- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 6th Standard CBSE Social Science question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 6th Standard CBSE Social Science books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place.

6th Standard CBSE Subjects
6th standard cbse study materials.

Study Materials for Other CBSE Board Standards

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

Latest CBSE 6th Standard CBSE Study Material Updates
What, Where, How and When Class 6 Case Study CBSE History Chapter 1

Last Updated on March 20, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Here you will find Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 6 Social Science Series.
What, Where, How and When Class 6 Case Study CBSE History Chapter 1 (PDF Download)
Case Study Questions
Question 1:
Read the following passage and answer the given questions provided below.
The word India comes from the Indus, called Sindhu in Sanskrit. The Iranians and the Greeks who came through the northwest about 2500 years ago and were familiar with the Indus, called it the Hindos or the Indos, and the land to the east of the river was called India. The name Bharata was used for a group of people who lived in the north-west, and who are mentioned in the Rigveda, the earliest composition in Sanskrit (dated to about 3500 years ago). Later it was used for the country.
There are several ways to finding out about the past. One is to search for and read books that were written long ago. These are called manuscripts, because they were written by hand. This word come from the Latin word ‘manu’, meaning hand. These were usually written on palm leaf, or on the specially prepared bark of a tree known as the birch, which grows in the Himalayas.
Over the years manuscripts were eaten away by insects, some were destroyed, but many have survived, often preserved in temples and monasteries. These books dealt with all kinds of subjects: religious beliefs and practices, the lives of kings, medicine and science.
Q. 1. The word India comes from the Indus River, what is Indus called in Sanskrit? (a) Sindh (b) Sindhu (c) Ravi (d) Beas
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: The word India comes from the Indus River, Indus is called ‘Sindhu’ in Sanskrit.
Q. 2. Greeks came through which direction about 2500 years ago in Indian subcontinent? (a) Northeast (b) Southeast (c) Southwest (d) Northwest
Ans. Option (d) is correct. Explanation: Greeks came through the northwest about 2500 years ago and were familiar with the Indus, called it the Hindos or the Indos.
Q.3. The name Bharata was used for a group of people who lived in the northwest, and who are mentioned in which Veda? (a) Yajurveda (b) Rigveda (c) Samaveda (d) Atharvaveda
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: The name Bharata was used for a group of people who lived in the north-west, and who are mentioned in the Rigveda, the earliest composition in Sanskrit (dated to about 3500 years ago). Later, the word was used for the country.
Q. 4. The word manuscript comes from which word? (a) Greek (b) Latin (c) French (d) Sanskrit
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: One way to know about past is to search for and read books that were written long ago. These are called manuscripts, because they were written by hand. This word come from the Latin word ‘manu’, meaning hand.
Q. 5. The manuscripts dealt with which kind of subjects? (a) Religious beliefs (b) Lives of kings (c) Medicine (d) All of the above
Ans. Option (d) is correct. Explanation: Over the years manuscripts were eaten away by insects, some were destroyed, but many have survived, often preserved in temples and monasteries. These books dealt with all kinds of subjects: religious beliefs and practices, the lives of kings, medicine and science.
We hope the given case study questions for What, Where, How and When Class 6 helps you in your learning.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science includes all the questions provided in NCERT Class 6 Social Science Text book of Geography The Earth: Our Habitat, History Our Pasts, Civics Social and Political Life. Here CBSE Class 6 SST all questions are solved with the detailed explanation to score good marks in the exams.
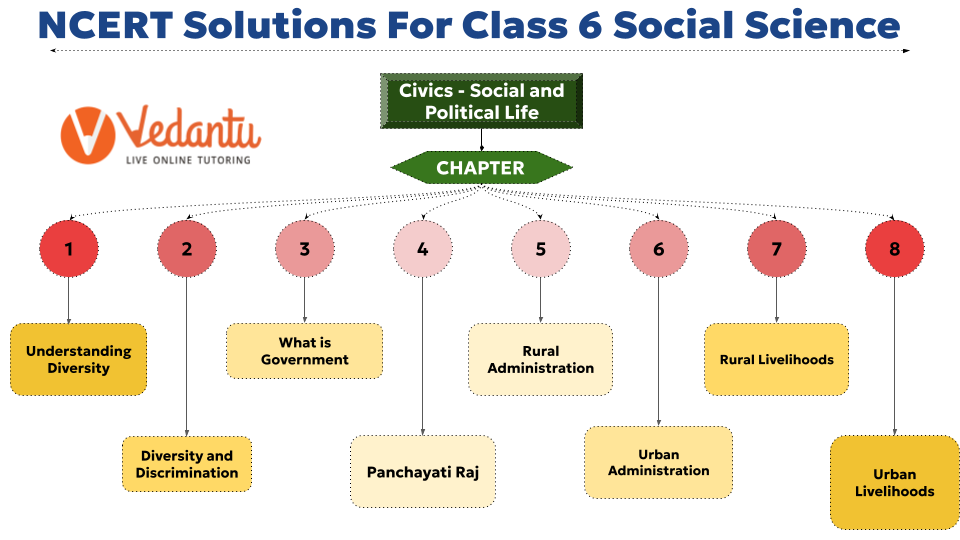
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography : The Earth: Our Habitat
- Chapter 1 The Earth in the Solar System
- Chapter 2 Globe Latitudes and Longitudes
- Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth
- Chapter 4 Maps
- Chapter 5 Major Domains of the Earth
- Chapter 6 Major Landforms of the Earth
- Chapter 7 Our Country India
- Chapter 8 India Climate Vegetation and Wildlife
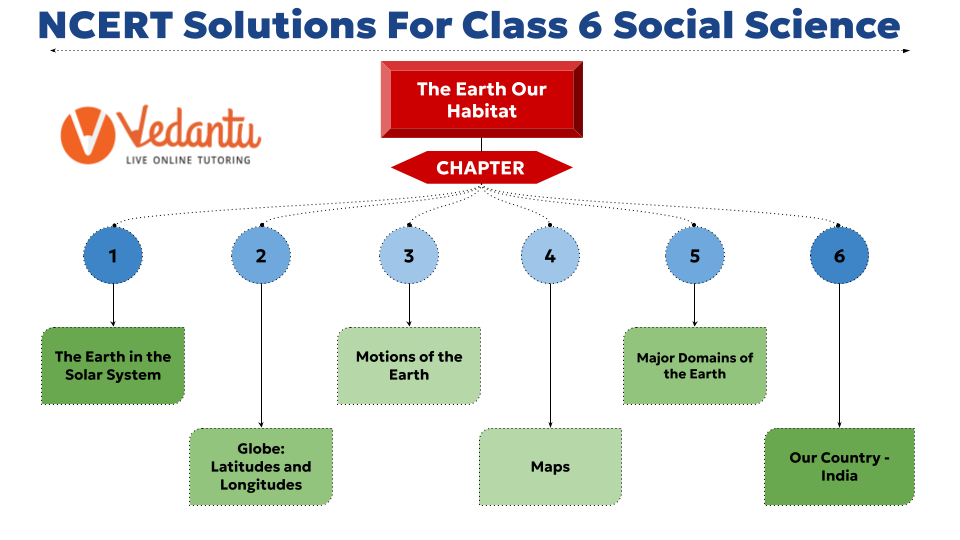
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History : Our Pasts – I
- Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When?
- Chapter 2 On The Trial of the Earliest People
- Chapter 3 From Gathering to Growing Food
- Chapter 4 In the Earliest Cities
- Chapter 5 What Books and Burials Tell Us
- Chapter 6 Kingdoms, Kings and an Early Republic
- Chapter 7 New Questions and Ideas
- Chapter 8 Ashoka, The Emperor Who Gave Up War
- Chapter 9 Vital Villages, Thriving Towns
- Chapter 10 Traders, Kings and Pilgrims
- Chapter 11 New Empires and Kingdoms
- Chapter 12 Buildings, Paintings, and Books
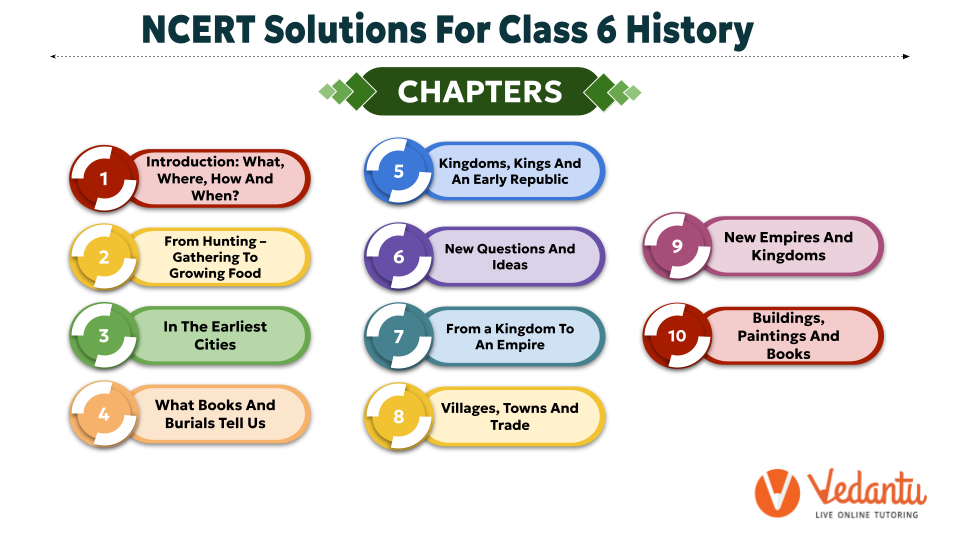
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Civics
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Civics : Social and Political Life – I
- Chapter 1 Understanding Diversity
- Chapter 2 Diversity and Discrimination
- Chapter 3 What is Government
- Chapter 4 Key Elements of a Democratic Government
- Chapter 5 Panchayati raj
- Chapter 6 Rural Administration
- Chapter 7 Urban Administration
- Chapter 8 Rural Livelihoods
- Chapter 9 Urban Livelihoods
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science (Download PDF)
NCERT Solutions Maths Science Social English Hindi Sanskrit RD Sharma
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 6
- Class 6 Social Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science
Download chapter-wise ncert solutions for class 6 social science.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science covers all the questions in the NCERT textbook for Class 6 Social Science – spread across subjects like History, Civics and Geography. Solving these questions will help the students learn Social Science proficiently. Students can use these solutions as the best source to revise the subject before the exams. These NCERT Solutions For Class 6 SST are also the best source for the students to self-analyse their performance.
Students are more likely to score more marks in the exams if they practise these solutions regularly. Find below the links to access the PDF format of the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 for subjects like History, Civics and Geography.
To ease the process of studying, detailed PDFs and solutions are provided on BYJU’S. These solutions are the best source of study material for students who find difficulty in answering textbook questions. These solutions help students to revise the entire syllabus a few days before the exam without any difficulty. Students will be able to find out the concepts at which they are weak and work on them for a better academic score. As the solutions contain thorough explanations, students will be able to score high marks in the Class 6 final exam.
Now, students can be confident about scoring good marks in CBSE Class 6 . These solutions address and solve all the doubts that the students may have regarding the subject. All they have to do is to learn the answers to these questions and practise. Students can find chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science subjects in the links below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History
History is a subject which includes the important events which occurred in our earlier days. It is very important for students to learn the chapters which are covered in the NCERT Textbook to score well in the annual exam. Students mainly find it difficult to learn the chapters as each one of them contains many dates and events related to it. For this purpose, the set of highly experienced faculty at BYJU’S prepare the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History in a comprehensive manner. Short-cut tips and tricks are explained so that students can easily remember all the events related to each chapter.
Please note: According to the NCERT Class 6 Social Science textbook 2023-24, Chapter 7 – ‘Ashoka, The King Who Gave Up War’ has been renamed as ‘From a Kingdom to an Empire’; Chapters 8 and 9 have been merged as ‘Chapter 8 – Villages, Towns and Trade’.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography
It is very important for the students to know about the earth that we live in, right from smaller classes. Having a strong knowledge of these concepts not only helps students in scoring good marks but also helps them to understand the changes that occur in our environment. The subject matter experts at BYJU’S draft the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography to improve confidence among students to score more marks. The important concepts are highlighted so that students will be able to frame proper answers to the questions that would appear in the exams.
The following chapters have been removed from the NCERT Class 6 Geography textbook 2023-24.
Major Landforms of the Earth
India: Climate, Wildlife and Vegetation
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Civics
The word ‘Civics’ refers to the study of the rights and duties of a citizen. Civics is a Social Science branch introduced to the students from Class 6. The objective of providing it as a subject is to help students understand the rights they possess in our country. To help students understand it better, our faculty, with vast experience in the subject, have designed the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Civics . Using these solutions will improve the way a student approaches a concept.
The following chapter has been removed from the NCERT Class 6 Civics textbook 2023-24.
Key Elements of a Democratic Government
The highly experienced faculty at BYJU’S design the solutions completely based on the latest syllabus of the CBSE board. Each and every exercise is solved in a comprehensive manner to make students well-versed in all the dates and events which are important for the exam. The online and PDF versions are available on BYJU’S to provide the best study material for the students.
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science to score well in the final exam.
Benefits of using NCERT Class 6 Social Science
Some of the benefits of solving NCERT Solutions Social Science Class 6 are as mentioned below:
- These solutions are prepared by the experts and cover all the questions from NCERT books.
- Students can build a strong hold on the concepts of the subject with these solutions.
- These NCERT Solutions are the best resource for students to prepare for the exams.
- These are designed following the latest NCERT syllabus, emphasising the important topics.
- Solving these solutions gives the students an advantage with practical questions.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science
How can i study for the class 6 social science examination using ncert solutions in a fast and productive way, will i get correct and detailed answers to the textbook questions in ncert solutions for class 6 social science, are ncert solutions for class 6 social science the most trustworthy guide for cbse students, how long should a student learn the answers to the textbook questions using the ncert solutions for class 6 social science, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
so much thankful to all the teachers who help the scholars by any means without any profit . It is really very very excellent thing for the all . May God bless you all teachers who do such a good helping hand to the poor especially . thanks
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 3 In the Earliest Cities
- Last modified on: 11 months ago
- Reading Time: 12 Minutes

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 In the Earliest Cities
Here in this article, we are providing Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science. In case study or passage-based questions, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ Questions based on it will be asked. For Social Science Subjects, there would be 5 case-based sub-parts questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.
In the Earliest Cities Class 6 Social Science Case Study Questions
Case Study Question 1:
Let us look at some of the objects that were made and found in Harappan cities. Most of the things that have been found by archaeologists are made of stone, shell and metal, including copper, bronze, gold and silver. Copper and bronze were used to make tools, weapons, ornaments and vessels. Gold and silver were used to make ornaments and vessels. Perhaps the most striking finds are those of beads, weights, and blades. The Harappans also made seals out of stone. These are generally rectangular and usually have an animal carved on them. The Harappans also made pots with beautiful black designs.
Cotton was probably grown at Mehrgarh about 7000 years ago. Actual pieces of cloth were found attached to the lid of a silver vase and some copper objects at Mohenjodaro. Archaeologists have also found spindle whorls, made of terracotta and faience. These were used to spin thread.
(i) The objects found in Harappan sites were made of (a) stone, shell and metal (b) copper, bronze and gold (c) silver (d) All of the above Ans. Option (d) is correct. Explanation: Most of the things that have been found by archaeologists in various Harappan sites are made of stone, shell and metal, including copper, bronze, gold and silver.
(ii) Which metals were used to make ornaments? (a) Gold and Silver (b) Copper and Bronze (c) Iron and Copper (b) All of these Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: Gold and silver were used to make ornaments and vessels.
(iii) When was the cotton grown? (a) 5000 years ago (b) 7000 years ago (c) 6000 years ago (d) 9000 years ago Ans. Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: Cotton was grown at Mehrgarh about 7000 years ago
(iv) What was/were the feature(s) of seals? (a) Made out of stone (b) Rectangular in shape (c) Animals carved on them (d) All of the above Ans. Option (d) is correct. Explanation: The Harappans made seals out of stone and these are generally rectangular and usually have an animal carved on them.
(v) A person who is trained to do only one kind of work? (a) Multitasker (b) Scholar (c) Specialist (d) None of the above Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: A specialist is a person who is trained to do only one kind of work, for example, cutting stone, polishing beads or carving seals.
Related Posts
Social science class 6 chapter list, latest chapter list (2023-24), cbse class 6 history chapters.
| Chapter 1 | What, Where, How and When? Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 2 | From Hunting – Gathering to Growing Food Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 3 | In the Earliest Cities Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 4 | What Books and Burials Tell Us Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 5 | Kingdoms, Kings and the Early Republic Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 6 | New Questions and Ideas Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 7 | From a Kingdom to an Empire Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 8 | Villages, Towns and Trade Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 9 | New Empires and Kingdoms Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 10 | Buildings, Paintings and Books Case Study Questions |
CBSE Class 6 Social & Political Life Chapters
| Chapter 1 | Diversity Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 2 | Diversity and Discrimination Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 3 | Government Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 4 | Local Government and Administration Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 5 | Rural Administration Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 6 | Urban Administration Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 7 | Rural Livelihoods Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 8 | Urban Livelihoods Case Study Questions |
CBSE Class 6 Geography Chapters – The Earth: Our Habitat
| Chapter 1 | The Earth in the Solar System Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 2 | Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 3 | Motions of the Earth Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 4 | Maps |
| Chapter 5 | Major Domains of the Earth Case Study Questions |
| Chapter 6 | Our Country: India Case Study Questions |
Old Chapter List
Class 6 Social Science Geography: The Earth – Our Habitat
Chapter 1 The Earth in the Solar System Chapter 2 Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth Chapter 4 Maps Chapter 5 Major Domains of the Earth Chapter 6 Major Landforms of the Earth Chapter 7 Our Country India Chapter 8 India Climate Vegetation and Wildlife
Class 6 Social Science History: Our Pasts – I
Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When? Chapter 2 On The Trial of the Earliest People Chapter 3 From Gathering to Growing Food Chapter 4 In the Earliest Cities Chapter 5 What Books and Burials Tell Us Chapter 6 Kingdoms, Kings and an Early Republic Chapter 7 New Questions and Ideas Chapter 8 Ashoka, The Emperor Who Gave Up War Chapter 9 Vital Villages, Thriving Towns Chapter 10 Traders, Kings and Pilgrims Chapter 11 New Empires and Kingdoms Chapter 12 Buildings, Paintings, and Books
Class 6 Social Science Civics: Social and Political Life – I
Chapter 1 Understanding Diversity Chapter 2 Diversity and Discrimination Chapter 3 What is Government Chapter 4 Key Elements of a Democratic Government Chapter 5 Panchayati raj Chapter 6 Rural Administration Chapter 7 Urban Administration Chapter 8 Rural Livelihoods Chapter 9 Urban Livelihoods
What is Case Study Question in Class 6 Social Science?
Case study questions typically present a specific scenario or case related to a historical event, geographical issue, or social problem. Students are expected to read and understand the details of the case and then answer a set of questions based on their understanding and knowledge of the subject matter.
Case study questions can be an effective way to assess students’ understanding and ability to apply social science concepts to practical situations. They also encourage students to think critically, analyze information, and draw informed conclusions – skills that are valuable both inside and outside the classroom.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- Social Science

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Question Answers - FREE PDF Download
Struggling with the vast world of Class 6 Social Science (History, Civics, Geography)? Vedantu's class 6 social science question answers are here to transform your learning. Master key concepts with clear explanations, confidently tackle practice questions and utilise them for effective revision before exams. But that's not all!

Class 6 NCERT solutions also act as a powerful self-assessment tool, helping you pinpoint areas for improvement. Download your FREE PDF today and watch your Social Science grades soar! Vedantu's Class 6 Social Science NCERT Solutions, aligned with the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 6 Social Science , provides clear explanations and covers all essential concepts. Master the subject and ace your exams!
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science Chapter-wise Book Links - Download the FREE PDF
S.No. | NCERT Solutions for Social Science Class 6 Chapter-Wise Book Links |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
Glance on NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
Class 6 NCERT social science has a vivid syllabus divided into three sections.
These sections have chapters related to our earth and our habitat, our past, and the aspects of social and political life.
To understand the context and fundamental principles of all these chapters, refer to the Class 6 sst solutions framed by the subject experts of Vedantu.
Students are likelier to score higher if they regularly practice solutions from the NCERT class 6th social science.
To ease the studying process, online PDFs for NCERT solutions class 6 sst are provided in detail at Vedantu.
These solutions for sst NCERT class 6 can be used by students as the best source for revising the subject before exams.
These NCERT solutions for class 6 social science also help self-analyse student results.
All questions with a thorough explanation to score high marks in the exams are solved here as per the CBSE NCERT class 6 social science.
Students can download NCERT Solutions for Social Science class 6 hassle-free from Vedantu.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science: Concepts and Chapter-Wise Links
Class 6 geography - the earth our habitat.
Get ready to explore the amazing planet we call home! The "The Earth Our Habitat" chapters will be your passport to a world of wonder. You'll delve into the mysteries of our planet, from the towering mountains to the vast oceans. Uncover the secrets of continents, globes, and maps while understanding how the Earth's movements affect our lives.
S.No. | NCERT Solutions Class 6 Geography Chapter-wise Links |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
Class 6 History - Our Past I
History buffs, assemble! Are you curious about the world before you? "Our Past I" is your gateway to a thrilling adventure through time. These chapters will unlock the secrets of our earliest ancestors, their tools, and the amazing journey of humankind from hunters and gatherers to settled communities.
S.No. | NCERT Solutions Class 6 History Chapter-wise Links |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
9 |
|
10 |
|
Class 6 Civics - Social and Political Life
Have you ever wondered how decisions are made in your community? Or why we follow certain rules in society? "Social and Political Life" will be your guide to understanding the intricate web of relationships and structures that shape our daily lives. These chapters will introduce you to diversity, how we live harmoniously, and the importance of rules and regulations. You'll also explore the role of government in creating a fair and just society.
S.No. | NCERT Solutions Class 6 Civics Chapter-wise Links |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
Benefits of NCERT Solutions for Social Science Class 6
Apart from the exclusive notes designed by the experts, download and follow the solutions for Social Science Class 6 to find accurate answers to all the exercise questions.
As mentioned earlier, the elaborate syllabus of NCERT class 6 social science has three sections.
Remove any confusion related to the answering formats and utilisation of concepts included in the chapters for answering such fundamental questions for social science class 6.
Know the NCERT class 6 social science all Chapter Name and download the specific files according to your curricular need.
Make your study sessions more convenient by adding these solutions to your class's 6th social science study material.
Resolve doubts by following the answers for NCERT solutions for class 6 social science compiled by the experts.
Learn how the experts have attempted the questions to develop your answering skills for sst NCERT class 6.
NCERT Solutions class 6 sst provides a comprehensive resource to help you excel in History, Civics, and Geography. Downloadable PDFs with clear explanations and practice questions make learning and revision efficient. Solutions for class 6 NCERT social science are more than just answers. They equip you with the tools to understand key concepts, improve critical thinking, and develop a love for social science.
Related Important Links for Class 6 Social Science
Along with this, students can also download additional study materials provided by Vedantu for CBSE Class 6 Social Science –
S.No. | Important Links For Class 6 Social Science |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science 2024-25
1. Which website provides the latest CBSE-prescribed class 6th social science syllabus?
Vedantu is a great platform that gives CBSE prescribed syllabus. It offers the best solution for students to easily cover the chapters like NCERT Solution for Class 6th SST. It is proven to be the best support in terms of gathering information as they are free downloadable PDFs.
2. How many chapters are covered in NCERT solutions for class 6 social science Civics subjects?
There are 8 chapters in NCERT Class 6 Social Science Civics. Below is a list of them. Find NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Civics at Vedantu, categorised and prepared to help you learn and score well.
Chapter 1 - Understanding Diversity
Chapter 2 - Diversity and Discrimination
Chapter 3 - What is Government?
Chapter 4 - Panchayati raj
Chapter 5 - Rural Administration
Chapter 6 - Urban Administration
Chapter 7 - Rural Livelihoods
Chapter 8 - Urban Livelihoods
3. What is SST NCERT class 6?
Social Science is a subject that needs practical acceptance and knowledge. The concepts are not limited to a textbook. Solving questions related to what you’ve learned is the best way to check what you have gained. In its widest definition, social is defined as the scientific study of society and how people interact with and impact the world surrounding them. Economics, geography, political science and history are mainly the sub-subjects of social science. It is a popular subject among students.
4. What is a democratic government from NCERT Solutions class 6 sst?
A democratic government is where the rulers are elected by the citizens of the country. The native people have a big role in choosing the government. People can take part in the decisions for them and their actions are exercised by them directly or through elected representatives. Elections are held to choose such a government. A democracy differs from a monarchy or dictatorship in that each citizen has their own right to vote and choose the way in which the government is administered.
5. Can I study class 6 NCERT social science on the Vedantu website?
Vedantu primarily focuses on the aspects that assist students in getting a firm grasp on this subject. Our experts research and make the best-detailed study material for the students to understand the concepts clearly. It is in easy and concise language. Vedantu has made NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science textbook, which will guide you to solve the NCERT questions quickly at free of cost. These solutions can also be accessed on the Vedantu app for free.
6. What do geography class 6 sst solutions include?
Geography subject tells us about our surroundings and places near or far from us. It also gives an overview of our solar system and the galaxies. Geography of Class 6 includes major physical divisions of India, major landforms, major domains and landforms, different maps, details of earth’s axis, different seasons in India, rotation revolution and angle of inclination of the earth, three heat zones of the earth etc. It will give you an overview of our earth.
7. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science are comprehensive explanations and answers to the questions in the Class 6 Social Science textbook, published by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT). These solutions cover the three main subjects within Social Science: History, Civics, and Geography.
8. How can NCERT Solutions help me in class 6 social science question answers?
Understanding concepts: The solutions provide clear explanations that break down complex social science concepts into easy-to-understand steps.
Improving learning: They offer solutions to various question formats, helping you practice applying your knowledge and improving your answering skills.
Effective revision: Solutions can be valuable for revising key topics before exams, ensuring you retain important information.
Self-assessment: By comparing your answers to the solutions, you can identify areas where you might need to focus more during revision.
9. Are Solutions enough for scoring well in NCERT social science class 6?
NCERT Solutions are a valuable resource, but they might not be sufficient. Consider using them alongside your textbook, class notes, and other reference materials for a well-rounded understanding.
10. Where can I find NCERT Solutions for Social Science class 6?
Several websites and educational platforms offer downloadable PDFs or online access to NCERT Solutions. Ensure the source is reputable and the solutions align with the latest CBSE curriculum.
11. What are some additional benefits of using NCERT Solutions for NCERT class 6 social science?
Save time: Ready-made solutions can save you time compared to finding answers on your own.
Boost confidence: Knowing you can access reliable explanations can increase your confidence in understanding.
Develop critical thinking: You can enhance your critical thinking skills by analysing different problem-solving approaches.
NCERT SOLUTIONS FOR CLASS 6
Cbse class 6 study materials.
Case Study Questions Class 6 History New Questions and Ideas
Case study questions class 6 history chapter 6 new questions and ideas.
CBSE Class 6 Case Study Questions History New Questions and Ideas. Important Case Study Questions for Class 6 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions New Questions and Ideas.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 6 History New Questions and Ideas
1.) What was the other name of Siddhartha as mentioned in (1)?
2.) Name the religion founded by Siddhartha as mentioned in (2)?
Ans. Mahajanpadas
The Buddha belonged to a small gana known as the (1) gana, and was a (2). When he was a young man, he left the comforts of his home in search of knowledge. He wandered for several years, meeting and holding discussions with other thinkers. He finally decided to find his own path to realisation, and meditated for days on end under a peepal tree at (3) in Bihar, where he attained enlightenment. After that, he was known as the Buddha or the Wise One. He then went to (4), near Varanasi, where he taught for the first time. He spent the rest of his life travelling on foot, going from place to place, teaching people, till he passed away at (5).
4.) Name the place where Buddha meditated for days also mentioned as (3) in the4 above para.
Ans. Buddha meditated for days under a peepal tree at Bodh Gaya in Bihar.
Ans. Buddha passed away at Kusinara.
1.) Fill in the blank marked (1).
5.) What was the language of the ordinary people?
Ans. Prakrit was the language of the ordinary people. Buddha taught in the same language.
Ans. Upanishads were part of the later vedic texts that recorded ideas of the thinkers of that time. Upanishad literally means ‘approaching and sitting near” and the texts contain conversation between teachers and students.
Ans. The four women thinkers are- Gargi, Apala, gosha and Maitreyi.
Ans. Vardhamana Mahavira
Ans. Vardhmana Mahavira taught a simple doctrine that men and women who wished to know the truth must leave their homes. And follow a very strict rule of ahimsa, which means not hurting or killing human beings.
1.) What were the followers of Mahavira known as?
Ans. The teachings of Mahavira are presently available at a place called Valabhi, in Gujarat.
Ans. Both Mahavira and Buddha felt that true knowledge can only be gained by people who left their homes. So they arranged an association for people who left their homes called sangha.
To begin with, both Jaina and Buddhist monks went from place to place throughout the year, teaching people. The only time they stayed in one place was during the (1), when it was very difficult to travel. Then, their supporters built temporary shelters for them in gardens, or they lived in natural caves in hilly areas. As time went on, many supporters of the bhikkhus and bhikkhunis, and they themselves, felt the need for more permanent shelters and so monasteries were built. These were known as (2). The earliest viharas were made of wood, and then of brick. Some were even in caves that were dug out in hills, especially in western India.
Ans. The supporters of the bhikkhus and the bhikkhunis felt the need for more permanent shelters and hence built monasteries.
1.) What was the new form of Buddhism called?
Ans. The bodhisattvas were the people who attained enlightenment. Once they attained enlightenment, they could live in complete isolation and meditate in peace.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, sikkim scert class 4 english chapter 5a the food we eat solution, ncert solutions class 6 math ganita prakash chapter 1 patterns in mathematics, ncert solutions class 6 social science chapter 1 locating places on the earth, the chair class 6 extra questions and answers.

Social Studies
Teacher's resources.

Test Generator

Assessment Sheets

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 Locating Places on the Earth
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 Locating Places on the Earth updated for academic session 2024-25. Class 6 Social Science Exploring Society – India and Beyond India Beyond Geography Chapter 1 solutions are given here in simplified format.
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 Locating Places Question Answers
- Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 Solutions
- Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 NCERT
- Class 6 Social Science all Chapter’s Answers
- Class 6 all Subject’s NCERT Solutions
Maps are like a treasure guide that helps us find places we want to visit. In this chapter, we learn about maps in detail. A map is a drawing of an area, whether it’s small like a village or large like the whole world. It shows us where things are and how to get there. Maps are usually viewed from the top, and they come in different types, such as physical maps that show natural features like mountains and rivers, political maps that show countries and cities, and thematic maps that provide specific information. Three key components of maps are distance, direction, and symbols, which help in understanding maps better.

Understanding Map Components: Distance, Direction, and Symbols When looking at a map, you might wonder how a large place can fit on a small piece of paper. This is possible because of the map’s scale, which represents the actual distance between two points. Directions on a map are indicated by arrows pointing north, south, east, and west, known as cardinal directions. There are also intermediate directions like northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest. Symbols are small drawings or signs used to represent different features on a map, such as buildings, roads, and rivers. These symbols make it easier to include a lot of details in a limited space.
Mapping the Earth is more complex because our planet is a sphere. A globe is a spherical representation of the Earth and gives a more accurate picture than a flat map. Globes can show the Earth’s geography and other celestial bodies. They help us understand how different places are connected. For instance, the North and South Poles are fixed points on a globe, and the Equator is an imaginary line that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Understanding these features on a globe helps us locate places more accurately.
Coordinates: Latitudes and Longitudes To locate any place on Earth, we use a system of coordinates, which includes latitudes and longitudes. Latitudes are imaginary lines that run parallel to the Equator and are measured in degrees from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the poles. Longitudes, on the other hand, run from the North Pole to the South Pole and are also measured in degrees, starting from 0° at the Prime Meridian. By using these two coordinates, we can pinpoint any location on Earth. For example, New York is located at 74°W longitude, while Delhi is at 77°E.
Longitude not only helps in locating places but also plays a crucial role in determining time. The Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each 15° apart, corresponding to one hour of time difference. The Prime Meridian at Greenwich is the reference point for calculating time across the world. As the Earth rotates from west to east, time increases as we move eastward and decreases as we move westward. Countries adopt standard time based on a meridian passing through them, like Indian Standard Time (IST), which is 5.5 hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
The International Date Line is an imaginary line located around 180° longitude, opposite the Prime Meridian. Crossing this line changes the date by one day; if you cross it eastward, you subtract a day, and if you cross it westward, you add a day. This line is not straight but zigzags to avoid dividing countries into different days. The concept of the International Date Line helps us understand how time and dates are coordinated globally, ensuring that the world functions smoothly despite the differences in local times.
The Grid System and its Applications The grid system of latitudes and longitudes allows us to locate any place on Earth with precision. Maps and globes are essential tools for understanding geography, time zones, and the Earth’s rotation. By learning about these concepts, students can better navigate the world and appreciate how interconnected different places are. Whether it’s determining the time in another country or finding a location on a map, the knowledge of latitudes, longitudes, and time zones is fundamental for exploring the Earth.

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

Case Study Based Questions: When People Rebel (1857 and After) | Social Studies (SST) Class 8 PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Case Study 1
Since the mid-eighteenth century, nawabs and rajas had seen their power erode. They had gradually lost their authority and honour. Residents had been stationed in many courts, the freedom of the rulers reduced, their armed forces disbanded, and their revenues and territories taken away by stages. Many ruling families tried to negotiate with the Company to protect their interests. For example, Rani Lakshmibai of Jhansi wanted the Company to recognise her adopted son as the heir to the kingdom after the death of her husband. Nana Saheb, the adopted son of Peshwa Baji Rao II, pleaded that he be given his father’s pension when the latter died. However, the Company, confident of its superiority and military powers, turned down these pleas. Awadh was one of the last territories to be annexed. In 1801, a subsidiary alliance was imposed on Awadh, and in 1856 it was taken over. Governor-General Dalhousie declared that the territory was being misgoverned and British rule was needed to ensure proper administration. The Company even began to plan how to bring the Mughal dynasty to an end. The name of the Mughal king was removed from the coins minted by the Company. In 1849, Governor-General Dalhousie announced that after the death of Bahadur Shah Zafar, the family of the king would be shifted out of the Red Fort and given another place in Delhi to reside in. In 1856, Governor-General Canning decided that Bahadur Shah Zafar would be the last Mughal king and after his death none of his descendants would be recognised as kings – they would just be called princes.
Question and Answer: 1 Mark
Q1: Who was the adopted son of Peshwa Baji Rao II? Ans: Nana Saheb, the adopted son of Peshwa Baji Rao II.
Q2: Who decided that Bahadur Shah Zafar would be the last Mughal King? Ans: In 1856, Governor-General Canning decided that Bahadur Shah Zafar would be the last Mughal king.
Question and Answer: 2 Mark
Q1: In 1849, what did Governor-general Dalhousi announce? Ans: In 1849, Governor-General Dalhousie announced that after the death of Bahadur Shah Zafar, the family of the king would be shifted out of the Red Fort and given another place in Delhi to reside in.
Q2: What did Rani Lakshmibai of Jhansi want? Ans: Rani Lakshmibai of Jhansi wanted the Company to recognise her adopted son as the heir to the kingdom after the death of her husband.
Case Study 2
In the countryside, peasants and zamindars resented the high taxes and the rigid methods of revenue collection. Many failed to pay back their loans to the moneylenders and gradually lost the lands they had tilled for generations. The Indian sepoys in the employ of the Company also had reasons for discontent. They were unhappy about their pay, allowances and conditions of service. Some of the new rules, moreover, violated their religious sensibilities and beliefs. Did you know that in those days many people in the country believed that if they crossed the sea they would lose their religion and caste?
So when in 1824, the sepoys were told to go to Burma by the sea route to fight for the Company, they refused to follow the order, though they agreed to go by the land route. They were severely punished, and since the issue did not die down, in 1856 the Company passed a new law which stated that every new person who took up employment in the Company’s army had to agree to serve overseas if required. Sepoys also reacted to what was happening in the countryside. Many of them were peasants and had families living in the villages. So the anger of the peasants quickly spread among the sepoys.
Another account we have from those days are the memoirs of Subedar Sitaram Pande. Sitaram Pande was recruited in 1812 as a sepoy in the Bengal Native Army. He served the English for 48 years and retired in 1860. He helped the British to suppress the rebellion though his own son was a rebel and was killed by the British in front of his eyes.
On retirement he was persuaded by his Commanding Officer, Norgate, to write his memoirs. He completed the writing in 1861 in Awadhi and Norgate translated it into English and had it published under the title From Sepoy to Subedar.
Here is an excerpt from what Sitaram Pande wrote:
It is my humble opinion that this seizing of Oudh filled the minds of the
Sepoys with distrust and led them to plot against the Government.
Agents of the Nawab of Oudh and also of the King of Delhi were sent all over India to discover the temper of the army. They worked upon the feelings of sepoys, telling them how treacherously the foreigners had behaved towards their king. They invented ten thousand lies and promises to persuade the soldiers to mutiny and turn against their masters, the English, with the object of restoring the Emperor of Delhi to the throne. They maintained that this was wholly within the army’s powers if the soldiers would only act together and do as they were advised.On the evening of 3 July 1857, over 3,000 rebels came from Bareilly, crossed the river Jamuna, entered Delhi, and attacked the British cavalry posts. The battle continued all through the night.
Q1: When the sepoys were told to go to Burma? Ans: In 1824, the sepoys were told to go to Burma.
Q2: When did the company pass a new law for the employees? Ans: In 1856 the Company passed a new law for the employees.
Q1: When Sitaram Pande was recruited? And for how many years did he serve? Ans: Sitaram Pande was recruited in 1812 as a sepoy in the Bengal Native Army. He served the English for 48 years.
Q2: What happened on the evening of 3rd July,1857? Ans: On the evening of 3 July 1857, over 3,000 rebels came from Bareilly, crossed the river Jamuna, entered Delhi, and attacked the British cavalry posts. The battle continued all through the night.
Case Study 3
On 8 April 1857, a young soldier, Mangal Pandey, was hanged to death for attacking his officers in Barrackpore. Some days later, some sepoys of the regiment at Meerut refused to do the army drill using the new cartridges, which were suspected of being coated with the fat of cows and pigs. Eighty-five sepoys were dismissed from service and sentenced to ten years in jail for disobeying their officers. This happened on 9 May 1857. The response of the other Indian soldiers in Meerut was quite extraordinary. On 10 May, the soldiers marched to the jail in Meerut and released the imprisoned sepoys. They attacked and killed British officers. They captured guns and ammunition and set fire to the buildings and properties of the British and declared war on the firangis. The soldiers were determined to bring an end to their rule in the country. But who would rule the land instead? The soldiers had an answer to this question – the Mughal emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar. Unnerved by the scale of the upheaval, the Company decided to repress the revolt with all its might. It brought reinforcements from England, passed new laws so that the rebels could be convicted with ease, and then moved into the storm centres of the revolt. Delhi was recaptured from the rebel forces in September 1857. The last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar was tried in court and sentenced to life imprisonment. He and his wife Begum Zinat Mahal were sent to prison in Rangoon in October 1858. Bahadur Shah Zafar died in the Rangoon jail in November 1862. The recapture of Delhi, however, did not mean that the rebellion died down after that. People continued to resist and battle the British. The British had to fight for two years to suppress the massive forces of popular rebellion. Lucknow was taken in March 1858. Rani Lakshmibai was defeated and killed in June 1858. A similar fate awaited Rani Avantibai, who after initial victory in Kheri, chose to embrace death when surrounded by the British on all sides. Tantia Tope escaped to the jungles of central India and continued to fight a guerrilla war with the support of many tribal and peasant leaders. He was captured, tried and killed in April 1859. Just as victories against the British had earlier encouraged rebellion, the defeat of rebel forces encouraged desertions. The British also tried their best to win back the loyalty of the people. They announced rewards for loyal landholders would be allowed to continue to enjoy traditional rights over their lands. Those who had rebelled were told that if they submitted to the British, and if they had not killed any white people, they would remain safe and their rights and claims to land would not be denied. Nevertheless, hundreds of sepoys, rebels, nawabs and rajas were tried and hanged.
Q1: When Mangal Pandey was hanged to death? Ans: On 8 April 1857, a young soldier, Mangal Pandey, was hanged to death.
Q2: What is the meaning of ‘Firangis’? Ans: The meaning of ‘Firangis’ is Foreigners. The term reflects an attitude of contempt.
Q1: Who was the last Mughal emperor? And when did he die? Ans: Bahadur Shah Zafar was the last Mughal emperor. Bahadur Shah Zafar died in the Rangoon jail in November 1862.
Q2: Where did Tantia Tope escape? And when was he captured? Ans: Tantia Tope escaped to the jungles of central India and continued to fight a guerrilla war with the support of many tribal and peasant leaders. He was captured, tried and killed in April 1859.
Case Study 4
The way in which people are spread across the earth surface is known as the pattern of population distribution. More than 90 per cent of the world’s population lives in about 30 per cent of the land surface. The distribution of population in the world is extremely uneven. Some areas are very crowded and some are sparely populated. The crowded areas are south and south east Asia, Europe and north eastern North America. Very few people live in high latitude areas, tropical deserts, high mountains and areas of equatorial forests. Many more people live north of the Equator than south of the Equator. Almost three-quarters of the world’s people live in two continents Asia and Africa.
Q1: What does “population distribution” mean, and why is it viewed as being uneven globally? Ans: Distribution of people across the Earth’s surface is commonly referred as “Population”. It is uneven because more than 90% of the world’s population occupies approximately 30% of its land surface, resulting in densely populated areas in some areas and sparsely populated areas in others.
Q2: Describe the most densely populated areas of the world and state some factors which contribute to this density.`1 Ans: South and Southeast Asia, Europe, and northeastern North America are among the continents with the densest populations. People are drawn to settle in these areas because of things like rich agricultural lands, easy access to resources, developed infrastructure, and urbanisation, which results in high population densities.
Q3: Why are some places with low population density, like high latitude areas and tropical deserts? Ans: Due to harsh environmental conditions, restricted resource availability, and difficulties in agriculture and human habitation, high latitude regions and tropical deserts have low population densities. In these areas, large human settlements are discouraged by the harsh climates and inadequate infrastructure.
Q4: State the role of equator in determining the residence of people on earth. Ans: The Equator influences population distribution because there are significantly more people living north of the Equator than south of it. This has occurred as a result of historical and geographic circumstances such as the existence of significant civilizations and favourable climatic conditions for settlement in the northern hemisphere.
Q5: How can addressing demographic issues and making plans for sustainable development be made easier with an understanding of the population distribution pattern? Ans: Planning for sustainable development and addressing demographic issues require an understanding of the population distribution pattern. It aids in the efficient resource allocation, infrastructure design, and implementation of policies to control population growth, ensure equitable regional development, and address issues with overcrowding and underdevelopment.
Case Study 5
Topography: People always prefer to live on plains rather than mountains and plateaus because these areas are suitable for farming, manufacturing and service activities. The Ganga plains are the most densely populated areas of the world while mountains like Andes, Alps and Himalayas are sparsely populated. Climate: People usually avoid extreme climates that are very hot or very cold like Sahara desert, polar regions of Russia, Canada and Antarctica. Soil: Fertile soils provide suitable land for agriculture. Fertile plains such as Ganga and Brahmaputra in India, Hwang-He, Chang Jiang in China and the Nile in Egypt are densely populated.
Q1: Why do people favour plains over mountains and plateaus for settlement, and how does this preference affect population distribution? Ans: Because they are good for farming, manufacturing, and service industries, people prefer to live on plains.Because of their fertile and ideal agricultural conditions, the Ganga plains are likely to have the world’s densest population. Mountains, on the other hand, have a low population density due to their difficult terrain and limited agricultural potential. These regions include the Andes, Alps, and Himalayas.
Q2: How does climate influence where people live, and why do people avoid harsh climates? Ans: People typically steer clear of extreme climates because of the difficulties they present for habitation and agricultural endeavours, such as the Sahara Desert, the polar regions of Russia, Canada, and Antarctica. Climates that are comfortable and moderate are better for settling and population growth.
Q3: Describe how fertile soil affects population distribution and give instances of densely populated regions with fertile plains. Ans: Agriculture, which is essential for human settlements, is supported by fertile soils. Due to their rich agricultural potential and historical significance, regions like the Nile in Egypt, the Ganga and Brahmaputra plains in India, Hwang-He and Chang Jiang in China, and the Ganga and Brahmaputra plains in India are populated densely.
Q4: What effects do geographical elements like topography and climate have on the economic activity and development prospects of various regions? Ans: The types of economic activities that can be pursued in various regions are influenced by geographic factors like topography and climate. Plains are ideal for farming, manufacturing, and services, which promotes economic growth and higher population densities. Economic opportunities and population density are restricted by harsh climates and challenging mountainous and plateau terrain.
Q5: What are the effects of population distribution patterns on resource management, infrastructure building, and urbanisation?
Ans: Population distribution patterns have significant implications for urbanisation, infrastructure development, and resource management. People’s concentration in densely populated areas necessitates well-planned cities and adequate infrastructure to meet the needs of the population. Sparsely populated areas, on the other hand, may face resource utilisation and development challenges due to limited demand and economic activity.
Case Study 6
In 1804, the world’s population reached one billion. A hundred and fifty five years later, in 1959, the world’s population reached 3 billion. This is often called population explosion. In 1999, 40 years later, the population doubled to 6 billion. The main reason for this growth was that with better food supplies and medicine, deaths were reducing, while the number of births still remained fairly high. Births are usually measured using the birth rate i.e. the number of live births per 1,000 people. Deaths are usually measured using the death rate i.e. the number of deaths per 1,000 people. Migrations is the movement of people in and out of an area.
Q1: State the concept of “population explosion” and what are some of the primary factors causing this rapid population growth? Ans: The rapid and significant increase world’s population is often termed as “population explosion”. The primary reasons of this expansion were improvements in food supplies and medicine, which resulted in lower death rates while birth rates remained relatively high.
Q2: Describe the peak in population growth, such as when the world’s population reached one billion, three billion, and six billion. Ans: In 1804, the world’s population was one billion, three billion in 1959, and six billion in 1999. These landmarks demonstrate the global population’s exponential growth over time.
Q3: Describe the factors which influence population change ,except natural growth? Ans: Aside from natural growth (births minus deaths), migration, or the movement of people into and out of an area, is another factor influencing population changes.
Q4: How have medical advances and improved food supplies affected population growth, and what challenges do countries face as a result of population growth? Ans: Population growth has been facilitated by improvements in food availability and medical technology. Population growth can, however, put a strain on infrastructure and resources and present difficulties in providing for a growing population’s needs, such as food, housing, and employment, which countries must address for long-term development.
Case Study 7
Migration is another way by which population size changes. People may move within a country or between countries. Emigrants are people who leave a country; Immigrants are those who arrive in a country. Countries like the United States of America and Australia have gained in-numbers by in-migration or immigration. Sudan is an example of a country that has experienced a loss in population numbers due to out-migration or emigration. The general trend of international migrations is from the less developed nations to the more developed nations in search of better employment opportunities. Within countries large number of people may move from the rural to urban areas in search of employment, education and health facilities.
Q1: Define migration and explain it’s affect on population size both within and between countries. Ans: Migration is the act through which individuals move from one area to another, either within the boundaries of a nation (internal migration) or between countries (international migration). This relocation of people influences the size of populations which eventually causes population growth in the countries of arrival (immigration) and therefore leading population decline in the countries of departure (emigration).
Q2: Give some examples of countries which experienced a rapid increase in population due to immigration and countries which experienced population decline due to emigration. Ans: Countries including the United States of America and Australia faced major growth in population through immigration, attracting people from all over the world. Whereas, a country like Sudan is an example of a population decline as people emigrate to other countries in search of better opportunities.
Q3: State some of the difficulties and advantages of migration ? Ans: Migration can pose difficulties for sending countries, such as labour shortages and the loss of skilled workers. At the same time, receiving countries may face issues with integration, cultural diversity, and social cohesion. However, migration has advantages such as a diverse workforce, cultural enrichment, and potential economic contributions to both sending and receiving countries.
| |424 docs|48 tests |
Top Courses for Class 8
| Last updated |
mock tests for examination
Video lectures, semester notes, past year papers, study material, case study based questions: when people rebel (1857 and after) | social studies (sst) class 8, practice quizzes, shortcuts and tricks, objective type questions, previous year questions with solutions, sample paper, important questions, viva questions, extra questions.

Case Study Based Questions: When People Rebel (1857 and After) Free PDF Download
Importance of case study based questions: when people rebel (1857 and after), case study based questions: when people rebel (1857 and after) notes, case study based questions: when people rebel (1857 and after) class 8, study case study based questions: when people rebel (1857 and after) on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.

COMMENTS
What is Case Study Question in Class 6 Social Science? Case study questions typically present a specific scenario or case related to a historical event, geographical issue, or social problem. Students are expected to read and understand the details of the case and then answer a set of questions based on their understanding and knowledge of the ...
CBSE 6th Standard CBSE Social Science English medium question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 6th Standard CBSE Social Science books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one ...
Answer- Himalayas. 4.) Manuscripts deal in what kind of subjects. Answer- manuscripts deal with all kinds of subjects: religious beliefs and practices, the lives of kings, medicine and science. Case 5: There were many other things that were made and used in the past. Those who study these objects are called (1).
What is Case Study Question in Class 6 Social Science? Case study questions typically present a specific scenario or case related to a historical event, geographical issue, or social problem. Students are expected to read and understand the details of the case and then answer a set of questions based on their understanding and knowledge of the ...
Document Description: Case Based Questions: New Questions and Ideas for Class 6 2024 is part of Social Studies (SST) Class 6 preparation. The notes and questions for Case Based Questions: New Questions and Ideas have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about Case Based Questions: New Questions and Ideas covers topics like Case 1: The Life of Buddha, Case 2 ...
Document Description: Case Based Questions: In the Earliest Cities for Class 6 2024 is part of Social Studies (SST) Class 6 preparation. The notes and questions for Case Based Questions: In the Earliest Cities have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about Case Based Questions: In the Earliest Cities covers topics like Case 1: The Discovery of Harappa, Case 2 ...
Ans: Striving for equality in the workplace and society is essential to reduce discrimination and promote fairness. The document Class 6 Civics Chapter 2 Case Based Questions - Diversity and Discrimination is a part of the Class 6 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 6 . All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6.
Here you will find Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 6 Social Science Series. What, Where, How and When Class 6 Case Study CBSE History Chapter 1 (PDF Download) Case Study Questions. Question 1:
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science Chapter 14 Economic Activities Around Us for session 2024-25 based on National Education Policy 2020. ... India and Beyond India Beyond Economics Section Question answers of exercises according to new education policy 2020. ... Case Study: AMUL Dairy Cooperative ...
Download Class 6 Social Science Important Questions with Answers PDF 2024. Get the PDF version of these important questions and complete your study material. Take your preparation to the next level and focus on how you can increase your answering skills. Find out how the experts have used the concepts of the chapters to answer such questions ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 6 Civics Understanding Diversity. Case 1. Ladakh is a desert in the mountains in the east of Jammu and Kashmir.The goats in this region are special because they produce pashmina wool.Being a desert did not mean that Ladakh did not attract its share of traders. It was considered a good trade route as it had many ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography : The Earth: Our Habitat. Chapter 1 The Earth in the Solar System. Chapter 2 Globe Latitudes and Longitudes. Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth. Chapter 4 Maps. Chapter 5 Major Domains of the Earth. Chapter 6 Major Landforms of the Earth. Chapter 7 Our Country India.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science includes all the questions provided in the NCERT textbooks, prescribed as per the latest 2023-24 curriculum. The study material provides easy access to subject-wise solutions so that students can easily prepare for the exams.
In the Earliest Cities Class 6 Social Science Case Study Questions. Case Study Question 1: Let us look at some of the objects that were made and found in Harappan cities. Most of the things that have been found by archaeologists are made of stone, shell and metal, including copper, bronze, gold and silver. Copper and bronze were used to make ...
Document Description: Case Based Questions: Kingdoms, Kings and an Early Republic for Class 6 2024 is part of Social Studies (SST) Class 6 preparation. The notes and questions for Case Based Questions: Kingdoms, Kings and an Early Republic have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about Case Based Questions: Kingdoms, Kings and an Early Republic covers topics like ...
There are a total of 36 questions in the CBSE Class 6 Social Science Sample Paper-1 with Solutions (2024-25). You will get short answer type questions as well as long answer type questions in this sample paper. Most of the answers are written in a point-wise manner so that you can easily learn and understand them.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Maths, Science, Social Science for Class Class 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11 and 12 by Experienced Subject Teachers. 100% FREE Exercise & Practice for CBSE, NCERT and ICSE. Book Solutions. RS AGGARWAL MATH SOLUTION; ... Social Science. CBSE Case Study Questions: ...
Table of Content. 1. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Question Answers - FREE PDF Download. 2. NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science Chapter-wise Book Links - Download the FREE PDF. 3. Glance on NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science. 4. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science: Concepts and Chapter-Wise Links.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 6 History New Questions and Ideas. Case study 1. Siddhartha, also known as (1), the founder of (2) was born about 2500 years ago. This was a time of rapid change in the lives of people. Some kings in the _____ were growing more powerful. New cities were developing, and life was changing in the villages as well.
Class 6. CBSE Social Studies Teacher's Resources. E-book. Test Generator. Maps. Assessment Sheets. Worksheets. Answer Key ...
Introduction of Case Based Questions: What is Government? in English is available as part of our Social Studies (SST) Class 6 for Class 6 & Case Based Questions: What is Government? in Hindi for Social Studies (SST) Class 6 course. Download more important topics related with notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 6 Exam by signing up for free. . Class 6: Class 6 Civics Chapter 3 Case ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History- Chapter-Wise. Chapter-1 What Where How and When. Chapter-2 On the Trail of the Earliest People. Chapter-3 From Hunting Gathering to Growing Food. Chapter-4 In the Earliest Cities. Chapter-5 What Books and Burials Tell Us.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies; NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Sociology; ... Class 6 Social Science Exploring Society - India and Beyond India Beyond Geography Chapter 1 solutions are given here in simplified format. ... Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 Locating Places Question Answers. Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 Solutions;
Document Description: Case Based Questions: From Hunting-Gathering to Growing Food for Class 6 2024 is part of Social Studies (SST) Class 6 preparation. The notes and questions for Case Based Questions: From Hunting-Gathering to Growing Food have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about Case Based Questions: From Hunting-Gathering to Growing Food covers topics ...
Introduction of Case Study Based Questions: When People Rebel (1857 and After) in English is available as part of our Social Studies (SST) Class 8 for Class 8 & Case Study Based Questions: When People Rebel (1857 and After) in Hindi for Social Studies (SST) Class 8 course. Download more important topics related with notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 8 Exam by signing up for free.