
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1 What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
- Break through writer’s block. Write your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot
Table of Contents
What is the introduction for a research paper, why is the introduction important in a research paper, craft a compelling introduction section with paperpal. try now, 1. introduce the research topic:, 2. determine a research niche:, 3. place your research within the research niche:, craft accurate research paper introductions with paperpal. start writing now, frequently asked questions on research paper introduction, key points to remember.
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow. It offers an overview of what to expect when reading the main body of your paper.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address. Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal Copilot is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal Copilot helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal Copilot, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2 For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3 Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction. Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic. Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects. Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought. Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance. Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through. Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review. A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following: Introduces the topic – Establishes the study’s significance – Provides an overview of the relevant literature – Provides context for the study using literature – Identifies knowledge gaps However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction: Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research Avoid direct quoting Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
1. Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
2. Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
3. Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
4. Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to write a high-quality conference paper, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without....
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a research proposal

What is a research proposal?
What is the purpose of a research proposal , how long should a research proposal be, what should be included in a research proposal, 1. the title page, 2. introduction, 3. literature review, 4. research design, 5. implications, 6. reference list, frequently asked questions about writing a research proposal, related articles.
If you’re in higher education, the term “research proposal” is something you’re likely to be familiar with. But what is it, exactly? You’ll normally come across the need to prepare a research proposal when you’re looking to secure Ph.D. funding.
When you’re trying to find someone to fund your Ph.D. research, a research proposal is essentially your “pitch.”
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research.
You’ll need to set out the issues that are central to the topic area and how you intend to address them with your research. To do this, you’ll need to give the following:
- an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls
- an overview of how much is currently known about the topic
- a literature review that covers the recent scholarly debate or conversation around the topic
➡️ What is a literature review? Learn more in our guide.
Essentially, you are trying to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into.
It is the opportunity for you to demonstrate that you have the aptitude for this level of research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas:
It also helps you to find the right supervisor to oversee your research. When you’re writing your research proposal, you should always have this in the back of your mind.
This is the document that potential supervisors will use in determining the legitimacy of your research and, consequently, whether they will invest in you or not. It is therefore incredibly important that you spend some time on getting it right.
Tip: While there may not always be length requirements for research proposals, you should strive to cover everything you need to in a concise way.
If your research proposal is for a bachelor’s or master’s degree, it may only be a few pages long. For a Ph.D., a proposal could be a pretty long document that spans a few dozen pages.
➡️ Research proposals are similar to grant proposals. Learn how to write a grant proposal in our guide.
When you’re writing your proposal, keep in mind its purpose and why you’re writing it. It, therefore, needs to clearly explain the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. You need to then explain what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
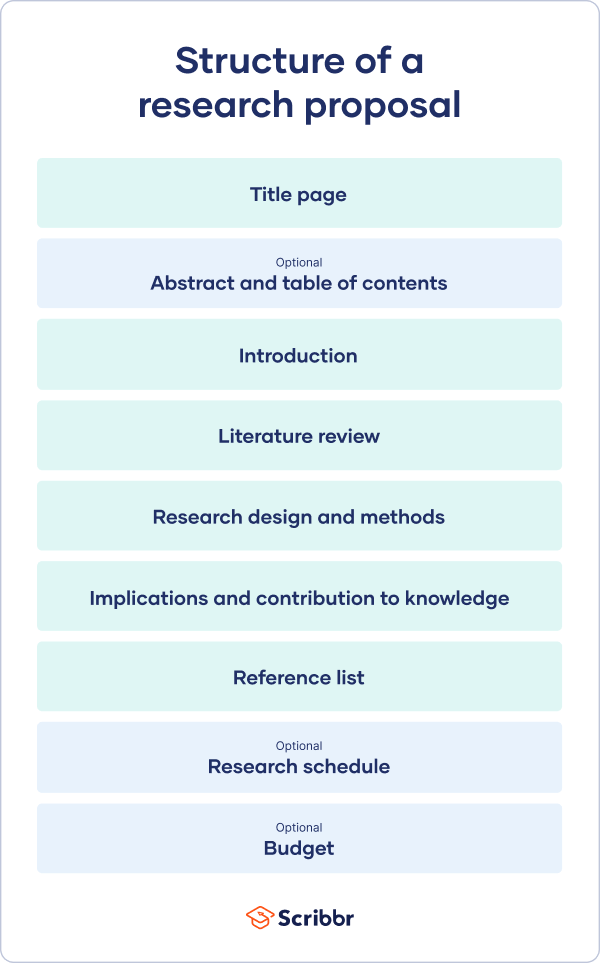
Generally, your structure should look something like this:
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Research Design
- Implications
If you follow this structure, you’ll have a comprehensive and coherent proposal that looks and feels professional, without missing out on anything important. We’ll take a deep dive into each of these areas one by one next.
The title page might vary slightly per your area of study but, as a general point, your title page should contain the following:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- The name of your institution and your particular department
Tip: Keep in mind any departmental or institutional guidelines for a research proposal title page. Also, your supervisor may ask for specific details to be added to the page.
The introduction is crucial to your research proposal as it is your first opportunity to hook the reader in. A good introduction section will introduce your project and its relevance to the field of study.
You’ll want to use this space to demonstrate that you have carefully thought about how to present your project as interesting, original, and important research. A good place to start is by introducing the context of your research problem.
Think about answering these questions:
- What is it you want to research and why?
- How does this research relate to the respective field?
- How much is already known about this area?
- Who might find this research interesting?
- What are the key questions you aim to answer with your research?
- What will the findings of this project add to the topic area?
Your introduction aims to set yourself off on a great footing and illustrate to the reader that you are an expert in your field and that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge and theory.
The literature review section answers the question who else is talking about your proposed research topic.
You want to demonstrate that your research will contribute to conversations around the topic and that it will sit happily amongst experts in the field.
➡️ Read more about how to write a literature review .
There are lots of ways you can find relevant information for your literature review, including:
- Research relevant academic sources such as books and journals to find similar conversations around the topic.
- Read through abstracts and bibliographies of your academic sources to look for relevance and further additional resources without delving too deep into articles that are possibly not relevant to you.
- Watch out for heavily-cited works . This should help you to identify authoritative work that you need to read and document.
- Look for any research gaps , trends and patterns, common themes, debates, and contradictions.
- Consider any seminal studies on the topic area as it is likely anticipated that you will address these in your research proposal.
This is where you get down to the real meat of your research proposal. It should be a discussion about the overall approach you plan on taking, and the practical steps you’ll follow in answering the research questions you’ve posed.
So what should you discuss here? Some of the key things you will need to discuss at this point are:
- What form will your research take? Is it qualitative/quantitative/mixed? Will your research be primary or secondary?
- What sources will you use? Who or what will you be studying as part of your research.
- Document your research method. How are you practically going to carry out your research? What tools will you need? What procedures will you use?
- Any practicality issues you foresee. Do you think there will be any obstacles to your anticipated timescale? What resources will you require in carrying out your research?
Your research design should also discuss the potential implications of your research. For example, are you looking to confirm an existing theory or develop a new one?
If you intend to create a basis for further research, you should describe this here.
It is important to explain fully what you want the outcome of your research to look like and what you want to achieve by it. This will help those reading your research proposal to decide if it’s something the field needs and wants, and ultimately whether they will support you with it.
When you reach the end of your research proposal, you’ll have to compile a list of references for everything you’ve cited above. Ideally, you should keep track of everything from the beginning. Otherwise, this could be a mammoth and pretty laborious task to do.
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to format and organize your citations. Paperpile allows you to organize and save your citations for later use and cite them in thousands of citation styles directly in Google Docs, Microsoft Word, or LaTeX.
Your project may also require you to have a timeline, depending on the budget you are requesting. If you need one, you should include it here and explain both the timeline and the budget you need, documenting what should be done at each stage of the research and how much of the budget this will use.
This is the final step, but not one to be missed. You should make sure that you edit and proofread your document so that you can be sure there are no mistakes.
A good idea is to have another person proofread the document for you so that you get a fresh pair of eyes on it. You can even have a professional proofreader do this for you.
This is an important document and you don’t want spelling or grammatical mistakes to get in the way of you and your reader.
➡️ Working on a research proposal for a thesis? Take a look at our guide on how to come up with a topic for your thesis .
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research. Generally, your research proposal will have a title page, introduction, literature review section, a section about research design and explaining the implications of your research, and a reference list.
A good research proposal is concise and coherent. It has a clear purpose, clearly explains the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. A good research proposal explains what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
You need a research proposal to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into. It is your opportunity to demonstrate your aptitude for this level or research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas clearly, concisely, and critically.
A research proposal is essentially your "pitch" when you're trying to find someone to fund your PhD. It is a clear and concise summary of your proposed research. It gives an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls, it elaborates how much is currently known about the topic, and it highlights any recent debate or conversation around the topic by other academics.
The general answer is: as long as it needs to be to cover everything. The length of your research proposal depends on the requirements from the institution that you are applying to. Make sure to carefully read all the instructions given, and if this specific information is not provided, you can always ask.

Research Proposal: A step-by-step guide with template
Making sure your proposal is perfect will drastically improve your chances of landing a successful research position. Follow these steps.
There’s no doubt you have the most cutting-edge research idea to date, backed up by a solid methodology and a credible explanation proving its relevance! There are thousands of research ideas that could change the world with many new ideologies.
The truth is, none of this would matter without support. It can be daunting, challenging, and uncertain to secure funding for a research project. Even more so when it isn’t well-thought-out, outlined, and includes every detail.
An effective solution for presenting your project, or requesting funding, is to provide a research proposal to potential investors or financiers on your behalf.
It’s crucial to understand that making sure your proposal is perfect will drastically improve your chances of landing a successful research position. Your research proposal could result in the failure to study the research problem entirely if it is inadequately constructed or incomplete.
It is for this reason that we have created an excellent guide that covers everything you need to know about writing a research proposal, and includes helpful tips for presenting your proposal professionally and improving its likelihood of acceptance!
What Is a Research Proposal?

Generally, a research proposal is a well-crafted, formal document that provides a thorough explanation of what you plan to investigate. This includes a rationale for why it is worth investigating, as well as a method for investigating it.
Research proposal writing in the contemporary academic environment is a challenging undertaking given the constant shift in research methodology and a commitment to incorporating scientific breakthroughs.
An outline of the plan or roadmap for the study is the proposal, and once the proposal is complete, everything should be smooth sailing. It is still common for post-graduate evaluation panels and funding applications to submit substandard proposals.
By its very nature, the research proposal serves as a tool for convincing the supervisor, committee, or university that the proposed research fits within the scope of the program and is feasible when considering the time and resources available.
A research proposal should convince the person who is going to sanction your research, or put another way, you need to persuade them that your research idea is the best.
Obviously, if it does not convince them that it is reasonable and adequate, you will need to revise and submit it again. As a result, you will lose significant time, causing your research to be delayed or cut short, which is not good.
A good research proposal should have the following structure
A dissertation or thesis research proposal may take on a variety of forms depending on the university, but most generally a research proposal will include the following elements:
- Titles or title pages that give a description of the research
- Detailed explanation of the proposed research and its background
- Outline of the research project
- An overview of key research studies in the field
- Description the proposed research design (approach)
So, if you include all these elements, you will have a general outline. Let’s take a closer look at how to write them and what to include in each element so that the research proposal is as robust as the idea itself.
A step-by-step guide to writing a research proposal
#1 introduction.
Researchers who wish to obtain grant funding for a project often write a proposal when seeking funding for a research-based postgraduate degree program, or in order to obtain approval for completing a thesis or PhD. Even though this is only a brief introduction, we should be considering it the beginning of an insightful discussion about the significance of a topic that deserves attention.
Your readers should understand what you are trying to accomplish after they read your introduction. Additionally, they should be able to perceive your zeal for the subject matter and a genuine interest in the possible outcome of the research.
As your introduction, consider answering these questions in three to four paragraphs:
- In what way does the study address its primary issue?
- Does that subject matter fall under the domain of that field of study?
- In order to investigate that problem, what method should be used?
- What is the importance of this study?
- How does it impact academia and society overall?
- What are the potential implications of the proposed research for someone reviewing the proposal?
It is not necessary to include an abstract or summary for the introduction to most academic departments and funding sources. Nevertheless, you should confirm your institution’s requirements.
#2 Background and importance
An explanation of the rationale for a research proposal and its significance is provided in this section. It is preferable to separate this part from the introduction so that the narrative flows seamlessly.
This section should be approached by presuming readers are time-pressed but want a general overview of the whole study and the research question.
Please keep in mind that this isn’t an exhaustive essay that contains every detail of your proposed research, rather a concise document that will spark interest in your proposal.
While you should try to take into account the following factors when framing the significance of your proposed study, there are no rigid rules.
- Provide a detailed explanation of the purpose and problem of the study. Multidimensional or interdisciplinary research problems often require this.
- Outline the purpose of your proposed research and describe the advantages of carrying out the study.
- Outline the major issues or problems to be discussed. These might come in the form of questions or comments.
- Be sure to highlight how your research contributes to existing theories that relate to the problem of the study.
- Describe how your study will be conducted, including the source of data and the method of analysis.
- To provide a sense of direction for your study, define the scope of your proposal.
- Defining key concepts or terms, if necessary, is recommended.
The steps to a perfect research proposal all get more specific as we move forward to enhance the concept of the research. In this case, it will become important to make sure that your supervisor or your funder has a clear understanding of every aspect of your research study.
#3 Reviewing prior literature and studies
The aim of this paragraph is to establish the context and significance of your study, including a review of the current literature pertinent to it.
This part aims to properly situate your proposed study within the bigger scheme of things of what is being investigated, while, at the same time, showing the innovation and originality of your proposed work.
When writing a literature review, it is imperative that your format is effective because it often contains extensive information that allows you to demonstrate your main research claims compared to other scholars.
Separating the literature according to major categories or conceptual frameworks is an excellent way to do this. This is a more effective method than listing each study one by one in chronological order.
In order to arrange the review of existing relevant studies in an efficient manner, a literature review is often written using the following five criteria:
- Be sure to cite your previous studies to ensure the focus remains on the research question. For more information, please refer to our guide on how to write a research paper .
- Study the literature’s methods, results, hypotheses, and conclusions. Recognize the authors’ differing perspectives.
- Compare and contrast the various themes, arguments, methodologies, and perspectives discussed in the literature. Explain the most prominent points of disagreement.
- Evaluate the literature. Identify persuasive arguments offered by scholars. Choose the most reliable, valid, and suitable methodologies.
- Consider how the literature relates to your area of research and your topic. Examine whether your proposal for investigation reflects existing literature, deviates from existing literature, synthesizes or adds to it in some way.
#4 Research questions and objectives
The next step is to develop your research objectives once you have determined your research focus.
When your readers read your proposal, what do you want them to learn? Try to write your objectives in one sentence, if you can. Put time and thought into framing them properly.
By setting an objective for your research, you’ll stay on track and avoid getting sidetracked.
Any study proposal should address the following questions irrespective of the topic or problem:
- What are you hoping to accomplish from the study? When describing the study topic and your research question, be concise and to the point.
- What is the purpose of the research? A compelling argument must also be offered to support your choice of topic.
- What research methods will you use? It is essential to outline a clear, logical strategy for completing your study and make sure that it is doable.
Some authors include this section in the introduction, where it is generally placed at the end of the section.
#5 Research Design and Methods
It is important to write this part correctly and organize logically even though you are not starting the research yet. This must leave readers with a sense of assurance that the topic is worthwhile.
To achieve this, you must convince your reader that your research design and procedures will adequately address the study’s problems. Additionally, it seeks to ensure that the employed methods are capable of interpreting the likely study results efficiently.
You should design your research in a way that is directly related to your objectives.
Exemplifying your study design using examples from your literature review, you are setting up your study design effectively. You should follow other researchers’ good practices.
Pay attention to the methods you will use to collect data, the analyses you will perform, as well as your methods of measuring the validity of your results.
If you describe the methods you will use, make sure you include the following points:
- Develop a plan for conducting your research, as well as how you intend to interpret the findings based on the study’s objectives.
- When describing your objectives with the selected techniques, it is important to also elaborate on your plans.
- This section does not only present a list of events. Once you have chosen the strategy, make sure to explain why it is a good way to analyse your study question. Provide clear explanations.
- Last but not least, plan ahead to overcome any challenges you might encounter during the implementation of your research design.
In the event that you closely follow the best practices outlined in relevant studies as well as justify your selection, you will be prepared to address any questions or concerns you may encounter.
We have an amazing article that will give you everything you need to know about research design .
#6 Knowledge Contribution and Relevance
In this section, you describe your theory about how your study will contribute to, expand, or alter knowledge about the topic of your study.
You should discuss the implications of your research on future studies, applications, concepts, decisions, and procedures. It is common to address the study findings from a conceptual, analytical, or scientific perspective.
If you are framing your proposal of research, these guide questions may help you:
- How could the results be interpreted in the context of contesting the premises of the study?
- Could the expected study results lead to proposals for further research?
- Is your proposed research going to benefit people in any way?
- Is the outcome going to affect individuals in their work setting?
- In what ways will the suggested study impact or enhance the quality of life?
- Are the study’s results going to have an impact on intervention forms, techniques, or policies?
- What potential commercial, societal, or other benefits could be derived from the outcomes?
- Policy decisions will be influenced by the outcomes?
- Upon implementation, could they bring about new insights or breakthroughs?
Throughout this section, you will identify unsolved questions or research gaps in the existing literature. If the study is conducted as proposed, it is important to indicate how the research will be instrumental in understanding the nature of the research problem.
#7 Adherence to the Ethical Principles
In terms of scientific writing style, no particular style is generally acknowledged as more or less effective. The purpose is simply to provide relevant content that is formatted in a standardized way to enhance communication.
There are a variety of publication styles among different scholarly disciplines. It is therefore essential to follow the protocol according to the institution or organization that you are targeting.
All scholarly research and writing is, however, guided by codes of ethical conduct. The purpose of ethical guidelines, if they are followed, is to accomplish three things:
1) Preserve intellectual property right;
2) Ensure the rights and welfare of research participants;
3) Maintain the accuracy of scientific knowledge.
Scholars and writers who follow these ideals adhere to long-standing standards within their professional groups.
An additional ethical principle of the APA stresses the importance of maintaining scientific validity. An observation is at the heart of the standard scientific method, and it is verifiable and repeatable by others.
It is expected that scholars will not falsify or fabricate data in research writing. Researchers must also refrain from altering their studies’ outcomes to support a particular theory or to exclude inconclusive data from their report in an effort to create a convincing one.
#8 The budget
The need for detailed budgetary planning is not required by all universities when studying historical material or academic literature, though some do require it. In the case of a research grant application, you will likely have to include a comprehensive budget that breaks down the costs of each major component.
Ensure that the funding program or organization will cover the required costs, and include only the necessary items. For each of the items, you should include the following.
- To complete the study in its entirety, how much money would you require?
- Discuss the rationale for such a budget item for the purpose of completing research.
- The source of the amount – describe how it was determined.
When doing a study, you cannot buy ingredients the way you normally would. With so many items not having a price tag, how can you make a budget? Take the following into consideration:
- Does your project require access to any software programs or solutions? Do you need to install or train a technology tool?
- How much time will you be spending on your research study? Are you required to take time off from work to do your research?
- Are you going to need to travel to certain locations to meet with respondents or to collect data? At what cost?
- Will you be seeking research assistants for the study you propose? In what capacity and for what compensation? What other aspects are you planning to outsource?
It is possible to calculate a budget while also being able to estimate how much more money you will need in the event of an emergency.
#9 Timeline
A realistic and concise research schedule is also important to keep in mind. You should be able to finish your plan of study within the allotted time period, such as your degree program or the academic calendar.
You should include a timeline that includes a series of objectives you must complete to meet all the requirements for your scholarly research. The process starts with preliminary research and ends with final editing. A completion date for every step is required.
In addition, one should state the development that has been made. It is also recommended to include other relevant research events, for instance paper or poster presentations . In addition, a researcher must update the timeline regularly, as necessary, since this is not a static document.
#10 A Concluding Statement
Presenting a few of the anticipated results of your research proposal is an effective way to conclude your proposal.
The final stage of the process requires you to reveal the conclusion and rationale you anticipate reaching. Considering the research you have done so far, your reader knows that these are anticipated results, which are likely to evolve once the whole study is completed.
In any case, you must let the supervisors or sponsors know what implications may be drawn. It will be easier for them to assess the reliability and relevance of your research.
It will also demonstrate your meticulousness since you will have anticipated and taken into consideration the potential consequences of your research.
The Appendix section is required by some funding sources and academic institutions. This is extra information that is not in the main argument of the proposal, but appears to enhance the points made.
For example, data in the form of tables, consent forms, clinical/research guidelines, and procedures for data collection may be included in this document.
Research Proposal Template
Now that you know all about each element that composes an ideal research proposal, here is an extra help: a ready to use research proposal example. Just hit the button below, make a copy of the document and start working!

Avoid these common mistakes
In an era when rejection rates for prestigious journals can reach as high as 90 percent, you must avoid the following common mistakes when submitting a proposal:
- Proposals that are too long. Stay to the point when you write research proposals. Make your document concise and specific. Be sure not to diverge into off-topic discussions.
- Taking up too much research time. Many students struggle to delineate the context of their studies, regardless of the topic, time, or location. In order to explain the methodology of the study clearly to the reader, the proposal must clearly state what the study will focus on.
- Leaving out significant works from a literature review. Though everything in the proposal should be kept at a minimum, key research studies must need to be included. To understand the scope and growth of the issue, proposals should be based on significant studies.
- Major topics are too rarely discussed, and too much attention is paid to minor details. To persuasively argue for a study, a proposal should focus on just a few key research questions. Minor details should be noted, but should not overshadow the thesis.
- The proposal does not have a compelling and well-supported argument. To prove that a study should be approved or funded, the research proposal must outline its purpose.
- A typographical error, bad grammar or sloppy writing style. Even though a research proposal outlines a part of a larger project, it must conform to academic writing standards and guidelines.
A final note
We have come to the end of our research proposal guide. We really hope that you have found all the information you need. Wishing you success with the research study.
We at Mind the Graph create high quality illustrative graphics for research papers and posters to beautify your work. Check us out here .

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
About Fabricio Pamplona
Fabricio Pamplona is the founder of Mind the Graph - a tool used by over 400K users in 60 countries. He has a Ph.D. and solid scientific background in Psychopharmacology and experience as a Guest Researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry (Germany) and Researcher in D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR, Brazil). Fabricio holds over 2500 citations in Google Scholar. He has 10 years of experience in small innovative businesses, with relevant experience in product design and innovation management. Connect with him on LinkedIn - Fabricio Pamplona .
Content tags
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
12 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
kindly assist me in writing the proposal in psychology education
Please,Kindly assist my in my phd thesis writing on personal and socio cultural factors as determinate of family planning adoption
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 5 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
17 Research Proposal Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project.
The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project’s viability and the researcher’s preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
The process holds value both externally (for accountability purposes and often as a requirement for a grant application) and intrinsic value (for helping the researcher to clarify the mechanics, purpose, and potential signficance of the study).
Key sections of a research proposal include: the title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, timeline, budget, outcomes and implications, references, and appendix. Each is briefly explained below.
Watch my Guide: How to Write a Research Proposal
Get your Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
Research Proposal Sample Structure
Title: The title should present a concise and descriptive statement that clearly conveys the core idea of the research projects. Make it as specific as possible. The reader should immediately be able to grasp the core idea of the intended research project. Often, the title is left too vague and does not help give an understanding of what exactly the study looks at.
Abstract: Abstracts are usually around 250-300 words and provide an overview of what is to follow – including the research problem , objectives, methods, expected outcomes, and significance of the study. Use it as a roadmap and ensure that, if the abstract is the only thing someone reads, they’ll get a good fly-by of what will be discussed in the peice.
Introduction: Introductions are all about contextualization. They often set the background information with a statement of the problem. At the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what the rationale for the study truly is. I like to see the research questions or hypotheses included in the introduction and I like to get a good understanding of what the significance of the research will be. It’s often easiest to write the introduction last
Literature Review: The literature review dives deep into the existing literature on the topic, demosntrating your thorough understanding of the existing literature including themes, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in the literature. It serves both to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and, to demonstrate how the proposed study will fit alongside the literature on the topic. A good literature review concludes by clearly demonstrating how your research will contribute something new and innovative to the conversation in the literature.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. Common points discussed in the research design and methods section include highlighting the research paradigm, methodologies, intended population or sample to be studied, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures . Toward the end of this section, you are encouraged to also address ethical considerations and limitations of the research process , but also to explain why you chose your research design and how you are mitigating the identified risks and limitations.
Timeline: Provide an outline of the anticipated timeline for the study. Break it down into its various stages (including data collection, data analysis, and report writing). The goal of this section is firstly to establish a reasonable breakdown of steps for you to follow and secondly to demonstrate to the assessors that your project is practicable and feasible.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. When applying for a scholarship, the budget should demonstrate that you are being responsible with your expensive and that your funding application is reasonable.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: A discussion of the anticipated findings or results of the research, as well as the potential contributions to the existing knowledge, theory, or practice in the field. This section should also address the potential impact of the research on relevant stakeholders and any broader implications for policy or practice.
References: A complete list of all the sources cited in the research proposal, formatted according to the required citation style. This demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the relevant literature and ensures proper attribution of ideas and information.
Appendices (if applicable): Any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or consent forms, that provide further information or support for the research proposal. These materials should be included as appendices at the end of the document.
Research Proposal Examples
Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section.
1. Education Studies Research Proposals
See some real sample pieces:
- Assessment of the perceptions of teachers towards a new grading system
- Does ICT use in secondary classrooms help or hinder student learning?
- Digital technologies in focus project
- Urban Middle School Teachers’ Experiences of the Implementation of
- Restorative Justice Practices
- Experiences of students of color in service learning
Consider this hypothetical education research proposal:
The Impact of Game-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Middle School Mathematics
Abstract: The proposed study will explore multiplayer game-based learning techniques in middle school mathematics curricula and their effects on student engagement. The study aims to contribute to the current literature on game-based learning by examining the effects of multiplayer gaming in learning.
Introduction: Digital game-based learning has long been shunned within mathematics education for fears that it may distract students or lower the academic integrity of the classrooms. However, there is emerging evidence that digital games in math have emerging benefits not only for engagement but also academic skill development. Contributing to this discourse, this study seeks to explore the potential benefits of multiplayer digital game-based learning by examining its impact on middle school students’ engagement and academic performance in a mathematics class.
Literature Review: The literature review has identified gaps in the current knowledge, namely, while game-based learning has been extensively explored, the role of multiplayer games in supporting learning has not been studied.
Research Design and Methods: This study will employ a mixed-methods research design based upon action research in the classroom. A quasi-experimental pre-test/post-test control group design will first be used to compare the academic performance and engagement of middle school students exposed to game-based learning techniques with those in a control group receiving instruction without the aid of technology. Students will also be observed and interviewed in regard to the effect of communication and collaboration during gameplay on their learning.
Timeline: The study will take place across the second term of the school year with a pre-test taking place on the first day of the term and the post-test taking place on Wednesday in Week 10.
Budget: The key budgetary requirements will be the technologies required, including the subscription cost for the identified games and computers.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: It is expected that the findings will contribute to the current literature on game-based learning and inform educational practices, providing educators and policymakers with insights into how to better support student achievement in mathematics.
2. Psychology Research Proposals
See some real examples:
- A situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team
- The effect of musical preference on running performance
- Relationship between self-esteem and disordered eating amongst adolescent females
Consider this hypothetical psychology research proposal:
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students
Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods .
Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels during exam weeks. This can affect both mental health and test performance. This study explores the potential benefits of mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation as a way to mediate stress levels in the weeks leading up to exam time.
Literature Review: Existing research on mindfulness-based meditation has shown the ability for mindfulness to increase metacognition, decrease anxiety levels, and decrease stress. Existing literature has looked at workplace, high school and general college-level applications. This study will contribute to the corpus of literature by exploring the effects of mindfulness directly in the context of exam weeks.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n= 234 ) will be randomly assigned to either an experimental group, receiving 5 days per week of 10-minute mindfulness-based interventions, or a control group, receiving no intervention. Data will be collected through self-report questionnaires, measuring stress levels, semi-structured interviews exploring participants’ experiences, and students’ test scores.
Timeline: The study will begin three weeks before the students’ exam week and conclude after each student’s final exam. Data collection will occur at the beginning (pre-test of self-reported stress levels) and end (post-test) of the three weeks.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: The study aims to provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress among college students in the lead up to exams, with potential implications for mental health support and stress management programs on college campuses.
3. Sociology Research Proposals
- Understanding emerging social movements: A case study of ‘Jersey in Transition’
- The interaction of health, education and employment in Western China
- Can we preserve lower-income affordable neighbourhoods in the face of rising costs?
Consider this hypothetical sociology research proposal:
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Interpersonal Relationships among Young Adults
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effects of social media usage on interpersonal relationships among young adults, using a longitudinal mixed-methods approach with ongoing semi-structured interviews to collect qualitative data.
Introduction: Social media platforms have become a key medium for the development of interpersonal relationships, particularly for young adults. This study examines the potential positive and negative effects of social media usage on young adults’ relationships and development over time.
Literature Review: A preliminary review of relevant literature has demonstrated that social media usage is central to development of a personal identity and relationships with others with similar subcultural interests. However, it has also been accompanied by data on mental health deline and deteriorating off-screen relationships. The literature is to-date lacking important longitudinal data on these topics.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n = 454 ) will be young adults aged 18-24. Ongoing self-report surveys will assess participants’ social media usage, relationship satisfaction, and communication patterns. A subset of participants will be selected for longitudinal in-depth interviews starting at age 18 and continuing for 5 years.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of five years, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between social media usage and interpersonal relationships among young adults, potentially informing social policies and mental health support related to social media use.
4. Nursing Research Proposals
- Does Orthopaedic Pre-assessment clinic prepare the patient for admission to hospital?
- Nurses’ perceptions and experiences of providing psychological care to burns patients
- Registered psychiatric nurse’s practice with mentally ill parents and their children
Consider this hypothetical nursing research proposal:
The Influence of Nurse-Patient Communication on Patient Satisfaction and Health Outcomes following Emergency Cesarians
Abstract: This research will examines the impact of effective nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and health outcomes for women following c-sections, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with patient surveys and semi-structured interviews.
Introduction: It has long been known that effective communication between nurses and patients is crucial for quality care. However, additional complications arise following emergency c-sections due to the interaction between new mother’s changing roles and recovery from surgery.
Literature Review: A review of the literature demonstrates the importance of nurse-patient communication, its impact on patient satisfaction, and potential links to health outcomes. However, communication between nurses and new mothers is less examined, and the specific experiences of those who have given birth via emergency c-section are to date unexamined.
Research Design and Methods: Participants will be patients in a hospital setting who have recently had an emergency c-section. A self-report survey will assess their satisfaction with nurse-patient communication and perceived health outcomes. A subset of participants will be selected for in-depth interviews to explore their experiences and perceptions of the communication with their nurses.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including rolling recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing within the hospital.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the significance of nurse-patient communication in supporting new mothers who have had an emergency c-section. Recommendations will be presented for supporting nurses and midwives in improving outcomes for new mothers who had complications during birth.
5. Social Work Research Proposals
- Experiences of negotiating employment and caring responsibilities of fathers post-divorce
- Exploring kinship care in the north region of British Columbia
Consider this hypothetical social work research proposal:
The Role of a Family-Centered Intervention in Preventing Homelessness Among At-Risk Youthin a working-class town in Northern England
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effectiveness of a family-centered intervention provided by a local council area in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth. This case study will use a mixed-methods approach with program evaluation data and semi-structured interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data .
Introduction: Homelessness among youth remains a significant social issue. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in addressing this problem and identify factors that contribute to successful prevention strategies.
Literature Review: A review of the literature has demonstrated several key factors contributing to youth homelessness including lack of parental support, lack of social support, and low levels of family involvement. It also demonstrates the important role of family-centered interventions in addressing this issue. Drawing on current evidence, this study explores the effectiveness of one such intervention in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth in a working-class town in Northern England.
Research Design and Methods: The study will evaluate a new family-centered intervention program targeting at-risk youth and their families. Quantitative data on program outcomes, including housing stability and family functioning, will be collected through program records and evaluation reports. Semi-structured interviews with program staff, participants, and relevant stakeholders will provide qualitative insights into the factors contributing to program success or failure.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Budget: Expenses include access to program evaluation data, interview materials, data analysis software, and any related travel costs for in-person interviews.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in preventing youth homelessness, potentially informing the expansion of or necessary changes to social work practices in Northern England.
Research Proposal Template
Get your Detailed Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
This is a template for a 2500-word research proposal. You may find it difficult to squeeze everything into this wordcount, but it’s a common wordcount for Honors and MA-level dissertations.
| Section | Checklist |
|---|---|
| Title | – Ensure the single-sentence title clearly states the study’s focus |
| Abstract (Words: 200) | – Briefly describe the research topicSummarize the research problem or question – Outline the research design and methods – Mention the expected outcomes and implications |
| Introduction (Words: 300) | – Introduce the research topic and its significance – Clearly state the research problem or question – Explain the purpose and objectives of the study – Provide a brief overview of |
| Literature Review (Words: 800) | – Gather the existing literature into themes and ket ideas – the themes and key ideas in the literature – Identify gaps or inconsistencies in the literature – Explain how the current study will contribute to the literature |
| Research Design and Methods (Words; 800) | – Describe the research paradigm (generally: positivism and interpretivism) – Describe the research design (e.g., qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods) – Explain the data collection methods (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations) – Detail the sampling strategy and target population – Outline the data analysis techniques (e.g., statistical analysis, thematic analysis) – Outline your validity and reliability procedures – Outline your intended ethics procedures – Explain the study design’s limitations and justify your decisions |
| Timeline (Single page table) | – Provide an overview of the research timeline – Break down the study into stages with specific timeframes (e.g., data collection, analysis, report writing) – Include any relevant deadlines or milestones |
| Budget (200 words) | – Estimate the costs associated with the research project – Detail specific expenses (e.g., materials, participant incentives, travel costs) – Include any necessary justifications for the budget items – Mention any funding sources or grant applications |
| Expected Outcomes and Implications (200 words) | – Summarize the anticipated findings or results of the study – Discuss the potential implications of the findings for theory, practice, or policy – Describe any possible limitations of the study |
Your research proposal is where you really get going with your study. I’d strongly recommend working closely with your teacher in developing a research proposal that’s consistent with the requirements and culture of your institution, as in my experience it varies considerably. The above template is from my own courses that walk students through research proposals in a British School of Education.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Class Group Name Ideas (for School Students)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 19 Top Cognitive Psychology Theories (Explained)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
8 thoughts on “17 Research Proposal Examples”
Very excellent research proposals
very helpful
Very helpful
Dear Sir, I need some help to write an educational research proposal. Thank you.

Hi Levi, use the site search bar to ask a question and I’ll likely have a guide already written for your specific question. Thanks for reading!
very good research proposal
Thank you so much sir! ❤️
Very helpful 👌
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation , appearing right after the table of contents . Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant topic .
Your introduction should include:
- Your topic, in context: what does your reader need to know to understand your thesis dissertation?
- Your focus and scope: what specific aspect of the topic will you address?
- The relevance of your research: how does your work fit into existing studies on your topic?
- Your questions and objectives: what does your research aim to find out, and how?
- An overview of your structure: what does each section contribute to the overall aim?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to start your introduction, topic and context, focus and scope, relevance and importance, questions and objectives, overview of the structure, thesis introduction example, introduction checklist, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about introductions.
Although your introduction kicks off your dissertation, it doesn’t have to be the first thing you write — in fact, it’s often one of the very last parts to be completed (just before your abstract ).
It’s a good idea to write a rough draft of your introduction as you begin your research, to help guide you. If you wrote a research proposal , consider using this as a template, as it contains many of the same elements. However, be sure to revise your introduction throughout the writing process, making sure it matches the content of your ensuing sections.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Begin by introducing your dissertation topic and giving any necessary background information. It’s important to contextualize your research and generate interest. Aim to show why your topic is timely or important. You may want to mention a relevant news item, academic debate, or practical problem.
After a brief introduction to your general area of interest, narrow your focus and define the scope of your research.
You can narrow this down in many ways, such as by:
- Geographical area
- Time period
- Demographics or communities
- Themes or aspects of the topic
It’s essential to share your motivation for doing this research, as well as how it relates to existing work on your topic. Further, you should also mention what new insights you expect it will contribute.
Start by giving a brief overview of the current state of research. You should definitely cite the most relevant literature, but remember that you will conduct a more in-depth survey of relevant sources in the literature review section, so there’s no need to go too in-depth in the introduction.
Depending on your field, the importance of your research might focus on its practical application (e.g., in policy or management) or on advancing scholarly understanding of the topic (e.g., by developing theories or adding new empirical data). In many cases, it will do both.
Ultimately, your introduction should explain how your thesis or dissertation:
- Helps solve a practical or theoretical problem
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Builds on existing research
- Proposes a new understanding of your topic
Perhaps the most important part of your introduction is your questions and objectives, as it sets up the expectations for the rest of your thesis or dissertation. How you formulate your research questions and research objectives will depend on your discipline, topic, and focus, but you should always clearly state the central aim of your research.
If your research aims to test hypotheses , you can formulate them here. Your introduction is also a good place for a conceptual framework that suggests relationships between variables .
- Conduct surveys to collect data on students’ levels of knowledge, understanding, and positive/negative perceptions of government policy.
- Determine whether attitudes to climate policy are associated with variables such as age, gender, region, and social class.
- Conduct interviews to gain qualitative insights into students’ perspectives and actions in relation to climate policy.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
I. Introduction
Human language consists of a set of vowels and consonants which are combined to form words. During the speech production process, thoughts are converted into spoken utterances to convey a message. The appropriate words and their meanings are selected in the mental lexicon (Dell & Burger, 1997). This pre-verbal message is then grammatically coded, during which a syntactic representation of the utterance is built.
Speech, language, and voice disorders affect the vocal cords, nerves, muscles, and brain structures, which result in a distorted language reception or speech production (Sataloff & Hawkshaw, 2014). The symptoms vary from adding superfluous words and taking pauses to hoarseness of the voice, depending on the type of disorder (Dodd, 2005). However, distortions of the speech may also occur as a result of a disease that seems unrelated to speech, such as multiple sclerosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
This study aims to determine which acoustic parameters are suitable for the automatic detection of exacerbations in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by investigating which aspects of speech differ between COPD patients and healthy speakers and which aspects differ between COPD patients in exacerbation and stable COPD patients.
Checklist: Introduction
I have introduced my research topic in an engaging way.
I have provided necessary context to help the reader understand my topic.
I have clearly specified the focus of my research.
I have shown the relevance and importance of the dissertation topic .
I have clearly stated the problem or question that my research addresses.
I have outlined the specific objectives of the research .
I have provided an overview of the dissertation’s structure .
You've written a strong introduction for your thesis or dissertation. Use the other checklists to continue improving your dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Scribbr. Retrieved July 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/introduction-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write A Proposal
Writing a Proposal involves several key steps to effectively communicate your ideas and intentions to a target audience. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each step:
Identify the Purpose and Audience
- Clearly define the purpose of your proposal: What problem are you addressing, what solution are you proposing, or what goal are you aiming to achieve?
- Identify your target audience: Who will be reading your proposal? Consider their background, interests, and any specific requirements they may have.
Conduct Research
- Gather relevant information: Conduct thorough research to support your proposal. This may involve studying existing literature, analyzing data, or conducting surveys/interviews to gather necessary facts and evidence.
- Understand the context: Familiarize yourself with the current situation or problem you’re addressing. Identify any relevant trends, challenges, or opportunities that may impact your proposal.
Develop an Outline
- Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content.
- Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution.
- Background/Context: Offer relevant background information and context to help the readers understand the situation.
- Objectives/Goals: Clearly state the objectives or goals of your proposal.
- Methodology/Approach: Describe the approach or methodology you will use to address the problem.
- Timeline/Schedule: Present a detailed timeline or schedule outlining the key milestones or activities.
- Budget/Resources: Specify the financial and other resources required to implement your proposal.
- Evaluation/Success Metrics: Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points and restate the benefits of your proposal.
Write the Proposal
- Grab attention: Start with a compelling opening statement or a brief story that hooks the reader.
- Clearly state the problem: Clearly define the problem or issue you are addressing and explain its significance.
- Present your proposal: Introduce your proposed solution, project, or idea and explain why it is the best approach.
- State the objectives/goals: Clearly articulate the specific objectives or goals your proposal aims to achieve.
- Provide supporting information: Present evidence, data, or examples to support your claims and justify your proposal.
- Explain the methodology: Describe in detail the approach, methods, or strategies you will use to implement your proposal.
- Address potential concerns: Anticipate and address any potential objections or challenges the readers may have and provide counterarguments or mitigation strategies.
- Recap the main points: Summarize the key points you’ve discussed in the proposal.
- Reinforce the benefits: Emphasize the positive outcomes, benefits, or impact your proposal will have.
- Call to action: Clearly state what action you want the readers to take, such as approving the proposal, providing funding, or collaborating with you.
Review and Revise
- Proofread for clarity and coherence: Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure a logical flow: Read through your proposal to ensure the ideas are presented in a logical order and are easy to follow.
- Revise and refine: Fine-tune your proposal to make it concise, persuasive, and compelling.
Add Supplementary Materials
- Attach relevant documents: Include any supporting materials that strengthen your proposal, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Appendices: Add any additional information that might be useful but not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Formatting and Presentation
- Follow the guidelines: Adhere to any specific formatting guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
- Use a professional tone and language: Ensure that your proposal is written in a clear, concise, and professional manner.
- Use headings and subheadings: Organize your proposal with clear headings and subheadings to improve readability.
- Pay attention to design: Use appropriate fonts, font sizes, and formatting styles to make your proposal visually appealing.
- Include a cover page: Create a cover page that includes the title of your proposal, your name or organization, the date, and any other required information.
Seek Feedback
- Share your proposal with trusted colleagues or mentors and ask for their feedback. Consider their suggestions for improvement and incorporate them into your proposal if necessary.

Finalize and Submit
- Make any final revisions based on the feedback received.
- Ensure that all required sections, attachments, and documentation are included.
- Double-check for any formatting, grammar, or spelling errors.
- Submit your proposal within the designated deadline and according to the submission guidelines provided.
Proposal Format
The format of a proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements of the organization or institution you are submitting it to. However, here is a general proposal format that you can follow:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization’s name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines.
2. Executive Summary:
- Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
- Summarize the problem, proposed solution, and anticipated benefits.
- Keep it brief and engaging, as this section is often read first and should capture the reader’s attention.
3. Introduction:
- State the problem or issue you are addressing and its significance.
- Provide background information to help the reader understand the context and importance of the problem.
- Clearly state the purpose and objectives of your proposal.
4. Problem Statement:
- Describe the problem in detail, highlighting its impact and consequences.
- Use data, statistics, or examples to support your claims and demonstrate the need for a solution.
5. Proposed Solution or Project Description:
- Explain your proposed solution or project in a clear and detailed manner.
- Describe how your solution addresses the problem and why it is the most effective approach.
- Include information on the methods, strategies, or activities you will undertake to implement your solution.
- Highlight any unique features, innovations, or advantages of your proposal.
6. Methodology:
- Provide a step-by-step explanation of the methodology or approach you will use to implement your proposal.
- Include a timeline or schedule that outlines the key milestones, tasks, and deliverables.
- Clearly describe the resources, personnel, or expertise required for each phase of the project.
7. Evaluation and Success Metrics:
- Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Identify specific metrics, indicators, or evaluation methods that will be used.
- Describe how you will track progress, gather feedback, and make adjustments as needed.
- Present a detailed budget that outlines the financial resources required for your proposal.
- Include all relevant costs, such as personnel, materials, equipment, and any other expenses.
- Provide a justification for each item in the budget.
9. Conclusion:
- Summarize the main points of your proposal.
- Reiterate the benefits and positive outcomes of implementing your proposal.
- Emphasize the value and impact it will have on the organization or community.
10. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Attach any relevant documents that provide further information but are not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Proposal Template
Here’s a basic proposal template that you can use as a starting point for creating your own proposal:
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to submit a proposal for [briefly state the purpose of the proposal and its significance]. This proposal outlines a comprehensive solution to address [describe the problem or issue] and presents an actionable plan to achieve the desired objectives.
Thank you for considering this proposal. I believe that implementing this solution will significantly contribute to [organization’s or community’s goals]. I am available to discuss the proposal in more detail at your convenience. Please feel free to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
Yours sincerely,
Note: This template is a starting point and should be customized to meet the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
Proposal Sample
Here’s a sample proposal to give you an idea of how it could be structured and written:
Subject : Proposal for Implementation of Environmental Education Program
I am pleased to submit this proposal for your consideration, outlining a comprehensive plan for the implementation of an Environmental Education Program. This program aims to address the critical need for environmental awareness and education among the community, with the objective of fostering a sense of responsibility and sustainability.
Executive Summary: Our proposed Environmental Education Program is designed to provide engaging and interactive educational opportunities for individuals of all ages. By combining classroom learning, hands-on activities, and community engagement, we aim to create a long-lasting impact on environmental conservation practices and attitudes.
Introduction: The state of our environment is facing significant challenges, including climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. It is essential to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills to understand these issues and take action. This proposal seeks to bridge the gap in environmental education and inspire a sense of environmental stewardship among the community.
Problem Statement: The lack of environmental education programs has resulted in limited awareness and understanding of environmental issues. As a result, individuals are less likely to adopt sustainable practices or actively contribute to conservation efforts. Our program aims to address this gap and empower individuals to become environmentally conscious and responsible citizens.
Proposed Solution or Project Description: Our Environmental Education Program will comprise a range of activities, including workshops, field trips, and community initiatives. We will collaborate with local schools, community centers, and environmental organizations to ensure broad participation and maximum impact. By incorporating interactive learning experiences, such as nature walks, recycling drives, and eco-craft sessions, we aim to make environmental education engaging and enjoyable.
Methodology: Our program will be structured into modules that cover key environmental themes, such as biodiversity, climate change, waste management, and sustainable living. Each module will include a mix of classroom sessions, hands-on activities, and practical field experiences. We will also leverage technology, such as educational apps and online resources, to enhance learning outcomes.
Evaluation and Success Metrics: We will employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures to evaluate the effectiveness of the program. Pre- and post-assessments will gauge knowledge gain, while surveys and feedback forms will assess participant satisfaction and behavior change. We will also track the number of community engagement activities and the adoption of sustainable practices as indicators of success.
Budget: Please find attached a detailed budget breakdown for the implementation of the Environmental Education Program. The budget covers personnel costs, materials and supplies, transportation, and outreach expenses. We have ensured cost-effectiveness while maintaining the quality and impact of the program.
Conclusion: By implementing this Environmental Education Program, we have the opportunity to make a significant difference in our community’s environmental consciousness and practices. We are confident that this program will foster a generation of individuals who are passionate about protecting our environment and taking sustainable actions. We look forward to discussing the proposal further and working together to make a positive impact.
Thank you for your time and consideration. Should you have any questions or require additional information, please do not hesitate to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
How to Write an Effective Research Proposal Introduction
Table of Contents
Every research proposal needs a well-written introduction. It serves as your first impression to potential readers and helps set the tone of the entire document. But learning how to write a proposal introduction that effectively conveys the main points of your research can be difficult. Don’t worry, though, because we’re here to help.
In this article, we’ll be sharing a step-by-step guide you can follow to start writing your introduction. We’ll also discuss the importance of this section in your paper and give tips to make it more effective.
If you’re ready to write an introduction that gets people interested in your research proposal , read on.
Why Your Introduction Matters
A research introduction is a vital part of any academic paper. It serves as an essential starting point for the reader, allowing them to understand the importance of the work and what it aims to solve.
The introduction of your proposal aims to achieve the following goals:
Introduce your topic
- State the problem your research aims to solve
- Provide context for your research
How Long Should a Proposal Introduction Be?
Research proposal introductions should be concise but also cover all the necessary points of your research. It can be a few paragraphs long. Don’t try to throw in all the information in one paragraph.
A good word count target would be around 500 to 1000 words . This is just a general figure. It’s still best to check the journal guidelines for the specific type of paper you’re writing.

How to Write a Proposal Introduction
The main job of an introduction is to let readers know what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This can usually be done with the help of a strong opening hook.
Your hook can be anything from an interesting fact, a trivial question, or a strong statement relevant to your topic. It needs to be something that will pique the reader’s interest.
Explain the background of your research topic.
After giving a general overview of the topic, provide additional context and explain why your proposed research is essential. Discuss relevant theories or prior studies on the topic and how they inform your work.
Explain your objectives.
Clearly state what objectives or goals your research seeks to accomplish in relation to the problem you have established. Ensure these objectives are S.M.A.R.T., Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
How you frame your objectives can vary depending on the type of paper you’re writing. An argumentative paper, it’s usually in the form of a thesis statement. If you’re working on an empirical paper, you can generally pose the objective as a research question.
Describe your methods.
How will you go about conducting your research? Are there any special techniques or tools that you plan on using? Be as detailed as possible so that readers understand how the research process will be carried out.
End with a summary.
Lastly, end your introduction with a summary statement that captures the main points of your proposal.
Ensure all the key elements discussed above (research question, background info, objectives, methods) are included in the conclusion. Keep it concise and focused while leaving room for further discussion in the body of the paper.
Final Words
A well-written introduction is crucial for any research paper. It helps to set the stage and provide readers with an understanding of your work’s purpose and overall focus.
An effective research introduction not only introduces the topic at hand but helps to build credibility for the researcher’s point of view and argument. Follow these steps on how to write a proposal introduction , and you should have no problem getting started.

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Proposal Generator Articles
Creative terms and conditions agreement in business proposal.
In business, proposals are essential for securing contracts and agreements with clients. However, a proposal is only complete with terms…
- Proposal Generator
Free guide to a statement of proposal sample
A statement of proposal is a document that outlines a proposed project or initiative in detail. It is typically used…
Free Proposal Letter for Training and Development for a Head Start
Training and development are essential to improve employees’ skills, knowledge, and productivity. A well-crafted training proposal can help an organization…
Detailed Guide to Free HR Consulting Proposal
HR consulting is an essential service for businesses of all sizes. HR consultants provide expert guidance to organizations on various…
Key Guide to Better Remote Work Proposal
The rise of remote work has been a significant trend in the business world over the last few years. With…
Guide to Free E-Commerce Proposal Template
E-commerce has become one of the most popular ways of doing business recently. With the increasing number of people using…
Reference.com
What's Your Question?
- History & Geography
- Science & Technology
- Business & Finance
- Pets & Animals
Crafting an Effective Research Proposal: Learning from Noteworthy PDF Examples
Research proposals are essential documents that outline the objectives, methodology, and significance of a research project. They serve as blueprints for researchers, guiding them through the process of conducting their investigations. While there are various formats and templates available, PDF examples of research proposals can be particularly beneficial in understanding the structure and content required for a successful proposal. In this article, we will explore some noteworthy PDF examples of research proposals and discuss what makes them effective.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research proposal sets the stage for the study by providing background information on the topic and stating the research problem or question. A well-crafted introduction should capture the reader’s interest and clearly articulate the significance of the proposed research.
One example of an effective introduction in a research proposal is a study on climate change’s impact on coastal communities. The introduction outlines key statistics related to rising sea levels and emphasizes the vulnerability of coastal areas to environmental changes. It also highlights gaps in existing literature and explains how the proposed study aims to address these gaps.
Literature Review
The literature review section demonstrates that you have thoroughly researched existing studies related to your topic and have identified a gap that your research will fill. It showcases your ability to critically analyze previous work while highlighting its relevance to your own study.
An exemplary PDF example of a literature review within a research proposal is one that explores mental health interventions among college students. This section summarizes various studies on mental health issues faced by college students, including stress, anxiety, and depression. It then highlights gaps in current intervention strategies and proposes new approaches based on emerging evidence.
Methodology
The methodology section describes how you will conduct your research, including details about data collection methods, sample selection criteria, and data analysis techniques. This section should demonstrate your ability to design a rigorous study that will yield reliable results.
A notable PDF example showcases a research proposal investigating the effects of a new teaching method on student performance in mathematics. The methodology section outlines the study’s design, including the selection of schools and participants, data collection through pre- and post-tests, and statistical analysis methods. It also discusses potential limitations and ethical considerations.
Significance and Expected Outcomes
The significance and expected outcomes section explains the potential impact of your research and how it contributes to existing knowledge in the field. It should highlight the practical implications of your findings and explain how they can be applied to real-world situations.
An informative PDF example of this section could be a research proposal on renewable energy sources. It discusses the significance of transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy for environmental sustainability. The proposal outlines expected outcomes such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions, increased energy efficiency, and long-term cost savings.
In conclusion, examining PDF examples of research proposals can provide valuable insights into crafting an effective proposal. By studying well-structured introductions, comprehensive literature reviews, detailed methodologies, and impactful significance sections, researchers can learn from successful proposals in their fields. These examples serve as guideposts for developing their own research proposals that are compelling, rigorous, and contribute meaningfully to their respective disciplines.
This text was generated using a large language model, and select text has been reviewed and moderated for purposes such as readability.
MORE FROM REFERENCE.COM


Introduction in Research
Ai generator.
Introduction in research serves as a critical component, setting the stage for the entire study. It provides context, explains the significance of the research, and outlines the objectives. For example, a self-introduction essay in the introduction can help personalize the research, making it relatable. This initial section is crucial for engaging readers and establishing the foundation for the subsequent analysis and discussion. Effective introductions ensure clarity and focus, guiding the reader through the research journey.
What is Introduction in Research
Introduction in research is the initial section that provides context, states the research problem, outlines objectives, and highlights the study’s significance. It engages readers, sets the stage for the research, and guides the direction of the entire study.
Introduction in Research Format

- Engage the reader with a broad context or compelling hook.
- Provide relevant details to set the stage for the research.
- Clearly define the specific research problem or question.
- Outline the main goals and aims of the research.
- Explain the importance and potential impact of the study.
- Briefly describe the research methods and approach used.
Introduction in Research Examples
Research introductions across various fields.
- Introduction in research serves as the opening passage, setting the stage for an exploration of the impact of climate change on coastal ecosystems. This study aims to understand the specific changes in marine biodiversity due to rising sea levels and temperatures.
- In this research, we examine the effects of social media on adolescent mental health. By analyzing various psychological factors, we aim to identify patterns and suggest strategies for healthier online interactions among teenagers.
- The research introduction delves into the relationship between economic policies and unemployment rates. This study investigates how different fiscal approaches have influenced job markets in the past decade, providing insights for future policy-making.
- This research investigates the role of renewable energy in reducing carbon emissions. The introduction outlines the current dependency on fossil fuels and the potential benefits of transitioning to sustainable energy sources.
- Our study explores the advancements in artificial intelligence and its applications in healthcare. The introduction discusses the growing reliance on AI for diagnostics and treatment, emphasizing the need for further research in this field.
- The focus of this research is the historical significance of the Silk Road in cultural exchanges between East and West. The introduction highlights key periods of interaction and the lasting impact on global trade and culture.
- In this study, we assess the effectiveness of online learning platforms in higher education. The introduction reviews the shift from traditional classrooms to digital environments, addressing both the benefits and challenges faced by students and educators.
- This research examines the psychological effects of childhood trauma on adult behavior. The introduction provides an overview of various types of trauma and their long-term consequences, setting the foundation for a detailed analysis.
- Our study aims to understand consumer behavior in the digital age. The introduction outlines the evolution of marketing strategies and their influence on purchasing decisions, particularly in the context of e-commerce.
- This research delves into the genetic factors contributing to common hereditary diseases. The introduction discusses recent breakthroughs in genomics and their implications for personalized medicine and preventative care.
- The focus of this study is the impact of urbanization on wildlife habitats. The introduction presents an overview of urban expansion and its detrimental effects on biodiversity, underscoring the need for sustainable development practices.
- In this research, we explore the relationship between diet and mental health. The introduction highlights the growing evidence linking nutritional choices to psychological well-being, advocating for a holistic approach to mental health care.
- This study examines the influence of political rhetoric on public opinion. The introduction reviews historical and contemporary examples, aiming to understand how leaders shape societal beliefs and attitudes through their speeches.
- Our research investigates the effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance. The introduction discusses the prevalence of sleep disorders and their impact on various cognitive functions, such as memory and decision-making.
- This research focuses on the challenges and opportunities of remote work. The introduction addresses the recent shift towards telecommuting, analyzing its effects on productivity, work-life balance, and employee satisfaction.
- In this study, we assess the role of technology in education reform. The introduction reviews current educational technologies and their potential to enhance learning experiences and outcomes in K-12 and higher education settings.
- The aim of this research is to evaluate the environmental impact of single-use plastics. The introduction outlines the scale of plastic pollution and its effects on ecosystems, advocating for alternative materials and waste management solutions.
Features of the Introduction in Research
- Context: Provides background information relevant to the research topic, setting the stage for the study.
- Problem Statement: Clearly defines the research problem or question being addressed in the study.
- Objectives: Outlines the main goals and aims of the research project.
- Significance: Explains the importance and potential impact of the research findings.
- Literature Review: Summarizes relevant previous studies and how they relate to the current research.
- Hypothesis: States the proposed explanation or prediction that the research will test.
- Scope: Defines the boundaries and limitations of the research.
- Methodology Overview: Briefly describes the research methods and approaches used to collect and analyze data.
Introduction in Research Proposal
Introduction in research proposal is crucial for setting the tone and direction of your study. A good introduction provides a clear context, highlights the significance, and outlines the research objectives. The introduction paragraph should engage readers, clearly state the research problem, and present the study’s goals. This foundational section is key to securing interest and support for your research, guiding readers through the rationale and planned approach. Crafting a compelling introduction ensures clarity and focus for the entire proposal.
Introduction in Research Paper
Introduction in research paper serves as the gateway to your study, establishing the context and significance of your work. A well-crafted research paper introduction outlines the research problem, states the objectives, and provides a brief overview of the methodology. This initial section aims to engage readers, setting the stage for a comprehensive exploration of the topic. By clearly defining the scope and purpose, the introduction ensures that readers understand the relevance and direction of the research, laying a strong foundation for the subsequent sections.
Introduction in Research Defense
Introduction in research defense is a pivotal part of presenting your study. This section provides an overview of the research problem, objectives, and significance. It sets the stage for the defense by summarizing key findings and methodologies. A strong introduction engages the audience, clarifies the purpose of the research, and highlights its contributions to the field. This initial part of the defense ensures that the audience understands the research context, laying the groundwork for a detailed discussion of the study’s results and implications.
Importance of Introduction in Research
Introduction in research is a critical component, as it sets the stage for the entire study. A well-crafted introduction paragraph provides essential context, clearly defines the research problem, and outlines the objectives. This section engages the reader, establishing the relevance and significance of the research. It guides the direction of the study, ensuring clarity and focus. By presenting a concise overview, the introduction helps readers understand the purpose and scope of the research, laying a strong foundation for the subsequent analysis and discussion.
What is the purpose of an introduction in research?
It provides background information and sets the context for the study.
What should be included in a research introduction?
The introduction should include the research problem, objectives, and significance of the study.
How long should an introduction be in a research paper?
It typically ranges from one to two pages, depending on the length of the paper.
Why is the introduction important in a research paper?
It engages the reader and establishes the foundation for the research.
What is a research problem in the introduction?
A research problem is the specific issue or question that the study aims to address.
How does the introduction relate to the research hypothesis?
The introduction outlines the hypothesis or research questions that will be tested or explored.
Can the introduction include a literature review?
Yes, a brief review of relevant literature is often included to provide context.
Should the introduction mention the research methodology?
Yes, it should give a brief overview of the methodology to be used.
What is the role of the thesis statement in the introduction?
The thesis statement summarizes the main point or argument of the research.
How does the introduction set the tone for the research paper?
It introduces the topic and approach, setting expectations for the reader.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Study protocol
- Open access
- Published: 02 July 2024
Improving medication adherence among persons with cardiovascular disease through m-health and community health worker-led interventions in Kerala; protocol for a type II effectiveness-implementation research-(SHRADDHA-ENDIRA)
- Jaideep C. Menon 1 ,
- Denny John 2 ,
- Aswathy Sreedevi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6037-9265 3 ,
- Chandrasekhar Janakiram 4 ,
- Akshaya R 3 ,
- Sumithra S 5 ,
- Aravind M S 6 ,
- Mathews Numpeli 7 ,
- Bipin Gopal 8 ,
- Renjini B A 7 ,
- Sajeev P K 9 ,
- Ravivarman Lakshmanaswamy 10 &
- Abhishek Kunwar 11
Trials volume 25 , Article number: 437 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
92 Accesses
7 Altmetric
Metrics details
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of mortality worldwide, and at present, India has the highest burden of acute coronary syndrome and ST-elevation myocardial infarction (MI). A key reason for poor outcomes is non-adherence to medication.
The intervention is a 2 × 2 factorial design trial applying two interventions individually and in combination with 1:1 allocation ratio: (i) ASHA-led medication adherence initiative comprising of home visits and (ii) m-health intervention using reminders and self-reporting of medication use. This design will lead to four potential experimental conditions: (i) ASHA-led intervention, (ii) m-health intervention, (iii) ASHA and m-health intervention combination, (iv) standard of care. The cluster randomized trial has been chosen as it randomizes communities instead of individuals, avoiding contamination between participants. Subcenters are a natural subset of the health system, and they will be considered as the cluster/unit. The factorial cluster randomized controlled trial (cRCT) will also incorporate a nested health economic evaluation to assess the cost-effectiveness and return on investment (ROI) of the interventions on medication adherence among patients with CVDs. The sample size has been calculated to be 393 individuals per arm with 4–5 subcenters in each arm. A process evaluation to understand the effect of the intervention in terms of acceptability, adoption (uptake), appropriateness, costs, feasibility, fidelity, penetration (integration of a practice within a specific setting), and sustainability will be done.
The effect of different types of intervention alone and in combination will be assessed using a cluster randomized design involving 18 subcenter areas. The trial will explore local knowledge and perceptions and empower people by shifting the onus onto themselves for their medication adherence. The proposal is aligned to the WHO-NCD aims of improving the availability of the affordable basic technologies and essential medicines, training the health workforce and strengthening the capacity of at the primary care level, to address the control of NCDs. The proposal also helps expand the use of digital technologies to increase health service access and efficacy for NCD treatment and may help reduce cost of treatment.
Trial registration
The trial has been registered with the Clinical Trial Registry of India (CTRI), reference number CTRI/2023/10/059095.
Peer Review reports
Administrative information
Note: the numbers in curly brackets in this protocol refer to SPIRIT checklist item numbers. The order of the items has been modified to group similar items (see http://www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/spirit-2013-statement-defining-standard-protocol-items-for-clinical-trials/ ).
Title {1} | SPIRIT guidance: Descriptive title identifying the study design, population, interventions, and, if applicable, trial acronym.
|
Trial registration {2a and 2b}. | SPIRIT guidance: Trial identifier and registry name. If not yet registered, name of intended registry. Item 2b is met if the register used for registration collects all items from the World Health Organization Trial Registration Data Set. |
Protocol version {3} | SPIRIT guidance: Date and version identifier. Version 3. 23 February 2024. |
Funding {4} | SPIRIT guidance: Sources and types of financial, material, and other support. Financial support from WHO, Geneva, Alliance for Health Policy and System research |
Author details {5a} | SPIRIT guidance: Affiliations of protocol contributors. Jaideep C Menon, Professor, Adult Cardiology, AIMS, Kochi Denny John, Adjunct Professor, Ramaiah University of applied Sciences Aswathy S, Professor, Community Medicine Chandrasekhar J, Professor, Public Health Dentistry Akshaya R, Senior Resident, Community Medicine Sumithra S, Senior Lecturer, St John’s research Institute Aravind MS, Research Associate, Public Health, AIMS, Kochi Mathews Numpeli, CHC MO, DHS, Govt of Kerala Bipin Gopal, State nodal Officer- NCDs, Kerala Renjini BA, MO, DHS, Govt of Kerala Sajeev PK, NHM Coordinator, Kalady Ravivarman L, WHO NCD officer, India Country Office Abhishek Kunwar, NPO NCD, WHO India |
Name and contact information for the trial sponsor {5b} | SPIRIT guidance: Name and contact information for the trial sponsor. Dr Sarah Rylance, Medical Officer for Chronic Respiratory Diseases, Focal point for NCD Research and Innovation World Health Organization HQ |
Role of sponsor {5c} | SPIRIT guidance: Role of study sponsor and funders, if any, in study design; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of data; writing of the report; and the decision to submit the report for publication, including whether they will have ultimate authority over any of these activities. Study sponsor does not have any role in the study design, collection, management, analysis and interpretation of data |
Introduction
Background and rationale {6a}.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of mortality worldwide, and at present, India has the highest burden of acute coronary syndrome and ST-elevation myocardial infarction (MI) [ 1 ]. A key reason for poor outcomes is non-adherence to medication. The WHO has reported that non-adherence to drugs in chronic conditions is as high as 50%, and 30% of re-admissions are related to non-compliance to medication. In its 2003 report [ 2 ], WHO states that “increasing the effectiveness of adherence interventions may have a far greater impact on the health of the population than any improvement in specific medical treatment.”
A systematic review published in 2015 on adherence to medication had eleven studies from India reporting adherence rates (using pills taken, prescribed doses taken, changes, etc.) using Morisky Medication Adherence Score (MMAS) in the range of 0–51.2% [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. The factors associated with non-adherence to medications were forgetfulness, difficulty in remembering, and stopping medication upon feeling better/worse.
Various interventions have been studied to increase medication adherence for cardiovascular disease in India. These include the use of combination therapy or polypill [ 9 , 10 , 11 ], use of community health workers (CHW) for simplified hypertension management with the aid of a smart-phone-based electronic decision support system [ 12 ], “task shifting” interventions to CHWs for CVD risk reduction through behavioral change [ 13 ], improving adherence to drugs, lifestyle changes, and clinical risk markers in patients of acute coronary syndromes [ 14 , 15 ] and use of CHWs and doctors in primary health center (PHC) to assess CVD risk with clinical decision support being provided through an m-health platform by doctors sitting remotely [ 16 ]. Studies have also identified the use of mobile technology by health workers in resource-limited settings for health delivery improvement [ 17 ]. The different studies mentioned have looked at m-health or CHWs alone to improve adherence to medication, lifestyle changes, or as a platform for treatment, with varied results.
We measured adherence in 2064 patients of coronary artery disease (CAD) the ENDIRA cohort using the MMAS-8 in the year 2019. Our results revealed poor adherence to chronic care medications in CAD patients. On an average, only 2.8 of the mandated 4 drugs (beta blocker, ACE Inhibitor /ARB, statin, and anti-platelet) were being taken by patients regularly [ 18 ]. The mean value of MMAS was 4 out of a possible 8, reflecting poor adherence [ 19 ]. A study on the feasibility of an m-health intervention in the same cohort for the prevention and management of CAD revealed that the use and ownership of mobiles was 88% (2015), 92% were willing to receive mobile health advice [ 19 ], 70% preferred voice calls over SMS, 85.9% would send self-recorded blood pressure, weight, and blood glucose to a doctor or community health worker [ 19 ]. Given that the results of our study revealed poor adherence and that use of m-health for CVD was both acceptable and feasible, the obvious next step would be in trying to improve adherence using these resources.
Objectives {7}
Primary objective.
To assess the effectiveness of using m-health and community health worker-led interventions for improving adherence to drugs in patients with cardiovascular disease using m-health and community health worker intervention individually and in combination in comparison to control group.
Secondary objective
To assess the effects of using the interventions (m-health and community health worker-led interventions) for improving adherence to drugs among heart disease patients on implementation outcomes such as acceptability and adoption.
To assess the cardiometabolic risk factors among first degree relatives of patients with heart disease
Trial design {8}
It is a 2 × 2 factorial design trial applying two interventions individually and in combination with a 1:1 allocation ratio. Two interventions are applied individually and in combination: (i) ASHA-led medication adherence initiative comprising of home visits, and (ii) m-health intervention using reminders and self-reporting of medication use. This design will lead to four potential experimental conditions: (i) ASHA-led intervention, (ii) m-health intervention, (iii) ASHA and m-health intervention combination, (iv) standard of care.
Methods: participants, interventions, and outcomes
Study setting {9}.
The study will be implemented in the ENDIRA (Epidemiology of Non-communicable Diseases in Rural Areas) cohort (n-114,064 individuals) which includes 2064 patients with heart disease in whom adherence to drugs for heart disease has already been assessed. The ENDIRA cohort is spread over 5 primary health centers consisting of 18 subcenters where the health details of all individuals have been recorded. In order to avoid contamination in the treatment allocation and its response, at least 10 km of distance among villages will be maintained and they will be clubbed into 4 groups.
The intervention will be implemented in Angamaly block consisting of five local self-government areas namely Mookkannoor, Kalady, Thuravoor, Karukutty, and Manjapra with a population of 18,638, 20,407, 20,475, 26,811, and 14,668 in Ernakulam district [ 20 ] in Kerala state, India, respectively.
Eligibility criteria {10}
The study samples will consist of adult community members with diagnosis of CAD, valvular disease, heart failure, and rhythm disorders in the target areas who provide informed consent.
Eligibility criteria
Diagnosed case of CAD who have received treatment for MI/STEMI/UA or diagnosed using a coronary angiogram or CT coronary angiogram or have undergone revascularization and are on medications.
Other cardiovascular cases such as rhythm disorders, valve disorders, and heart failure identified as pumping disorders by the community will also be a part of the study. Male or female aged 18 years or more will be considered.
Resident of village during the baseline survey.
Has no plans to migrate in next 12 months from the date of initiation of intervention.
Exclusion criteria
Persons who are bedridden and are unable to answer the questions.
Pregnant or lactating mothers
Individuals with cognitive impairment
Who will take informed consent? {26a}
Informed consent will be taken by the accredited social health activist of the area who will be collecting the data. The data collection will be through an application called SHRADDHA (which means care). The participant’s digital signature will be obtained on the tablet.
Additional consent provisions for collection and use of participant data and biological specimens {26b}
Blood samples will be collected to assess random blood sugar and HbA1c among cardiac patients with type 2 DM after obtaining consent. These samples will be tested using point-of-care devices and will not be stored. We will request consent for review of participants’ medical records, and for the collection of blood samples to assess random blood sugar and HbA1c among the cardiac patients with type 2 diabetes. But this trial does not involve collecting biological specimens for storage.
Interventions
Explanation for the choice of comparators {6b}.
Results of our study revealed poor adherence and that use of m-health for CVD was both acceptable and feasible. Various interventions have been studied to increase medication adherence for cardiovascular disease in India such as use of combination therapy or polypill, use of community health workers (CHW) for simplified hypertension management with the aid of a smart phone-based electronic decision support system, so we decided to use factorial study design where study units would be assigned to ASHA and no ASHA group. Following this they would be assigned to m-health and no m-health group. Thus, there are four arms to the study: namely ASHA, ASHA and m-health, m-health, and standard of care.
Intervention description {11a}
The intervention content is prepared after discussion with the stakeholders such as ASHAs, Medical Officers, and patients. Qualitative data would be obtained from unstructured or semi-structured interviews exploring the individual’s understanding of the use of medicines, potential obstacles and incentives to adherence, useful strategies to improve adherence. Interview guide for In-Depth-Interviews and Key-Informant Interviews will be developed after a thorough literature search. In-Depth Interviews will be done with the participants and their relatives to identify individual’s understanding of the use of medicines, potential obstacles and incentives to adherence, useful strategies to improve adherence, and other questions spontaneously raised during the interview. For Key-Informant Interviews, Health care providers such as doctors, the multipurpose health worker, ASHAs, and pharmacists (about 10) will be interviewed till saturation Is reached. Focus group discussions (FGD) will be conducted among adherent CVD patients and nonadherent CVD patients. About 3-4 such FGD will be conducted till data saturation is reached. This will be repeated at endline.
Community health worker directed visits to the house of the patient, where they will explain the use of drugs and the various roles of the different classes of drugs along with taking a pill count and giving health advice and counselling with a PowerPoint on a tablet. The frequency of visits is twice a month for the first 3 months, and once a month for the next 3 (11 visits in all). A schedule of visits with the areas to be highlighted in each visit such as diet, physical activity, tobacco, and alcohol will be prepared and given.
Before the commencement of the intervention training, sessions for community health workers (ASHAs) in the intervention arm will be conducted. This will comprise of three sessions of 6 h each and would include curriculum-based training modules on CVD, HTN, diabetes, dyslipidemia; awareness of the role each of the 4 classes of drugs in AS-CVD plays in secondary prevention; sensitization to the role of adherence in preventing recurrence; sensitization to the side effects of the drugs and counselling skill training. Role of lifestyle changes such as diet, physical activity, tobacco, and alcohol will also be carried out.
The envisaged m-health platform is a two-way system through which messages or jingles (audio clips) could be passed back and forth between the care provider (ASHA, Research assistant, or doctor) and the recipient (patient). Individual patient details gathered and entered on a Tab PC get stored on a central server. The data is anonymized and coded individually, with a 12-digit UID. In clusters where the m-health intervention is planned, individual patients could download and activate an already developed App, which is a free download from the Google play store [Ente app (my app)]. The individual patient would be able to access his personal health record as entered, by way of the App. This App would serve as a two-way channel of communication between the patient and caregiver. In the other clusters, individual patients could download their personal data and the App, with the communication channel remaining blocked.
Bi-monthly reminders via text or audio messages and weekly reminders on taking medicines at the time of a scheduled dose by way of a beep or tune and health advice by way of messages are sent for the first 3 months, followed by monthly reminders of text messages the next 3 and weekly drug reminder tunes.
Community health worker and m-health
Health worker (ASHA)-directed visits to the house of the patient, where they will explain the use of drugs and the various roles of the different classes of drugs along with taking a pill count and giving health advice and counselling. The frequency of visits is twice a month for the first 3 months, and once a month for the next 3. In addition, bi-monthly reminders via text or audio messages and weekly reminders on taking medicines at the time of a scheduled dose by way of a beep or tune and health advice by way of messages are sent for the first 3 months, followed by monthly reminders of text messages the next 3 and weekly drug reminder tunes.
Standard of care (SoC) is patient-initiated physician visit with health advice and treatment as prescribed by the treating doctor.
In all the groups, the patients can visit the doctor in case of any need or emergency.
After completion of baseline survey in all clusters, intervention will be implemented in intervention clusters for 6 months. All the participants in the intervention and control arms will be permitted to use standard treatment for CVD. Community health worker-directed visits to the house of the patient, where they will explain the use of drugs and the various roles of the different classes of drugs along with taking a pill count and giving health advice and counselling. The frequency of visits is twice a month for the first 3 months, and once a month for the next 3 (9 visits in all). Table 1 shows the timepoint for the intervention implementation.
Criteria for discontinuing or modifying allocated interventions {11b}
This is not applicable as the intervention is to improve medication adherence, so there will be no special criteria for discontinuing or modifying allocated intervention.
Strategies to improve adherence to interventions {11c}
The various interventions are for the improvement of adherence as measured by the Morisky Medication Adherence scale [ 21 ].
Relevant concomitant care permitted or prohibited during the trial {11d}
Relevant concomitant care is permitted.
Provisions for post-trial care {30}
This is a non-pharmacological intervention; therefore, there are no specific post trial care provisions.
Outcomes {12}
Primary, secondary, and other outcomes.
The primary outcome is the adherence of patients as measured by Morisky adherence scale [ 21 ] at the beginning of the study, midterm, and at the end. The secondary outcomes include Quality of Life (EuroQOL) [ 22 ], blood pressure, random blood sugar, HbA1c among the cardiac patients with type 2 diabetes, mortality events, and other unintended outcomes will also be recorded. The analysis will include change from baseline. Adherence is chosen as the main outcome as the objective is to study the impact of the various interventions singly and in combination on adherence in comparison to standard of care. Various symptoms, such as dyspnea, fatigue, edema, difficulty sleeping, depression, and chest pain associated with CVD limits activities of daily life [ 23 ]. Therefore, it is important to measure the quality of life before and after the intervention. Metabolic control can result from better adherence to medication and a better awareness of the importance to adhering to medication. Therefore, meeting targets of blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and HbA1c will be considered as secondary outcomes.
Participant timeline {13}
Sample size {14}.
Based on the learnings from the previous study, the rate of missing data due to electronic data collection will be low.
Phases 1 and 2: planning and baseline evaluation
The process of developing the intervention will start with the development of the initial concepts based on the available literature and interaction with healthcare professionals working in the rural areas.
Baseline study
Selection and training of team : The team will deliver the training to the selected project coordinator and the field staff. Field staff (part-time) will be recruited by the investigators on the advice of village head and/or NCD clinic in-charge. He/she should be a member of community preferably the accredited social health activist with an interest in health care and community, willingness to learn, and leadership qualities. A strong commitment to work in the community will be identified as an important criteria for the selection of all the team members. After a sensitization session of the data collectors/field staff, they will be asked to prepare a list of persons with cardiovascular disease including coronary artery disease, valvular disease, arrhythmias, and heart failure. Hands on sessions to download the App and collect data will be provided.
In Phase 2, baseline evaluation will be initiated in the study areas after obtaining the ethics committee approval. Written informed consent will be obtained from the study participants. Participants will receive a participant information sheet (PIS) outlining the rationale for the study, details on interventions, the steps, and protocols to be followed throughout the study, potential side effects and risks, benefits, a confidentiality statement, the option to withdraw from the study at any time, and the investigators’ contact information. The baseline survey performed by ASHAs will be done through a survey app called SHRADDHA. The variables collected would include (1) basic demographic information, including age, income, gender, marital status, religion, and occupation; (2) lifestyle-related factors such as physical activity, tobacco use, and alcohol consumption, dietary factors intake of fruits and vegetables, cooking oil and red meats; (3) disease details including for diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, stroke and CAD, COPD, and surgeries; and (4) current medications. Questions will be explained to each participant to help them get familiar with the contents, instructions for filling them out will be given, and the responses will be recorded. On the home visit, the Field staff/ASHA will also record height and weight, measure sugars with a glucometer, and take a photo of the most recent prescription. All of this will be recorded in the app. Glycosylated hemoglobin will also be measured among the cardiac patients with diabetes using the point of care device called Lumira Dx.
Sample size : Sample size was estimated assuming an improvement of 10% in medication adherence at the end of a 6-month period in either m-health or community health worker-led intervention compared to control group. This 10% improvement will lead to an effect size of 0.4 units in medication adherence through m-health or community health worker-led intervention and an effect size of 0.8 units in combined intervention (m-health and community health worker-led intervention) compared to the control group. The 10% was an assumption considering that large differences are not possible in a community setting and was based on another community-based study which has also used 10% improvement of adherence score [ 24 ].
To observe a difference of 0.4 units in the medication adherence between study groups, with a standard deviation of 1.8, 5% level of significance (adjusted for multiple comparison) and 80% power, the sample size needed will be 238 participants in each of the study groups. After accounting for a design effect (cluster effect) and 10% attrition, the number of participants required per group will be 393, a total of 1572 participants.
Recruitment {15}
Working through the public health system, keeping in mind the proximity of the ASHAs to the community, it is expected that adequate participant enrolment can be achieved. Monitoring and supervision by the project team will assist in timely completion. The time period of recruitment is from February to May, 2024. After the recruitment, the randomization will be done and intervention will be administered for 6 months. Expected to finish by November 2024 and endline assessment in December 2024.
Assignment of interventions: allocation
Sequence generation {16a}.
Allocation of intervention and sequence generation will be as follows. Codes will be randomly assigned to the four interventions (ASHA, m-health, ASHA + m-health, and control groups) namely A, B, C, and D. In the next step, randomization list will be generated using RANDOM ALLOC software. Eighteen subcenters will be randomized into 4 study groups (A, B, C, and D) using different permutations of ABCD. Each subcenter will be allocated random numbers ranging from 1 to 18 using random number generators and random shuffling of this number. Interventions will be allocation to the subcenters in the sequence of random shuffled numbers as per the randomization list.
Concealment mechanism {16b}
It will be an open-label trial as concealment is not possible. However, study site allocation will be done only after completing baseline assessment and agreements with sites to participate.
Implementation {16c}
The allocation sequence will be generated by the Statistician, enrolment will be by the Field coordinator and the Field coordinator will assign subcenter as it is a cluster randomized trial.
Assignment of interventions: blinding
Who will be blinded {17a}.
Data analysts will be blinded. The ASHA workers, patients, and outcome assessors are not blinded.
Procedure for unblinding if needed {17b}
In this study, the ASHA workers, patients, and outcome assessors will not be blinded. Only the data analysts will be blinded. The data analyst will be unblinded if there are any outlier biochemical values which requires immediate action so that the patient can be intimated.
Data collection and management
Plans for assessment and collection of outcomes {18a}.
The primary outcome adherence will be measured by Morisky 8-item adherence questionnaire which has been validated in various countries including India and in various disease conditions. The eight-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) is a structured self-report measure of medication-taking behavior that has been widely used in various cultures [ 25 , 26 , 27 ].It has a maximum score of 8.
The quality of life will be measured by the EuroQol five‐dimensions – 3‐level (EQ5D) which is a versatile quality of life (QOL) instrument with five dimensions (mobility, self‐care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression) and a visual analog scale. The questionnaire has also been found to be valid and reliable in various disease conditions including cardiovascular and cancer in India and neighboring countries [ 28 , 29 ].Random blood sugar among the patient and family member will be measured by the ASHA as per standard methods using a glucometer. Blood pressure will also be measured using the electronic Blood pressure will be recorded with the OMRON HEM 7124 automatic blood pressure monitor (Shimogyo-ku, Kyoto, Japan) by measuring upper arm BP. A laboratory technician will measure Glycosylated Haemoglobin using the Lumira Dx point of care device.
Real-time data entry will be monitored, and wherever there are difficulties with using the app, support will be provided by the field coordinator.
Plans to promote participant retention and complete follow-up {18b}
All efforts will be made to retain all participants in the study. As they are also part of the earlier ENDIRA study, there is a good rapport with the study group, local self-government, and frontline health workers. Loss to follow-up may result from migration to their children’s places of living or death or for other reasons. The characteristics of the patients who drop out will be recorded and compared to those who are in the study.
Data management {19}
As the data is collected through the SHRADDHA app, the data will be exported to excel and checked for completion each day. According to the data collected, feedback, and monitoring will be done to ensure correct and complete entries. Duplicate entries will be checked for and removed.
Confidentiality {27}
The data of the patients will be anonymized, and each patient will be assigned a unique id. From the app de-identified anonymized data will be stored in Excel. This will be stored confidentially before, during, and after the trial.
Plans for collection, laboratory evaluation, and storage of biological specimens for genetic or molecular analysis in this trial/future use {33}
In this study, blood samples will be collected to assess random blood sugar and HbA1c. These tests are done using point-of-care devices. The blood samples will not be stored in the current trial.
Statistical methods
Statistical methods for primary and secondary outcomes {20a}.
Several models will be run to test for the main outcomes, implementation outcomes, and related research questions. Mixed linear and logistic effects models as appropriate will be used to identify differences between the groups (ASHA, ASHA and m-health, m-health, control group), where random effects will be used for the clusters and fixed effects will be used for effects of ASHA workers and of m-health. The primary dependent variable in the models will be change in adherence measured by the Morisky scale. Models will also be fitted for the secondary outcomes such as change in blood pressure, random blood sugar, Hba1c levels, and quality of life. Subsequently, covariates such as age, sex, and co-morbidities will be added to the models to adjust for potential confounders.
Interim analyses {21b}
In this study, the intervention is done to improve the medication adherence through health education by ASHA workers, m-health, or both. Since the risk due to the intervention is minimal or none, interim analysis, and stopping guidelines have not been prescribed by the ethical committee and therefore there will not be any stopping guidelines.
Methods for additional analyses (e.g., subgroup analyses) {20b}
Subgroup analysis will not be carried out. However, for the primary and secondary outcome variables, covariates such as age, sex, and co-morbidities will be considered as potential confounders in the mixed effect model analysis.
Methods in analysis to handle protocol non-adherence and any statistical methods to handle missing data {20c}
Nonadherence will be managed by the intention to treat analysis and if there are too many missing data, imputations will be considered. Mixed method analysis will be considered for intention to treat analysis. Also depending on the percentage of data missingness and assumption for data missing in the study variables, appropriate missing data imputation technique will be used.
Plans to give access to the full protocol, participant-level data, and statistical code {31c}
Full protocol can be given. Full dataset can be given with the permission of the Institution, WHO, and Government.
Oversight and monitoring
Composition of the coordinating center and trial steering committee {5d}.
There is only one site for the study; therefore, the coordinating and steering committee will be situated at the site. The coordinating center is the Community Health Centre (CHC). The ASHA’s work is coordinated through the CHC by the National Health mission coordinators. The trial steering committee (TSC) monitors recruitment, communicates, and provides conflict resolution and timely advice. They meet every 6 weeks. Local organization and implementation is taken care of by the NHM coordinators and a responsible person reporting to the Principal Investigator from the Project management group. Trainings and other group meetings are conducted by the project management group. Consent is obtained by the ASHA. Periodic meetings are conducted by the Project management group (investigators) team to monitor progress. The stakeholder groups are apprised of the progress of the trial, role of intervention, and its possible benefit.
Composition of the data monitoring committee, its role and reporting structure {21a}
This study is measuring adherence which is a low-risk intervention; therefore, a data monitoring committee is not required. The project management group meets every 2 weeks. The Trial Steering Group and the independent Data Monitoring and Ethics Committee meet to review conduct throughout the trial period.
Adverse event reporting and harms {22}
As this study is measuring adherence of an intervention, no adverse events or serious adverse events and harms from the intervention are anticipated. But if there are any, they will be reported to relevant regulatory bodies such as Project management group, Trial steering Committee, District Health Authority, and Ethics Committee. Trial deviations will be reported to the ethical committee.
Frequency and plans for auditing trial conduct {23}
The meetings of the Project management group, Trial Steering group, independent data monitoring, and Ethics Committee periodically will also serve to audit the trial.
Plans for communicating important protocol amendments to relevant parties (e.g. trial participants, ethical committees) {25}
Before the start and at the start, there have been some minor modifications which has been updated to the ethical committee and subsequently uploaded in the CTRI.
Dissemination plans {31a}
The results of the study will be published in standard journals. Social media and Stakeholder workshops will be used to disseminate the findings. A lay summary will be shared with all participants.
The present study will promote much needed research and innovation for increasing adherence among patients with cardiovascular disease. The effect of different types of intervention alone and in combination will be assessed using a cluster randomized design involving 18 subcenter areas. This factorial cluster randomized controlled trial will benefit by increasing the drug adherence for NCD using m-health platform and frontline health workers. The trial will explore local knowledge, perceptions and empower people by shifting the onus onto themselves for their medication adherence.
The proposal is aligned to the WHO-NCD aims of improving the availability of affordable basic technologies and essential medicines, improving adherence for non-communicable diseases (NCDs). It also aligns to WHO-NCD aim of training the health workforce and strengthening the capacity of health systems, particularly at the primary care level, to address the control of NCDs. The proposal also helps expand the use of digital technologies to increase health service access and efficacy for NCD treatment and may help reduce the cost of treatment.
The proposal helps implementation of WHO-PEN protocol for Self-Care guidelines including utilizing frontline health workers in improving self-care in patients of heart disease, counselling to improving adherence and self-care, considering patients’ beliefs and concerns about drugs and their effect. The research is also aligned to the WHO-HEARTS package, both by way of A&T of the HEARTS where A- consists of information on CVD medicine and technology procurement, quantification, distribution, management, and handling of supplies at facility level. T- consists of guidance and examples on team-based care and task shifting related to the care of CVD. The research is also aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) goal in relation to NCD of reducing by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment.
There are significant expected implementation challenges to note. First, the trial involves working with the primary clinics providing NCD screening and detection services, and building an effective partnership with the state government of Kerala where the project will be implemented will be crucial for its success. Second, medication nonadherence for patients with chronic diseases is extremely common with 40–50% of patients prescribed medications for management of diabetes and hypertension [ 30 ]. There exist treatment-related barriers, such as treatment complexity, side effects (or fear of side effects), inconvenience, cost, and time, and other barriers such as poor practitioner-patient relationship, aspects of which are beyond the scope of the intervention [ 30 ].
If successful, the medication adherence intervention, using m-health and ASHAs, has the potential to constitute evidence-based practice for improving medication adherence for CVD in India, and in similar developing countries.
Trial status
The current protocol is version 3 dated 23–02-2024. The recruitment began on November 30, 2023 and is expected to be complete by May 30, 2024. The submission has been delayed due to unavoidable circumstances such as elections and heatwave.
Availability of data and materials {29}
The investigators will have access to the final data set. There are no contractual agreements which limit access to investigators. The investigators in the field collect the data and the data is with them. Any data required to support the protocol can be supplied on request.
Abbreviations
Angiotensin-converting enzyme
Angiotensin II receptor blocker
Accredited social health activist
- Coronary artery disease
Community health workers
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Cluster randomized control trial
Computed tomography
Clinical Trials Registry—India
Cardiovascular diseases
Epidemiology of Non-Communicable Diseases in Rural Areas
Hypertension
Low-middle-income countries
Mobile Health
Myocardial infarction
Morisky Medication Adherence Score
Non-communicable diseases
Primary health center
Quality of Life
Return on investment
Sustainable Development Goals
Short Message Service
ST elevation myocardial infarction
Unstable angina
World Health Organization
Sreeniwas Kumar A, Sinha N. Cardiovascular disease in India: A 360 degree overview. Medical Journal Armed Forces India. 2020;76(1):1–3.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sabaté E, ed. Adherence to Long-Term Therapies: Evidence for Action. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003.
Baroletti S, Dell’Orfano H. Medication adherence in cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2010;121:1455–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Prabhakaran D, Jeemon P, Roy A. Cardiovascular disease in India, Current epidemiology and future directions. Circulation. 2016;133:1605–20.
Akeroyd JM, Chan WJ, Kamal AK, Palaniappan L, Virani SS. Adherence to cardiovascular medications in the South Asian population: A systematic review of current evidence and future directions. World J Cardiol. 2015;7(12):938–47.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Fathima FN, Shanbhag DN, Hegde SKB, Sebastian B, Briguglio S. Cross Sectional Study of Adherence to Prescribed Medications among Individuals Registered at a High Risk Clinic in a Rural Area in Bangalore, India. Indian J Publ Health Research and Development. 2013;4(3):90–4.
Article Google Scholar
Venkatachalam J, Abrahm SB, Singh Z, Stalin P, Sathya GR. Determinants of Patient’s Adherence to Hypertension Medications in a Rural Population of Kancheepuram District inTamilNadu. SouthIndia Indian J Community Med. 2015;40:33–7.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Kumar N, Unnikrishnan B, Thapar R, Mithra P, Kulkarni V, Holla R, Bhagawan D, Mehta I. Factors associated with adherence to antihypertensive treatment among patients attention atertiary care hospital in Mangalore. South India IJCRR. 2014;6:77–85.
Google Scholar
Bahl VK, Jadhav UM, Thacker HP. Management of hypertension with the fixed combination of perindopril and amlodipine in daily clinical practice: results from the STRONG prospective, observational, multicenter study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2009;9:135–42.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Soliman EZ, Mendis S, Dissanayake WP, Somasundaram NP, Gunaratne PS, Jayasingne IK, Furberg CD. A Polypill for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a feasibility study of the World Health Organization. Trials. 2011;12:3.
Thom S, Poulter N, Field J, Patel A, Prabhakaran D, Stanton A, Grobbee DE, Bots ML, Reddy KS, Cidambi R, et al. Effects of a fixed-dose combination strategy on adherence and risk factors in patients with or at high risk of CVD:theUMPIRE randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;310:918–29.
Ajay VS, Tian M, Chen H, Wu Y, Li X, Dunzhu D, et al. A cluster-randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effects of a simplified cardiovascular management program in Tibet, China and Haryana, India: study design and rationale. BMC Public Health. 2014;14(1):924.
Jeemon P, Narayanan G, Kondal D, et al. Task shifting of frontline community health workers for cardiovascular risk reduction: design and rationale of a cluster randomised controlled trial (DISHAstudy) in India. BMC Public health. 2016;16:264.
Kamath DY, Xavier D, Gupta R, Devereaux PJ, Sigamani A, Hussain T, et al. Rationale and design of a randomized controlled trial evaluating community health worker–based interventions for the secondary prevention of acute coronary syndromes in India (SPREAD). Am Heart J. 2014;168(5):690–7.
Sharma KK, Gupta R, Mathur M, Natani V, Lodha S, Roy S, Xavier D. Non-physician health workers for improving adherence to medications and healthy lifestyle following acute coronary syndrome: 24-month follow-up study. Indian Heart J. 2016;68(6):832–40.
Peiris D, Praveen D, Kishor M, et al. SMART health India: A stepped-wedge, a cluster randomised controlled trial of a community health worker managed mobile health intervention for people assessed at high cardiovascular disease risk in rural India. PLOS One. 2019;14(3):e0213708.
Free C, Phillips G, Watson L, Galli L, Felix L, Edwards P, et al. The effectiveness of mobile-health technologies to improve health care service delivery processes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2013;10(1): e1001363.
Banerjee A, Menon JC, et al. A learning health system for secondary prevention in cardiovascular disease in Kerala using informatics and non-physician health workers (LHSCVD). Indian Heart J. 2018;70:S2.
Feinberg L, Menon JC, et al. Potential for mobile health (m-Health) prevention of cardiovascular diseases in Kerala: A population-based survey. Indian Heart J. 2017;69:182–99.
Angamaly Municipality City Population Census 2011-2024 | Kerala. [cited 2024 Jun 3]. Available from: https://www.census2011.co.in/data/town/803285-angamaly-kerala.html
Janežič A, Locatelli I, Kos M. Criterion validity of 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in patients with asthma. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(11):e0187835. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187835.PMID:29190693;PMCID:PMC5708647 .
EQ-5D-3LUserguide-23–07.pdf. [cited 2024 Jun 3]. Available from: https://euroqol.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/EQ-5D-3LUserguide-23-07.pdf
Heo S, Lennie TA, Okoli C, Moser DK. Quality of life in patients with heart failure: ask the patients. Heart Lung. 2009;38(2):100–8.
Xavier D, Gupta R, Kamath D, Sigamani A, Devereaux PJ, George N, et al. Community health worker-based intervention for adherence to drugs and lifestyle change after acute coronary syndrome: a multicentre, open, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4(3):244–53.
Surekha A, Fathima FN, Agrawal T, Misquith D. Psychometric Properties of Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS) in Known Diabetic and Hypertensive Patients in a Rural Population of Kolar District, Karnataka. Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development. 2016;7(2):250.
Grover A, Oberoi M. Self-reported Morisky eight item medication adherence scale is a reliable and valid measure of compliance to statins in hyperlipidemic patients in India. Indian Heart J. 2020;72(4):319–20.
Okello S, Nasasira B, Muiru ANW, Muyingo A. Validity and Reliability of a Self-Reported Measure of Antihypertensive Medication Adherence in Uganda. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(7):e0158499.
Mahesh PKB, Gunathunga MW, Jayasinghe S, Arnold SM, Senanayake S, Senanayake C, et al. Construct validity and reliability of EQ-5D-3L for stroke survivors in a lower middle-income setting. Ceylon Med J. 2019;64(2):52–8.
Tripathy S, Hansda U, Seth N, Rath S, Rao PB, Mishra TS, et al. Validation of the EuroQol Five-dimensions - Three-Level Quality of Life Instrument in a Classical Indian Language (Odia) and Its Use to Assess Quality of Life and Health Status of Cancer Patients in Eastern India. Indian J Palliat Care. 2015;21(3):282–8.
Kleinsinger F. The Unmet Challenge of Medication Nonadherence. Perm J. 2018;22:18–033. https://doi.org/10.7812/TPP/18-033 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Accredited Social Health Activists, Dr Naseema Najeeb CHC MO, Dr Sunil Kumar, and Mr Sunny V V.
Funded by WHO NCD Division and NCD Alliance, Geneva.
WHO Reference 2023/1376413–0.
The funding body does not have a role in the design, data collection, analysis, and interpretation of data.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Adult Cardiology, AIMS, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Kochi, India
Jaideep C. Menon
Ramaiah University of Applied Sciences, Bengaluru, India
Community Medicine, AIMS, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Kochi, India
Aswathy Sreedevi & Akshaya R
Public Health Dentistry, Amrita School of Dentistry, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Kochi, India
Chandrasekhar Janakiram
StJohn’s Research Institute, Bangalore, India
AIMS, Kochi, India
Aravind M S
MO, DHS, Govt of Kerala, Ernakulam, India
Mathews Numpeli & Renjini B A
NCD, DHS, Govt of Kerala, Kerala, Thiruvananthapuram, India
Bipin Gopal
CHC, Kalady, Kalady, India
India Country Office, New Delhi, India
Ravivarman Lakshmanaswamy
NPO NCD, WHO India, New Delhi, India
Abhishek Kunwar
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
➙JCM is the Chief investigator, conceived the study, led the proposal and protocol development, Funding Acquisition, Methodology, Writing – Original Draft Preparation, Review & Editing
➙DJ—Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – Original Draft Preparation, Review & Editing
➙AS—Development of proposal, Funding Acquisition, Methodology, Writing – Original Draft Preparation, Review & Editing
➙CJ—Development of proposal, Funding Acquisition, Methodology, Project Administration, Formal Analysis, Writing – Review & Editing
➙AR—Analysis, Project Administration, Supervision, Writing – Original Draft Preparation, Review & Editing
➙SS—Analysis, Sample calculation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing—Review & Editing
➙AMS—Project Administration, Supervision, Writing – Original Draft Preparation, Review & Editing
➙MN—Methodology, Project Administration, Supervision, Writing – Review & Editing
➙BG—Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – Review & Editing
➙RBA—Project administration, Methodology, Writing – Review & Editing,
➙RL—Investigation, Methodology, Writing – Review & Editing
➙AK—Investigation, Methodology, Writing – Review & Editing
➙All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Aswathy Sreedevi .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate {24}.
Ethical Review Board of Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences had approved the study dated 23–02-2024 number ECASM-AIMS-2024–098. Written, informed consent to participate will be obtained from all participants. Ethical approval has been obtained.
Consent for publication {32}
Informed consent has been obtained and the model consent form can be made available. No identifying images or other personal or clinical details of participants are presented here or will be presented in reports of the trial results.
Competing interests {28}
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Menon, J.C., John, D., Sreedevi, A. et al. Improving medication adherence among persons with cardiovascular disease through m-health and community health worker-led interventions in Kerala; protocol for a type II effectiveness-implementation research-(SHRADDHA-ENDIRA). Trials 25 , 437 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08244-0
Download citation
Received : 09 May 2024
Accepted : 11 June 2024
Published : 02 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08244-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Factorial study design
- Valvular disease
- Heart failure
- Implementation Research
- Medication adherence
- Morisky Medication Adherence Scale
ISSN: 1745-6215
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
A well written introduction will help make a compelling case for your research proposal. To begin with, the introduction must set context for your research by mentioning what is known about the topic and what needs to be explored further. In the introduction, you can highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge in your ...
Define your specific research problem and problem statement. Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study. Give an overview of the paper's structure. The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Research proposals, like all other kinds of academic writing, are written in a formal, objective tone. Keep in mind that being concise is a key component of academic writing; formal does not mean flowery. Adhere to the structure outlined above. Your reader knows how a research proposal is supposed to read and expects it to fit this template.
Research Proposal Sample. Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study. 1. Introduction. Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Learn step-by-step how to write a Research Proposal Introduction from the first sentence to the last paragraph.Struggling with developing ideas or a research...
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
2. Introduction. The introduction is crucial to your research proposal as it is your first opportunity to hook the reader in.A good introduction section will introduce your project and its relevance to the field of study. You'll want to use this space to demonstrate that you have carefully thought about how to present your project as interesting, original, and important research.
Research paper introduction example. The following introduction is taken from a research paper exploring the potential uses of the peach palm. We've highlighted each step we mentioned above. Note that some of the steps may overlap a bit; the goal is to include all four components. In this example, the thesis statement appears in Step 4 rather ...
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
A dissertation or thesis research proposal may take on a variety of forms depending on the university, but most generally a research proposal will include the following elements: Titles or title pages that give a description of the research. Detailed explanation of the proposed research and its background. Outline of the research project.
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level project, and one for a PhD-level ...
II. Research Proposal Writing A. Introduction. A research proposal is commonly written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project when enrolling for a research-based postgraduate degree. Graduate and post-graduate students also embark on a university dissertation to obtain a degree or get that Ph.D. Although it is just a course ...
The key thing is. to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas. Step 2: Describe the background. This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is ...
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
INTRODUCTION. A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under 'Research methodology II' section [Table 1] in this issue of IJA) and to ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students. Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods. Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels ...
Introduction to Writing Research Proposals In this handout we will discuss some of the basics of how to write a Research Proposal. The main goal of a Research Proposal is to convince someone to give you money. To that end, you will have be an expert salesperson and convince your audience, usually a panel of experts in the eld or a closely ...
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
Develop an Outline. Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content. Consider the typical structure of a proposal: Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution. Background/Context: Offer relevant ...
Hannah Skaggs. Hannah, a writer and editor since 2017, specializes in clear and concise academic and business writing. She has mentored countless scholars and companies in writing authoritative and engaging content. Write a research proposal with purpose and accuracy. Learn about the objective, parts, and key elements of a research proposal in ...
Lastly, end your introduction with a summary statement that captures the main points of your proposal. Ensure all the key elements discussed above (research question, background info, objectives, methods) are included in the conclusion. Keep it concise and focused while leaving room for further discussion in the body of the paper.
The introduction section of a research proposal sets the stage for the study by providing background information on the topic and stating the research problem or question. A well-crafted introduction should capture the reader's interest and clearly articulate the significance of the proposed research. ... A notable PDF example showcases a ...
What is Introduction in Research. Introduction in research is the initial section that provides context, states the research problem, outlines objectives, and highlights the study's significance. It engages readers, sets the stage for the research, and guides the direction of the entire study. Introduction in Research Format. Opening Sentence:
Background Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of mortality worldwide, and at present, India has the highest burden of acute coronary syndrome and ST-elevation myocardial infarction (MI). A key reason for poor outcomes is non-adherence to medication. Methods The intervention is a 2 × 2 factorial design trial applying two interventions individually and in combination with 1:1 ...