Starting a Business | How To

How to Write a Business Plan in 7 Steps
Published February 2, 2024
Published Feb 2, 2024
WRITTEN BY: Mary King
Get Your Free Ebook
Your Privacy is important to us.
This article is part of a larger series on Starting a Business .
Starting A Business?
Step 1: Gather Your Information
Step 2: outline your business plan, step 3: write each section, step 4: organize your appendix, step 5: add final details, step 6: add a table of contents, step 7: get feedback, bottom line.
A solid business plan helps you forecast your future business and is a critical tool for raising money or attracting key employees or business partners. A business plan is also an opportunity to show why and how your business will become a success. Learning how to write a business plan successfully requires planning ahead and conducting financial and market research.
How to write a business plan step-by-step:
- Gather your information
- Outline your business plan
- Write each section
- Organize your appendix
- Add final details
- Add a table of contents
- Get feedback.
Your first step is to get organized by gathering all your relevant business information. This will save you time completing the various sections of your business plan. At a minimum, you’ll want to have the following handy:
- Business name, contact information, and address
- Owner(s) names, contact information, and addresses
- Names, contact information, and addresses of any business partners (if you will be working with partners)
- Resume and relevant work history for yourself and any key partners or employees
- Any significant sales, commerce, traffic, and financial data and forecasts
- Customer data (if applicable)
- Any significant data about your nearest competitors’ commerce, traffic, or finances
Now it’s time to outline your business plan, making note of the sections you need to include and what data you want to include in each section. You can create an outline on your own or use a business plan template to help. Whichever route you choose, it is common to include these sections in your business plan outline:
- Introduction
- Executive summary
- Company overview
- Products and services
- Market and industry analysis
- Marketing strategy
- Sales strategy
- Management and organization
- Financial data, analysis, and forecasts
Connect the data you gathered in step one to specific sections of your outline. Make a note if you need to convert some information into charts or images to make them more compelling for potential investors. For example, you’ll want to include relevant work history in your management section and convert your sales forecasts into charts for your financial data section.
Now it’s time to write your business plan. Attack this one section at a time, adding the relevant data as you go.
Executive Summary
The executive summary is an overview of the business plan and should ideally be one, but no more than two, pages in length. Some investors actually only request the executive summary. So make it an informative, persuasive, and concise version of your business plan.
It can be easier to write the executive summary last, after the other sections. Then you can more clearly understand which sections of your business plan are the most important to highlight in the executive summary.
When learning how to write an executive summary for a business plan, remember to include the following:
- Business objectives : Your business objectives are specific and attainable goals for your business. Create at least four business objectives organized by bullet point. If you’re not sure how to phrase your objectives, read our SMART goals examples to understand how to do so.
- Mission statement: The mission statement discusses the aim, purpose, and values of your business. It’s typically a short statement from one sentence to several sentences in length. You may find that your mission statement evolves as your business grows. Learn more on how to write your mission statement in our guide.
Consider also including the following in your executive summary:
- Business description : Similar to a 30-second pitch, describing your business and what makes it unique
- Products and services : The type of products and services you’re providing and their costs
- Competitors : Your biggest competitors and why your business will succeed despite them
- Management and organization : The owners’ backgrounds and how they will help the business succeed; management structure within the business
- Business location (or facility) : Location benefits and the surrounding area
- Target market and ideal customer : Who your ideal customers are and why they’re going to purchase your products or services
- Financial data and projections : Provide brief financial data and projections relevant to your business, such as startup costs, at what month the business will be profitable, and forecasted sales data
- Financing needed : Explanation of the startup funding sources and the amount of financing being requested
The bullets above can be combined into several paragraphs. You can add or remove sections based on your business’ needs. For example, if you don’t have a physical location, you might remove that piece of information. Or, if a web presence is crucial to your success, include two to three sentences about your online strategy .
Company Overview
The company overview (sometimes also called a “business overview”) section highlights your company successes (if you’re already in business) or why it will be successful (if you’re a startup). In the opening paragraph or paragraphs, provide information like location, owners, hours of operation, products, and services.
How you structure this section depends on whether you’re a startup or an established business. A startup will discuss the general expenses and steps needed to open the business, such as permits, build-outs, rent, and marketing. An established business will briefly discuss the company’s financial performance over the past three years.
If you’re trying to raise capital from an investor or bank, include a chart listing the items your business will acquire with the capital. For example, if you’re purchasing equipment with the additional funding, list each piece of equipment and the associated cost. At the bottom of the chart, show the total of all expenses, which should be the requested amount of funding.
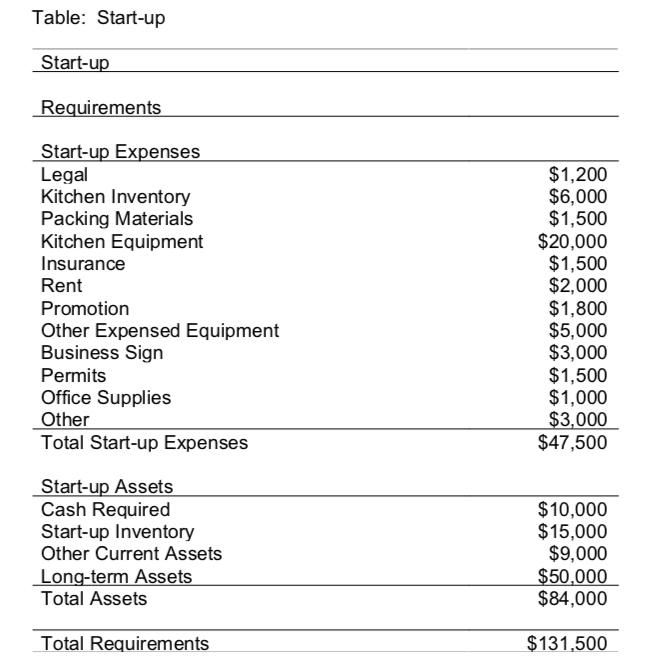
This startup cost table for a pizza restaurant separates startup expenses from startup assets.
Your company overview should cover the following:
- Location & Facilities : If you have a brick-and-mortar location or a facility, like a warehouse, describe it here. Detail the benefits of your location and the surrounding areas. Write about square footage, leases or ownership, the surrounding area, and a brief description of the population.
- Ownership : Briefly mention the company ownership team and their backgrounds. Show why these owners are likely to be successful in operating this business by providing certain details, such as each owner’s industry experience, previous employers, education, and awards. This will be discussed more in-depth in the management and organization section below.
- Competitive advantage : Ideally, your competitive advantage is what your business can do that your competitors cannot. It’s the one big differentiator that will make your company successful. Many investors are looking for specific competitive advantages, such as patents, proprietary tech, data, and industry relationships. If you don’t have these, describe the top aspect in which your business will do better than competitors, such as quality of products, quality of services, relationships with vendors, or marketing strategy.
Products & Services
The products and services section is the most flexible section because its structure depends on what your business sells. Regardless of what you’re selling, include a description of your business model to explain how your business makes money. Also include future products or services your business could provide one, two, or five years down the road.
List and describe all physical and digital products you plan to sell, as well as any services the business provides. Services don’t necessarily have to be sold for a cost—your business might offer entertainment, like live music or bar games as a free service.
Whether you’re selling products, services, or both, it’s important to discuss fulfillment, or how each will be delivered. If you make or sell physical products, describe how products will be sold, assembled, packed, and shipped. If your business is service-based, describe how a service, such as a window installation, will be ordered and completed. Where will the glass be purchased from and acquired, how will customers place orders, and how will the window be installed?
Market & Industry Analysis
The market and industry analysis section is where you analyze potential customers and the forces that influence your industry. This section is where you make the case as to why your business should succeed, ideally backed by data. You’ll want to do a deep dive into your competitors and discuss their challenges and successes. Learn more about sales targeting to improve how you approach your sales strategy.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation, or your target market, consists of the customers who are most likely to purchase your products or services. Describe these groups of customers based on demographics, including attributes like age, income, location, and buying habits. Additionally, if you’ll be operating with a business-to-business (B2B) model, use characteristics to describe the ideal businesses to which you’ll sell.
Once your target market is segmented into groups, use market research data to show that those customers are physically located near your business (or are likely to do business with you if you’re online). If you’re opening a daycare, for example, you’ll want to show the data on how many families are in a certain mile radius around your business. You can obtain this kind of data from a free resource, like the U.S. Census and ReferenceUSA .
Once you have at least three segments, briefly outline the strategy you’ll use to reach them. Most likely it will be a combination of marketing, pricing, networking, and sales.
Learn the best approach to product pricing in our guide.
Industry Analysis
Take a look at your business’s industry and explain why it’s a great idea to start a business in that niche. If you’re in a growing industry, a bank is more likely to lend your business capital because it’s predicted to be in demand and have additional customers. Learn about how to find a niche market .
Find industry statistics from a free tool, like the Bureau of Labor Statistics , or a paid tool like the Hoovers Industry Research , which provides professionally curated reports for over 1,000 industries.
Competitor Research
Wrap up the market and industry analysis section by analyzing at least five competitors within a five-mile radius (expand the radius, if needed). Create a table with the five competitors and mention their distance from your business (if applicable), along with their challenges, and successes.
During your analysis, you’ll want to frame their challenges as something you can improve upon. Persuade your reader that your business will provide superior products and services than the competitors.
Marketing Strategy & Implementation Summary
In the opening paragraphs of your marketing strategy and implementation summary, give an overview of the subsections below.
Include any industry trends you may take advantage of. If applicable, include the advertising strategy and budget, stating specific channels. Mention who in the business will be responsible for overseeing the marketing.
Include any platforms and tools the business will use, like your website, social media, email marketing, and video. If you’re hiring a company to do any online work, like creating a website or managing social media, briefly describe them and the overall cost (you can elaborate more on costs in the financial data section ).
Don’t forget to include a subsection for your traditional marketing plan. Traditional marketing encompasses anything not online, such as business cards, flyers, local media, direct mail, magazine advertising, and signage.
Sales Strategy
If sales is an important component of your business, include a section about your sales strategy. Describe the role of the salesperson (or persons), strategies they’ll use to close the deal with clients, lead follow-up procedures, and networking they’ll attend. Also, list any training your sales staff will attend.
Sales Forecast Table
A sales forecast table gives a high-level summary of where you expect your sales and expenses to occur for each of the next three years in business. In the paragraph before the table, state where you expect growth to come from and include a growth percentage rate. The annual sales forecast chart will be broken down further in the financial projections section below.
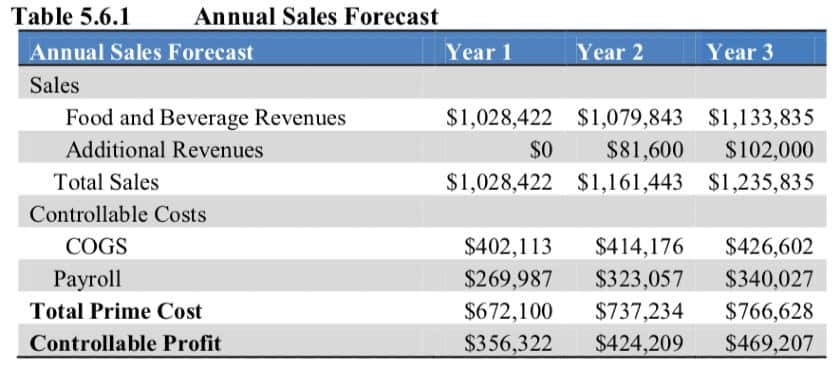
The annual sales forecast for this restaurant summarizes sales, cost, and profit for the first three years in business.
Pricing Strategy
In the pricing strategy section, discuss product/service pricing, competitor pricing, sales promotions , and discounts—basically anything related to the pricing of what you sell. You should discuss pricing in relation to product and service quality as well. Consider including an overview of pricing for specific products, e.g., pizza price discounts when ordering a specific number of pizzas for catering.
Milestones in a business plan are typically displayed in a table. They outline important tasks to do before the business opens (or expands, if already in business). For each milestone, include the name, estimated start and completion date, cost, person responsible, and department responsible (or outside company responsible). List at least seven milestones.
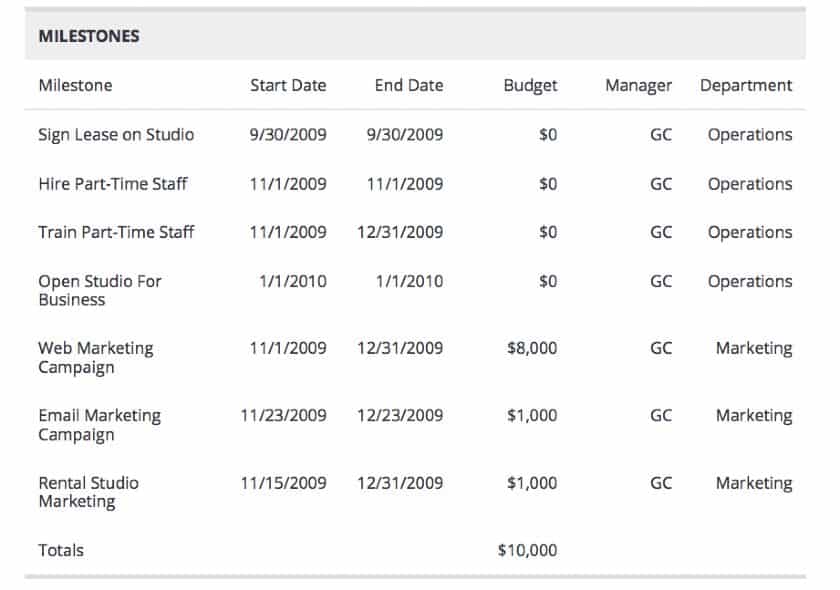
Milestones for this commercial photography business include hiring staff and completing marketing campaigns.
Management & Organization Summary
The management and organization summary is an in-depth look at the ownership background and key personnel. This is an important section because many investors say they don’t invest in companies, they invest in people. In this section, make the case why you and your team have the experience and knowledge to make this business a success.
Ownership Background
Discuss the owners’ backgrounds and place an emphasis on why that background will ensure the business succeeds. If you don’t have experience managing a retail business, consider finding a co-owner who does. Typically, banks won’t lend to someone who doesn’t have experience in the type of business they’re trying to open.
Management Team Gaps
If there are any experience or knowledge gaps within the management team, state them. List the consultants or employees you will hire to cover the gaps. Investors who know your industry well may recognize gaps within your business plan, and it’s important to state the gaps without waiting for the investor to bring it up. This makes it appear that you know the industry well.
Personnel Plan
The personnel plan outlines every position within your business for at least the next three years. In the opening paragraph, discuss the roles within the company and who will report to whom. Include a table with at least three years of salary projections for each employee in your business. Include a total salary figure at the bottom. This table may be broken down further into salaries for each month in the financial projections or appendix.
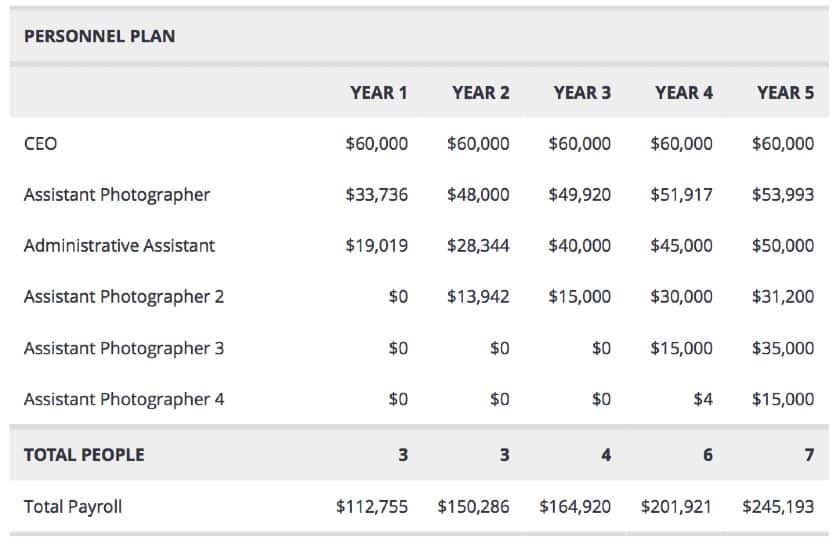
This commercial photography business has the CEO at the same salary every year, with their employees’ salaries increasing year over year.
Financial Data & Analysis
The financial data and analysis section is the most difficult part of a business plan. This section requires you to forecast income and expenses for the next three years. You’ll need a working knowledge of common financial statements, like the profit and loss statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
In the opening paragraphs of the financial data and analysis section, give an overview of the sections below. Discuss the break-even point and the projected profit at the first, second, and third year in business. State the assets and liabilities from the projected balance sheet as well.
If you’re getting a loan from a bank, say how long and from what source the loan will be repaid. One of the main pieces of information bankers want to ascertain from financial forecasting is if they will be paid back and how likely that is to happen.
You might also include the following financial reports:
- Break-even analysis : Break-even is when your business starts to make money. Break-even analysis is where you illustrate the point at which your revenue exceeds expenses and a profit occurs. In this section’s opening paragraph, state your monthly fixed costs and average percent variable costs (cost that changes with output, like labor or cost of goods). In the example below, variable costs increase 8% for every additional dollar made.
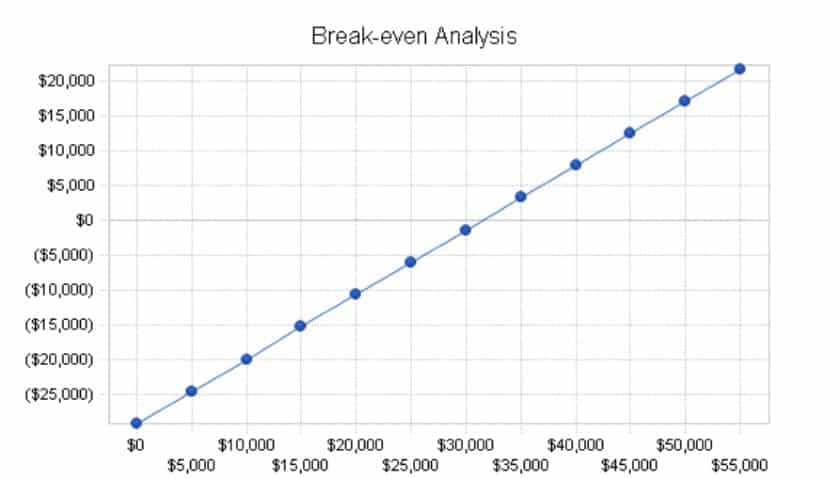
The break-even point for this document shredding business is $31,500 in a month.
- Projected profit & loss: The profit and loss table is a month-by-month breakdown of income and expenses (including startup expenses). Typically, you should expect your business to show a profit within the first year of operating and increase in years two and three. Be sure to show income and expenses month-by-month for the first two years in operation. Create a separate chart that shows income and expenses year-by-year for the first three years.
- Projected cash flow : The cash flow section shows your business’s monthly incoming and outgoing cash. It should cover the first two years in business. Mention what you plan to do with excess cash. See how to run a statement cash flow in QuickBooks Online .
- Projected balance sheet: The balance sheet shows the net worth of the business and the financial position of the company on a specific date. It focuses on the assets and liabilities of the business. Ideally, the balance sheet should show that the net worth of your business increases. Prepare a projected year-by-year balance sheet for the first three years.
- Business ratios: Also called financial ratios, these are a way to evaluate business performance. It’s helpful to compare your projected business ratios to the industry standard. Project your business ratios by year for the first three years.
The appendix is where you put information about the business that doesn’t fit in the above categories. What you put here largely depends on the type of business you’re creating. It’s a good idea to put any visual components in the appendix. A restaurant might add an image of the menu and an artist rendering of the interior and exterior, for example.
Consider including the following items in your business plan appendix:
- Artist mock-up of interior
- Building permits
- Equipment documentation
- Incorporation documents
- Leases and agreements
- Letters of recommendation
- Licenses and permits
- Marketing materials
- Media coverage
- Supplier agreements
An appendix isn’t required in a business plan, but it’s highly recommended for additional persuasion. Documents like media coverage, agreements, and equipment documentation show the investor and banker you’re serious about the business. If your appendix is more than 10 pages, consider creating a second table of contents just for the appendix.
Detailed Financial Projections
Put the more detailed projections in the appendix. The financial projections in the previous section is typically a year-by-year breakdown for three years in the future. But many bankers and investors want to see the first two years broken down month-by-month for at least the profit and loss statement, balance sheet, cash flow, and personnel plan.
Typically, you can print out the spreadsheet in smaller font and include it in the appendix. You don’t need to create additional charts for the appendix.
With all of your information organized, now it’s time to add the final details, like cover pages and a nondisclosure agreement (NDA).
- Cover Page: The cover page provides contact information about the business and its owner. The cover page should have the business name and who prepared it, including your name, address, phone number, and email address. Additionally, if the registered company name with the state is different from the business name, you may want to add that as a “company name.”
- Nondisclosure Agreement: An NDA ((also called a confidentiality agreement) is a legal document that safeguards business information. You’d want someone to sign it before reading your business plan if you believe they could use the information to their advantage and your disadvantage, such as to steal your business idea or marketing strategy.

Fit Small Business provides a free non-disclosure agreement.
Once your final details are added, proofread all the sections of your business plan, ensuring that the information is accurate and that all spelling and grammar are correct. If there are any illustrations, projections, or additional information you forgot to include, now is the time to add it.
The final step is adding a table of contents so that bankers and potential investors can easily navigate your business plan. A table of contents lists the sections and subsections of your business plan. All of the headers above (Executive Summary, Business Objectives, Company Overview, Products and Services, and so on) are considered sections of a business plan. You can number the sections for additional organization. For example, 1.0 is the executive summary, 1.1 is the business objectives, and 1.2 is the mission statement.
Editing and formatting can change the pagination of your business plan. So you’ll save yourself work if you finalize the business plan content first, then arrange the table of contents at the end.
Congratulations! You’ve captured your business idea and plan for profitability on paper. Before you send this business plan to loan officers and potential investors, ask friends, family, and other supportive business owners to read it and provide feedback. They may notice typos or other errors that you missed. They may also identify details you can add to make your business plan more persuasive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About How to Write a Business Plan
These are the most common questions I hear about writing a business plan.
What needs to be in a business plan?
What you should put in a business plan depends on its purpose and your industry. If you’re seeking funding from a bank or investor, you’re going to need most of the sections above, with a strong focus on your financial projections. If you are using your business plan to attract key employees (like a chef for your restaurant), mock-ups and vendor agreements will be more useful. Think about the information that will help your target reader make a decision about whether to get involved with your business—whether that is a location, a business model, or product idea—and be sure your business plan includes that information.
How do you write a business plan for a startup?
The business plan for a startup is similar to a business plan for an established business. The startup business plan will include startup costs, which will be listed by item and factored into the financial projections. Additionally, since your business hasn’t proven it can be successful yet, you may need additional information about the ownership, business model, market, and industry to convince the reader your business will succeed.
How long does it take to write a business plan?
A simple business plan may only take a couple of hours. However, for the business plan provided with this template, which includes financial projections, it may take over 60 hours to research the income and costs associated with running your business. You also have to format those costs into a chart, because it’s best to showcase the data with easy-to-understand charts.
Is writing a business plan hard?
Creating a business plan for funding from a bank or investor is a detailed process. Unless you have a background in financial statements, the financial projections may be difficult for the average business owner. But you can ask for help; it is common to hire a bookkeeper or accountant to assist you with financial projects to ensure your math is correct. Outside of the projections, most other business plan sections are simple, though you’ll want to give yourself time to make each section persuasive.
Every type of business, whether it’s a side hustle or a multimillion-dollar business, should have a business plan. The industry analysis and market segmentation sections validate your business idea. Researching and forecasting financial projections helps you logically think through income and expenses, which lessens the risk of business failure. Remember to get feedback on your business plan from business employees and associates. If necessary, have them sign an NDA before they review the plan.
About the Author

Find Mary On LinkedIn Twitter
Mary King is an expert restaurant and small business contributor at Fit Small Business. With more than a decade of small business experience, Mary has worked with some of the best restaurants in the world, and some of the most forward-thinking hospitality programs in the country. Mary’s firsthand operational experience ranges from independent food trucks to the grand scale of Michelin-starred restaurants, from small trades-based businesses to cutting-edge co-working spaces.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
How to make a business plan
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Small Business Tax Prep
Small Business Services
- Self-Employed
Small Business Owners
- Block Advisors News Center
- Build Your Business
- Manage Your Business
- All Categories
October 31, 2023
Block Advisors
How to Write a Business Plan Step-By-Step
October 31, 2023 • Block Advisors
QUICK ANSWER:
- A business plan outlines your business’s goals, services, financing, and more.
- Business plans vary in length and complexity but should always include an explanation of what your business will do and how it will do it.
- Business plans serve as a guide for business owners and employees and are key to boosting investor confidence.
Whether you’re a serial entrepreneur or just getting your first small business idea off the ground, creating a business plan is an important step. Good business planning will help you clarify your goals and objectives, identify strategies, and note any potential issues or roadblocks you might face.
Not every business owner chooses to write a business plan, but many find it to be a valuable step to take when starting a business. Creating a business plan can seem daunting and confusing at first. But taking the time to plan and research can be very beneficial, especially for first-time small business owners.
If you want to learn how to create a business plan or if you feel you just need a little business plan help, read on!
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan serves as a comprehensive document that outlines your business’s goals, services, financing, leadership, and more details essential to its success. Think of the plan as the who, what, and why of your new business:

Who are the major players in your business?
What goods or services do you offer and why are they important?
Why are you in business and why should customers choose you?
Business plans can range in complexity and length, but, at their core, all plans explain what the business will do and how it will do it. A business plan serves as a guide for business owners and employees and should boost investor confidence. Some important advantages of business plans include:
- Shows investors you have an in-demand product or service, a solid team to achieve business goals, and the potential for growth and scalability.
- Increases the likelihood of securing a business loan, locking in investments, or raising capital. >>Read: A Guide to Raising Capital as a Small Business Founder
- Helps recognize partnership opportunities with other companies.
- Identifies and defines competitors within your given industry.
Looking for an examples of a successful business plan? Check out the SBA’s business plan page for walkthroughs of different business plan outlines.
How to Write a Business Plan: 10 Simple Steps
Starting with a blank page is undoubtedly intimidating. So, begin with a structured business plan template including the key elements for each section. Once your outline is complete, it’ll be time to fill in the details. Don’t worry, you’ll know how to write a business plan in no time. We’ve broken each section down to help you write a business plan in a few simple steps.
1. Brainstorm and Draft an Executive Summary for Your Business Plan
This will be the first page of your business plan. Think of it as your business’ written elevator pitch. In this high level summary, include a mission statement, a short description of the products or services you will be providing, and a summary of your financial and growth projections.
This section will be the first part people read, but you may find it easier to write it last. Writing it after building out the rest of your plan may help you condense the most important information into a concise statement. You’ll need to streamline your thoughts from the other sections into a one page or less summary.
2. Create a Business Description
In this next section, describe your business. Add more specific details than the executive summary. You should include your business’s registered name, the address of your business’s location, basic information about your business structure , and the names of key people involved in the business.
The company description should also answer these two questions:
- Who are you?
- What do you plan to do?
Explain why you’re in business. Show how you are different from competitors. Tell investors why they should finance your company. This section is often more inspirational and emotional. Make sure you grab the reader’s attention. The goal is to get them to believe in your vision as much as you do.
What business structure is right for my company?
Answer these six questions to help you find your fit
3. Outline Your Business Goals
This section should serve as an objective statement. Explain what you want to accomplish and your timeline. Business goals and objectives give you a clear focus. They drive your business to success, so dream big. Include objectives that will help you reach each goal. Don’t forget to make your goals and objectives SMART – that is, they should be:
S pecific | M easurable | A ttainable | R elevant | T ime-bound
4. Conduct and Summarize Market Research
Next, outline your ideal customer with some research. Do the math to estimate the potential size of your target market. Make sure you are choosing the right market for your product, one with plenty of customers who want and need your product. Define your customer’s pain points. Explain your expertise in relation to the market. Show how your product or service fills an important gap and brings value to your customers. Use your findings to build out a value proposition statement.
5. Conduct a Competitive Analysis
In a similar way, you’ll also want to conduct and include a competitive analysis. The purpose of this analysis is to determine the strengths and weaknesses of competitors in your market, strategies that will give you a competitive advantage, and how your company is different. Some people choose to conduct a competitive analysis using the SWOT method .
6. Outline Your Marketing and Sales Strategies
Your marketing sales strategy can make or break your business. Your marketing plan should outline your current sales decisions as well as future marketing strategies. In this section, you should reiterate your value proposition, target markets, and customer segments. Then, include details such as:
- A launch plan
- Growth tactics and strategies
- A customer retention plan
- Advertising and promotion channels (i.e. social media, print, search engines, etc.)
7. Describe Your Product or Service
By this point, your products or services have probably been mentioned in several areas of the business plan. But it’s still important to include a separate section that outlines their key details. Describe what you’re offering and how it fits in the current market. Also include details about the benefits, production process, and life cycle of your products. If you have any trademarks or patents, include them here. This is also a good time to ask yourself, “Should my plan include visual aids?”
[ Read More Must-Have Tips to Start Your Small Business ]
8. Compile Financial Plans
Financial health is crucial to the success of any business. If you’re just starting your business, you likely won’t have financial data yet. However, you still need to prepare a budget and financial plan. If you have them, include income statements , balance sheets , and cash flow statements . You can also include reporting metrics such as net income and your ratio of liquidity to debt repayment ability.
If you haven’t launched your business yet, include realistic projections of the same information. Set clear financial goals and include projected milestones. Share information about the budget. What are the business operations costs? Ensure you are comprehensive when considering what costs you may need to prepare for.
9. Build a Management and Operations Plan
Identify your team members. Highlight their expertise and qualifications. Outline roles that still need to be filled now to establish your company and later as the business grows. Read More: 8 tax steps to take when hiring employees >>
Include a section detailing your logistics and operations plan. Consider all parts of your operation. Create a plan that provides details on suppliers, production, equipment, shipment and fulfillment, and inventory. This shows how your business will get done.
10. Create an Appendix – A Place for Additional Information and Documents
Lastly, assemble an organized appendix. This section can contain any other relevant information a reader might need to enhance their understanding of other sections. If you feel like the appendix is getting long, consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section. Appendices often include documents such as:
- Licenses and permits
- Bank statements
- Resumes of key employees
- Equipment leases
How to Create a Business Plan: The Bottom Line
A business plan helps you identify clear goals and provides your business direction. Many small business plans are 10-20 pages in length. But as long as the essentials are covered, feel empowered to build a plan that works for you and your company’s needs. Creating a business plan will help you identify your market and target customers, define business aims, and foster long-term financial health.
We’re ready to help you get your business started on the right foot today, and help you find long-term satisfaction as you pursue your business dream. Writing a business plan can be exciting. But if the steps to starting your business are feeling overwhelming, Block Advisors is here to help. Make an appointment today – our experts can assist you with tax prep , bookkeeping , payroll , business formation , and more .

Recommended for you
Defining employee compensation and taxable wages, a guide to raising capital as a small business founder, how to onboard new employees for their first day, find tax help in your area..
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » startup, writing a business plan here’s how to do it, step by step.
At the foundation of every strong business is a solid business plan. Looking to develop a business plan for your new venture? Here’s what to include in each step.

In our Startup2021 series, we're helping aspiring entrepreneurs navigate the new business climate of the COVID-19 era. Each week, we'll share an in-depth look at one step you can to take toward launching your business in 2021.
At the foundation of every strong business is a solid business plan. A business plan outlines important information regarding a company’s operations and goals, and serves as a blueprint for how to achieve those goals. This document not only helps entrepreneurs think through and research their venture thoroughly, it also demonstrates to investors the viability of the business idea.
If you’re looking to develop a business plan for your new venture, it’s important to include all the necessary information. Here are the nine sections to include in a strong business plan, step by step.
1. Executive summary.
Your business plan should begin with an executive summary, which outlines what your company is about and why it will succeed. This section includes your mission statement, a brief description of the product or service you are offering, a summary of your plans and basic logistical details about your team.
2. Company description.
Your company description should further detail the logistics of your business, such as its registered name, address and key people involved. Here, you should also provide specific information about your product or service, including who your business serves and what problem you solve for that population.
3. Market analysis.
Conducting thorough market research can help you understand the nature of your industry, as well as how to stand out from competitors. Include a summary of your research findings in this section. Consider any trends or themes that emerge, what other successful businesses in the field are doing (or failing to do) and how your business can do better.
[Read: How to Conduct a Market Analysis ]
4. Organization and management.
This section should include your business’s legal structure — for example, whether you are incorporating as an S or C corporation, forming a partnership or operating as an LLC or sole proprietor. Provide pertinent information on your leadership team and other key employees, including each relevant individual’s percent of ownership and extent of involvement.
Describe how you will attract and retain your customer base, including what makes you stand out from competitors, and detail the actual sales process.
5. Products/services.
Your product or service is the crux of your business idea, so you’ll want to ensure you make a strong case for it being on the market. Use this section to elaborate on your product or service throughout its life cycle, including how it works, who it serves, what it costs and why it is better than the competition. If you have any pending or current intellectual property, include this information here. You can also detail any research and development for your product or service in this section.
6. Marketing and sales.
In this section, you should explain what your marketing and sales strategies are, and how you will execute them. (Note that these strategies will likely evolve over time, and you can always make adjustments as needed.) Describe how you will attract and retain your customer base, including what makes you stand out from competitors, and detail the actual sales process.
[Read: 5 KPIs to Measure Your Business’s Marketing Success ]
7. Funding request.
If you’re seeking funding, this section is critical for investors to understand the level of funding you need. Specify what type of funding you need (debt or equity) and how much, as well as how that capital will be used. You should also include information on any future financial plans, such as selling your business or paying off debts.
8. Financial projections.
The goal of your financial projections section is to show that your business is viable and worth the investment. Offer a financial forecast for the next five years, using information from current or projected income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statements to support it. Graphs and charts can be an especially helpful tool in visualizing your business’s finances.
9. Appendix.
Finally, use the appendix for any information that could not fit or did not apply to other sections of the document. Information such as employee resumes, permits, credit history and receipts are often included in this section. If you have a long appendix, consider adding a table of contents to make it easier for the reader.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Become a small business member and save!
Become an integral voice in the world’s largest business organization when you join the U.S. Chamber of Commerce as a small business member. Members also receive exclusive discounts from B2B partners, including a special offer from FedEx that can help your business save hundreds a year on shipping. Become a member today and start saving!
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more startup tips
Micro-business vs. startup: what’s the difference, micro businesses: what are they and how do you start one, how to use ai tools to write a business plan.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
.jpeg)
How to Write the Perfect Business Plan: 10 Essential Steps
Whether you’re starting a new small business or are already years into operating one, a business plan is one of the best ways to clarify your long-term vision. Follow our step-by-step guide to writing a highly effective business plan.
Download Template
Fill the form below to download this template
Thank for you submitting the information.
Click below to download template.
Calculating Stripe fees for customer payments is easy with our calculator. Enter the payment amount to calculate Stripe's transaction fees and what you should charge to receive the full amount.
Our calculations are based on Stripe's per-transaction fees of 2.9% plus $0.30.
Calculate how much you’ll pay in Square fees for online, in-person, and manually-entered payments.
Enter your loan information to get an estimated breakdown of how much you'll pay over the lifetime of your loan.
PayPal fees can be confusing. Our calculator helps you understand how much you’ll pay in fees for common transaction methods.
hether you’re starting a new small business or are already years into operating one, a business plan is one of the best ways to clarify your long-term vision. While every business plan is different, there are several key elements to consider that will benefit you in the long run.
Follow our step-by-step guide to writing a highly effective business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that outlines your business goals and how you plan to achieve them. Ideally, this will become your roadmap for marketing, sales, finance, and growth.
In other words, a business plan is...
- An explanation of your overall vision.
- A valuable tool to plan and track your business fundamentals.
- An overview of your path to profitability, which can help get funding for your company.
Do You Need A Business Plan?
While it’s not a requirement, having a business plan is strongly recommended. In a recent QuickBooks survey , nearly 70% of current business owners recommended writing a business plan.
Creating a business plan is especially useful in the following scenarios:
- Applying for business loans
- Seeking additional rounds of funding or investors
- Growing your employee headcount
- Attracting top-level management candidates
- Looking for opportunities to scale your business
10 Steps To Creating A Comprehensive Business Plan
While not every business plan is the same, there are a few key steps you should take to create an effective and comprehensive document:
1. Create an executive summary
Think of an executive summary as your company's elevator pitch in written form. It should be 1 to 2 pages in length and summarize important information about your company and goals. If you are pitching your business plan to get funding, you should ensure your executive summary appeals to investors.
What should you include in an executive summary?
- An overview of your business
- Your company mission statement
- A concise description of products or services offered
- A description of your target market and customer demographics
- A brief analysis of your competition
- Financial projections and funding requirements
- Information about your management team
- Future plans and growth opportunities
- An overall summary of your business plan
2. Write your company description
Your company description is a more detailed and comprehensive explanation of your business. It should provide a thorough overview of your company, including your company history, your mission, your objectives, and your vision. A company description should help the reader understand the context and background of the business, as well as the key factors that contribute to its success.
What should you include in your company description?
- Official company name
- Type of business structure
- Physical address(es)
- Company history and background information
- Mission statement and core values
- Management team members and their qualifications
- Products and services offered
- Target market and customer segmentation
- Marketing and sales strategy
- Goals (both short- and long-term)
- Vision statement
Novo Note : The company description is your chance to expound on the pain points your company solves. It should also give a reader an accurate impression of who you are.
3. Conduct and outline market analysis
This is one of the most important steps in building a business plan. Here, you will assess the size and dynamics of the market your business operates in.
How to conduct a market analysis
Market analyses include both quantitative and qualitative data. You may want to conduct surveys or lean on existing industry research to gather this information. You’ll want to answer:
- What is the size of the market?
- How much revenue does your industry generate?
- What trends are impacting this industry?
- Where are opportunities for innovation?
- What are the most well-known companies in the industry? What tactics do they use to sell to customers? How do they price their offering?
- Where are there gaps in the market?
- What are your customer demographics? What problems do they have that need solving? What are their values, desires, and purchasing habits?
- What barriers to entry, if any, exist? These could include startup costs, legal requirements, environmental conditions that impact consumer behavior, and market saturation.
What is your target market?
In this section, you will specify the customer segment(s) you’re targeting . You can divide customers into small segments organized by age, location, income, and lifestyle. The goal is to describe what type of consumer will be most interested in your offering.
Novo Note : Regardless of your company’s size, understanding the trends and opportunities within your target market enables you to build a more effective marketing plan to distinguish yourself from the marketplace and grow your business. This analysis might also help you find potential customers or new products you could offer.
4. Analyze your competitors
After conducting a market analysis, you need to do a deep dive into your competitors. Look at how the competition is succeeding or failing and how each competitor has positioned itself. For example, you might want to evaluate your competitors’ brand, pricing, and distribution strategies.
How to conduct a competitive analysis
You’ll want to research your competitors and ask the following questions:
- What are their strengths?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are their customer reviews like?
- How do they price their offering(s)?
- What are their value propositions?
- What marketing and sales channels do they leverage?
- How are they growing and evolving?
Novo Note : After you develop a strong understanding of the competitive landscape, consider how your business is unique. Solidifying your competitive advantage can help you appeal to your target audience.
5. Describe your products or services
This is your chance to go into more detail about the products and services you offer! Use this opportunity to note where your offering or service differs from others in the industry. Highlight the standout features of your product, your company’s unique ability to solve customer problems, and your product roadmap.
What to include:
- Your product catalog
- Key differentiating features
- Information about the production process
- The resources required for production
- Plans for future product releases
6. Define your marketing and sales strategy
Your marketing plan describes your strategy for connecting with your target market and generating leads. It doesn't need to be full-fledged at this point, but it should answer who you're trying to sell to and how you plan to target them. Investors also want to know how you plan on selling your brand and breaking into the market, so make sure to consider their perspective as you develop your marketing strategy.
- Your sales and marketing budget
- Your key sales and marketing objectives
- Details about your sales process and sales goals
- Platforms or strategies you’ll employ to reach your target audience
- PR initiatives, content ideas, and social media strategies
7. Gather your business financials and outline financial projections
Your financials section lays out your company's past and current performance. You can also include a roadmap that dives into financial projections for your business. Aim to include projections for the next five years at a minimum.
- Income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Explanation of any significant changes
Novo Note : Novo offers integrations with accounting software like Quickbooks and Xero , allowing you to seamlessly access all your financial information within your business checking account .
.png)
8. Describe your organization
Your business plan should also include an organizational chart that maps your company’s structure.
What to include :
- Company’s management structure
- Other key personnel, along with their roles and responsibilities
- Expertise of your team (feature any specialists or experts)
Novo Note : This is also a good place to explain the legal structure of your company — for example, if you are an LLC , a corporation, or a sole proprietorship .
9. Outline your funding requests
If you’re looking for business funding, include an outline of any funding requests and requirements.
- Why you are requesting funding
- What the funding will be used for specifically
- Desired terms and conditions of funding
- The length of time over which the funding will be used
- Type of funding required (for example, debt or equity)
Novo Note : Propose a five-year funding plan, and aim to be as detailed as possible about how you will utilize the funds to grow your business.
10. Create an appendix
The last section, the appendix, includes supporting documents and additional information not listed elsewhere in your business plan. Not all of these items are necessary to include, so you’ll need to evaluate which are most relevant to your business. You might also want to include a table of contents to help keep the appendix organized.
Items to consider including:
- Bank statements
- Business credit history
- Legal documents
- Letters of reference
Sample Business Plans
Need an example to help you through the process? Check out the Small Business Administration’s downloadable examples or this even more in-depth one from Harvard Business School.
Tips For Creating A Great Business Plan
Here are some of our favorite tips for creating the most effective and efficient business plan:
- Keep it short and sweet : You want to be sure people will actually read your business plan, so stay on topic and to the point.
- Make it digestible : No need to use the fanciest terminology or draft up the most complex graphs. Keep wording and ideas simple and straightforward — it’s the most impactful way to get your information across.
- Triple-check your work : There’s nothing worse than noticing a grammar, spelling, or mathematical error when you’re presenting your vision. So proofread… and then proofread again!
- Start early : It’s never too late to write a business plan, but the earlier you do it, the stronger your strategy for growth and expansion will be from the start.
- Reference credible sources : If you are going to reference third-party research in your business plan, lean on sources that are widely recognized as authorities. Try tapping into trade associations and government resources, like U.S. Census data or data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
- Set yourself apart : Wherever you can, explain why your product or service stands out and how it can solve a problem.
- Be objective : Avoid the instinct to only showcase the good. Stakeholders and investors want to know that you are realistic and have a contingency plan if you hit a bump in the road.
Updating Your Business Plan
As with most situations in business (and life), things change! So don’t think that your business plan has to be set in stone after you create it. Instead, you should plan to return to it once a year and make updates.
Be sure to do the following when you review and update your business plan:
- Analyze your progress: Review your original business plan and compare it to your actual financial data. Are you moving in the right direction, or do you need to reevaluate your strategy?
- Consider whether your product offerings need to be adjusted: For example, decide if you want to diversify your product offerings or scale back and focus on a singular product.
- Reassess your overall goals: Perhaps your sales goals have changed with your new marketing strategy. Or maybe your customer’s needs have changed. In any case, be flexible where needed.
We know there’s a lot that goes into creating a business plan, but it’s worth it. There’s no one-size-fits-all formula for developing a business plan, but our steps outlined above will put you on the right track for developing a comprehensive, investor-friendly document.
Take time to review your business plan annually and make changes as your needs and goals change.
Novo Platform Inc. strives to provide accurate information but cannot guarantee that this content is correct, complete, or up-to-date. This page is for informational purposes only and is not financial or legal advice nor an endorsement of any third-party products or services. All products and services are presented without warranty. Novo Platform Inc. does not provide any financial or legal advice, and you should consult your own financial, legal, or tax advisors.
All-in-one money management
Take your business to new heights with faster cash flow and clear financial insights —all with a free Novo account. Apply in 10 minutes .
Why Your Startup Could Benefit from an Accelerator
Why should you convert your sole proprietorship to an llc, overdue invoice how to ask for payment professionally (with examples), spend less time managing your finances.
Take your business to new heights with faster cash flow and clear financial insights—all with a free Novo account. Apply online in 10 minutes.
More Articles On
Operating a business, the right way to pay yourself as a business owner, what business owners need to know about beneficial ownership information reporting, business continuity vs. disaster recovery: key differences.
Home > Business > Business Startup
How To Write a Business Plan

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .

Starting a business is a wild ride, and a solid business plan can be the key to keeping you on track. A business plan is essentially a roadmap for your business — outlining your goals, strategies, market analysis and financial projections. Not only will it guide your decision-making, a business plan can help you secure funding with a loan or from investors .
Writing a business plan can seem like a huge task, but taking it one step at a time can break the plan down into manageable milestones. Here is our step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan.
Table of contents
- Write your executive summary
- Do your market research homework
- Set your business goals and objectives
- Plan your business strategy
- Describe your product or service
- Crunch the numbers
- Finalize your business plan

By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Step 1: Write your executive summary
Though this will be the first page of your business plan , we recommend you actually write the executive summary last. That’s because an executive summary highlights what’s to come in the business plan but in a more condensed fashion.
An executive summary gives stakeholders who are reading your business plan the key points quickly without having to comb through pages and pages. Be sure to cover each successive point in a concise manner, and include as much data as necessary to support your claims.
You’ll cover other things too, but answer these basic questions in your executive summary:
- Idea: What’s your business concept? What problem does your business solve? What are your business goals?
- Product: What’s your product/service and how is it different?
- Market: Who’s your audience? How will you reach customers?
- Finance: How much will your idea cost? And if you’re seeking funding, how much money do you need? How much do you expect to earn? If you’ve already started, where is your revenue at now?
Step 2: Do your market research homework
The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research . This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to gather this information. Your method may be formal or more casual, just make sure that you’re getting good data back.
This research will help you to understand the needs of your target market and the potential demand for your product or service—essential aspects of starting and growing a successful business.
Step 3: Set your business goals and objectives
Once you’ve completed your market research, you can begin to define your business goals and objectives. What is the problem you want to solve? What’s your vision for the future? Where do you want to be in a year from now?
Use this step to decide what you want to achieve with your business, both in the short and long term. Try to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound benchmarks—that will help you to stay focused and motivated as you build your business.
Step 4: Plan your business strategy
Your business strategy is how you plan to reach your goals and objectives. This includes details on positioning your product or service, marketing and sales strategies, operational plans, and the organizational structure of your small business.
Make sure to include key roles and responsibilities for each team member if you’re in a business entity with multiple people.
Step 5: Describe your product or service
In this section, get into the nitty-gritty of your product or service. Go into depth regarding the features, benefits, target market, and any patents or proprietary tech you have. Make sure to paint a clear picture of what sets your product apart from the competition—and don’t forget to highlight any customer benefits.
Step 6: Crunch the numbers
Financial analysis is an essential part of your business plan. If you’re already in business that includes your profit and loss statement , cash flow statement and balance sheet .
These financial projections will give investors and lenders an understanding of the financial health of your business and the potential return on investment.
You may want to work with a financial professional to ensure your financial projections are realistic and accurate.
Step 7: Finalize your business plan
Once you’ve completed everything, it's time to finalize your business plan. This involves reviewing and editing your plan to ensure that it is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
You should also have someone else review your plan to get a fresh perspective and identify any areas that may need improvement. You could even work with a free SCORE mentor on your business plan or use a SCORE business plan template for more detailed guidance.
Compare the Top Small-Business Banks
Data effective 1/10/23. At publishing time, rates, fees, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
The takeaway
Writing a business plan is an essential process for any forward-thinking entrepreneur or business owner. A business plan requires a lot of up-front research, planning, and attention to detail, but it’s worthwhile. Creating a comprehensive business plan can help you achieve your business goals and secure the funding you need.
Related content
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business
- How to Get a Business License: What You Need to Know
- What Is a Cash Flow Statement?
Best Small Business Loans

5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2023 All Rights Reserved.
How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Conducting Market Research
Crafting a business plan, reviewing funding options, understanding legal requirements, implementing marketing strategies, how much does it cost to start a business, what should i do before starting a business, what types of funding are available to start a business, do you need to write a business plan, the bottom line.
Building an effective business launch plan
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Headshot-4c571aa3d8044192bcbd7647dd137cf1.jpg)
Starting a business in the United States involves a number of different steps, spanning legal considerations, market research, creating a business plan, securing funding, and developing a marketing strategy. It also entails decisions around a business’s location, structure, name, taxation, and registration.
This article covers the key steps involved in starting a business, as well as important aspects of the process for entrepreneurs to consider.
Key Takeaways
- Entrepreneurs seeking to develop their own business should start by conducting market research to understand their industry space and competition, and to target customers.
- The next step is to write a comprehensive business plan, outlining the company’s structure, vision, and strategy. Potential funders and partners may want to review the business plan in advance of signing any agreements.
- Securing funding is crucial in launching a business. Funding can come in the form of grants, loans, venture capital, or crowdfunded money; entrepreneurs may also opt to self-fund instead of or in combination with any of these avenues.
- Choosing a location and business structure can have many implications for legal aspects of business ownership, such as taxation, registration, and permitting, so it’s important to fully understand the regulations and requirements for the jurisdiction in which the business will operate.
- Another key aspect of launching a new business is having a strategic marketing plan that addresses the specifics of the business, industry, and target market.
Before starting a business, entrepreneurs should conduct market research to determine their target audience, competition, and market trends.
The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) recommends researching demographic data around potential customers to understand a given consumer base and reduce business risk. It also breaks down common market considerations as follows:
- Demand : Do people want or need this product or service?
- Market size : How many people might be interested?
- Economic indicators : These include income, employment rate, and spending habits of potential customers.
- Location : Where are the target market and the business located?
- Market saturation : How competitive is the business space, and how many similar offerings exist?
- Pricing : What might a customer be willing to pay?
Market research should also include an analysis of the competition (including their strengths and weaknesses compared to those of the proposed business), market opportunities and barriers to entry, industry trends, and competitors’ market share .
There are various methods for conducting market research, and the usefulness of different sources and methodologies will depend on the nature of the industry and potential business. Data can come from a variety of sources: statistical agencies, economic and financial institutions, and industry sources, as well as direct consumer research through focus groups, interviews, surveys, or questionnaires.
A comprehensive business plan is like a blueprint for a business. It will help lay the foundation for business development and can assist in decision making, day-to-day operations, and growth.
Potential investors or business partners may want to review and assess a business plan in advance of agreeing to work together. Financial institutions often request business plans as part of an application for a loan or other forms of capital.
Business plans will differ according to the needs and nature of the company and only need to include what makes sense for the business in question. As such, they can vary in length and structure depending on their intended purpose.
Business plans can generally be divided into two formats: traditional business plans and lean startup business plans. The latter is typically more useful for businesses that will need to adjust their planning quickly and frequently, as they are shorter and provide a higher-level overview of the company.
The process of funding a business can be as unique as the business itself—that is, it will depend on the needs and vision of the business and the current financial situation of the business owner.
The first step in seeking funding is to calculate how much it will cost to start the business. Estimate startup costs by identifying a list of expenses and putting a number to each of them through research and requesting quotes. The SBA has a startup costs calculator for small businesses that includes common types of business expenses.
From there, an entrepreneur will need to determine how to secure the required funding. Common funding methods include:
- Self-funding , also known as bootstrapping
- Seeking funding from investors, also known as venture capital
- Raising money by crowdfunding
- Securing a business loan
- Winning a business grant
Each method will hold advantages and disadvantages depending on the situation of the business. It’s important to consider the obligations associated with any avenue of funding. For example, investors generally provide funding in exchange for a degree of ownership or control in the company, whereas self-funding may allow business owners to maintain complete control (albeit while taking on all of the risk).
The availability of funding sources is another potential consideration. Unlike loans, grants do not have to be paid back—however, as a result, they are a highly competitive form of business funding. The federal government also does not provide grants for the purposes of starting or growing a business, although private organizations may. On the other hand, the SBA guarantees several categories of loans to support small business owners in accessing capital that may not be available through traditional lenders.
Whichever funding method (or methods) an entrepreneur decides to pursue, it’s essential to evaluate in detail how the funding will be used and lay out a future financial plan for the business, including sales projections and loan repayments , as applicable.
Legally, businesses operating in the U.S. are subject to regulations and requirements under many jurisdictions, across local, county, state, and federal levels. Legal business requirements are often tied to the location and structure of the business, which then determine obligations around taxation, business IDs, registration, and permits.
Choosing a Business Location
The location—that is, the neighborhood, city, and state—in which a business operates will have an impact on many different aspects of running the business, such as the applicable taxes, zoning laws (for brick-and-mortar, or physical locations), and regulations.
A business needs to be registered in a certain location; this location then determines the taxes, licenses, and permits required. Other factors to consider when choosing a location might include:
- Human factors : Such as the target audience for your business, and preferences of business owners and partners around convenience, knowledge of the area, and commuting distance
- Regulations and restrictions : Concerning applicable jurisdictions or government agencies, including zoning laws
- Regionally specific expenses : Such as average salaries (including required minimum wages), property or rental prices, insurance rates, utilities, and government fees and licensing
- The tax and financial environment : Including income tax, sales tax, corporate tax, and property tax, or the availability of tax credits, incentives, or loan programs
Picking a Business Structure
The structure of a business should reflect the desired number of owners, liability characteristics, and tax status. Because these have legal and tax compliance implications , it’s important to fully understand and choose a business structure carefully and, if necessary, consult a business counselor, lawyer, and/or accountant.
Common business structures include:
- Sole proprietorship : An unincorporated business that has just one owner, who pays personal income tax on profits
- Partnership : Options include a limited partnership (LP) or a limited liability partnership (LLP)
- Limited liability company (LLC) : A business structure that protects its owners from personal responsibility for its debts or liabilities
- Corporation : Options include a C corp , S corp , B corp , closed corporation , or nonprofit
Getting a Tax ID Number
A tax ID number is like a Social Security number for a business. Whether or not a state and/or federal tax ID number is required for any given business will depend on the nature of the business, as well as the location in which the business is registered.
If a business is required to pay state taxes (such as income taxes and employment taxes), then a state tax ID will be necessary. The process and requirements around state tax IDs vary by state and can be found on individual states’ official websites. In some situations, state tax IDs can also be used for other purposes, such as protecting sole proprietors against identity theft.
A federal tax ID, also known as an employer identification number (EIN) , is required if a business:
- Operates as a corporation or partnership
- Pays federal taxes
- Wants to open a business bank account
- Applies for federal business licenses and permits
- Files employment, excise, alcohol, tobacco, or firearms tax returns
There are further situations in which a business might need a federal tax ID number, specific to income taxation, certain types of pension plans, and working with certain types of organizations. Business owners can check with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) about whether they need an EIN.
Registering a Business
Registration of a business will depend on its location and business structure, and can look quite different depending on the nature and size of the business.
For example, small businesses may not require any steps beyond registering their business name with local and state governments, and business owners whose business name is their own legal name might not need to register at all. However, registration can include personal liability protection as well as legal and tax benefits, so it can be beneficial even if it’s not strictly required.
Most LLCs, corporations, partnerships, and nonprofits are required to register at the state level and will require a registered agent to file on their behalf. Determining which state to register with can depend on factors such as:
- Whether the business has a physical presence in the state
- If the business often conducts in-person client meetings in the state
- If a large portion of business revenue comes from the state
- Whether the business has employees working in the state
If a business operates in more than one state, it may need to file for foreign qualification in other states in which it conducts business. In this case, the business would register in the state in which it was formed (this would be considered the domestic state), and file for foreign qualification in any additional states.
Some businesses may decide to register with the federal government if they are seeking tax-exempt status or trademark protection, but federal registration is not required for many businesses.
Overall registration requirements, costs, and documentation will vary depending on the governing jurisdictions and business structure.
Obtaining Permits
Filing for the applicable government licenses and permits will depend on the industry and nature of the business, and might include submitting an application to a federal agency, state, county, and/or city. The SBA lists federally regulated business activities alongside the corresponding license-issuing agency, while state, county, and city regulations can be found on the official government websites for each region.
Every business should have a marketing plan that outlines an overall strategy and the day-to-day tactics used to execute it. A successful marketing plan will lay out tactics for how to connect with customers and convince them to buy what the company is selling.
Marketing plans will vary according to the specifics of the industry , target market, and business, but they should aim to include descriptions of and strategies around the following:
- A target customer : Including market size, demographics, traits, and relevant trends
- Unique value propositions or business differentiators : Essentially, an overview of the company’s competitive advantage with regard to employees, certifications, or offerings
- A sales and marketing plan : Including methods, channels, and a customer’s journey through interacting with the business
- Goals : Should cover different aspects of the marketing and sales strategy, such as social media follower growth, public relations opportunities, or sales targets
- An execution plan : Should detail tactics and break down higher-level goals into specific actions
- A budget : Detailing how much different marketing projects and activities will cost
The startup costs for any given business will vary greatly depending on the industry, business activity, and product or service offering. Home-based online businesses will usually cost less than those that require an office setting to meet with customers. The estimated cost can be calculated by first identifying a list of expenses and then researching and requesting quotes for each one. Use the SBA’s startup costs calculator for common types of expenses associated with starting a small business.
Entrepreneurs seeking to start their own business should fully research and understand all the legal and funding considerations involved, conduct market research, and create marketing and business plans. They will also need to secure any necessary permits, licenses, funding, and business bank accounts.
Startup capital can come in the form of loans, grants, crowdfunding, venture capital, or self-funding. Note that the federal government does not provide grant funding for the purposes of starting a business, although private sources do.
Business plans are comprehensive documents that lay out the most important information about a business. They are important references for the growth, development, and decision-making processes of a business, and financial institutions as well as potential investors and partners generally request to review them in advance of agreeing to provide funding or work together.
Starting a business is no easy feat, but research and preparation can help smooth the way. Having a firm understanding of the target market, competition, industry, business goals, business structure, funding requirements, tax and operating regulations, and marketing strategy, and conducting research and consulting experts where necessary, are all things that entrepreneurs can do to set themselves up for success.
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Loans .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Fund Your Business .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Pick Your Business Location .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Choose a Business Structure .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Get Federal and State Tax ID Numbers .”
Internal Revenue Service. “ Do You Need an EIN? ”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Register Your Business .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Apply for Licenses and Permits .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Marketing and Sales .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Grants .”
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1217476205-11cc214dcdcb47dd93434868ea14839e.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Start Your Business
Ready to start your business? Learn how to develop a great business idea, research customers, set up your legal structure, and plan for the future with these startup resources.

- Business ideas
- Market research
- Business models
- Legal requirements
Explore Topics

How to Start a Business With No Money
Karoki Githure
Oct. 29, 2023
Don’t let a lack of funding stop you—it’s still possible to start a lucrative business. You just need to harness existing resources, craft a viable business plan, and leverage networking for growth.
Briana Morgaine
Apr. 2, 2024
James Javier
Mar. 29, 2024
Jeff Smedsrud
Noah Parsons
Mar. 20, 2024

26 Businesses You Can Start for Free
Starting a business doesn’t have to drain your bank account. There are plenty of business options out there that require little to no start-up capital. Here is a list of our favorites.

Industry Startup Guides
Want to learn more about starting a specific type of business? Check out our growing list of industry startup guides for more detailed insights.

Free Download
Business Startup Checklist
Keep track of your progress and know what steps are coming up with this easy-to-use startup checklist.
Clarify your ideas and understand how to start your business with LivePlan

How to Start a Nonprofit
Jan. 5, 2024
Nonprofits are designed to pursue a mission, not generate profits. That doesn’t mean you can skip traditional startup steps—in fact, it may be even more crucial to your survival.

How to Start a Home-Based Business
Feb. 20, 2024

How to Start a Franchise
Questions to ask before starting a business
What are your strengths and weaknesses.
Your strengths and weaknesses will impact how effectively you operate as an entrepreneur. If you aren’t aware of what they are, then you’ll struggle to identify opportunities and problems before it’s too late.
Have you talked to the right people?
Don’t go into business alone. No, you don’t need to find a partner, but it’s worth chatting with people you trust to see how they respond to your idea and gather any advice they may have before starting.
Why are you starting a business?
Your reasons for starting a business will impact how likely you are to see it through. When the going gets tough, if you don’t have a firm reason for why you’re doing this, then you’ll struggle to keep going.
How much will it cost to start?
The cost of starting a business varies depending on the type, your location, and many other factors. The important thing is that you don’t just guess and actually budget and forecast your expenses beforehand.
Do you have a good business idea?
A good business idea is something that people want, and that solves a problem in their lives. If you’re unsure that your business does that, then you need to get out and validate it with potential customers.

Who are your competitors?
No business lacks competition. You need to know who they are, what they offer, and anything else that tells you how to position your business to be competitive.
Should you quit your job?
It can be tempting to go all in on a business idea immediately. However, entrepreneurship is hard and risky, and it may not be the wisest choice to cut your primary source of income. To know if it is the right time, you need to determine when your business will be profitable and sustainable.
How will you make money?
The business model is surprisingly overlooked by many business owners. They get caught up in the idea and the allure of entrepreneurship but fail to determine how they will make money. Don’t reinvent the wheel and explore some common options to see what fits your business.
12 steps to start your business

1. What to do before starting a business
Why are you starting a business? What does it take to be successful? Could you start with a side hustle? Let’s help you answer these and other vital questions before setting up your business.

2. Find the right business idea
Once you know why you want to start a business, it’s time to find your idea. Learn what it takes to develop a good idea and explore our curated lists of potential business ideas that may be a good fit.

3. Validate your business idea
How do you know if your business idea will work? By testing it out and verifying that you’re solving a real problem for real people. Here’s what you should do after coming up with your business idea.

4. Conduct market research
Who are your customers? Who are your competitors? What does the industry look like? Will you be able to successfully enter this market? These are necessary questions to answer through a bit of research.

5. Select your business model
How will you make money? This is answered with your business model, which covers how your costs, revenue streams, and customer expectations work together. And you don’t have to start from scratch—check out these common types of business models.

6. Price your products and services
What are your customers willing to pay? It’s difficult to know when starting out, but don’t let that stop you. Learn how to set initial prices and compare common pricing models that may work for your business.

7. Write your business plan
You need a business plan before starting a business. This isn’t about checking a box but improving your understanding of what it takes to run a successful business.

8. Make your business legal
Before setting up shop, you must check all the necessary legal boxes. Don’t worry about spending hours researching—we’ve compiled the most common legal requirements.

9. Set up your finances
You need a firm grasp of your startup costs and funding needs. Which requires you to forecast your sales, expenses, and cash flow. That may sound daunting, but we’ve broken it down into steps to follow and even cover setting up accounting and payroll systems.

10. Choose a business location
Will you be selling online? Running a traditional brick-and-mortar location? Maybe a bit of both? You need to consider where and how you’ll sell your products. Explore what to look for in a physical retail location and how to make a splash online.

11. Put together your team
Learn when it’s the right time to hire, what makes a good employee, and how to successfully grow your team. Even if you’re running a business solo, you should know how your team will grow.

12. Market your business
Learn the basics of creating a small business marketing plan, including what to prepare beforehand and how to track the impact of your marketing efforts.

Tips to start your business
Looking for additional guidance to help get your business off the ground? We’ve rounded up our favorite tips and resources from entrepreneurial experts to do just that.

Start stronger by writing a quick business plan
Start a business FAQ
What are the basic steps to start a business?
To start a business, you’ll need to:
- Identify and validate your business idea
- Conduct market research
- Select a business model and pricing strategy
- Write a business plan and financial plan
- Select your business structure
- Register your business
- Obtain licenses and permits
- Select an online or physical location
- Start building your team if necessary
- Promote your business
How much money do you usually need to start a business?
The amount of money needed to start a business varies greatly depending on the type and scale of the business. It could range from a few hundred dollars for a home-based service business to several thousand or even millions for a manufacturing or tech startup.
You must carefully consider and forecast your startup costs and cash flow to fully understand how much money you need to start.
What should I do first when starting a business?
The first step in starting a business is identifying a viable business idea and conducting market research to understand the demand, competition, and potential challenges. Additionally, it’s worth self-reflection to determine if you want to jump into entrepreneurship.
What do I need to start my first business?
At a minimum, you’ll need a business idea, a business plan, capital, a legal structure, a registered business name, necessary licenses and permits, a business bank account, and an accounting system.
How can I start a business with no money?
Starting a business with no money can be challenging but not impossible. You can consider service-based businesses that require minimal upfront costs. You can also minimize your upfront investment by starting your business as a side hustle while retaining a full or part-time job.
What 3 things make a business successful?
A clear and compelling value proposition, a strong understanding of the market and customers, and effective management and operations are three key elements that contribute to business success.
How can I start a simple business?
Starting a simple business often involves offering a service based on your skills or interests. This could be anything from pet sitting to graphic design. The key steps include identifying your service, understanding your market, setting prices, and promoting your business.
How do I start a beginner business?
As a beginner, start with a business idea that aligns with your skills and passions. Conduct market research, write a one-page business plan, and test if your idea resonates with your target customers. Start small, learn from the experience, and gradually grow your business.
How to start a business with only $100?
With only $100, consider a service-based or online business that requires minimal startup costs. This could be a consulting service, online tutoring, freelance writing, or selling handmade products. Use social media and free online tools for marketing and management to keep costs low.
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Start a Business in 15 Steps

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
1. Find the right opportunity
2. write a business plan, 3. choose a business structure, 4. get a federal tax id, 5. apply for licenses and permits, 6. open a business bank account, 7. understand your startup financing options, 8. get a business credit card, 9. choose the right accounting software, 10. prepare to pay your taxes, 11. protect yourself with business insurance, 12. establish your online presence, 13. set up a payments system, 14. hire employees, 15. get financing to grow your business.
Starting a business takes research, smarts and self-confidence — and a measure of fearlessness. You may already be asking yourself: How can I start my own business with no money? What's the right equipment? Am I getting the best advice?
Here are the essential steps on how to start a business, from choosing the right business idea, creating a solid business plan and structuring your company to opening a business bank account and choosing the right accounting software.
» MORE: 5 steps to turn your side gig into a full-fledged business

ZenBusiness
What business should you start? It depends on your expertise, plus how much time and money you’re able to invest. Some small-business ideas can be launched from home with little overhead, and e-commerce and remote businesses have become increasingly common in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
As you narrow your scope, you also want to be sure that your idea can actually make money . If you’re not sure what kind of business you want to run, use these lists to get the wheels turning:
50 best small-business ideas.
The 23 most profitable business ideas .
40 startup ideas to try .
16 e-commerce business ideas.
40 home business ideas to explore .
44 online business ideas you can start now .
Looking for tools to help grow your business?
Tell us where you're at in your business journey, and we'll direct you to the experience that fits.
on Nerdwallet's secure site
A strong business plan can help you prepare for every aspect of your business. Plus, you’ll need one to present to potential investors and lenders. This document should include details of the products or services you plan to offer, how you plan to make money, who you need on your team and more.
You’ll also want to include detailed financial projections, budgets and thorough explanations of how you plan to spend investor dollars or loans. Since cash flow projections will fluctuate as you adjust projected income and expenses, it helps to think of the plan’s financials as a living, changing document.
Ultimately, your business plan will help you chart a course for your business, anticipate potential roadblocks and work out how to overcome them — and will likely go through multiple iterations before your idea comes to fruition. Industry colleagues and accountants may be able to provide valuable feedback on how realistic your projections look and point out any overlooked costs.
How to write a business plan, step by step .
How to create a business budget .
Best business budgeting software tools .
5 tips to write a successful business plan .
How to write a successful business plan for a loan .
The legal structure of your business can affect everything from your taxes to what you're liable for. For example, there’s no legal distinction between a sole proprietorship and its owner. Limited liability companies (LLCs) and their owners, however, are considered separate entities by law, which can provide more personal asset protection.
Talking with a tax professional can help you choose the right business structure for you. And you can change your structure as your business grows.
How to choose the right business structure .
Pros and cons of a limited liability company .
LLC vs. sole proprietorship: How to choose .
Partnership vs. corporation: How to choose .
Getting an employer identification number (EIN) is necessary for most businesses to file taxes, open bank accounts and perform other essential tasks. Even if you don’t have employees, there are benefits to getting an EIN. It’s free to apply and the online application only takes a few minutes.
How to apply for an employer identification number .
Benefits of getting an EIN (even if you don’t have to) .
In general, restaurants need health inspections and liquor licenses. Hair stylists need cosmetology licenses. Your city may require you to apply for a business license regardless of what field you’re in. And if you’re renovating a space to sell products or perform services, you may need to ask local officials for a zoning change.
Set aside time early on to find out what licenses and permits you need before you can open your doors. While you don’t typically need a lawyer to apply for a business license, they can help you navigate the process and review other documents, like lease agreements or loans, before you sign them. Industry associations, city officials who work on economic development issues and local business associations, like your Chamber of Commerce, may be able to offer advice, too.
How to get a business license .
Do you need a business license to sell online?
How to find a startup lawyer .
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Keeping your business and personal finances separate is key to managing your business finances. It’s standard bookkeeping hygiene and makes it easier to deduct business expenses come tax time. A business bank account can help, and they’re simple to set up.
Best business bank accounts .
Best business bank accounts for freelancers .
Best free business checking accounts .
Best business bank accounts for LLCs .

Most businesses need a little capital to get started. However, the majority of business loans are not available to businesses that have been operating for less than six months, and most online lenders prefer at least a year in business. Startups should consider alternative financing options, or try to leverage other strengths of their business, such as strong credit or collateral. If your business does qualify for a loan, be sure to pay attention to interest rates, potential prepayment fees and personal liability terms.

Found Small Business Banking
Many business owners rely on their own savings to get started. You can also look into crowdfunding, personal loans, business grants and more. High-growth-potential startups may also be eligible for equity financing, which gives partial ownership, or equity, to investors in exchange for capital.
How do business loans work?
Best startup business loans.
Startup business grants .
Asset-based lending options.
Types of startup funding.
Crowdfunding for business .
Is equity financing right for your business?
Funding your business with a personal loan .
Is your to-do list overwhelming?
Business credit cards can also be used as a short-term financing solution to help you purchase necessary supplies and pay bills while cash flow is still shaky. Just be sure to spend within your limit and pay off your balance in full each month so you don’t get into a cycle of debt. Startup financing aside, business credit cards also make it easier to keep business and personal finances separate. As an added bonus, you can also earn rewards, such as cash back, on the money you spend.
Usually, you can qualify for a business credit card based on your personal credit score.
What is a business credit card?
How to get a business credit card .
Best small-business credit cards .
Best business credit cards for new businesses .
Best 0% APR business credit cards.
It’s essential that you keep records that show how much revenue you’re bringing in and how much you’re spending. Accounting software helps you track and analyze these numbers by generating reports and recording sales trends — and there are even some free options.
As your business grows, you may want to start working with a bookkeeper . This person can help ensure your records are complete and accurate, which makes it easier to file your taxes, apply for financing and more.
Best accounting software for small businesses .
Best online bookkeeping services .
Bookkeeping basics for small businesses.
Best free accounting software .
Know these 4 business financial metrics to track performance .
You'll have some new tax responsibilities as a business owner — including, potentially, the need to pay taxes throughout the year, not just during tax season. But you'll probably discover some new tax breaks , too.
Filing taxes can be complex, especially as a small-business owner. Developing a relationship with a tax professional early on can help set you up for success, and they can be a trusted adviser to your business later on.
A tax guide for small-business owners.
Self-employment tax, explained.
Best tax software for small businesses .
How estimated quarterly taxes work .
How to find the right tax advisor for your business .
It's important to protect your business and your personal assets, and business insurance exists to do just that. NerdWallet recommends that every business carry general liability insurance in case of legal claims.
You may also need insurance to comply with a contract, like to set up a booth at an event or work as a subcontractor on a larger project.
Best small-business insurance providers .
How much does business insurance cost?
What is general liability insurance?
What is a business owner’s policy (BOP)?
An online presence is critical for almost every business — especially if you want to sell products online. Setting up a website and social media profiles early on, even if they’re simple, can help you start developing relationships with potential customers right away.
Here’s what you need to know to start your business website:
How to build an e-commerce website .
The ultimate guide to small-business marketing .
The best ways to promote your business on social media .
6 Instagram tips for small-business owners .
8 best e-commerce website builders for small businesses .
The do’s and don’ts of using Facebook to drive business sales .
5 best places to advertise your business online .
If your business takes credit and debit cards, you'll likely need a payment processor and point-of-sale (POS) system. Lots of POS system providers double as processing companies, which can make the decision-making process simple. Remember to consider upfront hardware costs for card readers or POS registers, monthly POS software fees and processing fees. Online payments typically have higher processing fees than in-person payments, so be sure to consider the full range of fees when choosing your provider.
How to accept credit card payments.
What is credit card processing and how does it work?
Cheapest credit card processing companies.
Best point-of-sale (POS) systems .
Best credit card processing companies .
Best credit card readers for small businesses .
You may not need to hire employees right away — and some small-business owners prefer to remain solopreneurs throughout the life of their business. But if you do choose to hire, you’ll probably need workers’ compensation insurance, payroll software and more. Here’s what goes into hiring your first employees.
Ready to hire your first employee? Prep with these steps .
Strategies to attract good employees.
Tips for hiring remote workers.
Strategies to help retain employees.
How to choose the right payroll software for your business .
Best payroll software for small businesses.
What is workers’ compensation insurance?
Once you’ve been in business for six to 12 months, you may start qualifying for business loans. Financing can help your business grow and expand — by buying equipment, renovating an office or expanding your inventory, for instance — or float you through a slow season while you prepare for increased future revenue.
Here’s what you need to know about business loans, lines of credit and other financing options.
How to get a business loan .
SBA loans: What they are and how to qualify .
Equipment financing: What it is and top lenders.
Best small-business loans .
Types of business loans.
Should you grow your business? 6 questions to help you decide .
On a similar note...
BUSINESS STRATEGIES
How to start a business in 14 steps: a guide for 2024
- Cecilia Lazzaro Blasbalg
- Dec 3, 2023
- 31 min read
Get started by: Creating a website → | Getting a domain →

In the words of Steve Jobs, “The only way to do great work is to love what you do.” Starting your own business is one step towards doing work that you love. But from forming an idea to creating a business website , there are several essential steps and questions to consider before you dive in: What problem are you solving? Who is your target audience? What differentiates your product or service from existing offerings? And, most importantly, where exactly do you begin?
This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step of the journey: brainstorming ideas, perfecting your branding, registering your business and more. Use it as your trusted roadmap on how to start a business, empowering you to navigate the exciting world of entrepreneurship with confidence.
Ready to create a business website? Start building yours today .
How to start a business
Brainstorm and refine your business idea
Conduct market and competitor research
Pick a business name
Write up a business plan
Choose a legal structure for your business
Secure business capital and funding
Register your business and make it official
Apply for tax IDs, licenses and permits
Apply for business insurance
Organize your finances
Brand your business
Create a professional business website
Market and promote your business
Build a team
01. Brainstorm and refine your business idea
You might already have a great business idea that you can’t wait to start, or maybe you’re still in the early brainstorming stages of finding your niche. If the latter applies to you, think about what you’re passionate about and what skills you possess. The best business ideas often emerge from your interests and expertise, making it easier to stay motivated and dedicated throughout the journey.
Keep in mind that there are some very real, very unavoidable small business challenges to consider. Most business ideas require money, innovation and time to yield results—some may even come with financial risks. This is true for both brick-and-mortar businesses and online business ideas . That’s why as a first step, you’ll need to refine and test your idea to make sure it’s a viable option. Here are some effective ways to kickstart your brainstorming process:
Be realistic: While it’s important to choose a business idea that’s in line with your passions, it’s also crucial that there’s market demand for your product or service. Ask yourself, is your business idea scalable? Who’s your target market ? Do you have the necessary skills and expertise?
Test your idea in the real world: This can involve anything from a focus group to a small-scale pilot test. Another strategy is to build a landing page , which can help you generate and gauge interest. If you find that your idea doesn’t pique interest, it’s time to reassess. Consider how you can refresh your idea to bring something new to the table, or how you can adapt it to more directly address consumer needs.
Define your business model: As you think about ways to make money from your idea, think about the exact business model that will help you to grow your business in a manageable way. Think: How do you want your business to look a year from now? Two years from now? Five? Is it sustainable?

Popular business ideas to get you started
Dropshipping : Dropshipping is a great low-cost business idea that lets you sell products without needing to manage your own inventory. You simply need an eCommerce website , or a specific dropshipping website and a strong marketing strategy to get started.
Print on demand (POD): Another popular way to make money online , POD involves working with suppliers that print your designs on blank items, such as t-shirts and mugs, and ship the orders on your behalf. This is an effective way to put your own spin on a retail venture and start your own online store .
Freelancing: Freelance artists , writers and creatives can jumpstart their business by creating a portfolio website and monetizing their skills. Take Berlin-based illustrator and animator Rafael Varona for inspiration—his modern, visually engaging Wix website features artwork he’s done for leading companies including Disney, Google and Porsche.
Starting a service business : Service business ideas center around selling your expertise, skills or assistance—such as tutoring, dog walking, personal training or event planning. For inspiration, take a look at Whitehead Weddings + Events . Founder Anna Katherine Whitehead has built an elegant service website that showcases work samples, package offerings and more.
Selling handmade items: If you’ve got a knack for creating homemade jewelry, artwork, décor or clothing, you have a business idea just waiting to launch. Follow the lead of businesses like Tach Clothing , whose online Wix storefront features handmade crocheted clothing inspired by vintage fashion.
Boring businesses : Don't be fooled by the way these business sound, boring means anything but. These ventures are typically businesses that offer products or services that are essential but may not have flashy or attention-grabbing qualities. Think accounting firms, insurance companies, waste management services or industrial manufacturers.

How a successful business owner turned selling handmade items into a $2M business
Six and a half years ago, Amanda Buhse was working a 9-to-5 job as a graphic designer. Her day job was exhausting so Buhse and her best friend, a nurse, decided to meet a few times a week to decompress over a glass of wine and make candles together. The hobby stuck. Buhse eventually turned those evenings melting wax and cutting wicks into a bustling business.
Now she’s the owner and chief creative officer of Coal and Canary , a Canada-based online luxury candle company. Her candles are sold all over North America and have even made it into the glamorous gift bags handed out to VIPs at the Oscar and Grammy Awards.
What started as a passionate side hustle is now a $2M business. You can read more about Amanda’s business story here .
Other business ideas to consider:
Business ideas for teens
Small town business ideas
Part-time business ideas
Scalable business ideas
Family business ideas
Craft business ideas
B2B business ideas
Rental business ideas
Beauty business ideas
Is starting a business worth it?
Yes, starting a business is worth it. Business ownership can be a profitable venture, providing financial stability and potential for growth. Moreover, for people like Amanda Buhse, it offers the opportunity to escape the confines of a 9-to-5 job that may not bring you happiness or fulfillment. By taking the leap into entrepreneurship, you can create your own path and shape your future on your own terms.
More popular business ideas to consider
How to start an online business
How to start a consulting business
How to start a fitness business
How to start a fitness clothing line
How to start a makeup line
How to start a candle business
How to start a clothing business
How to start an online boutique
How to start a t-shirt business
How to start a jewelry business
How to start a subscription box business
How to start a beauty business
How to start a photography business
How to start a food business
How to start an interior design business
How to start a rental property business
How to start a painting business
How to start a gym business
How to start a babysitting business
How to start a plumbing business
How to start a coaching business
How to start a finance business
02. Conduct market and competitor research
When your business is still in its earliest stages, doing market research is critical. This step helps you understand your target audience’s needs and preferences, allowing you to tailor your products or services accordingly. It also enables you to evaluate the competitive landscape, identify market gaps and make informed decisions. All of this increases your chances of success and mitigates risk.
When it comes to consumer behavior, there are two sets of research: primary and secondary.
Primary research: This is the direct study of your target market by researching them firsthand, such as by conducting user interviews or holding focus groups. You’ll want to define who your customers are and further segment your market by age, location, language, spending power or even stage of life (for example, college students, newlyweds or retirees).
Secondary research: This consists of gathering information from external sources. Conduct an online search or reference public agencies like the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics as a good starting point. Down the line, you might also find internal data just as useful. You can turn to your own sales reports and see what trends took off right under your nose.
This combination of primary and secondary research can help you create a thorough SWOT analysis , which is an insightful way to measure and evaluate your overall business outlook against your competitors. To do this, create a table with four quadrants, where you'll rank your business’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
Strengths: Identify the areas where your business stands out. Then, turn to your competitors and ask yourself, “How can I do what they do, but better?” Look at the products and services they offer to help you understand what attracts their customers, and use this as inspiration to improve your own business strategy and competitive advantage .
Weaknesses: Be honest with yourself here. Answer this question as directly as you can: What do customers complain about or dislike? This will let you narrow in on one topic at a time, as opposed to tackling something abstract like, “What is wrong within my company?”
Opportunities: Think about your business in terms of growth. Consider different ways to expand and tap into new spaces, like running seasonal events, taking on a green initiative or testing out trends.
Threats: Be cautious of any external factors that can affect your business in a negative way. It can range from market fluctuations to consumers who no longer express interest in your offerings.
Remember to play to your understanding of what a specific audience needs. Identifying a gap in the market, or having an idea to make an existing product is an important part of market research for starting a business.
How one entrepreneur translated her understanding of her target audience into business success
Raquel “Rocky” Harris knows a thing or two about kicking ass. She’s a five-time Muay Thai champion, Team USA gold medalist, Fight Camp trainer (that’s basically the Peloton of boxing) and, most recently, a thriving entrepreneur (see our guide on how to become an entrepreneur ). Harris now uses Wix eCommerce to sell a collection of wellness products to athletes like herself as the founder of Warm Up .
“I was making my own hand sanitizer and thought ‘Why don’t they have sanitizers that kill fungus?’” she says. “There are always breakouts in boxing gyms due to common skin infections like ringworms. Tea tree soap is anti-fungal, so I started adding it to my hand sanitizers, which eventually evolved into my sweat butters.”
She launched her first product line while training clients and creating Wix sites for her colleagues, all while moving across the country to shoot workouts for Fight Camp. You can read more about her business story here .
Is it easy to start a business?
Creating a business doesn't have to be difficult or intimidating. It can start with a simple but strong idea, like Raquel Harris' realization that hand sanitizers would be all the more useful if they killed fungus, especially in boxing rings.
Starting a business does require dedication, hard work and careful planning—there's no way around that. While it may not be easy, per se, with the right mindset, research, resources and tools like Wix, anyone can embark on the entrepreneurial journey. The rewards of building a successful business can truly be fulfilling and worthwhile.

03. Pick a business name
Feeling satisfied with your business idea? The next step is to come up with a business name that will leave a strong first impression on potential clients.
You’ll want a name that’s catchy, memorable and scalable (i.e., is still relevant even if your business expands to new locations, niches or product offerings). If you need a little nudge, Wix’s free business name generator can help you brainstorm some ideas, or you can check out these best company names for further inspiration.
You’ll also want to make sure no one else has trademarked or registered your desired business name, which you can check via the U.S. Trademark Electronic Search System or with the Office of the Secretary of State for the state in which your business is located. And, remember you’ll eventually want to build a website for your business. Because your domain name will most likely be the same as your business name, make sure your desired name is available by doing a domain name search .
Learn more:
Small business name ideas
Tech business name ideas
Craft business name ideas
Clothing brand name ideas
Consulting business names
Marketing business names
eCommerce business names
Beauty business name ideas
Fitness business name ideas

04. Write up a business plan
Another essential step when starting a business is to come up with an organized plan. At its core, a business plan is a document that serves as a roadmap for how to structure, operate and manage your new venture. It serves multiple purposes, like helping to attract investors, earning the trust of banks and outlining the cost of starting your business . You can use a business plan template to get your thoughts on paper. No matter how you get started, your business plan should include these components:
Executive summary : Give a high-level view of your business proposal or concept. If you were to make a professional elevator pitch (explaining your business in about a minute), you’d be reciting this bit aloud.
Company description: Include your company’s name, the names of your founders, your locations and your mission statement . Your mission statement should include core values, goals and your guarantee to provide clients with quality service or products. Take a look at these powerful mission statement examples to gather inspiration for your own.
Industry analysis: Provide research about your industry, such as small business trends and growth. When writing this section, think about how large your industry is and how it’s expected to evolve. You should also consider who your competitors are, and make note of their strengths and weaknesses.
Customer analysis: Describe your target audience and how you plan to reach them. Clearly state the needs of your customers and specify how your product or service will meet them.
Organization and management: Provide an overview of your business' organization and leadership, encompassing any founders, executives, board members, employees or important stakeholders. Creating a visual representation—like an organizational chart—can assist in presenting your company's structure effectively.
Service or product offerings: Create a list of your existing and upcoming products and services. If you're still developing your business idea, write a concept statement to outline your vision. Additionally, incorporate a proof of concept (POC) to showcase the viability of your idea.
Marketing and sales: Outline how your business concept actually translates into sales. Explain your marketing strategies and tactics, including plans for advertising, promotions, pricing, distribution channels and digital marketing efforts, along with planned consumer touchpoints (website, mobile app, retail store, etc.).
Financial projections: Estimate how much money will be coming in—or share any data around early sales. Investors want to see hard numbers to justify their risk. Include a sales forecast (based on industry and market trends), expenses , sunk costs , overhead costs , anticipated break-even point, expected accounts receivable, an estimated cash flow (derived from your sales forecast and expenses) and expected profits or losses.
Operational plan: Wrap up with an action plan. If you have a team, write down how each member will contribute to achieving your company’s SMART goals and objectives. Answer questions like “Is there a timeline?” and “What are the milestones you wish to accomplish?” For both, think in terms of years and quarters.

How choosing the right business model and establishing a clear business plan helped this online business succeed
Based in Oldbury, right in the heart of England, Andrew Darby, Faye Darby, Craig Pritchard and Terri Pritchard sold their first piece of jewelry in January 2019. Their story began with Wix eCommerce and a little inspiration from their spouses: “Our wives love jewelry, so we thought, ‘Let's do something mid-range and affordable. Nice pieces that last well.’"
For these new entrepreneurs, the key to starting their business off on the right foot was, in their own words, also their biggest challenge, “The biggest challenge was having a business model so to speak—or a blueprint and sticking to that blueprint. Eventually when we found our blueprint, we got ourselves out of trying to sell here, there, and everywhere.”
And for this business, it's worked. As of April 2022, Darby Pritchards had an annual returning customer rate of over 20%. Read more about how they started their business here .
Looking for a business plan for a specific business idea:
How to create a clothing line business plan
How to create a consultant business plan
How to create a photographer business plan
How to create a bookkeeping business plan
How to create a virtual assistant business plan
How to create a real estate business plan
How to create a restaurant business plan
How to create a plumbing business plan

05. Choose a legal structure for your business
While there are different flavors of legal structures, choosing which one will best serve your needs is based on multiple factors, such as how much personal liability you want to have, taxes and business registration requirements. For example, a sole proprietorship is the easiest to file, but has the most personal liability. LLCs relieve you of many personal liabilities, but can come with hefty tax payments.
A great place to start is by reviewing your options via the U.S. Small Business Administration’s business structure breakdown .
The most common types of businesses or business entities in the U.S. include:
Sole proprietorship : This refers to a business owned by one individual who assumes all of its legal responsibility. Profits and losses from the business are reported on the owner's personal income tax return, and the owner is personally liable for any debts or legal issues that may arise, which could potentially put personal assets at risk.
Partnership : In this arrangement, two or more individuals or entities share ownership, responsibilities and profits. The partnership itself does not pay income tax; instead, the profits and losses "pass through" to the partners, who report them on their individual tax returns. Each partner is personally responsible for the debts and obligations of the partnership, which could potentially expose personal assets to business-related risks.
Corporations : This is a legal entity separate from its owners (shareholders) that can conduct business and incur liabilities in its own name. Corporations are subject to corporate income tax on profits, and its shareholders are generally not personally liable for the company's debts and legal obligations. If a corporation distributes dividends to its shareholders, they must pay personal income tax on these amounts. There are different types of corporations with varying legal implications, most notably C-corps and S-corps.
Limited Liability Company (LLC) : LLCs provide the limited liability protection of a corporation while allowing for the flexibility of a partnership. In terms of taxes, an LLC can choose to be taxed as a pass-through entity, where the profits and losses "pass through" to the owners' individual tax returns, or it can elect to be taxed as a corporation.
How do you know which one is right for you? We consulted with Shylene D’Addario, VP, associate general counsel with LegalZoom. Shylene offered the following insight:
"Sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations and LLCs are the most popular kinds of business structures, according to the IRS. But what type is best for you and why?
A sole proprietorship is best suited to a business owned by an individual or couple that doesn’t have employees or significant contracts with landlords, suppliers or subcontractors.
A business with two or more owners that hasn’t established an entity is treated as a general partnership. General partners typically share the management of the business and its profits and losses but don’t have any protection against liability for their partners’ negligence, misconduct or internal disputes.
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) provide their owners with protection against liability for company obligations. If your LLC can’t pay its debts or is unable to meet its obligations, only the business assets—and not personal assets—are at risk in a lawsuit. This flexibility and limited liability make LLCs a popular choice for small businesses of all types.
Corporations offer their owners (called 'shareholders') the same liability protection as LLCs. Corporations tend to have somewhat more complex recordkeeping and reporting requirements than LLCs, depending on the state in which you incorporate.
If you have additional questions about what kind of entity may be right for your needs, you can learn more on our website or LegalZoom can connect you with a business lawyer who can help advise you in this process."
Start an LLC with LegalZoom.
Do your research, and compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of the different business structures to find the right fit for you. A business lawyer can help advise you in this process, and the IRS’ guide to business structures can assist in evaluating tax implications.
What are the differences between starting a small business and an enterprise?
Starting an enterprise and starting a small business share some similarities but they differ greatly in scale, scope and goals.
Small businesses are typically, as the name suggests, small in scale. They often serve a local or niche market and have a limited number of employees. Enterprises are generally larger in scale, often with a broader geographic reach. They may have multiple locations and serve a larger customer base. Think a small, independent toy shop in a town versus a huge brand like Toys R us.
Small businesses are often owner-operated, where the owner is actively involved in day-to-day operations. Enterprises usually have a more complex ownership structure. They generally have multiple owners, shareholders and a board of directors. The owner's involvement in day-to-day operations can be limited, especially in larger enterprises.
Small businesses tend to offer a narrow range of products or services tailored to a specific customer base. They might focus on providing personalized, local solutions. Enterprises typically have a broader scope, offering a wide range of products or services. They often aim to capture a larger share of the market or diversify their offerings.
While small businesses can grow over time, they might not have aspirations for rapid or significant expansion. The primary goal may be to maintain a steady income or lifestyle. The primary goal of an enterprise is often rapid growth and scaling. They aim to expand their operations, market presence, and profitability.

06. Secure business capital and funding
The most common cause of startup failure is lack of financing (47%), according to a recent survey. Second to that is running out of cash (44%). Clearly, it’s never too early to start thinking about finances. You’ll need both sufficient capital and reliable cash flow to get your business off the ground.
Business funding can take many forms. From applying for grants and loans to reaching out to an angel investor or setting up a fundraising campaign, there are many different strategies here. Here are a few good ways to obtain capital:
Bootstrapping : This involves dipping into your own personal finances to fund your business. In some cases, the benefits of investing your own money may outweigh the challenges of having to depend on outsiders. This allows you to retain greater control over all aspects of your company, though you may face slower growth and potential personal risk.
Crowdfunding: This is a fast and easy way to share your ideas on a wide scale, get feedback and raise money at the same time. When choosing from one of the many crowdfunding sites available, consider the fees, terms and conditions of each, as well as the kind of audience they typically draw.
Small business grants: The biggest benefit of using grant money is that you won’t have to pay it back. A good place to begin looking for grants and eligibility is on the grants for community organizations page of the U.S. Small Business Administration website. Alternatively, you can check out private institutions that offer small business grants, including FedEx and the Second Service Foundation .
Credit cards: When used responsibly, credit cards can be a viable option for funding a new business. It’s advisable to open a business credit card just for this purpose; ideally one with a 0% introductory APR period and a rewards structure so you can earn cash back, credit statements or miles. This can also be a good way to build your business credit score, as long as you make on-time payments and keep a credit utilization of under 30% . You will need strong credit to obtain other types of financing.
Startup business loan : Small businesses can apply for loans from banks and other financial institutions through their offering of business banking services. First, you should know how much you need, and you should be able to demonstrate good reasons for it. Use the financial projections of your business plan to estimate an amount and determine the type of loan you need.
Business line of credit (LOC): This is a flexible loan that behaves similar to a credit card, letting you borrow and repay funds as needed. Business LOCs often have an annual income and time-in-business requirement, but new business owners may be able apply if they’re willing to put up collateral and have a good personal credit score ( over 670 ).
Angel investors: Often, angel investors are found through mutual contacts or even family members. That said, there are hundreds of other active high-net worth individuals who seed startups with their personal money, particularly in the early stages. You can check out Golden Seeds LLC (New York City) or Tech Coast Angels (Los Angeles) as just a few examples of angel investing firms who are involved in venture capital financing.

07. Register your business and make it official
Before you take your business out into the world, you’ll need to complete all the legal and formal paperwork. If you’re establishing a business in the U.S., your location and business structure will determine the steps you’ll need to take to register a business name .
Keep in mind that, according to the SBA , the benefits of registering your business include personal liability protection, legal and trademark protection, and tax benefits—all of which are crucial to the prosperity and expansion of any entrepreneurial operation .
Meanwhile, for those who are seeking to set up a business in the UK or EU , it's essential to familiarize yourself with the different requirements and rules for registering a business , relevant certifications and VAT.

How to start a business by state
How to start a business in Utah
How to start a business in Massachusetts
How to start a business in Oregon
How to start a business in Alabama
How to start a business in Missouri
How to start a business in Illinois
How to start a business in Maryland
How to start a business in Michigan
How to start a business in Connecticut
How to start a business in South Carolina
How to start a business in Tennessee
How to start a business in Minnesota
How to start a business in New York
How to start a business in Pennsylvania
How to start a business in Virginia
How to start a business in Indiana
How to start a business in Washington state

How these co-founders managed to register their business one step at a time
For Andrea Shubert, Co-founder of Strathcona Spirits when it came to registering their new business they found the following crucial:
"Don’t start with a 'no.' We didn’t think the distillery was going to happen because of all the red tape involved, but we kept applying for permits to do this or that. When they said yes, we thought: great, let’s move on to the next thing. The idea that everything is permitted is the best place to start from and just go from there.
And when you get a 'no,' which we definitely have a few times over the last five years, we typically dust ourselves off and continue on until we find our 'yes.'"
08. Apply for tax IDs, licenses and permits
As a registered U.S. business, you’re going to need to obtain your federal and state tax ID numbers , known as your employer identification number (EIN). This is how your business is recognized by the government when it comes to paying taxes on both the state and federal levels. Furthermore, you’ll need a tax ID number to hire employees, open a bank account and apply for relevant business licenses and permits.
Check your local government site to see what types of licenses and permits you might need to apply for. If your company’s activities are regulated by a federal agency, you’ll need a license (selling alcoholic beverages or broadcasting on public radio are two examples). You can review the SBA’s list of business requirements for federal licenses and permits for more information.
Applying for an EIN is free and you can do so online with the IRS’ EIN Assistant tool . That said, tax requirements vary by state. Visit your state’s website to check whether you need to get a state tax ID number to remain compliant. You'll also need to understand which IRS forms are relevant for your business, income statement , tax return process, income tax audit process and corporate tax payments, if any.
Taxes are a major responsibility for business owners, and that responsibility can vary significantly from business to business. According to Sabrina Papini, marketing director of eCommerce and marketplaces at Avalara , "A small business owner might be subjected to various types of taxes depending on their location, industry and business activities." Papini notes that in particular, business owners may be required to pay the following:
Sales tax: If your business sells goods or services to customers within a particular jurisdiction, you might need to collect and remit sales tax. The rate and regulations can vary based on the location and type of product or service sold.
State and local taxes: Depending on your business' location, there could be additional state and local taxes beyond sales tax. These could include business privilege taxes, property taxes, local business license fees and city-specific taxes.
Excise tax: Certain industries that deal with specific goods like alcohol, tobacco, fuel or other regulated products might be subject to excise taxes. These taxes are usually included in the product's price and are paid by the manufacturer, importer or distributor.
International taxes: The company could encounter various international taxes and fees if the business engages in international commerce. These may include value-added tax (VAT), goods and services tax (GST), customs duties or tariffs. If you're a U.S. business operating overseas, or a foreign business operating from the U.S., you should also check for any double taxation liabilities.
Tax considerations should be part of your operational plan from the beginning, Papini emphasizes. "[Using] automated tools, staying informed about tax changes and seeking professional guidance when necessary are critical strategies for managing tax and staying compliant with regulations . These steps will not only help protect your business from legal issues but also contribute to its growth and success."

09. Apply for business insurance
As a new small business owner, obtaining insurance is crucial to protect your venture from unforeseen risks and potential financial liabilities. Business insurance provides a safety net that can shield your assets and help your business stay afloat in case of accidents, lawsuits or other unexpected events.
When applying for insurance, you’ll want to first assess the nature of your business and identify the specific risks it may face. This includes any potential hazards, liabilities related to your products or services, and any potential lawsuits that might arise. Next, consider the coverage types that align with your business needs, such as general liability, professional liability, casualty or property insurance, etc.
A knowledgeable insurance broker can help you navigate the complexities of insurance policies and find the best rates and coverage options that fit your unique circumstances. Some types of insurance you might need to consider include:
Workers' compensation insurance: Mandatory in most states if you have employees, this insurance covers medical expenses and lost wages for employees who suffer work-related injuries or illnesses.
General liability insurance: This provides coverage for third-party bodily injury, property damage and related legal expenses resulting from accidents on your business premises or due to your products or services.
Professional liability insurance: Also known as “errors and omissions insurance,” this policy protects against claims of professional negligence, errors or omissions that may arise from providing professional services or advice.
Property insurance: This policy covers physical assets of the business, such as buildings, equipment, inventory and furniture against damage or loss from events like fire, theft or natural disasters.
Product liability insurance: This type of policy offers coverage for claims arising from injuries or property damage caused by a defective product sold by your business.
Business interruption insurance: If your business operations are interrupted due to a covered event, such as a fire or natural disaster, this will provide compensation for lost income and ongoing expenses.
Employment practices liability insurance (EPLI): An EPLI policy provides coverage for claims related to employment practices issues, such as wrongful termination, discrimination or harassment.

10. Organize your finances
Keeping a business running smoothly demands organized, detailed financials. As you put these systems in place, you’ll want to open a business bank account and consider how you’ll handle your business accounting.
Set up a business bank account
New small businesses should set up a business bank account for several reasons. First and foremost, separating your business finances from your personal finances is crucial for maintaining accurate and organized records. A dedicated business bank account enables you to track income, expenses and profits effectively, simplifying tax preparation and financial reporting.
Additionally, having a business bank account is usually required if you want a business loan or line of credit. It builds credibility with customers, peers and potential investors, as it demonstrates a professional approach to how you operate.
To open a business bank account, you’ll typically need to provide certain documents, including your business registration paperwork, employer identification number (EIN) or Social Security number (SSN). When setting up a business bank account, you’ll want to ask questions to make sure the bank can adequately handle your business needs. Make sure you ask about account fees, transaction limits, access to credit options and integration with financial accounting software to start.
Set up an accounting system
Having a meticulous bookkeeping system in place will help set your business up for success, especially when it comes to tracking expenses, paying taxes, managing invoices or handling payroll. There are a myriad of accounting apps and software options that can help you stay organized in this area, or you can hire a certified public accountant (CPA) to manage this for you.
With Wix, you can keep your books right from within the platform, eliminating the need for additional software and streamlining your workflow. You can manage customer invoices or product inventory directly from your website dashboard, or you can employ a number of accounting and payroll app integrations, such as QuickBooks and EasyTeam .
To fine tune your process, turn to this guide on small business accounting , which covers everything from creating financial statements to planning cash flow statements to managing balance sheets and more.

11. Brand your business
Building a brand is a vital part of understanding how to start a small business and shape a corporate identity . In a nutshell, branding is about creating a consistent voice, set of values and visual identity for your company. This can include everything from logo and brand colors to your company ethos, story and personality.
Brand visuals
When building your brand visuals, there are several key elements and assets you need to create to establish a cohesive visual identity:
Logo: A well-designed logo is the cornerstone of your brand visuals. It should be versatile, memorable and easily recognizable. You can get a professional design in minutes with Wix’s free logo maker .
Color palette: Choose a set of primary and secondary colors that reflect your brand's personality and evoke the desired emotions.
Typography: Select fonts that align with your brand's tone and are easy to read across different mediums.
Imagery: Decide on the type of images or illustrations that best represent your brand. This could include photography, illustrations or graphics.
Iconography: Create a set of custom icons or symbols that can be used consistently throughout your branding materials.
Website design: Ensure that your brand visuals and colors are integrated into your site design, including buttons, banners and overall layout.
Print materials: Consider how your brand visuals will translate to print materials like business cards, brochures and packaging. Not sure how to design a business card ? The Wix Business Card Maker can help you create a professional design in just six steps.
Email: Creating a business email takes just a handful of steps, and you can get a custom business email with Wix . Develop branded templates to maintain consistency in your online communications.

Brand story
According to Sitecore’s 2022 Brand Authenticity report, 70% of consumers want brands to connect with them on a more personal level. This is where your brand story comes into play.
Building a brand story is all about creating a compelling and authentic narrative that resonates with your target audience. Yaya Aaronsohn, head of brand maker at Wix, explains further. "At its core, branding hinges on trust—think of it as a relationship between two individuals: the customer and the brand, which represents the business. Within this relationship, authenticity plays a critical role. It builds trust and creates emotional bonds. It fosters consistency, engagement and reduces reputation risks."
A well-defined brand story can help you forge an emotional connection with customers, and should touch on your:
Origin story: Share the backstory of how and why your brand was created, including the challenges and inspirations that led to its inception.
Founder's journey: If applicable, humanize the brand by sharing the founder's personal journey and connection to the business.
Brand purpose: Clearly articulate the reason your brand exists, its core mission and the problem it aims to solve for its customers.
Brand values: Identify the guiding principles and values that drive your brand's decision-making and actions.
Evolution: Address how your brand has evolved over time and demonstrate your commitment to continuous improvement.
Brand voice
Brand voice establishes a consistent tone that reflects your personality and communication style. It further helps customers relate to the face behind the brand, which can translate directly to sales.
Your brand voice should remain consistent across all channels to reinforce your identity. Some key elements to include are:
Persona: Identify how you want to be perceived by your target audience and craft a tone that supports that identity.
Language: Use language that aligns with your chosen persona, such as authoritative, knowledgeable, down to earth or humorous.
Communication strategy: Set clear communication standards for how you’ll respond to customer comments, reviews, emails or phone calls.

12. Create a professional business website
Building a strong website and setting goals for your website is an absolute must when starting a business. For most prospective customers, investors and partners, your website will be their introduction to your business. It's a vital opportunity for you to create a positive first impression of your brand.
Expert advice from Amanda Buhse, Owner and Chief Creative Officer of Coal and Canary
"Something that I always heard growing up was that you could be the smallest fish in the sea, but if you have a professional website and branding, people will take you seriously. When I sent my website to potential retailers early on, we were making seven candles at a time out of my small kitchen. I think it goes to show that when you have a professional brand, the goals and dreams that you have are limitless." (Coal and Canary now produces more than 1,0000 hand-poured candles, a day from their 10,000 square foot warehouse.)
Learning how to make a business website is simple and doable for people of all skill levels. Follow the steps outlined below to get your online presence off the ground.
Ready to launch? Build a beautiful business website or eCommerce website today.
Find a business website template
Website builders make it easy to create a professional, well-designed website with a few clicks of the mouse. Wix offers more than 800 business templates , including more than 500 online store templates , encompassing everything from finance and fashion to crafts and consulting (and beyond).
To begin, simply choose a template and customize it to meet your needs. Alternatively, you can utilize Wix’s AI website builder tool, which translates information about your design and layout preferences into a professional website tailor-made to your needs—all in a matter of minutes.
If you need more inspiration, check out the best business websites of the past year.
Customize your tools and features
With the foundation of your website up and running, it’s time to fine-tune which tools and integrations you’ll use to help run your business.
Wix offers business owners a full assortment of native software solutions and built-in features that transform your site dashboard into a one-stop-shop for day-to-day operations. You can handle transactions with Wix Payments or Wix Point of Sale (POS) ; manage incoming payments with Wix Invoices ; schedule classes, workshops and appointments with Wix Bookings ; and even sell tickets with Wix Events & Tickets .
The Wix App Market offers hundreds of other third-party integrations that can help you manage payroll, expense tracking and more.
Choose a web host and domain name
After you’ve customized your template, you’re ready to move on to the next step: flipping the switch so that your site is visible to the public. This is a two-fold process.
First, you’ll need to pick a web hosting provider. Basically, this is just a tool that stores your website’s files so that they’re viewable online. Wix is the leading web hosting platform for small businesses , and it offers free website hosting that’s protected and reliable—complete with 24/7 security monitoring and integrated SSL certificates to keep your users safe.
Once you’ve selected a web host, you’ll need to connect your registered domain name to a hosting server. It will take a matter of minutes, but rest assured that when you purchase your website domain with Wix, you’ll also gain access to domain security and full customer support.

Optimize your business website for SEO
When it comes to starting a business online, it’s essential to have some basic knowledge of search engine optimization (SEO). SEO is the process of optimizing web content to improve your site’s ranking for searches of specific keywords. Rebecca Tomasis, SEO expert for Wix Blogs, explains further. "The higher you rank in search, and the more keywords you rank for—the greater your visibility, traffic and potential for conversions or sales."
For example, if you sell organic baby items, you want to integrate exact phrases, like “eco baby products” and “natural baby toys,” into your site content. This improves your chances of showing up in search results when people type those phrases into the search bar.
You can use keyword research tools such as Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs or Semrush (which has native integration with Wix ) to find terms to incorporate into your web content. You can also use the Wix SEO Hub as a resource for all things related to learning SEO.
Your overall SEO strategy should include the following:
Technical SEO: "Technical [SEO] involves elements such as your site speed, core web vitals, the site hierarchy and structure and navigation," Tomasis details. In other words, your website should, on a technical level, be responsive, quick to load (including on mobile) and easy for search engines to crawl. You should avoid things like dead links, duplicate content and large, slow-loading media files that can impact the user experience.
On-page optimization: Optimize your website's individual pages for the targeted keywords you’ve identified. Place the primary keyword in the page title, meta description, headings and content naturally.
High-quality content: Create high-quality, informative and engaging content that addresses the needs of your target audience. If you have a blog, well-written articles attract visitors and encourage them to spend more time on your site, signaling search engines about its relevance. "Make sure your content is helpful and answers the intent behind the search term as directly and as clearly as possible," says Tomasis. "Everything about the article—its structure, its data, its headings—should be optimized to meet the intent of the user searching."
Mobile-friendly design: Ensure your website is responsive and mobile-friendly. With the increasing number of mobile users, mobile optimization is crucial for SEO and user experience.
Local SEO: If your business serves a local audience, optimize for local SEO. Claim and optimize your Google My Business listing, ensure consistent NAP (name, address, phone) information across the web and encourage customer reviews.

13. Market and promote your business
Once you’ve launched your business and published your website, you can start building a small business marketing strategy that fuels business growth . A solid marketing strategy is essential for bringing in customers and taking your business to the next level. As Erin Shea, Senior Director of North America Marketing for VistaPrint shares, "Customers are the backbone of any successful small business and effective marketing is one of the best ways to build and sustain your community". According to Erin,
“Whether you’re engaging customers online or offline—remember that consistency is worth its weight in gold. A cohesive look to your marketing inspires confidence in your professionalism, builds credibility and strengthens customer rapport.”
Check out more of VistaPrint's 2024 marketing trends to help with your new business efforts.
Here are some of the most common marketing strategies to consider:
Paid advertising: By leveraging targeted advertisements, small businesses can reach a vast audience of potential customers who are actively searching for products or services related to their industry. Google Ads are particularly popular, letting businesses bid on relevant keywords, ensuring their ads appear prominently in search engine results. Wix users can manage Google Ad campaigns from their site dashboard, leaving one less external platform to worry about.
Social media marketing: Marketing on social media brings you massive exposure from diverse groups of people. Pick a platform that your target audience uses and maintain an active presence there. You can also implement paid social media marketing; for example, Wix users can boost sales with fully integrated Facebook and Instagram ads directly from their website builder.
Email marketing: A highly effective tactic, email marketing can promote your brand and build engagement . Using this method, you can reach customers directly, build a loyalty program and customize messages based on their individual interests. Wix users have access to a free email marketing tool with customizable templates, simple editing interface and advanced analytics.
Content marketing: This involves crafting and sharing valuable and relevant content in order to draw in your target audience. It can be done in a variety of ways, including publishing a blog, creating a podcast or making a YouTube channel. Use any of these outlets to share business updates, distribute relevant industry related news and build connections with potential customers.
Word of mouth: Positive word of mouth can give your brand's reputation and credibility a boost, increasing customer loyalty and customer acquisition. It’s a cost-effective strategy that can create a ripple effect, reaching a broader audience and generating organic growth for businesses.
Bear in mind that finding the right marketing strategy may take some time, experimentation and patience. But, Erin notes, consistency is key: "Whether you’re engaging customers online or offline, remember that consistency is worth its weight in gold. Even if you’re just starting out, try experimenting with different marketing tactics to see what works. As your sales grow, direct a greater portion of your revenue for your marketing budget and keep building.”

14. Build a team
As your business grows, it may be difficult for you to play multiple roles—which is where hiring employees and delegating tasks comes in. Even if you decide not to hire in-house staff, you may find yourself needing extra assistance from freelancers or independent contractors.
Read also: Human resources guide
When you begin the hiring process, factor in your budget, your needs and the company culture you want to portray. Creating a well-defined vision statement will help you find the right people to satisfy all of these requirements.
There are many effective ways to source talent for your team. A few ideas to get you started:
Online job platforms: Websites like Indeed, LinkedIn and Glassdoor offer job posting services where you can find potential team members.
Local job boards: Many communities have local job boards or websites where businesses can post job openings to attract candidates from the area.
College career centers: Contact career centers at local colleges and universities to connect with talented students or recent graduates seeking employment opportunities.
Networking events: Attend industry-specific business networking events or job fairs to meet potential candidates face-to-face and discuss job opportunities.
Social media: Utilize social media channels like Facebook, X (formerly Twitter) and Instagram to reach out to a broader audience and attract job seekers.
Freelance platforms: Websites like Upwork, Freelancer and Fiverr offer access to freelancers who can work on specific projects or provide specialized skills.
Industry-specific forums or groups: Join online forums or social media groups dedicated to a particular industry to discover talented professionals interested in relevant job opportunities.

How to start a business FAQ
How do you start a business as a beginner.
To start a business as a beginner, follow these essential 14 steps:
How much money do you usually need to start a business?
How do you get money to start a business, do you need a business degree to start a business, what do you need to start a business, can you start a business with no money, how to start a business online, how to start a business as a teenager, how to start a business as a student.
LegalZoom is a partner of Wix.
Related Posts
How to register a business name
How to name a business: a creative guide
Free business plan template for small businesses
Was this article helpful?

Ashley Ferro
How to Start a Coaching Business in 2024 Step By Step
Wondering how to start a coaching business and keep it afloat?
It's a tough nut to crack, but luckily, we've got the answers you need.
This comprehensive guide is designed to navigate you through the crucial steps. It will assist you in identifying your distinct coaching niche, establishing your business infrastructure with precision, and developing a business strategy poised for success.
We address key aspects including:
- selecting the appropriate legal structure
- implementing effective marketing strategies
- proficiently managing your finances
Upon completion, you will possess a profound understanding of how to start an online coaching business that is not only financially rewarding but also significantly influential in enriching people's lives.
Identifying your coaching niche
Selecting a specific niche in the coaching industry is crucial for the success of your coaching business. This specialization not only helps in standing out in a crowded market but also allows for more targeted and effective marketing strategies.
Whether you're considering career coaching, life coaching, health and wellness coaching, or any other area, focusing on a specific niche aligns your expertise with the needs of a particular group of clients.
{{block-start:focus-trainer}}
Why specialize?
- Expertise development : Specializing in a particular area allows you to develop deep expertise, which enhances your credibility and attractiveness to potential clients.
- Targeted marketing : A specific niche enables you to tailor your marketing efforts more effectively, reaching the people who are most likely to benefit from your services.
- Higher demand : Specialists often enjoy higher demand and can command better rates due to their perceived expertise in a specific field.
{{block-end:focus-trainer}}
Tips on identifying your target audience
- Assess your strengths and interests : Look at your own skills, experiences, and passions. What areas do you excel in? For instance, if you have a background in corporate training, career coaching might be a natural fit.
- Market research : Conduct thorough research to understand the needs and challenges of potential clients. This can involve reading industry reports, participating in relevant forums, and conducting surveys.
- Identifying gaps in the market : Look for areas that are underserved or have a growing demand. For example, the rise of remote working has created a demand for coaches specializing in helping professionals adapt to this new work environment.
- Consider your ideal client : Picture the type of client you want to work with. Are they corporate professionals, new mothers returning to work, or individuals seeking a career change? Understanding your ideal client's profile will guide you in refining your niche.
- Analyze competitors : Look at what other coaches in your desired field are doing. What services are they offering? What gaps can you fill? This can help you find a unique angle within your chosen niche.
- Trial and error : Sometimes, the best way to find your niche is through experience. Try working with different types of clients and see where you find the most success and fulfillment.
By carefully identifying and defining your coaching niche, you set the foundation for a focused, effective, and successful coaching practice. Remember, your niche should reflect a combination of your passion, expertise, and a market need, ensuring that your coaching business is not only profitable but also fulfilling.
Setting up your coaching business infrastructure
Establishing a solid business infrastructure not only legitimizes your business in the eyes of the law and your clients but also sets you up for operational success.
Here’s a guide to help you navigate this process:
How to start a coaching business online from the legal perspective
Step 1: choose your business structure.
Deciding whether to operate as a sole proprietorship or form a Limited Liability Company (LLC) is a key decision.
- Sole proprietorship : This is the simplest structure, with minimal paperwork and the owner having complete control. However, it offers no personal liability protection.
- LLC : This provides personal liability protection, separating your personal assets from the business. It’s more complex than a sole proprietorship but can offer tax advantages and increased credibility.
Step 2: Registering your business
The process involves choosing a business name and registering it with your state or local government.
This step might also include obtaining a federal Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS, especially if you plan to hire employees.
Step 3: Obtaining necessary licenses and permits
Depending on your location and the nature of your coaching services, you may need specific licenses or permits.
This could include a general business license or specific professional certifications.
{{block-start:focus-consulting}}
Setting up your coaching business legally is a breeze with these 3 easy steps:
1. Pick your business framework — go with either Sole Proprietorship or LLC.
2. Register your business with your state or local government.
3. Get any licenses and permits you might need for your coaching practice.
{{block-end:focus-consulting}}
Essential tools and systems for running a coaching business
1. profi as an all-in-one solution.
Profi stands out as a comprehensive platform specifically for coaches. It combines several functionalities into one streamlined service, potentially replacing multiple tools.
Key features include:
- Client management : Manage appointments, client information, and communications.
- Billing and payment processing : Handle invoicing and payments directly through the platform.
- Video calls and messaging : Conduct sessions and communicate securely with clients.
- Program development tools : Create and manage coaching programs and curricula.
- Marketing and engagement : Tools to enhance client engagement and market your services.
To learn more about how Profi can help you start and grow your coaching business, book a demo , or if you're a solo practitioner, you can start with Profi's free trial .
2. Insurance
Consider obtaining liability insurance to protect your business from potential lawsuits.
3. Professional development tools
Stay updated with coaching trends and techniques through continuous learning. This might include:
- Subscriptions to professional journals
- Online courses
- Membership in coaching associations
How to craft a coaching business plan
Creating a well-structured business plan is a critical step for the success of your coaching business. It not only provides a roadmap for your venture but also helps in attracting potential investors and partners.
Step 1: Define your business vision and goals
Begin by articulating the core purpose of your coaching business. This should capture your passion and what you aspire to achieve in the long run.
A strong vision statement serves as a guiding star, helping to steer all business decisions and strategies.
For example, "Empowering young professionals to achieve career excellence and personal fulfillment."
Setting SMART goals
- Specificity : Clearly outline what you aim to achieve. For example, "Launch an online coaching program for at least 20 participants by the end of the year."
- Measurability : Set benchmarks to track progress. This might include tracking website traffic or participant feedback.
- Achievability : Ensure your goals are realistic, given your current resources and market conditions.
- Relevance : Align each goal with your broader business vision. If your vision is to empower young professionals, a relevant goal could be developing career advancement workshops.
- Time-bound : Assign a clear timeline to each goal. For instance, "Increase client base by 15% in the next six months."
Balancing short-term and long-term objectives
Short-term objectives could include actions like creating your coaching website, networking with industry professionals, or completing a specialized coaching course.
Long-term aspirations might encompass broader ambitions like becoming a recognized leader in your coaching niche, expanding your business to include additional coaches, or publishing influential coaching material.
Step 2: Analyze your market
Analyzing the market involves a blend of comprehensive research and keen observation.
Start by diving into the coaching industry's current state and future trends. This involves studying industry reports and participating in relevant online forums.
Pinpoint the specific needs and preferences of your target audience. This can be achieved through surveys, direct interactions, or analyzing online discussions in niche-specific forums.
Performing competitor analysis
- Identifying competitors : Begin by listing out both your direct and indirect competitors. This helps in painting a clear picture of the current market landscape.
- Analyzing strengths and weaknesses : Examine your competitors' offerings, customer feedback, and marketing strategies to understand what they are doing well and where there might be gaps.
- Finding market opportunities : Look for unaddressed areas or niches that your competitors might have overlooked. This might involve unique services, specific client demographics, or innovative coaching approaches.
Step 3: Think of how to market your coaching business
Crafting effective marketing and operational strategies is vital for the growth and smooth functioning of your coaching business.
Marketing strategy
Developing a marketing strategy involves a mix of techniques:
- Digital marketing : This includes building a strong online presence, engaging potential clients through social media, and creating valuable content like blogs or videos.
- Networking : Here, you'll focus on forming connections within the industry, attending events, and actively participating in online forums.
- Referral programs : Encourage existing clients to refer new ones by offering incentives.
Operational plan
Efficient operations are crucial for the success of your business:
- Service delivery : Decide whether to offer sessions online or in-person and establish a reliable scheduling system.
- Client management : Implement a system to manage client information, track progress, and maintain communication.
- Daily operations : Allocate specific times daily for administrative tasks like responding to emails and updating social media.
This approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of both marketing outreach and the inner workings of your business operations.
Step 4: Financial planning and projections
In this crucial step, you'll lay the financial groundwork for your coaching business.
Estimating initial investment needs
Calculate expenses for getting your business off the ground. This includes:
- Licensing and legal fees.
- Marketing expenses, such as advertising and promotional materials.
- Website development costs, including domain registration and hosting.
- Office supplies and any necessary equipment.
Then, set aside funds for unexpected expenses.
Identifying revenue sources
Think beyond traditional one-on-one coaching. Consider:
- Group sessions or workshops.
- Online courses or digital products like ebooks.
- Speaking engagements or webinar hosting.
Projecting income and expenses
Create a detailed projection of your income and expenses. This should include:
- Regular operational costs like software subscriptions, rent (if applicable), and ongoing marketing expenses.
- Expected revenue from different services.
Also, prepare for both best-case and worst-case scenarios. This helps in:
- Anticipating challenges and planning for contingencies.
- Understanding the potential growth trajectory and making informed decisions.
A comprehensive financial plan not only prepares you for the initial phase of your business but also guides you through its growth stages.
Step 5: Leverage free resources
Expanding your toolkit with free resources can significantly streamline your business plan creation process.
- Online templates : Look for templates designed for coaching businesses. These templates help in organizing your plan and covering all essential aspects. Websites like Template.net offer a variety of business plan templates, including ones tailored for coaching services.
- Business plan guidance : Platforms like SCORE and Bplans offer comprehensive resources. They provide free business plan samples, which can be a great starting point. Additionally, they offer guidance and advice specific to the coaching industry, helping you refine your plan.
- Educational resources : Utilize free online courses and webinars that focus on business planning and strategy. Websites like Coursera and Khan Academy offer courses that can enhance your understanding of business fundamentals.
By utilizing these free resources, you can develop a well-structured and industry-specific business plan without incurring additional costs.
Step 6: Review and revise regularly
To ensure your coaching business stays relevant and successful, it's crucial to regularly update your business plan.
- Market evolution : Stay alert to changes in the coaching industry and market trends. This includes adapting to new technologies, shifting client needs, and emerging coaching methods.
- Client feedback : Incorporate feedback from your clients to refine your services and approaches.
- Personal growth : As you grow and learn in your coaching journey, let your business plan reflect your evolving expertise and new insights.
- Scheduled reviews : Set a regular schedule, like quarterly or biannually, to reassess and update your plan.
Continuously refining your business plan ensures that your coaching practice remains dynamic, adaptive, and aligned with both your professional goals and market realities.
Developing a strong brand and online presence
To create a distinctive brand and online presence for your coaching business:
Develop a unique brand identity
Developing a unique brand identity involves a deep understanding of your audience's specific needs and preferences, crafting a brand message and visual style that resonates with them, and using storytelling to connect emotionally.
It's about creating a brand that not only stands out but also genuinely reflects the values and benefits of your coaching services.
The key is to build a brand that feels personal and relatable to your target audience, thus fostering trust and recognition in the competitive coaching market.
{{block-start:focus-quote}}
“A brand is the set of expectations, memories, stories and relationships that, taken together, account for a consumer’s decision to choose one product or service over another.”
Seth Godin, Entrepreneur and Author
{{block-end:focus-quote}}
Creating an engaging and effective website
To create an engaging and effective website for your coaching business:
- Start with user-friendly platforms like Wix or WordPress . They offer easy navigation and design options suitable for all skill levels.
- Design your website to be visually attractive , ensuring it aligns with your brand’s style and ethos. Use colors, fonts, and images that represent your coaching philosophy.
- Ensure your website is easy to navigate . Clear menus and a well-organized layout help visitors find what they need quickly.
- Provide detailed information about your services . Clearly explain what you offer and how it benefits your clients.
- Include testimonials to build trust and credibility . They show prospective clients the success stories and positive experiences of others.
- Regularly update a blog with relevant and insightful content . This not only engages your audience but also improves your website’s search engine ranking.
- Make it easy for potential clients to contact you . Include a contact form, email address, and, if applicable, your business phone number.
A well-crafted website acts as a central hub for your coaching business, effectively showcasing your services and attracting potential clients.
Effective use of social media
For effective social media use in your coaching business:
- Choose platforms that align with your niche . LinkedIn is ideal for career coaching, while Instagram suits lifestyle coaching, for example.
- Regularly post content that offers real value to your audience . This could include tips, insights, or thought-provoking questions.
- Use your social media to tell stories , whether they're your own, your clients' success stories, or motivational anecdotes. This humanizes your brand and creates deeper connections.
- Foster a sense of community on your platforms . Engage with your followers, respond to comments, and create content that encourages interaction.
- Maintain a regular posting schedule and ensure your content is authentic to your brand.
By strategically using social media, you can significantly enhance your brand's visibility, connect with your target audience, and grow your coaching business.
How to design your coaching packages
When designing your coaching packages:
- Identify the specific challenges and goals of your target audience . This insight helps in creating packages that directly address these needs.
- Offer diverse packages , like 3-month programs, which can include various elements such as personalized sessions, group workshops, and resource access. Tailoring the length and content of these programs allows you to cater to different client preferences and commitment levels.
- Clearly outline what each package includes and the benefits it offers . This transparency helps clients understand the value they'll receive.
- While structure is important, allow some flexibility to modify packages based on individual client progress or changing needs.
- Set competitive yet sustainable prices for your packages . Consider offering different price points for different levels of service.
By thoughtfully designing your coaching packages to address specific client problems and offering varied structures and clear value, you can effectively meet the needs of your clients and strengthen the appeal of your coaching services.
Pricing strategies for your coaching business
To create a comprehensive pricing strategy for your coaching business:
Market analysis
When analyzing market prices for your coaching business, it's about looking at what others in your area are charging and understanding their reasons. This could be due to their experience, the type of coaching they offer, or who they're targeting.
It's also good to see how pricing trends are changing and how clients feel about different price points.
Remember, prices can vary in different locations. This research helps you figure out a good price for your services.
Value-based pricing
In value-based pricing, consider the unique impact and results your coaching provides.
This method involves setting prices based on the positive changes and outcomes your clients experience, rather than simply charging for the time spent. For example, if your coaching significantly improves a client's career or personal life, your pricing should reflect this transformative value.
This approach acknowledges the unique benefits and results of your coaching, aligning the price with the perceived value in the eyes of your clients.
Diverse pricing models
When considering pricing models for your coaching business, explore various options:
- Hourly rates : Suitable for individual sessions or short-term engagements, but this model might limit long-term income potential.
- Package deals : Create bundles, like a set of six sessions, priced at a flat rate. This encourages clients to commit to a series, enhancing client retention and providing more stable income.
- Subscription models : Offer ongoing support with a regular monthly fee. This model ensures a consistent revenue stream and can build long-term client relationships.
Each model has unique benefits and can be tailored to different types of coaching services and client needs.
Cost consideration
In pricing your coaching services, make sure to include all your costs like:
- Money spent on marketing
- Any materials you need for coaching
- Time you put into planning and conducting sessions
This will help you set prices that cover your expenses and ensure your business makes money.
Flexible adjustments
In pricing your coaching services, it's important to stay flexible and open to adjustments. Be ready to change your rates in response to how the market reacts, what your competitors are charging, or feedback from your clients.
Also, as you gain more experience and expertise, you might find it reasonable to increase your prices. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your pricing strategy ensures it stays relevant and reflects the value you provide.
Tiered pricing options
Tiered pricing options involve offering different service levels at various price points.
This strategy allows you to cater to a wider range of clients, from those seeking basic services to those wanting premium, comprehensive coaching. Each tier should provide increasing value, justifying the higher price.
For example, a basic package might include limited sessions and email support, while a premium package could offer more sessions, additional resources, and personalized support.
This approach not only broadens your client base but also allows clients to choose a service level that fits their needs and budget.
Trial and feedback
Introducing trial offers or introductory sessions at a special rate is an effective strategy to attract new clients and gather valuable feedback.
These trial sessions allow potential clients to experience your coaching style and the value you offer, which can lead to more informed decisions about continuing with your services.
Also, the feedback received during these trial periods is crucial. It helps you understand client expectations and satisfaction, providing insights that can guide adjustments in your service offerings and pricing structure to better align with market needs and preferences.
Transparency and communication
For transparency and communication in your pricing:
- Be clear and upfront about how much your coaching services cost . This includes detailing what each price includes, like the number of sessions or additional resources.
- Explain the value clients will receive from your services . This helps justify the cost and shows clients what they're investing in.
Open communication about pricing builds trust and establishes a positive relationship with potential clients. It shows you're honest and straightforward, which is important in a coaching relationship.
Operational considerations when starting a coaching business
In operational considerations for your coaching business:
- Choose between home-based or office space . Home-based setups offer cost efficiency and convenience, while an office space might provide a more professional ambiance for clients.
- Utilize comprehensive platforms like Profi, which provides scheduling, secure video calls, billing, and client management in one place. This streamlines various administrative tasks, making operations smoother.
- For marketing, consider a specialist who understands your niche market . For web development, hire a professional to ensure your website is user-friendly, SEO-optimized, and visually appealing.
Overcoming the challenges of starting a coaching business
Managing startup costs.
When managing startup costs for your coaching business, it's important to carefully plan and prioritize your initial investments. These costs typically include obtaining necessary certifications, marketing your services, setting up a professional website, and possibly securing a physical office space.
To effectively manage these expenses:
- Home office : Start with a home office to significantly reduce overhead costs.
- Digital marketing : Invest in cost-effective digital marketing strategies like social media engagement and content marketing, which can provide high returns at lower costs compared to traditional advertising.
- Affordable web solutions : Use affordable, user-friendly website platforms to create a professional online presence without incurring high development costs.
{{block-start:color-green}}
Pro Tip : Focus on lean management principles in the early stages of your business. This means prioritizing spending on essentials that directly contribute to client acquisition and retention, and avoiding overspending on non-essential items. Keeping overheads low initially allows you to invest more into areas that directly drive business growth.
{{block-end:color-green}}
Finding clients
Finding clients is a crucial challenge in establishing a coaching business. Effective marketing, credibility, and networking are key components in building a client base.
To enhance your client acquisition:
- Online presence : Strengthen your visibility with a robust online presence. Use social media and content marketing to showcase your expertise and connect with potential clients.
- Introductory offers : Attract clients by offering trial sessions or workshops. These can demonstrate your coaching style and effectiveness.
- Referral programs : Encourage existing clients to refer new ones by offering incentives, tapping into word-of-mouth marketing.
Pro Tip : Consistently engage with your audience through various online channels. Regular interaction, combined with providing valuable content, establishes trust and positions you as a go-to expert in your field. This approach can significantly enhance client acquisition efforts.
Handling time management and work-life balance
A common challenge in coaching businesses is managing time effectively and maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
To address this challenge:
- Efficient scheduling : Use tools like digital calendars or scheduling software to manage your time efficiently.
- Set boundaries : Establish clear work hours to prevent burnout and maintain personal time.
Pro Tip : Implement time management techniques like batching similar tasks and setting aside specific times for client sessions, administrative work, and personal activities. This helps create a balanced routine, ensuring productivity while maintaining personal well-being.
Embracing the journey of starting a coaching business
When it comes to starting a coaching business from scratch, let's be real: it's no walk in the park. You're bound to run into challenges, from crunching the numbers on costs to scouting out clients.
But remember, these are steps towards something bigger: a chance to shape your work life and make a real difference in others' lives. It's more than just a job; it's an opportunity to create positive change.
Embrace this journey, ready to learn and grow along the way.
Ashley Ferro is a content writer with 4+ years of experience creating engaging, SEO-friendly content across various topics ranging from service delivery, customer experience, onboarding, to workflow management. When she's not writing, Ashley loves traveling, trying new foods, and playing with her dog!
Generate more profit for your service practice
Without investing any more time. You've been helping others — it's time to help yourself
.webp)
Alina Trigubenko
.webp)
Link copied
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

April 1, 2024 , Filed Under: Uncategorized
What to Know Before Starting Your Business
Embarking on the journey of starting your own business can be exhilarating, daunting, and outright transformative. It’s a path paved with challenges, learning, and opportunities. Whether you’re driven by a passion for innovation or the dream of being your own boss, understanding the landscape ahead can make the difference between a fleeting attempt and a thriving enterprise. This article sheds light on key considerations and strategies for aspiring entrepreneurs, aiming to equip you with the knowledge to navigate the complex yet rewarding world of business.
Identifying Your Niche
Finding your niche is a critical first step in the business world. It’s not just about what you want to sell or offer; it’s about identifying a gap in the market that your business can fill. A well-defined niche helps in creating a focused marketing strategy and establishes a clear target audience. Consider conducting market research and competitor analysis to ensure your business idea has the potential to stand out.
Creating a Solid Business Plan
A robust business plan is your roadmap to success. It outlines your business goals, strategies, market analysis, financial forecasts, and potential challenges. It’s a living document that not only guides your startup phase but also assists in managing your business. A comprehensive plan attracts investors and serves as a tool for evaluating decisions and tracking progress.
In the quest for further resources and guidance on entrepreneurship, exploring various platforms for insights can be immensely beneficial. For those interested in gaining a deeper understanding of the nuances, online resources on how to run a business can provide valuable perspectives and advice from seasoned professionals. This can complement your existing knowledge and aid in refining your business strategies.
Building a Strong Brand
Your brand is the identity of your business; it’s what sets you apart in the market. A strong brand resonates with your target audience and creates loyalty. It encompasses your business name, logo, values, and communication strategy. Investing in your brand’s development and consistently presenting it across all platforms can significantly impact your business’s growth and perception.
Understanding Legal Requirements
Navigating the legal landscape is crucial for any startup. This includes choosing the right business structure , understanding tax obligations, and ensuring compliance with local, state, and federal regulations. Failing to address these aspects can lead to significant legal hurdles down the line. Consider consulting with a legal expert to get your business off to a proper legal start.
Maintaining Work-Life Balance
Starting and running a business requires dedication and hard work, but it’s crucial to maintain a healthy work-life balance. Burnout can hinder your progress and affect your decision-making. Setting boundaries, taking breaks, and pursuing hobbies or interests outside your business can enhance your overall productivity and well-being.
Financial Management
Effective financial management is the backbone of any successful business. It involves setting up a budget, managing cash flow , and determining funding sources. Whether it’s through personal savings, loans, or investors, securing enough capital is essential. Understanding your financial landscape also means planning for taxes and setting aside resources for unexpected expenses.
Expanding Your Network
Building a strong professional network is invaluable for any entrepreneur. Networking can open doors to new opportunities, partnerships, advice, and support. Attend industry events, join relevant online communities, and engage with other entrepreneurs through social media platforms. A robust network not only aids in the growth of your business but also enriches your entrepreneurial journey with diverse perspectives and relationships.
Embracing Digital Marketing
In today’s digital age, having a strong online presence is non-negotiable. Digital marketing strategies such as SEO , content marketing, social media advertising, and email marketing can drive traffic, generate leads, and boost sales. Utilizing these tools effectively involves understanding your audience, creating quality content, and constantly analyzing and adjusting your strategies based on performance metrics.
Staying Adaptable and Open to Learning
The business landscape is ever-changing, and adaptability is key to stay ahead. Be open to experimenting with new strategies, technologies, and business models. Continuous learning and being receptive to feedback can lead to innovative solutions and business improvement. Regularly review your business plan and strategies to ensure they align with current market trends and business needs.
Emphasizing Customer Satisfaction
Ultimately, the success of your business depends on the satisfaction of your customers. Delivering quality products or services, exceptional customer service, and valuing customer feedback are fundamental. Implement mechanisms to gather customer insights and respond to them constructively. Satisfied customers are likely to become repeat buyers and can become powerful advocates for your brand in a competitive market.
Launching a business is a venture filled with highs and lows, but proper preparation and awareness can set the foundation for a successful and fulfilling journey. It’s not just about having a great idea but also about strategically bringing that idea to life. By focusing on finding your niche, creating a detailed business plan, understanding legal requirements, managing finances wisely, building a strong brand, leveraging digital marketing, maintaining work-life balance, expanding your network, staying adaptable, and emphasizing customer satisfaction, you are laying the groundwork for a business that can withstand challenges and thrive in a competitive landscape.
The real voyage of discovery consists not in seeking new landscapes, but in having new eyes — Marcel Proust


Learning center series
A step by step guide to starting a bakery in 2024
- Published on March 11, 2024
- by Turgut Arisoy
- Last updated: 2 hours ago

Each morning, the intoxicating scent of fresh bread and pastries heralds the dawn; a symphony of flavors served warm from the oven in the journey of starting a bakery. You can be the conductor of this delicious orchestra, the creator of delights such as wedding cakes, cupcakes, and breads.
In a world where gluten-free, vegan, and small-batch artisanal bakeries rule the roost, it’s not merely about mixing flour, butter, and sugar. It’s about entrepreneurship, sustainability, trends, innovation, and yes, an unabashed love for all things sweet and savory. Welcome to the era where bread meets business, and passion kneads profitability.
This guide is your ultimate recipe to venture into the world of baking full-time, with insider tips and expert advice that will help you go from kneading dough in your home kitchen to opening your type of bakery by 2024. Let’s roll!
Delicious Earnings in the Oven 🍞 In May 2022, the median annual wage for bakery businesses was $32,780, showing the financial potential in the world of baking.
Step-by-Step Guide to Crafting Your Bakery Business Plan
Step 1: defining your bakery concept.
Understanding and defining your bakery type is the initial fundamental. It’s not just about deciding what type of pastries or loaves you’re enthusiastic to bake every day, but a more comprehensive view of your bakery’s skeleton.
- Is it a high-end patisserie or an eco-friendly neighborhood bake shop?
- Will it offer gluten-free or vegan options?
- What’s the distinctive selling proposition that makes your bakery stand out?
Jotting down these answers helps to establish the vision for your bakery. This phase isn’t just productive for your business plan but shapes your brand ultimately.
Step 2: Conducting Market Research
Understanding your local market can’t be skipped. Even if your buttery croissants are impressive, if they don’t align with local preferences, your bakery might suffer. To obtain valuable insights:
- Study your direct competition—other bakeries.
- Delve into indirect competition—supermarkets or cafes selling baked goods.
- Understand your target customer’s preferences—are they health-conscious, or do they favor indulgence?
- Gauge how much they’re willing to pay and how often they frequent bakeries.
The gathered data aids in avoiding potential pitfalls, harnessing market opportunities, and fine-tuning your bakery type.
Bakery Boom in the Business 🥖 In 2022, the market size of the bakery cafe and retail bakery sector in the United States reached a delicious high of 17 billion U.S. dollars, reflecting a significant rise from 13.3 billion U.S. dollars in the previous year.
Step 3: Financial Planning
Every aspiring baker’s dream of owning a bakery hinges on comprehensive financial planning. It encompasses:
- Start-up costs including acquiring a location, equipment costs, insurance, and licensing
- Operating expenses such as utility bills, salaries, and ingredient expenses
- A revenue forecast based on realistic estimations of sales and prices
Creating a well-structured financial plan provides a clear view of the investments required and an understanding of when the business becomes profitable. Unearth the critical financial details and true expenses associated with initiating a bakery business in 2024 through our comprehensive guide.
Each step not only builds your bakery cafes but also lays out clear tracks for launching and growing your bakery venture in 2024. By laying out and organizing these thoughts and plans, you’re preparing for a successful bakery marketing strategy. Metrobi facilitates bakery delivery operations, offering delivery services across more than 20 cities in the US, including Seattle .
Flourishing Flavors Across the U.S. 🍪 The market size of the bakery cafe sector in the U.S. has reached a delightful approximate total of 13.3 billion U.S. dollars , showcasing continuous growth over the last decade.
Essential Equipment for Your Bakery
Expeditiousness and food safety are key parameters for maintaining the integrity of a bakery business. Equipping the bakery business with the right set of tools and appliances and incorporating safety measures not only helps abide by the health guidelines but also enhances the overall efficiency of the baking process.
Baking Tools and Appliances
Baking is as much an art as it is a science. Each type of pastry, bread, or other baked goods requires specialized tools to create bakery products with exquisite taste and perfect texture. Essential professional-grade bakery items and appliances include everything from a commercial mixer and dough sheet to a commercial oven and proofing cabinet. At Metrobi, we extend our expertise to bakeries by offering delivery services across more than twenty cities in the United States, encompassing prompt same-day delivery options in New York City .
TIP – Make sure these tools and appliances are relevant to the bakery type you plan to open.
The commercial mixer is the workhorse of any bakery. Ranging in size, these mixers are designed to handle large quantities of dough and batter. They come in various types—planetary mixers, spiral mixers, and vertical cutter mixers—each with different functionalities to accommodate varying needs as bakery products.
TIP – You may need to adjust the size of the mixer depending on the anticipated volume of your bakery business.
Dough sheeters are also important bakery products. They are useful for making pastries or bread, and automate the laborious process of rolling out dough to a uniform thickness. Commercial ovens come in various types, including deck, convection, and roll-in rack ovens. Each type serves a different purpose and can significantly affect the quality of your baked goods.
TIP – Consider the space your bakery has. Some ovens may not fit, or you may need to consider a different type of oven to accommodate your baking needs in dining space.
Additionally, a proofing cabinet is critical for dough rising. It maintains a warm and humid environment, allowing dough to rise evenly and quickly.
TIP – There are different types of proofing cabinets. Some are built into other equipment like ovens in bakery kitchen.
Expanding Dough in the Bakery Industry 🍞 The US bakery market was valued at a substantial $99.47 billion in 2023 , with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.08% between 2023 and 2028.
Safety and Sanitation Equipment
Compliance with health codes and guidelines is a significant aspect of any food business. For bakery-cafes, incorporating safety and sanitation equipment is crucial to maintain cleanliness and minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
TIP – Each state has different health code regulations, so it’s essential to check local laws and guidelines.
Fire suppressant systems and fire extinguishers are fundamental safety equipment pieces every retail bakery owner should have. Other significant safety items include first-aid kits, anti-slip floor mats, and protective clothing.
In terms of sanitation, investing in top-quality dishwashing equipment is paramount. Other essential sanitation equipment includes handwashing stations, sanitizer dispensers, and waste disposal units, ensuring your baking business maintains a clean and healthy working environment.
Technology helps to optimize bakery operations. It plays a vital role in maintaining the quality of the baked goods while adhering to the safety regulations underlined by health guidelines. The right equipment can make your baking business more efficient, safer, and more productive to target customers. After all, a great baker is just as good as their tools.
Understanding Bakery Licensing and Regulations
Health department regulations.
Navigating health department regulations is a paramount step in starting a bakery business. Ensuring you’re keeping up can shield your business from potential legal consequences and, more importantly, underpin the health and safety of your future customers.
For instance, bakeries have to abide by the guidelines set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA governs every aspect of a food service business – starting from food storage to sanitation practices. One risk you should beware of is cross-contamination. Put simply, cross-contamination is the transfer of harmful substances or disease-causing microorganisms to food, usually by way of non-sanitized equipment or surfaces.
TIP – Depending on your location, you might also have local health codes that apply. Be sure to check your local health department’s regulations to see what rules you need to follow.
Acquiring a Food Service License
A food service license signifies that your type of bakery abides by local health and safety codes. Acquiring a bakery license involves multiple stages that can include submitting an application, an initial inspection, a possible reinspection, and payment of an application fee. Bear in mind, that operating without a bakery business license could result in the closure of your bakery and hefty fines.
Comparing Dough: Wholesale vs Retail Bakeries 💼 Commercial wholesale bakeries have cooked up significant success with $31 billion in revenue , towering over the earnings of retail bakeries. Moreover, the US boasted approximately 205,000 bakers in 2022, highlighting the extensive workforce behind this thriving industry.
Business Licenses and Permits
To kick off your bakery correctly, there are various forms of paperwork to tackle. Bakery business licenses, sales privilege license and permits are the legal prerequisites for opening any business, including a bakery. Consider these the entry tickets to the business spaces and world. At Metrobi, we specialize in distributing bakery goods , ensuring your products reach their destinations efficiently and safely.
General Business License
At the top of the list sits the general business license. This allows your bakery to operate in a particular city or state. It’s renewed periodically, often every one to three years. The fees for a generak business license vary by city and state, so it is important to check with your local government to understand the costs involved.
Specialized Permits
Depending on the nature of your bakery and your location, you may also need additional permits. These can include a bakery or food establishment permit, a sales permit, and a signage permit. The key here is to identify what applies to your business case and get it in place before opening your doors to loyal customers.
Understanding and following the required regulations and licensing procedures will instill trust and professionalism in your bakery. Not to mention, catering license keeps your business running smoothly, ensuring you meet your local, state, and federal requirements. With business continuity in mind, these cast-iron measures act as a solid foundation for the success and longevity of your bakery.
Rising Stars: The Home Baking Boom 🏡 By 2023, the market for home bakeries supplying baking ingredients is projected to reach $15.6 billion , indicating a significant rise in home baking ventures.
Effective Marketing Strategies for Your Bakery
Building a strong online presence.
The bakery industry thrives on sensory appeal. A strong online bakery presence gives you the platform to share appealing imagery and narrate your unique story. Whether you’re whipping up artisanal bread or sculpting bespoke cakes, sharing this process digitally reels in potential customers.
Social Media Engagement
1 in 3 people discover new brands and products through social media accounts. Harness the power of platforms such as Instagram and Facebook to showcase your best bakery creations, highlight loyal customer reviews, and promote special offers. These platforms can be useful for commercial bakeries and successful business.
Creating an Easy-to-Navigate Website
Your website is your digital storefront. Make it easy for visitors to find bakery opening hours, browse your product offerings, and place orders. Remember, a clear and user-friendly website equals satisfied customers.
Utilizing SEO Strategies
Improve your bakery’s online visibility by implementing Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategies. This includes using relevant keywords in your content and regularly posting blog articles on your website.
Local Bakery Marketing Strategies
Never underestimate the value of local marketing in a bakery business. Create a bond with your community and see your customer base grow. You need to provide a good customer service.
Joining Local Food Events
Participate in local food festivals, farmers’ markets, or community events. This offers the opportunity to showcase your products, attract new customers, and solidify your status within the local community.
Collaborating with Local Businesses
Form connections with local business owners for mutual benefit. For example, consider providing baked goods to local cafes or partnering with a culinary school for workshops.
Leveraging Local Media
Get your bakery featured in local newspapers, radio stations, and TV news for commercial space. This offers free publicity and helps increase your visibility within the community of business owners.
With these marketing strategies, your artisanal bakery business is well-positioned to attract a loyal customer base, both online and locally. Remember, the key to successful B2B marketing is staying true to your brand while effectively engaging your target audience.
Crunching the Numbers: America's Cookie Craze 🍪 Cookies ranked as the country’s second-favorite baked product, with sales soaring over eight billion U.S. dollars .
Home-based Bakery vs Storefront Bakery: Which is Right for You?
Pros and cons of a home-based bakery.
Launching your dream bakery right from your home kitchen can seem like a cozy idea. It’s wonderful to whip up tantalizing pastries in the comfort of your home, but it’s essential to be privy to the trade-offs. Begin your journey into entrepreneurship with our comprehensive guide on how to start a bakery business from home , which includes insights on navigating through legal requirements, setting up your kitchen, and implementing effective marketing strategies to ensure your venture is a delectable success.
1. Lower startup costs, flexibility in work hours, and the convenience of working from home are some of the most compelling perks.
2. Due to Cottage Food Laws, home bakers can typically operate without commercial-grade kitchen equipment, depending on local regulations.
1. Limited space to work and store ingredients, potential conflict balancing personal and work life in the same space, and restrictions on the types of food you can sell may be potential challenges of running a home bakery.
Moving from marketing efforts to operational plans, the choice of bakery location plays an integral role. Keep reading to compare this setup with its retail counterpart, and decode what might be more suitable for your aspirations. Uncover the ideal bakery locations by following our guide, which uncovers America’s secret favorites and top picks for memorable pastries and sweets.
Pros and Cons of a Storefront Bakery
A storefront bakery can infuse that irresistible ‘fresh bread’ scent into the heart of a bustling street. However, this appealing vision comes with its own set of benefits and hindrances.
1. Improved visibility, the ability to showcase your products to passersby, and an expanded workspace for baking and display can often provide a better customer experience.
2. Moreover, there’s the chance to turn the bakery into a community space and attract more foot traffic, which is less likely with a home bakery.
1. Higher initial costs, increased overhead costs such as rent and utility bills, and longer work hours may put more pressure on your specialty bakery to perform and generate profits.
Both home-based, storefront or wholesale bakery options have their unique pros and cons. It boils down to the baker’s aspirations, financial considerations, and the desired scalability. By now, you should have a clear comparison of the two types of bakeries to help you make your business decision.
Sealing the Dough: Steps Forward for Starting a Bakery
Starting your bakery might look like a mountain, but you’re now equipped to climb it. You’ve learned the basics of setting up a shop, the type of equipment you need, marketing essentials, and important legal matters.
Undoubtedly, it’s the sweet aroma of freshly baked bread, a delighted customer’s smile, and the fulfillment of your entrepreneurial dream that makes this journey rewarding.
So, you’re ready! And the only unanswered question is: What will your signature bake be? Your next step is to fine-tune your baking skills and craft that masterpiece that will have your customers coming back for more.
Remember, the secret ingredient of a successful bakery is the passion and love that goes into creating every treat. Keep that flame burning!
Now, roll up those sleeves, and let’s get that oven preheating. After all, the world is waiting to taste your magic. Just imagine, soon, ‘Baker Extraordinaire’ will be your new title. How does that sound?
Finding the best bakery location
Starting a bakery business from home
Discover the cost of opening a bakery business
‟I am able to do twice as many orders because I don't spend time delivering”
‟Reliability, Accuracy & Timeliness”
Bartleby’s Ice Cream Cakes
‟3 Metrobi Drivers together completed more than 170 deliveries for us.”
Diamond Bakery
‟Powerful Route Planning”
Rebel Bread

Success Stories
Jacobson Floral

P’s Patties

Hanato Floral Design

Quinlan-Wasserman

Secret Garden Rose

LuNo Culinary

DELIVER WITH METROBI
Grow with confidence

- 55 Court St floor 2, Boston, MA 02108
- [email protected]
- Team Metrobi
- Privacy policy
- Terms of service
- Write for us
Refer us to a company, you earn $250 and they earn $250. Learn more

- Shopify Delivery Planner App
- Delivery Management Software
- Atlanta courier service
- Boston courier service
- Chicago courier service
- Denver courier service
- Miami courier service
- New York City courier service
- Los Angeles courier service
- Philadelphia courier service
- San Francisco courier service
- Washington DC courier service
- See all locations
- Bulk Order Delivery Service
- Express Urgent Delivery Service
- Fixed Route Delivery Service
- On Demand Delivery Service
- Overnight Delivery Service
- Same Day Delivery Service
- Scheduled Delivery Service
- Wholesale Delivery Service
- See all delivery services
- Metrobi vs. Onfleet
- Metrobi vs. Roadie
- Artisan Food
- Food Producers
Want to access our large pool of drivers?
We started Metrobi to take operations off your plate. We provide drivers (rated 4.97/5), dedicated operation managers (70% cheaper), and routing software with a receiver notification system.
45 Ideas for a Business to Start With 50k

Have questions on formation, banking and taxes?
Schedule a FREE consultation with a formation and compliance expert today 📞

Starting a business with just $50k is absolutely a feasible option for aspiring entrepreneurs. Even though it’s not a million, $50,000 to invest in a new business is still a great starting point.
Whether you’ve always wanted to be your own boss and run a business or you have a passion project that you want to bring to life, there are many options available to you.
In this guide, we’re running over the top 45 ideas for a business to start with $50k as well as how to make your entrepreneurial goals a reality.
Finding the Right Business to Start
It’s essential to have a clear idea of what type of business you want to start and how you can utilize your skills and expertise to make it a success. Before you start investing your money into a new venture, you’ll want to assess your skills and expertise to ensure that you are taking the right path.
Assessing your skills and expertise is a must when starting a business with limited funds. You need to identify what you are good at and passionate about, and then look for opportunities that correspond to your skills. You can start by brainstorming your most lucrative skills and areas of expertise.
Do you have a background in marketing, social media, or accounting? Are you skilled in web design, content writing, or graphic design? Once you identify your strengths, you will be able to narrow down your choices and pick a business idea that aligns with your skills and expertise.
Most importantly, try and find a business venture in a field that you enjoy. If your startup idea makes you excited, you’ll find it easier to dedicate yourself to your new business.
45 Businesses to Start With a $50k Investment

With $50k, you have several business opportunities that you can venture into.
We’ve compiled a list of the top 45 ideas to get your creativity flowing!
1. Food truck: Start a mobile restaurant with a unique menu.
2. Coffee shop: Open a coffeehouse that offers premium coffee, snacks, and pastries.
3. Microbrewery: Create unique craft beers and sell them in your own brewery or taproom.
4. Ice cream parlor: Serve delicious ice cream and frozen treats in your own shop.
5. Personal training studio: Start a fitness studio that offers personal training sessions.
6. Social media marketing agency: Help businesses grow their social media presence.
7. Web design agency: Offer professional web design and development services to clients.
8. Graphic design agency: Create logos, brochures, and other design materials for clients.
9. Digital marketing agency: Offer services like SEO, PPC, and content marketing to businesses.
10. Event planning business: Plan and organize events like weddings, corporate events, and parties.
11. Clothing boutique: Start your own fashion boutique with trendy clothes and accessories.
12. Pet grooming business: Open a pet grooming salon that offers grooming services for dogs and cats.
13. Daycare center: Open a daycare center for young children.
14. Interior design business: Help clients create beautiful and functional spaces.
15. Photography studio: Start a photography business that offers portrait, wedding, and event photography.
16. Cleaning service: Offer cleaning services to homes and businesses.
17. Lawn care business: Start a lawn care service that offers mowing, trimming, and other maintenance services.
18. Handyman service: Offer handyman services like repairs, installations, and maintenance.
19. Painting business: Start a painting service that offers interior and exterior painting.
20. House flipping business: Buy and renovate houses to sell for a profit.
21. Real estate investing: Invest in rental properties or buy and sell homes.
22. Food delivery service: Deliver food from local restaurants to customers.
23. Car detailing business: Offer car detailing services to customers.
24. Mobile car wash: Start a mobile car wash service that offers car washing and detailing.
25. Car rental business: Start a car rental business that offers rental cars to customers.
26. Tour company: Offer guided tours of popular destinations.
27. Language school: Teach foreign languages to students.
28. Tutoring service: Offer tutoring services to students in a variety of subjects.
29. Virtual assistant business: Offer virtual assistant services to businesses and individuals.
30. Copywriting service: Offer copywriting services to businesses.
31. Translation service: Offer translation services for documents and websites.
32. Proofreading service: Offer proofreading services for documents and websites.
33. Bookkeeping service: Offer bookkeeping services to small businesses.
34. Financial planning service: Help individuals and businesses with financial planning.
35. T ax preparation service: Offer tax preparation services to individuals and businesses.
36. Freelance writing business: Start a freelance writing business and offer writing services to clients.
37. E-commerce store: Start an online store that sells products in a specific niche.
38. Dropshipping business: Start a business that uses dropshipping to sell products online.
39. Affiliate marketing business: Start a business that uses affiliate marketing to promote products and earn commissions.
40. Amazon FBA business: Start a business that uses Amazon FBA to sell products.
41. Stock trading: Invest in stocks to earn a profit.
42. Forex trading: Trade currencies on the foreign exchange market.
43. Cryptocurrency trading: Trade cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
44. Social media influencer: Build a following on social media and monetize your influence.
45. YouTube channel: Start a YouTube channel and monetize your content.
Remember, these are just brainstorming ideas. Do your research and due diligence to determine if a business idea is feasible and profitable in your specific location and market.
7 Steps to Start a Business with 50k

Starting a business is a challenging yet exciting endeavor. It requires careful planning and execution to ensure that your business will thrive and succeed in the long run. Take a look at the necessary steps to start a business.
1. Create a Business Plan
One of the most crucial steps in starting a business is creating a business plan . This will serve as a roadmap for outlining the strategies and objectives of the business.
Here is what you will need to do for creating a comprehensive business plan.
Identify Your Business Concept and Target Market
Determine the nature of your business and who your target customers are. Conduct market research to gather information about your potential customers, competitors, and industry trends.
Define Your Products or Services
Clearly define the products or services that your business will offer. List down the features, benefits, and unique selling points of your products or services.
Determine Your Marketing and Sales Strategies
Outline your marketing and sales strategies to attract and retain customers. Identify the channels and tactics that you will use to reach your target market.
Create a Financial Plan
A financial plan should include a startup budget, a projected income statement, and a cash flow statement. This will help you determine the financial viability of your business and the amount of funding that you will need.
Establish a Management Team
Determine the roles and responsibilities of your management team. Choose individuals with the right skills and expertise to help you run your business effectively.
2. Choose Your Business Structure
There are several different business structures you can choose from, each offering unique benefits and drawbacks. Taking the time to research each of the following will help you determine the best fit.
Sole Proprietorship
Sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common business structure. It is ideal for small businesses with one owner. The liability and taxation are the sole responsibility of the owner. The business profits and losses are considered individual income, and the owner can deduct business expenses. However, the owner’s personal assets are at risk if the business is involved in any legal disputes.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
Limited Liability Company (LLC) is a hybrid structure that combines the limited liability of a corporation with the simplicity and tax benefits of a partnership or sole proprietorship.
An LLC protects the personal assets of the owners from any legal disputes and has flexible taxation options.
However, setting up an LLC can be more costly than other structures, and the owners are subject to self-employment taxes.
Partnership
A partnership is a business structure for two or more owners who share the responsibilities and profits. There are two types of partnerships; general and limited.
A general partnership involves an equal share of profits, liabilities, and responsibilities among the partners.
A limited partnership involves only one general partner who has unlimited liability and controls the operations and limited partners who contribute capital but have limited liability.
Partnerships have the advantage of shared responsibility, but they can pose potential conflicts with partners and are subject to personal liability in case of legal disputes.
Corporation
A corporation is a business structure that separates business operations and liability from the owners. It provides limited liability to shareholders and has the potential for unlimited growth and access to capital.
However, corporations are heavily regulated, expensive to establish, and require more paperwork and legal formalities.
3. Register Your Business
Once you’ve chosen a business structure, you’ll need to register your business with the appropriate state agency.
After registering your business, you need to secure an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This will allow you to pay taxes, open a bank account, and hire employees if necessary.
You can apply for an EIN online using the IRS website .
4. Obtain Necessary Licenses and Permits
Depending on your business type, you may require additional licenses or permits to operate legally.
Check with your state and local agencies to ensure you have everything you need to get started and that you’re not at risk of any violations.
5. Open a Business Bank Account
Opening a business bank account is an important step towards managing your finances efficiently. Having a separate bank account for your business can help to keep your personal and business finances separate, making it easier to track your business expenses and profits.
A business bank account can also help to build credit for your business, which can be important if you plan to apply for financing in the future.
To open a business bank account you will need to provide information about your business such as the business name, address, and an EIN.
6. Hire and Train Your Staff
Hiring the right employees is a crucial aspect for any business to thrive. It is essential to have a well-developed hiring strategy in place to ensure you hire the right fit for your organization.
Properly hiring and training your staff can also save you valuable time and resources. More importantly, it can enhance the overall performance of your business.
7. Promote Your Business
Promoting your business is essential to its success. There are many ways to get the word out about your business and attract more customers. One of the best ways to promote your business is through digital marketing.
Digital marketing includes website content, social media marketing, search engine optimization, and email marketing.
There are also other ways to promote your business as well. You may find direct mail campaigns work well for your business or that you have considerable success when networking.
In short, remember to test and try a variety of strategies until you find the one that sticks.
Get Excited About Starting Your New Business
Starting a new business can be one of the most thrilling and rewarding experiences that you will ever undertake. However, it can also be challenging and daunting, particularly if you are not sure where to begin.
When in doubt, make sure to explore all the small business tools and resources offered by doola . Take advantage of online business entity formation, business banking solutions, bookkeeping, and much more.
You can also book a free consultation to learn how doola can help your new venture take off the ground!

What are some businesses I can start with 50k?
Some examples are a home cleaning service, a food truck, a personalized gift shop, a freelance consulting business, or an online store.
How do I determine which business is the best fit for me?
Consider your skills, interests, and the current market demand for your potential business. Conduct market research and create a business plan to help guide your decision-making process.
How long does it take to see a return on investment in a new business?
This depends on a variety of factors such as the industry, competition, and business model. It’s important to have a financial plan in place and be prepared for potential setbacks or slower growth.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when starting a new business?
Some mistakes include not conducting enough research, underestimating costs and expenses, not having a solid business plan, and not understanding the market or target audience.
How can I maximize my chances of success in a new business venture?
Network with other entrepreneurs and business professionals, stay up to date on industry trends, continuously learn and innovate, and prioritize exceptional customer service. Don’t be afraid to seek guidance or advice from mentors, coaches, or consultants as needed.
Table of contents

Free e-book
How to form a US LLC in 5 minutes
A beginner-friendly guide on the basics of LLCs. Learn about formation, banking, and taxes.
- LLC vs. C Corporation: The Ultimate Guide for Your Business
- Best State to Form My LLC In
- Wyoming vs. Delaware LLC
- LLC Fees by State
Keep reading
Start your dream business and keep it 100% compliant
Turn your dream idea into your dream business.

Schedule a FREE consultation with a US CPA today 📞
Cookie consent
By continuing to browse this website, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. Learn more.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
New York Takes Crucial Step Toward Making Congestion Pricing a Reality
The board of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority voted to approve a new $15 toll to drive into Manhattan. The plan still faces challenges from six lawsuits before it can begin in June.

By Winnie Hu and Ana Ley
New York City completed a crucial final step on Wednesday in a decades-long effort to become the first American city to roll out a comprehensive congestion pricing program, one that aims to push motorists out of their cars and onto mass transit by charging new tolls to drive into Midtown and Lower Manhattan.
The program could start as early as mid-June after the board of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, the state agency that will install and manage the program, voted 11-to-1 to approve the final tolling rates, which will charge most passenger cars $15 a day to enter at 60th Street and below in Manhattan. The program is expected to reduce traffic and raise $1 billion annually for public transit improvements.
It was a historic moment for New York’s leaders and transportation advocates after decades of failed attempts to advance congestion pricing even as other gridlocked cities around the world, including London, Stockholm and Singapore, proved that similar programs could reduce traffic and pollution.
While other American cities have introduced related concepts by establishing toll roads or closing streets to traffic, the plan in New York is unmatched in ambition and scale.
Congestion pricing is expected to reduce the number of vehicles that enter Lower Manhattan by about 17 percent, according to a November study by an advisory committee reporting to the M.T.A. The report also said that the total number of miles driven in 28 counties across the region would be reduced.
“This was the right thing to do,” Janno Lieber, the authority’s chairman and chief executive, said after the vote. “New York has more traffic than any place in the United States, and now we’re doing something about it.”
Congestion pricing has long been a hard sell in New York, where many people commute by car from the boroughs outside of Manhattan and the suburbs, in part because some of them do not have access to public transit.
New York State legislators finally approved congestion pricing in 2019 after Gov. Andrew M. Cuomo helped push it through. A series of recent breakdowns in the city’s subway system had underscored the need for billions of dollars to update its aging infrastructure.
It has taken another five years to reach the starting line. Before the tolling program can begin, it must be reviewed by the Federal Highway Administration, which is expected to approve it.
Congestion pricing also faces legal challenges from six lawsuits that have been brought by elected officials and residents from across the New York region. Opponents have increasingly mobilized against the program in recent months, citing the cost of the tolls and the potential environmental effects from shifting traffic and pollution to other areas as drivers avoid the tolls.
A court hearing is scheduled for April 3 and 4 on a lawsuit brought by the State of New Jersey, which is seen as the most serious legal challenge. The mayor of Fort Lee, N.J., Mark J. Sokolich, has filed a related lawsuit.
Four more lawsuits have been brought in New York: by Ed Day, the Rockland County executive; by Vito Fossella, the Staten Island borough president, and the United Federation of Teachers; and by two separate groups of city residents.
Amid the litigation, M.T.A. officials have suspended some capital construction projects that were to be paid for by the program, and they said at a committee meeting on Monday that crucial work to modernize subway signals on the A and C lines had been delayed.
Nearly all the toll readers have been installed, and will automatically charge drivers for entering the designated congestion zone at 60th Street or below. There is no toll for leaving the zone or driving around in it. Through traffic on Franklin D. Roosevelt Drive and the West Side Highway will not be tolled.
Under the final tolling structure, which was based on recommendations by the advisory panel, most passenger vehicles will be charged $15 a day from 5 a.m. to 9 p.m. on weekdays, and from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. on weekends. The toll will be $24 for small trucks and charter buses, and will rise to $36 for large trucks and tour buses. It will be $7.50 for motorcycles.
Those tolls will be discounted by 75 percent at night, dropping the cost for a passenger vehicle to $3.75.
Fares will go up by $1.25 for taxis and black car services, and by $2.50 for Uber and Lyft. Passengers will be responsible for paying the new fees, and they will be added to every ride that begins, ends or occurs within the congestion zone. There will be no nighttime discounts. (The new fees come on top of an existing congestion surcharge that was imposed on for-hire vehicles in 2019.)
The tolls will mostly be collected using the E-ZPass system. Electronic detection points have been placed at entrances and exits to the tolling zone. Drivers who do not use an E-ZPass will pay significantly higher fees — for instance, $22.50 instead of $15 during peak hours for passenger vehicles.
Emergency vehicles like fire trucks, ambulances and police cars, as well as vehicles carrying people with disabilities, were exempted from the new tolls under the state’s congestion pricing legislation .
As for discounts, low-income drivers who make less than $50,000 annually can apply to receive half off the daytime toll after their first 10 trips in a calendar month. In addition, low-income residents of the congestion zone who make less than $60,000 a year can apply for a state tax credit.
All drivers entering the zone directly from four tolled tunnels — the Lincoln, Holland, Hugh L. Carey and Queens-Midtown — will receive a “crossing credit” that will be applied against the daytime toll. The credit will be $5 round-trip for passenger vehicles, $12 for small trucks and intercity and charter buses, $20 for large trucks and tour buses, and $2.50 for motorcycles. No credits will be offered at night.
Grace Ashford contributed reporting.
Winnie Hu is a Times reporter covering the people and neighborhoods of New York City. More about Winnie Hu
Ana Ley is a Times reporter covering New York City’s mass transit system and the millions of passengers who use it. More about Ana Ley

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Download Now: Free Business Plan Template. Writing a business plan doesn't have to be complicated. In this step-by-step guide, you'll learn how to write a business plan that's detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Step 1: Gather Your Information. Your first step is to get organized by gathering all your relevant business information. This will save you time completing the various sections of your business plan. At a minimum, you'll want to have the following handy: Business name, contact information, and address. Owner (s) names, contact information ...
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
Step 7: Financial Analysis and Projections. It doesn't matter if you include a request for funding in your plan, you will want to include a financial analysis here. You'll want to do two things here: Paint a picture of your business's performance in the past and show it will grow in the future.
While your plan will be unique to your business and goals, keep these tips in mind as you write. 1. Know your audience. When you know who will be reading your plan—even if you're just writing it for yourself to clarify your ideas—you can tailor the language and level of detail to them.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
The Bottom Line. Knowing how to start a small business involves the key steps of market research, setting up a business plan, understanding the legal requirements, exploring funding options ...
Don't worry, you'll know how to write a business plan in no time. We've broken each section down to help you write a business plan in a few simple steps. 1. Brainstorm and Draft an Executive Summary for Your Business Plan. This will be the first page of your business plan.
Here are the nine sections to include in a strong business plan, step by step. 1. Executive summary. Your business plan should begin with an executive summary, which outlines what your company is about and why it will succeed. This section includes your mission statement, a brief description of the product or service you are offering, a summary ...
10 Steps To Creating A Comprehensive Business Plan. While not every business plan is the same, there are a few key steps you should take to create an effective and comprehensive document: . 1. Create an executive summary. Think of an executive summary as your company's elevator pitch in written form.
Step 2: Do your market research homework. The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research. This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to ...
Fact checked by. Vikki Velasquez. Starting a business in the United States involves a number of different steps, spanning legal considerations, market research, creating a business plan, securing ...
7. Write your business plan. You need a business plan before starting a business. This isn't about checking a box but improving your understanding of what it takes to run a successful business. 8. Make your business legal. Before setting up shop, you must check all the necessary legal boxes.
5 best places to advertise your business online. 13. Set up a payments system. If your business takes credit and debit cards, you'll likely need a payment processor and point-of-sale (POS) system ...
How to start a business. Brainstorm and refine your business idea. Conduct market and competitor research. Pick a business name. Write up a business plan. Choose a legal structure for your business. Secure business capital and funding. Register your business and make it official. Apply for tax IDs, licenses and permits.
Think of your business plan as a roadmap — a guide to help you structure, fund and operate your business. A good business plan gives you the chance to carefully consider every step of starting — or growing — your business so you can prepare for potential challenges. (If you're just getting started on your entrepreneurial journey, refer ...
By utilizing these free resources, you can develop a well-structured and industry-specific business plan without incurring additional costs. Step 6: Review and revise regularly. To ensure your coaching business stays relevant and successful, it's crucial to regularly update your business plan.
A robust business plan is your roadmap to success. It outlines your business goals, strategies, market analysis, financial forecasts, and potential challenges. It's a living document that not only guides your startup phase but also assists in managing your business. A comprehensive plan attracts investors and serves as a tool for evaluating ...
Step-by-Step Guide to Crafting Your Bakery Business Plan Step 1: Defining Your Bakery Concept. ... Navigating health department regulations is a paramount step in starting a bakery business. Ensuring you're keeping up can shield your business from potential legal consequences and, more importantly, underpin the health and safety of your ...
The best way to accomplish any business or personal goal is to write out every possible step it takes to achieve the goal. Then, order those steps by what needs to happen first. Some steps may ...
Starting a business is a challenging yet exciting endeavor. It requires careful planning and execution to ensure that your business will thrive and succeed in the long run. Take a look at the necessary steps to start a business. 1. Create a Business Plan. One of the most crucial steps in starting a business is creating a business plan. This ...
New York City completed a crucial final step on Wednesday in a decades-long effort to become the first American city to roll out a comprehensive congestion pricing program, one that aims to push ...