

How To Write An Editorial (7 Easy Steps, Examples, & Guide)
Writing an editorial is one of those things that sounds like it should be pretty straightforward. Easy, even.
But then you sit down to start typing. Your fingers freeze over the keyboard. You gaze into the perfectly blank white space of your computer screen.
Wait , you think. How do I write an editorial ?
Here’s how to write an editorial:
- Choose a newsworthy topic (Something with broad interest)
- Choose a clear purpose (This will guide your entire process)
- Select an editorial type (Opinion, solution, criticism, persuasive, etc)
- Gather research (Facts, quotes, statistics, etc)
- Write the editorial (Using an Editorial Template that includes an introduction, argument, rebuttal, and conclusion)
- Write the headline (Title)
- Edit your editorial (Grammar, facts, spelling, structure, etc)
In this article, we’ll go through each of these steps in detail so that you know exactly how to write an editorial.
What Is an Editorial? (Quick Definition)

Table of Contents
Before we jump into the mechanics of how to write an editorial, it’s helpful to get a good grasp on the definition of editorials.
Here is a simple definition to get us started:
An editorial is a brief essay-style piece of writing from a newspaper, magazine, or other publication. An editorial is generally written by the editorial staff, editors, or writers of a publication.
Of course, there’s a lot more to it than simply dashing out an essay.
There is the purpose, different types of editorials, elements of a good editorial, structure, steps to writing an editorial, and the actual mechanics of writing your editorial.
“In essence, an editorial is an opinionated news story.” – Alan Weintraut
What Is the Purpose of an Editorial?
The purpose of an editorial is to share a perspective, persuade others of your point of view, and possibly propose a solution to a problem.
The most important part is to pick one purpose and stick to it.
Rambling, incoherent editorials won’t do. They won’t get you the results or the response you might want.
When it comes to purpose, you want:
- Singular focus
- Personal connection
The first two probably make sense with no explanation. That last one (personal connection) deserves more attention.
The best editorials arise from personal passions, values, and concerns. You will naturally write with vigor and voice. Your emotion will find its way into your words.
Every bit of this will make your editorials instantly more compelling.
What Are the Different Types of Editorials?
There are two main types of editorials and a number of different subtypes.
One of the first steps in how to write an editorial is choosing the right type for your intended purpose or desired outcome.
The two main types of editorials:
Opinion Editorial
In an opinion editorial, the author shares a personal opinion about a local or national issue.
The issue can be anything from local regulations to national human trafficking.
Typically, the topic of an editorial is related to the topics covered in the publication. Some publications, like newspapers, cover many topics.
Solution Editorial
In a solution editorial, the author offers a solution to a local or national problem.
It’s often recommended for the author of solution editorials to cite credible sources as evidence for the validity of the proposed solution (BTW, research is also important for opinion editorials).
There are also several editorial subtypes based on purpose:
- Explain (you can explain a person, place, or thing)
- Criticism (you can critically examine a person, place, or thing)
- Praise (celebrate a person, place, or thing)
- Defend (you can defend a person, place, or thing)
- Endorsement (support a person, place, or thing)
- Catalyst (for conversation or change)
How To Write an Editorial (7 Easy Steps)
As a reminder, you can write an editorial by following seven simple steps.
- Choose a topic
- Choose a purpose
- Select an editorial type
- Gather research
- Write the editorial
- Write the headline
- Edit your editorial
If you want a short, visual explanation of how to write an editorial, check out this video from a bona fide New York Times Editor:
1) Choose a Newsworthy Topic
How do you choose a topic for your editorial?
You have several options. Your best bet is to go with a topic about which you feel strongly and that has broad appeal.
Consider these questions:
- What makes you angry?
- What makes your blood boil?
- What gets you excited?
- What is wrong with your community or the world?
When you write from a place of passion, you imbue your words with power. That’s how to write an editorial that resonates with readers.
2) Choose a Purpose
The next step for how to write an editorial is to choose your purpose.
What do you want to accomplish with your editorial? What ultimate outcome do you desire? Answering these questions will both focus your editorial and help you select the most effective editorial type.
Remember: a best practice is honing in on one specific purpose.
Your purpose might be:
- To trigger a specific action (such as voting)
- To raise awareness
- To change minds on an issue
3) Select a type
Now it’s time to select the best editorial type for your writing. Your type should align with your purpose.
In fact, your purpose probably tells you exactly what kind of editorial to write.
First, determine which major type of editorial best fits your purpose. You can do this by asking yourself, “Am I giving an opinion or offering a solution?”
Second, select your subtype. Again, look to your purpose. Do you want to explain? Persuade? Endorse? Defend?
Select one subtype and stick to it.
4) Gather Research
Don’t neglect this important step.
The research adds value, trust, credibility, and strength to your argument. Think of research as evidence. What kind of evidence do you need?
You might need:
- Research findings
All of these forms of evidence strengthen your argument.
Shoot for a mix of evidence that combines several different variations. For example, include an example, some statistics, and research findings.
What you want to avoid:
- Quote, quote, quote
- Story, story, story
Pro tip: you can find research articles related to your topic by going to Google Scholar.
For other evidence, try these sources:
- US Census Bureau
- US Government
- National Bureau of Economic Research
You might also want to check with your local librarian and community Chamber of Commerce for local information.
5) Write Your Editorial
Finally, you can start writing your editorial.
Aim to keep your editorial shorter than longer. However, there is no set length for an editorial.
For a more readable editorial, keep your words and sentences short. Use simple, clear language. Avoid slang, acronyms, or industry-specific language.
If you need to use specialized language, explain the words and terms to the reader.
The most common point of view in editorials is first person plural. In this point of view, you use the pronouns “we” and “us.”
When writing your editorial, it’s helpful to follow an Editorial Template. The best templates include all of the essential parts of an editorial.
Here is a basic Editorial template you can follow:
Introduction Response/Reaction Evidence Rebuttal Conclusion
Here is a brief breakdown of each part of an editorial:
Introduction: The introduction is the first part of an editorial. It is where the author introduces the topic that they will be discussing. In an editorial, the author typically responds to a current event or issue.
Response/Reaction: The response/reaction is the part of the editorial where the author gives their opinion on the topic. They state their position and give reasons for why they believe what they do.
Evidence: The evidence is typically a series of facts or examples that support the author’s position. These can be statistics, quotations from experts, or personal experiences.
Rebuttal: The rebuttal is the part of the editorial where the author addresses any arguments or counter-arguments that may be raised against their position. They refute these arguments and offer additional evidence to support their point of view.
Conclusion: The conclusion is the last part of an editorial. It wraps up the author’s argument and provides a final statement on the topic.
6) Write The Headline
Your headline must be catchy, not clickbait. There’s a fine line between the two, and it’s not always a clear line.
Characteristics of a catchy headline:
- Makes the reader curious
- Includes at least one strong emotion
- Clearly reveals the subject of the editorial
- Short and sweet
- Doesn’t overpromise or mislead (no clickbait)
Your headline will either grab a reader’s attention or it will not. I suggest you spend some time thinking about your title. It’s that important. You can also learn how to write headlines from experts.
Use these real editorial headlines as a source of inspiration to come up with your own:
- We Came All This Way to Let Vaccines Go Bad in the Freezer?
- What’s the matter with Kansas?
- War to end all wars
- Still No Exit
- Zimbabwe’s Stolen Election
- Running out of time
- Charter Schools = Choices
Suggested read: How To Write an Autobiography
7) Edit Your Editorial
The final step is to edit and proofread your editorial.
You will want to check your editorial for typos, spelling, grammatical, and punctuation mistakes.
I suggest that you also review your piece for structure, tone, voice, and logical flaws.
Your editorial will be out in the public domain where any troll with a keyboard or smartphone (which, let’s be honest, is everyone) can respond to you.
If you’ve done your job, your editorial will strike a nerve.
You might as well assume that hordes of people might descend on your opinion piece to dissect every detail. So check your sources. Check the accuracy of dates, numbers, and figures in your piece.
Double-check the spelling of names and places. Make sure your links work.
Triple-check everything.
Editorial Structures and Outlines
As you learn how to write an editorial, you have many choices.
One choice is your selection of structure.
There are several editorial structures, outlines, and templates. Choose the one that best fits your topic, purpose, and editorial type.
Every editorial will have a beginning, middle, and end.
Here are a few specific structures you can use:
- Problem, Solution, Call to Action
- Story, Message, Call to Action
- Thesis, Evidence, Recommendation
- Your View, Opposing Views, Conclusion
How Do You Start an Editorial?
A common way to start an editorial is to state your point or perspective.
Here are a few other ways to start your editorial:
- The problem
- Startling statement
- Tell a story
- Your solution
Other than the headline, the beginning of your editorial is what will grab your reader.
If you want to write an editorial that gets read, then you must write a powerful opening.
How Do You End an Editorial?
You can end with a call-to-action, a thoughtful reflection, or a restatement of your message.
Keep in mind that the end of your editorial is what readers will most likely remember.
You want your ending to resonate, to charge your reader with emotion, evidence, and excitement to take action.
After all, you wrote the editorial to change something (minds, policies, approaches, etc.).
In a few sections (see below), you will learn a few simple templates that you can “steal” to help you end your editorial. Of course, you don’t have to use the templates.
They are just suggestions.
Often, the best way to conclude is to restate your main point.
What Makes a Good Editorial?
Even if you learn how to write an editorial, it doesn’t mean the editorial will automatically be good. You may be asking, What makes a good editorial ?
A good editorial is clear, concise, and compelling.
Therefore, the best editorials are thought out with a clear purpose and point of view. What you want to avoid is a rambling, journal-type essay. This will be both confusing and boring to the reader.
That’s the last thing you want.
Here are some other elements of a good editorial:
- Clear and vivid voice
- Interesting point of view
- Gives opposing points of view
- Backed up by credible sources
- Analyzes a situation
“A good editorial is contemporary without being populist.” —Ajai Singh and Shakuntala Singh
How Do You Know If You’ve Written a Good Editorial?
Many people want to know how to tell if they have written a good editorial.
How do you know?
You can tell by the response you get from the readers. A good editorial sparks a community conversation. A good editorial might also result in some type of action based on the solution you propose.
An article by Ajai Singh and Shakuntala Singh in Mens Sana Monograph says this about good editorials:
It tackles recent events and issues, and attempts to formulate viewpoints based on an objective analysis of happenings and conflicting/contrary opinions. Hence a hard-hitting editorial is as legitimate as a balanced equipoise that reconciles apparently conflicting positions and controversial posturings, whether amongst politicians (in news papers), or amongst researchers (in academic journals).
Note that newsworthy events, controversy, and balance matter in editorials.
It’s also a best practice to include contradicting opinions in your piece. This lends credibility and even more balance to your peice.
Editorial Examples & Templates
As you write your own editorial, study the following example templates “stolen” from real editorials.
You can use these templates as “sentence starters” to inspire you to write your own completely original sentences.
Phrases for the beginning:
- It’s been two weeks since…
- Look no further than…
- The country can’t…
Phrases for the middle:
- That’s an astonishing failure
- It should never have come to this
- Other [counties, states, countries, etc.] are…
- Within a few days…
- Not everyone shares my [opinion, pessimism, optimism]
- Officials say…
Phrases for the end:
- Let’s commit to…
- Finally…
- If we can…we will…
Honestly, the best way to learn how to write an editorial is to read and study as many published editorials as possible. The more you study, the better you will understand what works.
Study more editorials at these links:
- New York Times editorials
- USA Today editorials
- The Washington Post
How To Write an Editorial for Students
Writing an editorial for students is virtually the same as writing an editorial at any other time.
However, your teacher or professor might give you specific instructions, guidelines, and restrictions. You’ll want to read all of these thoroughly, get clarity, and follow the “rules” as much as possible.
Writing an editorial is a skill that will come in handy throughout your life. Whether you’re writing a letter to the editor of your local paper or creating a post for your blog, being able to communicate your ideas clearly and persuasively is an important skill. Here are some tips to help you write an effective editorial:
- Know your audience. Who are you writing for? What are their concerns and interests? Keep this in mind as you craft your message.
- Make a clear argument. What is it that you want your readers to know? What do you want them to do? Be sure to state your case clearly and concisely.
- Support your argument with evidence. Use facts, statistics, and expert opinions to make your case.
- Use strong language . Choose words that will resonate with your readers and make them want to take action.
- Be persuasive, not blasting. You want your readers to be convinced by your argument, not turned off by aggressive language. Stay calm and collected as you make your case.
By following these tips, you can write an effective student editorial that will get results.
What Is an Editorial In a Newspaper?
The editorial section of a newspaper is where the publication’s editorial board weighs in on important issues facing the community. This section also includes columns from guest writers and staff members, as well as letters to the editor.
The editorial board is made up of the publication’s top editors, who are responsible for setting the tone and direction of the paper.
In addition to op-eds, the editorial section also features editorials, which are written by the editorial board and represent the official position of the paper on an issue.
While editorial boards may lean one way or another politically, they strive to present both sides of every issue in a fair and unbiased way.
Ultimately, the goal of the editorial section is to promote thoughtful discussion and debate on the topics that matter most to readers.
Final Thoughts: How To Write an Editorial
Whew , we have covered a lot of ground in this article. I hope that you have gained everything you need to know about how to write an editorial.
There are a lot of details that go into writing a good editorial.
If you get confused or overwhelmed, know that you are not alone. Know that many other writers have been there before, and have struggled with the same challenges.
Mostly, know that you got this .
Related posts:
- How To Write an Ode (7 Easy Steps & Examples)
- Jasper Commands Template: Ultimate Guide + 300 Commands
- Best AI Essay Writer (With Examples)
- The Best Writing Books for Beginners
National Institute of Health (On Editorials)
1 thought on “How To Write An Editorial (7 Easy Steps, Examples, & Guide)”
Pingback: How To Write a Manifesto: 20 Ultimate Game-Changing Tips - CHRISTOPHER KOKOSKI
Comments are closed.
How to Start an Editorial: Step-by-Step Guide

The “How to Start an Editorial: Step-by-Step Guide” provides a comprehensive roadmap for crafting persuasive editorials. It covers selecting a relevant topic, conducting research , creating a persuasive thesis, and organizing your thoughts.
Table of Contents
Learn how to start an editorial with a captivating introduction, build a strong case, and polish your work for publication. This guide will aid you in maneuvering through the process, ensuring your editorial resonates with readers and sparks meaningful conversation.
Understanding the Basics of How to Start an Editorial
Understanding the basics of how to start an editorial is essential. This skill helps anyone looking to craft a compelling piece that resonates with readers. An editorial, opinion journalism, presents the writer’s perspective on a specific topic or issue.
The goal of an editorial is not only to inform but also to persuade, engage, and potentially inspire action. To accomplish this, it is essential to comprehend how an editorial should be structured.
Crafting a Compelling Editoria
A well-structured editorial typically consists of four key components: the introduction, the thesis, the body, and the conclusion. Each element plays a vital role in communicating your ideas effectively and persuasively.
Introduction: This is where you grab your reader’s attention and pique their interest in the topic. Start with a strong hook, such as a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or an engaging anecdote. This technique entices readers to continue reading.
Thesis: The thesis is a concise statement of your central argument or opinion. It sets the tone for your editorial and serves as a roadmap for the points you’ll cover throughout the piece.
Body: The body of your editorial is in which you showcase your arguments, evidence, and examination to bolster your thesis. Organize your points logically and coherently, ensuring each paragraph focuses on a single idea or argument. Use concrete examples, facts, and expert opinions to strengthen your case and convince your readers.
Conclusion: In the conclusion, reiterate your thesis and summarize the main points you’ve made in the body. End with a strong closing statement that either calls for action, offers a solution, or poses a thought-stimulating query. This approach helps create a lasting impact on your readers.
By understanding the basic structure of an editorial, you’ll be better equipped to craft a persuasive and engaging piece. Keep these essential components in mind as you embark on your editorial writing journey, and you’ll be well on the path to crafting a compelling and thought-provoking editorial.
How to Start an Editorial: Brainstorming Ideas
When embarking on the journey of writing an editorial, one of the first steps is brainstorming ideas for a compelling and relevant topic. The subject matter should be exciting and provide value to your readers, sparking meaningful conversations and potentially inspiring change. As you brainstorm ideas, consider how to write an editorial title that accurately reflects the content and seizes the interest of your intended audience.
To generate topic ideas, focus on current events, trending issues, or subjects directly impacting your community. Consider the opinions, concerns, and debates surrounding these topics, as they can serve as a rich source of inspiration for your editorial. Make a list of potential subjects , then evaluate each based on relevance, timeliness, and potential impact on readers.
Once you’ve chosen a topic, start thinking about an engaging title that accurately reflects the essence of your editorial. A well-crafted title should be concise, clear, and thought-provoking, enticing readers to explore your piece further. Consider using powerful words, phrases, or questions that evoke emotion or provoke curiosity. Additionally, incorporating keywords related to your topic can help your editorial reach a wider audience through search engines and social media platforms.
As you finalize your title, ensure it aligns with your editorial’s central thesis and overall tone. It’s essential to strike a balance between capturing attention and accurately representing the content within your piece. If your title needs to be more accurate and sensationalized, you risk losing credibility with your readers.
Brainstorming ideas for an editorial involves identifying compelling topics, evaluating their relevance and impact, and crafting a captivating title that precisely represents the substance of your piece. By adhering to these steps, you can develop a robust foundation for your editorial, ensuring it resonates with readers and sparks meaningful conversations.

How to Start an Editorial: Conducting Research
When learning how to start an editorial writing, conducting thorough research is a critical step. Regardless of your chosen topic, gathering accurate information and understanding different perspectives are essential for crafting a well-informed and persuasive editorial . This will enable you to present a strong case for your viewpoint and build credibility with your readers.
Begin your research by identifying reputable sources of information, such as newspapers, academic journals, books, government reports, and expert opinions. These sources can provide valuable insights, facts, and data to support your arguments. Be sure to critically evaluate each source for accuracy, relevance, and credibility, as this will help you build a solid foundation for your editorial.
As you collect information, make note of opposing viewpoints and counterarguments. Addressing these in your editorial demonstrates your understanding of the topic ‘s complexity and showcases your ability to engage in a balanced and thoughtful discussion. This will make your arguments more persuasive and help you establish trust with your readers.
During the research process, you must remain open-minded and willing to adapt your initial ideas or thesis based on the evidence you encounter. This flexibility will lead to a more nuanced and well-rounded editorial.
Organize your research findings clearly and logically, grouping related ideas and evidence together. This will help you identify patterns and connections that can inform the structure of your editorial and enhance the flow of your arguments.
In summary, conducting research is vital to starting an editorial writing process. By gathering accurate information, understanding different perspectives, and organizing your findings, you can build a strong foundation for a persuasive and well-informed editorial that engages and informs your readers.
How to Start an Editorial: Crafting a Clear and Compelling Argument
Understanding how to start an editorial article involves mastering the art of crafting a clear and compelling argument. A persuasive editorial hinges on presenting a solid case for your viewpoint backed by evidence, logic, and an engaging writing style. Following these guidelines allows you to develop an argument that resonates with readers and effectively communicates your perspective.
Mastering the Art of Persuasion
Develop a clear thesis: Your thesis is your editorial’s central idea or argument. It should be a concise and specific statement that reflects your opinion on the topic. Be sure to state your thesis early in your editorial, preferably in the introduction, to set the stage for your argument.
Provide compelling evidence: Support your thesis with well-researched facts, statistics, and expert opinions. Use a variety of credible sources to present a diverse range of evidence that bolsters your argument. Remember to cite your sources to maintain transparency and credibility.
Address counterarguments: Acknowledging opposing viewpoints and addressing counterarguments demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of the topic and strengthens your position. You can further reinforce your argument by debunking or refuting these counterarguments.
Use persuasive language: The language you use in your editorial plays a significant role in swaying your readers. Employ persuasive techniques such as rhetorical questions, anecdotes, and analogies to engage your audience and make your argument more relatable and convincing.
Organize your thoughts logically: Ensure that your argument follows a coherent and orderly framework, with each paragraph concentrating on a singular point or piece of evidence. This will help readers follow your reasoning and make your editorial more coherent and persuasive.
Revise and edit: After writing your initial draft, take the time to revise and edit your editorial. Make certain that your argument is lucid, succinct, and well-supported and that your writing is free of errors and inconsistencies.
When learning how to start an editorial article, crafting a clear and compelling argument is essential. By developing a solid thesis, providing convincing evidence, addressing counterarguments, using persuasive language, and organizing your thoughts logically, you can create a persuasive editorial that engages readers and effectively communicates your viewpoint.

How to Start an Editorial: Structuring Your Editorial
Learning how to write an editorial page requires a solid understanding of the editorial structure, which is crucial in presenting your ideas coherently and persuasively. A well-structured editorial ensures readers can easily follow your reasoning and engage with your argument.
Structuring for Impactful Communication
Here are some essential steps to adhere to when structuring your editorial:
Introduction: Begin your editorial with a captivating introduction that hooks your readers and provides context for your topic. Use a thought-provoking question, an intriguing anecdote, or a surprising fact to grab their attention. Additionally, introduce your thesis statement, which outlines your central argument and sets the stage for the rest of your editorial.
Body Paragraphs: The body of your editorial should be organized into a series of paragraphs, each focusing on a single point or piece of evidence that supports your thesis. Use clear topic sentences to convey the main idea of each paragraph and maintain a logical flow throughout your editorial . Be sure to provide well-researched facts, statistics, and expert opinions to support your claims and address any counterarguments to strengthen your position.
Transition Sentences: Utilize transition sentences between paragraphs to create a smooth flow and maintain continuity in your argument. This will help guide your readers through your editorial and enhance its readability.
Conclusion: Conclude your editorial by summarizing your main points and restating your thesis in a fresh, compelling manner. The conclusion should create a long-lasting impact on your readers by offering a solution, urging action, or posing a thought-provoking question.
Editing and Proofreading: After completing your initial draft, carefully review your editorial for clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Check for grammatical errors, inconsistencies, and redundancies, and refine your language and style to ensure your argument is presented effectively.
By following these steps, you can structure your editorial to effectively communicate your ideas and persuade your readers. Mastering the art of structuring your editorial page is essential in producing an engaging and thought-provoking piece that encourages meaningful dialogue and inspires action.
How to Start an Editorial: Writing a Strong Opening Paragraph
Understanding how to start an editorial letter begins with crafting a solid opening paragraph that captures your reader’s focus and establishes the foundation for your argument. The introduction is a crucial component of your editorial, as it sets the tone and determines whether readers will be engaged enough to continue reading.
Strategies for Captivating Your Audience
Below are some pointers for producing a persuasive opening paragraph:
Use a Captivating Hook: Begin your editorial with a hook that immediately grabs your readers’ interest. his could encompass an astonishing fact, a thought-provoking inquiry, or an emotional anecdote relevant to your topic. A robust hook will pique your audience’s curiosity and encourage them to read further.
Provide Context: After capturing your reader’s attention, provide background information and context about your topic. This will aid your audience in comprehending the importance and relevance of the issue you are addressing. Be concise and avoid overwhelming your readers with too much information at the outset.
State your Thesis: Your thesis statement should be introduced early in your editorial, preferably within the opening paragraph. This statement should clearly articulate your central argument or opinion on the topic. A well-crafted thesis will serve as a roadmap for your readers, guiding them through your editorial and shaping their expectations.
Establish Your Credibility: Briefly highlights your expertise, experience, or other factors qualifying you to write about the topic. Establishing credibility from the outset will help your readers trust your perspective and be more open to your argument.
Engage Your Readers: Use a conversational tone to address your readers directly to create connection and engagement. This will help make your editorial more relatable and accessible, encouraging readers to continue reading and consider your viewpoint.
Writing a solid opening paragraph is essential when learning how to start an editorial letter. Using a captivating hook, providing context, stating your thesis, establishing your credibility, and engaging your readers, you can create an introduction that sets the stage for a persuasive and compelling editorial.
How to Start an Editorial: Adding Supporting Evidence
When learning how to write an editor’s note for a magazine, adding supporting evidence to your editorial is crucial in establishing credibility and persuading your readers. A well-researched and evidence-backed editorial will strengthen your argument and demonstrate your commitment to presenting a balanced and informed perspective.
Enhancing Your Editorial with Supporting Evidence
Here are some tips for incorporating supporting evidence into your editorial:
Use Various Sources: To create a robust argument, gather evidence from multiple reputable sources, such as academic journals, newspapers, government reports, and expert opinions. This will help ensure your editorial is well-rounded and credible, showcasing diverse perspectives and information.
Cite Your Sources: Be transparent about the origins of your evidence by citing your sources. This demonstrates your commitment to accuracy and allows your readers to verify your claims and explore the topic further.
Integrate Evidence Seamlessly: Incorporate your supporting evidence into your editorial naturally and unobtrusively. Employ unambiguous and succinct terminology to articulate your facts, statistics, and expert opinions, ensuring they support and enhance your argument without overwhelming your readers.
Address Counterarguments: Including evidence that addresses counterarguments or opposing viewpoints is essential in creating a balanced and persuasive editorial . By acknowledging and responding to these perspectives, you demonstrate your understanding of the topic’s complexity and further solidify your own argument.
Connect Evidence to Your Thesis: Ensure that each piece of evidence you present directly supports your thesis statement. This will help your readers understand the relevance of your evidence and follow your line of reasoning more easily.
Use Evidence Strategically: Be selective in the evidence you present, focusing on the most compelling and convincing information that supports your argument. Avoid overloading your editorial with excessive details, which may detract from your central message.
Adding supporting evidence is critical to writing an editor’s note for a magazine. By using various sources, citing your evidence, integrating it seamlessly, addressing counterarguments, and connecting your evidence to your thesis, you can create a persuasive and well-informed editorial that effectively communicates your viewpoint and resonates with your readers.

How to Start an Editorial: Wrapping Up with a Powerful Conclusion
Knowing how to write an editorial for a magazine involves mastering the art of crafting a powerful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression on your readers. The conclusion of your editorial should not only sum up your key arguments and restate your thesis but also provide a sense of closure and inspire further thought or action.
Strategies for Leaving a Lasting Impression
Here are some guidelines for crafting a compelling conclusion:
Reiterate Your Central Argument or Position: Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement freshly and engagingly. This will remind your readers of your central argument and reinforce the main message of your editorial.
Summarize Your Main Points: Briefly recaps your editorial’s key points and supporting evidence. This will help your readers remember your most compelling arguments and tie your ideas together cohesively.
Offer a Solution or Recommendation: If appropriate, present a solution or recommendation that addresses the issue or problem discussed in your editorial. This can demonstrate your commitment to positive change and encourage your readers to consider potential solutions.
Call-to-action: Urge your readers to take action or further think or discuss the topic. A solid call to action can inspire your audience to make a difference or explore the issue more deeply.
End with a Memorable Statement or Question: Conclude your editorial with a thought-provoking statement or question that leaves a lasting impression on your readers. This will encourage them to reflect on your argument and consider the broader implications of your editorial.
Maintain Your Tone: Ensure that the tone of your conclusion is consistent with the rest of your editorial. A cohesive tone will help create a sense of unity and polish in your writing.
Wrapping up your editorial with a powerful conclusion is essential in crafting a persuasive and engaging piece. By restating your thesis, summarizing your main points, offering a solution, calling for action, and ending with a memorable statement, you can leave a lasting impression on your readers and encourage them to engage with your ideas long after they have finished reading your magazine editorial.
What should I focus on when brainstorming ideas for an editorial?
Concentrate on current events, trending issues, or subjects that impact your community. Consider opinions, concerns, and debates surrounding these topics for inspiration. Evaluate each idea based on relevance, timeliness, and potential impact on readers.
How can I ensure my research is credible and accurate?
Use reputable sources of information, such as newspapers, academic journals, books, government reports, and expert opinions. Critically evaluate each source for accuracy, relevance, and credibility to build a solid foundation for your editorial.
What should I include in my editorial’s opening paragraph?
Use a captivating hook, provide context, state your thesis, establish credibility, and engage your readers to create a strong and engaging introduction.
What are some tips for writing a powerful conclusion?
Restate your thesis, summarize your main points, offer a solution or recommendation, call to action, end with a memorable statement or question, and maintain your tone to create a compelling and lasting conclusion.
How can I make sure my editorial is well-structured?
Organize your editorial into an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion, using clear topic and transition sentences to maintain a logical flow. Ensure that each paragraph focuses on a single point or piece of evidence and that your argument is coherent and persuasive.

Learn How To Develop Launch-Ready Creative Products
Download How to Turn Your Creativity into a Product, a FREE starter kit.

Advertisement
Create a Memorable Social Media Experience
Get the content planner that makes social media 10x easier.

Invite Your Customers To A Whole New World
Create a unique user experience.

Maximize Your Brand and Make Your Mark
Custom brand assets will take you to new heights.

Rank a Website: How to Implement Mobile Optimization

Storytelling: How to Understand the Neuroscience

Faceless Marketing: How to Create a Campaign

Email Marketing: How to Identify the Pros and Cons

Rank a Website: How to Analyze Your Link Profile

Business Ideas: How to Start Your Own Business
How To Write An Editorial
Last updated on: Nov 20, 2023
Learn How To Write An Editorial By Experts
By: Cordon J.
Reviewed By: Chris H.
Published on: Sep 14, 2021

An editorial is a newspaper article that presents the author’s point of view on different topics and issues. Students are often assigned to write editorials of school newspapers.
When assigned to write an editorial piece, you must understand the characteristics of an editorial that appeal to the reader.
Learn how to write an editorial with this complete guide. Also, find below some editorial topics and examples that may assist you when you begin writing your editorial.

On this Page
What is an Editorial?
An editorial is an article that expresses the editor's ideas and explains the issue at hand. Just because it is an opinion piece doesn’t mean that the author can write their thoughts merely. They can not write an editorial without conducting research and considering the facts.
To build their argument and persuade the readers, editorial writers must present authentic evidence that will support their opinions.
The aim of an editorial is to present an issue clearly and propose a solution to get rid of it.
Author’s need to address the people currently facing the issue. They also need to tell them what can be done to deal with the situation. If necessary, the author must speak to the government, asking them to take appropriate measures to help combat the situation.
Considering the research and effort that goes into writing an editorial, they can be considered similar to a research paper.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Types of an Editorial
Typically, there are four different types of editorials, where each serves a unique purpose.
Below is a detailed description of these types.
1. Explain and Interpret – this format gives editors a chance to explain how they tackled sensitive and controversial topics.
2. Criticize – such editorials while focusing on the problem rather than the solution criticize actions, decisions, or certain situations.
3. Persuade – in this format, you propose a solution and convince the readers to take appropriate actions.
4. Praise – this type of editorial is written to show support and commend a notable action of an organization or individual.
How to Write an Editorial?
With social media becoming more popular day by day where everyone can easily express their opinions, people aren't sure of how to write a strong editorial.
Editorials are based on the writer’s opinions. But, if you want the reader to take your word seriously, you must provide facts to support your opinion. Don’t ramble and rant about a personal issue.
Following are the important steps that will help you craft an impressive editorial.
1. Pick a Topic That Will Grab The Reader's Attention
The purpose of an editorial is to change the public’s belief about a particular topic. Or to encourage them to critically analyze issues and, more often than not, suggest a particular course of action.
When brainstorming ideas for your piece, make sure that it is interesting, has a current news angle, and serves a purpose. Sometimes writing on a controversial subject can really help attract the reader.
2. Research and Gather Facts
As an editorial writer, your job is to find the truth about a particular issue. Do your research and look for relevant information so that you can present facts along with your opinion. Go through credible sources only and gather the latest facts.
Check out this detailed blog on the types of research and how to conduct them. It will make this step easier for you.
3. Writing the Editorial
When writing an editorial, keep it short and clear, so the reader stays with you throughout the piece. It shouldn’t be longer than 600 to 800 words. Also, avoid using fancy jargon or technical terms.
- Introduction
Start the editorial with a unique and catchy question, statistics, facts, and quotations. You could also use any other sentence relevant to the topic that will help grab the reader's attention. Also, present your argument in the form of a thesis statement at this stage.
The body of your editorial piece should explain the issue at hand objectively without any trace of biasedness. Discuss each and every aspect of your topic. Address the 5 W’s and H (what, when, where, who, why, and how.)Start by addressing your opposition, people who have dissimilar views. You can also highlight the positive aspects of the opposition as long as they are factually correct.
Next, you need to refute the opposing side. Provide strong reasons and evidence that can help with the credibility of your stance.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
When addressing a problem, you need to propose a valid and applicable solution.
End the editorial with a strong, thought-provoking statement. Your reader must get a sense of closure and completeness from the ending.
4. Proofread and Edit
Don't forget to go through your article once you are done writing. This will help get rid of otherwise unnoticed mistakes and typos.
Editorial Example
EDITORIAL EXAMPLE PDF
Editorial Topics
Here are some interesting and good ideas to help you write an excellent editorial.
- The contribution of fast food is making us obese.
- Should PlayStations be blamed for the death of outdoor activities?
- The flip side of social media.
- Should recreational marijuana be legalized?
- How does recycling help save the environment?
- The evil that is the selfie culture.NBA season preview.
- Are e-cigarettes really safe for our health?
We hope that this blog helped answer all of your editorial writing-related queries. In case of any confusion generate sample editorials from our AI paper writer or, feel free to contact 5StarEssays.com and ask to write an essay for me .
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes a good editorial.
Great content needs to be informative, opinionated, and engaging. It should also teach without being pedantic or didactic in order for the reader's attention span to last as long they are reading. Also, keep it as brief as possible.
What are the elements of an editorial?
Following are the main elements of an editorial:
- Objective explanation
- Opposing opinions
- Writer’s opinions
What is editorial style?
Editors use a set of guidelines to help make their words as consistent and effective as possible. This is their specific writing style. It distinguishes their writing from anyone else.

Speech, Law
Cordon. is a published author and writing specialist. He has worked in the publishing industry for many years, providing writing services and digital content. His own writing career began with a focus on literature and linguistics, which he continues to pursue. Cordon is an engaging and professional individual, always looking to help others achieve their goals.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- How to Write A Bio – Professional Tips and Examples

- Learn How to Write an Article Review with Examples

- How to Write a Poem Step-by-Step Like a Pro

- How To Write Poetry - 7 Fundamentals and Tips

- Know About Appendix Writing With the Help of Examples

- List of Social Issues Faced By the World

- How To Write A Case Study - Easy Guide

- Learn How to Avoid Plagiarism in 7 Simple Steps

- Writing Guide of Visual Analysis Essay for Beginners

- Learn How to Write a Personal Essay by Experts

- Character Analysis - A Step By Step Guide

- Obesity Essay: A Complete Guide and Topics

- Thematic Statement: Writing Tips and Examples

- Expert Guide on How to Write a Summary

- How to Write an Opinion Essay - Structure, Topics & Examples

- How to Write a Synopsis - Easy Steps and Format Guide

- How to Get Better at Math - Easy Tips and Tricks

- How to Write a Movie Review - Steps and Examples

- Creative Writing - Easy Tips For Beginners

- Types of Plagiarism Every Student Should Know

People Also Read
- personal statement prompts
- literary analysis essay writing
- improve writing skills for high school students
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
CURATE YOUR FUTURE
My weekly newsletter “Financialicious” will help you do it.

In This Post
How to write an editorial, in 6 steps.
An editorial is an opinion-driven piece that brings awareness to current events or topics of importance. Here’s what to include.

Editorials assert an opinion or perspective using journalistic principles.
If you have a strong opinion about a topic, knowing how to write an editorial essay can help you land more media visibility and readership.
Editorial writing is when a columnist, journalist, or citizen submits an opinion-based article to a media outlet. A good editorial will be measured and fair; it will make a clear argument with an end goal to persuade readers, raise awareness on a particular issue, or both. Editorials give people a chance to present a supporting or opposing view on a topical issue, and they’re usually formatted as first-person essays.
Opinion editorials (Op-eds) can be a great way to land a byline or full article with a media publication. It can let you assert a stance more powerfully than you would in a quotation or interview.
Key Takeaways
- Also known as an opinion piece, an editorial asserts an author’s position, and often tackles recent events.
- Newspapers have allocated space for editorials from readers for years. The opinion-editorial section is sometimes abbreviated as “op-ed.”
- Editorials are written in first person, from the perspective of the writer, but they should still lean on credible sources.
- Readers should also know how the writer or organization reconciles apparently conflicting positions. True editorial coverage is earned, not purchased.
In this article, we’ll touch on what an editorial piece actually is, along with examples of editorial structure to help you organize your thoughts as you're brainstorming ideas.
What is Editorial Writing?
Every strong editorial has, at its core, a thought-provoking statement or call to action. Editorial writers formulate viewpoints based on experience, supporting evidence, objective analysis, and/or opinion.
Editorials perform very well online. These days, readers don’t always want information alone. They also want interpretation or analysis, whether that be through a newspaper article, a thesis statement, a newsletter , or an opinionated news story. Editorials are powerful, but they are also often biased.
Here's an example of an editorial I wrote recently for Fortune Magazine . This section of Fortune is called Commentary, and it publishes one to two pieces a day from non-staff writers on a variety of business topics.
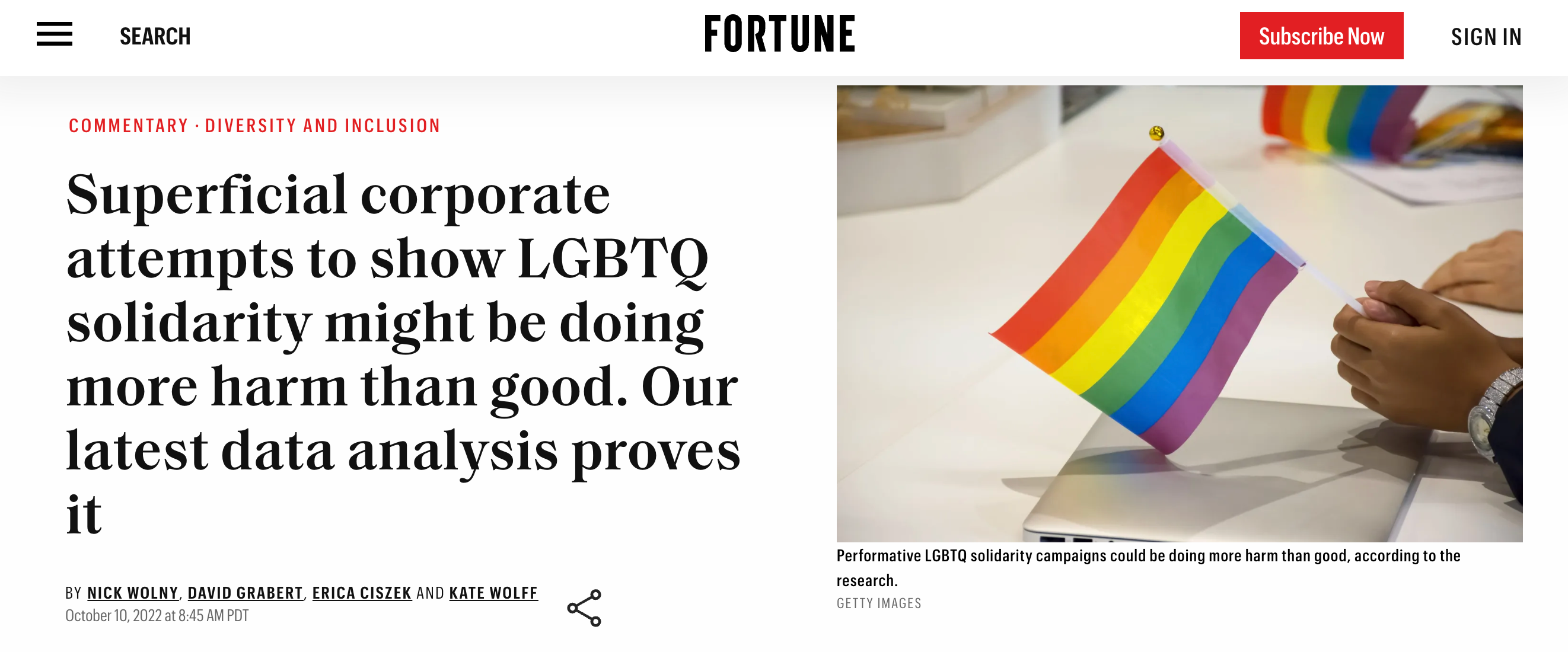
The specifics of this pitch are detailed in my “Pitching Publications 101” workshop.

Limited-Time Offer: ‘Pitching Publications 101’ Workshop
Get the ‘Pitching Publications 101’ Workshop and two other resources as part of the Camp Wordsmith® Sneak Peek Bundle , a small-bite preview of my company's flagship publishing program. Offer expires one hour from reveal.
Many media outlets rotate in opinion columnists to offer unique perspectives on a regular basis. Here’s a screenshot from The Washington Post opinion page ; the paper has over 80 opinion columnists, who write regularly about topics like policy, health, and climate change.
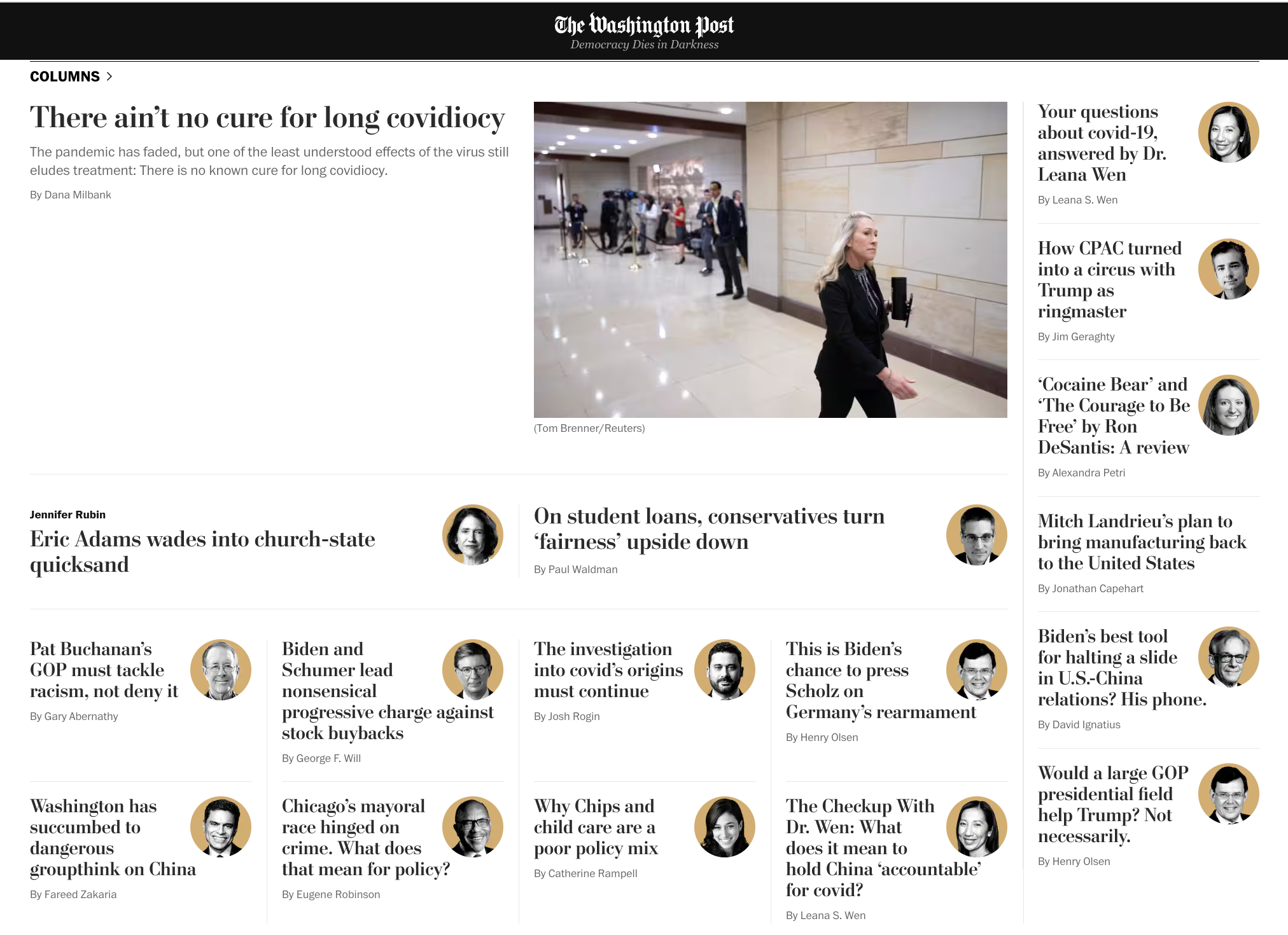
Large media publications usually have a separate section for opinion and commentary.
What Is an Editorial Board?
In contrast, you may have seen a newspaper or media publication release a statement from its editorial board. The editorial board consists of the publication’s editors, who together release a joint statement about a certain topic.
Examples of editorial topics include:
- An editorial board endorsing a local politician in a forthcoming election.
- Commentary on issues of local importance.
- Scientists announcing a newly published research paper that has mainstream relevance.
- Perspectives from citizens who come from various walks of life.
- Submitted opinion pieces in school newspapers or academic journals.
Good Examples of Published Editorials
The best way to get a feel for writing editorials is to see some effective editorial examples in action.
The Los Angeles Times and 70+ other newspapers condemned the actions of Scott Adams, the illustrator behind Dilbert cartoons. Since the cartoons were scheduled to run in the paper for a few more weeks, the editorial board released a statement updating readers on their decision to pull the cartoon, along with what next steps would be taken.

Many editorials are written by celebrities or public figures as a way to create awareness or touch on a controversial subject. Chrissy Teigen published an editorial on Medium about her miscarriage. Medium is an open-source publishing platform that many personalities use to make independent op-ed statements publicly.
A peer of mine, Zach McKenzie, wrote an editorial on the lack of sober queer spaces in Houston, America’s fourth-largest city. He pitched it to the Houston Chronicle, and an editor accepted and published his opinion piece.
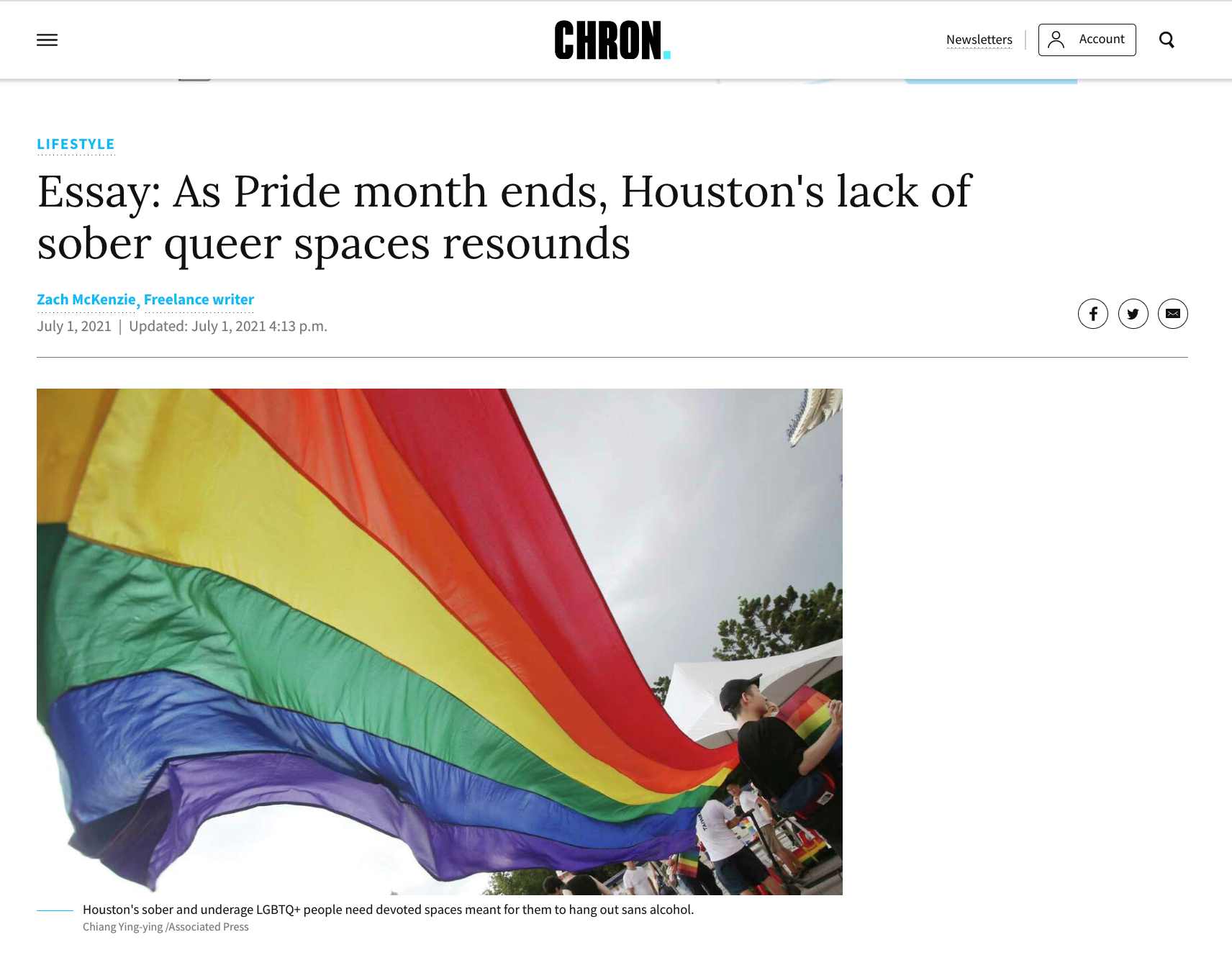
He later became a freelance writer for the paper. Since you'll often work with an editor on your editorial, this could open doors for freelance opportunities.
Editorials can also refute other editorials. These are sometimes formatted as letters to the editor instead. In 2011, Martin Lindstrom published an op-ed with The New York Times entitled “You Love Your iPhone. Literally” , which asserted that neuroimaging showed we feel human love for our smartphones. A response letter signed by a total of 45 neuroscientists was sent to the Times condemning the op-ed as scientifically inaccurate.
Types of Editorials
Editorials typically fall into one of four categories: explanation, criticism, persuasive essay, or praise.

No. 1: Explanation or Interpretation
Not all editorials have to be about controversial topics. Editorials written by a board or an organization might simply summarize main points of new research or a recent decision.
No. 2: Criticism
Criticism is by far the most popular type of editorial, because, well, we love the drama! 🍿
Opinion editorial usually disagrees with the status quo on a given topic, but does so in a well-researched way. An opinion editor will do more than simply fix grammatical errors; they often guide the contributor through the writing process and reinforce good editorial style.
No. 3: Persuasive Essay
Technically, an editorial can also simply be a persuasive essay, written in first person. As long as the main point has a good chance at catching a reader’s attention, editors will be interested in the piece.
No. 4: Praise
Sometimes, an opinion piece actually agrees with the status quo or current news angle, although these pieces are less common.
How to Write an Editorial in 6 Steps
- Pick a topic that has mainstream appeal.
- Lead with a summary of your opinion.
- State the facts.
- Summarize the opposition’s position.
- Refute the opposition.
- Offer readers a solution or reframe.
Step 1: Pick a Topic That Has Mainstream Appeal
If you want your essay to be published in a news outlet, it has to be, well, news!
Connect your thesis statement to a current event. Your topic should be one that the majority of the public can understand or relate with. Remember: Business is niche, media is broad. Make it mainstream.
Step 2: Lead With a Summary of Your Opinion
Editorial format usually opens with a summary of your thesis statement and/or new ideas in the first paragraph. In journalism, this section is known as the lede —part of the “inverted pyramid” writing process —and it’s the most important section of your article.
Remember, if readers can’t get oriented and understand your own opinion within the first few sentences, they’ll leave.
Related: How to Write a News Lead
Step 3: State the Facts
One detail any writers miss regarding how to write an editorial is giving sufficient background information. In some ways, you have to operate like a journalist when you begin writing editorials. Collect facts and outline the main points for your reader so they grasp the issue at hand.
Step 4: Summarize the Opposition’s Position
Good editorial presents both sides of the story. Even though this is an opinion-based essay, you want your editorial format to acknowledge common counter arguments.
Step 5: Refute the Opposition
This is the fun part! Use logic and evidence in your writing to reinforce your point. When you cite sources and statistics, your writing will pack more punch.
Step 6: Offer Readers a Solution or Reframe
Lastly, go into a clear conclusion and possible solutions. Don’t just dump an opinion on your reader and then leave them with nothing to do or consider. You’ve persuaded us with a hard-hitting editorial on a topic you feel strongly about—now ask us to do something!
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes a good editorial.
A good editorial will assert a clear and compelling point. The editorial should cite reputable sources in order to form its point, and should address why the opposing viewpoint is misguided.
What Is the Purpose of an Editorial?
An editorial provides contrast to day-to-day journalism with perspectives and commentary on recent events. Editorials are not objective; they are subjective and opinionated by design.
What Are Examples of Editorial Content?
An editorial could be a column in a magazine or newspaper, a public statement, a newsletter, or even a blog post. A letter to the editor is usually not considered an editorial.
Write Your First (or Next) Editorial This Year
You don’t have to be a journalist to pitch and write editorials, but you do have to have a point of view that will capture a reader’s attention. Study the writing process of editorials and you’ll have a better shot at getting your opinions published. ⬥
Thanks For Reading 🙏🏼
Keep up the momentum with one or more of these next steps:
📣 Share this post with your network or a friend. Sharing helps spread the word, and posts are formatted to be both easy to read and easy to curate – you'll look savvy and informed.
📲 Hang out with me on another platform. I'm active on Medium, Instagram, and LinkedIn – if you're on any of those, say hello.
📬 Sign up for my free email list. This is where my best, most exclusive and most valuable content gets published. Use any of the signup boxes on the site.
🏕 Up your writing game: Camp Wordsmith is a free online resources portal all about writing and media. Get instant access to resources and templates guaranteed to make your marketing hustle faster, better, easier, and more fun. Sign up for free here.
📊 Hire me for consulting. I provide 1-on-1 consultations through my company, Hefty Media Group. We're a certified diversity supplier with the National Gay & Lesbian Chamber of Commerce. Learn more here.

Welcome to the blog. Nick Wolny is a writer, editor and copy consultant based in Los Angeles.
A Beginner’s Guide on How to Write an Editorial
- Academic Writing Guides

Writing an editorial essay lets you share your viewpoint on or advocate for a particular cause with your audience. A great editorial article creates awareness on a matter and influences people’s positions on it. But how do you compose such an article?
This post shares valuable insights on how to write an editorial that impresses editors and influences readers. Keep reading to enhance your effectiveness and master how to write an editorial essay .
What Is an Editorial Paper?
Let’s start by answering the big question, “ What is an editorial paper ?” As the name suggests, an editorial article or paper expresses an editor’s stand on a matter and explains the issue at hand. However, it doesn’t mean that the editor exclusively expresses their thoughts. That’s why the writer must research the topic and include other people’s ideas on the subject.
A great editorial paper focuses on a given topic. The author must focus on why their target readers care about the topic and why some people might hold contrary views. That’s why understanding the two sides of a matter makes an editorial more interesting and acceptable to many audiences. You will also need to present readers with valid evidence that supports your opinions.
When your editorial addresses a problem, you must also present clear solutions. Tell your readers what should be done to address the situation. If necessary, speak to the relevant authorities that need to take appropriate measures to address particular situations. For instance, you can address the government or institutions that can midwife solutions.
How to Write an Editorial
The rise of social media has provided more people with a free platform to express their platforms. Consequently, people are no longer sure of what it takes to write editorials . However, it doesn’t mean that you can master how to write an editorial that impresses editors. This section shares insights to help you compose a great editorial that speaks to your constituents.
Choose an Attention-Grabbing Topic
Start your journey by selecting an interesting topic with current news value and serves a defined goal. At times, handling a controversial topic can attract people.
Research and Gather Facts
Next, gather the facts surrounding your topic before presenting it to your readers. You must research the facts so that your opinion isn’t based on your feelings. Use credible sources and collect the latest facts surrounding your topic.
Drafting the Editorial
Draft your paper to be short and clear, at least 600 to 800 words. Additionally, avoid using jargon.
- Introduction. Make its intro as attractive as possible. You can open it with relevant stats, a quote from a famous person your readers respect, or a thought-provoking question.
- Body. The body should address all the details surrounding your topic. It should follow the 5 W’s and H pattern (what, when, where, who, why, and how). This section should address opposition and provide evidence to support your stance. When addressing problems, propose valid and practical solutions.
- Conclusion. End your editorial with a strong, thought-provoking statement. Give your readers a sense of closure and completeness from this section.
Proofread and Edit
Polish your editorial by editing and proofing it for styling, grammar, and spelling perfection before submitting it.
Tips for Writing a Good Editorial
Do you want to master how to write an editorial article ? Below are tips to help you up your editorial writing game.
- Be decisive. A great editorial takes a firm position on a matter. Whenever you mention a contrary position, you immediately show readers why it’s inaccurate and why readers should agree with your stand.
- Provide fresh ideas. Research your topic well to provide readers with fresh ideas. Whereas people have ideas on specific issues, adding a fresh angle to them makes your article more valuable.
- Offer solutions. If you address a problem, your article should provide possible solutions. Don’t just describe problems for which you can’t prescribe solutions.
- Focus on your interests. Whenever possible, select a topic you are passionate about to be better placed to address an issue you care about. Do you care about quality education? Then don’t write on maternal health.
Types of Editorials
It’s essential to understand the types of editorials before you write an editorial for a chosen publication. We have four types of editorials, categorized based on their tone and purpose. These categories are:
- Explaining and Interpreting: These editorials let editors explain how they handle sensitive and controversial topics.
- Criticizing: Such editorials focus on the problem rather than the solution. They criticize actions, decisions, or particular situations.
- Persuading: These editorials propose solutions and convince readers to take appropriate actions towards a matter.
- Praising: Such editorials show support for and commend notable actions by organizations or individuals.
How Do Publications Choose Editorials?
So, how do newspapers and other publications choose an editorial for students ? Most major publications employ op-ed columnists to provide a given number of published editorials in a given year. Some college and high school newspapers have their own columnists who regularly provide editorial content. Most of these publications also solicit guest editorials from external sources. These editorials are like letters to editors but still receive a more generous word count.
The editors use their discretion to accept or reject some editorials. For instance, if they think an editorial touches a needlessly controversial subject or exposes the publication to legal implications, they reject it. In other cases, an editorial board may send the article to the writer to revise or streamline it before resubmitting it for publication.
Editorial Example
Whenever you are stuck on how to write an editorial,l examples will be of much help. This section contains an example regarding the educational system to inspire your writing.
A Critical Editorial Example: A Clarion Call to Reform a Flawed Education System
Our education system is flawed and outdated in many areas and needs urgent reforms. It has many outdated teaching methods that don’t fully engage students. For instance, rote learning stifles innovation and critical thinking, leaving learners ill-equipped when they enter the real world.
Class sizes are still too large, hindering personalized learner attention. Overworked instructors struggle to address student needs. The obsession with standardized testing emphasizes memorization over creative learning. Consequently, it stresses learners and undermines the joy of learning.
Further, the system is unequal. For example, wealthier districts receive more funding, while underprivileged schools lack basic resources. This inequality perpetuates a vicious cycle of disadvantage and limits opportunities for many underprivileged learners.
Thus, everyone must demand radical and immediate reforms. We must all demand innovative teaching methods, smaller class sizes, and equal funding to transform the education landscape. Let’s call for reforms and create an education system that empowers our children, into whose hands we’ll leave our nation.
Editorial Essay Topics
Mastering how to write an editorial paper requires you to choose appropriate topics. To help you do that, we have selected hot sample topics for editorial essay projects. Check them out to jumpstart your next assignment.
- The role of junk food in increasing obesity.
- Is PlayStation turning our children into zombies?
- The dark side of social media.
- Should governments legalize recreational marijuana?
- How does recycling promote a clean and healthy environment?
- The dark side of the selfie culture.
- Are e-cigarettes any safer than traditional ones?
Conclusion
There, you have everything you need to compose an editorial article that impresses readers and fetches good grades. We hope you will use all the valuable information this post shared on how to write an editorial to up your game.
- Citation Guides
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Essay Writing Guides
- Research Paper Topics
- Research Paper Writing Guides
- Study Tips and Tricks
Featured articles

Strategies for Writing a Great Problem Solution Essay
Composing an assignment on a problem and solution essay topic allows you to demonstrate your ability to resolve human challenges. It helps you understand human problems and how to be a part of the solution instead of allocating blame and pointing fingers. So, how do you compose a great problem solutions essay? This post has […]
Author: Marina Kean

Your Complete Guide to Writing a Compelling Leadership Essay
True leadership lies at the heart of human well-being and success. Every positive step humanity ever took required great and responsible leadership. Therefore, people have studied leadership for many edges to unravel its different underlying factors. But how do you write a great essay that demonstrates your grasp of this sacred call? This post shares […]
We use cookies to provide you with a good service. By using this website, you agree with our Cookie policy. Read more .

Quick Guide to Writing an Editorial for Students
The purpose of an editorial article is to present an author’s point on a certain issue. Such articles are based on the majority vote from the editorial board, which includes editors and managers. If you want to write an editorial that will present your point properly and resonate with your audience, you should know some basic rules, and college-writers.com is here to help you with some actionable tips.
An editorial piece can have a good impact on your career, especially if your company is a reputable newspaper. However, you should understand what a good editorial looks like, and what its key elements are. You should also think of the possible response from your readers. We hope that this guide will help you create an effective editorial in no time.
An Editorial Essay
Before you start writing an editorial essay, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the concept of an editorial article. Editorial articles present ideas and opinions of a newspaper’s editor. Most often, such articles focus on very important social issues.
Although such articles mostly focus on opinions, it doesn’t mean that they are not based on facts. Moreover, editorial articles have something in common with research papers because an author should research the issue and present evidence that will support his or her opinion. An editorial article should also suggest possible solutions.
An editorial article should speak to different types of audience. On the one hand, it should be intended for people who suffer from the discussed issue and give them some ideas on how the situation can be improved. On the other hand, an editorial article should also be intended for the government, encouraging it to solve the problem and also suggesting some necessary measures.
As you can see, editorial writing is somewhat similar to writing research papers. Once you’ve hot the necessary research material, the writing process becomes interesting and fun.
The Main Components of an Editorial Essay
Explain and interpret
The first thing you should do is to explain how the newspaper covered a certain sensitive or controversial issue.
Your goal is to not only criticize actions, decisions, and opinions but also to provide an alternative solution. We also recommend that you provide examples from real life that are familiar to your readers.
Offer your solutions. While the previous paragraph should illustrate the issue, this one must encourage your audience to take the right actions.
Mention people and organizations who do the right thing and who have already contributed to solving the problem. However, you may not include this part if the issue in question is new.
Writing Steps
Although editorials focus on the editor’s opinion and the newspaper’s stance, in general, writing it isn’t a simple task. If you want your readers to take your words seriously, you should clearly understand the difference between a fair and a biased point of view. Don’t use an editorial as an opportunity to spill your anger. Instead, we suggest that you follow these steps:
1. Find a relevant topic
It’s not easy to figure out how to write a good editorial. Every writer knows how important choosing relevant topics is. If you want to write an opinion that will be appreciated by the audience, you should only write about relevant issues. Nobody will want to read your opinion if the topic is irrelevant. Ask yourself, why is your opinion important? Do you need to present any statistical data? Do you need to provide certain facts? Why is your topic important at all? You can write about virtually anything, as long as this issue is relevant and you can present solutions that are actually valuable.
2. Do your research
There are many opinions on any issue and you should pick your side carefully. Even when you see a couple arguing, there is always his side, her side, and the truth. When it comes to important social issues, the situation gets even more complicated so you must be able to find the truth among many different opinions. Do your research and make sure that your point is unbiased.
3. Make sure that your opinion is valid
Your opinion must be valid. It means that you shouldn’t formulate your opinion based on emotions. Support it with facts and present these facts in an understandable manner. You should be able to find persuasive arguments and illustrate them with solid evidence. Coming up with a valid opinion is all about reasoning. Your language should be engaging and clear so that your audience can easily understand why your opinion is right.
4. Write an outline
Once you’ve got nice arguments that support your opinion, write an outline for your story. Decide which paragraphs will focus on statistics and where you will provide quotes. You may also acknowledge the opposite opinions and refute them. All these elements determine the structure of your essay or article so you should plan the structure before writing your paper.
When the outline is ready, start to write, filling every section of your paper with claims and pieces of evidence that support them. If you prepare for the writing process properly, you won’t have any problems creating a well-structured piece of writing.
5. Read your work
Read your paper aloud before submitting it. We recommend that you never skip this last step because you need to check your paper for plagiarism and any mistakes. Reading your text aloud is a great solution because, this way, you will quickly detect sentences that sound awkward and check the overall tone. Make sure that your paper sounds professional. Think about your readers and try to make them relate to your point.
Helpful Tips
Modern technology has introduced numerous challenges for newspapers because the competition constantly grows. Social media makes the situation more complicated than ever, adding the emotional element, which will be a problem if you want to write an editorial. These tips will help you write a nice paper, no matter what topic you’re working on.
- Find a newspaper with more than 100,000 copies If you want to be a successful writer, you should make sure that you will reach out to as many people as you can. When you find a good paper, choose relevant topics and offer logical solutions.
- Choose controversial topics To write an impressive editorial, you should choose a debatable topic. Controversial issues are a great opportunity for you because they help keep your readers engaged — everyone will continue to read to find out whether you agree with their own position or not, and why. You may also ask your readers relevant questions.
- Be honest You won’t be able to effectively support an opinion if you don’t actually agree with it. Sometimes, you may feel tempted to argue for a certain position just because it can make your essay controversial and engaging. However, we recommend that you be honest with your readers and only choose the right side. This way, your essay will be strong and authentic.
- Offer different solutions If you’re discussing a common problem that many of your readers are familiar with, make sure to provide different solutions. Consider each solution in terms of effectiveness and efficiency so that your readers can choose from among various options and decide which one will work for them.
Interesting Topics
Before you become a writer in a newspaper or magazine, you will have to write many editorial essays in high school. The most common formats of editorial essays are related to current events in the country and the world. Here are some topics that you may choose:
- Global warming and its consequences for the planet;
- Should gambling be legal?
- Causes, symptoms, and treatment of HIV;
- E-cigarettes: are they safe?
- Should marriage to animals be legal?
An editorial should provide the author’s viewpoint, without being too emotional or biased. It must also be informative but not instructive. It should encourage readers to take action without being annoying. It should also be persuasive, well-structured, and based on solid evidence. Last but not least, we recommend that you make it concise.
With us you get
- 10+ years experience in the custom writing market
- A wide range of services
- Satisfied and returning customers
- 6-hour delivery available
- Money-back guarantee
- 100% privacy guaranteed
- Professional team of experienced paper writers
- Only custom college papers
- Free amendments upon request
- Constant access to your paper writer
- Free extras by your request
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , what is academic writing: tips for students, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content.
How to Begin an Essay: 13 Engaging Strategies
ThoughtCo / Hugo Lin
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
An effective introductory paragraph both informs and motivates. It lets readers know what your essay is about and it encourages them to keep reading.
There are countless ways to begin an essay effectively. As a start, here are 13 introductory strategies accompanied by examples from a wide range of professional writers.
State Your Thesis Briefly and Directly
But avoid making your thesis a bald announcement, such as "This essay is about...".
"It is time, at last, to speak the truth about Thanksgiving, and the truth is this. Thanksgiving is really not such a terrific holiday...." (Michael J. Arlen, "Ode to Thanksgiving." The Camera Age: Essays on Television . Penguin, 1982)
Pose a Question Related to Your Subject
Follow up the question with an answer, or an invitation for your readers to answer the question.
"What is the charm of necklaces? Why would anyone put something extra around their neck and then invest it with special significance? A necklace doesn't afford warmth in cold weather, like a scarf, or protection in combat, like chain mail; it only decorates. We might say, it borrows meaning from what it surrounds and sets off, the head with its supremely important material contents, and the face, that register of the soul. When photographers discuss the way in which a photograph reduces the reality it represents, they mention not only the passage from three dimensions to two, but also the selection of a point de vue that favors the top of the body rather than the bottom, and the front rather than the back. The face is the jewel in the crown of the body, and so we give it a setting." (Emily R. Grosholz, "On Necklaces." Prairie Schooner , Summer 2007)
State an Interesting Fact About Your Subject
" The peregrine falcon was brought back from the brink of extinction by a ban on DDT, but also by a peregrine falcon mating hat invented by an ornithologist at Cornell University. If you cannot buy this, Google it. Female falcons had grown dangerously scarce. A few wistful males nevertheless maintained a sort of sexual loitering ground. The hat was imagined, constructed, and then forthrightly worn by the ornithologist as he patrolled this loitering ground, singing, Chee-up! Chee-up! and bowing like an overpolite Japanese Buddhist trying to tell somebody goodbye...." (David James Duncan, "Cherish This Ecstasy." The Sun , July 2008)
Present Your Thesis as a Recent Discovery or Revelation
"I've finally figured out the difference between neat people and sloppy people. The distinction is, as always, moral. Neat people are lazier and meaner than sloppy people." (Suzanne Britt Jordan, "Neat People vs. Sloppy People." Show and Tell . Morning Owl Press, 1983)
Briefly Describe the Primary Setting of Your Essay
"It was in Burma, a sodden morning of the rains. A sickly light, like yellow tinfoil, was slanting over the high walls into the jail yard. We were waiting outside the condemned cells, a row of sheds fronted with double bars, like small animal cages. Each cell measured about ten feet by ten and was quite bare within except for a plank bed and a pot of drinking water. In some of them brown silent men were squatting at the inner bars, with their blankets draped round them. These were the condemned men, due to be hanged within the next week or two." (George Orwell, "A Hanging," 1931)
Recount an Incident That Dramatizes Your Subject
"One October afternoon three years ago while I was visiting my parents, my mother made a request I dreaded and longed to fulfill. She had just poured me a cup of Earl Grey from her Japanese iron teapot, shaped like a little pumpkin; outside, two cardinals splashed in the birdbath in the weak Connecticut sunlight. Her white hair was gathered at the nape of her neck, and her voice was low. “Please help me get Jeff’s pacemaker turned off,” she said, using my father’s first name. I nodded, and my heart knocked." (Katy Butler, "What Broke My Father's Heart." The New York Times Magazine , June 18, 2010)
Use the Narrative Strategy of Delay
The narrative strategy of delay allows you to put off identifying your subject just long enough to pique your readers' interest without frustrating them.
"They woof. Though I have photographed them before, I have never heard them speak, for they are mostly silent birds. Lacking a syrinx, the avian equivalent of the human larynx, they are incapable of song. According to field guides the only sounds they make are grunts and hisses, though the Hawk Conservancy in the United Kingdom reports that adults may utter a croaking coo and that young black vultures, when annoyed, emit a kind of immature snarl...." (Lee Zacharias, "Buzzards." Southern Humanities Review , 2007)
Use the Historical Present Tense
An effective method of beginning an essay is to use historical present tense to relate an incident from the past as if it were happening now.
"Ben and I are sitting side by side in the very back of his mother’s station wagon. We face glowing white headlights of cars following us, our sneakers pressed against the back hatch door. This is our joy—his and mine—to sit turned away from our moms and dads in this place that feels like a secret, as though they are not even in the car with us. They have just taken us out to dinner, and now we are driving home. Years from this evening, I won’t actually be sure that this boy sitting beside me is named Ben. But that doesn’t matter tonight. What I know for certain right now is that I love him, and I need to tell him this fact before we return to our separate houses, next door to each other. We are both five." (Ryan Van Meter, "First." The Gettysburg Review , Winter 2008)
Briefly Describe a Process That Leads Into Your Subject
"I like to take my time when I pronounce someone dead. The bare-minimum requirement is one minute with a stethoscope pressed to someone’s chest, listening for a sound that is not there; with my fingers bearing down on the side of someone’s neck, feeling for an absent pulse; with a flashlight beamed into someone’s fixed and dilated pupils, waiting for the constriction that will not come. If I’m in a hurry, I can do all of these in sixty seconds, but when I have the time, I like to take a minute with each task." (Jane Churchon, "The Dead Book." The Sun , February 2009)
Reveal a Secret or Make a Candid Observation
"I spy on my patients. Ought not a doctor to observe his patients by any means and from any stance, that he might the more fully assemble evidence? So I stand in doorways of hospital rooms and gaze. Oh, it is not all that furtive an act. Those in bed need only look up to discover me. But they never do." ( Richard Selzer , "The Discus Thrower." Confessions of a Knife . Simon & Schuster, 1979)
Open with a Riddle, Joke, or Humorous Quotation
You can use a riddle , joke, or humorous quotation to reveal something about your subject.
" Q: What did Eve say to Adam on being expelled from the Garden of Eden? A: 'I think we're in a time of transition.' The irony of this joke is not lost as we begin a new century and anxieties about social change seem rife. The implication of this message, covering the first of many periods of transition, is that change is normal; there is, in fact, no era or society in which change is not a permanent feature of the social landscape...." (Betty G. Farrell, Family: The Making of an Idea, an Institution, and a Controversy in American Culture . Westview Press, 1999)
Offer a Contrast Between Past and Present
"As a child, I was made to look out the window of a moving car and appreciate the beautiful scenery, with the result that now I don't care much for nature. I prefer parks, ones with radios going chuckawaka chuckawaka and the delicious whiff of bratwurst and cigarette smoke." (Garrison Keillor, "Walking Down The Canyon." Time , July 31, 2000)
Offer a Contrast Between Image and Reality
A compelling essay can begin with a contrast between a common misconception and the opposing truth.
"They aren’t what most people think they are. Human eyes, touted as ethereal objects by poets and novelists throughout history, are nothing more than white spheres, somewhat larger than your average marble, covered by a leather-like tissue known as sclera and filled with nature’s facsimile of Jell-O. Your beloved’s eyes may pierce your heart, but in all likelihood they closely resemble the eyes of every other person on the planet. At least I hope they do, for otherwise he or she suffers from severe myopia (near-sightedness), hyperopia (far-sightedness), or worse...." (John Gamel, "The Elegant Eye." Alaska Quarterly Review , 2009)
- 'Whack at Your Reader at Once': Eight Great Opening Lines
- What Is a Compelling Introduction?
- How to Structure an Essay
- Writing a Descriptive Essay
- Hookers vs. Chasers: How Not to Begin an Essay
- Development in Composition: Building an Essay
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- How To Write an Essay
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- How to Write a Great Essay for the TOEFL or TOEIC
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- How to Develop and Organize a Classification Essay
- Contrast Composition and Rhetoric
- 6 Steps to Writing the Perfect Personal Essay
- A Guide to Using Quotations in Essays
- What Is Expository Writing?
- How It Works
- Essay Examples
How to Write a Compelling Newspaper Editorial
Are you looking for ways to write an excellent editorial for your readers? Here, we've put together a list of different stages you’ll need to develop an attractive newspaper article. You’ll discover that they are all that you need for your first trial.
Defining Editorial Essays
So, what is an editorial essay? If you know how to write a psychology essay you are already a bit familiar with this type of writing. Well, this is a question which we find from most authors. First, you must understand the meaning of the word editorial. It means a newspaper article which contains different ideas of the author. He or she can choose to write a piece on any topic, but mostly, these pieces talk about social issues. Of course, similar to all research papers, you’ll have to offer credible evidence that supports your findings.
Detailed research should be conducted to find the topic that the author wishes to discuss. An editorial should describe the problem and offer suitable solutions. For instance, if the author wants to talk about the issues associated with an obese population, he or she should also give a detailed account of how to deal with such a huge problem. A good example here is developing a message for all those suffering from obesity and for healthcare experts who need to handle it.
The authors also speak to the ruling local governments as they try to encourage them to take the necessary measures. So far, it’s clear that coming up with an editorial essay bears close similarities with writing a research or essay paper. Therefore, if you didn’t have any problems in writing college, university or high school papers, you’ll find it pretty easy when you decide to come up with an interesting editorial.
How Can You Write Different Editorial Essays?
You’ll discover that unlike other essays, editorials have a different classification. Here, instead of being classified according to their nature, they are grouped based on their purposes. Hence, there’s no way of coming up with the answer to “what is an editorial essay?” without first understanding the basic facts of all types. So, as you work on your essay, you could either:
- Describe/Explain/Interpret The Subject
Show how your newspaper article talks about the specific subject. Keep in mind that your argument needs to be debatable, controversial and sensitive to attract your audience. Take a look at this example: You might be an editor of a high school paper who chooses to talk about the different standards of writing to your readers.
- You Could Even Criticize The Problem
Critical thinking is something that all expert essay writers should use to make a meaningful and captivating piece which covers a vital issue. Remember that an excellent editorial piece criticizes certain cases or actions providing solutions to all the existing problems. Your main aim here is to allow the readers to identify the problem rather than just their solutions.
- You Can Also Persuade Your Audience By Showing Them The Central Argument Of The Editorial
Unlike the editorial essays which only criticize, persuasive papers concentrate on all suggested solutions without diving into the specific details of the problem. From the introduction or opening paragraph, the author should motivate his audience to take action when implementing the solution. Suitable examples of such essays are political endorsements.
These types of editorials appreciate organizations or people who have done beneficial and special deeds.
Are you still wondering what editorial essays are? If so, below are some exciting tips to help you understand such papers better!
Methods That Will Help You Come Up With an Attractive Editorial Essay
We are currently in the age of fierce writing competition because of the advancements in social media. Nowadays, you’ll find that a majority of people cannot write a persuasive newspaper editorial piece. Luckily, here are some essential tips and additional advice from various writing experts. As a young author, they should help you master the craft!
Try to choose the newspaper that is read by a wide-range of people. Such papers mostly talk about the relevant topics as well as offering essential facts as well as solutions to the current issues.
The importance of using such subjects is because they are quite debatable. Besides, they are one of the best ways of engaging your audience in the discussion. Here, it’s essential to ask them additional questions as you proceed with the research.
It’s worth mentioning that an author cannot take both sides of a controversial paper. Therefore, you should choose the one which you think is right based on your knowledge and experience.
As a young author, you should also provide multiple solutions that give your different audience choices. It’s crucial to test the efficiency and effectiveness of all solutions before offering them!
“To make any argument sound better, talk about several analogies. As the author, you have the right to choose between different social, political and cultural analogies as people often trust such fields. For instance, your research problem could be the credibility of different mobile spying applications.” Burke goes on to add that, “Look for similar issues in other technologically advanced countries where millions of people use such methods to keep their families safe. With editorials, you’re just looking for solutions as you discover what other states did to solve the specific issue.”
How Can You Write Newspaper Editorial
No matter the type of editorial piece you choose, your newspaper article should have specific features which you’ll need to keep in mind as an editor.
- An engaging introduction, followed by many body paragraphs and an attractive conclusion. As you can see, the structure is pretty similar to what we find in a good number of academic essays.
- A reasonable interpretation of the question or issue by using reliable facts, figures and statistics. Here, you should remember that complex problems need more attention than other simple topics.
- Use the most efficient news angle.
- Arguments offered by the opposing parties to show the essay is entirely unbiased and objective!
- As the author, you should also include your different viewpoints in the most formal language. Remember that impressive editorials do not concentrate on character traits when trying to persuade and attract the audience.
- Use professionalism and criticism to come up with possible solutions.
- Include a summary and a compelling call to action (CTA).
Before you even start writing your introduction , go through the various guidelines of the instructor. Here, you should consider factors such as content, formatting, and word count limitations. Now, the text below only provides specific answers to the question, “how to come up with an attractive editorial essay?”
Different Topics for Editorial Essays
Below, we will take you through the best essay subjects. In the process, we will also show you the most captivating research issues and suitable solutions for each!
1. Charter Schools/Institutions Are All About Making The Right Decision
For instance: “Public charter institutions are part of the public schooling program. Therefore, they follow all the recommended standards of learning. Such schools must show efficiency in all their proven methods of teaching. Otherwise, a good number of these institutions risk closure if they fail to bring high achievements. It’s the sole responsibility of the teachers to educate their students according to the standards of the United States of America learning system.”
2. Reality Television Programs Alternate and Develop Reality
Example: “The reality shows on our televisions make people lose touch with reality. Directors try to force their audience to believe that problems which players tackle every day also take place in our day to day lives. Besides, they force people to believe that their consequences are more serious than those of real-life situations.” “Interestingly, according to research done by Michigan University’s Dr. Gibson, viewing such TV shows for a long time results has certain challenges. For example, it leads to improved levels of aggression for a majority of people living in the United States. Therefore, such programs should come with various ranking to prevent those going through adolescence from watching them!”
Other topic ideas:
3. The Importance Of Higher Education In The United States
4. Causes And Consequences Of Subprime Crisis
5. Should We Legalize Marijuana For Its Relaxation Effect Or Is It Harmful To Our Brains?
6. Challenges Faced By Banning Cigarettes
7. Looking Back At the NBA Season: Primary Goals, Preparation, Expectation, Forecasts, Best Players, Discussions, and Results.
8. Essential Facts That Prove The Illegality Of Gambling
9. Proper Diabetes Treatment
10. Why The Government Allows Use Of Capital Punishment?
You can also get more amazing editorial essay examples as well as some of the most powerful research papers on expert academic writing websites . With that said, the following is a step-by-step approach to assist you in writing a captivating editorial piece!
Step-By-Step Approach to Assist You in Writing a Captivating Editorial Piece
Step 1: pick the best topic.
Here, the best method is to choose a controversial social issue and talk about it from all possible angles. Keep in mind that your audience is feels encouraged reading such an essay from one cover to another if it comes with a provoking or ‘loud’ title. So, it’s critical to come up with essential ideas while in the brainstorming process!
The subject should be recent and touch on the sensitive issues within your society. A uniquely written topic is a sure guarantee that the readers will go through your newspaper article extensively. So, remember to only use necessary evidence from all recent sources. You could even go through different argumentative essays to get a clear picture of what you’ll need when writing your piece.
STEP 2: Giving Your Opinion
Composing an editorial is just like writing an argumentative piece. Here, you have to choose a recently discussed, contradictive and of course debatable subject. In the process, you should also highlight your stand regarding this issue with the help of convincing evidence. An excellent editorial needs to even cover both the negative and the positives of the topic. In this case, you should take caution not to focus on only one side as it’s not just subjective but also unprofessional. If you come across some difficulties, consider looking at the professional editorial and editing services. They will assist you to continue and develop the main idea of your article.
STEP 3: Writing an Outline
Have you ever tried to come up with an outline for your research or term paper? Well, while writing an editorial piece having a framework is also a crucial step. It helps you stick to the main subject even when new ideas come up in the process. Furthermore, it enables you to come up with well-structured and organized concepts!
STEP 4: Now Composing an Editorial
Create an argument that’s based on the topic of concern and choose a headline that automatically captivates your readers. A suitable example is including an exclamation mark which should compel them to read your article. Besides, you could even have a question mark towards the end. When it comes to the main argument, ensure you support it with different analogies and examples. A wise strategy is pointing out positive and negative aspects of all issues.
Here Are Extra Prompts:
- Applying facts and statistics from all online primary sources or those you find in the library. These resources will help you in explaining your argument.
- Discuss the most captivating evidence towards the end!
- Avoid being too passive in other less powerful ideas to keep your readers interested throughout!
STEP 5: Conclusion or Possible Solutions
Your editorial should always have a conclusion based on constructive criticism. Keep in mind that you should still have two points of view: For instance, if you’re writing about the different government regulations aimed at reducing the use of tobacco, show why these strategies are more critical than others. Also, propose various alternative regulations.
In a nutshell, writing an editorial is a crucial step in your writing career. Besides, you may request for an efficient newspaper article from various online professionals to grab the attention of your audiences. Here, you’ll find fantastic sites which charge less custom writing fees!

- Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
- A Comprehensive Guide to Writing a Research Paper Outline
- Writing A Perfect Movie Review
- How to Create a Persuasive Essay Outline
- How to Write the Stanford University Application Essays in 2018


- Engaging With Sources Effectively
by acburton | Apr 30, 2024 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources
We’ve talked about the three ways to integrate sources effectively that allow writers to provide evidence and support for their argument, enter the scholarly conversation, and give credit to the original authors of the work that has helped and informed them. Sources also encourage writers to share their own knowledge and authority with others, help readers find additional sources related to the topic they are interested in, and protect you by giving credit where credit is due (thus avoiding plagiarism). In other words, sources are much more than just something we add on at the end of our writing!
When writing about a source or simply referencing it, we are positioning ourselves in response to, or in conversation with that source, with the goal of focusing our writing on our own argument/thesis. Sources do not stand on their own within a piece of writing and that is why, alongside finding strong and reputable sources worth responding to and making sure that we fully understand sources (even before writing about them), it is critical to engage with our sources in meaningful ways. But how exactly do we effectively engage with our sources in our writing?
Joseph Harris, in How To Do Things with Texts , presents four different ways of “rewriting the work of others”, three of which provide insight into the how of engaging sources. When a writer forwards the work of another writer, they are applying the concepts, topics, or terms from one reading, text, or situation to a different reading, text or situation. By countering the ideas found in source material, a writer argues “against the grain of a text” by underlining and countering ideas that a writer may be in disagreement with. Taking an approach is the adaptation of a theory or method from one writer to a new set of issues or texts. Harris’ book provides a thorough classification of methods to engage with a source. For something a little simpler, here are three basic ways you can get started effectively engaging with sources (Harris 5-7).
3 Basic Ways to Engage with Sources Effectively
- Disagree and Explain Why. Persuade your reader that the argument or information in a source should be questioned or challenged.
- Agree, But With Your Own Take. Add something new to the conversation. Expand a source’s insights or argument to a new situation or your own example. Provide new evidence and discuss new implications.
- Agree and Disagree Simultaneously. This is a nuanced approach to complex sources or complex topics. You can, for example, agree with a source’s overall thesis, but disagree with some of its reasoning or evidence.
Remember that this is not an exhaustive list. When engaging with others’ sources as a way to support our own ideas and argument, it is crucial that we engage with critical thinking, nuance, and objectivity to ensure that we are constructing unbiased, thoughtful, and compelling arguments.
Some of the different areas throughout your essay that will benefit from effective engagement with source material include: your thesis statement, analysis, and conclusion.
- Thesis Statement. The argument that you make in your thesis statement can challenge, weaken, support, or strengthen what is being argued by your source or sources.
Analysis. Thorough analysis in your body paragraphs emphasize the role of your argument in comparison to that found in your source material. Bring your analysis back to your thesis statement to reinforce the connection between the two.
- Conclusion. Consider the “big picture” or “takeaways” to leave your reader with.
There are many other, sometimes optional, essay sections or writing styles that benefit from critical engagement with a source. These can include literature reviews, reflections, critiques, and so on.
Strategies for Engaging Critically From Start to Finish
- Aim to dig deeper than surface level. Ask the ‘how’ and ‘why’ of a source, as well as ‘how’ and ‘why’ it is relevant to the topic at hand and the argument you are making.
- Ask yourself if you’ve addressed every possible question, concern, critique, or “what if” that comes to mind; put yourself in the place of your readers.
- Use TEAL body paragraph development as a template and guide for developing thorough analysis in your body paragraphs. Effectively engaging with your sources is essential to the analysis portion of the TEAL formula and to creating meaningful engagement with your sources.
- Visit the Writing Center for additional support on crafting engaging analyses and for other ways to engage with your source material from thesis to conclusion.
Our Newest Resources!
- Revision vs. Proofreading
- The Dos and Don’ts of Using Tables and Figures in Your Writing
- Synthesis and Making Connections for Strong Analysis
- Writing Strong Titles
Additional Resources
- Graduate Writing Consultants
- Instructor Resources
- Student Resources
- Quick Guides and Handouts
- Self-Guided and Directed Learning Activities

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Gather research (Facts, quotes, statistics, etc) Write the editorial (Using an Editorial Template that includes an introduction, argument, rebuttal, and conclusion) Write the headline (Title) Edit your editorial (Grammar, facts, spelling, structure, etc) In this article, we'll go through each of these steps in detail so that you know exactly ...
Thoroughly research your topic. Before you start the writing process, ensure you have a thorough knowledge of your topic —particularly if it's a complex issue. Read newspaper articles, scholarly journals, and history books to fully understand the topic and context surrounding it. 2. Pick a thesis statement.
Content, Content Creation, Content Writing, Creativity, Editorial Structure, Writing. Julia Clementson. The "How to Start an Editorial: Step-by-Step Guide" provides a comprehensive roadmap for crafting persuasive editorials. It covers selecting a relevant topic, conducting research, creating a persuasive thesis, and organizing your thoughts.
Below is a detailed description of these types. 1. Explain and Interpret - this format gives editors a chance to explain how they tackled sensitive and controversial topics. 2. Criticize - such editorials while focusing on the problem rather than the solution criticize actions, decisions, or certain situations. 3.
Step 1: Pick a Topic That Has Mainstream Appeal. If you want your essay to be published in a news outlet, it has to be, well, news! Connect your thesis statement to a current event. Your topic should be one that the majority of the public can understand or relate with. Remember: Business is niche, media is broad.
Drafting the Editorial. Draft your paper to be short and clear, at least 600 to 800 words. Additionally, avoid using jargon. Introduction. Make its intro as attractive as possible. You can open it with relevant stats, a quote from a famous person your readers respect, or a thought-provoking question. Body.
1. Decide on a topic. Since editorials are based on opinion, your topic should be arguable and have multiple points of view. Your essay will reflect your personal bias or the bias of the group you are representing, so you should expect some of your readers to disagree with your stance.
Develop a clear thesis. This needs to be a clear statement that tells the reader exactly what your editorial is about and where you stand on the issue. This may take one sentence or a whole paragraph. It depends on your writing style. Example: It is December 1918, and January 1919 is just days away.
The writer of the academic essay aims to persuade readers of an idea based on evidence. The beginning of the essay is a crucial first step in this process. In order to engage readers and establish your authority, the beginning of your essay has to accomplish certain business. Your beginning should introduce the essay, focus it, and orient ...
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
How to Write an Editorial. Jason Spingarn-Koff • February 5, 2014. The New York Times's editorial page editor Andrew Rosenthal provides seven tips for writing an effective editorial.
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis. For example, if you are analyzing ...
Your language should be engaging and clear so that your audience can easily understand why your opinion is right. 4. Write an outline. Once you've got nice arguments that support your opinion, write an outline for your story. Decide which paragraphs will focus on statistics and where you will provide quotes.
Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors. Use a plagiarism checker.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
In those cases, a useful starting point will be to come up with a strong analytical question that you will try to answer in your essay. Your answer to that question will be your essay's thesis. You may have many questions as you consider a source or set of sources, but not all of your questions will form the basis of a strong essay.
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
Use the Historical Present Tense. An effective method of beginning an essay is to use historical present tense to relate an incident from the past as if it were happening now. "Ben and I are sitting side by side in the very back of his mother's station wagon.
For many, getting started is the hardest part of anything. And that's understandable. First, because it turns whatever you're doing into a reality, which raises the stakes. Second, because where you start can easily dictate the quality of where you end up. College essays have their own special brand of DTDT.
STEP 4: Now Composing an Editorial. Create an argument that's based on the topic of concern and choose a headline that automatically captivates your readers. A suitable example is including an exclamation mark which should compel them to read your article. Besides, you could even have a question mark towards the end.
These steps will help you get your point across clearly and concisely: 1. Turn the topic into a question and answer it. Set up a big question in the title of your essay or within the first few sentences. Then, build up to answering that question in your thesis statement.
Good example. I wiped the sweat from my head and tried to catch my breath. I was nearly there—just one more back tuck and a strong dismount and I'd have nailed a perfect routine. Some students choose to write more broadly about themselves and use some sort of object or metaphor as the focus.
The Writing Center 193 Science Library Irvine, CA 92697-5695 (949)-824-8949 [email protected]
Creating a proposal essay: essential steps When you need to write my essay for me, you should understand it requires careful planning, thorough research, and meticulous execution.Discover the main steps to ensure your essay stands out: Plan: Structure your essay proposal outline with an introduction presenting the problem, body paragraphs proposing solutions supported by evidence, and a ...