What Is Happiness and Why Is It Important? (+ Definition)

It seems like an odd question, but is it? Do you know how to define happiness? Do you think happiness is the same thing to you as it is to others?
What’s the point of it all? Does it even make a difference in our lives?
In fact, happiness does have a pretty important role in our lives, and it can have a huge impact on the way we live our lives. Although researchers have yet to pin down the definition or an agreed-upon framework for happiness, there’s a lot we have learned in the last few decades.
This article will dive into the science of happiness, what it actually is, and why it matters.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Happiness & Subjective Wellbeing Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients identify sources of authentic happiness and strategies to boost wellbeing.

This Article Contains:
- A Look at the Oxford English Dictionary’s Definition of Happiness
What is the Meaning of Happiness in Positive Psychology?
The psychology behind human happiness, 8 examples that describe what a happy life looks like, why is happiness so important, 6 videos that explain happiness, a take-home message, a look at the oxford english dictionary ‘s definition of happiness.
First, let’s take a look at the definition of happiness so we’re all on the same page. Oxford English Dictionary ’s definition of “happiness” is a simple one: “ The state of being happy .”
Not exactly what we were looking for, was it? Perhaps we need to dive a little deeper. Oxford English Dictionary ’s definition of “happy” is a little more helpful: “ Feeling or showing pleasure or contentment .”
That’s better! So, happiness is the state of feeling or showing pleasure or contentment. From this definition, we can glean a few important points about happiness:
- Happiness is a state, not a trait; in other words, it isn’t a long-lasting, permanent feature or personality trait, but a more fleeting, changeable state.
- Happiness is equated with feeling pleasure or contentment, meaning that happiness is not to be confused with joy, ecstasy, bliss, or other more intense feelings.
- Happiness can be either feeling or showing, meaning that happiness is not necessarily an internal or external experience, but can be both.

Download 3 Free Happiness Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to discover authentic happiness and cultivate subjective well-being.
Download 3 Free Happiness Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
The meaning of happiness in Positive Psychology really depends on who you ask.
Happiness is often known by another name in positive psychology research: subjective wellbeing, or SWB.
Some believe happiness is one of the core components of SWB, while others believe happiness is SWB. Regardless, you’ll frequently find SWB used as a shorthand for happiness in the literature.
And speaking of the literature, you will find references to SWB everywhere. A quick Google search for the word “happiness” offers over 2 million results (as of January 6th, 2019). Further, a scan for the same term in two of psychology’s biggest online databases (PsycINFO and PsycARTICLES) returns 19,139 results from academic and other journals, books, dissertations, and more.
Is it difficult to define scientifically?
With so many takes on happiness, it’s no wonder that happiness is a little difficult to define scientifically; there is certainly disagreement about what, exactly, happiness is.
According to researchers Chu Kim-Prieto, Ed Diener, and their colleagues (2005), there are three main ways that happiness has been approached in positive psychology:
- Happiness as a global assessment of life and all its facets;
- Happiness as a recollection of past emotional experiences;
- Happiness as an aggregation of multiple emotional reactions across time (Kim-Prieto, Diener, Tamir, Scollon, & Diener, 2005).
Although they generally all agree on what happiness feels like—being satisfied with life, in a good mood, feeling positive emotions , feeling enjoyment, etc.—researchers have found it difficult to agree on the scope of happiness.
However, for our purposes in this piece, it’s enough to work off of a basic definition that melds the OED ‘s definition with that of positive psychologists: happiness is a state characterized by contentment and general satisfaction with one’s current situation.
Pleasure vs. happiness

The association between the two makes sense, and it’s common to hear the two words used interchangeably outside of the literature; however, when it comes to the science of positive psychology, it is important to make a distinction between the two.
Happiness, as we described above, is a state characterized by feelings of contentment and satisfaction with one’s life or current situation. On the other hand, pleasure is a more visceral, in-the-moment experience. It often refers to the sensory-based feelings we get from experiences like eating good food, getting a massage, receiving a compliment, or having sex.
Happiness , while not a permanent state, is a more stable state than pleasure. Happiness generally sticks around for longer than a few moments at a time, whereas pleasure can come and go in seconds (Paul, 2015).
Pleasure can contribute to happiness, and happiness can enhance or deepen feelings of pleasure, but the two can also be completely mutually exclusive. For example, you can feel a sense of happiness based on meaning and engagement that has nothing to do with pleasure, or you could feel pleasure but also struggle with guilt because of it, keeping you from feeling happy at the same time.
Happiness vs. meaning
Happiness and meaning have an even more distinct line between the two. Rarely are happiness and meaning confused or used interchangeably, and for good reason—they describe two very different experiences.
Humans may resemble many other creatures in their striving for happiness, but the quest for meaning is a key part of what makes us human, and uniquely so.
Roy Baumeister et al. (2013)
Unlike happiness, meaning is not a fleeting state that drifts throughout the day; it’s a more comprehensive sense of purpose and feeling of contributing to something greater than yourself.
As the quote from Baumeister and colleagues (2013) suggests, there are important distinctions between the methods of searching for and the benefits of experiencing happiness and meaning. Scott Barry Kaufman at Scientific American (2016) outlines these distinctions that Baumeister and his fellow researchers found between the two:
- Finding one’s life easy or difficult was related to happiness, but not meaning;
- Feeling healthy was related to happiness, but not meaning;
- Feeling good was related to happiness, not meaning;
- Scarcity of money reduced happiness more than meaning;
- People with more meaningful lives agreed that “relationships are more important than achievements;”
- Helping people in need was linked to meaning but not happiness;
- Expecting to do a lot of deep thinking was positively related to meaningfulness, but negatively with happiness;
- Happiness was related more to being a taker rather than a giver, whereas meaning was related more to being a giver than a taker;
- The more people felt their activities were consistent with the core themes and values of their self, the greater meaning they reported in their activities;
- Seeing oneself as wise, creative, and even anxious were all linked to meaning but had no relationship (and in some cases, even showed a negative relationship) to happiness (Kaufman, 2016).
Basically, although the two overlaps and each can contribute to the experience of the other, the two can be mutually exclusive (Baumeister et al., 2013).
Relevant reading: 19 Cliché Happiness Quotes & The (Lack Of) Science Behind Them
The origins and etymology of happiness (Incl. root words)
According to Etymology Online (n.d.), the word for “happy” in most languages came from the word for “lucky.” This suggests an interesting trend—perhaps our ancestors believed that happiness was largely a by-product of luck?
It also points to a possible difference of general opinion between earlier generations and our own 20th and 21st-century generations: that happiness was not a vital factor in a good life, but essentially a bonus that some lucky individuals got to experience.
Here’s what author Darrin McMahon writes about the origins and root words of the word “happiness:”
“It is a striking fact that in every Indo-European language, without exception, going all the way back to ancient Greek, the word for happiness is a cognate with the word for luck. Hap is the Old Norse and Old English root of happiness, and it just means luck or chance, as did the Old French heur, giving us bonheur, good fortune or happiness. German gives us the word Gluck, which to this day means both happiness and chance.”
(McMahon, 2006)
What does self-happiness mean?
Although the term is not used very often, “self-happiness” refers to a sense of happiness or satisfaction with one’s self. It is often associated with self-confidence, self-esteem, and other concepts that marry “the self” with feeling content and happy.
In general, it means that you are pleased with yourself and your choices, and with the person that you are.
Happiness can be defined as an enduring state of mind consisting not only of feelings of joy, contentment, and other positive emotions, but also of a sense that one’s life is meaningful and valued (Lyubomirsky, 2001).
Happiness energizes us and is a highly sought after state of being. But, what components make up happiness?
Martin Seligman (2002) argued that happiness has three dimensions that can be cultivated:
- The regular experience of pleasantness (the pleasant life)
- The frequent engagement in satisfying activities (the engaged life)
- The experience of a sense of connectedness to a greater whole (the meaningful life)
Although each dimension is important, the happiest people tend to be those who pursue the full life— they infuse their life with pleasure, engagement, and meaning (Seligman et al., 2005).
Building on Seligman’s three dimensions of happiness, Sirgy and Wu (2009) added the balanced life dimension.
According to these authors, balance in life is another key factor contributing to happiness because the amount of satisfaction derived from a single life domain is limited. One needs to be involved in multiple domains to satisfy the broad spectrum of human needs. As a result, cultivating a sense of balance is crucial for juggling these life domains.

Now that we know what happiness is, let’s dive a little deeper. What does psychology have to tell us about happiness?
There are many different theories of happiness, but they generally fall into one of two categories based on how they conceptualize happiness (or well-being):
- Hedonic happiness/well-being is happiness conceptualized as experiencing more pleasure and less pain; it is composed of an affective component (high positive affect and low negative affect) and a cognitive component (satisfaction with one’s life);
- Eudaimonic happiness/well-being conceptualizes happiness as the result of the pursuit and attainment of life purpose, meaning, challenge, and personal growth; happiness is based on reaching one’s full potential and operating at full functioning (AIPC, 2011).
Some theories see happiness as a by-product of other, more important pursuits in life, while others see happiness as the end-goal for humans. Some theories state that pursuing happiness is pointless (although pursuing other important experiences and feelings may contribute to greater happiness), and some assume that happiness can be purposefully increased or enhanced.
Although they differ on the specifics, these theories generally agree on a few points:
- It’s good to be happy, and people like being happy;
- Happiness is neither a totally fleeting, momentary experience nor a stable, long-term trait;
- At least some portion of our happiness is set by our genetics, but the amount varies from about 10% up to 50%;
- The pursuit and attainment of pleasure will rarely lead to happiness;
- There are many sources that contribute to or compose happiness (AIPC, 2011).
What sources create true personal happiness?
Taking together all the various theories and findings on happiness, we know that there are at least a few factors that are very important for overall happiness:
- Individual income;
- Labor market status;
- Physical health;
- Social relationships;
- Moral values;
- Experience of positive emotions (AIPC, 2011).
All of these factors can contribute to a happy life, but research has found that good relationships are a vital ingredient (Waldinger & Schulz, 2010).
When we are happy in our most important relationships (usually our spouse or significant other, our children and/or our parents, other close family members, and our closest friends), we tend to be happier.
We have some control over how our relationships go, so that leads us to an interesting and important question: can we increase our own happiness?
Can individuals learn how to be happy?
The answer from numerous studies is a resounding YES—you CAN learn how to be happier.
The degree to which you can increase your happiness will vary widely by which theory you subscribe to, but there are no credible theories that allow absolutely no room for individual improvement. To improve your overall happiness, the most effective method is to look at the list of sources above and work on enhancing the quality of your experiences in each one of them.
For example, you can work on getting a higher salary (although a higher salary will only work up to about $75,000 USD a year), improve your health , work on developing and maintaining high-quality relationships, and overall, find ways to incorporate more positive feelings into your daily life. This does assume basic access to safety as well as social equality.

Of course, what it looks like will depend on the individual—a happy life for one person may be another’s nightmare!
However, there are a few examples that can display a wide range of lives that can be conducive to happiness:
- A woman who lives alone, has excellent relationships with her nieces and nephews, gives to charity, and finds meaning in her work;
- A man who is happily married with three healthy children and a relatively low-paying job;
- A widow who enjoys regular visits with her children and grandchildren, along with volunteering for local charities;
- A cancer patient who has a wonderful support system and finds meaning in helping others make it through chemotherapy;
- A social worker who works 70-hour weeks with no overtime pay, to ensure the children on her caseload are in good hands;
- An unmarried man in a monastery who has no earthly possessions and no salary to speak of, but finds meaning in communing with his god;
- A teenager in a foster home who has several close friends and enjoys playing football on his school’s team;
- A man who lives with several pets, enjoys a high salary, and loves his job.
Each of these was pulled from real-world examples of people who are happy. They may not seem like they have it all, but they all have at least one of the ingredients from the list of sources mentioned earlier. We don’t need to have everything we want in order to be happy—true happiness can be obtained by finding joy in what we already have, however much or little that may seem.
What are some visions you associate with happiness? Are there any similarities with these dreams?
You might be wondering why happiness is considered such an important aspect of life, as there are many components of a meaningful life.
In some ways, science would agree with you. It appears that life satisfaction , meaning, and well-being can be linked with happiness, but happiness is not necessarily the overarching goal for everyone in life. It is still important because it has some undeniably positive benefits and co-occurring factors.
June Silny at Happify outlines 14 answers to the question, “ What’s so great about happiness, anyway? ”
- Happy people are more successful in multiple life domains, including marriage, friendship, income, work performance, and health.
- Happy people get sick less often and experience fewer symptoms when they do get sick.
- Happy people have more friends and a better support system.
- Happy people donate more to charity (and giving money to charity makes you happy, too).
- Happy people are more helpful and more likely to volunteer—which also makes you happier!
- Happy people have an easier time navigating through life since optimism eases pain, sadness, and grief.
- Happy people have a positive influence on others and encourage them to seek happiness as well, which can act as reinforcement.
- Happy people engage in deeper and more meaningful conversations.
- Happy people smile more, which is beneficial to your health.
- Happy people exercise more often and eat more healthily.
- Happy people are happy with what they have rather than being jealous of others.
- Happy people are healthier all around and more likely to be healthy in the future.
- Happy people live longer than those who are not as happy.
- Happy people are more productive and more creative, and this effect extends to all those experiencing positive emotions.
The relationship between mental health and happiness
As you can probably assume from the list above, there is a strong relationship between mental health and happiness! When happy people are healthier, have better relationships, make friends more easily, and find more success in life, it’s easy to see why happiness and mental health are related.
The sources that contribute to happiness are the same as those that provide people with a buffer or protection against mental illness, which explains the close relationship between the two.
A recent study explored the association between happiness and mental health in college students and found that a relatively strong, positive correlation connects the two factors (Shafiq, Nas, Ansar, Nasrulla, Bushra, & Imam, 2015). This correlation held, even when gender and socio-demographic variables were added to the mix.
The close tie between mental health and happiness is reason enough to make happiness an important priority for parents, educators, researchers, and medical professionals alike, along with the simple fact that we all like to feel happy!

17 Exercises To Increase Happiness and Wellbeing
Add these 17 Happiness & Subjective Well-Being Exercises [PDF] to your toolkit and help others experience greater purpose, meaning, and positive emotions.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
If you’re interested in learning more about happiness from a scientific perspective, there are a few videos you might want to check out, including:
Positive Psychology: The Science of Happiness by Professor Tal Ben-Shahar from WGBH Forum.
Shawn Achor – The Happiness Advantage: Linking Positive Brains to Performance TEDTalk from TEDx Talks
Positive Psychology – Happier by Professor Tal Ben-Shahar, Ph.D. from FightMediocrity
How to be Happy – The Science of Happiness and Feeling Positive in Life from Memorize Academy
The Surprising Science of Happiness TED Talk by Dan Gilbert from TED
How to Be Happy – The Secret of Authentic Happiness – Martin Seligman from Practical Psychology
I hope this piece was helpful and informative for you, and that you learned something new about the scientific study of happiness. It’s a fascinating area of research, and new findings are coming out all the time. Make sure you stay up to date on the happiness literature , as the findings can be of great use in helping you to live your best life!
What are your thoughts on happiness? Would you define it differently? What do you find is the most important ingredient for your own happiness? Let us know in the comments section below!
Thanks for reading, I hope you are all finding happiness in all your life journeys.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Happiness Exercises for free .
- AIPC. (2011). Happiness and positive psychology. Australian Institute of Professional Counsellors Article Library . Retrieved from https://www.aipc.net.au/articles/happiness-and-positive-psychology/
- Baumeister, R., Vohs, K. D., Aaker, J. L., & Gabinsky, E. N. (2013). Some key differences between a happy life and a meaningful life. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 8 , 505-516.
- Joseph Sirgy, M., & Wu, J. (2009). The pleasant life, the engaged life, and the meaningful life: What about the balanced life? Journal of Happiness Studies, 10 , 183-196.
- Kaufman, S. B. (2016). The differences between happiness and meaning in life. Scientific American . Retrieved from https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/beautiful-minds/the-differences-between-happiness-and-meaning-in-life/
- Kim-Prieto, C., Diener, E., Tamir, M., Scollon, C. N., & Diener, M. (2005). Integrating the diverse definitions of happiness: A time-sequential framework of subjective well-being. Journal of Happiness Studies, 6 , 261-300.
- Lyubomirsky, S. (2001). Why are some people happier than others? The role of cognitive and motivational processes in well-being. American Psychologist, 56(3) , 239.
- McMahon, D. (2006). Happiness: A history . Grove Press.
- Online Etymology Dictionary (n.d.). Happy . Retrieved from http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/behaviorism/
- Paul, M. (2015). The difference between happiness and pleasure. Huffington Post: Life . Retrieved from https://www.huffpost.com/entry/the-difference-between-happiness-and-pleasure_b_7053946
- Seligman, M. E. (2002). Authentic happiness: Using the new positive psychology to realize your potential for lasting fulfillment . Simon and Schuster.
- Seligman, M. E., Steen, T. A., Park, N., & Peterson, C. (2005). Positive psychology progress: empirical validation of interventions. American Psychologist, 60(5) , 410.
- Shafiq, S., Naz, R. A., Ansar, M., Nasrulla, T., Bushra, M., & Imam, S. (2015). Happiness as related to mental health among university students. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 5 , 124-132.
- Silny, J. (n.d.). What’s so great about happiness, anyway? (The answer: plenty!). Happify Daily . Retrieved from https://www.happify.com/hd/whats-so-great-about-happiness/
- Waldinger, R. J., & Schulz, M. S. (2010). What’s love got to do with it?: Social functioning, perceived health, and daily happiness in married octogenarians. Psychology and Aging, 25 , 422-431.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
His article was extremely helpful and enabled me to grasp the concept of the confusing question of what it means to be happy and the general meaning of happiness. I’m so glad I found this article to be honest.
I disagree with your comment that ‘Happiness is not a state but a trait.’ I see happiness as a purely internal construct. I choose to be happy regardless of the people or things going on around me. Those people who look for happiness in others, outside of themselves, bounce back and forth between some fleeting form of happiness and unhappiness. If they would instead see happiness as an internal construct, man vs himself, they wouldn’t be dependent on someone else for their personal feelings of happiness. Because really, you don’t have the power to change others… But you do have all the power you need to change how you choose to see and react to what’s around you. The ball of your happiness is 100% in your court.
The article was very helpful and informative
Just finished your article on happiness, or SWB and meaning . As stated in your article, happiness is fleeting and subject to feel good material goods and personal objectives. Having sex, kids, buying a new car, an opioid response. However, I thought life was supposed to have meaning that would contribute to my happiness. I chose a career based on what I thought I could contribute to my own and others lives. Rather naïve on my behalf and futile at this stage. I’m 72 years old and understand less now about the world as it is than ever before. I’ve seen the horrors of war and have moved forward from those days to marrying, having a family and building a career, the dopamine response, however I’ve lost the meaning of life and find myself unhappy, angry, reclusive and frustrated. I have done drugs, tried meditation and read books searching for meaning and happiness, which has been elusive at times. Your article helped put certain expectations of others and myself in perspective and what I need to do to achieve happiness and meaning. Thank you!
Thanks for this article. Nowadays, i do gratitude exercice in the morning, midday and before sleep. It’s help me stay more in positive thoughts. I like soo much.
I write: I am grateful for … ( 10x )
Thank you so much for this very insightful article. It really taught me a lot.
Thank you very much for the article. I think it will help me a lot. It has given me clear ideas of how I can try and attain some degree of happiness, and hence greater contentment. Happiness is important in individuals – I believe it is a key to tolerance and a stable society.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Embracing JOMO: Finding Joy in Missing Out
We’ve probably all heard of FOMO, or ‘the fear of missing out’. FOMO is the currency of social media platforms, eager to encourage us to [...]

The True Meaning of Hedonism: A Philosophical Perspective
“If it feels good, do it, you only live once”. Hedonists are always up for a good time and believe the pursuit of pleasure and [...]

Happiness Economics: Can Money Buy Happiness?
Do you ever daydream about winning the lottery? After all, it only costs a small amount, a slight risk, with the possibility of a substantial [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (50)
- Coaching & Application (57)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (45)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (29)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (18)
- Positive Parenting (4)
- Positive Psychology (33)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (17)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (38)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
3 Happiness Exercises Pack [PDF]
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is Happiness?
Defining Happiness, and How to Become Happier
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
Verywell/ Jiaqi Zhou
How to Cultivate Happiness
How to be a happier person.
Happiness is something that people seek to find, yet what defines happiness can vary from one person to the next. Typically, happiness is an emotional state characterized by feelings of joy, satisfaction, contentment, and fulfillment. While happiness has many different definitions, it is often described as involving positive emotions and life satisfaction.
When most people talk about the true meaning of happiness, they might be talking about how they feel in the present moment or referring to a more general sense of how they feel about life overall.
Because happiness tends to be such a broadly defined term, psychologists and other social scientists typically use the term ' subjective well-being ' when they talk about this emotional state. Just as it sounds, subjective well-being tends to focus on an individual's overall personal feelings about their life in the present.
Two key components of happiness (or subjective well-being) are:
- The balance of emotions: Everyone experiences both positive and negative emotions, feelings, and moods. Happiness is generally linked to experiencing more positive feelings than negative ones.
- Life satisfaction: This relates to how satisfied you feel with different areas of your life including your relationships, work, achievements, and other things that you consider important.
Another definition of happiness comes from the ancient philosopher Aristotle, who suggested that happiness is the one human desire, and all other human desires exist as a way to obtain happiness. He believed that there were four levels of happiness: happiness from immediate gratification, from comparison and achievement, from making positive contributions, and from achieving fulfillment.
Happiness, Aristotle suggested, could be achieved through the golden mean, which involves finding a balance between deficiency and excess.
Signs of Happiness
While perceptions of happiness may be different from one person to the next, there are some key signs that psychologists look for when measuring and assessing happiness.
Some key signs of happiness include:
- Feeling like you are living the life you wanted
- Going with the flow and a willingness to take life as it comes
- Feeling that the conditions of your life are good
- Enjoying positive, healthy relationships with other people
- Feeling that you have accomplished (or will accomplish) what you want in life
- Feeling satisfied with your life
- Feeling positive more than negative
- Being open to new ideas and experiences
- Practicing self-care and treating yourself with kindness and compassion
- Experiencing gratitude
- Feeling that you are living life with a sense of meaning and purpose
- Wanting to share your happiness and joy with others
One important thing to remember is that happiness isn't a state of constant euphoria . Instead, happiness is an overall sense of experiencing more positive emotions than negative ones.
Happy people still feel the whole range of human emotions—anger, frustrastion, boredom, loneliness, and even sadness—from time to time. But even when faced with discomfort, they have an underlying sense of optimism that things will get better, that they can deal with what is happening, and that they will be able to feel happy again.
Types of Happiness
There are many different ways of thinking about happiness. For example, the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle made a distinction between two different kinds of happiness: hedonia and eudaimonia.
- Hedonia: Hedonic happiness is derived from pleasure. It is most often associated with doing what feels good, self-care, fulfilling desires, experiencing enjoyment, and feeling a sense of satisfaction.
- Eudaimonia: This type of happiness is derived from seeking virtue and meaning. Important components of eudaimonic well-being including feeling that your life has meaning, value, and purpose. It is associated more with fulfilling responsibilities, investing in long-term goals, concern for the welfare of other people, and living up to personal ideals.
Hedonia and eudemonia are more commonly known today in psychology as pleasure and meaning, respectively. More recently, psychologists have suggested the addition of the third component that relates to engagement . These are feelings of commitment and participation in different areas of life.
Research suggests that happy people tend to rank pretty high on eudaimonic life satisfaction and better than average on their hedonic life satisfaction.
All of these can play an important role in the overall experience of happiness, although the relative value of each can be highly subjective. Some activities may be both pleasurable and meaningful, while others might skew more one way or the other.
For example, volunteering for a cause you believe in might be more meaningful than pleasurable. Watching your favorite tv show, on the other hand, might rank lower in meaning and higher on pleasure.
Some types of happiness that may fall under these three main categories include:
- Joy: A often relatively brief feeling that is felt in the present moment
- Excitement: A happy feeling that involves looking forward to something with positive anticipation
- Gratitude: A positive emotion that involves being thankful and appreciative
- Pride: A feeling of satisfaction in something that you have accomplished
- Optimism: This is a way of looking at life with a positive, upbeat outlook
- Contentment: This type of happiness involves a sense of satisfaction
While some people just tend to be naturally happier, there are things that you can do to cultivate your sense of happiness.
Pursue Intrinsic Goals
Achieving goals that you are intrinsically motivated to pursue, particularly ones that are focused on personal growth and community, can help boost happiness. Research suggests that pursuing these types of intrinsically-motivated goals can increase happiness more than pursuing extrinsic goals like gaining money or status.
Enjoy the Moment
Studies have found that people tend to over earn—they become so focused on accumulating things that they lose track of actually enjoying what they are doing.
So, rather than falling into the trap of mindlessly accumulating to the detriment of your own happiness, focus on practicing gratitude for the things you have and enjoying the process as you go.
Reframe Negative Thoughts
When you find yourself stuck in a pessimistic outlook or experiencing negativity, look for ways that you can reframe your thoughts in a more positive way.
People have a natural negativity bias , or a tendency to pay more attention to bad things than to good things. This can have an impact on everything from how you make decisions to how you form impressions of other people. Discounting the positive—a cognitive distortion where people focus on the negative and ignore the positive—can also contribute to negative thoughts.
Reframing these negative perceptions isn't about ignoring the bad. Instead, it means trying to take a more balanced, realistic look at events. It allows you to notice patterns in your thinking and then challenge negative thoughts.
Impact of Happiness
Why is happiness so important? Happiness has been shown to predict positive outcomes in many different areas of life including mental well-being, physical health, and overall longevity.
- Positive emotions increase satisfaction with life.
- Happiness helps people build stronger coping skills and emotional resources.
- Positive emotions are linked to better health and longevity. One study found that people who experienced more positive emotions than negative ones were more likely to have survived over a 13 year period.
- Positive feelings increase resilience. Resilience helps people better manage stress and bounce back better when faced with setbacks. For example, one study found that happier people tend to have lower levels of the stress hormone cortisol and that these benefits tend to persist over time.
- People who report having a positive state of well-being are more likely to engage in healthy behaviors such as eating fruits and vegetables and engaging in regular physical exercise.
- Being happy may make help you get sick less often. Happier mental states are linked to increased immunity.
Some people seem to have a naturally higher baseline for happiness—one large-scale study of more than 2,000 twins suggested that around 50% of overall life satisfaction was due to genetics, 10% to external events, and 40% to individual activities.
So while you might not be able to control what your “base level” of happiness is, there are things that you can do to make your life happier and more fulfilling. Even the happiest of individuals can feel down from time to time and happiness is something that all people need to consciously pursue.
Cultivate Strong Relationships
Social support is an essential part of well-being. Research has found that good social relationships are the strongest predictor of happiness. Having positive and supportive connections with people you care about can provide a buffer against stress, improve your health, and help you become a happier person.
In the Harvard Study of Adult Development, a longitudinal study that looked at participants over 80 years, researchers found that relationships and how happy people are in those relationships strongly impacted overall health.
So if you are trying to improve your happiness, cultivating solid social connections is a great place to start. Consider deepening your existing relationships and explore ways to make new friends.
Get Regular Exercise
Exercise is good for both your body and mind. Physical activity is linked to a range of physical and psychological benefits including improved mood. Numerous studies have shown that regular exercise may play a role in warding off symptoms of depression, but evidence also suggests that it may also help make people happier, too.
In one analysis of past research on the connection between physical activity and happiness, researchers found a consistent positive link.
Even a little bit of exercise produces a happiness boost—people who were physically active for as little as 10 minutes a day or who worked out only once a week had higher levels of happiness than people who never exercised.
Show Gratitude
In one study, participants were asked to engage in a writing exercise for 10 to 20 minutes each night before bed. Some were instructed to write about daily hassles, some about neutral events, and some about things they were grateful for. The results found that people who had written about gratitude had increase positive emotions, increased subjective happiness, and improve life satisfaction.
As the authors of the study suggest, keeping a gratitude list is a relatively easy, affordable, simple, and pleasant way to boost your mood. Try setting aside a few minutes each night to write down or think about things in your life that you are grateful for.
Find a Sense of Purpose
Research has found that people who feel like they have a purpose have better well-being and feel more fulfilled. A sense of purpose involves seeing your life as having goals, direction, and meaning. It may help improve happiness by promoting healthier behaviors.
Some things you can do to help find a sense of purpose include:
- Explore your interests and passions
- Engage in prosocial and altruistic causes
- Work to address injustices
- Look for new things you might want to learn more about
This sense of purpose is influenced by a variety of factors, but it is also something that you can cultivate. It involves finding a goal that you care deeply about that will lead you to engage in productive, positive actions in order to work toward that goal.
Press Play for Advice On Reaching Your Dreams
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast , featuring best-selling author Dave Hollis, shares how to create your best life. Click below to listen now.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
Challenges of Finding Happiness
While seeking happiness is important, there are times when the pursuit of life satisfaction falls short. Some challenges to watch for include:
Valuing the Wrong Things
Money may not be able to buy happiness, but there is research that spending money on things like experiences can make you happier than spending it on material possessions.
One study, for example, found that spending money on things that buy time—such as spending money on time-saving services—can increase happiness and life satisfaction.
Rather than overvaluing things such as money, status, or material possessions, pursuing goals that result in more free time or enjoyable experiences may have a higher happiness reward.
Not Seeking Social Support
Social support means having friends and loved ones that you can turn to for support. Research has found that perceived social support plays an important role in subjective well-being. For example, one study found that perceptions of social support were responsible for 43% of a person's level of happiness.
It is important to remember that when it comes to social support, quality is more important than quantity. Having just a few very close and trusted friends will have a greater impact on your overall happiness than having many casual acquaintances.
Thinking of Happiness as an Endpoint
Happiness isn’t a goal that you can simply reach and be done with. It is a constant pursuit that requires continual nurturing and sustenance.
One study found that people who tend to value happiness most also tended to feel the least satisfied with their lives. Essentially, happiness becomes such a lofty goal that it becomes virtually unattainable.
“Valuing happiness could be self-defeating because the more people value happiness, the more likely they will feel disappointed,” suggest the authors of the study.
Perhaps the lesson is to not make something as broadly defined as “happiness” your goal. Instead, focus on building and cultivating the sort of life and relationships that bring fulfillment and satisfaction to your life.
It is also important to consider how you personally define happiness. Happiness is a broad term that means different things to different people. Rather than looking at happiness as an endpoint, it can be more helpful to think about what happiness really means to you and then work on small things that will help you become happier. This can make achieving these goals more manageable and less overwhelming.
History of Happiness
Happiness has long been recognized as a critical part of health and well-being. The "pursuit of happiness" is even given as an inalienable right in the U.S. Declaration of Independence. Our understanding of what will bring happiness, however, has shifted over time.
Psychologists have also proposed a number of different theories to explain how people experience and pursue happiness. These theories include:
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
The hierarchy of needs suggests that people are motivated to pursue increasingly complex needs. Once more basic needs are fulfilled, people are then motivated by more psychological and emotional needs.
At the peak of the hierarchy is the need for self-actualization, or the need to achieve one's full potential. The theory also stresses the importance of peak experiences or transcendent moments in which a person feels deep understanding, happiness, and joy.
Positive Psychology
The pursuit of happiness is central to the field of positive psychology . Psychologists who study positive psychology are interested in learning ways to increase positivity and helping people live happier, more satisfying lives.
Rather than focusing on mental pathologies, the field instead strives to find ways to help people, communities, and societies improve positive emotions and achieve greater happiness.
Finley K, Axner M, Vrooman K, Tse D. Ideal levels of prosocial involvement in relation to momentary affect and eudaimonia: Exploring the golden mean . Innov Aging . 2020;4(Suppl 1):614. doi:10.1093/geroni/igaa057.2083
Kringelbach ML, Berridge KC. The neuroscience of happiness and pleasure . Soc Res (New York) . 2010;77(2):659-678.
Panel on Measuring Subjective Well-Being in a Policy-Relevant Framework; Committee on National Statistics; Division on Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education; National Research Council; Stone AA, Mackie C, editors. Subjective Well-Being: Measuring Happiness, Suffering, and Other Dimensions of Experience [Internet]. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US).
Lee MA, Kawachi I. The keys to happiness: Associations between personal values regarding core life domains and happiness in South Korea . PLoS One . 2019;14(1):e0209821. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0209821
Hsee CK, Zhang J, Cai CF, Zhang S. Overearning . Psychol Sci . 2013;24(6):852-9
Carstensen LL, Turan B, Scheibe S, et al. Emotional experience improves with age: evidence based on over 10 years of experience sampling . Psychol Aging . 2011;26(1):21‐33. doi:10.1037/a0021285
Steptoe A, Wardle J. Positive affect and biological function in everyday life . Neurobiol Aging . 2005;26 Suppl 1:108‐112. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.08.016
Sapranaviciute-Zabazlajeva L, Luksiene D, Virviciute D, Bobak M, Tamosiunas A. L ink between healthy lifestyle and psychological well-being in Lithuanian adults aged 45-72: a cross-sectional study . BMJ Open . 2017;7(4):e014240. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014240
Costanzo ES, Lutgendorf SK, Kohut ML, et al. Mood and cytokine response to influenza virus in older adults . J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci . 2004;59(12):1328‐1333. doi:10.1093/gerona/59.12.1328
Lyubomirsky S, Sheldon KM, Schkade D. Pursuing happiness: The architecture of sustainable change . Review of General Psychology. 2005;9 (2):111–131. doi:0.1037/1089-2680.9.2.111
The Harvard Gazette. Good genes are nice, but joy is better .
Zhang Z, Chen W. A systematic review of the relationship between physical activity and happiness . J Happiness Stud 20, 1305–1322 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-018-9976-0
Cunha LF, Pellanda LC, Reppold CT. Positive psychology and gratitude interventions: a randomized clinical trial . Front Psychol . 2019;10:584. Published 2019 Mar 21. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00584
Ryff CD. Psychological well-being revisited: advances in the science and practice of eudaimonia . Psychother Psychosom . 2014;83(1):10‐28. doi:10.1159/000353263
Whillans AV, Dunn EW, Smeets P, Bekkers R, Norton MI. Buying time promotes happiness . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2017;114(32):8523‐8527. doi:10.1073/pnas.1706541114
Gulacti F. The effect of perceived social support on subjective well-being . Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences . 2010;2(2):3844-3849. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.03.602
Mauss IB, Tamir M, Anderson CL, Savino NS. Can seeking happiness make people unhappy? [corrected] Paradoxical effects of valuing happiness [published correction appears in Emotion. 2011 Aug;11(4):767]. Emotion . 2011;11(4):807‐815. doi:10.1037/a0022010
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
Mind & Body Articles & More
Six ways happiness is good for your health, need some extra motivation to get happier check out the ways that well-being has been linked to good health..
Over the past decade, an entire industry has sprouted up promising the secrets to happiness. There are best-selling books like The Happiness Project and The How of Happiness , and happiness programs like Happify and Tal-Ben Shahar’s Wholebeing Institute .
Here at the Greater Good Science Center, we offer an online course on “The Science of Happiness” and boast a collection of research-based happiness practices on our new website, Greater Good in Action .
But all of these books and classes raise the question: Why bother? Many of us might prefer to focus on boosting our productivity and success rather than our positive emotions. Or perhaps we’ve tried to get happier but always seem to get leveled by setbacks. Why keep trying?

Recently, a critical mass of research has provided what might be the most basic and irrefutable argument in favor of happiness: Happiness and good health go hand-in-hand. Indeed, scientific studies have been finding that happiness can make our hearts healthier, our immune systems stronger, and our lives longer.
Several of the studies cited below suggest that happiness causes better health; others suggest only that the two are correlated—perhaps good health causes happiness but not the other way around. Happiness and health may indeed be a virtuous circle, but researchers are still trying to untangle their relationship. In the meantime, if you need some extra motivation to get happier , check out these six ways that happiness has been linked to good health.
1. Happiness protects your heart
Love and happiness may not actually originate in the heart, but they are good for it. For example, a 2005 paper found that happiness predicts lower heart rate and blood pressure. In the study, participants rated their happiness over 30 times in one day and then again three years later. The initially happiest participants had a lower heart rate on follow-up (about six beats slower per minute), and the happiest participants during the follow-up had better blood pressure.
Research has also uncovered a link between happiness and another measure of heart health: heart rate variability, which refers to the time interval between heartbeats and is associated with risk for various diseases. In a 2008 study , researchers monitored 76 patients suspected to have coronary artery disease. Was happiness linked to healthier hearts even among people who might have heart problems? It seemed so: The participants who rated themselves as happiest on the day their hearts were tested had a healthier pattern of heart rate variability on that day.
Over time, these effects can add up to serious differences in heart health. In a 2010 study , researchers invited nearly 2,000 Canadians into the lab to talk about their anger and stress at work. Observers rated them on a scale of one to five for the extent to which they expressed positive emotions like joy, happiness, excitement, enthusiasm, and contentment. Ten years later, the researchers checked in with the participants to see how they were doing—and it turned out that the happier ones were less likely to have developed coronary heart disease. In fact, for each one-point increase in positive emotions they had expressed, their heart disease risk was 22 percent lower.
2. Happiness strengthens your immune system
Do you know a grumpy person who always seems to be getting sick? That may be no coincidence: Research is now finding a link between happiness and a stronger immune system.
In a 2003 experiment , 350 adults volunteered to get exposed to the common cold (don’t worry, they were well-compensated). Before exposure, researchers called them six times in two weeks and asked how much they had experienced nine positive emotions—such as feeling energetic, pleased, and calm—that day. After five days in quarantine, the participants with the most positive emotions were less likely to have developed a cold.
Some of the same researchers wanted to investigate why happier people might be less susceptible to sickness, so in a 2006 study they gave 81 graduate students the hepatitis B vaccine. After receiving the first two doses, participants rated themselves on those same nine positive emotions. The ones who were high in positive emotion were nearly twice as likely to have a high antibody response to the vaccine—a sign of a robust immune system. Instead of merely affecting symptoms, happiness seemed to be literally working on a cellular level.
A much earlier experiment found that immune system activity in the same individual goes up and down depending on their happiness. For two months, 30 male dental students took pills containing a harmless blood protein from rabbits, which causes an immune response in humans. They also rated whether they had experienced various positive moods that day. On days when they were happier, participants had a better immune response, as measured by the presence of an antibody in their saliva that defends against foreign substances.
3. Happiness combats stress
Stress is not only upsetting on a psychological level but also triggers biological changes in our hormones and blood pressure. Happiness seems to temper these effects, or at least help us recover more quickly.
In the study mentioned above, where participants rated their happiness more than 30 times in a day, researchers also found associations between happiness and stress. The happiest participants had 23 percent lower levels of the stress hormone cortisol than the least happy, and another indicator of stress—the level of a blood-clotting protein that increases after stress—was 12 times lower.
Happiness also seems to carry benefits even when stress is inevitable. In a 2009 study , some diabolically cruel researchers decided to stress out psychology students and see how they reacted. The students were led to a soundproof chamber, where they first answered questions indicating whether they generally felt 10 feelings like enthusiasm or pride. Then came their worst nightmare: They had to answer an exceedingly difficult statistics question while being videotaped, and they were told that their professor would evaluate their response. Throughout the process, their heart was measured with an electrocardiogram (EKG) machine and a blood pressure monitor. In the wake of such stress, the hearts of the happiest students recovered most quickly.
4. Happy people have fewer aches and pains
Unhappiness can be painful—literally.
A 2001 study asked participants to rate their recent experience of positive emotions, then (five weeks later) how much they had experienced negative symptoms like muscle strain, dizziness, and heartburn since the study began. People who reported the highest levels of positive emotion at the beginning actually became healthier over the course of the study, and ended up healthier than their unhappy counterparts. The fact that their health improved over five weeks (and the health of the unhappiest participants declined) suggests that the results aren’t merely evidence of people in a good mood giving rosier ratings of their health than people in a bad mood.
A 2005 study suggests that positive emotion also mitigates pain in the context of disease. Women with arthritis and chronic pain rated themselves weekly on positive emotions like interest, enthusiasm, and inspiration for about three months. Over the course of the study, those with higher ratings overall were less likely to experience increases in pain.
5. Happiness combats disease and disability
Happiness is associated with improvements in more severe, long-term conditions as well, not just shorter-term aches and pains.
In a 2008 study of nearly 10,000 Australians, participants who reported being happy and satisfied with life most or all of the time were about 1.5 times less likely to have long-term health conditions (like chronic pain and serious vision problems) two years later. Another study in the same year found that women with breast cancer recalled being less happy and optimistic before their diagnosis than women without breast cancer, suggesting that happiness and optimism may be protective against the disease.
As adults become elderly, another condition that often afflicts them is frailty, which is characterized by impaired strength, endurance, and balance and puts them at risk of disability and death. In a 2004 study, over 1,550 Mexican Americans ages 65 and older rated how much self-esteem, hope, happiness, and enjoyment they felt over the past week. After seven years, the participants with more positive emotion ratings were less likely to be frail. Some of the same researchers also found that happier elderly people (by the same measure of positive emotion) were less likely to have a stroke in the subsequent six years; this was particularly true for men.
6. Happiness lengthens our lives
In the end, the ultimate health indicator might be longevity—and here, especially, happiness comes into play. In perhaps the most famous study of happiness and longevity, the life expectancy of Catholic nuns was linked to the amount of positive emotion they expressed in an autobiographical essay they wrote upon entering their convent decades earlier, typically in their 20s. Researchers combed through these writing samples for expressions of feelings like amusement, contentment, gratitude, and love. In the end, the happiest-seeming nuns lived a whopping 7-10 years longer than the least happy.
You don’t have to be a nun to experience the life-extending benefits of happiness, though. In a 2011 study , almost 4,000 English adults ages 52-79 reported how happy, excited, and content they were multiple times in a single day. Here, happier people were 35 percent less likely to die over the course of about five years than their unhappier counterparts.
These two studies both measured specific positive emotions, but overall satisfaction with one’s life—another major indicator of happiness—is also linked to longevity. A 2010 study followed almost 7,000 people from California’s Alameda County for nearly three decades, finding that the people who were more satisfied with life at the beginning were less likely to die during the course of the study.
While happiness can lengthen our lives, it can’t perform miracles. There’s some evidence that the link between happiness and longevity doesn’t extend to the ill —or at least not to the very ill.
A 2005 meta-analysis , aggregating the results of other studies on health and happiness, speculates that experiencing positive emotion is helpful in diseases with a long timeline but could actually be harmful in late-stage disease. The authors cite studies showing that positive emotion lowers the risk of death in people with diabetes and AIDS , but actually increases the risk in people with metastatic breast cancer , early-stage melanoma , and end-stage kidney disease . That increased risk might be due to the fact that happier people underreport their symptoms and don’t get the right treatment, or take worse care of themselves because they are overly optimistic.
More on Happiness
Explore the relationship between meaning & happiness
Discover the secret to a happy life .
Read Rick Hanson's "How to Trick Your Brain for Happiness."
Listen to Sonja Lyubomirsky on the myths of happiness .
Discover a better way to pursue happiness .
As the science of happiness and health matures, researchers are trying to determine what role, if any, happiness actually plays in causing health benefits. They’re also trying to distinguish the effects of different forms of happiness (including positive emotions and life satisfaction), the effects of “extreme” happiness, and other factors. For example, a new study suggests that we should look not just at life satisfaction levels but life satisfaction variability : Researchers found that low life satisfaction with lots of fluctuations—i.e., an unstable level of happiness—was linked to even earlier death than low life satisfaction alone.
All that said, the study of the health benefits of happiness is still young. It will take time to figure out the exact mechanisms by which happiness influences health, and how factors like social relationships and exercise fit in. But in the meantime, it seems safe to imagine that a happier you will be healthier, too.
About the Author
Kira M. Newman
Kira M. Newman is the managing editor of Greater Good . Her work has been published in outlets including the Washington Post , Mindful magazine, Social Media Monthly , and Tech.co, and she is the co-editor of The Gratitude Project . Follow her on Twitter!
You May Also Enjoy

This article — and everything on this site — is funded by readers like you.
Become a subscribing member today. Help us continue to bring “the science of a meaningful life” to you and to millions around the globe.
You are here: Home » Blog » Happiness
Why Is Happiness So Important? (For You & For The Greater Good)
Reviewed and fact-checked
We are committed to the highest standards of accuracy and reliability in our content. Every statement made on our website is meticulously fact-checked and supported by authoritative studies.
Read more about our processes here .
Updated on August 5, 2023
When you ask someone what they find most important in life, chances are that happiness is a part of their answer. Happiness is deemed one of the most important things in the world. In fact, this entire website is about happiness. But why is happiness so important exactly?
This question is a bit harder to answer, mostly because happiness is something subjective. However, there are plenty of evidence-based reasons that explain the importance of happiness. So even when you feel that happiness is the most important thing in your life, here are some actual reasons that back this up.
This article will answer many questions, like why happiness is more important than money and why more happiness will result in a more sustainable planet. At the end of this article, you’ll be able to explain the importance of happiness to somebody else!
The importance of happiness
Greater life satisfaction is linked to a healthier and longer life, happy people are more productive and likely to succeed, our current situation as a species, the current driver of our decision-making process, 1. happiness is correlated to sustainable actions, 2. focusing on happiness comes with many indirect benefits, 3. happiness is correlated to fewer conflicts, can focusing on happiness close the gap between the poor and the rich, closing words.
When discussing the importance of happiness, it’s critical to understand the difference between the personal importance and the greater importance of happiness.
For example, I find my own happiness important, because… well. Because I am a better person when I’m happy. I find my life more enjoyable when I’m in a good mood, so my happiness is important to me!
But there are also reasons why your happiness is important for the greater good. Whether it’s the society, your surroundings or the future of this planet: your happiness makes a difference.
Personal importance of happiness
It’s easy to understand why happiness is so important on a personal level. We all want to be happy, because happiness is a part of everyone’s actions. Whether it’s the goals you’re working towards, the people you socialize with, or the hobbies you engage in: it’s highly likely that you’re looking for happiness.
There is plenty of evidence-based research to back this up:
There are already plenty of studies and articles out there that support the correlation between happiness and living longer and more healtily. Happy people tend to live longer and healthier lives. If you don’t believe this, here’s some compelling studies:
- Happiness improves your cardiac health .
- Happy people are more likely to eat healthily and be more physically active .
- Unhappy people are more likely to catch a cold (sounds annoying, right?)
- Being happy helps reduce your stress levels .
- More positive and happy people are less likely to die (although the true nature of this observation is not yet fully understood).
Want more proof? If you Google the words “happiness vs health study”, Google will give you over 300 million results.
I’d say this goes a long way to explain the importance of happiness. But there’s more.
Philosopher and Nobel Prize winner Albert Schweitzer once said:
“Success is not the key to happiness; happiness is the key to success.” Albert Schweitzer
Is there any truth to this quote?
Yes, there is. For example, this study found that employee happiness is correlated to employee productivity and performance.
In fact, this interesting page breaks down whether or not happy people are really “worth more” than unhappy people. The page continues with some interesting observations about whether or not policymakers should focus more on the happiness of people.
This brings me to the more interesting question: what makes happiness so important for the greater good?
Sure, it’s clear that personal happiness is something we should all personally pursue. But what about the impact of personal happiness on society as a whole?
What makes happiness so important for the greater good
Happiness may be much more important for the greater good than you think.
This is something that I’ve been thinking of a lot lately. The impact of personal happiness on our society as a whole is something that – I feel – should be a much bigger topic these days.
In order to properly explain where I’m coming from, I need to zoom out a little.
If I told you that the human race is currently on a pathway to self-destruction, would you believe me?
I’m not saying that I’m convinced of some kind of doomsday scenario, but there are plenty of people who believe so. And when you look at the numbers, it’s a compelling case:
- Animal extinction rate is at an all-time high .
- Global warming is becoming more and more of a crisis. (Some people even believe that we’re past the point of no return ).
- Income inequality and the division between the rich and the poor seems to be only growing .
- The amount of children that are growing up in conflict areas is growing .
Do I need to go on?
Whether or not we as the human species are destroying this planet is not the topic of this article. However, it’s important to realize that there are simply a lot of worrisome things happening in the world right now.
And what’s the root-cause of these things?
If you ask me, it’s capitalism.
Google’s current definition of capitalism is:
“an economic and political system in which a country’s trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit.”
The decisions we make are generally controlled by our desire to profit. Whether it’s the policies created by our governments, or the execution of projects by the companies we work for: our decision-making process is controlled by economic profit. Whatever option generates the most monetary profit, that’s the option that’s most likely going to be chosen.
Capitalism demands efficiency, in order to increase profits and stay ahead of the pack. This demand for efficiency often comes at the cost of sustainability and global happiness levels.
Nonetheless, this type of decision-making has led to great things:
- It’s made us more connected. We can book a plane ticket and land on the other side of the world 30 hours later.
- About half of the global population carries a device that acts as a calculator, GPS, multimedia player, browser, alarm, browser and cellphone.
- Humans are so far developed, that we now have a human-made object over 22.8 billion kilometers in space from where we are now .
These are all fantastic achievements, that we may not have reached by now if we hadn’t used economic profit as the main driver for our decisions.
But then again, if you look at our current situation (remember the previous bullet list of negatives?), we may want to reconsider our approach for the future.
Examples of what makes happiness important for the greater good
Here’s one of my favorite quotes, ironically from someone who’s famous for helping business leaders generate more profits.
What got you here won’t get you there.
Capitalism may have gotten us to be the most advanced species to have ever lived (who knows?)
But will this same approach lead to a long, happy and sustainable life?
One of the best documentaries I’ve watched last year is “A Life On Our Planet” by David Attenborough . This documentary explores the current problems we have on our planet and provides interesting ways that can help us deal with these problems.
Interestingly enough, it’s clear that capitalism is not the answer.
In fact, I would go as far as to say that happiness is the answer. Even if you don’t agree, it’s still interesting to explore the concept of happiness as a driver for decision-making. What if companies and governments used happiness as the driver for their decisions, instead of profit? Would the world be a better place?
I think the answer is clear:
A 2012 article by Victor Corral-Verdugo, fittingly entitled The Positive Psychology of Sustainability , argues that the main values of sustainable behavior and positive psychology are quite similar. For example, both stress the importance of altruism and humanity, equity and fairness, responsibility, future orientation, and intrinsic motivation to name a few.
Based on previous research, Corral-Verdugo outlines some positive variables that cause people to engage in sustainable behavior.
One of these factors is happiness. It states that happiness is related to decreased consumption of resources and pro-ecological behaviors.
This is an interesting observation because it implies that happiness may help fix the climate issues that we’re facing. If happier people are more likely to act in a sustainable way, then it’s easy to see how more happiness results in more sustainable choices by governments and big corporations.
There are some admirable examples of companies that clearly demonstrate how to focus on employer happiness instead of corporate profit.
One that comes to mind is Zapier, a software company that made headlines by offering every employee a $10.000 relocation fund if they decided to move away from San Fransisco . Logically, this move didn’t improve their profit margins, and it was done as an experiment to help their employees relocate to places where the cost of living was lower.
Another interesting example is the CEO of Twitter, Jack Dorsey, who donated a huge chunk of his wealth ( roughly 28% ) to fund the development of a COVID-19 vaccine. You could argue that this $1 billion donation was a brilliant marketing move. But then again, it is one of the biggest donations when looking at the relative size of the donation to the net worth of the donator.
I’m personally much less impressed by Jeff Bezos’ cumulative $2.1 billion donations since they’re only 1.9% of his net worth .
These examples all share a commonality: the decisions were not based on maximum profit, but rather the happiness of the people.
Are these people worse-off as a result of their decisions?
Jack Dorsey is still one of the most wealthy people alive, but his donation helped fund the vaccine that will hopefully propel us out of this pandemic. Zapier could have made more profit if they hadn’t offered their employees the extravagant relocation bonus, but they didn’t. They are still a profitable company, but their decision also increased the happiness of their employees and increased their ability to hire smart and talented people.
In a world where everything is centered around profitability, it’s interesting to see how focusing on happiness can lead to indirect consequences that will end up benefitting profitability as well.
Before I go on, I want to acknowledge that this topic is highly controversial. Therefore, I’ve tried to use only factual sources here.
Based on yearly polls of happiness, Africa is often recognized as the unhappiest continent . Africa is also the continent with the most conflicts .
It’s easy to understand how conflict can negatively impact the happiness of the people involved.
Does that mean that Africa would be free of conflict if everyone magically woke up happy one day? No, because the continent is plagued by other – more severe – issues, like inequality, corruption, poverty, a horrible history of colonization, poor infrastructure and more.
But that’s not to say that more happiness would not lead to improvements. In fact, there is a strong case to be made that if governments would focus more on the happiness of others, the issues that are plaguing the content would be somewhat reduced. This well-written page explains it much better than I could .
An interesting, yet somewhat anecdotal, example that supports this idea is the country Costa Rica. This relatively small country manages to score high on the World Happiness Report every year , despite having one of the lowest GDPs. Even though there are multiple reasons for this relatively high score, it’s interesting to know that Costa Rica does not have a standing army.
Where the United States spend an incredible $732 billion per year on their military , Costa Rica spends next to nothing in comparison.
As a result, they don’t directly participate in conflicts around the world and have more money to spend on improving the lives of their people.
One of the biggest problems in the world right now is income inequality. The rich seem to only get richer, while poverty continues to be everywhere.
Will focusing on happiness close this gap?
I’d say it would. Imagine a company that focuses less on profits and more on employee happiness. At first, profit margins would decrease. Traditional investing methods would result in a lower valuation of said company. This lower valuation would lead directly to a lower level of wealth amongst shareholders.
In other words, the rich get less rich.
When this money is reserved for employee happiness instead, the life of employees would naturally be impacted positively. I mean, it’s not hard to imagine that more lenient deadlines would result in less stress at work, and therefore a happier life.
Unfortunately, there aren’t any studies that support this theory (yet!)
This is something that I’ll be publishing more about in the next couple of weeks.
💡 By the way : If you want to start feeling better and more productive, I’ve condensed the information of 100’s of our articles into a 10-step mental health cheat sheet here. 👇
This Cheat Sheet Will Help You Be Happier and More Productive
Thrive under stress and crush your goals with these 10 unique tips for your mental health.
Focusing on personal happiness is clearly important. But how does this happiness benefit the greater good? I hope this article has inspired you to think differently about the importance of your happiness.
By focusing more on the happiness of others , I believe we’re able to create a happier and more sustainable place for our children to grow up in.
What do you think? Do you disagree with anything in this article? Do you want to share your own story on what makes happiness important for you? I’d love to hear about it in the comments below!
Founder of Tracking Happiness, with over 100 interviews and a focus on practical advice, our content extends beyond happiness tracking. Hailing from the Netherlands, I’m a skateboarding enthusiast, marathon runner, and a dedicated data junkie, tracking my happiness for over a decade.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Welcome to Harvard
- Climate Solutions
What is the key to finding happiness? The Harvard community explores the physical, mental, social, and spiritual aspects of living a life filled with joy.
Explore moments of joy across campus
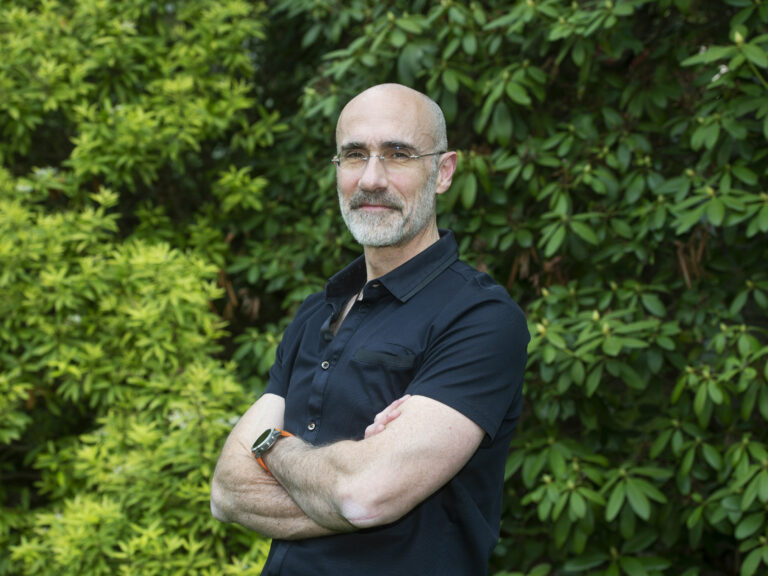

Learn how to be happy
Is there a formula for happiness, and can you apply it to your own life? Professor Arthur Brooks thinks so.
Read more from The Harvard Gazette
Studying happiness
Explore ancient Chinese philosophy, ethics, and political theory to challenge your assumptions of what it means to be happy, live a meaningful life, and change the world.
Understanding happiness
Learn how the origins of joy can improve the way we lead organizations—and our personal lives.
Practicing happiness
Research shows that short writing exercises reliving happy moments boosted the moods of adults recovering from addiction.
The Leadership and Happiness Laboratory
The Leadership and Happiness Laboratory conducts research and creates resources for leaders to learn the science of happiness, apply it in their own lives, and share it with others.
Learn about the lab
Managing Happiness
What if you can will yourself to be happy? This free online course gives participants data-backed strategies to make themselves happier.
Take the course
Health and happiness
Research has long indicated the link between our happiness and physical health. A study from the Harvard Chan School finds a host of health benefits that accompany an optimistic attitude.
Read more from the Harvard Chan School
Good genes are nice, but joy is better
When scientists began tracking the health of 268 Harvard sophomores in 1938, they hoped the study would reveal clues to leading healthy and happy lives. They got more than they ever expected.
Health and happiness go hand in hand
No matter your current state of happiness, there are ways to boost your outlook and give your mental and physical health a lift.
Linking happiness and wellbeing
A Harvard-led study found that younger adults have the lowest scores in a dozen wellbeing measures compared to other age groups.
Finding happiness in community

The value of relationships
Robert Waldinger, director of the Harvard Study of Adult Development, says one of the biggest surprises they encountered was that what makes people happy is also what helps keep them healthy—relationships.
A pet can change your life
Animals ease loneliness and boost oxytocin—the love hormone.

Mending fences
In a society roiled by division, how can we find common ground and build relationships with those who don’t share our views?

Reaching out
Research offers new reasons to pick up the phone and reconnect with that old friend.

Forgiveness can heal
Forgiveness transcends mere spiritual practice or good behavior—it fosters good mental health.

How do you measure and govern for happiness?
An international conference of academics, practitioners, corporate managers, and spiritual leaders at the Harvard Divinity School sought answers to the question of universal happiness.
Explore videos from the conference
Finding joy in our work

When working harder doesn’t work, reinvent your career

Playful summer learning

Fulfillment doesn't require big change

This summer, remember to refresh

Want to be happier? Make more free time.

Get out of your own way
You may also like
Related In Focus topics
- Healthy Living
- Mindfulness and Meditation
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Why does happiness matter?
Being happy is not just about feeling good. Research shows that it also makes us healthier, more productive – and nicer
D oes happiness matter? People react to this question in surprisingly different ways. Some suggest that there are far more significant things to worry about; others see happiness as vitally important and something that every human being ultimately wants in life. To explore this conundrum, we need to start by looking at what happiness actually means.
Happiness relates to how we feel, but it is more than just a passing mood. We are emotional beings and experience a wide range of feelings on a daily basis. Negative emotions – such as fear and anger – help us to get away from danger or defend ourselves. And positive emotions – such as enjoyment and hope – help us to connect with others and build our capacity to cope when things go wrong.
Trying to live a happy life is not about denying negative emotions or pretending to feel joyful all the time. We all encounter adversity and it’s completely natural for us to feel anger, sadness, frustration and other negative emotions as a result. To suggest otherwise would be to deny part of the human condition.
Happiness is about being able to make the most of the good times – but also to cope effectively with the inevitable bad times, in order to experience the best possible life overall. Or, in the words of the biochemist turned Buddhist monk Matthieu Ricard: “Happiness is a deep sense of flourishing, not a mere pleasurable feeling or fleeting emotion but an optimal state of being.”
One popular misconception about happiness is that happy people are somehow more likely to be lazy or ineffective. In fact research shows the opposite is true: happiness doesn’t just feel good, it actually leads to a wide range of benefits for our performance, health, relationships and more.
For example, economists at Warwick University showed different groups of people either a positive film clip or a neutral film clip and then asked them to carry out standard workplace tasks under paid conditions. The people who were primed to feel happy were 11% more productive than their peers, even after controlling for age, IQ and other factors. Similarly, researchers at Wharton Business School found that companies with happy employees outperform the stock market year on year and a team at UCL has discovered that people who are happy as young adults go on to earn more than their peers later in life.

In healthcare, doctors who are happy have been found to make faster and more accurate diagnoses , even when this happiness was induced simply by giving them the small gift of a sugary sweet. In education, schools that focus on children’s social and emotional wellbeing experience significant gains in academic attainment as well as improvements in pupil behaviour. Happiness has also been linked to better decision-making and improved creativity .
So, rather than success being the key to happiness, research shows that happiness could in fact be the key to success.
But it doesn’t just help us function better: happiness also brings substantial benefits for society as a whole. For example, a review of more than 160 studies found “clear and compelling evidence” that happier people have better overall health and live longer than their less happy peers. They are around half as likely to catch the cold virus and have a 50% lower risk of experiencing a cardiovascular event such as a heart attack or stroke.
Happier people are also less likely to engage in risky behaviour – for example, they are more likely to wear seat belts and less likely to be involved in road accidents . Happier people are even more financially responsible, tending to save more and have more control over their expenditures .
But perhaps most importantly of all, people who are happier are more likely to make a positive contribution to society . In particular, they are more likely to vote, do voluntary work and participate in public activities. They also have a greater respect for law and order and offer more help to others.
There is even evidence that happiness is contagious, so that happier people help others around them to become happier too. An extensive study in the British Medical Journal followed people over 20 years and found that their happiness affected others in their networks across “three degrees of separation”. In other words, how happy we are has a measurable impact on the mood of our friend’s friend’s friend.
When it comes to the happiness of society as a whole, however, the sad truth is that in recent decades we have become substantially richer but no happier . The positive benefits of higher incomes have been undermined by rising inequality and falling levels of trust and social cohesion. We’ve also reached the point where mental ill health is one of our greatest social challenges – causing more of the suffering in our society than either unemployment or poverty.
This is why increasing numbers of policymakers and leaders are now calling for measures of progress to be based on human wellbeing and happiness , not just economic factors such as growth in GDP. Here in the UK, the government has introduced a programme to measure national wellbeing , and influential figures – including former cabinet secretary Gus O’Donnell – are calling for wellbeing to become the overall measure of prosperity and the main guide to public policy.
This shift towards prioritising happiness is important because this also reflects what the majority of people want. In a YouGov poll commissioned by Action for Happiness , a majority (87%) of UK adults said they would prefer a society with the “greatest overall happiness and wellbeing”, rather than the “greatest overall wealth” (8%). The findings were consistent across all regions, age groups and social classes.
So happiness does matter – the scientific evidence is compelling. The pursuit of happiness is not some fluffy nice-to-have or middle-class luxury; it’s about helping people to live better lives and creating a society that is more productive, healthy and cohesive. As Aristotle said: “Happiness is the meaning and the purpose of life, the whole aim and end of human existence.”
Of course, being happy is not some magical cure-all. Happy people still get sick and lose loved ones – and not all happy people are efficient, creative or generous. But, other things being equal, happiness brings substantial advantages.
Perhaps the most powerful insight of all comes, not from the research, but from the responses I’ve heard from many hundreds of parents when asking them what they want above all for their children. Nearly all say something like: “I really just want them to be happy.”
Happiness is the thing we want most for the people we love the most. That’s why it matters so much.
Mark Williamson is director of Action for Happiness . For tips on how to be happier, read his 10 keys to happiness
- Health & wellbeing
- Happy for life
- Mental health

People in UK are overall less happy than before pandemic, ONS finds

Meet the loners

Ten tips for a better work-life balance

‘Commercial no-brainer’: why the role of happiness officer is taking off

Happiness officers: does every workplace need to hire someone to bring the joy?

Take the Oxford Happiness Questionnaire

Happiness among UK young people has hit 13-year low, study finds

Learning about joy from the Germans

To be happy you have to feel you belong

The big idea: is it time to stop worrying about stress?
Comments (…), most viewed.
Happiness Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on happiness.
Happiness is something which we can’t describe in words it can only be felt from someone’s expression of a smile. Likewise, happiness is a signal or identification of good and prosperous life. Happiness is very simple to feel and difficult to describe. Moreover, happiness comes from within and no one can steal your happiness.

Can Money Buy You Happiness?
Every day we see and meet people who look happy from the outside but deep down they are broken and are sad from the inside. For many people, money is the main cause of happiness or grief. But this is not right. Money can buy you food, luxurious house, healthy lifestyle servants, and many more facilities but money can’t buy you happiness.
And if money can buy happiness then the rich would be the happiest person on the earth. But, we see a contrary image of the rich as they are sad, fearful, anxious, stressed, and suffering from various problems.
In addition, they have money still they lack in social life with their family especially their wives and this is the main cause of divorce among them.
Also, due to money, they feel insecurity that everyone is after their money so to safeguard their money and them they hire security. While the condition of the poor is just the opposite. They do not have money but they are happy with and stress-free from these problems.
In addition, they take care of their wife and children and their divorce rate is also very low.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Happiness Comes from Within
As we now know that we can’t buy happiness with money and there is no other shortcut to happiness. It is something that you feel from within.
In addition, true happiness comes from within yourself. Happiness is basically a state of mind.
Moreover, it can only be achieved by being positive and avoiding any negative thought in mind. And if we look at the bright side of ourselves only then we can be happy.
Happiness in a Relationship
People nowadays are not satisfied with their relationship because of their differences and much other reason. But for being happy in a relationship we have to understand that there are some rules or mutual understanding that keeps a relationship healthy and happy.
Firstly, take care of yourself then your partner because if you yourself are not happy then how can you make your partner happy.
Secondly, for a happy and healthy relationship give you partner some time and space. In addition, try to understand their feeling and comfort level because if you don’t understand these things then you won’t be able to properly understand your partner.
Most importantly, take initiative and plan to go out with your partner and family. Besides, if they have plans then go with them.
To conclude, we can say that happiness can only be achieved by having positive thinking and enjoying life. Also, for being happy and keeping the people around us happy we have to develop a healthy relationship with them. Additionally, we also have to give them the proper time.
FAQs about Happiness
Q.1 What is True Happiness? A.1 True happiness means the satisfaction that you find worthy. The long-lasting true happiness comes from life experience, a feeling of purpose, and a positive relationship.
Q.2 Who is happier the rich or the poor and who is more wealthy rich or poor? A.2 The poor are happier then the rich but if we talk about wealth the rich are more wealthy then the poor. Besides, wealth brings insecurity, anxiety and many other problems.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Download the App


Happiness and Life Satisfaction
Self-reported life satisfaction differs widely between people and between countries. What explains these differences?
By Esteban Ortiz-Ospina and Max Roser
First published in 2013; most recent substantive revision February 2024.
How happy are people today? Were people happier in the past? How satisfied with their lives are people in different societies? And how do our living conditions affect all of this?
These are difficult questions to answer, but they are questions that undoubtedly matter for each of us personally. Indeed, today, life satisfaction and happiness are central research areas in the social sciences, including in ‘mainstream’ economics.
Social scientists often recommend that measures of subjective well-being should augment the usual measures of economic prosperity, such as GDP per capita . 1 But how can happiness be measured? Are there reliable comparisons of happiness across time and space that can give us clues regarding what makes people declare themselves ‘happy’?
In this topic page, we discuss the data and empirical evidence that might answer these questions. Our focus here will be on survey-based measures of self-reported happiness and life satisfaction. Here is a preview of what the data reveals.
- Surveys asking people about life satisfaction and happiness do measure subjective well-being with reasonable accuracy.
- Life satisfaction and happiness vary widely both within and among countries. It only takes a glimpse at the data to see that people are distributed along a wide spectrum of happiness levels.
- Richer people tend to say they are happier than poorer people; richer countries tend to have higher average happiness levels; and across time, most countries that have experienced sustained economic growth have seen increasing happiness levels. So, the evidence suggests that income and life satisfaction tend to go together (which still doesn’t mean they are one and the same).
- Important life events such as marriage or divorce do affect our happiness but have surprisingly little long-term impact. The evidence suggests that people tend to adapt to changes.
See all interactive charts on Happiness and Life Satisfaction ↓
Other research and writing on happiness and life satisfaction on Our World in Data:
- Are Facebook and other social media platforms bad for our well-being?
- Are people more likely to be lonely in so-called 'individualistic' societies?
- Are we happier when we spend more time with others?
- Collective pessimism and our inability to guess the happiness of others
- How important are social relations for our health and well-being?
- Is there a loneliness epidemic?
- There is a 'happiness gap' between East and West Germany
Happiness across the world today
The World Happiness Report is a well-known source of cross-country data and research on self-reported life satisfaction. The map here shows, country by country, the ‘happiness scores’ published this report.
The underlying source of the happiness scores in the World Happiness Report is the Gallup World Poll —a set of nationally representative surveys undertaken in more than 160 countries in over 140 languages.
The main life evaluation question asked in the poll is: “Please imagine a ladder, with steps numbered from 0 at the bottom to 10 at the top. The top of the ladder represents the best possible life for you, and the bottom of the ladder represents the worst possible life for you. On which step of the ladder would you say you personally feel you stand at this time?” (This is also known as the “Cantril Ladder”.)
The map plots the average answer that survey respondents provided to this question in different countries. As with the steps of the ladder, values in the map range from 0 to 10.
There are large differences across countries. According to the most recent figures, European countries top the ranking: Finland, Denmark, Iceland, Switzerland, and the Netherlands have the highest scores. In the same year, the lowest national scores correspond to Afghanistan, South Sudan, and other countries in central Sub-Saharan Africa.
You can click on any country on the map to plot time series for specific countries.
Self-reported life satisfaction tends to correlate with other measures of well-being—richer and healthier countries tend to have higher average happiness scores. (More on this in the section below .)
Happiness over time
Findings from the integrated values surveys.
In addition to the Gallup World Poll (discussed above), the Integrated Values Surveys provides cross-country data on self-reported life satisfaction. These are the longest available time series of cross-country happiness estimates that include non-European nations.
The Integrated Values Surveys collect data from a series of representative national surveys covering almost 100 countries, with the earliest estimates dating back to 1981. In these surveys, respondents are asked: “Taking all things together, would you say you are (i) Very happy, (ii) Rather happy, (iii) Not very happy, or (iv) Not at all happy”. This visualization plots the share of people answering they are “very happy” or “rather happy”.
As we can see, in most countries, the trend is positive: In most countries with data from two or more surveys, the most recent observation is higher than the earliest. In some cases, the improvement has been very large; in Albania, for example, the share of people who reported being ‘very happy’ or ‘rather happy’ went from 33.4% in 1998 to 73.9% in 2022.
Findings from Eurobarometer
The Eurobarometer survey collects data on life satisfaction as part of their public opinion surveys. For several countries, these surveys have been conducted at least annually for more than 40 years. The visualization here shows the share of people who report being ‘very satisfied’ or ‘fairly satisfied’ with their standards of living.
Two points are worth emphasizing. First, estimates of life satisfaction often fluctuate around trends. In France, for example, we can see that the overall trend is positive, yet there is a pattern of ups and downs. And second, despite fluctuations, decade-long trends have been generally positive for most European countries.
In most cases, the share of people who say they are ‘very satisfied’ or ‘fairly satisfied’ with their life has gone up over the full survey period. 2 Yet there are some clear exceptions, of which Greece is the most notable example. In 2007, around 67% of the Greeks said they were satisfied with their life, but five years later, after the financial crisis struck, the corresponding figure was down to 32.4%. Despite recent improvements, Greeks today are, on average, much less satisfied with their lives than they were before the financial crisis. No other European country in this dataset has gone through a comparable negative shock.
The distribution of life satisfaction
More than averages — the distribution of life satisfaction scores.
Most of the studies comparing happiness and life satisfaction among countries focus on averages. However, distributional differences are also important.
Life satisfaction is often reported on a scale from 0 to 10, with 10 representing the highest possible level of satisfaction. This is the so-called ‘Cantril Ladder’. This visualization shows how responses are distributed across steps in this ladder. In each case, the height of the bars is proportional to the fraction of answers at each score. Each differently-colored distribution refers to a world region, and for each region, we have overlaid the distribution for the entire world as a reference.
These plots show that in Sub-Saharan Africa—the region with the lowest average scores—the distributions are consistently to the left of those in Europe.
This means that the share of people who are ‘happy’ is lower in Sub-Saharan Africa than in Western Europe, independently of which score in the ladder we use as a threshold to define ‘happy’. Similar comparisons can be made by contrasting other regions with high average scores (e.g., North America, Australia, and New Zealand) against those with low average scores (e.g., South Asia).
Another important point to notice is that the distribution of self-reported life satisfaction in Latin America and the Caribbean is high across the board—it is consistently to the right of other regions with roughly comparable income levels, such as Central and Eastern Europe.
This is part of a broader pattern: Latin American countries tend to have a higher subjective well-being than other countries with comparable levels of economic development. As we will see in the section on the social environment , culture, and history matter for self-reported life satisfaction.
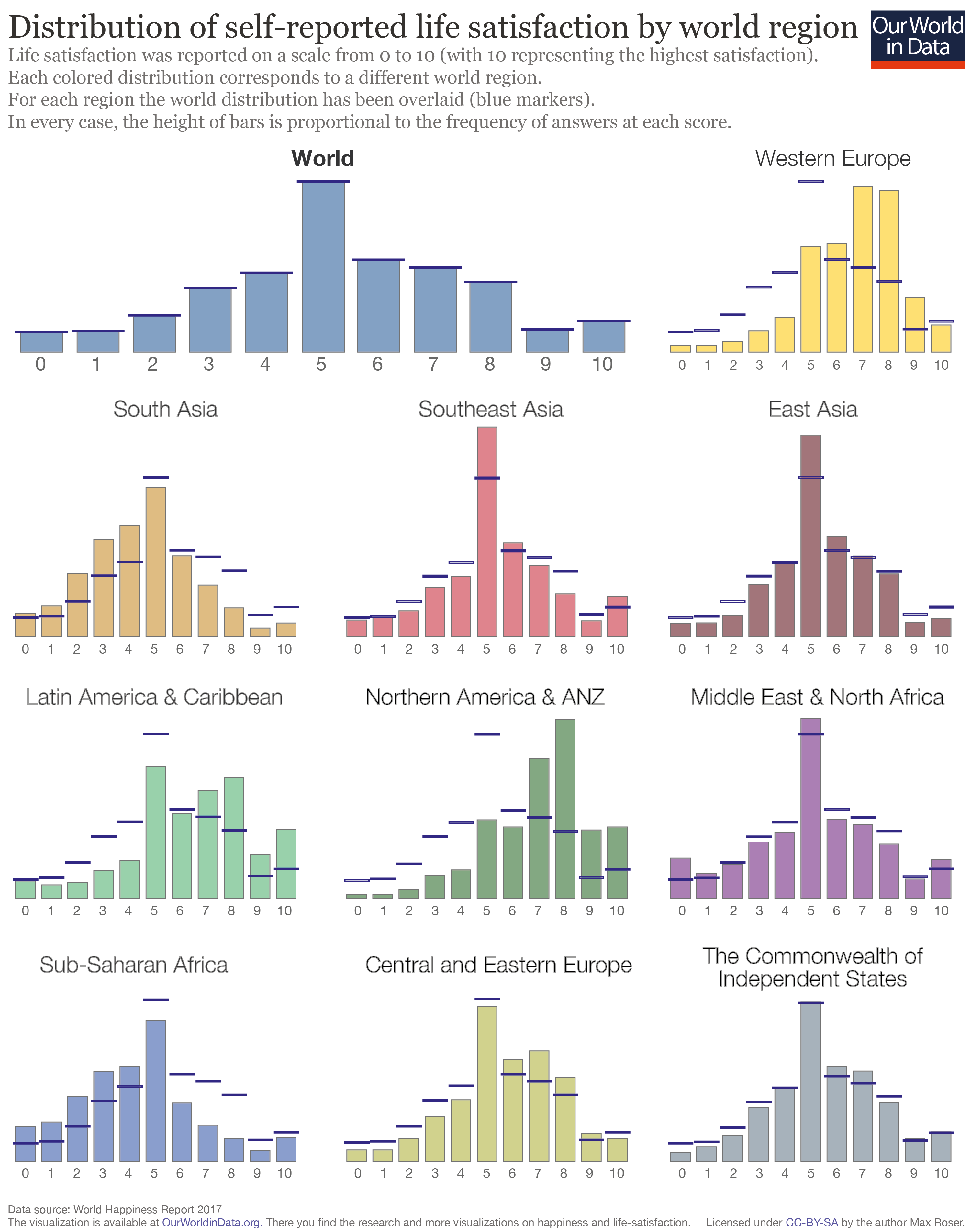
If you want data on country-level distributions of scores, the Pew Global Attitudes Survey provides such figures for more than 40 countries.
Differences in happiness within countries
Happiness inequality, happiness inequality in the us and other rich countries.
The General Social Survey (GSS) in the US is a survey administered to a nationally representative sample of about 1,500 respondents each year since 1972 and is an important source of information on long-run trends of self-reported life satisfaction in the country. 3
Using this source, Stevenson and Wolfers (2008) 4 show that while the national average has remained broadly constant, inequality in happiness has fallen substantially in the US in recent decades.
The authors further note that this is true both when we think about inequality in terms of the dispersion of answers, and also when we think about inequality in terms of gaps between demographic groups. They note that two-thirds of the black-white happiness gap has been eroded (although today, white Americans remain happier on average, even after controlling for differences in education and income), and the gender happiness gap has disappeared entirely (women used to be slightly happier than men, but they are becoming less happy, and today there is no statistical difference once we control for other characteristics). 5
The results from Stevenson and Wolfers are consistent with other studies looking at changes of happiness inequality (or life satisfaction inequality) over time. In particular, researchers have noted that there is a correlation between economic growth and reductions in happiness inequality—even when income inequality is increasing at the same time. The visualization here uses data from Clark, Fleche, and Senik (2015) 6 shows this. It plots the evolution of happiness inequality within a selection of rich countries that experienced uninterrupted GDP growth.
In this chart, happiness inequality is measured by the dispersion — specifically the standard deviation — of answers in the World Values Survey . As we can see, there is a broad negative trend. In their paper, the authors show that the trend is positive in countries with falling GDP.
Why could it be that happiness inequality falls with rising income inequality?
Clark, Fleche, and Senik argue that part of the reason is that the growth of national income allows for the greater provision of public goods, which in turn tightens the distribution of subjective well-being. This can still be consistent with growing income inequality since public goods such as better health affect incomes and well-being differently.
Another possibility is that economic growth in rich countries has translated into a more diverse society in terms of cultural expressions (e.g., through the emergence of alternative lifestyles), which has allowed people to converge in happiness even if they diverge in incomes, tastes, and consumption. Steven Quartz and Annette Asp explain this hypothesis in a New York Times article , discussing evidence from experimental psychology.
The link between happiness and income
The link across countries, higher national incomes go together with higher average life satisfaction.
If we compare life satisfaction reports from around the world at any given point in time, we immediately see that countries with higher average national incomes tend to have higher average life satisfaction scores. In other words, people in richer countries tend to report higher life satisfaction than people in poorer countries. The scatter plot here shows this.
Each dot in the visualization represents one country. The vertical position of the dots shows the national average self-reported life satisfaction in the Cantril Ladder (a scale ranging from 0-10 where 10 is the highest possible life satisfaction), while the horizontal position shows GDP per capita based on purchasing power parity (i.e., GDP per head after adjusting for inflation and cross-country price differences).
This correlation holds even if we control for other factors: Richer countries tend to have higher average self-reported life satisfaction than poorer countries that are comparable in terms of demographics and other measurable characteristics. You can read more about this in the World Happiness Report 2017 , specifically the discussion in Chapter 2.
As we show below, income and happiness also tend to go together within countries and across time .
The link within countries
Higher personal incomes go together with higher self-reported life satisfaction.
Above; we point out that richer countries tend to be happier than poorer countries. Here, we show that the same tends to be true within countries: richer people within a country tend to be happier than poorer people in the same country. The visualizations here show us this by looking at happiness by income quintiles.
Firstly, we show each country in individual panels: within each panel is a connected scatter plot for a specific country. This means that for each country, we observe a line joining five points: each point marks the average income within an income quintile (horizontal axis) against the average self-reported life satisfaction of people at that income quintile (vertical axis).
What does this visualization tell us? We see that in all cases, lines are upward sloping: people in higher income quintiles tend to have higher average life satisfaction. Yet in some countries, the lines are steep and linear (e.g., in Costa Rica, richer people are happier than poorer people across the whole income distribution), while in some countries, the lines are less steep and non-linear (e.g., the richest group of people in the Dominican Republic is as happy as the second-richest group).
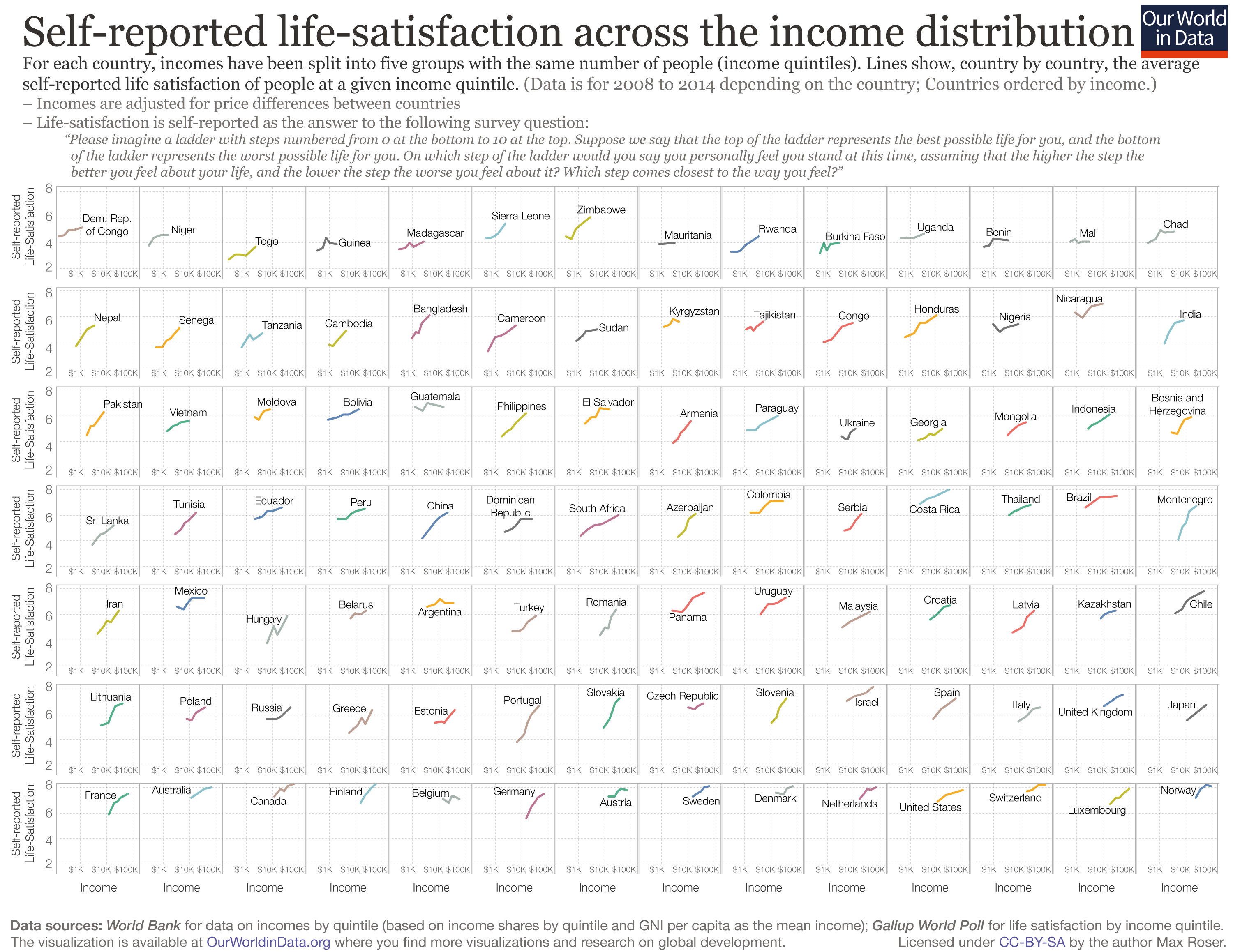
In a second visualization, we present the same data, but instead of plotting each country separately, showing all countries in one grid.
The resulting connected scatter plot may be messy, resembling a ‘spaghetti’ chart, but it is helpful to confirm the overall pattern: despite kinks here and there, lines are, by and large, upward-sloping.
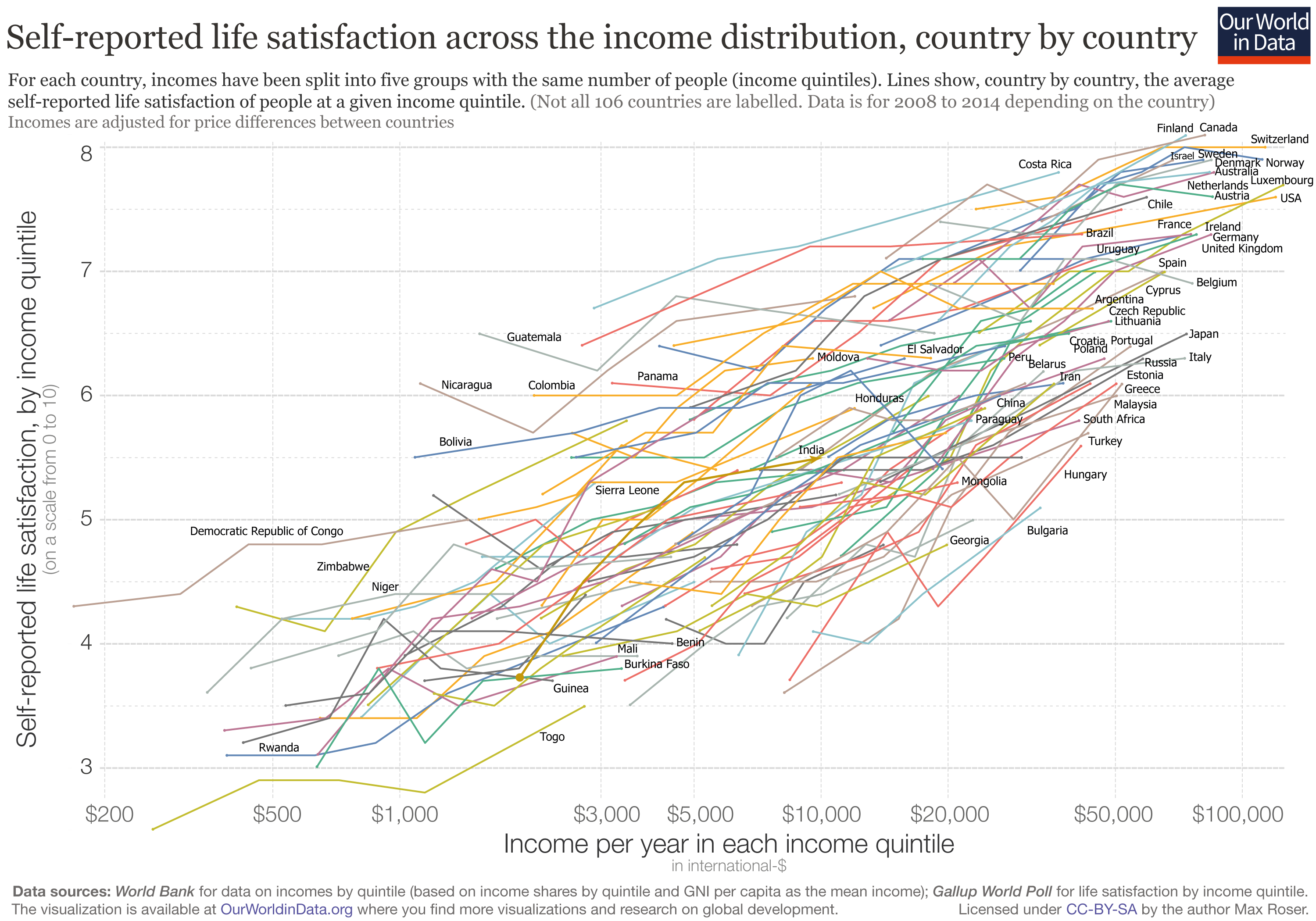
Looking across and within countries
A snapshot of the correlation between income and happiness—between and within countries.
Do income and happiness tend to go together? The visualization here shows that the answer to this question is yes, both within and across countries.
It may take a minute to wrap your head around this visualization, but once you do, you can see that it handily condenses the key information from the previous three charts into one.
To show the income-happiness correlation across countries, the chart plots the relationship between self-reported life satisfaction on the vertical axis and GDP per capita on the horizontal axis. Each country is an arrow on the grid, and the location of the arrow tells us the corresponding combination of average income and average happiness.
To show the income-happiness correlation within countries, each arrow has a slope corresponding to the correlation between household incomes and self-reported life satisfaction within that country. In other words, the slope of the arrow shows how strong the relationship between income and life satisfaction is within that country. ( This chart gives you a visual example of how the arrows were constructed for each country). 7
If an arrow points northeast, that means richer people tend to report higher life satisfaction than poorer people in the same country. If an arrow is flat (i.e., points east), that means rich people are, on average, just as happy as poorer people in the same country.
As we can see, there is a very clear pattern: richer countries tend to be happier than poorer countries (observations are lined up around an upward-sloping trend), and richer people within countries tend to be happier than poorer people in the same countries (arrows are consistently pointing northeast).
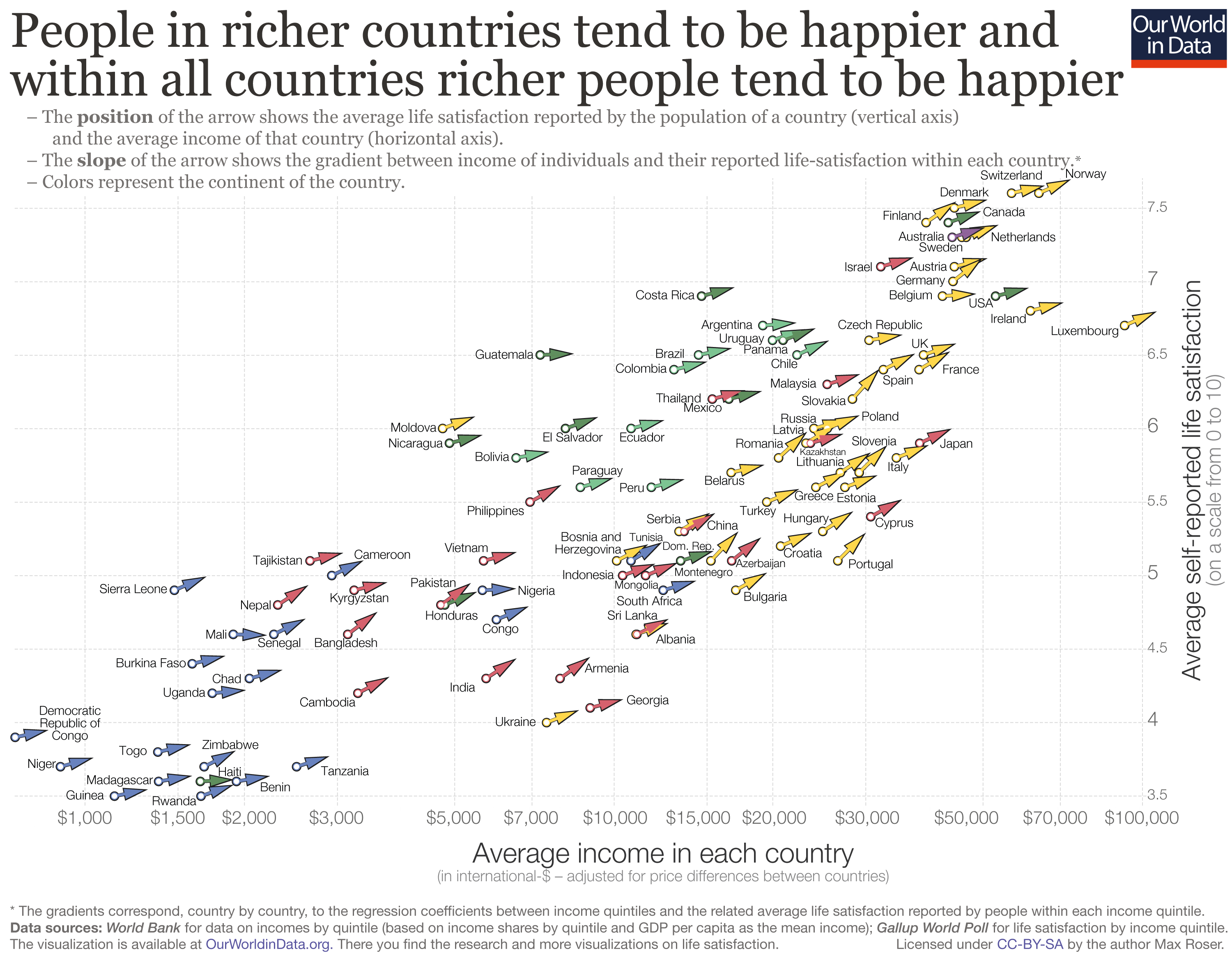
It’s important to note that the horizontal axis is measured on a logarithmic scale. The cross-country relationship we would observe on a linear scale would be different since, at high national income levels, slightly higher national incomes are associated with a smaller increase in average happiness than at low levels of national incomes. In other words, the cross-country relationship between income and happiness is not linear on income (it is ‘log-linear’). We use the logarithmic scale to highlight two key facts: (i) at no point in the global income distribution is the relationship flat, and (ii) a doubling of the average income is associated with roughly the same increase in the reported life satisfaction, irrespective of the position in the global distribution.
These findings have been explored in more detail in a number of recent academic studies. Importantly, the much-cited paper by Stevenson and Wolfers (2008) 8 shows that these correlations hold even after controlling for various country characteristics, such as the demographic composition of the population, and are robust to different sources of data and types of subjective well-being measures.
Economic growth and happiness
In the charts above, we show that there is robust evidence of a strong correlation between income and happiness across and within countries at fixed points in time. Here, we want to show that, while less strong, there is also a correlation between income and happiness across time. Or, put differently, as countries get richer, the population tends to report higher average life satisfaction.
The chart shown here uses data from the World Values Survey to plot the evolution of national average incomes and national average happiness over time. To be specific, this chart shows the share of people who say they are ‘very happy’ or ‘rather happy’ in the World Values Survey (vertical axis) against GDP per head (horizontal axis). Each country is drawn as a line joining the first and last available observations across all survey waves. 9
As we can see, countries that experience economic growth also tend to experience happiness growth across waves in the World Values Survey. This is a correlation that holds after controlling for other factors that also change over time (in this chart from Stevenson and Wolfers (2008), you can see how changes in GDP per capita compare to changes in life satisfaction after accounting for changes in demographic composition and other variables).
An important point to note here is that economic growth and happiness growth tend to go together on average . Some countries, in some periods, experience economic growth without increasing happiness. The experience of the US in recent decades is a case in point. These instances may seem paradoxical given the evidence—we explore this question in the following section.
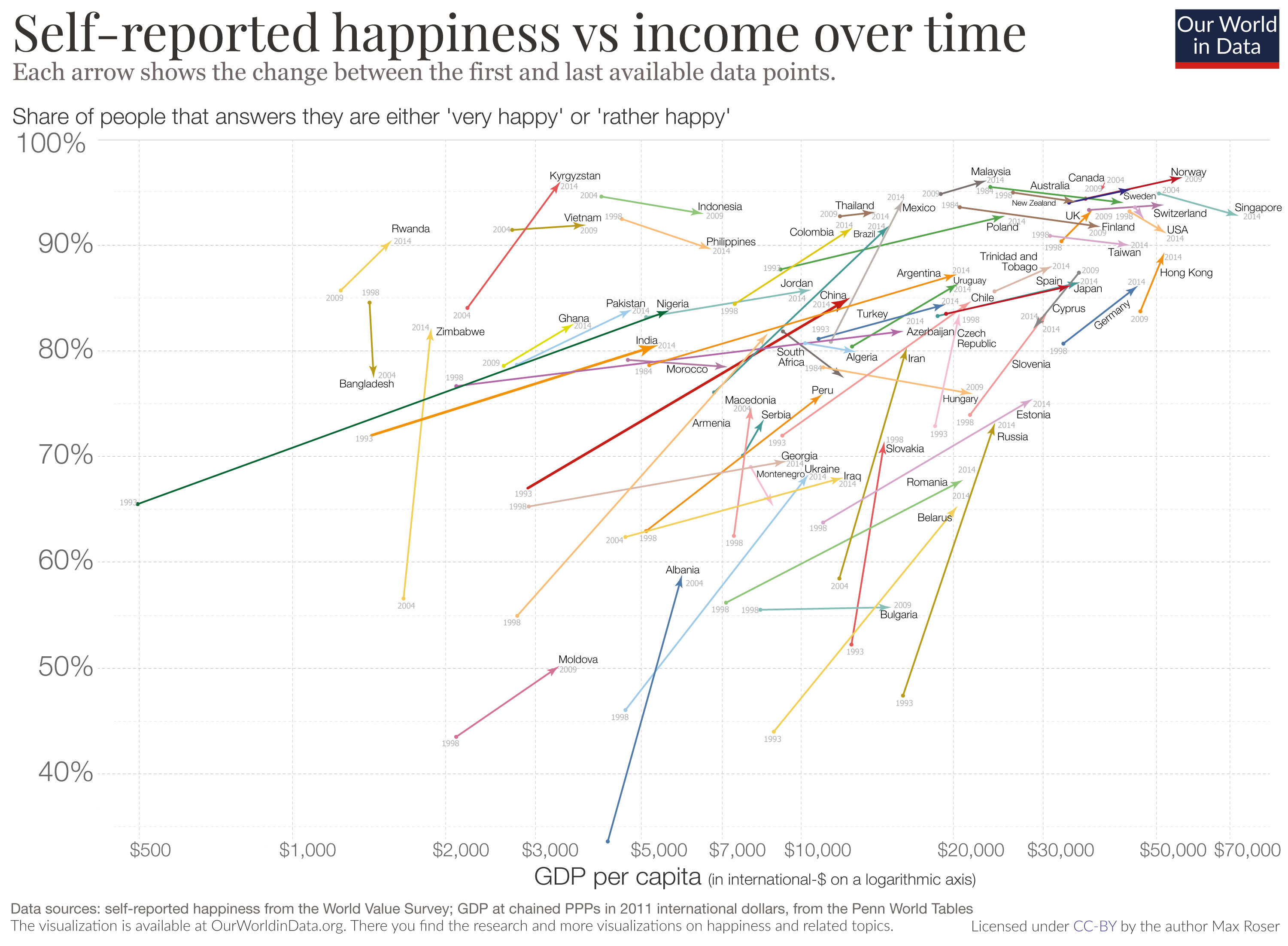
The Easterlin Paradox
The observation that economic growth does not always go together with increasing life satisfaction was first made by Richard Easterlin in the 1970s. Since then, there has been much discussion over what came to be known as the ‘Easterlin Paradox’.
At the heart of the paradox was the fact that richer countries tend to have higher self-reported happiness, yet in some countries for which repeated surveys were available over the course of the 1970s, happiness was not increasing with rising national incomes. This combination of empirical findings was paradoxical because the cross-country evidence (countries with higher incomes tended to have higher self-reported happiness) did not, in some cases, fit the evidence over time (countries seemed not to get happier as national incomes increased).
Notably, Easterlin and other researchers relied on data from the US and Japan to support this seemingly perplexing observation. If we look closely at the data underpinning the trends in these two countries, however, these cases are not, in fact, paradoxical.
Let us begin with the case of Japan. There, the earliest available data on self-reported life satisfaction came from the so-called ‘Life in Nation surveys’, which date back to 1958. At first glance, this source suggests that mean life satisfaction remained flat over a period of spectacular economic growth (see, for example, this chart from Easterlin and Angelescu 2011). 10 Digging a bit deeper, however, we find that things are more complex.
Stevenson and Wolfers (2008) 8 show that the life satisfaction questions in the ‘Life in Nation surveys’ changed over time, making it difficult—if not impossible—to track changes in happiness over the full period. The visualization here splits the life satisfaction data from the surveys into sub-periods where the questions remained constant. As we can see, the data is not supportive of a paradox: the correlation between GDP and happiness growth in Japan is positive within comparable survey periods. The reason for the alleged paradox is, in fact mismeasurement of how happiness changed over time.
In the US, the explanation is different but can once again be traced to the underlying data. Specifically, if we look more closely at economic growth in the US over the recent decades, one fact looms large: growth has not benefitted the majority of people. Income inequality in the US is exceptionally high and has been on the rise in the last four decades, with incomes for the median household growing much more slowly than incomes for the top 10%. As a result, trends in aggregate life satisfaction should not be seen as paradoxical: the income and standard of living of the typical US citizen have not grown much in the last couple of decades. (You can read more about this in our page on inequality and incomes across the distribution .)
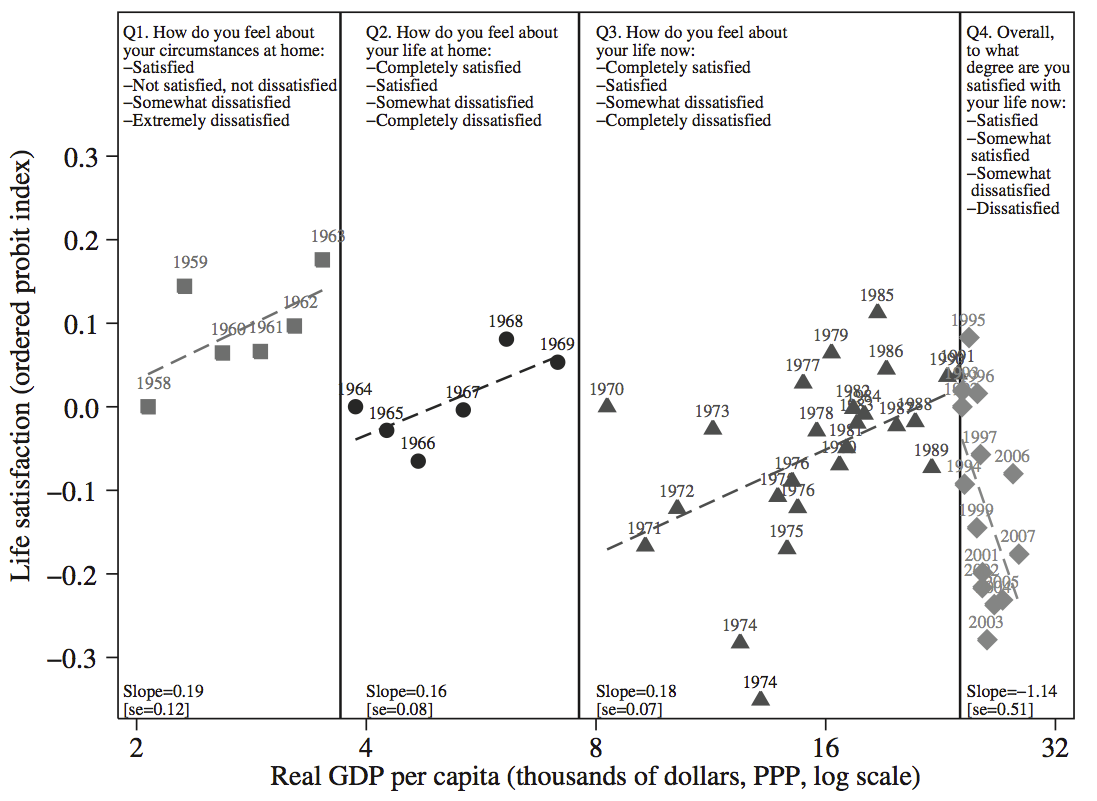
Health and life satisfaction
Life expectancy and life satisfaction.
Health is an important predictor of life satisfaction, both within and among countries. In this visualization, we provide evidence of the cross-country relationship.
Each dot in the scatterplot represents one country. The vertical position of the dots shows national life expectancy at birth, and the horizontal position shows the national average self-reported life satisfaction in the Cantril Ladder (a scale ranging from 0-10, where 10 is the highest possible life satisfaction).
As we can see, there is a strong positive correlation: countries where people tend to live longer are also countries where people tend to say more often that they are satisfied with their lives. A similar relationship holds for other health outcomes (e.g., life satisfaction tends to be higher in countries with lower child mortality ).
The relationship plotted in the chart clearly reflects more than just the link between health and happiness since countries with high life expectancy also tend to be countries with many other distinct characteristics. However, the positive correlation between life expectancy and life satisfaction remains after controlling for observable country characteristics, such as income and social protection. You can read more about this in the World Happiness Report 2017 , specifically the discussion in Chapter 2.
Life satisfaction through life events
How do common life events affect happiness.
Do people tend to adapt to common life events by converging back to a baseline level of happiness?
Clark et al. (2008) 12 use data from the German Socio-Economic Panel to identify groups of people experiencing significant life and labor market events and trace how these events affect the evolution of their life satisfaction. The visualization here shows an overview of their main findings. In each individual chart, the red lines mark the estimated effect of a different event at a given point in time (with ‘whiskers’ marking the range of confidence of each estimate).
In all cases, the results are split by gender, and time is labeled so that 0 marks the point when the corresponding event took place (with negative and positive values denoting years before and after the event). All estimates control for individual characteristics, so the figures show the effect of the event after controlling for other factors (e.g., income, etc.).
The first point to note is that most events denote the evolution of a latent situation: People grow unhappy in the period leading up to a divorce, while they grow happy in the period leading up to a marriage.
The second point is that single life events do tend to affect happiness in the short run, but people often adapt to changes. Of course, there are clear differences in the extent to which people adapt. In the case of divorce, life satisfaction first drops, then goes up and stays high. For unemployment, there is a negative shock both in the short and long run, notably among men. And for marriage, life satisfaction builds up before the wedding and fades out after it.
In general, the evidence suggests that adaptation is an important feature of well-being. Many common but important life events have a modest, long-term impact on self-reported happiness. Yet adaptation to some events, such as long-term unemployment, is neither perfect nor immediate.
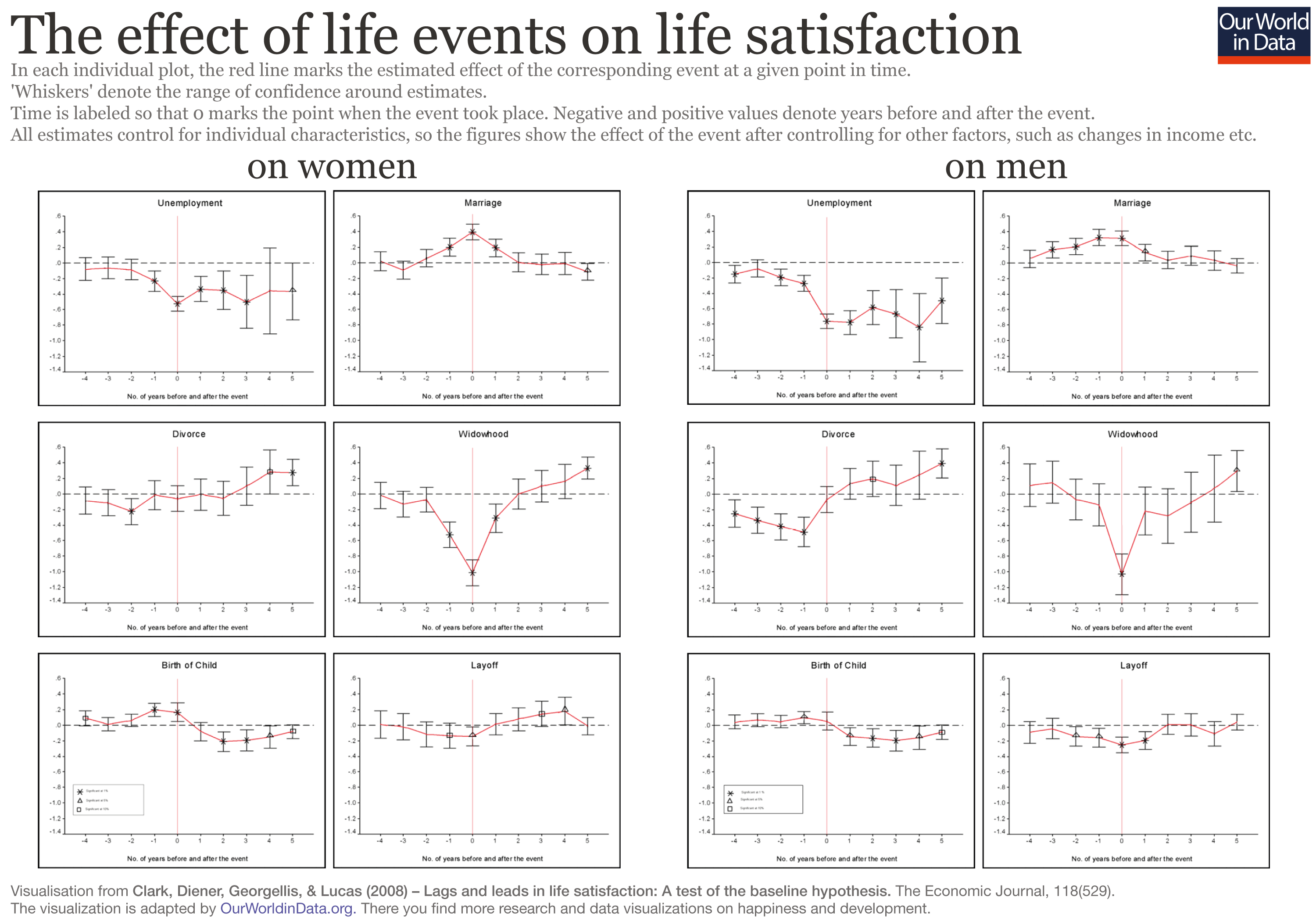
Does disability correlate with life satisfaction?
A number of papers have noted that long-term paraplegics do not report themselves as particularly unhappy when compared to non-paraplegics (see, for example, the much-cited paper by Brickman, Coates, and Janoff-Bulman, 1978). 13
This assertion has received attention because it tells us something about the very meaning of well-being and has important consequences for policy. It is, for example, considered in courts of law with respect to compensation for disability.
However, comparing differences in self-reported life satisfaction among people with different disability statuses is not an ideal source of evidence regarding the effect of tragedy on happiness. Non-paraplegics are potentially different from paraplegics in ways that are hard to measure. Better sources of evidence are longitudinal surveys, where people are tracked over time.
Oswald and Powdthavee (2008) 14 use data from a longitudinal survey in the UK to explore whether accidents leading to disability imply long-term shocks to life satisfaction.
The chart here, from Oswald and Powdthavee, shows the average reported life satisfaction of a group of people who became seriously disabled (at time T) and remained seriously disabled in the two following years (T+1 and T+2). Here, ‘seriously disabled’ means that disability prevented them from being able to do day-to-day activities.
As we can see—and as the authors show more precisely through econometric techniques—those entering disability suffer a sudden drop in life satisfaction and recover only partially. This supports the idea that while adaptation plays a role in common life events, the notion of life satisfaction is indeed sensitive to tragic events.
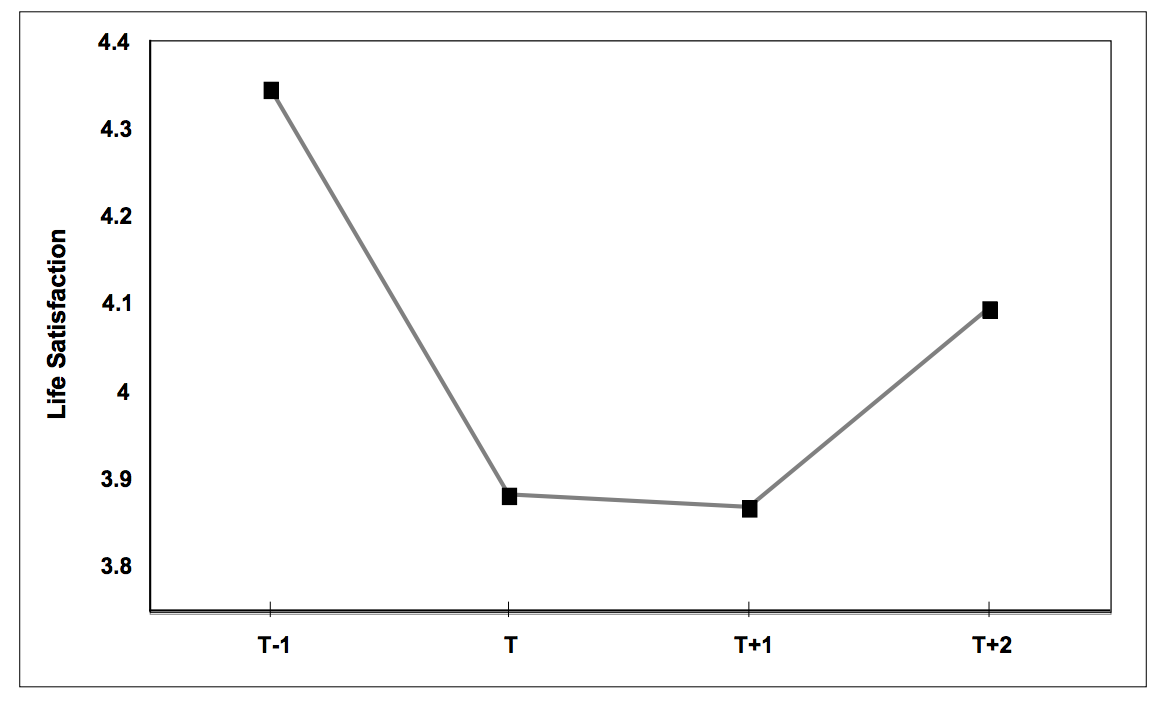
Life satisfaction and society
Culture and life satisfaction.
Comparisons of happiness among countries suggest that culture and history shared by people in a given society matter for self-reported life satisfaction. For example, as the chart here shows, culturally and historically similar Latin American countries have a higher subjective well-being than other countries with comparable levels of economic development. (This chart plots self-reported life satisfaction as measured in the 10-point Cantril ladder on the vertical axis against GDP per capita on the horizontal axis).
Latin America is not a special case in this respect. Ex-communist countries, for example, tend to have lower subjective well-being than other countries with comparable characteristics and levels of economic development.
Academic studies in positive psychology discuss other patterns. Diener and Suh (2002) write: “In recent years cultural differences in subjective well-being have been explored, with a realization that there are profound differences in what makes people happy. Self-esteem, for example, is less strongly associated with life satisfaction, and extraversion is less strongly associated with pleasant affect in collectivist cultures than in individualist cultures”. 15
To our knowledge, there are no rigorous studies exploring the causal mechanisms linking culture and happiness. However, it seems natural to expect that cultural factors shape the way people collectively understand happiness and the meaning of life.
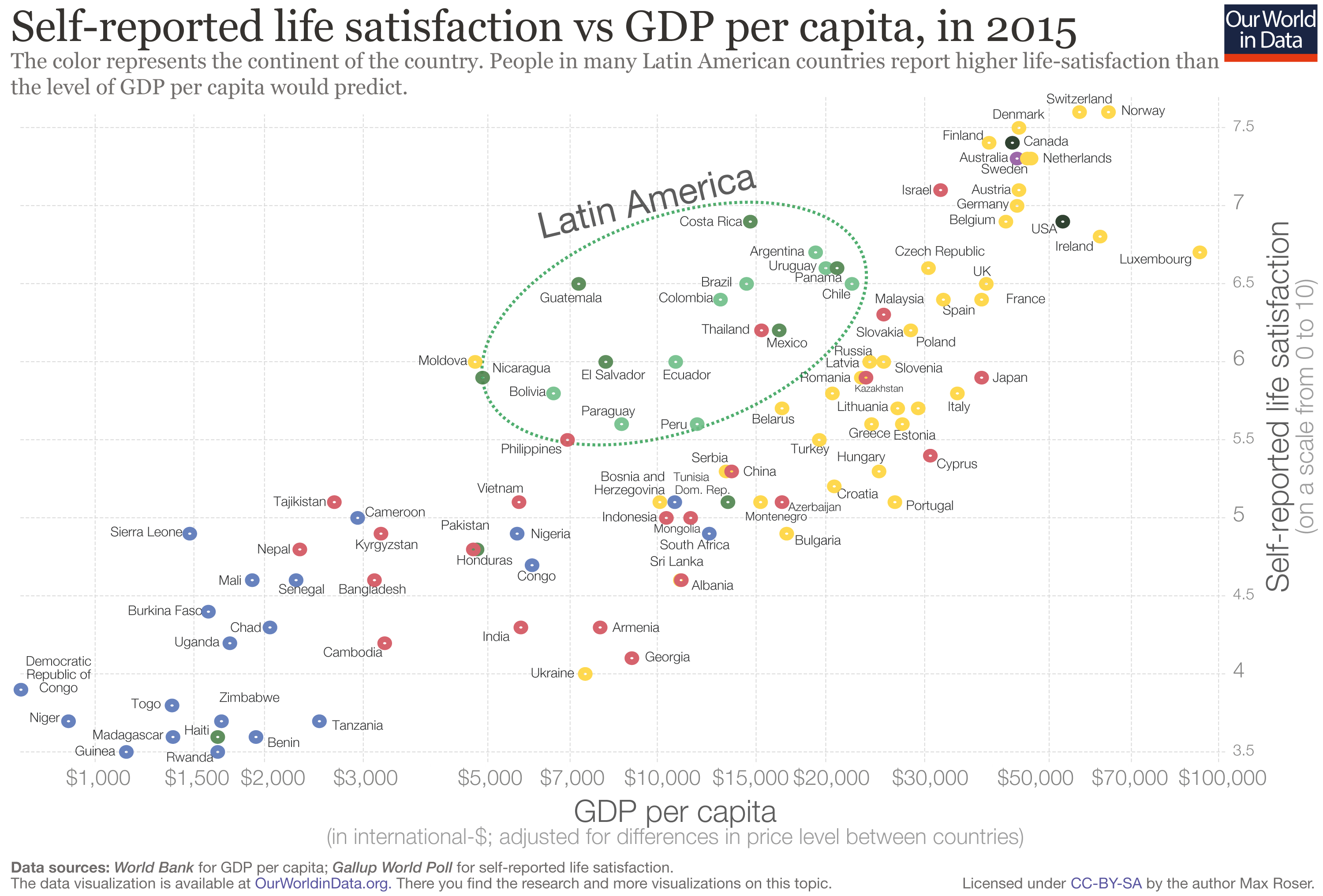
Sense of freedom and life satisfaction
A particular channel through which social environment may affect happiness is freedom: the society we live in may crucially affect the availability of options that we have to shape our own life.
This visualization shows the relationship between self-reported sense of freedom and self-reported life satisfaction using data from the Gallup World Poll . The variable measuring life satisfaction corresponds to country-level averages of survey responses to the Cantril Ladder question (a 0-10 scale, where 10 is the highest level of life satisfaction), while the variable measuring freedom corresponds to the share of people who agree with the statement “In this country, I am satisfied with my freedom to choose what I do with my life”. 16
As we can see, there is a clear positive relationship: countries, where people feel free to choose and control their lives, tend to be countries where people are happier. As Inglehart et al. (2008) 17 show this positive relationship holds even after we control for other factors, such as income and strength of religiosity.
Interestingly, this chart also shows that while there are some countries where the perceived sense of freedom is high but average life satisfaction is low (e.g., Rwanda), there are no countries where the perceived sense of freedom is low but average life satisfaction is high (i.e., there are no countries in the top left area of the chart).
To our knowledge, there are no rigorous studies exploring the causal mechanisms linking freedom and happiness. However, it seems natural to expect that self-determination and the absence of coercion are important components of what people consider a happy and meaningful life.
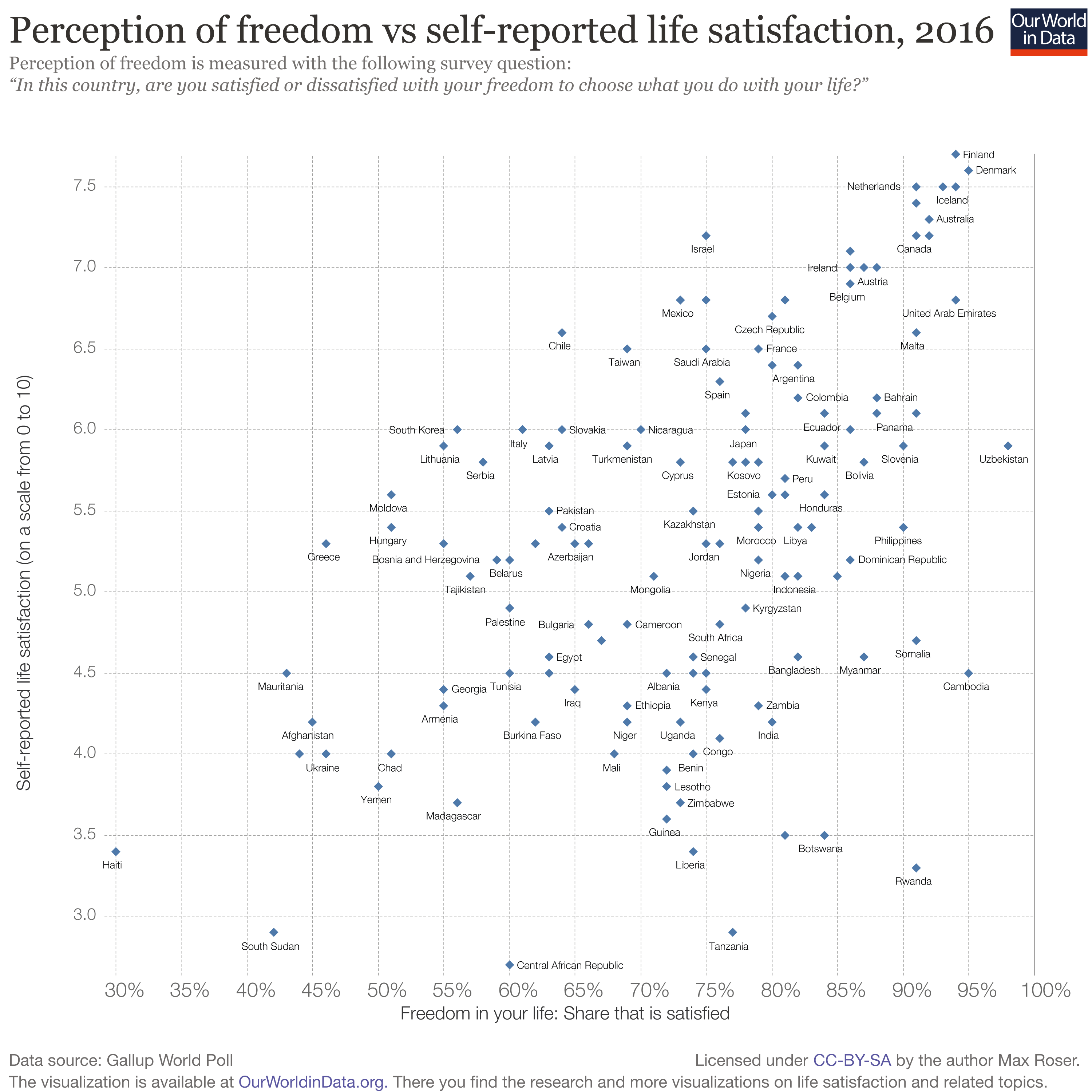
The link between media and gloominess
A number of studies have found that there is a link between emotional exposure to negative content in news and changes in mood.
Johnston and Davey (1997), 18 , for example, conducted an experiment in which they edited short TV news to display positive, neutral, or negative material and then showed them to three different groups of people. The authors found that people who watched the ‘negative’ clip were more likely to report a sad mood.
This link between emotional content in news and changes in mood is all the more important if we consider that media gatekeepers tend to prefer negative to positive coverage of newsworthy facts (see, for example, Combs and Slovic 1979 19 ).
Of course, mood is not the same as life satisfaction. Yet, as we discuss below in the section on measurement and data quality , surveys measuring happiness often do capture emotional aspects of well-being. In any case, people’s perceptions of what it means to lead a meaningful life are heavily influenced by their expectations of what is possible and likely to occur in their lives, and this has also been shown to depend on media exposure. 20
Data Quality and Measurement
Can ‘happiness’ really be measured.
The most natural way to attempt to measure subjective well-being is to ask people what they think and feel. Indeed, this is the most common approach.
In practice, social scientists tend to rely on questions inquiring directly about happiness or on questions inquiring about life satisfaction. The former tends to measure the experiential or emotional aspects of well-being (e.g., “I feel very happy”), while the latter tends to measure the evaluative or cognitive aspects of well-being (e.g., “I think I lead a very positive life”).
Self-reports about happiness and life satisfaction are known to correlate with things that people typically associate with contentment, such as cheerfulness and smiling. (In this scatter plot , you can see that countries where people have higher self-reported life satisfaction are also countries where people tend to smile more).
Experimental psychologists have also shown that self-reports of well-being from surveys turn out to correlate with activity in the parts of the brain associated with pleasure and satisfaction. Various surveys have confirmed that people who say they are happy also tend to sleep better and express positive emotions verbally more frequently.
Is ‘life satisfaction’ the same as ‘happiness’?
In this topic page, we discuss data and empirical research on happiness and life satisfaction. However, it is important to bear in mind that “life satisfaction” and “happiness” are not really synonyms. This is, of course, reflected in the data since self-reported measures of these two variables come from asking different kinds of questions.
The Integrated Values Surveys asks directly about happiness: “Taking all things together, would you say you are (i) Very happy, (ii) Rather happy, (iii) Not very happy, (iv) Not at all happy, (v) Don’t know.”
The Gallup World Poll, on the other hand, uses the Cantril Ladder question and asks respondents to evaluate their life: “Please imagine a ladder, with steps numbered from 0 at the bottom to 10 at the top. The top of the ladder represents the best possible life for you, and the bottom of the ladder represents the worst possible life for you. On which step of the ladder would you say you personally feel you stand at this time?”
As the following scatter plot shows, these two measures tend to be related (countries that score high in one measure also tend to score high in the other), yet they are not identical (there is substantial dispersion, with many countries sharing the same score in one variable but diverging in the other).
The differences in responses to questions inquiring about life satisfaction and happiness are consistent with the idea that subjective well-being has two sides: an experiential or emotional side and an evaluative or cognitive side. Of course, the limits between emotional and cognitive aspects of well-being are blurred in our minds, so in practice, both kinds of questions measure both aspects to some degree. Indeed, social scientists often construct ‘subjective well-being indexes’ where they simply average out results from various types of questions.
Are happiness averages really meaningful?
The most common way to analyze data on happiness consists of taking averages across groups of people. Indeed, cross-country comparisons of self-reported life satisfaction, such as those presented in ‘happiness rankings’, rely on national averages of reports on a scale from 0 to 10 (the Cantril Ladder).
Is it reasonable to take averages of life satisfaction scores? Or, in more technical terms, are self-reports of Cantril scores really a cardinal measure of well-being?
The evidence tells us that survey-based reports on the Cantril Ladder do allow cardinal measurement reasonably well—respondents have been found to translate verbal labels, such as ‘very good’ and ‘very bad’, into roughly the same numerical values. 21 22
But as with any other aggregate indicator of social progress, averages need to be interpreted carefully, even if they make sense arithmetically. For example, if we look at happiness by age in a given country, we may see that older people do not appear to be happier than younger people. Yet this may be because the average-by-age figure from the snapshot confounds two factors: the age effect (people from the same cohort do get happier as they grow older, across all cohorts) and the cohort effect (across all ages, earlier generations are less happy than more recent generations). If the cohort effect is very strong, the snapshot can even give a picture that suggests people become less happy as they grow older, even though the exact opposite is actually true for all generations.
This example is, in fact, taken from the real world: using data from the US, Sutin et al. (2013) 23 showed that self-reported feelings of well-being tend to increase with age across generations, but overall levels of well-being depend on when people were born.
How much does language matter for cross-country comparisons of happiness?
Linguistic differences are often seen as a major obstacle for making cross-country comparisons of happiness. However, there is evidence suggesting that comparability issues, at least with respect to language, are less problematic than many people think.
Studies have shown, for example, that in interviews in which respondents are shown pictures or videos of other individuals, respondents can broadly identify whether the individual shown to them was happy or sad; this is also true when respondents were asked to predict the evaluations of individuals from other cultural communities. (For evidence of this, see Sandvik et al., 1993; Diener and Lucas, 1999). 24
Studies have also shown that ‘indigenous emotions’ across cultures (i.e., feelings that are unique in that they do not have equivalents in the English language) are not experienced any more frequently or differently than commonly translated emotions. (See Scollon et al. 2005). 25
The conclusion, therefore, seems to be that there is some basic understanding among humans about what it means to be ‘happy’. Survey-based measures of self-reported life satisfaction are informative about cross-country differences, even if these comparisons are obviously noisy.
A French translation of this topic page is available on our site: Bonheur et satisfaction .
Interactive charts on happiness and life satisfaction
Particularly important was the Stiglitz-Sen-Fitoussi Commission . It also relates to Bhutan’s famous measurement of Gross National Happiness (GNH) as an indicator of progress (Wikipedia here ).
To be precise, in 27 out of 31 countries with data spanning longer than one decade, the estimate for 2016 is higher than the earliest available estimate.
The GSS asks people a very similar question to the Integrated Values Survey: “Taken all together, how would you say things are these days—would you say that you are very happy, pretty happy, or not too happy?”
Stevenson, Betsey, and Justin Wolfers. “Happiness inequality in the United States.” The Journal of Legal Studies 37.S2 (2008): S33-S79. An ungated earlier version of the paper is available here .
These results have been discussed in various blogs. Freakonomics provides a quick and interesting overview of the debate, specifically with regard to gender gaps .
Clark, Andrew E., Sarah Flèche, and Claudia Senik. “Economic growth evens out happiness: Evidence from six surveys.” Review of Income and Wealth (2015). An ungated earlier version of the paper is available here
To be precise, the gradients correspond, country by country, to the regression coefficients between income quintiles and the related average life satisfaction reported by people within each income quintile.
Stevenson, B. and Wolfers, J. (2008). Economic growth and subjective well-being: Reassessing the Easterlin Paradox. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity, 1-87. An earlier version is available online here .
The dataset includes observations for Egypt. However, we have excluded these observations from our analysis. This is because the survey for Egypt in the wave labeled 2014 is from 2012, which was a year characterized by extreme political instability in that country.
R.A. Easterlin and L. Angelescu – ‘Modern Economic Growth and Quality of Life: Cross-Sectional and Time Series Evidence’ in Land, Michalos, and Sirgy (ed.) (2011) – Handbook of Social Indicators and Quality of Life Research. Springer.
Chart from Stevenson B, Wolfers J (2008) - Economic Growth and Subjective Well-Being: Reassessing the Easterlin Paradox. Brookings Paper Econ Activ 2008 (Spring):1–87. Underlying data source: Life in Nation surveys, 1958–2007. Note from the authors: “The series in each of the four panels reports responses to a different life satisfaction question, and therefore comparisons should be made only within each panel. GDP per capita is at purchasing power parity in constant 2000 international dollars.”
Clark, A. E., Diener, E., Georgellis, Y., & Lucas, R. E. (2008). Lags and leads in life satisfaction: A test of the baseline hypothesis. The Economic Journal, 118(529).
Brickman, P., Coates, D., & Janoff-Bulman, R. (1978). Lottery winners and accident victims: Is happiness relative? . Journal of personality and social psychology, 36(8), 917. Chicago.
Oswald, A. J., & Powdthavee, N. (2008). Does happiness adapt? A longitudinal study of disability with implications for economists and judges. Journal of Public Economics, 92(5), 1061-1077.
Diener, E., Oishi, S., & Lucas, R. E. (2009). Subjective well-being: The Science of Happiness and Life Satisfaction. Oxford Handbook of Positive Psychology, 2, 187-194.
To be precise, the Gallup World Poll asks: “In this country, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with your freedom to choose what you do with your life?”
Inglehart, R., Foa, R., Peterson, C., & Welzel, C. (2008). Development, freedom, and rising happiness: A global perspective (1981–2007). Perspectives on psychological science, 3(4), 264-285.
Johnston, W. M., & Davey, G. C. (1997). The Psychological Impact of Negative TV News Bulletins: The Catastrophizing of Personal Worries. British Journal of Psychology, 88(1), 85-91.
Combs, B., & Slovic, P. (1979). Newspaper coverage of causes of death. Journalism Quarterly, 56(4), 837-849.
Riddle (2010), for example, found that people watching more vivid violent media gave higher estimates of the prevalence of crime in the real world. (Riddle, K. (2010). Always on my mind: Exploring how frequent, recent, and vivid television portrayals are used in the formation of social reality judgments. Media Psychology, 13(2), 155–179.)
Ferrer‐i‐Carbonell, A., & Frijters, P. (2004). How important is methodology for the estimates of the determinants of happiness?. The Economic Journal, 114(497), 641-659.
Van Praag, B.M.S. (1991). ‘Ordinal and cardinal utility: an integration of the two dimensions of the welfare concept’, Journal of Econometrics, vol. 50, pp. 69–89.
Sutin, A. R., Terracciano, A., Milaneschi, Y., An, Y., Ferrucci, L., & Zonderman, A. B. (2013). The effect of birth cohort on well-being The legacy of economic hard times. Psychological science, 0956797612459658.
Sandvik, E., Diener, E. and Seidlitz, L. (1993). ‘Subjective well-being: the convergence and stability of self and non-self report measures’, Journal of Personality, vol. 61, pp. 317–42. Diener, E. and Lucas, R.E. (1999). ‘Personality and subjective well-being’, in Kahneman et al. (1999) chapter 11.
Scollon, C. N., Diener, E., Oishi, S., & Biswas-Diener, R. (2004). Emotions across cultures and methods. Journal of cross-cultural psychology, 35(3), 304-326.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this topic page, please also cite the underlying data sources. This topic page can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Happiness
List of essays on happiness, essay on happiness – short essay (essay 1 – 150 words), essay on happiness – for kids and children (essay 2 – 200 words), essay on happiness – 10 lines on happiness written in english (essay 3 – 250 words), essay on happiness (essay 4 – 300 words), essay on happiness – ways to be happy (essay 5 – 400 words), essay on happiness – for school students (class 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 standard) (essay 6 – 500 words), essay on happiness – ways of developing happiness (essay 7 – 600 words), essay on happiness – sources of suffering, happiness and conclusion (essay 8 – 750 words), essay on happiness – long essay on happiness (essay 9 – 1000 words).
Happiness is defined by different people in different ways. When we feel positive emotions we tend to feel happy. That is what happiness is all about. Happiness is also regarded as the mental state of a person in an optimistic manner.
Every person defines happiness in his/her own manner. In whatever manner you may define happiness; the truth is that it is vital for a healthy and prosperous life.
In order to make students understand what true happiness is all about, we have prepared short essays for students which shall enlighten them further on this topic.
Audience: The below given essays are exclusively written for school students (Class 3, 4 ,5, 6 and 7 Standard).
Introduction:
Happiness is a state of mind and the feeling expressed when things are going great. It is what we feel when we get our first car, buy a new house or graduate with the best grades. Happiness should be distinguished from joy. When joy is a constant state of mind, happiness depends on events in our lives.
Importance of Happiness:
The opposite of happiness is sadness which is a state of negativity in the mindset. When we remain sad for an extended period of time it can lead to depression. To avoid this state of mind we must always remind ourselves of happenings in our lives that made us happy.
Conclusion:
Though life throws countless challenges at us on a daily basis, if we drown in those challenges we would definitely become depressed. It is important that we find positive things in our daily lives to get excited about and feel the happiness.
Happiness is a state of mind which makes you feel accomplished in life and having everything in this world without a single reason to repent. Well, although there can be no perfect definition of happiness; happiness is when you feel you’re at the top of the world where a sense of complete satisfaction prevails.
The meaning of happiness is relative and varies from people to people. For some, happiness is when you experience professional success, reunions with family and friends, eating out, reading books or watching good movies. While for others, happiness can be accomplished by some weekend activities which might help you de-stress and get the satisfaction of mind.
If you involve yourself in social activities where you help the needy and provide support to the weaker section of the society, you can experience happiness if not anything else. When a young boy flies a kite, plays with mud, and watches the nature, for him, that is the greatest happiness in the world.
The happiness of mind is often considered quite contrary to jealousy and anger which you experience once you have failed or unaccomplished any desired goal. You should always try to rehearse the ways of keeping yourself satisfied and keeping away from negativity to experience peace and happiness in life. True happiness begins where desire ends!
What is happiness? It is a state of being happy. But it does not mean to be happy all the time. Happiness is a feeling of something good that is happening in our life. We feel happy when we achieve something. But happiness is spread when our dear one is happy as well. Some people find true happiness in playing with their pets, while some may find happiness in staying engaged in creative work.
Happiness is often derived from channelizing thoughts to positive thinking. However, it is not as simple as it may sound.
To achieve the state of complete happiness one has to practice on improving the state of life by:
1. Staying contended in life with what you have. Cribbing and grumbling never lead to happiness.
2. Staying focused on the current life instead of daydreaming of the good days or old days.
3. Stop blaming for something that went terribly wrong in life. The life is all about moving on. Stop worrying and set new goals in life.
4. Being thankful to God for all the good things that you have in your life.
5. Having good people around you who can boost up positivity in your life.
Everyone desires to be happy in life. Happiness cannot be achieved without establishing complete control of one’s thoughts as it is very easy to be carried away by the waves of thoughts and emotions surrounding us. Remind yourself of the good things of your life and be thankful about it.
What is happiness? Some would state that happiness implies being well off. Others would state that for them, happiness intends to be sound. You will discover individuals saying that for them happiness implies having love in their life, having numerous companions, a great job, or accomplishing a specific objective. There are individuals, who trust that the want of a specific wish would make happiness in their life; however, it may not be so. Having true happiness is something which is desired by all.
The Path to Happiness:
There are small things which when incorporated into our daily lives, can lead us to the path of happiness. For instance, instead of thinking about problems, we should actually be thinking about the solutions. Not only will we be happier but we shall also be able to solve our problems faster. Similarly, once in a while, you start the day with the longing to achieve a few targets. Toward the day’s end, you may feel disappointed and miserable, in light of the fact that you haven’t possessed the capacity to do those things. Take a look at what you have done, not at what you have not possessed the capacity to do. Regularly, regardless of whether you have achieved a ton amid the day, you let yourself feel disappointed, due to some minor assignments you didn’t achieve. This takes away happiness from you.
Again, now and then, you go throughout the day effectively completing numerous plans, yet as opposed to feeling cheerful and fulfilled, you see what was not cultivated and feel troubled. It is out of line towards you.
Each day accomplishes something good which you enjoy doing. It may tend to be something little, such as purchasing a book, eating something you cherish, viewing your most loved program on TV, heading out to a motion picture, or simply having a walk around the shoreline. Even small things can bring great levels of happiness in our lives and motivate us for new goals.
Happiness is not what you feel from outside, rather it is something which comes from your inner soul. We should find happiness in us rather than searching for it in worldly desires.
Happiness is defined by different people in different ways. Some find happiness in having a luxurious life while some find it in having loving people around them rather than money. True happiness lies within us and our expectation of happiness. It is something that should be felt and cannot be explained in words.
Even though this simple word has a lot of meaning hidden in it, many fail to understand the real one or feel the real happiness. Finding happiness in the outer world is the main reason for this failure. Nothing can buy you happiness, whether be the favorite thing you desire for or the person you love the most or the career you build, unless and until you feel it within yourself.
Ways to be Happy:
Bring happiness and soulful life to yourself rather than expecting it from the outside world like things, money, etc. Being happy is not as easy as advised to be one happier person. To be content and happy with whatever you have and yourself it takes time and patience. You should practice to be a happier person in all moments and eventually you will notice that no sorrow can sink you down.
Whatever good or bad happened in your past shouldn’t bother your present. Learn to live today with more happiness than yesterday and forget about your past sadness for a harmonious life. Thankfulness to the life you got is another important character you should acquire to be happy. If you compare yourself with someone with better luxurious life, then you will never be happy or content and do it the other way.
Don’t depress your mind with bad and negative thoughts about yourself and around. Try to find every goodness in a situation you face and accept the things that already happened, whether good or bad. Never forget to choose merrier and positive people to be closer to you so that their vibes will also help you in being one merrier person.
Whenever you feel low and depressed never hesitate to go to those around you to find happiness. But be aware of those negative ones that may pull you even deeper into the bad thoughts. Always surround yourself with positive thinking and motivating people so that you can rise higher even from the deepest fall.
Happiness is nothing but a feeling that will be seeded into your soul only if you wish to and nothing other than yourself can indulge this feeling in you. Don’t spoil your life finding happiness somewhere else.
Happiness is a very complicated thing. Happiness can be used both in emotional or mental state context and can vary largely from a feeling from contentment to very intense feeling of joy. It can also mean a life of satisfaction, good well-being and so many more. Happiness is a very difficult phenomenon to use words to describe as it is something that can be felt only. Happiness is very important if we want to lead a very good life. Sadly, happiness is absent from the lives of a lot of people nowadays. We all have our own very different concept of happiness. Some of us are of the opinion that we can get happiness through money, others believe they can only get true happiness in relationships, some even feel that happiness can only be gotten when they are excelling in their profession.
As we might probably know, happiness is nothing more than the state of one being content and happy. A lot of people in the past, present and some (even in the future will) have tried to define and explain what they think happiness really is. So far, the most reasonable one is the one that sees happiness as something that can only come from within a person and should not be sought for outside in the world.
Some very important points about happiness are discussed below:
1. Happiness can’t be bought with Money:
A lot of us try to find happiness where it is not. We associate and equate money with happiness. If at all there is happiness in money then all of the rich people we have around us would never feel sad. What we have come to see is that even the rich amongst us are the ones that suffer depression, relationship problems, stress, fear and even anxiousness. A lot of celebrities and successful people have committed suicide, this goes a long way to show that money or fame does not guarantee happiness. This does not mean that it is a bad thing to be rich and go after money. When you have money, you can afford many things that can make you and those around you very happy.
2. Happiness can only come from within:
There is a saying that explains that one can only get true happiness when one comes to the realisation that only one can make himself/herself happy. We can only find true happiness within ourselves and we can’t find it in other people. This saying and its meaning is always hammered on in different places but we still refuse to fully understand it and put it into good use. It is very important that we understand that happiness is nothing more than the state of a person’s mind. Happiness cannot come from all the physical things we see around us. Only we through our positive emotions that we can get through good thoughts have the ability to create true happiness.
Our emotions are created by our thoughts. Therefore, it is very important that we work on having only positive thoughts and this can be achieved when we see life in a positive light.
Happiness is desired by every person. However, there are very few persons that attain happiness easily in life.
It is quite tough to get happiness in life as people usually link it with the things and the people around them. The simple fact is that happiness usually starts as well as finishes with your own life. All those people who understand this fact easily get the true happiness in their life.
Happiness in Relationships:
There are lots of people who link happiness with the money and there are few others also who link it with the personal relations. It is very important to know that if you are not happy with yourself then, it is not possible to remain happy in your relationship as well.
The problems in the relationship have been increasing speedily and the main cause behind it is the huge amount of expectation that we have from the other individual. We always want them to make us feel happy. For example, some people feel happy if their partner plans a surprise for them or if he/she buy them a new dress. But all these things are not a true source of happiness in life.
Ways of Developing Happiness:
The lack of happiness in the relationship not only exists in couples but also in the relationship of friends, sister – brother or parent-child.
The following are the few ways that help in creating happiness in the relationships:
1. Pay Attention to Yourself:
You should always pay attention to yourself to get happiness. You should not give importance to any other person in your life in comparison to yourself and also expect the same from that person. Giving too much importance to the other and not receiving anything back from them makes a person disappointed and happiness gets lost.
2. Have some Initiative:
You can make the plan of traveling outside yourself. Don’t wait for your parent, partner or kid to take you outside. You can ask them to come along with you if they want. But, if they decline your offer then, don’t get discouraged and carry on your trip plan along with full happiness.
3. Provide some Space:
It is necessary to provide some amount of space to every individual and spend some time with oneself. It helps in creating happiness.
Happiness is Necessary for Good Life:
It does not matter that whether you are a working expert, a schoolchild, a retired person or a housewife, happiness is necessary for everybody to live a good and happy life. Happiness is essential for an individual’s emotional comfort. A person who is not fit emotionally will feel an impact on his complete health that will drain very soon.
Unluckily, despite the fact that happiness is tremendously necessary, people do not give so much importance to all those habits which can keep them happy. They are so excessively captivated inside their professional lives as well as other nuts and bolts of life that they overlook to relish the happy memories of their life. It is also the main reason that problems like anxiety, stress, and depression are increasing gradually in people’s lives today.
Happiness is an internal feeling. It is a healthy emotion. Happiness helps us to stay fit both mentally and physically. Happiness helps in lowering stress and keeping away from any health issues. The reason of happiness may be different for different person. You just need to find out what actually makes you happy. So, if you want real happiness in life then, you need to understand that only you can make yourself happy.
“There is no way to happiness, happiness is the way” this sentence has been attributed to Buddha. Well, at least that’s what it says on one sticker in my dorm room. The fact is that man has occupied himself with the path to happiness for millennia. Something happened during our evolution that made us deeply question the purpose of our existence. People like Buddha are part of the answer, or at least they try to give us the answer.
Since these questions have troubled us there have been many who sought to answer them and by doing so, they formed philosophies and religions. The search for earthly happiness will make many do incredible deeds but if this energy is used in the wrong way it can cause great suffering. How can we know which recipe for happiness is the best one and what we should devote our time and attention to? The trick is, there is no right answer and as the first sentence of this essay states, there is no way to be happy because being happy is the way. That’s how I got my head around this problem, let me explain some more.
Source of Suffering:
At the expense of sounding Buddhist, when you think about most of the things that make us unhappy are material in nature. They are the things that we really do not need but they make us feel happy. This notion is not just something the wise man from the 6 th century BC India expressed but many more have said this before and after him. Socrates and Jesus to name just a few.
What I find interesting in the struggle for happiness is the paradox present in the instructions to reach it. One has a thought all through life to be good and hard working so he can get the things he wants and needs later on in life but then as you start to struggle for the money you realize that your life is turning into a money grabbing game. So, the source of happiness and stability becomes the source of all your anxiety and aggression. Naturally, we can see how some people thought that all material things stand on the path to our happiness.
But what about the immaterial, what if you are in love with someone you are not supposed to love? The above instruction would tell you to surrender your heart’s desire and you will be free from constraints. Is this happiness? Or is it the struggle to do and achieve the impossible the real source of happiness?
Source of Happiness:
People often forget that they are animals and like all of them they have a logic to their nature and their own specific needs. Like all the other animal’s people are caught in the struggle for existence and sometimes surviving the day can be a real ordeal if you get caught in the wrong circumstances. Men has made himself safe from most of the things that could have harmed him in nature but in doing so he forgot what he has made.
Think about the present from a historical perspective. Even a hundred years ago most people lost up to 80% of all their children to diseases, clean water was a rarity for most of our existence, and people actually had to labor to make food and to have enough to feed their family all through the year. The fact is we have a lot to be grateful for in the present age and the fact that some of us are unhappy because we do not have all our heart’s desires is just a symptom of collective infancy. Having all of your loved ones around you, with a roof to shelter under and with lots of delicious food is the only source of happiness man needs everything else should just be a bonus.
Happiness cannot be found by rejecting everything that is material or by earning more money then you can spend. The trick is to find balance by looking at yourself and the lives of people around you and by understanding that there is a lot to be grateful for, the trick is to stop searching for a path and to understand that we are already walking on one. As long as we are making any type of list of the prerequisite for our life of happiness, we will end up unsatisfied because life does not grant wishes we are the ones that make them come true. Often the biggest change in our lives comes from a simple change of perspective rather than from anything we can own.
Happiness is the state of emotional wellbeing and being contented. Happiness is expressed through joyful moments and smiles. It is a desirable feeling that everybody want to have at all times. Being happy is influenced by situations, achievements and other circumstances. Happiness is an inner quality that reflects on the state of mind. A peaceful state of mind is considered to be happiness. The emotional state of happiness is mixture of feelings of joy, satisfaction, gratitude, euphoria and victory.
How happiness is achieved:
Happiness is achieved psychologically through having a peaceful state of mind. By a free state of mind, I mean that there should be no stressful factors to think about. Happiness is also achieved through accomplishment of goals that are set by individuals. There is always happiness that accompanies success and they present feelings of triumph and contentment.
To enable personal happiness in life, it is important that a person puts himself first and have good self-perception. Putting what makes you happy first, instead of putting other people or other things first is a true quest towards happiness. In life, people tend to disappoint and putting them as a priority always reduces happiness for individuals. There is also the concept of practicing self-love and self-acceptance. Loving oneself is the key to happiness because it will mean that it will not be hard to put yourself first when making decisions.
It is important for an individual to control the thoughts that goes on in their heads. A peaceful state of mind is achieved when thoughts are at peace. It is recommended that things that cause a stressful state of mind should be avoided.
Happiness is a personal decision that is influenced by choices made. There is a common phrase on happiness; “happiness is a choice” which is very true because people choose if they want to be happy or not. Happiness is caused by circumstances and people have the liberty to choose those circumstance and get away from those that make them unhappy.
Happiness is also achieved through the kind of support system that an individual has. Having a family or friends that are supportive will enable the achievement of happiness. Communicating and interacting with the outside world is important.
Factors Affecting Happiness:
Sleep patterns influence the state of mind thus influence happiness. Having enough sleep always leads to happy mornings and a good state of mind for rest of the day. Sleep that is adequate also affects the appearance of a person. There is satisfaction that comes with having enough sleep. Enough rest increases performance and productivity of an individual and thus more successes and achievements are realized and happiness is experienced.
Another factor affecting happiness is the support network of an individual. A strong support network of family and friends results in more happiness. Establishing good relationships with neighbors, friends and family through regular interactions brings more happiness to an individual. With support network, the incidences of stressful moments will be reduced because your family and friends will always be of help.
Sexual satisfaction has been established to affect happiness. It is not just about getting the right partner anymore. It is about having a partner that will satisfy you sexually. There is a relationship between sex and happiness because of the hormones secreted during sexual intercourse. The hormone is called oxytocin and responsible for the happiness due to sexual satisfaction. Satisfaction also strengthens the relationships between the partners and that creates happiness.
Wealth also plays a significant role in happiness. There is a common phrase that is against money and happiness: “money cannot buy happiness” is this true? Personally, I believe that being financially stable contributes to happiness because you will always have peace of mind and many achievements. Peace of mind is possible for wealthy people because they do not have stressors here and then compared to poor people. Also, when a person is wealthy, they can afford to engage in luxurious activities that relaxes the mind and create happiness. For a person to be wealthy, they will have had many achievements in life. These achievement make them happy.
A good state of health is an important factor that influences the happiness of individuals. A healthy person will be happy because there are no worries of diseases or pain that they are experiencing. When a person is healthy, their state of mind is at peace because they are not afraid of death or any other health concerns. Not only the health of individuals is important, but also the health of the support system of the person. Friends and family’s state of health will always have an impact on what we feel as individuals because we care about them and we get worried whenever they are having bad health.
Communication and interactions are important in relation to an individual’s happiness. Having a support system is not enough because people need to communicate and interact freely. Whenever there are interactions like a social gathering where people talk and eat together, more happiness is experienced. This concept is witnessed in parties because people are always laughing and smiling in parties whenever they are with friends.
Communication is key to happiness because it helps in problem solving and relieving stressors in life. Sharing experiences with a support system creates a state of wellbeing after the solution is sought. Sometime when I am sad, I take my phone and call a friend or a family member and by the time the phone call is over, I always feel better and relieved of my worries.
Happiness is an important emotion that influences how we live and feel on a daily basis. Happiness is achieved in simple ways. People have the liberty to choose happiness because we are not bound by any circumstances for life. Factors that influence happiness are those that contribute to emotional wellbeing. Physical wellbeing also affects happiness. Every individual finds happiness in their own because they know what makes them happy and what doesn’t.
Emotions , Happiness , Psychology
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Which is More Important in Life: Love or Money | Essay
- Essay on My School
- Essay on Solar Energy
- Essay on Biodiversity
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview
Essays About Happiness: 5 Essay Examples and 6 Writing Prompts
Being happy and content is essential to living a successful life. If you are writing essays about happiness, start by reading our helpful guide.
Whenever we feel positive emotions rushing through our heads, chances are we are feeling happy. Happiness is what you feel when you enter the house, the smell of your favorite food being cooked or when you finally save up enough money to buy something you’ve wanted. It is an undeniably magical feeling.
Happiness can do wonders for your productivity and well-being; when you are happy, you are more energetic, optimistic, and motivated. So it is, without a doubt, important. However, do not become caught up in trying to be happy, as this may lead to worse problems. Instead, allow yourself to feel your emotions; be authentic, even if that means feeling a little more negative.
5 Top Essay Examples
1. causes of happiness by otis curtis, 2. how to be happy by tara parker-pope, 3. reflections on ‘happiness’ by shahzada sultan.
- 4. Happiness is Overrated by John Gorman
5. Toxic positivity by Suhani Mahajan
6 prompts for essays about happiness, 1. why is it important to be happy, 2. what is happiness to you, 3. the role of material things in happiness, 4. how does happiness make you more productive, 5. is true happiness achievable, 6. happiness vs. truth.
“If you don’t feel good about yourself you will have a similarly negative attitude towards others and education is one way of having good self-esteem, as it helps you to live life successfully and happily. Education is one way of getting that dream job and education is an essential cog in the wheel to living comfortably and happily. One English survey that included over 15,000 participants revealed that 81 percent of people who had achieved a good level of education had a high level of life satisfaction.”
Based on personal beliefs and research, Curtis’ essay describes different contributing causes to people’s happiness. These include a loving, stable family and good health. Interestingly, there is a positive correlation between education level and happiness, as Curtis cites statistics showing that education leads to high self-esteem, which can make you happier.
“Socratic questioning is the process of challenging and changing irrational thoughts. Studies show that this method can reduce depression symptoms. The goal is to get you from a negative mindset (“I’m a failure.”) to a more positive one (“I’ve had a lot of success in my career. This is just one setback that doesn’t reflect on me. I can learn from it and be better.”)”
Parker-Pope writes about the different factors of happiness and how to practice mindfulness and positivity in this guide. She gives tips such as doing breathing exercises, moving around more, and spending time in places and with people that make you happy. Most importantly, however, she reminds readers that negative thoughts should not be repressed. Instead, we should accept them but challenge that mindset.
“Happiness is our choice of not leaving our mind and soul at the mercy of the sways of excitement. Happiness cannot eliminate sorrow, suffering, pain or death from the scheme of things, but it can help keep fear, anxiety, sadness, hopelessness, pessimism and other fathers of unhappiness at bay.”
Sultan discusses what happiness means to her personally. It provides an escape from all the dreariness and lousy news of daily life, not eliminating negative thoughts but keeping them at a distance, even just for a moment. She writes that to be happy; we should not base our happiness on the outcomes of our actions. We cannot control the world around us, so we should not link our happiness to it. If something doesn’t go our way, that is just how the world works. It is useless to be sad over what we cannot control.
4. Happiness is Overrated by John Gorman
“Our souls do float across the sea of life, taking on water as they go, sinking ever so slightly — perhaps even imperceptibly — into despair. But our souls are not the bucket. Happiness itself is. And it’s the bucket we use to pour water out our souls and keep us afloat. What we really need is peace. Peace patches the holes in our souls and stops the leaking. Once we have peace, we will no longer need to seek happiness.”
In his essay, Gorman reflects on how he stopped trying to chase happiness and instead focused on finding peace in life. He writes that we are often so desperate looking for happiness that our lives become complicated, chaotic, and even depressing at times. He wants readers to do what they are passionate about and be their authentic selves; that way, they will find true happiness. You might also be interested in these essays about courage .
“That’s the mindset most of us have. Half of toxic positivity is just the suppression of 200% acceptable feelings such as anger, fear, sadness, confusion, and more. Any combination of such feelings is deemed “negative.” Honestly, mix ‘em up and serve them to me in a cocktail, eh? (Fine, fine, a mocktail. I reserve my right to one of those little umbrellas though.)
But by closing ourselves off to anything but positivity, we’re experiencing the same effects as being emotionally numb. Why are we doing this to ourselves?”
Mahajan writes about the phenomenon known as “toxic positivity” in which everyone is expected to be happy with their lives. It trivializes people’s misfortunes and sufferings, telling them to be happy with what they have instead. Mahajan opposes this, believing that everyone’s feelings are valid. She writes that it’s okay to be sad or angry at times, and the stigma around “negative feelings” should be erased. When we force ourselves to be happy, we may feel emotionally numb or even sad, the exact opposite of being happy.

Many would say that happiness aids you in many aspects of your life. Based on personal experience and research, discuss the importance of being happy. Give a few benefits or advantages of happiness. These can include physical, mental, and psychological benefits, as well as anything else you can think of.
Happiness means different things to different people and may come from various sources. In your essay, you can also explain how you define happiness. Reflect on this feeling and write about what makes you happy and why. Explain in detail for a more convincing essay; be sure to describe what you are writing about well.

Happiness has a myriad of causes, many of which are material. Research the extent to which material possessions can make one happy, and write your essay about whether or not material things can truly make us happy. Consider the question, “Can money buy happiness?” Evaluate the extent to which it can or cannot, depending on your stance.
Happiness has often been associated with a higher level of productivity. In your essay, look into the link between these two. In particular, discuss the mental and chemical effects of happiness. Since this topic is rooted in research and statistics, vet your sources carefully: only use the most credible sources for an accurate essay.
In their essays, many, including Gorman and Mahajan, seem to hold a more critical view of happiness. Our world is full of suffering and despair, so some ask: “Can we truly be happy on this earth?” Reflect on this question and make the argument for your position. Be sure to provide evidence from your own experiences and those of others.
In dystopian stories, authorities often restrict people’s knowledge to keep them happy. We are seeing this even today, with some governments withholding crucial information to keep the population satisfied or stable. Write about whether you believe what they are doing is defensible or not, and provide evidence to support your point.
For help with this topic, read our guide explaining “what is persuasive writing ?”
For help picking your next essay topic, check out our top essay topics about love .

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
What Is Happiness?
Reviewed by Psychology Today Staff
Happiness is an electrifying and elusive state. Philosophers, theologians, psychologists, and even economists have long sought to define it. And since the 1990s, a whole branch of psychology— positive psychology —has been dedicated to pinning it down. More than simply positive mood, happiness is a state of well-being that encompasses living a good life, one with a sense of meaning and deep contentment.
Feeling joyful has its health perks as well. A growing body of research also suggests that happiness can improve your physical health; feelings of positivity and fulfillment seem to benefit cardiovascular health, the immune system, inflammation levels, and blood pressure, among other things. Happiness has even been linked to a longer lifespan as well as a higher quality of life and well-being.
Attaining happiness is a global pursuit. Researchers find that people from every corner of the world rate happiness more important than other desirable personal outcomes, such as obtaining wealth, acquiring material goods, and getting into heaven.

Happiness is not the result of bouncing from one joy to the next; researchers find that achieving happiness typically involves times of considerable dis comfort. Genetic makeup, life circumstances, achievements, marital status, social relationships, even your neighbors—all influence how happy you are. Or can be. So do individual ways of thinking and expressing feelings. Research shows that much of happiness is under personal control.
Regularly indulging in small pleasures, getting absorbed in challenging activities, setting and meeting goals , maintaining close social ties, and finding purpose beyond oneself all increase life satisfaction. It isn't happiness per se that promotes well-being, it’s the actual pursuit that’s key.
For more, see How to Find Happiness.

Happy people live with purpose. They find joy in lasting relationships, working toward their goals, and living according to their values. The happy person is not enamored with material goods or luxury vacations. This person is fine with the simple pleasures of life—petting a dog, sitting under a tree, enjoying a cup of tea. Here are a few of the outward signs that someone is content.
- Is open to learning new things
- Is high in humility and patience
- Smiles and laughs readily
- Goes with the flow
- Practices compassion
- Is often grateful
- Exercises self-care
- Enjoys healthy relationships
- Is happy for other people
- Gives and receives without torment
- Lives with meaning and purpose
- Does not feel entitled and has fewer expectations
- Is not spiteful or insulting
- Does not hold grudges
- Does not register small annoyances
- Does not angst over yesterday and tomorrow
- Does not play games
- Is not a martyr or victim
- Is not stingy with their happiness
For more, see How To Find Happiness.

Misperceptions abound when it comes to what we think will make us happy. People often believe that happiness will be achieved once they reach a certain milestone, such as finding the perfect partner or landing a particular salary.
Humans, however, are excellent at adapting to new circumstances, which means that people will habituate to their new relationship or wealth, return to a baseline level of happiness, and seek out the next milestone. Fortunately, the same principle applies to setbacks—we are resilient and will most likely find happiness again.
Regarding finances specifically, research shows that the sweet spot for yearly income is between $60,000 and $95,000 a year, not a million-dollar salary. Earnings above $95,000 do not equate to increased well-being; a person earning $150,000 a year will not necessarily be as happy as a person earning a lot less.
The type of thoughts below exemplify these misconceptions about happiness:
- "I’ll be happy when I’m rich and successful."
- "I’ll be happy when I’m married to the right person."
- "Landing my dream job will make me happy."
- "I can’t be happy when my relationship has fallen apart."
- "I will never recover from this diagnosis."
- "The best years of my life are over."
For more, see The Science of Happiness.

Positive psychology is the branch of psychology that explores human flourishing. It asks how individuals can experience positive emotions, develop authentic relationships, find flow, achieve their goals, and build a meaningful life.
Propelled by University of Pennsylvania psychologist Martin Seligman , the movement emerged from the desire for a fundamental shift in psychology—from revolving around disease and distress to providing the knowledge and skills to cultivate growth, meaning, and fulfillment. For more, see Positive Psychology.

Every person has unique life experiences, and therefore unique experiences of happiness. That being said, when scientists examine the average trajectory of happiness over the lifespan, some patterns tend to emerge. Happiness and satisfaction begin relatively high, decrease from adolescence to midlife , and rise throughout older adulthood.
What makes someone happy in their 20s may not spark joy in their 80s, and joy in someone’s 80s may have seemed irrelevant in their 20s. It’s valuable for people to continue observing and revising what makes them happy at a given time to continue striving for fulfillment throughout their lifetime.
For more, see Happiness Over the Lifespan.

Health and happiness are completely intertwined. That’s not to say that people with illnesses can’t be happy, but that attending to one’s health is an important—and perhaps underappreciated—component of well-being.
Researchers have identified many links between health and happiness—including a longer lifespan—but it’s difficult to distinguish which factor causes the other. Making changes to diet , exercise, sleep, and more can help everyone feel more content.
For more, see Happiness and Health .

In life, there's always going to be someone with more. Jealousy and envy only make you feel worse. Fortunately, sympathetic joy offers a better path forward for you and others.

Quid-pro-quo kindness can be damaging to a relationship. Here's how to avoid it.

If any society seriously wishes to improve levels of wellbeing and overall harmony, the best place to start is childhood.

When friends are sexually involved, but don't consider their relationship romantic, some enjoy greater freedom regarding life and sexuality.

Discover how challenges that are not fun in the moment—but rewarding in retrospect—can grow resilience, deepen life satisfaction, and lead to transformative personal growth.

Having a supportive partner can encourage you to take creative risks and look for opportunities to continue to learn and grow.

There are lessons to be learned about our approach to life from how we play poker.

A new study suggests that happiness among singles and those in couples is similar.

The space that you're in can help you think and do, or not.

Discover the science behind the mental health benefits of this popular pastime.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Essay on Happiness in Life
Students are often asked to write an essay on Happiness in Life in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Happiness in Life
Understanding happiness.
Happiness is a feeling of joy, satisfaction, and contentment. It’s the positive emotion we feel when our needs are met or our desires are fulfilled.
Importance of Happiness
Happiness is crucial in life. It keeps us healthy, boosts our immune system, and makes us more creative. It also improves our relationships with others.
Finding Happiness
We find happiness in various ways. It can be through spending time with loved ones, pursuing hobbies, or helping others. Remember, true happiness comes from within, not from material possessions.
Happiness as a Choice
Happiness is a choice. We can choose to be happy by focusing on the positive aspects of life and maintaining a positive attitude.
250 Words Essay on Happiness in Life
Understanding the concept of happiness.
Happiness, an elusive yet essential concept, is often perceived as the ultimate goal of life. It’s a complex amalgamation of emotions, experiences, and a state of mind that is influenced by several factors. However, its definition varies from person to person, influenced by individual values, aspirations, and experiences.
The Role of Positive Emotions
Positive emotions play a significant role in fostering happiness. They enable us to appreciate the present, build resilience, and create a positive outlook towards life. They also enhance our ability to cope with adversity and maintain a sense of well-being, thereby contributing to our overall happiness.
Significance of Relationships
Relationships are another critical aspect of happiness. They provide emotional support, a sense of belonging, and a platform for sharing joys and sorrows. Quality relationships, whether familial, platonic, or romantic, contribute to a sustained sense of happiness.
The Pursuit of Meaning
While pleasure and positive emotions contribute to happiness, the pursuit of meaning is equally important. Engaging in activities that align with our values, interests, and passions provides a sense of purpose and fulfillment, thereby enhancing our happiness.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, happiness in life is not a destination, but a journey. It’s a dynamic state, influenced by one’s emotions, relationships, and pursuits. It’s about finding joy in the little things, cherishing relationships, pursuing meaningful activities, and maintaining a positive outlook. Ultimately, the key to happiness lies within us, and it’s our responsibility to unlock it.
500 Words Essay on Happiness in Life
Introduction: the concept of happiness.
Happiness, a seemingly simple concept, is a multifaceted and deeply personal idea. It is a universal goal that everyone strives to achieve. Yet, its definition varies widely among individuals, cultures, and societies. Philosophers, psychologists, and scholars have long explored the nature of happiness, its sources, and its significance in our lives.
Happiness is often associated with a state of mind that is content, satisfied, and filled with joy. However, this definition is only the tip of the iceberg. It is a complex amalgamation of emotional, psychological, and physiological elements. Psychologists often describe it as a combination of life satisfaction and having more positive emotions than negative ones. Yet, it’s important to understand that happiness is not a constant state of euphoria, but rather, a balance between the various emotions we experience.
The Pursuit of Happiness
The pursuit of happiness is a journey rather than a destination. It’s about finding joy in the journey itself, not just the end goal. Happiness is a dynamic process that evolves and changes with our experiences, perceptions, and personal growth. It is not a static state to be achieved, but a continuous process that needs to be nurtured and cultivated.
Many of us believe that happiness is tied to external factors such as wealth, success, or relationships. However, studies have shown that our circumstances account for only about 10% of our happiness levels. The rest is determined by our genes and, importantly, our actions and attitudes. This implies that we have significant control over our happiness.
Happiness and Wellbeing
Happiness plays a crucial role in our overall wellbeing. It is not only an end in itself but also a means to achieving other important outcomes in life. Happy individuals are found to be more productive, creative, and healthier. They tend to have stronger relationships and are more resilient in the face of adversity.
Practices for Cultivating Happiness
Cultivating happiness requires conscious effort. Practices such as mindfulness, gratitude, and positive thinking can significantly enhance our happiness. Mindfulness helps us live in the present moment and appreciate it, while gratitude shifts our focus from what’s wrong in our lives to what’s right. Positive thinking, on the other hand, helps us maintain an optimistic outlook on life, even in challenging situations.
Conclusion: The Essence of Happiness
In conclusion, happiness is a deeply personal and complex phenomenon. It’s not just about feeling good, but also about growing emotionally, being satisfied with life, and building meaningful relationships. It is an ongoing journey of self-discovery and personal growth. By understanding the nature of happiness and consciously adopting practices that cultivate it, we can enhance our wellbeing and lead more fulfilling lives.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on What Are the Qualities of a Good Leader
- Essay on Leadership Qualities
- Essay on Qualities of a True Leader
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

On Happiness as Harmony
Nov 25, 2018
Pedro Blas González
O f the many ways that we can exist as persons, happiness directs our glance inward, toward the essence of our individual being. This is the discovery of personhood as interiority. The ultimate form of happiness—joy—signals our participation in being.
The capacity to experience happiness is a dominant human trait. We can even think of this capacity for self-reflection as being divine in inspiration. No doubt, our ability to be happy plays a major role in our behavior. Few of us reflect on the fact that whether we are happy or not determines a large portion of our daily decision-making. Consider the inestimable sociopolitical cost of unhappiness. Humans who are unhappy often embrace destructive behavior against themselves or others. Most importantly, the worldview of unhappy people is often ruled by forms of self-loathing, which, more often than not, finds expression in the social and political arenas.
Happiness can be experienced as momentous and temporary. It can also inform our lives in a lasting way in the form of joy. This is because joy is a state of being human. This means that we literally encounter ourselves, our being as the persons whom we are, in being happy. Of course, we exist in several ways throughout our lives—as children, adults, and as elderly, among others. Yet fundamental to all human activities is our realization of the self as always being embedded in the world. Thus, joy is a form of being that recognizes the centrality of the self to the reality of the world.
The state of being happy allows us to reflect on what it means to be who we are as individuals. This lightness displays man’s harmony with existence, especially in lieu of being in the world. I often compare the airy lightness that we feel when we are happy with the adagio movement of a symphony. We can think of joy as an existential form of harmony that alerts us to the symmetry of the fullness of being. When reflecting on joy, the adagio from Rodrigo’s Concierto de Aranjuez and Bach’s “ Air on a G String ” often come to mind.
Perhaps happiness is more representative of personhood than even intelligence, in its ability to distinguish us from animals. No doubt, human beings possess the capacity to understand the vitality that makes us who we are as individuals. Aside from our biological make-up, human beings are also dominated by a lived-vitality that can be understood as the desire for self-knowledge. Our lived vitality, what we like to refer to as character, is also indicative of our existential fingerprint on creation. Unlike our physical fingerprints, our character is not reducible to mere biology.
S elf-knowledge is a foundational form of our understanding of the world around us. Self-knowledge exists as intuition of the human person—from the inside out. Thus, the highest form of knowledge a human can possess is that of oneself as an ontological entity. We know ourselves existentially. While philosophical materialism reduces our capacity for happiness to something that is physical in nature—that is, as a function of the brain, this still leaves us with the odd realization of having to express emotions whose origin is not physical stimuli. What we encounter when we reflect on the reality of our lives is our lived-essence as individual souls. Circa 2018, we still possess no scientific explanation of what it means to be a differentiated individual. Moreover, we certainly have no idea why we should come into existence in the first place. Existentially speaking, happiness, tragedy, misery, and life itself, only happen to individual persons.
In other words, while it is fruitful to discuss happiness with others, in private conversations or in round-table type arrangements, ultimately what we are discussing in those instances is the intellectualized articulation of a vital state of being. This is so, because when we attempt to communicate our state of happiness through language, we always fall short of the inwardly felt reality of the latter. The last word in happiness belongs to our experiencing it as a lived emotion, not words.
In writing about happiness, I am aware that the best that can be achieved here is a commentary on this basic human reality. I do not pretend to offer a textbook account of joy or happiness. Who can? Worthwhile commentary on the nature of happiness must reflect vital and existential existence. Happiness must be lived, and therefore, felt as a lived experience. This makes abstract and theoretical commentaries on happiness pointless. Commentary on happiness can offer us very little by way of a moral or spiritual return, for talking about happiness does not make people happy.
Writing that is not done in the form of, say, a memoir on the actual experience of happiness merely comes across as an intellectual curiosity. There is a marked difference in writing that explores its subject as a theoretical abstraction, and exploratory, autobiographical essays. Only the latter reflects the lived-world of the author, with all the color, trials, and tribulations that make life a vital and existential reality.
This is one reason why academic writing on happiness will always be theoretically sterile. How many people will benefit from such an enterprise? Reading academic textbooks on philosophy, one quickly realizes that the subjects in question are not people of flesh and blood, but some theoretical cardboard “agents” that do not exist. This is one reason given by José Ortega y Gasset for not reading academic journals. These agents are actually comical fabrications of people who apparently have too much time on their hands. It is hard to imagine Socrates, Boethius, or Thomas More, for example, paying much attention to theoretical agents, and not their own fate, as they prepared to die.
After reading academic philosophy for a long time, one comes to feel embarrassed for its inanity. Apparently, the ridiculous and laughable nature of such analytical inquiry is lost on both academic philosophers and the publishers profiting from such make-work fodder. What is the point of dragging philosophical reflection through a maze of laboratories, where persons who are endowed with free will are turned into deterministic, conditioned rat-specimens? These works may build academic careers, but rarely are they reflections on living and the attendant aspects of vital reality.
I nstead, I propose a kind of adventure of philosophical discovery that attempts to identify the importance of joy and happiness to productive living. Genuine reflection on happiness must come about through what I will refer to as fullness of being , which is encountered in vital symmetry. The fullness of being is manifested in vital-life, especially those forms that are ruled by a self-regulating, virtuous symmetry. It is hard to communicate the value of happiness and joy to other people if we do not experience it as a lived reality. This is why happiness is a truly curious and paradoxical human emotion.
Placing happiness and its importance to human existence under the scope of medical materialism, biologism, physicalism, and so forth, is an aberration that ranks high on the list of human follies. The latter materialist renditions of man are content to view happiness as a mere function or epiphenomenon—an offshoot—of the brain. Yet happiness is not a function of the body. Instead, happiness is a manner of being human, one that embraces the entirety of personhood. Reducing happiness to brain function is a fine example of how science is often at odds with lived existence.
In Man and People , the Spanish philosopher Ortega y Gasset writes about the differences between biological life and biographical existence. While the former is obvious, the latter signifies an existential category that lies outside the realm of science. We do not experience the interior reality of our lives by being convinced by abstractions, but through the essence of personhood. This is one reason why we can say that joy and happiness are interrelated modes of being. Science, we ought not to forget, is the study of matter, not of persons as existential entities. Whenever science tries to offer an account of human reality, it does so by taking inventory of the material realm. The problem is that human existence makes itself known as lived-experience of ourselves. Sentient people intuit the reality of their lives more readily than they do the objective world. Human existence resists being reduced to mere quantifiable phenomena. Why then our current insistence in reducing man to our alleged component parts? Reason may recognize a state of happiness in oneself or another, but it cannot reproduce vital happiness on demand. This is part of what Pascal means by “the heart has its own reasons.”
We must be vigilant in our approach regarding the nature and meaning of happiness. It is one thing to be happy and another to pay it lip service. The former is the stuff of vital reality, while the latter is better suited for public consumption. The former is what some people feel, while the latter fuels a cottage industry. How can our culture isolate happiness and bottle it for popular consumption? This is all too convenient and facile. The matter becomes complicated because, while science has nothing to offer in reflection on joy and happiness, psychobabble serves as a useful reminder of the intellectual and cultural inanity to which idle reasoning can lead.
Gifted essayists and thinkers have written about happiness in a spirited lyricism that complements this human emotion. Yet few who write about happiness are under the impression that happiness can be attained through the stroke of a pen or the clicking of keys. Even so, exploratory essays are more conducive to reflection on this vital aspect of human life than alleged studies or abstract theories.
It is a curiosity that many people who write about happiness today do so to refute the idea that happiness is attainable. This is consistent with our postmodern self-loathing. It should appear obvious to naysayers that, if happiness is unattainable in daily life, it is pointless to explain it away through theory. Happy people can’t be persuaded into believing that happiness is an illusion through the citation of a nauseating array of logical deductions or case studies. Yet as obvious as this truism may appear, Western culture and education have been taken hostage by those who relish the latter abuse of reason.
Human existence is governed by existential categories. One of these categories, which is not encountered as a thing among things in the world, is free will. The rhythm of a thoughtful essay flows, much as life, through unpredictable waters. This is why writers like Marcus Aurelius, Montaigne, and Pascal speak to readers across the centuries. People express their joy or happiness in unpredictable ways, precisely because these are not scientific categories that can be isolated and catalogued. It is useful to be reminded of this frequently. This is also why there can be no science or case studies that accurately predict the trajectory of happy lives, or the human capacity for attaining happiness.
W e must also recognize that because human behavior is fickle, formulas that aim to capture the essence of happiness will always be ineffective. Of course, this does not mean that there are no rational, sensible, or reasonable rules that we ought to follow that can lead to happiness. On the contrary, the basic principles that rule over human existence, as we have encountered these for millennia, can be counted on as guides for human felicity with no less regularity than we understand the phases of the moon.
Many miserable lives have been built through caprice. It is not difficult to see how many people actually do battle with life. Ironically, few of these people understand the conditions that make them unhappy. This is a worst-case scenario of the transparency of life. The philosopher Gabriel Marcel has the following to say in The Philosophy of Existentialism about our neglect of the human person as an ontological mystery:
Rather than to begin with abstract definitions and dialectical arguments which may be discouraging at the outset, I should like to start with a sort of global and intuitive characterization of the man in whom the sense of the ontological—the sense of being—is lacking, or, so to speak more correctly, of the man who has lost the awareness of this sense. Generally speaking, modern man is in this condition: if ontological demands worry him at all, it is only dully, as an obscure impulse.
Our differentiated existential condition makes every person responsible for uncovering objective universal principles that inform human existence. Failure to realize that human existence is regulated by time-proven principles often takes a toll on our lives. We can model some aspects of our lives, whether professional, moral, or spiritual, on the good examples set by exemplary people. However, we must be ready to tackle reality on its own terms, in our own existence. This means taking stock of our circumstances.
Every person encounters and responds to life’s demands according to our inherent capacity. In other words, we are equal to our lives. Every person is responsible for cultivating vital symmetry, harmony with life. Ortega y Gasset is correct to argue that we are our circumstances, and if we don’t save them, we cannot save ourselves. Our circumstances, according to Ortega, include the fundamental reality that is our incarnate life. Man’s ontological condition is measured as reality vis-à-vis the individual as a person. We do not encounter our life as one more thing in a universe of inanimate objects. This suggests that human existence, what is experienced as an existential reality, must embrace free will. This is one of the initial demands that a happy life makes of itself.
People who embrace spiritual autonomy exercise free will in order to tackle the demands of daily existence. This enables us to recognize that there are things that remain out of their control. Part of what it means to experience human existence as a differentiated person is the acceptance of mystery in human existence. In other words, the exercise of free will also means knowing when we do not possess knowledge or control over something. This realization keeps us humble and honest, in addition to keeping us from becoming cynical about things that may not be in our power to comprehend. Two aspects of the human condition that will always remain out of our control are luck and irony.
Among other ways, we can understand the human will to be a psycho-physical component of the person. Will is the capacity of autonomous persons to come to terms with the strife they must face in order to live as incarnate souls—and prosper. Again, we must make choices—some trivial, others deadly serious. We cannot evade having to make choices, for even the consideration of evasion is already a choice. Luck can be thought of as a timing mechanism of events that take place in our life. Luck may be fortuitous or otherwise. On a purely material level, where events are said to depend on each other through cause and effect, it is almost impossible to establish the existence of luck. However, what is ordinarily considered cause and effect—contingency—nevertheless affects people of flesh and blood. Human beings often internalize events that science will dismiss as explainable. Because it is out of our control, luck enters our life without warning. On the other hand, timing in life does not necessarily need to convey a sense of good or ill fortune. The timing of events in our life, one way or another, can be dictated by the choices we make. We are often the unsuspecting recipients, for good or ill, of other people’s free will.
Embedded in this multi-layered existential condition is our ability to experience happiness. We cannot will ourselves to be happy. This would be presumptuous on our part. Human happiness, as I have already alluded to, is a diffuse emotion. It cannot be coerced. Happiness is often experienced as a singular joy that we can experience without much ado. Happiness or its antithesis–unhappiness—often come about as the result of our outlook on life, the purpose and meaning of our lives, and our spiritual and emotional stability, in addition to the choices we make.
We must also keep in mind that self-conscious discussion about happiness tends to aggravate our unhappiness. One cannot grasp with the mind what is not felt vitally. The former is an academic exercise, while the latter remains the stuff of vital existence. Much can be said about the harm that psychoanalysis has done to the human psyche in the twentieth century. Self-help gurus and the self-indulgent industry they have created operate on the principle that everyone ought to be happy. The latter is one of many platitudes that our age embraces. Ours is perhaps the only time in recorded history when everyone is promised a happy life, regardless of our attention to the duty we owe ourselves to practice prudence.
Pedro Blas González is a professor of philosophy at Barry University.
The University Bookman
- Bookman Home
- Departments
- Search for:
Explore Past Articles
The University Bookman Follow
More than Regime Change, We Need a New Cosmological Vision
Revolution and Counter Revolution
What Is Happiness Essay
What is happiness? We can ask hundreds of people, and each of them would probably give different answers. One would say that happiness is to be with a loved one, the second would say that happiness is the stability, and the third, on the contrary, would say that happiness is the unpredictability. For someone, to be happy is to have a lot of money while for others – to be popular. All in all, there are plenty of different understandings of happiness.
Personally, I consider happiness as simplicity and peace when my family and friends are healthy and happy as well. I recognize that they all are dear to me and able to understand what is going on inside me. I know that they will support me in any situation doing everything that depends on them. In return, I am also ready to do much for them. What we do for others, helping them when they need our help, advice, or support and obtaining appreciation, is happiness because helping others, we are doing something very significant and necessary.
What does it mean to be happy? I think it is, primarily, a state of mind, it means to have harmony with yourself and the people around. Happiness is multi-faceted. Perhaps, the word “love” is the most appropriate one to describe my happiness as love is driven by our world. People create wonderful things concerning their job, hobby, or family. Love is life, and I am happy when I realize that I live up to the hilt.
However, some people might be unhappy even though they should be. For example, teenagers who have everything to live a happy life, including healthy family, close friends, and enough money to satisfy basic needs, ask their parents to buy the latest model of IPhone. In the case, parents could not afford it, some teenagers tend to feel unhappy. After all, one can be a successful leader and have millions as well as prestige, but do not have a loving family and emotional harmony.
In my opinion, material values are not a true measure of happiness. Happiness is the ability to be optimistic in spite of difficulties and the ability to overcome them successfully. Finally, challenges should be taken as the lessons that life presents us. Even the negative things teach something, give a new experience, or refer to the correct direction.
I believe that happiness is not a gift and not a given right as every person has its own happiness inside. Moreover, it is never too late to become happy. We can inspire and motivate ourselves and others to be happy. A stranger’s passing smile, warm rays of the sun penetrating the window, or a cup of freshly brewed coffee – happiness is in detail. Everyone chooses and prefers different sources. It is of great importance for people to enjoy moments of life, even the most insignificant ones.
We need to appreciate every moment in our lives remembering that happiness is within us. After all, time passes, and we are getting hurt by the fact that we did not appreciate the time when we had a chance. Therefore, living in peace and harmony with others, helping those who need your help, and avoiding things that you would regret about in future are paramount ways to find happiness and make others happy.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 29). What Is Happiness Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-happiness-essay/
"What Is Happiness Essay." IvyPanda , 29 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-happiness-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'What Is Happiness Essay'. 29 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "What Is Happiness Essay." October 29, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-happiness-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "What Is Happiness Essay." October 29, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-happiness-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "What Is Happiness Essay." October 29, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-happiness-essay/.
- Dagger and Its Scabbard Analysis
- I Taste a Liquor Never Brewed
- “The Yellow Wallpaper” Short Story by Gilman
- Love as a Multi-Faceted Concept
- John Updike's "A&P" Short Story Analysis
- Hobby Lobby Stores Inc.’s Mission
- The "Beowulf" Anglo-Saxony Epic Poem
- “Gently Penetrating...” Composition by Westerkamp
- Penetrating and Blunt Trauma
- Writings About Hobby - Home Brewing Beer
- The Key to Happiness and Satisfaction with Life
- Aesthetical Beauty's Understanding
- Happiness and Its Influence on Decision-Making
- History and Psychology in Proust’s “The Cookie”
- Self-Perception and Organizational Feelings Journal
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Does Work Make You Happy? Evidence from the World Happiness Report
- Jan-Emmanuel De Neve
- George Ward
Blue collar vs. white collar, employed vs. unemployed, self-employed vs. the rest.
A new analysis draws on data from hundreds of thousands of individuals across the globe, investigating the ways in which elements of people’s working lives drive their wellbeing. The type of job you have matters: white-collar and managerial workers are generally happier than blue-collar workers. Where you live also matters: life evaluation fluctuates according to country. Interestingly, in all countries, self-employed people report both more positive and more negative work experiences, suggesting that being your own boss is both rewarding and stressful. Being unemployed is miserable, and not just for the unemployed person: people who remain employed in areas with high unemployment also report lower overall wellbeing. Finally, while pay is important, certain non-monetary aspects of employment matter too: factors like autonomy and work-life balance can influence how happy you feel.
Since most of us spend a great deal of our lives working, it is inevitable that work plays a key role in shaping our levels of happiness. In a recent chapter of the World Happiness Report — published annually to coincide with the United Nation’s International Day of Happiness — we look more closely at the relationship between work and happiness. We draw largely upon the Gallup World Poll , which has been surveying people in over 150 countries around the world since 2006. These efforts allow us to analyze data from hundreds of thousands of individuals across the globe and investigate the ways in which elements of people’s working lives drive their wellbeing.
- JN Jan-Emmanuel De Neve is Associate Professor of Economics and Strategy at the Saïd Business School, University of Oxford, and an Associate Editor of the World Happiness Report .
- GW George Ward is a Ph.D. student at the Institute for Work and Employment Research, MIT Sloan School of Management.
Partner Center
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on Email
- Subscribe to our Newsletter

The One Thing It's More Important To Feel Than Happiness
Happiness is great, but it isn't everything..
- Marielisa Reyes
Written on May 03, 2024

We all want to live happy, fulfilling lives, but figuring out how to get there can be tough. What does it even mean to be truly happy, and how do we become our happiest selves?
And while happiness is great, it shouldn’t be the only thing we aim for. Dr. Amanda Hanson, a psychologist, explains why focusing solely on happiness might not be the best approach and suggests one thing we can strive for to make our lives more meaningful.
@midlifemuse Watch my free class about self-love. Link in bio ❤️ #midlifemuse #dramandahanson #amandahanson #selflove #psychologist #therapist #emotions #emotionalhealing #psychologytips #greyhairinfluencer #greyhair #midlife #beingemotional #heavyfeelings ♬ original sound - Dr. Amanda Hanson
“I don’t want to sit in rooms with just happy people ,” says Hanson. “I wanna sit in rooms where people tell me the stories of how they overcame their heartbreak.”
The stories of people who rise after being knocked down, who own the darkest moments of their lives and turn them into something beautiful.
But let’s be honest, most people don’t want that for themselves, especially those with children. “I just want my children to be happy,” parents say to Hanson.
And on the surface, there’s nothing wrong with this. Yes, we want our children to lead happy and fulfilling lives, so what?
Hanson continues, “But toxic positivity bypassing real emotions, difficult emotions, is not the goal here.”
What's more important for your emotional well-being than happiness?
If you truly want to succeed in life or heal from emotional trauma , you need to learn how to feel. How to feel the sadness, the anger, the shame, the resentment.
You need to learn how to feel the regret. To understand what it’s like to say, “I wish I could’ve done things differently.” Yes, we need to sit down with our emotions and consider it all.
@healingwithcharlie Replying to @Behi a brief breakdown on how to sit with your emotions #anxiousattachment #anxiousattachmentstyle #anxiouspreoccupied #anxiouspreoccupiedattachment #avoidant #avoidantattachment #avoidantattachmentstyle #fearfulavoidantattachment #disorganizedattachment #windowoftolerance #somatichealing #somatictherapy ♬ original sound - Healing with Charlie
Hanson ends, “The end goal in this lifetime is not happiness. The end goal is to feel everything,”
But how do we permit ourselves to feel? It might sound silly, but many of us were raised to suppress our emotions, leaving us unsure of how to connect with them on a deeper level.
So, how do we get in touch with our emotional side? Therapist Kim Egel discusses how to tap into your emotions especially if you’re new to that kind of thing.
RELATED: Happiness Isn't Sustainable — But These 3 Things Will Make You Content Forever
How To Feel Your Full Range Of Emotions
1. take a break.
As we rush through life, jumping from one activity to another, we often forget to take a breather. And this constant busyness leaves us with little time to process or understand our true emotions.
Which is why we need to learn how to slow down. Egel writes, “In order to tap into how you’re feeling you need time to ‘sit with and process your emotions.’”
Create room and time to allow yourself to feel your emotions. When you return from work, take 20-30 minutes to walk.
During this time allow yourself the room to sit with your emotions . Start with your day and then go from there.
And always remember, experiencing emotions, both the good and the bad, is what makes us human.
2. Name the emotion
As you’re processing, try to put a name to what you’re feeling. This can be tricky if you’re not used to it, but give it a shot.
Start with understanding if it’s a positive or negative emotion, suggests Egel. Then, see if you can match your feelings to one of the basic emotions we’re familiar with, like anger, sadness, or happiness.
RELATED: 10 Secrets To Being More Content (So Nobody Can Take Your Joy Away)
3. Feel it physically
Ask yourself where you feel your emotions. Is it in your throat or eyes? Or is it in your chest or hands?
Be curious about those sensations and explore them, summarizes Egel. Ask yourself if the sensations you feel are pleasant or unpleasant.
Feel these sensations for a minute or two and allow yourself to sit in the uncomfortable.
@withlovesabrinaflores this video is a love letter to everyone who feels very heavy sometimes but especially to all my fellow bpd babies :-) we’re just humans out here!!! feelin human emotions!!! havin human experiences!!!!! ♬ original sound - Sabrina Flores
4. Be compassionate
Always be kind to yourself, no matter what emotions you’re going through.
Egel writes, “If this is difficult for you to do, think about what you would say to your best friend If they were feeling your specific emotion.”
You might find yourself saying that you understand their struggle and that things will get better. You’ll reassure your friends that you’re there for them and that you support them.
And when we start talking to ourselves like we would to a friend or loved one, we slowly begin to treat ourselves with more kindness and respect. Which can help us appreciate and respect our emotions more.
Feeling your emotions isn’t a walk in the park; it can be pretty tough and uncomfortable. But by facing both the good and bad, you can start taking control of your emotions.
This can lead to a healthier relationship with yourself and those around you.
RELATED: 48 Realistic Laws Of Happiness To Manifest A Truly Content Life
Marielisa Reyes is a writer with a bachelor's degree in psychology who covers self-help, relationships, career, and family topics.
Our Newsletters
Get the best of YourTango delivered straight to your inbox — the biggest stories, actionable advice & horoscope predictions!
Explore our Floor Plans & Pricing

- Independent Senior Living
- Personal Care
- Senior Assisted Living
- SHINE® Memory Care
- Skilled Nursing
- Respite Care
- 100% Satisfaction Guarantee
- Ambassadors Club
- Sensations Dining
- Celebrations Activities & Events
- Dimensions Health & Fitness
- Expressions Concierge
- Impressions Housekeeping & Maintenance
- Connections Transportation
- Community Locations
- Schedule A Tour
Larry David Shares His Secrets To Happiness In Later Life
- Discovery Village At Westchase
- Larry David Shares His Secrets…

The quest for happiness doesn’t have an expiration date. Secrets to happiness in later life, as shared by Larry David, reveal that joy, fulfillment, and laughter can flourish at any age. These insights are not just philosophical musings but practical approaches that anyone can incorporate into their daily lives. Emphasizing the importance of community, humor, and staying active, Larry David’s advice resonates with many looking for contentment in their golden years.
Our community takes these secrets to happiness to heart, embedding them into our Senior Living services. We understand that happiness stems from a blend of physical well-being, mental stimulation, and emotional connections.
Cultivating a Sense of Humor and Embracing Laughter
Laughing is like a secret potion for a better life. Larry David shows us that finding fun in daily happenings can make our days lighter. It’s not about ignoring the hard stuff but finding moments of joy amid them. Imagine the simple act of sharing a joke with a friend or watching a comedy that makes you laugh till your sides hurt. Laughter has a magic way of making problems seem smaller.
Creating moments for laughter in your day is essential. Whether it’s a funny book, a show, or just silly conversations with friends, these are the sparks that light up our lives. Laughter also brings people closer, creating a shared joy that’s truly special. It’s about looking at the world with a twinkle in your eye, ready to find the humor hidden in the corners of everyday life.
Prioritizing Time with Loved Ones and Building Strong Relationships
Nothing beats the warmth of close relationships. Larry David values spending time with loved ones as a source of true happiness. In places like retirement communities, this means creating cherished moments with others, whether they’re family, friends, or new acquaintances. Activities that bring people together, like shared meals or group activities, are golden opportunities to deepen bonds.
Relationships are the heart of a happy life. They provide support, laughter, and a sense of belonging. Making time for those we care about, listening to their stories, and sharing our own weaves a tapestry of connections that enrich our lives immensely. It’s these connections that form the bedrock of a fulfilling life, offering love and support through thick and thin.
Adopting an Attitude of Gratitude and Appreciation
Gratitude turns what we have into enough. Larry David suggests focusing on our blessings, big and small. This might mean appreciating a kind gesture from a neighbor or the beauty of a sunset. In a community setting, showing gratitude can be as simple as thanking someone for their help or enjoying the nature around you. Recognizing the good in our lives can transform our outlook, filling us with happiness.
Keeping a gratitude journal or sharing what we’re thankful for can make appreciation a daily habit. It’s about seeing the good in every day, even on the tough ones. This practice not only enriches our own lives but also spreads positivity to those around us. Gratitude is contagious, after all. It fosters a community of kindness and appreciation where everyone feels valued and happy.
Join Our Happy Community
In our retirement community happiness starts with personalized care that meets the unique needs and preferences of each resident. We go beyond the basics to ensure that everyone in our community feels valued, understood, and connected.
We also believe in the power of staying physically and mentally active. Our senior living services include a range of programs that encourage movement, creativity, and learning. From fitness classes tailored to all abilities to art workshops and educational talks, we offer endless opportunities for residents to pursue new interests and reignite old passions.
Contact us to learn more about the vibrant life that awaits in our community, where we put the secrets to happiness into practice every day. Let us help you or your loved one find joy in every moment.
Related posts

Hi, I'm here to help
How may I assist you today?
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:

What It Means To Be Asian in America
The lived experiences and perspectives of asian americans in their own words.
Asians are the fastest growing racial and ethnic group in the United States. More than 24 million Americans in the U.S. trace their roots to more than 20 countries in East and Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent.
The majority of Asian Americans are immigrants, coming to understand what they left behind and building their lives in the United States. At the same time, there is a fast growing, U.S.-born generation of Asian Americans who are navigating their own connections to familial heritage and their own experiences growing up in the U.S.
In a new Pew Research Center analysis based on dozens of focus groups, Asian American participants described the challenges of navigating their own identity in a nation where the label “Asian” brings expectations about their origins, behavior and physical self. Read on to see, in their own words, what it means to be Asian in America.
- Introduction
Table of Contents
This is how i view my identity, this is how others see and treat me, this is what it means to be home in america, about this project, methodological note, acknowledgments.
No single experience defines what it means to be Asian in the United States today. Instead, Asian Americans’ lived experiences are in part shaped by where they were born, how connected they are to their family’s ethnic origins, and how others – both Asians and non-Asians – see and engage with them in their daily lives. Yet despite diverse experiences, backgrounds and origins, shared experiences and common themes emerged when we asked: “What does it mean to be Asian in America?”
In the fall of 2021, Pew Research Center undertook the largest focus group study it had ever conducted – 66 focus groups with 264 total participants – to hear Asian Americans talk about their lived experiences in America. The focus groups were organized into 18 distinct Asian ethnic origin groups, fielded in 18 languages and moderated by members of their own ethnic groups. Because of the pandemic, the focus groups were conducted virtually, allowing us to recruit participants from all parts of the United States. This approach allowed us to hear a diverse set of voices – especially from less populous Asian ethnic groups whose views, attitudes and opinions are seldom presented in traditional polling. The approach also allowed us to explore the reasons behind people’s opinions and choices about what it means to belong in America, beyond the preset response options of a traditional survey.
The terms “Asian,” “Asians living in the United States” and “Asian American” are used interchangeably throughout this essay to refer to U.S. adults who self-identify as Asian, either alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic identity.
“The United States” and “the U.S.” are used interchangeably with “America” for variations in the writing.
Multiracial participants are those who indicate they are of two or more racial backgrounds (one of which is Asian). Multiethnic participants are those who indicate they are of two or more ethnicities, including those identified as Asian with Hispanic background.
U.S. born refers to people born in the 50 U.S. states or the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, or other U.S. territories.
Immigrant refers to people who were not U.S. citizens at birth – in other words, those born outside the U.S., Puerto Rico or other U.S. territories to parents who were not U.S. citizens. The terms “immigrant,” “first generation” and “foreign born” are used interchangeably in this report.
Second generation refers to people born in the 50 states or the District of Columbia with at least one first-generation, or immigrant, parent.
The pan-ethnic term “Asian American” describes the population of about 22 million people living in the United States who trace their roots to more than 20 countries in East and Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent. The term was popularized by U.S. student activists in the 1960s and was eventually adopted by the U.S. Census Bureau. However, the “Asian” label masks the diverse demographics and wide economic disparities across the largest national origin groups (such as Chinese, Indian, Filipino) and the less populous ones (such as Bhutanese, Hmong and Nepalese) living in America. It also hides the varied circumstances of groups immigrated to the U.S. and how they started their lives there. The population’s diversity often presents challenges . Conventional survey methods typically reflect the voices of larger groups without fully capturing the broad range of views, attitudes, life starting points and perspectives experienced by Asian Americans. They can also limit understanding of the shared experiences across this diverse population.
Across all focus groups, some common findings emerged. Participants highlighted how the pan-ethnic “Asian” label used in the U.S. represented only one part of how they think of themselves. For example, recently arrived Asian immigrant participants told us they are drawn more to their ethnic identity than to the more general, U.S.-created pan-ethnic Asian American identity. Meanwhile, U.S.-born Asian participants shared how they identified, at times, as Asian but also, at other times, by their ethnic origin and as Americans.
Another common finding among focus group participants is the disconnect they noted between how they see themselves and how others view them. Sometimes this led to maltreatment of them or their families, especially at heightened moments in American history such as during Japanese incarceration during World War II, the aftermath of 9/11 and, more recently, the COVID-19 pandemic. Beyond these specific moments, many in the focus groups offered their own experiences that had revealed other people’s assumptions or misconceptions about their identity.
Another shared finding is the multiple ways in which participants take and express pride in their cultural and ethnic backgrounds while also feeling at home in America, celebrating and blending their unique cultural traditions and practices with those of other Americans.
This focus group project is part of a broader research agenda about Asians living in the United States. The findings presented here offer a small glimpse of what participants told us, in their own words, about how they identify themselves, how others see and treat them, and more generally, what it means to be Asian in America.
Illustrations by Jing Li
Publications from the Being Asian in America project
- Read the data essay: What It Means to Be Asian in America
- Watch the documentary: Being Asian in America
- Explore the interactive: In Their Own Words: The Diverse Perspectives of Being Asian in America
- View expanded interviews: Extended Interviews: Being Asian in America
- About this research project: More on the Being Asian in America project
- Q&A: Why and how Pew Research Center conducted 66 focus groups with Asian Americans

One of the topics covered in each focus group was how participants viewed their own racial or ethnic identity. Moderators asked them how they viewed themselves, and what experiences informed their views about their identity. These discussions not only highlighted differences in how participants thought about their own racial or ethnic background, but they also revealed how different settings can influence how they would choose to identify themselves. Across all focus groups, the general theme emerged that being Asian was only one part of how participants viewed themselves.
The pan-ethnic label ‘Asian’ is often used more in formal settings

“I think when I think of the Asian Americans, I think that we’re all unique and different. We come from different cultures and backgrounds. We come from unique stories, not just as a group, but just as individual humans.” Mali , documentary participant
Many participants described a complicated relationship with the pan-ethnic labels “Asian” or “Asian American.” For some, using the term was less of an active choice and more of an imposed one, with participants discussing the disconnect between how they would like to identify themselves and the available choices often found in formal settings. For example, an immigrant Pakistani woman remarked how she typically sees “Asian American” on forms, but not more specific options. Similarly, an immigrant Burmese woman described her experience of applying for jobs and having to identify as “Asian,” as opposed to identifying by her ethnic background, because no other options were available. These experiences highlight the challenges organizations like government agencies and employers have in developing surveys or forms that ask respondents about their identity. A common sentiment is one like this:
“I guess … I feel like I just kind of check off ‘Asian’ [for] an application or the test forms. That’s the only time I would identify as Asian. But Asian is too broad. Asia is a big continent. Yeah, I feel like it’s just too broad. To specify things, you’re Taiwanese American, that’s exactly where you came from.”
–U.S.-born woman of Taiwanese origin in early 20s
Smaller ethnic groups default to ‘Asian’ since their groups are less recognizable
Other participants shared how their experiences in explaining the geographic location and culture of their origin country led them to prefer “Asian” when talking about themselves with others. This theme was especially prominent among those belonging to smaller origin groups such as Bangladeshis and Bhutanese. A Lao participant remarked she would initially say “Asian American” because people might not be familiar with “Lao.”
“[When I fill out] forms, I select ‘Asian American,’ and that’s why I consider myself as an Asian American. [It is difficult to identify as] Nepali American [since] there are no such options in forms. That’s why, Asian American is fine to me.”
–Immigrant woman of Nepalese origin in late 20s
“Coming to a big country like [the United States], when people ask where we are from … there are some people who have no idea about Bhutan, so we end up introducing ourselves as being Asian.”
–Immigrant woman of Bhutanese origin in late 40s
But for many, ‘Asian’ as a label or identity just doesn’t fit
Many participants felt that neither “Asian” nor “Asian American” truly captures how they view themselves and their identity. They argue that these labels are too broad or too ambiguous, as there are so many different groups included within these labels. For example, a U.S.-born Pakistani man remarked on how “Asian” lumps many groups together – that the term is not limited to South Asian groups such as Indian and Pakistani, but also includes East Asian groups. Similarly, an immigrant Nepalese man described how “Asian” often means Chinese for many Americans. A Filipino woman summed it up this way:
“Now I consider myself to be both Filipino and Asian American, but growing up in [Southern California] … I didn’t start to identify as Asian American until college because in [the Los Angeles suburb where I lived], it’s a big mix of everything – Black, Latino, Pacific Islander and Asian … when I would go into spaces where there were a lot of other Asians, especially East Asians, I didn’t feel like I belonged. … In media, right, like people still associate Asian with being East Asian.”
–U.S.-born woman of Filipino origin in mid-20s
Participants also noted they have encountered confusion or the tendency for others to view Asian Americans as people from mostly East Asian countries, such as China, Japan and Korea. For some, this confusion even extends to interactions with other Asian American groups. A Pakistani man remarked on how he rarely finds Pakistani or Indian brands when he visits Asian stores. Instead, he recalled mostly finding Vietnamese, Korean and Chinese items.
Among participants of South Asian descent, some identified with the label “South Asian” more than just “Asian.” There were other nuances, too, when it comes to the labels people choose. Some Indian participants, for example, said people sometimes group them with Native Americans who are also referred to as Indians in the United States. This Indian woman shared her experience at school:
“I love South Asian or ‘Desi’ only because up until recently … it’s fairly new to say South Asian. I’ve always said ‘Desi’ because growing up … I’ve had to say I’m the red dot Indian, not the feather Indian. So annoying, you know? … Always a distinction that I’ve had to make.”
–U.S.-born woman of Indian origin in late 20s
Participants with multiethnic or multiracial backgrounds described their own unique experiences with their identity. Rather than choosing one racial or ethnic group over the other, some participants described identifying with both groups, since this more accurately describes how they see themselves. In some cases, this choice reflected the history of the Asian diaspora. For example, an immigrant Cambodian man described being both Khmer/Cambodian and Chinese, since his grandparents came from China. Some other participants recalled going through an “identity crisis” as they navigated between multiple identities. As one woman explained:
“I would say I went through an identity crisis. … It’s because of being multicultural. … There’s also French in the mix within my family, too. Because I don’t identify, speak or understand the language, I really can’t connect to the French roots … I’m in between like Cambodian and Thai, and then Chinese and then French … I finally lumped it up. I’m just an Asian American and proud of all my roots.”
–U.S.-born woman of Cambodian origin in mid-30s
In other cases, the choice reflected U.S. patterns of intermarriage. Asian newlyweds have the highest intermarriage rate of any racial or ethnic group in the country. One Japanese-origin man with Hispanic roots noted:
“So I would like to see myself as a Hispanic Asian American. I want to say Hispanic first because I have more of my mom’s culture in me than my dad’s culture. In fact, I actually have more American culture than my dad’s culture for what I do normally. So I guess, Hispanic American Asian.”
–U.S.-born man of Hispanic and Japanese origin in early 40s
Other identities beyond race or ethnicity are also important
Focus group participants also talked about their identity beyond the racial or ethnic dimension. For example, one Chinese woman noted that the best term to describe her would be “immigrant.” Faith and religious ties were also important to some. One immigrant participant talked about his love of Pakistani values and how religion is intermingled into Pakistani culture. Another woman explained:
“[Japanese language and culture] are very important to me and ingrained in me because they were always part of my life, and I felt them when I was growing up. Even the word itadakimasu reflects Japanese culture or the tradition. Shinto religion is a part of the culture. They are part of my identity, and they are very important to me.”
–Immigrant woman of Japanese origin in mid-30s
For some, gender is another important aspect of identity. One Korean participant emphasized that being a woman is an important part of her identity. For others, sexual orientation is an essential part of their overall identity. One U.S.-born Filipino participant described herself as “queer Asian American.” Another participant put it this way:
“I belong to the [LGBTQ] community … before, what we only know is gay and lesbian. We don’t know about being queer, nonbinary. [Here], my horizon of knowing what genders and gender roles is also expanded … in the Philippines, if you’ll be with same sex, you’re considered gay or lesbian. But here … what’s happening is so broad, on how you identify yourself.”
–Immigrant woman of Filipino origin in early 20s
Immigrant identity is tied to their ethnic heritage

Participants born outside the United States tended to link their identity with their ethnic heritage. Some felt strongly connected with their ethnic ties due to their citizenship status. For others, the lack of permanent residency or citizenship meant they have stronger ties to their ethnicity and birthplace. And in some cases, participants said they held on to their ethnic identity even after they became U.S. citizens. One woman emphasized that she will always be Taiwanese because she was born there, despite now living in the U.S.
For other participants, family origin played a central role in their identity, regardless of their status in the U.S. According to some of them, this attitude was heavily influenced by their memories and experiences in early childhood when they were still living in their countries of origin. These influences are so profound that even after decades of living in the U.S., some still feel the strong connection to their ethnic roots. And those with U.S.-born children talked about sending their kids to special educational programs in the U.S. to learn about their ethnic heritage.
“Yes, as for me, I hold that I am Khmer because our nationality cannot be deleted, our identity is Khmer as I hold that I am Khmer … so I try, even [with] my children today, I try to learn Khmer through Zoom through the so-called Khmer Parent Association.”
–Immigrant man of Cambodian origin in late 50s
Navigating life in America is an adjustment
Many participants pointed to cultural differences they have noticed between their ethnic culture and U.S. culture. One of the most distinct differences is in food. For some participants, their strong attachment to the unique dishes of their families and their countries of origin helps them maintain strong ties to their ethnic identity. One Sri Lankan participant shared that her roots are still in Sri Lanka, since she still follows Sri Lankan traditions in the U.S. such as preparing kiribath (rice with coconut milk) and celebrating Ramadan.
For other participants, interactions in social settings with those outside their own ethnic group circles highlighted cultural differences. One Bangladeshi woman talked about how Bengalis share personal stories and challenges with each other, while others in the U.S. like to have “small talk” about TV series or clothes.
Many immigrants in the focus groups have found it is easier to socialize when they are around others belonging to their ethnicity. When interacting with others who don’t share the same ethnicity, participants noted they must be more self-aware about cultural differences to avoid making mistakes in social interactions. Here, participants described the importance of learning to “fit in,” to avoid feeling left out or excluded. One Korean woman said:
“Every time I go to a party, I feel unwelcome. … In Korea, when I invite guests to my house and one person sits without talking, I come over and talk and treat them as a host. But in the United States, I have to go and mingle. I hate mingling so much. I have to talk and keep going through unimportant stories. In Korea, I am assigned to a dinner or gathering. I have a party with a sense of security. In America, I have nowhere to sit, and I don’t know where to go and who to talk to.”
–Immigrant woman of Korean origin in mid-40s
And a Bhutanese immigrant explained:
“In my case, I am not an American. I consider myself a Bhutanese. … I am a Bhutanese because I do not know American culture to consider myself as an American. It is very difficult to understand the sense of humor in America. So, we are pure Bhutanese in America.”
–Immigrant man of Bhutanese origin in early 40s
Language was also a key aspect of identity for the participants. Many immigrants in the focus groups said they speak a language other than English at home and in their daily lives. One Vietnamese man considered himself Vietnamese since his Vietnamese is better than his English. Others emphasized their English skills. A Bangladeshi participant felt that she was more accepted in the workplace when she does more “American” things and speaks fluent English, rather than sharing things from Bangladeshi culture. She felt that others in her workplace correlate her English fluency with her ability to do her job. For others born in the U.S., the language they speak at home influences their connection to their ethnic roots.
“Now if I go to my work and do show my Bengali culture and Asian culture, they are not going to take anything out of it. So, basically, I have to show something that they are interested in. I have to show that I am American, [that] I can speak English fluently. I can do whatever you give me as a responsibility. So, in those cases I can’t show anything about my culture.”
–Immigrant woman of Bangladeshi origin in late 20s
“Being bi-ethnic and tri-cultural creates so many unique dynamics, and … one of the dynamics has to do with … what it is to be Americanized. … One of the things that played a role into how I associate the identity is language. Now, my father never spoke Spanish to me … because he wanted me to develop a fluency in English, because for him, he struggled with English. What happened was three out of the four people that raised me were Khmer … they spoke to me in Khmer. We’d eat breakfast, lunch and dinner speaking Khmer. We’d go to the temple in Khmer with the language and we’d also watch videos and movies in Khmer. … Looking into why I strongly identify with the heritage, one of the reasons is [that] speaking that language connects to the home I used to have [as my families have passed away].”
–U.S.-born man of Cambodian origin in early 30s
Balancing between individualistic and collective thinking
For some immigrant participants, the main differences between themselves and others who are seen as “truly American” were less about cultural differences, or how people behave, and more about differences in “mindset,” or how people think . Those who identified strongly with their ethnicity discussed how their way of thinking is different from a “typical American.” To some, the “American mentality” is more individualistic, with less judgment on what one should do or how they should act . One immigrant Japanese man, for example, talked about how other Japanese-origin co-workers in the U.S. would work without taking breaks because it’s culturally inconsiderate to take a break while others continued working. However, he would speak up for himself and other workers when they are not taking any work breaks. He attributed this to his “American” way of thinking, which encourages people to stand up for themselves.
Some U.S.-born participants who grew up in an immigrant family described the cultural clashes that happened between themselves and their immigrant parents. Participants talked about how the second generation (children of immigrant parents) struggles to pursue their own dreams while still living up to the traditional expectations of their immigrant parents.
“I feel like one of the biggest things I’ve seen, just like [my] Asian American friends overall, is the kind of family-individualistic clash … like wanting to do your own thing is like, is kind of instilled in you as an American, like go and … follow your dream. But then you just grow up with such a sense of like also wanting to be there for your family and to live up to those expectations, and I feel like that’s something that’s very pronounced in Asian cultures.”
–U.S.-born man of Indian origin in mid-20s
Discussions also highlighted differences about gender roles between growing up in America compared with elsewhere.
“As a woman or being a girl, because of your gender, you have to keep your mouth shut [and] wait so that they call on you for you to speak up. … I do respect our elders and I do respect hearing their guidance but I also want them to learn to hear from the younger person … because we have things to share that they might not know and that [are] important … so I like to challenge gender roles or traditional roles because it is something that [because] I was born and raised here [in America], I learn that we all have the equal rights to be able to speak and share our thoughts and ideas.”
U.S. born have mixed ties to their family’s heritage

“I think being Hmong is somewhat of being free, but being free of others’ perceptions of you or of others’ attempts to assimilate you or attempts to put pressure on you. I feel like being Hmong is to resist, really.” Pa Houa , documentary participant
How U.S.-born participants identify themselves depends on their familiarity with their own heritage, whom they are talking with, where they are when asked about their identity and what the answer is used for. Some mentioned that they have stronger ethnic ties because they are very familiar with their family’s ethnic heritage. Others talked about how their eating habits and preferred dishes made them feel closer to their ethnic identity. For example, one Korean participant shared his journey of getting closer to his Korean heritage because of Korean food and customs. When some participants shared their reasons for feeling closer to their ethnic identity, they also expressed a strong sense of pride with their unique cultural and ethnic heritage.
“I definitely consider myself Japanese American. I mean I’m Japanese and American. Really, ever since I’ve grown up, I’ve really admired Japanese culture. I grew up watching a lot of anime and Japanese black and white films. Just learning about [it], I would hear about Japanese stuff from my grandparents … myself, and my family having blended Japanese culture and American culture together.”
–U.S.-born man of Japanese origin in late 20s
Meanwhile, participants who were not familiar with their family’s heritage showed less connection with their ethnic ties. One U.S.-born woman said she has a hard time calling herself Cambodian, as she is “not close to the Cambodian community.” Participants with stronger ethnic ties talked about relating to their specific ethnic group more than the broader Asian group. Another woman noted that being Vietnamese is “more specific and unique than just being Asian” and said that she didn’t feel she belonged with other Asians. Some participants also disliked being seen as or called “Asian,” in part because they want to distinguish themselves from other Asian groups. For example, one Taiwanese woman introduces herself as Taiwanese when she can, because she had frequently been seen as Chinese.
Some in the focus groups described how their views of their own identities shifted as they grew older. For example, some U.S.-born and immigrant participants who came to the U.S. at younger ages described how their experiences in high school and the need to “fit in” were important in shaping their own identities. A Chinese woman put it this way:
“So basically, all I know is that I was born in the United States. Again, when I came back, I didn’t feel any barrier with my other friends who are White or Black. … Then I got a little confused in high school when I had trouble self-identifying if I am Asian, Chinese American, like who am I. … Should I completely immerse myself in the American culture? Should I also keep my Chinese identity and stuff like that? So yeah, that was like the middle of that mist. Now, I’m pretty clear about myself. I think I am Chinese American, Asian American, whatever people want.”
–U.S.-born woman of Chinese origin in early 20s
Identity is influenced by birthplace

“I identified myself first and foremost as American. Even on the forms that you fill out that says, you know, ‘Asian’ or ‘Chinese’ or ‘other,’ I would check the ‘other’ box, and I would put ‘American Chinese’ instead of ‘Chinese American.’” Brent , documentary participant
When talking about what it means to be “American,” participants offered their own definitions. For some, “American” is associated with acquiring a distinct identity alongside their ethnic or racial backgrounds, rather than replacing them. One Indian participant put it this way:
“I would also say [that I am] Indian American just because I find myself always bouncing between the two … it’s not even like dual identity, it just is one whole identity for me, like there’s not this separation. … I’m doing [both] Indian things [and] American things. … They use that term like ABCD … ‘American Born Confused Desi’ … I don’t feel that way anymore, although there are those moments … but I would say [that I am] Indian American for sure.”
–U.S.-born woman of Indian origin in early 30s
Meanwhile, some U.S.-born participants view being American as central to their identity while also valuing the culture of their family’s heritage.
Many immigrant participants associated the term “American” with immigration status or citizenship. One Taiwanese woman said she can’t call herself American since she doesn’t have a U.S. passport. Notably, U.S. citizenship is an important milestone for many immigrant participants, giving them a stronger sense of belonging and ultimately calling themselves American. A Bangladeshi participant shared that she hasn’t received U.S. citizenship yet, and she would call herself American after she receives her U.S. passport.
Other participants gave an even narrower definition, saying only those born and raised in the United States are truly American. One Taiwanese woman mentioned that her son would be American since he was born, raised and educated in the U.S. She added that while she has U.S. citizenship, she didn’t consider herself American since she didn’t grow up in the U.S. This narrower definition has implications for belonging. Some immigrants in the groups said they could never become truly American since the way they express themselves is so different from those who were born and raised in the U.S. A Japanese woman pointed out that Japanese people “are still very intimidated by authorities,” while those born and raised in America give their opinions without hesitation.
“As soon as I arrived, I called myself a Burmese immigrant. I had a green card, but I still wasn’t an American citizen. … Now I have become a U.S. citizen, so now I am a Burmese American.”
–Immigrant man of Burmese origin in mid-30s
“Since I was born … and raised here, I kind of always view myself as American first who just happened to be Asian or Chinese. So I actually don’t like the term Chinese American or Asian American. I’m American Asian or American Chinese. I view myself as American first.”
–U.S.-born man of Chinese origin in early 60s
“[I used to think of myself as] Filipino, but recently I started saying ‘Filipino American’ because I got [U.S.] citizenship. And it just sounds weird to say Filipino American, but I’m trying to … I want to accept it. I feel like it’s now marry-able to my identity.”
–Immigrant woman of Filipino origin in early 30s
For others, American identity is about the process of ‘becoming’ culturally American
Immigrant participants also emphasized how their experiences and time living in America inform their views of being an “American.” As a result, some started to see themselves as Americans after spending more than a decade in the U.S. One Taiwanese man considered himself an American since he knows more about the U.S. than Taiwan after living in the U.S. for over 52 years.
But for other immigrant participants, the process of “becoming” American is not about how long they have lived in the U.S., but rather how familiar they are with American culture and their ability to speak English with little to no accent. This is especially true for those whose first language is not English, as learning and speaking it without an accent can be a big challenge for some. One Bangladeshi participant shared that his pronunciation of “hot water” was very different from American English, resulting in confusions in communication. By contrast, those who were more confident in their English skills felt they can better understand American culture and values as a result, leading them to a stronger connection with an American identity.
“[My friends and family tease me for being Americanized when I go back to Japan.] I think I seem a little different to people who live in Japan. I don’t think they mean anything bad, and they [were] just joking, because I already know that I seem a little different to people who live in Japan.”
–Immigrant man of Japanese origin in mid-40s
“I value my Hmong culture, and language, and ethnicity, but I also do acknowledge, again, that I was born here in America and I’m grateful that I was born here, and I was given opportunities that my parents weren’t given opportunities for.”
–U.S.-born woman of Hmong origin in early 30s

During the focus group discussions about identity, a recurring theme emerged about the difference between how participants saw themselves and how others see them. When asked to elaborate on their experiences and their points of view, some participants shared experiences they had with people misidentifying their race or ethnicity. Others talked about their frustration with being labeled the “model minority.” In all these discussions, participants shed light on the negative impacts that mistaken assumptions and labels had on their lives.
All people see is ‘Asian’
For many, interactions with others (non-Asians and Asians alike) often required explaining their backgrounds, reacting to stereotypes, and for those from smaller origin groups in particular, correcting the misconception that being “Asian” means you come from one of the larger Asian ethnic groups. Several participants remarked that in their own experiences, when others think about Asians, they tend to think of someone who is Chinese. As one immigrant Filipino woman put it, “Interacting with [non-Asians in the U.S.], it’s hard. … Well, first, I look Spanish. I mean, I don’t look Asian, so would you guess – it’s like they have a vision of what an Asian [should] look like.” Similarly, an immigrant Indonesian man remarked how Americans tended to see Asians primarily through their physical features, which not all Asian groups share.
Several participants also described how the tendency to view Asians as a monolithic group can be even more common in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“The first [thing people think of me as] is just Chinese. ‘You guys are just Chinese.’ I’m not the only one who felt [this] after the COVID-19 outbreak. ‘Whether you’re Japanese, Korean, or Southeast Asian, you’re just Chinese [to Americans]. I should avoid you.’ I’ve felt this way before, but I think I’ve felt it a bit more after the COVID-19 outbreak.”
–Immigrant woman of Korean origin in early 30s
At the same time, other participants described their own experiences trying to convince others that they are Asian or Asian American. This was a common experience among Southeast Asian participants.
“I have to convince people I’m Asian, not Middle Eastern. … If you type in Asian or you say Asian, most people associate it with Chinese food, Japanese food, karate, and like all these things but then they don’t associate it with you.”
–U.S.-born man of Pakistani origin in early 30s
The model minority myth and its impact

“I’ve never really done the best academically, compared to all my other Asian peers too. I never really excelled. I wasn’t in honors. … Those stereotypes, I think really [have] taken a toll on my self-esteem.” Diane , documentary participant
Across focus groups, immigrant and U.S.-born participants described the challenges of the seemingly positive stereotypes of Asians as intelligent, gifted in technical roles and hardworking. Participants often referred to this as the “model minority myth.”
The label “model minority” was coined in the 1960s and has been used to characterize Asian Americans as financially and educationally successful and hardworking when compared with other groups. However, for many Asians living in the United States, these characterizations do not align with their lived experiences or reflect their socioeconomic backgrounds. Indeed, among Asian origin groups in the U.S., there are wide differences in economic and social experiences.
Academic research on the model minority myth has pointed to its impact beyond Asian Americans and towards other racial and ethnic groups, especially Black Americans, in the U.S. Some argue that the model minority myth has been used to justify policies that overlook the historical circumstances and impacts of colonialism, slavery, discrimination and segregation on other non-White racial and ethnic groups.
Many participants noted ways in which the model minority myth has been harmful. For some, expectations based on the myth didn’t match their own experiences of coming from impoverished communities. Some also recalled experiences at school when they struggled to meet their teachers’ expectations in math and science.
“As an Asian person, I feel like there’s that stereotype that Asian students are high achievers academically. They’re good at math and science. … I was a pretty mediocre student, and math and science were actually my weakest subjects, so I feel like it’s either way you lose. Teachers expect you to fit a certain stereotype and if you’re not, then you’re a disappointment, but at the same time, even if you are good at math and science, that just means that you’re fitting a stereotype. It’s [actually] your own achievement, but your teachers might think, ‘Oh, it’s because they’re Asian,’ and that diminishes your achievement.”
–U.S.-born woman of Korean origin in late 20s
Some participants felt that even when being Asian worked in their favor in the job market, they encountered stereotypes that “Asians can do quality work with less compensation” or that “Asians would not complain about anything at work.”
“There is a joke from foreigners and even Asian Americans that says, ‘No matter what you do, Asians always do the best.’ You need to get A, not just B-plus. Otherwise, you’ll be a disgrace to the family. … Even Silicon Valley hires Asian because [an] Asian’s wage is cheaper but [they] can work better. When [work] visa overflow happens, they hire Asians like Chinese and Indian to work in IT fields because we are good at this and do not complain about anything.”
–Immigrant man of Thai origin in early 40s
Others expressed frustration that people were placing them in the model minority box. One Indian woman put it this way:
“Indian people and Asian people, like … our parents or grandparents are the ones who immigrated here … against all odds. … A lot of Indian and Asian people have succeeded and have done really well for themselves because they’ve worked themselves to the bone. So now the expectations [of] the newer generations who were born here are incredibly unrealistic and high. And you get that not only from your family and the Indian community, but you’re also getting it from all of the American people around you, expecting you to be … insanely good at math, play an instrument, you know how to do this, you know how to do that, but it’s not true. And it’s just living with those expectations, it’s difficult.”
–U.S.-born woman of Indian origin in early 20s
Whether U.S. born or immigrants, Asians are often seen by others as foreigners

“Being only not quite 10 years old, it was kind of exciting to ride on a bus to go someplace. But when we went to Pomona, the assembly center, we were stuck in one of the stalls they used for the animals.” Tokiko , documentary participant
Across all focus groups, participants highlighted a common question they are asked in America when meeting people for the first time: “Where are you really from?” For participants, this question implied that people think they are “foreigners,” even though they may be longtime residents or citizens of the United States or were born in the country. One man of Vietnamese origin shared his experience with strangers who assumed that he and his friends are North Korean. Perhaps even more hurtful, participants mentioned that this meant people had a preconceived notion of what an “American” is supposed to look like, sound like or act like. One Chinese woman said that White Americans treated people like herself as outsiders based on her skin color and appearance, even though she was raised in the U.S.
Many focus group participants also acknowledged the common stereotype of treating Asians as “forever foreigners.” Some immigrant participants said they felt exhausted from constantly being asked this question by people even when they speak perfect English with no accent. During the discussion, a Korean immigrant man recalled that someone had said to him, “You speak English well, but where are you from?” One Filipino participant shared her experience during the first six months in the U.S.:
“You know, I spoke English fine. But there were certain things that, you know, people constantly questioning you like, oh, where are you from? When did you come here? You know, just asking about your experience to the point where … you become fed up with it after a while.”
–Immigrant woman of Filipino origin in mid-30s
U.S.-born participants also talked about experiences when others asked where they are from. Many shared that they would not talk about their ethnic origin right away when answering such a question because it often led to misunderstandings and assumptions that they are immigrants.
“I always get that question of, you know, ‘Where are you from?’ and I’m like, ‘I’m from America.’ And then they’re like, ‘No. Where are you from-from ?’ and I’m like, ‘Yeah, my family is from Pakistan,’ so it’s like I always had like that dual identity even though it’s never attached to me because I am like, of Pakistani descent.”
–U.S.-born man of Pakistani origin in early 20s
One Korean woman born in the U.S. said that once people know she is Korean, they ask even more offensive questions such as “Are you from North or South Korea?” or “Do you still eat dogs?”
In a similar situation, this U.S.-born Indian woman shared her responses:
“I find that there’s a, ‘So but where are you from?’ Like even in professional settings when they feel comfortable enough to ask you. ‘So – so where are you from?’ ‘Oh, I was born in [names city], Colorado. Like at [the hospital], down the street.’ ‘No, but like where are you from?’ ‘My mother’s womb?’”
–U.S.-born woman of Indian origin in early 40s
Ignorance and misinformation about Asian identity can lead to contentious encounters

“I have dealt with kids who just gave up on their Sikh identity, cut their hair and groomed their beard and everything. They just wanted to fit in and not have to deal with it, especially [those] who are victim or bullied in any incident.” Surinder , documentary participant
In some cases, ignorance and misinformation about Asians in the U.S. lead to inappropriate comments or questions and uncomfortable or dangerous situations. Participants shared their frustration when others asked about their country of origin, and they then had to explain their identity or correct misunderstandings or stereotypes about their background. At other times, some participants faced ignorant comments about their ethnicity, which sometimes led to more contentious encounters. For example, some Indian or Pakistani participants talked about the attacks or verbal abuse they experienced from others blaming them for the 9/11 terrorist attacks. Others discussed the racial slurs directed toward them since the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. Some Japanese participants recalled their families losing everything and being incarcerated during World War II and the long-term effect it had on their lives.
“I think like right now with the coronavirus, I think we’re just Chinese, Chinese American, well, just Asian American or Asians in general, you’re just going through the same struggles right now. Like everyone is just blaming whoever looks Asian about the virus. You don’t feel safe.”
–U.S.-born man of Chinese origin in early 30s
“At the beginning of the pandemic, a friend and I went to celebrate her birthday at a club and like these guys just kept calling us COVID.”
–U.S.-born woman of Korean origin in early 20s
“There [were] a lot of instances after 9/11. One day, somebody put a poster about 9/11 [in front of] my business. He was wearing a gun. … On the poster, it was written ‘you Arabs, go back to your country.’ And then someone came inside. He pointed his gun at me and said ‘Go back to your country.’”
–Immigrant man of Pakistani origin in mid-60s
“[My parents went through the] internment camps during World War II. And my dad, he was in high school, so he was – they were building the camps and then he was put into the Santa Anita horse track place, the stables there. And then they were sent – all the Japanese Americans were sent to different camps, right, during World War II and – in California. Yeah, and they lost everything, yeah.”
–U.S.-born woman of Japanese origin in mid-60s

As focus group participants contemplated their identity during the discussions, many talked about their sense of belonging in America. Although some felt frustrated with people misunderstanding their ethnic heritage, they didn’t take a negative view of life in America. Instead, many participants – both immigrant and U.S. born – took pride in their unique cultural and ethnic backgrounds. In these discussions, people gave their own definitions of America as a place with a diverse set of cultures, with their ethnic heritage being a part of it.
Taking pride in their unique cultures

“Being a Pakistani American, I’m proud. … Because I work hard, and I make true my dreams from here.” Shahid , documentary participant
Despite the challenges of adapting to life in America for immigrant participants or of navigating their dual cultural identity for U.S.-born ones, focus group participants called America their home. And while participants talked about their identities in different ways – ethnic identity, racial (Asian) identity, and being American – they take pride in their unique cultures. Many also expressed a strong sense of responsibility to give back or support their community, sharing their cultural heritage with others on their own terms.
“Right now it has been a little difficult. I think it has been for all Asians because of the COVID issue … but I’m glad that we’re all here [in America]. I think we should be proud to be here. I’m glad that our families have traveled here, and we can help make life better for communities, our families and ourselves. I think that’s really a wonderful thing. We can be those role models for a lot of the future, the younger folks. I hope that something I did in the last years will have impacted either my family, friends or students that I taught in other community things that I’ve done. So you hope that it helps someplace along the line.”
“I am very proud of my culture. … There is not a single Bengali at my workplace, but people know the name of my country. Maybe many years [later] – educated people know all about the country. So, I don’t have to explain that there is a small country next to India and Nepal. It’s beyond saying. People after all know Bangladesh. And there are so many Bengali present here as well. So, I am very proud to be a Bangladeshi.”
Where home is
When asked about the definition of home, some immigrant participants said home is where their families are located. Immigrants in the focus groups came to the United States by various paths, whether through work opportunities, reuniting with family or seeking a safe haven as refugees. Along their journey, some received support from family members, their local community or other individuals, while others overcame challenges by themselves. Either way, they take pride in establishing their home in America and can feel hurt when someone tells them to “go back to your country.” In response, one Laotian woman in her mid-40s said, “This is my home. My country. Go away.”
“If you ask me personally, I view my home as my house … then I would say my house is with my family because wherever I go, I cannot marry if I do not have my family so that is how I would answer.”
–Immigrant man of Hmong origin in late 30s
“[If somebody yelled at me ‘go back to your country’] I’d feel angry because this is my country! I live here. America is my country. I grew up here and worked here … I’d say, ‘This is my country! You go back to your country! … I will not go anywhere. This is my home. I will live here.’ That’s what I’d say.”
–Immigrant woman of Laotian origin in early 50s
‘American’ means to blend their unique cultural and ethnic heritage with that in the U.S.

“I want to teach my children two traditions – one American and one Vietnamese – so they can compare and choose for themselves the best route in life.” Helen , documentary participant (translated from Vietnamese)
Both U.S.-born and immigrant participants in the focus groups shared their experiences of navigating a dual cultural environment between their ethnic heritage and American culture. A common thread that emerged was that being Asian in America is a process of blending two or more identities as one.
“Yeah, I want to say that’s how I feel – because like thinking about it, I would call my dad Lao but I would call myself Laotian American because I think I’m a little more integrated in the American society and I’ve also been a little more Americanized, compared to my dad. So that’s how I would see it.”
–U.S.-born man of Laotian origin in late 20s
“I mean, Bangladeshi Americans who are here, we are carrying Bangladeshi culture, religion, food. I am also trying to be Americanized like the Americans. Regarding language, eating habits.”
–Immigrant man of Bangladeshi origin in mid-50s
“Just like there is Chinese American, Mexican American, Japanese American, Italian American, so there is Indian American. I don’t want to give up Indianness. I am American by nationality, but I am Indian by birth. So whenever I talk, I try to show both the flags as well, both Indian and American flags. Just because you make new relatives but don’t forget the old relatives.”
–Immigrant man of Indian origin in late 40s

Pew Research Center designed these focus groups to better understand how members of an ethnically diverse Asian population think about their place in America and life here. By including participants of different languages, immigration or refugee experiences, educational backgrounds, and income levels, this focus group study aimed to capture in people’s own words what it means to be Asian in America. The discussions in these groups may or may not resonate with all Asians living in the United States. Browse excerpts from our focus groups with the interactive quote sorter below, view a video documentary focused on the topics discussed in the focus groups, or tell us your story of belonging in America via social media. The focus group project is part of a broader research project studying the diverse experiences of Asians living in the U.S.
Read sortable quotes from our focus groups
Browse excerpts in the interactive quote sorter from focus group participants in response to the question “What does it mean to be [Vietnamese, Thai, Sri Lankan, Hmong, etc.] like yourself in America?” This interactive allows you to sort quotes from focus group participants by ethnic origin, nativity (U.S. born or born in another country), gender and age.
Video documentary
Videos throughout the data essay illustrate what focus group participants discussed. Those recorded in these videos did not participate in the focus groups but were sampled to have similar demographic characteristics and thematically relevant stories.
Watch the full video documentary and watch additional shorter video clips related to the themes of this data essay.
Share the story of your family and your identity
Did the voices in this data essay resonate? Share your story of what it means to be Asian in America with @pewresearch. Tell us your story by using the hashtag #BeingAsianInAmerica and @pewidentity on Twitter, as well as #BeingAsianInAmerica and @pewresearch on Instagram.
This cross-ethnic, comparative qualitative research project explores the identity, economic mobility, representation, and experiences of immigration and discrimination among the Asian population in the United States. The analysis is based on 66 focus groups we conducted virtually in the fall of 2021 and included 264 participants from across the U.S. More information about the groups and analysis can be found in this appendix .
Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts, its primary funder. This data essay was funded by The Pew Charitable Trusts, with generous support from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative DAF, an advised fund of the Silicon Valley Community Foundation; the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation; the Henry Luce Foundation; The Wallace H. Coulter Foundation; The Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation; The Long Family Foundation; Lu-Hebert Fund; Gee Family Foundation; Joseph Cotchett; the Julian Abdey and Sabrina Moyle Charitable Fund; and Nanci Nishimura.
The accompanying video clips and video documentary were made possible by The Pew Charitable Trusts, with generous support from The Sobrato Family Foundation and The Long Family Foundation.
We would also like to thank the Leaders Forum for its thought leadership and valuable assistance in helping make this study possible. This is a collaborative effort based on the input and analysis of a number of individuals and experts at Pew Research Center and outside experts.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
‘He Is Our Sinatra’: Lin-Manuel Miranda on Why Marc Anthony — and His New Album, ‘Muevense’ — Are So Important (EXCLUSIVE)
By Lin-Manuel Miranda
Lin-Manuel Miranda
- Lin-Manuel Miranda Is Hopeful for Broadway’s Return 3 years ago
- Lin-Manuel Miranda on the Public Theater That Oskar Eustis Built 7 years ago

New York City is filled with Latin music icons, and legendary singer Marc Anthony and “Hamilton” / “In the Heights”/ “Encanto” composer Lin-Manuel Miranda are two in a long and illustrious legacy. With Anthony’s new album “Muevense” arriving this Friday — and him performing his new single, “Ale, Ale,” at the Latin American Music Awards tonight on Univision — Miranda took the time to pay tribute to “our Sinatra”: the man whose music, as you’ll see below, was the soundtrack to so much of his life.
Popular on Variety
It may have been your last Spring Break with your friends, screaming “Voy a reír, voy a bailar…” at the top of your lungs. It may have been blasting “No Me Conoces” during your first heartbreak (“Y AHORA RESULTA QUE NO SOY SUFICIENTE PARA TI, WHOAAA…” you sang to that empty bedroom). Or walking down the aisle to “Vivir Lo Nuestro”/ “Nadie Como Ella,” too many classics to count.
Here’s my Marc Anthony Story. My first album was “Otra Nota,” which I purchased at Nobody Beats The Wiz with my 13th birthday money in 1993, because “Palabras Del Alma” was already so inescapable that I had to hear the rest of the album. Even as a teenager, I knew that the passion and depth in this young man’s voice was beyond anything I’d ever heard in salsa. It forced me to double down on learning to dance salsa, so that by the time “Todo A Su Tiempo” came out in 1995, I was ready to tear up the dance floor at Mayra Linares’ quinceañera with all her gorgeous friends.
I was at the New York Puerto Rican Day Parade in 1997, watching Marc Anthony on the main stage on 86th Street and 5th Avenue, when Tito Puente came by on a passing float. He pointed at Marc, jumped down from his parade float, and took to the mainstage for a blistering timbale solo on the song already in progress, a passing of the torch I’ll never forget.
I went to see Marc Anthony’s Broadway debut in “The Capeman” that same year, and sang “Adios Hermanos” with my friends at graduation.
My mother reports that after she dropped me, her youngest child, off to college in 1998, she listened to “Contra La Corriente” for a month straight. “’YO TRATO, TRATO, TRATO, PERO NO TE OLVIDO…’ Lin-Manuel, I was so depressed at our empty nest and that album got me through it.”
When my son Francisco was born, Marc’s voice was singing on our childbirth playlist: “Si te vas, si te vaaas…”
I could go on, but these notes only have so much space.
All this to say, a new Marc Anthony album is always cause for celebration, and it speaks to the timelessness and consistency of his voice and his musical collaborators that at any moment you can turn on any radio station and within the same commercial-free music block, hear a song he recorded last year next to a song he recorded 30 years ago. He is our Sinatra, and when we hear him, we also hear the echoes of all the unforgettable moments in our own lives.
And now here comes “MUEVENSE,” a new soundtrack for the next chapter in Marc’s life and ours. The blistering title track, “Muevense,” which is all over ONE CHORD, but contains a universe of syncopation and will flood all dance floors. An ex-lover classic in “Punta Cana,” which joins “No Me Conoces,” “Hasta Ayer” and “Y Hubo Alguien” in the pantheon of “You Broke Up With Me and You’ll Always Regret It.” But “I’m Thriving” anthems, now in bachata mode! “Si Te Enamoro,” headed for your next wedding playlist immediately. “Ojala Te Duela,” a historic foray into mariachi with the great Pepe Aguilar, and confirms what we have always known: that lágrima in Marc’s voice transcends styles and musical boundaries. “En La Distancia,” by the great Colombian songwriter Fonseca, has one of the most exciting musical builds in Marc’s discography. “Ale Ale” is as close to a valedictory speech as you’ll ever hear Marc give, his “My Way.” “A Donde Vamos A Parar” is the breakup/crying on the dancefloor jam you’ve been waiting for, written by Marc’s namesake, the legendary Marco Antonio Solís. The album’s closer, “Amarte A La Antigua,” has the craziest held note into a key change you’ve ever heard, and will be a staple in our lives for years to come.
Thank you, Marc. Every new album is a promise of more life, more music, and more memories, and “Muevense” is up there with your best. See the rest of you on the dance floor.
More From Our Brands
Kendrick lamar, dua lipa, danny ocean, and all the songs you need to know, savannah vs. charleston: which southern city has the best luxury hotels, fanatics exec appeals injunction in draftkings noncompete case, be tough on dirt but gentle on your body with the best soaps for sensitive skin, grey’s anatomy promises to ‘pay off’ all that season 20 build-up in a ‘fiery… edge-of-your-seat’ finale, verify it's you, please log in.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The three dimensions of happiness. Happiness can be defined as an enduring state of mind consisting not only of feelings of joy, contentment, and other positive emotions, but also of a sense that one's life is meaningful and valued (Lyubomirsky, 2001). Happiness energizes us and is a highly sought after state of being.
Two key components of happiness (or subjective well-being) are: The balance of emotions: Everyone experiences both positive and negative emotions, feelings, and moods. Happiness is generally linked to experiencing more positive feelings than negative ones. Life satisfaction: This relates to how satisfied you feel with different areas of your ...
Happiness lengthens our lives In the end, the ultimate health indicator might be longevity—and here, especially, happiness comes into play. In perhaps the most famous study of happiness and longevity, the life expectancy of Catholic nuns was linked to the amount of positive emotion they expressed in an autobiographical essay they wrote upon ...
Our current situation as a species. The current driver of our decision-making process. Examples of what makes happiness important for the greater good. 1. Happiness is correlated to sustainable actions. 2. Focusing on happiness comes with many indirect benefits. 3. Happiness is correlated to fewer conflicts.
The Leadership and Happiness Laboratory conducts research and creates resources for leaders to learn the science of happiness, apply it in their own lives, and share it with others. ... Research has long indicated the link between our happiness and physical health. A study from the Harvard Chan School finds a host of health benefits that ...
As Aristotle said: "Happiness is the meaning and the purpose of life, the whole aim and end of human existence.". Of course, being happy is not some magical cure-all. Happy people still get ...
500+ Words Essay on Happiness. Happiness is something which we can't describe in words it can only be felt from someone's expression of a smile. Likewise, happiness is a signal or identification of good and prosperous life. Happiness is very simple to feel and difficult to describe. Moreover, happiness comes from within and no one can steal ...
Most of the studies comparing happiness and life satisfaction among countries focus on averages. However, distributional differences are also important. Life satisfaction is often reported on a scale from 0 to 10, with 10 representing the highest possible level of satisfaction. This is the so-called 'Cantril Ladder'.
It is important that we find positive things in our daily lives to get excited about and feel the happiness. Essay on Happiness - For Kids and Children (Essay 2 - 200 Words) Happiness is a state of mind which makes you feel accomplished in life and having everything in this world without a single reason to repent.
You might also be interested in these essays about courage. 5. Toxic positivity by Suhani Mahajan. "That's the mindset most of us have. Half of toxic positivity is just the suppression of 200% acceptable feelings such as anger, fear, sadness, confusion, and more. Any combination of such feelings is deemed "negative.".
Happiness is an electrifying and elusive state. Philosophers, theologians, psychologists, and even economists have long sought to define it. And since the 1990s, a whole branch of psychology ...
100 Words Essay on Happiness in Life Understanding Happiness. Happiness is a feeling of joy, satisfaction, and contentment. It's the positive emotion we feel when our needs are met or our desires are fulfilled. Importance of Happiness. Happiness is crucial in life. It keeps us healthy, boosts our immune system, and makes us more creative.
On Happiness as Harmony. Pedro Blas González. O f the many ways that we can exist as persons, happiness directs our glance inward, toward the essence of our individual being. This is the discovery of personhood as interiority. The ultimate form of happiness—joy—signals our participation in being. The capacity to experience happiness is a ...
We can ask hundreds of people, and each of them would probably give different answers. One would say that happiness is to be with a loved one, the second would say that happiness is the stability, and the third, on the contrary, would say that happiness is the unpredictability. For someone, to be happy is to have a lot of money while for others ...
from the 'prudential happiness' (or 'eudaimonic') and differs from the concept of happiness as life satisfaction itself or something similar, e.g. 'happiness as inv olving the realizing ...
Since most of us spend a great deal of our lives working, it is inevitable that work plays a key role in shaping our levels of happiness. In a recent chapter of the World Happiness Report ...
Stronger relationships. When you allow yourself to be content, you are also telling yourself to accept others as they are. The benefits of contentment are not limited to your own well-being; they ...
1. Health. Your health is very important to you as an individual. You should ensure that your body is healthy all the time so that you can be a happy person. Remember that when your body is aching, you will not be comfortable like you were …show more content…. Confidence. Confidence is very essential in life.
Friendship is an essential aspect of human life that brings joy, support, and companionship. It is a bond that goes beyond mere acquaintances and develops through shared experiences, trust, and understanding. Friends play a significant role in our lives, providing a sense of belonging and enriching our journey.
RELATED: 48 Realistic Laws Of Happiness To Manifest A Truly Content Life Marielisa Reyes is a writer with a bachelor's degree in psychology who covers self-help, relationships, career, and family ...
Understanding the importance of progress allows us to integrate a mindset of constant self-improvement, resulting in a more meaningful and fulfilling life. All things considered, understanding growth is key for pursuing happiness and productivity in regard to the advantages of development in many aspects of life and explaining why growth is ...
Our community takes these secrets to happiness to heart, embedding them into our Senior Living services. We understand that happiness stems from a blend of physical well-being, mental stimulation, and emotional connections. Cultivating a Sense of Humor and Embracing Laughter. Laughing is like a secret potion for a better life.
The terms "Asian," "Asians living in the United States" and "Asian American" are used interchangeably throughout this essay to refer to U.S. adults who self-identify as Asian, either alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic identity. "The United States" and "the U.S." are used interchangeably with "America" for variations in the writing.
In this heartfelt essay, 'Hamilton' / 'Encanto' composer Lin-Manuel Miranda explains why Marc Anthony's music has been so important in his life.