
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
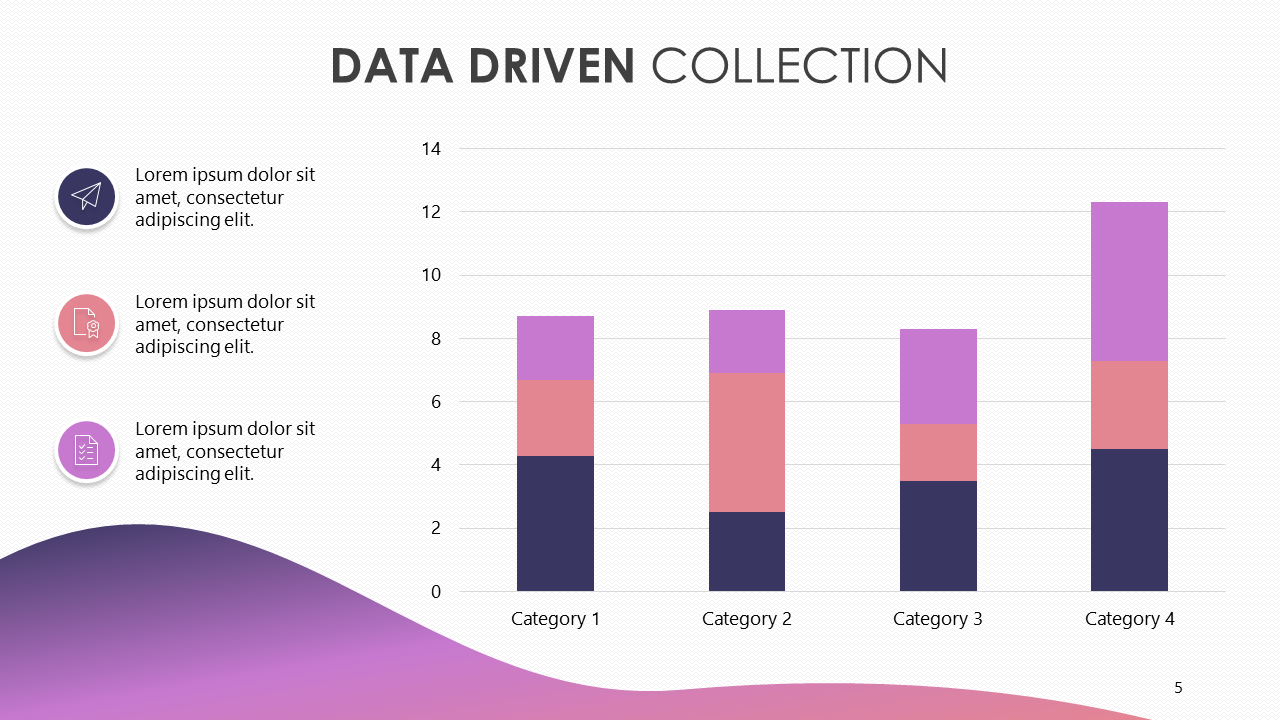
Tabular & Graphical Presentation of data
Published by Oscar Driessen Modified over 4 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Tabular & Graphical Presentation of data"— Presentation transcript:

Copyright © 2010, 2007, 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Eleventh Edition and the Triola.

Slide 1 Spring, 2005 by Dr. Lianfen Qian Lecture 2 Describing and Visualizing Data 2-1 Overview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Visualizing Data.
IB Math Studies – Topic 6 Statistics.

1 Introduction to biostatistics By Dr. S. Shaffi Ahamed Asst. Professor Dept. of Family & Community Medicine KKUH.

INTRODUCTION TO BIOSTATISTICS DR.S.Shaffi Ahamed Asst. Professor Dept. of Family and Comm. Medicine KKUH.

INTRODUCTION TO BIOSTATISTICS

McGraw-Hill/IrwinCopyright © 2009 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical Methods.

Frequency Distributions and Graphs

Descriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical Methods

July, 2000Guang Jin Statistics in Applied Science and Technology Chapter 3 Organizing and Displaying Data.

Data Presentation.
Copyright © 2011 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical Methods.

COURSE: JUST 3900 INTRODUCTORY STATISTICS FOR CRIMINAL JUSTICE Instructor: Dr. John J. Kerbs, Associate Professor Joint Ph.D. in Social Work and Sociology.

Frequency Distribution is a statistical technique to explore the underlying patterns of raw data. Preparing frequency distribution tables, we can.

1 Laugh, and the world laughs with you. Weep and you weep alone.~Shakespeare~

Chapter 2 Describing Data.

Dr.Shaikh Shaffi Ahamed Ph.D., Associate Professor Dept. of Family & Community Medicine.

Presentation Of Data. Data Presentation All business decisions are based on evaluation of some data All business decisions are based on evaluation of.

Copyright © 2010, 2007, 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 2-2 Frequency Distributions.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

CHAPTER 2 – Descriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical presentations.

Related Papers
Puja Setiawan
Why Study Statistics? Modern Statistics Statistics and Engineering The Role of the Scientist and Engineer in Quality Improvement A Case Study : Visually Inspecting Data to Improve Product Quality Two Basic Concepts - Population and Sample Treatment of Data Pareto Diagrams and Dot Diagrams Frequency Distributions Graphs of Frequency Distributions Stem-and-leaf Displays Descriptive Measures Quartiles and Percentiles The Calculation of x and s A Case Study: Problems with Aggregating Data
Hafiz Zahoor
Vinh San Nguyen
1. No. The first class frequency, for example, tells us only that there were 18 pennies with weights in the 2.40-2.49 grams class, but there is no way to tell the exact values of those 18 weights. 2. The sum of the relative frequencies should be 1.00 when proportions are used, and it should be 100% when percentages are used. 3. No. This is not a relative frequency distribution because the sum of the percentages is not 100%. It appears that each respondent was asked to indicate whether he downloaded the four types of material (and so the sum of the percentages could be anywhere from 0% to 400%), and not to place himself in one of the four categories (in which case the table would be a relative frequency distribution and the sum of the percentages would be 100%). 4. The gap in the frequencies suggests the table includes heights from two different populations. Considering the values, it appears that the two populations are elementary students and faculty/staff personnel at the school. 5. a. Class width: subtracting the first two lower class limits, 14−10 = 4. b. Class midpoints: the first class midpoint is (10+13)/2 = 11.5, and the others can be obtained by adding the class width to get 11.5, 15.5, 19.5, 23.5, 27.5. c. Class boundaries: the boundary between the first and second class is (13+14)/2 = 13.5, and the others can be obtained by adding or subtracting the class width to get 9.5, 13.5, 17.5, 21.5, 25.5, 29.5. 6. a. Class width: subtracting the first two lower class limits, 6−2 = 4. b. Class midpoints: the first class midpoint is (2+5)/2 = 3.5, and the others can be obtained by adding the class width to get 3.5, 7.5, 11.5, 15.5. c. Class boundaries: the boundary between the first and second class is (5+6)/2 = 5.5, and the others can be obtained by adding or subtracting the class width to get 1.5, 5.5, 9.5, 13.5, 17.5. 7. a. Class width: subtracting the first two lower class limits, 1.00−0.00 = 1.00. b. Class midpoints: the first class midpoint is (0.00+0.99)/2 = 0.495, and the others can be obtained by adding the class width to get 0.495, 1.495, 2.495, 3.495, 4.495. c. Class boundaries: the boundary between the first and second class is (0.99+1.00)/2 = 0.995, and the others can be obtained by adding or subtracting the class width to get-0.005, 0.995, 1.995, 2.995, 3.995, 4.995. 8. a. Class width: subtracting the first two lower class limits, 1.00−0.00 = 1.00. b. Class midpoints: the first class midpoint is (0.00+0.99)/2 = 0.495, and the others can be obtained by adding the class width to get 0.495, 1.495, 2.495, 3.495, 4.495, 5.495 c. Class boundaries: the boundary between the first and second class is (0.99+1.00)/2 = 0.995, and the others can be obtained by adding or subtracting the class width to get-0.005, 0.995, 1.995, 2.995, 3.995, 4.995, 5.995.
fekad alemachew
Faijun Nahar Mim
desalegn nega
Statistics can be defined in two senses: plural (as Statistical Data) and singular (as Statistical Methods). Plural sense: Statistics are collection of facts (figures). This meaning of the word is widely used when reference is made to facts and figures on sales, employment or unemployment, In this sense the word Statistics serves simply as data. But not all numerical data are statistics. Singular sense: Statistics is the science that deals with the methods of data collection, organization, presentation, analysis and interpretation of data. It refers the subject area that is concerned with extracting relevant information from available data with the aim to make sound decisions. According to this meaning, statistics is concerned with the development and application of methods and techniques for collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing and interpreting statistical data. B. Classification of Statistics Based on the scope of the decision, statistics can be classified into two; Descriptive and Inferential Statistics. Descriptive Statistics refers to the procedures used to organize and summarize masses of data. It is concerned with describing or summarizing the most important features of the data. It deals only the characteristics of the collected data without going beyond it. That is, this part deals with only describing the data collected without going any further: that is without attempting to infer(conclude) anything that goes beyond the data themselves. The methodology of descriptive statistics includes the methods of organizing (classification, tabulation, Frequency Distributions) and presenting (Graphical and Diagrammatic Presentation) data and calculations of certain indicators of data like Measures of Central Tendency and Measures of Dispersion (Variation) which summarize some important features of the data. Inferential (Inductive) Statistics includes the methods used to find out something about a population, based on the sample. It is concerned with drawing statistically valid conclusions about the characteristics of the population based on information obtained from sample. In this form of statistical analysis, descriptive statistics is linked with probability theory in order to generalize the results of the sample to the population. Performing hypothesis testing, determining relationships between variables and making predictions are also inferential statistics.
Muhammad Taimoor
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
MUSTAPHA NASIR USMAN
Sakiru A Adeosun
Abebe T Kassaye
Md. Mazharul Islam Jony
Kwaku Owusu-Bediako
Werner Haipumbu
toqeer H shah
Benson Njane
Nelson Abana
Kebede Abu Aragaw
Journel Ann Supremo
KRIPARAJ KUNNATH
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Data presentation: A comprehensive guide
Learn how to create data presentation effectively and communicate your insights in a way that is clear, concise, and engaging.
Raja Bothra
Building presentations

Hey there, fellow data enthusiast!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on data presentation.
Whether you're an experienced presenter or just starting, this guide will help you present your data like a pro. We'll dive deep into what data presentation is, why it's crucial, and how to master it. So, let's embark on this data-driven journey together.
What is data presentation?
Data presentation is the art of transforming raw data into a visual format that's easy to understand and interpret. It's like turning numbers and statistics into a captivating story that your audience can quickly grasp. When done right, data presentation can be a game-changer, enabling you to convey complex information effectively.
Why are data presentations important?
Imagine drowning in a sea of numbers and figures. That's how your audience might feel without proper data presentation. Here's why it's essential:
- Clarity : Data presentations make complex information clear and concise.
- Engagement : Visuals, such as charts and graphs, grab your audience's attention.
- Comprehension : Visual data is easier to understand than long, numerical reports.
- Decision-making : Well-presented data aids informed decision-making.
- Impact : It leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Types of data presentation:
Now, let's delve into the diverse array of data presentation methods, each with its own unique strengths and applications. We have three primary types of data presentation, and within these categories, numerous specific visualization techniques can be employed to effectively convey your data.
1. Textual presentation
Textual presentation harnesses the power of words and sentences to elucidate and contextualize your data. This method is commonly used to provide a narrative framework for the data, offering explanations, insights, and the broader implications of your findings. It serves as a foundation for a deeper understanding of the data's significance.
2. Tabular presentation
Tabular presentation employs tables to arrange and structure your data systematically. These tables are invaluable for comparing various data groups or illustrating how data evolves over time. They present information in a neat and organized format, facilitating straightforward comparisons and reference points.
3. Graphical presentation
Graphical presentation harnesses the visual impact of charts and graphs to breathe life into your data. Charts and graphs are powerful tools for spotlighting trends, patterns, and relationships hidden within the data. Let's explore some common graphical presentation methods:
- Bar charts: They are ideal for comparing different categories of data. In this method, each category is represented by a distinct bar, and the height of the bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar charts provide a clear and intuitive way to discern differences between categories.
- Pie charts: It excel at illustrating the relative proportions of different data categories. Each category is depicted as a slice of the pie, with the size of each slice corresponding to the percentage of the total value it represents. Pie charts are particularly effective for showcasing the distribution of data.
- Line graphs: They are the go-to choice when showcasing how data evolves over time. Each point on the line represents a specific value at a particular time period. This method enables viewers to track trends and fluctuations effortlessly, making it perfect for visualizing data with temporal dimensions.
- Scatter plots: They are the tool of choice when exploring the relationship between two variables. In this method, each point on the plot represents a pair of values for the two variables in question. Scatter plots help identify correlations, outliers, and patterns within data pairs.
The selection of the most suitable data presentation method hinges on the specific dataset and the presentation's objectives. For instance, when comparing sales figures of different products, a bar chart shines in its simplicity and clarity. On the other hand, if your aim is to display how a product's sales have changed over time, a line graph provides the ideal visual narrative.
Additionally, it's crucial to factor in your audience's level of familiarity with data presentations. For a technical audience, more intricate visualization methods may be appropriate. However, when presenting to a general audience, opting for straightforward and easily understandable visuals is often the wisest choice.
In the world of data presentation, choosing the right method is akin to selecting the perfect brush for a masterpiece. Each tool has its place, and understanding when and how to use them is key to crafting compelling and insightful presentations. So, consider your data carefully, align your purpose, and paint a vivid picture that resonates with your audience.
What to include in data presentation?
When creating your data presentation, remember these key components:
- Data points : Clearly state the data points you're presenting.
- Comparison : Highlight comparisons and trends in your data.
- Graphical methods : Choose the right chart or graph for your data.
- Infographics : Use visuals like infographics to make information more digestible.
- Numerical values : Include numerical values to support your visuals.
- Qualitative information : Explain the significance of the data.
- Source citation : Always cite your data sources.
How to structure an effective data presentation?
Creating a well-structured data presentation is not just important; it's the backbone of a successful presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a compelling and organized presentation that captivates your audience:
1. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is paramount. Consider their needs, interests, and existing knowledge about your topic. Tailor your presentation to their level of understanding, ensuring that it resonates with them on a personal level. Relevance is the key.
2. Have a clear message
Every effective data presentation should convey a clear and concise message. Determine what you want your audience to learn or take away from your presentation, and make sure your message is the guiding light throughout your presentation. Ensure that all your data points align with and support this central message.
3. Tell a compelling story
Human beings are naturally wired to remember stories. Incorporate storytelling techniques into your presentation to make your data more relatable and memorable. Your data can be the backbone of a captivating narrative, whether it's about a trend, a problem, or a solution. Take your audience on a journey through your data.
4. Leverage visuals
Visuals are a powerful tool in data presentation. They make complex information accessible and engaging. Utilize charts, graphs, and images to illustrate your points and enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Visuals should not just be an accessory; they should be an integral part of your storytelling.
5. Be clear and concise
Avoid jargon or technical language that your audience may not comprehend. Use plain language and explain your data points clearly. Remember, clarity is king. Each piece of information should be easy for your audience to digest.
6. Practice your delivery
Practice makes perfect. Rehearse your presentation multiple times before the actual delivery. This will help you deliver it smoothly and confidently, reducing the chances of stumbling over your words or losing track of your message.
A basic structure for an effective data presentation
Armed with a comprehensive comprehension of how to construct a compelling data presentation, you can now utilize this fundamental template for guidance:
In the introduction, initiate your presentation by introducing both yourself and the topic at hand. Clearly articulate your main message or the fundamental concept you intend to communicate.
Moving on to the body of your presentation, organize your data in a coherent and easily understandable sequence. Employ visuals generously to elucidate your points and weave a narrative that enhances the overall story. Ensure that the arrangement of your data aligns with and reinforces your central message.
As you approach the conclusion, succinctly recapitulate your key points and emphasize your core message once more. Conclude by leaving your audience with a distinct and memorable takeaway, ensuring that your presentation has a lasting impact.
Additional tips for enhancing your data presentation
To take your data presentation to the next level, consider these additional tips:
- Consistent design : Maintain a uniform design throughout your presentation. This not only enhances visual appeal but also aids in seamless comprehension.
- High-quality visuals : Ensure that your visuals are of high quality, easy to read, and directly relevant to your topic.
- Concise text : Avoid overwhelming your slides with excessive text. Focus on the most critical points, using visuals to support and elaborate.
- Anticipate questions : Think ahead about the questions your audience might pose. Be prepared with well-thought-out answers to foster productive discussions.
By following these guidelines, you can structure an effective data presentation that not only informs but also engages and inspires your audience. Remember, a well-structured presentation is the bridge that connects your data to your audience's understanding and appreciation.
Do’s and don'ts on a data presentation
- Use visuals : Incorporate charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
- Keep it simple : Avoid clutter and complexity.
- Highlight key points : Emphasize crucial data.
- Engage the audience : Encourage questions and discussions.
- Practice : Rehearse your presentation.
Don'ts:
- Overload with data : Less is often more; don't overwhelm your audience.
- Fit Unrelated data : Stay on topic; don't include irrelevant information.
- Neglect the audience : Ensure your presentation suits your audience's level of expertise.
- Read word-for-word : Avoid reading directly from slides.
- Lose focus : Stick to your presentation's purpose.
Summarizing key takeaways
- Definition : Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding.
- Importance : Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact.
- Types : Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
- Choosing methods : Select the right method based on data, audience, and purpose.
- Components : Include data points, comparisons, visuals, infographics, numerical values, and source citations.
- Structure : Know your audience, have a clear message, tell a compelling story, use visuals, be concise, and practice.
- Do's and don'ts : Do use visuals, keep it simple, highlight key points, engage the audience, and practice. Don't overload with data, include unrelated information, neglect the audience's expertise, read word-for-word, or lose focus.
FAQ's on a data presentation
1. what is data presentation, and why is it important in 2024.
Data presentation is the process of visually representing data sets to convey information effectively to an audience. In an era where the amount of data generated is vast, visually presenting data using methods such as diagrams, graphs, and charts has become crucial. By simplifying complex data sets, presentation of the data may helps your audience quickly grasp much information without drowning in a sea of chart's, analytics, facts and figures.
2. What are some common methods of data presentation?
There are various methods of data presentation, including graphs and charts, histograms, and cumulative frequency polygons. Each method has its strengths and is often used depending on the type of data you're using and the message you want to convey. For instance, if you want to show data over time, try using a line graph. If you're presenting geographical data, consider to use a heat map.
3. How can I ensure that my data presentation is clear and readable?
To ensure that your data presentation is clear and readable, pay attention to the design and labeling of your charts. Don't forget to label the axes appropriately, as they are critical for understanding the values they represent. Don't fit all the information in one slide or in a single paragraph. Presentation software like Prezent and PowerPoint can help you simplify your vertical axis, charts and tables, making them much easier to understand.
4. What are some common mistakes presenters make when presenting data?
One common mistake is trying to fit too much data into a single chart, which can distort the information and confuse the audience. Another mistake is not considering the needs of the audience. Remember that your audience won't have the same level of familiarity with the data as you do, so it's essential to present the data effectively and respond to questions during a Q&A session.
5. How can I use data visualization to present important data effectively on platforms like LinkedIn?
When presenting data on platforms like LinkedIn, consider using eye-catching visuals like bar graphs or charts. Use concise captions and e.g., examples to highlight the single most important information in your data report. Visuals, such as graphs and tables, can help you stand out in the sea of textual content, making your data presentation more engaging and shareable among your LinkedIn connections.
Create your data presentation with prezent
Prezent can be a valuable tool for creating data presentations. Here's how Prezent can help you in this regard:
- Time savings : Prezent saves up to 70% of presentation creation time, allowing you to focus on data analysis and insights.
- On-brand consistency : Ensure 100% brand alignment with Prezent's brand-approved designs for professional-looking data presentations.
- Effortless collaboration : Real-time sharing and collaboration features make it easy for teams to work together on data presentations.
- Data storytelling : Choose from 50+ storylines to effectively communicate data insights and engage your audience.
- Personalization : Create tailored data presentations that resonate with your audience's preferences, enhancing the impact of your data.
In summary, Prezent streamlines the process of creating data presentations by offering time-saving features, ensuring brand consistency, promoting collaboration, and providing tools for effective data storytelling. Whether you need to present data to clients, stakeholders, or within your organization, Prezent can significantly enhance your presentation-making process.
So, go ahead, present your data with confidence, and watch your audience be wowed by your expertise.
Thank you for joining us on this data-driven journey. Stay tuned for more insights, and remember, data presentation is your ticket to making numbers come alive! Sign up for our free trial or book a demo !
More zenpedia articles

How to present SWOT analysis presentation: Tips & templates

Rewards and recognition presentation: A comprehensive guide

Best practices to create and deliver effective presentations
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)
Presentation of Data

Statistics deals with the collection, presentation and analysis of the data, as well as drawing meaningful conclusions from the given data. Generally, the data can be classified into two different types, namely primary data and secondary data. If the information is collected by the investigator with a definite objective in their mind, then the data obtained is called the primary data. If the information is gathered from a source, which already had the information stored, then the data obtained is called secondary data. Once the data is collected, the presentation of data plays a major role in concluding the result. Here, we will discuss how to present the data with many solved examples.
What is Meant by Presentation of Data?
As soon as the data collection is over, the investigator needs to find a way of presenting the data in a meaningful, efficient and easily understood way to identify the main features of the data at a glance using a suitable presentation method. Generally, the data in the statistics can be presented in three different forms, such as textual method, tabular method and graphical method.
Presentation of Data Examples
Now, let us discuss how to present the data in a meaningful way with the help of examples.
Consider the marks given below, which are obtained by 10 students in Mathematics:
36, 55, 73, 95, 42, 60, 78, 25, 62, 75.
Find the range for the given data.
Given Data: 36, 55, 73, 95, 42, 60, 78, 25, 62, 75.
The data given is called the raw data.
First, arrange the data in the ascending order : 25, 36, 42, 55, 60, 62, 73, 75, 78, 95.
Therefore, the lowest mark is 25 and the highest mark is 95.
We know that the range of the data is the difference between the highest and the lowest value in the dataset.
Therefore, Range = 95-25 = 70.
Note: Presentation of data in ascending or descending order can be time-consuming if we have a larger number of observations in an experiment.
Now, let us discuss how to present the data if we have a comparatively more number of observations in an experiment.
Consider the marks obtained by 30 students in Mathematics subject (out of 100 marks)
10, 20, 36, 92, 95, 40, 50, 56, 60, 70, 92, 88, 80, 70, 72, 70, 36, 40, 36, 40, 92, 40, 50, 50, 56, 60, 70, 60, 60, 88.
In this example, the number of observations is larger compared to example 1. So, the presentation of data in ascending or descending order is a bit time-consuming. Hence, we can go for the method called ungrouped frequency distribution table or simply frequency distribution table . In this method, we can arrange the data in tabular form in terms of frequency.
For example, 3 students scored 50 marks. Hence, the frequency of 50 marks is 3. Now, let us construct the frequency distribution table for the given data.
Therefore, the presentation of data is given as below:
|
| |
|---|---|
| 10 | 1 |
| 20 | 1 |
| 36 | 3 |
| 40 | 4 |
| 50 | 3 |
| 56 | 2 |
| 60 | 4 |
| 70 | 4 |
| 72 | 1 |
| 80 | 1 |
| 88 | 2 |
| 92 | 3 |
| 95 | 1 |
|
|
|
The following example shows the presentation of data for the larger number of observations in an experiment.
Consider the marks obtained by 100 students in a Mathematics subject (out of 100 marks)
95, 67, 28, 32, 65, 65, 69, 33, 98, 96,76, 42, 32, 38, 42, 40, 40, 69, 95, 92, 75, 83, 76, 83, 85, 62, 37, 65, 63, 42, 89, 65, 73, 81, 49, 52, 64, 76, 83, 92, 93, 68, 52, 79, 81, 83, 59, 82, 75, 82, 86, 90, 44, 62, 31, 36, 38, 42, 39, 83, 87, 56, 58, 23, 35, 76, 83, 85, 30, 68, 69, 83, 86, 43, 45, 39, 83, 75, 66, 83, 92, 75, 89, 66, 91, 27, 88, 89, 93, 42, 53, 69, 90, 55, 66, 49, 52, 83, 34, 36.
Now, we have 100 observations to present the data. In this case, we have more data when compared to example 1 and example 2. So, these data can be arranged in the tabular form called the grouped frequency table. Hence, we group the given data like 20-29, 30-39, 40-49, ….,90-99 (As our data is from 23 to 98). The grouping of data is called the “class interval” or “classes”, and the size of the class is called “class-size” or “class-width”.
In this case, the class size is 10. In each class, we have a lower-class limit and an upper-class limit. For example, if the class interval is 30-39, the lower-class limit is 30, and the upper-class limit is 39. Therefore, the least number in the class interval is called the lower-class limit and the greatest limit in the class interval is called upper-class limit.
Hence, the presentation of data in the grouped frequency table is given below:
|
| |
|---|---|
| 20 – 29 | 3 |
| 30 – 39 | 14 |
| 40 – 49 | 12 |
| 50 – 59 | 8 |
| 60 – 69 | 18 |
| 70 – 79 | 10 |
| 80 – 89 | 23 |
| 90 – 99 | 12 |
|
|
|
Hence, the presentation of data in this form simplifies the data and it helps to enable the observer to understand the main feature of data at a glance.
Practice Problems
- The heights of 50 students (in cms) are given below. Present the data using the grouped frequency table by taking the class intervals as 160 -165, 165 -170, and so on. Data: 161, 150, 154, 165, 168, 161, 154, 162, 150, 151, 162, 164, 171, 165, 158, 154, 156, 172, 160, 170, 153, 159, 161, 170, 162, 165, 166, 168, 165, 164, 154, 152, 153, 156, 158, 162, 160, 161, 173, 166, 161, 159, 162, 167, 168, 159, 158, 153, 154, 159.
- Three coins are tossed simultaneously and each time the number of heads occurring is noted and it is given below. Present the data using the frequency distribution table. Data: 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1, 3, 0, 1, 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2, 1, 3, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 0.
To learn more Maths-related concepts, stay tuned with BYJU’S – The Learning App and download the app today!
| MATHS Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
PowerPoint Charts, Graphs, & Tables Made Easy | Tips & Tricks

In today's digital world, effective communication is key, especially in presentations. After all, in a world saturated with information, the power to express your message clearly and impactfully can make all the difference.
We know that conveying complex information can be challenging, but guess what? It doesn't have to be! After discussing this with our 200+ expert presentation designers , I've gathered their best practices and strategies to create this comprehensive guide.
Below, you will find expert tips and tricks for making, customizing, and presenting PowerPoint charts, graphs, and tables. Stay with us!

Today, we'll explore the following topics:
- PowerPoint Charts and Graphs
Tables in PowerPoint
Free powerpoint charts, graphs, and tables templates, ready to enhance your presentations our team at 24slides is here to help, powerpoint charts and graphs.
If you are thinking of adding tables to your PowerPoint presentation, let me first show you two other great options: charts and graphs.
Charts and graphs stand out for making complex information easy to read at a glance. They’re ideal for identifying trends, representing patterns, and making decisions easier. In addition, charts and graphs capture the audience's attention.
You have many types to choose from, and we'll go over the most important ones later. In the meantime, here are some examples:
Undoubtedly, one of the best ways to take your presentations to the next level.
But you may have a question in mind: What is the difference between a chart and a graph in PowerPoint? Charts refer to any visual representation of data, whether graphical or non-graphical (such as tables). Graphs, on the other hand, refer specifically to the graphical representation of data (such as bar charts).
In other words, all graphs are charts, but not all charts are graphs.
People often confuse these terms in PowerPoint, but they actually refer to different visual elements.
How to Make a Chart in PowerPoint?
First, go to the Insert tab. Then, click on Chart and select your favorite chart type. Finally, enter your data or copy it from somewhere else. Simple!
Here you have the detailed step-by-step instructions:
- Select the slide where you want to add the chart. Choose the Insert tab, then select the Illustrations group's Chart option.
- A dialog box for inserting charts will appear. Choose a category on the left, then double-click the chart you want on the right.
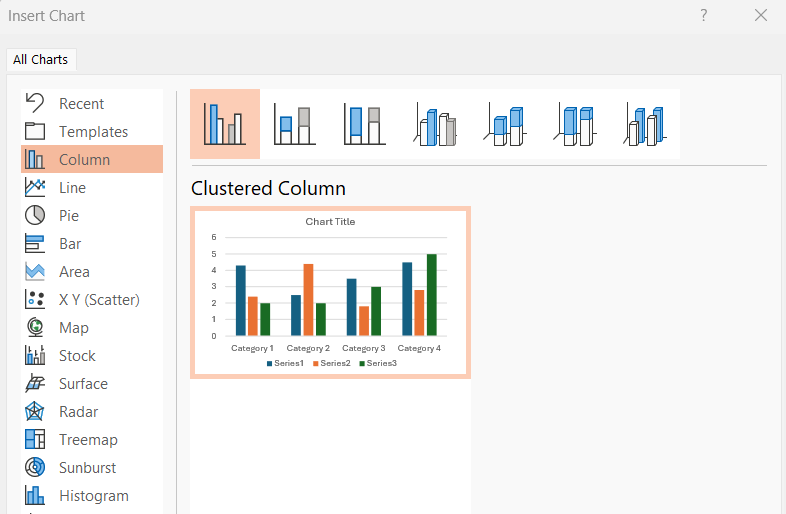
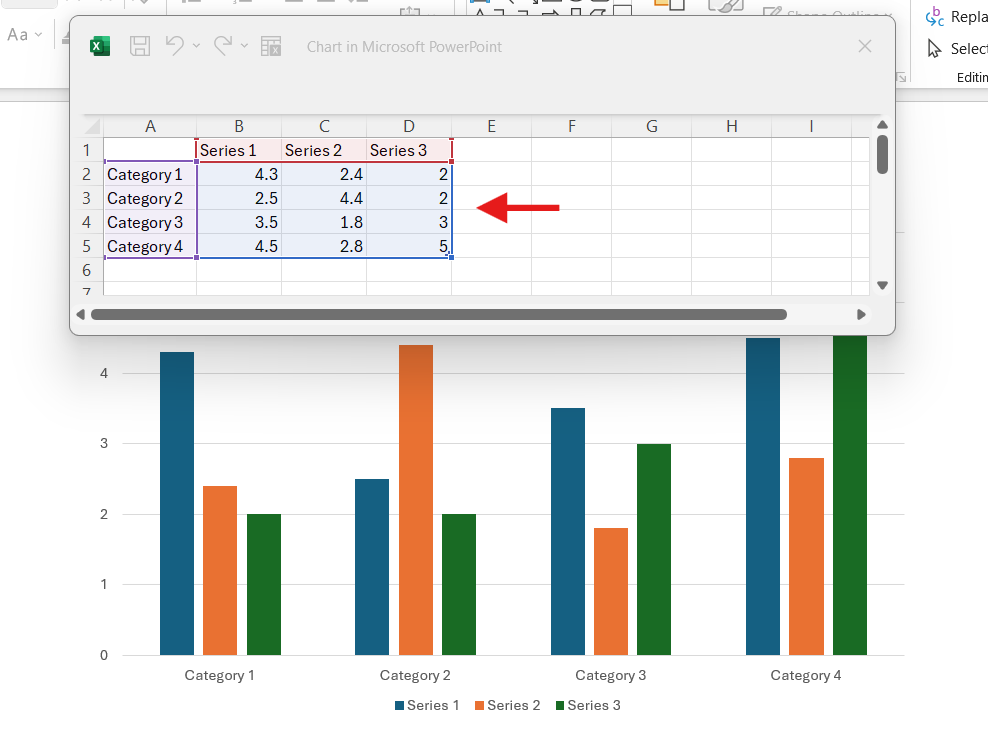
- When inserted, the chart appears alongside a spreadsheet. Here, you have to replace the placeholder data with your own details.
To edit your chart's content, use the selection handles in the spreadsheet to add or remove data.
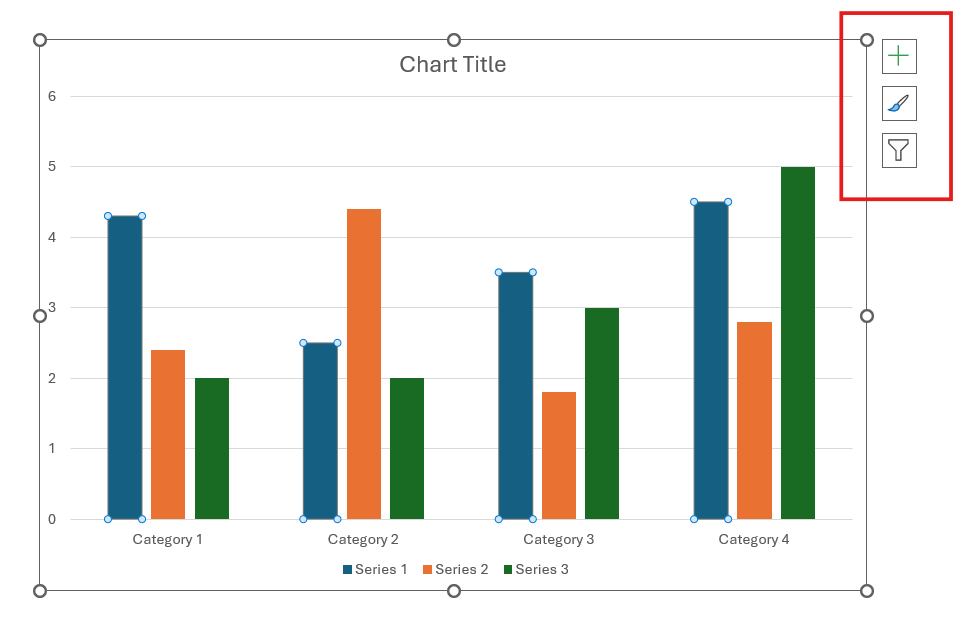
- When inserting a chart, you will see small buttons on the upper right side of the chart.
Format using the Chart Elements button. Click on “+” to tweak the chart title, data labels, and more. Use the Chart Styles button (brush) to change the chart's color or style. Finally, the Chart Filters button (funnel) will show or hide data from your chart.
Customizing Charts in PowerPoint
We already know about the power of PowerPoint charts, but we still have one more step to take: customizing them.
- Edit data: You can modify data directly in PowerPoint. Just double-click on the chart to open the associated Excel spreadsheet. Here, you can add, delete, or edit data. If you want to do it like a pro, check out how to Link or Embed an Excel File in PowerPoint.
- Change the design: Go to the design tab. Here, you can add or remove elements such as titles, captions, labels, etc.
- Change color and style: Select the format tab. In this section, you will find options to change the chart's color and style. You can even make individual changes.
- Add shape effects: Go to the format tab and unleash your creativity. You can add shadows, reflections, and 3D effects.
And there you have it; now you know how to customize your PowerPoint Chart. If you are looking for more inspiration, take a look at our detailed Flowchart and Gantt Chart articles.
Chart vs table
Is a chart better than a table?
We already know the importance of using tables in PowerPoint presentations. However, you may have a question in mind: are charts better than tables? The short answer is: it depends.
First off, think about what type of data you are dealing with and, most importantly, what message you are trying to get across.
Charts are great for showing trends, making comparisons, and connecting data points. They’re also visually appealing. Conversely, tables could be your perfect selection for numerical data and comprehensive details.
The most important types of charts in PPT and which one is best for you
We have checked out why adding visuals is a game-changer for your presentations. However, which one is best for your needs?
Based on our more than 10 years of expertise and creating around 17,500 slides per month, these are the charts most requested by our customers. Let's explore each one!
“Columns, bars, lines, and pie charts are top picks for clients because they're more descriptive and easier to get for the audience.” Briana/ Design Manager
Column Chart
Ideal for making comparisons. You can represent data in an attractive and clear way. It’s also a great option for showing changes over time. Here, you can emphasize the difference in quantities.
Imagine you're tracking sales for a store. If you have many categories of sales data and need to compare them, a column chart could be just what you need.
Download our Free Column Chart Template here.
Like the column chart, the bar chart can simplify complex information quickly , especially when comparing data. But, the horizontal layout might influence how people see things, potentially altering how they understand your data. Keep this in mind!
When you have long category labels or many categories, choose a bar chart instead of a column chart. Horizontal bars are easier to read and take up less space in the presentation.
Download our Free Bar Chart Template here.
The top choice for showing trends over time. You can even combine it with other charts. For example, you can add them to a column chart to display different data at a glance. This makes it easier for viewers to understand complex information.
But how to make a line graph in PowerPoint? First, click on the Insert tab. Then, click on Graph and select Line Graph. That's it—it's as simple as that.
Download our Free Line Chart Template here .
The best for showing proportions. Not only is it easy to understand, but you will also be able to illustrate percentages or parts of a whole.
Pie charts are easy to create, you need to figure out the percentages or proportions of each data category. But remember, keep the chart to six or fewer sections. This maintains data impact, avoiding confusion.
Download our Free Pie Chart Template here .
How to Use Charts and Graphs Effectively?
We already know how to use PowerPoint charts, graphs, and tables, but we want to go one step further. Here are the best tips for making effective PowerPoint presentations.
- Choose the right type of chart. Choose graphics that best suit your data. For example, use column or bar charts to compare categories, line charts to show trends over time, and pie charts to display parts of a whole.
- Be selective. Avoid using too much information, eliminate irrelevant details, and keep it simple. By focusing on the most important data points, you enhance the clarity of the information for your audience.
- Pay attention to color. When presenting data , keep in mind the consistency of the colors and make sure essential information stands out. Avoid using too many colors here, as this can be distracting.
- Add context. Make your titles clear and descriptive. Labels should also serve as a guide for viewers to understand everything easily. This could mean explaining trends, defining terms, or just describing where the data comes from.
- Consistency. Use the same style and format for your graphics and data. Ensure brand consistency in a presentation is key. This creates a professional and polished visual presentation.
- Be creative. Try unique ways to showcase your data, like infographics or custom graphics. For example, you can use a bar chart to compare categories and a line chart to show the trend over time.
Pro Tip: Creating a PowerPoint infographic is one of the most creative ways to present data. They provide a visually engaging and easy-to-follow format for presenting complex information. Briana/ Design Manager
PowerPoint tables help organize and display data in a structured way for presentations. They’re made up of rows and columns containing text, numerical data, or other information.
Tables are awesome for showing comparisons, summarizing information, sharing research findings, and planning. Because of all that, they are a top choice for visualizing financial or statistical data. They’re incredibly versatile and practical!
All you need to do is put the right labels on, and reading should be a breeze. Believe us, your audience will appreciate it. Do you want to present data in detail and make comparisons? Then, this is your best option.
People have been using PowerPoint tables for a long time. Why? That's simple: they’re easy to read.
Here's an example:

Download our Free Table Template here .
How to Make a Table in PowerPoint?
Inserting tables in PowerPoint is quite simple. Just click on Insert and then on Table . Next, just drag the mouse down to choose the number of rows and columns you need.
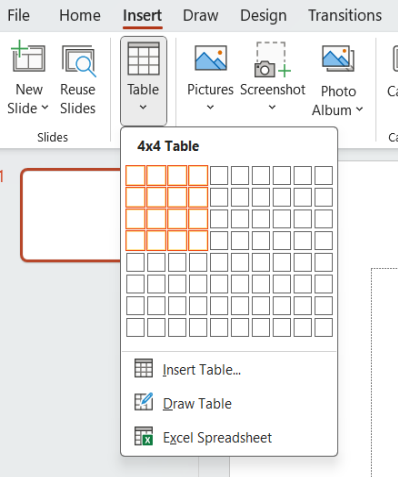
Should you require a bigger table? You can manually select the values for the columns and rows.
Customizing tables in PowerPoint
Now that we know how to create a table in PowerPoint, let's customize it. But first, let's learn how to add rows and columns in PowerPoint.
- How to add a row to a table in PowerPoint?
Click on a cell in the existing table. Go to the Layout tab in the ribbon and select Insert . Select Insert Rows Above or Insert Rows Below , depending on where you want to add the new row.
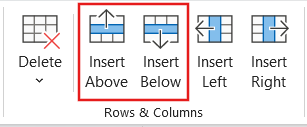
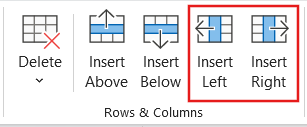
- How to add a column to a table in PowerPoint?
Click on an adjacent cell in the table. Go to the Layout tab in the ribbon and then select Insert . Choose either Insert Columns Left or Insert Columns Right , depending on where you want to add the new column.
Now that you have the structure of your table ready, let's give it some styling:
- Applying style in your table presentation
To edit your tables, first select a cell. Then, click on the Design tab to pick the style you like best. Finally, click on the drop-down arrow to see the complete Table Styles gallery .
That's it. Now you know how to use tables in PowerPoint.
How to Use Tables Effectively?
Tables are powerful tools for presenting data in a structured format. They can enhance clarity, facilitate comparisons, and convey complex information.
However, when you don't use them correctly, they can have the opposite effect, making the information flat and boring. So here are golden rules to help you:
Keep it simple
Don't overload your table with too much information. Focus on the most important information to keep it clear and easy to read. Remember, the powerful presentation of data is in simplicity.
Consider whether gridlines are necessary for your table. Removing them can make your board look cleaner and more professional.
Although many don't mention it, choosing the right words is vital. The more you can say of the same idea in fewer words, the better. Avoid using words or connectors that add nothing to the message.
Highlight key data points
Make your table pop using bold, italics, or fun colors to highlight important data or headings. This will make the table easier to read.
Consider adding shades for alternate rows to make your table easier to read. Make the shadow subtle, to avoid distraction from the data itself.
You can use color to emphasize backgrounds or text. No matter which method you opt for to add contrast, remember that “less is more” when creating an effective table.
Consistency
Consistency is crucial in tables, as it is in graphics. Ensure that the font style, size, and color are the same across the entire table. This helps maintain visual harmony.
Align your text and numbers properly so they're easier to read and give your table a polished look. If you will use decimals, think about aligning them to facilitate comparisons.
In this article, we have explored the benefits of incorporating visuals like charts, graphs, and presentation tables in PowerPoint. We also know how to add them and ensure they look good.
Just remember to pick the right chart and keep your presentations consistent.
And as I said at the beginning, conveying complex information doesn't have to be challenging! Our Templates by 24Slides platform has hundreds of free PowerPoint charts, graphs, and table templates.
You can download and combine different templates to create a shiny PowerPoint Presentation. All the examples in this article are fully customizable, allowing you to insert your data without worrying about design. Enjoy them!
Knowing how to use PowerPoint charts, graphs, and tables can make the difference between a successful presentation and a failed one. However, mastering the art of presenting data takes more time and effort.
The good news? You can always trust professionals to do the heavy work, allowing you to focus on improving your product or service — what really matters to your business.
With an average satisfaction score of 4.8 out of 5 from over 1.3 million redesigned slides, it's safe to say we're incredibly proud of the product we deliver.
We're the world's largest presentation design company.
Not only will you receive an attractive presentation, but we will create one that fits your brand's visual guidelines. Most importantly, it will help emphasize your message and engage your audience.

Ready to elevate your PowerPoint presentations? Explore this content!
- PowerPoint 101: The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- Mastering the Art of Presenting Data in PowerPoint
- The Ultimate Brand Identity Presentation Guide [FREE PPT Template]
- 7 Essential Storytelling Techniques for your Business Presentation
- The Cost of PowerPoint Presentations: Discover the hidden expenses you might overlook!
Create professional presentations online
Other people also read
How To Write Effective Emails That Will Improve Your Communi...

How to Make a Marketing Plan Presentation in PowerPoint

Alternative presentation styles: Takahashi

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Tabular Presentation of Data

Understanding tabular representation of statistical data
The statistical data usually refers to the aggregate of the numerical data which eventually contributes to its collection, interpretation, and analysis. Quantifying this data helps with the research and statistical operations. In the tabular presentation, the data is presented in the form of rows and columns, and this data positioning makes reading and understanding the data more feasible. The logical and statistical conclusions are derived from the presentation of the data.
Objectives of Tabular Data Presentation
The objectives of tabular data presentation are as follows.
The tabular data presentation helps in simplifying the complex data.
It also helps to compare different data sets thereby bringing out the important aspects.
The tabular presentation provides the foundation for statistical analysis.
The tabular data presentation further helps in the formation of graphs, as well as diagrams for the purpose of advanced data analysis.
Parts of the Table that are Used in the Tabulation
Some of the parts that are used in the table of tabular data presentation are as follows.
Table number: This is included for the purpose of identification and it provides for easy reference.
Title: It provides the nature of information which is included in the table. This information is included adjacent to table number.
Stub: This is provided on the left-side of tabular form. The specific issues that are mentioned in the stub are presented in the horizontal rows.
Caption: The caption is put on the top of columns within the table. The columns come with the specific unit within which figures are noted down.
Body: This is the most significant of the table and it is located in the middle or centre of the table. It is made up of numerical contents.
Footnote: The footnote gives the scope or potential for further explanation that might be required for any item which is included in the table. The footnote helps with the clarification of data that is mentioned within the table.
Information source: The information source is included on the bottom of the table. It gives the source related to the specific piece of information and the authenticity of the sources that are cited here helps in contributing to the credibility of the data.
You can check out the illustration of the tabular presentation of data through the provided sample included in the Vedantu notes related to this topic. The different forms of tabular analysis are quantitative analysis, qualitative analysis, spatial analysis, and temporal analysis. When it comes to limitations related to the tabular presentation of the data, they are lack of focus on the individual items, no scope or potential for description, and requiring expert knowledge.
Illustration Of A Tabular Representation of Data
Tabular presentation of data example is shown below.
Age group (in years) | Children (Female) | Total (X) | Children (Male) | Total (Y) | Grand total (X+Y) | ||
Residents | Non-Residents | Residents | Non- Residents | ||||
3-5 | 8 | 4 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 20 |
5-8 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
8-10 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
10-12 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 7 |
12-15 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
Total | 15 | 17 | 32 | 8 | 10 | 18 | 50 |
Test Your Knowledge –
1. Where Is A “Headnote” Placed In A Table?
A headnote comprises the main title
It follows the primary title within a small bracket
A headnote can be placed anywhere in the table
2. Which Of The Following is Used for Explanation of Column Figures?
Caption
Title
Forms of Tabular Analysis
Quantitative .
The quantitative tabular analysis provides a description and interpretation of items based on statistics. Such analysis is undertaken through numeric variables as well as statistical methods.
Qualitative
Qualitative analysis is done, taking into account various attributes that are non-numerical. For instance, it may include social status, nationality, and physical specifications, among others. In such classification, the attributes that are taken into consideration cannot be subjected to quantitative measurement.
Spatial
Categorisation, when done based on location such as a state, country, block, and district, etc., is called spatial analysis.
Temporal
In this analysis method, time becomes a variable for data analysis. Such consideration of time may be in the form of hours, days, weeks, and months among others.
Limitations of A Tabular Presentation
There are certain drawbacks to a table presentation of data that have been mentioned below.
Lack of Focus on Individual Items
Individual items are not presented distinctly. A tabular presentation shows data in an aggregated manner.
No Scope for Description
It is only the figures that are indicated in a tabular presentation. The attributes of those figures cannot be mentioned in tables. Moreover, the qualitative aspects of figures cannot be mentioned.
Requires Expert Knowledge
A layperson will not be able to decipher the intricacies that are mentioned in the figures within a tabular presentation. Its interpretation and analysis can only be undertaken by a person with the requisite expertise.
To know more about this topic and others, install the Vedantu app on your device and read from online study materials available over our platform.

FAQs on Tabular Presentation of Data
1. What is tabular data presentation?
The specific methods that are used for presenting statistical data in the tabular format is known as tabular presentation of data. The data is systematically and logically arranged within the rows and the columns with regards to the specific characteristics of the data. The tabular data presentation makes forthright interpretation as well as comprehensible dataset. This is the reason why tabular data presentation format is widely used in a number of applications where data needs to be organised and analysed.
2. What are the objectives related to data tabulation?
There are specific and well-defined objectives that are associated with the presentation of data tabulation. The data tabular presentation helps with the easy conversion of data into a simple and comprehensible form through tabulation. Besides data arrangement convenience, the tabular presentation of data also creates the foundation for statistical analysis. This statistical analysis might include dispersion, averages, and correlation amongst other factors. These well-laid out objectives are the primary reason behind the usage of tabular data presentation.
3. What are the primary benefits of using tabular presentation of data?
The tabular presentation of data helps with the organisation of data that is easy to understand and analyse. It also helps with the comparison of data. The data is presented in such a way that it helps reduce the time and effort of the user through the organisation as well as the simplicity of the data presentation. The easy organisation plus presentation of data in tabular form is one of the reasons why it is widely used in data analysis.
4. Can I rely on the tabular presentation of data notes from Vedantu?
Yes, you can rely on the Vedantu note for tabular presentation of data. These notes and chapters are compiled by well-qualified teachers or experts who have distinguished knowledge in the subject and who understand the comprehension skills of the students. These notes are carefully created to provide the best explanation of the topic and help students understand the concept in detail through text and illustrations wherever essential.
5. How can I access the tabular presentation of data notes provided by Vedantu?
If you want access to the Vedantu notes on tabular presentation of data then you can download it from the Vedantu app or website. These notes are available for download in the PDF file format for free. Once you are on the relevant section of the website, you will find the “Download PDF” button and when you click on that option, the file will be downloaded on your device. Now you can access the Vedantu notes even offline as per your convenience.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Korean J Anesthesiol
- v.70(3); 2017 Jun
Statistical data presentation
1 Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
Sangseok Lee
2 Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Data are usually collected in a raw format and thus the inherent information is difficult to understand. Therefore, raw data need to be summarized, processed, and analyzed. However, no matter how well manipulated, the information derived from the raw data should be presented in an effective format, otherwise, it would be a great loss for both authors and readers. In this article, the techniques of data and information presentation in textual, tabular, and graphical forms are introduced. Text is the principal method for explaining findings, outlining trends, and providing contextual information. A table is best suited for representing individual information and represents both quantitative and qualitative information. A graph is a very effective visual tool as it displays data at a glance, facilitates comparison, and can reveal trends and relationships within the data such as changes over time, frequency distribution, and correlation or relative share of a whole. Text, tables, and graphs for data and information presentation are very powerful communication tools. They can make an article easy to understand, attract and sustain the interest of readers, and efficiently present large amounts of complex information. Moreover, as journal editors and reviewers glance at these presentations before reading the whole article, their importance cannot be ignored.
Introduction
Data are a set of facts, and provide a partial picture of reality. Whether data are being collected with a certain purpose or collected data are being utilized, questions regarding what information the data are conveying, how the data can be used, and what must be done to include more useful information must constantly be kept in mind.
Since most data are available to researchers in a raw format, they must be summarized, organized, and analyzed to usefully derive information from them. Furthermore, each data set needs to be presented in a certain way depending on what it is used for. Planning how the data will be presented is essential before appropriately processing raw data.
First, a question for which an answer is desired must be clearly defined. The more detailed the question is, the more detailed and clearer the results are. A broad question results in vague answers and results that are hard to interpret. In other words, a well-defined question is crucial for the data to be well-understood later. Once a detailed question is ready, the raw data must be prepared before processing. These days, data are often summarized, organized, and analyzed with statistical packages or graphics software. Data must be prepared in such a way they are properly recognized by the program being used. The present study does not discuss this data preparation process, which involves creating a data frame, creating/changing rows and columns, changing the level of a factor, categorical variable, coding, dummy variables, variable transformation, data transformation, missing value, outlier treatment, and noise removal.
We describe the roles and appropriate use of text, tables, and graphs (graphs, plots, or charts), all of which are commonly used in reports, articles, posters, and presentations. Furthermore, we discuss the issues that must be addressed when presenting various kinds of information, and effective methods of presenting data, which are the end products of research, and of emphasizing specific information.
Data Presentation
Data can be presented in one of the three ways:
–as text;
–in tabular form; or
–in graphical form.
Methods of presentation must be determined according to the data format, the method of analysis to be used, and the information to be emphasized. Inappropriately presented data fail to clearly convey information to readers and reviewers. Even when the same information is being conveyed, different methods of presentation must be employed depending on what specific information is going to be emphasized. A method of presentation must be chosen after carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages of different methods of presentation. For easy comparison of different methods of presentation, let us look at a table ( Table 1 ) and a line graph ( Fig. 1 ) that present the same information [ 1 ]. If one wishes to compare or introduce two values at a certain time point, it is appropriate to use text or the written language. However, a table is the most appropriate when all information requires equal attention, and it allows readers to selectively look at information of their own interest. Graphs allow readers to understand the overall trend in data, and intuitively understand the comparison results between two groups. One thing to always bear in mind regardless of what method is used, however, is the simplicity of presentation.

| Variable | Group | Baseline | After drug | 1 min | 3 min | 5 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP | C | 135.1 ± 13.4 | 139.2 ± 17.1 | 186.0 ± 26.6 | 160.1 ± 23.2 | 140.7 ± 18.3 |
| D | 135.4 ± 23.8 | 131.9 ± 13.5 | 165.2 ± 16.2 | 127.9 ± 17.5 | 108.4 ± 12.6 | |
| DBP | C | 79.7 ± 9.8 | 79.4 ± 15.8 | 104.8 ± 14.9 | 87.9 ± 15.5 | 78.9 ± 11.6 |
| D | 76.7 ± 8.3 | 78.4 ± 6.3 | 97.0 ± 14.5 | 74.1 ± 8.3 | 66.5 ± 7.2 | |
| MBP | C | 100.3 ± 11.9 | 103.5 ± 16.8 | 137.2 ± 18.3 | 116.9 ± 16.2 | 103.9 ± 13.3 |
| D | 97.7 ± 14.9 | 98.1 ± 8.7 | 123.4 ± 13.8 | 95.4 ± 11.7 | 83.4 ± 8.4 |
Values are expressed as mean ± SD. Group C: normal saline, Group D: dexmedetomidine. SBP: systolic blood pressure, DBP: diastolic blood pressure, MBP: mean blood pressure, HR: heart rate. * P < 0.05 indicates a significant increase in each group, compared with the baseline values. † P < 0.05 indicates a significant decrease noted in Group D, compared with the baseline values. ‡ P < 0.05 indicates a significant difference between the groups.
Text presentation
Text is the main method of conveying information as it is used to explain results and trends, and provide contextual information. Data are fundamentally presented in paragraphs or sentences. Text can be used to provide interpretation or emphasize certain data. If quantitative information to be conveyed consists of one or two numbers, it is more appropriate to use written language than tables or graphs. For instance, information about the incidence rates of delirium following anesthesia in 2016–2017 can be presented with the use of a few numbers: “The incidence rate of delirium following anesthesia was 11% in 2016 and 15% in 2017; no significant difference of incidence rates was found between the two years.” If this information were to be presented in a graph or a table, it would occupy an unnecessarily large space on the page, without enhancing the readers' understanding of the data. If more data are to be presented, or other information such as that regarding data trends are to be conveyed, a table or a graph would be more appropriate. By nature, data take longer to read when presented as texts and when the main text includes a long list of information, readers and reviewers may have difficulties in understanding the information.
Table presentation
Tables, which convey information that has been converted into words or numbers in rows and columns, have been used for nearly 2,000 years. Anyone with a sufficient level of literacy can easily understand the information presented in a table. Tables are the most appropriate for presenting individual information, and can present both quantitative and qualitative information. Examples of qualitative information are the level of sedation [ 2 ], statistical methods/functions [ 3 , 4 ], and intubation conditions [ 5 ].
The strength of tables is that they can accurately present information that cannot be presented with a graph. A number such as “132.145852” can be accurately expressed in a table. Another strength is that information with different units can be presented together. For instance, blood pressure, heart rate, number of drugs administered, and anesthesia time can be presented together in one table. Finally, tables are useful for summarizing and comparing quantitative information of different variables. However, the interpretation of information takes longer in tables than in graphs, and tables are not appropriate for studying data trends. Furthermore, since all data are of equal importance in a table, it is not easy to identify and selectively choose the information required.
For a general guideline for creating tables, refer to the journal submission requirements 1) .
Heat maps for better visualization of information than tables
Heat maps help to further visualize the information presented in a table by applying colors to the background of cells. By adjusting the colors or color saturation, information is conveyed in a more visible manner, and readers can quickly identify the information of interest ( Table 2 ). Software such as Excel (in Microsoft Office, Microsoft, WA, USA) have features that enable easy creation of heat maps through the options available on the “conditional formatting” menu.
| Example of a regular table | Example of a heat map | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP | DBP | MBP | HR | SBP | DBP | MBP | HR |
| 128 | 66 | 87 | 87 | 128 | 66 | 87 | 87 |
| 125 | 43 | 70 | 85 | 125 | 43 | 70 | 85 |
| 114 | 52 | 68 | 103 | 114 | 52 | 68 | 103 |
| 111 | 44 | 66 | 79 | 111 | 44 | 66 | 79 |
| 139 | 61 | 81 | 90 | 139 | 61 | 81 | 90 |
| 103 | 44 | 61 | 96 | 103 | 44 | 61 | 96 |
| 94 | 47 | 61 | 83 | 94 | 47 | 61 | 83 |
All numbers were created by the author. SBP: systolic blood pressure, DBP: diastolic blood pressure, MBP: mean blood pressure, HR: heart rate.
Graph presentation
Whereas tables can be used for presenting all the information, graphs simplify complex information by using images and emphasizing data patterns or trends, and are useful for summarizing, explaining, or exploring quantitative data. While graphs are effective for presenting large amounts of data, they can be used in place of tables to present small sets of data. A graph format that best presents information must be chosen so that readers and reviewers can easily understand the information. In the following, we describe frequently used graph formats and the types of data that are appropriately presented with each format with examples.
Scatter plot
Scatter plots present data on the x - and y -axes and are used to investigate an association between two variables. A point represents each individual or object, and an association between two variables can be studied by analyzing patterns across multiple points. A regression line is added to a graph to determine whether the association between two variables can be explained or not. Fig. 2 illustrates correlations between pain scoring systems that are currently used (PSQ, Pain Sensitivity Questionnaire; PASS, Pain Anxiety Symptoms Scale; PCS, Pain Catastrophizing Scale) and Geop-Pain Questionnaire (GPQ) with the correlation coefficient, R, and regression line indicated on the scatter plot [ 6 ]. If multiple points exist at an identical location as in this example ( Fig. 2 ), the correlation level may not be clear. In this case, a correlation coefficient or regression line can be added to further elucidate the correlation.

Bar graph and histogram
A bar graph is used to indicate and compare values in a discrete category or group, and the frequency or other measurement parameters (i.e. mean). Depending on the number of categories, and the size or complexity of each category, bars may be created vertically or horizontally. The height (or length) of a bar represents the amount of information in a category. Bar graphs are flexible, and can be used in a grouped or subdivided bar format in cases of two or more data sets in each category. Fig. 3 is a representative example of a vertical bar graph, with the x -axis representing the length of recovery room stay and drug-treated group, and the y -axis representing the visual analog scale (VAS) score. The mean and standard deviation of the VAS scores are expressed as whiskers on the bars ( Fig. 3 ) [ 7 ].

By comparing the endpoints of bars, one can identify the largest and the smallest categories, and understand gradual differences between each category. It is advised to start the x - and y -axes from 0. Illustration of comparison results in the x - and y -axes that do not start from 0 can deceive readers' eyes and lead to overrepresentation of the results.
One form of vertical bar graph is the stacked vertical bar graph. A stack vertical bar graph is used to compare the sum of each category, and analyze parts of a category. While stacked vertical bar graphs are excellent from the aspect of visualization, they do not have a reference line, making comparison of parts of various categories challenging ( Fig. 4 ) [ 8 ].

A pie chart, which is used to represent nominal data (in other words, data classified in different categories), visually represents a distribution of categories. It is generally the most appropriate format for representing information grouped into a small number of categories. It is also used for data that have no other way of being represented aside from a table (i.e. frequency table). Fig. 5 illustrates the distribution of regular waste from operation rooms by their weight [ 8 ]. A pie chart is also commonly used to illustrate the number of votes each candidate won in an election.

Line plot with whiskers
A line plot is useful for representing time-series data such as monthly precipitation and yearly unemployment rates; in other words, it is used to study variables that are observed over time. Line graphs are especially useful for studying patterns and trends across data that include climatic influence, large changes or turning points, and are also appropriate for representing not only time-series data, but also data measured over the progression of a continuous variable such as distance. As can be seen in Fig. 1 , mean and standard deviation of systolic blood pressure are indicated for each time point, which enables readers to easily understand changes of systolic pressure over time [ 1 ]. If data are collected at a regular interval, values in between the measurements can be estimated. In a line graph, the x-axis represents the continuous variable, while the y-axis represents the scale and measurement values. It is also useful to represent multiple data sets on a single line graph to compare and analyze patterns across different data sets.
Box and whisker chart
A box and whisker chart does not make any assumptions about the underlying statistical distribution, and represents variations in samples of a population; therefore, it is appropriate for representing nonparametric data. AA box and whisker chart consists of boxes that represent interquartile range (one to three), the median and the mean of the data, and whiskers presented as lines outside of the boxes. Whiskers can be used to present the largest and smallest values in a set of data or only a part of the data (i.e. 95% of all the data). Data that are excluded from the data set are presented as individual points and are called outliers. The spacing at both ends of the box indicates dispersion in the data. The relative location of the median demonstrated within the box indicates skewness ( Fig. 6 ). The box and whisker chart provided as an example represents calculated volumes of an anesthetic, desflurane, consumed over the course of the observation period ( Fig. 7 ) [ 9 ].

Three-dimensional effects
Most of the recently introduced statistical packages and graphics software have the three-dimensional (3D) effect feature. The 3D effects can add depth and perspective to a graph. However, since they may make reading and interpreting data more difficult, they must only be used after careful consideration. The application of 3D effects on a pie chart makes distinguishing the size of each slice difficult. Even if slices are of similar sizes, slices farther from the front of the pie chart may appear smaller than the slices closer to the front ( Fig. 8 ).

Drawing a graph: example
Finally, we explain how to create a graph by using a line graph as an example ( Fig. 9 ). In Fig. 9 , the mean values of arterial pressure were randomly produced and assumed to have been measured on an hourly basis. In many graphs, the x- and y-axes meet at the zero point ( Fig. 9A ). In this case, information regarding the mean and standard deviation of mean arterial pressure measurements corresponding to t = 0 cannot be conveyed as the values overlap with the y-axis. The data can be clearly exposed by separating the zero point ( Fig. 9B ). In Fig. 9B , the mean and standard deviation of different groups overlap and cannot be clearly distinguished from each other. Separating the data sets and presenting standard deviations in a single direction prevents overlapping and, therefore, reduces the visual inconvenience. Doing so also reduces the excessive number of ticks on the y-axis, increasing the legibility of the graph ( Fig. 9C ). In the last graph, different shapes were used for the lines connecting different time points to further allow the data to be distinguished, and the y-axis was shortened to get rid of the unnecessary empty space present in the previous graphs ( Fig. 9D ). A graph can be made easier to interpret by assigning each group to a different color, changing the shape of a point, or including graphs of different formats [ 10 ]. The use of random settings for the scale in a graph may lead to inappropriate presentation or presentation of data that can deceive readers' eyes ( Fig. 10 ).

Owing to the lack of space, we could not discuss all types of graphs, but have focused on describing graphs that are frequently used in scholarly articles. We have summarized the commonly used types of graphs according to the method of data analysis in Table 3 . For general guidelines on graph designs, please refer to the journal submission requirements 2) .
| Analysis | Subgroup | Number of variables | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | Among items | Two per items | Variable width column chart |
| One per item | Bar/column chart | ||
| Over time | Many periods | Circular area/line chart | |
| Few periods | Column/line chart | ||
| Relationship | Two | Scatter chart | |
| Three | Bubble chart | ||
| Distribution | Single | Column/line histogram | |
| Two | Scatter chart | ||
| Three | Three-dimensional area chart | ||
| Comparison | Changing over time | Only relative differences matter | Stacked 100% column chart |
| Relative and absolute differences matter | Stacked column chart | ||
| Static | Simple share of total | Pie chart | |
| Accumulation | Waterfall chart | ||
| Components of components | Stacked 100% column chart with subcomponents |
Conclusions
Text, tables, and graphs are effective communication media that present and convey data and information. They aid readers in understanding the content of research, sustain their interest, and effectively present large quantities of complex information. As journal editors and reviewers will scan through these presentations before reading the entire text, their importance cannot be disregarded. For this reason, authors must pay as close attention to selecting appropriate methods of data presentation as when they were collecting data of good quality and analyzing them. In addition, having a well-established understanding of different methods of data presentation and their appropriate use will enable one to develop the ability to recognize and interpret inappropriately presented data or data presented in such a way that it deceives readers' eyes [ 11 ].
<Appendix>
Output for presentation.
Discovery and communication are the two objectives of data visualization. In the discovery phase, various types of graphs must be tried to understand the rough and overall information the data are conveying. The communication phase is focused on presenting the discovered information in a summarized form. During this phase, it is necessary to polish images including graphs, pictures, and videos, and consider the fact that the images may look different when printed than how appear on a computer screen. In this appendix, we discuss important concepts that one must be familiar with to print graphs appropriately.
The KJA asks that pictures and images meet the following requirement before submission 3)
“Figures and photographs should be submitted as ‘TIFF’ files. Submit files of figures and photographs separately from the text of the paper. Width of figure should be 84 mm (one column). Contrast of photos or graphs should be at least 600 dpi. Contrast of line drawings should be at least 1,200 dpi. The Powerpoint file (ppt, pptx) is also acceptable.”
Unfortunately, without sufficient knowledge of computer graphics, it is not easy to understand the submission requirement above. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an understanding of image resolution, image format (bitmap and vector images), and the corresponding file specifications.
Resolution is often mentioned to describe the quality of images containing graphs or CT/MRI scans, and video files. The higher the resolution, the clearer and closer to reality the image is, while the opposite is true for low resolutions. The most representative unit used to describe a resolution is “dpi” (dots per inch): this literally translates to the number of dots required to constitute 1 inch. The greater the number of dots, the higher the resolution. The KJA submission requirements recommend 600 dpi for images, and 1,200 dpi 4) for graphs. In other words, resolutions in which 600 or 1,200 dots constitute one inch are required for submission.
There are requirements for the horizontal length of an image in addition to the resolution requirements. While there are no requirements for the vertical length of an image, it must not exceed the vertical length of a page. The width of a column on one side of a printed page is 84 mm, or 3.3 inches (84/25.4 mm ≒ 3.3 inches). Therefore, a graph must have a resolution in which 1,200 dots constitute 1 inch, and have a width of 3.3 inches.
Bitmap and Vector
Methods of image construction are important. Bitmap images can be considered as images drawn on section paper. Enlarging the image will enlarge the picture along with the grid, resulting in a lower resolution; in other words, aliasing occurs. On the other hand, reducing the size of the image will reduce the size of the picture, while increasing the resolution. In other words, resolution and the size of an image are inversely proportionate to one another in bitmap images, and it is a drawback of bitmap images that resolution must be considered when adjusting the size of an image. To enlarge an image while maintaining the same resolution, the size and resolution of the image must be determined before saving the image. An image that has already been created cannot avoid changes to its resolution according to changes in size. Enlarging an image while maintaining the same resolution will increase the number of horizontal and vertical dots, ultimately increasing the number of pixels 5) of the image, and the file size. In other words, the file size of a bitmap image is affected by the size and resolution of the image (file extensions include JPG [JPEG] 6) , PNG 7) , GIF 8) , and TIF [TIFF] 9) . To avoid this complexity, the width of an image can be set to 4 inches and its resolution to 900 dpi to satisfy the submission requirements of most journals [ 12 ].
Vector images overcome the shortcomings of bitmap images. Vector images are created based on mathematical operations of line segments and areas between different points, and are not affected by aliasing or pixelation. Furthermore, they result in a smaller file size that is not affected by the size of the image. They are commonly used for drawings and illustrations (file extensions include EPS 10) , CGM 11) , and SVG 12) ).
Finally, the PDF 13) is a file format developed by Adobe Systems (Adobe Systems, CA, USA) for electronic documents, and can contain general documents, text, drawings, images, and fonts. They can also contain bitmap and vector images. While vector images are used by researchers when working in Powerpoint, they are saved as 960 × 720 dots when saved in TIFF format in Powerpoint. This results in a resolution that is inappropriate for printing on a paper medium. To save high-resolution bitmap images, the image must be saved as a PDF file instead of a TIFF, and the saved PDF file must be imported into an imaging processing program such as Photoshop™(Adobe Systems, CA, USA) to be saved in TIFF format [ 12 ].
1) Instructions to authors in KJA; section 5-(9) Table; https://ekja.org/index.php?body=instruction
2) Instructions to Authors in KJA; section 6-1)-(10) Figures and illustrations in Manuscript preparation; https://ekja.org/index.php?body=instruction
3) Instructions to Authors in KJA; section 6-1)-(10) Figures and illustrations in Manuscript preparation; https://ekja.org/index.php?body=instruction
4) Resolution; in KJA, it is represented by “contrast.”
5) Pixel is a minimum unit of an image and contains information of a dot and color. It is derived by multiplying the number of vertical and horizontal dots regardless of image size. For example, Full High Definition (FHD) monitor has 1920 × 1080 dots ≒ 2.07 million pixel.
6) Joint Photographic Experts Group.
7) Portable Network Graphics.
8) Graphics Interchange Format
9) Tagged Image File Format; TIFF
10) Encapsulated PostScript.
11) Computer Graphics Metafile.
12) Scalable Vector Graphics.
13) Portable Document Format.
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Organisational Behaviour
- Human Resource Management
- Entrepreneurship
- CBSE Class 11 Statistics for Economics Notes
Chapter 1: Concept of Economics and Significance of Statistics in Economics
- Statistics for Economics | Functions, Importance, and Limitations
Chapter 2: Collection of Data
- Methods of Data Collection
- Sources of Data Collection | Primary and Secondary Sources
- Direct Personal Investigation: Meaning, Suitability, Merits, Demerits and Precautions
- Indirect Oral Investigation : Suitability, Merits, Demerits and Precautions
- Difference between Direct Personal Investigation and Indirect Oral Investigation
- Information from Local Source or Correspondents: Meaning, Suitability, Merits, and Demerits
- Questionnaires and Schedules Method of Data Collection
- Difference between Questionnaire and Schedule
- Qualities of a Good Questionnaire and Types of Questionnaires
- What are the Published Sources of Collecting Secondary Data?
- What Precautions should be taken before using Secondary Data?
- Two Important Sources of Secondary Data: Census of India and Reports & Publications of NSSO
- What is National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO)?
- What is Census Method of Collecting Data?
- Sample Method of Collection of Data
- Methods of Sampling
- Father of Indian Census
- What makes a Sampling Data Reliable?
- Difference between Census Method and Sampling Method of Collecting Data
- What are Statistical Errors?
Chapter 3: Organisation of Data
- Organization of Data
- Objectives and Characteristics of Classification of Data
- Classification of Data in Statistics | Meaning and Basis of Classification of Data
- Concept of Variable and Raw Data
- Types of Statistical Series
- Difference between Frequency Array and Frequency Distribution
- Types of Frequency Distribution
Chapter 4: Presentation of Data: Textual and Tabular
- Textual Presentation of Data: Meaning, Suitability, and Drawbacks
Tabular Presentation of Data: Meaning, Objectives, Features and Merits
- Different Types of Tables
- Classification and Tabulation of Data
Chapter 5: Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data: Meaning , Features, Guidelines, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Types of Diagrams
- Bar Graph | Meaning, Types, and Examples
- Pie Diagrams | Meaning, Example and Steps to Construct
- Histogram | Meaning, Example, Types and Steps to Draw
- Frequency Polygon | Meaning, Steps to Draw and Examples
- Ogive (Cumulative Frequency Curve) and its Types
- What is Arithmetic Line-Graph or Time-Series Graph?
- Diagrammatic and Graphic Presentation of Data
Chapter 6: Measures of Central Tendency: Arithmetic Mean
- Measures of Central Tendency in Statistics
- Arithmetic Mean: Meaning, Example, Types, Merits, and Demerits
- What is Simple Arithmetic Mean?
- Calculation of Mean in Individual Series | Formula of Mean
- Calculation of Mean in Discrete Series | Formula of Mean
- Calculation of Mean in Continuous Series | Formula of Mean
- Calculation of Arithmetic Mean in Special Cases
- Weighted Arithmetic Mean
Chapter 7: Measures of Central Tendency: Median and Mode
- Median(Measures of Central Tendency): Meaning, Formula, Merits, Demerits, and Examples
- Calculation of Median for Different Types of Statistical Series
- Calculation of Median in Individual Series | Formula of Median
- Calculation of Median in Discrete Series | Formula of Median
- Calculation of Median in Continuous Series | Formula of Median
- Graphical determination of Median
- Mode: Meaning, Formula, Merits, Demerits, and Examples
- Calculation of Mode in Individual Series | Formula of Mode
- Calculation of Mode in Discrete Series | Formula of Mode
- Grouping Method of Calculating Mode in Discrete Series | Formula of Mode
- Calculation of Mode in Continuous Series | Formula of Mode
- Calculation of Mode in Special Cases
- Calculation of Mode by Graphical Method
- Mean, Median and Mode| Comparison, Relationship and Calculation
Chapter 8: Measures of Dispersion
- Measures of Dispersion | Meaning, Absolute and Relative Measures of Dispersion
- Range | Meaning, Coefficient of Range, Merits and Demerits, Calculation of Range
- Calculation of Range and Coefficient of Range
- Interquartile Range and Quartile Deviation
- Partition Value | Quartiles, Deciles and Percentiles
- Quartile Deviation and Coefficient of Quartile Deviation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation, and Examples
- Quartile Deviation in Discrete Series | Formula, Calculation and Examples
- Quartile Deviation in Continuous Series | Formula, Calculation and Examples
- Mean Deviation: Coefficient of Mean Deviation, Merits, and Demerits
- Calculation of Mean Deviation for different types of Statistical Series
- Mean Deviation from Mean | Individual, Discrete, and Continuous Series
- Mean Deviation from Median | Individual, Discrete, and Continuous Series
- Standard Deviation: Meaning, Coefficient of Standard Deviation, Merits, and Demerits
- Standard Deviation in Individual Series
- Standard Deviation in Discrete Series
- Standard Deviation in Frequency Distribution Series
- Combined Standard Deviation: Meaning, Formula, and Example
- How to calculate Variance?
- Coefficient of Variation: Meaning, Formula and Examples
- Lorenz Curveb : Meaning, Construction, and Application
Chapter 9: Correlation
- Correlation: Meaning, Significance, Types and Degree of Correlation
- Methods of Measurements of Correlation
- Scatter Diagram Correlation | Meaning, Interpretation, Example
- Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient in Statistics
- Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation | Assumptions, Merits and Demerits
- Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation | Methods and Examples
Chapter 10: Index Number
- Index Number | Meaning, Characteristics, Uses and Limitations
- Methods of Construction of Index Number
- Unweighted or Simple Index Numbers: Meaning and Methods
- Methods of calculating Weighted Index Numbers
- Fisher's Index Number as an Ideal Method
- Fisher's Method of calculating Weighted Index Number
- Paasche's Method of calculating Weighted Index Number
- Laspeyre's Method of calculating Weighted Index Number
- Laspeyre's, Paasche's, and Fisher's Methods of Calculating Index Number
- Consumer Price Index (CPI) or Cost of Living Index Number: Construction of Consumer Price Index|Difficulties and Uses of Consumer Price Index
- Methods of Constructing Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Wholesale Price Index (WPI) | Meaning, Uses, Merits, and Demerits
- Index Number of Industrial Production : Characteristics, Construction & Example
- Inflation and Index Number
Important Formulas in Statistics for Economics
- Important Formulas in Statistics for Economics | Class 11
What is Tabulation?
The systematic presentation of numerical data in rows and columns is known as Tabulation . It is designed to make presentation simpler and analysis easier. This type of presentation facilitates comparison by putting relevant information close to one another, and it helps in further statistical analysis and interpretation. One of the most important devices for presenting the data in a condensed and readily comprehensible form is tabulation. It aims to provide as much information as possible in the minimum possible space while maintaining the quality and usefulness of the data.
“Tabulation involves the orderly and systematic presentation of numerical data in a form designed to elucidate the problem under consideration.” – L.R. Connor
Objectives of Tabulation
The aim of tabulation is to summarise a large amount of numerical information into the simplest form. The following are the main objectives of tabulation:
- To make complex data simpler: The main aim of tabulation is to present the classified data in a systematic way. The purpose is to condense the bulk of information (data) under investigation into a simple and meaningful form.
- To save space: Tabulation tries to save space by condensing data in a meaningful form while maintaining the quality and quantity of the data.
- To facilitate comparison: It also aims to facilitate quick comparison of various observations by providing the data in a tabular form.
- To facilitate statistical analysis: Tabulation aims to facilitate statistical analysis because it is the stage between data classification and data presentation. Various statistical measures, including averages, dispersion, correlation, and others, are easily calculated from data that has been systematically tabulated.
- To provide a reference: Since data may be easily identifiable and used when organised in tables with titles and table numbers, tabulation aims to provide a reference for future studies.
Features of a Good Table
Tabulation is a very specialised job. It requires a thorough knowledge of statistical methods, as well as abilities, experience, and common sense. A good table must have the following characteristics:
- Title: The top of the table must have a title and it needs to be very appealing and attractive.
- Manageable Size: The table shouldn’t be too big or too small. The size of the table should be in accordance with its objectives and the characteristics of the data. It should completely cover all significant characteristics of data.
- Attractive: A table should have an appealing appearance that appeals to both the sight and the mind so that the reader can grasp it easily without any strain.
- Special Emphasis: The data to be compared should be placed in the left-hand corner of columns, with their titles in bold letters.
- Fit with the Objective: The table should reflect the objective of the statistical investigation.
- Simplicity: To make the table easily understandable, it should be simple and compact.
- Data Comparison: The data to be compared must be placed closely in the columns.
- Numbered Columns and Rows: When there are several rows and columns in a table, they must be numbered for reference.
- Clarity: A table should be prepared so that even a layman may make conclusions from it. The table should contain all necessary information and it must be self-explanatory.
- Units: The unit designations should be written on the top of the table, below the title. For example, Height in cm, Weight in kg, Price in ₹, etc. However, if different items have different units, then they should be mentioned in the respective rows and columns.
- Suitably Approximated: If the figures are large, then they should be rounded or approximated.
- Scientifically Prepared: The preparation of the table should be done in a systematic and logical manner and should be free from any kind of ambiguity and overlapping.
Components of a Table
A table’s preparation is an art that requires skilled data handling. It’s crucial to understand the components of a good statistical table before constructing one. A table is created when all of these components are put together in a systematic order. In simple terms, a good table should include the following components:
1. Table Number:
Each table needs to have a number so it may be quickly identified and used as a reference.
- If there are many tables, they should be numbered in a logical order.
- The table number can be given at the top of the table or the beginning of the table title.
- The table is also identified by its location using subscripted numbers like 1.2, 2.1, etc. For instance, Table Number 3.1 should be seen as the first table of the third chapter.
Each table should have a suitable title. A table’s contents are briefly described in the title.
- The title should be simple, self-explanatory, and free from ambiguity.
- A title should be brief and presented clearly, usually below the table number.
- In certain cases, a long title is preferable for clarification. In these cases, a ‘Catch Title’ may be placed above the ‘Main Title’. For instance , the table’s contents might come after the firm’s name, which appears as a catch title.
- Contents of Title: The title should include the following information: (i) Nature of data, or classification criteria (ii) Subject-matter (iii) Place to which the data relates (iv) Time to which the data relates (v) Source to which the data belongs (vi) Reference to the data, if available.
3. Captions or Column Headings:
A column designation is given to explain the figures in the column at the top of each column in a table. This is referred to as a “Column heading” or “Caption”.
- Captions are used to describe the names or heads of vertical columns.
- To save space, captions are generally placed in small letters in the middle of the columns.
4. Stubs or Row Headings:
Each row of the table needs to have a heading, similar to a caption or column heading. The headers of horizontal rows are referred to as stubs. A brief description of the row headers may also be provided at the table’s left-hand top.
5. Body of Table:
The table’s most crucial component is its body, which contains data (numerical information).
- The location of any one figure or data in the table is fixed and determined by the row and column of the table.
- The columns and rows in the main body’s arrangement of numerical data are arranged from top to bottom.
- The size and shape of the main body should be planned in accordance with the nature of the figures and the purpose of the study.
- As the body of the table summarises the facts and conclusions of the statistical investigation, it must be ensured that the table does not have irrelevant information.
6. Unit of Measurement:
If the unit of measurement of the figures in the table (real data) does not change throughout the table, it should always be provided along with the title.
- However, these units must be mentioned together with stubs or captions if rows or columns have different units.
- If there are large figures, they should be rounded up and the rounding method should be stated.
7. Head Notes:
If the main title does not convey enough information, a head note is included in small brackets in prominent words right below the main title.
- A head-note is included to convey any relevant information.
- For instance, the table frequently uses the units of measurement “in million rupees,” “in tonnes,” “in kilometres,” etc. Head notes are also known as Prefatory Notes .
8. Source Note:
A source note refers to the place where information was obtained.
- In the case of secondary data, a source note is provided.
- Name of the book, page number, table number, etc., from which the data were collected should all be included in the source. If there are multiple sources, each one must be listed in the source note.
- If a reader wants to refer to the original data, the source note enables him to locate the data. Usually, the source note appears at the bottom of the table. For example, the source note may be: ‘Census of India, 2011’.
- Importance: A source note is useful for three reasons: -> It provides credit to the source (person or group), who collected the data; -> It provides a reference to source material that may be more complete; -> It offers some insight into the reliability of the information and its source.
9. Footnotes:
The footnote is the last part of the table. The unique characteristic of the data content of the table that is not self-explanatory and has not previously been explained is mentioned in the footnote.
- Footnotes are used to provide additional information that is not provided by the heading, title, stubs, caption, etc.
- When there are many footnotes, they are numbered in order.
- Footnotes are identified by the symbols *, @, £, etc.
- In general, footnotes are used for the following reasons: (i) To highlight any exceptions to the data (ii)Any special circumstances affecting the data; and (iii)To clarify any information in the data.
.webp)
Merits of Tabular Presentation of Data
The following are the merits of tabular presentation of data:
- Brief and Simple Presentation: Tabular presentation is possibly the simplest method of data presentation. As a result, information is simple to understand. A significant amount of statistical data is also presented in a very brief manner.
- Facilitates Comparison: By grouping the data into different classes, tabulation facilitates data comparison.
- Simple Analysis: Analysing data from tables is quite simple. One can determine the data’s central tendency, dispersion, and correlation by organising the data as a table.
- Highlights Characteristics of the Data: Tabulation highlights characteristics of the data. As a result of this, it is simple to remember the statistical facts.
- Cost-effective: Tabular presentation is a very cost-effective way to convey data. It saves time and space.
- Provides Reference: As the data provided in a tabular presentation can be used for other studies and research, it acts as a source of reference.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Commerce - 11th
- Statistics for Economics
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 15 PPT Table Templates for Analytical Data Visualization

When it comes to managing bulk data, tables are an indispensable part of any business management.
Whether you wish to present data to clients or analyze the figures to define your business goals, arranging the information in tabular format gives always a green signal. It helps you evaluate the data in a feasible manner, enabling you to highlight the progress or shortcomings quickly.
Data tables are powerful business tools that add a visual pattern to the information and make it easier for the audience to identify needs and measure impact. Since one size never fits all, there are different types of data tables, each serving their specific purpose. Using rows and columns, you can segregate the information into distinct categories making it easy for your audience to grasp the facts and make informed decisions.
Moreover, the application of tables in PowerPoint presentations extends far beyond showcasing data. You can use them for comparing products, features, prices, etc. This allows you to perform a comprehensive competitive analysis that directs you to create growth-oriented strategies.
In this blog, we will focus on business-specific PPT table template collection, such as the comparison table, pricing table, product comparison chart, competitive advantage table, and more. Also, we will walk you through some tables categorized on basis of their number of columns which include — 2-column table, 3-column table, 5-column table, and 8-column table. Leaving no stone unturned, this blog will further provide you with some additional topic-specific single slides.
Let’s begin right away!
Template 1: Comparison PPT Table Template
Utilize this comparison table PPT template to analyze different attributes of your business. You will be able to discuss and compare company objectives, social media platform users, employee performance, etc. You can even compare features of a product, find viable solutions, and more. Download now.
Download this template
Template 2: Product Comparison Chart PowerPoint Presentation
Present comprehensive data with this PPT table template. It is replete with rows and columns created for different purposes. From comparing prices to accurately analyzing product attributes, the given design has a table for every requirement. Get it today.
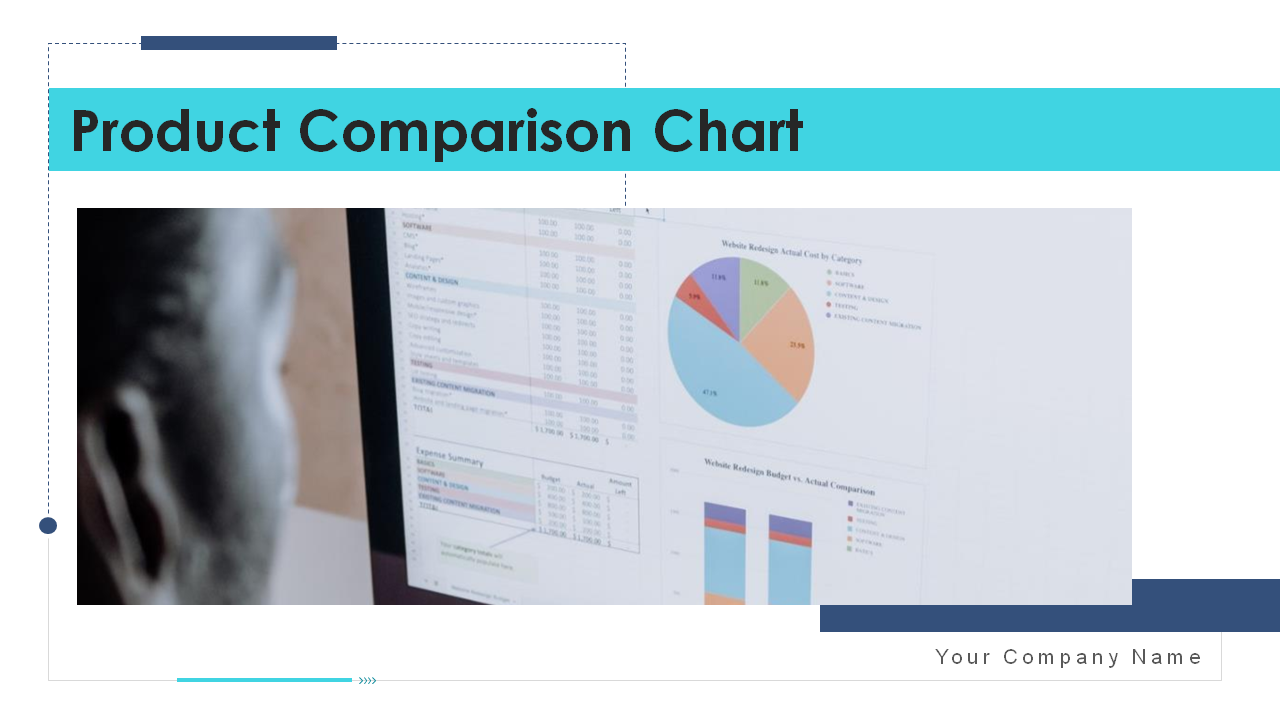
Template 3: Pricing PPT Table Template
Price selection plays a vital role in determining the turnover of the company. You can deploy this PowerPoint layout to analyze and showcase various price packages to attract potential customers. The given design will also help you calculate and plan your activities to achieve the desired profits. With this sample, you can analyze different factors, such as competitive prices, standout features, and more, to set an informed pricing value. Get it today.

Template 4: Benchmark Table Template PPT
Explore the set standards to get an idea of the existing competition. This benchmark table PowerPoint template will allow you to focus your efforts on goal achievement. You can scrutinize your competitors’ working methodology, evaluate marketing goals, set business goals, etc. It will also help you get a fair opinion about the market and trends. Get it now.
Template 5: Competitive Advantage PPT Table Template
Deploy this PPT complete deck to examine the competitive edge. With this theme, you can analyze various elements, such as cost and efficiency, brand image, market share, social impact, etc. You can also compare other attributes like price, quality, functionality, and more to ensure the strong foothold of your company. Grab this PPT now.

Template 6: Action Item Table PPT Presentation
Plans without proper execution are as good as vehicles without wheels. Ensure an effective and streamlined workflow with this high-quality action item table PPT template. The given sample will help you mention the task details like assigned to, related notes, due date, project status, etc. You can also mark the priority level for each action item to ensure and organize the project. Download it right away.

Template 7: Figure Table PowerPoint Template
Manage your database in an efficient manner with this predesigned figure table PPT template. You can illustrate multiple elements in a tabular format to gain a comprehensive perspective. The given design sample will help you elucidate components, such as weekly revenue sales report, company sales forecast, showcase ROI calculations emphasizing the profitability of investments, etc. It also includes slides dedicated to cost allocation, data comparison, sales plan, customer retention statistics, and more. Download it today.

Template 8: 2-Column PPT Table Template
You can benefit from this 2-column PPT design when you need to compare two components. It can help you segregate their properties, highlight the features, distinguish prices, etc. The given slides contain infographics for data integration, data storage technology, etc. Organize your data with this well-formatted column table PPT layout. Download it immediately.
Template 9: Three-Column PPT Table Template
Segment facts and figures in a well-organized manner with this 3-column table PPT design. This high-quality template will enable you to provide a clear and concise description of various elements. You can manage them in multiple ways as per your requirements. Get it now.
Template 10: Five-Column Table PPT Template
This PowerPoint design is suitable for comparing and contrasting five different components. It can offer detailed and comprehensive information allowing for a thorough decision. You can deploy this theme for business, research, and other purposes. It will enable you to depict the results in an easy-to-understand manner. Grab this PPT today.
Template 11: 8-column PPT Table Template
Don’t miss out on any important detail by using this 8-column table PPT design. This all-inclusive sample design fosters a systematic flow of information by arranging it into groups that clearly outline the concept. You can mention specifications, features, workflow, activities, and more. The tabular format helps you assess data easily and present it in a visually engaging manner. Download now.
Template 12: Competitive-comparison Table Presentation Slide
Utilize this content-ready competition comparison table PPT design template to evaluate multiple attributes of your competitors. This multi-dimensional table will help you analyze the strengths and shortcomings of your company. You can elucidate factors, such as revenue, profit, market share, product quality, employee count, and more. The given PowerPoint slide will help you gain an overview of your competition to channel your efforts accordingly. Get it immediately.
Template 13: Customer Touch Point Analysis PPT Table Design
Improve your customer engagement by analyzing various touch points with this infographic. The given PowerPoint design can benefit you in scrutinizing the strengths and weaknesses of the current customer strategy. You can use this slide for training, assessing the impact of each phase, and working on improving lead generation. This theme will support you in building a strong brand reputation, thereby promoting business growth. Download it right away.
Template 14: Financial Planning PPT Table Template
Create a descriptive financial infographic using this content-ready PPT design. The given table theme will benefit you to display multiple fiscal components, such as cost, revenue, profit, etc, arranged in a monthly order. It will help you gain a monetary business overview, allowing you to modify your plans and strategies. Grab this template immediately.
Template 15: PPT Table Template for Visualizing Business Information
Use this PPT slide to showcase your business information in a neat and organized way. The tabular format allows for a clear depiction of data and helps you put forward your case efficiently. You can use this design to segment different aspects or categories of your business, enabling better evaluation and comprehension. These organized details can be utilized for improving plans that support business growth and coordination. Grab this PPT slide immediately.
Let your data breathe with these professionally designed table templates. Our PowerPoint format collection will help you organize and represent details in a comprehensive way, promoting easy understanding and better audience engagement. These sample layouts are fully customizable, thereby saving your time and effort. Download them now.
P.S. Give your market research an edge by creating a useful demographic table with the help of PowerPoint templates featured in this informative guide .
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 12 Templates to Manage and Track Your Expense Reports
Top 10 powerpoint templates to make a descriptive supplier performance dashboard [free pdf attached].
![tabular presentation of data in statistics ppt Top 10 Product Pricing Templates to Balance Affordability and Profitability [Free PDF Attached]](https://www.slideteam.net/wp/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Top-10-Product-Pricing-Templates_1-1013x441.png)
Top 10 Product Pricing Templates to Balance Affordability and Profitability [Free PDF Attached]
![tabular presentation of data in statistics ppt Top 10 Subscription Plan Templates for Better Customer Engagement [Free PDF Attached]](https://www.slideteam.net/wp/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/1013x441no-button-3-1013x441.jpg)
Top 10 Subscription Plan Templates for Better Customer Engagement [Free PDF Attached]

Top 10 PowerPoint Templates to Create a Suggestive Demographics Table
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

--> Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

--> Sales funnel results presentation layouts
--> 3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

--> Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Future plan powerpoint template slide

--> Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

--> Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

--> Agenda powerpoint slide show

--> Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

--> Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

--> Meet our team representing in circular format

60 Effective PowerPoint Presentation Tips & Tricks (Giant List)
Here's a PowerPoint presentation tips and tricks guide that takes you through how to make a good PowerPoint presentation.

The best PowerPoint presentations shouldn’t be remembered. Instead, they should fall into the background to support you and the message you’re trying to get across.
Unlike good PowerPoint presentations , bad PowerPoint presentations are a distraction. You may remember them, but not in a good way.
You’ve seen them before. They might have millions of lines of text. Or a disjointed flow to the slides. Even worse, some slides feature ugly photos and poor design that detract from the message you’re trying to get across. That can even hurt your credibility as a professional or speaker.

This article will take you from finding your initial topic to learning how to make a great PowerPoint presentation. Our guide covers everything in between so that you learn how to present a PowerPoint like a pro.
These Microsoft PowerPoint presentation tips and guidelines are organized into sections. So cut straight to the advice you need and come back when you’re ready for the next steps.
Guide to Making Great Presentations (Free eBook Download)

Also, download our Free eBook: The Complete Guide to Making Great Presentations . It’s the deepest resource for learning effective presentation skills for a PPT.
This eBook covers the complete presentation process. It takes the PowerPoint tips and tricks you learn in this article further. Learn how to write your presentation, design it like a pro, and prepare it to present powerfully. It’s another great source for presentation design tips.
Master PowerPoint (Free Course): 15 Essential Tips
This article is full of helpful tips so you can build a powerful presentation. You can also find more PowerPoint tips in this video lesson:
To learn even more about how to make a PowerPoint look good, review the huge list of tips below.
What Makes a PowerPoint Presentation Effective?
Knowing how to use PowerPoint and work within it quickly is helpful. But more important is making a good presentation that hits all your goals. A great PowerPoint presentation is:
- Prepared to Win . Research, plan, and prepare your presentation professionally. It helps you deliver an effective message to your target audience.
- Designed Correctly . Your visual points should stand out without overwhelming your audience. A good PowerPoint visual shouldn’t complicate your message.
- Practiced to Perfection . Rehearse your timing and delivery so that your points land as practiced with a live audience.
- Delivered With Poise . Present with a relaxed inner calm and confident outward projection. Give your audience warmth, excitement, and energy.
- Free From Mistakes . Avoid typos, cheesy clip art, and mistakes like reading directly from your slides.
Consider this your all-inclusive guide to how to make a good presentation. We’ll look at preparing your presentation and explore how to design it in PowerPoint. Plus, we’ll cover how to practice and nail your delivery successfully come presentation time.
We’ll also address what not to do in these tips for PowerPoint presentations—so you can sidestep any big mistakes. Now let’s dig into these tips for effective PowerPoint presentations.
Killer Presentation Preparation Tips to Get Started Right
Before even opening PowerPoint, start by addressing these things. These Microsoft PowerPoint tips and tricks will ensure that you’re prepared for your presentation:
1. Know Your Stuff
Your presentation isn’t about your slides alone. It’s about the message you want to get across. Before filling in stats, facts and figures, think about the narrative that’ll be discussed, why, and in what order.
2. Write It Out
Start in a Word or Google doc, and storyboard or script the entire presentation. This will give you an idea of how the information presented will flow and how viewers will see it in sequence. Learn the complete writing process .
3. Highlight What’s Most Important
A presentation covers the most crucial pieces only. Whatever you’ve been working on that led to this—a paper, a work project, a new product design—doesn’t need to be shared in its entirety. Pick key points and put the rest in an “Appendix” to refer to during the Q&A session at the end.
4. Know Your Audience
How you talk to a room full of medical professionals should be different from the way you address a room full of young entrepreneurs. Everything, in fact, is different: your topic selection, the language you use, the examples you give to illustrate points. The little bits of humor you include should be tailored specifically with your target audience in mind.
Understand your audience’s needs to create a successful PowerPoint presentation. Customize your content to meet their specific requirements.
5. Rehearse! (Yes, Already)
It’s never too early to get used to the rhythm of your presentation and take note of points you want to emphasize. While saying it out loud, you’ll start to develop a “feel” for the material. You’ll notice that some things work well, while others don’t and might need to be worked around.
6. Rewrite After You Rehearse
As you’re rehearsing your presentation, you’re bound to stumble over sections that don’t quite flow naturally. Instead of reworking your delivery, it might be time to consider the content and rewrite the areas that served as stumbling blocks.
“Editing is hard. ‘It’s good enough,’ is a phrase wannabes use. Leaders take editing seriously.” – Anthony Trendl
The most important part of creating a great presentation is the writing stage. The second most important stage is rewriting.
7. Share With a Friend
If the stakes are high for your presentation, it’s never too early to get feedback from those that you trust. Here’s an article that helps you collaborate as a team on a PowerPoint presentation. Get PowerPoint design tips from those that you trust when you collaborate.
Simple Tips to Design Your PowerPoint Presentation Better
Second only to you (the information you bring and how you present it) is your PowerPoint slides. If not designed well, a PowerPoint can be disengaging or distracting (regardless of the content quality). Here are some presentation design tips to make sure this doesn’t happen to you:
8. Keep Your Slides Simple
This is one of the most important PowerPoint presentation tips to follow when designing your slides. Keep in mind that less is more (effective.) A cluttered slide is distracting. It causes confusion for an audience: Which part of the slide should I focus on? Should I read the slide or pay attention to the presenter?
A simple, visually appealing slide will engage your audience, keeping them on track with your main points. Here’s an example of a simple slide that serves its purpose perfectly:

Minimalist slide templates like Nook can help you resist the urge to clutter your slides.
9. Limit Words on Your Slides
Piggybacking on the last point, less is more effective. If possible, avoid bullets altogether. Otherwise cut them to just a few simple words. The audience should be listening, not reading.
10. Use High-Quality Photos and Graphics
One of the most important tips for quality PowerPoint presentations is to use high-quality photos and graphics.
Earlier in this tutorial, you saw Envato Elements, an all-you-can-download service with PPT tips inside of templates. Those pre-built designs are a beginner’s best friend. They’re even better when paired with Elements’ unlimited library of stock photos .
People are more likely to take you seriously if your presentation is visually appealing. Users view attractive design as more usable. Similarly, they’ll view a more attractive PowerPoint as more effective.
11. Use Accurate and Relevant Charts and Graphs
Charts and graphs can also be distracting if they’re not used right. Make sure your information design is simple and clean so that the audience doesn’t spend the entire time trying to decipher what your X axis says. Learn more about PPT data presentation .
12. Use High-Quality, Fresh Templates
Have you seen the old PowerPoint template that looks like worn paper and uses ink splashes? Yeah, so has your audience. Templates can be distracting if they’re too basic or if the design feels dated. You need one with great design options.
Costs are always a concern. But when you use Envato Elements, you’ve got everything you need to create a great PowerPoint presentation . That’s thanks to the incredible all-you-can-download subscription package.
The best PowerPoint tips and tricks can hardly compare to the value of using a template while building your presentation.
On Envato Elements, there are thousands of PowerPoint design templates that are ready to use. Instead of designing a presentation from scratch, start with a template! Just add your specifics to the placeholders.

Templates like Galaxi are impressively designed and waiting for your slide specifics.
The best PowerPoint design tips save you time. And there’s no tip more powerful than this one: use a pre-built template . It helps you master how to present a PowerPoint without spending all your time in the app.
13. Choose Appropriate Fonts
Fonts are an important part of engaging your audience. Fonts and typography choices have a subconscious effect on viewers. They can characterize your company’s presentation and brand either positively or negatively. Make sure that you’re choosing fonts that are professional and modern.
14. Choose Color Well
Like font choice, colors cause specific subconscious reactions from viewers. Choosing an outdated color combination for your presentation will render it ineffective.
Below is an example of the Popsicle PowerPoint template , which has a modern presentation color choice:

The Popsicle PowerPoint template highlights how harmonized color palettes can create beautiful slides.
15. Clean + Simple Formatting Makes All the Difference!
We’ve got a full tutorial on how to make a good presentation slide . Give it a read through and review the accompanying video. Just remember, less is more. The focus is you and your message , not your slides.
16. Make Sure All Objects Are Aligned
A simple way to create a well-designed presentation is to make sure all items on a slide are intentionally aligned. To do this, hold down Shift and select all the objects you want to include. Then choose Arrange in the options bar and apply Alignment Type .
17. Limit Punctuation
This isn’t the place for exclamation points. Emphasize your points (while speaking). Don’t enlist punctuation to do this for you. (Leave these at home!!!)
18. Avoid Over-Formatting Your Points
This PowerPoint presentation tip is simple. There’s no need to have every word of every bullet point capitalized, or to have all your bullet points in title case. If possible, drop bullets altogether. Again, the simpler, the better!
Limit your text formatting, including reducing the use of bullets, underline, and other effects. Compare the before example on the left to the revised version on the right.

19. Combine Information With Graphics in PowerPoint
One of the most powerful presentation skills for PPT is using infographics. With the right type of visuals, slides come to life and reduce the text in favor of graphics.
Infographics help combine information with graphics. It’s easier to explain complex ideas when you use visual formats that are intuitive.
Practice Presentation Tips: Rehearse, Rehearse, Rehearse!
Delivery is probably more important than the actual content. Here’s how to become more aware of your own unique ticks, and how to present like a polished pro:
20. I’ll Say It Again, Rehearse!
Just do it. Again and again. Experiment with pauses, gestures, and body language. Practice around one hour for every minute of your speech.
21. Practice With a Timer
Consistency is key to an effective PowerPoint presentation. The timing should be similar (ideally the same) each time you rehearse. This one will especially pay off when it’s time to present in front of your audience.
22. Slow It Down
Many of the best speakers today intentionally speak slowly. You’ll have the chance to emphasize, appear more thoughtful, and make your information easier to digest.
23. Pause More Often
Like the prior tip, pausing more often allows your main points to be emphasized and gives time for information to sink in. You need to let key points breathe a little before rushing into the next section.
24. Record Yourself
Use your phone’s voice recorder. Assess and critique yourself. Consider:
- Are your pauses too short or too long?
- Are you speaking slowly enough? Too slow?
- When you’re nervous, does your voice get high like the mice in Cinderella?

It’s always weird to hear your own voice recorded; don’t stress it. Use this as a time to adjust.
25. Choose Three Focal Points in the Room
If you stare at the same spot (or even creepier, the same person) the entire time, your presentation will be ineffective (and awkward.) People will be distracted by you, wondering what you’re staring at.
Try this: pick three points in the room (typically: left, center, right). Take time to direct your delivery toward each physical focal point in the room. Also, focus on the center when making your primary points.
26. Vary Your Sentence Length
This makes you sound more interesting, and it’s easier for your audience to follow. Think short and punchy. Or go long and complex for dramatic effect.
27. Modulate!
Don’t speak in monotone for your whole presentation. Be conscious of raising and lowering your voice tone. Otherwise, people will tune you out, and you’ll come across like the teacher in Charlie Brown.
28. Practice in Front of a Mirror
What you look like is as important as how you sound. Pretend you’re having a normal conversation, and allow your hands to move with your speech to emphasize your points. Just don’t get carried away! (I’m thinking Brene Brown or President Obama , not your Aunt Jamie after a few gin and tonics.)
29. Use “Present Mode” When Rehearsing
When you finally are ready to hit the Present button in PowerPoint, make sure you use the Present Mode option. This allows you (and only you) to view extra notes about each slide—just in case you forget something!
30. Practice With New Audiences
If possible, try doing a few real live test runs as a webinar or even at a local Toastmasters organization to get some feedback from a live audience.
31. Engage the Audience by Asking Questions
There’s no reason that a presentation should be one-sided. Why not invert the format and ask your audience a question?
To learn how to create a slide that kicks off a Q&A, use this article . These PowerPoint design tips help you create an engaging and exciting discussion.
Helpful Tips to Step Up and Deliver Come Presentation Time
When the actual day arrives, there are only a few last PowerPoint presentation tips and guidelines to keep in mind:
32. Take a Deep Breath
Deep breathing is proven to relieve stress. It’s simple, and it’ll help you remain calm and in the moment, even up to the last minute before starting.
33. Lighten Up Your Mood
Tell yourself a joke or watch a funny video clip. Do this before the presentation, of course. Research concludes that happy people are more productive. More productive is more focused and able to perform better.
34. Remind Yourself to Take It Slow
When we’re stressed or nervous (or both), we tend to speak faster. Consciously, take yet another deep breath and remind yourself to take it slow!
35. Read the Room
Every presentation room has a temperature. It’s your job as a speaker to gauge it and tailor your presentation to it.
Here’s a great example. Layoffs are coming at a company, and you’re asked to speak to an audience. Even if the audience isn’t personally affected by the actions, you’ve got to consider the morale of the workforce.

Skilled speakers have a knack for reading the energy of the room and adjusting their presentation on the fly.
The last thing that group will want to hear is how strong the economy is and why the company is the best place to work. That doesn’t mean that you’ve got to align to their uncertainty, but don’t go too far against the grain while presenting.
Robert Kennedy III is a master of bringing energy and aligning a speech to the audience. Here’s his advice for adjusting:
“It can be hard to wake up a “dead” crowd but go for it. Most of all, don’t take their energy personally. Focus on serving them with every bit of your fiber then leave empty.”
36. Fake It ‘Til You Make It!
Go forward with confidence. If you act confident, you’ll start to feel more confident. Move slowly with grace, speak clearly, smile, wear something nice. You’ll appear confident to all attendees (no matter how you feel internally).
PowerPoint Presentation Tips and Tricks to Help Avoid Mistakes (What Not to Do)
Most importantly, focus on what you can do to make your presentation better. There are a few important things not to do that we’ve got to address. Here are a handful of PowerPoint presentation tips and tricks to help you avoid missteps.
37. Stop With the Sound Effects
Sound effects are distracting and outdated. In most cases, avoid them. Add audio or music to your presentation to inject interest or highlight an important point, but it’s something to take extra care with. If you insert audio, then make sure your use really connects with your audience and has a fresh approach. Otherwise, it’s best to leave it out.
38. Don’t Use Flashy Slide Transitions
Again, this is distracting and outdated. Use transitions and subtle animations in your PowerPoint presentation. But you need to take care and do it right .
39. Beware of Clip Art
This PowerPoint presentation tip shouldn’t even have to be said. But please, please don’t use clip art. Use professional graphics instead.
40. Don’t Be Afraid to Be Afraid
The fear of public speaking is a real one. Many beginners think that if they’re feeling nervous that a presentation won’t go well or succeed. That might lead them to cancel the presentation.
Here’s a tip from expert Sandra Zimmer, who leads The Self-Expression Center on conquering your fears before you take the stage:
“Get out of your head and into your body. I do this through a grounding exercise that really works to calm nerves and bring you present in the moment.”
If you think that public speaking fears aren’t normal, you might never give your award-winning presentation. So don’t be afraid to be afraid, and acknowledge it’s part of the process!
41. Don’t Read Directly During Your PowerPoint Presentation
If you spend your entire presentation looking at the screen or your note cards, you’re sure to lose your audience’s attention. They’ll disengage from what you’re saying, and your presentation will fall flat.
Reading from your paper or screen also makes it look like you’re not prepared. Many people do it, but no one should. As a general rule, only present something you know well and have, at least mostly, memorized the main points of.
42. Don’t Miss Out on PowerPoint Customizations
Many new PowerPoint users often make significant mistakes when using Envato Elements designs.
The best way to see how to make a good presentation PPT is to start with designs from others. That means using a template, but that doesn’t mean you can’t customize them!

Don’t forget that PowerPoint templates are infinitely customizable. Think of them as guides with built-in presentation design tips.
To see more presentation tips that show you what not to do, make sure to check out our guide .
Work in PowerPoint More Effectively (Tips & Tricks to Level Up Your PPT Skills)
These PowerPoint tips will help you get the most out of the application to level up your next presentation. Let’s dive in.
43. Use the Visual Guides
When you’re designing your next PowerPoint presentation, it helps to create a sense of visual rhythm. Slides that have objects aligned and centered are more likely to resonate with an audience.
44. Use a Few Animations (Tastefully)
Animations in effective PowerPoint presentations are a slippery slope. We’ve all sat through presentations where there were so many objects in motion that it was easy to lose focus on the key ideas in the presentation.
But that’s why animations get an unfairly bad reputation. Use animations to create motion and hold an audience’s attention. Use them sparingly and on key elements on your slide, and you’ll capture that attention properly.
45. Stage Key Content With Animations
You just learned that animations should avoid being distracting. But there’s an important principle to using animations properly. It’s called staging content.
Staging content means that the content appears step by step. There’s nothing worse than overwhelming an audience with all your content at once. But when you stage content, bring it on step by step.
Take it from presentation pro Suzannah Baum :
“If you’re sharing a slide with lots of different points on it, using the animation to reveal those points one at a time is a way to keep the presenter’s content flowing smoothly.”
For more animation presentation tips and tricks, follow our guide .
46. Add a Video to Your PowerPoint
When you’re sharing a big idea in your presentation, it helps to share your perspective from a few different angles. Adding a video to supplement your content can do just that. Luckily, it’s easy to add and embed a YouTube video in your next PowerPoint presentation.
47. Add Charts & Graphs
Charts and graphs can help you tell stories with data. It’s easy for an audience to zone out when you throw a big data table or set of statistics at them.
instead, convert those to charts and graphs. Try out our tutorial to learn how to edit those graphs.
48. Build Your Own Infographics With SmartArt
Earlier in this tutorial, we gave you one of my favorite PowerPoint design tips: use infographic templates.
Here’s another. One of my favorite PowerPoint features is SmartArt, which allows you to build infographics right inside the app.
You don’t have to use another graphic design app like Photoshop or Illustrator to add visuals. Instead, try out SmartArt to help you build graphics that are easy to update.
49. Use Presenter View
Remember that when you use the PowerPoint, you’ re the presentation. The slides are just there to reinforce what you’ve got to say and support your speaking points.
That’s why I always recommend using Presenter view. More often than not, you’re going to have several displays. Presenter view shows your content on your screen, while your presentation is displayed on another screen.
50. Track Your PowerPoint Changes
One of my favorite PowerPoint design tips is to collaborate. Those who know you best will suggest compelling changes that are sure to help you succeed.
As you start collaborating on your presentation, it helps to keep track of proposed and included PowerPoint changes. Use this article to track changes made by others.
10 More Advanced PowerPoint Tips & Tricks
Really need to wow an audience with a good PowerPoint presentation? Give these tips a try to make an unforgettable impression:
51. Engage With an Interactive Quiz
A good PowerPoint presentation gets your audience involved. One of the best PowerPoint tricks is to do that with a quiz. By engaging audiences, a quiz makes your slides memorable.

By adding trivia, you’ll see how to present a PowerPoint in a way that people will love. Channel your inner game-show host today. MIDTEST is a good PowerPoint presentation with quiz slides.
52. Illustrate With Custom Image Masks
One of the top PowerPoint tips is to illustrate your slides. But you can go beyond simple, rectangular images on each slide.

The Burte template is full of PowerPoint tricks , including custom image masks. Image masks shape photos into unique works of art. And thanks to premium templates, you can style photos just like this. Masks overlay your photos onto geometric shapes, instantly elevating your style.
53. Print Handouts With Extra Notes
Wonder how to give a good presentation PPT that audiences will remember? Give them a piece of it to take home.
PowerPoint makes it easy to print handouts with room for notes on the page. This way, audiences can keep copies of your slides, along with their own notes. This is the perfect way to ensure everyone engages with and retains your content.
54. Make Bulk Edits With Master Slides
When you think about how to present a PowerPoint, consider your branding. That means keeping your logo front and center in the eyes of an audience. But if you’re working with a lengthy slide deck, this could seem daunting.
That’s where master slides come in. They’re common in premium layouts, and they’re a leading example of presentation skills for PPT. Master slides let you make bulk edits fast.
55. Shrink File Sizes for Sharing
Many of the top presentation tips involve making your slides more accessible. Often, that involves sharing them with audiences online.
You’ll often find that email clients and cloud services limit the size of files that you share. This can be a problem with large PPT slide decks. But there are a few quick steps you can take to reduce PPT file size. Cut graphics, scale down photos, and more.
56. Map Processes With Flowcharts
As you consider how to do a good PowerPoint presentation, think of ease of understanding. After all, you’re trying to explain something to your audience.

The Flowcharts in Infographics template seamlessly illustrates ideas and processes. A flowchart maps out a process in a visual way. Instead of resorting to endless narration, try a quick illustration like this. It saves you time and effort, and your audience is sure to thank you.
57. Use Brand-Specific Colors
Using presentation skills for PPT helps form an association between your message and branding. There’s no better way to do that than with your brand colors.
PowerPoint makes it easy to change color themes, adding your brand colors and logo to each slide. This is one of the top PowerPoint tricks for marketing presentations.
58. Build Social Media Posts in PPT
A good PowerPoint presentation doesn’t have to be shared through a projector. Use the app and templates to build amazing illustrations to use anywhere.

A template like Soffee helps you learn how to present a PowerPoint easily with a pre-built design.
Try using PowerPoint to create social media posts. It helps you engage with your audience, with no need to design custom layouts from scratch.
59. Be Industry-Specific
One of the top presentation tips in 2024 is to be industry-specific. That means avoiding generic layouts and choosing something more customized.
This offers two key advantages. First, you save time by having layouts built for you. Second, you gain design inspiration for your specific topic. Themed templates are truly the best of both worlds.

The Medical and Health template is a good PowerPoint presentation with a set theme.
60. Design for Online (Virtual) Sharing
Last but not least in our list of PowerPoint tips comes virtual presenting. More and more often, slides will be shared with online audiences around the globe.
Why not design your slides for that very purpose? And then learn how to share flawlessly with a global team? It’s one of the top presentation tips for 2024. Embrace it today.
More Great PowerPoint Tutorial Resources
We’ve built a resource for Microsoft PowerPoint that you’re sure to want to try. It includes countless PowerPoint tips and tricks. It’s called How to Use PowerPoint (Ultimate Tutorial Guide) and has all the PowerPoint design tips you need.
Discover More Top PowerPoint Template Designs From Envato Elements for 2024
You’ve just seen our favorite powerful PowerPoint presentation tips and guidelines to help you improve your speaking. We’ve also mentioned Envato Elements, an incredible all-you-can-download source for top PowerPoint designs .
Here are five of the best PowerPoint templates that you can use to create your best presentation yet:
1. Galaxi PowerPoint Template
Blast off to success with the help of this PowerPoint template! Think of the pre-built slide designs as pro PowerPoint design tips. They’re built by professional graphic designers. All the popular and modern slide styles that are perfect for your next presentation. Use Galaxi’s five styles and 30 designs to create a great presentation.
2. Masmax PowerPoint Template

We selected templates for this article that match the PowerPoint tips and tricks provided. Masmax fits the bill perfectly across its 234 unique slide designs. These slide designs are sure to align with the latest in design expectations.
3. STYLE Multipurpose PowerPoint Template V50

Style is subjective, but we can all agree that this template is stunning! The light and airy slide designs are built with fashion-focused designs in mind. But that doesn’t mean that it’s not perfect for most presentations. When learning to present a PowerPoint, remember that templates can be customized to suit your purpose.
4. Peachme Creative PowerPoint Template

Peachme has image-focused slides with splashy designs. The slides are colorful and perfect for a modern presentation. Don’t worry about remembering all the PowerPoint design tips because they’re included in the pre-built slides. Use Peachme’s designs for your presentation today.
5. Buizi Office Building Rent PowerPoint Template

Buizi markets itself as a real estate focused template. It’s ideal for that purpose because of the minimal, image-focused slide designs. But that also makes it a perfect choice for presentations in many fields.
We’ve just scratched the surface of PowerPoint design tips with these five options. Here are many more, bundled inside of the best roundups on Envato Tuts+:
How to Build a Good PowerPoint Presentation Quickly (In 2024)
You’ve already seen effective presentation skills PPT techniques. But you may be wondering exactly how to do a good PowerPoint presentation. It only takes a few clicks. Let’s learn how in just five steps.
For this mini-tutorial, we’ll use the Enjoy PowerPoint Template from Envato Elements. You’ll see that it’s a beautiful template that helps you learn how to present a PowerPoint by giving you every object and layout you need.

Let’s get started:
1. Choose Your Slides
As you can see, a template like Enjoy has dozens of unique slides inside. The key to how to give a good presentation PPT is to choose only the slides that you need.

One of the best PowerPoint tricks is to start by selecting slides you wish to use from your template.
In PowerPoint, scroll through the sidebar on the left to view different slide layouts. Right-click and choose Delete to remove unwanted designs. Plus, you can click and drag slide thumbnails to reorder them in the deck.
2. Add Text
Consider how to do a good PowerPoint presentation without investing a ton of time. That’s where premium templates come in.

One of our top presentation tips when working with a PPT is to lean on the pre-built text boxes for your content.
To add custom text, simply click and select the contents of any text box on your slide. Then, type in your own words. Repeat as needed throughout your slide deck.
3. Customize Fonts
With text selected, it’s easy to customize fonts on each slide. Find the Font section on PowerPoint’s Home tab. From there, you’ve got a variety of dropdown options.

Another of our top tips for presentation tricks is to use a custom font setting in your template.
Click to change the font, font size, and more. You can also use the buttons on the left to add bolds, italics, and more.
Need more custom font styles? As an Envato Elements subscriber, you’ve got instant access to thousands of custom fonts . Use them in your presentation with ease.
4. Insert Images
Slides like this one contain an image placeholder. That’s another advantage found only with premium templates. These make adding images a breeze.

Add images to your PPTX template for more visually interesting slides.
To get started, find an image file stored on your computer. Then, drag and drop it over the placeholder. PowerPoint will import it, sized and scaled for a perfect fit.
5. Change Colors
One of the top effective presentation skills is changing shape colors. This helps you control the look and feel of each slide.

With a shape selected, find the Shape Format tab on PowerPoint’s ribbon. Then, click on the Shape Fill dropdown. You’ll see a color chooser menu appear. Click on any thumbnail to apply it to the shape or browse through the Gradient and Texture options.
Start Putting These PowerPoint Presentation Tips & Tricks Into Use Today!
Learning to write, design, and present a PowerPoint presentation is an invaluable skill, no matter where you use it. If you’re a good communicator of important messages, you’ll never go hungry.
Luckily, improving PowerPoint presentations isn’t as hard as it seems. Follow these tips for PowerPoint presentations to design and deliver with greater confidence.
Remember: Less is more (effective) . Use PowerPoint presentation templates for better design and more effective visual impact. And you can customize a PPT template quickly , with the right workflow.
Related Articles

- Society ›
Demographics
Median age of immigrants in South Africa 2001-2022, by gender
In 2022, the median age of immigrants in South Africa was 34 years among men, and 33 years for women. Compared to 2011, the average age of male and female migrants in the country increased slightly from 31 years and 30 years, respectively.
Median age of immigrants in South Africa from 2001, 2011, and 2022, by gender
| Characteristic | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 36 | 37 |
| 2011 | 31 | 30 |
| 2022 | 34 | 33 |
Additional Information
Show sources information Show publisher information Use Ask Statista Research Service
Africa, South Africa
2001, 2011, and 2022
Other statistics on the topic
- African countries hosting the most refugees 2023
- Countries with the most international migrants in Africa 2020
- Estimated migration balance by region 2023
- World regions with more African migrants 2020

- Immediate access to statistics, forecasts & reports
- Usage and publication rights
- Download in various formats
* For commercial use only
Basic Account
- Free Statistics
Starter Account
- Premium Statistics
Professional Account
- Free + Premium Statistics
- Market Insights
1 All prices do not include sales tax. The account requires an annual contract and will renew after one year to the regular list price.
Statistics on " Immigration in Africa "
- Refugees and IDPs - worldwide 2000-2022
- Refugee population 2022, by region
- Number of stateless people globally 2000-2022
- Countries with the highest number of IDPs due to conflict worldwide 2022
- Population share of climate migrants globally 2050, by region
- Number of international migrants in Africa 2000-2020
- Distribution of international migrants in Africa 2019, by region
- Regions of origin of migrants in Africa 2020
- Number of international migrants in Africa 2020, by age group
- Number of emigrants from Africa 2000-2020
- Number of emigrants from Africa 2020, by region of origin
- Main destinations of African migrants 2019, by region
- Number of deaths of migrants in Africa 2014-2021
- Refugee population in Sub-Saharan Africa 2010-2022
- Number of asylum seekers in Africa 2020, by country
- Number of internally displaced persons in Africa 2023, by country
- Number of illegal border crossings in the EU 2022, by route
- Number of recorded deaths of migrants in the Mediterranean Sea 2019-2021, by origin
- Main causes of migrants' deaths in the Mediterranean Sea 2022
- Deaths of migrants on the Central Mediterranean Route 2014-2022
- Deaths of migrants on the Eastern Mediterranean Route 2014-2022
- Deaths of migrants on the Western Mediterranean Route 2014-2022
- Migrants being returned to Libya while trying to reach Europe 2019-2021
- Arrivals, deaths, and disappearances from West Africa to Canary Islands 2016-2020
- Sea accidents on the migration route from West Africa to the Canary Islands 2018-2020
- Deaths of migrants crossing the Western African Atlantic route 2014-2021
- Irregular immigrants arriving by land or sea in Spain 2023, by point of entry
Other statistics that may interest you Immigration in Africa
- Basic Statistic Estimated migration balance by region 2023
- Basic Statistic Refugees and IDPs - worldwide 2000-2022
- Basic Statistic Refugee population 2022, by region
- Premium Statistic Number of stateless people globally 2000-2022
- Basic Statistic Countries with the highest number of IDPs due to conflict worldwide 2022
- Premium Statistic Population share of climate migrants globally 2050, by region
Migrant population in Africa
- Premium Statistic Number of international migrants in Africa 2000-2020
- Premium Statistic Distribution of international migrants in Africa 2019, by region
- Premium Statistic Countries with the most international migrants in Africa 2020
- Premium Statistic Regions of origin of migrants in Africa 2020
- Premium Statistic Number of international migrants in Africa 2020, by age group
African migration flows
- Premium Statistic Number of emigrants from Africa 2000-2020
- Premium Statistic Number of emigrants from Africa 2020, by region of origin
- Basic Statistic Main destinations of African migrants 2019, by region
- Basic Statistic World regions with more African migrants 2020
- Basic Statistic Number of deaths of migrants in Africa 2014-2021
Asylum seekers, refugees, and IDPs
- Basic Statistic Refugee population in Sub-Saharan Africa 2010-2022
- Basic Statistic African countries hosting the most refugees 2023
- Basic Statistic Number of asylum seekers in Africa 2020, by country
- Basic Statistic Number of internally displaced persons in Africa 2023, by country
Illegal migration through Mediterranean routes
- Basic Statistic Number of illegal border crossings in the EU 2022, by route
- Basic Statistic Number of recorded deaths of migrants in the Mediterranean Sea 2019-2021, by origin
- Basic Statistic Main causes of migrants' deaths in the Mediterranean Sea 2022
- Basic Statistic Deaths of migrants on the Central Mediterranean Route 2014-2022
- Basic Statistic Deaths of migrants on the Eastern Mediterranean Route 2014-2022
- Basic Statistic Deaths of migrants on the Western Mediterranean Route 2014-2022
- Premium Statistic Migrants being returned to Libya while trying to reach Europe 2019-2021
Illegal migration through the Atlantic route
- Premium Statistic Arrivals, deaths, and disappearances from West Africa to Canary Islands 2016-2020
- Premium Statistic Sea accidents on the migration route from West Africa to the Canary Islands 2018-2020
- Basic Statistic Deaths of migrants crossing the Western African Atlantic route 2014-2021
- Premium Statistic Irregular immigrants arriving by land or sea in Spain 2023, by point of entry
Further Content: You might find this interesting as well

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This document provides information on various methods of presenting data, including tabular, graphical, and textual presentation. It discusses principles of data presentation and different types of tables, charts, and diagrams that can be used including simple tables, frequency distribution tables, bar charts, histograms, line graphs and pie ...
Oral Presentations. • Only include important results. • One report table might need to be broken down into as many as 8‐10 slides. • Don't paste huge tables onto slides and then say "sorry you can't read this"!! • Use large fonts and clear formatting. Table 1.
It provides objectives and rules for tabulating data, including arranging it logically and including totals. It describes key parts of an ideal table like the title, columns, body, and sources. Different types of tabulation are covered, including simple, grouped, and cross tabulation. Grouped frequency tables involve dividing a range into class ...
Presentation of data ppt. The document discusses various methods for presenting data, including tabular, visual, graphical and diagrammatical presentation. It provides guidelines for constructing effective tables, graphs, diagrams and choosing the appropriate method based on the type of data. Tables are useful for presenting exact data while ...
Slides Prepared by JOHN S. LOUCKS St. Edward's University Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical Presentations Part A Summarizing Qualitative Data Summarizing Quantitative Data Summarizing Qualitative Data Frequency Distribution Relative Frequency Distribution Percent Frequency Distribution Bar Graph Pie Chart Example: Marada Inn Guests staying at Marada Inn were asked to ...
26 Elements of a Table Ideal table should have Number Title Column headings Foot-notes Number Table number for identification in a report Title, place Describe the body of the table, variables, Time period (What, how classified, where and when) Column Variable name, No. , Percentages (%), etc., Heading Foot-note(s) - to describe some column/row headings, special cells, source, etc.,
Introduction (2) •Text, Tabular & Graphs for data and information presentation are very powerful communication tools. •Easy to understand, •Attract and sustain the interest of readers, •Efficiently present large amounts of complex information. Show the data. Induce the reader to think about the data being presented. Avoid distorting the ...
There are two major tools/techniques for presentation of data as follows:-Presentation in tabular form-Presentation in graphical form. 2.1 Tabular Presentation Data may be presented in the form of statistical tables. In one table only simple frequencies can be shown.
This page titled 1.3: Presentation of Data is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Anonymous via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. In this book we will use two formats for presenting data sets.
But not all numerical data are statistics. Singular sense: Statistics is the science that deals with the methods of data collection, organization, presentation, analysis and interpretation of data. It refers the subject area that is concerned with extracting relevant information from available data with the aim to make sound decisions.
There many forms of presentation of data of which the following three are well known: (i). Textual Presentation, (ii). Tabular Presentation, (iii). Diagrammatic Presentation. Here, we discuses in detail Tabular method of data presentation. DA table is a symmetric arrangement of statistical data in rows and columns.
PRESENTATION OF STATISTICAL DATA. The document provides information on data presentation and summarization techniques. It discusses how data can be organized through editing and classification. It also describes various methods of presenting data, including tabulation, graphs, diagrams, histograms, frequency curves, frequency polygons and ogives.
Tabulation of Data Ppt - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. 1. Tabulation involves systematically presenting numerical data in columns and rows according to salient characteristics to facilitate comparison and analysis. 2. The main objectives of tabulation are to simplify complex data, clarify characteristics, present facts concisely, and ...
Definition: Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding. Importance: Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact. Types: Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
Generally, the data in the statistics can be presented in three different forms, such as textual method, tabular method and graphical method. Presentation of Data Examples. Now, let us discuss how to present the data in a meaningful way with the help of examples. Example 1:
Here you have the detailed step-by-step instructions: Select the slide where you want to add the chart. Choose the Insert tab, then select the Illustrations group's Chart option. A dialog box for inserting charts will appear. Choose a category on the left, then double-click the chart you want on the right.
The objectives of tabular data presentation are as follows. The tabular data presentation helps in simplifying the complex data. It also helps to compare different data sets thereby bringing out the important aspects. The tabular presentation provides the foundation for statistical analysis. The tabular data presentation further helps in the ...
2. PRESENTATION OF DATA This refers to the organization of data into tables, graphs or charts, so that logical and statistical conclusions can be derived from the collected measurements. Data may be presented in (3 Methods): - Textual - Tabular or - Graphical. 3.
In this article, the techniques of data and information presentation in textual, tabular, and graphical forms are introduced. Text is the principal method for explaining findings, outlining trends, and providing contextual information. A table is best suited for representing individual information and represents both quantitative and ...
As a result of this, it is simple to remember the statistical facts. Cost-effective: Tabular presentation is a very cost-effective way to convey data. It saves time and space. Provides Reference: As the data provided in a tabular presentation can be used for other studies and research, it acts as a source of reference.
The given slides contain infographics for data integration, data storage technology, etc. Organize your data with this well-formatted column table PPT layout. Download it immediately. Download this template . Template 9: Three-Column PPT Table Template . Segment facts and figures in a well-organized manner with this 3-column table PPT design.
Tabulation. Nov 21, 2014 • Download as PPT, PDF •. 105 likes • 110,422 views. AI-enhanced description. N. Nirmal Singh. This document discusses different types of tabulation methods for presenting data. It defines tabulation as the systematic organization of data in rows and columns. The document outlines several types of tables including ...
Here's a PowerPoint presentation tips and tricks guide that takes you through how to make a good PowerPoint presentation. ... Learn more about PPT data presentation. 12. Use High-Quality, Fresh Templates ... It's easy for an audience to zone out when you throw a big data table or set of statistics at them. instead, convert those to charts and ...
Directly accessible data for 170 industries from 150+ countries and over 1 Mio. facts. ... Presentation Design; Animated videos; ... Please create an employee account to be able to mark statistics ...
The document discusses various types of graphic representations of data including graphs, diagrams, and charts. It describes graphs as a pictorial presentation of data using lines, bars, and dots. It explains the meaning and significance of graphs, compares tabular and graphic representations, and outlines general rules for constructing graphs.