Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Acids, Bases and Salts
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 2 acids, bases and salts.
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Acids, Bases and Salts. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Acids, Bases and Salts.

CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Acids, Bases and Salts
Case study : 1.
Based on the above paragraph answer the following questions:
Ans: It is a non- metallic oxide as carbon belongs to non- metals group i.e P – Block elements group 6.
Ans: Mg(OH)2 < Ca(OH)2 < NaOH.
CASE STUDY : 2
Following the above paragraph, answer the following questions;
iv) Does rain water or distilled water will conduct electricity?
Ans: Rain water will conduct electricity as it contains both positive and negative ions of different salts in it.
CASE STUDY : 3
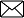
On heating gypsum at 373 K, it loses water molecules and becomes calcium sulphate hemihydrate ( CaSO 4 .½ H 2 O ). This is called Plaster of Paris.Plaster of Paris is a white powder and on mixing with water, it changes to gypsum once again giving a hard solid mass.
i) What is the molecular formula of gypsum?
v) What does this 2 denotes in CaSO4. 2 H2O?
Ans: 2 denotes the two water molecules as water of crystallisation.
CASE STUDY : 4
iv) Where does the sodium hydroxide solution is formed?
artificial fibres
CASE STUDY : 5 (Acids Bases and Salts)
i.e neutral salt is formed.
CASE STUDY : 6
Answer the following on the basis of above paragraph:
iii) What are the important of pH in everyday life?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, west bengal board class 6 math solution, west bengal board class 6 maths chapter 14 solutions রেখা, রেখাংশ, রশ্মি ও বিন্দু বিষয়ক বিস্তৃত ধারণা, ncert class 7 mathematics third chapter data handling exercise 3.1 3.2 3.3 solutions, assam scert class 8 history and political science chapter 1 solutions.

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Study Questions Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Re a son . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1:
A compound, X of sodium forms a white powder. It is a constituent of baking powder and is used in some antacids. When heated it gives a compound, Y which is anhydrous and absorbs water to become a hydrated salt. When this salt is kept in the open air, it loses water molecules in a process called efflorescence. When dissolved in water it forms a strong base and a weak acid, Z.
(i) What is the compound, X?
| CO |
Answer: (c) NaOH.
(ii) The compound, Y is
| CO | CO .10H O |
Answer: (c) Na2CO3.10H2O
(iii) What is the nature of the solution formed by dissolving Y in water?
Answer: (a) Alkaline
(iv) Identify the compound, Z.
| CO | O |
Answer: (b) H2CO3
(v) Sodium carbonate is a basic compound because it is a salt of a
Answer: (c) strong acid and weak base
Case Study 2:
pH is quite useful to us in a number of ways in daily life. Some of its applications are:
Control of pH of the soil : Plants need a specific pH range for proper growth. The soil may be acidic, basic, or neutral depending upon the relative concentration of H* and OH-. The pH of any soil can be determined by using pH paper. If the soil is too acidic, it can be corrected by adding lime to it. If the soil is too basic, it can be corrected by adding organic manure which contains acidic materials.
Regaining shine of a tarnished copper vessel by use of acids : A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lenion on the vessel, the surface is cleaned and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that copper oxide is basic in nature, which reacts with the acid (citric acid) present in lemon to form a salt (copper citrate) which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
Self-defence by animals through chemical warfare : Stings of bees and ants contain methanoic acid. When stung, it causes lot of pain and irritation. This can be cured by rubbing the affected area with mild base like baking soda.
(i) When black copper oxide placed in a beaker is treated with dilute HCl, its color changes to ( a) white (b) dark red (c) bluish-green (d) no change.
Answer: (c) bluish green
(ii) P is an aqueous solution of acid and Q is an aqueous solution of base. When these two are diluted separately, then (a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralization.
(b) pH of P decreases while that of Q increases till neutralization. (C) pH of both P and Q decrease. (d) pH of both P and Q increase.
Answer: (a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralisation.
(iii) Which of the following acids is present in bee sting? (a) Formic acid (b) Acetic acid (c) Citric acid (d) Hydrochloric acid
Answer: (c) Citric acid
(iv) Sting of ant can be cured by rubbing the affected area with soap because (a) it contains oxalic acid which neutralises the effect of formic acid (b) it contains aluminium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (d) none of these
Answer: (c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid
(v) The pH of soil X is 7.5 while that of soil Y is 4.5. Which of the two soils, should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH? (a) X only (b) Y only (c) Both X and Y (d) none of these
Answer: (b) Y only
Case Study 3: Acids, bases, and salts are essential substances in our daily lives and play crucial roles in various chemical reactions and processes. Acids are sour-tasting substances that can donate hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. They turn blue litmus paper red and have a pH value less than 7. Bases, on the other hand, are bitter-tasting substances that can accept hydrogen ions or donate hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water. They turn red litmus paper blue and have a pH value greater than 7. Salts are formed when acids react with bases, resulting in the neutralization process. They are formed by the combination of positive ions (cations) from bases and negative ions (anions) from acids. Understanding the properties and uses of acids, bases, and salts is important in various applications, such as in the preparation of medicines, household cleaning agents, and agricultural practices.
What are acids? a) Substances that can donate hydrogen ions when dissolved in water b) Substances that can accept hydrogen ions when dissolved in water c) Substances that turn blue litmus paper red d) Substances with a pH value less than 7 Answer: a) Substances that can donate hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
How are bases characterized? a) Sour-tasting substances b) Substances that can donate hydrogen ions c) Substances that turn red litmus paper blue d) Substances with a pH value less than 7 Answer: c) Substances that turn red litmus paper blue
What are salts formed from? a) Acids and bases b) Acids and metals c) Bases and metals d) Bases and water Answer: a) Acids and bases
What is the pH value of acids? a) Less than 7 b) Equal to 7 c) Greater than 7 d) Variable Answer: a) Less than 7
In which applications are acids, bases, and salts commonly used? a) Preparation of medicines b) Household cleaning agents c) Agricultural practices d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like

Class 10 Maths Surface Areas and Volumes Handwritten Notes by Toppers – Download PDF
Assertion reason questions class 10 science chapter 3 metals and non-metals, mcq class 10 social science history print culture and the modern world questions with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Case Based Questions - Acids, Bases and Salts
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Case Study - 1
A scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, called pH scale has been developed. The p in pH stands for ‘potenz’ in German, meaning power. On the pH scale we can measure pH generally from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very alkaline). pH should be thought of simply as a number which indicates the acidic or basic nature of a solution. Higher the hydronium ion concentration, lower is the pH value.
Answer the following on the basis of above paragraph: Q1: What does the scale represent when pH value increases from 7 to 14? Ans: It represents an increase in OH- ions concentration in the solution i.e. the increment in the strength of alkali. Q2: What is the pH value of milk of magnesia? Ans: It is 10. Q3: What are the important of pH in everyday life? Ans: We human beings, plants and animals all are sensitive to pH i.e. their body work on normal pH such as plants grow between the pH range of 6 to 8. Our human body work within the pH range of 7 to 7.8. Q4: What happens when the pH of mouth is lower than 5.5? Ans: Tooth decay starts in which the enamel gets corroded due to the much production of acids in mouth by bacteria. Q5: Two solutions X&Y. The pH of X is 4 and the pH of Y is 7. What is the nature of two solution? Ans: Solution X is acidic in nature and the solution Y is neutral in nature.
Case Study - 2
Salts of a strong acid and a strong base are neutral with pH value of 7. On the other hand, salts of a strong acid and weak base are acidic with pH value less than 7 and those of a strong base and weak acid are basic in nature, with pH value more than 7.
Answer the following in reference to the above paragraph: Q1: Classify the following as strong bases and weak bases: KOH, NaOH, CsOH, NH4OH Ans: Strong bases: KOH, NaOH, CsOH Weak base: NH 4 OH Q2: Write a reaction of a strong acid and a weak base? Ans: HCl(aq) + NH 4 OH(aq) → NH 4 Cl(aq) + H 2 O(aq) Q3: What happens when strong acids and bases react to each other? Explain by giving example. Ans: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H 2 O i.e. neutral salt is formed. Q4: Identify the following as strong acid: CH 3 COOH, H 2 SO 4 , HNO 3 , H 3 PO 4 , H 2 CO 3 , HCl. Ans: Strong acid: HCl, HNO 3 , H 2 SO 4 . Q5: Classify the following acis as strong or weak acid: acetic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid, oxalic acid. Ans: All are weak acid present in fruits and vegetables.
Case Study - 3
Sodium hydroxide When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (called brine), it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. The process is called the chlor-alkali process because of the products formed– chlor for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide.
Based on the above given information, answer the following questions: Q1: Write the chemical equation involved in this process? Ans: 2NaCl (aq)+ 2H 2 O(l) → 2 NaOH(aq) + Cl 2 (g) + H 2 (g) Q2: What are the substance that are formed at anode and cathode on chlor- alkali process? Ans: At anode Chlorine gas & at cathode hydrogen gas are formed. Q3: What are the uses of chlorine? Ans:
- Used for water treatment
- Disinfectants
- pesticides.
Q4: Where does the sodium hydroxide solution is formed? Ans: It is formed near the cathode. Q5: What are the uses of Sodium hydroxide? Ans:
- uses in making soaps and detergents
- artificial fibres
- paper making
Case Study - 4
Plaster of Paris On heating gypsum at 373 K, it loses water molecules and becomes calcium sulphate hemihydrate ( CaSO 4 .½ H 2 O ). This is called Plaster of Paris. Plaster of Paris is a white powder and on mixing with water, it changes to gypsum once again giving a hard solid mass. Water of crystallisation is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt. Five water molecules are present in one formula unit of copper sulphate. Chemical formula for hydrated copper sulphate is Cu SO 4 . 5H 2 O. Now you would be able to answer the question whether the molecule of Na2CO3 .10H2O is wet.
Answer the following questions on the basis of the above paragraph: Q1: What is the molecular formula of gypsum? Ans: CaSO 4 . 2H 2 O Q2: Write the equation of formation of plaster of paris by heating gypsum? Ans: CaSO 4 . 2H 2 O + heat ⇒ CaSO 4 . 1/2 H 2 O + 1^1/2 H 2 O Q3: What are the uses of Plaster of Paris? Ans: It is used by doctor for supporting of fractured bones, to make toys etc. Q4: Give the equation when POP is mixed with water? Ans: CaSO4. 1/2H2O + 1^1/2 H2O ⇒ CaSO4. 2H2O Q5: What does this 2 denotes in CaSO 4 . 2 H 2 O? Ans: 2 denotes the two water molecules as water of crystallisation.
Case Study - 5
Take solutions of glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, etc. n Fix two nails on a cork, and place the cork in a 100 mL beaker. Connect the nails to the two terminals of a 6 volt battery through a bulb and a switch, as shown in. Now pour some dilute HCl in the beaker and switch on the current. Repeat with dilute sulphuric acid. What do you observe? Repeat the experiment separately with glucose and alcohol solutions. What do you observe now? Does the bulb glow in all cases?
Following the above paragraph, answer the following questions; Q1: What was the changes occur in case of acids i.e HCl, H2SO4? Ans: The bulbs will start glowing as it contains hydrogen ions H+ ions (aq) as cation and Cl- or SO4^2- as anion. Q2: Why do glucose and alcohol do not conduct electricity? Ans: They do not contains free ions neither cation nor anion. To conduct electricity, free ions are required. Q3: Why do acids do not show acidic behaviour in absence of water? Ans: Acidic behaviour are shown by releasing of H+ ions from acids. To dissociate into H+ ions, the acids need medium i.e water. Q4: Does rain water or distilled water will conduct electricity? Ans: Rain water will conduct electricity as it contains both positive and negative ions of different salts in it. Q5: Why do aqueous solution of acids conduct electricity? Ans: The acid contains Hydrogen ions in solutions as well as anions. Due to the presence of free ions they conduct electricity.
Case Study - 6
The reaction between carbon dioxide and calcium hydroxide (lime water), Calcium hydroxide, which is a base, reacts with carbon dioxide to produce a salt and water. Since this is similar to the reaction between a base and an acid, we can conclude that nonmetallic oxides are acidic in nature.
Based on the above paragraph answer the following questions: Q1: What is the nature of Carbon dioxide? Ans: It is a non- metallic oxide as carbon belongs to non- metals group i.e P – Block elements group 6. Q2: Give another reaction of non- metallic oxide and a base? Ans: CO 2 (g) + 2NaOH(aq)→ Na 2 CO 3 (aq) + H 2 O(aq) Q3: Arrange the following bases in increasing order: NaOH, Ca(OH) 2 & Mg(OH) 2 . Ans: Mg(OH) 2 < Ca(OH) 2 < NaOH. Q4: Write the complete reaction between calcium hydroxide and carbon dioxide with physical states? Ans: Ca(OH) 2 (aq) + CO 2 (g) → CaCO 3 (s) + H 2 O(l) Q5: What is the nature of non- metallic oxide? Ans: The non- metallic oxide are acidic in nature because when they dissolved in water, they form acidic substance turning blue litmus into red.
Top Courses for Class 10
| Rating | |
mock tests for examination
Viva questions, objective type questions, important questions, semester notes, class 10 science chapter 2 case based questions - acids, bases and salts, sample paper, practice quizzes, video lectures, shortcuts and tricks, previous year questions with solutions, extra questions, past year papers, study material.

Case Based Questions: Acids, Bases and Salts Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: acids, bases and salts, case based questions: acids, bases and salts notes, case based questions: acids, bases and salts class 10, study case based questions: acids, bases and salts on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study Questions, by practicing this Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
A compound, X of sodium forms a white powder. It is a constituent of baking powder and is used in some antacids. When heated it gives a compound, Y which is anhydrous and absorbs water to become a hydrated salt. When this salt is kept in the open air, it loses water molecules in a process called efflorescence. When dissolved in water it forms a strong base and a weak acid, Z.
(i) What is the compound, X?
| CO |
Answer: (c) NaOH.
(ii) The compound, Y is
| CO | CO .10H O |
Answer: (c) Na2CO3.10H2O
(iii) What is the nature of the solution formed by dissolving Y in water?
Answer: (a) Alkaline
(iv) Identify the compound, Z.
| CO | O |
Answer: (b) H2CO3
(v) Sodium carbonate is a basic compound because it is a salt of a
Answer: (c) strong acid and weak base
Question 2:
pH is quite useful to us in a number of ways in daily life. Some of its applications are:
Control of pH of the soil : Plants need a specific pH range for proper growth. The soil may be acidic, basic, or neutral depending upon the relative concentration of H* and OH-. The pH of any soil can be determined by using pH paper. If the soil is too acidic, it can be corrected by adding lime to it. If the soil is too basic, it can be corrected by adding organic manure which contains acidic materials.
Regaining shine of a tarnished copper vessel by use of acids : A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lenion on the vessel, the surface is cleaned and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that copper oxide is basic in nature, which reacts with the acid (citric acid) present in lemon to form a salt (copper citrate) which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
Self-defence by animals through chemical warfare : Stings of bees and ants contain methanoic acid. When stung, it causes lot of pain and irritation. This can be cured by rubbing the affected area with mild base like baking soda.
(i) When black copper oxide placed in a beaker is treated with dilute HCl, its color changes to ( a) white (b) dark red (c) bluish-green (d) no change.
Answer: (c) bluish green
(ii) P is an aqueous solution of acid and Q is an aqueous solution of base. When these two are diluted separately, then (a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralization.
(b) pH of P decreases while that of Q increases till neutralization. (C) pH of both P and Q decrease. (d) pH of both P and Q increase.
Answer: (a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralisation.
(iii) Which of the following acids is present in bee sting? (a) Formic acid (b) Acetic acid (c) Citric acid (d) Hydrochloric acid
Answer: (c) Citric acid
(iv) Sting of ant can be cured by rubbing the affected area with soap because (a) it contains oxalic acid which neutralises the effect of formic acid (b) it contains aluminium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (d) none of these
Answer: (c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid
(v) The pH of soil X is 7.5 while that of soil Y is 4.5. Which of the two soils, should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH? (a) X only (b) Y only (c) Both X and Y (d) none of these
Answer: (b) Y only
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 2 Acids Bases Salts
Please refer to Chapter 2 Acids Bases Salts Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Acids Bases Salts
Case/Passage – 1 Marble’s popularity began in ancient Rome and Greece, where white and off-white marble were used to construct a variety of structures, from hand-held sculptures to massive pillars and buildings.

Question: A student added 10g of calcium carbonate in a rigid container, secured it tightly and started to heat it. After some time, an increase in pressure was observed, the pressure reading was then noted at intervals of 5 mins and plotted against time, in a graph as shown below. During which time interval did maximum decomposition took place?

(a) 15-20 min (b) 10-15 min (c) 5-10 min (d) 0-5 min
Question: Marble statues are corroded or stained when they repeatedly come into contact with polluted rain water.Identify the main reason.

(a) decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide (b) polluted water is basic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate (c) polluted water is acidic in nature hence it reacts with calciumcarbonate (d) calcium carbonate dissolves in water to give calcium hydroxide.
Question: Gas A, obtained above is a reactant for a very important biochemical process which occurs in the presence of sunlight. Identify the name of the process – (a) Respiration (b) Photosynthesis (c) Transpiration (d) Photolysis and buildings.
Question: The substance not likely to contain CaCO 3 is (a) Dolomite (b) A marble statue (c) Calcined gypsum (d) Sea shells.
Question: Calcium oxide can be reduced to calcium, by heating with sodium metal. Which compound would act as an oxidizing agent in the above process? (a) sodium (b) sodium oxide (c) calcium (d) calcium oxide Frothing in Yamuna:
Case/Passage – 2 The primary reason behind the formation of the toxic foam is high phosphate content in the wastewater because of detergents used in dyeing industries, dhobi ghats and households.Yamuna’s pollution level is so bad that parts of it have been labelled ‘dead’ as there is no oxygen in it for aquatic life to survive.

Question: High content of phosphate ion in river Yamuna may lead to: (a) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae (b) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and no effect of growth of algae (c) increased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae (d) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and decreased growth of algae
Question: Which of the following correctly represents the solutions in increasing order of their hydronium ion concentration? (a) P > Q > R > S (b) P > S > Q > R (c) S < Q < R < P (d) S < P < Q < R
Question: Which of the following statements is correct for the water with detergents dissolved in it? (a) low concentration of hydroxide ion (OH– )and high concentration of hydronium ion (H3 O +) (b) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH–)and low concentration of hydronium ion (H 3 O+) (c) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH–) as well as hydronium ion (H 3 O+) (d) equal concentration of both hydroxide ion (OH–) and hydronium ion (H 3 O+). The table provides the pH value of four solutions P, Q, R and S

Question: Predict the pH value of the water of river Yamuna if the reason for froth is high content of detergents dissolved in it. (a) 10-11 (b) 5-7 (c) 2-5 (d) 7
Question: If a sample of water containing detergents is provided to you, which of the following methods will you adopt to neutralize it? (a) Treating the water with baking soda (b) Treating the water with vinegar (c) Treating the water with caustic soda (d) Treating the water with washing soda

Related Posts

Metals And Non Metals Class 10 Science Notes And Questions

Nationalism in India Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions

CBSE Class 10 English Glimpses of India Summary
- Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Last Updated on May 15, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts.
| Acids Bases and Salts | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 10 | |
| Science | |
| Class 10 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |
Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Acids Bases and Salts
Question 1:
pH is quite useful to us in a number of ways in daily life. Some of its applications are:
Control of pH of the soil: Plants need a specific pH range for proper growth. The soil may be acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the relative concentration of H+ and OH-. The pH of any soil can be determined by using pH paper. If the soil is too acidic, it can be corrected by adding lime to it. If the soil is too basic, it can be corrected by adding organic manure which contains acidic materials.
Regaining shine of a tarnished copper vessel by use of acids: A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lemon on the vessel, the surface is cleaned and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that copper oxide is basic in nature, which reacts with the acid (citric acid) present in lemon to form a salt (copper citrate) which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
Self-defence by animals through chemical warfare: Stings of bees and ants contain methanoic acid. When stung, it causes lot of pain and irritation. This can be cured by rubbing the affected area with mild base like baking soda.
Read the above passage carefully and give the answer to the following questions:
(i) When black copper oxide placed in a beaker is treated with dilute HCl, its colour changes to (a) white (b) dark red (c) bluish green (d) no change.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: CuO + 2HCl → CuCl 2 + 2H 2 O, CuCl 2 is bluish green in colour.
(ii) P is an aqueous solution of acid and Q is an aqueous solution of base. When these two are diluted separately, then (a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralisation. (b) pH of P decreases while that of Q increases till neutralisation. (c) pH of both P and Q decrease. (d) pH of both P and Q increase.
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: On diluting, H+ ion concentration reduces per unit volume thus, pH increases. On the other hand, on diluting, OH– concentration also reduces, pOH increases and pH decreases. As, pOH + pH = 14. Thus, pH of Q (basic solution) decreases while that of P (acidic solution) increases on dilution.
(iii) Which of the following acids is present in bee sting? (a) Formic acid (b) Acetic acid (c) Citric acid (d) Hydrochloric acid
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Formic acid is the common name of methanoic acid, and it is present in bee sting
(iv) Sting of ant can be cured by rubbing the affected area with soap because (a) it contains oxalic acid which neutralises the effect of formic acid (b) it contains aluminium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (d) none of these.
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct
(v) The pH of soil X is 7.5 while that of soil Y is 4.5. Which of the two soils, should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH? (a) X only (b) Y only (c) Both X and Y (d) None of these
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: Soil Y is acidic. Hence, it should be treated with powdered chalk to reduce its acidity
Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 1
Topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Introduction to Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Definitions of Acids and Bases
- Properties of Acids and Bases
- Salts and their Types
- Importance and Uses of Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Preparation and Properties of Some Important Compounds
- Chemical Reactions of Acids and Bases
This chapter deals with the basic understanding of acids, bases, and salts, including their properties, reactions, pH scale, indicators, and practical applications.
Helpful Links for CBSE Class 10 Science Preparation
- Download 125 Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 220 Important Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 225 Practical Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 65 Important Numerical Problems for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 60 Important Diagram Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Physics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Heat Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 10 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 10 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on chemical reactions and equations for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on acids, bases and salts class 10 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of acids, bases and salts.
Q7: What is an acid?
A7: An acid is a substance that ionizes in water to produce hydrogen ions (H⁺) as the only positive ions. Examples include hydrochloric acid (HCl) found in gastric juices, citric acid in citrus fruits, acetic acid in vinegar, and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) in car batteries.
Q8: What are the properties of acids?
A8: Acids taste sour, turn blue litmus paper red, react with metals to produce hydrogen gas, and react with bases to form salts and water.
Q9: How do acids react with metals? Give examples.
A9: Acids react with metals to produce a salt and hydrogen gas. For example: 2HCl + Mg → MgCl₂ + H₂.
Q10: What is a base?
A10: A base is a substance that ionizes in water to produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻) as the only negative ions. Examples include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)₂].
Q11: What are the properties of bases?
A11: Bases taste bitter, feel slippery, turn red litmus paper blue, and react with acids to form salts and water.
Q12: Differentiate between acids and bases based on their taste, effect on litmus paper, and chemical behavior.
A12: Acids taste sour, turn blue litmus paper red, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas. Bases taste bitter, turn red litmus paper blue, and react with acids to form salts and water.

Related Posts
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 1st Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 2nd Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 3rd Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 4th Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 5th Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Acids, Bases and Salts Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject acids, bases and salts case study questions 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Baking powder produces carbon dioxide on heating, so it is used in cooking to make the batter spongy. Although, baking soda also produces CO 2 on heating, but it is not used in cooking because on heating, baking soda produces sodium carbonate along with carbon dioxide. Sodium carbonate, thus, produced, makes the taste bitter. Baking powder is the mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid. Generally, tartaric acid is mixed with baking soda to make baking powder. When baking powder is heated, NaHCO 3 decomposes to give CO 2 which makes bread and cake fluffy. Tartaric acid helps to remove bitter taste due to formation of sodium tartrate. \(2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+ \ \ \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{6} \mathrm{O}_{6} \quad \longrightarrow \quad 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{4} \mathrm{O}_{6}\) Baking soda Tartaric acid Carbon dioxide Sodium tartrate (i) On passing excess CO 2 gas in aqueous solution of sodium carbonate, the substance obtained is
| CO ·10H O | ·H O |
(ii) When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to acetic acid, it evolves a gas. Which of the following statements are true about the gas evolved? (I) It turns lime water milky (II) It extinguishes a burning splinter (III) It dissolves in a solution of sodium hydroxide (IV) It has a pungent odour
(iii) Select the correct statement regarding sodium hydrogen carbonate.
| are produced during the heating ofNaHCO |
(iv) Acetic acid was added to a solid X kept in a test tube. A colourless and odourless gas was evolved. The gas was passed through lime water which turned milky. It was concluded that
(v) Which of the following statements are correct regarding baking soda? (I) Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (II) On heating, baking soda gives sodium carbonate (III) It is used for manufacture of soap (IV) It is an ingredient of baking powder
Bleaching powder is also known as chloride of lime. It is a solid and yellowish white in colour. Bleaching powder can be easily identified by the strong smell of chlorine. When calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) reacts with chlorine, it gives calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder) and water is formed. Aqueous solution of bleaching powder is basic in nature. The material to be bleached is first passed through solution of NaOH to remove greasy matter. Then it is passed through aqueous solution of bleaching powder and very dil. HCI solution. HCI reacts with bleaching powder to liberate nascent oxygen which bleaches material. (i) Bleaching powder is used as
(ii) Bleaching powder is also known as
(iii) Bleaching powder gives smell of chlorine because it
(iv) Select the correct statement(s) regarding bleaching powder.
(v) Identify the product 'X' in the given reaction \(\mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2} \longrightarrow X+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
| ) |
The preparation of washing soda is carried out through following steps: Step-I: Manufacture of sodium hydrogen carbonate: \(\mathrm{NaCl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{NH}_{3}+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \longrightarrow \ \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+ \ \mathrm{NH}_{4} \mathrm{Cl}\) Sodium hydrogen carbonate Step-II : Thermal decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate: When dry crystals of sodium hydrogen carbonate are heated strongly, they decompose to form anhydrous sodium carbonate (soda ash). \(2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3(s)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3(s)}+\mathrm{CO}_{2(g)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(g)}\) Step-III : Recrystallisation of sodium carbonate: Sodium carbonate thus obtained is recrystallised to form crystals of washing soda. \(\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3(s)}+ 10 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3} \cdot 10 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(s)}\) Anhydrous Washing soda sodium carbonate (i) Some of the uses of washing soda are given below: (I) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water (II) It is used in glass industry (III) It is used in paper industry (IV) It is used in the manufacture of sodium compounds such as borax Select the correct option regarding uses of washing soda
(ii) What products will be formed along with water when sodium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid?
(iii) Chief raw materials for the manufacture of washing soda are
(iv) What is the action of sodium carbonate on litmus paper?
(v) What products will be obtained when solution of sodium carbonate and slaked lime is heated?
| and NaOH | |
| and NaOH |
"Indicator is a chemical compound which is added to the solution in very small amount to detect its acidic or basic nature:" As they show colour change in acidic and basic medium, they are also called acid-base indicators. In other words, "an acid-base indicator is that substance which possesses one colour in acidic medium and a different colour in alkaline medium:'' Indicators, basically, are coloured organic substances either extracted from plants (natural indicators) or synthesised in the laboratory (synthetic indicators). A few common acid base indicators are: Litmus, phenolphthalein, methyl orange etc. In addition to these there are some naturally occurring substances which have different smell in acidic and basic medium. These substances are called olfactory indicators. (i) Which one of the following will turn red litmus blue?
(ii) A solution turns blue litmus red. The pH of the solution is probably
(iii) A solution in test tube 'A' turns red litmus blue, evolves hydrogen gas on reaction with zinc and does not react with sodium carbonate. Whereas, solution in test tube 'B' turns blue litmus red, liberates hydrogen gas on reaction with zinc and evolves carbon dioxide gas with sodium carbonate. Identify 'A' and 'B'
(iv) Select the incorrect option
(v) Which one of the following can be used as an acid-base indicator by visually impaired student?
Acids turn blue litmus red but have no effect on red litmus. Bases turn red litmus blue but have no effect on blue litmus. The sample in which phenolphthalein remains colourless while methyl orange changes to pink/ red are acids while the samples in which phenolphthalein colour changes to pink and methyl orange changes to yellow are bases. Some observations of different sample solutions in litmus, phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicator are given in the table.
|
| ||||
| HCI | No colour change | Red | Colourless | Red/ Pink |
| H2 SO | No colour change | Red | Colourless | Red/ Pink |
| HNO | No colour change | Red | Colourless | Red/ Pink |
| CH COOH | No colour change | Red | Colourless | Red/ Pink |
| NaOH | Blue | No colour change | Pink | Yellow |
| Ca(OH) | Blue | No colour change | Pink | Yellow |
| KOH | Blue | No colour change | Pink | Yellow |
| Mg(OH) | Blue | No colour change | Pink | Yellow |
| NH OH | Blue | No colour change | Pink (Becomes colourless after sometime) | Yellow (Becomes colourless after sometime) |
(i) Which of the following substances does not turn red litmus solution to blue?
| PO | OH |
(ii) Phenolphthalein's colour in basic medium is ___________but in acid it is ___________ .
(iii) Which of the following acids are edible? (I) Citric acid (II) Tartaric acid (III) Hydrochloric acid (IV) Carbonic acid.
(iv) The colour of methyl orange in neutral solution is
(v) Which of the following cannot act as an indicator?

*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject acids, bases and salts case study questions 2021 answer keys.
\({ (i) }(\mathrm{b}): \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}\) (ii) (b) : \(\mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COONa}\) \(+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \uparrow+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) Carbon dioxide gas is evolved which turns limewater milky. It extinguishes a burning splinter since it is not a supporter of combustion. It dissolves in sodium hydroxide solution and it is an odourless gas. \({ (iii) }(\mathrm{c}): 2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3} \stackrel{\text { Heat }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) NaHCO 3 is soluble in water. \({ (iv) }(\mathbf{b}): \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} \longrightarrow\) \(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COONa}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) (v) (c): It is not used in manufacture of soap .
(i) (d) (ii) (d) (iii) (b): Bleaching powder gives chlorine on exposure to air by reacting with CO 2 . \(\mathrm{CaOCl}_{2}+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CaCO}_{3}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2}\) (iv) (d) \({ (v) }(\mathrm{a}): \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CaOCl}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
(i) (d) (ii) (c): Na2CO 3 reacts with dilute acids to give COgas with brisk effervescence. \(\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3(s)}+2 \mathrm{HCl}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaCl}_{(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)}\) \(+\mathrm{CO}_{2(g)} \uparrow\) Sodium Dil. Hydrochloric Sodium Water Carbon dioxide carbonate acid chloride (iii) (a): Chief raw materials for the manufacture of washing soda are sodium chloride (NaCl), ammonia (NH 3 ) and limestone (CaCO 3 ) (iv) (a): Sodium carbonate turns red litmus blue (v) (b): Sodium hydroxide and calcium carbonate are formed when the solution of sodium carbonate and slaked lime, Ca(OH) 2 is heated \(\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{CaCO}_{3}\)
(i) (b) : Baking soda (NaHCO 3 ) is basic in nature. (ii) (d) : The solution turns blue litmus red, hence it is acidic. (iii) (b): Acids turn blue litmus red, liberate hydrogen gas with zinc and evolve carbon dioxide gas with metal carbonates. Bases turn red litmus blue, evolve hydrogen gas with zinc and do not react with metal carbonates (iv) (b):
| Flowers of hydrangea plant (blue) | Blue | Blue |
(v) (c): Vanilla essence is an olfactory indicator. So, its smell is different in acidic and basic medium which can be detected easily by a visually impaired student.
(i) (c) (ii) (a) (iii) (b): Citric and tartaric acid are from organic substances such as lemon and tamarind respectively and they are edible. Hydrochloric acid though formed inside stomach is not edible. Carbonic acid is a mild acid and is edible in the form of soda water. (iv) (b) (v) (b)
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects
myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Download Case study questions for CBSE class 10 Science in PDF format from the myCBSEguide App . We have the new pattern case study-based questions for free download. Class 10 Science case study questions
This article will guide you through:
What are case study questions?
- Sample Papers with Case Study questions
- Class 10 Science Case Study question examples
- How to get case-based questions for free?
- How to attempt the case-based questions in Science?
Questions based on case studies are some real-life examples. The questions are asked based on a given paragraph i.e. Case Study. Usually, 4-5 questions are asked on the basis of the given passage. In most cases, these are either MCQs or assertion & reason type questions. Let’s take an example to understand. There is one paragraph on how nitrogen is generated in the atmosphere. On the basis of this paragraph, the board asks a few objective-type questions. In other words, it is very similar to the unseen passages given in language papers. But the real cases may be different. So, read this article till the end to understand it thoroughly.
What is CBE?
CBSE stands for competency-based education. The case study questions are part of this CBE. The purpose of CBE is to demonstrate the learning outcomes and attain proficiency in particular competencies.
Questions on Real-life Situations
As discussed the case study questions are based on real-life situations. Especially for grade 10 science, it is very essential to have the practical knowledge to solve such questions. Here on the myCBSEguide app, we have given many such case study paragraphs that are directly related to real-life implications of the knowledge.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App . There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions. In some cases, you will find that the question is not asked directly from the passage but is based on the concept that is discussed there. That’s why it is very much important to understand the background of the case study paragraph.
CBSE Case Study Sample Papers
You can download CBSE case study sample papers from the myCBSEguide App or Student Dashboard. Here is the direct link to access it.
Case Study Question Bank
As we mentioned that case study questions are coming in your exams for the last few years. You can get them in all previous year question papers issued by CBSE for class 1o Science. Here is the direct link to get them too.
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper , we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
Case-based Question -1
Read the following and answer any four questions: Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Phosphoric acid
- Carbonic acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Blue vitriol
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
Case-based Question -2
- V 1 + V 2 + V 3
- V 1 – V 2 +V 2
- None of these
- same at every point of the circuit
- different at every point of the circuit
- can not be determined
- 20 3 Ω 203Ω
- 15 2 Ω 152Ω
Case-based Question -3
- pure strips
- impure copper
- refined copper
- none of these
- insoluble impurities
- soluble impurities
- impure metal
- bottom of cathode
- bottom of anode
How to Attempt the Case-Based Questions in Science?
Before answering this question, let’s read the text given in question number 17 of the CBSE Model Question Paper.
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
See, there are only two sentences and CBSE is asking you 5 questions based on these two sentences. Now let’s check the first questions given there.
Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by a) Breathing b) Tissue respiration c) Organ respiration d) Digestion of food
Now let us know if you can relate the question to the paragraph directly. The two sentences are about energy and how it is obtained. But neither the question nor the options have any similar text in the paragraph.
So the conclusion is, in most cases, you will not get direct answers from the passage. You will get only an idea about the concept. If you know it, you can answer it but reading the paragraph even 100 times is not going to help you.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
3 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 10 Science”
Where is the answer
Class 10 Science MCQ
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- Chemical Reactions and Equations 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Acids, Bases, and Salts 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Metals and Non-Metals 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Carbon and its Compounds 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Periodic Classification of Elements 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Life Processes 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- How Do Organisms Reproduce 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Heredity and Evolution 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Light Reflection and Refraction 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts

| Study Reference for Class 10 Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts |
|---|

Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Class 10 NCERT Solutions
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapters:.
Why does tooth decay start when the pH of mouth is lower than 5.5?
What would be the colour of litmus in a solution of sodium carbonate, what is the common name of the compound caocl 2 , what is bleaching powder how is it prepared , contact form.
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Class 10 Science
- Chapter 2 Acid Bases And Salts
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 2 – cbse get free pdf.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts are prepared to help students in their CBSE exam preparation. This solution provides them with answers to the questions provided in the NCERT Class 10 textbooks. To score better marks in Class 10 Science examination, students should get well-versed with the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science provided here.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter – 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
Download most important questions for class 10 science chapter – 2 acids, bases and salts.
In this chapter, students will learn about the nature and behaviour of acids, bases and salts. This chapter mainly describes the chemical nature of acids, bases and salts and their reaction with metals, non-metals and with each other. It’s highly suggested that students make use of the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 while learning the main concepts. Also, this chapter is quite interesting as it involves many practical experiments to help learners understand the basics.
Every year, 3-4 questions from this chapter are asked in the Class 10 examination. This is also one of the important chapters, as the chances of scoring full marks on questions from this chapter are more. Hence, students are advised to practise all questions of this chapter using these NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science. Access the NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Science of this chapter from the link given below.
Practical-based multiple choice questions and subjective-based questions are regularly asked in previous year question papers.
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 The Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acid Bases and Salts
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access Answers to NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – Acids, Bases and Salts
In-text questions set 1 —> Page number 18
1. You are given three test tubes. The three test tubes contain distilled water, an acidic solution and the basic solution, respectively. There is only red litmus paper available in order to identify what is there in each test tube. How will you find out what is in each of the test tubes?
Solution: We can identify the content in each of the test tubes using red litmus paper. This can be done by noticing the colour change of the red litmus paper.
- On litmus paper, the three solutions in the test tubes are poured separately.
- The solution which turns red litmus to blue contains a basic solution.
- Divide the formed blue litmus paper into two parts.
- The solution from the test tube, which turns blue litmus paper to red, will be the acidic solution.
- The solution of the test tube, which does not change either red or blue litmus paper, contains water.
NOTE: After immediate distillation, distilled water has a pH of 7. However, within a few hours after distillation, it absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and turns slightly acidic with a pH of 5.8.
In-text questions set 2 —> Page number 22
1. Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Solution: Curd and sour food substances contain acids; these acidic substances combine with metal. This reaction turns food into poison, which damages people’s health.
2. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Solution: When an acid reacts with any metal, salt and hydrogen gas are formed.
Metal + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen gas
3. Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Solution: As the metal compound released is Calcium Chloride, the gas evolved here is CO 2 . Hence, metal A should be Calcium Carbonate. Hence, the reaction between Calcium Carbonate and HCl is
CaCO 3 (s) + 2HCl (Aq) → CaCl 2 ( Aq) + CO 2 (g) + H 2 O (l)
In-text questions set 3 Page number – 25
1. Why do HCl, HNO3, etc., show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show an acidic character?
Solution: Release of H + ion in water will make a compound acidic or non-acidic. Acids are substances which, upon dissociating with water, resulting in the production of Hydrogen ions. Some compounds show an acidic character as they dissociate in the aqueous solution, which results in the production of hydrogen ions (acids like HCl, HNO 3 ).
Compounds similar to glucose or alcohol do contain a hydrogen element, but they do not show signs of acidic nature. The fact is that the hydrogen in them will not separate from like the hydrogen in the acids. They will not separate to become hydrogen ions, on dissolving in the water.
2. Why does an aqueous solution of acid conduct electricity?
Solution: Charged particles are responsible for the conductance of electricity in an acid. These charged particles, called ions, are the reason behind the conductance of electricity in acid.
3. Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour of the dry litmus paper?
Solution: HCl does not give out Hydrogen ions; therefore, HCl does not show any acidic behaviour, and the colour of the litmus paper remains the same on reacting with HCl gas.
4. While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Solution: While diluting an acid, it is recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid because if water is added to a concentrated acid, it releases a huge amount of heat which may result in an explosion and can cause acid burns on the face, clothes and body parts. Hence, it is safe to add acid to water but not water to acid.
5. How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H 3 O + ) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted?
Solution: When acid is added to water, there will be a fixed amount of hydronium present in the fixed volume of the solution. If we dilute the solution, hydronium ions per volume of the solution decrease, and this, in turn, decreases Hydronium concentration in the solution.
6. How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH – ) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
Solution: When a base is dissolved in sodium hydroxide solution, its hydroxide ions increase, but it will reach saturation at some point. After saturation point, hydroxide ion concentration is not affected even after adding base further.
In-text questions set 4 Page number – 33
1. You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6, and the pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of these is acidic, and which one is basic?
Solution: In order to find the hydrogen ion concentration, we can use the rule that states, “The pH of any solution is inversely proportional to the hydrogen ion concentration.” Therefore, it means that the solution that has a lower pH number will have a higher hydrogen ion concentration. Hence, solution A will have a higher hydrogen ion concentration. In addition, solution B will be basic, and A will be acidic.
2. What effect does the concentration of H + (aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Solution: Hydrogen ion concentration decides the nature of the solution. If Hydrogen ion concentration increase, then the solution turns acidic and similarly, if Hydrogen ion concentration decreases, then the solution turns basic.
3. Do basic solutions also have H +( aq) ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Solution: Basic solutions have H + ions, but hydroxide ions present in basic solution are more in basic solution. Hence, Hydroxide ions turn the solution into basic.
4. Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide), or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Solution: If the soil is acidic in nature (PH below 7), then such fields should be treated with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate).
In-text questions set 5 Page number – 34-35
1. What is the common name of the compound CaOCl 2 ?
Solution: The common name of CaOCl 2 is bleaching powder.
2. Name the substance, which on treatment with chlorine, yields bleaching powder.
Solution: The substance, which on treatment with chlorine, yields bleaching powder is Calcium hydroxide.
3. Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Solution: Sodium carbonate is the compound which is used for softening hard water.
4. What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Solution: Heating sodium hydrocarbonate yields sodium carbonate, and carbon dioxide gas is liberated in the process.
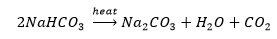
5. Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
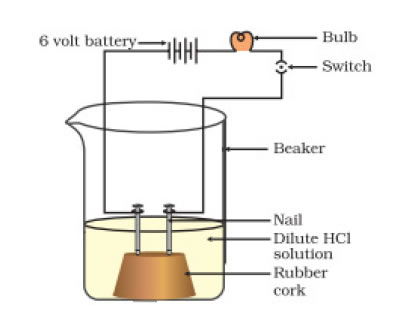
Solution: The chemical equation for the reaction of Plaster of Paris and water is
CaSO 4 .1/2H 2 O + 3/2H 2 O → CaSO 4 .2H 2 O
Exercise questions Page number – 33
1. A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be
a) 1 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 10
Solution: The answer is 10 because litmus paper turns blue when the solution reacts with a basic solution (PH more than 7). Hence, 10 is the answer.

2. A solution reacts with crushed eggshells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. The solution contains
a) NaCl (b) HCl (c) LiCl (d) KCl
Solution: The answer is HCl.
Eggshells contain calcium carbonate, which on reaction with HCl, liberates CO 2 gas, which turns lime water into milky.

CaCO 3 + 2HCl → CaCl 2 + H 2 O + CO 2
3. 10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be
(a) 4 mL (b) 8 mL (c) 12 mL (d) 16 mL
Solution: Since 10 ml of NaOH requires 8 mL of HCL, 20 ml of NaOH requires 8 x 2 = 16mL of HCl. Hence, the answer is option (d) 16mL.

4. Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion?
(a) Antibiotic (b) Analgesic (c) Antacid (d) Antiseptic
Solution: Indigestion is due to the excess production of acid in the stomach. Medicines used to treat indigestion is called Antacid.

5. Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.

=> Dilute sulphuric acid + zinc → Zinc Sulphate + Hydrogen Gas
=> H 2 SO 4 (aq) + Zn → ZnSO 4 (aq) + H 2 (g)

=> Dilute Hydrochloric + Magnesium → Magnesium Chloride + Hydrogen Gas
=> 2HCl(aq) + Mg → MgCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g)

=> Dilute Sulphuric Acid + Aluminium → Aluminium Sulphate + Hydrogen Gas
=> 3H 2 SO 4 (aq) + 2Al(s) → Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 (aq) + 3H 2 (g)

=> Dilute Hydrochloric Acid + Iron → Ferrous Chloride + Hydrogen Gas
=> 6HCl(aq) + 3Fe(s) → 3FeCl 2 (aq) + 3H 2 (g)

6. Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
Solution: Insert two nails into the wooden or rubber cork and place them on a beaker, as shown in the figure. Connect the iron nail to a bulb, a 6-volt battery and a wire connected to the switch. Pour some alcohol or glucose so as to dip the nails in glucose or alcohol. Turn the switch on, and you see the bulb not glowing despite of connection to the switch. Now empty the beaker and add the HCL solution. This time, the bulb glows. This proves acid can conduct electricity, but alcohol and glucose do not conduct electricity.
7. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rain water does?
- Distilled water does not contain any ionic compounds in it.
- Whereas rainwater has a lot more compounds.
- Rainwater has dissolved acidic gas, such as carbon dioxide from the air, and that forms carbonic acid. This means that it has hydrogen ions and carbonate ions. Therefore, with the presence of acids, rainwater can conduct electricity.

8. Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Solution: The acidic behaviour of acids is because of the presence of hydrogen ions. Hydrogen ions can only be produced in the presence of water, and therefore, water is definitely needed if acids are to show their acidic behaviour.

9. Five solutions, A, B, C, D and E, when tested with a universal indicator, showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9, respectively. Which solution is
(a) Neutral?
(b) Strongly alkaline?
(c) Strongly acidic?
(d) Weakly acidic?
(e) Weakly alkaline?
Solution: In increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration,
pH 11(C) < pH 9(E) < pH 7 (D) < pH 4 (A) < pH 1 (B)
PH11 – Strongly alkaline
pH9 – Weakly alkaline
PH7 – Neutral
pH4 – Weakly acidic
pH1 – Strongly acidic

10. Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH 3 COOH) is added to test tube B. Amount and concentration taken for both the acids are the same. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Solution: HCl is a strong acid, whereas acetic is a weaker acid. Fizzing occurs because of the production of the hydrogen gas obtained due to the reaction of the acid on the magnesium ribbon. Since HCl is a very strong acid, there is a lot of liberation of hydrogen gas from test tube A. Therefore, more fizzing takes place in test tube A.

11. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Solution: Fresh milk is turned to curd due to the production of lactic acid. Lactic acid reduces the pH of the milk.

12. A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Solution: (a) He shifted the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline to prevent milk from getting sour due to the production of lactic acid.
(b) This milk takes a long time to set into curd because the lactic acid produced here first neutralises the pH, and then the pH is reduced to turn the milk into curd.

13. Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why.
Solution: Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container because moisture can affect the Plaster of Paris by slowing down the setting of the plaster because of hydration. This will turn plaster useless.

14. What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Solution: The reaction of the acid + base gives a product of salt + water, which is considered a neutralisation reaction.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H 2 O
Mg(OH) 2 + H 2 CO 3 → MgCO 3 + 2H 2 O

15. Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
| 1. It is used as an electrolyte | 1. It can be used to test the garden soil for acidity. If bubbles are developed, then the soil is too acidic |
| 2. It can be used domestically as a water softener for laundry. | 2. If used on washing the car, then it will remove dead bug bodies without damaging the colour or the paint on the car. |

Topics included in NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – Acid, Bases and Salts
- Understanding the chemical properties of bases and acids
- How do acids and bases react with metals?
- How do metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates react with acids?
- How do acids and bases react with each other?
- The reaction of metallic oxides with acids
- The reaction of non–metallic oxide with base
- What do all acids and bases have in common?
- What happens to an acid or base in a water solution?
- How strong are acid or base solutions?
- Importance of pH in everyday life
- More about salts
- Family of salts
- pH of salts
- Chemicals from common salt
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 2 Science Acids, Bases and Salts
In this chapter, students will get a hold of basic knowledge of acids, bases and salts. Students can further learn by accessing the Class 10 NCERT Solutions , the various chemical properties of acids, bases and salts and their reaction with metals and non-metals.
Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 2 Science Acids, Bases and Salts
- There are a lot of practical-based questions in this solution, and these types of questions are often asked in CBSE Class 10 Science examination.
- Students will encounter questions on day-to-day examples of acids, bases and salts.
- One can perceive different kinds of reactions involved with acids, bases and salts.
Students can also access NCERT Solutions for Classes 1 to 12 of any subject to learn and revise key concepts at any time.
BYJU’S is India’s top education technology company that believes in a modern learning approach. Our resource materials include NCERT notes, books, animations, videos, info-graphics, NCERT exemplar solutions, sample papers and NCERT Solutions . Our study materials will not only help students understand the topic completely but also help them memorising the topic for a longer period of time.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2
List the concepts discussed in chapter 2 of ncert solutions for class 10 science., are the ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 2 the best reference guide for the students, why should i refer to byju’s ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 2, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
byjus is the best classes this is help me and I need byjus because I weak all the subjects.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 2 Class 10 - Acids, Bases and Salts
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Chapter 2 of Class 10, Acids, Bases and Salts, is going to teach you about the nature of solutions and various products that we use on a daily basis. These products or solutions are categorised into 2 categories which are acids and bases.
We, at Teachoo , will provide you with all the necessary sources such as concepts , NCERT questions along with extra questions made by our experts which will help you in clarifying all the concepts easily.
Firstly, you are going to learn about various strength tests which will help you check the power of a solution, both acidic and basic. The tests you are going to learn about are -
- Litmus Paper test
- pH scale test
Secondly, you are going to understand various reactions which occur when acidic and basic solutions are combined with each other. You will also learn about the reactions of acids and bases with metals.
Lastly, you will look at the category of Salts and their chemical properties as well as their uses in our day to day lives.
NCERT Questions
Questions from inside the book, teachoo questions, case based questions (mcq), assertion reasoning questions (mcq), mcq from past year papers, mcqs from ncert exemplar.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases And Salts
Get extra questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases And Salts with PDF. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These extra questions will be helpful to revise the important topics and concepts. You can easily download all the questions and answers in PDF format from our app.
Acids, Bases And Salts Class 10 Science Extra Questions with Answers
Question 1: The pH of a sample of vegetable soup was found to be 6.5. How is this soup likely to taste?
Answer: The taste will be slightly sour as it is weakly acidic.
Question 2: Which bases are called alkalies? Give an example of alkalies.
Answer: Soluble bases are called alkalies, e.g. sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Question 3: Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid indicating the physical state of the reactants and the products.
Answer: Na 2 CO 3 (s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + CO 2 (g) + H 2 O(l)
Question 4: Write a balanced chemical equation for a neutralisation reaction, mentioning the physical state of the reactants and the products.
Answer: NaOH(s) + 2HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H 2 O(l)
Question 5: What would be the colour of red litmus in a solution of sodium carbonate?
Answer: The red litmus will change to blue in sodium carbonate solution.
Question 6: Which gas is evolved when sodium hydrogencarbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid?
Answer: Carbon dioxide gas is evolved.
Question 7: Curd is not kept in copper and brass utensils. Why?
Answer: Curd and sour substances contain acids which react with brass and copper vessels to form poisonous salts which are harmful for our health.
Question 8: Name the gas usually liberated when a dilute acid reacts with a metal. What happens when a burning candle is brought near this gas?
Answer: H 2 gas is liberated. It burns with pop sound when burning candle is brought near the gas.
Question 9: What effect does an increase in concentration of H + (aq.) in a solution have on the pH of solution?
Answer: Higher the concentration, lower will be pH of the solution.
Question 10: Why does 1 M HC1 solution have a higher concentration of H+ ions than 1 M CH 3 COOH solution?
Answer: 1 M HCl has higher cone, of (H+) because it ionises completely in aqueous solution whereas CH 3 COOH does not as it is weak acid.
Question 11: Which gas is generally liberated when a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid reacts with an active metal?
Answer: Hydrogen gas is liberated when active metal reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Zn(s) + 2HCl (dil.) → ZnCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g)
Question 12: What is the colour of litmus in a solution of ammonium hydroxide?
Answer: Red litmus will turn blue in ammonium hydroxide.
Question 13: How will you test for the gas which is liberated when hydrochloric acid reacts with an active metal?
Answer: Bring a burning matchstick near the gas. It burns with ‘pop’ sound showing that it is hydrogen.
Question 14: Name the acid present in the following: (i) Tomato (ii) Vinegar (iii) Tamarind
Answer: (i) Oxalic acid (ii) Acetic acid (iii) Tartaric acid
Question 15: mL of water and 10 mL of sulphuric acid are to be mixed in a beaker (i) State the method that should be followed with reason. (ii) What is this process called?
Answer: (i) The acid is to be added slowly in water to prevent the mixture to be splashed. The reaction is highly exothermic therefore, constant cooling should be done.
(ii) The process is called dilution.
Question 16: Explain how antacid works.
Answer: Hyperacidity is caused by excess of hydrochloric acid in stomach. Antacid is basic in nature. It neutralizes excess of acid and gives relief from pain caused by hyperacidity.
Question 17: Name the natural source of each of the following acid (i) Citric acid. (ii) Oxalic acid. (iii) Lactic acid. (iv) Tartaric acid.
Answer: (i) Lemon and orange. (ii) Tomatoes and Guava. (iii) Sour milk (curd) (iv) Tamarind.
Question 18: A student detected the pH of four unknown solution A, B, C and D as follows 11, 5, 7 and 2. Predict the nature of the solution.
Answer: A is basic ‘B’ is acidic ‘C’ is natural and ‘D’ is strongly acidic.
Question 19: State the chemical name of Plaster of Paris. Write a chemical equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Answer: Calcium sulphate hemihydrate.
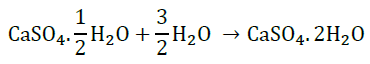
Question 20: State in brief the preparation of washing soda from baking soda. Write balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Answer: Sodium hydrogencarbonate (baking soda) on heating gives sodium carbonate which on recrystallisation gives washing soda.
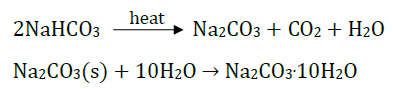
Question 21: What is the colour of FeSO 4 .7H 2 O crystals? How does this colour change upon heating? Give balanced chemical equation for the changes.
Answer: Pale green is the colour of FeSO 4 .7H 2 O crystals. It becomes dirty white on heating.
Question 22: Classify the following salts into acidic, basic and neutral: Potassium sulphate, ammonium chloride, sodium carbonate, sodium chloride.
Answer: Neutral: Potassium sulphate, Sodium chloride
Acidic: Ammonium chloride
Basic: Sodium carbonate
Question 23: A student dropped few pieces of marble in dilute HC1 contained in a test tube. The evolved gas was passed through lime water.
(i) What change would be observed in lime water?
(ii) Write balanced chemical equation for the above change.
Answer: (i) Lime water will turn milky due to formation of calcium carbonate.
(ii) Ca(OH) 2 (aq) + CO 2 (g) → CaCO 3 (s) + H 2 O(l)
Question 24: What happens when chlorine is passed over slaked lime at 313K? Write chemical equation of the reaction involved and state two uses of the product obtained.
Answer: Bleaching powder is formed.
(i) It is used as bleaching agent in paper and textile industries. (ii) It is used as disinfectant in purification of drinking water
Question 25: What is meant by ‘water of crystallisation’ of a substance?
Answer: The water molecules associated with a crystalline substance is called ‘water of crystallisation’.
Question 26: (a) Define olfactory indicators. Name two substances which can be used as olfactory indicator. (b) Choose strong acids from the following: CH 3 COOH, H 2 SO 4 , H 2 CO 3 , HNO 3
Answer: (a) Those substances whose smell (odour) changes in acidic or basic solution are called olfactory indicators, e.g. onion and vanilla.
(b) H 2 SO4 and HNO 3 are strong acids.
Question 27: Explain the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on the following with chemical equation: (i) Magnesium ribbon (ii) Sodium hydroxide (iii) Crushed egg shells
Answer: (i) Hydrogen gas will be formed Mg(s) + 2HCl (dil) → MgCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g)
(ii) Sodium chloride and water will be formed NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H 2 O
(iii) Crushed egg shell are made up of CaCO 3 which reacts with dil HCl to give brisk effervescence due to CO 2 CaCO 3 (s) + 2HCl CaCl 2 + H2O + CO 2
Question 28: (i) Give the constituents of baking powder (ii) Why cake or bread swells on adding baking powder? Write chemical equation.
Answer: (i) Baking powder containing sodium hydrogen carbonate and tartaric acid. (ii) It is due to carbon dioxide
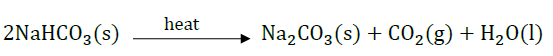
Question 29: (a) Write the name given to bases that are highly soluble in water. Give an example. (b) How is tooth decay related to pH? How can it be prevented? (c) Why does bee sting cause pain and irritation? Rubbing of baking soda on the sting area gives relief. How?
Answer: (a) Alkali, e.g. NaOH (Sodium hydroxide).
(b) Lower the pH, more will be tooth decay. Acid reacts with Ca3(PO4)2 and cause tooth decay. It can be prevented by brushing teeth after every meal.
(c) It is due to formic acid. Sodium hydrogencarbonate (Baking soda) neutralises formic acid giving relief.
Question 30: A white powder is added while baking breads and cakes to make them soft and fluffy. Write the name of the powder. Name its main ingredients. Explain the function of each ingredient. Write the chemical reaction taking place when the powder is heated during baking.
Answer: Baking powder. It consists of sodium hyrogencarbonate and tartaric acid. Sodium hydrogencarbonate gives CO 2 which makes cake soft and fluffy. Tartaric acid neutralizes the bitterness due to sodium carbonate produced.
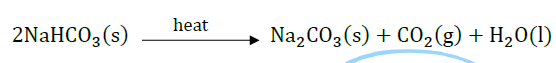
Question 31: “Sodium hydrogencarbonate is a basic salt”. Justify the statement. How is it converted into washing soda? Explain.
Answer: Sodium hydrogencarbonate is a salt of sodium hydroxide (strong base) and carbonic acid (weak acid). It is basic salt. It is converted into washing soda by heating followed by crystallization.
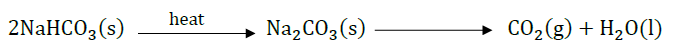
Question 32: (a) What is universal indicator? (b) Write the chemical equation involved in the preparation of sodium hydroxide. Name the process.
Answer: (a) Universal indicator is the mixture of synthetic indicators which is used to find pH of solutions.
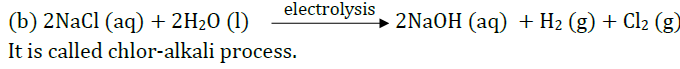
Question 33: A gas ‘X’ reacts with lime water and forms a compound ‘Y’ which is used as a bleaching agent in chemical industry. Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y\ Give the chemical equation of the reactions involved.
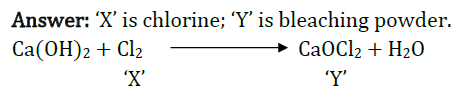
Question 34: (i) Name the compound which is obtained from baking soda and is used to remove permanent hardness of water. (ii) Write its chemical formula. (iii) What happens when it is recrystallised from its aqueous solution?
Answer: (i) Sodium carbonate is obtained from baking soda and is used to remove hardness of water. (ii) Na 2 CO 3 (iii) It changes to washing soda, Na 2 CO 3 .10H 2 O
Question 35: What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Answer: The reaction between acid and base to form salt and water is called neutrilisation reaction. Examples: KOH + HNO 3 → KNO 3 + H 2 O 2NaOH + H 2 SO 4 → Na 2 SO 4 + 2H 2 O
Question 36: What is tooth enamel chemically? State the condition when it starts corroding. What happens when food particles left in the mouth after eating degrade? Why do doctors suggest use of tooth powder/toothpaste to prevent tooth decay?
Answer: It is made up of calcium phosphate. It starts corroding due to acid formed in mouth. The food particles which are left in mouth form acids which cause tooth decay. Toothpaste and tooth powder are basic and neutralise acid formed in mouth which prevents tooth decay.
Question 37: What is Plaster of Paris chemically? How is it prepared? List its two important uses.
Answer: Calcium sulphate hemihydrate. It is prepared by heating gypsum at 373 K.
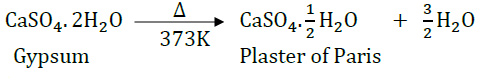
(i) It is used to prepare chalks. (ii) It is used to make casts and moulds.
Question 38: What is baking soda chemically called? Give reaction involved in its preparation. Write one of its uses.
Answer: Sodium hydrogencarbonate. NH 3 + CO 2 + H 2 O + NaCl → NaHCO 3 + NH 4 Cl OR NaCO 3 + CO 2 + H 2 O → 2NaHCO 3 It is used as an antacid.
Question 39: (a) What is an alkali? Give an example. (b) Why do HCl, HNO 3 , etc. show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Answer: (a) Soluble bases are called alkalies, e.g. sodium hydroxide is an alkali.
(b) HCl, HNO 3 ionise in aqueous solution, whereas alcohol and glucose do not show acidic characters because they do not ionise in aqueous solution.
Question 40: A compound which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening when mixed with proper quantity of water. (i) Identify the compound. (ii) Write the chemical equation for its preparation. (iii) Mention one important use of this compound.
Answer: (i) Plaster of Paris
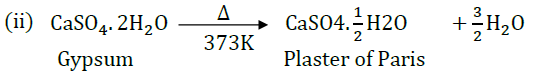
(iii) It is used for plastering fractured bones.
Question 41: Name the products formed in each case when (a) hydrochloric acid reacts with caustic soda. (b) granulated zinc reacts with caustic soda. (c) carbon dioxide is passed into lime water.

Question 42: State reason for the following statements: (i) Tap water conducts electricity whereas distilled water does not. (ii) Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not turn blue litmus red whereas dilute hydrochloric acid does. (iii) During summer season, a milk man usually adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk. (iv) For a dilution of acid, acid is added into water and not water into acid. (v) Ammonia is a base but does not contain hydroxyl group.
Answer: (i) Tap water contains ions which conduct electricity, distilled water does not contain ions.
(ii) Dry HCl does not form ions but HCl gives H + and Cl – .
(iii) Baking soda does not allow milk to change to lactic acid which makes milk sour.
(iv) Adding water to acid is highly exothermic. Therefore, water is added to acid very slowly with cooling.
(v) Ammonia dissolves in water and forms H – Therefore, it is basic in nature.
Question 43: (a) State the chemical properties on which the following uses of baking soda are based: (i) as an antacid (ii) as a soda acid fire extinguisher (iii) to make bread and cake soft and spongy. (b) How is washing soda is obtained from baking soda? Write balanced chemical equation.
Answer: (a) (i) It is weakly basic in nature and naturalize hyperacidity. (ii) It liberates CO 2 with H 2 SO 4 , which extinguish fire. (iii) It liberates CO 2 on heating which makes bread and cake soft and sponge
Baking soda on heating gives sodium carbonate which on crystallisation from hydrated washing soda.
Na 2 CO 3 + 10H 2 O → Na 2 CO 3 .10H 2 O
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy

- Revision Notes
- __Social Science
- NCERT Solutions
- Important Questions
Saturday, June 22, 2024
Acids, bases, and salts notes | class 10 science chapter 2.

Certainly! Here are some detailed notes on the chapter "Acids, Bases, and Salts" from the NCERT Class 10 Science textbook:
Introduction
- Acids : Acids are substances that release hydrogen ions ( H + H^+ H + ) in aqueous solution. They have a sour taste and turn blue litmus paper red.
- Bases : Bases are substances that release hydroxide ions ( O H − OH^- O H − ) in aqueous solution. They have a bitter taste and turn red litmus paper blue.
Properties of Acids:
- Taste : Sour taste.
- Effect on Litmus : Turns blue litmus paper red.
- Reaction with Metals : Acids react with active metals to produce hydrogen gas. Example: 2HCl + Zn → ZnCl 2 + H 2 \text{Example: } \text{2HCl} + \text{Zn} \rightarrow \text{ZnCl}_2 + \text{H}_2
- Reaction with Metal Carbonates and Bicarbonates : Acids react with metal carbonates and bicarbonates to produce carbon dioxide gas. Example: 2HCl + Na 2 CO 3 → 2NaCl + CO 2 + H 2 O \text{Example: } \text{2HCl} + \text{Na}_2\text{CO}_3 \rightarrow \text{2NaCl} + \text{CO}_2 + \text{H}_2\text{O}
Properties of Bases:
- Taste : Bitter taste.
- Effect on Litmus : Turns red litmus paper blue.
- Reaction with Fats and Oils : Bases react with fats and oils to form soap. Example: NaOH + H 3 CCO 2 H → Soap + Water
- Indicators : Substances that change color in the presence of acids or bases.
- Examples : Litmus, phenolphthalein, methyl orange.
- pH Scale : A scale used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution.
- pH Values :
- pH < 7 indicates an acidic solution.
- pH = 7 indicates a neutral solution.
- pH > 7 indicates a basic (alkaline) solution.
Importance of pH in Everyday Life
- Acid Rain : Harmful effects of acid rain on plants, buildings, and aquatic life.
- pH in Soil : Importance of pH in determining soil fertility and plant growth.
- pH in Human Body : Importance of maintaining pH balance in the blood and digestive system.
- Formation : Salts are formed by the reaction between acids and bases.
- Properties : Salts may be acidic, basic, or neutral depending on the nature of the acids and bases involved in their formation.
- Examples : NaCl , CaCO 3 , CuSO
Uses of Salts
- Food Preservation : Use of salts like sodium chloride (table salt) for preserving food.
- Healthcare : Use of salts in medicines and healthcare products.
- Industry : Use of salts in industries such as textile, leather, and glass.
Preparation of Salts
- Methods : Preparation of salts by neutralization reactions.
- Example : Preparation of CuSO 4 \text{CuSO}_4 from CuO \text{CuO} and H 2 SO 4 \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 H 2 .
- Understanding acids, bases, and salts is crucial for understanding various chemical reactions in daily life, industrial processes, and environmental impacts.
These notes cover the essential concepts and applications of acids, bases, and salts as taught in Class 10 Science. They provide a comprehensive overview of the chapter, helping students grasp both theoretical and practical aspects of these substances.
Certainly! The NCERT Class 10 Science textbook typically includes chapters covering various topics in physics, chemistry, and biology. Here's a list of chapters commonly found in the NCERT Class 10 Science book:
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Metals and Non-Metals
- Carbon and its Compounds
- Periodic Classification of Elements
- Life Processes
- Control and Coordination
- How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Heredity and Evolution
- Light - Reflection and Refraction
- The Human Eye and the Colourful World
- Electricity
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Sources of Energy
- Our Environment
- Management of Natural Resources
These chapters cover fundamental concepts in science for Class 10 students and are structured to provide a comprehensive understanding of each topic.
About Padhlo Bacho alistarbot is a blogger resources site is a provider of high quality blogger template with premium looking layout and robust design. The main mission of templatesyard is to provide the best quality blogger templates.
No comments:
Post a comment.
- Follow on Twitter
- Subscribe on Youtube
Search This Blog
Report Abuse
Management of natural resources notes | class 10 science chapter 16.

Recent Post
Contact form.


COMMENTS
CASE STUDY : 5 (Acids Bases and Salts) Salts of a strong acid and a strong base are neutral with pH value of 7. On the other hand, salts of a strong acid and weak base are acidic with pH value less than 7 and those of a strong base and weak acid are basic in nature, with pH value more than 7. Answer the following in reference to the above ...
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to ...
Case Study/Passage Based Questions on Acids, Bases and Salts. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Question 1: pH is quite useful to us in a number of ways in daily life. Some of its applications are: Control of pH of the soil : Plants need a specific pH range for proper growth. The soil may be acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the ...
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Acids, Bases and Salts Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. The acidic behaviour of acids is due to the presence of hydrogenil (H + )ions in them. They produce hydrogen ions in the presence of water. Water is a polar solvent and this property of water helps in weakening the bond between the ions and makes ...
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science. Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given ...
The Case Based Questions: Acids, Bases and Salts is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 10 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
Case study-based questions Question 1 Salt is an ionic compound that results from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base.It is composed of related numbers of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negative ions) so that the product is electrically neutral (without a net charge). They may be simple salts such as NaCl, KCl, and ...
Case Study Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: A compound, X of sodium forms a white powder. It is a constituent of baking powder and is used in some antacids.
Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Acids Bases Salts. Marble's popularity began in ancient Rome and Greece, where white and off-white marble were used to construct a variety of structures, from hand-held sculptures to massive pillars and buildings. Question: A student added 10g of calcium carbonate in a rigid container, secured it tightly and ...
Acids, Bases and Salts Case Study Questions (CSQ's) Select the number of questions for the test: TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Acids, Bases and Salts chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert advice.
Learn Acids, Bases, and Salts Class 10 | Class 10 Science Chapter 2 | Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 2 | case study Questions | case study based question | case ...
Q12: Differentiate between acids and bases based on their taste, effect on litmus paper, and chemical behavior. A12: Acids taste sour, turn blue litmus paper red, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas. Bases taste bitter, turn red litmus paper blue, and react with acids to form salts and water. Hello students, we are providing case ...
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Acids, Bases and Salts Case Study Questions 2021. 10th Standard CBSE. Reg.No. : Science. Time : 00:30:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 20. Baking powder produces carbon dioxide on heating, so it is used in cooking to make the batter spongy. Although, baking soda also produces CO 2 on heating, but it is not used in ...
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples. ... Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up.
Practice. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,600 Mastery points! In this unit, we will be talking about the basic concepts of acids, bases, and salts. We will cover acid and base definitions, reactions, strength (pH), chemical compounds of salts, and their uses.
Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study: Here, Students can read Class 10 Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Based Questions with Answers in PDF File format. Apart from this ...
Here you will find NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts that are useful resources in covering entire syllabus and have in depth analysis of chapters. These Cass 10 NCERT Solutions are prepared as per the accordance of latest CBSE guidelines so you can score maximum marks. The definitions of Acids and Bases in terms of furnishing of H+ and OH- ions, General ...
In this chapter, students will learn about the nature and behaviour of acids, bases and salts. This chapter mainly describes the chemical nature of acids, bases and salts and their reaction with metals, non-metals and with each other. It's highly suggested that students make use of the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 while ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Exercise Questions. Question 1: A solution turns red litmus blue; its pH is likely to be: (a) 1. (b) 4. (c) 5. (d) 10. Answer: (d) 10. A solution which turns the colour of red litmus to blue must be basic in nature. A basic solution has a pH value of greater than 7.
2HCl + Zn → ZnCl 2 + H 2. Hydrogen gas is evolved with the formation of the corresponding salt. Q.20. Give two characteristics each of acids and bases. Answer: Two characteristics of acids: Acids are sour in taste. They produce H+ ions upon dilution. Two characteristics of bases: Bases are bitter in taste.
Chapter 2 of Class 10, Acids, Bases and Salts, is going to teach you about the nature of solutions and various products that we use on a daily basis. These products or solutions are categorised into 2 categories which are acids and bases. We, at Teachoo, will provide you with all the necessary sources such as concepts, NCERT questions along ...
Answer: (i) Lemon and orange. (ii) Tomatoes and Guava. (iii) Sour milk (curd) (iv) Tamarind. Question 18: A student detected the pH of four unknown solution A, B, C and D as follows 11, 5, 7 and 2. Predict the nature of the solution. Answer: A is basic 'B' is acidic 'C' is natural and 'D' is strongly acidic.
Explore the fundamental concepts of acids, bases, and salts in chemistry through this comprehensive guide for Class 10 students. Learn about their properties...
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts CBSE Class 10 SCIENCE Question Type MCQ No. of Questions 85 Useful for Class 10 Studying Students Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts MCQs with Answers Q.1. Which one of the following is acidic?(a) Lemon juice (b) Tomatoes (c) Milk (d) All Answer (d)All … Continue reading MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science ...
Formation: Salts are formed by the reaction between acids and bases. Properties: Salts may be acidic, basic, or neutral depending on the nature of the acids and bases involved in their formation. Examples: NaCl, CaCO 3, CuSO Uses of Salts. Food Preservation: Use of salts like sodium chloride (table salt) for preserving food.