Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.

Literature Reviews
- What is a Literature Review?
- Six Steps to Writing a Literature Review
- Finding Articles
- Try A Citation Manager
- Avoiding Plagiarism
Selecting a Research Topic
The first step in the process involves exploring and selecting a topic. You may revise the topic/scope of your research as you learn more from the literature. Be sure to select a topic that you are willing to work with for a considerable amount of time.
When thinking about a topic, it is important to consider the following:
Does the topic interest you?
Working on something that doesn’t excite you will make the process tedious. The research content should reflect your passion for research so it is essential to research in your area of interest rather than choosing a topic that interests someone else. While developing your research topic, broaden your thinking and creativity to determine what works best for you. Consider an area of high importance to your profession, or identify a gap in the research. It may take some time to narrow down on a topic and get started, but it’s worth the effort.
Is the Topic Relevant?
Be sure your subject meets the assignment/research requirements. When in doubt, review the guidelines and seek clarification from your professor.
What is the Scope and Purpose?
Sometimes your chosen topic may be too broad. To find direction, try limiting the scope and purpose of the research by identifying the concepts you wish to explore. Once this is accomplished, you can fine-tune your topic by experimenting with keyword searches our A-Z Databases until you are satisfied with your retrieval results.
Are there Enough Resources to Support Your Research?
If the topic is too narrow, you may not be able to provide the depth of results needed. When selecting a topic make sure you have adequate material to help with the research. Explore a variety of resources: journals, books, and online information.
Adapted from https://jgateplus.com/home/2018/10/11/the-dos-of-choosing-a-research-topic-part-1/
Why use keywords to search?
- Library databases work differently than Google. Library databases work best when you search for concepts and keywords.
- For your research, you will want to brainstorm keywords related to your research question. These keywords can lead you to relevant sources that you can use to start your research project.
- Identify those terms relevant to your research and add 2-3 in the search box.
Now its time to decide whether or not to incorporate what you have found into your literature review. E valuate your resources to make sure they contain information that is authoritative, reliable, relevant and the most useful in supporting your research.
Remember to be:
- Objective : keep an open mind
- Unbiased : Consider all viewpoints, and include all sides of an argument, even ones that don't support your own
Criteria for Evaluating Research Publications
Significance and Contribution to the Field
• What is the author’s aim?
• To what extent has this aim been achieved?
• What does this text add to the body of knowledge? (theory, data and/or practical application)
• What relationship does it bear to other works in the field?
• What is missing/not stated?
• Is this a problem?
Methodology or Approach (Formal, research-based texts)
• What approach was used for the research? (eg; quantitative or qualitative, analysis/review of theory or current practice, comparative, case study, personal reflection etc…)
• How objective/biased is the approach?
• Are the results valid and reliable?
• What analytical framework is used to discuss the results?
Argument and Use of Evidence
• Is there a clear problem, statement or hypothesis?
• What claims are made?
• Is the argument consistent?
• What kinds of evidence does the text rely on?
• How valid and reliable is the evidence?
• How effective is the evidence in supporting the argument?
• What conclusions are drawn?
• Are these conclusions justified?
Writing Style and Text Structure
• Does the writing style suit the intended audience? (eg; expert/non-expert, academic/non- academic)
• What is the organizing principle of the text?
- Could it be better organized?
Prepared by Pam Mort, Lyn Hallion and Tracey Lee Downey, The Learning Centre © April 2005 The University of New South Wales.
Analysis: the Starting Point for Further Analysis & Inquiry
After evaluating your retrieved sources you will be ready to explore both what has been found and what is missing . Analysis involves breaking the study into parts, understanding each part, assessing the strength of evidence, and drawing conclusions about its relationship to your topic.
Read through the information sources you have selected and try to analyze, understand and critique what you read. Critically review each source's methods, procedures, data validity/reliability, and other themes of interest. Consider how each source approaches your topic in addition to their collective points of intersection and separation . Offer an appraisal of past and current thinking, ideas, policies, and practices, identify gaps within the research, and place your current work and research within this wider discussion by considering how your research supports, contradicts, or departs from other scholars’ research and offer recommendations for future research.
Top 10 Tips for Analyzing the Research
- Define key terms
- Note key statistics
- Determine emphasis, strengths & weaknesses
- Critique research methodologies used in the studies
- Distinguish between author opinion and actual results
- Identify major trends, patterns, categories, relationships, and inconsistencies
- Recognize specific aspects in the study that relate to your topic
- Disclose any gaps in the literature
- Stay focused on your topic
- Excluding landmark studies, use current, up-to-date sources
Prepared by the fine librarians at California State University Sacramento.
Synthesis vs Summary
Your literature review should not simply be a summary of the articles, books, and other scholarly writings you find on your topic. It should synthesize the various ideas from your sources with your own observations to create a map of the scholarly conversation taking place about your research topics along with gaps or areas for further research.

Bringing together your review results is called synthesis. Synthesis relies heavily on pattern recognition and relationships or similarities between different phenomena. Recognizing these patterns and relatedness helps you make creative connections between previously unrelated research and identify any gaps.
As you read, you'll encounter various ideas, disagreements, methods, and perspectives which can be hard to organize in a meaningful way. A synthesis matrix also known as a Literature Review Matrix is an effective and efficient method to organize your literature by recording the main points of each source and documenting how sources relate to each other. If you know how to make an Excel spreadsheet, you can create your own synthesis matrix, or use one of the templates below.
Because a literature review is NOT a summary of these different sources, it can be very difficult to keep your research organized. It is especially difficult to organize the information in a way that makes the writing process simpler. One way that seems particularly helpful in organizing literature reviews is the synthesis matrix. Click on the link below for a short tutorial and synthesis matrix spreadsheet.
- Literature Review and Synthesis
- Lit Review Synthesis Matrix
- Synthesis Matrix Example
A literature review must include a thesis statement, which is your perception of the information found in the literature.
A literature review:
- Demonstrates your thorough investigation of and acquaintance with sources related to your topic
- Is not a simple listing, but a critical discussion
- Must compare and contrast opinions
- Must relate your study to previous studies
- Must show gaps in research
- Can focus on a research question or a thesis
- Includes a compilation of the primary questions and subject areas involved
- Identifies sources
https://custom-writing.org/blog/best-literature-review
Organizing Your Literature Review
The structure of the review is divided into three main parts—an introduction, body, and the conclusion.
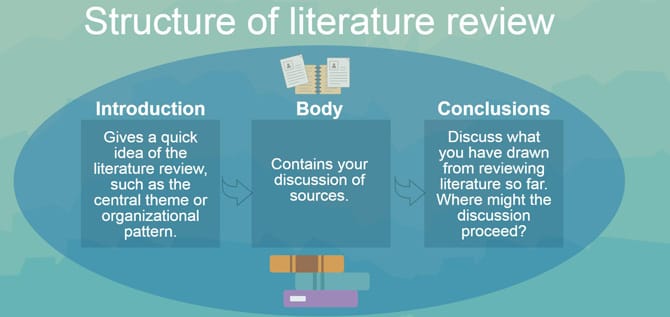
Introduction
Discuss what is already known about your topic and what readers need to know in order to understand your literature review.
- Scope, Method, Framework: Explain your selection criteria and similarities between your sources. Be sure to mention any consistent methods, theoretical frameworks, or approaches.
- Research Question or Problem Statement: State the problem you are addressing and why it is important. Try to write your research question as a statement.
- Thesis : Address the connections between your sources, current state of knowledge in the field, and consistent approaches to your topic.
- Format: Describe your literature review’s organization and adhere to it throughout.
Body
The discussion of your research and its importance to the literature should be presented in a logical structure.
- Chronological: Structure your discussion by the literature’s publication date moving from the oldest to the newest research. Discuss how your research relates to the literature and highlight any breakthroughs and any gaps in the research.
- Historical: Similar to the chronological structure, the historical structure allows for a discussion of concepts or themes and how they have evolved over time.
- Thematic: Identify and discuss the different themes present within the research. Make sure that you relate the themes to each other and to your research.
- Methodological: This type of structure is used to discuss not so much what is found but how. For example, an methodological approach could provide an analysis of research approaches, data collection or and analysis techniques.
Provide a concise summary of your review and provide suggestions for future research.
Writing for Your Audience
Writing within your discipline means learning:
- the specialized vocabulary your discipline uses
- the rhetorical conventions and discourse of your discipline
- the research methodologies which are employed
Learn how to write in your discipline by familiarizing yourself with the journals and trade publications professionals, researchers, and scholars use.
Use our Databases by Title to access:
- The best journals
- The most widely circulated trade publications
- The additional ways professionals and researchers communicate, such as conferences, newsletters, or symposiums.
- << Previous: What is a Literature Review?
- Next: Finding Articles >>
- Last Updated: Jan 18, 2024 1:14 PM
- URL: https://niagara.libguides.com/litreview
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Literature review

How to write a literature review in 6 steps
How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.

How to write a systematic literature review [9 steps]
How do you write a systematic literature review? What types of systematic literature reviews exist and where do you use them? Learn everything you need to know about a systematic literature review in this guide

What is a literature review? [with examples]
Not sure what a literature review is? This guide covers the definition, purpose, and format of a literature review.

Writing a Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- Step 1: Choosing a Topic
- Step 2: Finding Information
- Step 3: Evaluating Content
- Step 4: Taking Notes
- Step 5: Synthesizing Content
- Step 6: Writing the Review
- Step 7: Citing Your Sources
- Meet the Library Team
- Off-Campus & Mobile Access
- Research Help
- Other Helpful Guides
Library Hours
*Hours may differ on holidays and when classes are out of session. Up-to-date hours can be found here: https://library.llu.edu/all-library-hours .
Monday: 7:00am - 10:00pm
Tuesday: 7:00am - 10:00pm
Wednesday: 7:00am - 10:00pm
Thursday: 7:00am - 10:00pm
Friday: 7:00am - 4:00pm
Saturday: Closed
Sunday: 10:00am - 10:00pm
Steps To Write a Literature Review
- << Previous: What is a Literature Review?
- Next: Step 1: Choosing a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 9:42 AM
- URL: https://libguides.llu.edu/literaturereview
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
Who is my subject librarian.
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write a Literature Review
This guide has a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA) License.

This license lets others remix, tweak, and build upon your work non-commercially, as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms.
- Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) License Deed
This guide is organized around the 7 steps in the graphic to the left to help you understand the process of writing a literature review.
This guide will help you to
- Define a literature review
- Recognize that different fields of study have their own way to perform and write literature reviews
- Prepare to search the literature
- Read critically -- analyze and synthesize
- Prepare to write a literature review
At the end of the tutorial, you will find a quiz that you can submit through Canvas for course credit.
Graphic from Literature Review (2009) by Machi and McEvoy.
Text description of "Literature Review Process" for web accessibility
If you have questions related to a field or discipline, consider reaching out to a Subject Librarian by email, phone, or by scheduling an appointment for a free consultation:
- Subject Librarians
- Next: What's a Literature Review? >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .

Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Stellar Literature Review (with Help from AI)

Table of contents

Aren’t all of us mini versions of Sherlock Holmes when browsing data and archives for a research piece? As we go through the process, a comprehensive literature review is an essential toolkit to make your research shine.
A literature review consists of scholarly sources that validate the content. Its primary objective is to offer a concise summary of the research and to let you explore relevant theories and methodologies. Through this review, you can identify gaps in the existing research and bridge them with your contribution.
The real challenge is how to write an excellent literature review. Let’s learn.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is an introduction to your research. It helps you put your perspective to the table, along with a summary of the theme.
What does my literature review communicate?
- Explanation of your research: how the information was collected, the research method, the justification of the chosen data sources, and an overview of the data analysis.
- Framework: the journey from where the concept began and how it is presented.
- Connects the previous and current research:
It presents the broader scope of your research by connecting it to the existing data and debates and underlining how your content fits the prevailing studies.
In an era of information overload, a literature review must be well-structured.
Let’s learn all about the structure and style of a literature review that’ll help you strengthen your research.
Literature review– structure and style
Begin with a question and end it with the solution– the key to structuring a literature review. It resembles an essay’s format, with the first paragraph introducing the readers to the topic and the following explaining the research in-depth.
The conclusion reiterates the question and summarizes the overall insights of your research. There’s no word count restriction. —it depends on the type of research. For example, a dissertation demands lengthy work, whereas a short paper needs a few pages.
In a literature review, maintaining high quality is vital, with a focus on academic writing style. Informal language should be avoided in favor of a more formal tone.
The content avoids contractions, clearly differentiating between previous and current research through the use of past and present tense. Wordtune assists in establishing a formal tone, enhancing your work with pertinent suggestions. This AI-powered tool ensures your writing remains genuine, lucid, and engaging.

The option of refining the tonality offers multiple possibilities for rephrasing a single sentence. Thus, pick the best and keep writing.
Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
Your friendly step-by-step guide to writing a literary review (with help from AI)
Do you find it challenging to begin the literature review? Don’t worry! We’re here to get you started with our step-by-step guide.
1. Narrow down the research scope
Simply begin with the question: What am I answering through my research?
Whether it’s cooking or painting, the real challenge is the prep-up for it rather than performing the task. Once you’re done, it smoothly progresses. Similarly, for your literature review, prepare the groundwork by narrowing down the research scope.
Browse and scoop out relevant data inclining well with your research. While you can’t cover every aspect of your research, pick a topic that isn’t too narrow nor too broad to keep your literature review well-balanced.
2. Hunt relevant literature
The next question: Does this data align with the issue I’m trying to address?
As you review sources of information, hunt out the best ones. Determine which findings help in offering a focused insight on your topic. The best way to pick primary sources is to opt for the ones featured in reliable publications. You can also choose secondary sources from other researchers from a reasonable time frame and a relevant background.
For example, if your research focuses on the Historical Architecture of 18th-century Europe, the first-hand accounts and surveys from the past would hold more weight than the new-age publications.
3. Observe the themes and patterns in sources
Next comes: What is the core viewpoint in most of the research? Has it stayed constant over time, or have the authors differed in their points of view?
Ensure to scoop out the essential aspects of what each source represents. Once you have collected all this information, combine it and add your interpretations at the end. This process is known as synthesis.
Synthesize ideas by combining arguments, findings and forming your new version.
4. Generate an outline
The next question: How can I organize my review effectively? When navigating multiple data sources, you must have noticed a structure throughout the research. Develop an outline to make the process easier. An outline is a skeletal format of the review, helping you connect the information more strategically.
Here are the three different ways to organize an outline– Chronologically, Thematically, or by Methodology.You can develop the outline chronologically, starting from the older sources and leading to the latest pieces. Another way of organizing is to thematically divide the sections and discuss each under the designated sub-heading.
You can even organize it per the research methods used by the respective authors. The choice of outline depends on the subject. For example, in the case of a science paper, you can divide the information into sections like introduction, types of equipment, method, procedure, findings, etc. In contrast, it’s best to present it in divisions based on timelines like Ancient, Middle Ages, Industrial revolutions, etc., for a history paper.
If you’re confused about how to structure the data, work with Wordtune.

With the Generate with AI feature, you can mention your research topic and let Wordtune curate a comprehensive outline for your study.

Having a precise prompt is the key to getting the best results.
5. Start filling!
Your next question must be: Am I ready to compose all the parts of the literature review?
Once you’re ready with the basic outline and relevant sources, start filling in the data. Go for an introductory paragraph first to ensure your readers understand the topic and how you will present it. Ensure you clearly explain the section in the first sentence.
However, if beginning from the first paragraph seems intimidating, don’t worry! Add the main body content to the sub-headings, then jump to the introduction.
Add headings wherever possible to make it more straightforward and guide your readers logically through different sources. Lastly, conclude your study by presenting a key takeaway and summarizing your findings. To make your task easier, work with Wordtune. It helps align your content with the desired tone and refine the structure.
6. Give attention to detail and edit
The last question: Am I satisfied with the language and content written in the literature review? Is it easy to understand?
Once you’re done writing the first draft of a literature review, it’s time to refine it. Take time between writing and reading the draft to ensure a fresh perspective. It makes it easier to spot errors when you disconnect from the content for some time. Start by looking at the document from a bird's eye to ensure the formatting and structure are in order.
After reviewing the content format, you must thoroughly check your work for grammar, spelling, and punctuation. One of the best approaches to editing and proofreading is to use Wordtune . It helps simplify complex sentences, enhance the content quality, and gain prowess over the tonality.
The dos and don’ts of writing a literature review
Writing a stellar literature review requires following a few dos and don'ts. Just like Sherlock Holmes would never overlook a hint, you must pay attention to every minute detail while writing a perfect narrative. To help you write, below are some dos and don'ts to remember.

Composing a literature review demands a holistic research summary, each part exhibiting your understanding and approach. As you write the content, make sure to cover the following points:
- Keep a historical background of the field of research. Highlight the relevant relation between the old studies and your new research.
- Discuss the core issue, question, and debate of your topic.
- Theories lay the foundation of research. While you’re writing a literature review, make sure to add relevant concepts and ideas to support your statements.
- Another critical thing to keep in mind is to define complex terminologies. It helps the readers understand the content with better clarity.
Examples of comprehensive literature reviews
Aren’t good examples the best way to understand a subject? Let’s look into a few examples of literature reviews and analyze what makes them well-written.
1. Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
An overview of scholarly sources is included in the literature review, which explores critical thinking in American education. The introduction stating the subject’s importance makes it a winning literature review. Following the introduction is a well-defined purpose that highlights the importance of research.
As one keeps reading, there is more clarity on the pros and cons of the research. By dividing information into parts with relevant subheadings, the author breaks a lengthy literature review into manageable chunks, defining the overall structure.
Along with other studies and presented perspectives, the author also expresses her opinion. It is presented with minimal usage of ‘I,’ keeping it person-poised yet general. Toward the conclusion, the author again offers an overview of the study. A summary is further strengthened by presenting suggestions for future research as well.
2. The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review
This literature review is thematically organized on how technology affects language acquisition. The study begins with an introduction to the topic with well-cited sources. It presents the views of different studies to help readers get a sense of different perspectives. After giving these perspectives, the author offers a personalized opinion.
One of the critical aspects that makes this a good literature review is a dedicated paragraph for definitions. It helps readers proceed further with a clear understanding of the crucial terminologies. There’s a comparison of the modern and previous studies and approaches to give an overall picture of the research.
Once the main body is composed, the author integrates recommendations for action-based tips. Thus, the literature review isn’t just summarizing the sources but offering actions relevant to the topics. Finally, the concluding paragraph has a brief overview with key takeaways.
Wordtune: your writing buddy!
A literature review demands the right balance of language and clarity. You must refine the content to achieve a formal tone and clear structure. Do you know what will help you the most? Wordtune !.
The real-time grammar checker leaves no scope for errors and lets you retain precision in writing. This writing companion is all you need for stress-free working and comprehensive literature review development.
Let the narrative begin
A literary review isn't just about summarizing sources; it's about seamlessly bringing your perspective to the table. Always remember to set a narrative for added interest and a brilliant composition. With structure and style being the pillars of a stellar literature review, work with Wordtune to ensure zero compromises on the quality.
Share This Article:

The Official Wordtune Guide

An Expert Guide to Writing Effective Compound Sentences (+ Examples)
How I Turned Clutter into Cash: 10 Proven Instagram Copywriting Hacks
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

Literature Review Guide
- Lit Reviews: What You Need to Know Before You Start
Here are a Few Examples of Literature Reviews
- Choose Your Research Topic
- Tips for Database Searching
- Evaluate Your Results
- Synthesize Your Articles
Slides from Workshop on 01/30/24
https://bit.ly/3vFDntg
Understanding Peer-reviewed Journal Articles vs. Scholarly Sources
Peer Reviewed Articles
- Group of experts in the author's discipline reviews and evaluates an article to ensure quality
- Often double-blind, so reviewers' & author's identities are concealed from each other
- High level of rigor
- When you limit for peer reviewed in a database, you're typically actually limiting to peer reviewed journals . So you might find book reviews or letters to the editor. However, all the research articles will be peer reviewed.
Scholarly Sources
- Intended for academic audience, usually within specific field
- Authored by academics, specialists, or researchers in the field (not by journalists). Includes author's credentials
NOTE: Although the term peer reviewed & scholarly are often used interchangeably, some scholarly works are not peer reviewed (such as dissertations, books, and book chapters), but all peer reviewed articles are scholarly.

NOTE: Right click on image to view larger in another tab

Ebook - The Literature Review: Six Steps to Success
Ebook - Succeeding With Your Literature Review: A Handbook for Students
Ebook - Writing the Literature Review
Ebook - Conducting Your Literature Review
All scholarly journal articles include a review of the literature, usually after the introduction paragraph. Take a look at this example journal article:
MacKinnon, C. J., Smith, N. G., Henry, M., Milman, E., Berish, M., Farrace, A., Körner, A., Chochinov, H. M., & Cohen, S. R. (2016). A Pilot Study of Meaning-Based Group Counseling for Bereavement. Omega: Journal of Death & Dying, 72(3), 210–233. https://doi.org/10.1177/0030222815575002
https://www.academia.edu/download/83475030/A_pilot_study_of_meaning-based_group_cou20220408-13993-1bj1mkp.pdf
Sometimes, a literature review can be a stand-alone work (tip: the title may contain the phrase, literature review) Take a look at this literature review journal article:
Dalechek, D. E., Caes, L., McIntosh, G., & Whittaker, A. C. (2024). Anxiety, history of childhood adversity, and experiencing chronic pain in adulthood: A systematic literature review and meta‐analysis. European Journal of Pain. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.2232
All dissertations include a review of the literature in the chapter 2. Take a look at this example dissertation:
Shah, F. A. (2023). Promotions and Rewards: Perceptions of Minority Women in Corporate America (Order No. 30530620). Available from Dissertations & Theses @ Adler University. (2839630623). https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/promotions-rewards-perceptions-minority-women/docview/2839630623/se-2
- Next: Choose Your Research Topic >>
- Last Updated: Jan 30, 2024 5:57 PM
- URL: https://library.adler.edu/literature_review_guide
TAFT COLLEGE
Literature Review: What is a Literature Review?
What is a literature review.
- Organize & Compose
- Evaluating Information
- Citing, Paraphrasing, and Formatting

- Writing a Literature Review: Six Steps to Get You from Start to Finish If you are new to the process of synthesizing information from what can seem like a massive amount of "literature," these suggestions from a UC Merced Sociology professor can help you tackle the project.
When conducting a literature review a researcher must have three quite distinct skills. He or she must be
- adept at searching online databases and print indexes.
- able to evaluate critically what has been read.
- able to incorporate the selected readings into a coherent, integrated, meaningful account.
Portions of this LibGuide have been borrowed from LibGuides at the following colleges and universities:
- Boston College
- University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
- Austin Peay State University
- Santa Rosa Junior College
A literature review surveys published information (books, scholarly articles, and other documents) relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory. The "literature" of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic.
Sometimes a literature review is a brief summary of those sources, but more commonly it is a summary and a synthesis. A synthesis can be a reorganization of the information to provide a new interpretation, make comparisons between old and new information, or track the intellectual progression of an idea or concept. A literature review can also provide an evaluation of the sources in order to advise readers on their relevance or importance.
Here are a few types of Literature Reviews often used in undergraduate research:
- Narrative Review: Describes what related research has already been conducted and how that research informs the thesis of the paper
- Critical Review: Provides a more detailed examination of the literature that compares and evaluates a number of perspectives.
- Conceptual Review: Groups literature according to concepts, or categories, or themes in order to provide a snapshot of where things are with a particular field of research.
What is the Purpose of a Literature Review?
Generally speaking, a literature provides an overview of the significant literature published on a topic. For researchers of all levels and disciplines, a literature review can:
- Set up the starting point for research by summarizing, comparing, and evaluating existing sources in the area of interest.
- Help understand the direction of the further research and areas worth focusing on.
- Provide access to the most important information on a certain topic by picking out sources that are valid, meaningful, and relevant, summarizing them and turning them into a single concise report.
- Help researchers not to duplicate work that has been done before.
- Provide a detailed analysis of methods used in other researches.
- Identify gaps and contradictions in existing sources and highlight the most important findings.
- Identify current research in the field.
Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Some Tips on Recording the Information Found, on Taking Notes etc.:
- It is sometimes sufficient to browse the text quickly. The introduction or conclusion often give a gist of the thesis and main points. Still, often a researcher must read much or all of a work, especially if it is of an authoritative or technical nature.
- Begin with most recent studies and work backwards. A recent article’s list of references or bibliography might provide you with valuable works to consult.
- If the report/article has an abstract, read it first.
- Don’t trust your memory. Record all research. You'll never remember who said what if you neglect to take adequate notes!
- Write down the complete citation for each work. Don't forget the page nos. for later use in the notes and bibliography. For Internet citations, note the URL.
- Avoid "grandfather" citations. Return to original source.
- Write all direct quotations precisely, word-for-word. Use quotation marks. Failure to put a direct text in quotes (or to credit the author) sets the stage for plagiarism.
- Avoid copying too many direct quotations. Most of the review should be primarily in your own words with appropriate documentation of others’ ideas.
- Do not stress just a single source or two. It is usually important in a literature review to provide evidence you consulted and used a wide range of resources.
- For a contentious topic, present the opposing positions. Be objective. Do not overemphasize one side.
- Sample Literature Reviews from the University of West Florida
- Example: Writing a Short Literature Review from CUNY This is an excellent example of an APA literature review from how a student gathered information from the literature to composing and formatting the entire paper.
- Sample Literature Reviews from University of LaVerne This guide provides sample published literature reviews from a wide variety of disciplines.
- Next: Research >>
- Last Updated: Jan 29, 2024 9:12 AM
- URL: https://lib.taftcollege.edu/c.php?g=963864

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
Steps in the literature review process.
- What is a literature review?
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- You may need to some exploratory searching of the literature to get a sense of scope, to determine whether you need to narrow or broaden your focus
- Identify databases that provide the most relevant sources, and identify relevant terms (controlled vocabularies) to add to your search strategy
- Finalize your research question
- Think about relevant dates, geographies (and languages), methods, and conflicting points of view
- Conduct searches in the published literature via the identified databases
- Check to see if this topic has been covered in other discipline's databases
- Examine the citations of on-point articles for keywords, authors, and previous research (via references) and cited reference searching.
- Save your search results in a citation management tool (such as Zotero, Mendeley or EndNote)
- De-duplicate your search results
- Make sure that you've found the seminal pieces -- they have been cited many times, and their work is considered foundational
- Check with your professor or a librarian to make sure your search has been comprehensive
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of individual sources and evaluate for bias, methodologies, and thoroughness
- Group your results in to an organizational structure that will support why your research needs to be done, or that provides the answer to your research question
- Develop your conclusions
- Are there gaps in the literature?
- Where has significant research taken place, and who has done it?
- Is there consensus or debate on this topic?
- Which methodological approaches work best?
- For example: Background, Current Practices, Critics and Proponents, Where/How this study will fit in
- Organize your citations and focus on your research question and pertinent studies
- Compile your bibliography
Note: The first four steps are the best points at which to contact a librarian. Your librarian can help you determine the best databases to use for your topic, assess scope, and formulate a search strategy.
Videos Tutorials about Literature Reviews
This 4.5 minute video from Academic Education Materials has a Creative Commons License and a British narrator.
Recommended Reading
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Home → Academic Writing → How to Start a Literature Review (Like a Pro)
How to Start a Literature Review (Like a Pro)
Jordan Kruszynski
- June 26, 2023

Ah, how to start a literature review – those words will be all too familiar to battle-hardened researchers, but to the rest of us, they may be a bit of a mystery.
Are you a student trying to get ahead of the game with your first literature review? Or are you a professional looking to learn more about literature reviews? If so, then this post is for you.
In this article, we’ll discuss how to start a literature review, the types of sources used in literature reviews, and the benefits of writing them. We’ll also outline the steps for preparing and writing your own literature review.
Read on and let the magic begin!
Literature Reviews – The Researcher’s Friend
A literature review is an essential part of any research project. It is a compilation of all the literature and research related to a particular topic. It is used to provide context and background for a research project. Literature reviews are important for two primary reasons. First, they provide a comprehensive and objective review of the existing literature on a topic. Second, they provide support for any conclusions or hypotheses that may be drawn from the research.
Literature reviews are used in many different fields, including business, education, and the sciences. They are used to provide an overview of a topic and to support the conclusions and hypotheses of a research project.
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical appraisal of existing research on a particular topic . It is a systematic and comprehensive review of all the published work in a particular field. The purpose of a literature review is to provide an overview of the existing research on a topic, to identify gaps in the literature, and to propose new directions for future research.
The literature review is an important part of the research process and should be conducted thoroughly and objectively. It should include a critical analysis of the existing literature, an evaluation of the research methods used, and an assessment of the quality of the evidence.
Types of Literature Review
There are several different types of literature reviews. They include narrative reviews, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and scoping reviews.
- Narrative reviews are the most common type of literature review. They provide an overview of the existing literature on a topic. Narrative reviews typically include an introduction, a review of the literature, and a conclusion.
- Systematic reviews are more rigorous and comprehensive than narrative reviews. They involve rigorous and systematic searches of the literature and include a critical appraisal of the evidence. Systematic reviews are typically used in clinical research.
- Meta-analyses are reviews that combine the results of multiple studies to evaluate the overall effect of a particular treatment or intervention. Meta-analyses are more rigorous and comprehensive than narrative reviews and systematic reviews.
- Scoping reviews are used to identify the range of research on a particular topic. They are typically used to identify gaps in the literature and to propose new directions for future research.
Sourcing Pieces for Your Review
When conducting a literature review, it is important to use a variety of sources. These sources include journal articles, books, conference proceedings, dissertations, and other academic sources. It is also important to use a variety of search strategies to identify the most relevant and up-to-date sources.
Research papers will probably form the bulk of your literature review, and this is where Audemic can help – simply load any papers you want to use into the app, and you can organise them intuitively to make sourcing a breeze.
It is important to note that not all sources are created equal. Some sources may be more reliable than others. When evaluating sources for your literature review, it is important to consider their credibility, relevance, accuracy, and objectivity.
Benefits of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews are an essential part of any research project. They provide an overview of the existing literature on a topic and can be used to identify gaps in the literature, as well as propose new directions for future research. They also provide support for any conclusions or hypotheses that may be drawn from the research.
Literature reviews can also help researchers save time and money. By conducting a thorough and comprehensive review of the existing literature, researchers can avoid redundant research and save time and money.
How to Start a Literature Review
Now that you understand the purpose and benefits of a literature review, it’s time to learn how to start one. The first step in starting a literature review is to identify a topic. Once you have identified a topic, you can start searching for sources.
When searching for sources, it is important to use a variety of search strategies, such as keyword searches, author searches, and database searches. It is also important to use a variety of sources, such as journal articles, books, conference proceedings, and dissertations.
Preparing for Your Literature Review
Once you have identified and located the sources for your literature review, it is time to start preparing. Before you begin writing, it is important to read and analyse each source. This will help you identify the key points of each source and understand how it contributes to the literature on your topic.
It is also important to organise your sources. This can be done by creating a spreadsheet or using a reference management software, such as Mendeley or Zotero. This will help you keep track of your sources and make it easier to cite them in your literature review.
Did somebody say Zotero? Audemic features Zotero integration, so you can not only organise your sources, but also listen to them when you need a change of pace. Nice, eh?
Searching for Sources for Your Review
Now that you have identified a topic and prepared your sources, it’s time to start searching for additional sources. When searching for sources, it is important to use a variety of search strategies. These search strategies include keyword searches, author searches, database searches, and library catalogue searches.
It is also important to use a variety of sources. These sources include journal articles, books, conference proceedings, dissertations, and other academic sources. It is also important to consider the credibility, relevance, accuracy, and objectivity of each source.
Writing and Structuring Your Literature Review
Once you have identified and located the sources for your literature review, it is time to start writing. When writing your literature review, it is important to keep the structure and organisation in mind. Your literature review should include an introduction, a review of the literature, and a conclusion.
- When writing your introduction , it is important to provide context for your topic. This should include an explanation of the purpose of the literature review and a description of the research question.
- The review of the literature should provide an overview of the existing literature on the topic. It should include a summary of each source and an analysis of the evidence. It should also include an evaluation of the research methods used and an assessment of the quality of the evidence.
- Finally, the conclusion should summarise the key points of the literature review and provide recommendations for future research.
Final Thoughts
A literature review is an essential part of any research project, so it pays to master this critical academic skill. And with the guidance in this post, you should be well on your way to knowing how to start a literature review for yourself. By putting it into practice, you can unlock your writing potential and produce a thorough, engaging and comprehensive literature review.
So what are you waiting for? Search for those sources and get started! And why not use Audemic to speed up the review process and boost it into the cosmos!
Keep striving, researchers! ✨
Table of Contents
Related articles.

How to Publish a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
You’re in academia. You’re going steady. Your research is going well and you begin to wonder: ‘How exactly do I get a

Behind the Scenes: What Does a Research Assistant Do?
Have you ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes in a research lab? Does it involve acting out the whims of

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction: Hook, Line, and Sinker
Want to know how to write a research paper introduction that dazzles? Struggling to hook your reader in with your opening sentences?

Blog Podcast
Privacy policy Terms of service
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Discover more from Audemic: Access any academic research via audio
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step One: Decide on your areas of research: Before you begin to search for articles or books, decide beforehand what areas you are going to research. Make sure that you only get articles and books in those areas, even if you come across fascinating books in other areas. A literature review I am currently working on, for example, explores ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
review. Once you complete these six steps, you will have a complete draft of your literature review. The great thing about this process is that it breaks down into manageable steps something that seems enormous: writing a literature review. I think that Foss and Walter's system for writing the literature review really can work for a
1. Claims, conclusions, and findings about the constructs you are investigating. 2. Definitions of terms. 3. Calls for follow-up studies relevant to your project. 4. Gaps you notice in the ...
Your literature review should not simply be a summary of the articles, books, and other scholarly writings you find on your topic. It should synthesize the various ideas from your sources with your own observations to create a map of the scholarly conversation taking place about your research topics along with gaps or areas for further research.
The six steps you need to follow to produce an excellent Literature Review for your research studies in any fields.Source: https://hub.wiley.com/community/ex...
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
6. Write your literature review. Regardless of the structure you chose, a review should always include the following three sections: An introduction, which should give the reader an outline of why you are writing the review and explain the relevance of the topic. A body, which divides your literature review into different sections. Write in ...
How to write a literature review in 6 steps. How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.
What is a Literature Review? Steps to Write a Literature Review. Step 1: Choosing a Topic ; Step 2: Finding Information ; Step 3: Evaluating Content ; Step 4: Taking Notes ; Step 5: Synthesizing Content ; Step 6: Writing the Review ; Step 7: Citing Your Sources ; Library Services Toggle Dropdown. Meet the Library Team ; Off-Campus & Mobile ...
Ideally some time should pass between when you finish the writing step and when you edit. This helps you review your writing with fresh eyes so that you can more easily spot errors and oversights. First, look at your paper from a bird's-eye view: make sure the formatting is neat and consistent and the overall organization of ideas makes sense ...
This guide will help you to. Define a literature review. Recognize that different fields of study have their own way to perform and write literature reviews. Prepare to search the literature. Read critically -- analyze and synthesize. Prepare to write a literature review. Graphic from Literature Review (2009) by Machi and McEvoy.
2. Definitions of terms. 3. Calls for follow-up studies relevant to your project. 4. Gaps you notice in the literature. 5. Disagreement about the constructs you are investigating. When you find ...
The topic must at least be: interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary), an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and.
Similarly, for your literature review, prepare the groundwork by narrowing down the research scope. Browse and scoop out relevant data inclining well with your research. While you can't cover every aspect of your research, pick a topic that isn't too narrow nor too broad to keep your literature review well-balanced. 2.
Sometimes, a literature review can be a stand-alone work (tip: the title may contain the phrase, literature review) Take a look at this literature review journal article: Dalechek, D. E., Caes, L., McIntosh, G., & Whittaker, A. C. (2024). Anxiety, history of childhood adversity, and experiencing chronic pain in adulthood: A systematic ...
For researchers of all levels and disciplines, a literature review can: Set up the starting point for research by summarizing, comparing, and evaluating existing sources in the area of interest. Help understand the direction of the further research and areas worth focusing on. Provide access to the most important information on a certain topic ...
The Literature Review by Diana Ridley The Literature Review is a step-by-step guide to conducting a literature search and writing up the literature review chapter in Masters dissertations and in Ph.D. and professional doctorate theses. The author provides strategies for reading, conducting searches, organizing information and writing the review.
The first step in starting a literature review is to identify a topic. Once you have identified a topic, you can start searching for sources. When searching for sources, it is important to use a variety of search strategies, such as keyword searches, author searches, and database searches. It is also important to use a variety of sources, such ...
The first step is pretty obvious. You have to decide what to write about. Once you decide, about half the battle is over. But we need to make a distinction between your topic and your research question. A topic is the broad topic you are studying. The research question is the narrow topic on which you are writing your literature review.
Schedule a free 1-1 strategy session with me to see how I can help you achieve your research goals:https://academicenglishnow.com/schedule?utm_source=YouTube...