

15 Informative Speech Examples to Inspire Your Next Talk
- The Speaker Lab
- May 13, 2024
Table of Contents
A good informative speech is one of the most effective tools in a speaker’s arsenal. But with so many potential topics out there, it can be tough to know where to start. That’s why we’ve compiled 15 informative speech examples to help you find your perfect subject. Whether you’re unearthing secrets from history for your listeners or delving into future technologies, informative speeches can prove to be the recipe for the perfect talk.
But crafting an effective informative speech is about more than just picking a topic. You have to research topics, put your thoughts in order, and speak up clearly and confidently. In this post, we’ll explore strategies for each step of the process, so you can create a speech that informs, engages, and makes a lasting impact on your listeners. Let’s get started.
15 Informative Speech Examples
If you’re looking for some inspiration for your next informative speech, look no further. Below are 15 examples of informative speech topics that are sure to engage and educate your audience.
- The history and evolution of social media platforms
- The benefits and drawbacks of renewable energy sources
- The impact of sleep deprivation on mental and physical health
- The role of emotional intelligence in personal and professional success
- The science behind climate change and its potential consequences
- The importance of financial literacy for young adults
- The influence of artificial intelligence on various industries
- The benefits of regular exercise and a balanced diet
- The history and cultural significance of a specific art form or genre
- The impact of technology on interpersonal communication
- The psychology behind procrastination and effective strategies to overcome it
- The role of diversity and inclusion in fostering innovation and creativity
- The importance of mental health awareness and resources for students
- The future of space exploration and its potential benefits for humanity
- The impact of globalization on local economies and cultures
These topics cover a wide range of subjects, from technology and science to psychology and culture. By choosing one of these informative speech examples, you’ll have plenty of material to work with to create an engaging and educational presentation.
Remember, the key to a successful informative speech is to choose a topic that you’re passionate about and that will resonate with your audience. Do your research, organize your thoughts, and practice your delivery to ensure that your message comes across loud and clear.
What Is an Informative Speech?
If you’ve ever been to a conference or seminar, chances are you’ve heard an informative speech. But what exactly is an informative speech? Simply put, it’s a type of speech designed to educate the audience on a particular topic. The goal is to provide interesting and useful information, ensuring the audience walks away with new knowledge or insights. Unlike persuasive speeches that aim to convince the audience of a viewpoint, informative speeches focus on explaining a subject clearly and objectively.
Types of Informative Speeches
Informative speeches come in various forms, each with its own purpose. The most common types are definition, explanation, description, and demonstration speeches. Depending on the objective, an informative speech can take on different structures and styles.
For example, a definition speech aims to explain a concept or term, while a demonstration speech shows the audience how to perform a task or process. An explanatory speech, on the other hand, provides a detailed account of a complex subject, breaking it down into digestible parts.
Purpose of Informative Speeches
At its core, the purpose of an informative speech is to share knowledge with the audience. These speeches are characterized by their fact-based, non-persuasive nature. The focus is on delivering information in an engaging and accessible way.
A well-crafted informative speech not only educates but also sparks curiosity and encourages further learning. By dedicating yourself to providing valuable information and appealing to your audience’s interests, you can succeed as an informative speaker.
Strategies for Selecting an Informative Speech Topic
Choosing the right topic is crucial for an effective informative speech. You want a subject that is not only interesting to you but also relevant and engaging for your audience. Consider their knowledge level, background, and expectations when selecting your topic.
One strategy is to focus on a subject you’re passionate about or have expertise in. This allows you to speak with authority and enthusiasm, making your speech more compelling. Another approach is to address current events or trending topics that are on people’s minds.
When brainstorming potential topics, consider your speech’s purpose and the type of informative speech you want to deliver. Is your goal to define a concept, explain a process, describe an event, or demonstrate a skill? Answering these questions will help guide your topic selection.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
How to Write an Informative Speech
Now that you’ve selected your topic, it’s time to start writing your informative speech. The key to a successful speech is thorough preparation and a clear, organized structure. Let’s break down the steps involved in crafting an engaging and informative presentation.
Researching Your Topic
Before you start writing, it’s essential to conduct thorough research on your topic. Gather facts, statistics, examples, and other supporting information for your informative speech. These things will help you explain and clarify the subject matter to your audience.
As you research, use reliable sources such as academic journals, reputable websites, and expert opinions to ensure the accuracy and credibility of your information. Take notes and organize your findings in a way that makes sense for your speech’s structure.
Structuring Your Speech
A typical informative speech structure includes three main parts, namely, an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should grab the audience’s attention, establish your credibility , and preview the main points you’ll cover.
The body of your speech is where you’ll present your main points and supporting evidence. Use clear transitions between each point to maintain a logical flow. The conclusion should summarize your key takeaways and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Outlining Your Speech
Creating an outline is a crucial step in organizing your thoughts and ensuring a coherent flow of information. Start by listing your main points and then add subpoints and supporting details for each section.
A well-structured outline will serve as a roadmap for your speech, keeping you on track and helping you stay focused on your key messages. It also makes the writing process more efficient and less overwhelming.
Writing Your Draft
With your outline in hand, it’s time to start writing your draft. Focus on presenting information clearly and concisely, using simple language and avoiding jargon. Provide examples and analogies throughout your informative speech in order to illustrate complex ideas and make them more relatable to your audience.
As you write, keep your audience in mind and tailor your language and examples to their level of understanding. Use transitions to link your ideas and maintain a smooth flow throughout the speech.
Editing and Revising
Once you’ve completed your draft, take the time to edit and revise your speech. First, check for clarity, accuracy, and logical organization. Then, eliminate unnecessary details, repetition, and filler words.
Read your speech aloud to identify any awkward phrasing or unclear passages. Lastly, seek feedback from others and be open to making changes based on their suggestions. Remember, the goal is to create a polished and effective informative speech.
Delivering an Informative Speech
You’ve written a fantastic informative speech, but now comes the real challenge: delivering it effectively. The way you present your speech can make all the difference in engaging your audience and ensuring they retain the information you’re sharing.
Practicing Your Speech
Practice makes perfect, and this couldn’t be more true when it comes to public speaking. Rehearse your speech multiple times to build confidence and familiarity with the content. Practice in front of a mirror, family members, or friends to get comfortable with your delivery.
As you practice, focus on your pacing, intonation, and body language. Aim for a conversational tone and maintain eye contact with your audience. The more you practice, the more natural and engaging your delivery will become.
Using Visual Aids
Visual aids such as slides, charts, or props can enhance your informative speech by making complex information more accessible and engaging. When utilized in your informative speech, they can help illustrate key points, provide visual examples, and break up the monotony of a purely verbal presentation.
Of course, it’s important to ensure your visuals are clear, relevant, and easy to understand. Otherwise, they may end up obscuring your points instead of clarifying them. In light of this, avoid cluttering your slides with too much text or overwhelming your audience with too many visuals. Use them strategically to support your message, not distract from it.
Engaging Your Audience
Engaging your audience is crucial for a successful informative speech. Use rhetorical questions, anecdotes, or interactive elements to keep them involved and attentive. Encourage participation, if appropriate, and maintain a conversational tone to create a connection with your listeners.
Pay attention to your audience’s reactions and adapt your delivery accordingly. If you sense confusion or disinterest, try rephrasing your points or providing additional examples to clarify your message. Remember, your goal is to educate and inspire your audience, so keep them at the forefront of your mind throughout your speech.
Handling Nerves
It’s normal to feel nervous before and during a speech, but there are strategies to help you manage those nerves . Take deep breaths, visualize success, and focus on your message rather than your anxiety. Remember, your audience wants you to succeed, and a little nervousness can actually enhance your performance by showing enthusiasm and authenticity.
If you find yourself getting overwhelmed, take a moment to pause, collect your thoughts, and regain your composure. Smile, make eye contact, and remind yourself that you’ve prepared thoroughly and have valuable information to share.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To deliver an effective informative speech, it’s important to be aware of common pitfalls and mistakes. One of the biggest errors is overloading your audience with too much information. Remember, less is often more when it comes to public speaking.
Another mistake is failing to organize your content logically or using complex jargon without explanation. Make sure your speech has a clear structure and that you’re explaining any technical terms or concepts in a way that your audience can understand.
Finally, don’t neglect the importance of practice and preparation. Winging it or relying too heavily on notes can lead to a disjointed and unengaging speech. Take the time to rehearse, refine your delivery, and internalize your key points.
By avoiding these common mistakes and focusing on the strategies we’ve discussed, you’ll be well on your way to delivering an informative speech that educates, engages, and inspires your audience.
Tips for Delivering a Compelling Informative Speech
Once you’ve chosen your topic and done your research, it’s time to focus on delivering a compelling speech. Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Start with a strong attention-grabbing opening that draws your audience in and sets the tone for your speech.
- Use clear, concise language and avoid jargon or technical terms that your audience may not understand.
- Incorporate storytelling, examples, and anecdotes to make your points more relatable and memorable.
- Use visual aids , such as slides or props, to enhance your message and keep your audience engaged.
- Practice your delivery and timing to ensure that you stay within your allotted time and maintain a natural, conversational tone.
By following these tips and choosing a topic that you’re passionate about, you’ll be well on your way to delivering an informative speech that educates and inspires your audience.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
20 Bonus Topics for Informative Speeches
In case the informative speech examples above didn’t pique your interest, we have several more for you to consider. Ranging from topics like science and technology to history and education, these 20 topics are perfect for your next presentation.
- The history and development of virtual reality technology
- The benefits and challenges of remote work
- The science behind the formation of hurricanes and tornadoes
- The impact of social media on political campaigns and elections
- The importance of sustainable fashion and its environmental benefits
- The role of emotional support animals in mental health treatment
- The history and cultural significance of a specific cuisine or dish
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine ecosystems
- The benefits and risks of gene editing technology
- The psychology behind conspiracy theories and their spread online
- The importance of digital privacy and data security in the modern age
- The role of music therapy in healthcare and wellness
- The impact of deforestation on biodiversity and climate change
- The history and evolution of a specific sport or athletic event
- The benefits and challenges of alternative education models
- The science behind the human immune system and how vaccines work
- The impact of mass incarceration on communities and families
- The role of storytelling in preserving cultural heritage and traditions
- The importance of financial planning for retirement and old age
- The impact of urban agriculture on food security and community development
Choosing a Topic That Resonates With Your Audience
When selecting a topic for your informative speech, it’s important to consider your audience and what will resonate with them. Think about their interests, backgrounds, and knowledge levels, and choose a topic that will be both informative and engaging.
For example, if you’re speaking to a group of high school students, you may want to choose a topic that relates to their experiences or concerns, such as the impact of social media on mental health or the importance of financial literacy for young adults. If you’re speaking to a group of business professionals, you may want to focus on topics related to industry trends, leadership strategies, or emerging technologies.
By choosing a topic that resonates with your audience, you’ll be more likely to capture their attention and keep them engaged throughout your speech. And remember, even if you’re not an expert on the topic, you can still deliver an informative and engaging speech by doing your research and presenting the information in a clear and accessible way.
FAQs on Informative Speech Examples
What is an example of informative speech.
An example includes breaking down the impacts of climate change, detailing causes, effects, and potential solutions.
What are the 3 types of informative speeches?
The three main types are explanatory (breaks down complex topics), descriptive (paints a picture with words), and demonstrative (shows how to do something).
What are the 5 useful topics of an informative speech?
Top picks include technology advances, mental health awareness, environmental conservation efforts, cultural diversity appreciation, and breakthroughs in medical research.
What is an effective informative speech?
An effective one delivers clear info on a specific topic that educates listeners without overwhelming them. It’s well-researched and engaging.
Informative speech examples are everywhere, if you know where to look. From TED Talks to classroom lectures, there’s no shortage of inspiration for your next presentation. All you have to do is find a topic that lights your fire while engaging your audience.
Remember, a great informative speech is all about clarity, organization, and engagement. By following the tips and examples we’ve covered, you’ll be well on your way to delivering an informative speech that educates, enlightens, and leaves a lasting impression. So go ahead, pick your topic, and start crafting your own informative speech today!
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write an Informative Speech
Last Updated: April 30, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Lynn Kirkham . Lynn Kirkham is a Professional Public Speaker and Founder of Yes You Can Speak, a San Francisco Bay Area-based public speaking educational business empowering thousands of professionals to take command of whatever stage they've been given - from job interviews, boardroom talks to TEDx and large conference platforms. Lynn was chosen as the official TEDx Berkeley speaker coach for the last four years and has worked with executives at Google, Facebook, Intuit, Genentech, Intel, VMware, and others. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,393,400 times.
An informative speech tells an audience about a process, event, or concept. Whether you’re explaining how to grow a garden or describing a historical event, writing an informative speech is pretty straightforward. Knowing the topic inside and out is key, so start by conducting thorough research. Organize your speech logically so your audience can easily follow, and keep your language clear. Since speeches are recited out loud, be sure to set aside time after writing to perfect your delivery.
Researching the Topic

- Suppose your prompt instructs you to inform the audience about a hobby or activity. Make a list of your clubs, sports, and other activities, and choose the one that interests you most. Then zoom in on one particular aspect or process to focus on in your speech.
- For instance, if you like tennis, you can’t discuss every aspect of the sport in a single speech. Instead, you could focus on a specific technique, like serving the ball.

- For example, if your speech is about a historical event, find primary sources, like letters or newspaper articles published at the time of the event. Additionally, include secondary sources, such as scholarly articles written by experts on the event.
- If you’re informing the audience about a medical condition, find information in medical encyclopedias, scientific journals, and government health websites.
Tip: Organize your sources in a works cited page. Even if the assignment doesn’t require a works cited page, it’ll help you keep track of your sources. [3] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For instance, if your speech is on growing plants from seeds, explain the process step-by-step to a friend or relative. Ask them if any parts in your explanation seemed muddy or vague.
- Break down the material into simple terms, especially if you’re addressing a non-expert audience. Think about how you’d describe the topic to a grandparent or younger sibling. If you can’t avoid using jargon, be sure to define technical words in clear, simple terms.

- For example, if your speech is on the poet Charles Baudelaire, a strong thesis would be, “I am here to explain how city life and exotic travel shaped the key poetic themes of Charles Baudelaire’s work.”
- While the goal of an informative speech isn't to make a defensible claim, your thesis still needs to be specific. For instance, “I’m going to talk about carburetors” is vague. “My purpose today is to explain how to take apart a variable choke carburetor” is more specific.

- For instance, a speech meant to persuade an audience to support a political stance would most likely include examples of pathos, or persuasive devices that appeal to the audience's emotions.
- On the other hand, an informative speech on how to grow pitcher plants would present clear, objective steps. It wouldn't try to argue that growing pitcher plants is great or persuade listeners to grow pitcher plants.
Drafting Your Speech

- Delivering memorized remarks instead of reading verbatim is more engaging. A section of a speaking outline would look like this: III. YMCA’s Focus on Healthy Living A. Commitment to overall health: both body and mind B. Programs that support commitment 1. Annual Kid’s Day 2. Fitness facilities 3. Classes and group activities

- For example, you could begin with, “Have you ever wondered how a figure skater could possibly jump, twist, and land on the thin blade of an ice skate? From proper technique to the physical forces at play, I’ll explain how world-class skaters achieve jaw-dropping jumps and spins.”
- Once you've established your purpose, preview your speech: “After describing the basic technical aspects of jumping, I’ll discuss the physics behind jumps and spins. Finally, I’ll explain the 6 types of jumps and clarify why some are more difficult than others.”
- Some people prefer to write the speech's body before the introduction. For others, writing the intro first helps them figure out how to organize the rest of the speech.

- For instance, if your speech is about the causes of World War I, start by discussing nationalism in the years prior to the war. Next, describe the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand, then explain how alliances pulled the major players into open warfare.
- Transition smoothly between ideas so your audience can follow your speech. For example, write, “Now that we’ve covered how nationalism set the stage for international conflict, we can examine the event that directly led to the outbreak of World War I: the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. [11] X Research source

- For instance, your conclusion could point out, “Examining the factors that set the stage for World War I shows how intense nationalism fueled the conflict. A century after the Great War, the struggle between nationalism and globalism continues to define international politics in the twenty-first century.”

- Typically, speeches aren’t read verbatim. Instead, you’ll memorize the speech and use a bare bones outline to stay on track.
Avoid information overload: When you compose your speech, read out loud as you write. Focus on keeping your sentence structures simple and clear. Your audience will have a hard time following along if your language is too complicated. [14] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
Perfecting Your Delivery

- While it’s generally okay to use slightly different phrasing, try to stick to your complete outline as best you can. If you veer off too much or insert too many additional words, you could end up exceeding your time limit.
- Keep in mind your speaking outline will help you stay focused. As for quotes and statistics, feel free to write them on your notecards for quick reference.
Memorization tip: Break up the speech into smaller parts, and memorize it section by section. Memorize 1 sentence then, when you feel confident, add the next. Continue practicing with gradually longer passages until you know the speech like the back of your hand.

- Instead of slouching, stand up tall with your shoulders back. In addition to projecting confidence, good posture will help you breathe deeply to support your voice.

- Have them point out any spots that dragged or seemed disorganized. Ask if your tone was engaging, if you used body language effectively, and if your volume, pitch, and pacing need any tweaks.

- If you keep exceeding the time limit, review your complete sentence outline. Cut any fluff and simplify complicated phrases. If your speech isn’t long enough, look for areas that could use more detail or consider adding another section to the body.
- Just make sure any content you add is relevant. For instance, if your speech on nationalism and World War I is 2 minutes too short, you could add a section about how nationalism manifested in specific countries, including Britain, Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Serbia.
Sample Informative Speeches

Expert Q&A

- You're probably much better at informative speeches than you think! If you have ever told your parents about your day at school or explained to a friend how to make chicken noodle soup, you already have experience giving an informative speech! Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If you get nervous, try to relax, take deep breaths, and visualize calming scenery. Remember, there’s nothing to worry about. Just set yourself up for success by knowing the material and practicing. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- When composing your speech, take your audience into consideration, and tailor your speech to the people you’re addressing. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-realworldcomm/chapter/11-1-informative-speeches/
- ↑ https://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/a-primer-on-communication-studies/s11-01-informative-speeches.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_page_basic_format.html
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/communication/chapter/11-1-informative-speeches/
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/informative-speaking
- ↑ https://rasmussen.libanswers.com/faq/337550
- ↑ Lynn Kirkham. Public Speaking Coach. Expert Interview. 20 November 2019.
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/oralcommunication/guides/how-to-outline-a-speech
- ↑ https://wac.colostate.edu/resources/writing/guides/informative-speaking/
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/structuring-speech
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/speeches/
- ↑ https://www.speechanddebate.org/wp-content/uploads/High-School-Competition-Events-Guide.pdf
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/communication/chapter/10-4-physical-delivery/
About This Article

To write an informative speech, start with an introduction that will grab your audience's attention and give them an idea of where the rest of your speech is headed. Next, choose 3 important points that you want to make to form the body of your speech. Then, organize the points in a logical order and write content to address each point. Finally, write a conclusion that summarizes the main points and ends with a message that you want your audience to take away from it. For tips on researching topics for an informative speech, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Tiffany Caroline
Aug 27, 2019
Did this article help you?
Linda Howard
Sep 9, 2022
Jul 30, 2017
Jasmine Guzman
Jun 4, 2017
Brenden Shelton
Oct 15, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
50 Interesting Informative Speech Topics for College
26 September, 2020
15 minutes read
Author: Mathieu Johnson
Informative speeches grant speakers a responsible mission of educating people about significant ideas and themes. They’re also about sharing thoughts and opinions on this or that topic, aimed at expanding understanding and providing listeners with relevant insights for further deliberation. Therefore, it’s a particular type of speeches given to put things into sharp focus and offer food for thought. Read up to know which informative speech topics have the most impact.

What is an informative speech?
As mentioned above, it’s a kind of speech that, well, informs the audience about your topic. Sounds simple enough, but simplicity is deceptive, and there are enough secrets behind this science. Specifically, not all people are fully aware of the fact that the “what” question is a key element that needs to be answered, for with informative speeches, you want to choose a topic most likely to be well received.
Of course, you can speak about something you already know, but you can also talk about the topic which is absolutely new to you. In this case, however, you must make sure that the theme will be relatively easy to research and studied before speech delivery. Another important point worth noticing is that organizational requirements and type of information for informative speech usually intertwines with those for an informative essay, for the latter is often an extension of the first.
How to write an informative speech?
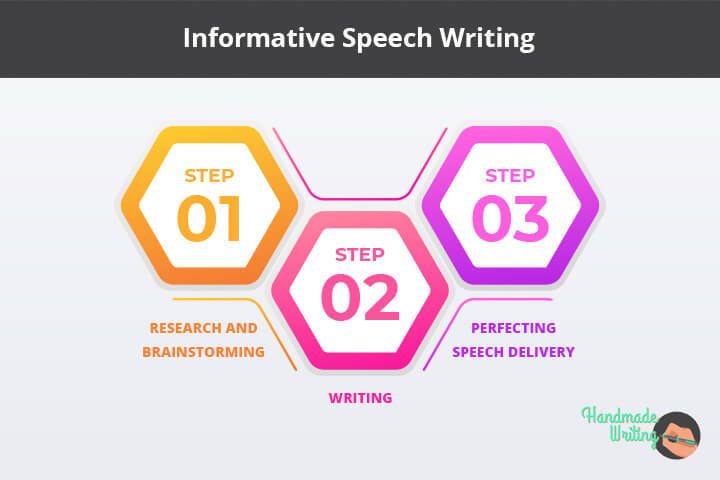
So, now it’s time to move from theory to practice and write an informative speech. But where do you start from?
Although there are many different processes involved in the process, we’ll narrow them to essentials to help you better grasp the idea of how a perfect speech should be tailored.
Stage 1. Research and Brainstorming
Think about the topic.
The first and most crucial step is about choosing the right topic. We’ve mentioned before that it’s vital to select the issue you feel free to talk about. However, there are also cases when professors assign a specific task for you. Either way, the point here is to conduct thorough research based on the given or chosen topic.
If you want to explain the history of some company, band or event, for example, make sure to deliver the message clearly, without going here and there. For this, consider talking about particular points which will cover the whole speech and help the audience quickly digest it. Otherwise, your speech will depart from the topic, and listeners will find it challenging to follow your thoughts.
Gather Evidence
Every scholarly work proves its credibility by the inclusion of relevant sources to show both the audience and the instructor that you’ve put enough effort into the work to sound authoritative. This is a great chance to get a good mark, but more importantly, earn trust from listeners. To cite the evidence correctly, you can search for some facts, stats, or numbers in a variety of sources. These include textbooks, books, and encyclopedias (online ones work as well), scholarly articles, reputable news bureaus, and government documents. If these are hard to find for you, think of alternatives, like online journals and magazines. But be careful and don’t use sources from there if they are not credible and reputable. As an example, use The New York Times, The Guardian, Harvard Business Review, SAJE journals, Forbes, etc.
Also, keep in mind that the evidence you’ll use should depend on the subject of your talk. If it’s about science, check scientific publications. If it’s about medicine – embark upon texts on this specific sphere. Finally, don’t forget to create a works cited page at the end of your speech and put all your sources there. Even if your instructor does not specify such a requirement, create a list anyways. This will help you keep references organized, and you will be able to pick a suitable one from the list.
Generate a Nice Thesis
A thesis is the core of impactful speech that tells listeners about its focal points. It also reveals the purpose of your speech and provides the audience with an insight into what the speech is all about. Notably, your thesis should not exceed the length of one-two sentences and be as precise as possible. More so, thesis, like the speech itself, is not about convincing people to take your topic stance immediately. Rather, it’s about informing listeners about significant events or cases which they could analyze and make relevant conclusions themselves. No need to push them or force to change the perspective, just try to be genuine and honest with people you’re talking to. Considering that it’s a scholarly piece of work, there’s no room for appealing to emotions or subjective claims. So in informative speeches, objectivity is the key player.

Informative speech outline
The outline is a skeleton of your speech that briefly explains each of your points. This is basically a list of short sentences which reveal the meaning of your main speech ideas. Remember that this list is not for the audience; it’s for your own use. So the task here is to write about every point in a way you’ll understand. You can also use notecards instead of paper so that it’ll be much easier for you not to get lost in a sea of ideas and organize the speech properly. Tip: include numbers and capital letters for headings, and bullet points or other figures to mark subheadings.
If you are still unsure on whether you can cope with your task – you are in the right place to get help. Our essay writers will easily answer the to the question “Who can write my speech?”
Stage 2. Writing
Once the sketches are ready and you have a clear understanding of what to speak about, move on straight to writing.
Craft an Engaging Intro
What does engaging stand for in this case? It denotes some speech elements which will be enticing for listeners from the first sentence. It’s a common practice to start speeches with different hooks to call for more people’s attention. There are a plethora of techniques you can use to make an unforgettable first impression: jokes, anecdotes, examples from personal life, interesting statistics, rhetorical questions, quotes of famous people. You can even invent your own attention-grabber which will help you knock down listeners.
Give More Detail in the Main Body
Once you managed to create impact by the introduction and made sure everyone will be eager to listen to you further, you need to expand the explanation of key speech ideas in a well-structured, organized manner. Like in regular life, you start a story from the beginning to the end, while gradually moving from one idea to another. The same goes for informative speech – you need to ensure that the flow of your narration is logical and concise, fully elaborated, and precise. Also, don’t forget about making transitions between sentences. They will make your speech flow naturally, helping the audience to process the information much easier and effortlessly.
Wrap Everything Up in Conclusion
The ending of your informative speech should restate the main idea and the thesis you’ve mentioned in the introduction. There’s no need to say new things that will only confuse your audience. Instead, all the conclusion needs is a nice wrapping of the already stated claims.
So basically you want to review your main points and thereby deliver listeners a message which they will perceive as a major takeaway from what you’ve just told them. However, the introductory part should by no means repeat previous information word by word. It’s just a short restatement that covers up the main points.
Proofread and Edit the Final Version
Once the text is written entirely, it’s a must for you to double check it to avoid possible mistakes. If your informative speech turns out not as informative as expected due to grammatical or lexical errors, you’ll not be taken seriously, which we bet is not the purpose of delivering your talk. So, to prevent casualties from happening, you’ll need to use reliable editing and proofreading tools. Grammarly is an excellent source for this. Its accurate algorithm detects all kinds of mistakes and fixes them on the fly in a matter of seconds. And you can also check the text for plagiarism to make sure that it has no analogs anywhere on the web.

Stage 3. Perfecting Speech Delivery
Memorize your speech.
Half work is done – you have a writing piece. Now it’s time to learn it. Of course, it’ll take you time to do this, but with a little patience and enough time, you can memorize it even faster than expected. Besides, it’s not recommended to learn the speech from A to Z, inside out and upside down by heart. If your instructor is indulgent enough, feel free to memorize your talk in a way that allows you to explain your ideas clearly and consistently. To facilitate the process of learning, you can memorize sentence by sentence until you’re confident. And even if you forget something during delivery, you can always count on the outline that’ll give you a hint on what to talk about next.
Practice Reading Speech Aloud
When the final product is finally ready and polished, you need to concentrate on reading it.
Practice the speech in a mirror, to a friend/relative/pet, or record yourself to trace the tone and intonation. This way, you’ll make sure that your informative speech is brilliant and you deliver it just the way you wanted. Besides, this practice can help you critically evaluate the flaws and correct them before the actual delivery. Have enough time for this, because even experienced speakers always rehearse their speeches. Finally, focus on the way you use gestures, the way you stand and look at the audience, and facial expressions.

List of informative speech topics
There are lots of easy informative speech topics to choose from, but we offer you to review our topics list with some of the most alluring ones to get you started. Let’s examine pro informative topics that’ll help you write a memorable speech.
Topics for informative speech about music
- Frank Sinatra – a beloved father of music
- The drastic evolution of french music
- Deep house – the most popular music style among youngsters
- Why did rock and roll became an epitome of popular dance music
- Why does reggae music most known under the name of Bob Marley
- The psychological and physical benefits of listening to music
- Chill, lounge and electronica has market the era of progressive sound
- The impact of rap music on society at large
- The art of playing the violin
- The evolution of jazz music and its connection to historical movements
Informative speech topics about animals
- Why are so many animals under extinction today and how do we fix it?
- Why dogs are considered as humans best friend?
- The history and evolution of polar bears
- Why does rhinos horn trimming in South Africa still allowed
- How to properly raise chinchillas
- The most dangerous types of dogs on the planet
- Staggering intellectual abilities of elephants baffle even scientists
- How to keep snakes away and save your life
- Different types of butterflies
- The history of bees and their role in the world
Topics for informative speech about global warming
- Patterns in climate change: rising temperatures and flooding
- What Effects does Climate Change have on the Earth and its Inhabitants?
- What are the practical solutions to global warming
- What is global warming and what causes it?
- The future of global warming: dismal predictions and statistics
- Controversial opinions about global warming
- The greenhouse effect as the top one reason of climate change
- The global issue of global warming: what’s next?
- Humans are responsible for the emergence and progress of global warming
- Sanctions against generation of greenhouses: will they ever take place?
Informative speech ideas about sports
- How sports improve human physical and psychological health
- Is golf the game of the past?
- The real life of sport teams: from trainings to furious games
- Can roller skating be considered a kind of sport?
- What’s more dangerous: white water rafting or ice diving?
- The history of sports: whom do we owe respect?
- Hockey 101: gear, playing techniques, team spirit
- Why is boxing the most dangerous type of sports
- The most unusual kinds of sports humans have invented
- The importance and potential threat of football for the world
Interesting speech topics about food and drinks
- How to bake a cake and not put on weight
- Why does alcohol bring so much trouble to contemporary youth?
- There are no superfoods, the study shows
- Does fast food really cause addiction?
- The secret ingredient of Coca Cola and why you’ll never want to drink it again
- If the fruit diet useful for health?
- Why bananas can save the world
- Eating vegetables and olive oil is a golden ticket to rejuvenation
- What’s the difference between natural and processed foods?
- Why eating pizza is the worst way to get away with cooking
As you can see from the list of topics for speeches, informative speech is a perfect occasion to explore interesting themes in depth and share your knowledge with people who are most likely to learn new things with you. Discovering a variety of topics and writing them on paper is perhaps the most engaging task your instructor has ever assigned you. And if you find it challenging to come with the right idea for a good topic, just send a “ write my speech ” request, and we’ll complete your order in no time.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
25 Topics for an Informative Speech

3-minute read
- 20th November 2023
Have you been asked to give an informative speech, or do you simply want to practice your public speaking skills ? If the answer to either question is yes, then the first thing you need to do is choose a topic for your speech. But with so many potential topics, how can you pick just one? In this post, we’ve narrowed down 25 topics for an informative speech to help you find the one that works best for you.
Choosing a Topic
Informative speeches aim to educate the audience on a particular subject or industry. Unlike persuasive speeches , informative ones are not meant to convince the listener to believe or act a certain way; they are meant to be purely descriptive and explanatory.
The best topics for informative speeches are engaging, interesting, valuable, and relevant to the target audience . Choose a topic about which you have a comprehensive understanding or one you intend to research substantially. After all, it’s easy to deliver an engaging presentation and educate your audience when you’re extremely knowledgeable about the topic! Next, let’s take a look at 25 interesting topics for an informative speech, organized by subject.
Science and Technology
● The impact of artificial intelligence on society
● Recent advancements in space exploration
● Recent breakthroughs in medical research
● The science behind climate change and its effects
● The evolution of social media
● What is 3D printing?
Health and Wellness
● The effect of regular exercise on overall health
● How sleep impacts brain functioning
● Understanding stress and stress management techniques
● How does sugar impact the body?
● Key figures in the Civil Rights movement
● Significant women in history
● Sculpture of the Renaissance
● A history of fashion in the Victorian era
● An exploration of the Olympics from their beginning
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
● The history and impact of open-access education
● An exploration of virtual learning over the past 25 years
● How high schools differ around the world
● A look back at education in 19th-century America and the way it compares to current methods
● The history of homework
The Environment and Sustainability
● How to reduce your carbon footprint
● What is zero-waste living?
● The significance of global water conservation
● The impact of air pollution on public health
● The impact of oil spills on the environment
Tips for Giving an Informative Speech
If you’re giving an informative speech, remember to:
● Do your research! Gather information from credible, authoritative sources when composing your speech. Avoid sources that discuss strictly the opinion of the author and look for solid, factual evidence to support your topic.
● Consider your audience. Do they have at least a baseline knowledge of the topic? The answer to this question will help determine how deep you should go in your explanations and what kind of language to use.
● Organize your ideas . Before you begin writing, create a comprehensive outline that includes the introduction, main ideas, and conclusion.
● Use anecdotes or examples to make your content more engaging and relevant to your audience.
● Anticipate potential questions and jot down notes you can easily refer to.
Here’s one last essential speech writing tip: to ensure a smooth delivery and enhance your writing, have your speech professionally proofread and edited. Our editors can make sure your informative speech effectively conveys your message and engages your audience. Send in your free sample today to get started.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
Informative speech examples
4 types of informative speeches: topics and outlines
By: Susan Dugdale | Last modified: 08-05-2023
The primary purpose of an informative speech is to share useful and interesting, factual, and accurate information with the audience on a particular topic (issue), or subject.
Find out more about how to do that effectively here.
What's on this page
The four different types of informative speeches, each with specific topic suggestions and an example informative speech outline:
- description
- demonstration
- explanation
What is informative speech?
- The 7 key characteristics of an informative speech

We all speak to share information. We communicate knowledge of infinite variety all day, every day, in multiple settings.
Teachers in classrooms world-wide share information with their students.
Call centers problem solve for their callers.
News outlets (on and offline) issue reports on local, national and international events and issues, people of interest, weather, traffic flow around cities...
Health care professionals explain the treatment of addictive behaviors, the many impacts of long Covid, the development of new treatments...
Specialist research scientists share their findings with colleagues at conferences.
A pastry chef demonstrates how to make perfect classic croissants.
The range of informative public speaking is vast! Some of us do it well. Some of us not so well - largely because we don't fully understand what's needed to present what we're sharing effectively.
Return to Top
The key characteristics of an informative speech
So, what are the key characteristics or essential elements, of this type of speech? There are seven.
1. Objectivity
The information you give is factual, neutral and objective. You make no attempt to persuade or push (advocate) a particular viewpoint.
Your personal opinions: feelings thoughts, or concerns about the topic you're presenting are not given. This is not a persuasive speech.
As an example, here's an excerpt from a Statistics Department report on teenage births in New Zealand - the country I live in.
Although it's a potentially a firecracker subject: one arousing all sorts of emotional responses from outright condemnation of the girls and their babies to compassionate practical support, the article sticks to the facts.
The headline reads: "Teenage births halved over last decade"
"The number of teenage women in New Zealand giving birth has more than halved over the last decade, Stats NZ said today.
There were 1,719 births registered to teenage women (those aged under 20 years) in 2022, accounting for around 1 in every 34 births that year. In 2012, there were 3,786 births registered to teenage mothers, accounting for around 1 in every 16 births that year."
For more see: Statistics Department NZ - Teenage births halved over last decade
You present your information clearly and concisely, avoiding jargon or complex language that may confuse your audience.
The candidate gave a rousing stump speech , which included a couple of potentially inflammatory statements on known wedge issues .
If the audience is familiar with political jargon that sentence would be fine. If they're not, it would bewilder them. What is a 'stump speech' or a 'wedge issue' ?
Stump speech: a candidate's prepared speech or pitch that explains their core platform.
Wedge issue: a controversial political issue that divides members of opposing political parties or the same party.
For more see: political jargon examples
3. Relevance
The content shared in your speech should be relevant and valuable. It should meet your audience's needs or spark their curiosity.
If the audience members are vegetarians, they're highly unlikely to want to know anything about the varying cuts of beef and what they are used for.
However, the same audience might be very interested in finding out more about plant protein and readily available sources of it.
4. Organizational pattern
The speech should have a logical sequential structure with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion.
If I am giving a demonstration speech on how to bake chocolate chip cookies, to be effective it needs to move through each of the necessary steps in the correct order.
Beginning with how to spoon the mixture on to the tray, or how to cool the cookies on a wire rack when you've taken them out of the oven, is confusing.
5. Research and credibility
Informative speeches are based on thorough research and reliable sources to ensure accuracy and credibility. And sources need to be properly cited.
My friend told me, my mother says, or I saw it on Face Book is neither authoritative nor enough. ☺
Example: My speech is on literacy rates in USA. To be credible I need to quote and cite reputable sources.
- https://www.apmresearchlab.org/10x-adult-literacy
- https://www.thinkimpact.com/literacy-statistics/
6. Visual aids
Slides, charts, graphs, or props are frequently used to help the audience fully understand what they're being told.
For example, an informative speech on the rise and fall of a currency's daily exchange rate is made a great deal easier to follow and understand with graphs or charts illustrating the key points.
Or for a biographical speech, photos of the person being talked about will help hold the attention of your audience.
7. Effective delivery
To be effective your speech needs to be delivered in a way that captures and hold the audience's attention. That means all aspects of it have been rehearsed or practiced.
If you're demonstrating, you've gone through every step to ensure you have the flow of material right.
If you're using props (visual aids) of any sort you've made sure they work. Can they be seen easily? Do they clearly illustrate the point you're making?
Is your use of the stage (or your speaking space) good? Does your body language align with your material? Can your voice be heard? Are you speaking clearly?
Pulling together a script and the props you're going to use is only part of the task of giving a speech. Working on and refining delivery completes it.
To give a successful speech each of these seven aspects needs to be fine-tuned: to hook your audience's interest, to match their knowledge level, your topic, your speech purpose and, fit within the time constraints you've been given.
Types of informative speeches
There are four types of informative speeches: definition, description, explanation and demonstration. A speech may use one, or a mix of them.
1. Informing through definition
An informative speech based on definition clearly, and concisely, explains a concept * , theory, or philosophy. The principal purpose is to inform the audience, so they understand the main aspects of the particular subject being talked about.
* Definition of concept from the Cambridge dictionary - an abstract principle or idea
Examples of topics for definition or concept speeches
A good topic could be:
- What is global warming?
- What are organics?
- What are the core beliefs of Christianity?
- What is loyalty?
- What is mental health?
- What is modern art?
- What is freedom?
- What is beauty?
- What is education?
- What are economics?
- What is popular culture?
These are very broad topic areas- each containing multiple subtopics, any of which could become the subject of a speech in its own right.
Example outline for a definition or concept informative speech
Speech title:.
What is modern art?
- people who want an introductory overview of modern art to help them understand a little more about what they're looking at - to place artists and their work in context
Specific purpose:
- to provide a broad outline/definition of modern art

Modern art refers to a broad and diverse artistic movement that emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and continued to develop throughout the 20th century.
It is characterized by a radical departure from traditional artistic styles and conventions and encompasses a wide range of artistic styles, techniques, and media, reflecting the cultural, social, and technological changes of the time.
Key characteristics or main points include:
- Experimentation and innovation : Modern artists sought to break away from established norms and explore new ways of representing the world. They experimented with different materials, techniques, and subjects, challenging the boundaries of traditional art forms.
- Abstraction : Modern art often features abstract and non-representational elements, moving away from realistic depictions. Artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Piet Mondrian explored pure abstraction, using shapes, lines, and colors to convey emotions and ideas.
- Expression of the inner self : Many modern artists aimed to convey their inner emotions, thoughts, and experiences through their work. This led to the development of various movements like Expressionism (See work of Evard Munch) and Surrealism (See work of Salvador Dali).
- Rejection of academic conventions : Artists sought to break free from the rigid rules of academic art and embrace more individualistic and avant-garde approaches. For example: Claude Monet, (1840 -1926) Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Édouard Manet
- Influence of industrialization and urbanization : The rapid changes brought about by industrialization and urbanization in the 19th and 20th centuries influenced modern art. Artists were inspired by the dynamics of the modern world and its impact, often negative, on human life.
- Multiple art movements : Modern art encompasses a wide array of movements and styles, for example Cubism, Futurism, Dadaism, Abstract Expressionism, Pop Art... Each movement brought its own unique perspective on art and society.
- Focus on concept and process : Modern artists began to emphasize the underlying ideas and concepts behind their work, giving greater importance to the creative process itself.
Modern art should not be confused with contemporary art. While modern art refers specifically to the artistic developments of the early to mid-20th century, contemporary art encompasses art created by artists living and working in the present day. The transition from modern art to contemporary art happened around the late 20th century- 1950s onward.
References:
- mymodernmet.com/abstract artists
- differencess.com/expressionism vs surrealism
- lorimcnee.com/artists who died without recognition
- industrial revolution the influence on art
- mymodernmet.com/important art movements
- theartstory.org/conceptual-art
- Image: The Scream, Edvard Munch
2. Informing through description
Informing through description means creating detailed, vivid verbal pictures for your audience to make what you're talking about come to life in the minds of those listening which in turn, will make your subject matter memorable.
Examples of good informative speech topics that could be used for descriptive speeches
- How I celebrate Christmas
- My first day at school
- My home town
- A time I feared for my life
- A time when I felt contented and happy
My first car
- An object I find fascinating: lotus shoes, bustles, corsets, panniers (These are historical items of women's clothing.)
- Working from home: the joys, the hazards
- My dream home, job, or holiday
- An event I'll never forget
- The most valuable or interesting thing I own
- Martin Luther King, Benjamin Franklin, President Lincoln... a notable person from the past or present, including someone you may know: a family member, friend or yourself, or a public figure (an artist, singer, dancer, writer, entrepreneur, inventor...)
Example outline for a descriptive informative speech
- to take the audience with me back to the time when we bought our first car and have them appreciate that car's impact on our lives
Central idea:
Our Austin A50 was a much-loved car

About the car:
- English, Austin A50, 1950ish model - curvy, solid, a matron of cars
Background to purchase:
- 1974 - we were 20 and 21 - young and broke
- The car cost $200 - a lot of money for me at that time. I raided my piggy bank to buy it.
- It was a trade up from the back of the motorbike - now I could sit side by side and talk, rather than sit behind and poke my husband, when I wanted to say important things like, 'Slow down', or 'I'm cold'. The romance of a motorbike is short-lived in winter. It diminishes in direct proportion to the mountain of clothes needing to be put on before going anywhere - coats, scarf, boots, helmet... And this particular winter was bitter: characterized by almost impenetrable grey fog and heavy frosts. It was so cold the insides of windows of the old house we lived in iced up.
- It was tri-colored - none of them dominating - bright orange on the bonnet, sky blue on the rear doors and the roof, and matt black on the front doors and the boot. (Bonus - no one would ever steal it - far too easily identified!)
- The chrome flying A proudly rode the bonnet.
- The boot, (trunk lid) was detachable. It came off - why I can't remember. But it needed to be opened to fill the tank, so it meant lifting it off at the petrol station and leaning it up against the boot while the tank filled, and then replacing it when done.
- There were bench seats upholstered in grey leather (dry and cracked) front and back with wide arm rests that folded down.
- The windows wound up and down manually and, in the rear, there were triangle shaped opening quarter-windows.
- The mouse-colored lining that had been on the doors and roof was worn, torn and in some patches completely missing. Dust poured in through the crevices when we drove on the metal roads that were common where we lived.
- It had a column gear change - 4 gears, a heater that didn't function, proper old-school semaphore trafficators indicators that flicked out from the top of the door pillars and blinked orange, a clutch that needed a strong push to get it down, an accelerator pedal that was slow to pick up and a top speed of around 50 mph.
Impact/benefits:
We called her Prudence. We loved, and remember, her fondly because:
- I was taught to drive in her - an unforgettable experience. I won the bunny hopping record learning to coordinate releasing the clutch and pressing down on the accelerator. Additionally, on metal roads, I found you needed to slow before taking corners. Sliding on two wheels felt precarious. The bump back down to four was a relief.
- We did not arrive places having to disrobe - take off layers of protective clobber.
- We could talk to each without shouting and NOW our road trips had a soundtrack - a large black portable battery driven tape player sat on the back parcel shelf blasting out a curious mix of Ry Cooder, Bach, Mozart's Flute Concerto, Janice Joplin... His choice. My choice. Bliss.
- My father-in-law suggested we park it down the street rather than directly outside his house when we visited. To him Prudence was one eccentricity too many! An embarrassment in front of the neighbors. ☺
- austinmemories.com/styled-33/styled-39/index.html
- wikipedia.org/Austin_Cambridge
- archive.org/1956-advertisement-for-austin-a-50
3. Informing through demonstration
Informing through demonstration means sharing verbal directions about how to do a specific task: fix, or make, something while also physically showing the steps, in a specific chronological order.
These are the classic 'show-n-tell', 'how to' or process speeches.
Examples of process speech topics:
- How to bake chocolate chip cookies
- How to use CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) correctly
- How to prepare and plant a tub of vegetables or flowers
- How to read a topographic map
- How to make a tik-tok reel
- How to knit a hat
How to brainstorm material for a speech
For literally 100s more demonstration topic ideas
A demonstrative informative speech outline example
To demonstrate the brainstorming process and to provide practical strategies (helpful tips) for freeing and speeding up the generation of ideas
Main ideas:
Understanding brainstorming - explanation of what brainstorming is and its benefits
Preparing for brainstorming - the starting point - stating the problem or topic that needs brainstorming, working in a comfortable place free from distractions, encouraging open-mindedness and suspension of judgment.
Techniques for brainstorming : (Show and tell on either white board or with large sheets of paper that everyone can see) mind mapping, and free writing. Take topic ideas from audience to use.
Example : notes for maid of honor speech for sister

Benefits : Demonstrate how mind maps can help visually organize thoughts and connections, how free writing allows ideas to flow without stopping to judge them
Encourages quantity over quality - lots of ideas - more to choose from. May generate something you'd never have thought of otherwise.
Select, refine, develop (show and tell)
For more see: brainstorm examples
4. Informing through explanation
Informing through explanation is explaining or sharing how something works, came to be, or why something happened, for example historical events like the Civil War in the United States. The speech is made stronger through the use of visuals - images, charts of data and/or statistics.
Examples of explanatory informative speech topics
- How did the 1919 Treaty of Versailles contribute to the outbreak of World War Two?
- What led to The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865)?
- Why is there an increase in type two diabetes and problems associated with obesity in first world countries, for example, in UK and USA?
- How do lungs work?
- What causes heart disease?
- How electric vehicles work?
- What caused the Salem witch trials?
- How does gravitation work?
- How are rainbows formed?
- Why do we pay taxes?
- What is cyberbullying? Why is it increasing?
Example explanatory informative speech outline
The Treaty of Versailles: how did it contribute to the outbreak of World War Two

- to explain how the Treaty of Versailles (1919) was a significant causal factor leading up World War two
Central ideas:
Historical context : World War One, 'the war to end all wars' ended in 1918. The Allied Powers: USA, UK, France, Italy and Japan, met in Paris at the Paris Peace Conference 1919 to work out the details and consequences of the Treaty of Versailles, which would impact the defeated Central Powers, principally Germany.
These included:
- territorial boundary changes which stripped Germany of land in Europe, and established new nations - e.g. Poland and Czechoslovakia
- military restrictions - the disarmament of the German military, restrictions on weapons and technology, demilitarization of the Rhineland
- reparations - demands that they were unable to meet, plus being forced to accept a "war guilt" clause (Article 231) had an enormous impact, economically and psychologically. The country plunged into deep recession - albeit along with many other countries. (The Great Depression 1929-1939 which ended with the beginning of World War Two.)
The League of Nations - The League of Nations was an international diplomatic group developed after World War I as a way to solve disputes between countries before they erupted into open warfare. Despite being active in its set up, USA refused to join it - a stance that weakened its effectiveness.
Controversies within Germany: Public anger and resentment, plus political instability as result of reparations, territory loss and economic hardships
Controversies with Treaty partners: The Treaty's perceived fairness and effectiveness: Italy and Japan felt their settlements were inadequate compared to what had been taken by UK, USA and France.
The rise of 'isms' Simmering discontent eventually emerged as the rise of Fascism in Italy, Nazism in Germany and Statism (a mix of nationalism, militarism and “state capitalism”) in Japan.
Expansionist Nationalism Spread of expansionist nationalism - a state's right to increase its borders because it is superior in all ways. Therefore, Hitler was 'right' to take back what had previously been regarded as German territory (Czechoslovakia and Austria), and to go after more, all the while goading the Allied Powers to act. When his armies went into Poland, Britain declared war against Germany - 21 years after the end of the last.
- history.com/treaty-of-versailles-world-war-ii-guilt-effects
- tinyurl.com/Treaty-of-Versailles
- Image: tinyurl.com/signing-Treaty-of-Versailles
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Informative Speech Outline – Template & Examples

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

Informative speeches are used in our day-to-day lives without even noticing it, we use these speeches whenever we inform someone about a topic they didn’t have much knowledge on, whenever we give someone instructions on how to do something that they haven’t done before, whenever we tell someone about another person. Informative speaking is fairly new to the world of public speaking. Ancient philosophers like Aristotle, Cicero and, Quintilian envisioned public speaking as rhetoric, which is inherently persuasive.
In this article:
What is an Informative Speech?
Here are some ways to prepare for your speech, 1. develop support for your thesis, 2. write your introduction and conclusion, 3. deliver the speech, example of an informative speech outline.

An informative speech is designed to inform the audience about a certain topic of discussion and to provide more information. It is usually used to educate an audience on a particular topic of interest. The main goal of an informative speech is to provide enlightenment concerning a topic the audience knows nothing about. The main types of informative speeches are descriptive, explanatory, demonstrative, and definition speeches. The topics that are covered in an informative speech should help the audience understand the subject of interest better and help them remember what they learned later. The goal of an informative speech isn’t to persuade or sway the audience to the speaker’s point of view but instead to educate. The details need to be laid out to the audience so that they can make an educated decision or learn more about the subject that they are interested in.
It is important for the speaker to think about how they will present the information to the audience.
Informative Speech Preparation

When you are preparing your informative speech, your preparation is the key to a successful speech. Being able to carry your information across to the audience without any misunderstanding or misinterpretation is very important.
1. Choose Your Topic
Pick a topic where you will explain something, help people understand a certain subject, demonstrate how to use something.
2. Make a Thesis Statement
Think about what point you are trying to get across, What is the topic that you want to educate your audience on? “I will explain…” “I will demonstrate how to…” “I will present these findings…”
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
3. Create Points That Support Your Thesis
Take a moment to think about what would support your thesis and take a moment to write the points down on a sheet of paper. Then, take a moment to elaborate on those points and support them.
Typical Organization for an Informative Speech:
How to Speech: 4 Key steps to doing what you are talking about.
Example: Step One: Clean the chicken of any unwanted feathers and giblets. Step Two: Spice the chicken and add stuffings. Step Three: Set oven to 425 degrees Fahrenheit. Step Four: Place chicken in the oven and cook for an hour.
History/ What Happened Speech: Points listing from the beginning to the latest events that you want to discuss in your speech.
Example: First, Harry met Sally. Second, Harry took Sally out to the roadhouse. Third, Harry and Sally started their courtship. Fourth, Harry and Sally moved in together and adopted a dog named Paco.
What is it Speech: Two to Four main points that discuss the key elements of your subject.
Example: First, there must be four wheels. Second, the car’s engine must be functioning. Third, the doors must be functional. Fourth, in order to get to your destination, the car’s steering has to be functional.
Explain it Speech: Two to Four main points that go through the key elements of the topic to explain it.
Example: Firstly, the car drives by the engine that powers it to move forward. Secondly, by the wheels that rotate in a forward or backward motion. Thirdly, the car’s engine is powered by gas which gives it the ability to function and essentially move the car.
Write down support for your points. Take some time to research your topic thoroughly. It is good to gather statistics, expert opinions, facts, and much more to make your speech unique and effective.
There are three main types of support you should use to strengthen your speech:
Interest supports.
Interest supports are used to increase the audience’s interest in the topic you are presenting.
- Personal experiences
- Interaction (e.g., Questions to the audience)
Evidence Supports
Evidence increases solid factual support in your speech. Examples of evidence supported are statistics, expert opinions, direct quotations. Studies, surveys, and facts.
Multimedia Aids
Multimedia aids such as posters with pictures and writing, DVDs, music or recordings on a stereo player, videotapes, and PowerPoint presentations.
Write your introduction. Provide a quick attention getter, state your thesis, elaborate on why it is important to you and your audience. It is expected that you preview your main points in the introduction by listing all your main points of discussion in your introduction.
Write your conclusion. Tie the speech together, build to a higher point and give it a sense of conclusion.
Practice your speech until you feel confident. Present your material as effectively as possible.
Informative Speech Outline

Creating an outline for an informative speech will help you organize your ideas and information to share with your audience in an effective manner. A well-planned outline will ensure that all the important information is included in your speech and ensure that you don’t wander off-topic.
Topic: This will be the title of your speech.
Purpose: To inform the audience about the topic.
Thesis: A theme statement that clearly describes the topic and points made in the presentation.
- Introduction
- Attention-grabbing opening statement
- Reason to listen to the speech
- Thesis statement
- Preview of points to be covered
- First main point
- First subpoint
- Supporting detail
- Second subpoint
- Second main point
- Third main point
- Restatement of main points
- Restatement of thesis
- Concluding remarks
When developing an outline, follow these rules to ensure a successful speech:
- Include one idea for every point, subpoint, or supporting detail.
- If there is one point, there must be a second point. If there is one supporting point, there should be a second supporting point.
- Be consistent. If you are using full sentences to describe points and subpoints, use full sentences throughout the outline. Ensure that the verb tense is consistent throughout your outline as well.
Informative Speech Outline Examples

Topic: Adoption
Purpose: To inform people about adoption
Thesis: Adoption is the act of transferring parental rights and duties to someone other than the adopted person’s biological parents. The number of children adopted each year by American families is an estimate only.
- What do Edgar Allan Poe, John Lennon, Steve Jobs, and Eleanor Roosevelt all have in common? They were all adopted. Adoption is the act of transferring parental rights and duties to someone other than the adopted person’s biological parents. The adoption process is lengthy, expensive, and varies from country to country and even state to state. Not only does adoption vary from state to state, but sometimes the adoption process even varies within regions of a state.
- Many children get adopted every year. No one knows how adoption works.
- Adoption is a life-changing event, not just for the children involved but also for every single family made whole through adoption.
- Adoption processes vary from place to place. Types of adoption. Benefits and detriments to adoption. Many children who are adopted have experienced neglect and abuse.
- Adoption processes vary from place to place.
- The adoption process varies from state to state.
- It is more expensive in certain states than in others.
- The amount of paperwork throughout the process also depends on the state legislature.
- The adoption process varies within a state.
- In certain states, the adoption process is different from one region to the next.
- The process is different depending on the child protection laws set in each region inside a state.
- Types of adoption
- There are different types of adoption.
- There is step-parent or other family member adoption
- There is also adoption across state lines
- The more traditional adoption types are commonly known.
- There is private adoption which is most commonly found throughout the U.S.
- Adoption through foster care is a good thing to try for first-time adopters.
- The adoption process is expensive.
- There are a lot of upfront expenses.
- You are subjected to adoption agency fees to help you find a suitable match for your family.
- You also have to pay to adopt the child you want to adopt.
- There are a lot of big expenses in terms of the child too.
- Readying a living space to suit a child’s wants and needs can be expensive.
- Many new expenses come to light like healthcare, school, etc.
- Adoption processes vary from state to state. There are many different types of adoption. Adoption can be expensive, so you have to ensure that you are financially capable of caring for another human being.
- Adoption is the act of transferring parental rights and duties to someone other than the adopted person’s biological parents. The number of children adopted each year by American families is an estimate only.
- Adoption is an absolutely life-changing adventure, but everyone needs to be more educated before walking into a demanding process. There will be many emotions, expenses, and frustration, but it truly is worth it in the end.
Topic: Snakebites and how they’re treated
Purpose: To inform the audience of the dangers of snakes and how to respond to being bitten by a snake.
Thesis: Snakebites are dangerous and could ultimately lead to loss of life if not acted upon correctly.
- Imagine that you and your friend are walking in the woods, one sunny day in the fall when leaves cover the ground. Suddenly, your friend accidentally steps on a snake and gets bitten.
- Your friend’s chance of survival depends on your knowledge of acting promptly and taking proper measures in this situation.
- Today I will inform you about three common poisonous snakes seen in our country and explain to you the effects of a snake bite.
- Three poisonous snakes. Effects of the snake’s venom. How to administer first aid in the event of a snake bite.
- Three poisonous snakes
- There are two types of Rattlesnakes.
- William Pinkston: Responsible for more deaths in this country.
- Western diamondback: found from Texas to Eastern California.
- Copperhead and Cottonmouth
- Before striking, it opens its mouth wide to reveal its white inside.
- That’s how it got its name.
- The effects of snake venom on the human body
- Hepatotoxic
- Destroys blood vessels and red blood cells.
- Deadly and fatal to the victim.
- It affects the optic nerves in the eyes, causing blindness.
- It affects the nerves controlling the respiratory muscles, causing suffocation and eventually leading to death if left untreated.
- How to administer first aid in the event of a snake bite.
- Immobilize the bitten area slightly lower than the heart.
- Apply a flat constricting band 2-4 inches above the bite.
- With a sterile scalpel or knife, make one incision that connects the fang marks.
- Squeeze venom gently from the incision with your fingers for 30 minutes.
- Get the victim to the hospital as soon as possible.
- Snake bites are dangerous and could ultimately lead to loss of life if not acted upon correctly.
- Snake bites are dangerous and could ultimately lead to loss of life if they are not cared for properly, and the victim doesn’t get the necessary treatment in time.
Informative speeches have one main goal: to inform the audience of a specific topic of interest. For you to have an effective and successful informative speech, it is important to do your research and draw up an informative speech outline. The speech outline ensures that you do not wander off topic or get carried away with one point.
If, on the other hand, you have to prepare persuasive speech, we have a guide on outlining and preparing for it the right way right here .
Avoid Any Awkward Silence With These 35+ Topics to Talk About
16 Tips to Help You Write Like a Pro
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

14 Informative Speeches
Speeches to Educate, Explain, or Describe
In this chapter . . .
In this chapter we examine our first type of public speech, the informative speech. This is used in lectures, briefings, and anytime you want to transmit fact-based information to an audience. We cover what makes an informative speech unique, the types of informative speeches, and how to construct this type of speech.
What is an informative Speech? Defining what an informative speech is can be both straight-forward and somewhat tricky at the same time. Very simply, an informative speech can first be defined as a speech based entirely and exclusively on facts. An informative speech conveys knowledge, a task that every person engages in every day in some form or another. Whether giving someone who is lost driving directions, explaining the specials of the day as a server, or describing the plot of a movie to friends, people engage in forms of informative speaking daily.
An informative speech does not attempt to convince the audience that one thing is better than another. It does not advocate a course of action or incorporate opinion as its basis. This can be the tricky part of developing an informative speech because some opinion statements sound like facts (since they are generally agreed upon by many people) but are really opinions.
For example, in an informative speech on George Washington, you might want to say, “George Washington was one of the greatest presidents in the history of the United States.” While this statement may be agreed upon by many people, it’s not irrefutable, meaning someone could argue against this claim. However, you could include this statement in an informative speech if you present the opinion from a reputable source: “Ron Chernow, in his 2011 best-selling biography of George Washington, describes the first president as one of the greatest presidents in the history of the United States.” That is an acceptable way of presenting an opinion within the framework of a factual speech. While you may not be able to avoid opinion, you don’t want your central idea, your main points, and most of your supporting material to be opinion or argument in an informative speech.
Additionally, you should never take sides on an issue in an informative speech, nor should you “spin” the facts to influence the opinions of the listeners. Even if you are informing the audience about differences in views on controversial topics, you should simply and clearly explain the issues.
This doesn’t mean that an informative speech will have no effect on the audience. An audience can learn things from an informative speech that will affect what they do or how they think about something—that’s their choice. Your only focus is to provide the clearest and most factual information you can.
Types of Informative Speeches
While the topics to choose from for informative speeches are nearly limitless, they can be categorized according to five broad categories based on the primary goal of the speech. Understanding the type of informative speech that you will be giving can help you to figure out the best way to research and speechwriting.
Type 1: History
An informative speech on the history or development of something. Your focus is to explain to an audience how something came into existence. History speeches can be about objects, places, ideas, or even events. For example, imagine your informative speech was on the history of the football (the object, not the game). Someone at some point in history was the first to develop what is considered the modern football. Who was it? What was it originally made of? How did it evolve into the football that is used by the NFL today? For the history of a place, like a university, you would describe the specific year it opened, the number of students who were initially enrolled, and how it got its name. It’s also possible to provide the history of an idea, like “democracy.” By explaining the civilizations and cultures that adopted forms of democracy throughout history, it’s possible to provide an audience with a better understanding of how the idea has been shaped into what it has become today.
Type 2: Biography
A biographical speech is similar to a history one, but in this case the subject is a person, whether living or deceased. As with histories of objects, places, or ideas, there are specific and irrefutable facts that provide the details of someone’s life. Your focus is to tell the audience about someone’s life.
Type 3: Processes
Process speeches are informative speeches that explain how to do something or how something is achieved. These speeches require you to provide steps that will help your audience understand how to accomplish a specific task or process. We see examples of “how-to” presentations frequently—especially on YouTube. There’s a second type of process speech that focuses not on how the audience can achieve a result, but on how a process is achieved. The goal is understanding of a process instead of the performance of a process. After a speech on how to change a car tire, for example, the audience members could probably do it (they might not want to, but they would know the steps). However, after a speech on how a bill goes through Congress, the audience would understand this important part of democracy but not be ready to serve in Congress. Either way, if your speech aims at teaching the audience how something works, it’s a process speech.
Type 4: Ideas and Concepts
It is possible to have an informative speech about an idea or concept where your primary focus isn’t on the history of the idea, but how it exists now. In the examples above, we have seen two types of speeches about democracy: democracy as the topic of a speech that focuses on its history and democracy in a speech that focuses on a process in democratic legislation. In this fourth type of informative speech, you could focus on the concept of democracy as interpreted, for example, in three different countries. Your speech is neither about history nor about process but focuses on the definition itself.
Type 5: General
Sometimes an informative speech topic doesn’t lend itself to a focus on history, process, or concept. In those cases, the topics tend to fall into the general category of informative speeches. The focus in this type of informative speech is determined by the topic. For example, imagine a speech about customs to know when traveling in Japan. This isn’t a speech about the history of anime , nor a biography of a former emperor. It’s not about the process of planning a trip to Japan, nor is it about the concept of kawaii . Customs of Japan falls into the “general” type of informative speech.
Tips for Informational Speeches
Use the type of speech to determine the structure.
Identifying the type of informative speech being given can help in several ways (conducting research, writing the introduction and conclusion), but the biggest benefit is that the type of informative speech being given will help determine the organizational pattern that is best for a speech.
For example, a How-To speech must be in chronological order (step 1, step 2, step 3). Similarly, most speeches that focus on providing history or biography will be organized chronologically, but not always. It makes sense to use chronology to explain the history of the football from the moment it was first developed to where it’s today, but for an informative speech on Benjamin Franklin a student might choose a topical pattern (idea 1, idea 2, idea 3) as their three main points: 1) His time as a printer, 2) His time as an inventor, 3) His time as a diplomat. These main points are not in strict chronological order because Franklin was a printer, inventor, and diplomat at the same time during periods of his whole life. However, this example would still be one way to inform an audience about him without using the chronological organizational pattern.
As for general informative speeches, since the topics that can be included in this category are so diverse and cover a range of possible subject matter, the way they are organized will be varied as well and may use chronological, spatial, or topical structures. (Refer to Chapter x on speech structure and organization).
Keep Your Topic Specific
One of the biggest and most common mistakes students make is pursuing a topic that is much too broad. Let’s consider the example of a student who proposes the topic “To inform my audience about the Civil War.” The Civil War was, conservatively speaking, four years long, resulted in over 750,000 casualties, and arguably changed the course of human history. To think that it’s possible to cover all of that in a speech is unrealistic. Even a very experienced professor in American history would find it difficult to deliver a one-hour lecture that accomplished that goal.
The better approach in this case is to be as specific as possible. A revised specific purpose for this speech might be something like “To inform my audience about the Gettysburg Address.” This topic is much more compact (the Gettysburg Address is only a few minutes long) and doing research will be easier—although you will still find hundreds of sources on it. An even more specific topic would be “To inform my classmates of the specific places in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania that are considered haunted.”
Avoid Fake Informative Speech Topics
Sometimes students think that because something sounds like an informative speech topic, it’s one. This happens a lot with political issues that are usually partisan in nature. Some students may feel that the speech topic “To inform my audience why William Henry Harrison was a bad president” sounds factual, but really this is an opinion—in other words, it’s a fake informational speech because it’s a persuasive speech disguised as an informational speech. Similarly, a few topics that include conspiracy and paranormal subject matter are usually mistaken for good informative topics as well. It is common for a student to propose the topic “To inform my audience about the existence of extraterrestrials,” thinking it’s a good topic. After all, there is plenty of evidence to support the claim, right? There are pictures of unidentified objects in the sky that people claim are from outer space, there are people who claim to have seen extraterrestrials, and most powerful of all, there are people who say that they have been abducted by aliens and taken into space.
The problem here, as you have probably already guessed, is that these facts are not irrefutable. Not every single person who sees something unknown in the sky will agree it’s an alien spacecraft, and there can be little doubt that not everyone who claims to have been abducted by a UFO is telling the truth. This isn’t to say that you can’t still do an informative speech on alien sites. For example, two viable options are “To inform my audience about the SETI Project” or “To inform my audience of the origin of the Area 51 conspiracy.” However, these types of speeches can quickly devolve into opinion if you aren’t careful, which would then make them persuasive speeches. Even if you start by trying to be objective, unless you can present each side equally, it will end up becoming a persuasive speech. Additionally, when a speaker picks such a topic, it’s often because of a hidden desire to persuade the audience about them.
Be Selective about Content
Even if you have chosen a specific and focused topic, you must still make choices about what you can and cannot include. Writing an informative speech isn’t about dumping enormous amounts of information on your audience that you can only get to by speaking at breakneck speed. It’s about carefully choosing what to include, making it interesting and clear, and presenting it to your audience at a comfortable pace. What’s better: too much information that audiences can’t grasp or less information for audiences that hear every word? Regardless of the topic, you will never be able to cover everything that is known about your topic, so don’t try. Select the things that will best help the audience gain a general understanding of the topic that will interest them, and that they hopefully will find valuable.
Be Accurate, Clear, and Interesting
A good informative speech conveys accurate information to the audience clearly and keeps the listener interested in the topic. Achieving all three of these goals—accuracy, clarity, and interest—is the key to being an effective speaker. If information is inaccurate, incomplete, or unclear, it will be of limited usefulness to the audience.
Part of being accurate is making sure that your information is current. Even if you know a great deal about your topic or wrote a good paper on the topic in a high school course, you will need to verify the accuracy and completeness of what you know, especially if it’s medical or scientific information.
What defines “interesting?” In approaching the informative speech, you should keep in mind the good overall principle that the audience is asking, “what’s in it for me?” The audience is either consciously or unconsciously wondering “What in this topic for me? How can I use this information? Of what value is this speech content to me? Why should I listen to it?”
Keep in Mind Audience Diversity
Finally, remember that not everyone in your audience is the same, so an informative speech should be prepared with audience diversity in mind. If the information in a speech is too complex or too simplistic, it will not hold the interest of the listeners. Determining the right level of complexity can be hard. Audience analysis is one important way to do this (see Chapter 2). Do the members of your audience belong to different age groups? Did they all go to public schools in the United States, or are some of them international students? Are they all students majoring in the same subject, or is there a mixture of majors? Never assume that just because an audience is made up of students, they all share a knowledge set.
Learning how to give informative speeches will serve you well in your college career and your future work. Keep in mind the principles in this chapter but also those of the previous chapters: relating to the informational needs of the audience, using clear structure, and incorporating interesting and attention-getting supporting evidence.
Something to Think About
Here are three general topics for informative speeches. Write specific purposes for them and explain how you would answer the WIIFM question.
- Type 1 diabetes
- The psychological effects of using social media
Public Speaking as Performance Copyright © 2023 by Mechele Leon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Informative Speeches — Types, Topics, and Examples

What is an informative speech?
An informative speech uses descriptions, demonstrations, and strong detail to explain a person, place, or subject. An informative speech makes a complex topic easier to understand and focuses on delivering information, rather than providing a persuasive argument.
Types of informative speeches
The most common types of informative speeches are definition, explanation, description, and demonstration.

A definition speech explains a concept, theory, or philosophy about which the audience knows little. The purpose of the speech is to inform the audience so they understand the main aspects of the subject matter.
An explanatory speech presents information on the state of a given topic. The purpose is to provide a specific viewpoint on the chosen subject. Speakers typically incorporate a visual of data and/or statistics.
The speaker of a descriptive speech provides audiences with a detailed and vivid description of an activity, person, place, or object using elaborate imagery to make the subject matter memorable.
A demonstrative speech explains how to perform a particular task or carry out a process. These speeches often demonstrate the following:
How to do something
How to make something
How to fix something
How something works

How to write an informative speech
Regardless of the type, every informative speech should include an introduction, a hook, background information, a thesis, the main points, and a conclusion.
Introduction
An attention grabber or hook draws in the audience and sets the tone for the speech. The technique the speaker uses should reflect the subject matter in some way (i.e., if the topic is serious in nature, do not open with a joke). Therefore, when choosing an attention grabber, consider the following:
What’s the topic of the speech?
What’s the occasion?
Who’s the audience?
What’s the purpose of the speech?

Common Attention Grabbers (Hooks)
Ask a question that allows the audience to respond in a non-verbal way (e.g., a poll question where they can simply raise their hands) or ask a rhetorical question that makes the audience think of the topic in a certain way yet requires no response.
Incorporate a well-known quote that introduces the topic. Using the words of a celebrated individual gives credibility and authority to the information in the speech.
Offer a startling statement or information about the topic, which is typically done using data or statistics. The statement should surprise the audience in some way.
Provide a brief anecdote that relates to the topic in some way.
Present a “what if” scenario that connects to the subject matter of the speech.
Identify the importance of the speech’s topic.
Starting a speech with a humorous statement often makes the audience more comfortable with the speaker.
Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the audience needs to know to understand the speech in its entirety.
The thesis statement shares the central purpose of the speech.
Demonstrate

Preview the main ideas that will help accomplish the central purpose. Typically, informational speeches will have an average of three main ideas.
Body paragraphs
Apply the following to each main idea (body) :
Identify the main idea ( NOTE: The main points of a demonstration speech would be the individual steps.)
Provide evidence to support the main idea
Explain how the evidence supports the main idea/central purpose
Transition to the next main idea

Review or restate the thesis and the main points presented throughout the speech.
Much like the attention grabber, the closing statement should interest the audience. Some of the more common techniques include a challenge, a rhetorical question, or restating relevant information:
Provide the audience with a challenge or call to action to apply the presented information to real life.
Detail the benefit of the information.
Close with an anecdote or brief story that illustrates the main points.
Leave the audience with a rhetorical question to ponder after the speech has concluded.
Detail the relevance of the presented information.

Before speech writing, brainstorm a list of informative speech topic ideas. The right topic depends on the type of speech, but good topics can range from video games to disabilities and electric cars to healthcare and mental health.
Informative speech topics
Some common informative essay topics for each type of informational speech include the following:
Informative speech examples
The following list identifies famous informational speeches:
“Duties of American Citizenship” by Theodore Roosevelt
“Duty, Honor, Country” by General Douglas MacArthur
“Strength and Dignity” by Theodore Roosevelt
Explanation
“Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death” by Patrick Henry
“The Decision to Go to the Moon” by John F. Kennedy
“We Shall Fight on the Beaches” by Winston Churchill
Description
“I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King, Jr.
“Pearl Harbor Address” by Franklin Delano Roosevelt
“Luckiest Man” by Lou Gehrig
Demonstration
The Way to Cook with Julia Child
This Old House with Bob Vila
Bill Nye the Science Guy with Bill Nye
Informative Speech Topics and Ideas: The Ultimate Guide
Before proceeding to the main topic, let us get some idea on Informative speech. Well, it is the type of speech that gives information about a particular subject to audiences.
Its main goal is to help audiences to recognize the information presented by you. Additionally, it makes a complex topic simple to understand providing different opinions and perspectives.
It also provides engaging information which is unique and desired by the audience.
Besides, informative speech can include objects, procedures, events, and other innovative ideas. This does not include the limited list as it is the topic plan that every useful speech contains. Speech can only be handy if it delivers genuine and informative information.
Informative speech describes the topic of your interest. For an instance, if you are giving an informative speech on coffee, focus on the topic.
Think about, what does coffee do, why do you love coffee, and how does it affect your health.
Also, to get rid of the health effect how much coffee do you need to drink per day. You can also conclude by summarizing all these things in a creative way. This makes your speech more interesting.
When you present, you might like to expand some topics or reduce the others. Here, you should be sensitive to your audience and think too much like this can distract the topic.
So focus on your plan and subject. Keep in mind, informative speech just to inform audiences. Do not pick up the topic based on your view as it is a convincing speech.
Remember, too much argumentative speech attempting to influence might take your audiences away.
These kinds of speech are polemical and are wrongly argumentative. You can also find places and time to make an appropriate polemical speech. But, it is not good to include it in the middle of the speech.
You can mention like “Coffee encourages me to work, giving me company during the work. I start my day with a cup of coffee.
It also inspires me to carry out research well. Yet, it can affect my health as well. So, I need to be conscious and drink coffee to the limit”. You can add more here describing different circumstances.
Table of Contents
Informative Speech Topics in History:
Informative speech topics in health and medicine:, informative speech topics in teaching, education, and students:, informative speech topics in music:, informative speech topics in food:, informative speech topics on environment:, informative speech topics in technology:, informative speech topics on economy:, informative speech topics in life:, other informative speech topics, 1. introduction, body, and conclusion, 2. clear, influential, and grabbing introduction, 3. seamless transitions, 4. do not forget to summarize at last, sample of informative speech, a) note list of wide-ranging subject area corresponding your knowledge and expertise, b) focus on the subject area relevant you don’t know yet but would love to, c) pick up the particular purpose of your speech, d) from the list of your topics, pick the one you can express clearly, a) carry out the initial research, b) think about how your research might change your topic, a) think about your audiences earlier than writing the speech, b) summarize your speech, c) elaborate the key points to make it interesting, d) write an introduction, e) write conclusion, a) make sufficient time to practice your speech, b) practice slowing down, c) if possible practice your speech with your friends, 1) make sure you do not speak fast, 2) practice speaking clearly and comprehensibly, 3) speak with your parents and friends, 4) get help from the internet, 5) carry out the outline properly, 6) understand the difference between persuasive and informative speech, 1) the audiences, 2) languages, 4) try to become clear and concise, 5) use audio or visuals if possible, informative speech topics.

- The Great Depression
- Famous riots
- The British Royal Family
- Women in the military
- Unique funeral customs across the world
- The origin of alphabets
- The history of tobacco use
- The evolution of marriage
- Top secret government experiments
- The most fascinating accidental inventions
- History of witchcraft
- The history of language
- History of beauty products
- The Industrial Revolution
- The Middle Ages
- How did the Olympics come to be?
- Albert Einstein’s Contributions to Science
- Helen Keller’s Life
- History of art and expression
- Civil disobedience
- Why do we celebrate Valentine’s day?
- Where did fortune cookies come from
- A look into World wars
- Understanding cults
- Evolution of comic books
- Most exciting prison breaks of history
- Why have street gangs been so prevalent?
- Life and Works of Mahatma Gandhi
- Most shocking murders the world has seen
- Evolution of immigration in the US
- Life and Works of Mother Teresa
- People Who Changed the World
- How the Earth was formed
- How antibiotics came to be
- The history of greyhound dogs
- Different philosophical perspectives
- Evolution of movies
- How Modern art came to be
- Understanding Millenials and Gen-Z
- History of Superstitions
- History of Genocide
- Indian Culture
- Haitian Music
- The trucking industry
- The 80’s: more than just denim and hairdos
- The funniest inventions ever
- An analysis of smoking in movies through the years
- Women in space
- World’s most wanted criminals
- Most ridiculous laws throughout history
- Medicines from nature
- Memory loss
- How the brain works
- Mental illnesses
- Fast food culture
- Basic first aid
- Lucid dreams
- Organ donation
- Medicinal properties of ginger
- Why I am better than you: A look into Narcissistic Disorder
- Are home remedies actually worth it?
- How DNA testing changed the world
- How vitamins can enrich your everyday life
- Why you need to stretch before your workout
- Different personality disorders
- The true horror of chemical warfare
- How makeup affects your skin
- Birth control and its negative effects
- Leaps made by stem cell research
- Signs of early on-set Alzheimers
- How vaccines work
- How to avoid wrinkles
- Understanding insomnia
- Understanding addiction
- How nicotine deteriorates your life
- Herbs as medicine
- Life as a child of a drug addict
- Why do we itch?
- Botox: the good and the bad
- Human cadavers – history of, uses of
- How to have a better memory
- DNA evidence.
- The intelligence of dolphins
- Is dark chocolate healthy?
- Importance of vitamins and minerals
- Pros and cons of LASIK surgery
- Weight Issues.
- Teen pregnancy
- How stress can cripple your health
- How a vegan diet can better your life
- Why understanding health is vital to your weight loss journey
- Unique medical conditions
- Crazy things people have done on an adrenaline rush
- Why does our body crave danger?
- How to make an income while a student
- How to survive freshman year
- How to take the GRE
- How to get a student job on campus
- How to save money while in college
- Virtual learning and its impact on Modern Education
- Education and its role in unemployment
- Great vacation bargains for students
- Ethnic diversity for a more open learning experience
- What to do in your senior year
- Why do you need a college degree?
- Moving out of the dorm to an apartment off-campus
- Freebies and discounts for students
- How to pay off your student loans in 10 years
- Graduation checklist
- How to pick a major you care about
- The evolution of testing
- The basics of financial aid
- How to get that great internship
- Current issues in education and what we can do about them
- Basics of getting a fellowship
- Learning disabilities teachers should be aware of
- Banned books
- Why travel is beneficial to education.
- Diploma mills
- Poverty and its impact on students
- A look at the different testing methods
- Online learning: A breakthrough in Modern Education
- What to do on spring break?
- Is homeschooling an effective learning method?
- The history of your favorite musical group
- How music has changed the world
- What music has been to society
- Classical and Modern Music: A comparison
- The benefits of Music Therapy
- Music and its effects on mood
- Music and its effects on plant growth
- Music and its effects on the psychological response of infants
- The impact your favorite artist has had in the music world
- The evolution of music
- How different genres of music promote empowerment through self-expression
- Modern earphones and tinnitus
- Music and devotion explained through the life of an artist
- How our brain reacts to music
- How music can be used in rehabilitation
- Does our music tastes define our personality?
- What really makes a rockstar?
- Strangest musical instruments across the world
- Food additives: What are they and how they affect us
- Food etiquettes across different countries
- The food crisis
- We are what we eat
- Culinary modernism
- The most exotic foods you can eat
- Different types of coffee
- Can peanut butter and jelly get any better than it is?
- Understanding the food chain
- Understanding food allergies
- Understanding nutrition
- Playing matchmaker: Condiments in foods
- Baking your own bread
- Wedding cakes: The bigger the better?
- How to plan a diet that works
- How to make the perfect cocktail
- A quick guide to wine tasting
- Junk food: More than just a packet of chips
- Food disorders: What we can do to help
- What is better than sliced bread?
- How branding is shaping our perception of food
- Cereal, soda, and obesity
- Eggs: the most versatile food
- How to go green in our eating habits
- A practical guide to balanced eating
- Are superfoods all that they claim to be?
- How to master herbs and spices
- How to make your own pasta
- How to pair your wine with your food?
- How to plan a culinary itinerary?
- Ocean pollution and how serious the issue has become
- Organic agriculture: Why the switch is worth it
- The true impact of Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
- Pollution laws and who it is actually protecting
- Is it over for coal?
- Plant species that have gone extinct
- Animal species that have gone extinct
- Our environment is dying and here’s why
- Water shortage across the globe
- How much of what we eat is pesticides and insecticides?
- Domestic wastes and how to better manage it
- What we can do to protect our environment?
- COVID-19 as a blessing to Mother Nature
- How a meat-based diest impacts the environment
- How to preserve finite resources?
- How we are contributing to global pollution
- How Global Warming is coming for us
- How corporations are destroying our environment
- Are rainforests going extinct?
- Genetically modified crops: Boon or curse?
- How would life adjust without electricity?
- 3D printers have been a game-changer
- Evolution of computer programming
- Gadgets I love most
- Useful websites
- The internet as a boon or curse for human interaction
- How Google became the widespread power that is is
- Choosing a digital camera
- New technologies
- Biometrics: New development or a threat to biological data?
- Pros and cons of going electric
- How do 3D glasses work?
- Violence and Video Games: Is this still a thing?
- Evolution of content consumption
- How to stay safe online?
- How the content we consume makes us
- How to start a good personal inventory
- How search engines work
- Social Networking
- The Evolution of video games
- VR gaming: Blurring the line of reality
- The downside of smartphones
- Pros and Cons of Smartphones
- Is freedom of speech real over the Internet?
- How technology has compromised our safety
- Are blogs the new diaries?
- How to build better credit
- What you need to know about online banking security
- Is your money safe?
- Taxing the rich: Is that the solution?
- The best investment tactics
- How to beat the market
- How to get a credit card
- Price hike in the agricultural field
- Where does our currency come from?
- The ever-increasing cost of education
- How education affects economy
- Economic impacts of people growing their own foods
- Why you need to save money
- How to eat well on just $5 a day?
- The budgeting secret you’ve needed all your life
- How to get along with your roommate
- Some inexpensive places to take your date
- What to do when your roommate moves out
- Being Confident.
- Believing in Yourself.
- Breaking Bad Habits.
- Being Optimistic in Life.
- Being a Positive Talker.
- Types of birth control
- How to fall for the right person
- Choosing the right tires for your car
- How to perform a magic trick
- How a single parent upbringing affects the child
- How to build your own brand?
- How to achieve Goals
- How Does Self-motivation Work?
- Different leadership styles and how they help employee productivity
- Handling Responsibility
- Importance of Discipline
- Importance of Meditation
- Powerful Communication
- The most dangerous jobs
- Should assisted suicide be legalized?
- The secret for a lasting marriage
- How to grow your own home garden
- How to retain good employees
- How to recognize toxic behaviors
- How to master negotiations
- Become a more persuasive speaker
- The benefits of reading every day
- Differences in male and female communication
- Muscle cars
- Antique collecting
- Dog training
- My first job
- Overcoming conflict
- Favorite place
- My favorite food
- Prohibition
- Airplane stunts
- Model railroading
- Roadside attractions
- Multi-Level marketing
- Why are smiles contagious
- Is it love or simply a habit?
- Interesting world records
- Favorite TV Shows
- The Welfare system
- City planning
- Reality TV shows
- Coin collecting
- Ice cream making
- Reality of a dream
- What winners do to win?
- Near-death experiences
- The beauty of wolves
- Funeral oration
- Pesticide use in agriculture
- How to change a flat tire
- How to drive a stick shift
What to include in informative speech?
Know what to include in an informative speech.
Usually, an informative speech contains an introduction, an informative body, and a meaningful and convincing conclusion. You have to follow the format one after another.
While working on the introduction part, you have to be clean to draw the attention of the audience. Generally, an introduction is a gateway to the key points.
The way you present the introduction part of the speech can influence the audience. It should have a clear relationship between the presenter and the topic.
Add some interesting example that attracts them and does not get bored. Focusing more on the body, develop the speech. Make sure your audiences will listen with an interest from the start.
While delivering an informative speech, the body should harmonize the main points. It must also present the information. Better follow the given time limit and convey information in an understandable way. This makes the audience convenient to engage and understand.
You need to think about a comfortable and natural way of presenting the speech. This way your speech gets appreciated by the audience. Here, the presenter should reveal a vibrant interest or desire for the topic. Keep the correct eye contact. The advancement from one point to another should not look uncomfortable.
In the conclusion part, do not forget to summarize your previous points. The main goal of the conclusion is to end with the main points of the speech. This will set your information in the mind of audiences. The ending should be the medium speaker signals the speech is heading towards an end.
Besides, analyze and repeat the most projecting ideas, innovations, or features of the speech. You should conclude the speech in a similar flow used during the speech. The essential thing to note down is that ending the speech is important. It needs to take the attention of the audience until the last hour.
For your ease, here are some samples that can be helpful for efficient informative speech.
How to write informative speech?
1) pick up the the topic.
The informative speech should cover all the procedures and ideas focusing on the topic. Better to start with a larger image and convincing points that you are confident to speak on.
For an instance, work on the subjects that you usually do or love to do. You can also include the activities that you have been practicing for years. The more you understand the topic, the easier it will be to carry out the useful speech.
Spend some time on the speech that builds up the confidence to deliver the speech. Prepare and come with a long-tail list. This benefits you with more choices to improve the speech that you love to present.
For example, if you like traveling, you might have lots of interesting travel experiences. You will feel comfortable speaking on that topic. Also, you love researching more on the topic of your interest.
Better include these kinds of topics in the list of your subject area. For an instance, you can say that you want to become a tech blogger. But you might not know much about the subject.
You can show it, saying you need to research more on the topic to pursue your aim. This makes your speech and subject influential.
First of all, find out the time you take to cover the topic and focus on completing the speech within the allocated time.
Pick up the particular purpose of the speech to direct the attention of your audience.
Think about making your speech influential. Only delivering the important speech is not going to help to attract your audiences.
Delivering the thing that your audiences already know might bore them. So make it interesting including the practical things and add your experience as well.
Be precise with the topic, do not move away from the topic. Suppose, you are speaking on the National animal of a country.
Focus on the topic of national animals, do not divert your speech explaining more about the country. Your speech may look meaningless.
Deep research and understanding of the topic make your speech more remarkable and appealing.
Better focus on a particular topic that you can express without too much work. If you try to speak about an unfamiliar topic, you might be in trouble later. Better pick up the topic workable for you to speak.
2) Research on the topic
One of the rules to write an informative speech is -Know your subject. Carry out your research with proper understanding and honesty. You can do this by utilizing trustworthy resources to write the notes.
While gathering research elements, divide the resources that you will use in the speech. Also, try to learn more about the subject area related to the topic. You may have to respond to the queries about the speech topic. Better learn the things that are helpful to answer the queries.
For an instance, you are speaking about European culture. If the audience asks about it, you should be smart enough to answer to the query.
Once you complete your research, find something new that makes your speech more effective. Instead of ignoring it, take some time to prepare it.
When preparing an informative speech on social media, you understand different things during the research. You may find the research on Social media Myth more interesting. If you have more confidence to speak on the social media myths, you can pursue it. You have done lots of research that makes you able to deliver the speech in an interesting way.
3) About writing the speech
It is ideal to expect your audiences are a little familiar with your topic. Keeping in mind, you may still deliver the background information of the related topic. Beware of the shortcuts you use while explaining the topic. Until your task says otherwise, do not rush to clarify anything.
Nobody desires to know about the actors and actresses when you are giving a speech in the movie. You do not need to provide lots of background information as they are already familiar with the topic.
List out the information you are willing to include and keep it in logical order. To carry out how to informative speech, including the reason for what you are doing and how you do it will be fine.
For example, if your speech is on preparing hamburgers, you should explain every step you carry out. Additionally, do not forget to explain how you use the ingredient for the perfect result. This makes your speech interesting.
Better elaborate on the main points to make your informative speech more interesting and informative. The common method to carry out the speech is to emerge with the key points. These key points for a speech should be in sequential order or spatial order.
This procedure helps to give a useful, informative, and engaging speech. For an instance, start the speech on My trip to Lumbini with a short introduction of Lumbini. Then, your experience while visiting Lumbini and conclude with summarizing them.
The introduction is the main gateway to your speech. It should take the attention of audiences and let them understand what you are talking about. Usually, if your speech is long or complicated, make sure to provide the points you aim to cover.
Better start the speech with interesting jokes or quotes related to your topic. Make sure you will not speak out of the topic. This will be useful to build a strong connection between your speech and the audience. Yet, it might go wrong if you prefer unpleasant statements or meaningless jokes.
For an instance, starting the speech as “I just came from the universe” might sound weird. This can make your speech boring and unimpressive. Better try some relevant sentences and speech.
The conclusion should sum up the key points of your speech. Better conclude the speech with your opinion. The audience usually remembers the first and last things they hear.
Thus, be sure, you are in the right sequence to deliver your message to your audiences. It will help to start and conclude your speech with some essential memorizing messages.
Attempt to put your conclusion into the introduction. Emerging with a complete circle provides will make your speech in the heart of your audience.
For an instance, you used some precise jokes or quotes making the speech impressive. If your movie speech started with a story about an actor struggling to make his career.
It might sound useless and inappropriate with the topic. So, talk about the thing that is necessary and appropriate.
4) Practicing your speech
Practice makes us perfect so make enough time to practice your speech. Include or cut off the points as necessary.
Try completing your speech in the precise time. Even if you are not assigned the time limitation, do not make the speech long and boring. You might not know this while delivering the speech. Better think about it earlier than you give the speech.
If you are speaking for some event, be sure that it does not cross the time limitation. Audiences might get your speech boring if you take a too long time or you may have to end with an incomplete speech. So, be sure that it works according to the time.
While presenting in a mass of people, you might f try to end the speech instantly. You may also speak quickly and in that way, audiences might not understand you.
To be sure the audiences enjoy what you present, attempt to slow down. Better use, video recorder while practicing. This way you can analyze your speech by yourself. It will be effective if you point out the mistakes and work to fix that.
Try to include dramatic pauses to make your speech more attractive. Dramatic pauses can strike a particular bit of information providing the audience time to reflect.
Best speakers use them carefully with great consequence. You have to be alert about the list of information. Make some time to practice after you list out the information.
You might be nervous to present in front of a huge mass of people. So, try practicing in front of your friend. This makes you able to build confidence.
Being nervous will mess up your speech. Better prepare well by working with your friends. Get feedback from them as an audience and work on the drawbacks. If you go with the wrong plan then recover from the mistake. This gives you the strength to deliver an interesting speech.
So, these are some effective ways to write informative speeches. Following these points will help to deliver an interesting speech.
Tips for Informative Speech
Now, let us proceed towards the tips to make your informative speech more efficient
While presenting in front of lots of people, it is likely to get nervous. When you get nervous, you try to complete the speech by talking quickly.
This might make the speech confusing and unimpressive. Think about it, while practicing try to slow down and make your speech clear and loud.
Even if you are good at writing the speech, it will not be effective unless you speak clearly. If you mumble while speaking, it might sound unclear. So, practice more and more until you speak clearly and comprehensibly.
You are most likely good at informative speech but you might not realize that. You can speak with your parents and friends about different topics of your interest. This builds up your confidence to speak in public.
If you are having a problem deciding on the topic of your speech, get help from the internet. There, you can find lots of websites with a list of prospective and interesting topics.
Or else, you can also think about the time you spend the most. For an instance, you spend most of your time cooking. Talk about cooking the dishes that you are proficient at.
Your outline plays a significant role to help you take your speech in an organized way. Yet, you should not take it lightly.
When you work on the speech, you might get that some points mentioned in the outline is unnecessary. You can add essential points and remove the points which you do not need. As outline helps to find necessary points, do it properly.
Persuasive and informative speeches are two different things. You should know that. Persuasive speech is convincing while informative speech gives information about a particular topic.
Simple ways to approach an informative speech
Think about your audience. This is the most challenging as the speaking circumstances, forums, and topics can vary. Before presenting the speech, analyze who your audiences are? Why are they present in your speech? Focusing on these details, you can explore the best ways to present your speech.
If you are speaking about lung cancer, you should know its basics as well. Some audiences might not understand the depth.
So start your speech from the basics. Do not presume that audiences are familiar with the background of your topic. Again, do not assume they do not know. This is the main reason, knowing the audience is essential. Besides, it depends on the situation of the speech.
Use proper language. Speak the language that audiences desire to listen to. You deliver the speech with the goal to provide useful information to the audience.
If audiences do not understand what you speak, the speech becomes useless. The main target of an informative speech is to give knowledge about a particular topic.
If you can explain well the topic in simple language better use it. Try to make the speech simple and understandable.
Do not rush to complete the speech quickly. Instead, think about educating your audiences with your speech. Explain the term if necessary.
Understanding the time flow of the speech will be helpful to make your speech effective. Speakers should create a link between their topic and the interest of audiences.
Here describe the significance of the topic. Also, express the main points with some interesting examples and quotes.
A speaker confessing their own experience encourages the audiences to share the same interest.
To become a good speaker, you have to be clear and concise at first. Spend lots of time on simple concepts instead of the harder ones.
Since giving many examples to prove a single point might not work well. This way your audiences may find your speech boring.
Better, explore some new ideas and prepare the topic well. Try to provide detailed information. Most of the audience gets influenced by details and descriptive presentation.
Try practicing using audio or visuals if possible. They help to find out your mistake. You can improve after you know where the mistake is.
Additionally, informative speech can be effective with demo presentation and visual support. So, using them properly helps to deliver your speech in a proper way.
The above-mentioned topics and tips for informative speech should help you prepare and deliver a powerful informative speech. If you have any suggestions or feedback, please let me know in the comment below.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.1 Informative Speeches
Learning objectives.
- Identify common topic categories for informative speeches.
- Identify strategies for researching and supporting informative speeches.
- Explain the different methods of informing.
- Employ strategies for effective informative speaking, including avoiding persuasion, avoiding information overload, and engaging the audience.
Many people would rather go see an impassioned political speech or a comedic monologue than a lecture. Although informative speaking may not be the most exciting form of public speaking, it is the most common. Reports, lectures, training seminars, and demonstrations are all examples of informative speaking. That means you are more likely to give and listen to informative speeches in a variety of contexts. Some organizations, like consulting firms, and career fields, like training and development, are solely aimed at conveying information. College alumni have reported that out of many different speech skills, informative speaking is most important (Verderber, 1991). Since your exposure to informative speaking is inevitable, why not learn how to be a better producer and consumer of informative messages?
Creating an Informative Speech
As you’ll recall from Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , speaking to inform is one of the three possible general purposes for public speaking. The goal of informative speaking is to teach an audience something using objective factual information. Interestingly, informative speaking is a newcomer in the world of public speaking theorizing and instruction, which began thousands of years ago with the ancient Greeks (Olbricht, 1968). Ancient philosophers and statesmen like Aristotle, Cicero, and Quintilian conceived of public speaking as rhetoric, which is inherently persuasive. During that time, and until the 1800s, almost all speaking was argumentative. Teaching and instruction were performed as debates, and even fields like science and medicine relied on argumentative reasoning instead of factual claims.

Until the 1800s, even scientific fields and medicine relied on teaching that was based on debate and argument rather than the informative-based instruction that is used today.
Monash University – Surgery Workshop 2012 – CC BY-NC 2.0.
While most instruction is now verbal, for most of modern history, people learned by doing rather than listening, as apprenticeships were much more common than classroom-based instruction. So what facilitated the change from argumentative and demonstrative teaching to verbal and informative teaching? One reason for this change was the democratization of information. Technical information used to be jealously protected by individuals, families, or guilds. Now society generally believes that information should be shared and made available to all. The increasing complexity of fields of knowledge and professions also increased the need for informative speaking. Now one must learn a history or backstory before actually engaging with a subject or trade. Finally, much of the information that has built up over time has become commonly accepted; therefore much of the history or background information isn’t disputed and can now be shared in an informative rather than argumentative way.
Choosing an Informative Speech Topic
Being a successful informative speaker starts with choosing a topic that can engage and educate the audience. Your topic choices may be influenced by the level at which you are speaking. Informative speaking usually happens at one of three levels: formal, vocational, and impromptu (Verderber, 1991). Formal informative speeches occur when an audience has assembled specifically to hear what you have to say. Being invited to speak to a group during a professional meeting, a civic gathering, or a celebration gala brings with it high expectations. Only people who have accomplished or achieved much are asked to serve as keynote speakers, and they usually speak about these experiences. Many more people deliver informative speeches at the vocational level, as part of their careers. Teachers like me spend many hours lecturing, which is a common form of informative speaking. In addition, human resources professionals give presentations about changes in policy and provide training for new employees, technicians in factories convey machine specifications and safety procedures, and servers describe how a dish is prepared in their restaurant. Last, we all convey information daily in our regular interactions. When we give a freshman directions to a campus building, summarize the latest episode of American Idol for our friend who missed it, or explain a local custom to an international student, we are engaging in impromptu informative speaking.
Whether at the formal, vocational, or impromptu level, informative speeches can emerge from a range of categories, which include objects, people, events, processes, concepts, and issues. An extended speech at the formal level may include subject matter from several of these categories, while a speech at the vocational level may convey detailed information about a process, concept, or issue relevant to a specific career.

Subjects of informative speaking at the vocational level usually relate to a speaker’s professional experience or expertise.
Peter Long – Business Meeting – CC BY 2.0.
Since we don’t have time to research or organize content for impromptu informative speaking, these speeches may provide a less detailed summary of a topic within one of these categories. A broad informative speech topic could be tailored to fit any of these categories. As you draft your specific purpose and thesis statements, think about which category or categories will help you achieve your speech goals, and then use it or them to guide your research. Table 11.1 “Sample Informative Speech Topics by Category” includes an example of how a broad informative subject area like renewable energy can be adapted to each category as well as additional sample topics.
Table 11.1 Sample Informative Speech Topics by Category
Speeches about objects convey information about any nonhuman material things. Mechanical objects, animals, plants, and fictional objects are all suitable topics of investigation. Given that this is such a broad category, strive to pick an object that your audience may not be familiar with or highlight novel relevant and interesting facts about a familiar object.
Speeches about people focus on real or fictional individuals who are living or dead. These speeches require in-depth biographical research; an encyclopedia entry is not sufficient. Introduce a new person to the audience or share little-known or surprising information about a person we already know. Although we may already be familiar with the accomplishments of historical figures and leaders, audiences often enjoy learning the “personal side” of their lives.
Speeches about concepts are less concrete than speeches about objects or people, as they focus on ideas or notions that may be abstract or multifaceted. A concept can be familiar to us, like equality, or could literally be a foreign concept like qi (or chi ), which is the Chinese conception of the energy that flows through our bodies. Use the strategies discussed in this book for making content relevant and proxemic to your audience to help make abstract concepts more concrete.
Speeches about events focus on past occasions or ongoing occurrences. A particular day in history, an annual observation, or a seldom occurring event can each serve as interesting informative topics. As with speeches about people, it’s important to provide a backstory for the event, but avoid rehashing commonly known information.
Informative speeches about processes provide a step-by-step account of a procedure or natural occurrence. Speakers may walk an audience through, or demonstrate, a series of actions that take place to complete a procedure, such as making homemade cheese. Speakers can also present information about naturally occurring processes like cell division or fermentation.

Informative speeches about processes provide steps of a procedure, such as how to make homemade cheese.
Joel Kramer – curdle – CC BY 2.0.
Last, informative speeches about issues provide objective and balanced information about a disputed subject or a matter of concern for society. It is important that speakers view themselves as objective reporters rather than commentators to avoid tipping the balance of the speech from informative to persuasive. Rather than advocating for a particular position, the speaker should seek to teach or raise the awareness of the audience.
Researching an Informative Speech Topic
Having sharp research skills is a fundamental part of being a good informative speaker. Since informative speaking is supposed to convey factual information, speakers should take care to find sources that are objective, balanced, and credible. Periodicals, books, newspapers, and credible websites can all be useful sources for informative speeches, and you can use the guidelines for evaluating supporting materials discussed in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” to determine the best information to include in your speech. Aside from finding credible and objective sources, informative speakers also need to take time to find engaging information. This is where sharp research skills are needed to cut through all the typical information that comes up in the research process to find novel information. Novel information is atypical or unexpected, but it takes more skill and effort to locate. Even seemingly boring informative speech topics like the history of coupons can be brought to life with information that defies the audience’s expectations. A student recently delivered an engaging speech about coupons by informing us that coupons have been around for 125 years, are most frequently used by wealthier and more educated households, and that a coupon fraud committed by an Italian American businessman named Charles Ponzi was the basis for the term Ponzi scheme , which is still commonly used today.
As a teacher, I can attest to the challenges of keeping an audience engaged during an informative presentation. While it’s frustrating to look out at my audience of students and see glazed-over eyes peering back at me, I also know that it is my responsibility to choose interesting information and convey it in a way that’s engaging. Even though the core content of what I teach hasn’t change dramatically over the years, I constantly challenge myself to bring that core information to life through application and example. As we learned earlier, finding proxemic and relevant information and examples is typically a good way to be engaging. The basic information may not change quickly, but the way people use it and the way it relates to our lives changes. Finding current, relevant examples and finding novel information are both difficult, since you, as the researcher, probably don’t know this information exists.
Here is where good research skills become necessary to be a good informative speaker. Using advice from Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” should help you begin to navigate through the seas of information to find hidden treasure that excites you and will in turn excite your audience.

To avoid boring an audience, effective informative speakers possess good research skills and the ability to translate information to be engaging and relevant for an audience.
Niall Kennedy – Sleep – CC BY-NC 2.0.
As was mentioned earlier, the goal for informative speaking is to teach your audience. An audience is much more likely to remain engaged when they are actively learning. This is like a balancing act. You want your audience to be challenged enough by the information you are presenting to be interested, but not so challenged that they become overwhelmed and shut down. You should take care to consider how much information your audience already knows about a topic. Be aware that speakers who are very familiar with their speech topic tend to overestimate their audience’s knowledge about the topic. It’s better to engage your topic at a level slightly below your audience’s knowledge level than above. Most people won’t be bored by a brief review, but many people become lost and give up listening if they can’t connect to the information right away or feel it’s over their heads.
A good informative speech leaves the audience thinking long after the speech is done. Try to include some practical “takeaways” in your speech. I’ve learned many interesting and useful things from the informative speeches my students have done. Some of the takeaways are more like trivia information that is interesting to share—for example, how prohibition led to the creation of NASCAR. Other takeaways are more practical and useful—for example, how to get wine stains out of clothing and carpet or explanations of various types of student financial aid.
Organizing and Supporting an Informative Speech
You can already see that informing isn’t as easy as we may initially think. To effectively teach, a speaker must present quality information in an organized and accessible way. Once you have chosen an informative speech topic and put your research skills to the test in order to locate novel and engaging information, it’s time to organize and support your speech.
Organizational Patterns
Three organizational patterns that are particularly useful for informative speaking are topical, chronological, and spatial. As you’ll recall, to organize a speech topically, you break a larger topic down into logical subdivisions. An informative speech about labor unions could focus on unions in three different areas of employment, three historically significant strikes, or three significant legal/legislative decisions. Speeches organized chronologically trace the development of a topic or overview the steps in a process. An informative speech could trace the rise of the economic crisis in Greece or explain the steps in creating a home compost pile. Speeches organized spatially convey the layout or physical characteristics of a location or concept. An informative speech about the layout of a fire station or an astrology wheel would follow a spatial organization pattern.
Methods of Informing
Types of and strategies for incorporating supporting material into speeches are discussed in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , but there are some specific ways to go about developing ideas within informative speeches. Speakers often inform an audience using definitions, descriptions, demonstrations, and explanations. It is likely that a speaker will combine these methods of informing within one speech, but a speech can also be primarily organized using one of these methods.
Informing through Definition
Informing through definition entails defining concepts clearly and concisely and is an important skill for informative speaking. There are several ways a speaker can inform through definition: synonyms and antonyms, use or function, example, and etymology (Verderber, 1991). Defining a concept using a synonym or an antonym is a short and effective way to convey meaning. Synonyms are words that have the same or similar meanings, and antonyms are words that have opposite meanings. In a speech about how to effectively inform an audience, I would claim that using concrete words helps keep an audience engaged. I could enhance your understanding of what concrete means by defining it with synonyms like tangible and relatable . Or I could define concrete using antonyms like abstract and theoretical .
Identifying the use or function of an object, item, or idea is also a short way of defining. We may think we already know the use and function of most of the things we interact with regularly. This is true in obvious cases like cars, elevators, and smartphones. But there are many objects and ideas that we may rely on and interact with but not know the use or function. For example, QR codes (or quick response codes) are popping up in magazines, at airports, and even on t-shirts (Vuong, 2011). Many people may notice them but not know what they do. As a speaker, you could define QR codes by their function by informing the audience that QR codes allow businesses, organizations, and individuals to get information to consumers/receivers through a barcode-like format that can be easily scanned by most smartphones.

An informative speaker could teach audience members about QR codes by defining them based on their use or function.
Douglas Muth – My QR Code – CC BY-SA 2.0.
A speaker can also define a topic using examples, which are cited cases that are representative of a larger concept. In an informative speech about anachronisms in movies and literature, a speaker might provide the following examples: the film Titanic shows people on lifeboats using flashlights to look for survivors from the sunken ship (such flashlights weren’t invented until two years later) (The Past in Pictures, 2012); Shakespeare’s play Julius Caesar includes a reference to a clock, even though no mechanical clocks existed during Caesar’s time (Scholasticus K., 2012). Examples are a good way to repackage information that’s already been presented to help an audience retain and understand the content of a speech. Later we’ll learn more about how repackaging information enhances informative speaking.
Etymology refers to the history of a word. Defining by etymology entails providing an overview of how a word came to its current meaning. The Oxford English Dictionary is the best source for finding etymology and often contains interesting facts that can be presented as novel information to better engage your audience. For example, the word assassin , which refers to a person who intentionally murders another, literally means “hashish-eater” and comes from the Arabic word hashshashin . The current meaning emerged during the Crusades as a result of the practices of a sect of Muslims who would get high on hashish before killing Christian leaders—in essence, assassinating them (Oxford English Dictionary Online, 2012).
Informing through Description
As the saying goes, “Pictures are worth a thousand words.” Informing through description entails creating verbal pictures for your audience. Description is also an important part of informative speeches that use a spatial organizational pattern, since you need to convey the layout of a space or concept. Good descriptions are based on good observations, as they convey what is taken in through the senses and answer these type of questions: What did that look like? Smell like? Sound like? Feel like? Taste like? If descriptions are vivid and well written, they can actually invoke a sensory reaction in your audience. Just as your mouth probably begins to salivate when I suggest that you imagine biting into a fresh, bright yellow, freshly cut, juicy lemon wedge, so can your audience be transported to a setting or situation through your descriptions. I once had a student set up his speech about the history of streaking by using the following description: “Imagine that you are walking across campus to your evening class. You look up to see a parade of hundreds upon hundreds of your naked peers jogging by wearing little more than shoes.”
Informing through Demonstration
When informing through demonstration , a speaker gives verbal directions about how to do something while also physically demonstrating the steps. Early morning infomercials are good examples of demonstrative speaking, even though they are also trying to persuade us to buy their “miracle product.” Whether straightforward or complex, it’s crucial that a speaker be familiar with the content of their speech and the physical steps necessary for the demonstration. Speaking while completing a task requires advanced psycho-motor skills that most people can’t wing and therefore need to practice. Tasks suddenly become much more difficult than we expect when we have an audience. Have you ever had to type while people are reading along with you? Even though we type all the time, even one extra set of eyes seems to make our fingers more clumsy than usual.
Television chefs are excellent examples of speakers who frequently inform through demonstration. While many of them make the process of speaking while cooking look effortless, it took much practice over many years to make viewers think it is effortless.

Television chefs inform through demonstration. Although they make it seem easy, it is complex and difficult.
Gordonramsaysubmissions – gordon ramsay 7 – CC BY 2.0.
Part of this practice also involves meeting time limits. Since television segments are limited and chefs may be demonstrating and speaking live, they have to be able to adapt as needed. Demonstration speeches are notorious for going over time, especially if speakers haven’t practiced with their visual aids / props. Be prepared to condense or edit as needed to meet your time limit. The reality competition show The Next Food Network Star captures these difficulties, as many experienced cooks who have the content knowledge and know how to physically complete their tasks fall apart when faced with a camera challenge because they just assumed they could speak and cook at the same time.
Tips for Demonstration Speeches
- Include personal stories and connections to the topic, in addition to the “how-to” information, to help engage your audience.
- Ask for audience volunteers (if appropriate) to make the demonstration more interactive.
- Include a question-and-answer period at the end (if possible) so audience members can ask questions and seek clarification.
- Follow an orderly progression. Do not skip around or backtrack when reviewing the steps.
- Use clear signposts like first , second , and third .
- Use orienting material like internal previews and reviews, and transitions.
- Group steps together in categories, if needed, to help make the information more digestible.
- Assess the nonverbal feedback of your audience. Review or slow down if audience members look lost or confused.
- Practice with your visual aids / props many times. Things suddenly become more difficult and complicated than you expect when an audience is present.
- Practice for time and have contingency plans if you need to edit some information out to avoid going over your time limit.
Informing through Explanation
Informing through explanation entails sharing how something works, how something came to be, or why something happened. This method of informing may be useful when a topic is too complex or abstract to demonstrate. When presenting complex information make sure to break the topic up into manageable units, avoid information overload, and include examples that make the content relevant to the audience. Informing through explanation works well with speeches about processes, events, and issues. For example, a speaker could explain the context surrounding the Lincoln-Douglas debates or the process that takes place during presidential primaries.
“Getting Plugged In”
TED Talks as a Model of Effective Informative Speaking
Over the past few years, I have heard more and more public speaking teachers mention their use of TED speeches in their classes. What started in 1984 as a conference to gather people involved in Technology, Entertainment, and Design has now turned into a worldwide phenomenon that is known for its excellent speeches and presentations, many of which are informative in nature. [1] The motto of TED is “Ideas worth spreading,” which is in keeping with the role that we should occupy as informative speakers. We should choose topics that are worth speaking about and then work to present them in such a way that audience members leave with “take-away” information that is informative and useful. TED fits in with the purpose of the “Getting Plugged In” feature in this book because it has been technology focused from the start. For example, Andrew Blum’s speech focuses on the infrastructure of the Internet, and Pranav Mistry’s speech focuses on a new technology he developed that allows for more interaction between the physical world and the world of data. Even speakers who don’t focus on technology still skillfully use technology in their presentations, as is the case with David Gallo’s speech about exotic underwater life. Here are links to all these speeches:
- Andrew Blum’s speech: What Is the Internet, Really? http://www.ted.com/talks/andrew_blum_what_is_the_internet_really.html
- Pranav Mistry’s speech: The Thrilling Potential of Sixth Sense Technology. http://www.ted.com/talks/pranav_mistry_the_thrilling_potential_of_sixthsense_technology.html
- David Gallo’s speech: Underwater Astonishments. http://www.ted.com/talks/david_gallo_shows_underwater_astonishments.html
- What can you learn from the TED model and/or TED speakers that will help you be a better informative speaker?
- In what innovative and/or informative ways do the speakers reference or incorporate technology in their speeches?
Effective Informative Speaking
There are several challenges to overcome to be an effective informative speaker. They include avoiding persuasion, avoiding information overload, and engaging your audience.
Avoiding Persuasion
We should avoid thinking of informing and persuading as dichotomous, meaning that it’s either one or the other. It’s more accurate to think of informing and persuading as two poles on a continuum, as in Figure 11.1 “Continuum of Informing and Persuading” (Olbricht, 1968). Most persuasive speeches rely on some degree of informing to substantiate the reasoning. And informative speeches, although meant to secure the understanding of an audience, may influence audience members’ beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors.
Figure 11.1 Continuum of Informing and Persuading
Speakers can look to three areas to help determine if their speech is more informative or persuasive: speaker purpose, function of information, and audience perception (Verderber, 1991). First, for informative speaking, a speaker’s purpose should be to create understanding by sharing objective, factual information. Specific purpose and thesis statements help establish a speaker’s goal and purpose and can serve as useful reference points to keep a speech on track. When reviewing your specific purpose and thesis statement, look for words like should / shouldn’t , good / bad , and right / wrong , as these often indicate a persuasive slant in the speech.
Second, information should function to clarify and explain in an informative speech. Supporting materials shouldn’t function to prove a thesis or to provide reasons for an audience to accept the thesis, as they do in persuasive speeches. Although informative messages can end up influencing the thoughts or behaviors of audience members, that shouldn’t be the goal.
Third, an audience’s perception of the information and the speaker helps determine whether a speech is classified as informative or persuasive. The audience must perceive that the information being presented is not controversial or disputed, which will lead audience members to view the information as factual. The audience must also accept the speaker as a credible source of information. Being prepared, citing credible sources, and engaging the audience help establish a speaker’s credibility. Last, an audience must perceive the speaker to be trustworthy and not have a hidden agenda. Avoiding persuasion is a common challenge for informative speakers, but it is something to consider, as violating the speaking occasion may be perceived as unethical by the audience. Be aware of the overall tone of your speech by reviewing your specific purpose and thesis to make sure your speech isn’t tipping from informative to persuasive.

Words like should / shouldn’t , good / bad , and right / wrong in a specific purpose and/or thesis statement often indicate that the speaker’s purpose is tipping from informative to persuasive.
Hans Splinter – balance – CC BY-ND 2.0.
Avoiding Information Overload
Many informative speakers have a tendency to pack a ten-minute speech with as much information as possible. This can result in information overload , which is a barrier to effective listening that occurs when a speech contains more information than an audience can process. Editing can be a difficult task, but it’s an important skill to hone, because you will be editing more than you think. Whether it’s reading through an e-mail before you send it, condensing a report down to an executive summary, or figuring out how to fit a client’s message on the front page of a brochure, you will have to learn how to discern what information is best to keep and what can be thrown out. In speaking, being a discerning editor is useful because it helps avoid information overload. While a receiver may not be attracted to a brochure that’s covered in text, they could take the time to read it, and reread it, if necessary. Audience members cannot conduct their own review while listening to a speaker live. Unlike readers, audience members can’t review words over and over (Verderber, 1991). Therefore competent speakers, especially informative speakers who are trying to teach their audience something, should adapt their message to a listening audience. To help avoid information overload, adapt your message to make it more listenable.
Although the results vary, research shows that people only remember a portion of a message days or even hours after receiving it (Janusik, 2012). If you spend 100 percent of your speech introducing new information, you have wasted approximately 30 percent of your time and your audience’s time. Information overload is a barrier to effective listening, and as good speakers, we should be aware of the limitations of listening and compensate for that in our speech preparation and presentation. I recommend that my students follow a guideline that suggests spending no more than 30 percent of your speech introducing new material and 70 percent of your speech repackaging that information. I specifically use the word repackaging and not repeating . Simply repeating the same information would also be a barrier to effective listening, since people would just get bored. Repackaging will help ensure that your audience retains most of the key information in the speech. Even if they don’t remember every example, they will remember the main underlying point.
Avoiding information overload requires a speaker to be a good translator of information. To be a good translator, you can compare an unfamiliar concept with something familiar, give examples from real life, connect your information to current events or popular culture, or supplement supporting material like statistics with related translations of that information. These are just some of the strategies a good speaker can use. While translating information is important for any oral presentation, it is especially important when conveying technical information. Being able to translate complex or technical information for a lay audience leads to more effective informing, because the audience feels like they are being addressed on their level and don’t feel lost or “talked down to.” The History Channel show The Universe provides excellent examples of informative speakers who act as good translators. The scientists and experts featured on the show are masters of translating technical information, like physics, into concrete examples that most people can relate to based on their everyday experiences.

Comparing the turbulent formation of the solar system to the collisions of bumper bars and spinning rides at an amusement park makes the content more concrete.
Alexander Svensson – Ferris Wheel – CC BY 2.0.
Following the guidelines established in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” for organizing a speech can also help a speaker avoid information overload. Good speakers build in repetition and redundancy to make their content more memorable and their speech more consumable. Preview statements, section transitions, and review statements are some examples of orienting material that helps focus an audience’s attention and facilitates the process of informing (Verderber, 1991).
Engaging Your Audience
As a speaker, you are competing for the attention of your audience against other internal and external stimuli. Getting an audience engaged and then keeping their attention is a challenge for any speaker, but it can be especially difficult when speaking to inform. As was discussed earlier, once you are in the professional world, you will most likely be speaking informatively about topics related to your experience and expertise. Some speakers fall into the trap of thinking that their content knowledge is enough to sustain them through an informative speech or that their position in an organization means that an audience will listen to them and appreciate their information despite their delivery. Content expertise is not enough to be an effective speaker. A person must also have speaking expertise (Verderber, 1991). Effective speakers, even renowned experts, must still translate their wealth of content knowledge into information that is suited for oral transmission, audience centered, and well organized. I’m sure we’re all familiar with the stereotype of the absentminded professor or the genius who thinks elegantly in his or her head but can’t convey that same elegance verbally. Having well-researched and organized supporting material is an important part of effective informative speaking, but having good content is not enough.
Audience members are more likely to stay engaged with a speaker they view as credible. So complementing good supporting material with a practiced and fluent delivery increases credibility and audience engagement. In addition, as we discussed earlier, good informative speakers act as translators of information. Repackaging information into concrete familiar examples is also a strategy for making your speech more engaging. Understanding relies on being able to apply incoming information to life experiences.
Repackaging information is also a good way to appeal to different learning styles, as you can present the same content in various ways, which helps reiterate a point. While this strategy is useful with any speech, since the goal of informing is teaching, it makes sense to include a focus on learning within your audience adaptation. There are three main learning styles that help determine how people most effectively receive and process information: visual, auditory, and kinesthetic (Fleming, 2012). Visual learners respond well to information presented via visual aids, so repackage information using text, graphics, charts and other media. Public speaking is a good way to present information for auditory learners who process information well when they hear it. Kinesthetic learners are tactile; they like to learn through movement and “doing.” Asking for volunteers to help with a demonstration, if appropriate, is a way to involve kinesthetic learners in your speech. You can also have an interactive review activity at the end of a speech, much like many teachers incorporate an activity after a lesson to reinforce the material.
“Getting Real”
Technical Speaking
People who work in technical fields, like engineers and information technology professionals, often think they will be spared the task of public speaking. This is not the case, however, and there is actually a branch of communication studies that addresses public speaking matters for “techies.” The field of technical communication focuses on how messages can be translated from expert to lay audiences. I actually taught a public speaking class for engineering students, and they basically had to deliver speeches about the things they were working on in a way that I could understand. I ended up learning a lot more about jet propulsion and hybrid car engines than I ever expected!
Have you ever been completely lost when reading an instruction manual for some new product you purchased? Have you ever had difficulty following the instructions of someone who was trying to help you with a technical matter? If so, you’ve experienced some of the challenges associated with technical speaking. There are many careers where technical speaking skills are needed. According to the Society for Technical Communication, communicating about specialized or technical topics, communicating by using technology, and providing instructions about how to do something are all examples of technical speaking (Society for Technical Communication, 2012). People with technical speaking skills offer much to organizations and businesses. They help make information more useable and accessible to customers, clients, and employees. They can help reduce costs to a business by reducing unnecessary work that results from misunderstandings of instructions, by providing clear information that allows customers to use products without training or technical support and by making general information put out by a company more user friendly. Technical speakers are dedicated to producing messages that are concise, clear, and coherent (Society for Technical Communication, 2012). Such skills are used in the following careers: technical writers and editors, technical illustrators, visual designers, web designers, customer service representatives, salespeople, spokespeople, and many more.
- What communication skills that you’ve learned about in the book so far do you think would be important for a technical speaker?
- Identify instances in which you have engaged in technical speaking or received information from a technical speaker. Based on what you have learned in this chapter, were the speakers effective or not, and why?
Sample Informative Speech
Title: Going Green in the World of Education
General purpose: To inform
Specific purpose: By the end of my speech, the audience will be able to describe some ways in which schools are going green.
Thesis statement: The green movement has transformed school buildings, how teachers teach, and the environment in which students learn.
Introduction
Attention getter: Did you know that attending or working at a green school can lead students and teachers to have less health problems? Did you know that allowing more daylight into school buildings increases academic performance and can lessen attention and concentration challenges? Well, the research I will cite in my speech supports both of these claims, and these are just two of the many reasons why more schools, both grade schools and colleges, are going green.
Introduction of topic: Today, I’m going to inform you about the green movement that is affecting many schools.
Credibility and relevance: Because of my own desire to go into the field of education, I decided to research how schools are going green in the United States. But it’s not just current and/or future teachers that will be affected by this trend. As students at Eastern Illinois University, you are already asked to make “greener” choices. Whether it’s the little signs in the dorm rooms that ask you to turn off your lights when you leave the room, the reusable water bottles that were given out on move-in day, or even our new Renewable Energy Center, the list goes on and on. Additionally, younger people in our lives, whether they be future children or younger siblings or relatives, will likely be affected by this continuing trend.
Preview statement: In order to better understand what makes a “green school,” we need to learn about how K–12 schools are going green, how college campuses are going green, and how these changes affect students and teachers.
Transition: I’ll begin with how K–12 schools are going green.
- In order to garner support for green initiatives, the article recommends that local leaders like superintendents, mayors, and college administrators become involved in the green movement.
- Once local leaders are involved, the community, students, parents, faculty, and staff can be involved by serving on a task force, hosting a summit or conference, and implementing lessons about sustainability into everyday conversations and school curriculum.
- The US Green Building Council’s website also includes a tool kit with a lot of information about how to “green” existing schools.
- For example, Fossil Ridge High School in Fort Collins, Colorado, was built in 2006 and received LEED certification because it has automatic light sensors to conserve electricity and uses wind energy to offset nonrenewable energy use.
- To conserve water, the school uses a pond for irrigation, has artificial turf on athletic fields, and installed low-flow toilets and faucets.
- According to the 2006 report by certified energy manager Gregory Kats titled “Greening America’s Schools,” a LEED certified school uses 30–50 percent less energy, 30 percent less water, and reduces carbon dioxide emissions by 40 percent compared to a conventional school.
- Many new building materials, carpeting, and furniture contain chemicals that are released into the air, which reduces indoor air quality.
- So green schools purposefully purchase materials that are low in these chemicals.
- Natural light and fresh air have also been shown to promote a healthier learning environment, so green buildings allow more daylight in and include functioning windows.
Transition: As you can see, K–12 schools are becoming greener; college campuses are also starting to go green.
- According to the Sturm College of Law’s website, the building was designed to use 40 percent less energy than a conventional building through the use of movement-sensor lighting; high-performance insulation in the walls, floors, and roof; and infrared sensors on water faucets and toilets.
- Electric car recharging stations were also included in the parking garage, and the building has extra bike racks and even showers that students and faculty can use to freshen up if they bike or walk to school or work.
- Some of the dining halls on campus have gone “trayless,” which according to a 2009 article by Calder in the journal Independent School has the potential to dramatically reduce the amount of water and chemical use, since there are no longer trays to wash, and also helps reduce food waste since people take less food without a tray.
- The Renewable Energy Center uses slow-burn technology to use wood chips that are a byproduct of the lumber industry that would normally be discarded.
- This helps reduce our dependency on our old coal-fired power plant, which reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- The project was the first known power plant to be registered with the US Green Building Council and is on track to receive LEED certification.
Transition: All these efforts to go green in K–12 schools and on college campuses will obviously affect students and teachers at the schools.
- Many schools are literally going green by including more green spaces such as recreation areas, gardens, and greenhouses, which according to a 2010 article in the Journal of Environmental Education by University of Colorado professor Susan Strife has been shown to benefit a child’s cognitive skills, especially in the areas of increased concentration and attention capacity.
- Additionally, the report I cited earlier, “Greening America’s Schools,” states that the improved air quality in green schools can lead to a 38 percent reduction in asthma incidents and that students in “green schools” had 51 percent less chance of catching a cold or the flu compared to children in conventional schools.
- The report “Greening America’s Schools” notes that a recent synthesis of fifty-three studies found that more daylight in the school building leads to higher academic achievement.
- The report also provides data that show how the healthier environment in green schools leads to better attendance and that in Washington, DC, and Chicago, schools improved their performance on standardized tests by 3–4 percent.
- According to the article in Education Week that I cited earlier, the Sustainability Education Clearinghouse is a free online tool that provides K–12 educators with the ability to share sustainability-oriented lesson ideas.
- The Center for Green Schools also provides resources for all levels of teachers, from kindergarten to college, that can be used in the classroom.
- The report “Greening America’s Schools” claims that the overall improved working environment that a green school provides leads to higher teacher retention and less teacher turnover.
- Just as students see health benefits from green schools, so do teachers, as the same report shows that teachers in these schools get sick less, resulting in a decrease of sick days by 7 percent.
Transition to conclusion and summary of importance: In summary, the going-green era has impacted every aspect of education in our school systems.
Review of main points: From K–12 schools to college campuses like ours, to the students and teachers in the schools, the green movement is changing the way we think about education and our environment.
Closing statement: As Glenn Cook, the editor in chief of the American School Board Journal , states on the Center for Green Schools’s website, “The green schools movement is the biggest thing to happen to education since the introduction of technology to the classroom.”
Ash, K. (2011). “Green schools” benefit budgets and students, report says. Education Week , 30 (32), 10.
Calder, W. (2009). Go green, save green. Independent School , 68 (4), 90–93.
The Center for Green Schools. (n.d.). K–12: How. Retrieved from http://www.centerforgreenschools.org/main-nav/k-12/buildings.aspx
Eastern Illinois University. (n.d.). Renewable Energy Center. Retrieved from http://www.eiu.edu/sustainability/eiu_renewable.php
Kats, G. (2006). Greening America’s schools: Costs and benefits. A Capital E Report. Retrieved from http://www.usgbc.org/ShowFile.aspx?DocumentID=2908
Strife, S. (2010). Reflecting on environmental education: Where is our place in the green movement? Journal of Environmental Education , 41 (3), 179–191. doi:10.1080/00958960903295233
Sturm College of Law. (n.d.). About DU law: Building green. Retrieved from http://www.law.du.edu/index.php/about/building-green
USGBC. (n.d.). About us. US Green Building Council . Retrieved from https://new.usgbc.org/about
Key Takeaways
- Getting integrated: Informative speaking is likely the type of public speaking we will most often deliver and be audience to in our lives. Informative speaking is an important part of academic, professional, personal, and civic contexts.
- Informative speeches teach an audience through objective factual information and can emerge from one or more of the following categories: objects, people, concepts, events, processes, and issues.
- Effective informative speaking requires good research skills, as speakers must include novel information, relevant and proxemic examples, and “take-away” information that audience members will find engaging and useful.
The four primary methods of informing are through definition, description, demonstration, or explanation.
- Informing through definition entails defining concepts clearly and concisely using synonyms and antonyms, use or function, example, or etymology.
- Informing through description entails creating detailed verbal pictures for your audience.
- Informing through demonstration entails sharing verbal directions about how to do something while also physically demonstrating the steps.
- Informing through explanation entails sharing how something works, how something came to be, or why something happened.
- An effective informative speaker should avoid persuasion by reviewing the language used in the specific purpose and thesis statements, using objective supporting material, and appearing trustworthy to the audience.
- An effective informative speaker should avoid information overload by repackaging information and building in repetition and orienting material like reviews and previews.
- An effective informative speaker engages the audience by translating information into relevant and concrete examples that appeal to different learning styles.
- Getting integrated: How might you use informative speaking in each of the following contexts: academic, professional, personal, and civic?
- Brainstorm potential topics for your informative speech and identify which topic category each idea falls into. Are there any risks of persuading for the topics you listed? If so, how can you avoid persuasion if you choose that topic?
- Of the four methods of informing (through definition, description, demonstration, or explanation), which do you think is most effective for you? Why?
Fleming, N., “The VARK Helpsheets,” accessed March 6, 2012, http://www.vark-learn.com/english/page.asp?p=helpsheets .
Janusik, L., “Listening Facts,” accessed March 6, 2012, http://d1025403.site.myhosting.com/files.listen.org/Facts.htm .
Olbricht, T. H., Informative Speaking (Glenview, IL: Scott, Foresman, 1968), 1–12.
Oxford English Dictionary Online, accessed March 6, 2012, http://www.oed.com .
The Past in Pictures, “Teaching Using Movies: Anachronisms!” accessed March 6, 2012, http://www.thepastinthepictures.wildelearning.co.uk/Introductoryunit!.htm .
Scholasticus K, “Anachronism Examples in Literature,” February 2, 2012, accessed March 6, 2012, http://www.buzzle.com/articles/anachronism-examples-in-literature.html .
Society for Technical Communication, “Defining Technical Communication,” accessed March 6, 2012, http://www.stc.org/about-stc/the-profession-all-about-technical-communication/defining-tc .
Verderber, R., Essentials of Informative Speaking: Theory and Contexts (Belmont, CA: Wadsworth, 1991), 3.
Vuong, A., “Wanna Read That QR Code? Get the Smartphone App,” The Denver Post , April 18, 2011, accessed March 6, 2012, http://www.denverpost.com/business/ci_17868932 .
- “About TED,” accessed October 23, 2012, http://www.ted.com/pages/about . ↵
Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Speech Crafting →
How to Write an Informative Speech Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide

It’s the moment of truth — the anxiety-inducing moment when you realize writing the outline for your informative speech is due soon. Whether you’re looking to deliver a report on the migratory patterns of the great white stork or give a lecture on the proper techniques of candle making, knowing how to write an effective outline is essential.
That’s why we’ve put together this complete, step-by-step guide on how to write an informative speech outline. From selecting a topic to transitioning during your speech, this guide will have you well on your way to writing a compelling informative speech outline . So grab your pen and paper, put on your thinking cap, and let’s get started!
What is an Informative Speech Outline?
An informative speech outline is a document used to plan the structure and core content of a public speech. It’s used by speakers to ensure their talk covers all the important points, stays on-topic and flows logically from one point to another. By breaking down complex topics into smaller, concise sections, an effective outline can help keep a speaker organized, set objectives for their talk, support key points with evidence and promote audience engagement. A well-structured outline can also make a presentation easier to remember and act as an invaluable reminder if nerves ever get the better of the speaker. On one hand, an informative speech outline enables speakers to cover multiple ideas in an efficient manner while avoiding digressions. On the other hand, it’s important that speakers remain flexible to adjust and adapt content to meet audience needs. While there are some tried-and-tested strategies for creating outlines that work, many successful speakers prefer to tweak and modify existing outlines according to their personal preferences. In conclusion, preparing an informative speech outline can boost confidence and create an effective structure for presentations. With this in mind, let’s now look at how to structure an informative speech outline
How to Structure an Informative Speech Outline
The structure of your informative speech outline should be based on the points you need to cover during your presentation. It should list out all of the main points in an organized and logical manner, along with supporting details for each point. The main structure for an informative speech should consist of three parts: the introduction, body and conclusion.
Introduction
When starting to craft your structure, begin by introducing the topic and giving a brief synopsis of what the audience can expect to learn from your speech. By setting up what they will gain from your presentation, it will help keep them engaged throughout the rest of your talk. Additionally, include any objectives that you want to achieve by the end of your speech.
The body of an informative speech outline typically consists of three parts: main points, sub-points, and supporting details. Main points are the core topics that the speaker wishes to cover throughout the speech. These can be further broken down into sub-points, that explore the main ideas in greater detail. Supporting details provide evidence or facts about each point and can include statistics, research studies, quotes from experts, anecdotes and personal stories . When presenting an informative speech, it is important to consider each side of the topic for an even-handed discussion. If there is an argumentative element to the speech, consider incorporating both sides of the debate . It is also important to be objective when presenting facts and leave value judgments out. Once you have determined your main points and all of their supporting details, you can start ordering them in a logical fashion. The presentation should have a clear flow and move between points smoothly. Each point should be covered thoroughly without getting overly verbose; you want to make sure you are giving enough information to your audience while still being concise with your delivery.
Writing an informative speech outline can be a daunting yet rewarding process. Through the steps outlined above, speakers will have created a strong foundation for their speech and can now confidently start to research their topics . The outline serves as a guiding map for speakers to follow during their research and when writing their eventual speech drafts . Having the process of developing an informative speech broken down into easy and manageable steps helps to reduce stress and anxiety associated with preparing speeches .
- The introduction should be around 10-20% of the total speech duration and is designed to capture the audience’s attention and introduce the topic.
- The main points should make up 40-60% of the speech and provide further detail into the topic. The body should begin with a transition, include evidence or examples and have supporting details. Concluding with a recap or takeaway should take around 10-20% of the speech duration.
While crafting an informative speech outline is a necessary step in order for your presentation to run smoothly, there are many different styles and approaches you can use when creating one. Ultimately though, the goal is always to ensure that the information presented is factual and relevant to both you and your audience. By carefully designing and structuring an effective outline, both you and your audience will be sure to benefit greatly from it when it comes time for delivering a successful presentation .
Now that speakers know how to create an effective outline, it’s time to begin researching the content they plan to include in their speeches. In the next section we’ll discuss how to conduct research for an informative speech so speakers are armed with all the facts necessary to deliver an interesting and engaging presentation .
How to Research for an Informative Speech
When researching an informative speech, it’s important to find valid and reliable sources of information. There are many ways that one can seek out research for an informative speech, and no single method will guarantee a thorough reliable research. Depending on the complexity of the topic and the depth of knowledge required, a variety of methods should be utilized. The first step when researching for an informative speech should be to evaluate your present knowledge of the subject. This will help to determine what specific areas require additional research, and give clues as to where you might start looking for evidence. It is important to know the basic perspectives and arguments surrounding your chosen topic in order to select good sources and avoid biased materials. Textbooks, academic journals, newspaper articles, broadcasts, or credible websites are good starting points for informational speeches. As you search for information and evidence, be sure to use trustworthy authors who cite their sources. These sources refer to experts in the field whose opinions add credibility and can bolster your argument with facts and data. Evaluating these sources is particularly important as they form the foundation of your speech content and structure. Analyze each source critically by looking into who wrote it and evaluating how recent or relevant it is to the current conversation on your chosen topic. As with any research paper, one must strive for accuracy when gathering evidence while also surveying alternative positions on a topic. Considering both sides of a debate allows your speech to provide accurate information while remaining objective. This will also encourage audience members to draw their conclusions instead of taking your word for it. Furthermore, verifying sources from multiple angles (multiple avenues) ensures that information is fact-checked versus opinionated or biased pieces which might distort accuracy or mislead an audience member seeking truth about a controversial issue. At this stage in preparing for an informative speech, research should have been carried out thoroughly enough to allow confidently delivering evidence-based statements about a chosen topic. With all of this necessary groundwork completed, it’s time to move onto the next stage: sourcing different types of evidence which will allow you to illustrate your point in an even more helpful way. It is now time to transition into discussing “Sources & Evidence”.
Sources and Evidence
When crafting an informative speech outline, it is important to include accurate sources and valid evidence. Your audience needs to be sure that the content you are presenting not only reflects a clear understanding of the topic but is also backed up with reliable sources. For example, if you are speaking about climate change, include research studies, statistics, surveys and other forms of data that provide concrete evidence that supports your argument or position. Additionally, be sure to cite any sources used in the speech so that your audience can double-check the accuracy. In some cases, particularly when discussing sensitive topics, each side of the issue should be addressed. Not only does this make for a more balanced discussion, it also allows you to show respect for different points of view without compromising your own opinion or position. Presenting both sides briefly will demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter and show your ability to present a well-rounded argument. Knowing how to source accurately and objectively is key to creating an informative speech outline which will be compelling and engaging for an audience. With the right sources and evidence utilized correctly, you can ensure that your argument is both authoritative and convincing. With these fundamentals in place, you can move on to developing tips for crafting an informative speech for maximum impact and engagement with the listeners.
Tips for Crafting an Informative Speech
When crafting an informative speech, there are certain tips and tricks that you can use to make sure your outline is the best it can be. Firstly, if you are speaking about a controversial issue, make sure you present both sides of the argument in an unbiased manner. Rely on researching credible sources, and discuss different points of views objectively. Additionally, organize and prioritize your points so that they are easy to follow and follow a logical progression. Begin with introducing a succinct thesis statement that briefly summarizes the main points of your speech. This will give the audience a clear idea of what topics you will be discussing and help retain their attention throughout your speech. Furthermore, be mindful to weave in personal anecdotes or relevant stories so that the audience can better relate to your ideas. Make sure the anecdotes have a purpose and demonstrate the key themes effectively. Acquiring creative ways to present data or statistics is also important; avoid inundating the audience with too many facts and figures all at once. Finally, ensure that all visual aids such as props, charts or slides remain relevant to the subject matter being discussed. Visual aids not only keep listeners engaged but also make difficult concepts easier to understand. With these handy tips in mind, you should be well on your way to constructing an effective informative speech outline! Now let’s move onto exploring some examples of effective informative speech outlines so that we can get a better idea of how it’s done.
Examples of Effective Informative Speech Outlines
Informative speeches must be compelling and provide relevant details, making them effective and impactful. In order to create an effective outline, speakers must first conduct extensive research on the chosen topic. An effective informative speech outline will clearly provide the audience with enough information to keep them engaged while also adhering to a specific timeframe. The following are examples of how to effectively organize an informative speech: I. Introduction: A. Stimulate their interest – pose a question, present intriguing facts or establish a humorous story B. Clearly state the main focus of the speech C. Establish your credibility– explain your experience/research conducted for the speech II. Supporting Points: A. Each point should contain facts and statistics related to your main idea B. Each point should have its own solid evidence that supports it III. Conclusion: A. Summarize supporting points B. Revisit your introduction point and explain how it’s been updated/changed through the course of the discussion C. Offer a final statement or call to action IV. Bibliography: A. Cite all sources used in creating the speech (provide an alphabetical list) Debate both sides of argument if applicable: N/A
Commonly Asked Questions
What techniques can i use to ensure my informative speech outline is organized and cohesive.
When crafting an informative speech outline, there are several techniques you can use to ensure your speech is organized and cohesive. First of all, make sure your speech follows a logical flow by using signposting , outlining the main ideas at the beginning of the speech and then bulleting out your supporting points. Additionally, you can use transitions throughout the speech to create a smooth order for your thoughts, such as ‘next’ and ‘finally’. Furthermore, it is important that each point in your outline has a specific purpose or goal, to avoid rambling and confusion. Finally, use visual aids such as charts and diagrams to emphasise key ideas and add clarity and structure to your speech. By following these techniques , you can ensure your informative speech outline is well organized and easy to follow.
How should I structure the order of the information in an informative speech outline?
The structure of an informative speech outline should be simple and organized, following a linear step-by-step process. First, you should introduce the topic to your audience and provide an overview of the main points. Next, give an explanation of each point, offer evidence or examples to support it, and explain how it relates to the overall subject matter. Finally, you should conclude with a summary of the main points and a call for action. When structuring the order of information in an informative speech outline, it is important to keep topics distinct from one another and stick to the logical progression that you have established in your introduction. Additionally, pay attention to chronology if appropriate; when discussing historical events, for example, make sure that they are presented in the correct order. Moreover, use transition phrases throughout your outline to help move ideas along smoothly. Finally, utilize both verbal and visual aids such as diagrams or graphics to illustrate complex knowledge effectively and engage your audience throughout your presentation.
What are the essential components of an informative speech outline?
The essential components of an informative speech outline are the introduction, body, and conclusion. Introduction: The introduction should establish the topic of your speech, provide background information, and lead into the main purpose of your speech. It’s also important to include a strong attention-grabbing hook in order to grab the audience’s attention. Body: The body is where you expand on the main points that were outlined in the introduction. It should provide evidence and arguments to support these points, as well as explain any counterarguments that might be relevant. Additionally, it should answer any questions or objections your audience may have about the topic. Conclusion: The conclusion should restate the purpose of your speech and summarize the main points from the body of your speech. It should also leave your audience feeling inspired and motivated to take some kind of action after hearing your speech. In short, an effective informative speech outline should strongly focus on bringing all of these elements together in a cohesive structure to ensure that you deliver an engaging presentation that educates and informs your audience.
Protect your data
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy . You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.
- Career Advice
- The Purpose of Informative...
The Purpose of Informative Speech - Rules, Types, and Topic Ideas
10 min read · Updated on February 20, 2023

Does the thought of public speaking leave you quaking in your boots?
When you were in school, you were probably required, at some point, to get up in front of the class and give a speech about something. Perhaps your teacher wanted you to give a 15-minute presentation about making a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, or you had to talk about what happens when a star explodes. Both of these are examples of informative speeches.
Now you have a career and your boss has asked you to give an informative speech about a new project that's on the horizon. If you've been lucky enough to live without having to give a presentation in the past, you may be wondering about the purpose of an informative speech. What are the rules? Are there different types of informative speech? How do you pick topics and generate ideas? Well, put on your learning hat and let's dive into these questions.
What is an informative speech?
Basically, an informative speech is when you verbalize a message to give someone else information. In that context, giving someone directions to your house is a miniature informative speech. Informative speeches are used by companies to present details about a new policy, describe procedures, and set expectations.
The content of an informative speech is educational and objective. It's based on facts and, often, visuals are used as supporting evidence to help cement the information into the audience's mind. No matter which type of informative speech you deliver, the overall objective should be education.
There are four goals of an informative speech. They are to be accurate, give meaningful information, articulate the message clearly, and be engaging. In other words, make it memorable and truthful in a way that people can easily understand.
4 types of informative speech
There are countless types of informative speech; however, there are four types that are commonly used .
Definition
A definition speech aims to explain what something means. The topic is likely something the audience knows little about. The easiest way to define concepts is by using synonyms or antonyms. You could also talk about how something is used or what it does as a way to define it. Another very effective way to deliver a definition-style informative speech is to use examples. Examples help your audience to assimilate the information in their brain for easier retention.
Demonstration
If you're going to deliver a demonstration speech, it's imperative that you're intimately familiar with the topic. You also must be able to think quickly to overcome any challenge that may occur during your demonstration. Above all else, be sure to practice, practice, practice! Talking and doing something at the same time involves psycho-motor skills that can be hard to accomplish with people looking.
Think of every television chef - Gordon Ramsay, Rachel Ray, or Julia Child. Their broadcasts are the epitome of a demonstration type of informative speech. Gordon Ramsay goes through the process of scrambling eggs and at the same time, he's telling you what to do, when to do it, and how to do it. Just because they make it look easy, doesn't mean you'll be able to wing it.
The really great thing about demonstration speeches is that you can do things like ask for volunteers from the audience, fill in any empty space in your speech with the definition of what you're working with, and have a clear sequence of steps to complete to ensure that the information is fully delivered.
Description
A description type of informative speech relies on the five human senses to deliver information. You could be talking about a new restaurant and the hunger associated with the smells that come from the kitchen, or your speech could be something that advises your employees about a rebranding initiative and the vibrant colors in the new logo.
Either way, you're giving the audience a mental picture of what you're talking about. This is called spatial pattern organization and allows the people listening to you to arrange concepts in their minds to evoke a sensory reaction.
Explanation
You have to be careful with explanation speeches as they can quickly become boring for your audience, especially if you're presenting complicated information. Of course, you can break up the information into units. Avoid word vomiting on your audience and use examples to explain the content in a way that your audience can relate to.
What are the rules for informative speech?
First and foremost, an informative speech isn't meant to persuade anyone of anything. Your informative speech may inspire people to change their minds about a topic; however, that isn't the goal. The goal of informative speaking is to give information. Persuasive speaking, often used in sales roles, is meant to get someone to do something or act in a particular way, based on information that is shared with them.
You may deliver an informative speech on solar panels and how their use on a residential dwelling lowers utility bills. The goal of your speech is simply to explain the correlation between the use of solar and the effect on the electricity bill that the resident receives each month. However, there may be some audience members who run home and get solar panels. Even though your informative speech ended up persuading that audience member to do something, that doesn't change the fact that your speech was informative. It's all about intent.
How do you start an informative speech?
Before you get up in front of your audience, there are several things to consider when you start building your informative speech.
Who is your audience? Of course, knowing the specific people you'll be presenting to is imperative. You need to also consider what they may or may not already know. This could greatly impact how much or how little information you need to share.
What will you be talking about? The answer to this question defines the basis of your speech. Take into account where your passions lie and, conversely, what you don't like about the topic. If you want to keep your audience engaged, you have to keep any biases you may have about the subject in check so that they don't influence your message.
How long does the speech need to be? If you only have 5 minutes, a high-level overview may be all you have time to discuss. However, if you'll be in the spotlight for 30 minutes or more, you can spend a bit more time on the things you feel your audience may not be as familiar with. This will aid comprehension and knowledge retention.
Where will you physically give the speech? This is especially important if you'll have visuals. If you're in a large auditorium, the visuals you present need to be seen by the people in the back. If you're in a small conference room, it won't present much of an issue.
Why are you giving the speech? If you know the different types of speeches, answering the “why” will be easy. Your goal will be to inform someone about something in a demonstrative or descriptive way.
After you answer those questions, you can craft your presentation. When you get in front of your audience, remember to be engaging.
You only have a few seconds to grab their attention. The standard advice is to open with a joke, but that may not always be appropriate. Think about every speech or presentation you've had to attend. What were the things that made it memorable for you? Use those elements in your own speech.
Don't forget about your body language
Your audience isn't only listening to the words you say. They're also watching your posture, hand gestures, and facial expressions. When you need to give an informative speech, it's quite possible that the content is simply boring but, if you're an engaging orator, the audience will be more apt to follow along because they enjoy watching you.
It can be argued that body language says as much as our words. If you're smiling, the audience will assume you like the topic. If you slump over a podium, the audience may guess that you're not confident in what you're talking about.
The wrong body language can turn off your entire audience. Not only will they miss what you're saying, but they will also question your authority to tell them anything. They certainly won't walk away with the knowledge that you want them to possess. On the other hand, the right body language will improve audience engagement and assist in getting your message across.
Informative speech topics vary by career
You may have had to give informative speeches at school, but don't think graduation saves you from ever having to give one again. Almost every career path you can take could present an opportunity for you to give an informative speech.
Good news! If you find a career you love, giving informative speeches will be a breeze, and narrowing down your list of ideas will also lead you to easy informative speech topics.
Here are some examples of careers that require frequent informative speeches.
Teachers : Since informative speeches are, by nature, educational, it makes sense that teachers and professors use them to develop learning environments for their students. Teachers are also good at turning boring material into fun, informative speeches to engage students and promote knowledge retention.
Journalist : You must have a passion for relaying information if you decide to go into journalism. This career is filled with informative speeches on a daily basis. Journalists are the ones the public relies on to get pertinent information about critical events that are happening in the world.
Docent/Curator : If you've ever been to a museum and had someone guide you through the exhibits explaining the nature of the pieces being presented, you watched someone give an informative speech.
Doctor : Wait a second, doctors don't give speeches. Yes, they do! A lot! When a doctor describes your ailment or injury and what you have to do to take care of it, that's an informative speech. Additionally, many doctors present on topics at association events. Those are informative speeches, too.
Mechanic : This one may stump you, too. At what point does a mechanic give an informative speech? The moment he or she starts explaining what's wrong with your car and what needs to be done to fix it.
It doesn't matter what career you fall into, you will likely have to give an informative speech at some point - although some careers will require it more often than others.
Key takeaways
Anything you need to tell someone can technically be considered an informative speech, as long as your goal is to give information and not try to change their mind about the topic. It doesn't matter if you're giving a 2-minute set of directions to someone or providing an hour-long oration over a complex concept; your informative speech needs to be:
Well thought out
Truthful
Audience-centered
One immutable truth is that you will see some sort of requirement for communication skills in every single job description you read. That's because communication is a highly sought-after soft skill that will first be judged during your interview - another form of informative speech.
TopResume would love to be a part of your career journey. We can help you with career advice and interview preparation, so that your speech-giving skills are up to par. Submit your resume for a free resume review and step into that interview room with confidence.
Recommended reading:
15 Free Resources to Improve Presentation and Public Speaking Skills
Ask Amanda: How Can I Become Better at Public Speaking?
10 Easy Ways to Improve Nonverbal Communication Skills
Related Articles:
Don't “Snowplow” Your Kids' Job Search — Set Them Up for Success Instead
What Kind of Job Candidate Are You?
Why December is the Best Time of Year to Look for a Job
See how your resume stacks up.
Career Advice Newsletter
Our experts gather the best career & resume tips weekly. Delivered weekly, always free.
Thanks! Career advice is on its way.
Share this article:
Let's stay in touch.
Subscribe today to get job tips and career advice that will come in handy.
Your information is secure. Please read our privacy policy for more information.

Delivering an informative speech: 7 key tips every speaker should follow
- Filed under: Public speaking tips and tricks , Speaking tips , Speech delivery
Delivering an informative speech seems somehow easier than giving a big sales pitch or giving a speech at a conference.
There are all sorts of speeches in the world that seem difficult ( persuasive , impromptu , etc.), and therefore giving an informative speech seems like a piece of cake.
However, here’s the challenge. If you’re trying to communicate with people, it’s not about the information coming out of your mouth and it’s not necessarily about the information on the PowerPoint slides. Mostly, it’s about the information your audience understands and can remember.
So, never lose sight of that. You’ve got to really figure out how can you convey this information.
Table of Contents
How do you deliver an informative speech?
Here is a brief overview of what you should keep in mind in order to deliver a great speech.
Additional reading:
- How to deliver a ceremonial speech? A Full Guide
- How to Give an Award Acceptance Speech?
What is the purpose of an informative speech?
Now, tet’s dive in and see how to get your audience to understand you and to remember your message(s).
#1 The main purpose of an informative speech is to be Memorable
So, here’s the dirty little secret: It’s incredibly easy to give an informational speech.
BUT: It’s much harder when a transfer of information, from your brain into the brains and memories of the audience, is required.
That’s why your focus should not just be giving a speech, but also giving an effective informational speech.
So, you need to remember that the main goal of your speech is to deliver your message as clearly as possible and to be memorable. Your audience wants to know exactly what information you have.
How do you write a good informative speech?
The good news is that you don’t have to be wildly entertaining while delivering an informational speech. Remember:
- You’re not the comedian for the night.
- You don’t have to be incredibly charming during your speech
- You’re not the master of ceremonies
Nevertheless, we still need a specific goal for this speech.
#2 Brainstorm all the ideas you want to communicate
I do not recommend that you sit down and just try to type a 20-page speech. For some people, it’s easier to sit back, relax and have a notepad. You may want to take notes on your phone or tablet. It doesn’t really matter.
But rather than thinking in terms of entire paragraphs and flow, brainstorm ideas that you should be able to communicate in 10 seconds, or less 10 words or less.
Recommended books
How to Deliver a TED Talk: Secrets of the World's Most Inspiring Presentations
Jeremy Donovan
Resonate: Present Visual Stories that Transform Audiences
Nancy Duarte
Confessions of a Public Speaker
Scott Berkun
Talk Like TED: The 9 Public-Speaking Secrets of the World's Top Minds
Carmine Gallo
The Checklist Manifesto: How to Get Things Right
Atul Gawande
The First 20 Hours: How to Learn Anything... Fast!
Josh Kaufman
Just start brainstorming on every idea on your topic that you might want to communicate to the audience.
Some things to remember:
- Don’t check things out
- Don’t scrutinize
- Don’t be critical
- Dump it all out there
#3 Isolate the ideas you want people to remember
After brainstorming, you have to figure out the messages you want to communicate in this informational speech.
Therefore, usually, it takes a lot of time to isolate the ideas, messages, and information you want people to understand and remember.
Next, figure out now how to make this information memorable.
It’s just this basic, low-level goal of trying to communicate information in a way that people can digest.
#4 No more than five key points for the speech
An exercise for you: think of the best speaker you’ve seen give an speech in the last few years.
If you had to recall, how many numbers, facts or bits of information do you remember?
I’ve asked this question for years and quite often people don’t remember anything, or they remember two or three points. Occasionally, someone will remember five ideas or five bits of information from the best speaker.
That’s the main reason I am suggesting to keep your speech focused on no more than five key points of information.
#5 Avoid providing too much information
The biggest problem most people have when they’re giving speeches is they give away too much information. They just throw it all out there and try to talk about an hour’s worth of information for 20 minutes.
This kind of speech is abstract and disconnected.
Since there are no examples, no case studies and no stories, nobody remembers anything.
- How to write a speech: 20 good and effective tips
- How to Outline a Presentation: A Complete Guide From a Pro
How to prepare for an informative speech?
#6 practice your speech and practice with the video camera.
In order to figure out whether your speech is any good – and whether you can deliver it properly – it is important to practice. The less time you prepare and practice, the greater the probability that no one will listen to and retain what you have to say.
Practice in front of a video camera
The best way to see how you look and sound is to practice in front of a video camera. If you are a bit lazy and skip that part then there’s an excellent chance you’re never going to improve.
The best thing about practicing in front of a video camera is that, unlike your friends, it does not kill you with kindness by saying, “Hey, best speech ever!” It gives you honest feedback about what to improve.
Here are some tips regarding how to practice your speech in front of a video camera:
- Watch yourself and write down everything you liked about your first try
- Write down everything you didn’t like about this speech
- If you finished, do it again, and this time, try to avoid the mistakes you wrote down earlier.
- Keep practicing until you are satisfied with what you see and hear
If you do this, you’re going to be in good shape.
- Prepared speech: 10 effective tips on how to practice a speech
- How to be comfortable in front of a video camera? 14 great tips
#7 Test your speech beforehand
The good news about informational speeches is that they are very easy to test, whether it works or not.
Send your video to a couple of people
Now, if you’ve done what I’ve asked thus far, I want you to take that last video that you’re proud of and send it to three or four people who are similar to the audience you’ll be speaking to in real life. Ask them to watch it once and to call you right away.
Ask them to tell you the messages they remember from the speech
Ask them, “Tell me…what messages do you remember from my speech? What are the main takeaways?”
It’s completely irrelevant whether or not they liked your speech or found you charismatic or charming. You’re simply trying to figure out if they retained the information.
Did they throw back in your face those five ideas that were important (at least at some conceptual level)?
If so, congratulations! You are five for five and that’s a one hundred present success rate. There’s not a professional speaker in the entire world who can ever do better than that.
If they don’t remember your message(s), you have failed
However, if they remember only a couple of those messages (or none) and they’re just telling you, “You’re great and fantastic,” that means you failed.
That means you now have empirical evidence that the way you conveyed the information in your presentation didn’t work.
You need to take your speech, tear it up, throw it away and start again. If your audience doesn’t remember your messages, it’s not their fault – it is your fault.
Final words about delivering an informational speech
I am sure that if you follow these tips about how to give an effective speech, you will deliver a great speech in the future.
What I hope you really took away is the idea that it’s not about what comes out of your mouth or even if you have great eye contact. It’s about whether or not people understand and remember the information you are trying to convey.
You’re going to really use your judgment to figure out one of the handfuls of ideas that this audience really has to know, and then spend your time making it more understandable and memorable with examples, case studies, and stories.
Posts about public speaking you may also like

How to speak with confidence in public?
No matter what your field of expertise is, public speaking can make or break your career. If that sentence fills you with self-doubt, you’re not

Stage fright: A Helpful Illustrated Guide
The stage fright is one of the most common fears in people, so let us today have a closer what is it. In this article,

Public speaking FAQs: Answers To the Top 22 Most Common Questions
There are a bunch of public speaking related questions that I keep hearing (and probably will keep hearing) during my training sessions or business consulting
- Tags: Impromptu speaking , Impromptu talk , Prepare a speech , Prepared speech , Public presentation , Speech preparation process , Speech tips , Speech writing tips , Unprepared speech , Unprepared speech topics , Writing a speech
Recommended gear

Best Portable Speakers For The Presentations

Best Video Cameras for Public Speakers

Best rresenter remotes for public speakers

Best Portable Thumb Drives And Hard Drives for the Presentations
Who is janek tuttar.
My name is Janek Tuttar , and I am the founder and author of Speak and Conquer website.
I have been teaching public speaking at Estonian Entrepreneurship University of Applied Sciences
Here, I am sharing the wisdom of how to cope in different public speaking situations.
More information about Janek »

Share this post

Hi! My name is Janek Tuttar, and I am the founder and author of SpeakAndConquer.com.
I have been teaching and blogging about public speaking since spring 2007. Here, I am sharing the wisdom of how to cope in different public speaking situations.
Send me an e-mail: [email protected]
LEGAL INFORMATION
This site is owned and operated by Janek Tuttar. SpeakAndConquer.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com.
This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.

Best teleprompters

Best Computer Mice for the Presentations

Best Laptop Backpacks for Public Speakers

13.1 What is an Informative Speech?
An informative speech can first be defined as a speech based entirely and exclusively on facts. Basically, an informative speech conveys knowledge, a task that every person engages in every day in some form or another. Whether giving someone who is lost driving directions, explaining the specials of the day as a server, or describing the plot of a movie to friends, people engage in forms of informative speaking daily. Secondly, an informative speech does not attempt to convince the audience that one thing is better than another. It does not advocate a course of action.
Consider the following two statements:
George Washington was the first President of the United States.
In each case, the statement made is what can be described as irrefutable, meaning a statement or claim that cannot be argued. In the first example, even small children are taught that having two apples and then getting two more apples will result in having four apples. This statement is irrefutable in that no one in the world will (or should!) argue this: It is a fact.
Similarly, with the statement “George Washington was the first President of the United States,” this again is an irrefutable fact. If you asked one hundred history professors and read one hundred history textbooks, the professors and textbooks would all say the same thing: Washington was the first president. No expert, reliable source, or person with any common sense would argue about this.
(Someone at this point might say, “No, John Hanson was the first president.” However, he was president under the Articles of Confederation for a short period—November 5, 1781, to November 3, 1782—not under our present Constitution. This example shows the importance of stating your facts clearly and precisely and being able to cite their origins.)
Informative Speech is Not a Persuasive Speech
Informative speech is fundamentally different from a persuasive speech in that it does not incorporate opinion as its basis. This can be the tricky part of developing an informative speech, because some opinion statements sometimes sound like facts (since they are generally agreed upon by many people), but are really opinion. For example, in an informative speech on George Washington, you might say, “George Washington was one of the greatest presidents in the history of the United States.” While this statement may be agreed upon by most people, it is possible for some people to disagree and argue the opposite point of view. The statement “George Washington was one of the greatest presidents in the history of the United States” is not irrefutable, meaning someone could argue this claim. If, however, you present the opinion as an opinion from a source, that is acceptable: it is a fact that someone (hopefully someone with expertise) holds the opinion. You do not want your central idea, your main points, and the majority of your supporting material to be opinion or argument in an informative speech.
Unlike in persuasive speeches, in an informative speech, you should never take sides on an issue, nor should you “spin” the issue in order to influence the opinions of the listeners. Even if you are informing the audience about differences in views on controversial topics, you should simply and clearly describe and explain the issues. This is not to say, however, that the audience’s needs and interests have nothing to do with the informative speech. We come back to the WIIFM principle (“What’s in it for me?”) because even though an informative speech is fact-based, it still needs to relate to people’s lives in order to maintain their attention.
Why Informative Speech Is Important
The question may arise here, “If we can find anything on the Internet now, why bother to give an informative speech?” The answer lies in the unique relationship between audience and speaker found in the public speaking context. The speaker can choose to present information that is of most value to the audience. Secondly, the speaker is not just overloading the audience with data. As we have mentioned before, that’s not really a good idea because audiences cannot remember great amounts of data and facts after listening. The focus of the content is what matters. This is where the specific purpose and central idea come into play. Remember, public speaking is not a good way to “dump data” on the audience, but to make information meaningful.
Finally, although we have stressed that the informative speech is fact-based and does not have the purpose of persuasion, information still has an indirect effect on someone. If a classmate gives a speech on correctly using the Heimlich Maneuver to help a choking victim, the side effect (and probably desired result) is that the audience would use it when confronted with the situation.
It’s About Them: Public Speaking in the 21st Century Copyright © 2022 by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Home — Essay Samples — Literature — Leonardo Da Vinci — Informative Speech Outline: Leonardo Da Vinci
Informative Speech Outline: Leonardo Da Vinci
- Categories: Italian Renaissance Leonardo Da Vinci
About this sample

Words: 697 |
Published: Jun 6, 2024
Words: 697 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, early life and education, artistic achievements, scientific explorations, legacy and impact.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Arts & Culture Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1848 words
3 pages / 1217 words
3.5 pages / 1498 words
2 pages / 887 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Leonardo Da Vinci
If you could talk to anyone in history, who would it be? This thought-provoking question opens a door to a realm of possibilities and hypothetical conversations with individuals who have left an indelible mark on the course of [...]
Leonardo da Vinci is a name synonymous with genius, artistry, and innovation. Born in 1452 in the small town of Vinci, Italy, he lived a life that was marked by unparalleled creativity and ingenuity. From his artistic [...]
There are certain individuals in the world who have transformed the word "success." They have reached the heights of it and are known as legends. Leonardo Da Vinci is among those individuals who are claimed to be the greats of [...]
Leonardo da Vinci, a polymath of the Italian Renaissance, is widely regarded as one of the most diversely talented individuals to have ever lived. His achievements spanned across a multitude of disciplines, including art, [...]
Leonardo da Vinci was a one of a kind talent that the world may never see again. His inquisitive nature and desire to learn helped him achieve some of the most marvelous works that mankind has ever seen. He was a painter, [...]
The transition movement that took place between the 14th and 17th century in Italy is known as the Renaissance time or by definition "rebirth". The philosophy that took place in the period is one of the humanism or the focus on [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

ENG 102, Trale, Boyce: AI Resources
- Library Resources
- AI Resources
- Video Tips
- Annotated Bib
- MLA Style (9th ed.)
These resources and tips can give you a better understanding of how artificial intelligence tools can be used in your academic research.
Use these tools responsibly, ethically and under the guidance of your instructor to ensure compliance with CCAC's Academic Integrity policy.
Used effectively, AI tools can help with your understanding of a subject and shouldn't be used as a shortcut to completing your assignments.
- More on Ethics & Academic Integrity
- CCAC Student Code of Academic Conduct

"Create an Image of Students Using a Laptop in a College Library." Microsoft Copilot, 10 May 2024.
Is AI Reliable?
AI generators collate a response based on your prompt. The output can be impressive, but it is based on an analysis of words and phrases found throughout websites and then generated based on the prompt. Results can be inaccurate, nonsensical, biased and lack any supporting resources. Make certain to check the output!
Useful For:
Brainstorming & search terms
Generating outlines
Focusing a topic
Understanding difficult subjects
Not Recommended For:
Writing an essay or speech
Providing references
Verifiable information
Unbiased perspectives
What Is A Prompt?
An AI prompt is a specific instruction you give a powerful computer program, like telling a barista your coffee order. The clearer your prompt, the better the AI understands what you want it to do, like write an essay or translate a text.
"AI Prompt Definition." Google Gemini, 8 May 2024.
Define the goal: Identify the purpose of the prompt and what the output should be.
Be specific: Include precise instructions and keywords or phrases.
Stay concise: Keep each prompt short, but continue the conversation with follow up prompts.
Provide the output: Define what you want: an outline, list of terms, or a short paragraph of ideas.
A series of prompts can be a conversation with the AI tool. This back-and-forth chat allows you to give directions and then build on ideas, refining each step as you progress through the interaction.

Prompt Examples
Brainstorming, developing search terms, creating outlines.
Smart Student: ChatGPT Prompting: Your Ticket to Superior Research and Learning
AI & Critical Thinking
Smart Student: Here's What AI is Doing to Your Critical Thinking Skills
Popular AI Tools

- Gemini Created by Google, Gemini has multimodal capabilities across text, images, audio, video and code.

- Copilot Developed by Microsoft, Copilot can assist with various tasks and integrate with the Office suite.

- ChatGPT Developed by OpenAI, ChatGPT 3.5 can generate conversations based on the prompts on any topic.

- Perplexity Created by Anthropic, Perplexity is a cross between an AI generator and a search engine; it will respond to prompts and provide links to the websites or other sources it used to answer your question
Why Cite AI?
If you're using AI tools for any of your research, you should include that in your citations, just like you would any other source. Even if you are using AI to help with a draft or outline, you'll want to acknowledge that with a sentence at the beginning or end of the paper that says something like, "This paper was produced with drafting support from Google Gemini AI." Your instructor might have specific conventions for how they would like to list this as well, so it is always best practice to check in with them!
Building blocks
- Author: Do not treat the AI as an author; MLA is reserving that for human authors. Omit the author section of the citation.
- Title of source: Describe what was generated by the AI tool. If you have not included information about the prompt in the text of your essay, you need to do that here.
- Title of container: The name of the AI tool.
- Version: Name the version of the AI tool as specifically as possible.
- Date: Include the date the content was generated.
- Location: Give the URL for the tool. If possible, give the URL for the specific content. ( Note: the style guide post is slightly out of date; you can now send someone a URL of your ChatGPT conversation. This is the URL you should use in your citation.)
"Prompt text" prompt. AI tool , version of tool, company that made the tool, date text was generated. URL.
- In-text citation: ("Describe the symbolism")
- Works Cited: “Describe the symbolism of the green light in the book The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald” prompt. ChatGPT , 13 Feb. version, OpenAI, 8 Mar. 2023, https://chat.openai.com/share/dccb3610-1db9-4eed-88b1-cdb06f67982a .
Check out the MLA Style Guide for more information.
- Author: Use the creator of the AI as the author (e.g. OpenAI, Google, etc.)
- Date: Include the date the content was generated.
- Title: Use the name of the AI tool (e.g. ChatGPT, Bard)
- Description: In brackets, clarify that this is a large language model, or another specific type of generative AI.
Company that made the tool (date text was generated). AI tool ( version of tool) [Large language model]. URL.
- In-text citation: (OpenAI, 2023)
- References: OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT (Mar 14 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/share/dccb3610-1db9-4eed-88b1-cdb06f67982a.
Check out the APA Style Guide for more information .
Chicago Style
In Chicago, you'll cite generative AI differently depending on whether or not you included the prompt in the text of your paper. If you included it in your paper, you don't need to repeat it in the citation.
- Author: Treat the AI as the author. If you're footnoting quoted text, say "Text generated by [the AI tool]."
- Date: Include the date the content was generated.
- Publisher: Use the company that created the AI (e.g. OpenAI, Google)
- Location: Give the URL for the tool. If possible, give the URL for the specific content.
Prompt already included in paper:
1. Text generated by [name of the AI tool], date, Company that made the tool, URL.
Prompt not yet included in paper:
1. [Name of the AI tool], response to "prompt," date text was generated, Company that made the tool, URL.
- Prompt already included in paper: 1. Text generated by ChatGPT, March 7, 2023, OpenAI, https://chat.openai.com/share/dccb3610-1db9-4eed-88b1-cdb06f67982a .
- Prompt not yet included in paper: 1. ChatGPT, response to “Explain how to make pizza dough from common household ingredients,” March 7, 2023, OpenAI, https://chat.openai.com/share/dccb3610-1db9-4eed-88b1-cdb06f67982a .
Check out the Chicago Style Guide for more information
Content adapted from University of Maryland: AI & Information Literacy, Cite Correctly
- << Previous: Library Resources
- Next: Video Tips >>
- Last Updated: Jun 5, 2024 8:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ccac.edu/eng-trale

Oratorical Speech for Elementary
Ai generator.
Good [morning/afternoon/evening] everyone,
Today, I want to talk to our young students about something very important: the joy of learning and the incredible journey you are all on. As elementary students, you are at the beginning of an exciting adventure filled with new discoveries, fun challenges, and endless possibilities. Let’s explore how you can make the most of your time in school and develop a love for learning that will last a lifetime.
Embrace Curiosity
First and foremost, always be curious. Curiosity is the spark that lights the fire of learning. Ask questions, explore new things, and never be afraid to wonder about the world around you. Whether it’s why the sky is blue, how plants grow, or what makes a story exciting, your curiosity will lead you to new and amazing discoveries.
Enjoy the Journey
Learning is not just about getting the right answers or perfect grades; it’s about enjoying the process of discovering new things. Each day at school is an opportunity to learn something new, make new friends, and have fun. Embrace each day with excitement and joy. Remember, it’s okay to make mistakes along the way because that’s how we learn and grow.
Be Kind and Respectful
One of the most important lessons you will learn in school is how to be kind and respectful to others. Treat your classmates, teachers, and everyone you meet with kindness and respect. Help others when they need it, share, and be a good friend. These actions not only make your school a happier place but also help you build strong and lasting friendships.
Work Hard and Persevere
Sometimes, learning new things can be challenging, but don’t give up! Work hard and keep trying, even when things are difficult. Remember, every great achievement starts with small steps and lots of practice. If you keep working hard and never give up, you can achieve anything you set your mind to.
Explore Your Passions
Each of you has unique talents and interests. Find what you love to do, whether it’s reading, drawing, playing sports, or solving puzzles, and spend time doing it. Exploring your passions makes learning fun and helps you discover what makes you happy. Your interests might even lead you to exciting opportunities in the future.
Listen and Learn from Others
Your teachers, parents, and classmates have so much to teach you. Listen to them, ask for help when you need it, and learn from their experiences. Everyone you meet has something valuable to share, and by listening and learning from others, you can grow and improve every day.
Celebrate Your Achievements
Every time you learn something new or achieve a goal, take a moment to celebrate. Be proud of your hard work and accomplishments, no matter how big or small. Celebrating your successes helps you stay motivated and reminds you of the joy of learning.
Have Fun and Be Creative
Learning is not just about studying and working hard; it’s also about having fun and being creative. Use your imagination, play games, and enjoy your time at school. Creativity and play are important parts of learning and can make your school experience much more enjoyable.
In conclusion, elementary school is a wonderful time filled with opportunities to learn, grow, and have fun. Embrace curiosity, enjoy the journey, be kind and respectful, work hard, explore your passions, listen to others, celebrate your achievements, and always have fun and be creative. These principles will help you make the most of your time in school and develop a lifelong love for learning.
Remember, you are the future, and the skills and knowledge you gain today will help you achieve amazing things tomorrow. Enjoy every moment of your educational journey, and always strive to be the best you can be.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Speech Writing /
Vote of Thanks Speech for Students in English

- Updated on
- Jun 3, 2024

A vote of thanks is a formal speech that expresses gratitude to a special guest or person for honourable contributions. A vote of thanks speech is concluded by expressing your gratitude, summarising the main points of the event and sending an uplifting message. In this article, we will look at some samples of speech on the vote of thanks. Keep reading to learn more.
Table of Contents
- 1 Importance of Vote of Thanks
- 2 Speech on Vote of Thanks for School Event
- 3 Speech on Vote of Thanks for Chief Guest
- 4 Speech on Vote of Thanks for Guest Lecture
- 5 FAQs
Importance of Vote of Thanks
A vote of thanks is a formal speech that concludes your speech by thanking a guest or special person for their contribution. A vote of thanks is a vital part of an event because it shows that you value each member and their contribution. It has importance in several aspects:
- Expression of Gratitude: It allows us to express our gratitude to those who have supported and made the event possible. It helps us to build positive relationships.
- Closure: A vote of thanks helps provide closure to the event. It is something that summarizes the whole event, key highlights and achievements.
- Sense of encouragement: Acknowledging and appreciating the efforts of other people in the vote of thanks encourages them to better future performance. It inspires people to remain motivated and engaged towards the organization’s goal.
- Acknowledgement of contributions: A vote of thanks is a formal way of acknowledging other’s efforts that made the event possible.
- Purpose of courtesy: Appreciating individuals for their support or contribution reflects professional etiquette by highlighting the value of respect in networking.
- Social Networking: Respecting the contributions of others shows that you value them. This can help you improve your professional relationships while also helping to build new ones.
Also Read: Essay on Voting for School Students
Speech on Vote of Thanks for School Event
Also Read: Speech on President of India for School Students in English
Speech on Vote of Thanks for Chief Guest
Also Read: Here are Interesting Children’s Day Speech for Students
Speech on Vote of Thanks for Guest Lecture
Also Read: Welcome Speech in English for Learning and Growth of School Students: Long and Short
Ans: A vote of thanks is a formal speech that expresses gratitude to a guest or special person for their contributions. There are ways to conclude the speech by delivering a ‘Vote of Thanks’, as per the event.
Ans: A vote of thanks is a vital part of an event because it shows that you value each member and their contribution. It is important as it is a way to express your gratitude towards the other team members. It provides closure to your speech by summarising all of the key highlights of the events and the achievements. It promotes a sense of encouragement and acknowledgement to the tea members, which acts as a professional courtesy.
Ans: Make sure to start your speech with a warm greeting. It should be short and simple. You can start your speech by extending your gratitude towards a special guest on behalf of the party that is hosting the event.
Popular English Speech Topics
For more information on such interesting speech topics for your school, visit our speech writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Bhumika Sharma
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Below are 15 examples of informative speech topics that are sure to engage and educate your audience. The history and evolution of social media platforms. The benefits and drawbacks of renewable energy sources. The impact of sleep deprivation on mental and physical health. The role of emotional intelligence in personal and professional success.
The three circles are labeled: "things I am interested in," "things my audience cares about," and "things I can research.". The center point where these three circles overlap is the sweet spot for your speech topic. When (Length): The length of your speech can drastically impact how in-depth you dive into the topic.
Informative Speech Idea In 5 Steps. 1. Step One - Make a List. Make a short list of your personal interests and informative speech topic ideas. To help you determine your interests on an informative speech topic, think about your favorite objects, products, people, animals, events, places, processes, procedures, concepts, policies, theories ...
2. Include a hook, thesis, and road map of your speech in the introduction. It's common to begin a speech with an attention-grabbing device, such as an anecdote, rhetorical question, or quote. [8] After getting the audience's attention, state your thesis, then preview the points your speech will cover.
Writing. Stage 3. Perfecting Speech Delivery. List of informative speech topics. Topics for informative speech about music. Informative speech topics about animals. Topics for informative speech about global warming. Informative speech ideas about sports. Interesting speech topics about food and drinks.
If you're giving an informative speech, remember to: Do your research! Gather information from credible, authoritative sources when composing your speech. Avoid sources that discuss strictly the opinion of the author and look for solid, factual evidence to support your topic. Consider your audience.
Structuring an Informative Speech. Typically, informative speeches have three parts: Introduction; Body; Conclusion; In this section, we discuss the three parts of an informative speech, calling attention to specific elements that can enhance the effectiveness of your speech. As a speaker, you will want to create a clear structure for your speech.
For example, an informative speech on the rise and fall of a currency's daily exchange rate is made a great deal easier to follow and understand with graphs or charts illustrating the key points. Or for a biographical speech, photos of the person being talked about will help hold the attention of your audience. 7.
Educating your audience with informative speech topics you feel passionate about is the primary goal. Browse this list and let your enthusiasm shine through.
As you can see, knowing that you want to inform your audience is just a small part of your speech. To make your speech as effective as possible, write with the right type of speech in mind. 1. Choose Your Topic. Before starting your informative speech outline example, you need to know what you're writing about.
Follow these 10 steps to help you write an informative speech: 1. Select your topic. Pick a topic that relates to the goals of your informative speech. Professionals giving informative speeches to their coworkers, for example, might consider different topics than students giving informative speeches as part of a public speaking class. In ...
Informative speeches are used in our day-to-day lives without even noticing it, we use these speeches whenever we inform someone about a topic they didn't have much knowledge on, whenever we give someone instructions on how to do something that they haven't done before, whenever we tell someone about another person.
An informative speech conveys knowledge, a task that every person engages in every day in some form or another. Whether giving someone who is lost driving directions, explaining the specials of the day as a server, or describing the plot of a movie to friends, people engage in forms of informative speaking daily.
The most common types of informative speeches are definition, explanation, description, and demonstration. A definition speech explains a concept, theory, or philosophy about which the audience knows little. The purpose of the speech is to inform the audience so they understand the main aspects of the subject matter.
2. Make an introduction - Introduce yourself and the topic of your speech, as well as any relevant background information that the audience needs to understand the topic better. 3. Present facts and evidence - Use facts and evidence to support the points you make in your speech.
2) Research on the topic. a) Carry out the initial research. b) Think about how your research might change your topic. 3) About writing the speech. a) Think about your audiences earlier than writing the speech. b) Summarize your speech. c) Elaborate the key points to make it interesting. d) Write an introduction.
Most persuasive speeches rely on some degree of informing to substantiate the reasoning. And informative speeches, although meant to secure the understanding of an audience, may influence audience members' beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors. Figure 11.1 Continuum of Informing and Persuading.
When crafting an informative speech outline, there are several techniques you can use to ensure your speech is organized and cohesive. First of all, make sure your speech follows a logical flow by using signposting, outlining the main ideas at the beginning of the speech and then bulleting out your supporting points.
Basically, an informative speech is when you verbalize a message to give someone else information. In that context, giving someone directions to your house is a miniature informative speech. Informative speeches are used by companies to present details about a new policy, describe procedures, and set expectations.
Examine nine types of informative speeches below: 1. Descriptive speeches. The purpose of a descriptive speech is often to create a visual image for audiences about a specific object, place or person to help them more deeply understand it. It's typically best to use this type of speech when you want to depict something specific for an audience ...
We've outlined five steps for writing an informative speech. It'll help you take all those thoughts and share them with the audience in a clear and deliberate manner. ... This will give you three pertinent details to share about your topic while you bolster them with interesting facts, statistics, and narratives. Or, if your informative ...
Here is a brief overview of what you should keep in mind in order to deliver a great speech. #1 Be memorable. The main goal of your speech is to deliver your message as clearly as possible and to be memorable. #2 Brainstorm all the ideas you want to communicate. Brainstorm ideas that you should be able to communicate in 10 seconds, or less 10 ...
An informative speech can first be defined as a speech based entirely and exclusively on facts. Basically, an informative speech conveys knowledge, a task that every person engages in every day in some form or another. Whether giving someone who is lost driving directions, explaining the specials of the day as a server, or describing the plot ...
This speech aims to provide an overview of Leonardo da Vinci's life, his multifaceted contributions, and the lasting impact of his work on both his contemporaries and future generations. By delving into his early years, artistic achievements, scientific explorations, and legacy, we can appreciate the breadth of his genius and the enduring ...
Location: Give the URL for the tool. If possible, give the URL for the specific content. Format. Prompt already included in paper: 1. Text generated by [name of the AI tool], date, Company that made the tool, URL. Prompt not yet included in paper: 1. [Name of the AI tool], response to "prompt," date text was generated, Company that made the ...
Oratorical Speech for Elementary. Good [morning/afternoon/evening] everyone, Today, I want to talk to our young students about something very important: the joy of learning and the incredible journey you are all on. As elementary students, you are at the beginning of an exciting adventure filled with new discoveries, fun challenges, and endless ...
A vote of thanks is a formal speech that expresses gratitude to a special guest or person for honourable contributions. A vote of thanks speech is concluded by expressing your gratitude, summarising the main points of the event and sending an uplifting message. In this article, we will look at some samples of speech on the vote of thanks.