- Open access
- Published: 25 November 2023

Systematic review and research agenda for the tourism and hospitality sector: co-creation of customer value in the digital age
- T. D. Dang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0930-381X 1 , 2 &
- M. T. Nguyen 1
Future Business Journal volume 9 , Article number: 94 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
2104 Accesses
1 Citations
Metrics details
A Correction to this article was published on 07 February 2024
This article has been updated
The tourism and hospitality industries are experiencing transformative shifts driven by the proliferation of digital technologies facilitating real-time customer communication and data collection. This evolution towards customer value co-creation demands a paradigm shift in management attitudes and the adoption of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Metaverse. A systematic literature review using the PRISMA method investigated the impact of customer value co-creation through the digital age on the tourism and hospitality sector. The primary objective of this review was to examine 27 relevant studies published between 2012 and 2022. Findings reveal that digital technologies, especially AI, Metaverse, and related innovations, significantly enhance value co-creation by allowing for more personalized, immersive, and efficient tourist experiences. Academic insights show the exploration of technology’s role in enhancing travel experiences and ethical concerns, while from a managerial perspective, AI and digital tools can drive industry success through improved customer interactions. As a groundwork for progressive research, the study pinpoints three pivotal focal areas for upcoming inquiries: technological, academic, and managerial. These avenues offer exciting prospects for advancing knowledge and practices, paving the way for transformative changes in the tourism and hospitality sectors.
Introduction
The tourism and hospitality industry is constantly evolving, and the digital age has brought about numerous changes in how businesses operate and interact with their customers [ 1 ]. One such change is the concept of value co-creation, which refers to the collaborative process by which value is created and shared between a business and its customers [ 2 , 3 ]. In order to facilitate the value co-creation process in tourism and hospitality, it is necessary to have adequate technologies in place to enable the participation of all stakeholders, including businesses, consumers, and others [ 4 , 5 ]. Thus, technology serves as a crucial enabler for value co-creation. In the tourism and hospitality industry, leading-edge technology can be crucial in co-creation value processes because it can facilitate the creation and exchange of value among customers and businesses [ 6 , 7 ]. For example, the development of cloud computing and virtual reality technologies has enabled new forms of collaboration and co-creation that were not possible before [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Recent technologies like AI, Metaverse, and robots have revolutionized tourism and hospitality [ 11 , 12 , 13 ]. These technologies are used in various ways to enhance the customer experience and drive business success. AI can personalize the customer experience using customer data and personalized recommendations [ 14 ]. It can also optimize operations by automating tasks and improving decision-making. The metaverse, or virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, are being used to offer immersive and interactive experiences to customers [ 10 , 11 ]. For example, VR and AR can create virtual tours of hotels and destinations or offer interactive experiences such as virtual cooking classes or wine tastings [ 15 ]. Robots are being used to aid and interact with customers in various settings, including hotels, restaurants, and tourist attractions. For example, robots can provide information, answer questions, and even deliver room services [ 12 , 16 ]. The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the crucial interplay between public health, sustainable development, and digital innovations [ 17 ]. Globally, the surge in blockchain applications, particularly in the business, marketing and finance sectors, signifies the technological advancements reshaping various industries [ 18 ]. These developments, coupled with integrating digital solutions during the pandemic, highlight the pervasive role of technology across diverse sectors [ 19 , 20 , 21 ]. These insights provide a broader context for our study of the digital transformation in the tourism and hospitality sectors. Adopting new technologies such as AI, the Metaverse, blockchain and robots is helping the tourism and hospitality industry deliver customers a more personalized, convenient, and immersive experience [ 22 ]. As these technologies continue to evolve and become more prevalent, businesses in the industry need to stay up-to-date and consider how they can leverage these technologies to drive success [ 23 , 24 ].
Despite the growing body of literature on customer value co-creation in the tourism and hospitality sector, it remains scattered and fragmented [ 2 , 25 , 26 ]. To consolidate this research and provide a comprehensive summary of the current understanding of the subject, we conducted a systematic literature review using the PRISMA 2020 (“ Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ”) approach [ 27 , 28 ]. This systematic review aims to explore three primary areas of inquiry related to the utilization of AI and new technologies in the tourism and hospitality industry: (i) From a technology perspective, what are the main types of AI and latest technologies that have been used to enhance co-creation values in tourism and hospitality?; (ii) From an academic viewpoint—What are the future research directions in this sector?; (iii) From a managerial standpoint—How can these technologies be leveraged to enhance customer experiences and drive business success?. In essence, this study contributes valuable insights into the dynamic realm of customer value co-creation in the digital age within the tourism and hospitality sector. By addressing the research questions and identifying gaps in the literature, our systematic literature review seeks to provide novel perspectives on leveraging technology to foster industry advancements and enhance customer experiences.
The remaining parts of this article are structured in the following sections: “ Study background ” section outlines pertinent background details for our systematic literature review. In “ Methodology ” section details our research objectives, queries, and the systematic literature review protocol we used in our study design. In “ Results ” section offers the findings based on the analyzed primary research studies. Lastly, we conclude the article, discuss the outstanding work, and examine the limitations to the validity of our study in “ Discussion and implications ” section.
Study background
Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, the tourism sector is experiencing significant transformations. Despite the substantial impact on the tourism industry, the demand for academic publications about tourism remains unabated. In this recovery phase, AI and novel technologies hold immense potential to assist the tourism and hospitality industry by tackling diverse challenges and enhancing overall efficiency. In this section, the study provides some study background for the review processes.
The relationship between tourism and hospitality
Tourism and hospitality are closely related industries, as the hospitality industry plays a crucial role in the tourism industry [ 29 ]. Academics and practitioners often examine tourism and hospitality because they are related industries [ 2 , 30 ]. Hospitality refers to providing travelers and tourists accommodation, food, and other services [ 31 ]. These can include hotels, resorts, restaurants, and other types of establishments that cater to the needs of travelers [ 32 ]. On the other hand, the tourism industry encompasses all the activities and services related to planning, promoting, and facilitating travel [ 31 ]; transportation, tour operators, travel agencies, and other businesses that help facilitate tourist travel experiences [ 33 ]. Both industries rely on each other to thrive, as travelers need places to stay and eat while on vacation, and hospitality businesses rely on tourists for their income [ 32 , 33 , 34 ].
In recent years, the tourism industry has undergone significant changes due to the increasing use of digital technologies, enabling the development of new forms of tourism, such as “smart tourism” [ 8 , 10 ]. Smart tourism refers to using digital technologies to enhance the customer experience and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the industry [ 1 ]. These technologies, including AI and Metaverse, can be used in various aspects of the tourism industry, such as booking and reservation processes, customer service, and the management of tourist attractions [ 4 , 11 ]. The hospitality industry, which includes hotels and restaurants, is closely linked to the tourism industry and is also adopting intelligent technologies to improve the customer experience and increase efficiency [ 1 , 22 ]. Recent studies have explored the impact of these technologies on the tourism and hospitality sectors and have identified both benefits and challenges for stakeholders [ 10 , 35 , 36 ].
Customer value co-creation in tourism and hospitality
Customer value co-creation in tourism and hospitality refers to the process by which customers and businesses collaborate to create value by exchanging services, information, and experiences [ 2 , 33 ]. This process involves the customer and the business actively creating value rather than simply providing a product or service to the customer [ 37 ]. Studies have found that customer value co-creation in tourism and hospitality can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty [ 2 ]. When customers feel that they can contribute to the value of their experience, they are more likely to feel a sense of ownership and involvement, which can lead to a more positive overall evaluation of the experience [ 5 , 38 ]. In the tourism industry, customer value co-creation can increase satisfaction with the destination, trips, accommodation, services, and overall experiences [ 4 ]. These can be achieved by allowing customers to choose their room amenities or providing opportunities to interact with staff and other guests [ 5 , 39 ]. Customer value co-creation in tourism and hospitality can be a powerful solution for businesses to increase customer satisfaction and loyalty. By actively involving customers in creating value, businesses can create a more personalized and engaging experience for their customers.
AI, Metaverse, and new technologies in tourism and hospitality
The impact of AI, the Metaverse, and new technologies on the tourism and hospitality industries is an area of active research and debate [ 2 , 4 , 29 , 40 ]. First, using AI and new technology in tourism and hospitality can improve the customer experience, increase efficiency, and reduce costs [ 13 , 41 , 42 , 43 ]. For instance, chatbots and virtual assistants facilitate tasks like room bookings or restaurant reservations for customers. Concurrently, machine learning (ML) algorithms offer optimized pricing and marketing strategies and insights into customer perceptions within the tourism and hospitality sectors [ 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 ]. However, there are also concerns about the potential negative impact of AI on employment in the industry [ 48 ]. Second, The emergence of the Metaverse, a virtual shared space where people can interact in real time, can potentially revolutionize the tourism and hospitality industries [ 10 ]. For example, VR and AR experiences could allow travelers to visit and explore destinations without leaving their homes [ 15 , 49 ], while online events and social gatherings could provide new business opportunities to connect with customers [ 11 ]. However, it is unclear how the Metaverse will evolve and its long-term impact on the tourism and hospitality industries [ 4 , 10 , 11 ]. Last, other emerging technologies, such as blockchain, AI-Robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT), can potentially transform the tourism and hospitality industries [ 18 , 45 , 48 ]. For example, blockchain could be used to secure and track the movement of travel documents [ 18 ], while IoT-enabled devices could improve the efficiency and personalization of the customer experience [ 50 ]. As with AI and the Metaverse, it is difficult to predict the exact impact of these technologies on the industry, but they are likely to play a significant role in shaping its future [ 18 , 40 ]. In the aftermath of the pandemic, the healthcare landscape within the tourism and hospitality sector is undergoing significant transformations driven by the integration of cutting-edge AI and advanced technologies [ 38 , 51 , 52 ]. These technological advancements have paved the way for personalized and seamless experiences for travelers, with AI-powered chatbots playing a pivotal role in addressing medical inquiries and innovative telemedicine solutions ensuring the well-being of tourists [ 52 , 53 ].
This study background provides essential context for the subsequent systematic literature review, as it contextualizes the field’s key concepts, frameworks, and emerging technologies. By examining these aspects, the study aims to contribute valuable insights into the post-pandemic recovery of the tourism and hospitality industry, paving the way for future research opportunities and advancements in the field.
Methodology
This study meticulously adopted a systematic literature review process grounded in a pre-defined review protocol to provide a thorough and objective appraisal [ 54 ]. This approach was geared to eliminate potential bias and uphold the integrity of study findings. The formulation of the review protocol was a collaborative effort facilitated by two researchers. This foundational document encompasses (i) Clear delineation of the study objectives, ensuring alignment with the research aim; (ii) A thorough description of the methods used for data collection and assessment, which underscores the replicability of our process; (iii) A systematic approach for synthesizing and analyzing the selected studies, promoting consistency and transparency.
Guiding the current review process was the PRISMA methodology, a renowned and universally esteemed framework that has set a gold standard for conducting systematic reviews in various scientific disciplines [ 27 , 28 ]. The commendable efficacy of PRISMA in service research substantiates its methodological robustness and reliability [ 55 ]. It is not only the rigorous nature of PRISMA but also its widespread acceptance in service research that accentuates its fittingness for this research. Given tourism and hospitality studies’ intricate and evolving nature, PRISMA is a robust compass to guide our SLR, ensuring methodological transparency and thoroughness [ 56 , 57 ]. In essence, the PRISMA approach does not merely dictate the procedural intricacies of the review but emphasizes clarity, precision, and transparency at every phase. The PRISMA methodology presents the research journey holistically, from its inception to its conclusions, providing readers with a clear and comprehensive understanding of the approach and findings [ 58 ].
Utilizing the goal-question-metrics approach [ 59 ], our study aims to analyze current scientific literature from the perspectives of technicians, researchers, and practitioners to comprehend customer value co-creation through the digital age within the Tourism and Hospitality sector. In order to accomplish this goal, we formulated the following research questions:
What are the main types of AI and new technologies used to enhance value co-creation in the tourism and hospitality industries?
What are the future research directions in customer value co-creation through AI and new technologies in the tourism and hospitality sector?
How do managers in the tourism and hospitality sector apply AI and new technologies to enhance customer co-creation value and drive business success?
The subsequent subsections will provide further details regarding our search and analysis strategies.
Search strategy and selection criteria
We collected our data by searching for papers in the Scopus and Web of Science databases, adhering to rigorous scientific standards. We included only international peer-reviewed academic journal articles, excluding publications like books, book chapters, and conference proceedings [ 60 , 61 , 62 ]. The research process covered the period from 2009 to 2022, as this timeframe aligns with the publication of the first studies on value co-creation in the tourism industry in 2009 and the first two studies on value co-creation in general in 2004 [ 63 , 64 ]. The selection of sources was based on criteria such as timelines, availability, quality, and versatility, as discussed by Dieste et al. [ 2 ]. We employed relevant keywords, synonyms, and truncations for three main concepts: tourism and hospitality, customer value co-creation, and AI and new technologies in smart tourism and hospitality. To ensure transparency and comprehensiveness, we followed the PRISMA inclusion criteria, detailed in Table 1 , and utilized topic and Boolean/phrase search modes to retrieve papers published from 2009 to 2022. The final search string underwent validation by experts to ensure accuracy and comprehensiveness:
A PRISMA diagram was produced to understand better this study’s search strategy and record selection.
Study selection and analysis procedure
The current study utilized the PRISMA framework to document our review process. One hundred two papers were retrieved during the initial search across the databases. Table 1 outlines the criteria for selecting the studies based on scope and quality. The study adhered to the PRISMA procedure (as shown in Fig. 1 ) and applied the following filters:
We identified and removed 17 duplicate records during the ‘identification’ step.
We excluded 27 publications in the ‘Screening’ step based on the title and abstract.
We excluded 31 publications based on the entire text in the eligibility step.
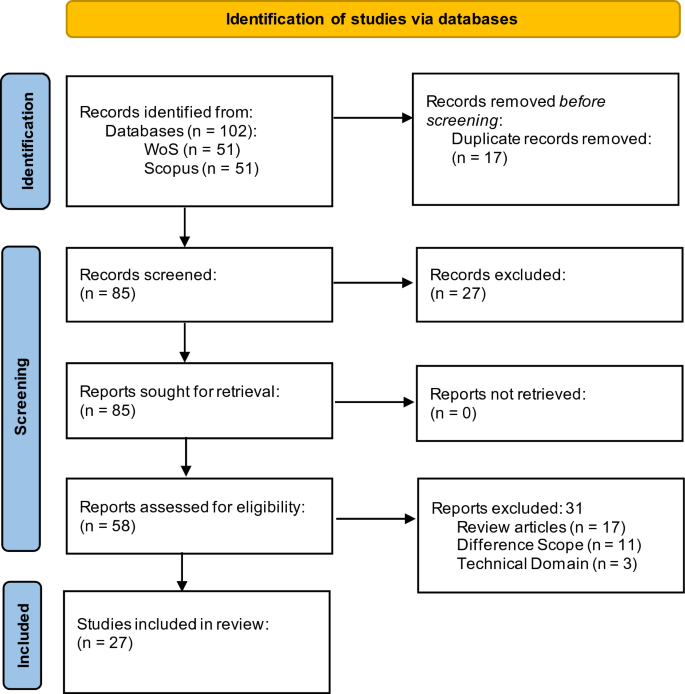
PRISMA flow diagram
As a result, we were left with a final collection of 27 journal articles for downloading and analysis. Two trained research assistants conducted title and abstract screenings separately, and any disagreements about inclusion were resolved by discussing them with the research coordinator until an agreement was reached. Papers not in English, papers from meetings, books, editorials, news, reports, and patents were excluded, as well as unrelated or incomplete papers and studies that did not focus on the tourism and hospitality domain. A manual search of the reference lists of each paper was conducted to identify relevant papers that were not found in the database searches. After this process, 27 papers were left for a full-text review.
This study used the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) to evaluate the quality of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research studies included [ 65 , 66 ]. According to the findings, the quality of the study met the standards of a systematic review. Additional information can be obtained from Additional file 1 : Appendix 1.
In this section, we will report the results of our data analysis for each research question. We will begin by describing the characteristics of the studies included in the systematic literature review, such as (1) publication authors, titles, years and journals, topics, methods, and tools used in existing studies. Then each facet was elaborated by the following questions: (i) What are the main types of AI and new technologies used to enhance value co-creation in the tourism and hospitality industries? (ii) What are the future research directions in customer value co-creation through AI and new technologies in the tourism and hospitality sector? (iii) How do managers in the tourism and hospitality sector apply AI and new technologies to enhance customer co-creation value and drive business success?
Studies demographics
Figure 2 shows the yearly publication of articles on customer co-creation of value in tourism and hospitality through AI and new technologies. The chart’s data suggests two main findings. Firstly, the research on customer value co-creation in tourism and hospitality through AI and new technologies is still in its early stages (1 paper in 2012). However, the annual number of published articles from 2017 to the present appears to be generally increasing. This trend implies that the application of value co-creation in this field is gaining academic attention and is becoming an emerging research area. Based on this trend, we anticipate seeing more studies on this topic published in the following years.
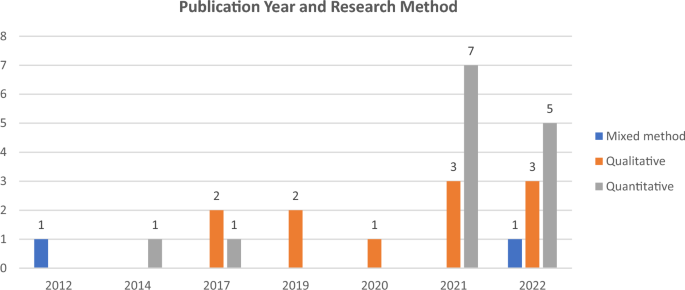
Publication Years with research methods
Regarding research type, 14 papers (52%) conducted quantitative research, employing statistical analysis, structural equation modeling, and data mining methods. Meanwhile, 11 papers (41%) conducted qualitative research using interviews, thematic analysis, and descriptive analysis. Only two papers (7%) used mixed research (combining quantitative and qualitative methods). The survey and interview methods (both individual and group) were found to be more common than other research methods. This suggests that interviews provide greater insight into participant attitudes and motivations, enhancing accuracy in quantitative and qualitative studies. Additionally, certain studies employed content analysis, big data analysis using UGC, and data from online platforms, social media, and big data.
Regarding the publishing journals, we found that 27 papers were published in 22 journals (refer to Table 2 ), where three journals had more than one paper on co-creation value through AI and new technologies in tourism and hospitality, indicating their keen interest in this topic. Most publications were in the Journal of Business Research, with four studies on co-creation value through AI and new technologies in tourism and hospitality. Two related studies were published in the Tourism Management Perspectives and Journal of Destination Marketing & Management. This distribution indicates that most current research on co-creation value through AI and new technologies in tourism and hospitality was published in journals in the tourism and hospitality management field. However, some journals in the computer and AI field have also published papers on co-creation value through AI and new technologies in tourism and hospitality, including Computers in Industry, Computers in Human Behavior, Computational Intelligence, and Neuroscience.
Regarding data analytics tools, SmartPLS, AMOS, NVivo and PROCESS tools are the 5 most popular software graphic tools used in studies, while Python and R are the two main types of programming languages used. In total, 27 studies, 14 refer to using AI applications and data analytics in this research flow. Metaverse and relative technologies such as AR and VR were included in 8 studies. Three studies used service robots to discover the value co-creation process. There are include two studies that have used chatbots and virtual assistants.
Publication years and journals
In recent systematic literature reviews focusing on general services, tourism, and hospitality, there has been a notable emphasis on traditional factors shaping customer experience [ 26 , 67 , 68 ]. However, this study uniquely positions itself by emphasizing the digital age’s profound impact on value co-creation within this sector. The subsequent part digs more into the specifics of this study, building on these parallels. The detailed findings offer nuanced insights into how value co-creation in tourism and hospitality has evolved, providing a more extensive understanding than previous works.
Result 1—technology viewpoints: What are the main types of AI and new technologies used to enhance value co-creation in the tourism and hospitality industries?
Several types of AI and new technologies have been used to enhance co-creation values in the tourism and hospitality industry. Nowadays, AI, ML, and deep learning can all be used to enhance customer value co-creation in the tourism and hospitality industry [ 42 , 69 , 70 ]. There are some AI applications identified through the review process:
First, personalization and customized recommendations: AI and ML can be used to analyze customer data, such as their past bookings, preferences, and reviews, to personalize recommendations and experiences for them [ 7 , 69 , 71 , 72 ]. Cuomo et al. examine how data analytics techniques, including AI and ML, can improve traveler experience in transportation services. Applying AI and ML can help customers discover new experiences and activities they may not have considered otherwise [ 13 ]. Relating to data mining applications, Ngamsirijit examines how data mining can be used to create value in creative tourism. Moreover, the study also discusses the need for co-creation to create a successful customer experience in creative tourism and ways data mining can enhance the customer experience [ 73 ].
Second, user-generated content and sentiment analysis: ML and Natural Language Processing (NLP) can be used to analyze user-generated content such as reviews and social media posts to understand customer needs and preferences [ 12 , 37 ]. This can help businesses identify opportunities to create customer value [ 74 ]. NLP can analyze customer reviews and feedback to understand the overall sentiment toward a hotel or destination [ 75 ]. This can help businesses identify areas for improvement and create a better customer experience [ 70 ]. In the study using NLP to analyze data from Twitter, Liu et al. examine the impact of luxury brands’ social media marketing on customer engagement. The authors discuss how big data analytics and NLP can be used to analyze customer conversations and extract valuable insights about customer preferences and behaviors [ 74 ].
Third, recent deep learning has developed novel models that create business value by forecasting some parameters and promoting better offerings to tourists [ 71 ]. Deep learning can analyze large amounts of data and make more accurate predictions or decisions [ 39 , 41 ]. For example, a deep learning model could predict the likelihood of a customer returning to a hotel based on their past bookings and interactions with the hotel [ 72 ].
Some applications of the latest technologies that have been used to enhance co-creation values in tourism and hospitality include
Firstly, Chatbots and virtual assistants can enhance customer value co-creation in the tourism and hospitality industry in several ways: (i) Improved customer service: Chatbots and virtual assistants can be used to answer customer questions, provide information, and assist with tasks such as booking a room or making a reservation [ 45 ]. These tools can save customers and staff time and improve customer experience [ 76 ]; (ii) Increased convenience: Chatbots and virtual assistants can be accessed 24/7, meaning customers can get help or assistance anytime [ 50 ]. These tools can be handy for traveling customers with questions or who need assistance outside regular business hours [ 44 ]; (iii) Personalization: Chatbots and virtual assistants can use natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond to customer inquiries in a more personalized way [ 45 , 70 ]. This can help improve the customer experience and create a more favorable impression of the business. Moreover, this can save costs and improve customers [ 16 ].
Secondly, metaverse technologies can enhance customer value co-creation in the tourism and hospitality industry in several ways: (i) Virtual tours and experiences: Metaverse technologies can offer virtual tours and experiences to customers, allowing them to visit and explore destinations remotely [ 77 ]. This technology can be beneficial for customers who are unable to travel due to pandemics or who want to preview a destination before deciding to visit in person [ 49 ]; (ii) Virtual events: Metaverse technologies can be used to host virtual events, such as conferences, workshops, or trade shows, which can be attended by customers from anywhere in the world [ 9 ]. This can save time and money for businesses and customers and increase the reach and impact of events; (iii) Virtual customer service: Metaverse technologies can offer virtual customer service, allowing customers to interact with businesses in a virtual setting [ 25 ]. This can be especially useful for customers who prefer to communicate online or in remote areas; (iv) Virtual training and education : Metaverse technologies can offer virtual training and education to employees and customers [ 41 ]. Metaverse can be an effective and convenient way to deliver training and can save time and money for both businesses and customers [ 7 ]; (v) Virtual reality (VR) experiences: Metaverse technologies can be used to offer VR experiences to customers, allowing them to immerse themselves in virtual environments and participate in activities that would be difficult or impossible to do in the real world [ 77 ]. This can enhance the customer experience and create new business opportunities to offer unique and memorable experiences [ 71 ].
Thirdly, IoT and robots can enhance customer value co-creation in the tourism and hospitality sector in several ways: (i) One way is by providing personalized and convenient customer experiences [ 12 ]. For example, hotels can use IoT-enabled devices to allow guests to control the temperature and lighting in their rooms, as well as access hotel amenities such as room service and concierge services [ 50 ]; (ii) In addition, robots can be used to provide assistance and enhance the customer experience in various ways [ 16 , 40 ]. For example, robots can be used to deliver items to guest rooms, assist with check-in and check-out processes, and provide information and directions to guests [ 12 ]; (iii) Both IoT and robots can be used to gather customer feedback and data in real-time, which can help to improve the quality and effectiveness of tourism and hospitality services [ 76 ]. For example, hotels can use IoT-enabled devices to gather data on guest preferences and needs, which can be used to tailor services and experiences to individual customers. This can help to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty [ 76 ]. Overall, using IoT and robots in the tourism and hospitality sector can help improve the industry’s efficiency and effectiveness and enhance the customer experience.
Result 2—academic viewpoints: What are the future research directions in customer value co-creation through AI and new technologies in the tourism and hospitality sector?
From an academic perspective, there are several potential future research directions in customer value co-creation through the digital age in the tourism and hospitality sector. Some possibilities include: (1) Understanding how different technologies and platforms facilitate co-creation: Researchers could investigate how different technologies and platforms, such as social media, mobile apps, or virtual reality, enable or inhibit co-creation in the tourism and hospitality industry; (2) Investigating the impact of co-creation on business performance: Researchers could examine the relationship between co-creation and business performance in the tourism and hospitality sector and identify the factors that drive success in co-creation initiatives; (3) Investigating the impact of AI and automation on co-creation: As AI and automation technologies become more prevalent in the industry, research could focus on the impact these technologies have on co-creation and value creation, including the potential for AI to facilitate or hinder co-creation; (4) Investigating the impact of the Metaverse on customer behaviour: Research could focus on understanding how the Metaverse affects customer behaviour and decision-making, and how companies can use this information to facilitate co-creation and value creation [ 9 ]; (5) Analysing the use of social media and other digital platforms for co-creation: Researchers could study how companies in the tourism and hospitality sector use social media and other digital platforms to facilitate co-creation with customers, and the impact that these platforms have on value creation [ 7 , 45 , 78 ]. Researchers could investigate how social interactions and communities in the Metaverse enable or inhibit co-creation in the tourism and hospitality industry and the impact on customer satisfaction and loyalty; (6) Examining the ethical implications of the Metaverse and AI: Researchers could explore the ethical considerations surrounding the use of the Metaverse and AI in the tourism and hospitality sector, such as issues related to privacy and data security, and the potential for these technologies to perpetuate or exacerbate societal inequalities [ 48 , 75 , 77 ].
Result 3—Management viewpoints: How do managers in the tourism and hospitality sector apply AI and new technologies to enhance customer co-creation value and drive business success?
There are several ways managers in the tourism and hospitality industry can apply AI and new technologies to enhance customer experiences and drive business success. We suggest four main possibilities: (1) Implementing chatbots or virtual assistants to encourage customer co-creation: Managers can use chatbots or virtual assistants to provide quick and convenient customer service, helping businesses respond to customer inquiries and resolve issues more efficiently [ 76 ]. Then, encourage customer co-creation by inviting customers to participate in the creation of new experiences and products by gathering feedback and ideas through online forums and focus groups [ 45 ]. This can help build a sense of community and engagement and can also lead to the development of new, innovative products and experiences that will attract more customers [ 50 , 79 ]; (2) Leveraging personalization technologies and using predictive analytics: Managers can use AI-powered personalization technologies to analyze customer data and preferences and offer personalized recommendations and experiences [ 42 , 72 , 80 ]. This can help businesses better understand and anticipate customer needs and create more tailored and satisfying experiences that drive co-creation value. Managers can leverage AI-powered predictive analytics technologies to analyze data and predict future customer behavior or trends [ 75 ]. This can help businesses anticipate customer needs and make informed decisions about resource allocation and planning, enhancing co-creation value. Managers can use personalization technologies and predictive analytics to analyze customer feedback and identify areas for improvement [ 37 ]. These can help businesses better understand customer needs and preferences and create more satisfying and valuable experiences that drive co-creation value [ 7 , 36 , 41 ]; (3) Using the Metaverse to facilitate co-creation: Managers can leverage the Metaverse to allow customers to design and customize their own experiences, which can help create value in collaboration with customers [ 25 , 71 , 77 ]. Managers can use VR and AR technologies to create immersive and interactive customer experiences in the Metaverse [ 81 ]. This can help businesses differentiate themselves and stand out in a competitive market. Managers can use data analysis tools to understand how customers behave in the Metaverse and use this information to create more personalized and satisfying experiences [ 9 ]. Managers can leverage the Metaverse to facilitate co-creation with customers, for example, by enabling customers to design and customize their own experiences [ 49 , 81 ]. This can help businesses create value in collaboration with customers; (4) Integrating AI-robotics into operations to support value co-creation: Analyse your business processes to identify tasks that can be automated using AI-powered robotics, such as check-in and check-out, room service, or concierge services [ 12 , 82 ]. Managers can consider using AI-powered robots for tasks such as check-in and check-out or for delivering amenities to guests. Use AI and the latest technologies to streamline the booking and check-in process, making it faster and more convenient for customers [ 16 ]. This can include using virtual assistants to handle booking inquiries or facial recognition technology to allow customers to check in at their hotel simply by showing their faces. These can help businesses reduce labor costs and improve efficiency, enhancing co-creation value [ 16 ]. We summarize three viewpoints in Fig. 3 below.
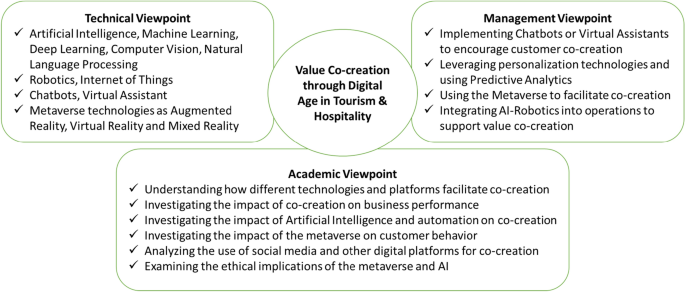
Summary of value co-creation through the Digital Age in Tourism and Hospitality
Combining these three viewpoints as a research agenda for tourism and hospitality in the AI and digital age holds immense potential. It addresses critical aspects such as customer experience enhancement, leveraging customer-generated content, and exploring cutting-edge technologies to create value co-creation opportunities. Researching these areas allows the industry to stay at the forefront of the digital revolution and deliver exceptional customer experiences that drive business success in the next few years.
Discussion and implications
This study aimed to develop a systematic literature review of customer value co-creation in the hospitality and tourism industry using the PRISMA protocol [ 27 ]. The study findings highlighted that tourism and hospitality should take advantage of AI and new technologies, as it brings significant advantages. Value co-creation in the tourism and hospitality sector refers to creating value through the collaboration and participation of multiple stakeholders, including tourists, employees, and the industry [ 2 ]. AI, Metaverse, and other new technologies can significantly enhance value co-creation in this sector by enabling more personalized, immersive, and efficient tourist experiences [ 40 , 80 , 81 ].
From a technology viewpoint, the study reveals that manifestations of customer value co-creation through the digital age are related to AI and the latest technologies such as Metaverse, robots, IoT, chatbots, intelligence systems, and others that shape co-creation [ 42 ]. AI applications and new technologies can help shape customer value co-creation in this sector. AI can follow the rules, think like an expert, learn from data, and even create virtual and augmented reality experiences [ 4 , 10 ]. Chatbots, personalization, predictive analytics, and robotics are examples of how AI and technology can create unique and fun travel experiences [ 16 , 40 , 74 , 83 ].
From an academic viewpoint, researchers look at ways technology can help people enjoy their travels and stay in hotels by boosting the value co-creation process [ 2 ]. They are looking at how different technologies, like social media, can help people create value for themselves and others [ 45 , 84 ]. They are also looking at how AI and the virtual world can change people’s decisions and how companies can use this information to help people [ 77 , 80 ]. Finally, researchers are looking into the ethical issues of using technology in tourism and hospitality [ 48 , 75 , 77 ].
From the manager’s viewpoint, managers in the tourism and hospitality industry can use AI and new technologies to create better customer experiences and drive success [ 70 , 80 ]. These can include using chatbots or virtual assistants to help customers and get their feedback [ 50 , 76 ], using personalization technologies to understand customer needs [ 69 ], using the Metaverse to have customers design their own experiences [ 10 ], and using AI-robotics to automate tasks [ 16 , 82 ].
In light of the findings from this systematic literature review, policymakers in the tourism and hospitality sectors must revisit and revitalize current strategies. Embracing digital age technologies, especially AI and metaverse tools, can significantly enhance customer value co-creation. This necessitates targeted investments in technology upgradation, capacity-building, and skilling initiatives. While the initial resource allocation may appear substantial, the long-term returns regarding elevated customer satisfaction, increased tourism inflow, and industry-wide growth are undeniable. Policymakers must ensure a collaborative approach, engaging stakeholders across the value chain for streamlined adoption and implementation of these advancements.
Overall, the use of AI, Metaverse, and other new technologies can significantly enhance co-creation value in the tourism and hospitality sector by enabling more personalized, immersive, and efficient experiences for tourists and improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the industry as a whole [ 15 ].
Theoretical implications
The systematic literature review using the PRISMA method on customer value co-creation through the digital age in the tourism and hospitality sector has several theoretical implications.
First, this research paper addresses earlier suggestions that emphasize the significance of further exploring investigations on customer value co-creation in the hospitality and tourism sector [ 2 , 85 ].
Second, the review highlights the importance of adopting a customer-centric approach in the tourism and hospitality industry, in which customers’ needs and preferences are central to the design and delivery of services [ 35 , 86 ]. This shift towards customer value co-creation is driven by the increasing use of digital technologies, such as the IoT, AI, and ML, which enable real-time communication and data gathering from customers [ 1 , 40 ].
Third, the review highlights the role of digital technologies in enabling personalized and convenient customer experiences, which can help improve satisfaction and loyalty [ 87 ]. Using AI-powered chatbots and personalized recommendations based on customer data can enhance the customer experience, while using IoT-enabled devices can allow guests to control and access hotel amenities conveniently [ 12 ].
Fourth, the review suggests that adopting digital technologies in the tourism and hospitality sector can increase the industry’s efficiency and effectiveness [ 88 ]. Businesses use ML algorithms to automate tasks and analyze customer data, which can help streamline processes and identify areas for improvement [ 39 , 80 ].
Overall, the systematic literature review using the PRISMA method sheds light on adopting a customer-centric approach and leveraging digital technologies for customer value co-creation in tourism and hospitality. Over the next five years, researchers should focus on exploring the potential of emerging technologies, developing conceptual frameworks, and conducting applied research to drive meaningful transformations in the industry. By aligning strategies with these implications, organizations can thrive in the dynamic digital landscape and deliver exceptional customer experiences, ultimately contributing to their success and competitiveness in the market [ 2 , 4 , 15 , 29 , 33 , 89 ].
Practical implications
The systematic literature review using the PRISMA method on customer value co-creation through the digital age in the tourism and hospitality sector has several management implications for organizations in this industry.
First, the review suggests that adopting a customer-centric approach, in which customers’ needs and preferences are central to the design and delivery of services, is crucial for success in the digital age [ 40 , 86 ]. Therefore, managers should focus on understanding and meeting the needs and preferences of their customers and consider how digital technologies can be leveraged to enable real-time communication and data gathering from customers [ 15 , 80 ].
Second, the review highlights the importance of using digital technologies like the IoT, AI, and ML to enable personalized and convenient customer experiences [ 40 , 50 ]. Managers should consider how these technologies can enhance the customer experience and improve satisfaction and loyalty [ 36 , 39 ].
Third, the review suggests that adopting digital technologies in the tourism and hospitality sector can lead to increased efficiency and effectiveness in the industry [ 7 , 16 ]. Therefore, managers should consider how these technologies can streamline processes and identify areas for improvement [ 42 ]. Further, regarding privacy concerns, managers must spend enough resources to secure their customers’ data to help boost the customer value co-creation process [ 48 , 77 ].
Fourth, policymakers can foster an environment conducive to value co-creation by incorporating customer-centric strategies and leveraging digital technologies. Effective policies can enhance customer experiences, promote sustainable growth, and drive economic development, ensuring a thriving and competitive industry in the digital age.
The practical implications of applying AI and new technology for managerial decision-making in the tourism and hospitality industry are vast and promising [ 90 ]. Managers can navigate the dynamic digital landscape and drive meaningful co-creation with customers by embracing a customer-centric approach, leveraging personalized technologies, addressing efficiency and data security considerations, and strategically adopting AI-powered tools. By staying abreast of technological advancements and harnessing their potential, businesses can thrive in the next five years and beyond, delivering exceptional customer experiences and enhancing value co-creation in the industry.
Limitations and future research
The research, anchored in the PRISMA methodology, significantly enhances the comprehension of customer value co-creation within the digital ambit of the tourism and hospitality sectors. However, it is essential to underscore certain inherent limitations. Firstly, there might be publication and language biases, given that the criteria could inadvertently favor studies in specific languages, potentially sidelining seminal insights from non-English or lesser-known publications [ 91 ]. Secondly, the adopted search strategy, governed by the choice of keywords, databases, and inclusion/exclusion guidelines, might have omitted pertinent literature, impacting the review’s comprehensiveness [ 57 ]. Furthermore, the heterogeneous nature of the studies can challenge the synthesized results’ generalizability. Finally, the swiftly evolving domain of this research underscores the ephemeral nature of the findings.
In light of these limitations, several recommendations can guide subsequent research endeavors. Scholars are encouraged to employ a more expansive and diverse sampling of studies to curtail potential biases. With the digital technology landscape in constant flux, it becomes imperative to delve into a broader spectrum of innovations to discern their prospective roles in customer value co-creation [ 18 ]. Additionally, varied search strategies encompassing multiple databases can lend a more holistic and inclusive character to systematic reviews [ 27 ]. Moreover, future research could investigate the interplay between political dynamics and the integration of novel technologies, enriching the understanding of value co-creation in a broader socio-political context. Lastly, integrating sensitivity analyses can ascertain the findings’ robustness, ensuring the conclusions remain consistent across diverse search paradigms, thereby refining the review’s overall rigor.
In conclusion, this review highlights the pivotal role of digital technologies in customer value co-creation within the tourism and hospitality sectors. New AI, blockchain and IoT technology applications enable real-time communication and personalized experiences, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Metaverse technologies offer exciting opportunities for immersive interactions and virtual events. However, privacy and data security challenges must be addressed. This study proposed a comprehensive research agenda addressing theoretical, practical, and technological implications. Future studies should aim to bridge research gaps, investigate the impact of co-creation on various stakeholders, and explore a more comprehensive array of digital technologies in the tourism and hospitality sectors. This study’s findings provide valuable insights for fostering innovation and sustainable growth in the industry’s digital age. Despite the valuable insights gained, we acknowledge certain limitations, including potential biases in the search strategy, which underscore the need for more inclusive and diverse samples in future research.
Availability of data and materials
The review included a total of 27 studies published between 2012 and 2022.
Change history
07 february 2024.
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-023-00293-2
Abbreviations
- Artificial intelligence
Augmented reality
Internet of Things
Machine learning
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Virtual reality
Pencarelli T (2020) The digital revolution in the travel and tourism industry. J Hosp Tour Insights 22(3):455–476
Google Scholar
Carvalho P, Alves H (2022) Customer value co-creation in the hospitality and tourism industry: a systematic literature review. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 35(1):250–273
Aman J, Abbas J, Mahmood S, Nurunnabi M, Bano S (2019) The influence of Islamic religiosity on the perceived socio-cultural impact of sustainable tourism development in Pakistan: a structural equation modeling approach. Sustainability 11(11):3039
Buhalis D, Lin MS, Leung D (2022) Metaverse as a driver for customer experience and value co-creation: implications for hospitality and tourism management and marketing. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 35(2):701–716
Grissemann US, Stokburger-Sauer NE (2012) Customer co-creation of travel services: the role of company support and customer satisfaction with the co-creation performance. Tour Manag 33(6):1483–1492
Pham LH, Woyo E, Pham TH, Dao TXT (2022) Value co-creation and destination brand equity: understanding the role of social commerce information sharing. J Hosp Tour Insights
Troisi O, Grimaldi M, Monda A (2019) Managing smart service ecosystems through technology: how ICTs enable value cocreation. Tour Anal 24(3):377–393
Buonincontri P, Micera R (2016) The experience co-creation in smart tourism destinations: a multiple case analysis of European destinations. J Hosp Tour Insights 16(3):285–315
Jung TH, tom Dieck MC (2017) Augmented reality, virtual reality and 3D printing for the co-creation of value for the visitor experience at cultural heritage places. J Place Manag Dev 10:140–151
Koo C, Kwon J, Chung N, Kim J (2022) Metaverse tourism: conceptual framework and research propositions. Curr Issues Tour 1–7
Dwivedi YK et al (2022) Metaverse beyond the hype: Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int J Inf Manag 66:102542
Zhang X, Balaji M, Jiang Y (2022) Robots at your service: value facilitation and value co-creation in restaurants. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 34(5):2004–2025
Neuhofer B, Magnus B, Celuch K (2021) The impact of artificial intelligence on event experiences: a scenario technique approach. Electron Mark 31(3):601–617
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Abbas J, He C, Pilař L, Shah SAR (2023) Tourism, urbanization and natural resources rents matter for environmental sustainability: the leading role of AI and ICT on sustainable development goals in the digital era. Resour Pol 82:103445
Zhu J, Cheng M (2022) The rise of a new form of virtual tour: Airbnb peer-to-peer online experience. Curr Issues Tour 25(22):3565–3570
Xie L, Liu C, Li D (2022) Proactivity or passivity? An investigation of the effect of service robots’ proactive behaviour on customer co-creation intention. Int J Hosp Manag 106:103271
Wang Q, Huang R (2021) The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on sustainable development goals—a survey. Environ Res 202:111637
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Önder I, Gunter U (2022) Blockchain: Is it the future for the tourism and hospitality industry? Tourism Econ 28(2):291–299
Wang Q, Su M (2020) Integrating blockchain technology into the energy sector—from theory of blockchain to research and application of energy blockchain. Comput Sci Rev 37:100275
Wang Q, Li R, Zhan L (2021) Blockchain technology in the energy sector: from basic research to real world applications. Comput Sci Rev 39:100362
CAS Google Scholar
Wang Q, Su M, Zhang M, Li R (2021) Integrating digital technologies and public health to fight Covid-19 pandemic: key technologies, applications, challenges and outlook of digital healthcare. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(11):6053
Abbas J, Mubeen R, Iorember PT, Raza S, Mamirkulova G (2021) Exploring the impact of COVID-19 on tourism: transformational potential and implications for a sustainable recovery of the travel and leisure industry. Curr Res Behav Sci 2:100033
PubMed Central Google Scholar
Elkhwesky Z, El Manzani Y, Elbayoumi Salem I (2022) Driving hospitality and tourism to foster sustainable innovation: a systematic review of COVID-19-related studies and practical implications in the digital era. Tour Hosp Res 14673584221126792
Shah SAR, Zhang Q, Abbas J, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Pilař L (2023) Technology, urbanization and natural gas supply matter for carbon neutrality: a new evidence of environmental sustainability under the prism of COP26. Resour Pol 82:103465
Ahmed KE-S, Ambika A, Belk R (2022) Augmented reality magic mirror in the service sector: experiential consumption and the self. J Serv Manag
Doran A, Pomfret G, Adu-Ampong EA (2022) Mind the gap: a systematic review of the knowledge contribution claims in adventure tourism research. J Hosp Tour Manag 51:238–251
Page MJ et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Rev 10(1):1–11
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, P. Group* (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151(4):264–269
So KKF, Li X, Kim H (2020) A decade of customer engagement research in hospitality and tourism: a systematic review and research agenda. J Hosp Tour 44(2):178–200
Han H (2021) Consumer behavior and environmental sustainability in tourism and hospitality: a review of theories, concepts, and latest research. J Sustain Tour 29(7):1021–1042
Medlik S (2012) Dictionary of travel, tourism and hospitality. Routledge
Reisinger Y, Kandampully J, Mok C (2001) Concepts of tourism, hospitality, and leisure services. Service quality management in hospitality, tourism, and leisure, pp 1–14
Binkhorst E, Den Dekker T (2013) Agenda for co-creation tourism experience research. In: Marketing of tourism experiences, Routledge, 219–235
Abbas J, Al-Sulaiti K, Lorente DB, Shah SAR, Shahzad U (2022) Reset the industry redux through corporate social responsibility: the COVID-19 tourism impact on hospitality firms through business model innovation. In: Economic growth and environmental quality in a post-pandemic world, Routledge, pp 177–201
Buhalis D, Harwood T, Bogicevic V, Viglia G, Beldona S, Hofacker C (2019) Technological disruptions in services: lessons from tourism and hospitality. J Serv Manag 30:484–506
Sengupta P, Biswas B, Kumar A, Shankar R, Gupta S (2021) Examining the predictors of successful Airbnb bookings with Hurdle models: evidence from Europe, Australia, USA and Asia-Pacific cities. J Bus Res 137:538–554
Gonzalez-Rodriguez MR, Díaz-Fernández MC, Bilgihan A, Shi F, Okumus F (2021) UGC involvement, motivation and personality: comparison between China and Spain. J Dest Mark Manag 19:100543
Abbas J (2020) The impact of coronavirus (SARS-CoV2) epidemic on individuals mental health: the protective measures of Pakistan in managing and sustaining transmissible disease. Psychiatr Danub 32(3–4):472–477
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Neuhofer B, Buhalis D, Ladkin A (2014) A typology of technology-enhanced tourism experiences. Int J Tour Res 16(4):340–350
Samala N, Katkam BS, Bellamkonda RS, Rodriguez RV (2020) Impact of AI and robotics in the tourism sector: a critical insight. J Tour Futures 8(1):73–87
De Carlo M, Ferilli G, d’Angella F, Buscema M (2021) Artificial intelligence to design collaborative strategy: An application to urban destinations. J Bus Res 129:936–948
Grundner L, Neuhofer B (2021) The bright and dark sides of artificial intelligence: a futures perspective on tourist destination experiences. J Dest Mark Manag 19:100511
Al-Sulaiti I (2022) Mega shopping malls technology-enabled facilities, destination image, tourists’ behavior and revisit intentions: implications of the SOR theory. Front Environ Sci 1295
Alimamy S, Gnoth J (2022) I want it my way! The effect of perceptions of personalization through augmented reality and online shopping on customer intentions to co-create value. Comput Hum Behav 128:107105
Lee M, Hong JH, Chung S, Back K-J (2021) Exploring the roles of DMO’s social media efforts and information richness on customer engagement: empirical analysis on Facebook event pages. J Travel Res 60(3):670–686
Abaalzamat KH, Al-Sulaiti KI, Alzboun NM, Khawaldah HA (2021) The role of Katara cultural village in enhancing and marketing the image of Qatar: evidence from TripAdvisor. SAGE Open 11(2):21582440211022736
Al-Sulaiti KI, Abaalzamat KH, Khawaldah H, Alzboun N (2021) Evaluation of Katara cultural village events and services: a visitors’ perspective. Event Manag 25(6):653–664
Khaliq A, Waqas A, Nisar QA, Haider S, Asghar Z (2022) Application of AI and robotics in hospitality sector: a resource gain and resource loss perspective. Technol Soc 68:101807
Yin CZY, Jung T, Tom Dieck MC, Lee MY (2021) Mobile augmented reality heritage applications: meeting the needs of heritage tourists. Sustainability 13(5):1–18
Buhalis D, Moldavska I (2021) Voice assistants in hospitality: using artificial intelligence for customer service. J Hosp Tour Technol 13(3):386–403
Abbas J (2021) Gestión de crisis, desafíos y oportunidades sanitarios transnacionales: la intersección de la pandemia de COVID-19 y la salud mental global. Investigación en globalización, 3 (2021), 1–7
Micah AE et al (2023) Global investments in pandemic preparedness and COVID-19: development assistance and domestic spending on health between 1990 and 2026. Lancet Glob Health 11(3):e385–e413
Hau LN, Thuy PN (2022) Enabling customer co-creation behavior at a distance: the case of patients using self-monitoring handheld devices in healthcare. Serv Bus 16(1):99–123
Brereton P, Kitchenham BA, Budgen D, Turner M, Khalil M (2007) Lessons from applying the systematic literature review process within the software engineering domain. J Syst Softw 80(4):571–583
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14(3):207–222
Lin Z, Rasoolimanesh SM (2022) Sharing tourism experiences in social media: a systematic review. Anatolia 1–15
Page MJ, Moher D, McKenzie JE (2022) Introduction to PRISMA 2020 and implications for research synthesis methodologists. Res Synth Methods 13(2):156–163
PubMed Google Scholar
Snyder H (2019) Literature review as a research methodology: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 104:333–339
Caldiera VRBG, Rombach HD (1994) The goal question metric approach. Encycl Softw Eng 528–532
Hopfenbeck TN, Lenkeit J, El Masri Y, Cantrell K, Ryan J, Baird J-A (2018) Lessons learned from PISA: a systematic review of peer-reviewed articles on the programme for international student assessment. Scand J Educ Res 62(3):333–353
Kitchenham B, Brereton OP, Budgen D, Turner M, Bailey J, Linkman S (2009) Systematic literature reviews in software engineering–a systematic literature review. Inf Softw Technol 51(1):7–15
Dieste O, Grimán A, Juristo N (2009) Developing search strategies for detecting relevant experiments. Empir Softw Eng 14(5):513–539
Prahalad CK, Ramaswamy V (2004) Co-creation experiences: the next practice in value creation. J Interact Mark 18(3):5–14
Vargo SL, Lusch RF (2014) Evolving to a new dominant logic for marketing. In: The service-dominant logic of marketing, Routledge, pp 21–46
Hong et al QN (2018) Mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT), version 2018. Registration of copyright vol 1148552, no 10
Pace R et al (2012) Testing the reliability and efficiency of the pilot mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT) for systematic mixed studies review. Int J Nurs Stud 49(1):47–53
Beck J, Rainoldi M, Egger R (2019) Virtual reality in tourism: a state-of-the-art review. Tour Rev 74(3):586–612
Pahlevan-Sharif S, Mura P, Wijesinghe SN (2019) A systematic review of systematic reviews in tourism. J Hosp Tour Manag 39:158–165
Cuomo MT, Colosimo I, Celsi LR, Ferulano R, Festa G, La Rocca M (2022) Enhancing traveller experience in integrated mobility services via big social data analytics. Technol Forecast Soc Change 176:121460
Chiu M-C, Huang J-H, Gupta S, Akman G (2021) Developing a personalized recommendation system in a smart product service system based on unsupervised learning model. Comput Ind 128:103421
Cranmer EE, tom Dieck MC, Fountoulaki P (2020) Exploring the value of augmented reality for tourism. Tour Manag Perspect 35:100672
Lin S (2022) Implementation of personalized scenic spot recommendation algorithm based on generalized regression neural network for 5G smart tourism system. Comput Intell Neurosci 2022
Ngamsirijit W (2014) Value creation in creative tourism: co-creation through data mining. Int J Intell 2(2–3):255–276
Liu X, Shin H, Burns AC (2021) Examining the impact of luxury brand’s social media marketing on customer engagement: Using big data analytics and natural language processing. J Bus Res 125:815–826
Hew J-J, Tan GW-H, Lin B, Ooi K-B (2017) Generating travel-related contents through mobile social tourism: Does privacy paradox persist? Telemat Inform 34(7):914–935
Lalicic L, Weismayer C (2021) Consumers’ reasons and perceived value co-creation of using artificial intelligence-enabled travel service agents. J Bus Res 129:891–901
Hilken T et al (2022) Disrupting marketing realities: a research agenda for investigating the psychological mechanisms of next-generation experiences with reality-enhancing technologies. Psychol Mark 39(8):1660–1671
Brejla P, Gilbert D (2014) An exploratory use of web content analysis to understand cruise tourism services. Int J Tour Res 16(2):157–168
Li Z, Wang D, Abbas J, Hassan S, Mubeen R (2022) Tourists’ health risk threats amid COVID-19 era: role of technology innovation, transformation, and recovery implications for sustainable tourism. Front Psychol 12:769175
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Liburd J, Duedahl E, Heape C (2022) Co-designing tourism for sustainable development. J Sustain Tour 30(10):2298–2317
Serravalle F, Ferraris A, Vrontis D, Thrassou A, Christofi M (2019) Augmented reality in the tourism industry: a multi-stakeholder analysis of museums. Tour Manag Perspect 32:100549
Xie L, Liu X, Li D (2022) The mechanism of value cocreation in robotic services: customer inspiration from robotic service novelty. J Hosp Mark Manag 31(8):962–983
Huang M-H, Rust RT (2021) Engaged to a robot? The role of AI in service. J Serv Res 24(1):30–41
Mamirkulova G, Mi J, Abbas J, Mahmood S, Mubeen R, Ziapour A (2020) New silk road infrastructure opportunities in developing tourism environment for residents better quality of life. Glob Ecol Conser 24:e01194
Rihova I, Buhalis D, Gouthro MB, Moital MJTM (2018) Customer-to-customer co-creation practices in tourism: lessons from customer-dominant logic. Tour Manag 67:362–375
Rahimian S, ShamiZanjani M, Manian A, Esfidani MR (2021) A framework of customer experience management for hotel industry. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 33(5):1413–1436
Ameen N, Tarhini A, Reppel A, Anand A (2021) Customer experiences in the age of artificial intelligence. Comput Hum Behav 114:106548
Iranmanesh M, Ghobakhloo M, Nilashi M, Tseng M-L, Yadegaridehkordi E, Leung N (2022) Applications of disruptive digital technologies in hotel industry: a systematic review. Int J Hosp Manag 107:103304
Wang S, Abbas J, Al-Sulati KI, Shah SAR (2023) The impact of economic corridor and tourism on local community’s quality of life under one belt one road context. Evaluat Rev 0193841X231182749
Akhmedova A, Manresa A, Escobar Rivera D, Bikfalvi A (2021) Service quality in the sharing economy: a review and research agenda. Int J Consum Stud 45(4):889–910
Henry BM, Tomaszewski KA, Walocha JA (2016) Methods of evidence-based anatomy: a guide to conducting systematic reviews and meta-analysis of anatomical studies. Ann Anat Anatomischer Anz 205:16–21
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology (HCMUT), Vietnam National University Ho Chi Minh City (VNUHCM), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
T. D. Dang & M. T. Nguyen
Eastern International University, Thu Dau Mot, Binh Duong Province, Vietnam
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
DTD, conceived the research idea and designed the study in collaboration with NMT. DTD took the lead in writing the manuscript, with significant contributions from NMT. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript to ensure accuracy and clarity. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to T. D. Dang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This material is the authors’ original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere. The paper is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article has been revised: the affiliation is corrected for the co-author “M. T. Nguyen”.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Quality assessment of included studies.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions

About this article
Cite this article.
Dang, T.D., Nguyen, M.T. Systematic review and research agenda for the tourism and hospitality sector: co-creation of customer value in the digital age. Futur Bus J 9 , 94 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-023-00274-5
Download citation
Received : 31 May 2023
Accepted : 06 November 2023
Published : 25 November 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-023-00274-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Customer value co-creation
- Tourism and hospitality
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, customer experience in the hotel industry: a systematic literature review and research agenda.
International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management
ISSN : 0959-6119
Article publication date: 18 January 2023
Issue publication date: 17 July 2023
Academic research on customer experience (CX) in the hospitality industry has recently experienced vast growth as managers have increasingly focused on delivering distinctive experiences to their guests. Despite the relevance of this topic, studies conducted in this area within the hotel context are scarce and dispersed. This paper aims to classify the main academic studies and to present a definition of hotel CX, a conceptual model, emerging trends and future research gaps.
Design/methodology/approach
A systematic literature review (SLR) was selected as the research methodology. Adapted from preferred reporting items of SLR and meta-analysis statements, this study entailed an in-depth review of 46 articles published in English between 2006 and 2021. The articles were compiled using keyword searches in Scopus and Web of Science.
This study facilitates an understanding of the hotel CX. The conceptual framework derived from the SLR includes the entire set of antecedents, consequences, mediators and moderators of this concept. The results also illustrate the topic’s academic evolution and expose major guidelines that can help determine areas for future research.
Originality/value
This study adds value to the hospitality research literature via SLR. The framework of CX in the hotel industry synthesizes the existing knowledge on this topic and identifies research gaps. The proposed framework allows for the improvement of future hotel CX studies.
- Systematic literature review
- Customer experience
- Hotel industry
Acknowledgements
This study was conducted under the framework of the Research UAM Group TECHNOCONS “Consumer Behavior and Technology.” This research was supported by the Professorship Excellence Program in accordance with the multi-year agreement signed by the Government of Madrid and the Autonomous University of Madrid, UAM (Line #3) and by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, grant number PID2020-113561RB-I00.
Veloso, M. and Gomez-Suarez, M. (2023), "Customer experience in the hotel industry: a systematic literature review and research agenda", International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management , Vol. 35 No. 8, pp. 3006-3028. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-04-2022-0517
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2022, Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Global trends in hospitality ☆
Lerzan aksoy.
a Fordham University, Gabelli School of Business, New York, NY, United States
Sunmee Choi
b School of Business, Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea
c Dean of College of Business and Management, VinUniversity, Hanoi, Viet Nam
Tarik Dogru
d Florida State University, Dedman College of Hospitality, Tallahassee, FL, United States
Timothy Keiningham
e St. John’s University, Peter J. Tobin College of Business, Queens, NY, United States
Melanie Lorenz
f Florida Atlantic University, College of Business, Boca Raton, FL, United States
J. Bruce Tracey
g Cornell University, School of Hotel Administration, SC Johnson College of Business, Ithaca, NY, United States
The disruptions to the global hospitality industry have been accelerated, particularly after the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic. As such, it is even more important for scholars to focus on future research that addresses the most relevant and important industry-specific challenges. In this paper, we analyze the recent hospitality research and industry trends to identify the topics that have received the most attention, and then compare these trends to the survey results from two key industry stakeholders – academics (N = 67) and practitioners (N = 235) – regarding the most important short- and longer-terms research priorities. Overall, the findings suggest that both stakeholder groups have placed supply and demand characteristics, as well as technology, as the industry’s most pressing priorities in both the short- and longer-term future. The relative importance of safety and cleanliness is expected to decline over time while environmental sustainability will gain increasing attention in the future.
1. Introduction
The global hospitality industry, which includes hotels and other types of accommodations, as well as restaurants, bars, casinos, cruise ships, travel agencies, tour operators, and similar organizations, accounted for roughly $4.5 trillion in consumer spending during 2020 ( Hospitality Global Market Report, 2020 ). More broadly, the travel and tourism segments accounted for 10.3% of the global GDP in 2019, totaling $8.9 trillion ( WTTC, 2020b ). Unfortunately, it is not surprising that many of the firms that operate within service- and labor-intensive industries have suffered immensely because of the COVID-19 pandemic. As a result of the extensive scope of this global crisis, pre-pandemic industry trend projections alone are unlikely to be helpful in guiding future academic research and managerial actions. The overarching aim of this research is to provide needed insight into the most important short- and long-term trends from the perspectives of hospitality academics and practitioners by combining historic trends with prognostications from both such stakeholders.
This investigation is conducted in three parts: (1) a review of articles in the leading academic hospitality journals; (2) a review of articles in hospitality trade journals; and (3) a survey of hospitality academics and practitioners. By doing so, we identify critical gaps in the literature and significant differences in the perspectives of academics and practitioners—both in terms of established areas of interest and their future expectations.
As might be expected, the findings point to a short-term focus on disease prevention and related issues, which subsequently declines in importance over the longer term. Nonetheless, technology and supply and demand issues stand out amongst both academics and practitioners alike as key trends in both the short- and long-term. In general, however, when significant differences exist between academics and practitioners (e.g., sustainability, branding), practitioners tend to place greater importance on more immediate financial well-being needs, while academics focus on broader, longer-term trends. By identifying the gaps in the literature and differences in the perceived importance of various trends, this investigation offers insight for rigorous and relevant academic research agendas to help guide the recovery of the hospitality industry through the extreme turbulence caused by COVID-19.
2. Literature review
2.1. scope: global hospitality industry.
The travel and tourism sector is recognized as an important driver for job creation and a dynamic engine of employment opportunities ( Dogru and Bulut, 2018 , Wttc, 2020a ). In 2019, one in 10 jobs (total 330 million jobs) were supported by the global travel and tourism sector, and one quarter of all net new jobs were created by this sector over the last five years ( WTTC, 2020b ).
In 2020, however, this industry faced unprecedented challenges and threats from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic ( WTTC, 2020b ). Community lockdowns, social distancing requirements, stay-at-home orders, travel and mobility restrictions, and dining limitations have resulted in a temporary suspension of many hospitality businesses and significantly decreased the demand for businesses that were allowed to continue to operate ( Bartik et al., 2020 , Gursoy and Chi, 2020 ). While the optimistic scenario projects a 30% reduction in jobs and GDP compared with 2019, the pessimistic scenario projects a 60% reduction in jobs and a 62% reduction in GDP compared with 2019 ( WTTC, 2020b ).
Of all industries, the global hospitality industry is among the hardest hit, while facing reductions of >90% of activities in some markets ( Fernandes, 2020 ). An above average representation of SMEs in sectors such as accommodation and food services have been particularly affected by the crisis ( OECD, 2020 ). As of 22 June 2020, 513 companies in the restaurant segment filed for bankruptcy ( WTTC, 2020c ). Large firms have also suffered from the downturn ( WTTC, 2020c ). For example, Marriott International, which has 174,000 employees globally, placed tens of thousands of workers on furlough, and Hilton Worldwide notified lenders in March 2020 that they would be borrowing a precautionary $1.75 billion under a revolving loan to preserve money and to maintain flexibility ( Nicola et al., 2020 ).
In contrast, it has been suggested that the travel and tourism sector is poised to be the key sector in driving the recovery of the global economy post COVID-19 by generating new jobs, driving visitors back to destinations, and having a positive economic domino effect on suppliers across the entire supply chain ( Dogru and Bulut, 2018 , Wttc, 2020a ). Projected recovery plans involve rebuilding traveler confidence, developing innovative and digital technologies, and offering more affordable products ( WTTC, 2020d ). Transitioning from crisis management to recovery, hospitality is preparing for the “new normal” by ensuring operational excellence; assuring a safe experience for staff and guests through enhanced cleanliness and hygiene best practices; rebuilding trust and confidence through transparency and communication; and implementing new enabling policies ( WTTC, 2020e ).
Having discussed the scope, importance, and disciplinary range of the industry as well as the status and future outlook, the next section explores the academic and practitioner literatures to compare – across disciplines – trends that may influence the current and future developments in the hospitality industry. The goals are to derive important insights about the state of the respective literatures, as well as to identify discrepancies between academics and practitioners in an effort to promote research that is more aligned with the industry’s challenges and that helps stimulate timely and actionable solutions. This is particularly important in the time of COVID-19 as traditional ways of doing business have been hampered, and innovative solutions are desperately needed.
3. Study 1: Review & categorization of academic literature
The goal of Study 1 is to gauge what hospitality researchers believe to be the most important industry trends based upon the topics published in some of the leading academic hospitality journals. This effort is intended to provide a broad overview of the current state of the literature, with the expectation that the topics represent what academic researchers perceive to be of current or future importance in the hospitality industry.
3.1. Procedure & samples
To review and categorize the literature comprehensively, we deviated from the traditional literature approach and instead used a systematic review. First, the research team decided to examine the articles that were published in the following five hospitality research journals: Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, Tourism Management, and International Journal of Hospitality Management . These journals were selected because they publish research that is directly aligned with industry-specific challenges and priorities, and they are considered leading journals in the hospitality field (e.g., listed as “A” outlets by the Australian Business Deans Council on journal quality). The period of January 2018 to the end of the year 2020 was chosen to reflect the most recent trends, and we examined all articles including the ones published online but not yet in press.
Following the selection of the journals, two coders (both with advanced degrees and conduct hospitality-specific research) independently reviewed all articles (N = 1,459) and coded them based on disciplinary domain (e.g., consumer behavior, human resources, operations management, etc.) and main focus (e.g., use and utility of social media, employee engagement, efficiency, etc.) to identify the academic origin and primary research themes. The number of articles for each of the journals and interrater agreement indices are list in Table 1 .
Articles by journal and interrater agreements.
3.2. Results
The analysis identified five main disciplinary domains: consumer behavior/marketing, organizational behavior/human resource management, strategic management, operations management, and finance/economic/law/accounting. Articles of topics that did not fit any main discipline (e.g., research methodology, education, tourism, literature reviews, food and beverage, and entrepreneurship) were sorted into the category “others”. Of 1,459 articles reviewed, the majority fell into the consumer behavior/marketing discipline (652 articles; 44.69%), followed by organizational behavior/human resource management (280 articles; 19.19%), and strategic management (191 articles; 13.09%). To a lesser extent, articles could be placed into finance/economics/law/accounting (102 articles; 6.99%), or operations management (86 articles; 5.89%). 145 articles were summarized in the “others” category (9.94%). Within each of the disciplines, counts of the key words associated with the main focus of the studies were used to identify the primary trends and research themes. We will discuss the most prominent ones in the following paragraphs. Table 2 provides a complete overview of all trends by discipline, the distribution and count, as well as exemplary citations.
Overview of research trends per discipline.
The major research trends within the consumer behavior/marketing discipline focused on the customer experience (e.g., eWOM, social influences, emotions, and customer satisfaction; 29%), followed by online content (e.g., online reviews, online ratings, social media; 14%), brand and branding issues (e.g., brand love, brand personality, authenticity; 7%), and co-creation (e.g., customer-centricity, user generated content; 7%).
Research in the organizational behavior/ human resource management discipline focused on employee job attitudes and participation (e.g., engagement, innovative and creative behaviors, OCB; 29%), talent, recruiting, and retention management (e.g., job crafting, mentoring, training, selection; 18%), employee well-being (e.g., work-family conflict, work-life balance, burnout, bullying; 16%), and leadership (e.g., ethical, transformational, authentic leadership; 16%).
Strategic management articles examined the impact of firm-level policies, strategies, and practices (e.g., green practices, management strategies, transparency, and accountability; 18%), innovation, intellectual capital, and knowledge (e.g., knowledge sharing, collaboration, product, service, process innovations; 17%), performance management (e.g., profitability, survival, profit chain; 17%), and CSR (e.g., different strategies, influences of CSR on brand equity and reputation; 11%).
Finance/Economics/Law/Accounting articles centered on performance (e.g., efficiency, financial performance matrices and assessments, economic growth, revenue; 32%), governance (e.g., M&A, investments, ownership; 23%), risk (e.g., policy uncertainty, credit risk, risk management; 10%), and local and community impact (e.g., market structure, local environment, discrimination; 10%).
Finally, operations management articles highlighted trends such as revenue management (e.g., pricing, forecasting, modeling, rate conditions, discounting; 34%), technology (e.g., robotics, logistic robots, blockchain, key-less technology; 13%), supply chain, distribution, and procurement (e.g., lean techniques, supplier relationships, transparency; 11%), and sustainability (e.g., waste and water management, carbon footprint, packaging; 9%).
4. Study 2: Review & categorization of trade literature
The goal of Study 2 was to gauge the sentiment of hospitality practitioners and identify what they believe to be the most important topics related to the industry. In general, the expectation is that the topics covered in the hospitality trade literature represent either current needs or expected future needs within the industry. Given the fast turnaround for publication, in comparison to the academic literature, discussed topics may be more time-sensitive and driven by recent development.
4.1. Procedure & samples
To assess topic areas of interest to practitioners, we followed the same process described in the academic literature review and conducted a systematic review of three of the most widely circulated trade publications: Hotel Magazine , Hotels , and Hotel Business . As with the academic literature review, we examined the time period from January 2018 to September 2020, the most recently available issues at the time of writing. It should be noted that while hotels are the featured focus of these outlets, they include content that considers many other industry segments (e.g., food and beverage, OTAs, cruise, etc.).
As before, two coders independently evaluated 1,365 articles and classified each according to content areas discussed. It is important to note that content areas used to code these trade publications were not mutually exclusive, as articles regularly discussed multiple topics (average of 2.06 topics per article). Interrater reliability was calculated using Cohen’s Kappa (k = 0.75, p < .001), indicating substantial agreement between coders ( Landis & Koch, 1977 ).
4.2. Results
Analysis of the text allowed us to define a set of overarching trend categories (see Table 3 for complete overview). Of these 34 trend categories, five (each > 10%), namely technology (e.g., AI, mobile applications, and blockchain; 22%), consumer segments/preferences (e.g. segmentation, guest expectations and experiences; 14%), corporate portfolios (e.g., diversification, expansion; 12%), employee management (e.g., training, education, compensation; 12%) as well as travel and tourism (e.g. travel habits, regional analysis; 11%) accounted for the majority of topics (>70%). Our analysis was based on trade publications with a largely set format, containing designated sections for topics such as food and beverage and design. As such, these categories may be overrepresented in this analysis.
Overview of trade publication trends.
In comparing the results of the academic literature review and the review of trade publications, we see that most interests between academics and practitioners do align. Both groups place considerable emphasis on each of the disciplinary foci, namely, consumer behavior/marketing, organizational behavior/human resource management, strategic management, finance/economics/law/accounting, and operations management. However, and most notably, practitioners seem to place a much greater emphasis on technology than academics, as this is by far the most discussed topic in trade publications.
5. Study 3: Assessment of short- & long-term trends by academics and hospitality industry professionals
The goals of Study 3 were to: (a) gauge what hospitality academics and practitioners believe to be the major trends impacting the industry in both the short-term (1 to 3 years) and long-term (4–10 years); (b) identify any significant differences between these perspectives; and (c) assess the general level of economic optimism regarding the hospitality industry over both the short- and long-term. The need to distinguish one to three year trends from longer term trends in part reflects a desire to mitigate respondents’ expected emphasis on the COVID-19 pandemic; it is hoped that this distinction will allow for the separation of long-term trends from those that may be pandemic-specific. Furthermore, perceptions about economic outlook may differ based on stakeholder status and if so, may offer some explanation for any differences that may be identified.
5.1. Data and measures
Sample : Data for this study was collected via an online survey. As the survey was designed to reach both academic researchers and hospitality practitioners, respondents were drawn from several sources. To gain insight into academia’s perceptions of hospitality industry trends, a survey was sent to the editorial review board members of seven journals: Cornell Hospitality Quarterly , International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management , International Journal of Hospitality Management , Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research , Tourism Management , Annals of Tourism Research , and Journal of Sustainable Tourism . The latter two journals were included to broaden the sample of hospitality scholars and include those who conduct tourism research that informs hospitality management practice. In total, 67 completed responses were received. To gain insight into hospitality practitioners’ perceptions of industry trends, a survey was sent to hospitality school alumni from ESSEC Business School in Paris, France, Cornell University’s School of Hotel Administration (and members of the Advisory Boards of the School’s Centers and Institutes), and Florida State University. In total, 235 completed responses were received. Respondents fell into one of three primary groups: (1) academic (22.2%), (2) current or former hospitality industry practitioner (51.0%), and (3) other (26.8%); the “other” category was largely made up of individuals who supply services to the hospitality industry (e.g., consultant). Overall, the respondents were 62.7% male; 15.2% age 18–34, 44.9% age 35–54, 39.9% age 55 and older; 72.6% White, 14.2% Asian or Pacific Islander, 6.6% Hispanic or Latino, 1.0%% Black or African American, 4.6% Other Racial/Ethnic Identification.
Academic respondents were 36.5% Full Professor (tenured/tenure track), 22.2% Associate Professor (tenured/tenure track), 4.8% Assistant Professor (tenured/tenure track), 1.6% Clinical Professor (non-tenure track), 4.8% Adjunct Professor (non-tenure track), 12.7% Senior Lecturer, 11.1% Lecturer, 6.3% Emeritus Professor (retired). Hospitality practitioner respondents were 27.9% Executive/C-Level Management, 30.5% Administrative (e.g. GM, Restaurant Manager, Department Manager, Assistant Manager, etc.), 12.3% Sales and Marketing, 8.4% Data Analytics, 7.1% Revenue Management, 5.8% Hospitality Operations (e.g. Front Desk Agent, Guest Room Attendant, Guest Service Agent, etc.), 4.5% Human Resources, 3.2% Technology (e.g. System Operator, IT Specialist, etc.). See Fig. 1 for the respective details.

Academic and practitioner positions held by respondents.
In total, respondents were from 42 countries (plus Hong Kong), with 64.5% from the United States. See Fig. 2 for the respective details.

Top 20 countries of respondents.
Measures : The overriding aim of the survey was to identify both short-term (1–3 years) and long-term (4–10 years) trends in the hospitality industry. To help ensure that respondents were prepared to think about these issues separately, the survey began with the following text:
“For the first few questions, we ask that you think about what are the most important 1) short-term trends (current environment through the next 3 years) and 2) long-term trends (4 to 10 years into the future) impacting the hospitality industry separately .”
Respondents were first asked to list “the five most important trends impacting the hospitality industry in the current environment through the next 3 years ”, and their “prediction for the economic health of the hospitality industry in the current environment through the next 3 years ”. Respondents were then asked to list “the five most important trends impacting the hospitality industry over the longer term ( i.e. 4 to 10 years in the future) ”, and their “prediction for the economic health of the hospitality industry over the longer term ( i.e. 4 to 10 years in the future) ”. 1 Additionally, we included two measures that in the context of the pandemic may influence an individual’s disposition and perceptions about what may be important. The first measure included two questions that asked about the economic impact that COVID-19 may have had on respondents: (a) “How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted your employment status in 2020”, and (b) “How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted your total household income in 2020?” Response choice alternatives for the first item ranged were: temporarily furloughed, job eliminated, pay reduced without reduction in hours, pay reduced with deduction in hours, accepted buyout package/early retirement, and no change to employment status. Response choice alternatives for the second item were: increased significantly, decreased significantly, and no change in household income related to COVID-19 pandemic.
The second measure assessed the respondents’ general level of optimism and pessimism using the 10-item Life Orientation Test, developed and validated by Scheier, Carver, and Bridges (1994) . A principle components analysis (Varimax rotation, Eigenvalues > 1) revealed three significant factors. Reliability analysis, however, found that only one component achieved a Cronbach’s Alpha level of 0.7 or higher (i.e., 0.717). Specifically, this factor was comprised of three items associated with pessimism: (a) I hardly ever expect things to go my way; (b) If something can go wrong for me, it will; and (c) I rarely count on good things happening to me. Further analyses using median-based groupings on the expected trends and industry economic health indicators, however, revealed very few statistically significant differences (and as a result, very little additional insight). As a result, it appears that respondents’ general level of pessimism has little impact on their perceptions of hospitality trends.
5.2. Analyses and results
Personal Economic Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic : In contrast to the non-significant findings associated with an individual’s pessimism, there were significant differences in the personal economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic across the two industry stakeholder groups. Specifically, academic respondents were much less likely to be negatively impacted economically as a result of COVID-19 than were hospitality industry practitioners. Almost 80% of academic respondents (79.7%) indicated that they experienced no change to their employment status as a result of the pandemic. That number dropped to 35.1% for hospitality practitioner respondents (see Fig. 3 ). Similarly, 25% of academic respondents indicated that their household income had dropped significantly because of the pandemic, whereas 61% of hospitality practitioners saw a significant drop in household income (see Fig. 4 ). As such, any differences across the stakeholder groups may be explained in part by the personal economic impact of COVID-19.

Impact of COVID-19 on employment status.

Impact of COVID-19 on 2020 household income.
Expected Industry Health Over the Short- and Long-term : Despite differing levels of economic harm caused by COVID-19 on academics and practitioners, the projected health of the industry in the short- and long-term was remarkably similar among the groups (see Fig. 5 ). That, however, does not mean that there was general agreement in the outlook. Regarding their short-term outlook, both groups of respondents were almost evenly divided as to whether they were optimistic or pessimistic about the future (see Fig. 5 ).

Level of economic optimism for the hospitality industry over the next 3 years Fig. 5 (continued): Level of economic optimism for the hospitality industry over the next 3 years.
Regarding their long-term outlook, however, 75% or more of respondents (regardless of group) were somewhat or very optimistic about the economic health of the hospitality industry (see Fig. 6 ). Moreover, there were no statistically significant differences between the mean levels of economic optimism for any group.

Level of economic optimism for the hospitality industry over the next 4 to 10 years Fig. 6 (continued): Level of economic optimism for the hospitality industry over the next 4 to 10 years.
In sum, we did not observe any salient differences across the industry stakeholder groups regarding perceptions about pessimism and expected industry health. However, the personal economic impact of COVID-19 may explain, at least in part, differences across the stakeholder groups regarding the nature and perceived importance of future industry trends (although we do not make any major claims about the theoretical relevance of this finding).
Most Important Trends Impacting the Hospitality Industry : Respondents were asked to list the five most important trends impacting the hospitality over the short-term (i.e., “current environment through the next 3 years”) and the longer-term (i.e., “4 to 10 years in the future”). To assess the trends proposed by respondents, two independent coders read through all trends collected, and based upon this review developed a mutually agreed upon coding structure. Each coder, working separately, assigned codes to each trend. Codes were then compared for consistency, resulting in an initial agreement rate of 85%. Discrepancies were discussed and resolved for all divergent codes.
Respondents’ perceptions of the most important short- and long-term trends for both hospitality academics and practitioners combined are displayed in Fig. 7 . For the short-term, the most cited topics included: 1) sanitation, cleanliness, and health; 2) demand, supply, and revenue; 3) technology; 4) COVID-19; 5) travel policies and issues, 6) economic and competitive issues; 7) employee well-being; and 8) consumer confidence/sentiment. A similar list emerged for the longer-term priorities, though the relative importance of some topics changed: 1) demand, supply, and revenue; 2) technology; 3) economic and competitive issues; 4) travel policies and issues; 5) sanitation, cleanliness, and health; 6) environmental and sustainability issues; 7) employee well-being; and 8) customer and guest issues.

Expected hospitality trends (all respondents).
The most obvious initial takeaway from examining differences in anticipated short- and long-term trends is the significant and expected decline in pandemic related issues in the longer term. In fact, all significant declining trends have an obvious relationship to concerns over health, safety, and disease prevention. Another major takeaway is the comparatively low perceived importance of environmental and sustainability concerns in the short- versus the long-term (where these concerns rose significantly).
To examine differences by type of respondent, short- and long-term trends were distinguished by academic, hospitality industry, and other employment groups (see Fig. 8 , Fig. 9 , Fig. 10 , respectively). Fig. 8 shows the expected short- and long-term trends for academic respondents. Unlike the aggregate trends shown in Fig. 7 , the pandemic did not alter the top two expected trends; they are the same for both the short- and long-term: (a) technology and (b) demand, supply, and revenue. Moreover, environmental and sustainability mentions rise significantly over the long-term, becoming the third most important expected trend. Pandemic related issues become much less prominent in the longer term, with the highest ranked issue being sanitation (ranked number nine).

Expected hospitality trends (academic).

Expected hospitality trends (hotel industry practitioner).

Expected hospitality trends (other).
Fig. 9 shows the expected short- and long-term trends for hospitality industry respondents. The pattern of responses was similar to those of the academic respondents. The most important trend for hospitality industry respondents is supply and demand/revenue in both the short- and long-term. Technology is similarly important, ranking third in the short-term and second in the long-term. Unlike academic respondents, however, while environmental/sustainability rises significantly over the long-term, it did not reach the top five trends (rising to number seven). Additionally, branding rises significantly in importance over the longer term, becoming the tenth most mentioned long-term trend; by contrast, only 4.3% of academics mentioned branding, making it the twenty-third most mentioned long-term trend.
Fig. 10 shows the expected short- and long-term trends for respondents in the other category (primarily industry supplier) respondents. After examining both the academic and hospitality industry data, it is evident that respondents in this group tend to see trends in the industry differently. For example, technology never rises to the top three trends in either the short- or long-term. Moreover, no trends showed statistically significant increases in importance over the longer term, whereas numerous trends showed significant declines from the short to the long-term. It is possible that these differences are in part, impacted by the diverse nature of respondents’ involvement with and stakeholder position associated with the hospitality industry (e.g., supplier, consultant).
Because one aim of this investigation is to gauge the differences in perspectives between academics and hospitality industry practitioners, Fig. 11 , Fig. 12 provide direct comparisons between expected hospitality trends for these two groups. Examining both the short-term trends ( Fig. 11 ) and long-term trends ( Fig. 12 ) reveals that academics are much more likely to believe that technology related trends are important; this occurs despite technology being a top three trend for both academics and hospitality practitioners. Similarly, academic respondents are much more likely to believe that environmental/sustainability issues represent an important trend; in this case, however, this represents a large difference in the relative perception of this issue as an important trend by the two groups. Environmental/sustainability issues are the ninth most mentioned short-term trend for academics whereas they are the eighteenth most mentioned trend for hospitality industry practitioners. While the perception of this issue becomes significantly more important in the long-term for both groups, it is much more frequently mentioned by academics. Specifically, it is the third most mentioned long-term trend for academics, and the seventh most mentioned trend for hospitality industry practitioners. Another often mentioned trend where academics and practitioners differed significantly is food and beverage in the short-term. In terms of most mentioned short-term trends, the issue is similar for both academics and practitioners (seventh vs. tenth respectively). But in terms of percentage of respondents, almost twice as many academic respondents mentioned the issue compared to hospitality industry practitioners (28.4% vs. 14.3% respectively).

Expected hospitality trends current to 3 years (academic vs practitioner).

Expected hospitality trends 4 to 10 years (academic vs practitioner).
Additionally, academic researchers were more likely to mention innovation as a short-term trend (11.9%) while only 3.0% of hospitality industry practitioners did. By contrast, 13.6% of hospitality industry practitioners mentioned cost control as a short-term industry trend, while only 4.5% of academic respondents mentioned this issue as a priority.
6. Conclusions
Taken together, the results from studies 1, 2, and 3 provide important insights for both academic researchers and practitioners in the hospitality industry. Perhaps the most obvious and expected finding is that COVID-19 has pushed safety, and disease prevention issues to the forefront in the short-term. Moreover, although the importance of these issues appears to decrease over the longer term, given the significant and yet-to-be discovered implications of the current pandemic, we expect continued attention will be given to sanitation, cleanliness, and related issues.
However, our findings also suggest that future research should continue to focus on the topics that were important prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. First, and perhaps reinforced by the pandemic, technology-related issues remain at or near the top for both academics and practitioners in both the short- and long-term. Interestingly, despite technology being much more widely discussed in hospitality trade publications than in the hospitality academic literature prior to the pandemic, academic respondents were significantly more likely to mention technology as an important short- and long-term issue than were hospitality practitioner respondents, making it the most mentioned trend for both time frames. Why trade journals focus more on technology yet academics mention technology more is not possible to determine from this study (particularly given the structured formats and editorial calendars of trade publications), but it does point to a general alignment on the importance of technology between academics and practitioners.
Our review of the recently published hospitality research indicates several opportunities to extend the current body of knowledge about the roles and relevance of technology. For example, several studies have demonstrated positive effects associated with interactive- (e.g., Morosan & DeFranco, 2019 ) and AI-based technologies (e.g., Pillai & Sivathanu, 2020 ) that have been introduced to enhance or improve the consumer experience. These findings point to the need to consider the relative and/or differential influence of emerging technologies for customer satisfaction, loyalty, engagement, and related outcomes. Moreover, Cho, Bonn, Susskind, and Giunipero’s (2018) study on the supplier relationships in the independent restaurant segment demonstrated that information technology may be an important moderator of the relationship between a restaurant’s supplier dependence and market responsiveness. The results from this study suggests that further consideration is needed to examine the multi-level influences associated with technology (e.g. individual/customer versus unit/restaurant), as well as the extent to which technology may be an antecedent, mediator, and/or moderator within technology-embedded frameworks.
Another topic in which hospitality academics and practitioners agreed was the importance of supply, demand, and revenue issues for both the short- and long-term. Interestingly, while the academic literature provides some coverage of these topics (typically under disciplines related to finance/economics/law/accounting and operations management ), the total number of studies in this area was relatively small given its recognized importance by both academics and practitioners. Similarly, the trade literature devoted little space to supply and demand issues (see Table 3 ). However, given the significant economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the need for additional research into issues related to supply, demand, and revenue optimization, at least for the foreseeable future, appears well-justified. For example, studies in this domain have examined the use and applicability of predictive forecasting (e.g., Arbelo, Arbelo-Pérez, & Pérez-Gómez, 2018 ) and revenue management practices (e.g., Noone, Enz, & Canina, 2019 ) within and across industry segments. In addition, studies have demonstrated support for a wide array of individual (e.g., gender; Choi, Joe, & Mattila, 2018 ) and contextual (e.g., rate conditions; Arenoe & van der Rest, 2020 ) factors that may influence both individual- (e.g., consumer price evaluations) and aggregate-level outcomes (e.g., hotel pricing strategies). Thus, and similar to research on technology, we encourage future studies to examine the relative importance of key demand characteristics (e.g., customers’ willingness to pay), as well as explore the relevance of contingencies that may influence the efficacy and utility of demand, supply, and revenue management practices (e.g., distribution channel management).
Another noteworthy finding was the perceived relevance of environmental/sustainability. This issue is widely considered to be important across all industries ( unglobalcompact.org 2020 ), which is consistent with our finding that 41.8% of academic researchers mentioned environmental/sustainability issues as important over the longer term (making it the third most mentioned trend). However, our findings also indicated that this topic has received comparably much lower attention in the academic literature (i.e., 3.7% of all published articles), which is reflected by the dispersed treatment of this topic across multiple disciplines and stakeholder groups (e.g., strategic management, operations management, consumer behavior, etc.) By contrast, 6.4% of trade industry articles covered sustainability issues pre-pandemic. Yet while 19.5% of hospitality practitioners mentioned this issue as an important longer-term trend, it falls to seventh place behind financial and operational issues. Based on these findings, it appears there is a need for multi- and cross-disciplinary studies to extend our understanding about the roles and relevance of environmental and sustainability issues, especially policies, programs, and systems that can be linked to business outcomes that resonate with priorities expressed by industry practitioners (e.g. demand, supply, and revenue).
One noteworthy point of divergence between academics and practitioners is the perceived importance of trends and priorities associated with branding. While branding topics have been widely addressed in both the academic and trade literatures, this topic was seldom mentioned by academic respondents as a short- or longer-term priority. In contrast, 16.9% of hospitality industry practitioners mentioned branding as an important long-term trend. This difference may reflect the general tendency of internal stakeholders (i.e. industry practitioners) to focus more on immediate and tangible concerns versus external stakeholders (i.e., industry-focused academics) who may focus more on more longer-term and broader priorities ( Khan, 2019 , King et al., 2011 , Vong, 2017 , Wenzel et al., 2020 ). We see similar divergence—with likely similar causes—with several other less mentioned trends, such as innovation, differentiation, and cost control.
These findings point to additional opportunities for hospitality academic researchers to address gaps in the literature on topics believed to be important by both academia and practitioners. Moreover, the findings reinforce the need for academic researchers to carefully consider and integrate managerial relevance with academic rigor to their investigations. In this way, academic researchers can better assist the hospitality industry—which has suffered greatly from the pandemic—to recover more quickly and thrive in the long term.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Lerzan Aksoy: Data curation, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Sunmee Choi: Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. Tarik Dogru: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Timothy Keiningham: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. Melanie Lorenz: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Dan Rubin: Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Software. J. Bruce Tracey: .
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Biographies
Lerzan Aksoy's research interests are in service research, including customer satisfaction, employee satisfaction, innovation and social innovation, its relationship to loyalty, firm performance and societal wellbeing. A prolific writer, Professor Aksoy has co-authored or edited five books. Her most recent book, The Wallet Allocation Rule, is a New York Times and USA Today bestseller. Professor Aksoy's research has received more than a dozen prestigious scientific awards, including the Marketing Science Institute/H. Paul Root Award from the Journal of Marketing, Citations of Excellence “Top 50” Award and Robert Johnston Outstanding Paper Award (3 times) from the Journal of Service Management. Her articles have been published in top tier journals such as the Journal of Marketing, Journal of Marketing Research, Marketing Science, Journal of Academy of Marketing Science, Journal of Interactive Marketing, Harvard Business Review, MIT Sloan Management Review, Journal of Service Research and Journal of Service Management. She is associate editor for the Journal of Service Research and was selected “Best Reviewer of the Year” among the editorial review board members of both the Journal of Service Research and Journal of Service Management. Dr. Aksoy served as co-chair of AMA SERVSIG (American Marketing Association - Service Special Interest Group) and worked with Filene Research Institute doing research with credit unions. She currently serves on the Board of Trustees of Marketing Edge, is a member of the Academic Council of the AMA and serves as the academic partner for the American Innovation Index. She has also been featured in media including CNN, CNBC and publications such as The Wall Street Journal, BrandWeek and Harvard Business Online. Professor Aksoy is a keynote speaker at academic and industry conferences. She has provided executive training and consulting to credit unions and companies including Sony, Ford, Pfizer, Nielsen and L'Oreal.
Sunmee Choi is Dean of College of Business and Management at VinUniversity in Hanoi, Vietnam, while taking a three-year leave of absence from School of Business at Yonsei University in Seoul, Korea. The areas of her research interest include service operations management, revenue management, demand-forecasting methods, distribution channel management, and customer experience management. Her work has been published in journals such as Journal of Business Research, Journal of Service Management, Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research, International Journal of Hospitality Management, Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management, and Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Marketing. Sunmee received her M.S. and Ph.D. from the School of Hotel Administration at Cornell University.
Tarik Dogru earned his doctorate in hospitality management from the University of South Carolina and MBA from Zonguldak Karaelmas University, Turkey. Prior to joining the faculty of the FSU Dedman College of Hospitality, Dr. Dogru served as an assistant professor at Boston University (2016-18), an adjunct faculty member at the University of South Carolina (2013-16), and a research assistant at Ahi Evran University, Turkey (2009-12). He has taught a variety of courses in business and hospitality schools at undergraduate and graduate levels. The range of Dr. Dogru’s research interests spans topics in hospitality finance, corporate finance, behavioral finance, real estate investment, hotel investments, sharing economy, tourism economics, climate change, and block chain technology. Dr. Dogru is a highly productive researcher who publishes in many prestigious hospitality and tourism journals — Tourism Management, Annals of Tourism Research, Journal of Travel Research, International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, International Journal of Hospitality Management, Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, Tourism Analysis, International Journal of Tourism Research, and Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights. He serves on the editorial board of Tourism Economics and Tourism Analysis and as a reviewer for several academic journals.
Timothy Keiningham, is the J. Donald Kennedy Endowed Chair in E-Commerce. He received the American Marketing Association’s Christopher Lovelock Career Contributions to the Services Discipline Award for teaching, research, and service that has had the greatest long-term impact on the development of the services discipline. This is the highest award presented in the field of service marketing. Dr. Keiningham was named one of the Top 50 Undergraduate Business Professors by Poets & Quants. He is author of the NY Times bestseller The Wallet Allocation Rule and author/editor of eight other books on customer loyalty. His research has been accepted in top-tier journals in marketing (e.g., Journal of Marketing, Journal of Marketing Research, Marketing Science, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science), strategy (e.g., Harvard Business Review and MIT Sloan Management Review) and service management (e.g., Journal of Service Research, and Journal of Service Management). His research has received several awards. Dr. Keiningham’s work aims to bridge the gap between leading scientific research and management best practices. To advance management practice and inform his scientific research, he serves as chief strategy and client officer at Rockbridge Associates. Prior to joining Rockbridge, he worked for seventeen years in senior officer positions at Ipsos (the world’s 3rd largest market research firm); the last seven years he served as Global Chief Strategy Officer and EVP at Ipsos Loyalty. Dr. Keiningham received a BA from Kentucky Wesleyan College, an MBA from Vanderbilt University, and a PhD from Staffordshire University (UK).
Melanie Lorenz is an experienced Assistant Professor. A native of Germany, she has worked in banking and consulting. She then decided to become an academic, and earned her PhD in Marketing from the University of Alabama in 2016. She has been an Assistant Professor at the University of Toledo. Her focus is in International Business and Marketing; her research has been published in the Journal of World Business, International Marketing Review, and Academy of Management Learning and Education, among others.
Dan Rubin is assistant professor of marketing at St. John’s University, Peter J. Tobin School of Business. His research focusing on consumer behavior has been published in top-tier journals including the Journal of Consumer Psychology, Journal of Business Research, and Journal of Consumer Marketing. Dr. Rubin received his PhD from Baruch College.
J. Bruce Tracey is the Kenneth and Marjorie Blanchard Professor of Human Resource Management at Cornell University's Nolan School of Hotel Administration, where he has taught courses in human resources and organizational management for undergraduate, graduate, and professional audiences throughout North America, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. Professor Tracey's research considers a wide range of topics that examine the effectiveness of HR policies, practices, and systems. His work has been published in diverse outlets such as the Journal of Applied Psychology, Journal of Management, University of Pennsylvania Journal of Labor and Employment Law, and the Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, where he is currently serving in his second term as Editor. Sponsors for Professor Tracey's research and consulting include Four Seasons Hotels and Resorts, Hilton Worldwide, and Marriott International, and he has been cited in the New York Times, Bloomberg, Forbes, USA Today, Fast Company, among other popular press outlets.
☆ Author order is alphabetical. All authors contributed equally.
1 While we initially considered asking respondents to rank-order pre-defined categories and trends based on our academic and practitioner literature review, we decided that the results would not have been able to reflect the unprecedented turbulence in the industry that COVID-19 has created. Thus, open ended questions, while more difficult to code, will provide more in-depth insights.
- Arbelo A., Arbelo-Pérez M., Pérez-Gómez P. Estimation of profit efficiency in the hotel industry using a Bayesian stochastic frontier model. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly. 2018; 59 (4):364–375. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arenoe B., van der Rest J.P.I. Does willingness to pay for rate conditions depend on the booking window? A novel time-dependent conjoint analysis approach. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly. 2020; 61 (2):213–222. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bartik, A. W., Bertrand, M., Cullen, Z. B., Glaeser, E. L., Luca, M., & Stanton, C. T. (2020). How are small businesses adjusting to COVID-19? Early evidence from a survey (No. w26989). National Bureau of Economic Research.
- Cho M., Bonn M.A., Susskind A., Giunipero L. Restaurant dependence/autonomy in the supply chain and market responsiveness: The moderating roles of information technology adoption and trust. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. 2018; 30 (9):2945–2964. [ Google Scholar ]
- Choi C., Joe S.J., Mattila A.S. Reference price and its asymmetric effects on price evaluations: The moderating role of gender. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly. 2018; 59 (2):189–194. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dogru T., Bulut U. Is tourism an engine for economic recovery? Theory and empirical evidence. Tourism Management. 2018; 67 :425–434. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fernandes, Nuno, Economic Effects of Coronavirus Outbreak (COVID-19) on the World Economy (March 22, 2020). IESE Business School Working Paper No. WP-1240-E, Available at SSRN: 10.2139/ssrn.3557504. [ CrossRef ]
- Gursoy, D., & Chi, C. G. (2020). Effects of COVID-19 pandemic on hospitality industry: review of the current situations and a research agenda. 29(5), 527-529, DOI: 10.1080/19368623.2020.1788231.
- Hospitality Global Market Report (2020). Available at: Last accessed December 6, 2020.
- Khan M.A. A systematic assessment of gaps between academic research and industry participation in hospitality management discipline. International Journal of Hospitality Management. 2019; 82 :82–90. [ Google Scholar ]
- King C., Funk D.C., Wilkins H. Bridging the gap: An examination of the relative alignment of hospitality research and industry priorities. International Journal of Hospitality Management. 2011; 30 (1):157–166. [ Google Scholar ]
- Landis J.R., Koch G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33 :159–174. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morosan C., DeFranco A. Using interactive technologies to influence guests’ unplanned dollar spending in hotels. International Journal of Hospitality Management. 2019; 82 (September):242–251. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nicola M., Alsafi Z., Sohrabi C., Kerwan A., Al-Jabir A., Iosifidis C.…Agha R. The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus and COVID-19 pandemic: A review. International Journal of Surgery. 2020; 78 :185–193. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Noone B.M., Enz C.A., Canina L. The uniqueness of revenue management approaches in nontraditional settings: The case of the golf industry. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research. 2019; 43 (5):633–655. [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD, 2020. Coronavirus (COVID-19): SME Policy Responses.
- Pillai R., Sivathanu B. Adoption of AI-based chatbots for hospitality and tourism. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. 2020; 32 (10):3199–3226. [ Google Scholar ]
- Scheier M.F., Carver C.S., Bridges M.W. Distinguishing optimism from neuroticism (and trait anxiety, self-mastery, and self-esteem): A re-evaluation of the Life Orientation Test. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1994; 67 (6):1063–1078. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- unglobalcompact.org (2020), Business as a Force for Good, United Nations Global Compact. Available at: https://www.unglobalcompact.org/what-is-gc/mission (Accessed September 19, 2020).
- Vong F. Relevance of academic research to hospitality practitioners. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Education. 2017; 29 (3):116–128. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wenzel M., Stanske S., Leiberman M.B. Strategic response to crisis. Strategic Management Journal. 2020; 41 :v7–v8. doi: 10.1002/smj.3161. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WTTC, 2020a. Global Economic Impact and Trends. Available at: https://wttc.org/Research/Economic-Impact .
- WTTC, 2020b. Recovery Scenarios 2020 & Economic Impact from COVID-19. Available at: https://wttc.org/Research/Economic-Impact/Recovery-Scenarios-2020-Economic-Impact-from-COVID-19 .
- WTTC, 2020c. To Recovery & Beyond. Available at: https://wttc.org/Research/Insights .
- WTTC, 2020d. 100 Million Jobs Recovery Plan. Available at: https://wttc.org/Portals/0/Documents/Press%20Releases/WTTC%20and%20CEOs%20present%20plan%20to%20save%20100%20million%20jobs.pdf?ver=2020-10-09-104603-973 .
- WTTC, 2020e. Leading Global Protocols for the New Normal. Available at: https://wttc.org/COVID-19/Safe-Travels-Global-Protocols-Stamp .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A literature review helps researchers to understand the historical development of knowledge in an area of study (Creswell, Citation 2012) ... Tourism and hospitality industry are highly customer-focused and quality of service is a major source of competitive advantage. The survival and success of tourism and hospitality businesses depends on an ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on ...
O'Neill, J. W., & Follmer, K. (2020). A Multilevel Review of Hospitality Industry Work-Family Conflict Research and a Strategy for Future Research. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 44(1), 3-44. ... As with the academic literature review, we examined the time period from January 2018 to September 2020, the most recently available ...
Abstract. This article provides a systematic literature review of the hospitality, leisure, tourism, business, and management literature on luxury hospitality. We use a data-driven quantitative method (i.e., bibliometric review) to provide an integrated view of extant luxury hospitality research. The bibliographic coupling analysis allowed us ...
A systematic literature review using the PRISMA method investigated the impact of customer value co-creation through the digital age on the tourism and hospitality sector. The primary objective of this review was to examine 27 relevant studies published between 2012 and 2022. ... The hospitality industry, which includes hotels and restaurants, ...
A systematic review of the contemporary literature is considered to identify and classify research that focuses on the hospitality industry in the time of COVID-19. The systematic review's primary purpose is to identify, summarize, and analyze the findings of all relevant individual studies that are addressing predefined research questions ...
A CONCEPTUAL LITERATURE REVIEW ON SERVICE QUALITY AND CUSTOMER LOYALTY IN THE HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY DURING THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of California State Polytechnic University, Pomona Inulfillment Partial F Of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science In Hospitality Management. By. SongXin Xu. 2022
Literature review An approach to finding relevant hospitality industry academic literature was deployed with the use of keyword searches utilising Google Scholar and journal databases held in the electronic libraries of Lander University and New Mexico State University. Keywords included, and were not limited to
While the COVID-19 pandemic has dealt the hospitality industry and the academia with uncharted challenges, it also presents great research opportunities for hospitality scholars. The magnitude of this crisis and its devastating effects on operations, employees, and customers are unrivaled compared to previous crises.
This study reports on a systematic review of the published literature used to reveal the current research investigating the hospitality industry in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic. The presented review identified relevant papers using Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Science Direct databases. Of the 175 articles found, 50 papers met the predefined inclusion criteria.
Analytics, Business Analytics, Hospitality, Hotels, Literature Review Nowada ys, there is a wide variety of information systems in which the tourism and hotel industry have not stayed behind.
We conducted a narrative literature review to analyze the importance of the dimensions of working hours, salary, professional development, leadership, and management, working atmosphere, work itself, and infrastructure as driving forces of job satisfaction in the Alpine hospitality industry. In the following sections, we elaborate on each of ...
The results also illustrate the topic's academic evolution and expose major guidelines that can help determine areas for future research.,This study adds value to the hospitality research literature via SLR. The framework of CX in the hotel industry synthesizes the existing knowledge on this topic and identifies research gaps.
The tourism and hospitality industry highly vulnerable to environmental, political, and socioeconomic factors, ... Section two is a review of relevant literature; section three investigates the interconnectedness structure between different tourism and hospitality markets; section four presents the regression analysis and section five concludes ...
Management & Science University. This systematic review paper aims to enhance knowledge of corporate sustainability initiatives in the. hospitality industry as it has been researched by earlier ...
A Literature Review Exploring the Challenges for Fair Work in the Hospitality Industry 1. Introduction The Fair Work Convention's Vision is: By 2025, people in Scotland will have a world-leading working life where fair work drives success, wellbeing and prosperity for individuals, businesses, organisations and for society.
The purpose of this study is to examine the current literature pertaining to the impact of COVID-19 on the global hospitality industry. The research has a two-fold approach. First, a succinct examination of the literature highlights the significant negative effects of the pandemic on the multiple fields of hospitality.
This study aimed to examine the conceptual development, trends, and intellectual structures in the literature on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry. This study applied the bibliometric review method to analyze 1165 Scopus-indexed documents. Descriptive analyses, citation analysis, co-citation analysis, and keyword co-occurrence analysis were used to investigate the ...
Computational intelligence in the hospitality industry: a literature review. The quantification of techniques used in the hospitality sector is visually depicted in Fig. 2 showing that, inside CI, ML is the most used set of methodologies in the hospitality industry. Inside this area, the most used methodologies appeared to be probabilistic ...
Organisational Learning in the Hospitality Industry: A Literature Review 11 identi ed and measured using di erent constructs and facilitating factors (Bhatnagar & Sharma, 2005; Goh & Richards, 1997).
The company engages, listens, and responds to consumer sentiments as is evidenced in their brand messaging strategy about young women and their shifting self-confidence and self-image in their early/mid-teens. They have also run campaigns on aging and skin care as women advance through life. They use accurate size models and strive to make ...
Based on a systematic review of the literature, this paper represents one of the first attempts to capture the state of the literature on fraud in the hospitality industry. Systematic Literature Reviews (SLR) offer a reliable process for aggregating literature on a particular topic and identifying areas of investigation within and gaps in the ...
As with the academic literature review, we examined the time period from January 2018 to September 2020, the most recently available issues at the time of writing. ... Effects of COVID-19 pandemic on hospitality industry: review of the current situations and a research agenda. 29(5), 527-529, DOI: 10.1080/19368623.2020.1788231. Hospitality ...
The construction industry is scrutinized and criticized for its impact on environmental degradation. Nowadays, while the lean construction philosophy and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim to alleviate the adverse environmental effects of the construction industry, their synergies remain unclear and ambiguous. Therefore, this study aims to explore the synergies between lean construction ...
Methods. A SLR method was used to synthesise the research on VCD across the fields of tourism and hospitality. The aim of this method is to minimise bias in the review of literature with a wide variety of different combinations of topic, subject matter, location and variables (Pickering & Byrne, Citation 2014).An SLR maps what is known, and thus pinpoints gaps on what is yet to be known ...
Table 1. Hospitality internships literature profile. 1. Beggs et al. (2008) "The purpose of this study was to examine differences in the perceptions of internships between college students studying travel and tourism and practitioners in the field." (p. 31) 2. Amissah et al. (2019)
The purpose of this narrative review of the recent literature is to analyze the outcomes, complications, and implant survival of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) carried out on people with hemophilia (PWH). It has been shown that TKA substantially alleviates preoperative pain and improves knee function and the patient's quality of life. However, the complication rates of TKA range between 8.5% ...