- Subscribe Now

Pandemic in 2021: How the Philippines responded to COVID-19
Already have Rappler+? Sign in to listen to groundbreaking journalism.
This is AI generated summarization, which may have errors. For context, always refer to the full article.

The second year of the coronavirus pandemic in the Philippines was, in a number of ways, similar to the first.
Lockdowns remained for the most part of the year as two waves of COVID-19 ravaged the country. While several millions of Filipinos were able to get vaccinated throughout the year, experts flagged the vaccination campaign’s sluggish pace.
In the middle of it all, lawmakers investigated alleged anomalies involving billions of pesos in the Duterte administration’s pandemic contracts. These were probed in marathon Senate hearings that went on for months on end.
It was not until the latter part of the year until new daily coronavirus cases were reported only in the hundreds, restrictions were eased, and mandatory face shield policies were dropped – finally giving some kind of sense that, perhaps, the Philippines was getting out of the woods. (READ: Does wearing a face shield protect against COVID-19? )
While the holidays may be looking up for many Filipinos, the threat of a new variant of concern looms, and experts say that there is still a need to practice “risk-based” decisions when choosing activities and engagements despite the relatively low cases.
Here’s a list of stories reviewing what happened during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021.
As the Philippines’ vaccination campaign began in March, one of the government’s main goals was to get as many Filipinos vaccinated. We monitored the arrival and rollout of the vaccines in these trackers, as well as where COVID-19 cases were most prevalent. We also chronicle the significant events in the pandemic in a running timeline.
- TRACKER: The Philippines’ COVID-19 vaccine distribution
- TRACKER: Status of vaccination in Metro Manila
- TRACKER: The Philippines’ plans for COVID-19 boosters, third doses
- MAPS: COVID-19 in the Philippines
- TIMELINE: The novel coronavirus pandemic
Things we learned about COVID-19
These stories and explainers explore new information about the virus as they came.
Why did we need to pay attention to the virus when it mutated?
- EXPLAINER: Ano ang pagkakaiba ng mutation, variant, at strain?
- What we know so far about new COVID-19 variant found in PH
- FAST FACTS: The coronavirus Lambda variant
- What the surge fueled by the Delta variant taught us
- Beyond the Stories: Ano’ng dapat malaman tungkol sa Omicron variant?
How did the public and health experts tackle the ivermectin debate, when it was floated as a possible alternative treatment to COVID-19?
- COVID-19: The Philippines’ race for a cure
- Are we missing out on alternative treatments for COVID-19?
- EXPLAINER: Myths and facts about ivermectin
- In fierce Ivermectin debate, doctors remind: ‘Do no harm’
How did we learn to understand the dynamics of new variants and vaccines, and was herd immunity the only goal?
- Can COVID-19 vaccines in the Philippines beat Delta?
- 5 myths about COVID-19 vaccines debunked
- EXPLAINER: COVID-19 patients at PGH mostly unvaccinated
- In COVID-19 battle, herd immunity isn’t the only goal the PH needs to reach
- COVID-19 holiday plans: What would experts do?
Plight of health workers
Two deadly surges took an unprecedented toll on health workers employed in a healthcare system which had problems spilling over from before the pandemic began.
The release to workers of their benefits mandated by law was also a rocky discussion as the Department of Health’s spending was put under scrutiny.
- Overworked, underpaid health workers are walking away as Delta ravages PH
- Are the doctors alright? Frontliners in remote areas feel Manila’s neglect
- Doctors plead with gov’t: ‘We can’t fight this virus with antiquated methods’
- How Philippine contact tracers lost track of the virus
- Philippine contact tracers: The forgotten frontliners
- Underpaid health workers walk out, call for Duque resignation at mass protests
- What you should know about COVID-19 hazard pay, special risk allowance
The Duterte COVID-19 response
The pandemic response of President Rodrigo Duterte was not without criticism on matters of public health policy, public funds management, and governance.
- PH scores lowest among ASEAN countries in gov’t pandemic response – survey
- ‘NCR Plus’ bubble vs COVID-19 pointless with lax LGU borders
- PH may be among last in Southeast Asia to reach herd immunity
- What you need to know about Duterte’s COVID-19 loans
- Many unknowns in Duterte’s COVID-19 jab as PH fights vaccine hesitancy
- EXPLAINER: What went wrong with Duterte’s pandemic response?
- EXPLAINER: The Philippines’ fight vs vaccine hesitancy
- Hesitancy not a major driver for PH’s low vaccination rates
- President Duterte, you can still get COVID-19 under control
- Duterte’s longest SONA leaves Filipinos hanging on pandemic recovery
- Often-ignored COA fuels pandemic outrage vs Duterte gov’t
- DOH’s poor use of P67 billion COVID-19 funds led to ‘missed opportunities’ – auditors
- DOH failed to spend P2.07 billion after parking it in PS-DBM in 2020
- How the Duterte gov’t shut out local PPE producers during a pandemic
- PH’s last-minute quarantine changes force travelers to spend thousands
Jobs and economy
The health crisis coincided with an economic crisis that was experienced locally and globally. Here’s what it was like for Filipinos in 2021.
- Philippines offers nurses in exchange for vaccines from Britain, Germany
- Labor secretary Bello aims to deploy more nurses, healthcare staff overseas
- With fresh lockdowns, 3.88 million Filipinos jobless in August 2021
- Philippines lowers 2021 economic growth target over fresh lockdowns, Delta
- Delta variant puts Philippine economy among most vulnerable in Asia
- COVID-19 pandemic to cost PH P41.4 trillion over next 4 decades – NEDA
- Philippine GDP growth slows but beats forecasts at 7.1% in Q3 2021
- Philippines raises deployment cap of healthcare workers to 7,000
Despair, ‘bayanihan’ amid crisis
The Philippines recorded millions of positive cases and tens of thousands dead – with more added to the health department’s daily tally. These are stories of people behind the numbers, as well as how Filipinos in the country and abroad banded together in times of crisis.
- Philippines’ COVID-19 surge tears through families
- Facebook as lifeline: Desperate Filipinos turn to strangers for help
- Community pantries: Is it a ‘revolution’ when Filipinos just want to give?
- ‘Take care of your neighbor’: Communities battle doubts about COVID-19 vaccines
- Healthcare professionals turn to TikTok to fact-check, debunk health myths
- Through virus surge and separation, Filipinos in Indonesia closer than ever
- ‘Last year was nothing compared to now’: Learning from India’s second wave
The Pharmally controversy
As Filipinos struggled to survive, lawmakers investigated allegations of misspending in the government’s pandemic funds. These anomalies, which sprung from irregularities found by the Commission on Audit, had ties to the President himself.
- Biggest pandemic supplier has links to ex-Duterte adviser Michael Yang
- Pharmally had P625,000 capital before bagging P8 billion in COVID-19 contracts
- Pharmally bags P2 billion more deals in 2021
- PANOORIN: Bakit kahina-hinala ang pagkakuha ng Pharmally ng mga kontrata sa pandemya?
- ‘We swindled gov’t’: Pharmally changed expiry date of medical-grade face shields
- 2 days after bombshell testimony, Pharmally exec can’t be contacted by Senate panel
- Furious Duterte seeks to block Cabinet, witnesses from appearing in Senate probe
- Rigged favors for Pharmally, substandard supplies are graft – senators
- Pharmally’s Krizle Mago recants Senate testimony: ‘It was a pressured response’
- ‘Sue us instead’: Jailed Pharmally execs still won’t budge over missing documents
– Rappler.com
Add a comment
Please abide by Rappler's commenting guidelines .
There are no comments yet. Add your comment to start the conversation.
How does this make you feel?
Related Topics

Michelle Abad
Recommended stories, {{ item.sitename }}, {{ item.title }}, department of health, here’s what you need to know about pertussis or whooping cough.
DOH loses P338 million due to alleged hospital project irregularities in Albay

Why screening for breast cancer even without symptoms is important

CA junks DOH plea on P8.1-billion barangay health stations project

DOH, FDA advise against gluta IV drip for skin whitening
year-end stories
Generative ai’s wild 2023: ‘hallucinate’ as word of the year, $27b in investments.

Business Sense: 2023 is generative AI’s breakout year

#SharePhilippines: Philippine festivals come alive again in 2023

How House lawmakers flexed their political muscle in 2023

The top 10 most viewed Rappler Live Jam episodes of 2023

Checking your Rappler+ subscription...
Upgrade to Rappler+ for exclusive content and unlimited access.
Why is it important to subscribe? Learn more
You are subscribed to Rappler+
Supporting the Philippines’ COVID-19 Emergency Response
Beneficiaries
For Vilma Campos , a Quezon City resident and mother of five, life has improved since her family received their vaccinations. “My daughter has resumed working, so has my husband,” she said. “Life is no longer that difficult.”
Before COVID-19 hit, Vilma’s job was taking care of children. When the authorities started implementing quarantine restrictions, she, her daughter, and her spouse lost their jobs. Vilma said her family was always wondering where to get the next meal. “What gave us hope was the arrival of vaccines,” she said. “Things have improved and I really wish we can all overcome this pandemic.”
The Philippines was one of the countries hit hardest by COVID-19 in the East Asia and Pacific region. To manage the spread of the virus, authorities implemented strict quarantine restrictions and health protocols, restricted mobility of people as wells as the operational capacity of businesses. As a result, the Philippine economy suffered. In 2020, GDP contracted 9.5 percent, driven by significant declines in consumption and investment growth, and exacerbated by the sharp slowdown in exports, tourism, and remittances. Many Filipinos lost jobs and experienced food shortages and difficulties accessing health care. Due to global shortages, procurement of COVID-19 vaccines, medical supplies, personal protective equipment (PPE), reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test machines, and test kits proved challenging in the early phases of the pandemic.
The project supported the country’s efforts to scale up vaccination across the national territory, strengthen the country’s health system, and overcome the impact of the pandemic especially on the poor and the most vulnerable. Besides vaccines, the project supported procurement of PPE, essential medical equipment such as mechanical ventilators, cardiac monitors, portable x-ray machines; laboratory equipment and test kits; and ambulances. The project also supported construction and refurbishment of negative pressure isolation rooms and quarantine facilities, as well as the expansion of the country’s laboratory capacity at the national and sub-national levels for prevention of and preparedness against emerging infectious diseases. It funded retrofitting of the national reference laboratory – the Research Institute for Tropical Medicine (RITM) – as well as six sub-national and public health laboratories in Baguio, Cebu, Davao, and Manila, and the construction and expansion of laboratory capacity in priority regions without such facilities.
During year1 to year 2, the following results were achieved:
- The project supported the procurement and deployment of 33 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine across the country. The project supported pediatric vaccination for 7.5 million children. With the support of development partners including the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, and Asian Infrastructure and Investment Bank, the Philippines administered more than 137 million vaccines (more than 126 million first and second doses, and more than 10 million booster doses) by March of 2022.
- The project helped scale up testing capacity from 1,000 RT-PCR tests per day to 24,979 per day.
- The project supported the procurement of 500 mechanical ventilators, 119 portable x-ray machines, 70 infusion pumps, 50 RT-PCR machines, and 68 ambulances.
- As a result of the strong vaccination rates and strengthened health response capacity, the Philippines is now much better able to manage the pandemic.
The Philippines COVID-19 Emergency Response Project supported the procurement and deployment of 33 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine across the country. The project also supported pediatric vaccination for 7.5 million Filipino children.
Bank Group Contribution
The World Bank through the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) provided $900 million of funding in total for the emergency response project. The project provided $100 million for medical and laboratory equipment and supplies; $500 million for primary vaccine doses, ancillaries, and end-to-end logistics; and $300 million for boosters and additional doses, and end-to-end logistics.
The World Bank collaborated with the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Asian Infrastructure and Investment Bank (AIIB) on project preparation and vaccines financing. The Bank worked with the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), and the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) on the Vaccine Introduction Readiness Tool (VIRAT) and Vaccine Readiness Assessment Tool (VRAF) Tool 2.0, which is used to assess status, gaps, and issues in four domains: planning and management, supply and distribution, program delivery, and supporting systems and infrastructure. Australia, through the AGaP Trust Fund, provided a US$300,000 grant to support implementation. The World Bank also collaborated with UNICEF to address vaccine hesitancy and with the WHO to procure RT-PCR machines and test kits.
Looking Ahead
The Philippine government is considering additional support for scaling up testing capacity. Equipment has been acquired and civil works commissioned through the project are now in use. An action plan is being developed for continued implementation of environmental and social safeguards employed in the project, such as COVID-19 waste management and assessment of accessibility of vulnerable groups to health care services. These will be institutionalized using the manuals developed and through directive issuances by the Department of Health. The project also supports the development of National Action Plan Towards Increased Accessibility of Health Care Facilities for Vulnerable Groups. The World Bank is also supporting the Department of Health and priority LGUs in strengthen local health systems for Universal Health Coverage.
Philippines Covid-19 Emergency Response Project
Philippines Covid-19 Emergency Response Project Additional Financing
Philippines COVID-19 Emergency Response Project – Additional Financing 2
Department of Health Covid-19 Tracker.
Department of Health Covid-19 Updates on Covid-19 Vaccines
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
- Open access
- Published: 21 September 2021
Local government responses for COVID-19 management in the Philippines
- Dylan Antonio S. Talabis 1 , 2 ,
- Ariel L. Babierra 1 , 2 ,
- Christian Alvin H. Buhat 1 , 2 ,
- Destiny S. Lutero 1 , 2 ,
- Kemuel M. Quindala III 1 , 2 &
- Jomar F. Rabajante 1 , 2 , 3
BMC Public Health volume 21 , Article number: 1711 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
551k Accesses
25 Citations
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
Responses of subnational government units are crucial in the containment of the spread of pathogens in a country. To mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Philippine national government through its Inter-Agency Task Force on Emerging Infectious Diseases outlined different quarantine measures wherein each level has a corresponding degree of rigidity from keeping only the essential businesses open to allowing all establishments to operate at a certain capacity. Other measures also involve prohibiting individuals at a certain age bracket from going outside of their homes. The local government units (LGUs)–municipalities and provinces–can adopt any of these measures depending on the extent of the pandemic in their locality. The purpose is to keep the number of infections and mortality at bay while minimizing the economic impact of the pandemic. Some LGUs have demonstrated a remarkable response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The purpose of this study is to identify notable non-pharmaceutical interventions of these outlying LGUs in the country using quantitative methods.
Data were taken from public databases such as Philippine Department of Health, Philippine Statistics Authority Census, and Google Community Mobility Reports. These are normalized using Z-transform. For each locality, infection and mortality data (dataset Y ) were compared to the economic, health, and demographic data (dataset X ) using Euclidean metric d =( x − y ) 2 , where x ∈ X and y ∈ Y . If a data pair ( x , y ) exceeds, by two standard deviations, the mean of the Euclidean metric values between the sets X and Y , the pair is assumed to be a ‘good’ outlier.
Our results showed that cluster of cities and provinces in Central Luzon (Region III), CALABARZON (Region IV-A), the National Capital Region (NCR), and Central Visayas (Region VII) are the ‘good’ outliers with respect to factors such as working population, population density, ICU beds, doctors on quarantine, number of frontliners and gross regional domestic product. Among metropolitan cities, Davao was a ‘good’ outlier with respect to demographic factors.
Conclusions
Strict border control, early implementation of lockdowns, establishment of quarantine facilities, effective communication to the public, and monitoring efforts were the defining factors that helped these LGUs curtail the harm that was brought by the pandemic. If these policies are to be standardized, it would help any country’s preparedness for future health emergencies.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Since the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of cases have already reached 82 million worldwide at the end of 2020. In the Philippines, the number of cases exceeded 473,000. As countries around the world face the continuing threat of the COVID-19 pandemic, national governments and health ministries formulate, implement and revise health policies and standards based on recommendations by world health organization (WHO), experiences of other countries, and on-the-ground experiences. Early health measures were primarily aimed at preventing and reducing transmission in populations at risk. These measures differ in scale and speed among countries, as some countries have more resources and are more prepared in terms of healthcare capacity and availability of stringent policies [ 1 , 2 ].
During the first months of the pandemic, several countries struggled to find tolerable, if not the most effective, measures to ‘flatten’ the COVID-19 epidemic curve so that health facilities will not be overwhelmed [ 3 , 4 ]. In responding to the threat of the pandemic, public health policies included epidemiological and socio-economic factors. The success or failure of these policies exposed the strengths or weaknesses of governments as well as the range of inequalities in the society [ 5 , 6 ].
As national governments implemented large-scale ‘blanket’ policies to control the pandemic, local government units (LGUs) have to consider granular policies as well as real-time interventions to address differences in the local COVID-19 transmission dynamics due to heterogeneity and diversity in communities. Some policies in place, such as voluntary physical distancing, wearing of face masks and face shields, mass testing, and school closures, could be effective in one locality but not in another [ 7 – 9 ]. Subnational governments like LGUs are confronted with a health crisis that have economic, social and fiscal impact. While urban areas have been hot spots of the COVID-19 pandemic, there are health facilities that are already well in placed as compared to less developed and deprived rural communities [ 10 ]. The importance of local narratives in addressing subnational concerns are apparent from published experiences in the United States [ 11 ], China [ 12 , 13 ], and India [ 14 ].
In the Philippines, the Inter-Agency Task Force on Emerging Infectious Diseases (IATF) was convened by the national government in January 2020 to monitor a viral outbreak in Wuhan, China. The first case of local transmission of COVID-19 was confirmed on March 7, 2020. Following this, on March 8, the entire country was placed under a State of Public Health Emergency. By March 25, the IATF released a National Action Plan to control the spread of COVID-19. A community quarantine was initially put in place for the national capital region (NCR) starting March 13, 2020 and it was expanded to the whole island of Luzon by March 17. The initial quarantine was extended up to April 30 [ 5 , 15 ]. Several quarantine protocols were then implemented based on evaluation of IATF:
Community Quarantine (CQ) refers to restrictions in mobility between quarantined areas.
In Enhanced Community Quarantine (ECQ), strict home quarantine is implemented and movement of residents is limited to access essential goods and services. Public transportation is suspended. Only economic activities related to essential and utility services are allowed. There is heightened presence of uniformed personnel to enforce community quarantine protocols.
Modified Enhanced Community Quarantine (MECQ) is implemented as a transition phase between ECQ and GCQ. Strict home quarantine and suspension of public transportation are still in place. Mobility restrictions are relaxed for work-related activities. Government offices operates under a skeleton workforce. Manufacturing facilities are allowed to operate with up to 50% of the workforce. Transportation services are only allowed for essential goods and services.
In General Community Quarantine (GCQ), individuals from less susceptible age groups and without health risks are allowed to move within quarantined zones. Public transportation can operate at reduced vehicle capacity observing physical distancing. Government offices may be at full work capacity or under alternative work arrangements. Up to 50% of the workforce in industries (except for leisure and amusement) are allowed to work.
Modified General Community Quarantine (MGCQ) refers to the transition phase between GCQ and the New Normal. All persons are allowed outside their residences. Socio-economic activities are allowed with minimum public health standard.
LGUs are tasked to adopt, coordinate, and implement guidelines concerning COVID-19 in accordance with provincial and local quarantine protocols released by the national government [ 16 ].
In this study, we identified economic and demographic factors that are correlated with epidemiological metrics related to COVID-19, specifically to the number of infected cases and number of deaths [ 17 , 18 ]. At the regional, provincial, and city levels, we investigated the localities that differ with the other localities, and determined the possible reasons why they are outliers compared to the average practices of the others.
We categorized the data into economic, health, and demographic components (See Table 1 ). In the economic setting, we considered the number of people employed and the number of work hours. The number of health facilities provides an insight into the health system of a locality. Population and population density, as well as age distribution and mobility, were used as the demographic indicators. The data (as of November 10, 2020) from these seven factors were analyzed and compared to the number of deaths and cumulative cases in cities, provinces or regions in the Philippines to determine the outlier.
The Philippine government’s administrative structure and the availability of the data affected its range for each factor. Regional data were obtained for the economic component. For the health and demographic components, data from cities and provinces were retrieved from the sources. Due to the NCR exhibiting the highest figures in all key components, an investigation was conducted to identify an outlier among its cities. The z -transform
where x is the actual data, μ is the mean and σ is the standard deviation were applied to normalize the dataset. Two sets of normalized data X and Y were compared by assigning to each pair ( x , y ), where x ∈ X and y ∈ Y , its Euclidean metric d given by d =( x − y ) 2 . Here, the Y ’s are the number of COVID-19 cases and deaths, and X ’s are the other demographic indicators. Since 95% of the data fall within two standard deviations from the mean, this will be the threshold in determining an outlier. This means that if a data pair ( x , y ) exceeds, by two standard deviations, the mean of the Euclidean metric values between the sets X and Y , the pair is assumed to be an outlier.
To identify a good outlier, a bias computation was performed. In this procedure, Y represents the normalized data set for the number of deaths or the number of cases while X represents the normalized data set for every factor that were considered in this study. The bias is computed using the metric
for all x in X and y in Y . To categorize a city, province, or region as a good outlier, the bias corresponding to this locality must exceed two standard deviations from the mean of all the bias computations between the sets X and Y .
Results and discussion
The data used were the reported COVID-19 cases and deaths in the Philippines as of November 10, 2020 which is 240 days since community lockdowns were implemented in the country. Figure 1 shows the different lockdowns implemented per province since March 15. It can be seen that ECQ was implemented in Luzon and major cities in the country in the first few weeks since March 15, and slowly eased into either GCQ or MGCQ as time progressed. By August, the most stringent lockdown was MECQ in the National Capital Region (NCR) and some nearby provinces. Places under MECQ on September were Iloilo City, Bacolod City, and Lanao del Sur, with the last province as the lone community to be placed under MECQ the month after. By November 1, 2020, communities were either placed under GCQ or MGCQ.
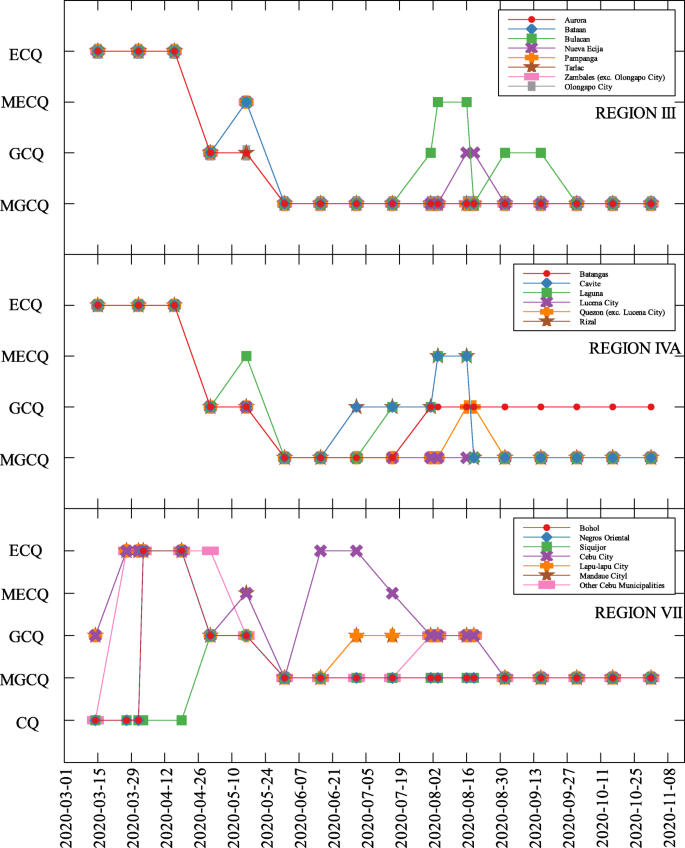
COVID-19 community quarantines in Regions III, IVA and VII
Comparison of economic, health, and demographic components and COVID-19 parameters
The economic, health and demographic components were compared to COVID-19 cases and deaths. These comparisons were done for different community levels (regional, provincial, city/metropolitan) (See Tables 2 , 3 , and 4 ). Figure 2 summarizes the correlation of components to COVID-19 cases and deaths at the regional level. In all components, correlations with other parameters to both COVID-19 cases and deaths are close. Every component except Residential Mobility and GRDP have slightly higher correlation coefficient for COVID-19 cases as compared to COVID-19 deaths.
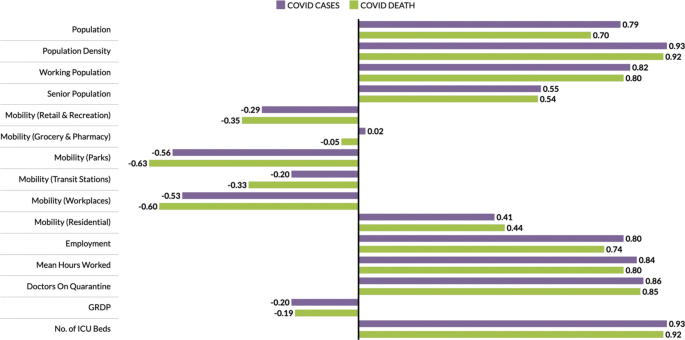
Correlation of components to COVID-19 cases and deaths at the regional level
Among the components, the number of ICU beds component has the highest correlation with COVID-19 parameters. This makes sense as this is one of the first-degree measures of COVID-19 transmission. Population density comes in second, followed by mean hours worked and working population, which are all related to how developed the region is economy-wise. Regions having larger population density also have a huge working population and longer working hours [ 24 ]. Thus, having a huge population density implies high chance of having contact with each other [ 25 , 26 ]. Another component with high correlation to the cases and deaths is the number of doctors on quarantine, which can be looked at two ways; (i) huge infection rate in the region which is the reason the doctors got exposed or are on quarantine, and (ii) lots of doctors on quarantine which resulted to less frontliners taking care of the infected individuals. All definitions of mobility and the GDP are not strongly correlated to any of the COVID-19 measures.
In each data set, outliers were identified depending on their distance from the mean. For simplicity, we denote components that are compared with COVID-19 cases by (C) and with COVID-19 deaths by (D). The summary of outliers among regions in the Philippines is shown in Figs. 3 and 4 . Data is classified according to groups of component. In each outlier region, non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPI) implemented and their timing are identified.
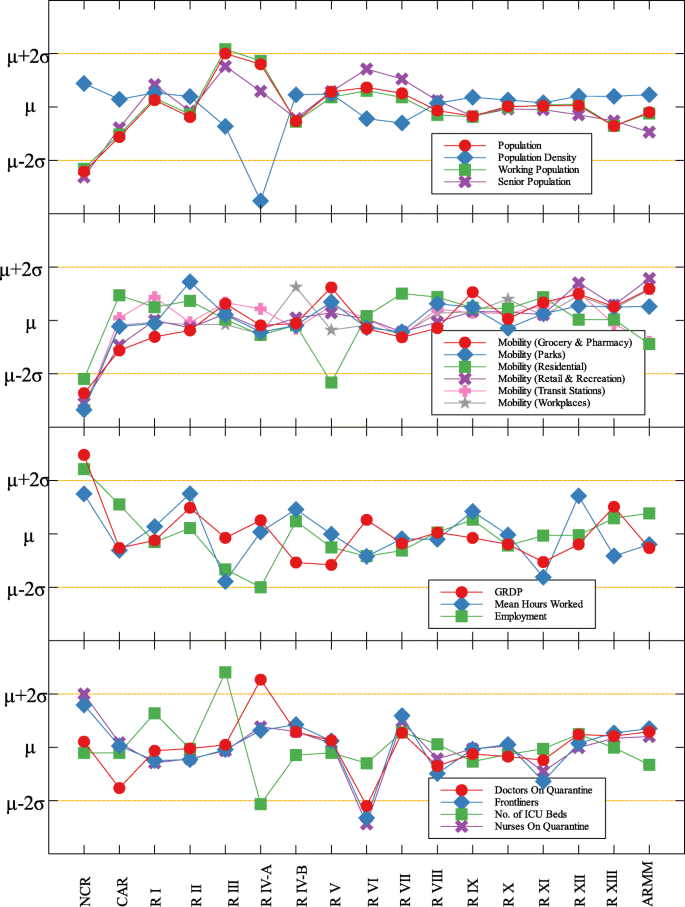
Outliers among regions in the Philippines with respect to COVID-19 cases
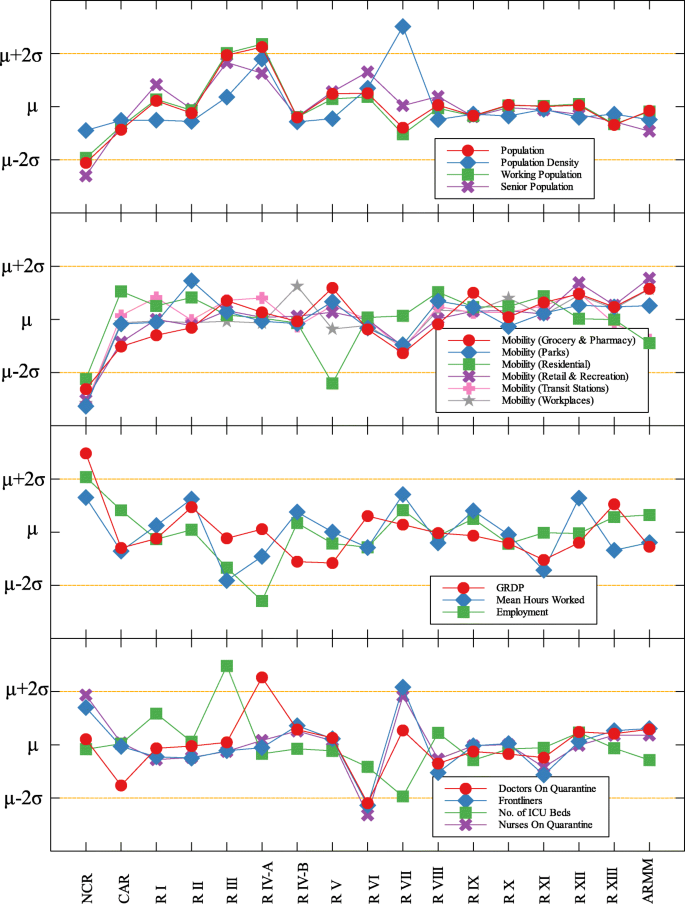
Outliers among regions in the Philippines with respect to COVID-19 deaths
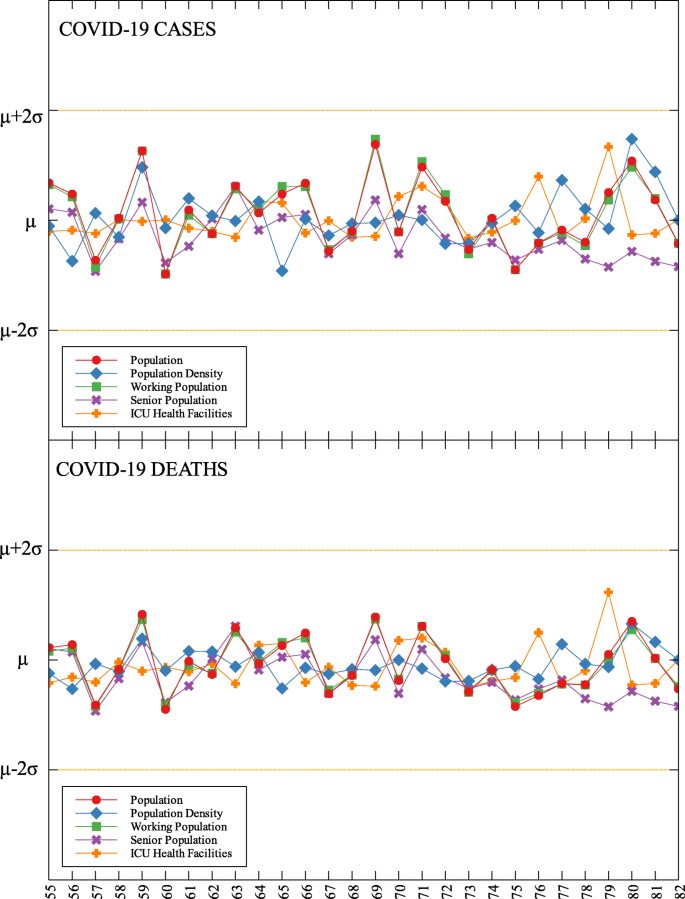
Region III is an outlier in terms of working population (C) and the number of ICU beds (C) (see Fig. 5 and Table 5 ). This means that considering the working population of the region, the number of COVID-19 infections are better than that of other regions. Same goes with the number of ICU beds in relation to COVID-19 deaths. Region III is comprised of Aurora, Bataan, Nueva Ecija, Pampanga, Tarlac, Zambales, and Bulacan. This good performance might be attributed to their performance especially on their programs against COVID-19. As early as March 2020, the region had been under a community lockdown together with other regions in Luzon. Being the closest to NCR, Bulacan has been the most likely to have high number of COVID-19 cases in the region. But the province responded by opening infection control centers which offer free healthcare, meals, and rooms for moderate-severe COVID-19 patients [ 27 ]. They have also implemented strict monitoring of entry-exit borders, organization of provincial task force and incident command center, establishment of provincial quarantine facilities for returning overseas Filipino workers, mandated municipal quarantine facilities for asymptomatic cases, and mass testing, among others [ 27 ]. Most of which have been proven effective in reducing the number of COVID-19 cases and deaths [ 28 ].
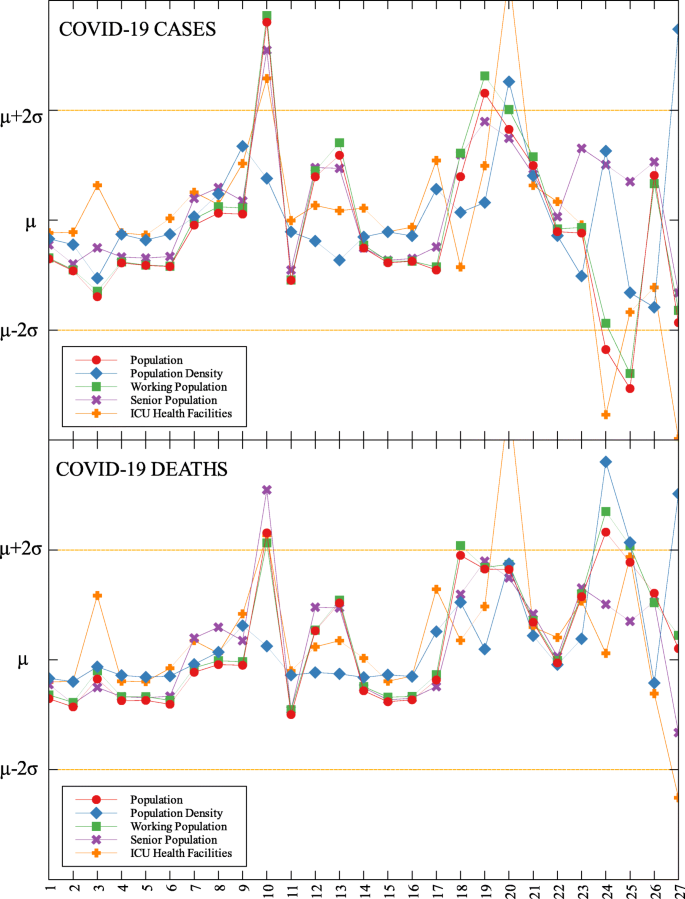
Outliers among the provinces in Luzon with respect to COVID-19 cases and deaths
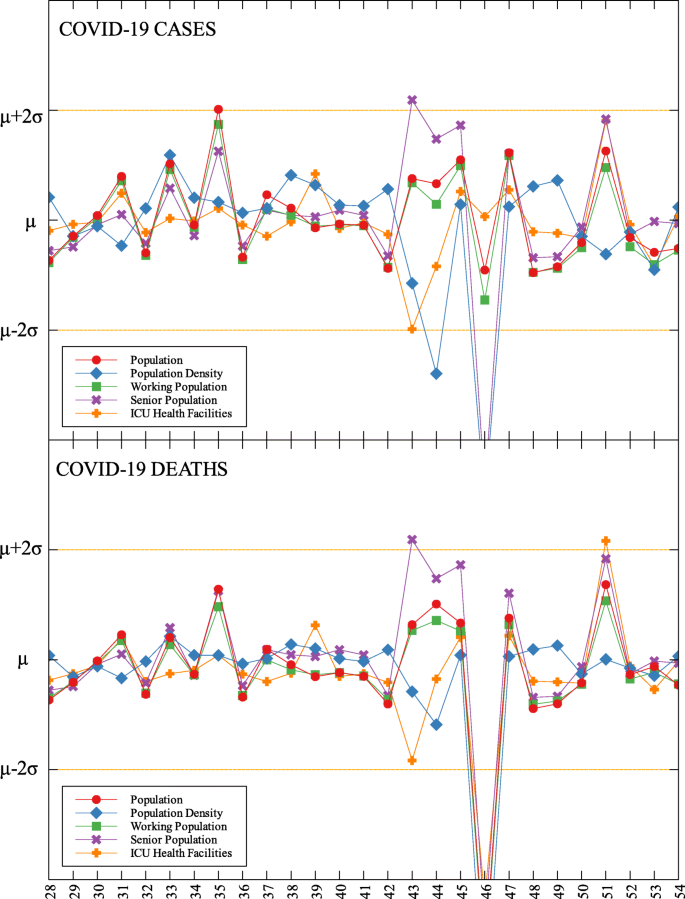
Outliers among the provinces in Visayas with respect to COVID-19 cases and deaths
Outliers among the provinces in Mindanao with respect to COVID-19 cases and deaths
Region IV-A is an outlier in terms of population and working population (D) and doctors on quarantine (D) (see Fig. 5 and Table 5 ). Considering their population and working population, the COVID-19 death statistics show better results compared to other regions. Same goes with the number of doctors in the region which are in quarantine in relation to the reported COVID-19 deaths. This shows that the region is doing well in terms of decreasing the COVID-19 fatalities compared to other regions in terms of populations and doctors on quarantine. Region IV-A is comprised of Batangas, Cavite, Laguna, Quezon, and Rizal. Same with Region III, they have been under the community lockdown since March of last year. Provinces of the region such as Rizal have been proactive in responding to the epidemic as they have already suspended classes and distributed face masks even before the nationwide lockdown [ 29 ]. Despite being hit by natural calamities, the region still continue ramping up the response to the pandemic through cash assistance, first aid kits, and spreading awareness [ 30 ].
An interesting result is that NCR, the center of the country and the most densely populated, is a good outlier in terms of GRDP (C) and GRDP (D). Cities in the region launched various programs in order to combat the disease. They have launched mass testings with Quezon City, Taguig City, and Caloocan City starting as early as April 2020. Pasig City started an on-the-go market called Jeepalengke. Navotas, Malabon, and Caloocan recorded the lowest attack rate of the virus. Caloocan city had good strategies for zoning, isolation and even in finding ways to be more effective and efficient. Other programs also include color-coded quarantine pass, and quarantine bands. It is also possible that NCR may just have a very high GRDP compared to other regions. A breakdown of the outliers within NCR can be seen in Fig. 8 .
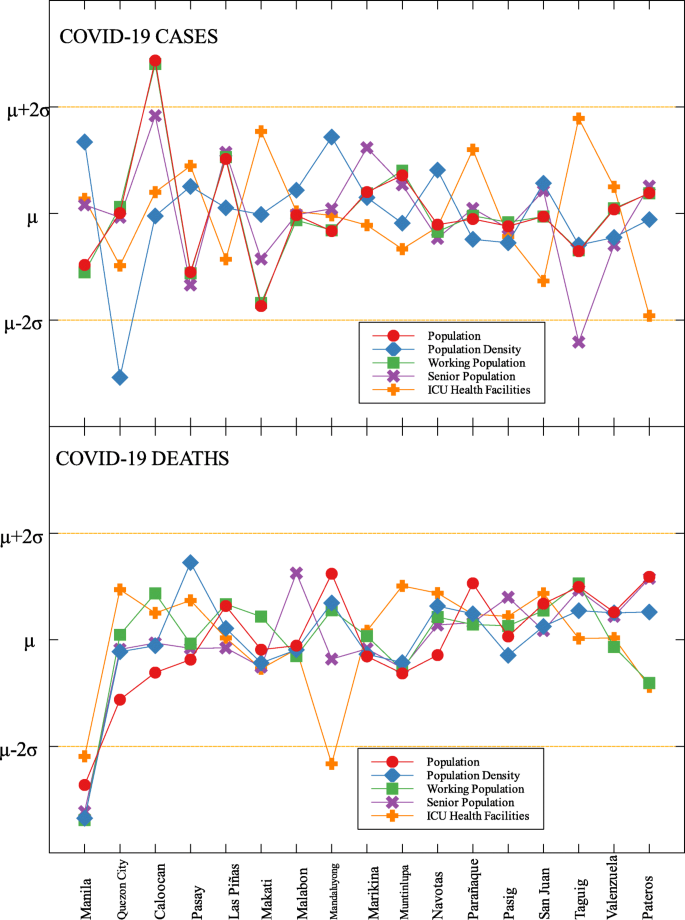
Outliers in the national capital region with respect to COVID-19 cases and deaths
Region VII is also an outlier in terms of population density (D) and frontliners (D) (see Fig. 6 and Table 5 ). This means that given the population density and the number of frontliners in the region, their COVID-related deaths in the region is better than the rest of the country. This region consists of four provinces (Cebu, Bohol, Negros Oriental, and Siquijor) and three highly urbanized cities (Cebu City, Lapu-Lapu City, and Mandaue City), referred to as metropolitan Cebu. This significant decline may be explained by how the local government responded after they were placed in stricter community quarantine measures despite the rest of the country easing in to more lenient measures. Due to the longer and stricter quarantine in Cebu, the lockdown had a greater impact here than in other areas where restrictions were eased earlier [ 31 ]. Dumaguete was one of the destinations of the first COVID case in the Philippines [ 32 ], their local government was able to keep infections at bay early on. Siquijor was also COVID-19-free for 6 months [ 33 ]. The compounded efforts of the different provinces in the region can account for the region being identified as an outlier.
Among the metropolitan cities, Davao came out as a good outlier in terms of population (C) and working population (C) (see Figs. 7 , 9 , and Table 5 ). This result may be attributed to their early campaign on consistent communication of COVID-19-related concerns to the public [ 34 ]. They were also able to set up transportation for essential workers early on [ 35 ].
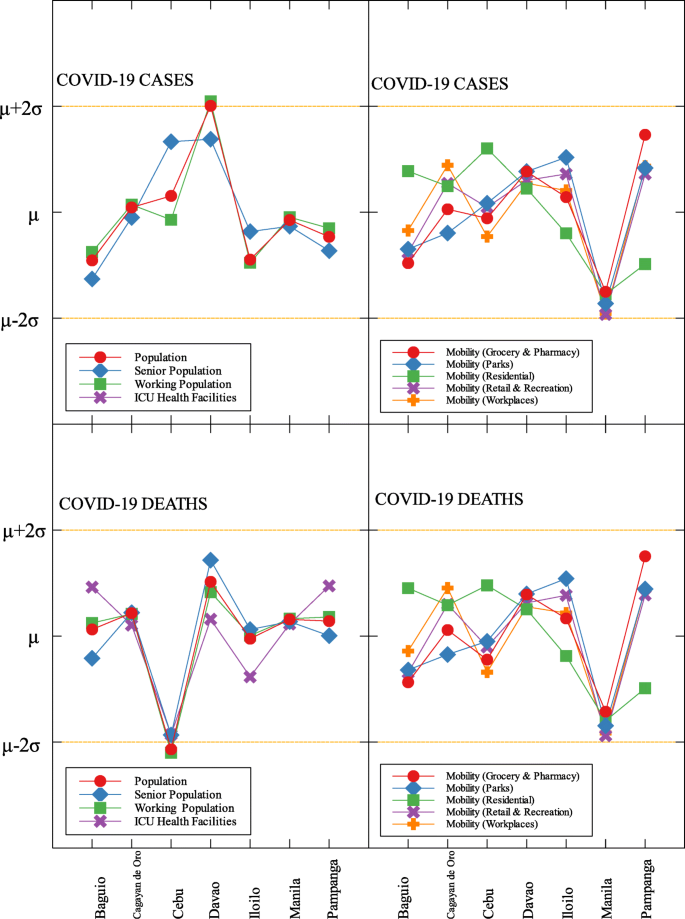
Outliers among metropolitan areas in the Philippines with respect to COVID-19 cases and deaths
This study identified outliers in each data group and determined the NPIs implemented in the locality. Economic, health and demographic components were used to identify these outliers. For the regional data, three regions in Luzon and one in Visayas were identified as outliers. Apart from the minimum IATF recommended NPIs, various NPIs were implemented by different regions in containing the spread of COVID-19 in their areas. Some of these NPIs were also implemented in other localities yet these other localities did not come out as outliers. This means that one practice cannot be the sole explanation in determining an outlier. The compounding effects of practices and their timing of implementation are seen to have influenced the results. A deeper analysis of daily data for different trends in the epidemic curve is considered for future research.
Correlation tables, outliers and community quarantine timeline
Availability of data and materials.
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, Ren R, Leung KSM, Lau EHY, Wong JY, Xing X, Xiang N, Wu Y, Li C, Chen Q, Li D, Liu T, Zhao J, Liu M, Tu W, Chen C, Jin L, Yang R, Wang Q, Zhou S, Wang R, Liu H, Luo Y, Liu Y, Shao G, Li H, Tao Z, Yang Y, Deng Z, Liu B, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Shi G, Lam TTY, Wu JT, Gao GF, Phil D, Cowling BJ, Yang B, Leung GM, Feng Z. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(13):1199–207.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Hsiang S, Allen D, Annan-Phan S, Bell K, Bolliger I, Chong T, Druckenmiller H, Huang LY, Hultgren A, Krasovich E, Lau P, Lee J, Rolf E, Tseng J, Wu T. The effect of large-scale anti-contagion policies on the covid-19 pandemic. Nature. 2020; 584:262–67.
Anderson R, Heesterbeek JAP, Klinkenberg D, Hollingsworth T. Comment how will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the covid-19 epidemic?Lancet. 2020; 395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30567-5 .
Buhat CA, Torres M, Olave Y, Gavina MK, Felix E, Gamilla G, Verano KV, Babierra A, Rabajante J. A mathematical model of covid-19 transmission between frontliners and the general public. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinforma. 2021; 10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-021-00295-6 .
Ocampo L, Yamagishic K. Modeling the lockdown relaxation protocols of the philippine government in response to the covid-19 pandemic: an intuitionistic fuzzy dematel analysis. Socioecon Plann Sci. 2020; 72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2020.100911 .
Weible C, Nohrstedt D, Cairney P, Carter D, Crow D, Durnová A, Heikkila T, Ingold K, McConnell A, Stone D. Covid-19 and the policy sciences: initial reactions and perspectives. Policy Sci. 2020; 53:225–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11077-020-09381-4 .
Article Google Scholar
Wibbens PD, Koo WW-Y, McGahan AM. Which covid policies are most effective? a bayesian analysis of covid-19 by jurisdiction. PLoS ONE. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0244177 .
Mintrom M, O’Connor R. The importance of policy narrative: effective government responses to covid-19. Policy Des Pract. 2020; 3(3):205–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/25741292.2020.1813358 .
Google Scholar
Chin T, Kahn R, Li R, Chen JT, Krieger N, Buckee CO, Balsari S, Kiang MV. Us-county level variation in intersecting individual, household and community characteristics relevant to covid-19 and planning an equitable response: a cross-sectional analysis. BMJ Open. 2020; 10(9). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039886 .
OECD. The territorial impact of COVID-19: managing the crisis across levels of government. 2020. https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/the-territorial-impact-of-covid-19-managing-the-crisis-across-levels-of-government-d3e314e1/#biblio-d1e5202 . Accessed 20 Feb 2007.
White ER, Hébert-Dufresne L. State-level variation of initial covid-19 dynamics in the united states. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240648 .
Lin S, Huang J, He Z, Zhan D. Which measures are effective in containing covid-19? — empirical research based on prevention and control cases in China. medRxiv. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.28.20046110 . https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2020/03/30/2020.03.28.20046110.full.pdf .
Mei C. Policy style, consistency and the effectiveness of the policy mix in China’s fight against covid-19. Policy Soc. 2020; 39(3):309–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/14494035.2020.1787627. http://arxiv.org/abs/https: //doi.org/10.1080/14494035.2020.1787627.
Dutta A, Fischer HW. The local governance of covid-19: disease prevention and social security in rural india. World Dev. 2021; 138:105234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105234 .
Vallejo BM, Ong RAC. Policy responses and government science advice for the covid 19 pandemic in the philippines: january to april 2020. Prog Disaster Sci. 2020; 7:100115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdisas.2020.100115 .
Inter-Agency Task Force for the Management of Emerging Infectious Diseases. Omnibus guidelines on the implementation of community quarantine in the Philippines. 2020. https://doh.gov.ph/node/27640 . Accessed 20 Feb 2020.
Roy S, Ghosh P. Factors affecting covid-19 infected and death rates inform lockdown-related policymaking. PloS ONE. 2020; 15(10):0241165. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241165 .
Pullano G, Valdano E, Scarpa N, Rubrichi S, Colizza V. Evaluating the effect of demographic factors, socioeconomic factors, and risk aversion on mobility during the covid-19 epidemic in france under lockdown: a population-based study. Lancet Digit Health. 2020; 2(12):638–49.
Department of Health. COVID-19 tracker. 2020. https://doh.gov.ph/covid19tracker . Accessed 25 Nov 2020.
Authority PS. Philippine population density (based on the 2015 census of population). 2020. https://psa.gov.ph/content/philippine-population-density-based-2015-census-population . Accessed 11 Apr 2020.
Google. COVID-19 community mobility report. 2020; https://www.google.com/covid19/mobility?hl=en. Accessed 25 Nov 2020.
Authority PS. Labor force survey. 2020. https://psa.gov.ph/statistics/survey/labor-and-employment/labor-force-survey?fbclid=IwAR0a5GS7XtRgRmBwAcGl9wGwNhptqnSBm-SNVr69cm8sCVd9wVmcoKHRCdU . Accessed 11 Apr 2020.
Authority PS. https://psa.gov.ph/grdp/tables?fbclid=IwAR3dKvo3B5eauY7KcWQG4VXbuiCrzFHO4b-f1k5Od76ccAlYxUimUIaqs94 . Accessed 11 Apr 2020. 2020.
Peterson E. The role of population in economic growth. SAGE Open. 2017; 7:215824401773609. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244017736094 .
Buhat CA, Duero JC, Felix E, Rabajante J, Mamplata J. Optimal allocation of covid-19 test kits among accredited testing centers in the philippines. J Healthc Inform Res. 2021; 5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41666-020-00081-5 .
Hamidi S, Sabouri S, Ewing R. Does density aggravate the covid-19 pandemic?: early findings and lessons for planners. J Am Plan Assoc. 2020; 86:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/01944363.2020.1777891 .
Philippine News Agency. Bulacan shares anti-COVID-19 best practices. 2020. https://mb.com.ph/2020/08/16/bulacan-shares-anti-covid-19-best-practices/ . Accessed Mar 2020.
Buhat CA, Villanueva SK. Determining the effectiveness of practicing non-pharmaceutical interventions in improving virus control in a pandemic using agent-based modelling. Math Appl Sci Eng. 2020; 1:423–38. https://doi.org/10.5206/mase/10876 .
Hallare K. Cainta, Rizal suspends classes, distributes face masks over coronavirus threat. 2020. https://newsinfo.inquirer.net/1238217/cainta-rizal-suspends-classes-distributes-face-masks-over-coronavirus-threat . Accessed Mar 2020.
Relief International. Responding to COVID-19 in the Aftermath of Volcanic Eruption. 2020. https://www.ri.org/projects/responding-to-covid-19-in-the-aftermath-of-volcanic-eruption/. Accessed Mar 2020.
Macasero R. Averting disaster: how Cebu City flattened its curve. 2020. https://www.rappler.com/newsbreak/explainers/how-cebu-city-flattened-covid-19-curve/ . Accessed Mar 2020.
Edrada EM, Lopez EB, Villarama JB, Salva-Villarama EP, Dagoc BF, Smith C, Sayo AR, Verona JA, Trifalgar-Arches J, Lazaro J, Balinas EGM, Telan EFO, Roy L, Galon M, Florida CHN, Ukawa T, Villaneuva AMG, Saito N, Nepomuceno JR, Ariyoshi K, Carlos C, Nicolasor AD, Solante RM. First covid-19 infections in the philippines: a case report. Trop Med Health. 2020; 48(30). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41182-020-00218-7 .
Macasero R. Coronavirus-free for 6 months, Siquijor reports first 2 cases. 2020. https://www.rappler.com/nation/siquijor-coronavirus-cases-august-2-2020 . Accessed Mar 2020.
Davao City. Mayor Sara, disaster radio journeying with dabawenyos. 2020. https://www.davaocity.gov.ph/disaster-risk-reduction-mitigation/mayor-sara-disaster-radio-journeying-with-dabawenyos . Accessed Mar 2020.
Davao City. Davao city free rides to serve GCQ-allowed workers. 2020. https://www.davaocity.gov.ph/transportation-planning-traffic-management/davao-city-free-rides-to-serve-gcq-allowed-workers/ . Accessed Mar 2020.
Download references
Acknowledgements
JFR is supported by the Abdus Salam International Centre for Theoretical Physics Associateship Scheme.
This research is funded by the UP System through the UP Resilience Institute.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Mathematical Sciences and Physics, University of the Philippines Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines
Dylan Antonio S. Talabis, Ariel L. Babierra, Christian Alvin H. Buhat, Destiny S. Lutero, Kemuel M. Quindala III & Jomar F. Rabajante
University of the Philippines Resilience Institute, University of the Philippines, Quezon City, Philippines
Faculty of Education, University of the Philippines Open University, Laguna, Philippines
Jomar F. Rabajante
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors are involved in drafting the manuscript and in revising it. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dylan Antonio S. Talabis .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable. We used secondary data. These are from the public database of the Philippine Department of Health ( https://www.doh.gov.ph/covid19tracker ) and Philippine Statistics Authority Census ( https://psa.gov.ph )

Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
S. Talabis, D.A., Babierra, A.L., H. Buhat, C.A. et al. Local government responses for COVID-19 management in the Philippines. BMC Public Health 21 , 1711 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11746-0
Download citation
Received : 19 April 2021
Accepted : 30 August 2021
Published : 21 September 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11746-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Local government
- Quantitative methods
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Transparency Seal
- PIDS Vision, Mission and Quality Policy
- Strategic Plan 2019-2025
- Organizational Structure
- Bid Announcements
- Site Statistics
- Privacy Notice

- Research Agenda
- Research Projects
- Research Paper Series
- Guidelines in Preparation of Articles
- Editorial Board
- List of All Issues
- Disclaimer and Permissions
- Inquiries and Submissions
- Subscription
- Economic Policy Monitor
- Discussion Paper Series
- Policy Notes
- Development Research News
- Economic Issue of the Day
- Annual Reports
- Special Publications
Working Papers
Monograph Series
Staff Papers
Economic Outlook Series
List of All Archived Publications
- Other Publications by PIDS Staff
- How to Order Publications
- Rate Our Publications
- Press Releases
- PIDS in the News
- PIDS Updates
- Legislative Inputs
- Database Updates
- GIS-based Philippine Socioeconomic Profile
- Socioeconomic Research Portal for the Philippines
- PIDS Library
- PIDS Corners
- Infographics
- Infographics - Fact Friday
- Infographics - Infobits
The Philippines’ Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic: Learning from Experience and Emerging Stronger to Future Shocks
- Celia M. Reyes
- COVID-19 pandemic
- whole-of-government approach
- COVID-19 policy responses
- macroeconomic response
- public health shock
- Philippine economy
- crisis response
- food security
- overseas Filipino workers
- human development
- income distribution
- basic education
- crisis communication
- risk communication
- COVID-19 recovery
- local government units
- fiscal response to pandemic
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic hit the Philippine economy and society unprecedentedly. To protect the people, the government had to act decisively and identify solutions to contain the rapid spread of the virus and the devastating economic and social disruption caused by the pandemic. This book compiles papers assessing the strategies, policies, and recovery efforts that the government had implemented during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. It discusses the challenges that the country had experienced and the government's responses in the areas of health, macroeconomy, food security, labor, social protection, poverty, education, digitalization, fiscal policy, and crisis and risk communication. Learning from these experiences, this book provides recommendations to help the Philippines recover from the current crisis and build better resilience to future shocks.
This publication has been cited 4 times
- Alviar, DC. 2023. Sapat ba ang teknolohiya upang epektibong magturo? Mga aral mula sa PIDS . Tutubi News Magazine.
- Daily Guardian . 2024. COVID-19 school closures led to significant learning losses – expert . DailyGuardian .
- Manila Standard Business. 2023. PIDS: Technology key to learning amid crises . Manila Standard.
- Nazario, Dhel. 2023. NAST PHL set to introduce new members, recognize outstanding Filipino scientists . Manila Bulletin.

Download Publication
Please let us know your reason for downloading this publication. May we also ask you to provide additional information that will help us serve you better? Rest assured that your answers will not be shared with any outside parties. It will take you only two minutes to complete the survey. Thank you.
Related Posts
Publications.

Video Highlights

- How to Order Publications?
- Opportunities
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- SAGE - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Journalism, public health, and COVID-19: some preliminary insights from the Philippines
In this essay, we engage with the call for Extraordinary Issue: Coronavirus, Crisis and Communication. Situated in the Philippines, we reflect on how COVID-19 has made visible the often-overlooked relationship between journalism and public health. In covering the pandemic, journalists struggle with the shrinking space for press freedom and limited access to information as they also grapple with threats to their physical and mental well-being. Digital media enable journalists to report even in quarantine, but new challenges such as the wide circulation of health mis-/disinformation and private information emerge. Moreover, journalists have to contend with broader structural contexts of shutdown not just of a mainstream broadcast but also of community newspapers serving as critical sources of pandemic-related information. Overall, we hope this essay broadens the dialogue among journalists, policymakers, and healthcare professionals to improve the delivery of public health services and advance health reporting.
Introduction
In this essay, we reflect on how COVID-19 has brought to our attention the often-overlooked relationship between journalism and public health. We draw initial insights from critical analysis of media and public health ( Henderson and Hilton, 2018 ) to suggest that health reporting in the country during the pandemic can be connected to journalistic practices, technological changes, and structural constraints. For journalism to advance public health, it needs to contend with the pandemic and the context into which it is uniquely situated – both of which are moving targets and difficult to predict. In this essay, we pay attention to the Philippines not just because it has one of the highest COVID 19-related cases and deaths in the world but also because the country is at the crossroads of changes in digital media and shrinking space for media freedom, as evidenced by the shutdown of the country’s biggest media network, closing or suspension of community newspapers, and passage of laws that may restrict free speech. In doing so, we hope to broaden dialogue among journalists, policymakers, and healthcare professionals to improve the delivery of public health services as well as advance health reporting.
Similar to other countries, the public health system in the Philippines was unprepared for and overburdened by COVID-19. The first case was reported on January 30 when a Chinese woman reached the country from Wuhan, China, and then a few days later her male companion died of the virus – making it the first recorded death outside of China ( Department of Health (DOH), 2020b ; Ramzy and May, 2020 ; World Health Organization (WHO), 2020a ). By March 7, the first case of local transmission was confirmed ( DOH, 2020a ; WHO, 2020a ). To date, there are 112,593 confirmed cases, 6,263 new cases, and 2,115 deaths in the country ( WHO, 2020b ) – making the Philippines as one of the most highly impacted in Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific Region. Equally alarming is the number of doctors, nurses, and other hospital staff who get infected and die of COVID-19 ( CNN Philippines, 2020a ; McCarthy, 2020 ). Recently, professional medical and allied medical associations have called for a unified and calibrated response and temporary quarantine of the country’s capital to avoid a total collapse of the healthcare system ( Batnag, 2020 ). Critical but seldom discussed are the challenges of journalism in making sense of the rapid spread and devastating impact of COVID-19 in the Philippines and how the pandemic is also gradually transforming journalism in the country.
Journalism and public health work together to broaden health information sources, facilitate public understanding of health, and mobilize support for or against public health policy ( Henderson and Hilton, 2018 ; Larsson et al., 2003 ; Vercellesi et al., 2010 ) and this relationship is magnified during pandemics. The relationship between journalism and public health has mostly been explained based on journalistic roles and news framing. During the 2009 H1N1, for instance, Klemm et al. (2017) found that journalists shifted from ‘watchdogs’ to ‘cooperative’ roles. Holland et al. (2014) further argued that the 2009 H1N1 enabled journalists to be reflexive of their roles especially with conflicts of interest among experts and decision makers. News framing has likewise informed the conversations between journalism and public health. For example, Krishnatray and Gadekar (2014) found that fear and panic dominated the frames used by journalists in their news stories about the 2009 H1N1. In this essay, we hope to engage with ongoing discussion about journalism and public health by reflecting on how health reporting during COVID-19 in the Philippines relates to broader, emergent, and interconnected issues of journalistic practices, technological changes, and structural constraints in the country.
Reporting from home
COVID-19, along with the ensuing quarantines, poses challenges to existing journalistic practices that typically require fieldwork, but it also encourages journalists in the Philippines to reimagine news production. We observe that access to information has generally been limited because government offices have not been in full operation while virtual press briefings do not allow for a more open discussion between journalists and officials. To illustrate, Ilagan (2020) reported that most routine requests for information have not been processed since March 2020 when government offices were wholly or partly closed due to the ongoing quarantine. The Philippines is among many governments in the world that had to suspend the processing of freedom-of-information (FOI) requests because of the pandemic ( McIntosh, 2020 ). FOI officers working from home could not address requests because they lacked Internet connection, laptop computers, and scanners, including digital copies of files. They also found it difficult to coordinate remotely with record custodians. While some national agencies have been proactive in providing information on COVID-19, the same cannot be said for many local government units. Ilagan (2020) further noted that ‘[un]like frontline agencies at the national level, local governments do not proactively publish data on their websites’. Information about plans to combat the impact of the virus are usually available, but more prodding is needed to find out how these plans are being implemented and funded. Camus (2020) also reported that journalists were prohibited from covering what is happening in hospitals and other high-risk areas. More and more press briefings have thus taken place online, but reporters have found it harder to demand answers because officials and their staff often screen questions. For instance, Camus (2020) wrote that some questions from journalists were ignored while official reports from the government were consistently discussed.
Moreover, we observe that the pandemic has taken a toll on both the physical and mental well-being of journalists. Reported cases of journalists experiencing high levels of stress, undergoing self-quarantines, and at least one news anchor contracting the virus point to the need for broader safety measures at the organizational level of news outlets. The National Union of Journalists of the Philippines (NUJP) lamented the limited mental health support for journalists by saying that ‘there are hardly any readily available and sustained support systems for colleagues experiencing mental health issues’ ( Adel, 2020 ). Safeguarding the physical and psychological well-being of journalists during pandemics or any type of crisis does not rest on individuals alone but should be demanded from news organizations and advocated for by professional associations. Yet some journalists have been able to navigate the consequences of COVID-19 on the profession by reimagining newsgathering, taking advantage of online resources as well as doing collaborations.
First, journalists have been coping with the challenge of limited access to information by interviewing sources through phones and attending webinars with experts to learn more about the pandemic ( Tantuco, 2020 ). Bolledo (2020) said that journalists had to adapt in light of the global health crisis changing media operations. By adapting, he referred to Reuters’ approaches to comprehensive newsgathering, which focus on open-source and non-mainstream techniques such as ‘citizen and collaborative journalism’ and ‘social journalism’. In practice, this set of methods includes monitoring Facebook and Twitter feeds, joining Facebook groups created for a specific cause or geographical area, following hashtags and using keywording to find leads and sources. Bolledo (2020) also emphasized the need to fact-check information gathered using these methods, highlighting the importance of news values and the 5Ws and one H in reporting. Second, to address the barriers in online press briefings, journalists organized themselves to raise their unanswered questions in media group chats of government organizations ( Ilagan, 2020 ). Third, the NUJP organized peer support networks critical for minimizing stress and trauma among journalists who reported about and during COVID-19. Finally, in an effort to prevent contracting and spreading the virus among co-workers, journalists are maintaining records of their activities and a list of sources whom they interacted for purposes of contact tracing ( Camus, 2020 ). The new methods employed in health reporting, as creative responses to the constraints brought upon by COVID-19, partly illustrate how an emerging practice may turn into professional norm ( Henderson and Hilton, 2018 ) in health reporting during pandemic.
Double-edged sword
At the onset of COVID-19, journalism in the Philippines has struggled with ongoing technological changes that bring about double-edged consequences. On one hand, digital media has enabled journalists to help Filipinos make better sense of the pandemic – from reporting infections and deaths regularly to covering press conferences organized by agencies at the frontlines of COVID-19 response. Through Facebook live videos, Zoom , and other video conferencing applications, journalists are able to talk about their lived experiences in covering COVID-19. Various groups inside and outside of the Philippines have been hosting a series of webinars on how to cover the pandemic. Media groups in the Philippines meanwhile have also organized press briefings that tackle the state of news reporting in the country. In the forum titled ‘Intrepid Journalism in the Time of Corona’ organized by This Side Up Manila , two journalists discussed the state of news from the early stages of the pandemic to the declaration of enhanced community quarantine (ECQ). Early in the live video, they shared their frustrations about the consequences of COVID-19 on fieldwork and storytelling. According to the reporters, covering COVID-19 is different from reporting about natural disasters or conflict zones because they felt that there was no end in sight to the pandemic. As a result, they reminded themselves and their colleagues to find a balance and slow down as the pandemic may be prolonged and even put the lives of their families at risk. These webinars, which are in theory accessible to anyone in the world, also allow journalists to share their experiences with and learn from their counterparts in other countries. For instance, Hivos organized a webinar titled ‘Data Driven Reporting During Covid-19’ with journalists from the Philippines, Kenya, and Mexico to find out how they have been affected by and coping with the pandemic. The journalists said they have found collaboration or working with other journalists and members of the academe and civil society as key in reporting when fieldwork is not possible. Like the Philippines, too, Kenya and Mexico also experience barriers in accessing and reporting information while their governments too are also mandating policies that could restrict press freedom ( Hivos, 2020 ).
On the other hand, digital media has complicated the work of journalists as they had to deal with the spread of health mis- and/or disinformation. To partly explain the diffusion of online fake news (e.g. mass testing and vaccines), we engage with Tandoc et al. (2018) who emphasized the characteristics of technology and the role of audiences. For instance, social media made it challenging for journalists to delineate information sources from each other, especially given the evolving science of COVID-19. Because science is evolving, journalists tend to rely heavily on expert opinion, without verifying the experts’ assumptions. Correcting mis- and/ or disinformation about the pandemic was likewise difficult because journalists had limited understanding of what counted as fake news among Filipinos. Another problem that journalists had to contend with while working during the pandemic is the recent ‘data breach’ that used Facebook profiles of real people ( Robles et al., 2020 ). The rise of fake Facebook accounts is counterproductive not just to fight against health mis- and/or disinformation but also places the identities of journalists at risk. To a large extent, the proliferation of health mis- and/ or disinformation is inextricably connected to the social context not just of COVID-19 but also the Philippines. As Tandoc et al. (2018) pointed out, ‘fake news needs the nourishment of troubled times in order to take root. Social tumult and divisions facilitate our willingness to believe news that confirms our enmity toward another group’ (p. 149). While it created new issues, COVID-19 has also reinforced existing problems in the country and one of those is the shrinking space for free speech.
Shutdowns, suspensions, and shrinking spaces
The pandemic is also laying bare pre-existing conditions hounding the Philippine press in a supposed democracy. For instance, the government passed ‘The Bayanihan to Heal as One Act’ (Republic Act No. 11469) to give the president emergency powers that would enable him to quickly respond to COVID-19. Human rights and media advocates criticized this law as it included a provision penalizing ‘fake news’, which can easily be used and abused by those in power to file complaints against individuals, including journalists ( Freedom for Media, Freedom for All Network, 2020 ). Again this posed another challenge to journalists and the audience who both use social media as a means to get and share information. In similar vein, the passage of the ‘ Anti-Terrorism Act of 2020 ’ (Republic Act No. 11479) received pushback for its broad provisions. Human rights groups also say that the law has essentially also criminalized intent, which could send a chilling effect especially among journalists who might be working on stories critical of the government.
On 5 May 2020, ABS-CBN, the country’s largest media network, went off-air after its broadcast franchise expired. The House of Representatives, which oversees the granting of franchises, refused ABS-CBN’s bid for a renewal, which ultimately led the media giant to close its broadcast operations and lay off thousands of employees. This development comes after the conviction of Rappler executive editor Maria Ressa and former researcher-writer Reynaldo Santos Jr for supposedly violating the Cybercrime Prevention Act of 2012 (Republic Act No. 10175). The shutdown is seen as the latest in a series of attacks and threats against news organizations deemed as critical of the current administration ( Gutierrez, 2020 ; Pago, 2020 ). Community journalism is neither spared. At least half of some 60 community newspapers have suspended or ceased printing due to economic losses caused by the quarantine, according to estimates from the Philippine Press Institute, the national association of newspapers. The NUJP also raised economic difficulties confronting many freelance journalists, especially those who work on contract in broadcast, since the start of the lockdown. Suspension of operations means that contractual media workers would not be able to earn because work is not available. The halt in the production of news by ABS-CBN and various papers across the archipelago means that people, especially those in far-flung areas, have fewer sources of news at a time when getting information is most crucial. Again, these developments point to how pandemic reportage may be tied to political landscape in the country ( Henderson and Hilton, 2018 ).
COVID-19 is transforming the practice and business of journalism. On one hand, the pandemic and the ensuing quarantine restrictions have prompted news organizations and journalists to adapt and take advantage of digital media to continue gathering and presenting news. On the other hand, the pandemic has also exposed journalists and audiences alike to further mis- and/ or disinformation as well as to government’s new efforts to stamp out ‘fake news’. These developments run in parallel with threats to press freedom and journalist safety. In a pandemic, journalists are not mere observers or mere reporters as they also face the same risks everyone else is exposed to ( CNN Philippines, 2020b ). By laying out the current media environment in this essay, we hope to expand and deepen the conversation between and among journalists, policymakers, and healthcare professionals about public health reporting. In line with Larsson et al. (2003) , we encourage further conversations between journalists and healthcare professionals to collectively identify gaps in health reporting and broaden understanding of ‘fake news’ and how it thrives in social media. Consistent with Tandoc et al. (2018) , we also recommend that journalists and healthcare professionals listen to their audience to help understand what counts as health-related ‘fake news’ for them. Moreover, we invite policymakers to protect democratic spaces that enable journalists, healthcare professionals, and citizens alike to gather and share information related to COVID-19. At a time when disseminating reliable information and holding the powerful to account have never been more critical, we deem it necessary to understand where journalists are coming from to understand both the long-standing and emerging issues they have to grapple with in a pandemic.
Authors’ note: The views provided in this essay do not represent the official views of the authors’ institutional affiliations.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.

- Adel R. (2020) Aside from PPEs, journalists need mental health support during pandemic . Philstar.com , 4 May . Available at: https://www.philstar.com/headlines/2020/05/04/2011831/aside-ppes-journalists-need-mental-health-support-during-pandemic
- Anti-Terrorism Act of 2020 (Republic Act [RA] No. 11479) 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- Batnag D. (2020) Doctors and nurses in the Philippines urge government to put Manila back on coronavirus lockdown . The Straits Times , 1 August . Available at: https://www.straitstimes.com/asia/se-asia/philippines-doctors-urge-time-out-as-coronavirus-cases-surge
- Bayanihan to Heal as One Act (Republic Act [RA] No. 11469) 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bolledo JR. (2020) Newsgathering in the ‘new normal’ [Webinar] . Journalism Studies Association of the Philippines, Quezon City, NCR, Philippines, 24 July. [ Google Scholar ]
- Camus MR. (2020) Journalism in times of COVID-19 . Philippine Daily Inquirer , 22 March . Available at: https://newsinfo.inquirer.net/1246259/journalism-in-times-of-covid-19
- CNN Philippines (2020. a) COVID-19 cases among healthcare workers now at 1,245; death toll at 27 . CNN Philippines , 27 April . Available at: https://www.cnnphilippines.com/news/2020/4/27/covid-cases-PH-healthworkers.html
- CNN Philippines (2020. b) Remembering World Press Freedom Day: Filipino journalists also ‘heroes’ in COVID-19 fight . CNN Philippines , 3 May . Available at: https://cnnphilippines.com/news/2020/5/3/journalism-World-Press-Freedom.html?fbclid=IwAR3atwW-TpGDi3VXHpG_ka1rhioIBFMQCCLNE0pAIRvtGsQxbI7jlConDMA
- Cybercrime Prevention Act of 2012 (Republic Act [RA] No. 10175) 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Department of Health (DOH) (2020. a) DOH confirms local transmission of COVID-19 in PH; reports 6th case , 7 March . Available at: https://www.doh.gov.ph/doh-press-release/doh-confirms-local-transmission-of-covid-19-in-ph#:~:text=The%20Department%20of%20Health%20(DOH,had%20no%20recent%20travel%20history
- Department of Health (DOH) (2020. b) DOH reveals more negative 2019-NCOV cases; confirms first NCOV ARD death in PH , 2 February . Available at: https://www.doh.gov.ph/press-release/DOH-reveals-more-negative-2019-nCoV-cases-confirms-first-nCoV-ARD-death-in-PH
- Freedom for Media, Freedom for All Network (2020) Press freedom further restricted amid COVID-19 pandemic . Philippine Center for Investigative Journalism , 4 May . Available at: https://pcij.org/article/4009/state-of-media-freedom-in-ph-2
- Gutierrez J. (2020) Leading Philippine broadcaster, target of Duterte’s Ire, forced off the air . The New York Times , 5 May . Available at: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/05/05/world/asia/philippines-abs-cbn-duterte.html
- Henderson L, Hilton S. (2018) The media and public health: where next for critical analysis? Critical Public Health 28 ( 4 ): 373–376. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hivos (2020) Press under pressure: the view from investigative journalists . Hivos , 25 May . Available at: https://www.hivos.org/blog/press-under-pressure-the-view-from-investigative-journalists/
- Holland K, Sweet M, Blood RW. (2014) A legacy of the swine flu global pandemic: journalists, expert sources, and conflicts of interest . Journalism 15 ( 1 ): 53–71. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ilagan K. (2020) Quarantine curbs access to information . Philippine Center for Investigative Journalism , 5 June . Available at: https://pcij.org/article/4080/test-4
- Klemm C, Das E, Hartman T. (2017) Changed priorities ahead: journalists’ shifting role perceptions when covering public health crises . Journalism 20 ( 9 ): 1223–1241. [ Google Scholar ]
- Krishnatray P, Gadekar R. (2014) Construction of death in H1N1 news in The Times of India . Journalism 15 ( 6 ): 731–753. [ Google Scholar ]
- Larsson A, Oxman AD, Carling C, et al. (2003) Medical messages in the media – barriers and solutions to improving medical journalism . Health Expectations 6 ( 4 ): 323–331. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCarthy J. (2020) Pandemic claims the lives of doctors in the Philippines at startling rates . NPR , 3 April . Available at: https://www.npr.org/sections/coronavirus-live-updates/2020/04/03/826804519/pandemic-claims-doctors-in-the-philippines-at-startling-rates
- McIntosh T. (2020) Governments delay access to information due to COVID-19 . Global Investigative Journalism Network , 31 March . Available at: https://gijn.org/2020/03/31/governments-delay-access-to-information-due-to-covid-19/
- Pago A. (2020) Journalists struggle to cover the pandemic as space for media freedom shrinks . Philippine Center for Investigative Journalism , 6 May . Available at: https://pcij.org/article/4046/journalists-struggle-to-cover-the-pandemic-as-space-for-media-freedom-shrinks
- Ramzy A, May T. (2020) Philippines reports first coronavirus death outside China . The New York Times , 2 February . Available at: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/02/02/world/asia/philippines-coronavirus-china.html
- Robles A, Bloomberg and DPA (2020) Who is behind surge in fake Facebook accounts in the Philippines? South China Morning Post , 8 June . Available at: https://www.scmp.com/week-asia/politics/article/3088067/who-behind-surge-fake-facebook-accounts-philippines
- Tandoc EC, Jr, Lim ZW, Ling R. (2018) Defining ‘fake news’ . Digital Journalism 6 ( 2 ): 137–153. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tantuco V. (2020) How the COVID-19 pandemic is affecting the media . Rappler , 7 May . Available at: https://rappler.com/newsbreak/in-depth/how-covid-19-pandemic-affecting-media
- Vercellesi L, Minghetti P, Di Croce M, et al. (2010) Recommendations for health reporting: proposal of a working paper . Health Education Journal 69 ( 1 ): 48–62. [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2020. a) Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in the Philippines , 20 May . Available at: https://www.who.int/philippines/emergencies/covid-19-in-the-philippines
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2020. b) WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard , 5 August . Available at: https://covid19.who.int/region/wpro/country/ph
RTI uses cookies to offer you the best experience online. By clicking “accept” on this website, you opt in and you agree to the use of cookies. If you would like to know more about how RTI uses cookies and how to manage them please view our Privacy Policy here . You can “opt out” or change your mind by visiting: http://optout.aboutads.info/ . Click “accept” to agree.

Fighting COVID-19 in the Philippines
8 ways usaid reachhealth supports pandemic response.
As COVID-19 swept the world in 2020, the Philippines became Southeast Asia’s most affected country.
RTI International has been supporting the COVID-19 response in the Philippines through ReachHealth , a five-year United States Agency for International Development (USAID) project that strengthens and improves access to family planning and maternal and child health services.
Building on 14 years of RTI experience working with local governments in the Philippines to improve health outcomes, the USAID ReachHealth Project supports the COVID-19 response in 15 priority local government units across the country. Working closely with the Department of Health (DOH), the Department of Interior and Local Governance, UN agencies, the private sector, and civil society organizations, we strengthen the government’s emergency and ongoing response at all levels.
Our support has included operationalizing nationwide COVID-19 policies, rolling out vaccines, helping facilities access national COVID-19 financing and testing kits, strengthening the capacities of health workers on infection prevention and control and case management, improving contact tracing, and supporting risk communication and community engagement efforts. Most recently, ReachHealth has helped the country prepare for the roll out of child vaccines and the safe reopening of in-person schools.
Since ReachHealth began supporting the Philippines' pandemic response, we have trained over 20,000 people and reached nearly 37 million people with messages on preventing gender-based violence and COVID-19’s spread.
Here are eight of the important ways we have and continue to respond to COVID-19 in the Philippines:
1. Strengthening community health and support systems
Barangay Health Emergency Response Teams, or BHERTs, usually connect community members to health facilities — but during times of emergency their work becomes more important than ever. These neighborhood-based teams formed the frontline of efforts to delay COVID-19’s spread and locally contain the pandemic by communicating risk, facilitating contact tracing and vaccination, and connecting communities with broader local health systems. ReachHealth works to ensure BHERTs in hotspot communities are active, effective, and trained on critical elements of the COVID-19 community response, including essential behaviors to prevent the virus’ spread, infection prevention and control, vaccination and testing protocols, contact tracing, and quarantine and isolation. ReachHealth has helped train over 7,800 people on contact tracing and rapid response so far.
2. Increasing vaccine coverage
In 2021, ReachHealth collaborated with the DOH and local actors to plan for vaccine rollouts. We developed public messaging for local governments to spread the word, updated FAQs for community health responders like BHERTs, and supported health facility planning and preparation. Once vaccines were available, ReachHealth also helped speed up the roll out by deploying 28 mobile vaccine teams across the country to ensure even the most remote communities got access. ReachHealth has established or supported over 200 vaccination sites in the Philippines. More than 2.8 million Filipinos have been fully vaccinated with ReachHealth’s support.

Grace Jose receives a COVID vaccine at a vaccination site in Caloocan City. Photo by Christian Rieza/USAID ReachHealth
3. Strengthening health and testing facilities
Throughout the pandemic, the science on COVID-19 and how to address it has evolved. To help health facilities keep up, ReachHealth provided training to over 5,000 people on case management and over 3,000 people on infection prevention and control. We also partnered with local governments to establish 10 additional mobile testing units and four community testing centers in vulnerable areas. As COVID-19 testing increased, so did the demand for accredited labs that could process tests quickly. By providing support , ReachHealth helped increase the number of accredited labs across the country and reduced testing times to just a few hours in eight labs in Mindanao and Luzon.

Vilma Cabral gets tested for COVID-19 at a USAID-supported community-based testing center in the Philippines. Photo by Rosana Ombao for USAID
4. Supporting a data-driven response
The DOH collaborated with the World Health Organization to launch a mobile application, COVID KAYA , that supports frontline responders with contact tracing and case monitoring. The introduction of any new, centralized data system across regions with varying needs and infrastructure can be challenging and uneven. Our team provided technical assistance to help local governments roll out the application, and directly trained officials, health workers, and personnel from health epidemiology units on its use.
5. Addressing gender-based violence
In the Philippines, 1 in 20 women and girls aged 15-49 have experienced sexual violence. COVID-19 lockdowns and quarantines brought extended periods of restricted movement and home confinement for millions of people — an unprecedented situation that worsened violence against women and children at home. ReachHealth supported the continued functioning of gender-based violence (GBV) services, such as a 24-hour helpline, while a messaging campaign, Hindi kailangang magtiis! (You don’t need to suffer in silence!), sought to prevent GBV and to let people know about available services. Since October 2020, this campaign has reached over 9 million Filipinos on Facebook alone.
6. Distributing essential equipment and supplies
Frontline health workers needed personal protective equipment (PPE) to care for their patients safely. In partnership with the Armed Forces of the Philippines, ReachHealth supported the distribution of PPE donated by the US Defense Threat Reduction Agency to 109 hospitals, rural health units, and quarantine facilities in vulnerable areas across the country. We also partnered with Proctor & Gamble to distribute more than 700,000 face masks. ReachHealth is now providing PPE and communication materials to local schools to aid in the safe reopening of in-person classes.
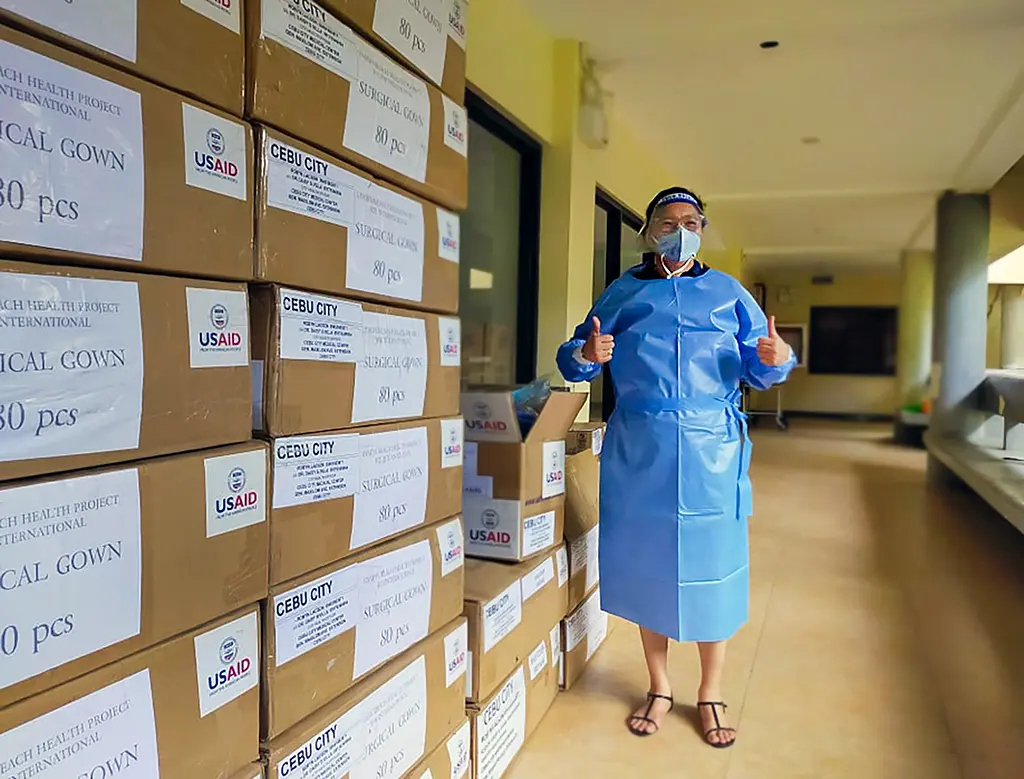

Boxes of personal protective equipment destined for health facilities during the COVID-19 pandemic in Cebu City, Philippines. Photo by Robyn Lacson/USAID ReachHealth
7. Prioritizing water, sanitation, and hygiene
Although water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) was not a focus area for ReachHealth, our team recognized that good sanitation and hygiene are critical to slowing the spread of COVID-19. We developed a tool to assess and prioritize sites for handwashing stations and installed these facilities in more than 200 quarantine centers, shelters, and public spaces. We also incorporated WASH messaging into our trainings and messaging campaigns and partnered with the DOH and Procter & Gamble to procure and distribute 70,000 hygiene kits to adults and young people. We have reached over 2.5 million Filipinos with WASH support so far, and our team continues to collaborate with local WASH organizations to bolster their ongoing work.
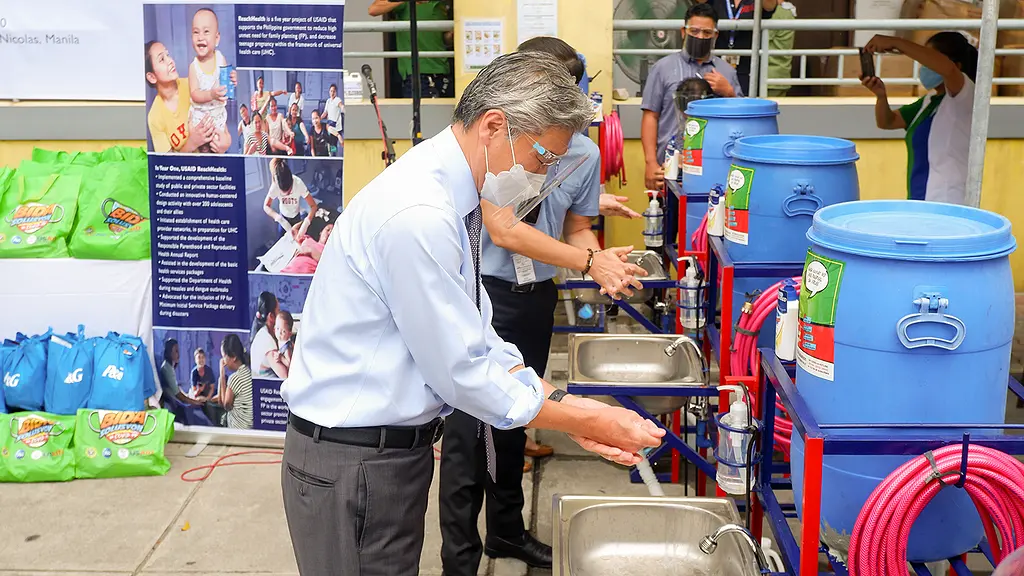

U.S. Ambassador Sung Kim uses one of the 16 handwashing stations installed in facilities and communities around the city. Photo by Rosana Ombao/USAID ReachHealth
8. Keeping our focus on family planning
Family planning (FP) continues to be an essential health service, especially in times of social and economic uncertainty. While our team stepped up to contribute their expertise to the COVID-19 response, they remain committed to expanding access to quality FP services across the Philippines. In March 2020, 25% of surveyed health centers reported a disruption in FP services and 81% saw a decline in people seeking FP care. From creating online resources to helping service providers improve their teleconsultation abilities, our team rapidly adapted approaches to accommodate the new normal and ensure all Filipinos could continue to access FP care. More than 2,000 teleconsultations on family planning have occurred since.
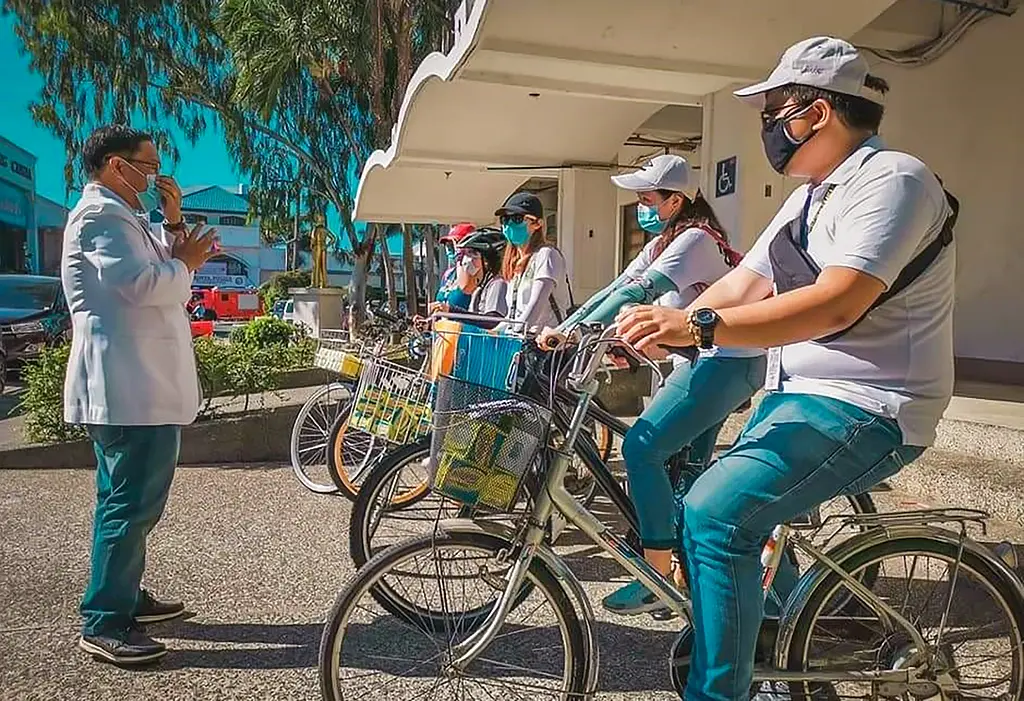

A team of "Nurses on Wheels" delivers family planning supplies to neighborhood health stations in Cainta. Photo by Mon Joshua Vergara/Cainta Municipal Health Office
- U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
- Global Health
- Global Health Security
- COVID-19 Research + Response
- Health Systems Strengthening
- Primary Health Care in Low- and Middle-Income Countries
- Interventions and Prevention Programs
- Philippines
ReachHealth: Strengthening Access to Critical Services for Filipino Families
Assessing the availability of essential family planning services during covid-19 in the philippines, from hotspots to bright spots: fighting covid-19 in the barangays of the philippines, hope on wheels: delivering vaccines to remote communities, stopping the spread: making covid testing accessible for filipinos.
Content Search
Philippines
Impact Report: COVID-19 Response in the Philippines
In the past six months, UNHCR has mobilized quickly to support the government-led response to COVID-19 in the Philippines. Help us continue to deliver sustainable & vital services including health, water, sanitation and hygiene to many more forcibly displaced families.
UNHCR Philippines, with the support of donors, in coordination with partners, and together with other United Nations agencies in the country, has mobilized rapidly and comprehensively to help the government respond to this unprecedented crisis – particularly in communities with refugees, asylum seekers, internally displaced populations, and persons at risk of statelessness. They are among the most vulnerable to COVID-19, and they cannot be left behind in the response.
PREPOSITIONING TO RESPOND TO A GLOBAL PANDEMIC
Building on its experience in SARS and ebola outbreaks noting that the health crisis is a global challenge that must be addressed through solidarity and cooperation, in March UNHCR endeavoured to mobilize its resources to effectively combat the public health emergency urging governments and partners that the most vulnerable – including refugees, asylum seekers, stateless and the internally displaced – should be able to access health facilities and services in a non-discriminatory manner.
UNHCR has followed the guidance of the World Health Organization (WHO) and identified a number of prevention and response activities in displacement situations that include:
RAPID RESPONSE
Together with other UN agencies in the Philippines, UNHCR augmented government response efforts in containing the spread of the pandemic and decreasing morbidity and mortality, as well as ensuring protection and assistance for forcibly displaced populations.
Life-Saving Assistance
Providing core relief items, hygiene kits, and personal protective equipment to vulnerable communities and to support duty bearers in their response
Ensuring the continuity of direct assistance to refugees and asylum seekers amid the pandemic
Community Level Health Awareness
Conducting awareness raising sessions and distributing localized COVID-19 information materials focusing on hygiene, respiratory symptoms and signs, referral mechanisms, infection prevention information.
SUSTAINABLE RECOVERY
UNHCR joins the government and other humanitarian partners in helping ensure that the people of the Philippines can emerge stronger and be better prepared to withstand future emergencies.
Information Management
UNHCR Philippines has a functional cooperation with government agencies in instituting a systematic information management & reporting mechanism that maps displacement incidences to gauge the extent of protection provided to internally displaced persons (IDPs)
Information management has become a useful tool in providing targeted assistance as information is derived from evidence-based needs, gaps, as well as displacement trends and analysis gathered by a strong Protection Cluster network
Capacity Building
- UNHCR is strengthening the information management capacity of government partners to ensure continuity in refugee status determination procedures, protection monitoring, case management, as well as reporting and mitigating potential protection risks for displaced people amid the public health emergency
Quick Impact Projects
- UNHCR is mainstreaming and integrating the impact of COVID-19 into the planning and design of quick impact projects, which promote community empowerment, help foster peaceful co-existence, and strengthen resilience of forcibly displaced populations.
As we move from rapid response to sustainable recovery, you can help ensure that more forcibly displaced families in Mindanao are better prepared and equipped to withstand future emergencies. In the next few months, the impact of COVID-19 will be integrated into the design and implementation of quick impact projects, prioritizing water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) facilities.
Related Content
Philippines + 2 more
Asia and the Pacific: Weekly Regional Humanitarian Snapshot (27 February - 4 March 2024)
Consolidated rapid assessments report: floods and landslides due to northeast monsoon and low pressure area - mindanao, philippines (16 february 2024), philippines: mindanao floods - dref operation (appeal mdrph053), philippines: fulfilling our humanitarian mission in 2023.
Plan International's websites
Find the Plan International website you are looking for in this list
COVID-19 response in the Philippines
Support for girls and young women.
The COVID-19 pandemic is severely challenging the Philippines. We’re supporting the most vulnerable children, especially girls, and young women affected by this crisis.
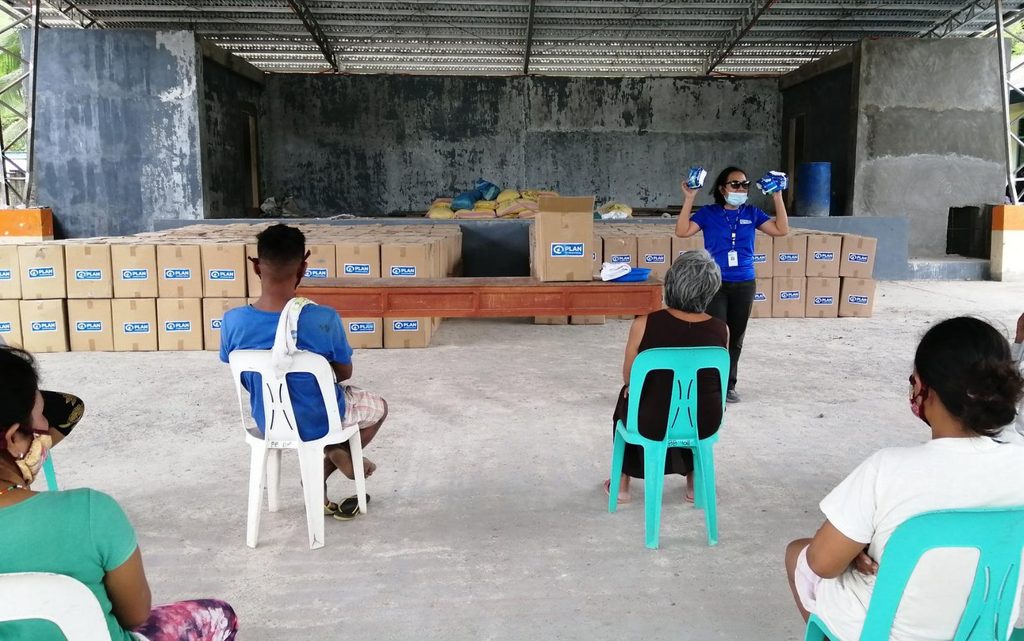

How we’re responding
We’re working with partners to reach the most vulnerable children, especially girls.
Children's stories
Rising above covid-19: an 18 year old girl’s journey, realisations of a young woman during covid-19, girl promotes mental wellbeing during pandemic, latest insights, the fragile state of unemployed youth during covid-19, girls’ needs unmet, voices unheard amid covid-19– plan international philippines study, plan international philippines covid-19 response impact report, impact of covid-19 on filipino girls and young women.
This study analyses the impact of COVID-19 on Filipino girls and young women aged 13 to 24 years old.
Download options
Full report
Executive summary

Cookie preferences updated. Close
This popup will be triggered by a user clicking something on the page.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Response to COVID 19 in the Philippines. The Philippines has been severely affected by COVID-19. As of 17 January 2022, the Philippines has recorded over 3 million confirmed cases of her COVID-19, with over 52,700 deaths, according to the latest WHO figures. Since March 2020, the country has taken strict measures to contain the spread of the ...
Despite being one of the hardest hit countries in Southeast Asia in 2021, the Philippines has had to wait for vaccines from wealthy countries. The country now has over 3.5 million confirmed cases ...
Delta variant puts Philippine economy among most vulnerable in Asia. COVID-19 pandemic to cost PH P41.4 trillion over next 4 decades - NEDA. Philippine GDP growth slows but beats forecasts at 7. ...
Low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) with weak health systems are especially vulnerable during the COVID-19 pandemic. In this paper, we describe the challenges and early response of the Philippine Government, focusing on travel restrictions, community interventions, risk communication and testing, from 30 January 2020 when the first case was reported, to 21 March 2020.
The term "pasaway" is a Filipino word loosely refers to an importunate, stubborn, or obstinate person. Amid the lockdown, the term pasaway referred to people violating government- imposed health protocols. Feared for spreading the virus, the pasaway became the bane of the government's pandemic response.
The Philippine response to COVID-19 has been described as being one of the longest and strictest lockdowns in the world. Why has the Philippine government relied heavily on draconian measures in its "war" against COVID-19? And what discourse informed the framing of its response as a war against the virus? This article argues that the government's reliance on draconian measures was a ...
When the COVID-19 pandemic struck in the Philippines, the World Bank supported the country's efforts to scale up vaccination, strengthen its health system, and counter the impact of the pandemic, especially on the poor and the most vulnerable. In addition to support for procurement and deployment of 33 million doses of vaccines, the project funded purchases of emergency medical/laboratory ...
Responses of subnational government units are crucial in the containment of the spread of pathogens in a country. To mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Philippine national government through its Inter-Agency Task Force on Emerging Infectious Diseases outlined different quarantine measures wherein each level has a corresponding degree of rigidity from keeping only the essential ...
2. Policies and measures undertaken in response to COVID-19 On 7 March 2020, the country's COVID-19 alert level system was raised to Code Red Sub-level 1 following the first reported localized transmission. A State of Public Health Emergency was declared throughout the Philippines on 8 March 2020 through Proclamation no. 922. On 12 March 2020 ...
New cases of COVID-19 in the Philippines, 30 January-21 March 2020 Community transmission reported in the Philippines Number of new cases 1 e 0 20 40 60 80 1 e 1 ar 1 ar Declaration of state of public health emergency WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic Fig. 1b. Timeline of key events and developments in the Philippines, 30 January-21 March 2020
The World Health Organization (WHO) has been working with Ministries of Health worldwide to prepare and respond to COVID-19. In the Philippines, WHO country office in the Philippines and its partners have been working with the Department of Health and subnational authorities to respond to the pandemic. The country level response is done with support from the WHO regional office and headquarters.
Impact Report: COVID-19 Response in the Philippines. In the past six months, UNHCR has mobilized quickly to support the government-led response to COVID-19 in the Philippines. Help us continue to deliver sustainable & vital services including health, water, sanitation and hygiene to many more forcibly displaced families.
This kind of community engagement promoted by NICE could be utilized in the Philippine setting where the deficient COVID-19 response has been mainly military-led. 2 The inadequacy of this top-down style and the tactics of scare are glaring as the country's number of cases and deaths have worsened from mid-March 2021.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic hit the Philippine economy and society unprecedentedly. To protect the people, the government had to act decisively and identify solutions to contain the rapid spread of the virus and the devastating economic and social disruption caused by the pandemic. This book compiles papers assessing the ...
Abstract. In this essay, we engage with the call for Extraordinary Issue: Coronavirus, Crisis and Communication. Situated in the Philippines, we reflect on how COVID-19 has made visible the often-overlooked relationship between journalism and public health. In covering the pandemic, journalists struggle with the shrinking space for press ...
As COVID-19 swept the world in 2020, the Philippines became Southeast Asia's most affected country. RTI International has been supporting the COVID-19 response in the Philippines through ReachHealth, a five-year United States Agency for International Development (USAID) project that strengthens and improves access to family planning and maternal and child health services.
HOT OFF THE PRESS—An anthology about the pandemic response in the Philippines is now available at the Ateneo University Press. Titled Lockdown and Lowdown: The Politics of COVID-19 Pandemic Response in the Philippines, this compendium presents accounts of the COVID-19 pandemic response from the perspective of local governments within the frame of national-local political relations and ...
COVID-19 in the Philippines Situation Report 01. More situation reports from WHO. WHO Western Pacific. WHO Global. More from the Western Pacific. COVID-19 technical guidance. COVID-19 advice for the public. COVID-19 outbreak page. COVID-19 news from the region.
The Philippines COVID-19 Emergency Response Project supported the procurement and deployment of 33 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine across the country. The project also supported pediatric ...
Always follow your national health authority's advice. Symptoms of COVID-19 can vary, but mild cases often experience fever, cough, and fatigue. Moderate cases may have difficulty breathing or mild pneumonia. While severe cases may have severe pneumonia, other organ failure & possible death. Anyone experiencing difficulty breathing should ...
Exactly 100 days have passed since the first confirmed COVID-19 case was announced in the Philippines on 30 January 2020, with a 38-year old female from Wuhan testing positive for the novel ...
Philippines. Impact Report: COVID-19 Response in the Philippines Format News and Press Release Source. UNHCR; Posted 30 Sep 2020 Originally published 30 Sep 2020 Origin View original.
Girls' needs unmet, voices unheard amid COVID-19- Plan International Philippines study. A new study by humanitarian and girls' rights organization Plan International Philippines reveals how the COVID-19 pandemic systematically impacts the lives ….