- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →

Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Creative Problem-Solving & Why Is It Important?

- 01 Feb 2022
One of the biggest hindrances to innovation is complacency—it can be more comfortable to do what you know than venture into the unknown. Business leaders can overcome this barrier by mobilizing creative team members and providing space to innovate.
There are several tools you can use to encourage creativity in the workplace. Creative problem-solving is one of them, which facilitates the development of innovative solutions to difficult problems.
Here’s an overview of creative problem-solving and why it’s important in business.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving?
Research is necessary when solving a problem. But there are situations where a problem’s specific cause is difficult to pinpoint. This can occur when there’s not enough time to narrow down the problem’s source or there are differing opinions about its root cause.
In such cases, you can use creative problem-solving , which allows you to explore potential solutions regardless of whether a problem has been defined.
Creative problem-solving is less structured than other innovation processes and encourages exploring open-ended solutions. It also focuses on developing new perspectives and fostering creativity in the workplace . Its benefits include:
- Finding creative solutions to complex problems : User research can insufficiently illustrate a situation’s complexity. While other innovation processes rely on this information, creative problem-solving can yield solutions without it.
- Adapting to change : Business is constantly changing, and business leaders need to adapt. Creative problem-solving helps overcome unforeseen challenges and find solutions to unconventional problems.
- Fueling innovation and growth : In addition to solutions, creative problem-solving can spark innovative ideas that drive company growth. These ideas can lead to new product lines, services, or a modified operations structure that improves efficiency.

Creative problem-solving is traditionally based on the following key principles :
1. Balance Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Creative problem-solving uses two primary tools to find solutions: divergence and convergence. Divergence generates ideas in response to a problem, while convergence narrows them down to a shortlist. It balances these two practices and turns ideas into concrete solutions.
2. Reframe Problems as Questions
By framing problems as questions, you shift from focusing on obstacles to solutions. This provides the freedom to brainstorm potential ideas.
3. Defer Judgment of Ideas
When brainstorming, it can be natural to reject or accept ideas right away. Yet, immediate judgments interfere with the idea generation process. Even ideas that seem implausible can turn into outstanding innovations upon further exploration and development.
4. Focus on "Yes, And" Instead of "No, But"
Using negative words like "no" discourages creative thinking. Instead, use positive language to build and maintain an environment that fosters the development of creative and innovative ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving and Design Thinking
Whereas creative problem-solving facilitates developing innovative ideas through a less structured workflow, design thinking takes a far more organized approach.
Design thinking is a human-centered, solutions-based process that fosters the ideation and development of solutions. In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar leverages a four-phase framework to explain design thinking.
The four stages are:

- Clarify: The clarification stage allows you to empathize with the user and identify problems. Observations and insights are informed by thorough research. Findings are then reframed as problem statements or questions.
- Ideate: Ideation is the process of coming up with innovative ideas. The divergence of ideas involved with creative problem-solving is a major focus.
- Develop: In the development stage, ideas evolve into experiments and tests. Ideas converge and are explored through prototyping and open critique.
- Implement: Implementation involves continuing to test and experiment to refine the solution and encourage its adoption.
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
While there are many useful tools in the creative problem-solving process, here are three you should know:
Creating a Problem Story
One way to innovate is by creating a story about a problem to understand how it affects users and what solutions best fit their needs. Here are the steps you need to take to use this tool properly.
1. Identify a UDP
Create a problem story to identify the undesired phenomena (UDP). For example, consider a company that produces printers that overheat. In this case, the UDP is "our printers overheat."
2. Move Forward in Time
To move forward in time, ask: “Why is this a problem?” For example, minor damage could be one result of the machines overheating. In more extreme cases, printers may catch fire. Don't be afraid to create multiple problem stories if you think of more than one UDP.
3. Move Backward in Time
To move backward in time, ask: “What caused this UDP?” If you can't identify the root problem, think about what typically causes the UDP to occur. For the overheating printers, overuse could be a cause.
Following the three-step framework above helps illustrate a clear problem story:
- The printer is overused.
- The printer overheats.
- The printer breaks down.
You can extend the problem story in either direction if you think of additional cause-and-effect relationships.
4. Break the Chains
By this point, you’ll have multiple UDP storylines. Take two that are similar and focus on breaking the chains connecting them. This can be accomplished through inversion or neutralization.
- Inversion: Inversion changes the relationship between two UDPs so the cause is the same but the effect is the opposite. For example, if the UDP is "the more X happens, the more likely Y is to happen," inversion changes the equation to "the more X happens, the less likely Y is to happen." Using the printer example, inversion would consider: "What if the more a printer is used, the less likely it’s going to overheat?" Innovation requires an open mind. Just because a solution initially seems unlikely doesn't mean it can't be pursued further or spark additional ideas.
- Neutralization: Neutralization completely eliminates the cause-and-effect relationship between X and Y. This changes the above equation to "the more or less X happens has no effect on Y." In the case of the printers, neutralization would rephrase the relationship to "the more or less a printer is used has no effect on whether it overheats."
Even if creating a problem story doesn't provide a solution, it can offer useful context to users’ problems and additional ideas to be explored. Given that divergence is one of the fundamental practices of creative problem-solving, it’s a good idea to incorporate it into each tool you use.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a tool that can be highly effective when guided by the iterative qualities of the design thinking process. It involves openly discussing and debating ideas and topics in a group setting. This facilitates idea generation and exploration as different team members consider the same concept from multiple perspectives.
Hosting brainstorming sessions can result in problems, such as groupthink or social loafing. To combat this, leverage a three-step brainstorming method involving divergence and convergence :
- Have each group member come up with as many ideas as possible and write them down to ensure the brainstorming session is productive.
- Continue the divergence of ideas by collectively sharing and exploring each idea as a group. The goal is to create a setting where new ideas are inspired by open discussion.
- Begin the convergence of ideas by narrowing them down to a few explorable options. There’s no "right number of ideas." Don't be afraid to consider exploring all of them, as long as you have the resources to do so.
Alternate Worlds
The alternate worlds tool is an empathetic approach to creative problem-solving. It encourages you to consider how someone in another world would approach your situation.
For example, if you’re concerned that the printers you produce overheat and catch fire, consider how a different industry would approach the problem. How would an automotive expert solve it? How would a firefighter?
Be creative as you consider and research alternate worlds. The purpose is not to nail down a solution right away but to continue the ideation process through diverging and exploring ideas.

Continue Developing Your Skills
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, marketer, or business leader, learning the ropes of design thinking can be an effective way to build your skills and foster creativity and innovation in any setting.
If you're ready to develop your design thinking and creative problem-solving skills, explore Design Thinking and Innovation , one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses. If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author
Creative Problem Solving Explained
Creative problem solving is based on the belief that everyone is creative and can enhance their creative abilities with discipline.
Creative problem solving is a deliberate approach to solving complex problems. While creativity is an innate part of creative problem solving, the process uses a variety of steps and strategies designed to bring to the table solutions that are actionable and effective.
It’s a proven approach to use innovative ideas and views of a problem to develop viable options that can be brought to bear on the challenge. It can also redefine the problem, coming at it from a new perspective that results in an effective solution.
It also has powerful applications for addressing your greatest workflow challenges. Using creative problem solving lets you identify, refine, iterate, and select the best options to improve workflows using new technologies like automation.
Fundamentals of Creative Problem Solving
Many people hear “creative problem solving” and think it’s about brainstorming answers. However, creative problem solving is about much more. Creative answers to problems do not just appear magically but are the result of deliberate processes.
To work well, creative problem solving is rooted in two assumptions:
- Everyone is creative in some manner
- You can learn and enhance someone’s creative abilities
Those are powerful assumptions. They help to dispel the idea that there are “creative types” and “noncreative types.” All participants can be empowered to engage in the process by supporting and reinforcing the innate presence of creativity.
Alex Osborn helped define and formalize the idea of creative problem solving. He believed that two types of thinking are critical to creative problem solving.
Convergent Thinking focuses on the norms of problem solving and focuses on finding a singular solution that's well defined. Divergent Thinking is the opposite, with multiple options being considered after fostering creativity as part of the problem solving process.
Both play a role and have value in problem solving. Typically, both are used as part of the process.
For example, divergent thinking can create multiple ideas for possible solutions. Convergent thinking can whittle those down to a few or one idea to implement.
Principles of Creative Problem Solving
Here is a closer look at some key tenets of creative problem solving.
Reframe the Problem as a Question
Begin by restating the problem as a question or series of open-ended questions. The problem becomes more approachable with multiple possibilities available, and participants can be invited into the process.
By contrast, problems presented as declarative statements are often met by silence. These statements often lead to a limited response or no response at all.
There's a shift when asked as a question rather than a statement. The challenge is not an obstacle but rather an opportunity to solve. It opens the door to brainstorming and ideation.
Suspend Judgment
All too often, ideas that are generated in problem solving spaces are quickly dismissed. This instantaneous judgment has short- and long-term impacts.
First, it immediately dismisses the presented idea and the presenter. What’s more, the dismissal can have a chilling effect on others, stymieing the idea generation process.
There’s a time when judging presented ideas – when convergent thinking is at play. In the beginning, immediate judgment should be suspended.
Even the most implausible ideas presented at the beginning of the process may play a role later as long as they are still considered viable. If poisoned early in the process, they will unlikely be given any value later.
‘Yes, And’ Instead of ‘No, But’
The word “no” can have a similarly stifling effect on the creative problem solving work. "But," whether preceded by "yes” or "no," can close the conversation. It acts to negate everything that has come before.
You can create and maintain a more positive, encouraging tone using "yes, and" language instead of "no, but" language.
More positive language helps build on previously generated ideas. It creates an additive approach to the process instead of a dismissive one.
One Approach to Creative Problem Solving
Having a clearly defined approach to solving problems helps participants understand the scope and scale of the work. While multiple approaches can be used, here is one way to frame the engagement.
1. Clarify the Problem
The most critical step to creative problem solving is identifying and articulating the problem or goal. While it may appear to be easy to do so, often, what people think the problem is is not the true problem.
The critical step is to break down the problem, analyze it and understand the core issue.
One approach is to use the "five whys." Start by asking yourself, "Why is this a problem?" Once you have the answer, ask, "Why else?" four more times.
This iterative process can often refine and revise to unearth the true issue that needs to be addressed. You can ask other questions to further refine, such as:
- Why is this problem important to us?
- What is stopping us from solving this problem?
- Where will we be differently 6-12 months after solving the problem?
2. Define Evaluation Criteria
The creative problem solving process is likely to generate many potential ideas. It’s important to establish the process by which the ideas will be evaluated and, if selected, deployed.
These processes may have important factors, such as budget, staffing and time. The process needs to address what you seek to accomplish, avoid and act on. The process should be articulated to the participants in the problem solving and those affected by the outcomes.
3. Research the Problem
You want a clear understanding of the problem, which may require lots or a little research. Understand the common problem, how others may deal with it, and potential solutions.
4. Develop Creative Challenges
Once the problem is articulated and researched, it’s time to frame them. “Creative challenges” are simple and brief, question-based concepts. For example, "How can we …" or “What would it mean if …" These challenges will form the basis of your problem solving. They should be broadly focused and not include any evaluation criteria.
5. Create Ideas
Idea generation is what most people envision when they think of brainstorming or solving problems.
Start by taking just one of the creative challenges. Give yourself or the team some time to build at least 50 ideas. That may seem like a lot, but it can spark conversation and construction.
The ideas may or may not solve the presented challenge. By capturing them on paper or a computer (many programs support idea generation), you can have them readily available to organize, expand on, evaluate, and flesh out.
Be sure to use the following rules in this stage:
- Write down every idea
- Ensure no one critiques presented ideas
- Don’t stop until you’ve reached 50
- Present the full list of ideas and then ask if anyone has anything else to add
- If you have time, sleep on the ideas and return the next day. Try to add 25 more.
6. Sort and Assess Ideas
Take a break and reconvene to look at the ideas using the evaluation criteria. Combine ideas, then use the evaluation criteria to whittle down the list.
Some ideas may be implementable immediately. Others may need further analysis to prioritize.
7. Create a Plan
When you have your shortlist, create an action plan that outlines the steps necessary to implement the ideas. By breaking down the ideas into actionable steps, you’ll be better able to put them into play and see the results.
Problem Solving Your Workflows
When it comes to coming up with creative answers to your workflow problems, we have a variety of resources for you listed below. In addition, we're always interested in providing objective, experienced ideas through our Customer Success and Services teams.
- Reframe Your Business Processes
- Process Redesign Tips
- What is Business Process Re-Engineering?
- Process Improvement Examples
- https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-creative-problem-solving
- https://www.mindtools.com/a2j08rt/creative-problem-solving
- https://www.creativeeducationfoundation.org/what-is-cps/
- https://innovationmanagement.se/2010/06/02/the-basics-of-creative-problem-solving-cps/
- https://asana.com/resources/convergent-vs-divergent
Tags creativity problem solving process improvement
Categories Business Ideas Workflow Ideas Project Management

Marketing the world's best workflow automation software and drinking way too much coffee. Connect with me on LinkedIn at https://www.linkedin.com/in/michaelraia/
Subscribe to Receive the Latest Workflow Automation Tips
Subscribe →
Business Ideas
Customer corner, department focus, employee spotlight, flowchart friday, industry focus, productivity points, productivity tips, project management, using integrify, workflow ideas.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Understanding the Psychology of Creativity
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Michael H / DigitalVision / Getty Images
What Is Creativity?
When does creativity happen, types of creativity, what does it take to be creative, creativity and the big five, how to increase creativity, frequently asked questions.
What is creativity? Creativity involves the ability to develop new ideas or utilize objects or information in novel ways. It can involve large-scale ideas that have the potential to change the world, such as inventing tools that impact how people live, or smaller acts of creation such as figuring out a new way to accomplish a task in your daily life.
This article explores what creativity is and when it is most likely to happen. It also covers some of the steps that you can take to improve your own creativity.
Studying creativity can be a tricky process. Not only is creativity a complex topic in and of itself, but there is also no clear consensus on how exactly to define creativity. Many of the most common definitions suggest that creativity is the tendency to solve problems or create new things in novel ways.
Two of the primary components of creativity include:
- Originality: The idea should be something new that is not simply an extension of something else that already exists.
- Functionality: The idea needs to actually work or possess some degree of usefulness.
In his book Creativity: Flow and the Psychology of Discovery and Invention , psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi suggested that creativity can often be seen in a few different situations.
- People who seem stimulating, interesting, and have a variety of unusual thoughts.
- People who perceive the world with a fresh perspective, have insightful ideas and make important personal discoveries. These individuals make creative discoveries that are generally known only to them.
- People who make great creative achievements that become known to the entire world. Inventors and artists such as Thomas Edison and Pablo Picasso would fall into this category.
Experts also tend to distinguish between different types of creativity. The “four c” model of creativity suggests that there are four different types:
- “Mini-c” creativity involves personally meaningful ideas and insights that are known only to the self.
- “ Little-c” creativity involves mostly everyday thinking and problem-solving. This type of creativity helps people solve everyday problems they face and adapt to changing environments.
- “Pro-C” creativity takes place among professionals who are skilled and creative in their respective fields. These individuals are creative in their vocation or profession but do not achieve eminence for their works.
- “Big-C” creativity involves creating works and ideas that are considered great in a particular field. This type of creativity leads to eminence and acclaim and often leads to world-changing creations such as medical innovations, technological advances, and artistic achievements.
Csikszentmihalyi suggests that creative people tend to possess are a variety of traits that contribute to their innovative thinking. Some of these key traits include:
- Energy: Creative people tend to possess a great deal of both physical and mental energy. However, they also tend to spend a great deal of time quietly thinking and reflecting.
- Intelligence: Psychologists have long believed that intelligence plays a critical role in creativity. In Terman’s famous longitudinal study of gifted children, researchers found that while high IQ was necessary for great creativity, not all people with high IQs are creative. Csikszentmihalyi believes that creative people must be smart, but they must be capable of looking at things in fresh, even naïve, ways.
- Discipline: Creative people do not just sit around waiting for inspiration to strike. They are playful, yet they are also disciplined in the pursuit of their work and passions.
Certain personality traits are also connected to creativity. According to the big five theory of personality , human personality is made up of five broad dimensions:
- Conscientiousness
- Extroversion
- Agreeableness
- Neuroticism
Each dimension represents a continuum, so for each trait, people can be either high, low, or somewhere between the two.
Openness to experience is a big five trait that is correlated with creativity. People who are high on this trait are more open to new experiences and ideas. They tend to seek novelty and enjoy trying new things, meeting new people, and considering different perspectives.
However, other personality traits and characteristics can also play a role in creativity. For example, intrinsic motivation , curiosity, and persistence can all determine how much people tend to pursue new ideas and look for novel solutions.
While some people seem to come by creativity naturally, there are things that you can do to increase your own creativity .
Some strategies that can be helpful for improving creativity include:
- Being open to new ideas : Openness to experience is the personality trait that is most closely correlated with creativity. Focus on being willing to try new things and explore new ideas.
- Be persistent : Creativity is not just about sitting around waiting for inspiration to strike. Creative people spend time working to produce new things. Their efforts don't always work out, but continued practice builds skills that contribute to creativity.
- Make time for creativity : In addition to being persistent, you also need to devote time specifically toward creative efforts. This might mean setting aside a little time each day or each week specifically to brainstorm, practice, learn, or create.
Csikszentmihalyi has noted that creativity requires both a fresh perspective combined with discipline. As Thomas Edison famously suggested, genius is 1% inspiration and 99% perspiration.
A Word From Verywell
Creativity is a complex subject and researchers are still working to understand exactly what factors contribute to the ability to think creatively. While some people seem to come by creativity naturally, there are also things you can do to build and strengthen this ability.
The late Maya Angelou also suggested that thinking creativity helps foster even greater creativity, "The important thing is to use it. You can’t use up creativity. The more you use it, the more you have," she suggested.
Creativity does not reside in one single area of the brain; many areas are actually involved. The frontal cortex of the brain is responsible for many of the functions that play a part in creativity.
However, other parts of the brain impact creativity as well, including the hippocampus (which is important to memory) and the basal ganglia (which is essential in the memory of how to perform tasks). The white matter of the brain, which keeps the various parts of the brain connected, is also essential for creative thinking.
Research suggests that people can train their brains to be more creative. Engaging in cognitively stimulating tasks, going on a walk, finding sources of inspiration, and meditating are a few strategies that may help boost creative thinking abilities.
The "big five" are the broad categories of traits that make up personality. The five dimensions are openness, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism. Each trait involves a range between two extremes, and people can be either at each end or somewhere in the middle.
American Psychological Association. The science of creativity .
Csikszentmihalyi M. Creativity: Flow and the Psychology of Discovery and Invention . New York: HarperCollins; 2013.
Kaufman J, Beghetto R. Beyond big and little: The four C model of creativity . Review of General Psychology . 2009;13(1):1-12. doi:10.1037/a0013688
Kaufman SB, Quilty LC, Grazioplene RG, et al. Openness to experience and intellect differentially predict creative achievement in the arts and sciences . J Pers . 2016;84(2):248-258. doi:10.1111/jopy.12156
Elliot J. Conversations With Maya Angelou . Jackson, Miss.: University Press of Mississippi; 1998.
Cavdarbasha D, Kurczek J. Connecting the dots: your brain and creativity . Front Young Minds . 2017;5:19. doi:10.3389/frym.2017.00019
Sun J, Chen Q, Zhang Q, Li Y, Li H, Wei D, Yang W, Qiu J. Training your brain to be more creative: brain functional and structural changes induced by divergent thinking training . Hum Brain Mapp . 2016;37(10):3375-87. doi:10.1002/hbm.23246
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
https://thesecondprinciple.com
The work of leslie owen wilson, ed. d..

Types of creative thinking
What are the types of creative thinking and how does the process work.
Creative thinking is much more than using your imagination to crank out lots of new ideas. Creative thinking is a lifestyle, a personality trait, a way of perceiving the world, a way of interacting with other people, and a way of living and growing . Gary Davis
© Leslie Owen Wilson email
To create – the most complex type of cognition:
Since the 1950s cognitive psychologists and researchers have been trying to explain the differences in diverse types of thinking. In 1956 Benjamin Bloom with others developed a hierarchical listing, or taxonomy, annotating the complexity of the differences in varied levels of cognition. Most teachers are generally familiar with this work, known as Bloom’s Taxonomy, and it starts from simplest forms of thinking progressing to those that are more complex as: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and lastly evaluation.
To be frank the original progressive array never set quite right with me as I always thought to synthesize something surely one had to evaluate it first. But who was I to challenge the taxonomy of these respected cognitive researchers?
Apparently, I was not alone in this criticism because in 2000-2001 a revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy was put forth and reworked. This effort was based on some of Bloom’s criticisms of his own work and led by one of his former students, Lorin Anderson, in conjunction with the efforts of one of the taxonomy’s original authors and a longtime colleague of Bloom’s, David Krathwohl. The revised work recognized the conundrum between synthesis and evaluation and also reworked the taxonomy changing the original nouns to verbs in hierarchical array – remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, and lastly, create. Here “to create” attains its rightful place as the most complex form of human thinking.
Unfortunately, much of what we do in school concentrates, not on creating, but on remembering, understanding and applying. Like many others I would like this to change. I think that the world will need all the creative thinkers we can muster if we are to solve today’s and tomorrow’s problems.
The interplay of two types of thinking — Convergence and divergence equals creative thinking
Partly because it is tied to the profitability in business, a great deal of effort has been put forth in defining creative problem-solving and in training folks in how to do it. In this genre one of the more common definitions of creativity has to do with dissecting creative thought into a process of dual exchanges through the melding of two types of thinking – convergence and divergence . In this dance of paired thinking, as we look for solutions or innovations the object is to go through a series of steps first diverging (expanding ideas) and then converging (narrowing possibilities) until a solution is found; a course of action resolved; and end foreseen; or a product conceptualized.
Definitions of divergent thinking usually include the ability to elaborate, and think of diverse and original ideas with fluency and speed. Ideating and brainstorming are premiere examples of exercises using this type of thinking. What if . . . ? How about . . .? Could we try this or that idea . . . ? are types of questions that can lead to divergent thought patterns.
Metaphorically, whether we live in areas with snow, most of us have seen movies or cartoons where a small snowball rolls down a hill picking up more snow and getting larger and larger. This is like divergent thinking. The primary object of this form of cognition is to think of possibilities, to connect the dots, to find solutions, to generate new and different ideas.
Convergent thinking is defined as the ability to use logical and evaluative thinking to critique and narrow ideas to ones best suited for given situations, or set criteria . We use this type of thinking when we make crucial and well-formed decisions after appraising an array of ideas, information, or alternatives. Metaphorically this like herding cattle toward a chute as we are looking for a narrow band of solutions, or one great idea.
In creative production both thought processes are necessary as one first diverges ideas in numerous quantities and then narrows and refines the array through convergent thought processes. Specifically, in creative problem solving, or in any complex problem-solving activity for that matter, one needs to be able to weave in and out of divergent and convergent thought patterns in order to effectively arrive at an appropriate conclusion specific for a given situation.
Unfortunately, too often the processes involved in schooling concentrate on convergent thought, and ignore or undervalue divergent thinking. Children need exposure to both types of thinking in order to be adept at solving problems quickly and well . This is a premiere life skill!
Divergent Thinking Abilities – A strong part of creative thinking and behaviors
Adapted and modified from the works of Williams, F. E.
Creative production is often characterized by the divergent nature of human thought and action. Divergence is usually indicated by the ability to generate many, or more complex or complicated, ideas from one idea or from simple ideas or triggers. Traditionally the eight elements below are ones commonly thought of as inherent elements of creative production, as well as attributes associated with creative problem solving abilities.
Fluency – The ability to generate a number of ideas so that there is an increase of possible solutions or related products.
Flexibility – The ability to produce different categories or perceptions whereby there are a variety of different ideas about the same problem or thing.
Elaboration – The ability to add to, embellish, or build on an idea or product.
Originality – The ability to create fresh, unique, unusual, totally new, or extremely different ideas or products
Complexity – The ability to conceptualize difficult, intricate, many layered or multifaceted ideas or products.
Risk-taking – The willingness to be courageous, adventuresome, daring — trying new things or taking risks in order to stand apart.
Imagination – The ability to dream up, invent, or to see, to think, to conceptualize new ideas or products – to be ingenious.
Curiosity – The trait of exhibiting probing behaviors, asking and posing questions, searching, being able to look deeper into ideas, and the wanting to know more about something.
Melding Synthetic, Analytical, and Practical Thought:
Robert Sternberg is one of my favorite authors. Long ago he paired with Wendy M. Williams to write a valuable little gem that can help teachers or parents trying to understand children and creativity — How to develop student creativity (1996, ASCD). While it is an older work, it is still a treasure. Indeed, the work is wonderfully succinct and adaptable enough so that someone in business could imaginatively bridge Sternberg and Williams’ ideas into the workplace. In How to develop . . . the authors define creative work as the balance between three abilities that can be learned and practiced. Below I have summarized their ideas and added a few of my own.
According to Sternberg and Williams creative work consists of the application and melding of three types of thinking, all of which they contend can be learned or enhanced. They feel that creativity is a balance between these three metacomponents:
Analytical ability – Again, this includes the ability to think convergently in that it requires critical thinking and appraisal as one analyzes and evaluates thoughts, ideas, and possible solutions. This type of thinking is key in the realm of creative work because not all ideas are good ones, some need to be culled. Creative people use this type of thinking to consider implications and project possible responses, problems, and outcomes. Commonly we think of this ability as “critical thinking” at its best.
Synthetic (creative) ability – This obviously includes divergent thinking as it is the ability to think of or generate new, novel, and interesting ideas. But it is also the ability to spontaneously make connections between ideas, or groups of things — ones that often go unnoticed, or undiscovered by others. Wm. J. J. Gordon’s concept of Synectics is a primary example of this type of thinking.
Practical ability – The world is full of people who have good ideas, as well as ones who can pick ideas apart. However, the basic key to creative work must include the ability to use practical thinking. This is the ability to translate abstractions and theories into realistic applications. It is the skill to sell or communicate one’s ideas to others, to make others believe that ideas, works, or products are valuable, different, useful, innovative, unusual, or worthy of consideration. This type of thinking is prized in the context of being creative because it is how one finds a potential audience for one’s creative work. An innovation or invention needs an audience, a consumer, a user, and implementor. Indeed, ideas are just ideas if no one knows about them or no one uses them.
*A teaching challenge – Use and combine the 3 levels of thinking created by Robert Sternberg and Wendy Williams to create diverse activities in order to help students explore aspects of intelligence and creativity.
___________________________
The more you know –
Here are internal and external links to related articles about types of creative thinking and ways to increase creative thinking. Unfortunately many of the external links are not ad free, but they are still very informative and worth the “dodge the ads” effort.
Internal links:
- Advice for thinking creatively
- Blockages and Barriers to Creativity
- Return to the site’s Master Index
External Links:
- Cleverism – Idea Generation
- Natalie Shoemaker — She gives you 5 ways to boost divergent thinking
- Psychology Today – Scott Barry Kaufman discusses convergence and divergence
- Creately.com – While it is an extension of an Australian commercial site selling templates and software to facilitate group processes and communication, this page “herds” many of the ideas on creative thinking from notable, outside authors. These methods were originally designed to help people, as well as organizational groups, think creatively and outside the proverbial box. The folks at Creately have adeptly capitalized on the ideas of others and offered viewers visual teasers on an array of problem solving methods. The page unfortunately does not lead you back to the original authors or to their books and resources, like Edward DeBono’s Six thinking hats or to SCAMPER’s original developer Alex Osborn, or those by SCAMPER author , Bob Eberl e . But, the page is well worth checking out for an overview of some of the available techniques. If you want to know more, and find free techniques and ideas, you will have to follow the bread crumbs on the web. You may wish to start with some of my pages, inserted links, and my related bibliographies on creativity and creative resources.
- 7 Types of thinking – A concise overview of different types of thinking from Anthony Metivier’s pages on Magnetic Memory Method .

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 5 min read
Understanding Creativity
Tools and techniques for creative thinking.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

It is important to start with a clear definition of what we mean by creativity, as there are two completely different types. The first is technical creativity , where people create new theories, technologies or ideas. This is the type of creativity we discuss here. The second is artistic creativity , which is more born of skill, technique and self-expression. Artistic creativity is beyond the scope of these articles.
Many of the techniques in this chapter have been used by great thinkers to drive their creativity. Albert Einstein, for example, used his own informal variant of Provocation to trigger ideas that led to the Theory of Relativity. But anyone can learn to be technically creative, and use these tools. They are designed to help you devise creative and imaginative solutions to problems, and help you to spot opportunities that you might otherwise miss.
Approaches to Creativity
There are two main strands to technical creativity: programmed thinking and lateral thinking. Programmed thinking relies on logical or structured ways of creating a new product or service. Examples of this approach are Morphological Analysis and the Reframing Matrix .
The other main strand uses "Lateral Thinking." Examples of this are Brainstorming , Random Input and Provocation. Lateral Thinking has been developed and popularized by Edward de Bono, whose books you can find in the appropriate articles.
Programmed Thinking and Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking recognizes that our brains are pattern recognition systems, and that they do not function like computers. It takes years of training before we learn to do simple arithmetic – something that computers do very easily. On the other hand, we can instantly recognize patterns such as faces, language, and handwriting. The only computers that begin to be able to do these things do it by modeling the way that human brain cells work. Even then, computers will need to become more powerful before they approach our ability to handle patterns.
The benefit of good pattern recognition is that we can recognize objects and situations very quickly. Imagine how much time would be wasted if you had to do a full analysis every time you came across a cylindrical canister of effervescent fluid. Most people would just open their can of fizzy drink. Without pattern recognition, we would starve or be eaten. We could not cross the road safely.
Unfortunately, we get stuck in our patterns. We tend to think within them. Solutions we develop are based on previous solutions to similar problems. Normally it does not occur to us to use solutions belonging to other patterns.
We use lateral thinking techniques to break out of this patterned way of thinking.
Lateral thinking techniques help us to come up with startling, brilliant and original solutions to problems and opportunities.
It is important to point out that each type of approach has its strength. Logical, disciplined thinking is enormously effective in making products and services better. It can, however, only go so far before all practical improvements have been carried out. Lateral thinking can generate completely new concepts and ideas, and brilliant improvements to existing systems. In the wrong place, however, it can be sterile or unnecessarily disruptive.
Taking the Best of Each
A number of techniques fuse the strengths of the two different strands of creativity. Techniques such as the Concept Fan use a combination of programmed and lateral thinking. DO IT and Min Basadur's Simplex embed the two approaches within problem-solving processes. While these may be considered 'overkill' when dealing with minor problems, they provide excellent frameworks for solving difficult and serious ones.
The Creative Frame of Mind
Often the only difference between creative and uncreative people is self-perception. Creative people see themselves as creative and give themselves the freedom to create. Uncreative people do not think about creativity and do not give themselves the opportunity to create anything new.
Being creative may just be a matter of setting aside the time needed to take a step back and allow yourself to ask yourself if there is a better way of doing something. Edward de Bono calls this a "Creative Pause." He suggests that this should be a short break of maybe only 30 seconds, but that this should be a habitual part of thinking. This needs self-discipline, as it is easy to forget.
Another important attitude shift is to view problems as opportunities for improvement. While this is something of a cliché, it is true. Whenever you solve a problem, you have a better product or service to offer afterward.
Using Creativity
Creativity is sterile if action does not follow from it. Ideas must be evaluated, improved, polished and marketed before they have any value. Other sections of Mind Tools lay out the evaluation, analysis and planning tools needed to do this. They also explain the time and stress management techniques you will need when your creative ideas take off.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Starbursting.
Understanding New Ideas by Brainstorming Questions
Kano Model Analysis
Delivering Products That Will Delight
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 20% off your first year of Mind Tools
Our on-demand e-learning resources let you learn at your own pace, fitting seamlessly into your busy workday. Join today and save with our limited time offer!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Pain Points Podcast - Balancing Work And Kids

Pain Points Podcast - Improving Culture
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points podcast - what is ai.
Exploring Artificial Intelligence
Pain Points Podcast - How Do I Get Organized?
It's Time to Get Yourself Sorted!
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Contingency planning.
Developing a Good "Plan B"
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
7 Types of Critical Thinking: A Guide to Analyzing Problems
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally about various issues and situations. It involves applying different types of thinking skills to different problems and challenges. Some of the main types of critical thinking are: Analytical Thinking, Creative Thinking, Decision-Making, Problem-Solving, Reflection , Open-mindedness, Good communication
Sanju Pradeepa

Have you ever had a problem that was too big to solve right away? Or perhaps you just couldn’t figure out how to approach it? Whether it’s a personal, academic, or professional problem, having the right set of critical thinking skills can help.
Critical thinking is all about carefully evaluating data and making rational decisions. In other words, it’s the skill of analyzing information from many different points of view before drawing a conclusion. It’s an ongoing process that involves gathering information, asking questions, and considering various solutions.
In this guide, we’ll go over different types of critical thinking skills and provide examples of how to apply these skills when approaching a problem from any angle. We’ll also look at ways to sharpen your critical thinking skills so you can tackle any challenge with ease. So let’s get started.
Table of Contents
What is “critical thinking”.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze a problem or situation and come up with a rational, informed solution. It’s an essential skill for all kinds of processes, from problem solving to decision-making to creative thinking.
In order to tackle complex problems, you need to be able to think critically and evaluate the information at your disposal in order to come up with the best solution.
Critical thinking involves breaking down a problem into its component parts and analyzing it systematically to determine how best to proceed. It requires the ability to think objectively and make informed judgments based on facts and evidence rather than just guesswork or opinion. It also involves the use of several different types of critical thinking skills, such as:
- Analytical Thinking : This type of critical thinking skill involves analyzing data or information in order to draw logical conclusions or find solutions. It’s important for problem-solving and decision-making since it helps you find solutions through careful analysis.
- Creative Thinking: This type of critical thinking skill requires imagination and open-mindedness in order to come up with innovative ideas and solutions. It can help you identify new ways of looking at a situation or find different solutions to a problem.
- Problem-Solving Thinking : This type of critical thinking skill involves developing strategies in order to solve problems quickly and effectively.
Different Types of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information in order to come to a conclusion or make decisions. But did you know that there are different types of critical thinking?
Let’s break down those types of critical thinking skills into 7 different titles and learn them one by one:
1. Analytical Thinking

It is all about taking the pieces of a problem, digging into them, and methodically finding a solution. Analytical thinking is a key element in working through problems and coming up with the best plan of action for success.
So, what does analytical thinking involve? It involves being able to break a problem down into smaller bits and pieces, understanding how each piece interconnects, and developing strategies for solving each individual piece by gathering information relating to it.
Analyzing how each piece of the puzzle affects the next requires you to really understand how they connect together, and using this approach can help you come up with better solutions that can help improve the overall situation.
You’ll also need to make sure any strategies or solutions you come up with are grounded in evidence-based research so that your conclusions are reliable.
Here are some key skills necessary for effective analytical thinking:
- Evaluating: being able to review facts and make judgments about them depending on the situation at hand
- Investigating means asking questions about various aspects of a problem and doing research so that you can identify its root causes.
- Synthesizing: Combining different pieces of data or information together to create new solutions or approaches to existing problems
- Reasoning logically means connecting bits of data together in order to evaluate different possibilities that could help solve the problem or issue at hand.
With these analytical thinking skills, you can start breaking down any problem into smaller, manageable parts, think logically through how they connect together, assess what evidence is needed to make decisions, and draw conclusions based on facts rather than just opinions or hunches.
2. Creative Thinking and Idea Generation

Do you ever feel like your thoughts are stuck in a rut ? Creative thinking and idea generation can help you come up with fresh solutions to problems and break out of that rut.
Creative thinking is an essential critical thinking tool. It can help you look at an issue from a different point of view or think of new ways to approach the problem. Here are some tips for giving your creative thinking skills an extra boost:
- Challenge assumptions. Even if something seems obvious, take some time to question it and consider other possibilities.
- Brainstorm different solutions . Try writing down potential solutions, no matter how wild they may seem, then look for patterns between them or ideas that can be combined into something new.
- Consider different perspectives. Even if the issue seems cut and dry from one perspective, try to imagine it from other angles and think about how the issue appears from those views.
- Take a break and come back later with fresh eyes: sometimes taking a step away from the problem is enough to give you the necessary distance to discover new ideas or paths of exploration.
These strategies will help dramatically improve your ability to generate new ideas and jumpstart your creative thinking process whenever you need it.

3. Decision-Making

When it comes to critical thinking, decision-making is an essential skill. It’s not just about being able to evaluate a situation; it’s about being able to make a well-informed decision that will bring the best results.
Here are four key components of decision-making:
- Goal Setting : Take time to first identify what you want to accomplish with your decision.
- Analyzing Alternatives: Evaluate the pros and cons of potential solutions before choosing one.
- Risk assessment: estimate the possible risks associated with each potential solution, based on current evidence.
- Implementation: Once the decision is made, start working on implementation tasks and track results for ongoing improvement or refinement.
By following these steps, you’ll be in a better position to make decisions that have positive outcomes for you and those involved in the decision-making process.
The ability to think critically and make sound decisions can not only help you solve problems quickly but can also lead to more successful long-term strategies for your business or organization.
4. Problem-Solving

It is one of the most essential types of critical thinking skills. Problem-solving involves taking all the pieces of a problem and figuring out how to resolve it. This can involve coming up with new solutions, making decisions, devising strategies, and identifying patterns and trends.
It’s an invaluable skill in many aspects of life and can help you create effective solutions to a wide range of problems. To use your problem-solving skills effectively, keep these tips in mind:
- Break the problem down into smaller, manageable parts . Breaking down a problem into smaller chunks makes it easier to work on and understand.
- Look for connections between pieces. Try to identify any connections between different aspects or pieces of the problem to gain insights that may help you solve it more efficiently.
- Don’t get overwhelmed by the scope of the challenge at hand; take it one step at a time and remember that even small victories can help move you closer to finding a solution.
- Think creatively when coming up with possible solutions or strategies; often the best solution is not obvious at first glance.
- Keep track of what works and what doesn’t ; this will give you valuable insights for future problem-solving endeavors as well as feedback on your progress towards resolving the current one at hand.
5. Reflection and Assessing Evidence

Now it’s time to take a look at your own cognitive activity. Reflection and assessing evidence are two types of critical thinking skills that help you make sure you’re not jumping to conclusions without considering the pros and cons of a situation.
When it comes to reflection, this involves being honest with yourself and taking a deep look at the way your thoughts, feelings, and beliefs are informing your decisions. At its core, reflection allows you to objectively evaluate the evidence that’s in front of you so that you can make an informed assessment about what the best next step is for a given problem or situation.
Assessing evidence is also critical for coming up with effective solutions. This means carefully examining the available data and making sure you have all of the necessary information before reaching an opinion or making a decision. It involves looking at multiple perspectives and interpretations of any given issue so that you can form an educated conclusion about how best to solve it.
6. Open-mindedness

It is a critical thinking skill that is all about trying to understand something from different perspectives and being able to appreciate the difference in opinions. Open-mindedness allows you to analyze a problem from multiple angles and consider different solutions or ways of approaching it.

Here are some tips for developing open-mindedness as a critical thinking skill:
- Listen carefully and actively to others ; rather than just hearing words, try to understand their point of view.
- Ask questions without judgmen t and without assuming your own opinion is the right one.
- Pay attention to how other people view the same situation differently than you do.
- Think critically and evaluate arguments objectively, without assumptions or preconceived ideas about what the answer should be or which course of action should be taken.
- Suspend judgment until you have enough information about a topic or situation; don’t jump to conclusions too quickly.
- Prioritize respect when engaging with others who have different perspectives. Be willing to put in the effort required to understand why they think that way and why that might be important to them in their lives or work.
- Avoid making assumptions about what someone else believes; find out more first before passing judgment on someone’s opinion or actions.
By developing this type of open-mindedness, you can become more aware of how your personal biases may impact your ability to think critically, improving your overall decision-making skills over time and helping you become a more valuable asset as part of any team or organization.
7. Good communication

Good communication is an important part of the critical thinking process. That’s because having good communication skills helps you be more persuasive, helping you convince people of ideas and solutions that are well thought-out. It also allows you to better explain and justify your reasoning to others, which is essential when looking at complex problems.
To have strong communication skills, it’s important to think before you speak. You should also take the time to clearly articulate your thoughts, using simple yet powerful language. Additionally, having an open mind is key. It allows you to consider different angles and perspectives on any issue or problem that you might face.
Here are some tips for good communication:
- Take a moment to succinctly formulate your thoughts before speaking or writing them down.
- Ask questions when necessary, and listen carefully to what others have to say.
- Stay open-minded in conversations, as this will help broaden your knowledge of the situation.
- Speak clearly and use accurate language so that your message won’t be misunderstood.
While it’s true that critical thinking skills can’t be taught in just a few days, plenty of work and practice can go a long way toward equipping you to think critically about the problems in your life. With the right practice and guidance, you can become a master at analyzing issues, discerning cause and effect, and integrating facts to formulate your strategy.
If you’re looking to hone your critical thinking skills, start by breaking down a problem into its component parts. Assess the evidence, identify assumptions, and determine the best course of action. With practice and dedication, you can develop the analytical skills to resolve complex problems and make better decisions in the future.
- 6 Main Types of Critical Thinking Skills (With Examples) by Jamie Birt (2022) from Indeed.com
- Critical thinking From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- Critical thinking is the one skillset you can’t afford not to master By Maggie Wooll (2022) from BetterUp (https://www.betterup.com/)
Call to Action
If you want to improve yourself and achieve your goals, you need to take action. Don’t wait for the perfect moment or the right opportunity. Start today with one small step and build momentum.

Let’s boost your self-growth with Believe in Mind.
Interested in self-reflection tips, learning hacks, and knowing ways to calm down your mind? We offer you the best content which you have been looking for.
Follow Me on
You May Like Also
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7 Module 7: Thinking, Reasoning, and Problem-Solving
This module is about how a solid working knowledge of psychological principles can help you to think more effectively, so you can succeed in school and life. You might be inclined to believe that—because you have been thinking for as long as you can remember, because you are able to figure out the solution to many problems, because you feel capable of using logic to argue a point, because you can evaluate whether the things you read and hear make sense—you do not need any special training in thinking. But this, of course, is one of the key barriers to helping people think better. If you do not believe that there is anything wrong, why try to fix it?
The human brain is indeed a remarkable thinking machine, capable of amazing, complex, creative, logical thoughts. Why, then, are we telling you that you need to learn how to think? Mainly because one major lesson from cognitive psychology is that these capabilities of the human brain are relatively infrequently realized. Many psychologists believe that people are essentially “cognitive misers.” It is not that we are lazy, but that we have a tendency to expend the least amount of mental effort necessary. Although you may not realize it, it actually takes a great deal of energy to think. Careful, deliberative reasoning and critical thinking are very difficult. Because we seem to be successful without going to the trouble of using these skills well, it feels unnecessary to develop them. As you shall see, however, there are many pitfalls in the cognitive processes described in this module. When people do not devote extra effort to learning and improving reasoning, problem solving, and critical thinking skills, they make many errors.
As is true for memory, if you develop the cognitive skills presented in this module, you will be more successful in school. It is important that you realize, however, that these skills will help you far beyond school, even more so than a good memory will. Although it is somewhat useful to have a good memory, ten years from now no potential employer will care how many questions you got right on multiple choice exams during college. All of them will, however, recognize whether you are a logical, analytical, critical thinker. With these thinking skills, you will be an effective, persuasive communicator and an excellent problem solver.
The module begins by describing different kinds of thought and knowledge, especially conceptual knowledge and critical thinking. An understanding of these differences will be valuable as you progress through school and encounter different assignments that require you to tap into different kinds of knowledge. The second section covers deductive and inductive reasoning, which are processes we use to construct and evaluate strong arguments. They are essential skills to have whenever you are trying to persuade someone (including yourself) of some point, or to respond to someone’s efforts to persuade you. The module ends with a section about problem solving. A solid understanding of the key processes involved in problem solving will help you to handle many daily challenges.
7.1. Different kinds of thought
7.2. Reasoning and Judgment
7.3. Problem Solving
READING WITH PURPOSE
Remember and understand.
By reading and studying Module 7, you should be able to remember and describe:
- Concepts and inferences (7.1)
- Procedural knowledge (7.1)
- Metacognition (7.1)
- Characteristics of critical thinking: skepticism; identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions; reasoning and problem solving skills (7.1)
- Reasoning: deductive reasoning, deductively valid argument, inductive reasoning, inductively strong argument, availability heuristic, representativeness heuristic (7.2)
- Fixation: functional fixedness, mental set (7.3)
- Algorithms, heuristics, and the role of confirmation bias (7.3)
- Effective problem solving sequence (7.3)
By reading and thinking about how the concepts in Module 6 apply to real life, you should be able to:
- Identify which type of knowledge a piece of information is (7.1)
- Recognize examples of deductive and inductive reasoning (7.2)
- Recognize judgments that have probably been influenced by the availability heuristic (7.2)
- Recognize examples of problem solving heuristics and algorithms (7.3)
Analyze, Evaluate, and Create
By reading and thinking about Module 6, participating in classroom activities, and completing out-of-class assignments, you should be able to:
- Use the principles of critical thinking to evaluate information (7.1)
- Explain whether examples of reasoning arguments are deductively valid or inductively strong (7.2)
- Outline how you could try to solve a problem from your life using the effective problem solving sequence (7.3)
7.1. Different kinds of thought and knowledge
- Take a few minutes to write down everything that you know about dogs.
- Do you believe that:
- Psychic ability exists?
- Hypnosis is an altered state of consciousness?
- Magnet therapy is effective for relieving pain?
- Aerobic exercise is an effective treatment for depression?
- UFO’s from outer space have visited earth?
On what do you base your belief or disbelief for the questions above?
Of course, we all know what is meant by the words think and knowledge . You probably also realize that they are not unitary concepts; there are different kinds of thought and knowledge. In this section, let us look at some of these differences. If you are familiar with these different kinds of thought and pay attention to them in your classes, it will help you to focus on the right goals, learn more effectively, and succeed in school. Different assignments and requirements in school call on you to use different kinds of knowledge or thought, so it will be very helpful for you to learn to recognize them (Anderson, et al. 2001).
Factual and conceptual knowledge
Module 5 introduced the idea of declarative memory, which is composed of facts and episodes. If you have ever played a trivia game or watched Jeopardy on TV, you realize that the human brain is able to hold an extraordinary number of facts. Likewise, you realize that each of us has an enormous store of episodes, essentially facts about events that happened in our own lives. It may be difficult to keep that in mind when we are struggling to retrieve one of those facts while taking an exam, however. Part of the problem is that, in contradiction to the advice from Module 5, many students continue to try to memorize course material as a series of unrelated facts (picture a history student simply trying to memorize history as a set of unrelated dates without any coherent story tying them together). Facts in the real world are not random and unorganized, however. It is the way that they are organized that constitutes a second key kind of knowledge, conceptual.
Concepts are nothing more than our mental representations of categories of things in the world. For example, think about dogs. When you do this, you might remember specific facts about dogs, such as they have fur and they bark. You may also recall dogs that you have encountered and picture them in your mind. All of this information (and more) makes up your concept of dog. You can have concepts of simple categories (e.g., triangle), complex categories (e.g., small dogs that sleep all day, eat out of the garbage, and bark at leaves), kinds of people (e.g., psychology professors), events (e.g., birthday parties), and abstract ideas (e.g., justice). Gregory Murphy (2002) refers to concepts as the “glue that holds our mental life together” (p. 1). Very simply, summarizing the world by using concepts is one of the most important cognitive tasks that we do. Our conceptual knowledge is our knowledge about the world. Individual concepts are related to each other to form a rich interconnected network of knowledge. For example, think about how the following concepts might be related to each other: dog, pet, play, Frisbee, chew toy, shoe. Or, of more obvious use to you now, how these concepts are related: working memory, long-term memory, declarative memory, procedural memory, and rehearsal? Because our minds have a natural tendency to organize information conceptually, when students try to remember course material as isolated facts, they are working against their strengths.
One last important point about concepts is that they allow you to instantly know a great deal of information about something. For example, if someone hands you a small red object and says, “here is an apple,” they do not have to tell you, “it is something you can eat.” You already know that you can eat it because it is true by virtue of the fact that the object is an apple; this is called drawing an inference , assuming that something is true on the basis of your previous knowledge (for example, of category membership or of how the world works) or logical reasoning.
Procedural knowledge
Physical skills, such as tying your shoes, doing a cartwheel, and driving a car (or doing all three at the same time, but don’t try this at home) are certainly a kind of knowledge. They are procedural knowledge, the same idea as procedural memory that you saw in Module 5. Mental skills, such as reading, debating, and planning a psychology experiment, are procedural knowledge, as well. In short, procedural knowledge is the knowledge how to do something (Cohen & Eichenbaum, 1993).
Metacognitive knowledge
Floyd used to think that he had a great memory. Now, he has a better memory. Why? Because he finally realized that his memory was not as great as he once thought it was. Because Floyd eventually learned that he often forgets where he put things, he finally developed the habit of putting things in the same place. (Unfortunately, he did not learn this lesson before losing at least 5 watches and a wedding ring.) Because he finally realized that he often forgets to do things, he finally started using the To Do list app on his phone. And so on. Floyd’s insights about the real limitations of his memory have allowed him to remember things that he used to forget.
All of us have knowledge about the way our own minds work. You may know that you have a good memory for people’s names and a poor memory for math formulas. Someone else might realize that they have difficulty remembering to do things, like stopping at the store on the way home. Others still know that they tend to overlook details. This knowledge about our own thinking is actually quite important; it is called metacognitive knowledge, or metacognition . Like other kinds of thinking skills, it is subject to error. For example, in unpublished research, one of the authors surveyed about 120 General Psychology students on the first day of the term. Among other questions, the students were asked them to predict their grade in the class and report their current Grade Point Average. Two-thirds of the students predicted that their grade in the course would be higher than their GPA. (The reality is that at our college, students tend to earn lower grades in psychology than their overall GPA.) Another example: Students routinely report that they thought they had done well on an exam, only to discover, to their dismay, that they were wrong (more on that important problem in a moment). Both errors reveal a breakdown in metacognition.
The Dunning-Kruger Effect
In general, most college students probably do not study enough. For example, using data from the National Survey of Student Engagement, Fosnacht, McCormack, and Lerma (2018) reported that first-year students at 4-year colleges in the U.S. averaged less than 14 hours per week preparing for classes. The typical suggestion is that you should spend two hours outside of class for every hour in class, or 24 – 30 hours per week for a full-time student. Clearly, students in general are nowhere near that recommended mark. Many observers, including some faculty, believe that this shortfall is a result of students being too busy or lazy. Now, it may be true that many students are too busy, with work and family obligations, for example. Others, are not particularly motivated in school, and therefore might correctly be labeled lazy. A third possible explanation, however, is that some students might not think they need to spend this much time. And this is a matter of metacognition. Consider the scenario that we mentioned above, students thinking they had done well on an exam only to discover that they did not. Justin Kruger and David Dunning examined scenarios very much like this in 1999. Kruger and Dunning gave research participants tests measuring humor, logic, and grammar. Then, they asked the participants to assess their own abilities and test performance in these areas. They found that participants in general tended to overestimate their abilities, already a problem with metacognition. Importantly, the participants who scored the lowest overestimated their abilities the most. Specifically, students who scored in the bottom quarter (averaging in the 12th percentile) thought they had scored in the 62nd percentile. This has become known as the Dunning-Kruger effect . Many individual faculty members have replicated these results with their own student on their course exams, including the authors of this book. Think about it. Some students who just took an exam and performed poorly believe that they did well before seeing their score. It seems very likely that these are the very same students who stopped studying the night before because they thought they were “done.” Quite simply, it is not just that they did not know the material. They did not know that they did not know the material. That is poor metacognition.
In order to develop good metacognitive skills, you should continually monitor your thinking and seek frequent feedback on the accuracy of your thinking (Medina, Castleberry, & Persky 2017). For example, in classes get in the habit of predicting your exam grades. As soon as possible after taking an exam, try to find out which questions you missed and try to figure out why. If you do this soon enough, you may be able to recall the way it felt when you originally answered the question. Did you feel confident that you had answered the question correctly? Then you have just discovered an opportunity to improve your metacognition. Be on the lookout for that feeling and respond with caution.
concept : a mental representation of a category of things in the world
Dunning-Kruger effect : individuals who are less competent tend to overestimate their abilities more than individuals who are more competent do
inference : an assumption about the truth of something that is not stated. Inferences come from our prior knowledge and experience, and from logical reasoning
metacognition : knowledge about one’s own cognitive processes; thinking about your thinking
Critical thinking
One particular kind of knowledge or thinking skill that is related to metacognition is critical thinking (Chew, 2020). You may have noticed that critical thinking is an objective in many college courses, and thus it could be a legitimate topic to cover in nearly any college course. It is particularly appropriate in psychology, however. As the science of (behavior and) mental processes, psychology is obviously well suited to be the discipline through which you should be introduced to this important way of thinking.
More importantly, there is a particular need to use critical thinking in psychology. We are all, in a way, experts in human behavior and mental processes, having engaged in them literally since birth. Thus, perhaps more than in any other class, students typically approach psychology with very clear ideas and opinions about its subject matter. That is, students already “know” a lot about psychology. The problem is, “it ain’t so much the things we don’t know that get us into trouble. It’s the things we know that just ain’t so” (Ward, quoted in Gilovich 1991). Indeed, many of students’ preconceptions about psychology are just plain wrong. Randolph Smith (2002) wrote a book about critical thinking in psychology called Challenging Your Preconceptions, highlighting this fact. On the other hand, many of students’ preconceptions about psychology are just plain right! But wait, how do you know which of your preconceptions are right and which are wrong? And when you come across a research finding or theory in this class that contradicts your preconceptions, what will you do? Will you stick to your original idea, discounting the information from the class? Will you immediately change your mind? Critical thinking can help us sort through this confusing mess.
But what is critical thinking? The goal of critical thinking is simple to state (but extraordinarily difficult to achieve): it is to be right, to draw the correct conclusions, to believe in things that are true and to disbelieve things that are false. We will provide two definitions of critical thinking (or, if you like, one large definition with two distinct parts). First, a more conceptual one: Critical thinking is thinking like a scientist in your everyday life (Schmaltz, Jansen, & Wenckowski, 2017). Our second definition is more operational; it is simply a list of skills that are essential to be a critical thinker. Critical thinking entails solid reasoning and problem solving skills; skepticism; and an ability to identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions. Excellent deductive and inductive reasoning, and problem solving skills contribute to critical thinking. So, you can consider the subject matter of sections 7.2 and 7.3 to be part of critical thinking. Because we will be devoting considerable time to these concepts in the rest of the module, let us begin with a discussion about the other aspects of critical thinking.
Let’s address that first part of the definition. Scientists form hypotheses, or predictions about some possible future observations. Then, they collect data, or information (think of this as making those future observations). They do their best to make unbiased observations using reliable techniques that have been verified by others. Then, and only then, they draw a conclusion about what those observations mean. Oh, and do not forget the most important part. “Conclusion” is probably not the most appropriate word because this conclusion is only tentative. A scientist is always prepared that someone else might come along and produce new observations that would require a new conclusion be drawn. Wow! If you like to be right, you could do a lot worse than using a process like this.
A Critical Thinker’s Toolkit
Now for the second part of the definition. Good critical thinkers (and scientists) rely on a variety of tools to evaluate information. Perhaps the most recognizable tool for critical thinking is skepticism (and this term provides the clearest link to the thinking like a scientist definition, as you are about to see). Some people intend it as an insult when they call someone a skeptic. But if someone calls you a skeptic, if they are using the term correctly, you should consider it a great compliment. Simply put, skepticism is a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided. People from Missouri should recognize this principle, as Missouri is known as the Show-Me State. As a skeptic, you are not inclined to believe something just because someone said so, because someone else believes it, or because it sounds reasonable. You must be persuaded by high quality evidence.
Of course, if that evidence is produced, you have a responsibility as a skeptic to change your belief. Failure to change a belief in the face of good evidence is not skepticism; skepticism has open mindedness at its core. M. Neil Browne and Stuart Keeley (2018) use the term weak sense critical thinking to describe critical thinking behaviors that are used only to strengthen a prior belief. Strong sense critical thinking, on the other hand, has as its goal reaching the best conclusion. Sometimes that means strengthening your prior belief, but sometimes it means changing your belief to accommodate the better evidence.
Many times, a failure to think critically or weak sense critical thinking is related to a bias , an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice. Everybody has biases, but many people are unaware of them. Awareness of your own biases gives you the opportunity to control or counteract them. Unfortunately, however, many people are happy to let their biases creep into their attempts to persuade others; indeed, it is a key part of their persuasive strategy. To see how these biases influence messages, just look at the different descriptions and explanations of the same events given by people of different ages or income brackets, or conservative versus liberal commentators, or by commentators from different parts of the world. Of course, to be successful, these people who are consciously using their biases must disguise them. Even undisguised biases can be difficult to identify, so disguised ones can be nearly impossible.
Here are some common sources of biases:
- Personal values and beliefs. Some people believe that human beings are basically driven to seek power and that they are typically in competition with one another over scarce resources. These beliefs are similar to the world-view that political scientists call “realism.” Other people believe that human beings prefer to cooperate and that, given the chance, they will do so. These beliefs are similar to the world-view known as “idealism.” For many people, these deeply held beliefs can influence, or bias, their interpretations of such wide ranging situations as the behavior of nations and their leaders or the behavior of the driver in the car ahead of you. For example, if your worldview is that people are typically in competition and someone cuts you off on the highway, you may assume that the driver did it purposely to get ahead of you. Other types of beliefs about the way the world is or the way the world should be, for example, political beliefs, can similarly become a significant source of bias.
- Racism, sexism, ageism and other forms of prejudice and bigotry. These are, sadly, a common source of bias in many people. They are essentially a special kind of “belief about the way the world is.” These beliefs—for example, that women do not make effective leaders—lead people to ignore contradictory evidence (examples of effective women leaders, or research that disputes the belief) and to interpret ambiguous evidence in a way consistent with the belief.
- Self-interest. When particular people benefit from things turning out a certain way, they can sometimes be very susceptible to letting that interest bias them. For example, a company that will earn a profit if they sell their product may have a bias in the way that they give information about their product. A union that will benefit if its members get a generous contract might have a bias in the way it presents information about salaries at competing organizations. (Note that our inclusion of examples describing both companies and unions is an explicit attempt to control for our own personal biases). Home buyers are often dismayed to discover that they purchased their dream house from someone whose self-interest led them to lie about flooding problems in the basement or back yard. This principle, the biasing power of self-interest, is likely what led to the famous phrase Caveat Emptor (let the buyer beware) .
Knowing that these types of biases exist will help you evaluate evidence more critically. Do not forget, though, that people are not always keen to let you discover the sources of biases in their arguments. For example, companies or political organizations can sometimes disguise their support of a research study by contracting with a university professor, who comes complete with a seemingly unbiased institutional affiliation, to conduct the study.
People’s biases, conscious or unconscious, can lead them to make omissions, distortions, and assumptions that undermine our ability to correctly evaluate evidence. It is essential that you look for these elements. Always ask, what is missing, what is not as it appears, and what is being assumed here? For example, consider this (fictional) chart from an ad reporting customer satisfaction at 4 local health clubs.
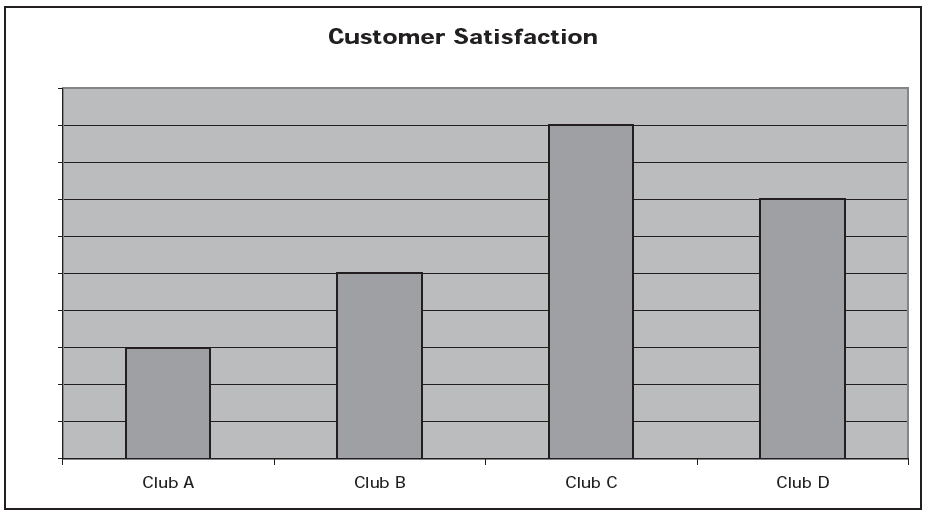
Clearly, from the results of the chart, one would be tempted to give Club C a try, as customer satisfaction is much higher than for the other 3 clubs.
There are so many distortions and omissions in this chart, however, that it is actually quite meaningless. First, how was satisfaction measured? Do the bars represent responses to a survey? If so, how were the questions asked? Most importantly, where is the missing scale for the chart? Although the differences look quite large, are they really?
Well, here is the same chart, with a different scale, this time labeled:
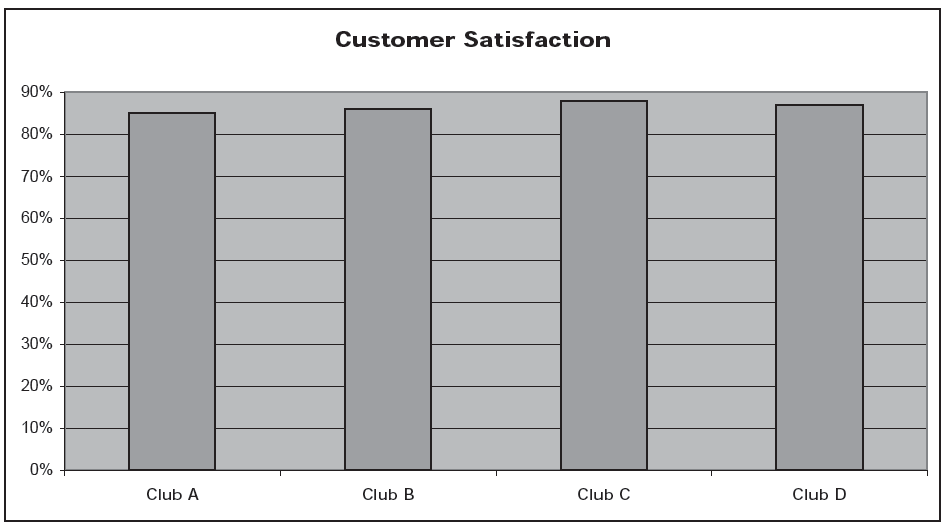
Club C is not so impressive any more, is it? In fact, all of the health clubs have customer satisfaction ratings (whatever that means) between 85% and 88%. In the first chart, the entire scale of the graph included only the percentages between 83 and 89. This “judicious” choice of scale—some would call it a distortion—and omission of that scale from the chart make the tiny differences among the clubs seem important, however.
Also, in order to be a critical thinker, you need to learn to pay attention to the assumptions that underlie a message. Let us briefly illustrate the role of assumptions by touching on some people’s beliefs about the criminal justice system in the US. Some believe that a major problem with our judicial system is that many criminals go free because of legal technicalities. Others believe that a major problem is that many innocent people are convicted of crimes. The simple fact is, both types of errors occur. A person’s conclusion about which flaw in our judicial system is the greater tragedy is based on an assumption about which of these is the more serious error (letting the guilty go free or convicting the innocent). This type of assumption is called a value assumption (Browne and Keeley, 2018). It reflects the differences in values that people develop, differences that may lead us to disregard valid evidence that does not fit in with our particular values.
Oh, by the way, some students probably noticed this, but the seven tips for evaluating information that we shared in Module 1 are related to this. Actually, they are part of this section. The tips are, to a very large degree, set of ideas you can use to help you identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions. If you do not remember this section, we strongly recommend you take a few minutes to review it.
skepticism : a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided
bias : an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice
- Which of your beliefs (or disbeliefs) from the Activate exercise for this section were derived from a process of critical thinking? If some of your beliefs were not based on critical thinking, are you willing to reassess these beliefs? If the answer is no, why do you think that is? If the answer is yes, what concrete steps will you take?
7.2 Reasoning and Judgment
- What percentage of kidnappings are committed by strangers?
- Which area of the house is riskiest: kitchen, bathroom, or stairs?
- What is the most common cancer in the US?
- What percentage of workplace homicides are committed by co-workers?
An essential set of procedural thinking skills is reasoning , the ability to generate and evaluate solid conclusions from a set of statements or evidence. You should note that these conclusions (when they are generated instead of being evaluated) are one key type of inference that we described in Section 7.1. There are two main types of reasoning, deductive and inductive.
Deductive reasoning
Suppose your teacher tells you that if you get an A on the final exam in a course, you will get an A for the whole course. Then, you get an A on the final exam. What will your final course grade be? Most people can see instantly that you can conclude with certainty that you will get an A for the course. This is a type of reasoning called deductive reasoning , which is defined as reasoning in which a conclusion is guaranteed to be true as long as the statements leading to it are true. The three statements can be listed as an argument , with two beginning statements and a conclusion:
Statement 1: If you get an A on the final exam, you will get an A for the course
Statement 2: You get an A on the final exam
Conclusion: You will get an A for the course
This particular arrangement, in which true beginning statements lead to a guaranteed true conclusion, is known as a deductively valid argument . Although deductive reasoning is often the subject of abstract, brain-teasing, puzzle-like word problems, it is actually an extremely important type of everyday reasoning. It is just hard to recognize sometimes. For example, imagine that you are looking for your car keys and you realize that they are either in the kitchen drawer or in your book bag. After looking in the kitchen drawer, you instantly know that they must be in your book bag. That conclusion results from a simple deductive reasoning argument. In addition, solid deductive reasoning skills are necessary for you to succeed in the sciences, philosophy, math, computer programming, and any endeavor involving the use of logic to persuade others to your point of view or to evaluate others’ arguments.
Cognitive psychologists, and before them philosophers, have been quite interested in deductive reasoning, not so much for its practical applications, but for the insights it can offer them about the ways that human beings think. One of the early ideas to emerge from the examination of deductive reasoning is that people learn (or develop) mental versions of rules that allow them to solve these types of reasoning problems (Braine, 1978; Braine, Reiser, & Rumain, 1984). The best way to see this point of view is to realize that there are different possible rules, and some of them are very simple. For example, consider this rule of logic:
therefore q
Logical rules are often presented abstractly, as letters, in order to imply that they can be used in very many specific situations. Here is a concrete version of the of the same rule:
I’ll either have pizza or a hamburger for dinner tonight (p or q)
I won’t have pizza (not p)
Therefore, I’ll have a hamburger (therefore q)
This kind of reasoning seems so natural, so easy, that it is quite plausible that we would use a version of this rule in our daily lives. At least, it seems more plausible than some of the alternative possibilities—for example, that we need to have experience with the specific situation (pizza or hamburger, in this case) in order to solve this type of problem easily. So perhaps there is a form of natural logic (Rips, 1990) that contains very simple versions of logical rules. When we are faced with a reasoning problem that maps onto one of these rules, we use the rule.
But be very careful; things are not always as easy as they seem. Even these simple rules are not so simple. For example, consider the following rule. Many people fail to realize that this rule is just as valid as the pizza or hamburger rule above.
if p, then q
therefore, not p
Concrete version:
If I eat dinner, then I will have dessert
I did not have dessert
Therefore, I did not eat dinner
The simple fact is, it can be very difficult for people to apply rules of deductive logic correctly; as a result, they make many errors when trying to do so. Is this a deductively valid argument or not?
Students who like school study a lot
Students who study a lot get good grades
Jane does not like school
Therefore, Jane does not get good grades
Many people are surprised to discover that this is not a logically valid argument; the conclusion is not guaranteed to be true from the beginning statements. Although the first statement says that students who like school study a lot, it does NOT say that students who do not like school do not study a lot. In other words, it may very well be possible to study a lot without liking school. Even people who sometimes get problems like this right might not be using the rules of deductive reasoning. Instead, they might just be making judgments for examples they know, in this case, remembering instances of people who get good grades despite not liking school.
Making deductive reasoning even more difficult is the fact that there are two important properties that an argument may have. One, it can be valid or invalid (meaning that the conclusion does or does not follow logically from the statements leading up to it). Two, an argument (or more correctly, its conclusion) can be true or false. Here is an example of an argument that is logically valid, but has a false conclusion (at least we think it is false).
Either you are eleven feet tall or the Grand Canyon was created by a spaceship crashing into the earth.
You are not eleven feet tall
Therefore the Grand Canyon was created by a spaceship crashing into the earth
This argument has the exact same form as the pizza or hamburger argument above, making it is deductively valid. The conclusion is so false, however, that it is absurd (of course, the reason the conclusion is false is that the first statement is false). When people are judging arguments, they tend to not observe the difference between deductive validity and the empirical truth of statements or conclusions. If the elements of an argument happen to be true, people are likely to judge the argument logically valid; if the elements are false, they will very likely judge it invalid (Markovits & Bouffard-Bouchard, 1992; Moshman & Franks, 1986). Thus, it seems a stretch to say that people are using these logical rules to judge the validity of arguments. Many psychologists believe that most people actually have very limited deductive reasoning skills (Johnson-Laird, 1999). They argue that when faced with a problem for which deductive logic is required, people resort to some simpler technique, such as matching terms that appear in the statements and the conclusion (Evans, 1982). This might not seem like a problem, but what if reasoners believe that the elements are true and they happen to be wrong; they will would believe that they are using a form of reasoning that guarantees they are correct and yet be wrong.
deductive reasoning : a type of reasoning in which the conclusion is guaranteed to be true any time the statements leading up to it are true
argument : a set of statements in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion
deductively valid argument : an argument for which true beginning statements guarantee that the conclusion is true
Inductive reasoning and judgment
Every day, you make many judgments about the likelihood of one thing or another. Whether you realize it or not, you are practicing inductive reasoning on a daily basis. In inductive reasoning arguments, a conclusion is likely whenever the statements preceding it are true. The first thing to notice about inductive reasoning is that, by definition, you can never be sure about your conclusion; you can only estimate how likely the conclusion is. Inductive reasoning may lead you to focus on Memory Encoding and Recoding when you study for the exam, but it is possible the instructor will ask more questions about Memory Retrieval instead. Unlike deductive reasoning, the conclusions you reach through inductive reasoning are only probable, not certain. That is why scientists consider inductive reasoning weaker than deductive reasoning. But imagine how hard it would be for us to function if we could not act unless we were certain about the outcome.
Inductive reasoning can be represented as logical arguments consisting of statements and a conclusion, just as deductive reasoning can be. In an inductive argument, you are given some statements and a conclusion (or you are given some statements and must draw a conclusion). An argument is inductively strong if the conclusion would be very probable whenever the statements are true. So, for example, here is an inductively strong argument:
- Statement #1: The forecaster on Channel 2 said it is going to rain today.
- Statement #2: The forecaster on Channel 5 said it is going to rain today.
- Statement #3: It is very cloudy and humid.
- Statement #4: You just heard thunder.
- Conclusion (or judgment): It is going to rain today.
Think of the statements as evidence, on the basis of which you will draw a conclusion. So, based on the evidence presented in the four statements, it is very likely that it will rain today. Will it definitely rain today? Certainly not. We can all think of times that the weather forecaster was wrong.
A true story: Some years ago psychology student was watching a baseball playoff game between the St. Louis Cardinals and the Los Angeles Dodgers. A graphic on the screen had just informed the audience that the Cardinal at bat, (Hall of Fame shortstop) Ozzie Smith, a switch hitter batting left-handed for this plate appearance, had never, in nearly 3000 career at-bats, hit a home run left-handed. The student, who had just learned about inductive reasoning in his psychology class, turned to his companion (a Cardinals fan) and smugly said, “It is an inductively strong argument that Ozzie Smith will not hit a home run.” He turned back to face the television just in time to watch the ball sail over the right field fence for a home run. Although the student felt foolish at the time, he was not wrong. It was an inductively strong argument; 3000 at-bats is an awful lot of evidence suggesting that the Wizard of Ozz (as he was known) would not be hitting one out of the park (think of each at-bat without a home run as a statement in an inductive argument). Sadly (for the die-hard Cubs fan and Cardinals-hating student), despite the strength of the argument, the conclusion was wrong.
Given the possibility that we might draw an incorrect conclusion even with an inductively strong argument, we really want to be sure that we do, in fact, make inductively strong arguments. If we judge something probable, it had better be probable. If we judge something nearly impossible, it had better not happen. Think of inductive reasoning, then, as making reasonably accurate judgments of the probability of some conclusion given a set of evidence.
We base many decisions in our lives on inductive reasoning. For example:
Statement #1: Psychology is not my best subject
Statement #2: My psychology instructor has a reputation for giving difficult exams
Statement #3: My first psychology exam was much harder than I expected
Judgment: The next exam will probably be very difficult.
Decision: I will study tonight instead of watching Netflix.
Some other examples of judgments that people commonly make in a school context include judgments of the likelihood that:
- A particular class will be interesting/useful/difficult
- You will be able to finish writing a paper by next week if you go out tonight
- Your laptop’s battery will last through the next trip to the library
- You will not miss anything important if you skip class tomorrow
- Your instructor will not notice if you skip class tomorrow
- You will be able to find a book that you will need for a paper
- There will be an essay question about Memory Encoding on the next exam
Tversky and Kahneman (1983) recognized that there are two general ways that we might make these judgments; they termed them extensional (i.e., following the laws of probability) and intuitive (i.e., using shortcuts or heuristics, see below). We will use a similar distinction between Type 1 and Type 2 thinking, as described by Keith Stanovich and his colleagues (Evans and Stanovich, 2013; Stanovich and West, 2000). Type 1 thinking is fast, automatic, effortful, and emotional. In fact, it is hardly fair to call it reasoning at all, as judgments just seem to pop into one’s head. Type 2 thinking , on the other hand, is slow, effortful, and logical. So obviously, it is more likely to lead to a correct judgment, or an optimal decision. The problem is, we tend to over-rely on Type 1. Now, we are not saying that Type 2 is the right way to go for every decision or judgment we make. It seems a bit much, for example, to engage in a step-by-step logical reasoning procedure to decide whether we will have chicken or fish for dinner tonight.
Many bad decisions in some very important contexts, however, can be traced back to poor judgments of the likelihood of certain risks or outcomes that result from the use of Type 1 when a more logical reasoning process would have been more appropriate. For example:
Statement #1: It is late at night.
Statement #2: Albert has been drinking beer for the past five hours at a party.
Statement #3: Albert is not exactly sure where he is or how far away home is.
Judgment: Albert will have no difficulty walking home.
Decision: He walks home alone.
As you can see in this example, the three statements backing up the judgment do not really support it. In other words, this argument is not inductively strong because it is based on judgments that ignore the laws of probability. What are the chances that someone facing these conditions will be able to walk home alone easily? And one need not be drunk to make poor decisions based on judgments that just pop into our heads.
The truth is that many of our probability judgments do not come very close to what the laws of probability say they should be. Think about it. In order for us to reason in accordance with these laws, we would need to know the laws of probability, which would allow us to calculate the relationship between particular pieces of evidence and the probability of some outcome (i.e., how much likelihood should change given a piece of evidence), and we would have to do these heavy math calculations in our heads. After all, that is what Type 2 requires. Needless to say, even if we were motivated, we often do not even know how to apply Type 2 reasoning in many cases.
So what do we do when we don’t have the knowledge, skills, or time required to make the correct mathematical judgment? Do we hold off and wait until we can get better evidence? Do we read up on probability and fire up our calculator app so we can compute the correct probability? Of course not. We rely on Type 1 thinking. We “wing it.” That is, we come up with a likelihood estimate using some means at our disposal. Psychologists use the term heuristic to describe the type of “winging it” we are talking about. A heuristic is a shortcut strategy that we use to make some judgment or solve some problem (see Section 7.3). Heuristics are easy and quick, think of them as the basic procedures that are characteristic of Type 1. They can absolutely lead to reasonably good judgments and decisions in some situations (like choosing between chicken and fish for dinner). They are, however, far from foolproof. There are, in fact, quite a lot of situations in which heuristics can lead us to make incorrect judgments, and in many cases the decisions based on those judgments can have serious consequences.
Let us return to the activity that begins this section. You were asked to judge the likelihood (or frequency) of certain events and risks. You were free to come up with your own evidence (or statements) to make these judgments. This is where a heuristic crops up. As a judgment shortcut, we tend to generate specific examples of those very events to help us decide their likelihood or frequency. For example, if we are asked to judge how common, frequent, or likely a particular type of cancer is, many of our statements would be examples of specific cancer cases:
Statement #1: Andy Kaufman (comedian) had lung cancer.
Statement #2: Colin Powell (US Secretary of State) had prostate cancer.
Statement #3: Bob Marley (musician) had skin and brain cancer
Statement #4: Sandra Day O’Connor (Supreme Court Justice) had breast cancer.
Statement #5: Fred Rogers (children’s entertainer) had stomach cancer.
Statement #6: Robin Roberts (news anchor) had breast cancer.
Statement #7: Bette Davis (actress) had breast cancer.
Judgment: Breast cancer is the most common type.
Your own experience or memory may also tell you that breast cancer is the most common type. But it is not (although it is common). Actually, skin cancer is the most common type in the US. We make the same types of misjudgments all the time because we do not generate the examples or evidence according to their actual frequencies or probabilities. Instead, we have a tendency (or bias) to search for the examples in memory; if they are easy to retrieve, we assume that they are common. To rephrase this in the language of the heuristic, events seem more likely to the extent that they are available to memory. This bias has been termed the availability heuristic (Kahneman and Tversky, 1974).
The fact that we use the availability heuristic does not automatically mean that our judgment is wrong. The reason we use heuristics in the first place is that they work fairly well in many cases (and, of course that they are easy to use). So, the easiest examples to think of sometimes are the most common ones. Is it more likely that a member of the U.S. Senate is a man or a woman? Most people have a much easier time generating examples of male senators. And as it turns out, the U.S. Senate has many more men than women (74 to 26 in 2020). In this case, then, the availability heuristic would lead you to make the correct judgment; it is far more likely that a senator would be a man.
In many other cases, however, the availability heuristic will lead us astray. This is because events can be memorable for many reasons other than their frequency. Section 5.2, Encoding Meaning, suggested that one good way to encode the meaning of some information is to form a mental image of it. Thus, information that has been pictured mentally will be more available to memory. Indeed, an event that is vivid and easily pictured will trick many people into supposing that type of event is more common than it actually is. Repetition of information will also make it more memorable. So, if the same event is described to you in a magazine, on the evening news, on a podcast that you listen to, and in your Facebook feed; it will be very available to memory. Again, the availability heuristic will cause you to misperceive the frequency of these types of events.
Most interestingly, information that is unusual is more memorable. Suppose we give you the following list of words to remember: box, flower, letter, platypus, oven, boat, newspaper, purse, drum, car. Very likely, the easiest word to remember would be platypus, the unusual one. The same thing occurs with memories of events. An event may be available to memory because it is unusual, yet the availability heuristic leads us to judge that the event is common. Did you catch that? In these cases, the availability heuristic makes us think the exact opposite of the true frequency. We end up thinking something is common because it is unusual (and therefore memorable). Yikes.
The misapplication of the availability heuristic sometimes has unfortunate results. For example, if you went to K-12 school in the US over the past 10 years, it is extremely likely that you have participated in lockdown and active shooter drills. Of course, everyone is trying to prevent the tragedy of another school shooting. And believe us, we are not trying to minimize how terrible the tragedy is. But the truth of the matter is, school shootings are extremely rare. Because the federal government does not keep a database of school shootings, the Washington Post has maintained their own running tally. Between 1999 and January 2020 (the date of the most recent school shooting with a death in the US at of the time this paragraph was written), the Post reported a total of 254 people died in school shootings in the US. Not 254 per year, 254 total. That is an average of 12 per year. Of course, that is 254 people who should not have died (particularly because many were children), but in a country with approximately 60,000,000 students and teachers, this is a very small risk.
But many students and teachers are terrified that they will be victims of school shootings because of the availability heuristic. It is so easy to think of examples (they are very available to memory) that people believe the event is very common. It is not. And there is a downside to this. We happen to believe that there is an enormous gun violence problem in the United States. According the the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were 39,773 firearm deaths in the US in 2017. Fifteen of those deaths were in school shootings, according to the Post. 60% of those deaths were suicides. When people pay attention to the school shooting risk (low), they often fail to notice the much larger risk.
And examples like this are by no means unique. The authors of this book have been teaching psychology since the 1990’s. We have been able to make the exact same arguments about the misapplication of the availability heuristics and keep them current by simply swapping out for the “fear of the day.” In the 1990’s it was children being kidnapped by strangers (it was known as “stranger danger”) despite the facts that kidnappings accounted for only 2% of the violent crimes committed against children, and only 24% of kidnappings are committed by strangers (US Department of Justice, 2007). This fear overlapped with the fear of terrorism that gripped the country after the 2001 terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center and US Pentagon and still plagues the population of the US somewhat in 2020. After a well-publicized, sensational act of violence, people are extremely likely to increase their estimates of the chances that they, too, will be victims of terror. Think about the reality, however. In October of 2001, a terrorist mailed anthrax spores to members of the US government and a number of media companies. A total of five people died as a result of this attack. The nation was nearly paralyzed by the fear of dying from the attack; in reality the probability of an individual person dying was 0.00000002.
The availability heuristic can lead you to make incorrect judgments in a school setting as well. For example, suppose you are trying to decide if you should take a class from a particular math professor. You might try to make a judgment of how good a teacher she is by recalling instances of friends and acquaintances making comments about her teaching skill. You may have some examples that suggest that she is a poor teacher very available to memory, so on the basis of the availability heuristic you judge her a poor teacher and decide to take the class from someone else. What if, however, the instances you recalled were all from the same person, and this person happens to be a very colorful storyteller? The subsequent ease of remembering the instances might not indicate that the professor is a poor teacher after all.
Although the availability heuristic is obviously important, it is not the only judgment heuristic we use. Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman examined the role of heuristics in inductive reasoning in a long series of studies. Kahneman received a Nobel Prize in Economics for this research in 2002, and Tversky would have certainly received one as well if he had not died of melanoma at age 59 in 1996 (Nobel Prizes are not awarded posthumously). Kahneman and Tversky demonstrated repeatedly that people do not reason in ways that are consistent with the laws of probability. They identified several heuristic strategies that people use instead to make judgments about likelihood. The importance of this work for economics (and the reason that Kahneman was awarded the Nobel Prize) is that earlier economic theories had assumed that people do make judgments rationally, that is, in agreement with the laws of probability.
Another common heuristic that people use for making judgments is the representativeness heuristic (Kahneman & Tversky 1973). Suppose we describe a person to you. He is quiet and shy, has an unassuming personality, and likes to work with numbers. Is this person more likely to be an accountant or an attorney? If you said accountant, you were probably using the representativeness heuristic. Our imaginary person is judged likely to be an accountant because he resembles, or is representative of the concept of, an accountant. When research participants are asked to make judgments such as these, the only thing that seems to matter is the representativeness of the description. For example, if told that the person described is in a room that contains 70 attorneys and 30 accountants, participants will still assume that he is an accountant.
inductive reasoning : a type of reasoning in which we make judgments about likelihood from sets of evidence
inductively strong argument : an inductive argument in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion that is probably true
heuristic : a shortcut strategy that we use to make judgments and solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
availability heuristic : judging the frequency or likelihood of some event type according to how easily examples of the event can be called to mind (i.e., how available they are to memory)
representativeness heuristic: judging the likelihood that something is a member of a category on the basis of how much it resembles a typical category member (i.e., how representative it is of the category)
Type 1 thinking : fast, automatic, and emotional thinking.
Type 2 thinking : slow, effortful, and logical thinking.
- What percentage of workplace homicides are co-worker violence?
Many people get these questions wrong. The answers are 10%; stairs; skin; 6%. How close were your answers? Explain how the availability heuristic might have led you to make the incorrect judgments.
- Can you think of some other judgments that you have made (or beliefs that you have) that might have been influenced by the availability heuristic?
7.3 Problem Solving
- Please take a few minutes to list a number of problems that you are facing right now.
- Now write about a problem that you recently solved.
- What is your definition of a problem?
Mary has a problem. Her daughter, ordinarily quite eager to please, appears to delight in being the last person to do anything. Whether getting ready for school, going to piano lessons or karate class, or even going out with her friends, she seems unwilling or unable to get ready on time. Other people have different kinds of problems. For example, many students work at jobs, have numerous family commitments, and are facing a course schedule full of difficult exams, assignments, papers, and speeches. How can they find enough time to devote to their studies and still fulfill their other obligations? Speaking of students and their problems: Show that a ball thrown vertically upward with initial velocity v0 takes twice as much time to return as to reach the highest point (from Spiegel, 1981).
These are three very different situations, but we have called them all problems. What makes them all the same, despite the differences? A psychologist might define a problem as a situation with an initial state, a goal state, and a set of possible intermediate states. Somewhat more meaningfully, we might consider a problem a situation in which you are in here one state (e.g., daughter is always late), you want to be there in another state (e.g., daughter is not always late), and with no obvious way to get from here to there. Defined this way, each of the three situations we outlined can now be seen as an example of the same general concept, a problem. At this point, you might begin to wonder what is not a problem, given such a general definition. It seems that nearly every non-routine task we engage in could qualify as a problem. As long as you realize that problems are not necessarily bad (it can be quite fun and satisfying to rise to the challenge and solve a problem), this may be a useful way to think about it.
Can we identify a set of problem-solving skills that would apply to these very different kinds of situations? That task, in a nutshell, is a major goal of this section. Let us try to begin to make sense of the wide variety of ways that problems can be solved with an important observation: the process of solving problems can be divided into two key parts. First, people have to notice, comprehend, and represent the problem properly in their minds (called problem representation ). Second, they have to apply some kind of solution strategy to the problem. Psychologists have studied both of these key parts of the process in detail.
When you first think about the problem-solving process, you might guess that most of our difficulties would occur because we are failing in the second step, the application of strategies. Although this can be a significant difficulty much of the time, the more important source of difficulty is probably problem representation. In short, we often fail to solve a problem because we are looking at it, or thinking about it, the wrong way.
problem : a situation in which we are in an initial state, have a desired goal state, and there is a number of possible intermediate states (i.e., there is no obvious way to get from the initial to the goal state)
problem representation : noticing, comprehending and forming a mental conception of a problem
Defining and Mentally Representing Problems in Order to Solve Them
So, the main obstacle to solving a problem is that we do not clearly understand exactly what the problem is. Recall the problem with Mary’s daughter always being late. One way to represent, or to think about, this problem is that she is being defiant. She refuses to get ready in time. This type of representation or definition suggests a particular type of solution. Another way to think about the problem, however, is to consider the possibility that she is simply being sidetracked by interesting diversions. This different conception of what the problem is (i.e., different representation) suggests a very different solution strategy. For example, if Mary defines the problem as defiance, she may be tempted to solve the problem using some kind of coercive tactics, that is, to assert her authority as her mother and force her to listen. On the other hand, if Mary defines the problem as distraction, she may try to solve it by simply removing the distracting objects.
As you might guess, when a problem is represented one way, the solution may seem very difficult, or even impossible. Seen another way, the solution might be very easy. For example, consider the following problem (from Nasar, 1998):
Two bicyclists start 20 miles apart and head toward each other, each going at a steady rate of 10 miles per hour. At the same time, a fly that travels at a steady 15 miles per hour starts from the front wheel of the southbound bicycle and flies to the front wheel of the northbound one, then turns around and flies to the front wheel of the southbound one again, and continues in this manner until he is crushed between the two front wheels. Question: what total distance did the fly cover?
Please take a few minutes to try to solve this problem.
Most people represent this problem as a question about a fly because, well, that is how the question is asked. The solution, using this representation, is to figure out how far the fly travels on the first leg of its journey, then add this total to how far it travels on the second leg of its journey (when it turns around and returns to the first bicycle), then continue to add the smaller distance from each leg of the journey until you converge on the correct answer. You would have to be quite skilled at math to solve this problem, and you would probably need some time and pencil and paper to do it.
If you consider a different representation, however, you can solve this problem in your head. Instead of thinking about it as a question about a fly, think about it as a question about the bicycles. They are 20 miles apart, and each is traveling 10 miles per hour. How long will it take for the bicycles to reach each other? Right, one hour. The fly is traveling 15 miles per hour; therefore, it will travel a total of 15 miles back and forth in the hour before the bicycles meet. Represented one way (as a problem about a fly), the problem is quite difficult. Represented another way (as a problem about two bicycles), it is easy. Changing your representation of a problem is sometimes the best—sometimes the only—way to solve it.
Unfortunately, however, changing a problem’s representation is not the easiest thing in the world to do. Often, problem solvers get stuck looking at a problem one way. This is called fixation . Most people who represent the preceding problem as a problem about a fly probably do not pause to reconsider, and consequently change, their representation. A parent who thinks her daughter is being defiant is unlikely to consider the possibility that her behavior is far less purposeful.
Problem-solving fixation was examined by a group of German psychologists called Gestalt psychologists during the 1930’s and 1940’s. Karl Dunker, for example, discovered an important type of failure to take a different perspective called functional fixedness . Imagine being a participant in one of his experiments. You are asked to figure out how to mount two candles on a door and are given an assortment of odds and ends, including a small empty cardboard box and some thumbtacks. Perhaps you have already figured out a solution: tack the box to the door so it forms a platform, then put the candles on top of the box. Most people are able to arrive at this solution. Imagine a slight variation of the procedure, however. What if, instead of being empty, the box had matches in it? Most people given this version of the problem do not arrive at the solution given above. Why? Because it seems to people that when the box contains matches, it already has a function; it is a matchbox. People are unlikely to consider a new function for an object that already has a function. This is functional fixedness.
Mental set is a type of fixation in which the problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past, even though the solution may no longer be useful. It is commonly seen when students do math problems for homework. Often, several problems in a row require the reapplication of the same solution strategy. Then, without warning, the next problem in the set requires a new strategy. Many students attempt to apply the formerly successful strategy on the new problem and therefore cannot come up with a correct answer.
The thing to remember is that you cannot solve a problem unless you correctly identify what it is to begin with (initial state) and what you want the end result to be (goal state). That may mean looking at the problem from a different angle and representing it in a new way. The correct representation does not guarantee a successful solution, but it certainly puts you on the right track.
A bit more optimistically, the Gestalt psychologists discovered what may be considered the opposite of fixation, namely insight . Sometimes the solution to a problem just seems to pop into your head. Wolfgang Kohler examined insight by posing many different problems to chimpanzees, principally problems pertaining to their acquisition of out-of-reach food. In one version, a banana was placed outside of a chimpanzee’s cage and a short stick inside the cage. The stick was too short to retrieve the banana, but was long enough to retrieve a longer stick also located outside of the cage. This second stick was long enough to retrieve the banana. After trying, and failing, to reach the banana with the shorter stick, the chimpanzee would try a couple of random-seeming attempts, react with some apparent frustration or anger, then suddenly rush to the longer stick, the correct solution fully realized at this point. This sudden appearance of the solution, observed many times with many different problems, was termed insight by Kohler.
Lest you think it pertains to chimpanzees only, Karl Dunker demonstrated that children also solve problems through insight in the 1930s. More importantly, you have probably experienced insight yourself. Think back to a time when you were trying to solve a difficult problem. After struggling for a while, you gave up. Hours later, the solution just popped into your head, perhaps when you were taking a walk, eating dinner, or lying in bed.
fixation : when a problem solver gets stuck looking at a problem a particular way and cannot change his or her representation of it (or his or her intended solution strategy)
functional fixedness : a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver cannot think of a new use for an object that already has a function
mental set : a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past
insight : a sudden realization of a solution to a problem
Solving Problems by Trial and Error
Correctly identifying the problem and your goal for a solution is a good start, but recall the psychologist’s definition of a problem: it includes a set of possible intermediate states. Viewed this way, a problem can be solved satisfactorily only if one can find a path through some of these intermediate states to the goal. Imagine a fairly routine problem, finding a new route to school when your ordinary route is blocked (by road construction, for example). At each intersection, you may turn left, turn right, or go straight. A satisfactory solution to the problem (of getting to school) is a sequence of selections at each intersection that allows you to wind up at school.
If you had all the time in the world to get to school, you might try choosing intermediate states randomly. At one corner you turn left, the next you go straight, then you go left again, then right, then right, then straight. Unfortunately, trial and error will not necessarily get you where you want to go, and even if it does, it is not the fastest way to get there. For example, when a friend of ours was in college, he got lost on the way to a concert and attempted to find the venue by choosing streets to turn onto randomly (this was long before the use of GPS). Amazingly enough, the strategy worked, although he did end up missing two out of the three bands who played that night.
Trial and error is not all bad, however. B.F. Skinner, a prominent behaviorist psychologist, suggested that people often behave randomly in order to see what effect the behavior has on the environment and what subsequent effect this environmental change has on them. This seems particularly true for the very young person. Picture a child filling a household’s fish tank with toilet paper, for example. To a child trying to develop a repertoire of creative problem-solving strategies, an odd and random behavior might be just the ticket. Eventually, the exasperated parent hopes, the child will discover that many of these random behaviors do not successfully solve problems; in fact, in many cases they create problems. Thus, one would expect a decrease in this random behavior as a child matures. You should realize, however, that the opposite extreme is equally counterproductive. If the children become too rigid, never trying something unexpected and new, their problem solving skills can become too limited.
Effective problem solving seems to call for a happy medium that strikes a balance between using well-founded old strategies and trying new ground and territory. The individual who recognizes a situation in which an old problem-solving strategy would work best, and who can also recognize a situation in which a new untested strategy is necessary is halfway to success.
Solving Problems with Algorithms and Heuristics
For many problems there is a possible strategy available that will guarantee a correct solution. For example, think about math problems. Math lessons often consist of step-by-step procedures that can be used to solve the problems. If you apply the strategy without error, you are guaranteed to arrive at the correct solution to the problem. This approach is called using an algorithm , a term that denotes the step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution. Because algorithms are sometimes available and come with a guarantee, you might think that most people use them frequently. Unfortunately, however, they do not. As the experience of many students who have struggled through math classes can attest, algorithms can be extremely difficult to use, even when the problem solver knows which algorithm is supposed to work in solving the problem. In problems outside of math class, we often do not even know if an algorithm is available. It is probably fair to say, then, that algorithms are rarely used when people try to solve problems.
Because algorithms are so difficult to use, people often pass up the opportunity to guarantee a correct solution in favor of a strategy that is much easier to use and yields a reasonable chance of coming up with a correct solution. These strategies are called problem solving heuristics . Similar to what you saw in section 6.2 with reasoning heuristics, a problem solving heuristic is a shortcut strategy that people use when trying to solve problems. It usually works pretty well, but does not guarantee a correct solution to the problem. For example, one problem solving heuristic might be “always move toward the goal” (so when trying to get to school when your regular route is blocked, you would always turn in the direction you think the school is). A heuristic that people might use when doing math homework is “use the same solution strategy that you just used for the previous problem.”
By the way, we hope these last two paragraphs feel familiar to you. They seem to parallel a distinction that you recently learned. Indeed, algorithms and problem-solving heuristics are another example of the distinction between Type 1 thinking and Type 2 thinking.
Although it is probably not worth describing a large number of specific heuristics, two observations about heuristics are worth mentioning. First, heuristics can be very general or they can be very specific, pertaining to a particular type of problem only. For example, “always move toward the goal” is a general strategy that you can apply to countless problem situations. On the other hand, “when you are lost without a functioning gps, pick the most expensive car you can see and follow it” is specific to the problem of being lost. Second, all heuristics are not equally useful. One heuristic that many students know is “when in doubt, choose c for a question on a multiple-choice exam.” This is a dreadful strategy because many instructors intentionally randomize the order of answer choices. Another test-taking heuristic, somewhat more useful, is “look for the answer to one question somewhere else on the exam.”
You really should pay attention to the application of heuristics to test taking. Imagine that while reviewing your answers for a multiple-choice exam before turning it in, you come across a question for which you originally thought the answer was c. Upon reflection, you now think that the answer might be b. Should you change the answer to b, or should you stick with your first impression? Most people will apply the heuristic strategy to “stick with your first impression.” What they do not realize, of course, is that this is a very poor strategy (Lilienfeld et al, 2009). Most of the errors on exams come on questions that were answered wrong originally and were not changed (so they remain wrong). There are many fewer errors where we change a correct answer to an incorrect answer. And, of course, sometimes we change an incorrect answer to a correct answer. In fact, research has shown that it is more common to change a wrong answer to a right answer than vice versa (Bruno, 2001).
The belief in this poor test-taking strategy (stick with your first impression) is based on the confirmation bias (Nickerson, 1998; Wason, 1960). You first saw the confirmation bias in Module 1, but because it is so important, we will repeat the information here. People have a bias, or tendency, to notice information that confirms what they already believe. Somebody at one time told you to stick with your first impression, so when you look at the results of an exam you have taken, you will tend to notice the cases that are consistent with that belief. That is, you will notice the cases in which you originally had an answer correct and changed it to the wrong answer. You tend not to notice the other two important (and more common) cases, changing an answer from wrong to right, and leaving a wrong answer unchanged.
Because heuristics by definition do not guarantee a correct solution to a problem, mistakes are bound to occur when we employ them. A poor choice of a specific heuristic will lead to an even higher likelihood of making an error.
algorithm : a step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution to a problem
problem solving heuristic : a shortcut strategy that we use to solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
confirmation bias : people’s tendency to notice information that confirms what they already believe
An Effective Problem-Solving Sequence
You may be left with a big question: If algorithms are hard to use and heuristics often don’t work, how am I supposed to solve problems? Robert Sternberg (1996), as part of his theory of what makes people successfully intelligent (Module 8) described a problem-solving sequence that has been shown to work rather well:
- Identify the existence of a problem. In school, problem identification is often easy; problems that you encounter in math classes, for example, are conveniently labeled as problems for you. Outside of school, however, realizing that you have a problem is a key difficulty that you must get past in order to begin solving it. You must be very sensitive to the symptoms that indicate a problem.
- Define the problem. Suppose you realize that you have been having many headaches recently. Very likely, you would identify this as a problem. If you define the problem as “headaches,” the solution would probably be to take aspirin or ibuprofen or some other anti-inflammatory medication. If the headaches keep returning, however, you have not really solved the problem—likely because you have mistaken a symptom for the problem itself. Instead, you must find the root cause of the headaches. Stress might be the real problem. For you to successfully solve many problems it may be necessary for you to overcome your fixations and represent the problems differently. One specific strategy that you might find useful is to try to define the problem from someone else’s perspective. How would your parents, spouse, significant other, doctor, etc. define the problem? Somewhere in these different perspectives may lurk the key definition that will allow you to find an easier and permanent solution.
- Formulate strategy. Now it is time to begin planning exactly how the problem will be solved. Is there an algorithm or heuristic available for you to use? Remember, heuristics by their very nature guarantee that occasionally you will not be able to solve the problem. One point to keep in mind is that you should look for long-range solutions, which are more likely to address the root cause of a problem than short-range solutions.
- Represent and organize information. Similar to the way that the problem itself can be defined, or represented in multiple ways, information within the problem is open to different interpretations. Suppose you are studying for a big exam. You have chapters from a textbook and from a supplemental reader, along with lecture notes that all need to be studied. How should you (represent and) organize these materials? Should you separate them by type of material (text versus reader versus lecture notes), or should you separate them by topic? To solve problems effectively, you must learn to find the most useful representation and organization of information.
- Allocate resources. This is perhaps the simplest principle of the problem solving sequence, but it is extremely difficult for many people. First, you must decide whether time, money, skills, effort, goodwill, or some other resource would help to solve the problem Then, you must make the hard choice of deciding which resources to use, realizing that you cannot devote maximum resources to every problem. Very often, the solution to problem is simply to change how resources are allocated (for example, spending more time studying in order to improve grades).
- Monitor and evaluate solutions. Pay attention to the solution strategy while you are applying it. If it is not working, you may be able to select another strategy. Another fact you should realize about problem solving is that it never does end. Solving one problem frequently brings up new ones. Good monitoring and evaluation of your problem solutions can help you to anticipate and get a jump on solving the inevitable new problems that will arise.
Please note that this as an effective problem-solving sequence, not the effective problem solving sequence. Just as you can become fixated and end up representing the problem incorrectly or trying an inefficient solution, you can become stuck applying the problem-solving sequence in an inflexible way. Clearly there are problem situations that can be solved without using these skills in this order.
Additionally, many real-world problems may require that you go back and redefine a problem several times as the situation changes (Sternberg et al. 2000). For example, consider the problem with Mary’s daughter one last time. At first, Mary did represent the problem as one of defiance. When her early strategy of pleading and threatening punishment was unsuccessful, Mary began to observe her daughter more carefully. She noticed that, indeed, her daughter’s attention would be drawn by an irresistible distraction or book. Fresh with a re-representation of the problem, she began a new solution strategy. She began to remind her daughter every few minutes to stay on task and remind her that if she is ready before it is time to leave, she may return to the book or other distracting object at that time. Fortunately, this strategy was successful, so Mary did not have to go back and redefine the problem again.
Pick one or two of the problems that you listed when you first started studying this section and try to work out the steps of Sternberg’s problem solving sequence for each one.
a mental representation of a category of things in the world
an assumption about the truth of something that is not stated. Inferences come from our prior knowledge and experience, and from logical reasoning
knowledge about one’s own cognitive processes; thinking about your thinking
individuals who are less competent tend to overestimate their abilities more than individuals who are more competent do
Thinking like a scientist in your everyday life for the purpose of drawing correct conclusions. It entails skepticism; an ability to identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions; and excellent deductive and inductive reasoning, and problem solving skills.
a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided
an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice
a type of reasoning in which the conclusion is guaranteed to be true any time the statements leading up to it are true
a set of statements in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion
an argument for which true beginning statements guarantee that the conclusion is true
a type of reasoning in which we make judgments about likelihood from sets of evidence
an inductive argument in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion that is probably true
fast, automatic, and emotional thinking
slow, effortful, and logical thinking
a shortcut strategy that we use to make judgments and solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
udging the frequency or likelihood of some event type according to how easily examples of the event can be called to mind (i.e., how available they are to memory)
judging the likelihood that something is a member of a category on the basis of how much it resembles a typical category member (i.e., how representative it is of the category)
a situation in which we are in an initial state, have a desired goal state, and there is a number of possible intermediate states (i.e., there is no obvious way to get from the initial to the goal state)
noticing, comprehending and forming a mental conception of a problem
when a problem solver gets stuck looking at a problem a particular way and cannot change his or her representation of it (or his or her intended solution strategy)
a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver cannot think of a new use for an object that already has a function
a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past
a sudden realization of a solution to a problem
a step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution to a problem
The tendency to notice and pay attention to information that confirms your prior beliefs and to ignore information that disconfirms them.
a shortcut strategy that we use to solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2020 by Ken Gray; Elizabeth Arnott-Hill; and Or'Shaundra Benson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 5: Thinking and Analysis
Solving problems creatively, learning objectives.
- Identify the value of creative thinking in education
- Describe the role of creative thinking skills in problem-solving
Creative Thinking Fiction and Facts
As you continue to develop your creative thinking skills, be alert to perceptions about creative thinking that could slow down progress. Remember that creative thinking and problem-solving are ways to transcend the limitations of a problem and see past barriers. It’s a way to think “outside of the box.”
Problem-Solving with Creative Thinking
Creative problem-solving is a type of problem-solving. It involves searching for new and novel solutions to problems. Unlike critical thinking, which scrutinizes assumptions and uses reasoning, creative thinking is about generating alternative ideas— practices and solutions that are unique and effective. It’s about facing sometimes muddy and unclear problems and seeing how “things” can be done differently—how new solutions can be imagined. [2]
Resources for Creative Thinking
- Creative Thinking Skills
- 45 Websites on Creative Thinking and Creative Skills
- Creativity Techniques A To Z
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Harris, Robert. "Introduction to Creative Thinking." Virtual Salt . 2 Apr 2012. Web. 16 Feb 2016. ↵
- "Critical and Creative Thinking, MA." University of Massachusetts Boston . 2016. Web. 16 Feb 2016. ↵
- College Success. Authored by : Linda Bruce. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

The 4 Types of Critical Thinking Skills – Explained!
Critical thinking skills are the mental process involved in processing information. They help us with problem solving, decision making, and thinking critically.

There are four types of “thinking skills”: convergent or analytical thinking , divergent thinking, critical thinking and creative thinking. We use these skills to help us understand the world around us, think critically, solve problems, make logical choices and develop our own values and beliefs.
The 4 Types of Thinking Skills
The 4 types of thinking skills are:
1. Convergent Analytical Thinking
Convergent thinking is the process of coming up with the best answer to a question using our memory, resources around us, or logic.
This thinking skill does not require significant creativity or lateral thinking strategies . It is not the best for solving problems that are complex or require thinking out of the box. Instead, it uses very straightforward thought processes. A convergent thinker simply needs to apply already established procedures and memory recall to reach the ‘correct’ answer.
Convergent thinking is very commonly used for standardized and multiple choice tests. These sorts of tests simply assess our knowledge and ability to apply knowledge to simple and logical situations.
The key elements required to be a skilled convergent thinker are: speed, accuracy and logic.
2. Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking is the exact opposite of convergent thinking. It involves coming up to solutions, paths forward or new ideas when there is no single correct answer.
Questions like “should I study to become a doctor or a lawyer?” may not have a simple answer. You might be good at both, and both options might bring you happiness and a good life. So, which option should you choose?
To come up with solutions to questions without clear answers, you need to break down the possibilities and analyze each part. You might create a pros and cons list, a Venn diagram or a table to lay out your options and consider each one in turn.
We often encourage divergent thinking from a very young age. For example, we encourage children to play or simply ‘be playful’ in order to solve problems and discover how their world is complex and full of possibility.
3. Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking skills involve analyzing something in order to form a judgement about it.
A critical thinker does not take the assumptions of a topic for granted. Instead, the critical thinking involves ‘critiquing’ what your are viewing using your available intellectual knowledge.
People who think critically can use three processes to develop critical insights on a topic: deduction, induction and abduction.
Deduction includes the critical thinking skills that involve drawing conclusions based on the facts at hand. You have all the facts available to you to come to a clear and unambiguous conclusion about a topic. For example, a doctor does blood tests to determine if someone has a virus. The blood tests come back positive, so we can deduce that you definitely have that virus. Deduction is a great skill to use if you want to solve problems.
Induction includes the critical thinking skills that involve drawing conclusions based on a generalization . You don’t have all the exact information at hand. However, you think critically and realize are aware of patterns, clues and a methodology that can help you induce the answer. For example, you come to the doctor exhibiting a fever, sneezing and coughing. The doctor doesn’t do tests, but they induce that you probably have influenza because your symptoms are characteristic of someone with the flu.
Abduction includes the critical thinking skills that involve coming to a conclusion that is the most likely or logical based on the small amount of knowledge that you have. You can’t be sure of the answer, but you can think critically and make an educated guess. For example, you may see that a cat is on the roof. The most logical answer is that the cat got up there by climbing a nearby tree and jumping from it to the roof, but you can’t be sure.
Read about more examples of critical thinking on our full write-up.
4. Creative Thinking
Creative thinking involves thinking about a topic in unusual, unconventional and alternative ways to generate new ideas about an established topic. A creative thinker will try to address an issue from a perspective that hasn’t been used before.
While creative thinking may appear illogical, it is in fact a great driver of human development. Creative thinkers identify gaps in marketplaces or new, easier, faster and better ways of doing things. When a creative thinker comes up with a great new way of approaching an issue, their new method can become the new orthodoxy.
See Also: Creative Thinking Examples
Get a Pdf of this article for class
Enjoy subscriber-only access to this article’s pdf
How to Maintain your Thinking when School is Over
You need to keep your mind active in order to maintain improve your critical thinking skills.
When I finished high school, I stopped thinking mathematically . I stopped using calculus, trigonometry, geometry, etc. in my daily life. Ten years on, my critical thinking skills that involve mathematics are very poor.
By contrast, I kept reading and writing in the ten years since graduating high school. I am much better at these creative and critical thinking skills than I was when I was at high school. That’s because I continued to exercise those creative and critical thinking skills aspects of my mind on a regular basis.
Some ways to maintain your mind’s neural pathways and keep up strong critical thinking skills include:
- Doing Sudoku quizzes daily
- Doing Crosswords daily
- Reading a book per month
- Completing mathematical quizzes regularly
- Taking courses in community college
- Doing brain exercise apps focused on critical thinking
How to Improve your Critical Thinking Skills
To improve your critical thinking skills, you need to go beyond just maintaining your mind.
You cannot just keep doing the same thing day-in, day-out and expect to get better. Critical thinkers are always working on self-improvement.
Instead, you need to exercise new parts of your brain by studying regularly and keep creating new neural pathways in your mind. This emphasizes the importance of education for critical thinking.
You always need to be thinking about things that are new and difficult for you to understand.
The things that you learn need to be difficult. It’s through the difficulty and discomfort in thinking that you are improving your critical thinking and problem solving skills. It’s just like going to the gym: no pain, no gain.
Some ways to improve your critical thinking skills include:
- Taking college courses (or one of these alternatives ) in topics that you find very difficult
- Taking classes in an online school
- Learning using new learning strategies that make you uncomfortable
- Taking up new and diverse hobbies
The more you think, the better you will get at being a critical thinkers. You’ll become faster, more creative and overall better at thinking if you practice and try out new strategies.
Tools to Help you Think Better
There are also some tools that we call cognitive tools that help you with your critical thinking skills. These tools don’t do the thinking for you, but they help you to become a good critical thinker.
Thinking tools can help critical thinkers include:
- Helping you structure your thoughts
- Giving you a blueprint or scaffold for finding new angles to approach a topic
- Providing prompts to move your thinking forward
Some tools that can help your thinking skills include:
1. A Brainstorming Mind Map
A brainstorming mind map can be made with a simple piece of paper. Simply write the topic at the top of the piece of paper and scrawl any and all key things you can think about down onto the paper. During the brainstorming process , no ideas are bad ideas. You can use critical thinking to critique and dismiss some of your ideas later on; but the brainstorming session can help get your mind moving and exercise those critical thinking skills.
2. A Radar Chart
A radar (or spider) chart is very similar to a brainstorming mind map, but it also shows the links between concepts.
To create a spider chart , write the topic you’re thinking about in the middle of the piece of paper.
When you come up with a new idea, write it near the middle of the paper and draw a line from the topic in the center to the idea. If you come up with new ideas or sub-ideas based on that first key idea, you can write them down and draw a line from one idea to the other. Whenever you come up with related ideas, you should draw a line between them to show their relationship.
3. A Process Chart
A process chart shows the sequence of steps from a question to its logical answer. Often in science and mathematics classes, you need to provide your process chart to your teacher to show how you came to your conclusions . You may hear your teacher tell you to “show your critical thinking skills”!
4. A Spreadsheet
Even a simple spreadsheet using Excel or Google Sheets can help with your critical thinking. It will help you lay out ideas into an easy-to-read table to help you keep track of your thoughts, your processes and your different categories. Categorizing ideas into columns and rows can help you to identify new patterns in data.
5. A Pros and Cons List
A simple pros and cons list can help you to get your ideas out of your brain and onto paper. Once it’s on paper, you can go through the list systematically and compare the pros and cons directly with one another. Once you’ve done this, you may have a better idea of what conclusions to come to.
6. De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats
Another strategy for helping your thinking skills is to use De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats. These are six metaphorical ‘hats’ that you can put on. Each hat represents a different way to look at a topic. When you ‘put the hat on’, you have to think from the perspective of the hat. These hats are great for your critical thinking.
The six hats are:
- Red Hat: Think about your feelings, emotions and hunches about a topic
- White Hat: Think about the information that’s available to you and what it can reveal about the topic
- Yellow Hat: Think about the benefits and value in the situation you’re thinking about.
- Black Hat: Think about the risks, difficulties and challenges that a situation you’re thinking about may cause.
- Green Hat: Think about the alternatives and creative approaches you can apply to a topic.
- Blue Hat: Think about the processes you can use and how to manage the situation logically.
Related: 5 Types of Skills
Final Thoughts
Thinking skills are necessary for problem solving, decision making, and thinking critically. They help you do your job better, make smart decisions, and improve your own life. You can classify your thinking skills into: convergent thinking, divergent thinking, critical thinking, and creative skills. You could also use strategies such as De Bono’s thinking hats, a pros and cons list or a process chart to help you think .
Make sure you keep your mind active, try new things and do quizzes to maintain your thinking skills throughout your life.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
3 thoughts on “The 4 Types of Critical Thinking Skills – Explained!”
Professor Chris, I have a question. As you outline, “There are four types of ‘thinking skills'”.
1. convergent or analytical thinking, 2. divergent thinking, 3. critical thinking and 4. creative thinking.
All four are processes of “thinking”. This leads me to ask, “What is the description of the process of thinking?”
W. Edwards Deming, American engineer, statistician and professor observed:
”If you can’t describe what you are doing as a process, you don’t know what you are doing.”
If we can’t describe thinking as a specific process, we don’t know what we are doing.
Without knowing the specific process of thinking, we don’t know how to perform: analytical thinking, divergent thinking, critical thinking or creative thinking.
I repeat my question. “What is the description of the process of thinking?” Thank you for your time, Ted

Definitions are such tricky things! It’s hard to find consensus in the scholarly community about a simple definition of anything, really. Although, I’d agree on the face of it that thinking is a process (and the knowledge or idea is the product). You might be interested in the concept of process thinking , which we often juxtapose to systems thinking (which, really, also involves ‘thinking as a process’), but as you have teased out this fact that thinking is inevitably a process, I wanted to give you a nudge to a resource that’ll help you go deeper on the topic.
All the best! Chris
This is interesting! Learning these four types of thinking skills would definitely help me with either school or work.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Homo Creativus pp 265–286 Cite as
Creative Problem Solving: From Evolutionary and Everyday Perspectives
- Gerard J. Puccio 10 &
- Monika Modrzejewska-Świgulska 11
- First Online: 08 June 2022
560 Accesses
Part of the book series: Creativity in the Twenty First Century ((CTFC))
Humans by nature are creative problem solvers. The purpose of this chapter is to explore the connections between biological evolution and creativity. Here, the authors make three principal arguments. First, through the arc of human history creative problem solving has been a competitive advantage for the human species. Thus, it is argued that creative thinking is an innate human trait and fundamental to the human experience. Second, everyday acts of creativity serve to underscore the fact that humans are bestowed with a capacity to creatively solve problems. Third, while humans are naturally gifted with the prowess to engage in creative thinking, deliberate creativity methods, such as Creative Problem Solving, can be leveraged to purposefully breed creative solutions. The chapter concludes by examining at a macro-level the polarity between creativity and conformity and describes how this dialectic serves to facilitate cultural evolution.
- Creative problem solving
- Everyday creativity
- Conformity bias
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Allman, W. F. (1996). The dawn of creativity. U.S. News & World Report , 120 (20), 53–58.
Google Scholar
Ansary, T. (2019). The invention of yesterday: A 50,000—Year history of human culture, conflict, and connection. Hachette Book Group.
Basadur, M., Graen, G. B., & Scandura, T. A. (1986). Training effects on attitudes toward divergent thinking among manufacturing engineers. Journal of Applied Psychology, 71 (4), 612–617. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.71.4.612
Article Google Scholar
Benyus, J. M. (1997). Biomimicry: Innovation inspired by nature . William Morrow and Company.
Campbell, D. T. (1960). Blind variation and selective retention in creative thought as in other knowledge processes. Psychological Review, 67 , 380–400. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0040373
Carruthers, P. (2002). Human creativity: Its cognitive basis, its evolution, and its connections with childhood pretence. The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science, 53 (2), 225–249. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjps/53.2.225
Chmielińska, A., & Modrzejewska-Świgulska, M. (2020). Women’s life (re)decisions: Report from biographical narrations. Przegląd Badań Edukacyjnych, 30 , 87–105.
Craft, A. (2001). Little c creativity. In A. Craft, B. Jeffrey, & M. Leibling (Eds.), Creativity in education (pp. 45–61). Continuum.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1996). Creativity: Flow and the psychology of discovery and invention. HarperCollins.
Darwin, C. (2003). The origin of species: By means of natural selection of the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life . Signet Classics.
de Bono, E. (1977). Lateral thinking . Penguin Books.
Dunbar, R., Barrett, L., & Lycett, J. (2007). Evolutionary psychology: A beginners’ guide . Oneworld Publications.
Firestien, R. L., & McCowan, R. J. (1988). Creative problem solving and communication behaviors in small groups. Creativity Research Journal, 1 , 106–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/10400418809534292
Gabora, L., & Kaufman, S. C. (2010). Evolutionary approaches to creativity. In J. C. Kaufman & R. J. Sternberg (Eds.), Cambridge handbook of creativity (pp. 279–300). Cambridge University Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Gordon, W. J. J. (1961). Synectics . Harper & Row.
Gould, S. J. (1996, October). Creating the creators. Discover , 17 (10), 42–54.
Hargadon, A. (2003). How breakthroughs happen: The surprising truth about how companies innovate . Harvard Business School Press.
Hunter, J. E., & Schmidt, F. L. (1996). Intelligence and job performance: Economic and social implications. Psychology, Public Policy, and Law, 2 , 447–472. https://doi.org/10.1037/1076-8971.2.3-4.447
Isaksen, S. G., Dorval, K. B., & Treffinger, D. J. (1994). Creative approaches to problem solving . Kendall/Hunt.
Isaksen, S. G., & Treffinger, D. J. (2004). Celebrating 50 years of reflective practice: Versions of creative problem solving. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 38 (2), 75–101. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2162-6057.2004.tb01234.x
Johansson, F. (2004). The Medici effect: Breakthrough insights at the intersection of ideas, concepts and cultures . Harvard Business School Press.
Johnson, B. (1996). Polarity management: Identifying and managing unsolvable problems . HRD Press.
Jung, C. G. (1960). The transcendent function In R. F. C. Hull (Trans.), The Collected works of C. G. Jung (Vol. 8). Princeton University Press (original work published in 1947).
Kaufman, J. C. (2016). Creativity 101 . Springer Publishing.
Kuhn, S. L. (2012). Emergent patterns of creativity and innovation in early technologies. In S. Elias (Ed.), Origins of human innovation and creativity (pp. 69–87). Elsevier.
Lewin, K. (1951). Field theory in social science: Selected theoretical papers . Harper.
MacKinnon, D. W. (1962). The nature of nurture of creative talent. The American Psychologist, 17 , 484–495. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0046541
Meadow, A., & Parnes, S. J. (1959). Evaluation of training in creative problem solving. Journal of Applied Psychology, 43 (3), 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0046040
Mithen, S. (2006). The singing Neanderthals: The origins of music, language, mind, and body . Harvard University Press.
Modrzejewska-Świgulska, M. (2013). Twórczość codzienna jako zasób wspierający dobrostan ludzi [Everyday creativity as a resource supporting people’s well-being]. In K. J. Szmidt, & M. Modrzejewska-Świgulska (Eds.), Zasoby twórcze człowieka. Wprowadzenie do pedagogiki pozytywnej (pp. 83–107). Wydawnictwo Uniwersytet Łódzkiego.
Modrzejewska-Świgulska, M. (2014). Twórczość codzienna w narracjach pedagogów [Everyday creativity in educator’s narrations]. Wydawnictwo Uniwersytet Łódzkiego.
Modrzejewska-Świgulska, M. (2015). Twórczość codzienna w praktyce i teorii . [Everyday creativity in practice and theory]. In J. Uszynska-Jarmoc & B. Kunat (Eds.), Twórczość codzienna jako aktywność całożyciowa człowieka (pp. 23–36). Trans Humana.
Morriss-Kay, G. M. (2010). The evolution of human artistic creativity. Journal of Anatomy, 216 (2), 158–176. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01160.x
Murdock, M. C., & Puccio, G. J. (1993). A contextual organizer for conducting creativity research. In S. G. Isaksen, M. C. Murdock, R. L. Firestien, & D. J. Treffinger (Eds.), Understanding and recognizing creativity: The emergence of a discipline (pp. 249–280). Ablex.
Murray, D. K. (2009). Borrowing brilliance: The six steps to business innovation by building on the ideas of others. Gotham Books.
National Center on Education and the Economy. (2008). Tough choices or tough times: The report on the new commission on the skills of the American workforce. Wiley.
Nielsen, D., & Thurber, S. (2016). The secrets of the highly creative thinker: How to make connections others don’t . BIS Publishing.
Osborn, A. F. (1953a). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving . Scribner’s Sons.
Osborn, A. F. (1953b, November 11). This I Believe [Interview]. Edward R. Murrow Papers; Tufts Digital Archive. https://dl.tufts.edu/concern/audios/nv935c52m
Palmer, D. (2010). Origins: Human evolution revealed . Mitchell Beazley.
Parnes, S. J. (1985). The creative studies project. In S. G. Isaksen (Ed.), Frontiers of creativity research (pp. 156–188). Bearly Limited.
Parnes, S. J., & Meadow, A. (1959). Effects of “brainstorming” instructions on creative problem solving by trained and untrained subjects. Journal of Educational Psychology, 50 (4), 171–176. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0047223
Parnes, S. J., & Noller, R. B. (1972). Applied creativity: The creative studies project: Part II—Results of the two-year program. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 6 , 164–186.
Puccio, G. J. (2012, December). Creativity as a life skill . TEDx Gramercy. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ltPAsp71rmI
Puccio, G. J. (2017). From the dawn of humanity to the 21st century: Creativity as an enduring survival skill. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 51 , 330–334. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.203
Puccio, G. J. (2020). Polarities in creativity: Revisiting Amabile’s componential model. In R. Reiter-Palmon, C. Fisher, & J. S. Mueller (Eds.), Creativity at work: A Festschrift in honor of Teresa Amabile (pp. 143–156). Palgrave Macmillan.
Puccio, G. J., Burnett, C., Acar, S., Yudess, J. A., Holinger, M., & Cabra, J. F., (2018). Creative problem solving in small groups: The effects of creativity training on idea generation, solution creativity, and leadership effectiveness. The Journal of Creative Behavior . Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.381
Puccio, G. J., & Cabra, J. F. (2009). Creative problem solving: Past, present, and future. In T. Rickards, H. A. Runco, & S. Moger (Eds.), The Routledge companion to creativity (pp. 327–337). Routledge.
Puccio, G. J., & Cabra, J. F. (2010). Organizational creativity: A systems perspective. In J. Kaufmann & R. J. Sternberg (Eds.), The cambridge handbook of creativity (pp. 145–173). Cambridge University Press.
Puccio, G. J., Cabra, J. F., & Schwagler, N. (2018). Organizational creativity: A practical guide for innovators and entrepreneurs . Sage.
Puccio, G. J., Firestien, R. L., Coyle, C., & Masucci, C. (2006). A review of the effectiveness of CPS training: A focus on workplace issues. Creativity and Innovation Management, 15 , 19–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8691.2006.00366.x
Puccio, G. J., Mance, M., Barbero-Switalski, L., & Reali, P. D. (2012). Creativity rising: Creative thinking and creative problem solving in the 21st century . ICSC Press.
Puccio, G. J., Mance, M., & Murdock, M. C. (2011). Creative leadership: Skills that drive change (2nd ed.). Sage.
Puccio, G. J., Murdock, M. C., & Mance, M. (2005). Current developments in creative problem solving for organizations. The Korean Journal of Thinking & Problem Solving, 15 , 43–76.
Rhodes, M. (1961). An analysis of creativity. Phi Delta Kappan, 42, 305 – 310 . https://www.jstor.org/stable/20342603
Richards, R. (1999). Everyday creativity. In M. A. Runco & S. R. Pritzker (Eds.), Encyclopedia of creativity (Vol. 1, pp. 683–687). Academic Press.
Rose, L. H., & Lin, H. T. (1984). A meta-analysis of long-term creativity training programs. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 18 , 11–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2162-6057.1984.tb00985.x
Richards, R. (2010). Everyday creativity: Process and way of life—Four key issues. In J. C. Kaufman & R. J. Sternberg (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of creativity (pp. 189–215). Cambridge University Press.
Roth, G., & Dicke, U. (2005). Evolution of the brain and intelligence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9 , 250–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2005.03.005
Roth, G., & Dicke, U. (2017). Evolution of cognitive brains: Mammals. In S. Watanabe, M. a. Hofman, & T. Shimizu (Eds.), Evolution of the brain, cognition, and emotion in vertebrates (pp. 125–146). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-56559-8_6
Runco, M. A. (2006). Reasoning and personal creativity. In J. C. Kaufman & J. Bear (Eds.), Creativity and reason in cognitive development (pp. 99–116). University Press Cambridge.
Runco, M. A., & Jaeger, G. J. (2012). The standard definition of creativity. Creativity Research Journal, 24 , 92–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/10400419.2012.650092
Scott, G., Leritz, L., & Mumford, M. (2004). The effectiveness of creativity training: A quantitative review. Creativity Research Journal, 16 (4), 361–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/10400410409534549
Spivey, N. (2005). How art made the world: A journey to the origins of human creativity . Basic Books.
Sternberg, R. J., & Lubart, T. I. (1995). Defying the crowd: Cultivating creativity in a culture of conformity . The Free Press.
Szmidt, K. J. (2018). Teoretyczno-badawcze nurty w polskiej kreatologii [Theoretic-research trends in Polish creatology]. Nauki o Wychowaniu, Studia Interdyscypliarne, 7 (2), 8–43.
Talbot, R. J. (1997). Taking style on board (or how to get used to the idea of creative adaptors and uncreative innovators). Creativity and Innovation Management, 6 (3), 177–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8691.00066
Treffinger, D. J. (1995). Creative problem solving: Overview and educational implications. Educational Psychology Review, 7 , 191–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02213375
Trilling, B., & Fadel, C. (2009). 21st century skills: Learning for life in our times . Jossey-Bass.
van der Steur, J. (2018). The power of polarities: An innovative method to transform individuals, teams, and organizations. Based on Carl Jung’s theory of the personality. Polarity Institute.
Wilson, E. O. (2017). The origins of creativity. Liveright Publishing.
Download references

Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Creativity and Change Leadership Department, The State University of New York, Buffalo, NY, USA
Gerard J. Puccio
University of Lodz, Łódź, Poland
Monika Modrzejewska-Świgulska
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gerard J. Puccio .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
LaPEA, Université de Paris, Boulogne-Billancourt, France
Todd Lubart
Marion Botella
Samira Bourgeois -Bougrine
Xavier Caroff
Jerome Guegan
Christophe Mouchiroud
Julien Nelson
Franck Zenasni
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Puccio, G.J., Modrzejewska-Świgulska, M. (2022). Creative Problem Solving: From Evolutionary and Everyday Perspectives. In: Lubart, T., et al. Homo Creativus. Creativity in the Twenty First Century. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99674-1_15
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99674-1_15
Published : 08 June 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-99672-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-99674-1
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 2: Thinking Creatively
Chapter 2 learning outcomes.
After reading this chapter, you should be able to do the following:
- Identify eight creative thinking ideas to boost your personal creativity.
- Explain three ways to enhance team collaboration and creativity.
- Identify three threats to team creativity.
- Describe the “shape of ideation” as it is graphed from a team ideation session.
- Describe the SCAMPER technique for brainstorming.
- List three barriers to creativity.
- List three benefits of doing creativity exercises.
- List ten reasons businesses nurture creativity and innovation.
Inspiration or Perspiration
A century ago, Thomas Edison thought deeply about what drives invention or, as we call it today, innovation. One of his famous sayings, “Genius is 1 percent inspiration and 99 percent perspiration,” stresses that innovation involves more than just great ideas. Edison knew from his own experience that the systematic hard work of trial-and-error experimentation paid off. His inventions, like the lightbulb and the phonograph, emerged through thousands of attempts as he refined the process step by step ( [1] ).
Thomas Edison knew breakthroughs do not come from “lightbulb” moments (pun intended). His quote captures this concept perfectly.
“Genius is 1% inspiration and 99% perspiration” (Thomas Edison)
Personal creativity.
Not everyone considers themselves creative, but most of us do have the ability to be creative. We use our creative minds more often than we think. Whenever you solve a problem, try something new, or give advice to a friend, you are probably using creative thought.
Just like doing physical exercise to work out your body, sometimes you need to do mental exercises in order to work out your mind. Play the video below to learn about the following eight creative thinking tips you can put into practice to help boost your creativity.
- Schedule Creative Free Time
- Set a Timer
- Think Quantity Over Quality
- Become an “Idea Machine”
- Switch Up Your Routine
- Look at Something Familiar Through a New Lens
- Read More Often
- Freewrite More Often
Play the “8 Creative Thinking Exercises to Boost Your Creativity” YouTube Video below to see if there is an exercise to boost your creative thinking. [2] Transcript for “8 Creative Thinking Exercises to Boost Your Creativity” Video [PDF–New Tab] . Closed captioning is available on YouTube.
There is a misconception that creativity is this thing that happens in the shower, a strike of lightning that you get out of nowhere, but the reality is creativity is not a moment in time, it’s a process and it takes time to develop.
If you were to generate a list of possible solutions to any given problem you may notice that the first few on the list will be similar to ideas other people may also come up with, but as you get to the bottom of the list you may find your ideas become more unique. This is because we solve problems every day in our lives and we are good at it. If I asked you how you will get to work today since your car is being repaired at the service center, you might say, “I’ll get a ride with a friend,” or “I’ll take the bus,” or “My mechanic loaned me a vehicle.” If I then asked you to think of some other ways you might get to work, I’m sure your ideas will become more novel as you provide additional possibilities. These novel ideas may not always be feasible, but while you are brainstorming new ideas, don’t judge them for feasibility, just get the ideas first (quantity), then later evaluate each idea on how well it resolves the problem or takes advantage of the opportunity.
Commands for Being Creative
- Get Stupid! Throw out what you know and start from somewhere new. Try drawing an image of a telephone. What did you draw? Something you have seen? Did you think to draw a phone that does not exist yet? Lose the concept of what you think a phone is and start thinking about what a phone might be in the future.
- Want the Box. Constraints are necessary for creativity. The more boundaries you have the more creative you will be.
- Can the critic. Don’t listen to the critic inside you that always tells you, “that’s a bad idea.” Ignore this voice.
Explore the Concept – Personal Creativity Exercise – SIT Technique
Doing daily creative warm-up exercises may help you become a more flexible thinker in your job and help you approach work challenges with less fear and a more playful attitude.
- Take any household product you use daily, such as a coffee cup, a hairbrush, a toothbrush, a pen, a notebook, a laptop, etc.
- Addition Technique: Add something to the product to change it. What can it now do or be used for?
- Subtraction Technique: Subtract or take away a part of the product. What can it now do or be used for?
- Answer Example: For the addition technique, you might add another handle to a mug, making it easier to hold or making it into a sippy cup for toddlers (if you also added a lid). For the subtraction technique, you might subtract or remove the handle on the mug altogether turning it into a travel mug that will fit in a car cup holder.
SCAMPER Technique for Brainstorming
Creative thinking and problem-solving are essential parts of the design process to turn ideas into innovation and break the barriers against creativity. One of the successful methods used in creative thinking is the SCAMPER technique. While there are different creative thinking and problem-solving techniques such as reversed brainstorming , Hurson’s thinking model , the Six Hats of critical thinking , and Lego Serious Play , SCAMPER is considered one of the easiest and most direct methods. The SCAMPER technique is based very simply on the idea that what is new is actually a modification of existing old things around us. [3]
What does the SCAMPER acronym stand for?
- S–Substitute (e.g., components, materials, people)
- C–Combine (e.g., mix, combine with other assemblies or services, integrate)
- A–Adapt (e.g., alter, change function, use part of another element)
- M–Modify/Magnify (e.g., increase or reduce in scale, change shape, modify attributes)
- P–Put to other uses (e.g., more than one way to use, more than one function)
- E–Eliminate (e.g., remove elements, simplify, reduce to core functionality)
- R–Rearrange/Reverse (e.g., turn inside out or upside down) [4]
Click on the information icon beside each of the letters below to learn more about SCAMPER.
Transcript for “SCAMPER” H5P [PDF–New Tab] .
Benefits of Doing Creativity Exercises
Creativity exercises offer many benefits for individuals, groups, or companies who use them, including the following: [5]
- Improved flexible thinking: Creativity exercises improve your mental flexibility. You may see the possibility of small shifts or changes to a project that you didn’t notice before.
- Discovery of multi-dimensional ideas: If you or your team have been working in the same field for a long time, you might use the same ideas repeatedly. Creativity exercises help you discover entirely new solutions to repetitive problems.
- Embracing work challenges: With enough practice, work challenges become something to look forward to as an opportunity to show and improve your mental creativity rather than a test delaying your progress.
- Seeing new concepts: Some creativity exercises help develop your creative vision, allowing you to see objects, ideas, and problems in a new way. This is highly beneficial when looking for a novel solution to a business challenge.
- Improved teamwork: Creativity exercises help individuals and groups improve teamwork skills like communication, problem-solving, and unity.
Team Creativity
Team creativity is based on having open debates, and a free flow of ideas . For that to happen, trust must exist among team members. Where trust is lacking–so will creativity. D uring brainstorming sessions, it is important to let everyone know that no idea is bad, no one will be judged, and all innovation comes with some risks. Listed be low are a few ideas on how to enhance creativity and collaboration in teams, as well as a list of some of the threats that may impair team creativity.
Enhancing Creativity and Collaboration in Teams
- Complementary Skill Sets. Collaboration works best when team members have complementary and diverse skill sets required to complete the project. Companies may also consider collaborating with customers, experts in the field, or experts in technical, design, marketing, and finance areas. [6]
- Appreciating Others . Engaging in purposeful conversations and the ability to resolve conflicts are essential ingredients for collaboration. The team needs time to get to know each other not just as professionals, but as human beings, to build trust through informal social interaction. [7]
- Open Communication. Encourage people to voice their ideas and opinions. Team members need to know it is okay to share their ideas and opinions, and that this is actually valued. When team members feel comfortable sharing their thoughts, it’s more likely to foster the kinds of discussions required to generate creative solutions. [8]
- Facilitate Diverse Ways of Working. People have their own ways of doing things. Some people like to work in teams; others prefer to work alone. Some enjoy using a pencil and notepad to jot down their thoughts, while others always make notes on their tablets or make voice recordings on their phones. Managers and team leaders need to allow people to choose how they work – as long as they do their jobs and do them well – they’re happier, and that can prompt more creativity. [9]
- Prevent Internal Competition. Competition for a promotion, pay raise, bonus, or anything else among team members has a negative effect on team creativity. Team members will try to promote their own ideas, or even not share ideas within the team, and rather share them outside the team with the team leader, or upper management. No internal competition among team members should exist. [10]
- Establish Ground Rules. Include rules such as “nobody gets to monopolize the conversation,” and “nobody gets to be quiet all the time.” Establish what happens when someone is late to a meeting. Will you allow using computers and phones in the meeting (hint: do you want their full attention or not?) Make sure you keep a “parking lot” list of things so you do not forget any ideas. [11]
Threats to Team Creativity
Social Loafing: This is the tendency for group members to slack off. These members may think their ideas are dispensable or may see other members working hard, and believe they do not need to contribute. [12]
Conforming: Members may conform due to the desire to be liked. If they believe their teammates will be critical of their suggestions, they will be more likely to agree rather than disagree. [13]
Production Blocking: This can occur when members cannot express their ideas because others are expressing their own. When working alone, individuals can work without interruption of thought, whereas when working in a group, members may forget their ideas or may not get time to speak. [14]
Performance Matching: When working in a team for an excessive amount of time, members will start to develop the same tendencies. Members that achieve higher ideals than the group may lower their standards, whereas members that work at a slower pace may increase their efforts. Overall, the team will plateau and may find it more difficult to generate unique ideas over time. [15]
Team Ideation Session: Graphing the Process
What happens in our thinking process when we are given a problem to solve in a specific amount of time? As described by Stefan Mumaw in the LinkedIn Learning, Creativity Boot Camp course. If we graphed this ideation process for a group trying to solve a problem or take advantage of an opportunity, we would see a graph (refer to Figure 2.1 below) that at first has many ideas, but after a short period of time the group feels they have exhausted all the good ideas, and the ideas dwindle almost to a halt. What happens next, is that someone offers a different, silly, or absurd idea, then more ideas come from that idea and the tide has turned. These ideas are more unique and are often the best ideas that get generated during the session and they appear on the graph after initial ideas have dwindled. The graph resembles the letter “M” with the first arc being higher than the second arc. This graph shape is known as the shape of ideation because it consistently reveals itself this way. [16]
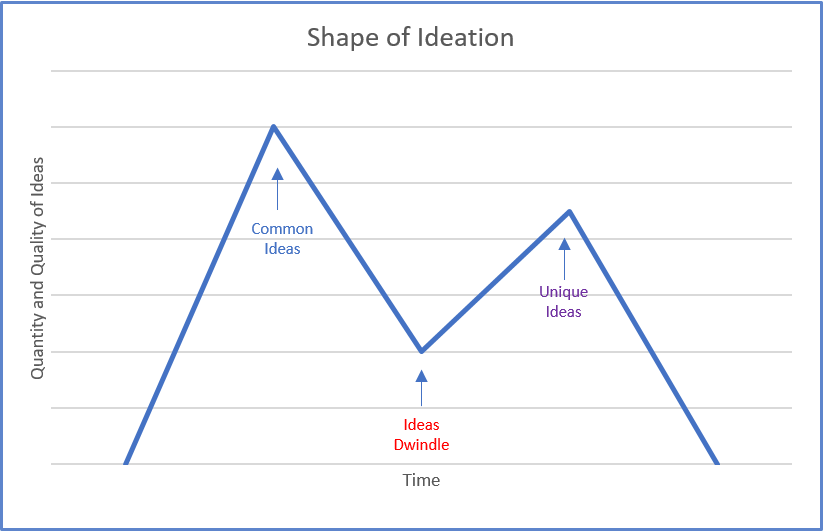
Explore the Concept – Team Creativity Exercise – Telephone Pictionary
In every creative team, it is essential to have a little bit of abstract thinking. The team-building exercise of telephone Pictionary does just that and it can be played in larger groups or small ones. Sometimes, interpreting those you work with can be a real challenge. This game deals with this issue in a fun and enlightening way.
Use strips of paper with song titles or lyrics written on them, such as “Ice, Ice Baby,” “Singing in the Rain” or famous quotes, like “Crying over spilled milk,” “A Pinch to Grow an Inch” or movie titles or phrases, like “There’s No Place Like Home,” “May the Force Be With You.” Each team member starts with their phrase. They write it out on the first page of their notebook as best they can.
All notebooks are passed to the left after 30 seconds. That person then has 30 seconds to interpret the drawing and, on the next page in the notebook, write down what they think the drawing is depicting. The next person draws what the last person wrote (without looking back at the drawings in the notebook). The notebook gets passed again and again until it makes it back to the original owner. Once each notebook is back where it started, the owner of the notebook shows each page to the group to see how the original phrase got interpreted down the line.
This exercise really demonstrates how meaning can get misconstrued and the importance of explaining things with other people’s sensibilities taken into account. [17]
Barriers to Creativity
Below is a list of some of the things that can be barriers to personal, team, and organizational creativity. [18]
- Functional fixedness . You see objects, components, and things around you, and you can’t imagine them doing different functions than what they’re designed to do. [19]
- Structural fixedness . You find it really hard to imagine objects having a different structure than what you’re used to. [20]
- Relational fixedness . You find it very hard to imagine two objects having a relationship that wasn’t there before. [21]
- Self-censorship. Get the critic out of your mind. Stop telling yourself your ideas are not good enough.
- Micro-Management. Micro-Management stifles a person’s ability to be creative as micromanagers provide too much detail related to how a particular task or problem should be tackled. This reduces the ability for the person to think for themselves and add their own creative flair.
- Overthinking. Overthinking about a problem or task uses the logical conscious side of our mind. Often creativity comes from the subconscious mind so rather than overthinking it might be wise to go for a walk or simply start daydreaming.
- Concerns about Image. Image risks are where people worry about the impression that people will have of them after suggesting an idea.
- Lack of Time. Lack of time and/or opportunity. People often feel that they are too busy with their day-to-day efforts to have time to focus on being creative. Resolve this by setting some planned time aside each and every day for creative efforts.
- Lack of Sleep. Lack of sleep not only forms barriers to creativity but to most other things too! Try and lead a healthy well-balanced life with lots of exercise and water and healthy nutrition.
- Criticism. Criticism from others can off-put you from proceeding any further with your ideas. Try and dismiss negative thinkers or win them over by demonstrating the validity of your idea with a prototype.
- Rules, Policies, and Procedures. If the organization that you work in has lots of rules, policies, and procedures then these can sometimes stifle creativity due to the bureaucracy that they create. If you can’t advance your project forward without five signatures then you will find it difficult to maintain momentum.
- Fear of Rejection. Just having that underlying fear that others will reject your ideas can be a barrier to creativity. Work with your passions, enjoy your creative moments, and don’t let others put you off.
- Stress. Stress is not only a distraction that drains the energy we might channel into being creative, it is also very bad for our health and concentration.
- Lack of Motivation , commitment, skills to perform creative tasks, or employee preparation to persist.
- Lack of organizational or managerial support or sufficient resources for creative work.
Importance of Creativity and Innovation to Business
Creativity fuels innovation. Creativity is a thought process, while innovation is an action. For a business to survive it needs both. Some of the top reasons businesses nurture creativity and innovation include:
- Innovation helps organizations grow.
- Innovation keeps organizations relevant.
- Innovation helps organizations differentiate themselves.
- Innovation increases productivity in the workplace by sparking excitement and feelings of purpose in employees.
- Innovation improves a team’s problem-solving skills by challenging the team to dive deeper and develop novel solutions.
- Innovation helps organizations position themselves as innovators in the marketplace.
- Innovation helps organizations generate more profits.
- Innovation helps organizations reduce expenses.
- Innovation helps organizations attract employees, investors, partners, and contractors.
- Innovation helps organizations gain a competitive advantage.
Key Takeaways
- Eight creative thinking tips you can try any time. Schedule creative free time, Set a timer, Think quantity over quality, Become an “Idea Machine,” Switch up your routine, Look at something familiar through a new lens, Read more often, and Freewrite more often.
- Commands for being creative. Get stupid! Want the box. Can the critic.
- The SCAMPER technique for brainstorming is based very simply on the idea that what is new is actually a modification of existing old things around us
- Benefits of doing creativity exercises. Improved flexible thinking, Discovery of multi-dimensional ideas, Embracing work challenges, See ing new concepts, and Improved teamwork.
- Team creativity is based on having open debates, and a free flow of ideas .
- Enhancing creativity and collaboration in teams. Collaboration works best when team members have complementary skill sets required to complete the project. Engaging in purposeful conversations and the ability to resolve conflicts are essential ingredients for collaboration. Open communication must be there. Facilitate diverse ways of working. Establish ground rules for working together.
- Threats to team creativity. Social loafing, Conformity, Production blocking, and Performance matching.
- Team ideation session: Graphing the process. When given a problem to solve in a specific amount of time what happens in our thinking process? If we graphed this ideation process we would see a graph that at first has many ideas, but after a short period of time the group feels they have exhausted all the good ideas, and the ideas stall. What happens next, is that someone offers a different, silly, or absurd idea, then more ideas come from that idea and the tide has turned. The best ideas often come after this turn in the graph. This is known as the shape of ideation because it consistently reveals itself this way. [22]
- Barriers to creativity. Functional, structural, and relational fixedness; self-censorship; micro-management; overthinking; concerns about image; lack of time; lack of sleep; criticism; rules, policies, and procedures; fear of rejection; stress; lack of motivation; and lack of organizational or managerial support.
- Importance of Creativity and Innovation to Business.
- Innovation helps organizations generate more growth and profits.
End-of-Chapter Exercises
- Take a Quiz to See How Creative You Are. Complete one or more of the following quizzes. Huffpost How Creative Are You? , What Percent Creative Are You? , What’s Your Creative Type? , MindTools How Creative Are You? , Are You In The Top 10% of the Most Creative People in the World? , and Are You Actually Creative? . Did you learn anything new about yourself or were the results what you expected?
- Grab a partner to try this creative exercise. Together you are going to write down as many cereal box toys as you can think of if boxes of cereal were around during the days of the wild, wild, west. You have three minutes to compile one list together; write down as many ideas as you can.
- Compare Groups. How many ideas did you and your partner come up with in three minutes? Sometimes people say they don’t have time to come up with more ideas, but as you can see given only three minutes you and your partner were able to come up with some ideas. So time is not a problem, motivation may be an issue when it comes to thinking creatively. For this exercise you may have been motivated because the exercise was silly and fun, you had a partner to work with, maybe your professor was observing you, and you only had three minutes to finish the task. This exercise is adapted from one called Wild Westios shared in the LinkedIn Learning, Creativity Boot Camp module.
- Grab a partner. You have five minutes to create the ultimate desk. Discuss and sketch it out.
- Compare Groups. How many desks had a beverage dispenser? How many desks were mobile, roll or fly? How many desks have some sort of water feature? How many desks come with some sort of extra person, such as a chef or masseuse? How many desks have a large flat surface? Why a large flat surface? Because that is what you know. We start with what we know a desk to be. We attach ideas to what we know, so we become improvers. We have to stop starting with other people’s solutions and we have to ask questions. What is a desk and what does a desk need to do? We insert restrictions that are not really there. This exercise is adapted from one called Ultimate Desk shared in the LinkedIn Learning, Creativity Boot Camp module.
- Squiggles. This exercise should take you five minutes. Take a sheet of paper and draw 5 to 10 squiggles in different shapes and sizes. Now turn your squiggles into birds. Think about the main characteristics of a bird (beak, tail, legs) and start adding them. First, draw a beak which is a simple triangle – make variations in size and position. Then, do the same with the tale, which is also a triangle. Finally, add legs that are made out of sticks. That is how simple it is! Take a look at the drawings and spend a minute considering how easily the brain finds patterns. [23]
- Write a Six-Word Story. Ernest Hemingway, one of the greatest authors of all time, was once challenged to write a complete story in just six words. Never one to shy from a challenge, he wrote: “For sale: baby shoes, never worn.” What would your complete six-word story be? [24]
- Packaging Yourself. If you were a product, available for sale at your favourite retail store, what store would you be sold in? What would the packaging look like? What would your catchy product title be? What would it say on the box? This is not just an exercise in creative thinking, but of establishing your own personal brand in a fun and inventive way. [25]
- Find Creative Uses for Everyday Objects. A pen is just a pen…or is it? What do you have around you right now that could be used for something completely different? Alton Brown, the chef who knows his science, refuses to buy objects that have just one use. He finds ways to use kitchen tools in the most inventive ways. So what can you do with that stapler, the pair of scissors, or that old bookend? [26]
Self-Check Exercise – Quiz – Thinking Creativity
Additional resources.
- LinkedIn Learning Creativity Bootcamp Training
- 50 Fun Creativity Exercises to Boost the Power of Your Creative Mind
- 21 Ways to Boost Your Personal Creativity
- 5 Team Building Exercises Guaranteed to Spark Creativity
- Business Innovation – Canada Periodical Fund – Canada.ca
- Innovation Canada (ic.gc.ca)
- MaRS Discovery District
- Discover Your Creative Type
- 18 Creativity Exercises to Try at Work
- 5 Innovative Games for Creative Ideas
- 9 Ways to Dramatically Improve You Creativity
(Note: This list of sources used is NOT in APA citation style instead the auto-footnote and media citation features of Pressbooks were utilized to cite references throughout the chapter and generate a list at the end of the chapter.)
Media Attributions
- The Shape of Ideation © Stefan Mumaw adapted by Kerri Shields is licensed under a All Rights Reserved license
- Otazo, K. (n.d.). Innovation takes perspiration. https://www.strategy-business.com/article/li00010 ↵
- Johnson, S. (2010, September 17). 8 creative thinking exercises to boost your creativity. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/pfg9a9diN40 ↵
- Elmansy, R. (n.d.). A guide to SCAMPER technique for creative thinking. https://www.designorate.com/a-guide-to-the-scamper-technique-for-creative-thinking/ ↵
- Serrat, O. (2009, February 31). The SCAMPER technique. https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/27643/scamper-technique.pdf ↵
- Indeed. (2021, March 19). 18 creativity exercises to improve creative thinking and problem-solving at work. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/creativity-exercise ↵
- Creativity at Work. (n.d.). 12 ways to enhance creativity and collaboration in teams. https://www.creativityatwork.com/12-ways-to-enhance-creativity-and-collaboration-in-teams/ ↵
- Kelly. (2019, August 22). Four strategies to enhance your team's creativity. https://www.creativityatwork.com/12-ways-to-enhance-creativity-and-collaboration-in-teams/ ↵
- Solomon, Y. (n.d.). How to build a brilliantly creative team. https://www.inc.com/yoram-solomon/8-steps-to-build-superior-team-creativity.html ↵
- Kaur, S. (n.d.). Team making portfolio: Teach creativity. https://sandeepartly.wordpress.com/team-creativity/ ↵
- Mumaw, S. (2014, November 19). Creativity boot camp. [Video]. LinkedIn Learning. https://www.linkedin.com/learning/creativity-boot-camp?u=2167290 ↵
- Merritt, J. (2022, June 7). The 30 most effective team building activities for creative teams. https://www.getrodeo.io/blog/team-building-activities ↵
- Innovation-Creativity. (n.d.). Creativity barriers. https://www.innovation-creativity.com/barriers-to-creativity/#:~:text=Barriers%20To%20Creativity%20Include%3A%201%20Functional%20fixedness.%20Functional,creativity%20but%20to%20most%20other%20things%20too%21%20 ↵
- Ozment, D. (2020, September 22). Fixedness: Your main barrier to creative thinking. https://drewboyd.com/fixedness-your-main-barrier-to-creative-thinking/ ↵
- Strimaityte, A. (2019, November 26). We might think creativity is a talent and not something everyone can have, but luckily that is not true. Creativity is a muscle that you can train. https://innovationlab.net/blog/9-best-exercises-to-spark-creativity-in-ideation/ ↵
- Sugget, P. (2020, February 6). Creative exercises to get the wheels turning. https://www.thebalancecareers.com/creative-brain-exercises-39352 ↵
- Sugget, P. (2020, February 6). Creative exercises to get the wheels turning. https://www.thebalancecareers.com/creative-brain-exercises-39352 ↵
is based very simply on the idea that what is new is actually a modification of existing old things around us.
If we graphed this ideation process we would see a graph that at first has many ideas, but after a short period of time the group feels they have exhausted all the good ideas, and the ideas stall. What happens next, someone offers a different, silly, or absurd idea, then more ideas come from that idea and the tide has turned. The best ideas often come after this turn in the graph.
You see objects, components, and things around you, and you can’t imagine them doing different functions than what they’re designed to do.
You find it really hard to imagine objects having a different structure than what you’re used to.
You find it very hard to imagine two objects having a relationship that wasn’t there before.
Leading Innovation, 2nd Edition Copyright © 2023 by Kerri Shields is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

What Is Creativity? – Understanding Imaginative Problem Solving
Creativity: Do you know what the meaning of this word is? Most people would respond with the simplest answer, being that it is something you create, such as art or music. However, is this the complete creativity definition? When delving into the subject, you will discover that this only covers the tip of the iceberg, and when you have to define creativity, there is a lot more involved. So, we are going to try and unravel the complex question, “What is creativity?”
Table of Contents
- 1 Developing a Creativity Definition
- 2.1 Various Sections of the Brain Involved in Creativity
- 3.1.1 Being Creative Can Help to Stabilize Emotions
- 3.1.2 Creating Is Stimulating
- 3.1.3 Stress Relief
- 3.1.4 Creativity Can Help to Improve Empathy
- 3.1.5 Creativity Improves Brain Plasticity
- 3.2 The Basic Stages of Creativity
- 4.1 Set Goals
- 4.2 Be a Risk Taker
- 4.3 Build Confidence
- 4.4 Brainstorm Ideas
- 4.5 Keep a Journal
- 4.6 Go Out and Find Inspiration
- 4.7 Ask Others for Their Input
- 4.8 Unwind and Relax
- 5.1 What Is Creativity?
- 5.2 Can You Describe Creativity as a Skill?
- 5.3 Are There More Creative People Than Others?
Developing a Creativity Definition
You can define creativity by saying it is about rising above the conventional way of thinking, to improve and create unique approaches to ideas. Creativity can be seen as an ability; you can either have a natural ability to perform, or you can learn and improve on what you have, as everybody has something they can tap into.
There are also many facets to creativity, and it can be subjective as many might measure creativity differently and include things like imagination, gratification, the value of an idea, differences in the creative process, and how original the idea is.

The idea of creativity today means thinking out of the box, understanding there might be limits to what you can do, trying to overcome these, and improving on the results. Creativity involves more than just thinking things up, it is taking those ideas and developing them. For example, if it is an item you wish to make, then you have to imagine, design, and build it, or if it is a new concept or idea, you should be able to test it out and prove that it works.
The way we think of or define creativity today is something that has only recently come into being. This is because, in past cultures, any ideas were seen more as discoveries or reproductions of what already existed.
Creativity as we know it today only started evolving during the early parts of the 20th century when the focus was placed on the individual and the different types of personalities, which has since developed over the years.
Creativity and the Brain
With the development of science and technology, today you can visually see what happens in the brain. When it comes to creativity and any other skill, both mental and physical, all originate in the brain. When learning a skill, it is the neurons going off in a particular part of the brain, until what you are learning becomes second nature.
Creativity is a skill that rises above the more traditional ways of thought and new or unique ideas are formed.

Sometimes, this process is easier for some than others and it all depends on how the brain forms connections or a network in the brain. When these networks are highly active, the more creative you can be. Some of these networks have been identified and are as follows.
- Executive attention : This helps the brain to focus and disregard other distractions and to control responses. Mainly situated in the brain’s prefrontal cortex.
- Imagination network : The place where you daydream and imagine scenarios and ideas. This network can involve the prefrontal cortex and areas of the parietal lobe.
- Salience network : Regions in the brain that is responsible for deciding which stimuli should be taken note of. For example, if you see something familiar and you form an appropriate response.
When all the networks are firing effectively, you could have an epiphany or a seemingly unexpected creative moment. A famous example is Archimedes in his bathtub, who coined the term “eureka”. However, this does not happen randomly and out of nowhere; there are thought processes in motion.
- Convergent thinking : This is where you use a variety of different information and look for a single solution to the problem. For example, puzzles or multiple-choice questions, where you have one solution, but you need to sift through information to get to the correct answer.
- Divergent thinking : This involves coming up with multiple ideas for a solution. For example, how many applications can you think of for a specific object? Some ideas can be conventional, while others are more original, which closely links this process to creative thinking as well as problem-solving.
When looking at a creativity psychology definition, does it mean that those who are more creative are also more intelligent? There has been a lot of research on the matter, but this subject is still relatively new, and the complete answer to this question is still pending.
However, some research has indicated a few links between intelligence as well as creativity. You can say that intelligence can be categorized as a type of creativity, but you can also say that creativity is a type of intelligence.

These two aspects of the human mind can both overlap and have a lot of things in common. They both process information, which is then formulated into a solution. Intelligence can easily be measured, while creativity is more difficult to define and measure. Generally, those that have high intelligence are more creative.
Also, those that are highly creative, can have high intelligence. However, even though there is research in favor of both ideas, it is not absolute and there is no definitive research that proves either case.
Creativity and intelligence are more parts of the same process, and the skills tend to overlap, but they are not dependent on one another. So, technically, you can be either of these or both. As you can already see, creativity is a complex topic. Research has discovered that it can include several thought processes. Besides what we have already discussed, research has indicated that more processes go into creativity, including the following.
In the end, coming up with a creativity definition is difficult as it is such a complex subject that involves multiple brain processes, which use different parts of the brain. So, creativity cannot be limited to a single part of the brain.
For example, scientists believed creativity was generated by the right side of the brain, or the right hemisphere. However, recent discoveries point to more areas involved than a single section or half of the brain.
Various Sections of the Brain Involved in Creativity
There are various sections of the brain that play a part in the creative process. These include the hippocampus, frontal cortex, basal ganglia, and white matter of the brain. White matter is what connects the different brain structures. So, if the connections between the brain structures work more efficiently, the more effective the brain can process information. This could mean better, faster, and more creative ideas.
- Hippocampus : This is a part of the brain responsible for learning and memory, which involves storing and retrieving these memories. By retrieving various memories and experiences you may have had, you can use your imagination and use these memories to create new and different ideas.
- Frontal cortex : This structure has been seen as playing a central role in creativity, as we depend on it for various functions related to creative thinking. For example, short-term memory
- Basal ganglia : This can be found deep within the brain and is responsible for processing how to do tasks. Many times, these tasks will seem automatic, for example, riding a bike. When developing and practicing, creative tasks can become easier.
There has been some research into the various functions of different parts of the brain, especially in those who have difficulty or who have sustained an injury. Scientists can then measure the differences between a normal brain versus a damaged brain. For example, research has discovered a direct association between creative thinking and the hippocampus.
Where participants who had some form of damage to the area, showed they had lower scores when given a test that measures divergent thinking. Specifically, the Torrance Test of Creativity, which evaluates the potential for creativity.
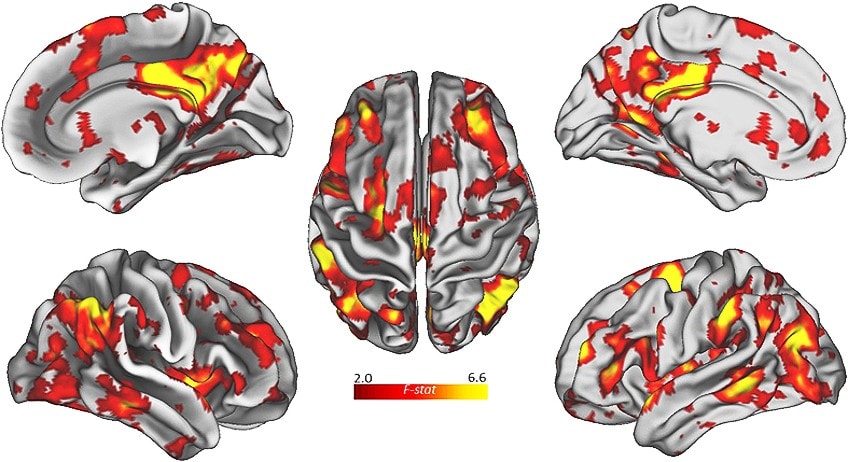
Today, we also have access to things like MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans or EEG (electroencephalogram) images. The MRI creates a detailed image of the brain, while the EEG tests the electrical activity within the brain. Using these tools, scientists can study the brain more effectively. Studies done this way have shown that for participants who had these scans done while performing creative tasks, scientists can observe where in the brain the activity is processed.
From these tests, it can be determined that creativity originated from more than one section of the brain but requires a network of processes from different parts of the brain, depending on the task at hand.
Is Creativity Important?
Some people say that they are simply not creative, and in many cases in schools, the creative subjects are placed below other subjects deemed more important. So, why should we look closer at creativity? We all want to be good at something, and this requires a lot of time and dedication to develop new skills. But we all cannot be everything at once, so why should you consider spending a bit more time developing your creativity?
In this day and age of development and technology, there is always a place for unique thinking to help grow business ideas.

Many companies and businesses appreciate creative qualities and are searching for those who can apply lateral thinking. A survey that was done by IBM showed that creativity is seen as the main quality needed for a successful business.
Various other surveys also show how creativity can be important. Even though the surveys might not be scientific and are more opinions of individuals, they are still something that should be taken into account. If you combine it with scientific research, this just proves that creativity plays an important role in everyday life.
A creative person is someone who can come up with good, original ideas, and can bring them into reality, something any business can successfully utilize.
Benefits of Creativity
The studies concerning creativity might only be beginning, and there is a lot still to learn and discover about the brain. However, there have been quite a few discoveries concerning the benefits of creativity, even though how it all works is still in process.

Being Creative Can Help to Stabilize Emotions
Many therapies involve creative tasks such as art, dance, and music. These activities and creative activities can help those who suffer from mental disorders like depression, anxiety, dementia, Alzheimer’s, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Working through difficult emotions can be done through various creative outlets.
Creating Is Stimulating
When you are in the process of creating something, not only are you more relaxed, but it can also be energizing and stimulating, as well as help you to focus. Your attention is on the current task, and there is some excitement about what the outcome will be.

Stress Relief
This is one of the more apparent advantages of focusing on creative activities or tasks. When participating in a creative task, you bring more awareness to the here and now, while momentarily putting aside thoughts of yesterday and tomorrow. This helps to reduce stress and can bring about a feeling of calm and accomplishment.
If you are doing something you enjoy, you are also freer in the creative process, without deadlines and other stressors that could hold you back.
Creativity Can Help to Improve Empathy
It has been proven that certain forms of creativity can help to improve a person’s feelings of empathy. By viewing other people’s art and forms of creativity, it can develop a certain understanding of others, their culture, and their situations.
Creativity Improves Brain Plasticity
Brain plasticity is the ability of the brain to modify or change the activity in response to whatever stimuli and then reorganize the connections. For example, in the way we form a new habit. Being creative can help to stimulate the various connections in the brain.
This is said to help improve the way we live.
The Basic Stages of Creativity
You might have come across someone that says that they do not possess any creativity, however, all of us possess a certain degree of creativity. The only main difference is how you display your creativity. For some, it might be in art or music, while others use their creativity in work or simply in the way they look at the world.
Whatever the case, creativity ultimately originates from the way we think.

Since creativity is such a complex subject, there are various methods people can use during the creative process. However, there are a few stages that are common, and which were first expressed by a social psychologist, Graham Wallas. He made known these stages in a book in the early 20th century called, The Art of Thought . Below is a short description of these five stages.
Ways to Improve Creativity
Is there a way to become more creative? Some people have a natural talent for certain things, but even they can benefit from improving their skills. So, yes you can always improve on creativity, and it is a useful skill that anybody can learn, no matter where you are in life.
Creativity definition: is being able to come up with unique ideas that can help solve problems, aid in better communication, or simply entertain. If you want to improve your creative abilities, there are a few things you can do.
For anything to work, you need to commit yourself to the process, and setting goals is a way to do this. Do not put off what you want to do, decide to do it, and set yourself a time for developing new skills. As with all things, to get good at something, you need to practice.
You also need to know everything about whatever you are interested in. As you learn and understand a subject, it will become easier and better for you to come up with more novel and unique ideas.
Be a Risk Taker
To advance in certain areas, there is always a certain amount of risk involved. For example, sharing a painting in a class might be daunting, but the positive critique will make you a better painter in the future. You might not succeed every time, but nothing is wasted as you also learn from your mistakes. So, next time you try, it may be even better than you anticipated.

Build Confidence
When it comes to a lack of confidence, this can be something that is quite debilitating and stops you from doing what you want. Insecurity is something that can stifle creativity, so try to work on building your confidence by rewarding yourself or being less critical of your work.
Try to avoid negative thoughts, even if you do not do well, to begin with, see it as a learning curve, and move on.
Brainstorm Ideas
Brainstorming is used in schools and is a way to help develop creativity. Again, the main thing is to let go of any negative thoughts and criticism, and to write down any ideas. The point is to come up with a lot of ideas in as little time as possible.

You can then look at all the ideas and improve on them, and so work your way to a possible solution. This is a great method for problem-solving and utilizing creative thinking skills. There are other methods or techniques you can try.
- Mind maps : This as well as flow charts are a great way to help connect ideas and it is an original way to find answers to challenging questions.
- Six thinking hats technique : This is a way to incorporate the various ways people think to come up with the best solution. For example, there are six colored hats each connected to a different thinking process to help form a solution more cohesively as a group.
- Thought experiments : Creating hypothetical situations where you have to think through the consequences of an idea or theory.
Keep a Journal
An effective way to help with the creative process is to keep a journal. Whenever you have an idea, make sure to write it down, even if it is not relevant to your current project. This is a great way to keep track of ideas and also look back on what you have already achieved, and maybe come up with more possible ideas.
This can also be a way to challenge yourself in the future, to continually grow from what you have done in the past. Make sure you try new things, instead of falling back on old ideas and using the same solution all the time.
Go Out and Find Inspiration
Going out to find inspiration can be just what you need to come up with new ideas. You can visit a museum, travel, listen to music, and read a book you would not normally choose. Engage in activities you would not normally do, to get out of your comfort zone and experience new things. You should also love and enjoy what you are doing because this is the best way to boost creativity. If you love something, then it is easier to do, and you will commit to it without having problems or making excuses.

Ask Others for Their Input
Take your ideas and bounce them off others and get their input and advice. You do not have to be alone in the process, while others might have the answer to your problem. Learning from others can only help to improve your creative abilities and outcomes.
Asking for help should not be seen as a weakness, as everyone has their own knowledge base and experience, it can only help. A fresh perspective might just be what is needed.
Unwind and Relax
Sometimes, things can get overwhelming and nothing is coming to mind. This might be a good time to simply stop what you are doing and do something else. Go and run, walk, or simply relax and read a book. Your mind needs to relax as well, and in so doing, the answer you were looking for might just appear.

In the end, creativity is something we all possess, it is just a matter of how we express it. Creativity is a skill that helps you to better understand the world we live in and to take make observations, use and compare them with existing knowledge, and then form new ideas and applications others have not thought of. It is proof of how wonderful and complex our minds are.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is creativity.
The creativity psychology definition describes it as an ability to produce original and unique thoughts, ideas, and possibilities, to help solve problems, aid in communication, and can also be a form of entertainment.
Can You Describe Creativity as a Skill?
Some individuals seem to have a natural-born talent; however, creativity is a skill that can be developed. Creativity starts with the basis of knowledge and learning and then can be enhanced by practicing the way you think. Being creative can mean experimenting, imagining, exploring, and questioning things around us.
Are There More Creative People Than Others?
As mentioned, some people have a natural talent for performing certain tasks, but everybody can be creative – it just takes a little more practice and dedication to develop creativity. A lot more research must still be done in this field.

Isabella studied at the University of Cape Town in South Africa and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts majoring in English Literature & Language and Psychology. Throughout her undergraduate years, she took Art History as an additional subject and absolutely loved it. Building on from her art history knowledge that began in high school, art has always been a particular area of fascination for her. From learning about artworks previously unknown to her, or sharpening her existing understanding of specific works, the ability to continue learning within this interesting sphere excites her greatly.
Her focal points of interest in art history encompass profiling specific artists and art movements, as it is these areas where she is able to really dig deep into the rich narrative of the art world. Additionally, she particularly enjoys exploring the different artistic styles of the 20 th century, as well as the important impact that female artists have had on the development of art history.
Learn more about Isabella Meyer and the Art in Context Team .
Cite this Article
Isabella, Meyer, “What Is Creativity? – Understanding Imaginative Problem Solving.” Art in Context. May 16, 2022. URL: https://artincontext.org/what-is-creativity/
Meyer, I. (2022, 16 May). What Is Creativity? – Understanding Imaginative Problem Solving. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/what-is-creativity/
Meyer, Isabella. “What Is Creativity? – Understanding Imaginative Problem Solving.” Art in Context , May 16, 2022. https://artincontext.org/what-is-creativity/ .
Similar Posts

How to Remove Permanent Marker from Plastic – An Easy Guide

Implied Lines in Art – A Key Element of Cohesive Composition

How to Polish Epoxy Resin – The Ins and Outs of Polishing Epoxy Resin

Ceramic Ideas – Inspirational Ideas for Handmade Ceramic Projects

How to Paint on Resin – Your Detailed Guide to Painting on Resin

Why Are NFTs Bad for the Environment? – NFT Carbon Footprint
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
One common approach divides the types of thinking into problem solving and reasoning, but other kinds of thinking, such as judgment and decision making, have been suggested as well. Problem solving is a systematic search through a range of possible actions in order to reach a predefined goal. It involves two main types of thinking: divergent,
A second route involves "System 2" processes: thinking that is slow, deliberate, and conscious. "Creativity can use one or the other or a combination of the two," he said. "You might use Type 1 thinking to generate ideas and Type 2 to critique and refine them." Which pathway a person uses might depend, in part, on their expertise.
Creative problem solving is based on the belief that everyone is creative and can enhance their creative abilities with discipline. Creative problem solving is a deliberate approach to solving complex problems. While creativity is an innate part of creative problem solving, the process uses a variety of steps and strategies designed to bring to ...
1. Put Yourself in a Box. Creative thinking is about "thinking outside the box," but putting limitations on your problem-solving can help you think more freely and innovatively. For example, if someone tells you to make dinner, you may struggle to come up with a meal you don't always cook.
Creative problem-solving is a type of problem-solving. It involves searching for new and novel solutions to problems. Unlike critical thinking, which scrutinizes assumptions and uses reasoning, creative thinking is about generating alternative ideas—practices and solutions that are unique and effective. It's about facing sometimes muddy and ...
CPS is a comprehensive system built on our own natural thinking processes that deliberately ignites creative thinking and produces innovative solutions. Through alternating phases of divergent and convergent thinking, CPS provides a process for managing thinking and action, while avoiding premature or inappropriate judgment. It is built upon a ...
"Mini-c" creativity involves personally meaningful ideas and insights that are known only to the self. "Little-c" creativity involves mostly everyday thinking and problem-solving. This type of creativity helps people solve everyday problems they face and adapt to changing environments. "Pro-C" creativity takes place among professionals who are skilled and creative in their ...
Key Points. Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using your creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that you can focus your mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.
Humans are innate creative problem-solvers. Since early humans developed the first stone tools to crack open fruit and nuts more than 2 million years ago, the application of creative thinking to solve problems has been a distinct competitive advantage for our species (Puccio 2017).Originally used to solve problems related to survival, the tendency toward the use of creative problem-solving to ...
This type of thinking is prized in the context of being creative because it is how one finds a potential audience for one's creative work. An innovation or invention needs an audience, a consumer, a user, and implementor. Indeed, ideas are just ideas if no one knows about them or no one uses them. Analytical Thinking.
The creative problem-solving process Footnote 1 is a systematic approach to problem-solving that was first proposed by Alex Osborn in 1953 in his landmark book Applied Imagination.The approach went through several refinements over a period of five years. Osborn began with a seven-step model that reflected the creative process (orientation, preparation, analysis, hypothesis, incubation ...
Approaches to Creativity. There are two main strands to technical creativity: programmed thinking and lateral thinking. Programmed thinking relies on logical or structured ways of creating a new product or service. Examples of this approach are Morphological Analysis and the Reframing Matrix. The other main strand uses "Lateral Thinking."
On completion of this chapter, the readers will be able to: Identify the appropriate problem-solving tool to use for a specific situation or to match his or her preferred thinking style. Apply a range of thinking tools to assist in the ideation and idea refinement stages of creative thinking tasks. Deliver creative ideas for further development ...
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Types of Critical Thinking: 1 Analytical Thinking 2 Creative Thinking 3 Decision-Making 4 Problem-Solving 5 Reflection 6 Open-mindedness 7 Good communication.
Module 7: Thinking, Reasoning, and Problem-Solving. This module is about how a solid working knowledge of psychological principles can help you to think more effectively, so you can succeed in school and life. You might be inclined to believe that—because you have been thinking for as long as you can remember, because you are able to figure ...
Creative problem-solving is a type of problem-solving. It involves searching for new and novel solutions to problems. Unlike critical thinking, which scrutinizes assumptions and uses reasoning, creative thinking is about generating alternative ideas— practices and solutions that are unique and effective. It's about facing sometimes muddy ...
Creative thinking and problem-solving are essential parts of the design process to turn ideas into innovation and break the barriers against creativity. One of the successful methods used in creative thinking is the SCAMPER technique. ... Lack of sleep not only forms barriers to creativity but to most other things too! Try and lead a healthy ...
They help us with problem solving, decision making, and thinking critically. There are four types of "thinking skills": convergent or analytical thinking, divergent thinking, critical thinking and creative thinking. We use these skills to help us understand the world around us, think critically, solve problems, make logical choices and ...
Abstract. Humans by nature are creative problem solvers. The purpose of this chapter is to explore the connections between biological evolution and creativity. Here, the authors make three principal arguments. First, through the arc of human history creative problem solving has been a competitive advantage for the human species.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis . Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another.
Creative thinking and problem-solving are essential parts of the design process to turn ideas into innovation and break the barriers against creativity. One of the successful methods used in creative thinking is the SCAMPER technique. ... Lack of sleep not only forms barriers to creativity but to most other things too! Try and lead a healthy ...
The idea of creativity today means thinking out of the box, understanding there might be limits to what you can do, trying to overcome these, and improving on the results. Creativity involves more than just thinking things up, it is taking those ideas and developing them. For example, if it is an item you wish to make, then you have to imagine ...