LIVE MASTERCLASS: 7 Strategies For Parents To Help Your Child Earn $100,000 College Scholarships & Ace The New 2024 Digital SAT. Enroll Free!

SAT Essay Samples | Low vs High-Scoring Examples
The SAT Essay is often used as an extra way to impress admissions officers with your overall academic preparedness. But what does a good essay look like vs a bad one? To make life easier, the College Board has provided some helpful SAT essay samples that you can study over.
Besides helping you get into college, here are a number of other SAT Essay benefits to consider .
SAT Essay Samples Prompt
Expect to see prompt directions like the ones below:
“As you read the passage below, consider how Paul Bogard uses:
- evidence, such as facts or examples, to support claims.
- reasoning to develop ideas and to connect claims and evidence.
- stylistic or persuasive elements, such as word choice or appeals to emotion, to add power to the ideas expressed.”
SAT Essay Samples Passage
“ Adapted from Paul Bogard, “Let There Be Dark.” ©2012 by Los Angeles Times. Originally published December 21, 2012.
At my family’s cabin on a Minnesota lake, I knew woods so dark that my hands disappeared before my eyes. I knew night skies in which meteors left smoky trails across sugary spreads of stars. But now, when 8 of 10 children born in the United States will never know a sky dark enough for the Milky Way, I worry we are rapidly losing night’s natural darkness before realizing its worth. This winter solstice, as we cheer the days’ gradual movement back toward light, let us also remember the irreplaceable value of darkness.
All life evolved to the steady rhythm of bright days and dark nights. Today, though, when we feel the closeness of nightfall, we reach quickly for a light switch. And too little darkness, meaning too much artificial light at night, spells trouble for all.
Already the World Health Organization classifies working the night shift as a probable human carcinogen, and the American Medical Association has voiced its unanimous support for “light pollution reduction efforts and glare reduction efforts at both the national and state levels.” Our bodies need darkness to produce the hormone melatonin, which keeps certain cancers from developing, and our bodies need darkness for sleep. Sleep disorders have been linked to diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease and depression, and recent research suggests one main cause of “short sleep” is “long light.” Whether we work at night or simply take our tablets, notebooks and smartphones to bed, there isn’t a place for this much artificial light in our lives.
The rest of the world depends on darkness as well, including nocturnal and crepuscular species of birds, insects, mammals, fish and reptiles. Some examples are well known—the 400 species of birds that migrate at night in North America, the sea turtles that come ashore to lay their eggs—and some are not, such as the bats that save American farmers billions in pest control and the moths that pollinate 80% of the world’s flora. Ecological light pollution is like the bulldozer of the night, wrecking habitat and disrupting ecosystems several billion years in the making. Simply put, without darkness, Earth’s ecology would collapse…
In today’s crowded, louder, more fast-paced world, night’s darkness can provide solitude, quiet and stillness, qualities increasingly in short supply. Every religious tradition has considered darkness invaluable for a soulful life, and the chance to witness the universe has inspired artists, philosophers and everyday stargazers since time began. In a world awash with electric light…how would Van Gogh have given the world his “Starry Night”? Who knows what this vision of the night sky might inspire in each of us, in our children or grandchildren?
Yet all over the world, our nights are growing brighter. In the United States and Western Europe, the amount of light in the sky increases an average of about 6% every year. Computer images of the United States at night, based on NASA photographs, show that what was a very dark country as recently as the 1950s is now nearly covered with a blanket of light. Much of this light is wasted energy, which means wasted dollars. Those of us over 35 are perhaps among the last generation to have known truly dark nights. Even the northern lake where I was lucky to spend my summers has seen its darkness diminish.
It doesn’t have to be this way. Light pollution is readily within our ability to solve, using new lighting technologies and shielding existing lights. Already, many cities and towns across North America and Europe are changing to LED streetlights, which offer dramatic possibilities for controlling wasted light. Other communities are finding success with simply turning off portions of their public lighting after midnight. Even Paris, the famed “city of light,” which already turns off its monument lighting after 1 a.m., will this summer start to require its shops, offices and public buildings to turn off lights after 2 a.m. Though primarily designed to save energy, such reductions in light will also go far in addressing light pollution. But we will never truly address the problem of light pollution until we become aware of the irreplaceable value and beauty of the darkness we are losing.”
SAT Essay Samples Directions
Here is how the essay directions will be worded format-wise on test day.
“Write an essay in which you explain how Paul Bogard builds an argument to persuade his audience that natural darkness should be preserved. In your essay, analyze how Bogard uses one or more of the features in the directions that precede the passage (or features of your own choice) to strengthen the logic and persuasiveness of his argument. Be sure that your analysis focuses on the most relevant features of the passage.
Your essay should not explain whether you agree with Bogard’s claims, but rather explain how Bogard builds an argument to persuade his audience.”
Essay Sample Response (Low Scoring)
“In “Let there be dark,” Paul Bogard talks about the importance of darkness.
Darkness is essential to humans. Bogard states, “Our bodies need darkness to produce the hormone melatonin, which keeps certain cancers from developing, and our bodies need darkness for sleep, sleep. Sleep disorders have been linked to diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease and depression and recent research suggests are main cause of “short sleep” is “long light.” Whether we work at night or simply take our tablets, notebooks and smartphones to bed, there isn’t a place for this much artificial light in our lives.” (Bogard 2). Here, Bogard talks about the importance of darkness to humans. Humans need darkness to sleep in order to be healthy.
Animals also need darkness. Bogard states, “The rest of the world depends on darkness as well, including nocturnal and crepuscular species of birds, insects, mammals, fish and reptiles. Some examples are well known—the 400 species of birds that migrate at night in North America, the sea turtles that come ashore to lay their eggs—and some are not, such as the bats that save American farmers billions in pest control and the moths that pollinate 80% of the world’s flora. Ecological light pollution is like the bulldozer of the night, wrecking habitat and disrupting ecosystems several billion years in the making. Simply put, without darkness, Earth’s ecology would collapse…” (Bogard 2). Here Bogard explains that animals, too, need darkness to survive.”
Essay Sample Response (High Scoring)
“In response to our world’s growing reliance on artificial light, writer Paul Bogard argues that natural darkness should be preserved in his article “Let There be dark”. He effectively builds his argument by using a personal anecdote, allusions to art and history, and rhetorical questions.
Bogard starts his article off by recounting a personal story – a summer spent on a Minnesota lake where there was “woods so dark that [his] hands disappeared before [his] eyes.” In telling this brief anecdote, Bogard challenges the audience to remember a time where they could fully amass themselves in natural darkness void of artificial light. By drawing in his readers with a personal encounter about night darkness, the author means to establish the potential for beauty, glamour, and awe-inspiring mystery that genuine darkness can possess. He builds his argument for the preservation of natural darkness by reminiscing for his readers a first-hand encounter that proves the “irreplaceable value of darkness.” This anecdote provides a baseline of sorts for readers to find credence with the author’s claims.
Bogard’s argument is also furthered by his use of allusion to art – Van Gogh’s “Starry Night” – and modern history – Paris’ reputation as “The City of Light”. By first referencing “Starry Night”, a painting generally considered to be undoubtedly beautiful, Bogard establishes that the natural magnificence of stars in a dark sky is definite. A world absent of excess artificial light could potentially hold the key to a grand, glorious night sky like Van Gogh’s according to the writer. This urges the readers to weigh the disadvantages of our world consumed by unnatural, vapid lighting. Furthermore, Bogard’s alludes to Paris as “the famed ‘city of light’”. He then goes on to state how Paris has taken steps to exercise more sustainable lighting practices. By doing this, Bogard creates a dichotomy between Paris’ traditionally alluded-to name and the reality of what Paris is becoming – no longer “the city of light”, but more so “the city of light…before 2 AM”. This furthers his line of argumentation because it shows how steps can be and are being taken to preserve natural darkness. It shows that even a city that is literally famous for being constantly lit can practically address light pollution in a manner that preserves the beauty of both the city itself and the universe as a whole.
Finally, Bogard makes subtle yet efficient use of rhetorical questioning to persuade his audience that natural darkness preservation is essential. He asks the readers to consider “what the vision of the night sky might inspire in each of us, in our children or grandchildren?” in a way that brutally plays to each of our emotions. By asking this question, Bogard draws out heartfelt ponderance from his readers about the affecting power of an untainted night sky. This rhetorical question tugs at the readers’ heartstrings; while the reader may have seen an unobscured night skyline before, the possibility that their child or grandchild will never get the chance sways them to see as Bogard sees. This strategy is definitively an appeal to pathos, forcing the audience to directly face an emotionally-charged inquiry that will surely spur some kind of response. By doing this, Bogard develops his argument, adding guttural power to the idea that the issue of maintaining natural darkness is relevant and multifaceted.
Writing as a reaction to his disappointment that artificial light has largely permeated the presence of natural darkness, Paul Bogard argues that we must preserve true, unaffected darkness. He builds this claim by making use of a personal anecdote, allusions, and rhetorical questioning.”
For more test strategies, college admissions, and scholarship application tips sign up for our FREE classes happening right now!
Related Articles

A Complete Guide to Guaranteed SAT and ACT Score Scholarships
Jun 11, 2024
Prep Expert Student Spotlight: Alejandro’s SAT Prep Course Experience
May 28, 2024

Cracking the Code of SAT Idioms
May 7, 2024
Written by Prep Expert
More from prep expert.

Everything You Need to Know About ACT Idioms
If you’ve ever been stumped by an idiom on the ACT, you’re not the only one. Preparing for questions about…

Harvard Brings Back Standardized Testing Requirements
Harvard College has just joined the ranks of Ivy League schools that have recently made the decision to reinstate standardized…

How to Improve Your ACT Score by 10 Points
Achieving a high score on the ACT opens doors to a multitude of opportunities, including scholarships, competitive programs, and more.…
$200 OFF COUPON CODE
Subscribe to our emails and get $200 OFF any Prep Expert Online Course.
Enter the coupon code SHARKTANK200 to save $200 OFF any Prep Expert Online Course!
By providing your email address, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions
No thanks, I’d prefer to pay full price.
What Is the SAT Essay?
College Board
- February 28, 2024
The SAT Essay section is a lot like a typical writing assignment in which you’re asked to read and analyze a passage and then produce an essay in response to a single prompt about that passage. It gives you the opportunity to demonstrate your reading, analysis, and writing skills—which are critical to readiness for success in college and career—and the scores you’ll get back will give you insight into your strengths in these areas as well as indications of any areas that you may still need to work on.
The Essay section is only available in certain states where it’s required as part of SAT School Day administrations. If you’re going to be taking the SAT during school , ask your counselor if it will include the Essay section. If it’s included, the Essay section will come after the Reading and Writing and Math sections and will add an additional 50 minutes .
What You’ll Do
- Read a passage between 650 and 750 words in length.
- Explain how the author builds an argument to persuade an audience.
- Support your explanation with evidence from the passage.
You won’t be asked to agree or disagree with a position on a topic or to write about your personal experience.
The Essay section shows how well you understand the passage and are able to use it as the basis for a well-written, thought-out discussion. Your score will be based on three categories.
Reading: A successful essay shows that you understood the passage, including the interplay of central ideas and important details. It also shows an effective use of textual evidence.
Analysis: A successful essay shows your understanding of how the author builds an argument by:
- Examining the author’s use of evidence, reasoning, and other stylistic and persuasive techniques
- Supporting and developing claims with well-chosen evidence from the passage
Writing: A successful essay is focused, organized, and precise, with an appropriate style and tone that varies sentence structure and follows the conventions of standard written English.
Learn more about how the SAT Essay is scored.
Want to practice? Log in to the Bluebook™ testing application , go to the Practice and Prepare section, and choose full-length practice test . There are 3 practice Essay tests. Once you submit your response, go to MyPractice.Collegeboard.org , where you’ll see your essay, a scoring guide and rubric so that you can score yourself, and student samples for various scores to compare your self-score with a student at the same level.
After the Test
You’ll get your Essay score the same way you’ll get your scores for the Reading and Writing and Math sections. If you choose to send your SAT scores to colleges, your Essay score will be reported along with your other section scores from that test day. Even though Score Choice™ allows you to choose which day’s scores you send to colleges, you can never send only some scores from a certain test day. For instance, you can’t choose to send Math scores but not SAT Essay scores.
Until 2021, the SAT Essay was also an optional section when taking the SAT on a weekend. That section was discontinued in 2021.
If you don’t have the opportunity to take the SAT Essay section as part of the SAT, don’t worry. There are other ways to show your writing skills as part of the work you’re already doing on your path to college. The SAT can help you stand out on college applications , as it continues to measure the writing and analytical skills that are essential to college and career readiness. And, if you want to demonstrate your writing skills even more, you can also consider taking an AP English course .
Related Posts
How to get ready for the digital sat on a school day.
Advanced Placement
What is AP English?
Taking the sat during school, how long does the sat take.
SAT School Day with Essay
If you are taking a state-provided SAT, you may be required, or have the option, to answer an essay question as part of your test. The SAT Essay is a lot like a typical college writing assignment that asks you to analyze a text. It shows colleges that you're able to read, analyze, and write at the college level.
The SAT Essay asks you to use your reading, analysis, and writing skills. You'll be asked to:
- Read a passage.
- Explain how the author builds an argument to persuade an audience.
- Support your explanation with evidence from the passage.
SAT Essay Overview
- Total questions: 1 prompt, with points to consider and directions
- Time allotted: 50 minutes to read and analyze the passage and to develop a written response
What the SAT Essay Measures
The SAT Essay shows how well you understand the passage and use it as the basis for a well-written, well-thought-out response. Your essay will be scored on three dimensions, each on a 2–8 scale:
- Reading: A successful essay shows that you understood the passage, including the interplay of central ideas and important details. It also shows effective use of textual evidence.
- Examining the author's use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive techniques (or other elements of your choosing)
- Supporting your claims and points effectively
- Focusing on those features of the passage that are most relevant for completing the task
- Writing: A successful essay is cohesive, organized, and precise, uses an appropriate style and tone, has varied sentences, and observes the conventions of standard written English.
The Essay Prompt
The prompt shown below is nearly identical to the one that will appear on the SAT.
As you read the passage below, consider how [the author] uses:
- Evidence, such as facts or examples, to support claims.
- Reasoning to develop ideas and to connect claims and evidence.
- Stylistic or persuasive elements, such as word choice or appeals to emotion, to add power to the ideas expressed.
Write an essay in which you explain how [the author] builds an argument to persuade [their] audience that [author's claim]. In your essay, analyze how [the author] uses one or more of the features listed above (or features of your own choice) to strengthen the logic and persuasiveness of [their] argument. Be sure that your analysis focuses on the most relevant features of the passage. Your essay should not explain whether you agree with [the author's] claims, but rather explain how [the author] builds an argument to persuade [their] audience.
The Essay Passage
All passages have these things in common:
- Written for a broad audience
- Argue a point
- Express subtle views on complex subjects
- Use logical reasoning and evidence to support claims
- Examine ideas, debates, or trends in the arts and sciences or in civic, cultural, or political life
- Always taken from published works
All the information you need to write your essay will be included in the passage or in notes about it.
SAT Essay Scoring Guide
| Score | Reading | Analysis | Writing |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | The response demonstrates thorough comprehension of the source text. The response shows an understanding of the text's central idea(s) and of most important details and how they interrelate, demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of the text. The response is free of errors of fact or interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes skillful use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating a complete understanding of the source text. | The response offers an insightful analysis of the source text and demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of the analytical task. The response offers a thorough, well-considered evaluation of the author's use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student's own choosing. The response contains relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim(s) or point(s) made. The response focuses consistently on those features of the text that are most relevant to addressing the task. | The response is cohesive and demonstrates a highly effective use and command of language. The response includes a precise central claim. The response includes a skillful introduction and conclusion. The response demonstrates a deliberate and highly effective progression of ideas both within paragraphs and throughout the essay. The response has a wide variety in sentence structures. The response demonstrates a consistent use of precise word choice. The response maintains a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a strong command of the conventions of standard written English and is free or virtually free of errors. |
| 3 | The response demonstrates effective comprehension of the source text. The response shows an understanding of the text's central idea(s) and important details. The response is free of substantive errors of fact and interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes appropriate use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating an understanding of the source text. | The response offers an effective analysis of the source text and demonstrates an understanding of the analytical task. The response competently evaluates the author's use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student's own choosing. The response contains relevant and sufficient support for claim(s) or point(s) made. The response focuses primarily on those features of the text that are most relevant to addressing the task. | The response is mostly cohesive and demonstrates effective use and control of language. The response includes a central claim or implicit controlling idea. The response includes an effective introduction and conclusion. The response demonstrates a clear progression of ideas both within paragraphs and throughout the essay. The response has variety in sentence structures. The response demonstrates some precise word choice. The response maintains a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a good control of the conventions of standard written English and is free of significant errors that detract from the quality of writing. |
| 2 | The response demonstrates some comprehension of the source text. The response shows an understanding of the text's central idea(s) but not of important details. The response may contain errors of fact and/or interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes limited and/or haphazard use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating some understanding of the source text. | The response offers limited analysis of the source text and demonstrates only partial understanding of the analytical task. The response identifies and attempts to describe the author's use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student's own choosing, but merely asserts rather than explains their importance; Or one or more aspects of the response's analysis are unwarranted based on the text. The response contains little or no support for claim(s) or point(s) made. The response may lack a clear focus on those features of the text that are most relevant to addressing the task. | The response demonstrates little or no cohesion and limited skill in the use and control of language. The response may lack a clear central claim or controlling idea or may deviate from the claim or idea over the course of the response. The response may include an ineffective introduction and/or conclusion. The response may demonstrate some progression of ideas within paragraphs but not throughout the response. The response has limited variety in sentence structures; sentence structures may be repetitive. The response demonstrates general or vague word choice; word choice may be repetitive. The response may deviate noticeably from a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a limited control of the conventions of standard written English and contains errors that detract from the quality of writing and may impede understanding. |
| 1 | The response demonstrates little or no comprehension of the source text. The response fails to show an understanding of the text's central idea(s), and may include only details without reference to central idea(s). The response may contain numerous errors of fact and/or interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes little or no use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating little or no understanding of the source text. | The response offers little or no analysis or ineffective analysis of the source text and demonstrates little or no understanding of the analytical task. The response identifies without explanation some aspects of the author's use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student's choosing; Or numerous aspects of the response's analysis are unwarranted based on the text. The response contains little or no support for claim(s) or point(s) made, or support is largely irrelevant. The response may not focus on features of the text that are relevant to addressing the task; Or the response offers no discernible analysis (e.g., is largely or exclusively summary). | The response demonstrates little or no cohesion and inadequate skill in the use and control of language. The response may lack a clear central claim or controlling idea. The response lacks a recognizable introduction and conclusion. The response does not have a discernible progression of ideas. The response lacks variety in sentence structures; sentence structures may be repetitive. The response demonstrates general and vague word choice; word choice may be poor or inaccurate. The response may lack a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a weak control of the conventions of standard written English and may contain numerous errors that undermine the quality of writing. |
SAT Essay Practice
To practice for the SAT Essay:
- Download Bluebook™ .
- Go to Practice and Prepare on the Bluebook homepage, and select SAT Essay Practice . (You can access the essay practice with the same sign-in credentials provided by your school.)
- After you've finished the practice test in Bluebook, go to My Practice and sign in with the same credentials provided by your school to view your essay response, prompt, self-scoring rubric, and additional student sample essays.
SAT Practice Essays and Score Explanations—Digital
NOTE: The Essay is only available in certain states where it's required as part of SAT School Day administrations. If you're going to be taking the SAT on a school day, ask your counselor if it will include the Essay section.
SAT Practice Essay 1—Digital
This full-length, official SAT practice essay was written by the same people who wrote the SAT. Download it to get started.
SAT Practice Essay 1 Score Explanations—Digital
Download student sample essays—and the explanations that show why they received the score they did—for SAT Practice Essay 1.
SAT Practice Essay 2—Digital
Sat practice essay 2 score explanations—digital.
Download student sample essays—and the explanations that show why they received the score they did—for SAT Practice Essay 2.
SAT Practice Essay 3—Digital
Sat practice essay 3 score explanations—digital.
Download student sample essays—and the explanations that show why they received the score they did—for SAT Practice Essay 3.

SAT Essay Prompts (10 Sample Questions)
What does it take to get a high SAT Essay score, if not perfect it? Practice, practice and more practice! Know the tricks and techniques of writing the perfect SAT Essay, so that you can score perfect as well. That’s not a far off idea, because there actually is a particular “formula” for perfecting the SAT Essay test. Consider that every prompt has a format, and what test-takers are required to do remain the same- even if the passage varies from test to test.
The SAT Essay test will ask you to read an argument that is intended to persuade a general audience. You’ll need to discuss how proficient the author is in arguing their point. Analyze the argument of the author and create an integrated and structured essay that explains your analysis.
On this page, we will feature 10 real SAT Essay prompts that have been recently released online by the College Board. You can utilize these Essay SAT prompts as 10 sample SAT Essay questions for easy practice. This set of SAT Essay prompts is the most comprehensive that you will find online today.
The predictability of the SAT Essay test necessitates students to perform an organized analytical method of writing instead of thinking up random ideas on their own. Consider that what you will see before and after the passage remains consistent. It is recommended that you initially read and apply the techniques suggested in writing the perfect SAT Essay (🡨link to SAT Essay —- SAT Essay Overview: How to Get a Perfect Score) before proceeding on using the following essay prompts for practice.
Check our SAT Reading Practice Tests
10 Official SAT Essay Prompts For Practice

Practice Test 1
“Write an essay in which you explain how Jimmy Carter builds an argument to persuade his audience that the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge should not be developed for industry.”
Practice Test 2
“Write an essay in which you explain how Martin Luther King Jr. builds an argument to persuade his audience that American involvement in the Vietnam War is unjust.”
Practice Test 3
“Write an essay in which you explain how Eliana Dockterman builds an argument to persuade her audience that there are benefits to early exposure to technology.”
Practice Test 4
“Write an essay in which you explain how Paul Bogard builds an argument to persuade his audience that natural darkness should be preserved.”
Practice Test 5
“Write an essay in which you explain how Eric Klinenberg builds an argument to persuade his audience that Americans need to greatly reduce their reliance on air-conditioning.”
Practice Test 6
“Write an essay in which you explain how Christopher Hitchens builds an argument to persuade his audience that the original Parthenon sculptures should be returned to Greece.”
Practice Test 7
“Write an essay in which you explain how Zadie Smith builds an argument to persuade her audience that public libraries are important and should remain open”
Practice Test 8
“Write an essay in which you explain how Bobby Braun builds an argument to persuade his audience that the US government must continue to invest in NASA.”
Practice Test 9
“Write an essay in which you explain how Richard Schiffman builds an argument to persuade his audience that Americans need to work fewer hours.”
Practice Test 10
“Write an essay in which you explain how Todd Davidson builds an argument to persuade his audience that the US government must continue to fund national parks.”
Visit our SAT Writing Practice Tests
What Is An Example Of A SAT Essay That Obtained A Perfect Score?

Here is an example of Practice Test 4 above and how a perfect SAT Essay in response to it looks like. This has been published in the College Board website.
Answer Essay with Perfect Score:
In response to our world’s growing reliance on artificial light, writer Paul Bogard argues that natural darkness should be preserved in his article “Let There be dark”. He effectively builds his argument by using a personal anecdote, allusions to art and history, and rhetorical questions.
Bogard starts his article off by recounting a personal story – a summer spent on a Minnesota lake where there was “woods so dark that [his] hands disappeared before [his] eyes.” In telling this brief anecdote, Bogard challenges the audience to remember a time where they could fully amass themselves in natural darkness void of artificial light. By drawing in his readers with a personal encounter about night darkness, the author means to establish the potential for beauty, glamour, and awe-inspiring mystery that genuine darkness can possess. He builds his argument for the preservation of natural darkness by reminiscing for his readers a first-hand encounter that proves the “irreplaceable value of darkness.” This anecdote provides a baseline of sorts for readers to find credence with the author’s claims.
Bogard’s argument is also furthered by his use of allusion to art – Van Gogh’s “Starry Night” – and modern history – Paris’ reputation as “The City of Light”. By first referencing “Starry Night”, a painting generally considered to be undoubtedly beautiful, Bogard establishes that the natural magnificence of stars in a dark sky is definite. A world absent of excess artificial light could potentially hold the key to a grand, glorious night sky like Van Gogh’s according to the writer. This urges the readers to weigh the disadvantages of our world consumed by unnatural, vapid lighting. Furthermore, Bogard’s alludes to Paris as “the famed ‘city of light’”. He then goes on to state how Paris has taken steps to exercise more sustainable lighting practices. By doing this, Bogard creates a dichotomy between Paris’ traditionally alluded-to name and the reality of what Paris is becoming – no longer “the city of light”, but moreso “the city of light…before 2 AM”. This furthers his line of argumentation because it shows how steps can be and are being taken to preserve natural darkness. It shows that even a city that is literally famous for being constantly lit can practically address light pollution in a manner that preserves the beauty of both the city itself and the universe as a whole
Finally, Bogard makes subtle yet efficient use of rhetorical questioning to persuade his audience that natural darkness preservation is essential. He asks the readers to consider “what the vision of the night sky might inspire in each of us, in our children or grandchildren?” in a way that brutally plays to each of our emotions. By asking this question, Bogard draws out heartfelt ponderance from his readers about the affecting power of an untainted night sky. This rhetorical question tugs at the readers’ heartstrings; while the reader may have seen an unobscured night skyline before, the possibility that their child or grandchild will never get the chance sways them to see as Bogard sees. This strategy is definitively an appeal to pathos, forcing the audience to directly face an emotionally-charged inquiry that will surely spur some kind of response. By doing this, Bogard develops his argument, adding gutthral power to the idea that the issue of maintaining natural darkness is relevant and multifaceted.
Writing as a reaction to his disappointment that artificial light has largely permeated the prescence of natural darkness, Paul Bogard argues that we must preserve true, unaffected darkness. He builds this claim by making use of a personal anecdote, allusions, and rhetorical questioning.
Related Topic: SAT Requirements
This response scored a 4/4/4.
Reading—4: This response demonstrates thorough comprehension of the source text through skillful use of paraphrases and direct quotations. The writer briefly summarizes the central idea of Bogard’s piece ( natural darkness should be preserved ; we must preserve true, unaffected darkness ), and presents many details from the text, such as referring to the personal anecdote that opens the passage and citing Bogard’s use of Paris’ reputation as “The City of Light.” There are few long direct quotations from the source text; instead, the response succinctly and accurately captures the entirety of Bogard’s argument in the writer’s own words, and the writer is able to articulate how details in the source text interrelate with Bogard’s central claim. The response is also free of errors of fact or interpretation. Overall, the response demonstrates advanced reading comprehension.
Analysis—4: This response offers an insightful analysis of the source text and demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of the analytical task. In analyzing Bogard’s use of personal anecdote, allusions to art and history, and rhetorical questions , the writer is able to explain carefully and thoroughly how Bogard builds his argument over the course of the passage. For example, the writer offers a possible reason for why Bogard chose to open his argument with a personal anecdote, and is also able to describe the overall effect of that choice on his audience ( In telling this brief anecdote, Bogard challenges the audience to remember a time where they could fully amass themselves in natural darkness void of artificial light. By drawing in his readers with a personal encounter…the author means to establish the potential for beauty, glamour, and awe-inspiring mystery that genuine darkness can possess…. This anecdote provides a baseline of sorts for readers to find credence with the author’s claims ). The cogent chain of reasoning indicates an understanding of the overall effect of Bogard’s personal narrative both in terms of its function in the passage and how it affects his audience. This type of insightful analysis is evident throughout the response and indicates advanced analytical skill.
Writing—4: The response is cohesive and demonstrates highly effective use and command of language. The response contains a precise central claim ( He effectively builds his argument by using personal anecdote, allusions to art and history, and rhetorical questions ), and the body paragraphs are tightly focused on those three elements of Bogard’s text. There is a clear, deliberate progression of ideas within paragraphs and throughout the response. The writer’s brief introduction and conclusion are skillfully written and encapsulate the main ideas of Bogard’s piece as well as the overall structure of the writer’s analysis. There is a consistent use of both precise word choice and well-chosen turns of phrase ( the natural magnificence of stars in a dark sky is definite , our world consumed by unnatural, vapid lighting , the affecting power of an untainted night sky ). Moreover, the response features a wide variety in sentence structure and many examples of sophisticated sentences ( By doing this, Bogard creates a dichotomy between Paris’ traditionally alluded-to name and the reality of what Paris is becoming – no longer “the city of light”, but moreso “the city of light…before 2AM” ). The response demonstrates a strong command of the conventions of written English. Overall, the response exemplifies advanced writing proficiency.
Related Topics:
- Practice Tests for SAT Reading
- SAT Writing And Language Practice Tests
- SAT Languages Test
- SAT Essay Test SAT Writing Practice Tests
- SAT Science Test, Topics & Subjects Content
- SAT Registration
- SAT Test Dates
- SAT vs ACT, Which One Should You Take?
- Why Take the SAT?

The SAT Essay
Written by tutor ellen s..
The SAT has undergone a significant number of changes over the years, generally involving adjustments in the scoring rubric, and often in response to steadily-declining or increasingly-perfect test scores. When the SAT was changed in 2005, however, they made some significant changes to the test that students see. One of these changes was the addition of the writing section, based on the original SAT II subject test, which includes a timed essay. In including a timed essay on an otherwise multiple-choice test, the SAT throws a problem at students that they are generally unprepared to solve.
Because high school classes usually don’t discuss timed essays, students can have difficulty when faced with the SAT essay. You’ll need a different set of skills to tackle the SAT essay, and ideally a completely separate amount of time to practice those skills. In this lesson I’ll give you an overview of the differences between timed essays and at-home essays, and share my tips for successfully completing a well-organized, well-thought-out SAT essay.
First, the differences. In a timed essay, you’re given the prompt on the spot rather than having an idea of what the topic will be beforehand, as you would if you were writing an essay for an English class. On the SAT, you get one prompt and one prompt only, so you don’t even have the benefit of choosing one that works for you – you have to write about whatever they give you. In addition you’re writing everything out longhand, which eats up more time than you might think and makes it harder to make edits and corrections – particularly if you have bad handwriting and you’re worried about staying legible. And just forget about rearranging paragraphs and reorganizing whole sentences – you’ll never have time for that!
The Difference Between the SAT Essay and At-Home Essays
All of this means that you have to be much more organized right from the get-go than you would be in a natural writing process. You’ll need to read the question, think for a few moments, and then immediately form an opinion so you can start the actual writing as soon as possible. So for all timed essays, and the SAT essay in particular, I strongly emphasize the importance of prewriting. Prewriting can take many forms, from word clouds to concept nets, but for the SAT, I recommend the basic straightforward outline – with a few tweaks. Here’s my formula for SAT essay outlines.
How to Outline Your Essay
First, read the prompt through a couple of times. SAT essay prompts usually follow a set format involving the statement of an opinion, and then asking whether you agree or disagree with that opinion. Let’s take an example from the January 2014 test date, courtesy of the College Board website:
Some see printed books as dusty remnants from the preelectronic age. They point out that electronic books, or e-books, cost less to produce than printed books and that producing them has a much smaller impact on natural resources such as trees. Yet why should printed books be considered obsolete or outdated just because there is something cheaper and more modern? With books, as with many other things, just because a new version has its merits doesn’t mean that the older version should be eliminated.
Assignment: Should we hold on to the old when innovations are available, or should we simply move forward? Plan and write an essay in which you develop your point of view on this issue. Support your position with reasoning and examples taken from your reading, studies, experience, or observations. ( Source. )
he first thing I recommend when confronted with an SAT essay prompt is to ask yourself the question “Do I agree or disagree with the premise of the prompt?” That’ll usually be the last sentence of the first paragraph in the prompt. In this case, do you agree that “just because a new version has its merits doesn’t mean that the older version should be eliminated”? Now write the phrase “I agree” or “I disagree” at the top of your scratch paper accordingly. Put some asterisks around it so you remember to keep checking back in with it during the writing. This opinion is the most important part of your essay, so you want it to be clear in your mind. Next, ask yourself “Why do I agree?” or “Why do I disagree?” The first sentence you say to yourself in response to that question is your rough thesis statement. Jot that down under the first phrase. So, my response to our example would look like this:
* I agree * While the new version might have its merits, the original often has merits of its own.
Again, this is very rough at this stage, but on the SAT you’re trying to prewrite fast, so don’t worry too much about that. On to the body paragraphs!
On a 25-minute essay, you probably won’t have enough time for a full five-paragraph structure with three sub-examples for each point. Two body paragraphs and two examples of each will suffice. You never want to rely on just a single example, though, or you’ll likely lose points for not supporting your statements enough. Write out a template for the body of your essay that looks like this:
I. Main point 1 A. Example 1 B. Example 2 II. Main point 2 A. Example 1 B. Exampple 2
Remember, it’s an outline, so no full sentences. Write only as much as you need to remind yourself of your points. So for our example, my outline would look like this:
I. The “Tangible” aspects A. A book never runs out of battery B. Can read it in the sun, by the pool or in the bathtub – places you wouldn’t want to take a piece of electronics II. The “non-tangible” aspects A. The smell of a new book, tactile sense of turning pages, experience of closing it when you finish B. Ability to get lost in a book, to lose sense of place and become the story
At this point I can see a slight revision I’d make to my original thesis statement, which is the idea that an e-book can never mimic the tactile experience of reading (smelling the book, turning pages, etc.) I’ll quickly adjust my thesis to say:
While the new version might have its merits, the original offers a tactile experience that the new can’t hope to achieve – an experience that can’t be mimicked by technology.
Perfect. All told, your prewriting should have taken you 3 to 5 minutes, most of which was thinking. Now, on to the paper itself!
Writing Your Essay
Okay, here’s my biggest timed-essay secret: don’t start with the introduction. Start by skipping five or six lines down the page, leaving space for an introduction that will be inserted later. Start with your first body paragraph. Work from your outline, converting your points into full sentences and connecting them with transitions, and you should be at a good start. Once both body paragraphs are written, continue on and write your conclusion. Then, go back and write your introduction in the space you left at the beginning. That way, you’ll know what you’re introducing since it’s already written.
I generally recommend about 15 minutes of writing time for the body paragraphs, followed by 5 minutes for the intro and conclusion. Depending on how quickly you got your prewriting done, that leaves you with one or two minutes to look it over, fixing any spelling mistakes or sloppy handwriting. Don’t try to change too much, though – when you’re writing everything out longhand, changes require erasing. We do so much writing on computers these days that sometimes we forget how long it takes to erase a whole sentence and rewrite it. A better tactic is to think through each sentence in your head before you write it down, making sure you have it phrased the way you want it before you put pencil to paper. But don’t spend too long – try it a few times and you’ll find that writing four full paragraphs longhand actually takes about 25 minutes to do – on a good day. You should expect to be writing pretty much continuously for the entire 25 minutes.
Keeping Track of Time, Staying Comfortable, and More Advice
Speaking of which, when you practice your timed essays, pay attention to how your hand feels while you’re writing. The first few times you’ll likely be sore; your hand might even cramp up from writing so hard. It’s tiring to write for that long, so make sure you’re helping yourself. Write lightly on the paper – it’s easy to start pressing down super hard when you’re nervous and panicking. Writing lightly will not only help stave off the hand cramps, it’ll also make erasing much easier when you need to do it. Sit back in your chair while you write – you don’t need to be three inches from your paper to see the words you’re putting down, and hunching over will just make you press harder. Bring your attention to your breathing – are you holding your breath? Why? Try breathing deeply and slowly while you write – it’ll calm your brain and help you think.
Finally, a word about the writing itself – don’t forget you’re on a clock here. Often, you begin to notice as you write that your opinion about the topic is evolving, changing, developing nuances and side areas you want to explore. I know this sounds weird, but you’ve got to try to rein that in – those are all fine things to be thinking about ordinarily, and in an at-home essay I’d say go for it, but you don’t have time to change what you’re writing about in this situation. Sometimes, you’ll even get halfway through a timed essay and realize that you actually don’t agree like you thought you did. Save that thought for later. You’ve got the outline of an organized essay, and that’s what you should be writing. It doesn’t matter at this point if you actually still agree with what you’re saying, all that matters is that you state a clear opinion and communicate it well. After all, the test grader doesn’t even know you – how’s she to know that you don’t really think this anymore? Stay confident and get your original idea out on paper.
For example, the outline I gave above is a perfectly accurate depiction of my opinion on the topic – as it relates to books. However, if we were to start talking about, say, writing essays…I’d probably say that no, I don’t think we should hold on to writing essays out by hand when there are computers available. After all, I’m writing this article on a computer. I’ve copied and pasted multiple paragraphs of information back and forth around this lesson as I was looking for appropriate ways to introduce concepts, and that would have taken forever if I had been writing by hand. But if that thought had occurred to me midway through writing my timed essay about books, I would have acknowledged it for the briefest of moments and then disregarded it. My essay is about books. I’ll just stick to that so I can keep it clean and organized.
Don’t worry about the test graders thinking “But what about X?” – they know you only had 25 minutes and can’t possibly fit every aspect of the argument into that amount of time – or space, for that matter. The scoring rubric focuses on what is present, not what is omitted. As long as you have a clear point of view and are communicating it well, you’ll fulfill their criteria. Remember, this essay’s not in the critical reading section, it’s in the writing section. They’re not in the business of judging the merits of your opinion, just how clearly you’ve communicated it and how well you’ve supported it.
Your timed essays will probably turn out very different than the essays you write at home for class. They might seem stiff, straightforward or brusque; with a limited amount of time you can’t create the subtle, nuanced arguments that your English teachers are probably looking for. But what you can do is create a well-organized, concise presentation of a relatively straightforward point of view, supported by concrete examples that all point toward the same central concept. The SAT essay responds well to a formulaic approach, so while it may take some practice, you will eventually be able to handle a 25-minute essay prompt with confidence.
- How can we change the underlined section to best set up the information that follows?
- How can we best change the underlined section, or is it good as it is?
- The result was an explosion of mural painting that spread throughout California and the southwestern United States in the 1970s. It was the Chicano mural movement
- What are some strategies I can use to make my writing more persuasive?
HIGH SCHOOL
- ACT Tutoring
- SAT Tutoring
- PSAT Tutoring
- ASPIRE Tutoring
- SHSAT Tutoring
- STAAR Tutoring
GRADUATE SCHOOL
- MCAT Tutoring
- GRE Tutoring
- LSAT Tutoring
- GMAT Tutoring
- AIMS Tutoring
- HSPT Tutoring
- ISAT Tutoring
- SSAT Tutoring
Search 50+ Tests
Loading Page
math tutoring
- Elementary Math
- Pre-Calculus
- Trigonometry
science tutoring
Foreign languages.
- Mandarin Chinese
elementary tutoring
- Computer Science
Search 350+ Subjects
- Video Overview
- Tutor Selection Process
- Online Tutoring
- Mobile Tutoring
- Instant Tutoring
- How We Operate
- Our Guarantee
- Impact of Tutoring
- Reviews & Testimonials
- About Varsity Tutors
FREE SAT Writing Practice Tests
All sat writing resources, free sat writing diagnostic tests, sat writing diagnostic test 1, sat writing diagnostic test 2, sat writing diagnostic test 3, sat writing diagnostic test 4, sat writing diagnostic test 5, sat writing diagnostic test 6, sat writing diagnostic test 7, sat writing diagnostic test 8, sat writing diagnostic test 9, sat writing diagnostic test 10, sat writing diagnostic test 11, sat writing diagnostic test 12, sat writing diagnostic test 13, sat writing diagnostic test 14, sat writing diagnostic test 15, sat writing diagnostic test 16, sat writing diagnostic test 17.
Our free SAT Writing Practice Tests are each a selection of 10 to 12 questions, which will give you a cross-section of topics from the Writing section of the official SAT. You might think of them as little quizzes, which you can use to hone your skills. To get a more comprehensive idea of the concepts you need to review, try one of the Full-Length SAT Writing Practice Tests. These tests simulate the writing portion of the SAT, which gives you valuable text experience and can help you learn to pace yourself so you can be sure you’ll have enough time to finish the real test. The results pages for the longer-form tests offer tons of useful feedback, including detailed explanations of the answers and links to additional concept-specific practice opportunities. The results of the complete practice tests can also help you streamline your SAT study plan by revealing the topics on which you need to focus. Once you’ve had the chance to do some review, you can gauge your progress by taking another Full-Length SAT Writing Practice Test. Whether you need top SAT Writing tutors in New York , SAT Writing tutors in Chicago , or top SAT Writing tutors in Los Angeles , working with a pro may take your studies to the next level. SAT Writing Section What is the Writing Section of the SAT exam? The SAT Writing Section tests your ability to understand and effectively respond to writing prompts and to demonstrate your knowledge of various grammatical and semantic rules, as well as conventions about how to construct the clearest sentences and paragraphs. On the exam, you will be expected both to identify present errors and suggest preferable alternative sentence and paragraph constructions to display your knowledge of the aforementioned rule types. Varsity Tutors offers resources like a free SAT prep book to help with your self-paced study, or you may want to consider an SAT Writing tutor . What kinds of multiple-choice questions appear on the SAT Writing section? In addition to the separate Essay portion of the SAT Writing section, three different question types appear on the SAT Writing section: Identifying Sentence Errors, Improving Sentences, and Improving Paragraphs. These do not appear in equal ratios, however: of the 49 questions, 25 will be Identifying Sentence Errors, 18 will be Improving Sentences, and 6 will be Improving Paragraphs. Identifying Sentence Error questions consist of a sentence with four sections of its text underlined, as well as a “No Error” option. One of the four underlined portions of the sentence may contain a grammatical or usage error; it is your job to determine whether or not the sentence contains an error, and if it does, to select the answer choice that corresponds to the section of text that contains that error. There is never more than one error in a Identifying Sentence Error sentence, and you are not tested about how to fix the grammatical error that you identify—your job is to simply point out the part of the sentence that contains the error. Improving Sentence questions present you with a sentence which is either completely or partially underlined. This sentence may or may not contain a grammatical or usage error. Of the five possible answer choices, the first one reproduces the underlined portion of the sentence exactly, while the other options each make one change to that section. It is your job to select the option that makes the sentence clear and grammatically correct. If a sentence contains no errors, you should select the option that reproduces the underlined section of the sentence exactly. Some Improving Sentence questions may reference a passage, but will direct you to at most one or two sentences for you to consider. Improving Paragraph questions test your knowledge of how to best formulate paragraphs by providing you with a passage that has its sentences numbered and then asking you about proposed changes to that paragraph. Sentence order, sentence design, and proper sentence and paragraph transitions are all fair game in this portion of the Writing Section. Questions and their answers often refer to sentence numbers so that they do not have to quote entire sentences each time they refer to them. Certain Improving Paragraph questions may give you the option of leaving an indicated sentence or a certain part of the paragraph as it is written, but not all questions give you this option. Which specific grammar concepts are covered on the SAT Writing Section? Subject-verb agreement, proper tense usage, gerunds and infinitives, parallel sentence structure, subject-pronoun agreement, the use of appropriate prepositions, similar object comparisons, active vs. passive voice, and proper use of conjunctions are among the grammatical rules you should be familiar with in preparation for the exam. The Varsity Tutors Learning Tools free SAT Practice Tests contains questions that test each of these concepts. How much is the SAT Writing Section worth on the SAT? In total, the SAT Writing Section is worth 800 points, just like the other two sections: SAT Critical Reading and SAT Math. But this section is different in that it is not composed solely of multiple-choice questions, although these do constitute a majority of the section. Additionally, there is an essay, which is always the first section on any given SAT. The essay composes 30% of the overall total SAT Writing Section score, while the multiple-choice problems make up the remaining 70%. How is the SAT Writing Section graded? For the Essay Section, two separate graders each read the essay and submit a score on a scale from 1 to 6, where 6 is the highest score an essay can receive, and 1 the lowest. Generally, these graders are grading each essay on how well it asserts and defends a particular position in response to the question asked, while providing specific and detailed examples to illustrate and support its argument; however, other factors are also taken into consideration when determining an essay’s score; these include use of proper grammar and correct spelling, as well as effective construction of a variety of sentence types. The Writing Section’s multiple-choice questions are graded like the SAT’s other multiple-choice-based sections. Correct answers are tallied, and then incorrect answers are multiplied by ¼ and subtracted from the total. Answers left blank do not count against the overall score. These portion totals are then added together to make up the overall raw SAT Writing score, which is then combined with the Essay score and reported in terms of a 200-800 scale. How many questions are on the SAT Writing Section? How much time do I have for each part of the SAT Writing Section? In total, each SAT Writing section contains 49 multiple-choice questions and an essay prompt. You are given 35 minutes to complete the multiple-choice questions, which appear in two sections, one 25 minutes long, the other 10 minutes long. You are given 25 minutes to compose an essay in response to the essay prompt. So, in total, the entire SAT Writing section takes 60 minutes to complete. There is a caveat, however, that may lead to you having to complete two writing sections on your SAT. For testing purposes, the College Board includes an additional ungraded experimental section on each one of its officially administered tests to gather data about the quality of new problems. This additional section is 25 minutes long, and tests Critical Reading, Writing, or Math. While you will notice that you complete two versions of a certain section, there is no way to tell which section is the “real” one that determines your score in that area, and which is the experimental section that does not affect your score. So, the best course of action is to treat every section as if it is affecting your score. Do I get a break during the SAT Writing section? While students are given breaks between certain sections of the SAT, they are not given breaks during any sections, and it is not recommended that you stop to rest during a section. The SAT is designed to be completed in a certain amount of time, without much extra time, and you don’t want to run the risk of not completing the section (and hence losing points) just because you stopped to take a break. How much time should I spend on each multiple-choice question on the SAT Writing Section? Given that there are 49 multiple-choice question in two separate sections (one 25 mins, the other 10 mins) on the SAT Writing section, you could easily do the math to find that you have less than a minute per question. This should be your rough guide for how to spend your time. In some cases, you will spend less time on a question, and in others, more time, but in general, you should be mindful of this limit. Last, any one-size-fits-all time-allocation recommendations will not work in all situations, but they do provide a basic guideline for effectively using the limited time you have available. Should I guess on the SAT Writing Section? Guessing on the SAT Writing Section’s multiple-choice questions is advisable or inadvisable for the same reasons it would be for any other multiple-choice question on the exam. Incorrect multiple-choice answers receive a penalty of ¼ of a point which, in sum, can add up. In contrast, blank answers do not count towards your overall score, so they do not count against you at all whatsoever. A good rule of thumb is to use your knowledge of grammar, proper sentence and paragraph construction, and other semantic rules to eliminate three of the five answer responses. If you can confidently do this, then you might want to guess between the remaining answers. Studying for the SAT Writing Section: Essay Should I read the whole quotation and question before writing my the SAT Writing essay? Always read the entire essay prompt on the SAT before responding to it! Reading the entire question is always essential for formulating and asserting an effective position on some issue. Often, the questions are more complicated than they initially seem, and you want to make sure not to read your own questions into them (and then spend 25 minutes answering a question not asked). Rereading the question two or three times is a good idea that helps you be sure that you didn’t misread or misunderstand it. Often, however, students spend too much time reading and rereading the quotation to mine it for ideas about what to write. Know that this essay is not about explicating the quotation included; the authors of the test include the quotation, instead, to give you food for thought. You should be using your own experiences, knowledge and ideas to fashion your essay, not just the content of the quotation. How should I study for the SAT Writing section's essay writing portion? While it may seem difficult to study for an essay-based section, you can effectively prepare for the SAT Essay section by doing the following five things: 1.) Read up on the SAT Essay and learn about what makes it unique when compared to other standardized tests’ essay sections. 2.) Read over a few SAT Essay prompts and try out one or two by taking them in 25 minutes, just like the real exam section. Having a qualified, competent friend, teacher, or tutor read over this essay and provide you with feedback will help you figure out what you need to work on in particular. 3.) After you have a better sense of what you need to work on, you should then brainstorm examples you might draw on from your life. You might draw examples from books you have read, recent news stories you have seen, friends’ experiences that you have heard about, or other events you know about. Sometimes you can even draw examples from popular media like movies and music. Take a sample SAT Essay prompt and brainstorm ideas that you might use to respond to it or a similar question. 4.) Focus on honing your ability to write a strong, coherent, and relevant thesis statement. You can improve this skill by reading SAT Essay Prompts and quickly formulating a position that you could support in an essay, one that you could develop and pursue for at least two to three body paragraphs. Using too simplistic of a thesis statement and realizing that you have run out of material to discuss halfway through the SAT Essay on test day is a terrible position to be in. Reviewing the basic format of an SAT Essay might be helpful too, but if you have already been recently writing timed essays, this step may be superfluous. 5.) Complete at least two to three more full essays and focus on what kinds of examples you might need to develop an inventory of. Having a solid example tool box will be endlessly useful to you on test day, as you can use many different examples for different kinds of essays, and will not have to spend as much time trying to hurriedly come up with examples. How should I use my time when writing the essay on the SAT Writing section? You shouldn’t tackle any SAT question without thinking about how you are approaching it, and the same can be said for the SAT Essay. For this section, it’s crucial that you be aware of how you are using your time, and make efficient use of it. Like other timed writing assignments, the SAT Essay portion of the Writing Section requires you to quickly understand the question being asked of you, take a position, formulate your examples, outline, draft, and revise. You are given only twenty-five minutes in which to write your essay, so consider organizing your time like this: Reading Question and Formulating a Position: 2-3 minutes Brainstorming Reasons, Commentary and Paragraph Structure: 4 minutes Drafting the Essay - 15-17 minutes Revising and Editing - 2 minutes Keep in mind that eyeing your watch every two seconds to ensure that you’re on track will not be of help to you, and will, in fact, hurt your progress on the essay. But having a general sense of how you should be progressing will prevent you from leaving the essay section with little more than a well-developed outline. Can I use a prewritten essay on the SAT Writing section? No, you cannot use a prewritten essay on the SAT; however, arriving with a fresh example bank ready and waiting in your short-term memory is just as good. Also, if you’ve been practicing responding to SAT prompts, then it should be a piece of cake to tackle a new one, because you can tackle each prompt in the same way: by reading the prompt, taking a position, briefly outlining that position with examples, drafting your essay from your outline, and finally, revising and editing your essay. How is the SAT Writing section's essay section graded? The essay composes 30% of the overall total SAT Writing Section score, while the remaining multiple choice sections make up the remaining 70%. Each essay is given a score between 1 and 6 by two independent graders. Each SAT essay is graded on how effectively it asserts a position in a thesis statement in response to the question asked, and how well it supports that thesis statement with details and examples. Other aspects of the essay including spelling, grammar, and sentence variety are also taken into consideration when determining an essay’s grade. In addition to the SAT Writing practice tests and SAT Writing tutoring , you may also want to consider taking some of our SAT Writing flash cards . Studying for the SAT Writing Section: Multiple-Choice Questions How should I study for the Improving Sentences, Identifying Sentence Errors and Improving Paragraphs portions of the SAT Writing Section? Use the following tips to study effectively for the SAT Writing section’s multiple-choice questions: 1.) Refamiliarize yourself with English grammar, style, and usage conventions, as all of the SAT Writing section’s multiple-choice questions test your understanding of grammar, style, and usage rules in some way. Focusing on the rules and conventions that you don’t completely understand or that underlie problems you often miss is the most efficient way to raise your SAT Writing score. However, thinking about the grammar rules should only be part of the study process. 2.) Start practicing each type of question that appears on the SAT Writing section. Don’t rush through these, though! When you miss a question, figure out where you went wrong, or what point you misunderstood. If you don’t spend enough time analyzing the questions you miss, your studying will not be as effective. Varsity Tutors offers free SAT Writing Practice Tests for you to use in preparing for the SAT's Writing section. Our free SAT Writing Practice Tests are written by teachers, professors, content specialists, and tutors. Explanations are given for each question, so if you miss a question, you can find out where you went wrong. Varsity Tutors also offers free SAT Writing Diagnostic Tests, free SAT Writing Flashcards, and free SAT Writing Questions of the Day, as well as other free SAT Writing resources. 3.) Eventually, take a complete 25-minute SAT Writing Section and then check your overall score. Identify which kinds of questions you tend to get wrong and focus on improving your performance in those particular areas (i.e. those particular grammar rules or question types). This is the best way to improve your score. See if you can confidently explain not only why the correct answer is correct in any given problem, but also why incorrect answers are incorrect. 4.) Make sure to take at least two or three full practice tests before taking the actual exam. This way you can develop a tolerance for the somewhat exhausting task of completing the whole test in one sitting. e essay section with little more than a well-developed outline. Can I use a prewritten essay on the SAT Writing section? No, you cannot use a prewritten essay on the SAT; however, arriving with a fresh example bank ready and waiting in your short-term memory is just as good. Also, if you’ve been practicing responding to SAT prompts, then it should be a piece of cake to tackle a new one, because you can tackle each prompt in the same way: by reading the prompt, taking a position, briefly outlining that position with examples, drafting your essay from your outline, and finally, revising and editing your essay. How is the SAT Writing section's essay section graded? The essay composes 30% of the overall total SAT Writing Section score, while the remaining multiple choice sections make up the remaining 70%. Each essay is given a score between 1 and 6 by two independent graders. Each SAT essay is graded on how effectively it asserts a position in a thesis statement in response to the question asked, and how well it supports that thesis statement with details and examples. Other aspects of the essay including spelling, grammar, and sentence variety are also taken into consideration when determining an essay’s grade. Studying for the SAT Writing Section: Multiple-Choice Questions How should I study for the Improving Sentences, Identifying Sentence Errors and Improving Paragraphs portions of the SAT Writing Section? Use the following tips to study effectively for the SAT Writing section’s multiple-choice questions: 1.) Refamiliarize yourself with English grammar, style, and usage conventions, as all of the SAT Writing section’s multiple-choice questions test your understanding of grammar, style, and usage rules in some way. Focusing on the rules and conventions that you don’t completely understand or that underlie problems you often miss is the most efficient way to raise your SAT Writing score. However, thinking about the grammar rules should only be part of the study process. 2.) Start practicing each type of question that appears on the SAT Writing section. Don’t rush through these, though! When you miss a question, figure out where you went wrong, or what point you misunderstood. If you don’t spend enough time analyzing the questions you miss, your studying will not be as effective. Varsity Tutors offers free SAT Writing Practice Tests for you to use in preparing for the SAT's Writing section. Our free SAT Writing Practice Tests are written by teachers, professors, content specialists, and tutors. Explanations are given for each question, so if you miss a question, you can find out where you went wrong. Varsity Tutors also offers free SAT Writing Diagnostic Tests, free SAT Writing Flashcards, and free SAT Writing Questions of the Day, as well as other free SAT Writing resources. 3.) Eventually, take a complete 25-minute SAT Writing Section and then check your overall score. Identify which kinds of questions you tend to get wrong and focus on improving your performance in those particular areas (i.e. those particular grammar rules or question types). This is the best way to improve your score. See if you can confidently explain not only why the correct answer is correct in any given problem, but also why incorrect answers are incorrect. 4.) Make sure to take at least two or three full practice tests before taking the actual exam. This way you can develop a tolerance for the somewhat exhausting task of completing the whole test in one sitting.
Free SAT Writing Practice Tests
Practice tests by concept, identifying sentence errors practice test, identifying agreement errors practice test, identifying modifier-word modified agreement errors practice test, identifying noun-noun agreement errors practice test, identifying pronoun-antecedent agreement errors practice test, identifying subject-verb agreement errors practice test, identifying no errors or other errors practice test, identifying other errors practice test, identifying sentences that contain no errors practice test, identifying phrase, clause, and sentence errors practice test, identifying conjunction errors practice test, identifying correlative conjunction errors practice test, identifying other conjunction errors practice test, identifying subordinate conjunction errors practice test, identifying modifier placement errors practice test, identifying ambiguous modifier errors practice test, identifying dangling modifier errors practice test, identifying misplaced or interrupting modifier errors practice test, identifying other phrase, clause, and sentence errors practice test, identifying ambiguity and redundancy errors practice test, identifying parallel structure errors practice test, identifying sentence fragment and sentence combination errors practice test, identifying punctuation errors practice test, identifying punctuation errors: commas practice test, identifying punctuation errors: comma splices practice test, identifying punctuation errors: commas for dependent clauses practice test, identifying punctuation errors: commas for introductory or interrupting phrases practice test, identifying punctuation errors: commas in lists practice test, identifying punctuation errors: other punctuation practice test, identifying apostrophe errors practice test, identifying colon errors practice test, identifying other punctuation errors practice test, identifying quotation mark errors practice test, identifying semicolon errors practice test, identifying word usage errors practice test, identifying adjective and adverb errors practice test, identifying comparative and superlative errors practice test, identifying other adjective and adverb errors practice test, identifying other usage errors practice test, identifying conventional and idiomatic usage errors practice test, identifying errors involving commonly confused words practice test, identifying preposition errors practice test, identifying pronoun errors practice test, identifying pronoun errors: ambiguity practice test, identifying pronoun errors: case practice test, identifying pronoun errors: inconsistent usage practice test, identifying pronoun errors: incorrect usage practice test, identifying verb errors practice test, identifying other verb errors practice test, identifying verb mood errors practice test, identifying verb tense errors practice test, identifying verb voice errors practice test, improving paragraphs practice test, analyzing, combining, and moving content practice test, analyzing content practice test, identifying sentence purpose practice test, identifying sentence relationships practice test, other content analyses practice test, separating, combining, or moving sentences practice test, combining sentences practice test, moving sentences practice test, separating sentences practice test, improving and correcting sentences practice test, rewriting a full sentence practice test, avoiding ambiguity and redundancy in a full sentence practice test, sentence improvements and errors practice test, increasing the effectiveness of a full sentence practice test, rewriting a sentence fragment practice test, avoiding ambiguity and redundancy in a sentence fragment practice test, correcting grammatical errors in a sentence fragment practice test, increasing contextual relevance in a sentence fragment practice test, increasing the effectiveness of a sentence fragment practice test, revising introductions and transitions in a sentence fragment practice test, revising word choice, style, and tone in a sentence fragment practice test, rewriting a single word practice test, correcting single-word grammatical errors practice test, increasing the contextual relevance of a single word practice test, increasing the effectiveness of a single word practice test, revising a single word of introductions and transitions practice test, revising a single word to avoid ambiguity and redundancy practice test, revising word choice, style, and tone practice test, inserting or deleting content practice test, deleting content practice test, inserting content practice test, improving sentences practice test, correcting agreement errors practice test, correcting modifier-word modified agreement errors practice test, correcting noun-noun agreement errors practice test, correcting pronoun-antecedent agreement errors practice test, correcting subject-verb agreement errors practice test, correcting other errors and recognizing no errors practice test, correcting other errors practice test, recognizing sentences that contain no errors practice test, correcting phrase, clause, and sentence errors practice test, correcting conjunction errors practice test, correcting correlative conjunction errors practice test, correcting other conjunction errors practice test, correcting subordinate conjunction errors practice test, correcting modifier placement errors practice test, correcting ambiguous modifier errors practice test, correcting dangling modifier errors practice test, correcting misplaced or interrupting modifier errors practice test, correcting other phrase, clause, and sentence errors practice test, correcting ambiguity and redundancy errors practice test, correcting parallel structure errors practice test, correcting sentence fragment and sentence combination errors practice test, correcting punctuation errors practice test, correcting punctuation errors: commas practice test, correcting punctuation errors: comma splices practice test, correcting punctuation errors: commas for dependent clauses practice test, correcting punctuation errors: commas for introductory or interrupting phrases practice test, correcting punctuation errors: commas in lists practice test, correcting punctuation errors: other commas practice test, correcting punctuation errors: other punctuation practice test, correcting apostrophe errors practice test, correcting colon errors practice test, correcting other punctuation errors practice test, correcting quotation mark errors practice test, correcting semicolon errors practice test, correcting word usage errors practice test, correcting adjective and adverb errors practice test, correcting comparative and superlative errors practice test, correcting other adjective and adverb errors practice test, correcting other usage errors practice test, correcting conventional and idiomatic usage errors practice test, correcting preposition errors practice test, correcting pronoun errors practice test, correcting pronoun errors: ambiguity practice test, correcting pronoun errors: case practice test, correcting pronoun errors: inconsistent usage practice test, correcting pronoun errors: incorrect usage practice test, correcting verb errors practice test, correcting other verb errors practice test, correcting verb mood errors practice test, correcting verb tense errors practice test, correcting verb voice errors practice test.

| Email address: | |
| Your name: | |
| Feedback: |
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., 5 sat essay tips for a great score.
Thinking about tackling the SAT Essay? Here's what you need to know: you'll be asked to read a text (typically a speech or editorial of some sort) and discuss how the author effectively builds an argument. This might be a familiar task if you’ve done it in school, but if not, don’t worry. The format is straightforward, and with some practice, you can learn how to write a great SAT essay.
What is the SAT essay?
The SAT essay is optional and costs an additional fee of $17.00. Currently, only 25 colleges and universities require the SAT essay. You can find a searchable list of school requirements for the essay here . If there is any chance that you might apply to one of those schools, you should sign up for the essay. If you are not sure where you will apply, you should strongly consider signing up for the essay. Your essay score will appear on every score report you send to colleges, regardless of whether or not the school requires an essay.
Here are 5 tips for writing a killer SAT essay, should you decide to add on that section:

1. Stay Objective
The thing to remember here is that ETS (the company that writes the test) is not asking you for your opinion on a topic or a text. So be sure to maintain formal style and an objective tone. Tip: Avoid “I” and “you.
2. Keep It Tidy
Handwriting is becoming a lost art. Unfortunately, this is one occasion where your skill with a pencil matters. Graders read tons of essays each day. If they cannot decipher your script, they will lower your score. Do yourself a favor and write legibly.
3. (Indented) Paragraphs Are Your Friend
Remember the basic essay structure you learned in school: introductory paragraph, body paragraphs and a conclusion? The SAT essay graders love it! Your introduction should describe the text and paraphrase the argument being made, as well as introduce the specific elements of the passage and argument that you will discuss in the essay. Your conclusion should restate the goal of the passage/argument and sum up the points you made.
Read More: SAT Tips and Strategies
4. For Example…
Use your body paragraphs to back up your thesis statement by citing specific examples. Use short, relevant quotes from the text to support your points.
5. Don't Worry About the Exact Terms for Things
Blanking on terminology? When describing how the author builds his or her argument, “appeal to the emotions” is fine instead of specifically referencing “pathos.” And “comparison of two things” can be used instead of referring to a metaphor. If you do know the official terms, though, feel free to use them!
Build the right SAT prep plan for you
Our private tutors will help you build a prep plan that's customized to your score goals, study habits, and schedule.
Find a Tutor

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
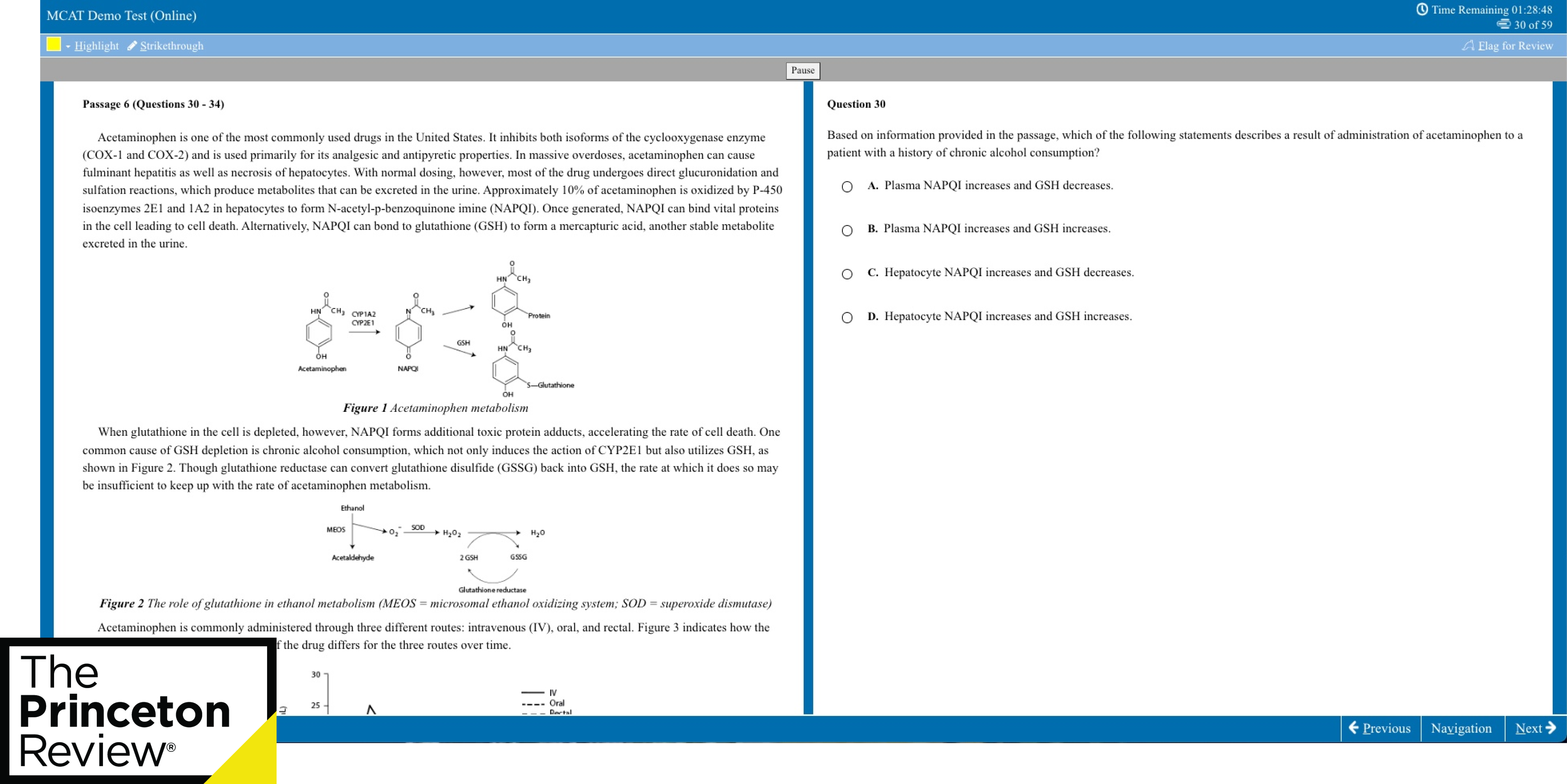
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
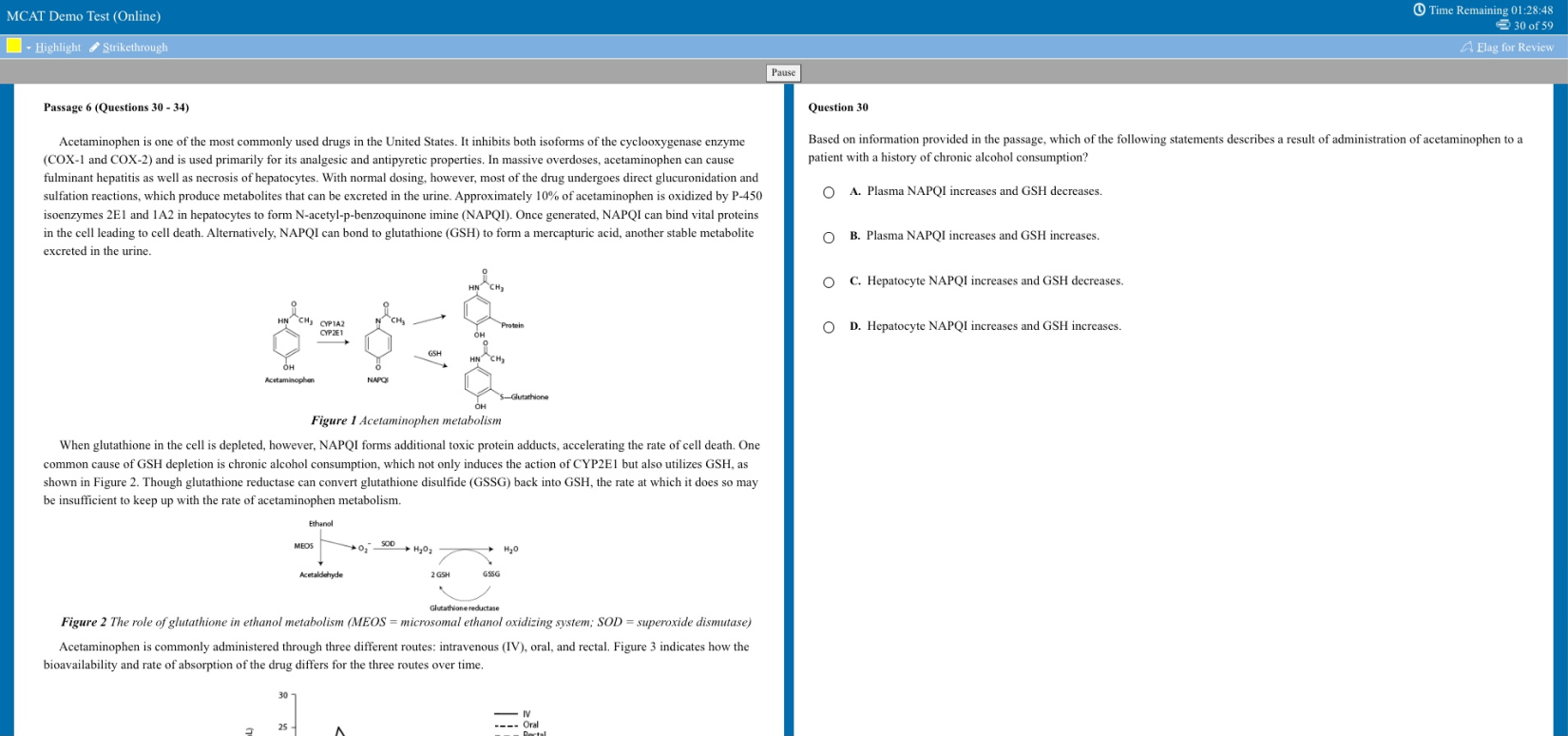
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
8 Best SAT Essay Examples To Prepare For Your Test
Are you looking for the top SAT essay examples? Take a look at our guide containing the best examples to prepare for your examination.
Are you busy preparing for the SAT essay? The College Board is responsible for administering the SAT, which is essential for determining college decisions. In addition, writing is important for every field of study, which is why the SAT values the essay. As a result, your SAT essay score can have an impact not only on the entirety of your test performance but also on your college admissions decisions. Therefore, it may be helpful to look at a few sample essay prompts, allowing you to determine how you can maximize your performance on your essay.
1. The Value of Struggle
2. the topic of greed, 3. politicians and personal character, 4. demonstrating a lack of knowledge, 5. fame and fortune, 6. truth and lies, 7. expectations and public figures, 8. quick reaction times, what should i write in my sat essay, how long should my sat essay be, what should i do before i write my sat essay.
Prompt: Do we only value the things that we struggle for?
Plan your response carefully, and make sure you support your point of view with specific examples. The examples can come from history, a personal anecdote from high school, or knowledge of particular subjects.
This is a very common type of SAT writing prompt. In the prompt, the essay alludes to absolutism. In this case, the absolute is that we only value things we struggle for. Unless we struggle for it, we will never love it. In general, taking an absolute point of view will unnecessarily pigeonhole you into an impossible argument. Therefore, it is essential to change your response slightly. Instead, it would help if you talked about situations where you value things you struggle for and do not value things you struggle for. Just because you do not struggle for it doesn’t mean it is not valuable.
For example, you may not necessarily have valued your relationships with your siblings. If you are lucky, you may get along well with your siblings without stressing about it. This could be an example you can use in your essay. Likewise, you value your relationships with your family members but do not struggle for them. Then, you might want to share an example of something that you value after struggling for it.

Prompt: Is greed always a bad thing?
Greed is a driving force behind a lot of decisions that we make. There are some situations where greed is terrible and others where greed is good. You don’t want to take the standpoint that greed is always wrong. For example, greed is something that can help you maximize your score on the SAT. Because you want to go to an established college, someone could say you are greedy. It depends on how you use that motivation. Because you are channeling it for a positive force, such as doing well on the SAT, it is not necessarily bad. You can also talk about athletes who are greedy for success and decide to channel that motivation into excelling in their chosen field.
On the other hand, there are situations where greed might be bad. For example, you may want to point out a famous person who has gone to jail for financial misdeeds. You might even want to talk about Bernie Madoff , who ran one of the largest Ponzi schemes in history. He hurt many people out of greed and ended up paying a steep price for it. It would be best if you wrapped up the essay by discussing specific circumstances where greed is bad and others where greed is good. Then, you can talk about how that difference can guide our decisions and make us better people.
Prompt: Should you consider the personal character of a politician before deciding to vote for that person?
Anyone who has recently paid attention to politics has likely seen many attack ads. They are trying to convince people to vote for politicians based on personal character instead of what they might do (or not) for the country. Even though the personal character is not necessarily the most important thing you should think about, it should play a role in your decision-making process.
As you write this essay, you may want to use an example of a situation where the personal character is important for deciding who to vote for. For example, you may want to talk about Richard Nixon, who was forced to resign after the press unveiled the Watergate scandal. While Richard Nixon did many great things in the office, such as opening up China, the Watergate scandal demonstrated that he could not be trusted. Because he lost the trust of the people, he would not be able to govern effectively, forcing him out of office.
Another example includes Bill Clinton, who is widely known to have cheated on his wife with Monica Lewinsky. Despite this, he was not forced to resign from office, and he is widely respected as a good president, if not a good person. He presided over one of the largest economic expansions in US history, and he was the last person to have a balanced budget. In this case, despite his personal character flaws, he was able to govern effectively.
There are plenty of other examples you can use to write this essay, but it all comes down to whether someone’s personal character has an impact on their ability to govern. If their individual character flaws do not impact their ability to govern effectively, then it might not impact their potential success as a leader. On the other hand, if someone’s personal character flaws completely remove their ability to govern effectively, then you may want to vote for someone else. You can use these general points to craft a strong essay. You might also be wondering, which colleges require SAT essay section for consideration .
Prompt: Are you required to admit your lack of knowledge before you are able to learn something?
This essay prompt is one that just about everyone can relate to. The premise of the essay is clear: if you feel like you already know everything, you will not be able to learn something new. At the same time, it is possible for you to learn something without admitting that you totally lack knowledge. You simply need to be open to a new point of view. You might be able to pull an example of this from the classroom.
For example, the first day you walked into chemistry class, you probably didn’t know the first thing about chemistry. You did not necessarily need to admit your lack of knowledge before you can start learning something new. This could be an example you can use that goes against the premise of the prompt.
On the other hand, there are situations where admitting a lack of knowledge can help you learn something new. For example, you may want to point out a discussion that you recently had with an expert in a certain area. By admitting that you did not know anything, you might have allowed that person to teach you. If you acted like you knew everything, that expert may not have wanted to teach you anything. By admitting your lack of knowledge, you open yourself up to new sources of information.
To do well on this essay, you will need to specify when admitting a lack of knowledge can help you learn something and when it is unnecessary. That difference will help you maximize your SAT essay score. You might also be interested in these GRE writing examples .

Prompt: Is fame always a good thing?
Fame and fortune have been popular topics of discussion recently. There are many people who believe that famous people lead lives of comfort and luxury. Many people believe that they lead lives that the rest of us can only dream of. Even though it may look nice to be a famous person, it is not always a good thing. Therefore, you should immediately take the point of view that there are situations where fame can be good, but there are other situations where fame can be bad.
You might want to start with an example of a situation where fame is good. You can talk about almost any famous athlete, actor, or actress. You can talk about how their fame has landed them a lot of endorsement deals, making them enormous sums of money that they can use to support a luxurious lifestyle, their children, and future generations. Clearly, there are situations where fame can be a good thing.
On the other hand, you will need to use examples where fame might not necessarily be a good thing. For example, you may want to talk about the tremendous mental health issues that Britney Spears has suffered because of her fame and her conservatorship. Or, you may want to talk about the mental health struggles that a lot of famous musicians have, such as Kurt Cobain (who ultimately committed suicide).
You might also want to talk about the tremendous anxiety that Naomi Osaka struggles with when she has to talk to the press. Despite her tennis success and fortune, she doesn’t always appear happy on the tennis court. Based on the examples you choose, you will ultimately have to decide when fame is a good thing and when fame is a bad thing. The answer varies from person to person, and there is not necessarily a right or wrong answer. You simply need to write a strong essay that supports your point of view.
Prompt: Is it always important to tell 100 percent of the truth?
Growing up, we are always taught to tell the truth. It is easier to tell children that they should tell the truth no matter what. At the same time, life is not black and white. There are some situations where shades of grey matter. When you write this essay, you should not do it as a “yes or no” answer. Instead, you need to talk about when it is important to tell the truth and when telling a lie, even a lie of omission, is important.
For example, you may want to take the point of view that telling a lie is a good thing if it benefits the person listening. You might want to use an example of explaining life and death to a small child. If your child really loves your next-door neighbor, but your next-door neighbor is dying of cancer, you don’t necessarily want to tell the child that the neighbor has cancer. The child might not be able to understand this. Instead, you may want to say that the person is not feeling well.
On the other hand, there are plenty of situations where telling the truth is a good thing. For example, you definitely don’t want to lie to your significant other about major financial issues. You probably don’t want to lie to your family members about major events in your life. If you lie to people important to you, particularly if you hurt them, it can damage your relationship with them, causing irreparable harm. When you close this essay, you will have to define when it is okay to lie to someone and when it is not. You might find it easier to say that lying is okay when it benefits the person you are talking to. You will need to use specific examples to write a strong essay.
Prompt: Do we expect too much from our public figures?
As a society, we tend to hold our public figures in high esteem. What this means is that we also hold them to a higher standard. Therefore, things that might not necessarily get us fired from our jobs could force a public figure to resign. At the same time, public figures are people, not superheroes. Therefore, do we expect too much from them?
You may want to start by discussing whether it is appropriate to place high expectations on the shoulders of public figures. After all, they have only earned that position by demonstrating that they may have more knowledge, wisdom, or personal capacity than the average person. Therefore, it should only make sense that we would hold them to a higher level. Then, you may want to share some of the high expectations we place on public figures. We expect them to defend the country, help those less fortunate, and foster scientific and economic growth.
On the other hand, you may want to talk about situations where the expectations we have for public figures are not necessarily reasonable. For example, you may want to discuss the expectation that public figures should immediately end a global pandemic. Or, you may want to talk about situations where public figures fall short because of events outside their control.
For example, our public figures are still accountable to the law. They are not dictators and could fall victim to significant companies or politicians who do not cooperate with them. When you finish this essay, you may want to discuss the difference between reasonable and unreasonable expectations. How do you define reasonable and unreasonable? You may even want to take the point that what is reasonable or unreasonable can vary from person to person.
Prompt: Is it better for us to react instinctively in times of crisis?
They call them reflexes for a reason, you want to respond as quickly as possible when there is a crisis. Evolutionarily, we would expect our reflexes to guide us in the right direction, but that is not always the case. For this essay, you will need to specify when it is better to react instinctively and when it is better to take a slower approach.
For example, you might want to talk about slamming on the brakes when trying to avoid an accident. If a child crosses the street in front of you, you don’t have time to pause, think, and decide whether you want to swerve or stop. Therefore it would be best if you reacted instinctively. If you wait too long, you will hit the child, leading to a catastrophe. In this situation, your reflexes are good.
Then, there are situations where it is better to take a more thought-out approach. For example, you might want to talk about a politician behind a desk trying to deal with energy, climate, or military crises. It may be prudent for politicians to reach out to their advisers, get everyone’s input, and decide what to do next. To write a strong essay, you will have to decide when it is crucial to react instinctively and when it is essential to pause for a moment and take a step back. Then, if you choose strong examples, you can write a solid response.
Looking for more? Check out these SAT writing tips .
FAQs About SAT Essay Examples
It would help if you used specific, varied examples to write a strong essay. The models need to support your point of view. It would help if you tried to choose examples from your personal life, current events, and history to demonstrate an extensive knowledge base. With a bit of test prep, you could get a perfect score.
There is no set length for your SAT essay. A five-paragraph essay is an excellent rule of thumb, but it is not required. It is more critical to show that you know how to organize your essay using paragraphs. There will be a time limit, so your essay cannot be super long.
It is always helpful to spend a couple of minutes brainstorming and outlining your essay before you start writing. You only have so many sheets of paper, so you need your essay to be organized before you begin. Think about your central claim, your sentence structure, and word choice. Next, write your thesis statement, topic sentences, and examples you want to use before you start writing your new SAT essay. Then, step by step, you will have a template around which you can build your central idea.
For help with this topic, read our guide explaining what is persuasive writing ? If you’re still stuck, check out our general resource of essay writing topics .
SAT Writing and Language: Practice tests and explanations
The SAT writing and language test consists of 44 multiple-choice questions that you'll have 35 minutes to complete. The questions are designed to test your knowledge of grammatical and stylistic topics.
The SAT Writing and Language questions ask about a variety of grammatical and stylistic topics. If you like to read and/or write, the SAT may frustrate you a bit because it may seem to boil writing down to a couple of dull rules.
- 30 SAT Grammar Practice Tests
SAT Writing and Language Practice Tests
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 1
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 2
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 3
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 4
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 5
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 6
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 7
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 8
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 9
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 10
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 11
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 12
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 13
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 14
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 15
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 16
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 17
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 18
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 19
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: A Sweet Discovery
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: René Descartes: The Father of Modern Philosophy
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Novel: Introspection to Escapism
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Interning: A Bridge Between Classes and Careers
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: In Defense of Don Quixote
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Women's Ingenuity
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Working from Home: Too Good to Be True?
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Is Gluten-Free the Way to Be?
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Antarctic Treaty System in Need of Reform
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Finding Pluto
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Public Relations: Build Your Brand While Building for Others
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Film, Culture, and Globalization
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Vitamin C—Essential Nutrient or Wonder Drug?
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Familiar Myth
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: America's Love for Streetcars
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Educating Early
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Age of the Librarian
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Unforeseen Consequences: The Dark Side of the Industrial Revolution
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Remembering Freud
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Success in Montreal
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Sorting Recyclables for Best Re-Use
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Interpreter at America's Immigrant Gateway
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Software Sales: A Gratifying Career
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Art of Collecting
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The UN: Promoting World Peace
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: DNA Analysis in a Day
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Will You Succeed with Your Start-Up?
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Edgard Varèse's Influence
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: From Here to the Stars
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The UK and the Euro
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Coffee: The Buzz on Beans
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Predicting Nature's Light Show
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 20
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 21
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 22
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 23
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 24
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 25
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 26
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 27
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 28
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 29
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 30
- New SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 31
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Physician Assistants
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Maria Montessori
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Platonic Forms
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Eureka Effect
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Carrot or the Stick?
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Promise of Bio-Informatics
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: What is Art?
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Little Tramp
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Who Really Owns American Media?
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Dangers of Superstition
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Skepticism and the Scientific Method
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Magic of Bohemia
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Careers in Engineeringd
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: An American Duty
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: Idol Worship in Sports
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test: The Secret Life of Photons
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 32: The Romani People
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 33: Into the Abyss
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 34: The Doctor Is In
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 35: Maslow's Hierarchy and Violence
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 36: Folklore
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 37: Age of the Drone
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 38: Policing Our Planet
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 39: The Bullroarer
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 40: Astrochemistry
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 41: Blood Ties
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 42: Out with the Old and the New
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 43: Extra, Extra
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 44: Parthenon
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 45: Where Have all the Cavemen Gone?
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 46: Chiroptera
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 47: The Tyrannical and the Taciturn
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 48
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 49
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 50: The Giants of Theater
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 51: Gravity, It's Everywhere
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 52: Do the Numbers Lie?
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 53: Draw Your Home
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 54: The Online Job Hunt
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 55: The Glass Menagerie
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 56: For Richer or For Poorer
- SAT Writing and Language Practice Test 57: Hypocrisy of Hippocratic Humorism
New SAT SAT Writing & Language Practice Tests Pdf Download
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 1
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 2
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 3
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 1 Answer Explanations
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 2 Answer Explanations
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 3 Answer Explanations
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 4 pdf download
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 5 pdf download
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 6 pdf download
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 7 pdf download
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 8 pdf download
- New SAT Writing & Language Practice Test 9 pdf download

More Information
- HOW TO ACE THE SAT WRITING AND LANGUAGE TEST: A STRATEGY
- Introduction to SAT Writing and Language Strategy
- The SAT Writing and Language Test-Words
- The SAT Writing and Language Test-Words and Punctuation in Reverse
- The SAT Writing and Language Test-Punctuation
- The SAT Writing and Language Test-Precision Questions
- The SAT Writing and Language Test-Consistency Questions

Home > College Admissions > SAT > SAT Practice Test
SAT Practice Test
Exam summary.
0 of 10 Questions completed
Information
You have already completed the exam before. Hence you can not start it again.
Exam is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the exam.
You must first complete the following:
Exam complete. Results are being recorded.
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), ( 0 )
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0 , ( 0 ) 0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0 )
- SAT Algebra 0%
- SAT Geometry & Trigonometry 0%
- SAT Problem Solving & Data Analysis 0%
Congrats on taking our SAT Sample Quiz. Take one of our full-length SAT practice tests or one of our study sets. Everything is 100% free!
1 . Question
What percentage does 90 represent in relation to 360?
2 . Question
7 added to 4 times a quantity y is equal to 62. Which equation represents this condition?
- a. 7(4y) = 62
- b. 7 – 4y = 62
- c. 7 + 4y = 62
- d. 4y – 7 = 62
3 . Question
For a cost of $57, how many pounds of avocados were bought at a rate of $19 per pound?
4 . Question
| x | f(x) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 65 |
| 1 | 73 |
| 2 | 81 |
The table displays three sets of values for x and their corresponding f(x) values for a linear function f. What equation accurately represents the definition of f(x)?
- a. f(x) = 6x + 65
- b. f(x) = 8x + 65
- c. f(x) = 65x + 73
- d. f(x) = 73x + 81
5 . Question
If \frac{x}{15}=20 , what is the value of \frac{15}{x} ?
6 . Question
What is the equation that defines line p in the xy-plane, given that it passes through the point (-4, 6) and has a slope of 6?
- a. y = 6x + 30
- b. y = 6x – 30
- c. y = 6 + 30x
- d. y = 6x – 30x
7 . Question
2.5b + 5r = 80
The provided equation expresses the connection between the quantity of biscuits (b) and raisins (r) that a reviewer business can handle in a single day. If the business is tending to 16 raisins on a specific day, what is the capacity for biscuits that it can manage on the same day?
8 . Question
In a specific rectangular area, the length-to-width ratio is 45 : 15. If the width of the region grows by 8 units, how should the length be adjusted to uphold this ratio?
- a. It must decrease by 24.5 units.
- b. It must increase by 24.5 units.
- c. It must decrease by 24 units.
- d. It must increase by 24 units.
9 . Question
In a circle with center O, the arc XY measures 105°. What is the degree measure of the angle XOY that corresponds to this arc?
10 . Question
In a right triangle, the side lengths are 3\sqrt3 , 2\sqrt3 ,and \sqrt{70} units. What is the area of the triangle in square units?
*Enter in just the number for your answer.
All SAT Practice Tests
If you want some more in-depth prep, use a free SAT practice test listed below.
- Practice Exams = Timed and Full-Length
- Practice Sets = Not Timed and Smaller Sets of Questions
SAT Practice Exam #1
SAT Practice Exam #2
SAT Practice Exam #3
SAT Practice Exam #4
SAT Math Practice Sets
SAT Reading & Writing Practice Sets
Use Our SAT Prep (100% Free)
Prepare for your SAT with Test-Guide.com. We offer 4 full-length exams and 32+ practice sets. Everything is updated for the SAT Digital Exam.
Official SAT PDF Practice Exams
If you want to study using PDFs, use the links below. These are full-length practice exams provided by the CollegeBoard.
| | |
| | |
| | |
| |
Overview of the SAT
The SAT is an entrance exam used by colleges and universities to help make decisions about admissions.
The SAT is administered by the CollegeBoard and is given 7 times per year. The exam is a timed, mainly multiple-choice exam, taken by students in high school.
Beginning in the spring of 2024, the SAT will be going fully digital. The digital SAT (DSAT) will have some formatting and content changes to it, along with some other changes. You can review those changes below.
New SAT (Digital SAT)
This exam will be given to students starting in spring of 2024.
| Section | Number of Questions | Time Limit (Mins) |
|---|---|---|
| Reading & Writing | 54 | 64 (Two 32-Minute Modules) |
| Math | 44 | 70 (Two 35-Minute Modules) |
Old SAT (Written Exam)
This exam will be given to students up until spring of 2024.
| Section | Number of Questions | Time Limit (Mins) |
|---|---|---|
| Reading | 52 | 65 |
| Writing & Language | 44 | 35 |
| Math (With calculator) | 38 | 55 |
| Math (Without calculator) | 20 | 25 |
The biggest difference between the old SAT and the digital SAT is that the digital SAT is taken completely online and has combined some sections to streamline the exam.
Scoring of the SAT
You will receive a score for math and a score for reading/writing. Each of those scores will be between 200 and 800 .
Your total score will be the sum of those two scores. You can receive a total score between 400 and 1600 on the SAT.
The average SAT score is 1060. Learn more about good SAT scores .
Registering for the SAT and Test Dates
You can register for the SAT online via the CollegeBoard site .
You will need to do the following when registering for the SAT:
- Have a Valid Photo ID
- Upload a Photo of Yourself When Registering Online
- Pay Registration Fees
- Print Your Admission Ticket
It will cost your $60 to take the SAT. There may be some additional fees like canceling, changing test center, etc..
The SAT is typically given 7 times per year. The exam is given on Saturdays. You can expect the exam to be given in these months:
- Early March
- Late August
- Early October
- Early November
- Early December
You can find exact dates on the official website .
Steps for Using SAT Practice
When using our free SAT practice tests, we recommend the following steps to get the most out of your time:
- Take 1 practice exam from each subject.
- Determine which subject you struggled the most with.
- Focus on that 1 subject moving forward. Take additional practice exams in that subject, study important concepts, and invest in a course if need be.
- Take a practice exam on that subject again and see where you stand. Continue to focus on that subject if you need more help or move on to another subject if you did well on this practice exam.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 for other subjects.
Benefits of Using SAT Practice Questions
There are many benefits to using SAT questions during your prep process. Some of those benefits include:
Help With Timing
The SAT exam is a timed test. Keeping a steady pace is critical to achieving a high score.
You can improve your decision making and your time by taking practice exams.
Test Familiarity
All standardized tests, including the SAT, have their own unique way of presenting questions and answer choices.
You will gain more familiarity and comfort with the SAT question style as you take more practice quizzes. On the real exam day, there will be no surprises.
Efficient Studying
When you take many practice exams, you will get a sense of your test strengths and weaknesses.
Many students mistakenly spend time working on their strengths while ignoring their weaknesses.
Knowing which subjects you struggle with will help you focus your study time.
Work On Problem Solving
Tests like the SAT measure your ability to solve problems, not just memorize information. It is critical to have strong problem-solving abilities.
The answer explanations provided in our score reports can help you understand how to solve problems that you may be struggling with.
Frequently Asked Questions
When is the sat going to the digital format.
The SAT will be switching to the digital format in the spring of 2024.
How many questions are on the SAT?
There are 154 questions on the old SAT (written version).
There are 98 questions on the new SAT (digital version).
How much time do you have to take the SAT?
You will have 3 hours and 15 minutes to take the old SAT (written version).
You will have 2 hours and 14 minutes to take the new SAT (digital version).
Can I use a calculator on the math section of the SAT?
There will be 1 math section in which you can use a calculator and 1 math section in which you cannot use a calculator on the old SAT (written version).
You will be permitted to use a calculator on all math modules on the new SAT (digital version).
What is a good way to practice for the SAT?
We recommend taking 1 practice exam for each subject. You can then determine which subject gave you the most trouble and focus your studies on that subject.

- Authored By: Adam Groden
- Last Updated: January 19, 2024
Get in touch with us
Are you sure you want to logout?
Study abroad.

SAT Essay Examples For High Scoring Student
Sat essay examples.
Just like with essays on other exams, the secret to excelling on the SAT essay section is by pre-planning the examples and evidence that you wish to use. But you might be wondering how it can be done on the new SAT essay as the whole point of the essay is to use information from the given passage while answering and you don’t know about the essay ahead of time.
Well, the truth is that while the specifics of each example depend on the passage and obviously change with each exam, the pattern of the examples you choose to discuss can be defined, and therefore, planned ahead of time.

In this blog, we will discuss a few good SAT essay examples that will help you in formulating almost any essay SAT gives you. By practicing examples of the most common types of essays asked on SAT, you will cut down on planning time during the exam and increase the amount and quality of content you can write in a limited time. This will help build your confidence and enable you to walk into any SAT essay exam with a positive attitude.
If you are looking for an answer to the question, “Is there an essay on the SAT?”, here it is: The College Board in January 2021 announced that the essay portion of the SAT will no longer be asked after June 2021. Some schools with school day testing still offer the SAT essay section. Therefore, now it’s no longer possible to take the SAT Essay, unless your school offers it during SAT School Day Testing.

While the SAT Essay scores were already made optional by most colleges, this means that the SAT Essay cancelled section is now not required by the College Board. It will also probably result in changes in college applications such as not considering the essay scores for ACT or SAT anymore, in addition to requiring more writing samples for placement.
For every passage, you should play for its particular strengths. If there are a lot of statistics or facts involved, you can discuss those in your essay. If it dwells more on personal appeals or anecdotes to emotion, you can discuss those. But if you struggle with analysing in a limited amount of time, it is best to memorize these types of examples beforehand so that you get a helpful checklist to get through while you read the essay prompt. This will point you in the right direction.

Below we have discussed a few examples of SAT essays on different topics such as evidence and reasoning that you can use as stellar evidence to support your thesis. We have also guided you on how you can use the evidence type to support your thesis across a range of SAT essay prompts for each example. After you go through the blog, you will realize how helpful pre-planned high-scoring student SAT essay examples are.
Example of Evidence
The most fundamental technique that the author uses to build an argument is by supporting his points with the help of evidence. Many different kinds of evidence can be used by the author to support his/her claim. But here we will discuss a single one (facts and statistics) that is commonly seen in official SAT Essay prompts.

Example 1: Facts and Statistics
Using facts and statistics to bolster one’s argument is one of the most reliable techniques authors use to build an argument. It is more commonly seen in essays written about social studies-related and scientific topics where specific facts and data are readily available.
How to Identify it?
Statistics are usually found in the form of specific numbers about the topic under study. It may be shown in the form of tables, percentage, or as a way to communicate other information. Below are a few examples of statistics from an official essay prompt of SAT , “Let There Be Dark” written by Paul Bogard.

Example: In United States, 8 children born out of 10 will never get to know a sky dark enough for the Milky Way
Example: In Western Europe and the United States, the increase in the amount of light in the sky is about 6% on an average year

Non-numerical information can also be used to depict factual evidence. You will often encounter facts being presented with references to the research survey, study, expert, or other sources from which they have been derived. Below is another example from the same topic.
Example: The World Health Organization already classifies working during night shifts as potentially carcinogenic for humans.

Why is it Persuasive?
Statistics and facts are persuasive argument building methods as the author is not just making up random points for why the argument could be possibly right. There is actually some data, statistics, research, or other types of reliable information that backs up the author’s argument.
In the above examples, Paul Bogard reveals specific information regarding the issues with light pollution (when he says that most children in the United States won’t be fortunate enough to see the Milky Way) to back up his argument that light pollution is a real issue. He then proceeds to present information indicating how light pollution is a major problem (working during the night is carcinogenic for humans).
By presenting valid facts and information instead of just forcing a subjective opinion and beating about the bush, Paul Bogard empowers the reader to connect the dots themselves. This gives the reader a power or ownership over the argument, rendering it more persuasive. This is because the reader concludes the same statements even on his own, rather than blindly trusting Bogard on telling them what to think.
Example Type 2: Anecdotes
Another technique often used by authors as an alternative to presenting evidence with facts or statistics is using the anecdote. This type of evidence can be found more commonly in speeches or other types of SAT essay prompts that are personally directed towards the reader.
An anecdote refers to a short story about a real event or a person. It is when an author goes about discussing their own personal experiences or that of someone else they know or have heard of. Below is an anecdote example from an official SAT essay prompted that has been taken from the foreword by Jimmy Carter, a former U.S. President.
One of the most humbling and unforgettable experiences of our lives happened on the coastal plain. During our trip, we had expected to see the caribou. However, to our amazement, we saw the migration of thousands of caribou along with their newborn calves.
The sweep of tundra surrounding us was flooded with life in a matter of a few minutes with the sounds of clicking hooves and grunting animals filling the air. It was a once-in-a-lifetime experience to see the dramatic procession of the herd of the Porcupine caribou. We now understand why this special birthplace has been described as “America’s Serengeti” by many.
Although anecdotes are not facts or statistics, they can be a reliable technique to express information because it’s more interesting for the reader to go through the anecdote rather than read dry, boring facts. People tend to trust the experiences more if they can personally relate or connect with them, although it does not always mean that the statement is true.
In the example stated above, instead of talking about the statistics supporting the creation of wildlife refuges, rather an anecdote is used by Jimmy Carter to represent the same point using illustrations of the wonders of nature, which works more effectively. By allowing the readers to vicariously experience this majestic event of the migration of the caribou, Carter stimulates the empathetic sense of the reader towards wildlife preservation and therefore makes it more likely for the reader to agree with him on the topic of wildlife preservation.
Conclusion
We hope that the essay prompts given above help you in your SAT preparation and in getting a SAT good essay score. Don’t forget to check out our other blogs on how to prepare effectively for the SAT.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. why is it helpful to prepare sat essay examples.
The SAT essay examples will help you get a sat good essay score as they have several things in common with the exam pattern:
- All of these passages try to convince the reader of the veracity of the claim of the author.
- All of these are around the same length.
- All of these can be analysed and written about in a relatively short time period
2. How can essay example practice help to get a good SAT essay score?
By practising these essay examples you will have a decent idea ahead of time regarding argument-building techniques that will help you greatly on the test day and increase your overall SAT essay score.
3. Will the techniques used by the author on the SAT be complex?
The main techniques used by the author won’t be too complex. This is because you just can’t afford the time to analyse and write about complicated techniques. Therefore, you can prepare yourself beforehand with SAT essay examples found across persuasive passages on many common topics.

Relevant Articles

How Should You Calculate Cumulative GPA for all Semesters?
Introduction In today’s college admissions environment, your Cumulative Grade Point …
How Should You Calculate Cumulative GPA for all Semesters? Read More »
Strategies for Success: Mastering the Digital SAT Scoring System
Securing good marks on the digital SAT is important for …
Strategies for Success: Mastering the Digital SAT Scoring System Read More »

Is the Digital SAT Easier? New Format & Adaptive Testing
With multiple speculations on the introduction of the newer SAT …
Is the Digital SAT Easier? New Format & Adaptive Testing Read More »

Is the Digital SAT Harder? Exploring Changes, Similarities & Prep
High school students take the SAT or Scholastic Assessment Test …
Is the Digital SAT Harder? Exploring Changes, Similarities & Prep Read More »

With Turito Study Abroad

Get an Expert Advice from Turito

With Turito CAP.

With Turito Coding.

With Turito RoboNinja

1-on-1 tutoring for the undivided attention

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, sat essay rubric: full analysis and writing strategies.

We're about to dive deep into the details of that least beloved* of SAT sections, the SAT essay . Prepare for a discussion of the SAT essay rubric and how the SAT essay is graded based on that. I'll break down what each item on the rubric means and what you need to do to meet those requirements.
On the SAT, the last section you'll encounter is the (optional) essay. You have 50 minutes to read a passage, analyze the author's argument, and write an essay. If you don’t write on the assignment, plagiarize, or don't use your own original work, you'll get a 0 on your essay. Otherwise, your essay scoring is done by two graders - each one grades you on a scale of 1-4 in Reading, Analysis, and Writing, for a total essay score out of 8 in each of those three areas . But how do these graders assign your writing a numerical grade? By using an essay scoring guide, or rubric.
*may not actually be the least belovèd.
Feature image credit: Day 148: the end of time by Bruce Guenter , used under CC BY 2.0 /Cropped from original.
UPDATE: SAT Essay No Longer Offered
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});.
In January 2021, the College Board announced that after June 2021, it would no longer offer the Essay portion of the SAT (except at schools who opt in during School Day Testing). It is now no longer possible to take the SAT Essay, unless your school is one of the small number who choose to offer it during SAT School Day Testing.
While most colleges had already made SAT Essay scores optional, this move by the College Board means no colleges now require the SAT Essay. It will also likely lead to additional college application changes such not looking at essay scores at all for the SAT or ACT, as well as potentially requiring additional writing samples for placement.
What does the end of the SAT Essay mean for your college applications? Check out our article on the College Board's SAT Essay decision for everything you need to know.
The Complete SAT Essay Grading Rubric: Item-by-Item Breakdown
Based on the CollegeBoard’s stated Reading, Analysis, and Writing criteria, I've created the below charts (for easier comparison across score points). For the purpose of going deeper into just what the SAT is looking for in your essay, I've then broken down each category further (with examples).
The information in all three charts is taken from the College Board site .
The biggest change to the SAT essay (and the thing that really distinguishes it from the ACT essay) is that you are required to read and analyze a text , then write about your analysis of the author's argument in your essay. Your "Reading" grade on the SAT essay reflects how well you were able to demonstrate your understanding of the text and the author's argument in your essay.
|
|
|
|
(Inadequate) | The response demonstrates little or no comprehension of the source text. The response fails to show an understanding of the text’s central idea(s), and may include only details without reference to central idea(s). The response may contain numerous errors of fact and/or interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes little or no use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating little or no understanding of the source text. |
|
(Partial) | The response demonstrates some comprehension of the source text. The response shows an understanding of the text’s central idea(s) but not of important details. The response may contain errors of fact and/or interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes limited and/or haphazard use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating some understanding of the source text. |
|
(Proficient) | The response demonstrates effective comprehension of the source text. The response shows an understanding of the text’s central idea(s) and important details. The response is free of substantive errors of fact and interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes appropriate use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating an understanding of the source text. |
|
(Advanced) | The response demonstrates thorough comprehension of the source text. The response shows an understanding of the text’s central idea(s) and of most important details and how they interrelate, demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of the text. The response is free of errors of fact or interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes skillful use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating a complete understanding of the source text. |
You'll need to show your understanding of the text on two different levels: the surface level of getting your facts right and the deeper level of getting the relationship of the details and the central ideas right.
Surface Level: Factual Accuracy
One of the most important ways you can show you've actually read the passage is making sure you stick to what is said in the text . If you’re writing about things the author didn’t say, or things that contradict other things the author said, your argument will be fundamentally flawed.
For instance, take this quotation from a (made-up) passage about why a hot dog is not a sandwich:
“The fact that you can’t, or wouldn’t, cut a hot dog in half and eat it that way, proves that a hot dog is once and for all NOT a sandwich”
Here's an example of a factually inaccurate paraphrasing of this quotation:
The author builds his argument by discussing how, since hot-dogs are often served cut in half, this makes them different from sandwiches.
The paraphrase contradicts the passage, and so would negatively affect your reading score. Now let's look at an accurate paraphrasing of the quotation:
The author builds his argument by discussing how, since hot-dogs are never served cut in half, they are therefore different from sandwiches.
It's also important to be faithful to the text when you're using direct quotations from the passage. Misquoting or badly paraphrasing the author’s words weakens your essay, because the evidence you’re using to support your points is faulty.
Higher Level: Understanding of Central Ideas
The next step beyond being factually accurate about the passage is showing that you understand the central ideas of the text and how details of the passage relate back to this central idea.
Why does this matter? In order to be able to explain why the author is persuasive, you need to be able to explain the structure of the argument. And you can’t deconstruct the author's argument if you don’t understand the central idea of the passage and how the details relate to it.
Here's an example of a statement about our fictional "hot dogs are sandwiches" passage that shows understanding of the central idea of the passage:
Hodgman’s third primary defense of why hot dogs are not sandwiches is that a hot dog is not a subset of any other type of food. He uses the analogy of asking the question “is cereal milk a broth, sauce, or gravy?” to show that making such a comparison between hot dogs and sandwiches is patently illogical.
The above statement takes one step beyond merely being factually accurate to explain the relation between different parts of the passage (in this case, the relation between the "what is cereal milk?" analogy and the hot dog/sandwich debate).
Of course, if you want to score well in all three essay areas, you’ll need to do more in your essay than merely summarizing the author’s argument. This leads directly into the next grading area of the SAT Essay.
The items covered under this criterion are the most important when it comes to writing a strong essay. You can use well-spelled vocabulary in sentences with varied structure all you want, but if you don't analyze the author's argument, demonstrate critical thinking, and support your position, you will not get a high Analysis score .
|
|
|
|
(Inadequate) | The response offers little or no analysis or ineffective analysis of the source text and demonstrates little or no understanding of the analytic task. The response identifies without explanation some aspects of the author’s use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student’s choosing, Or numerous aspects of the response’s analysis are unwarranted based on the text. The response contains little or no support for claim(s) or point(s) made, or support is largely irrelevant. The response may not focus on features of the text that are relevant to addressing the task, Or the response offers no discernible analysis (e.g., is largely or exclusively summary). |
|
(Partial) | The response offers limited analysis of the source text and demonstrates only partial understanding of the analytical task. The response identifies and attempts to describe the author’s use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student’s own choosing, but merely asserts rather than explains their importance, or one or more aspects of the response’s analysis are unwarranted based on the text. The response contains little or no support for claim(s) or point(s) made. The response may lack a clear focus on those features of the text that are most relevant to addressing the task. |
|
(Proficient) | The response offers an effective analysis of the source text and demonstrates an understanding of the analytical task. The response competently evaluates the author’s use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student’s own choosing. The response contains relevant and sufficient support for claim(s) or point(s) made. The response focuses primarily on those features of the text that are most relevant to addressing the task. |
|
(Advanced) | The response offers an insightful analysis of the source text and demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of the analytical task. The response offers a thorough, well-considered evaluation of the author’s use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student’s own choosing. The response contains relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim(s) or point(s) made. The response focuses consistently on those features of the text that are most relevant to addressing the task. |
Because this category is so important, I've broken it down even further into its two different (but equally important) component parts to make sure everything is as clearly explained as possible.
Part I: Critical Thinking (Logic)
Critical thinking, also known as critical reasoning, also known as logic, is the skill that SAT essay graders are really looking to see displayed in the essay. You need to be able to evaluate and analyze the claim put forward in the prompt. This is where a lot of students may get tripped up, because they think “oh, well, if I can just write a lot, then I’ll do well.” While there is some truth to the assertion that longer essays tend to score higher , if you don’t display critical thinking you won’t be able to get a top score on your essay.
What do I mean by critical thinking? Let's take the previous prompt example:
Write an essay in which you explain how Hodgman builds an argument to persuade his audience that the hot dog cannot, and never should be, considered a sandwich.
An answer to this prompt that does not display critical thinking (and would fall into a 1 or 2 on the rubric) would be something like:
The author argues that hot dogs aren’t sandwiches, which is persuasive to the reader.
While this does evaluate the prompt (by providing a statement that the author's claim "is persuasive to the reader"), there is no corresponding analysis. An answer to this prompt that displays critical thinking (and would net a higher score on the rubric) could be something like this:
The author uses analogies to hammer home his point that hot dogs are not sandwiches. Because the readers will readily believe the first part of the analogy is true, they will be more likely to accept that the second part (that hot dogs aren't sandwiches) is true as well.
See the difference? Critical thinking involves reasoning your way through a situation (analysis) as well as making a judgement (evaluation) . On the SAT essay, however, you can’t just stop at abstract critical reasoning - analysis involves one more crucial step...
Part II: Examples, Reasons, and Other Evidence (Support)
The other piece of the puzzle (apparently this is a tiny puzzle) is making sure you are able to back up your point of view and critical thinking with concrete evidence . The SAT essay rubric says that the best (that is, 4-scoring) essay uses “ relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim(s) or point(s) made. ” This means you can’t just stick to abstract reasoning like this:
That explanation is a good starting point, but if you don't back up your point of view with quoted or paraphrased information from the text to support your discussion of the way the author builds his/her argument, you will not be able to get above a 3 on the Analysis portion of the essay (and possibly the Reading portion as well, if you don't show you've read the passage). Let's take a look of an example of how you might support an interpretation of the author's effect on the reader using facts from the passage :
The author’s reference to the Biblical story about King Solomon elevates the debate about hot dogs from a petty squabble between friends to a life-or-death disagreement. The reader cannot help but see the parallels between the two situations and thus find themselves agreeing with the author on this point.
Does the author's reference to King Solomon actually "elevate the debate," causing the reader to agree with the author? From the sentences above, it certainly seems plausible that it might. While your facts do need to be correct, you get a little more leeway with your interpretations of how the author’s persuasive techniques might affect the audience. As long as you can make a convincing argument for the effect a technique the author uses might have on the reader, you’ll be good.

Say whaaat?! #tbt by tradlands , used under CC BY 2.0 /Cropped and color-adjusted from original.
Did I just blow your mind? Read more about the secrets the SAT doesn’t want you to know in this article .
Your Writing score on the SAT essay is not just a reflection of your grasp of the conventions of written English (although it is that as well). You'll also need to be focused, organized, and precise.
|
|
|
|
(Inadequate) | The response demonstrates little or no cohesion and inadequate skill in the use and control of language. The response may lack a clear central claim or controlling idea. The response lacks a recognizable introduction and conclusion. The response does not have a discernible progression of ideas. The response lacks variety in sentence structures; sentence structures may be repetitive. The response demonstrates general and vague word choice; word choice may be poor or inaccurate. The response may lack a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a weak control of the conventions of standard written English and may contain numerous errors that undermine the quality of writing. |
|
(Partial) | The response demonstrates little or no cohesion and limited skill in the use and control of language. The response may lack a clear central claim or controlling idea or may deviate from the claim or idea over the course of the response. The response may include an ineffective introduction and/or conclusion. The response may demonstrate some progression of ideas within paragraphs but not throughout the response. The response has limited variety in sentence structures; sentence structures may be repetitive. The response demonstrates general or vague word choice; word choice may be repetitive. The response may deviate noticeably from a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a limited control of the conventions of standard written English and contains errors that detract from the quality of writing and may impede understanding. |
|
(Proficient) | The response is mostly cohesive and demonstrates effective use and control of language. The response includes a central claim or implicit controlling idea. The response includes an effective introduction and conclusion. The response demonstrates a clear progression of ideas both within paragraphs and throughout the essay. The response has variety in sentence structures. The response demonstrates some precise word choice. The response maintains a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a good control of the conventions of standard written English and is free of significant errors that detract from the quality of writing. |
|
(Advanced) | The response is cohesive and demonstrates a highly effective use and command of language. The response includes a precise central claim. The response includes a skillful introduction and conclusion. The response demonstrates a deliberate and highly effective progression of ideas both within paragraphs and throughout the essay. The response has a wide variety in sentence structures. The response demonstrates a consistent use of precise word choice. The response maintains a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a strong command of the conventions of standard written English and is free or virtually free of errors. |
Because there's a lot of different factors that go into calculating your Writing score, I've divided the discussion of this rubric area into five separate items:
Precise Central Claim
Organization, vocab and word choice, sentence structure, grammar, etc..
One of the most basic rules of the SAT essay is that you need to express a clear opinion on the "assignment" (the prompt) . While in school (and everywhere else in life, pretty much) you’re encouraged to take into account all sides of a topic, it behooves you to NOT do this on the SAT essay. Why? Because you only have 50 minutes to read the passage, analyze the author's argument, and write the essay, there's no way you can discuss every single way in which the author builds his/her argument, every single detail of the passage, or a nuanced argument about what works and what doesn't work.
Instead, I recommend focusing your discussion on a few key ways the author is successful in persuading his/her audience of his/her claim.
Let’s go back to the assignment we've been using as an example throughout this article:
"Write an essay in which you explain how Hodgman builds an argument to persuade his audience that the hot dog cannot, and never should be, considered a sandwich."
Your instinct (trained from many years of schooling) might be to answer:
"There are a variety of ways in which the author builds his argument."
This is a nice, vague statement that leaves you a lot of wiggle room. If you disagree with the author, it's also a way of avoiding having to say that the author is persuasive. Don't fall into this trap! You do not necessarily have to agree with the author's claim in order to analyze how the author persuades his/her readers that the claim is true.
Here's an example of a precise central claim about the example assignment:
The author effectively builds his argument that hot dogs are not sandwiches by using logic, allusions to history and mythology, and factual evidence.
In contrast to the vague claim that "There are a variety of ways in which the author builds his argument," this thesis both specifies what the author's argument is and the ways in which he builds the argument (that you'll be discussing in the essay).
While it's extremely important to make sure your essay has a clear point of view, strong critical reasoning, and support for your position, that's not enough to get you a top score. You need to make sure that your essay "demonstrates a deliberate and highly effective progression of ideas both within paragraphs and throughout the essay."
What does this mean? Part of the way you can make sure your essay is "well organized" has to do with following standard essay construction points. Don't write your essay in one huge paragraph; instead, include an introduction (with your thesis stating your point of view), body paragraphs (one for each example, usually), and a conclusion. This structure might seem boring, but it really works to keep your essay organized, and the more clearly organized your essay is, the easier it will be for the essay grader to understand your critical reasoning.
The second part of this criteria has to do with keeping your essay focused, making sure it contains "a deliberate and highly effective progression of ideas." You can't just say "well, I have an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, so I guess my essay is organized" and expect to get a 4/4 on your essay. You need to make sure that each paragraph is also organized . Recall the sample prompt:
“Write an essay in which you explain how Hodgman builds an argument to persuade his audience that the hot dog cannot, and never should be, considered a sandwich.”
And our hypothetical thesis:
Let's say that you're writing the paragraph about the author's use of logic to persuade his reader that hot dogs aren't sandwiches. You should NOT just list ways that the author is logical in support of his claim, then explain why logic in general is an effective persuasive device. While your points might all be valid, your essay would be better served by connecting each instance of logic in the passage with an explanation of how that example of logic persuades the reader to agree with the author.
Above all, it is imperative that you make your thesis (your central claim) clear in the opening paragraph of your essay - this helps the grader keep track of your argument. There's no reason you’d want to make following your reasoning more difficult for the person grading your essay (unless you’re cranky and don’t want to do well on the essay. Listen, I don’t want to tell you how to live your life).
In your essay, you should use a wide array of vocabulary (and use it correctly). An essay that scores a 4 in Writing on the grading rubric “demonstrates a consistent use of precise word choice.”
You’re allowed a few errors, even on a 4-scoring essay, so you can sometimes get away with misusing a word or two. In general, though, it’s best to stick to using words you are certain you not only know the meaning of, but also know how to use. If you’ve been studying up on vocab, make sure you practice using the words you’ve learned in sentences, and have those sentences checked by someone who is good at writing (in English), before you use those words in an SAT essay.
Creating elegant, non-awkward sentences is the thing I struggle most with under time pressure. For instance, here’s my first try at the previous sentence: “Making sure a sentence structure makes sense is the thing that I have the most problems with when I’m writing in a short amount of time” (hahaha NOPE - way too convoluted and wordy, self). As another example, take a look at these two excerpts from the hypothetical essay discussing how the author persuaded his readers that a hot dog is not a sandwich:
Score of 2: "The author makes his point by critiquing the argument against him. The author pointed out the logical fallacy of saying a hot dog was a sandwich because it was meat "sandwiched" between two breads. The author thus persuades the reader his point makes sense to be agreed with and convinces them."
The above sentences lack variety in structure (they all begin with the words "the author"), and the last sentence has serious flaws in its structure (it makes no sense).
Score of 4: "The author's rigorous examination of his opponent's position invites the reader, too, to consider this issue seriously. By laying out his reasoning, step by step, Hodgman makes it easy for the reader to follow along with his train of thought and arrive at the same destination that he has. This destination is Hodgman's claim that a hot dog is not a sandwich."
The above sentences demonstrate variety in sentence structure (they don't all begin with the same word and don't have the same underlying structure) that presumably forward the point of the essay.
In general, if you're doing well in all the other Writing areas, your sentence structures will also naturally vary. If you're really worried that your sentences are not varied enough, however, my advice for working on "demonstrating meaningful variety in sentence structure" (without ending up with terribly worded sentences) is twofold:
- Read over what you’ve written before you hand it in and change any wordings that seem awkward, clunky, or just plain incorrect.
- As you’re doing practice essays, have a friend, family member, or teacher who is good at (English) writing look over your essays and point out any issues that arise.
This part of the Writing grade is all about the nitty gritty details of writing: grammar, punctuation, and spelling . It's rare that an essay with serious flaws in this area can score a 4/4 in Reading, Analysis, or Writing, because such persistent errors often "interfere with meaning" (that is, persistent errors make it difficult for the grader to understand what you're trying to get across).
On the other hand, if they occur in small quantities, grammar/punctuation/spelling errors are also the things that are most likely to be overlooked. If two essays are otherwise of equal quality, but one writer misspells "definitely" as "definately" and the other writer fails to explain how one of her examples supports her thesis, the first writer will receive a higher essay score. It's only when poor grammar, use of punctuation, and spelling start to make it difficult to understand your essay that the graders start penalizing you.
My advice for working on this rubric area is the same advice as for sentence structure: look over what you’ve written to double check for mistakes, and ask someone who’s good at writing to look over your practice essays and point out your errors. If you're really struggling with spelling, simply typing up your (handwritten) essay into a program like Microsoft Word and running spellcheck can alert you to problems. We've also got a great set of articles up on our blog about SAT Writing questions that may help you better understand any grammatical errors you are making.
How Do I Use The SAT Essay Grading Rubric?
Now that you understand the SAT essay rubric, how can you use it in your SAT prep? There are a couple of different ways.
Use The SAT Essay Rubric To...Shape Your Essays
Since you know what the SAT is looking for in an essay, you can now use that knowledge to guide what you write about in your essays!
A tale from my youth: when I was preparing to take the SAT for the first time, I did not really know what the essay was looking for, and assumed that since I was a good writer, I’d be fine.
Not true! The most important part of the SAT essay is using specific examples from the passage and explaining how they convince the reader of the author's point. By reading this article and realizing there's more to the essay than "being a strong writer," you’re already doing better than high school me.

Change the object in that girl’s left hand from a mirror to a textbook and you have a pretty good sketch of what my junior year of high school looked like.
Use The SAT Essay Rubric To...Grade Your Practice Essays
The SAT can’t exactly give you an answer key to the essay. Even when an example of an essay that scored a particular score is provided, that essay will probably use different examples than you did, make different arguments, maybe even argue different interpretations of the text...making it difficult to compare the two. The SAT essay rubric is the next best thing to an answer key for the essay - use it as a lens through which to view and assess your essay.
Of course, you don’t have the time to become an expert SAT essay grader - that’s not your job. You just have to apply the rubric as best as you can to your essays and work on fixing your weak areas . For the sentence structure, grammar, usage, and mechanics stuff I highly recommend asking a friend, teacher, or family member who is really good at (English) writing to take a look over your practice essays and point out the mistakes.
If you really want custom feedback on your practice essays from experienced essay graders, may I also suggest the PrepScholar test prep platform ? I manage the essay grading and so happen to know quite a bit about the essay part of this platform, which gives you both an essay grade and custom feedback for each essay you complete. Learn more about how it all works here .
What’s Next?
Are you so excited by this article that you want to read even more articles on the SAT essay? Of course you are. Don't worry, I’ve got you covered. Learn how to write an SAT essay step-by-step and read about the 6 types of SAT essay prompts .
Want to go even more in depth with the SAT essay? We have a complete list of past SAT essay prompts as well as tips and strategies for how to get a 12 on the SAT essay .
Still not satisfied? Maybe a five-day free trial of our very own PrepScholar test prep platform (which includes essay practice and feedback) is just what you need.
Trying to figure out whether the old or new SAT essay is better for you? Take a look at our article on the new SAT essay assignment to find out!
Laura graduated magna cum laude from Wellesley College with a BA in Music and Psychology, and earned a Master's degree in Composition from the Longy School of Music of Bard College. She scored 99 percentile scores on the SAT and GRE and loves advising students on how to excel in high school.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
No extra time allowed! #5: Grade the essay, using the official essay rubric to give yourself a score out of 8 in the reading, analysis, and writing sections. #6: Repeat steps 4 and 5. Choose the prompts you think will be the hardest for you so that you can so that you're prepared for the worst when the test day comes.
Essay Sample Response (High Scoring) "In response to our world's growing reliance on artificial light, writer Paul Bogard argues that natural darkness should be preserved in his article "Let There be dark". He effectively builds his argument by using a personal anecdote, allusions to art and history, and rhetorical questions.
You can read the full text of the passage associated with the prompt (part of Practice Test 5) via our complete collection of official SAT essay prompts.. In the following SAT essay format, I've broken down an SAT essay into introduction, example paragraphs, and conclusion.Since I'm writing in response to a specific prompt, some of the information and facts in the template will only be useful ...
If your state offers SAT Essay as part of its in-school testing, you can find practice essay prompts and scoring explanations below. ... Download student sample essays—and the explanations that show why they received the score they did—for SAT Practice Essay 1. PDF; 461.99 KB;
Here are a couple of examples of statistics from an official SAT essay prompt, "Let There Be Dark" by Paul Bogard: Example: 8 of 10 children born in the United States will never know a sky dark enough for the Milky Way. Example: In the United States and Western Europe, the amount of light in the sky increases an average of about 6% every year.
the SAT Essay scoring rubric at . ... consider how Paul Bogard uses • evidence, such as facts or examples, to support claims. • reasoning to develop ideas and to connect claims and evidence. • stylistic or persuasive elements, such as word choice or appeals to emotion, ... are writing is legible to those readers.
College Board. February 28, 2024. The SAT Essay section is a lot like a typical writing assignment in which you're asked to read and analyze a passage and then produce an essay in response to a single prompt about that passage. It gives you the opportunity to demonstrate your reading, analysis, and writing skills—which are critical to ...
The SAT Essay is a lot like a typical college writing assignment that asks you to analyze a text. It shows colleges that you're able to read, analyze, and write at the college level. The SAT Essay asks you to use your reading, analysis, and writing skills. You'll be asked to: Read a passage. Explain how the author builds an argument to persuade ...
You can utilize these Essay SAT prompts as 10 sample SAT Essay questions for easy practice. This set of SAT Essay prompts is the most comprehensive that you will find online today. The predictability of the SAT Essay test necessitates students to perform an organized analytical method of writing instead of thinking up random ideas on their own.
How to Outline Your Essay. First, read the prompt through a couple of times. SAT essay prompts usually follow a set format involving the statement of an opinion, and then asking whether you agree or disagree with that opinion. Let's take an example from the January 2014 test date, courtesy of the College Board website:
In addition to the separate Essay portion of the SAT Writing section, three different question types appear on the SAT Writing section: Identifying Sentence Errors, Improving Sentences, and Improving Paragraphs. ... Take a sample SAT Essay prompt and brainstorm ideas that you might use to respond to it or a similar question. 4.) Focus on honing ...
Here are 5 tips for writing a killer SAT essay, should you decide to add on that section: 1. Stay Objective. The thing to remember here is that ETS (the company that writes the test) is not asking you for your opinion on a topic or a text. So be sure to maintain formal style and an objective tone.
The SAT examination begins with a 25-minute writing task: The essay. You have no choice of topic: you have to write on the prompt given in a text box. For example you may see something like: Time has a doomsday book, on whose pages he is continually recording illustrious names. But as often as a new name is written there, an old one disappears.
This is the argument you need to deconstruct in your essay. Writing an SAT essay consists of four major stages: Reading: 5-10 minutes. Analyzing & Planning: 7-12 minutes. Writing: 25-35 minutes. Revising: 2-3 minutes. There's a wide time range for a few of these stages, since people work at different rates.
Based on the examples you choose, you will ultimately have to decide when fame is a good thing and when fame is a bad thing. The answer varies from person to person, and there is not necessarily a right or wrong answer. You simply need to write a strong essay that supports your point of view. 6. Truth and Lies.
Looking at successful SAT essay examples can help prep you for the writing portion of the SAT. See sources for SAT sample essays to get your best score. ... Types of Writing; Essays; SAT Writing Examples: Sources for Sample Essays By Matt Salter, B.A. , Staff Writer . Updated September 13, 2022 Image Credits.
SAT Essay Writing Guide with Sample Prompts (Fifth Edition) - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Besides the sample essays, the book provides information about the revised SAT test and its scoring process. It also includes detailed guidance on the new SAT essay section: why the essay should be taken, format of the essay tasks, how to develop a top ...
The SAT writing and language test consists of 44 multiple-choice questions that you'll have 35 minutes to complete. The questions are designed to test your knowledge of grammatical and stylistic topics. The SAT Writing and Language questions ask about a variety of grammatical and stylistic topics. If you like to read and/or write, the SAT may ...
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
SAT Essay prompts are unlike any other writing assignment. The questions are extremely general, asking things like "is the world changing for the better," but they only ever require a very simplistic thesis statement about a complex idea.
Take a SAT practice test to prepare for your exam. Our practice exams are 100% free, full-length, and include answer explanations. ... Answer Some Sample Questions with Our Free SAT Practice Test Below . For our full-length SAT exams and practice sets (100% free), ... Reading & Writing: 54: 64 (Two 32-Minute Modules) Math: 44: 70 (Two 35-Minute ...
How to Write an SAT Essay, Step by Step. Learn the ins and outs of writing a perfect-scoring SAT essay by following along as we go through the reading, analyzing and planning, writing, and revising stages of a sample essay. You'll get to see the whole process, from scribbled handwritten planning notes to the polished final product.
Below are a few examples of statistics from an official essay prompt of SAT, "Let There Be Dark" written by Paul Bogard. Example: In United States, 8 children born out of 10 will never get to know a sky dark enough for the Milky Way. Example: In Western Europe and the United States, the increase in the amount of light in the sky is about 6% ...
SAMPLE ESSAY PROMPT FOR THE CSN . ENGLISH PLACEMENT EXAM . 1. Prepare a multiple-paragraph writing sample of about 300-600 words on the topic below. Plan, write, review and edit. Read the prompt carefully before you begin to plan and write. Many people are philanthropists, giving money to those in need. Also, many people believe that those
The SAT essay rubric says that the best (that is, 4-scoring) essay uses " relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim (s) or point (s) made. " This means you can't just stick to abstract reasoning like this: The author uses analogies to hammer home his point that hot dogs are not sandwiches.