
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

1 What is Action Research for Classroom Teachers?
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
- What is the nature of action research?
- How does action research develop in the classroom?
- What models of action research work best for your classroom?
- What are the epistemological, ontological, theoretical underpinnings of action research?
Educational research provides a vast landscape of knowledge on topics related to teaching and learning, curriculum and assessment, students’ cognitive and affective needs, cultural and socio-economic factors of schools, and many other factors considered viable to improving schools. Educational stakeholders rely on research to make informed decisions that ultimately affect the quality of schooling for their students. Accordingly, the purpose of educational research is to engage in disciplined inquiry to generate knowledge on topics significant to the students, teachers, administrators, schools, and other educational stakeholders. Just as the topics of educational research vary, so do the approaches to conducting educational research in the classroom. Your approach to research will be shaped by your context, your professional identity, and paradigm (set of beliefs and assumptions that guide your inquiry). These will all be key factors in how you generate knowledge related to your work as an educator.
Action research is an approach to educational research that is commonly used by educational practitioners and professionals to examine, and ultimately improve, their pedagogy and practice. In this way, action research represents an extension of the reflection and critical self-reflection that an educator employs on a daily basis in their classroom. When students are actively engaged in learning, the classroom can be dynamic and uncertain, demanding the constant attention of the educator. Considering these demands, educators are often only able to engage in reflection that is fleeting, and for the purpose of accommodation, modification, or formative assessment. Action research offers one path to more deliberate, substantial, and critical reflection that can be documented and analyzed to improve an educator’s practice.
Purpose of Action Research
As one of many approaches to educational research, it is important to distinguish the potential purposes of action research in the classroom. This book focuses on action research as a method to enable and support educators in pursuing effective pedagogical practices by transforming the quality of teaching decisions and actions, to subsequently enhance student engagement and learning. Being mindful of this purpose, the following aspects of action research are important to consider as you contemplate and engage with action research methodology in your classroom:
- Action research is a process for improving educational practice. Its methods involve action, evaluation, and reflection. It is a process to gather evidence to implement change in practices.
- Action research is participative and collaborative. It is undertaken by individuals with a common purpose.
- Action research is situation and context-based.
- Action research develops reflection practices based on the interpretations made by participants.
- Knowledge is created through action and application.
- Action research can be based in problem-solving, if the solution to the problem results in the improvement of practice.
- Action research is iterative; plans are created, implemented, revised, then implemented, lending itself to an ongoing process of reflection and revision.
- In action research, findings emerge as action develops and takes place; however, they are not conclusive or absolute, but ongoing (Koshy, 2010, pgs. 1-2).
In thinking about the purpose of action research, it is helpful to situate action research as a distinct paradigm of educational research. I like to think about action research as part of the larger concept of living knowledge. Living knowledge has been characterized as “a quest for life, to understand life and to create… knowledge which is valid for the people with whom I work and for myself” (Swantz, in Reason & Bradbury, 2001, pg. 1). Why should educators care about living knowledge as part of educational research? As mentioned above, action research is meant “to produce practical knowledge that is useful to people in the everyday conduct of their lives and to see that action research is about working towards practical outcomes” (Koshy, 2010, pg. 2). However, it is also about:
creating new forms of understanding, since action without reflection and understanding is blind, just as theory without action is meaningless. The participatory nature of action research makes it only possible with, for and by persons and communities, ideally involving all stakeholders both in the questioning and sense making that informs the research, and in the action, which is its focus. (Reason & Bradbury, 2001, pg. 2)
In an effort to further situate action research as living knowledge, Jean McNiff reminds us that “there is no such ‘thing’ as ‘action research’” (2013, pg. 24). In other words, action research is not static or finished, it defines itself as it proceeds. McNiff’s reminder characterizes action research as action-oriented, and a process that individuals go through to make their learning public to explain how it informs their practice. Action research does not derive its meaning from an abstract idea, or a self-contained discovery – action research’s meaning stems from the way educators negotiate the problems and successes of living and working in the classroom, school, and community.
While we can debate the idea of action research, there are people who are action researchers, and they use the idea of action research to develop principles and theories to guide their practice. Action research, then, refers to an organization of principles that guide action researchers as they act on shared beliefs, commitments, and expectations in their inquiry.
Reflection and the Process of Action Research
When an individual engages in reflection on their actions or experiences, it is typically for the purpose of better understanding those experiences, or the consequences of those actions to improve related action and experiences in the future. Reflection in this way develops knowledge around these actions and experiences to help us better regulate those actions in the future. The reflective process generates new knowledge regularly for classroom teachers and informs their classroom actions.
Unfortunately, the knowledge generated by educators through the reflective process is not always prioritized among the other sources of knowledge educators are expected to utilize in the classroom. Educators are expected to draw upon formal types of knowledge, such as textbooks, content standards, teaching standards, district curriculum and behavioral programs, etc., to gain new knowledge and make decisions in the classroom. While these forms of knowledge are important, the reflective knowledge that educators generate through their pedagogy is the amalgamation of these types of knowledge enacted in the classroom. Therefore, reflective knowledge is uniquely developed based on the action and implementation of an educator’s pedagogy in the classroom. Action research offers a way to formalize the knowledge generated by educators so that it can be utilized and disseminated throughout the teaching profession.
Research is concerned with the generation of knowledge, and typically creating knowledge related to a concept, idea, phenomenon, or topic. Action research generates knowledge around inquiry in practical educational contexts. Action research allows educators to learn through their actions with the purpose of developing personally or professionally. Due to its participatory nature, the process of action research is also distinct in educational research. There are many models for how the action research process takes shape. I will share a few of those here. Each model utilizes the following processes to some extent:
- Plan a change;
- Take action to enact the change;
- Observe the process and consequences of the change;
- Reflect on the process and consequences;
- Act, observe, & reflect again and so on.
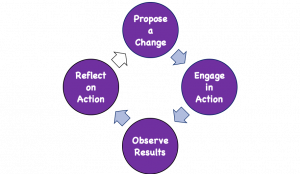
Figure 1.1 Basic action research cycle
There are many other models that supplement the basic process of action research with other aspects of the research process to consider. For example, figure 1.2 illustrates a spiral model of action research proposed by Kemmis and McTaggart (2004). The spiral model emphasizes the cyclical process that moves beyond the initial plan for change. The spiral model also emphasizes revisiting the initial plan and revising based on the initial cycle of research:
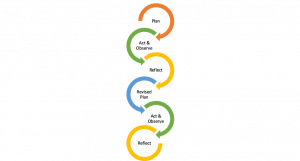
Figure 1.2 Interpretation of action research spiral, Kemmis and McTaggart (2004, p. 595)
Other models of action research reorganize the process to emphasize the distinct ways knowledge takes shape in the reflection process. O’Leary’s (2004, p. 141) model, for example, recognizes that the research may take shape in the classroom as knowledge emerges from the teacher’s observations. O’Leary highlights the need for action research to be focused on situational understanding and implementation of action, initiated organically from real-time issues:
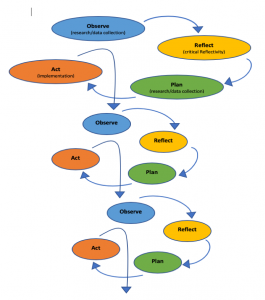
Figure 1.3 Interpretation of O’Leary’s cycles of research, O’Leary (2000, p. 141)
Lastly, Macintyre’s (2000, p. 1) model, offers a different characterization of the action research process. Macintyre emphasizes a messier process of research with the initial reflections and conclusions as the benchmarks for guiding the research process. Macintyre emphasizes the flexibility in planning, acting, and observing stages to allow the process to be naturalistic. Our interpretation of Macintyre process is below:
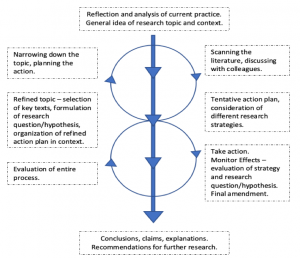
Figure 1.4 Interpretation of the action research cycle, Macintyre (2000, p. 1)
We believe it is important to prioritize the flexibility of the process, and encourage you to only use these models as basic guides for your process. Your process may look similar, or you may diverge from these models as you better understand your students, context, and data.
Definitions of Action Research and Examples
At this point, it may be helpful for readers to have a working definition of action research and some examples to illustrate the methodology in the classroom. Bassey (1998, p. 93) offers a very practical definition and describes “action research as an inquiry which is carried out in order to understand, to evaluate and then to change, in order to improve educational practice.” Cohen and Manion (1994, p. 192) situate action research differently, and describe action research as emergent, writing:
essentially an on-the-spot procedure designed to deal with a concrete problem located in an immediate situation. This means that ideally, the step-by-step process is constantly monitored over varying periods of time and by a variety of mechanisms (questionnaires, diaries, interviews and case studies, for example) so that the ensuing feedback may be translated into modifications, adjustment, directional changes, redefinitions, as necessary, so as to bring about lasting benefit to the ongoing process itself rather than to some future occasion.
Lastly, Koshy (2010, p. 9) describes action research as:
a constructive inquiry, during which the researcher constructs his or her knowledge of specific issues through planning, acting, evaluating, refining and learning from the experience. It is a continuous learning process in which the researcher learns and also shares the newly generated knowledge with those who may benefit from it.
These definitions highlight the distinct features of action research and emphasize the purposeful intent of action researchers to improve, refine, reform, and problem-solve issues in their educational context. To better understand the distinctness of action research, these are some examples of action research topics:
Examples of Action Research Topics
- Flexible seating in 4th grade classroom to increase effective collaborative learning.
- Structured homework protocols for increasing student achievement.
- Developing a system of formative feedback for 8th grade writing.
- Using music to stimulate creative writing.
- Weekly brown bag lunch sessions to improve responses to PD from staff.
- Using exercise balls as chairs for better classroom management.
Action Research in Theory
Action research-based inquiry in educational contexts and classrooms involves distinct participants – students, teachers, and other educational stakeholders within the system. All of these participants are engaged in activities to benefit the students, and subsequently society as a whole. Action research contributes to these activities and potentially enhances the participants’ roles in the education system. Participants’ roles are enhanced based on two underlying principles:
- communities, schools, and classrooms are sites of socially mediated actions, and action research provides a greater understanding of self and new knowledge of how to negotiate these socially mediated environments;
- communities, schools, and classrooms are part of social systems in which humans interact with many cultural tools, and action research provides a basis to construct and analyze these interactions.
In our quest for knowledge and understanding, we have consistently analyzed human experience over time and have distinguished between types of reality. Humans have constantly sought “facts” and “truth” about reality that can be empirically demonstrated or observed.
Social systems are based on beliefs, and generally, beliefs about what will benefit the greatest amount of people in that society. Beliefs, and more specifically the rationale or support for beliefs, are not always easy to demonstrate or observe as part of our reality. Take the example of an English Language Arts teacher who prioritizes argumentative writing in her class. She believes that argumentative writing demonstrates the mechanics of writing best among types of writing, while also providing students a skill they will need as citizens and professionals. While we can observe the students writing, and we can assess their ability to develop a written argument, it is difficult to observe the students’ understanding of argumentative writing and its purpose in their future. This relates to the teacher’s beliefs about argumentative writing; we cannot observe the real value of the teaching of argumentative writing. The teacher’s rationale and beliefs about teaching argumentative writing are bound to the social system and the skills their students will need to be active parts of that system. Therefore, our goal through action research is to demonstrate the best ways to teach argumentative writing to help all participants understand its value as part of a social system.
The knowledge that is conveyed in a classroom is bound to, and justified by, a social system. A postmodernist approach to understanding our world seeks knowledge within a social system, which is directly opposed to the empirical or positivist approach which demands evidence based on logic or science as rationale for beliefs. Action research does not rely on a positivist viewpoint to develop evidence and conclusions as part of the research process. Action research offers a postmodernist stance to epistemology (theory of knowledge) and supports developing questions and new inquiries during the research process. In this way action research is an emergent process that allows beliefs and decisions to be negotiated as reality and meaning are being constructed in the socially mediated space of the classroom.
Theorizing Action Research for the Classroom
All research, at its core, is for the purpose of generating new knowledge and contributing to the knowledge base of educational research. Action researchers in the classroom want to explore methods of improving their pedagogy and practice. The starting place of their inquiry stems from their pedagogy and practice, so by nature the knowledge created from their inquiry is often contextually specific to their classroom, school, or community. Therefore, we should examine the theoretical underpinnings of action research for the classroom. It is important to connect action research conceptually to experience; for example, Levin and Greenwood (2001, p. 105) make these connections:
- Action research is context bound and addresses real life problems.
- Action research is inquiry where participants and researchers cogenerate knowledge through collaborative communicative processes in which all participants’ contributions are taken seriously.
- The meanings constructed in the inquiry process lead to social action or these reflections and action lead to the construction of new meanings.
- The credibility/validity of action research knowledge is measured according to whether the actions that arise from it solve problems (workability) and increase participants’ control over their own situation.
Educators who engage in action research will generate new knowledge and beliefs based on their experiences in the classroom. Let us emphasize that these are all important to you and your work, as both an educator and researcher. It is these experiences, beliefs, and theories that are often discounted when more official forms of knowledge (e.g., textbooks, curriculum standards, districts standards) are prioritized. These beliefs and theories based on experiences should be valued and explored further, and this is one of the primary purposes of action research in the classroom. These beliefs and theories should be valued because they were meaningful aspects of knowledge constructed from teachers’ experiences. Developing meaning and knowledge in this way forms the basis of constructivist ideology, just as teachers often try to get their students to construct their own meanings and understandings when experiencing new ideas.
Classroom Teachers Constructing their Own Knowledge
Most of you are probably at least minimally familiar with constructivism, or the process of constructing knowledge. However, what is constructivism precisely, for the purposes of action research? Many scholars have theorized constructivism and have identified two key attributes (Koshy, 2010; von Glasersfeld, 1987):
- Knowledge is not passively received, but actively developed through an individual’s cognition;
- Human cognition is adaptive and finds purpose in organizing the new experiences of the world, instead of settling for absolute or objective truth.
Considering these two attributes, constructivism is distinct from conventional knowledge formation because people can develop a theory of knowledge that orders and organizes the world based on their experiences, instead of an objective or neutral reality. When individuals construct knowledge, there are interactions between an individual and their environment where communication, negotiation and meaning-making are collectively developing knowledge. For most educators, constructivism may be a natural inclination of their pedagogy. Action researchers have a similar relationship to constructivism because they are actively engaged in a process of constructing knowledge. However, their constructions may be more formal and based on the data they collect in the research process. Action researchers also are engaged in the meaning making process, making interpretations from their data. These aspects of the action research process situate them in the constructivist ideology. Just like constructivist educators, action researchers’ constructions of knowledge will be affected by their individual and professional ideas and values, as well as the ecological context in which they work (Biesta & Tedder, 2006). The relations between constructivist inquiry and action research is important, as Lincoln (2001, p. 130) states:
much of the epistemological, ontological, and axiological belief systems are the same or similar, and methodologically, constructivists and action researchers work in similar ways, relying on qualitative methods in face-to-face work, while buttressing information, data and background with quantitative method work when necessary or useful.
While there are many links between action research and educators in the classroom, constructivism offers the most familiar and practical threads to bind the beliefs of educators and action researchers.
Epistemology, Ontology, and Action Research
It is also important for educators to consider the philosophical stances related to action research to better situate it with their beliefs and reality. When researchers make decisions about the methodology they intend to use, they will consider their ontological and epistemological stances. It is vital that researchers clearly distinguish their philosophical stances and understand the implications of their stance in the research process, especially when collecting and analyzing their data. In what follows, we will discuss ontological and epistemological stances in relation to action research methodology.
Ontology, or the theory of being, is concerned with the claims or assumptions we make about ourselves within our social reality – what do we think exists, what does it look like, what entities are involved and how do these entities interact with each other (Blaikie, 2007). In relation to the discussion of constructivism, generally action researchers would consider their educational reality as socially constructed. Social construction of reality happens when individuals interact in a social system. Meaningful construction of concepts and representations of reality develop through an individual’s interpretations of others’ actions. These interpretations become agreed upon by members of a social system and become part of social fabric, reproduced as knowledge and beliefs to develop assumptions about reality. Researchers develop meaningful constructions based on their experiences and through communication. Educators as action researchers will be examining the socially constructed reality of schools. In the United States, many of our concepts, knowledge, and beliefs about schooling have been socially constructed over the last hundred years. For example, a group of teachers may look at why fewer female students enroll in upper-level science courses at their school. This question deals directly with the social construction of gender and specifically what careers females have been conditioned to pursue. We know this is a social construction in some school social systems because in other parts of the world, or even the United States, there are schools that have more females enrolled in upper level science courses than male students. Therefore, the educators conducting the research have to recognize the socially constructed reality of their school and consider this reality throughout the research process. Action researchers will use methods of data collection that support their ontological stance and clarify their theoretical stance throughout the research process.
Koshy (2010, p. 23-24) offers another example of addressing the ontological challenges in the classroom:
A teacher who was concerned with increasing her pupils’ motivation and enthusiasm for learning decided to introduce learning diaries which the children could take home. They were invited to record their reactions to the day’s lessons and what they had learnt. The teacher reported in her field diary that the learning diaries stimulated the children’s interest in her lessons, increased their capacity to learn, and generally improved their level of participation in lessons. The challenge for the teacher here is in the analysis and interpretation of the multiplicity of factors accompanying the use of diaries. The diaries were taken home so the entries may have been influenced by discussions with parents. Another possibility is that children felt the need to please their teacher. Another possible influence was that their increased motivation was as a result of the difference in style of teaching which included more discussions in the classroom based on the entries in the dairies.
Here you can see the challenge for the action researcher is working in a social context with multiple factors, values, and experiences that were outside of the teacher’s control. The teacher was only responsible for introducing the diaries as a new style of learning. The students’ engagement and interactions with this new style of learning were all based upon their socially constructed notions of learning inside and outside of the classroom. A researcher with a positivist ontological stance would not consider these factors, and instead might simply conclude that the dairies increased motivation and interest in the topic, as a result of introducing the diaries as a learning strategy.
Epistemology, or the theory of knowledge, signifies a philosophical view of what counts as knowledge – it justifies what is possible to be known and what criteria distinguishes knowledge from beliefs (Blaikie, 1993). Positivist researchers, for example, consider knowledge to be certain and discovered through scientific processes. Action researchers collect data that is more subjective and examine personal experience, insights, and beliefs.
Action researchers utilize interpretation as a means for knowledge creation. Action researchers have many epistemologies to choose from as means of situating the types of knowledge they will generate by interpreting the data from their research. For example, Koro-Ljungberg et al., (2009) identified several common epistemologies in their article that examined epistemological awareness in qualitative educational research, such as: objectivism, subjectivism, constructionism, contextualism, social epistemology, feminist epistemology, idealism, naturalized epistemology, externalism, relativism, skepticism, and pluralism. All of these epistemological stances have implications for the research process, especially data collection and analysis. Please see the table on pages 689-90, linked below for a sketch of these potential implications:
Again, Koshy (2010, p. 24) provides an excellent example to illustrate the epistemological challenges within action research:
A teacher of 11-year-old children decided to carry out an action research project which involved a change in style in teaching mathematics. Instead of giving children mathematical tasks displaying the subject as abstract principles, she made links with other subjects which she believed would encourage children to see mathematics as a discipline that could improve their understanding of the environment and historic events. At the conclusion of the project, the teacher reported that applicable mathematics generated greater enthusiasm and understanding of the subject.
The educator/researcher engaged in action research-based inquiry to improve an aspect of her pedagogy. She generated knowledge that indicated she had improved her students’ understanding of mathematics by integrating it with other subjects – specifically in the social and ecological context of her classroom, school, and community. She valued constructivism and students generating their own understanding of mathematics based on related topics in other subjects. Action researchers working in a social context do not generate certain knowledge, but knowledge that emerges and can be observed and researched again, building upon their knowledge each time.
Researcher Positionality in Action Research
In this first chapter, we have discussed a lot about the role of experiences in sparking the research process in the classroom. Your experiences as an educator will shape how you approach action research in your classroom. Your experiences as a person in general will also shape how you create knowledge from your research process. In particular, your experiences will shape how you make meaning from your findings. It is important to be clear about your experiences when developing your methodology too. This is referred to as researcher positionality. Maher and Tetreault (1993, p. 118) define positionality as:
Gender, race, class, and other aspects of our identities are markers of relational positions rather than essential qualities. Knowledge is valid when it includes an acknowledgment of the knower’s specific position in any context, because changing contextual and relational factors are crucial for defining identities and our knowledge in any given situation.
By presenting your positionality in the research process, you are signifying the type of socially constructed, and other types of, knowledge you will be using to make sense of the data. As Maher and Tetreault explain, this increases the trustworthiness of your conclusions about the data. This would not be possible with a positivist ontology. We will discuss positionality more in chapter 6, but we wanted to connect it to the overall theoretical underpinnings of action research.
Advantages of Engaging in Action Research in the Classroom
In the following chapters, we will discuss how action research takes shape in your classroom, and we wanted to briefly summarize the key advantages to action research methodology over other types of research methodology. As Koshy (2010, p. 25) notes, action research provides useful methodology for school and classroom research because:
Advantages of Action Research for the Classroom
- research can be set within a specific context or situation;
- researchers can be participants – they don’t have to be distant and detached from the situation;
- it involves continuous evaluation and modifications can be made easily as the project progresses;
- there are opportunities for theory to emerge from the research rather than always follow a previously formulated theory;
- the study can lead to open-ended outcomes;
- through action research, a researcher can bring a story to life.
Action Research Copyright © by J. Spencer Clark; Suzanne Porath; Julie Thiele; and Morgan Jobe is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Original Language Spotlight
- Alternative and Non-formal Education
- Cognition, Emotion, and Learning
- Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Education and Society
- Education, Change, and Development
- Education, Cultures, and Ethnicities
- Education, Gender, and Sexualities
- Education, Health, and Social Services
- Educational Administration and Leadership
- Educational History
- Educational Politics and Policy
- Educational Purposes and Ideals
- Educational Systems
- Educational Theories and Philosophies
- Globalization, Economics, and Education
- Languages and Literacies
- Professional Learning and Development
- Research and Assessment Methods
- Technology and Education
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Action research.
- Eileen S. Johnson Eileen S. Johnson Oakland University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264093.013.696
- Published online: 29 May 2020
Action research has become a common practice among educational administrators. The term “action research” was first coined by Kurt Lewin in the 1930s, although teachers and school administrators have long engaged in the process described by and formally named by Lewin. Alternatively known as practitioner research, self-study, action science, site-based inquiry, emancipatory praxis, etc., action research is essentially a collaborative, democratic, and participatory approach to systematic inquiry into a problem of practice within a local context. Action research has become prevalent in many fields and disciplines, including education, health sciences, nursing, social work, and anthropology. This prevalence can be understood in the way action research lends itself to action-based inquiry, participation, collaboration, and the development of solutions to problems of everyday practice in local contexts. In particular, action research has become commonplace in educational administration preparation programs due to its alignment and natural fit with the nature of education and the decision making and action planning necessary within local school contexts. Although there is not one prescribed way to engage in action research, and there are multiple approaches to action research, it generally follows a systematic and cyclical pattern of reflection, planning, action, observation, and data collection, evaluation that then repeats in an iterative and ongoing manner. The goal of action research is not to add to a general body of knowledge but, rather, to inform local practice, engage in professional learning, build a community practice, solve a problem or understand a process or phenomenon within a particular context, or empower participants to generate self-knowledge.
- action research cycle
- educational practice
- historical trends
- philosophical assumptions
- variations of action research
You do not currently have access to this article
Please login to access the full content.
Access to the full content requires a subscription
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Education. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 14 May 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.66.15.189]
- 185.66.15.189
Character limit 500 /500
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Action Research in Education
Introduction.
- Chapters and Articles
- Theory and Ethics
- Practical Texts for Individual Teachers
- Collaborative Inquiry and School-Wide Teams for Administrators and School Leaders
- Action Research in Teacher Education
- Action Research in Graduate Education
- PAR Inquiry Processes
- Youth Participatory Action Research (YPAR)
- Critical Participatory Action Research
- Critical Youth Participatory Action Research
- International Perspectives
- Exemplary Case Studies
- Practitioner Journals for Action Researchers across All Disciplines
- Research Journals for Action Researchers across All Disciplines
- Journals Primarily for English/Language Arts/Literacy Educators, Teacher Educators, and Researchers
- Action Research Organizations
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Ethical Research with Young Children
- Grounded Theory
- Methodologies for Conducting Education Research
- Mixed Methods Research
- Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques
- Qualitative Research Design
- Social Science and Education Research
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- English as an International Language for Academic Publishing
- Girls' Education in the Developing World
- History of Education in Europe
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Action Research in Education by Mary Beth Hines , Kerry Armbruster , Adam Henze , Maria Lisak , Christina Romero-Ivanova , Leslie Rowland , Lottie Waggoner LAST REVIEWED: 15 January 2020 LAST MODIFIED: 15 January 2020 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199756810-0140
Educational action research involves participants conducting inquiry into their own practices in order to improve teaching and learning, practices and programs. This means that the researcher is a participant in the activity being investigated, be it in schools or community centers—wherever teaching and learning occur. In Guiding School Improvement with Action Research ( Sagor 2000 , cited under Collaborative Inquiry and School-Wide Teams for Administrators and School Leaders ), Richard Sagor describes action research as “a disciplined process of inquiry conducted by and for those taking the action . . .[in order to] assist the “actor” in improving and/or refining his or her actions” (p. 3). The term “educational action research” encompasses a variety of approaches with different goals (see Historical Overviews of Educational Action Research ). While no consensus exists on a taxonomy that best describes its variations (modes, goals, epistemologies, politics, processes), most analyses identify the following types: (1) “Teacher research” signifies P-16 teacher-conducted inquiry designed to explore research questions related to educational improvement. It is often used interchangeably with “practitioner research/participant inquiry,” although this is a broader term that also refers to projects initiated by others in the educational experience (e.g., administrators, staff, community members). (2) “Participatory action research” (PAR) emphasizes equal, collaborative participation among university and/or school personnel and/or others with vested interests in education, working toward the shared goal of producing educational change. (3) “Youth participatory action research” (YPAR) includes young people as research partners and agents of change. (4) “Critical action research” refers to investigations of underlying power relations present in one’s situated educational practices. All educational action research is designed to impact local policy and practice. Critiques of action research object to this focus on the micro level, claiming that it does not impact education beyond the immediate audience. However, this viewpoint obscures the fact that qualitative action research case studies and cross-case analyses are generalizable to theory, thus carrying the potential to create widespread change. Another critique centers on the limited effectiveness of connecting action research with social justice. However, others argue that social justice is inextricably woven into action research because the inquiry stems from grassroots movements that emphasize social change ( Cochran-Smith and Lytle 2009 , cited under Books ) and privileges the educator’s “insider” knowledge alongside the outside researcher’s formal academic training. The following criteria were used for selecting the texts cited in this article: (1) texts that were peer-reviewed, (2) texts explicitly described as action research (or a synonymous term) by the writer or other scholars, (3) texts cited more frequently than other texts on the same issue, (4) texts originally written in English. These criteria guidelines eliminated the use of dissertations, conference papers, blogs, or pedagogical narratives that were not described as action research (or a comparable term), or reports written in other languages.
Historical Overviews of Educational Action Research
This section contains key texts in defining and outlining the history of educational action research. The scholars whose works are included are among the most cited, recognized, and respected in this field. These articles and books will aid in understanding the spectrum of issues that led to action research’s inception as well as its implementations, changes, and ideologies. This section is broken into shorter works ( Chapters and Articles ) and longer works ( Books ) that will guide the reader in gaining a better understanding of action research’s past and its growth as an area of study.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Education »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Academic Achievement
- Academic Audit for Universities
- Academic Freedom and Tenure in the United States
- Action Research in Education
- Adjuncts in Higher Education in the United States
- Administrator Preparation
- Adolescence
- Advanced Placement and International Baccalaureate Courses
- Advocacy and Activism in Early Childhood
- African American Racial Identity and Learning
- Alaska Native Education
- Alternative Certification Programs for Educators
- Alternative Schools
- American Indian Education
- Animals in Environmental Education
- Art Education
- Artificial Intelligence and Learning
- Assessing School Leader Effectiveness
- Assessment, Behavioral
- Assessment, Educational
- Assessment in Early Childhood Education
- Assistive Technology
- Augmented Reality in Education
- Beginning-Teacher Induction
- Bilingual Education and Bilingualism
- Black Undergraduate Women: Critical Race and Gender Perspe...
- Blended Learning
- Case Study in Education Research
- Changing Professional and Academic Identities
- Character Education
- Children’s and Young Adult Literature
- Children's Beliefs about Intelligence
- Children's Rights in Early Childhood Education
- Citizenship Education
- Civic and Social Engagement of Higher Education
- Classroom Learning Environments: Assessing and Investigati...
- Classroom Management
- Coherent Instructional Systems at the School and School Sy...
- College Admissions in the United States
- College Athletics in the United States
- Community Relations
- Comparative Education
- Computer-Assisted Language Learning
- Computer-Based Testing
- Conceptualizing, Measuring, and Evaluating Improvement Net...
- Continuous Improvement and "High Leverage" Educational Pro...
- Counseling in Schools
- Critical Approaches to Gender in Higher Education
- Critical Perspectives on Educational Innovation and Improv...
- Critical Race Theory
- Crossborder and Transnational Higher Education
- Cross-National Research on Continuous Improvement
- Cross-Sector Research on Continuous Learning and Improveme...
- Cultural Diversity in Early Childhood Education
- Culturally Responsive Leadership
- Culturally Responsive Pedagogies
- Culturally Responsive Teacher Education in the United Stat...
- Curriculum Design
- Data Collection in Educational Research
- Data-driven Decision Making in the United States
- Deaf Education
- Desegregation and Integration
- Design Thinking and the Learning Sciences: Theoretical, Pr...
- Development, Moral
- Dialogic Pedagogy
- Digital Age Teacher, The
- Digital Citizenship
- Digital Divides
- Disabilities
- Distance Learning
- Distributed Leadership
- Doctoral Education and Training
- Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) in Denmark
- Early Childhood Education and Development in Mexico
- Early Childhood Education in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Childhood Education in Australia
- Early Childhood Education in China
- Early Childhood Education in Europe
- Early Childhood Education in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Early Childhood Education in Sweden
- Early Childhood Education Pedagogy
- Early Childhood Education Policy
- Early Childhood Education, The Arts in
- Early Childhood Mathematics
- Early Childhood Science
- Early Childhood Teacher Education
- Early Childhood Teachers in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Years Professionalism and Professionalization Polici...
- Economics of Education
- Education For Children with Autism
- Education for Sustainable Development
- Education Leadership, Empirical Perspectives in
- Education of Native Hawaiian Students
- Education Reform and School Change
- Educational Statistics for Longitudinal Research
- Educator Partnerships with Parents and Families with a Foc...
- Emotional and Affective Issues in Environmental and Sustai...
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- Environmental and Science Education: Overlaps and Issues
- Environmental Education
- Environmental Education in Brazil
- Epistemic Beliefs
- Equity and Improvement: Engaging Communities in Educationa...
- Equity, Ethnicity, Diversity, and Excellence in Education
- Ethics and Education
- Ethics of Teaching
- Ethnic Studies
- Evidence-Based Communication Assessment and Intervention
- Family and Community Partnerships in Education
- Family Day Care
- Federal Government Programs and Issues
- Feminization of Labor in Academia
- Finance, Education
- Financial Aid
- Formative Assessment
- Future-Focused Education
- Gender and Achievement
- Gender and Alternative Education
- Gender, Power and Politics in the Academy
- Gender-Based Violence on University Campuses
- Gifted Education
- Global Mindedness and Global Citizenship Education
- Global University Rankings
- Governance, Education
- Growth of Effective Mental Health Services in Schools in t...
- Higher Education and Globalization
- Higher Education and the Developing World
- Higher Education Faculty Characteristics and Trends in the...
- Higher Education Finance
- Higher Education Governance
- Higher Education Graduate Outcomes and Destinations
- Higher Education in Africa
- Higher Education in China
- Higher Education in Latin America
- Higher Education in the United States, Historical Evolutio...
- Higher Education, International Issues in
- Higher Education Management
- Higher Education Policy
- Higher Education Research
- Higher Education Student Assessment
- High-stakes Testing
- History of Early Childhood Education in the United States
- History of Education in the United States
- History of Technology Integration in Education
- Homeschooling
- Inclusion in Early Childhood: Difference, Disability, and ...
- Inclusive Education
- Indigenous Education in a Global Context
- Indigenous Learning Environments
- Indigenous Students in Higher Education in the United Stat...
- Infant and Toddler Pedagogy
- Inservice Teacher Education
- Integrating Art across the Curriculum
- Intelligence
- Intensive Interventions for Children and Adolescents with ...
- International Perspectives on Academic Freedom
- Intersectionality and Education
- Knowledge Development in Early Childhood
- Leadership Development, Coaching and Feedback for
- Leadership in Early Childhood Education
- Leadership Training with an Emphasis on the United States
- Learning Analytics in Higher Education
- Learning Difficulties
- Learning, Lifelong
- Learning, Multimedia
- Learning Strategies
- Legal Matters and Education Law
- LGBT Youth in Schools
- Linguistic Diversity
- Linguistically Inclusive Pedagogy
- Literacy Development and Language Acquisition
- Literature Reviews
- Mathematics Identity
- Mathematics Instruction and Interventions for Students wit...
- Mathematics Teacher Education
- Measurement for Improvement in Education
- Measurement in Education in the United States
- Meta-Analysis and Research Synthesis in Education
- Methodological Approaches for Impact Evaluation in Educati...
- Mindfulness, Learning, and Education
- Motherscholars
- Multiliteracies in Early Childhood Education
- Multiple Documents Literacy: Theory, Research, and Applica...
- Multivariate Research Methodology
- Museums, Education, and Curriculum
- Music Education
- Narrative Research in Education
- Native American Studies
- Nonformal and Informal Environmental Education
- Note-Taking
- Numeracy Education
- One-to-One Technology in the K-12 Classroom
- Online Education
- Open Education
- Organizing for Continuous Improvement in Education
- Organizing Schools for the Inclusion of Students with Disa...
- Outdoor Play and Learning
- Outdoor Play and Learning in Early Childhood Education
- Pedagogical Leadership
- Pedagogy of Teacher Education, A
- Performance Objectives and Measurement
- Performance-based Research Assessment in Higher Education
- Performance-based Research Funding
- Phenomenology in Educational Research
- Philosophy of Education
- Physical Education
- Podcasts in Education
- Policy Context of United States Educational Innovation and...
- Politics of Education
- Portable Technology Use in Special Education Programs and ...
- Post-humanism and Environmental Education
- Pre-Service Teacher Education
- Problem Solving
- Productivity and Higher Education
- Professional Development
- Professional Learning Communities
- Program Evaluation
- Programs and Services for Students with Emotional or Behav...
- Psychology Learning and Teaching
- Psychometric Issues in the Assessment of English Language ...
- Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Samp...
- Quantitative Research Designs in Educational Research
- Queering the English Language Arts (ELA) Writing Classroom
- Race and Affirmative Action in Higher Education
- Reading Education
- Refugee and New Immigrant Learners
- Relational and Developmental Trauma and Schools
- Relational Pedagogies in Early Childhood Education
- Reliability in Educational Assessments
- Religion in Elementary and Secondary Education in the Unit...
- Researcher Development and Skills Training within the Cont...
- Research-Practice Partnerships in Education within the Uni...
- Response to Intervention
- Restorative Practices
- Risky Play in Early Childhood Education
- Scale and Sustainability of Education Innovation and Impro...
- Scaling Up Research-based Educational Practices
- School Accreditation
- School Choice
- School Culture
- School District Budgeting and Financial Management in the ...
- School Improvement through Inclusive Education
- School Reform
- Schools, Private and Independent
- School-Wide Positive Behavior Support
- Science Education
- Secondary to Postsecondary Transition Issues
- Self-Regulated Learning
- Self-Study of Teacher Education Practices
- Service-Learning
- Severe Disabilities
- Single Salary Schedule
- Single-sex Education
- Single-Subject Research Design
- Social Context of Education
- Social Justice
- Social Network Analysis
- Social Pedagogy
- Social Studies Education
- Sociology of Education
- Standards-Based Education
- Statistical Assumptions
- Student Access, Equity, and Diversity in Higher Education
- Student Assignment Policy
- Student Engagement in Tertiary Education
- Student Learning, Development, Engagement, and Motivation ...
- Student Participation
- Student Voice in Teacher Development
- Sustainability Education in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Higher Education
- Teacher Beliefs and Epistemologies
- Teacher Collaboration in School Improvement
- Teacher Evaluation and Teacher Effectiveness
- Teacher Preparation
- Teacher Training and Development
- Teacher Unions and Associations
- Teacher-Student Relationships
- Teaching Critical Thinking
- Technologies, Teaching, and Learning in Higher Education
- Technology Education in Early Childhood
- Technology, Educational
- Technology-based Assessment
- The Bologna Process
- The Regulation of Standards in Higher Education
- Theories of Educational Leadership
- Three Conceptions of Literacy: Media, Narrative, and Gamin...
- Tracking and Detracking
- Traditions of Quality Improvement in Education
- Transformative Learning
- Transitions in Early Childhood Education
- Tribally Controlled Colleges and Universities in the Unite...
- Understanding the Psycho-Social Dimensions of Schools and ...
- University Faculty Roles and Responsibilities in the Unite...
- Using Ethnography in Educational Research
- Value of Higher Education for Students and Other Stakehold...
- Virtual Learning Environments
- Vocational and Technical Education
- Wellness and Well-Being in Education
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Young Children and Spirituality
- Young Children's Learning Dispositions
- Young Children's Working Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.66.15.189]
- 185.66.15.189

Action research in the classroom: A teacher's guide
November 26, 2021
Discover best practices for action research in the classroom, guiding teachers on implementing and facilitating impactful studies in schools.
Main, P (2021, November 26). Action research in the classroom: A teacher's guide. Retrieved from https://www.structural-learning.com/post/action-research-in-the-classroom-a-teachers-guide
What is action research?
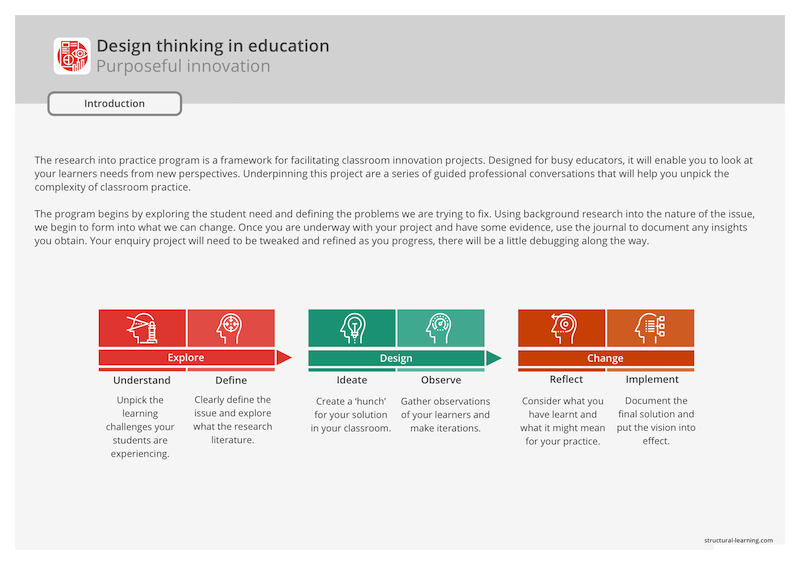
Action research is a participatory process designed to empower educators to examine and improve their own practice. It is characterized by a cycle of planning , action, observation, and reflection, with the goal of achieving a deeper understanding of practice within educational contexts. This process encourages a wide range of approaches and can be adapted to various social contexts.
At its core, action research involves critical reflection on one's actions as a basis for improvement. Senior leaders and teachers are guided to reflect on their educational strategies , classroom management, and student engagement techniques. It's a collaborative effort that often involves not just the teachers but also the students and other stakeholders, fostering an inclusive process that values the input of all participants.
The action research process is iterative, with each cycle aiming to bring about a clearer understanding and improvement in practice. It typically begins with the identification of real-world problems within the school environment, followed by a circle of planning where strategies are developed to address these issues. The implementation of these strategies is then observed and documented, often through journals or participant observation, allowing for reflection and analysis.
The insights gained from action research contribute to Organization Development, enhancing the quality of teaching and learning. This approach is strongly aligned with the principles of Quality Assurance in Education, ensuring that the actions taken are effective and responsive to the needs of the school community.
Educators can share their findings in community forums or through publications in journals, contributing to the wider theory about practice . Tertiary education sector often draws on such studies to inform teacher training and curriculum development.
In summary, the significant parts of action research include:
- A continuous cycle of planning, action, observation, and reflection.
- A focus on reflective practice to achieve a deeper understanding of educational methodologies.
- A commitment to inclusive and participatory processes that engage the entire school community.
Creating an action research project
The action research process usually begins with a situation or issue that a teacher wants to change as part of school improvement initiatives .
Teachers get support in changing the ' interesting issue ' into a 'researchable question' and then taking to experiment. The teacher will draw on the outcomes of other researchers to help build actions and reveal the consequences .
Participatory action research is a strategy to the enquiry which has been utilised since the 1940s. Participatory action involves researchers and other participants taking informed action to gain knowledge of a problematic situation and change it to bring a positive effect. As an action researcher , a teacher carries out research . Enquiring into their practice would lead a teacher to question the norms and assumptions that are mostly overlooked in normal school life . Making a routine of inquiry can provide a commitment to learning and professional development . A teacher-researcher holds the responsibility for being the source and agent of change.
Examples of action research projects in education include a teacher working with students to improve their reading comprehension skills , a group of teachers collaborating to develop and implement a new curriculum, or a school administrator conducting a study on the effectiveness of a school-wide behavior management program.
In each of these cases, the research is aimed at improving the educational experience for students and addressing a specific issue or problem within the school community . Action research can be a powerful tool for educators to improve their practice and make a positive impact on their students' learning.

Potential research questions could include:
- How can dual-coding be used to improve my students memory ?
- Does mind-mapping lead to creativity?
- How does Oracy improve my classes writing?
- How can we advance critical thinking in year 10?
- How can graphic organisers be used for exam preparation?
Regardless of the types of action research your staff engage in, a solid cycle of inquiry is an essential aspect of the action research spiral. Building in the process of reflection will ensure that key points of learning can be extracted from the action research study.
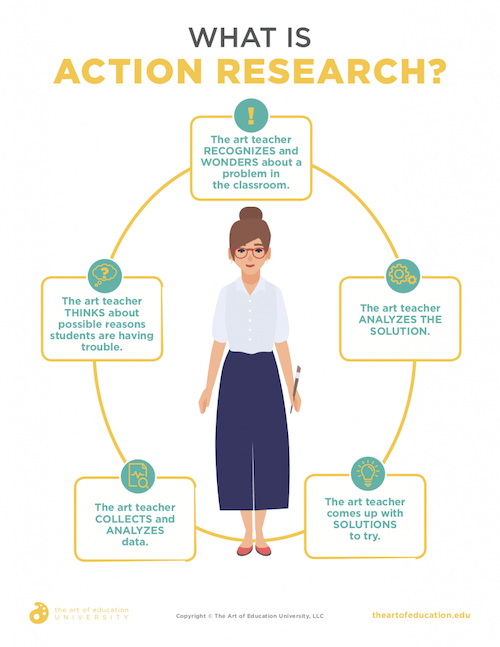
What is an action research cycle?
Action research in education is a cycle of reflection and action inquiry , which follows these steps:
1. Identifying the problem
It is the first stage of action research that starts when a teacher identifies a problem or question that they want to address. To make an a ction research approach successful, the teacher needs to ensure that the questions are the ones 'they' wish to solve. Their questions might involve social sciences, instructional strategies, everyday life and social management issues, guide for students analytical research methods for improving specific student performance or curriculum implementation etc. Teachers may seek help from a wide variety of existing literature , to find strategies and solutions that others have executed to solve any particular problem. It is also suggested to build a visual map or a table of problems, target performances, potential solutions and supporting references in the middle.
2. Developing an Action Plan
After identifying the problem, after r eviewing the relevant literature and describing the vision of how to solve the problem; the next step would be action planning which means to develop a plan of action . Action planning involves studying the literature and brainstorming can be used by the action research planner to create new techniques and strategies that can generate better results of both action learning and action research. One may go back to the visual map or table of contents and reorder or colour-code the potential outcomes. The items in the list can be ranked in order of significance and the amount of time needed for these strategies.
An action plan has the details of how to implement each idea and the factors that may keep them from their vision of success . Identify those factors that cannot be changed –these are the constants in an equation. The focus of action research at the planning stage must remain focused on the variables –the factors that can be changed using actions. An action plan must be how to implement a solution and how one's instruction, management style, and behaviour will affect each of the variables.
3. Data Collection
Before starting to implement a plan of action , the researcher must have a complete understanding of action research and must have knowledge of the type of data that may help in the success of the plan and must assess how to collect that data. For instance, if the goal is to improve class attendance, attendance records must be collected as useful data for the participatory action. If the goal is to improve time management, the data may include students and classroom observations . There are many options to choose from to collect data from. Selecting the most suitable methodology for data collection will provide more meaningful , accurate and valid data. Some sources of data are interviews and observation. Also, one may administer surveys , distribute questionnaires and watch videotapes of the classroom to collect data.
4. Data Analysis and Conclusions
At this action stage, an action researcher analyses the collected data and concludes. It is suggested to assess the data during the predefined process of data collection as it will help refine the action research agenda. If the collected data seems insufficient , the data collection plan must be revised. Data analysis also helps to reflect on what exactly happened. Did the action researcher perform the actions as planned? Were the study outcomes as expected? Which assumptions of the action researcher proved to be incorrect?
Adding details such as tables, opinions, and recommendations can help in identifying trends (correlations and relationships). One must share the findings while analysing data and drawing conclusions . Engaging in conversations for teacher growth is essential; hence, the action researcher would share the findings with other teachers through discussion of action research, who can yield useful feedback. One may also share the findings with students, as they can also provide additional insight . For example, if teachers and students agree with the conclusions of action research for educational change, it adds to the credibility of the data collection plan and analysis. If they don't seem to agree with the data collection plan and analysis , the action researchers may take informed action and refine the data collection plan and reevaluate conclusions .
5. Modifying the Educational Theory and Repeat
After concluding, the process begins again. The teacher can adjust different aspects of the action research approach to theory or make it more specific according to the findings . Action research guides how to change the steps of action research development, how to modify the action plan , and provide better access to resources, start data collection once again, or prepare new questions to ask from the respondents.
6. Report the Findings
Since the main approach to action research involves the informed action to introduce useful change into the classroom or schools, one must not forget to share the outcomes with others. Sharing the outcomes would help to further reflect on the problem and process, and it would help other teachers to use these findings to enhance their professional practice as an educator. One may print book and share the experience with the school leaders, principal, teachers and students as they served as guide to action research. Or, a community action researcher may present community-based action research at a conference so people from other areas can take advantage of this collaborative action. Also, teachers may use a digital storytelling tool to outline their results.
There are plenty of creative tools we can use to bring the research projects to life. We have seen videos, podcasts and research posters all being used to communicate the results of these programs. Community action research is a unique way to present details of the community-related adventures in the teacher profession, cultivate expertise and show how teachers think about education , so it is better to find unique ways to report the findings of community-led action research.
Final thoughts on action-research for teachers
As we have seen, action research can be an effective form of professional development, illuminating the path for teachers and school leaders seeking to refine their craft. This cyclical process of inquiry and reflection is not merely a methodological pursuit but a profound professional journey. The definition of action research, as a systematic inquiry conducted by teachers, administrators, and other stakeholders in the teaching/learning environment, emphasizes the collaborative nature of improving educational strategies and outcomes.
Action research transcends traditional disciplinary practices by immersing educators in the social contexts of their work, prompting them to question and adapt their methods to meet the evolving needs of their students . It is a form of reflective practice that demands critical thinking and flexibility, as one navigates through the iterative stages of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.
The process of action research is inherently participatory, encouraging educators to engage with their learning communities to address key issues and social issues that impact educational settings. This method empowers professionals within universities and schools alike to take ownership of their learning and development, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and participatory approaches.
In summary, action research encapsulates the essence of what it means to be a learning professional in a dynamic educational landscape. It is the embodiment of a commitment to lifelong learning and a testament to the capacity of educators to enact change . The value of action research lies in its ability to transform practitioners into researchers, where the quest for knowledge becomes a powerful conduit for change and innovation. Thus, for educators at every level, embracing the rigorous yet rewarding path of action research can unveil potent insights and propel educational practice to new heights.

Key Papers on Action Research
- Utilizing Action Research During Student Teaching by James O. Barbre and Brenda J. Buckner (2013): This study explores how action research can be effectively utilized during student teaching to enhance professional pedagogical disposition through active reflection. It emphasizes developing a reflective habit of mind crucial for teachers to be effective in their classrooms and adaptive to the changing needs of their students.
- Repositioning T eacher Action Research in Science Teacher Education by B. Capobianco and A. Feldman (2010): This paper discusses the promotion of action research as a way for teachers to improve their practice and students' learning for over 50 years, focusing on science education. It highlights the importance of action research in advancing knowledge about teaching and learning in science.
- Action research and teacher leadership by K. Smeets and P. Ponte (2009): This article reports on a case study into the influence and impact of action research carried out by teachers in a special school. It found that action research not only helps teachers to get to grips with their work in the classroom but also has an impact on the work of others in the school.
- Teaching about the Nature of Science through History: Action Research in the Classroom by J. Solomon, Jon Duveen, Linda Scot, S. McCarthy (1992): This article reports on 18 months of action research monitoring British pupils' learning about the nature of science using historical aspects. It indicates areas of substantial progress in pupils' understanding of the nature of science.
- Action Research in the Classroom by V. Baumfield, E. Hall, K. Wall (2008): This comprehensive guide to conducting action research in the classroom covers various aspects, including deciding on a research question, choosing complementary research tools, collecting and interpreting data, and sharing findings. It aims to move classroom inquiry forward and contribute to professional development.
These studies highlight the significant role of action research in enhancing teacher effectiveness, student learning outcomes, and contributing to the broader educational community's knowledge and practices.
Enhance Learner Outcomes Across Your School
Download an Overview of our Support and Resources
We'll send it over now.
Please fill in the details so we can send over the resources.
What type of school are you?
We'll get you the right resource
Is your school involved in any staff development projects?
Are your colleagues running any research projects or courses?
Do you have any immediate school priorities?
Please check the ones that apply.
Download your resource
Thanks for taking the time to complete this form, submit the form to get the tool.
Classroom Practice
Innovative Education in VT
A blog exploring innovative, personalized, student-centered school change
Why do action research?
5 benefits of doing action research in the classroom.

Teachers are constantly tinkering, creating, learning, and growing. Action research is a slightly formalized version of what skilled teachers do every day.
By honoring action research as systematic professional inquiry, we empower teachers to improve their practice. It’s easy to get started undertaking a small, powerful action research project in your classroom. Let’s see what it can look like.
What it looks like and why it’s worth it
Classrooms are complex social environments. In addition to subject matter and developmental expertise, teachers possess very specific knowledge about the learning dynamics of a classroom. Teachers understand that everything from the culture of the school to the current dating status of particular class members may influence the success of a lesson.
This complexity means that large-scale education research has limited applicability on a day-to-day basis. There are just too many contextual factors affecting the implementation of any generalized approach. This means that most of the daily dilemmas of teaching, top-down policies and large-scale research are not detailed or nuanced enough to be useful.
Here are 5 benefits of doing action research in the classroom
1. action research powers professional growth.
Action research is a powerful form of teacher-driven professional development.
In Action Research for Professional Development , Jane McNiff suggests starting with the question “How do I improve my work?” She argues that action research is fundamentally a professional improvement strategy.
At the Middle Grades Institute each summer, participants seeking graduate credit use the Institute to launch their action research. Then, they present their findings to peers at a statewide gathering in January of each year.
2. Action research makes change manageable
Action research helps teachers focus on one aspect of their practice they would like to improve. Specific questions and a finite time period bind each iteration. This ensures natural pauses for reflection and planning.
Victoria Smith, a Language Arts teacher at Crossett Brook Middle School in Waterbury, Vermont, focused her research on a single unit where she experimented with a choice model which had been inspired by the art teacher at her school .
Michael Crocker, at The Cabot School, in Cabot VT, focused his research on a single day. He examined whether and how digital devices could enhance a field trip.

In the rapidly shifting world of education, action research helps prioritize which changes are worthy of extra attention. Action researchers pick a slice of their practice and dive into the research literature, then they use data to evaluate success and draw conclusions.
3. Action research promotes collaboration
The systematic nature of action research promotes purposeful collaboration.
A team from Hazen Union Middle School, in Hardwick, Vermont, sought to create a new interdisciplinary unit called “I Belong,” so they worked together on an action research project to document and study the results .
Educators can also collaborate between schools to share and compare related approaches. Check out this study looking at how student goal-setting is enhanced by digital tools , conducted by educators from Wallingford Elementary School and Shrewsbury Mountain School, in central Vermont.
4. Action research loves being shared
If you’ve ever wondered how to improve a certain aspect of your practice, then it’s entirely likely another teacher is wondering how to improve that exact same aspect of their own practice.
Get together and share
The Middle Grades Conference each January provides a venue for discussing action research and professional learning by teachers from around the state. Educators prepare presentations showcasing their driving question as well as the method they used to investigate it. They also prepare a short summary of their findings. The topics they pursue impact not only their own teaching but also intersect with issues and initiatives affecting teachers statewide.
Educators at Mill River Union High School showcased both the qualitative —

and quantitative —

nature of their action research project. It examined the effect of formal professional development on the amount and nature of tech integration at the school.
In my experience, it is one of the best conferences to attend or at which to present. It’s a low-key way for educators to be seen as and receive recognition for, being experts in their classrooms. It also gives educators a way to peer into other classrooms and see solutions to common issues in teaching.
Get a chance to publish
Sam Nelson, a social studies teacher at Shelburne Community School in Vermont, recently published his action research in the journal Middle Grades Review . The article details his evolution in creating opportunities for students to practice within a proficiency-based learning environment.
5. Action research can power systems change
The share-ability of action research makes it a useful vehicle for influencing school and district policy, as argued in this ASCD article, Guiding School Improvement with Action Research .
That Mill River Union High School study on the effectiveness of professional development allowed the team to document the positive impact of intensive professional learning. The results allowed them to advocate for continued support moving forward.
Similarly, a team at Lamoille Union Middle School pioneered Student Led Conferences at the school. Their thorough data collection showed nearly unanimous support by parents and students, providing a strong rationale to expand the practice.
Experts in systemic change recognize that rapid cycles of experimentation and evaluation are more effective than detailed long term action planning. Some schools are even incorporating action research into their evaluation system.
The call to action (research)
Imagine the transformative potential if all teachers have the time and support to conduct action research. In the mean time, I hope that you have the chance to engage in professional inquiry that will benefit you, your teaching, and your students.
Next week, we’re going to break down the action research process into workable steps, so that wherever you are with your practice, you can begin designing your own small, manageable action research project to power up your teaching. Until then, consider the starting point, and think of one aspect of your teaching practice you’d like to improve.
What will you research?
Related posts.

How to get started with action research

Unpacking a great action research project

#vted Reads: with Alex Shevrin Venet

Top 10 ways to spend a snow day

#vted Reads: The Successful Middle School

What's your inquiry question?
- ← 8 methods for reflection in project-based learning
- Assessment in Proficiency-Based Classrooms →


Life LeGeros
Life has worked in various roles in K-12 education, including classroom teacher, assistant principal, math department head, state agency administrator, and school board teacher representative. His dissertation focused on the impact of math teachers' knowledge on the growth of their students. He believes in teacher leadership, student empowerment, and challenging the status quo. He loves being immersed in tech-rich and outdoor environments, though not simultaneously. Find him on Twitter @lifelegeros.
4 thoughts on “ Why do action research? ”
Pingback: Phys ed 2.0: More learning, less suffering - Innovation: Education
I get a lot of information, thanks
thanks for post.
Action research is very relevant in business because there is always room for improvement with running a business. Action research offers opportunity for continued ideas. In business, the goal is to improve processes. Action research is beneficial in settings in which continued improvement is the focus.
Thanks for sharing
What do you think? Cancel reply
- Tes Explains
What is action research?

Action research is a practice-based research method, designed to bring about change in a context. In the context of schools, it might be a teacher-led investigation, usually conducted within the teacher’s own school or classroom.
When a problem or question is identified, an initiative is devised to address it. Following implementation, the impact is then assessed and reflected upon. This reflection may lead to amendments to the initiative, before repeating the process again.
Where can I see this in action?
In 2021, teacher and apprenticeship manager Dave Shurmer conducted research that looked at the impact that increased physical activity has on pupils’ academic attainment in literacy and numeracy.
He asked pupils to skip for two minutes before English or maths lessons. At the end of the term, pupils sat a Sats practice paper. Shurmer compared the data from before and after the term for a conditioned and unconditioned group, and found that when the pupils skipped before lessons once a week, they went on to gain an extra mark on their test papers. When they skipped twice a week, they gained an extra two marks.
In 2022, English teacher Katie Packman wrote about her action research project for Tes : after struggling to enthuse key stage 3 students in creative writing, she decided to introduce a workshopping approach. For one hour a week, students were given free rein to choose a creative writing project to develop. She held one-on-one tutorials to give feedback, and students had to plan and then draft their piece, and continue to work on it or start planning their next piece, until their next tutorial. In the end-of-year assessment results, 27 out of 28 students had made expected progress, and 65 per cent of those had made higher-than-expected progress.
Further reading:
- How to lead whole-class guided reading in schools
- Action research in the classroom: a quick guide
- Active learning: make a drama out of teaching punctuation
- “Front loading” and how it can support learning
- Why we use action research as CPD
The Education Endowment Foundation (EEF) is an independent charity dedicated to breaking the link between family income and educational achievement.
To achieve this, it summarises the best available evidence for teachers; its Teaching and Learning Toolkit, for example, is used by 70 per cent of secondary schools.
The charity also generates new evidence of “what works” to improve teaching and learning, by funding independent evaluations of high-potential projects, and supports teachers and senior leaders to use the evidence to achieve the maximum possible benefit for young people.

education, community-building and change
What is action research and how do we do it?
In this article, we explore the development of some different traditions of action research and provide an introductory guide to the literature.
Contents : what is action research · origins · the decline and rediscovery of action research · undertaking action research · conclusion · further reading · how to cite this article . see, also: research for practice ., what is action research.
In the literature, discussion of action research tends to fall into two distinctive camps. The British tradition – especially that linked to education – tends to view action research as research-oriented toward the enhancement of direct practice. For example, Carr and Kemmis provide a classic definition:
Action research is simply a form of self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own practices, their understanding of these practices, and the situations in which the practices are carried out (Carr and Kemmis 1986: 162).
Many people are drawn to this understanding of action research because it is firmly located in the realm of the practitioner – it is tied to self-reflection. As a way of working it is very close to the notion of reflective practice coined by Donald Schön (1983).
The second tradition, perhaps more widely approached within the social welfare field – and most certainly the broader understanding in the USA is of action research as ‘the systematic collection of information that is designed to bring about social change’ (Bogdan and Biklen 1992: 223). Bogdan and Biklen continue by saying that its practitioners marshal evidence or data to expose unjust practices or environmental dangers and recommend actions for change. In many respects, for them, it is linked into traditions of citizen’s action and community organizing. The practitioner is actively involved in the cause for which the research is conducted. For others, it is such commitment is a necessary part of being a practitioner or member of a community of practice. Thus, various projects designed to enhance practice within youth work, for example, such as the detached work reported on by Goetschius and Tash (1967) could be talked of as action research.
Kurt Lewin is generally credited as the person who coined the term ‘action research’:
The research needed for social practice can best be characterized as research for social management or social engineering. It is a type of action-research, a comparative research on the conditions and effects of various forms of social action, and research leading to social action. Research that produces nothing but books will not suffice (Lewin 1946, reproduced in Lewin 1948: 202-3)
His approach involves a spiral of steps, ‘each of which is composed of a circle of planning, action and fact-finding about the result of the action’ ( ibid. : 206). The basic cycle involves the following:
This is how Lewin describes the initial cycle:
The first step then is to examine the idea carefully in the light of the means available. Frequently more fact-finding about the situation is required. If this first period of planning is successful, two items emerge: namely, “an overall plan” of how to reach the objective and secondly, a decision in regard to the first step of action. Usually this planning has also somewhat modified the original idea. ( ibid. : 205)
The next step is ‘composed of a circle of planning, executing, and reconnaissance or fact-finding for the purpose of evaluating the results of the second step, and preparing the rational basis for planning the third step, and for perhaps modifying again the overall plan’ ( ibid. : 206). What we can see here is an approach to research that is oriented to problem-solving in social and organizational settings, and that has a form that parallels Dewey’s conception of learning from experience.
The approach, as presented, does take a fairly sequential form – and it is open to a literal interpretation. Following it can lead to practice that is ‘correct’ rather than ‘good’ – as we will see. It can also be argued that the model itself places insufficient emphasis on analysis at key points. Elliott (1991: 70), for example, believed that the basic model allows those who use it to assume that the ‘general idea’ can be fixed in advance, ‘that “reconnaissance” is merely fact-finding, and that “implementation” is a fairly straightforward process’. As might be expected there was some questioning as to whether this was ‘real’ research. There were questions around action research’s partisan nature – the fact that it served particular causes.
The decline and rediscovery of action research
Action research did suffer a decline in favour during the 1960s because of its association with radical political activism (Stringer 2007: 9). There were, and are, questions concerning its rigour, and the training of those undertaking it. However, as Bogdan and Biklen (1992: 223) point out, research is a frame of mind – ‘a perspective that people take toward objects and activities’. Once we have satisfied ourselves that the collection of information is systematic and that any interpretations made have a proper regard for satisfying truth claims, then much of the critique aimed at action research disappears. In some of Lewin’s earlier work on action research (e.g. Lewin and Grabbe 1945), there was a tension between providing a rational basis for change through research, and the recognition that individuals are constrained in their ability to change by their cultural and social perceptions, and the systems of which they are a part. Having ‘correct knowledge’ does not of itself lead to change, attention also needs to be paid to the ‘matrix of cultural and psychic forces’ through which the subject is constituted (Winter 1987: 48).
Subsequently, action research has gained a significant foothold both within the realm of community-based, and participatory action research; and as a form of practice-oriented to the improvement of educative encounters (e.g. Carr and Kemmis 1986).
Exhibit 1: Stringer on community-based action research
A fundamental premise of community-based action research is that it commences with an interest in the problems of a group, a community, or an organization. Its purpose is to assist people in extending their understanding of their situation and thus resolving problems that confront them….
Community-based action research is always enacted through an explicit set of social values. In modern, democratic social contexts, it is seen as a process of inquiry that has the following characteristics:
• It is democratic , enabling the participation of all people.
• It is equitable , acknowledging people’s equality of worth.
• It is liberating , providing freedom from oppressive, debilitating conditions.
• It is life enhancing , enabling the expression of people’s full human potential.
(Stringer 1999: 9-10)
Undertaking action research
As Thomas (2017: 154) put it, the central aim is change, ‘and the emphasis is on problem-solving in whatever way is appropriate’. It can be seen as a conversation rather more than a technique (McNiff et. al. ). It is about people ‘thinking for themselves and making their own choices, asking themselves what they should do and accepting the consequences of their own actions’ (Thomas 2009: 113).
The action research process works through three basic phases:
Look -building a picture and gathering information. When evaluating we define and describe the problem to be investigated and the context in which it is set. We also describe what all the participants (educators, group members, managers etc.) have been doing.
Think – interpreting and explaining. When evaluating we analyse and interpret the situation. We reflect on what participants have been doing. We look at areas of success and any deficiencies, issues or problems.
Act – resolving issues and problems. In evaluation we judge the worth, effectiveness, appropriateness, and outcomes of those activities. We act to formulate solutions to any problems. (Stringer 1999: 18; 43-44;160)
The use of action research to deepen and develop classroom practice has grown into a strong tradition of practice (one of the first examples being the work of Stephen Corey in 1949). For some, there is an insistence that action research must be collaborative and entail groupwork.
Action research is a form of collective self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own social or educational practices, as well as their understanding of those practices and the situations in which the practices are carried out… The approach is only action research when it is collaborative, though it is important to realise that action research of the group is achieved through the critically examined action of individual group members. (Kemmis and McTaggart 1988: 5-6)
Just why it must be collective is open to some question and debate (Webb 1996), but there is an important point here concerning the commitments and orientations of those involved in action research.
One of the legacies Kurt Lewin left us is the ‘action research spiral’ – and with it there is the danger that action research becomes little more than a procedure. It is a mistake, according to McTaggart (1996: 248) to think that following the action research spiral constitutes ‘doing action research’. He continues, ‘Action research is not a ‘method’ or a ‘procedure’ for research but a series of commitments to observe and problematize through practice a series of principles for conducting social enquiry’. It is his argument that Lewin has been misunderstood or, rather, misused. When set in historical context, while Lewin does talk about action research as a method, he is stressing a contrast between this form of interpretative practice and more traditional empirical-analytic research. The notion of a spiral may be a useful teaching device – but it is all too easy to slip into using it as the template for practice (McTaggart 1996: 249).
Further reading
This select, annotated bibliography has been designed to give a flavour of the possibilities of action research and includes some useful guides to practice. As ever, if you have suggestions about areas or specific texts for inclusion, I’d like to hear from you.
Explorations of action research
Atweh, B., Kemmis, S. and Weeks, P. (eds.) (1998) Action Research in Practice: Partnership for Social Justice in Education, London: Routledge. Presents a collection of stories from action research projects in schools and a university. The book begins with theme chapters discussing action research, social justice and partnerships in research. The case study chapters cover topics such as: school environment – how to make a school a healthier place to be; parents – how to involve them more in decision-making; students as action researchers; gender – how to promote gender equity in schools; writing up action research projects.
Carr, W. and Kemmis, S. (1986) Becoming Critical. Education, knowledge and action research , Lewes: Falmer. Influential book that provides a good account of ‘action research’ in education. Chapters on teachers, researchers and curriculum; the natural scientific view of educational theory and practice; the interpretative view of educational theory and practice; theory and practice – redefining the problem; a critical approach to theory and practice; towards a critical educational science; action research as critical education science; educational research, educational reform and the role of the profession.
Carson, T. R. and Sumara, D. J. (ed.) (1997) Action Research as a Living Practice , New York: Peter Lang. 140 pages. Book draws on a wide range of sources to develop an understanding of action research. Explores action research as a lived practice, ‘that asks the researcher to not only investigate the subject at hand but, as well, to provide some account of the way in which the investigation both shapes and is shaped by the investigator.
Dadds, M. (1995) Passionate Enquiry and School Development. A story about action research , London: Falmer. 192 + ix pages. Examines three action research studies undertaken by a teacher and how they related to work in school – how she did the research, the problems she experienced, her feelings, the impact on her feelings and ideas, and some of the outcomes. In his introduction, John Elliot comments that the book is ‘the most readable, thoughtful, and detailed study of the potential of action-research in professional education that I have read’.
Ghaye, T. and Wakefield, P. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book one: the role of the self in action , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 146 + xiii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: dialectical forms; graduate medical education – research’s outer limits; democratic education; managing action research; writing up.
McNiff, J. (1993) Teaching as Learning: An Action Research Approach , London: Routledge. Argues that educational knowledge is created by individual teachers as they attempt to express their own values in their professional lives. Sets out familiar action research model: identifying a problem, devising, implementing and evaluating a solution and modifying practice. Includes advice on how working in this way can aid the professional development of action researcher and practitioner.
Quigley, B. A. and Kuhne, G. W. (eds.) (1997) Creating Practical Knowledge Through Action Research, San Fransisco: Jossey Bass. Guide to action research that outlines the action research process, provides a project planner, and presents examples to show how action research can yield improvements in six different settings, including a hospital, a university and a literacy education program.
Plummer, G. and Edwards, G. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book two: dimensions of action research – people, practice and power , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 142 + xvii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: exchanging letters and collaborative research; diary writing; personal and professional learning – on teaching and self-knowledge; anti-racist approaches; psychodynamic group theory in action research.
Whyte, W. F. (ed.) (1991) Participatory Action Research , Newbury Park: Sage. 247 pages. Chapters explore the development of participatory action research and its relation with action science and examine its usages in various agricultural and industrial settings
Zuber-Skerritt, O. (ed.) (1996) New Directions in Action Research , London; Falmer Press. 266 + xii pages. A useful collection that explores principles and procedures for critical action research; problems and suggested solutions; and postmodernism and critical action research.
Action research guides
Coghlan, D. and Brannick, D. (2000) Doing Action Research in your own Organization, London: Sage. 128 pages. Popular introduction. Part one covers the basics of action research including the action research cycle, the role of the ‘insider’ action researcher and the complexities of undertaking action research within your own organisation. Part two looks at the implementation of the action research project (including managing internal politics and the ethics and politics of action research). New edition due late 2004.
Elliot, J. (1991) Action Research for Educational Change , Buckingham: Open University Press. 163 + x pages Collection of various articles written by Elliot in which he develops his own particular interpretation of action research as a form of teacher professional development. In some ways close to a form of ‘reflective practice’. Chapter 6, ‘A practical guide to action research’ – builds a staged model on Lewin’s work and on developments by writers such as Kemmis.
Johnson, A. P. (2007) A short guide to action research 3e. Allyn and Bacon. Popular step by step guide for master’s work.
Macintyre, C. (2002) The Art of the Action Research in the Classroom , London: David Fulton. 138 pages. Includes sections on action research, the role of literature, formulating a research question, gathering data, analysing data and writing a dissertation. Useful and readable guide for students.
McNiff, J., Whitehead, J., Lomax, P. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project , London: Routledge. Practical guidance on doing an action research project.Takes the practitioner-researcher through the various stages of a project. Each section of the book is supported by case studies
Stringer, E. T. (2007) Action Research: A handbook for practitioners 3e , Newbury Park, ca.: Sage. 304 pages. Sets community-based action research in context and develops a model. Chapters on information gathering, interpretation, resolving issues; legitimacy etc. See, also Stringer’s (2003) Action Research in Education , Prentice-Hall.
Winter, R. (1989) Learning From Experience. Principles and practice in action research , Lewes: Falmer Press. 200 + 10 pages. Introduces the idea of action research; the basic process; theoretical issues; and provides six principles for the conduct of action research. Includes examples of action research. Further chapters on from principles to practice; the learner’s experience; and research topics and personal interests.
Action research in informal education
Usher, R., Bryant, I. and Johnston, R. (1997) Adult Education and the Postmodern Challenge. Learning beyond the limits , London: Routledge. 248 + xvi pages. Has some interesting chapters that relate to action research: on reflective practice; changing paradigms and traditions of research; new approaches to research; writing and learning about research.
Other references
Bogdan, R. and Biklen, S. K. (1992) Qualitative Research For Education , Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Goetschius, G. and Tash, J. (1967) Working with the Unattached , London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
McTaggart, R. (1996) ‘Issues for participatory action researchers’ in O. Zuber-Skerritt (ed.) New Directions in Action Research , London: Falmer Press.
McNiff, J., Lomax, P. and Whitehead, J. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project 2e. London: Routledge.
Thomas, G. (2017). How to do your Research Project. A guide for students in education and applied social sciences . 3e. London: Sage.
Acknowledgements : spiral by Michèle C. | flickr ccbyncnd2 licence
How to cite this article : Smith, M. K. (1996; 2001, 2007, 2017) What is action research and how do we do it?’, The encyclopedia of pedagogy and informal education. [ https://infed.org/mobi/action-research/ . Retrieved: insert date] .
© Mark K. Smith 1996; 2001, 2007, 2017
Last Updated on December 7, 2020 by infed.org

Action Research: Steps, Benefits, and Tips

Introduction
History of action research, what is the definition of action research, types of action research, conducting action research.
Action research stands as a unique approach in the realm of qualitative inquiry in social science research. Rooted in real-world problems, it seeks not just to understand but also to act, bringing about positive change in specific contexts. Often distinguished by its collaborative nature, the action research process goes beyond traditional research paradigms by emphasizing the involvement of those being studied in resolving social conflicts and effecting positive change.
The value of action research lies not just in its outcomes, but also in the process itself, where stakeholders become active participants rather than mere subjects. In this article, we'll examine action research in depth, shedding light on its history, principles, and types of action research.

Tracing its roots back to the mid-20th century, Kurt Lewin developed classical action research as a response to traditional research methods in the social sciences that often sidelined the very communities they studied. Proponents of action research championed the idea that research should not just be an observational exercise but an actionable one that involves devising practical solutions. Advocates believed in the idea of research leading to immediate social action, emphasizing the importance of involving the community in the process.
Applications for action research
Over the years, action research has evolved and diversified. From its early applications in social psychology and organizational development, it has branched out into various fields such as education, healthcare, and community development, informing questions around improving schools, minority problems, and more. This growth wasn't just in application, but also in its methodologies.
How is action research different?
Like all research methodologies, effective action research generates knowledge. However, action research stands apart in its commitment to instigate tangible change. Traditional research often places emphasis on passive observation , employing data collection methods primarily to contribute to broader theoretical frameworks . In contrast, action research is inherently proactive, intertwining the acts of observing and acting.
The primary goal isn't just to understand a problem but to solve or alleviate it. Action researchers partner closely with communities, ensuring that the research process directly benefits those involved. This collaboration often leads to immediate interventions, tweaks, or solutions applied in real-time, marking a departure from other forms of research that might wait until the end of a study to make recommendations.
This proactive, change-driven nature makes action research particularly impactful in settings where immediate change is not just beneficial but essential.
Action research is best understood as a systematic approach to cooperative inquiry. Unlike traditional research methodologies that might primarily focus on generating knowledge, action research emphasizes producing actionable solutions for pressing real-world challenges.
This form of research undertakes a cyclic and reflective journey, typically cycling through stages of planning , acting, observing, and reflecting. A defining characteristic of action research is the collaborative spirit it embodies, often dissolving the rigid distinction between the researcher and the researched, leading to mutual learning and shared outcomes.
Advantages of action research
One of the foremost benefits of action research is the immediacy of its application. Since the research is embedded within real-world issues, any findings or solutions derived can often be integrated straightaway, catalyzing prompt improvements within the concerned community or organization. This immediacy is coupled with the empowering nature of the methodology. Participants aren't mere subjects; they actively shape the research process, giving them a tangible sense of ownership over both the research journey and its eventual outcomes.
Moreover, the inherent adaptability of action research allows researchers to tweak their approaches responsively based on live feedback. This ensures the research remains rooted in the evolving context, capturing the nuances of the situation and making any necessary adjustments. Lastly, this form of research tends to offer a comprehensive understanding of the issue at hand, harmonizing socially constructed theoretical knowledge with hands-on insights, leading to a richer, more textured understanding.
Disadvantages of action research
Like any methodology, action research isn't devoid of challenges. Its iterative nature, while beneficial, can extend timelines. Researchers might find themselves engaged in multiple cycles of observation, reflection, and action before arriving at a satisfactory conclusion. The intimate involvement of the researcher with the research participants, although crucial for collaboration, opens doors to potential conflicts. Through collaborative problem solving, disagreements can lead to richer and more nuanced solutions, but it can take considerable time and effort.
Another limitation stems from its focus on a specific context: results derived from a particular action research project might not always resonate or be applicable in a different context or with a different group. Lastly, the depth of collaboration this methodology demands means all stakeholders need to be deeply invested, and such a level of commitment might not always be feasible.
Examples of action research
To illustrate, let's consider a few scenarios. Imagine a classroom where a teacher observes dwindling student participation. Instead of sticking to conventional methods, the teacher experiments with introducing group-based activities. As the outcomes unfold, the teacher continually refines the approach based on student feedback, eventually leading to a teaching strategy that rejuvenates student engagement.
In a healthcare context, hospital staff who recognize growing patient anxiety related to certain procedures might innovate by introducing a new patient-informing protocol. As they study the effects of this change, they could, through iterations, sculpt a procedure that diminishes patient anxiety.
Similarly, in the realm of community development, a community grappling with the absence of child-friendly public spaces might collaborate with local authorities to conceptualize a park. As they monitor its utilization and societal impact, continual feedback could refine the park's infrastructure and design.
Contemporary action research, while grounded in the core principles of collaboration, reflection, and change, has seen various adaptations tailored to the specific needs of different contexts and fields. These adaptations have led to the emergence of distinct types of action research, each with its unique emphasis and approach.
Collaborative action research
Collaborative action research emphasizes the joint efforts of professionals, often from the same field, working together to address common concerns or challenges. In this approach, there's a strong emphasis on shared responsibility, mutual respect, and co-learning. For example, a group of classroom teachers might collaboratively investigate methods to improve student literacy, pooling their expertise and resources to devise, implement, and refine strategies for improving teaching.
Participatory action research
Participatory action research (PAR) goes a step further in dissolving the barriers between the researcher and the researched. It actively involves community members or stakeholders not just as participants, but as equal partners in the entire research process. PAR is deeply democratic and seeks to empower participants, fostering a sense of agency and ownership. For instance, a participatory research project might involve local residents in studying and addressing community health concerns, ensuring that the research process and outcomes are both informed by and beneficial to the community itself.
Educational action research
Educational action research is tailored specifically to practical educational contexts. Here, educators take on the dual role of teacher and researcher, seeking to improve teaching practices, curricula, classroom dynamics, or educational evaluation. This type of research is cyclical, with educators implementing changes, observing outcomes, and reflecting on results to continually enhance the educational experience. An example might be a teacher studying the impact of technology integration in her classroom, adjusting strategies based on student feedback and learning outcomes.
Community-based action research
Another noteworthy type is community-based action research, which focuses primarily on community development and well-being. Rooted in the principles of social justice, this approach emphasizes the collective power of community members to identify, study, and address their challenges. It's particularly powerful in grassroots movements and local development projects where community insights and collaboration drive meaningful, sustainable change.
Key insights and critical reflection through research with ATLAS.ti
Organize all your data analysis and insights with our powerful interface. Download a free trial today.
Engaging in action research is both an enlightening and transformative journey, rooted in practicality yet deeply connected to theory. For those embarking on this path, understanding the essentials of an action research study and the significance of a research cycle is paramount.
Understanding the action research cycle
At the heart of action research is its cycle, a structured yet adaptable framework guiding the research. This cycle embodies the iterative nature of action research, emphasizing that learning and change evolve through repetition and reflection.
The typical stages include:
- Identifying a problem : This is the starting point where the action researcher pinpoints a pressing issue or challenge that demands attention.
- Planning : Here, the researcher devises an action research strategy aimed at addressing the identified problem. In action research, network resources, participant consultation, and the literature review are core components in planning.
- Action : The planned strategies are then implemented in this stage. This 'action' phase is where theoretical knowledge meets practical application.
- Observation : Post-implementation, the researcher observes the outcomes and effects of the action. This stage ensures that the research remains grounded in the real-world context.
- Critical reflection : This part of the cycle involves analyzing the observed results to draw conclusions about their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Revision : Based on the insights from reflection, the initial plan is revised, marking the beginning of another cycle.
Rigorous research and iteration
It's essential to understand that while action research is deeply practical, it doesn't sacrifice rigor . The cyclical process ensures that the research remains thorough and robust. Each iteration of the cycle in an action research project refines the approach, drawing it closer to an effective solution.
The role of the action researcher
The action researcher stands at the nexus of theory and practice. Not just an observer, the researcher actively engages with the study's participants, collaboratively navigating through the research cycle by conducting interviews, participant observations, and member checking . This close involvement ensures that the study remains relevant, timely, and responsive.
Drawing conclusions and informing theory
As the research progresses through multiple iterations of data collection and data analysis , drawing conclusions becomes an integral aspect. These conclusions, while immediately beneficial in addressing the practical issue at hand, also serve a broader purpose. They inform theory, enriching the academic discourse and providing valuable insights for future research.
Identifying actionable insights
Keep in mind that action research should facilitate implications for professional practice as well as space for systematic inquiry. As you draw conclusions about the knowledge generated from action research, consider how this knowledge can create new forms of solutions to the pressing concern you set out to address.

Collecting data and analyzing data starts with ATLAS.ti
Download a free trial of our intuitive software to make the most of your research.

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Importance of Action Research in Teacher Education Programs

Related Papers
Gregory Hine
This research paper explores the experiences of three teacher-researchers, ‘Simone’, ‘Damian ’ and ‘Michael’, who undertook an Action Research project in their respective schools as part of their postgraduate studies. As Head of Professional Learning, Simone conducted a research project designed to investigate how to improve a Peer Observation Program operating at her secondary school. Damian, also a Head of Professional Learning, explored ways to improve the profile of the existing Professional Development program at his secondary school, with a particular emphasis on overhauling the Staff Mentor Program. Michael, a Head of Junior School, investigated ways to reduce the number of playground incidents resulting from primary students not adhering to playground policy rules. The paper initially outlines the construct of Action Research in the light of its applicability to educational research. Particular reference is made to the benefits of Action Research for those in the teaching pr...
Jose Augusto Faienda Wanina
This paper is about the perception of student teachers concerning their role as researchers and the impact of action research in their professional development. This paper is a product of joint collaboration with master-level student teachers of the Faculty of Education of the University of Prishtina. Qualitative data collected through reflective writings, open-ended questionnaires and various research project reports implemented by student teachers themselves were analyzed using inductive methods. Findings support the fact that action research is a major component in teacher professional development. According to teacher-researchers, action research has a major impact not only on the improvement of teaching practices and better student achievements, but also on increasing the collaboration among peer teachers and fostering a new culture where teachers assume their responsibilities to implement action research in their own classrooms. Key terms: Action research, professional develop...
La investigación acción como estrategia de reflexión, mejora y cambio en la práctica docente de la enseñanza de lenguas
Mayoral V . Pedro José , Fernando Peralta-Castro
La investigación acción como estrategia de reflexión, mejora y cambio en la práctica docente de la enseñanza de lenguas Action Research as a strategy for reflection, improvement and change in Language Teaching Practice A pesquisa-ação como estratégia para reflexão, aprimoramento e mudança na prática docente do ensino de línguas
Peggy Willcuts
The overall purpose of this action research study was to explore the experiences of ten middle school science teachers involved in a three-year partnership program between scientists and teachers at a Department of Energy national laboratory, including the impact of the program on their professional development, and to improve the partnership program by developing a set of recommendations based on the study’s findings. This action research study relied on qualitative data including field notes recorded at the summer academies and data from two focus groups with teachers and scientists. Additionally, the participating teachers submitted written reflections in science notebooks, participated in open-ended telephone interviews that were transcribed verbatim, and wrote journal summaries to the Department of Energy at the end of the summer academy. The analysis of the data, collaboratively examined by the teachers, the scientists, and the science education specialist acting as co-researchers on the project, revealed five elements critical to the success of the professional development of science teachers. First, scientist-teacher partnerships are a unique contribution to the professional development of teachers of science that is not replicated in other forms of teacher training. Second, the role of the science education specialist as a bridge between the scientists and teachers is a unique and vital one, impacting all aspects of the professional development. Third, there is a paradox for classroom teachers as they view the professional development experience from two different lenses – that of learner and that of teacher. Fourth, learning for science teachers must be designed to be constructivist in nature. Fifth, the principles of the nature of science must be explicitly showcased to be seen and understood by the classroom teachers.
Dr. Denise Payton
Effective Teaching in Higher Education for the 21st Century Adult Learner by Denise Murchison Payton MA, Fayetteville State University, 1999 BA, North Carolina A&T State University, 1979 Doctoral Study Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements for the Degree of
Gail Furman
This exploratory study gathered information about the use of action research within doctor of education programs in educational leadership and explored faculty understanding of and perspectives on action research. Survey data established that action research is used infrequently to meet dissertation requirements. Contributing factors include lack of clarity regarding the nature of action research (AR) and concerns about methodological legitimacy. Because the development of collaborative leadership skills and the pursuit of social justice objectives are inherent to the action research process, these results call for additional discussion regarding this distinctive methodology and its role in the preparation of educational leaders at the doctoral level.
Australian Journal of Teacher Education
Majida Dajani
Jeew Hemraj
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Elena Sparrow
Daniel Breiman
Carlene Boucher
Leading & Managing
Martin Bassett , Carol Cardno , Chris Wood
alara.net.au
Pieter Du Toit
Samah Zakareya
Canadian Journal of Action Research
Michele Jacobsen
IJELS AIAC , Alemu Anshu
Janice Stewart
The Counseling Psychologist
William Hanson
Paul Newton
Prof. Dr. Maya Khemlani David
mana legend
Razia Ghanchi-Badasie
Bulent Avci
Kristina A Hesbol
Timothy Teehan
Ensuring Quality in English Language Teacher Education
Lina Mukhopadhyay
Akua-Kisiwaa Adefope
Kristina Hesbol , T. Lange
Elizabeth Murphy
Linda Shear
Patricia Briscoe
Shawn Boone
The Qualitative Report
Berdine Gordon-Littréan
Todd Dinkelman , Todd S. Hawley , J.B. Mayo Jr
Brock Education Journal
Snezana Ratkovic
Stephanie Storms
Ambreen Shahriar
In Researching translation and interpreting.
Brenda Nicodemus
International Journal of Educational Methodology
GLenda Rivera
Comfort Oghu
Melanie Mollan-Moscoso
Faaletino Roberts
ProQuest LLC
Jamelyn C Tobery-Nystrom
Dorian Stoilescu
Leslie Patterson
Dissertation
Dr. Sonya McCoy-Wilson
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- New! Member Benefit New! Member Benefit
- Featured Analytics Hub
- Resources Resources
- Member Directory
- Networking Communities
- Advertise, Exhibit, Sponsor
- Find or Post Jobs
- Learn and Engage Learn and Engage
- Bridge Program
- Compare AACSB-Accredited Schools
- Explore Programs
- Advocacy Advocacy
- Featured AACSB Announces 2024 Class of Influential Leaders
- Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging
- Influential Leaders
- Innovations That Inspire
- Connect With Us Connect With Us
- Accredited School Search
- Accreditation
- Learning and Events
- Advertise, Sponsor, Exhibit
- Tips and Advice
- Is Business School Right for Me?
Recognizing the Value of Educational Research
- A recent survey shows that research on teaching and learning is not valued at many AACSB-accredited schools across the U.S. and Canada.
- One reason that business schools might not recognize research on teaching and learning is that the journal quality lists they commonly use to assess faculty intellectual contributions focus primarily on discipline-based scholarship.
- STEM fields already place equal value on research on teaching and learning within individual disciplines. By following their lead, two Canadian scholars argue, business schools will enrich their students’ learning experiences.
If business educators were asked to define the purpose of business schools, they likely would emphasize the need to “prepare the next generation of leaders.” But if this is the case, why do so few business schools prioritize research that advances teaching and curricular design?
Researcher Sanobar Siddiqui first explored this question as the subject of her doctoral dissertation. “One of my thesis findings was that the tenure system’s lack of rewards impedes business academics from pursuing research in teaching and learning,” she explains.
Now an assistant professor of accounting at the University of Regina’s Faculty of Business Administration in Canada, Siddiqui wanted to learn why so many business schools do not value research on teaching and learning (RoTL). This response is puzzling, she says, given that Standard 7 of the AACSB Business Accreditation Standards accepts “scholarship of teaching and learning” as documentation to indicate a business school’s teaching effectiveness and impact.
She and Camillo Lento, a professor with the Faculty of Business Administration at Lakehead University in Thunder Bay, Ontario, published a paper on the status of RoTL in the April 2022 edition of the International Journal of Educational Management . The paper’s findings are based on a survey in which Siddiqui and Lento asked educators two questions:
- How do AACSB-accredited business schools in the U.S. and Canada define “teaching effectiveness,” according to AACSB’s Standard 7?
- Do these schools consider research on teaching and learning in their promotion and tenure decisions?
This topic is particularly important, says Siddiqui, because business schools serve such diverse student audiences. Moreover, learner success is integral to every business school’s mission. Many of the instructional strategies “that we use in class are not research-informed or evidence-based. Hence, we are shortchanging our students,” she says. “Our teaching needs to catch up with the changes we see in our classroom.”
‘A Last Priority’
Siddiqui and Lento received 78 responses to their survey; in the second phase of their study, they conducted semi-structured interviews with 11 educators in the U.S. and Canada.
Among survey respondents, 42 percent noted that they were “unaware of an explicit teaching effectiveness definition” at their schools, but 58 percent said the policies in place at their schools communicated “an implied definition.” Only one respondent could quote a definition of teaching effectiveness from the school’s website.
Respondents noted a lack of “perceived respect and value” for RoTL, describing this line of scholarship as “a last priority” at their schools. As one educator put it, “Our department does not really care about teaching as long as you are cranking out strong scholarship.”
Schools that consider educational research for tenure and faculty qualification tend to focus on journal quality alone, not on whether published articles are discipline-based.
The good news is that 55 percent of respondents noted that their schools did take RoTL into account when making tenure decisions. Siddiqui and Lento found that these schools have two things in common. First, they focus on journal quality alone for the purposes of tenure and faculty qualification, not on whether faculty’s published articles are discipline-based.
Second, these schools are more likely to consider RoTL when faculty include this work “as part of a larger research plan that includes discipline-based research.” Only faculty following teaching tracks are likely to receive tenure based solely on publications in education-focused journals.
Additionally, teaching-oriented schools are more likely than research-oriented schools to recognize RoTL. While this makes outward sense, Siddiqui wonders why prolific faculty who produce innovative scholarship on pedagogical issues that are critical to business education cannot “be hired, promoted, and awarded just like discipline-based researchers” at research-oriented institutions.
What Perpetuates the Stigma?
Siddiqui and Lento point to several factors that could be driving the lack of recognition of RoTL among AACSB-accredited schools:
No consensus about teaching quality. Although many individual educational institutions have defined teaching effectiveness based on existing research, business schools have not yet established a shared definition of what constitutes effective teaching. However, the co-authors emphasize, more dedicated research could produce findings that inspire a common language around teaching and learning.
The complex nature of determining teaching quality. Schools often evaluate the quality of faculty’s research by whether the work appears in academic journals that are rated highly by certain journal quality lists . However, they find they cannot use a similar approach to evaluate the quality of faculty’s teaching, says Lento. “The evaluation of teaching effectiveness is much more complex and requires many more sources of information, possibly compiled into a teaching dossier that is unique to an educator.”
A lack of attention in business doctoral programs. Most doctoral programs train young researchers to study topics related to their disciplines of choice. As a result of this early training, RoTL “may come with a stigma as it is outside of traditional discipline-specific research,” Lento says.
Lento admits that the reasons listed above are speculative. He and Siddiqui would like to see other researchers conduct follow-up studies that take deeper dives into the broader stigma surrounding RoTL.
Changing Mindsets, Taking Action
In the meantime, Siddiqui and Lento call on business school administrators and faculty to work together to create a “shared and precise definition of teaching effectiveness.” Educators can start by defining teaching quality within their own institutions.
From there, Siddiqui and Lento say that schools can take any or all the following actions to change mindsets about RoTL:
- Set appropriate objectives, incentives, and evaluation mechanisms.
- Create and nurture communities of practice that help like-minded faculty pursue research focused on solving issues they face in their classrooms.
- Consider weighing education research in peer-reviewed articles more heavily, particularly for faculty in teaching-focused roles.
- Recognize RoTL for accreditation and tenure and normalize it as a legitimate form of scholarship.
- Make seed funds available to faculty who pursue RoTL.
- Give awards and incentives to faculty who use research-informed teaching in their classrooms.
- Consider hiring tenure-track academics who also are expert educators with an expressed interest in pursuing RoTL. These scholars can investigate and develop “research-informed teaching tools ready to be put into practice in almost any business classroom,” says Siddiqui. This outcome, she emphasizes, is an indication of how RoTL contributes to the advancement of business disciplines.
- Encourage and teach RoTL in doctoral programs, with the aim of improving and advancing the quality of teaching at business schools.
Siddiqui points out that information on the websites of AACSB-accredited schools “are replete with research centers, research chairs and scholars, core research focus areas, research awards, annual research celebration reports, intellectual contributions, and grant-funding awards.”
There is no reason, she says, that schools could not also highlight information about their teaching philosophies, teaching awards, student feedback, educational leadership and professional development, and faculty research on teaching and learning.
Two B-School Perspectives
So far, Siddiqui and Lento’s paper has captured the attention of other like-minded educators in the business school community. This includes Nicola Charwat, associate dean of teaching and learning and senior lecturer of business law and taxation at Monash University’s Monash Business School (MBS) in Caulfield East, Australia.
MBS prioritizes scholarship on teaching and learning (SoTL) where appropriate, she says, through efforts that include identifying quality education-oriented journals and valuing publication in those journals equally to publication in discipline-based journals. The school uses “a consultative process” to identify journals specializing in teaching and learning that are equivalent to discipline-based journals rated as A*, A, B, and C on the quality list compiled by the Australian Business Deans Council.
“We have also instituted a Business Education and Research Group, which has been awarding both practice- and research-output-focused grants to staff for three years,” Charwat says. “Alongside these efforts, of course, there are moves in the university in line with the broader trend of raising the profile of teaching and ensuring its status is on par with other work of the university.”
Educators in STEM disciplines have long recognized educational research in tenure decisions and regularly reward academics who pursue RoTL in their disciplines.
Despite these changes, Charwat notes that the perception remains that accomplishments related to educational research are “somehow lesser” than those related to discipline-related scholarship. Additionally, many faculty remain uncertain about how to approach educational research. In response, MBS has built communities of practice dedicated to teaching and is now working “to increase awareness of and opportunities to undertake SoTL and education research,” Charwat says.
Charwat says that the questions raised in Siddiqui and Lento’s paper are “essential” to business education, and that their article “has prompted us to start exploring the patterns of our own SoTL and education research.” MBS faculty, she adds, might also pursue a similar study focused on AACSB-accredited schools in Australia.
Another educator who read the article with interest is Martin Lockett, former dean and professor of strategic management at Nottingham University Business School China (NUBS China) in Zhejiang. Lockett explains that NUBS China uses the Academic Journal Guide , which is produced by the Chartered Association of Business Schools (CABS), to support tenure decisions and to classify faculty under AACSB accreditation standards.
But in the CABS guide, only four journals focused on teaching and learning are rated as 3, 4, or 4*, which are the targets that NUBS China uses to qualify faculty as Scholarly Academics under AACSB accreditation or for internal recognition of quality research, Lockett says.
This has led to worry among the school’s teaching-oriented faculty that if they focus on RoTL, they risk being classified as “additional faculty,” unless they can consistently publish in the few education-focused journals listed by CABS. That concern, Lockett says, deters most faculty from pursuing RoTL in any substantial way.
While this scenario is all too common at institutions with research-focused missions, it is not mandated by AACSB accreditation standards, emphasizes Stephanie Bryant, AACSB’s chief accreditation officer. She clarifies that whether a business school considers educational scholarship for the purpose of accreditation or tenure is its choice, based on the parameters it has set for its individual mission. “The standards do not say anywhere, or imply, that educational research is not valued,” Bryant stresses. The devaluation of RoTL, she adds, “is a school perspective.”
Time to ‘Balance the Scales’
The stigma surrounding RoTL at AACSB-accredited business schools could be lifted, say Siddiqui and Lento, if administrators acknowledge the benefits that fostering cultures of teaching and learning bring to all business school stakeholders. These advantages include a wider scope of scholarship and more evidence-based pedagogical tools for faculty, richer learning experiences and better learning outcomes for students, and more well-rounded job candidates for employers.
Educators in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines already know this, says Siddiqui. STEM departments have long recognized educational research in tenure decisions and regularly reward academics who pursue RoTL in their disciplines.
As one example, Siddiqui points to Carl Edwin Wieman, winner of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize in Physics. Wieman established the Carl Wieman Science Education Initiative at the University of British Columbia in Canada to encourage evidence-based teaching methods focused on improving undergraduate science education. Since its inception, the initiative has hired fellows who are interested in conducting education research, particularly based in the disciplines in which they have earned their doctorates. It also has inspired the creation of teaching materials in science education, a dedicated website, and a sister initiative at the University of Colorado Boulder in the United States.
Business schools, says Siddiqui, could achieve comparable results by raising awareness of the importance of RoTL, disseminating RoTL findings beyond peer-reviewed journals, and driving research-informed teaching methods that advance business education.
This year, the co-authors published a second paper that finds that scholarly and practice academics who developed rigorous research skills in their doctoral programs and who publish discipline-based research are more likely to pursue RoTL research. Here, Siddiqui and Lento more directly call on business school deans to reward and incentivize this line of research by creating communities of practice and expanding their journal ranking frameworks to include relevant peer-reviewed publications.
It is imperative, Siddiqui and Lento argue, that business schools place studies based on classroom settings on equal footing with studies based on corporate settings. “Research on teaching and learning balances the scales,” Siddiqui says, “by utilizing evidence-based, efficient, and effective teaching to foster deep learning amongst diverse student audiences.”
- accreditation
- administration
- faculty engagement
- Welsh leads equity-centered research practice partnership to reduce racial disparities in school discipline
Media Inquiries
- 615-322-6397 Email
Latest Stories
- Class of 2024 honors loved ones in “The hands that held our hands”
- Vanderbilt joins Meharry Medical College, Fisk University in hosting Tri-Institutional Seminar series
May 13, 2024, 11:51 AM
By Jenna Somers

Last year, Richard Welsh reported findings on the persistence of racial disparities in exclusionary school discipline practices. Despite suspensions declining over the past decade as schools reformed their policies, exclusionary disciplinary rates remained higher for African American students. Across the South, in-school suspensions (ISS) are particularly prevalent and disruptive to the education of racially minoritized students. Given these facts, Welsh has embarked on a new co-design process of ISS that leverages an existing research-practice partnership with a school district in Georgia to crack the code on truly resolving racial inequities in school discipline policies and practices.
Supported by a $474,178 grant from the William T. Grant Foundation and a $125,000 grant from the American Institutes of Research Equity Initiative, Welsh is leading a three-year project with the school district to understand the role of race and power in equity-centered research-practice partnerships, how the dynamics of the partnership affect partnership activities, and how these activities influence research use by school administrators, district leaders, and school board members.
“These are the three key decisionmakers who can advance racial equity in school districts through policies, programs, and personnel. They make decisions about codes of conduct, which disciplinary programs to implement, and who to hire, including behavioral specialists to support students’ social-emotional development,” said Welsh, associate professor of education and public policy at Vanderbilt Peabody College of education and human development.
“Improving the use of research evidence among education leaders via equity-centered research-practice partnerships can possibly lead to disruptive decisions necessary to addressing persistent racial inequities in school discipline. Also, turning the analytical lens on ourselves to examine how inequities might manifest in the partnership has implications for partnership and student outcomes,” Welsh added.
The research team will analyze their interviews with key decision makers, research-practice partnership primary investigators, and co-design team members. They will also observe school board meetings, school discipline committee meetings, and partnership meetings, as well as co-design workshops, district- and school-level documents, and materials to record the partnering process as well as the use of research evidence and disruptive decision-making. By engaging in cycles of disciplined inquiry to improve ISS processes, the partnership aims to reach its goal of improving youth outcomes.
The co-design process includes working with a team of school leaders and school personnel at three middle schools to analyze and reimagine their ISS process and infrastructure.
Keep Reading

Welsh’s study reveals persistent racial disparities in school exclusionary discipline, recommends promising reforms

Welsh’s essay emphasizes need for antiblackness framework to reduce inequality in school discipline

Welsh’s study reveals the importance of parental trust in schools for reducing exclusionary discipline
Explore story topics.
- Education and Psychology
- Ideas In Action
- Ideas in Action Featured
- Peabody College
- peabody-home
- Richard Welsh
- Vanderbilt Peabody College of education and human development

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Action research is a process for improving educational practice. Its methods involve action, evaluation, and reflection. It is a process to gather evidence to implement change in practices. Action research is participative and collaborative. It is undertaken by individuals with a common purpose.
Of particular importance is the shift toward viewing teaching as a form of inquiry. Action Research and Changing Teaching Practice in ELA Education ... This seems to reflect similar trends in social studies research in general that emphasizes history education. Action research studies focused on the topic of history education provide evidence ...
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin.A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social sciences, particularly in educational settings.
The primary purpose of action research in education is to identify specific challenges within the classroom and develop practical solutions based on evidence-based practices. By incorporating action research, educators can continuously improve their teaching methodology. It helps in enhancing student engagement, retention and overall achievement.
Action research has become a common practice among educational administrators. The term "action research" was first coined by Kurt Lewin in the 1930s, although teachers and school administrators have long engaged in the process described by and formally named by Lewin. Alternatively known as practitioner research, self-study, action science ...
Greg teaches in the undergraduate and postgraduate degrees, and his research interests are in leadership, leadership development, secondary mathematics pedagogy, and action research. Email: [email protected]. Please cite as: Hine, G. S. C. (2013). The importance of action research in teacher education programs.
The analysis showed that action research played an important role in forming a research-based education. The teachers wrote about 'implementing research' into their teaching, using a vocabulary inspired by the evidence-based teaching perspective; a top-down perspective (cf. Levinsson Citation 2013 ; Wollscheid and Opheim Citation 2016 ).
Discuss action research in PK-12, as well as in higher education settings The first book to focus on the importance and application of action research exclusively in educational settings Offers world perspectives on action research in education Written by a team of international scholars The Wiley Handbook of Action Research in Education is an ...
Introduction. Educational action research involves participants conducting inquiry into their own practices in order to improve teaching and learning, practices and programs. This means that the researcher is a participant in the activity being investigated, be it in schools or community centers—wherever teaching and learning occur.
The self-study framework grounds action research as one form of teacher-research, which has emerged as a methodology in educational research to help teachers engage in inquiry (Pinnegar & Hamilton, 2009). Action research is emancipatory because it "demands that practitioners take a hard look at the structures and social arrangements that ...
Action research in education is known for improving the teachers' and administrators' professional practice and is deemed favourable by most educationists for solving problems in education. It is ...
Action research is a participatory process designed to empower educators to examine and improve their own practice. It is characterized by a cycle of planning, action, observation, and reflection, with the goal of achieving a deeper understanding of practice within educational contexts. This process encourages a wide range of approaches and can ...
There are several benefits of using action research in education, including the following: It helps teachers to become more reflective practitioners. Through reflection, teachers can learn new strategies for improving student outcomes. It helps teachers to develop a shared understanding of teaching and learning.
This issue of Educational Action Research addresses many of these issues of people and positionality. In so doing, ... By emphasising collaborative action research Messiou draws attention to the importance of involvement in the process of action research. Furthermore, the focus on developing inclusion in schools shows how action research can ...
This paper studies the early formulation of the Action Research theory as suggested by Lewin in 1946. It covers its echo around the world, including main critiques against it, especially during the second half of the twentieth century. The paper also stresses the importance of using Action Research in education through studying the promising ...
the professional disposition of teachers, action r esearch encourages teachers to becom e continuous. learners within their classrooms and schools (Mil ls, 2011). Because of the professional ...
In the rapidly shifting world of education, action research helps prioritize which changes are worthy of extra attention. Action researchers pick a slice of their practice and dive into the research literature, then they use data to evaluate success and draw conclusions. 3. Action research promotes collaboration.
Action research is almost invariably eclectic in its use of specific data collection strategies. For example, research projects might incorporate a combination of such strategies as surveys (face-to-face, paper-pencil, and/or online), individual and small-group interviews (e.g. focus groups), in-depth case studies, observations of people's ...
Action research is a practice-based research method, designed to bring about change in a context. In the context of schools, it might be a teacher-led investigation, usually conducted within the teacher's own school or classroom. When a problem or question is identified, an initiative is devised to address it.
The approach is only action research when it is collaborative, though it is important to realise that action research of the group is achieved through the critically examined action of individual group members. (Kemmis and McTaggart 1988: 5-6) ... Elliot, J. (1991) Action Research for Educational Change, Buckingham: Open University Press. 163 ...
Introduction. Action research stands as a unique approach in the realm of qualitative inquiry in social science research. Rooted in real-world problems, it seeks not just to understand but also to act, bringing about positive change in specific contexts. Often distinguished by its collaborative nature, the action research process goes beyond ...
1 The importance of action research in teacher education programs: Three testimonies. 2016 •. Gregory Hine. This research paper explores the experiences of three teacher-researchers, 'Simone', 'Damian ' and 'Michael', who undertook an Action Research project in their respective schools as part of their postgraduate studies.
Educational Action Research, has its foundations in the writings of John Dewey, the great American educational philosopher of the 1920s and 30s, ... knowledgeable educators at the school or district site is still important for successful teacher research to occur. Also, universities, educational agencies, and districts may encourage teacher ...
Two researchers want to persuade more business schools to encourage, support, and reward faculty who conduct rigorous research on teaching and learning. A recent survey shows that research on teaching and learning is not valued at many AACSB-accredited schools across the U.S. and Canada. One reason that business schools might not recognize ...
Given these facts, Welsh has embarked on a new co-design process of ISS that leverages an existing research-practice partnership with a school district in Georgia to crack the code on truly ...