

Problem-solving in Leadership: How to Master the 5 Key Skills
The role of problem-solving in enhancing team morale, the right approach to problem-solving in leadership, developing problem-solving skills in leadership, leadership problem-solving examples.
Other Related Blogs
What’s the Role of Problem-solving in Leadership?
- Getting to the root of the issue: First, Sarah starts by looking at the numbers for the past few months. She identifies the products for which sales are falling. She then attempts to correlate it with the seasonal nature of consumption or if there is any other cause hiding behind the numbers.
- Identifying the sources of the problem: In the next step, Sarah attempts to understand why sales are falling. Is it the entry of a new competitor in the next neighborhood, or have consumption preferences changed over time? She asks some of her present and past customers for feedback to get more ideas.
- Putting facts on the table: Next up, Sarah talks to her sales team to understand their issues. They could be lacking training or facing heavy workloads, impacting their productivity. Together, they come up with a few ideas to improve sales.
- Selection and application: Finally, Sarah and her team pick up a few ideas to work on after analyzing their costs and benefits. They ensure adequate resources, and Sarah provides support by guiding them wherever needed during the planning and execution stage.
- Identifying the root cause of the problem.
- Brainstorming possible solutions.
- Evaluating those solutions to select the best one.
- Implementing it.

- Analytical thinking: Analytical thinking skills refer to a leader’s abilities that help them analyze, study, and understand complex problems. It allows them to dive deeper into the issues impacting their teams and ensures that they can identify the causes accurately.
- Critical Thinking: Critical thinking skills ensure leaders can think beyond the obvious. They enable leaders to question assumptions, break free from biases, and analyze situations and facts for accuracy.
- Creativity: Problems are often not solved straightaway. Leaders need to think out of the box and traverse unconventional routes. Creativity lies at the center of this idea of thinking outside the box and creating pathways where none are apparent.
- Decision-making: Cool, you have three ways to go. But where to head? That’s where decision-making comes into play – fine-tuning analysis and making the choices after weighing the pros and cons well.
- Effective Communication: Last but not at the end lies effective communication that brings together multiple stakeholders to solve a problem. It is an essential skill to collaborate with all the parties in any issue. Leaders need communication skills to share their ideas and gain support for them.
How do Leaders Solve Problems?
Business turnaround, crisis management, team building.
Process improvement
Ace performance reviews with strong feedback skills..
Master the art of constructive feedback by reviewing your skills with a free assessment now.
Why is problem solving important?
What is problem-solving skills in management, how do you develop problem-solving skills.

Top 15 Tips for Effective Conflict Mediation at Work
Top 10 games for negotiation skills to make you a better leader, manager effectiveness: a complete guide for managers in 2023, 5 proven ways managers can build collaboration in a team.

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
How to write a memo: 8 steps with examples

Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test

Jump to section
What’s a memorandum?
How to write a business memo in 8 steps, when to write a memo, 5 examples of memos, unleashing the power of effective memos.
Whether you’re planning a meeting or working on a project with dozens of moving parts, effective communication is the key to success.
But it’s hard to keep everyone in the loop all the time. You can’t always host a 1:1 meeting or talk to coworkers face-to-face when new information arises. Sometimes, all you need is a short notification that alerts everyone at the same time — and does so quickly.
Memos provide a streamlined channel for internal communication. In a short space, you can share vital information with clarity and impact. Here’s the step-by-step process of how to write a memo with specific examples, from crafting a compelling header to including action plans and timelines.
A memorandum, also known as a memo, is a concise written message that quickly and efficiently shares vital information. This could come in the form of an email, Slack announcement, or a piece of paper on a bulletin board, depending on the workplace.
A well-structured memo offers lots of information in a short space. It does everything from announcing changes in company policy to providing vital project updates, all without wasting readers’ time. Anyone can write an email, but memo-writing is a learned skill that takes time to truly perfect.

To create a succinct and comprehensive memo, formatting is key. Just like a professional email , every piece of information plays a role in making the memo easily digestible and actionable — from subject line to salutation .
Here’s a step-by-step approach to ensure your messages are both effective and clear:
1. Start with a header
To set the stage, always start with a comprehensive header. The header should include the date and the general subject, along with who the memo is to and from. These elements offer context and ensure that readers quickly grasp the basic premise, aiding quick decision-making about the action they need to take.
2. Craft a clear objective statement
The first paragraph of your memo should directly express its purpose in an objective statement or problem statement . This not only helps the recipients understand the memo's relevance, but also ensures they grasp its intent swiftly.
Think of a cover letter . The first line is usually something like “I am writing to…” A memo should have the same clarity so readers immediately know what they’re looking at and why.

3. Provide a comprehensive body paragraph
The body of the memo is where you'll develop your main points, so it should be as comprehensive as possible despite the short space. Always start with critical details as early as possible, then move towards less significant but still pertinent information.
To enhance readability, structure the body using bullet points or numbered lists. And remember to stay away from unnecessary jargon that may confuse your readers. A memo’s goal is brevity, so make sure it’s easy to understand.
4. Provide background information
If your memo references previous events, circumstances, or memos, include a brief background section. This provides context, orients your readers, and ties your current communication to past events or actions, offering a holistic understanding of the situation at hand.
5. Include action items and timelines
Memos often need to include a call to action that tells readers what to do next, whether that’s to acknowledge receipt or find a meeting room ASAP. Clearly define the steps they need to take, identify the parties responsible, and specify the deadlines for these tasks.
By doing so, you encourage accountability and create a shared understanding of expectations, fostering a more organized and efficient work environment .

6. Add a summary
If your memo tackles a complex issue or is particularly lengthy, add a short conclusion to summarize the most important points. In the absence of face-to-face cues, reiterating the main points through a brief summary reinforces the essential elements of your message, aiding comprehension.
7. Include your contact information
As hard as you may try, communication isn’t always clear. People might have questions about what to do next, and failing to provide a clear path toward those answers could add unnecessary hurdles.
To avoid this, always add your contact information at the end of your memo, whether that’s your desk location or your Slack handle. This lets your colleagues reach out if they have questions or need further clarification on any points.
8. Add attachments if necessary
If you reference other documents, graphs, or materials, either attach them or provide accessible links. This ensures that your readers have all the resources at their disposal to fully understand and act upon the memo. Linking out also keeps you from adding too much information to the memo itself.
According to Gallup’s 2022 State of the Global Workplace Report, 41% of employees wish they could change their company’s engagement or culture . And communication falls into that category. Meetings, emails, and effective memos all support the interactions that uplift strong culture .
Knowing when to write a memo helps you choose the right type of communication for the situation and avoid information silos . Here are some scenarios where memos shine:
Inform about company policies or changes: If your organization is undergoing changes in policies, procedures, or strategies, a memo is an excellent way to update staff. It ensures uniform understanding and gives everyone the chance to ask questions as soon as possible, saving time and stunting the spread of misinformation.
Raise awareness about an issue: If a significant issue is impacting your organization's functioning, a memo brings it to everyone's attention. In this situation, a memo is also vital for overall engagement and the employee experience because it keeps people in the loop on important issues and reinforces the value of their contributions.
Provide updates on a project: Memos are a great tool for informing stakeholders about a project's progress, timeline adjustments, or resource requirements. Informing everyone of all the project's deadlines and ongoing developments prevents roadblocks and helps projects run smoothly.
Make a request: A memo effectively communicates formal requests, including those for resources, approvals, or feedback . By clearly articulating the reasons and potential benefits of your request, a memo acts as a persuasive tool for support or approval. It can also anticipate and address possible questions.
Recognize employee achievement: Memos are also a method for acknowledging outstanding employee performance a nd achievements like a promotion . This has the multipurpose effect of expressing recognition for hard work while emphasizing company values , boosting morale , and fostering a positive work environment.

To help you better visualize how to write a good memo, here are five memo examples for different situations:
1. Change in policy memo
This example not only outlines changes in company policy, but also explains the reasons behind the change. It encourages questions and tells readers exactly where to go for more information, offering transparency and support.
To: [person or department name]
From: [person or department name]
Date: [insert date]
Subject: [subject] Policy Change
I'm writing to inform you of an important update regarding [policy]. Effective [date], we will be implementing changes to [specific details of the policy changes].
The purpose of this change is to [explain the rationale behind the change and its benefits]. We believe that these adjustments will contribute to [goal].
Please take the time to review the attached document outlining the updated policy in detail. Should you have any questions or concerns, feel free to reach out to [contact person or department].
Thank you for your attention to this matter.
Best regards,
2. Project update memo
An update memo keeps everyone informed about a project's progress, any changes to the original plan, or any challenges along the way. This ongoing communication helps preempt problems and ensures everyone is working towards the same goals.
Subject: [project name] Update
Here’s an update on the progress of [project name]. Here are the key developments since our last update:
- [a summary of tasks and milestones]
- [any challenges or issues and how they were resolved]
- [any adjustments to the project timeline or scope, if applicable]
Overall, we’re making steady progress and remain on track to meet our goals. Please stay vigilant and continue to give your best effort to ensure the successful completion of this project.
If you have any questions or need further clarification, please don't hesitate to reach out to me. Let's keep up the excellent work!
3. Issue alert memo
This type of memo raises awareness about a specific issue affecting the company, a department, or a specific project. Besides highlighting the problem, it may also suggest potential steps to address it, encouraging proactive problem-solving within the organization.
Subject: [subject] Issue
I'm writing to bring your attention to an issue with [subject]. It has come to our attention that [describe the issue and its impact on the company or employees].
We understand the potential challenges that this may pose and are actively working on resolving the situation. In the meantime, we encourage everyone to [provide any necessary instructions or precautions].
Rest assured that we’re taking this matter seriously, and we will keep you updated on any progress or further instructions. If you have any insights or suggestions related to this issue, please share them with [contact person or department].
Thank you for your understanding and cooperation.

4. Request memo
A request memo formalizes a need for resources, feedback, or approval. By clearly outlining the reasons behind the request, you effectively communicate the need for these items and the impact they could have on the team.
Subject: [specific request]
Hi [person or department name],
I hope this message finds you well. I'm writing to formally request [specific request]. This is because [provide a concise explanation of the request, including its importance and potential benefits for the company].
I’ve attached a detailed proposal outlining the specifics of the request, including [details, supporting data, and relevant information].
Should you have any questions or require further information, please don't hesitate to reach out to me. I appreciate your attention.
5. Employee recognition memo
According to data from Gallup, employees who don’t experience enough recognition are twice as likely to say they’ll quit in the next year .
A memo is a quick way to give kudos and celebrate an employee's achievement or contribution to the company. Not only does it express appreciation for hard work , but it also boosts morale and fosters a healthy environment for everyone.
Subject: Quick kudos
Let’s all take a moment to appreciate [employee name] from [department/team]’s exceptional performance and dedication. They have consistently demonstrated [specific achievements, qualities, or contributions].
Their hard work and commitment to excellence have been truly remarkable and deserving of recognition. [employee name]’s efforts reflect positively on the entire team and contribute to our overall success as a company.
Please join me in congratulating [employee name] for their outstanding achievement. We appreciate their continued dedication and professionalism. Let's celebrate this milestone and continue to inspire and support one another in our respective roles.
Warmest congratulations once again!
Mastering how to write a memo is an essential skill in the corporate world because it lets you convey a message with clarity and simplicity.
Whether you're drafting a project update or learning how to write a memo to your boss, you can become a better communicator and break down silos. Never underestimate the power of a well-structured and purposeful memo.

Elizabeth Perry
Content Marketing Manager, ACC
What is lateral thinking? 7 techniques to encourage creative ideas
How improving your concentration helps your memory, learn what process mapping is and how to create one (+ examples), curious wanting to learn more is key to career success, how to introduce yourself in an interview: examples & tips, how to prioritize tasks: 7 tips to perfect your workflow, how to make a daily schedule: tips and examples, learn how to be ambitious: 5 tips to focus on the goals that matter, squirrel how to increase attention span so you get stuff done, similar articles, how to write an exciting promotion announcement, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, write thank you letters after interviews to stand out as job applicant, 8 tips on how to write a professional email (with examples), write an intro email to a new team to start your job on the right foot, what’s a project scope, and how do you write one, how to write a linkedin summary that impresses recruiters, how to send a reminder email that’s professional and effective, how to write a follow-up email 2 weeks after an interview, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
How do I Write a Memo About Solving a Problem?
by Melvin Richardson
Published on 26 Sep 2017
Many organizations have problems, and to write a memo about solving a problem you should follow specific steps. . Before you can write a memo you need all the information pertaining to the problem as well as the individuals involved. Sometimes solving a problem is a matter of improving communication.
Determine or define the problem is. Your memo should start with a problem statement. This is a quick summary of what the problem is. Make sure you put this information in the simplest terms possible so everyone involved will understand the problem.
Find out possible causes of the problem. Your action plan can be geared towards eliminating the causes.
Write out who and what is affected by the problem. List all people and departments affected and explain how. For example, an inadequate computer system will affect the customer service department because it will not be able to take calls as quickly. This can reduce the profitability of a company because poor customer service can cause a loss of market share.
Make a list of the possible solutions to the problem. One solution could be a complete upgrade to the computer system. Another possible solution is to hire more customer service representatives to handle the excess of calls due to a poor system. Write down as many solutions to the problem as you can come up with.
Recommend the best possible solution. Explain why the method you chose is the best. Determine who will help implement it. Your recommendation should include the costs that will be incurred. Make sure the solution has a starting time and ending time. Outline the individuals or departments that will participate in the solution.
- 0 Shopping Cart $ 0.00 -->

Build your skills! Take our eLearning courses on TITAN!
World-class eLearning courses with videos, exercises, downloads, and a certificate of completion. Get started today!

Today’s post is by Suzanne Paling, author of The Sales Leader’s Problem Solver ( CLICK HERE to get your copy).
Articles on the subject of leadership run the gamut, from the four essential qualities to the 30+ characteristics. Internet searches on the word leader offer up myriad choices including: integrity, passion, patience, delegation, clarity, creativity and fearlessness – valid and important traits all.
To my surprise, one trait seldom gets mentioned – problem solving. Think about it. Acknowledging and effectively dealing with an issue (especially if it’s caused difficulties for a prolonged period of time) showcases leadership abilities.
In my new book The Sales Leader’s Problem Solver ; I take the reader through the process of solving 15 of the most common sales force conundrums. At the end of every chapter, I talk about how the act of solving a dilemma enhances the person’s leadership credentials.
While the problems featured in the book are sales specific, the process for solving a problem has applications for leaders in different departments throughout the company. I offer the following suggestions:
Gather Data
Take the time to speak with others in your organization about the issue. Once you have a better understanding of the issue, get away from anecdotal information. Seek out unbiased facts and figures.
Most of us tend to read and rely on a regular group of reports. Step out of your comfort zone. Ask people in different departments about their favorite reports. CFOs are often great sources of new information. Assemble data that backs up, shows the extent of; or reinforce people’s claims about the problem.
Forget company politics. Pretend no one could tell you “no.” Be bold. Think it through. How would you go about solving this problem? What changes would need to be made? Simply put, if you had the authority to do so, how would you take care of this difficulty?
Put it in Writing
Take all the information you’ve assembled and create an easy-to-read report. Use charts and graphs to showcase any relevant factual data. Make your case.
People often balk at this, citing past examples of suggesting changes or solutions and being turned down. Don’t let that deter you. Stand your ground. Creating a document shows commitment and courage.
Present it to Your Supervisor
While meeting, Skyping or speaking on the phone with your boss, calmly mention the report you’ve put together. Say something like, “I’ve been giving some thought to the ongoing dilemma with the lack of prospecting for new business on the part of some sales reps. I’ll be sending you a memo with some suggestions for dealing with the issue. When you’ve had a chance to look it over, I’d like to discuss it with you and hear your thoughts.”
That’s it. Unless you get asked questions, move on to the next item on the agenda. Most direct supervisors will curious about what you’ve written. Often, sales leaders express surprise at how quickly their boss reads the report and gets back to them.
Be Open to Compromise
Your direct supervisor sees problems from a different vantage point than yours. A level or two removed from those you manage, she might have a different perspective on the situation. Don’t get so attached to the information you put in the report that you can’t listen to her opinions. No doubt, she’ll have a good idea or two as well.
Agree on a Solution
Come together on a solution for the problem that both you and your boss can agree on. Discuss how best to share this information with appropriate parties.
Speaking to the Rep Involved
Approach the first meeting with the idea of doing a lot of listening. Make no attempt to solve the problem during that initial conversation. Ask open-ended questions and hear what the person has to say. Show them the information that you’ve put together and encourage them to look it over for a day or two.
During subsequent meetings, offer the rep your full support. Provide the time and resources necessary for them to show improvement. But put a timeline on solving the problem. Let them know they have to be performing at a certain level by a certain date or you will have to put them on probation.
Once you’ve begun the process of solving the problem, think about how it got started in the first place. What can be done going forward to mitigate the possibility of it reoccurring? Make adjustments where necessary to hiring, orientation, and training. Update any policy and procedure manuals to reflect any changes.
Leaders don’t bring problems to their direct supervisors, they bring solutions. Whether an individual runs a big company with hundreds of employees or an entry level employee gets put in charge of a small one-off project for the first time – successfully solving a problem represents a career enhancing opportunity.

Did you enjoy this post? If so, I highly encourage you to take about 30 seconds to become a regular subscriber to this blog . It’s free, fun, practical, and only a few emails a week (I promise!). SIGN UP HERE to get the thought LEADERS blog conveniently delivered right to your inbox!
Photo: Solution of Grade 9th Math problem by arjin j
Leave a Reply
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Our Course Offerings
Leadership skills, communication skills.
Communications: Foundations Communications: Applications Principles of Chart Design Strategic Client Engagement Storytelling for Leaders Storytelling for Salespeople Compelling Executive Presence Advanced Facilitation Skills
Individual Skills
Conflict Resolution Everything is Negotiable thoughtLEADERSHIP: Innovation Building Personal Resilience Time Management Mastery
Coaching & Consulting
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Power of Leaders Who Focus on Solving Problems
- Deborah Ancona
- Hal Gregersen

Can you get people excited about the problems that excite you?
There’s a new kind of leadership taking hold in organizations. Strikingly, these new leaders don’t like to be called leaders, and none has any expectation that they will attract “followers” personally — by dint of their charisma, status in a hierarchy, or access to resources. Instead, their method is to get others excited about whatever problem they have identified as ripe for a novel solution. Having fallen in love with a problem, they step up to leadership — but only reluctantly and only as necessary to get it solved. Leadership becomes an intermittent activity as people with enthusiasm and expertise step up as needed, and readily step aside when, based on the needs of the project, another team member’s strengths are more central. Rather than being pure generalists, leaders pursue their own deep expertise, while gaining enough familiarity with other knowledge realms to make the necessary connections. They expect to be involved in a series of initiatives with contributors fluidly assembling and disassembling.
In front of a packed room of MIT students and alumni, Vivienne Ming is holding forth in a style all her own. “Embrace cyborgs,” she calls out, as she clicks to a slide that raises eyebrows even in this tech-smitten crowd. “ Really . Fifteen to 25 years from now, cognitive neuroprosthetics will fundamentally change the definition of what it means to be human.”
- Deborah Ancona is the Seley Distinguished Professor of Management at MIT’s Sloan School of Management and the founder of the MIT Leadership Center.
- Hal Gregersen is a Senior Lecturer in Leadership and Innovation at the MIT Sloan School of Management , a globally recognized expert in navigating rapid change, and a Thinkers50 ranked management thinker. He is the author of Questions Are the Answer: A Breakthrough Approach to Your Most Vexing Problems at Work and in Life and the coauthor of The Innovator’s DNA: Mastering the Five Skills of Disruptive Innovators .
Partner Center
More From Forbes
How to solve a problem like a leader.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Often leaders will think they are driving a problem-solving culture by insistent, or even just encouraging, team members to utilize the tools and templates of problem-solving.
However, most organizations then respond with either sterile and uninspired efforts or at worse, malicious compliance. Shaping the culture of good problem-solving behaviors will naturally encourage people to pick up those same tools with the right intent.
After nearly three decades of coaching at every level, from entry-level employees to experienced CEOs of multi-billion-dollar corporations, author and advisor Jamie Flinchbaugh has worked with over 300 companies worldwide in Lean transformation, including Intel, Harley-Davidson, Crayola, BMW, and Amazon. In his new book, People Solve Problems: The Power of Every Person, Every Day, Every Problem , Flinchbaugh shifts the conversation and argues that organizations focus too much on problem-solving tools and templates and miss other critical elements that make a more significant difference: getting the right behaviors and building the right capabilities.
Problem-solving is not usually completed in a straight line, with fixed questions and predetermined ... [+] answers, say experts
Problem-solving is not usually completed in a straight line, with fixed questions and predetermined answers. Instead, it requires learning, agility, curiosity, and intuition. “This is certainly the case as problems are not puzzles. Whereas a puzzle may have a correct answer, a problem is often unbounded, requiring firstly, the need to understand its scope before exploring solutions, more accurately, different solutions”, says Lebene Soga of Henley Business School. While each problem may not be unique, each requires its own line of inquiry. And each situation solver cannot just follow a script but must leverage their strengths and overcome their weaknesses. “The formulaic approaches to problem-solving may be useful elsewhere but not when we are confronted with wicked problems.”
Attempting to solve or “solutionize” wicked problems requires an understanding of complexity, risks, and more importantly, people,” Soga adds. This is where the right coaching becomes necessary as you do not want leaders rushing to solve problems which often leads to more significant problems. The flexibility and personal engagement that coaching enables to make it the most powerful leverage point for improving problem-solving.
Best Travel Insurance Companies
Best covid-19 travel insurance plans.
In a similar vein, the head of the management discipline at the University of Newcastle Australia, Ashish Malik, reflecting on his two decades of research on the global information technology industry, noted, “the essence of leadership is to take decisions on a range of problems—which may vary on a continuum from simple to complex, for some there are known solutions, while for others there is no known solution or a script ready. Therefore, decision-making is a courageous exercise, and for the first-time leaders, it is a watershed moment.” Leaders often employ many systematic and less planned tools and techniques to solve complex problems, such as using evidence-based and metricized approaches to solving known and unknown issues. In his research, Malik, Sinha, and Blumenfeld found that the use of Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma methodologies was very prevalent in offshore outsourcing call centers , BPOs , and IT Industry in India as a useful tool for approaching complex tasks operational and leadership problems.
Problem-solving is not a recipe with known inputs, established steps, and a predictable outcome. Curiosity allows us to enter problem-solving as a learning process because we must close our knowledge gaps before closing our performance gaps. Intuition is helpful because when trekking through uncharted territory, as most problem solving is done, it requires making essential adjustments such as when to go slower, when to start over, and even where to start. Analytical and data-driven methods are critical but insufficient when navigating such a journey as problem-solving.
In summary, excellent and practical tools help us perform better in most domains, and problem-solving is no exception, however, much like many of those exact domains, the skill, capability, and talent that we bring to the task far outweigh those tools in their impact on performance.
Disclosure: One source mentioned in this article, Lebene Soga, is employed by the same University as this article’s author, though both reside on different campuses

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Why Problem-Solving Skills Are Essential for Leaders in Any Industry

- 17 Jan 2023
Any organization offering a product or service is in the business of solving problems.
Whether providing medical care to address health issues or quick convenience to those hungry for dinner, a business’s purpose is to satisfy customer needs .
In addition to solving customers’ problems, you’ll undoubtedly encounter challenges within your organization as it evolves to meet customer needs. You’re likely to experience growing pains in the form of missed targets, unattained goals, and team disagreements.
Yet, the ubiquity of problems doesn’t have to be discouraging; with the right frameworks and tools, you can build the skills to solve consumers' and your organization’s most challenging issues.
Here’s a primer on problem-solving in business, why it’s important, the skills you need, and how to build them.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Problem-Solving in Business?
Problem-solving is the process of systematically removing barriers that prevent you or others from reaching goals.
Your business removes obstacles in customers’ lives through its products or services, just as you can remove obstacles that keep your team from achieving business goals.

Design Thinking
Design thinking , as described by Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar in the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , is a human-centered , solutions-based approach to problem-solving and innovation. Originally created for product design, design thinking’s use case has evolved . It’s now used to solve internal business problems, too.
The design thinking process has four stages :

- Clarify: Clarify a problem through research and feedback from those impacted.
- Ideate: Armed with new insights, generate as many solutions as possible.
- Develop: Combine and cull your ideas into a short list of viable, feasible, and desirable options before building prototypes (if making physical products) and creating a plan of action (if solving an intangible problem).
- Implement: Execute the strongest idea, ensuring clear communication with all stakeholders about its potential value and deliberate reasoning.
Using this framework, you can generate innovative ideas that wouldn’t have surfaced otherwise.
Creative Problem-Solving
Another, less structured approach to challenges is creative problem-solving , which employs a series of exercises to explore open-ended solutions and develop new perspectives. This is especially useful when a problem’s root cause has yet to be defined.
You can use creative problem-solving tools in design thinking’s “ideate” stage, which include:
- Brainstorming: Instruct everyone to develop as many ideas as possible in an allotted time frame without passing judgment.
- Divergent thinking exercises: Rather than arriving at the same conclusion (convergent thinking), instruct everyone to come up with a unique idea for a given prompt (divergent thinking). This type of exercise helps avoid the tendency to agree with others’ ideas without considering alternatives.
- Alternate worlds: Ask your team to consider how various personas would manage the problem. For instance, how would a pilot approach it? What about a young child? What about a seasoned engineer?
It can be tempting to fall back on how problems have been solved before, especially if they worked well. However, if you’re striving for innovation, relying on existing systems can stunt your company’s growth.
Related: How to Be a More Creative Problem-Solver at Work: 8 Tips
Why Is Problem-Solving Important for Leaders?
While obstacles’ specifics vary between industries, strong problem-solving skills are crucial for leaders in any field.
Whether building a new product or dealing with internal issues, you’re bound to come up against challenges. Having frameworks and tools at your disposal when they arise can turn issues into opportunities.
As a leader, it’s rarely your responsibility to solve a problem single-handedly, so it’s crucial to know how to empower employees to work together to find the best solution.
Your job is to guide them through each step of the framework and set the parameters and prompts within which they can be creative. Then, you can develop a list of ideas together, test the best ones, and implement the chosen solution.
Related: 5 Design Thinking Skills for Business Professionals
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need
1. problem framing.
One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you’re trying to solve.
“Before you begin to generate solutions for your problem, you must always think hard about how you’re going to frame that problem,” Datar says in the course.
For instance, imagine you work for a company that sells children’s sneakers, and sales have plummeted. When framing the problem, consider:
- What is the children’s sneaker market like right now?
- Should we improve the quality of our sneakers?
- Should we assess all children’s footwear?
- Is this a marketing issue for children’s sneakers specifically?
- Is this a bigger issue that impacts how we should market or produce all footwear?
While there’s no one right way to frame a problem, how you do can impact the solutions you generate. It’s imperative to accurately frame problems to align with organizational priorities and ensure your team generates useful ideas for your firm.
To solve a problem, you need to empathize with those impacted by it. Empathy is the ability to understand others’ emotions and experiences. While many believe empathy is a fixed trait, it’s a skill you can strengthen through practice.
When confronted with a problem, consider whom it impacts. Returning to the children’s sneaker example, think of who’s affected:
- Your organization’s employees, because sales are down
- The customers who typically buy your sneakers
- The children who typically wear your sneakers
Empathy is required to get to the problem’s root and consider each group’s perspective. Assuming someone’s perspective often isn’t accurate, so the best way to get that information is by collecting user feedback.
For instance, if you asked customers who typically buy your children’s sneakers why they’ve stopped, they could say, “A new brand of children’s sneakers came onto the market that have soles with more traction. I want my child to be as safe as possible, so I bought those instead.”
When someone shares their feelings and experiences, you have an opportunity to empathize with them. This can yield solutions to their problem that directly address its root and shows you care. In this case, you may design a new line of children’s sneakers with extremely grippy soles for added safety, knowing that’s what your customers care most about.
Related: 3 Effective Methods for Assessing Customer Needs
3. Breaking Cognitive Fixedness
Cognitive fixedness is a state of mind in which you examine situations through the lens of past experiences. This locks you into one mindset rather than allowing you to consider alternative possibilities.
For instance, your cognitive fixedness may make you think rubber is the only material for sneaker treads. What else could you use? Is there a grippier alternative you haven’t considered?
Problem-solving is all about overcoming cognitive fixedness. You not only need to foster this skill in yourself but among your team.
4. Creating a Psychologically Safe Environment
As a leader, it’s your job to create an environment conducive to problem-solving. In a psychologically safe environment, all team members feel comfortable bringing ideas to the table, which are likely influenced by their personal opinions and experiences.
If employees are penalized for “bad” ideas or chastised for questioning long-held procedures and systems, innovation has no place to take root.
By employing the design thinking framework and creative problem-solving exercises, you can foster a setting in which your team feels comfortable sharing ideas and new, innovative solutions can grow.

How to Build Problem-Solving Skills
The most obvious answer to how to build your problem-solving skills is perhaps the most intimidating: You must practice.
Again and again, you’ll encounter challenges, use creative problem-solving tools and design thinking frameworks, and assess results to learn what to do differently next time.
While most of your practice will occur within your organization, you can learn in a lower-stakes setting by taking an online course, such as Design Thinking and Innovation . Datar guides you through each tool and framework, presenting real-world business examples to help you envision how you would approach the same types of problems in your organization.
Are you interested in uncovering innovative solutions for your organization’s business problems? Explore Design Thinking and Innovation —one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses —to learn how to leverage proven frameworks and tools to solve challenges. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author

University of Nairobi Leadership Problem-Solving Memo
by ella | Feb 4, 2024 | Writing
Description
Leadership problem solving memo.
Imagine you are the leader of the design department in a growing organization in a high tech industry. Over the past three months, the sales in the organization have declined due to poor designs and software malfunctions and your department has been identified as part of the problem. As the department leader, you want to involve your team in identifying and solving any problems within your department.
Using the module required readings, videos, and your personal experience, prepare a two-page memo to your team. Provide a problem-solving process the organization can establish for such situations to properly identify such problems. Justify why you believe the approaches are best for the department.
NOTE: Keep in mind that you are not trying to solve the problem of the decline in sales, but rather you are introducing a problem-solving protocol . You do not know what is causing the problem, so solving it is not an option at this point .
Your well-written memo must adhere to the following parameters:
- 2 pages in length using APA memo format (Links to an external site.) , with the inclusion of APA citations and referencing formatted.
- Be supported by six references, with at least four credible references. Remember, you must support your thinking and prior knowledge with references; all facts must be supported; in-text references used throughout the assignment must be included in an APA-formatted reference list.
Order a similar assignment, and have writers from our team of experts write it for you, guaranteeing you an A
- BSU Memory Loss Case Study

- Online Flipbook
- Online Catalog
- Online Magazine
- Online Brochure
- Digital Booklet
- Business Proposal
- Real Estate Flyer
- Multimedia Presentation
- Ebook Online
- Online Photo Album
- Online Portfolio
- Company Newsletter
- Lead Generation
- Document Tracking
- PDF Statistics
- Virtual Bookshelf
- Flipbook App
Knowledge Base > Business Proposals > 5 Efficient Tips on How to End a Memo
5 Efficient Tips on How to End a Memo
Today, we are more and more often using digital communication. Instead of communicating via traditional letters, we simply send text messages or use online meetings, so the classic memo seems to have almost no place in the modern office.
In reality, however, writing memos in a formal style is crucial for effective communication with your supervisor and coworkers. Good memos can help you plan more effectively, solve problems, promote transparency within the company, and advance your career.
A well-written memo can cut through bureaucratic red tape and convey key corporate information to the right people in a clear and simple way, especially if you ensure it ends correctly.
In this article, we will explain how to write a business memo and how to end it. We will also present aesthetically pleasing templates for such documents, that you can later use to create your memo with our proposal builder .
What is a business memo and when do you need it?
A business memo is a short document used to communicate information within a company. It must be concise and direct. It is less formal than a business letter but should still be professional and to the point.
Such a memo is written when a problem arises; thus, its purpose is to identify a problem and provide a solution or distribute some relevant information.

Business memos are meant to help busy readers who need to find new information just by glancing at the text. A business note of this kind is aimed at readers who are browsing the new information for key topics and issues that interest them.
The formal memo can be similar to a press release but is intended primarily for internal use rather than for the press. For example, you can include in this business document the news that you have hired a new specialist or the notification of a change of date for a business trip.
How to write a great memo in 7 steps?
1. start with a title.
There is nothing wrong with starting a memo with the subject line “Memorandum” or “Memo”. But you can add in a few words about the topic. “Memo: New Employee” is a very good, simple topic. If you want, you can add a bit of personalization to it. “New employee” is great, but if you want to build a team, add a phrase to it for your readers – for example, “Memo: Your new colleague”.
2. Present the most important information in the opening paragraph
This is what’s crucial. The content and importance of the memo should be immediately apparent to the reader. If you’re hiring a new employee you need to state the key points right away, like the employee’s name, their job title, and where he or she will be working, and let readers move on to the next question or issue.
Don’t write that the company is expanding, and constantly hiring – but do say who, for example, is to prepare the workstation and so on.
3. The memo should be concise
You need to create it in a clear and precise manner that is both professional and friendly. Short sentences are the key to achieving this look, avoid passive mode or words like will or shall.
Avoid using jargon and pretentious language when writing. Instead of writing “a new employee will arrive tomorrow”, write “new worker arrives on May 6th”. It is also a good idea to avoid negative words by writing in a positive tone – this is more productive.

4. Add a summary
If your memo takes up several pages, it’s a good idea to present a summary in the first or last paragraph. You can often add it as the first line or first sentence of such a long message – business people don’t read long text. The executive summary is a concise summary of the memo’s purpose and content, so it’s useful for those who are busy or looking for key information.
5. Use text formatting
To help readers find what they are looking for, use formatting features such as headings, bolding, etc. The points you list can be formatted as an ordered or unordered list with bullet points. When you write a memo in an email, add links. This allows the reader to quickly jump to the main points of the memo and their location in the document.
6. Present your memo as an interactive PDF
Publuu allows you to convert PDF documents into business proposals. With PDF formatting, and its ability to add links, your business proposals and other notes will look beautiful and be very impressive.
With Publuu analytics, you can easily see who is reading your proposals and ask for feedback – and your proposal’s archive will be stored securely in the cloud.
Publuu’s business proposal example
View more business proposal examples
MAKE YOUR OWN
7. Add a call to action
The end of a note is a good place for a call to action, so the reader knows exactly what to do next. This also sets the reader up positively and helps create a team spirit. Adding team-specific directives to the memo helps get to the point quickly and without contradiction.
5 tips on how to end a memo
Here are some quick tips on how to write memos and end them in a professional way! They can also apply to other short paragraphs like an incident report or customer or employee file.

The author’s signature may or may not appear at the bottom of the last section of the note if it is in written format or a PDF scan. The reader should know simply who the author of the note is, your signature is sufficient. When you write a note, the content is more important than the author or his job title.

There should be no more than one or two sentences in the last paragraph (depending on the topic of the memo). Let the facts speak for themselves. It is up to the reader to come to a conclusion. Most memos end with a short summary and recommended action, but this generally depends on the company policies.

You should, however, add a positive tone to the ending of your memo. When you write a memo keeping in mind the positive tone, you can affect what follows the memo and any future correspondence between you and the reader. For example, add something like “Let’s make a great team together” to your notification about a new employee.

Be professional. Since a memo is a business document that is often kept in an archive, it is important to write it in the correct format and formal style. You’ll still have to be clear and easy to understand when you write a memo for your coworkers.

A salutation as in a business letter is unnecessary. If you’re sending a digital memo, include your contact information like your e-mail address in place of a signature if you’re not sure if the recipient has access to it.
Effective business memos templates

You can use this sample memo as an inspiration when writing a note of your own. Be sure to adjust it to your company and the specific audience that’s going to read it.

This simple memo template is great when writing short, self-contained messages. It can take one page or more!

This memo template showcases how to use this format to take a specific action. Use it for any new procedure in your company!

This prism memo is also great if you want to write a memo from any event.

This memo template can help in writing a perfect business memo using the Word tool package.

This colorful memo template is perfect for many cultures and examples.

The simple and clear design of this memo makes it easy to present news, summarize meetings or begin a new policy change in your company.

The blue shapes in this memo look professional but soft – they won’t detach from the content and the conclusion of the memo.
A business memo is a document that is distributed to company employees to share information. It should be professional and specific, even though it is less formal than business letters. Your memo will look elegantly presented as a Publuu business proposal.
End it elegantly and briefly. If you follow our rules you will get to the point quickly and eliminate any potential problems.
You may be also interested in:
What is a Business Proposal? A Simple Guide for Your Business How To Write A Business Proposal? Top Business Proposal Template Websites
Aesthetics and minimalism enthusiast. Loves to explore the world, and travel is the meaning of her life. Amateur photographer and passionate about dogs. At work, she points her energy into crafting content that reflects her interest in literature and design.
Recent posts

- Flipbook Expert (13)
- PDF Expert (20)
- Catalogs (33)
- Brochures (44)
- Magazines (29)
- Real Estates (17)
- Portfolios (15)
- Booklets (13)
- Presentations (19)
- Education (8)
- Newsletters (13)
- Photo Albums (7)
- Ebooks (28)
- Business Proposals (16)
- Marketing Tips (53)
Popular articles

Convert your PDF to flipbook today!
Go beyond boring PDF and create digital flipbook for free. Register with Publuu for free today and check out all the smart options we prepared for you!
This site uses cookies. Learn more about the purpose of their use and changing cookie settings in your browser. By using this website you agree to the use of cookies in accordance with your current browser settings.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A policy memo is a practical, professionally written document that can vary in length from one page to over twenty-five pages. It provides analysis and recommendations directed to a predetermined audience regarding a specific situation, topic, or issue. A well-written policy memo reflects attention to the policy problem. It is well organized and structured in a clear and concise style that assumes the reader possesses limited knowledge of, as well as little time to conduct research about, the topic of concern. There is no thesis statement or overall theoretical framework underpinning the document; the focus is on describing one or more specific policy recommendations and their supporting action items.
Bhasin, Tavishi and Charity Butcher. “Teaching Effective Policy Memo Writing and Infographics in a Policy Programme.” European Political Science 21 (2022): 1-17; Davis, Jennifer. Guide to Writing Effective Policy Memos. MIT OpenCourseWare, Water and Sanitation Infrastructure Planning in Developing Countries, Spring 2004; Judge, Andrew. "Designing and Implementing Policy Writing Assessments: A Practical Guide." Teaching Public Administration 39 (2021): 351-368; Pennock, Andrew. “The Case for Using Policy Writing in Undergraduate Political Science Courses.” PS: Political Science and Politics 44 (January 2011): 141-146.
How to Approach Writing a Policy Memo
Benefits of Writing a Policy Memo
Writing a policy memo is intended to support the following learning outcomes:
- Helps students learn how to write academically rigorous, persuasive papers about a specific “real-world” issue;
- Teaches how to choose and craft a document’s content based on the needs of a particular audience [rather than for a general readership];
- Prepares students to write an effective position paper in non-academic settings;
- Promotes researching, organizing, and writing a persuasive paper that emphasizes presenting evidence-based recommendations rather than simply reporting a study's findings;
- Teaches students to be client-oriented and to better anticipate the assumptions and concerns of their targeted readership;
- Encourages reflective thinking about the cause and consequential effect of a particular recommendation and to anticipate what questions stakeholder groups may have; and,
- Enables students to create original work that synthesizes policy-making research into a clearly written document advocating change and specific courses of action.
Do not approach writing a policy memo in the same way as you would an academic research paper . Yes, there are certain commonalities in how the content is presented [e.g., a well-written problem statement], but the overarching objective of a policy memo is not to discover or create new knowledge. It is focused on providing to a predetermined group of readers the rationale for choosing a particular policy alternative and/or specific courses of action leading to positive social and political change within society. In this sense, most policy memos possess a component of advocacy and advice intended to promote evidence-based dialog about an issue.
Essential Elements of an Effective Policy Memo Focus and Objectives The overall content of your memo should be strategically aimed at achieving the following goal: convincing your target audience about the accuracy of your analysis and, by extension, that your policy recommendations are valid. Avoid lengthy digressions and superfluous narration that can distract the reader from understanding the policy problem. Note that your target audience is defined in two ways: by the decision-makers who can advocate for or implement change and by individuals and groups most likely impacted by your policy recommendations should they be implemented. Professionally Written Always keep in mind that a policy memorandum is a tool for decision-making. Keep it professional and avoid hyperbole and clever or indeterminate language that could undermine the credibility of your document. The presentation and content of the memo should be polished, easy to understand, and free of jargon. Writing professionally does not imply that you can’t be passionate about your topic, but your policy recommendations should be evidence-based and grounded in solid reasoning and a succinct writing style. Evidence-based A policy memo is not an argumentative debate paper. The reader should expect your recommendations to be based upon evidence that the problem exists and understand the consequences [both good and bad] of adopting particular policy alternatives. To address this, policy memos should include a clear cost-benefit analysis that considers anticipated outcomes, the potential impact on stakeholder groups you have identified, clear and quantifiable performance goals, and how success will be measured. Accessibility A policy memo requires clear and simple language that avoids unnecessary jargon and concepts of an academic discipline. Do not skip around. Use one paragraph to develop one idea or argument and make that idea or argument explicit within the first one or two sentences. Your memo should have a straightforward, explicit organizational structure that provides well-explained arguments arranged within a logical sequence of reasoning [think in terms of an if/then logic model--if this policy recommendation, then this action; if this benefit, then this potential cost; if this group is allocated resources, then this group may be excluded]. Presentation Style The visual impact of your memo affects the reader’s ability to grasp your ideas quickly and easily. Include a table of contents and list of figures and charts, if necessary. Subdivide the text using clear and descriptive headings to guide the reader. Incorporate devices such as capitalization, bold text, and bulleted items, but be consistent, and don’t go crazy; the purpose is to facilitate access to specific sections of the paper for successive readings. If it is difficult to find information in your document, policy makers will not use it. Practical and Feasible Your memorandum should provide a set of actions based on what is actually happening in reality. Do not base your policy recommendations on future scenarios or hypothetical situations that could be interpreted as unlikely to occur or that do not appear possible because you have not adequately explained the circumstances supporting these scenarios. Here again, your cost-benefit analysis can be essential to validating the practicality and feasibility of your recommendations. Explicit Transparency Provide specific criteria to assess either the success or failure of the policies you are recommending. As much as possible, this criteria should be derived from your cost/benefit analysis. Do not hide or under-report information that does not support your policy recommendations. Just as you would note the limitations of your study in a research paper, a policy memo should describe issues of weakness of your analysis. Explain why they may arise and why your recommendations are still valid despite these issues. Be open and straightforward because doing so strengthens your arguments and it will help the reader assess the overall impact of recommended policy changes.
NOTE: Technically, it would not be wrong for your policy memo to argue for maintaining the status quo. However, the general objective of a policy memo assignment is to critically examine opportunities for transformative change and to highlight the risks of on-going complacency. If you choose to argue for maintaining the current policy trajectory, in whole or in part, be concise in identifying and systematically refuting all relevant policy options. Again, it must be rooted in an evidence-based cost/benefit analysis. Whether maintaining current policies is short-term or long-term [and these need to be clearly defined], you must explain concisely why each possible outcome of maintaining the status quo would be preferable to any alternative policy options and recommended courses of action. If your argument for maintaining the status quo is short-term, explain what factors in the future could trigger a policy-related course correction.
Herman, Luciana. Policy Memos. John F. Kennedy School of Government. Harvard University; How to Write a Public Policy Memo. Student Learning Center. University of California, Berkeley; Policy Memo. Thompson Writing Program, Writing Studio. Duke University; Policy Memo Guidelines. Cornell Fellows Program. Cornell University; Memo: Audience and Purpose. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Policy Memo Requirements and Guidelines, 2012-2013 edition. Institute for Public Policy Studies. University of Denver; Thrall, A. Trevor. How to Write a Policy Memo. University of Michigan--Dearborn, 2006; Mastro, Oriana Skylar. "Teach What you Preach: A Comprehensive Guide to the Policy Memo as a Methods Teaching Tool." Journal of Political Science Education 17 (2021): 326-340; Writing Effective Memos. Electronic Hallway. Daniel J. Evans School of Public Affairs. University of Washington; Writing Effective Policy Memos. Water & Sanitation Infrastructure Planning syllabus. Spring 2004. Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Structure and Writing Style
The contents of a policy memo can be organized in a variety of ways. Below is a general template adapted from the “Policy Memo Requirements and Guidelines, 2012-2013 edition” published by the Institute for Public Policy Studies at the University of Denver and from suggestions made in the book, A Practical Guide for Policy Analysis: The Eightfold Path to More Effective Problem-Solving [Eugene Bardach. 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2012] . Both sources provide useful approaches to writing a policy memo in the event your professor does not provide specific guidance. Overall, the tone of your writing should be formal but assertive. Note that the most important consideration in terms of writing style is professionalism, not creativity. I. Cover Page Provide a complete and informative cover page that includes the document title, date, the full names and titles of the writer or writers [i.e., Joe Smith, Student, Department of Political Science, University of Southern California]. The title of the policy memo should be formally written and specific to the policy issue [e.g., “Charter Schools, Fair Housing, and Legal Standards: A Call for Equal Treatment”]. For longer memos, consider including a brief executive summary that highlights key findings and recommendations.
II. Introduction and Problem Definition A policy memorandum should begin with a short summary introduction that defines the policy problem, provides important contextual background information, and explains what issues are being covered. This is followed by a short justification for writing the memo, why a decision needs to be made [answering the “So What?” question], and an outline of the recommendations you make or key themes the reader should keep in mind. Summarize your main points in a few sentences, then conclude with a description of how the remainder of the memo is organized.
III. Methods This is usually where other research about the problem or issue of concern is summarized. Describe how you plan to identify and locate the information on which your policy memo is based. This may include peer-reviewed journals and books as well as possible professionals you interviewed, databases and websites you explored, or legislative histories or relevant case law that you used. Remember this is not intended to be a thorough literature review; only choose sources that persuasively support your position or that help lay a foundation for understanding why actions need to be taken.
IV. Issue Analysis This section is where you explain in detail how you examined the issue and, by so doing, persuade the reader of the appropriateness of your analysis. This is followed by a description of how your analysis contributes to the current policy debate. It is important to demonstrate that the policy issue may be more complex than a basic pro versus con debate. Very few public policy debates can be reduced to this type of rhetorical dichotomy. Be sure your analysis is thorough and takes into account all factors that may influence possible strategies that could advance a recommended set of solutions.
V. Proposed Solutions Write a brief review of the specific solutions you evaluated, noting the criteria by which you examined and compared different proposed policy alternatives. Identify the stakeholders impacted by the proposed solutions and describe in what ways they will benefit from your proposed solution. Focus on identifying solutions that have not been proposed or tested elsewhere. Offer a contrarian viewpoint that challenges the reader to take into account a new perspective on the research problem. Note that you can propose solutions that may be considered radical or unorthodox, but they must be realistic and politically feasible.
VI. Strategic Recommendations Solutions are just opinions until you provide a path that delineates how to get from where you are to where you want to go. Describe what you believe are the best recommended courses of action [i.e., "action items"]. In writing this section, state the broad approach to be taken, with specific, practical steps or measures that should be implemented. Be sure to also state by whom and within what time frame these actions should be taken. Conclude by highlighting the consequences of maintaining the status quo [or if supporting the status quo, why change at this time would be detrimental]. Also, clearly explain why your strategic recommendations are best suited for addressing the current policy situation.
VI. Limitations As in any academic paper, you must describe limitations to your analysis. In particular, ask yourself if each of your recommendations are realistic, feasible, and sustainable, and in particular, that they can be implemented within the current bureaucratic, economic, political, cultural, social, or other type of contextual climate in which they reside. If not, you should go back and clarify your recommendations and provide further evidence as to why the recommendation is most appropriate for addressing the issue. It does not necessarily undermine the overall recommendations of your study if the limitation cannot be overcome, but you must clearly acknowledge this. Place the limitation within the context of a critical issue that needs further study in concurrence with possible implementation [i.e., findings indicate service learning promotes civic engagement, but there is a lack of data on the types of service learning programs that exist among high schools in South Central Los Angeles].
VII. Cost-Benefit Analysis This section may be optional but, in some cases, your professor may ask you to include an explicit summary analysis of the costs and benefits of each recommendation. If you are asked to include a separate cost-benefit analysis, be concise and brief. Since most policy memos do not have a formal conclusion, the cost-benefit analysis can act as your conclusion by summarizing the key differences among policy alternatives and recommended courses of action.
Bardach, Eugene. A Practical Guide for Policy Analysis: The Eightfold Path to More Effective Problem-Solving . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2012; Herman, Luciana. Policy Memos. John F. Kennedy School of Government. Harvard University; How to Write a Public Policy Memo. Student Learning Center. University of California, Berkeley; Policy Memo Guidelines. Cornell Fellows Program. Cornell University; Memo: Audience and Purpose. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Pennock, Andrew. “The Case for Using Policy Writing in Undergraduate Political Science Courses.” PS: Political Science and Politics 44 (January 2011): 141-146; Policy Memo Requirements and Guidelines, 2012-2013 edition. Institute for Public Policy Studies. University of Denver; Thrall, A. Trevor. How to Write a Policy Memo. University of Michigan--Dearborn, 2006; Sajedinejad, S., et al. From Research to Impact: A Toolkit for Developing Effective Policy Briefs . Toronto, Ontario: Policy Bench, Fraser Mustard Institute of Human Development, University of Toronto, 2021; What Are Policy Briefs. FAO Corporate Document Repository. United Nations; Writing Effective Memos. Electronic Hallway. Daniel J. Evans School of Public Affairs. University of Washington; Writing Effective Policy Memos. Water & Sanitation Infrastructure Planning syllabus. Spring 2004. Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Proofreading the Memo
Problems to Avoid
The style and arrangement of an effectively written memo can differ because no two policies, nor their intended audience of readers, are exactly the same. Nevertheless, before you submit your policy memo, be sure you proofread the document so that you avoid these common problems. If you identify one or more of these problems, you should rewrite or re-organize the content accordingly.
1. Acknowledge the Law of Unintended Consequences . No policy analysis is complete until you have identified for whom the policy actions are supposed to benefit and identify what groups may be impacted by the consequences of their implementation. Review your memo and make sure you have clearly delineated who could be helped and who could be potentially harmed or excluded from benefiting from your recommended policy actions. As noted by Wilcoxen, this is also important because describing who may or may not benefit can help you anticipate which stakeholder groups will support your policy recommendations and which groups will likely oppose it. Calculating potential "winners" and "losers" will help reveal how much it may cost to compensate those groups excluded from benefiting. By building this compensation into your policy recommendations, you are better able to show the reader how to reduce political obstacles.
2. Anticipate the Reader's Questions . Examine your recommended courses of action and identify any open-ended, declarative, indeterminate, or ambiguous statements that could lead the reader to have to ask further questions. For example, you declare that the most important factor supporting school choice among parents is distance from home. Without clarification or additional information, this could lead the reader to ask numerous questions, such as, why or by what means do you know this, what distance is considered to be too far, what factors contribute to parent's decision about school choice and distance from schools, or what age group does this most apply to. Clarify these types of open-ended statements so that your policy recommendations can be more fully understood and accepted as valid.
3. Be Concise . Being succinct in your writing does not relate to the overall length of the policy memo or the amount of words you use. It relates to your ability to provide a lot of information clearly and without superfluous detail. Strategies include r eviewing long paragraphs and breaking them up into parts, looking for long sentences and eliminating unnecessary qualifiers and modifiers, and deleting prepositional phrases in favor of adjectives or adverbs. The overarching goal is to be thorough and precise in how your ideas are presented and to avoid writing that uses too many words or excessively technical expressions.
4. Focus on the Results . While it is important that your memo describe the methods by which you gathered and analyzed the data informing your policy recommendations, the content should focus on explaining the results of your analysis and the logic underpinning your recommendations. Remember your audience. The reader is presumably a decision-maker with limited knowledge of the issue and who has little time to contemplate the methods of analysis. The validity of your findings will be determined primarily by your reader's determination that your policy recommendations and supporting action items are realistic and rooted in sound reasoning. Review your memo and make sure the statement about how you gathered the data is brief and concise. If necessary, technical issues or raw data can be included in an appendix.
5. Minimize Subjective Reasoning . Although the memo should be persuasive, avoid emphasizing your personal opinion about the topic. A policy memo should be written in a professional tone with recommendations based upon empirical reasoning while, at the same time, reflecting a level of passion about your topic. However, being passionate does not imply being opinionated. The memo should emphasize presenting all of the facts a reader would need to reach their own conclusions about the validity of your recommendations.
6. Use of Non-textual Elements . Review all tables, charts, figures, graphs, or other non-textual elements and make sure they are labeled correctly. Examine each in relation to the text, making sure they are described adequately and that they relate to the overall content of your memo. If these elements are located in appendices, make sure references to them within the text are correct [i.e., reference to Figure 2 is actually the table you want the reader to look at].
Bardach, Eugene and Eric M. Pataschnik. A Practical Guide for Policy Analysis: The Eightfold Path to More Effective Problem-Solving . 5th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2016; Herman, Luciana. Policy Memos. John F. Kennedy School of Government. Harvard University; How to Write a Public Policy Memo. Student Learning Center. University of California, Berkeley; Memo: Audience and Purpose. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Policy Memo Requirements and Guidelines, 2012-2013 edition. Institute for Public Policy Studies. University of Denver; Wilcoxen, Peter J. Tips on Writing a Policy Memo. PAI 723, Economics for Public Decisions Course Syllabus. Maxwell School of Citizenship and Public Affairs, Syracuse University.
Writing Tip
Difference Between a Policy Memo and a Policy Brief
A policy memo and a policy brief share much in common. They both describe the rationale for choosing particular policy alternatives or courses of action, they both contain persuasive language, and both documents are written for non-experts, such as, practitioners, politicians, non-governmental agency workers, lobbyists, and others who work on or regularly make decisions about the issue addressed in the document. Both documents are free of jargon or technical terminology and focus on communicating the practical implications of prior policy research to a specific audience based on available evidence.
Ironically, however, a policy memo is typically shorter in length than a policy “brief.” A policy memo usually ranges from one to twent-five pages, while a policy brief can be anywhere from twenty to more than a hundred pages in length depending on the complexity of the topic. Therefore:
- A policy brief is commonly produced in response to a request from a decision-maker concerning an issue that requires more thorough information to address the underlying policy problem or they are produced by an advocacy group or organization for the purpose of influencing a specific policy, often in an urgent tone. Non-textual elements , such as, figures, charts, graphs, or diagrams, are often included.
- A policy memo is concisely written and presents information, ideas, and recommendations clearly so the reader can quickly scan the document for the most relevant points. Policy memos focus on brevity and often synthesize existing evidence in language that is direct, specific, and with minimal background information or historical context. Non-textual elements are only included if necessary.
Guide to Writing an Effective Policy Memo. Leadership for Educational Equity, New York; Policy Briefs. The Writing Center, University of North Carolina; Policy Memo. Writing Studio, Duke University; Manny, Karoline. What is a Policy Brief/Memo? Grace Doherty Library, Centra College; Sajedinejad, S., et al. From Research to Impact: A Toolkit for Developing Effective Policy Briefs . Toronto, Ontario: Policy Bench. Fraser Mustard Institute of Human Development, University of Toronto, 2021.
Another Writing Tip
Citing Sources
Policy memos generally do not include extensive footnotes, endnotes, further readings, or a bibliography. However, if you use supporting information in a memo, cite the source in the text. For example, you may refer to a study that supported a specific assertion by referencing it in the following manner: "A study published in 2012 by the Eagleton Center for Public Interest Polling showed that public opinion towards China was....” However, some assignments may require a formal list of references. Before writing your memo, be sure you are clear about how your professor wants you to cite any sources referred to in your analysis.
Policy Memo. Thompson Writing Program, Writing Studio. Duke University.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Using Non-Textual Elements
Policy memos are not just text-based but frequently include numeric tables and charts or other non-textual elements, such as photographs, maps, and illustrations. However, it is important that you use non-textual elements judiciously and only in relation to supplementing and clarifying arguments made in the text so as not to distract the reader from the main points of your memo . As with any non-textual elements, describe what the reader is seeing and why the data is important to understanding the policy problem.
Still Yet Another Writing Tip
Including Appendices
The purpose of an appendix is to provide supplementary material that is not an essential part of the main text but which may be helpful in providing the reader with more complete information. If you have information that is vital to understanding an issue discussed in the memo, it can be included in one or more appendices. However, if you have a lot of information, don't write a five page memo and include twenty pages of appendices. Memos are intended to be succinct and clearly expressed. If there is a lot of data, refer to the source and summarize it, or discuss with your professor how it should be included.
- << Previous: Writing Field Notes
- Next: Writing a Reflective Paper >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Leadership Problem Solving Memo
Pssst… we can write an original essay just for you..
Any subject. Any type of essay. We’ll even meet a 3-hour deadline.
writers online
Subject: Leadership Problem Solving Memo
As you might all have known, the last few months have been quite challenging for this company. Reducing sales have become the primary issue, which influenced the subject challenge. Unfortunately, the design department has been listed as the primary driver behind the significant difficulties recorded in the organization. Poor designs and software malfunctions are the primary cause of declining sales. As one of the vital departments in the organization, the executives have raised the issue, precisely creating a sense of urgency. Thus, as your departmental leader, I believe that each team member has a critical role to play in minimizing the adverse effects of this problem. In this case, the memo will address the creative problem-solving process, precisely focusing on the Osborne-Parnes innovative problem-solving model.
According to Dostál (2015), problem-solving is a non-routine procedure, which is oriented towards altering an unfavorable organizational situation. Notably, Shen and Tzeng (2018) state that with the complexity of regulatory challenges in matters of sustainability, the need for advanced modern computational methods to support decision-making is inevitable. In times of need, employees are encouraged to embrace a disruptive approach, which disrupts the status quo, and focuses on identifying the problems within their workplace and across the firm’s products and services (Basadur, Gelade & Basadur, 2014). In other words, to cope with stressful situations, it is advisable to implement a thought process that facilitates the generation of ideas via which organizations can successfully remove undesired obstructions. Besides, the willingness to solve a problem is a crucial factor that enables organizations to alienate the challenges at hand. Thus, by comprehending the relevant phases of the problem-solving approach, organizational teams can strategically overcome the problem at hand.
As suggested in the Osborne-Parnes model, the ideal problem-solving strategy should implement a six-stage procedure. The team will realize that each of the essential steps plays a significant role in facilitating organizational development. As a consequence , the team will be implementing this six-phased approach to minimize the adverse effects of deteriorating sales. The first phase that the team will embrace is forecasting and perceiving the threats affecting the department. The significance of this phase is to increase sensitivity and create a sense of urgency regarding the subject problem (Dostál, 2015). Next, the team will proceed by gathering critical data regarding the identified threats in phase one above. In this step, the team should comprehend the problems linked to the unfavorable situation, evaluate the origin, and recommend options to minimize the challenge. Consequently, this step will be crucial for understanding the factors characterizing the threat; hence, identifying and categorizing them accurately.
Next, we shall define the issue and expound on all the aspects affecting the organization. As suggested by Bardach and Patashnik (2019), this step should be used to assemble some evidence from the collected data in the second phase above. Thus, for this team, the third step will embrace critical thinking to define the issue at hand, and all the attributes are characterizing this problem. Also, we must create opinions through a brainstorming phase, thereby suggesting relevant alternatives to solve the challenge. Walton and Toniolo (2016) note that alternative solutions are discussed and arguments brought forward before reaching the ideal intervention. Therefore, from the available options, the team can proceed to the negotiation phase in which they identify the complete responsibility for the situation at hand.
Lastly, once the problem and ideal solutions are identified, the team can proceed to the implementation phase. This stage requires the unit to zone in on a specific action plan to eliminate the unfavorable status quo (Van Aken, & Berends, 2018). Notably, we are expected to evaluate the results of this action plan, thereby establish a control cycle to prevent the problem from recurring in the future. Overall, I believe in this creative approach because it provides a step-by-step methodology for analyzing the problematic situation. Consequently, it is justifiable to implement the Osbarne-Parnes problem-solving theory since it challenges conventional thinking and adopts innovative solutions suitable for organizational development. In conclusion, we will be reviewing the steps discussed above during the next meeting . For all questions and clarifications, I will be addressing them when the team converges to discuss the problem.
Remember! This is just a sample.
Save time and get your custom paper from our expert writers.
In case you can’t find a sample example, our professional writers are ready to help you with writing your own paper. All you need to do is fill out a short form and submit an order

Four of the biggest problems facing education—and four trends that could make a difference
Eduardo velez bustillo, harry a. patrinos.

In 2022, we published, Lessons for the education sector from the COVID-19 pandemic , which was a follow up to, Four Education Trends that Countries Everywhere Should Know About , which summarized views of education experts around the world on how to handle the most pressing issues facing the education sector then. We focused on neuroscience, the role of the private sector, education technology, inequality, and pedagogy.
Unfortunately, we think the four biggest problems facing education today in developing countries are the same ones we have identified in the last decades .
1. The learning crisis was made worse by COVID-19 school closures
Low quality instruction is a major constraint and prior to COVID-19, the learning poverty rate in low- and middle-income countries was 57% (6 out of 10 children could not read and understand basic texts by age 10). More dramatic is the case of Sub-Saharan Africa with a rate even higher at 86%. Several analyses show that the impact of the pandemic on student learning was significant, leaving students in low- and middle-income countries way behind in mathematics, reading and other subjects. Some argue that learning poverty may be close to 70% after the pandemic , with a substantial long-term negative effect in future earnings. This generation could lose around $21 trillion in future salaries, with the vulnerable students affected the most.
2. Countries are not paying enough attention to early childhood care and education (ECCE)
At the pre-school level about two-thirds of countries do not have a proper legal framework to provide free and compulsory pre-primary education. According to UNESCO, only a minority of countries, mostly high-income, were making timely progress towards SDG4 benchmarks on early childhood indicators prior to the onset of COVID-19. And remember that ECCE is not only preparation for primary school. It can be the foundation for emotional wellbeing and learning throughout life; one of the best investments a country can make.
3. There is an inadequate supply of high-quality teachers
Low quality teaching is a huge problem and getting worse in many low- and middle-income countries. In Sub-Saharan Africa, for example, the percentage of trained teachers fell from 84% in 2000 to 69% in 2019 . In addition, in many countries teachers are formally trained and as such qualified, but do not have the minimum pedagogical training. Globally, teachers for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects are the biggest shortfalls.
4. Decision-makers are not implementing evidence-based or pro-equity policies that guarantee solid foundations
It is difficult to understand the continued focus on non-evidence-based policies when there is so much that we know now about what works. Two factors contribute to this problem. One is the short tenure that top officials have when leading education systems. Examples of countries where ministers last less than one year on average are plentiful. The second and more worrisome deals with the fact that there is little attention given to empirical evidence when designing education policies.
To help improve on these four fronts, we see four supporting trends:
1. Neuroscience should be integrated into education policies
Policies considering neuroscience can help ensure that students get proper attention early to support brain development in the first 2-3 years of life. It can also help ensure that children learn to read at the proper age so that they will be able to acquire foundational skills to learn during the primary education cycle and from there on. Inputs like micronutrients, early child stimulation for gross and fine motor skills, speech and language and playing with other children before the age of three are cost-effective ways to get proper development. Early grade reading, using the pedagogical suggestion by the Early Grade Reading Assessment model, has improved learning outcomes in many low- and middle-income countries. We now have the tools to incorporate these advances into the teaching and learning system with AI , ChatGPT , MOOCs and online tutoring.
2. Reversing learning losses at home and at school
There is a real need to address the remaining and lingering losses due to school closures because of COVID-19. Most students living in households with incomes under the poverty line in the developing world, roughly the bottom 80% in low-income countries and the bottom 50% in middle-income countries, do not have the minimum conditions to learn at home . These students do not have access to the internet, and, often, their parents or guardians do not have the necessary schooling level or the time to help them in their learning process. Connectivity for poor households is a priority. But learning continuity also requires the presence of an adult as a facilitator—a parent, guardian, instructor, or community worker assisting the student during the learning process while schools are closed or e-learning is used.
To recover from the negative impact of the pandemic, the school system will need to develop at the student level: (i) active and reflective learning; (ii) analytical and applied skills; (iii) strong self-esteem; (iv) attitudes supportive of cooperation and solidarity; and (v) a good knowledge of the curriculum areas. At the teacher (instructor, facilitator, parent) level, the system should aim to develop a new disposition toward the role of teacher as a guide and facilitator. And finally, the system also needs to increase parental involvement in the education of their children and be active part in the solution of the children’s problems. The Escuela Nueva Learning Circles or the Pratham Teaching at the Right Level (TaRL) are models that can be used.
3. Use of evidence to improve teaching and learning
We now know more about what works at scale to address the learning crisis. To help countries improve teaching and learning and make teaching an attractive profession, based on available empirical world-wide evidence , we need to improve its status, compensation policies and career progression structures; ensure pre-service education includes a strong practicum component so teachers are well equipped to transition and perform effectively in the classroom; and provide high-quality in-service professional development to ensure they keep teaching in an effective way. We also have the tools to address learning issues cost-effectively. The returns to schooling are high and increasing post-pandemic. But we also have the cost-benefit tools to make good decisions, and these suggest that structured pedagogy, teaching according to learning levels (with and without technology use) are proven effective and cost-effective .
4. The role of the private sector
When properly regulated the private sector can be an effective education provider, and it can help address the specific needs of countries. Most of the pedagogical models that have received international recognition come from the private sector. For example, the recipients of the Yidan Prize on education development are from the non-state sector experiences (Escuela Nueva, BRAC, edX, Pratham, CAMFED and New Education Initiative). In the context of the Artificial Intelligence movement, most of the tools that will revolutionize teaching and learning come from the private sector (i.e., big data, machine learning, electronic pedagogies like OER-Open Educational Resources, MOOCs, etc.). Around the world education technology start-ups are developing AI tools that may have a good potential to help improve quality of education .
After decades asking the same questions on how to improve the education systems of countries, we, finally, are finding answers that are very promising. Governments need to be aware of this fact.
To receive weekly articles, sign-up here

Consultant, Education Sector, World Bank

Senior Adviser, Education
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
What to know about the crisis of violence, politics and hunger engulfing Haiti

A long-simmering crisis over Haiti’s ability to govern itself, particularly after a series of natural disasters and an increasingly dire humanitarian emergency, has come to a head in the Caribbean nation, as its de facto president remains stranded in Puerto Rico and its people starve and live in fear of rampant violence.
The chaos engulfing the country has been bubbling for more than a year, only for it to spill over on the global stage on Monday night, as Haiti’s unpopular prime minister, Ariel Henry, agreed to resign once a transitional government is brokered by other Caribbean nations and parties, including the U.S.
But the very idea of a transitional government brokered not by Haitians but by outsiders is one of the main reasons Haiti, a nation of 11 million, is on the brink, according to humanitarian workers and residents who have called for Haitian-led solutions.
“What we’re seeing in Haiti has been building since the 2010 earthquake,” said Greg Beckett, an associate professor of anthropology at Western University in Canada.

What is happening in Haiti and why?
In the power vacuum that followed the assassination of democratically elected President Jovenel Moïse in 2021, Henry, who was prime minister under Moïse, assumed power, with the support of several nations, including the U.S.
When Haiti failed to hold elections multiple times — Henry said it was due to logistical problems or violence — protests rang out against him. By the time Henry announced last year that elections would be postponed again, to 2025, armed groups that were already active in Port-au-Prince, the capital, dialed up the violence.
Even before Moïse’s assassination, these militias and armed groups existed alongside politicians who used them to do their bidding, including everything from intimidating the opposition to collecting votes . With the dwindling of the country’s elected officials, though, many of these rebel forces have engaged in excessively violent acts, and have taken control of at least 80% of the capital, according to a United Nations estimate.
Those groups, which include paramilitary and former police officers who pose as community leaders, have been responsible for the increase in killings, kidnappings and rapes since Moïse’s death, according to the Uppsala Conflict Data Program at Uppsala University in Sweden. According to a report from the U.N . released in January, more than 8,400 people were killed, injured or kidnapped in 2023, an increase of 122% increase from 2022.
“January and February have been the most violent months in the recent crisis, with thousands of people killed, or injured, or raped,” Beckett said.
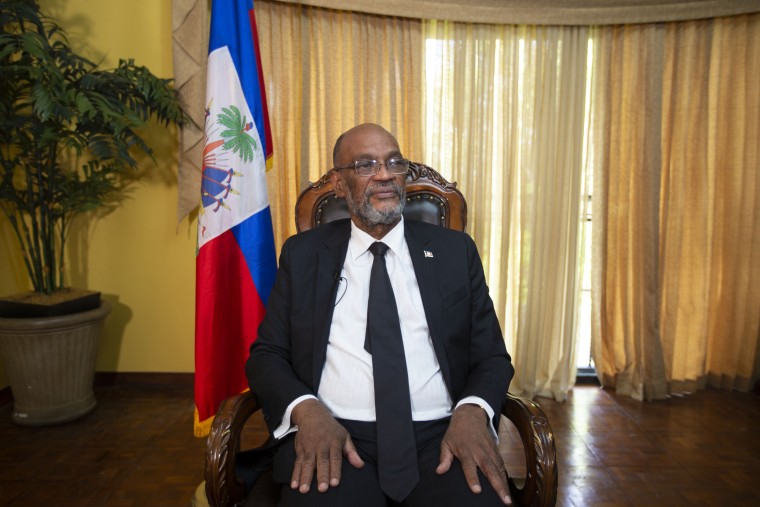

Armed groups who had been calling for Henry’s resignation have already attacked airports, police stations, sea ports, the Central Bank and the country’s national soccer stadium. The situation reached critical mass earlier this month when the country’s two main prisons were raided , leading to the escape of about 4,000 prisoners. The beleaguered government called a 72-hour state of emergency, including a night-time curfew — but its authority had evaporated by then.
Aside from human-made catastrophes, Haiti still has not fully recovered from the devastating earthquake in 2010 that killed about 220,000 people and left 1.5 million homeless, many of them living in poorly built and exposed housing. More earthquakes, hurricanes and floods have followed, exacerbating efforts to rebuild infrastructure and a sense of national unity.
Since the earthquake, “there have been groups in Haiti trying to control that reconstruction process and the funding, the billions of dollars coming into the country to rebuild it,” said Beckett, who specializes in the Caribbean, particularly Haiti.
Beckett said that control initially came from politicians and subsequently from armed groups supported by those politicians. Political “parties that controlled the government used the government for corruption to steal that money. We’re seeing the fallout from that.”
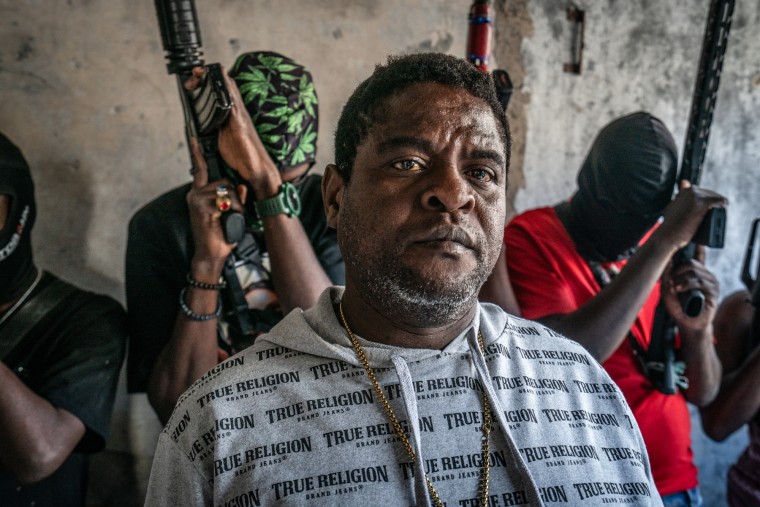

Many armed groups have formed in recent years claiming to be community groups carrying out essential work in underprivileged neighborhoods, but they have instead been accused of violence, even murder . One of the two main groups, G-9, is led by a former elite police officer, Jimmy Chérizier — also known as “Barbecue” — who has become the public face of the unrest and claimed credit for various attacks on public institutions. He has openly called for Henry to step down and called his campaign an “armed revolution.”
But caught in the crossfire are the residents of Haiti. In just one week, 15,000 people have been displaced from Port-au-Prince, according to a U.N. estimate. But people have been trying to flee the capital for well over a year, with one woman telling NBC News that she is currently hiding in a church with her three children and another family with eight children. The U.N. said about 160,000 people have left Port-au-Prince because of the swell of violence in the last several months.
Deep poverty and famine are also a serious danger. Gangs have cut off access to the country’s largest port, Autorité Portuaire Nationale, and food could soon become scarce.
Haiti's uncertain future
A new transitional government may dismay the Haitians and their supporters who call for Haitian-led solutions to the crisis.
But the creation of such a government would come after years of democratic disruption and the crumbling of Haiti’s political leadership. The country hasn’t held an election in eight years.
Haitian advocates and scholars like Jemima Pierre, a professor at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, say foreign intervention, including from the U.S., is partially to blame for Haiti’s turmoil. The U.S. has routinely sent thousands of troops to Haiti , intervened in its government and supported unpopular leaders like Henry.
“What you have over the last 20 years is the consistent dismantling of the Haitian state,” Pierre said. “What intervention means for Haiti, what it has always meant, is death and destruction.”
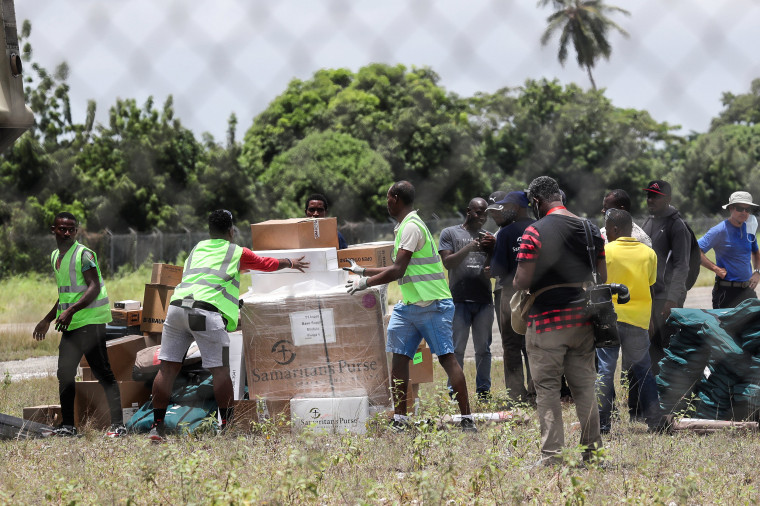

In fact, the country’s situation was so dire that Henry was forced to travel abroad in the hope of securing a U.N. peacekeeping deal. He went to Kenya, which agreed to send 1,000 troops to coordinate an East African and U.N.-backed alliance to help restore order in Haiti, but the plan is now on hold . Kenya agreed last October to send a U.N.-sanctioned security force to Haiti, but Kenya’s courts decided it was unconstitutional. The result has been Haiti fending for itself.
“A force like Kenya, they don’t speak Kreyòl, they don’t speak French,” Pierre said. “The Kenyan police are known for human rights abuses . So what does it tell us as Haitians that the only thing that you see that we deserve are not schools, not reparations for the cholera the U.N. brought , but more military with the mandate to use all kinds of force on our population? That is unacceptable.”
Henry was forced to announce his planned resignation from Puerto Rico, as threats of violence — and armed groups taking over the airports — have prevented him from returning to his country.
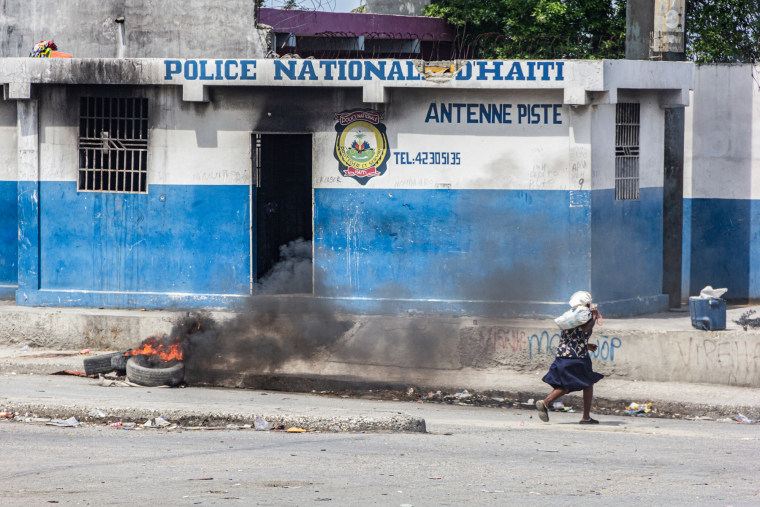

Now that Henry is to stand down, it is far from clear what the armed groups will do or demand next, aside from the right to govern.
“It’s the Haitian people who know what they’re going through. It’s the Haitian people who are going to take destiny into their own hands. Haitian people will choose who will govern them,” Chérizier said recently, according to The Associated Press .
Haitians and their supporters have put forth their own solutions over the years, holding that foreign intervention routinely ignores the voices and desires of Haitians.
In 2021, both Haitian and non-Haitian church leaders, women’s rights groups, lawyers, humanitarian workers, the Voodoo Sector and more created the Commission to Search for a Haitian Solution to the Crisis . The commission has proposed the “ Montana Accord ,” outlining a two-year interim government with oversight committees tasked with restoring order, eradicating corruption and establishing fair elections.
For more from NBC BLK, sign up for our weekly newsletter .
CORRECTION (March 15, 2024, 9:58 a.m. ET): An earlier version of this article misstated which university Jemima Pierre is affiliated with. She is a professor at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, not the University of California, Los Angeles, (or Columbia University, as an earlier correction misstated).
Patrick Smith is a London-based editor and reporter for NBC News Digital.
Char Adams is a reporter for NBC BLK who writes about race.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A decision memo is a collaborative document or communication channel where employees can cooperatively solve organizational problems by channeling multiple perspectives into a shared feedback loop ...
Brainstorming possible solutions. Evaluating those solutions to select the best one. Implementing it. Sharpening problem-solving skills is crucial for taking the initiative, decision-making, and critical reflection. Social responsibility and personal brand are also enhanced through effective problem-solving.
Leadership Problem Solving Memo Imagine you are the leader of the design department in a growing organization in a high tech industry. Over the past three months, the sales in the organization have declined due to poor designs and software malfunctions and your department has been identified as part of the problem. As the department leader, you want to involve your team in identifying and ...
Read more on Business writing or related topic Decision making and problem solving John Baldoni is an internationally recognized executive coach and leadership educator. His most recent book is ...
6. Add a summary. If your memo tackles a complex issue or is particularly lengthy, add a short conclusion to summarize the most important points. In the absence of face-to-face cues, reiterating the main points through a brief summary reinforces the essential elements of your message, aiding comprehension. 7.
Before you can write a memo you need all the information pertaining to the problem as well as the individuals involved. Sometimes solving a problem is a matter of improving communication. Determine or define the problem is. Your memo should start with a problem statement. This is a quick summary of what the problem is.
Leadership. Leaders don't bring problems to their direct supervisors, they bring solutions. Whether an individual runs a big company with hundreds of employees or an entry level employee gets put in charge of a small one-off project for the first time - successfully solving a problem represents a career enhancing opportunity.
Read more on Decision making and problem solving or related topic Leading teams Rebecca Zucker is an executive coach and a founding partner at Next Step Partners , a leadership development firm.
Summary. There's a new kind of leadership taking hold in organizations. Strikingly, these new leaders don't like to be called leaders, and none has any expectation that they will attract ...
Problem-solving is not a recipe with known inputs, established steps, and a predictable outcome. Curiosity allows us to enter problem-solving as a learning process because we must close our ...
A status memo is a kind of progress report. This type of memo is often used by a project manager or team leader. They confirm where the team is on a project and what remains to be done. A problem-solving memo is one that addresses an issue and provides a solution. It's like a directive memo, although in some cases the writer might ask for ...
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need. 1. Problem Framing. One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you're trying to solve.
View Leadership Problem Solving Memo draft.docx from ORG 502 at Colorado State University, Global Campus. Decision Making Model Tinyan Ng Colorado State University - Global Campus ORG 502 - Effective ... Monroe, T. (2014). Creative problem solving in a fast-paced, guidance-rich environment. Defense AT&L Magazine, 43 (4), 20-23. Oroszi, T. (2018).
Leadership Problem Solving Memo. Imagine you are the leader of the design department in a growing organization in a high tech industry. Over the past three months, the sales in the organization have declined due to poor designs and software malfunctions and your department has been identified as part of the problem. As the department leader ...
MAKE YOUR OWN. 7. Add a call to action. The end of a note is a good place for a call to action, so the reader knows exactly what to do next. This also sets the reader up positively and helps create a team spirit. Adding team-specific directives to the memo helps get to the point quickly and without contradiction.
LEADERSHIP PROBLEM SOLVING MEMO 3 implementation (Tarvin, 2019). Documentations of the agreements are essential, and that will be done to promote a better understanding of the implications and other details (Gartenstein, 2018). This will follow the protocol on contingencies that will enable us to address the issues even if the circumstances change (Harich & Rosas, 2019).
Below is a general template adapted from the "Policy Memo Requirements and Guidelines, 2012-2013 edition" published by the Institute for Public Policy Studies at the University of Denver and from suggestions made in the book, A Practical Guide for Policy Analysis: The Eightfold Path to More Effective Problem-Solving [Eugene Bardach. 4th ...
Critical thinking skills allow nurse leaders to solve problems in the workplace and develop potential solutions for these issues. The attribute of critical thinking allows nurse leaders to assist other staff in problem solving and decision making. ... Module 02 Written Assignment Leadership Attributes Memo. Madeline Herrmann School of Nursing ...
We are adopting measurable standards for these leadership and problem-solving behaviors. The standards are: Align on standards and goals. Find and embrace the "red". Use Navy problem-solving methods to get at root cause. Fix or elevate barriers. Encourage learning through trust and respect. Specify ownership.
2 Leadership Problem Solving Memo DATE: October 25, 2020 TO: Design Department Staff FROM: Jonathan Walker, Design Department Director SUBJECT: Declining Sales Memo Greetings Design Team: As you may be aware sales for the organization have decreased over the past several months due to some design and software malfunctions. We are in the process of determining strategies to identify was to ...
Subject: Leadership Problem Solving Memo. As you might all have known, the last few months have been quite challenging for this company. Reducing sales have become the primary issue, which influenced the subject challenge. ... According to Dostál (2015), problem-solving is a non-routine procedure, which is oriented towards altering an ...
Unfortunately, we think the four biggest problems facing education today in developing countries are the same ones we have identified in the last decades. 1. The learning crisis was made worse by COVID-19 school closures. Low quality instruction is a major constraint and prior to COVID-19, the learning poverty rate in low- and middle-income ...
Date: 29 th July 2020 From: the Design Department Leader To: the Design Team Subject: Leadership Problem Solving Memo As you might all have known, the last few months have been quite challenging for this company. Reducing sales have become the primary issue, which influenced the subject challenge. Unfortunately, the design department has been listed as the primary driver behind the significant ...
Chaos has gutted Port-au-Prince and Haiti's government, a crisis brought on by decades of political disruption, a series of natural disasters and a power vacuum left by the president's assassination.