
Rhetorical Questions in Essays: 5 Things you should Know

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Rhetorical questions can be useful in writing. So, why shouldn’t you use rhetorical questions in essays?
In this article, I outline 5 key reasons that explain the problem with rhetorical questions in essays.
Despite the value of rhetorical questions for engaging audiences, they mean trouble in your university papers. Teachers tend to hate them.
There are endless debates among students as to why or why not to use rhetorical questions. But, I’m here to tell you that – despite your (and my) protestations – the jury’s in. Many, many teachers hate rhetorical questions.
You’re therefore not doing yourself any favors in using them in your essays.
Rhetorical Question Examples
A rhetorical question is a type of metacommentary . It is a question whose purpose is to add creative flair to your writing. It is a way of adding style to your essay.
Rhetorical questions usually either have obvious answers, or no answers, or do not require an answer . Here are some examples:
- Are you seriously wearing that?
- Do you think I’m that gullible?
- What is the meaning of life?
- What would the walls say if they could speak?
I understand why people like to use rhetorical questions in introductions . You probably enjoy writing. You probably find rhetorical questions engaging, and you want to draw your marker in, engage them, and wow them with your knowledge.
1. Rhetorical Questions in Academic Writing: They Don’t belong.
Rhetorical questions are awesome … for blogs, diaries, and creative writing. They engage the audience and ask them to predict answers.
But, sorry, they suck for essays. Academic writing is not supposed to be creative writing .
Here’s the difference between academic writing and creative writing:
- Supposed to be read for enjoyment first and foremost.
- Can be flamboyant, extravagant, and creative.
- Can leave the reader in suspense.
- Can involve twists, turns, and surprises.
- Can be in the third or first person.
- Readers of creative writing read texts from beginning to end – without spoilers.
Rhetorical questions are designed to create a sense of suspense and flair. They, therefore, belong as a rhetorical device within creative writing genres.
Now, let’s look at academic writing:
- Supposed to be read for information and analysis of real-life ideas.
- Focused on fact-based information.
- Clearly structured and orderly.
- Usually written in the third person language only.
- Readers of academic writing scan the texts for answers, not questions.
Academic writing should never, ever leave the reader in suspense. Therefore, rhetorical questions have no place in academic writing.
Academic writing should be in the third person – and rhetorical questions are not quite in the third person. The rhetorical question appears as if you are talking directly to the reader. It is almost like writing in the first person – an obvious fatal error in the academic writing genre.
Your marker will be reading your work looking for answers , not questions. They will be rushed, have many papers to mark, and have a lot of work to do. They don’t want to be entertained. They want answers.
Therefore, academic writing needs to be straight to the point, never leave your reader unsure or uncertain, and always signpost key ideas in advance.
Here’s an analogy:
- When you came onto this post, you probably did not read everything from start to end. You probably read each sub-heading first, then came back to the top and started reading again. You weren’t interested in suspense or style. You wanted to find something out quickly and easily. I’m not saying this article you’re reading is ‘academic writing’ (it isn’t). But, what I am saying is that this text – like your essay – is designed to efficiently provide information first and foremost. I’m not telling you a story. You, like your teacher, are here for answers to a question. You are not here for a suspenseful story. Therefore, rhetorical questions don’t fit here.
I’ll repeat: rhetorical questions just don’t fit within academic writing genres.
2. Rhetorical Questions can come across as Passive
It’s not your place to ask a question. It’s your place to show your command of the content. Rhetorical questions are by definition passive: they ask of your reader to do the thinking, reflecting, and questioning for you.
Questions of any kind tend to give away a sense that you’re not quite sure of yourself. Imagine if the five points for this blog post were:
- Are they unprofessional?
- Are they passive?
- Are they seen as padding?
- Are they cliché?
- Do teachers hate them?
If the sub-headings of this post were in question format, you’d probably – rightly – return straight back to google and look for the next piece of advice on the topic. That’s because questions don’t assist your reader. Instead, they demand something from your reader .
Questions – rhetorical or otherwise – a position you as passive, unsure of yourself, and skirting around the point. So, avoid them.
3. Rhetorical Questions are seen as Padding
When a teacher reads a rhetorical question, they’re likely to think that the sentence was inserted to fill a word count more than anything else.
>>>RELATED ARTICLE: HOW TO MAKE AN ESSAY LONGER >>>RELATED ARTICLE: HOW TO MAKE AN ESSAY SHORTER
Rhetorical questions have a tendency to be written by students who are struggling to come to terms with an essay question. They’re well below word count and need to find an extra 15, 20, or 30 words here and there to hit that much-needed word count.
In order to do this, they fill space with rhetorical questions.
It’s a bit like going into an interview for a job. The interviewer asks you a really tough question and you need a moment to think up an answer. You pause briefly and mull over the question. You say it out loud to yourself again, and again, and again.
You do this for every question you ask. You end up answering every question they ask you with that same question, and then a brief pause.
Sure, you might come up with a good answer to your rhetorical question later on, but in the meantime, you have given the impression that you just don’t quite have command over your topic.
4. Rhetorical Questions are hard to get right
As a literary device, the rhetorical question is pretty difficult to execute well. In other words, only the best can get away with it.
The vast majority of the time, the rhetorical question falls on deaf ears. Teachers scoff, roll their eyes, and sigh just a little every time an essay begins with a rhetorical question.
The rhetorical question feels … a little ‘middle school’ – cliché writing by someone who hasn’t quite got a handle on things.
Let your knowledge of the content win you marks, not your creative flair. If your rhetorical question isn’t as good as you think it is, your marks are going to drop – big time.
5. Teachers Hate Rhetorical Questions in Essays
This one supplants all other reasons.
The fact is that there are enough teachers out there who hate rhetorical questions in essays that using them is a very risky move.
Believe me, I’ve spent enough time in faculty lounges to tell you this with quite some confidence. My opinion here doesn’t matter. The sheer amount of teachers who can’t stand rhetorical questions in essays rule them out entirely.
Whether I (or you) like it or not, rhetorical questions will more than likely lose you marks in your paper.
Don’t shoot the messenger.
Some (possible) Exceptions
Personally, I would say don’t use rhetorical questions in academic writing – ever.
But, I’ll offer a few suggestions of when you might just get away with it if you really want to use a rhetorical question:
- As an essay title. I would suggest that most people who like rhetorical questions embrace them because they are there to ‘draw in the reader’ or get them on your side. I get that. I really do. So, I’d recommend that if you really want to include a rhetorical question to draw in the reader, use it as the essay title. Keep the actual essay itself to the genre style that your marker will expect: straight up the line, professional and informative text.
“97 percent of scientists argue climate change is real. Such compelling weight of scientific consensus places the 3 percent of scientists who dissent outside of the scientific mainstream.”
The takeaway point here is, if I haven’t convinced you not to use rhetorical questions in essays, I’d suggest that you please check with your teacher on their expectations before submission.
Don’t shoot the messenger. Have I said that enough times in this post?
I didn’t set the rules, but I sure as hell know what they are. And one big, shiny rule that is repeated over and again in faculty lounges is this: Don’t Use Rhetorical Questions in Essays . They are risky, appear out of place, and are despised by a good proportion of current university teachers.
To sum up, here are my top 5 reasons why you shouldn’t use rhetorical questions in your essays:

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Classroom Wall Decoration Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 31 Cute & Cozy Play Corner Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 24 Steiner-Waldorf Classroom Design Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Kindergarten Decoration Ideas
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Should you use Rhetoric Questions in an Essay?
Rhetorical questions are questions asked to make a point or to create a dramatic effect rather than to get an answer.
Many college professors discourage using rhetorical questions in essays, and the majority agree that they can be used only in specific circumstances.
While they are helpful for the person writing an essay, if you want to include them in an essay, ensure that you rephrase them into a sentence, indirect question, or statement.
It is essential to say that there is only minimal space for including rhetorical questions in academic writing.
This post will help you discover why professors discourage using rhetorical questions in essays and when it is okay to use them. Let's dive in!
Why do professors discourage the use of rhetorical questions in academic papers?
We love rhetorical questions for the flair they add to written pieces. They help authors achieve some sense of style when writing essays. However, since they have an obvious answer, no answer, or require no answer, they have no place in academic writing, not even the essay hooks. They are a way to engage the audience by letting them keep thinking of the answer as they read through your text. Avoid using rhetorical essays in academic writing unless you are doing creative writing. There is no room for suspense in academic writing. Let’s find out why professors discourage them so badly in any form of academic writing, not just essay writing alone!
1. Because they don't belong in academic writing
Rhetorical questions are awesome; they can help engage your readers and keep them interested in your writing. However, they are only perfect for creative writing, diaries, and blogs and are not appropriate for academic writing. This is because academic writing is about logic, facts, and arguments, while rhetorical questions are about entertainment. The two are incompatible; the questions do not belong in academic writing.
Rhetorical questions are typically utilized in creative writing to create flair and suspense. However, academic writing does not need flair or suspense. Because most academic writing assignments are based on facts, evidence, arguments, and analysis. Thus, there is no need for the creation of flair or suspense. In other words, there is no space for rhetorical questions in academic writing.
Another thing that shows that rhetorical questions don't belong in academic writing is that they are usually written in the first person. The fact that they are written in the first person means they do not fit in academic writing, where students are usually urged to write in the third person. So while it is okay for rhetorical questions to feature in creative writing where the author addresses the reader, it is not okay for the questions to feature in academic writing where everything should be matter-of-fact.
Lastly, rhetorical questions do not belong in academic writing because readers of academic works do not expect to see them. When you start reading an academic paper, you expect answers, and you don't expect suspense, flair, or entertainment. Therefore, you will most likely be confused and even upset when you see rhetorical questions in an academic paper.
2. Because they come across as passive
When writing an academic paper as a student, you are expected to show your mastery of the content; you are expected to demonstrate your command of the content. What you are not likely to do is to pose rhetorical questions, and this is because the questions are passive and, therefore, unsuitable for academic papers. Specifically, passive voice is unsuitable for academic papers because it is dull and lazy. What is appropriate and recommended for academic papers is active voice, and this is because it is clear and concise.
You now know why you should not use passive rhetorical questions in academic papers. Another reason why you should not use passive rhetorical questions is that they will make you sound as if you are unsure of yourself. If you are sure about the points and arguments you are making in your paper, you will not ask passive rhetorical questions. Instead, you will develop your paper confidently from the introduction to the conclusion.
When you ask your readers passive rhetorical questions, you will make them Google or think about the answer. These are not the things that readers want to be doing when reading academic papers. They want to see well-developed ideas and arguments and be informed, inspired, and educated. Thus, you should spare them the need to do things they do not plan to do by not using rhetorical questions in your academic paper.
3. Because they are seen as padding
When your professor sees a rhetorical question in your essay, they will think you are just trying to fill the minimum word count. In other words, they will think you are trying to cheat the system by filling the word count with an unnecessary sentence. This could lead to you getting penalized, which you do not want for your essay if you are aiming for a top grade.
Why do professors see rhetorical questions as padding? Well, it is because struggling students are the ones who typically use rhetorical questions in their essays. Therefore, when professors see these questions, they assume that the student struggled to meet the word count, so they throw in a few rhetorical questions.
4. Because they are hard to get right
It is not easy to ask rhetorical questions correctly, especially in essays. This is because there are several things to consider when asking them, including the location, the words, the punctuation, and the answer. Most of the time, when students ask rhetorical questions in their papers, professors roll their eyes because most students ask them wrong.
The correct way to ask a rhetorical question is to ask it in the right place, in the right way, and to use the correct punctuation. You will discover how to do these things in the second half of this post. Don't just ask a rhetorical question for the sake of it; ask only when necessary.
5. Because professors hate them
If the other reasons why professors discourage rhetorical questions have not convinced you to give up on using them, this one should. Professors hate rhetorical questions, and they don't like them because they feel the questions don't belong in academic papers. Therefore, when you use them, you risk irking your professor and increasing your likelihood of getting a lower grade. So if you don't want a lower grade, you should give rhetorical questions a wide berth.
Your professor might love rhetorical questions. However, including rhetorical questions in your essay is a risk you do not want to take. Because your hunch about them liking rhetorical questions might be wrong, resulting in a bad grade for you.
When to use rhetorical questions in academic papers
You now know professors do not like seeing rhetorical questions in academic papers. However, this does not mean you cannot use them. There are situations when it is okay to use rhetorical questions in your academic papers. Below you will discover the instances when it is appropriate to use rhetorical questions in your essays.
1. When introducing your essay
When introducing your essay, you must try to grab the reader's attention with your first two or three sentences. The best way to do this is to use a hook statement – an exciting statement that makes the reader want to read the rest of the paper to find out more. And the best way to write a hook statement is as a rhetorical question.
When you write your hook statement as a rhetorical question, you will make your reader think about the question and the topic before they continue to read your introduction . This will most likely pique their interest in the topic and make them want to read the rest of your essay.
Therefore, instead of starting your essay with a dull and ordinary hook statement, you should start it with a powerful rhetorical question. This will undoubtedly hook your reader. Below is a good example of a rhetorical question hook statement:
Where could the world be without the United Nations?
Starting your essay with the question above will definitely hook any reader and give the reader an idea of the angle you want to take in your essay.
2. When you want to evoke emotions
Most academic papers are supposed to be written in the third person and should also be emotionless, well-organized, and to the point. However, there are some that can be written in the first person. Good examples of such essays include personal essays and reflective essays.
When you are writing personal essays, it is okay to express emotions. And one of the best ways to do it is by using rhetorical questions. These questions are perfect for evoking emotions because they make the reader think and reflect. And making your reader think and reflect is an excellent way to make them relate to your story.
The most appropriate way to use rhetorical questions to evoke emotions is to make your questions target specific feelings such as rage, hope, happiness, sadness, and so on. Targeted questions will help your reader think about certain things and feelings, which will undoubtedly influence what they will feel thereafter. Below is an excellent example of a rhetorical question used to evoke emotions:
Doesn't everyone deserve to be free?
This question makes you feel compassion for those who are not free and makes you think about them and the things they are going through.
3. When you want to emphasize something
Using a rhetorical question to emphasize a point is okay, especially in a personal essay. The right way to do this is to make the statement you want to highlight and ask a rhetorical question immediately after. Emphasizing a statement using a rhetorical question will help drive your message home, and it will also help leave an impact on the reader. Below is an excellent example of a rhetorical question used to emphasize the statement before it:
Nearly 1000 racehorses die or get injured every year. Is the killing and maiming of horses justified in this age of cars and underground trains?
The rhetorical question above brings into sharp focus the statement about the number of horses killed yearly and makes the reader think about the number of horses killed or injured annually.
4. When you want to make a smooth transition
One of the best ways to transition from one topic to the next is by using a rhetorical question. It is essential to transition smoothly from one point to the next if you want your essay to have an excellent flow.
A rhetorical question can help you to make a smooth transition from one point to the next by alerting the reader to a new topic. Below is an excellent example of a rhetorical question used to make a smooth transition from one paragraph to the next:
Did you know malaria remains one of Africa's leading causes of infant mortality? The tropical disease accounted for over half a million infant deaths in 2020.
The statement above smartly alerts the reader about a new topic and introduces it in a smooth and calculated manner.
Mistakes to avoid when using rhetorical questions
If you decide to use rhetorical questions in your essays, there are some mistakes you should avoid.
1. Overusing them
Using rhetorical questions in academic papers is okay, but you should never overuse them. The number of rhetorical questions in your essay should never exceed two, and more than two rhetorical questions are just too many for an essay.
2. Using them in research papers
Research papers are the most formal of academic papers. Most professors who give research paper assignments do not fancy seeing rhetorical questions in them. Therefore, you should never use rhetorical questions in research papers.
3. Never use them as your thesis statement
Your thesis statement should be a statement that is logical, concise, and complete. It should never be a question, let alone a rhetorical one.
As you have discovered in this article, rhetorical questions should ideally not be used in essays. This is because they do not belong, professors hate them, and so on. However, as you have also discovered, there are some situations when it is okay to use rhetorical questions. In other words, you can use rhetorical questions in the right circumstances. The fact that you now know these circumstances should enable you to use rhetorical questions in your essays, if necessary, correctly.
You should talk to us if you are too busy to write your essay or edit it to make it professional enough. Our company provides both essay writing and essay editing services at affordable rates. Contact us today for assistance or simply order your essay using our essay order page.
What are rhetorical questions?
Rhetorical questions are questions asked to make a point rather than to get an answer. They are often used in creative writing to create a dramatic effect or a sense of suspense.
When and how to use rhetorical questions in essays
Professors hate rhetorical questions in essays . You should only use them sparingly and when necessary. Otherwise, you should not use them at all.
What mistakes should you avoid when using rhetorical questions in essays?
You should never use a rhetorical question instead of a good thesis statement . You should also never use a rhetorical question in a research paper.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.


Rhetorical Question

Rhetorical Question Definition
What is a rhetorical question? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to get an answer—most commonly, it's asked to make a persuasive point. For example, if a person asks, "How many times do I have to tell you not to eat my dessert?" he or she does not want to know the exact number of times the request will need to be repeated. Rather, the speaker's goal is to emphasize his or her growing frustration and—ideally—change the dessert-thief's behavior.
Some additional key details about rhetorical questions:
- Rhetorical questions are also sometimes called erotema.
- Rhetorical questions are a type of figurative language —they are questions that have another layer of meaning on top of their literal meaning.
- Because rhetorical questions challenge the listener, raise doubt, and help emphasize ideas, they appear often in songs and speeches, as well as in literature.
How to Pronounce Rhetorical Question
Here's how to pronounce rhetorical question: reh- tor -ih-kuhl kwes -chun
Rhetorical Questions and Punctuation
A question is rhetorical if and only if its goal is to produce an effect on the listener, rather than to obtain information. In other words, a rhetorical question is not what we might call a "true" question in search of an answer. For this reason, many sources argue that rhetorical questions do not need to end in a traditional question mark. In the late 1500's, English printer Henry Denham actually designed a special question mark for rhetorical questions, which he referred to as a "percontation point." It looked like this: ⸮ (Here's a wikipedia article about Denham's percontation point and other forms of "irony punctuation.")
Though the percontation point has fallen out of use, modern writers do sometimes substitute a traditional question mark with a period or exclamation point after a rhetorical question. There is a lively debate as to whether this alternative punctuation is grammatically correct. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- In general, rhetorical questions do require a question mark.
- When a question is a request in disguise, you may use a period. For instance, it is ok to write: "Will you please turn your attention to the speaker." or "Can you please go to the back of the line."
- When a question is an exclamation in disguise, you may use an exclamation point. For instance, it is okay to write: "Were they ever surprised!"
- When asking a question emotionally, you may use an exclamation point. For instance, " Who could blame him!" and "How do you know that!" are both correct.
Rhetorical Questions vs. Hypophora
Rhetorical questions are easy to confuse with hypophora , a similar but fundamentally different figure of speech in which a speaker poses a question and then immediately answers it. Hypophora is frequently used in persuasive speaking because the speaker can pose and answer a question that the audience is likely to be wondering about, thereby making the thought processes of the speaker and the audience seem more aligned. For example, here is an example of hypophora used in a speech by Dwight Eisenhower:
When the enemy struck on that June day of 1950, what did America do? It did what it always has done in all its times of peril. It appealed to the heroism of its youth.
While Eisenhower asked this question without expecting an answer from his audience, this is an example of hypophora because he answered his own question. In a rhetorical question, by contrast, the answer would be implied in the question—to pose a rhetorical question, Eisenhower might have said instead, "When the enemy struck, who in their right mind would have done nothing to retaliate?"
Rhetorical Questions vs. Aporia
Rhetorical questions are also related to a figure of speech called aporia . Aporia is an expression of doubt that may be real, or which may be feigned for rhetorical effect. These expressions of doubt may or may not be made through the form of a question. When they are made through the form of a question, those questions are sometimes rhetorical.
Aporia and Rhetorical Questions
When someone is pretending doubt for rhetorical effect, and uses a question as part of that expression of doubt, then the question is rhetorical. For example, consider this quotation from an oration by the ancient Greek orator Demosthenes:
I am at no loss for information about you and your family; but I am at a loss where to begin. Shall I relate how your father Tromes was a slave in the house of Elpias, who kept an elementary school near the Temple of Theseus, and how he wore shackles on his legs and a timber collar round his neck? Or how your mother practised daylight nuptials in an outhouse next door to Heros the bone-setter, and so brought you up to act in tableaux vivants and to excel in minor parts on the stage?
The questions Demosthenes poses are examples of both aporia and rhetorical question, because Demosthenes is feigning doubt (by posing rhetorical questions) in order to cast insulting aspersions on the character of the person he's addressing.
Aporia Without Rhetorical Questions
If the expression of doubt is earnest, however, then the question is not rhetorical. An example of aporia that is not also a rhetorical question comes from the most famous excerpt of Shakespeare's Hamlet:
To be or not to be—that is the question. Whether ‘tis nobler in the mind to suffer The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune, Or to take arms against a sea of troubles, And by opposing end them?
While Hamlet asks this question without expecting an answer (he's alone when he asks it), he's not asking in order to persuade or make a point. It's a legitimate expression of doubt, which leads Hamlet into a philosophical debate about whether one should face the expected miseries of life or kill oneself and face the possible unknown terrors of death. It's therefore not a rhetorical question, because Hamlet asks the question as an opening to actually seek an answer to the question he is obsessing over.
Rhetorical Question Examples
Rhetorical question examples in literature.
Rhetorical questions are particularly common in plays, appearing frequently in both spoken dialogue between characters, and in monologues or soliloquies, where they allow the playwright to reveal a character's inner life.
Rhetorical Questions in Shakespeare's The Merchant of Venice :
In his speech from Act 3, Scene 1 of Shakespeare's The Merchant of Venice , Shylock uses rhetorical questions to point out the indisputable similarities between Jews and Christians, in such a way that any listener would find him impossible to contradict:
I am a Jew. Hath not a Jew eyes? Hath not a Jew hands, organs, dimensions, senses, affections, passions? fed with the same food, hurt with the same weapons, subject to the same diseases, healed by the same means, warmed and cooled by the same winter and summer, as a Christian is? If you prick us, do we not bleed? if you tickle us, do we not laugh? if you poison us, do we not die? and if you wrong us, shall we not revenge? If we are like you in the rest, we will resemble you in that. If a Jew wrong a Christian, what is his humility? Revenge. If a Christian wrong a Jew, what should his sufferance be by Christian example? Why, revenge. The villainy you teach me, I will execute, and it shall go hard but I will better the instruction.
Rhetorical questions in Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet :
In this soliloquy from Act 2, Scene 2 of Romeo and Juliet , Juliet poses a series of rhetorical questions as she struggles to grasp the difficult truth—that her beloved Romeo is a member of the Montague family:
Thou art thyself, though not a Montague. What's Montague? it is nor hand, nor foot, Nor arm, nor face, nor any other part Belonging to a man. O, be some other name! What's in a name? that which we call a rose By any other name would smell as sweet; So Romeo would, were he not Romeo call'd Retain that dear perfection which he owes Without that title. Romeo, doff thy name, And for that name which is no part of thee Take all myself.
Rhetorical Question Examples in Political Speeches
Rhetorical questions often "challenge" the listener to contradict what the speaker is saying. If the speaker frames the rhetorical question well, it gives the impression that his or her view is true and that it would be foolish, or even impossible, to contradict the speaker's argument. In other words, rhetorical questions are great for speeches.
Rhetorical Questions in Ronald Reagan's 1980 Republican National Convention Acceptance Address:
In this speech, Reagan uses a series of rhetorical questions—referred to as "stacked" rhetorical questions—to criticize the presidency of his predecessor and running opponent, Jimmy Carter:
Can anyone look at the record of this Administration and say, "Well done"? Can anyone compare the state of our economy when the Carter Administration took office with where we are today and say, "Keep up the good work"? Can anyone look at our reduced standing in the world today say, "Let's have four more years of this"?
Rhetorical Questions in Hillary Clinton's 2016 Democratic National Convention Speech:
In this portion of her speech, Clinton argues that her opponent Donald Trump is not temperamentally fit to become president:
A president should respect the men and women who risk their lives to serve our country—including Captain Khan and the sons of Tim Kaine and Mike Pence, both Marines. So just ask yourself: Do you really think Donald Trump has the temperament to be commander-in-chief?
Rhetorical Question Examples in Song Lyrics
Love has left even the best musicians of our time feeling lost, searching for meaning, and—as you might expect—full of rhetorical questions. Musicians such as Tina Turner, Jean Knight, and Stevie Wonder have all released hits structured around rhetorical questions, which allow them to powerfully express the joy, the pain, and the mystery of L-O-V-E.
Rhetorical Questions in "What's Love Got to do with It" by Tina Turner
What's love got to do, got to do with it What's love but a second hand emotion What's love got to do, got to do with it Who needs a heart when a heart can be broken
Rhetorical Questions in "Mr. Big Stuff" by Jean Knight
Now because you wear all those fancy clothes (oh yeah) And have a big fine car, oh yes you do now Do you think I can afford to give you my love (oh yeah) You think you're higher than every star above
Mr. Big Stuff Who do you think you are Mr. Big Stuff You're never gonna get my love
Rhetorical Questions in "Isn't She Lovely" by Stevie Wonder
Isn't she lovely Isn't she wonderful Isn't she precious Less than one minute old I never thought through love we'd be Making one as lovely as she But isn't she lovely made from love
Stevie Wonder wrote "Isn't She Lovely" to celebrate the birth of his daughter, Aisha. The title is a perfect example of a rhetorical question, because Wonder isn't seeking a second opinion here. Instead, the question is meant to convey the love and amazement he feels towards his daughter.
Why Do Writers Use Rhetorical Questions?
Authors, playwrights, speech writers and musicians use rhetorical questions for a variety of reasons:
- To challenge the listener
- To emphasize an idea
- To raise doubt
- To demonstrate that a previously asked question was obvious
The examples included in this guide to rhetorical questions have largely pointed to the persuasive power of rhetorical questions, and covered the way that they are used in arguments, both real and fictional. However, poets also frequently use rhetorical questions for their lyrical, expressive qualities. Take the poem below, "Danse Russe (Russian Dance)" by William Carlos Williams:
If when my wife is sleeping and the baby and Kathleen are sleeping and the sun is a flame-white disc in silken mists above shining trees,— if I in my north room dance naked, grotesquely before my mirror waving my shirt round my head and singing softly to myself: "I am lonely, lonely. I was born to be lonely. I am best so!" If I admire my arms, my face, my shoulders, flanks, buttocks against the yellow drawn shades,— Who shall say I am not the happy genius of my household?
The rhetorical question that concludes this poem has the effect of challenging the reader to doubt Williams' happiness—daring the listener to question this intimate, eccentric portrait of the poet's private world. By ending the poem in this way, Williams maintains a delicate balance. Throughout the poem, he draws the reader in and confides secrets of his interior life, but the question at the end is an almost defiant statement that he does not require the reader's approval. Rather, the reader—like the mirror—is simply there to witness his happy solitude.
Other Helpful Rhetorical Question Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Rhetorical Questions: A general explanation with a variety of examples, as well as links to specific resources with punctuation rules.
- The Dictionary Definition of Rhetorical Question: A basic definition with some historical information.
- A detailed explanation of rhetorical questions , along with related figures of speech that involve questions.
- A video of Ronald Reagan's 1980 Republican National Convention Speech, in which he asks stacked rhetorical questions.
- An article listing the greatest rhetorical questions in the history of pop music.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1961 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 41,348 quotes across 1961 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Figurative Language
- Figure of Speech
- Anachronism
- Antimetabole
- Common Meter
- Rising Action
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Juxtaposition
- Bildungsroman
- Alliteration
- Internal Rhyme
- Antanaclasis
- Anadiplosis
- End-Stopped Line

- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
How to Use Rhetorical Questions in Essay Writing Effectively
Table of contents
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay
Instantly enhance your writing in real-time while you type. With LanguageTool
Get started for free
Rhetorical Questions: Learn What They Are and How To Use Them
You’ve probably heard of the term “rhetorical question,” but do you know what it means? And no, that’s not a rhetorical question. Don’t worry—we’ll tell you exactly what they are with easy-to-understand explanations and examples.

Rhetorical Question: Quick Summary
A rhetorical question is a question that is not meant to be answered, but is asked to make a point or create a desired effect.
Pretend you’ve worked on a puzzle for three days. You finally finished, and then your teenage brother destroys it in a second. You might ask:
- Are you crazy?
This is a rhetorical question because you aren’t expecting a response. Instead, you’re emphasizing shock or confusion (and maybe heartbreak).
If it looks like a question and sounds like a question, it must require an answer, right?
Well, no, not always.
Rhetorical questions aren’t meant to be answered. Below, we’ll explain what they are and how to use them.
What’s a Rhetorical Question?
A rhetorical question is a statement that’s formulated as a question that is not meant to be answered. Instead, it creates an effect or emphasizes a point.
Consider the following scenario: You’re watching the news with a friend and hear that someone in your town has won the lottery. You might say to your friend
Can you imagine?
It’s technically a question, but you aren’t expecting a “yes” or “no” response. Instead, the point you’re trying to make is more similar to stating “Imagine that.”
The real meaning of rhetorical questions is often implied or suggested, but not explicitly stated.
Rhetorical questions are extremely common. They can be found in everyday speech and writing, but also in literature and persuasive texts, like debates, speeches, essays, and marketing advertisements.
What Are the Different Types of Rhetorical Questions?
There are different types of rhetorical questions, with each of them serving a distinct purpose.
Hypophora (Anthypophora)
Hypophora (also known as anthypophora ) is when a speaker or writer poses a question and then immediately provides an answer to it. It engages the audience or reader by anticipating their questions and addressing them directly.
What’s the easiest way to improve our public education system? Pay teachers more.
What is the key to success in business? Forming strong relationships with your customers and clients.
How can we improve income inequality in our society? Easy—raise the minimum wage.
It should be noted that there is disagreement among scholars regarding the precise definition of hypophora and anthypophora. The Century Dictionary defines hypophora as the inquiry, while anthypophora refers to the response. Nowadays, both terms have come to encompass both the questioning and answering elements of the technique.
Epiplexis is a type of rhetorical question that is used to rebuke or reprimand the audience. It challenges and engages the audience in a pointed and sometimes confrontational manner. This type of rhetorical device is meant to persuade (or shame) the audience into accepting the speaker’s perspective.
I can’t believe you skipped class. Do you not care about your education or future?
That’s horrible. How could you think such a thing?
Are you really going to let fear stop you from reaching your fullest potential?
As a rhetorical device, erotesis is asked to elicit a strong response, either in affirmation or denial, but they typically anticipate a negative response.
Do you really think it’s okay that basic healthcare is only accessible to those who can afford it?
Is it really worth it to risk your career just to impress someone?
Do you actually think it’s a good idea to stay up all night before the big exam?
How Do You Punctuate a Rhetorical Question?
That’s a good question, and one that doesn’t have a definitive answer. The punctuation used for a rhetorical question can vary depending on the context. Some options include using a question mark, period, or exclamation mark. However, some experts argue that a question mark should always be used for any type of question, whether it’s rhetorical or not.
We’d recommend punctuating rhetorical questions with a question mark.
Here’s a fun fact for you: In the 1580s, Henry Denham proposed using a reverse question mark for these particular types of questions. Known as a percontation mark , it never became standard.

Examples of Rhetorical Questions
Below, you ’ ll find several examples of rhetorical questions.
Rhetorical Questions Found in Literature
William Shakespeare often used rhetorical questions in his writing. A few of them are:
Shall I compare thee to a summer’s day? (Sonnet 18)
Was he not born of [ a] woman? (Macbeth)
Can one desire too much of a good thing? (As You Like It)
Common Rhetorical Questions Used in Everyday Speech
Are you kidding me?
Isn’t that the craziest thing you’ve ever seen?
Did you really think I would believe that?
Can’t you take a joke?
What’s the harm in trying?
Do you think I was born yesterday?
Who do you think you are?
Using Rhetorical Questions in Your Writing
Keep in mind that rhetorical questions can:
- Keep readers engaged.
- Draw attention to something important.
- Encourage reflection.
In short, rhetorical questions can be a powerful tool for writers to use to engage their audience and emphasize their ideas. Another great tool for writers to use is LanguageTool—a multilingual spelling and grammar checker that goes above and beyond to elevate your writing.
Wasn’t this the most helpful, easy-to-understand guide on rhetorical questions you’ve ever read?

Unleash the Professional Writer in You With LanguageTool
Go well beyond grammar and spell checking. Impress with clear, precise, and stylistically flawless writing instead.
Works on All Your Favorite Services
- Thunderbird
- Google Docs
- Microsoft Word
- Open Office
- Libre Office
We Value Your Feedback
We’ve made a mistake, forgotten about an important detail, or haven’t managed to get the point across? Let’s help each other to perfect our writing.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What Is a Rhetorical Question?

3-minute read
- 4th April 2023
Rhetorical questions can be an effective tool for writers and speakers to connect with their audience and convey their message more effectively. In this article, we’ll discuss rhetorical questions, how to use them, and some examples.
Definition of a Rhetorical Question
A rhetorical question is a question that isn’t meant to be answered. It’s asked to make a point or create an effect rather than to elicit an actual response. Here are a few examples:
· Are you kidding me? ‒ Used to express disbelief or shock
· Do you think I was born yesterday? ‒ Used to express suspicion or doubt
· Why not? – Used to express willingness to try something
How to Use a Rhetorical Question
Rhetorical questions are rhetorical devices often used in writing and speech to engage the audience, emphasize a point, or provoke thought. They can be used to introduce a topic, make a statement, or open an argument.
Conversational Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions are used in everyday speech and conversations. For example:
· Who knows? ‒ Indicates that no one knows the answer
· Isn’t that the truth? ‒ Used to express agreement with something
Introducing a Topic
Rhetorical questions are a common strategy in essay writing to introduce a topic or persuade the reader . Here are some essay questions with rhetorical questions you could use to introduce the topic:
Essay Question: Why should we care about climate change?
Rhetorical Question Introduction: Would you like to live on a dying planet?
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Essay Question: Are dress codes a good idea for school?
Rhetorical Question Introduction: Wouldn’t you like the freedom to choose what you want to wear?
Famous Examples of Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions are a powerful and effective device to use in speech and writing, which is why you can find countless examples, from past and present figures, using them. Here are a few examples:
Here, Obama is using rhetorical questions to emphasize a point to his audience about what type of nation America is. The questions demonstrate his stance on immigration in America.
Dr. King used a variety of literary devices in his writing and speeches to inspire and invoke change and action in his audience. Here, he poses the rhetorical question, “Now, what does all of this mean in this great period of history?” to get his audience thinking. There’s no obvious answer here. He’s setting up his response to this seemingly unanswerable question.
Here, Sojourner Truth is speaking at the 1851 Women’s Convention to persuade the audience that women should have the right to vote like men. She’s emphasizing that she can do everything a man can do and more (childbirth), but she can’t vote like a man because she’s a woman.
Rhetorical questions are statements pretending to be a question. They’re not to be answered, as their answer should be obvious or there isn’t an obvious answer.
You can use rhetorical questions to emphasize a point, introduce a topic, or encourage your audience to think critically about an issue. If you’re looking to enhance your speaking or writing, check out our Literary Devices page to learn more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
What are rhetorical questions and should I be using them?
Believe it or not, you use rhetorical questions daily. Learn how to use them in the right way

Hugo Whitehead
Believe it or not, you use rhetorical questions daily. But, being able to harness them in the right way, will make your writing better than ever before!
What is a rhetorical question?
A rhetorical question is a literary technique used by writers for dramatic effect or to make a point. Unlike a normal question, they do not intend to be answered directly. Instead, they are used as a persuasive device to shape the way an audience thinks about a certain topic.
Why should you use them in your writing?
Rhetorical questions are a powerful but often underutilized technique that can add diversity and flair to your writing. They can explain or pinpoint something to the reader without explicitly saying or writing it. This added complexity forces the reader to engage, consider, and hypothesize about what they have read. This in turn creates a dramatic effect, making your writing much more entertaining to the reader.
To get the most out of your rhetorical questions, read them out loud to make sure they evoke the effect you intended, whether that be revealing the unknown, making a point or subtly influencing the reader.
Where and when can they be used?
Rhetorical questions can be used in most types of writing. Let's consider some examples.
They can be used to reveal a character's perception of the world without explicitly saying it. See the example below:
"What has the world come to?"
Without directly saying that the character is upset by the state of the world, it forces the reader to piece this together themselves.
By using a rhetorical question with an intended answer, the speaker can engage the audience through a common experience.
Do you hate doing the dishes? Then, I've got a solution for you!
Sometimes you can answer a question with a rhetorical question if the answer to the first question is seemingly obvious.
"Does Nick like chocolate?", asked Craig. "Is the Pope Catholic?"
Appropriate use of rhetorical question can be thought-provoking, lead the reader to arrive at a conclusion on their own and potentially have greater impact on the reader.
If you prick us, do we not bleed? If you tickle us, do we not laugh? If you poison us, do we not die? And if you wrong us, shall we not revenge?
"The Merchant of Venice" - William Shakespeare
Outwrite: The essential writing tool
Powered by artificial intelligence, Outwrite detects and corrects your spelling and grammar mistakes, as well as giving you rephrasing suggestions to improve the quality, clarity, and eloquence of your writing.
To learn more about language techniques, check out our articles on Similes and Quotation marks .

- Literary Terms
When and How to Write a Rhetorical Question
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write a Rhetorical Question
How to Write a Rhetorical Question
It’s best not to set out with the goal of writing a rhetorical question – that’s likely to make them sound forced. Instead, just try to write naturally, just as you would speak, and notice when the rhetorical questions appear.
The exception to this is when you’re writing an aporia to transition between steps in an argument (see section 6). In this case, you should:
- Think about what question the section is trying to answer
- Then simply phrase it as a question rather than a sentence. The question should be direct so that the reader knows exactly where you’re going in the argument.
When to Use Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions are found in all forms of literature, from poetry to philosophy to history. However, there are a few places where rhetorical questions are especially helpful:
Formal Essays
- In the transitions between sections. We’ll see an example in the next section
- Introductions . A good essay should raise a question and then answer it through argument. So it can be very effective in the introduction. Raise a rhetorical question, and then use your thesis statement to answer the question.
Creative Writing
- The opening and transitions of speeches . A good speech is often structured a lot like an essay, so you might want to have the orator (speaker) begin with a rhetorical question that he or she will then go on to make a speech about.
- Opening Sentence . In writing a novel or short story, the opening sentence is often the hardest thing to write. So experiment with rhetorical questions here. Can you come up with a question that gives the reader a hint of what the story is going to be about, what its major themes are, etc.?
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website

- Freelancing
- Trending Stories

What are Rhetorical Questions? A Deep Dive into Their Meaning and Significance. This article provides readers with a comprehensive toolkit for creating questions that resonate with an audience, leaving a lasting impact and influencing their perception.
Rhetorical questions are like special questions in how we talk and write. They don’t need answers, but they make you think or underline a point. You see them a lot in everyday talk, big speeches, ads, and in books. They’re like bridges that connect the person talking or writing with the people listening.
So, what are rhetorical questions? Why are they important? Well, they’re everywhere, so that shows they matter. They help share ideas, whether you’re talking to a big audience or just chatting with friends.
Rhetorical questions are like tools for talking and writing. They make sure people really understand the message. They’re not just for one kind of talk; you can use them in school, at work, or in regular conversations.
Rhetorical questions are like magic because they make you think. They get your brain going and help you understand things better. So, next time you hear one, know it’s not just a question – it’s a way to keep our conversations and thoughts moving.
Table of Contents
What are rhetorical questions and their characteristics?
What are rhetorical questions? Rhetorical questions are like a special type of question. Unlike regular questions that expect answers, rhetorical questions are more like statements in disguise. They’re here to get you thinking, not to hear your response. These questions don’t follow the typical question rules; instead, they’re like a secret weapon for writers and speakers to pack a punch with their ideas.
Rhetorical questions have some special features that make them stand out. They’re like little brain teasers, making you ponder and sparking your thoughts. They often use fancy language tricks like metaphors, exaggeration, or wordplay to make a big impact. For example, when someone asks, “Is the sky blue?” to point out the obvious, they’re using a rhetorical question.
History and origin: What are rhetorical questions?
Rhetorical questions have been around for ages, all the way back to ancient Greece. In those days, people really admired the skill of convincing and public speaking. Wise folks like Aristotle and Plato, famous Greek philosophers, used rhetorical questions in their talks. These questions helped them catch the attention of their listeners and make their arguments strong.
But rhetorical questions didn’t stop there. They found their way into all sorts of communication. They were used in religious sermons, political speeches, and even in the writings of famous authors like William Shakespeare. The fact that they’ve been around for so long shows just how powerful and persuasive they can be.
What are the rhetorical questions’ variations and forms?
Rhetorical questions come in all sorts of variations and forms. They can be sly or right out in the open, serious or funny, and sometimes they really make you think. What are rhetorical questions? Here are a few common types:
1. Hypophora:
2. rhetorical exclamatory questions:, 3. rhetorical tag questions:.
This is when a question is asked, and then the answer is given right away. It’s like a question and a follow-up response all in one. For example, “How can we overcome adversity? The answer lies in our resilience and determination.”
These questions are a mix of rhetorical questions and exclamations. They often express strong feelings or amazement. For instance, “Could you believe the incredible beauty of the sunset?”
These questions are used to seek agreement or confirmation, but the person asking them doesn’t expect a direct answer. For example, “It’s a beautiful day, isn’t it?”
These different flavors of rhetorical questions give communicators a whole toolbox to work with. They help connect with the audience in various ways, making communication more effective and engaging.
What are rhetorical questions’ functions?
Rhetorical questions play a unique role in our conversations and writing. By understanding their role, you can become a more effective communicator in a wide range of contexts. What are rhetorical questions? Here are the various functions of rhetorical questions:
- Engaging the audience:
- Stating a point:
- Challenging assumptions:
- Creating a sense of agreement:
- Capturing attention:
- Aiding recall:
- Stirring emotions:
- Enhancing engagement:
- Repetition:
- Antithesis:
A. Persuasion and argumentation
Rhetorical questions serve as powerful tools for persuasion and argumentation. When used strategically, they can influence the beliefs, opinions, and decisions of an audience. Here’s how:
1. Engaging the audience:
Rhetorical questions invite the audience to actively think about a topic. For example, “Can we afford to ignore the urgent need for change?” This question prompts the audience to consider the consequences of inaction, making them more receptive to the speaker’s viewpoint.
2. Stating a point:
Rhetorical questions can be a subtle way to make a point without coming across as confrontational. For instance, “Is it wise to continue down this unsustainable path?” The question implies that the current path is unwise, without directly stating it.
3. Challenging assumptions:
By posing rhetorical questions, speakers or writers can challenge the audience’s assumptions. For example, “Are we really as secure as we believe?” This question prompts the audience to reevaluate their sense of security, opening them to a new perspective.
4. Creating a sense of agreement:
Rhetorical questions can be used to seek agreement from the audience. When a speaker asks, “Don’t we all want a better future?” They are rallying the audience around a shared ideal.
In persuasive contexts, rhetorical questions can sway opinions, inspire action, and strengthen arguments. They do this by encouraging the audience to see things from the speaker’s viewpoint.
B. Emphasis and engagement
Rhetorical questions are masters of emphasis and engagement, often used to grab attention and hold it. Here’s how they achieve this:
1. Capturing attention:
Rhetorical questions pique the audience’s interest. They disrupt the ordinary flow of information and encourage the audience to focus on the question, preparing them for what comes next.
2. Aiding recall:
Because rhetorical questions prompt the audience to think actively, the information presented following the question is more likely to be remembered. This aids in the retention of key messages.
3. Stirring emotions:
Rhetorical questions can evoke strong emotional responses. They can make the audience feel a sense of urgency, wonder, or empathy. For example, “What if you had the power to change someone’s life?” This question tugs at the heartstrings, creating an emotional connection.
4. Enhancing engagement:
Rhetorical questions engage the audience as active participants in the communication process. This is especially valuable in education, encouraging critical thinking and participation.
In sum, rhetorical questions are essential for holding the audience’s attention. They evoke emotions and emphasize key points, making them a valuable tool in various forms of communication.
C. Rhetorical devices and figures of speech
What are rhetorical questions? Rhetorical questions are intertwined with various rhetorical devices and figures of speech. These devices add depth and artistry to the use of rhetorical questions. Let’s explore a few key examples:
1. Metaphor:
Rhetorical questions often employ metaphors to convey complex ideas. “Is life but a fleeting moment in the grand tapestry of time?” This question uses the metaphor of life as a moment and time as a tapestry to provoke contemplation.
2. Repetition:
Repeated rhetorical questions can have a powerful effect. “Can we change? Can we improve? Can we make a difference?” This repetition reinforces the message and emphasizes the importance of change.
3. Antithesis:
Antithesis involves presenting contrasting ideas. Rhetorical questions can be used to set up antithesis, like, “Do we choose to stand still, or do we dare to move forward?” This contrast encourages the audience to consider both sides of the argument.
4. Hyperbole:
Rhetorical questions sometimes employ exaggeration for effect. “Could that be any more obvious?” This hyperbolic question makes a point by emphasizing the blatant nature of the situation.
Examples: What are rhetorical questions?
You might be wondering, “What are these rhetorical questions all about?” Well, they’re questions that don’t need real answers. They’re used to make a point or get you thinking. Let’s see how they work in real life, from famous speeches to everyday talk.
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” Speech:
- Shakespeare’s Hamlet:
- Patrick Henry’s “Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death” Speech:
- When expressing surprise:
- When offering compliments:
- When seeking agreement:
- In parenting:
- Bounty Paper Towels:
A. From famous speeches and literature
Rhetorical questions have made their mark in famous speeches and literature throughout history. Here, we explore how renowned figures have harnessed the power of rhetorical questions to engage, persuade, and inspire:
1. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” Speech:
In his 1963 speech, Dr. King asked rhetorical questions challenging the status quo and envisioning a fairer society.” Is the American dream an elusive fantasy for some and a harsh reality for others?” These questions highlighted African-American injustices and envisioned a more inclusive future.
2. Shakespeare’s Hamlet:
Shakespeare often used rhetorical questions to explore his characters’ inner thoughts. In “Hamlet,” the titular character muses, “To be or not to be, that is the question.” This profound question encapsulates Hamlet’s contemplation of life, death, and the human condition.
3. Patrick Henry’s “Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death” Speech:
Delivered in 1775, Henry’s speech was a rallying cry for American independence. He asked, “Is life so dear, or peace so sweet, as to be purchased at the price of chains and slavery?” These questions challenged the audience to consider the true cost of submission to British rule.
B. In everyday conversation
Rhetorical questions aren’t just for fancy speeches. We use them in everyday talk to show surprise, give compliments, ask for agreement, or teach.
1. When expressing surprise:
“Could it be any colder today?” This question shows we’re shocked by the freezing weather.
2. When offering compliments:
“Is there anything you can’t do?” This is a way of saying someone is super talented.
3. When seeking agreement:
“Don’t we all want a better life?” This question brings people together by talking about shared goals.
4. In parenting:
Parents use rhetorical questions to teach. “What happens when you don’t finish your homework on time?” It makes kids think about the consequences.
C. In advertising and marketing
Have you ever seen a catchy ad or slogan that made you think? Well, that’s the magic of rhetorical questions in marketing.
Nike’s famous slogan, “Just do it,” is a rhetorical question. It challenges consumers to question their own hesitations and inspires them to take action.
“Think Different.” This tagline poses a rhetorical question, prompting consumers to ponder the benefits of Apple products. It also encourages them to think about individuality and creativity.
3. Bounty Paper Towels:
“Why use ordinary paper towels when you can have the quicker picker-upper?” This question emphasizes Bounty’s paper towels’ benefits, making consumers ponder their superior qualities.
These questions make us curious and get us thinking about the product.
The psychology of rhetorical questions
What are rhetorical questions? Ever wonder why these questions grab our attention? It’s because they work with how our brains think. Let’s explore why they’re so powerful.
- Engaging critical thinking:
- Highlighting key points:
- Retaining information:
- Guiding the audience:
- Creating empathy:
- Eliciting emotional responses:
- Fostering engagement:
- Encouraging critical thinking:
- Stimulating class participation:
- Enhancing memory:
- Improving communication:
A. Cognitive processes and impact on the audience
Rhetorical questions are not just linguistic tools; they have a profound impact on the way our minds work. Let’s learn cognitive processes and how rhetorical questions influence the audience’s thinking:
1. Engaging critical thinking:
Rhetorical questions make us think. When we hear one, our brains look for answers, which helps us think critically.
2. Highlighting key points:
These questions point out important stuff. For example, “What are the consequences of climate change?” makes us focus on how serious climate change is.
3. Retaining information:
When we hear a rhetorical question, we remember the info that comes after it better. This is useful for learning new things.
4. Guiding the audience:
Rhetorical questions guide our thoughts. For instance, “Can we afford to ignore the urgent need for change?” helps us think about how important it is to make a change.
B. Emotional appeal and connection
Rhetorical questions can evoke emotions and establish connections with the audience. Here’s how they accomplish this:
1. Creating empathy:
Rhetorical questions get us involved in the conversation. For example, “Have you ever experienced the feeling of loss?” makes us feel the speaker understands us.
2. Eliciting emotional responses:
By their very nature, rhetorical questions can prompt strong emotional reactions. They can be used to spark feelings of empathy, sadness, wonder, or even anger. However, it depends on the context and content of the question.
3. Fostering engagement:
Rhetorical questions don’t just make us think. They also make us feel. This gets us more interested in the message, and we’re more likely to remember it.
C. Rhetorical questions in education and learning
Rhetorical questions aren’t just for speeches and ads. They’re also used in classrooms to help students learn better.
1. Encouraging critical thinking:
Teachers use rhetorical questions to make students think and analyze things. For example, “What do you think will happen if we change this variable in the experiment?”
2. Stimulating class participation:
Rhetorical questions can make learning fun. When a teacher asks one, it gets students talking and learning together.
3. Enhancing memory:
Rhetorical questions help us remember stuff. This is super helpful for students because they can remember what they learn.
4. Improving communication:
Learning how to use rhetorical questions helps students talk and write better. It’s not just for school; it helps in other parts of life, too!
The psychology behind rhetorical questions shows us how they make us think, feel, and learn in different ways. Whether it’s a big speech, a classroom, or an ad, these questions make a big impact.
Common misconceptions: What are rhetorical questions?
There are some things people get mixed up about rhetorical questions. Let’s clear these up so you can understand them better.
- Response expectation:
- Interrogative structure:
- Loss of impact:
- Insincerity:
- Context matters:
- Cultural differences:
- Linguistic nuances:
- Translation challenges:
A. Rhetorical questions vs. literal questions
People sometimes mix up rhetorical questions with regular ones. Let’s see how they’re different:
1. Purpose:
Regular questions are meant to get answers. Rhetorical questions aren’t looking for answers; they’re making a point or getting us thinking.
2. Response expectation:
When someone asks a regular question like “What time is it?” They want a real answer, like “It’s 3:30.” But with a rhetorical question like “Is this the best you can do?” they don’t want an answer; they’re showing something could be better.
3. Interrogative structure:
Regular questions follow the usual rules, like using question words (who, what, where, when, why). Rhetorical questions often break those rules.
Understanding this difference helps us communicate better. Mixing up rhetorical questions with real ones can cause confusion.
B. Effectiveness and overuse
Rhetorical questions are great, but they lose their power if we use them too much.
1. Loss of impact:
When we use these questions too often, they become less exciting. Imagine if a whole speech was just one question after another. It would get boring, right?
2. Insincerity:
If we use too many rhetorical questions, it might seem like we’re not being honest or we’re trying to trick someone. We don’t want that!
3. Context matters:
Rhetorical questions work best when they fit the situation. In some cases, a simple statement might be better than a question. We should use these questions thoughtfully.
C. Cultural and linguistic variations
The use and understanding of rhetorical questions can vary across cultures and languages. It’s important to recognize this. Common misconceptions in this regard include:
1. Cultural differences:
What is considered persuasive or engaging in one culture might not be so in another? The way rhetorical questions are received and their cultural appropriateness can vary significantly.
2. Linguistic nuances:
Different languages may have their own nuances when it comes to rhetorical questions. Some languages use it more, while others prefer direct expression.
3. Translation challenges:
Translating unanswerable questions between languages can be challenging. This happens because the question might not have the same effect in another language due to language and cultural differences.
It’s important to understand and respect these differences. In a world where we communicate with many cultures and languages, it’s a reminder that good communication is about more than just words. You need to get the culture and language context right to communicate well.
How to use rhetorical questions effectively?
What are rhetorical questions? Are you looking to employ rhetorical questions to enhance your communication skills? In this section, we’ll provide practical guidance on using rhetorical questions effectively.
- Know your purpose:
- Clarity and simplicity:
- Consider your audience:
- Use varied forms:
- Timing matters:
- Visual and auditory impact:
- Prior knowledge:
- Interests and values:
- Age and education level:
- Cultural sensitivity:
- Metaphor and Simile:
- Parallelism:
A. Tips for writers and speakers
Follow these tips for writers and speakers to wield rhetorical questions effectively.
1. Know your purpose:
Clearly define the purpose of your rhetorical question. Are you aiming to engage, persuade, or emphasize a point? Your intent should guide the crafting of the question.
2. Clarity and simplicity:
Keep your rhetorical questions clear and simple. Complex questions can confuse the audience and dilute the impact. Choose words and structures that are easily understood.
3. Consider your audience:
Tailor your questions to your audience’s knowledge, interests, and expectations. Avoid questions that might alienate or confuse them.
4. Use varied forms:
Experiment with different forms of rhetorical questions. Consider hypophora (posing a question and then answering it), rhetorical tag questions (inviting agreement), and exclamatory questions (conveying strong emotions).
5. Timing matters:
Think about the timing of your rhetorical questions. Place them strategically within your speech or text to maximize their effect. A well-timed question can captivate the audience’s attention.
6. Visual and auditory impact:
Use vocal and physical cues to accentuate your rhetorical questions. Adjust your tone, volume, and body language to draw attention to the question.
B. Tailoring rhetorical questions to the audience
Adapting your rhetorical questions is crucial for effective communication. Here’s how to do it:
1. Prior knowledge:
Consider what your audience already knows about the topic. Align questions with your audience’s understanding and guide them to more complex ideas.
2. Interests and values:
Reflect on the interests and values of your audience. Craft questions that resonate with their concerns and priorities. This demonstrates that you understand and empathize with their perspective.
3. Age and education level:
Adjust question complexity based on your audience’s age and education. Use straightforward language for a general audience and intricate questions for experts.
4. Cultural sensitivity:
Be aware of cultural nuances. Certain cultural contexts may require more sensitivity in topic and question choice.. Respect and adapt to these variations.
C. Balancing rhetorical questions with other rhetorical techniques
Rhetorical questions, when combined with other techniques, boost their persuasive power.
1. Anaphora:
Anaphora repeats a word or phrase at the start of sentences. Combining rhetorical questions with anaphora can create a rhythmic and persuasive effect. For instance, “What can we do? What can we change? What can we achieve?”
2. Metaphor and Simile:
Use metaphors and similes alongside rhetorical questions to illustrate your point. For example, “Just as a ship needs a strong captain, do we not need a strong leader in our journey forward?”
3. Parallelism:
Employ parallel sentence structures with rhetorical questions for symmetry and impact. “Are we ready to act? Are we ready to commit? Are we ready to make a difference?”
4. Allusion:
Balancing rhetorical questions with other techniques creates a well-rounded, persuasive message. Each technique enhances engagement and impact, making your message more effective.
Ethical considerations: What are rhetorical questions?
While rhetorical questions can be a valuable tool for communication, there are ethical considerations to keep in mind. Not all situations are suitable for their use, and understanding these considerations is crucial to using rhetorical questions responsibly.
- Transparency:
- Balanced presentation:
- Respect for diverse perspectives:
- Fact-checking:
- Personal integrity:
- Honesty in intention:
- Ethical boundaries:
- Advertising and marketing:
- Public speaking and politics:
- Media and journalism:
A. Avoiding manipulation and deceit
In rhetoric and persuasion, using rhetorical questions effectively balances impact and manipulation. Here’s how to avoid crossing that line:
1. Transparency:
Be transparent about your intentions when using rhetorical questions. If your question is meant to persuade, inform your audience of your perspective. Avoid posing questions solely to manipulate their emotions or opinions.
2. Balanced presentation:
Present a balanced view of the topic at hand. Also, avoid simplifying complex topics with rhetorical questions. Moreover, you should not manipulate the narrative to serve your agenda.
3. Respect for diverse perspectives:
Acknowledge that there may be multiple valid viewpoints on a subject. Avoid using rhetorical questions to belittle or dismiss opposing opinions. Foster respectful and open dialogue instead.
4. Fact-checking:
Make sure your rhetorical questions rely on accurate info. Misrepresenting facts or using false premises can lead to deceit.
B. Maintaining authenticity and honesty
Authenticity and honesty should underpin the use of rhetorical questions:
1. Personal integrity:
Use rhetorical questions that align with your values and beliefs. Avoid employing questions that compromise your personal integrity or authenticity.
2. Honesty in intention:
Reflect on the actual purpose of your rhetorical questions. Do they provoke real thought or just deceive? Ensure your intent is honest.

3. Ethical boundaries:
Recognize the ethical boundaries in various contexts. Consider consequences and prioritize honesty and authenticity in interactions.
C. Ethical guidelines for using rhetorical questions in various contexts
Different contexts may require different ethical considerations when using rhetorical questions:
1. Education:
In educational settings, rhetorical questions can be used to stimulate critical thinking. However, educators must ask unbiased questions. These questions should encourage open discussion, not impose a specific viewpoint.
2. Advertising and marketing:
Ethical advertising and marketing aim to inform and persuade consumers honestly. Rhetorical questions engage but should not deceive. Adhering to advertising standards and being transparent about product claims is essential.
3. Public speaking and politics:
In public discourse, rhetorical questions often appear in speeches and politics. Public figures should use them sincerely, avoiding deception or emotional exploitation.
4. Media and journalism:
Journalists must use rhetorical questions responsibly in news reporting. These questions should make readers think but not manipulate the news.
No matter where you use them, you need to be ethical. Ethical use of rhetorical questions involves open, honest, and respectful discussions.
Following these ethical guidelines allows communicators to use rhetorical questions while maintaining integrity.
Whether you’re a student learning rhetoric or a professional enhancing persuasive skills, understanding ‘what is a rhetorical question’ boosts your language and discourse proficiency.
These questions influence, engage, evoke emotions, encourage critical thinking, and simplify complex ideas. Mastering rhetorical questions shape narratives, inspires action, and leaves a lasting impact.
Study famous speeches, literature, or ads to see how they use rhetorical questions. Practice crafting your own, adapting them to contexts and audiences, and refine your technique.
No Comments
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Rhetorical Questions in an Essay: Can You Use Rhetorical Questions in an Essay?
Rhetorical questions are some of the most widely employed figures of speech in literature. Many people use them in spoken or written form.
So, what is a rhetorical question? A rhetorical question is a statement formulated in form of a question; it is a question with an obvious answer or no answer at all.
Speakers and writers include rhetorical questions in their speeches and writings to engage the audience. They make the audience’s role more dynamic and exciting.
In this article, we look deeper at the role of rhetorical questions in an essay. Therefore, as a student or an essay writer read it comprehensively. Equip yourself with more knowledge and sharpen your essay-writing skills.
Can You Use Rhetorical Questions in an Essay?
You can definitely use rhetorical questions in an essay. They are an effective writing technique to use, especially in narrative and persuasive essays. They give the reader a chance to pause and consider the query. Because of this, they are good at grabbing a reader’s attention. Furthermore, they get the reader to consider their own thoughts on the subject at hand.
New Service Alert !!!
We are now taking exams and courses
Rhetorical questions channel attention to essential points, inject dramatic emphasis, or foster debates. These objectives get achieved when these questions are placed strategically in the paper. Writers use them in essays to formulate and grow critical pointers and themes. In addition, such writers employ them in their essays to reinforce particular key points in their arguments.
Although rhetorical questions are useful tools for getting people to think about a subject, it’s crucial to avoid overusing them. A reader may become confused and fail to grasp your main point if you employ too many. You can engage rhetorical questions more effectively if you use one or two in your essay and then provide a thorough explanation of your response.
Similarly, it is worth noting that not all essays accommodate the use of rhetorical questions. Academic and college application essays are examples of such essays. Remember, academic papers should be straight to the point. Instructors do not expect questions, but answers.
How to Write a Rhetorical Question in an Essay
Many linguists and literature experts are against the use of rhetorical questions in essays. However, the role these figures of speech play in an essay is unparalleled. Therefore, if you decide to use one in your essay, how do you write it? Please stick around and find out more.
In the title of your essay
Because they grab the reader’s attention, rhetorical questions are alluring to utilize in essays. They cannot, however, be successful in the essay’s body. Therefore, if you feel compelled to employ a rhetorical question, use it for the essay’s title.
Also see: can the title of an essay be a question?
In the introduction of your essay
If you address the query in the argument, you may utilize it in the introduction. You should take note of the fact that you must respond to the question and cannot rely on the reader to do so.
An excellent way to apply this literary technique would be to pose the question in the first paragraph. Then, before moving on to the essay’s body, use the thesis statement to provide an answer.
In argumentative essays
You may use a rhetorical question to get a reader to perceive or behave a certain way. Therefore, you can use them when creating argumentative essays. When utilized properly, a question like this can frequently increase the weight of a claim and support your argument.
However, unless required, you shouldn’t use this type of writing in your argumentative or persuasive essay. It is best to rephrase them as complete sentences even if you believe the rhetorical question would seem far more accessible or persuasive.
Despite their role, there are common mistakes that you should avoid when writing rhetorical questions in your essay. These mistakes include;
- Using them in the thesis statement of your essay. Remember, a thesis statement is written to answer a question rather than ask one. You would rather commence your introduction with a rhetoric question and answer it in the thesis statement.
- Overusing them in your essay . When you overuse rhetorical questions, it makes your essay annoying to the reader and makes it less impactful.
- Employing them in academic and research papers . Academic papers are written based on research and facts. They should, therefore, be straightforward and answer questions rather than asking.
The use of rhetorical questions in an essay is allowed and viable. As an essay writer ensure to use them strategically and sparingly for them to serve the intended purpose. All the best in your future writing.

What is a rhetorical question? Why do we use them? Learn about types, definition, and examples
Why would you ask a question that doesn’t expect an answer? There are several reasons, but chances are you’re using a rhetorical question .
In this article, we’ll take a look at what rhetorical questions are, why we use them, the different types, and plenty of examples.

What is a rhetorical question?
A rhetorical question is a type of question that we ask to emphasize a point or create a certain effect, without expecting an answer.
Although they take the form of a question, rhetorical questions are really just figures of speech. You are not supposed to provide a response; only perhaps to reflect on the message being conveyed.
For example, if I’m having a terrible day, I might comment “ Could this day get any worse? “. I’m not expecting you to come up with a list of things that could happen to make my day worse. It’s just a way of expressing despair, perhaps hoping for some sympathy.
In another example, a father might say to his child “ How many times do I have to ask you to clear the table when you’ve finished eating? “. He is not expecting that the child has kept count and will answer with a number. He is really saying “I wish you would learn to clear the table after you eat, without being reminded.”
These questions can be used in literature, poetry, debates, persuasive writing, and everyday conversation.
Before we look at why we use rhetorical questions, here are some more common examples:
- Can’t you do anything right?
- Who do you think you are?
- Isn’t it a beautiful day?
- Did you get dressed in the dark?
- Guess what?
- How should I know?
- Would it kill you to admit I’m right?
- Why do bad things always happen to me?
- How many times do I have to tell you?
- What is he thinking?
- Who’s counting?
- Can you blame her?
- Are you kidding me?
Keep reading for more helpful examples with specific purposes like persuasion, agreeing, and disagreeing.
Why do we use rhetorical questions?
We can use rhetorical questions to:
- Persuade people
- Evoke emotions
- Provoke thought
- Guide narrative
- Express frustration
- Convey agreement or disagreement
- Introduce a surprise or a plot twist
- Answer a question or make a point with humor or sarcasm
Let’s look at a few of these uses in more detail.

Persuasive rhetorical questions
If you are speaking or writing to persuade someone about something, rhetorical questions can help you ridicule an argument, inspire action, challenge beliefs, and encourage personal reflection.
Some phrases that might be used in persuasive rhetorical questions include:
- Don’t you think that…
- Wouldn’t you rather…
- Do you really believe that…
- Can we afford to…
- Isn’t it about time…
- Is this really…
- Can you imagine…
- Why don’t we…
You’ll often hear phrases like these in speeches, debates, and essays.
Here are some examples with more context:
- Is this really what we have lowered ourselves to?
- Isn’t it about time we took action to protect our environment?
- Can we afford to ignore the needs of the most vulnerable in our society?
- Can you imagine a world without homelessness?
- Do you really believe that they can keep their promises?
- Wouldn’t you rather be able to enter the workplace debt-free?
Using rhetorical questions effectively can help you engage your audience and make a compelling argument.
Avoiding direct criticism
Another purpose of rhetorical questions is to avoid direct criticism or to soften the blow of a harsh message by using humor. For instance:
Did you get dressed in the dark? The implication is that you are not well dressed or your clothes don’t match. The use of humor through this rhetorical question makes the comment less direct.
What time do you call this? You could say this to someone who has arrived late, especially if you have been waiting a long time for them.
Are you kidding me? This can be said in excitement or exasperation. For the latter, it’s a kinder way of saying “What you just said is so unacceptable, I hope it isn’t true.”
Different types of rhetorical question
There are several types of rhetorical question that take a specific form or serve a specific purpose. Let’s take a closer look at anthypophora , epiplexis , and erotesis .
Anthypophora and hypophora: Answering your own question
Technically, ‘hypophora’ refers to the question and ‘anthypophora’ refers to the answer in this literary device where the speaker (or writer) poses a question and then immediately answers it .
In reality, both terms are used interchangeably to refer to the device as a whole.
Anthypophora is often used by speakers to address questions the audience might have in their minds, demonstrating like-minded thinking and keeping control of the discourse. It can also help change the direction of a speech, catch the audience’s attention, or emphasize a point.
Examples of this type of rhetorical question with an answer include:
- So, where are we going to find the money to fund this project? We will reassign some budget from X and Y.
- What was the result of all of this? We made a new discovery.
- Who is going to benefit from this policy? You all are.
- What is the motto of this business? Success through unity. What does that mean? It means we all have a part to play.
- Finally, she was safe. Or was she? The door creaked open to reveal a shady figure.
Epiplexis: Provoking remorse or shame
The purpose of epiplexis as a rhetorical device is to reproach, rebuke, admonish, or shame the listener or reader and convert them to the speaker or writer’s way of thinking.
You might hear this type of rhetorical question in a debate, a political speech, or a piece of persuasive writing. Equally, it can be used when a parent is reprimanding a child, an employer is chiding an employee, and so on.
Here are some examples of epiplexis:
- Why would you do such a thing?
- Who would want to let these children starve when it’s in your power to feed them?
- Do you think money grows on trees?
- You have been late to work three days in a row. Are you trying to get yourself fired?
- Why are you using that kind of language?
- Do you want to end up in the emergency room over this?
- How many times do I have to ask you to tidy your room?
Erotesis: Stirring emotions
Erotesis is designed to elicit a strong emotional response from the audience. When the question is posed, the expected response, whether spoken or unspoken, is already obvious (and is often a resounding ‘no’).
This type of question can stir an audience’s emotions and appeal to their sentiments.
Examples of erotesis include:
- Are we going to let the other side win?
- Do you want to be stuck in this job for the rest of your life?
- Is it really worth risking your house for this investment?
- Do you want to miss out on this once-in-a-lifetime opportunity?
You’ll often hear this type of language in advertising campaigns, rallies, and any scenario where a person is trying to get others on their side.
You might also want to read about indirect questions which, although not strictly rhetorical, are sometimes asked with no intention of receiving a response.

Rhetorical question examples
We have already given plenty of examples, but here are some more that might help if you’re still learning about rhetorical questions in English:
Common rhetorical questions
Although there is no fixed list of rhetorical questions in English – you are free to have fun creating your own – there are certain examples that occur regularly in everyday speech and have become idiomatic in nature.
Here are some examples of common rhetorical questions with their meanings:
| Rhetorical question | Definition |
|---|---|
| Do I look like I was born yesterday? | I’m not as naive/stupid/inexperienced as you think. |
| Do you kiss your mother with that mouth? | A warning against using coarse language |
| Who cares? | It doesn’t matter/I don’t care. |
| How should I know? | I don’t know, and you shouldn’t expect me to know. |
| Were you born in a barn? | You seem unsophisticated or messy. (Or a direct instruction to close a door behind you.) |
| Why not? | Yes/okay. |
| How many times do I have to tell/ask you? | I’m fed up of repeating myself. |
| What time do you call this? | You’re late. |
| What is he thinking? | Expresses surprise/confusion/disagreement with someone’s actions |
| Do you think money grows on trees? Do you think I’m made of money? | I don’t have an endless supply of money to spend on you. |
| What’s that got to do with the price of fish? | That’s irrelevant. (Read more about this ) |
Examples of rhetorical questions in literature
William Shakespeare was a master of rhetorical questions, using them to uncover the inner thoughts and motivations of his characters.
One of the most profound examples is the iconic soliloquy ‘To be, or not to be’ in Hamlet, as the character contemplates life and death.
We also see Juliet questioning the importance of a name in Romeo and Juliet :
What’s in a name? That which we call a rose By any other name would smell as sweet
In Julius Caesar , Brutus asks “Who is here so vile that will not love his country?”, knowing that nobody will speak up. Later, Marc Antony, reflecting on Caesar’s conquests, says “Did this in Caesar seem ambitious?”
And the famous line ‘Shall I compare thee to a summer’s day?’ comes from Shakespeare’s Sonnet 18.
There are plenty of other examples of rhetorical questions in poetry.
Percy Bysshe Shelley’s poem Ode to the West Wind ends with a rhetorical question:
The trumpet of a prophecy! O Wind, If Winter comes, can Spring be far behind?
And William Wordsworth used several rhetorical questions in this stanza of his poem The Solitary Reaper :
Will no one tell me what she sings?— Perhaps the plaintive numbers flow For old, unhappy, far-off things, And battles long ago: Or is it some more humble lay, Familiar matter of to-day? Some natural sorrow, loss, or pain, That has been, and may be again?
Funny rhetorical questions for ‘yes’
If you want a witty or sarcastic way to answer a question with a definite ‘yes’, try one of these rhetorical affirmatives:
- Is water wet?
- Is the sky blue?
- Is the sun hot?
- Is the Pope Catholic?
- Does a bear poop in the woods?
- Do fish swim?
- Do birds fly?
- What’s the opposite of ‘no’?
- Do snakes have knees?
Note that these are colloquial expressions and should only be used in casual settings.
Rhetorical questions are common in English, from the intricate plays of Shakespeare to political speeches to marketing strategies to everyday conversations.
They provoke thought, stir emotions, challenge norms, and subtly guide our thinking – but they all have one thing in common: a question asked for effect, with no answer expected.
We hope this guide has helped broaden your vocabulary as you learn how to use rhetorical questions yourself!
What is the purpose of a rhetorical question?
A rhetorical question is usually used for persuasion, emphasis, engagement, emotion, or dramatic effect, rather than to seek an answer. Depending on the context and the type of rhetoric used, it can serve different purposes.
How should you punctuate rhetorical questions?
It’s usually best to punctuate rhetorical questions with a question mark, as they take the form of a question.
In cases where the question is used as an exclamation, you could use an exclamation mark instead. For example: “What were you thinking!”
How are rhetorical questions used in persuasive writing?
Rhetorical questions are often used in persuasive writing to ridicule an argument, inspire action, expose emotions, or provoke thought. They serve as powerful tools for engaging the reader and making them think carefully about what is written.
Are rhetorical questions used in everyday speech?
Yes, rhetorical questions are commonly used in everyday speech to express opinions or make personal remarks without expecting a response. We also use them when affirmation or denial is implicit, so the person who asks the question already knows the answer.

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Can I Use Rhetorical Questions in an Essay (Quick Answer)
by Antony W
November 1, 2021

A rhetorical question is a powerful literary technique that lets you make a point or add a dramatic effect in an essay.
Unlike a standard question, being rhetoric doesn’t evoke direct response. Rather, it tends to be persuasive in form, and it helps an author shape the way his or her target readers look at an issue or think about a topic.
Given the diversity and flair they add in writing, and the extent to which the engage readers to consider and hypothesize what they just read, can you really use rhetorical questions in an essay or should you avoid them completely?
Can I Use Rhetorical Questions in an Essay?
It’s not advisable to use rhetorical questions in an essay. While they are perfect for helping you come to grip with the essay topic in question, they’re not useful for the person reading the essay.
You could include them in the essay as indirect questions, but the best approach is to rephrase the questions into statements or not use them at all.
To understand why teachers hate rhetorical questions in essays, it’s important to look at the difference between creative and essay writing.
As you can see from the table above, rhetoric questions seek to spark excitement and suspense, which is the exact opposite of what academic writing is all about.
To take this even further, below are reasons why you shouldn’t use rhetorical question in academic writing.
1. Rhetorical Questions Add Unnecessary Words to an Essay
You don’t have much writing real estate when writing an essay. With a tight word count limit, rhetorical equations are an obvious waste of resources.
Again, questions don’t tell a story, describe your claim, or defend your argument in an essay. And rightly so, they tend to leave readers with more questions than answers.
2. Rhetorical Questions Introduce Redundancy
You might think for the moment that rhetorical questions are good for introducing a point. But isn’t it better to get to the point?
Besides, we don’t think that essay readers, from college admissions committee to professors who have dozens of argumentative essays to review even have the patience to read questions you present.
The issue here is rhetorical questions introduce redundancy in the essay, taking up the space that you have otherwise used to explain an idea or an issue better.
Instead of filling the essay with questions, which may leave the reader unsure, go straight to the point and make your ideas clear .
3. Rhetorical Questions Accost Readers
Academic writing isn’t your place to ask questions because they change the tone and perspective of an essay just as quickly.
They are passive in form. In other words, using them in academic writing means you’re asking your readers to do the thinking and reflection for you
When you change from answering readers’ most important questions on an issue to questioning them instead, you accost them. Readers don’t appreciate when you aggressively demand something from them.
4. Rhetorical Questions Make Lousy Assumption that a Reader Knows
While you’re welcome to use rhetorical questions in improving your creative writing , you shouldn’t do in academic writing.
Often with rhetorical questions, writers tend to assume that the audience already know the answer, which may not exactly be the case.
Since we don’t know if a reader knows the answer to a question, it’s best to express the question as a statement or else you risk being misunderstood.
Think about it:
Your instructor gave you an essay assignment because they want to see how you answer the question. In other words, they’re looking for answers, evidence, and arguments to your claim (position). They neither want to be entertained nor left in suspense.
How to Ask Rhetorical Question in an Essay?
While we generally don’t recommend using rhetoric questions in an essay, there’s one exception to this rule. You can use rhetorical questions:
In the Title of an Essay
It’s tempting to use rhetorical questions in an essay because they draw in the attention of the reader.
However, they can’t be effective in the body section of the essay, and we’ve already told you why.
So if you feel the urge to use rhetorical questions, use it as a title for the essay.
In the Introduction of an Essay
You may use it in the introduction provided you answer the question in the argument.
Notice here that you have to answer the question, not leave the reader to answer it for you.
An effective way to implement this literary device would be to ask the question in the opening paragraph and then use the thesis statement to answer the question before you get to the body part of the essay .
In Argumentative Essays
Rhetorical questions can be good for persuading a reader to think or act in a certain way. As such, you may use them in writing argumentative essays .
If used correctly, such a question can often strengthen the magnitude of a claim and solidify your position.
However, you really shouldn’t include this kind of writing in your argument or persuasive essay unless it’s absolutely necessary.
Even if you feel like the rhetorical question would sound a lot more readable or convincing, it would be best to rephrase them in complete statements.
Get Essay Writing Help
With all that said, feel free to get in touch with Help for Assessment writers if you need assistance with your essay writing.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Rhetorical Questions – Definition, Examples & Meaning
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

In the study of language, a rhetorical question is recognized as a figurative inquiry employed in dialogue, not with the expectation of a response, but to provoke thought, or underscore a declaration. This stylistic device is not aimed at gathering information but serves to draw attention or reinforce an argument. This type of loaded question is a common and effective tool in the realms of academic writing , literature, marketing, debates, and daily communication.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Rhetorical questions in a nutshell
- 2 Definition: Rhetorical questions
- 3 Examples of rhetorical questions
- 4 The 3 types
- 5 Effects & purposes
- 6 Benefits & problems
- 7 Rhetorical question vs. leading question
Rhetorical questions in a nutshell
A rhetorical question is a stylistic tool with a figurative question mark that seeks no response because the answer is implied or obvious.
Definition: Rhetorical questions
The etymology of the term “rhetorical” traces back to the Greek language, where “rhetorikos,” means “skilled in speaking.” It is a figure of speech in the form of a question posed for stylistic and dramatic effect rather than to elicit an answer. Unlike regular questions, which seek information or clarification, rhetorical questions are used to make a point , persuade , provoke thought , or create a dramatic effect. Despite not expecting an answer, they are still questions in form and should be punctuated accordingly with an ordinary question mark to maintain grammatical correctness and brevity.
They are designed to encourage the listener or reader to consider the implied answer within the context of the question itself, rather than to respond verbally. They are commonly used in literature, speeches, and everyday conversation to emphasize a point, express irony, or lead the audience toward a particular conclusion. When talking about academic writing, rhetorical questions have no place in it since they are used for creative flair instead of clarity.
- You’re asking me if I want to go on an all-expenses-paid trip? Is the sky blue?
- Who in their right mind would turn down such an opportunity?
- How can we expect to achieve success if we don’t put in the effort?
Examples of rhetorical questions
Rhetorical inquiries are employed across various contexts to engage audiences, provoke thought, emphasize points, or express emotions. Below you will find examples in different contexts and their functions.
Everyday life
Here are common example sentences used in daily communications.
- Do I look like I was born yesterday?
- Is money growing on trees?
- Have you ever seen me arrive late to anything?
Rhetorical inquiries in literature are often used to provoke thought, emphasize themes, or convey the characters’ emotions succinctly. Here are some short popular examples from various literary works.
- All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others, aren’t they?
- Was he not born of (a) woman?
- Can’t repeat the past? Why, of course, you can!
Below you’ll find several examples that could be seen in marketing and media.
- Want to save money on your car insurance?
- Why settle for less when you can have the best?
- Isn’t it time we talk about mental health?
In speeches and debates, especially of a political nature, figurative questions can be used to provoke an audience’s thoughts and guide them to a specific answer.
- How long will we tolerate injustice and remain silent?
- Is it not our duty to ensure every citizen has access to healthcare?
- Do we want to live in a society where education is a privilege and not a right?
Rhetorical questions with obvious answers
Most rhetorical inquiries asked have an obvious, implied answer.
- Is the sky blue?
- Don’t you want to win?
- Are you serious?
Rhetorical questions that have no answers
A rhetorical inquiry is often a hypothetical question with no real answer implied. These are typically used to make a strong negative point or to prompt further discussion.
- Why bother?
The 3 types
Rhetorical questions frequently appear in fiction, non-fiction, speeches, and everyday conversation. Some are so common they’re clichés . They come in three forms – anthypophora, erotesis, and epiplexis. Respectively, they argue the point, reinforce a point, or attack the question’s target.
| Question that immediately answers itself. | What do we stand for? We stand for freedom, justice, and equality for all. | Control the discussion and guide thoughts in a specific direction before any objections arise. | |
| Question used to challenge the audience. | Do you call this justice, to let the guilty walk free while the innocent suffer? | Criticize or condemn to provoke the audience and make them reflect on their actions or beliefs. | |
| Question used to evoke a strong reaction. | How can we expect to achieve peace by continuing to prepare for war? | Persuade or convince the audience by highlighting the obviousness or absurdity of the situation. |
Below you’ll find an image encompassing all types, their functions, and additional examples.
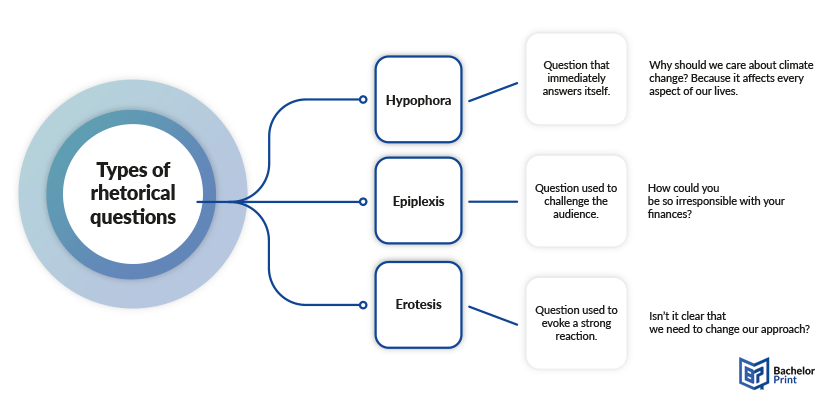
Effects & purposes
In the world of communication and rhetoric, rhetorical questions are powerful tools that can have profound effects on the listener or reader. Here are some of the theoretical and psychological impacts they have, along with plenty of examples.
Engagement and interest
Figurative questions draw the audience’s attention and engage them more deeply in the subject.
- Have you ever wondered what it means to live a good life?
This question invites the audience to reflect personally on the concept of a good life, making them more invested in the ensuing discussion.
They emphasize a point or highlight an issue, making it more memorable or striking.
- Is freedom of speech not the foundation of a democratic society?
By questioning the importance of free speech, the speaker underscores its critical role in democracy.
Provoking thought
Rhetorical questions encourage the audience to critical thinking and reflect on their beliefs or assumptions.
- What does it profit a man if he gains the whole world but loses his soul?
This question, derived from biblical context, prompts deep contemplation about the value of material vs. spiritual wealth.
Irony or sarcasm
They can convey irony or sarcasm , critiquing a situation without directly stating the criticism.
- Oh, because we all have the luxury of time, don’t we?
Used in a context where time is limited, this question sarcastically comments on the unrealistic expectations of having ample time.
Rhetorical questions can strengthen a persuasive argument by leading the audience to an intended conclusion.
- Can we really afford to ignore the environmental crisis any longer?
This question implies that the cost of inaction is too high, persuading the audience towards recognizing the urgency of environmental issues.
Building connection
They can create a sense of connection and rapport by involving the audience in the conversation.
- Haven’t we all been in a situation where we wished we had spoken up?
This question resonates with common human experiences, building a bond with the audience.
Challenging assumptions
Rhetorical questions challenge the audience to reconsider their assumptions or preconceived notions.
- Do we truly believe that all men are created equal?
It prompts the audience to reflect on their personal beliefs and the societal values around equality. By questioning the sincerity of the belief in equality, it encourages individuals to consider inconsistencies between stated values and actual practices or policies and societal justice.
Expressing frustration
They can express frustration , disbelief , or incredulity about a situation or behavior.
- Are we seriously still debating this issue?
This question expresses frustration over the prolonged discussion of what the speaker perceives as an obvious or resolved matter.
Benefits & problems
Since we have already discussed possible effects, these questions can offer several benefits in communication, but they also come with potential drawbacks. Understanding both can help in effectively leveraging rhetorical questions for desired outcomes.
Below, you’ll see several advantages rhetorical questions can offer.
| They engage the audience by encouraging them to think about the question and its implications, making the communication more interactive and thought-provoking. | |
| Rhetorical questions are excellent for emphasizing a point or highlighting an issue, making the message more memorable and impactful. They’re especially useful for headlines. | |
| By leading the audience to consider a question and its obvious answer, the audience is subtly guided to agree with the speaker’s viewpoint, making them a powerful tool. | |
| They can add dramatic effect or intrigue to a speech or writing, capturing the audience’s attention and maintaining their interest. | |
| Rhetorical questions encourage reflection and critical thinking, prompting the audience to ponder deeper meanings and implications. |
While there are numerous advantages, disadvantages can also arise when using rhetorical inquiries that may make you consider using them.
| If the implied answer is not clear to the audience, rhetorical questions can lead to confusion or misinterpretation, potentially diluting the message’s effectiveness. | |
| Frequent use of rhetorical questions can become tiresome and may diminish their impact, leading to disengagement or annoyance among the audience. | |
| Some audiences may perceive rhetorical questions as patronizing or condescending, especially if the implied answer seems to undermine their intelligence or opinions. | |
| The effectiveness can vary significantly across different cultures. In some contexts, they might not be as easily understood, affecting the communication’s impact. | |
| In situations where direct communication is necessary, relying too much on rhetorical questions can obscure the message, making it less straightforward and harder to grasp. |
We have created an image encompassing both pros and cons, as listed in the tables above.
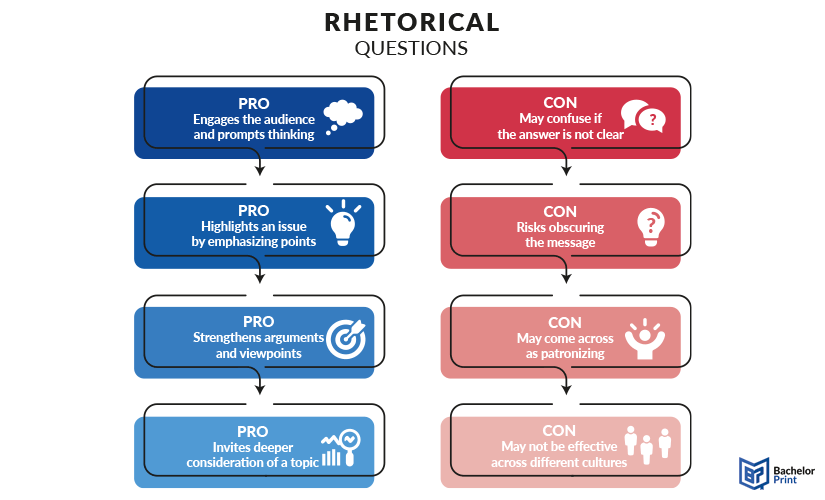
Rhetorical question vs. leading question
A leading question (also, a suggestive question) is a question that prompts or encourages the desired answer . It’s often used in legal contexts, interviews, or surveys to guide the respondent toward a specific response, sometimes subtly implying it.
The key difference lies in their intent : rhetorical questions aim to engage thought or emphasize a point without expecting a response, while leading questions seek to elicit a specific response, steering the conversation or testimony in a desired direction. Below, you’ll find examples of leading questions.
- You saw the defendant at the scene, didn’t you?
- Don’t you agree that the product works wonders?
What are rhetorical questions and their types?
It is a question that is asked for a specific purpose rather than obtaining information. The types include anthypophora (or hypophora), epiplexis, and erotesis.
Why do authors and public speakers use rhetorical questions?
To better illustrate, emphasize, and reiterate the (persuasive) points they want to make. Rhetorical questions can also invite further, unguided thought — even if they’re unanswerable. Open-ended queries make good starting points for free-flowing seminars and rhetorical debates.
Is a rhetorical question ever inappropriate?
Occasionally, it can be. Poorly timed, targeted, or phrased rhetorical questions often appear to talk down to the reader — or appear to tell them what they should think. Accidental, pathetic humor (bathos) may result from questions that are too obscure or niche to be relatable or mistakenly express a truly unpopular opinion.
What is a rhetorical question example?
“How should I know?” is a question that shows frustration, while expecting no answer.
How do you know if a question is rhetorical?
Rhetorical means that it is made for style or effect, meaning a rhetorical question is used for mere effect, rather than an answer or information. In casual conversations you can tell from context clues that there’s no point in answering this seemingly complex question.
I am so so happy I found BachelorPrint!!! I was first working with Book1One,...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Playcanvas |
| Zweck | Display our 3D product animations |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | playcanv.as, playcanvas.as, playcanvas.com |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint
- Essay Editor
Rhetorical Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide

A rhetorical analysis essay is a part of the AP English Language and Composition exam. Due to its unorthodox purpose, rhetorical analysis can be hard to master at first. This article will help you understand what a rhetorical analysis essay is, learn about main rhetorical analysis strategies, and find out how to write a rhetorical analysis.
What is a rhetorical analysis?
As you can probably guess, a rhetorical analysis is a type of analytical essay. Alongside a synthesis essay and argument essay, it is included in the free response section of the AP English exam.
Unlike most essays, a rhetoric analysis does not aim to persuade the audience. Instead, it presents a thorough study of a text’s rhetoric. The writers are expected to carefully examine a given text, deduce the author’s intention, and analyze whether it was achieved and by which means.
Rhetorical analysis strategies
To write a rhetorical analysis essay, you should read the presented text and divide it into several different components. Then, by analyzing these components and how they intertwine together to create a cohesive message, you can uncover how exactly the author managed to express their ideas in the text.
Generally, a rhetorical essay focuses on persuasive texts. The authors of these texts always employ common devices and approaches to convince their audience. That’s why the basis of any rhetorical essay is dissecting rhetorical analysis strategies that the author applied.
There are three main strategies used in rhetoric:
- Ethos . Ethos refers to a strategy where the author presents themselves as a figure of authority in their domain. This may include mentioning the author’s achievements to prove they have expertise on a subject.
- Pathos . This strategy aims to evoke strong emotions in the audience. If an author sounds inspirational or impassioned, it is a clear sign they use the pathos strategy.
- Logos . The logos strategy appeals to the logical side of the audience. It is one of the most common ways to persuade a reader in academic writing as it involves dissecting evidence and using trusted sources to sway the audience.
These rhetorical analysis strategies act as a guide for rhetorical essay writers. Knowing them will help you better understand what you should look for before starting your analysis.
Rhetorical analysis outline
Like other academic essays, a rhetorical analysis consists of three main parts: introduction, main body, and conclusion.
- The introduction of a rhetorical analysis should help the readers understand what the essay is going to be about or, rather, whom. In this part, you can focus on informing the audience about the subject of your analysis and its author. After this comes your thesis statement. In a rhetorical analysis thesis, you should express your argument about the author’s use of rhetorical devices and whether they had the intended effect.
- The main body of your essay should be dedicated to examining these devices and rhetorical analysis strategies. Each paragraph should cover a separate point and include evidence.
- The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis provides a brief overview of the arguments and ties them back to the essay thesis.
By following this rhetorical analysis outline, you can craft a cohesive essay worth the highest marks.
How to write rhetorical analysis essays: a step-by-step guide
It is easy to learn how to write a rhetorical analysis when you know what to do. Let’s explore the steps you need to take to write a perfect rhetorical analysis.
Step 1. Study the text
The obvious first step during your writing process should be reading the given text. The entirety of your essay will hedge on this text, so consider thoughtfully reading it and marking everything you think may be useful for your analysis.
Step 2. Create a plan
While we have already covered the basic outline of a rhetorical analysis, this step involves a more in-depth approach. Write down which topics will be covered in each paragraph of your paper. This is where you can also note which evidence can be used in your arguments. The following questions can help you formulate your outline:
- What was the author’s intention?
- Does the author use any rhetorical analysis strategies or devices to support their purpose?
- Does the author make any mistakes in using any of the strategies or devices? How can you detect it?
- What could the author have used to convey their message more effectively?
Step 3. Introduce the topic
At this point, you can start your essay by crafting the introduction. Talk about the author and what kind of text you will analyze. At the end, add your thesis statement that will indicate what you will be examining in your paper.
Step 4. Provide evidence
In the main body, you need to use examples from the text to illustrate your arguments. This is where you should apply your plan. Note that each paragraph is dedicated to a separate component of the text. So if you want to elaborate on the author’s approach to following the logos strategy, make sure to separate it from your analysis of the pathos strategy.
Step 5. Finish your essay
Restate your thesis in different words and give a quick recap of all the evidence you provided. After you are finished, reread your essay and make necessary corrections if needed.
Summary: rhetorical analysis essay
Rhetorical essays are some of the most difficult academic essays for writing. To craft a well-done rhetorical analysis, you must possess a keen knowledge of the art of rhetoric and how it can be applied to writing contemporary texts.
If you still struggle with how to write a rhetorical analysis, give a try to essay generator Aithor . Aithor is a state-of-the-art text generator that helps students and academics from all fields with academic writing. Use Aithor to create a rhetorical essay outline, assist in writing, or generate an example of how a perfect rhetorical analysis essay should look like.
Related articles
Classification essay guide.
A classification essay is a powerful tool in academic writing, enabling writers to break down broad topics into organized categories for better understanding. This guide will show you how to write a classification essay, from designing a perfect outline to selecting compelling topics. Continue reading to learn how to create a clear, insightful, and engaging classification essay. What is a Classification Essay? A Brief Overview A classification essay is a type of academic writing that involves ...
Argumentative Essay: A Comprehensive Guide to Academic Writing
An argumentative essay is one of the most common pieces of academic writing. It tests your ability to analyze a topic and use solid arguments to defend your position. In this article, you will learn how to write an argumentative essay and find argument essay examples. What is an argumentative essay? In academic writing, an argumentative essay is a paper where a writer provides arguments for and against a certain topic. The purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the audience to accep ...
How to Write a Good Conclusion For a Lab Report
Writing a good conclusion for your science lab report can be the difference between a good grade and a great one. It's your last chance to show you understand the experiment and why it matters. This article will help you learn how to write a lab conclusion that sums up your work and shows your teacher that you understood what you did. What Should Be in Your Lab Report Conclusion? A good lab report conclusion wraps up your lab work in a neat package. When you're thinking about how to write a c ...
How to Write a Reaction Paper Nice and Easy
In the world of student home assignments there lives an interesting and creative project, a reaction essay, by name. It deals with the person's feedback on a movie, book, article, a piece of work, evoking thoughts and emotions. What is the essence of this paper? How to write a perfect one? Let's get acquainted with this issue. At first, imagine the situation when you've just watched a deep philosophical movie or read an article that cut you to the very heart. You feel like thunderstruck. You ne ...
How to Write a Business Report With Example
One of the most effective ways to convey essential information is through a business report. This article will guide you through the purpose of a business report, provide valuable writing tips, outline how to format your business report correctly and offer an example for better understanding. What is the Purpose of a Business Report? A business report serves as a critical tool for decision-making within an organization. Its primary purpose is to analyze a particular situation or issue, evalua ...
A Guide to Writing a Great Short Essay
As a student, you're no stranger to the countless writing assignments your teachers toss your way. When you see that your next assignment is a short essay, you might think, "Oh, this will be easy!" I mean, it's only a few hundred words, right? How hard could it be? But here's the thing: writing a short essay can sometimes be even harder than writing a longer paper. So, let's work together and figure out how to make your short essays really stand out! The Basics of a Short Essay Format A short ...
Full Guide to Writing an Analytical Essay
In academic writing, an analytical essay is considered one of the most difficult papers. Not only does it require an extensive understanding of the topic, but also a high level of critical thinking skills. In this article, we’ll break down what analytical essays are, their structure, and how to write an analytical essay for the first time. What is an analytical essay? Analytical writing focuses on demonstrating how exactly an author arrived at a given conclusion. It showcases the entire thoug ...
Writing a Compare and Contrast Essay: A Complete Guide
Compare and contrast essay is an academic text that encourages authors to take a look at the differences between two or more subjects. Read this article to find out how to write a comparative essay for your assignment. What is a compare and contrast essay? As the name suggests, compare and contrast papers aim to provide two main perspectives on separate subjects by finding their similarities and dissecting their differences. Oftentimes, the purpose of compare and contrast essays is to presen ...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Academic writing
Avoid rhetorical questions
Published on November 26, 2014 by Shane Bryson . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

An example of such a question is:
Who could disagree with the statement that our political system is effective?
What the questions suggests is that “No intelligent person can dispute that our political system is effective.”
There are a few problems here.
The main problem with this type of question is that almost always there is someone who will answer in a way you don’t anticipate. Another issue is that often such questions are used in place of careful argument, and they are a poor substitution.
Finally, they take up more space than it would take to simply state the point, and they lack the clarity and conviction of a good declarative statement.
Other interesting articles
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Begging the question fallacy
- Hasty generalization fallacy
- Equivocation fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bryson, S. (2023, July 23). Avoid rhetorical questions. Scribbr. Retrieved July 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-writing/avoid-rhetorical-questions/
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

WRITERS HELPING WRITERS®
Helping writers become bestselling authors
What You Can Learn from Rhetorical Questions in Your Manuscript
October 20, 2020 by LISA HALL WILSON

It is such an easy thing to do. Once you become aware of author intrusion and what that looks like in limited third person, first person, or deep POV, the easy workaround becomes a rhetorical question. A rhetorical question is used to create dramatic effect or make a point rather than elicit an answer. Instead of telling the reader how the character feels or inserting information into the story, you have the character wonder about the information instead.
Here’s a paragraph from a manuscript I’ve stuffed in a drawer.
Laurel slunk deeper into her seat. The two other reporters and the admin glanced at her, but mostly they stared at their notebooks. She straightened in her seat and hooked her hair behind her ears. Why was everyone acting so sullen?
There it is. The rhetorical question that’s slipped in to replace the bit of author intrusion I had there. Problem solved, right? Maybe. Except, when I do a search for question marks, there’s 22 rhetorical questions in eight pages. TWENTY-TWO?? Hmmm…

I saw this trend of overusing rhetorical questions in my student’s work too and the question marks began jumping off the page at me. The problem is that the author intrusion or narrator voice we’re trying to avoid by using rhetorical questions ends up being a crutch that prevents us from taking that next step to go deeper with our character.
So I challenged myself to limit the rhetorical questions to one per chapter. One. And here are the benefits of stretching yourself in this way.
Rhetorical Questions Aren’t Wrong
Rhetorical questions have their place in internal dialogue, the goal shouldn’t be to completely eliminate them (mostly, rhetorical questions are fair game in dialogue). They can offer great surprise for the reader.
But most of the time, the character’s rhetorical questions are offering information the reader already knows the character is thinking about. You’re repeating information instead of moving the story ahead. You’ve just tied an anchor to the pace of your novel right there. Why waste valuable space on the page repeating things the reader already knows?
Flip-Flopping
Readers want characters that stand for something. They want characters who have decided to press on towards a particular goal no matter what the cost – there’s no turning back. To do this well, your character needs to plant a flag, draw a line in the sand, pick a path, choose a side.
While we hope rhetorical questions help us create tension and uncertainty in characters (and therefore readers), over-using them allows the character to waffle. This waffling or hesitation makes the character harder to cheer for, harder to relate to. Instead, force them to be decisive and live with the consequences. Take a rhetorical question in your manuscript and have the character think of the answer to the question instead. For instance:
Could she trust him?
Could become: He’d betrayed her before and nothing stopped him from doing it again. But maybe he was her only chance at a relationship. The ache in her chest kicked up, a sharp penetrating throb over her sternum. No, she couldn’t trust him, but she didn’t trust herself to make a good decision either.
The rhetorical question is a shortcut that’s meant to increase tension, but many times the shortcut undermines the emotional potential in a scene. It’s a lost opportunity to go deeper. There’s more emotional depth to the answer than the rhetorical question offered.
Try Starting with the Rhetorical Question
Back-to-back rhetorical questions point to weak writing or undeveloped characters. I’m a pantser at heart, so my first drafts are riddled with rhetorical questions. Case in point:

But could she do it? Could she go back to the farm—to him? Could they fix their marriage? Did she even want to?
I have begun to see these paragraphs as fluorescent sticky tabs marking a place I need to revisit and go deeper with the emotions.
In revisions, get curious about how the character would answer those questions. Start with the rhetorical question as a launching point for going deeper. What are the implications of one or more possible answers?
In the paragraph above, the female character is trying to decide if she should give her marriage another chance. There’s so much depth to plumb there. If she goes back to him, what kind of person does that make her? Would her opinion of herself change if it doesn’t work out? Why is it so hard to decide – what’s at risk? What parts of herself are upset and why is she refusing to listen to them? What would a stronger person do? Why can’t she do that?
Are the Rhetorical Questions Always Coming from One Character?
This was a pretty humbling question to ask myself, because I saw a trend in my first drafts where there was always one POV character who overused rhetorical questions to an embarrassing level. The other POV characters would have a reasonable use of rhetorical questions, but there would be one with back-to-back paragraphs of rhetorical questions. *womp womp*
Has this happened to you too? It’s a signal to me that I don’t know my character well enough. I don’t know WHY they’re doing/thinking certain things, what’s motivating them, what emotions are involved or at risk, or even what they really want. The rhetorical questions allowed me to waffle and skim, to avoid the hard work of going deeper. I had to stop being a lazy writer and get curious about aspects of this character I didn’t have an answer for yet.
Going deeper with the emotions in a scene allows the reader to connect with the character. Rhetorical questions can be a great starting point to diving deep into emotions, so don’t be discouraged if you find quite a few!

If Lisa had a super-power it would be breaking down complicated concepts into digestible practical steps. Lisa loves helping writers “go deeper” and create emotional connections with readers using deep point of view! Hang out with Lisa on Facebook at Confident Writers where she talks deep point of view.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Reader Interactions
October 22, 2020 at 2:52 pm
Thanks so much. I constantly use rhetorical questions in my writing as a crutch. I kept wondering “Is this good writing?” (haha). I couldn’t put my finger on how to replace them. Your examples really help.
October 21, 2020 at 1:28 pm
Cool Article. I was heading in this direction, but this article confirms what I was doing. And, yes, you are so right. We can come up with some amazing things we didn’t know was in our character’s heads. It’s fun.
October 20, 2020 at 5:41 pm
Lisa, definitely one of your best posts! Like you are looking over my shoulder to make sure I’m using deeper POV instead of taking the shortcut. I will be checking out my manuscript during edits to make my writing the best it can be.
October 20, 2020 at 6:34 pm
Glad it was helpful! l
October 20, 2020 at 10:42 am
You gave me some good food for thought here, Lisa. First, I never thought about how many times I might use retoricals and if I overuse them (great idea to look for question marks!) and second, I have to ask myself if I use them to waffle too much when I should be going deeper. Thank you!
October 20, 2020 at 12:37 pm
I saw them overused in the work I was critiquing and saw why they were being over-used. And when I looked at some of my own first drafts I saw the same issue. I love it when something new pops out at me to take my writing even deeper.
Breakout English
Writing an Article – Rhetorical Questions
Writing rhetorical questions is a literary device that professional writers love to hate, but if you’re writing an article for an exam, they can be a very useful tool. You may need to write an article in Cambridge Preliminary (PET) or First (FCE) and in Trinity ISE I, II, or III. Writing an article is a new addition to the Preliminary (PET) exam in 2020, but personally, I think it is a nice option for B1 candidates to show their ability. So why are rhetorical questions a good option for writing articles?

What is a rhetorical question?
A rhetorical question is a question which is asked for effect and doesn’t need to be answered. Sometimes the answer to rhetorical questions is obvious or sometimes the asker will go on to answer it themselves.
As you can see by the way I used a rhetorical question in the introduction to this blog, they encourage a reader to keep reading. The psychological effect of rhetorical questions can be quite powerful because you can spark interest, intrigue and even controversy if used effectively.
When and how often should you be writing rhetorical questions?
They are a great tool for articles and possibly reviews or letters , but that’s where I would draw the line. A rhetorical question has no place in formal writing, which means avoid them in essays, reports and proposals. Articles are generally neutral or informal in exams, so I think they are a great place to show off a few questions.
Use rhetorical questions sparingly . The best place for them is at the end of your 1st paragraph and in the final paragraph as a way to make the ending interesting. One or two questions throughout the text is more than enough.
The materials: Rhetorical question cards
These rhetorical question cards have sentence stems on them so that you can practice writing questions for different topics that could come up in the exam. Brainstorm a series of topics and then try writing a question for each one.

Possible procedure:
- Cut up question cards and give one set to each pair
- On the board, have a list of six possible article topics (like the example above)
- One student rolls a dice which determines the topic everyone has to write about
- Each pair turns over a question card and writes a rhetorical question related to the topic
- Compare and contrast, correct errors and put the best on the board
- Replace the used topic with a new one
- Rinse and repeat
EXAM PART : Writing Part 2 – Article, Preliminary (PET), FIrst (FCE), ISE I, ISE II, ISE III
EXAM SKILLS : Creating cohesion and maintaining reader’s interest
TIME: 20 minutes
PREPARATION: One set of question cards per pair of students, list of article topics appropriate for the level

- Speech Writing
- Delivery Techniques
- PowerPoint & Visuals
- Speaker Habits
- Speaker Resources
Speech Critiques
- Book Reviews
- Browse Articles
- ALL Articles
- Learn About Us
- About Six Minutes
- Meet Our Authors
- Write for Us
- Advertise With Us
How to Use Rhetorical Questions in Your Speech
A rhetorical question is a common rhetorical device where a question is asked by a speaker, but no answer is expected from the audience . This distinguishes it from explicit verbal audience interaction where a speaker asks a question, and then waits for a response or calls on someone to answer it.
You are certainly aware of this technique, but are you aware that you can use a rhetorical question in at least nine different ways ? No? Read on!
This article identifies nine ways to use rhetorical questions, and provides examples throughout.
- Speech Quotations
- Rhetorical Questions
- Triads (the Rule of Three)
- Parallelism
Strategies when asking rhetorical questions
Like other speech techniques, rhetorical questions can be used in a variety of ways, depending on the needs of the speaker and the speech.
It is rarely necessary to ask a rhetorical question; there is nearly always another way to convey the same idea without using a question. But rhetorical questions, like other rhetorical devices, add variety and interest to a speech.
Here are nine strategies that can be fulfilled (often in combination) with a carefully crafted rhetorical question:
1. Engage the audience to think with a rhetorical question.
The most popular use of a rhetorical question is to engage your audience to think. If your entire speech is a series of statements, your audience may passively listen and absorb little. On the other hand, you can make them active participants in your speech by inviting them to think about your arguments. This is most effective if they are asked to think about an issue from a fresh perspective.
For example, suppose you are delivering a goal achievement seminar. While many people feel that external forces prevent them from realizing their goals, you might engage your audience to think about their self-defeating behaviors:
Setting goals is easy, but achieving them isn’t. How are you sabotaging yourself?
2. Invite your audience to agree with you by asking a rhetorical question.
To persuade your audience, they must see you as credible . One way to build credibility is to convince your audience that you are similar to them and share their beliefs. One way to do this is by asking a rhetorical question where the answer has the audience agreeing with you, perhaps even nodding their head in agreement.
For example, suppose you are speaking at a networking event for working mothers, and you represent a local health spa:
Given how hard you work — both at the office and at home — don’t you deserve a day at the spa?
[When your audience silently answers “Yes, I do deserve that”, the effect is that they see themselves as more similar to you.]
3. Stir emotions by asking a rhetorical question.
Effective speakers know how to stir audience emotions. Rhetorical questions do this by making the audience a partner in your emotional statements . Instead of delivering one-way emotional statements, you can involve your audience more emotionally by hooking them with a rhetorical question.
For example, suppose you are at a political rally. Instead of saying:
They’ve never done anything to help us.
What have they ever done to help us?
The latter version is stronger, because it triggers an emotional response by having the audience thinking “Nothing! They’ve done nothing!”
4. Emphasize a previous statement with a rhetorical question.
Rhetorical questions can be used as an exclamation point on a preceding statement. While the preceding statement may be a factual statement, a rhetorical question forces your audience to think hard about it .
For example, suppose you are speaking out against gang violence in your community:
17 of our sons and daughters have already died in gang-related crime. How many will it take before we act?
5. Invoke misdirection with a rhetorical question.
Careful use of misdirection in a speech is an effective way of generating audience surprise , and this results in them being active participants. One form of misdirection is when you make a statement which leads in one direction, and then follow it up with a statement that pulls in the opposite direction.
For example, suppose you are trying to motivate your sales department:
Financial analysts in our industry predict that sales are going to be down next year. But does that prediction apply to us? [… and then you go on to show why it does not…]
In the above example, the rhetorical question followed a contrasting statement. But this pattern can be reversed with the rhetorical question preceding a contrasting statement. For example:
Why would anyone care about the polling data, when it has proven to be inaccurate in the past? The primary reason is that polling firms have been using entirely different methods this time…
6. Ask and answer a rhetorical question your audience may be thinking.
Thorough audience analysis will reveal many questions that members of your audience may have. Rather than waiting to address these questions following your speech (e.g. in a Q&A session), you can address them in the body of your speech by asking the question and immediately answering it.
For example, imagine that you are speaking to a new parents’ support group:
As a new parent, you often wonder: What can I do to give my child an intellectual jump start? The answer is reading aloud to them every day.
Or, consider another example:
Why is it important to exercise our right to vote? Voting is a duty of active citizenship!
7. Answer a question with another rhetorical question.
A common technique to answer a question (either one you have raised, or one coming from your audience) is to respond with a rhetorical question. This is done when the two questions (the one you were asked, and the one you responded with) have the same answer (typically, either “yes” or “no”).
For example:
Will we win the contract? Is the sky blue?
The obvious answer to the second question is “yes”, and this implies the answer to the first is also “yes”.
Do you think we should give up on our school and close it? Do pigs fly?
This time, the obvious answer to the second question is “no”, and this implies the answer to the first is also “no”.
Beware when using this technique as it can sound cliche to your audience. If you can, make the second question fresh and unique to your audience.
8. Ask a series of rhetorical questions to highlight divergent thoughts.
When speaking about a particularly complex issue, one technique that reinforces this complexity is to ask a series of questions which, if answered, would all point in different directions.
How can we stop bullying in school? Is the answer to educate the bullies? Or educate those being bullied? Do we need more supervision on playgrounds? How about stricter penalties for offenders? […]
A series of questions like this might be used in the opening of a speech, while the body of the speech might follow up on the individual questions one by one.
9. Ask a series of rhetorical questions to highlight convergent thoughts.
A series of rhetorical questions can also be used in situations where, if the questions were answered, all of the answers would point in the same direction. This technique is a variation on repetition and could be used to emphasize a point repeatedly.
Who has turned around our club and made it prosperous? Who is tireless in her devotion to this club? Who is our undisputed leader? Of course I am speaking of our club president Laurelle who we honor here today.
What do you think?
That’s not a rhetorical question. I really do want to hear what you think. Please add a comment to share your ideas about how to use rhetorical questions.
Please share this...
This is one of many public speaking articles featured on Six Minutes . Subscribe to Six Minutes for free to receive future articles.
Add a Comment Cancel reply
E-Mail (hidden)
Subscribe - It's Free!
| Follow Us |
Similar Articles You May Like...
- Speech Preparation #6: Add Impact with Rhetorical Devices
- What is Charisma? Can it be Learned?
- How to Write Memorable Speech Lines (Chiasmus)
- 8 Ways to Use Contrast in Your Speeches
- Speech Critique: Ken Robinson (TED 2006)
- Why Successful Speech Outlines follow the Rule of Three
Find More Articles Tagged:
16 comments.
Thanks, Andrew, for this incredibly helpful article on using the rhetorical question. Already incorporated one of your suggestions in a speech I am writing.
This is really a set of useful tips. And all the articles coming in this series are useful and effective tips and inputs. Thank you for sharing all these valid points and eye openers.
Thanks Andrew – that’s a very thorough and thought-provoking look at rhetorical questions. I never realised there was so much to them!
What do you think are the *limits* of their use, though? I ask because I once attended a talk where (to my mind) the speaker *overused* rhetorical questions. From a listener’s viewpoint, that felt frustrating because it was as though the speaker repeatedly asked for dialogue, only to move on without waiting for our answers. So the talk was a monologue just *masquerading* as dialogue.
In what ways, then, might a presenter attempt to judge when they had the “right” number of rhetorical questions in their talk, compared with real questions or other techniques? I wonder if there should be at least as many real questions as rhetorical questions, to maintain balance. What do you think?
I agree that rhetorical questions can be overused, but I don’t think one can give a general rule about what the “right” number or ratio is. It depends wildly on the purpose and nature of the presentation.
For example, in his TED talk, Ken Robinson used rhetorical questions 26 times (as part of his personal speaking style), and doesn’t ask any questions where he expects a response from the audience.
It would be good if there was *some* guideline people could fall back on – if not mathematical, maybe something like “ask a couple of trusted colleagues their opinions about the rhetorical questions in your talk”. Or “keep only the rhetorical questions you’d use in a one-to-one conversation”. That second one sounds like a promising rule of thumb, but I’ll continue to think about a guideline that might work. Thanks for the Ken Robinson link – it’s really useful to consider a real example like that. Like you, the 1st time I watched Ken’s talk, I didn’t really notice all the rhetorical questions. But now I’m aware of them, they’re quite obtrusive, which to me rings alarm bells. So *if* he uses them as part of his regular style, I think someone who listened to a couple of his talks would quickly start to be distracted by them. Also, such wide use lessens their power. Anyway, thanks again for sparking this line of thought on a useful speech technique. I’m a lot more aware of the uses for rhetorical questions now!
Extremely good points and well-articulated. The use of the rhetorical question is far more powerful than most speakers realize so your article gives excellent advice.
from Paris, France
Andrew —
You have a GREAT site which I just found.
I preparing a contest speech at Toastmasters in Paris and was looking for some writing advice – and found your wonderful site. Keep up the good work. Joy,
if you ask a topic question and you prepared for the answer in speech way , it will be consider it a question and answer? like they did in pageant. they already a topic question and they prepared a answered in speech formed.
Very helpful! I’m strategically commencing a defence for gross misconduct for an employee and this will be a unique and suprising approach. My thought is to ask initially if the employee is guilty and then answer that he is but not guilty because…….here, I will commence my mitigating evidence. I will try to introduce other rhetoricals throughout…..very good, thanks!
Thank you for your help Andrew, but I have a question. If I am trying to write a persuasive speech, which one of these methods should I use? I looked through them all and found that all of them were really interesting and intriguing. Please answer soon.
With great thanks, Henry
Hi. The things which you have share about is really interesting and useful.
It is a great tool. Thanks for doing it. Edna
I’m not sure if this is another category or fits in with one of the 9 mentioned, but I use rhetorical questions to force a point.
“So Johny has a key to the house. he regularly takes food from the kitchen. He’s been a bully at school. The principle has had him in his office because he’s threatening people.
And you think it’s not reasonable that he stole money off the counter?”
What is answer of “that is good for the customer”(make it a rhetorical question)help me to understand
Thank you we looked through this in our classroom in our high school.
Do you happen to have any info on how to write one for a photography paper?
Recent Tweets
RT @geek_speaker How many ways can you use rhetorical questions in your speech? http://t.co/6dG39M4d via @6minutes — Anil Dilawri Nov 19th, 2012
Interesting > RT @geek_speaker: How many ways can you use rhetorical questions in your speech? http://t.co/fo1GfK2W via @6minutes — VizwerxGroup Nov 19th, 2012
Do you use questions in your speech? Great tip to consider: 9 ways to embrace your speech with rhetorical questions. http://t.co/jygpVr99 — Clondalkin TM D22 Nov 19th, 2012
Do you think rhetorical questions help your #speaking? http://t.co/B2nBRkJg from @6minutes — Donn King Nov 19th, 2012
How many ways can you use rhetorical questions in your speech? http://t.co/sWihtVw9 via @6minutes — Joel Heffner Nov 20th, 2012
How many ways can you use rhetorical questions in your speech? http://t.co/LYE8oMJZ via @6minutes — Desi Ivanova Dec 4th, 2012
How many ways can you use rhetorical questions in your speech http://t.co/6Wg4ufPG — Book to Speak Dec 5th, 2012
Great insights from @6Minutes: How to Use Rhetorical Questions in Your Speech http://t.co/c8mGTzZtY5 — Christopher Witt (@CPWitt) Feb 28th, 2014
How to Use Rhetorical Questions in Your Speech https://t.co/uvDe8ZWd13 by @6minutes — @patelmehulg Jan 28th, 2017
How to Use Rhetorical Questions in Your Speech https://t.co/BLwBPFPZsg by @6minutes — @tarini_kd Sep 1st, 2017
2 Blog Links
Links of the Week: Week of Nov 5-11 « Creating Communication — Nov 10th, 2012
Seriously, stay out of my room | The Suburban Crab — Jan 21st, 2013
Featured Articles
- Majora Carter (TED, 2006) Energy, Passion, Speaking Rate
- Hans Rosling (TED, 2006) 6 Techniques to Present Data
- J.A. Gamache (Toastmasters, 2007) Gestures, Prop, Writing
- Steve Jobs (Stanford, 2005) Figures of speech, rule of three
- Al Gore (TED, 2006) Humor, audience interaction
- Dick Hardt (OSCON, 2005) Lessig Method of Presentation
Books We Recommend
| [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
| [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
| [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
| Follow Six Minutes |
Six Minutes Copyright © 2007-2019 All Rights Reserved.
Read our permissions policy , privacy policy , or disclosure policy .
Comments? Questions? Contact us .

15 Examples of Powerful Rhetorical Devices to Level Up Your Communication Skills
- The Speaker Lab
- July 9, 2024
Table of Contents
When it comes to mastering the art of public speaking, there are plenty of skills you might focus on improving. One such skill is the use of rhetorical devices in your speech. From Abraham Lincoln to modern-day authors, these tools have shaped unforgettable narratives and compelling arguments. In this article, we’ll explore some key examples of rhetorical devices that you can incorporate into your own writing to captivate and persuade. By the end, you’ll see how these techniques quietly work behind the scenes to make words come alive.
What Are Rhetorical Devices?
Before we study some examples of rhetorical devices, let’s first define what they actually are. Rhetorical devices are techniques or language used to convey a point or convince an audience. And they’re not just for English teachers or literature buffs—politicians, businesspeople, and even your favorite novelists all use rhetorical devices to persuade and impact their audiences.
While there’s some overlap with literary devices like metaphors, rhetorical devices are specifically designed to appeal to the reader’s sensibilities. In other words, they make an argument more compelling, memorable, and persuasive by tapping into emotions, logic, credibility, and style.
Common Types of Rhetorical Devices
So what exactly are these mysterious rhetorical devices? There are actually dozens of different techniques, each with its own unique effect. Some of the most common types include:
- Ethos: Appeal to the credibility and character of the speaker
- Pathos: Appeal to the emotions of the audience
- Logos: Appeal to logic and reason
- Repetition: Repeating words or phrases for emphasis
- Analogies: Comparing two things to show similarities
- Rhetorical questions: Asking a question for effect, not an answer
These are just a few examples, but they give you a sense of the variety and power of rhetorical devices. Each one serves a specific purpose in crafting a persuasive message.
Purpose of Using Rhetorical Devices in Writing
Of course, you may be wondering why you should bother with all these rhetorical devices in the first place. Can’t you just say what you mean and call it a day? You certainly could, but if you want your writing to have a real impact, rhetorical devices are key.
The purpose of using rhetorical devices in writing is to:
- Engage the reader’s emotions and imagination
- Make your arguments more memorable and persuasive
- Establish your credibility and authority on the topic
- Add style and flair to your prose
Essentially, rhetorical devices are like secret weapons that help your writing pack a punch. They take your arguments from bland to brilliant by tapping into the power of language.
Of course, like any tool, rhetorical devices must be used skillfully and strategically. You can’t just sprinkle them in willy-nilly and expect your writing to improve. It takes practice and finesse to wield them effectively.
But don’t worry—in the next section, we’ll cover some concrete rhetorical devices examples to help you get started. For now, just remember: rhetorical devices are help give your speech a polished feel. Learn to use them wisely, and your writing will reap the benefits.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
15 Examples of Rhetorical Devices in Literature and Everyday Language
Now that we’ve covered the basics of what rhetorical devices are and why they matter, let’s dive into some specific examples. Once you start looking for them, you can find these devices everywhere, whether it’s in famous speeches, classic literature, pop songs, and even everyday conversations. Let’s dive in.
Rhetorical Questions
A rhetorical question is a question asked for effect, not expecting an answer. These questions are designed to make the reader or listener think, emphasizing a point or provoking an emotional response.
- “If you prick us, do we not bleed? If you tickle us, do we not laugh? If you poison us, do we not die? And if you wrong us, shall we not revenge?” ( The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare)
- “Are you kidding me?” (Everyday speech)
Alliteration
Alliteration is the repetition of initial consonant sounds in a series of words. It creates a rhythmic, musical quality that makes phrases more memorable.
- “Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers.” (Tongue twister)
- “‘Cause, baby, now we got bad blood.” (“Bad Blood” by Taylor Swift)
Another example of a rhetorical device is an allusion. This technique makes an indirect reference to a person, place, event, or literary work. It relies on the reader’s existing knowledge to make a connection and thus enrich the meaning of the text.
- “I feel like I’m carrying the weight of the world on my shoulders.” (Reference to Greek myth of Atlas)
- “If you’re Juliet, then I’m your Romeo.” (Allusion to Shakespeare’s play, Romeo and Juliet )
Amplification
Amplification involves repeating a word or expression while adding more detail to clarify meaning. It’s used to emphasize certain points and expand on important ideas.
- “Love, true love, will follow you forever.” ( The Princess Bride )
- “A person who has good thoughts cannot ever be ugly. You can have a wonky nose and a crooked mouth and a double chin and stick-out teeth, but if you have good thoughts it will shine out of your face like sunbeams and you will always look lovely.” (The Twits by Roald Dahl)
An analogy is a comparison between two things to show their similarities. It helps explain complex ideas by relating them to more familiar concepts.
- “Life is like a box of chocolates. You never know what you’re gonna get.” ( Forrest Gump )
- “Finding a good man is like finding a needle in a haystack.” (Common expression)
Anaphora is the repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of successive clauses. Not only does it create a powerful rhythmic effect, but it also emphasizes key themes or ideas.
- “I have a dream that one day…” (Repeated throughout MLK’s famous speech)
- “It rained on his lousy tombstone, and it rained on the grass on his stomach. It rained all over the place.” (Catcher in the Rye by J.D. Salinger)
Antanagoge involves placing a criticism and compliment together to lessen the impact. It’s a way of simultaneously acknowledging a fault and offering a positive perspective.
- “The car is not pretty, but it runs great.” (Everyday speech)
- “April showers bring May flowers.” (Common expression)
Antimetabole
As you’ve seen in some examples already, rhetorical devices often utilize repetition to create a certain effect. Antimetabole is no different. In order to use this technique, a writer must repeat words or phrases in reverse order for emphasis. The inverted parallelism creates a memorable, catchy effect.
- “Ask not what your country can do for you, but what you can do for your country.” (JFK’s inaugural address)
- “When the going gets tough, the tough get going.” (Common expression)
Antiphrasis
Antiphrasis uses a word with an opposite meaning for ironic or humorous effect. It’s a form of sarcasm or understatement that draws attention to the contrast between what is said and reality.
- “Oh, I love being stuck in traffic.” (Sarcastic everyday speech)
- “I was awakened by the dulcet tones of Frank, the morning doorman, alternately yelling my name, ringing my doorbell, and pounding on my apartment door…” ( Filthy Rich by Dorothy Samuels)
Antithesis juxtaposes two contrasting ideas in parallel structure. The stark contrast not only emphasizes the conflict between the ideas but also adds vibrancy to the language.
- “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” (Neil Armstrong)
- “To err is human; to forgive, divine.” (Alexander Pope)
An appositive is a noun or noun phrase that renames another noun right beside it. It adds both extra details and context about the original noun.
- “My brother, a talented musician, taught himself guitar.” (Everyday speech)
- “Mr. Knightley, a sensible man about seven or eight-and-thirty, was not only a very old and intimate friend of the family, but particularly connected with it, as the elder brother of Isabella’s husband.” ( Emma by Jane Austen)
Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds in nearby words. Much like alliteration, it creates a musical or rhythmic effect that can make language more memorable.
- “The rain in Spain stays mainly in the plain.” (Song lyric from My Fair Lady )
- “Goodnight, sleep tight, don’t let the bedbugs bite.” (Common expression)
Asyndeton refers to a practice in literature whereby the author purposely leaves out conjunctions in the sentence, while maintaining the grammatical accuracy of the phrase. It helps speed up the rhythm of the prose being constructed.
- “I came, I saw, I conquered.” (Julius Caesar)
- “Live, laugh, love.” (Everyday expression)
Cacophony is the use of words with sharp, harsh, hissing, and unmelodious sounds—primarily those of consonants—in order to achieve desired results. For instance, the author might be trying to create a spooky atmosphere or engage the reader’s auditory senses.
- “My stick fingers click with a snicker/And, chuckling, they knuckle the keys.” (“Player Piano” by John Updike)
- “Beware the Jabberwock, my son./The jaws that bite, the claws that catch.” (“Jabberwocky” by Lewis Carroll)
Chiasmus is a “two-part sentence or phrase, where the second part is a reversal of the first.” As you may notice from the examples below, this rhetorical device is strikingly similar to antimetabole. However, whereas antimetabole uses the same or similar wording in reverse, chiasmus merely “mirrors related concepts by repeating elements of a sentence.” As a result, chiasmus allows for a bit more freedom of expression while still creating a parallel sentence structure.
- “I’d rather laugh with the sinners than cry with the saints.” (Billy Joel)
- “Genuine righteousness leads to life, but the pursuit of evil brings death.” (Proverbs 11:19)
As you can see, rhetorical devices can be found anywhere, from political speeches to pop songs to everyday expressions. By understanding how these techniques work, you can harness their power in your own writing and speech.
How to Effectively Use Rhetorical Devices in Your Writing
Mastering the art of using rhetorical devices can take your writing to the next level. In order to truly harness the power of rhetorical devices, however, you need to approach them strategically and with purpose. Let’s break it down.
Identify Your Purpose
Before you start adding rhetorical devices to your writing, take a step back and consider your purpose. What do you want to achieve with your piece? Are you trying to persuade your audience, evoke emotion, or simply inform them? When you understand your goal, you can choose the most appropriate devices to support your message.
Choose Appropriate Devices
Once you’ve identified your purpose, it’s time to select the rhetorical devices that will best serve your writing. This is where really understanding the different types of devices comes in handy. For example, if you want to create a sense of urgency, you might opt for rhetorical devices such as repetition or hyperbole . If you’re aiming to establish credibility, then you might lean towards allusion or ethos .
Use Them Sparingly
While using rhetorical devices is a great way to make your speeches shine, it’s important not to go overboard. In fact, overusing these techniques can actually weaken your writing and make it feel gimmicky or insincere. Instead, use them sparingly and strategically, like a chef adding just the right amount of seasoning to enhance a dish.
Ensure Clarity
While rhetorical devices can add depth and impact to your writing, they should never come at the expense of clarity. Your audience should still be able to easily understand your message, even with the added flourishes. If a device is making your writing confusing or convoluted, then it’s time to rethink its use.
Practice and Revise
Like any skill, effectively using rhetorical devices takes practice. When you write, experiment with different techniques and see how they impact your work. Don’t be afraid to revise and refine your use of devices as you go. Over time, you’ll develop a keen sense of when and how to deploy these powerful tools for maximum impact.
By following these guidelines and continually honing your craft, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the art of using rhetorical devices in your writing. Remember, the goal is not to show off your literary prowess, but rather to enhance your message and engage your audience on a deeper level.
The Impact of Rhetorical Devices on Audience Engagement
If you’re looking for ways to engage your audience, then rhetorical devices are great examples of how to do so effectively. But that’s not all that they can do. Rhetorical devices can also create emphasis, evoke emotions, enhance memorability, and establish credibility. If you’re a writer, then understanding the impact these techniques can have on your audience is crucial.
Creating Emphasis
One of the most powerful ways rhetorical devices engage audiences is by creating emphasis. Rhetorical devices like repetition, amplification, and antithesis, for example, can highlight key ideas or arguments, making them stand out in the reader’s mind. By strategically emphasizing certain points, you can guide your audience’s attention and ensure your most important messages hit home.
Evoking Emotions
Rhetorical devices are also incredibly effective at evoking emotions in your audience. Whether you want to inspire, motivate, or persuade, techniques like metaphor , hyperbole, and rhetorical questions can tap into your reader’s feelings and create a powerful emotional connection. And when your audience feels something, they’re more likely to stay engaged and invested in your message.
Enhancing Memorability
If you want someone to remember your speech, then rhetorical devices are crucial. Techniques such as alliteration, assonance, and chiasmus create a sense of rhythm and balance in your writing. By crafting passages with these rhetorical devices, you can ensure that your ideas don’t just sound good, but also linger long after your audience has finished reading.
Establishing Credibility
Finally, rhetorical devices can play a crucial role in establishing your credibility as a writer. By skillfully employing techniques such as allusion, ethos, and logos, you demonstrate your expertise and authority on a subject. When your audience perceives you as knowledgeable and trustworthy, they’re more likely to engage with your ideas and take your message to heart.
By understanding the impact of rhetorical devices on audience engagement and using them effectively in your writing, you can take your work to new heights. Whether you’re crafting a persuasive essay, a compelling blog post, or a powerful speech, these techniques are your secret weapon for captivating your audience and leaving a lasting impression. So go forth and wield them wisely.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Examples of Rhetorical Devices in Famous Speeches
Throughout history, great orators and writers have used rhetorical devices in order to captivate their audiences and drive home their points. Below are several famous speeches and essays that showcase the power of these techniques. So if you are looking for examples of how to use rhetorical devices effectively, then you’ve come to the right place.
“The Gettysburg Address” by Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln’s “Gettysburg Address” is a short speech, but it packs a rhetorical punch. In just a few minutes, Lincoln manages to honor the fallen soldiers, reaffirm the principles of the Declaration of Independence, and call on his audience to dedicate themselves to the unfinished work of the war.
One of the key devices Lincoln uses is antithesis, the juxtaposition of contrasting ideas. “The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here,” he says, contrasting the fleeting nature of words with the permanence of actions.
Lincoln also employs epistrophe (the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses) when he says, “of the people, by the people, for the people.” This technique drives home the central theme of the speech: that the war was fought in order to preserve a government based on popular sovereignty.
“I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King, Jr.
One of the most iconic speeches in American history, Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” is a masterclass in the use of rhetorical devices. Throughout the speech, King employs techniques like anaphora, allusion, and metaphor to paint a vivid picture of his vision for a more just and equal society.
The well-known line from King’s speech “I have a dream” illustrates the power of anaphora, as it is repeated throughout his speech in order to emphasize his wish for equality. King also makes use of allusion, referencing the Declaration of Independence, the Gettysburg Address, and the Bible to tie his message to the larger American and Christian traditions. In addition, his metaphors, like “the Negro lives on a lonely island of poverty in the midst of a vast ocean of material prosperity,” make abstract concepts concrete and emotionally resonant.
“We Shall Fight on the Beaches” by Winston Churchill
Delivered at a time when Britain stood alone against the might of Nazi Germany, Winston Churchill’s “We Shall Fight on the Beaches” speech is a stirring call to arms. Churchill uses a variety of rhetorical devices to inspire his audience and project confidence in the face of overwhelming odds.
One of the most prominent devices in the speech is anaphora. Churchill repeats the phrase “we shall fight” multiple times, each time in a different context: “we shall fight in France, we shall fight on the seas and oceans, we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air.” This repetition hammers home the message of defiance and determination.
Churchill also makes use of metaphor, comparing the British Empire and its allies to “the old lion” and Nazi Germany to “the new and terrible enemy.” These vivid images help to paint the conflict in stark, almost mythic terms.
“Friends, Romans, Countrymen” by William Shakespeare
Though not a real-life speech, Mark Antony’s funeral oration in Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar is a fictional example of rhetorical mastery. Antony’s speech is a brilliant manipulation of the crowd’s emotions, turning them against Brutus and the other conspirators and inciting them to riot.
One of Antony’s key techniques is irony. Throughout the speech, he repeatedly refers to Brutus as an “honorable man,” while providing evidence that contradicts this characterization. This irony helps to undermine Brutus’s credibility and cast doubt on his motives.
Antony also makes effective use of pathos, the appeal to emotion . He shows the crowd Caesar’s wounded body and reads his will, which leaves money to the citizens of Rome. These actions stir up feelings of grief and gratitude in the crowd, making them more receptive to Antony’s message.
These famous speeches demonstrate the power of rhetorical devices to shape opinion, stir emotion, and even change the course of history. When we study how great orators and writers have used these techniques, we can learn to communicate our own ideas more effectively and persuasively.
FAQs on Rhetorical Devices
What is an example of a rhetorical device.
Anaphora, the repetition of words at the start of successive phrases, helps create emotional impact. Think MLK’s “I Have a Dream” speech.
What are the three most common rhetorical devices?
Alliteration, metaphor, and hyperbole top the list.
What is an example of a rhetorical technique?
Antithesis pairs opposites to highlight contrast. For instance, the statement “to err is human; to forgive, divine” employs antithesis.
The magic of effective communication often lies in mastering various rhetorical devices. Whether you’re crafting an inspiring speech or penning a thought-provoking essay, understanding these tools is crucial.
You’ve now seen how simple yet impactful techniques such as metaphors, analogies, and antitheses enrich our language. These aren’t just academic exercises; they’re practical strategies you can apply today. So as you write your next piece, remember to create emphasis with repetition, evoke emotions with vivid imagery, and add rhythm with alliteration. Happy writing!
- Last Updated: July 3, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Rhetorical questions in argument
The author in this model essay never answers or presents counterarguments to his many rhetorical questions. So why would the author choose to conclude a paragraph and write this essay in the form of questions? By allowing, inviting, and 'opening up' to counterarguments, counterclaims, and rebuttals, don't questions weaken or worsen an argumentative essay?
- argumentation
2 Answers 2
In asking a question in this manner, the author uses (or tries to use!) rhetorical questions . The author does not expect a response - indeed, such a response is not possible, because the responder has way to insert himself or herself into the piece. These questions are not meant for "allowing, inviting, and 'opening up' to counterarguments." It appears the author's intent is to ask questions that (to the author) have obvious answers in a way to engage the reader more.
Rather than looking at an artificial, bad example, it would be more helpful to look at a canonical good example: the speech given by the Corcyrean Envoy at Sparta prior as told by Thucydides . In the opening of the speech, the envoy effectively makes use of several rhetorical questions.
In the piece you're referring to, I see four questions. The two in the first paragraph aren't rhetorical questions. The second question there is a clarification of the first, and the first is setting up an ostensibly stronger claim than the claim to be proved, on the idea that if you prove the stronger claim, you thereby prove the weaker claim as well. It's not a rhetorical question because the writer proceeds to attempt to answer the question. Similarly with the question in the third paragraph: the writer raises this question as a possible objection to the argument he's presenting, and proceeds to answer the question to rebut that possible objection. The question at the end of the second paragraph is the only rhetorical question in the piece. Rhetorical questions are questions that are not intended to be answered (and that the writer doesn't proceed to try to answer). They pose a question with a seemingly obvious answer in order to use that implied answer as a step in their argument. They can be effective argumentative tactics in persuasive writing in general, but I always discouraged them when teaching philosophical writing because the gold-standard of clarity in an argument is having all the premises of an argument stated explicitly. Dan Dennett advises to always try answering rhetorical questions (similar to his advice to always have a "ding" go off in your mind when you come across the words "of course," "obviously," etc. in an argument), to guard against arguments sneaking in unquestioned assumptions.
You must log in to answer this question.
- Featured on Meta
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
Hot Network Questions
- Questions about writing a Linear Algebra textbook, with Earth Science applications
- Did any other European leader praise China for its peace initiatives since the outbreak of the Ukraine war?
- A web site allows upload of pdf/svg files, can we say it is vulnerable to Stored XSS?
- A Ring of Cubes
- "Will make Elysian shades not too fair, too divine." in John Keats's "Lamia"
- Is "double-lowercase-L" a ligature (Computer Modern Italic)?
- Implementation of Euler-Maruyama numerical solver
- Error concerning projectile motion in respected textbook?
- Why do "dual frequency" or low frequency switching regulators exist when higher frequency is better?
- Power pedals on a fully MTB (riding flat roads), later on road/gravel bike
- Equivalence of first/second choice with naive probability - I don't buy it
- How can I sort all levels except the innermost level?
- Looking for title of old Star Trek TOS book where Spock is captured and gets earring
- How should I deal with curves in new deck boards during installation?
- Reference about cancellation property for semigroups
- Whom did Rashi call "oker harim"
- How to delete an island whose min x less than -1
- Problem computing a limit
- bpy.app.timers.register is lagging Blender
- A model suffering from omitted variable bias can be said to be unidentified?
- Histogram manipulation
- Eliminate some numbers so that each of the three rows contains the numbers 1 through 9 each exactly once
- Which interpreter for "Unicode text, UTF-8 text executable"
- Does the word זֶרַע (zer'a) refer to physical or spiritual descendants in Isaiah 53:10?
- Career Advice
Anatomy of an AI Essay
How might you distinguish one from a human-composed counterpart? After analyzing dozens, Elizabeth Steere lists some key predictable features.
By Elizabeth Steere
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

baona /iStock/Getty images Plus
Since OpenAI launched ChatGPT in 2022, educators have been grappling with the problem of how to recognize and address AI-generated writing. The host of AI-detection tools that have emerged over the past year vary greatly in their capabilities and reliability. For example, mere months after OpenAI launched its own AI detector, the company shut it down due to its low accuracy rate.
Understandably, students have expressed concerns over the possibility of their work receiving false positives as AI-generated content. Some institutions have disabled Turnitin’s AI-detection feature due to concerns over potential false allegations of AI plagiarism that may disproportionately affect English-language learners . At the same time, tools that rephrase AI writing—such as text spinners, text inflators or text “humanizers”—can effectively disguise AI-generated text from detection. There are even tools that mimic human typing to conceal AI use in a document’s metadata.
While the capabilities of large language models such as ChatGPT are impressive, they are also limited, as they strongly adhere to specific formulas and phrasing . Turnitin’s website explains that its AI-detection tool relies on the fact that “GPT-3 and ChatGPT tend to generate the next word in a sequence of words in a consistent and highly probable fashion.” I am not a computer programmer or statistician, but I have noticed certain attributes in text that point to the probable involvement of AI, and in February, I collected and quantified some of those characteristics in hopes to better recognize AI essays and to share those characteristics with students and other faculty members.
I asked ChatGPT 3.5 and the generative AI tool included in the free version of Grammarly each to generate more than 50 analytical essays on early American literature, using texts and prompts from classes I have taught over the past decade. I took note of the characteristics of AI essays that differentiated them from what I have come to expect from their human-composed counterparts. Here are some of the key features I noticed.
AI essays tend to get straight to the point. Human-written work often gradually leads up to its topic, offering personal anecdotes, definitions or rhetorical questions before getting to the topic at hand.
AI-generated essays are often list-like. They may feature numbered body paragraphs or multiple headings and subheadings.
The paragraphs of AI-generated essays also often begin with formulaic transitional phrases. As an example, here are the first words of each paragraph in one essay that ChatGPT produced:
- “In contrast”
- “Furthermore”
- “On the other hand”
- “In conclusion.”
Notably, AI-generated essays were far more likely than human-written essays to begin paragraphs with “Furthermore,” “Moreover” and “Overall.”
AI-generated work is often banal. It does not break new ground or demonstrate originality; its assertions sound familiar.
AI-generated text tends to remain in the third person. That’s the case even when asked a reader response–style question. For example, when I asked ChatGPT what it personally found intriguing, meaningful or resonant about one of Edgar Allan Poe’s poems, it produced six paragraphs, but the pronoun “I” was included only once. The rest of the text described the poem’s atmosphere, themes and use of language in dispassionate prose. Grammarly prefaced its answer with “I’m sorry, but I cannot have preferences as I am an AI-powered assistant and do not have emotions or personal opinions,” followed by similarly clinical observations about the text.
AI-produced text tends to discuss “readers” being “challenged” to “confront” ideologies or being “invited” to “reflect” on key topics. In contrast, I have found that human-written text tends to focus on hypothetically what “the reader” might “see,” “feel” or “learn.”
AI-generated essays are often confidently wrong. Human writing is more prone to hedging, using phrases like “I think,” “I feel,” “this might mean …” or “this could be a symbol of …” and so on.
AI-generated essays are often repetitive. An essay that ChatGPT produced on the setting of Rebecca Harding Davis’s short story “Life in the Iron Mills” contained the following assertions among its five brief paragraphs: “The setting serves as a powerful symbol,” “the industrial town itself serves as a central aspect of the setting,” “the roar of furnaces serve as a constant reminder of the relentless pace of industrial production,” “the setting serves as a catalyst for the characters’ struggles and aspirations,” “the setting serves as a microcosm of the larger societal issues of the time,” and “the setting … serves as a powerful symbol of the dehumanizing effects of industrialization.”
Editors’ Picks
- Technology in the Classroom: What the Research Tells Us
- Animated AI TAs Coming to Morehouse
- ‘Did I Insult Them?’
AI writing is often hyperbolic or overreaching. The quotes above describe a “powerful symbol,” for example. AI essays frequently describe even the most mundane topics as “groundbreaking,” “vital,” “esteemed,” “invaluable,” “indelible,” “essential,” “poignant” or “profound.”
AI-produced texts frequently use metaphors, sometimes awkwardly. ChatGPT produced several essays that compared writing to “weaving” a “rich” or “intricate tapestry” or “painting” a “vivid picture.”
AI-generated essays tend to overexplain. They often use appositives to define people or terms, as in “Margaret Fuller, a pioneering feminist and transcendentalist thinker, explored themes such as individualism, self-reliance and the search for meaning in her writings …”
AI-generated academic writing often employs certain verbs. They include “delve,” “shed light,” “highlight,” “illuminate,” “underscore,” “showcase,” “embody,” “transcend,” “navigate,” “foster,” “grapple,” “strive,” “intertwine,” “espouse” and “endeavor.”
AI-generated essays tend to end with a sweeping broad-scale statement. They talk about “the human condition,” “American society,” “the search for meaning” or “the resilience of the human spirit.” Texts are often described as a “testament to” variations on these concepts.
AI-generated writing often invents sources. ChatGPT can compose a “research paper” using MLA-style in-text parenthetical citations and Works Cited entries that look correct and convincing, but the supposed sources are often nonexistent. In my experiment, ChatGPT referenced a purported article titled “Poe, ‘The Fall of the House of Usher,’ and the Gothic’s Creation of the Unconscious,” which it claimed was published in PMLA , vol. 96, no. 5, 1981, pp. 900–908. The author cited was an actual Poe scholar, but this particular article does not appear on his CV, and while volume 96, number 5 of PMLA did appear in 1981, the pages cited in that issue of PMLA actually span two articles: one on Frankenstein and one on lyric poetry.
AI-generated essays include hallucinations. Ted Chiang’s article on this phenomenon offers a useful explanation for why large language models such as ChatGPT generate fabricated facts and incorrect assertions. My AI-generated essays included references to nonexistent events, characters and quotes. For example, ChatGPT attributed the dubious quote “Half invoked, half spontaneous, full of ill-concealed enthusiasms, her wild heart lay out there” to a lesser-known short story by Herman Melville, yet nothing resembling that quote appears in the actual text. More hallucinations were evident when AI was generating text about less canonical or more recently published literary texts.
This is not an exhaustive list, and I know that AI-generated text in other formats or relating to other fields probably features different patterns and tendencies . I also used only very basic prompts and did not delineate many specific parameters for the output beyond the topic and the format of an essay.
It is also important to remember that the attributes I’ve described are not exclusive to AI-generated texts. In fact, I noticed that the phrase “It is important to … [note/understand/consider]” was a frequent sentence starter in AI-generated work, but, as evidenced in the previous sentence, humans use these constructions, too. After all, large language models train on human-generated text.
And none of these characteristics alone definitively point to a text having been created by AI. Unless a text begins with the phrase “As an AI language model,” it can be difficult to say whether it was entirely or partially generated by AI. Thus, if the nature of a student submission suggests AI involvement, my first course of action is always to reach out to the student themselves for more information. I try to bear in mind that this is a new technology for both students and instructors, and we are all still working to adapt accordingly.
Students may have received mixed messages on what degree or type of AI use is considered acceptable. Since AI is also now integrated into tools their institutions or instructors have encouraged them to use—such as Grammarly , Microsoft Word or Google Docs —the boundaries of how they should use technology to augment human writing may be especially unclear. Students may turn to AI because they lack confidence in their own writing abilities. Ultimately, however, I hope that by discussing the limits and the predictability of AI-generated prose, we can encourage them to embrace and celebrate their unique writerly voices.
Elizabeth Steere is a lecturer in English at the University of North Georgia.

Some Community Colleges See Level Funding Despite Lean State Budgets
In some states, community college systems have seen wins this budget season even when lawmakers were looking to cut c
Share This Article
More from teaching.

Our students have been drifting away, Helen Kapstein writes, but we want them to drift back to the mindset of being c

We See You, Student Parents
Alex Rockey recommends eight principles for transforming academic access for them through mobile-friendly courses.

Beyond the Research
Michel Estefan offers a roadmap for helping graduate student instructors cultivate their distinct teaching style.
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Britain’s Next Prime Minister Has Shown Us Who He Is, and It’s Not Good

By Oliver Eagleton
Mr. Eagleton is a journalist and the author of “The Starmer Project.” He wrote from London.
The outcome seems predestined. The British Conservative Party, moribund after 14 years in office and struggling to defend its record of routine corruption and economic mismanagement , is heading into Thursday’s general election with the backing of just 20 percent of the electorate. The opposition Labour Party, having run a colorless campaign whose main aim was to channel frustration with the government, is projected to win a huge parliamentary majority. That means that Labour’s leader, Keir Starmer , will be the country’s next prime minister.
How is he likely to govern? A former lawyer with a bland rhetorical style and a tendency to modify his policies, Mr. Starmer is accused by critics on the left and right alike of lacking conviction. He is labeled an enigma, a man who stands for nothing, with no plans and no principles. His election manifesto, which The Telegraph pronounced “the dullest on record,” appears to confirm the sense that he is a void and that the character of his administration defies prediction.
But a closer look at Mr. Starmer’s back story belies this narrative. His politics are, in fact, relatively coherent and consistent. Their cardinal feature is loyalty to the British state. In practice, this often means coming down hard on those who threaten it. Throughout his legal and political career, Mr. Starmer has displayed a deeply authoritarian impulse, acting on behalf of the powerful. He is now set to carry that instinct into government. The implications for Britain — a country in need of renewal, not retrenchment — are dire.
Mr. Starmer has seldom dwelt on the specifics of his legal career, and his personal motives are, of course, unknowable. But it seems clear, based on his track record, that Mr. Starmer’s outlook began to take shape around the turn of the millennium. By that time, he had gained a reputation as a progressive barrister who worked pro bono for trade unionists and environmentalists. But in 1999 he surprised many of his colleagues by agreeing to defend a British soldier who had shot and killed a Catholic teenager in Belfast. Four years later, he was hired as a human rights adviser to the Northern Ireland Policing Board — a role in which he reportedly helped police officers justify the use of guns, water cannons and plastic bullets.
Feted by the judicial establishment, Mr. Starmer was hired to run the Crown Prosecution Service in 2008, putting him in charge of criminal prosecutions in England and Wales. Professional success brought him closer to the state, which he repeatedly sought to shield from scrutiny. He did not bring charges against the police officers who killed Jean Charles de Menezes , a Brazilian migrant who was mistaken for a terrorist suspect and shot seven times in the head. Nor did Mr. Starmer prosecute MI5 and MI6 agents who faced credible accusations of complicity in torture. Nor were so-called spy cops — undercover officers who infiltrated left-wing activist groups and manipulated some of their members into long-term sexual relationships — held accountable.
He took a different tack with those he saw as threatening law and order. After the 2010 student demonstrations over a rise in tuition fees, he drew up legal guidelines that made it easier to prosecute peaceful protesters. The following year, when riots erupted in response to the police killing of Mark Duggan , Mr. Starmer organized all-night court sittings and worked to increase the severity of sentencing for people accused of participating. During his tenure, state prosecutors fought to extradite Gary McKinnon, an I.T. expert with autism who had embarrassed the U.S. military by gaining access to its databases, and worked to drag out the case against the WikiLeaks editor Julian Assange.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Rep. Pat Ryan Becomes 10th Congress Member Calling For Biden Replacement: Here’s The Full List
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Rep. Pat Ryan, D-N.Y., on Wednesday joined nine other Democratic lawmakers urging Biden to step aside in the presidential race—as calls from within the party for Biden to drop his re-election bid continue to trickle in despite his insistence he’s staying in the contest.
President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump participate in the first presidential debate ... [+] at CNN Studios in Atlanta, Georgia, United States on June 27, 2024. (Photo by Kyle Mazza/Anadolu via Getty Images)
Rep. Pat Ryan, D-N.Y., tweeted Wednesday Biden is “no longer the best candidate to defeat Trump,” and asked him to step aside “to deliver on his promise to be a bridge to a new generation of leaders.”
Sen. Michael Bennet, D-Colo., predicted Tuesday on CNN Trump “is on track . . . to win this election, and maybe win it by a landslide,” stopping short of calling on Biden to step aside and adding that “the White House, in the time since that disastrous debate . . . has done nothing to really demonstrate they have a plan to win this election.”
Rep. Mikie Sherrill, D-N.J. , urged Biden not to run for reelection and “help lead us through a process toward a new nominee” in a statement Tuesday, saying the “stakes are too high” for a second Trump presidency, making him the ninth elected Democrat to call on Biden to step aside.
Reps. Adam Smith, D-Wash., Jerry Nadler, D-N.Y., Mark Takano, D-Calif., and Joe Morelle, D-N.Y., all said Biden should withdraw from the race at a discussion of Democratic lawmakers Sunday, The New York Times and NBC News reported, citing sources with knowledge of the talks—though Nadler later walked back his push for Biden to drop out.
Rep. Angie Craig, D-Minn., called on Biden to step down from the race after Biden’s sit-down interview with ABC News’ George Stephanopoulos citing both Biden’s poor debate performance and his “lack of a forceful response” in the week since the debate—Biden once again claimed in that interview the debate was a “bad episode” and not a sign of a condition, and refused to take a cognitive test.
Rep. Mike Quigley, D-Ill. , argued Biden should drop out of the race in an interview with MSNBC ’s Chris Hayes, saying the “only thing” Biden has left to cement his legacy and “prevent utter catastrophe is to step down and let someone else do this.”
Rep. Seth Moulton, D-Mass. : Moulton lamented he no longer has confidence Biden could defeat former President Donald Trump in the November election, telling Boston NPR station WBUR Biden should “step aside to let new leaders rise up.”
Rep. Lloyd Doggett, D-Texas: Doggett was the first sitting Democratic lawmaker to push for Biden to step aside last week, explaining he “had hoped that the debate would provide some momentum,” but Biden instead “failed to effectively defend his many accomplishments and expose Trump’s many lies.”
Rep. Raúl Grijalva, D-Ariz. , joined Doggett as the second sitting congressional Democrat calling on Biden to step down, telling The New York Times Biden has a “responsibility” to remove himself from the race.
Julian Castro : The Obama-era secretary of housing and urban development and early 2020 Democratic primary candidate argued Biden should “absolutely” take himself out of the race, saying Vice President Kamala Harris should take over on the Democratic ticket.
Former Rep. Tim Ryan, D-Ohio: Biden’s former opponent for the 2020 nomination said he believes Harris is the party’s “best path forward” in a Newsweek op-ed , calling Harris an opportunity for “generational change.”
Wealthy Biden supporters: Billionaires Christy Walton, Michael Novogratz and Reed Hastings—all of whom have given to pro-Biden or anti-Trump groups at various points—have urged Biden to step aside, while Mark Cuban has said Democrats should assess whether another person can step in as the nominee.
The New York Times Editorial Board: “To serve his country, President Biden should leave the race” the left-leaning panel declared in a headline the day after the debate, followed by similar calls from the editorial boards of The Chicago Tribune, The Atlanta Journal-Constitution and The Boston Globe.
Thomas Friedman: Acknowledging his friendship with Biden and describing how he wept while watching what he called a “heartbreaking” debate, the Pulitzer Prize-winning New York Times columnist wrote that Biden “has no business running for re-election” and the Democratic Party should conduct a new “open process in search of a Democratic presidential nominee.”
Nicholas Kristof: In a column published just hours after the debate ended, fellow New York Times columnist Kristof wrote that Biden’s debate performance “reinforced the narrative” he is too old to serve as president, and urged the president to announce his retirement before the convention, giving his delegates the chance to select another Democratic nominee, such as Michigan Gov. Gretchen Whitmer, Ohio Sen. Sherrod Brown or Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo.
Paul Krugman: “The best president of my life needs to withdraw,” was the headline on a third New York Times columnist’s plea , with Krugman acknowledging “maybe some Biden loyalists will consider this a betrayal, given how much I have supported his policies, but I fear that we need to recognize reality.”
David Remnick: The editor of the New Yorker wrote that Biden appeared to “wander into senselessness onstage,” and that remaining on the ticket “would be an act not only of self-delusion but of national endangerment.”
David Ignatius: Reiterating a view he expressed in a September column that Biden should not run, The Washington Post foreign affairs columnist wrote in a post-debate piece that Biden has been insulated by his close circle of aides and confidants, including his wife, Jill Biden, who have dismissed calls that he should step aside and “have been protective—to a fault.”
Mark Leibovich: The Atlantic staff writer and former New York Times Magazine national correspondent headlined his column “Time To Go, Joe” after the debate, calling it a “disaster” and writing that Biden “looked old, sounded old, and yes, is in fact very, very old.”
Joe Scarborough: Declaring that he “love[s]” Biden, the host of MSNBC’s “Morning Joe” (a program Biden reportedly follows closely) gently suggested the morning after the debate that the president should bow out of the race, asking the rhetorical question “if he were CEO, and he turned in a performance like that, would any corporation in America keep him on?”
Chandler West: Former White House director of photography from January 2021 through May 2022, West wrote on Instagram that “it’s time for Joe to go,” Axios reported, citing screenshots of West’s story in which he said White House operatives have said privately for months that Biden is “not as strong as he was just a couple of years ago,” and a subsequent text message from West to Axios predicting that the debate is “not gonna be the last” bad day for Biden.
James Carville: Biden “shouldn’t be” the nominee, the longtime Democratic political consultant told Politico , after saying the Biden campaign used his name in a post-debate fundraising text without his permission, and also told Axios he thinks Biden will end his campaign before Election Day, paraphrasing a quote by economist Herb Stein, “that which can’t continue . . . won’t.”
Andrew Yang: Biden’s former 2020 opponent for the Democratic nomination wrote in his blog that he was “wrong” for having confidence Biden’s team could prepare him for the debate, describing Biden as “old and shuffling” when he saw him in February, while writing that Biden is “running an unwinnable race” and “doing wrong by the country” for continuing his candidacy.
Cenk Uygur: Less than 30 minutes into the debate, the host and founder of left-wing political podcast, The Young Turks, who also briefly ran for the Democratic nomination this year, tweeted that the show would “start talking about who should replace Biden. Because at this point it’s obvious that it definitely MUST happen.”
Biden has rebuffed the calls to step aside in the race, telling congressional Democrats in a letter Monday “it’s time for [discussions about his debate performance] to end.”
What To Watch For
Some Democrats have expressed careful skepticism about Biden’s future in the race, but have stopped short of calling on him to step aside. Former House Speaker Nancy Pelosi, D-Calif., said on MSNBC in the days following the debate “I think it’s a legitimate question to say this is an episode or this is a condition,” referring to Biden’s cognitive abilities. She said Wednesday on the network that “time is running out” for Biden to decide if he’ll stay in the race—an odd statement that suggests he might still drop his bid despite his repeated insistence he’ll keep running. Rep. James Clyburn, D-S.C., a former member of the party’s leadership, said he’d like Biden to remain the nominee but argued Harris should replace him if Biden stands down. Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear, who has been floated as a replacement for Biden on the ticket, told reporters he will continue to support Biden “so long as he continues to be in the race,” but added “only he can make decisions about his candidacy.”
Key Background
The presidential debate last month was considered the most important night of the 2024 campaign cycle—and an opportunity for Biden to reassure voters concerned that he is too old to run for president. But Biden was widely viewed to have done the opposite, losing his train of thought within minutes of the debate beginning, speaking so softly at times it was hard to understand what he was saying, giving disjointed answers and often standing with a blank stare on his face, his mouth agape, while Trump was speaking. Abysmal reviews , even from some of Trump’s fiercest critics, instantly poured in on social media, and by the end of the debate, Democrats were reportedly privately discussing the possibility of replacing him on the ticket, multiple outlets reported.
There is no formal mechanism for replacing Biden as the nominee if he doesn’t step aside voluntarily. He has won nearly 3,900 of the 4,000 available delegates in the primaries who are beholden (but not legally required) to vote to formally nominate Biden at the Democratic convention in August. In an unprecedented and highly unlikely scenario, the delegates could spurn Biden and vote to select another nominee. Or Biden could withdraw from the race before the convention, giving his delegates the opportunity to cast their votes for another candidate. If he were to withdraw after the August convention, party rules state that the Democratic National Committee’s approximately 500 members could convene a special meeting to select a new nominee by majority vote. Harris would be the most obvious choice for a replacement, but Whitmer and California Gov. Gavin Newsom are other names commonly floated by pundits and the press. Both have defended him publicly following the debate.
Further Reading
Can Democrats Replace Biden? Here’s What Would Happen If Biden Leaves 2024 Race. (Forbes)
Biden Says ‘I Don’t Debate As Well As I Used To’ In Fiery Speech After Rocky Thursday Face-Off With Trump (Forbes)
These Are The Likely Democratic Presidential Candidates If Biden Drops Out—As Rough Debate Prompts Calls To Stand Down (Forbes)
Biden’s Debate Performance Torched—Even By Trump Foes—Over Weak Voice And Verbal Stumbles: ‘Hard To Watch’ (Forbes)
Biden Loses Train Of Thought And Corrects Himself Repeatedly In Debate With Trump (Forbes)
CORRECTION (7/9): This story has been updated to reflect how many House Democrats are currently calling for Biden to drop out.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Rhetorical questions can be useful in writing. So, why shouldn't you use rhetorical questions in essays? Here's 5 key reasons to explain the problem with rhetorical questions in essays.
Rhetorical questions are used in various forms of writing and rhetoric. They can be found in literature and are often used in persuasive writing, like essays, debates, and speeches of all kinds, whether political or a commencement speech. They're also common in everyday conversation as figures of speech and in marketing advertisements.
Discover the definition of rhetorical questions, see examples, and learn how to use them for more effective writing.
Rhetorical questions are questions asked to make a point or to create a dramatic effect rather than to get an answer. Many college professors discourage using rhetorical questions in essays, and the majority agree that they can be used only in specific circumstances.
A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to get an answer—most commonly, it's asked to make a persuasive point. For example, if a person asks, "How many times do I have to tell you not to eat my dessert?" he or she does not want to know the exact number of times the request will need to be repeated. Rather, the speaker's goal is to ...
Learn how to use rhetorical questions effectively in your essays! Our guide covers everything you need to know to make your writing more engaging.
A rhetorical question is asked to make a point or create an effect. We'll elaborate on this and provide several examples of rhetorical questions.
Rhetorical questions can be an effective tool for writers and speakers to connect with their audience and convey their message more effectively. In this article, we're exploring rhetorical questions, how to use them, and looking at examples.
A rhetorical question is a literary technique used by writers for dramatic effect or to make a point. Unlike a normal question, they do not intend to be answered directly. Instead, they are used as a persuasive device to shape the way an audience thinks about a certain topic.
Technically, though, we can't. Oh, we can answer questions about rhetoric, but rhetorical questions are, by definition, questions no one expects to be answered.
Clear explanation of when and how to write a Rhetorical Question. It's best not to set out with the goal of writing a rhetorical question - that's likely to make them sound forced. Instead, just try to write naturally, just as you would speak, and notice when the rhetorical questions appear.
Rhetorical questions are like tools for talking and writing. They make sure people really understand the message. They're not just for one kind of talk; you can use them in school, at work, or in regular conversations. Rhetorical questions are like magic because they make you think.
The use of rhetorical questions in an essay is allowed and viable. As an essay writer ensure to use them strategically and sparingly for them to serve the intended purpose.
A rhetorical question is a type of question that we ask to emphasize a point or create a certain effect, without expecting an answer. Although they take the form of a question, rhetorical questions are really just figures of speech. You are not supposed to provide a response; only perhaps to reflect on the message being conveyed.
A rhetorical question is a powerful literary technique that lets you make a point or add a dramatic effect in an essay. Unlike a standard question, being rhetoric doesn't evoke direct response. Rather, it tends to be persuasive in form, and it helps an author shape the way his or her target readers look at an issue or think about a topic.
Definition: Rhetorical questions. The etymology of the term "rhetorical" traces back to the Greek language, where "rhetorikos," means "skilled in speaking.". It is a figure of speech in the form of a question posed for stylistic and dramatic effect rather than to elicit an answer. Unlike regular questions, which seek information or ...
This article will help you understand what a rhetorical analysis essay is, learn about main rhetorical analysis strategies, and find out how to write a rhetorical analysis.
A rhetorical question is a question asked not as a genuine inquiry but rather to suggest something or to make a point. An example of such a question is:
A rhetorical question is used to create dramatic effect or make a point rather than elicit an answer. Instead of telling the reader how the character feels or inserting information into the story, you have the character wonder about the information instead. Here's a paragraph from a manuscript I've stuffed in a drawer.
Writing rhetorical questions is a literary device that professional writers love to hate, but if you're writing for an exam, they can be a very useful tool.
It is rarely necessary to ask a rhetorical question; there is nearly always another way to convey the same idea without using a question. But rhetorical questions, like other rhetorical devices, add variety and interest to a speech.
What are rhetorical questions? A rhetorical question is a question asked in order to create a dramatic effect or to make a point, rather than to get an answer. For example, the question 'and what time do you call this?' is asked or written merely for effect with no answer expected.
Discover 15 powerful rhetorical devices examples that can enhance your writing and engage your audience effectively.
Rhetorical questions are questions that are not intended to be answered (and that the writer doesn't proceed to try to answer). They pose a question with a seemingly obvious answer in order to use that implied answer as a step in their argument. They can be effective argumentative tactics in persuasive writing in general, but I always ...
AI essays tend to get straight to the point. Human-written work often gradually leads up to its topic, offering personal anecdotes, definitions or rhetorical questions before getting to the topic at hand. AI-generated essays are often list-like. They may feature numbered body paragraphs or multiple headings and subheadings.
Guest Essay. Britain's Next Prime Minister Has Shown Us Who He Is, and It's Not Good ... A former lawyer with a bland rhetorical style and a tendency to modify his policies, Mr. Starmer is ...
Ten sitting Democratic members of Congress have now called on Biden to step aside—though Biden has so far vowed to stay in the race.