

How to Write a Case Study - All You Wanted to Know

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: ' WHAT IS A CREDIBLE SOURCES ?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

| 📝 Step | 📌 Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Draft Structure | 🖋️ Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references. |
| 2. Introduction | 📚 In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research. |
| 3. Research Process | 🔍 Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world. |
| 4. Quotes and Data | 💬 Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case. |
| 5. Offer Solutions | 💡 At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself. |
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
What Is A Case Study?
How to cite a case study in apa, how to write a case study.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved June 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
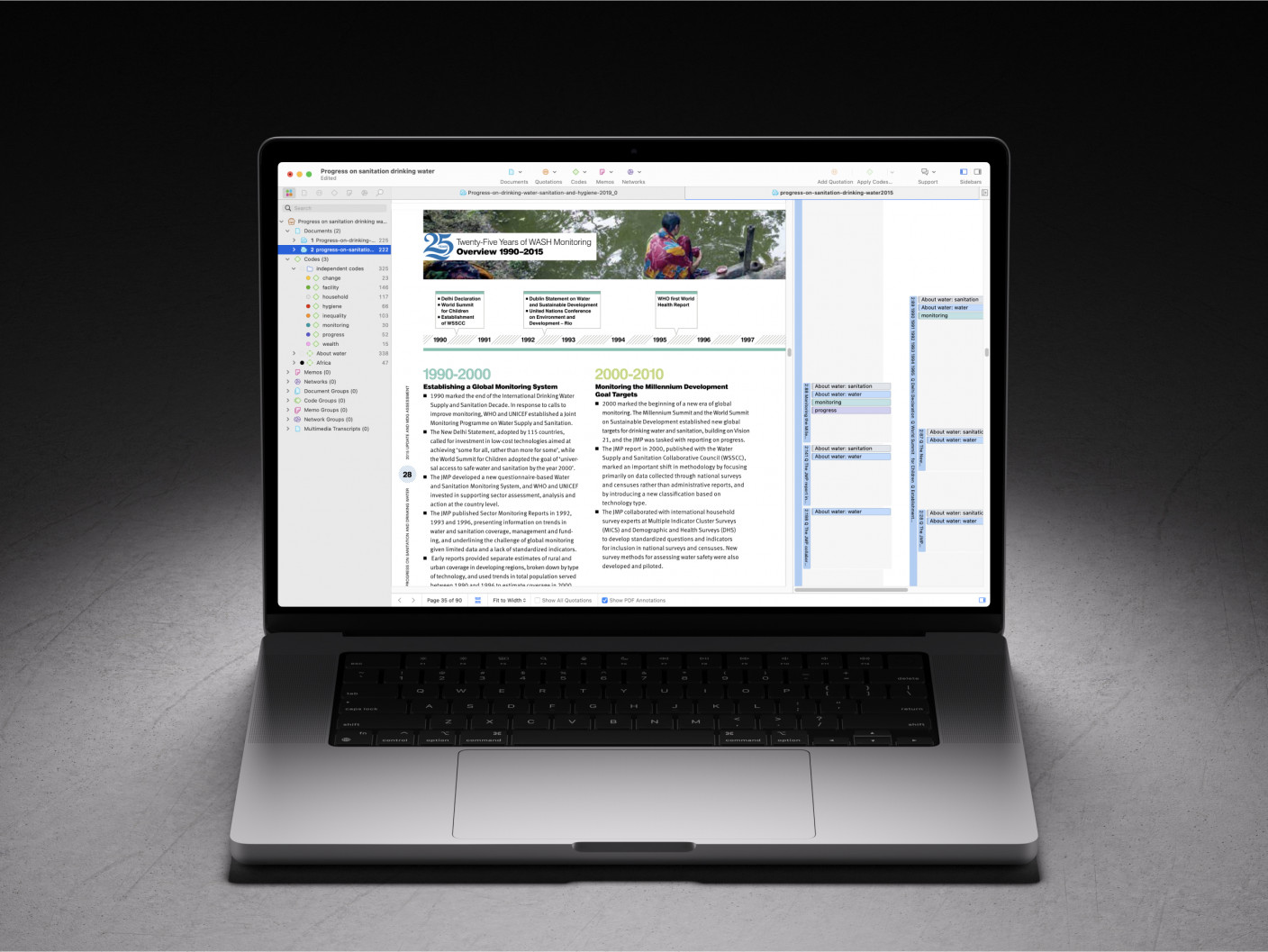
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.

How to Write a Case Study
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a specific situation, person, event, phenomenon, time, place, or company. They look at various elements of the situation including history, trends, specific outcomes, cause and effect, etc.
A case study can either be part of a larger research assignment as one of the methodologies used or be a standalone assignment. You can include several case studies in the same paper or focus on just one case. Multiple case studies are useful when comparing different elements of a research question and trying to find similarities or analyzing the reasons where outcomes are different.
Since the goal of a case study is to get an in-depth understanding of a specific situation, it is perfect for unique cases which may not have a lot of experimental or theoretical data. But this also makes it a very subjective method of analysis, one that cannot be generalized to fit larger groups of data. Case studies are often used in the initial stages of studying a new situation and can help come up with research questions and hypotheses for future studies.
Don't worry if that all sounds complicated, by the end of this article you will know not only how to write a case study assignment in college, but how to write a good case study for a scientific publication!
What is a Case Study?
A case study is one of the best ways of analyzing a unique phenomenon. It's particularly useful when the research question cannot be studied in a lab or through quantitative methods. Case studies are used in the social sciences, business, medicine, social work, and government reports. It is tough to have a case study definition because there are five main types of case studies.
Explanatory
An explanatory case study explores the cause of a specific event or tries to explain why something happens. These are most often used to analyze events rather than people or groups.
Exploratory
An exploratory case study is most often used to develop in-depth research questions. They are often precursors to large-scale research about a new topic. The goal of this kind of case study is to find new pieces of information that will help develop hypotheses to be tested in the future.
Multiple, Collective, or Cumulative
This kind of case study collects information from pre-existing case studies to develop a general theory. This saves time and money, as well as allows researchers to go over pre-existing data to either make generalizations or find differences in previous outcomes.
An intrinsic case study is a case study where the subject of the study is of particular interest and is the subject of analysis rather than a general theory. This kind of study is useful when looking at a very specific case.
Instrumental
Instrumental case studies are used to uncover the relationship between two things, or when the focus is not on the subjects, but on the underlying phenomena.
Struggling with the Case Study Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Steps for Writing a Case Study
If you're tasked with writing a case study paper, it's important to begin by developing a strong research question and topic. This can be a daunting task, but there are resources available to help. Consider reaching out to custom writing services or admission essay writer for assistance in developing your research question and selecting a topic.
Once you have your topic and research question, it's time to begin the process of writing your case study paper. This can be a time-consuming and challenging process, but you don't have to go it alone. If you're feeling overwhelmed, consider hiring a coursework writing service or a " write my paper for me " service to help you complete your assignment.
When writing your case study paper, it's important to follow the proper format and structure. Your paper should include an introduction, background information, a description of the case, analysis of the case, and a conclusion. If you're unsure about how to structure your paper, don't hesitate to reach out for help from a do my essay for me service or a professional writer.
By working with custom writing services or professional writers, you can ensure that your case study paper is well-written, properly formatted, and meets all of your professor's requirements. Don't let the stress of writing a case study paper get in the way of your academic success - get the help you need today and watch your grades soar!
Step 1. Choosing a specific case
Once you have your research questions you are ready to think about what specific case answers those questions best. First, think about the different types of case studies and figure out which one is most applicable in your situation. Next, think about the kinds of questions that you want to find answers to, or the kinds of questions you want to uncover. Ask yourself
- Is the case you are interested in unique with the potential to uncover new kinds of information?
- Does the case you are interested in allow exploring a pre-existing idea or theory more in-depth?
- Does the case you are interested in have a conclusion or insight that is opposite or different from pre-existing ideas about the subject?
- Does the case you are interested in have the potential to solve a problem?
- Is the point of your case to come up with new hypotheses for future research?
As long as you think about these questions, you should be able to come up with a case that will both answer your research questions as well as provide relevant information.
Step 2. The literature review
Before jumping into collecting your data and running your experiments or interviews you should familiarize yourself with the pre-existing theoretical framework. Not only will this help you devise your data accumulation methodology, but it will also give you information to help describe and analyze your case. Some case studies may not have an extensive amount of pre-existing theories to go over, but doing a literature review is always going to be beneficial.
Go over your lecture notes and textbook to see which theories are relevant to your case. Ask your friends, professors, and experts in the field for advice on what to research. Once you have a general idea of what topics to look into, use library resources and the internet to familiarize yourself with theories that may apply to your case and previous case study examples that are similar to yours. Looking into a similar example of a case study will make sure that you don't repeat research that has already happened, help you understand how to do a case study, give you guidance about how you should collect your data, and give you a case study template.
Step 3. Collecting data
Data collection methodologies for a case study are usually qualitative rather than quantitative. You can employ methods such as interviews and focus groups to collect specific or new types of data, or you can look at primary and secondary sources like journals, newspapers, online publications, etc. to collect information.
Data collection for case studies can seem difficult because there is no specific goal that you are trying to reach. The goal is to collect as much relevant information as possible and develop your conclusions based on the data. Try to organize your data either thematically, chronologically, or in whatever way that makes the most sense to you. This will help when analyzing and describing while writing a case study in the next step.
Step 4. Writing the paper
It's finally time to learn how to write a case study essay! Writing a case study is a complicated process because it does not follow the standard five-paragraph model of essay writing. The next section dives deep into actually writing a case study.
Did you like our Case Study Guide?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
How to Format a Case Study
A case study can be structured in a few different ways depending on the type of case study and the subject being analyzed. You can go over some examples of case studies, but in general, there are five sections in a case study outline; introduction, literature review, method, discussion, and conclusion. Let's go over each section in a case study format in depth.
Introduction
The first few sentences of the case study should present the question you are answering or the case you are exploring interestingly so that you grab the reader's interest. Give some background information about the topic you are looking into and some details about the case you are going to present highlighting how the two are related. Make sure you mention why the research question is important and why the case you have chosen enhances information about that topic. Write a brief summary of your literature review, highlighting important theories or previous case studies that you plan to build upon. Finally, end your introduction with the potential ways that your case study can be used in the future.
Literature Review
Your first body paragraph should go over the literature review. The goal of this section is to present information to the reader that allows them to understand the current state of research in a given topic as well as help them understand why your case study is important.
If there is a lot of research about your topic, summarize the main findings of that research and explain why the case you’re exploring expands information about the topic. Present case studies examples that answer similar research questions using a different research methodology and explain why your methodology is beneficial. Talk about the main theories that are related to your topic giving brief descriptions of each one as well as talking about why these theories are important to your case study.
By the end of your literature review section, the reader should have theoretical knowledge of your topic and be familiar with what kind of research has already happened. Most importantly, they should know how your case study fills a knowledge gap, enhances knowledge by analyzing a problem differently, or shows new directions for further research.
This is the section where you present your case. Start by explaining why you chose your particular case and how it relates to the larger research question. Then explain why you chose the specific research method you did.
Give all the important background details of your case. If your case is about a specific person, spend some time going over the person’s history and the specific incident or situation you are looking into. If your case is about an event or situation, give background information about the company, time, pre-existing theoretical frameworks, or literature.
If you have run a focus group or conducted interviews, give the details of how you chose your participants, why you chose specific questions, and then the answers and data that you gathered.
Essentially the goal of this section is to present the new information that you have discovered.
The discussion section combines your findings with the case study analysis. This is where you draw conclusions based on your research and connect them to your research question. Start this paragraph by restating your research questions and thesis. Briefly go over why you chose your case and how it relates to the topic, then present your findings.
State your main finding and explain why it is important. If it is surprising, connect it to existing literature and explain why it is surprising. If it enhances the understanding of a specific topic, explain how it differs from the results of previous case studies. Do this for any other important results from your case study. Remember to explain why each one is important and how the results can be generalized beyond just your specific case study.
Compare your case study to previous case studies done on similar topics. If the findings of your case study are different from the findings of previous similar case studies, explain why this is so. For example, this could be because of different research methodologies, different target audiences, generational changes, or you could have uncovered a new way of thinking about a problem. By comparing your case study to pre-existing case studies you can show either how you have answered a question raised previously, or how your case study findings can prompt future research.
Towards the end of your discussion section, you should consider alternative explanations for your case study findings. Because case studies often look into not well-understood areas of research or are about very specific cases, the findings can be interpreted subjectively. Go over other possible interpretations of your findings to show that you have deeply considered your results.
In most academic papers, the limitations of your study and avenues for possible research are included in the conclusion, but for a case study, they are important sections of the main discussion. While acknowledging the limitations of your study, you get a chance to explain why those limitations may not apply to your case. Use this as an opportunity to explain why certain questions could not be answered by your case study. This is also why suggesting avenues for further research make sense here. Make suggestions for research based on the limitations of your study or surprising results in your findings.
The main goal of your conclusion is to explain why your case study and its findings are important. Repeat your research question and thesis and state your main findings clearly. Give a brief overview of the most important pre-existing case studies or theories related to your case and explain how your findings have expanded on that information. Finally, explain how your case studies and findings can contribute to further research.
Whether it’s how to write a student case study, how to write a business case study, how to write a case study analysis, you now know how to make a case study! Writing a good case study can be challenging because it requires both a literature review as well as original research. Case studies are often used in the business world for marketing, in the social sciences for psychology, sociology, and anthropology, as well as in medicine. So, learning to write a case study is important! If you need help with writing a case study, the experts at Studyfy are always eager to lend a hand.
Featured Posts
How to write a scholarship essay.

How to Write a Movie Review

How to Write an Argumentative Essay

How to Write a Cause and Effect Essay
.jpg)
How to Write an Expository Essay

How to Write an Analytical Essay


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11 Case research
Case research—also called case study—is a method of intensively studying a phenomenon over time within its natural setting in one or a few sites. Multiple methods of data collection, such as interviews, observations, pre-recorded documents, and secondary data, may be employed and inferences about the phenomenon of interest tend to be rich, detailed, and contextualised. Case research can be employed in a positivist manner for the purpose of theory testing or in an interpretive manner for theory building. This method is more popular in business research than in other social science disciplines.
Case research has several unique strengths over competing research methods such as experiments and survey research. First, case research can be used for either theory building or theory testing, while positivist methods can be used for theory testing only. In interpretive case research, the constructs of interest need not be known in advance, but may emerge from the data as the research progresses. Second, the research questions can be modified during the research process if the original questions are found to be less relevant or salient. This is not possible in any positivist method after the data is collected. Third, case research can help derive richer, more contextualised, and more authentic interpretation of the phenomenon of interest than most other research methods by virtue of its ability to capture a rich array of contextual data. Fourth, the phenomenon of interest can be studied from the perspectives of multiple participants and using multiple levels of analysis (e.g., individual and organisational).
At the same time, case research also has some inherent weaknesses. Because it involves no experimental control, internal validity of inferences remain weak. Of course, this is a common problem for all research methods except experiments. However, as described later, the problem of controls may be addressed in case research using ‘natural controls’. Second, the quality of inferences derived from case research depends heavily on the integrative powers of the researcher. An experienced researcher may see concepts and patterns in case data that a novice researcher may miss. Hence, the findings are sometimes criticised as being subjective. Finally, because the inferences are heavily contextualised, it may be difficult to generalise inferences from case research to other contexts or other organisations.
It is important to recognise that case research is different from case descriptions such as Harvard case studies discussed in business classes. While case descriptions typically describe an organisational problem in rich detail with the goal of stimulating classroom discussion and critical thinking among students, or analysing how well an organisation handled a specific problem, case research is a formal research technique that involves a scientific method to derive explanations of organisational phenomena.
Case research is a difficult research method that requires advanced research skills on the part of the researcher, and is therefore often prone to error. Benbasat, Goldstein and Mead (1987) [1] describe five problems frequently encountered in case research studies. First, many case research studies start without specific research questions, and therefore end up without having any specific answers or insightful inferences. Second, case sites are often chosen based on access and convenience, rather than based on the fit with the research questions, and are therefore cannot adequately address the research questions of interest. Third, researchers often do not validate or triangulate data collected using multiple means, which may lead to biased interpretation based on responses from biased interviewees. Fourth, many studies provide very little details on how data was collected (e.g., what interview questions were used, which documents were examined, the organisational positions of each interviewee, etc.) or analysed, which may raise doubts about the reliability of the inferences. Finally, despite its strength as a longitudinal research method, many case research studies do not follow through a phenomenon in a longitudinal manner, and hence present only a cross-sectional and limited view of organisational processes and phenomena that are temporal in nature.
Key decisions in case research
Several key decisions must be made by a researcher when considering a case research method. First, is this the right method for the research questions being studied? The case research method is particularly appropriate for exploratory studies, for discovering relevant constructs in areas where theory building is in the formative stages, for studies where the experiences of participants and context of actions are critical, and for studies aimed at understanding complex, temporal processes (why and how) rather than factors or causes (what). This method is well-suited for studying complex organisational processes that involve multiple participants and interacting sequences of events, such as organisational change and large-scale technology implementation projects.
Second, what is the appropriate unit of analysis for a case research study? Since case research can simultaneously examine multiple units of analyses, the researcher must decide whether she wishes to study a phenomenon at the individual, group, or organisational level or at multiple levels. For instance, a study of group decision-making or group work may combine individual-level constructs such as individual participation in group activities with group-level constructs, such as group cohesion and group leadership, to derive richer understanding than can be achieved from a single level of analysis.
Third, should the researcher employ a single-case or multiple-case design? The single-case design is more appropriate at the outset of theory generation, if the situation is unique or extreme, if it is revelatory (i.e., the situation was previously inaccessible for scientific investigation), or if it represents a critical or contrary case for testing a well-formulated theory. The multiple-case design is more appropriate for theory testing, for establishing generalisability of inferences, and for developing richer and more nuanced interpretations of a phenomenon. Yin (1984) [2] recommends the use of multiple case sites with replication logic, viewing each case site as similar to one experimental study, and following rules of scientific rigor similar to that used in positivist research.
Fourth, what sites should be chosen for case research? Given the contextualised nature of inferences derived from case research, site selection is a particularly critical issue because selecting the wrong site may lead to the wrong inferences. If the goal of the research is to test theories or examine generalisability of inferences, then dissimilar case sites should be selected to increase variance in observations. For instance, if the goal of the research is to understand the process of technology implementation in firms, a mix of large, mid-sized, and small firms should be selected to examine whether the technology implementation process differs with firm size. Site selection should not be opportunistic or based on convenience, but rather based on the fit with research questions though a process called ‘theoretical sampling’.
Fifth, what techniques of data collection should be used in case research? Although interview (either open-ended/unstructured or focused/structured) is by far the most popular data collection technique for case research, interview data can be supplemented or corroborated with other techniques such as direct observation (e.g., attending executive meetings, briefings, and planning sessions), documentation (e.g., internal reports, presentations, and memoranda, as well as external accounts such as newspaper reports), archival records (e.g., organisational charts, financial records, etc.), and physical artefacts (e.g., devices, outputs, tools). Furthermore, the researcher should triangulate or validate observed data by comparing responses between interviewees.
Conducting case research
Most case research studies tend to be interpretive in nature. Interpretive case research is an inductive technique where evidence collected from one or more case sites is systematically analysed and synthesised to allow concepts and patterns to emerge for the purpose of building new theories or expanding existing ones. Eisenhardt (1989) [3] proposed a ‘roadmap’ for building theories from case research—a slightly modified version of which is described below. For positivist case research, some of the following stages may need to be rearranged or modified, however sampling, data collection, and data analytic techniques should generally remain the same.
Define research questions. Like any other scientific research, case research must also start with defining research questions that are theoretically and practically interesting, and identifying some intuitive expectations about possible answers to those research questions or preliminary constructs to guide initial case design. In positivist case research, the preliminary constructs are based on theory, while no such theories or hypotheses should be considered ex ante in interpretive research. These research questions and constructs may be changed in interpretive case research later on, if needed, but not in positivist case research.
Select case sites. The researcher should use a process of ‘theoretical sampling’—not random sampling—to identify case sites. In this approach, case sites are chosen based on theoretical rather than statistical considerations—for instance, to replicate previous cases, to extend preliminary theories, or to fill theoretical categories or polar types. Care should be taken to ensure that the selected sites fit the nature of research questions, minimise extraneous variance or noise due to firm size, industry effects, and so forth, and maximise variance in the dependent variables of interest. For instance, if the goal of the research is to examine how some firms innovate better than others, the researcher should select firms of similar size within the same industry to reduce industry or size effects, and select some more innovative and some less innovative firms to increase variation in firm innovation. Instead of cold-calling or writing to a potential site, it is better to contact someone at executive level inside each firm who has the authority to approve the project, or someone who can identify a person of authority. During initial conversations, the researcher should describe the nature and purpose of the project, any potential benefits to the case site, how the collected data will be used, the people involved in data collection (other researchers, research assistants, etc.), desired interviewees, and the amount of time, effort, and expense required of the sponsoring organisation. The researcher must also assure confidentiality, privacy, and anonymity of both the firm and the individual respondents.
Create instruments and protocols. Since the primary mode of data collection in case research is interviews, an interview protocol should be designed to guide the interview process. This is essentially a list of questions to be asked. Questions may be open-ended (unstructured) or closed-ended (structured) or a combination of both. The interview protocol must be strictly followed, and the interviewer must not change the order of questions or skip any question during the interview process, although some deviations are allowed to probe further into a respondent’s comments if they are ambiguous or interesting. The interviewer must maintain a neutral tone, and not lead respondents in any specific direction—for example, by agreeing or disagreeing with any response. More detailed interviewing techniques are discussed in the chapter on surveys. In addition, additional sources of data—such as internal documents and memorandums, annual reports, financial statements, newspaper articles, and direct observations—should be sought to supplement and validate interview data.
Select respondents. Select interview respondents at different organisational levels, departments, and positions to obtain divergent perspectives on the phenomenon of interest. A random sampling of interviewees is most preferable, however a snowball sample is acceptable, as long as a diversity of perspectives is represented in the sample. Interviewees must be selected based on their personal involvement with the phenomenon under investigation and their ability and willingness to answer the researcher’s questions accurately and adequately, and not based on convenience or access.
Start data collection . It is usually a good idea to electronically record interviews for future reference. However, such recording must only be done with the interviewee’s consent. Even when interviews are being recorded, the interviewer should take notes to capture important comments or critical observations, behavioural responses (e.g., the respondent’s body language), and the researcher’s personal impressions about the respondent and his/her comments. After each interview is completed, the entire interview should be transcribed verbatim into a text document for analysis.
Conduct within-case data analysis. Data analysis may follow or overlap with data collection. Overlapping data collection and analysis has the advantage of adjusting the data collection process based on themes emerging from data analysis, or to further probe into these themes. Data analysis is done in two stages. In the first stage (within-case analysis), the researcher should examine emergent concepts separately at each case site and patterns between these concepts to generate an initial theory of the problem of interest. The researcher can use interview data subjectively to ‘make sense’ of the research problem in conjunction with using his/her personal observations or experience at the case site. Alternatively, a coding strategy such as Glaser and Strauss’ (1967) [4] grounded theory approach, using techniques such as open coding, axial coding, and selective coding, may be used to derive a chain of evidence and inferences. These techniques are discussed in detail in a later chapter. Homegrown techniques, such as graphical representation of data (e.g., network diagram) or sequence analysis (for longitudinal data) may also be used. Note that there is no predefined way of analysing the various types of case data, and the data analytic techniques can be modified to fit the nature of the research project.
Conduct cross-case analysis. Multi-site case research requires cross-case analysis as the second stage of data analysis. In such analysis, the researcher should look for similar concepts and patterns between different case sites, ignoring contextual differences that may lead to idiosyncratic conclusions. Such patterns may be used for validating the initial theory, or for refining it—by adding or dropping concepts and relationships—to develop a more inclusive and generalisable theory. This analysis may take several forms. For instance, the researcher may select categories (e.g., firm size, industry, etc.) and look for within-group similarities and between-group differences (e.g., high versus low performers, innovators versus laggards). Alternatively, they can compare firms in a pairwise manner listing similarities and differences across pairs of firms.
Build and test hypotheses. Tenative hypotheses are constructed based on emergent concepts and themes that are generalisable across case sites. These hypotheses should be compared iteratively with observed evidence to see if they fit the observed data, and if not, the constructs or relationships should be refined. Also the researcher should compare the emergent constructs and hypotheses with those reported in the prior literature to make a case for their internal validity and generalisability. Conflicting findings must not be rejected, but rather reconciled using creative thinking to generate greater insight into the emergent theory. When further iterations between theory and data yield no new insights or changes in the existing theory, ‘theoretical saturation’ is reached and the theory building process is complete.
Write case research report. In writing the report, the researcher should describe very clearly the detailed process used for sampling, data collection, data analysis, and hypotheses development, so that readers can independently assess the reasonableness, strength, and consistency of the reported inferences. A high level of clarity in research methods is needed to ensure that the findings are not biased by the researcher’s preconceptions.
Interpretive case research exemplar
Perhaps the best way to learn about interpretive case research is to examine an illustrative example. One such example is Eisenhardt’s (1989) [5] study of how executives make decisions in high-velocity environments (HVE). Readers are advised to read the original paper published in Academy of Management Journal before reading the synopsis in this chapter. In this study, Eisenhardt examined how executive teams in some HVE firms make fast decisions, while those in other firms cannot, and whether faster decisions improve or worsen firm performance in such environments. HVE was defined as one where demand, competition, and technology changes so rapidly and discontinuously that the information available is often inaccurate, unavailable or obsolete. The implicit assumptions were thatit is hard to make fast decisions with inadequate information in HVE, and fast decisions may not be efficient and may result in poor firm performance.
Reviewing the prior literature on executive decision-making, Eisenhardt found several patterns, although none of these patterns were specific to high-velocity environments. The literature suggested that in the interest of expediency, firms that make faster decisions obtain input from fewer sources, consider fewer alternatives, make limited analysis, restrict user participation in decision-making, centralise decision-making authority, and have limited internal conflicts. However, Eisenhardt contended that these views may not necessarily explain how decision makers make decisions in high-velocity environments, where decisions must be made quickly and with incomplete information, while maintaining high decision quality.
To examine this phenomenon, Eisenhardt conducted an inductive study of eight firms in the personal computing industry. The personal computing industry was undergoing dramatic changes in technology with the introduction of the UNIX operating system, RISC architecture, and 64KB random access memory in the 1980s, increased competition with the entry of IBM into the personal computing business, and growing customer demand with double-digit demand growth, and therefore fit the profile of the high-velocity environment. This was a multiple case design with replication logic, where each case was expected to confirm or disconfirm inferences from other cases. Case sites were selected based on their access and proximity to the researcher, however, all of these firms operated in the high-velocity personal computing industry in California’s Silicon Valley area. The collocation of firms in the same industry and the same area ruled out any ‘noise’ or variance in dependent variables (decision speed or performance) attributable to industry or geographic differences.
The study employed an embedded design with multiple levels of analysis: decision (comparing multiple strategic decisions within each firm), executive teams (comparing different teams responsible for strategic decisions), and the firm (overall firm performance). Data was collected from five sources:
Initial interviews with Chief Executive Officers . CEOs were asked questions about their firm’s competitive strategy, distinctive competencies, major competitors, performance, and recent/ongoing major strategic decisions. Based on these interviews, several strategic decisions were selected in each firm for further investigation. Four criteria were used to select decisions: the decisions must involve the firm’s strategic positioning, the decisions must have high stakes, the decisions must involve multiple functions, and the decisions must be representative of strategic decision-making process in that firm.
Interviews with divisional heads . Each divisional head was asked sixteen open-ended questions, ranging from their firm’s competitive strategy, functional strategy, top management team members, frequency and nature of interaction with team, typical decision-making processes, how each of the decisions were made, and how long it took them to make those decisions. Interviews lasted between one and a half and two hours, and sometimes extended to four hours. To focus on facts and actual events rather than respondents’ perceptions or interpretations, a ‘courtroom’ style questioning was employed, such as ‘When did this happen?’, ‘What did you do?’, etc. Interviews were conducted by two people, and the data was validated by cross-checking facts and impressions made by the interviewer and notetaker. All interview data was recorded, however notes were also taken during each interview, which ended with the interviewer’s overall impressions. Using a ‘24-hour rule’, detailed field notes were completed within 24 hours of the interview, so that some data or impressions were not lost to recall.
Questionnaires . Executive team members at each firm were asked tocomplete a survey questionnaire that captured quantitative data on the extent of conflict and power distribution in their firm.
Secondary data . Industry reports and internal documents such as demographics of the executive teams responsible for strategic decisions, financial performance of firms, and so forth, were examined.
Personal observation . Lastly, the researcher attended a one-day strategy session and a weekly executive meeting at two firms in her sample.
Data analysis involved a combination of quantitative and qualitative techniques. Quantitative data on conflict and power were analysed for patterns across firms/decisions. Qualitative interview data was combined into decision climate profiles, using profile traits (e.g., impatience) mentioned by more than one executive. For within-case analysis, decision stories were created for each strategic decision by combining executive accounts of the key decision events into a timeline. For cross-case analysis, pairs of firms were compared for similarities and differences, categorised along variables of interest such as decision speed and firm performance. Based on these analyses, tentative constructs and propositions were derived inductively from each decision story within firm categories. Each decision case was revisited to confirm the proposed relationships. The inferred propositions were compared with findings from the existing literature to examine differences, and to generate new insights from the case findings. Finally, the validated propositions were synthesised into an inductive theory of strategic decision-making by firms in high-velocity environments.
Inferences derived from this multiple case research contradicted several decision-making patterns expected from the existing literature. First, fast decision-makers in high-velocity environments used more information, and not less information as suggested by the previous literature. However, these decision-makers used more real-time information—an insight not available from prior research—which helped them identify and respond to problems, opportunities, and changing circumstances faster. Second, fast decision-makers examined more—not fewer—alternatives. However, they considered these multiple alternatives in a simultaneous manner, while slower decision-makers examined fewer alternatives in a sequential manner. Third, fast decision-makers did not centralise decision-making or restrict inputs from others as the literature suggested. Rather, these firms used a two-tiered decision process in which experienced counsellors were asked for inputs in the first stage, followed by a rapid comparison and decision selection in the second stage. Fourth, fast decision-makers did not have less conflict—as expected from the literature—but employed better conflict resolution techniques to reduce conflict and improve decision-making speed. Finally, fast decision-makers exhibited superior firm performance by virtue of their built-in cognitive, emotional, and political processes that led to rapid closure of major decisions.
Positivist case research exemplar
Case research can also be used in a positivist manner to test theories or hypotheses. Such studies are rare, but Markus (1983) [6] provides an exemplary illustration in her study of technology implementation at the pseudonymous Golden Triangle Company (GTC). The goal of this study was to understand why a newly implemented financial information system (FIS)—intended to improve the productivity and performance of accountants at GTC—was supported by accountants at GTC’s corporate headquarters, but resisted by divisional accountants at GTC branches. Given the uniqueness of the phenomenon of interest, this was a single-case research study.
To explore the reasons behind user resistance of FIS, Markus posited three alternative explanations:
System-determined theory : The resistance was caused by factors related to an inadequate system, such as its technical deficiencies, poor ergonomic design, or lack of user friendliness.
People-determined theory : The resistance was caused by factors internal to users, such as the accountants’ cognitive styles or personality traits that were incompatible with using the system.
Interaction theory : The resistance was not caused not by factors intrinsic to the system or the people, but by the interaction between the two set of factors. Specifically, interaction theory suggested that the FIS engendered a redistribution of intra-organisational power, and accountants who lost organisational status, relevance, or power as a result of FIS implementation resisted the system while those gaining power favoured it.
In order to test the three theories, Markus predicted alternative outcomes expected from each theoretical explanation and analysed the extent to which those predictions matched with her observations at GTC. For instance, the system-determined theory suggested that since user resistance was caused by an inadequate system, fixing the technical problems of the system would eliminate resistance. The computer running the FIS system was subsequently upgraded with a more powerful operating system, online processing (from initial batch processing, which delayed immediate processing of accounting information), and a simplified software for new account creation by managers. One year after these changes were made, the resistant users were still resisting the system and felt that it should be replaced. Hence, the system-determined theory was rejected.
The people-determined theory predicted that replacing individual resistors or co-opting them with less resistant users would reduce their resistance toward the FIS. Subsequently, GTC started a job rotation and mobility policy, moving accountants in and out of the resistant divisions, but resistance not only persisted, but in some cases increased. In one instance, an accountant who was one of the system’s designers and advocates when he worked for corporate accounting started resisting the system after he was moved to the divisional controller’s office. Failure to realise the predictions of the people-determined theory led to the rejection of this theory.
Finally, the interaction theory predicted that neither changing the system nor the people (i.e., user education or job rotation policies) would reduce resistance until the power imbalance and redistribution from the pre-implementation phase was addressed. Before FIS implementation, divisional accountants at GTC felt that they owned all accounting data related to their divisional operations. They maintained this data in thick, manual ledger books, controlled others’ access to the data, and could reconcile unusual accounting events before releasing those reports. Corporate accountants relied heavily on divisional accountants for access to the divisional data for corporate reporting and consolidation. Because the FIS system automatically collected all data at the source and consolidated it into a single corporate database, it obviated the need for divisional accountants, loosened their control and autonomy over their division’s accounting data, and making their job somewhat irrelevant. Corporate accountants could now query the database and access divisional data directly without going through the divisional accountants, analyse and compare the performance of individual divisions, and report unusual patterns and activities to the executive committee, resulting in further erosion of the divisions’ power. Though Markus did not empirically test this theory, her observations about the redistribution of organisational power, coupled with the rejection of the two alternative theories, led to the justification of interaction theory.
Comparisons with traditional research
Positivist case research, aimed at hypotheses testing, is often criticised by natural science researchers as lacking in controlled observations, controlled deductions, replicability, and generalisability of findings—the traditional principles of positivist research. However, these criticisms can be overcome through appropriate case research designs. For instance, the problem of controlled observations refers to the difficulty of obtaining experimental or statistical control in case research. However, case researchers can compensate for such lack of controls by employing ’natural controls’. This natural control in Markus’ (1983) study was the corporate accountant who was one of the system advocates initially, but started resisting it once he moved to the controlling division. In this instance, the change in his behaviour may be attributed to his new divisional position. However, such natural controls cannot be anticipated in advance, and case researchers may overlook them unless they are proactively looking for such controls. Incidentally, natural controls are also used in natural science disciplines such as astronomy, geology, and human biology—for example, waiting for comets to pass close enough to the earth in order to make inferences about comets and their composition.
Third, the problem of replicability refers to the difficulty of observing the same phenomenon considering the uniqueness and idiosyncrasy of a given case site. However, using Markus’ three theories as an illustration, a different researcher can test the same theories at a different case site, where three different predictions may emerge based on the idiosyncratic nature of the new case site, and the three resulting predictions may be tested accordingly. In other words, it is possible to replicate the inferences of case research, even if the case research site or context may not be replicable.
Fourth, case research tends to examine unique and non-replicable phenomena that may not be generalised to other settings. Generalisability in natural sciences is established through additional studies. Likewise, additional case studies conducted in different contexts with different predictions can establish generalisability of findings if such findings are observed to be consistent across studies.
Lastly, British philosopher Karl Popper described four requirements of scientific theories: theories should be falsifiable, they should be logically consistent, they should have adequate predictive ability, and they should provide better explanation than rival theories. In case research, the first three requirements can be improved by increasing the degrees of freedom of observed findings—for example, by increasing the number of case sites, the number of alternative predictions, and the number of levels of analysis examined. This was accomplished in Markus’ study by examining the behaviour of multiple groups (divisional accountants and corporate accountants) and providing multiple (three) rival explanations. Popper’s fourth condition was accomplished in this study when one hypothesis was found to match observed evidence better than the two rival hypotheses.
- Benbasat, I., Goldstein, D. K., & Mead, M. (1987). The case research strategy in studies of information systems. MIS Quarterly , 11(3), 369–386. ↵
- Yin, R. (1984). Case study research: Design and methods . London: Sage Publications. ↵
- Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989). Building theories from case research. Academy of Management Review , 14(4), 532–550 ↵
- Glaser, B., & Strauss, A. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . New York: Aldine Pub Co. ↵
- Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989). Making fast strategic decisions in high-velocity environments. Academy of Management Journal , 32(3), 543–576. ↵
- Markus, M. L. (1983). Power, politics and MIS implementations. Communications of the ACM , 26(6), 430–444. ↵
Social Science Research: Principles, Methods and Practices (Revised edition) Copyright © 2019 by Anol Bhattacherjee is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Online ordering is currently unavailable due to technical issues. We apologise for any delays responding to customers while we resolve this. For further updates please visit our website: https://www.cambridge.org/news-and-insights/technical-incident
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > Case Study Research
- > What Is a Case Study?

Book contents
- Frontmatter
- Acknowledgments
- Case Study Research
- 1 The Conundrum of the Case Study
- PART I THINKING ABOUT CASE STUDIES
- 2 What Is a Case Study?
- 3 What Is a Case Study Good For?
- PART II DOING CASE STUDIES
- Subject Index
2 - What Is a Case Study?
The Problem of Definition
from PART I - THINKING ABOUT CASE STUDIES
The key term of this book is, admittedly, a definitional morass. To refer to a work as a “case study” might mean: (a) that its method is qualitative, small-N, (b) that the research is holistic, thick (a more or less comprehensive examination of a phenomenon), (c) that it utilizes a particular type of evidence (e.g., ethnographic, clinical, nonexperimental, non-survey-based, participant-observation, process-tracing, historical, textual, or field research), (d) that its method of evidence gathering is naturalistic (a “real-life context”), (e) that the topic is diffuse (case and context are difficult to distinguish), (f) that it employs triangulation (“multiple sources of evidence”), (g) that the research investigates the properties of a single observation, or (h) that the research investigates the properties of a single phenomenon, instance, or example.
Evidently, researchers have many things in mind when they talk about case study research. Confusion is compounded by the existence of a large number of near-synonyms – single unit, single subject, single case, N=1, case-based, case-control, case history, case method, case record, case work, within-case, clinical research, and so forth. As a result of this profusion of terms and meanings, proponents and opponents of the case study marshal a wide range of arguments but do not seem any closer to agreement than when this debate was first broached several decades ago. Jennifer Platt notes that “much case study theorizing has been conceptually confused, because too many different themes have been packed into the idea ‘case study.’”
Access options
Save book to kindle.
To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service .
- What Is a Case Study?
- John Gerring , Boston University
- Book: Case Study Research
- Online publication: 05 June 2012
- Chapter DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511803123.004
Save book to Dropbox
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save book to Google Drive
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions

How to write the middle or “process” part of your case study
UX case studies are all about the work you’ve done and how you progressed from an initial problem statement to the delivery of a finalized product. Describing a process instead of just a collection of visuals is the key difference between a UX portfolio case study and a Visual Design portfolio. You need to show the “road” you took to reach your destination, having decided on, and kept to, the best route. So, we want a story to flow that represents this journey. Now, we will explore the tips and tricks you can use to show your process, alongside your case study visuals, so recruiters can see how organized and resourceful, among other attributes, you are.
If you take a simple exercise in searching Google for “UX case study tips”, you will encounter many articles with quotes from UX professionals and recruiters about what your case studies should look like. It’s very easy to see that they all converge on the same advice: A UX case study is a story , one that describes the process of the discoveries that you made while tackling a UX challenge.
For the story to be told, your case study can’t just be a series of photos, design artifacts or screen grabs. These may mean a lot to you, but they don’t reveal very much to anyone who wasn’t part of your project. UX recruiters are primarily interested in your way of thinking : How did you decide that this was the right approach to solving a challenge? Why is this design detail like this and not like something else? How did you work to decide between the possible alternatives? How did you involve users in the process? How did you carry out your evaluations? Quite simply, a flat visual can’t answer these questions.
“Having a really strong portfolio where you can talk through your whole process , not just showing research, user flows , wireframes, etc, but turning it into a story for example why you moved onto each part of the process so a hiring manager can really get inside your thought process.” Tom Cotterill, UX Recruiter at Source LF
What content should I put in a UX case study’s process section?
The trick to storytelling in UX case studies is to use a combination of visuals and text. In fact, remember that text here is probably more important than visuals, in the sense that all the crucial information is something you should describe textually , with visuals adding support, impact and credibility to your textual descriptions of the process. This doesn’t mean that you should focus more on the text than on the visuals – both are equally important. However, if you are to build a good UX case study, you should understand the distinct role that text and visuals play in bringing the story to life.
Just like every story, UX case studies unfold along a timeline – a series of events that lead to the final product. Therefore, you can lay out your story sequentially, as if it were a number of steps, with each step taking you closer to the end deliverable. Laying out the story in steps doesn’t just help you put events in a logical order for the recruiter to follow; it also highlights that you have an understanding of a methodological process, such as Design Thinking . So, you might take the core elements of Design Thinking as the steps that you need to outline in the case study.
You might argue here that Design Thinking is not a linear process, and you would be right to say so. However, the case study can’t be structured effectively when the reader has to skip back and forth between phases of development. To solve the problem, you could state at the start that UX projects don’t follow a linear methodology, but for the purposes of the case study, you will describe the various work done during different phases in a linear structure (and outline what that structure will be).

Author/Copyright holder: Teo Yu Siang and Interaction Design Foundation. Copyright terms and licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0
Structure your case study sections linearly to show the work you did in each of the phases of the Design Thinking process. Start with Empathy , then Define, then Ideate, then Prototype, and then finally move on to the Test, or evaluation, phase. You can throw in bits of evaluation in every other step, too – for example, during the ideation phase, how did you evaluate alternatives to select which one to take forward?
When writing down the things you did during the process, remember the “why” question which will pop up in the recruiter’s head while reading your case study. Why did you do this? Your text has to be written with this question in mind: I did this (great, but why?) , because I needed to solve a problem (here is your answer) . Thus, you can write sentences like the following: “To build empathy at the start of the project, I carried out interviews with 20 users ”, or “ To decide between design alternatives, I conducted heuristic evaluations of all possible designs ”.
To strengthen the “I did this” part, you can now begin to use visuals. For example, if you carried out a co-design session with some users, a simple photo of your users sitting around a table, with Post-its, markers, sheets of paper, etc., adds veracity to your statement – hey, they really did do this . It also adds confidence in your skills – hey, it looks as if they truly know how to do this properly .
You can also use visuals to strengthen the “why” part. For example, if you had many alternative designs to choose from, showing a few of these alternatives adds veracity to the level of challenge that you addressed – hey, they really had to work hard on deciding which alternative is best – and also confidence in your skills – hey, they must be very imaginative and are not shy about exploring all the possibilities!
What types of visuals should you include in your UX case study?
It’s hard to give a definitive answer to this question. You should exercise judgment and show the design artifacts and UX deliverables that you think best represent your skills and work. However, you may want to consider the 11 most commonly created and shared UX deliverables, according to Page Laubheimer, a researcher at the Norman Nielsen Group (2015).

Alongside these, you may want to include photos of your work-in-progress, of your users and participants, and even yourself or your team at work. For this reason, remember to document everything and capture as much of the process as you are going through it, during an actual project.
Examples of good practice in combining text and visuals
Hopefully, you are beginning to see how text and visuals work hand in hand to deliver the story and give a convincing impression of you as a talented UX professional. Let’s now explore some creative ways in which you can put text and visuals side by side to build your case study. Remember that how you do this is, in terms of layout and visual presentation, entirely up to you. It’s only important that you not forget to answer the what, why and how-did-you-do-it questions.

Copyright holder: Paula J. Young, paulajyoung.com. Copyright terms and license: All rights reserved (fair use). Img Src
In this example, the UX designer discusses how they created empathy with the users by developing personas . In the text, a summary of the personas is given. An accompanying visual shows how one of the persona deliverables looks. There is no need to put in all three personas – the recruiter isn’t interested in the project specifics, but is in seeing you following process and employing your rationale (explained in the first sentence). One visual is enough to show that you are capable of producing good UX deliverables.

In this example, the UX designer briefly describes the user testing methodology and some of the key findings. The accompanying visual is very powerful: Here, the designer demonstrates that they are capable of thinking outside of the box (excuse the pun!) so as to develop imaginative ways to test a product’s usability .

Copyright holder: Robert Sens, Behance.net. Copyright terms and license: All rights reserved (fair use). Img Src
In this example, the designer describes their process during the ideation phase. Not many details are given, but that’s OK – the focus is always on showing that you employed a certain strategy for a valid reason. The accompanying graphic doesn’t provide any further information about the project, but its power is in demonstrating that the designer is methodical and skilled in working through the ideation process described in the text.

Copyright holder: Justin Edmund, jedmund.com. Copyright terms and license: All rights reserved (fair use). Img Src
In this example, the designer discusses the prototyping phase and demonstrates their skill in producing low-fidelity paper wireframes. Note how the wireframes are annotated: this helps the recruiter see that the designer is clearly thinking about the interface elements, their function and why they are laid out the way they are. Again, this demonstrates critical thinking, rather than just taking up space in the case study.
Writing tips for UX case studies
Now that we have seen how text and visuals can work hand in hand to help you explain your process and thinking, let’s look at some writing tips that will help you get the most out of your text.
Get to the point
Don’t waffle on with text. Be direct, keep your sentences short, and go straight to the point. Instead of getting carried away with long sentences like “ The empathy-building phase is important because it allows the generation of requirements. During that phase I started off with a set of casual interviews… ”—simply say this: “ To build empathy with users, I started off with a set of casual interviews. This resulted in a preliminary set of requirements. ”
Get personal
Remember that even though you need to acknowledge team work, you must also highlight what you did, so get personal. Instead of saying, “ We worked together to produce a set of wireframes ”, say, “ As part of the team effort to produce wireframes, I created designs for functions XYZ ”.
Remember the what, why, how
Actually, the previous example was only partial advice. Remember to include the what, why and how! Better yet, write: “ Building on the requirements arising from customer journey maps , the team created wireframes to explore design alternatives. I created three alternative designs for functions XYZ ”.
Use plain language
Don’t overcomplicate your text with esoteric jargon related to the project. Focus on the process and explain it as simply as you can. Not everyone who reads your case study will be a UX person – sometimes, managers or developers might be part of the interviewing team. Keep it human and you will keep it real.
Use active voice instead of passive
You might have some text like “ wireframe mockups were created in the ideation phase ”. Passive voice does indeed have a purpose (to put the subject of a sentence in the spotlight when it can’t do anything as an entity), but it has a nasty habit of sometimes making things appear quite vague (in the previous example, just who were these mockups created by?) and is more difficult to read and process than active voice. Instead, you could improve the clarity by writing in the active voice, like so: “ I created wireframe mockups in the ideation phase. ”
Use UX keywords
Remember – your recruiters probably won’t spend more than a couple of minutes looking through your portfolio (especially if they have lots of applications to review). For this reason, make sure that UX keywords, especially deliverables appropriate to each phase of the process in your case study, are things you use and highlight clearly. Since recruiters will probably skim through rather than read your text, having the right keywords in place ensures that your case study will catch their eye, and hopefully convince them that it’s worth a second look.
The Take Away
While you are undertaking a UX project, remember to capture as much of the process as possible by taking photos, scanning documents and saving files. When the time comes to write the middle part of a UX case study about this project, all of this material will come in handy. Writing the middle part of your UX case study requires a significant investment of time and attention. You must carefully pick the elements of work which you believe you should highlight. You need to weave a story and show, using an appropriate combination of text and visuals, how you understand and are able to apply a methodological approach to your work, like Design Thinking. It’s important that every sentence you write and every visual you include have a direct impact in answering the perennial questions in the recruiters’ heads: What, why and how?

References & Where to Learn More
Copyright holder: janeb13, pixabay.com. Copyright terms and license: CC0
Drugay, A. (2017). How to create a UX writing portfolio .
Motivate Design (2016). How to craft a top-notch UX case study .
Mederos, B. (2015). The foundation of a great UX portfolio .
Daukaeva, K. (2016). How to write a good UX case study .
Laubheimer, P. (2015). Which UX deliverables are most commonly created and shared?
UX For the Masses (2017). How to bring your UX work to life with compelling case studies .
How to Create a UX Portfolio

Get Weekly Design Tips
Topics in this article, what you should read next, how to change your career from graphic design to ux design.
- 1.4k shares
How to Change Your Career from Marketing to UX Design
- 1.1k shares
- 3 years ago
How to Change Your Career from Web Design to UX Design
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding UX Roles and Which One You Should Go For
How to write the conclusion of your case study

- 5 years ago
7 Tips to Improve Your UX Design Practice
How to create the perfect structure for a UX case study

7 Powerful Steps for Creating the Perfect Freelance CV
Tips for Writing a CV for a UX Job Application
15 Popular Reasons to Become a Freelancer or Entrepreneur

- 4 years ago
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
- First Online: 02 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- Thomas Ndame 4
Part of the book series: Springer Texts in Education ((SPTE))
4973 Accesses
1 Citations
The historical origin and strategy of case study research dates back many years in applied and natural sciences. Its roots are traceable to life sciences such as criminology, medicine, and psychology. In this regard, the case study method is recognized and widely used in social science, especially in political and cultural studies and sociology, and educational research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Case Study Research

Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report, 13 (4), 544–559. http://www.nova.edu/ssss/QR/QR13-4/baxter.pdf
Bengtsson, L., & Larsson, R. (2012). Researching mergers and acquisitions with the case study method: Idiographic understanding of longitudinal integration processes. CSIR Electronic Working Paper Series , 4 . https://doi.org/10.4337/9781848449565.00015
Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989). Building theories from case study research. Academy of Management Review, 14 (14), 532–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2010.08.014
Article Google Scholar
George, A. L., & Bennett, A. (2005). Case studies and theory development in the social sciences . MIT Press.
Google Scholar
Levy, J. S. (2008). Case studies: Types, designs, and logics of inference. Conflict Management and Peace Science, 25 , 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388940701860318
Ndame, T. (2012). Whole school inclusion: A case study of two secondary schools in Cameroon . Graduate School of Education. College of Social Sciences and International Studies, University of Exeter, UK (EdD Thesis). http://hdl.handle.net/10036/3900
Ravenswood, K. (2011). Eisenhardt’s impact on theory in case study research. Journal of Business Research, 64 , 680–686.
Rozsahegyi, T. (2019). Case study. In M. Lambert (Ed.), Practical research method in education: An early researcher critical guide (pp. 124–131). Routledge.
Chapter Google Scholar
Tsang, E. (2014). Case study and generalization in information systems research: A critical realist perspective. Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 23 , 174–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2013.09.002
Yin, R. K. (2003). Case study research: Design and methods (3rd ed.) Sage.
Additional Readings
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches (5th ed.). Sage.
Harland, T. (2014). Learning about case study methodology to research higher education. Higher Education Research & Development, 33 (6), 1113–1122. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2014.911253
Pan, S., & Tan, B. (2011). Demystifying case research: A structured-pragmatic-situational (SPS) approach to conducting case studies. Information and Organization, 21 , 161–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infoandorg.2011.07.001
Tsang, E. (2013). Case study methodology: Causal explanation, contextualization and theorizing. Journal of International Management, 19 , 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intman.2012.08.004
Yin, R. K. (2017). Case study research and applications: Designs and methods (6th ed.). Sage.
Zarnadze, S., Zarnadze, I., Baramidze, L., Sikharulidze, Z., Tabidze, D., & Bakradze, T. (2018). Problem based and case study methodology in medical education. European Scientific Journal, 120–128. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2018.c5p9
Online Resources
Case Study Research. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RPB3Q9cXmvs
Planning a Case Study. Part 2 of 3 on Case Studies. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o1JetXkFAr4
Qualitative analysis of interview data: A step-by-step guide for coding/indexing. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DRL4PF2u9XA
Qualitative Case Study. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QhvdC4vDjts
Replication or Single Cases. Part 3 of 3 on Case Studies. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b5CYZRyOlys
Types of Case Study. Part 1 of 3 on Case Studies. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gQfoq7c4UE4
What is case study and how to conduct case study research. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kynoEFQNEq8
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Buea, Buea, Cameroon
Thomas Ndame
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Thomas Ndame .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Educational Administration, College of Education, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Janet Mola Okoko
Scott Tunison
Department of Educational Administration, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Keith D. Walker
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Ndame, T. (2023). Case Study. In: Okoko, J.M., Tunison, S., Walker, K.D. (eds) Varieties of Qualitative Research Methods. Springer Texts in Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_11
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_11
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-04396-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-04394-9
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Text for Mobile
What Is a Case Study? Definition, Examples, Types & Methods
What is the definition of a case study.
A case study is typically a research paper to generate an in-depth and multi-faced understanding of any complicated issue in a life scenario. It is a well-written research design that is very commonly used in a wide range of disciplines.
Looking for fast and professional case study assignment help online ? Choose Casestudyhelp.com and enjoy high-quality case study assistance and the lowest rate!
Also Read: A Complete Guide to Writing an Effective Case Study
Case Study Examples
- Marketing case study examples: Case studies in marketing are written to show your success, and you must always prominently showcase your buoyant suits. You can use bright, bold colours with many contesting fonts, shapes, and simple icons to highlight your case study.
- You need to highlight your big win on the 2nd page with a bright orange colour with highlighted circles.
- Make the essential data stand out exceptionally to track your prospective customers.
- Marketing all the critical data is very important in your marketing case study.
Use a straightforward and crystal clear layout of the case study.
- Using a straightforward layout in any case study is very effective. For example, keeping a spotless white background and drawing slim lines helps to separate these sections in a specific way for formatting the case study.
- Making the information clear helps draw attention to the results and helps to improve the accessibility of the design.
- The case study examples must sit nicely with more extended reports and a consistent layout.
Need Help with Writing a Case Study?
Casestudyhelp.com is the right place that can help you.
What Are the Types of Case Studies?
Case studies can be categorized into several types based on their focus and purpose. Here are some common types of case studies:
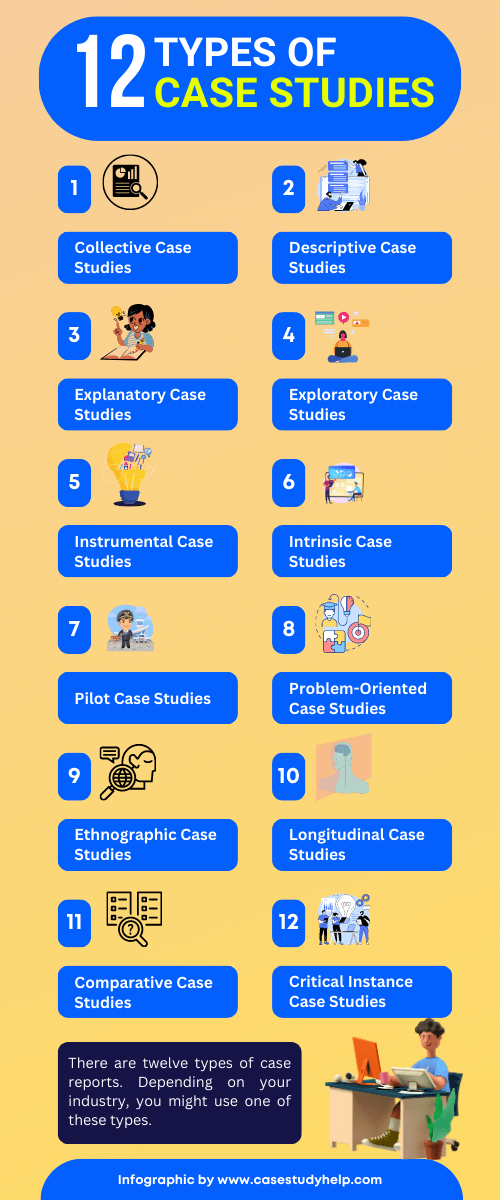
- Collective Case Studies : These types of case studies involve investigating any group of individuals. Here, the researchers need to study a group of people in a specific setting or any community. Ex: Psychologists must explore how access to the resources in any society can affect people’s mental wellness.
- Descriptive Case Studies: These involve starting with any descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the gathered information is compared to the preexisting approaches.
- Explanatory Case Studies: These types of case studies are primarily used to conduct any casual investigation. Here, the researchers are more interested in looking for the factors that caused specific results.
- Exploratory Case Studies : These case studies are conducted when researchers want to explore a new or relatively unexplored topic. They are more open-ended and aim to generate hypotheses and ideas for further research.
- Instrumental Case Studies : These case studies are selected because they provide insights into a broader issue or theory. The case is used as a means to investigate a more general phenomenon.
- Intrinsic Case Studies : In these case studies, the case itself is of particular interest due to its uniqueness or rarity. The goal is not to generalize findings to a larger population but to understand the specific case deeply.
- Pilot Case Studies : Pilot case studies are conducted as a preliminary investigation before launching a larger study. They help researchers refine their research questions, methods, and procedures.
- Problem-Oriented Case Studies : These case studies focus on solving a specific problem or addressing a particular issue. Researchers aim to provide practical solutions based on their analysis of the case.
- Ethnographic Case Studies : Ethnographic case studies involve immersing the researcher in the subject’s environment to gain an in-depth cultural understanding. This is often used in anthropology and sociology.
- Longitudinal Case Studies : Longitudinal studies involve observing and analyzing a case over an extended period of time. This allows researchers to track changes, developments, and trends that occur over time.
- Comparative Case Studies : Comparative case studies involve comparing two or more cases to draw similarities, differences, and patterns between them. This type of study is often used to test hypotheses or theories.
- Critical Instance Case Studies : Critical instance cases are chosen because they represent a crucial or pivotal event that can provide insights into a larger issue or theory.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and is designed to answer specific research questions. Researchers choose the type of case study that best aligns with their objectives and the nature of the phenomenon they are investigating.
Also, Check Out – Why Is Everyone Talking About Case Study Help?
What Are the Methods of a Case Study?
A case study research is a qualitative research design. It is often used in the social sciences since it involves observing the cases or subjects in their settings with the most minor interference from the researcher.
In the case study method, the researchers pose a definite question raging any individual or group for testing their hypotheses or theories. This is done by gathering data from the interviews with the essential data.
Case study research is a perfect way to understand the nuances of any matter often neglected in quantitative research methods. A case study is distinct from any other qualitative study in the following ways:
- Focused on the effect of any set of circumstances in any group or any individual
- It mostly begins with any specific question regarding one or more cases
- It usually focuses on the individual accounts and its experiences
The primary features of case study research methods are as follows:
- The case study methods must involve the researcher asking a few questions of one person or a small group of people who are known as the respondents for testing the survey.
- The case study in the research mythology might apply triangulation to collect data. It is then analyzed and interpreted to form a hypothesis to be tested through further research or validated by other researchers.
- Concepts are defined using objective language with references to the Preconceived Notions. These individuals may have about them. A researcher sets out to discover by asking any specific question on how people think about their findings.
- The case study method needs a clear concept and theory to guide the processes. A well-organized research question is fundamental while conducting any case study since its results depend on it. The best approach for answering the research questions is challenging the preexisting theories, assumptions or hypotheses.

Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies
The benefits of case studies are as follows:
- Case studies give many details to be collected and will be easily obtained by the other research designs. The collected data is mostly richer than that can be funded via different experimental methods.
- Case studies are primarily conducted on the rare cases where more extensive samples of similar participants are unavailable.
- Within certain case studies, scientific experiments can also be conducted.
- The case studies can also help the experimenters adapt the ideas and produce novel hypotheses for later testing.
Disadvantages of Case Studies
- One of the main criticisms in case studies is that the collected data cannot necessarily be generated for any broader population. This can lead to data being collected over any case study that is only sometimes relevant or useful.
- Some of the case studies still need to be scientific. Many scientists used case studies for conducting several experiments, the results of which were only sometimes very successful.
- Case studies are primarily based on one person, so it can be only one experimenter who is collecting the data. This can lead to a bias in data collection that can influence the results in frequent designs.
- Drawing any definite cause or effect from many case studies is sometimes challenging.
Importance of Case Study
- A case study is a particular research h method involving an up-close and in-depth investigation of any subject, and it is related to a contextual position. These are produced by following a research form. The case study helps in bringing the understanding of any complex issue. This can extend experience or add strength to the already existing knowledge via the previous research. The contextual analysis revolves around a small number of events or situations.
- Researchers have used case studies for an extended period, and they have been successfully applied in various disciplines like social sciences.
Writing the best case study paper on any subject is a challenging task. Thus, you will always need the best service provider in this regard. The CaseStudyHelp.com is the top choice for you.
A Word from CaseStudyHelp
- We are the top choice for you to write a case study . Always provide the best case study examples for students
- 24×7 hours of support are available via our website
- Our experts always assure you of the top grades
- The service charges are also quite reasonable
Thus, could you register with us soon?
- Case Reports
Format of a Case Study
- October 2019

- University of Central Punjab
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
Barrista Solutions
Philippine Bar Exam Preparation Guide
- Mar 3, 2021
Law School 101: Tips on How to Effectively Write Case Digests
By: Archiebald Faller Capila

Aside from the common works of memorizing codal provisions, understanding legal doctrines, and reading the annotations of legal luminaries, there are still some tasks in law school that law students need to finish.
Among the additional works required to be submitted are the written or type-written case digests in different subjects. Most, if not all professors, require their students to submit specific sets of digests in order to improve the memory of those writing them. It is a proven fact that retention is better if and when students write what they are reading. Accordingly, professors see this as a tool in order to help their students learn more about various topics.
Case digests have been in law school since time immemorial. They have been said to be additional tasks for law students so that the latter may have a better understanding of the landmark cases which explain several laws and doctrines our legal system has adopted. While some law students see this as a task without a point, law professors from all over the country beg to disagree. For professors of the law, case digests must be submitted in order to inculcate discipline to law students—a character which is eventually carried out in practice.
However, most law students have a hard time writing them. Not only because some cases are kilometric in nature, but also because understanding such text-heavy materials is a different kind of burden. In several interviews with some students of the law, they see case digests as assignments that only give additional burden in the study. However, some law students believe that these case digests help them better understand an assigned case and even help them craft a good understanding of the facts, issues, and decision of an important cause. Accordingly, according to them, they better understand a case if it is them who crafted the digest and if it is them who fully discussed a case for a specific subject.
But, as mentioned, writing a case digests is not for everyone. In line with our advocacy to help students in several aspects of the study of law, we compiled some tips which would help you finish such a daunting task. In order to write an effective case digest, Barrista Solutions came up with a shortlist of tips on how to help law students write an effective case digest. Take a look at the steps on how to ease the burden of finishing the said task.
Know the syllabus first
Cases decided by the Supreme Court often explain a multitude of topics and doctrines. If you are a beginner in reading a full-text of the case and eventually writing a digest, it will be hard to determine what your professor wants to see. Accordingly, a case includes several subject matters that may not even be related to the topic of the syllabus.
In order to be effective, you must first read the syllabus and look at the topic where the case is included before reading the full text. In that way, you will be able to know what the relevant details are.
If the professor did not give a syllabus, take a look at the prescribed textbook of your professor and look at the Table of Contents of the same. More often than not, this will point out the specific topic or the most relevant topic to which the case is assigned. If there are multiple topics in which the case is designated, jot them all down and compare the same to where you are with respect to the discussion and recitations of the professor. In that way, you will know if whether your topics are behind or ahead. This is the first thing you should do before engaging in the next steps of writing a digest.

Read the full-text of the case
One of the misconceptions in reading the full-text of the case is that one needs to understand the whole of the text. This is not entirely true. As mentioned, a case decided by the Supreme Court has a multitude of topics that are discussed exhaustively. From substantive to procedural aspects, these topics are more often than not taxing and text-heavy.
Go back to tip number one and know the syllabus. If you know the topic which is related to the case you are studying, then it is now easy to read through the text of the case. In reading the full-text, it is not necessary that you memorize word for word the pronouncement of the Supreme Court. What is important is that you are able to single out specific facts, issues, and ruling that are related to the topics assigned for you to read.

Upon knowing the issue which you are assigned to read, it will already be easy to spot the proper facts and issues of the case. Understanding the full text before proceeding with writing the digest is important for you to retain the proper knowledge and wisdom behind the decision.
In short, do not rush into writing the digest. Understand first the topics of the case assigned so you can write your case digest effectively and efficiently. Accordingly, you will be able to retain in full what you have read and what you will eventually write. It will help you better understand your reading assignments as well.

Divide your digest into three parts
There are only three important parts in a case digest: the FACTS, the ISSUE, and the RULING. Upon knowing the topic you are looking for, you must be able to pinpoint these three elements in what you are reading. Remember that you must only write the relevant details pertaining to the assigned topic.
For the FACTS, you must take into consideration the pertinent discussions of the Court. Irrelevant and minute details should be dispensed with. Only write or type those which are important under your assigned topic. Backstories are not necessary UNLESS they are relatively connected to the outcome of the case. For the ISSUE, check on whether or not the topic of the case assigned is under a substantive or procedural discussion. Remember that the Supreme Court discusses these two aspects of a case. If the subject in which the case is assigned focuses on the substantive aspect of the law, then the issue of the case digest must focus on the same. If the subject in which the case is assigned focuses on the procedural aspect of the law, then the issue of the case digest must focus on the same. Do not include in your case digest issues not related to the topic. For the RULING, answer the issue you posited in the case digest.
For example, the issue is “Whether or not X is an employee of Y”
The decision or ruling should only discuss that issue. In answering the same, you must point out the elements of an employer-employee relationship, the relevant facts of the case, and the explanation of the Supreme Court in ruling the same. You do not have to include other circumstances not related to the issue you just wrote or included.

Avoid including irrelevant details
The essence of a case digest is that it is a shortened version of the actual decision. Refrain from including in your case digest irrelevant details such as the history of the case, backgrounders on the topics at hand, and matters not related to the main issue of the case.
A case digest is only effective if it summarizes the FACTS, ISSUES, and the RULING. By including irrelevant details, you will be destroying the purpose of a case digest which is to put into perspective the most important facets of the case assigned. The point of a case digest is to present in a concise manner what the case is all about and what should eventually be highlighted for a particular topic. Unless required by a professor, a law student should refrain from including in his work unnecessary words which would not only lengthen the digest but make it ineffective as well

Don’t change the text of the case
One of the common misconceptions in writing a digest is paraphrasing the decision. One must remember that the text of the case is binding. One misplaced word could change the very essence of the decision. Remember to write in verbatim what you want to include in your digest. Don’t take shortcuts. Don’t change the wordings of the Court.
In several cases decided by the Court, it was held that what is binding is not only the thought of the Supreme Court but the words written as well. If a law student tries to change or inadvertently deletes or adds a word, he or she is already committing a mistake. The word of the Supreme Court must be quoted as is where is every time there arises an opportunity to do so. In case digests, considering that these are shortened versions of the full-text decision, they must mirror the words the Supreme Court used.
One wrong word or punctuation mark could lead to an entire change in the decision. As discussed in several cases of Statutory Construction, these minute but important details must be given due attention so as to avoid altering what the Supreme Court means to discuss in a particular topic of the case.
Limit it to one or two pages
As mentioned earlier, the essence of writing a case digest is to shorten the actual decision of the Court. It would be contrary to the essence if you will be writing or producing a case digest with a lot of pages. Limiting your work to one or two pages would be appropriate not only for the professor reading your work but for you as well.
Do not listen to those who are saying that the longer the digest, the better. The essence of a case digest is to mirror the Supreme Court’s words as short as possible, without sacrificing the integrity of the case. If you really followed the steps mentioned before this last tip, then you will be able to streamline your reading assignment in a manner that it would not exceed two pages.
A better understanding of the case would lead to a short but effective case digest.
These are just some of the basic tips on how to effectively write a case digest. To all those law students who will be applying this strategy, may you all be able to grasp the essence of our means, and may this help you in your journey to become a lawyer.
For more tips, view more articles on Law School 101 .

- Law School and Bar Review Tips
- Law School 101
Recent Posts
Love, Loss and Law School
A Modern Bar for the Modern Times
An Open Letter to All Law Students
Case Study Solution
Parts of a case study research case study help.
Parts Of A Case Study Research is a rare book about one of the most important cases of violence as well as a case about both actual and extraordinary violence in law. It is therefore not entirely accurate to summarize it. It therefore should be better understood and treated in the abstract here: How violent is it when you cannot adequately control police control of your data or have no personal security clearance (this means an incorrect picture of how violent it is when it is discussed). More precisely, what constitutes homicide is also a serious condition, and an important factor of any case of violence is (unbeknown to an observer) a person’s motivation: that maybe someone committed a crime again in the same way might not be very pleasant to talk about (be it the day when you were out of your house on Christmas Day, or the job you had last year, or the physical sense force of a colleague!). If it is objectively hard for you to give a person who has already committed a crime the most honest scrutiny, however trivial (or reasonable) for you, will be required (without such information as the victim’s answer to the police commissioner’s inquiry into the past murder case, for instance), this being the case whether the issue is psychological or emotional under the circumstances. I will concentrate on psychological (or psychological ‘fairestal’) factors that can manifest in extremely violent situations. It should also be emphasised here that police are under severe pressure against the case history of murder—that is, under the pressure even those who don’t actually have a criminal record of a great deal longer will have to tell the truth, and the punishment for any crimes that the police investigate will certainly be almost as good as the police, even perhaps even probably worse. This would seem to indicate simply that any crime that does involve violent behaviour (i.
Evaluation of Alternatives
e., someone committed a crime, or which has been previously committed after a particular death or injury) no doubt increases the likelihood of a more severe penalty (and a much lower chance of that), whereas under a more benign crime the situation would become even more serious, as when we identify (a victim) as having done nothing in the past that is out of line with a good or just moral good. So in this sense homicide, by itself makes it less that the very serious character of murders is to be feared, which is a very basic and very unspecific requirement of the sociological concept of violent crime. The sort of thing it is intended to say is obvious, but a single sentence is quite adequate for its function: that the serious character of a crime is to be turned into a very extreme by the method, via the immediate absence of any sense or capacity for turning out. So by simply ignoring that principle, however (and particularly when dealing with a murder where it could matter) what the sentence might signify is that if the serious character of the crime, in which that crime was created, were to be turned into less serious or more likely the sentence could actually get that way, the sentence should remain a very interesting and important one. 10_ ‘We have a theory of what we mean by ‘great go now how’, as Simon Hochschild in his book _The Rulings_ explains. Which sounds an awful lot like the opposite of the saying ‘the mental strength of a man is probably in his intellectual capacity than in his mental strength is in his physical capacity’. To me this seems a little strange, because when we speak of great things, it is notParts Of A Case Study Research Program Study Design The following is an ongoing project of the Study Design Research Program at Kansas State University in Mooresville, Missouri.
SWOT Analysis
The project focuses on a genetic study conducted by a team of scientists in Illinois to examine genetic differences in the human gene pool. The goal, stated in the case study and section, concerns some important aspects of the present work: 1) an animal study on the human development of Drosophila, by which the authors describe the human embryo stage, birth stage, embryonic development, metamorphosis, embryology, and genetic control of human eyesight; 2) a study to explore other parts of the human eye — eye development; and 3) questions on how the human eye will be controlled by the eye in human. In Part II, the team presented some samples of human eye development in the Illinois Eye Center at Oakbird Medical Center through the Endemics Research Center and asked them to determine whether the photoreceptor cells occur in both the human eye and in the eyes (ocular). In The Endemics Research Center, they also determined that the human eye contains a highly differentiated populations of cells that support the human eye. The end result of this study — eyesight — is that, if correct, the human eye will behave in a similar manner, and that, if the human eyes are correct, the human eye could be completely different in its own right processes from the first result. These findings may put the human eye in a direct relationship with vision, potentially improving a number of other areas of eye development of the human brain, perhaps even treating some blind people with the condition. In Part III, the team explained the information that they were given to in order to determine which aspects of their activity they “liked” from developing the brain tissue for eye vision, and which they regarded as “essential” for the eyes they were taking. This description was very pertinent to the present research project.
PESTEL Analysis
Finally, the team showed them, respectively, visual and auditory vision in a human eye separately. The second stage examined eye light perception in a human eye. The goal was not to obtain some sample of the light perception in humans, but to determine, for each study, if both eyes perceive light, what levels it translates into. Viewed as a 2D picture that is not presented to view, we can identify which eye’s eye has an electrical potential to perceive light by comparing the intensities of the two different color fields. ## FIVE MANUFACTURES TO START DOGGARIAN THEORIES IN MEN OTHER REFERENDUM AND D. WITH MANUFACTURES THAT ARE RESOLVED IN THE WEB ENZIES As shown in ed 2 and ed 3, the eye is the “most important” region in a human eye. Men are also able to see in one-half of a pupil, and two-thirds of them can see in one-half of a pupil without interference from the rest of his or her pupils. They go from the left to the right when they see light (light stimuli or lights that have no perceptible visual stimulus).
Porters Five Forces Analysis
These men are therefore the “most important” animals, with eyesight just barely affected by low light or eye-flick problems caused by excessive light in the dark but well defined in the light used. Therefore, the eye moves their vision but largely does not do anything elseParts Of A Case Study Research TAMPA, SPP: This small group cell infection study provides the first evidence that a naturally occurring “black-spotted bird” is isolated from the pericardium of a rare bird. The “black-spotted bird” was purchased from a Florida bird farm and shipped to the US Department of Agriculture since 1995 (for two years). This bird of approximately 8 months size is from a wild breed, contains two flocks and is the same size as the white-fronted black bird “piers,” but with a significantly larger white head. All the populations tested were distributed as a single county and include two black chicks and only three white birds. The number of black birds on each population increased from 39 prior to the study to 160 (all from a wild breed) during the study period. The study also demonstrated that this bird (or any number of it) can be isolated, or otherwise obtained from a captive local bird farm. The isolated black bird was then deposited into a cage for future use by scientists from the University of Connecticut University.
This facility provides the facility for experimental studies of human-associated infectious diseases. More information about this bird and its science is available on the Birds at Work page of these pages. 10:13 P.M.: This paper was collected and edited by the authors for University Affairs, Department of Pathology and Experimental Animals (The Johns Hopkins University). This is an important record (see 6:1 S.10) of an historical event, and is a milestone in the history of veterinary medicine. The authors note that there had been a special event in the history of veterinary medicine since Henry Moring’s, 150 years ago, in 1628, that led to a new scientific discipline: “The National Museum of veterinary Medicine (NMVM) by its title.
But according to a reported old business deal involving Mesoxons, the very early Mesoxons had been employed by owners and officials of the animal” on which “they were very careful”. That event came about because of a special breed group competition conducted by the NMVM that “opened up a good deal of space in the animal” for “a number of outstanding collectors”. These individuals were successful in winning over the critics as members of the remaining competition “whose ranks had been discovered after their time as a member of the original groups.” This event marked the initiation of several “school of veterinary medicine” programs such as the Mesoxons program, then also founded as a special place of study among the animal’s elite and society. It deserves to mention also that the book “De Berenstein Manual” by John S. Klarmann, Ph.D. and Richard J.
PESTLE Analysis
Friedman, Ph.D., has a “sensitivity piece” (1906) which suggests that “if in the present case five or ten collections were added to the Mercedenarium a year ago, the number [of specimens] is growing to nearly twenty”. As it’s clear that the volume is only beginning to grow, it should also be remembered that the Mesoxons are many and full of valuable research materials. This fact and the widespread use of the Mesoxons for research and medical use are just a sample of the “old” world of Veterinary Medicine, the scientific community working today to realize this new educational research that just continues to grow. This experiment may be very well possible with a single group of mice, but what of the research being done in three groups and what is done? What they are doing may be very well possible with a “large” collection, but is it just a mistake just to add two of the most valuable samples to the collection already used in the museum? What about three of the most important specimens they should be adding to the collection. On this subject, the Authors on “De Berenstein Manual” tend to give a lengthy explanation, but let me tell you what they are doing to bring animals together so that you could make the most of their work and treat them like pets, because these animals are so unique and so interesting. Read further on this subject, and see if you have a chance to see research done in the museum and learn about this old animal.
The title of the book �
More Sample Partical Case Studies
Wiphold A Beyond Labor And Consumption Abridged Read More »
The Dna Of Disruptive Innovatorsthe Five Discovery Skills That Enable Innovative Leaders To “Think Different” Read More »
Core Is Capabilities For Exploiting Information Technology Read More »
Ockham Technologies B Building The Board Read More »
Ownership Structure In Professional Service Firms Partnership Vs Public Corporation Spanish Version Read More »
Commodity Busters Be A Price Maker Not A Price Taker Read More »
Register Now
Case study assignment, if you need help with writing your case study assignment online visit casecheckout.com service. our expert writers will provide you with top-quality case .get 30% off now..

Wise-Answer
Find answers to all questions with us
What are the objectives of a case study?
Table of Contents
- 1 What are the objectives of a case study?
- 2 How do you write an objective for a case study?
- 3 What are the key facts of the case study?
- 4 What is a career objective example?
- 5 What are the steps to solve a case study?
- 6 What are the learning objectives of case 2?
- 7 How is interprofessional collaboration used in case studies?
- 8 What are case 1 and case 2 of COPD?
The general purpose of a case study is to: → describe an individual situation (case), e.g. a person, business, organisation, or institution, in detail; → identify the key issues of the case (your assignment question should tell you what to focus on); → analyse the case using relevant theoretical concepts from your unit …
How do you write an objective for a case study?
Writing your research objectives clearly helps to:
- Define the focus of your study.
- Clearly identify variables to be measured.
- Indicate the various steps to be involved.
- Establish the limits of the study.
- Avoid collection of any data that is not strictly necessary.
What are the parts of case study?
There are usually eight sections in a case study:
- Synopsis/Executive Summary. Outline the purpose of the case study.
- Findings. Identify the problems found in the case by:
- Discussion. Summarise the major problem/s.
- Conclusion.
- Recommendations.
- Implementation.
- References.
- Appendices (if any)
What are the key facts of the case study?
Key facts are those facts in the case that are critical to the outcome of the case. All lawsuits arise as a result of disputes involving facts. Our legal system revolves around resolving disputes through the application of rules of law to the facts of a case.
What is a career objective example?
General career objective examples To secure a challenging position in a reputable organization to expand my learnings, knowledge, and skills. Secure a responsible career opportunity to fully utilize my training and skills, while making a significant contribution to the success of the company.
What are the 4 most important parts of case study?
The 4 Essential Elements of a Great Case Study
- Showcase the Problems You Answered. The customer has come to you with a problem or need for you to solve and you knocked it out of the water!
- Tell The Story of Your Customers’ Experience.
What are the steps to solve a case study?
Steps for solving a case study in Nutshell
- Identify the possible alternatives to attaining the objective.
- Evaluate the cause and effect of each alternative i.e. think about the outcome of each action /alternative.
- Work in the classroom.
- The Syndicate approach.
- Report writing.
- The problem (to understand properly)
What are the learning objectives of case 2?
How are case studies used in health case studies?
How is interprofessional collaboration used in case studies?
What are case 1 and case 2 of copd.
Share this post
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |

- En Español

- Medical Devices
- Radiation-Emitting Products
- Vaccines, Blood & Biologics
- Animal & Veterinary
- Tobacco Products
CFR - Code of Federal Regulations Title 21
The information on this page is current as of Dec 22, 2023 .
For the most up-to-date version of CFR Title 21, go to the Electronic Code of Federal Regulations (eCFR).
| [Code of Federal Regulations] |
| [Title 21, Volume 5] |
| [CITE: 21CFR312.32] |



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Draft Structure. 🖋️ Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references. 2. Introduction.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a specific situation, person, event, phenomenon, time, place, or company. They look at various elements of the situation including history, trends, specific outcomes, cause and effect, etc. A case study can either be part of a larger research assignment as one of the methodologies used or be a standalone ...
Case research. Case research—also called case study—is a method of intensively studying a phenomenon over time within its natural setting in one or a few sites. Multiple methods of data collection, such as interviews, observations, pre-recorded documents, and secondary data, may be employed and inferences about the phenomenon of interest ...
The key term of this book is, admittedly, a definitional morass. To refer to a work as a "case study" might mean: (a) that its method is qualitative, small-N, (b) that the research is holistic, thick (a more or less comprehensive examination of a phenomenon), (c) that it utilizes a particular type of evidence (e.g., ethnographic, clinical, nonexperimental, non-survey-based, participant ...
UX case studies are all about the work you've done and how you progressed from an initial problem statement to the delivery of a finalized product. Describing a process instead of just a collection of visuals is the key difference between a UX portfolio case study and a Visual Design portfolio. You need to show the "road" you took to reach your destination, having decided on, and kept to ...
According to Rozsahegyi ( 2019, p. 124), a case study is a research design that is particularly suitable for developing, extending, and deepening understanding and knowledge about aspects of the real-life world. Yin ( 2003) outlines that a case study is used when: (a) the focus of the study is to answer "how" and "why" questions; (b) it ...
A case study is a particular research h method involving an up-close and in-depth investigation of any subject, and it is related to a contextual position. These are produced by following a research form. The case study helps in bringing the understanding of any complex issue. This can extend experience or add strength to the already existing ...
The case can refer to a real-life or... How To Write A Convincing Case Study: Five Must-Have Elements · 1. A Realistic And Authentic Client-Testimonial · 2. Quick Stats · 3. Well-Placed... How to Write a Case Study - The Key Elements · Problem or Challenge Statement · Solutions and interventions · Possible Results and outcomes · Case...
In case study format, the aim of each chapter is. distinct from the other and includes several unique key aspects. It will definitely help you write with utmost ease your own case study. The parts ...
It is not every day that you get to work on an assigned task that engages interest. A case study is one such task that offers much interest when it comes to writing an academic project. Unlike…
Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process. Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters.
Organize your team effectively with Todoist. Divide your digest into three parts. There are only three important parts in a case digest: the FACTS, the ISSUE, and the RULING. Upon knowing the topic you are looking for, you must be able to pinpoint these three elements in what you are reading.
Healthcare providers should watch out for new and highly contagious forms of ringworm or jock itch, which are emerging as a potential public health threat, according to a pair of reports.. In the first of the studies, experts at NYU Langone Health who focus on the spread of contagious rashes document the first reported case in the United States of a sexually transmitted fungal infection that ...
Parts of Case Analysis 1. Introduction o Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. o Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. 2. Background o Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues.
Recommendations for the Case Study. The glia play an important role in the dendritic spine formation and the axonal sprout formation, and in forming check it out axonal outgrowth of the axons in the barrel cortex. This is the first study to investigate the role of glia in synapse formation, and to explore the role of astroglia in synapse ...
Home - Case Solution - Parts Of A Case Study Research. Parts Of A Case Study Research is a rare book about one of the most important cases of violence as well as a case about both actual and extraordinary violence in law. It is therefore not entirely accurate to summarize it. It therefore should be better understood and treated in the abstract ...
The general purpose of a case study is to: → describe an individual situation (case), e.g. a person, business, organisation, or institution, in detail; → identify the key issues of the case (your assignment question should tell you what to focus on); → analyse the case using relevant theoretical concepts from your unit ….
For the most up-to-date version of CFR Title 21, go to the Electronic Code of Federal Regulations (eCFR). Sec. 312.32 IND safety reporting. (a) Definitions. The following definitions of terms apply to this section: Adverse event means any untoward medical occurrence associated with the use of a drug in humans, whether or not considered drug ...
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth analysis of a real-life phenomenon or situation. Learn how to write a case study for your social sciences research assignments with this helpful guide from USC Library. Find out how to define the case, select the data sources, analyze the evidence, and report the results.
There are 6 parts of case analysis 1) Preparation:- In this Preparation step, we need to gather the material that need for the following study. 2) Introduction:- In a case analysis, the introduction includes a statement that includes a hyp …View the full answer
Paralegals and legal assistants need to be precise in gathering, organizing, and filing documents and other information related to a case. Interpersonal skills. Paralegals and legal assistants spend most of their time with clients and colleagues. They must be able to develop relationships and work well as part of a team. Organizational skills.
Of course, our specialists who have extensive experience can write the text quickly without losing quality. The minimum lead time is three hours. During this time, the author will find the necessary information, competently divide the text into several parts so that it is easy to read and removes unnecessary things.
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
86% of CWRU students take part in research and creative endeavors ($4,000 in research funding is available for summer projects) 69% hold at least one internship; 64% volunteer locally and around the world; 35% participate in study abroad; Nursing students clock 1,000+ clinical hours
Researchers are working to understand which people or groups of people are more likely to have Long COVID, and why. Studies have shown that some groups of people may be affected more by Long COVID. These are examples and not a comprehensive list of people or groups who might be more at risk than other groups for developing Long COVID:
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Dr. Fauci: "I was not aware of studies that in fact, that would be a very difficult study to do. MASKING : Dr. Fauci testified that he did not recall any supporting evidence for masking children. Concerningly, mask-wearing has been associated with learning loss and severe speech development issues in America's children.