Sling is now Sling by Toast! Learn more
More Features

- Restaurants
- Get Started


Restaurant Business Plan: What To Include, Plus 8 Examples
- Business Growth & Management , Templates & Guides
Do you want to ensure the success of your new foodservice endeavor? Write a restaurant business plan.
In this article, the experts at Sling tell you why a business plan is vital for both new and existing businesses and give you tips on what to include.
Table Of Contents
What Is A Restaurant Business Plan?
Why is a restaurant business plan important, questions to ask first, what to include in an effective restaurant business plan, how to format a restaurant business plan, efficient workforce management is essential for success.

At its most basic, a restaurant business plan is a written document that describes your restaurant’s goals and the steps you will take to make those goals a reality.
This business plan also describes the nature of the business itself, financial projections, background information, and organizational strategies that govern the day-to-day activity of your restaurant.

A restaurant business plan is vital for the success of your endeavor because, without one, it is very difficult — sometimes even impossible — to obtain funding from an investor or a bank.
Without that all-important starting or operational capital, you may not be able to keep your doors open for long, if at all.
Even if funding isn’t a primary concern, a business plan provides you — the business owner or manager — with clear direction on how to translate general strategies into actionable plans for reaching your goals.
The plan can help solidify everything from the boots-on-the-ground functional strategy to the mid-level business strategy all the way up to the driving-force corporate strategy .
Think of this plan as a roadmap that guides your way when things are going smoothly and, more importantly, when they aren’t.
If you want to give your restaurant the best chance for success, start by writing a business plan.

Sitting down to write a restaurant business plan can be a daunting task.
As you’ll see in the What To Include In An Effective Restaurant Business Plan section below, you’ll need a lot of information and detail to ensure that the final document is both complete and effective.
Instead of starting with word one, it is hugely beneficial to answer a number of general questions first.
These questions will help you narrow down the information to include in your plan so the composition process feels less difficult.
The questions are:
- What problem does the business’s product or service solve?
- What niche will the business fill?
- What is the business’s solution to the problem?
- Who are the business’s customers?
- How will the business market and sell its products to them?
- What is the size of the market for this solution?
- What is the business model for the business?
- How will the business make money?
- Who are the competitors?
- How will the business maintain a competitive advantage?
- How does the business plan to manage growth?
- Who will run the business?
- What makes those individuals qualified to do so?
- What are the risks and threats confronting the business?
- What can you do to mitigate those risks and threats?
- What are the business’s capital and resource requirements?
- What are the business’s historical and projected financial statements?
Depending on your business, some of these questions may not apply or you may not have applicable answers.
Nevertheless, it helps to think about, and try to provide details for, the whole list so your finished restaurant business plan is as complete as possible.
Once you’ve answered the questions for your business, you can transfer a large portion of that information to the business plan itself.
We’ll discuss exactly what to include in the next section.
In this section, we’ll show you what to include in an effective restaurant business plan and provide a brief example of each component.
1) Executive Summary
You should always start any business plan with an executive summary. This gives the reader a brief introduction into common elements, such as:
- Mission statement
- Overhead costs
- Labor costs
- Return on investment (ROI)
This portion of your plan should pique the reader’s interest and make them want to read more.
Fanty & Mingo’s is a 50-seat fine-dining restaurant that will focus on Sweruvian (Swedish/Peruvian) fusion fare.
We will keep overhead and labor costs low thanks to simple but elegant decor , highly skilled food-prep staff, and well-trained servers.
Because of the location and surrounding booming economy, we estimate ROI at 20 percent per annum.
2) Mission Statement
A mission statement is a short description of what your business does for its customers, employees, and owners.
This is in contrast to your business’s vision statement which is a declaration of objectives that guide internal decision-making.
While the two are closely related and can be hard to distinguish, it often helps to think in terms of who, what, why, and where.
The vision statement is the where of your business — where you want your business to be and where you want your customers and community to be as a result.
The mission statement is the who , what , and why of your business — it’s an action plan that makes the vision statement a reality
Here’s an example of a mission statement for our fictional company:
Fanty and Mingo’s takes pride in making the best Sweruvian food, providing fast, friendly, and accurate service. It is our goal to be the employer of choice and offer team members opportunities for growth, advancement, and a rewarding career in a fun and safe working environment.
3) Company Description

In this section of your restaurant business plan, you fully introduce your company to the reader. Every business’s company description will be different and include its own pertinent information.
Useful details to include are:
- Owner’s details
- Brief description of their experience
- Legal standing
- Short-term goals
- Long-term goals
- Brief market study
- An understanding of the trends in your niche
- Why your business will succeed in these market conditions
Again, you don’t have to include all of this information in your company description. Choose the ones that are most relevant to your business and make the most sense to communicate to your readers.
Fanty & Mingo’s will start out as an LLC, owned and operated by founders Malcolm Reynolds and Zoe Washburne. Mr. Reynolds will serve as managing partner and Ms. Washburne as general manager.
We will combine atmosphere, friendly and knowledgeable staff, and menu variety to create a unique experience for our diners and to reach our goal of high value in the fusion food niche.
Our gross margin is higher than industry average, but we plan to spend more on payroll to attract the best team.
We estimate moderate growth for the first two years while word-of-mouth about our restaurant spreads through the area.
4) Market Analysis
A market analysis is a combination of three different views of the niche you want to enter:
- The industry as a whole
- The competition your restaurant will face
- The marketing you’ll execute to bring in customers
This section should be a brief introduction to these concepts. You can expand on them in other sections of your restaurant business plan.
The restaurant industry in our chosen location is wide open thanks in large part to the revitalization of the city’s center.
A few restaurants have already staked their claim there, but most are bars and non-family-friendly offerings.
Fanty & Mingo’s will focus on both tourist and local restaurant clientele. We want to bring in people that have a desire for delicious food and an exotic atmosphere.
We break down our market into five distinct categories:
- High-end singles
- Businessmen and businesswomen
We will target those markets to grow our restaurant by up to 17 percent per year.

Every restaurant needs a good menu, and this is the section within your restaurant business plan that you describe the food you’ll serve in as much detail as possible.
You may not have your menu design complete, but you’ll likely have at least a handful of dishes that serve as the foundation of your offerings.
It’s also essential to discuss pricing and how it reflects your overall goals and operating model. This will give potential investors and partners a better understanding of your business’s target price point and profit strategy.
We don’t have room to describe a sample menu in this article, but for more information on menu engineering, menu pricing, and even a menu template, check out these helpful articles from the Sling blog:
- Menu Engineering: What It Is And How It Can Increase Profits
- Restaurant Menu Pricing: 7 Tips To Maximize Profitability
- How To Design Your Menu | Free Restaurant Menu Template
6) Location
In this section, describe your potential location (or locations) so that you and your investors have a clear image of what the restaurant will look like.
Include plenty of information about the location — square footage, floor plan , design , demographics of the area, parking, etc. — to make it feel as real as possible.
We will locate Fanty & Mingo’s in the booming and rapidly expanding downtown sector of Fort Wayne, Indiana.
Ideally, we will secure at least 2,000 square feet of space with a large, open-plan dining room and rich color scheme near the newly built baseball stadium to capitalize on the pre- and post-game traffic and to appeal to the young urban professionals that live in the area.
Parking will be available along side streets and in the 1,000-vehicle parking garage two blocks away.
7) Marketing

The marketing section of your restaurant business plan is where you should elaborate on the information you introduced in the Market Analysis section.
Go into detail about the plans you have to introduce your restaurant to the public and keep it at the top of their mind.
Fanty & Mingo’s will employ three distinct marketing tactics to increase and maintain customer awareness:
- Word-of-mouth/in-restaurant marketing
- Partnering with other local businesses
- Media exposure
We will direct each tactic at a different segment of our potential clientele in order to maximize coverage.
In the process of marketing to our target audience, we will endeavor to harness the reach of direct mail and broadcast media, the exclusivity of the VIP party, and the elegance of a highly trained sommelier and wait staff.
8) Financials
Even though the Financials section is further down in your restaurant business plan, it is one of the most important components for securing investors and bank funding.
We recommend hiring a trained accountant to help you prepare this section so that it will be as accurate and informative as possible.
Fanty & Mingo’s needs $250,000 of capital investment over the next year and a half for the following:
- Renovations to leased space
- Dining room furniture
- Kitchen and food-prep equipment
- Liquor license
Projected profit and loss won’t jump drastically in the first year, but, over time, Fanty & Mingo’s will develop its reputation and client base. This will lead to more rapid growth toward the third and fourth years of business.

Most entrepreneurs starting a new business find it valuable to have multiple formats of their business plan.
The information, data, and details remain the same, but the length and how you present them will change to fit a specific set of circumstances.
Below we discuss the four most common business plan formats to cover a multitude of potential situations.
Elevator Pitch
An elevator pitch is a short summary of your restaurant business plan’s executive summary.
Rather than being packed full of details, the elevator pitch is a quick teaser of sorts that you use on a short elevator ride (hence the name) to stimulate interest in potential customers, partners, and investors
As such, an effective elevator pitch is between 30 and 60 seconds and hits the high points of your restaurant business plan.
A pitch deck is a slide show and oral presentation that is designed to stimulate discussion and motivate interested parties to investigate deeper into your stakeholder plan (more on that below).
Most pitch decks are designed to cover the executive summary and include key graphs that illustrate market trends and benchmarks you used (and will use) to make decisions about your business.
Some entrepreneurs even include time and space in their pitch deck to demonstrate new products coming down the pipeline.
This won’t necessarily apply to a restaurant business plan, but, if logistics permit, you could distribute small samples of your current fare or tasting portions of new dishes you’re developing.
Stakeholder Plan (External)
A stakeholder plan is the standard written presentation that business owners use to describe the details of their business model to customers, partners, and potential investors.
The stakeholder plan can be as long as is necessary to communicate the current and future state of your business, but it must be well-written, well-formatted, and targeted at those looking at your business from the outside in.
Think of your stakeholder plan as a tool to convince others that they should get involved in making your business a reality. Write it in such a way that readers will want to partner with you to help your business grow.
Management Plan (Internal)
A management plan is a form of your restaurant business plan that describes the details that the owners and managers need to make the business run smoothly.
While the stakeholder plan is an external document, the management plan is an internal document.
Most of the details in the management plan will be of little or no interest to external stakeholders so you can write it with a higher degree of candor and informality.
After you’ve created your restaurant business plan, it’s time to take steps to make it a reality.
One of the biggest challenges in ensuring that your business runs smoothly and successfully is managing and optimizing your team. The Sling app can help.
Sling not only includes powerful and intuitive artificial-intelligence-based scheduling tools but also many other features to help make your workforce management more efficient, including:
- Time and attendance tracking
- Built-in time clock
- Labor cost optimization
- Data analysis and reporting
- Messaging and communication
- And much more…
With Sling, you can schedule faster, communicate better, and organize and manage your work from a single, integrated platform. And when you use Sling for all of your scheduling needs, you’ll have more time to focus on bringing your restaurant business plan to life.
For more free resources to help you manage your business better, organize and schedule your team, and track and calculate labor costs, visit GetSling.com today.
See Here For Last Updated Dates: Link
This content is for informational purposes and is not intended as legal, tax, HR, or any other professional advice. Please contact an attorney or other professional for specific advice.
Find the article useful? Share with others:
Related articles

How To Write Your Ideal Restaurant Mission Statement + 15 Inspiring Examples
Whether you run a one-person food cart, a small eatery with fewer than five empl...

12 Examples of Small Business Goals, Plus How to Achieve Your Own
Want to improve the way your business operates? Learn some of the more common bu...

55 Restaurant Marketing Tips To Win Your Market
Discover the best restaurant marketing tips and learn how you can harness onlin...
Get started today
Schedule faster, communicate better, get things done.
ZenBusinessPlans
100+ Sample Food Business Plans and Templates
Food generally is an essential consumable item. A lot of entrepreneurs these days are seriously on the lookout for profitable and trending food business ideas to start a new business. Choosing the right niche is the first and most important step for any business initiative.
Increasing population and desire to have easy access to food are the factors that create more opportunities in the food industry. Starting up a business is the best way to get out of the rat race and into being your own boss. But when it comes to the food industry, there are many things that can go wrong.
Even before the pandemic, restaurant owners were finding it difficult to fill chef spaces. But since COVID became a worldwide problem, this situation has become worse. The shutting down of social places meant that long-time workers in the food business have swapped to new job roles.
Don’t let this doom and gloom put you off, though, as we have some amazing ideas to help you get past these struggles and create a successful food business in 2023! If you keep your business small before you try reaching for the stars, you will be more likely to push through those barriers.
Sample Business Plans for Food Industry
1. charcuterie business plan.
Charcuterie is a display of prepared meats paired with cheeses and plain vegetables on a traditional board. Charcuterie is the culinary art of preparing meat products such as bacon, salami, ham, sausage, terrines, galantines, ballotines, pâtés, and confit professionally. Till today, this has remained a popular way to feed guests on a budget for small parties or wine tastings, and a person that prepares charcuterie is called a Charcutier.
2. Food Truck Business Plan
We said we would talk about food trucks, and here we are! A food truck is the best way to get your meals and hot snacks to festival-goers, but you can also use them like a classic restaurant. Some people set up shop in a location, clamp their truck to the floor and buy benches for their customers to sit on.
You still have that fun alfresco feeling without having to pay for top restaurant prices. We suggest using a food truck if your concepts aren’t time-consuming. If you have a dish that takes a long time to create, then your customers will be less likely to stick around for their meal.
This is because trucks are considered a fast food option. Instead of a normal fast food restaurant, though, many customers expect a more exciting menu from a truck in comparison.
The burgers are more than just a burger; they have 5 extra ingredients that make your mouth water from just smelling it. You can afford to be more creative in a food truck, as you won’t have to pay the same licenses or permits. This means you can use more ingredients and charge the same price as a normal burger.
3. Nano Brewery Business Plan
In simple terms, a nano brewery is a brewery (plant) that produces a small amount of beer per time; it is a small-scale brewery that can’t be compared to conventional brewery plants or microbrewery plants and it is usually owned independently. Any entrepreneur that has some cash and brewing technique can comfortably start his or her own nano brewery business.
4. Religious Coffee Shop Business Plan
According to reports, 7 in 10 Americans drink coffee every week; 62% drink coffee every day, making it second only to water. There are over 24,000 coffee shops in the United States, with an average sell rate of 230 cups per day.
Truth be told, coffee has become a crucial part of a cultural revolution, and owing to some amazing trends, it seems that growth will continue. Churches, ministries, and entrepreneurs in the United States are beginning to leverage coffee’s popularity and are gradually turning it into an opportunity for outreach and faith development.
5. Cocktail Bar Business Plan
A cocktail bar is a bar or small restaurant where cocktails are the main drinks available; a characteristic feature of many standard cocktail bars is a wide selection of assorted cocktail drinks available by the glass. A cocktail is a mixed drink typically made with a distilled beverage (such as gin, brandy, vodka, whiskey, tequila, cachaça, or rum) that is mixed with other ingredients. If beer is one of the ingredients, the drink is called a beer cocktail.
6. Fruit Juice Shop Business Plan
A fruit juice bar, or fruit juice shop is a small, informal restaurant where juice and in most cases, smoothies are made and served to customers. Fruit juice is ideally 100 percent pure juice made from the flesh of fresh fruit or from whole fruit, depending on the type used.
7. Cold Storage Business Plan
A cold storage business is a commercial facility for storing perishable products such as fruits, vegetables, meat, fish, furs, etc. under controlled conditions for longer periods. Based on the storage conditions, cold storage may be classified into three categories – short-term or temporary storage, long-term storage, and frozen storage.
Available data shows that the U.S. cold storage market size was estimated at USD 15.84 billion in 2019 and is expected to reach USD 16.43 billion in 2020.
8. Funnel Cake Business Plan
A funnel cake shop is a business that bakes and sells funnel cakes. Please note that the name “funnel cake” was derived from the method of squeezing batter through a funnel in a circular pattern into hot oil to achieve a dizzying pattern of crispy-fried dough.
The funnel cake business is a niche idea in the cake and bakery industry and available statistics have it that the global bakery product market size was estimated at USD 203.8 billion in 2018.
9. Fig and Coconut Jam Business Plan
A fig and coconut jam production company is a niche jam, jelly, and preserves business that produces and sells fig and coconut jam. Fig and coconut jam can be used like other jams as a fruit spread for toast, scones, cakes, and other baked goods, and it can also be used as a condiment for savory foods.
10. Cotton Candy Business Plan
A cotton candy business is a business that makes and sells cotton candies most especially at children’s parties, parks, stadiums et al. Cotton candy, which is also known as fairy floss and candy floss, is a spun-sugar confection that resembles cotton. The U.S. candy market is expected to reach a value of USD 19.6 billion by 2025, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc.
11. Hot Dog Vendor Business Plan
A hot dog vendor business is a business that sells different types of hot dogs and drinks from a shop, cart, or food truck. Hot dogs are prepared commercially by mixing the ingredients (meats, spices, binders, and fillers) in vats where rapidly moving blades grind and mix them all together. This mixture is forced through tubes for cooking.
The market size of the Hot Dog and Sausage Production industry is $19.2bn in 2023 and the industry is expected to increase by 3.6 percent going forward.
12. Crepe Restaurant Business Plan
A crepe restaurant is a niche restaurant that serves crepes (pancakes) as its main menu. A crepe is a French pancake that is made with a thin batter containing flour, eggs, melted butter, salt, milk, and water. Crepes can be filled with a variety of sweet or savory mixtures. Savory buckwheat crepes are always served for lunch and dinner in a crepe restaurant while sweet crepes are for dessert or snack.
13. Food Hub Business Plan
A food hub business as defined by the USDA is “a centrally located facility with a business management structure facilitating the aggregation, storage, processing, distribution, and/or marketing of locally/regionally produced food products.
Food hubs also fill gaps in food system infrastructures, such as transportation, product storage, and product processing. Available data shows that there are about 212 food hubs in the United States and industry data indicates that local food sales totaled at least $12 billion in 2014 and estimates that the market value could hit $20 billion.
Before Starting a Food Business, Test your idea
First off, you should be testing your ideas before putting a deposit on a business loan. Finding the problems early on will stop you from diving into a money pit. Use our advice like a checklist to guide you through this testing phase, and be ready to receive criticism. Remember, you cannot improve or create a strong foundation if you ignore everyone’s advice.
a. Feedback From 3rd Parties
The main reason why people think about creating a food business is because their friends or family say they should. They drool over your stews, make heart-eyes over your steaks, and lovingly long for another bite. Well, in reality, your friends and family are probably boosting your ego or sugar-coating their reaction.
We aren’t saying they are lying necessarily, but they might ignore some of your poorer meals because they know you are trying your best. Your customers won’t be so forgiving. To make sure your friends aren’t saying you are better than you are, you need a true third party to judge your food tasting sessions.
You could ask your co-workers to take the plate and make an anonymous comment. If they are mostly positive, that’s great; you can then adjust your recipes, packaging, service standards in accordance with all the positive and negative feedback.
You could also talk to local companies in the same area of business as you. Ask them if your packaging is appropriate, if they have advice for a new business owner, and anything else that you are worried about. Doing this beginner networking is a great way to start a community too. Local businesses are normally more friendly than chains and will be happy to help you on your journey.
b. Perfect “One Food” Business idea At A Time
You might feel as though you need a whole menu of amazing food, but in reality, you have to remember that you are starting at the bottom. Having one fantastic idea and putting a lot of effort into it would be a more successful business venture than spreading your ideas too thin.
When it comes to testing, your test group may become overwhelmed if they are given too many options. It wouldn’t be uncommon for the group to start comparing dishes to each other rather than their normal experiences.
In the testing group, you want these “customers” to tell you if your ideas will make it, if they are good enough to be sold and if there is a problem that can be fixed. If they have a lot to look at, they will simply tell you which one is the best. Once you find the best variation of that one food product, you can then start to work on another.
c. Look After The “Other” 20% Of Your Online Food Order Customers
There are normally 3 types of customers in the food industry; the ones who enjoy your food enough to try it again another time or simply not dismiss it; ones who will absolutely love your food and will keep coming back; and those who like to try new foods on a whim.
If the first type of person doesn’t like your food, they will simply not return. If the second type of person has a bad experience, they will try again. If this second visit redeems the food, they will remain loyal, but if it doesn’t save their experience, they will either drop into the first type or not come back.
Depending on how good your business is, you might have either a large percentage of lovers and a low percentage of “it’s fine” ers, or it can be the other way around. However, around 20% of your customers will likely be the third type.
Going to restaurants and vendors or trying new sweets on a whim is a growing hobby for many people. The third type wants to be the first ones to experience this unique and potentially viral adventure. These people will likely make a review on whatever social media network they use, and this can either boom or bury your business.
These people will not hesitate to share their lengthy and detailed opinions about your business. Of course, you should always take these opinions with a pinch of salt, as a negative review on a blog often gets more traction than a positive one; however, you should take note of what they are saying. Pleasing these reviewers will make your business look good online, and it can help you create a big fan base.

How To Write a Winning Food Business Plan + Template

Creating a business plan is essential for any business. Still, it can be beneficial for food businesses that want to improve their strategy or raise funding.
A well-crafted business plan not only outlines the vision for your company but also documents a step-by-step roadmap of how you will accomplish it. To create an effective business plan, you must first understand the components essential to its success.
This article provides an overview of the key elements that every food business owner should include in their business plan.
Download the Ultimate Business Plan Template
What is a Food Business Plan?
A food business plan is a formal written document describing your company’s business strategy and feasibility. It documents the reasons you will be successful, your areas of competitive advantage, and it includes information about your team members. Your business plan is a key document that will convince investors and lenders (if needed) that you are positioned to become a successful venture.
Why Write a Food Business Plan?
A food business plan is required for banks and investors. The document is a clear and concise guide to your business idea and the steps you will take to make it profitable.
Entrepreneurs can also use this as a roadmap when starting their new company or venture, especially if they are inexperienced in starting a business.
Writing an Effective Food Business Plan
The following are the key components of a successful food business plan:
Executive Summary
The executive summary of a food business plan is a one- to two-page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which you will present in full in the rest of your business plan.
- Start with a one-line description of your food company
- Provide a short summary of the key points in each section of your business plan, which includes information about your company’s management team, industry analysis, competitive analysis, and financial forecast among others.
Company Description
This section should include a brief history of your company. Include a short description of how your company started, and provide a timeline of milestones your company has achieved.
If you are just starting your food business, you may not have a long company history. Instead, you can include information about your professional experience in this industry and how and why you conceived your new venture. If you have worked for a similar company before or have been involved in an entrepreneurial venture before starting your food firm, mention this.
Industry Analysis
The industry or market analysis is an important component of a food business plan. Conduct thorough market research to determine industry trends and document the size of your market.
Questions to answer include:
- What part of the food industry are you targeting?
- How big is the market?
- What trends are happening in the industry right now (and if applicable, how do these trends support your company’s success)?
You should also include sources for the information you provide, such as published research reports and expert opinions.
Customer Analysis
This section should include a list of your target audience(s) with demographic and psychographic profiles (e.g., age, gender, income level, profession, job titles, interests). You will need to provide a profile of each customer segment separately, including their needs and wants.
For example, a food business’ customers may include restaurants, grocery stores, caterers, and food trucks.
You can include information about how your customers make the decision to buy from you as well as what keeps them buying from you.
Develop a strategy for targeting those customers who are most likely to buy from you, as well as those that might be influenced to buy your products or food services with the right marketing.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis helps you determine how your product or service will be different from competitors, and what your unique selling proposition (USP) might be that will set you apart in this industry.
For each competitor, list their strengths and weaknesses. Next, determine your areas of competitive differentiation and/or advantage; that is, in what ways are you different from and ideally better than your competitors.
Below are sample competitive advantages your food business may have:
- Unique menu items
- Strong industry reputation
- Proven track record of success
- Low-cost production
- Local sourcing
Marketing Plan
This part of the business plan is where you determine and document your marketing plan. . Your plan should be clearly laid out, including the following 4 Ps.
- Product/Service : Detail your product/service offerings here. Document their features and benefits.
- Price : Document your pricing strategy here. In addition to stating the prices for your products/services, mention how your pricing compares to your competition.
- Place : Where will your customers find you? What channels of distribution (e.g., partnerships) will you use to reach them if applicable?
- Promotion : How will you reach your target customers? For example, you may use social media, write blog posts, create an email marketing campaign, use pay-per-click advertising, launch a direct mail campaign. Or you may promote your food business via word-of-mouth marketing or by exhibiting at food trade shows.
Operations Plan
This part of your food business plan should include the following information:
- How will you deliver your product/service to customers? For example, will you do it in person or over the phone only?
- What infrastructure, equipment, and resources are needed to operate successfully? How can you meet those requirements within budget constraints?
The operations plan is where you also need to include your company’s business policies. You will want to establish policies related to everything from customer service to pricing, to the overall brand image you are trying to present.
Finally, and most importantly, in your Operations Plan, you will lay out the milestones your company hopes to achieve within the next five years. Create a chart that shows the key milestone(s) you hope to achieve each quarter for the next four quarters, and then each year for the following four years. Examples of milestones for a food business include reaching $X in sales. Other examples include expanding to a second location or launching a new product line.
Management Team
List your team members here including their names and titles, as well as their expertise and experience relevant to your specific food industry. Include brief biography sketches for each team member.
Particularly if you are seeking funding, the goal of this section is to convince investors and lenders that your team has the expertise and experience to execute on your plan. If you are missing key team members, document the roles and responsibilities you plan to hire for in the future.
Financial Plan
Here you will include a summary of your complete and detailed financial plan (your full financial projections go in the Appendix).
This includes the following three financial statements:
Income Statement
Your income statement should include:
- Revenue : how much revenue you generate.
- Cost of Goods Sold : These are your direct costs associated with generating revenue. This includes labor costs, as well as the cost of any equipment and supplies used to deliver the product/service offering.
- Net Income (or loss) : Once expenses and revenue are totaled and deducted from each other, this is the net income or loss.
Sample Income Statement for a Startup Food Business
| Revenues | $ 336,090 | $ 450,940 | $ 605,000 | $ 811,730 | $ 1,089,100 |
| $ 336,090 | $ 450,940 | $ 605,000 | $ 811,730 | $ 1,089,100 | |
| Direct Cost | |||||
| Direct Costs | $ 67,210 | $ 90,190 | $ 121,000 | $ 162,340 | $ 217,820 |
| $ 67,210 | $ 90,190 | $ 121,000 | $ 162,340 | $ 217,820 | |
| $ 268,880 | $ 360,750 | $ 484,000 | $ 649,390 | $ 871,280 | |
| Salaries | $ 96,000 | $ 99,840 | $ 105,371 | $ 110,639 | $ 116,171 |
| Marketing Expenses | $ 61,200 | $ 64,400 | $ 67,600 | $ 71,000 | $ 74,600 |
| Rent/Utility Expenses | $ 36,400 | $ 37,500 | $ 38,700 | $ 39,800 | $ 41,000 |
| Other Expenses | $ 9,200 | $ 9,200 | $ 9,200 | $ 9,400 | $ 9,500 |
| $ 202,800 | $ 210,940 | $ 220,871 | $ 230,839 | $ 241,271 | |
| EBITDA | $ 66,080 | $ 149,810 | $ 263,129 | $ 418,551 | $ 630,009 |
| Depreciation | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 4,200 |
| EBIT | $ 60,880 | $ 144,610 | $ 257,929 | $ 413,351 | $ 625,809 |
| Interest Expense | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 |
| $ 53,280 | $ 137,010 | $ 250,329 | $ 405,751 | $ 618,209 | |
| Taxable Income | $ 53,280 | $ 137,010 | $ 250,329 | $ 405,751 | $ 618,209 |
| Income Tax Expense | $ 18,700 | $ 47,900 | $ 87,600 | $ 142,000 | $ 216,400 |
| $ 34,580 | $ 89,110 | $ 162,729 | $ 263,751 | $ 401,809 | |
| 10% | 20% | 27% | 32% | 37% | |
Balance Sheet
Include a balance sheet that shows your assets, liabilities, and equity. Your balance sheet should include:
- Assets : All of the things you own (including cash).
- Liabilities : This is what you owe against your company’s assets, such as accounts payable or loans.
- Equity : The worth of your business after all liabilities and assets are totaled and deducted from each other.
Sample Balance Sheet for a Startup Food Business
| Cash | $ 105,342 | $ 188,252 | $ 340,881 | $ 597,431 | $ 869,278 |
| Other Current Assets | $ 41,600 | $ 55,800 | $ 74,800 | $ 90,200 | $ 121,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $ 146,942 | $ 244,052 | $ 415,681 | $ 687,631 | $ 990,278 |
| Fixed Assets | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 |
| Accum Depreciation | $ 5,200 | $ 10,400 | $ 15,600 | $ 20,800 | $ 25,000 |
| Net fixed assets | $ 19,800 | $ 14,600 | $ 9,400 | $ 4,200 | $ 0 |
| $ 166,742 | $ 258,652 | $ 425,081 | $ 691,831 | $ 990,278 | |
| Current Liabilities | $ 23,300 | $ 26,100 | $ 29,800 | $ 32,800 | $ 38,300 |
| Debt outstanding | $ 108,862 | $ 108,862 | $ 108,862 | $ 108,862 | $ 0 |
| $ 132,162 | $ 134,962 | $ 138,662 | $ 141,662 | $ 38,300 | |
| Share Capital | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Retained earnings | $ 34,580 | $ 123,690 | $ 286,419 | $ 550,170 | $ 951,978 |
| $ 34,580 | $ 123,690 | $ 286,419 | $ 550,170 | $ 951,978 | |
| $ 166,742 | $ 258,652 | $ 425,081 | $ 691,831 | $ 990,278 | |
Cash Flow Statement
Include a cash flow statement showing how much cash comes in, how much cash goes out and a net cash flow for each year. The cash flow statement should include:
- Cash Flow From Operations
- Cash Flow From Investments
- Cash Flow From Financing
Below is a sample of a projected cash flow statement for a startup food business.
Sample Cash Flow Statement for a Startup Food Business
| Net Income (Loss) | $ 34,580 | $ 89,110 | $ 162,729 | $ 263,751 | $ 401,809 |
| Change in Working Capital | $ (18,300) | $ (11,400) | $ (15,300) | $ (12,400) | $ (25,300) |
| Plus Depreciation | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 4,200 |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $ 21,480 | $ 82,910 | $ 152,629 | $ 256,551 | $ 380,709 |
| Fixed Assets | $ (25,000) | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | $ (25,000) | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Cash from Equity | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Cash from Debt financing | $ 108,862 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ (108,862) |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $ 108,862 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ (108,862) |
| Net Cash Flow | $ 105,342 | $ 82,910 | $ 152,629 | $ 256,551 | $ 271,847 |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $ 0 | $ 105,342 | $ 188,252 | $ 340,881 | $ 597,431 |
| Cash at End of Period | $ 105,342 | $ 188,252 | $ 340,881 | $ 597,431 | $ 869,278 |
You will also want to include an appendix section which will include:
- Your complete financial projections
- A complete list of your company’s business policies and procedures related to the rest of the business plan (marketing, operations, etc.)
- Any other documentation which supports what you included in the body of your business plan.
A well-written food business plan is a critical tool for any entrepreneur looking to start or grow their food company. It not only outlines your business vision but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it.
Finish Your Food Business Plan in 1 Day!
- Purchase History

Business Plan Template for a Food and Beverage Business
by I.J. Karam | Jan 12, 2023 | Business Plans

A business plan is an essential tool for any entrepreneur looking to start a food and beverage business. It outlines the goals and strategies for your company, and serves as a roadmap for success. In this guide, we will walk you through the process of creating a business plan for your food and beverage business, covering everything from market research and financial projections to marketing and operations. Whether you’re looking to open a restaurant, a food truck, or a catering business, this food and beverage business plan template guide will provide you with all the information you need to get started.
Before we start, we suggest you check our ready-made Food & Beverage business plan templates in Word with automatic financial plans in Excel. They will save you tons of time and efforts and will help you build a restaurant, food truck or any other type of F&B business plan in record time.
Now, let’s dive in and learn how to create a business plan for your food and beverage business.
Executive Summary for an F&B Business Plan
An executive summary is a brief overview of the main points of your business plan. It should be written last, after the rest of the plan has been completed, and should be no more than two pages long. In the executive summary for a food and beverage business, you should include the following key points:
- Business concept: Explain what your business is, what products or services you will offer, and what makes your business unique.
- Target market: Describe your target customers and the market you will be serving.
- Financial projections: Summarize your financial projections, including projected sales and profits.
- Management and ownership: Outline the management and ownership structure of your business, including key members of your team and their qualifications.
- Marketing and sales strategy: Explain how you plan to market and sell your products or services, including your pricing strategy and how you will reach your target market.
- Operations plan: Describe your operations plan, including how you will source ingredients, prepare and serve your products, and manage your inventory.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points of your business plan and explain why you believe your business will be successful.
The executive summary serves as an introduction to your business plan, and should be written in clear, concise language that is easy for potential investors or lenders to understand.
Here is a sample executive summary for an F&B business:
Our business, [Business Name], is a new restaurant concept that specializes in serving locally sourced, organic, and sustainable cuisine. We will offer a range of dishes that cater to a variety of dietary restrictions and preferences, including vegetarian, vegan, and gluten-free options.
Our target market is health-conscious individuals and families in the [city/region] area who are looking for delicious and nutritious meal options. We have conducted extensive market research and have identified a strong demand for our type of food in the area.
We project sales of $500,000 in the first year, with a profit margin of 8%. Our restaurant will be owned and managed by [name], a seasoned restaurant professional with over 10 years of experience in the industry. Our team also includes a highly skilled head chef, a marketing expert, and a dedicated operations manager.
To reach our target market, we will launch an extensive marketing campaign that includes social media advertising, email marketing, and local collaborations. We will also offer a loyalty program and host events and promotions to attract customers.
Our restaurant will have a fully equipped kitchen, a dedicated prep area, and a stylish dining area that can accommodate up to 50 customers. We will source ingredients from local farmers and producers, and will have strict quality control measures in place to ensure that all dishes are prepared to the highest standards.
We are confident that our unique concept, experienced team, and comprehensive business plan will position us for success in the competitive food and beverage market. We are excited to bring our delicious and nutritious food to the community and become a go-to destination for healthy and sustainable dining options
The Problem Opportunity
In this section you need to cite the key problems encountered in the Food and Beverage (F&B) Industry and then show how your own business will solve in an effective manner.
As an example, key problems in the F&B industry can include:
- High competition in the market
- Rising food and labor costs
- Seasonal fluctuations in demand
- Limited access to funding
Here are potent solutions that your F&B business may want to offer to solve the above cited problems:
- Differentiate your business and offer a unique dining experience, conduct market research and tailor your offering to the needs of your target audience, and utilize effective marketing techniques to build brand awareness and reach new customers. Foster customer loyalty through loyalty programs or other incentives.
- Implement cost-saving measures and explore options for automating tasks or processes, increase efficiency by streamlining operations and implementing technology solutions, and offer value-priced menu items or promotions to attract cost-conscious customers.
- Explore options for offering products or services outside of traditional operating hours, utilize social media and other digital marketing techniques to reach new customers and increase visibility, and consider offering catering or delivery services to generate additional revenue.
- Research different funding options and create a compelling business plan, build relationships with potential investors or lenders and demonstrate the strength of your management team, and consider alternative forms of financing, such as crowdfunding or pre-sales.
Mission & Vision for a F&B Business
Mission: Our mission at [Your Company Name] is to provide our customers with a unique and enjoyable dining experience that combines high-quality food with exceptional customer service. We strive to create a warm and welcoming atmosphere that encourages customers to come back time and time again.
Vision: Our vision is to become the premier destination for [Your Cuisine] in [City/Region] and to establish ourselves as a leader in the F&B industry. We aim to achieve this through continuous innovation, the use of high-quality ingredients, and a commitment to excellence in every aspect of our business. We believe that by consistently exceeding our customers’ expectations, we can build a loyal following and achieve long-term success.
Products and Services
[Your Company Name] offers a wide range of high-quality food and beverage options to suit the tastes and preferences of our customers. Our menu features a variety of [Your Cuisine]-inspired dishes, including appetizers, entrees, and desserts. We offer a range of options to accommodate dietary preferences and restrictions, including vegetarian, vegan, and gluten-free options.
Our dishes are made with fresh, locally-sourced ingredients and prepared by our talented team of chefs. We take pride in the quality of our ingredients and the care that goes into preparing each dish. We are constantly innovating and experimenting with new flavors and techniques to keep our menu fresh and exciting.
In addition to our dining options, we also offer catering services for events of all sizes. Our catering team can create customized menus to suit the needs of your event and can provide all necessary equipment and staff to ensure a successful and stress-free event. We have experience catering a wide range of events, including weddings, corporate functions, and private parties.
We are dedicated to providing exceptional customer service and strive to create a memorable dining experience for every customer. Our team is trained to provide personalized service and to assist with any special requests or dietary needs. We have a variety of seating options available, including indoor and outdoor seating, and we offer a range of amenities to make our customers’ experience more enjoyable, such as free Wi-Fi and a selection of games and activities.
It is also a good idea to include your menu with pricing in this section:

Business Model Canvas for an F&B Business
Value Proposition:
- High-quality, delicious food made with fresh, locally-sourced ingredients.
- Exceptional customer service and a memorable dining experience.
- A wide range of menu options that cater to a variety of tastes and dietary preferences.
Customer Segments:
- Foodies: Customers who are passionate about food and are always seeking out new and exciting dining experiences.
- Health-conscious individuals: Customers who are looking for healthy and sustainable options when dining out.
- Time-poor individuals and families: Customers who are looking for convenient and quick dining options, including delivery and takeout.
- Social groups: Customers who are looking for a lively and welcoming atmosphere for group gatherings, such as birthdays, celebrations, or corporate events.
- Dine-in: Customers can visit the restaurant and enjoy their meals on-site.
- Takeout and delivery: Customers can order meals to be picked up or delivered to their homes or offices.
- Online ordering: Customers can place orders and make payments online.
- Social media: The business can use social media platforms to reach and communicate with customers.
Customer Relationships:
- Personalized service: The business will strive to create a memorable dining experience for every customer through personalized attention and care.
- Loyalty program: The business may offer a loyalty program to reward repeat customers and encourage customer retention.
- Online reviews and ratings: The business will monitor and respond to online reviews and ratings in order to maintain a positive reputation and to gather feedback from customers.
Revenue Streams:
- Sales of food and beverages: The primary source of revenue for the business will be the sale of food and beverages to customers.
- Catering services: The business may offer catering services for events such as corporate functions, parties, or weddings.
- Merchandise: The business may sell branded merchandise, such as t-shirts, hats, or tote bags.
Key Resources:
- Kitchen facilities and equipment: The business will need a fully-equipped kitchen and necessary cooking and food preparation equipment in order to prepare and serve meals.
- Staff: The business will need a team of chefs, servers, and other staff in order to operate.
- Marketing and branding materials: The business will need marketing and branding materials, such as menus, signage, and social media assets, in order to promote itself and its products and services.
Key Partners:
- Suppliers: The business will need to establish relationships with suppliers of fresh ingredients and other necessary supplies.
- Delivery partners: The business may work with third-party delivery partners in order to offer delivery services to customers.
- Event venues and organizers: The business may partner with event venues and organizers in order to provide catering services.
Key Activities:
- Menu development: The business will need to continuously develop and update its menu in order to keep it fresh and interesting.
- Food preparation and cooking: The business will need to prepare and cook meals to a high standard in order to deliver a superior product to customers.
- Customer service: The business will need to provide exceptional customer service in order to create a memorable dining experience for every customer.
- Marketing and promotion: The business will need to promote itself and its products and services in order to attract customers.
Key Expenses:
- Ingredient and supply costs: The business will incur costs for ingredients and other necessary supplies.
- Staff salaries and benefits: The business will need to pay salaries and benefits to its team of chefs, servers, and other staff.
- Rent and utilities: The business will need to pay rent and utilities for its kitchen and dining facilities.
- Marketing and promotional expenses: The business will incur costs for marketing and promotional activities.
SWOT Analysis for an F&B Business
- Strong brand recognition: Our business has a strong reputation and is well-known in the local community.
- Experienced team: Our team has a wealth of experience in the food and beverage industry and is able to provide high-quality products and services to our customers.
- High-quality ingredients: We use only the freshest and highest-quality ingredients in our dishes, which sets us apart from our competitors.
- Unique menu offerings: Our menu features a variety of unique and innovative dishes that are not offered by other restaurants in the area.
Weaknesses:
- Limited seating: Our premises have limited seating, which may limit our ability to accommodate larger groups or parties.
- Lack of online presence: We do not currently have a strong online presence, which may limit our ability to attract new customers through social media or online reviews.
- Limited catering experience: While we have experience in restaurant operations, we have limited experience in catering and events, which may be a weakness in terms of expanding into these areas.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand for healthy options: There is a growing demand for healthier options in the food and beverage industry, and we have the opportunity to capitalize on this trend by offering more plant-based and organic dishes on our menu.
- Expansion into catering and events: There is a strong demand for catering and event services in our area, and we have the opportunity to expand our business into these areas.
- Partnership opportunities: We have the opportunity to partner with other local businesses or organizations to offer special promotions or events.
- Competition: There is strong competition in the food and beverage industry, and we may face challenges from established competitors as well as new entrants to the market.
- Changes in consumer preferences: Consumer preferences may change over time, and we may need to adapt our offerings to meet the evolving needs and tastes of our customers.
- Economic downturns: Economic downturns or other external factors may impact consumer spending and could affect the demand for our products and services.
Market Trends
The food and beverage industry is a dynamic and rapidly-evolving sector, and it is important for businesses to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and developments. According to recent industry data, some of the current trends in the F&B industry include:
- Health and wellness: Consumers are increasingly seeking out healthy and sustainable options when dining out. This includes a demand for plant-based and vegetarian options, as well as a focus on locally-sourced and organic ingredients. In fact, a survey by the National Restaurant Association found that nearly 60% of consumers are more likely to visit a restaurant that offers healthy options.
- Convenience and delivery: With busy lifestyles, many consumers are looking for convenient dining options, including delivery and takeout. This trend has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has led to an increase in online ordering and contactless payment options. In fact, a report by the NPD Group found that off-premises dining, including delivery and takeout, now accounts for over half of all restaurant sales in the United States.
- Experiential dining: In addition to good food, many customers are seeking out dining experiences that are memorable and unique. This can include interactive or immersive elements, such as live music or interactive cooking demonstrations. A survey by Zagat found that 75% of consumers are willing to pay more for a unique dining experience.
- Plant-based options: The demand for plant-based options continues to grow, with many consumers looking for healthier and more sustainable options. This trend includes a wide range of plant-based alternatives, including vegetarian, vegan, and flexitarian options. A report by the Good Food Institute found that the market for plant-based meat alone is expected to reach $85 billion by 2030.
- The F&B industry is a large and growing sector, with the global food and beverage market projected to reach $31 trillion by 2024. The industry is highly competitive, with many players vying for a share of the market.
We believe that by adapting to the latest trends and offering a range of options that meet the needs and preferences of our customers, we can continue to grow and succeed in the competitive F&B industry.
Local Market Trends
Here is it a good idea to discuss how local market trends support your own F&B business idea. You can use local market report or the results of a survey you have done.
Target Customers
Our target customers are individuals and families who are seeking high-quality, delicious food and exceptional customer service. We aim to attract a diverse customer base and to appeal to a range of demographics, including:
- Foodies: Customers who are passionate about food and are always seeking out new and exciting dining experiences. These customers are typically willing to pay a premium for high-quality ingredients and innovative dishes.
- Health-conscious individuals: Customers who are looking for healthy and sustainable options when dining out. This includes a demand for plant-based, vegetarian, and vegan options, as well as a focus on locally-sourced and organic ingredients.
- Time-poor individuals and families: Customers who are looking for convenient and quick dining options, including delivery and takeout. These customers value efficiency and appreciate options that allow them to enjoy good food without spending a lot of time preparing it themselves.
- Social groups: Customers who are looking for a lively and welcoming atmosphere for group gatherings, such as birthdays, celebrations, or corporate events. These customers appreciate a range of seating options and amenities, such as outdoor seating or private dining rooms, and value personalized service.
We believe that by catering to these diverse groups and offering a range of options to meet their needs and preferences, we can establish ourselves as a premier destination for food and beverage in [City/Region].
Competitive Analysis in the local F&B Market
The food and beverage industry is highly competitive, with many players vying for a share of the market. It is important for businesses to understand the competitive landscape in order to effectively position themselves and to develop strategies for success.
Some of the key players in the [Your City/Region] market for [Your Cuisine] include:
- [Competitor 1]: This competitor is known for its wide range of menu options and convenient location. Its strengths include a diverse menu that caters to a variety of tastes and dietary preferences, as well as a central location that is easily accessible by public transportation. However, it has several weaknesses, including inconsistency in the quality of its food and a reputation for subpar customer service.
- [Competitor 2]: This competitor is known for its high-quality ingredients and innovative dishes. Its strengths include a focus on using fresh, locally-sourced ingredients and an emphasis on culinary creativity. However, it has a higher price point than some of its competitors, which may be a deterrent for some customers.
- [Competitor 3]: This competitor has a strong brand presence and a loyal customer base. Its strengths include a well-established reputation and a strong marketing campaign that has helped to build customer loyalty. However, it has limited menu options and may not appeal to customers who are looking for a wider range of choices.
Competitive Advantages
In order to differentiate ourselves from these competitors and establish a competitive advantage, we will focus on the following:
- Quality: We will use high-quality ingredients and prepare our dishes with care and attention to detail in order to deliver a superior product to our customers. This will help us to stand out from competitors who may have a reputation for inconsistency in the quality of their food.
- Service: We will provide exceptional customer service and strive to create a memorable dining experience for every customer. By focusing on personalized service and attention to detail, we can differentiate ourselves from competitors who may have a reputation for subpar customer service.
- Innovation: We will stay attuned to the latest trends and developments in the industry and will continuously innovate and experiment with new flavors and techniques in order to keep our menu fresh and exciting. This will help us to attract food-savvy customers who are always looking for new and exciting dining experiences.
- Price: While we will use high-quality ingredients and offer exceptional customer service, we will also be mindful of pricing in order to make our products and services accessible to a wider range of customers. By offering competitive pricing and value for money, we can appeal to price-sensitive customers while still delivering a high-quality product.
We believe that by focusing on these areas, we can differentiate ourselves from our competitors and establish a strong position in the market.
Operating Plan
- Menu: Our menu will feature a wide range of dishes made with fresh, locally-sourced ingredients. We will offer a mix of classic and contemporary dishes to appeal to a variety of tastes and dietary preferences, including vegetarian, vegan, and gluten-free options. We will regularly update and refresh our menu to keep it interesting and to reflect the latest trends and flavors.
- Kitchen and food preparation: Our kitchen will be fully equipped with the necessary cooking and food preparation equipment, including ovens, stoves, refrigerators, and storage facilities. We will maintain strict hygiene standards and follow all food safety regulations. Our chefs will be trained in the latest culinary techniques and will be responsible for preparing and cooking meals to a high standard.
- Service: Our service staff will be trained in the latest customer service techniques and will be responsible for providing exceptional service to our customers. They will be responsible for taking orders, serving meals, and handling payments, as well as for maintaining the cleanliness and appearance of the dining area.
- Hours of operation: Our restaurant will be open seven days a week, from [opening time] to [closing time]. We will also offer delivery and takeout services during these hours.
- Staffing: Our staff will include a team of chefs, servers, and other support personnel. We will maintain a schedule that ensures that we have sufficient staff on hand at all times to meet the needs of our customers.
- Facilities: Our restaurant will be located in a prime location, with convenient access for customers and sufficient seating and dining space to accommodate our expected volume of business. We will maintain the cleanliness and appearance of our facilities at all times.
- Suppliers: We will work with a network of trusted suppliers to source the freshest ingredients and other necessary supplies. We will maintain strong relationships with our suppliers and will work with them to ensure that we have a consistent supply of high-quality ingredients. We will also regularly review our supplier relationships to ensure that we are getting the best value for money.
- Financial management: We will use financial management software to track our income and expenses and to create financial reports. We will also maintain accurate and up-to-date records of all financial transactions.
- Legal and regulatory compliance: We will ensure that we are fully compliant with all relevant legal and regulatory requirements, including those related to food safety, employment, and business licensing. We will also carry the necessary insurance to protect our business and our customers.
- Risk management: We will identify and assess potential risks to our business and will implement measures to mitigate or prevent these risks. This may include having contingency plans in place for unexpected events or disruptions, such as natural disasters or equipment failures.
Marketing Plan for an F&B Business
Target Market:
Our target market is foodies, health-conscious individuals, time-poor individuals and families, and social groups. We will use market research to gather information about the preferences and behaviors of these customer segments and will tailor our marketing efforts to appeal to them. For example, we will use social media and email marketing to target foodies with promotions and updates about new menu items and events, and we will highlight the healthy and sustainable aspects of our ingredients and dishes to appeal to health-conscious individuals. We will also focus on the convenience and speed of our delivery and takeout services to attract time-poor individuals and families, and we will use social media and event sponsorship to promote our restaurant as a lively and welcoming place for group gatherings.
Marketing Mix:
- Product: Our products will include a wide range of dishes made with fresh, locally-sourced ingredients. We will offer a mix of classic and contemporary dishes to appeal to a variety of tastes and dietary preferences, including vegetarian, vegan, and gluten-free options. We will also offer catering services for events such as corporate functions, parties, and weddings. We will differentiate our products by highlighting their high quality and unique flavors, as well as by offering a wide range of options to cater to different tastes and preferences.
- Price: Our pricing will be competitive with other restaurants in the area, taking into account the quality of our ingredients and the level of service we provide. We will offer various pricing options, such as discounts for early bird diners and special deals for group bookings. We will also use upselling techniques to encourage customers to upgrade their meals or add extra items, such as appetizers or desserts.
- Place: Our restaurant will be located in a prime location, with convenient access for customers and sufficient seating and dining space to accommodate our expected volume of business. We will also offer delivery and takeout services to customers who prefer to dine at home. We will ensure that our restaurant is well-maintained and attractive, and that our online ordering and delivery systems are easy to use and reliable.
- Promotion: We will use a variety of marketing and promotional techniques to attract and retain customers. These may include traditional advertising methods, such as print and radio ads, as well as digital marketing techniques, such as social media and email marketing. We will also utilize word-of-mouth referrals and customer reviews to spread the word about our business. We will use social media to engage with customers and to promote our products and events, and we will use email marketing to send newsletters and special offers to our subscribers. We will also consider sponsoring local events or partnering with other businesses to reach new customers.
Marketing Budget:
Our marketing budget will be [amount] per year. This budget will be allocated to various marketing and promotional activities, such as advertising, social media marketing, email marketing, and event sponsorship. We will regularly review and adjust our marketing budget in order to ensure that we are getting the best return on investment. We will track the performance of our marketing efforts using metrics such as website traffic, social media engagement, and sales conversions, and we will use this data to optimize our campaigns and allocate our budget accordingly.
Hiring Plan
We will be hiring for the following positions:
- Chefs: We will be looking for chefs with a passion for food and a strong understanding of culinary techniques and trends. Candidates should have relevant culinary qualifications and experience, as well as strong organizational and time management skills.
- Servers: We will be looking for servers who are friendly, knowledgeable, and efficient, with a strong focus on customer service. Candidates should have experience in the hospitality industry, as well as excellent communication and interpersonal skills.
- Kitchen staff: We will be looking for kitchen staff with strong attention to detail and the ability to work well as part of a team. Candidates should have relevant food handling qualifications and experience, as well as good physical fitness and the ability to work under pressure.
Qualifications and experience: We will require all candidates to have relevant qualifications and experience for the positions they are applying for. For example, chefs will be required to have culinary qualifications and experience, while servers will be required to have experience in the hospitality industry.
Recruitment process: Our recruitment process will involve the following steps:
- Advertising: We will advertise the positions using a variety of methods, including job boards, social media, and local media.
- Resume screening: We will review resumes and cover letters to shortlist candidates who meet the minimum qualifications and experience requirements.
- Interviews: We will conduct interviews with shortlisted candidates to assess their fit for the positions and our company culture.
- Reference checks: We will contact the references provided by candidates to verify their qualifications and experience.
- Offer and acceptance: We will make job offers to successful candidates and will work with them to finalize the terms of their employment.
Selection criteria: In addition to qualifications and experience, we will also consider the following factors when making hiring decisions:
- Fit with our company culture: We will look for candidates who align with our values and who will thrive in our dynamic and collaborative work environment.
- Customer service skills: We will prioritize candidates who have strong customer service skills and who are able to create a positive and memorable dining experience for our customers.
- Teamwork and collaboration: We will look for candidates who are able to work well as part of a team and who are willing to contribute to the overall success of the business.
Financial Plan for an F&B Business
A financial plan for a food and beverage business outlines the financial projections and strategies for the business. It includes detailed information on projected income, expenses, and profits, as well as information on funding and investment.
The main components of a financial plan for an F&B business include:
- Sales forecast: A projection of the business’s expected sales over a certain period of time, usually 3-5 years. The forecast should be based on market research and should take into account the target market, competition, and pricing strategy.
- Expense budget: A detailed breakdown of the business’s expected expenses, including costs for ingredients, labor, rent, utilities, marketing, and other operational expenses.
- Profit and loss statement: A summary of the business’s projected income and expenses over a certain period of time, which helps to determine the profitability of the business.
- Break-even analysis: A calculation of the point at which the business will begin to turn a profit, taking into account fixed and variable costs.
- Cash flow statement: A projection of the business’s expected cash inflows and outflows over a certain period of time, which helps to determine the business’s liquidity.
- Funding and investment: Information on the business’s funding needs and sources, including information on loans, grants, and investments.
- Financial ratios: A set of calculations that help to evaluate the overall financial health of the business, such as profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and solvency ratios.
- Assumptions: A list of the assumptions that have been made in the financial projections, such as projected sales growth, pricing strategy, and operating costs.
For a more detailed guide on how to build a detailed financial plan for your F&B business you might be interested to check our coffee shop financial plan guide , restaurant financial plan guide , food truck financial plan guide or bakery financial plan guide .
Sales Forecast
Let’s assume that [Your Restaurant] has a seating capacity of 100 and that the occupancy rate is 63.00% in Year 1, 70.58% in Year 2 and 78.90% in Year 3.
Also let’s assume that the average check is 25 USD.
This gives us the below revenue forecast for the next three years:
Year 1: 100 x 63.00% x 365 x 25 = 574,900 USD
Year 2: 100 x 70.58% x 365 x 25 = 644,000 USD
Year 3: 100 x 78.90% x 365 x 25 = 720,000 USD
The sales forecast is shown in the chart below:

Income Statement Forecast for an F&B Business
Below you can find the profit and loss statement forecast for the next three years:
| Less COGS | (101,775) | (114,000) | (127,500) |
| Less SG&A expenses | (347,500) | (362,600) | (388,700) |
| Less depreciation | (24,750) | (27,000) | (27,000) |
| Less interest expense | – | – | – |
| Pre-tax income | 100,875 | 140,400 | 176,800 |
| Less taxes | (30,263) | (42,120) | (53,040) |
Cash Flow Statement Forecast for an F&B Business
Below you can find the statement of cash flows forecast for the next three years:
| Net income | 70,613 | 98,280 | 123,760 |
| Plus depreciation | 24,750 | 27,000 | 27,000 |
| Less increase in inventory | (10,356) | (1,719) | (675) |
| Less increase in accounts receivable | – | – | – |
| Plus increase in accounts payable | 8,512 | 1,413 | 555 |
| Less investment | (270,000) | – | – |
| Plus net new equity capital raised | 292,182 | – | – |
| Less dividends paid | – | – | – |
| Plus net new long-term debt | – | – | – |
| Plus net new bank borrowings | – | – | – |
| Beginning cash balance | – | 115,700 | 240,674 |
| Ending cash balance | 115,700 | 240,674 | 391,314 |
Balance Sheet Forecast for an F&B Business
Below you can find the balance sheet forecast for the next three years:
| Cash | 115,700 | 240,674 | 391,314 |
| Inventory | 10,356.3 | 12,075.0 | 12,750.0 |
| Accounts receivable | – | – | – |
| – | – | – | |
| Gross property, plant & equipment | 270,000 | 270,000 | 270,000 |
| Less accumulated depreciation | (24,750) | (51,750) | (78,750) |
| – | – | – | |
| Accounts payable | 8,512 | 9,925 | 10,479 |
| Bank notes payable | – | – | – |
| Long-term debt | – | – | – |
| Shareholders equity | 362,795 | 461,075 | 584,835 |
Risk Management
We will take the following measures to manage financial risks:
- Diversification: We will diversify our revenue streams by offering a range of products and services, such as catering and events, in addition to our regular restaurant operations. This will help to reduce our dependence on any one particular source of income and will provide a buffer against any downturns in the market.
- Cost control: We will regularly review our expenses and will implement cost-saving measures where possible. This could include negotiating better rates with suppliers, reducing waste and spoilage, and streamlining our operations.
- Insurance: We will carry the necessary insurance to protect our business against financial losses due to events such as accidents, natural disasters, and equipment failures. This will help to ensure that we are able to recover from any unexpected setbacks and continue to operate smoothly.
Startup Capital
Our startup capital will come from the following sources:
- Investment: [amount] from [investor/s] – We will receive investment from [investor/s] in exchange for an ownership stake in our business.
- Loans: [amount] from [lender/s] – We will take out loans from [lender/s] to finance the start-up costs of our business, such as purchasing equipment and inventory.
Our startup capital will be used to cover the following costs:
- Equipment: [amount] – This includes the cost of purchasing kitchen and dining room equipment, such as ovens, refrigerators, and furniture.
- Inventory: [amount] – This includes the cost of purchasing food and beverage items to stock our restaurant.
- Rent: [amount] – This includes the cost of leasing our premises.
- Salaries: [amount] – This includes the wages and benefits that we will pay to our employees.
- Marketing: [amount] – This includes the cost of promoting our business, such as advertising and social media marketing.
We expect that our startup capital will be sufficient to cover the costs of setting up and operating our business for the first three months. After this point, we expect to be generating sufficient revenue to cover our expenses and to begin turning a profit.
Key People / Founders
[Founder 1]
[Name] is the co-founder and CEO of [Business Name].
[He/She] has [number] years of experience in the food and beverage industry, having worked in a variety of roles in restaurants and catering companies.
[He/She] has a passion for creating innovative and delicious dishes, and has a track record of success in menu development and kitchen management.
[He/She] will be responsible for overseeing the day-to-day operations of the business, as well as developing and implementing strategies for growth and expansion.
[Founder 2]
[Name] is the co-founder and COO of [Business Name].
[He/She] has [number] years of experience in business management and finance, having worked in a variety of roles in startups and small businesses.
[He/She] has a strong understanding of financial planning and risk management, and has a track record of success in driving profitability and growth.
[He/She] will be responsible for managing the financial operations of the business, including budgeting, forecasting, and fundraising.
Key Milestones
- Finalize business plan and secure funding.
- We will finalize our business plan and secure funding from investors and/or lenders.
- This will involve presenting our plan to potential investors and negotiating the terms of investment.
- Lease premises and purchase equipment
- We will sign a lease for our restaurant premises and purchase the necessary equipment to set up our kitchen and dining room.
- This will involve conducting market research to find the best location and negotiating the terms of the lease, as well as purchasing and installing the equipment.
- Hire and train staff
- We will hire and train a team of chefs, servers, and other staff to operate our restaurant.
- This will involve advertising job openings, conducting interviews, and providing on-the-job training to ensure that our staff are prepared to provide high-quality service to our customers.
- Launch our restaurant
- We will open the doors to our restaurant and begin serving customers.
- This will involve finalizing the menu, ordering and stocking inventory, and preparing the restaurant for operation.
- Launch our catering service
- We will launch our catering service and begin accepting bookings for events.
- This will involve building a team of catering staff, developing our catering menu, and promoting our services to potential customers.
- Expand our geographical reach
- We will open a second location in a neighboring town.
- This will allow us to expand our customer base and to capture a new market.
In conclusion, our proposed F&B business is a viable and profitable venture that will meet the needs of the local community for high-quality, delicious food and beverages. Our experienced management team, strong marketing strategies, and commitment to using only the freshest, locally sourced ingredients will set us apart from our competitors. We are confident that our business plan will attract the necessary funding and support to make our vision a reality. With your support and investment, we can bring our F&B business to life and provide our customers with an unparalleled dining experience.

Download a Ready-Made Business Plan, Choose Your Industry:
- F&B Business Plans
- Services Business Plans
- Retail Business Plans
- Tourism Business Plans
- Tech Business Plans
Recent Posts
- Bed and Breakfast Business Model Canvas: A Complete Guide
- Restaurant Business Model Canvas
- How to Create a Bar Business Plan
- Gym Financial Plan Template [2024 Guide]
- Laundry Financial Plan Template [2024 Guide]
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

A SAMPLE BUSINESS PLAN FOR SMALL FOOD BUSINESSES

Related Papers
Arditya Setyawan
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Food Truck Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Food Truck Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your food truck business plan.
We have helped over 100,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their food trucks.
Food Truck Business Plan Example & Template
Below is a template to help you create each section of your food truck business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck is a new food truck located in Portland owned by local critically acclaimed chef, Zane Benedict. The menu will consist of popular food options that consist of burgers, sandwiches, gyros, and tacos uniquely made with the creativity and uniqueness that Chef Zane can offer. Chef Zane’s eclectic style and consistency make him a favorite among Portland foodies and his food truck will garner a loyal following amongst young professionals and college students.
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will be located in the immensely popular food truck pod known as Cartopia. Chef Zane will receive lots of exposure by being a part of this community as there are plenty of neighboring food trucks, bars, nightlife, and entertainment options nearby. With the popular location of Cartopia and an impressive Instagram social media following, Zesty Zane’s Food Truck is destined to become a local go-to dining destination for anyone craving delicious, interesting fare at an affordable price.
Products Served
The following are the products to be offered by Zesty Zane’s Food Truck:
- Sandwiches & paninis
- Assorted non-alcoholic beverages
Customer Focus
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will target customers in Portland who live, work, or socialize near Cartopia. This area is frequented by numerous young professionals, college students, and the late-night crowd who regularly eat at food trucks. Anyone seeking trendy dining options are the target customers of Zesty Zane’s Food Truck.
Management Team
Chef Zane has worked in the culinary industry for over ten years and is accustomed to the long, demanding hours of operating a kitchen. He attended culinary school in San Francisco and returned home to Portland to be a part of the world-renowned food scene that Portland has built for itself. After working under three award-winning chefs, Chef Zane is ready to venture out on his own and start his own business as a food truck.
Chef Zane Benedict will be the food truck owner and operator of his food truck. He will operate the food truck Tuesday through Sunday from 11:00 am until 1:00 am. Chef Zane will also employ two part-time cooks to assist him during peak hours of operation.
Success Factors
The following success factors will set Zesty Zane’s Food Truck apart from the competition:
- Exceptional cuisine made fresh with locally sourced ingredients.
- An eclectic menu that is unlike any other in the Portland food scene.
- Convenient location: Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will be located in a highly-trafficked food truck pod that is frequented by college students, young professionals, and night-life regulars.
- Delicious food at a good price. Zesty Zane’s food items will be cheaper than other food truck dishes without sacrificing quality.
Financial Highlights
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck is seeking $40,000 in debt financing to open its food truck. The funding will be dedicated for the purchase of the food truck, cooking supplies and equipment, working capital, three months worth of payroll expenses and opening inventory. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Purchase of food truck – $20,000
- Food truck kitchen supplies and equipment – $10,000
- Opening inventory – $2,000
- Working capital (to include 3 months of overhead expenses) – $3,000
- Marketing (website design and management) – $5,000
The following graph outlines the pro forma financial projections for Zesty Zane’s Food Truck:
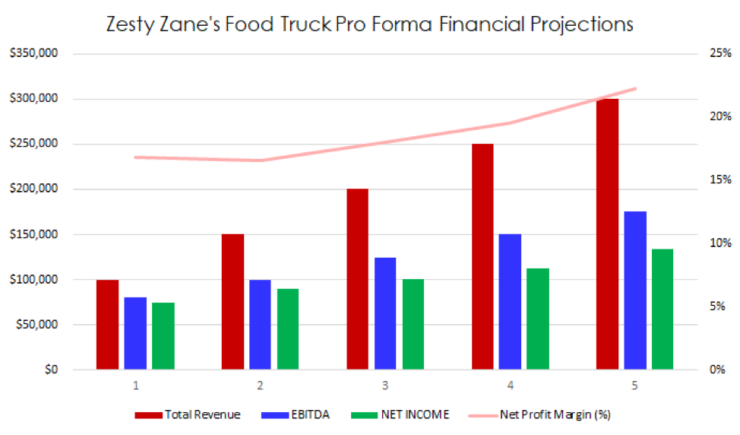
Company Overview
Who is zesty zane’s food truck.
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck is a startup food truck business located in Portland, Oregon. The menu offerings are eclectic, made-to-order, bistro-type dishes served fresh and fast in the entertainment district of Portland. The ingredients are locally-sourced from independent food growers and artisans in and around the Portland region. The dishes are incorporated with an ingenious twist to commonly known popular food menu items. The menu options are simple dishes commonly seen at food trucks, but Chef Zane adds his own spin to the typical fare – sandwiches, gyros, burgers, and tacos all made his way unlike any other food establishment.
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck is owned and operated by Zane Benedict, a local Chef classically trained in culinary school and under the most prestigious chefs in Portland. Chef Zane is known for his creativity, consistency, and quickness in the kitchen and his dishes receive multiple positive reviews in the restaurants Zane has been employed. Chef Zane specializes in fine French, Italian, and Mediterranean cuisine with a creative twist not typically found in other restaurant establishments.
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck History
After graduating from culinary school in 2008, Chef Zane Benedict worked as a sous chef in three different restaurants in Portland. All of the chefs Zane worked under were award-winning, locally-acclaimed chefs that frequently trained their apprentices to prepare dishes up to their expectation and standards.
Chef Zane learned a great deal from these chefs and garnered a reputation himself for his creativity and consistency. Now that Zane feels he has learned as much as he can from the senior chefs, he would like to venture out on his own and start his own business. Due to the large amount of capital required to open a full-scale restaurant, Chef Zane decided a food truck business was the most cost-effective option for his operation.
Since incorporation, Zesty Zane’s Food Truck has achieved the following milestones:
- Developed the food truck’s branding image, social media, and website.
- Has a soft hold on a used food truck that recently went out of business.
- Developed and finalized the menu of the dishes Chef Zane will serve.
- Obtained a food permit license to be able to prepare and sell food and drinks in Portland County.
- Obtained a sales and use tax permit for use in Portland County.
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck Products
The following are the types of menu items Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will produce:
Food Truck Industry Analysis
Food truck vendors will continue to perform well over the next five years, benefiting from consumers with deeper pockets who are able to spend on pricier gourmet food options. Revenues are expected to increase to $1.4 billion during this time period.
Food Truck industry operators are expected to continue to experience growth, as generally positive economic conditions and momentum from the gourmet food movement propel growth.
Consumers nowadays demand higher-quality food, a wider variety of styles and tastes, better presentation and, most importantly, more healthy menu options. Therefore, operators that include healthy options on their menus will be best situated for success over the next five years. Vendors that continue to offer unique food options will also be in a strong position by carving out a niche and developing a loyal customer base.
The food truck industry will also benefit from an increase in the urban population, which is expected to comprise the majority of the US population in five years. The food truck industry benefits from agglomeration because it relies on high foot traffic. Additionally, urban dwellers are also more likely to purchase meals rather than cooking at home due to their above-average incomes and limited spare time.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will target the population of Portland that frequently dines in the entertainment district. There is a large food truck area of Portland known as Cartopia, where Chef Zane will set up his business. This area is home to numerous dining establishments, nightlife, bars, clubs, and food trucks. The target market of this area are usually young professionals and college students who have disposable income.
The precise demographics for Portland, Oregon are:
| Total | Percent | |
|---|---|---|
| Total population | 590,157 | 100% |
| Male | 284,873 | 48.30% |
| Female | 305,284 | 51.70% |
| Under 5 years | 41,749 | 7.10% |
| 5 to 9 years | 43,509 | 7.40% |
| 10 to 14 years | 41,324 | 7.00% |
| 15 to 19 years | 43,301 | 7.30% |
| 20 to 24 years | 48,119 | 8.20% |
| 25 to 34 years | 106,407 | 18.00% |
| 35 to 44 years | 73,788 | 12.50% |
| 45 to 54 years | 64,669 | 11.00% |
| 55 to 59 years | 35,109 | 5.90% |
| 60 to 64 years | 27,995 | 4.70% |
| 65 to 74 years | 39,539 | 6.70% |
| 75 to 84 years | 17,394 | 2.90% |
| 85 years and over | 7,254 | 1.20% |
| Total housing units | 260,024 | 100% |
Customer Segmentation
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will primarily target the following customer profile:
- Local residents of Portland who partake in late-night activities such as socializing with friends or bar-hopping
- Business professionals that work and reside in the Portland Cartopia area – law offices, hospitals, clinics, insurance agencies, retail, and schools
- College students who are in search of fast, cheap, and trendy eats
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will be competing with other food trucks in the Portland community. A profile of each competitor is below.
Potato Champion
Potato Champion is a local favorite of Portland foodies that is also located in Cartopia. Started in 2008, Potato Champion quickly established itself as a fan favorite for late night food. Potato Champion serves a limited menu of hand cut, twice fried Belgian style fries, a variety of dipping sauces, and their own version of the Canadian classic Poutine, as well as other fry related dishes. They pride themselves in using the highest quality ingredients and focus on an inventive menu that combines tastes from all over the world with one of the most popular foods found on the globe, the french fry.
Potato Champion is open for lunch, dinner, and late-night. They are available for catering and delivery through Postmates. Followers of Potato Champion are also able to purchase swag from their store that includes music, bags, pins, and hoodies.
Started by John Eads in 2009, Pyro Pizza was built out of a 8’x16’ food cart that he custom-built with a cast iron wood fire oven. Aside from wood fired pizza, John also makes his own sodas using all real ingredients and natural cane sugar. John’s belief is that good ingredients make good food. His crew makes many components in-house and sources regional flour, pepperoni, sausage, blue cheese, soda ingredients, and seasonal produce all from Portland businesses and farms. In 2015, Pyro’s expanded to a new sandwich cart, Pyro’s Wicked Wiches – a scratch-made sandwich, soup, chips and cookie food cart.
Pyro’s serves an assortment of wood fire pizzas made from scratch. Their choices are margherita, marinara, arugula and mushroom, pepperoni, quattro formaggi, fennel sausage, veggie bianca, breadsticks, salads, and sodas.
Chicken and Guns
Chicken and Guns is another local favorite among Portland foodies. Also found in Cartopia, Chicken and Guns serves up Latin American chicken, wings, tacos, salad, soup, and their “guns” are crispy seasoned potatoes. The chicken is served by the quarter, half, or whole bird. Another item they are acclaimed for is their peruvian aji sauce, habanero carrot sauce and chimichurri sauce. They have been named the best fried chicken in Portland by the PDX Eater.
Chicken and Guns is open everyday from 11:00 am to 10:00 pm for takeout and delivery options. With a large Instagram and social media following, there is always destined to be a line at the Chicken and Guns food truck.
Competitive Advantage
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck offers several advantages over its competition. Those advantages are:
Food Truck Marketing Plan
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will offer a unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Delicious food made fresh with locally sourced ingredients using exquisite techniques.
- Located in the ultra-hip food truck area known as Cartopia.
- Great food at a great price. The menu offerings of Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will be accessible to customers of all walks of life.
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Zesty Zane’s Food Truck are as follows:
Social Media
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck’s main source of marketing will be through social media, primarily their Instagram page. Chef Zane has become adept at taking appealing photographs of his dishes. He will post pictures of his menu and add details on the location and hours of operation. His food truck account already has over 3,000 followers and he posts daily “Coming Soon” teaser photos.
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will be parked in the immensely popular food truck hub known as Cartopia of Portland. There are dozens of food trucks located in this pod and there is always a crowd of people. Cartopia hosts bands, art shows, shopping events, and other social gatherings to enhance the entertainment vibe of the pod. By being part of Cartopia, Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will receive lots of exposure and traffic.
SEO Website Marketing
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck plans to invest funds into maintaining a strong SEO presence on search engines like Google and Bing. When a person types in “local food truck” or “top food trucks in Portland”, Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will appear in the top three choices. Zesty Zane’s will also invest in their website also to ensure that it is user friendly, always up to date, and displays professional photographs of its menu items and location.
Third Party Delivery Sites
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will maintain a presence on sites like GrubHub, Uber Eats, Doordash, and Postmates so that people looking for local food with the option of delivery will see Zesty Zane’s listed.
The pricing of Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will be moderate and on par with other food trucks so customers feel they receive value when purchasing their menu items.
Operations Plan
The operations plan for Zesty Zane’s Food Truck is relatively simple as its overhead and cost is small. The functional roles for its employees are as follows:
Operation Functions:
- Chef Zane will run the food truck operation. He will be in charge of inventory, menu creation, food truck marketing, customer service, and bookkeeping. Chef Zane will work every day that he chooses to open the food truck. Chef Zane plans on operating the food truck Tuesday through Sunday 11:00 am to 1:00 am.
- Two part-time cooks that will alternate helping Chef Zane during the hours of operation. As business picks up, there will be two cooks at the same time assisting Chef Zane during peak hours.
Milestones:
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck aims to open in the next 3 months. The following are the milestones needed in order to obtain this goal.
4/15/202X – Purchase food truck
5/1/202X – Finalize menu
5/15/202X – Social media and advertising campaign begins
6/1/202X – Finish cleaning up the food truck and prepare it for operation
6/10/202X – Purchase food and drink inventory, stock truck, and park it at Cartopia
6/11/202X – Grand Opening of Zesty Zane’s Food Truck
Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will be owned and operated by Chef Zane Benedict.
Chef Zane Benedict, Food Truck Owner
Chef Zane Benedict is a Portland native who attended culinary school in San Francisco and returned to Portland to become a part of the world-renowned food scene Portland is uniquely known for. Zane was trained under three different chefs at fine dining establishments in downtown Portland and was awarded Best Sous Chef of Portland in 2017. Chef Zane has won two local culinary competitions, placed runner-up in a statewide competition, and participated in a cooking competition show on the Food Network.
Chef Zane has received numerous awards for his creativity and consistency of his food while being able to prepare dishes in a short amount of time. His ability to prepare food under pressure allows him the unique skill of serving numerous customers without having them undergo long wait times. This will keep customers happy and coming back for more.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Zesty Zane’s Food Truck will come from the menu items being offered daily.
The cost drivers will be the ingredients and products needed to make the menu items (oil, bread, meat, chicken, produce, drinks) as well as the cooking materials (pots, pans, bowls, plates, utensils, etc.). Other cost drivers will be the overhead expenses of payroll for the part-time employees and propane for the food truck.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
- Food Truck Marketing (website design and management) – $5,000
Key Assumptions
The following table outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and in order to pay off the business loan.
Initial Number of Customers Per Day: 50
Average Menu Item Cost: $9.00
Average Order per Customer: $15.00
Annual Cost for Maintenance of Truck: $10,000
Financial Projections
Income statement.
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
Food Truck Business Plan FAQs
What is a food truck business plan.
A food truck business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your food truck business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your food truck business plan using our Food Truck Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Food Truck Companies?
There are a variety of types of food trucks, each specializing in a specific type of cuisine or food item. There are food trucks that sell burgers, cookies, ice cream, tacos, pizza, sandwiches, salads and more.
What Are the Main Sources of Revenues and Expenses for a Food Truck Business?
The primary source of revenue for food truck businesses is its food and beverage sales.
The key expenses for a food truck business are food costs, salaries, and transportation expenses.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Food Truck Business?
Food truck businesses are typically funded through small business loans, personal savings, crowdfunding and credit card financing. A well-crafted food truck business plan is essential to securing funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Food Truck Business?
Starting a food truck business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Food Truck Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed business plan for your food truck that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your food truck business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your food truck business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Food Truck Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your food truck business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your food truck business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Food Truck Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your food truck business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your food truck business. Food truck marketing includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful food truck business:
- How to Start a Food Truck Business
Where Can I Get a Food Truck Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free food truck business plan template PDF here . This is a sample food truck business plan template you can use in PDF format.

Other Business Plan Templates
Catering Business Plan Template Bakery Business Plan Template Coffee Shop Business Plan Template Event Venue Business Plan Template

Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan Template & PDF Example
- July 24, 2024
- Business Plan

Creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial for launching and running a successful fast food restaurant. This plan serves as your roadmap, detailing your vision, operational strategies, and financial plan. It helps establish your fast food restaurant’s identity, navigate the competitive market, and secure funding for growth.
This article not only breaks down the critical components of a fast food restaurant business plan, but also provides an example of a business plan to help you craft your own.
Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or new to the food and beverage industry, this guide, complete with a business plan example, lays the groundwork for turning your fast food restaurant concept into reality. Let’s dive in!
Our fast food restaurant business plan is structured to cover all essential aspects needed for a comprehensive strategy. It outlines the restaurant’s operations, marketing strategy, market environment, competitors, management team, and financial forecasts.
- Executive Summary : Offers a snapshot of your fast food restaurant’s business idea, market study, team, and money plan.
- Restaurant & Location: Talks about the restaurant’s look, features, and why the spot is good for customers.
- Menu & Pricing: Shows what food your place serves and how much it costs.
- Key Stats: Tells about how big the market is, how it’s growing, and important numbers for fast food.
- Key Trends : Points out new changes in fast food, like healthier options or tech for ordering.
- Key Competitors: Look at the main other fast food places and how your restaurant is different.
- SWOT : Lists your restaurant’s strengths, weaknesses, chances, and risks.
- Marketing Plan : Plans for how to get and keep customers.
- Timeline : Important steps and goals from starting to the first year.
- Management: Gives information on who runs the restaurant and their jobs.
- Financial Plan: Shows how your restaurant might do money-wise over 5 years, including sales, profit, and costs.

Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan

Fully editable 30+ slides Powerpoint presentation business plan template.
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary introduces the business plan for your fast food restaurant , providing a concise overview of your establishment and its offerings. It should highlight your market positioning, the variety of fast food items and services you provide, its location, size, and a summary of daily operations.
This section should also delve into how your fast food restaurant will fit into the local market, including the number of direct competitors in the vicinity, identifying who they are, along with your restaurant’s unique selling points that set it apart from these competitors.
Moreover, it should include information about the management and co-founding team, outlining their roles and contributions to the restaurant’s success. Additionally, a synopsis of your financial projections, including revenue and profits for the next five years, should be included here to give a clear overview of your restaurant’s financial strategy.
Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan Executive Summary Example

Business Overview
The business overview should clearly define the restaurant’s key features, including its specific cuisine or theme, strategic location, facility design, and menu offerings. Highlighting what sets your restaurant apart in the competitive fast food market, such as unique culinary concepts or sustainable practices, is key for attracting interest and investment.
Example: “FlavorFusion,” a fast food restaurant specializing in fusion tacos, is located in the lively Midtown area, known for its vibrant food scene. The restaurant boasts a modern, 2,000 square-foot space with an energetic and contemporary vibe, seating for 50 patrons, and an additional outdoor area. The menu features a variety of gourmet fusion tacos made with high-quality, locally-sourced ingredients, catering to a diverse clientele.
Market Overview
This section should analyze the fast food market’s size, growth trends, and key industry developments. It positions your restaurant within the industry and highlights its potential to capitalize on current consumer trends like online ordering and plant-based options.
Example: FlavorFusion enters a market valued at $331 billion, growing at a 5.1% CAGR. Amidst intense competition from five local fast food outlets, FlavorFusion stands out with its unique fusion menu and focus on sustainability, aligning with the growing demand for innovative and eco-friendly dining options.
Management Team
Detailing the management team’s background and roles is essential. This part of the summary should emphasize their experience in the food and beverage industry and their roles in ensuring the restaurant’s operational excellence and financial health.
Example: The CEO/CFO of FlavorFusion, with extensive experience in business strategy and financial management, oversees the restaurant’s overall strategy and financial planning. The General Manager, responsible for day-to-day operations, ensures efficient restaurant functioning and high customer satisfaction.
Financial Plan
Clearly outlining the financial goals and projections is key. This section should include revenue targets and profit margins, offering insight into the restaurant’s financial health and growth potential.
Example: FlavorFusion aims to achieve $1.5 million in annual revenue with an 18% EBITDA margin by 2028. Supported by a strong business model, innovative menu, and effective marketing strategies , the restaurant is positioned for significant growth in the dynamic fast food market.
For a Fast Food Restaurant, the Business Overview section can be effectively divided into 2 main categories:
Restaurant & Location
Provide a detailed description of the restaurant’s physical environment, focusing on its design, ambiance, and welcoming atmosphere that appeals to customers. Mention the restaurant’s location, emphasizing its accessibility and convenience for customers, such as proximity to busy shopping areas or availability of parking. Explain why this location is particularly beneficial in attracting your target customer base.
Menu & Pricing
Describe the variety of fast food items and beverages offered, ranging from classic favorites to unique specialties that differentiate your restaurant from competitors. Detail your pricing strategy , ensuring it aligns with the quality of food served and appeals to the market segment you are targeting. Highlight any special deals, combo offers, or loyalty programs that add value for customers, promoting frequent visits and customer loyalty.

Industry Size & Growth
In the Market Overview of your fast food restaurant business plan, start by looking at how big the fast food industry is and how much it could grow. This helps you see how much room there is in the market and where you might grow.
Key Market Trends
Talk about what’s new in the fast food world, like how people want different and healthy options, meals they can get quickly, and new kinds of food. Mention how people are looking for good food that fits their busy lives and how they like to try new flavors from different places.
Competitive Landscape
A competitive analysis is a crucial component of your fast food restaurant’s business plan. It provides insights into how your restaurant compares to its competitors in the market. This analysis is instrumental in identifying your restaurant’s unique selling points and understanding the competitive landscape.
A thorough competitive analysis helps in shaping a well-informed business plan, ensuring that your restaurant is positioned to meet market demands and customer expectations effectively.
Identifying Your Competitors in the Fast Food Industry
Identifying competitors is the first step in understanding your position in the fast food market. Start by mapping out local fast food restaurants. For instance, if your restaurant specializes in burgers, your direct competitors include nearby burger joints like McDonald’s or Burger King , as well as local favorites like “Bob’s Burgers.” Don’t overlook indirect competitors such as Subway or Chipotle, which offer alternative fast dining options.
Use online tools like Google Maps to get a geographical sense of competitor distribution. Platforms like Yelp and TripAdvisor offer customer reviews and ratings, providing insights into competitors’ strengths and weaknesses . For example, if several reviews mention the quick service at “Fast Eats,” this is a key strength of your competitor.

Fast food competitors’ strategies
Analyzing the strategies of these competitors involves several aspects. Start with their menu offerings. For example, if “Healthy Bites” down the street is gaining popularity with its vegan options, it indicates a market trend towards healthier fast food.
Pricing strategy is another crucial aspect. Compare your prices with those of “Dollar Saver Menu” at McDonald’s or the premium options at “Shake Shack.” This comparison will help you understand where your restaurant fits in the market.
Marketing tactics in fast food can range from social media campaigns, like Wendy’s witty Twitter presence, to local billboard advertising. Pay attention to how competitors engage with customers online and the types of promotions they run.
Customer experience is also key. For instance, Chick-fil-A is renowned for its customer service. Visit competitors and note the service speed, order accuracy, and overall customer satisfaction.
Operational efficiency, especially in fast food, is a game-changer. Observe if competitors like Domino’s are using technology, like their pizza tracking system, to enhance efficiency and customer experience.
What’s your fast food restaurant’s value proposition?
Now, reflect on your restaurant’s unique value proposition . Perhaps your restaurant offers a unique fusion cuisine that isn’t available elsewhere in your area, or maybe you use locally sourced ingredients, which appeals to health-conscious consumers.
Identify market gaps through customer feedback and market trends . For example, the growing popularity of plant-based diets has led to the success of chains like “Beyond Meat.” If there’s a rising demand for plant-based fast food in your area that competitors aren’t meeting, this could be a niche for your restaurant.
Consider your location: A fast food restaurant located near a university might cater to students with budget-friendly deals, unlike a restaurant in a business district that might focus on quick service for office workers.

First, do a SWOT analysis for your fast food restaurant . Talk about Strengths (like a great menu and quick service), Weaknesses (like lots of competition or high costs), Opportunities (like more people wanting fast, tasty food), and Threats (like changes in what people want to eat or less money to spend on eating out).

Marketing Plan
Next, make a marketing plan that shows how you’ll get and keep customers. You can use ads, special deals, fun posts on social media, and events in the community.
Marketing Channels
Selecting the right marketing channels enables effective communication with potential customers and helps drive foot traffic to your restaurant. Employing diverse channels aids in enhancing brand visibility and engagement.
Digital Marketing
Utilize the digital landscape to your advantage:
- Social Media Presence: Utilize Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, TikTok, and other relevant platforms to showcase menu items, engage with followers through interactive content, host contests, and share user-generated content.
- Online Ordering Platforms: Partner with popular food delivery apps and maintain a user-friendly website with a seamless ordering system. Highlight exclusive online deals and promotions to attract online customers.
- Content Marketing : Produce engaging content such as blog posts, videos, or infographics about your recipes, behind-the-scenes kitchen stories, or spotlighting local ingredients. This content can be shared on your website and social media platforms to captivate your audience.
Local Advertising
Connect with the community through various local marketing strategies:
- Geo-targeted Ads: Invest in targeted online advertisements focused on your restaurant’s vicinity to capture the attention of nearby residents and commuters.
- Community Engagement: Participate in local events, sponsor local sports teams, or host charity fundraisers to increase community involvement and foster a positive brand image.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Forge partnerships with local businesses, gyms, schools, or corporate offices for joint promotional events or meal deals.
Promotional Activities
Entice potential customers with compelling offers and promotions:
- Limited-time Offers: Introduce seasonal specials, combo deals, or promotional menu items to generate excitement and attract new customers.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Implement loyalty cards or digital reward systems where frequent diners can earn points redeemable for discounts, free items, or exclusive perks.
- Referral Incentives : Encourage existing customers to refer friends and family by providing incentives such as discounts on their next order or free add-ons.

Sales Channels
Strategically employing various sales channels ensures efficient transactions and enhances customer satisfaction.
In-Store Upselling
Maximize sales during customer visits:
- Upsize Options: Offer upsized meals or meal add-ons for a nominal price increase to increase average order value.
- Combo Deals: Create bundled meal deals comprising popular items at a discounted price to encourage customers to spend more.
- Limited-time Add-ons : Introduce temporary add-ons or upgrades to entice customers into trying new menu items.
Online Ordering and Delivery
Enhance convenience and accessibility for customers:
- Efficient Online Ordering: Ensure a user-friendly online ordering system on your website and partnering delivery platforms, enabling customers to place orders seamlessly.
- Delivery Services: Optimize delivery operations to provide timely and efficient service, ensuring the food quality matches the in-store experience.
- Curbside Pickup: Offer a convenient pickup option for customers who prefer a quick in-and-out experience.
Subscription Services or Meal Plans
Encourage repeat business and secure recurring revenue streams:
- Subscription Plans: Create subscription-based meal plans offering weekly or monthly meal bundles at discounted rates for loyal customers.
- Meal Packages: Develop curated meal packages for families, individuals, or specific dietary preferences that customers can subscribe to for regular delivery or pickup.
Strategy Timeline
Lastly, make a clear timeline with important steps for starting your restaurant, getting the word out, getting more customers, and growing your business. This helps you stay on track and focused.
The Management section focuses on the fast food restaurant’s management and their direct roles in daily operations and strategic direction. This part is crucial for understanding who is responsible for making key decisions and driving the fast food restaurant towards its financial and operational goals.
For your fast food restaurant business plan, list the core team members, their specific responsibilities, and how their expertise supports the business.

The Financial Plan section is a comprehensive analysis of your financial projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability. It lays out your fast food restaurant’s approach to securing funding, managing cash flow, and achieving breakeven.
This section typically includes detailed forecasts for the first 5 years of operation, highlighting expected revenue, operating costs and capital expenditures.
For your fast food restaurant business plan, provide a snapshot of your financial statement (profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow statement), as well as your key assumptions (e.g. number of customers and prices, expenses, etc.).
Make sure to cover here _ Profit and Loss _ Cash Flow Statement _ Balance Sheet _ Use of Funds

Related Posts

Steakhouse Business Plan Template & PDF Example
Bubble Tea Business Plan Template & PDF Example

Bar Business Plan Template & PDF Example
- July 22, 2024
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIGipServerwww_ou_edu_cms_servers | session | This cookie is associated with a computer network load balancer by the website host to ensure requests are routed to the correct endpoint and required sessions are managed. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| language | session | This cookie is used to store the language preference of the user. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _ga_QP2X5FY328 | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. |
| _gat_UA-189374473-1 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| browser_id | 5 years | This cookie is used for identifying the visitor browser on re-visit to the website. |
| WMF-Last-Access | 1 month 18 hours 11 minutes | This cookie is used to calculate unique devices accessing the website. |
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Food Preparation Business Plan
Start your own food preparation business plan
What's For Dinner?
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
What’s For Dinner? is an exciting, new business with a unique approach to helping people enjoy home cooked meals with their families. Customers will come to our Plano, TX location and prepare 12 meals that they pre-select from a menu in a party atmosphere. In two hours, they will have a month’s worth of meals to put in their freezer.
By focusing on our competitive edge (no direct competitors in the Dallas/Ft. Worth area), our customers, and their needs, What’s For Dinner? will increase sales to a point that exceeds $1.3M in three years.
What’s For Dinner? is owned jointly by Alan and Kim Kirby as an S Corporation. Alan and Kim have 15 years of experience in the food service and entertainment industries, as a party planner and personal chef, respectively. They know the kinds of food preparation available in the Collin County area. With two teenaged children, have experienced the frustration of trying to feed a whole family healthy food both cheaply and quickly. Alan’s existing contacts with local social and community groups, and Kim’s ongoing relationships with food distributors, specialty grocers, and high-end clients will all help to generate high sales from early in the first year.
What’s For Dinner offers several advantages to its target market:
- Relatively inexpensive meal preparation: ~$15 for a four-person meal.
- Fun, social, party atmosphere.
- Convenient: eat your prepared meals in your home, when you want.
- Saves time: no shopping, no prep, no clean up.
- For seniors, special menus and transportation assistance make meals easy.
- And, best of all, not having to decide “What’s For Dinner?”
The purpose of this plan is two-fold. The first is to acquire funding of $259,708. The second is to lay the foundations of the company’s vision, philosophy, and strategy, to ensure that we know where we are going and how to get there.

1.1 Mission
What’s For Dinner? is a specialized business that provides a variety of people with the opportunity to prepare health conscious, yet savory meals that can be frozen to take home and eat at a later time. The purpose of this process is to both optimize the time investment needed to prepare the quality of meals that What’s For Dinner? will become known for, within the clients’ current schedules, and also for them to practice the proper health conscious behavior that has become the target lifestyle of a health deficient society.
What’s For Dinner? will provide a unique and distinctive service that will unite a party-like atmosphere with professional food preparation that will attract a growing repeat customer base. What’s For Dinner? will allow families and busy professionals the ability to prepare a variety of meals quickly in a fun atmosphere, away from home, thus giving people more of what they are looking for – time.
Our goal is to be a self-sustaining corporate enterprise within 3 years from the company’s inception to begin expanding our menu offerings within 3 months and its location offerings within 4 years. What’s For Dinner? will employ 4 individuals full time within 3 years, and will hit net profit goals of $100,000 by the end of its second year of existence.
In short, we will be in the business of helping our customers to relieve their daily stresses of what to fix their families for dinner by providing them with a great menu choice of meals that they will prepare.
1.2 Keys to Success
The keys to success in this business are:
- Creating a high level of customer satisfaction in our service and products, which will lead to customer retention each month.
- Marketing: getting our name out to the public, primarily through an intensive marketing campaign driven by our customers (word of mouth) with a supplemental vehicle of standardized and conventional marketing tactics.
- Great product quality and variety that will be used to aid in customer retention and growth.
- Finances: as our customer base increases we will be better able to lower our supply costs by buying more in bulk through food service distributors.
- Variety of menus offered based on seasons, trends and customer preferences.
- Exceeding our customers’ expectations by offering them a higher quality of food for a competitive price.
- What’s For Dinner’s website will be an efficient and convenient place for customers to register and pay for parties.
1.3 Objectives
The objectives for What’s For Dinner? in the first three years of operation include:
- To exceed customers’ expectations for food service and food service products.
- To increase the number of clients served by 25% per year through superior service.
- To develop a sustainable start-up business that is profitable.
- To achieve an after tax net profit of $134K by year three.
- To achieve a net income of more than 10% of sales by the third year.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
What’s For Dinner? is a unique business where customers come to our Plano, TX location and prepare twelve pre-chosen meals that will be taken home and frozen until they are ready to cook and serve. All of the planning, shopping, food preparation and containers are provided with no worries to the customer. The meals will be prepared in a party like atmosphere where customers will have separate workstations to prepare their meals and have a good time with friends, both new and old.
Our goal is to provide our customers with home cooked meals that their families will enjoy, while saving them time and effort and relieve stress from that age-old question of What’s For Dinner?
The scheduling aspect of our company will be combination of a standard walk-up scheduling procedure, a phone messaging service and an intensive highly-interactive e-commerce website that will allow the customer to not only schedule parties but also to pay online, using standard secure technology.
2.1 Start-up Summary
The start-up expenses include:
- Rent expenses include a deposit and rent for one month at $28.75 per square foot for 1,854 square feet, in the total amount of $5,182.
- Utilities expenses for one month.
- Insurance deposit and first month.
- Sales & Marketing expenses including stationery, brochures, outdoor signage.
- Website development.
- Office, kitchen and janitorial supply expenses.
- Leasehold improvements, including contractors fees and permits.
The required start-up assets of $50,000 include:
- Kitchen Equipment (long-term assets)
- Prep Tables (long-term assets)
- Cooking utensils
- Various Kitchen Utensils
- Computer and small business software
Please note that the long-term assets above will be depreciated using G.A.A.P. approved straight-line depreciation method.
The purpose of this business plan is to secure $259,708 in funding. This loan appears in the long-term liability row of the attached Start-up Funding table.
The following chart and table summarize the start-up assumptions.
| Start-up Funding | |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $196,708 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $93,000 |
| Total Funding Required | $289,708 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $59,000 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $34,000 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $0 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $34,000 |
| Total Assets | $93,000 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | |
| Current Borrowing | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $259,708 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $259,708 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | |
| Alan Kirby | $15,000 |
| Kim Kirby | $15,000 |
| Other | $0 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Total Planned Investment | $30,000 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | ($196,708) |
| Total Capital | ($166,708) |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $93,000 |
| Total Funding | $289,708 |
| Start-up | |
| Requirements | |
| Start-up Expenses | |
| Legal | $1,500 |
| Stationery etc. | $400 |
| Office Supplies | $500 |
| Kitchen Supplies | $1,000 |
| Janitorial Supplies | $400 |
| Insurance | $719 |
| Rent | $5,182 |
| Utilities | $1,085 |
| Sales and Marketing | $2,800 |
| Website Development | $4,000 |
| Leasehold Improvements | $140,000 |
| Licenses/Permits | $422 |
| Construction Fees / Permits | $35,000 |
| Outdoor Sign | $3,500 |
| Miscellaneous | $200 |
| Total Start-up Expenses | $196,708 |
| Start-up Assets | |
| Cash Required | $34,000 |
| Start-up Inventory | $9,000 |
| Other Current Assets | $8,000 |
| Long-term Assets | $42,000 |
| Total Assets | $93,000 |
| Total Requirements | $289,708 |

2.2 Company Ownership
What’s For Dinner? is a privately held Sub Chapter S-corporation. This allows for the protection allowed by the corporate legal structure combined with the “fall through” Generally Accepted Accounting Principals that will make personal financial sense to the corporations principle owners. The principle owners of What’s For Dinner? are Alan and Kim Kirby; each owns a 50% stake in the company. This company operates under the jurisdiction of the State of Texas and the United States of America.
What’s For Dinner? will provide its customers with twelve home cooked meals that they will freeze until customers are ready to serve them. These meals will be chosen from a set menu designed weekly by us and the meals will be prepared in our location. All of the planning, shopping, food preparation, recipe directions and containers will be provided to help make it as easy as possible for our customers to enjoy their time at our establishment.
Our customers will prepare their meals in a fun, party-like atmosphere where they can relax, meet new friends or spend time with old friends while preparing dinners for their families for the next month.
The Key benefits our customers will receive from using What’s For Dinner? are:
- Spend less time in the kitchen
- Less money on groceries & eating out – it keeps you from being tempted to eat out
- Home style meals & better eating
- Able to sit down at the table together as a family – including conversation and socialization
- Clean up is easy, because prep is done outside the home, and all meals come in disposable containers
- Less time spent on grocery shopping
- In 2 hours you will have 12 dinners for you and your family
- We create the menus – order the ingredients – slice, dice, chop and prepare
- Social hour preparing dinners
Our menus and portion sizes are tailored for the group and individual customers. Seniors get added benefits, with diabetic, low-cholesterol, and low-sodium choices. Families can increase portion sizes for a small fee to accommodate more children or guests.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
The Dallas area’s meal preparation market is untapped. As a matter of fact, there is no other business of this kind in the Dallas/Ft. Worth area. Though there are no exact replicas of our company there are some types of companies that we would have to consider to be indirect competitors. These include such companies and service professionals as caterers and those that will come to your home and prepare meals for you to freeze. What’s For Dinner?, at this time, has few direct competitors, with exception to area restaurants and your basic home cooking. At the inception of What’s For Dinner?, there will be no type of company like ours in the area, thus giving us the overwhelming competitive advantage of first entry.
The What’s For Dinner? market is primarily in the Collin County area: Plano, Frisco, Allen and McKinney. We will be focusing on households in these areas that have more than one person. Primarily, those households whose income is over $50,000, with someone under the age of 18 living there. As a secondary target market, we will market to the elderly population in the aforementioned areas. Initially, the greater portion of our customers will be busy, working class people and the growing group of single-parent families, but it will be of great benefit now and in the future to market our services to the highest growing population demographic – senior citizens.
The following statistics were taken from Table DP-1 Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2000 for Collin County.
4.1 Market Segmentation
What’s For Dinner? has three distinct target populations:
- Family households with children under 18 years old. This group of people is generally busier than other families with their time split between work, home and their children’s activities. This group may be single parent households, which only adds to the stress resulting from lack of time, coupled with the need for proper meals for their children. This provides them with a desire to provide their families with good meals and free time to enjoy being together.
- Family households with no children living at their home. This group has a need for our services, as hectic schedules, professional careers, and daily demands on time come up against the need for tasty, healthy meals. Depending on their work and home situations this demographic could use our service to enhance their selection of meals all the while minimizing their time in the kitchen. This group does recognize the benefits of our service and want to enjoy making meals for themselves and socializing through our business.
- Senior and Elderly Citizens. This group (65 and older) is the fastest growing portion of the population, and needs our services for several reasons:
- A good portion of this group is simply unable to cook nutritious meals and does not have the knowledge or skills to continue to effectively maneuver themselves in the kitchen.
- Many seniors do not have the time, energy, or means to make it to the grocery store.
We will market several menus designed for the diet needs of the senior populace (diabetic, low cholesterol, low sodium), with pick-up and drop-off coordinated with a local senior-transportation center. All prep and measuring will be done beforehand, so they will need only to stir and combine ingredients. In addition to meeting their practical needs, we will create the social experience that this group consistently hunts for, and help them to enhance their lifestyle through a higher quality of health.

| Market Analysis | |||||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| Households with children | 10% | 73,864 | 81,250 | 89,375 | 98,312 | 108,144 | 10.00% |
| Households with no children | 10% | 58,404 | 64,244 | 70,668 | 77,735 | 85,509 | 10.00% |
| Seniors | 12% | 25,852 | 28,954 | 32,428 | 36,319 | 40,677 | 12.00% |
| Total | 10.33% | 158,120 | 174,448 | 192,471 | 212,366 | 234,330 | 10.33% |
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
These target market segments were chosen based on their greater need for our services. Families with children are very busy, and they can end up spending a great deal on fast food and junk food because they don’t have time to cook healthy meals at home. Busy working couples and individuals without children are also busy, and may not have the skills or desire to plan and cook entire meals at home just for themselves; they can spend a lot on going out to eat. Seniors have special challenges in obtaining and preparing quality ingredients to feed themselves, including the loneliness of cooking for oneself. Options like “Meals on Wheels” are generally last-resorts, and many would prefer alternate food preparation arrangements, if any were available at a reasonable price – fixed incomes can be hard on the palate.
Our marketing strategies for all groups will emphasize our relatively inexpensive, fun, and easy approach to preparing healthy meals. We will vary our serving sizes, menu options, and level of preparation for each group; the family-size entree just right for a family of four makes no sense for a single individual. Different sized families have different needs, and it will be our goal to look to accommodate most family sizes through our variations in serving size.
4.3 Service Business Analysis
Our service is unique among Dallas meal preparation options. There are no direct competitors for What’s For Dinner? The closest competitors are personal chefs, who will come to your home and prepare your chosen meals for you and freeze them, at a very high price. Our target market segments cannot afford personal chefs.
Our indirect competitors are area restaurants. These include family-oriented, inexpensive diners and casual restaurants, as well as fast food and takeout. We will generally not be competing with upscale, adult-oriented restaurants, since those are “special occasion” locations, and do not fulfill local residents’ daily meal needs.
Our competitor restaurants compete on price, perceived convenience, and atmosphere. They succeed when they convince customers that going out to eat is an affordable “treat” that is easier and more pleasant than preparing meals at home. In truth, the restaurants with the lowest prices also offer poor quality food and atmosphere, and the struggle to get children ready, out the door, and have them behave in a restaurant setting can make these choices less appealing in families’ realities than in their imagination. For all customers, the time it takes to get ready, travel to a restaurant, order dinner, eat, pay, and get home make going out to a eat a full-evening’s commitment – hardly the convenience it claims.
With the introduction of What’s For Dinner? to the Dallas market, we will revolutionize the way that the community looks at cooking convenience. Our prices really are much lower than restaurant meals, with much higher quality meals. In addition, our “convenience” comes in two ways – preparing meals at a set time, outside the daily routine, so they are ready in advance, and eating and minimal clean-up right in the customer’s own home, which saves time and energy at the end of a long day.
4.3.1 Competition and Buying Patterns
Even though What’s For Dinner? has no direct competitors, we will set up our business as if we are entering an already aggressive and hostile market. This is aimed at helping us to become successful through a constant drive for increased service model efficiencies and marketing effectiveness. We will strive to excel in customer service excellence, continuing our menu varieties and achieving the highest standards for our food products. As owners, we feel that word of mouth and customer retention are significant factors in our success. Our convenient locations, sanitary facilities, competitive pricing structure and honorable reputation will all play a part in satisfying our customers and increasing our clientele at an accelerating rate. What’s For Dinner? will focus on these factors and always strive to improve our business model and service offerings. We will strive to be the very best in our industry and will not rest until we not only have the largest market share in our industry, but also have the most satisfied customers.
The buying patterns of our customer base will be affected by our initial meal prep party prices. We have concluded through our exhaustive focus market groups that we could set our prices high, since there is no direct competitor, but we feel that to attract and retain customers and be able to steadily grow our customer base, so we should price ourselves at a lower level first. By setting ourselves at the lower end of our pricing range, we will not only gain the attention of the vast majority of our target markets, but we will also be able to start our revenue streams off with an upward growth pattern. The price that we will choose will be reasonable for our customers and be adequate for the business to maintain a gross margin around 25%.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
What’s For Dinner? will gradually gain market share in the four focal geographic markets (Plano, Frisco, Allen and McKinney) by leveraging its competitive edges. These edges are superior attention to detail in the local food service market, a revolutionary food-servicing outlook and excellent nutritional meals at competitive price. These advantages have been unavailable in this market for some time. We will market our services with a targeted advertising campaign and networking.
5.1 Competitive Edge
What’s For Dinner? will begin with a critical competitive edge: we have no direct competitors in the Dallas/Ft. Worth area. By being the first-mover and (for at least a while) the only service of our kind, we will have the initial market buzz that is normally reserved for the first company of its kind into a given market. Our positioning is very hard to match, but only if we maintain focus on our strategy, marketing, business development, and fulfillment of quality and customer service will we be able to continually grow and outpace the “copy-cat” businesses that are sure to follow our market lead. We are aware that the tendency to relax due to lack of competition could weaken our competitive edge. What’s For Dinner? will be operated as if our direct competitors were conducting the same service business that we are in and we will be looking for additional enhancements to our operating procedures from day one.
In addition to our unique positioning, we offer the following advantages to our customers:
- High quality meals
- Relatively low prices
- Time saving meal preparation
- Reducing mess in customers’ kitchens
- Reducing stress around meal prep
- Saving them from that perennial problem of deciding, “What’s for Dinner?”
5.2 Marketing Strategy
As a food service business, our main goal is to provide high quality food with excellent customer service. Our challenge as a new company is to quickly establish a reputation for such quality among our potential markets. With this in mind, the initial focus of our marketing strategy will be to get our name and reputation out to the public to create “buzz.” Creating brand recognition for our new concept will be the first measurable milestone in our marketing strategy.
This will be one of the most important factors when measuring success within the first couple of months after inception. The basis for our ideology is simple; the more people that hear our name and become familiar with our services, the more people will use it. The marketing campaign will involve a targeted advertising campaign, different specials to entice the customers to try our business and a very intense networking campaign. All of these tactics will be used to help gain a loyal clientele aimed at fostering our happy customer base.
At start-up, we will begin a focused advertising campaign toward target segments in our geographical area. We will update our advertising campaign regularly to fill in gaps based on follow-up research: do people recognize our name? Do they know what we do? What is their impression of our services’ costs and quality?Marketing campaigns will work via:
- Local area newspapers that are viewed by our target market.
- Homeowner associations’, churches’ and specific groups’ newsletters.
- Direct mail advertisements/flyers to our target market purchased through a direct mailing company with lists specifically of our target market.
- Various flyers and pamphlets that will be available at many shopping centers and grocery stores throughout the area.
- Yellow pages advertisement.
- Dynamic website.
- Registered keyword searches that will lead to our website.
- Various Radio advertisements.
- Various event sponsorships.
What’s For Dinner? will also have a networking campaign that will start with the owner’s contacts and friends attending our first months’ meal prep parties. This will be the “word of mouth” campaign that will feature:
- Private parties with discounts for the host/hostess of the party. This will encourage them to invite 11 friends that will be introduced to our business and will be return customers.
- Special discounts to return customers when referring new customers.
5.3 Sales Strategy
In the food service business, as in any customer service intensive business, sales revenue is our lifeblood. The way in which we present ourselves to our customers and deal with the public will determine the success of our business. The food service industry is facilitated by repeat business and referrals. In order to continuously compete against other food providers, we need to enhance our repeat customer service business by making this our main sales focus. We cannot expect to have a satisfied customer by selling them one month’s of meals and then never seeing them again. We must make our sales strategy revolve around making the customer’s experience with us the best it possibly can, and further, making every effort to get our current customer base to visit us again. It is much more expensive to get new customers than to keep the customers you already have. Our customers cannot stop eating, but they could stop using our services. We will be selling our service to our current customers each time they come, in order to have repeat business and new business through their word of mouth.
These are just a few of the ways we will sell to our customers to gain repeat business and word of mouth advertising:
- High levels of customer service; friendly, comforting and entertaining
- Good variety of menus from which to choose
- The best quality of foods and ingredients
- Creating a fun and social atmosphere for our customers, so they want to return
- Reminders at each party to sign up for the next month’s party, along with the next month’s menu and samples
- A follow up and reminder program for our current customers that will be done through email and mail.
- Focus a specific portion of our advertising campaign on getting our repeat customers to come back and visit us
- Allow our best repeat customers to get special quantity specific discounts.
- Enlist a comprehensive and highly interactive e-commerce initiative to help to accommodate our customer’s payment and scheduling options.
The What’s For Dinner? website will serve as a productive and consistent selling tool. Our website will be set up to explain what we offer and the many benefits customers will receive for using our meal prep services. The website will help “close the sale;” customers will be able to register for the meal prep party they would like to attend and accepting payments online. This will be our main source of registrations for parties. The ease of use allowed by the Internet will be key to driving our customer pipeline. Our sales and marketing campaigns will help focus our customer traffic through our website, so that people can see how easy it will be to interact with our company. This element of efficiency will also help enhance our bottom line by allowing for a 24 hour customer service mechanism without having to keep a customer rep staffed all the time.
5.3.1 Sales Forecast
Through our research of other businesses like ours in Seattle, WA and Omaha, NE, we found that all of them quickly increased their sales over their first year. All of these researched companies went from their first month of 100 customers on average to over 1,000 customers within their first year of business. One company opened in Seattle against two other competitors and now has over 2,000 customers with three different locations.
We are optimistic that What’s For Dinner? will grow and prosper just as these other companies have, but we want to set reasonable forecasts for growth. We have therefore taken a conservative approach in preparing our Sales Forecast Table.
The following table and chart give a run-down on forecasted sales. We have forecasted that sales will increase each month with the exception of the summer months, when vacations and other seasonal activities may reduce purchases. Once we get our first few customers, our sales will increase through customer retention, and gaining new customers through networking. We expect sales to grow incrementally over the first year, reaching profitability by the fifth month of operation.
After the first year of operation, we expect sales to continue increasing, from 10% the first year up to 25% by the third year. As sales increase, we will make modifications to our facility and hire new employees to share in the work. Our proposed location allows room for expansion. Based on our research, and the size of our potential market, we expect to reach close to one million dollars in sales by the end of 2005.
Our direct costs of sales listed here are inventory used up in sales, including the meal ingredients and additional supplies, such as themed-party decorations, containers, napkins, and so on. Fixed operating expenses are listed in the Profit and Loss.
| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | |||
| Party Fees | $857,674 | $1,072,093 | $1,340,116 |
| Other Fees | $24,505 | $30,631 | $38,289 |
| Total Sales | $882,179 | $1,102,724 | $1,378,405 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Ingredients | $612,624 | $765,780 | $957,225 |
| Other Supplies | $44,109 | $55,136 | $68,920 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $656,733 | $820,917 | $1,026,146 |
5.4 Milestones
The accompanying table lists important program milestones, with dates and budgets for each. The milestone schedule indicates our emphasis on planning for implementation. What the table doesn’t show is the commitment behind it. Our business plan includes complete provisions for plan -vs. – actual analysis, and we will follow-up often to discover variances and course corrections.
What’s For Dinner? will have several milestones, including:
- Business plan completion. This will be done as a roadmap for the organization. This will be an indispensable tool for the ongoing performance and improvement of the company.
- Building set up.
- Our first meal prep party.
- Profitability.
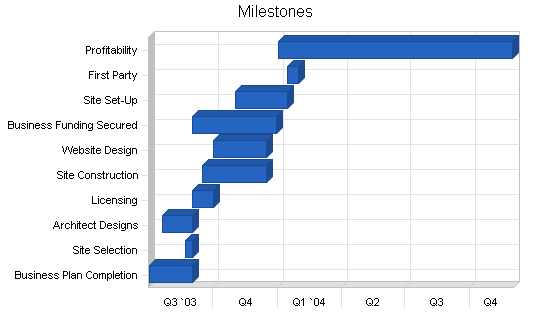
| Milestones | |||||
| Milestone | Start Date | End Date | Budget | Manager | Department |
| Business Plan Completion | 7/1/2003 | 9/1/2003 | $250 | Alan Kirby | Administration |
| Site Selection | 8/22/2003 | 9/1/2003 | $0 | Alan Kirby | Administration |
| Architect Designs | 7/20/2003 | 9/1/2003 | $5,000 | Alan Kirby | Administration |
| Licensing | 9/1/2003 | 10/1/2003 | $500 | Alan Kirby | Administration |
| Site Construction | 9/15/2003 | 12/15/2003 | $0 | Alan Kirby | Administration |
| Website Design | 10/1/2003 | 12/15/2003 | $1,280 | Alan Kirby | Web |
| Business Funding Secured | 9/1/2003 | 12/30/2003 | $0 | Alan Kirby | Administration |
| Site Set-Up | 11/1/2003 | 1/15/2004 | $0 | Alan Kirby | Administration |
| First Party | 1/15/2004 | 1/30/2004 | $0 | Alan Kirby | Administration |
| Profitability | 1/1/2004 | 12/1/2004 | $0 | Alan Kirby | Administration |
| Totals | $7,030 | ||||
Web Plan Summary
The What’s For Dinner? website will be the virtual business card, party scheduler and payment acceptance source all rolled into one. It will showcase our services and highlight the benefits of using our company. The website will be a crucial portal for party scheduling, as well as having availability cross-referenced with party menus. Customers will also use this website to register for their parties and pay for them using PayPal, which accepts MasterCard, Discover Card, Visa, or e-checks.
6.1 Website Marketing Strategy
The What’s For Dinner? website will be a strategic and very important part of our marketing mix. It will be used as a marketing tool to attract new customers, and as a sales tool to schedule parties, select menus, and pay. We will be promoting our website in all marketing programs, including newspaper ads, yellow page ads, business cards and flyers. We will also purchase targeted key word searches to help potential customers find our website. In addition, our website will feature prominently on all napkins, packaging, and receipts which current customers bring home, making repeat business easy and convenient.
Our main internet strategy is to direct the majority of our potential clients to our website first, as the introduction to our services, prices, and availability. This will reduce the time necessary for staff to provide basic information over the phone, allowing them to answer customer questions and provide more details, once customers know who we are, what we do, and how we might help them.
To encourage customers to use the website, we will offering special discounts to those who register their parties with our website and pay online. Our website must be easy to access and navigate, and must answer every customer question we can anticipate. It must use a legitimate, well-respected security feature and a reliable payment method. If it is all these things, many of our repeat customers will be happy to save time by researching party options and scheduling them online.
Clearly, we expect website use to be highest among younger, internet-savvy customers. We anticipate that our senior customers will use phone and direct contacts for most scheduling and payment interactions.
6.2 Development Requirements
The What’s For Dinner? website will be developed with the technical resources of a local web design artist. He has designed websites for over 325 businesses, most with e-commerce capabilities. He is designing a database interface which will let us adjust the schedule and track click/sales ratios, and easily update menu offerings.
As the website development progresses, he will work with a local graphic artist we have hired to come up with the website logo and graphics. We are still researching hosting possibilities, but feel our needs will be best served by subcontracting out the hosting of the site and the technical back-end supporting.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
The What’s For Dinner? management team will initially consist of the founders/owners themselves, Alan and Kim Kirby. We do not anticipate the need to hire anyone else on a full time basis during the first year, because all of the services that a normal small business needs will be outsourced. These services include the e-commerce infrastructure, accounting, marketing, and legal services. We do plan to employ one part-time employee from the beginning to help with cleaning and dishwashing.
Alan and Kim have 15 years of experience in the food service and entertainment industries, as a party planner and personal chef, respectively. Until the second year, Kim will continue to work part-time as a personal chef for several couples in Plano, doing the prep work and menu planning for What’s for Dinner? in the mornings. Alan will host the majority of the parties, after having prepared test batches of every menu item with Kim. The owners anticipate possibly hiring local high-school students as sous-chefs in years 2 and 3; Kim’s experience with local restaurants has shown that these students can often do quite well, paid only minimally in exchange for professional restaurant and food preparation training. Alan’s existing contacts with local social and community groups, and Kim’s ongoing relationships with food distributors, specialty grocers, and high-end clients will all help to generate high sales from early in the first year.
Throughout the first two years we will conduct an aggressive cost analysis as to what our capabilities are as owners and with what activities we need assistance.
7.1 Personnel Plan
The following table summarizes our personnel expenditures for the first three years, with compensation increasing from $34K the first year to about $60K in the third. We believe this plan is a fair compromise between fairness and expedience, and meets the commitment of our mission statement. The detailed monthly personnel plan for the first year is included in the appendices.
| Personnel Plan | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Alan Kirby | $24,000 | $30,000 | $40,000 |
| Kim Kirby | $5,000 | $7,500 | $10,000 |
| Part-time cleaner | $5,000 | $7,500 | $10,000 |
| Total People | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Total Payroll | $34,000 | $45,000 | $60,000 |
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
What’s For Dinner expects strong sales, based on research into our target market, similar businesses in other parts of the country, lack of direct competition, and the experience, reputations, and know-how of its owners/managers. By steadily repaying our long-term loan and holding down costs, we will generate a net profit midway through the first year and increase net worth dramatically by year 3. Our major fixed expenses are payroll and rent.
8.1 Important Assumptions
The financial plan depends on important assumptions, most of which are shown in the following table as annual assumptions. The monthly assumptions are included in the appendices.
Three of the more important underlying assumptions are:
- We assume a relatively strong economy, without major new recessions. Although an ailing economy would not allow us the growth that we anticipate, we believe that it would not drastically hurt the business because the service is economically feasible. The $175 session fee breaks down to $14.58 per meal – a deal hard to beat at even a fast-food restaurant for a family of four to six.
- We assume that our market needs will be seasonal, with a decrease in sales during the summer months.
| General Assumptions | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Current Interest Rate | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% |
| Tax Rate | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 |
8.2 Break-even Analysis
The following chart and table summarize our break-even analysis. With fixed costs of $10,520 per month at the outset (to cover payroll and other operating costs), and variable costs (inventory) at 74% of sales, we need to bill $41,167 to cover our costs. We do not expect to reach break-even until the sixth month into the business operation.
| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $39,503 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Percent Variable Cost | 74% |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $10,095 |
8.3 Projected Profit and Loss
What’s For Dinner?’s projected profit and loss is shown in the following table, with sales increasing from $10K the first month to close to $1.4M by the third year. We will reach profitability in the middle of our first year.
We are projecting very conservatively regarding cost of sales and gross margin. Our costs of sales are based on grocery store prices, which will decrease once we are to consistently able to buy our food in larger quantities from a food distributor. This will significantly lower our cost of sales, and increase our gross margin more than in this projection. We prefer to project conservatively so that we make sure we have enough cash.
The Sales and Marketing Expenses vary from the food preparation industry norms. Our Sales and Marketing Expenses will be to consistently maintain our advertising and promotions, while our biggest marketing will be word of mouth from our customers. We are budgeting for a high level of service from our website hosting company and payment processor, since the website is a key component of our Sales and Marketing Strategies.
The detailed monthly projections are included in the appendices.
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $882,179 | $1,102,724 | $1,378,405 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $656,733 | $820,917 | $1,026,146 |
| Other Costs of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $656,733 | $820,917 | $1,026,146 |
| Gross Margin | $225,446 | $281,807 | $352,259 |
| Gross Margin % | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $34,000 | $45,000 | $60,000 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 |
| Depreciation | $4,200 | $4,200 | $4,200 |
| Rent | $53,304 | $54,000 | $54,500 |
| Utilities | $13,160 | $14,476 | $15,924 |
| Office Supplies | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Insurance | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 |
| Payroll Taxes | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Accountant | $3,000 | $3,200 | $3,500 |
| Lawyer | $1,000 | $1,100 | $1,100 |
| Bank Charges | $180 | $180 | $180 |
| Website Payment Fees | $600 | $700 | $800 |
| Website Hosting & Support | $1,500 | $1,600 | $1,650 |
| Repairs and Maintenance | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $121,144 | $134,656 | $152,054 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $104,302 | $147,151 | $200,205 |
| EBITDA | $108,502 | $151,351 | $204,405 |
| Interest Expense | $17,342 | $15,861 | $14,316 |
| Taxes Incurred | $20,870 | $31,510 | $44,614 |
| Net Profit | $66,089 | $99,780 | $141,276 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 7.49% | 9.05% | 10.25% |
8.4 Projected Cash Flow
The following cash flow projections show the annual amounts only. Cash flow projections are critical to our success. The monthly cash flow is shown in the illustration, with one bar representing the cash flow per month, and the other the monthly cash balance. The annual cash flow figures are included here and the more important detailed monthly numbers are included in the appendices.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $882,179 | $1,102,724 | $1,378,405 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $882,179 | $1,102,724 | $1,378,405 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $882,179 | $1,102,724 | $1,378,405 |
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $34,000 | $45,000 | $60,000 |
| Bill Payments | $758,414 | $1,055,142 | $1,197,241 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $792,414 | $1,100,142 | $1,257,241 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $22,080 | $22,080 | $22,080 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $814,494 | $1,122,222 | $1,279,321 |
| Net Cash Flow | $67,685 | ($19,498) | $99,083 |
| Cash Balance | $101,685 | $82,187 | $181,270 |
8.5 Projected Balance Sheet
The balance sheet in the following table shows managed but sufficient growth of net worth, and a sufficiently healthy financial position. Our negative net worth, due to borrowed capital for start-up, makes a significant increase by the second year, and becomes positive in year three. It is common for start-up businesses to have a negative net worth their first few years.
The monthly estimates are included in the appendices.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $101,685 | $82,187 | $181,270 |
| Inventory | $137,714 | $172,142 | $215,178 |
| Other Current Assets | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $247,399 | $262,329 | $404,448 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $4,200 | $8,400 | $12,600 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $37,800 | $33,600 | $29,400 |
| Total Assets | $285,199 | $295,929 | $433,848 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $148,189 | $81,220 | $99,942 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $148,189 | $81,220 | $99,942 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $237,628 | $215,548 | $193,468 |
| Total Liabilities | $385,817 | $296,768 | $293,410 |
| Paid-in Capital | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($196,708) | ($130,619) | ($30,838) |
| Earnings | $66,089 | $99,780 | $141,276 |
| Total Capital | ($100,619) | ($838) | $140,438 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $285,199 | $295,929 | $433,848 |
| Net Worth | ($100,619) | ($838) | $140,438 |
8.6 Business Ratios
Business ratios for the years of this plan are shown below. Industry profile ratios based on the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) code 2099, Food Preparation, are shown for comparison.
The following table outlines some of the more important ratios from the Food Preparation industry. The final column, Industry Profile, details specific ratios based on the industry as it is classified by the Standard Industry Classification (SIC) code, 2099.
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 5.54% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Inventory | 48.29% | 58.17% | 49.60% | 11.58% |
| Other Current Assets | 2.81% | 2.70% | 1.84% | 22.16% |
| Total Current Assets | 86.75% | 88.65% | 93.22% | 53.03% |
| Long-term Assets | 13.25% | 11.35% | 6.78% | 46.97% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 51.96% | 27.45% | 23.04% | 27.29% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 83.32% | 72.84% | 44.59% | 20.18% |
| Total Liabilities | 135.28% | 100.28% | 67.63% | 47.47% |
| Net Worth | -35.28% | -0.28% | 32.37% | 52.53% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 30.90% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 17.88% | 16.00% | 15.03% | 16.61% |
| Advertising Expenses | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 1.28% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | 11.82% | 13.34% | 14.52% | 1.33% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 1.67 | 3.23 | 4.05 | 1.54 |
| Quick | 0.74 | 1.11 | 1.89 | 0.98 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 135.28% | 100.28% | 67.63% | 55.42% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | -86.42% | -15658.38% | 132.36% | 2.12% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | 30.49% | 44.37% | 42.85% | 4.76% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | 7.49% | 9.05% | 10.25% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | 0.00% | 0.00% | 100.60% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Inventory Turnover | 10.91 | 5.30 | 5.30 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 6.12 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 42 | 27 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 3.09 | 3.73 | 3.18 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.09 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 0.38 | 0.27 | 0.34 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $99,209 | $181,110 | $304,506 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 6.01 | 9.28 | 13.99 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.31 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 52% | 27% | 23% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 0.74 | 1.11 | 1.89 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9.82 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Party Fees | 0% | $10,500 | $17,500 | $26,250 | $35,000 | $44,297 | $66,445 | $66,445 | $66,445 | $99,667 | $112,125 | $149,500 | $163,500 |
| Other Fees | 0% | $300 | $500 | $750 | $1,000 | $1,266 | $1,898 | $1,898 | $1,898 | $2,848 | $3,204 | $4,271 | $4,671 |
| Total Sales | $10,800 | $18,000 | $27,000 | $36,000 | $45,563 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $102,515 | $115,329 | $153,771 | $168,171 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Ingredients | $7,500 | $12,500 | $18,750 | $25,000 | $31,641 | $47,461 | $47,461 | $47,461 | $71,191 | $80,089 | $106,786 | $116,786 | |
| Other Supplies | $540 | $900 | $1,350 | $1,800 | $2,278 | $3,417 | $3,417 | $3,417 | $5,126 | $5,766 | $7,689 | $8,409 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $8,040 | $13,400 | $20,100 | $26,800 | $33,919 | $50,878 | $50,878 | $50,878 | $76,316 | $85,856 | $114,474 | $125,194 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Alan Kirby | 0% | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 |
| Kim Kirby | 0% | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 |
| Part-time cleaner | 0% | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 | $417 |
| Total People | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Total Payroll | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | |
| General Assumptions | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Current Interest Rate | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | 7.00% | |
| Tax Rate | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | 24.00% | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | $10,800 | $18,000 | $27,000 | $36,000 | $45,563 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $102,515 | $115,329 | $153,771 | $168,171 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $8,040 | $13,400 | $20,100 | $26,800 | $33,919 | $50,878 | $50,878 | $50,878 | $76,316 | $85,856 | $114,474 | $125,194 | |
| Other Costs of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $8,040 | $13,400 | $20,100 | $26,800 | $33,919 | $50,878 | $50,878 | $50,878 | $76,316 | $85,856 | $114,474 | $125,194 | |
| Gross Margin | $2,760 | $4,600 | $6,900 | $9,200 | $11,644 | $17,466 | $17,466 | $17,466 | $26,198 | $29,473 | $39,297 | $42,977 | |
| Gross Margin % | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | 25.56% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | |
| Depreciation | $350 | $350 | $350 | $350 | $350 | $350 | $350 | $350 | $350 | $350 | $350 | $350 | |
| Rent | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | $4,442 | |
| Utilities | $980 | $1,030 | $1,030 | $1,030 | $1,030 | $980 | $980 | $980 | $1,280 | $1,280 | $1,280 | $1,280 | |
| Office Supplies | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | |
| Insurance | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 15% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Accountant | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | |
| Lawyer | $500 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $500 | |
| Bank Charges | $15 | $15 | $15 | $15 | $15 | $15 | $15 | $15 | $15 | $15 | $15 | $15 | |
| Website Payment Fees | $50 | $50 | $50 | $50 | $50 | $50 | $50 | $50 | $50 | $50 | $50 | $50 | |
| Website Hosting & Support | 0% | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 |
| Repairs and Maintenance | 15% | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $10,395 | $9,945 | $9,945 | $9,945 | $9,945 | $9,895 | $9,895 | $9,895 | $10,195 | $10,195 | $10,195 | $10,695 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($7,635) | ($5,345) | ($3,045) | ($745) | $1,698 | $7,570 | $7,570 | $7,570 | $16,003 | $19,278 | $29,102 | $32,282 | |
| EBITDA | ($7,285) | ($4,995) | ($2,695) | ($395) | $2,048 | $7,920 | $7,920 | $7,920 | $16,353 | $19,628 | $29,452 | $32,632 | |
| Interest Expense | $1,504 | $1,493 | $1,483 | $1,472 | $1,461 | $1,451 | $1,440 | $1,429 | $1,418 | $1,408 | $1,397 | $1,386 | |
| Taxes Incurred | ($2,193) | ($1,641) | ($1,087) | ($532) | $57 | $1,469 | $1,471 | $1,474 | $3,500 | $4,289 | $6,649 | $7,415 | |
| Net Profit | ($6,946) | ($5,198) | ($3,441) | ($1,685) | $180 | $4,651 | $4,659 | $4,667 | $11,084 | $13,581 | $21,056 | $23,481 | |
| Net Profit/Sales | -64.32% | -28.88% | -12.75% | -4.68% | 0.40% | 6.81% | 6.82% | 6.83% | 10.81% | 11.78% | 13.69% | 13.96% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $10,800 | $18,000 | $27,000 | $36,000 | $45,563 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $102,515 | $115,329 | $153,771 | $168,171 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $10,800 | $18,000 | $27,000 | $36,000 | $45,563 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $102,515 | $115,329 | $153,771 | $168,171 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $10,800 | $18,000 | $27,000 | $36,000 | $45,563 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $68,343 | $102,515 | $115,329 | $153,771 | $168,171 | |
| Expenditures | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | $2,833 | |
| Bill Payments | $480 | $14,790 | $26,201 | $34,869 | $42,144 | $51,001 | $78,542 | $60,501 | $62,351 | $115,990 | $110,789 | $160,756 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $3,314 | $17,624 | $29,034 | $37,703 | $44,977 | $53,834 | $81,375 | $63,334 | $65,184 | $118,824 | $113,622 | $163,589 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | $1,840 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $5,154 | $19,464 | $30,874 | $39,543 | $46,817 | $55,674 | $83,215 | $65,174 | $67,024 | $120,664 | $115,462 | $165,429 | |
| Net Cash Flow | $5,646 | ($1,464) | ($3,874) | ($3,543) | ($1,254) | $12,669 | ($14,872) | $3,169 | $35,491 | ($5,335) | $38,309 | $2,742 | |
| Cash Balance | $39,646 | $38,183 | $34,309 | $30,766 | $29,512 | $42,181 | $27,309 | $30,478 | $65,969 | $60,633 | $98,942 | $101,685 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $34,000 | $39,646 | $38,183 | $34,309 | $30,766 | $29,512 | $42,181 | $27,309 | $30,478 | $65,969 | $60,633 | $98,942 | $101,685 |
| Inventory | $9,000 | $8,844 | $14,740 | $22,110 | $29,480 | $37,311 | $55,966 | $55,966 | $55,966 | $83,948 | $94,441 | $125,922 | $137,714 |
| Other Current Assets | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $51,000 | $56,490 | $60,923 | $64,419 | $68,246 | $74,822 | $106,146 | $91,274 | $94,444 | $157,917 | $163,075 | $232,864 | $247,399 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 | $42,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $350 | $700 | $1,050 | $1,400 | $1,750 | $2,100 | $2,450 | $2,800 | $3,150 | $3,500 | $3,850 | $4,200 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $42,000 | $41,650 | $41,300 | $40,950 | $40,600 | $40,250 | $39,900 | $39,550 | $39,200 | $38,850 | $38,500 | $38,150 | $37,800 |
| Total Assets | $93,000 | $98,140 | $102,223 | $105,369 | $108,846 | $115,072 | $146,046 | $130,824 | $133,644 | $196,767 | $201,575 | $271,014 | $285,199 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $13,927 | $25,047 | $33,474 | $40,476 | $48,362 | $76,525 | $58,484 | $58,476 | $112,355 | $105,422 | $155,646 | $148,189 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $0 | $13,927 | $25,047 | $33,474 | $40,476 | $48,362 | $76,525 | $58,484 | $58,476 | $112,355 | $105,422 | $155,646 | $148,189 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $259,708 | $257,868 | $256,028 | $254,188 | $252,348 | $250,508 | $248,668 | $246,828 | $244,988 | $243,148 | $241,308 | $239,468 | $237,628 |
| Total Liabilities | $259,708 | $271,795 | $281,075 | $287,662 | $292,824 | $298,870 | $325,193 | $305,312 | $303,464 | $355,503 | $346,730 | $395,114 | $385,817 |
| Paid-in Capital | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) | ($196,708) |
| Earnings | $0 | ($6,946) | ($12,144) | ($15,585) | ($17,270) | ($17,090) | ($12,439) | ($7,780) | ($3,113) | $7,972 | $21,553 | $42,608 | $66,089 |
| Total Capital | ($166,708) | ($173,654) | ($178,852) | ($182,293) | ($183,978) | ($183,798) | ($179,147) | ($174,488) | ($169,821) | ($158,736) | ($145,155) | ($124,100) | ($100,619) |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $93,000 | $98,140 | $102,223 | $105,369 | $108,846 | $115,072 | $146,046 | $130,824 | $133,644 | $196,767 | $201,575 | $271,014 | $285,199 |
| Net Worth | ($166,708) | ($173,654) | ($178,852) | ($182,293) | ($183,978) | ($183,798) | ($179,147) | ($174,488) | ($169,821) | ($158,736) | ($145,155) | ($124,100) | ($100,619) |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

Food and Beverages Business Plan Sample
Download the food and beverage business plan sample in pdf, mission statement.
To create an ideal environment:
To inspire and nurture the human spirit – one person, one cup and one neighborhood at a time.
To provide the world’s ultimate coffee shop experience with the highest quality products, most inviting stores, friendliest staff, and best value.
Find out more about our mission by downloading the PDF here
Services Overview
Coffee Club will be a coffee house and café that offers pastries, seasonal ice creams, sorbet, wine, and quick menu items. Coffee Club will focus on providing a healthful fare with selections supplied by local bakers, using quality ingredients and minimally processed foods.
To view the full service overview, click here to download it in pdf

Market Overview
The Company is entering the market at a time when the industry in which it operates is experiencing substantial growth. According to market research firm IBIS World, the Coffee & Snack Shops Industry has seen an average annual growth rate of 5.8% over the last five years, positioning industry revenue to be around $47.7 billion in 2018. The Coffee & Snack Shops industry is projected to see an average annual growth rate of 1.4% over the next five years, placing industry revenue at $51 billion in 2022.
Market Analysis Summary
COFFEE & SNACK SHOPS
The Coffee and Snack Shops industry has taken advantage of the rising economic tide over the five years to 2018, posting substantial growth in each year since 2013.
As one of the nimblest industries within the broader foodservice sector, coffee, and snack shops have been able to adjust to changing consumer preferences as spending has picked up and consumers have increasingly opted for more convenient and affordable menu items. Stores that once specialized in catering to the unhealthy whims of consumers have strategically shifted to provide healthier, gourmet menu items.
Download the full coffee shop market analysis in pdf.
Pro Tips: Learn how to write a market analysis in business plan to create a perfect coffee shop business plan.
Target Market
The target market of Coffee Club is as follows
1. High School Students and Professionals
Coffee Club anticipates its food and beverage customers will be high school students aged 17-18 years and professionals aged between 25 to 59 years working in the proximity of the anticipated location. Regarding the employment scenario, 68% of people aged between 15 and 64 in the US had a paid job, and out of which, around 73% of men had a paid job in comparison to 63% of women.
For more detailed information on the target market, download the pdf here
Organizational Structure

Competitive Analysis

Here is a pdf download of the full Competitive Analysis
Competitive Advantages
The following is a listing of the primary competitive advantages of the Company upon entering the market.
- Congenial customer service
- A central location with greater foot traffic
- Parking facility available for customers
- Soothing ambiance for calm eating
- Excellent visibility from the Main Road
For a complete list of competitive advantages, click here to download a pdf
SWOT Analysis
- experience and knowledge of the owner
- customer service commitment
- scope and quality of menu items
- restaurant specializing in wholesome food
- intended location is an ideal location having excellent visibility from the main road
- new concept for book lovers
- high foot traffic area
- regular improvement and creativity
- offering competitive prices
- parking and takeaway facility
- appealing display of the food and beverage served
- the eye-catching ambiance of the shop with a book reading section
For a comprehensive SWOT guide, click here to download in pdf
Marketing Strategies
Social Media
The company will set up profiles on platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. These will be used to engage its target audience through photos, videos, or information on upcoming deals, discounts and the new arrival.
A well-optimized website with proper site structure, page layout, and clear and easy navigation, along with targeted keywords embedded throughout the site will be constructed and will ensure proper search engine placement and saturation. The Company’s website is an important marketing asset. Along with SEO, the website will be easily navigable, highly informative, and will serve as a platform to generate new business.
For more information about market strategies, click here.

Click here to download a detailed guide on the milestone.
Fund Requirement

To learn more about funding requirements, click here to download the pdf
Projected Income Statement
Coffee Club intends to deploy its funding to maximize growth and profitability. In the Income Statement table below, gross margin equals sales minus direct costs. The “bottom line” or profit (as measured before and after interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) equals gross margin minus operating expenses.

A complete projected income statement can be obtained by downloading the PDF here
Pro tips: Learn how to make an income statement with our free to download income statement templates to make a stunning one for you .
Need Nearest Business Plan Writing Services
Looking for a professional business plan writing services near me ? Contact us to achieve your company’s goals and get funded.
Download our free sample business plan pdf to learn how to write an elegant and professional business plan like this one.
Click to view the sample business plan. Our experienced MBA business plan writers professionally write each business plan and work with you to develop a winning plan.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

Sample Food Business Plan
Food business plan sample.
With the high deficit in food/restaurants to serve a growing urban population, there is great potential for profitability in starting a food /restaurant business. But this business would not just succeed automatically when entered into without any form of planning.
It requires careful planning and organization to enable it succeed.
Hence, the development of a viable food business plan would do much in guiding the business to profitability and stability.
Read: List of Food Business Name Suggestions
It is in the light of this that this food business plan sample has been developed to guide intending investors interested in this sector to on how to carefully write their business plans following the procedures listed in this article.
This is how a food business plan sample should look like;
SAMPLE FOOD BUSINESS PLANS:
- Juice bar business plan
- Ice cream factory business plan
- Hot dog cart business plan
- Cupcake shop business plan
- Coffee shop business plan
- Catering business plan
- Pizza shop business plan
- Liquor store business plan
- Microbrewery business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Cooking class business plan
- Food concession stand business plan
- Food truck business plan
- Food cart business plan
- Milk distribution business plan
- Frozen food business plan
- Food kiosk business plan
- Fast food business plan
- Street food business plan
- Executive Summary
- Market Analysis/Trends
- Target Market
- Competitive Advantage
- Sales and Marketing Strategy
- Pricing Strategy
- Financial Projection
- Payment Options
- Publicity and Advertising Strategy
- Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Providing quality and hygienic restaurant services to our underserved clients, and communities, Food Haven restaurant LLC provides round the clock restaurant services to its esteemed clients around the Washington DC area, with plans of expanding nationwide. This is based on the understanding that people have different needs and have their varying schedules spread round the clock.
To this end, because the body needs some replenishment of energy after a hectic day’s work, Food Haven restaurant comes to the rescue as it will be providing comprehensive care services to the food needs of the and by extension, the society.
Among the restaurant services to be provided by Food Haven are Mexican dishes, Intercontinental dishes, among other dishes served at our restaurants
MARKET ANALYSIS/TRENDS
Market analysis carried out by Food Haven restaurants have discovered that apart from the desire to eat good food to quench their hunger, there are those clients who’s interest in not to satisfy hunger. In fact, they are not necessarily hungry but are just out to satisfy their curiosity by sampling dishes from other parts of the world. For example, clients who are not Indians might want to have a taste of Indian menu.
This might be because they learnt about it from friends or saw it somewhere such as in a TV program or the internet and want to have a try because they thought it might taste good. Food Haven seeks to provide these services through the hiring of capable hands skilled in a wide array of restaurant services.
OUR TARGET MARKET
Due to the fact that food is one of the basic requirements needed for survival, Food Haven LLC seeks to make these abundantly available in different variants.
However Food Haven restaurants LLC has a certain category of people that makes up its target market and these include visiting tourists, neighbouring businesses, families, and corporate bodies among several other category of targeted clientele.
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
In a market full of innovations and ingenious business ideas, we plan on not being left out of this great business opportunity as we will be providing services that will ensure that we capture a good share of the food/restaurant market.
This we try to achieve through going a step further to make home and office deliveries and also the provision of other outdoor catering services especially at the request of our clients.
SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
Food Haven LLC will be adopting flexible marketing methodologies to ensure it stays afloat and catches up with current market innovations in the food industry. Because the industry is constantly changing, coupled with the change in client preferences, we intend adopting a sales and marketing strategy that will capture these areas of choice fluctuations.
Some of the sales and marketing strategies we will be adopting include direct marketing and online marketing to showcase our rich services to potential clients. Also, fliers and banners will be printed, distributed, advertising our services to the general public.
PRICING STRATEGY
The pricing strategy adopted by Food Haven LLC intends to be pocket and customer friendly.
Although certain aspects of our services such as intercontinental dishes are quite expensive as compared with the daily foods being consumed by most Americans, we at Food Haven intend striking a balance between profitability and client satisfaction. Compared to other restaurants offering similar services, our pricing regime will be among the friendliest.
FINANCIAL PROJECTION
The financial projection (profits) envisaged by Food Haven LLC within the next three years includes the following brief representations below;
– First Year $150,000 – Second Year $300,000 – Third Year $770,000
PAYMENT OPTIONS
Food Haven LLC seeks to provide a wide variety of payment options aimed at creating ease in the payment of bills by our esteemed customers. These include almost all the payment platforms such as through cheques, mobile payments, POS options, and of course payment through cash.
However, we seem to add other payment options as soon as they are available to reduce the stress on our clients, as they are most likely to return if they are satisfied with our services.
PUBLICITY AND ADVERTISING STRATEGY
The advert and publicity strategy to be used by Food Haven LLC includes the deployment of ICT tools such as the internet to make our presence felt.
Also, fliers, banners and other advert strategies will be used to showcase our services. In addition, we will be using the local radio in passing across knowledge of our services.
SUSTAINABILITY AND EXPANSION STRATEGY
Food Haven LLC plans to expand from its current location in Washington DC to 50 outlets within this region within the next 6 years. Our long term expansion strategy is to spread our tentacles across the United States with a target of hitting the 200 mark in the number of outlets spread across the United States of America.
This is an example of a food business plan sample and intends to shed light on what a food business plan should contain.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Sample Business Plans
- Food, Beverage & Restaurant
Food Truck Business Plan
With the expanding popularity of street food and drinks, trying global cuisine, and busy schedules, the street vendor culture is increasing. The interesting thing is you are going to join this market in the period when the demand is growing.
With the selection of the food truck, buying equipment, and hiring the right people, have you forgotten to plan your business thoroughly? If yes, then here is our food truck business plan template with examples that will help you plan yours.
From industry trends to various examples; we have covered it all. So, let’s wait no more and proceed.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan offers strategic direction for your food truck business, helping you set and achieve your goals.
- The executive summary is an important part, so keep it briefly engaging.
- Conducting a thorough industry analysis is crucial to understanding the food truck market, including its size, trends, key players, and local demographics.
- With high competition in the food industry, you need a robust marketing plan.
- Keep your financial projections practical and do not have extravagant expectations.
Food Truck Industry Highlights
Before diving right into the business plan guide, let’s go through some food industry trends and statistics:
- The industry size of street vendors in the USA was around $2.29 billion in 2021.
- In the US, there were 67,271 food trucks in 2022, growing at an average annual rate of 18.1% per year over the five years 2017-2022.
- The popularity of plant-based diets as in vegan options is growing.
- From Thai food to spicy Mexican food, food trucks are serving everything and anything showcasing the popularity of street food.
- Food trucks are not limited to evenings, they are exploring new markets like corporate campuses, universities, and residential areas for breakfast and lunch time too.
How to Write a Food Truck Business Plan (Description + Examples)
1. executive summary.
An executive summary is the summary of the whole business plan. It is the first section of the business plan and probably the only section your readers will go through.
It is normally the part that business owners prefer to write at the end because, till then they will have a keen understanding of the whole business plan.
Start your summary with a brief introduction to your business (about who you are and what services you will provide). After that, mention the other things like:
- Products and services
- Business goals
- Food truck objectives
- Mission statement
- Market Opportunity
- Target market
- Food truck business concept
- Financial summary
- Financial projections
Here is an example of a mission statement:
Tip: the executive summary is a quick overview, so keep it simple and engaging.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Company Overview
Provide detailed information about your food truck business in this section. It includes the food truck concept, name, location, legal structure of your business, and everything else about your business.
Here is an example of a business description made by the use of Upmetrics:

Also, do not forget to mention the type of food truck you are going to start, for instance, your business might be the one from below:
- Gourmet food trucks
- Taco trucks
- Pizza trucks
- Burger and sandwich trucks
- Dessert trucks
If you already have another local food truck and this is the other one, then write the business history about your food business.
After that, mention the vision and mission of your food truck business along with the future goals. Include the names, qualifications, and specializations of the owners.
3. Industry Analysis
The industry analysis will give you all the details about the food industry you are going to enter. It will support you in a better understanding of your business.
Here are some types of questions you might ask while conducting a food industry analysis:
- What is the current size of the food truck industry in the USA?
- What are the major trends in the food truck industry?
- Who are the huge players in the industry and what is their market share?
- How is technology affecting the food truck industry?
- What is the average price range and spending limit of the customers?
In short, industry analysis will help you have a better understanding of the market and support you in making informed decisions.
4. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis will help you to know the price point and positioning of your business in the food industry. This way you will also get to know about your direct and indirect competitors, as in other food trucks in your location.
Start your competitive analysis section by listing all your competitors with all their plus points and negative points. Some of the questions you might ask to know your competitors are:
- What food items does their menu include?
- What is their market share?
- What are their USPs and what do their customers like about them the most?
- How much does a food truck cost?
- What is their pricing strategy?
- What are the weaknesses through which you can have a competitive advantage?
After getting all the above answers, analyze your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to get a better understanding of your USPs.
This way you can get to know the USP of a food truck business. Once you get the USP, flaunt it in your own business plan.
5. Market Analysis
Competition in the restaurant industry is high, and to get a small gap to enter the market is a huge opportunity. Once you enter the market, it is time to define and mention your target market first.
Your target audience will depend on the type of food truck services you provide and the location of your food truck.
Once you know who you are going to serve, then understand the market by knowing the current trends and customer preferences. For example, some of the market trends for a food truck are:
- Health conscious diet
- Local sourcing
- Food transparency
- Kiosks (contactless ordering and payment)
- Creative menu items
At the end of the market analysis, do mention the regulatory environment a food business needs to follow in the particular location.
6. Sample Menu
One of the most necessary steps to launch your food truck business is designing the sample menu. Generally, food truck businesses provide fast-preparing meals.
A sample menu forces you to think about what will you make and serve your customers. Consider where you will store uncooked food, what you will need to prepare that food, and what you will use to serve that food to your customers.
Your menu should be in coordination with your target customers; for example, if you have students around the corner then design your menu with fast-serving dishes.
The menu is also a part of your branding, so keep the color and design of the menu the same as your food truck. Here is an example of including your menu in the food truck business plan:

7. Sales and Marketing Plan
You can see a food truck in the corner of every alley, so you need to reach customers and not wait for them to come to you. For that, you will need a food truck marketing strategy in place. Some of the strategies are:
Create a professional and mobile-friendly website including your location, contact information, and images of the food items you offer. This will help local customers find you online.
Social media marketing
Maintain active profiles on TikTok, Twitter, FaceBook, Instagram, and all other major social media platforms to spread your reach. It will help your target market to recognize you and will interest them to visit your food truck.
Loyalty programs
Think of implementing a loyalty program to reward your existing customers. You can offer free food dishes, BOGO offers, discounts, or any other such thing. These programs can help you increase the customer retention rate and encourage them to visit your business more.
Community engagement
Participate in food truck gatherings, local events as a stall, and other fun food festivals. Engage with the local community by sponsoring or collaborating with local organizations. Building a strong local reputation can help you reach a wide customer base.
Email marketing
Send regular newsletters, special offers, discounts, and event invitations to everyone whose details you got from your website. Email marketing can be a powerful tool for customer retention and engagement.
8. Management team
Letting your readers or investors know who is behind your food truck will allow them to understand your business more.
The management team is all about who is behind the wheels of your food truck and what are their roles. If you are starting a new food truck, then showcasing your experienced managers or head chef will make your business look stronger.
Here is an example of a management team:

9. Business Operations
In the entire business plan we have talked about goals, but here is the point where you have to mention what will you do to fulfill those goals.
Everyday goals
They are the heart and soul of your food truck business. From buying the most qualitative food items to fulfilling customers’ needs and everything in between is included.
Long-term goals
It’s all about milestones: the moments that make you pop the champagne. Picture celebrating your 10,000th delivery, hitting that milestone sales figure you’ve dreamt of, or expanding your team.
10. Financial Plan
For a successful food truck business, you will need a proper financial plan with realistic financial projections. In this section add the financial statements like income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet for 3-5 years.
- Income statement
An income statement is also known as a profit and loss statement, which describes the profitability of the business by deducting expenses from revenue.
The income statement is one of the important things your investors will focus on. So, don’t be greedy and display huge impractical numbers.
- Balance sheet
Balance sheets display your assets and liabilities. Although they can contain a lot of details, like equity, goodwill, other intangible assets, etc.
- Cash flow statement
Your cash flow statement helps you see how much money you need to start or grow your business and avoid running out of money. This cash flow should be maintained even for certain months after launch that is before you start making profits.
Surprisingly, you can make a profit but still face financial problems that could lead to bankruptcy. Therefore, you will need proper cash flow planning to avoid such circumstances. Here is an example of a 5-year cash flow statement:
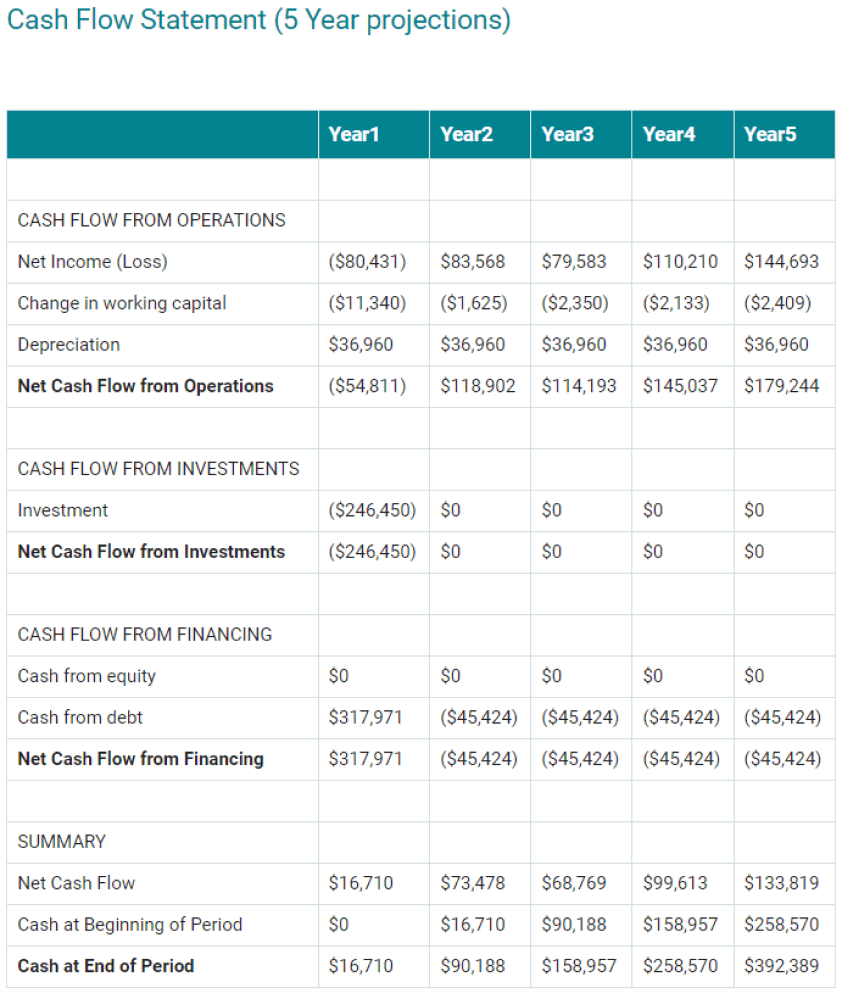
Why Do You Need a Business Plan for Your Food Truck?
If you are wondering why there is a lot more voice for a business plan, then consider this:
- A food-truck business plan offers a strategic direction to your business goals and helps you achieve them.
- A business plan will also help you understand the finances of your business and help you to secure funding.
- It will clarify the vision of your food truck, so you can focus on the daily operations.
- Also, it allows you to know specific risks you might face in the future, as a result, you will be prepared.
Now that you have plenty of reasons to have a food truck business plan, start writing one.
Related Food Truck Resources
- Food Truck Financial Plan
- How Much Does It Cost To Start A Food Truck
- How to Start a Food Truck Business
Download a Food Truck business plan template
Ready to kick-start your business plan writing process? And not sure where to start? Here you go, download our free food truck business plan pdf , and start writing.
This intuitive, modern, and investment-ready template is designed specifically for food truck businesses. It includes step-by-step instructions & examples to help in creating your own food-truck business plan.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
Write Your Business Plan with AI
Lastly! With the help of our food truck business plan template, you know how to write a business plan. So, you are a step closer to starting or expanding your food truck business exciting, right?
You know what else is exciting? Making your business planning process a lot smoother than this; yes, it is possible with the AI assistant of Upmetrics.
So, take a deep breath as we will take care of your business plan, and focus only on your business operations.
Related Posts
Food Processing Business Plan
Food Bank Business Plan
400+ Business Plan Example
Best AI Business Plan Tools
Frequently asked questions, can i start a food truck business without a formal business plan.
You can start a food truck business without a professional business plan, but it is not advisable, as a business plan will act as your roadmap. If you are going to start your business with bootstrapping, then you can take the risk of not writing a food truck business plan.
How often should I update my food truck business plan?
Your food truck business plan is a live document. So, you can edit it wherever and whenever you want. Ideally, you can read and edit your business plan once a month or as many times as required.
What should I include in the financial projections section of the business plan?
In a food truck business plan, you will need various estimated financial statements like
- Break-even analysis
- Sales forecast
- Uses of Funds
- Financial ratios
What are some tips for writing a food truck business plan template?
Some tips for writing a food truck business plan are:
- Be clear and concise about your goals
- Use data and statistics to support all your claims
- Be practical and realistic about your financial projections
- Ask friends and family to give feedback on your plan
- Read and re-read it before presenting it to your investors
What is the ideal length for a food truck business plan template?
Generally, the length of a business plan is around 15-35 pages. It also depends on the audience of your business plan, the type of your business, and the type of your business plan. As for a one-page business plan, the length is going to be 1 page.
About the Author

Vinay Kevadiya
Vinay Kevadiya is the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He enjoys sharing his insights on business planning and other relevant topics through his articles and blog posts. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Advertisement
Supported by
Harris Plans to Ban Grocery ‘Price Gouging.’ What Does the Evidence Say?
Price increases when demand exceeds supply are textbook economics. The question is whether, and how much, the pandemic yielded an excess take.
- Share full article

By Jim Tankersley and Jeanna Smialek
Reporting from Washington
Vice President Kamala Harris’s economic agenda for her presidential campaign features an argument that blames corporate price gouging for high grocery prices.
That message polls well with swing voters. It has been embraced by progressive groups , which regularly point to price gouging as a driver of rapid inflation, or at least something that contributes to rapid price increases. Those groups cheered the announcement late Wednesday that Ms. Harris would call for a federal ban on corporate price gouging on groceries in an economic policy speech on Friday.
But the economic argument over the issue is complicated.
Economists have cited a range of forces for pushing up prices in the recovery from the pandemic recession, including snarled supply chains, a sudden shift in consumer buying patterns , and the increased customer demand fueled by stimulus from the government and low rates from the Federal Reserve. Most economists say those forces are far more responsible than corporate behavior for the rise in prices in that period.
Biden administration economists have found that corporate behavior has played a role in pushing up grocery costs in recent years — but that other factors have played a much larger one.
The Harris campaign announcement on Wednesday cited meat industry consolidation as a driver of excessive grocery prices, but officials did not respond on Thursday to questions about the evidence Ms. Harris would cite or how her proposal would work.
There are examples of companies telling investors in recent years that they have been able to raise prices to increase profits. But even the term “price gouging” means different things to different people.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The food and beverage industry includes all businesses involved in the production, distribution, and sale of food and drinks. The global food and drink market is expected to grow at an annual rate of 11.9%, reaching a market volume of $3.8 billion by 2027. This increase sharply contrasts the declining industry performance over the last three years.
The breakout of the funding is below: Restaurant Build-Out and Design - $100,000. Kitchen supplies and equipment - $100,000. Opening inventory - $25,000. Working capital (to include 3 months of overhead expenses) - $25,000. Marketing (advertising agency) - $25,000.
Free Download: Sample Food and Beverage Business Plan Templates. The food and beverage sector is booming. Restaurant openings rose 10% in 2023 compared to 2022 — even higher than in pre-pandemic years. From fine dining to food trucks, farmers to brewers, and wholesalers to coffee makers, there are opportunities across the food and beverage ...
5) Menu. Every restaurant needs a good menu, and this is the section within your restaurant business plan that you describe the food you'll serve in as much detail as possible. You may not have your menu design complete, but you'll likely have at least a handful of dishes that serve as the foundation of your offerings.
Whether planning to open a small food truck or an expensive fine-dine restaurant, you'll do great as long as you serve good food and have a solid business plan. This library of food, beverage, and restaurant business plan examples here can inspire and guide you as you begin to plan your business. So, we got you covered on that part.
The Plan. Our restaurant business plan is structured to cover all essential aspects needed for a comprehensive strategy. It outlines the restaurant's operations, marketing strategy, market environment, competitors, management team, and financial forecasts. Executive Summary: Offers an overview of the restaurant's business concept, market ...
Here you go, download our free restaurant business plan pdf, and start writing. This intuitive, modern, and investment-ready template is designed specifically for restaurants. It includes step-by-step instructions & examples to help in creating your own restaurant business plan.
Sample Business Plans for Food Industry 1. Charcuterie Business Plan. Charcuterie is a display of prepared meats paired with cheeses and plain vegetables on a traditional board. Charcuterie is the culinary art of preparing meat products such as bacon, salami, ham, sausage, terrines, galantines, ballotines, pâtés, and confit professionally.
The executive summary of a food business plan is a one- to two-page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which you will present in full in the rest of your business plan. Start with a one-line description of your food company. Provide a short summary of the key points in each section of your business plan ...
A business plan is an essential tool for any entrepreneur looking to start a food and beverage business. It outlines the goals and strategies for your company, and serves as a roadmap for success. In this guide, we will walk you through the process of creating a business plan for your food and beverage business, covering everything from market ...
The following plan for a completely fictional business is used for a monthly entrepreneur workshop at Oklahoma State University's Food & Agricultural Products Center, entitled "Food Business Basics: A Guide to Starting Your Own Food Business.". This mock business plan focuses on a whipped topping business, but the format is appropriate ...
The breakout of the funding is below: Purchase of food truck - $20,000. Food truck kitchen supplies and equipment - $10,000. Opening inventory - $2,000. Working capital (to include 3 months of overhead expenses) - $3,000. Food Truck Marketing (website design and management) - $5,000.
Our fast food restaurant business plan is structured to cover all essential aspects needed for a comprehensive strategy. It outlines the restaurant's operations, marketing strategy, market environment, competitors, management team, and financial forecasts. Executive Summary: Offers a snapshot of your fast food restaurant's business idea ...
To increase the number of clients served by 25% per year through superior service. To develop a sustainable start-up business that is profitable. To achieve an after tax net profit of $134K by year three. To achieve a net income of more than 10% of sales by the third year. Company Summary.
1. High School Students and Professionals. Coffee Club anticipates its food and beverage customers will be high school students aged 17-18 years and professionals aged. between 25 to 59 years working in the proximity of the anticipated location. Regarding the employment scenario, 68% of people aged between 15 and 64 in the US had a paid job ...
Donny's Food Truck - Sample Business Plan CONFIDENTIAL You may utilize this business plan as a starting point for your own, but you do not have permission to reproduce, copy, resell, publish, or distribute this plan as it exists here. Page 1 SMALL BUSINESS PLAN SAMPLE DONNY'S FOOD TRUCK BUSINESS PLAN PRESENTED TO INDIVIDUAL OR COMPANY NAME
Food Cafe Business Plan Outline. This is the standard food cafe business plan outline which will cover all important sections that you should include in your business plan. Executive Summary. Introducing Rodeo Mexican Cafe. Funding Requirement & Capitalization Plan. Summary of Financial Highlights. The Cafe. The Rodeo Experience.
Writing a fast food restaurant business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan.
food business plan sample With the high deficit in food/restaurants to serve a growing urban population, there is great potential for profitability in starting a food /restaurant business. But this business would not just succeed automatically when entered into without any form of planning.
Food Truck Industry Highlights. Before diving right into the business plan guide, let's go through some food industry trends and statistics: The industry size of street vendors in the USA was around $2.29 billion in 2021.; In the US, there were 67,271 food trucks in 2022, growing at an average annual rate of 18.1% per year over the five years 2017-2022. ...
She applauded Ms. Harris's plan to combat grocery price gouging. Mr. Furman, by contrast, said there was a risk that policies meant to curb corporate price gouging could instead keep the economy ...
A business plan is a detailed blueprint for the activities needed to establish a business (i.e. the details of a product or service, the market for that product or service, and the management of the business providing that product or service). A business plan is also the 'yardstick' by which a business owner measures success in meeting ...