( 3 , 2 ) ( 3 , 2 )
( 2 , 3 ) ( 2 , 3 )
( 3 , 4 ) ( 3 , 4 )
( 5 , −4 ) ( 5 , −4 )
no solution
infinitely many solutions
ⓐ no solution, inconsistent, independent ⓑ one solution, consistent, independent
( 6 , 1 ) ( 6 , 1 )
( −3 , 5 ) ( −3 , 5 )
( 2 , 3 2 ) ( 2 , 3 2 )
( − 1 2 , −2 ) ( − 1 2 , −2 )
( 2 , −1 ) ( 2 , −1 )
( −2 , 3 ) ( −2 , 3 )
( 1 , 3 ) ( 1 , 3 )
( 4 , −3 ) ( 4 , −3 )
( 6 , 2 ) ( 6 , 2 )
( 1 , −2 ) ( 1 , −2 )
ⓐ Since both equations are in standard form, using elimination will be most convenient. ⓑ Since one equation is already solved for x , using substitution will be most convenient.
ⓐ Since one equation is already solved for y , using substitution will be most convenient. ⓑ Since both equations are in standard form, using elimination will be most convenient.
160 policies
Mark burned 11 calories for each minute of yoga and 7 calories for each minute of jumping jacks.
Erin burned 11 calories for each minute on the rowing machine and 5 calories for each minute of weight lifting.
The angle measures are 55 and 35.
The angle measures are 5 and 85.
The angle measures are 42 and 138.
The angle measures are 66 and 114.
The length is 60 feet and the width is 35 feet.
The length is 60 feet and the width is 38 feet.
It will take Clark 4 hours to catch Mitchell.
It will take Sally 1 1 2 1 1 2 hours to catch up to Charlie.
The rate of the boat is 11 mph and the rate of the current is 1 mph.
The speed of the canoe is 7 mph and the speed of the current is 1 mph.
The speed of the jet is 235 mph and the speed of the wind is 30 mph.
The speed of the jet is 408 mph and the speed of the wind is 24 mph.
206 adults, 347 children
42 adults, 105 children
13 dimes and 29 quarters
19 quarters and 51 nickels
3 pounds peanuts and 2 pounds cashews
10 pounds of beans, 10 pounds of ground beef
120 ml of 25% solution and 30 ml of 50% solution
125 ml of 10% solution and 125 ml of 40% solution
$42,000 in the stock fund and $8000 in the savings account
$1750 at 11% and $5250 at 13%
Bank $4,000; Federal $14,000
$41,200 at 4.5%, $24,000 at 7.2%
ⓐ C ( x ) = 15 x + 25 , 500 C ( x ) = 15 x + 25 , 500
ⓑ R ( x ) = 32 x R ( x ) = 32 x
ⓓ 1,500 1,500 ; when 1,500 benches are sold, the cost and revenue will be both 48,000
ⓐ C ( x ) = 120 x + 150,000 C ( x ) = 120 x + 150,000
ⓑ R ( x ) = 170 x R ( x ) = 170 x
ⓓ 3,000 3,000 ; when 3,000 benches are sold, the revenue and costs are both $510,000
( 2 , −1 , 3 ) ( 2 , −1 , 3 )
( −2 , 3 , 4 ) ( −2 , 3 , 4 )
( −3 , 4 , −2 ) ( −3 , 4 , −2 )
( −2 , 3 , −1 ) ( −2 , 3 , −1 )
infinitely many solutions ( x , 3 , z ) ( x , 3 , z ) where x = z − 3 ; y = 3 ; z x = z − 3 ; y = 3 ; z is any real number
infinitely many solutions ( x , y , z ) ( x , y , z ) where x = 5 z − 2 ; y = 4 z − 3 ; z x = 5 z − 2 ; y = 4 z − 3 ; z is any real number
The fine arts department sold 75 adult tickets, 200 student tickets, and 75 child tickets.
The soccer team sold 200 adult tickets, 300 student tickets, and 100 child tickets.
ⓐ [ 3 8 −3 2 5 −3 ] [ 3 8 −3 2 5 −3 ] ⓑ [ 2 −5 3 8 3 −1 4 7 1 3 2 −3 ] [ 2 −5 3 8 3 −1 4 7 1 3 2 −3 ]
ⓐ [ 11 9 −5 7 5 −1 ] [ 11 9 −5 7 5 −1 ] ⓑ [ 5 −3 2 −5 2 −1 −1 4 3 −2 2 −7 ] [ 5 −3 2 −5 2 −1 −1 4 3 −2 2 −7 ]
{ x − y + 2 z = 3 2 x + y − 2 z = 1 4 x − y + 2 z = 0 { x − y + 2 z = 3 2 x + y − 2 z = 1 4 x − y + 2 z = 0
{ x + y + z = 4 2 x + 3 y − z = 8 x + y − z = 3 { x + y + z = 4 2 x + 3 y − z = 8 x + y − z = 3
ⓐ [ −2 3 0 −2 4 −1 −4 4 5 −2 −2 −2 ] [ −2 3 0 −2 4 −1 −4 4 5 −2 −2 −2 ] ⓑ [ −2 3 0 −2 4 −1 −4 4 15 −6 −6 −6 ] [ −2 3 0 −2 4 −1 −4 4 15 −6 −6 −6 ] ⓒ [ −2 3 0 −2 3 4 −13 −16 −8 15 −6 −6 −6 ] [ −2 3 0 −2 3 4 −13 −16 −8 15 −6 −6 −6 ]
ⓐ [ 4 1 −3 2 2 −3 −2 −4 5 0 4 −1 ] [ 4 1 −3 2 2 −3 −2 −4 5 0 4 −1 ] ⓑ [ 8 2 −6 4 2 −3 −2 −4 5 0 4 −1 ] [ 8 2 −6 4 2 −3 −2 −4 5 0 4 −1 ] ⓒ [ 14 −7 −12 −8 2 −3 −2 −4 5 0 4 −1 ] [ 14 −7 −12 −8 2 −3 −2 −4 5 0 4 −1 ]
[ 1 −1 2 0 −3 −4 ] [ 1 −1 2 0 −3 −4 ]
[ 1 −1 3 0 −5 8 ] [ 1 −1 3 0 −5 8 ]
The solution is ( 4 , −1 ) . ( 4 , −1 ) .
The solution is ( −2 , 0 ) . ( −2 , 0 ) .
( 6 , −1 , −3 ) ( 6 , −1 , −3 )
( 5 , 7 , 4 ) ( 5 , 7 , 4 )
infinitely many solutions ( x , y , z ) , ( x , y , z ) , where x = z − 3 ; y = 3 ; z x = z − 3 ; y = 3 ; z is any real number.
infinitely many solutions ( x , y , z ) , ( x , y , z ) , where x = 5 z − 2 ; y = 4 z − 3 ; z x = 5 z − 2 ; y = 4 z − 3 ; z is any real number.
ⓐ −14 ; −14 ; ⓑ −28 −28
ⓐ 2 ⓑ −15 −15
ⓐ 3 ⓑ 11 ⓒ 2
ⓐ −3 −3 ⓑ 2 ⓒ 3
( − 15 7 , 24 7 ) ( − 15 7 , 24 7 )
( −2 , 0 ) ( −2 , 0 )
( −9 , 3 , −1 ) ( −9 , 3 , −1 )
( −6 , 3 , −2 ) ( −6 , 3 , −2 )
infinite solutions
The solution is the grey region.
No solution.
ⓐ { 30 m + 20 p ≤ 160 2 m + 3 p ≤ 15 { 30 m + 20 p ≤ 160 2 m + 3 p ≤ 15 ⓑ
ⓐ { a ≥ p + 5 a + 2 p ≤ 400 { a ≥ p + 5 a + 2 p ≤ 400 ⓑ
ⓐ { 0.75 d + 2 e ≤ 25 360 d + 110 e ≥ 1000 { 0.75 d + 2 e ≤ 25 360 d + 110 e ≥ 1000 ⓑ
ⓐ { 140 p + 125 j ≥ 1000 1.80 p + 1.25 j ≤ 12 { 140 p + 125 j ≥ 1000 1.80 p + 1.25 j ≤ 12 ⓑ

Section 4.1 Exercises
( 0 , 2 ) ( 0 , 2 )
( 2 , 4 ) ( 2 , 4 )
( −2 , 2 ) ( −2 , 2 )
( 3 , 3 ) ( 3 , 3 )
( 6 , −4 ) ( 6 , −4 )
No solutions, inconsistent, independent
1 point, consistent and independent
infinite solutions, consistent, dependent
( 1 , −4 ) ( 1 , −4 )
( −3 , 2 ) ( −3 , 2 )
( −1 / 2 , 5 / 2 ) ( −1 / 2 , 5 / 2 )
( −5 , 4 ) ( −5 , 4 )
( 0 , 10 ) ( 0 , 10 )
( 4 , −2 ) ( 4 , −2 )
( 4 , 0 ) ( 4 , 0 )
( 4 , 5 ) ( 4 , 5 )
( 7 , 12 ) ( 7 , 12 )
( −3 , −5 ) ( −3 , −5 )
( 2 , −3 ) ( 2 , −3 )
( −11 , 2 ) ( −11 , 2 )
( 6 / −9 , 24 / 7 ) ( 6 / −9 , 24 / 7 )
infinitely many
ⓐ substitution ⓑ elimination
ⓐ elimination ⓑ substituion
Answers will vary.
Section 4.2 Exercises
−7 −7 and −19 −19
22 and −67 −67
Eighty cable packages would need to be sold to make the total pay the same.
Mitchell would need to sell 120 stoves for the companies to be equal.
8 and 40 gallons
1000 calories playing basketball and 400 calories canoeing
Oranges cost $2 per pound and bananas cost $1 per pound
Package of paper $4, stapler $7
Hot dog 150 calories, cup of cottage cheese 220 calories
Owen will need 80 quarts of water and 20 quarts of concentrate to make 100 quarts of lemonade.
53.5 53.5 degrees and 36.5 36.5 degrees
16 degrees and 74 degrees
134 degrees and 46 degrees
37 degrees and 143 degrees
16 ° 16 ° and 74 ° 74 °
45 ° 45 ° and 45 ° 45 °
Width is 41 feet and length is 118 feet.
Width is 10 feet and length is 40 feet.
1.5 1.5 hour
Boat rate is 16 mph and current rate is 4 mph.
Boat rate is 18 mph and current rate is 2 mph.
Jet rate is 265 mph and wind speed is 22 mph.
Jet rate is 415 mph and wind speed is 25 mph.
Section 4.3 Exercises
110 adult tickets, 190 child tickets
6 good seats, 10 cheap seats
92 adult tickets, 220 children tickets
13 nickels, 3 dimes
42 dimes, 8 quarters
17 $10 bills, 37 $20 bills
80 pounds nuts and 40 pounds raisins
9 pounds of Chicory coffee, 3 pounds of Jamaican Blue Mountain coffee
10 bags of M&M’s, 15 bags of Reese’s Pieces
7.5 7.5 liters of each solution
80 liters of the 25% solution and 40 liters of the 10% solution
240 liters of the 90% solution and 120 liters of the 75% solution
$1600 at 8%, 960 at 6%
$28,000 at 9%, $36,000 at 5.5 % 5.5 %
$8500 CD, $1500 savings account
$55,000 on loan at 6% and $30,000 on loan at 4.5 % 4.5 %
ⓐ C ( x ) = 5 x + 6500 C ( x ) = 5 x + 6500
ⓑ R ( x ) = 10 x R ( x ) = 10 x
ⓓ 1,500; when 1,500 water bottles are sold, the cost and the revenue equal $15,000
Section 4.4 Exercises
( 4 , 5 , 2 ) ( 4 , 5 , 2 )
( 7 , 12 , −2 ) ( 7 , 12 , −2 )
( −3 , −5 , 4 ) ( −3 , −5 , 4 )
( 2 , −3 , −2 ) ( 2 , −3 , −2 )
( 6 , −9 , −3 ) ( 6 , −9 , −3 )
( 3 , −4 , −2 ) ( 3 , −4 , −2 )
( −3 , 2 , 3 ) ( −3 , 2 , 3 )
( −2 , 0 , −3 ) ( −2 , 0 , −3 )
x = 203 16 ; y = –25 16 ; z = –231 16 ; x = 203 16 ; y = –25 16 ; z = –231 16 ;
( x , y , z ) ( x , y , z ) where x = 5 z + 2 ; y = −3 z + 1 ; z x = 5 z + 2 ; y = −3 z + 1 ; z is any real number
( x , y , z ) ( x , y , z ) where x = 5 z − 2 ; y = 4 z − 3 ; z x = 5 z − 2 ; y = 4 z − 3 ; z is any real number
$20, $5, $10
Section 4.5 Exercises
ⓐ [ 2 4 −5 3 −2 2 ] [ 2 4 −5 3 −2 2 ] ⓑ [ 3 −2 −1 −2 −2 1 0 5 5 4 1 −1 ] [ 3 −2 −1 −2 −2 1 0 5 5 4 1 −1 ]
ⓐ [ 2 −5 −3 4 −3 −1 ] [ 2 −5 −3 4 −3 −1 ] ⓑ [ 4 3 −2 −3 −2 1 −3 4 −1 −4 5 −2 ] [ 4 3 −2 −3 −2 1 −3 4 −1 −4 5 −2 ]
{ 2 x − 4 y = −2 3 x − 3 y = −1 { 2 x − 4 y = −2 3 x − 3 y = −1
{ 2 x − 2 y = −1 2 y − z = 2 3 x − z = −2 { 2 x − 2 y = −1 2 y − z = 2 3 x − z = −2
ⓐ [ 3 2 1 4 −6 −3 ] [ 3 2 1 4 −6 −3 ] ⓑ [ 12 8 4 4 −6 −3 ] [ 12 8 4 4 −6 −3 ] ⓒ [ 12 8 4 24 −10 −5 ] [ 12 8 4 24 −10 −5 ]
ⓐ [ 2 1 −4 5 6 −5 2 3 3 −3 1 −1 ] [ 2 1 −4 5 6 −5 2 3 3 −3 1 −1 ] ⓑ [ 2 1 −4 5 6 −5 2 3 3 −3 1 −1 ] [ 2 1 −4 5 6 −5 2 3 3 −3 1 −1 ] ⓒ [ 2 1 −4 5 6 −5 2 3 −4 7 −6 7 ] [ 2 1 −4 5 6 −5 2 3 −4 7 −6 7 ]
[ 1 −2 3 −4 0 5 −11 17 0 1 −10 7 ] [ 1 −2 3 −4 0 5 −11 17 0 1 −10 7 ]
( 1 , −1 ) ( 1 , −1 )
( −2 , 5 , 2 ) ( −2 , 5 , 2 )
infinitely many solutions ( x , y , z ) ( x , y , z ) where x = 1 2 z + 4 ; y = 1 2 z − 6 ; z x = 1 2 z + 4 ; y = 1 2 z − 6 ; z is any real number
infinitely many solutions ( x , y , z ) ( x , y , z ) where x = 5 z + 2 ; y = −3 z + 1 ; z x = 5 z + 2 ; y = −3 z + 1 ; z is any real number
Section 4.6 Exercises
ⓐ 6 ⓑ −14 −14 ⓒ −6 −6
ⓐ 9 ⓑ −3 −3 ⓒ 8
( 7 , 6 ) ( 7 , 6 )
( −9 , 3 ) ( −9 , 3 )
inconsistent
Section 4.7 Exercises
ⓐ false ⓑ true
ⓐ { f ≥ 0 p ≥ 0 f + p ≤ 20 2 f + 5 p ≤ 50 { f ≥ 0 p ≥ 0 f + p ≤ 20 2 f + 5 p ≤ 50 ⓑ
ⓐ { c ≥ 0 a ≥ 0 c + a ≤ 24 a ≥ 3 c { c ≥ 0 a ≥ 0 c + a ≤ 24 a ≥ 3 c ⓑ
ⓐ { w ≥ 0 b ≥ 0 27 w + 16 b > 80 3.20 w + 1.75 b ≤ 10 { w ≥ 0 b ≥ 0 27 w + 16 b > 80 3.20 w + 1.75 b ≤ 10 ⓑ
ⓐ { w ≥ 0 r ≥ 0 w + r ≥ 4 270 w + 650 r ≥ 1500 { w ≥ 0 r ≥ 0 w + r ≥ 4 270 w + 650 r ≥ 1500 ⓑ
Review Exercises
( 3 , −1 ) ( 3 , −1 )
one solution, consistent system, independent equations
( 3 , 1 ) ( 3 , 1 )
( 4 , −1 ) ( 4 , −1 )
elimination
50 irises and 150 tulips
10 calories jogging and 10 calories cycling
35 ° 35 ° and 55 ° 55 °
the length is 450 feet, the width is 264 feet
1 2 1 2 an hour
the rate of the jet is 395 mph, the rate of the wind is 7 mph
41 dimes and 11 pennies
46 2 3 46 2 3 liters of 30% solution, 23 1 3 23 1 3 liters of 60% solution
$29,000 for the federal loan, $14,000 for the private loan
( −3 , 2 , −4 ) ( −3 , 2 , −4 )
[ 4 3 0 −2 1 −2 −3 7 2 −1 2 −6 ] [ 4 3 0 −2 1 −2 −3 7 2 −1 2 −6 ]
{ x − 3 z = −1 x − 2 y = −27 − y + 2 z = 3 { x − 3 z = −1 x − 2 y = −27 − y + 2 z = 3
ⓐ [ 1 −3 −2 4 4 −2 −3 −1 2 2 −1 −3 ] [ 1 −3 −2 4 4 −2 −3 −1 2 2 −1 −3 ] ⓑ [ 2 −6 −4 8 4 −2 −3 −1 2 2 −1 −3 ] [ 2 −6 −4 8 4 −2 −3 −1 2 2 −1 −3 ] ⓒ [ 2 −6 −4 8 4 −2 −3 −1 0 −6 −1 5 ] [ 2 −6 −4 8 4 −2 −3 −1 0 −6 −1 5 ]
( −2 , 5 , −2 ) ( −2 , 5 , −2 )
ⓐ { b ≥ 0 n ≥ 0 b + n ≤ 40 12 b + 18 n ≥ 500 { b ≥ 0 n ≥ 0 b + n ≤ 40 12 b + 18 n ≥ 500 ⓑ
Practice Test
( 2 , 1 ) ( 2 , 1 )
( 2 , −2 , 1 ) ( 2 , −2 , 1 )
15 liters of 1% solution, 5 liters of 5% solution
The candy cost $20; the cookies cost $5; and the popcorn cost $10.
ⓐ { C ≥ 0 L ≥ 0 C + 0.5 L ≤ 50 L ≥ 3 C { C ≥ 0 L ≥ 0 C + 0.5 L ≤ 50 L ≥ 3 C ⓑ
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/intermediate-algebra/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Lynn Marecek
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Intermediate Algebra
- Publication date: Mar 14, 2017
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/intermediate-algebra/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/intermediate-algebra/pages/chapter-4
© Feb 9, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Alg2.4 Exponential Functions and Equations
In this unit, students build on their understanding of exponential functions from an earlier course. Previously, they saw functions whose domain is the integers. Here, they write, interpret, and evaluate exponential functions whose domain is the real numbers. In the second half of the unit, students learn about logarithms in base 2 and 10 as a way to express the exponent that makes an exponential equation true. They then use logarithms to solve exponential equations and to answer questions about exponential functions. During this time, students encounter the constant \(e\) and learn that it is used to model situations with continuous growth rates, leading to working with the natural logarithm. The unit ends with an exposure to logarithmic functions.
Growing and Shrinking
- 1 Growing and Shrinking
- 2 Representations of Growth and Decay
Understanding Non-Integer Inputs
- 3 Understanding Rational Inputs
- 4 Representing Functions at Rational Inputs
- 5 Changes Over Rational Intervals
- 6 Writing Equations for Exponential Functions
- 7 Interpreting and Using Exponential Functions
Missing Exponents
- 8 Unknown Exponents
- 9 What is a Logarithm?
- 10 Interpreting and Writing Logarithmic Equations
- 11 Evaluating Logarithmic Expressions
The Constant $e$
- 12 The Number $e$
- 13 Exponential Functions with Base $e$
- 14 Solving Exponential Equations
Logarithmic Functions and Graphs
- 15 Using Graphs and Logarithms to Solve Problems (Part 1)
- 16 Using Graphs and Logarithms to Solve Problems (Part 2)
- 17 Logarithmic Functions
- 18 Applications of Logarithmic Functions
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 4 Answer Key
Anyone who wishes to prepare Grade concepts can get a strong foundation by accessing the Eureka Math Book Answer Key. People of highly subject expertise prepared the solutions in a concise manner for easy grasping. Start answering all the questions given in Eureka Math Book Grade 2 Answer Key. Refer to our Eureka Math Answers Grade 2 chapter 4 to enhance your math skills and also to score good marks in the exams.
Engage NY Eureka Math 2nd Grade Module 4 Lesson 4 Answer Key
Eureka’s Math Answer Key for Grade 2 meets the content and intent of the school curriculum. By using the Eureka Math Grade 2 Answer Key, you can understand the topics of all chapters easily. Detailed solutions provided make it easy for you to grab Knowledge and learn the underlying concepts. Download Eureka Math Answers Grade 2 pdf for free. Tp the links and practise well for the exams.
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 4 Problem Set Answer Key
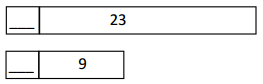
Answer: 23 – 9 = 24 – 10 = 14.
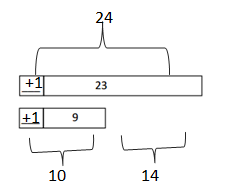
Answer: 32 – 19 = 33 – 20 = 13.
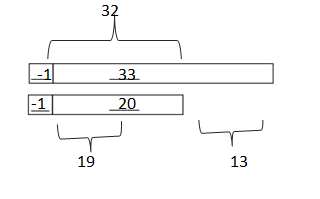
c. 50 – 29 = ___51-30_______ = ___21___
Answer: 50 – 29 = 51 – 30 = 21.
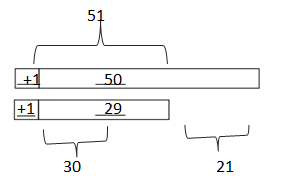
d. 47 – 28 = __49 – 30________ = __19____
Answer: 47 – 28 = 49 – 30 = 19.
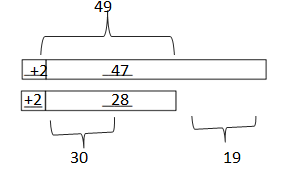
Answer: 29 + 46 = 30 + 45 = 75.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Draw and label a tape diagram to add tens. 29 + 46 = 75. 30 + 45 = 75. 29 + 46 = 30 + 45 = 75.
b. 38 + 45 = ___40_+_43_____ = __83____
Answer: 38 + 45 = 40 + 43 = 83.
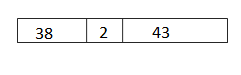
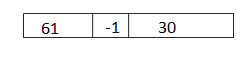
c. 61 + 29 = __60_+_30______ = __90____
Answer: 61 + 29 = 60 + 30 = 90.
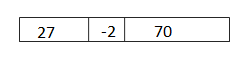
d. 27 + 68 = ____25_+_70____ = __95____
Answer: 27 + 68 = 70 + 25 = 95.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Draw and label a tape diagram to add tens. 27 + 68 = 95. 70 + 25 = 95. 27 + 68 = 70 + 25 = 95.
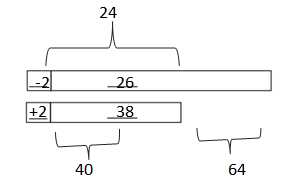
Question 1. Solve. Draw a tape diagram or number bond to add or subtract tens. Write the new number sentence. a. 26 + 38 = _24_+_40_______ = __64____
Answer: 26 + 38 = 24 + 40 = 64.
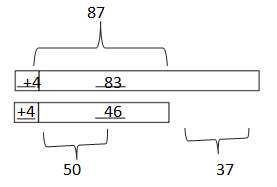
b. 83 – 46 = _87_-__50______ = __37____
Answer: 83 – 46 = 87 – 50 = 37.
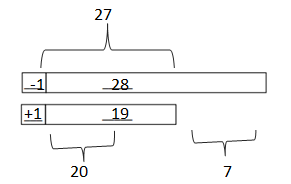
Question 2. Craig checked out 28 books at the library. He read and returned some books. He still has 19 books checked out. How many books did Craig return? Draw a tape diagram or number bond to solve.
Answer: The number of books did Craig return = 9.
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 4 Homework Answer Key
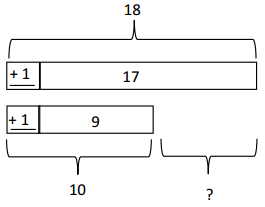
Answer: 17 – 9 = 18 – 10 = 8.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Draw and label a tape diagram to subtract tens. 17 – 9 = 8. 18 – 10 = 8. 17 – 9 = 18 – 10 = 8.

Answer: 33 – 19 = 34 – 20 = 14.
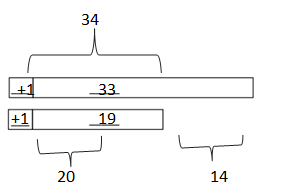
c. 60 – 29 = ___61_-_30_____ = ___31___
Answer: 60 – 29 = 61 – 30 = 31.
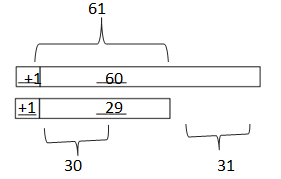
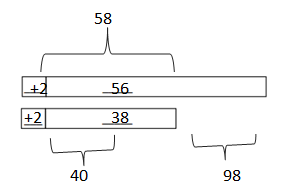
d. 56 – 38 = ___58_-_40_____ = ___18___
Answer: 56 – 38 = 58 – 40 = 18.
Answer: 28 + 43 = 71.
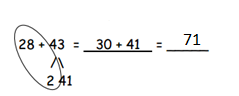
b. 49 + 26 = ___50_+_25____ = _75____
Answer: 49 + 26 = 75.
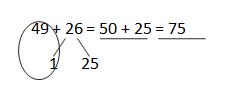
c. 43 + 19 = __45__+__17___ = _62____
Answer: 43 + 19 = 62.
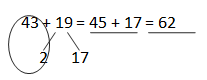
d. 67 + 28 = _70__+__25____ = ___95___
Answer: 67 + 28 = 95.
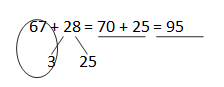
Question 3. Kylie has 28 more oranges than Cynthia. Kylie has 63 oranges. How many oranges does Cynthia have? Draw a tape diagram or number bond to solve.
Answer: The number of oranges does Cynthia has = 35.
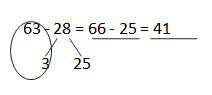
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Precalculus
- Signup / Login

How to Use a Math Medic Answer Key
Written by Luke Wilcox published 3 years ago
Answer key might be the wrong term here. Sure, the Math Medic answer keys do provide the correct answers to the questions for a lesson, but they have been carefully designed to do much more than this. They are meant to be the official guide to teaching the lesson, providing specific instructions for what to do and say to make a successful learning experience for your students.
Before we look at the details of the answer key, let's make sure we understand the instructional model first.
Experience First, Formalize Later (EFFL)
A typical Math Medic lesson always has the same four parts: Activity, Debrief Activity, QuickNotes, and Check Your Understanding. Here are the cliff notes:
Activity: Students are in groups of 2 - 4 working collaboratively through the questions in the Activity. The teacher is checking in with groups and using questions, prompts, and cues to get students to refine their communication and understanding. As groups finish the activity, the teacher asks students to go to the whiteboard to write up their answers to the questions.
Debrief Activity: In the whole group setting, the teacher leads a discussion about the student responses to the questions in the activity, often asking students to explain their thinking and reasoning about their answers. The teacher then formalizes the learning by highlighting key concepts and introducing new vocabulary, notation, and formulas.
QuickNotes: The teacher uses direct instruction to summarize the learning from the activity in the QuickNotes box - making direct connections to the learning targets for the lesson.
Check Your Understanding: Students are then asked to apply their learning from the lesson to a new context in the Check Your Understanding (CYU) problem. This can be done individually or in small groups. The CYU is very flexible in it's use, as it can be used as an exit ticket, a homework problem, or a quick review the next day.
How Do I See EFFL in the Answer Key?
You will see EFFL in the answer key like this:

Anything written in blue is something we expect our students to produce. This might not be quite what we expect by the end of the lesson, but provides us with a starting point when we move to formalization.
Anything written in red is an idea added by the teacher - the formalization of the learning that happened during the Activity. Students are expected to add these "notes" to their Activity using a red pen or marker.
What Do Students Write Down For Notes?
By the end of the lesson, students will have written down everything you see on the Math Medic Answer Keys. The most important transition is when students finish the Activity and we move to Debrief Activity. "Students, now is the time for you to put down your pencils and get out your your red Paper Mate flair pens" We give each student a Paper Mate flair pen at the beginning of the school year and tell them they must cherish and protect it with their life. They all think we should be sponsored by Paper Mate (anyone have any leads on this?)
The lessons you see on Math Medic are all of the notes we use with our students. We do not have some secret collection of guided notes.
Do Students Have Access to Answer Keys?
Yes! Any student can create a free Math Medic account to get access to the answer keys. We often send students to the website when they are absent from a lesson or when we don't quite finish the lesson in class. We are comfortable with students having access to these answer keys because we do not think Math Medic lessons should be used as a summative assessment or be used for a grade (unless it's for completion). Our lessons are meant to be the first steps in the formative process of learning new concepts.
Math Medic Help

Home > CC2 > Chapter 4 > Lesson 4.2.1
Lesson 4.1.1, lesson 4.1.2, lesson 4.2.1, lesson 4.2.2, lesson 4.2.3, lesson 4.2.4, lesson 4.3.1, lesson 4.3.2, lesson 4.3.3.
© 2022 CPM Educational Program. All rights reserved.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- enVision Math
- EngageNY Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Texas Go Math Grade 4 Lesson 2.4 Answer Key Relate Hundredths and Decimals
Refer to our Texas Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key Pdf to score good marks in the exams. Test yourself by practicing the problems from Texas Go Math Grade 4 Lesson 2.4 Answer Key Relate Hundredths and Decimals.
Essential Question
How can you record hundredths as fractions and decimals? Answer: We know that, The representation of the hundredths in the place-value chart is: 0.01 So, The representation of the hundredths in the form of a fraction is: \(\frac{1}{100}\) Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The representation of the hundredths in the form of a fraction is: \(\frac{1}{100}\) The representation of the hundredths in the form of a decimal number is 0.01
Unlock the problem
In the 2008 Summer Olympic Games, the winning time in the men’s 100-meter butterfly race was only \(\frac{1}{100}\) second faster than the second-place time. What decimal represents this fraction of a second? • Circle the numbers you need to use. Answer: It is given that In the 2008 Summer Olympic Games, the winning time in the men’s 100-meter butterfly race was only \(\frac{1}{100}\) second faster than the second-place time Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The numbers we need to use are: 1 and 100
You can write hundredths as fractions or decimals.

Mathematical Processes Explain how the size of one-tenth is related to the size one hundredth. Answer: We know that, One-hundredth is the tenth of the one-tenth Hence, from the above, We can conclude that One-hundredth = \(\frac{1}{10}\) × One-tenth
Alicia Won her 400-meter freestyle race by 4\(\frac{25}{100}\) seconds. How can you write this mixed number as a decimal?

Share and Show

Write the fraction or mixed number and the decimal shown by the model.

Mathematical Processes Are 0.5 and 0.50 equivalent? Explain. Answer: The given decimal numbers are: 0.5 and 0.50 Now, We know that, If zero is placed on the right side as the last digit in the decimal number, then that zero don’t have any value So, 0.5 = 0.50 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that 0.5 and 0.50 are equivalent
Problem Solving

Question 6. Write Math Explain how one whole, one-tenth, and one hundredth are related. Answer: We know that, “One-whole” is represented as 1 “One-tenth” is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of 1 “One-hundredth” is \(\frac{1}{10}\) of “One-tenth” and \(\frac{1}{100}\) of 1 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that One-hundredth = \(\frac{1}{10}\) of “One-tenth” = \(\frac{1}{100}\) of 1
Sense or Nonsense?

Daily Assessment Task
Fill in the bubble completely to show your answer.

TEXAS Test Prep

Texas Go Math Grade 4 Lesson 2.4 Homework and Practice Answer Key
Relate Hundredths and Decimals

Whose statement makes sense? whose statement is nonsense? Explain your reasoning. Answer: It is given that Emma said, “It is seventy-five hundredths of a mile to Waterslide Park.” Charles said, “It is seven and five-tenths miles to Waterslide Park.” Now, The representation of seventy-five hundredths in the Standard form is: 0.75 The representation of seven and five-tenths in the Standard form is: 7.5 It is given that The Waterslide park is: 0.75 miles Hence, from the above, We can conclude that Emma’s statement makes sense Charles’s statement makes not sense
Question 3. Jake said he has \(\frac{8}{100}\) of a dollar in his pocket. Margie said that the decimal for \(\frac{8}{100}\) is 0.8. What error did she make? What is the decimal form for \(\frac{8}{100}\)? Answer: It is given that Jake said he has \(\frac{8}{100}\) of a dollar in his pocket. Margie said that the decimal for \(\frac{8}{100}\) is 0.8 Now, The representation of \(\frac{8}{100}\) in the decimal form is: 0.08 Now, 0.8 represents only one digit after the decimal point But, From the given fraction, The digits after the decimal point must have 2 So, The error made by Margie is: The misinterprettion of digits after the decimal point Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The error made by Margie is: The misinterprettion of digits after the decimal point The representation of \(\frac{8}{100}\) in the decimal form is: 0.08
Lesson Check

Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.

COMMENTS
Answer Key Eureka Math® Grade 2 Module 4 TEKS EDITION Special thanks go to the Gordon A. Cain Center and to the Department of Mathematics at Louisiana State University for their support in the development of
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 10 Exit Ticket Answer Key. Question 1. Solve using the algorithm. Draw chips and bundle when you can. 27 + 137 = 164. Draw and bundle place value disks on the place value chart. 1 x 100 = 100. 3 x 10 = 30. 7 x 1 = 7.
The source for the homework pages is the full module PDF at this address:https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-2-mathematics-module-4
Engage NY Eureka Math 2nd Grade Module 2 Lesson 10 Answer Key Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 2 Lesson 10 Problem Set Answer Key. Use the RDW process to solve. Draw a tape diagram for each step. Problem 1 has been started for you. Question 1. Maura's ribbon is 26 cm long. Colleen's ribbon is 14 cm shorter than Maura's ribbon.
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
Engage NY Eureka Math 5th Grade Module 2 Lesson 10 Answer Key Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 2 Lesson 10 Problem Set Answer Key. ... Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 2 Lesson 10 Homework Answer Key. Question 1. Estimate the product. Solve using an area model and the standard algorithm. ... e. 73 × 2.4 ≈ __73_____ × ___2.4____ = __175.2_____ Answer ...
13. 2 (3u + 7) = -4 (3 - 2u) -6. 8 (2f - 2) = 7 (3f + 2) Solving equations with the variable on each side. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
10.1 Finding Composite and Inverse Functions; 10.2 Evaluate and Graph Exponential Functions; 10.3 Evaluate and Graph Logarithmic Functions; 10.4 Use the Properties of Logarithms; 10.5 Solve Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
In the second half of the unit, students learn about logarithms in base 2 and 10 as a way to express the exponent that makes an exponential equation true. They then use logarithms to solve exponential equations and to answer questions about exponential functions. During this time, students encounter the constant and learn that it is used to ...
10.2 Practice Solutions. G 10.2 Practice Solutions.notebook 2 April 19, 2013 Oct 21-5:48 PM. Directions: Find the surface area. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. 13M i 6 in 52 n Directions: Find the lateral area. Leave in terms of and round to the nearest tenth. 20 20.1 cm
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Statistics and Probability with Applications - 9781319244323, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Statistics and Probability with Applications includes answers to chapter exercises ...
Exercise 8. Exercise 9. Exercise 10. Exercise 11. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Big Ideas Math Algebra 2: A Common Core Curriculum - 9781608408405, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
You can find the source for the homework pages at the link below. click on the "full module" PDF:https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-2-mathematics-module-4
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 4 Exit Ticket Answer Key. Question 1. Solve. Draw a tape diagram or number bond to add or subtract tens. Write the new number sentence. ... Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 4 Homework Answer Key. Question 1. Solve. Draw and label a tape diagram to subtract 10, 20, 30, 40, etc.
Lesson 2.4 Homework Answer Key Go Math Grade 2 Question 2. Draw and label points for 310, 348, and 420. Answer: Explanation: 1. Here is a number line between 400 and 500 2. There are 10 lines dividing the total distance into 10 equal parts. 3. One whole is divided into 10 equal parts. 4. At each new line we are adding 1.
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
List of Figures 3.1 Technical Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 3.2 The ALEKS Website for K-12 Education ...
Lesson 10.5. Section 10.6: Lesson 10.6. Exercise 1. Exercise 2. Exercise 3. Exercise 4. Exercise 5. Exercise 6. Exercise 7. ... you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for McDougal Littell Algebra 2 Practice Workbook includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the ...
A typical Math Medic lesson always has the same four parts: Activity, Debrief Activity, QuickNotes, and Check Your Understanding. Here are the cliff notes: Activity:Students are in groups of 2 - 4 working collaboratively through the questions in the Activity. The teacher is checking in with groups and using questions, prompts, and cues to get ...
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
The representation of the given model in the form of a decimal number is: 0.68. Go Math Lesson 2.4 4th Grade Answer Key Question 3. Answer: The given model is: Now, From the above model, We can observe that. The representation of the given model in the form of a fraction = (The number of shaded parts) ÷ (The total number of parts) = 8 100.
Exercise 91. Exercise 92. Exercise 93a. Exercise 93b. Exercise 93c. Exercise 94. Exercise 95. Exercise 96. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to College Algebra - 9780321729682, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.