
Research Methodology Example
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Methodology Chapter Template
If you’re working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a research methodology chapter , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through a research methodology from a dissertation that earned full distinction , step by step. We start off by discussing the core components of a research methodology by unpacking our free methodology chapter template . We then progress to the sample research methodology to show how these concepts are applied in an actual dissertation, thesis or research project.
If you’re currently working on your research methodology chapter, you may also find the following resources useful:
- Research methodology 101 : an introductory video discussing what a methodology is and the role it plays within a dissertation
- Research design 101 : an overview of the most common research designs for both qualitative and quantitative studies
- Variables 101 : an introductory video covering the different types of variables that exist within research.
- Sampling 101 : an overview of the main sampling methods
- Methodology tips : a video discussion covering various tips to help you write a high-quality methodology chapter
- Private coaching : Get hands-on help with your research methodology

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Methodology Example
Research methodology example: frequently asked questions, is the sample research methodology real.
Yes. The chapter example is an extract from a Master’s-level dissertation for an MBA program. A few minor edits have been made to protect the privacy of the sponsoring organisation, but these have no material impact on the research methodology.
Can I replicate this methodology for my dissertation?
As we discuss in the video, every research methodology will be different, depending on the research aims, objectives and research questions. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your literature review to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research methodology chapter here .
Where can I find more examples of research methodologies?
The best place to find more examples of methodology chapters would be within dissertation/thesis databases. These databases include dissertations, theses and research projects that have successfully passed the assessment criteria for the respective university, meaning that you have at least some sort of quality assurance.
The Open Access Thesis Database (OATD) is a good starting point.
How do I get the research methodology chapter template?
You can access our free methodology chapter template here .
Is the methodology template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the template and you are free to use it as you wish.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study’s overall validity and reliability. The methodology section of a research paper answers two main questions: How was the data collected or generated? And, how was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and always written in the past tense.
Kallet, Richard H. "How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004): 1229-1232.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you chose affects the results and, by extension, how you interpreted their significance in the discussion section of your paper.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and, as a consequence, undermines the value of your analysis of the findings.
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. The methodology section of your paper should clearly articulate the reasons why you have chosen a particular procedure or technique.
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a multiple choice questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The method must be appropriate to fulfilling the overall aims of the study. For example, you need to ensure that you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring. For any problems that do arise, you must describe the ways in which they were minimized or why these problems do not impact in any meaningful way your interpretation of the findings.
- In the social and behavioral sciences, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow other researchers to adopt or replicate your methodology. This information is particularly important when a new method has been developed or an innovative use of an existing method is utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects . 5th edition. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The e mpirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences . This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for formulating hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation.
- The i nterpretative group of methods is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . Interpretive methods focus on analytically disclosing the meaning-making practices of human subjects [the why, how, or by what means people do what they do], while showing how those practices arrange so that it can be used to generate observable outcomes. Interpretive methods allow you to recognize your connection to the phenomena under investigation. However, the interpretative group requires careful examination of variables because it focuses more on subjective knowledge.
II. Content
The introduction to your methodology section should begin by restating the research problem and underlying assumptions underpinning your study. This is followed by situating the methods you used to gather, analyze, and process information within the overall “tradition” of your field of study and within the particular research design you have chosen to study the problem. If the method you choose lies outside of the tradition of your field [i.e., your review of the literature demonstrates that the method is not commonly used], provide a justification for how your choice of methods specifically addresses the research problem in ways that have not been utilized in prior studies.
The remainder of your methodology section should describe the following:
- Decisions made in selecting the data you have analyzed or, in the case of qualitative research, the subjects and research setting you have examined,
- Tools and methods used to identify and collect information, and how you identified relevant variables,
- The ways in which you processed the data and the procedures you used to analyze that data, and
- The specific research tools or strategies that you utilized to study the underlying hypothesis and research questions.
In addition, an effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods for gathering data should have a clear connection to your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom. Also be sure to explain how older data is still relevant to investigating the current research problem.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors? Describe how you plan to obtain an accurate assessment of relationships, patterns, trends, distributions, and possible contradictions found in the data.
- Provide background and a rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a justification for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of data being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate to addressing the research problem.
- Provide a justification for case study selection . A common method of analyzing research problems in the social sciences is to analyze specific cases. These can be a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis that are either examined as a singular topic of in-depth investigation or multiple topics of investigation studied for the purpose of comparing or contrasting findings. In either method, you should explain why a case or cases were chosen and how they specifically relate to the research problem.
- Describe potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE : Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic. If necessary, consider using appendices for raw data.
ANOTHER NOTE : If you are conducting a qualitative analysis of a research problem , the methodology section generally requires a more elaborate description of the methods used as well as an explanation of the processes applied to gathering and analyzing of data than is generally required for studies using quantitative methods. Because you are the primary instrument for generating the data [e.g., through interviews or observations], the process for collecting that data has a significantly greater impact on producing the findings. Therefore, qualitative research requires a more detailed description of the methods used.
YET ANOTHER NOTE : If your study involves interviews, observations, or other qualitative techniques involving human subjects , you may be required to obtain approval from the university's Office for the Protection of Research Subjects before beginning your research. This is not a common procedure for most undergraduate level student research assignments. However, i f your professor states you need approval, you must include a statement in your methods section that you received official endorsement and adequate informed consent from the office and that there was a clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university. This statement informs the reader that your study was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. In some cases, the approval notice is included as an appendix to your paper.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but concise. Do not provide any background information that does not directly help the reader understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how the data was analyzed in relation to the research problem [note: analyzed, not interpreted! Save how you interpreted the findings for the discussion section]. With this in mind, the page length of your methods section will generally be less than any other section of your paper except the conclusion.
Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional methodological approach; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall process of discovery.
Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data, or, gaps will exist in existing data or archival materials. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose.
Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in and of itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. "How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section." Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Blair Lorrie. “Choosing a Methodology.” In Writing a Graduate Thesis or Dissertation , Teaching Writing Series. (Rotterdam: Sense Publishers 2016), pp. 49-72; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Kallet, Richard H. “How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper.” Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004):1229-1232; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. “The Method Chapter: Describing Your Research Plan.” In Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . (Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications, 2015), pp. 87-115; What is Interpretive Research. Institute of Public and International Affairs, University of Utah; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
To locate data and statistics, GO HERE .
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between the application of theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics . Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship. S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Methods and the Methodology
Do not confuse the terms "methods" and "methodology." As Schneider notes, a method refers to the technical steps taken to do research . Descriptions of methods usually include defining and stating why you have chosen specific techniques to investigate a research problem, followed by an outline of the procedures you used to systematically select, gather, and process the data [remember to always save the interpretation of data for the discussion section of your paper].
The methodology refers to a discussion of the underlying reasoning why particular methods were used . This discussion includes describing the theoretical concepts that inform the choice of methods to be applied, placing the choice of methods within the more general nature of academic work, and reviewing its relevance to examining the research problem. The methodology section also includes a thorough review of the methods other scholars have used to study the topic.
Bryman, Alan. "Of Methods and Methodology." Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 3 (2008): 159-168; Schneider, Florian. “What's in a Methodology: The Difference between Method, Methodology, and Theory…and How to Get the Balance Right?” PoliticsEastAsia.com. Chinese Department, University of Leiden, Netherlands.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: May 15, 2024 9:53 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
Published on 25 February 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
It should include:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected and analysed your data
- Any tools or materials you used in the research
- Why you chose these methods
- Your methodology section should generally be written in the past tense .
- Academic style guides in your field may provide detailed guidelines on what to include for different types of studies.
- Your citation style might provide guidelines for your methodology section (e.g., an APA Style methods section ).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a research methodology, why is a methods section important, step 1: explain your methodological approach, step 2: describe your data collection methods, step 3: describe your analysis method, step 4: evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made, tips for writing a strong methodology chapter, frequently asked questions about methodology.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Your methods section is your opportunity to share how you conducted your research and why you chose the methods you chose. It’s also the place to show that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated .
It gives your research legitimacy and situates it within your field, and also gives your readers a place to refer to if they have any questions or critiques in other sections.
You can start by introducing your overall approach to your research. You have two options here.
Option 1: Start with your “what”
What research problem or question did you investigate?
- Aim to describe the characteristics of something?
- Explore an under-researched topic?
- Establish a causal relationship?
And what type of data did you need to achieve this aim?
- Quantitative data , qualitative data , or a mix of both?
- Primary data collected yourself, or secondary data collected by someone else?
- Experimental data gathered by controlling and manipulating variables, or descriptive data gathered via observations?
Option 2: Start with your “why”
Depending on your discipline, you can also start with a discussion of the rationale and assumptions underpinning your methodology. In other words, why did you choose these methods for your study?
- Why is this the best way to answer your research question?
- Is this a standard methodology in your field, or does it require justification?
- Were there any ethical considerations involved in your choices?
- What are the criteria for validity and reliability in this type of research ?
Once you have introduced your reader to your methodological approach, you should share full details about your data collection methods .
Quantitative methods
In order to be considered generalisable, you should describe quantitative research methods in enough detail for another researcher to replicate your study.
Here, explain how you operationalised your concepts and measured your variables. Discuss your sampling method or inclusion/exclusion criteria, as well as any tools, procedures, and materials you used to gather your data.
Surveys Describe where, when, and how the survey was conducted.
- How did you design the questionnaire?
- What form did your questions take (e.g., multiple choice, Likert scale )?
- Were your surveys conducted in-person or virtually?
- What sampling method did you use to select participants?
- What was your sample size and response rate?
Experiments Share full details of the tools, techniques, and procedures you used to conduct your experiment.
- How did you design the experiment ?
- How did you recruit participants?
- How did you manipulate and measure the variables ?
- What tools did you use?
Existing data Explain how you gathered and selected the material (such as datasets or archival data) that you used in your analysis.
- Where did you source the material?
- How was the data originally produced?
- What criteria did you use to select material (e.g., date range)?
The survey consisted of 5 multiple-choice questions and 10 questions measured on a 7-point Likert scale.
The goal was to collect survey responses from 350 customers visiting the fitness apparel company’s brick-and-mortar location in Boston on 4–8 July 2022, between 11:00 and 15:00.
Here, a customer was defined as a person who had purchased a product from the company on the day they took the survey. Participants were given 5 minutes to fill in the survey anonymously. In total, 408 customers responded, but not all surveys were fully completed. Due to this, 371 survey results were included in the analysis.
Qualitative methods
In qualitative research , methods are often more flexible and subjective. For this reason, it’s crucial to robustly explain the methodology choices you made.
Be sure to discuss the criteria you used to select your data, the context in which your research was conducted, and the role you played in collecting your data (e.g., were you an active participant, or a passive observer?)
Interviews or focus groups Describe where, when, and how the interviews were conducted.
- How did you find and select participants?
- How many participants took part?
- What form did the interviews take ( structured , semi-structured , or unstructured )?
- How long were the interviews?
- How were they recorded?
Participant observation Describe where, when, and how you conducted the observation or ethnography .
- What group or community did you observe? How long did you spend there?
- How did you gain access to this group? What role did you play in the community?
- How long did you spend conducting the research? Where was it located?
- How did you record your data (e.g., audiovisual recordings, note-taking)?
Existing data Explain how you selected case study materials for your analysis.
- What type of materials did you analyse?
- How did you select them?
In order to gain better insight into possibilities for future improvement of the fitness shop’s product range, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 8 returning customers.
Here, a returning customer was defined as someone who usually bought products at least twice a week from the store.
Surveys were used to select participants. Interviews were conducted in a small office next to the cash register and lasted approximately 20 minutes each. Answers were recorded by note-taking, and seven interviews were also filmed with consent. One interviewee preferred not to be filmed.
Mixed methods
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches. If a standalone quantitative or qualitative study is insufficient to answer your research question, mixed methods may be a good fit for you.
Mixed methods are less common than standalone analyses, largely because they require a great deal of effort to pull off successfully. If you choose to pursue mixed methods, it’s especially important to robustly justify your methods here.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Next, you should indicate how you processed and analysed your data. Avoid going into too much detail: you should not start introducing or discussing any of your results at this stage.
In quantitative research , your analysis will be based on numbers. In your methods section, you can include:
- How you prepared the data before analysing it (e.g., checking for missing data , removing outliers , transforming variables)
- Which software you used (e.g., SPSS, Stata or R)
- Which statistical tests you used (e.g., two-tailed t test , simple linear regression )
In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis ).
Specific methods might include:
- Content analysis : Categorising and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
- Thematic analysis : Coding and closely examining the data to identify broad themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying communication and meaning in relation to their social context
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process.
Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if you did not take the most standard approach to your topic. In this case, discuss why other methods were not suitable for your objectives, and show how this approach contributes new knowledge or understanding.
In any case, it should be overwhelmingly clear to your reader that you set yourself up for success in terms of your methodology’s design. Show how your methods should lead to results that are valid and reliable, while leaving the analysis of the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results for your discussion section .
- Quantitative: Lab-based experiments cannot always accurately simulate real-life situations and behaviours, but they are effective for testing causal relationships between variables .
- Qualitative: Unstructured interviews usually produce results that cannot be generalised beyond the sample group , but they provide a more in-depth understanding of participants’ perceptions, motivations, and emotions.
- Mixed methods: Despite issues systematically comparing differing types of data, a solely quantitative study would not sufficiently incorporate the lived experience of each participant, while a solely qualitative study would be insufficiently generalisable.
Remember that your aim is not just to describe your methods, but to show how and why you applied them. Again, it’s critical to demonstrate that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated.
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions
The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions .
2. Cite relevant sources
Your methodology can be strengthened by referencing existing research in your field. This can help you to:
- Show that you followed established practice for your type of research
- Discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating existing research
- Present a novel methodological approach to address a gap in the literature
3. Write for your audience
Consider how much information you need to give, and avoid getting too lengthy. If you are using methods that are standard for your discipline, you probably don’t need to give a lot of background or justification.
Regardless, your methodology should be a clear, well-structured text that makes an argument for your approach, not just a list of technical details and procedures.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research. Developing your methodology involves studying the research methods used in your field and the theories or principles that underpin them, in order to choose the approach that best matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. interviews, experiments , surveys , statistical tests ).
In a dissertation or scientific paper, the methodology chapter or methods section comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/methodology/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write Research Methodology
Last Updated: May 21, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Alexander Ruiz, M.Ed. and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Alexander Ruiz is an Educational Consultant and the Educational Director of Link Educational Institute, a tutoring business based in Claremont, California that provides customizable educational plans, subject and test prep tutoring, and college application consulting. With over a decade and a half of experience in the education industry, Alexander coaches students to increase their self-awareness and emotional intelligence while achieving skills and the goal of achieving skills and higher education. He holds a BA in Psychology from Florida International University and an MA in Education from Georgia Southern University. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, several readers have written to tell us that this article was helpful to them, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 521,435 times.
The research methodology section of any academic research paper gives you the opportunity to convince your readers that your research is useful and will contribute to your field of study. An effective research methodology is grounded in your overall approach – whether qualitative or quantitative – and adequately describes the methods you used. Justify why you chose those methods over others, then explain how those methods will provide answers to your research questions. [1] X Research source
Describing Your Methods

- In your restatement, include any underlying assumptions that you're making or conditions that you're taking for granted. These assumptions will also inform the research methods you've chosen.
- Generally, state the variables you'll test and the other conditions you're controlling or assuming are equal.

- If you want to research and document measurable social trends, or evaluate the impact of a particular policy on various variables, use a quantitative approach focused on data collection and statistical analysis.
- If you want to evaluate people's views or understanding of a particular issue, choose a more qualitative approach.
- You can also combine the two. For example, you might look primarily at a measurable social trend, but also interview people and get their opinions on how that trend is affecting their lives.

- For example, if you conducted a survey, you would describe the questions included in the survey, where and how the survey was conducted (such as in person, online, over the phone), how many surveys were distributed, and how long your respondents had to complete the survey.
- Include enough detail that your study can be replicated by others in your field, even if they may not get the same results you did. [4] X Research source

- Qualitative research methods typically require more detailed explanation than quantitative methods.
- Basic investigative procedures don't need to be explained in detail. Generally, you can assume that your readers have a general understanding of common research methods that social scientists use, such as surveys or focus groups.

- For example, suppose you conducted a survey and used a couple of other research papers to help construct the questions on your survey. You would mention those as contributing sources.
Justifying Your Choice of Methods

- Describe study participants specifically, and list any inclusion or exclusion criteria you used when forming your group of participants.
- Justify the size of your sample, if applicable, and describe how this affects whether your study can be generalized to larger populations. For example, if you conducted a survey of 30 percent of the student population of a university, you could potentially apply those results to the student body as a whole, but maybe not to students at other universities.

- Reading other research papers is a good way to identify potential problems that commonly arise with various methods. State whether you actually encountered any of these common problems during your research.

- If you encountered any problems as you collected data, explain clearly the steps you took to minimize the effect that problem would have on your results.

- In some cases, this may be as simple as stating that while there were numerous studies using one method, there weren't any using your method, which caused a gap in understanding of the issue.
- For example, there may be multiple papers providing quantitative analysis of a particular social trend. However, none of these papers looked closely at how this trend was affecting the lives of people.
Connecting Your Methods to Your Research Goals

- Depending on your research questions, you may be mixing quantitative and qualitative analysis – just as you could potentially use both approaches. For example, you might do a statistical analysis, and then interpret those statistics through a particular theoretical lens.

- For example, suppose you're researching the effect of college education on family farms in rural America. While you could do interviews of college-educated people who grew up on a family farm, that would not give you a picture of the overall effect. A quantitative approach and statistical analysis would give you a bigger picture.

- If in answering your research questions, your findings have raised other questions that may require further research, state these briefly.
- You can also include here any limitations to your methods, or questions that weren't answered through your research.

- Generalization is more typically used in quantitative research. If you have a well-designed sample, you can statistically apply your results to the larger population your sample belongs to.
Template to Write Research Methodology

Community Q&A
- Organize your methodology section chronologically, starting with how you prepared to conduct your research methods, how you gathered data, and how you analyzed that data. [13] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Write your research methodology section in past tense, unless you're submitting the methodology section before the research described has been carried out. [14] X Research source Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Discuss your plans in detail with your advisor or supervisor before committing to a particular methodology. They can help identify possible flaws in your study. [15] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://expertjournals.com/how-to-write-a-research-methodology-for-your-academic-article/
- ↑ http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/methodology
- ↑ https://www.skillsyouneed.com/learn/dissertation-methodology.html
- ↑ https://uir.unisa.ac.za/bitstream/handle/10500/4245/05Chap%204_Research%20methodology%20and%20design.pdf
- ↑ https://elc.polyu.edu.hk/FYP/html/method.htm
About This Article

To write a research methodology, start with a section that outlines the problems or questions you'll be studying, including your hypotheses or whatever it is you're setting out to prove. Then, briefly explain why you chose to use either a qualitative or quantitative approach for your study. Next, go over when and where you conducted your research and what parameters you used to ensure you were objective. Finally, cite any sources you used to decide on the methodology for your research. To learn how to justify your choice of methods in your research methodology, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prof. Dr. Ahmed Askar
Apr 18, 2020
Did this article help you?
M. Mahmood Shah Khan
Mar 17, 2020
Shimola Makondo
Jul 20, 2019
Zain Sharif Mohammed Alnadhery
Jan 7, 2019
Lundi Dukashe
Feb 17, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Project Methodology Templates with Samples and Examples

Vaishali Rai
Project management is confusing. Have you ever been in a situation like this, sitting at your project meeting, perhaps feeling out of your depth, and finding it hard to follow the conversation around you? It may be due to unstructured and unorganized execution of the project's principles. You also might need to apply a suitable project management methodology.
What is project management methodology?
A project management methodology is a set of principles, techniques, and procedures Project Managers use to execute and manage projects. There are several methodologies and all require different workflows, deliverables, and project management software development. The project management methodologies facilitate team collaboration by directing team members to work for a common objective.
Are your projects complex or straightforward? Whatever the case may be, these Top 10 Project Management Cycle Templates will help you organize and track every bit of it!
When a project is carried out systematically, chances of success are better. Project managers are responsible for planning tasks, tracking progress, and delivering results. Here’s when a project methodology comes in. It includes certain procedures that help you structure your team’s workflow.
There are many project methodologies available for the systematic execution of a project. Choosing the best one among a landscape of methodologies can be overwhelming. Some of these work well in specific projects or industries. However, Product managers select the methodology that best suits the way their teams work.
Here, in this blog, we'll talk about project methodologies and templates you can use in your projects.
Let’s explore!
Template 1: Project Management Methodologies PowerPoint Presentation Slides
This PPT displays an elaborative project agenda, including the project brief essential to operate efficiently. The layout also consists of details about the company's products. Showcase the progress summary, and the milestones achieved and reflect on the potential goals. Download now!

Download now!
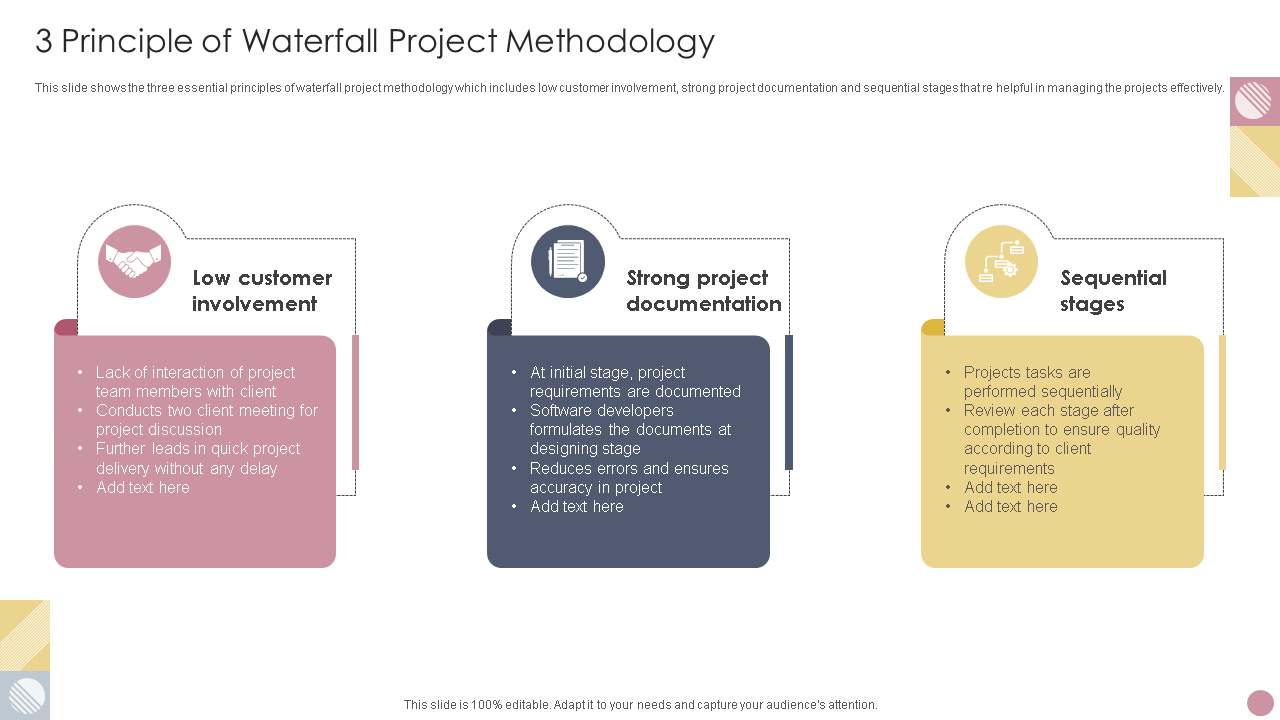
Template 2: Three Principles of Waterfall Project Methodology
This PPT is designed while keeping in mind the linear approach, meaning that the tasks are organized in a sequence. This template allows you to map the tasks from beginning to end and work accordingly. It includes three essential waterfall project methodology principles: low customer involvement, robust project documentation, and sequential stages that smoothen up the project management process. Download now!
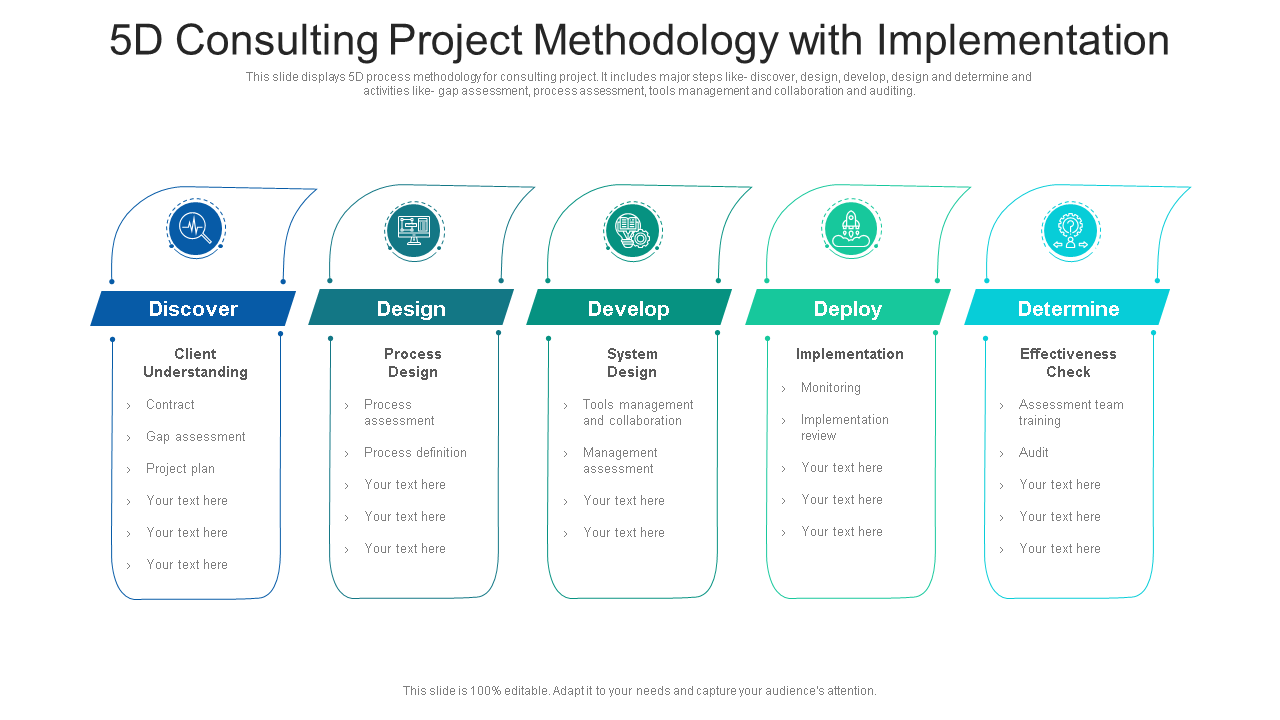
Template 3: 5D Consulting Project Methodology with Implementation
This PPT Template portrays a five-dimensional visualization process for consulting projects. It includes major steps like discovering, designing, developing, designing, and determining while considering budgetary and cost requirements. It also comprises activities like process assessment, tools management, collaboration, etc., that aid in accurate project deployment and maintenance. Download now!
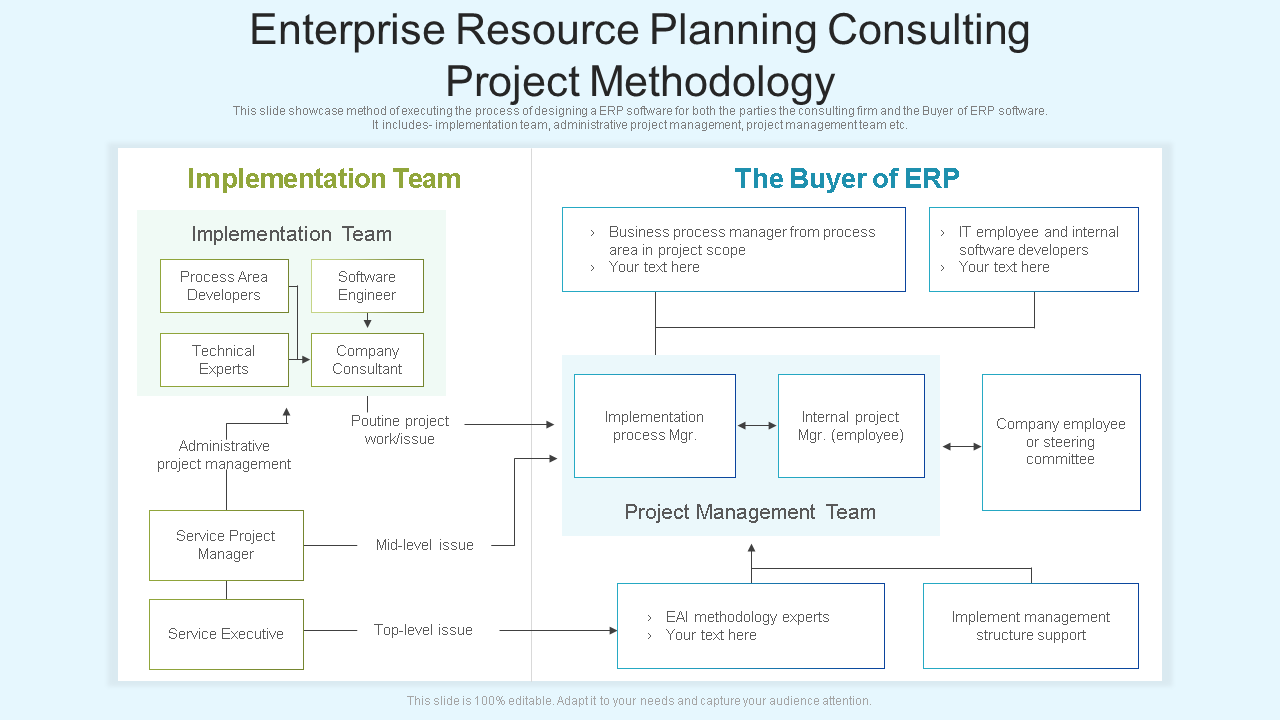
Template 4: Enterprise Resource Planning Consulting Project Methodology
This template displays an execution method for designing ERP software for both parties; the consulting firm and the buyer. It includes the implementation team, administrative project management, project management team, etc. Ace your resource planning game by organizing, identifying, and listing the resources required to complete a project. Get it now!
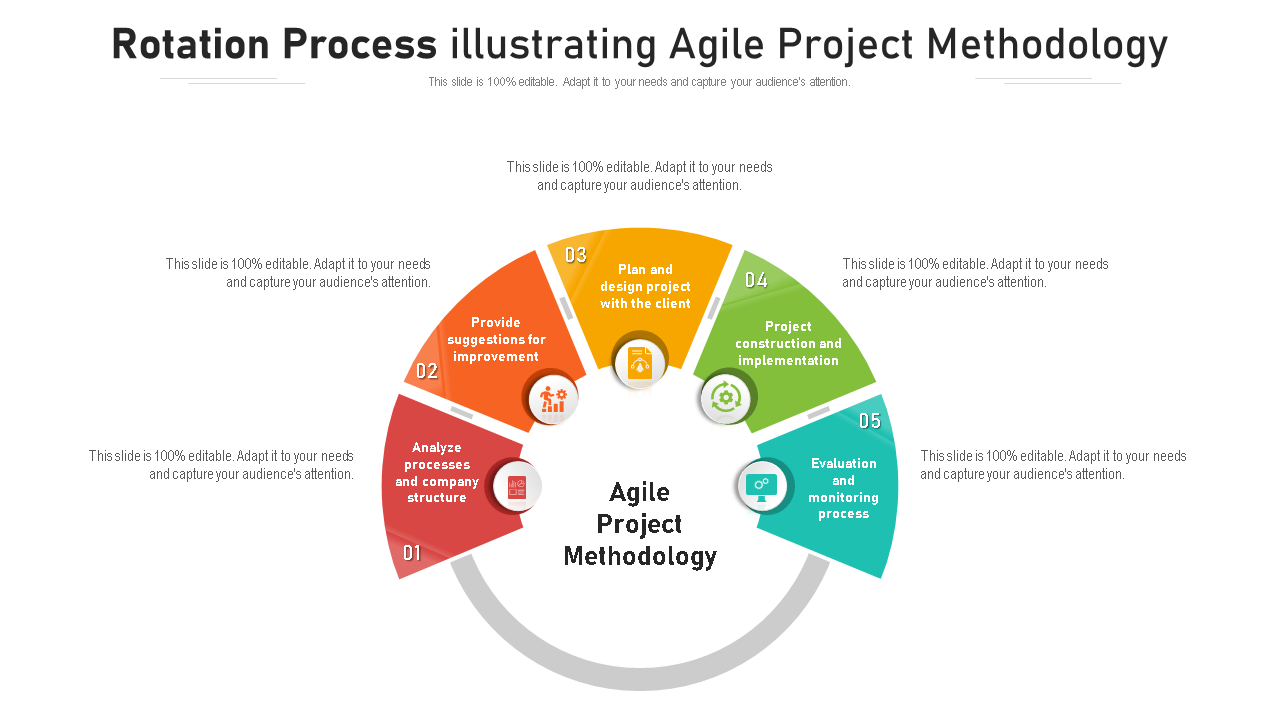
Template 5: Rotation Process Illustrating Agile Project Methodology
Agile is more of an approach than a methodology. It is collaborative, fast and effective, data-backed, and values individuals over processes. This template lets you analyze processes, provide suggestions, plan & design projects, project construction, and evaluate & monitor processes. Download now!
Template 6: Consulting Project Methodology for Supply Chain and Logistics
This template exhibits consulting project methodology for supply chain and logistics. It includes the five-step process of mapping, internal audit, gap assessment, solution design, and implementation. The topics discussed in this slide are gap analysis, solution design, implementation, internal audit, and mapping. Download this versatile template now!
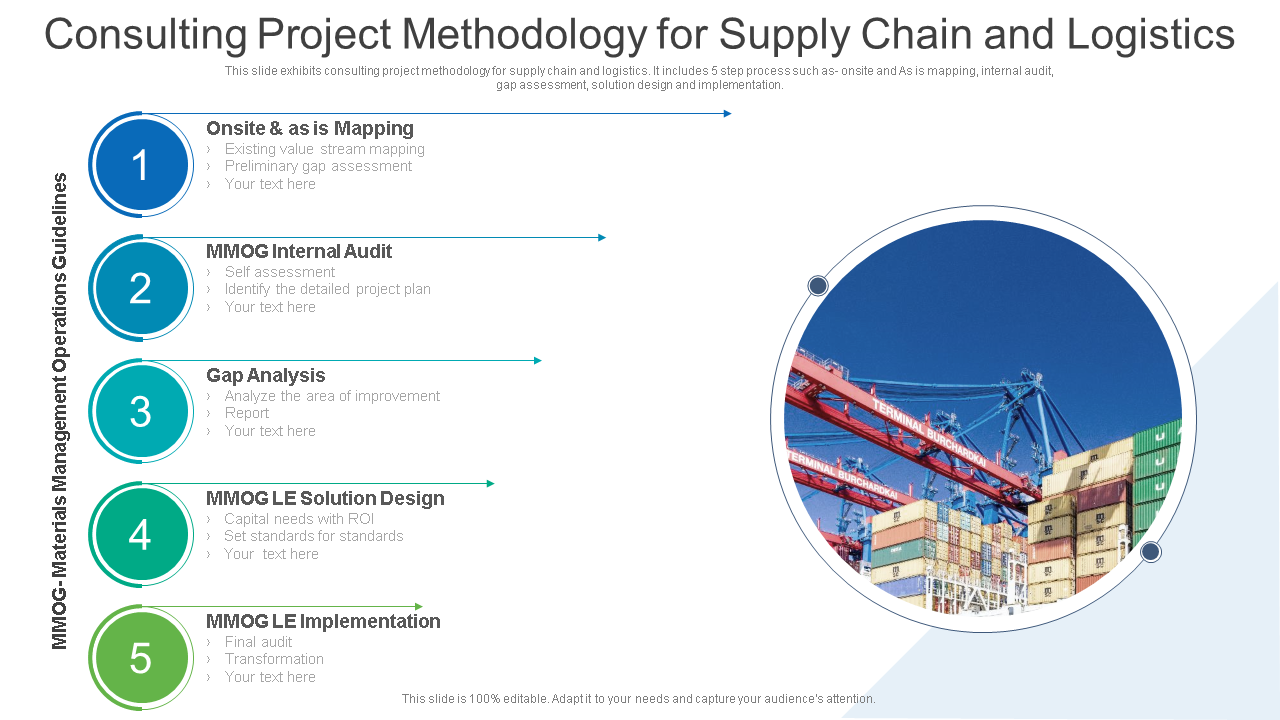
Template 7: Project Management Methodology Including Planning
This methodology is the one most used by project managers. It portrays the tasks in a chronological manner involving designing, developing, testing, and deploying a project. If you're looking for a comprehensive guide to your next project, look no further than this. Download it now!
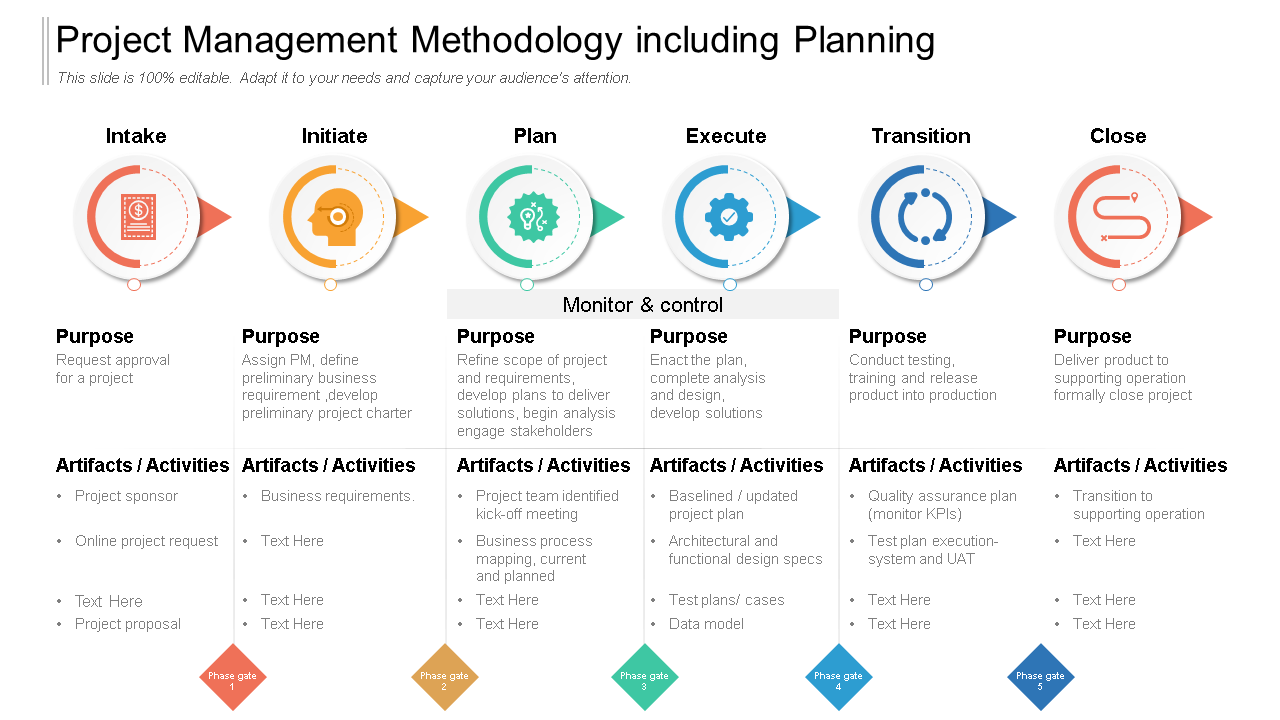
Template 8: Project Management and Implementation Methodology Overview
Project management and implementation methodology plays a significant role in ensuring successful delivery of projects. This template explains how these methods can be used to ensure the successful delivery of projects, along with some tips for implementing them. They also include a variety of practical examples to help you understand how the methodology can be applied in a real-world scenario. Get it now!
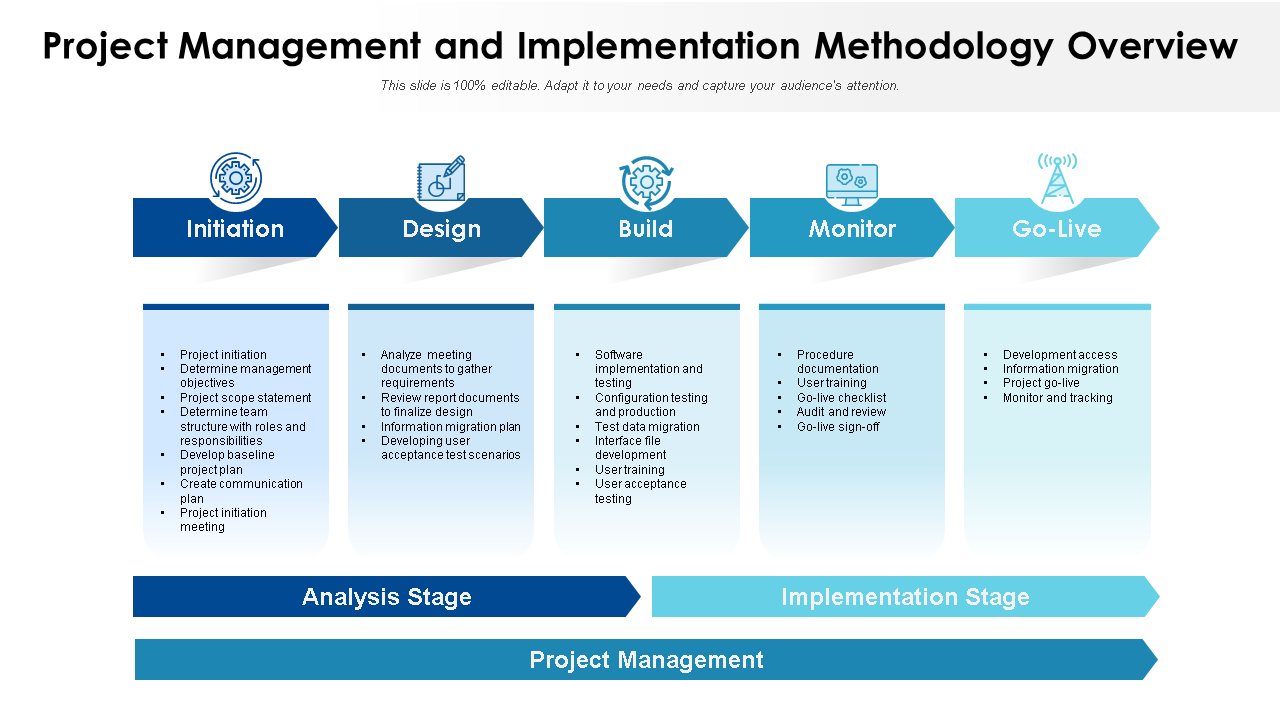
Template 9: Waterfall vs Agile Development Methodology for Project
This two-stage process template for projects is explicit and effective. It combines clarity and concise expression to achieve holistic project development by enabling client/stakeholder collaboration. It encourages frequent interaction of team members, making them resolve any complexities and meet requirements before deadlines. Download this now!
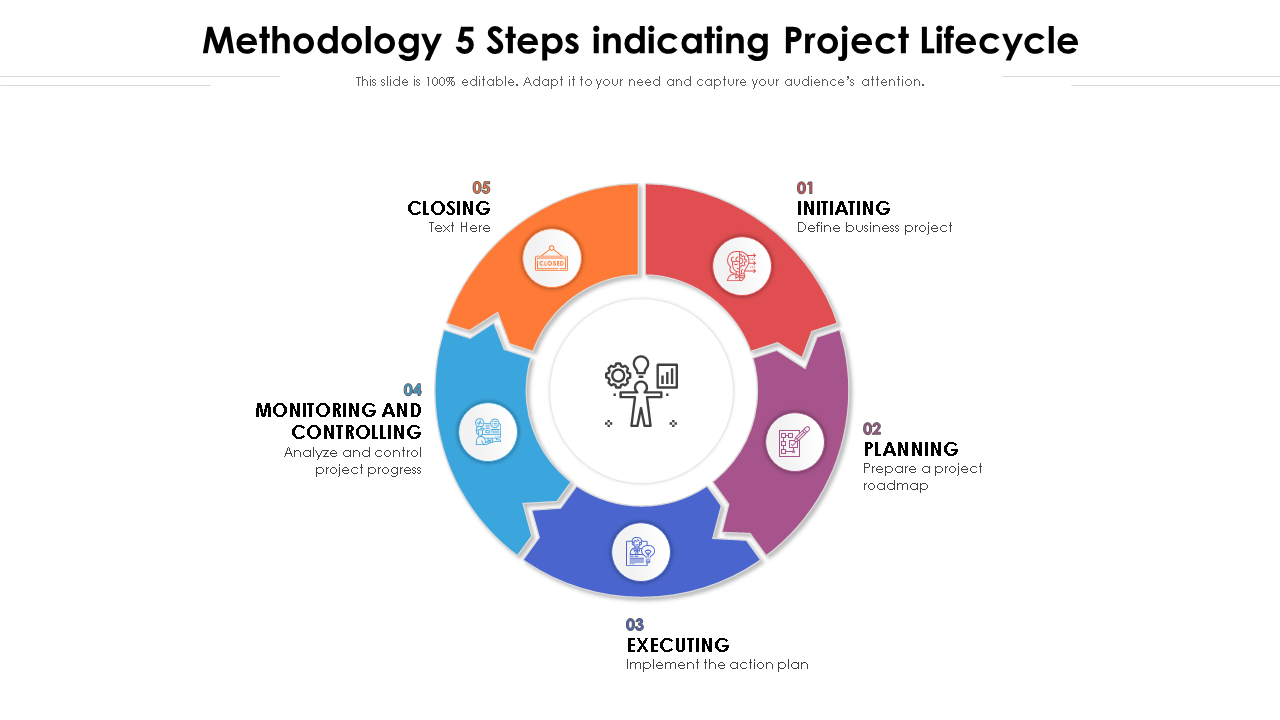
Template 10: Methodology Five Steps Indicating Project Lifecycle
Strategically important complex projects that are long-term, resource-heavy, and extensive, require flexible project management methodology. This template includes five steps of a project lifecycle that helps bring more cohesion to your project. Keep every team member on the same page with this helpful and 100% customizable template. Download now!
Manage Your Projects Well
By choosing the right project management methodology at the right time and the right place, you’ll be able to make your projects more efficient. Finding the perfect project methodology also helps implement processes right for you, your team, and your organization.
We hope that the above set of templates serves as the ultimate tool in your belt!
FAQs on Project Methodology
What is a project methodology.
A project management methodology is a detailed manual to supervise project completion. A project team uses this set of defined processes to initiate, plan, and execute the project. The type of project methodology you choose establishes the way of work organization, prioritization, and completion.
The project management methodology aims to standardize, structure, and organize work requirements and methods. This helps focus on what works best and enables the repetition of successful aspects and learning from mistakes, resulting in a continuous improvement process.
What are the five project methodologies?
Here are five common project methodologies used by Project Managers to manage workflow:
- Agile : This method is best suited for projects which require extreme flexibility and speed. It focuses less on documentation and more on customer satisfaction. Agile methodology is good for products with a faster release cycle.
- Scrum : Scrum methodology has an iterative project management style. It follows the principles followed in Agile methodology. In this method, the work is done in sessions known as ‘Sprints’. Here, the Scrum Master facilitates the process instead of a Project Manager.
- Waterfall : It is based on traditional methods and mainly focuses on following the processes. Here, much emphasis is given to project documentation.
- Critical Path Method : This methodology is a step-by-step method and works best for projects with independent tasks. Its key role is to measure and prioritize tasks.
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique : This method is commonly used along with CPM (Critical Path Method). It is mostly used by businesses that are looking for expansion. It measures progress to create timelines and budgets.
- Critical Chain Method : A separate classification, this methodology is more advanced than the CPM methodology. Here, goals are created based on constraints while focusing on cost-saving benefits.
What are the three major types of project methodologies?
Here are three major types of methodologies commonly used:
- Scrum method : Scrum is the most widely used agile methodology for project management. It allows you to do more by scheduling tasks in short cycles named sprints. It enables you to work as a dedicated team to analyze processes, meet requirements, and meet deadlines. It also helps you receive continuous feedback rather than using final evaluations. The scrum methodology is mostly used to develop new projects, compile budgets, and organize annual reports.
- Waterfall method : This method is linear and phase-based. It arranges and organizes tasks chronologically, which helps identify major areas of errors. Documentation is a huge part of waterfall methodology. It entails precise details about what you’re doing and how you’re doing it. This methodology doesn’t provide any room for flexibility.
- Lean and Six Sigma method : Lean and Six Sigma method is famous for its ability to manage the resource and time wastage that occurs in other methodologies. It is an approach to continuous improvement that is divided into two types of initiatives- Ongoing improvement initiatives and project-based initiatives. Each of these is associated with a set of methods and tools for you to employ. Ultimately, this methodology is based on the Kaizen principle that aims at making small changes on a daily basis for continuous improvement in small, easy steps.
How do you prepare a project methodology?
A good project method will represent the convergence of many factors, such as your scope, professional experience, and the research done. Here’s how you can prepare a project methodology in five steps:
- Communicate deliverables : A solid plan requires proper research and pre-planning. So, the first step is to set clear objectives, cost & budget, project requirements, and deliverables to work upon.
- Define the process : Choose the project methodology that best suits your team’s workflow and organizational structure. Sit with your team and draft a process that matches your work style and project requirements.
- Communicate risks and deadlines : Analyzing the ability to manage risks while meeting project deadlines is the next step in preparing a methodology. You need to observe the level of risk you can handle based on the size of the project.
- Determine task dependencies : Next, it is important to understand if you can perform tasks while keeping room for flexibility to alter the processes.
Define client/ stakeholder collaboration : Finally, you need to oversee the level of involvement you need from your stakeholders and clients in a project. It also defines team roles and assignments to help break down bigger projects into small and easy tasks.
Related posts:
- [Updated 2023] An All-Encompassing Guide to Project Planning (With 30+ PowerPoint Templates to Help You Get Started)
- [Updated 2023] Top 20 One Page Project Plans, Project Proposals, and Executive Summaries for Project Management
- Top 10 Research Paper Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 10 Project Report Templates With Samples And Examples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Project Management Checklist Templates With Samples and Examples (Free PDF Attached)

Top 10 Project Management Cycle Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Your Methods

Ensure understanding, reproducibility and replicability
What should you include in your methods section, and how much detail is appropriate?
Why Methods Matter
The methods section was once the most likely part of a paper to be unfairly abbreviated, overly summarized, or even relegated to hard-to-find sections of a publisher’s website. While some journals may responsibly include more detailed elements of methods in supplementary sections, the movement for increased reproducibility and rigor in science has reinstated the importance of the methods section. Methods are now viewed as a key element in establishing the credibility of the research being reported, alongside the open availability of data and results.
A clear methods section impacts editorial evaluation and readers’ understanding, and is also the backbone of transparency and replicability.
For example, the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology project set out in 2013 to replicate experiments from 50 high profile cancer papers, but revised their target to 18 papers once they understood how much methodological detail was not contained in the original papers.
What to include in your methods section
What you include in your methods sections depends on what field you are in and what experiments you are performing. However, the general principle in place at the majority of journals is summarized well by the guidelines at PLOS ONE : “The Materials and Methods section should provide enough detail to allow suitably skilled investigators to fully replicate your study. ” The emphases here are deliberate: the methods should enable readers to understand your paper, and replicate your study. However, there is no need to go into the level of detail that a lay-person would require—the focus is on the reader who is also trained in your field, with the suitable skills and knowledge to attempt a replication.
A constant principle of rigorous science
A methods section that enables other researchers to understand and replicate your results is a constant principle of rigorous, transparent, and Open Science. Aim to be thorough, even if a particular journal doesn’t require the same level of detail . Reproducibility is all of our responsibility. You cannot create any problems by exceeding a minimum standard of information. If a journal still has word-limits—either for the overall article or specific sections—and requires some methodological details to be in a supplemental section, that is OK as long as the extra details are searchable and findable .
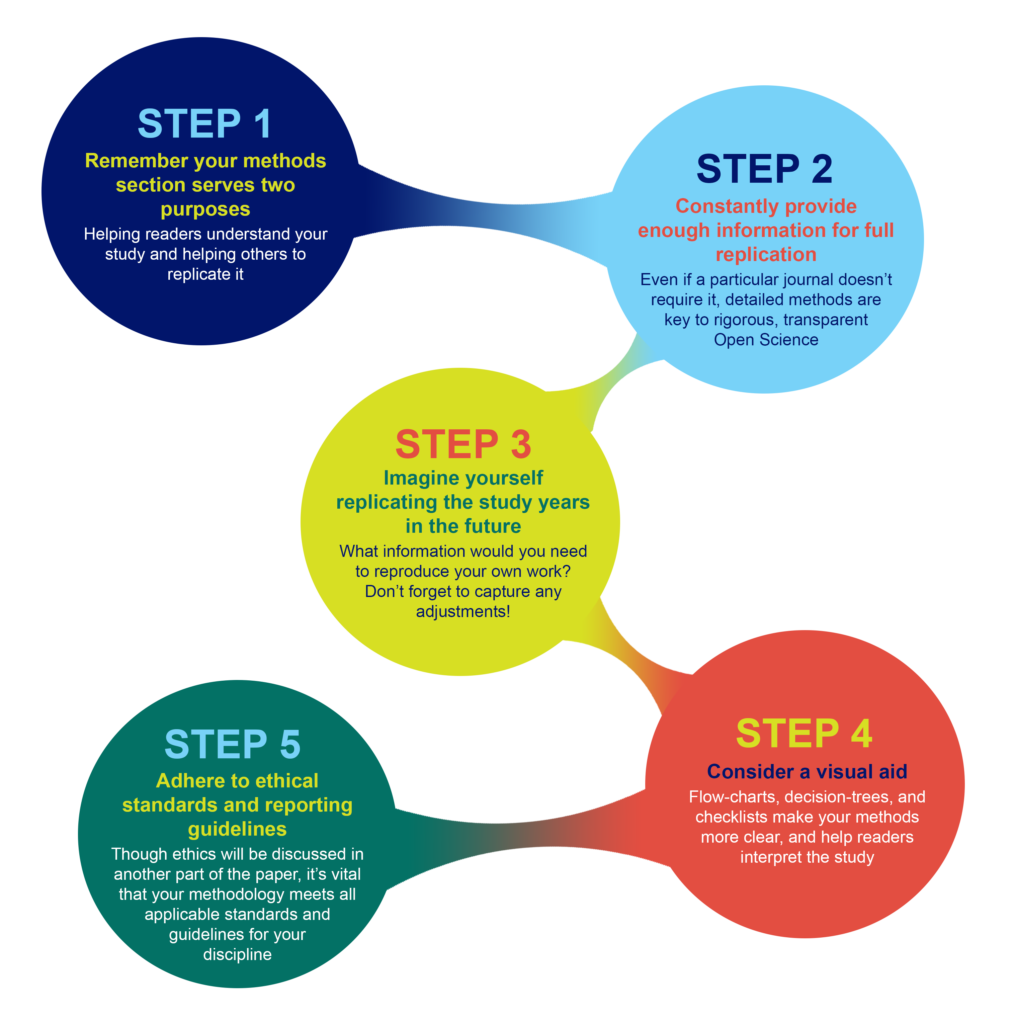
Imagine replicating your own work, years in the future
As part of PLOS’ presentation on Reproducibility and Open Publishing (part of UCSF’s Reproducibility Series ) we recommend planning the level of detail in your methods section by imagining you are writing for your future self, replicating your own work. When you consider that you might be at a different institution, with different account logins, applications, resources, and access levels—you can help yourself imagine the level of specificity that you yourself would require to redo the exact experiment. Consider:
- Which details would you need to be reminded of?
- Which cell line, or antibody, or software, or reagent did you use, and does it have a Research Resource ID (RRID) that you can cite?
- Which version of a questionnaire did you use in your survey?
- Exactly which visual stimulus did you show participants, and is it publicly available?
- What participants did you decide to exclude?
- What process did you adjust, during your work?
Tip: Be sure to capture any changes to your protocols
You yourself would want to know about any adjustments, if you ever replicate the work, so you can surmise that anyone else would want to as well. Even if a necessary adjustment you made was not ideal, transparency is the key to ensuring this is not regarded as an issue in the future. It is far better to transparently convey any non-optimal methods, or methodological constraints, than to conceal them, which could result in reproducibility or ethical issues downstream.
Visual aids for methods help when reading the whole paper
Consider whether a visual representation of your methods could be appropriate or aid understanding your process. A visual reference readers can easily return to, like a flow-diagram, decision-tree, or checklist, can help readers to better understand the complete article, not just the methods section.
Ethical Considerations
In addition to describing what you did, it is just as important to assure readers that you also followed all relevant ethical guidelines when conducting your research. While ethical standards and reporting guidelines are often presented in a separate section of a paper, ensure that your methods and protocols actually follow these guidelines. Read more about ethics .
Existing standards, checklists, guidelines, partners
While the level of detail contained in a methods section should be guided by the universal principles of rigorous science outlined above, various disciplines, fields, and projects have worked hard to design and develop consistent standards, guidelines, and tools to help with reporting all types of experiment. Below, you’ll find some of the key initiatives. Ensure you read the submission guidelines for the specific journal you are submitting to, in order to discover any further journal- or field-specific policies to follow, or initiatives/tools to utilize.
Tip: Keep your paper moving forward by providing the proper paperwork up front
Be sure to check the journal guidelines and provide the necessary documents with your manuscript submission. Collecting the necessary documentation can greatly slow the first round of peer review, or cause delays when you submit your revision.
Randomized Controlled Trials – CONSORT The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) project covers various initiatives intended to prevent the problems of inadequate reporting of randomized controlled trials. The primary initiative is an evidence-based minimum set of recommendations for reporting randomized trials known as the CONSORT Statement .
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses – PRISMA The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ( PRISMA ) is an evidence-based minimum set of items focusing on the reporting of reviews evaluating randomized trials and other types of research.
Research using Animals – ARRIVE The Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments ( ARRIVE ) guidelines encourage maximizing the information reported in research using animals thereby minimizing unnecessary studies. (Original study and proposal , and updated guidelines , in PLOS Biology .)
Laboratory Protocols Protocols.io has developed a platform specifically for the sharing and updating of laboratory protocols , which are assigned their own DOI and can be linked from methods sections of papers to enhance reproducibility. Contextualize your protocol and improve discovery with an accompanying Lab Protocol article in PLOS ONE .
Consistent reporting of Materials, Design, and Analysis – the MDAR checklist A cross-publisher group of editors and experts have developed, tested, and rolled out a checklist to help establish and harmonize reporting standards in the Life Sciences . The checklist , which is available for use by authors to compile their methods, and editors/reviewers to check methods, establishes a minimum set of requirements in transparent reporting and is adaptable to any discipline within the Life Sciences, by covering a breadth of potentially relevant methodological items and considerations. If you are in the Life Sciences and writing up your methods section, try working through the MDAR checklist and see whether it helps you include all relevant details into your methods, and whether it reminded you of anything you might have missed otherwise.
Summary Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your methods is keeping it readable AND covering all the details needed for reproducibility and replicability. While this is difficult, do not compromise on rigorous standards for credibility!

- Keep in mind future replicability, alongside understanding and readability.
- Follow checklists, and field- and journal-specific guidelines.
- Consider a commitment to rigorous and transparent science a personal responsibility, and not just adhering to journal guidelines.
- Establish whether there are persistent identifiers for any research resources you use that can be specifically cited in your methods section.
- Deposit your laboratory protocols in Protocols.io, establishing a permanent link to them. You can update your protocols later if you improve on them, as can future scientists who follow your protocols.
- Consider visual aids like flow-diagrams, lists, to help with reading other sections of the paper.
- Be specific about all decisions made during the experiments that someone reproducing your work would need to know.

Don’t
- Summarize or abbreviate methods without giving full details in a discoverable supplemental section.
- Presume you will always be able to remember how you performed the experiments, or have access to private or institutional notebooks and resources.
- Attempt to hide constraints or non-optimal decisions you had to make–transparency is the key to ensuring the credibility of your research.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…

Thesis, major paper, and major project proposals
- Definitions
- Introductory section
- Literature review
Methodology
- Schedule/work plan
- Other potential elements
- Proposal references
- Ask for help

The methodology section can include (but isn't limited to):
- A description of the research design and methods
- A description of data-gathering instruments
- Methods of data collection
- Ethical considerations
- Analysis strategies and techniques
- Potential participants
- Rationale for your choice of methodological choices
- How the methodology is appropriate for the organization or participants
- The advantages and disadvantages of the methodology
- References to scholarly literature that support the chosen research design and methods
If you are unsure if including the methodology is required in your thesis, major project, or research paper proposal, please consult with your instructor or advisor.
This information regarding the methodology section of a proposal was gathered from RRU thesis and major project handbooks, current in 2020, from programs in the Faculty of Social and Applied Sciences, the Faculty of Management, and the College of Interdisciplinary Studies. If the details here differ from the information provided in the handbook for your project, please follow the handbook's directions.
Image credit: Image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay

- In SAGE Research Methods Project Planner ; access via this link requires a RRU username and password.
Data Collection
How Do I Write About Theory?
- In SAGE Research Methods: Writing Up ; look for the How Do I Write About Theory? drop down option. Access via this link requires a RRU username and password.
How Do I Write My Methodology Section?
- In SAGE Research Methods: Writing Up ; look for the How Do I Write My Methodology Section? drop down option. Access via this link requires a RRU username and password.
Research Ethics
Image credit: Image by Mohamed Assan from Pixabay
- << Previous: Literature review
- Next: Schedule/work plan >>
- Last Updated: Jan 8, 2024 12:29 PM
- URL: https://libguides.royalroads.ca/proposals

studioprogetto.net
helping you conduct any research project easily
7-Step Guide on How to Write Methodology of a Project
The methodology section helps the reader to understand how you collected data, the tools used, and the philosophy behind the steps you took. The section helps readers to determine the research veracity of your work. It can determine whether the paper meets desired conditions or it will fall short.
Creating a methodology is one of the most difficult tasks even though it can be a few paragraphs or pages in a paper that is hundreds of pages long. It must capture the type of research you did, how you collected data, the approach during analysis, tools used, and the rationale for all these actions.
Why is methodology important? It provides your philosophy on data collection and handling. It can tell a reader whether your data is valid and, therefore, whether your conclusions are justified. By the time the reader is interacting with the data, he will know that it has been collected professionally.
Here are crucial tips on how to write a project methodology section that captures the imagination of every reader.
- Understand the methodology section
To understand what to include in methods section, you must know the role that the section plays in a research paper. The chapter helps a reader to examine the validity of the data you are using to make conclusions. Notice that the section involves a revelation of the methods used to collect data, tools used during analysis, and the challenges you encountered.
A reader can determine whether those were the best methods or tools available. If you overlooked or assumed too much about research, your paper will miss the mark. The secret is to use the best methods and tools, anticipating the strongest outcomes.
- Use samples as a guide
One of the best guides on how to write a methodology for a project is a sample. The samples feature what you are expected to produce at the end of the writing process. You only should be cautious to obtain the samples from credible sources. A poor quality sample will mislead you instead, resulting in poor performance.
- Gather details on your research methodology
How have you executed your research methodology section? Did you use questionnaires or interviews? What analysis tools did you use? The information must be accurately captured in the section. Remember that transcripts of the interviews and the questionnaires used have to be attached at the end of the paper. Know what you used and the steps you took. A reader can test these assertions.
- Use past tense
One of the tricks on how to write a good research methodology chapter is to master the tense. The section comes from research carried out long before and the data analyzed. It is, therefore, only logical to use past tense in your writing.
- The chapter is descriptive
Use descriptive words when crafting the topic. The reader wants to visualize you collecting data and analyzing it. It is written in such a way that if the reader follows your steps, he will arrive at a similar conclusion. Language is a crucial trick on how to write methodology of a project. It explains the fact that research is already complete.
- Revisit your objectives and research questions
The research question and objectives will guide you on how to write methodology of project. All the data you collect and how you analyze it should help you to answer the research questions and meet these objectives. The two must, therefore, be tied to the methodology section.
- Discuss obstacles
Discuss the shortcomings you experienced. Such challenges are a part of every academic project. They show that your research is not conclusive, paving way for improvements in the future.
Plan your methodology section to be accurate and represent the objectives you set before the start. Use samples to guide you through the writing process. You may also hire professional writing assistants to enable you to draft the best chapter.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write a Research Proposal
Writing a Research proposal involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and comprehensive document. Here is an explanation of each step:
1. Title and Abstract
- Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research.
- Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal.
2. Introduction:
- Provide an introduction to your research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
- Clearly state the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Discuss the background and context of the study, including previous research in the field.
3. Research Objectives
- Outline the specific objectives or aims of your research. These objectives should be clear, achievable, and aligned with the research problem.
4. Literature Review:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings, identify gaps, and highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to employ to address your research objectives.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques you will use.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate and suitable for your research.
6. Timeline:
- Create a timeline or schedule that outlines the major milestones and activities of your research project.
- Break down the research process into smaller tasks and estimate the time required for each task.
7. Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for your research, such as access to specific databases, equipment, or funding.
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources to carry out your research effectively.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise during your research and explain how you plan to address them.
- If your research involves human subjects, explain how you will ensure their informed consent and privacy.
9. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
- Clearly state the expected outcomes or results of your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and significance of your research in advancing knowledge or addressing practical issues.
10. References:
- Provide a list of all the references cited in your proposal, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
11. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans.
Research Proposal Format
The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your research proposal, highlighting the research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
3. Introduction:
- Introduce the research topic and provide background information.
- State the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the research.
- Review relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings and identify gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Explain how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
5. Research Objectives:
- Clearly state the specific objectives or aims of your research.
- Ensure that the objectives are clear, focused, and aligned with the research problem.
6. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to use.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate for your research.
7. Timeline:
8. Resources:
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources effectively.
9. Ethical Considerations:
- If applicable, explain how you will ensure informed consent and protect the privacy of research participants.
10. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
11. References:
12. Appendices:
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a template for a research proposal:
1. Introduction:
2. Literature Review:
3. Research Objectives:
4. Methodology:
5. Timeline:
6. Resources:
7. Ethical Considerations:
8. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
9. References:
10. Appendices:
Research Proposal Sample
Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study
1. Introduction
Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes by comparing them with traditional face-to-face instruction. The study will explore various aspects of online education, such as instructional methods, student engagement, and academic performance, to provide insights into the effectiveness of online learning.
2. Objectives
The main objectives of this research are as follows:
- To compare student learning outcomes between online and traditional face-to-face education.
- To examine the factors influencing student engagement in online learning environments.
- To assess the effectiveness of different instructional methods employed in online education.
- To identify challenges and opportunities associated with online education and suggest recommendations for improvement.
3. Methodology
3.1 Study Design
This research will utilize a mixed-methods approach to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. The study will include the following components:
3.2 Participants
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study.
3.3 Data Collection
The research will employ the following data collection methods:
- Quantitative: Pre- and post-assessments will be conducted to measure students’ learning outcomes. Data on student demographics and academic performance will also be collected from university records.
- Qualitative: Focus group discussions and individual interviews will be conducted with students to gather their perceptions and experiences regarding online education.
3.4 Data Analysis
Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical software, employing descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis. Qualitative data will be transcribed, coded, and analyzed thematically to identify recurring patterns and themes.
4. Ethical Considerations
The study will adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Informed consent will be obtained, and participants will have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
5. Significance and Expected Outcomes
This research will contribute to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the impact of online education on student learning outcomes. The findings will help educational institutions and policymakers make informed decisions about incorporating online learning methods and improving the quality of online education. Moreover, the study will identify potential challenges and opportunities related to online education and offer recommendations for enhancing student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
6. Timeline
The proposed research will be conducted over a period of 12 months, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
The estimated budget for this research includes expenses related to data collection, software licenses, participant compensation, and research assistance. A detailed budget breakdown will be provided in the final research plan.
8. Conclusion
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes through a comparative study with traditional face-to-face instruction. By exploring various dimensions of online education, this research will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges associated with online learning. The findings will contribute to the ongoing discourse on educational practices and help shape future strategies for maximizing student learning outcomes in online education settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?
- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Write a Project Proposal (Examples & Template Included)

Table of Contents
What is a project proposal, types of project proposals, project proposal vs. project charter, project proposal vs. business case, project proposal vs. project plan, project proposal outline, how to write a project proposal, project proposal example, project proposal tips.
- ProjectManager & Project Proposals
A project proposal is a project management document that’s used to define the objectives and requirements of a project. It helps organizations and external project stakeholders agree on an initial project planning framework.
The main purpose of a project proposal is to get buy-in from decision-makers. That’s why a project proposal outlines your project’s core value proposition; it sells value to both internal and external project stakeholders. The intent of the proposal is to grab the attention of stakeholders and project sponsors. Then, the next step is getting them excited about the project summary.
Getting into the heads of the audience for which you’re writing the project proposal is vital: you need to think like the project’s stakeholders to deliver a proposal that meets their needs.
We’ve created a free project proposal template for Word to help structure documents, so you don’t have to remember the process each time.

Get your free
Project Proposal Template
Use this free Project Proposal Template for Word to manage your projects better.
In terms of types of project proposals, you can have one that’s formally solicited, informally solicited or a combination. There can also be renewal and supplemental proposals. Here’s a brief description of each of them.
- Solicited project proposal: This is sent as a response to a request for proposal (RFP) . Here, you’ll need to adhere to the RFP guidelines of the project owner.
- Unsolicited project proposal: You can send project proposals without having received a request for a proposal. This can happen in open bids for construction projects , where a project owner receives unsolicited project proposals from many contractors.
- Informal project proposal: This type of project proposal is created when a client asks for an informal proposal without an RFP.
- Renewal project proposal: You can use a renewal project proposal when you’re reaching out to past customers. The advantage is that you can highlight past positive results and future benefits.
- Continuation project proposal: A continuation project proposal is sent to investors and stakeholders to communicate project progress.
- Supplemental project proposal: This proposal is sent to investors to ask for additional resources during the project execution phase.
A project proposal is a detailed project document that’s used to convince the project sponsor that the project being proposed is worth the time, money and effort to deliver it. This is done by showing how the project will address a business problem or opportunity. It also outlines the work that will be done and how it will be done.
A project charter can seem like the same thing as a project proposal as it also defines the project in a document. It identifies the project objectives, scope, goals, stakeholders and team. But it’s done after the project has been agreed upon by all stakeholders and the project has been accepted. The project charter authorizes the project and documents its requirements to meet stakeholders’ needs.
A business case is used to explain why the proposed project is justified. It shows that the project is worth the investment of time and money. It’s more commonly used in larger companies in the decision-making process when prioritizing one project over another.
The business case answers the questions: what is the project, why should it be taken up, who will be involved and how much will it cost? It’s therefore related to a project proposal, but the project proposal comes before the business case and is usually part of the larger proposal.
Again, the project proposal and the project plan in this case are very similar documents. It’s understandable that there would be some confusion between these two project terms. They both show how the project will be run and what the results will be. However, they’re not the same.
The project proposal is a document that aims to get a project approved and funded. It’s used to convince stakeholders of the viability of the project and their investment. The project plan, on the other hand, is made during the planning phase of the project, once it’s been approved. It’s a detailed outline of how the project will be implemented, including schedule, budget, resources and more.
All the elements in the above project proposal outline are present in our template. This free project proposal template for Word will provide you with everything you need to write an excellent project proposal. It will help you with the executive summary, project process, deliverables, costs—even terms and conditions. Download your free template today.
There are several key operational and strategic questions to consider, including:
- Executive summary: This is the elevator pitch that outlines the project being proposed and why it makes business sense. While it also touches on the information that’ll follow in the project proposal, the executive summary should be brief and to the point.
- Project background: This is another short part of the proposal, usually only one page, which explains the problem you’ll solve or the opportunity you’re taking advantage of with the proposed project. Also, provide a short history of the business to put the company in context to the project and why it’s a good fit.
- Project vision & success criteria: State the goal of the project and how it aligns with the goals of the company. Be specific. Also, note the metrics used to measure the success of the project.
- Potential risks and mitigation strategies: There are always risks. Detail them here and what strategies you’ll employ to mitigate any negative impact as well as take advantage of any positive risk.
- Project scope & deliverables: Define the project scope, which is all the work that has to be done and how it will be done. Also, detail the various deliverables that the project will have.
- Set SMART goals: When setting goals, be SMART. That’s an acronym for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. All your goals would be defined by those five things.
- Project approach: Define the approach you’ll use for the contract. There are several different types of contracts used in construction , for example, such as lump sum, cost plus, time and materials, etc. This is also a good place to describe the delivery method you’ll use.
- Expected benefits: Outline the benefits that will come from the successful completion of the project.
- Project resource requirements: List the resources, such as labor, materials, equipment, etc., that you’ll need to execute the project if approved.
- Project costs & budget: Detail all the costs, including resources, that’ll be required to complete the project and set up a budget to show how those costs will be spent over the course of the project.
- Project timeline: Lay out the project timeline , which shows the project from start to finish, including the duration of each phase and the tasks within it, milestones, etc.
In addition to these elements, it’s advisable to use a cover letter, which is a one-page document that helps you introduce your project proposal and grab the attention of potential clients and stakeholders.
To make the best proposal possible, you’ll want to be thorough and hit on all the points we’ve listed above. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a persuasive priority proposal.
1. Write an Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a quick overview of the main elements of your project proposal, such as your project background, project objectives and project deliverables, among other things. The goal is to capture the attention of your audience and get them excited about the project you’re proposing. It’s essentially the “elevator pitch” for the project life cycle. It should be short and to the point.
The executive summary should be descriptive and paint a picture of what project success looks like for the client. Most importantly, it should motivate the project client; after all, the goal is getting them to sign on the dotted line to get the project moving!
2. Provide a Project Background
The project background is a one-page section of your project proposal that explains the problem that your project will solve. You should explain when this issue started, its current state and how your project will be the ideal solution.
- Historic data: The history section outlines previously successful projects and those that could have run more smoothly. By doing so, this section establishes precedents and how the next project can be more effective using information from previous projects.
- Solution: The solution section addresses how your project will solve the client’s problem. Accordingly, this section includes any project management techniques , skills and procedures your team will use to work efficiently.
3. Establish a Project Vision & Success Criteria
You’ll need to define your project vision. This is best done with a vision statement, which acts as the north star for your project. It’s not specific as much as it’s a way to describe the impact your company plans to make with the project.
It’s also important to set up success criteria to show that the project is in fact doing what it’s proposed to do. Three obvious project success criteria are the triple constraint of cost, scope and time. But you’ll need to set up a way to measure these metrics and respond to them if they’re not meeting your plan.
4. Identify Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
To reduce the impact of risk in your project, you need to identify what those risks might be and develop a plan to mitigate them . List all the risks, prioritize them, describe what you’ll do to mitigate or take advantage of them and who on the team is responsible for keeping an eye out for them and resolving them.
5. Define Your Project Scope and Project Deliverables
The project scope refers to all the work that’ll be executed. It defines the work items, work packages and deliverables that’ll be delivered during the execution phase of your project life cycle. It’s important to use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to define your tasks and subtasks and prioritize them.
6. Set SMART Goals for Your Project Proposal
The best mindset when developing goals and objectives for your project proposal is to use the SMART system :
- Specific – Make sure your goals and objectives are clear, concise and specific to the task at hand.
- Measurable – Ensure your goals and objectives are measurable so it’s obvious to see when things are on track and going well, and conversely, when things are off track and issues need to be addressed. Measurable goals make it easy to develop the milestones you’ll use to track the progress of the project and identify a reasonable date for completion and/or closure.
- Attainable – It’s important every project has a “reach” goal. Hitting this goal would mean an outstanding project that extends above and beyond expectations. However, it’s important that the project’s core goal is attainable, so morale stays high and the job gets done with time and resources to spare.
- Relevant – Make sure all of your goals are directly relevant to the project and address the scope within which you’re working.
- Time-Based – Timelines and specific dates should be at the core of all goals and objectives. This helps keep the project on track and ensures all project team members can manage the work that’s ahead of them.
7. Explain What’s Your Project Approach
Your project approach defines the project management methodology , tools and governance for your project. In simple terms, it allows project managers to explain to stakeholders how the project will be planned, executed and controlled successfully.
8. Outline The Expected Benefits of Your Project Proposal
If you want to convince internal stakeholders and external investors, you’ll need to show them the financial benefits that your project could bring to their organization. You can use cost-benefit analysis and projected financial statements to demonstrate why your project is profitable.
9. Identify Project Resource Requirements
Project resources are critical for the execution of your project. The project proposal briefly describes what resources are needed and how they’ll be used. Later, during the planning phase, you’ll need to create a resource management plan that’ll be an important element of your project plan. Project requirements are the items, materials and resources needed for the project. This section should cover both internal and external needs.
10. Estimate Project Costs and Project Budget
All the resources that you’ll need for your project have a price tag. That’s why you need to estimate those costs and create a project budget . The project budget needs to cover all your project expenses, and as a project manager, you’ll need to make sure that you adhere to the budget.

11. Define a Project Timeline
Once you’ve defined your project scope, you’ll need to estimate the duration of each task to create a project timeline. Later during the project planning phase , you’ll need to create a schedule baseline, which estimates the total length of your project. Once the project starts, you’ll compare your actual project schedule to the schedule baseline to monitor progress.
Now let’s explore some project proposal examples to get a better understanding of how a project proposal would work in the real world. For this example, let’s imagine a city that’s about to build a rapid transit system. The city government has the funds to invest but lacks the technical expertise and resources that are needed to build it, so it issues a request for proposal (RFP) document and sends it to potential builders.
Then, the construction companies that are interested in executing this rapid transit project will prepare a project proposal for the city government. Here are some of the key elements they should include.
- Project background: The construction firm will provide an explanation of the challenges that the project presents from a technical perspective, along with historical data from similar projects that have been completed successfully by the company.
- Project vision & success criteria: Write a vision statement and explain how you’ll track the triple constraint to ensure the successful delivery of the project.
- Potential risks and mitigation strategies: List all risks and how they’ll be mitigated, and be sure to prioritize them.
- Project scope & deliverables: The work that’ll be done is outlined in the scope, including all the deliverables that’ll be completed over the life cycle of the project.
- Set SMART goals: Use the SMART technique to define your project goals by whether they’re specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound.
- Project approach: Define the methodology that the project manager will employ to manage the project. Also, figure out what type of contract will be used to define the project.
- Expected benefits: Show how the project will deliver advantages to the company and define what these benefits are in a quantifiable way.
- Project resource requirements: List all the resources, such as labor, materials, equipment, etc., needed to execute the project.
- Project costs & budget: Estimate the cost of the project and lay that out in a project budget that covers everything from start to finish.
- Project timeline: Outline the project schedule, including phases, milestones and task duration on a visual timeline.
Whatever project proposal you’re working on, there are a few tips that apply as best practices for all. While above we suggested a project proposal template that would have a table of contents, meaning it would be many pages long, the best-case scenario is keeping the proposal to one or two pages max. Remember, you’re trying to win over stakeholders, not bore them.
Speaking of project stakeholders , do the research. You want to address the right ones. There’s no point in doing all the work necessary to write a great proposal only to have it directed to the wrong target audience. Whoever is going to read it, though, should be able to comprehend the proposal. Keep the language simple and direct.
When it comes to writing, get a professional. Even a business document like a project proposal, business case or executive summary will suffer if it’s poorly constructed or has typos. If you don’t want to hire a professional business writer, make sure you get someone on your project team to copy, edit and proof the document. The more eyes on it, the less likely mistakes will make it to the final edition.
While you want to keep the proposal short and sweet, it helps to sweeten the pot by adding customer testimonials to the attachments. Nothing sells a project plan better than a customer base looking for your product or service.
ProjectManager & Project Proposals
ProjectManager allows you to plan proposals within our software. You can update tasks for the project proposal to signify where things stand and what’s left to be done. The columns allow you to organize your proposal by section, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) of sorts.
When building a project proposal, it’s vital to remember your target audience. Your audience includes those who are excited about the project, and see completion as a gain for their organization. Conversely, others in your audience will see the project as a pain and something to which they aren’t looking forward. To keep both parties satisfied, it’s essential to keep language factual and concise.
Our online kanban boards help you think through that language and collaborate on it effectively with other team members, if necessary. Each card shows the percentage completed so everyone in the project management team is aware of the work done and what’s left to be done.
As you can see from the kanban board above, work has begun on tasks such as product documentation and design. Tasks regarding stakeholder feedback, ideation, market research and more have been completed, and there’s a good start on the engineering drawings, 3D rendering, supply chain sourcing and translation services.
A PDF is then attached to the card, and everyone added to the task receives an email notifying them of the change. This same process can be used throughout the life-cycle of the project to keep the team updated, collaborating, and producing a first-class project proposal. In addition to kanban boards, you can also use other project management tools such as Gantt charts , project dashboards, task lists and project calendars to plan, schedule and track your projects.
Project proposals are just the first step in the project planning process. Once your project is approved, you’ll have to solidify the plan, allocate and manage resources, monitor the project, and finally hand in your deliverables. This process requires a flexible, dynamic and robust project management software package. ProjectManager is online project management software that helps all your team members collaborate and manage this process in real-time. Try our award-winning software with this free 30-day trial .

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
Sandeep Kashyap
How to write a perfect project proposal in 2024?

Introduction
The primary purpose of writing a project proposal is to secure funding, gain approval, or secure resources from the most important stakeholders of a project.
For that, you need to explain the following in simple terms in a project proposal:
- What do you want to do and what are your goals for the project?
- How are you going to achieve your goals?
- How are stakeholders going to benefit from the project?
- What do you want from stakeholders?
- How are you going to use the money and resources granted by stakeholders?
In this post, we will learn about all these about writing a perfect project proposal in 2024. We will look at different types of project proposals, a project proposal template, and a real-world example of a project proposal.
What is a project proposal?
A project proposal is a project management document that outlines a project’s objectives, timeline, budget, goals, and requirements.
It is primarily written for stakeholders to secure funding, gain approval, and secure resources. However, other types of project proposals are also sent to win projects from clients.
A project manager should have a good understanding of the project and its key stakeholders for writing an effective project proposal. It is because a manager needs to get into the heads of the project’s stakeholders to understand what they expect from a project and write an effective project proposal accordingly to ensure buy-in for the project.
Benefits of writing a strong project proposal
Writing a strong project proposal offers a surprising number of benefits beyond simply securing funding or approval. Here are five key benefits of writing an effective project proposal:
- Clearly defines the project to increase the chances of success
- Makes it easy for stakeholders to mutually understand the project
- Ensures everyone involved is on the same page about goals, roles, and expectations
- Helps identify potential roadblocks early for proactive planning of solutions
- It can attract funding, and talent, and even serve as a marketing tool
Difference between a project proposal, a project charter, and a project plan
It is important to note that a project proposal is different from a project charter and project plan. Let’s understand the difference between these terms.
Project proposal vs. project charter
A project charter is a formal document that outlines the project’s goals, objectives , and resource requirements for a shared understanding of the team. It can’t be created until the project proposal is approved. Whereas a project proposal is written during the initiation phase.
Project proposal vs. project plan
A project plan is a detailed guide that provides step-by-step instructions for executing, monitoring, and managing the approved project. It is created during the planning stage after the project charter and project scope is defined. Whereas, a project proposal is a persuasive tool for securing project approval and resources.
Read more: Project management plan – everything you need to know about
Project proposal types
Project proposals are of six different types. Each has a different goal. A manager may have to write a project proposal for external and internal stakeholders to run a project successfully. Therefore, it is important to know about the different types of project proposals.
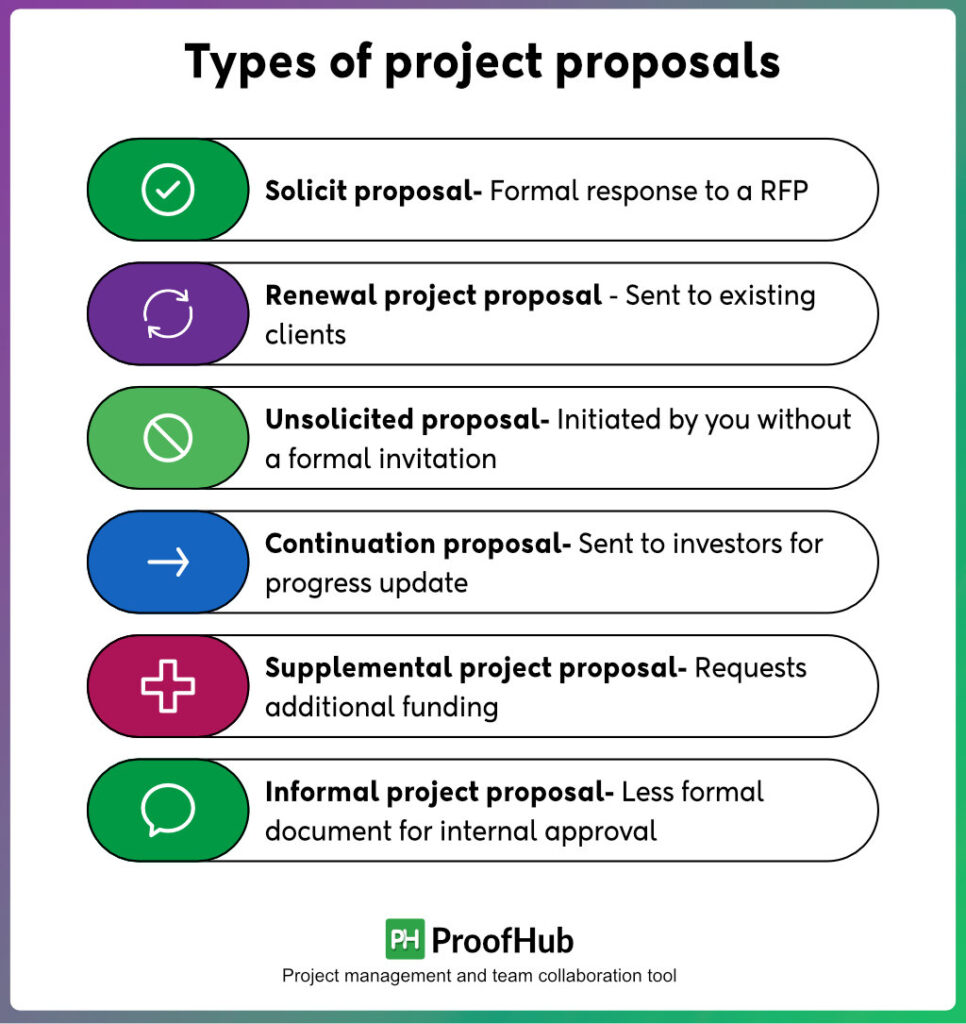
1. Solicited project proposal
A solicited project proposal is sent in response to a request for proposal (RFP). RFP is a document sent by a company to vendors to seek out resources required for a project. It includes the details of the scope of the work and the payment company pays for the resources.
RFP is sent to many vendors. Thus, while writing a solicited project proposal, you need to keep in mind that you may be competing against other vendors to secure a project. Thus, you need to keep your tone persuasive.
2. Unsolicited project proposal
This type of proposal is sent without having received a request for a proposal (RFP). A company has not sent a request for proposal to vendors but you know that the company is seeking resources from third-party vendors. You may or may not be competing against the other vendors in this type of proposal.
3. Informal project proposal
It is a type of project proposal that is created when a client makes an informal request for a project proposal from vendors. It means there is no formal RFP. Thus, the rules for writing a project proposal are less concrete. You can follow any format that can secure you a project.
4. Renewal project proposal
A project manager writes this type of proposal to existing clients to extend their services to the client. In this type of proposal, you focus on highlighting past achievements to secure a renewal for the future.
5. Continuation project proposal
The purpose of the continuation project proposal is to inform the client that the project is beginning and communicate the progress. You are not persuading the client with this type of proposal.
6. Supplemental project proposal
As the name suggests, this type of proposal is sent to the stakeholders who are already involved in a project to secure additional resources. The purpose is to convince the client to invest additional resources during the project execution phase.
How to write a winning project proposal?
You need to include certain elements in the project proposal to make sure it is good. Have a look at the steps to learn how to format a project proposal.

A. Pre-writing stage
The pre-writing stage is crucial for creating a compelling and successful project proposal. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
1. Understanding the audience
The first step is to identify decision-makers and understand the mindset of the audience for which you are writing a proposal. Thoroughly research the client’s needs, goals, and expectations. This includes understanding their industry, current challenges, and past projects.
Determine who will be reviewing and approving the proposal. This will help you adjust the tone, level of detail, and overall focus to cater to their expertise and interests. Tailor your proposal to directly address their specific concerns and priorities.
2. Project requirements gathering
To create an effective project proposal that has a higher chance of getting accepted, gather the project requirements. Usually, it is mentioned in the Request for Proposal (RFP) where specific requirements, evaluation criteria, submission deadlines, and any other instructions are provided.
If there is no RFP, schedule meetings or interviews with key stakeholders to gain a deeper understanding of the project requirements. This allows you to ask clarifying questions, gather feedback, and ensure your proposal aligns perfectly with their expectations.
3. Team brainstorming
Writing a project proposal is teamwork. Involve your team in brainstorming sessions to make a strong proposal. When a team is involved, it diversifies perspectives and expertise, leading to a more comprehensive and well-rounded proposal. Discuss the project goals, potential solutions, and resource needs with your team. Refine the proposal concept based on the collective knowledge and ensure everyone is aligned on the final approach.
B. Writing the proposal
1. start with writing an executive summary .
An executive summary is a concise overview of what a project is all about. It talks about the most important details or information of the project.
It primarily talks about the problem a project will solve, the solution a project will provide, and the benefits stakeholders will get from investing in this project.
It is important to keep in mind to explain these items briefly as you are going to explain the problem and solution in detail later in your proposal.
The purpose of writing an executive summary is to pique the interest of the stakeholders in a project. It is like the elevator pitch of an entrepreneur whose purpose is to attract the stakeholders for further discussion.
2. Explain the problem in the project background
The project background is a one-page section that focuses on highlighting the opportunity by talking about the project problems you are going to solve. It talks about the problem and its history such as statistics, references, and start date.
It discusses what has been done so far to solve the problem by others or earlier projects. What is the current state of the problem, and how your project will focus on solving it?
This section indicates the opportunity and the next section of vision explains how you are going to seize the opportunity.
3. Project vision and solution
Project vision is the section where you present the solution to the problem. Vision statement defines your vision for the project, the solution you are going to work on, and how it will solve the problems.
This section tells what goals and objectives you are going to achieve from the project. Thus, it also acts as a north star or success criterion for your project.
Now, stakeholders know what a project is all about; the problems, the solution, and the objectives. And they are interested to know how you will achieve the proposed objectives of a project.
The next sections of a project proposal talk about the project approach, scope, deliverables, milestones, budget, resources, and timeline.
Read more: Project objectives: learn how to write them for business growth
4. Project scope and deliverables
This section describes all the work items you need to work on a project. It involves breaking a large project into small tasks so that stakeholders can easily understand the project scope.
It also includes describing key milestones and project deliverables during the execution phase of your project life cycle.
The purpose is to provide stakeholders with enough information to make decisions about funding and resources.
5. Project timeline
Project stakeholders have a clear idea about the scope of the project. But the very next question that comes to stakeholders’ minds is how much time a project will take to complete.
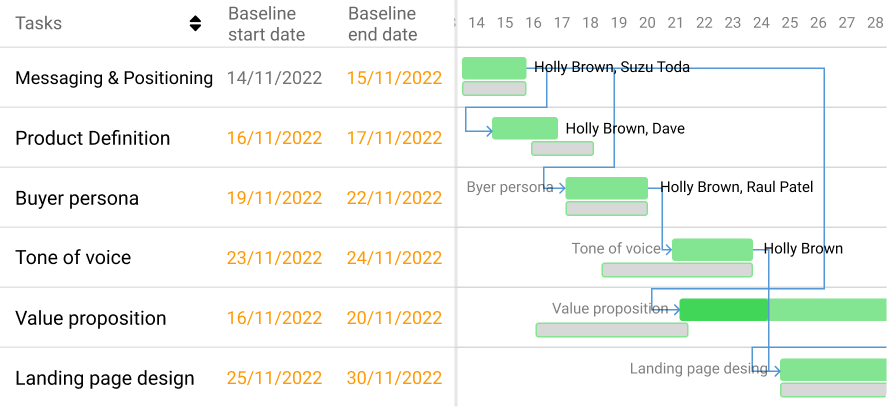
You need to propose an estimated timeline for the project describing when the key deliverables and milestones will be delivered and achieved.
6. Project methodology
With every project, the risks of cost, scope, time, and quality are associated. Thus, you need an effective project management approach to manage these risks.
In this section, you explain to stakeholders about the project approach you are going to use for project management . It includes defining project management methodology, tools, and governance for your project.
79% of teams worldwide use digital collaboration tools . The choice of your project management tool is going to influence how the project will be planned, executed, and managed and its potential risks are identified and mitigated successfully.
ProofHub is an all-in-one project management and team collaboration software that provides you with a centralized platform to collaborate with a team on a project proposal.
ProofHub strengthens your project proposal’s “Implementation Plan” by providing a platform to meticulously define tasks, assign roles, and track progress . Its work plan section allows for a detailed breakdown of the project with clear task dependencies and time estimates, visualized through a Gantt chart .
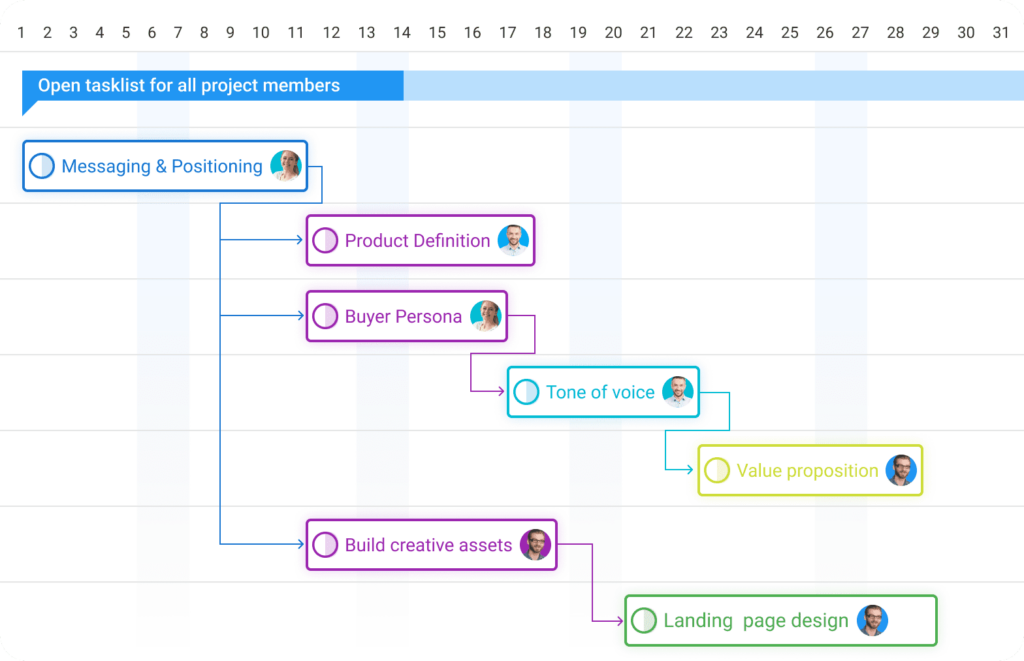
Team members can be assigned to specific tasks, ensuring accountability, while resource allocation demonstrates a well-planned approach.
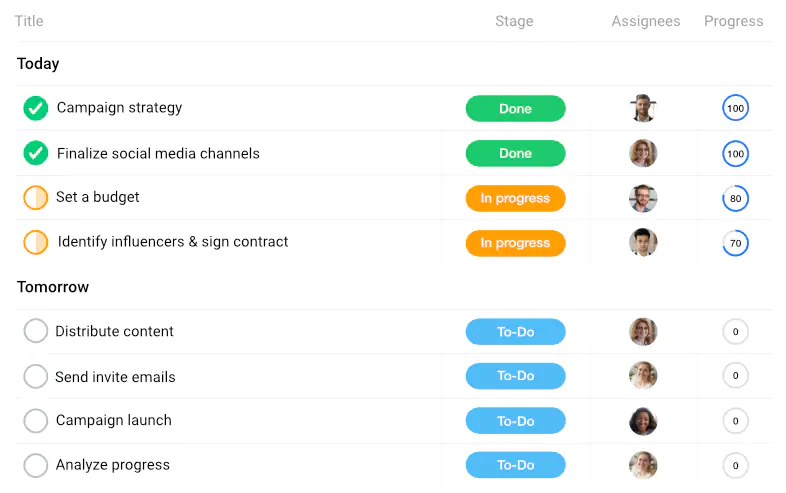
Real-time progress updates, collaborative discussions within tasks, and reporting capabilities showcase transparency and proactive management.
By incorporating ProofHub, your proposal presents a clear picture of efficient execution, giving the reader confidence in your ability to deliver the project successfully.
Learn more about ProofHub’s collaboration capabilities !
7. Project resource requirements
Project resource requirements talk about the resources you need to complete your project which includes materials, human resources, and technology. It is a key section that is crucial for the success of the project because every project needs resources to convert a plan into action.
This section of the project proposal briefly describes the project resources you need for the project and how you are going to utilize these resources.
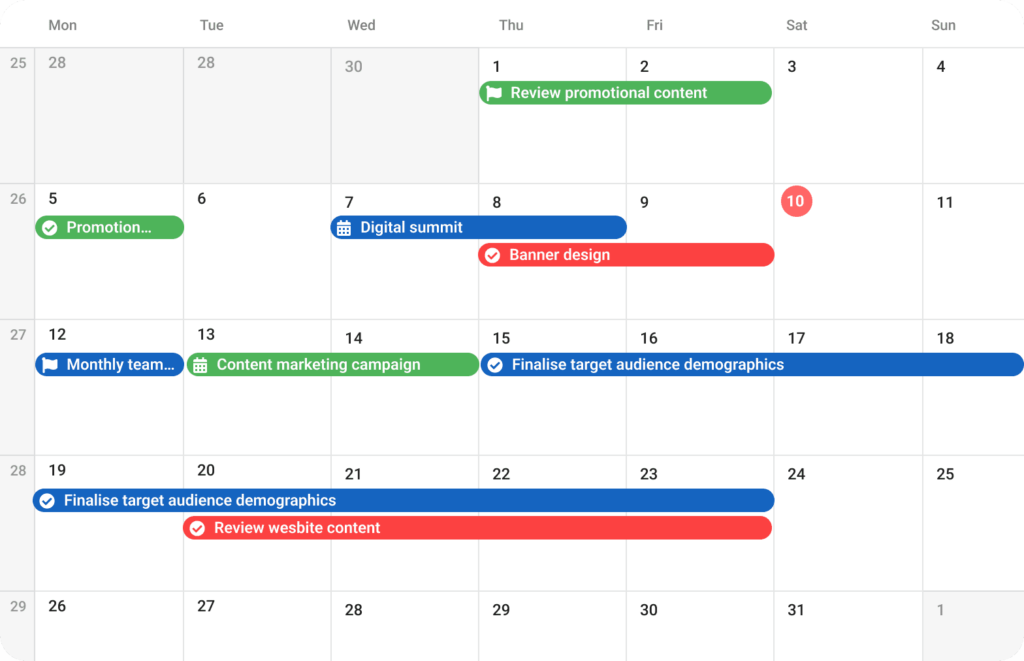
It does not explain the nitty gritty details of resource allocation. But, it gives a fair idea of why you need specific resources for your project and how these will be utilized.
Read more: 2024 guide to project resource management: processes, challenges & tools
8. Estimate project costs and budget
Project resources come at a price. Thus, in this section, you will define the project costs and create a project budget. It is the responsibility of a project manager to write this section in such a way that it covers all the project expenses.
At the same time, it also provides the opportunity for stakeholders to jump in and help you mitigate unexpected costs.
It also includes estimating project costs everything from the cost of project technology to team salaries and materials.
9. Closing statement
At this point of a project proposal, stakeholders have complete information about the project: scope, cost, time, objectives, and impact. You just have to briefly summarize the problem your project addresses and remind stakeholders about the benefits they will get from this project.
You can use cost-benefit analysis to demonstrate why your project is profitable. Thus, in this section, you wrap up your project proposal with a persuasive and confident conclusion to convince stakeholders to close the deal.
I hope these steps help you write a winning project proposal. Now, let’s have a look at some practical tips from experts to write a winning proposal.
Additional tips to write a perfect project proposal
Here are the five practical project proposal tips for writing a proposal:
- Clarity and conciseness: Do not use jargon or make your proposal overly complex. Keep it simple so that project sponsors can understand it easily.
- Strong value proposition: You want your project proposal to be accepted. Give strong emphasis on the benefits of your project and how it addresses the existing problems.
- Compelling visuals: Make your proposal compelling so that project sponsors read it. If it is not persuasive and visually interesting, project sponsors may not read it.
- Proofreading and editing: Do not make silly grammatical mistakes and fact check and proofread your proposal. Wherever required provide statistics to back your claims.
- Use collaboration tools: A project proposal involves explaining about project scope, cost, time, and resources. Use a project management tool like ProofHub to create a plan and collaborate with a team to create an effective project proposal.
Project proposal examples
A project proposal in project management is primarily sent to the stakeholders to secure funding, gain approvals, and request resources from stakeholders.
Here is a real-world example to get an idea of how to write a proposal for a project:
Project Proposal: Implementation of a CRM System to manage company customers, prospects, and leads
1. Executive
The Customer Success Manager at XYZ Corporation is proposing the implementation of a new Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system.
Currently, the company is using a legacy system that makes it difficult to manage data and ensure the alignment between the sales and marketing teams. It results in poor customer service to the customer and missed opportunities.
The new CRM system streamlines the company’s customer interactions, improves data management, and enhances overall customer satisfaction.
This results in enhanced customer relationships, improved operational efficiency, and increased business growth.
2. Background
- Lack of centralized data management system
- Lack of alignment between marketing and sales departments
- Not able to provide exceptional customer experience due to operational inefficiencies
3. Vision
- Implementing CRM to improve customer data management by centralizing all customer information into a single database
- Enhance communication and collaboration among sales, marketing, and customer service teams
- Increase customer satisfaction and retention through personalized and timely interaction
4. Project scope
- Researching and selecting a suitable CRM solution based on the specific needs and requirements of XYZ Corporation.
- Customizing the CRM system to align with the company’s business processes and workflows.
- Migrating existing customer data from legacy systems into the new CRM platform.
- Phase 1: Research and Selection (1 week)
- Phase 2: Customization and Configuration (2 weeks)
- Phase 3: Data Migration (1 week)
- Phase 4: Training and Adoption (2 weeks)
- Phase 5: Go-Live and Deployment (2 weeks)
5. Project management approach
Hybrid project management : Waterfall during the planning of each phase of the project and Agile during the implementation of the CRM.
6. Project resource and budget
The estimated budget for the CRM implementation project is $50,000, including software licensing fees, customization costs, training expenses, and implementation services.
7. Project risks and mitigation
- Potential resistance from employees toward adopting new technology
- Integration challenges with existing systems and applications:
Mitigation:
- Addressed through providing training sessions for employees to ensure hassle-free adoption of the CRM system.
- Managed through careful planning and coordination with IT vendors and stakeholders.
8. Conclusion
The implementation of a CRM system for XYZ Corporation enhances customer relationships, improves operational efficiency, and drives business growth. We seek approval from the executive management team to proceed with the implementation of the CRM system as outlined in this proposal.
Project management proposal template
Trying to manage a project without project management is like trying to play a football game without a game plan. – Karen Tate
A project management proposal template provides the framework and detailed proposal outlining to create a project proposal. It outlines the sections you need to include in a project proposal and the instructions in each section. By following the instructions in the template, you know how to make a project proposal, customized to your business needs.
Here is the project management proposal template:
1. Executive Summary
In this section, you will summarize the complete project proposal and add the most important details of the project.
Outline the following details in brief in the executive summary:
- Project background and vision
- Project goals and deliverables
- Project budget, timeframe, resource, and success criteria
2. Project Background
In this section, you will talk about the problem a project is going to solve or the business opportunity a project intends to grab. Explain it in-depth because it forms the basis of the project.
Here is what you need to include:
- Project history and stats of similar projects
- The basis upon which the project is created
3. Project vision
This section includes the project vision statement. You explain the solution to the project problem and define the goals of the project.
Here is what you need to do:
- Write a project vision
- Present a solution
- Write the SMART goals you want to achieve
4. Project plan
It includes multiple sections as below:
4.1 Project scope and deliverables
Project scope defines all the work you need to do to complete the project.
Project deliverable is something that is of the end-user or customer value.
4.2 Project timeline
Every project has a start and an end date. Similarly, there is a timeframe for each task and deliverable.
4.3 Project approach
Every project follows an approach to project management and uses project management tools. For example, construction projects follow the Waterfall methodology whereas software development projects follow the Agile methodology.
4.4 Project risks
A project risk is something that can impact the cost, time, and scope of the project.
List here all the project risks, likelihood, impact, mitigation plan, and risk owners in a table.
4.5 Project resource requirements
Project sponsors need to know about the details of the resources required to approve the budget for the Project Proposal.
Define the project resource requirements here in the table:
- Technology requirements
- Human resources requirements
- Material requirements
4.6 Project estimated cost and return on investment
A project sponsor wants to know the project costs and return on investments.
4.7 Project ownership and communication plan
This section includes the details of the key stakeholders of the project.
- Project sponsor: who owns the project
- Project customer: who the project is being delivered to
- Manager: who is responsible for managing the project and informing the status to stakeholders
5. Call to action
In this section, provide your contact details for the client to get in touch with any questions or allow the project sponsor to authorize the project if they are happy with the project proposal.
It is important to keep in mind the above-mentioned are the standard sections that are included in most project proposals. If you want to add some other elements to your project proposal, you can add the sections as per your needs to format a project proposal.
Create a winning project proposal with the right tool
A good project proposal convinces stakeholders why the project should be carried out. It should clearly describe project problems, project objectives, benefits for stakeholders, your requirements from stakeholders, and how you will utilize the secured resources. You need to have a good understanding of the project and project sponsors and stakeholders before writing a project proposal.
To create an effective project proposal, you need cross-collaboration between departments to gather key details and project management software to plan a project.
That’s where a feature-rich project management software, ProofHub, comes into play. It helps you with team collaboration and project planning for the project proposal. You can create a project plan using a Gantt chart , create tasks using task management software , and collaborate with the team using chat and a centralized file-sharing system .
Organize, manage, and collaborate seamlessly with ProofHub – All-in-one solution for projects, tasks, and teams
Related articles
- How to manage projects with a tool like ProofHub
- 10 Common project management challenges (and How to solve them)
- Project objectives: learn how to write them for business growth
- The 11 best project management software for your team
How long should a project proposal be?
A project proposal should not be too long. Ideally, a project proposal should take 1-2 pages but it also depends on the complexity of the project and the format you choose.
What section of a proposal presents a list of project costs?
Project costs are briefly covered in the Project Cost section. However, it depends on the template you choose. The detailed breakdown of the project costs is attached with the project proposal in the reference document.
What section of a proposal identifies the key issues and discusses the project goals?
Project background and project vision are the sections that talk about the key issues and project goals. However, it is explained in brief in the executive summary also.

- Share on LinkedIn
- Email this Page
- Share on Facebook
- Share on WhatsApp
Try ProofHub, our powerful project management and team collaboration software, for free !
No per user fee. No credit card required. Cancel anytime.
How to Write AI Prompts for Project Managers
By Lulu Richter | May 6, 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Writing prompts for AI tools is tricky. We’ll teach you how to engineer prompts for AI that can help project managers get their job done faster.
In this article, you’ll learn how to write project management prompts for AI , see examples of prompts by methodology and project phase , and find a downloadable cheat sheet for writing your own custom prompts.
What Are ChatGPT and Generative AI prompts?
ChatGPT and generative AI are types of artificial intelligence technology that answer questions and generate content. The user provides a prompt, and the AI generates results based on large-language models and internet search results.
Prompts can be questions, statements, commands, or instructions. The results will differ based on how the prompt is phrased and the specific directions it contains.
How ChatGPT and Generative AI Can Help Project Managers
Generative AI can save project managers time by simplifying tasks and generating fast results for all kinds of work, including project management. Below are some of the best use cases for generative AI for project managers :
- Generating and Filling Templates: Generative AI can create and fill templates for all kinds of uses, such as project plans, schedules, meeting agendas, communication plans, and more.
- Brainstorming and Organizing: Use AI to brainstorm ideas, then organize your thoughts into coherent content or lists.
- Writing Outlines and Drafts: ChatGPT is great for creating outlines and first drafts of written content for project updates, newsletters, blogs, speeches, and more.
- Summarizing: Generative AI can pull out and organize key data from dense meeting notes, project data, reports, and webinars.
- Translation: Generative AI can quickly translate text into different languages, which saves you time when providing materials to global team members or clients, or producing foreign language versions of your content.
- Iterations: AI can be used to test different kinds of messaging by simplifying and fleshing out copy, as well as changing the tone, adding examples, and more.
How to Write Project Management Prompts for Generative AI
Writing prompts for AI is a skill that you can learn and refine. When writing prompts for project management, give the AI instructions to think and respond like a project manager would, and be thorough in your instructions.
Ethan Mollick is an Associate Professor of Management at Wharton who specializes in innovation and AI. He outlined the process of creating successful AI prompts to produce better results on the first try. We’ve recreated the steps below from his findings to help you craft successful AI prompts for project management:
- Give the AI a Role: In order for the AI to create from the right perspective, tell it who or what it is (i.e., what its professional role is). State the job title and the type of company or projects it works on. Think of the role as the character you need the AI to play when crafting its response.
- Prompt the AI with Specific Expertise: Add the knowledge required for the AI to act in character for the prompt. If you would like it to have specific project management methodologies or certifications, list them. Tell the AI how much experience it should have in a given field or which experts to reference.
- Give the AI a Tone of Voice: Specify the voice you want it to respond in. Use words such as “academic” and “professional” if you would like a formal tone, or “friendly” and “natural” if you prefer a more casual response.
- State Your Goal: State the ultimate goal of the response. What are you trying to achieve? This can be anything from “create a project schedule” to “summarize these meeting notes” to “outline the steps of a software development project,” or any other concrete task. Let the AI know what you expect to gain with the prompt you are giving it.
- Give the AI a Task with Step-by-Step Instructions: Lay out the steps required to complete the prompt. List the results the response should include, and clearly define your expectations. Be very specific.
- Give Examples: Copy and paste or upload examples of the kind of results you want. Often, the more examples you provide, the better the output will be. Pro Tip: ChatGPT-4 and Google Gemini both make it easy to upload images to your prompt using the + sign or image upload button near the prompt entry text field.
- State Any Constraints: Tell the AI what you don’t want it to do. If there are methodologies it should ignore or things it should exclude, list them.
- Define the Format for the Output: Provide specific details about the format or structure desired for the output, such as a paragraph form or a numbered list. Give it a word count or sentence limit, or ask it to respond in a list or in paragraphs.
Using the steps above, you can create your own prompt to receive results from a project management perspective. Using these steps, we generated an example of a prompt below and its output to create a project schedule using ChatGPT 3.5. To use it yourself, replace the text within the brackets in each section with relevant information to your own project needs and role requirements:
“You are an [experienced project manager] at a [large Fortune 100 tech company] that [specializes in B2B sales]. You have [10 years of experience and are certified by the Project Management Institute and are a Scrum Master]. Your tone is [professional and direct]. You are [managing a software development project] and need to [schedule milestones and deadlines]. [Create a project schedule for an app development project] that includes [a start and end date with milestones and deadlines based on the average time needed to complete each task]. These should include [time for research, ideation, testing, and execution]. An example [project timeline template is attached]. Do not include [time needed for monitoring results or task assignments]. The output for this task should be [easy to edit and read, in a table format, with dates].”
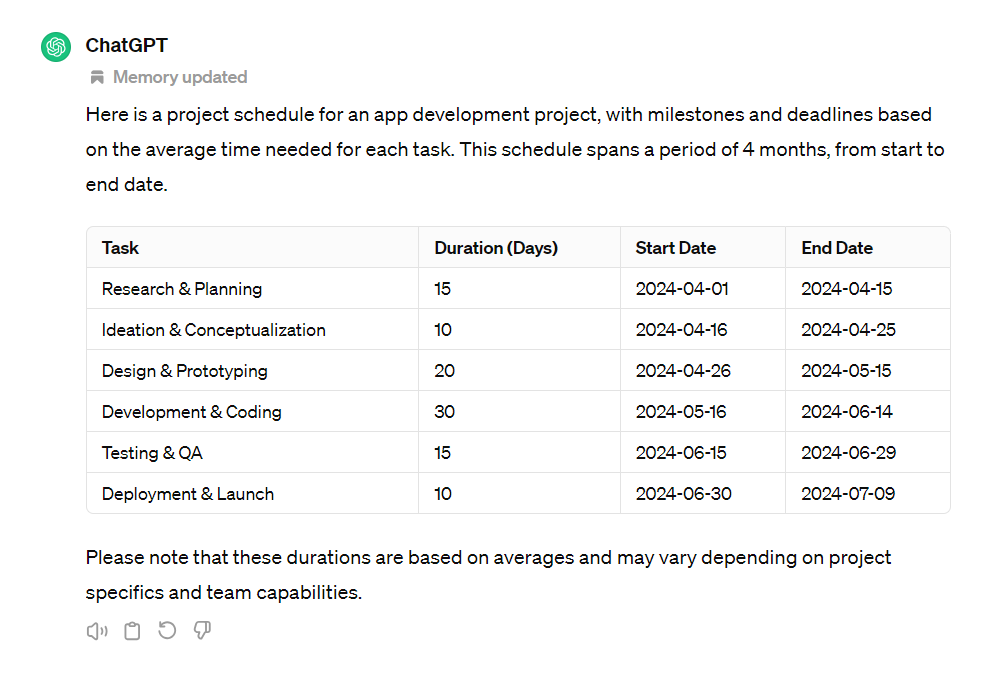
How to Write Project Management Prompts for AI Cheat Sheet
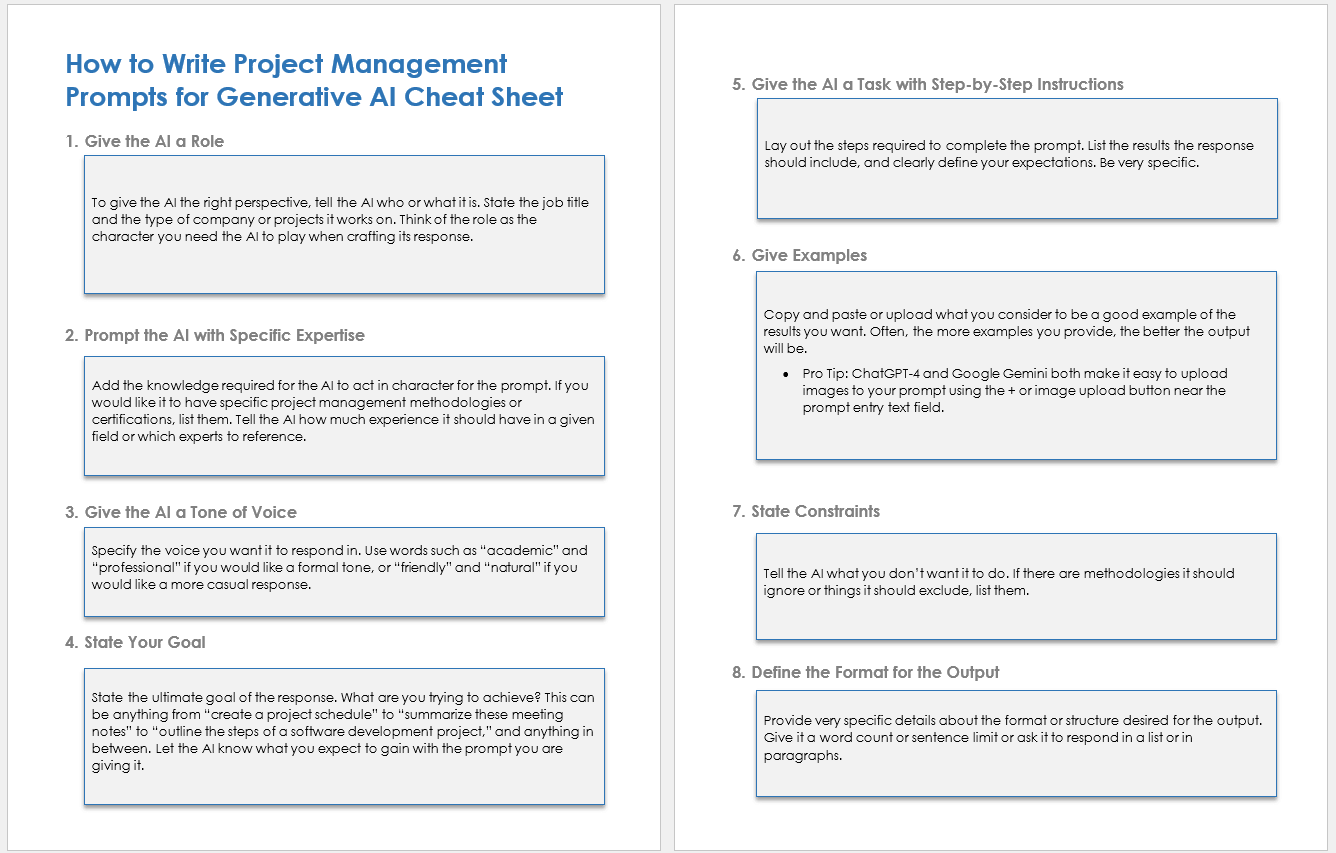
Download the How to Write Project Management Prompts for AI Cheat Sheet for Adobe PDF
Download and use this cheat sheet to save the steps to write successful AI prompts for project managers. Keep it handy and use it as a quick reference tool, or share it with your team to help them in their own work.
Tips for Writing AI Prompts
We have the tips to help you start writing AI prompts. With Linda Henry , who has been managing projects for more than 20 years, we’ve put together a list of best practices for writing and customizing AI prompts.
- Always Edit the Results: No tool is perfect, so always be sure to edit the results of generative AI. This will not only ensure there are no errors, but it will help make your writing sound more human as well.
- Give the AI a Role: Tell the AI who it is and what kind of expertise it has. It will use that information to generate better results. “Tell it who it is and what type of writing you need, give it a tone of voice and be very specific about the angle it should be using,” says Henry.
- Check the Facts: As with all research, be sure to fact-check any statistics or statements that the AI returns. “Sometimes you can ask the AI itself where it got certain facts or statements, and it will either give you the source or reveal its inaccuracy,” Henry advises.
- Don’t Worry About Length: Don’t be afraid to write a long prompt. Tell the AI everything it needs to know to do the job well, even if you include multiple paragraphs or long lists.
- Forget What You Know About Search Engines: AI tools use the language you use to gain context into your questions. “Prompt the AI like you’re talking to a person, not like you’re searching keywords on a search engine,” says Henry.
- Be Clear and Specific: The results of AI are only as good as the prompt, so tell it clearly and specifically what you want it to include. At the same time, if there are things you would like to leave out of your results, tell it that, too.
- Give Examples: AI tools can use examples as references to generate more relevant results. If you have an example that you like of the thing you are asking for, upload or link to it in your prompt.
- Customize Your Bot: ChatGPT can be customized to the user to give more personalized results. Press Crtl+Shift+I on a PC or Cmd+Shift+I on Mac to bring up the Customize ChatGPT window, and fill in the text box to create rules about the tone of voice, role, or types of responses you would like to see in your following responses.
- Use Complete Sentences: Don’t leave the AI guessing. “Create a project plan template” will give you much better results than just typing “project plan.”
- Experiment and Iterate: If the results aren’t quite what you were looking for, clarify ambiguities in your prompt as needed. “Play around with it,” says Henry. “If it doesn’t give me the results I want, I ask myself, ‘How can I ask this better?’ Sometimes all you need to do is tell it to ‘try again from this other perspective,’” Henry explains.
- Add Context: Give the AI as much context into your questions as you can. Include links to more information, and don’t use acronyms — spell out the whole words. Use keywords in your prompt as necessary to ensure your results are relevant.
- Specify the Format: Tell the AI what format you would like your results to take. Ask for your results in a table or list or as paragraphs. As generative AI improves, it will be able to handle additional formatting tasks.
- Be Patient: AI will not always get it right on the first try. Be patient when creating prompts and receiving results, and keep trying until you get the results you need.
- Check for Comprehension: If your results continue to be lacking, ask the AI if it understands what you want it to do. Its response can help tell you which part of your prompt it is having trouble with and help you tweak it for better understanding.
- Try Different Tools to Find Your Preference: As more and more AI tools become available, you might need to try a variety to determine the best one for your work. If an AI tool is not producing the results you would like, try a different one and see if the company offers any best practices for interacting with it. Google Gemini provides a guide to creating prompts for its tool. It suggests focusing on persona, task, content, and format when writing a prompt using its AI tool in Google Workspace.
ChatGPT Prompt Examples for Project Management Methodologies
Using the steps above, we’ve created examples of AI prompts for project managers based on various methodologies and phases of project management. Use these examples to craft your own prompts based on your experience and the needs of your team.
Agile Methodology AI Prompt Example
AI prompts for Agile project managers should establish the adaptability, collaboration, empathy, leadership, and facilitation skills required to be successful in the role, as in the prompt below:
You are an [experienced project manager] at a [midsize startup] that [owns and operates eleven coffee shops in Manhattan]. You have [an MBA in business and a Disciplined Agile Coach certification from the Project Management Institute]. Your tone is [clear, direct, empathetic, and adaptable]. You are [opening a new location] and need to [create a project plan]. [Create a project plan for a new coffee shop location] that includes [everything required from setting up the space to opening day]. This should include [a list of required purchases, a schedule for setting up the space, organizing, cleaning, and training employees, a marketing to-do list, and list of important contacts]. An example [project plan template is attached]. Do not include [time required for construction or build out]. The output for this task should be [easy to read and edit, in a table, or paragraph, or list format where necessary].
Critical Path Method (CPM) AI Prompt Example
AI prompts for project managers using the critical path method should emphasize the necessity for pre-planning and task sequencing to deliver projects within a strict time frame. The prompt should focus on deliverables and structured planning framed with an analytical approach, as seen below:
You are an [experienced construction project manager] at a [small agency] that [builds sets and props for tradeshows, plays, concerts, sporting events, and more]. You have [a deep understanding of the critical path method and structured planning]. Your tone is [clear, concise, direct, and analytical]. You are [building a large set for a new Broadway play] and need to [create a construction schedule and budget]. [Create a template] that includes [a detailed construction schedule over a 2 month period with time and budget estimates based on the average time and budget needed for similar projects of this scale using the critical path method]. This should include [time for design concepting and approvals, lead time for materials, time to build the sets, transportation to the venue, set up, and repairs and revisions ahead of opening night, as well as a section for notes]. An example [construction project plan template is attached]. Do not include [anything to do with the performance of the play, the actors, costumes, venue choice, or ticket sales]. The output for this task should be [easy to edit and read, with dates, over a 2 month period, in a table format with time estimations included].
This prompt will produce the template below, which can be customized to suit your needs:
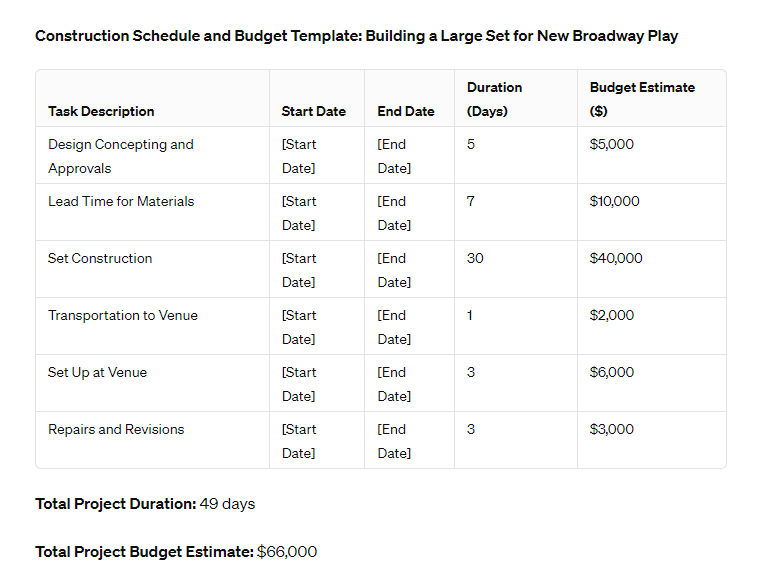
Kanban AI Prompt Example
AI prompts for PMs using Kanban methodology should reflect the continuous nature of the work, as well as task prioritization and shorter project timelines. ChatGPT can generate a table-formatted Kanban template or help to prioritize tasks or tickets in a list using the prompt below:
You are an [experienced manager of a team of software engineers] at a [large tech company] that [provides software as a service]. You have [Kanban certification from the Management and Strategy Institute]. Your tone is [adaptable, positive, and empathetic, and you are focused on both the needs of the business and maintaining a realistic workload for your team]. You are [overseeing the launch of a new product feature] and need to [prioritize and assign customer service tickets to your team]. [Create a Kanban board template] that includes [space to track work to do, work in progress, and completed work, as well as who each task is assigned to]. An example [Kanban board template is attached]. Do not include [dates or time estimates]. The output for this task should be [in a table format, and easy to read and edit].
Lean Methodology AI Prompt Example
AI prompts for project managers using the Lean methodology should emphasize the need to minimize waste while maximizing value. Use phrases that are unique or critical to this methodology, such as “Just-in-Time production” and “continuous improvement,” or give the AI a role that includes certification in Lean methodologies.
You are an [experienced manager] at a [large international company] that [manufactures automobiles]. You have [30 years of experience in the industry and are a certified Lean Six Sigma Green Belt]. Your tone is [diligent and organized, and you are focused on the big picture]. You are [starting a new product line] and need to [change an assembly line for the new product]. [Create a production schedule] that includes [every step required to change a product assembly line from one product to another]. This should include [a schedule of tasks, critical milestones, a risk management plan, and an estimate of the costs involved based on similar projects]. An example [project schedule is attached]. Do not include [time required for product development, marketing, or packaging]. The output for this task should be [a timeline, with tables or paragraphs where necessary].
Scrum Team AI Prompt Example
AI prompts for project managers who use Scrum should emphasize the flexibility required to be successful in the role. Be sure to use phrases that are unique to Scrum, and give the AI a high-level Scrum certification for best results, as demonstrated below:
You are a [project manager and Scrum Master] at a [large technology company] that [creates and maintains POS software for retail and restaurant businesses]. You have [a Professional Scrum Master III certification]. Your tone is [flexible, professional, and direct]. You are [rolling out a new version of your app] and need to [work through a task backlog that includes the final phase of development and testing]. [Create a template for a Scrum sprint planning template] that includes [all required tasks for a final round of development and testing before deployment] and a total sprint duration of [three weeks]. This should also include [a sprint backlog section and a list of upcoming, in-progress, and completed tasks, as well as a section to summarize the daily Scrum meeting]. An example [Scrum sprint planning template is attached]. Do not include [start and end dates]. The output for this task should be [a timeline with estimated durations of tasks and their priority, as well as a table to organize tasks by upcoming, in-progress, and completed status].
Six Sigma AI Prompt Example
AI prompts for Six Sigma should emphasize how the methodology uses data and statistical analysis to drive decision-making and problem solving. Use words and phrases that are relevant for Six Sigma, such as “focus on quality,” “customer-centric approach,” and “Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control (DMAIC),” or give the AI a role that includes certification in Six Sigma methodologies.
You are an [experienced project manager] at a [medium-sized company] that [provides customer support for healthcare organizations]. You have [a Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification and 10 years of experience in healthcare administration]. Your tone is [warm, professional, empathetic, and understanding]. You are [training a new hire] and need to [create a training schedule]. [Create a training schedule for a new employee] that includes [two weeks of hands-on training in healthcare customer service based on findings and best practices from past successful employees]. This should include [time for learning healthcare terms and requirements, training on customer service and phone manners, sensitivity training, and training on insurance costs and communication]. An example [training template is attached]. Do not include [sections for notes]. The output for this task should be [in a list or table format, a timeline that spans two workweeks, filled with the learnings for each day and the number of hours for each].

Waterfall Methodology AI Prompt Example
AI prompts for project managers using the Waterfall methodology should focus on managing dependencies and the methodical progression of tasks. AI is great for generating task sequences and identifying dependencies in a list of tasks using a prompt like the one below:
You are an [experienced project manager] at a [large financial institution] that [operates in the government sector]. You have [a Project Management Professional certification from PMI]. Your tone is [methodical, analytical, and detail-oriented]. You are [in the process of approving a new loan for a government project] and need to [organize the steps required to ensure compliance]. [Create a work breakdown structure with a detailed task list with dependencies] that includes [all elements required to review and approve a government loan for a public works project in New York City]. These should include [up-to-date compliance requirements, all necessary documents for review, and reviews and sign-offs from all necessary parties]. An example [work breakdown structure template is attached]. Do not include [a Gantt chart]. The output for this task should be [a sequential task list with dependencies identified and highlighted].
ChatGPT Prompt Examples for Project Management Phases
You might find it useful to cater your AI prompts to the specific phase of a project you are in. AI can be used to generate project charters and plans, create task lists for execution or templates for monitoring progress, summarize meeting notes and create agendas, and more. We’ve provided an example of a prompt for each of the five phases of project management below.
Project Initiation AI Prompt Example
In the project initiation phase, managers are concerned with organizing project information and creating charters, plans, task lists, and more. AI can make these tasks simpler using a prompt such as the one below:
You are an [experienced Agile project manager] at a [small company] that [designs and sells clothing at boutique retail stores]. You have [15 years of experience in retail and fashion design]. Your tone is [casually professional]. You are [launching a new clothing line] and need to [set up an ad campaign to reach boutiques that might want to sell it]. [Create a project charter] that includes [everything required to organize and begin this project]. It should include [general project information, information about the project team and stakeholders, a detailed scope of the project (including what is out of scope), a communication plan, and space for notes and links to other project information]. An example [project charter template is attached]. Do not include [a project schedule]. The output for this task should be [in distinct sections that are easy to read and edit].
Project Definition and Planning AI Prompt Example
During the project definition and planning phase, the project manager works with the team to set goals and expectations for the project and determine how success will be measured. You can use AI to help generate SMART goals , scope statements , communication plans , and more using a prompt like the one below:
You are an [experienced project manager] at a [large hardware manufacturing company] that [builds and supplies machines for electronics companies]. You have [an M.S. in Electrical Engineering and are a certified Lean Six Sigma Green Belt]. Your tone is [direct and detail-oriented]. You are [building a dielectric etch system for a new client] and need to [set SMART goals for the project]. [Create SMART goals for this project] that include [considerations for the manufacturing and delivery of the machine]. It should include [a focus on maintaining quality and consistency in the build and the machine’s output]. An example [SMART goal is attached]. Do not include [excessive details about timelines or scheduling]. The output for this task should be [in paragraph format with complete sentences for each of the SMART letter acronyms for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound].
Project Execution AI Prompt Example
During the project execution phase, the project manager’s role is to oversee and ensure that work is completed according to the project schedule and communicate status with team members and stakeholders. AI can help by generating project plans and task lists, creating meeting agendas, and more. Ease the project execution phase by using a prompt like the one below:
You are an [experienced Agile project manager] at a [marketing agency] that [creates ad campaigns for clients]. You have [10 years of experience managing work in creative fields and are a Certified Project Manager]. Your tone is [detail-oriented and professional]. You are [running an ad campaign for a client in the restaurant industry] and need to [assign and manage project tasks]. [Create a project schedule] that includes [a timeline, a task list, and assignments]. These should include [everything required to run a local print ad campaign for a restaurant]. An example [marketing project plan template is attached]. Do not include [financial or budget information]. The output for this task should be [in a table format with all columns required to assign tasks and track their status].
Project Monitoring and Reporting AI Prompt Example
You can also use AI to ease the project monitoring and reporting phase by summarizing project status from provided metrics, generating status emails, and more. Edit the prompt below with your own project information to help reduce the time required for status updates:
You are an [experienced Agile project manager] at a [midsize company] that [creates software for construction]. You have [a Disciplined Agile Coach certification from the Project Management Institute]. Your tone is [direct, professional, and detail-oriented]. You are [monitoring an ongoing software development project] and need to [provide a status update to stakeholders]. [Create a status update email template] that includes [space for project status, estimated date of completion, upcoming tasks, and risks and roadblocks]. An example [email status report template is attached]. The output for this task should be [in paragraph formatting, with space to fill in details].
Project Closing AI Prompt Example
Project closing often requires a lot of tasks for the project manager, such as post-mortem meetings, logging project details for storage, gathering and recording lessons learned, and more. You can use AI to make these tasks simpler using a prompt like the one below:
You are an [experienced Agile project manager] at a [large software company] that [develops mobile games]. You have [a Project Management Professional certification from PMI]. Your tone is [professional, clear, and direct]. You are [finishing the last updates to a mobile game] and need to [document the project and close it out]. [Create the agenda for a post-mortem meeting] that includes [lessons learned and project details, such as total budget and development schedule, metrics for success, and things to avoid on similar projects in the future]. An example [post-mortem meeting template is attached]. Do not include [a project schedule]. The output for this task should be [easy to read and edit].
Standardize and Streamline AI Prompts with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get more done.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover a better way to streamline workflows and eliminate silos for good.
'ZDNET Recommends': What exactly does it mean?
ZDNET's recommendations are based on many hours of testing, research, and comparison shopping. We gather data from the best available sources, including vendor and retailer listings as well as other relevant and independent reviews sites. And we pore over customer reviews to find out what matters to real people who already own and use the products and services we’re assessing.
When you click through from our site to a retailer and buy a product or service, we may earn affiliate commissions. This helps support our work, but does not affect what we cover or how, and it does not affect the price you pay. Neither ZDNET nor the author are compensated for these independent reviews. Indeed, we follow strict guidelines that ensure our editorial content is never influenced by advertisers.
ZDNET's editorial team writes on behalf of you, our reader. Our goal is to deliver the most accurate information and the most knowledgeable advice possible in order to help you make smarter buying decisions on tech gear and a wide array of products and services. Our editors thoroughly review and fact-check every article to ensure that our content meets the highest standards. If we have made an error or published misleading information, we will correct or clarify the article. If you see inaccuracies in our content, please report the mistake via this form .
How to use ChatGPT to write code: What it can and can't do for you

One of the more intriguing discoveries about ChatGPT is that it can write pretty good code. I first tested this out last year when I asked it to write a WordPress plugin my wife could use on her website. ChatGPT did a fine job, but it was a very simple project.
How to use ChatGPT to write: Resumes | Excel formulas | Essays | Cover letters
So, how can you use ChatGPT to write code as part of your daily coding practice? Here's a quick summary:
- ChatGPT can produce both useful and unusable code. For best results, provide clear and detailed prompts.
- ChatGPT excels in assisting with specific coding tasks or routines, rather than building complete applications from scratch.
- Use ChatGPT to find and choose the right coding libraries for specific purposes, and engage in an interactive discussion to narrow down options.
- Be cautious about the ownership of AI-generated code and always verify the code's reliability. Don't blindly trust the generated output.
- Treat interactions with ChatGPT as a conversation. Refine your questions based on the AI's responses to get closer to the desired output.
Now, let's explore ChatGPT in considerably more depth.
What types of coding can ChatGPT do well?
There are two important facts about ChatGPT and coding. The first is that the AI can, in fact, write useful code.
The second is that it can get completely lost, fall down a rabbit hole, chase its own tail, and produce unusable garbage.
Also: The best free AI courses
I found this out the hard way. After I finished the WordPress plugin, I decided to see how far ChatGPT could go.
I wrote out a very careful prompt for a Mac application, including detailed descriptions of user interface elements, interactions, what would be provided in settings, how they would work, and so on. Then, I fed the prompt to ChatGPT.
ChatGPT responded with a flood of text and code. Then, it stopped mid-code. When I asked it to continue, it vomited out even more code and text. I requested continue after continue, and it dumped out more and more code. But... none of it was usable . It didn't identify where the code should go, how to construct the project, and -- when I looked carefully at the code produced -- it left out major operations I requested, leaving in simple text descriptions stating "program logic goes here".
Also: Yikes! Microsoft Copilot failed every single one of my coding tests
After a bunch of repeated tests, it became clear to me that if you ask ChatGPT to deliver a complete application, it will fail. A corollary to this observation is that if you know nothing about coding and want ChatGPT to build you something, it will fail.
Where ChatGPT succeeds -- and does so very well -- is in helping someone who already knows how to code to build specific routines and get specific tasks done. Don't ask for an app that runs on the menu bar. But if you ask ChatGPT for a routine to put a menu on the menu bar, and then paste that into your project, the tool will do quite well.
Also, keep in mind that while ChatGPT appears to have a tremendous amount of domain-specific knowledge (and it often does), it lacks wisdom . As such, the tool may be able to write code, but it won't be able to write code containing the nuances for very specific or complex problems that require deep experience to understand.
Also: How to use ChatGPT to create an app
Use ChatGPT to demo techniques, write small algorithms, and produce subroutines. You can even get ChatGPT to help you break down a bigger project into chunks, and then you can ask it to help you code those chunks.
So, with that in mind, let's look at some specific steps for how ChatGPT can help you write code.
How to use ChatGPT to write code
1. narrow down and sharpen up your request.
This first step is to decide what you are going to ask of ChatGPT -- but not yet ask it anything. Decide what you want your function or routine to do, or what you want to learn about to incorporate into your code. Decide on the parameters you're going to pass into your code and what you want to get out. And then look at how you're going to describe it.
Also: How to write better ChatGPT prompts
Imagine you're paying a human programmer to do this task. Are you giving that person enough information to be able to work on your assignment? Or are you too vague and the person you're paying is more likely to either ask questions or turn in something entirely unrelated to what you want?
Here's an example. Let's say I want to be able to summarize any web page. I want to feed it something like this article and get back a short summary that's well-considered and appropriate. As my input, I'll specify a web page URL. As my output, it's a block of text with a summary.
2. Use ChatGPT to explore libraries and resources
Continuing with the example above, a very old school way of extracting web page data was to find the text between HTML paragraph tags.
But with the rise of AI tools , it makes more sense to use an AI library to do an intelligent extract and summary. One of the places ChatGPT excels (and it's also an area you can easily verify to avoid its authoritative-but-wrong behavior pattern) is finding libraries and resources.
Also: How to make ChatGPT provide sources and citations
OpenAI (the maker of ChatGPT) sells API access to the GPT-3 and GPT-4 engines that will do exactly what we want. But in the case of this example, let's assume we don't want to pay transaction fees.
So let's look at interacting with ChatGPT to figure out how to use such a tool, for free, with a project that runs in PHP.
I started with a prompt that was designed to elicit information about what libraries would provide the functionality I wanted. A library (for those of you reading along who aren't programmers) is a body of code a programmer can access that does a lot of the heavy lifting for a specific purpose. A big part of modern programming is finding and choosing the right libraries, so this is a good starting point.
In this case, I'm looking at blocks of code written by other people that will summarize text. Here's my first prompt:
Describe ten different open source AI libraries (and the languages they work with) that I can use to generate a summary of the main core contents of any web page, ignoring any ads or embedded materials.
This prompt gave me exactly what I wanted, including a mention of OpenAI's offerings. I think OpenAI would do great here, but for this hypothetical project, I don't want to budget for API fees. So. I'll narrow down the question:
Are any of these free?
ChatGPT hedged its bets with its answer. Here's what it said: "Yes, all ten of these AI libraries are open source and free to use. However, some of them may have usage limits or require payment for access to additional features or resources." So, based on that, I clarified my query:
Which of these libraries have no usage limits and don't require any additional payment or licensing?
Notice how this is very much a conversation. I don't have to re-ask the originating question. I'm just drilling down in the same way I might if I had an expert at hand and was seeking clarification. In this case, ChatGPT gave me eight library choices, but none of them mentioned the PHP language that I was planning to code in. So, here's the next prompt:
Of those 8 libraries, can I use any with PHP?
It returned three libraries, but I wasn't sure about what each did. So, another question:
What's the difference between Sumy, Gensim, and NLTK?
I still wasn't sure, so I clarified my use plan and then asked:
If I want to create summaries of web page news articles, which library would work better?
The answer I got was clear and promising: "Sumy is specifically designed for text summarization, which is the task of creating a summary that captures the most important information from a piece of text." So, now it was time to see what was involved in using Sumy with PHP. I asked my last question for this part of the project:
Can you explain how to use Sumy from PHP?
Feel free to play along on your computer and paste these prompts into your instance of ChatGPT. Notice that, in step one, I decided what program module I was going to get help on. Then, in this step, I had a conversation with ChatGPT to decide what library to use and how to integrate it into my project.
Also: The best AI chatbots
That may not seem like programming, but I assure you it is. Programming isn't just blasting lines of code onto a page. Programming is figuring out how to integrate all the various resources and systems together, and how to talk to all the various components of your solution. Here, ChatGPT helped me do that integration analysis.
By the way, I was curious whether Google's Gemini AI (formerly Bard) could help in the same way. Gemini can't actually write code, but it did give some extra insights into the planning aspect of programming over ChatGPT's responses. So, don't hesitate to use multiple tools to triangulate on answers you want. Here's that story: Gemini vs. ChatGPT: Can Gemini help you code? Since I wrote that article, Google added some coding capabilities to Gemini, but they're not all that great. You can read about it here: I tested Google Gemini's new coding skills. It didn't go well . And even more recently, I dug into Gemini Advanced . It's still not passing many tests.
Also: How I test an AI chatbot's coding ability - and you can too
Coding is next.
3. Ask ChatGPT to write example code
OK, let's pause here. This article is entitled "How to use ChatGPT to write code." And it will. But what we're really doing is asking ChatGPT to write example code.
Also: BASIC turns 60: Why simplicity was this programming language's blessing and its curse
Let's be clear: Unless you're writing a very small function (like the line sorter/randomizer ChatGPT wrote for my wife), ChatGPT isn't going to be able to write your final code. First, you're going to have to maintain it. ChatGPT is terrible at modifying already-written code. Terrible, as in, it doesn't do it. So, to get new code, you have to ask ChatGPT to generate something new. As I found previously, even if your prompt is virtually identical, ChatGPT may change what it gives you in very unexpected ways.
So, bottom line: ChatGPT can't maintain your code, or even tweak it.
That limitation means you have to do it yourself. As we know, the first draft of a piece of code is rarely the final code. So, even if you were to expect ChatGPT to generate final code, it would really be a starting point, one where you need to take it to completion, integrate it into your bigger project, test it, refine it, debug it, and so on.
Also: I asked ChatGPT to write a short Star Trek episode. It actually succeeded
But that doesn't mean the example code is worthless -- far from it. Let's take a look at a prompt I wrote based on the project I described earlier. Here's the first part:
Wite a PHP function called summarize_article. As input, summarize_article will be passed a URL to an article on a news-related site like ZDNET.com or Reuters.com.
I'm telling ChatGPT the programming language it should use. I'm also telling it the input but, while doing so, providing two sites as samples to help ChatGPT understand the style of article. Honestly, I'm not sure ChatGPT didn't ignore that bit of guidance. Next, I'll tell it how to do the bulk of the work:
Inside summarize_article, retrieve the contents of the web page at the URL provided. Using the library Sumy from within PHP and any other libraries necessary, extract the main body of the article, ignoring any ads or embedded materials, and summarize it to approximately 50 words. Make sure the summary consists of complete sentences. You can go above the 50 words to finish the last sentence, if necessary.
This is very similar to how I'd instruct an employee. I'd want that person to know that they weren't only restricted to Sumy. If they needed another tool, I wanted them to use it.
Also: How to get a perfect face match using Midjourney AI
I also specified an approximate number of words to create bounds for what I wanted as a summary. A later version of the routine might take that number as a parameter. I then ended by saying what I wanted as a result:
Once processing is complete, code summarize_article so it returns the summary in plain text.
The resulting code is pretty simple. ChatGPT did call on another library (Goose) to retrieve the article contents. It then passed that summary to Sumy with a 50-word limit and then returned the result. But once the basics are written, it's a mere matter of programming to go back in and add tweaks, customize what's passed to the two libraries, and delivering the results.
One interesting point of note. When I originally tried this test in early 2023, ChatGPT created a sample call to the routine it wrote, using a URL from after 2021. At that time, in March 2023, ChatGPT's dataset only went to 2021. Now, the ChatGPT knowledge base extends to the end of December 2023. But my point is that ChatGPT made up a sample link that it couldn't possibly know about:
https://www.reuters.com/business/retail-consumer/teslas-musk-says-fremont-california-factory-may-be-sold-chip-shortage-bites-2022-03-18/
I checked that URL against both Reuters' site and the Wayback Machine, and it doesn't exist. Never assume ChatGPT is accurate. Always double-check everything it gives you.
Does ChatGPT replace programmers?
Not now -- or, at least -- not yet. ChatGPT programs at the level of a talented first-year programming student, but it's lazy (like that first-year student). The tool might reduce the need for entry-level programmers, but at its current level, I think it will just make life easier for entry-level programmers (and even programmers with more experience) to write code and look up information. It's definitely a time-saver, but there are few programming projects it can do on its own -- at least now. In 2030? Who knows.
How do I get coding answers in ChatGPT?
Just ask it. You saw above how I used an interactive discussion dialog to narrow down the answers I wanted. When you're working with ChatGPT, don't expect one question to magically do all your work for you. But use ChatGPT as a helper and resource, and it will give you a lot of very helpful information. Of course, test that information -- because, as John Schulman, a co-founder of OpenAI, says , "Our biggest concern was around factuality, because the model likes to fabricate things."
Is the code generated by ChatGPT guaranteed to be error-free?
Hell, no! But you also can't trust the code human programmers write. I certainly don't trust any code I write. Code comes out of the code-making process incredibly flawed. There are always bugs. Before you ship, you need to test, test, and test again. Then, alpha test with a few chosen victims. Then beta test with your wider user community. Even after all that, there will be bugs. Just because an AI is playing at this coding thing doesn't mean it can do bug-free code. Do not trust. Always verify. And you still won't have it fully bug-free. Such is the nature of the universe.
How detailed should my description of a programming issue be when asking ChatGPT?
Detailed. Look at it this way: the more you leave open for interpretation, the more the AI will go its own way. When I give prompts to ChatGPT to help me while programming, I imagine I'm assigning a programming task to one of my students or someone who works for me. Did I give that person enough details to go off and create a first draft or will that person have to ask me a ton of additional questions? Worse, will that person have so little guidance that they'll go off in entirely the wrong direction? Don't be lazy here. ChatGPT can save you hours or even days programming (it has for me), but only if you give it useful instructions to begin with.
If I use ChatGPT to write my code, who owns it?
As it turns out, there's not a lot of case law yet to definitively answer this question. The US, Canada, and the UK require something that's copyrighted to have been created by human hands, so code generated by an AI tool may not be copyrightable. There are also issues of liability based on where the training code came from and how the resulting code is used. ZDNET did a deep dive on this topic, spoke to legal experts, and produced the following three articles. If you're concerned about this issue (and if you're using AI to help with code, you should be), I recommend you give them a read.
- Who owns the code? If ChatGPT's AI helps write your app, does it still belong to you?
- If you use AI-generated code, what's your liability exposure?
- A thorny question: Who owns code, images, and narratives generated by AI?
What programming languages does ChatGPT know?
Most of them. I tested common modern languages , like PHP, Python, Java, Kotlin, Swift, C#, and more. But then I had the tool write code in obscure dark-age languages like COBOL, Fortran, Forth, LISP, ALGOL, RPG (the report program generator, not the role-playing game), and even IBM/360 assembly language.
As the icing on the cake, I gave it this prompt:
Write a sequence that displays 'Hello, world' in ascii blinking lights on the front panel of a PDP 8/e
The PDP 8/e was my very first computer , and ChatGPT actually gave me instructions for toggling in a program using front-panel switches. I was impressed, gleeful, and ever so slightly afraid.
Can ChatGPT help me with data analysis and visualization tasks?
Yes, and a lot of it can be done without code. Check out my entire article on this topic: The moment I realized ChatGPT Plus was a game-changer for my business .
I also did a piece on generated charts and tables: How to use ChatGPT to make charts and tables
But here's where it gets fun. In the article above, I asked ChatGPT Plus "Make a bar chart of the top five cities in the world by population," and it did. But do you want code? Try asking:
Make a bar chart of the top five cities in the world by population in Swift. Pull the population data from online. Be sure to include any necessary libraries.
By adding "in Swift," you're specifying the programming language. By specifying where the data comes from and forcing ChatGPT Plus to include libraries, it knows to bring in the other resources the program needs. That's why, fundamentally, programming with an AI's help requires you to know things about programming. But if you do, it's cool. Because three sentences can get you a nice chunk of annotated code. Cool, huh?
How does ChatGPT handle the differences between dialects and implementations of a given programming language?
We don't have exact details on this issue from OpenAI, but our understanding of how ChatGPT is trained can shed some light on this question. Keep in mind that dialects and implementations of programming languages (and their little quirks) change much more rapidly than the full language itself. This reality makes it harder for ChatGPT (and many programming professionals) to keep up.
Also: How I used ChatGPT to write a custom JavaScript bookmarklet
As such, I'd work off these two assumptions:
- The more recent the dialectic change, the less likely ChatGPT knows about it, and
- The more popular a language overall, the more training data it likely has learned from, and therefore the more accurate it will be.
What's the bottom line? ChatGPT can be a very helpful tool. Just don't ascribe superpowers to it. Yet.
You can follow my day-to-day project updates on social media. Be sure to follow me on Twitter at @DavidGewirtz , on Facebook at Facebook.com/DavidGewirtz , on Instagram at Instagram.com/DavidGewirtz , and on YouTube at YouTube.com/DavidGewirtzTV .
How to use ChatGPT (and how to access GPT-4o)
Code faster with generative ai, but beware the risks when you do, how i test an ai chatbot's coding ability - and you can too.
Introduction to gpt-4o
GPT-4o ("o" for "omni") is designed to handle a combination of text, audio, and video inputs, and can generate outputs in text, audio, and image formats.
Before GPT-4o, users could interact with ChatGPT using Voice Mode, which operated with three separate models. GPT-4o will integrate these capabilities into a single model that's trained across text, vision, and audio. This unified approach ensures that all inputs—whether text, visual, or auditory—are processed cohesively by the same neural network.
Current API Capabilities
Currently, the API supports {text, image} inputs only, with {text} outputs, the same modalities as gpt-4-turbo . Additional modalities, including audio, will be introduced soon. This guide will help you get started with using GPT-4o for text, image, and video understanding.
Getting Started
Install openai sdk for python, configure the openai client and submit a test request.
To setup the client for our use, we need to create an API key to use with our request. Skip these steps if you already have an API key for usage.
You can get an API key by following these steps:
- Create a new project
- Generate an API key in your project
- (RECOMMENDED, BUT NOT REQUIRED) Setup your API key for all projects as an env var
Once we have this setup, let's start with a simple {text} input to the model for our first request. We'll use both system and user messages for our first request, and we'll receive a response from the assistant role.
Image Processing
GPT-4o can directly process images and take intelligent actions based on the image. We can provide images in two formats:
- Base64 Encoded
Let's first view the image we'll use, then try sending this image as both Base64 and as a URL link to the API
Base64 Image Processing
Url image processing, video processing.
While it's not possible to directly send a video to the API, GPT-4o can understand videos if you sample frames and then provide them as images. It performs better at this task than GPT-4 Turbo.
Since GPT-4o in the API does not yet support audio-in (as of May 2024), we'll use a combination of GPT-4o and Whisper to process both the audio and visual for a provided video, and showcase two usecases:
- Summarization
- Question and Answering
Setup for Video Processing
We'll use two python packages for video processing - opencv-python and moviepy.
These require ffmpeg , so make sure to install this beforehand. Depending on your OS, you may need to run brew install ffmpeg or sudo apt install ffmpeg
Process the video into two components: frames and audio
Example 1: summarization.
Now that we have both the video frames and the audio, let's run a few different tests to generate a video summary to compare the results of using the models with different modalities. We should expect to see that the summary generated with context from both visual and audio inputs will be the most accurate, as the model is able to use the entire context from the video.
Visual Summary
Audio summary.
- Visual + Audio Summary
The visual summary is generated by sending the model only the frames from the video. With just the frames, the model is likely to capture the visual aspects, but will miss any details discussed by the speaker.
The results are as expected - the model is able to capture the high level aspects of the video visuals, but misses the details provided in the speech.
The audio summary is generated by sending the model the audio transcript. With just the audio, the model is likely to bias towards the audio content, and will miss the context provided by the presentations and visuals.
{audio} input for GPT-4o isn't currently available but will be coming soon! For now, we use our existing whisper-1 model to process the audio
The audio summary is biased towards the content discussed during the speech, but comes out with much less structure than the video summary.
Audio + Visual Summary
The Audio + Visual summary is generated by sending the model both the visual and the audio from the video at once. When sending both of these, the model is expected to better summarize since it can perceive the entire video at once.
After combining both the video and audio, we're able to get a much more detailed and comprehensive summary for the event which uses information from both the visual and audio elements from the video.
Example 2: Question and Answering
For the Q&A, we'll use the same concept as before to ask questions of our processed video while running the same 3 tests to demonstrate the benefit of combining input modalities:
- Visual Q&A
- Audio Q&A
- Visual + Audio Q&A
Comparing the three answers, the most accurate answer is generated by using both the audio and visual from the video. Sam Altman did not discuss the raising windows or radio on during the Keynote, but referenced an improved capability for the model to execute multiple functions in a single request while the examples were shown behind him.
Integrating many input modalities such as audio, visual, and textual, significantly enhances the performance of the model on a diverse range of tasks. This multimodal approach allows for more comprehensive understanding and interaction, mirroring more closely how humans perceive and process information.
Currently, GPT-4o in the API supports text and image inputs, with audio capabilities coming soon.
- Latest Articles
- Top Articles
- Posting/Update Guidelines
- Article Help Forum
- View Unanswered Questions
- View All Questions
- View C# questions
- View C++ questions
- View Javascript questions
- View Visual Basic questions
- View Python questions
- CodeProject.AI Server
- All Message Boards...
- Running a Business
- Sales / Marketing
- Collaboration / Beta Testing
- Work Issues
- Design and Architecture
- Artificial Intelligence
- Internet of Things
- ATL / WTL / STL
- Managed C++/CLI
- Objective-C and Swift
- System Admin
- Hosting and Servers
- Linux Programming
- .NET (Core and Framework)
- Visual Basic
- Web Development
- Site Bugs / Suggestions
- Spam and Abuse Watch
- Competitions
- The Insider Newsletter
- The Daily Build Newsletter
- Newsletter archive
- CodeProject Stuff
- Most Valuable Professionals
- The Lounge
- The CodeProject Blog
- Where I Am: Member Photos
- The Insider News
- The Weird & The Wonderful
- What is 'CodeProject'?
- General FAQ
- Ask a Question
- Bugs and Suggestions
C# in Browser via WebAssembly (without Blazor)

- Download the samples

Introduction
C# programs (as well as programs written in many other software languages) can now be run in almost any browser via WebAssembly - Wasm for short.
On top of being written in better languages, WebAssembly programs usually run faster than JavaScript/TypeScript programs, because they are compiled (at least to the intermediary language, some are even compiled to the native machine assembly language). Also as strongly typed languages they have considerably smaller and faster built-in types.
Avalonia is a great multiplatform framework for building UI applications. Avalonia can be used for building desktop applications for Windows, MacOS, Linux, Browser WebAssembly applications and mobile applications for iOS, Android and Tizen.
On top of everything else, Avalonia allows reusing most of the code between different platforms.
Here is a website demonstrating Avalonia controls built as Avalonia in-browser application: Avalonia Demo :
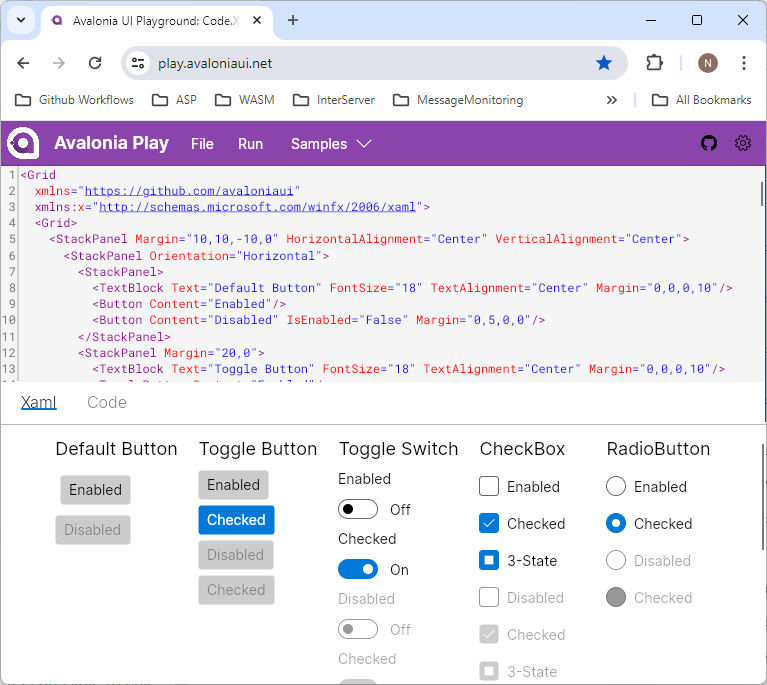
In this article we shall talk only about in-browser Avalonia via Wasm.
Why "Without Blazor"
Initial Microsoft's WebAssembly supporting product was called Blazor (client side version) and was released as part of ASP.NET. Blazor can be used for doing non-visual operations and also to modify the HTML tree in C#.
However, I saw some complaints about Blazor stability and performance when it comes to interaction with HTML/JavaScript. Here is one place on the web mentioning Blazor stability and performance problems . I remember seeing similar complaints on other websites as well.
Because of those problems, this article focuses on using System.Runtime.InteropServices.JavaScript package which became part of .NET's WebAssembly SDK. This package is reported to provide better performance and more stable interactions with JavaScript.
The latest version of Avalonia also uses this library.
The Main Problem with WebAssembly - Lack of good Samples and good Documentation
While C# via Wasm is ready for prime time, the main problem is it being a relatively new technology it has very few good samples and good documentation available on-line.
The main purpose of this article is to provide easy to understand samples and good documentation covering all or most of C#-in-browser functionality.
Article Outline
Here are the topics this article covers:
- Creating Wasm projects and embedding them into browser code.
- Calling Browser JavaScript methods from Wasm C# and vice versa - calling Wasm C# methods from in-browser JavaScript.
- Calling C# Program.Main method from JavaScript.
- Running Avalonia visual applications in browser.
Using ASP.NET Core for Samples
Browser based programming always implies a server - in all samples here I use ASP.NET due to the fact that ASP.NET is a great powerful, well tested, proven technology from Microsoft that works well with my favorite Visual Studio 2022 and allows keeping HTML/JavaScript client code together in the same project with the server code.
For the sake of speed and clarity I try avoiding ASP.NET code generation; instead I use ASP.NET as a Web and Data Server and the middle tier.
While ASP.NET is my choice for the server, exactly the same approach to deploying and running WebAssembly can be applied to any other server technology.
Samples Source Code Location
The samples' source code is located at Web Assembly Samples .
JavaScript calling C# Method Sample
Important note.
I'll go over the first sample with a great detail explaining almost everything with regards to the WebAssembly. This level of detail will not be maintained for the rest of the samples (since by that time you'll understand already how the WebAssembly works). So it is important to read this section, while the rest of the sample related sections you can read selectively depending on your needs.
Sample Location
This sample is located within JSCallingDotNetSample folder (its solution file has the same name).
Sample Code Overview
JSCallingDotNetSample solution has two projects in it:
- JSCallingDotNetSample - an ASP.NET 8.0 project. Please, make sure this is your start up project.
- Greeter - a C# .NET 8.0 library.

How the Solution and the Projects were Created
In order to create the solution and the main ASP.NET project, I started Visual Studio 2022, clicked "Create a new project" option and chose "ASP.NET Core Web APP (Razor Pages)":

Then I entered the name of the solution ("JSCallingDotNetSample") and made sure that the solution is created one directory above the project (and not in the same directory) by unselecting "Place solution and project in the same directory" check box.
Then to create the project containing C# code I right-clicked on the solution within the solution explorer, chose Add->New Project and then selected "Class Library" template:

Note, that while in all samples, below, the ASP.NET projects are created in the same fashion, some C#-only projects will be created differently. Sometimes we would have to choose C# Console project (instead of class library) template and for Avalonia samples it will be even more fun and I'll give details about creating Avalonia Wasm projects below when we get to the topic.
Note that there are no project dependencies - the ASP.NET main project does not depend on the C# project. Though later I'll show how to introduce a build dependency between the projects.
Running the Project
In order to run the project successfully - first build the Greeter project. Under the project's bin/Debug/net8.0-browser/wwwroot folder a subfolder _framework will be created:

Copy this _framework folder over under the wwwroot folder of the JSCollingDotNetSample ASP.NET project.

Note that the folder should not become part of the source code (even though it has been moved under a source code folder). If you are using git you have to add this folder with its content to the git .ignore file (this is what a small red STOP icon before the folder means).
Build and run the main JSCallingDotNetSample project - first for a second or two you'll see a message "Please wait while Web Assembly is Loading!" and then it will be overridden by a message generated by C# code:

C#-only Greeter Project
The C# Greeter project contains C# code called by JavaScript (from ASP.NET project). It has only one static class JSInteropCallsContainer and the class has a single method Greet that takes an array of strings (names) and returns a greeting string "Hello <name1>, <name2>, ... <name_N>!!!":
Note that the class is static and partial and the method Greet(...) has JSExport attribute - this allows the method to be called from JavaScript.
Take a look at the project file - Greeter.csproj:
Note the highlighted differences from a usual C# Library project:
- The Sdk is set to Microsoft.NET.Sdk.WebAssembly .
- TargetFramework is set to net8.0-browser .
- <AllowUnsafeBlocks>true</AllowUnsafeBlocks> .
This three changes allow the project to produce (as a result of a build) _framework folder containing .wasm and other files needed for deployment.
JSCallingDotNetSample Code
Here I explain the changes made to the files within JSCallingDotNetSample ASP.NET project after creating it using "ASP.NET Core Web App (Razor Pages)" template.
Minor Modifications
For the sake of simplification, I removed the wwwroot/lib folder - since I do not plan to use either bootstrapper or jQuery.
I also greatly simplified the _Layout.cshtml file located under Pages/Shared folder, removing its footer, header and CSS classes.
Modifications to Program.cs File
I removed some unneeded lines from Progam.cs file and added Mime Types required by WebAssembly
The mime types are added to a FileExtensionContentTypeProvider object which is then assigned to be the provider for the static files:
Adding wasmRunner.js File
I added wasmRunner.js file to wwwroot folder (the same folder that contains copied _framework folder).
Here is the content of the file:
The file is well documented in-code. Here are the most important lines from that file:
- We load the dotnet object from ./_framework/dotnet.js file. JavaScript import { dotnet } from ' ./_framework/dotnet.js'
- We create two methods from dotnet - one returns an object containing all the C# exports to JavaScript and the other returns configuration for the WebAssembly project and the web site. JavaScript const { getAssemblyExports, getConfig } = await dotnet.create();
- We call getConfig() method to get the config config object: const config = getConfig();
- We use getAssemblyExport(...) method to get the export object containing all C# exports: JavaScript const exports = await getAssemblyExports(config.mainAssemblyName);
- We call the exported C# Greeter.JSInteropCallsContainer.Greet(...) method and save the result in variable text : const text = exports.Greeter.JSInteropCallsContainer.Greet([ ' Nick' , ' Joe' , ' Bob' ]);
- Finally we assign the obtained text to be the inner text of our div element with id="out" : document.getElementById( " out" ).innerText = text;
Modifying Index.cshtml File
The last file that I change is Pages/Index.cshtml file. I changed its content to be:
Note that it has a div element with id equals to "out", whose content will be replaced with the text.
Also note that it loads the module wamsRunner.js from wwwroot folder (this is what ~/ means).
Improving Performance of in-Browser C#
The in-browser performance of C# code can be improved in many ways. Most important is compiling C# AOT (ahead of time). This might increase the size of .wasm files but will greatly improve the performance.
Our sample demonstrates how to use AOT compilation in Release configuration.
You can create release AOT version of Greeter by going to the Greeter project folder on the command line and executing the following command:
It will create the _framework folder under bin\Release\net8.0-browser\publish\wwwroot folder.
This folder _framework will contain the optimized version of .wasm files. Move or copy this folder under JSCallingDotNetSample/wwwroot folder in exactly the same fashion as before and now when you run the project it will load the optimized .wasm files.
Important Note : AOT compilation of projects can take a lot of time - even 10-15 minutes if the project is large enough. In our case, however, our project is very small and the AOT building should take only a couple of seconds.
Take another look at Greeter.csproj project file. The AOT instructions are contained within a PropertyGroup conditioned on Release Configuration:
Creating Build Dependency and Copying _framework Folder using a Post Build Event
Note that in Debug configuration we can set the project Greeter to be build before the main JSCallingDotNetSample project without setting the project dependency.
In order to do it right, click on the solution JSCallingDotNetSample in the solution explorer and choose "Project Dependencies..." menu item:

In the open dialog choose JSColldingDotNetSample under Projects and within "Depends on" panel made sure the checkbox is checked. Then press "OK" button.

This will ensure that Greeter project builds before the main ASP.NET JSCallingDotNetSample project.
Now to copy the _framework folder automatically under Debug mode we add the following lines to the end of JSColldingDotNetSample.csproj file:
Note, that this can be done only for the Debug option, because Release would require a publish step on Greeter project. Of course it should be possible to automate it also, but at this point I do not want to spend time figuring it out.
Example of C# Calling JavaScript Program
This sample is located within DotNetCallingJSSample folder (its solution has the same name as the folder). It is built on top of the previous sample.
It modifies our exported method
to depend on another method
whose implementation is provided within JavaScript.
JSInteropCallsContainer class within Greeter project has two methods instead of one.
Greeter.GetGreetingWord() is an extra method that's not implemented. It is marked as partial and it has JSImport("getGreetingWord", "CSharpMethodsJSImplementationsModule") attribute:
The attribute parameters signify that the program expects GetGreetingWord() method to be implemented by JavaScript getGreetingWord() method within JavaScript module named "CSharpMethodsJSImplementationsModule". A bit of a forward reference, but not the end of the world.
The method Greet(params string[] names) has been slightly modified to get the greeting word from GetGreetingWord() method instead of it being hardcode to "Hello":
The only file changed within main DotNetCallingJSSample project is wwwroot/wasmRunner.js. It has one line modified and one method call inserted:
Note that on top of the methods getAssemblyExport(...) and getConfig(...) (that we already used in the previous sample) we also obtain method setModuleImports(...) from await dotnet.create() call.
We then use setModuleImports(...) method to set up getGreetingWord() method within "CSharpMethodsJSImplementationsModule" module to always return "Hi".
Now, rebuild the main project DotNetCallingJSSample (to force also the rebuilding Greeter project and copying _framework folder) and run it. We shall see "Hi Nick, Joe, Bob!!!" - the greeting is "Hi" instead of "Hello":
Running C# Main Method in Web Assembly Sample
Next I'll show how run a C# Program.Main method from JavaScript. The corresponding sample is located under JSCallingCSharpMainMethodSample/JSCallingCSharpMainMethodSample.sln solution.
First of all rebuild and try running the main project JSCallingCSharpMainMethodSample. Press F12 to open the devtools in your browser. Click on the Console tab. You will see whatever is printed to the console:

Line "Welcome to WebAssembly Program.Main(string[] args)!!!", then line "Here are the arguments passed to Program.Main:" and finally "arg1", "arg2" and "arg3" are each printed on its own line.
The Greeter project in that solution has only one simple file C# Program.cs:
It will print to console "Welcome to WebAssembly Program.Main(string[] args)!!!" and then if there are some arguments passed to the main, it will aso print the line "Here are the arguments passed to Program.Main:" and then it will print each argument on its own line.
Now look at Greeter.csproj file:
Note - we added <RuntimeIdentifier>browser-wasm</RuntimeIdentifier> , we changed the OutputType to "Exe" and we added the StartupObject line
Within JSCallingCSharpMainMethodSample (main) project the only file changed is wasmRunner.js:
We get dotnetRuntime from await dotnet.create() and then call its dotnetRuntime.runMain(...) method to call the Program.Main(...) method of C#:
Note that the second argument passed to dotnetRuntime.runMain(...) should be an array of strings. These are the strings that will be passed over to Program.Main(string[] args) as args . This is why the program printed "arg1", "arg2" and "arg3" to the console. If you change the arguments within that array you shall see the corresponding changes in the program's output.
Run Avalonia in Browser via WebAssembly
Small intro to avalonia in browser.
Avalonia can run on many platforms including in-browser via WebAssembly.
Avalonia in Browser sample project is located under AvaInBrowserSample/AvaInBrowserSample.sln solution.
Open the solution, and make AvaInBrowserSample ASP.NET project to be your startup project.
Try rebuilding AvaInBrowserSample project and then run it in the debugger. After a couple of seconds Avalonia application is going to appear in the browser:

When you press button "Change Text" the first word of the phrase above toggles between "Hello" and "Hi" while the rest of the text stays the same.
Avalonia code is very simple - custom code is located only in MainView.xaml and MainView.xaml.cs files.
The button's callback triggers change of the text within the TextBox :
Creating Client C# Avalonia Project
Here I show how to create the Avalonia-in-Browser project using Avalonia Templates.
Note that I assume that we are inside the Solution Folder - AvaInBrowserSample.
To create an Avalonia WebAssembly project I use instructions from Creating Avalonia Web Assembly Project :
- I install wasm-tools (or make sure they are installed and up-to-date) by running dotnet workload install wasm-tools from a command line.
- I update to the latest Avalonia dotnet templates by running command: dotnet new install avalonia.templates
- I create folder AvaCode for the Avalonia projects and cd to it using the command line.
- From within that folder, I run from the command line: dotnet new avalonia.xplat
- This will create the shared project AvaCode (within the same-named folder) and a number of platform specific projects.
- I remove most of the platform specific projects leaving only AvaCode.Browser (for building the Avalonia WebAssembly bundle) and AvaCode.Display (for debugging and faster prototyping if needed).
Then I add those three project to my AvaInBrowserSample solution using Visual Studio. I place those projects in a separate solution folder AvaCode:
Note that the 3 Avalonia projects are at the top of the image within AvaCode Solution folder.
Now I can build my Avalonia functionality (within AvaCode project) and test it by running it from AvaCode.Desktop project.
I can also test it in the browser by changing the directory to AvaCode.Browser project and executing command "dotnet run" on the command line.
Changes to the Main Project
To make my main ASP.NET project display Avalonia's MainView, I copied the app.cs file from AvaCode.Browser/wwwroot folder into AvaInBrowserSample/wwwroot/css/ folder of the ASP.NET project.
Then I modified the _Layout.cshtml file to have a link to this app.css file, then I added the style that has some magic words: style="margin: 0px; overflow: hidden" to be <body> tag and simplified the area inside the <body> tag to make sure that @RenderBody() call is straight under the tag:
Now we need to modify wasmRunner.js file. It will look almost the same as the one from the previous section, but there will be some extra calls between dotnet. and .create() methods:
The last file to change is Index.cshtml. This file gets uses some CSS classes defined within app.cs file that we copied from AvaCode.Browser project. Without those CSS classes, Avalonia does not take correct space (all space) of the browser:
This article explains embedding C# .NET code into a browser and provides some easy to understand samples.
This article, along with any associated source code and files, is licensed under The MIT License

Comments and Discussions
Use Ctrl+Left/Right to switch messages, Ctrl+Up/Down to switch threads, Ctrl+Shift+Left/Right to switch pages.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
You don't need a lot of detail here - just a brief outline will do. Section 2 - The Methodology. The next section of your chapter is where you'll present the actual methodology. In this section, you need to detail and justify the key methodological choices you've made in a logical, intuitive fashion.
Step 1: Explain your methodological approach. Step 2: Describe your data collection methods. Step 3: Describe your analysis method. Step 4: Evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made. Tips for writing a strong methodology chapter. Other interesting articles.
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section: ... How to Write Research Methodology. ... Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used. ...
Provide the rationality behind your chosen approach. Based on logic and reason, let your readers know why you have chosen said research methodologies. Additionally, you have to build strong arguments supporting why your chosen research method is the best way to achieve the desired outcome. 3. Explain your mechanism.
The methodology section of your paper describes how your research was conducted. This information allows readers to check whether your approach is accurate and dependable. A good methodology can help increase the reader's trust in your findings. First, we will define and differentiate quantitative and qualitative research.
In this video, we walk you through a research methodology from a dissertation that earned full distinction, step by step. We start off by discussing the core components of a research methodology by unpacking our free methodology chapter template. We then progress to the sample research methodology to show how these concepts are applied in an ...
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects. 5th edition.Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences.
Learn how to write a strong methodology chapter that allows readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research. A good methodology chapter incl...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
Here are the steps to follow when writing a methodology: 1. Restate your thesis or research problem. The first part of your methodology is a restatement of the problem your research investigates. This allows your reader to follow your methodology step by step, from beginning to end. Restating your thesis also provides you an opportunity to ...
A quantitative approach and statistical analysis would give you a bigger picture. 3. Identify how your analysis answers your research questions. Relate your methodology back to your original research questions and present a proposed outcome based on your analysis.
Waterfall: It is based on traditional methods and mainly focuses on following the processes. Here, much emphasis is given to project documentation. Critical Path Method: This methodology is a step-by-step method and works best for projects with independent tasks. Its key role is to measure and prioritize tasks.
Your Methods Section contextualizes the results of your study, giving editors, reviewers and readers alike the information they need to understand and interpret your work. Your methods are key to establishing the credibility of your study, along with your data and the results themselves. A complete methods section should provide enough detail ...
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Other interesting articles.
This information regarding the methodology section of a proposal was gathered from RRU thesis and major project handbooks, current in 2020, from programs in the Faculty of Social and Applied Sciences, the Faculty of Management, and the College of Interdisciplinary Studies. If the details here differ from the information provided in the handbook ...
Example of a methodology in a research paper. The following example of a methodology in a research paper provides insight into the structure and content to consider when writing your own: This research article discusses the psychological and emotional impact of a mental health support program for employees. The program provided prolonged and ...
For example, if a project is behind schedule, switching to a more agile methodology such as Kanban or Scrum may help to get things back on track. On the other hand, if budget constraints are an issue, switching to a more 'slender' methodology such as the lean methodology may be the best course of action.
The secret is to use the best methods and tools, anticipating the strongest outcomes. Use samples as a guide; One of the best guides on how to write a methodology for a project is a sample. The samples feature what you are expected to produce at the end of the writing process. You only should be cautious to obtain the samples from credible sources.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
This free project proposal template for Word will provide you with everything you need to write an excellent project proposal. It will help you with the executive summary, project process, deliverables, costs—even terms and conditions. Download your free template today. ProjectManager's project proposal template.
The pre-writing stage is crucial for creating a compelling and successful project proposal. Here's a breakdown of the key steps involved: 1. Understanding the audience. The first step is to identify decision-makers and understand the mindset of the audience for which you are writing a proposal.
ChatGPT and generative AI are types of artificial intelligence technology that answer questions and generate content. The user provides a prompt, and the AI generates results based on large-language models and internet search results. Prompts can be questions, statements, commands, or instructions.
Use ChatGPT to demo techniques, write small algorithms, and produce subroutines. You can even get ChatGPT to help you break down a bigger project into chunks, and then you can ask it to help you ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
GPT-4o ("o" for "omni") is designed to handle a combination of text, audio, and video inputs, and can generate outputs in text, audio, and image formats. Background. Before GPT-4o, users could interact with ChatGPT using Voice Mode, which operated with three separate models. GPT-4o will integrate these capabilities into a single model that's ...
Then to create the project containing C# code I right-clicked on the solution within the solution explorer, chose Add->New Project and then selected "Class Library" template: Note that in all samples, below, the main project created in the same fashion, some C# projects will be created differently.