
- > Marketing

What is Service Marketing? Characteristics and Types
- Vrinda Mathur
- Jul 19, 2023

There is a noteworthy increase in service startups these days. Businesses of all sizes are shifting to a service-oriented marketing strategy.
The emergence of a thriving service industry has resulted in a shrinking of the distinctions between commodities and services. For many firms, commodities and services are inextricably linked. Even for organizations that focus solely on the manufacturing of goods, services are an essential component of their business operations. The easy part for businesses is creating a service; the more difficult part is marketing the service. How would you characterize your service marketing strategy? How do you promote your service-based company?
This blog will teach you everything you need to know about service marketing, including practical suggestions and strategies.
What is Service Marketing ?
Intangibility, perishability, heterogeneity, and inseparability are all features of service marketing. There are numerous distinctions between service marketing and general marketing. In general, perceived value is the driving reason behind the channelization of service marketing .
The buyer's primary motivation is to examine the outcome of the services. The competency of the service supplier is unimportant. For example, both technical tools and specialists can be used to optimize an internet advertising strategy. If the results obtained utilizing both are the same, this is referred to as "online advertising optimization."
As a result, we can argue that "value" explains service marketing. This entails establishing a positive interaction with your customers and earning their trust.
This marketing strategy is applicable to both B2B (business to business) and B2C (business to customer) services. Service marketing is used to drive firms in the following industries:
Hospitality,
Telecommunications,
Tourism,
Entertainment,
Financial Services,
Health Care Services,
Professional Services
Service marketing is a high-level sort of marketing that requires you to establish a high level of trust with your target audience. Building your consumers' trust in your services makes them more ready to sign the contract since they believe you have the essential skills to deliver the promised service value.
Unlike a one-time transaction involving product sales, service marketing is a notion that necessitates high-level human connection.
Characteristics of Service Marketing
Since some services required different tactics, service marketing arose as a distinct subject of study. Before they can be researched as a separate entity, these services must have some characteristics. Let us examine some of these peculiarities :
Intangibles are services.
Customers can only experience services, not test, keep, or use actual things. The purchase of a service is contingent on the customer's knowledge and comprehension of what the company has to offer. Because the selection is not focused on appearances or other physical criteria, a potential customer can take their time examining the numerous service possibilities before selecting one.
Heterogeneity:
Services entail a variety of processes that are subject to human variation and are provided by specific persons. Because services vary in substance and quality, some clients want highly customized services. Variability suggests that you are willing to accept fewer possibilities to regularize service delivery.
Performance is related to services:
The higher the quality of service, the more likely the firm will succeed. A wonderful example of a performance-related service is the hospitality business. A good restaurant experience is likely to result in repeat business, but a bad experience may result in customer loss.
Expendability:
Service performances, unlike physical assets, are transient (they cannot be stored or counted). Perishability indicates that demand is subject to wide swings. There is no inventory to function as a bridge between demand and supply, and dormant services cannot be retained.
Services are inseparable from providers:
A user does not take the service away from the supplier, but rather uses it. The service is maintained by the provider, and it is continuously given to other consumers. As a result, providers are essential to the supply of a service.
The prices of services vary:
A tangible product is normally the same price for every buyer, whereas the price of a service can vary. The cost of a plumber's repair might vary depending on the job's complexity, the amount of time required to finish the work, and the materials utilized. The more complicated the project, the more changeable the pricing.
Transfer of No-Ownership:
In service marketing, people receive the service but do not own it. Product ownership can be transferred in product marketing, but not in service. For example, a taxi user may pay a particular amount to the taxi driver, but this does not imply that he gains ownership of the cab just by paying that amount. As a result, service fees are paid here.
Also Read | What is Service Marketing? Features and Types
Types of Service Marketing:
Service marketing can be classified into three types: internal, external, and interactive. They are described below :

Types of Service Marketing
Marketing for Internal Services:
Internal service marketing refers to the promotion of services within an organization, specifically between the corporation and its employees. It focuses on personnel development and training in order to boost service productivity. It thinks that employees are the most important factor in promoting service activities, and that they should be well-treated and properly taught to handle clients.
Such businesses also decentralize power to their employees, allowing them to make their own decisions. Giving them decision-making authority would strengthen their loyalty and make them take responsibility for their actions.
Marketing of External Services:
Business-to-consumer (B2C) service marketing is another term for it. The company promotes its goods to the target markets here. To provide satisfaction and generate value, the company can employ a variety of marketing strategies to attract customers and provide its offering. As a result of the increased rivalry, the company should focus on strengthening its offering.
External marketing is a broad category of marketing that businesses use to enhance sales and brand exposure. It includes all of the activities that businesses typically engage in with their customers. External marketing includes sales promotion, personal selling, direct sales, offers, and direct marketing.
Marketing of Interactive Services:
Simply said, it refers to the combination of internal and external service marketing. It emphasizes the importance of staff interacting with consumers while serving them. Employees should engage and treat customers effectively, keep commitments, provide customer happiness and value, and ultimately contribute to the company's goals.
Interaction between your company's staff and customers constitutes interactive marketing. It happens in shop stalls, bank customer service counters, hotels, restaurants, and any other site where employees and consumers interact. Interaction marketing promotes consumer decision-making because the client requires assistance in making a decision, and your company's personnel assist him in doing so. If the representative delivers good and valuable information on what clients are seeking for, the conversion rate will rise.
Also Read | Business Market: Types, Characteristics & Examples
What is the Service Marketing Mix ?
The service marketing mix, often known as an expanded marketing mix, is an essential component of the design of a service plan. The service marketing mix has seven Ps as opposed to four in the product marketing mix. Simply said, the service marketing mix considers the service to be a product in and of itself. It does, however, introduce three more P's that are essential for optimal service delivery.
The service marketing mix, often known as the extended marketing mix, is an important component of the design of a service plan. This marketing mix consists of the seven Ps. Let's go over them in greater depth :
Your core product is a solution that meets your consumers' needs. This section should include a list of your service's primary qualities, both on their own and in comparison to other suppliers. These characteristics will serve as the cornerstone for your service marketing strategy. These could range from design, technology, and user experience to security.
Place:
Location In the case of services, the location determines where the service product will be located. Petrol stations are best placed along roads or in cities. A location with low traffic is not a good location for a petrol station. Similarly, a software company will fare better in a city or in the middle of nowhere than in a town or in the middle of nowhere.
While pricing has an impact on both customer retention and customer satisfaction, the price of a product is a significant decision in this regard. To correctly target your consumers, you should understand their price sensitivity range (as well as the pricing your competitors are giving). While pricing is often regarded as an indicator of general quality, intangible services place greater emphasis on price. When you charge a fee for your services, you are effectively pricing happiness. Product line pricing, economy pricing, and penetration pricing are all prominent pricing strategies employed by service providers.
Physical proof:
We've already said that you've kept previous pledges and have neutral evidence to back up your claims. This contributes to the development of trust. All physical aspects involved in the service delivery, from the physical location to all items or objects that have a role in providing information about the service, are considered physical evidence.
Promotion relates to positioning, such as locating your internet presence in the most appropriate location to reach clients. Your "what" is refined further with the use of positioning. For instance, what type of adverts or content you will run (Adwords or Facebook) and what type of messaging you would employ.
The focus of service marketing is on the people. Your credibility and the success of your service are dependent on your ability to build trust with your clients. Time and effort are required for successful client relationships. The way your customers will judge your service is partially dependent on how well you define your communication systems, so pay particular attention to this step.
And, as you are aware, service marketing is about more than simply the finished product. Process-centric standards aid in the establishment of your brand as one of dependability and consistency, ensuring that clients' expectations are met. How do you handle customer service? All of these procedures must be rigorously managed in order to provide a consistent client experience.
To summarize, service marketing is a method for a corporation to promote intangible, non-divisible, and time-limited services. It is done in a variety of methods in light of the expanding global service sector. It is also extremely different from product marketing, and there are other considerations. Service marketing has grown in importance in recent years as more and more services, such as education, banking, and hospitality, have become popular items.
Also Read | Product Marketing Vs Product Management
Share Blog :
Be a part of our Instagram community
Trending blogs
5 Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Elasticity of Demand and its Types
An Overview of Descriptive Analysis
What is PESTLE Analysis? Everything you need to know about it
What is Managerial Economics? Definition, Types, Nature, Principles, and Scope
5 Factors Affecting the Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
6 Major Branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Scope of Managerial Economics
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: The Shortest Path Algorithm
Different Types of Research Methods
Latest Comments
BLANK ATM CARD
GET RICH WITH BLANK ATM CARD, Whatsapp: +18033921735 I want to testify about Dark Web blank atm cards which can withdraw money from any atm machines around the world. I was very poor before and have no job. I saw so many testimony about how Dark Web Online Hackers send them the atm blank card and use it to collect money in any atm machine and become rich {[email protected]} I email them also and they sent me the blank atm card. I have use it to get 500,000 dollars. withdraw the maximum of 5,000 USD daily. Dark Web is giving out the card just to help the poor. Hack and take money directly from any atm machine vault with the use of atm programmed card which runs in automatic mode. You can also contact them for the service below * Western Union/MoneyGram Transfer * Bank Transfer * PayPal / Skrill Transfer * Crypto Mining * CashApp Transfer * Bitcoin Loans * Recover Stolen/Missing Crypto/Funds/Assets Email: [email protected] Text & Call or WhatsApp: +18033921735 Website: https://darkwebonlinehackers.com
KATHY BOMBACH
BUY IELTS CERTIFICATE FOR SALE, DRIVERS LICENSE FOR SALE, US PASSPORT FOR SALE, UK PASSPORT FOR FOR SALE : WhatsApp:+1 242 652 6983 UK driver's license for sale, a German id card for sale, Australian driver's license for sale, Australian passport for sale, We produce the optimal quality of real database registered documents, (buy passport online)where we record all the client’s information in the supposed database system,==========Keywords: UK passport for sale, Grenada passport for sale, Grenada citizenship by investment , Malta passport for sale,Malta citizenship by investment, German passport for sale, Israel passport for sale, French driver's licence for sale ,UK driver's licence for sale, German id card for sale, Australian driver's licence for sale, Australian passport for sale,Canadian passport for sale, Canadian id card for sale, Florida driver's licence for sale,New York id card for sale,California id card for sale, Nevada driver's licence for sale, Washington id card for sale, Belgian passport for sale,Dutch passport for sale , Fake birth certificate for sale , Netherlands id card for sale , Fake UK passport for sale ,Fake USA passport for sale, Texas id card for sale , Arizona id card for sale, Dubai id for sale, Dubai work permit for sale,IELTS for sale Dubai, IELTS for sale UAE , IELTS for sale USA, Ukrainian passport for sale, Russian passport for sale,Expungement lawyer for hire, How to Clear criminal records, Second citizenship for sale, IELTS for sale Kuwait ,Fake social security card for sale, UK birth certificate for sale, French birth certificate for sale, Fake passports for sale,Fake id card for sale, Fake driver's licence for sale, Buy fake id cards, English certificate for sale, Toefl certificate for sale,How to obtain IELTS without exam, Buy fake Canadian passport, Buy fake British passport, ==========We are the best International Documentation Services ( Buy Real / Buy Fake Passports , Buy Real / Buy Fake Drivers License,Buy Real / Buy Fake Id Cards , Buy Novelty Documents , Buy Fake Home Loan Documents ,Buy Fake High School Diploma Certificates , Buy Fake Social Security Cards , Buy Fake Bank Statements.Buy Novelty documents Online. Contact Us if you are interested in any of our services.Email us: – -WhatsApp: +1 242 652 6983 -Link :dynamicdocuments.online -Email:[email protected] ================================================================TAGS: DRIVER’S LICENSES FOR SALE, IELTS BUY CERTIFICATE, IELTS CERTIFICATE FOR SALE IN DUBAI,IELTS CERTIFICATE FOR SALE IN INDIA, IELTS CERTIFICATE FOR SALE IN MALAYSIA,IELTS CERTIFICATE FOR SALE IN PAKISTAN, IELTS CERTIFICATE FOR SALE IN PHILIPPINES,IELTS FOR SALE, PASSPORTS FOR SALE, SECOND CITIZENSHIP FOR SALE, ======================================================================== -Links:dynamicdocuments.online -Email: [email protected] Are you looking for a professional and dedicated company where you can obtain a driving license without test? buy driver license online available at the best rates. We have specialization in the making of real ID driver license and are involved in this industry for a very long period of time. You can buy real driver’s license legally from our company and get it delivered at your preferred region inside a short period. We always assure that our customers are satisfied with our driving license services. No compromises are made by our company in the production of fake and real driving license online. -WhatsApp: –+1 242 652 6983 -Link : dynamicdocuments.online -Email:[email protected] Obtain Fake and Real Driving License Online with the assistance of ProfessionalsBuy Drivers License Online . Buy uk id card onlineBuy German id card onlineBuy US id card onlineBuy Australian id card onlineBuy Ireland id card onlineBuy Austria id card onlineBuy Swiss id card onlineBuy. France id card onlineBuy china id card online Buy Identity card buy id card online buy an id card online Apply for a Social Security number online Buy Social Security number custom glock 19 gen 5 for sale cheap glock 19 gen 5 for sale glock 19 gen 5 for sale PSYCHEDELIC MUSHROOMS FOR SALE BUY MAGIC MUSHROOMS ONLINE BUY MAGIC MUSHROOM buy nembutal online m&s medicals buy nembutal online ?????????????????????????????????????????????????????? buy high quality undetectable counterfeit banknotes for sale, banknotes for sale Buy Registered Drivers License Online Buy Real Drivers License Online Buy Fake Drivers License Online Buy Passport Online Buy Registered Passport Online Buy Real And Fake Registered Passport Online Buy Registered IELTS | TOEFL Certificate Online Buy United State Passport online Buy Finland Passport online Buy UK Passport online Buy a German passport online German passport application German passport online Buy the United States Driver's License Online Buy Finland driving license online Buy UK driver's license online Buy a German driver's license online Buy German driver's license online German driving license Buy New Zealand driver's license online Buy Latvian driver's license online Buy Ireland driver's license online Buy New Zealand passport online Buy Latvia Passport online Buy Ireland Passport online Buy Denmark Passport online Buy Portugal Passport online Buy Portuguese Passport Online Buy Real And Fake Portuguese Passport Online Buy Cyprus Passport for Sale Buy Luxembourg Passport online Buy Turkish passport online Buy Dutch passport online Buy Norwegian passport online Buy Poland Passport online Buy Romania Passport online Buy Serbian passport online Buy Singapore Passport online Buy Greece Passport online Buy Hungarian passport online Buy a French passport online Buy US passport online Buy Romanian passport online Buy Slovenian passport online Buy Slovak passport online Buy Spanish passport online Buy a Swiss passport online Buy Thailand Passport online Buy Chile Passport online Buy Croatian passport online Buy Canadian passport online Buy Costa Rica Passport online Buy Estonian passport online Buy Australia Passport online Buy Denmark driving license online Buy Portugal driving license online Buy Cyprus Driver License For Sale Buy Luxembourg driver's license online Buy Turkish driver's license online Buy Dutch driver's license online Buy Norwegian driver's license online Buy Romania driver's license onlineBuy Serbian driver's license online Buy Australian driver's license online Buy a German passport online Email:[email protected]
Marketing91
Service Marketing – Definition, Importance, Characteristics and Strategy For Marketing
June 13, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
Definition: Service marketing is involved in designing, delivering, and doing post-delivery analysis of services for optimizing reach, measuring customer satisfaction , and standing-out from identical services offered by other market players.
Service marketing, as defined by the American Marketing Association is-
“For the sale of good, the various satisfaction, activities, as well as benefits on offer for sale, are elements of service marketing”. Sir William Beveridge defines service marketing as, “Social efforts that comprise of government exertions to battle 5 evils (illness, ignorance, wants, squalor and disease) within the society”.
Hasenfeld describes service marketing as –
“Action made by an organization that preserves and progress the happiness and workings of people.”
All the above service marketing definition provides information in part as happiness and functioning of people is well and good. It ignores the perception and the spirit of service marketing, which is very important in the grand scheme of things.
Service marketing strategies anticipate the needs of target audiences and try to meet their requirements for ensuring optimum value for the users/purchasers.
Marketing service strives to achieve-
- Attracting new customers
- Retaining existing customers
- Selling them upgraded services
- Channelizing referrals from existing customers
Table of Contents
What is a Services Marketing Strategy ?
A service marketing strategy comes into play for marketing service.
Service Marketing incorporates intangibility, perishability, heterogeneity, and inseparability sorts of characteristics. There are a lot of differences between service marketing and general marketing. In general, the perceived value is the driving force based on which service marketing is channelized.
The buyer’s main motive is to look at the result achieved from the services. The competence of the service provider doesn’t count for much.
For instance, both technology tools, as well as experts, can optimize an online advertisement campaign. If the results achieved are the same using both, it is termed “online advertising optimization.”
So, we can conclude that service marketing is explained by “value”. This means building a healthy rapport with your customers and gaining their trust.
The customers need to feel confident that the service marketer can bring the desired result.
Moreover, it requires high human interaction in the service industry, contrary to one-time interaction in product purchase. Service is a universal concept and is present in all business transactions.
Services are not only responsible for adding more economic values to a county but also play a key role in boosting employment and new job growth via services jobs.
In recent times, another form of service marketing i.e. Digital Service Marketing is also gaining lots of prevalence around the world. Let us understand what it is-
Digital Services Marketing Strategies

These are services that assist businesses to advertise online. They use various channels such as SEO, social media, and websites to promote their agenda.
The likes of SEM’s, content marketing, SMM, Digital advertising are all included under digital service marketing. The growing significance of the internet has assisted the boom of digital service marketing.
Now, after being clear about what service marketing is, let us now understand why it is so important nowadays-
Importance of Services Marketing Strategies
Key reasons why service marketing is crucial for optimizing the reach, conversions, and profits of a brand are-
1. Development of Secondary and Primary Sector
The smooth running of primary and secondary sectors depends on different services. Thus, the service industry, as a whole plays an important role in the efficient working of these sectors.
2. Rise in employment
Aviation, brokerages, tourism, hospitality, software, entertainment, retail, BPO’s are some of the sectors that get employments from the service industry. The entire country gets benefited as a result.
3. Upturn in National Income
If the service sector is expanding and growing, this will help in National Income. There would be the same amount of development and growth in the country as any other sector.
4. Assistance to basic services
Basic services of the country like post offices, insurance, courts, transport, banks , telecommunications, educational institute, hospitality get assistance from the service sector. These services are vital for a common man in their daily lives
5. Boost a nation’s image
Services like ITES, BPO will enhance a country’s image in front of the world. This portrays a bright future for the nation in front of the world.
6. Upturn in exports
Quality service sectors will bring in more demand from countries outside the international borders. These, in turn, boost the exports and helps to rake in foreign currency that adds to the economic stability of a country.
7. Opportunities for more women
There is a rise in demand for working women in the service sector. This has opened up new avenues for women to work and be equal to men at work.
Categories of Services in Service Marketing Strategies

1) People Processing Services
It requires the physical presence of users
2) Product/Possession Processing Services
It is associated with a specific product or possession like packers & movers services
3) Mental Stimulus Processing Services
It is associated with services that influence mental abilities, behavior, religious beliefs, lifestyle, or perceptions of users
4) Information Processing Services
Such services are associated with specific types of intangible products where information is considered as a product
Classification of Services Marketing
There are a lot of services available in the market. So, as a result, it is hard to classify service marketing, but the following classifications have been widely accepted:
1. End User basis
B2B services like advertising, consultancy, and marketing research. Moreover, services to the consumer are the ones that are provided straight to the end-users. These services include counseling, laundry, hairdressing, and package holiday.
2. Tangibility Basis
Tangible products such as watches, refrigerators, AC’s and televisions are examples that can be bought by the end-user. Services that are intangible and they can only feel the benefit derived from the service. For instance, Spa’s, educational institutions, and consultancy firms.
3. Specialization basis
Only experienced and qualified people with proper degrees to back their abilities are known as professional services. Their skills are recognized by various authorities to provide proof of their knowledge. For instance, Health care, audit, counseling, legal services.
Opposite to professional service providers is non-professional servicemen. They don’t possess any professional degree or educational qualification. These non-professional service providers are equally important to society as professionals. For instance, Painters, domestic help, and gardeners.
4. Labour intensive basis
The high involvement of humans in achieving a work can be called a people-based service. For instance, security services, catering, automobile repairs, and event management .
Contrary to people based service is equipment based service. In this service, equipment plays a significant role. Here, humans play a minimum role, or they are absent in some cases. For instance, ATMs, vending machines, etc.
5. Profit Basis
The running of a business with the end intention to earn profits by providing services is known as Commercial services. For instance, a jewelry shop, Hair salons, etc.
Services provided due to philanthropic reasons minus profit intention are known as Social Services. The main objective is to serve society. For instance, Old age homes, Street dogs safety centers, orphanages, etc.
Characteristics of Services Marketing
1. perishability.
The benefits derived from services cannot be resold, saved, stored, and returned once utilized. Once service is delivered, it cannot be taken back or transferred to another user. For instance, a dissatisfied customer cannot ask a barber to undo the haircut that he has received.
2. Inseparability
The service is produced by the service provider and consumed by the customer at the same time. A cobbler polishing his customer’s shoes is delivering his service, and the customer is getting his problem solved then and there.
3. Intangibility
The services provided by any service provider cannot be seen, touched, smelt, seen. Services don’t have a physical existence. One of the most defining features of service that sets it apart from a product. This is a challenge for the service provider to add tangibility to intangible service offerings.
4. Heterogeneous
Every service has its unique offering, and hence, its benefits cannot be copied. Products can be mass-produced in factories, but the services provided cannot be repeated.
Here is a video by Marketing91 on Service Marketing.
Services Marketing Challenges

Different challenges that service marketing campaigns may face are-
This is one of the vital elements of services. The customer of your service should have full faith in your skills. Trust is not built overnight but gradually over time.
The process of service adds to the overall value proposition of the service provided. Kindness, flexibility, and responsiveness are a few of the processes involved in the service industry.
3. Customization
A service provider should always possess the flexibility of providing services according to the demands of the customers. One size fits all is not the way to go in the service industry.
Top Hacks for Services Marketing Campaigns
Services are intangible, and that is why they need specific types of marketing services that can optimize the service quality and customer experience to develop a long-term business relation. Some of the steps you can incorporate in your service marketing strategies are-
- You should offer Use Incentives
- It is crucial to stay in touch with users via email
- Make use of Social Marketing along with Business Cards
- Always stay connected with the Community and Network
- Try to be in the news with effective PR
- Compete with other marketed players on value and not on price
Services Marketing Examples
Both B2C and B2B have great examples of service marketing.
Airbnb in the B2C segment has an exceptional presence alongside Uber , which is a problem-solving service.
In B2B, Hubspot offers software and solutions to other businesses. They have set an industry benchmark in the quality of service.
Strategies for Marketing Service And Product Marketing In Conclusion!
On the concluding note, we would like to suggest that service industries should also opt for aggressive service marketing campaigns in the same way as manufacturing companies do.
The service marketing triangle includes the company , employee , and customer.
In this, the company makes a promise to the customer, employee and company together enable that promise, and then, finally, employees deliver that promise to the customer. All in all, marketing services will include internal marketing , external marketing, and interactive marketing services.
Now, it is your turn to tell us how important do you consider service marketing for optimizing the role of the services industry in boosting the economy of a country!
We are here to listen to your thoughts and unique Service Marketing definition in the comment section below.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Services Marketing
Related posts:
- Service triangle or The service marketing triangle
- Service Differentiation and 7 Ways to Differentiate Service from Competitor
- 4 types of service processing – How to categorize service processes?
- What is Service Strategy? Meaning, Importance and Process
- Customer Service: Definition, Importance, Benefits and Tips
- Industrial Marketing – Definition, Strategy and Characteristics
- Importance of Customer Service
- Service Marketing Mix – 7 P’s of marketing
- Difference between product marketing mix and service marketing mix
- The Servqual Model – Definition, Dimensions, Gaps and Advantages Service
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
Services Marketing: Characteristics, Innovations, and More
While most may have heard of service marketing, the process of bringing a service to market, not everyone realizes that it’s a whole different science from product marketing. In this blog, we will look into the pillars of service marketing, its characteristics, and recent innovations.

Table of Contents
What is service marketing, effects of the right service marketing, the 4 characteristics of service marketing, 4 innovations in service marketing, looking for service marketing solutions, more about pixel506, key takeaways.
First things first―what are services? Services are non-physical items that can be provided by businesses and paid for by consumers. Services include but are not limited to banking, communication, education, medical treatments, beauty treatments, transportation, tourism, and insurance.
Selling a service is very different from selling a product. When you sell computers or computer parts, the buyer can hold and feel them. But when you sell a service, your audience is buying something that they will never own. For example, when traveling on an airplane, travelers pay for a service―to be brought from Point A to Point B. They don’t buy the airline, the plane, or the seat. When visiting a hair salon, consumers pay for a service―to have their hair cut. They don’t buy the hair salon, the hairdressing tools, or the hair products.
When selling a service, you are selling an experience. That experience has a perceived value. Airlines can promote their services, as can hair salons. By using service marketing, a company can display its offerings and benefits to increase end-customer value.
So, what is service marketing exactly? Service marketing is the process of bringing a service to market. This includes every step of the journey; from deciding the service’s messaging, to launching and marketing the service in a way that creates desire, and thus revenue.
At Pixel506, we have successfully helped multiple businesses identify opportunities to improve their service marketing efforts to increase customer satisfaction.
Case Study: The Lombardy Hotel, NYC
Hotel guests don’t purchase the hotel, the room, or even the bed they sleep in, they purchase a service―a clean, comfortable, and safe accommodation to stay in for one or multiple nights. Apart from the occasional walk-in, most travelers book their hotel rooms online via a mobile app or website. And thus, as a hotel owner, you want potential guests to land on your website and think, “this is my kind of place.”
One example is the work that Pixel506 did for The Lombardy Hotel in New York . We were tasked with updating the hotel’s website to reflect the hotel’s unique services, amenities, and local attractions as well as create a seamless online booking experience.
Our team successfully amplified the user experience with intuitive navigation and clear copy defining the hotel's personality. Call-to-actions pepper the website inviting visitors to connect further with the hotel. The easy booking process encourages visitors to check rates and book directly with the hotel without having to go through a travel agent or third-party website.
With Pixel506, The Lombardy created new and effective tools for communication through digital marketing channels and valuable content for the hotel's website and social media platforms. Brand engagement increased as did direct bookings through the website.
It is now easier for visitors to navigate to different pages and locate the services and information they need to make a decision or book a room. Although we can’t influence the way guests are greeted at check-in or treated during their stay, we were able to market the hotel’s services in a way that speaks to their audiences and their needs. By putting the customer experience first, potential guests now choose the services that they need quickly.
[READ CASE STUDY]
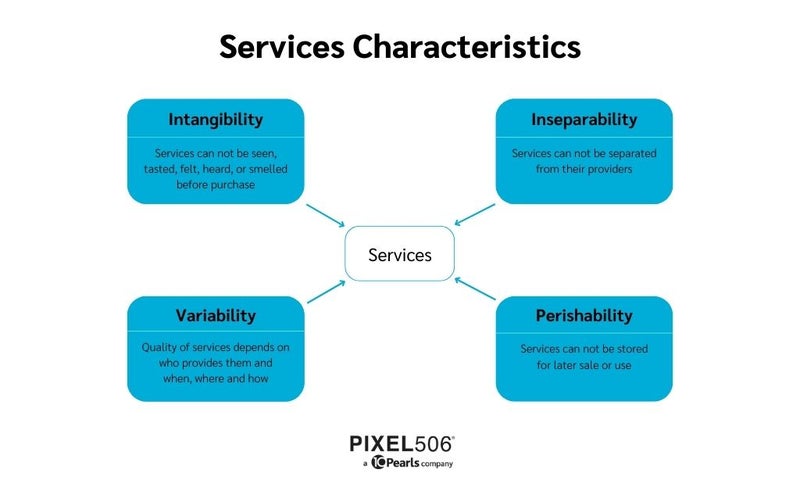
- Service marketing has four distinctive characteristics; intangibility, inseparability, variability, and perishability.
1.Intangibility
McDougall and Snetsinger (1990) defined intangibility as “the lack of physical evidence” and “the degree to which a product or a service cannot provide a clear concrete image”. Services cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled before buying.
For example, a customer of a hair salon only has an appointment and the promise of a fresh haircut. The salon wants to convey the idea that its service is professional yet personalized. They need to position themselves as such and truly commit to it. The salon’s exterior and interior should look clean and showcase high-quality products, the staff needs to dress properly, and be welcoming and approachable towards customers. The tools and equipment need to look clean and modern. The salon’s value proposition should extend to its online presence; its website, social media, email campaigns, loyal customer programs, and other communication should convey feelings of professional service and quality.
2.Inseparability
The definition of inseparability in the dictionary is “the quality or state of being incapable of being separated or divided.” One of the characteristics of service marketing is inseparability. When purchasing a product, most customers can separate the product from the staff member who provides it. However, when purchasing a service, customers commonly purchase a service at the time they want to consume them. This can make it challenging to separate the service they receive from the business or staff member who provides the service.
For example, a restaurant sells goods, as well as provides services―they prepare and serve food, set and clean tables, provide a menu, and may even offer entertainment. When visiting a restaurant, the customer will consume their meal while at the restaurant. But even if their meal is satisfactory, their overall experience can be bad due to service, the atmosphere, or even the restaurant’s location. It can be challenging for guests to separate the service they receive from the quality of the food because many factors can influence their experience. Every interaction is inseparable from the overall experience.
3.Variability
Variability means a lack of consistency and measures how much data or experiences vary. When purchasing a physical item, the product is consistent regardless of the store or online vendor selling it. When purchasing services, there is greater variability―there will always be changes in the experience of the same service provided by different vendors.
For example, when dealing with insurance claims, one staff member may be responsive and helpful, while another could be unpleasant and apathetic. Even the quality of the service being provided by a single staff member is variable. The level of service they provide could be different from one customer to another and could be greatly affected by their workload and state of mind. The quality of the service a consumer receives may depend on which vendor they choose, and which staff attends to them.
4.Perishability
Perishable goods refer to products and services that have an expiration date. Services, like foods, are perishable, meaning that services can not be stored for later use. Foods may go bad if they are not consumed in a certain period, the same applies to some services. Movie tickets, theater reservations, doctor’s appointments, and hotel bookings can not be stored or kept for later use. When left unused, the service vanishes, and a new ticket or another reservation will need to be made.
There are several steps that businesses can take to adjust the demand and supply of their services. For example, hotel rates for the same room will vary depending on peak season or off-peak. Part-time employees may be hired during the peak season to share the workload and serve more tourists.
We define service innovation in digital marketing as the implementation of new strategies and services that differentiates from the previous methods used to create value for customers. During the COVID-19 pandemic, businesses had to change the way they operate, communicate, and deliver their products and services. Now that the pandemic is winding down, some of these innovations in service marketing will stick around.
1.24/7 customer support
Nowadays, customers expect to be able to browse and purchase products and services at all times of the day. Whether they want to order groceries online, schedule a car service appointment, or plan a doctor’s appointment, customers are no longer willing to be restricted to office hours to get help. Businesses that are unable to respond promptly or offer online ordering and booking run the risk of losing customers.
2.Automated customer support
Customer service automation is the process of addressing clients' requests with minimal human-to-human touchpoints. If there is no staff available to speak with customers (before, during, or after office hours), customers expect automated customer support services to assist them. Chatbots, self-service portals, and automated email replies have become commonplace in general customer service and they aren't going anywhere.
3.Cashless and contactless payments
The pandemic has boosted the use of cashless and contactless payments and this trend isn’t going away. When paying for products and services, customers want to be able to complete transactions without having to carry cash or hand over their credit or debit card. Quick touch points using a card or phone are preferred. Cashless and contactless payments are not new but the COVID-19 pandemic rapidly accelerated the demand for them across industries worldwide.
4.Personalized experiences
Contactless experiences don’t mean the human connection gets lost, instead, it should enhance it. Nowadays, people expect streamlined services and personalized experiences. For example, when checking into a hotel, guests don't want to be treated like they're just another credit card number. Instead, they want to feel that their business is valued, that hoteliers know who they are, and what they like. A HubSpot research shows that personalization helps satisfy consumer expectations and drive repeat sales in almost 93% of customers. The more customized the service, the higher the satisfaction rate.
These four innovations may not exist entirely because of COVID-19, but the pandemic has accelerated them.
Being in the service industry ourselves, we understand your challenges. Whether you’re in education, hospitality, legal, transportation, or any other industry, we can help you market your services and dominate your competition. You can think of Pixel506 as your own 'internal marketing team,' we may be working remotely but we are always here to help and answer your questions. Our experts know how to create, implement, and manage digital marketing strategies for service companies. Outsourcing your marketing efforts to Pixel506 saves you both time and money and allows you to focus on scaling your business. If you’re looking for an established agency to help you with your marketing efforts, complete our form or contact us at contact us .
Pixel506 is a digital innovation agency that helps companies with creative solutions, providing strategy, technology, and digital marketing services. We power UX, marketing, and software development teams to create products and services that boost sales in the digital space. Since 2009, we have helped numerous companies with their product marketing as well as service marketing strategies. We have our roots in Brooklyn, New York, but our nearshoring teams are located in Costa Rica, Colombia, Perú, and Nicaragua. Our team of talented and skilled professionals will help you market your services and grow your client base. Feel free to contact us for more information or to request a quote. We look forward to helping you grow your business with strategic marketing innovations and personalized solutions.
- Service marketing is a type of marketing that is used to market a service rather than a product. Differing from product marketing, service marketing is more focused on building relationships and providing value to the customer.
- Recent innovations in service marketing include 24/7 customer support, automated customer support, cashless and contactless payments, and personalized experiences.
- A professional digital innovation agency, such as Pixel506, can help you market your services and grow your client base.
Do you want more leads? Let's start the process of creating a service marketing strategy that gets real results.
Want to learn how our Nearshore teams can enhance your business growth? Contact us today!
Most popular articles.
- The Importance of Quality Assurance in Software Development
- How to Decide What to Create Content About for Your Brand
- 4 Successful Nearshoring Partnerships
More Like This
- Job Search Websites
- Freelance Jobs Websites
- Find Freelance Writing Jobs
- Lucrative Freelance Jobs
- Legit Ways to Make Money from Home
- Freelance Project Management Software
- CRM for Freelancers
- Time Tracking Software
- Video Conferencing Software
- Work from Home Tools
- Email Marketing Software
- Paraphrasing Tools
- Self-Employment Guide
- Personal Branding Guide
What is Service Marketing?
- SMART Goals Definition
- Project Management Basics
- What is CRM?
- Why Is Time Management Important?
- Tips for Managing Time
- Overcome Parkinson’s Law
- How to Use Pomodoro Technique
- Best Productivity Tools
- Best Organization Apps
- Productivity Quotes
- Time Management Quotes
- High-Income Skills
- Employability Skills
- Communication Skills
- Self-Management Skills
- Project Management Skills
- Management Skills
- People Management Skills
What is Service Marketing? Definition, Strategies, Examples
Nowadays, there is a noticeable rise in service startups. Businesses of all sizes are moving towards a service-oriented marketing approach.
The presence of a vibrant service sector has led to the narrowing down of the differences between goods and services. For many businesses, goods and services are interconnected. Even for companies that focus on the production of goods, services represent an integral part of their business operations.
The easier part for businesses is to create a service, the harder part is to market the service. How do you define your service marketing strategy? How do you market your service-based business?
In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about service marketing including effective tips and tactics.
Let's get started.
Service marketing is an exclusive branch of marketing that sprung up in the early '80s because some specialized services required unique strategies, unlike physical marketing strategies. It centers on the business of non-physical intangible or, better said, abstract goods .
This form of marketing applies to both B2B (business to business) and B2C (business to customers) services. Examples of sectors that use service marketing to drive their businesses include:
- Hospitality,
- Telecommunications Services,
- Entertainment Services,
- Financial Services,
- Health Care Services,
- Professional Services,
- Car Rental Services,
- Trade Services, etc.
Service marketing is a high-grade type of marketing that needs you to build a considerable level of trust with your target audience . Building the trust of your customers in your services enables them to be more willing to sign the contract since they trust that you have the necessary skills to deliver the promised service value.
Unlike a one-off transaction that involves the sales of products, service marketing is a concept that requires high-level human interaction.
Characteristics of Service Marketing
Service marketing emerged as a special field of study due to some services that needed different strategies. These services must have some peculiarities before they can be studied as a separate entity. Let's take a look at some of those peculiarities.
- Heterogeneity – Services involve various processes that are subject to human variation and are delivered by certain personnel. Some clients request highly customized services because services are naturally variable in substance and quality. Variability implies that you are open to fewer opportunities to regularize the delivery of services .
- Intangibility – Services are abstract, i.e. they lack physical form. They cannot be controlled with any of our bodily senses like sight, touch, or smell. This characteristic implies that ownership cannot be changed or transferred . Value is derived from the consumption of experience of that service. You cannot evaluate the quality of service before purchase or consumption.
- Perishability – Unlike physical goods, service performances are temporal (they cannot be stored or enumerated). Perishability implies that demands are prone to wide-ranging fluctuations . No inventory acts as an intermediary between demand and supply and dormant services cannot be retained.
- Inseparability – Unlike goods, the concept of production and consumption of services cannot be dissociated. For goods, the production and consumption of physical products are two entirely different processes. An implication is that services are highly labor-intensive . Also, there are fewer opportunities to substitute capital for human labor.
- People Involvement – Service marketing is in the hands of people who provide services to need the needs and wants of their customers.
These five characteristics give rise to different problems in service marketing. Services are by nature complex, multi-dimensional, sophisticated, and multi-layered compared to standardized products. There are benefits attached to services.
Service marketing involves interactions between companies and clients, and between customers and other customers.
How to Define Your Service Marketing Strategy
The best marketing strategies all start from a simple and actionable plan and a genuine evaluation of where your business is today. You want to know how much customers value your services.
Which of your services sells the best and which sells the worst? What services offer a high profit margin? These are questions that need to be check-marked for you to build an effective marketing strategy.
Some decades ago, service companies rarely made use of marketing strategies compared to manufacturing companies. Compared to manufacturing companies, service firms:
- Often handle advertisement internally instead of going out to agencies
- Rarely come up with sales training programs
- Rarely meet marketing experts for consultations
- Do not run sales analysis in the environment around them.
There are various reasons why these service firms did not initially use marketing strategies. Some had lots of demand and did not see the need for a marketing plan. Others felt it was unprofessional to employ the use of marketing.
Later on, some of these service firms started experiencing a decline in demands for services, leading to low sales. They started using marketing agencies to boost their sales.
Service-based businesses need some elements of external marketing to be successful. It is what promotes your services to your target audience.
Defining a marketing plan for your service-based business is essential to your business' growth. Your strategy should focus on satisfying the needs of your target audience and building a long-term relationship with them through consistent interaction.
Below is a guide on how you can define a successful service marketing strategy.
1. Know the Key Elements of a Successful Strategy
One key element is for you to characterize your customers by their needs. You can do this by doing thorough market research on different customers and approaching them in a more friendly way than your rivals in the market.
The next step is to make the most of your business strengths to meet the various needs of customers. For instance, if you notice that some sets of audiences prioritize quality in service, your marketing strategy should convince them that you can provide the high-quality service they want.
2. Do a SWOT Analysis
Your business strategy must take account of your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Detailed research on your existing customers can say much about your SWOT.
After doing your analysis, look at the potential effects that each element of the SWOT analysis can have on your strategy.

3. Develop your Marketing Strategy
With insight into your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, you can maximize the positive information and minimize the effects of the negative information.
You can also write out some questions that your marketing actions will answer. Review these questions regularly and tick whenever you have completely answered them.

How to Market a Service-Based Business
Service-based businesses offer services to its target audience. Before you begin to market your service to customers, you need to understand some concepts.
You need to study and understand your customer's personalities, the dynamics of your target audience, their reaction when they are satisfied with your service, and their reaction when you do not meet their expectations.
Also, you can study how your existing customers knew about your service and how they were convinced to patronize you . It helps you in knowing the right points to hit when marketing your business.
After understanding your customers, there are some proven methods you can apply when marketing your business. They include email marketing, SEO, performance marketing, webinars, direct outreach, and referral marketing.
1. Email Marketing
The use of emails is one of the best ways to market your service-based business. After identifying your target audience, you can use email marketing to build and automate your email campaigns. You can set that up using email marketing software such as ConvertKit, MailChimp, and other MailChimp alternatives .
The welcome email is what you send to your customers when they join your email list. You can personalize your emails based on the user's preference.
Provide social proofs in your emails, people love it when there are proofs to back up the efficiency of service . Also, ensure your emails are reader-friendly. Do not employ the use of sophisticated words with the mindset of impressing your clients. You can miss out on passing the message you intend to pass to your target audience.

SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is a great way of promoting your service business . There is no doubt that if a random customer goes on the web to search for a service, he or she is most likely to click on any of the first five websites that appear on Google SERP (Search Engine Results Page).
If you want your website or blog to rank high, you need to do some SEO optimization. People still find it hard to understand how the Google search algorithm works on the internet. Here are some SEO tips to help you market your business.
- Use quality content
- Use search keywords in your content, and
- Use SEO-optimized titles, headers, and URLs.
- Use SEO tools to improve your rankings including keyword research tools .

3. Performance Marketing
Performance marketing is another good way of up-scaling your service business. It is the combination of brand marketing and paid advertising to achieve one goal.
This type of marketing involves an affiliate and a retailer. It is a win-win for both parties because the retailer only pays when the desired action has taken place.
Performance marketing is an umbrella that houses affiliate marketing and other types of marketing . The affiliate helps you market your service. Once they can convert a large audience, you pay them for their service and in turn, get a large number of people to offer your services to.

4. Webinars
You can also leverage webinars to boost your services and amass a large audience. To use webinars, you first identify a topic that interests your target market.
Here are ways to find a topic:
- Define your target audience
- Understand their pain points
- Use irresistible titles to capture their attention
The next step is to prepare your webinar. Ensure you are the person that hosts it. For this step, here are a few things to do.
- Use the best webinar software platforms
- Create your content
- Test run the devices you want to use to host the webinar
Promote Your Webinar
No matter how resourceful your webinar is, it needs promotions for it to get to a larger audience. Here are a few tips on how to promote your webinar.
- Add call-to-action clicks on your website
- Send promotional emails
- Post blog contents emphasizing the webinar
- Use social media platforms and possibly run Facebook Ads .
After a wonderful promotion, convert your webinar attendees into sales. The best way to do that is to:
- Focus on delivering valued content
- Showcase your expertise level
- Advertise your service at the end of the webinar.

5. Direct Outreach
Direct outreach is another great marketing tool. Customers patronize services based on emotions and justify them with logic. It involves reaching out to your customers via email or phone, including cold calling.
6. Referral Marketing
In the business world today, there is no doubt that referrals boost market sales. Referral marketing is a process where existing customers refer other people to your services.
Unlike other types of marketing that you directly contact a large audience, your existing customers do the work for you. Referral marketing helps your business gain more customers through word-of-mount testimonials from people who used your services .
One thing you need to do as a brand for referral marketing to work out is to offer quality and satisfactory services. Once you do that, the rest is easy. Customers are always naturally eager to talk to a friend or two about the service they enjoyed from a business.

Service Marketing Tips and Tactics
Some of the best service marketing tips and tactics you can use to attract more customers, generate more sales and Return on Investment (ROI) include:
1. Entice Your Audience with Incentives
No matter the services you offer as a business, you have lots of competitors out there trying to gain the attention of the same customers you are targeting.
How do you want to attract these customers to your service? How do you want to convince them that you offer services better than your competitors?
Incentives, promos, and add-ons are ways you can use to win customers to your side. Everyone appreciates extra efforts that service-based businesses add without charging extra costs. Incentives also attract new customers to your service.
2. Prioritize Your Value Over Prices
Most businesses always want to compete over prices in a bid to attract customers. However, if you want to reduce your prices, it might hurt you in the end because the lower you go, the lower your rivals will go just to snatch the market. Will you keep going lower? Will you reduce quality because you want to cut costs?
Smart service-based businesses compete based on values . Although there might be ranges in price, the one with the best values always wins. Once the standard of your business is offering high-quality services, you do not have to cut costs to attract customers. Intentional customers will take you as their ‘go-to' brand for your type of service .
3. Communicate Effectively
Communicating the results of services involves more personal interactions than delivering details concerning the sales of a product. Customers enjoy it when you constantly update them on your services other than just keeping them waiting for the final results . You need to keep an efficient communication funnel with customers.
You can effectively communicate via emails, phone numbers, CRM software , or social media. With social media, a single message can travel as fast as the speed of light within the blink of an eye. You can also schedule messages. It will save you the stress of sitting down all day forwarding messages to various customers.
4. Earn the Trust of Your Audience
Trust is one of the major building blocks of service-based marketing. When marketing your service, your main reference is the service itself. But what is more important is what other people (existing customers) have to say about you.
When marketing yourself, all you have to convince people is words. But when one or two people can testify about your services, it saves you the stress of proving your efficacy to each customer.
One good way to earn the trust of your audience is to deliver as expected, or more than expected . Once your customers are satisfied with your service, they will naturally tell others that need your service about their fruitful experience with your brand. Your brand gains new customers in the process.
Deliver quality services to the new customers and they will in return keep spreading glowing reviews about your brand. Reviews from your customers are very effective for attracting new customers.
5. Leverage Social Networking
Social media accounts help you to communicate effectively. The importance of social networking cannot be overemphasized. Most successful businesses have multiple social media accounts to reach out to a larger audience easily and quickly.
As a business, you need to create a website that has information about your services. You can use website builder tools like Wix and Squarespace to create the website. Then create accounts on social media like Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Instagram, etc.
Provide links to your media accounts on your website. Market your service business on these accounts regularly. You can even hire social media managers on freelance job websites like Upwork and Fiverr to manage your social media accounts on your behalf.
Service Marketing Types
The term ‘marketing' talks about creating awareness about your business, what you have to offer, and how your solution can benefit lots of people .

Here are the three types of service marketing: internal marketing, external marketing, and interactive marketing.
1. Internal Marketing
This is the type of marketing done by the company to its employees . Your employees need to be aware of what your service offers. It is done through empowerment programs and training. Your employees should be ambassadors of your service.
2. External Marketing
External marketing is the most common type of marketing. It is done by the company to its customers.
This type of marketing is the one that drags sales into your business because you are directly reaching out to the target audience. External marketing is done through advertisements, promotions, online PR.
3. Interactive Marketing
This type of marketing is between the employees and customers . In a marketing funnel, different employees have where they directly interact with customers.
Interactive marketing is done through customer support, interactions on social media, and personal employees. An example is when the customer service department of a service-based business attends to the welfare of customers.
Examples of Service Marketing
There are two classes of service marketing examples. We have B2B (Business to Business) service marketing examples and B2C (Business to Customer) service marketing examples.
B2B Services Marketing Examples
1. jbarrows sales training.

JBarrows Sales Training is one of the best service providers that provides consultancy and sales training services to some of the world’s leading service establishments like G2 Crowd, Slack, etc.
These companies use JB services to ensure that their teams hold high-quality meetings with the target markets . The sales training offered by JBarrows also helps to improve the quality of interactions during the sales process.
JBarrows Sales Training employs actionable strategies to help small and large-scale companies achieve desirable results.

Cience is a B2B service provider that uses multi-channel prospecting to help companies grow. With highly accurate research, they provide outbound sales processes that enable qualified meetings with your target audiences. Clients are assured of positive results.
Cience is among the top 10 fastest-growing marketing companies in the US. They have been able to serve different clients in hundreds of industries.
B2C Service Marketing Examples

Uber is a transportation business that connects available drivers with customers via mobile apps. For customers, it is a fast and convenient service compared to commercial transit buses. For the drivers, they get to earn an income while transporting people to their desired destination.
The online transport giant builds credibility by in-app reviews dropped by customers after each ride. Its primary value is flexibility for both parties.

Airbnb is an online market where people can find nearby accommodations. The company can sort customers' needs such as duration, costs, accommodation, location, etc. Customers enjoy a quality user experience when they use Airbnb and this boosts the company's reviews in return.
What are the 7 P's of Service Marketing?
There are 7 P's of service marketing . They include product, price, place, promotion, people, process, and physical evidence.

Product is what the word ‘marketing' centers on. It is whatever you have to offer as a solution to meet your customers' needs . In this case, it could be information, your blog, or even a consulting service. The perks of your service and its advantage over other rival service providers should be obvious to your target audience.
Your product has to be well defined in terms of its primary attributes and its extended attributes. The attributes of your service are the building block of your marketing strategy.
If your service design is faulty, no amount of marketing strategy can earn you a large audience. Products can include technology, UI/UX design, securities, transportation medium, and more.
Regardless of the value that you offer, pricing is a key determiner in acquiring customers and their final satisfaction. Before placing a price tag on your service, it would be best if you know the audience's price expectation range (and what your rivals are charging for the same service). It would help you know if you are charging far above the average or far below their expectations.
Talking about services, the price might not correctly indicate the quality. It is like putting a price on an abstract feeling.
There are several price strategies used in service marketing. They include:
Penetration Pricing
For this type of pricing, you start with low charges to acquire a large audience. As your brand begins to grow, you increase your charges.
In this way, you are slowly increasing your price rate on your audience. It may not have a one-time effect on them, compared to when you go from a low price to a ridiculously high price at once. An example of a company that adopted this strategy is Sky TV.
Economy Pricing
Economy pricing means setting a low price that is difficult for your competitors in the market to beat. But take note that this low price must still be profitable for your business. As long as it remains profitable, it is a good pricing strategy.
Premium Pricing
Premium pricing refers to when you place high prices on your service. You have to justify the reason why you are pricing at a premium or else competitors will look the other way at your competitors. One easy way to justify premium pricing is to deliver a unique, top-notch, and quality service.
Product Line Pricing
This pricing strategy refers to when you break down your services into small tiers or categories with specific prices per category. It means that your prices increase as you offer a higher number of services with higher value.
An example is a car washing company for different categories of car cleaning. They can have different price tags for basic wash, wash with wax, and full package.
Geographical Pricing
This pricing strategy depends on the location of the company in any part of the world. Variations in prices can arise from the location of a company. Countries that place more value on your services or where there are higher tax rates would offer services for higher prices.
For offline services such as legal services, healthcare, household upkeep, etc, proximity is an important factor to consider . The closer you are to your target audience, the higher the chances of increasing sales. Accessibility is not an excuse for your audience when marketing your services to them once you are situated close to them.
For online services where sales and purchases are made virtually, there are still some determining factors for high purchase probability. The common ones include:
- Security status of payment
- Ease of payment
- Account management
- Type of transaction
- Variety of payment methods
4. Promotion
Promotion refers to the mediums through which you advertise your services to your intended target audience. It plays a major role in whatever perspective the target audience has when they look at your service. Your positioning has to complement your promotion. Promotion leads to brand recognition and evaluation of your services .
Positioning (where exactly you are promoting your service) has a major role in the perception of your service. For example, where do you want to promote your service? Is it on Facebook Ads? Is it on Adwords? Also, what contents will they contain?
People refer to the target audience you are promoting and marketing your services to. The success and credibility of your service depend on how you can develop a good relationship with your target markets. It is essential to develop and manage customer relationships efficiently.
You need to pay close attention to what your customers want. It is one of the determining factors for the success of your service marketing campaign.
Unlike physical products, service marketing is not only about the results. The process is an important concept to consider when rendering services.
When you can define your process clearly and properly, customers will perceive your service as a credible and dependable one. It will assure them that their expectations will be met.
Having an effective process for handling your customer support is essential. It is very important to swiftly attend to any issues your customers have. Poor customer support processes will affect the satisfaction level of your customer with your service.
As a service business, solving your customer's issues is not the only important (result) factor but how quickly, efficiently, and gently you attend to it (process) matters.
7. Physical Evidence
Physical evidence affects a customer's satisfaction with abstract services. Since these services are intangible (cannot be seen, felt, or touched), customers depend on stories from existing customers to put their trust in you.
Reviews, accreditations, and stamps are what build a customer's trust in a service provider. Trust is built when you prove the promises you make when marketing your services to your target audience. Also, if no claims are negating your promises, it is easier to build trust in your customers' minds.
Was This Article Helpful?
Anastasia belyh.
Anastasia has been a professional blogger and researcher since 2014. She loves to perform in-depth software reviews to help software buyers make informed decisions when choosing project management software, CRM tools, website builders, and everything around growing a startup business.
Anastasia worked in management consulting and tech startups, so she has lots of experience in helping professionals choosing the right business software.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Characteristics of service marketing

Related Papers
Journal of Services Marketing
Sabine Benoit
G. K. Deshmukh
.{BSTRACT: In present era delivery of betler quatity eustomer services has become a skategic practice for firms in aimost all sectcrs' Eetter quality services are an abstract term whose explanation varies from customer to customer. Further services ar* intangible in nature thus it is very difficult-for organisations to understand and practice the rhilosophy of providing quality serviees. Customer's satisfaction lan only be attained by organisations if they are abie to provide qualrry serviees at affordable prioes after rnatching customer's expectations. The policies of Governraent and regulators ha're forced financia! institutions to proiide quality ,.*i.., to customers. Further awareness of customer rights have also increascd over the years wtricir tras *uO" iojuv;J'.rrro,,,.*, urry practical and demanding. Due to its import3nt rrine organisations are paying too much utt*rtiln ro, enhancement ofservice qualrty.
Marketing Science
dawn iacobucci iacobucci
Stephen L Vargo
Professor Jochen Wirtz
Nothing stands still. Technology evolves dramatically, customer needs keep changing, and new industries emerge. To forge ahead in this highly competitive landscape, businesses increasingly rely on service and service products to create and capture value. The Essentials of Services Marketing, Second Edition is written in response to this global transformation of our economies to services.
ruel muico , Joshua Noel Cañeda
Putting up a business has been a dream of many people. However, there are many aspects to be considered in entering the world of business, because every business has its own purpose. As known, the main purpose of business is to earn profit which funds the costs of operating the business as well as providing for the life needs of the proprietor. In addition, a business offers value through products and services to customers who pay for the value with cash or its equivalents. Businesses provide jobs for the people of a local community where it operates. It helps in the enhancement of the country’s international relation with other countries by means of investments, which lead to the improvement of the country’s economy. There are two types of business that people can choose from, the product-oriented business and service-oriented business. Both product and service-oriented businesses sell a product. But the ultimate difference between the two is that the product-oriented business actually sells a physical, tangible product, while the service-oriented business owners sell skills as the main product. The service-based businesses are the ones wherein work is performed in a professional manner by an individual or team for the benefit of the customers. The typical service-oriented businesses provide intangible products such as accounting, banking, consulting, cleaning, landscaping, education, insurance, treatment and transportation services. Service-oriented businesses rely on people and the client experience, which can be risky. On the other hand, product-based businesses can be assured that the product is going to be the same from customer to customer, making the customer’s experience fairly predictable, such as McDonalds, KFC, Ford Motor Company, Toyota Motors, Unilever and many more. As any business owner will tell, employees are one of the most important factors in any company. Whether the business is a large multinational organization or a small start-up that is just beginning to grow, the people you employ are absolutely vital. Because one of the major challenges for a start-up business is establishing reputation – ensuring that the company name is synonymous with good work, quality service and professionalism. With your employees acting as the face of the business, it is vital that the right people are on-board. It can take years to build a reputation and seconds to destroy one, so it is sensible to put procedures in place to protect the interests of the business and the employees in it. But in many instances even with the right people in the business there will be a scenario that can challenge the reputation of the business. The dictum that “Customers are always right!” is drilled into every young retail or hospitality worker, and has somehow made its way into the psyches of established business owners. It is used to convince customers that good service will be received from the company and to convince employees to give customers good service. It advocates that customer complaints should be treated seriously so that customers do not feel cheated or deceived. But the problem is, the customer is not always right, and always having this as a viewpoint can result in serious disservice to the business, employees, and customers. However, it was pointed out that customers can be dishonest, have unrealistic expectations that can lead to misunderstanding. The purpose of this study is to highlight the problems in the measurement of service quality, why the management seems to ignore some of the costs of poor service quality, as well as the repercussions of this, and how to implement service quality correctly in organizations.
Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences (PEN)
snehal pawar
International Journal of Scientific Management and Development
The research intends the Studying the effects of Service offering Potential on Marketing performance and competitive advantage with using service orientation as mediating role, a conceptual model was developed and tested. In order to this, a conceptual model was developed and tested. For this purpose, Four hypotheses were developed and tested. This study, from the purpose point of view can be considered as an applicable study and survey in terms of method of execution with correlation approach. The population includes Heads and deputy Bank Saderat Esfahan. Due to the limited size of population, the entire population was considered as the sample and no sampling was done. Data collection tool in this study is 24 question questionnaire designed by researcher and its validity was acknowledged by supervisor and advisors professors and management experts. The reliability of questionnaire was also confirmed by the Alpha index of 0.83. The questions of questionnaire are divided into demographic and main questions for testing hypotheses. From the 160 distributed questionnaires 145 were back (rate of return= 90%) and used to analyze data. Collected data were analyzed by SmartPLS software through two levels of statistical tests: descriptive level which involves frequency, percentage, cumulative percentage, mean and standard deviation and perceptive level which involves regression modeling, ANOVA, nonparametric test of Kolmogorov-Smirnov and nonparametric test of Friedman. Study findings based on structural equation outputs suggested appropriate goodness of fit indices GFI and DF. The findings revealed that all of the research hypotheses were supported.
International Journal of Services Technology and Management
Marko Ropret
RELATED PAPERS
Binus Business Review
anwar basalamah
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine
alex karagrigoriou
Ankara Medical Journal
Ayhan Ozhasenekler
Turkish Journal of Agriculture - Food Science and Technology
Devrim ÖZCAN
Brandi Simpson Miller
Advanced Powder Technology
Xiaoshu Cai
Elizaveta Permyakova
מחקרי ארץ יהודה ה
Amos Frumkin
Revista Direito e Práxis
André Carneiro Leão
GENEALO Wasquehal
Dominique M Delgrange
ARTEKS : Jurnal Teknik Arsitektur
Nisrina Dewi Salsabila
Journal of Wood Science
Kenichi Kuroda
International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chee Kuan Wong
Planeacion de un proyecto socioformativo
NANCY FABIOLA ANGOLI GARCíA
Apunts. Educació física i esports
Jean-paul Micallef
PLoS Medicine
Wanpen Chaicumpa
Scientific Reports
Fabio Polesel
Tadesse Dukessa
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Journal of Services Marketing: Volume 24 Issue 5
Table of contents, service quality, trust, commitment and service differentiation in business relationships.
While service quality, trust and commitment are frequently cited as critical to achieving important firm outcomes, the role of service differentiation in this framework is largely…
The role of intimacy in service relationships: an exploration
Relationship marketing is now commonly acknowledged as an alternative marketing paradigm. However, despite the use of the relationship metaphor in marketing contexts for many…

Characteristics of services – a new approach uncovers their value
Four characteristics have been regularly applied to services: intangibility, heterogeneity, inseparability, perishability (IHIP). More and more exceptions occur which have…
Testing a branch performance model in a New Zealand bank
This study aims to develop and test a comprehensive model that begins with management commitment/concern and progresses through intermediate links of service climate and in‐role…
Service brand equity and employee brand commitment
The aims of this article are to measure the brand equity of service firms (luxury hotels) using a customer perspective, to identify factors that predict customers’ brands…
A CIT investigation of other customers' influence in services
This paper aims to explore the different forms of other customers' influence in various service settings.
Synergistic effects of operant knowledge resources
Building on the service‐centered dominant logic, this paper aims to investigate the effects of firm knowledge (knowledge of customers, industry, and practices) and synergistic…

Online date, start – end:
Copyright holder:, open access:.
- Dr Rebekah Russell-Bennett
- Dr. Mark Rosenbaum
Further Information
- About the journal (opens new window)
- Purchase information (opens new window)
- Editorial team (opens new window)
- Write for this journal (opens new window)
We’re listening — tell us what you think
Something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
11.1 Classification of Services
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- 1 Define services.
- 2 List the classification of services.
- 3 Describe the characteristics of services.
Services Defined
You may have heard that the United States’ economy is primarily considered a service economy. But do you know why this is? Figure 11.2 provides the answer. It outlines the percentage each industry contributed to the gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020. 3 (A quick refresher from your economics course: the GDP is a measure of the total monetary value of all finished goods and services generated within a country’s borders during a specified period of time.) Which industries are the largest contributor to the GDP? Service industries. (Note that this figure does not include smaller industries such as utilities, or mining and agriculture.) When you total the service industries, they make up a whopping 67 percent of GDP versus only 10.8 percent for manufacturing.
In a nutshell, services are the nonphysical, intangible economic activities. On the other hand, physical goods are the things we can touch or handle, commonly called tangibles. Do you realize that, as you read this textbook, you’re participating in the services sector of the economy? That’s because education is considered part of the service sector. The service sector also includes things like banking, medical treatment, transportation, insurance, and many more categories. Based on the fact that the majority of contributions to the GDP in the United States are services, and more than half of the country’s workforce is employed in producing “intangibles,” it’s critical to understand this important sector from a marketing perspective.
Consider the challenges to marketers when selling services as opposed to products. A consumer can’t touch or see the service before they purchase, so it’s difficult to examine or evaluate benefits. Think about it: you can’t take a service out for a test drive the way you might if you were buying a new car. Yet it’s just as crucial for organizations that provide services to build brand awareness and brand loyalty.
Classification of Services
Services are classified as people-based services or equipment-based services. And within those classifications, there are subcategories (see Figure 11.3 ).
People-Based Services
People-based services are when people primarily deliver the service, rather than equipment or machinery (see Figure 11.4 for examples). It’s the individuals delivering the service, and the knowledge and skills that they possess, that add value and allow the service to be performed. People-based services can be broken down further into these subcategories:
- services provided by unskilled labor: parking lot attendants, babysitters, and janitors
- services provided by skilled labor: plumbers, caterers, and hairstylists
- services provided by professionals: doctors, attorneys, college professors, and accountants
Equipment-Based Services
Equipment-based service firms utilize equipment, machinery, and other forms of technology to perform service tasks (see Figure 11.5 ). Similar to people-based services, equipment-based services can be further broken down into subcategories:
- automated services: car washes and parking meters
- equipment-based services operated by relatively unskilled operators: dry-cleaning equipment
- equipment-based services operated by skilled operators: X-ray machines and ultrasound equipment
There is another way to categorize services, according to well-known author and professor Christopher Lovelock (1940–2008). He proposed four broad categories of services:
- people processing: services toward people’s bodies
- possession processing: services toward possessions
- mental stimulus processing: services toward people’s mind
- information processing: services toward intangible assets 4
In Figure 11.6 , the categories are defined on a two-dimensional matrix, wherein one of the dimensions is the direct recipient of the service and the other is the nature of the service act. 5
Link to Learning
If you plan to continue toward a marketing degree, you’ll want to familiarize yourself with Christopher Lovelock’s work. You can run a search on Amazon.com for his books or a search in your browser for articles and more information. Start by reading his Wikipedia page to learn about his academic background and achievements.
Let’s look at each of these categories in more depth. The first two categories (people processing and possession processing) involve tangible actions directed toward a person’s physical body or property, whereas mental stimulus processing and information processing involve intangible actions directed toward a person’s mind or information. We’ll expand on this in the following sections.
People Processing
In people processing services, the customer is a direct recipient of the service, and the production and consumption of the service are simultaneous. Consider examples of services where you must be present in the service facility in order to interact with the service provider and receive the service, such as barbershops or hair salons, physical therapists’ offices, or restaurants.
Possession Processing
The difference between people processing and possession processing is that the service is directed toward the customer’s physical possessions. In other words, production and consumption are separate. Your only involvement is dropping off the item that requires service or repair and explaining the problem. For example, once you have taken your car in for an oil change, you do not need to be physically at the location for the oil change to occur. Similarly, once you’ve dropped your clothes off at the dry cleaner’s, you don’t need to be physically present when the cleaning process is performed. These services are tangible because the direct recipient is one of your possessions rather than you as a person.
Mental Stimulus Processing
In its simplest explanation, mental stimulus processing is when the services interact with your mind rather than your body. Time and mental effort are required from the customer to receive this type of service. What you’re doing right now—reading this textbook—is a prime example of mental stimulus processing. Other examples include psychotherapy or counseling services. The key here is that services rendered in this category are intangible.
Information Processing
Information processing is the most intangible form of service, although it can be transformed into a tangible service output like reports, books, letters, DVDs, etc. Some examples of information processing services are things like meeting with your financial advisor regarding investment advice, legal services, and banking. 6
Service Industry Stats and a Changing Industry
If you’d like more insight into service industries, check out the US Bureau of Labor Statistics website . It categorizes industries and provides interesting statistics on employment.
Companies are launching new services every day. Think about it—services like Uber didn’t exist 20 years ago. As a marketer, understanding services and their business models is critical. Start here and read about on-demand service companies and how services—and apps—are changing the industry. And also check out this article about the top 15 service businesses for 2022 .
Characteristics of Services
As outlined in Figure 11.2 , service industries contribute the major percentage of the US GDP. It’s important to understand that this shift from the manufacturing sector to the service sector isn’t limited to the United States. Increasingly, the world economy is being characterized as a service economy. Looking at economic history, we can see a natural evolution in developing countries from the agricultural industry to the service sector as the mainstay of the economy. That’s why it’s critical for marketers to understand the characteristics of services.
As we pointed out above, some services come from physical products, such as getting a haircut or having your income tax return prepared by a professional. But other services are completely intangible. When you rent a hotel room, travel on an airplane, visit your doctor, attend a professional sporting event, or get advice from a lawyer or an accountant, you’re buying a service, so a marketer needs to consider the characteristics of services in order to get the right marketing messages to the right target market (see Figure 11.7 ).
Service Intangibility
By their very nature, services are intangible . This means they can’t be seen, tasted, felt, smelled, or heard before they are purchased. Consider the last time you purchased automobile insurance for your car. Other than the physical policy the company sends you (the only tangible asset), what you’ve paid for is completely intangible—it’s the company’s promise to pay claims against the policy.
Intangible services have a number of implications in marketing. The very fact that there’s nothing to touch, hear, smell, and so on typically increases the level of uncertainty that a consumer faces when choosing between services offered by your organization or those of competitors. Intangible services can seldom be tried out, inspected, or even given a “test drive” by a customer. Customers have to rely on the word of the marketers in order to assess what they’re actually going to get in return for what they’ve paid. In effect, they are buying a promise.
Savvy marketers reduce this uncertainty by creating physical “evidence” that allows the consumer to picture the service before it is purchased. For example, a hair salon may have imaging software that predicts how you would look with different hairstyles or colors. Companies like Zenni and Eyebuydirect have a virtual mirror that allows you to “try on eyeglasses” and see how the selected frames look on your face before you purchase. 7
Service Inseparability
The order of production and consumption between a physical product and a service differs. Think about a box of Girl Scout cookies, a physical good or product. The cookies were produced, stored, sold, and finally consumed. That’s not the way it works with services. Like goods, services are sold, but they are produced and consumed simultaneously. They can’t be separated from the service providers, whether they are people or equipment. 8 For example, try to get money out of your bank on a weekend or evening without an ATM, or try to get a haircut without the physical presence of your stylist. That’s the concept of service inseparability —you can’t separate the delivery of the service from the presence of the customer. In other words, the service provider is physically connected to the service and is evaluated on the basis of their communication skills, language, demeanor, personal hygiene, and clothing.
The impact to the marketer in these services—in which the service provider and customer must both be present—is how service providers (sometimes called frontline employees) conduct themselves in the presence of the customer because it may determine the likelihood of repeat business. 9 There are also other marketing implications with this concept, such as customer cooperation and participation, not to mention the influence from other customers who may be present.
Service Variability
Have you ever gone to a restaurant and had stellar customer service? You were seated promptly by a cheerful hostess; the busser filled up your water glass and refilled it several times during the evening; the waitstaff was attentive but not to the point of being annoying; and your dirty dishes were cleared promptly. But perhaps the next time you visit the same restaurant, your experience isn’t quite as amazing. The hostess isn’t as cheerful, and it takes her several minutes to seat you. It takes a while for someone to refill your water glass. The waitstaff isn’t nearly as attentive as they were during your first visit. What went wrong?
Perhaps what you’ve experienced is what’s known as service variability —the quality of the service depends on who provides it, when it is provided, and how it is provided. For example, Delta Air Lines prides itself on improving peoples’ lives and exceeding customer expectations. 10 However, because services are provided by humans who have human experiences where they may not be feeling well or they are having a bad day, the service may be variable between employees. One Delta employee may be cheerful and efficient, while another lags due to their energy and state of mind.
This is a challenge to marketers because products generally have little variability: each unit is built to certain specifications. For example, if you buy an Apple iPad Pro and your classmate purchases the same model, it’s likely that the two iPads will be virtually identical. The case color may be different, but otherwise they are the same. That’s not the case with a service, where there will undoubtedly be variations in the quality of the service depending on who offers the service, when it is offered, and at which location. Service-based companies need to rely on standardizing processes to the extent possible, frequent audits, customer surveys, and most importantly, customer feedback.
Service Perishability
Unlike most goods, services can’t be produced and stored for later use or sale. Services are, in effect, performances by the service provider. That’s the concept of service perishability . Did you miss tonight’s concert because of traffic? Too bad, because a ticket for tonight’s concert can’t be used for tomorrow night’s performance. Hotel rooms that are not occupied, airline seats that are not purchased, and unused gym memberships cannot be reclaimed. 11 Because these items can’t be stored for later use, they are considered a perishable service. This is particularly important for marketers because the perishability factor and the fluctuating demand poses special problems in capacity planning, scheduling, product planning, and pricing. 12
One way that marketers deal with this problem is by manipulating demand. Consider how many restaurants offer “happy hours” with discounted food and drinks during the late afternoon or early evening. Restaurants do this because this time is typically the period where there is a lull before the start of the dinner rush.
Careers In Marketing
You might be curious about the salaries of marketing jobs. There are numerous online resources that provide guides, but the best step to take is to check out popular sites like Monster, Indeed, and LinkedIn to view current job positions. They may not all include the salary, but most will include salary ranges. The following is a list of a few of resources to get you started.
- Monster: “High-Paying Marketing Jobs”
- Acadium: “How Much Do Marketers Make? Marketing Job Salaries in 2022”
- All Business Schools: “Marketing Manager Salaries and Job Outlook”
- Indeed: “Entry Level Marketing Salary in United States”
Knowledge Check
It’s time to check your knowledge on the concepts presented in this section. Refer to the Answer Key at the end of the book for feedback.
- Service variability
- Service inseparability
- Service perishability
- Service intangibility
- People-based services: unskilled labor
- Equipment-based services: unskilled operator
- People-based services: professionals
- Equipment-based services: skilled operator
- People-based services: skilled labor
- Equipment-based services: automated service
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Dr. Maria Gomez Albrecht, Dr. Mark Green, Linda Hoffman
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Marketing
- Publication date: Jan 25, 2023
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/11-1-classification-of-services
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 8. Services Marketing
Ray Freeman and Kelley Glazer
Learning Objectives
- Explain the meaning of services marketing
- Describe the differences between marketing services and marketing products
- Describe the characteristics of a marketing orientation and its benefits
- Define key services marketing terminology
- Explain the PRICE concept of marketing
- Provide examples of the 8 Ps of services marketing
- Gain knowledge of key service marketing issues and trends

Marketing is a continuous, sequential process through which management plans, researches, implements, controls, and evaluates activities designed to satisfy the customers’ needs and wants, and meet the organization’s objectives. According to Morrison (2010), services marketing “is a concept based on a recognition of the uniqueness of all services; it is a branch of marketing that specifically applies to the service industries”(p. 767).
Marketing in the tourism and hospitality industry requires an understanding of the differences between marketing goods and marketing services. To be successful in tourism marketing, organizations need to understand the unique characteristics of their tourism experiences, the motivations and behaviours of travelling consumers, and the fundamental differences between marketing goods and services.
The Evolution of Marketing
Until the 1930s, the primary objective of businesses was manufacturing, with little thought given to sales or marketing. In the 1930s, a focus on sales became more important; technological advances meant that multiple companies could produce similar goods, creating increased competition. Even as companies began to understand the importance of sales, the needs and wants of the customer remained a secondary consideration (Morrison, 2010).
In 1944, the first television commercial, for Bulova watches, reached 4,000 sets (Davis, 2013). The decades that followed, the 1950s and 1960s, are known as an era when marketing began to truly take off, with the number of mediums expanding and TV ad spending going from 5% of total TV revenues in 1953 to 15% just one year later (Davis, 2013).

The era from approximately 1950 to around 1970 was known as a time of marketing orientation (Morrison, 2010). Customers had more choice in product, this required companies to shift focus to ensure that consumers knew how their products matched specific needs. This was also the time where quality of service and customer satisfaction became part of organizational strategy. We began to see companies develop internal marketing departments, and in the 1960s, the first full-service advertising agencies began to emerge.
Societal marketing emerged in the 1970s when organizations began to recognize their place in society and their responsibility to citizens (or at least the appearance thereof). This change is demonstrated, for example, by natural resource extraction companies supporting environmental management issues and implementing more transparent policies. This decade saw the emergence of media we are familiar with today (the first hand-held mobile phone was launched in 1973) and the decline of traditional marketing through vehicles such as print; the latter evidenced by the closure of LIFE Magazine in 1972 amid complaints that TV advertising was too difficult to compete with (Davis, 2013).
The mid-1990s ushered in the start of the online marketing era. E-commerce (electronic commerce) revolutionized every industry, perhaps impacting the travel industry most of all. Tourism and hospitality service providers began making use of this technology to optimize marketing to consumers; manage reservations; facilitate transactions; partner and package itineraries; provide (multiple) customer feedback channels; collect, mine, analyze, and sell data; and automate functions. The marketing opportunities of this era appear limitless. Table 8.1 summarizes the evolution of marketing over the last century.
Typically, the progression of marketing in tourism and hospitality has been 10 to 20 years behind other sectors. Some in the industry attribute this to the traditional career path in the tourism and hospitality industry where managers and executives worked their way up the ranks (e.g., from bellhop to general manager) rather than through a postsecondary business education. It was commonly believed that to be a leader in this industry one had to understand the operations inside-out, so training and development of managers was based on technical and functional capabilities, rather than marketing savvy. And, as we’ll learn next, marketing services and experiences is distinct and sometimes more challenging than marketing goods. For these reasons, most businesses in the industry have been developing marketing skills for only about 30 years (Morrison, 2010).
Differences Between Goods and Services

There are four key differences between goods and services. According to numerous scholars (Regan; Rathmell; Shostack; Zeithaml et al. in Wolak, Kalafatis, & Harris, 1998) services are:
- Heterogeneous
- Inseparable (simultaneously produced and consumed)
The rest of this section details what these concepts mean.
Intangibility
Tangible goods are ones the customer can see, feel, and/or taste ahead of payment. Intangible services, on the other hand, cannot be “touched” beforehand. An airplane flight is an example of an intangible service because a customer purchases it in advance and doesn’t “experience” or “consume” the product until he or she is on the plane.
Heterogeneity
While most goods may be replicated identically, services are never exactly the same; they are heterogeneous . Variability in experiences may be caused by location, time, topography, season, the environment, amenities, events, and service providers. Because human beings factor so largely in the provision of services, the quality and level of service may differ between vendors or may even be inconsistent within one provider. We will discuss quality and level of service further in Chapter 9.
Inseparability
A physical good may last for an extended period of time (in some cases for many years). In contrast, a service is produced and consumed at the same time. A service exists only at the moment or during the period in which a person is engaged and immersed in the experience.

Perishability
Services and experiences cannot be stored; they are highly perishable . In contrast, goods may be held in physical inventory in a lot, warehouse, or a store until purchased, then used and stored at a person’s home or place of work. If a service is not sold when available, it disappears forever. Using the airline example, once the airplane takes off, the opportunity to sell tickets on that flight is lost forever, and any empty seats represent revenue lost.
Planning for Services Marketing
To ensure effective services marketing, tourism marketers need to be strategic in their planning process. Using a tourism marketing system requires carefully evaluating multiple alternatives, choosing the right activities for specific markets, anticipating challenges, adapting to these challenges, and measuring success (Morrison, 2010). Tourism marketers can choose to follow a strategic management process called the PRICE concept , where they:
- P: plan (where are we now?)
- R: research (where would we like to be?)
- I: implement (how do we get there?)
- C: control (how do we make sure we get there?)
- E: evaluate (how do we know if we got there?)
In this way, marketers can be more assured they are strategically satisfying both the customer’s needs and the organization’s objectives (Morrison, 2010). The relationship between company, employees, and customers in the services marketing context can be described as a services marketing triangle (Morrison, 2010), which is illustrated in Figure 8.5.
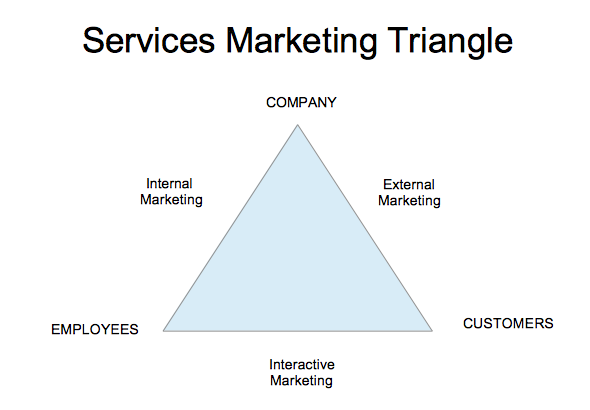
In traditional marketing, a business broadcasts messaging directly to the consumer. In contrast, in services marketing, employees play an integral component. The communications between the three groups can be summarized as follows (Morrison, 2010):
- External marketing: promotional efforts aimed at potential customers and guests (creating a promise between the organization and the guest)
- Internal marketing: training, culture, and internal communications (enabling employees to deliver on the promise)
- Interactive marketing: direct exchanges between employees and guests (delivering the promise)
The direct and indirect ways that a company or destination reaches its potential customers or guests can be grouped into eight concepts known as the 8 Ps of services marketing .
8 Ps of Services Marketing
The 8 Ps are best described as the specific components required to reach selected markets. In traditional marketing, there are four Ps: price, product, place, and promotion. In services marketing, the list expands to the following (Morrison, 2010):
- Product: the range of product and service mix offered to customers
- Place: how the product will be made available to consumers in the market, selection of distribution channels, and partners
- Promotion: specific combination of marketing techniques (advertising, personal sales, public relations, etc.)
- Pricing: part of a comprehensive revenue management and pricing plan
- People: developing human resources plans and strategies to support positive interactions between hosts and guests
- Programming: customer-oriented activities (special events, festivals, or special activities) designed to increase customer spending or length of stay, or to add to the appeal of packages
- Partnership: also known as cooperative marketing, increasing the reach and impact of marketing efforts
- Physical evidence: ways in which businesses can demonstrate their marketing claims and customers can document their experience such as stories, reviews, blog posts, or in-location signage and components
It’s important that these components all work together in a seamless set of messages and activities known as integrated marketing communications, or IMC, to ensure the guests receive a clear message and an experience that meets their expectations.
Integrated Marketing Communications

Integrated marketing communications (IMC) involves planning and coordinating all the promotional mix elements (including online and social media components) to be as consistent and mutually supportive as possible. This approach is much superior to using each element separately and independently.
Tour operators, attractions, hotels, and destination marketing organizations will often break down marketing into separate departments, losing the opportunity to ensure each activity is aligned with a common goal. Sometimes a potential visitor or guest is bombarded with messaging about independent destinations within a region, or businesses within a city, rather than one consistent set of messages about the core attributes of that destination.
It’s important to consider how consumers use various and multiple channels of communication and reach out to them in a comprehensive and coherent fashion. As a concept, IMC is not new, but it is more challenging than ever due to the numerous social media and unconventional communication channels now available. Each channel must be well maintained and aligned around the same messages, and selected with the visitor in mind. Too often businesses and destinations deploy multiple channels and end up neglecting some of these, rather than ensuring key platforms are well maintained (Eliason, 2014).
In order to better understand our guests, and the best ways to reach them, let’s take a closer look at the consumer as the starting and focal point of any marketing plan.
Consumer Behaviour in Tourism and Hospitality
Customers use their senses to see, hear, smell, and touch (and sometimes taste) to decipher messages from businesses, deciding on a product or service based on their perception of the facts rather than, at times, the actual facts. A number of factors have been shown to impact the choices the consumer makes, including personal factors, which reflect needs, wants, motivations, previous experience, and a person’s lifestyle, and interpersonal factors, such as culture, social class, family, and opinion leaders.
Perception Is Reality
The area of perception can be further broken down to screens and filters, biases, selective retention, and closure (Morrison, 2010). Let’s look at these concepts in more detail.

The world is filled with things that stimulate people. People are exposed to thousands of messages every day. Some stimuli come from the people around us; for example, a person on the bus might be wearing a branded cap, the bus may have advertising pasted all over it, and free newspapers distributed at the bus station could be filled with advertising. The human brain cannot absorb and remember all of these messages; people will screen out most of the stimuli they are exposed to. They may remember a piece or segment of a message they have seen or heard.
Take a Closer Look: 100 BC Moments Vending Machine
As part of a 2012 integrated campaign, Destination BC (then operating as Tourism BC) created a vending machine that offered users the opportunity to experience moments that could be part of their visit to British Columbia. At 14 feet tall, this vending machine dispensed free items like bikes, surfboards, and discounts on flights to encourage people to travel British Columbia. This experiential innovation was a way to provide a tangible element to intangible services. It was complemented by an online and social media campaign using the hashtag #100BCMoments and special web landing page at 100BCMoments.com. A video of the San Fransisco installation earned hundreds of thousands of views on YouTube; cutting through the clutter both in person and online. Watch it here: Giant Tourism BC Vending Machine comes to San Francisco : www.youtube.com/watch?v=VWbQtK4N8cM

Perceptual Biases
Everyone has perceptual biases; each person sees things from his or her own unique view of the world. An advertising message can be received and changed to something very different from the marketer’s intended statement.
Selective Retention
Once messages have made it through the screens, filters, and biases, they still may not be retained for long. Customers will practise selective retention, holding on only to the information that supports their beliefs and attitudes.

The brain does not like incomplete images. There is a state of psychological tension present until the image is complete (closure). Where information is unavailable to round out the images, the mind adds the missing data. Over time, through the use of imagery and music (such as jingles), messages are ingrained in a customer’s mind, and he or she automatically adds the company’s name, whether it is mentioned or not.
Applying Psychology to Marketing
Marketers may determine a degree of predictability about customer perceptions. Customers are likely to:
- Screen out information that they are already familiar with
- Notice and retain information to satisfy a need they are aware of (want)
- Purchase services that reflect the image they perceive themselves to project
- Notice and retain things out of the norm
- Attach credibility to personal information rather than commercially generated information
Customers are less likely to:
- Use perceptual biases to distort information received on an interpersonal basis
- Absorb complicated information that requires effort to comprehend
- Notice and retain information about a competitive service or product if they are satisfied with another brand
Tourism marketers are in the business of reminding and making customers aware of their needs. Customers have to be motivated to act on satisfying their wants and needs, while marketers need to trigger the process by supplying objectives and potential motives.
Spotlight On: Tourism Victoria’s Visitor Centre
Tourism Victoria’s Visitor Centre is a member of the Visitor Centre Network. Staff are available to provide travellers with tourist information, assistance, and advice. The Tourism Victoria Visitor Centre provides travellers with a wide range of services, including professional visitor counselling, helpful travel information and literature, and accommodation reservations (Tourism Victoria, 2015).
Consumer Decision-Making Process

In 1968, Kollat, Blackwell and Engel released the first edition of a book called Consumer Behavior where they identified a distinct five-step pattern for consumer decision-making (1972). These steps are: need recognition, information search, pre-purchase evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation.
Here are some critical components at each stage:
- Need recognition: For this process to start there needs to be a stimulus; a need must be triggered and identified.
- Information search: The customer begins to consult different sources of information; personal (marketer dominated) and intrapersonal (non-marketer) factors will likely be used.
- Pre-purchase evaluation: After researching the choices, the customer starts to evaluate options using both objective criteria, such as price and location, and subjective criteria, such as the perceived status of the product or service.
- Purchase: The customer intends to buy the product or service that best matches the criteria, although he or she can still be influenced by a number of factors, such as friends and family who disagree with the purchase, or a change in personal finances.
- Post-purchase evaluation: After use, the customer evaluates the purchase against expectations; if these don’t match, the customer will be either dissatisfied (expectations not met) or impressed (expectations exceeded). For this reason, it’s best for hospitality and tourism providers to “under promise” and “over deliver.”
Spotlight On: BC Ferries Vacations
BC Ferries Vacations offers over 70 unique travel packages to 40 destinations, connecting travellers to unbeatable scenery, accommodations, and activities. With world-class hotels, activities, and adventures to choose from, travellers can experience BC’s pristine wildlife or urban coastal culture with each customized vacation package. BC Ferries Vacations travel experts help travellers create a personalized vacation complete with ferry reservations to bring all-in-one convenience, quality, and value. And, in partnership with some of BC’s best hotels, BC Ferries Vacations is able to provide customers with the best rates, customer service, and overall experiences, whether travelling to Vancouver, Victoria, the north coast, or to remote and amazing destinations in-between (BC Ferries Services, 2015).
In order to reach consumers and stimulate need, tourism marketers can employ a number of traditional and online channels. These are detailed in the next section.
Reaching the Consumer
Marketers have more choices than ever when it comes to broadcasting their message to consumers. Potential travellers and guests will respond, in varying degrees, to traditional channels and emerging online communications tools. There are many choices in marketing and communication channels, each with strengths and weaknesses. Determining the right mix, frequency, and message depends heavily on establishing objectives, completing research, performing a situational analysis, and creating a positioning approach (Morrison, 2010). Let’s take a closer look at communications channels that may form part of the marketing mix.
Traditional Channels
Mass media is best described as the use of channels that reach very large markets. Examples include national newspapers and radio or television advertising. The immediate advantage of using mass media is the ability to reach multiple target markets in significant numbers. Disadvantages include the high expense and difficulty in effective target marketing and measuring return.

Out-Of-Home (OOH)
Out-of-home (OOH) channels refer to four major categories: billboards, transit, alternative outdoor, and street furniture. OOH advertising plays an important role in the tourism and hospitality industry as it provides an opportunity to inform travellers in unfamiliar territory. Transit advertising includes airports, rail, and taxi displays. Alternative outdoor refers to arenas, stadiums, and digital media. Street furniture includes bus shelters, kiosks, and shopping malls.
Print Media
Print media includes newspapers, magazines, journals, and directories. There is an increased trend away from traditional purchased print advertising toward editorial features, as these are more trusted by consumers. A print ad and an editorial feature created together is known as an advertorial .
Spotlight On: The Tartan Group
Founded in the 1990s in Victoria, The Tartan Group is a public relations firm focusing on tourism and hospitality clients including Clayoquot Wilderness Resort, Harmony Hotel, Inn at Laurel Point, and Hotel Zed. The staff have extensive experience working in the industry, and the organization has relationships with multiple tourism associations and press groups. For more information, visit the Tartan Group website : www.tartangroup.ca
Online Channels
As discussed in Chapter 7, the internet is nearly twice as important as travel agents as an information source for travel (Deloitte, 2015). There are an estimated 3 billion people around the globe with internet access, and social media has become truly integrated into the travel and hospitality industry. TripAdvisor and similar sites have become the customer’s first point of connection with tourism and hospitality products and experiences. This can be both an opportunity and a threat: an opportunity to open the channels of communication, but a threat if negative information about the travel or hospitality organization is widely spread. As online distribution expands, empowered and savvy travellers are unbundling the booking component and self-booking directly (Deloitte, 2015).
Internet and mobile technology are referred to as interactive media . For tourism and hospitality businesses, there are significant advantages to creating an online presence: it’s cost effective, it provides global reach, it allows a business to be available 24/7, and it provides a reciprocal communication platform for customers.
Social Media and Reputation Management
There are also challenges with online marketing, including being noticed within the volume of information customers are exposed to, and loss of control in delivering a message. Despite these challenges, as more consumers seek real-time information online, tourism marketers are responding with increasingly sophisticated online marketing strategies. This section draws from resources and expertise provided by WorldHost Training Services (2013).
Social Media
Social media is a broad term that refers to web-based and mobile applications used for social interaction and the exchange of content. Social networking is the act of using social media. Unlike traditional media such as newspapers, magazines, and television, social media is largely powered by user-generated content. This refers to content created and shared by consumers rather than by marketers, journalists, experts, and other paid professionals, although they too contribute to social networks.
Word of Mouth in the Age of Social Media
Social networking has transformed how many people interact with businesses and share experiences with others, in a communication channel known as word of mouth where customers share directly with each other. Consumers now have a variety of channels on which to express likes and dislikes, many of which have large audiences. Some of this commentary is made in real time, on a smartphone, while the customer is still in the business (WorldHost, 2013).
Advertising and Trust
Social networks, and review sites in particular, are used more and more to seek information and advice on things to do and products and services to purchase. Travellers and locals alike check out these sites for ideas on where to stay, eat, relax, shop, and explore. These channels are highly trusted. A survey of over 28,000 consumers in 56 countries found that consumers trust the advice of people they know (92%) and consumer opinions posted online (70%) more than any other advertising source (Nielsen, 2012).
Online Reviews = Business Success
Research shows a direct correlation between consumer reviews and purchase decisions. A 2011 survey by Phocuswright found that three in four active travellers cite reviews and photos as influential in choosing activities (PR Newswire, 2011). A 2011 study conducted by Harvard Business School found that, for independent restaurants, a one-star increase in Yelp ratings led to a 5% to 9% increase in revenue (Luca, 2011). And, according to a study by the Cornell Center for Hospitality Research, if a hotel increases its review score on Travelocity by 1 point on a 5-point scale, it can raise its price by 11.2% without affecting demand (Anderson, 2012).
Understanding Customer Needs
As we have discussed, service plays an important role in shaping customer impressions, where the ultimate goal of a tourism or hospitality business is to exceed expectations. Every customer has different wants and needs, but virtually all customers expect the following basic needs to be taken care of:
- Convenience
- Good service
To fully satisfy customers, businesses must deliver in all four areas. If they meet the basic needs listed above, they’ll create a passive customer — one who is satisfied, but not likely to write a review or mention a business to others.

On the other hand, failure to deliver on the promise can result in a disappointed customer undoing all the efforts of the marketing plan. For this reason, the entire process must be well coordinated and well executed.
Bringing it All Together
The role of destination bc.
Destination BC is responsible for executing key components of the provincial government’s tourism strategy (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Innovation, 2011). As we learned in the last chapter, this provincial destination marketing organization has been mandated to fulfill several key marketing and leadership responsibilities critical to the long-term sustainable growth of the provincial tourism industry. This includes marketing British Columbia domestically, nationally, and internationally as a tourist destination (Destination BC, n.d.). Its first three-year corporate and marketing strategy was released in November 2014 articulating its new vision, mission, and goals.
Take a Closer Look: Online Reputation Management
This guide from Destination BC’s Tourism Business Essentials series helps businesses understand how to manage their online reputation and includes tips for responding to reviews and other best practice. To get a copy of the guide, visit the Online Reputation Management Guide [PDF] : www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Programs/Guides-Workshops-and-Webinars/Guides/Tourism-Business-Essentials-Guides/TBE-Guide-Online-Reputation-Management-2nd-Edition-Sep-2014-(2).pdf.aspx
Market Segmentation
Tourism marketers, including the team at Destination BC, choose target markets for their efforts through market segmentation techniques, where potential visitors are separated by:
- Demographics
- Countries of origin
- Trip purposes
- Trip planning and arrangements
- Psychographics and lifestyles
- Special interests
- Technology uses
The Canadian Tourism Commission’s award-winning Explorer Quotient program provides tourism marketers with detailed psychographic and travel motivations information (Canadian Tourism Commission, 2008; 2012). It allows destinations and experiences to market themselves to target audiences based on psychographic profiles (their psychological tendencies) rather than geographic segments.
Take a Closer Look: EQ (Explorer Quotient)
Destination Canada’s EQ tool allows businesses to segment their customers in a new and innovative way. EQ offers a range of online resources from an EQ Quiz (so you can identify what type of traveller you are) to business toolkits and more. Explore this new tourism marketing tool by visiting the Explorer Quotient tool : http://en.destinationcanada.com/resources-industry/explorer-quotient
BC’s Tourism and Hospitality Key Markets
BC’s key target tourism markets can be broken down into three main categories: nearby markets, top priority markets, and emerging markets (BC Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Innovation, 2011).
Nearby markets are BC, Alberta, and Washington State, which are characterized by high volume and strong repeat visitation. Marketing activities to these areas are led by the regions, communities, and/or sectors such as ski. Top priority markets of Ontario, California, Germany, Japan, United Kingdom, South Korea, Australia are characterized by high revenue and high spending per visitor. Marketing efforts here are led by Destination BC. Emerging markets , which include China, India, and Mexico, are monitored and explored by Destination BC.
Performance Measurement and Evaluation
In order to measure its success in the realm of destination marketing, Destination BC has introduced a tool called the net promoter score (NPS) , a metric designed to monitor customer engagement. The NPS indicates the likelihood of travellers recommending a destination to friends, family, or colleagues. NPS is based on responses to the question, How likely are you to recommend [British Columbia] as a travel destination to a friend, family member, or colleague? Responses are scored from 0 = “not at all likely” to 10 = “extremely likely.” Respondents are divided into three categories:
- Detractors (scores of 0 to 6): Unhappy visitors, unlikely to tell others to visit and might even damage the reputation of a destination through negative word of mouth
- Passives (scores of 7 or 8): Marginally satisfied visitors not excited enough to tell others about their travel experience
- Promoters (scores of 9 or 10): Loyal enthusiasts likely to return and rave about their travel experience
NPS is calculated by subtracting the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters: NPS = % of detractors — % of supporters. The intention to recommend a travel destination, reported by the NPS, is a proxy measure of overall satisfaction with the travel experience. Satisfaction with the travel experience and the intention to recommend greatly increase the likelihood of a return visit to British Columbia. And word-of-mouth advocacy, either face-to-face or through social media, is critical for attracting first-time visitors to British Columbia.
Destination BC uses NPS as a performance measurement tool (among others) to help determine the overall effectiveness of online and integrated marketing communications strategies (Destination BC, 2013). Furthermore, Destination BC has developed the Remarkable Experiences program to “enable tourism operators to become experts in areas such as service design and digital marketing” (Destination BC, 2014).
Spotlight On: Aboriginal Travel Services
Aboriginal Travel Services (ATS) is BC’s first Aboriginal-owned travel agency, focusing on business and leisure needs of companies, First Nations bands, and individual tourists. Located on Coast Salish territories in downtown Vancouver, ATS reinvests profits into Aboriginal communities by way of youth scholarships in tourism and hospitality. The agency was developed as a social enterprise, with the dual purpose of selling travel services that provide cultural and economic opportunities to the communities it serves and committing to investing in the Aboriginal communities and tourism initiatives (Aboriginal Travel Services, 2015). For more information, visit the Aboriginal Travel Services website : www.aboriginaltravelservices.com
Effective planning, research, customer understanding, integrated marketing communications, and using online customer service strategies to support effective marketing are fundamental requirements for successful services marketing. However, it is critical that marketers understand the key trends and issues that will help to identify tomorrow’s marketing strategies (Government of Canada, 2013).
Trends and Issues

Tourism marketers in BC need to monitor trends in the following areas that may impact the success of their marketing efforts:
- Demographic shifts (aging population, the rise of millennials), and socioeconomics (cultural changes, economic decline/growth)
- Political, economic, and geographic changes (emerging or declining economies)
- Trip purpose (growth of multipurpose trips)
- Psychographic changes (special interests, healthy lifestyles, sustainability)
- Behavioural adaptations (free independent travel, decreasing brand loyalty)
- Product-related trends (emerging niches)
- Distribution channels (online travel agencies, virtual travel)
Remaining abreast of information in these areas is critical to the success of any services marketing plan, which should be continually monitored and adapted as the landscape changes.
Effective services marketing in the tourism and hospitality sector requires marketers to gain a solid understanding of the differences between the marketing of goods and services. Successful organizations use market research to learn the preferences and behaviours of key customer segments. Through a strategic planning process, organizations and destinations develop a marketing orientation designed to identify customer needs and trigger their wants, while striving to meet organizational objectives. Activities are designed to support integrated marketing communications across multiple platforms with reciprocal communications — that is, not just broadcasting information, but having conversations with customers. Savvy marketers will leverage these conversations to keep up with evolving customer interests while seeking an understanding of emerging trends in order to anticipate needs and wants. Engaged marketers also know that social media and integrated marketing communications must be complemented with remarkable customer service, which ultimately supports successful marketing strategy.
Chapter 9 will delve further into the components of delivering exceptional customer service as a key component of industry success.
- 8 Ps of services marketing: refers to product, place, promotion, pricing, people, programming, partnership, and physical evidence
- Advertorial: print content (sometimes now appearing online) that is a combination of an editorial feature and paid advertising
- Customer needs: gaps between what customers have and what they would like to have
- Customer wants: needs of which customers are aware
- E-commerce: electronic commerce; performing business transactions online while collecting rich data about consumers
- Emerging markets: markets for BC that are monitored and explored by Destination BC — China, India, and Mexico
- Heterogeneous: variable, a generic difference shared by all services
- Intangible: untouchable, a characteristic shared by all services
- Integrated marketing communications (IMC): planning and coordinating all the promotional mix elements and internet marketing so they are as consistent and as mutually supportive as possible
- Interactive media: online and mobile platforms
- Interpersonal factors: the influence of cultures, social classes, family, and opinion leaders on consumers
- Marketing: a continuous, sequential process through which management plans, researches, implements, controls, and evaluates activities designed to satisfy the customers’ needs and wants, and its own organization’s objectives
- Marketing orientation: the understanding that a company needs to engage with its markets in order to refine its products and services, and promotional efforts
- Market segmentation: specific groups of people with a similar profile, allowing marketers to target their messaging
- Mass media: the use of channels that reach very large markets
- Nearby markets: markets for BC, identified by Destination BC as BC, Alberta, and Washington State, characterized by high volume and strong repeat visitation
- Net promoter score (NPS): a metric designed to monitor customer engagement, reflecting the likelihood that travellers will recommend a destination to friends, family, or colleagues
- Out-of-home (OOH): channels in four major categories: billboards, transit, alternative outdoor, and street furniture
- Passive customer: a guest who is satisfied (won’t complain, but won’t celebrate the business either)
- Perishable : something that is only good for a short period of time, a characteristic shared by all services
- Personal factors: the needs, wants, motivations, previous experiences, and objectives of consumers that they bring into the decision-making process
- PRICE concept: an acronym that helps marketers remember the need to plan, research, implement, control, and evaluate the components of their marketing plan
- Print media: newspapers, magazines, journals, and directories
- Services marketing: marketing that specifically applies to services such as those provided by the tourism and hospitality industries; differs from the marketing of goods
- Services marketing triangle: a model for understanding the relationship between the company, its employees, and the customer; differs from traditional marketing where the business speaks directly to the consumer
- Social media: refers to web-based and mobile applications used for social interaction and the exchange of content
- Societal marketing: marketing that recognizes a company’s place in society and its responsibility to citizens (or at least the appearance thereof)
- Tangible: goods the customer can see, feel, and/or taste ahead of payment
- Top priority markets: markets for BC identified as a top priority for Destination BC — Ontario, California, Germany, Japan, United Kingdom, South Korea, Australia — which are characterized by high revenue and high spend per visitor
- Tourism marketing system: an approach that guides the planning, execution, and evaluation of tourism marketing efforts (PRICE concept is an approach to this)
- Word of mouth: information about a service experience passed along orally or through other social information sources from past customers to potential customers
- Should services be marketed exactly the same as manufactured products and packaged goods? Why or why not?
- Name at least three reasons for tourism marketers to do marketing research.
- Why is segmentation so important to effective marketing?
- What does integrated marketing communications achieve?
- What stages do customers usually go through when they make decisions about buying travel services?
- Name the three types of market priorities for British Columbia’s tourism experiences (according to Destination BC). What geographic segments are found in each?
- What is the net promoter score (NPS) for a destination with 20% detractors and 80% supporters?
- Why is delivering great experiences an important part of services marketing? Give five reasons.
- What characteristics do you agree with, which ones do you not? Why?
- Select one of the experiences (preferably in BC) matched to your profile and determine how it fits your type.
- How does the website of that company market to your traveller type? What visuals or key words do they use to get your attention?
Case Study: The Wickaninnish Inn
Located in Tofino, the Wickaninnish Inn (or “the Wick,” as it’s affectionately known) is a world-recognized high-end property famous for offering four seasons of luxury experiences on BC’s “wild coast.” But how does the Wick stay top-of-mind with tourism consumers? A quick look at their marketing mix offers some answers:
- Product: The inn has long been a leader in offering experiences that go above and beyond a room in a luxury hotel, starting with their storm-watching packages in the late fall, a time that was once their off-season.
- Place: Reservations can be made online on the inn’s website, via a toll-free number, through OTA sites including TripAdvisor (where reviews are constantly monitored in order to engage with customers), and other reservation services including the HelloBC program. The staff constantly engages with, and monitors their customers, tracking trends in traveller purchasing behaviour to ensure it is front and centre with the inn’s target markets.
- Promotion: The inn has a well-maintained, visually rich website and social media presence on Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, Pinterest, Google+, and Flickr (a presence that shifts constantly depending on where consumers can be found online). Its site features a media page with blogs, press releases, and high-resolution photos and videos to ensure journalists can easily post a story at any time.
- Pricing: The inn has a comprehensive revenue management and pricing plan that includes packaging and promotions for all seasons. The pricing reflects offering value to guests, while confidently staying at the higher end of the scale.
- People: Not only does the inn attract and train staff who deliver on its promise of exceptional experiences, the Wick also has a multi-person team responsible for sales, marketing, and media (blogging, press releases, photography, hosting familiarization tours).
- Programming: Programs include packaging under themes such as elopement, natural, seasonal, romantic, spa, and culinary. Many packages include the involvement of hotel personnel such as an elopement coordinator or concierge to help guests plan specific value-added and memorable components of their experience, such as a last-minute wedding (Wickaninnish Inn, 2015).
- Partnership: The Wick partners with other experience providers and events such as the Tofino Saltwater Classic — a fishing tournament hosted by Brendan Morrison of the Vancouver Canucks. By supporting the event as a platinum sponsor (Tofino Saltwater Classic, 2014), the representatives from the inn meet new potential guests and solidifies its place in the community.
- Physical evidence: In addition to familiarization tours (see Chapter 7 for definition), the media team ensures the inn is considered for a number of high-profile awards, and celebrates wins by broadcasting these as they occur (e.g., Travel and Leisure Awards World’s Best Winner 2014). Prize logos are placed on the inn’s home page online, in print ads, and in physical locations on the property. The inn also has a regular consumer newsletter that celebrates achievements and shares promotions with past and future guests.
Thinking about this example, answer the following questions:
- Imagine the inn received a review on TripAdvisor that showed a customer was not satisfied. How might it deal with this?
- Visit the company’s website at www.wickinn.com . Who are the target customers? How is this conveyed on the site?
- What are the prices for packages and accommodations? What does the price signal to you about the experience you might have at this hotel?
- Do an online search for “Wick Inn” using your favourite search engine. What are the first five links that come up? How do these present the property? What hand does the inn’s staff have in these results?
- Look at the community of Tofino as it is presented online and name five potential partners for the Wick.
Aboriginal Travel Services. (2015). Aboriginal Travel Services. Retrieved from www.aboriginaltravelservices.com
Anderson, C. (2012). The impact of social media on lodging performance. Retrieved from www.hotelschool.cornell.edu/research/chr/pubs/reports/abstract-16421.html
BC Ferries Services. (2015). BC Ferries vacations. Retrieved from: www.bcferriesvacations.com
British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Innovation. (2011). Gaining the edge: A five year strategy for tourism in British Columbia. [PDF] Retrieved from: www.jtst.gov.bc.ca/tourismstrategy/documents/mjti_tourismstrategyreport_fnl.pdf
Canadian Tourism Commission. (2008). The explorer quotient: A deeper understanding of the modern traveller . [PDF] Retrieved from: www.ttracanada.ca/sites/default/files/uploads/ctc._the_explorer_quotient_-_a_deeper_understanding_of_the_m.pdf
Canadian Tourism Commission. (2012). EQ profiles . [PDF] Retrieved from: https://en-corporate.canada.travel/sites/default/files/pdf/Resources/ctc_eq_profiles_2012-eng-lowres.pdf
Davis, K. (2013, July 17). A (kind of) brief history of marketing (infographic). Entrepreneur. Retrieved from www.entrepreneur.com/article/227438
Deloitte. (2015). Hospitality 2015 game changers or spectators? Retrieved from www2.deloitte.com/ie/en/pages/consumer-business/articles/hospitality-2015.html
Destination BC. (n.d.). About us . Retrieved from: www.destinationbc.ca/About-Us.aspx
Destination BC. (2013). Net promoter score. Retrieved from: www.destinationbc.ca/Resources/Monitoring-and-Evaluation/Net-Promoter-Score.aspx#.VOZd1_nF9Z9
Destination BC. (2014). Remarkable experiences program . Retrieved from: http://strategy.destinationbc.ca/how-we-will-win/foster-remarkable-experiences/remarkable-experiences-program/
Eliason, K. (2014, December 23). The importance of integrated marketing communications. Retrieved from www.portent.com/blog/internet-marketing/raining-marketing-importance-integrated-marketing-communications.htm
Government of Canada. (2013). FedNor: A guide to using market research and marketing measurement for successful tourism destination marketing . Retrieved from: http://fednor.gc.ca/eic/site/fednor-fednor.nsf/eng/fn03327.html
Kollat, D., Blackwell, R., & Engel, J. (1972). The current status of consumer behavior research: Developments during the 1968-1972 period. Proceedings of the Third Annual Conference of the Association for Consumer Research. Chicago, IL : Association for Consumer Research, pp. 576-585.
Luca, M. (2011, September 16). Reviews, reputation, and revenue: The case of Yelp.com . [PDF] Retrieved from www.hbs.edu/faculty/Publication%20Files/12-016_0464f20e-35b2-492e-a328-fb14a325f718.pdf
Morrison, A. M. (2010). Hospitality & travel marketing (4th ed., international ed.). Clifton Park, NY: Delmar Cengage Learning.
Nielsen. (2012, April 10). Global consumers’ trust in ‘earned’ advertising grows in importance. Retrieved from www.nielsen.com/us/en/press-room/2012/nielsen-global-consumers-trust-in-earned-advertising-grows.html
PR Newswire. (2011, January 11). Smart phones, social media and local search create marketing mojo in the travel industry, new report says . Retrieved from www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/smart-phones-social-media-and-local-search-create-marketing-mojo-in-the-travel-industry-new-report-says-113262519.html
Tofino Saltwater Classic. (2014). Tofino saltwater classic . Retrieved from www.tofinosaltwaterclassic.com
Tourism Victoria. (2015). Visitors centre . Retrieved from: www.tourismvictoria.com/plan/visitor-centre
Wickaninnish Inn. (2015). Elopement wedding packages . Retrieved from www.wickinn.com/package-type/elopement
Wolak, R., Kalafatis, S., & Harris, P. (1998). An investigation into four characteristics of services. [PDF] Journal of Empirical Generalisations in Marketing Science, 3 , 22-43. Retrieved from http://members.byronsharp.com/empgens/emp1.pdf
WorldHost Training Services. (2013). Remarkable service in the age of social media . Retrieved from: www.worldhosttraining.com/elearning/
Attributions
Figure 8.1 Vintage Ad #1,203: This Cheap Hotel Does Not Compute by Jamie is used under a CC BY 2.0 license.
Figure 8.2 1970s Advertising – Poster – Peter Max Don’t Smoke Cigarettes (USA) by Daniel Anyes Arroyo is used under a CC BY-NC 2.0 license.
Figure 8.3 British Columbia Parliament Christmas Lights by James Wheeler is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 license.
Figure 8.4 Empty Flight by Rex Roof is used under a CC BY 2.0 license.
Figure 8.5 Services Marketing Triangle by LinkBC is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 license.
Figure 8.6 Pacific Centre igloo by Janis Behan is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 license.
Figure 8.7 Army Photography Contest – 2007 – FMWRC – Arts and Crafts – Eye of the Holder by US Army is used under a CC BY 2.0 license.
Figure 8.8 BC Tourism Vending Machine by davitydave is used under a CC BY 2.0 license.
Figure 8.9 Precious Treasure by Dave Sutherland is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 license.
Figure 8.10 Victoria’s Inner Harbour at Night 2012 by Gord McKenna is used under a CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 license.
Figure 8.11 Out of Home Advertising for Grouse Mountain by LinkBC is used under a CC BY 2.0 license.
Figure 8.12 Fairmont Empress and Helijet Partnership by LinkBC is used under a CC BY 2.0 license.
Figure 8.13 Wreath makin’ – an unhappy customer (pas moi) by Katy is used under a CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 license.
Figure 8.14 Twitter escultura de arena by Rosaura Ochoa is used under a CC BY 2.0 license.
Long Descriptions
Figure 8.1 long description: A man holds up a calculator looking confused. He says, “Are you kidding me? A big double bed, television, air conditioning, and only $12.95 a night? It doesn’t compute.” [Return to Figure 8.1]
Figure 8.5 long description: Internal marketing is used between the company and its employees. External marketing is used between the company and its customers. Interactive marketing is used between the employees and the customers. [Return to Figure 8.5]
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC Copyright © 2015 by Ray Freeman and Kelley Glazer is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
4 Characteristics of Service: Intangibility, Inseparability, Variability, Perishability

A service is any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything.
Services do not always emerge out of physical products . When somebody rents a hotel room, deposits money in a bank, travels on an airplane, visits a physician, gets a haircut, gets a car repaired, watches a professional sport, watches a movie, and gets advice from a lawyer, he/she buys a service.
When designing marketing programs, a company must consider the characteristics of services.
Four characteristics of service are;
- intangibility,
- inseparability,
- variability and
- perishability.

Let’s discuss the 4 characteristics of the service.
Intangibility – Services Cannot Be Felt Before Buying.
Services are intangible in nature. It means that services can not be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled before they are bought.
For example, an airline passenger has only a ticket and the promise of a safe and comfortable journey.
As the buyers are interested in service quality, the service provider must add tangible dimensions. The place, price, equipment, and communication material must indicate the service quality as claimed by the service provider.
Consider a bank that wants to convey the idea that its service is quick and efficient. It must make this positioning strategy tangible in every aspect of customer contact.
The bank’s physical setting must suggest quick and efficient service: Its exterior and interior should have clear lines; internal traffic flow should be planned carefully; waiting for lines should seem short at teller windows and ATMs, and background music should be light and upbeat. The bank’s staff should be busy and properly dressed.
The equipment – computers, copy machines, desks – should look modern. The bank’s ads and other communications should suggest efficiency, with clean and simple designs and carefully chosen words and photos that communicate the bank’s positioning.
The bank should choose a name and symbol for its service that suggest speed and efficiency. It is pricing for various services should be kept simple and clear.
Inseparability – Services Are Generated and Consumed Together.
Inseparability is a major characteristic of services. It means that services are generated and consumed simultaneously and can not be separated from their providers, whether they are people or machines.
As the customer remains present as the service is produced, provider customer interaction is important in services marketing. The result of services is affected by both the provider and the customer.
Variability – Service Quality Never Stay The Same.
Variability is another important characteristic of services, which means that their quality may vary greatly, depending on who provides them and when, where, and how they are provided.
For example, the Sheraton hotel has a reputation for providing better service than others.
One employee may be cheerful and efficient within a particular Sheraton hotel, while another may be unpleasant and slower. Even the quality of a single Sheraton employee’s service varies according to his or her energy and the state of mind at the time of each customer dealing.
Service variability can be managed in several ways. Employees can be selected and trained carefully to provide good service. Employee incentives can be introduced that emphasize service quality. Customer satisfaction can be checked regularly through suggestion and complaint systems, customer surveys, and comparison shopping.
Perishability – Services Cannot Be Stored.
Services are perishable, which means that services can not be stored for later sale or use. A ticket for the evening show of a movie can not be used for watching the night show.
The perishability of services has important implications for service providers. In the case of steady demand, perishability is not a problem.
But where demand fluctuates, service providers face adjustment problems.
For example, public transportation companies have to own much more equipment then they would as demand is not ever throughout the day.
Service providers can several steps to make better demand-supply adjustments.
Different prices can be charged at different times on the demand side, which will shift some demand from peak periods to off-peak periods. On the supply side, part-time employees can be hired to cater to peak demand.

- Call to +1 844 889-9952
Services Marketing Concept
Introduction, characteristics of services, what is service marketing, jet star and service marketing, relationship marketing, importance of service quality, reference list.
A service can be defined as an indefinable product. It is the act of performing something for the sake of someone or something. A service differs from a product in that; a product is tangible whereas a service can not be touched. Another difference is that a product can be purchased and consumed at a later date while a service is consumed at the time and point of purchase and cannot be stored in any form. It can not be owned and perishes after purchase. A service is like an experience that changes with time. It is very difficult to receive exactly the same service at different times. One can walk up into a hotel and receive excellent service and experience a poor service on another visit.
Thereby, most of the service marketers put more emphasis on the nature of services, which include inseparability, intangibility, perishability, variability and right of ownership. This paper looks at the characteristics of services that distinguish them from products, the definition of service marketing and gives a brief overview of how this concept is used in service industries. It also gives a brief overview of an airline company (jet star) and how it uses service marketing to promote its services. Finally, it looks at relationship marketing and the importance of service quality to service industries.
Services have specific characteristics that are not found in products. One of these characteristics is inseparability; this means that the point of consumption and the provider of the service can not be separated. A service cannot be touched physically. An example of a service is a life insurance whereby the insurer receives a certificate but the service offered is intangible. Another characteristic of a service is that it is perishable and can not be stored to be consumed at a later date. It has to be consumed at the point of purchase for it to be termed as a service (Levitt 1981). One can not receive exactly the same kind of service since it can not be repeated.
Services are variable and they can never be identical especially because of the involvement of human resources. For instance, going to the same salon frequently for a similar service might experience variance in the level of customer satisfaction or speed. Last but not least, one can never acquire right of ownership from a service because it is just an experience. For instance, a mechanic may service ones car but that does not give him the right to own either the service or the equipment used by the mechanic.
This can be defined as a form of marketing that deals with the sale of services. Unlike the selling of products, selling of services is a tricky undertaking that requires a different marketing approach. Many companies offer both services and products but use different approaches for marketing (Zeithaml et al 1985). For instance, a computer shop may also offer services to its customers such as computer repair but use different approaches to market them. The main goal for service marketers is to not to persuade customers to purchase a particular product but to persuade them to do business with a given company located in a specific place.
For instance, a hotel offers service to its clients: it provides drinks or food that can be available in other hotels and it is, therefore, the responsibility of the marketer to convince people that a particular hotel is the best and its facilities are of high quality. Just like in marketing of products, service marketing covers issues such as the service on offer, the price, what makes it superior to other similar services and why people should go for that service excluding others. However, since services are intangible, service marketers have a hard task trying to convince consumers that the services being offered are of high quality and will have some benefits accrued to them.
Different marketers use different approaches when it comes to marketing; this depends on how they want people to perceive the company and the kind of information they want people to believe in regarding that particular company. For instance, a security company may want to portray itself as trustworthy and dependable while as a tourism company may want to portray itself as adventurous. Marketers should keep this in mind because at the end of the day, what is important is to convince people why they should go for a particular service offered by a particular company (Lovelock 1983).
Some marketing schools give reliable techniques for service marketing while others are developed by people who are involved in service marketing. This can be through practicing marketing in a real situation where one gets an opportunity to learn more about people, their preferences and what they look for in a service. The main objective behind this encounter is to establish a long lasting relationship with the consumers so that in future they will come back for the same service in that particular company. This can only be achieved if the service is of the right quality and the brand does not play a major role like in the case of product marketing where the value of the product plays a significant role.
Jet Star is an airline company based in Australia. It is one of the low cost companies with headquarters in Melbourne Victoria. Jet Star is an auxiliary of Qantas airlines, which was created to respond to the threats of competition from other low-cost airlines. Jet Star’s parent company is a strong firm that has withstood the test of time. It has a strong brand name preferred by many customers for both domestic and international air travel. As a form of service marketing, it offers other services that make air travel comfortable and more relaxed. On the domestic routes, Jet Star offers drinks and food to customers while on international routes especially on Airbus A330; it offers its services in two classes.
This has led to an increase in its annual profit especially from 2004 to 2008 when the service was in its initial stages. In 2007, Jet Star won the World Airline Award for low cost services and this gave it a competitive advantage over its rival firms (Rochfort 2009). The low cost service targets low income earners and middle class business people who rely on other means of transport due to the high charges of flights. Initially, these low cost services led to increased business which forced Jet Star to look for other aircrafts to cater for the increased demand for its services. Having introduced a low cost carrier service (LCC), Jet Star has increased its market share and is able to fight the threat from competitors. However, the future of this marketing strategy is not certain and the company has to look for other services to compliment the LCC. Such services include diversification of its services to other domestic areas that have no airlines, expansion into the international market and development of human resources.
Although the Australian economy has been doing well and the future is promising, Jet Star has to overcome some obstacles before it realises its full potential. First, there is the government requirement which it has to adhere to before being allowed to expand its services, increased capital costs, skilled labour requirements and rivalry from other firms (Rochfort 2009). Another major risk is that the company is not guaranteed of a ready market in the rural areas. However, the company’s technological developments have boosted its standing in regard to observing keeping clean environmental through the efficient use of energy. This has also had an impact on the sociological and cultural differences since consumers want firms to be more socially responsible.
Relationship marketing is a concept that has evolved through time to incorporate service marketing. It can be defined as the process of attracting and promoting good customer relationship. In the marketing literature, the genesis of contemporary relationship marketing as we are acquainted to today can be drawn back to an extract by Schneider (1980) in which he observes: “What is surprising is that researchers and businessmen have concentrated far more on how to attract customers to products and services than on how to retain customers” (p60).
The major concept behind relationship marketing is to attract and retain loyal customers as well as honouring their commitment and performance. It is a concept that was widely used in the ancient times although many modern marketers are relying on this concept (Egan 2001). Because of intense competition and rivalry, many service industries have realised the importance of relationship marketing and the benefits accrued to it.
Marketers and customers in service organisations such as hotels, banks and hospitals have to interact with each other in order to strengthen the bond that exists between them for better results. As a form of relationship marketing, Jet Star provides reserved seating where customers are allowed to book their seats in advance; a service that was launched in 2006 as the first service of its kind in Australia. It also provides online booking for customers who may not make it to the booking offices due to various reasons. Because of its good services and relationship with its customers, it was recognised as the official airline for the Australia Rugby league and its aircrafts were decorated with advertisements to mark the relationship with the national league in 2008 (O’Sullivan 2010).
Defining and determining quality service is of significance to providers of all services. As rivalry in service industries has augmented, the concept of service quality has turned out to be more and more important. Service quality has been recognised as a determinant of market size, return on investment and cost reduction (Anderson & Zeithaml 1984). Additionally, Devlin and Dong (1994) observe that in a progressively competitive environment, service quality is vital to business success. In their study, they connected the concept of service quality to customer contentment. In due course, it is customer satisfaction or contentment that leads to an increase in market share and profits.
Service organisations basically offer two forms of quality: technical quality and practical quality. Technical quality is the extent to which a business is able to do things in the “right” way as measured alongside some technological “industry standard.” Nevertheless, in service sectors, understanding of the technical quality of services is an area of service professionals. For that reason, Parasuraman, et al (1985) made a conclusion that consumers naturally rely on understanding properties when assessing service quality. They developed the SERVQUAL scale. This scale was premeditated to expose extensive areas of high or low service quality and can be used to show service quality trends over time, particularly when used with other service quality procedures.
A service is an intangible service that is consumed at the point of purchase. It has no right of ownership and this differentiates it from products. Service marketing can, therefore, be defined as a form of marketing that is undertaken for the purpose of creating awareness of a given service provided in a particular company. To make service marketing more beneficial, marketers should aim to create good relationship between customers and suppliers. This is called relationship marketing. To put into practice effectual relationship marketing, any organization, regardless of size, has to create and uphold a good relationship with its clientele, employees and all its stakeholders. The customer-supplier liaison is to a great extent an important issue in relationship marketing and unquestionably across the whole marketing discipline. Besides the formation of good relationship marketing, service organizations should aim at providing service of high quality as this will attract more customers.
Anderson, C. and Zeithaml, C. P. 1984. Stage of the Product Life Cycle, Business Strategy, and Business Performance, Academy of Management Journal, 5-24. Web.
Devlin, S J. & Dong H. K. 1994. Service Quality From the Customer Perspective, Marketing Research, Vol. 6, No. 1, 5-13. Web.
Egan, J, 2001. Relationship Marketing: Exploring relational strategies in marketing. Pearson Education Limited. Edinburgh Gate, England. Web.
Levitt, T. 1981. Marketing Intangible Products and Product Intangibles, Harvard Business Review, pp. 94-102. Web .
Lovelock, H. 1983. Classifying Services to Gain Strategic Marketing Insights, Journal of Marketing, Vol. 47, pp. 9-20. Web.
O’Sullivan, M. 2010. Qantas to Receive First Boeing 787 in 2012. Qantas . Web.
Parasuraman, A, et al. 1985. A Conceptual Model of Service Quality and Its Implications for Future Research, Journal of Marketing 49 (Fall), 41-50. Web.
Rochfort, S. 2009. Qantas revs up Jet star expansion . The Sydney Morning Herald. Web.
Schneider, B. 1980. The Service Organization: Climate Is Crucial. Organizational Dynamics. 9 (2), 52-65. Web.
Zeithaml, V. A, et al. 1985. Problems and Strategies in Services Marketing, Journal of Marketing, Vol. 49, pp. 33-46. Web.
Cite this paper
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
BusinessEssay. (2022, November 8). Services Marketing Concept. https://business-essay.com/services-marketing-concept/
"Services Marketing Concept." BusinessEssay , 8 Nov. 2022, business-essay.com/services-marketing-concept/.
BusinessEssay . (2022) 'Services Marketing Concept'. 8 November.
BusinessEssay . 2022. "Services Marketing Concept." November 8, 2022. https://business-essay.com/services-marketing-concept/.
1. BusinessEssay . "Services Marketing Concept." November 8, 2022. https://business-essay.com/services-marketing-concept/.
Bibliography
BusinessEssay . "Services Marketing Concept." November 8, 2022. https://business-essay.com/services-marketing-concept/.
- Marketing Events Role in Consumer Behavior
- The New Brain Company: Marketing
- Customer Management in Car Mechanical Services Industry
- Service Marketing in the Restaurant Business
- Marketing Principles Concept in Business
- The Use of Market Research in Business
- Retail Petrol Outlets: Marketing Mix Elements
- Pricing Policies: Market Conditions and Costing
- The Crisis of the Oil Market
- Marketing Effects on Consumer Behavior and Decision-Making
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services Editing Proofreading Rewriting
- Extra Tools Essay Topic Generator Thesis Generator Citation Generator GPA Calculator Study Guides Donate Paper
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us About Us Testimonials FAQ
- Studentshare
- Characteristics of Service Marketing - Intangibility, Perishability, Inseparability, Variability
Characteristics of Service Marketing - Intangibility, Perishability, Inseparability, Variability - Essay Example

- Subject: Marketing
- Type: Essay
- Level: Masters
- Pages: 10 (2500 words)
- Downloads: 0
Extract of sample "Characteristics of Service Marketing - Intangibility, Perishability, Inseparability, Variability"
- Service Marketing
- Cited: 0 times
- Copy Citation Citation is copied Copy Citation Citation is copied Copy Citation Citation is copied
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Characteristics of Service Marketing - Intangibility, Perishability, Inseparability, Variability
Different characteristics of services, marketing of service products in the cbd dental center in perth, australia, unique services of southwest airlines, why the hospitality service industry is among the fastest-growing industries in the world, the concept of service quality, marketing plan for australian college information centre, separating the creation of a value into goods marketing and services marketing, increasing of customer information of a service.

- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY
Characteristics of Service Marketing
Services typically have several distinctive characteristics or features from goods retailing. These are intangibility, perishability, inconsistency, fluctuation and consumer dependent. A service is anything which can be offered to the customers in order to satisfy their need, wants and desire and intangible, inseparable, variable and perishable in nature.
In India, service jobs now account for 70 per cent of all jobs and 65 per cent of gross domestic product. The peculiar characterised services create challenges and opportunities to the service marketers.
Some of the characteristics of service marketing are as follows:- 1. Service is a Performance 2. Service do not involve any ownership transfer 3. Intangibility 4. Variability 5. Perishability 6. Need is the Origin
7. Natural Shift 8. Strongest Area for Growth 9. Deregulation and Service Marketing 10. No Obsolesce 11. Consumption Inseparability 12. Simultaneity 13. Inconsistency 14. Fluctuation 15. Consumer Dependent 16. Ownership 17. Heterogeneity 18. Pricing of Service.
Characteristics of Service Marketing: Intangibility, Variability, Perishability, Natural Shift, Inseparability and Many More…
6 important characteristics of service marketing – service is a performance, services do not involve any ownership transfer, intangibility, inseparability, variability and perishability.
What exactly are the characteristics of a service? In fact, many organizations do have service elements to the product they sell, for example McDonald’s sell physical products i.e. burgers but consumers are also concerned about the quality and speed of service, are staff cheerful and welcoming and do they serve with a smile on their face?
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Keeping in mind the above criterion the following are the characteristics of services:
Characteristic # 1. Service is a performance:
While products are produced, services are performed. In most cases, services are totally unconnected to any physical product.
Characteristic # 2. Services do not involve any ownership transfer:
Usually, a service does not result in the ownership of anything. In other words, unlike in product marketing, there is no title/ ownership transfer. Another outcome of simultaneous production and consumption is that service producers find themselves playing a role as part of the product itself and as an essential ingredient in the service experience for the consumer.
When you buy a product you become its owner -be it a pencil, book, shirt, refrigerator, or car. In case or service, you may pay for its use but you never own it. In case of service the payment is not for purchase, but only for the use or access to or for hire of items or facilities.
Characteristic # 3. Intangibility:
Unlike physical products, services are intangible; they cannot be seen, touched, or smelt. Also, the consumer cannot sample a service in advance. Accordingly, it becomes difficult for the consumer to judge a service before it is bought; he cannot know its exact outcome in advance.
In other words, you cannot hold or touch a service unlike a product. In saying that although services are intangible the experience consumers obtain from the service has an impact on how they will perceive it. What do consumers perceive from customer service, the location, and the inner presentation of where they are purchasing the service?
Characteristic # 4. Inseparability:
Inseparability is the next unique feature of services. Services cannot be separated from the service providers. A product when produced can be taken away from the producer. However a service is produced at or near the point of purchase.
Visiting a restaurant, you order your meal, the waiting and delivery of the meal, the service provided by the waiter/rest is all a part of the service production process and is inseparable, the staffs in a restaurant are as a part of the process as well as the quality of food provided.
In fact services are marked by two kinds of inseparability:
i. Inseparability of production and consumption
ii. Inseparability of the service from the person who possesses the skill and performs the service.
Characteristic # 5. Variability:
Services are also marked by variability or heterogeneity. This is so because of three reasons- First, inseparability of the service from the provider leads to some variability. Second, services are highly people sensitive. Third, in services, the effect varies depending on when and where the service is provided.
Characteristic # 6. Perishability:
Services are perishable as well. They cannot be stored. This is so because of the fact that services are produced and consumed simultaneously. There is no inventory in case of a service. Services last a specific time and cannot be stored like a product for later use. If traveling by train, coach or air the service will only last the duration of the journey. The service is developed and used almost simultaneously. Again because of this time constraint consumers demand more.
Service Marketing Characteristics – Need is the Origin, Natural Shift, Strongest Area for Growth, Deregulation and Service Marketing and No Obsolescence
1. Need is the origin- Service marketing concepts and strategies have developed in response to tremendous growth of service industries.
2. Natural shift-
With the advent of education, healthcare, and software consultancy services, the service sector has secured a prominent position in the nation’s economy. Hence, it is vital for businesses to establish a department dedicated to the marketing of services.
Marketing services is no easy task for organizations. Service marketers must excel in attracting prospective customers to the service organization, leveraging all seven P’s of the service marketing mix.
1. Helps in Building Relationships
Service marketing fosters long-term relationships with target customers. Since service marketers do not have a tangible product to offer, they rely on comprehending the customers’ needs and demands. They strive to satisfy them through relevant service offerings in the most efficient manner.
In this process, trust and loyalty are cultivated among the customers towards the service organization, culminating in long-term relationships. These relationships aid in generating repeated purchases as well as word-of-mouth promotion.
2. Assists in Affecting Customers’ Perception
Several interaction points are designed for our target customers while delivering the services. The overall buying process of the customer is influenced by the cumulative effect of these interaction points. These include the people involved in providing the services, their processes and methodologies, and the surrounding physical evidence . These interaction points play a crucial role in shaping the perception of the target customers.
3. Involves Customers’ Feedback
The marketing approach for services differs significantly from that of tangible products, as consumers play a pivotal role in the marketing process. In this context, customer feedback is sought and analysed to enhance the effectiveness of service marketing .
This approach fosters a healthy relationship with customers, resulting in their loyalty towards the service organization.
4. Helps in Differentiating the Service Organization
Service organisations offering similar services or products to the market can effectively differentiate themselves using the service marketing approach. Service marketing emphasises the unique features of the services provided by an organisation, making it a preferred choice over its competitors.
For instance, service marketing is the reason why people distinguish between Domino’s and Pizza Hut, even though both deliver similar products.
5. Offers Higher Customer Retention
In today’s world of fierce competition, marketers are vying for a limited pool of customers. Consequently, it becomes more crucial to retain existing customers than to attract new ones.
In service marketing, customer needs and feedback are analysed to deliver the desired services. Therefore, by offering customised services, customers are satisfied, leading to higher customer retention.
More Like This:
Define service marketing – the essentials and key concepts.
- Marketing in Financial Services
- Service Recovery
- Service Market Segmentation
Latest Articles
Related stories, seo white label services: secret to your agency’s success, what is service addressable market (sam), service marketing strategies for education services.
thank you…got my response well
Leave A Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Join our newsletter and stay updated!
© EduPepper | All Rights Reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
According to Wirtz (2012) these services have the power to influence behaviour and shape attitudes by affecting people's minds. Examples of such services include education, theatre performances among others. Information processing involves the use of technology or brain power towards customers' assets.
Conclusion. To summarize, service marketing is a method for a corporation to promote intangible, non-divisible, and time-limited services. It is done in a variety of methods in light of the expanding global service sector. It is also extremely different from product marketing, and there are other considerations.
Sir William Beveridge defines service marketing as, "Social efforts that comprise of government exertions to battle 5 evils (illness, ignorance, wants, squalor and disease) within the society". Hasenfeld describes service marketing as -. "Action made by an organization that preserves and progress the happiness and workings of people.".
This essay critically discusses how the characteristics of services influence international expansion of service organisations. It will shed light on the definition of service and its categories, followed by an explanation on what service organisation strategy is and also define international expansion.
2.Inseparability. The definition of inseparability in the dictionary is "the quality or state of being incapable of being separated or divided.". One of the characteristics of service marketing is inseparability. When purchasing a product, most customers can separate the product from the staff member who provides it.
It is no longer as important to stress the characteristics of service marketing; rather, modern research highlights the similarities between products and services in an effort to build a new and common basis for research in marketing. ... grouped the presentations according to a broad set of 40 research topics commonly found in recent calls for ...
Services marketing is a specialized branch of marketing which emerged as a separate field of study in the early 1980s, following the recognition that the unique characteristics of services required different strategies compared with the marketing of physical goods. Services marketing typically refers to both business to consumer (B2C) and ...
earlier studies. Marketing managers of service firms can use the study to identify the challenges that are unique to their services and therefore focus on the most critical issues facing them. I. Introduction Most of the challenges in service marketing arise from the basic characteristics of services like
Implications for services marketing Many scholars argue that the distinction between services and goods based on the IHIP is deeply flawed since the customer does not make a difference between the two (e.g. Vargo and Figure 3 Customer integration approach to characterize services 365 Characteristics of services - a new approach uncovers their ...
Service marketing is an exclusive branch of marketing that sprung up in the early '80s because some specialized services required unique strategies, unlike physical marketing strategies. It centers on the business of non-physical intangible or, better said, abstract goods.
State of current knowledge. Service innovation and design, transformative service research, service branding, accountability, service logic, digitalization and other topics have been suggested as important research priorities ( Ostrom et al., 2015 ). These are, of course, central research topics in the field of service marketing today.
The research intends the Studying the effects of Service offering Potential on Marketing performance and competitive advantage with using service orientation as mediating role, a conceptual model was developed and tested. In order to this, a conceptual model was developed and tested. For this purpose, Four hypotheses were developed and tested.
Synergistic effects of operant knowledge resources. Joanna Phillips Melancon, David A. Griffith, Stephanie M. Noble, Qimei Chen. Building on the service‐centered dominant logic, this paper aims to investigate the effects of firm knowledge (knowledge of customers, industry, and practices) and synergistic…. HTML.
When you rent a hotel room, travel on an airplane, visit your doctor, attend a professional sporting event, or get advice from a lawyer or an accountant, you're buying a service, so a marketer needs to consider the characteristics of services in order to get the right marketing messages to the right target market (see Figure 11.7).
uncovers their value. Sabine Moeller. Department for Market-oriented Management, European Business School (EBS), Oestrich-Winkel, Germany. Abstract. Purpose - Four characteristics have been ...
Service marketing is an advertising technique used when a business wants to offer services to customers. This is unique in that the aim is to persuade a customer to purchase something they cannot physically own but addresses their wants and needs. Rather than viewing a product, a potential customer is only able to view the benefits the service ...
The 8 Ps are best described as the specific components required to reach selected markets. In traditional marketing, there are four Ps: price, product, place, and promotion. In services marketing, the list expands to the following (Morrison, 2010): Product: the range of product and service mix offered to customers.
Let's discuss the 4 characteristics of the service. Intangibility - Services Cannot Be Felt Before Buying. Services are intangible in nature. It means that services can not be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled before they are bought. For example, an airline passenger has only a ticket and the promise of a safe and comfortable journey.
It also gives a brief overview of an airline company (jet star) and how it uses service marketing to promote its services. Finally, it looks at relationship marketing and the importance of service quality to service industries. Characteristics of services. Services have specific characteristics that are not found in products.
Extract of sample "Characteristics of Service Marketing - Intangibility, Perishability, Inseparability, Variability". 1. Introduction The revolution in technology and the growth the marketing world has witnessed in every frontier has made the concept of service marketing gain more relevance. Companies who deal in services are looking towards ...
The peculiar characterised services create challenges and opportunities to the service marketers. Some of the characteristics of service marketing are as follows:- 1. Service is a Performance 2. Service do not involve any ownership transfer 3. Intangibility 4. Variability 5.
Evolution of Service Marketing. As an academic field, service marketing has been in existence from few past decades. Fisk, Brown and Bitner (1993) studied the service marketing literature from its nascent stage in 1953 to its maturity in 1993.They divided this evolution into three stages-. Crawling Out (1953-1979)- In the first stage ...
Service marketing emphasises the unique features of the services provided by an organisation, making it a preferred choice over its competitors. For instance, service marketing is the reason why people distinguish between Domino's and Pizza Hut, even though both deliver similar products. 5. Offers Higher Customer Retention.