

How to structure AQA A-level History Essays
- Dr Janet Rose
- December 14, 2019
For AQA History , at both AS and A level, you need to know how to write two types of essay – a block essay and a point-by-point essay. To be able to structure AQA history essays you’ll need to know these essay styles and where to use them.
Introductions
You don’t really need an introduction for the source questions. In the exam you will be pressed for time so it is sensible to just start with your analysis of extract A. However, for the essay questions you will need a short, clear introduction that references the question and states your line of argument.
The most helpful tip I can give you is this; write the introduction last . Why do I advise this? Because if you state your line of argument and what you intend to include, you then have to make sure your whole essay and conclusion matches your introduction. Obviously you should have a plan to follow but it is far, far easier to write the body of your essay and your conclusion, then make the introduction fit the essay you have just written. It makes writing the introduction a breeze because you will know exactly what you have argued, which evidence you have used, the order you have presented your material and what you have concluded.
No Surprises
Remember there should be no surprises for your marker or examiner in history. You are not writing a best seller where you build up the tension and then do a dramatic ‘ta da’ reveal. That will only confuse your examiner and lose you marks – potentially a lot of marks. What we want is a nice, clear format where we can see exactly what you are arguing, exactly what evidence you are using, and exactly what you have concluded. Importantly, we want to know this at the start of the essay. If you make your marker or examiner keep stopping, re-reading chunks, and going back and forth to try and understand your argument, you’ll just end up with an unhappy and frustrated reader. And this is the person who is going to award your marks! Be clear. Be concise. Get to the point quickly. Give evidence to back up your points. Reach a judgement.
History Essay: How to write an A-Grade Essay
Block Essays
For AQA you use these for the extract questions; the two sources for AS and the three sources for A level. You write the essay in blocks of text which are focused on one area.
For the source questions you don’t need to get too clever with hopping back and forth between sources and points. Decide and plan what you need to say and then write it clearly, with a clear assessment of each source, in big chunks of work. Do not worry about an introduction– just get straight into the analysis. First address Source A in a block, then Source B in another block and (for A level) Source C in a final block.
Remember that you need to assess the sources. Keep doing that all the way through. Assess each source as you write the block and do a mini summary at the end of each section. You can then bring the sources together in a very short conclusion at the end (no more than a couple of lines) where you can summarise your convincing/valuable assessment of the sources. It is very important that you make a clear judgement for each source, as that is what the question asks you to do.
By the way, when we talk about blocks it does not mean you have to cram everything into one enormous paragraph. If you have plenty to say (and hopefully you will) you should use a sensible paragraph structure. The reason it is called a block essay is that you deal with one section completely, in this case each source, before moving on to the next section.
Point-by-point essays
Point-by-Point essays are much trickier to master but are well worth the effort as, done properly, they tend to achieve higher marks. For AQA you can use this style for everything that is not a source question. The key to an excellent point-by-point essay is all in the planning; it will only come out well in the writing if you know exactly what you are going to argue and the order in which you are going to introduce evidence and points. So it is crucial that you make yourself a good plan!
Essentially, all the AQA essay questions at both AS and A level ask you to argue ‘for or against’ a hypothesis. They will look something like this:
‘Victorian governments in the years 1867 to 1886 had little interest in social reform.’ Explain why you agree or disagree with this view.
‘Henry VII had successfully established monarchical authority by 1509.’ Assess the validity of this view.
Your job, therefore, is to find evidence from your course for both sides of the argument i.e. both ‘for’ and ‘against’ the hypothesis. You absolutely must have evidence for both sides – not just one side. The evidence goes down on your plan, divided into ‘for’ and ‘against’ the hypothesis. Whichever side you end with more evidence for, or more convincing evidence for, that is the side you will conclude is most persuasive.
History Exams – How to avoid being narrative

Imagine it like a tennis match
Imagine it like a tennis match, where the ball starts on one side of the tennis court, is played and then sails over to the opposing side. A point-by-point argument is like this – it is oppositional, with two opposing sides. You should aim to bounce back and forth between the points and the two sides of the argument. Begin with one of the points from your plan, either for or against the hypothesis. Deal with the point in detail, using clear examples as evidence and linking it firmly to the question. That’s your opening shot.
Next, pop straight over to the opposing view and deal with that point, again using clear examples and linking to the question. Repeat this ‘back and forth’ technique until you have covered all the points and evidence in your plan.
To do this really well it is usually better to put up the side of your argument that you will oppose first. You outline the ‘other’ side of the argument and show that you understand the opposing view. Then you switch over to the other side of the hypothesis, i.e. ‘your’ argument, and use powerful evidence to back it up. Remember this is all about argument and analysis.
Back to our tennis match analogy; the ball is your argument, which bounces back and forth between the players, but you need ‘your’ side to end each point with the big shot – the one that wins the game.
How to use Provenance in History Exams
The Conclusion
You must conclude in line with the most persuasive and convincing evidence you have included in your plan. This sounds really obvious, but I have lost count of how many A-level history essays I have marked that argue effectively for one point of view, but then conclude in favour of the other side. The most common reason for this happening is that the student has moved off their plan when writing up the essay. Follow your plan!
At the end of the essay your conclusion should sum up all the main points of argument and then should reach a judgement. Don’t sit on the fence, no matter how tempting it is. You need to make a judgement. The conclusion should mirror your introduction and the main points of argument in the body of the essay, so the work ends up as a coherent, clear argument from introduction to conclusion.
The point-by-point essay takes practice, so it will help if you can get some feedback from your teacher or tutor, or even a parent who will be able to tell you if your argument is clear and makes sense to the reader. Do persevere, however, because when you get the technique right it will gain you more marks in the end.
Do you need help with History Essays?
Our history team is ready to help you. all our historians are graduates, experienced teachers, and skilled at getting our students the very best grades., you can contact a tutor here , or contact our friendly and knowledgeable office team to get a bespoke tutor match.
The Tutor Team Guarantee
How can we help you, share this post.
0333 987 4603

- Privacy Policy
- Handbook & Policies
Privacy Overview

A Level History Essay Structure – A Guide
- Post author By admin
- Post date December 1, 2022
- No Comments on A Level History Essay Structure – A Guide
Getting an A Level History essay structure right is by no means an easy task. In this post we will look at how we can build a structure from which our essay can develop.

Here you can see the most simplified essay structure for tackling A level History essays. All students should be familiar with this structure. We have broken the essay down into an introduction and conclusion as well as 3 separate parts of content. Running through the entire essay at the side is our line of argument. Whilst this may seem fairly simple, many students still fail to adequately follow this structure, when writing essay answers under exam conditions.
The reasons this structure works well is that it enables you to cover 3 different factors of content. These can be aligned 2-1 or 1-2 on either side of the argument. Your essay is now balanced (covering both sides of the argument), whilst at the same time being decisive in terms of your line of argument and judgement. It is also consistent with the amount you can write in the exam time given for (20-25) mark essay questions.
Expanded A level History Essay Structure

Let’s look at an expanded essay structure. Again, we have our introduction and conclusion as well as 3 separate parts of content. Now we can see that we have added whether or not each of our parts of content agrees or disagrees with the question premise. In order to have a balanced essay we can see on this example that; Content 1 agrees, Content 2 disagrees, and Content 3 can go either way. This overall A Level History essay structure ensures a balanced essay that also reaches judgement.
Furthermore, we have now broken down each individual part of Content/Factor. This can be seen as a mini essay in its own right. The Content/Factor is introduced and linked to the question as well as being concluded and linked to the question. Then we write 2 to 3 separate points within the body of the Content/Factor. We have 2 points that agree with the overall argument of this section of content. This strongly backs up our argument.
Then we can also potentially (this doesn’t have to be done always, but when done right creates a more nuanced analysis) add a third point that balances that particular section of content. However, it doesn’t detract from the overall argument of this factor/content. E.g. In the short term ‘point 3’ occurred but of much greater significance was ‘point 1’ and ‘point 2.’
How To Improve Further at A Level History
Pass A Level History – is our sister site, which shows you step by step, how to most effectively answer any A Level History extract, source or essay question. Please click the following link to visit the site and get access to your free preview lesson. www.passalevelhistory.co.uk
Previous and Next Blog Posts
Previous – A Level History Questions – Do and Avoid Guide – passhistoryexams.co.uk/a-level-history-questions-do-and-avoid-guide/
Next – A Level History Coursework Edexcel Guide – passhistoryexams.co.uk/a-level-history-coursework-edexcel/
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

How to Write An A-Level History Essay Structure
A major part of your A-level history coursework includes writing essays. While an essay essentially informs a reader about a certain topic, it is more than just writing all the information. So, examiners, especially during the A-levels, tend to focus on tricky things or skills like how well you have responded to the question, analysed the evidence, and built the arguments.
Unless you are exceptionally blessed, you need time to hone these skills, and poor grades are, thus, common in the beginning. Luckily, these abilities can be learned. Usually, when students struggle with such write-ups, they consider searching online: ‘Can I pay someone to write my essay ?’ to ease their academic burden. However, this guide has discussed some main steps to writing an A-level history essay. These will help you create a high-scoring essay.
Steps to Follow When Writing an A-level History Essay
Here are some crucial steps to writing a history essay:
1. Read the Question Carefully
Some students recite a prepared response without assessing what they are actually writing, resulting in a poorly-graded essay. Therefore, it is crucial to read the question several times to comprehend it. In addition, doing so will help you understand the importance of careful reading and annotation settings, such as identifying potential arguments to support your essay writing.
2. Create an Outline
Make an outline after you’ve finished analysing the essay question. This approach reduces the possibility of error when you hit a major roadblock. Furthermore, it acts as a roadmap when you can’t assemble your ideas in the essay.
The outline helps you brainstorm and comprehend what is essential to mention in your essay. Therefore, it’s a good idea to compile a list of key arguments supporting and refuting your position. You can also take help from A-level history essay examples online to understand how to go about the task. You are now prepared to move towards the introduction.
3. What Should Be in A History Essay Introduction?
You can state your main argument in the essay introduction. This is an exciting approach because it demonstrates you have a strong viewpoint and are willing to argue, focusing on keywords from the beginning. It also reveals to an examiner you have planned your essay, know what you will say, and can back it up with good evidence. However, usually, students don’t know how to start or what should be in a history essay introduction?
Therefore, any write-up introduction is often personalised. You can start with an interesting quote, disagree with the question, define a significant event, or do something else to set the scene, making it compelling. It will also show you have comprehensive knowledge of the subject matter, understand the problems at stake, and how to deal with them. This type of introduction will captivate readers, impress them, and pique their interest.
4. Write Main Body Paragraphs
Now you know what should be in a history essay introduction; it’s time to work on the main body paragraphs. You will support your case in the main body. However, remember you are making arguments, not telling a story.
You’ve already distinguished the keywords in the question. So, now it’s time to put them to use. Each paragraph must reference the keywords in a meaningful way. Be ruthless – you should carefully select only what is required to back up your argument.
5. Conclude Your History Essay
In conclusion, you summarise what you have written in the main body. This is the last thing an examiner reads. A good conclusion can save a bad essay and seal the deal on a good note.
It is the point where you tie the threads of your argument together and hammer home your points, leaving the audience in no doubt about your answer.
You should refer specifically to the question’s keywords and reinforce the points you made in the main body. But, above all, it should not contain anything new and restate your argument.
How to Answer A Source Question In A-Level History?
You might need to write the answer source question in your history essay, but you don’t know how to answer a source question in a-level history, so here are some tips you can keep in mind while writing an answer:
• Indicate how dependable you might expect the source of a particular type of question to be • Avoid using the word ‘biased’ • Indicate the source’s specific purpose • Include information about the author, the audience, or the time • Mention what is exaggerated or omitted, and then return to your question
Thus, following these tips, you will better understand how to answer a source question in a-level history.
A-Level History Essay Examples
Now you know how to work on a history essay.
Here’s a list of A-level history essay example topics you can work on: • The soldiers from India who fought in World War I • The involvement of America in the Korean War • Examples of music created due to political causes • What were the events that led to the Roman Empire’s demise? • The hippie movement of the 1960s • The incidents that led to Saudi Arabia’s emergence • The British music industry’s foray into the US market
These are some topics you can write on. Moreover, if you still feel it’s not easy for you to write A-level history essays, you can always consider taking essay writing services from us to meet your academic requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how many paragraphs should an a level history essay be.
An A-level history essay should have at least three paragraphs, but four paragraphs are also recommended.
2. How do you write a 20-mark history essay a level?
For writing a 20-marks history A-level essay, you should begin with a brief introduction. So, you should be presenting your thesis statement at this stage. Then, the main body of the argument should follow the pattern of Point, Evidence, and Describe.
Make a point at this stage, back it up with some evidence, and explain what it indicates. You must also evaluate these points to get excellent marks while demonstrating your claim is stronger. Finally, summarise your arguments to conclude, but don’t add new information.
3. How do you write a high school history essay?
Writing a high school history essay requires students to follow essential steps, including:
• Consider the background information that the reader should be aware of in the introductory paragraph • Define any keywords • Assess which ideas will require the cited assistance • Determine how each idea contributes to the main argument • Make a list of key points to go over in the conclusion
Administrator - AUTHOR
Recent post.

May 6, 2022
How To Write an Informative Essay Like Expert Essay Writers?

March 2, 2022 March 15, 2022

February 22, 2022 March 15, 2022
How to Write Your Dissertation the Right Way: Do’s and Don’ts
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Winner of UK’s Best Tutoring Centre BOOK YOUR FREE TRIAL

Step-by-Step Guide to Effective A-Level History Essay Writing
Step-by-Step Guide to Effective A-Level History Essay Writing : A-Level History entails demonstrating strong essay writing skills. Well-crafted essays require an organised approach: from properly interpreting the question to researching arguments to employing proper structure and style conventions. Follow this step-by-step process to produce polished A-Level History essays ready to earn top marks.
Step 1 – Analyse and Understand the Question
The first crucial step is decoding what the essay question is asking you to do. Underline key directive words like “assess,” “compare,” “discuss,” etc. Consider what the examiner wants you to accomplish in your response. Get clarification from your teacher if needed. Also underline the key themes, time period, and any named factors to focus your answer.
Step 2 – Brainstorm and Plan Arguments
After dissecting the question prompt, start freely brainstorming related arguments and evidence supporting different perspectives. Map out an initial broad thesis and the main points of analysis you will make. Prioritise providing depth of evidence over breath on a sprawling topic. Remember quality over quantity.
Step 3 – Research and Gather Evidence
Now conduct targeted research and gather historical evidence to support the analytical arguments sketched out. Compile factual support from lectures, textbooks, academic journals, primary source documents, and reputable websites. Choose precise evidence to reinforce key points. Avoid overly relying on generic background information.
Step 4 – Craft Strong Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement presents the main argumentative position you will take in the essay. It should directly respond to the parameters of the question. The thesis needs to be clear, focused, conveyed in 1-2 sentences, and backed by the analysis to follow. This roadmap guides readers effectively.
Step 5 – Outline Essay Structure and Flow
Organise research, arguments, and evidence into a structured outline establishing logical flow. Typical structure is: Introduction with thesis statement, 2-4 body paragraphs making analytical arguments, conclusion summarising arguments. Each element should build towards proving your thesis.
Step 6 – Write Clear Topic Sentences
Now compose clear topic sentences introducing the main point of each paragraph. Good topic sentences relay the essence of that section’s argument while linking back to the central thesis. They act as navigational signposts for readers to follow the progression.
Step 7 – Flesh Out Body Paragraphs
Within each body paragraph, logically expand on its topic sentence. Provide historical context and incorporate relevant evidence sources using quotes, examples, data, etc to back the main point. Analyse how evidence relates and prove conclusions. Transition smoothly between ideas and paragraphs.
Step 8 – Wrap Up with Strong Conclusion
Echo your original thesis and summarise the main arguments made in the essay to reinforce the concluding takeaway. Do not simply restate points but show how they come together to form a new understanding that compellingly answers the initial question. End powerfully.
Step 9 – Check Accuracy, Clarity and Flow
With the full draft complete, scrutinise the accuracy of historical facts, dates, names, and terminology. Verify evidence fully supports arguments. Assess clarity of phrasing and transition sentences between ideas. Revise disjointed sections and rework ineffective arguments needing stronger factual backing.
Step 10 – Polish Writing Style
Apply finishing touches by proofreading for proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Vary sentence structure and vocabulary. Cut excess verbiage using clear, concise language. Check that style, tone, and diction are appropriate for an academic history essay. Now your essay is submission-ready!
This strategic approach helps produce A-Level History essays demonstrating strong analysis, research, and writing skills. Partner with an experienced tutor like A Team Tutors for constructive feedback perfecting essay technique and scoring top marks on A-Level exams.
A-Team Academy is the perfect place for students who want to get ahead in their studies. Our free trial lessons and assessments are a great way to see if our teaching style is a good fit for you, we have experienced tutors that can help you reach your full potential . A-Team Academy Birmingham
Categorized in:
About the Author
“A Good Education Has The Power To Transform Not Only One Life But The Lives Of Those Around Them.” Amin Miah – Director
Check latest articles from this author:
Achieve gcse exam success at birmingham gcse exam centre – the region’s top scoring venue, choosing the right a level subjects: a student’s guide to making the best selections for university admissions and future careers, exploring the benefits of the igcse curriculum: why it’s worth considering, related articles, how to choose your a-levels like a pro: expert university prep tips, ace gcse biology: the key concepts and skills to master, common gcse english grammar pitfalls and how to avoid them, previous article, from classroom to world stage: cambridge international’s impact on student success, next article.
1772 Coventry Rd, Yardley, B26 1PB
305 Soho Rd, Handsworth, B21 9SA

Call for registration
- : 0121 517 0110
[email protected]
Opening times, useful links.

Alevels, HomeschoolLife, StudyFromHome, HomeEducation, OnlineLearning, IndependentStudy, AlevelJourney, HomeschoolSuccess, DistanceLearning, ExamPrep, SelfDirectedLearning, EducateAtHome, HomeschoolCommunity, AlevelChallenges, RemoteLearning, StudyGoals, AlevelTips, HomeschoolingAdventures, StudentLife, HomeschoolWinning
Copyright © 2023-2030 A-Team Academy
Please Enter your Email Address
To get instant access to this valuable past paper, simply enter your email address below.

Learning Today, Leading Tomorrow "

A Level History: Essay Writing and Revision Tips

A Level History poses a unique challenge, requiring not only a profound understanding of historical events but also the ability to articulate complex ideas in well-structured essays. Excelling in A Level History necessitates effective essay writing skills and strategic revision strategies. In this extensive guide, we will delve into essential tips for A Level History essay writing and effective revision approaches to help you succeed in this demanding subject.
I. A Level History Essay Writing Tips
a. understand the question.
1. Thorough Reading: Take the time to comprehend the essay question thoroughly. Identify key terms and requirements.
2. Thesis Formation: Clearly articulate a thesis statement that directly addresses the question.
b. Plan Your Essay
1. Structured Outline: Create a well-organized essay structure with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
2. Logical Flow: Ensure a coherent flow of ideas, with each paragraph contributing to the overall argument.
c. Effective Introduction
1. Context Establishment: Provide historical context to orient the reader.
2. Thesis Statement: Clearly state your argument or position in the introduction.
d. Develop a Strong Argument
1. Evidence-Based: Support your argument with evidence from historical sources.
2. Analysis: Analyze the significance of the evidence and its relevance to the overall argument.
e. Use of Historical Terminology
1. Precision in Terminology: Demonstrate a command of historical terminology relevant to the topic.
2. Contextual Usage: Use terms in their historical context to showcase understanding.

f. Counterarguments and Evaluation
1. Consideration of Counterarguments: Address potential counterarguments to strengthen your position.
2. Critical Evaluation: Assess the strengths and weaknesses of different historical perspectives.
g. Conclusion
1. Summarization of Key Points: Recapitulate the main points of your argument.
2. Restate Thesis: Reinforce your thesis in the conclusion.
h. Language and Style
1. Clarity: Write clearly and concisely, avoiding unnecessary complexity.
2. Varied Sentence Structure: Use a mix of sentence structures for readability.
II. A Level History Revision Strategies
a. organized revision schedule.
1. Prioritization of Topics: Identify weaker areas and prioritize them in your revision schedule.
2. Consistent Review: Regularly review topics instead of cramming.
b. Active Engagement with Sources
1. Primary and Secondary Source Engagement: Actively engage with both primary and secondary sources.
2. Critical Analysis: Develop skills to critically analyze historical documents.
c. Mind Maps and Diagrams
1. Visual Representation: Create mind maps or diagrams to visually represent historical events and connections.
2. Conceptual Understanding: Utilize visuals to enhance your conceptual understanding.
d. Practice Essay Writing
1. Timed Practice: Simulate exam conditions with timed essay writing.
2. Feedback Seek: Seek feedback from teachers or peers to enhance your writing skills.
e. Flashcards for Key Dates and Facts
1. Key Dates Memorization: Create flashcards for essential historical dates and facts.
2. Regular Review: Consistently review flashcards for better retention.
f. Group Study Sessions
1. Discussion Participation: Engage in group study sessions for diverse perspectives.
2. Concept Explanation: Teach concepts to peers to reinforce your understanding.
g. Past Papers and Marking Schemes
1. Exam Simulation: Practice with past papers to familiarize yourself with the exam format.
2. Marking Schemes Analysis: Analyze marking schemes to understand expectations.
h. Utilize Online Resources
1. Online Lectures: Watch online lectures to supplement your understanding.
2. Interactive Quizzes: Utilize online quizzes for self-assessment.
III. Conclusion
A Level History demands a multifaceted approach, combining effective essay writing skills with strategic revision strategies. Understanding essay question nuances, meticulous planning, and developing a robust argument with historical evidence are crucial elements of successful A Level History essays. In terms of revision, an organized schedule, active engagement with sources, and varied study techniques contribute to a comprehensive understanding of historical events. By adopting these tips, you can navigate the complexities of A Level History with confidence, mastering both the art of essay writing and the nuances of historical analysis. Remember, excellence in A Level History is not just about memorization but about the ability to critically analyze and interpret the past.
You Might Also Like

The Secret to Getting off the Waitlist
So how would you go about making a letter of continued interest while you’re on the waiting status? Here’s a guide we’ve got for you.

How to Leverage your Summer to Boost Admissions
Summer programs offer students the chance to explore new areas, interests, and exciting fields. Here you can check some summer programs - Read our blog

Sample College Essays
Sample Exemplar Essays to help you figure out on how to Write and Form your essay which stands out of the rest

Free Resources

How to write an introduction for a history essay

Every essay needs to begin with an introductory paragraph. It needs to be the first paragraph the marker reads.
While your introduction paragraph might be the first of the paragraphs you write, this is not the only way to do it.
You can choose to write your introduction after you have written the rest of your essay.
This way, you will know what you have argued, and this might make writing the introduction easier.
Either approach is fine. If you do write your introduction first, ensure that you go back and refine it once you have completed your essay.
What is an ‘introduction paragraph’?
An introductory paragraph is a single paragraph at the start of your essay that prepares your reader for the argument you are going to make in your body paragraphs .
It should provide all of the necessary historical information about your topic and clearly state your argument so that by the end of the paragraph, the marker knows how you are going to structure the rest of your essay.
In general, you should never use quotes from sources in your introduction.
Introduction paragraph structure
While your introduction paragraph does not have to be as long as your body paragraphs , it does have a specific purpose, which you must fulfil.
A well-written introduction paragraph has the following four-part structure (summarised by the acronym BHES).
B – Background sentences
H – Hypothesis
E – Elaboration sentences
S - Signpost sentence
Each of these elements are explained in further detail, with examples, below:
1. Background sentences
The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis , your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about.
Background sentences explain the important historical period, dates, people, places, events and concepts that will be mentioned later in your essay. This information should be drawn from your background research .
Example background sentences:
Middle Ages (Year 8 Level)
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15 th and 16 th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges.
WWI (Year 9 Level)
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe.
Civil Rights (Year 10 Level)
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times.
2. Hypothesis
Once you have provided historical context for your essay in your background sentences, you need to state your hypothesis .
A hypothesis is a single sentence that clearly states the argument that your essay will be proving in your body paragraphs .
A good hypothesis contains both the argument and the reasons in support of your argument.
Example hypotheses:
Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery.
Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare.
The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders.
Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1 st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state.
3. Elaboration sentences
Once you have stated your argument in your hypothesis , you need to provide particular information about how you’re going to prove your argument.
Your elaboration sentences should be one or two sentences that provide specific details about how you’re going to cover the argument in your three body paragraphs.
You might also briefly summarise two or three of your main points.
Finally, explain any important key words, phrases or concepts that you’ve used in your hypothesis, you’ll need to do this in your elaboration sentences.
Example elaboration sentences:
By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period.
Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined.
The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results.
While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period.
4. Signpost sentence
The final sentence of your introduction should prepare the reader for the topic of your first body paragraph. The main purpose of this sentence is to provide cohesion between your introductory paragraph and you first body paragraph .
Therefore, a signpost sentence indicates where you will begin proving the argument that you set out in your hypothesis and usually states the importance of the first point that you’re about to make.
Example signpost sentences:
The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20 th century.
The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Putting it all together
Once you have written all four parts of the BHES structure, you should have a completed introduction paragraph. In the examples above, we have shown each part separately. Below you will see the completed paragraphs so that you can appreciate what an introduction should look like.
Example introduction paragraphs:
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15th and 16th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges. Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies, but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery. By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period. The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe. Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare. Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined. The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success. The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders. The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results. The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20th century.
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times. Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state. While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period. The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Additional resources

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
How to Write a History Essay?
04 August, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
There are so many types of essays. It can be hard to know where to start. History papers aren’t just limited to history classes. These tasks can be assigned to examine any important historical event or a person. While they’re more common in history classes, you can find this type of assignment in sociology or political science course syllabus, or just get a history essay task for your scholarship. This is Handmadewriting History Essay Guide - let's start!

Purpose of a History Essay
Wondering how to write a history essay? First of all, it helps to understand its purpose. Secondly, this essay aims to examine the influences that lead to a historical event. Thirdly, it can explore the importance of an individual’s impact on history.
However, the goal isn’t to stay in the past. Specifically, a well-written history essay should discuss the relevance of the event or person to the “now”. After finishing this essay, a reader should have a fuller understanding of the lasting impact of an event or individual.
Need basic essay guidance? Find out what is an essay with this 101 essay guide: What is an Essay?
Elements for Success
Indeed, understanding how to write a history essay is crucial in creating a successful paper. Notably, these essays should never only outline successful historic events or list an individual’s achievements. Instead, they should focus on examining questions beginning with what , how , and why . Here’s a pro tip in how to write a history essay: brainstorm questions. Once you’ve got questions, you have an excellent starting point.
Preparing to Write

Evidently, a typical history essay format requires the writer to provide background on the event or person, examine major influences, and discuss the importance of the forces both then and now. In addition, when preparing to write, it’s helpful to organize the information you need to research into questions. For example:
- Who were the major contributors to this event?
- Who opposed or fought against this event?
- Who gained or lost from this event?
- Who benefits from this event today?
- What factors led up to this event?
- What changes occurred because of this event?
- What lasting impacts occurred locally, nationally, globally due to this event?
- What lessons (if any) were learned?
- Why did this event occur?
- Why did certain populations support it?
- Why did certain populations oppose it?
These questions exist as samples. Therefore, generate questions specific to your topic. Once you have a list of questions, it’s time to evaluate them.
Evaluating the Question

Seasoned writers approach writing history by examining the historic event or individual. Specifically, the goal is to assess the impact then and now. Accordingly, the writer needs to evaluate the importance of the main essay guiding the paper. For example, if the essay’s topic is the rise of American prohibition, a proper question may be “How did societal factors influence the rise of American prohibition during the 1920s? ”
This question is open-ended since it allows for insightful analysis, and limits the research to societal factors. Additionally, work to identify key terms in the question. In the example, key terms would be “societal factors” and “prohibition”.
Summarizing the Argument
The argument should answer the question. Use the thesis statement to clarify the argument and outline how you plan to make your case. In other words. the thesis should be sharp, clear, and multi-faceted. Consider the following tips when summarizing the case:
- The thesis should be a single sentence
- It should include a concise argument and a roadmap
- It’s always okay to revise the thesis as the paper develops
- Conduct a bit of research to ensure you have enough support for the ideas within the paper
Outlining a History Essay Plan

Once you’ve refined your argument, it’s time to outline. Notably, many skip this step to regret it then. Nonetheless, the outline is a map that shows where you need to arrive historically and when. Specifically, taking the time to plan, placing the strongest argument last, and identifying your sources of research is a good use of time. When you’re ready to outline, do the following:
- Consider the necessary background the reader should know in the introduction paragraph
- Define any important terms and vocabulary
- Determine which ideas will need the cited support
- Identify how each idea supports the main argument
- Brainstorm key points to review in the conclusion
Gathering Sources
As a rule, history essays require both primary and secondary sources . Primary resources are those that were created during the historical period being analyzed. Secondary resources are those created by historians and scholars about the topic. It’s a good idea to know if the professor requires a specific number of sources, and what kind he or she prefers. Specifically, most tutors prefer primary over secondary sources.
Where to find sources? Great question! Check out bibliographies included in required class readings. In addition, ask a campus Librarian. Peruse online journal databases; In addition, most colleges provide students with free access. When in doubt, make an appointment and ask the professor for guidance.
Writing the Essay
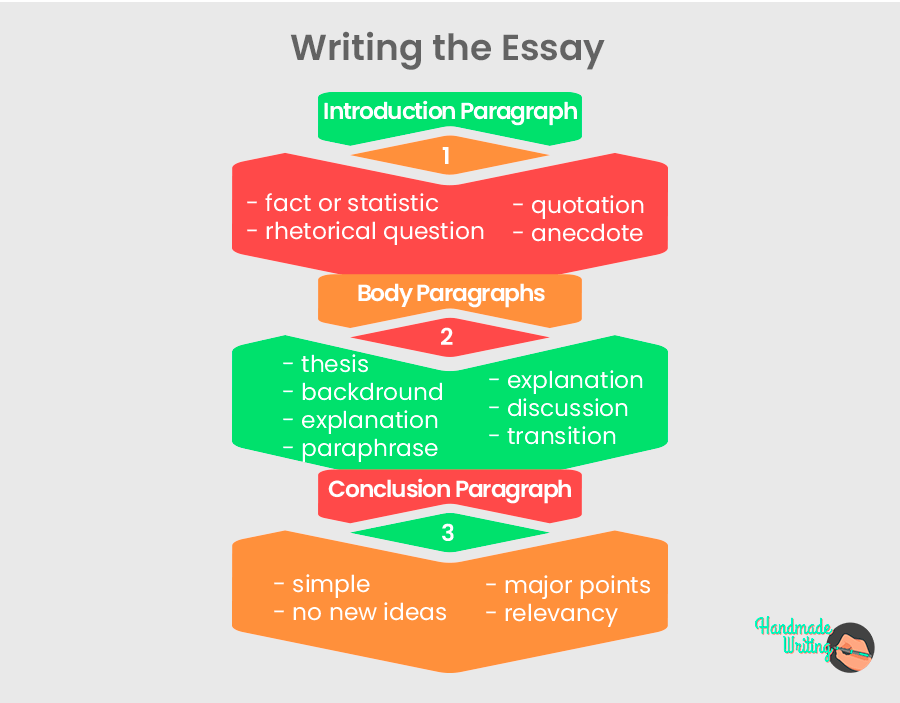
Now that you have prepared your questions, ideas, and arguments; composed the outline ; and gathered sources – it’s time to write your first draft. In particular, each section of your history essay must serve its purpose. Here is what you should include in essay paragraphs.
Introduction Paragraph
Unsure of how to start a history essay? Well, like most essays, the introduction should include an attention-getter (or hook):
- Relevant fact or statistic
- Rhetorical Question
- Interesting quotation
- Application anecdote if appropriate
Once you’ve captured the reader’s interest, introduce the topic. Similarly, present critical historic context. Namely, it is necessary to introduce any key individuals or events that will be discussed later in the essay. At last, end with a strong thesis which acts as a transition to the first argument.
Body Paragraphs
Indeed, each body paragraph should offer a single idea to support the argument. Then, after writing a strong topic sentence, the topic should be supported with correctly cited research. Consequently, a typical body paragraph is arranged as follows:
- Topic sentence linking to the thesis
- Background of the topic
- Research quotation or paraphrase #1
- Explanation and analysis of research
- Research quotation or paraphrase #2
- Transition to the next paragraph
Equally, the point of body paragraphs is to build the argument. Hence, present the weakest support first and end with the strongest. Admittedly, doing so leaves the reader with the best possible evidence.
Conclusion Paragraph
You’re almost there! Eventually, conclusion paragraphs should review the most important points in the paper. In them, you should prove that you’ve supported the argument proposed in the thesis. When writing a conclusion paragraph keep these tips in mind:
- Keep it simple
- Avoid introducing new information
- Review major points
- Discuss the relevance to today
Problems with writing Your History essay ? Try our Essay Writer Service!

Proofreading Your Essay
Once the draft is ready and polished, it’s time to proceed to final editing. What does this process imply? Specifically, it’s about removing impurities and making the essay look just perfect. Here’s what you need to do to improve the quality of your paper:
- Double check the content. In the first place, it’s recommended to get rid of long sentences, correct vague words. Also, make sure that all your paragrahps contain accurate sentences with transparent meaning.
- Pay attention to style. To make the process of digesting your essay easier, focus on crafting a paper with readable style, the one that is known to readers. Above all, the main mission here is to facilitate the perception of your essay. So, don’t forget about style accuracy.
- Practice reading the essay. Of course, the best practice before passing the paper is to read it out loud. Hence, this exercise will help you notice fragments that require rewriting or a complete removal.
History Essay Example
Did you want a history essay example? Take a look at one of our history essay papers.
Make it Shine
An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it’s achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine:
- Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it’s the first impression the professor will have of the paper.
- State a clear thesis. A strong thesis is easier to support.
- Incorporate evidence critically. If while researching you find opposing arguments, include them and discuss their flaws.
- Cite all the research. Whether direct quotations or paraphrases, citing evidence is crucial to avoiding plagiarism, which can have serious academic consequences.
- Include primary and secondary resources. While primary resources may be harder to find, the professor will expect them—this is, after all, a history essay.
History Essay Sample
Ready to tackle the history essay format? Great! Check out this history essay sample from an upper-level history class. While the essay isn’t perfect, the professor points out its many strengths.
Remember: start early and revise, revise, revise . We can’t revise history, but you can revise your ideas until they’re perfect.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Resources you can trust
Essay writing template

A useful essay planning template for A-level students to help them to construct an argument in response to any essay question, for coursework or exam conditions. Includes prompts for introductions and conclusions, and a framework for each paragraph.
All reviews
Have you used this resource?
Resources you might like

How to write an A Level History essay?
How to write a History Essay? In general, essay writing involves the organization of arguments to support or challenge a given view in the question statement. In the context of A Level History essay writing, it is important to adopt an argumentative style of writing to convince your reader that your stand is sound and well-analyzed. However, it is insufficient to weave a continuous line of arguments and submit your script with the expectation that you have just aced the examination. In this article, we will examine some key considerations that will support your efforts to create a good essay.
1: Read the question carefully The first step to do well for A Level History essay is to read the question. Some students are eager to skip the reading process and attempt the writing immediately, which can lead to fatal errors. It is imperative that you read the question and pick out the keywords. Pay attention to the command words, like “assess”. Also, identify the given view in the question statement to find out what is the opposing view, in order to take a clear stand in your introduction. During our JC History Tuition , we conduct class discussions to guide students through the reading process, by using example essay questions. Through proper reading and annotation setting, you will realise the importance of careful reading, such as the identification of possible arguments to support your essay writing.
2: Set your essay outline Once you have analyzed the essay question, plan your essay outline. By deriving a rough guideline on how you can arrange your ideas in the essay, this approach minimizes the potential error in which you arrive at a stumbling block and you are unable to decide on the direction of your subsequent paragraphs. The outline should be written in five minutes or less. Focus your efforts on the listing of key arguments that support your stand and those that challenge it. Under each argument, you can list down examples that come to your mind. Now, you are ready to write.
3: Acknowledge the given view in the question Similar to how individuals engage in intellectual debates, it is important that you acknowledge the view stated in the question. Failure to do so, you may risk being marked down for the ‘inability to answer the question’. To do this, you should explain how the given view answers the question.
Example Question: “The effectiveness of the United Nations (UN) peacekeeping efforts depended solely on the Security Council.” How far do you agree with this view in the period of 1945 to 1991?
4: Align the arguments to your stand This alignment of argument depends on the direction stated in your stand (which should be stated in your ‘Introduction’. With reference to the above question, if your stand is that you disagree and argue that the effectiveness of the UN did not depend on the Security Council, but rather the General Assembly, then your second paragraph should provide an analysis of the limitations of the Security Council’s role.
Bear in mind that the analysis of factors in every essay question cannot be memorised and stored piecewise in your own revision notes. It is a misleading approach that limits your thinking ability. Instead, our JC History Tuition will feature numerous question practices to widen the scope of assessments, such that you will be familiar with the possible perspectives in a given topic.
What’s Next? Practice makes perfect! I strongly encourage you to attempt more essays. Once you start, you will realise that this perceived sense of hesitation and reluctance can be overcome. Furthermore, your worries (Can I complete my essays on time? How do I remember so many examples?) will dissipate as you practice more often. I do not deny that writing can be a frictional process at the start. Do not give up. Your determination will bring you closer to your goal.
You might also like

Recent Posts
- What is the steel trigger price mechanism?
- How did Pakistan came into existence?
- What is Article 370?
- What is the Instrument of Accession?
- What is the United Nations Partition Plan?
- Approaches to Governance
- Approaches to National Unity
- Conflict and Cooperation
- Economic Development after Independence
- History Essays
- History Tuition
- JC History Syllabus
- JC History Tuition
- Regional Conflicts and Cooperation
- Safeguarding International Peace and Security
- Social Studies Tuition
- Study Notes and Tips
- The Cold War
- The Cold War in Asia
- Understanding the Global Economy
- Cold War and Southeast Asia
- Economic Development
- Exam Skills
- Four Asian Tigers
- Global Economy
- History SBCS
- Superpower Relations
- Uncategorized
- United Nations

- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

1J The British Empire - Essay Plans
Subject: History
Age range: 16+
Resource type: Unit of work
Last updated
21 August 2020
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This bundle contains 96 exam essay plans that covers all 6 themes for the AQA Alevel course. They are detailed plans which each contain an example judgement. It also contains 14 less structured plans to further exam questions or smaller questions with judgements which are useful to think about.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Block Essays. For AQA you use these for the extract questions; the two sources for AS and the three sources for A level. You write the essay in blocks of text which are focused on one area. For the source questions you don't need to get too clever with hopping back and forth between sources and points. Decide and plan what you need to say and ...
Now as to how to structure the paragraph itself: The first line of the paragraph should be a signpost sentence - it should summarise your argument for that paragraph. This gives the examiner a clear idea of what is coming in the next 300-400 words. There is a commonly used mark scheme with most exam boards, which rewards the P.E.E structure.
This template has been successfully used by high achieving A-level History students previously. can also be tailored to teach essay structure to lower secondary school - Year 7s and 11s. Creative Commons "NoDerivatives"
In order to have a balanced essay we can see on this example that; Content 1 agrees, Content 2 disagrees, and Content 3 can go either way. This overall A Level History essay structure ensures a balanced essay that also reaches judgement. Furthermore, we have now broken down each individual part of Content/Factor.
Steps to Follow When Writing an A-level History Essay. Here are some crucial steps to writing a history essay: 1. Read the Question Carefully. Some students recite a prepared response without assessing what they are actually writing, resulting in a poorly-graded essay. Therefore, it is crucial to read the question several times to comprehend it.
Step-by-Step Guide to Effective A-Level History Essay - 10-step process to craft analytical structured A-Level History essays ... Step 2 - Brainstorm and Plan Arguments. ... Organise research, arguments, and evidence into a structured outline establishing logical flow. Typical structure is: Introduction with thesis statement, 2-4 body ...
You should begin each section of your essay with a statement which should contain your main point, following this comes the Evidence which supports the point you are making (any facts or figures) and the analysis should explain why this supports your point and your main line of argument referring back to the question. All history essays begin ...
This resource contains x9 A4 essay plan templates. This includes 5-6 full points with Point, Evidence, Analysis and counter arguments, and space to fill in introduction and conclusions. Essay plans are a fantastic way to put your learned knowledge into practice. Familiarising yourself with essay titles is a great way to approach revision.
1) A block essay does what is says on the tin. You write the essay in blocks of text which are focused on one area. For AQA you use these for the source questions; the two sources for AS and the ...
Section 1: Unravelling the Marking Rubric. In order to excel in your A-Level H2 History essay and reach the highest marks, it is essential to understand and adhere to the marking rubric provided ...
A Level History poses a unique challenge, requiring not only a profound understanding of historical events but also the ability to articulate complex ideas in well-structured essays. Excelling in A Level History necessitates effective essay writing skills and strategic revision strategies. In this extensive guide, we will delve into essential tips for A Level History essay writing and ...
the History Paper The Challenges of Writing About (a.k.a., Making) History At first glance, writing about history can seem like an overwhelming task. History's subject matter is immense, encompassing all of human affairs in the recorded past — up until the moment, that is, that you started reading this guide.
25 Mark Essay Template for the AQA A-Level History Specification Source analysis template for paper 1 30 marker is available to download at: https://www.tes.com/teac
An essay plan is a way to identify, select, and order the points you want to make in your essay. It helps you to work out your argument and your structure before writing, which should make the writing process more efficient and focussed. Sometimes essay plans are set as formative assignments so tutors can provide feedback before you write your ...
docx, 23.2 KB. This resource is a planning sheet, setting out the structure required for an AQA A-Level History essay. This planning sheet may also be applicable for other exam boards such as OCR, WJEC and Edexcel but I would refer to your mark schemes for some more clarity. I have used this exact structure to get 25/25 on multiple essays and ...
To achieve the correct structure for your argument, it is crucial to understand the separate parts that make up a written essay. If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece. Most essays will require you to write: 1 Introduction Paragraph; 3 Body Paragraphs
1. Background sentences. The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis, your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about. Background sentences explain the important historical ...
Make it Shine. An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it's achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine: Write a substantial introduction.
A useful essay planning template for A-level students to help them to construct an argument in response to any essay question, for coursework or exam conditions. Includes prompts for introductions and conclusions, and a framework for each paragraph. 8.15 KB. Free download.
1: Read the question carefully The first step to do well for A Level History essay is to read the question. Some students are eager to skip the reading process and attempt the writing immediately, which can lead to fatal errors. It is imperative that you read the question and pick out the keywords. Pay attention to the command words, like ...
pdf, 465.23 KB. pdf, 350.88 KB. This bundle contains 96 exam essay plans that covers all 6 themes for the AQA Alevel course. They are detailed plans which each contain an example judgement. It also contains 14 less structured plans to further exam questions or smaller questions with judgements which are useful to think about.
Exam paper questions organised by topic and difficulty. Our worksheets cover all topics from GCSE, IGCSE and A Level courses. Give them a try and see how you do! Exam paper questions organised by topic and difficulty. ... A Level History. Choose from your exam board: AQA A Level History. Past Papers. Edexcel A Level History. Past Papers. OCR A ...