

Problem-solving flowchart: A visual method to find perfect solutions
Reading time: about 7 min
“People ask me questions Lost in confusion Well, I tell them there's no problem Only solutions” —John Lennon, “Watching the Wheels”
Despite John Lennon’s lyrics, nobody is free from problems, and that’s especially true in business. Chances are that you encounter some kind of problem at work nearly every day, and maybe you’ve had to “put out a fire” before lunchtime once or twice in your career.
But perhaps what Lennon’s saying is that, no matter what comes our way, we can find solutions. How do you approach problems? Do you have a process in place to ensure that you and your co-workers come to the right solution?
In this article, we will give you some tips on how to find solutions visually through a problem-solving flowchart and other methods.
What is visual problem-solving?
If you are a literal thinker, you may think that visual problem-solving is something that your ophthalmologist does when your vision is blurry. For the rest of us, visual problem-solving involves executing the following steps in a visual way:
- Define the problem.
- Brainstorm solutions.
- Pick a solution.
- Implement solutions.
- Review the results.
How to make your problem-solving process more visual
Words pack a lot of power and are very important to how we communicate on a daily basis. Using words alone, you can brainstorm, organize data, identify problems, and come up with possible solutions. The way you write your ideas may make sense to you, but it may not be as easy for other team members to follow.
When you use flowcharts, diagrams, mind maps, and other visuals, the information is easier to digest. Your eyes dart around the page quickly gathering information, more fully engaging your brain to find patterns and make sense of the data.
Identify the problem with mind maps
So you know there is a problem that needs to be solved. Do you know what that problem is? Is there only one problem? Is the problem sum total of a bunch of smaller problems?
You need to ask these kinds of questions to be sure that you are working on the root of the issue. You don’t want to spend too much time and energy solving the wrong problem.
To help you identify the problem, use a mind map. Mind maps can help you visually brainstorm and collect ideas without a strict organization or structure. A mind map more closely aligns with the way a lot of our brains work—participants can bounce from one thought to the next defining the relationships as they go.
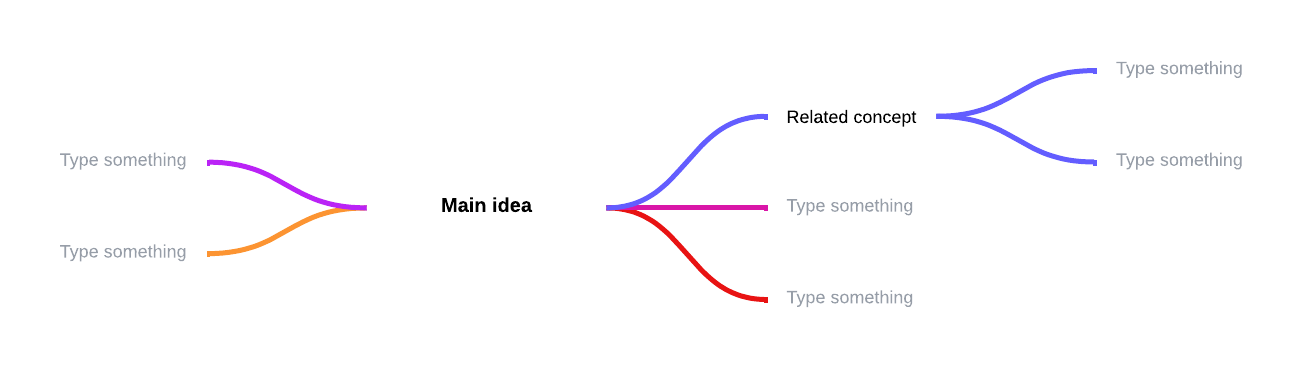
Mind mapping to solve a problem includes, but is not limited to, these relatively easy steps:
- In the center of the page, add your main idea or concept (in this case, the problem).
- Branch out from the center with possible root causes of the issue. Connect each cause to the central idea.
- Branch out from each of the subtopics with examples or additional details about the possible cause. As you add more information, make sure you are keeping the most important ideas closer to the main idea in the center.
- Use Collaborative AI to generate or expand on your ideas, so your mind map is as complete as possible.
Alternatively, you could use mind maps to brainstorm solutions once you discover the root cause. Try our free mind map template or add the mind map shape library to quickly start your own mind map.
Create a problem-solving flowchart
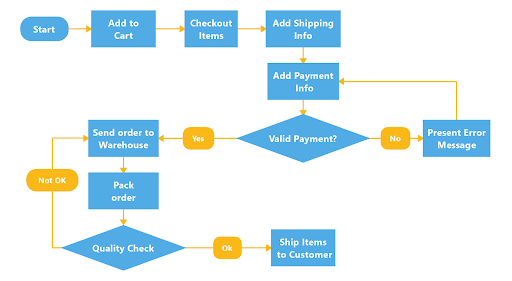
A mind map is generally a good tool for non-linear thinkers. However, if you are a linear thinker—a person who thinks in terms of step-by-step progression making a flowchart may work better for your problem-solving strategy. A flowchart is a graphical representation of a workflow or process with various shapes connected by arrows representing each step.
Whether you are trying to solve a simple or complex problem, the steps you take to solve that problem with a flowchart are easy and straightforward. Using boxes and other shapes to represent steps, you connect the shapes with arrows that will take you down different paths until you find the logical solution at the end.
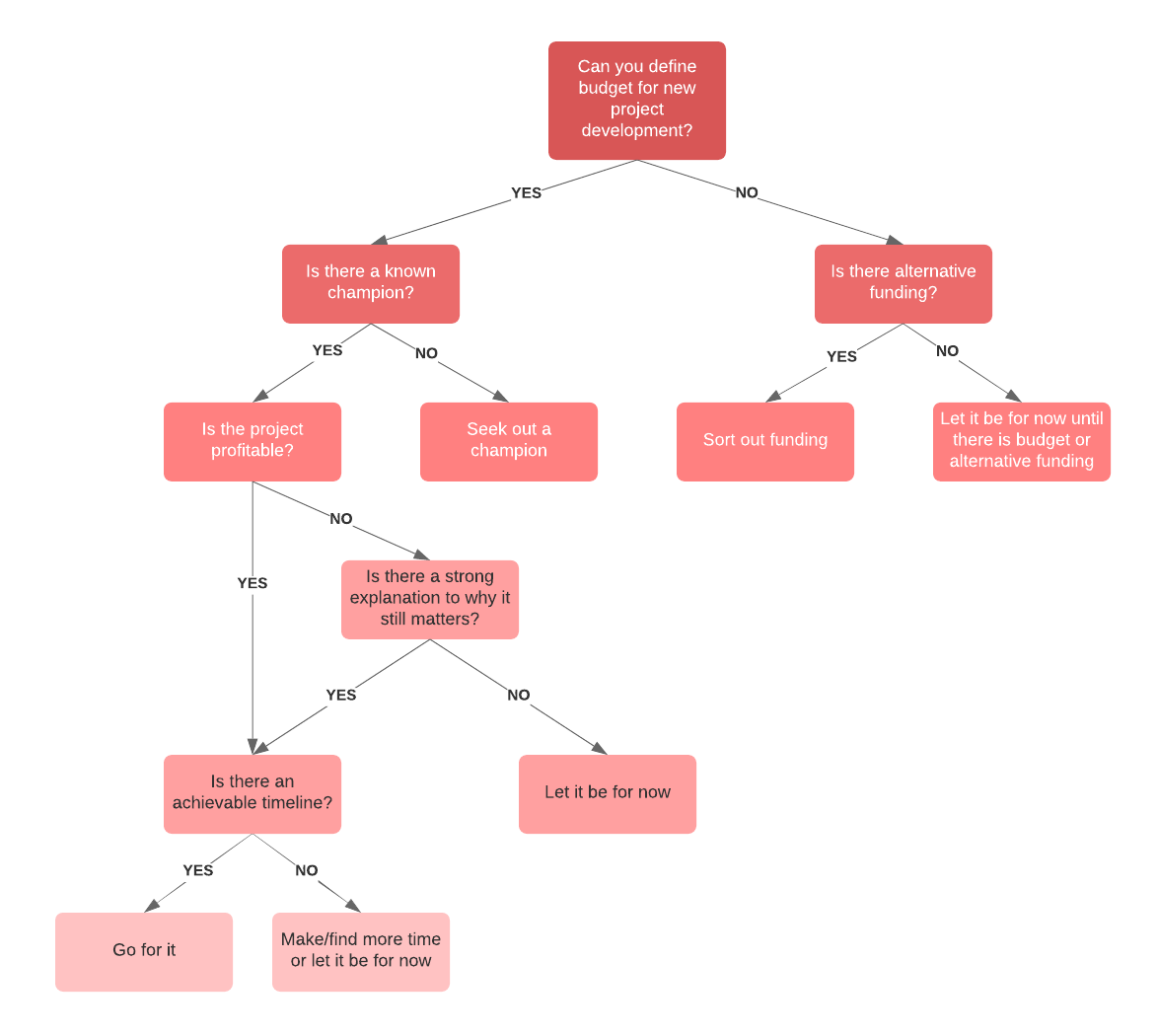
Flowcharts or decision trees are best used to solve problems or answer questions that are likely to come up multiple times. For example, Yoder Lumber , a family-owned hardwood manufacturer, built decision trees in Lucidchart to demonstrate what employees should do in the case of an injury.
To start your problem-solving flowchart, follow these steps:
- Draw a starting shape to state your problem.
- Draw a decision shape where you can ask questions that will give you yes-or-no answers.
- Based on the yes-or-no answers, draw arrows connecting the possible paths you can take to work through the steps and individual processes.
- Continue following paths and asking questions until you reach a logical solution to the stated problem.
- Try the solution. If it works, you’re done. If it doesn’t work, review the flowchart to analyze what may have gone wrong and rework the flowchart until you find the solution that works.
If your problem involves a process or workflow , you can also use flowcharts to visualize the current state of your process to find the bottleneck or problem that’s costing your company time and money.
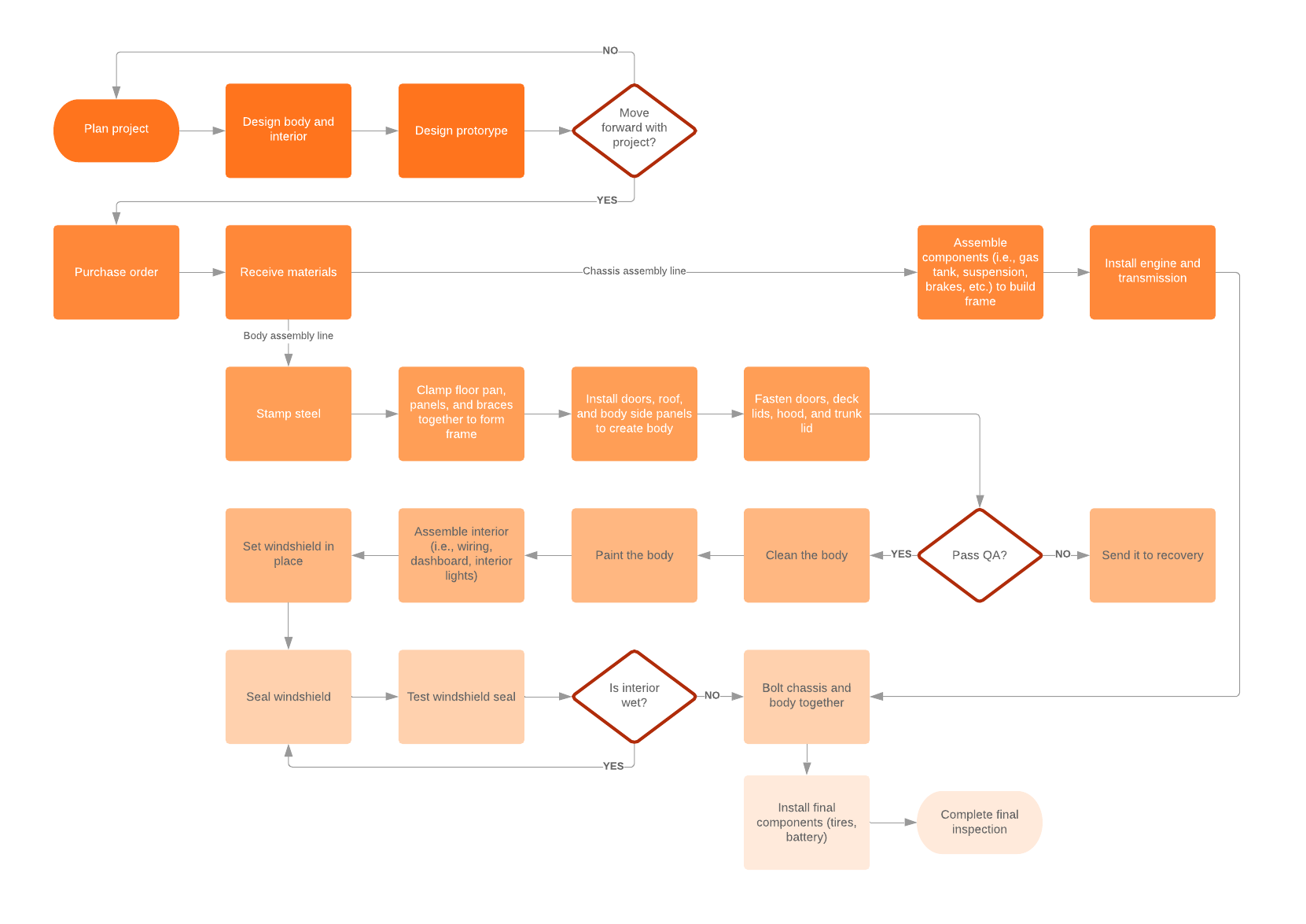
Lucidchart has a large library of flowchart templates to help you analyze, design, and document problem-solving processes or any other type of procedure you can think of.
Draw a cause-and-effect diagram
A cause-and-effect diagram is used to analyze the relationship between an event or problem and the reason it happened. There is not always just one underlying cause of a problem, so this visual method can help you think through different potential causes and pinpoint the actual cause of a stated problem.
Cause-and-effect diagrams, created by Kaoru Ishikawa, are also known as Ishikawa diagrams, fishbone diagrams , or herringbone diagrams (because they resemble a fishbone when completed). By organizing causes and effects into smaller categories, these diagrams can be used to examine why things went wrong or might go wrong.
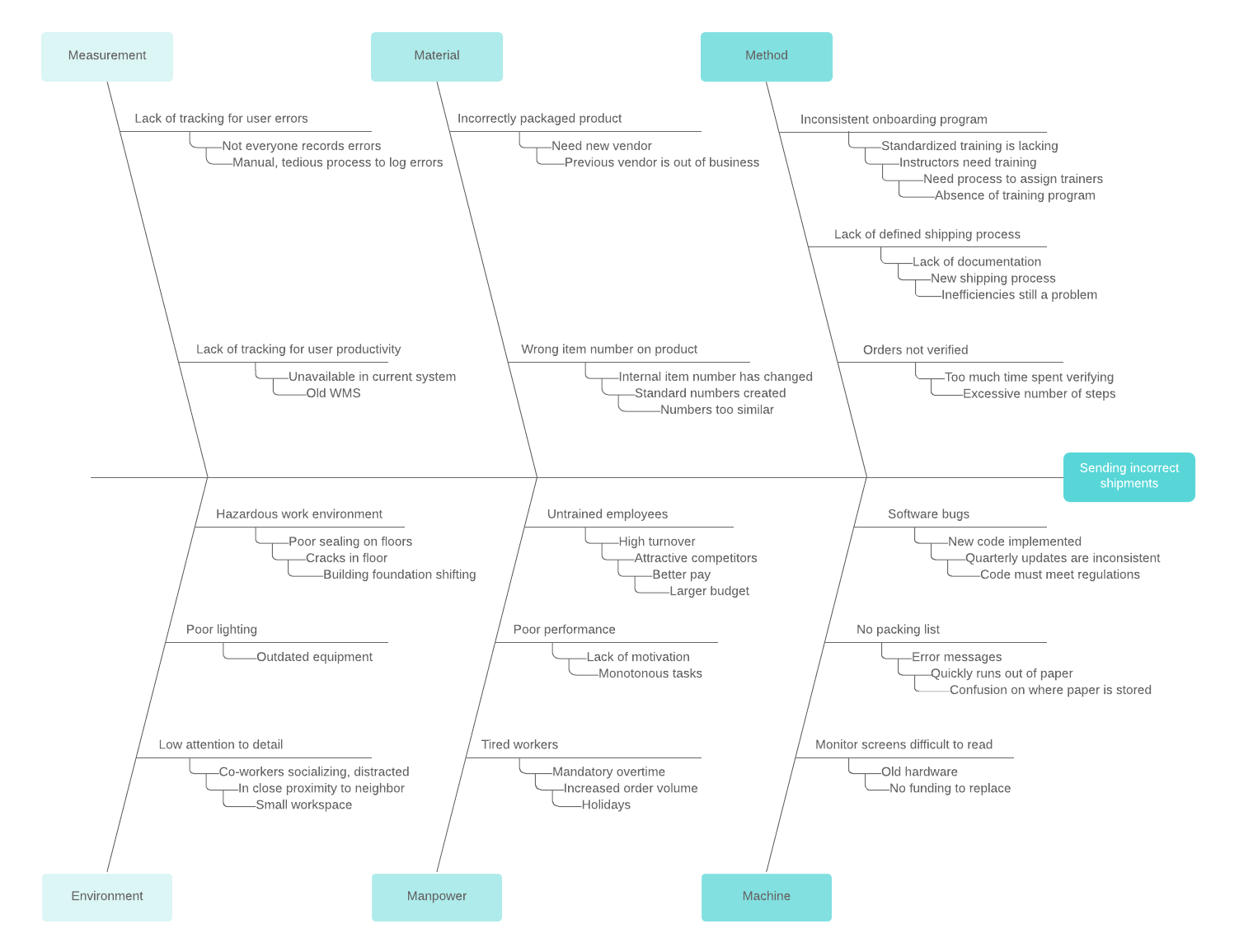
To perform a cause-and-effect analysis, follow these steps.
1. Start with a problem statement.
The problem statement is usually placed in a box or another shape at the far right of your page. Draw a horizontal line, called a “spine” or “backbone,” along the center of the page pointing to your problem statement.
2. Add the categories that represent possible causes.
For example, the category “Materials” may contain causes such as “poor quality,” “too expensive,” and “low inventory.” Draw angled lines (or “bones”) that branch out from the spine to these categories.
3. Add causes to each category.
Draw as many branches as you need to brainstorm the causes that belong in each category.
Like all visuals and diagrams, a cause-and-effect diagram can be as simple or as complex as you need it to be to help you analyze operations and other factors to identify causes related to undesired effects.
Collaborate with Lucidchart
You may have superior problem-solving skills, but that does not mean that you have to solve problems alone. The visual strategies above can help you engage the rest of your team. The more involved the team is in the creation of your visual problem-solving narrative, the more willing they will be to take ownership of the process and the more invested they will be in its outcome.
In Lucidchart, you can simply share the documents with the team members you want to be involved in the problem-solving process. It doesn’t matter where these people are located because Lucidchart documents can be accessed at any time from anywhere in the world.
Whatever method you decide to use to solve problems, work with Lucidchart to create the documents you need. Sign up for a free account today and start diagramming in minutes.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
How you can use creative problem solving at work.
Sometimes you're faced with challenges that traditional problem solving can't fix. Creative problem solving encourages you to find new, creative ways of thinking that can help you overcome the issue at hand more quickly.
Dialogue mapping 101: How to solve problems through visuals
Dialogue mapping is a facilitation technique used to visualize critical thinking as a group. Learn how you and your team can start dialogue mapping today to solve problems and bridge gaps in knowledge and understanding (plus get a free template!).
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .
Visualization for innovation: How to use flowcharts for smarter problem solving

In December 1921, industrial psychologists Lillian Gilbreth and Frank Bunker Gilbreth presented a new model for problem solving to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers in New York City.
Their “process chart” — known today as a flowchart — is a method of visualizing a process in order to improve it. More than one hundred years later, companies from manufacturing to tech startups use flowcharts to pinpoint bottlenecks, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making for their biggest challenges.
How flowcharts simplify problem solving
Visualizing a problem lets us see it in its entirety and process how different components interact. That’s because, according to the Gestalt Principles , with visual representation, our minds can quickly perceive individual elements as a whole and understand a problem better.
“Every detail of a process is more or less affected by every other detail,” the Gilbreths theorized . “Therefore, the entire process must be presented in such [a] form that it can be visualized all at once before any changes are made in any of its subdivisions.”
Once you see how individual elements work together to create a process, you can take steps to modify elements to improve the whole.
- What is a problem-solving flowchart?
A problem-solving flowchart is a flowchart that helps process improvement, troubleshooting, or decision-making. Flowcharts use shapes, symbols, and connecting arrows to map out a problem or flow. This technique illustrates how many steps are in a process, entry and endpoints, the flow of information and materials, and any branches or decision points.
For example, this problem-solving flowchart template shows how you can use a flowchart to troubleshoot a technical problem. The flow guides users through basic questions and actions to a likely solution.
Use this template
- When to use a flowchart for problem solving
Flowcharts can be useful in several instances:
- When you’re aware of a problem, but aren’t sure of the root cause or the best way to solve it.
- When you want to improve a product or service or specific outcomes, like delivery time.
- When you’re entering a new market and want to create solutions that are a market fit for real customer problems.
- The stages of problem solving
To understand how to use flowcharts for problem solving, we’ll use the double diamond design-thinking process . This approach divides problem solving into four stages: discover, define, develop, and deliver. Most people start problem solving in the middle of the diamonds, believing that they know the problem and can start on solutions right away. Instead, you should start even earlier.

https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/our-resources/the-double-diamond
1. Discover
Starting with research helps people understand, rather than simply assume, the problem. Design Council co-founder Jonathan Ball advises , “Go back and ask, ‘Have I been asked to solve the right problem?’”
Problem-solving requests normally come to product or engineering teams from leadership or customers. Statements like “This isn’t selling well” or “This process takes too long” describe pain points, but they’re too vague to form functional solutions.
There are multiple ways to explore the root of a problem:
- Qualitative user research like user interviews
- Quantitative user research like user testing and heatmap tracking
- Workshops, like Upwork’s problem-solving workshop with Miro that led participants through brainstorming, discussing, and voting on top problems to solve
- Flowcharts to illustrate challenges in the “as-is” process .
As-is process mapping
Flowcharts can help solve problems by first mapping out the problematic process. If a process map doesn’t exist, isn’t updated, or hasn’t been well communicated, this is the best starting point.
Ask all teams involved to participate in mapping out the current process. During the process, you may identify bottlenecks or areas of misunderstanding.
Next, refine your discovery into a single statement. A problem statement should explain who is affected, their end goal, the challenge, and the impact of the challenge. Here’s an example of a problem statement:
“Users of [software name] encounter frustration when they try to customize a monthly sales report. They are not able to customize the data within the platform reporting, and instead are abandoning the process and exporting raw data to compile outside of the platform. This takes longer, makes it harder for them to reach business goals, and lowers satisfaction with the software.”
You can get to the heart of a problem by asking why solving the problem is important and how the problem originated. Miro’s problem statement template is useful for this exercise.
Once you’ve defined the problem, you’re ready to move to the second diamond — the solution space. Flowcharts are ideal for mapping out potential solutions for testing. Just like an as-is process map, a proposed or to-be process map illustrates how a process should work, showing entry points, decision points, actions, parties, and endpoints.
In the development stage, use testing to reject ideas that don’t work and refine your solution. “The earlier and more often you can prototype and test, the better the outcome will be,” shares Ball.
It’s important to note that changing a process isn’t always the solution to your problems. Simply visualizing it and addressing misplaced expectations can also be a solution.
Once you ship a solution, your work isn’t done. Communicate the update to users, collect feedback, track outcomes, and commit to continuous improvement .
- How to make a visual problem-solving flowchart
Interested in trying your hand at visual problem solving? The specific techniques for visual problem solving are as numerous as there are problems, but below we’ll outline three to get you started. All of them use Miro as their foundation, which allows for collaboration in real time, so you can create effective visuals to guide your process.
1. Cyclical problem-solving process
This structured problem-solving process by Senior UX Designer Marcos Rezende walks teams through eight steps for tackling organizational challenges. It includes identifying the problem, gathering and analyzing data, generating solutions, and implementing them. Because this process is cyclical, it’s valuable for continuous improvement.
2. Cross-functional flowchart
If you’re attempting to solve internal workflow problems, a cross-functional flowchart can help you pinpoint challenges across silos. This template from Hiro Studio walks teams through outlining process steps and their relationships, identifying unnecessary complexity or duplication, and uncovering opportunities for improvement.
Consultant John White explains why this technique is effective: “When we document a process flow, we get everyone on the same page by removing assumptions of what we think is happening, and we document what is actually happening.”
Embed intro video: https://miro.com/miroverse/cross-functional-flowchart/
3. Problem tree
Instead of a traditional flowchart, this technique visualizes a problem as a tree. This visualization approach is designed to give a holistic view of a problem (the tree trunk) with its impacts (branches) and root causes (roots).
- Frameworks for decision-making
Beyond flowcharts, visualization can help leaders make better decisions by framing decision criteria in visual form. Here are a few ways you can illustrate your thought process in visual form for more effective decisions.
1. Risk matrix template
This risk matrix template helps leaders visualize the likelihood of adverse events happening by placing them on a matrix from rare to very likely and trivial to extreme.
2. Project scope template
How often do you need to argue that a request is “out of scope”? This simple framework helps you define a project scope at the beginning, so you have a touchstone to return to as a project evolves. This helps to manage goals, increase clarity, and keep projects within timeline and budget.
2. Priority matrix template
When you have competing priorities, deciding how to invest your time and budget is difficult. To determine the best outcomes, use this priority matrix template to map out initiatives by urgency and importance. This brings agility to your team and keeps your focus on what matters most.
You can find more decision-making visualization templates here .
- From visualization to optimization: How visual problem solving leads to innovation
Over a century after its birth, the flowchart remains a valuable tool to help companies approach a problem differently, using visual cues to understand all the moving parts.
With flowcharts and other visual tools, you can:
- Explore and define the right problem to solve
- Map out current processes to pinpoint the root cause of problems
- Propose and test new workflows and solutions
- Visualize a problem at a high level and work through frameworks for better decisions
Visualizing problems helps our brains “see” problems and solutions where we might have otherwise missed a connection. Using problem-solving flowcharts as a tool, you’ll set your teams up for better communication and innovation, too.
Ready to create flowcharts with just a few easy clicks?
Keep reading, unlocking clarity: mastering flow diagrams for complex process improvement.
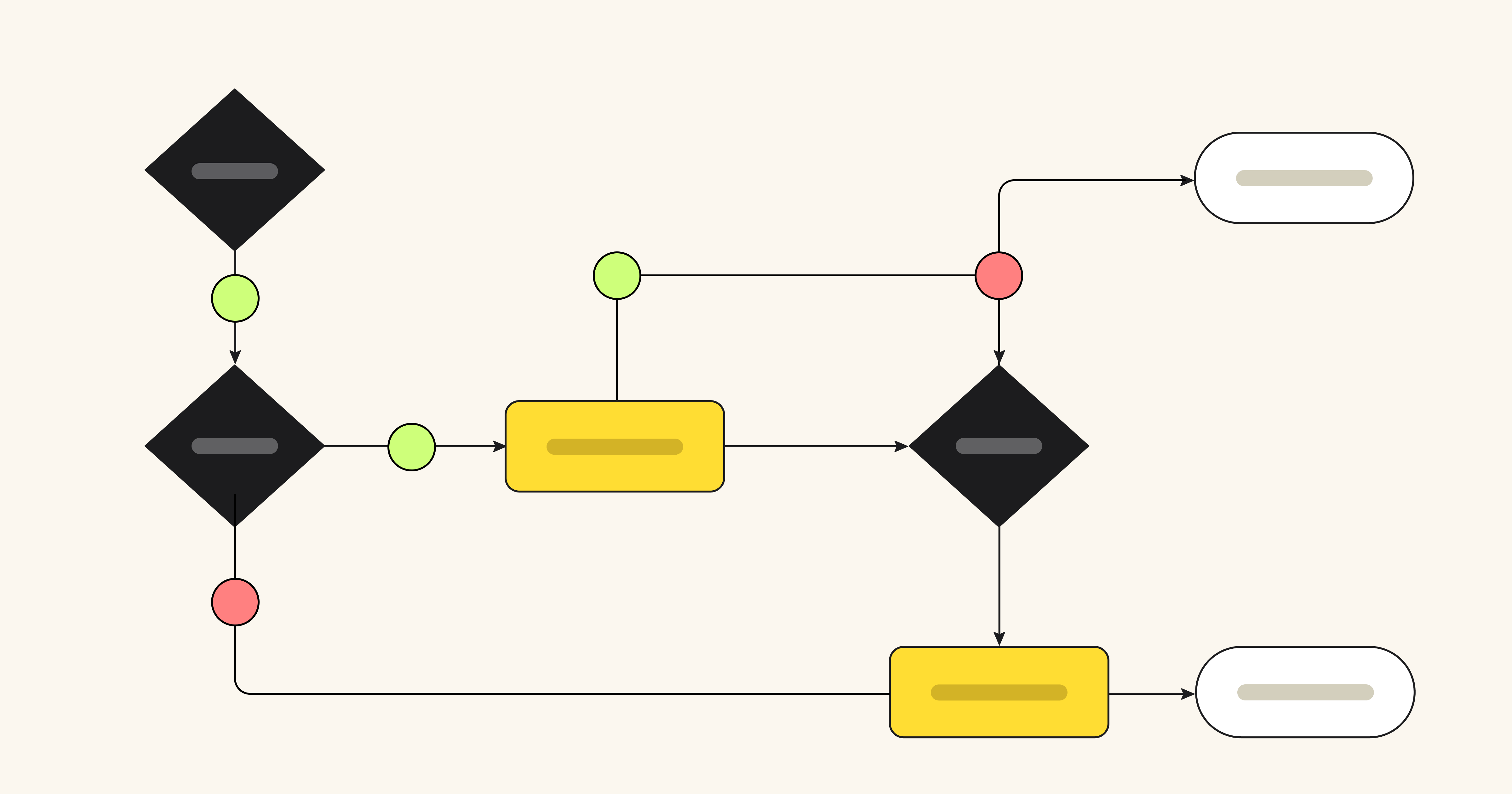
Diagram design 101: Tips for effective visual diagrams to supercharge innovation
Achieve continuous improvement with as-is and to-be process mapping
System Flowchart - A Complete Guide
A flowchart is often used to manage, analyze, design a process in many different fields. It is a useful tool that everyone should learn to help solve problems easier and more efficiently.
System flowchart is one of the common variations of the flowchart . But what is it exactly? What should you keep in mind when creating one?
Do not worry! This article will answer all the unanswered questions regarding the system flow chart. Without further delay, let's get into the flowchart tutorial!
What Is System Flowchart
As you may have already known, a flow chart is a graph that shows process flow, decisions, and outcomes. They are common tools of quality control that are utilized in many fields. There are four basic categories of flowcharts:
- Document flowcharts show you the flow of documents from one business unit to another.
- Data flowcharts let you see the overall data flow in a system.
- Program flowcharts show you a program’s control in a system. They are also one of the essential tools in programming. We have already covered it in an article, so check it out on our website!
- System flowcharts are the diagram type that shows you the flow of data and how decisions can affect the events surrounding it.
Like other types of flowcharts, system flowcharts consist of start/end terminals, processes, and decisions, all connected by arrows showing the flow and how data moves in the flow.

Are System Flowchart And Data Flowchart The Same
Some people might think that system flowcharts and data flowcharts are the same. However, the truth is far from it. They might have common symbols, but they are not the same things.
Data flowcharts show how data flows in the system. In other words, data flowcharts show where the data goes, then process all that data and output them.
However, data flowcharts do not show you the decisions, only the data flow. On the other hand, system flowcharts show you the data flow and its outcomes.
What Are Input And Output
Input is the data that the system receives, while output is the data that the system sends out. To put it in a nutshell, you can think of input as what comes in, while output is what you receive at the end of the program.
In a system, the process usually involves feeding the system with a source of input. Then, that input will be processed and modified in some way to produce the output that you will get in the end.
Imagine a kitchen where the chef receives basic components like eggs, flour, milk (input). He then transforms these components into something different, a cake (output). That is how a system works.
System Flowchart Examples
Example 1: a car's cruise control.
In this example, we will look at a car's cruise control. Cruise control allows the car to stay at the desired speed that the driver set. It works by adding or cutting the fuel according to the car’s speed.
To keep the car at a constant speed, we will have a major component called a speed sensor that records the car's speed. If the car is too slow, we can speed it up by adding more fuel, while if the car is too fast, we can slow it down by cutting some fuel.
A simple flow chart for this system should be like this:

Example 2: A Library Management System
Back in the day, it was harder for librarians to manage borrowed books before the digital age. Nowadays, a library would have a digital management system that allows people to borrow and return books to the librarian much easier.
The system starts with the user logging into their account. The system will then verify the user, allowing them to access all the library's services, such as changing passwords, borrowing, and returning if they pass all the verification steps.
The library management system should have a basic flow chart like this one below:

Example 3: Profit/Loss Calculating System
Profit is one of the important aspects that business runners often care about. It is one of the duties of finance teams. Usually, if the production cost is higher than the income, it is a loss. If the income is higher than the cost, it means you have profit.
The system is simple. It will compare the cost and the income to determine your profit or loss. The detailed flow chart of this system will be like this:

Example 4: Hospital's Medical Services
In a hospital, hundreds of medical cases arrive every day. To manage all those medical cases, they usually have to follow a long procedure to register and process their patients.
Usually, the procedure starts with a patient, or patients, arriving at the hospital. Then they will register the patient into their system, have a doctor record their health conditions, and give prescriptions. If the patient needs a follow-up session, the doctor will arrange an appointment.
The detailed hospital flow chart should be as follows:

System Flowchart Guideline
A flow chart tutorial would not be completed without a guideline. As with other types of flowcharts, for system flowcharts, you should follow the current standard guideline below:
- Step 1: Start the system.
- Step 2: Begin Process 1.
- Step 3: Check conditions and decide (Decision, "yes" or "no" answer)
- Step 4: Proceed according to the Decision. If it is "yes", proceed to Process 3. If it is "no", proceed to Process 2 and return to Step 2.
- Step 5: End of the system.
It also helps if you remember the following flowchart tips:
- Do not add more than one start/stop. Flowcharts should only have one start and one end.
- The flow of processes is generally from top to bottom or left to right, not the other way around.
- It is important not to make the arrows cross each other, as the flowchart is more confusing with crossing lines.
System flowcharts are one of the most basic tools you should learn to use. With a system flowchart , it might be easier to look at complex processes of your system to figure out bottlenecks and problems, thus saving you from a lot of headaches when trying to find and solve them.
Related Guides
Flowchart guides, brought to you by, zen flowchart.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

Nine essential problem solving tools: The ultimate guide to finding a solution
October 26, 2023 by MindManager Blog
Problem solving may unfold differently depending on the industry, or even the department you work in. However, most agree that before you can fix any issue, you need to be clear on what it is, why it’s happening, and what your ideal long-term solution will achieve.
Understanding both the nature and the cause of a problem is the only way to figure out which actions will help you resolve it.
Given that most problem-solving processes are part inspiration and part perspiration, you’ll be more successful if you can reach for a problem solving tool that facilitates collaboration, encourages creative thinking, and makes it easier to implement the fix you devise.
The problem solving tools include three unique categories: problem solving diagrams, problem solving mind maps, and problem solving software solutions.
They include:
- Fishbone diagrams
- Strategy maps
- Mental maps
- Concept maps
- Layered process audit software
- Charting software
- MindManager
In this article, we’ve put together a roundup of versatile problem solving tools and software to help you and your team map out and repair workplace issues as efficiently as possible.
Let’s get started!
Problem solving diagrams
Mapping your way out of a problem is the simplest way to see where you are, and where you need to end up.
Not only do visual problem maps let you plot the most efficient route from Point A (dysfunctional situation) to Point B (flawless process), problem mapping diagrams make it easier to see:
- The root cause of a dilemma.
- The steps, resources, and personnel associated with each possible solution.
- The least time-consuming, most cost-effective options.
A visual problem solving process help to solidify understanding. Furthermore, it’s a great way for you and your team to transform abstract ideas into a practical, reconstructive plan.
Here are three examples of common problem mapping diagrams you can try with your team:
1. Fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams are a common problem solving tool so-named because, once complete, they resemble the skeleton of a fish.
With the possible root causes of an issue (the ribs) branching off from either side of a spine line attached to the head (the problem), dynamic fishbone diagrams let you:
- Lay out a related set of possible reasons for an existing problem
- Investigate each possibility by breaking it out into sub-causes
- See how contributing factors relate to one another
Fishbone diagrams are also known as cause and effect or Ishikawa diagrams.
2. Flowcharts
A flowchart is an easy-to-understand diagram with a variety of applications. But you can use it to outline and examine how the steps of a flawed process connect.
Made up of a few simple symbols linked with arrows indicating workflow direction, flowcharts clearly illustrate what happens at each stage of a process – and how each event impacts other events and decisions.
3. Strategy maps
Frequently used as a strategic planning tool, strategy maps also work well as problem mapping diagrams. Based on a hierarchal system, thoughts and ideas can be arranged on a single page to flesh out a potential resolution.
Once you’ve got a few tactics you feel are worth exploring as possible ways to overcome a challenge, a strategy map will help you establish the best route to your problem-solving goal.
Problem solving mind maps
Problem solving mind maps are especially valuable in visualization. Because they facilitate the brainstorming process that plays a key role in both root cause analysis and the identification of potential solutions, they help make problems more solvable.
Mind maps are diagrams that represent your thinking. Since many people struggle taking or working with hand-written or typed notes, mind maps were designed to let you lay out and structure your thoughts visually so you can play with ideas, concepts, and solutions the same way your brain does.
By starting with a single notion that branches out into greater detail, problem solving mind maps make it easy to:
- Explain unfamiliar problems or processes in less time
- Share and elaborate on novel ideas
- Achieve better group comprehension that can lead to more effective solutions
Mind maps are a valuable problem solving tool because they’re geared toward bringing out the flexible thinking that creative solutions require. Here are three types of problem solving mind maps you can use to facilitate the brainstorming process.
4. Mental maps
A mental map helps you get your thoughts about what might be causing a workplace issue out of your head and onto a shared digital space.
Because mental maps mirror the way our brains take in and analyze new information, using them to describe your theories visually will help you and your team work through and test those thought models.
5. Idea maps
Idea maps let you take advantage of a wide assortment of colors and images to lay down and organize your scattered thought process. Idea maps are ideal brainstorming tools because they allow you to present and explore ideas about the best way to solve a problem collaboratively, and with a shared sense of enthusiasm for outside-the-box thinking.
6. Concept maps
Concept maps are one of the best ways to shape your thoughts around a potential solution because they let you create interlinked, visual representations of intricate concepts.
By laying out your suggested problem-solving process digitally – and using lines to form and define relationship connections – your group will be able to see how each piece of the solution puzzle connects with another.
Problem solving software solutions
Problem solving software is the best way to take advantage of multiple problem solving tools in one platform. While some software programs are geared toward specific industries or processes – like manufacturing or customer relationship management, for example – others, like MindManager , are purpose-built to work across multiple trades, departments, and teams.
Here are three problem-solving software examples.
7. Layered process audit software
Layered process audits (LPAs) help companies oversee production processes and keep an eye on the cost and quality of the goods they create. Dedicated LPA software makes problem solving easier for manufacturers because it helps them see where costly leaks are occurring and allows all levels of management to get involved in repairing those leaks.
8. Charting software
Charting software comes in all shapes and sizes to fit a variety of business sectors. Pareto charts, for example, combine bar charts with line graphs so companies can compare different problems or contributing factors to determine their frequency, cost, and significance. Charting software is often used in marketing, where a variety of bar charts and X-Y axis diagrams make it possible to display and examine competitor profiles, customer segmentation, and sales trends.
9. MindManager
No matter where you work, or what your problem-solving role looks like, MindManager is a problem solving software that will make your team more productive in figuring out why a process, plan, or project isn’t working the way it should.
Once you know why an obstruction, shortfall, or difficulty exists, you can use MindManager’s wide range of brainstorming and problem mapping diagrams to:
- Find the most promising way to correct the situation
- Activate your chosen solution, and
- Conduct regular checks to make sure your repair work is sustainable
MindManager is the ultimate problem solving software.
Not only is it versatile enough to use as your go-to system for puzzling out all types of workplace problems, MindManager’s built-in forecasting tools, timeline charts, and warning indicators let you plan, implement, and monitor your solutions.
By allowing your group to work together more effectively to break down problems, uncover solutions, and rebuild processes and workflows, MindManager’s versatile collection of problem solving tools will help make everyone on your team a more efficient problem solver.
Download a free trial today to get started!
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager
Visual problem solving with flowcharts and mind maps

What’s life without problems? Probably a little boring, if we’re being honest. If everything were perfect all the time, there would be no challenges, and things would get pretty monotonous. This is a rather optimistic view on what many believe to be an aggravating part of life. No matter how you feel about problems, one thing is true: problems are inevitable . You can’t always control how many problems you encounter in your life, but you can learn better ways to solve them. So, what can we do for those really complex issues that aren’t easily solved? Visual problem solving is the perfect way to see solutions and break down complex issues.
Make your own flowchart with Gleek .
What is visual problem solving?
Visual problem solving is the process of using aids like charts or diagrams to display all the aspects of a problem in order to find viable solutions. When problem solving, sometimes it’s hard to see what’s causing the problem, or other relationships and correlations that are affecting whatever it is you’re working on. Two common methods for problem solving include mind maps and flowcharts . A mind map is a non-linear diagram, used for making new ideas or breaking down complex issues. A flowchart is a linear diagram, used for making action plans and describing processes.
5 steps to solve problems
Identify the true problem
Maybe you know what the issue is in clear terms, or perhaps it’s still a little confusing. A good way to get a concrete vision of the problem you need to solve is to pose it as a question, or a short statement. You might come up with something like ‘our sales have dropped’, or, as a question ‘what can we do to increase sales?’.
Get information
Now that you have a clear objective to solve, the next step is to gather all the relevant information that pertains to the issue. This can look like statistics, comments from customers, employee feedback, and more. Once you’ve collected the data, you’ll need to analyze it from all angles to get a clear view on the topic.
Brainstorming session
Get any and all potential solution ideas out on the table. Doesn’t matter how silly an idea seems, just put anything that comes to mind on the drawing board. This is where your visual aids will really come in handy, especially mind maps. You might need more than one chart, depending on how complicated the issue is.
Choose the best idea(s)
Whether on your own or with a team, you’ll have to eliminate the potential solutions that just won’t work. To find the solution that’ll work best, it’s good to analyze it in the same way you did the problem – by looking at potential outcomes, and all facets involved.
Make an action plan
So you think you’ve found the perfect solution! Now what? If your problem is complicated, usually the solution will be too. Here is where another visual aid, like a flowchart, will be helpful. Map out the specific steps you need in order to implement your solution. Then, it’s time to put your plan into action.
These are just the basic steps you can use to start problem solving. You may find that other actions are needed during your own journey.
Common mistakes when problem solving
Mistakes? We all make them from time to time. Here are some common mistakes we are prone to when trying to fix problems.
Undefined problem – When identifying the problem, it’s possible that the problem is too big, multi-faceted, or too complex to tackle all at once. A way to avoid this is to break the problem down into chunks, following common themes.
More problems arise – This isn’t always a direct result of anything we do, but it can happen nonetheless. The best way to deal with more problems that arise when you’re trying to solve the original one is to think of the possible things that could go wrong during the solution stage. When you’re prepared for any situation, you’ll rarely have any setbacks.
No action plan – Finding a way to solve your problem doesn’t mean that the planning is over. On the contrary, you need to create a strategy to properly execute your solution so you won’t end up with a half-solved problem and even more issues than you started with.
When to use flowcharts
One way to chart your problems and progress is through flowcharts. For those who like to think in a step-by-step or linear fashion, flowcharts are the best way to visualize things. Let’s have a look at some situations that are best suited to flowcharts.
Big problems – Flowcharts can help break down a large problem or solution into specific steps or stages from start to finish.
Decision trees – This type of flowchart is helpful when diagramming actions that will happen as a result of other actions, whether they be in a software system or actions taken by people.
Cause and effect – Similar to a decision tree, a cause and effect flowchart is where you can analyze the potential results of various actions, past or present.
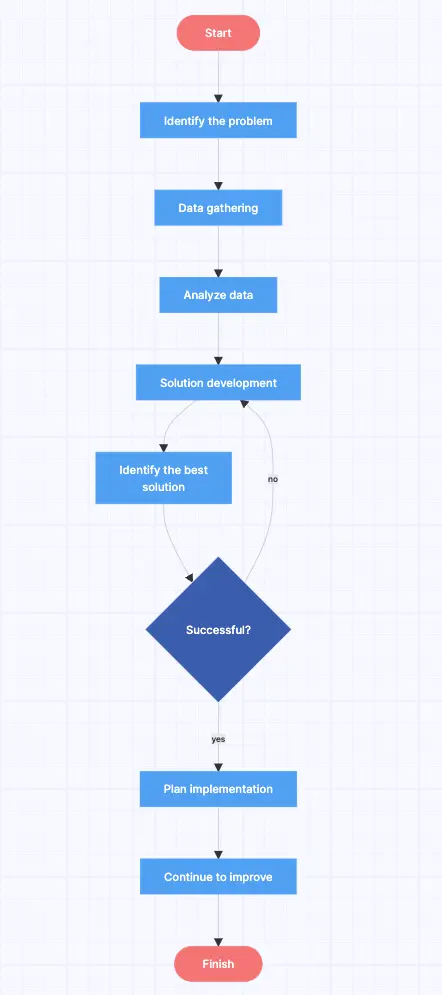
Check out our 20 flowchart templates that you can also easily edit !
When to use mind maps
Mind maps are great for brainstorming sessions, and non-linear problem solving. Here are some situations that are best visualized through a mind map.
Finding the problem – So, what is the problem exactly? Sometimes it’s hard to see. Making a mind map offers you the opportunity to see all the moving parts involved with a situation, and how they relate to one another, and can help you suss out the true problem.
Core and branching ideas – You start with a core idea, such as ‘online sales’, then add related ideas or issues branching off from that, like maybe ‘ad revenue’, or ‘social media campaigns’. Then those ideas can have their own branches. This is an easy way to analyze all aspects of a problem.
Source: Problem Solving with Mind Maps (Tutorial)
Looking to create your own flowchart? Gleek has the solution for you. With Gleek, you can create your own flowcharts using a text-based command center, without ever using your mouse. Not only can you create flowcharts, you can create many other UML-based diagrams that will wow your colleagues and bring new life to your presentations. Get started for free today .
Related posts
Uses for cross-functional flowcharts
20 editable flowchart templates & examples
What are flowchart symbols? Here’s a handy guide with examples
A step-by-step guide to creating a flowchart in Google Docs
7 stages of the product development process (flowchart example)
back to all posts
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
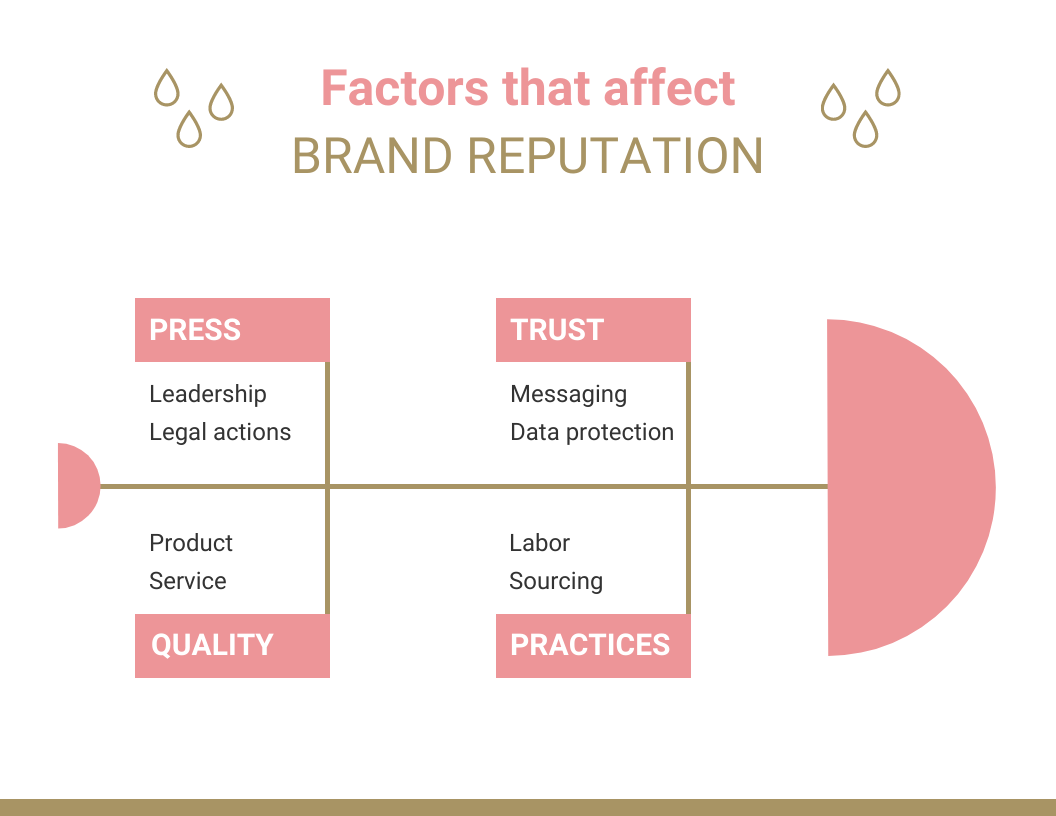
Blog Data Visualization How to Use Fishbone Diagrams to Solve Complex Problems
How to Use Fishbone Diagrams to Solve Complex Problems
Written by: Lydia Hooper Sep 10, 2021

Oftentimes, diagrams are used for visualizing and explaining complex topics, patterns and systems to others. But they are often also useful for helping us explore and better understand these things ourselves.
Fishbone diagrams (or cause and effect diagrams) are specifically used to help us solve complex problems.
Let’s say your team is looking to better understand why a certain product is not as successful as you’d like it to be. By creating a fishbone diagram, you can investigate the causes of certain outcomes, thereby identify how to improve them moving forward:

CREATE THIS DIAGRAM TEMPLATE
Let’s go through what a fishbone diagram is, when you should and should not use it, how to create a fishbone diagram and how to conduct fishbone analysis. You can then create your own fishbone diagram using Venngage’s Diagram Maker —no design experience required.
Table of contents:
What is a fishbone diagram, when to use a fishbone diagram, when not to use a fishbone diagram, how businesses can use fishbone diagrams.
- How to create and use a fishbone diagram
Fishbone diagrams are also known as Ishikawa diagrams, named after Professor Kaoru Ishikawa who was a pioneer in the field of quality management and who created this unique visualization.
Although they were initially used for quality improvement, today fishbone diagrams can be helpful for all kinds of problem-solving. For example, this one lists different factors that can lead to a healthy lifestyle.

Return to Table of Contents
Here’s what fishbone diagrams are best used for.
Addressing complex problems
As you can see, the fishbone diagram example above allows a viewer to see several factors at once, making it a great diagram for sharing a lot of complex information.
The most important thing about these diagrams is that they help teams recognize the reasons behind specific outcomes, or in other words—the root causes that lead to effects. They are ideal for addressing complex problems that have multiple causes, such as climate change:
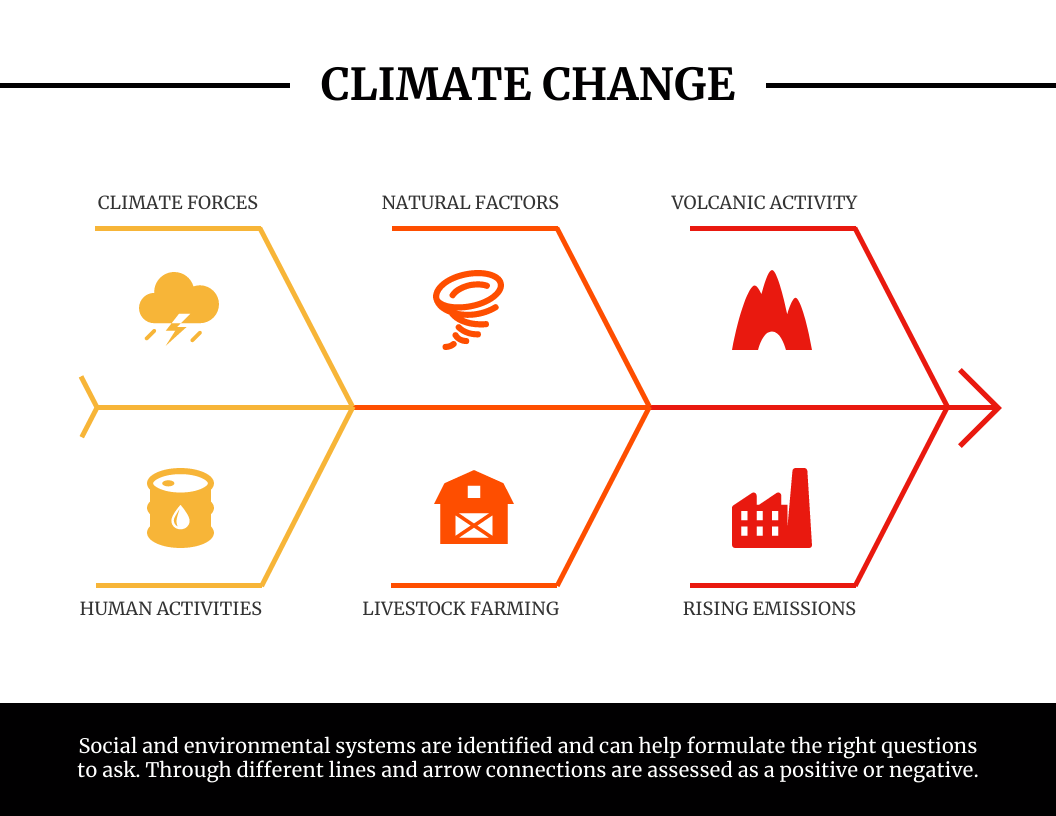
Facilitating reflective analysis
Fishbone diagrams are useful for reflective analysis.
If teams are primarily focused on KPIs, these diagrams can provide context that is otherwise missing, helping folks better understand what’s causing numbers to rise or fall.
Teams can identify where mistakes are being made, revenue is being lost, as well as what activities are leading to the best results.
Planning for desired outcomes
Fishbone diagrams are also helpful for future planning. By referencing a fishbone diagram, teams can better identify the best methods for reaching desired outcomes and plan actions accordingly.
You can customize this fishbone diagram template to develop concrete plans for improving customer satisfaction:

There are a few situations where you should use a different form of data visualization instead of fishbone diagrams.
When there’s one cause of multiple problems
While fishbone diagrams are ideal for scenarios in which there are multiple causes for a single problem, it’s not ideal for the reverse: when there is a common cause for several separate problems. If you are seeking to show this, a mind map might be a better fit.

CREATE THIS MIND MAP TEMPLATE
When the order of causes and effects maters
If you want to show specific sequences of causes and effects, a flowchart is the better option:

CREATE THIS CHART TEMPLATE
Related: What is a Problem-Solving Flowchart & How to Make One
When you’re looking at correlation, not causation
It’s critical to also remember that correlation and causation are two entirely different things. The quintessential example of this is how ice cream sales and sunscreen sales both rise in summer, but one type of these sales is not leading to the other.
If you are wanting to describe correlation instead of causation, a scatterplot is a common visualization.

Now that you know generally when to use and not to use these diagrams, let’s look at the two major ways businesses use fishbone diagrams to help them solve complex problems.
Analyze how conditions and motivations lead to actions and outcomes
Companies, employees, and customers face problems regularly. Declining leads, cash flow, productivity, satisfaction, retention—all of these problems have causes. Knowing these causes can make all the difference.
Here’s an example of a fishbone diagram that details the many factors that can contribute to missed deadlines:

It’s a big deal to be able to do this type of analysis. Not analyzing things like environments, people, and processes can lead to major unintended consequences.
For example:
- Poor training of employees can lead to inconsistencies in the workplace.
- Flawed KPIs can lead to disasters as dramatic as legal consequences, as Wells Fargo experienced .
- Artificial intelligence (AI) if implemented without human leadership can lead to errors, hazards, and institutionalized bias, as Bain consultancy describes.
- Outsourcing of labor overseas can reduce company loyalty and eliminate jobs domestically and eventually abroad, according to Investopedia .
Strategize based on how actions or inactions lead to positive or negative impacts
If you really want to change outcomes and impacts, analysis alone will be insufficient. Fishbone diagrams can also help companies plan improvements in policies, management, systems, etc.
This fishbone diagram example outlines some of the many factors that can lead to low productivity:

Once you’ve pinpointed the causes of problems, it’s much easier to take action to solve them.
How to create and use a fishbone diagram
1. select the outcome or effect you want to investigate.
What problem are you solving? What impacts or outcomes do you want to better understand? What do you want to improve?
Once you know this, you can select a Venngage fishbone diagram template and begin easily creating your diagram. Start by specifying as much as possible the key outcome on the right of the diagram, at the head.

2. Identify big categories of causes
Some of the more common categories are:
- Environment
- Measurement
You can use these categories if they make sense, or you may think of others that are more appropriate. It’s generally smart to use a total of four, six or eight categories.
A simple fishbone diagram would just include only these categories, like in this example:

In your design, you can use colors to help people distinguish categories from one another.
3. Generate a comprehensive list of contributing factors
Depending on the topic, you may want to dive deeper. The main categories can inspire you to think more critically about multiple factors that may lie in each of them.
This deeper dive will likely require team dialogues and/or conversations with different employees, customers, and other stakeholders. There may be other research you want to do such as reading case studies, observing behaviors, and/or conducting competitor analysis.
You can consider breaking the diagram into top and bottom halves, if that can add additional meaning, like in this example:

The diagram should adapt to your growing list. Add all the branches that are relevant to the right off the main stem extending from the head on the left. Use short phrases that describe the cause precisely and succinctly.
4. Analyze and reflect
Chances are that as you generated the categories and lists of causes, you began to consider all the things that are contributing to the outcome you selected. Even if you haven’t developed a completely exhaustive list, you are now ready to pause, take a step back, and think things through in a different way.
To pivot from thinking about the problem to thinking about the solution takes a shift in mindset. Being able to see everything at once in a fishbone diagram can facilitate this. It can help you expand your thinking and witness more fully the immense possibilities for change.
Visuals can also elicit emotions, and that’s important too. You may need to feel your sadness or anger about missed opportunities and other losses, and you will definitely be buoyed by feelings of curiosity and excitement about what you may be able to change.
Fishbone diagrams are powerful tools for reflection, but make no mistake, it’s the reflection that gets you really ready to change things.
5. Plan and take action
The journey to the root has prepared you to solve the problem at hand. Depending on how many categories and causes you’ve unearthed, and the support and resources you have, you can begin to prioritize which causes you will address first, and what you will work to shift over the long term. You might set new goals, and possibly new measures, accordingly.
The diagram you’ve created can be shared to help educate and motivate stakeholders to take action. You can add your brand colors and design details like icons using Venngage so it’s not only useful but visually engaging as well.
Summary: Use a fishbone diagram for root cause analysis, reflective analysis, future planning and more
Fishbone diagrams are not just attractive visuals for impressing others. They are visual tools that help us do some of the most valuable work there is: solving complex problems.
They can spur us to investigate and name what we can change. And because they are visual, we can continue to reference them as we make these changes, so we can stay on track.
Start creating a fishbone diagram today using Venngage’s drag-and-drop editor and easy-to-edit templates. No design experience required.
START CREATING FOR FREE
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

How to create a problem-solving flow chart
Problem-solving is one of those topics that we’ve often discussed on this site (check out our Problem Solving guide ). We think it’s one of THE vital skills of business. Why? Because you’ll come across problems every day, and you need to arm yourself with the right tools to solve them.
A problem-solving flowchart is one of those tools. It’ll help you take a problem statement, break the problem down into likely causes helping you get to the bottom of what’s gone wrong.
In this post, we’ll cover
- What is a Problem Solving Flow Chart
- How to create a Problem Solving flow chart
- Example 1 of Problem Solving flow chart
- Example 2 of Problem Solving Flow chart
- What flow chart shapes to use
- When should you use a flow chart
- 7 tips on creating your Problem Solving chart
Key Benefits & Likely issues with the tool
Let’s get started!
What is a Problem Solving Flowchart
A Problem Solving flow chart is a diagram that uses shapes, arrows, and text to show a moving sequence of actions and/or activities that help solve a problem.
How to create a Problem Solving flowchart
- Describe your problem.
- Pose Yes/No Questions that can help identify the cause of the problem
- Question each stage of the process until it is fully examined
- Repeat steps 2 & 3 until you have identified a solution
- Try the solution; if it is successful in addressing the root cause, then you’ve fixed your problem. If not, repeat the process until you have a solution that works.
A problem-solving flowchart attempts to identify a root cause/solution to the trigger that is causing the problem allowing you to change the process and prevent the problem from occurring.
Let’s now demonstrate the effectiveness of a problem solving flowchart by showing some examples.
Example 1 Problem solving flow chart
In our first example, we’re going to start with something simple to show you the principle of the tool.
We have been given a cup of tea and we don’t like it!
Let’s use a problem-solving flow chart to find out what’s gone wrong.
We’ve used Excel to capture this flow chart using flowchart shapes (insert –> shapes), you can, of course, use other applications to do this, you don’t’ have to have specialized flow chart software to do this. ( there’s a great flowchart in Excel video here ). Or you can simply use a pen and paper.
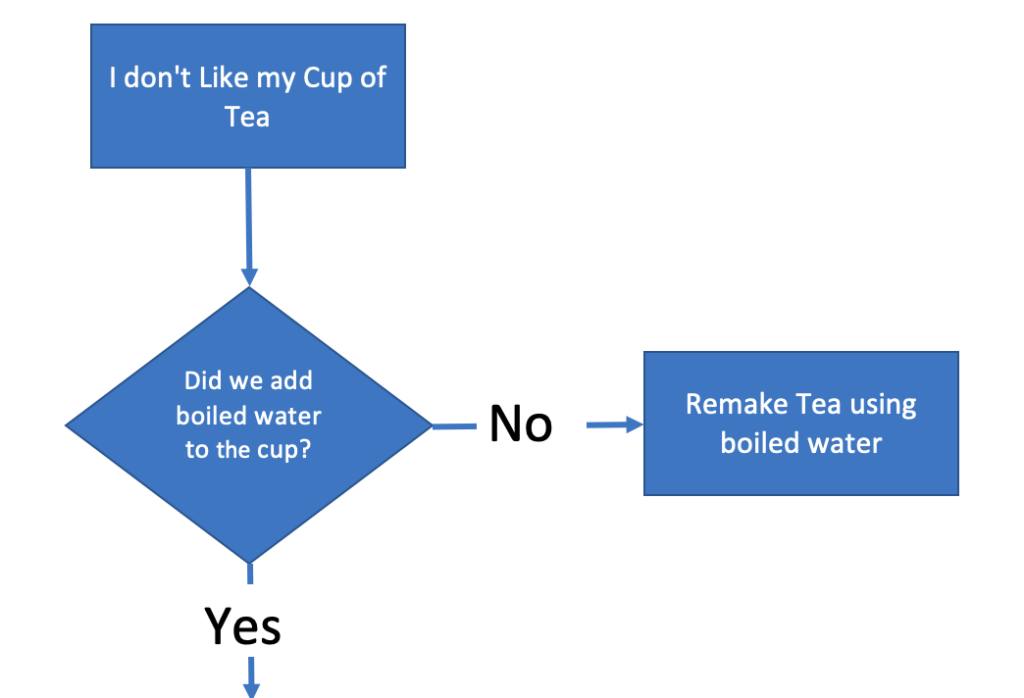
Use a rectangle and add your problem statement.
Remember to keep your problem statement unambiguous and straightforward. Here we’ve used “I don’t like my cup of tea.”

Now that we’ve got our problem statement, we’re going to start asking questions.
We’re going to examine the variables that go into a cup of tea in an attempt to find out what’s gone wrong.
** TIP** – Work through your process – rather than start from scratch, if you have a documented process, work through that examining each step to ascertain if there are issues. If not, you might find it useful to research and sketch out the process before starting with your flowchart.
We have a process for the cup of tea, which is:
1/ Boil Water
2/ Place Breakfast Tea teabag in the cup
3/ Add Water
4/ Leave to sit for 2 mins
4/ Remove teabag
5/ Add milk
6/ Add sugar
So our problem solving flow chart needs to examine each of those steps to determine where the failure has occurred.
We’ll add a question shape (diamond), connect out problem statement to it using an arrow to check if we boiled the kettle. Our Diagram will now look like:

As a question, we want two possible routes – Yes and No.
Our process asks us to boil the kettle if we did, and the answer is Yes, then we can go to the next process step.
If the answer is No, then we have a problem. Our tea will be cold.
Here we can do one of two things. We can terminate the flow chart, or we can add an activity to rectify the problem (this might be to remake the drink or to perhaps heat the drink up in the microwave).
Our flow chart now looks like this:
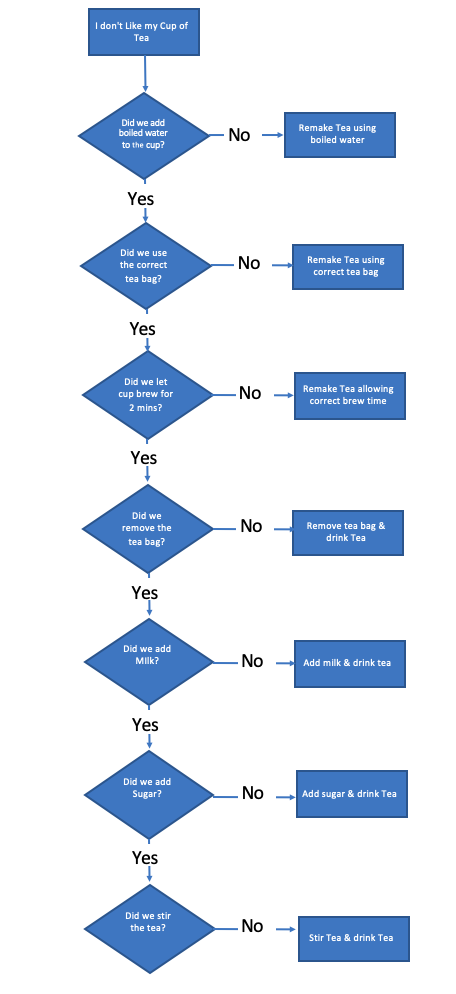
Step 2 in our Tea making process was to add a Breakfast-tea tea bag.
So, once again, we’ll ask a question about that step.
“Did we add an English Breakfast teabag.”
As before, we’ll use a question shape, using Yes or No answers. If we performed the process step correctly, we’d move on. If we didn’t, we’ll either end the problem solving (we’ve found the root cause), or we’ll add a corrective action.
Now we’ll repeat this process until we’ve reviewed the whole process.
Our finished flowchart looks like this.
However, we’re not finished.
What happens if we follow the flow chart, and we find we didn’t use boiled water. We remake the tea using boiled water, and we still don’t like it?
We need to ask some further questions.
We need to update our flow chart to validate that we solved the problem and what to do if we didn’t.
So for each step of the process, our problem solving flowchart now looks like this.
Here’s our completed flow chart.
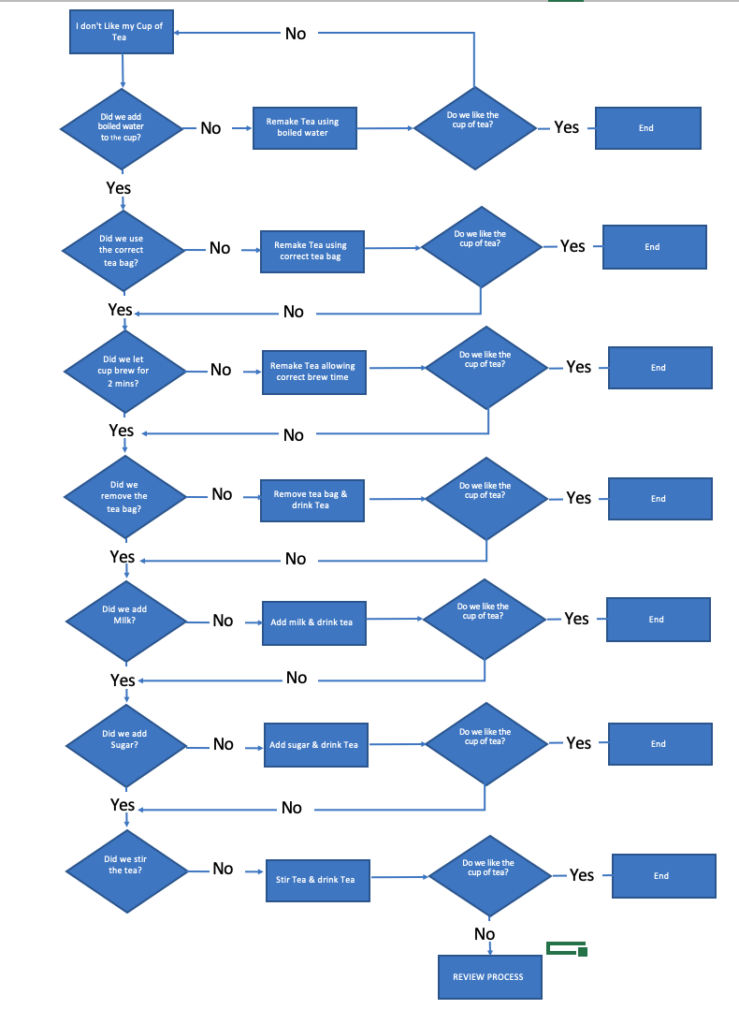
As you can see, we’ve identified the problem, and we’ve described a corrective action.
But there’s a problem here. With this flowchart, you can still follow it, validating the process, and still end up with a cup of tea that’s unsatisfactory.
Why is that?
Well, it’s perfectly possible that we started out with a process that’s incorrect. What happens if the process called for using an incorrect tea bag from the start?
So we’ll simplify things by adding a block at the end that if you’re still not happy at the end of reviewing the steps, a full review of the process will be undertaken. This is a simple answer to this problem, and I would expect that you would expand this section in more detail if you were creating a flowchart yourself.
So what does a more complex process look like, how about we look at a business problem?
Example 2 Problem Solving flow chart
OK, so example 1 may have been a bit simple, and you are maybe looking for something in a business context.
So in Example 2, let’s look at a scenario that’s a little more complex.
Let’s assume that your organization has received a non-conforming part. You have been assigned to work with the Vendor to:
- Find out what went wrong
- Prevent recurrence
We’re going to use a problem solving flow chart to help us do that.
As with the first example, we’re going to state the problem.
“The part is non conforming.”
Using the production process from the Vendor, we’ll work through the stages to see if we can spot what’s gone wrong.
The diagram below shows an analysis of the first two steps of the production process using a problem-solving flow chart.
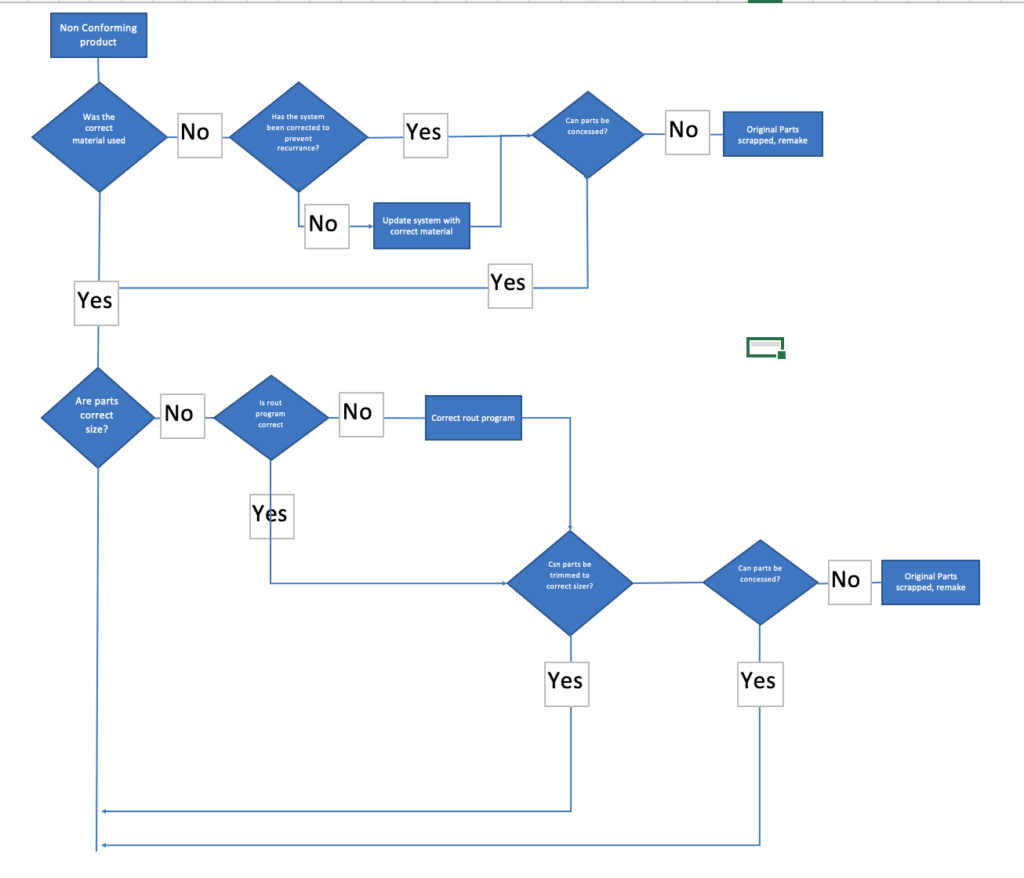
The first thing you’ll notice is that on one process step, there may be many questions to ascertain the potential issue.
Some of these may be complex and require careful thought.
There may be multiple variables (systems, processes, tools, inputs, etc.) that may require attention.
You will need to analyze each process step, in full, to be sure you have caught all the possible causes of the fault.
Which Flow chart shapes should you use.
A problem solving flow chart usually utilizes only a small number of shapes. We show these in the table below.
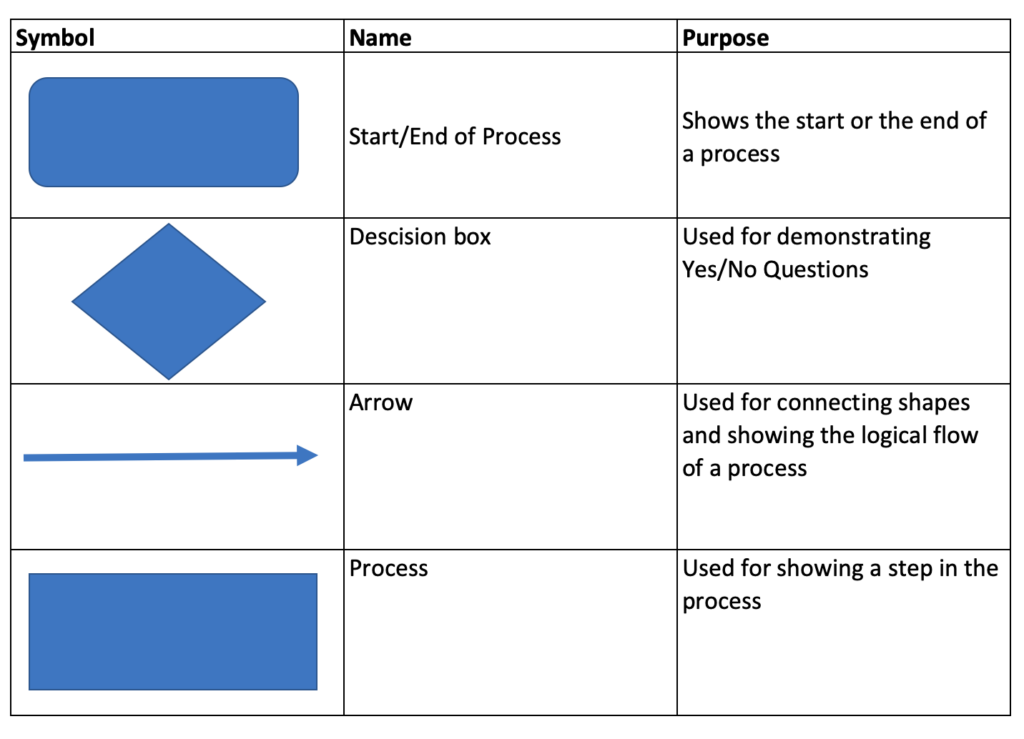
When should you use a Problem Solving flow chart
There are many many problem tools available.
A flow chart lends itself to be used when:
- You are looking for a tool that is simple to use
- You are looking to use a tool that does not require complex software
- You want to validate a process.
- You want something that facilitates collaboration
- You want something that you can use to communicate with others
7 Tips on creating great problem solving flow charts
1/ Use standard shapes!
2/ Make it easy to follow!
3/ Keep things on one page
4/ Don’t overload your boxes with text
5/ Go into enough detail. Don’t try and simplify activities as it might hide problems from being seen.
6/ Collaborate. Where you can utilize a team to help document the problem and the activities do so. The more knowledge of the process, the better chance you’ll have of locating the issue.
7/ Use a consistent direction to flow your process, moving things around the page can confuse people who might look at it.
A flow chart can provide you with a great advantage when looking to solve problems. Some of the key benefits include
- A visual aide that’s easy to understand
- Simple to use, does not require hours and hours of training
- A tool that facilitates collaboration
- Effective for aiding communication
- Provides an effective method of analysing a process
However, as with everything, there are some issues to look out for
- Flowchart fails to capture all process steps and therefore root cause analysis is hit and miss
- Lack of knowledge of the process by the individual compiling the flowchart results in inaccurate problem solving
- Inconsistent flow of process makes maps confusing
- Complex processes may be better suited to other tools (fishbone etc)
- Inconsistent formatting and/or use of shapes result in flowchart that is difficult to utilise.
There are a great many tools out there for problem-solving, and flow charts can be used either as a stand-alone tool or conjunction with one of these other tools.
Flowcharts can make for a great problem-solving tool.
They’re simple to use, effective, and facilitate collaboration.
We hope you’ve found our article useful, in particular the example walkthroughs.
If you’re looking to use the tool, we’d love some feedback from you and hearing how you’ve got on. Why not fire us a message on twitter or use the comments section below.
This article is part of our Problem Solving Guide.
Our Content
- Calculators
- Career Skills
- Communications
- Human Resources
- Strategy and Leadership
- Supply Chain Management

Harness the A3 problem solving template to effectively solve problems
We recently explored the way visual thinking can be used on Conceptboard , so now we’re taking it a step further and look at how visual thinking can be used to collaboratively solve problems using a methodology pioneered by Toyota and presently used worldwide by practitioners of lean sigma : the A3 problem solving template.
Visual thinking is a great way to unlock creative potential. Our brain’s capacity to hold visual elements is huge, so when you start thinking visually you are able to tap into an extensive resource that feels effortless. And dare we say it, fun!
Discover visual collaboration
To explore alternative brainstorming techniques, check out these 15 brainstorming techniques and templates you can use collaboratively with your team.
The A3 problem solving template to drive continuous improvement
There are hundreds of ways to problem solve, from mind mapping , to design thinking or customer journey mapping . But the simple effectiveness of the A3 template is hard to beat.
The basis of the A3 problem solving template is collectively mapping out a flow chart to break down complex processes, and highlighting the flaws in the system. From there, teams need to re-do the chart, highlight the key changes they need to make to improve the system. Then, create a plan of attack to implement those changes. It is a simple way to get everyone on the same page to visually solve problems. Remote or co-located teams can easily collaborate in real time on an A3 template using Conceptboard’s simple template featuring a rectangular space broken into four quadrants.
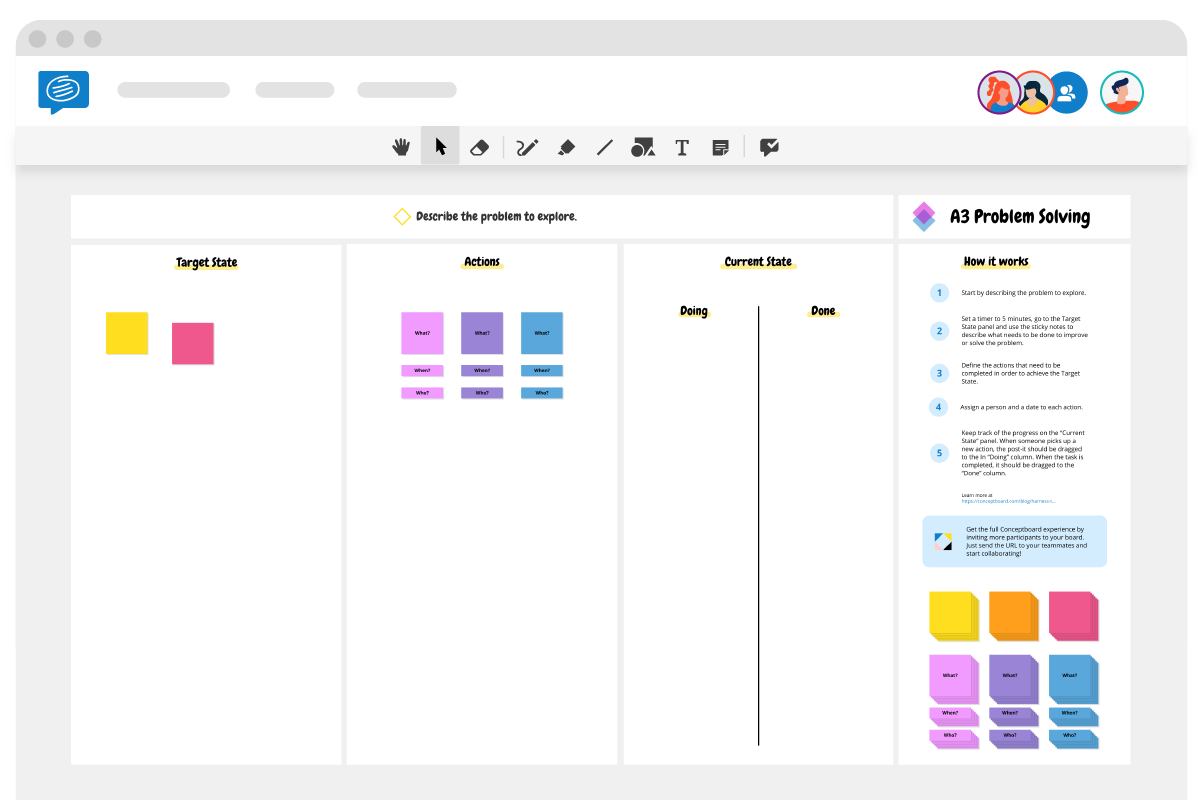
Use template
To get started, book a meeting time (at least an hour) for your team and send them a link to the collaborative board. Then, conduct the problem solving session in four simple steps:
- Detail the problem you are trying to solve in the top left quadrant.
- In the next quadrant underneath, as a team, illustrate the problem as a system including steps and links. You can do this using the pen, sticky notes, graphics or images. Then talk about each step as a group and give each step a general rating as to how well it’s functioning. This should result in a frame of reference of the current state of the system.
- In the third quadrant, again as a team, draw a visual map of the target state: that is what the ideal system would look like. You can highlight areas of focus where you want to try and do things differently, and what the intended results will be.
- Comparing these two visual maps, you should now be able to assess what actions need to be taken to achieve the target state. List these in the final quadrant. To make sure the list is actionable, detail Who, will do WHAT, by WHEN.
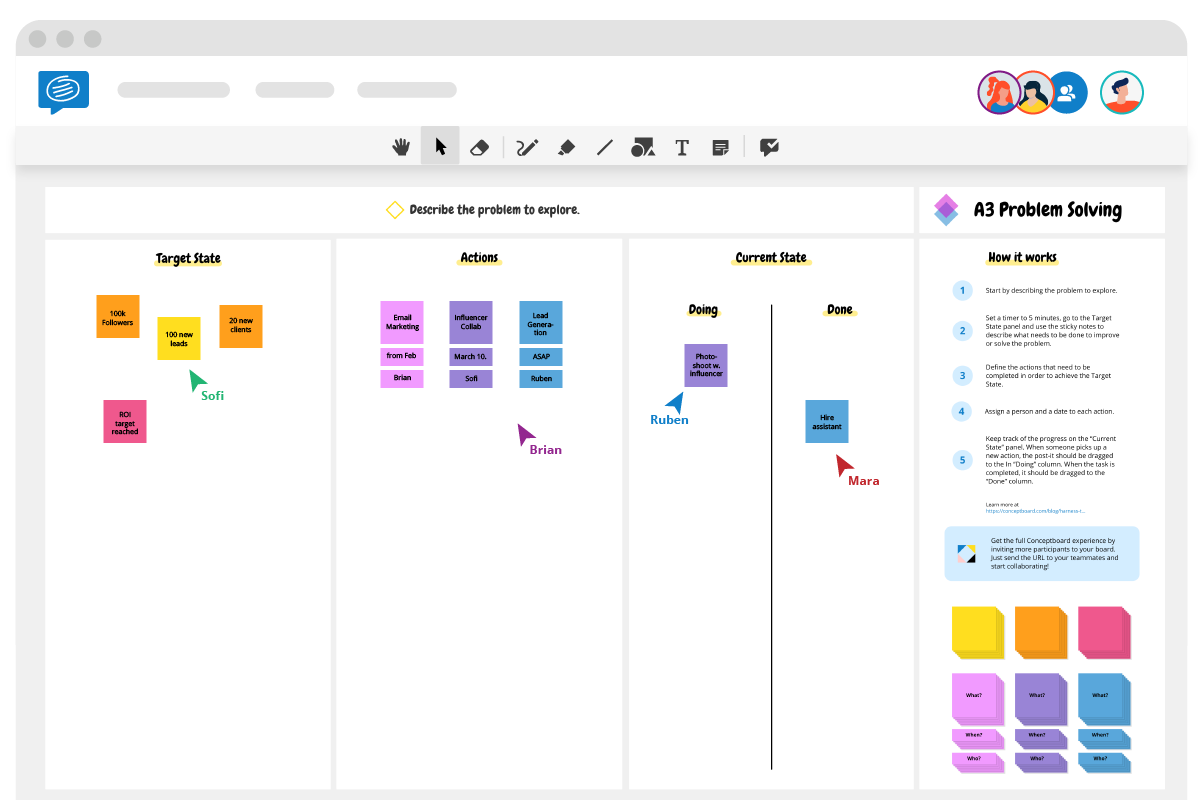
Once you have completed the four quadrants and an actionable list, make sure you send the link to the shared file to all stakeholders or involved team members. You could also export it in PDF form and print it on an A3 sheet once you are done filling it out.
The A3 methodology is extremely powerful as it enables you to synthesize different points of view into one manageable approach. This will create a shared understanding of the problem, as well as the effects it has on different departments within the business. If you want to learn more about how collective visual thinking can be used, watch this great TED Talk by Tom Wujec.
Feel free to explore Conceptboard’s free library of templates that will save you time and money in the planning process, allowing you to focus on the bigger picture .
More interesting articles for you

OZG 2.0: The future of digital administration in Germany is FIM
Since its introduction in 2017, the Online Access Act (OZG) has aimed to make it easier for citizens and companies to access administrative services and make them available digitally.

Unwrap the Joy: Elevate Your Team’s Holiday Spirit with Our Exclusive Christmas Game Template!
The holiday season is upon us, and at Conceptboard, we’re thrilled to unwrap the gift of festive cheer with our special Christmas Game Template!
Wireframe Template – A structure to build something great | Free Template
By using Wireframe Templates, you can streamline your workflow and ensure a more efficient and effective design process.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post Comment
Experience the power of visual collaboration
Experience how Conceptboard boosts your team’s hybrid collaboration and communication.
No credit card
No commitments
Start right now
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples
What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples
Published on January 2, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 29, 2024.
A fishbone diagram is a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot possible solutions. It is also called an Ishikawa diagram, after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa, as well as a herringbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram.
Fishbone diagrams are often used in root cause analysis , to troubleshoot issues in quality management or product development. They are also used in the fields of nursing and healthcare, or as a brainstorming and mind-mapping technique many students find helpful.
Table of contents
How to make a fishbone diagram, fishbone diagram templates, fishbone diagram examples, advantages and disadvantages of fishbone diagrams, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about fishbone diagrams.
A fishbone diagram is easy to draw, or you can use a template for an online version.
- Your fishbone diagram starts out with an issue or problem. This is the “head” of the fish, summarized in a few words or a small phrase.
- Next, draw a long arrow, which serves as the fish’s backbone.
- From here, you’ll draw the first “bones” directly from the backbone, in the shape of small diagonal lines going right-to-left. These represent the most likely or overarching causes of your problem.
- Branching off from each of these first bones, create smaller bones containing contributing information and necessary detail.
- When finished, your fishbone diagram should give you a wide-view idea of what the root causes of the issue you’re facing could be, allowing you to rank them or choose which could be most plausible.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

There are no built-in fishbone diagram templates in Microsoft programs, but we’ve made a few free ones for you to use that you can download below. Alternatively, you can make one yourself using the following steps:
- In a fresh document, go to Insert > Shapes
- Draw a long arrow from left to right, and add a text box on the right-hand side. These serve as the backbone and the head of the fish.
- Next, add lines jutting diagonally from the backbone. These serve as the ribs, or the contributing factors to the main problem.
- Next, add horizontal lines jutting from each central line. These serve as the potential causes of the problem.
Lastly, add text boxes to label each function.
You can try your hand at filling one in yourself using the various blank fishbone diagram templates below, in the following formats:
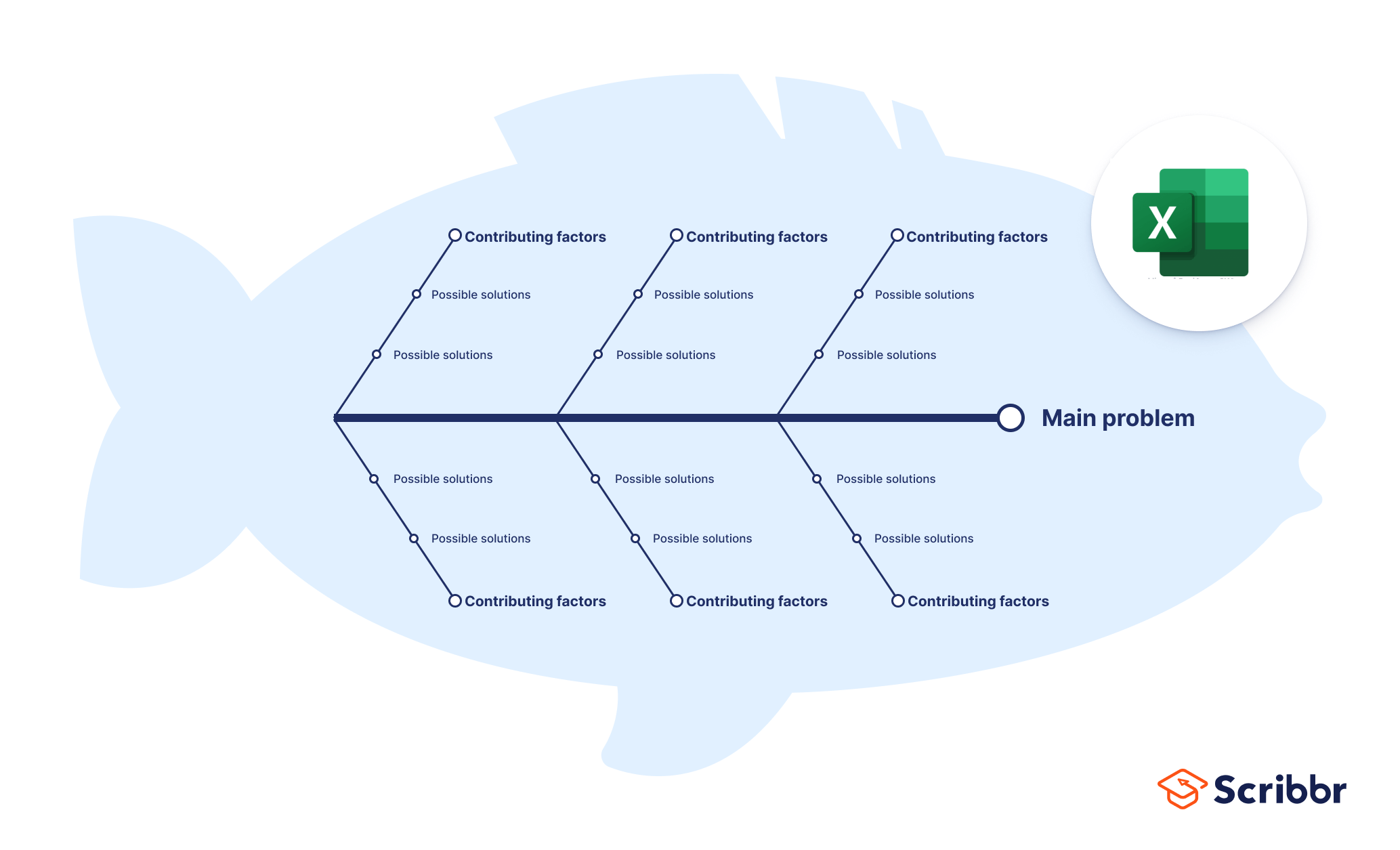
Fishbone diagram template Excel
Download our free Excel template below!
Fishbone diagram template Word
Download our free Word template below!
Fishbone diagram template PowerPoint
Download our free PowerPoint template below!
Fishbone diagrams are used in a variety of settings, both academic and professional. They are particularly popular in healthcare settings, particularly nursing, or in group brainstorm study sessions. In the business world, they are an often-used tool for quality assurance or human resources professionals.
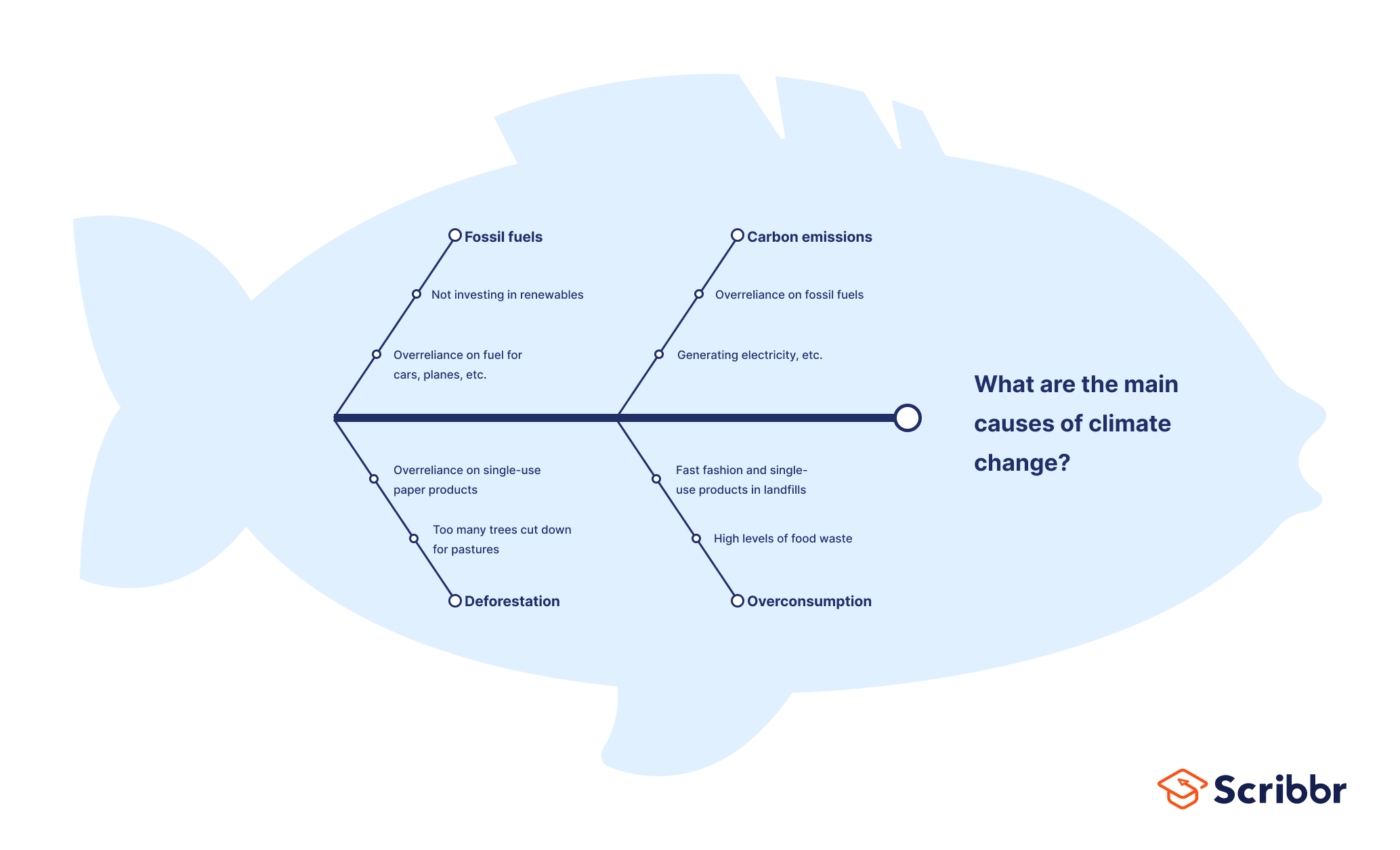
Fishbone diagram example #1: Climate change
Let’s start with an everyday example: what are the main causes of climate change?
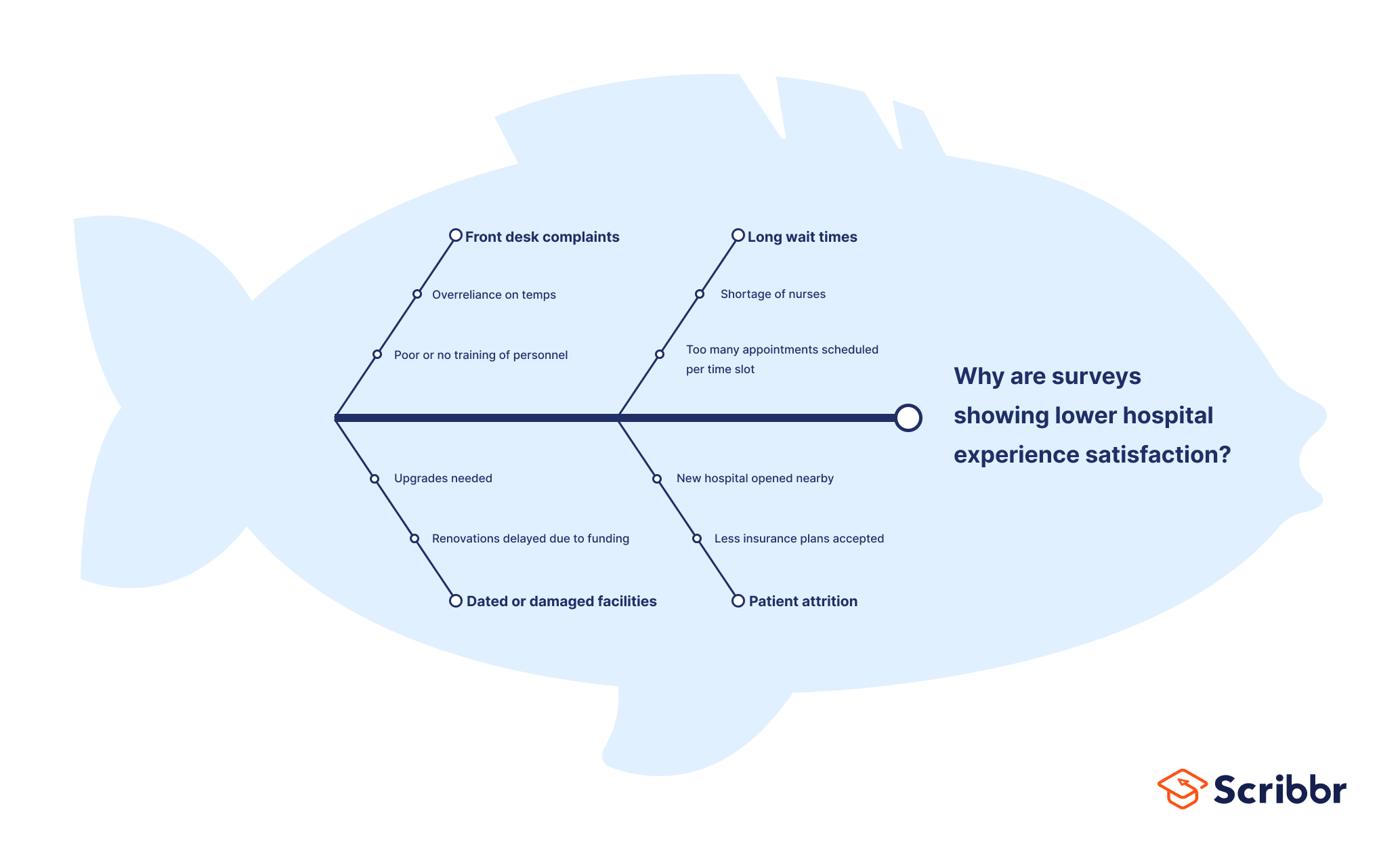
Fishbone diagram example #2: Healthcare and nursing
Fishbone diagrams are often used in nursing and healthcare to diagnose patients with unclear symptoms, or to streamline processes or fix ongoing problems. For example: why have surveys shown a decrease in patient satisfaction?
Fishbone diagram example #3: Quality assurance
QA professionals also use fishbone diagrams to troubleshoot usability issues, such as: why is the website down?
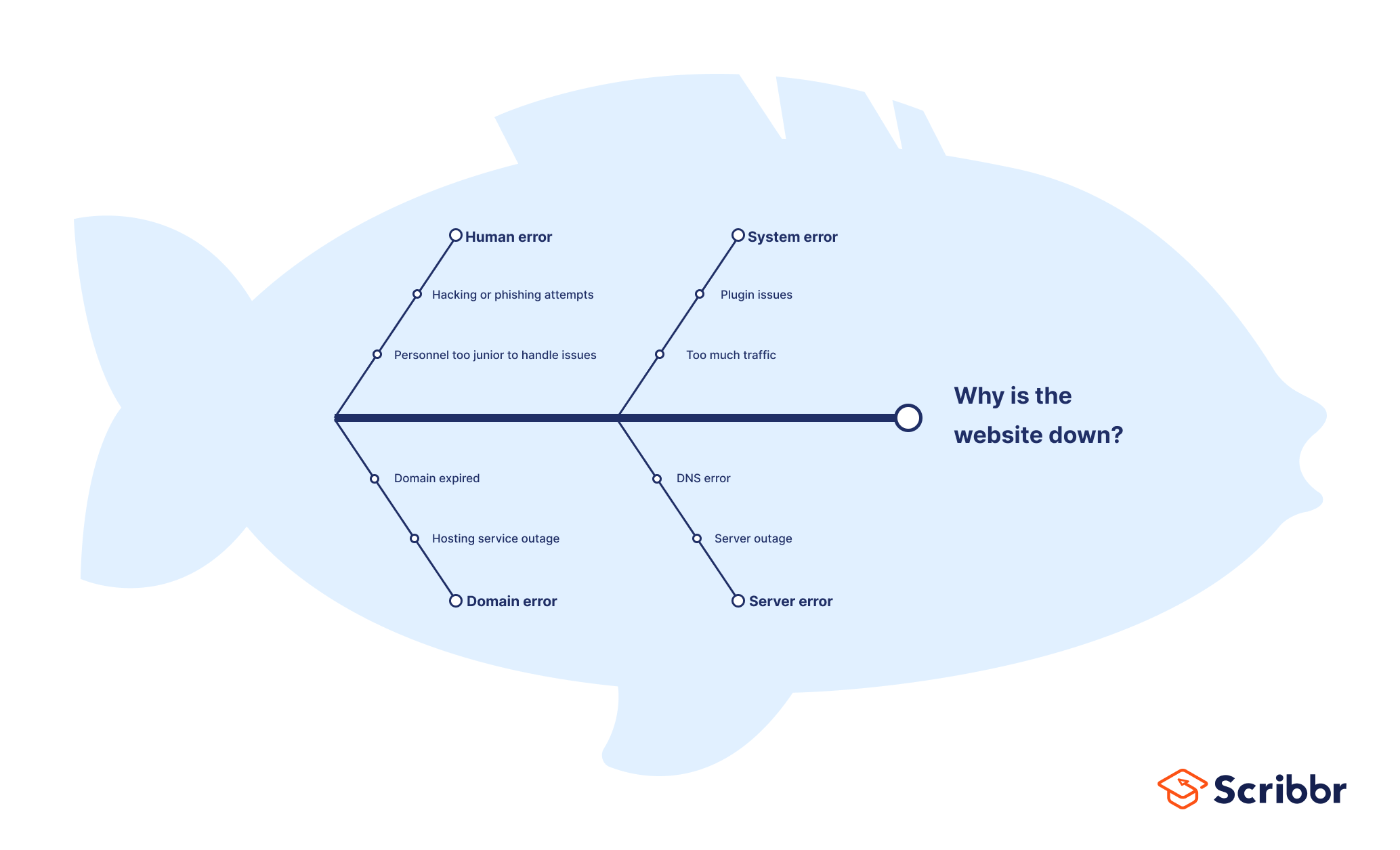
Fishbone diagram example #4: HR
Lastly, an HR example: why are employees leaving the company?
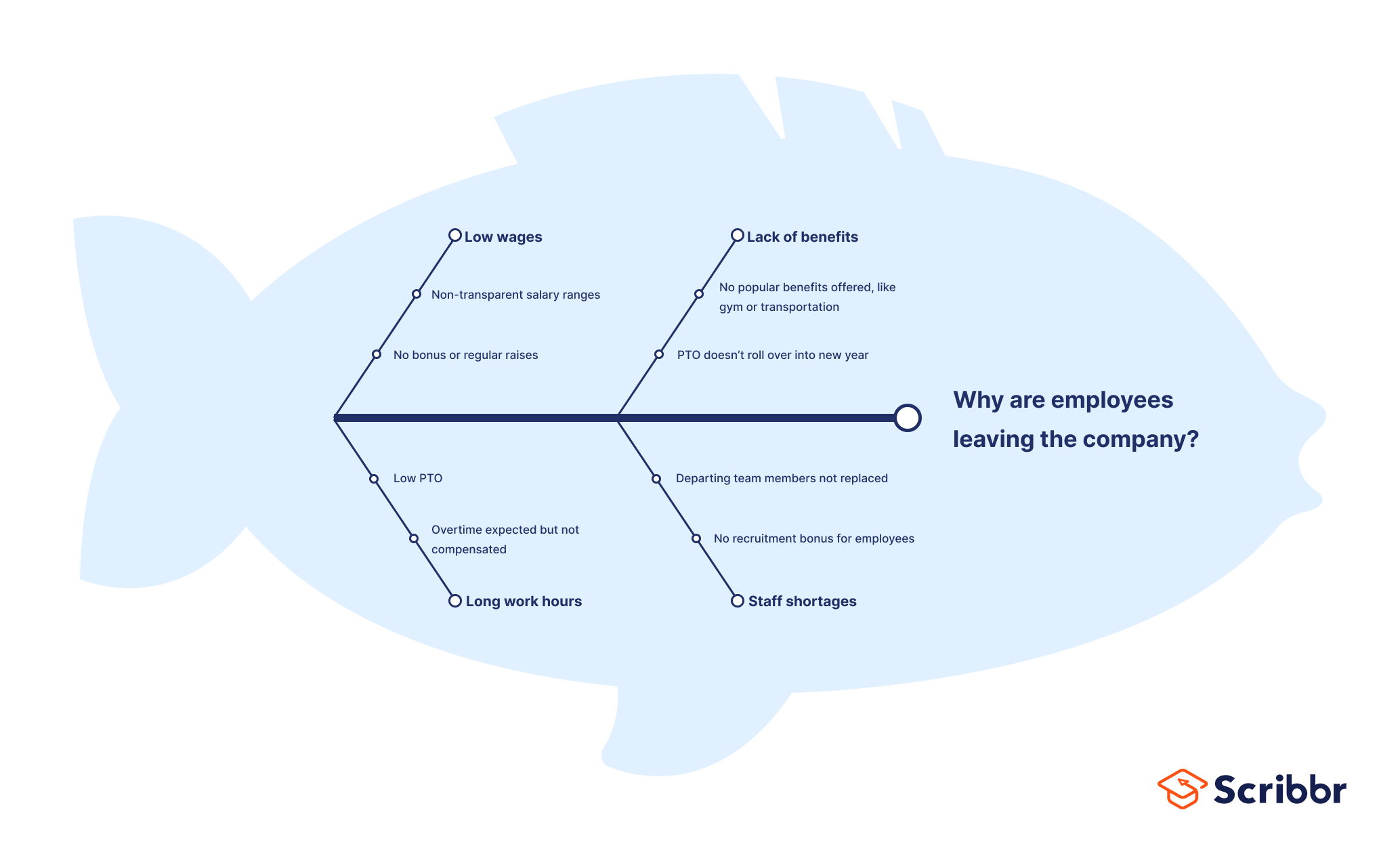
Fishbone diagrams come with advantages and disadvantages.
- Great tool for brainstorming and mind-mapping, either individually or in a group project.
- Can help identify causal relationships and clarify relationships between variables .
- Constant iteration of “why” questions really drills down to root problems and elegantly simplifies even complex issues.

Disadvantages
- Can lead to incorrect or inconsistent conclusions if the wrong assumptions are made about root causes or the wrong variables are prioritized.
- Fishbone diagrams are best suited to short phrases or simple ideas—they can get cluttered and confusing easily.
- Best used in the exploratory research phase, since they cannot provide true answers, only suggestions.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Fishbone diagrams have a few different names that are used interchangeably, including herringbone diagram, cause-and-effect diagram, and Ishikawa diagram.
These are all ways to refer to the same thing– a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot solutions.
Fishbone diagrams (also called herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, and Ishikawa diagrams) are most popular in fields of quality management. They are also commonly used in nursing and healthcare, or as a brainstorming technique for students.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2024, January 29). What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/fishbone-diagram/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, data collection | definition, methods & examples, exploratory research | definition, guide, & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Flowchart Maker
Online flowchart maker to visualize processes and workflows, visualize your workflows and processes to identify operational bottlenecks and areas for improvement..
- Professionally designed Flowchart templates to map processes faster
- Embed to web pages or export as JPEGs, PNGs, SVGs or PDFs
- Powerful sharing options to get feedback on your workflows
- Synced previews and live mouse tracking to map processes as a team
Flowchart Templates
Scientific Method - Flowchart Example

Sprint Tasks Flowchart
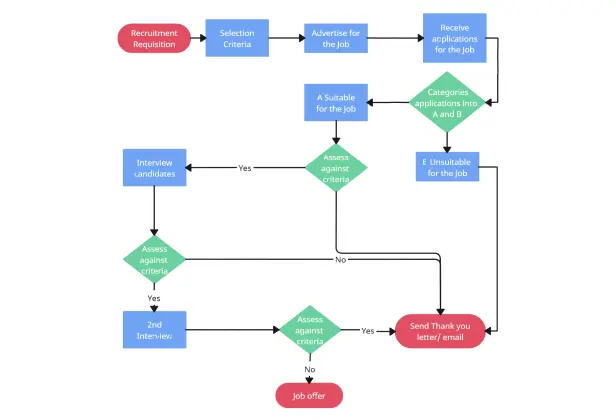
Recruitment Process Flowchart
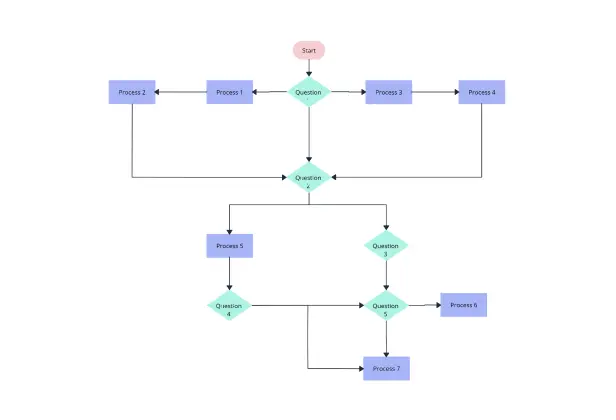
Meeting Flowchart Template

Flowchart Template with Multiple Ends
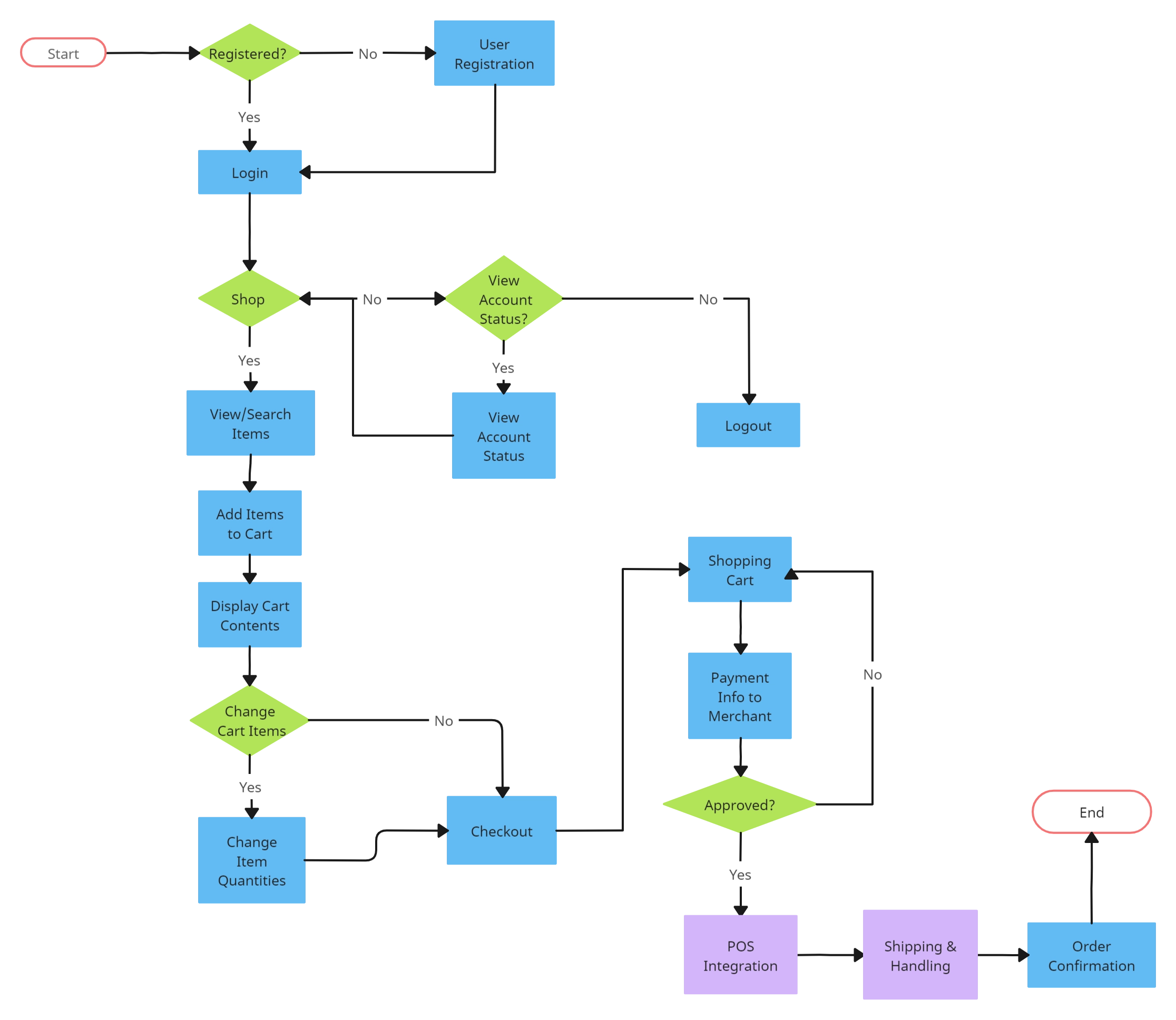
E-commerce - Order Process Flowchart
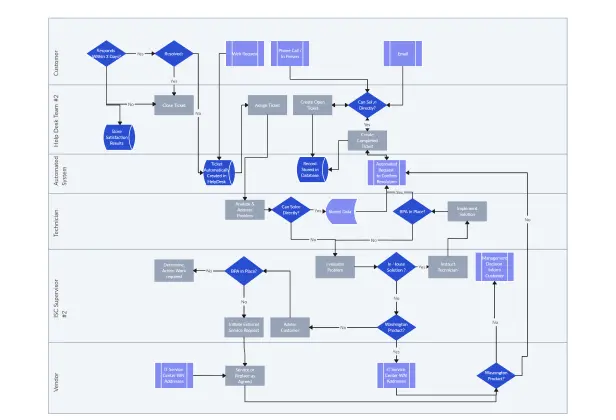
Help Desk Flowchart Example

Remote Hiring Process
What is a Flowchart?
A flowchart is a diagram that visually represents the progression of steps of a process or workflow. They are commonly used as decision-making, problem-solving, system designing, and educational tools.
There are multiple types of flowcharts including:
- Process flowchart - shows the steps of a process in sequential order.
- Workflow chart - visualizes a workflow or actions that need to be carried out to achieve a goal.
- Data flow chart - represents how data is processed within a system.
- Swimlane flowchart - illustrates process steps along with responsible owners or departments.
What are Flowcharts Used for?
Flowcharts are used across multiple industries;
- To clarify process steps or workflows and their respectful owners.
- To analyze existing processes to identify inefficiencies and necessary improvements.
- To collaborate on planning and designing new processes and to build a common understanding of them.
- To standardize processes by allowing team members to follow a single set of steps consistently.
- To train and guide new and existing employees on performing their tasks accurately.
How to Create a Flowchart Collaboratively
Identify the process or the workflow you and your team want to document or visualize. And then define the purpose and goals of the flowchart.
Gather the team members who will be involved in creating the flowchart. Create a Creately workspace for your flowchart. Add the team as collaborators with edit access to allow them to work together. You can easily track the changes they make with real-time cursor tracking and synced previews.
Identify the different steps involved in executing this process. If several people are responsible for carrying out the process, collaborate and get their input for an accurate visualization.
Using the standard flowchart symbols available in the Creately flowchart maker, convert the listed steps into a flowchart.
First, drag and drop the Start/End symbol onto the canvas. Using the Plus Create option, add the next symbol depending on whether it’s a process/step/operation or decision. Make sure to use the correct flowchart symbol to represent your data.
Connect the shapes with arrows highlighting the flow of the process or workflow. Creately’s Plus Create automatically recognizes the flow and adds the relevant connector as you draw the flowchart.
Customize the flowchart as necessary with Creately’s preset color themes before sharing it with stakeholders for feedback.
Review the flowchart frequently and update it as the process it represents, undergoes changes.
Flowchart Symbols
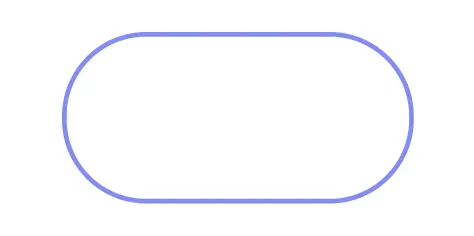
Terminal / Terminator
Represents the start or end of a process or system.

Represent a process, action step, or operation.
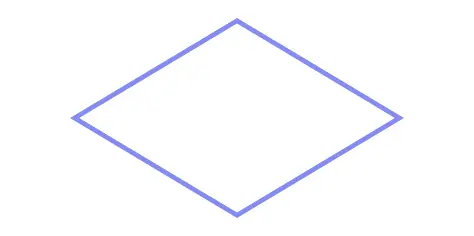
Shows the data inputs or outputs of a process.
Represents the decision point of a process.
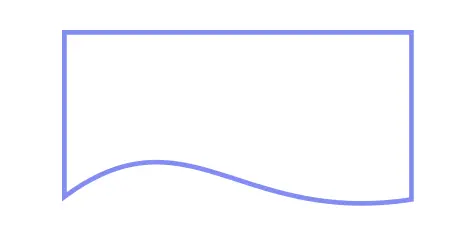
Indicates a document or report in a process flow.
Stored Data
Represents a data storage device or location, such as a database, file, or other form of data storage.
Direct Data
Indicate a step in the process where data is directly entered or obtained from an external source, such as a user, sensor, or other system.

Internal Storage
Represents an internal storage location, such as a register or buffer.

Manual Input
Represents a step in the process where data is manually entered by a user or operator.
Predefined Process
Represents a subroutine or a predefined process that is called upon during the process.
Flowchart Resources
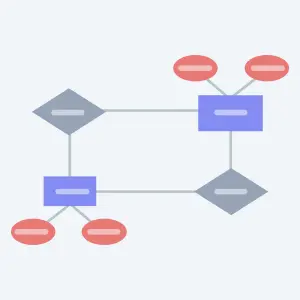
Flowcharts are widely popular and one of the most frequently diagram types. They are great for mapping the flow of steps, decisions that need to be made etc in a process. However flowcharts have just more than the process names, their flow...
Everyone has problems, and we spend most of our working lives solving them. For those who find this quite negative, problems can be also termed as Issues, Challenges or Opportunities. Some people are especially gifted at problem-solving...
A basic flowchart shows how micro processes are sequentially linked together in an operation. They are basically one dimensional, just showing the processes without going into much detail about the attributes of the particular process...
Flowcharts are easier to draw compared to other diagrams, but it doesn’t hurt to have flowchart examples to get started quickly. It’s much easier to change an existing diagram than to draw one from scratch. Our users have access to hundreds...
Every organization needs a set of rules to guide its members. Standard operating procedures (SOPs) are established for this purpose. SOPs are an essential part of any business and are necessary to ensure the quality and consistency of...
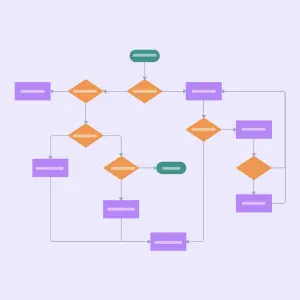
User flow diagrams are indispensable in mastering user experience. They allow you to understand how users interact with your app or website, the steps they take to complete a task or achieve a goal on your website. This will help you create...
Business process reengineering is a crucial element in the agenda of many large as well as small companies in many industries, with manufacturing and banking/ finance being the leading sectors. It allows organizations to view their business...
Whether you are planning a project or your week, a workflow can help you organize and document the tasks you need to stay focused and keep track of them. In this guide, we will discuss: what is a workflows, how to create one along with...
FAQs About Flowcharts
- Involve people who really know and live the process such as front-line employees.
- When analyzing a process using a flowchart, first create a high-level overview to identify the major components of the process and then drill down.
- Include as many people involved in the implementation of the process as possible to get a complete understanding.
- Keep the flowchart as simple and understandable as possible to ensure all stakeholders can follow it.
- Analyze the flowchart from front to back or from the process owner’s point of view and from back to front or from the customer’s point of view.

Designorate
Design thinking, innovation, user experience and healthcare design
How to Create the Systems Thinking Diagrams
Complex systems can’t be seen as individual parts. We need a broader perspective to see the whole pattern that causes the problem, as many factors as affecting both the current state and the desired state of the system. The systems thinking theory was first introduced by Jay Forrester and members of the Society for Organizational Learning at MIT in his book, The Fifth Discipline, to help us see a complex system as a framework with interrelationships between different internal and external elements that affect the system.
Related articles:
The Six Systems Thinking Steps to Solve Complex Problems
What Does Systems Thinking Teach us About the Problems of Problem-Solving Practice
Design Schools Should Teach Systems Thinking, and This is Why
What is Systems Thinking?
Systems thinking (Also known as system dynamics) is an approach to address problems by looking into them as a whole rather than small parts and considering the dynamic nature of the problem. Each element affects the other elements in the system. The approach helps us to present the root solution by considering the impact of this solution on different parts of the system. Systems thinking extend to seeing the world around ad complex interested systems that influence each other rather than isolated systems. The below video visualises what systems thinking mean:
Think about reducing the price of a specific product to ncrease sales. This will negatively affect the quality of the product and increase external competitiveness. Therefore, the systems thinking diagram provides us with a visual aid to understand the connection between different factors in the system.
Characteristics of the Systems Thinking
Before building the systems diagrams, we first need to understand the general principles that control the complex systems known as The 11 Laws of the Fifth Discipline (Check What Does the Systems Thinking Teach us About the Problems of Problem-Solving Practice ). These principles were highlighted in the Fifth Discipline theory by Peter Senge in his book, The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organization . These principles are below: 1- Today’s problems come from yesterday’s solutions. So, before adopting any new solutions, it is very important to understand the history of the existing problem. 2- The harder you push, the harder the system pushes back in a phenomenon known as “compensative feedback.” 3- Behavior grows better before it grows worse 4- The easy way out usually leads back in, therefore, the best solution is to understand the problem from a systematic approach to eliminate it. 5- The cure can be worse than the disease 6- Faster is slower. For example, If the solution aims to increase the system productivity beyond its optimal rate, the system may actually slow down to compensate for this change in growth rate. 7- Cause and effect are not closely related in time and space
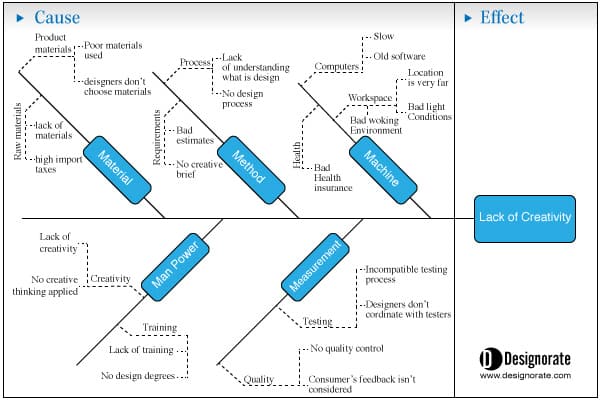
8- Small changes can produce big results—but the areas of the highest leverage are often the least obvious 9- You can have your cake and eat it too — but not all at once. The systems thinking method teaches us that we need to look at the big picture. We can provide a complete solution that accomplishes all of the required goals if we consider achieving these solutions based on a determined timeline. 10- Dividing an elephant in half does not produce two small elephants. The problems need to be seen as a whole rather than as individual parts. 11- There is no blame. One of the common difficulties when solving problems is to point the finger at someone as the sole guilty person. However, in system thinking, everyone is part of a whole system
Structure of the Systems Thinking Diagrams
In order to build the systems thinking diagram, we need to clearly identify the elements of the system and how it interacts with each other. Building the systems diagrams requires four steps; identify the events, identify the pattern of behaviour, build the system, and determine the mental models.
Step 1: Event
The first step is to identify the problem at hand that we would like to learn about. This may include one or more related problems to be addressed. For example:
- Customers wait for a long time at the reception
- The unsatisfied patients at the hospital reception in the systems thinking in healthcare setup
Step 2: Patterns of Behaviors
The next step is to observe the patterns that show the relationship between different elements involved in the system. These elements represent the potential causes of the problem (effect). The Cause Effect Diagram can help identify the different causes that may involve the problem highlighted in the previous step.
Charts like the one below can show the positive and negative relation between different factors and how they contribute to the main problem that need to be analyzed in the system.
Step 3: System
After identifying the potential causes for the final effect. The relation between every two elements in the system is controlled by the feedback loops. The loops either show positive or negative relations, as shown in the figure below. Sometimes, the relationship is referred to as Same/Opposite instead of Positive(+)/Negative(-).
Based on the above relation, there are two types of loops that are classified based on how they change the system:
Balanced feedback loops
This loop is the natural loop elements that tend to naturalize the impact of the change. For example, talking to each patient in the hospital reception office increases the waiting time, which positively increases the patient’s unsatisfactory. In this example, the feedback “patient unsatisfactory” decreases the impact of the change “talking to the patients.”
Reinforcing Feedback Loops
In contrast to the balanced loop, in the reinforcing loop, the feedback increases the impact of the change. Both are moving in the same positive direction. In our example, reducing the time at the reception office reduces the waiting time and, subsequently, reduces the patient’s unsatisfactory.
Once we build the relationship between different factors, we can add external factors that affect the system, such as the parking lots available for the patients or the medicine and governmental support…etc.
Identifying Gaps and Delays
In some cases, the current state of one of the elements stands as a barrier to achieving the intended goal or contributing to increasing the problem. These states are known as gaps. For example, the limited number of reception personnel halts any initiative to reach higher patient satisfaction. This factor is set as a gap in the system.
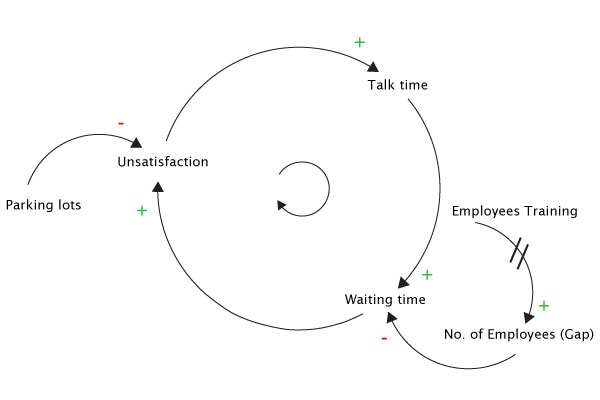
Once the gaps are defined, we can clearly see if our initiative may work out or if we need to fix these gaps before moving further to solving the problems in the system.
As highlighted Fifth Element Theory, the cause and effect may be separated by time and place. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the time delay in the feedback loops. For example, training reception employees to handle patients’ problems more efficiently may take time to see its impact on the system. These delays are represented in the systems by double slashes on the loop.
Further details can be added to the systems diagram, such as adding numerical data that show exactly how each element is affected by the other elements in the system.
Step 4: Mental Models
At the end of the process, the model guides us through the next steps required to achieve the intended goal. For example, improving the customer experience at the hospital front desk may involve the following:
– Increase the parking lots in front of the hospital
– Train the personnel to handle a large number of customers
– Wait for the government to provide better medicine prices…etc.
The below workshop from MIT Open Courses provides another practical example of applying the system dynamics using the Fishbone diagram :
The systems thinking diagrams allow us to effectively apply the theory to understand the different elements in the complex systems by visualizing the relation between them and determining the form of this relation. Once the systems diagram is complete, we’ll better understand of how it works, its gaps, the delays in the system, and how to improve the system based on the concluded data.
Wait, Join my Newsletters!
As always, I try to come to you with design ideas, tips, and tools for design and creative thinking. Subscribe to my newsletters to receive new updated design tools and tips!
Dr Rafiq Elmansy
As an academic and author, I've had the privilege of shaping the design landscape. I teach design at the University of Leeds and am the Programme Leader for the MA Design, focusing on design thinking, design for health, and behavioural design. I've developed and taught several innovative programmes at Wrexham Glyndwr University, Northumbria University, and The American University in Cairo. I'm also a published book author and the proud founder of Designorate.com, a platform that has been instrumental in fostering design innovation. My expertise in design has been recognised by prestigious organizations. I'm a fellow of the Higher Education Academy (HEA), the Design Research Society (FDRS), and an Adobe Education Leader. Over the course of 20 years, I've had the privilege of working with esteemed clients such as the UN, World Bank, Adobe, and Schneider, contributing to their design strategies. For more than 12 years, I collaborated closely with the Adobe team, playing a key role in the development of many Adobe applications.
You May Also Like

How Inclusive Design Reshaped Microsoft Products

How to Evaluate Design Ideas

Using the TRIZ Method for Creative Problem Solving

Measuring Design Thinking Impact

What are Design Research Types and Applications?

Service Design Thinking: Putting Your Consumer First
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Sign me up for the newsletter!
Taking a systems thinking approach to problem solving
Systems thinking is an approach that considers a situation or problem holistically and as part of an overall system which is more than the sum of its parts. Taking the big picture perspective, and looking more deeply at underpinnings, systems thinking seeks and offers long-term and fundamental solutions rather than quick fixes and surface change.
A systems thinking approach might be the ideal way to tackle essentially systemic problems. Our article sets out the basic concepts and ideas.
What is systems thinking?
When we consider the concepts of a car, or a human being we are using a systems thinking perspective. A car is not just a collection of nuts, bolts, panels and wheels. A human being is not simply an assembly of bones, muscles, organs and blood.
The history of systems thinking is itself innately complex, with roots in many important disciplines of the 20th century including biology, computing and data science. As a discipline, systems thinking is still evolving today.
How can systems thinking be applied to problem solving?
A popular way of applying a systems thinking lens is to examine the issue from multiple perspectives, zooming out from single and visible elements to the bigger and broader picture (e.g. via considering individual events, and then the patterns, structures and mental models which give rise to them).
Systems thinking is best applied in fields where problems and solutions are both high in complexity. There are a number of characteristics that can make an issue particularly compatible with a systems thinking approach:
Areas where systems thinking is often useful include health, climate change, urban planning, transport or ecology.
What is an example of a systems thinking approach to problem solving?
Beneath the waterline and invisible, lie deeper and longer-term trends or patterns of behavior. In our example this might be internal fighting in the political party which overshadows and obstructs its public campaigning and weakens its leadership and reputation.
The electoral system in the country may also be problematic or unfair, making the party so fearful and defensive against losing its remaining support base, that it has no energy or cash to campaign on a more positive agenda and win new voters.
Mental models
At the very base of the iceberg, deepest under the water, lie the mental models that allow the rest of the iceberg to persist in this shape. These include the assumptions, attitudes, beliefs and motivations which drive the behaviors, patterns and events seen further up in the iceberg.
When is a systems thinking approach not helpful?
If you are looking for a quick answer to a simple question, or an immediate response to a single event, then systems thinking may overcomplicate the process of solving your problem and provide you with more information than is helpful, and in slower time than you need.
A final word…
The biggest problems in the real world are rarely simple in nature and expecting a quick and simple solution to something like climate change or cancer would be naive.
Whether you think of it as zooming out to the big picture while retaining a focus on the small, or looking deeper under the water at the full shape of the iceberg, systems thinking can be a powerful tool for finding solutions that recognize the interactions and interdependence of individual elements in the real world.
You may also like
Systems thinking for school leaders: a comprehensive approach to educational management, how systems thinking enhances decision making skills: a quick guide, what is systems thinking, 5 ways to apply systems thinking to your business operations: a strategic guide, download this free ebook.
Problem Flow Diagram Software
The easiest and most powerful Problem Flow Diagram tool in the world.
Create Problem Flow Diagram online
Design the flow of solving problems using Problem Flow Diagram. Our Problem Flow Diagram software comes with a full set of Problem Flow Diagram icons and connectors that allows you to easily visualize your solution. Without a doubt, Visual Paradigm Online is the best Problem Flow Diagram software to create Problem Flow Diagrams.
A rich collection of Problem Flow Diagram template and example are provided to help you get a head-start when creating your own Problem Flow Diagrams. Following are some of these templates. Click Edit to start now. No registration needed!
Feature Highlights
Communicate and collaborate faster than ever with the best online diagram tool around.
Simple Yet Powerful
Intuitive drawing tools with precision control support. Apply formatting with the quick formatting tools.
Diagrams in MS Products
View and edit your diagrams directly in MS Office products such as Word, Excel, OneNote, etc.
Import Visio Drawing
VP Online is an online Visio alternative. Make a switch now to enjoy a lower cost and higher productivity.
Export and Sharing
Share your work with other by printing or exporting diagrams into images (PNG, JPG, SVG, GIF) or PDF.

Pre-Ready Templates
Create professional diagrams using a variety of templates. 2000's of ready-to-use templates are available.

Team Collaboration
Collaborate on your best ideas with the real-time diagram editor. Add comments for discussions.
Much more than a problem flow diagram software
Get Started Now
Create diagrams and charts in a simple and flexible way.
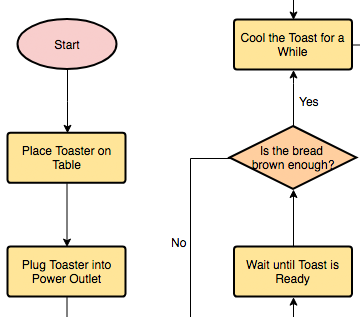
- Technical diagrams: UML , ERD , DFD , PERT , Network diagram , Wiring , PFD , P&ID , and more
- Business diagrams: ArchiMate , BPMN , SWOT , Value Chain , Value Stream Mapping , Org. Chart , and more
- Cloud architecture design tool: AWS , Azure , Google Cloud , IBM , Oracle , Alibaba , Tencent
- Powerful Flowchart , Floor plan , Mind map and Venn diagram tool
- Process Map Designer with templates like Customer Journey Mapping , Competitor Analysis , Root Cause , etc
©2024 by Visual Paradigm. All rights reserved.
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Security Overview
Learn Creative Problem Solving Techniques to Stimulate Innovation in Your Organization
By Kate Eby | October 20, 2017 (updated August 27, 2021)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations need processes in place to make strong, well-informed, and innovative decisions. Problem solving - in particular creative problem solving (CPS) - is a key skill in learning how to accurately identify problems and their causes, generate potential solutions, and evaluate all the possibilities to arrive at a strong corrective course of action. Every team in any organization, regardless of department or industry, needs to be effective, creative, and quick when solving problems.
In this article, we’ll discuss traditional and creative problem solving, and define the steps, best practices, and common barriers associated. After that, we’ll provide helpful methods and tools to identify the cause(s) of problematic situations, so you can get to the root of the issue and start to generate solutions. Then, we offer nearly 20 creative problem solving techniques to implement at your organization, or even in your personal life. Along the way, experts weigh in on the importance of problem solving, and offer tips and tricks.
What Is Problem Solving and Decision Making?
Problem solving is the process of working through every aspect of an issue or challenge to reach a solution. Decision making is choosing one of multiple proposed solutions — therefore, this process also includes defining and evaluating all potential options. Decision making is often one step of the problem solving process, but the two concepts are distinct.
Collective problem solving is problem solving that includes many different parties and bridges the knowledge of different groups. Collective problem solving is common in business problem solving because workplace decisions typically affect more than one person.
Problem solving, especially in business, is a complicated science. Not only are business conflicts multifaceted, but they often involve different personalities, levels of authority, and group dynamics. In recent years, however, there has been a rise in psychology-driven problem solving techniques, especially for the workplace. In fact, the psychology of how people solve problems is now studied formally in academic disciplines such as psychology and cognitive science.

Joe Carella is the Assistant Dean for Executive Education at the University of Arizona . Joe has over 20 years of experience in helping executives and corporations in managing change and developing successful business strategies. His doctoral research and executive education engagements have seen him focus on corporate strategy, decision making and business performance with a variety of corporate clients including Hershey’s, Chevron, Fender Musical Instruments Corporation, Intel, DP World, Essilor, BBVA Compass Bank.
He explains some of the basic psychology behind problem solving: “When our brain is engaged in the process of solving problems, it is engaged in a series of steps where it processes and organizes the information it receives while developing new knowledge it uses in future steps. Creativity is embedded in this process by incorporating diverse inputs and/or new ways of organizing the information received.”

Laura MacLeod is a Professor of Social Group Work at City University of New York, and the creator of From The Inside Out Project® , a program that coaches managers in team leadership for a variety of workplaces. She has a background in social work and over two decades of experience as a union worker, and currently leads talks on conflict resolution, problem solving, and listening skills at conferences across the country.
MacLeod thinks of problem solving as an integral practice of successful organizations. “Problem solving is a collaborative process — all voices are heard and connected, and resolution is reached by the group,” she says. “Problems and conflicts occur in all groups and teams in the workplace, but if leaders involve everyone in working through, they will foster cohesion, engagement, and buy in. Everybody wins.”
10 tips that will make you more productive.

Uncover the top three factors that are killing your productivity and 10 tips to help you overcome them.
Download the free e-book to overcome my productivity killers
Project Management Guide
Your one-stop shop for everything project management

Ready to get more out of your project management efforts? Visit our comprehensive project management guide for tips, best practices, and free resources to manage your work more effectively.
View the guide
What Is the First Step in Solving a Problem?
Although problem solving techniques vary procedurally, experts agree that the first step in solving a problem is defining the problem. Without a clear articulation of the problem at stake, it is impossible to analyze all the key factors and actors, generate possible solutions, and then evaluate them to pick the best option.

Dr. Elliott Jaffa is a behavioral and management psychologist with over 25 years of problem solving training and management experience. “Start with defining the problem you want to solve,” he says, “And then define where you want to be, what you want to come away with.” He emphasizes these are the first steps in creating an actionable, clear solution.

Bryan Mattimore is Co-Founder of Growth Engine, an 18-year old innovation agency based in Norwalk, CT. Bryan has facilitated over 1,000 ideation sessions and managed over 200 successful innovation projects leading to over $3 billion in new sales. His newest book is 21 Days to a Big Idea . When asked about the first critical component to successful problem solving, Mattimore says, “Defining the challenge correctly, or ‘solving the right problem’ … The three creative techniques we use to help our clients ‘identify the right problem to be solved’ are questioning assumptions, 20 questions, and problem redefinition. A good example of this was a new product challenge from a client to help them ‘invent a new iron. We got them to redefine the challenge as first: a) inventing new anti-wrinkle devices, and then b) inventing new garment care devices.”
What Are Problem Solving Skills?
To understand the necessary skills in problem solving, you should first understand the types of thinking often associated with strong decision making. Most problem solving techniques look for a balance between the following binaries:
- Convergent vs. Divergent Thinking: Convergent thinking is bringing together disparate information or ideas to determine a single best answer or solution. This thinking style values logic, speed, and accuracy, and leaves no chance for ambiguity. Divergent thinking is focused on generating new ideas to identify and evaluate multiple possible solutions, often uniting ideas in unexpected combinations. Divergent thinking is characterized by creativity, complexity, curiosity, flexibility, originality, and risk-taking.
- Pragmatics vs. Semantics: Pragmatics refer to the logic of the problem at hand, and semantics is how you interpret the problem to solve it. Both are important to yield the best possible solution.
- Mathematical vs. Personal Problem Solving: Mathematical problem solving involves logic (usually leading to a single correct answer), and is useful for problems that involve numbers or require an objective, clear-cut solution. However, many workplace problems also require personal problem solving, which includes interpersonal, collaborative, and emotional intuition and skills.
The following basic methods are fundamental problem solving concepts. Implement them to help balance the above thinking models.
- Reproductive Thinking: Reproductive thinking uses past experience to solve a problem. However, be careful not to rely too heavily on past solutions, and to evaluate current problems individually, with their own factors and parameters.
- Idea Generation: The process of generating many possible courses of action to identify a solution. This is most commonly a team exercise because putting everyone’s ideas on the table will yield the greatest number of potential solutions.
However, many of the most critical problem solving skills are “soft” skills: personal and interpersonal understanding, intuitiveness, and strong listening.
Mattimore expands on this idea: “The seven key skills to be an effective creative problem solver that I detail in my book Idea Stormers: How to Lead and Inspire Creative Breakthroughs are: 1) curiosity 2) openness 3) a willingness to embrace ambiguity 4) the ability to identify and transfer principles across categories and disciplines 5) the desire to search for integrity in ideas, 6) the ability to trust and exercise “knowingness” and 7) the ability to envision new worlds (think Dr. Seuss, Star Wars, Hunger Games, Harry Potter, etc.).”
“As an individual contributor to problem solving it is important to exercise our curiosity, questioning, and visioning abilities,” advises Carella. “As a facilitator it is essential to allow for diverse ideas to emerge, be able to synthesize and ‘translate’ other people’s thinking, and build an extensive network of available resources.”
MacLeod says the following interpersonal skills are necessary to effectively facilitate group problem solving: “The abilities to invite participation (hear all voices, encourage silent members), not take sides, manage dynamics between the monopolizer, the scapegoat, and the bully, and deal with conflict (not avoiding it or shutting down).”
Furthermore, Jaffa explains that the skills of a strong problem solver aren’t measurable. The best way to become a creative problem solver, he says, is to do regular creative exercises that keep you sharp and force you to think outside the box. Carella echoes this sentiment: “Neuroscience tells us that creativity comes from creating novel neural paths. Allow a few minutes each day to exercise your brain with novel techniques and brain ‘tricks’ – read something new, drive to work via a different route, count backwards, smell a new fragrance, etc.”
What Is Creative Problem Solving? History, Evolution, and Core Principles
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a method of problem solving in which you approach a problem or challenge in an imaginative, innovative way. The goal of CPS is to come up with innovative solutions, make a decision, and take action quickly. Sidney Parnes and Alex Osborn are credited with developing the creative problem solving process in the 1950s. The concept was further studied and developed at SUNY Buffalo State and the Creative Education Foundation.
The core principles of CPS include the following:
- Balance divergent and convergent thinking
- Ask problems as questions
- Defer or suspend judgement
- Focus on “Yes, and…” rather than “No, but…”
According to Carella, “Creative problem solving is the mental process used for generating innovative and imaginative ideas as a solution to a problem or a challenge. Creative problem solving techniques can be pursued by individuals or groups.”
When asked to define CPS, Jaffa explains that it is, by nature, difficult to create boundaries for. “Creative problem solving is not cut and dry,” he says, “If you ask 100 different people the definition of creative problem solving, you’ll get 100 different responses - it’s a non-entity.”
Business presents a unique need for creative problem solving. Especially in today’s competitive landscape, organizations need to iterate quickly, innovate with intention, and constantly be at the cutting-edge of creativity and new ideas to succeed. Developing CPS skills among your workforce not only enables you to make faster, stronger in-the-moment decisions, but also inspires a culture of collaborative work and knowledge sharing. When people work together to generate multiple novel ideas and evaluate solutions, they are also more likely to arrive at an effective decision, which will improve business processes and reduce waste over time. In fact, CPS is so important that some companies now list creative problem solving skills as a job criteria.
MacLeod reiterates the vitality of creative problem solving in the workplace. “Problem solving is crucial for all groups and teams,” she says. “Leaders need to know how to guide the process, hear all voices and involve all members - it’s not easy.”
“This mental process [of CPS] is especially helpful in work environments where individuals and teams continuously struggle with new problems and challenges posed by their continuously changing environment,” adds Carella.
Problem Solving Best Practices
By nature, creative problem solving does not have a clear-cut set of do’s and don’ts. Rather, creating a culture of strong creative problem solvers requires flexibility, adaptation, and interpersonal skills. However, there are a several best practices that you should incorporate:
- Use a Systematic Approach: Regardless of the technique you use, choose a systematic method that satisfies your workplace conditions and constraints (time, resources, budget, etc.). Although you want to preserve creativity and openness to new ideas, maintaining a structured approach to the process will help you stay organized and focused.
- View Problems as Opportunities: Rather than focusing on the negatives or giving up when you encounter barriers, treat problems as opportunities to enact positive change on the situation. In fact, some experts even recommend defining problems as opportunities, to remain proactive and positive.
- Change Perspective: Remember that there are multiple ways to solve any problem. If you feel stuck, changing perspective can help generate fresh ideas. A perspective change might entail seeking advice of a mentor or expert, understanding the context of a situation, or taking a break and returning to the problem later. “A sterile or familiar environment can stifle new thinking and new perspectives,” says Carella. “Make sure you get out to draw inspiration from spaces and people out of your usual reach.”
- Break Down Silos: To invite the greatest possible number of perspectives to any problem, encourage teams to work cross-departmentally. This not only combines diverse expertise, but also creates a more trusting and collaborative environment, which is essential to effective CPS. According to Carella, “Big challenges are always best tackled by a group of people rather than left to a single individual. Make sure you create a space where the team can concentrate and convene.”
- Employ Strong Leadership or a Facilitator: Some companies choose to hire an external facilitator that teaches problem solving techniques, best practices, and practicums to stimulate creative problem solving. But, internal managers and staff can also oversee these activities. Regardless of whether the facilitator is internal or external, choose a strong leader who will value others’ ideas and make space for creative solutions. Mattimore has specific advice regarding the role of a facilitator: “When facilitating, get the group to name a promising idea (it will crystalize the idea and make it more memorable), and facilitate deeper rather than broader. Push for not only ideas, but how an idea might specifically work, some of its possible benefits, who and when would be interested in an idea, etc. This fleshing-out process with a group will generate fewer ideas, but at the end of the day will yield more useful concepts that might be profitably pursued.” Additionally, Carella says that “Executives and managers don’t necessarily have to be creative problem solvers, but need to make sure that their teams are equipped with the right tools and resources to make this happen. Also they need to be able to foster an environment where failing fast is accepted and celebrated.”
- Evaluate Your Current Processes: This practice can help you unlock bottlenecks, and also identify gaps in your data and information management, both of which are common roots of business problems.
MacLeod offers the following additional advice, “Always get the facts. Don’t jump too quickly to a solution – working through [problems] takes time and patience.”
Mattimore also stresses that how you introduce creative problem solving is important. “Do not start by introducing a new company-wide innovation process,” he says. “Instead, encourage smaller teams to pursue specific creative projects, and then build a process from the ground up by emulating these smaller teams’ successful approaches. We say: ‘You don’t innovate by changing the culture, you change the culture by innovating.’”
Barriers to Effective Problem Solving
Learning how to effectively solve problems is difficult and takes time and continual adaptation. There are several common barriers to successful CPS, including:
- Confirmation Bias: The tendency to only search for or interpret information that confirms a person’s existing ideas. People misinterpret or disregard data that doesn’t align with their beliefs.
- Mental Set: People’s inclination to solve problems using the same tactics they have used to solve problems in the past. While this can sometimes be a useful strategy (see Analogical Thinking in a later section), it often limits inventiveness and creativity.
- Functional Fixedness: This is another form of narrow thinking, where people become “stuck” thinking in a certain way and are unable to be flexible or change perspective.
- Unnecessary Constraints: When people are overwhelmed with a problem, they can invent and impose additional limits on solution avenues. To avoid doing this, maintain a structured, level-headed approach to evaluating causes, effects, and potential solutions.
- Groupthink: Be wary of the tendency for group members to agree with each other — this might be out of conflict avoidance, path of least resistance, or fear of speaking up. While this agreeableness might make meetings run smoothly, it can actually stunt creativity and idea generation, therefore limiting the success of your chosen solution.
- Irrelevant Information: The tendency to pile on multiple problems and factors that may not even be related to the challenge at hand. This can cloud the team’s ability to find direct, targeted solutions.
- Paradigm Blindness: This is found in people who are unwilling to adapt or change their worldview, outlook on a particular problem, or typical way of processing information. This can erode the effectiveness of problem solving techniques because they are not aware of the narrowness of their thinking, and therefore cannot think or act outside of their comfort zone.
According to Jaffa, the primary barrier of effective problem solving is rigidity. “The most common things people say are, ‘We’ve never done it before,’ or ‘We’ve always done it this way.’” While these feelings are natural, Jaffa explains that this rigid thinking actually precludes teams from identifying creative, inventive solutions that result in the greatest benefit.
“The biggest barrier to creative problem solving is a lack of awareness – and commitment to – training employees in state-of-the-art creative problem-solving techniques,” Mattimore explains. “We teach our clients how to use ideation techniques (as many as two-dozen different creative thinking techniques) to help them generate more and better ideas. Ideation techniques use specific and customized stimuli, or ‘thought triggers’ to inspire new thinking and new ideas.”
MacLeod adds that ineffective or rushed leadership is another common culprit. “We're always in a rush to fix quickly,” she says. “Sometimes leaders just solve problems themselves, making unilateral decisions to save time. But the investment is well worth it — leaders will have less on their plates if they can teach and eventually trust the team to resolve. Teams feel empowered and engagement and investment increases.”
Strategies for Problem Cause Identification
As discussed, most experts agree that the first and most crucial step in problem solving is defining the problem. Once you’ve done this, however, it may not be appropriate to move straight to the solution phase. Rather, it is often helpful to identify the cause(s) of the problem: This will better inform your solution planning and execution, and help ensure that you don’t fall victim to the same challenges in the future.
Below are some of the most common strategies for identifying the cause of a problem:
- Root Cause Analysis: This method helps identify the most critical cause of a problem. A factor is considered a root cause if removing it prevents the problem from recurring. Performing a root cause analysis is a 12 step process that includes: define the problem, gather data on the factors contributing to the problem, group the factors based on shared characteristics, and create a cause-and-effect timeline to determine the root cause. After that, you identify and evaluate corrective actions to eliminate the root cause.
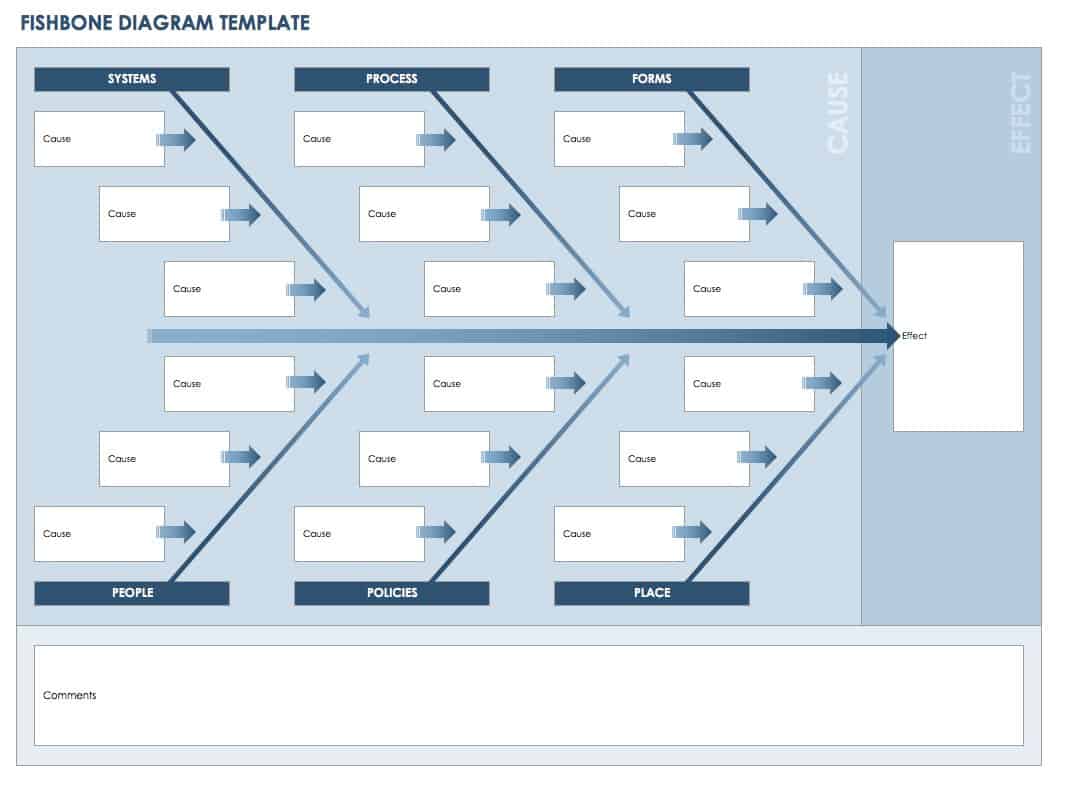
Download Fishbone Diagram Template - Excel
Download 5 Whys Template Excel | Word | PDF
Problem Solving Techniques and Strategies
In this section, we’ll explain several traditional and creative problem solving methods that you can use to identify challenges, create actionable goals, and resolve problems as they arise. Although there is often procedural and objective crossover among techniques, they are grouped by theme so you can identify which method works best for your organization.
Divergent Creative Problem Solving Techniques
Brainstorming: One of the most common methods of divergent thinking, brainstorming works best in an open group setting where everyone is encouraged to share their creative ideas. The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible – you analyze, critique, and evaluate the ideas only after the brainstorming session is complete. To learn more specific brainstorming techniques, read this article .
Mind Mapping: This is a visual thinking tool where you graphically depict concepts and their relation to one another. You can use mind mapping to structure the information you have, analyze and synthesize it, and generate solutions and new ideas from there. The goal of a mind map is to simplify complicated problems so you can more clearly identify solutions.
Appreciative Inquiry (AI): The basic assumption of AI is that “an organization is a mystery to be embraced.” Using this principle, AI takes a positive, inquisitive approach to identifying the problem, analyzing the causes, and presenting possible solutions. The five principles of AI emphasize dialogue, deliberate language and outlook, and social bonding.
Lateral Thinking: This is an indirect problem solving approach centered on the momentum of idea generation. As opposed to critical thinking, where people value ideas based on their truth and the absence of errors, lateral thinking values the “movement value” of new ideas: This means that you reward team members for producing a large volume of new ideas rapidly. With this approach, you’ll generate many new ideas before approving or rejecting any.
Problem Solving Techniques to Change Perspective
Constructive Controversy: This is a structured approach to group decision making to preserve critical thinking and disagreement while maintaining order. After defining the problem and presenting multiple courses of action, the group divides into small advocacy teams who research, analyze, and refute a particular option. Once each advocacy team has presented its best-case scenario, the group has a discussion (advocacy teams still defend their presented idea). Arguing and playing devil’s advocate is encouraged to reach an understanding of the pros and cons of each option. Next, advocacy teams abandon their cause and evaluate the options openly until they reach a consensus. All team members formally commit to the decision, regardless of whether they advocated for it at the beginning. You can learn more about the goals and steps in constructive controversy here .
Carella is a fan of this approach. “Create constructive controversy by having two teams argue the pros and cons of a certain idea,” he says. “It forces unconscious biases to surface and gives space for new ideas to formulate.”
Abstraction: In this method, you apply the problem to a fictional model of the current situation. Mapping an issue to an abstract situation can shed extraneous or irrelevant factors, and reveal places where you are overlooking obvious solutions or becoming bogged down by circumstances.
Analogical Thinking: Also called analogical reasoning , this method relies on an analogy: using information from one problem to solve another problem (these separate problems are called domains). It can be difficult for teams to create analogies among unrelated problems, but it is a strong technique to help you identify repeated issues, zoom out and change perspective, and prevent the problems from occurring in the future. .
CATWOE: This framework ensures that you evaluate the perspectives of those whom your decision will impact. The factors and questions to consider include (which combine to make the acronym CATWOE):
- Customers: Who is on the receiving end of your decisions? What problem do they currently have, and how will they react to your proposed solution?
- Actors: Who is acting to bring your solution to fruition? How will they respond and be affected by your decision?
- Transformation Process: What processes will you employ to transform your current situation and meet your goals? What are the inputs and outputs?
- World View: What is the larger context of your proposed solution? What is the larger, big-picture problem you are addressing?
- Owner: Who actually owns the process? How might they influence your proposed solution (positively or negatively), and how can you influence them to help you?
- Environmental Constraints: What are the limits (environmental, resource- and budget-wise, ethical, legal, etc.) on your ideas? How will you revise or work around these constraints?
Complex Problem Solving
Soft Systems Methodology (SSM): For extremely complex problems, SSM can help you identify how factors interact, and determine the best course of action. SSM was borne out of organizational process modeling and general systems theory, which hold that everything is part of a greater, interconnected system: This idea works well for “hard” problems (where logic and a single correct answer are prioritized), and less so for “soft” problems (i.e., human problems where factors such as personality, emotions, and hierarchy come into play). Therefore, SSM defines a seven step process for problem solving:
- Begin with the problem or problematic situation
- Express the problem or situation and build a rich picture of the themes of the problem
- Identify the root causes of the problem (most commonly with CATWOE)
- Build conceptual models of human activity surrounding the problem or situation
- Compare models with real-world happenings
- Identify changes to the situation that are both feasible and desirable
- Take action to implement changes and improve the problematic situation
SSM can be used for any complex soft problem, and is also a useful tool in change management .
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): This method helps teams anticipate potential problems and take steps to mitigate them. Use FMEA when you are designing (redesigning) a complex function, process, product, or service. First, identify the failure modes, which are the possible ways that a project could fail. Then, perform an effects analysis to understand the consequences of each of the potential downfalls. This exercise is useful for internalizing the severity of each potential failure and its effects so you can make adjustments or safeties in your plan.
Download FMEA Template
Problem Solving Based on Data or Logic (Heuristic Methods)
TRIZ: A Russian-developed problem solving technique that values logic, analysis, and forecasting over intuition or soft reasoning. TRIZ (translated to “theory of inventive problem solving” or TIPS in English) is a systematic approach to defining and identifying an inventive solution to difficult problems. The method offers several strategies for arriving at an inventive solution, including a contradictions matrix to assess trade-offs among solutions, a Su-Field analysis which uses formulas to describe a system by its structure, and ARIZ (algorithm of inventive problem solving) which uses algorithms to find inventive solutions.
Inductive Reasoning: A logical method that uses evidence to conclude that a certain answer is probable (this is opposed to deductive reasoning, where the answer is assumed to be true). Inductive reasoning uses a limited number of observations to make useful, logical conclusions (for example, the Scientific Method is an extreme example of inductive reasoning). However, this method doesn’t always map well to human problems in the workplace — in these instances, managers should employ intuitive inductive reasoning , which allows for more automatic, implicit conclusions so that work can progress. This, of course, retains the principle that these intuitive conclusions are not necessarily the one and only correct answer.
Process-Oriented Problem Solving Methods
Plan Do Check Act (PDCA): This is an iterative management technique used to ensure continual improvement of products or processes. First, teams plan (establish objectives to meet desired end results), then do (implement the plan, new processes, or produce the output), then check (compare expected with actual results), and finally act (define how the organization will act in the future, based on the performance and knowledge gained in the previous three steps).
Means-End Analysis (MEA): The MEA strategy is to reduce the difference between the current (problematic) state and the goal state. To do so, teams compile information on the multiple factors that contribute to the disparity between the current and goal states. Then they try to change or eliminate the factors one by one, beginning with the factor responsible for the greatest difference in current and goal state. By systematically tackling the multiple factors that cause disparity between the problem and desired outcome, teams can better focus energy and control each step of the process.
Hurson’s Productive Thinking Model: This technique was developed by Tim Hurson, and is detailed in his 2007 book Think Better: An Innovator’s Guide to Productive Thinking . The model outlines six steps that are meant to give structure while maintaining creativity and critical thinking: 1) Ask “What is going on?” 2) Ask “What is success?” 3) Ask “What is the question?” 4) Generate answers 5) Forge the solution 6) Align resources.
Control Influence Accept (CIA): The basic premise of CIA is that how you respond to problems determines how successful you will be in overcoming them. Therefore, this model is both a problem solving technique and stress-management tool that ensures you aren’t responding to problems in a reactive and unproductive way. The steps in CIA include:
- Control: Identify the aspects of the problem that are within your control.
- Influence: Identify the aspects of the problem that you cannot control, but that you can influence.
- Accept: Identify the aspects of the problem that you can neither control nor influence, and react based on this composite information.
GROW Model: This is a straightforward problem solving method for goal setting that clearly defines your goals and current situation, and then asks you to define the potential solutions and be realistic about your chosen course of action. The steps break down as follows:
- Goal: What do you want?
- Reality: Where are you now?
- Options: What could you do?
- Will: What will you do?
OODA Loop: This acronym stands for observe, orient, decide, and act. This approach is a decision-making cycle that values agility and flexibility over raw human force. It is framed as a loop because of the understanding that any team will continually encounter problems or opponents to success and have to overcome them.
There are also many un-named creative problem solving techniques that follow a sequenced series of steps. While the exact steps vary slightly, they all follow a similar trajectory and aim to accomplish similar goals of problem, cause, and goal identification, idea generation, and active solution implementation.
| Identify Goal | Define Problem | Define Problem |
| Gather Data | Define Causes | Identify Options |
| Clarify Problem | Generate Ideas | Evaluate Options |
| Generate Ideas | Choose the Best Solution | Implement Solution |
| Select Solution | Take Action | - |
MacLeod offers her own problem solving procedure, which echoes the above steps:
“1. Recognize the Problem: State what you see. Sometimes the problem is covert. 2. Identify: Get the facts — What exactly happened? What is the issue? 3. and 4. Explore and Connect: Dig deeper and encourage group members to relate their similar experiences. Now you're getting more into the feelings and background [of the situation], not just the facts. 5. Possible Solutions: Consider and brainstorm ideas for resolution. 6. Implement: Choose a solution and try it out — this could be role play and/or a discussion of how the solution would be put in place. 7. Evaluate: Revisit to see if the solution was successful or not.”
Many of these problem solving techniques can be used in concert with one another, or multiple can be appropriate for any given problem. It’s less about facilitating a perfect CPS session, and more about encouraging team members to continually think outside the box and push beyond personal boundaries that inhibit their innovative thinking. So, try out several methods, find those that resonate best with your team, and continue adopting new techniques and adapting your processes along the way.
Improve Problem Solving with Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

The Art of Effective Problem Solving: A Step-by-Step Guide
Author: Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
Whether we realise it or not, problem solving skills are an important part of our daily lives. From resolving a minor annoyance at home to tackling complex business challenges at work, our ability to solve problems has a significant impact on our success and happiness. However, not everyone is naturally gifted at problem-solving, and even those who are can always improve their skills. In this blog post, we will go over the art of effective problem-solving step by step.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let’s get started!
Problem Solving Methodologies
Individuals and organisations can use a variety of problem-solving methodologies to address complex challenges. 8D and A3 problem solving techniques are two popular methodologies in the Lean Six Sigma framework.
Methodology of 8D (Eight Discipline) Problem Solving:
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
The 8D process consists of the following steps:

- Form a team: Assemble a group of people who have the necessary expertise to work on the problem.
- Define the issue: Clearly identify and define the problem, including the root cause and the customer impact.
- Create a temporary containment plan: Put in place a plan to lessen the impact of the problem until a permanent solution can be found.
- Identify the root cause: To identify the underlying causes of the problem, use root cause analysis techniques such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts.
- Create and test long-term corrective actions: Create and test a long-term solution to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
- Implement and validate the permanent solution: Implement and validate the permanent solution’s effectiveness.
- Prevent recurrence: Put in place measures to keep the problem from recurring.
- Recognize and reward the team: Recognize and reward the team for its efforts.
Download the 8D Problem Solving Template
A3 Problem Solving Method:
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
The A3 problem-solving procedure consists of the following steps:
- Determine the issue: Define the issue clearly, including its impact on the customer.
- Perform root cause analysis: Identify the underlying causes of the problem using root cause analysis techniques.
- Create and implement a solution: Create and implement a solution that addresses the problem’s root cause.
- Monitor and improve the solution: Keep an eye on the solution’s effectiveness and make any necessary changes.
Subsequently, in the Lean Six Sigma framework, the 8D and A3 problem solving methodologies are two popular approaches to problem solving. Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Step 1 – Define the Problem
The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause. To avoid this pitfall, it is critical to thoroughly understand the problem.
To begin, ask yourself some clarifying questions:
- What exactly is the issue?
- What are the problem’s symptoms or consequences?
- Who or what is impacted by the issue?
- When and where does the issue arise?
Answering these questions will assist you in determining the scope of the problem. However, simply describing the problem is not always sufficient; you must also identify the root cause. The root cause is the underlying cause of the problem and is usually the key to resolving it permanently.
Try asking “why” questions to find the root cause:
- What causes the problem?
- Why does it continue?
- Why does it have the effects that it does?
By repeatedly asking “ why ,” you’ll eventually get to the bottom of the problem. This is an important step in the problem-solving process because it ensures that you’re dealing with the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
Once you have a firm grasp on the issue, it is time to divide it into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes tackling the problem easier and reduces the risk of becoming overwhelmed. For example, if you’re attempting to solve a complex business problem, you might divide it into smaller components like market research, product development, and sales strategies.
To summarise step 1, defining the problem is an important first step in effective problem-solving. You will be able to identify the root cause and break it down into manageable parts if you take the time to thoroughly understand the problem. This will prepare you for the next step in the problem-solving process, which is gathering information and brainstorming ideas.
Step 2 – Gather Information and Brainstorm Ideas

Gathering information and brainstorming ideas is the next step in effective problem solving. This entails researching the problem and relevant information, collaborating with others, and coming up with a variety of potential solutions. This increases your chances of finding the best solution to the problem.
Begin by researching the problem and relevant information. This could include reading articles, conducting surveys, or consulting with experts. The goal is to collect as much information as possible in order to better understand the problem and possible solutions.
Next, work with others to gather a variety of perspectives. Brainstorming with others can be an excellent way to come up with new and creative ideas. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas when working in a group, and make an effort to actively listen to what others have to say. Be open to new and unconventional ideas and resist the urge to dismiss them too quickly.
Finally, use brainstorming to generate a wide range of potential solutions. This is the place where you can let your imagination run wild. At this stage, don’t worry about the feasibility or practicality of the solutions; instead, focus on generating as many ideas as possible. Write down everything that comes to mind, no matter how ridiculous or unusual it may appear. This can be done individually or in groups.
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the next step in the problem-solving process, which we’ll go over in greater detail in the following section.
Step 3 – Evaluate Options and Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the third step in effective problem solving, and it entails weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, considering their feasibility and practicability, and selecting the solution that is most likely to solve the problem effectively.
To begin, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. This will assist you in determining the potential outcomes of each solution and deciding which is the best option. For example, a quick and easy solution may not be the most effective in the long run, whereas a more complex and time-consuming solution may be more effective in solving the problem in the long run.
Consider each solution’s feasibility and practicability. Consider the following:
- Can the solution be implemented within the available resources, time, and budget?
- What are the possible barriers to implementing the solution?
- Is the solution feasible in today’s political, economic, and social environment?
You’ll be able to tell which solutions are likely to succeed and which aren’t by assessing their feasibility and practicability.
Finally, choose the solution that is most likely to effectively solve the problem. This solution should be based on the criteria you’ve established, such as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and your overall goals.
It is critical to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to problems. What is effective for one person or situation may not be effective for another. This is why it is critical to consider a wide range of solutions and evaluate each one based on its ability to effectively solve the problem.
Step 4 – Implement and Monitor the Solution

When you’ve decided on the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. The fourth and final step in effective problem solving is to put the solution into action, monitor its progress, and make any necessary adjustments.
To begin, implement the solution. This may entail delegating tasks, developing a strategy, and allocating resources. Ascertain that everyone involved understands their role and responsibilities in the solution’s implementation.
Next, keep an eye on the solution’s progress. This may entail scheduling regular check-ins, tracking metrics, and soliciting feedback from others. You will be able to identify any potential roadblocks and make any necessary adjustments in a timely manner if you monitor the progress of the solution.
Finally, make any necessary modifications to the solution. This could entail changing the solution, altering the plan of action, or delegating different tasks. Be willing to make changes if they will improve the solution or help it solve the problem more effectively.
It’s important to remember that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to start from scratch. This is especially true if the initial solution does not effectively solve the problem. In these situations, it’s critical to be adaptable and flexible and to keep trying new solutions until you find the one that works best.
To summarise, effective problem solving is a critical skill that can assist individuals and organisations in overcoming challenges and achieving their objectives. Effective problem solving consists of four key steps: defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives and selecting the best solution, and implementing the solution.
You can increase your chances of success in problem solving by following these steps and considering factors such as the pros and cons of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and making any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, keep in mind that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to go back to the beginning and restart. Maintain your adaptability and try new solutions until you find the one that works best for you.
- Novick, L.R. and Bassok, M., 2005. Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press.
Was this helpful?

Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website www.learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.

The Power of 5 Whys to get Results

The Power of Mistakes: Lessons Learned from Failure
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…
Computersciencementor | Hardware, Software, Networking and programming
Algorithm and flowchart explained with examples, what is algorithm and flowchart.
Algorithm and flowchart are programming tools. A Programmer uses various programming languages to create programs. But before actually writing a program in a programming language, a programmer first needs to find a procedure for solving the problem which is known as planning the program. The program written without proper pre-planning have higher chances of errors. The tools that are used to plan or design the problem are known as programming tools. Algorithm and flowchart are widely used programming tools.

The word “algorithm” relates to the name of the mathematician Al- khowarizmi , which means a procedure or a technique. Programmer commonly uses an algorithm for planning and solving the problems.
An algorithm is a specific set of meaningful instructions written in a specific order for carrying out or solving a specific problem.
Types of Algorithm:
The algorithm and flowchart are classified into three types of control structures.
- Branching(Selection)
- Loop(Repetition)
According to the condition and requirement, these three control structures can be used.
In the sequence structure, statements are placed one after the other and the execution takes place starting from up to down.
Whereas in branch control, there is a condition and according to a condition, a decision of either TRUE or FALSE is achieved. In the case of TRUE, one of the two branches is explored; but in the case of FALSE condition, the other alternative is taken. Generally, the ‘IF-THEN’ is used to represent branch control.
Write an algorithm to find the smallest number between two numbers
Write an algorithm to check odd or even number.
The Loop or Repetition allows a statements or block of statements to be executed repeatedly based on certain loop condition. ‘While’ and ‘for’ construct are used to represent the loop structure in most programming languages. Loops are of two types: Bounded and Unbounded loop. In bounded loop, the number of iterations is fixed while in unbounded loops the condition has to satisfy to end the loop.
An algorithm to calculate even numbers between 20 and 40
Write an algorithm to input a natural number, n, and calculate the odd numbers equal or less than n.
Characteristics of a good algorithm.
- The Finite number of steps:
After starting an algorithm for any problem, it has to terminate at some point.
- Easy Modification.
There can be numbers of steps in an algorithm depending on the type of problem. It supports easy modification of Steps.
- Easy and simple to understand
A Simple English language is used while writing an algorithm. It is not dependent on any particular programming language. People without the knowledge of programming can read and understand the steps in the algorithm.
An algorithm is just a design of a program. Every program needs to display certain output after processing the input data. So one always expects the result as an output from an algorithm. It can give output at different stages. The result obtained at the end of an algorithm is known as an end result and if the result is obtained at an intermediate stage of process or operation then the result is known as an intermediate result. Also, the output has to be as expected having some relation to the inputs.
The first design of flowchart goes back to 1945 which was designed by John Von Neumann . Unlike an algorithm, Flowchart uses different symbols to design a solution to a problem. It is another commonly used programming tool.
In general, a flowchart is a diagram that uses different symbols to visually present the flow of data. By looking at a flow chart one can understand the operations and sequence of operations performed in a system. This is why flowchart is often considered as a blueprint of a design used for solving a specific problem.
A flowchart is defined as a symbolic or a graphical representation of an algorithm that uses different standard symbols.
Flowchart Symbols:
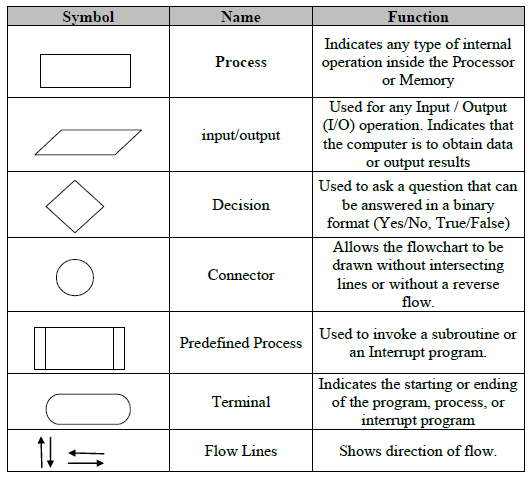
Guidelines for drawing a flowchart.
- The Title for every flowchart is compulsory.
- There must be START and END point for every flowchart.
- The symbols used in flowchart should have only one entry point on the top. The exit point for symbols (except for decision/diamond symbol) is on the button.
- There should be two exit points for decision symbol; exit points can be on the bottom and one side or on the sides.
- The flow of flowchart is generally from top to bottom. But in some cases, it can also flow to upward direction
- The direction of the flow of control should be indicated by arrowheads.
- The operations for every step should be written inside the symbol.
- The language used in flowchart should be simple so that it can be easily understood.
- The flowlines that show the direction of flow of flowchart must not cross each other.
- While connecting different pages of the same flowchart, Connectors must be used.
Some examples of algorithm and flowchart.
Example1: To calculate the area of a circle
Step1: Start
Step2: Input radius of the circle say r
Step3: Use the formula πr 2 and store result in a variable AREA
Step4: Print AREA
Step5: Stop Flowchart:
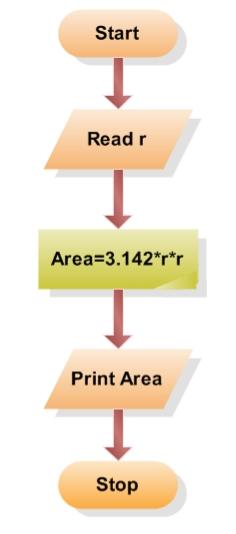
Related Posts
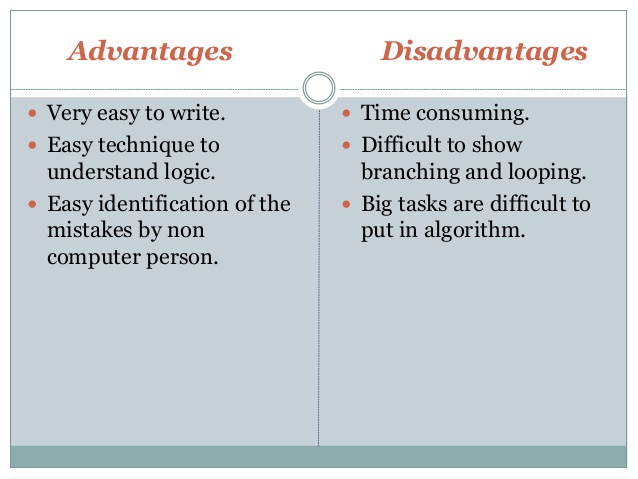
Sampurna shrestha
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Why Britain Just Ended 14 Years of Conservative Rule
Last week, the center-left labour party won the british general election in a landslide..

Hosted by Natalie Kitroeff
Featuring Mark Landler
Produced by Rob Szypko , Nina Feldman and Will Reid
Edited by Brendan Klinkenberg
With Paige Cowett
Original music by Dan Powell , Diane Wong and Marion Lozano
Engineered by Alyssa Moxley
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
For more than a decade, Britain has been governed by the Conservative Party, which pushed its politics to the right, embracing smaller government and Brexit. Last week, that era officially came to an end.
Mark Landler, the London bureau chief for The Times, explains why British voters rejected the Conservatives and what their defeat means in a world where populism is on the rise.
On today’s episode

Mark Landler , the London bureau chief for The New York Times.

Background reading
Five takeaways from the British general election.
The Conservatives have run Britain for 14 years. How have things changed in that time?
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Michael Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson, Nina Lassam and Nick Pitman.
Natalie Kitroeff is the Mexico City bureau chief for The Times, leading coverage of Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean. More about Natalie Kitroeff
Mark Landler is the London bureau chief of The Times, covering the United Kingdom, as well as American foreign policy in Europe, Asia and the Middle East. He has been a journalist for more than three decades. More about Mark Landler
Advertisement

COMMENTS
How do you approach problems? Do you have a process in place to ensure that you and your co-workers come to the right solution? Learn how to find solutions visually through a problem-solving flowchart and other methods.
A problem-solving flowchart is a flowchart that helps process improvement, troubleshooting, or decision-making. Flowcharts use shapes, symbols, and connecting arrows to map out a problem or flow. This technique illustrates how many steps are in a process, entry and endpoints, the flow of information and materials, and any branches or decision ...
Problem-Solving Flowcharts is a graphical representation used to break down problem or process into smaller, manageable parts, identify the root causes and outline a step-by-step solution. It helps in visually organizing information and showing the relationships between various parts of the problem. This type of flowcharts consists of different ...
With a system flowchart, it might be easier to look at complex processes of your system to figure out bottlenecks and problems, thus saving you from a lot of headaches when trying to find and solve them.
Problem solving tools help you and your team unlock great efficiency and results when analyzing and overcoming organizational issues. Learn more.
Visual problem solving is the process of using aids like charts or diagrams to display all the aspects of a problem in order to find viable solutions. When problem solving, sometimes it's hard to see what's causing the problem, or other relationships and correlations that are affecting whatever it is you're working on. Two common methods for problem solving include mind maps and . A mind ...
Fishbone diagram is perfect for root cause analysis, planning, and more. Learn how you can use fishbone diagrams for complex business problems.
In this article and video, we look at how to create and use flow charts, and explore how they can help you to solve problems in your processes.
Visual problem solving with flowcharts and mind maps. Why most people fail to solve problems and how visual problem solving can make it easier for anyone.
Discover how to use a problem-solving flow chart to visualize and solve complex problems. Follow a simple guide and download a free template in Excel.
The basis of the A3 problem solving template is collectively mapping out a flow chart to break down complex processes, and highlighting the flaws in the system.
Diagnose the situation so that your focus is on the problem, not just its symptoms. Helpful problem-solving techniques include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect diagrams to define and analyze root causes.
A fishbone diagram is a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot possible solutions. It is also called an Ishikawa diagram, after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa, as well as a herringbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram. Fishbone diagrams are often used in root cause ...
A flowchart is a diagram that visually represents the progression of steps of a process or workflow. They are commonly used as decision-making, problem-solving, system designing, and educational tools.
Solving complex problems can be achieved through systems thinking, a process that fits the problem, and system dynamics, which is an approach to model systems by emphasizing their feedback loops.
The systems thinking diagrams help us to understand complex systems and problems. Here is a step-by-step guide to create them.
Systems thinking is an approach that considers a situation or problem holistically and as part of an overall system which is more than the sum of its parts. Taking the big picture perspective, and looking more deeply at underpinnings, systems thinking seeks and offers long-term and fundamental solutions rather than quick fixes and surface change.
Design the flow of solving problems using Problem Flow Diagram. Our Problem Flow Diagram software comes with a full set of Problem Flow Diagram icons and connectors that allows you to easily visualize your solution.
Source: Business School, McKinsey, "Bulletproof Problem Solving" by Charles Conn and Robert McLean The Mutually Exclusive Collectively Exhaustive diagram plots the levers and impacts in ...
Effective problem solving is critical for success. Learn the necessary skills, best practices, and creative techniques to identify causes and solutions.
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
In general, a flowchart is a diagram that uses different symbols to visually present the flow of data. By looking at a flow chart one can understand the operations and sequence of operations performed in a system. This is why flowchart is often considered as a blueprint of a design used for solving a specific problem.
Also called: cause-and-effect diagram, Ishikawa diagram. This cause analysis tool is considered one of the seven basic quality tools. The fishbone diagram identifies many possible causes for an effect or problem. It can be used to structure a brainstorming session.
Why Britain Just Ended 14 Years of Conservative Rule Last week, the center-left Labour Party won the British general election in a landslide.