens when you spend a really long time at one place, a quarter century at one place, is you start to feel responsibility for a lot of things related to the organization and the people in the organization," Cohen said. "And I realized that the best thing I could do for me and everyone else was to do what I wanted to do, to make the right decision for me and my family."
CEO David Solomon tapped Cohen to help craft Goldman's digital bank as cohead of the consumer and wealth-management division in late 2020. Goldman reshuffled that division in 2022 amid significant losses and plans to sell the consumer-lending unit GreenSky , which the bank bought for $1.7 billion the year prior. She went on leave as Goldman continued to pull back from the business.
Her exit also comes as several Goldman partners and senior women have left the firm. Beth Hammack , a longtime Goldman partner and cohead of the global financial group, is also set to step down.
From Goldman to Cloudflare
Cohen told BI that while she was on sabbatical , she was in regular contact with Solomon — as well as John Waldron, the president and chief operating officer, and others — about coming back.
She said that more recently she started gathering advice because "it would be crazy for me while on sabbatical to not make a proactive decision about what I was going to do next." It was during those conversations that Cohen decided to think about doing something different.
Cloudflare is different; it's an enterprise technology firm with much less brand-name recognition than Cohen's former employer. But it plays a significant role in the world of technology.
The company aims to make the internet more secure and dependable. That could mean ensuring that sensitive company data handled by remote employees is protected from hackers, or enabling large websites to load quickly. It has said that more than 20% of internet traffic uses its security services and that it blocks an average of 182 billion threats a day.
"Everything that we're doing right now is impacted by the reliability and security of the internet," Cohen said. "I have young kids. The world that they're going to live in will be massively impacted by how companies like Cloudflare evolve."
Cloudflare says its clients include IBM, Shopify, L'Oréal, and Canva. Founded in 2009, it went public in 2019, and Cloudflare's stock price is up about 70% over the past year. Goldman was one of the lead banks on the initial public offering, a Cloudflare announcement at the time said. Cloudflare said it had nearly 3,700 employees globally at the end of 2023.
Cohen has long known the Cloudflare cofounders Matthew Prince, its CEO, and Michelle Zatlyn, its president and COO, but she didn't work with them while at Goldman. She said that during recent discussions with Prince and Zatlyn she realized moving to Cloudflare would allow her to marry her Wall Street experience and passion for technology.
"It was in the context of having that conversation, the 'aha' of not only am I really interested in enterprise technology, but there are real things that I've done over the last 25 years that are additive to a company that's at this stage," she said.
Having spent 20 years inking deals within Goldman Sachs' investment-banking unit, Cohen is no stranger to the boardroom. She'll bring experience in connecting with C-suites, but it'll be to sell them on the idea that "security and the connectivity cloud are board and CEO-level topics," she said.
"I'm really excited to be at the center of what I think is driving the world, and not just read about what's going on in cloud and AI, but actually be part of building it and helping the world build a better internet," she said.
Cohen's advice to Goldman's top brass
Cohen joined Goldman in 1999 as an investment-banking analyst after graduating from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Seen as a rising star, she made partner in 2014 and joined the bank's management committee — responsible for strategy, policy, and management decisions across the firm — in 2018. She became the youngest person to join Goldman's management committee .
Related stories
After nearly 20 years in M&A, she was tapped by then-CEO Lloyd Blankfein to be the chief strategy officer. She said this role set her up to learn more about integrating strategy with emerging technology, which became a driving force at Goldman Sachs.
When she was named cohead of the consumer and wealth-management business, Cohen became part of a major pivot for Goldman Sachs , which for most of its history ignored retail customers in favor of institutional clients. While the appointment entered her into the discussion about CEO candidates, the move to retail had already been in motion and had internal critics. The bank ultimately shifted away from its money-losing efforts to sell Main Street products and restructured in 2022. Cohen also went on medical leave during that year.
Cohen and other leaders have acknowledged they did "too much too quickly" regarding the consumer business. "We did some things well, we built a great deposits platform that we have continued to scale, and we created a credit card that is incredibly popular with consumers," she said. "And there are other things that we didn't do as well.
"We entered that business when I was in the investment bank, and a lot had already been done by the time I became involved," she added. "I certainly wasn't perfect, but it's always difficult when you show up where lots of decisions have been made and lots of things have been done, and then figuring out what are you going to undo, focusing on the undoing and the fixing, plus focusing on growing and the people and everything else."
That restructure resulted in Cohen's most recent role, as head of platform solutions overseeing transaction banking, credit cards, and enterprise partnerships. It's one of Goldman's three major business divisions.
Several female executives have left the bank in recent years, with many of them pursuing career opportunities elsewhere. Still, Cohen said her story "is aspirational to any woman that walks inside of Goldman Sachs."
She described diversity and inclusion as a "strategic imperative" and said she believed leadership would continue to focus on diversifying its top ranks. "No one's giving up inside of Goldman Sachs on this topic," she said.
"They know that having inclusive teams will help them be a better company, " she added. "And so has everything gone right? Absolutely not. Is there more work to do? Absolutely."
She said that the more diversity and inclusion are discussed as strategic imperatives in the same meetings where leaders talk about revenue growth and margins and market share, "the more it becomes part of running the business."
When asked what advice she'd give to leaders on bringing more women into senior ranks, Cohen said to "just keep going" and "keep trying new things."
Running toward her future
Cohen has encouraged people to consider whether they're happy in their jobs and whether they're still learning.
"If you decide to be here, and decide to do what you're doing, you own it," she told the Financial Times last March.
Cohen said that while she's had the chance to learn from successes and failures during her time at Goldman, this career move is "really more running towards than running away from something."
"As you think about my career at Goldman, I was inching towards this whole idea of how do you take technology platforms and use them as client-facing solutions. Goldman Sachs has built world-class technology platforms. We run one of the best trading businesses in global banking and markets. We could not do that without a world-class technology platform," she said.
"But the reality is Goldman Sachs is not a technology firm," Cohen added.
In a statement, Prince described Cohen as "incredible."
"Anyone who has worked with her can attest she operates at a different clock speed," Prince said. He added that after her 25 years at Goldman Sachs, "she could have gone anywhere, and we're honored that she'll be joining us as our first-ever chief strategy officer."
While the departure of one of Goldman's top executives may surprise some, it's an obvious fit to those who know and have worked closely with Cohen, like Goldman's chief information officer, Marco Argenti .
Cohen recalled that when she broke the news to Argenti, he told her, 'This is exactly what you should do," adding, "This is exactly the right company."
"I think it's just one of those things where it all lines up," she said. "The sector lines up, the company lines up, the team lines up."
Watch: How Twitter panic took down Silicon Valley Bank
- Main content
Advertisement
Supported by
Saudi Arabia Plans $40 Billion Push Into Artificial Intelligence
The Middle Eastern country is creating a gigantic fund to invest in A.I. technology, potentially becoming the largest player in the hot market.
- Share full article

By Maureen Farrell and Rob Copeland
The government of Saudi Arabia plans to create a fund of about $40 billion to invest in artificial intelligence, according to three people briefed on the plans — the latest sign of the gold rush toward a technology that has already begun reshaping how people live and work.
In recent weeks, representatives of Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund have discussed a potential partnership with Andreessen Horowitz, one of Silicon Valley’s top venture capital firms, and other financiers, said the people, who were not authorized to speak publicly. They cautioned that the plans could still change.
The planned tech fund would make Saudi Arabia the world’s largest investor in artificial intelligence. It would also showcase the oil-rich nation’s global business ambitions as well as its efforts to diversify its economy and establish itself as a more influential player in geopolitics. The Middle Eastern nation is pursuing those goals through its sovereign wealth fund, which has assets of more than $900 billion.
Officials from the Saudi fund have discussed the role Andreessen Horowitz — already an active investor in A.I. and whose co-founder Ben Horowitz is friends with the fund’s governor — could play and how such a fund would work, the people said. The $40 billion target would dwarf the typical amounts raised by U.S. venture capital firms and would be eclipsed only by SoftBank, the Japanese conglomerate that has long been the world’s largest investor in start-ups.
The Saudi tech fund, which is being put together with the help of Wall Street banks, will be the latest potential entrant into a field already awash in cash. The global frenzy around artificial intelligence has pushed up the valuations of private and public companies as bullish investors race to find or build the next Nvidia or OpenAI. The start-up Anthropic, for instance, raised more than $7 billion in one year alone — a flood of money virtually unheard-of in the venture capital world.
The cost of funding A.I. projects is steep. Sam Altman, the chief executive of OpenAI, has reportedly sought a huge sum from the United Arab Emirates government to boost manufacturing of chips needed to power A.I. technology.
Saudi representatives have mentioned to potential partners that the country is looking to back an array of tech start-ups tied to artificial intelligence, including chip makers and the expensive, expansive data centers that are increasingly necessary to power the next generation of computing, according to four people with knowledge of those efforts, who were not authorized to speak publicly. It has even considered starting its own A.I. companies.
Two of the people said that Saudi’s new investment push is likely to take off in the second half of 2024. A $40 billion fund could make both the Saudi Arabian government and Andreessen Horowitz key players in races to corner various businesses related to the field.
Mr. Horowitz and Yasir al-Rumayyan, the governor of the Public Investment Fund, have discussed the possibility of the Silicon Valley firm setting up an office in the country’s capital, Riyadh, one person with knowledge of the conversations said.
Other venture capitalists may participate in the kingdom’s tech fund, two people briefed on the plans said.
Partly because of its enormous financial clout and growing ambitions, those in international business circles closely monitor moves made by the Public Investment Fund, which was created in 1971.
In 2018, just as Saudi Arabia was becoming a major destination for investment firms and entrepreneurs seeking financial backing, the country’s agents killed the dissident Saudi journalist Jamal Khashoggi in the kingdom’s Istanbul consulate, which for a spell seemed to damage the nation’s reputation among international financiers.
In 2022, the Saudi government invested billions into a firm run by former President Donald J. Trump’s son-in-law Jared Kushner, among others, which was seen by many as a political move. One of its recent deals to merge its LIV Golf upstart with the PGA Tour raised the ire of golfers, but the pact is also controversial in part because of Saudi Arabia’s human rights record.
Saudi Arabia, which poured $3.5 billion into Uber in 2016, has largely struggled with technology investing. It handed $45 billion to SoftBank for the Japanese firm’s $100 billion Vision fund, which was channeled into dozens of enterprises including the now-bankrupt real estate firm WeWork and other failed start-ups, such as the robotic pizza-making company Zume.
Many in Silicon Valley and on Wall Street have welcomed the nation back into the fold. During this year’s Super Bowl, Mr. Horowitz hosted Mr. al-Rumayyan, according to two people briefed on their activities.
The two men also spent time together before and after the game, the people said, with Mr. Horowitz giving Mr. al-Rumayyan tours of Las Vegas, his adopted city, and introducing the investor to his friends in music and sports.
Maureen Farrell writes about Wall Street, focusing on private equity, hedge funds and billionaires and how they influence the world of investing. More about Maureen Farrell
Rob Copeland is a finance reporter, writing about Wall Street and the banking industry. More about Rob Copeland
Explore Our Coverage of Artificial Intelligence
News and Analysis
Gov. Bill Lee of Tennessee signed a bill to prevent the use of A.I. to copy a performer’s voice. It is the first such measure in the United States.
French regulators said Google failed to notify news publishers that it was using their articles to train its A.I. algorithms, part of a wider ruling against the company for its negotiating practices with media outlets.
Apple is in discussions with Google about using Google’s generative A.I. model called Gemini for its next iPhone.
The Age of A.I.
By interacting with data about genes and cells, A.I. models have made some surprising discoveries and are learning what it means to be alive. What could they teach us someday ?
Covariant, a robotics start-up, is using the technology behind chatbots to build robots that learn skills much like ChatGPT does.
When Google released Gemini, a new chatbot, the company quickly faced a backlash. The episode unleashed a fierce debate about whether A.I. should be guided by social values.
A.I.’s booming growth is radically reshaping an already red-hot data center market, raising questions about whether these sites can be operated sustainably .
Few companies better illustrate how A.I. is changing Silicon Valley deal-making than Anthropic, one of the world’s hottest A.I. start-ups .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Prospective buyers prefer that the company owners have performance metrics, revenue history, and any other paperwork ready. A business exit strategy ensures that company managers have systems in place for recording essential information on a regular basis. 2. Get a better understanding of revenue streams. An exit plan requires that one keeps ...
This strategy means possibly severing relationships with employees, partners, clients, customers, and anyone else involved with the day-to-day or general operations of your business. 8. Declare Bankruptcy. As far as small business exit strategy planning goes, this last method is the option that you can't really plan for.
Business Exit Strategy: An entrepreneur's strategic plan to sell his or her investment in a company he or she founded. An exit strategy gives a business owner a way to reduce or eliminate his or ...
A business exit strategy is a plan that an owner or executive creates and follows to liquidate their stake in a business, ideally at a substantial profit. A successful business exit strategy requires careful planning and should be periodically revised to best reflect the current business conditions.
An exit strategy is a business plan that outlines how and when a founder, CEO, investor, or other stakeholder will liquidate a company. There are several types of liquidity events you may plan for, including: Public offerings. Mergers. Acquisitions. Liquidations. Types of exit strategies. Below is a basic overview of the most common exit ...
Follow these steps to develop a business exit strategy: determine when you want to leave, define what you want to achieve, identify potential buyers or successors, evaluate and increase the current value of your business and assemble the right team. Write an exit plan, create a communication plan, develop a contingency plan and build a data room.
A business's primary goal is long-term value generation to its customers, itself, and its stakeholders. Having a thoughtful exit strategy shows the maturity of a business's Leadership towards longevity and value creation. There are many facets of the journey from owner motivation to financial strategies.
An exit strategy is often thought of as the way to end a business — which it can be — but in best practice, it's a plan that moves a business toward long-term goals and allows a smooth transition to a new phase, whether that involves re-imagining business direction or leadership, keeping financially sustainable or pivoting for challenges.
An exit strategy is a proactive plan to shift out of or liquidate an investment position, business transaction or venture. ... Creating an exit strategy is a smart business decision from the get ...
Below are some seven common types of exit strategies: 1. Initial Public Offering (IPO): An IPO is when a private company begins selling its shares to the public. This is a popular exit strategy for startup companies looking to expand. After an IPO, a business owner may choose to sell the business, or stay on board. 2.
Now that you know what creating an exit strategy involves and how exits can differ for startups versus established businesses, follow these tips when executing your plans. 1. Bring in outside expertise. You need to build your own professional team for the sales process because your buyer will almost certainly have one.
You should plan this strategy at least three to five years in advance (ideally ten years) with the understanding that your goals and business may evolve over time. 1. Identify your expectations ...
What business owners need next is an effective exit plan to tackle the obstacles ahead. The Exit Strategy Business Plan: Once business owners have the proper motivation, they need a plan to make achieve their goals. A Value Acceleration Plan designed by a Certified Exit Planning Advisor (CEPA) can help outline what the business owner needs to do.
Business Exit Plan Strategy Component #1: Valuation. Your exit strategy should begin with a valuation, or appraisal, of your company. The process of valuing your company involves three steps, the first being an assessment of the current value of your business. Once this value is calculated, you should then plan how to both preserve and increase ...
You leave the firm cleanly, plus you gain the earnings from the sale. Liquidate: Sell everything at market value and use the revenue to pay off any remaining debt. It is a simple approach, but also likely to reap the least revenue as a business exit plan. Since you are simply matching your assets with buyers, you probably will be eager to sell ...
An exit strategy is a plan for wrapping up your involvement in a business. For most people, that means readying the business for a change of owner. Executing a well thought-out exit strategy can increase your sale price, while ensuring the business continues to thrive after you've left. This can also be called succession planning.
Some business exit strategies to consider are liquidation, selling the business, management buyouts, employee stock ownership, IPOs ,. and family succession. Preparation involves timing, valuation, legal and financial preparations, enhancing business attractiveness, and developing a transition plan. Execution requires engaging professional ...
This brings us to what I call the exit strategy canvas (ESC) as a template for your exit plan. The main goal of the ESC is to document the essential building blocks of your exit strategy and create a shared language for communicating and iterating on your exit plan. I recommend that you lay out the ESC on one page to focus on what is absolutely ...
Exit Strategy: An exit strategy is a contingency plan that is executed by an investor, trader, venture capitalist or business owner to liquidate a position in a financial asset or dispose of ...
Key elements of a business exit strategy. Your exit strategy is more than a few thoughts you had one night or a quick discussion with your business partner. It's a written plan of action that accounts for the following: The date you plan to enact the exit strategy. The business valuation you will reach before exiting.
According to Investopedia, an exit strategy is a plan for selling or disposing of a financial or business asset when certain conditions have been met or exceeded.It is used by investors, traders ...
An EOT is a type of employee ownership option that is widely used in the U.K. but is just gaining ground in the U.S.Although similar, an EOT is different from the more popular employee stock ...
Understanding the financial worth of your hospitality business is essential before you can proceed with a succession plan or exit strategy. Hire a professional appraiser to give you an accurate ...
It's never too early to start planning for the sale of your business. What you don't want is to leave it too late. Whether your company is brand new or well-seasoned, right now could be the best time for you to consider how you will exit it. Early planning means you and your advisors can develop a strategy that ensures the best outcome.
As a standalone, more focused business, Ice Cream's management team will have operational and financial flexibility to grow its business, allocate capital and resources in support of the company's distinct strategy, including further optimising its manufacturing and logistics network, and developing wide-reaching, flexible, distribution ...
The Bank of Japan's strategy for an orderly exit from years of massive stimulus unraveled on an overcast day in December when Governor Kazuo Ueda and two deputies gathered at the bank's Tokyo ...
Investors cheered the plan, sending shares in Unilever, one of the world's biggest consumer goods companies, up nearly 6% at one point. ... advertising strategies, corporate governance ...
Stephanie Cohen, one of the highest-profile women on Wall Street, is leaving Goldman Sachs. Cohen is joining the tech company Cloudflare as its first chief strategy officer. Cohen's exit comes ...
The government of Saudi Arabia plans to create a fund of about $40 billion to invest in artificial intelligence, according to three people briefed on the plans — the latest sign of the gold rush ...