
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Last modified on: 2 months ago
- Reading Time: 8 Minutes
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts .

| CBSE | |
| U | Class 10 Students |
| Science | |
| Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Yes | |
| Important Link |
Case Study/Passage Based Questions on Acids, Bases and Salts
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
pH is quite useful to us in a number of ways in daily life. Some of its applications are:
Control of pH of the soil : Plants need a specific pH range for proper growth. The soil may be acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the relative concentration of H* and OH-. The pH of any soil can be determined by using pH paper. If the soil is too acidic, it can be corrected by adding lime to it. If the soil is too basic, it can be corrected by adding organic manure which contains acidic materials.
Regaining shine of a tarnished copper vessel by use of acids : A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lenion on the vessel, the surface is cleaned and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that copper oxide is basic in nature, which reacts with the acid (citric acid) present in lemon to form a salt (copper citrate) which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
Self-defence by animals through chemical warfare : Stings of bees and ants contain methanoic acid. When stung, it causes lot of pain and irritation. This can be cured by rubbing the affected area with mild base like baking soda.
(i) When black copper oxide placed in a beaker is treated with dilute HCl, its colour changes to ( a) white (b) dark red (c) bluish green (d) no change.
(ii) P is an aqueous solution of acid and Q is an aqueous solution of base. When these two are diluted separately, then (a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralisation. (b) pH of P decreases while that of Q increases till neutralisation. (C) pH of both P and Q decrease. (d) pH of both P and Q increase.
(iii) Which of the following acids is present in bee sting? (a) Formic acid (b) Acetic acid (c) Citric acid (d) Hydrochloric acid
(iv) Sting of ant can be cured by rubbing the affected area with soap because (a) it contains oxalic acid which neutralises the effect of formic acid (b) it contains aluminium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (d) none of these
(v) The pH of soil X is 7.5 while that of soil Y is 4.5. Which of the two soils, should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH? (a) X only (b) Y only (c) Both X and Y (d) none of these
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
3 thoughts on “ Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts ”
question no. 1 bit (iii) answer is wrong. It will be option (a). Otherwise you had done a great job for students.
That answer of question 3 in 1 case study is incorrect it should be formic acid Hope that would be corrected… Thank you for your efforts 😊
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Acids, Bases and Salts
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 2 acids, bases and salts.
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Acids, Bases and Salts. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Acids, Bases and Salts.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Acids, Bases and Salts
Case study : 1.
Based on the above paragraph answer the following questions:
Ans: It is a non- metallic oxide as carbon belongs to non- metals group i.e P – Block elements group 6.
Ans: Mg(OH)2 < Ca(OH)2 < NaOH.
CASE STUDY : 2
Following the above paragraph, answer the following questions;
iv) Does rain water or distilled water will conduct electricity?
Ans: Rain water will conduct electricity as it contains both positive and negative ions of different salts in it.
CASE STUDY : 3
On heating gypsum at 373 K, it loses water molecules and becomes calcium sulphate hemihydrate ( CaSO 4 .½ H 2 O ). This is called Plaster of Paris.Plaster of Paris is a white powder and on mixing with water, it changes to gypsum once again giving a hard solid mass.
i) What is the molecular formula of gypsum?
v) What does this 2 denotes in CaSO4. 2 H2O?
Ans: 2 denotes the two water molecules as water of crystallisation.
CASE STUDY : 4
iv) Where does the sodium hydroxide solution is formed?
artificial fibres
CASE STUDY : 5 (Acids Bases and Salts)
i.e neutral salt is formed.
CASE STUDY : 6
Answer the following on the basis of above paragraph:
iii) What are the important of pH in everyday life?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, assam scert class 8 geography and economics chapter 12 solutions, ncert class 7 mathematics second chapter fractions and decimals exercise 2.1 solutions, rs aggarwal class 5 solutions chapter 8, ncert class 7 mathematics first chapter integers exercise 1.3 solutions.
- Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Last Updated on May 15, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts.
| Acids Bases and Salts | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 10 | |
| Science | |
| Class 10 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |
Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Acids Bases and Salts
Question 1:
pH is quite useful to us in a number of ways in daily life. Some of its applications are:
Control of pH of the soil: Plants need a specific pH range for proper growth. The soil may be acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the relative concentration of H+ and OH-. The pH of any soil can be determined by using pH paper. If the soil is too acidic, it can be corrected by adding lime to it. If the soil is too basic, it can be corrected by adding organic manure which contains acidic materials.
Regaining shine of a tarnished copper vessel by use of acids: A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lemon on the vessel, the surface is cleaned and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that copper oxide is basic in nature, which reacts with the acid (citric acid) present in lemon to form a salt (copper citrate) which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
Self-defence by animals through chemical warfare: Stings of bees and ants contain methanoic acid. When stung, it causes lot of pain and irritation. This can be cured by rubbing the affected area with mild base like baking soda.
Read the above passage carefully and give the answer to the following questions:
(i) When black copper oxide placed in a beaker is treated with dilute HCl, its colour changes to (a) white (b) dark red (c) bluish green (d) no change.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: CuO + 2HCl → CuCl 2 + 2H 2 O, CuCl 2 is bluish green in colour.
(ii) P is an aqueous solution of acid and Q is an aqueous solution of base. When these two are diluted separately, then (a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralisation. (b) pH of P decreases while that of Q increases till neutralisation. (c) pH of both P and Q decrease. (d) pH of both P and Q increase.
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: On diluting, H+ ion concentration reduces per unit volume thus, pH increases. On the other hand, on diluting, OH– concentration also reduces, pOH increases and pH decreases. As, pOH + pH = 14. Thus, pH of Q (basic solution) decreases while that of P (acidic solution) increases on dilution.
(iii) Which of the following acids is present in bee sting? (a) Formic acid (b) Acetic acid (c) Citric acid (d) Hydrochloric acid
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Formic acid is the common name of methanoic acid, and it is present in bee sting
(iv) Sting of ant can be cured by rubbing the affected area with soap because (a) it contains oxalic acid which neutralises the effect of formic acid (b) it contains aluminium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (d) none of these.
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct
(v) The pH of soil X is 7.5 while that of soil Y is 4.5. Which of the two soils, should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH? (a) X only (b) Y only (c) Both X and Y (d) None of these
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: Soil Y is acidic. Hence, it should be treated with powdered chalk to reduce its acidity
Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 1
Topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Introduction to Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Definitions of Acids and Bases
- Properties of Acids and Bases
- Salts and their Types
- Importance and Uses of Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Preparation and Properties of Some Important Compounds
- Chemical Reactions of Acids and Bases
This chapter deals with the basic understanding of acids, bases, and salts, including their properties, reactions, pH scale, indicators, and practical applications.
Helpful Links for CBSE Class 10 Science Preparation
- Download 125 Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 220 Important Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 225 Practical Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 65 Important Numerical Problems for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 60 Important Diagram Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Physics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Heat Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 10 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 10 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on chemical reactions and equations for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on acids, bases and salts class 10 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of acids, bases and salts.
Q7: What is an acid?
A7: An acid is a substance that ionizes in water to produce hydrogen ions (H⁺) as the only positive ions. Examples include hydrochloric acid (HCl) found in gastric juices, citric acid in citrus fruits, acetic acid in vinegar, and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) in car batteries.
Q8: What are the properties of acids?
A8: Acids taste sour, turn blue litmus paper red, react with metals to produce hydrogen gas, and react with bases to form salts and water.
Q9: How do acids react with metals? Give examples.
A9: Acids react with metals to produce a salt and hydrogen gas. For example: 2HCl + Mg → MgCl₂ + H₂.
Q10: What is a base?
A10: A base is a substance that ionizes in water to produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻) as the only negative ions. Examples include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)₂].
Q11: What are the properties of bases?
A11: Bases taste bitter, feel slippery, turn red litmus paper blue, and react with acids to form salts and water.
Q12: Differentiate between acids and bases based on their taste, effect on litmus paper, and chemical behavior.
A12: Acids taste sour, turn blue litmus paper red, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas. Bases taste bitter, turn red litmus paper blue, and react with acids to form salts and water.

Related Posts
myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Download Case study questions for CBSE class 10 Science in PDF format from the myCBSEguide App . We have the new pattern case study-based questions for free download. Class 10 Science case study questions
This article will guide you through:
What are case study questions?
- Sample Papers with Case Study questions
- Class 10 Science Case Study question examples
- How to get case-based questions for free?
- How to attempt the case-based questions in Science?
Questions based on case studies are some real-life examples. The questions are asked based on a given paragraph i.e. Case Study. Usually, 4-5 questions are asked on the basis of the given passage. In most cases, these are either MCQs or assertion & reason type questions. Let’s take an example to understand. There is one paragraph on how nitrogen is generated in the atmosphere. On the basis of this paragraph, the board asks a few objective-type questions. In other words, it is very similar to the unseen passages given in language papers. But the real cases may be different. So, read this article till the end to understand it thoroughly.
What is CBE?
CBSE stands for competency-based education. The case study questions are part of this CBE. The purpose of CBE is to demonstrate the learning outcomes and attain proficiency in particular competencies.
Questions on Real-life Situations
As discussed the case study questions are based on real-life situations. Especially for grade 10 science, it is very essential to have the practical knowledge to solve such questions. Here on the myCBSEguide app, we have given many such case study paragraphs that are directly related to real-life implications of the knowledge.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App . There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions. In some cases, you will find that the question is not asked directly from the passage but is based on the concept that is discussed there. That’s why it is very much important to understand the background of the case study paragraph.
CBSE Case Study Sample Papers
You can download CBSE case study sample papers from the myCBSEguide App or Student Dashboard. Here is the direct link to access it.
Case Study Question Bank
As we mentioned that case study questions are coming in your exams for the last few years. You can get them in all previous year question papers issued by CBSE for class 1o Science. Here is the direct link to get them too.
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper , we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
Case-based Question -1
Read the following and answer any four questions: Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Phosphoric acid
- Carbonic acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Blue vitriol
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
Case-based Question -2
- V 1 + V 2 + V 3
- V 1 – V 2 +V 2
- None of these
- same at every point of the circuit
- different at every point of the circuit
- can not be determined
- 20 3 Ω 203Ω
- 15 2 Ω 152Ω
Case-based Question -3
- pure strips
- impure copper
- refined copper
- none of these
- insoluble impurities
- soluble impurities
- impure metal
- bottom of cathode
- bottom of anode
How to Attempt the Case-Based Questions in Science?
Before answering this question, let’s read the text given in question number 17 of the CBSE Model Question Paper.
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
See, there are only two sentences and CBSE is asking you 5 questions based on these two sentences. Now let’s check the first questions given there.
Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by a) Breathing b) Tissue respiration c) Organ respiration d) Digestion of food
Now let us know if you can relate the question to the paragraph directly. The two sentences are about energy and how it is obtained. But neither the question nor the options have any similar text in the paragraph.
So the conclusion is, in most cases, you will not get direct answers from the passage. You will get only an idea about the concept. If you know it, you can answer it but reading the paragraph even 100 times is not going to help you.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
3 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 10 Science”
Where is the answer
Class 10 Science MCQ
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Bihar Board
James Dyson Award
Cfa institute, srm university.
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Exam 2024 with Answers
Download case study questions for class 10 science to prepare for the cbse board exam 2024. these multiple choice type questions with answers are published by the cbse board to provide sample questions to students..

CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions 2024: Get here the questions based on case studies to practise for the CBSE Class 10 Science exam 2024. The CBSE Class 10 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful for understanding how the source based or case based questions are asked in the board exam. This question bank is published by the CBSE Board itself which makes it a very reliable source for the board exam preparations. Each question has five sub-questions with each followed by four options and a correct answer. Students can easily download these sample questions in PDF format and refer to the same for their exam preparations.
Note: Check the reduced CBSE Syllabus for Class 10 Science for 2024 Exam and then practise the case study questions accordingly for the CBSE Class 10 Board Exam 2024.
Important* Important Last Minute Tips and Resources for CBSE Class 10 Science Exam 2024
SCIENCE- Class X
Sample Case Studies
1. Read the following and answer any four questions from 1.1 to 1.5:
Marble’s popularity began in ancient Rome and Greece, where white and off-white marble were used to construct a variety of structures, from hand-held sculptures to massive pillars and buildings.

1.1 The substance not likely to contain CaCO 3 is
a) Dolomite
b) A marble statue
c) Calcined gypsum
d) Sea shells.
Answer: c) Calcined gypsum
1.2 A student added 10g of calcium carbonate in a rigid container, secured it tightly and started to heat it. After some time, an increase in pressure was observed, the pressure reading was then noted at intervals of 5 mins and plotted against time, in a graph as shown below. During which time interval did maximum decomposition took place?
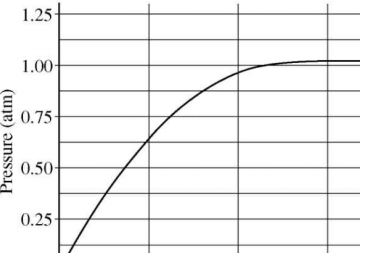
a) 15-20 min
b) 10-15 min
c) 5-10 min
Answer: d) 0-5 min
1.3 Gas A, obtained above is a reactant for a very important biochemical process which occurs in the presence of sunlight. Identify the name of the process -
a) Respiration
b) Photosynthesis
c) Transpiration
d) sphotolysis
Answer: b) Photosynthesis
1.4 Marble statues are corroded or stained when they repeatedly come into contact with polluted rain water. Identify the main reason.

a) decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide
b) polluted water is basic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
c) polluted water is acidic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
d) calcium carbonate dissolves in water to give calcium hydroxide.
Answer: c) polluted water is acidic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
1.5 Calcium oxide can be reduced to calcium, by heating with sodium metal. Which compound would act as an oxidizing agent in the above process?
b) sodium oxide
d) calcium oxide
Answer: d) calcium oxide
2. Read the following and answer any four questions from 2.1 to 2.5:
The reaction between MnO2 with HCl is depicted in the following diagram. It was observed that a gas with bleaching abilities was released.
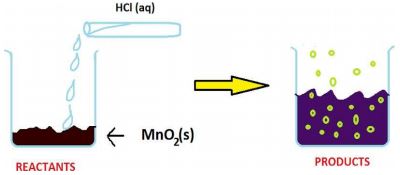
2.1 The chemical reaction between MnO 2 and HCl is an example of:
a) displacement reaction
b) combination reaction
c) redox reaction
d) decomposition reaction
Answer: c) redox reaction
2.2 Chlorine gas reacts with _______ to form bleaching powder.
a) dry Ca(OH) 2
b) dil. solution of Ca(OH) 2
c) conc. solution of Ca(OH) 2
Answer: a) dry Ca(OH) 2
2.3 Identify the correct statement from the following:
a) MnO 2 is getting reduced whereas HCl is getting oxidized
b) MnO 2 is getting oxidized whereas HCl is getting reduced.
c) MnO 2 and HCl both are getting reduced.
d) MnO 2 and HCl both are getting oxidized.
Answer: a) MnO 2 is getting reduced whereas HCl is getting oxidized
2.4 In the above discussed reaction, what is the nature of MnO 2 ?
a) Acidic oxide
b) Basic oxide
c) Neutral oxide
d) Amphoteric oxide
Answer: b) Basic oxide
2.5 What will happen if we take dry HCl gas instead of aqueous solution of HCl?
a) Reaction will occur faster.
b) Reaction will not occur.
c) Reaction rate will be slow.
d) Reaction rate will remain the same.
Answer: b) Reaction will not occur.
Also, check below other important study material released by the CBSE Board:
CBSE Class Maths Case Study Questions for All Chapters (Published by CBSE)
MCQs for Class 10 English Footprints without Feet (Published by CBSE)
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- UPSC Answer Key 2024
- UPSC Question Paper 2024
- UPSC Exam Analysis 2024
- UPSC Prelims Cut Off 2024
- Bihar BEd Admit Card 2024
- IAS Exam Last Minute Tips 2024
- NTA NET Admit Card 2024
- APSC SO Result 2024
- APSC SO Admit Card 2024
- UPSC CSE Admit Card 2024
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
New MSP for Kharif Crops: मोदी सरकार की दूसरी बड़ी सौगात, 14 खरीफ फसलों की MSP में बढ़ोतरी, देखें नई दरें
Modi Cabinet 2024 with Portfolios: कौन बनेगा स्पीकर, किसे मिली किस मंत्रालय की कमान और किसका बदला मंत्रालय? सब जानें
PM Kisan Beneficiary Status: डायरेक्ट Link से देखें PM-Kisan Samman Nidhi बेनिफिशियरी स्टेटस
Spot the 3 Differences Between the Car Mechanic Pictures in 31 Seconds
Discover the Surprising Reason Behind Nvidia's Recent Success!
Lok Sabha Results Rajasthan 2024: सबसे अधिक और सबसे कम मतों से जीतने वाले प्रत्याशी कौन है?
Are You a Visual Genius? Find the Octopus Hidden Among Mushrooms in 8 Seconds!
Vande Bharat Sleeper Trains: पहली वंदे भारत स्लीपर ट्रेन कब और किसी रूट पर दौड़ेगी?
Vande Bharat Sleeper Train: कैसे ये आधुनिक इंटीरियर दे रहा है लग्ज़री का एहसास, तस्वीरों में देखें
Chenab Rail Bridge: कश्मीर की खूबसूरत घाटी में देखें, अद्भुत इंजीनियरिंग का नमूना
PM Kisan Samman Nidhi: कौन है पात्र और क्या है आवेदन प्रक्रिया? सभी डिटेल्स यहां देखें
Durg University Result 2024 OUT at durguniversity.ac.in: Direct Link to Download UG, PG Marksheet
Word Search Puzzle: Only the smartest readers can find the word “smart” in 5 seconds!
RRB ALP Recruitment 2024: Vacancies Increased to 18799, Check Details
Seek and Find Puzzle: Prove You Are in the Top 1% By Finding the Hidden Umbrella in 7 Seconds
Nalanda University Campus: A Testament to Centuries of Learning Finally Revived
ANU Result 2024 OUT at nagarjunauniversity.co.in: Direct Link to Download UG, PG Marksheet
ASTU Result 2024 OUT at astu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet PDF
Dr MGR Medical University Result 2024 OUT at tnmgrmu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
Brain Teaser: Only High IQ Can Tell What’s Wrong With The Desert Picture In 8 Seconds!

Class 10 Science Case Study Questions PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Are you searching for a comprehensive resource to improve your understanding and problem-solving skills in Class 10 Science? Look no further! In this article, we will explore the world of Class 10 Science case study questions and provide you with an opportunity to download a PDF resource containing a collection of case study questions designed specifically for this subject. Let’s dive in and enhance your knowledge!
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

Table of Contents
CBSE Class 10th – SCIENCE: Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions provide a practical and real-life context for applying scientific concepts and principles. These questions require you to analyze a given scenario, identify relevant information, and utilize your scientific knowledge to solve problems or draw conclusions. Case study questions assess your ability to think critically, make connections, and apply scientific principles in a practical setting.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science
To support your preparation for Class 10 Science examinations, we have created a comprehensive PDF resource containing a collection of case study questions designed specifically for this subject. This PDF includes a variety of case studies covering different topics in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. It will provide you with ample practice opportunities to enhance your analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of elements
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Light reflection and refraction
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Human eye and colorful world
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Electricity
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Magnetic effects of current
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Our Environment
The above Case studies for Class 10 Science will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 10 Science Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for the benefit of Class 10 students.
- Class 10th Maths Case Study Questions
Benefits of Case Study Questions
Engaging with case study questions in Class 10 Science offers several benefits. Let’s explore some of them:
- Real-life application: Case study questions allow you to apply scientific concepts to real-life situations, enhancing your understanding of their practical relevance.
- Critical thinking skills: Analyzing case studies promotes critical thinking by challenging you to evaluate information, identify patterns, and draw logical conclusions.
- Problem-solving abilities: Case study questions require you to identify problems, propose solutions, and make informed decisions based on scientific evidence.
- Holistic learning: By examining different aspects of a case, you gain a broader perspective on scientific concepts and their interconnections.
- Preparation for higher education: Case study questions prepare you for future academic pursuits by developing skills necessary for scientific research and analysis.
Understanding the Structure of Case Study Questions
Case study questions typically present a scenario or a problem related to a scientific concept. The questions may require you to analyze data, interpret graphs, or propose solutions based on the given information. It is important to read the case study carefully, identify key details, and understand the context before attempting to answer the questions.
Tips for Analyzing and Answering Case Study Questions
To effectively analyze and answer case study questions, consider the following tips:
- Read the case study thoroughly: Take your time to understand the scenario, paying attention to key details and any scientific concepts mentioned.
- Identify the problem or objective: Determine the main question or objective that the case study aims to address. This will guide your analysis and help you stay focused.
- Break down the questions: Carefully read each question and break it down into smaller parts. Identify the specific information or data required to answer each question accurately.
- Apply scientific knowledge: Utilize your understanding of scientific principles and concepts to analyze the case study. Make connections between the given information and relevant scientific theories.
- Support your answers: Whenever possible, support your answers with scientific evidence or reasoning. Refer to specific data, graphs, or concepts from the case study to justify your conclusions.
Subject-wise Approach to Case Study Questions
Let’s explore how to approach case study questions in the subjects of Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.
In Physics case study questions, focus on understanding the principles and laws governing the given scenario. Analyze the data provided and apply relevant formulas and concepts to solve the problem. Consider factors such as motion, forces, energy, and electrical circuits, depending on the context of the case study.
Chemistry case study questions often involve analyzing chemical reactions, properties of substances, or experimental data. Pay attention to the details of the case study, such as reactants, products, conditions, and observations. Apply your knowledge of chemical reactions, bonding, and periodic trends to interpret and solve the problem.
Biology case study questions revolve around biological processes, organisms, and ecological relationships. Analyze the provided information, such as species interactions, environmental factors, or experimental results. Apply your understanding of biological concepts, such as genetics, evolution, ecosystems, and cellular processes, to address the questions effectively.
Importance of Practicing Case Study Questions
Practicing case study questions in Class 10 Science is crucial for several reasons:
- Application of knowledge: Case study questions enable you to apply scientific knowledge to real-life situations, enhancing your understanding and practical skills.
- Analytical thinking: Regular practice of case study questions hones your analytical thinking skills by challenging you to analyze complex scenarios and make informed decisions.
- Comprehensive understanding: Engaging with case studies offers a holistic understanding of scientific concepts, allowing you to grasp their practical implications and interconnections.
- Exam preparation: Practicing case study questions familiarizes you with the question patterns and formats commonly seen in Class 10 Science examinations, boosting your confidence and performance.
Case study questions offer a valuable opportunity to apply scientific knowledge in practical contexts. By engaging with these questions, you can develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills necessary for success in Class 10 Science. Remember to carefully analyze the case study, apply your scientific understanding, and justify your answers with relevant evidence. Regular practice of case study questions will greatly enhance your overall performance in examinations.
Where can I find Class 10 Science case study questions?
You can download a comprehensive PDF resource containing Class 10 Science case study questions from schools.studyrate.in This resource is specifically designed to provide you with ample practice material.
Why is practicing case study questions important for exam preparation?
Regular practice of case study questions enhances your ability to apply scientific knowledge in practical contexts, improving your analytical thinking and problem-solving abilities. This ultimately contributes to better performance in Class 10 Science examinations.
How should I approach Class 10 Science case study questions?
Read the case study carefully, identify the problem or objective, and analyze the given information. Apply your scientific knowledge to address the questions and support your answers with relevant evidence.
You Might Also Like
Assertion reason questions class 10 science chapter 8 how do organisms reproduce, (2024) class 10 science handwritten notes pdf download, extra questions of class 10 social science geography chapter 6 manufacturing industries pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Expert

CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions Download Free PDF
If you are looking for the CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions in PDF, then you are in the right place. CBSE 10th Class Case Study for the Science Subject is available here. These Case studies can help the students to solve the different types of questions that are based on the case study.

CBSE Board will be asking case study questions based on Science subjects in the upcoming board exams. Thus, it becomes an essential resource to study.
The Science Subject case study for class 10th covers a wide range of chapters from the Science. Students willing to score good marks in their board exams can use it. The questions are highly interactive and it allows students to use their thoughts and skills to solve such kinds of questions.
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning . Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of elements
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Light reflection and refraction
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Human eye and colorful world
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Electricity
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Magnetic effects of current
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Our Environment
The above Case studies for CBSE Class 10 Science will help you to score good marks in the Case Study questions that have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study have been developed by experts of cbseexperts.com for benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 10 Science Assertion and Reason Questions
Case Study Type Questions in Science Class 10
Case Study Type Questions in Science Class 10 include the information or data. Students willing to solve them are required to read the passage carefully and then solve them. While solving the paragraph the ideal way is to highlight the key information or given data.
Because later it will ease them to write the final answers. Science Case study type questions consist of 4 to 5 questions that should be answered in an MCQ manner.
While reading the paragraph students will get the clue in between about the possible answer of the question. They should definitely highlight those questions. This is the best way to solve such kind of Case study Type Questions.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
Case Based Questions for Class 10 Science PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science
If you are in search of case study questions for CBSE Class 10 Science, you have come to the right place. We are offering chapter-wise case study questions for CBSE Class 10 Science. These questions are based on passages given, and are designed to help students practice and improve their marks in the exam.
Chapter Wise CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science
Chapter Wise CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science are questions that are designed to test a student's understanding of scientific concepts and their ability to apply them to real-world situations. These questions are based on the chapters in the Class 10 Science syllabus and are typically presented in the form of a case study or a scenario.
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Chemical Reactions & Equations
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Acids, Bases & Salts
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Metals & Non-metals
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Carbon & Its compounds
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Life Processes
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Control & Coordination
- CBSE Case Study Questions: How do Organisms Reproduce?
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Heredity & Evolution
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Light- Reflection & Refraction
- CBSE Case Study Questions: The Human Eye & the Colourful World
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Electricity
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Our Environment
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Magnetic Effects of Current
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Periodic Classification of Elements
- CBSE Case Study Questions: Sources of Energy
Weightage of CBSE Case Study Questions in Class 10 Science
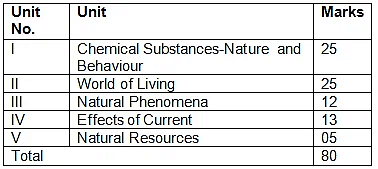
Why are Case Study Questions important in Science Class 10 ?
Case study questions are important in Science Class 10 for several reasons:
- Develops problem-solving skills: Case study questions require students to apply their knowledge to solve real-world problems. This develops their problem-solving skills and helps them to think critically.
- Enhances analytical skills: Case study questions involve analyzing a given scenario or problem and applying scientific concepts to find a solution. This helps students to develop their analytical skills and improves their ability to apply scientific concepts to real-world situations.
- Improves retention and understanding: Case study questions require students to apply the concepts they have learned in the chapter to solve problems. This helps them to better understand the concepts and retain them for a longer period.
- Enhances communication skills: Case study questions often require students to explain their thought process and reasoning. This improves their communication skills and helps them to articulate their ideas more clearly.
- Prepares for competitive exams: Case study questions are often included in competitive exams such as the Olympiad, NTSE, and JEE. Practicing case study questions in Class 10 Science helps students to prepare for these exams and enhances their chances of success.
Overall, case study questions are an effective way to engage students in Science Class 10 and develop their problem-solving, analytical, and communication skills. They also help students to apply scientific concepts to real-world situations and prepare them for higher-level science education.
Class 10 Science Curriculum at Glance
The Class 10 Science curriculum covers a wide range of topics that provide students with a solid foundation in scientific concepts. Here is a brief overview of the Class 10 Science curriculum:
- Chemical Reactions and Equations: Types of chemical reactions, balancing chemical equations, and the concept of oxidation and reduction.
- Acids, Bases, and Salts: Properties of acids and bases, pH scale, and preparation and properties of salts.
- Metals and Non-Metals: Physical and chemical properties of metals and non-metals, their reactions with water, acids, and other substances, and corrosion of metals.
- Carbon and Its Compounds: Covalent bonding in carbon compounds, properties of carbon compounds, and some important carbon compounds such as ethanol, ethanoic acid, and ethene.
- Periodic Classification of Elements: The history of the periodic table, modern periodic law, and the periodic trends in properties of elements.
- Life Processes: Basic concepts of nutrition, respiration, transport, and excretion in living organisms, and their mechanisms.
- Control and Coordination: The nervous system, the endocrine system, and their role in control and coordination in humans and other animals.
- How Do Organisms Reproduce?: Reproduction in animals and plants, modes of reproduction, and reproductive health.
- Heredity and Evolution: Basic concepts of heredity, inheritance patterns, and the role of variations in evolution.
- Light - Reflection and Refraction: Reflection and refraction of light, spherical mirrors, lenses, and their applications.
- Human Eye and Colourful World: The structure and functioning of the human eye, the correction of vision defects, and the concepts of dispersion and scattering of light.
- Electricity: Electric current, electric potential, electric circuits, and the heating effect of electric current.
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Magnetic field, magnetic field lines, magnetic field due to a current-carrying conductor, and the concept of an electromagnet.
- Sources of Energy: Different sources of energy, conventional and non-conventional sources of energy, and their advantages and disadvantages.
- Our Environment: Ecosystem, food chains and food webs, and environmental issues such as pollution and depletion of resources.
- Sustainable Management of Natural Resources: Conservation of natural resources, management of forests and wildlife, and sustainable management of resources.
The Class 10 Science curriculum provides a strong foundation in scientific concepts and prepares students for higher-level science education.
Students can also access CBSE Case Study Questions of all subjects of Class 10:
- CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics
- CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science SST
- CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 English
- CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Hindi
- CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Sanskrit
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science
What are case-based questions for class 10 science.
Case-based questions for Class 10 Science are problem-solving exercises that present real-world scenarios or situations using scientific concepts and require the student to analyze and apply their scientific knowledge and skills to solve the problem.
How can case-based questions for Class 10 Science help me prepare for my exams?
Case-based questions for Class 10 Science can provide a practical and interactive way for students to apply their scientific knowledge and skills to real-world scenarios. It can help students to understand the concepts better and improve their problem-solving abilities.
What types of topics are covered in case-based questions for Class 10 Science?
Case-based questions for Class 10 Science typically cover all the topics and chapters in the Class 10 Science curriculum, including physics, chemistry, and biology.
Top Courses for Class 10
FAQs on Case Based Questions for Class 10 Science
| 1. What are CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science? |
| 2. How are CBSE Case Study Questions weighted in Class 10 Science exams? |
| 3. Why are Case Study Questions important in Science Class 10? |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a Class 10 Science Case Study Question? |
| 5. How can students prepare for CBSE Case Study Questions in Class 10 Science? |
mock tests for examination
Previous year questions with solutions, important questions, case based questions for class 10 science, study material, viva questions, objective type questions, semester notes, shortcuts and tricks, sample paper, practice quizzes, past year papers, extra questions, video lectures.

Case Based Questions for Class 10 Science Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions for class 10 science, case based questions for class 10 science notes, case based questions for class 10 science class 10, study case based questions for class 10 science on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts 2024-25
- Class 10 Important Question
- Chapter 2: Acids, Bases And Salts

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-2 Important Questions with Answers - Free PDF Download
Class 10 Board exams are a crucial period of student life for scoring good marks. Thus students need to know equations, reactions, and formulas and be able to solve the same. Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 will assist students in mastering chemistry concepts. They will gain enough knowledge in the theory of the second chapter in Science through these problems.
If you plan to prepare for JEE and NEET examination , it is crucial to settle a good command in chemistry since the 10th standard. These questions will help you have a good base for chemistry preparation for 10th class and competitive exams. In Chapter 2 of Class 10 , students will be familiar with the behaviour of acids, bases, and salts. Also, they will learn how reactions of these three occur with metals and non-metals . The concept of acids mixing up with bases to form salts turns to be very interesting as it has an excellent practical approach. Thus, it becomes easy for students to learn various reactions to this subject. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions for other chapters:
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions | ||
Sl.No | Chapter No | Chapter Name |
1 | Chapter 1 |
|
2 | Chapter 2 | Acids, Bases and Salts |
3 | Chapter 3 |
|
4 | Chapter 4 |
|
5 | Chapter 5 |
|
6 | Chapter 6 |
|
7 | Chapter 7 |
|
8 | Chapter 8 |
|
9 | Chapter 9 |
|
10 | Chapter 10 |
|
11 | Chapter 11 |
|
12 | Chapter 12 |
|
13 | Chapter 13 |
|
14 | Chapter 14 |
|
15 | Chapter 15 |
|
16 | Chapter 16 |
|

Related Chapters
Study Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2- Acids Bases and Salts
1 mark questions.
An acid can react with
$\text{AgCl}$
$\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
$PbS{{O}_{4}}$
$\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
Ans: The correct answer is (b) $N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}$
Which of the following gives $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ on heating?
Ans: The correct answer is (c) Limestone
Plaster of Paris is made from
Slaked Lime
Gypsum
Ans: The correct answer is (d) Gypsum
4. Which is a base and not alkali?
$\text{NaOH}$
$\text{KOH}$
$\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{3}}}$
Ans: The correct answer is (c) $\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{3}}}$
5. Chemical formula of baking soda is
$\text{MgS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
$\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
$\text{MgC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
Ans: The correct answer is (c) $\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
The H+ ion concentration of a solution is $\text{1}\text{.0 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-5}}}\,\text{m}$. The solution is
(d) Amphoteric
Ans: The correct answer is (a) Acidic
An aqueous solution with pH-zero is
(d) Amphoteric
Ans: The correct answer is (a) Acidic
The setting of Plaster of Paris takes place due to
Dehydration
Hydration
Ans: The correct answer is (d) Hydration
9. The difference of water molecules is gypsum and Plaster of Paris is
$\dfrac{5}{2}$
$\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\dfrac{3}{2}$
Ans: The correct answer is (d) $\dfrac{3}{2}$
The odor of acetic acid resembles that of
Burning Plastic
Kerosene
Ans : The correct answer is (c) Vinegar
11. Washing soda has the formula
$\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{.7}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
$\mathsf{N}{{\mathsf{a}}_{\mathsf{2}}}\mathsf{C}{{\mathsf{O}}_{\mathsf{3}}}\mathsf{.10}{{\mathsf{H}}_{\mathsf{2}}}\mathsf{O}$
$\mathsf{N}{{\mathsf{a}}_{\mathsf{2}}}\mathsf{C}{{\mathsf{O}}_{\mathsf{3}}}\mathsf{.}{{\mathsf{H}}_{\mathsf{2}}}\mathsf{O}$
$\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
Ans: The correct answer is (b) $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{.10}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
Plaster of Paris hardens by
Giving off $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
Changing into $\text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
Combining with water
Giving out water
Ans: The correct answer is (c) Combining with water
Which of the following is evolved when $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is heated?
$\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
$\text{CO}$
${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
No
Ans: The correct answer is (a) $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
14. A drop of the liquid sample was put on the pH paper, the paper turned blue. The liquid sample must be of
Lemon Juice
Sodium bicarbonate
Ethanoic acid
Ans: The correct answer is (c) Sodium bicarbonate
15. If the pH of the solution is 13, it means that it is
Weakly acidic
Weakly basic
Strongly acidic
Strongly Basic
Ans: The correct answer is (d) Strongly Basic
16. How is the concentration of hydronium ions $\left( {{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}} \right)$ affected when a solution of acid is diluted?
Ans: If an acid solution is diluted, the hydronium ion concentration decreases.
17. What effect does the concentration of ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions have on the nature of the solution?
Ans: A higher concentration of ${{\mathsf{H}}^{\mathsf{+}}}$ ions turns the solution acidic in nature.
18. What is the common name of the compound $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$?
Ans: The common name of the compound is Bleaching powder.
19. Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Ans : Slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) yields bleaching powder in treatment with chlorine.
20. Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Ans: The compound which is used for softening hard water is Sodium carbonate.
21. A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be
Ans: The correct answer is (d) $10$
22. A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. The solution contains
$NaCl$
$HCl$
$LiCl$
$KCl$
Ans: The correct answer is (b) $\text{HCl}$
23. $10mL$ of a solution of $NaOH$ is found to be completely neutralized by $8mL$ of a given solution of $HCl$. If we take $20mL$ of same solution of $NaOH$, the amount of $HCl$ solution required to neutralize it will be
$4mL$
$8mL$
$12mL$
$16mL$
Ans: The correct answer is (d) $\text{16mL}$
24. Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion?
Antibiotics
Antiseptic
Ans: The correct answer is (c) Antacid
25. Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicators showed pH as $4,\,1,\,11,\,7$ and $9$ respectively. Which solution is:
strongly alkaline?
Ans: C
strongly acidic?
Ans: B
weakly acidic?
Ans: A
weakly alkaline?
26. ‘A’ is a soluble acidic oxide and ‘B’ is a soluble base. Compared to pH of pure water. What will be the pH of (a) solution of A (b) solution of B?
Ans: Since ‘A’ is acidic, the pH will be less than $7$. On the other hand, since ‘B’ is basic, pH will be more than $7$.
2 Marks Questions
1. What happens to the crystals of washing soda when exposed to air?
Ans: Upon exposure of washing soda crystals to air, the following reaction takes place:
$\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{.10}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\xrightarrow{\text{air}}\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{.}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\,\,\text{+}\,\,\text{9}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
In the reaction, the white crystals of washing soda turn into washing powder (white powder). Efflorescence occurs in the washing soda.
2. What is the chemical name of washing soda? Name three raw materials used in making washing soda by Solvay process?
Ans: The chemical name of washing soda $\left( \text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{.10}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O} \right)$ is sodium carbonate decahydrate.
Ammonia, Brine, and Limestone are used to make washing soda by the Solvay process.
3. What is efflorescence? Give an example?
Ans: Upon exposure to air, the loss of the molecules of water of crystallization from a substance is defined as efflorescence. For example, in the reaction given below, the crystals of washing soda turn into washing powder when exposed to air.
4. Why is sodium hydrogen carbonate an essential ingredient in antacids?
Ans: Sodium hydrogen carbonate $\left( \text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \right)$ is an essential ingredient in antacids because of the basic nature of the salt. It neutralizes the $HCl$ acid released in the stomach. The following reaction takes place,
$\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\,\,\text{+}\,\,\text{HCl}\to \text{NaCl}\,\,\text{+}\,\,{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\,\,\text{+}\,\,\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
5. Give the name and formula of two
strong monobasic acids
Ans: The required answer is:
Hydrochloric acid $\left( \text{HCl} \right)$, Nitric acid $\left( \text{HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \right)$
two weak dibasic acids
Carbonic acid $\left( {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \right)$, oxalic acid $\left( {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} \right)$
6. Why alkalis like sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide should not be left exposed to air?
Ans: Alkalis are hygroscopic in nature. Upon exposure to air, they absorb moisture from the surrounding atmosphere and get dissolved in it.
7. Dry ammonia has no action on litmus paper but a solution of ammonia in water turns red litmus paper blue. Why is it so?
Ans: Dry ammonia has no action on the litmus paper because it contains no hydroxyl ions in the absence of water. On dissolving in water, it forms ammonium hydroxide $\left( \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH} \right)$, which is basic in nature because it dissociates to give $\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}^{\text{+}}$ and $\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}$ ions. Thus, red litmus paper turns blue.
$\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\left( \text{g} \right)\,\,\text{+}\,{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\left( \text{aq} \right) $
$\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\left( \text{aq} \right)\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}^{\text{+}}\left( \text{aq} \right)\,\,\text{+}\,\,\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}\left( \text{aq} \right)$
8. Bleaching powder forms a milky solution in water. Explain.
Ans: Bleaching powder reacts with water to form $\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}$, which has a milky appearance. The reaction is given by,
$\text{CaOC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ +}\,\,{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\,\,\text{+}\,\,\text{2HCl}$
9. Why does not an acid show any acidic behavior in the absence of water?
Ans: Water is an ionizing compound. In its presence, acids form an aqueous solution and get ionized. This results in the release of ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ions and hence, acidic behavior is shown.
10. Fresh milk has a pH of $6$. What will be the pH value if milk changes into a curd? Justify.
Ans: Lactose is converted to lactic acid when milk changes into a curd. Because of the greater acidic nature, the pH value decreases.
11. What is the reaction between hydrogen in concentration ion concentration of an aqueous solution and pH?
Ans: The reaction is given as
$\text{pH=-log}\left[ {{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}} \right]$, where ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ is hydrogen in concentration
12. How will you show that acetic acid is monobasic acid?
Ans: When acetic acid reacts with a basic solution, only one ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ion is replaced by the base, which shows acetic acid is a monobasic acid. For example,
$\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{COOH}\,\,\text{+ NaOH}\to \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{COONa}\,\,\text{+}\,\,{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
13. Why should curd and sour substance not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Ans: Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc metals. These metals react with acids present in curd and sour substances to form poisonous soluble salts. Hence, storing curd and sour substances in brass or copper vessels makes them unfit for consumption.
14. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Ans: When an acid reacts with a metal, hydrogen gas is liberated. For example,
$\text{Zn + C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{ZnC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
We bring a burning splinter near the liberated gas. If the gas is hydrogen, it burns with a pop sound.
15. Why does an aqueous solution of acid conduct electricity?
Ans: Water is a polarizing compound. Acid gets ionized in an aqueous solution and $H^+$ ions are released. These ions conduct electricity.
16. Why does dry HCl gas not change the color of the dry litmus paper?
Ans: When litmus paper comes in contact with ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions, the color of the paper changes. These ions are produced only upon dissolution of $\text{HCl}$ gas in water. Therefore, dry $\text{HCl}$ does not change the color of dry litmus paper.
17. While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Ans: The addition of water to acid leads to a highly exothermic reaction. The intensity of the heat produced can break the glass container or cause severe burns to the person adding it. On the other hand, adding acid to water with constant stirring aids the absorption of the heat produced by water, and any harm/damage is avoided.
18. How is the concentration of hydroxide ions $\left( O{{H}^{-}} \right)$ affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
Ans: The dissolution of excess base in a solution of sodium hydroxide will release more hydroxide $\left( \text{O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}} \right)$ ions. Therefore, it will lead to an increase in the concentration of hydroxide ions.
19. Do basic solutions also have ${{H}^{+}}$ ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Ans: The ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions are present in both acidic and basic solutions. A solution is acidic if the concentration of ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions is more than $\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}$ ions. On the other hand, a solution is basic if the concentration of $\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}$ ions concentration is more than the ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions.
20. Do basic solutions also have ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Ans : Acidic and basic solutions both have ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions. The difference is that in acids ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions concentration is more than $\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}$ ions concentration while in basic solution $\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}$ ions concentration is more than ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions concentration.
21. You have two solutions ‘A’ and ‘B’. The pH of solution ‘A’ is $6$ and pH of solution ‘B’ is $8$. Which solution has more hydrogen ions concentration? Which is acidic and which one is basic?
Ans: On a pH scale, any solution having pH value less than $7$ is considered acidic and that with a pH value of more than $7$ is basic. Hence, according to the given pH values, solution ‘A’ is acidic in nature, while solution ‘B’ is basic. Also, since ‘A’ is acidic, it has a greater concentration of hydrogen ions.
22. What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Ans: On heating, a solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate, sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water are produced.
$\text{2NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + heat}\to \text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
23. Write an equation to show the reaction between plaster of Paris and water.
Ans: The reaction is as follows:
$\text{CaS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{.}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O + }\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{CaS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{.2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
24. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rainwater does?
Ans: The presence of small amounts of acid in rainwater aids the conduction of electricity. Distilled water is pure water and lacks ions. Therefore, it cannot conduct electricity.
25. Why do acids not show acidic behavior in the absence of water?
Ans: Acids produce hydrogen ions or hydronium ions only in presence of water. Therefore, it shows acidic behavior only in the presence of water.
26. Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid is added to test tube A, while acetic acid is added to test B. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Ans : The concentration of ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$ ions in test tube A will be more than that in test tube B because hydrochloric acid is stronger than acetic acid. Therefore, the faster reaction in test tube A will lead to vigorous fizzing.
27. Fresh milk has a pH of $6$. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Ans: Bacterial action on fresh milk turns it into curd. Hence, the lactose in the fresh milk is turned into lactic acid. Because of the formation of more acid, the pH will be lower than $6$.
28. Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Ans: A hard mass of gypsum is formed when the Plaster of Paris comes in contact with moisture. Therefore, it should be stored in a moisture-proof container.
29. Kazi and Priyam want to prepare dil ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$. Kazi added conc ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ to water slowly with constant stirring & cooling whereas Priyam added water to conc ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$. Name the student who was correct and why?
Ans: The addition of water to concentrated acid leads to a highly exothermic reaction. The intensity of the heat produced can break the glass container or cause severe burns to the person adding it. On the other hand, adding acid to water with constant stirring aids the absorption of the heat produced by water and any harm/damage is avoided. Hence, Kazi was correct.
30. A first aid manual suggests that vinegar should be used to treat wasp sting and baking soda for bee stings.
What does this information tell you about the chemical nature of the wasp stings?
Ans: Vinegar (acetic acid) is acidic in nature and it is to be used to heal or neutralize the effect of wasp stings, it implies that the chemical present in the stings is basic.
If there were no baking soda in the house, what other household substance could you use to treat bee stings?
Ans: Ammonium Hydroxide $\left( \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH} \right)$ can be used to treat bee stings
31. A compound ‘X’ on electrolysis in an aqueous solution produces a strong base. ‘Y’ along with two gases ‘A’ and ‘B’. ‘B’ is used in the manufacture of bleaching powder. Identify X, Y, A, and B. Write chemical equations.
Ans : The chemical equations may be written as:
$\text{2NaCl}\left( \text{aq} \right)\text{ + 2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{2NaOH}\left( \text{aq} \right)\text{ + C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)$
$\text{X}\to \text{NaCl}$
$\text{Y}\to \text{NaOH}$
$ \text{A}\to {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} $
$ \text{B}\to \text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$
32. A yellow powder X gives a pungent smell if left open in the air. It is prepared by the Reaction of dry compound Y with chlorine gas. It is used for disinfecting drinking water. Identify X and Y. Write the reaction involved.
Ans : The reaction is written as:
$\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{CaOC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
$\text{X}\to \text{CaOC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$
$\text{Y}\to \text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}$
33. A few drops of phenolphthalein indicator were added to an unknown solution A. It acquired pink color. Now another unknown solution B was added to it drop by drop and the solution becomes colorless. Predict the nature of A & B.
Ans: Phenolphthalein turns pink in color when it is dissolved in a basic solution and the pink color becomes colorless on dissolution with an acid. Hence, according to the given question, we can say that solution ‘A’ is basic in nature, while solution ‘B’ is acidic.
3 Marks Questions
1. (a) Name the raw materials used in the manufacture of sodium carbonate by the Solvay process?
Ans: The raw materials used are- sodium hydroxide, limestone, and ammonia.
(b) How is sodium hydrogen carbonate separated from a mixture of $N{{H}_{4}}Cl$ and $NaHC{{O}_{3}}$?
Ans: Sodium hydrogen carbonate $\left( \text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \right)$ settles down as a precipitate because it is sparingly soluble in water. However, $\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}$ remains dissolved in the solution. The precipitate is removed by filtration.
2. Write equations for the following reactions
Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules
Ans: The reaction can be written as:
$\text{Zn}\left( \text{S} \right)\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\left( \text{dil} \right)\to \text{ZnS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\left( \text{aq} \right)\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)$
Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
$\text{Mg}\left( \text{S} \right)\text{ + 2HCl}\left( \text{dil} \right)\to \text{MgC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{aq} \right)\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)$
Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminum powder.
$\text{2Al}\left( \text{S} \right)\text{ + 3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\left( \text{dil} \right)\to \text{A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\left( \text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} \right)}_{\text{3}}}\left( \text{aq} \right)\text{ + 3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)$
3. (a) An aqueous solution has a pH value of $7.0$. Is this solution acidic, basic, or neutral?
Ans: The nature of the solution is neutral.
If ${{H}^{+}}$ concentration of a solution is $1\times 1{{0}^{-2}}$ mol ${{L}^{-1}}$ what will be its pH value?
Ans: It is given that,
${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}\text{=1}\!\!\times\!\!\text{1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-2}}}\text{ mol}\,{{\text{L}}^{\text{-1}}}$
$\text{pH=log}\left[ \dfrac{\text{1}}{{{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}} \right]$
$ \text{=-log}\left[ {{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}} \right]$
$\text{=-log}\left[ \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-2}}} \right]$
$ \text{=-}\left( \text{-2} \right)\text{log10}$
$\text{pH=2}$
(c) Which has higher pH value: $1-M\,\,HCl$ or $1-M\,\,NaOH$?
Ans: A solution with $\text{1}\,\text{M}\,\,\text{NaOH}$ is basic in nature and will have a higher pH value.
A solution with $\text{1M}\,\,\text{HCl}$ is acidic in nature and will have a lower pH value.
4. What will you observe when:
Red litmus is introduced into a solution of sodium sulphate.
Ans: No colour change will occur because the solution of $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and water is almost neutral.
Methyl orange is added to dil $HCl$.
Ans: The color of methyl Orange will change to reddish.
Blue litmus is introduced into a solution of ferric chloride
Ans: $\text{FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ solution will form ferric hydroxide and hydrochloric acid, when it reacts with water. The presence of a strong acid will make the solution acidic in nature. Therefore, the blue litmus will change to red.
5. A first aid manual suggests that vinegar should be used to treat wasp sting and baking soda for bee stings.
What does this information tell you about the chemical name of the wasp sting?
Ans: Vinegar (acetic acid) is acidic in nature and if it is to be used to heal or neutralize the effect of wasp stings, it implies that the chemical present in the stings is basic.
If there were no baking soda in the house, what other household substances would you use to treat as stings?
Ans: Baking soda is basic in nature. If it is used to treat bee stings, it implies that the stings must be acidic. In case of unavailability of baking soda in the house, a solution of ammonium hydroxide $N{{H}_{4}}OH$ can be used for the same.
6. Does Tartaric acid help in making a cake or bread fluffy. Justify.
Ans: No, tartaric acid does not make cake/bread fluffy because no carbon dioxide is released during baking. Its role is to react with the $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ formed by the decomposition of $\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$.
$ CH\left( OH \right)COOH+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+CH\left( OH \right)COONa+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}} $
$ \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,| $
$ CH\left( OH \right)COOH\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,CH\left( OH \right)COONa\, $
Tartaric acid Disod. Tartarate
If this reaction does not occur, the $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ will impart a bitter taste to the cake.
7. Explain why?
Common salt becomes sticky during the rainy season.
Ans: On exposure to moist air, common salt becomes sticky because it contains impurities of magnesium chloride, which has a tendency to become liquid.
Blue vitriol changes to white upon heating.
Ans: Blue vitriol $\left( \text{CuS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{.5}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O} \right)$ changes to anhydrous copper sulphate $\left( \text{CuS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} \right)$ on heating, which is white in colour.
8. A compound X of sodium is commonly used in the kitchen for making crispy pakoras. It is also used for curing acidity in the stomach. Identify ‘X’. What is its chemical formula? State the reaction that takes place when it is heated during cooking?
Ans: Compound X can be identified as baking powder (or baking soda). Chemically, the compound is sodium hydrogen carbonate $\left( \text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \right)$. On heating the compound, the following reaction occurs:
$\text{2NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow{\text{heat}}\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\left( \text{s} \right)\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\left( \text{l} \right)\text{ + C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)$
9. Explain why-
Anhydrous calcium chloride is used in desiccators
Ans: The hygroscopic nature of anhydrous calcium chloride makes it readily absorb moisture and therefore, it is used as a desiccator.
If a bottle full of concentrated ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ is left open in the atmosphere by accident, the acid starts flowing out the bottle of its own.
Ans: Concentrated sulphuric acid is highly hygroscopic. It begins to absorb moisture from the air and gets diluted. Because of the increase in volume, the acid starts flowing out of the bottle.
10. How is plaster of Paris chemically different from gypsum? How may these be interconverted? Write one use of plaster of Paris?
Ans: Plaster of Paris is the anhydrous form of gypsum. It is prepared by heating gypsum.
Plaster of Paris is used in surgical bandages for setting fractured bones. Before applying on the fractured bone, it is mixed with water, which results in hydration and it changes into gypsum. The hard mass of the gypsum keeps the bones in position.
Plaster of Paris and Gypsum may be interconverted by the reaction:
$CaS{{O}_{4}}\dfrac{1}{2}{{H}_{2}}O+\dfrac{3}{2}{{H}_{2}}O\to CaS{{O}_{4}}2{{H}_{2}}O$
Plaster of Paris Gypsum
11. (a) What is the action of red litmus on
Dry ammonia gas
Ans: As no hydroxyl ions are released, red litmus has no action on dry ammonia gas.
Solution of ammonia gas in water?
Ans: Ammonium hydroxide is formed when ammonia is passed through water. It turns red litmus blue because it dissociates to give hydroxyl ions.
(b) State the observations you would make on adding ammonium hydroxide to an aqueous solution of
ferrous sulphate
Ans: Double decomposition reaction gives a green precipitate of ferrous hydroxide.
$FeS{{O}_{4}}\left( aq \right)+2N{{H}_{4}}OH\left( aq \right)\to Fe{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}+{{\left( N{{H}_{4}} \right)}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\left( aq \right)$
(Green ppt.)
Aluminum chloride?
Ans: Double decomposition reaction gives a white precipitate of aluminum hydroxide.
$AlC{{l}_{3}}\left( aq \right)+3N{{H}_{4}}OH\left( aq \right)\to Al{{\left( OH \right)}_{3}}+3N{{H}_{4}}Cl\left( aq \right)$
(White ppt.)
12. State the chemical property in each case on which the following uses of baking soda are based
As an antacid
Ans: The weakly alkaline nature of baking soda neutralizes the hydrochloric acid formed in the stomach.
$\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + HCl}\to \text{NaCl + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O + C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
As a constituent of baking powder. Give the chemical for baking soda
Ans: Using baking soda while baking makes the cake porous and fluffy. It is because carbon dioxide gas is evolved in the form of bubbles when baking.
$\text{2NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow{\text{heat}}\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O + C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
The chemical formula of baking soda is $\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$.
13. Metal compound ‘A’ reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction, if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Ans: We can say that ‘A’ is a salt of calcium because one of the products is calcium chloride.
The burning candle is extinguished, indicating the formation of carbon dioxide by the reaction of ‘A’ with hydrochloric acid.
Upon reaction with hydrochloric acid, calcium carbonate produces calcium chloride and carbon dioxide. Hence, ‘A’ is calcium carbonate.
The chemical equation can be given as:
$\text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + HCl}\to \text{CaC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
14. Why do $\text{HCl,}\,\,\text{HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ etc. show acidic characters in aqueous solution while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Ans: In their aqueous form, compounds like hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, release hydrogen ions, which signals acidic character.
On the other hand, compounds like alcohol and glucose cannot release hydrogen ions. Therefore, they show no acidic properties.
15. You have two solutions ‘A’ and ‘B’. The pH of solution ‘A’ is $6$ and pH of solution ‘B’ is $8$. Which solution has more hydrogen ions concentration? Which is acidic and which one is basic?
16. Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his field with quicklime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate).
Ans: Quicklime (calcium oxide), slaked lime (calcium hydroxide), and chalk (calcium carbonate) are basic in nature. Hence, a farmer would use them to neutralize the effect of acidic soil conditions.
17. A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
Why does he shift the pH of the milk from $6$ to slightly alkaline?
Ans: Sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) is a base. Hence, in addition to milk, the solution would become slightly alkaline. This implies that the pH value would become greater than $6$ (slightly alkaline) on the addition of a very small amount of baking soda.
Why does this milk take a long time to set a curd?
Ans: A neutralization reaction between the lactic acid of the curd and sodium hydrogen carbonate will prolong the time taken by milk to set as curd.
18. What is a neutralization reaction? Give two examples.
Ans: Neutralization reaction is the reaction between an acid and a base to produce salt and water. For example:
$ \text{NaOH + HCl}\to \text{NaCl + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O} $
$ \text{KOH + HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\to \text{KN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
19. Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Ans: The uses of washing soda are as follows:
Cleansing agent.
Permanently removing the hardness of the water.
Used in paper, glass, and soap industries.
The uses of baking soda are as follows:
Production of baking powder.
As an antacid.
20. Compound P forms enamel of teeth. It is the hardest substance of the body. It does not dissolve in water but it is corroded when pH in the mouth is below $5.5$. How does toothpaste prevent dental decay?
Ans: The compound P is $\text{Ca}_{\text{3}{{\left(\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} \right)}_{\text{2}}}}$.
Bacterial action on the remaining food particles in the mouth produces acids from the degradation of sugar. Toothpaste is usually basic in nature. It helps in neutralizing the excess acid and prevents tooth decay.
21. The oxide of a metal M was water-soluble when a blue litmus strip was dipped in this solution, it did not go any change in color. Predict the nature of oxide.
Ans: The nature of the metal oxide is basic in nature. On dissolution in water, it forms a metal hydroxide. This hydroxide is basic in nature, as the blue litmus did not undergo any change in color.
$\text{MO + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{M}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}$
22. A road tanker carrying acid was involved in an accident and its contents spilled on the road, iron drain covers began melting and fizzing as the acid ran over them. A specialist was called to see if the acid actually leaked into the nearby river.
Explain how the specialist could carry out a simple test to see if the river water contains some acid or not.
Ans: The expert can use a simple litmus paper test to determine if the river water contains acid or not. If the expert dips a strip of blue litmus paper into the sample of river water and the color changes to red, it implies that the river water has been affected by the acid spill.
The word melting is incorrectly used in the report. Suggest a better name that should have been used.
Ans: The word melting can be replaced with corrosion.
Explain why drain covers began fizzing as the acid rain over them.
Ans: Hydrogen gas is evolved when iron reacts with an acid.
23. A compound ‘A’ on heating at $370K$ gives ‘B’ used as plaster for supporting defractured bones in the right position. ‘B’ on mixing with water changes to ‘A’. Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ and write the chemical reaction.
Ans: The reaction can be given by:
$CaS{{O}_{4}}\dfrac{1}{2}{{H}_{2}}O+1\frac{1}{2}{{H}_{2}}O\to CaS{{O}_{4}}2{{H}_{2}}O$
Plaster of Paris Gypsum
‘B’ ‘A’
24. A student heated a few crystals of copper sulphate in a dry boiling tube.
What will be the color of the copper sulphate after heating?
Ans: Copper Sulphate becomes white in color after heating.
Will you notice water droplets in the boiling tube?
Ans : Yes, water droplets will be present in the boiling tube.
Where have these come from?
Ans : Even though copper sulphate crystals seem to be dry, they contain water of crystallization. The water droplets are formed because of this water crystallization.
5 Marks Questions
(a) The pH of rainwater collected from two cities A and B was found to be $6$ and $5$ respectively. The water of which city is more acidic? Find out the ratio of hydrogen ion concentration in the two samples of rainwater?
Ans: Lower pH value is an indication of greater acidic nature. Hence, the rain water of city B is more acidic.
We know that,
$ \text{pH=-log}\left[ {{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}} \right] $
$ \text{=log}\left[ \dfrac{\text{1}}{{{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}} \right] $
For city A,
$\text{log}\left[ \dfrac{\text{1}}{{{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}} \right]\text{=6} $
$ \left[ \dfrac{\text{1}}{{{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}} \right]\text{=anti log6} $
$ \text{=1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{6}}} $
$ \left[ {{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}} \right]\text{=1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-6}}} $
For city B,
$ \text{log}\left[ \dfrac{\text{1}}{{{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}} \right]\text{=5} $
$ \left[ \dfrac{\text{1}}{{{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}} \right]\text{=anti log5=1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{5}}} $
$ \left[ {{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}} \right]\text{=1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-5}}} $
Hence, the ratio is,
$\dfrac{\text{city}\,\text{A}}{\text{city}\,\text{B}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-6}}}}{\text{1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-5}}}} $
$ \text{=}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{10}} $
(b) Arrange the following in order (ascending) of their pH values.
$NaOH$ solution, Blood, lemon Juice.
Ans: The increasing order of pH values for the given solution is:
Lemon juice < Blood < $\text{NaOH}$ solution.
(a) Why does an aqueous solution of acid conduct electricity?
Ans: Water is a polarizing compound. In an aqueous solution form, acid dissociates to give ions. Electricity is conducted by the free movement of these ions.
How does the concentration of hydrogen ions ${{\left[ {{H}_{3}}O \right]}^{+}}$ change when the solution of an acid is diluted with water?
Ans: Dilution aids the process of dissociation of acid into ions. Thus, the concentration of ${{\left[ {{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{O} \right]}^{\text{+}}}$ ions increase on dilution.
Which has higher pH. A concentrated or dilute solution of $HCl$?
Ans: The number of ions per unit volume decreases with an increase in ${{\left[ {{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{O} \right]}^{\text{+}}}$ ions. Therefore, pH will increase on dilution.
What would you observe on adding dil $HCl$ acid to
Sodium bicarbonate is placed in a test tube.
Ans: A brick effervescence from the evolution of $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is observed.
$\text{NaHC}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\left( \text{s} \right)\text{ + HCl}\left( \text{aq} \right)\to \text{NaCl}\left( \text{aq} \right)\text{ + C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\left( \text{aq} \right)$
Zinc metal in a test tube.
Ans: A brick effervescence from the evolution of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ is observed.
$\text{Zn}\left( \text{s} \right)\text{ + 2HCl}\left( \text{aq} \right)\to \text{ZnCl}\left( \text{aq} \right)\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\left( \text{g} \right)$
A road tanker carrying acid was involved in an accident and its contents spilled on the road. At the side of the road iron drain cover began melting and fizzing as the acid ran over them. A specialist was called to see if the acid actually leaked into the nearby river.
Explain why specialists could carry out sample tests to see if the river water contains some acid or not.
Suggest a better report name for the word ‘melting’
Ans: The chemical reaction of drain cover (made of iron) with the acid can be called corrosion.
Explain why the drain covers began fizzing as the acid ran over them.
Ans: Hydrogen gas is evolved when iron reacts with an acid (like sulphuric acid or hydrochloric acid). The release of hydrogen is accompanied by effervescence and hence, the fizzing on the covers was observed.
Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when:
Dilute Sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
Ans: Zinc + Sulphuric acid $\to $ Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
$Zn+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to ZnS{{O}_{4}}+{{H}_{2}}$
Ans: Magnesium + Hydrochloric acid $\to $Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen gas
$Mg+{{2HCl}}\to MgC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}$
Dilute Sulphuric acid reacts with aluminum powder
Ans: Aluminum + Sulphuric acid $\to $ Aluminum sulphate + Hydrogen gas
$2Al+3{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to A{{l}_{2}}{{\left( S{{O}_{4}} \right)}_{3}}+3{{H}_{2}}$
Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
Ans: Iron + Hydrochloric acid $\to $Iron chloride + Hydrogen
$Fe+{{2HCl}}\to FeC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}$
Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorized as acids. Describe an activity
Ans: The following activity can prove that alcohol and glucose both contain hydrogen but are not categorized as acids.
Apparatus required: - Beaker, nails, battery, connecting wires, bulb, switch and alcohols.
The experiment is set up as shown
Ethyl alcohol is taken in the beaker.
The bulb does not glow when the switch is in on position.
The alcohol is replaced with a glucose solution. The bulb still does not glow.
6. A compound X is bitter in taste. It is a component of washing powder & reacts with dil. $\text{HCl}$ to produce brisk effervescence due to colorless, odorless gas Y which turns lime water milky due to formation of Z. When an excess of is passed, milkiness
disappears due to the formation of P. Identify X, Y, And Z & P.
Ans: The chemical reactions are as follows:
$ N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)\text{ }+\text{ }2HCl\left( aq \right)\to 2NaCl\left( aq \right)\text{ }+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)\text{ }+\text{ }C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right) $
$ Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}\left( aq \right)\text{ }+\text{ }C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to CaC{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)\text{ }+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right) $
$ CaC{{O}_{3}}\left( s \right)\text{ }+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}O\left( l \right)\text{ }+\text{ }C{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\to Ca{{\left( HC{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}\left( aq \right)$
$Ca{{\left( OH \right)}_{2}}$ is lime water
$CaC{{O}_{3}}$
is the white precipitate
$ X\to N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}} $
$Y\to C{{O}_{2}} $
$ Z\to CaC{{O}_{3}} $
$ P\to Ca{{\left( HC{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} $
7. When gas passes through a saturated solution of ammoniacal brine, two compounds ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are formed. ‘Y’ is used as an antacid and decomposes to form another solid ‘Z’. Identify ‘X’, ‘Y’, ‘Z’ and write chemical equations.
Ans: The chemical reactions are as follows:
$NaC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}+N{{H}_{3}}\to N{{H}_{4}}Cl+NaHC{{O}_{3}}$ $2NaHC{{O}_{3}}\underrightarrow{heat}\,\,N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}$
(Sodium hydrogencarbonate) (Sodium carbonate)
$ X\to N{{H}_{4}}Cl $
$ Y\to NaHC{{O}_{3}} $
$ Z\to N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}} $
8. A substance ‘X’ is used in the kitchen for making tasty crispy pakoras and is also an Ingredient of antacid. Name the substance ‘X’.
How does ‘X’ help to make cakes and bread soft and spongy?
Ans: The chemical reaction is as follows:
$2NaHC{{O}_{3}}\underrightarrow{heat}\,\,N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}$
(Sodium hydrogen carbonate) (Sodium carbonate)
The $C{{O}_{2}}$ gas escapes as bubbles, leaving behind pores. These pores make the cake/bread soft and spongy.
Is the pH value of the solution of ‘X’ is lesser than or greater than $\text{7}\text{.0}$?
Ans: Being salt of a strong base, the pH of the solution will be more than $7.0$.
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 - Free PDF Download
In the final examination of 10th board, around 3-4 questions are mandatorily asked from chapter acids, bases, and salts. Thus, there are maximum chances that students will score full marks from its questions. Students need good study material to prepare well and master it. Vedantu experts provide a free PDF for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Important Questions. It is to ensure students need not search for study material from other websites.
The conceptual questions of Acids, Bases, and Salts need good practice. Hence, it is better if students try every question of this chapter. It is not that easy to get into a deep study of each concept. So we have a free PDF for Ch 2 Science Class 10 Important Questions for students that cover every concept as stated according to CBSE guidelines. There is a complete range of questions ranging from MCQs to subjective long-answer-type questions with maximum chances to be asked in the exams. However, students need to go through all topics and subtopics of this chapter to know their importance.
Ch 2 Science Class 10 Important Questions Concepts to Cover
The questions prepared in the PDF are from experts' knowledge and precisely according to CBSE guidelines. CBSE follows the pattern according to NCERT books and Acid Bases and Salts Class 10 Important Questions. However, know the important concepts covered under this chapter to prepare well and master it.
A Basic Introduction to Acids Bases and Salts
The fundamental introduction covers the knowledge of acids bases and salts that students have studied in previous classes. It includes the Litmus paper test, the taste of acid and base, and basic needs for these compounds in our day to day life.
Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases
Chemical properties for acid and base are tested in the school labs to find appropriate results. However, certain reactions are conducted to find the chemical properties of acids and bases. Some such properties are listed below.
Acid and Bases Reacting with Metals
Students will perform experiments in the lab and write down reactions for an acid’s reaction and base with metal. Acids react with metal and form salt along with Hydrogen gas. Bases react with the metal to form salt and hydrogen gas.
Acids and Bases Reaction with Each Other
Base along with acid together combine and react to form salt and water. It means it is the concept that the effect of acid nullifies if the base is added to it or vice versa.
Acids Reacting with Metallic Oxides
Acid, along with metal oxides, will produce salt and water. Thus metal oxides are the basic oxides that produce salts when reacted with acid.
Bases Reacting with Non-Metallic Oxides
When a base reacts with non-metallic oxide, it produces salt and water. It states that non-metallic oxides have acidic properties.
Common Properties of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases in water.
Here students will learn about common properties that both base and acids show. One such common behaviour is in an aqueous form; both acids and bases can conduct electricity due to free ions. It is the common property between the two.
Strong and Weak Acids and Base
To find how strong are acids and bases, students will come across the concept of pH scale. The lesser pH value means more acidic the compound is. If pH value is 7, that means it is a neutral compound or acts as salt. If pH goes above 7, the compound starts showing basic properties. Thus more the pH value, more basic the compound is. Strength of acid goes down if it approaches near seven according to pH scale. Strength of a base increases if the pH value goes on increasing to 14.
More to Know About Salts
Here students encounter properties, formation, and uses of salts in our day to day life. The pH value of salts is generally ranging from 7 to 7.8. These are considered as neutral compounds (neither acidic nor basic).
Throughout the concept of Ch 2 Class 10 Science, students will be conducting certain experiments to note their final observations for the final compound formed. However, to remind them of the exams point of view, it could be challenging for them. Thus, acids bases and salts Class 10 Important Questions PDF can help them grow their concepts precisely.
Topics Covered in NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – Acid, Bases and Salts
Section 2.1 understanding the chemical properties of acids and bases.
2.1.1 Acids and Bases in the Laboratory
2.1.2 How do Acids and Bases React with Metals?
2.1.3 How do Metal Carbonates and Metal Hydrogen Carbonates React with Acids?
2.1.4 How do Acids and Bases React with each other?
2.1.5 Reaction of Metallic Oxides with Acids
2.1.6 Reaction of a Non-metallic Oxide with Base
Section 2.2 What Do All Acids and All Bases Have in Common?
2.2.1 What Happens to an Acid or a Base in a Water Solution?
Section 2.3 How Strong are Acid or Base Solutions?
2.3.1 Importance of pH in Everyday Life
Section 2.4 More About Salts
2.4.1 Family of Salts
2.4.2 pH of Salts
2.4.3 Chemicals from Common Salt
2.4.4 Are the Crystals of Salts Really Dry?
Important Questions of Acids Bases and Salts Class 10
Based on certain experiments conducted by students in their labs, a list of CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Important Questions are prepared. These questions are generally asked in the exams, and students need to be very precise in answering them. This chapter has the highest marks weightage, which can come in one mark, three marks, and five marks questions. Hence the PDF prepared carries different types of questions along with the answering pattern. Some of such Chapter 2 Science Class 10 Important Questions are listed below.
How will you distinguish acids from bases for their chemical properties?
What happens when an acid reacts with a metal? Explain with a suitable reaction example.
Explain metallic oxides reacting with acids.
Are non-metallic oxides acidic in nature? Justify your statement with suitable examples.
Why should you not keep sour substances in copper or brass utensils?
How can you say that acids in aqueous solution conduct electricity?
Is it possible for dry HCl change the colour for dry litmus paper? If no, then why?
Why is it good to add acids to water drop by drop rather than adding water to acids?
State different chemical properties of bases.
What happens when excess base is diluted into the water? What happens to the present concentration of OH- ions?
Suppose you have two compounds. One has pH as five another having 9. Which compound will be having more H+ ions? Also, describe which one is acidic or basic. Give reasons for each.
What happens to red litmus when kept in acid?
How are salts formed?
Which is common salt widely used?
All the Class 10 Science Ch 2 Important Questions stated above are most likely to be asked in the finals of 10th standard. These are crucial questions that students need to prepare well before exams for Ch 2 Class 10.
Benefits of Acid Bases and Salts Class 10 Important Questions
Students will come across various chemical properties of acids and bases in Ch 2 Class 10. However, the experimental results can make it challenging for them to prepare well for exams. Thus there is a need to work on Class 10th Science Chapter 2 Important Questions first. Know various features of having PDF for important questions of Acids Bases And Salts Class 10.
Practical Focus of Chapter 2: Chapter 2 of Class 10 is practical-based, requiring a strong command of concepts for effective coverage and preparation. Vedantu's expert-prepared PDF ensures comprehensive coverage of all essential concepts.
Application of Concepts in Real Life: Students will engage with diverse questions grounded in day-to-day life examples within the Acids, Bases, and Salts Class 10 Important Questions. This approach facilitates a precise understanding of each concept.
Reference Guides for Final Exams: These important questions serve as valuable reference guides, aiding students in thorough preparation for their final exams by aligning with the exam syllabus.
Accessible Language and Interactivity: The questions and answers are crafted in elementary and interactive language, promoting better understanding. This approach not only enhances comprehension but also contributes to scoring good grades and securing full marks in the questions posed.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 Science Study Materials |
|
|
|
|
|
Important questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 is a decent way to prepare well for final boards. It is the best reference guide for those who are preparing for competitive exams. Thus the chapter questions are the base for students who are planning their career in science. Answers to these important questions are explained precisely with graphs, tables of observations, and diagrams. Hence students need not look anywhere else for final solutions. These solutions are prepared in clear and simple language to acquire excellent grades according to students' concerns.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts 2024-25
1. How can Vedantu’s Important Questions for Chapter 2 “Acids, Bases, and Salts” of Class 10 Science help me in board exam preparation?
Vedantu's Important Questions are a crucial tool for CBSE Board exam preparation. As these questions have been carefully selected after rigorous research by our experts, you must avail of their complete benefit. When you go over these questions, you end up completing all the content of a particular chapter. Moreover, you understand how to compose answers in board examinations. Students lose marks in exams due to their inability to provide impressionable answers. Vedantu's Important Questions provide a perfect guide for forming answers to differently marked questions.
2. Is Chapter 2 “Acids, Bases and Salts” of Class 10 Science important?
Chapter 2 “Acids, Bases and Salts” of Class 10 Science is a vital chapter from the CBSE Board examination viewpoint. Many important questions are asked from this chapter in the exams. The concepts taught in this chapter are also crucial for upcoming academic years. Hence you must pay close attention to the concepts of this chapter and also practice them thoroughly.
Refer to Vedantu’s Important Questions for Chapter 2 “Acids, Bases, and Salts” of Class 10 Science to go through the important questions from this chapter. These important questions are available at free of cost on Vedantu(vedantu.com) and mobile app.
3. Which important questions can be asked in board examinations from “Acids, Bases, and Salts”?
As we have mentioned, Chapter 2" Acids, Bases, and Salts" is a very important chapter. Quite a few important questions can be asked from this chapter like:
What is the chemical formula of baking soda? (One Mark)
How will you show that amino acid is a monobasic acid? (Two Marks)
What is a neutralization reaction? Give two examples. (Three Marks)
You can find over 90 important questions from this chapter on Vedantu.
4. How do we measure the strength of acids and bases?
The strength of acids and bases is measured using a pH indicator. The pH indicator is a universal indicator that measures the concentration of H+ or OH- ions in a solution. The pH scale has a range from 0 to 14 wherein 0 being highly acidic and 14 being highly basic. A pH of 7 stands for a neutral solution. A pH lower than 7 indicates the acidity of a solution whereas a pH higher than 7 shows the alkaline nature of a solution.
5. What is the significance of pH in our daily lives?
pH plays a vital role in our daily lives as well:
Human body works at its optimum level at the pH of 7-7.8
Different types of plants grow well in soils of specific pH.
If the pH of our mouth is lower than 5.5 it can trigger mouth decay.
Our food is digested well at a particular pH range. An imbalance in this can cause acidity which must then be neutralized using antacids.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 1st Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 2nd Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 3rd Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 4th Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 5th Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Case Study Questions
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Redox reactions are those reactions in which oxidation and reduction occur Simultaneously. A redox reaction is made up of two half reactions. In the first half reaction, oxidation takes place and in second half reaction, reduction occurs. Oxidation is a process in which a substance loses electrons and in reduction, a substance gains electrons. The substance which gains electrons is reduced and acts as an oxidising agent. On the other hand, a substance which loses electrons is oxidised and acts as a reducing agent. (i) Which of the following is a redox reaction?
| \({ (a) \ } \mathrm{CaCO}_{3} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaO}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) | \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{H}_{2}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{HCl}\) |
| \({ (c) \ } \mathrm{CaO}+2 \mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaCl}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) | \(\text { (d) } \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{NaCl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) |
(ii) Identify the reaction in which H2 02 is acting as a reducing agent.
| \(\text { (a) } \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) | \(\text { (b) } 2 \mathrm{Hl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{I}_{2}\) |
| \(\text { (c) } \mathrm{Cl}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{O}_{2}\) | \(\text { (d) } 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{3}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) |
(iii) For the following reactions, identify the one in which H 2 S acts as a reducing agent.
| \(\text { (a) } \mathrm{CuSO}_{4}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CuS}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}\) | \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{Cd}\left(\mathrm{NO}_{3}\right)_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CdS}+2 \mathrm{HNO}_{3}\) |
| \(\text { (c) } 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{S}\) | (d) None of these |
(iv) For the following reaction, identify the correct statement. \(\mathrm{ZnO}+\mathrm{CO} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\)
| is being oxidised | |
(v) In the following reaction, which substance is reduced? \(\mathrm{PbS}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbSO}_{4}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
| O | O |
| ion concentration in the solution |
(ii) If the pH of a solution is 8, then its [H + ] ion is
(iii) In terms of acidic strength, which one of the following is in the correct increasing order?
(iv) Which of the following compounds does not give H + ions in aqueous solution?
| PO | H OH | CO | COOH |
(v) Four solutions labelled as P, Q, Rand Shave pH values 1, 9, 3 and 13 respectively. Which of the following statements about the given solutions is incorrect?
Baking powder produces carbon dioxide on heating, so it is used in cooking to make the batter spongy. Although, baking soda also produces CO 2 on heating, but it is not used in cooking because on heating, baking soda produces sodium carbonate along with carbon dioxide. Sodium carbonate, thus, produced, makes the taste bitter. Baking powder is the mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid. Generally, tartaric acid is mixed with baking soda to make baking powder. When baking powder is heated, NaHCO 3 decomposes to give CO 2 which makes bread and cake fluffy. Tartaric acid helps to remove bitter taste due to formation of sodium tartrate. \(2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+ \ \ \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{6} \mathrm{O}_{6} \quad \longrightarrow \quad 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{4} \mathrm{O}_{6}\) Baking soda Tartaric acid Carbon dioxide Sodium tartrate (i) On passing excess CO 2 gas in aqueous solution of sodium carbonate, the substance obtained is
| CO ·10H O | ·H O |
(ii) When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to acetic acid, it evolves a gas. Which of the following statements are true about the gas evolved? (I) It turns lime water milky (II) It extinguishes a burning splinter (III) It dissolves in a solution of sodium hydroxide (IV) It has a pungent odour
(iii) Select the correct statement regarding sodium hydrogen carbonate.
| are produced during the heating ofNaHCO |
(iv) Acetic acid was added to a solid X kept in a test tube. A colourless and odourless gas was evolved. The gas was passed through lime water which turned milky. It was concluded that
(v) Which of the following statements are correct regarding baking soda? (I) Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (II) On heating, baking soda gives sodium carbonate (III) It is used for manufacture of soap (IV) It is an ingredient of baking powder
The chemical reactivity of an element depends upon its electronic configuration. All elements having less than eight electrons in the outermost shell show chemical reactivity. During chemical reactions, atoms of all elements tend to achieve a completely filled valence shell. Metals are electropositive in nature. They have tendency to lose one or more electrons present in the valence shell of their atoms to form cations and achieve nearest noble gas configuration. The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from one element to other are known as ionic or electrovalent compounds. (i) The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are: X : 2 Y: 2, 8, 7 Z : 2, 8, 2 Which of the following is correct regarding these elements?
(ii) Element X reacts with element Y to form a compound Z. During the formation of compound Z, atoms of X lose one electron each whereas atoms of Y gain one electron each. Which of the following properties is not shown by compound Z?
(iii) Which of the following is correct representation of formation of magnesium chloride?
(iv) The electronic configuration of sodium ion is
(v)Which of the following represents an electropositive element?
A hydrocarbon (P) has the molecular formula C 10 H 22 .A hydrocarbon (Q) has two carbon atoms less than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. A hydrocarbon (R) has two carbon atoms more than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. (i) What is the molecular formula of (Q) ?
| H | H | H | H |
(ii) To which homologous series do the compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong?
(iii) What is the molecular formula of (R) ?
(iv) Identify the correct statement about compounds (P), (Q) and (R) .
| unit. |
(v) Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are
The recurrence of properties of the elements after a certain regular intervals, when they are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic numbers, is called periodicity. There are a number of physical properties such as atomic size, metallic and non -metallic character, etc. which show periodic variation. In periodic table, various properties vary differently from moving left to right in a period and going down in a group. In a period, properties vary because from moving left to right in a period, number of shells remain same but valence electron increases by one number hence nuclear charge increases. In a group, on going down, number of valence shells increases while number of valence electrons remains same. (i) From top to bottom in a group of the periodic table, the electropositive character of the element
(ii) Which element has the largest size in the second period?
(iii) Which of the following elements has three valence electrons?
(iv) In the periodic table, the metallic character of elements (a) decreases from left to right and decreases down the group (b) decreases from left to right and increases down the group (c) increases from left to right and increases down the group (d) increases from left to right and decreases down the group (v) Which of the following increases along the period?
The small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal. It is a narrow tube of about 6 metres which lies coiled in the abdomen. The length of small intestine varies in different animals depending on the type of food they eat. (i) Humans are not able to digest cellulose whereas they are able to digest starch due to
(iii) Butter cannot be digested in the stomach as lipase and bile are(a) released in small intestine
(iv) Which of the following is a correct statement? (a) Herbivores have shorter small intestine as they eat grasses (b) Carnivores have larger small intestine as they eat meat (c) Herbivores have larger small intestine as they eat grasses (d) None of these (v) Various types of movements are generated by the ______ layer of the small intestine.
(iii) Which of the following animals shows double circulatory pathway?
(v) Select the option which properly represents pulmonary circulation in humans. \(\text { (a) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \text { Right ventricle }\) \(\text { (b) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Right ventricle }\) \(\text { (c) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \rightarrow \text { Left auricle }\) \(\text { (d) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}>\text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \gg \text { Left auricle }\)
Spore formation, method of asexual reproduction is used by unicellular as well as multicellular organisms.Spores are microscopic units which could be air borne or are present in soil, etc. (i) A slice of bread kept in open for sometime shows growing white cottony mass which later turns black. This happens because (a) bacterial spores present in air germinate on the surface of bread slice (b) fungal spores present in air germinate on the surface of bread slice (c) protozoan microbes start feeding on bread slice (d) none ef these. (ii) Spore formation can be seen in
(iii) Bulb like structure at top of erect hyphae where spores are produced is
Gregor Mendel conducted hybridisation experiments on garden peas for seven years and proposed the laws of inheritance in living organisms. He investigated characters in the garden pea plant that were manifested as two opposing traits, e.g., tall or dwarf plants, yellow and green seeds, etc. (i) Among the seven pairs of contrasting traits in pea plant as studied by Mendel, the number of traits related to flower, pod and seed respectively were
(ii) The colour based contrasting traits in seven contrasting pairs, studied by Mendel in pea plant were
(iii) Refer to the given table of contrasting traits in pea plants studied by Mendel.
| Character | Dominant trait | Recessive trait |
| (i) Seed colour | ||
| (ii) Flower colour | ||
| (iii) Pod shape | ||
| (iv) Flower position |
Which of the given traits is correctly placed? (a) (i), (ii) and (iii) only (b) (ii), (iii) and (iv) only (c) (ii) and (iii) only (d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) (iv) Some of the dominant traits studied by Mendel were (a) round seed shape, green seed colour and axial flower position (b) terminal flower position, green pod colour and inflated pod shape (c) violet flower colour, green pod colour and round seed shape (d) wrinkled seed shape, yellow pod colour and axial flower position. (v) Which of the following characters was not chosen by Mendel?
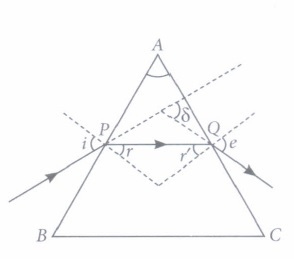
(ii) The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called
(iii) When a ray is refracted through a prism, then
| i=\(\angle\)\(\begin{equation} \delta \end{equation}\) | i=\(\angle\)e+\(\angle\)\(\begin{equation} \delta \end{equation}\) |
| \(\begin{equation} \delta \end{equation}\)= \(\angle\)e | i > \(\angle\)r |
(iv) The angle of deviation depends on
(v) The rectangular surfaces of a prism are known as
Some harmful non-biodegradable chemicals, i.e., pesticides (e.g., DDT) and heavy metals (e.g., mercury, arsenic cadmium, etc.) enter the bodies of organism through the food chain and go on concentrating at each trophic level. This phenomenon is called bio-magnification or biological magnification. (i) Refer to the given food chain Phytoplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Zooplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Small fish \(\longrightarrow\) Large fish \(\longrightarrow\) Fish eating birds If concentration of DDT in small fish is estimated to be 0.5 ppm, then amount of DDT in zooplankton and large fish would respectively be
(ii) Refer to the given table.
According to the given data. The correct order in a food chain will be
| C D A B | D A E C |
| E A D B | E A B D |
| P Q R | Q R P |
| R Q S | Q S R |
(iv) Higher amount of DDT disturb calcium metabolism of birds. This results in
(v) When animals are sprayed with poisons, they may die immediately, but their bodies still contain the poison. The poison in their bodies will then be passed on to the animals which eat them. What would be the consequence of a mass poisoning of the rabbit population in a grazing food chain and why? (a) Plants would die quickly as they are eaten by rabbits (b) Grasshopper would die quickly as all the animals in the food web would be affected (c) Western rattlesnakes would quickly become poisoned as they eat rabbits (d) Hawk would become poisoned as they feed on rabbits
(v) Greenhouse effect is due to
| and depletion of CO | and CO |
| and depletion of O |
Energy flow is the key function of an ecosystem. It is determined by the two basic laws of thermodynamics. Flow of energy in our ecosystem is unidirectional. Green plants capture approximately about 1% of the solar energy incident on the earth to carry out the process of photosynthesis. In an ecosystem, transfer of energy follows 10 percent law, i.e., only 10% energy is transferred from one trophic level to another and remaining 90% of energy is lost in respiration. (i) Read the given statements and select the incorrect one(s). I. At each trophic level organisms utilise energy in respiration. II. Only 10 percent of the solar radiations that fall on earth is used by green plants. III. Green plants are the ultimate source of entire energy as most of the food chain begin with them. IV. A food chain usually consist of 3-4 trophic levels.
(ii) Refer to the given flow chart. Plants \(\rightarrow\) Rat \(\rightarrow\) Snake 20 units 2 units 0.2 unit The given flow chart states that (a) flow of energy in an ecosystem is unidirectional (b) as we move along in a food chain the number of individuals at each trophic level decreases (c) only 10% of the total energy becomes available to next trophic level (d) both (a) and (c). (iii) Nearly 90% of the energy is wasted while moving from one trophic level to other. This energy is used in
(v) Which of the following correctly states the processes involved in energy transfer between the trophic levels?
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject case study questions answer keys.
(I) (b) : H 2 is oxidised to HCI while Cl 2 is reduced to HCl. (ii) (c) \((iii) (c): 2 \mathrm{Fe} \mathrm{Cl}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{s}\) H 2 Sitself gets oxidised to Sand reduces FeCl 3 to FeCI 2 (iv) (a ): ZnO is reduced to Zn and CO is oxidised to CO 2 (v) (b) : H 2 O 2 is reduced to water by removal of oxygen.
(i) (c): As the pH value increases from 7 to 14, it represents decrease in H+ ion concentration in the solution. (ii) (c) : pH = -log l0 [H + ] = 8 log l0 [H + ] =-8 [H + ] = 10 - 8 mol/L (iii) (a) (iv) (b): C 2 H 5 OH is not an ionic compound, it is a covalent compound and hence does not give H + ions in aqueous solution. (v) (c) : (a) Lower the pH of the solution, more acidic is the solution and higher is the [H + ] ions Thus, solution P (pH = 1) has higher [H + ] ions than solution R (pH = 3). (b) Higher the pH of the solution, more basic is the solution and higher is the [OH - ] ions Thus, solution Q (pH = 9) has lower [OH - ] ions than solution S (pH = l3). (c) Solution P (pH = 1) is acidic which turns blue litmus solution red whereas solution Q (pH = 9) is basic which turns red litmus solution blue. (d) Solution P (pH = 1) is highly acidic while solution S (pH = l3) is highly basic and solution Q (pH = 9) is weakly basic.
\({ (i) }(\mathrm{b}): \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}\) (ii) (b) : \(\mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COONa}\) \(+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \uparrow+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) Carbon dioxide gas is evolved which turns limewater milky. It extinguishes a burning splinter since it is not a supporter of combustion. It dissolves in sodium hydroxide solution and it is an odourless gas. \({ (iii) }(\mathrm{c}): 2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3} \stackrel{\text { Heat }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) NaHCO 3 is soluble in water. \({ (iv) }(\mathbf{b}): \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} \longrightarrow\) \(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COONa}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) (v) (c): It is not used in manufacture of soap .
(i) (d) (Ii) (b): '2' is an ionic compound \({ (iii) }(\mathrm{a}): \mathrm{Mg} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}+2 e^{-}\) \(\mathrm{Cl}+e^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\) \(\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgCl}_{2}\) 2,8,2 2,8 2,8,7 2,8,8 \((\text { iv })(\mathrm{d}): \mathrm{Na} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}^{+}+e^{-}\) 2,8,1 2,8 (v) (c): (a) and (d) represent electronegative elements and (b) represents a noble gas.
(i) (c) : Molecular formula of (Q) is CSH1Sas it has two carbon atoms less than (P). (ii) (c): Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are alkanes having general formula C n H 2n+2 . (iii) (a): Molecular formula of (R) is C 12 H 26 as it has two carbon atoms more than (P) (iv) (b): Compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong to same homologous series so they have different physical properties but similar chemical properties. They have same general formula C n H 2n+2 .They . differ by 2 carbon atoms and 4 hydrogen atoms. (v) (a)
(i) (a): As the size of the atom increases down the group, electropositive character increases. (ii) (c): Li is the first element of the second period. As the size decreases in the period from left to right, therefore, Li is the largest atom in the period. (iii) (c): Al (Z = 13) : 2, 8, 3 (iv) (b): Metallic character of elements decreases from left to right and increases down the group. (v) (a): As we move from left to right along a period, the number of valence electrons increases from 1 to 8.
(i) (a): In human, cellulose is indigestible as it cannot be broken into smaller molecules due to absence of cellulase enzyme. (ii) (b): Finger-like projections that come out from mucosa of intestine form villi. Cells lining the villi produce numerous microscopic projections called microvilli giving a brush border appearance which increase the surface area for absorption enormously. Villi has a good supply of capillaries and a large lymph vessel for absorption of nutrients. If the inner lining of the small intestine will be smooth, the surface for absorption will be reduced. (iii) (a) (iv) (c) (v) (b)
(i) (c): A- Artery: Carries blood from heart to different body parts. It is thick-walled and elastic. It acts as a "pressure reservoir" for maintaining the blood flow. B - Capillary : Nutrients, hormones, gases, etc. can diffuse into tissue cells through capillaries and vice versa. It is thin-walled, and only one cell layer thick resting on basement membrane. C - Vein: Brings blood from different body parts to the heart. It is thin-walled and act as low-resistance conduct for blood flow. D - Pulmonary vein: Two pulmonary veins from each lung transport the oxygenated blood to the left atrium. (ii) (d): In amphibians, the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the gills/lungs/skin and the right atrium gets the deoxygenated blood from other body parts. However, they get mixed up in the single ventricle which pumps out mixed blood i.e., incomplete double circulation (iii) (d): Whale is a mammal and in mammals, two separate circulatory pathways are found - systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation. Oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods received by the left and right atria respectively pass on to the left and right ventricles. Thus, oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods are not mixed. This is referred to as double circulation. (iv) (a) (v) (c): Pulmonary circulation is the movement of blood between heart and lungs. During this pathway deoxygenated blood entering the right atrium, moves into the right ventricle. From here it moves through the pulmonary arch into the lungs for oxygenation. Then from lungs the oxygenated blood moves into the left atrium through pulmonary veins.
(i) (b): The tiny spores of bread mould (Rhizopus) are always present in air. On coming in contact with moist surface of bread slice they settle on it and germinate to form new fungal hyphae which first look like white cottony mass and later turns black. (ii) (a): Mucor (fungus) reproduces asexually through spore formation. (iii) (d) (iv) (c) : Bacteria produce endospore which is a dormant and tough structure that enables bacteria to remain dormant for extended periods under unfavorable conditions. (v) (d)
(i) (a) : Characters studied by Mendel are as follows:
| Trait studied | Dominant | Recessive | |
| 1 | Plant height | Tall (T) | Dwarf (t) |
| 2 | Flower position | Axial (A) | Terminal (a) |
| 3 | Flower colour | Violet (V) or (W) | White (v) or (w) |
| 4 | Pod shape | Full or Inflated (I) or (C) | Constricted (i) or (c) |
| 5 | Pod colour | Green (G) or (Y) | Yellow (g) or (y) |
| 6 | Seed shape | Round (R) or (W) | Wrinkled (r) or (w) |
| 7 | Seed colour | Yellow (Y) or (G) | Green (y) or (g) |
(i) (a): The angle between the two refracting surfaces of a prism is called angle of prism. (ii) (b): The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called angle of deviation. (iii) (d): As the ray of light enters from rarer medium (air) to denser medium (glass), the angle of incidence is more than angle of refraction. (iv) (c): More be the refractive index, more be the angle of deviation and it also depends on the refractive index of prism. (v) (c): The refraction of light takes place through rectangular surfaces.
(i) (c): No two magnetic field lines are found to cross each other. If two field lines crossed each other, it would mean that at the point of intersection, the compass needle would point in two directions at the same time, which is not possible. (ii) (d): The magnetic field and hence the magnetic line of force exist in all the planes all around the magnet. (iii) (d): The relative strength of the magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines and the direction of the magnetic field is obtained by tangent to the field lines at the point of intersect. (iv) (d): The magnetic field lines due to a bar magnet are closed continuous curves directed from N to S outside the magnet and directed from S to N inside the magnet. Hence option (d) is correct. v) (d): Inside a bar magnet, the direction of field lines is from south pole to north pole
(i) (a): Due to bio-rnagnification, the concentration of DDT will always be less in zooplanktons than large fish (ii) (c) (iii) (b) : Due to bio-rnagnification the nonbio-degradable chemicals such as DDT accumulate and go on concentrating at each trophic level. (iv) (d) : Higher amounts of DDT disturb calcium metabolism of birds resulting in thinning of egg shells and their prematllre breaking that kills the embryos. (v) (d)
( i) (b) : In the given pie chart, gases P, Q, Rand S respectively are CO 2 , CH 4 , CFCs and N 2 O. Methane is produced by incomplete combustion of biomass. (ii) (c): Methane (gas Q) is produced by incomplete biomass combustion and incomplete decomposition mostly by anaerobic methanogens. Flooded paddy fields, marshes and cattles are the major source of this gas. (iii) (c) : CO 2 is the principal greenhouse gas that helps to keep the earth warm. (iv) (d) (v) (c)
(i) (b): 1% of solar radiation is captured by plants. Sun is the ultimate source of all energy. (ii) (d) (iii) (d) (iv) (d): The given pyramid is pyramid of energy that shows the two basic laws of thermodynamics. (v) (c): Light energy from the sun is converted to chemical energy in producers via photosynthesis. This chemical energy is then transferred to primary consumer, then subsequently to secondary consumer via feeding.
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
CBSE Class 10th - SCIENCE : Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. For Science subjects, there would be 5 case-based sub-parts questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.
| 1. Chemical Reactions & Equations | |
| 2. Acids, Bases & Salts | |
| 3. Metals & Non-metals | |
| 4. Carbon & Its Compounds | |
| 5. Periodic Classification of Elements | |
| 6. Life Processes | |
| 8. How Do Organisms Reproduce | |
| 9. Heredity & Evolution | |
| 10. Light-Reflection & Refraction | |
| 11. The Human Eye & the Colourful World | |
| 12. Electricity | |
| 13. Magnetic Effects of Electric Current | |
| 15. Our Environment |

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- CBSE Class 10 Results 2024 : CBSE Class 10 Answer Book Photocopy Applications Open 4 June, 2024, 6:17 pm
- CBSE 10th 2024-25 : Social Science Official Competency Focused Practice Questions released by CBSE 28 May, 2024, 4:12 pm
- CBSE Class 10 Revaluation Application 2024 Process Begins : How to Apply, Fees, Direct Link & Step-by-Step Guide 21 May, 2024, 4:02 pm
- CBSE Class 10 Result 2024 Latest Update : Verification of Marks, Revaluation & Photocopy of Answer Sheet; Check Complete Process 14 May, 2024, 11:55 am
- CBSE Class 10 Result 2024 Out: 93.60% Pass Percentage, JNV and Kendriya Vidyalaya shine with 99.09% score 13 May, 2024, 5:05 pm
- CBSE Class 10th Result 2024 Out : Supplementary, Re-verification & Re-evaluation Date Released; Check Details Here 13 May, 2024, 3:15 pm
- CBSE 10th Toppers List 2024: Check Toppers Name, Marks, Pass Percentage, Merit List, District & Result Full Statistics 13 May, 2024, 1:30 pm
- CBSE 10th Results 2024 Out : CBSE 10th Result Declared; Check Scorecard Here from Direct Link 13 May, 2024, 1:01 pm
- CBSE 10th 2024-25 : Science Official Competency Focused Practice Questions released by CBSE 7 May, 2024, 4:43 pm

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2
Home » CBSE » Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – Acids Bases And Salts
Science is an essential subject which helps you to comprehend changes in the natural and physical world. Chapter 2 of Class 10 Science is about ‘Acids, Bases, And Salts’. The chapter covers all the important topics that are related to the understanding of chemical reactions and how these chemical substances work with each other.
Quick Links
Going through the important questions will help you analyse your weak points, and you can overcome them to score well in your exams. It’s important to read NCERT books, which are an important resource for enhancing your learning abilities by offering a deeper conceptual understanding of each subject matter. It will help engineering and medical aspirants as well. Students are advised to refer to the Extramarks question bank of Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 to help them score well in the examinations.
Extramarks is one of the best online learning platforms for lakhs of students across the country for all classes from Class 1 to Class 12. Students rely on our comprehensive study materials such as NCERT chapter-wise solutions, CBSE revisions, past years’ solved question papers, etc. to prepare for their exams.
Extramarks experts have curated important questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 is a useful resource for students preparing for science. CBSE Class 10 is a vital stage in career-making as it helps you to make important decisions about your future career prospects. To help students excel in science subjects, we are providing the CBSE Class 10 important questions for science subjects. These questions will help students understand the types of questions asked on exams. It will give students good practise, and they will be able to face the board exam with full preparation.
These questions are available for all the chapters and cover the entire CBSE Class 10 Science syllabus. The questions are aligned with the CBSE exam pattern after analysing the previous year’s question paper pattern and the types of questions asked and by referring to the latest NCERT textbooks and exemplar books.
Our question Chapter 2 Class 10 Science Important Questions plays a vital role in scoring excellent marks in the board exams. Our subject experts have provided detailed answers with step-by-step instructions for students to understand the different concepts used in each of these questions.
Extramarks believes in incorporating the best learning experiences through its own repository. To enjoy the maximum benefit of these resources, students just need to register themselves at Extramarks’ official website and stay ahead of the competition. Apart from our question and answer solutions for Science Class 10 Chapter 2 Important Questions, students can refer to other study materials on our website to step up their preparation.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2022-23
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions are also available for the following chapters:
| 1 | |
| 2 | Acids, Bases and Salts |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | Periodic Classification of Elements |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 | |
| 12 | |
| 13 | |
| 14 | |
| 15 | |
| 16 | |
Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – With Solutions
The question bank of Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Important Questions covers different topics from the chapters. The questions are carefully picked from the exam point of view and cover MCQs, fill in the blanks, short answer questions, and long answer questions. By solving these questions from our Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2, students will be able to fully revise the chapter Acids, Bases, and Salts.
Given below are a set of a few questions and answers from our question bank Important Questions in Class 10 Science Chapter 2: Acids, Bases, and Salts
Question 1: Which of the following gives CO 2 on heating?
Answer1: The correct answer is (c) Limestone
Explanation: Slaked lime Ca(OH)2 on heating gives calcium oxide and water. Limestone CaCO3 on heating gives calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CaCO3 + heat CaO + CO2
Ca(OH)2 + heat CaO + H2O
Question 2: Chemical formula of baking soda is
Answer 2: The correct answer is (c) NaHCO3
Explanation: Chemical formula for baking soda is sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate NaHCO3.
Question3: The odour of acetic acid resembles that of
- Burning Plastic
Answer 3: The correct answer is (c) Vinegar
Explanation: Acetic acid is also known as ethanoic acid, and the formula is CH3COOH. Vinegar is a dilute solution of acetic acid (ethanoic acid) in water. So, the odour of acetic acid resembles vinegar.
Question 4: A drop of the liquid sample was put on the pH paper, and the pH paper turns blue. The liquid sample must be of
- Lemon Juice
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Ethanoic acid
Answer 4: The correct answer is (c) Sodium bicarbonate
Explanations: Bases change red litmus paper solution to blue. The liquid sample could be sodium bicarbonate. Another option is that all are acidic.
Question 5: Farmers neutralise the effect of acidity on the soil by adding
(A) Slaked Lime
(C) Caustic Soda
(D) Baking Soda
Answer 5: Correct Option is (A) Slaked lime
Explanations: Option A is correct. A few quantities of quicklime or slaked lime are used. If the solution is acidic, it decreases the solubility of minerals and affects the availability of nutrients. Thus, a small quantity of slaked lime solution is added to convert the acidic soil. Lime is alkaline, which neutralises the soil. While iron sulphate, aluminium sulphate is acidic and can be used to reduce the alkalinity of the soil.
Question 6: CuSO 4 .5H 2 O In this Compound, the water molecule is called –
(A) Pure Water
(B) Water of Crystallisation
(C) Soda Water
(D) None of these
Answer 6: Correct option is (B)
Explanations: The exact number of water molecules chemically bonded to a salt molecule within the hydrated crystalline compounds is called water of crystallisation. It is essential for the maintenance of a particular crystal. Blue crystals copper sulphate contains five molecules of water CuSO4.5H2O and is also known as blue vitriol.
Question 7: Two solutions, A and B, have pH values of 5 and 8, respectively. Which solution will be basic?
Answer7: Solution B will be basic as its pH value is 8.
Explanations: Solutions having a pH greater than 7 are basic. So, solution B is basic(pH value 7 to 14). Solution A pH value is 5, so it is acidic (1 to 7).
Question 8: The setting of the plaster of Paris takes place due to
- Dehydration
Answer 8: The correct answer is (d) Hydration
Explanation: The setting of the plaster of Paris takes place by hydration due to the formation of a solid crystalline hydrate, and the hardening of the plaster of Paris is a hydration reaction, which is the reverse of the dehydration of gypsum. Plaster of Paris quickly sets to shard mass when made into a thin paste with a water solution. A slight expansion takes place in this process, and heat evolves. This process is exothermic. Students can refer to important questions from Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Question 9: Which salt is Neutral salt?
(A) NH 4 Cl
(B) CH 3 COONH 4
(C) CH 3 COONa
(D) Na 2 CO 3
Answer 9: Correct Option is (B) ammonium acetate
Explanations: Option B is correct. Ammonium acetate is a WAWB type of salt. It has ammonium and acetate ions from acetic acid.
It will have neutral pH. The remaining option is acidic or basic salt behaviour.
Question 10: If the pH of the solution is 13, it means that it is
- Weakly acidic
- Weakly basic
- Strongly acidic
- Strongly Basic
Answer 10: The correct answer is (d) Strongly Basic
Explanations: A solution with pH 13 is a strong base as the basicity increases from 7 to 14. At pH 7, it is less basic and moving to 14, it increases.
Question 11: Name the acid-base indicator extracted from Lichen.
Answer 11: Litmus
Explanation: Litmus is a natural indicator extracted from Lichen. A purple dye indicator is extracted from a plant termed Lichen. This natural dye is called a litmus solution and is generally used as an indicator.
Question 12: Complete & balance the following chemical equations :
(i) NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) →
(ii) CaCO 3 (s) + H 2 O(l) + CO 2 (g) →
(iii) HCl(aq) + H 2 O(l) →
(i) 2NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2(g)
(ii) CaCO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) → Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
(iii) HCl(aq)+H2O(l)→H3O+(aq)+Cl−(aq)
Explanations:
- i) Zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce zincate sodium and hydrogen. This reaction takes place at a temperature near 550°C.
- ii) Calcium carbonate reacts with carbon dioxide and water to produce calcium hydrogen carbonate. The reaction proceeds at room temperature.
iii)Hydrochloric acid, HCl, is strong, so right from the start, you should expect it to ionise completely in an aqueous solution. In other words, every molecule of hydrochloric acid added to water will donate its proton H+ to the water molecule to form a hydronium ion, H3O+. Hydrochloric acid’s ionisation will also produce chloride anions, Cl-.
Question 13: Sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce
(D) All of the above
Answer 13: Correct Option is (D)
Explanations: Sodium carbonate is a base that reacts with an acid, like, hydrochloric acid, to give salt along with carbon dioxide and water. Brisk effervescence is observed by indicating the presence of carbon dioxide CO2 gas. The reaction is shown as follows ,
Na2CO3 + 2HCl 2NaCl + CO2 + H2O
Students can refer to important questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Question 14: Which of the following medicines is used for treating indigestion?
- Antibiotics
- Antiseptic
Answer 14: The correct answer is (c) Antacid
Explanations: Antacid is used for treating indigestion. Indigestion causes acidity in the stomach. We add antacids to neutralise it.
Antacids are basic and hence neutralise the acids.
Question 15: Bleaching powder forms a milky solution in water. Explain.
Answer 15: Bleaching powder reacts with water to form Ca(OH)2, which has a milky appearance. The reaction is given by,
CaOCl2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl
Explanations: When bleaching powder (CaOCl2) gets dissolved in water, the solution turns milky due to the formation of Ca (OH)2
Question 16: Why should curd and sour substance not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Answer 16: Brass is an alloy of copper Cu and zinc Zn metals. Both metals react with acids present in curd and sour substances to form poisonous soluble salts. Hence, storing curd and acidic substances in brass or copper vessels makes them unfit for consumption.
Explanations: Curd and sour substances contain acids. Acids interact with metals to develop salt and hydrogen gas. Hence, if such substances are kept in a copper container, the acid will interact, and the container will be corroded. Therefore it may spoil the food.
Metal + Acid → Salts + Hydrogen
Lactic acid is an organic acid that consists of the -COOH group. Hence, it is a weak acid because of the presence of this alkali group.
- Lactic acid(C3H6O3) forms in cow milk because of the breaking down of bacteria.
- Fresh milk does not contain lactic acid. Dairy products such as yoghurt, cheese and condensed milk have high levels of lactic acid.
- The acidic taste of substances contains acids such as vinegar containing acetic acid, tamarind, grapes containing tartaric acid, and lemons and oranges containing citric acid.
Question 17: Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rainwater does?
Answer 17: The presence of little amounts of acid in rainwater aids the conduction of electricity. Distilled water is pure water & lacks ions. Therefore, it cannot conduct electricity.
Explanations: Electricity needs ” ions” to move in electrolytes. Distilled water contains no ions and does not conduct electricity.
Question 18: What is the exact chemical formula of POP (Plaster of Paris)?
(A) CaSO 4 .2H 2 O
(B) CaSO 4 .3H 2 O
(C) CaSO 4 .1/2H 2 O
(D) CaCO 3 .1/2H 2 O
Answer 18: Correct Option is C
Explanations: On heating gypsum at 373 K, it loses water molecules and becomes calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO4.½ H2O). It is called Plaster of Paris.
Question 19: While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Answer 19: Adding water to acid produces a highly exothermic chemical reaction. The intensity of the heat formed can break the glass container or cause severe burns to the person diluting it. On the other hand, adding acid to water with constant stirring aids the absorption of the heat produced by water, and any harm/damage is avoided during the process.
Explanations: While diluting an acid, it is recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid because if water is added to a concentrated acid, it releases a huge amount of heat which may result in an explosion and can cause acid burns on the face, clothes and body parts. Thus it is safe to add acid to water rather than water to acid.
Question 20: Which gas is generally liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with a suitable ex. How will you identify and test for the presence of this gas?
Answer 20: Hydrogen gas is liberated when an acid reacts with a metal. For example: Take some pieces of zinc granules in a test tube and add H2SO4 to it. Shake it and pass the gas evolved into a soap solution. Bubbles are formed in the soap solution. These soap bubbles contain hydrogen gas. The chemical equation of the reaction is:
H2SO4+ Zn → ZnSO4 + H2↑
Identification test- Hydrogen gas is identified by bringing a burning candle near the soapy bubbles. The candle will burn with a pop sound.
Explanations: When an acid reacts with metal, salt and hydrogen gas are formed.
Metal + acid → Salt + Hydrogen gas↑
When a burning candle or matchstick is brought near hydrogen gas, it burns with a popup sound.
Question 21: Name the sodium compound used to soften hard water.
Answer 21 : Sodium carbonate is used for softening hard water.
Explanation: Washing soda(Na2CO3.10H2O) is the sodium compound used to soften hard water.
Question 22: Fresh milk has a pH value of 6. How do you suppose the pH will change as it converts into curd? Explain your answer.
Answer 22: Fresh milk is turned to curd due to the formation of lactic acid. Lactic acid reduces the pH value of the milk.
Explanations: The pH of milk is 6. The pH will reduce as it changes to curd because it is acidic. The acids present in it reduce the pH.
Question 23: Why does an aqueous solution of acid conduct electricity?
Answer 23: Charged particles are directly responsible for the conductance of electricity in an acid. These charged particles, called ions(cations/anions), are the reason behind the conductance of electricity in acid.
Explanations: Acids tend to dissociate into hydronium ions (H3O+) or hydrogen ions(H+) in an aqueous solution. Because of the movement of these ions, the solution can conduct electricity. Hence, an aqueous solution of acid can conduct electricity.
Question 24: 10 ml of a solution of sodium hydroxide NaOH is neutralised by 8 ml of a given solution of hydrochloric acid HCl. When we take 20 ml of the same solution of sodium hydroxide NaOH, the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be
(a) 4 ml (b) 8 ml (c) 12 ml (d) 16 ml
Answer 24: Since 10 ml of NaOH requires 8 ml of HCl, 20 ml of NaOH requires 8 x 2 = 16ml of HCl. Hence the answer is an option (d) 16ml.
Explanations: It is given that
10ml of NaOH neutralises 8ml Solution of HCl
So 1 ml of NaOH neutralises = 8/10 = 4/5ml Solution of HCl
Therefore, 20 ml of NaOH will neutralise = 4/5x 20= 16 ml solution of HCl.
Hence, 16 ml of HCl solution will be required to neutralise the 20 ml NaOH.The correct answer is (d)
Question 25: Write word equations and then balanced chemical equations for the reaction taking place when
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid interacts with zinc granules.
(b) Dilute hydrochloric acid interacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) Dilute sulphuric acid interacts with aluminium powder.
(d) Dilute hydrochloric acid interacts with iron filings.
Answer 25: Solutions are
- dilute sulphuric acid interacts with zinc granules-
Dilute Sulphuric acid(aq) + Zinc → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen gas
H2SO4(aqueous) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
- b) dilute hydrochloric acid interacts with magnesium ribbon-
Dilute Hydrochloric acid + Magnesium → Magnesium Chloride + Hydrogen Gas
2HCl(aq) + Mg(s) → MgCl2(aqueous) + H2(g)
- c) dilute sulphuric acid interacts with aluminium powder-
Dilute Sulphuric Acid + Aluminium(s) → Aluminium Sulphate + Hydrogen Gas
3H2SO4(aq) + 2Al(s) → Al2(SO4)3(aqueous) + 3H2(g)
- d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings-
Dilute Hydrochloric Acid + Iron(s) → Ferrous Chloride + Hydrogen Gas
6HCl(aq) + 3Fe(s) → 3FeCl2(aqueous) + 3H2(g)↑
Question 26: A milkman adds a very less amount of baking soda to fresh milk-
- a) Why does he shift the pH value of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
- b) Why does this milk take as much time to set as curd?
Answer 26: a) In alkaline conditions, milk does not set as curd easily due to the formation of lactic acid as in the acidic condition.
- b) Since this milk is slightly more basic than normal milk, acids produced to set the curd are neutralised by the base mix to the milk. Hence, it takes a longer time for the curd to set.
Explanations: a) He shifted the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline to prevent milk from getting sour due to the production of lactic acid.
- b) This milk takes a long time to set into curd because the lactic acid produced here first neutralises the pH then the pH is reduced to turn the milk into curd.
Question 27: Give two main important uses of Washing Soda and Baking Soda.
Answer 27: Uses of Washing Soda are:
- a) It is used to remove the permanent hardness of the water.
- b) It is utilised in glass, soap, paper industries and factories.
Uses of Baking Soda are-
- a) It is used as baking powder. Baking powder is a combination of baking soda and tartaric acid. Baking powder makes bread or cake and pastries fluffy.
- b) It is mainly used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
Explanations: Uses of washing soda: As cleansing agent and removing permanent hardness of the water.
They are used in the glass, soap and paper industries.
Uses of baking soda: For making baking powder as an antacid ingredient.
Question 28: Explain why Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Give reasons.
Answer 28: Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container because moisture can affect the plaster of Paris by slowing down the setting of the dressing application because of hydration. It will turn the plaster useless.
Explanations: Plaster of Paris (POP) should be stored in a moisture-proof container because it is a powdery mass that can absorb water or moisture to form a hard solid mass known as gypsum. The reaction takes place as follows:
CaSO4.½ H2O + 1½ H2O → CaSO4.2H2O
Plaster Of Paris water gypsum(hard solid)
Question 29: What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Answer 29: A reaction in which an acid and base react with each other to give salt and water is termed a neutralisation reaction. In this reaction, energy is evolved in the form of heat.
For example:- NaOH + HCl ⟶ NaCl + H2O
Base + Acid ⟶ Salt + water
(ii) During indigestion (caused due to the production of excess hydrochloric acid in the stomach), we administer an antacid (generally milk of magnesia, Mg(OH)2, which is basic). The antacid neutralises the excess acids and thus gives relief from indigestion.
Mg(OH)2 + 2HCl → MgCl2+2H2O
Explanations: The reaction of the acid + base gives a product of salt + water, which is considered a neutralisation reaction.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Mg(OH)2 + H2CO3 → MgCO3 + 2H2O
Question 30: Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH 3 COOH) is added to test tube B. Amount and concentration taken for both the acids are equal. In which test tubes A and B will the fizzing occur intensely and vigorously. Give reasons.
Answer 30: HCl is a stronger acid than CH3COOH. Therefore, the H+ ions concentration in test tube A will be higher than in test tube B. Hence, the reaction will occur faster in test tube A than in test tube B. So, fizzing will occur more vigorously in test tube B.
Explanations: When an acid reacts with magnesium metal, hydrogen gas is produced, which causes fizzing. Stronger acids have more hydrogen ions (H+ )in them. Thus, fizzing will occur strongly in test tube A, in which hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added. It is because HCl is a stronger acid than CH3COOH, and therefore, during the chemical reaction with magnesium metal, HCl will produce more hydrogen gas, due to which fizzing will be more vigorous in test-tube A.
Question 31: Five solutions, A, B, C, D and E, tested with a universal indicator, showed pH of 4,1,11,7 and 9, respectively. Which solution is
(a) neutral?
(b) strongly alkaline?
(c) strongly acidic?
(d) weakly acidic?
(e) weakly alkaline?
Arrange the pH value in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration
Answer 31 :
Explanation: a) Neutral = Solution D with pH=7
- b) Strongly Alkaline= Solution C with pH=11
- c) Strongly Acidic= Solution B with pH=1
- d) Weakly Acidic= Solution A with pH=4
- e) Weakly Alkaline= Solution E with pH=9
Arrange the pH value in increasing order of Hydrogen-ion Concentration.
The pH value can be arranged in the increasing order of the concentration of hydrogen ions as follows:
11<9<7<4<1
Student can refer to important questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Question 32: You are given three test tubes. These three test tubes contain distilled water, acidic and basic solutions, respectively. Only red litmus paper is available to identify what is there in each test tube. How will you separate what is in each of the three test tubes?
Answer 32: We can identify the content in each test tube using red litmus paper. It can be done by noticing the colour change of the red litmus paper.
- The three solutions in the test tubes are poured separately onto litmus paper.
- The solution that changes red litmus to blue contains a basic solution.
- Divide the formed blue litmus paper into two parts.
- The solution from the test tube, which turns blue litmus paper red, will be the acidic solution.
- The solution of the test tube, which does not change either red or blue litmus paper, contains water.
Explanations: Red litmus paper is a base indicator that turns blue in the presence of a base.
Let us consider the three test tubes, A, B, and C. Put the given red litmus paper in every solution. If the colour of red litmus paper turns to blue (as in test tube A), then it is a base, and if there is no change in colour, it is either acidic or neutral.
Now, a drop of the solutions from test tube A is put on the red litmus paper. The same process is repeated with solutions B and C. If either of them changes colour to blue, it is basic (let’s suppose B). Hence, out of three, one is removed as a base.
Out of the remaining two test tubes (A and C), any solution can be acidic or neutral. If we test them for acidic or neutral, a few drops of basic solution are added with a drop of each of the remaining two solutions separately, and then the nature of the drops of the mixtures is checked. If the colour of red litmus changes to blue, then the second solution is neutral (C), and if there is no change in colour, the second solution is acidic (A). It is because acidic and basic solutions neutralise each other. This way, each test tube’s contents can be checked and identified.
Question 33: A student was asked to collect apparatus from the lab store to experiment on the sample’s pH. Identify the article that he is not supposed to pick.
- Litmus paper
Answer 33 : (B) petri dish
Explanations: In the above-given options, all options are used for experimenting on the pH process, except Petri dish.
Question 34: An aqueous solution turns the red litmus solution to blue. Excess addition of which of the following given solutions would reverse the change?
(a) Baking powder
(c) Ammonium hydroxide solution
(d) Hydrochloric acid
Answer 34: The correct option is (d) Hydrochloric acid
Explanation: When the solution turns red litmus to blue, the solution should be basic. Adding acid can neutralise its effect; thus, (d) Hydrochloric acid is the correct answer.
Question 35: What happens when a solution of an acid is added with a solution of a base in a test tube?
(i) The temperature of the solution increases
(ii) The temperature of the solution reduces
(iii) The temperature of the solutions remains the same
(iv) Salt formation takes place
(a) (i) option only
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer 35: The correct option is (d) (i) and (iv)
Explanations: when an aqueous solution of an acid is mixed with a base solution, salt and water are formed. this chemical reaction is known as a neutralisation reaction. heat is evolved in this reaction. therefore, it is an exothermic reaction and increases the temperature of the solution. hence, the correct answer is option d..
Question 36: Which of the following salts does not contain water of crystallisation?
(a) Blue vitriol
(b) Baking soda
(c) Washing soda
Answer 36: The correct option is (b) Baking soda
Explanation: Baking sodas are white amorphous powder, whereas other salts given in the question are crystalline.
Blue vitriol is CuSO4.5H2O
Baking soda is NaHCO3
Washing soda is Na2CO3.10H2O
Gypsum is CaSO4.2H2O
Hence, the correct answer is option b.
Question 37: During the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas on a humid day, the gas is generally passed through the guard tube containing calcium chloride salt. The role of calcium chloride salt taken in the guard tube is to-
(a) absorb the released gas
(b) moisten the gas
(c) absorb moisture from the gas
(d) absorb chloride Cl – ions from the evolved gas
Answer 37: The correct option is (c) to absorb moisture from the gas
Explanation: Calcium is a good dehydrating agent. It has the characteristic property of absorbing moisture. Thus it is used as a desiccant to dry gases and Hydrocarbons in industries and labs. Calcium chloride taken in the guard tube behaves as a dehydrating agent. It absorbs moisture from the hydrogen chloride(HCl) gas that flows through it to obtain dry hydrogen chloride gas. Thus option c is correct.
Question 38: Calcium phosphate is present in tooth enamel. Its nature is
(a) basic nature
(c) neutral
(d) amphoteric
Answer 38: The correct option is (a) basic nature
Explanation: The phosphate ion present in calcium phosphate is a strong base, and it forms a strong salt. Hence, calcium phosphate is basic.
Calcium phosphate is a basic salt formed by the reaction of a strong base, calcium hydroxide and a weak acid, phosphoric acid.
2H3PO4 + 3Ca(OH)2 → Ca3(PO4) 2 + 6H2O
(Phosphoric acid) (Calcium hydroxide) (Calcium phosphate)
Hence, the correct answer is option a.
Question 39: Sodium carbonate is a basic salt because it is a salt of
(a) strong acid and strong base
(b) weak acid and weak base
(c) strong acid and weak base
(d) weak acid and strong base
Answer 39: The answer is (d) weak acid and strong base
Explanation: Salt is formed by weak acid and a strong base from strong salt. Here, sodium is a strong base, & carbonate is a weak acid. If sodium hydroxide, a strong base, reacts with carbonic acid, a weak acid, sodium carbonate salt and water are produced.
2NaOH + H2CO3 → Na2CO3 + 2H2O
Hence, the correct answer is option d.
Question 40: A soil sample is mixed with water & allowed to settle. The clear supernatant solution changes the pH paper to yellowish-orange. Which of the following options would change the colour of this pH paper to greenish-blue?
(a) Lemon juice
(b) Vinegar
(c) Common salt
(d) An antacid
Answer 40: The correct answer is (d) An antacid
Explanation: The sample solution turns pH paper yellowish-orange, confirming the sample’s acidic nature. To make the colour greenish-blue, we must add an antacid because it is basic. Hence the correct answer is d.
Question 41: Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of acidic strength
- Water < Acetic acid < Hydrochloric acid
- Water < Hydrochloric acid< Acetic acid
- Acetic acid< water < Hydrochloric acid
- Hydrochloric acid< water <Acetic acid
Answer 41: The correct option is (a) Water < Acetic acid < Hydrochloric acid.
Explanation- Water is neutral in its pure form, Acetic acid is a weak organic acid, and Hydrochloric acid is a mineral acid. So it is a strong acid. Hence, the correct answer is option a.
Question 42: Sodium hydrogen carbonate, when mixed with acetic acid, evolves a gas. Which of the following given statements are true about how the gas evolved?
(i) It changes lime water milky
(ii) It extinguishes a burning splinter
(iii) It dissolves in a solution of (NaOH) sodium hydroxide
(iv) It has a pungent smell
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer 42: The correct option is (b) (i) (ii)and (iii)
Explanation- Reaction between Sodium hydrogen carbonate and acetic acid leads to the evolution of carbon-dioxide gas. CO2 turns the lime water milky and extinguishes a burning splinter.
When sodium hydrogen carbonate is combined with acetic acid, the following reaction takes place-
NaHCO3 + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + CO2↑ + H2O
Evolved gas is carbon dioxide, a fire extinguisher and, hence, extinguishes a burning splinter.
On transfer, the carbon dioxide gas evolved through lime water, turning lime water milky due to forming a white precipitate of calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
The carbon dioxide gas, a non-metallic oxide, dissolves in a sodium hydroxide solution to form sodium carbonate and water.
CO2 + 2NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O
Question 43: What should be done if a few drops of concentrated acid accidentally spill over a student’s hand?
(a) Wash the hand with saline solution
(b) Wash the hand immediately with sufficient water & apply a paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate
(c) After washing hands with plenty of water, apply a solution of sodium hydroxide on the hand
(d) Neutralise the acids with a strong alkali
Answer 43: The correct option is (b) Wash the hand immediately with plenty of water and apply a paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate. If a few drops of concentrated acid accidentally spill over the hand, it should be washed immediately with plenty of water to remove the acid from the hand. After this, a paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate should be applied to neutralise the remaining acid on hand. Sodium hydroxide or strong alkali is highly corrosive and will burn the hand.
Explanation: Washing the affected hand with plenty of water will reduce the concentration of the acid. The remaining traces of the acid can be neutralised by applying a paste of Hydrogen carbonate, which is basic. NaOH is also a base; it is corrosive and is not used to neutralise the acid. Hence, the correct answer is option b.
Question 44: Common salt, besides being used in the kitchen, can also be utilised as the raw material for making –
(i) Washing soda
(ii) slaked lime
(iii) baking soda
(iv) bleaching powder
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer 44: The correct option is (c) (i) and (iii)
Explanation: Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) prepared by the Solvay process, which is the reaction of sodium chloride, ammonia and carbon dioxide in water. Calcium carbonate is used in the reaction to get carbon dioxide gas. Washing soda is sodium carbonate (Na2CO3.10H2O) prepared from sodium chloride. As only washing soda and baking soda has a compound of sodium so the correct option is c.
Question 45: One of the constituents of baking powder is sodium hydrogen carbonate; the other constituent is
(a) hydrochloric acid
(b) tartaric acid
(c) acetic acid
(d) sulphuric acid
Answer 45: The correct option is (b) tartaric acid
Explanation: A mild edible acid and Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate are used to form baking powder. Here, acetic or citric acid can also be used in place of tartaric acid. Baking powder combines baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) and a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid. Hence, the correct answer is option b.
Question 46: The pH of the gastric juices released during digestion is
(a) less than 7
(b) more than 7
(c) equal to 7
(d) equal to 0
Answer 46: The correct option is (a) less than 7
Explanation: The pH value is acidic to below 7 to ensure an easy breakdown of food particles. The pH of stomach juices is between 1 to 4 range. Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid (HCl) that helps in the digestion of food. Hydrochloric acid(HCl) is one of the components of gastric juice. The pH of gastric juice is about 1-2. Hence, the correct answer is option a.
Question 47: Which one of the following can be used as an acid-base indicator by a visually impaired student?
(b) Turmeric
(c) Vanilla essence
(d) Petunia leaves
Answer 47: The correct option is (c) Vanilla essence
Explanation: Vanilla essence can be utilised as an olfactory indicator. Therefore it can be used as an acid-base indicator by visually impaired students. So option c is correct.
Question 48: Which of the following is acidic?
(a) Lime juice
(b) Human blood
(c) Lime water
(d) Antacid
Answer 48: The correct option is (a) Lime juice
Explanation – Lime juice has citric acid in it. Thus it is acidic. Human blood is slightly basic (pH value is 7.4). Lime water Ca(OH)2 & antacids are basic. Lime juice is sour, and it contains citric acid. Hence, the correct answer is option a.
Question 49: Which of the following is used to dissolve gold?
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Sulphuric acid
(c) Nitric acid
(d) Aqua regia
Answer 49: The correct answer is (d) Aqua regia
Explanation: Gold is a noble metal that will not react even with strong acids, hence aqua regia, a mixture of concentrated Nitric acid & conc. Hydrochloric acid(HCl) in the ratio of 1:3 is used to dissolve gold, refer to important questions in Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Question 50: Match the following chemical compounds given in Column (A) with their appropriate application given in Column (B)-
(a) A—(iii), B—(i), C—(iv),and D—(ii)
(b) A—(iii), B—(iv), C—(i), and D—(ii)
(c) A—(iii), B—(iv), C—(i), and D—(ii)
(d) A—(iii), B—(iv), C—(i), and D—(ii)
Answer 50: The correct option is (c) A—(iii), B—(iv), C—(i), D—(ii)
Explanation: Bleaching powder is utilised for bleaching (decolourising) purposes. Baking
soda is an antacid because it neutralises the excess acid in our stomach to eliminate the pain. It is a mild non-corrosive basic salt. Washing soda is mainly used in the glass industry. Aqueous sodium chloride (NaCl)on electrolysis yields hydrogen and chlorine gases. Hence, the correct answer is option c.
Question 51: Identify the correct representation of the reaction occurring during the chlor-alkali process –
(i) 2NaCl(l) + 2H 2 O(l) → 2NaOH(l) + Cl 2 (g) + H 2 (g)
(ii) 2NaCl(aq) + 2H 2 O(aq) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl 2 (g) + H 2 (g)
(iii) 2NaCl(aq) + 2H 2 O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl 2 (aq) + H 2 (aq)
(iv) 2NaCl (aq) + 2H 2 O (l) → 2NaOH (aq) + Cl 2 (g) + H 2 (g)
Answer 51: The correct answer is (iv) 2NaCl (aq) + 2H2O (l) → 2NaOH (aq) + Cl2 (g) + H2 (g)
Explanation: When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (called brine), it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide near the cathode. This process is called the chlor-alkali process because of the products formed-chlor for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide(NaOH). Chlorine gas(Cl2) is given off at the anode, & hydrogen gas at the cathode.
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aqueous) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
So the correct answer is option iv.
Question 52: Name the acid in ant sting and give its chemical formula. Also, provide a common method to relieve the discomfort caused by the ant sting.
Answer 52: Ant sting releases formic acid. The chemical formula of this methanoic acid is HCOOH. Rubbing baking soda on the affected area can relieve the discomfort caused by the ant sting.
Explanation: The acid present in the ant’s sting is methanoic. Its chemical formula is HCOOH, and its common name is formic acid. The mild base, as baking soda on the stung area, gives relief.
Question 53: What happens when nitric acid is added to an eggshell?
Answer 53: Nitric acid dissolved eggshell, made up of Calcium carbonate. Calcium carbonate reacting with nitric acid yields Calcium Nitrate and carbon-di-oxide gas.
Explanation: Eggshell is composed of calcium carbonate, which dissolves in nitric acid and produces carbon dioxide gas.
CaCO3 + 2HNO3→ Ca(NO3)2 +H2O +CO2
Question 54: For making a cake, baking powder is taken. If at home, your mother picks baking soda instead of baking powder in the cake,
(a) how will it affect the taste of the cake & why?
(b) how can baking soda be turned into baking powder?
(c) what is the role of tartaric acid mixed with baking soda?
Answer 54: a) If we use baking soda instead of baking powder, the cake will taste bitter. After baking soda, sodium carbonate will be formed, making the cake taste bitter.
so 2NaHCO3 +heat→ Na2CO3+CO2+H2O
- b) Baking soda can be turned into baking powder by mixing an edible weak acid like tartaric acid.
- c) If tartaric acid is dissolved in water, it releases hydrogen ions. Hydrogen ions interact with Sodium Carbonate to produce carbon dioxide, making the cake fluffy .
Explanation: The chemical name of baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). It is a mild basic non-corrosive salt.
- a) When your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in a cake, the taste of the cake will be bitter because of the formation of sodium carbonate.
b)Baking soda can be changed into baking powder by mixing a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid.
- c) Tartaric acid is combined with baking soda to neutralise the sodium carbonate; hence, the cake will not taste bitter.
Question 55: A metal carbonate X reacting with acid gives a gas which, when passed through a solution Y, gives the carbonate back. On the other hand, a gas G obtained at the anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry Y, and it gives a compound Z, used for disinfecting drinking water. Identity X, Y, G and Z.
Answer 55: X is showing calcium. When calcium carbonate interacts with HCl, it gives out CO2 gas.
CaCO3 + 2HCl→ CaCl2+CO2+H2O
When carbon dioxide CO2 is passed into lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of Calcium carbonate.
CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O white ppt calcium carbonate
Thus, solution Y shows lime water
If chlorine gas is passed on dry lime water, it gives bleaching powder used to disinfect water.
2NaCl + 2H2O→ 2NaOH + H2 + Cl2
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Hence, the metal carbonate X is CaCO3, and Solution Y is lime water [Ca(OH)2], gas G is chlorine (Cl2), Y is dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2], Z is bleaching powder (CaOCl2).
Question 56: A sulphate salt of the Group 2 element of the Periodic Table is a white, soft substance that can be moulded into different shapes by making dough. If this compound is left in the open for some time, it becomes a solid mass & cannot be used for moulding purposes. Identify the sulphate salt & why does it show such behaviour? Give the reaction involved.
Answer 56: The sulphate salt should be calcium sulphate, a white and soft substance. Calcium sulphate is popularly known as the plaster of paris.
The Plaster of Paris has half a molecule of water of crystallisation. When we leave the plaster of paris open for some time, it absorbs moisture to gain several molecules of crystallisation. This newly formed compound is known as gypsum, which is hard to make moulds.
Explanation: Calcium sulphate is a salt of group 2 element (calcium), a white, soft substance that can be moulded into different shapes by making dough. It is commonly known as the Plaster of Paris. When this compound is left open for some time, it changes to gypsum, giving a hard solid mass.
CaSO4.½ H2O + 1 ½ H2O → CaSO4.2H2O
(Plaster of Paris) (Gypsum)
Question 57: What are strong & weak acids? In this following list of acids, separate strong acids from weak acids-
Hydrochloric acid(HCl), Acetic acid, Citric acid, Nitric acid, formic acid, and sulphuric acid.
Answer 57: The strength of acids depends on the number of hydrogen ions (H+ ions) produced. Acids that give rise to maximum hydrogen ions are said to be strong acids, and acids that give fewer hydrogen ions are said to be weak.
Hydrochloric acid, nitric acid & sulphuric acid get ionised completely, so they are strong acids.
Citric acid, acetic acid, and formic acid get ionised partially, so they are weak acids.
Explanations: Strong acids are those that get completely ionised, and weak acids are those that get partially ionised.
Hydrochloric acid is Strong Acid
citric acid- Weak Acid
acetic acid- Weak Acid
nitric acid – Strong Acid
formic acid- Weak Acid
sulphuric acid- Strong Acid
Question 58: What will be the action of the following substances on litmus paper? Dry hydrochloric acid HCl gas, Moistened NH 3 gas, Lemon juice, Carbonated soft drink, curd, and Soap solution.
Answer 58: Dry HCl gas- No effect
Moistened NH3 gas- Turns litmus paper into blue colour
Lemon juice- Turns litmus paper into red colour
Carbonated soft drink- Turns litmus paper into blue colour
Curd- Turns litmus paper into red colour
Soap solution- Turns litmus paper into blue colour
Explanation: Dry HCl gas will not affect litmus paper.
Moistened NH3 gas will convert red litmus to blue.
Lemon juice will change blue litmus to red.
Carbonated soft drinks will turn blue litmus to red.
The curd will change from blue litmus to red.
Soap solution will change red litmus to blue.
Question 59: A student prepared solutions of (i) an acid & (ii) a base in two separate beakers. She forgot to label the solutions, & litmus paper was unavailable in the laboratory. As both the solutions are colourless, how will she distinguish between the two?
Answer 59: Students can use the Phenolphthalein indicator to check the nature of the solution.
Explanation: Students can distinguish acid and base by using other indicators like phenolphthalein (pink colour in acidic medium), methyl orange (red colour in acidic medium), turmeric (red colour in basic medium) etc.
Benefits of Solving Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2
Science demands a lot of practice with conceptual clarity. Classes 8, 9 and 10 are very important for students to develop a strong fundamental knowledge. We recommend students access Extramarks comprehensive set of Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2. By solving questions and going through the solutions daily, students will gain confidence to solve various problems from the acid-base reactions and equations Chapter 2.
Below are some benefits of frequently solving questions from our Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2:
- By referring to the detailed step-by-step solutions given in our solutions, students will better learn about all the balanced chemical equations and the chemical reactions topics covered in Chapter 2 of the Class 10 Science syllabus.
- The questions & answers are based on the latest CBSE syllabus and as per NCERT exam guidelines. So students can rely on them fully.
- The questions covered in our set of Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 are based on various topics covered in the Acid-base reactions and equations chapter. So while solving these questions, students can revise the chapter and clarify any doubts.
- Practising questions similar to exam questions would help students perform better in their exams and score good marks.
Extramarks provides comprehensive learning solutions for students from Class 1 to Class 12. We have other study resources on our website, along with important questions and answers. Students can click on the links given below to access some of these resources:
- NCERT books
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE previous year’s question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 In the question, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below the question. Assertion (A): Baking powder is used in making cakes. Reason (R): The carbon dioxide gas released when baking powder is mixed with water (which is present in the dough) causes the cake to rise and makes it spongy.
(a) Both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Marks: 1 Ans
Please register to view this section
Cbse class 10 science important questions, chapter 1 - chemical reactions and equations.

Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals
Chapter 4 - carbon and its compounds, chapter 6 - life processes, chapter 7 - control and coordination, chapter 8 - how do organisms reproduce, chapter 9 - heredity and evolution, chapter 10 - light reflection and refraction, chapter 11 - human eye and colourful world, chapter 12 - electricity, chapter 13 - magnetic effects of electric current, chapter 14 - sources of energy, chapter 15 - our environment, chapter 16 - management of natural resources, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. why should students refer to the ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science chapter 2.
Students of Class 10 Science find it difficult to understand the various new concepts covered in this chapter. Doubts during class hours can be solved by clarifying with their teachers or using reference material per their needs. So, selecting the right study material requires a lot of understanding of the current CBSE syllabus. The NCERT exemplar answers for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 provided all the topics in the prescribed textbook.
2. Is the study resource of Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 enough to score good marks?
The solutions provided by subject experts are concise and written from an examination perspective. The answers to the exercise questions are clearly explained with examples. They are 100% accurate. These solutions will help students prepare for the exam as we follow the NCERT books and adhere to the CBSE Science syllabus guidelines. These NCERT solutions will assist students in developing a conceptual foundation that explains all of the key concepts in an easy-to-understand language. This exercise covers all topics and subtopics that could be expected in your Class 10 Science exams.
Along with the study materials provided by the Extramarks team, students should always refer to the official NCERT textbooks and exemplars supplied as part of the CBSE curriculum.
3. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 the best reference guide for the students?
To prepare well for the CBSE exams, students should choose the reference guide that helps them grasp concepts effortlessly and also provides solutions. For this purpose, the teachers at Extramarks have prepared chapter-wise solutions to guide the students. It can be referred to while answering the textbook questions to get a clear idea about the important concepts from the exam perspective.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study Questions With Answers. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids ...
CASE STUDY : 5 (Acids Bases and Salts) Salts of a strong acid and a strong base are neutral with pH value of 7. On the other hand, salts of a strong acid and weak base are acidic with pH value less than 7 and those of a strong base and weak acid are basic in nature, with pH value more than 7. Answer the following in reference to the above ...
Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts.
The Chapter wise Important case study based questions with their solved answers in CBSE Class 10 Science can be accessed from the table below: CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions ...
Case Study Class 10 Science: Here, you will get class 10 Science case study questions and answers pdf at free of cost. Along with you can also download case study questions class 10 Science chapter wise for getting higher marks in board examinations. Sharda University Admission - 100% Scholarship upto - Limited Time Offer - Apply Now ...
Case Study Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: A compound, X of sodium forms a white powder. It is a constituent of baking powder and is used in some antacids.
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App. There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Acids, Bases and Salts Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. The acidic behaviour of acids is due to the presence of hydrogenil (H + )ions in them. They produce hydrogen ions in the presence of water. Water is a polar solvent and this property of water helps in weakening the bond between the ions and makes ...
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science. Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given ...
Document Description: Case Based Questions: Acids, Bases and Salts for Class 10 2024 is part of Class 10 preparation. The notes and questions for Case Based Questions: Acids, Bases and Salts have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Case Based Questions: Acids, Bases and Salts covers topics like Case Study - 1, Case Study - 2, Case Study - 3, Case Study - 4 ...
The CBSE Class 10 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful for understanding how the source based or case based questions are asked in the board exam.
To support your preparation for Class 10 Science examinations, we have created a comprehensive PDF resource containing a collection of case study questions designed specifically for this subject. This PDF includes a variety of case studies covering different topics in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. It will provide you with ample practice ...
Such types of questions are solved by reading the given scenario in the paragraph. CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Case Study. Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations Case Study. Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases & Salts Case Study. Science Chapter 3 Metals & Non-Metals Case Study. Science Chapter 4 Carbon & Its Compounds Case Study.
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science. In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2: Acids, Bases and Salts. CBSE Case Study Questions: Acids, Bases & Salts ; CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3: Metals and Non-metals. CBSE Case Study Questions: Metals & Non-metals ; CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4: Carbon and its compounds
Class 10 Board exams are a crucial period of student life for scoring good marks. Thus students need to know equations, reactions, and formulas and be able to solve the same. Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 will assist students in mastering chemistry concepts. They will gain enough knowledge in the theory of the second chapter in Science through these problems.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. 10th Standard CBSE. Reg.No. : Science. Time : 00:30:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 20. Chemical equation is a method of representing a chemical reaction with the help of symbols and formulae of the substances involved in it.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Case Study Questions. Redox reactions are those reactions in which oxidation and reduction occur Simultaneously. A redox reaction is made up of two half reactions. In the first half reaction, oxidation takes place and in second half reaction, reduction occurs. Oxidation is a process in which a substance loses ...
Physics Chapters for Case Study Questions. Light - Reflection and Refraction. The Human Eye and The Colourful World. Electricity. Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Science students. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving ...
For Science subjects, there would be 5 case-based sub-parts questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions. Chapters. Download. 1. Chemical Reactions & Equations. Click Here. 2. Acids, Bases & Salts. Click Here.
Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 - With Solutions. The question bank of Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Important Questions covers different topics from the chapters. The questions are carefully picked from the exam point of view and cover MCQs, fill in the blanks, short answer questions, and long answer questions.
Download case study question pdfs for CBSE Class 10th Maths, CBSE Class 10th English, CBSE Class 10th Sciece, CBSE Class 10th SST. As the CBSE 10th Term-1 Board Exams are approaching fast, you can use these worksheets for FREE for practice by students for the new case study formats for CBSE introduced this year.