Center for Teaching
Bloom’s taxonomy.
| Armstrong, P. (2010). Bloom’s Taxonomy. Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching. Retrieved [todaysdate] from https://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/blooms-taxonomy/. |
Background Information | The Original Taxonomy | The Revised Taxonomy | Why Use Bloom’s Taxonomy? | Further Information

The above graphic is released under a Creative Commons Attribution license. You’re free to share, reproduce, or otherwise use it, as long as you attribute it to the Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching. For a higher resolution version, visit our Flickr account and look for the “Download this photo” icon.

Background Information
In 1956, Benjamin Bloom with collaborators Max Englehart, Edward Furst, Walter Hill, and David Krathwohl published a framework for categorizing educational goals: Taxonomy of Educational Objectives . Familiarly known as Bloom’s Taxonomy , this framework has been applied by generations of K-12 teachers and college instructors in their teaching.
The framework elaborated by Bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation. The categories after Knowledge were presented as “skills and abilities,” with the understanding that knowledge was the necessary precondition for putting these skills and abilities into practice.
While each category contained subcategories, all lying along a continuum from simple to complex and concrete to abstract, the taxonomy is popularly remembered according to the six main categories.
The Original Taxonomy (1956)
Here are the authors’ brief explanations of these main categories in from the appendix of Taxonomy of Educational Objectives ( Handbook One , pp. 201-207):
- Knowledge “involves the recall of specifics and universals, the recall of methods and processes, or the recall of a pattern, structure, or setting.”
- Comprehension “refers to a type of understanding or apprehension such that the individual knows what is being communicated and can make use of the material or idea being communicated without necessarily relating it to other material or seeing its fullest implications.”
- Application refers to the “use of abstractions in particular and concrete situations.”
- Analysis represents the “breakdown of a communication into its constituent elements or parts such that the relative hierarchy of ideas is made clear and/or the relations between ideas expressed are made explicit.”
- Synthesis involves the “putting together of elements and parts so as to form a whole.”
- Evaluation engenders “judgments about the value of material and methods for given purposes.”
The 1984 edition of Handbook One is available in the CFT Library in Calhoun 116. See its ACORN record for call number and availability.
Barbara Gross Davis, in the “Asking Questions” chapter of Tools for Teaching , also provides examples of questions corresponding to the six categories. This chapter is not available in the online version of the book, but Tools for Teaching is available in the CFT Library. See its ACORN record for call number and availability.
The Revised Taxonomy (2001)
A group of cognitive psychologists, curriculum theorists and instructional researchers, and testing and assessment specialists published in 2001 a revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy with the title A Taxonomy for Teaching, Learning, and Assessment . This title draws attention away from the somewhat static notion of “educational objectives” (in Bloom’s original title) and points to a more dynamic conception of classification.
The authors of the revised taxonomy underscore this dynamism, using verbs and gerunds to label their categories and subcategories (rather than the nouns of the original taxonomy). These “action words” describe the cognitive processes by which thinkers encounter and work with knowledge:
- Recognizing
- Interpreting
- Exemplifying
- Classifying
- Summarizing
- Implementing
- Differentiating
- Attributing
In the revised taxonomy, knowledge is at the basis of these six cognitive processes, but its authors created a separate taxonomy of the types of knowledge used in cognition:
- Knowledge of terminology
- Knowledge of specific details and elements
- Knowledge of classifications and categories
- Knowledge of principles and generalizations
- Knowledge of theories, models, and structures
- Knowledge of subject-specific skills and algorithms
- Knowledge of subject-specific techniques and methods
- Knowledge of criteria for determining when to use appropriate procedures
- Strategic Knowledge
- Knowledge about cognitive tasks, including appropriate contextual and conditional knowledge
- Self-knowledge
Mary Forehand from the University of Georgia provides a guide to the revised version giving a brief summary of the revised taxonomy and a helpful table of the six cognitive processes and four types of knowledge.
Why Use Bloom’s Taxonomy?
The authors of the revised taxonomy suggest a multi-layered answer to this question, to which the author of this teaching guide has added some clarifying points:
- Objectives (learning goals) are important to establish in a pedagogical interchange so that teachers and students alike understand the purpose of that interchange.
- Organizing objectives helps to clarify objectives for themselves and for students.
- “plan and deliver appropriate instruction”;
- “design valid assessment tasks and strategies”;and
- “ensure that instruction and assessment are aligned with the objectives.”
Citations are from A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives .
Further Information
Section III of A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives , entitled “The Taxonomy in Use,” provides over 150 pages of examples of applications of the taxonomy. Although these examples are from the K-12 setting, they are easily adaptable to the university setting.
Section IV, “The Taxonomy in Perspective,” provides information about 19 alternative frameworks to Bloom’s Taxonomy, and discusses the relationship of these alternative frameworks to the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy.

Teaching Guides
- Online Course Development Resources
- Principles & Frameworks
- Pedagogies & Strategies
- Reflecting & Assessing
- Challenges & Opportunities
- Populations & Contexts
Quick Links
- Services for Departments and Schools
- Examples of Online Instructional Modules

Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, Seventh Edition (2020)

Table of Contents | Supplemental Resources | Introduction (PDF)
Official source for APA Style The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, Seventh Edition is the official source for APA Style.
Widely adopted With millions of copies sold worldwide in multiple languages, it is the style manual of choice for writers, researchers, editors, students, and educators in the social and behavioral sciences, natural sciences, nursing, communications, education, business, engineering, and other fields.
Authoritative and easy to use Known for its authoritative, easy-to-use reference and citation system, the Publication Manual also offers guidance on choosing the headings, tables, figures, language, and tone that will result in powerful, concise, and elegant scholarly communication.
Scholarly writing It guides users through the scholarly writing process—from the ethics of authorship to reporting research through publication.
- Spiral-Bound $44.99
- Paperback $31.99
- Hardcover $54.99
- Course adoption

|
|
|
|

It is an indispensable resource for students and professionals to achieve excellence in writing and make an impact with their work.
7 reasons why everyone needs the 7th edition of APA’s bestselling Publication Manual

Full color with first-ever tabbed version

Guidelines for ethical writing and guidance on the publication process

Expanded student-specific resources; includes a sample paper

100+ new reference examples, 40+ sample tables and figures
New chapter on journal article reporting standards

Updated bias-free language guidelines; includes usage of singular “they”

One space after end punctuation!
What’s new in the 7th edition?
Full color All formats are in full color, including the new tabbed spiral-bound version.
Easy to navigate Improved ease of navigation, with many additional numbered sections to help users quickly locate answers to their questions.
Best practices The Publication Manual (7th ed.) has been thoroughly revised and updated to reflect best practices in scholarly writing and publishing.
New student resources Resources for students on writing and formatting annotated bibliographies, response papers, and other paper types as well as guidelines on citing course materials.
Accessibility guidelines Guidelines that support accessibility for all users, including simplified reference, in-text citation, and heading formats as well as additional font options.
New-user content Dedicated chapter for new users of APA Style covering paper elements and format, including sample papers for both professional authors and student writers.
Journal Article Reporting Standards New chapter on journal article reporting standards that includes updates to reporting standards for quantitative research and the first-ever qualitative and mixed methods reporting standards in APA Style.
Bias-free language guidelines New chapter on bias-free language guidelines for writing about people with respect and inclusivity in areas including age, disability, gender, participation in research, race and ethnicity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality
100+ reference examples More than 100 new reference examples covering periodicals, books, audiovisual media, social media, webpages and websites, and legal resources.
40+ new sample tables and figures More than 40 new sample tables and figures, including student-friendly examples such as a correlation table and a bar chart as well as examples that show how to reproduce a table or figure from another source.
Ethics expanded Expanded guidance on ethical writing and publishing practices, including how to ensure the appropriate level of citation, avoid plagiarism and self-plagiarism, and navigate the publication process.

7th edition table of contents
- Front Matter
- 1. Scholarly Writing and Publishing Principles
- 2. Paper Elements and Format
- 3. Journal Article Reporting Standards
- 4. Writing Style and Grammar
- 5. Bias-Free Language Guidelines
- 6. Mechanics of Style
- 7. Tables and Figures
- 8. Works Credited in the Text
- 9. Reference List
- 10. Reference Examples
- 11. Legal References
- 12. Publication Process
- Back Matter
List of Tables and Figures
Editorial Staff and Contributors
Acknowledgments
Introduction (PDF, 94KB)
Types of Articles and Papers
1.1 Quantitative Articles 1.2 Qualitative Articles 1.3 Mixed Methods Articles 1.4 Replication Articles 1.5 Quantitative and Qualitative Meta-Analyses 1.6 Literature Review Articles 1.7 Theoretical Articles 1.8 Methodological Articles 1.9 Other Types of Articles 1.10 Student Papers, Dissertations, and Theses
Ethical, legal, and professional standards in publishing
Ensuring the Accuracy of Scientific Findings
1.11 Planning for Ethical Compliance 1.12 Ethical and Accurate Reporting of Research Results 1.13 Errors, Corrections, and Retractions After Publication 1.14 Data Retention and Sharing 1.15 Additional Data-Sharing Considerations for Qualitative Research 1.16 Duplicate and Piecemeal Publication of Data 1.17 Implications of Plagiarism and Self-Plagiarism
Protecting the Rights and Welfare of Research Participants and Subjects
1.18 Rights and Welfare of Research Participants and Subjects 1.19 Protecting Confidentiality 1.20 Conflict of Interest
Protecting Intellectual Property Rights
1.21 Publication Credit 1.22 Order of Authors 1.23 Authors’ Intellectual Property Rights During Manuscript Review 1.24 Authors’ Copyright on Unpublished Manuscripts 1.25 Ethical Compliance Checklist
Required Elements
2.1 Professional Paper Required Elements 2.2 Student Paper Required Elements
Paper Elements
2.3 Title Page 2.4 Title 2.5 Author Name (Byline) 2.6 Author Affiliation 2.7 Author Note 2.8 Running Head 2.9 Abstract 2.10 Keywords 2.11 Text (Body) 2.12 Reference List 2.13 Footnotes 2.14 Appendices 2.15 Supplemental Materials
2.16 Importance of Format 2.17 Order of Pages 2.18 Page Header 2.19 Font 2.20 Special Characters 2.21 Line Spacing 2.22 Margins 2.23 Paragraph Alignment 2.24 Paragraph Indentation 2.25 Paper Length
Organization
2.26 Principles of Organization 2.27 Heading Levels 2.28 Section Labels
Sample papers
Overview of Reporting Standards
3.1 Application of the Principles of JARS 3.2 Terminology Used in JARS
Common Reporting Standards Across Research Designs
3.3 Abstract Standards 3.4 Introduction Standards
Reporting Standards for Quantitative Research
3.5 Basic Expectations for Quantitative Research Reporting 3.6 Quantitative Method Standards 3.7 Quantitative Results Standards 3.8 Quantitative Discussion Standards 3.9 Additional Reporting Standards for Typical Experimental and Nonexperimental Studies 3.10 Reporting Standards for Special Designs 3.11 Standards for Analytic Approaches 3.12 Quantitative Meta-Analysis Standards
Reporting Standards for Qualitative Research
3.13 Basic Expectations for Qualitative Research Reporting 3.14 Qualitative Method Standards 3.15 Qualitative Findings or Results Standards 3.16 Qualitative Discussion Standards 3.17 Qualitative Meta-Analysis Standards
Reporting Standards for Mixed Methods Research
3.18 Basic Expectations for Mixed Methods Research Reporting
Effective scholarly writing
Continuity and Flow
4.1 Importance of Continuity and Flow 4.2 Transitions 4.3 Noun Strings
Conciseness and Clarity
4.4 Importance of Conciseness and Clarity 4.5 Wordiness and Redundancy 4.6 Sentence and Paragraph Length 4.7 Tone 4.8 Contractions and Colloquialisms 4.9 Jargon 4.10 Logical Comparisons 4.11 Anthropomorphism
Grammar and usage
4.12 Verb Tense 4.13 Active and Passive Voice 4.14 Mood 4.15 Subject and Verb Agreement
4.16 First- Versus Third-Person Pronouns 4.17 Editorial “We” 4.18 Singular “They” 4.19 Pronouns for People and Animals (“Who” vs. “That”) 4.20 Pronouns as Subjects and Objects (“Who” vs. “Whom”) 4.21 Pronouns in Restrictive and Nonrestrictive Clauses (“That” vs. “Which”)
Sentence Construction
4.22 Subordinate Conjunctions 4.23 Misplaced and Dangling Modifiers 4.24 Parallel Construction
Strategies to Improve Your Writing
4.25 Reading to Learn Through Example 4.26 Writing From an Outline 4.27 Rereading the Draft 4.28 Seeking Help From Colleagues 4.29 Working With Copyeditors and Writing Centers 4.30 Revising a Paper
General Guidelines for Reducing Bias
5.1 Describe at the Appropriate Level of Specificity 5.2 Be Sensitive to Labels
Reducing Bias by Topic
5.3 Age 5.4 Disability 5.5 Gender 5.6 Participation in Research 5.7 Racial and Ethnic Identity 5.8 Sexual Orientation 5.9 Socioeconomic Status 5.10 Intersectionality
Punctuation
6.1 Spacing After Punctuation Marks 6.2 Period 6.3 Comma 6.4 Semicolon 6.5 Colon 6.6 Dash 6.7 Quotation Marks 6.8 Parentheses 6.9 Square Brackets 6.10 Slash
6.11 Preferred Spelling 6.12 Hyphenation
Capitalization
6.13 Words Beginning a Sentence 6.14 Proper Nouns and Trade Names 6.15 Job Titles and Positions 6.16 Diseases, Disorders, Therapies, Theories, and Related Terms 6.17 Titles of Works and Headings Within Works 6.18 Titles of Tests and Measures 6.19 Nouns Followed by Numerals or Letters 6.20 Names of Conditions or Groups in an Experiment 6.21 Names of Factors, Variables, and Effects
6.22 Use of Italics 6.23 Reverse Italics
Abbreviations
6.24 Use of Abbreviations 6.25 Definition of Abbreviations 6.26 Format of Abbreviations 6.27 Unit of Measurement Abbreviations 6.28 Time Abbreviations 6.29 Latin Abbreviations 6.30 Chemical Compound Abbreviations 6.31 Gene and Protein Name Abbreviations
6.32 Numbers Expressed in Numerals 6.33 Numbers Expressed in Words 6.34 Combining Numerals and Words to Express Numbers 6.35 Ordinal Numbers 6.36 Decimal Fractions 6.37 Roman Numerals 6.38 Commas in Numbers 6.39 Plurals of Numbers
Statistical and Mathematical Copy
6.40 Selecting Effective Presentation 6.41 References for Statistics 6.42 Formulas 6.43 Statistics in Text 6.44 Statistical Symbols and Abbreviations 6.45 Spacing, Alignment, and Punctuation for Statistics
Presentation of Equations
6.46 Equations in Text 6.47 Displayed Equations 6.48 Preparing Statistical and Mathematical Copy for Publication
6.49 List Guidelines 6.50 Lettered Lists 6.51 Numbered Lists 6.52 Bulleted Lists
General Guidelines for Tables and Figures
7.1 Purpose of Tables and Figures 7.2 Design and Preparation of Tables and Figures 7.3 Graphical Versus Textual Presentation 7.4 Formatting Tables and Figures 7.5 Referring to Tables and Figures in the Text 7.6 Placement of Tables and Figures 7.7 Reprinting or Adapting Tables and Figures
7.8 Principles of Table Construction 7.9 Table Components 7.10 Table Numbers 7.11 Table Titles 7.12 Table Headings 7.13 Table Body 7.14 Table Notes 7.15 Standard Abbreviations in Tables and Figures 7.16 Confidence Intervals in Tables 7.17 Table Borders and Shading 7.18 Long or Wide Tables 7.19 Relation Between Tables 7.20 Table Checklist 7.21 Sample Tables
Sample tables
7.22 Principles of Figure Construction 7.23 Figure Components 7.24 Figure Numbers 7.25 Figure Titles 7.26 Figure Images 7.27 Figure Legends 7.28 Figure Notes 7.29 Relation Between Figures 7.30 Photographs 7.31 Considerations for Electrophysiological, Radiological, Genetic, and Other Biological Data 7.32 Electrophysiological Data 7.33 Radiological (Imaging) Data 7.34 Genetic Data 7.35 Figure Checklist 7.36 Sample Figures
Sample figures
General Guidelines for Citation
8.1 Appropriate Level of Citation 8.2 Plagiarism 8.3 Self-Plagiarism 8.4 Correspondence Between Reference List and Text 8.5 Use of the Published Version or Archival Version 8.6 Primary and Secondary Sources
Works Requiring Special Approaches to Citation
8.7 Interviews 8.8 Classroom or Intranet Sources 8.9 Personal Communications
In-Text Citations
8.10 Author–Date Citation System 8.11 Parenthetical and Narrative Citations 8.12 Citing Multiple Works 8.13 Citing Specific Parts of a Source 8.14 Unknown or Anonymous Author 8.15 Translated, Reprinted, Republished, and Reissued Dates 8,16 Omitting the Year in Repeated Narrative Citations 8.17 Number of Authors to Include in In-Text Citations 8.18 Avoiding Ambiguity in In-Text Citations 8.19 Works With the Same Author and Same Date 8.20 Authors With the Same Surname 8.21 Abbreviating Group Authors 8.22 General Mentions of Websites, Periodicals, and Common Software and Apps
Paraphrases and Quotations
8.23 Principles of Paraphrasing 8.24 Long Paraphrases 8.25 Principles of Direct Quotation 8.26 Short Quotations (Fewer Than 40 Words) 8.27 Block Quotations (40 Words or More) 8.28 Direct Quotation of Material Without Page Numbers 8.29 Accuracy of Quotations 8.30 Changes to a Quotation Requiring No Explanation 8.31 Changes to a Quotation Requiring Explanation 8.32 Quotations That Contain Citations to Other Works 8.33 Quotations That Contain Material Already in Quotation Marks 8.34 Permission to Reprint or Adapt Lengthy Quotations 8.35 Epigraphs 8.36 Quotations From Research Participants
Reference Categories
9.1 Determining the Reference Category 9.2 Using the Webpages and Websites Reference Category 9.3 Online and Print References
Principles of Reference List Entries
9.4 Four Elements of a Reference 9.5 Punctuation Within Reference List Entries 9.6 Accuracy and Consistency in References
Reference elements
9.7 Definition of Author 9.8 Format of the Author Element 9.9 Spelling and Capitalization of Author Names 9.10 Identification of Specialized Roles 9.11 Group Authors 9.12 No Author
9.13 Definition of Date 9.14 Format of the Date Element 9.15 Updated or Reviewed Online Works 9.16 Retrieval Dates 9.17 No Date
9.18 Definition of Title 9.19 Format of the Title Element 9.20 Series and Multivolume Works 9.21 Bracketed Descriptions 9.22 No Title
9.23 Definition of Source 9.24 Format of the Source Element 9.25 Periodical Sources 9.26 Online Periodicals With Missing Information 9.27 Article Numbers 9.28 Edited Book Chapter and Reference Work Entry Sources 9.29 Publisher Sources 9.30 Database and Archive Sources 9.31 Works With Specific Locations 9.32 Social Media Sources 9.33 Website Sources 9.34 When to Include DOIs and URLs 9.35 Format of DOIs and URLs 9.36 DOI or URL Shorteners 9.37 No Source
Reference Variations
9.38 Works in Another Language 9.39 Translated Works 9.40 Reprinted Works 9.41 Republished or Reissued Works 9.42 Religious and Classical Works
Reference List Format and Order
9.43 Format of the Reference List 9.44 Order of Works in the Reference List 9.45 Order of Surname and Given Name 9.46 Order of Multiple Works by the Same First Author 9.47 Order of Works With the Same Author and Same Date 9.48 Order of Works by First Authors With the Same Surname 9.49 Order of Works With No Author or an Anonymous Author 9.50 Abbreviations in References 9.51 Annotated Bibliographies 9.52 References Included in a Meta-Analysis
Author Variations
Date Variations
Title Variations
Source Variations
Textual Works
10.1 Periodicals 10.2 Books and Reference Works 10.3 Edited Book Chapters and Entries in Reference Works 10.4 Reports and Gray Literature 10.5 Conference Sessions and Presentations 10.6 Dissertations and Theses 10.7 Reviews 10.8 Unpublished Works and Informally Published Works
Data Sets, Software, and Tests
10.9 Data Sets 10.10 Computer Software, Mobile Apps, Apparatuses, and Equipment 10.11 Tests, Scales, and Inventories
Audiovisual Media
10.12 Audiovisual Works 10.13 Audio Works 10.14 Visual Works
Online Media
10.15 Social Media 10.16 Webpages and Websites
General Guidelines for Legal References
11.1 APA Style References Versus Legal References 11.2 General Forms 11.3 In-Text Citations of Legal Materials
Legal Reference Examples
11.4 Cases or Court Decisions 11.5 Statutes (Laws and Acts) 11.6 Legislative Materials 11.7 Administrative and Executive Materials 11.8 Patents 11.9 Constitutions and Charters 11.10 Treaties and International Conventions
Preparing for Publication
12.1 Adapting a Dissertation or Thesis Into a Journal Article 12.2 Selecting a Journal for Publication 12.3 Prioritizing Potential Journals 12.4 Avoiding Predatory Journals
Understanding the Editorial Publication Process
12.5 Editorial Publication Process 12.6 Role of the Editors 12.7 Peer Review Process 12.8 Manuscript Decisions
Manuscript Preparation
12.9 Preparing the Manuscript for Submission 12.10 Using an Online Submission Portal 12.11 Writing a Cover Letter 12.12 Corresponding During Publication 12.13 Certifying Ethical Requirements
Copyright and Permission Guidelines
12.14 General Guidelines for Reprinting or Adapting Materials 12.15 Materials That Require Copyright Attribution 12.16 Copyright Status 12.17 Permission and Fair Use 12.18 Copyright Attribution Formats
During and After Publication
12.19 Article Proofs 12.20 Published Article Copyright Policies 12.21 Open Access Deposit Policies 12.22 Writing a Correction Notice 12.23 Sharing Your Article Online 12.24 Promoting Your Article
Credits for Adapted Tables, Figures, and Papers
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Sample Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper
This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader
Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication). These differences mostly extend to the title page and running head. Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper.
However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style.
Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples. Those authored by [AF] denote explanations of formatting and [AWC] denote directions for writing and citing in APA 7.
APA 7 Student Paper:
Apa 7 professional paper:.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format
APA Format for Students & Researchers
In this guide, students and researchers can learn the basics of creating a properly formatted research paper according to APA guidelines.
It includes information on how to conceptualize, outline, and format the basic structure of your paper, as well as practical tips on spelling, abbreviation, punctuation, and more. The guide concludes with a complete sample paper as well as a final checklist that writers can use to prepare their work for submission.
APA Paper Formatting Basics
- All text should be double-spaced
- Use one-inch margins on all sides
- All paragraphs in the body are indented
- Make sure that the title is centered on the page with your name and school/institution underneath
- Use 12-point font throughout
- All pages should be numbered in the upper right hand corner
- The manual recommends using one space after most punctuation marks
- A shortened version of the title (“running head”) should be placed in the upper left hand corner
Table of Contents
Here’s a quick rundown of the contents of this guide on how to do APA format.
Information related to writing and organizing your paper:
- Paper and essay categories
General paper length
- Margin sizes
- Title pages
- Running Heads
- APA Outline
- APA Abstract
- The body of papers
- APA headings and subheadings
- Use of graphics (tables and figures)
Writing style tips:
Proper tone.
- Reducing bias and labels
- Abbreviation do’s and don’ts
- Punctuation
- Number rules
Citing Your Sources:
- Citing Sources
- In-text Citations
- Reference Page
Proofing Your Paper:
- Final checklist
- Submitting your project
APA Information:
- What is APA
- APA 7 Updates
What you won’t find in this guide: This guide provides information related to the formatting of your paper, as in guidelines related to spacing, margins, word choice, etc. While it provides a general overview of APA references, it does not provide instructions for how to cite in APA format.
For step-by-step instructions for citing books, journals, how to cite a website in APA format, information on an APA format bibliography, and more, refer to these other EasyBib guides:
- APA citation (general reference guide)
- APA In-text citation
- APA article citation
- APA book citation
- APA citation website
Or, you can use our automatic generator. Our APA formatter helps to build your references for you. Yep, you read that correctly.
Writing and Organizing Your APA Paper in an Effective Way
This section of our guide focuses on proper paper length, how to format headings, spacing, and more! This information can be found in Chapter 2 of the official manual (American Psychological Association, 2020, pp. 29-67).
Categories of papers
Before getting into the nitty-gritty details related to APA research paper format, first determine the type of paper you’re about to embark on creating:
Empirical studies
Empirical studies take data from observations and experiments to generate research reports. It is different from other types of studies in that it isn’t based on theories or ideas, but on actual data.
Literature reviews
These papers analyze another individual’s work or a group of works. The purpose is to gather information about a current issue or problem and to communicate where we are today. It sheds light on issues and attempts to fill those gaps with suggestions for future research and methods.
Theoretical articles
These papers are somewhat similar to a literature reviews in that the author collects, examines, and shares information about a current issue or problem, by using others’ research. It is different from literature reviews in that it attempts to explain or solve a problem by coming up with a new theory. This theory is justified with valid evidence.
Methodological articles
These articles showcase new advances, or modifications to an existing practice, in a scientific method or procedure. The author has data or documentation to prove that their new method, or improvement to a method, is valid. Plenty of evidence is included in this type of article. In addition, the author explains the current method being used in addition to their own findings, in order to allow the reader to understand and modify their own current practices.
Case studies
Case studies present information related an individual, group, or larger set of individuals. These subjects are analyzed for a specific reason and the author reports on the method and conclusions from their study. The author may also make suggestions for future research, create possible theories, and/or determine a solution to a problem.
Since APA style format is used often in science fields, the belief is “less is more.” Make sure you’re able to get your points across in a clear and brief way. Be direct, clear, and professional. Try not to add fluff and unnecessary details into your paper or writing. This will keep the paper length shorter and more concise.
Margin sizes in APA Format
When it comes to margins, keep them consistent across the left, right, top, and bottom of the page. All four sides should be the same distance from the edge of the paper. It’s recommended to use at least one-inch margins around each side. It’s acceptable to use larger margins, but the margins should never be smaller than an inch.
Title pages in APA Format
The title page, or APA format cover page, is the first page of a paper or essay. Some teachers and professors do not require a title page, but some do. If you’re not sure if you should include one or not, ask your teacher. Some appreciate the page, which clearly displays the writer’s name and the title of the paper.
The APA format title page for student papers includes six main components:
- the title of the APA format paper
- names of all authors
- institutional affiliation
- course number and title
- instructor’s name
Title pages for professional papers also require a running head; student papers do not.
Some instructors and professional publications also ask for an author’s note. If you’re required or would like to include an author’s note, place it below the institutional affiliation. Examples of information included in an author’s note include an ORCID iD number, a disclosure, and an acknowledgement.
Here are key guidelines to developing your title page:
- The title of the paper should capture the main idea of the essay, but should not contain abbreviations or words that serve no purpose. For example, instead of using the title “A Look at Amphibians From the Past,” title the paper “Amphibians From the Past.” Delete the unnecessary fluff!
- Center the title on the page and place it about 3-4 lines from the top.
- The title should be bolded, in title case, and the same font size as your other page text. Do not underline or italicize the title. Other text on the page should be plain (not bolded , underlined, or italicized ).
- All text on the title page should be double-spaced. The APA format examples paper below displays proper spacing, so go take a look!
- Do not include any titles in the author’s name such as Dr. or Ms. In contrast, for your instructor’s name, use the form they prefer (e.g., Sagar Parekh, PhD; Dr. Minako Asato; Professor Nathan Ian Brown; etc.).
- The institutional affiliation is the school the author attends or the location where the author conducted the research.
In a hurry? Try the EasyBib title page maker to easily create a title page for free.
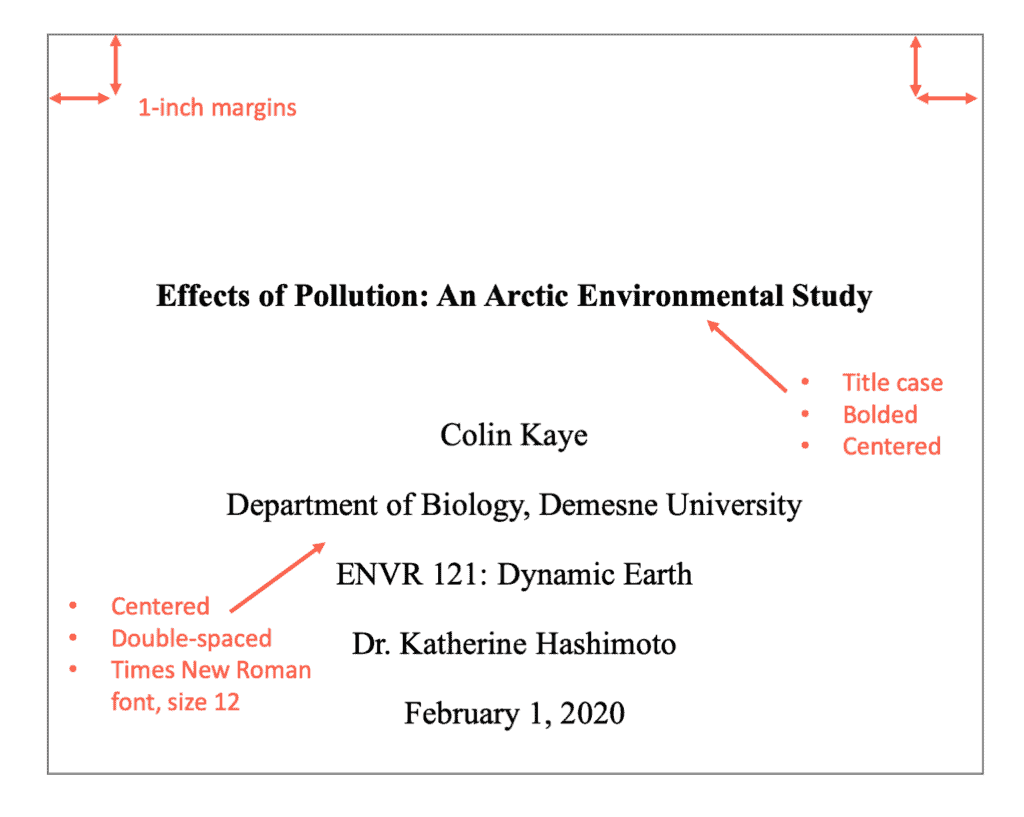
Sample of an APA format title page for a student paper:
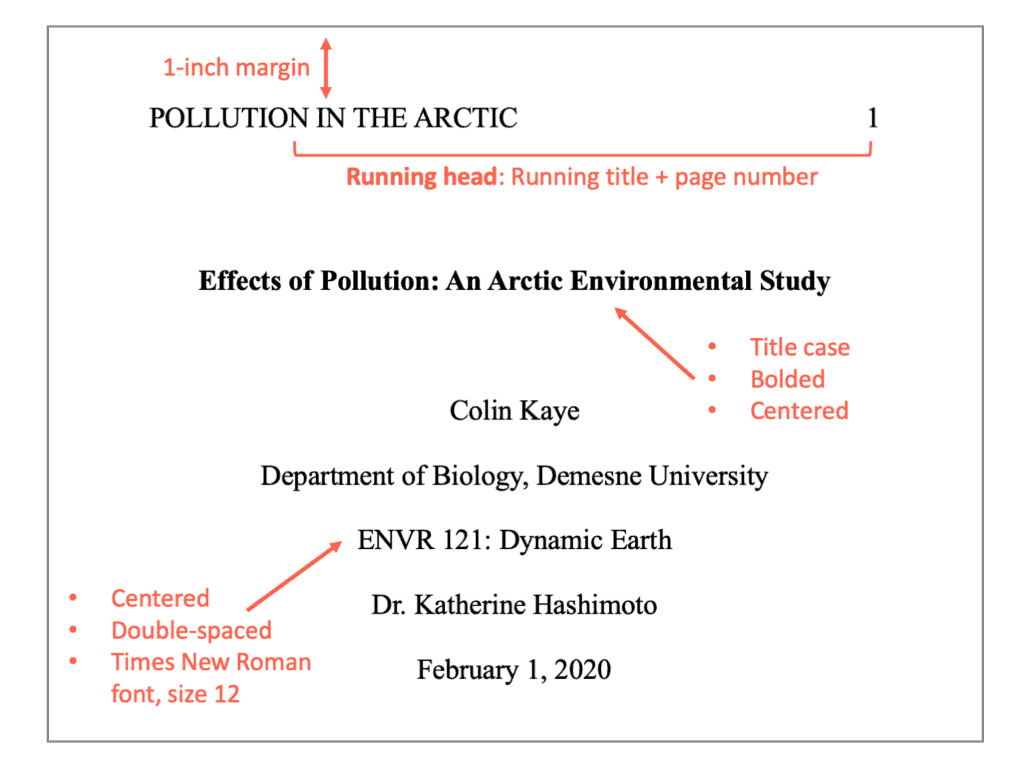
Sample of title page for a professional paper:
Running heads in APA Format
The 7th edition of the American Psychological Association Publication Manual (p. 37) states that running heads are not required for student papers unless requested by the instructor. Student papers still need a page number included in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The 6th edition required a running head for student papers, so be sure to confirm with your instructor which edition you should follow. Of note, this guide follows the 7th edition.
Running heads are required for professional papers (e.g., manuscripts submitted for publication). Read on for instructions on how to create them.
Are you wondering what is a “running head”? It’s basically a page header at the top of every page. To make this process easier, set your word processor to automatically add these components onto each page. You may want to look for “Header” in the features.
A running head/page header includes two pieces:
- the title of the paper
- page numbers.
Insert page numbers justified to the right-hand side of the APA format paper (do not put p. or pg. in front of the page numbers).
For all pages of the paper, including the APA format title page, include the “TITLE OF YOUR PAPER” justified to the left in capital letters (i.e., the running head). If your full title is long (over 50 characters), the running head title should be a shortened version.

Preparing outlines in APA Format
Outlines are extremely beneficial as they help writers stay organized, determine the scope of the research that needs to be included, and establish headings and subheadings.
There isn’t an official or recommended “APA format for outline” structure. It is up to the writer (if they choose to make use of an outline) to determine how to organize it and the characters to include. Some writers use a mix of roman numerals, numbers, and uppercase and lowercase letters.
Even though there isn’t a required or recommended APA format for an outline, we encourage writers to make use of one. Who wouldn’t want to put together a rough outline of their project? We promise you, an outline will help you stay on track.
Here’s our version of how APA format for outlines could look:

Don’t forget, if you’re looking for information on APA citation format and other related topics, check out our other comprehensive guides.
How to form an abstract in APA
An APA format abstract (p. 38) is a summary of a scholarly article or scientific study. Scholarly articles and studies are rather lengthy documents, and abstracts allow readers to first determine if they’d like to read an article in its entirety or not.
You may come across abstracts while researching a topic. Many databases display abstracts in the search results and often display them before showing the full text of an article or scientific study. It is important to create a high quality abstract that accurately communicates the purpose and goal of your paper, as readers will determine if it is worthy to continue reading or not.
Are you wondering if you need to create an abstract for your assignment? Usually, student papers do not require an abstract. Abstracts are not typically seen in class assignments, and are usually only included when submitting a paper for publication. Unless your teacher or professor asked for it, you probably don’t need to have one for your class assignment.
If you’re planning on submitting your paper to a journal for publication, first check the journal’s website to learn about abstract and APA paper format requirements.
Here are some helpful suggestions to create a dynamic abstract:
- Abstracts are found on their own page, directly after the title or cover page.
- Professional papers only (not student papers): Include the running head on the top of the page.
- On the first line of the page, center the word “Abstract” (but do not include quotation marks).
- On the following line, write a summary of the key points of your research. Your abstract summary is a way to introduce readers to your research topic, the questions that will be answered, the process you took, and any findings or conclusions you drew. Use concise, brief, informative language. You only have a few sentences to share the summary of your entire document, so be direct with your wording.
- This summary should not be indented, but should be double-spaced and less than 250 words.
- If applicable, help researchers find your work in databases by listing keywords from your paper after your summary. To do this, indent and type Keywords : in italics. Then list your keywords that stand out in your research. You can also include keyword strings that you think readers will type into the search box.
- Active voice: The subjects reacted to the medication.
- Passive voice: There was a reaction from the subjects taking the medication.
- Instead of evaluating your project in the abstract, simply report what it contains.
- If a large portion of your work includes the extension of someone else’s research, share this in the abstract and include the author’s last name and the year their work was released.
APA format example page:

Here’s an example of an abstract:
Visual design is a critical aspect of any web page or user interface, and its impact on a user’s experience has been studied extensively. Research has shown a positive correlation between a user’s perceived usability and a user’s assessment of visual design. Additionally, perceived web quality, which encompasses visual design, has a positive relationship with both initial and continued consumer purchase intention. However, visual design is often assessed using self-report scale, which are vulnerable to a few pitfalls. Because self-report questionnaires are often reliant on introspection and honesty, it is difficult to confidently rely on self-report questionnaires to make important decisions. This study aims to ensure the validity of a visual design assessment instrument (Visual Aesthetics of Websites Inventory: Short version) by examining its relationship with biometric (variables), like galvanic skin response, pupillometry, and fixation information. Our study looked at participants assessment of a webpage’s visual design, and compared it to their biometric responses while viewing the webpage. Overall, we found that both average fixation duration and pupil dilation differed when participants viewed web pages with lower visual design ratings compared to web pages with a higher visual design rating.
Keywords : usability, visual design, websites, eye tracking, pupillometry, self-report, VisAWI
The body of an APA paper
On the page after the title page (if a student paper) or the abstract (if a professional paper), begin with the body of the paper.
Most papers follow this format:
- At the top of the page, add the page number in the upper right corner of all pages, including the title page.
- On the next line write the title in bold font and center it. Do not underline or italicize it.
- Begin with the introduction and indent the first line of the paragraph. All paragraphs in the body are indented.
Sample body for a student paper:

Most scientific or professional papers have additional sections and guidelines:
- Start with the running head (title + page number). The heading title should be in capital letters. The abstract page should be page 2.
- The introduction presents the problem and premise upon which the research was based. It goes into more detail about this problem than the abstract.
- Begin a new section with the Method and use this word as the subtitle. Bold and center this subtitle. The Method section shows how the study was run and conducted. Be sure to describe the methods through which data was collected.
- Begin a new section with the Results . Bold and center this subtitle. The Results section summarizes your data. Use charts and graphs to display this data.
- Draw conclusions and support how your data led to these conclusions.
- Discuss whether or not your hypothesis was confirmed or not supported by your results.
- Determine the limitations of the study and next steps to improve research for future studies.
Sample body for a professional paper:

Keep in mind, APA citation format is much easier than you think, thanks to EasyBib.com. Try our automatic generator and watch how we create APA citation format references for you in just a few clicks. While you’re at it, take a peek at our other helpful guides, such as our APA reference page guide, to make sure you’re on track with your research papers.
Proper usage of headings & subheadings in APA Format
Headings (p. 47) serve an important purpose in research papers — they organize your paper and make it simple to locate different pieces of information. In addition, headings provide readers with a glimpse to the main idea, or content, they are about to read.
In APA format, there are five levels of headings, each with a different formatting:
- This is the title of your paper
- The title should be centered in the middle of the page
- The title should be bolded
- Use uppercase and lowercase letters where necessary (called title capitalization)
- Place this heading against the left margin
- Use bold letters
- Use uppercase and lowercase letters where necessary
- Place this heading against the left side margin
- End the heading with a period
- Indented in from the left margin
Following general formatting rules, all headings are double spaced and there are no extra lines or spaces between sections.
Here is a visual APA format template for levels of headings:

Use of graphics (tables and figures) in APA Format
If you’re looking to jazz up your project with any charts, tables, drawings, or images, there are certain APA format rules (pp. 195-250) to follow.
First and foremost, the only reason why any graphics should be added is to provide the reader with an easier way to see or read information, rather than typing it all out in the text.
Lots of numbers to discuss? Try organizing your information into a chart or table. Pie charts, bar graphs, coordinate planes, and line graphs are just a few ways to show numerical data, relationships between numbers, and many other types of information.
Instead of typing out long, drawn out descriptions, create a drawing or image. Many visual learners would appreciate the ability to look at an image to make sense of information.
Before you go ahead and place that graphic in your paper, here are a few key guidelines:
- Follow them in the appropriate numerical order in which they appear in the text of your paper. Example : Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, Figure 3.
- Example: Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, Figure 3
- Only use graphics if they will supplement the material in your text. If they reinstate what you already have in your text, then it is not necessary to include a graphic.
- Include enough wording in the graphic so that the reader is able to understand its meaning, even if it is isolated from the corresponding text. However, do not go overboard with adding a ton of wording in your graphic.
- Left align tables and figures
In our APA format sample paper , you’ll find examples of tables after the references. You may also place tables and figures within the text just after it is mentioned.
Is there anything better than seeing a neatly organized data table? We think not! If you have tons of numbers or data to share, consider creating a table instead of typing out a wordy paragraph. Tables are pretty easy to whip up on Google Docs or Microsoft Word.
General format of a table should be:
- Table number
- Choose to type out your data OR create a table. As stated above, in APA format, you shouldn’t have the information typed out in your paper and also have a table showing the same exact information. Choose one or the other.
- If you choose to create a table, discuss it very briefly in the text. Say something along the lines of, “Table 1 displays the amount of money used towards fighting Malaria.” Or, “Stomach cancer rates are displayed in Table 4.”
- If you’re submitting your project for a class, place your table close to the text where it’s mentioned. If you’re submitting it to be published in a journal, most publishers prefer tables to be placed in the back. If you’re unsure where to place your tables, ask!
- Include the table number first and at the top. Table 1 is the first table discussed in the paper. Table 2 is the next table mentioned, and so on. This should be in bold.
- Add a title under the number. Create a brief, descriptive title. Capitalize the first letter for each important word. Italicize the title and place it under the table number.
- Only use horizontal lines.
- Limit use of cell shading.
- Keep the font at 12-point size and use single or double spacing. If you use single spacing in one table, make sure all of the others use single spaces as well. Keep it consistent.
- All headings should be centered.
- In the first column (called the stub), center the heading, left-align the information underneath it (indent 0.15 inches if info is more than one line).
- Information in other columns should be centered.
- General . Information about the whole table.
- Specific . Information targeted for a specific column, row, or cell.
- Probability . Explains what certain table symbols mean. For example, asterisks, p values, etc.
Here’s an APA format example of a table:
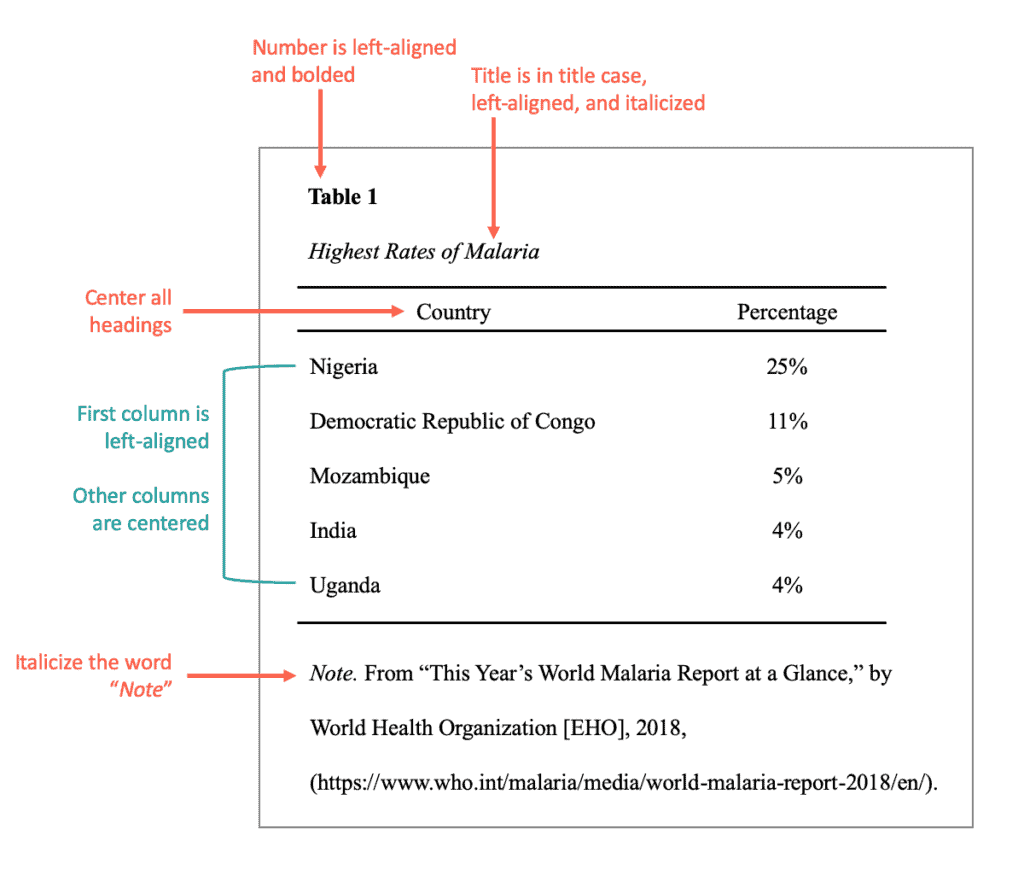
We know putting together a table is pretty tricky. That’s why we’ve included not one, but a few tables on this page. Scroll down and look at the additional tables in the essay in APA format example found below.
Figures represent information in a visual way. They differ from tables in that they are visually appealing. Sure, tables, like the one above, can be visually appealing, but it’s the color, circles, arrows, boxes, or icons included that make a figure a “figure.”
There are many commonly used figures in papers. Examples APA Format:
- Photographs
- Hierarchy charts
General format of a figure is the same as tables. This means each should include:
- Figure number
Use the same formatting tables use for the number, title, and note.
Here are some pointers to keep in mind when it comes to APA format for figures:
- Only include a figure if it adds value to your paper. If it will truly help with understanding, include it!
- Either include a figure OR write it all out in the text. Do not include the same information twice.
- If a note is added, it should clearly explain the content of the figure. Include any reference information if it’s reproduced or adapted.
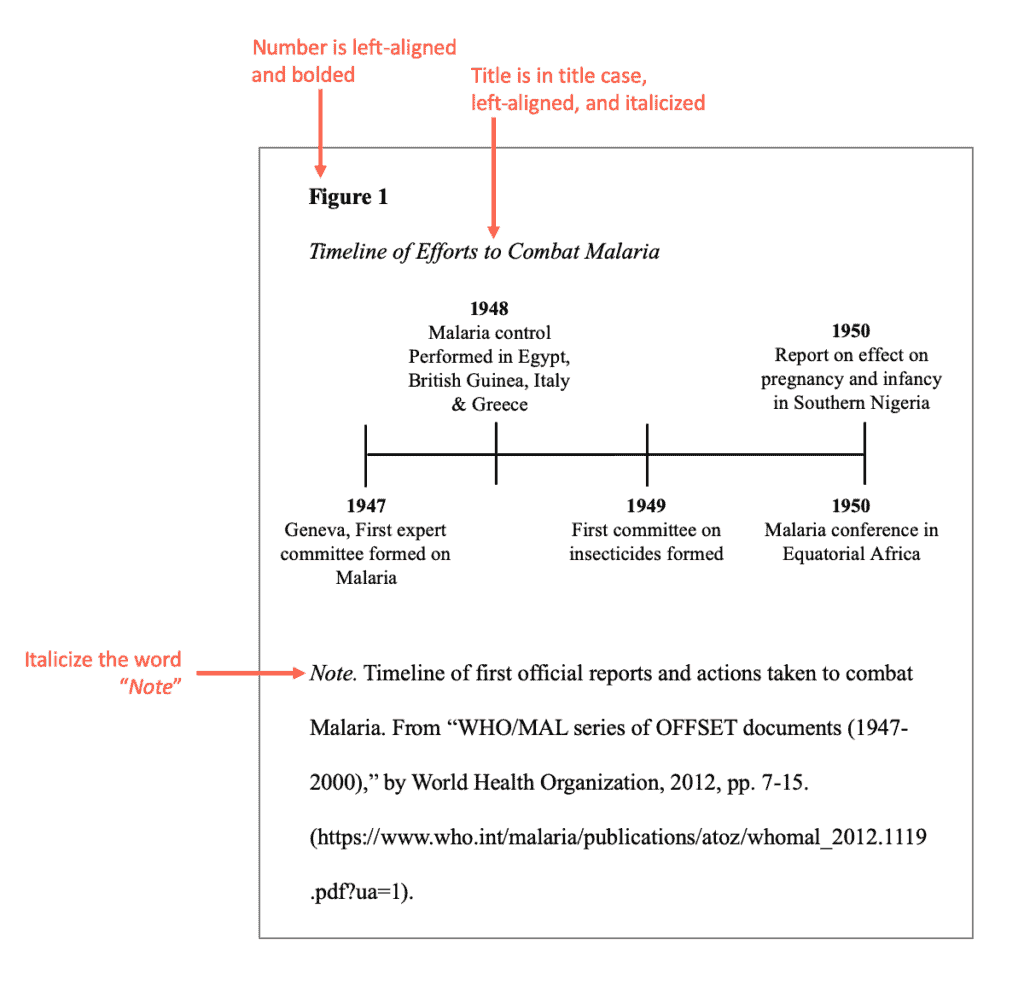
APA format sample of a figure:
Photographs:
We live in a world where we have tons of photographs available at our fingertips.
Photographs found through Google Images, social media, stock photos made available from subscription sites, and tons of other various online sources make obtaining photographs a breeze. We can even pull out our cell phones, and in just a few seconds, take pictures with our cameras.
Photographs are simple to find, and because of this, many students enjoy using them in their papers.
If you have a photograph you would like to include in your project, here are some guidelines from the American Psychological Association.
- Create a reference for the photograph. Follow the guidelines under the table and figure sections above.
- Do not use color photos. It is recommended to use black and white. Colors can change depending on the reader’s screen resolution. Using black and white ensures the reader will be able to view the image clearly. The only time it is recommended to use color photos is if you’re writing about color-specific things. For example, if you’re discussing the various shades of leaf coloration, you may want to include a few photographs of colorful leaves.
- If there are sections of the photograph that are not related to your work, it is acceptable to crop them out. Cropping is also beneficial in that it helps the reader focus on the main item you’re discussing.
- If you choose to include an image of a person you know, it would be respectful if you ask their permission before automatically including their photo in your paper. Some schools and universities post research papers online and some people prefer that their photos and information stay off the Internet.
B. Writing Style Tips
Writing a paper for scientific topics is much different than writing for English, literature, and other composition classes. Science papers are much more direct, clear, and concise. This section includes key suggestions, explains how to write in APA format, and includes other tidbits to keep in mind while formulating your research paper.
Verb usage in APA
Research experiments and observations rely on the creation and analysis of data to test hypotheses and come to conclusions. While sharing and explaining the methods and results of studies, science writers often use verbs.
When using verbs in writing, make sure that you continue to use them in the same tense throughout the section you’re writing. Further details are in the publication manual (p. 117).
Here’s an APA format example:
We tested the solution to identify the possible contaminants.
It wouldn’t make sense to add this sentence after the one above:
We tested the solution to identify the possible contaminants. Researchers often test solutions by placing them under a microscope.
Notice that the first sentence is in the past tense while the second sentence is in the present tense. This can be confusing for readers.
For verbs in scientific papers, the APA manual recommends using:
- Past tense or present perfect tense for the explantation of the procedure
- Past tense for the explanation of the results
- Present tense for the explanation of the conclusion and future implications
If this is all a bit much, and you’re simply looking for help with your references, try the EasyBib.com APA format generator . Our APA formatter creates your references in just a few clicks. APA citation format is easier than you think thanks to our innovative, automatic tool.
Even though your writing will not have the same fluff and detail as other forms of writing, it should not be boring or dull to read. The Publication Manual suggests thinking about who will be the main reader of your work and to write in a way that educates them.
How to reduce bias & labels
The American Psychological Association strongly objects to any bias towards gender, racial groups, ages of individuals or subjects, disabilities, and sexual orientation (pp. 131-149). If you’re unsure whether your writing is free of bias and labels or not, have a few individuals read your work to determine if it’s acceptable.
Here are a few guidelines that the American Psychological Association suggests :
- Only include information about an individual’s orientation or characteristic if it is important to the topic or study. Do not include information about individuals or labels if it is not necessary.
- If writing about an individual’s characteristic or orientation, for essay APA format, make sure to put the person first. Instead of saying, “Diabetic patients,” say, “Patients who are diabetic.”
- Instead of using narrow terms such as, “adolescents,” or “the elderly,” try to use broader terms such as, “participants,” and “subjects.”
- “They” or “their” are acceptable gender-neutral pronouns to use.
- Be mindful when using terms that end with “man” or “men” if they involve subjects who are female. For example, instead of using “Firemen,” use the term, “Firefighter.” In general, avoid ambiguity.
- When referring to someone’s racial or ethnic identity, use the census category terms and capitalize the first letter. Also, avoid using the word, “minority,” as it can be interpreted as meaning less than or deficient. Instead, say “people of color” or “underrepresented groups.”
- When describing subjects in APA format, use the words “girls” and “boys” for children who are under the age of 12. The terms, “young woman,” “young man,” “female adolescent,” and “male adolescent” are appropriate for subjects between 13-17 years old; “Men,” and “women,” for those older than 18. Use the term, “older adults.” for individuals who are older. “Elderly,” and “senior,” are not acceptable if used only as nouns. It is acceptable to use these terms if they’re used as adjectives.
Read through our example essay in APA format, found in section D, to see how we’ve reduced bias and labels.
Spelling in APA Format
- In APA formatting, use the same spelling as words found in Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary (American English) (p. 161).
- If the word you’re trying to spell is not found in Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary, a second resource is Webster’s Third New International Dictionary .
- If attempting to properly spell words in the psychology field, consult the American Psychological Association’s Dictionary of Psychology
Thanks to helpful tools and features, such as the spell checker, in word processing programs, most of us think we have everything we need right in our document. However, quite a few helpful features are found elsewhere.
Where can you find a full grammar editor? Right here, on EasyBib.com. The EasyBib Plus paper checker scans your paper for spelling, but also for any conjunction , determiner, or adverb out of place. Try it out and unlock the magic of an edited paper.
Abbreviation do’s and don’ts in APA Format
Abbreviations can be tricky. You may be asking yourself, “Do I include periods between the letters?” “Are all letters capitalized?” “Do I need to write out the full name each and every time?” Not to worry, we’re breaking down the publication manual’s abbreviations (p. 172) for you here.
First and foremost, use abbreviations sparingly.
Too many and you’re left with a paper littered with capital letters mashed together. Plus, they don’t lend themselves to smooth and easy reading. Readers need to pause and comprehend the meaning of abbreviations and quite often stumble over them.
- If the abbreviation is used less than three times in the paper, type it out each time. It would be pretty difficult to remember what an abbreviation or acronym stands for if you’re writing a lengthy paper.
- If you decide to sprinkle in abbreviations, it is not necessary to include periods between the letters.
- Example: While it may not affect a patient’s short-term memory (STM), it may affect their ability to comprehend new terms. Patients who experience STM loss while using the medication should discuss it with their doctor.
- Example : AIDS
- The weight in pounds exceeded what we previously thought.
Punctuation in APA Format
One space after most punctuation marks.
The manual recommends using one space after most punctuation marks, including punctuation at the end of a sentence (p. 154). It doesn’t hurt to double check with your teacher or professor to ask their preference since this rule was changed recently (in 2020).
The official APA format book was primarily created to aid individuals with submitting their paper for publication in a professional journal. Many schools adopt certain parts of the handbook and modify sections to match their preference. To see an example of an APA format research paper, with the spacing we believe is most commonly and acceptable to use, scroll down and see section D.
For more information related to the handbook, including frequently asked questions, and more, here’s further reading on the style
It’s often a heated debate among writers whether or not to use an Oxford comma (p. 155), but for this style, always use an Oxford comma. This type of comma is placed before the words AND and OR or in a series of three items.
Example of APA format for commas: The medication caused drowsiness, upset stomach, and fatigue.
Here’s another example: The subjects chose between cold, room temperature, or warm water.
Apostrophes
When writing a possessive singular noun, you should place the apostrophe before the s. For possessive plural nouns, the apostrophe is placed after the s.
- Singular : Linda Morris’s jacket
- Plural : The Morris’ house
Em dashes (long dash) are used to bring focus to a particular point or an aside. There are no spaces after these dashes (p. 157).
Use en dashes (short dash) in compound adjectives. Do not place a space before or after the dash. Here are a few examples:
- custom-built
- 12-year-old
Number rules in APA Format
Science papers often include the use of numbers, usually displayed in data, tables, and experiment information. The golden rule to keep in mind is that numbers less than 10 are written out in text. If the number is more than 10, use numerals.
APA format examples:
- 14 kilograms
- seven individuals
- 83 years old
- Fourth grade
The golden rule for numbers has exceptions.
In APA formatting, use numerals if you are:
- Showing numbers in a table or graph
- 4 divided by 2
- 6-month-olds
Use numbers written out as words if you are:
- Ninety-two percent of teachers feel as though….
- Hundred Years’ War
- One-sixth of the students
Other APA formatting number rules to keep in mind:
- World War II
- Super Bowl LII
- It’s 1980s, not 1980’s!
Additional number rules can be found in the publication manual (p. 178)
Need help with other writing topics? Our plagiarism checker is a great resource for anyone looking for writing help. Say goodbye to an out of place noun , preposition , or adjective, and hello to a fully edited paper.
Overview of APA references
While writing a research paper, it is always important to give credit and cite your sources; this lets you acknowledge others’ ideas and research you’ve used in your own work. Not doing so can be considered plagiarism , possibly leading to a failed grade or loss of a job.
APA style is one of the most commonly used citation styles used to prevent plagiarism. Here’s more on crediting sources . Let’s get this statement out of the way before you become confused: An APA format reference and an APA format citation are two different things! We understand that many teachers and professors use the terms as if they’re synonyms, but according to this specific style, they are two separate things, with different purposes, and styled differently.
A reference displays all of the information about the source — the title, the author’s name, the year it was published, the URL, all of it! References are placed on the final page of a research project.
Here’s an example of a reference:
Wynne-Jones, T. (2015). The emperor of any place . Candlewick Press.
An APA format citation is an APA format in-text citation. These are found within your paper, anytime a quote or paraphrase is included. They usually only include the name of the author and the date the source was published.
Here’s an example of one:
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is even discussed in the book, The Emperor of Any Place . The main character, Evan, finds a mysterious diary on his father’s desk (the same desk his father died on, after suffering from a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy attack). Evan unlocks the truth to his father and grandfather’s past (Wynne-Jones, 2015).
Both of the ways to credit another individual’s work — in the text of a paper and also on the final page — are key to preventing plagiarism. A writer must use both types in a paper. If you cite something in the text, it must have a full reference on the final page of the project. Where there is one, there must be the other!
Now that you understand that, here’s some basic info regarding APA format references (pp. 281-309).
- Each reference is organized, or structured, differently. It all depends on the source type. A book reference is structured one way, an APA journal is structured a different way, a newspaper article is another way. Yes, it’s probably frustrating that not all references are created equal and set up the same way. MLA works cited pages are unique in that every source type is formatted the same way. Unfortunately, this style is quite different.
- Most references follow this general format:
Author’s Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year published). Title of source . URL.
Again, as stated in the above paragraph, you must look up the specific source type you’re using to find out the placement of the title, author’s name, year published, etc.
For more information on APA format for sources and how to reference specific types of sources, use the other guides on EasyBib.com. Here’s another useful site .
Looking for a full visual of a page of references? Scroll down and take a peek at our APA format essay example towards the bottom of this page. You’ll see a list of references and you can gain a sense of how they look.
Bonus: here’s a link to more about the fundamentals related to this particular style. If you want to brush up or catch up on the Modern Language Association’s style, here’s a great resource on how to cite websites in MLA .
In-text APA citation format
Did you find the perfect quote or piece of information to include in your project? Way to go! It’s always a nice feeling when we find that magical piece of data or info to include in our writing. You probably already know that you can’t just copy and paste it into your project, or type it in, without also providing credit to the original author.
Displaying where the original information came from is much easier than you think.Directly next to the quote or information you included, place the author’s name and the year nearby. This allows the reader of your work to see where the information originated.
APA allows for the use of two different forms of in-text citation, parenthetical and narrative Both forms of citation require two elements:
- author’s name
- year of publication
The only difference is the way that this information is presented to the reader.
Parenthetical citations are the more commonly seen form of in-text citations for academic work, in which both required reference elements are presented at the end of the sentence in parentheses. Example:
Harlem had many artists and musicians in the late 1920s (Belafonte, 2008).
Narrative citations allow the author to present one or both of the required reference elements inside of the running sentence, which prevents the text from being too repetitive or burdensome. When only one of the two reference elements is included in the sentence, the other is provided parenthetically. Example:
According to Belafonte (2008), Harlem was full of artists and musicians in the late 1920s.
If there are two authors listed in the source entry, then the parenthetical reference must list them both:
(Smith & Belafonte, 2008)
If there are three or more authors listed in the source entry, then the parenthetical reference can abbreviate with “et al.”, the latin abbreviation for “and others”:
(Smith et al., 2008)
The author’s names are structured differently if there is more than one author. Things will also look different if there isn’t an author at all (which is sometimes the case with website pages). For more information on APA citation format, check out this page on the topic: APA parenthetical citation and APA in-text citation . There is also more information in the official manual in chapter 8.
If it’s MLA in-text and parenthetical citations you’re looking for, we’ve got your covered there too! You might want to also check out his guide on parenthetical citing .
Would you benefit from having a tool that helps you easily generate citations that are in the text? Check out EasyBib Plus!
References page in APA Format
An APA format reference page is easier to create than you probably think. We go into detail on how to create this page on our APA reference page . We also have a guide for how to create an annotated bibliography in APA . But, if you’re simply looking for a brief overview of the reference page, we’ve got you covered here.
Here are some pointers to keep in mind when it comes to the references page in APA format:
- This VIP page has its very own page. Start on a fresh, clean document (p. 303).
- Center and bold the title “References” (do not include quotation marks, underline, or italicize this title).
- Alphabetize and double-space ALL entries.
- Use a readable font, such as Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, or Lucida (p. 44).
- Every quote or piece of outside information included in the paper should be referenced and have an entry.
- Even though it’s called a “reference page,” it can be longer than one page. If your references flow onto the next page, then that’s a-okay.
- Only include the running head if it is required by your teacher or you’re writing a professional paper.
Sample reference page for a student paper:
Here’s another friendly reminder to use the EasyBib APA format generator (that comes with EasyBib Plus) to quickly and easily develop every single one of your references for you. Try it out! Our APA formatter is easy to use and ready to use 24/7.
Final APA Format Checklist
Prior to submitting your paper, check to make sure you have everything you need and everything in its place:
- Did you credit all of the information and quotes you used in the body of your paper and show a matching full reference at the end of the paper? Remember, you need both! Need more information on how to credit other authors and sources? Check out our other guides, or use the EasyBib APA format generator to credit your sources quickly and easily. EasyBib.com also has more styles than just the one this page focuses on.
- 12-pt. Times New Roman
- 11-pt. Calibri, Arial, Georgia
- 10-pt. Lucida, Sans Unicode, Computer Modern
- If you created an abstract, is it directly after the title page? Some teachers and professors do not require an abstract, so before you go ahead and include it, make sure it’s something he or she is expecting.
- Professional paper — Did you include a running head on every single page of your project?
- Student paper — Did you include page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of all your pages?
- Are all headings, as in section or chapter titles, properly formatted? If you’re not sure, check section number 9.
- Are all tables and figures aligned properly? Did you include notes and other important information directly below the table or figure? Include any information that will help the reader completely understand everything in the table or figure if it were to stand alone.
- Are abbreviations used sparingly? Did you format them properly?
- Is the entire document double spaced?
- Are all numbers formatted properly? Check section 17, which is APA writing format for numbers.
- Did you glance at the sample paper? Is your assignment structured similarly? Are all of the margins uniform?
Submitting Your APA Paper
Congratulations for making it this far! You’ve put a lot of effort into writing your paper and making sure the t’s are crossed and the i’s are dotted. If you’re planning to submit your paper for a school assignment, make sure you review your teacher or professor’s procedures.
If you’re submitting your paper to a journal, you probably need to include a cover letter.
Most cover letters ask you to include:
- The author’s contact information.
- A statement to the editor that the paper is original.
- If a similar paper exists elsewhere, notify the editor in the cover letter.
Once again, review the specific journal’s website for exact specifications for submission.
Okay, so you’re probably thinking you’re ready to hit send or print and submit your assignment. Can we offer one last suggestion? We promise it will only take a minute.
Consider running your paper through our handy dandy paper checker. It’s pretty simple.
Copy and paste or upload your paper into our checker. Within a minute, we’ll provide feedback on your spelling and grammar. If there’s a pronoun , interjection , or verb out of place, we’ll highlight it and offer suggestions for improvement. We’ll even take it a step further and point out any instances of possible plagiarism.
If it sounds too good to be true, then head on over to our innovative tool and give it a whirl. We promise you won’t be disappointed.
What is APA Format?
APA stands for the American Psychological Association . In this guide, you’ll find information related to “What is APA format?” in relation to writing and organizing your paper according to the American Psychological Association’s standards. Information on how to cite sources can be found on our APA citation page. The official American Psychological Association handbook was used as a reference for our guide and we’ve included page numbers from the manual throughout. However, this page is not associated with the association.
You’ll most likely use APA format if your paper is on a scientific topic. Many behavioral and social sciences use this organization’s standards and guidelines.
What are behavioral sciences? Behavioral sciences study human and animal behavior. They can include:
- Cognitive Science
- Neuroscience
What are social sciences? Social sciences focus on one specific aspect of human behavior, specifically social and cultural relationships. Social sciences can include:
- Anthropology
- Political Science
- Human Geography
- Archaeology
- Linguistics
What’s New in the 7th Edition?
This citation style was created by the American Psychological Association. Its rules and guidelines can be found in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . The information provided in the guide above follows the 6th edition (2009) of the manual. The 7th edition was published in 2020 and is the most recent version.
The 7th edition of the Publication Manual is in full color and includes 12 sections (compared to 8 sections in the 6th edition). In general, this new edition differentiates between professional and student papers, includes guidance with accessibility in mind, provides new examples to follow, and has updated guidelines.We’ve selected a few notable updates below, but for a full view of all of the 7th edition changes visit the style’s website linked here .
- Paper title
- Student name
- Affiliation (e.g., school, department, etc.)
- Course number and title
- Course instructor
- 6th edition – Running head: SMARTPHONE EFFECTS ON ADOLESCENT SOCIALIZATION
- 7th edition – SMARTPHONE EFFECTS ON ADOLESCENT SOCIALIZATION
- Pronouns . “They” can be used as a gender-neutral pronoun.
- Bias-free language guidelines . There are updated and new sections on guidelines for this section. New sections address participation in research, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality.
- Spacing after sentences. Add only a single space after end punctuation.
- Tables and figures . The citing format is now streamlined so that both tables and figures should include a name and number above the table/figure, and a note underneath the table/figure.
- 6th ed. – (Ikemoto, Richardson, Murphy, Yoshida 2016)
- 7th ed. – (Ikemoto et al., 2016)
- Citing books. The location of the publisher can be omitted. Also, e-books no longer need to mention the format (e.g., Kindle, etc.)
- Example: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-019-0153-5
- Using URLs. URLs no longer need to be prefaced by the words “Retrieved from.”
New citing information . There is new guidance on citing classroom or intranet resources, and oral traditions or traditional knowledge of indigenous peoples.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) (2020). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000

Published October 31, 2011. Updated May 14, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Sample Paper
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
We should not use “et al.” in APA reference list entries. If the number of authors in the source is up to and including 20, list all author names and use an ampersand (&) before the final author’s name. If the number of authors is more than 20, list the first 19 authors’ names followed by an ellipsis (but no ampersand), and then add the final author’s name. An example of author names in a reference entry having more than 20 authors is given below:
Author Surname1, F. M., Author Surname2, F. M., Author Surname3, F. M., Author Surname4, F. M., Author Surname5, F. M., Author Surname6, F. M., Author Surname7, F. M., Author Surname8, F. M., Author Surname9, F. M., Author Surname10, F. M., Author Surname11, F. M., Author Surname12, F. M., Author Surname13, F. M., Author Surname14, F. M., Author Surname15, F. M., Author Surname16, F. M., Author Surname17, F. M., Author Surname18, F. M., Author Surname19, F. M., . . . Last Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year).
Alvarez, L. D., Peach, J. L., Rodriguez, J. F., Donald, L., Thomas, M., Aruck, A., Samy, K., Anthony, K., Ajey, M., Rodriguez, K. L., Katherine, K., Vincent, A., Pater, F., Somu, P., Pander, L., Berd, R., Fox, L., Anders, A., Kamala, W., . . . Nicole Jones, K. (2019).
Note that, unlike references with 2 to 20 author names, the symbol “&” is not used here before the last author’s name.
APA 7, released in October 2019, has some new updates. Here is a brief description of the updates made in APA 7.
Different types of papers and best practices are given in detail in Chapter 1.
How to format a student title page is explained in Chapter 2. Examples of a professional paper and a student paper are included.
Chapter 3 provides additional information on qualitative and mixed methods of research.
An update on writing style is included in Chapter 4.
In chapter 5, some best practices for writing with bias-free language are included.
Chapter 6 gives some updates on style elements including using a single space after a period, including a citation with an abbreviation, the treatment of numbers in abstracts, treatment for different types of lists, and the formatting of gene and protein names.
In Chapter 7, additional examples are given for tables and figures for different types of publications.
In Chapter 8, how to format quotations and how to paraphrase text are covered with additional examples. A simplified version of in-text citations is clearly illustrated.
Chapter 9 has many updates: listing all author names up to 20 authors, standardizing DOIs and URLs, and the formatting of an annotated bibliography.
Chapter 10 includes many examples with templates for all reference types. New rules covering the inclusion of the issue number for journals and the omission of publisher location from book references are provided. Explanations of how to cite YouTube videos, power point slides, and TED talks are included.
Chapter 11 includes many legal references for easy understanding.
Chapter 12 provides advice for authors on how to promote their papers.
For more information on some of the changes found in APA 7, check out this EasyBib article .
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Paragraphs: Organization (MEAL Plan)
Organization video playlist.
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Academic Paragraphs: Introduction to Paragraphs and the MEAL Plan (video transcript)
- Academic Paragraphs: Examples of the MEAL Plan (video transcript)
Duke University's Thompson Writing Program (n.d.) recommends that you organize the material within a paragraph according to the MEAL plan:
Main Idea: Your topic sentence stating the concrete claim the paragraph is advancing. Evidence: Paraphrase or direct quotations from the source material you are using to support your topic sentence's claim. Analysis: Your explanation and evaluation of the evidence; explaining the evidence you provided and its relevance in your own words. Lead Out: Concluding; preparing your reader to transition to the next paragraph (and the next claim).
The MEAL plan matches the general format of academic writing on many levels: that of assertion, evidence, and explanation. Many students make the mistake of writing toward a topic sentence or claim, rather than from one; keeping the MEAL plan in mind as you write will help you begin your paragraphs strongly and develop your analysis thoroughly.
Duke University Thompson Writing Program. (n.d.). Paragraphing: The MEAL plan . http://twp.duke.edu/sites/twp.duke.edu/files/file-attachments/meal-plan-2-1.original.pdf
Outlining Strategies
Outlining your first draft by listing each paragraph's topic sentence can be an easy way to ensure that each of your paragraphs is serving a specific purpose in your paper. You may find opportunities to combine or eliminate potential paragraphs when outlining—first drafts often contain repetitive ideas or sections that stall, rather than advance, the paper's central argument .
Additionally, if you are having trouble revising a paper, making an outline of each paragraph and its topic sentence after you have written your paper can be an effective way of identifying a paper's strengths and weaknesses.
Related Resources
- Previous Page: Topic Sentences
- Next Page: Transitions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
UIJRT » United International Journal for Research & Technology
- Call For Papers - June 2024
- [email protected]
- ISSN: 2582-6832
- Google Scholar

Academic Performance of Grade 7 Students in Biology Through Close Reading Strategies
- Author(s): Jestine Jaranilla Jaramiel and Jhonner Dichoso Ricafort
PAPER DETAILS
- Educational Management
- Paper ID: UIJRTV5I80001
- Pages: 01-10
The study, “Academic Performance of Grade 7 Students in Biology through Close Reading Strategies,” aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of close reading strategies in improving the academic performance of Grade 7 students in Biology. The study utilized the one-group pretest-posttest and descriptive methods and involved twenty-two (22) Grade 7 students from a private non-sectarian school in Sorsogon City, Philippines. It used pre-and post-tests and modules on selected Biology topics as instruments. The study indicated that close reading strategies significantly impacted students’ academic performance. Following the application of close reading strategies, the students’ performance in Biology improved, with t-values of 3.95, 5.92, 12.31, 8.30, and 16.78, all exceeding the critical value of 2.080. Additionally, these strategies enhanced their reading comprehension skills, which are essential for understanding scientific concepts. The findings suggest integrating close reading strategies into Biology instruction can benefit students’ academic performance. Teachers and educators can utilize these strategies to enhance critical thinking skills, comprehension, and academic performance in science education. Furthermore, this research provides evidence that close reading strategies can effectively improve students’ academic performance and be an instructional tool in Biology education.
Related Papers
Junior high school students’ attitudes regarding the recreational use of marijuana, level of acceptability of human circulatory system model for non-biology major and biology major teachers, motivation, attitude, and language learning styles of senior high school students, practices of elementary schools on the implementation of school-based feeding program from pre-pandemic to post-pandemic, effect of station rotation model in learning grade 10 physics, factors that influence technical vocational students’ choice of specialization in relation to their academic performance in deped division of sorsogon, comprehensible inputs to scaffold comprehension of l2 learners, school-based management journey of select school in sorsogon city, metacognitive skills of grade 10 students, financial management of school heads in magallanes districts.

UIJRT is a open access, peer-reviewed & multidisciplinary engineering, technology and science journal that publishes original review and research articles.
- Privacy Policy
- Refund Policies
Author's Links
- Call For Papers
- Area of Publication
- Current Issue
- Past Issues
- Processing Fee
- Submit Manuscript
- Editorial Board Members
Have you any query?
- E-Mail: [email protected]
- E-Mail: [email protected]
- Phone: +91-7007979966
Social Site Profiles

© 2019-2024 UIJRT - United International Journal for Research & Technology - All Rights Reserved.

Privacy Overview
For conference & paper publication.
- ISSN Approved Journal
- Open Access Journal
- Fast Indexing Journal

Paragraph Templates for an Argumentative Research Paper on a Controversial Issue

- Word Document File
Description
Directions: I designed these templates for an argumentative research paper on a controversial issue. Students choose a controversial issue in America and find reputable research to support their stance on it. The research paper consists of three main points: background (or history) of the controversial issue, argument, and counterargument, which the student addresses and refutes.
I designed the below templates to provide scaffolding for lower-level students. While the templates for the argument and counter-argument paragraphs are more straightforward, there are countless ways for students to address the background section of the research paper; therefore, I provided sample sentences that students could use instead, but they will need to fill in their own information and arrange the sentences in an effective manner. Each template is also accompanied by an example paragraph to provide students with greater guidance. Please note that the content of the example paragraphs is fictional.
I would also suggest providing students with a list of topic choices before the unit begins. Have them turn in their top three choices to you. After you have student choices, you can pick which one each student will research. This allows you to limit the number of students researching the same topic and the flexibility to steer students away from topics that they may not be mature enough to address in a professional way.
Questions & Answers
Loverofenglish22.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

Prevent plagiarism, run a free plagiarism check.
- Knowledge Base
How to Avoid Plagiarism | Tips on Citing Sources
Published on October 10, 2021 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas without properly crediting the original author. Sometimes plagiarism involves deliberately stealing someone’s work, but more often it happens accidentally, through carelessness or forgetfulness.When you write an academic paper, you build upon the work of others and use various credible sources for information and evidence. To avoid plagiarism, you need to correctly incorporate these sources into your text.

You can avoid plagiarism by :
- Keeping track of the sources you consult in your research
- Paraphrasing or quoting from your sources (by using a paraphrasing tool and adding your own ideas)
- Crediting the original author in an in-text citation and in your reference list
- Using a plagiarism checker before you submit
- Use generative AI tools responsibly (outputs may be detected by an AI detector )
Even accidental plagiarism can have serious consequences , so take care with how you integrate sources into your writing.
Table of contents
Keeping track of your sources, avoiding plagiarism when quoting, avoiding plagiarism when paraphrasing, citing your sources correctly, using a plagiarism checker, using ai tools responsibly, checklist: plagiarism prevention, free lecture slides, frequently asked questions.
One of the most common ways that students commit plagiarism is by simply forgetting where an idea came from and unintentionally presenting it as their own. You can easily avoid this pitfall by keeping your notes organized and compiling a list of citations as you go.
Clearly label which thoughts are yours and which aren’t in your notes, highlight statements that need citations, and carefully mark any text copied directly from a source with quotation marks.
In the example below, red indicates a claim that requires a source, blue indicates information paraphrased or summarized from a source, and green indicates a direct quotation.
Notes for my paper on global warming
- Greenhouse gas emissions trap heat and raise global temperatures [cite details]
- Causes more severe weather: hurricanes, fires, water scarcity [cite examples]
- Animal habitats across the world are under threat from climate change [cite examples]
- Just this year, 23 species have been declared extinct (BBC News 2021)
- “Animals are changing shape… some are growing bigger wings, some are sprouting longer ears and others are growing larger bills” in order to cool off (Zeldovich 2021)
Managing sources with the Scribbr Citation Generator
To make your life easier later, make sure to write down the full details of every source you consult. That includes not only books and journal articles, but also things like websites, magazine articles, and videos. This makes it easy to go back and check where you found a phrase, fact, or idea that you want to use in your paper.
Scribbr’s Citation Generator allows you to start building and managing your reference list as you go, saving time later. When you’re ready to submit, simply download your reference list!
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Prevent plagiarism. run a free check..
Quoting means copying a piece of text word for word. The copied text must be introduced in your own words, enclosed in quotation marks , and correctly attributed to the original author.
In general, quote sparingly. Quotes are appropriate when:
- You’re using an exact definition, introduced by the original author
- It is impossible for you to rephrase the original text without losing its meaning
- You’re analyzing the use of language in the original text
- You want to maintain the authority and style of the author’s words
Long quotations should be formatted as block quotes . But for longer blocks of text, it’s usually better to paraphrase instead.
Paraphrasing means using your own words to explain something from a source.
Paraphrasing does not mean just switching out a few words from a copy-pasted text. To paraphrase properly, you should rewrite the author’s point in your own words to show that you have fully understood it.
Every time you quote or paraphrase, you must include an in-text or footnote citation clearly identifying the original author. Each citation must correspond to a full reference in the reference list or bibliography at the end of your paper.
This acknowledges the source of your information, avoiding plagiarism, and it helps your readers locate the source for themselves if they would like to learn more.
There are many different citation styles, each with its own rules. A few common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago . Your instructor may assign a particular style for you to use, or you may be able to choose. The most important thing is to apply one style consistently throughout the text.
The examples below follow APA Style.
Citing a single source
| In-text citation | The novel’s central theme is voiced by Cersei Lannister: “when you play the game of thrones you win or you die. There is no middle ground.” (Martin, 2002, p. 403). |
| Reference list | Martin, G. R. R. (2002). (Reprint ed.). Bantam. |
Citing multiple sources
If you quote multiple sources in one sentence, make sure to cite them separately so that it’s clear which material came from which source.
| In-text citation | Martin’s narrative can be read as a classic “zero-sum game” (Morgenstern and von Neumann, 1980, p.98), where players in the “game of thrones” either “win or … die” (Martin, 2002, p. 403), with no other outcomes possible. |
| Reference list | Martin, G. R. R. (2002). (Reprint ed.). Bantam. Morgenstern, O., & von Neumann, J. (1980). (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. |
To create correctly formatted source citations, you can use our free Citation Generator.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
And if you’re citing in APA Style, consider using Scribbr’s Citation Checker , a unique tool that scans your citations for errors. It can detect inconsistencies between your in-text citations and your reference list, as well as making sure your citations are flawlessly formatted.
Most universities use plagiarism checkers like Turnitin to detect potential plagiarism. Here’s how plagiarism checkers work : they scan your document, compare it to a database of webpages and publications, and highlight passages that appear similar to other texts.
Consider using a plagiarism checker yourself before submitting your paper. This allows you to identify issues that could constitute accidental plagiarism, such as:
- Forgotten or misplaced citations
- Missing quotation marks
- Paraphrased material that’s too similar to the original text
Then you can easily fix any instances of potential plagiarism.
There are differences in accuracy and safety between plagiarism checkers. To help students choose, we conducted extensive research comparing the best plagiarism checkers .
Generative AI tools like ChatGPT can be helpful at different stages of the writing and research process. However, these tools can also be used to plagiarize in various ways (whether intentionally or unintentionally). When using these tools, it’s important to avoid the following:
- AI-assisted plagiarism: Passing off AI-generated text as your own work (e.g., research papers, homework assignments)
- Plagiarism : Using the tool to paraphrase content from another source and passing it off as original work
- Self-plagiarism : Using the tool to rewrite a paper you previously submitted
It’s important to use AI tools responsibly and to be aware that AI-generated outputs may be detected by your university’s AI detector .
When using someone else’s exact words, I have properly formatted them as a quote .
When using someone else’s ideas, I have properly paraphrased , expressing the idea completely in my own words.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
Every source I cited is included in my reference list or bibliography .
I have consistently followed the rules of my required citation style .
I have not committed self-plagiarism by reusing any part of a previous paper.
I have used a reliable plagiarism checker as a final check.
Your document should be free from plagiarism!
Are you a teacher or professor who would like to educate your students about plagiarism? You can download our free lecture slides, available for Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Accidental plagiarism is one of the most common examples of plagiarism . Perhaps you forgot to cite a source, or paraphrased something a bit too closely. Maybe you can’t remember where you got an idea from, and aren’t totally sure if it’s original or not.
These all count as plagiarism, even though you didn’t do it on purpose. When in doubt, make sure you’re citing your sources . Also consider running your work through a plagiarism checker tool prior to submission, which work by using advanced database software to scan for matches between your text and existing texts.
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker takes less than 10 minutes and can help you turn in your paper with confidence.
To avoid plagiarism when summarizing an article or other source, follow these two rules:
- Write the summary entirely in your own words by paraphrasing the author’s ideas.
- Cite the source with an in-text citation and a full reference so your reader can easily find the original text.
Plagiarism can be detected by your professor or readers if the tone, formatting, or style of your text is different in different parts of your paper, or if they’re familiar with the plagiarized source.
Many universities also use plagiarism detection software like Turnitin’s, which compares your text to a large database of other sources, flagging any similarities that come up.
It can be easier than you think to commit plagiarism by accident. Consider using a plagiarism checker prior to submitting your paper to ensure you haven’t missed any citations.
Some examples of plagiarism include:
- Copying and pasting a Wikipedia article into the body of an assignment
- Quoting a source without including a citation
- Not paraphrasing a source properly, such as maintaining wording too close to the original
- Forgetting to cite the source of an idea
The most surefire way to avoid plagiarism is to always cite your sources . When in doubt, cite!
If you’re concerned about plagiarism, consider running your work through a plagiarism checker tool prior to submission. Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker takes less than 10 minutes and can help you turn in your paper with confidence.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Avoid Plagiarism | Tips on Citing Sources. Scribbr. Retrieved June 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/plagiarism/how-to-avoid-plagiarism/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, consequences of mild, moderate & severe plagiarism, types of plagiarism and how to recognize them, what is self-plagiarism | definition & how to avoid it, what is your plagiarism score.
Follow the event on:
In collaboration with, guidelines for science and research abstract submissions.
Read this page carefully before submitting your abstract for WindEurope’s Annual Event 2025.
At the end of the page, you will find the button that will bring you to the abstract submission portal (Oxford Abstracts).
| 10 June – 6 September 2024 | | December 2024 – March 2025 | |
| 11 September – 11 October 2024 | Members of WindEurope and the European Academy of Wind Energy (EAWE) will review, evaluate, and score abstracts in their field of expertise. This helps the programme committee to build a high-quality programme and keep commercial content out. | 8-10 April 2025 |
Session chairs and presenters attend a final briefing session in the speakers’ room of the venue before their session starts. |
| Early December 2024 | Based on the outcomes of the review, the programme committee creates session proposals for the technical track using the highest scoring abstracts. Notifications of selection will be sent by WindEurope to those selected for an oral presentation or to produce a poster. | April 2025 | General proceedings accessible to full conference delegates on and to WindEurope’s Members in the of the WindEurope website. will be published 4 to 6 weeks after submission, in open access in a dedicated volume of the IOP edited by EAWE. |
Essential requirements for abstracts
- Abstracts should be submitted in English.
- Your abstract must describe work that has been done at the moment of submission , not work that will be done.
- Your abstract should contain new unpublished work and should not describe work presented at other conferences.
- No sales pitches – abstracts should not contain overly promotional or commercial content, but rather strive to present data or results that can contribute to bringing the sector forward. WindEurope reserves the right to refuse/reject overly commercial abstracts.
- Your abstract should be submitted under the correct topic for a correct review.
- Your abstract cannot exceed 1,500 words (not including references).
- Your abstract should contain a complete reference list (not included in the word count).
- Abbreviations should be defined on first use .
- Science and research abstracts can only submitted in PDF (incl. text plus graphs, charts, or images as necessary, and embedded fonts). Please include abstract title, presenting author, co-authors and affiliations in your PDF.
Abstract submission and structure
Abstracts submitted under the science and research submission group must follow the following structure and rules:
- The abstract must be submitted as in PDF format
- The PDF file includes text plus graphs, charts, or images as necessary, and embedded fonts. Please include abstract title, presenting author, co-authors, and affiliations in your PDF too.
- The abstract must respect the word limit of maximum 1,500 words
- It should contain a complete reference list that is not included in the given word count
- The style of writing may be brief and incomplete, as long as the essential steps in the research are clear and convincing
Submitted abstracts should be divided in 5 sections :
- Introduction : Briefly describe the work to be discussed in your presentation.
- Approach : Briefly describe the approach you used.
- Main body of the abstract
- Conclusions : Outline the significant implications you’re your paper has for the industry.
- Learning objectives : If this abstract is selected and presented at the conference, what will delegates learn? Focus on what your abstract will enable them to do in their own job.
How are abstracts rated?
All abstracts are anonymously reviewed and collectively assessed by the Conference Scientific Committee from the European Academy of Wind Energy (EAWE) . For each abstract, the committee will provide:
- a numerical grade (0-5)
- a recommended presentation method
- a comment on the abstract
Who is reviewing my abstract?
All science and research abstracts are assigned for review to members of the Conference Scientific Committee from the European Academy of Wind Energy (EAWE) and then assessed by the committee at a dedicated meeting.
Science and research content at our events is organised in cooperation with the European Academy of Wind Energy (EAWE) , a world-leading wind energy academic & research community. The Academy will bring delegates leading edge wind energy research results, keeping Europe at the forefront of wind energy innovation. This offers a forum for in-depth presentations and discussions on progress and results of wind-energy related scientific research.
Numerical grading
The abstracts will be evaluated against the following criteria:
- The abstract has to describe work that has been done at the moment of writing the extended abstract, not work that will be done.
- While the style of writing may be brief and incomplete, the essential steps in the research must be clear and convincing.
- The abstract should contain new work, not yet published.
- The abstract should include a complete reference list.
- The methodology and results should be plausible and free of errors.
- The work in the abstract should be up-to-date as regards previous knowledge and the contribution of others.
- The work should be scientifically/technically relevant.
Reviewers will grade each abstract on a scale of 0-5, keeping the criteria listed above in mind.
- 0: Reject = None of the criteria are met
- 1: Very poor = Little or no accomplishment of the criteria
- 2: Poor = Some criteria are achieved but on a superficial level
- 3: Average = Abstract has fulfilled the criteria but is not remarkable
- 4: Good = Abstract performs strongly with regards to most criteria
- 5: Excellent = Abstract is exemplary with regards to all/most criteria
Recommendations made by abstract reviewers
The Conference Scientific Committee will make a recommendation on the presentation format for each abstract, intended as a guide for the Programme Committee, using these options:
- I strongly recommend that this abstract is selected for an oral presentation
- This abstract is more suitable for an oral presentation than poster presentation
- This abstract is more suitable for poster presentation than an oral presentation
- I strongly recommend that this abstract is selected for poster presentation
- This abstract should be rejected
The Conference Scientific Committee reviewers will explain their grades and recommendations by leaving a comment in the appropriate field. Comments will be available to authors upon request.
Abstract selection process
After the review is completed, the programme committee members receive the overview of all scored abstracts. Based on the scores, the reviewers’ comments and planned session topics, the programme committee will draft session proposals and select which abstracts are eligible for an oral presentation in a session and which are eligible to produce a poster. These proposals are the base to determine the technical and scientific programme outline for the conference.
For abstracts selected for either an oral presentation or a poster, WindEurope is happy to offer speakers and listed poster a complimentary 3-day Conference and Exhibition pass.
Kindly note that only one presenter per abstract is invited if selected. We cannot allow multiple presenters per abstracts.
Scientific paper publication (scientific proceedings)
Eligibility of scientific paper publications
If you submit an abstract under the science and research track, your abstract may be selected for publication in a specific open access volume of the IOP Journal of Physics: Conference Serie . Selected abstracts will be invited to submit a paper based on their abstract. Selected papers will be published depending on the peer-review outcome.
Selected abstracts eligible for a scientific publication will be contacted individually by the WindEurope Conference Secretariat.
Timeline for scientific papers
- Draft paper submission: 10 February 2025
Draft papers will be reviewed by EAWE in view of their publication in the IOP Journal of Physics Conference Series
- Final paper submission: 25 March 2025
IOP Journal of Physics: Conference Series
Please find some points to keep in mind about the scientific publications. More detailed information, planning for publication and review will be shared in due time by the conference secretariat to eligible candidates.
- Conference Series operates a publishing licence, under which authors retain copyright of their papers and they no longer need to sign and submit copyright assignment forms. Any author who wishes to publish in IOP Conference Series must agree to the terms of the licence and by submitting a paper for publication it is assumed all authors of the paper agree, in full, to the terms of the licence.
- IOP Conference Series uses author-supplied PDFs for all online and print publication. Authors are asked to prepare their papers using Microsoft Word or LaTeX, according to the journal guidelines and templates, and then convert these files to PDF.
By submitting an abstract to the WindEurope Annual Event 2025 and if your abstract is selected for a speaking slot or a poster, you implicitly give your permission to WindEurope asbl/vzw to reproduce your presentation file and/or poster file in the conference proceedings of the event. However, this does not forfeit your right to publish your presentation file and/or poster file in any other medium, nor does WindEurope retain any exclusive rights over it.
Event Ambassadors
We use cookies to provide you with a better experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy .
Keysight and AIST Partner for Quantum Research

Harnessing the power of quantum technologies promises to spur widespread innovation by using the fundamental laws of quantum mechanics to solve problems that are impossible using current technologies. However, building a strong quantum ecosystem takes time and requires significant investments from both national governments and private industry. These efforts also require the cooperation of the academic and government quantum research communities.
Recognizing this need, Keysight and Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to collaborate on quantum research and to drive the industrialization of quantum technologies.
Related Resources
“We’re in the early days of quantum, and while there is steady scientific progress, we need sustained collaboration among all members of the quantum community to make this a viable commercial technology,” said Dr. Eric Holland, general manager for Keysight’s Quantum Engineering Solutions group. “By formalizing a quantum collaboration with our long-time partner AIST, Keysight will be able to help quantum move forward as an industry with our unique expertise and solutions.”
Under the terms of the agreement, Keysight and AIST will focus extensively on exploring quantum control technologies, low-temperature electronics device technology, and modeling and simulation, as well as the standardization of these items in fields such as quantum computing and quantum sensing.
At the center of the collaboration will be the Global Research Center for Quantum-AI Fusion Technology Business Development (G-QuAT), a revolutionary research facility that will feature a 1,000-qubit quantum computer. AIST will integrate and link the G-QuAT’s evaluation testbeds, device manufacturing capabilities, and computing infrastructure with Keysight's quantum control technologies and 5G / 6G evaluation technologies.
“Japan has an ambitious 10-year plan to become a leader in quantum and Keysight is synergistically aligned to help deliver on these plans,” said Holland. “Linking our quantum control technologies to the G-QuAT facility will truly make it a world-class quantum research facility.”
The cooperation is expected to drive new technological developments and market creation, helping to help industrialize quantum technologies in Japan and globally.
Related Articles
Spectrum's arbitrary waveform generator precise enough for quantum research, infineon expands quantum computing commitment, takes part in six new research projects, keysight commissioned research finds automated testing remains a significant challenge for organizations, report abusive comment.
ChatGPT Goes to Law School
71 Journal of Legal Education 387 (2022)
16 Pages Posted: 25 Jan 2023 Last revised: 20 Oct 2023
Jonathan H. Choi
University of Southern California; University of Southern California Gould School of Law
Kristin E. Hickman
University of Minnesota - Twin Cities - School of Law
Amy Monahan
University of Minnesota Law School
Daniel Schwarcz
Date Written: January 23, 2023
How well can AI models write law school exams without human assistance? To find out, we used the widely publicized AI model ChatGPT to generate answers on four real exams at the University of Minnesota Law School. We then blindly graded these exams as part of our regular grading processes for each class. Over 95 multiple choice questions and 12 essay questions, ChatGPT performed on average at the level of a C+ student, achieving a low but passing grade in all four courses. After detailing these results, we discuss their implications for legal education and lawyering. We also provide example prompts and advice on how ChatGPT can assist with legal writing.
Keywords: ChatGPT, law school, AI, natural language processing, Legal Data, NLP, Legal NLP, Legal Analytics, natural language understanding, evaluation, machine learning, artificial intelligence, artificial intelligence and law
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Jonathan H. Choi (Contact Author)
University of southern california ( email ).
2250 Alcazar Street Los Angeles, CA 90089 United States
University of Southern California Gould School of Law ( email )
699 Exposition Blvd. Los Angeles, CA 90089 United States
University of Minnesota - Twin Cities - School of Law ( email )
229 19th Avenue South Minneapolis, MN 55455 United States 612-624-2915 (Phone)
University of Minnesota Law School ( email )
229 19th Avenue South Minneapolis, MN 55455 United States
HOME PAGE: http://www.law.umn.edu/profiles/daniel-schwarcz
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, university of minnesota law school legal studies research paper series.
Subscribe to this journal for more curated articles on this topic
Legal Education eJournal
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Legal Writing eJournal
Subscribe to this free journal for more curated articles on this topic
Law Educator: Courses, Materials & Teaching eJournal
Empirical legal studies ejournal, experimental legal studies ejournal, legal information, technology & law librarianship ejournal, artificial intelligence ejournal, artificial intelligence - law, policy, & ethics ejournal, generative ai ejournal, innovation in legal education ejournal, legal, medical & applied linguistics ejournal, libraries & information technology ejournal.
Top 150 Mechanical Engineering Research Topics [Updated]

Mechanical engineering is an intriguing discipline that holds significant sway in shaping our world. With a focus on crafting inventive machinery and fostering sustainable energy initiatives, mechanical engineers stand as pioneers in driving technological progress. However, to make meaningful contributions to the field, researchers must carefully choose their topics of study. In this blog, we’ll delve into various mechanical engineering research topics, ranging from fundamental principles to emerging trends and interdisciplinary applications.
How to Select Mechanical Engineering Research Topics?
Table of Contents
Selecting the right mechanical engineering research topics is crucial for driving impactful innovation and addressing pressing challenges. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the best research topics:
- Identify Your Interests: Start by considering your passions and areas of expertise within mechanical engineering. What topics excite you the most? Choosing a subject that aligns with your interests will keep you motivated throughout the research process.
- Assess Current Trends: Stay updated on the latest developments and trends in mechanical engineering. Look for emerging technologies, pressing industry challenges, and areas with significant research gaps. These trends can guide you towards relevant and timely research topics.
- Conduct Literature Review: Dive into existing literature and research papers within your field of interest. Identify gaps in knowledge, unanswered questions, or areas that warrant further investigation. Building upon existing research can lead to more impactful contributions to the field.
- Consider Practical Applications: Evaluate the practical implications of potential research topics. How will your research address real-world problems or benefit society? Choosing topics with tangible applications can increase the relevance and impact of your research outcomes.
- Consult with Advisors and Peers: Seek guidance from experienced mentors, advisors, or peers in the field of mechanical engineering. Discuss your research interests and potential topics with them to gain valuable insights and feedback. Their expertise can help you refine your ideas and select the most promising topics.
- Define Research Objectives: Clearly define the objectives and scope of your research. What specific questions do you aim to answer or problems do you intend to solve? Establishing clear research goals will guide your topic selection process and keep your project focused.
- Consider Resources and Constraints: Take into account the resources, expertise, and time available for your research. Choose topics that are feasible within your constraints and align with your available resources. Balancing ambition with practicality is essential for successful research endeavors.
- Brainstorm and Narrow Down Options: Generate a list of potential research topics through brainstorming and exploration. Narrow down your options based on criteria such as relevance, feasibility, and alignment with your interests and goals. Choose the most promising topics that offer ample opportunities for exploration and discovery.
- Seek Feedback and Refinement: Once you’ve identified potential research topics, seek feedback from colleagues, advisors, or experts in the field. Refine your ideas based on their input and suggestions. Iteratively refining your topic selection process will lead to a more robust and well-defined research proposal.
- Stay Flexible and Open-Minded: Remain open to new ideas and opportunities as you progress through the research process. Be willing to adjust your research topic or direction based on new insights, challenges, or discoveries. Flexibility and adaptability are key qualities for successful research endeavors in mechanical engineering.
By following these steps and considering various factors, you can effectively select mechanical engineering research topics that align with your interests, goals, and the needs of the field.
Top 50 Mechanical Engineering Research Topics For Beginners
- Analysis of the efficiency of different heat exchanger designs.
- Optimization of airfoil shapes for enhanced aerodynamic performance.
- Investigation of renewable energy harvesting using piezoelectric materials.
- Development of smart materials for adaptive structures in aerospace applications.
- Study of vibration damping techniques for improving vehicle ride comfort.
- Design and optimization of suspension systems for off-road vehicles.
- Analysis of fluid flow characteristics in microchannels for cooling electronics.
- Evaluation of the performance of different brake systems in automotive vehicles.
- Development of lightweight materials for automotive and aerospace industries.
- Investigation of the effects of friction stir welding parameters on joint properties.
- Design and testing of a small-scale wind turbine for rural electrification.
- Study of the dynamics of flexible multibody systems in robotics.
- Development of a low-cost prosthetic limb using 3D printing technology.
- Analysis of heat transfer in electronic packaging for thermal management.
- Investigation of energy harvesting from vehicle suspension systems.
- Design and optimization of heat sinks for electronic cooling applications.
- Study of material degradation in composite structures under various loading conditions.
- Development of bio-inspired robotic mechanisms for locomotion.
- Investigation of the performance of regenerative braking systems in electric vehicles.
- Design and analysis of an autonomous agricultural robot for crop monitoring.
- Optimization of gas turbine blade profiles for improved efficiency.
- Study of the aerodynamics of animal-inspired flying robots (bio-drones).
- Development of advanced control algorithms for robotic manipulators.
- Analysis of wear mechanisms in mechanical components under different operating conditions.
- Investigation of the efficiency of solar water heating systems.
- Design and optimization of microfluidic devices for biomedical applications.
- Study of the effects of additive manufacturing parameters on part quality.
- Development of assistive devices for individuals with disabilities.
- Analysis of the performance of different types of bearings in rotating machinery.
- Investigation of the feasibility of using shape memory alloys in actuator systems.
- Design and optimization of a compact heat exchanger for space applications.
- Study of the effects of surface roughness on friction and wear in sliding contacts.
- Development of energy-efficient HVAC systems for buildings.
- Analysis of the performance of different types of fuel cells for power generation.
- Investigation of the feasibility of using biofuels in internal combustion engines.
- Design and testing of a micro-scale combustion engine for portable power generation.
- Study of the mechanics of soft materials for biomedical applications.
- Development of exoskeletons for rehabilitation and assistance in mobility.
- Analysis of the effects of vehicle aerodynamics on fuel consumption.
- Investigation of the potential of ocean wave energy harvesting technologies.
- Design and optimization of energy-efficient refrigeration systems.
- Study of the dynamics of flexible structures subjected to dynamic loads.
- Development of sensors and actuators for structural health monitoring.
- Analysis of the performance of different cooling techniques in electronics.
- Investigation of the potential of hydrogen fuel cells for automotive applications.
- Design and testing of a small-scale hydroelectric power generator.
- Study of the mechanics of cellular materials for impact absorption.
- Development of unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) for environmental monitoring.
- Analysis of the efficiency of different propulsion systems in space exploration.
- Investigation of the potential of micro-scale energy harvesting technologies for powering wireless sensors.
Top 50 Mechanical Engineering Research Topics For Intermediate
- Optimization of heat exchanger designs for enhanced energy efficiency.
- Investigating the effects of surface roughness on fluid flow in microchannels.
- Development of lightweight materials for automotive applications.
- Modeling and simulation of combustion processes in internal combustion engines.
- Design and analysis of novel wind turbine blade configurations.
- Study of advanced control strategies for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
- Analysis of wear and friction in mechanical components under varying operating conditions.
- Investigation of thermal management techniques for high-power electronic devices.
- Development of smart materials for shape memory alloys in actuator applications.
- Design and fabrication of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) for biomedical applications.
- Optimization of additive manufacturing processes for metal 3D printing.
- Study of fluid-structure interaction in flexible marine structures.
- Analysis of fatigue behavior in composite materials for aerospace applications.
- Development of energy harvesting technologies for sustainable power generation.
- Investigation of bio-inspired robotics for locomotion in challenging environments.
- Study of human factors in the design of ergonomic workstations.
- Design and control of soft robots for delicate manipulation tasks.
- Development of advanced sensor technologies for condition monitoring in rotating machinery.
- Analysis of aerodynamic performance in hypersonic flight vehicles.
- Study of regenerative braking systems for electric vehicles.
- Optimization of cooling systems for high-performance computing (HPC) applications.
- Investigation of fluid dynamics in microfluidic devices for lab-on-a-chip applications.
- Design and optimization of passive and active vibration control systems.
- Analysis of heat transfer mechanisms in nanofluids for thermal management.
- Development of energy-efficient HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems.
- Study of biomimetic design principles for robotic grippers and manipulators.
- Investigation of hydrodynamic performance in marine propeller designs.
- Development of autonomous agricultural robots for precision farming.
- Analysis of wind-induced vibrations in tall buildings and bridges.
- Optimization of material properties for additive manufacturing of aerospace components.
- Study of renewable energy integration in smart grid systems.
- Investigation of fracture mechanics in brittle materials for structural integrity assessment.
- Development of wearable sensors for human motion tracking and biomechanical analysis.
- Analysis of combustion instability in gas turbine engines.
- Optimization of thermal insulation materials for building energy efficiency.
- Study of fluid-structure interaction in flexible wing designs for unmanned aerial vehicles.
- Investigation of heat transfer enhancement techniques in heat exchanger surfaces.
- Development of microscale actuators for micro-robotic systems.
- Analysis of energy storage technologies for grid-scale applications.
- Optimization of manufacturing processes for lightweight automotive structures.
- Study of tribological behavior in lubricated mechanical systems.
- Investigation of fault detection and diagnosis techniques for industrial machinery.
- Development of biodegradable materials for sustainable packaging applications.
- Analysis of heat transfer in porous media for thermal energy storage.
- Optimization of control strategies for robotic manipulation tasks in uncertain environments.
- Study of fluid dynamics in fuel cell systems for renewable energy conversion.
- Investigation of fatigue crack propagation in metallic alloys.
- Development of energy-efficient propulsion systems for unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs).
- Analysis of airflow patterns in natural ventilation systems for buildings.
- Optimization of material selection for additive manufacturing of biomedical implants.
Top 50 Mechanical Engineering Research Topics For Advanced
- Development of advanced materials for high-temperature applications
- Optimization of heat exchanger design using computational fluid dynamics (CFD)
- Control strategies for enhancing the performance of micro-scale heat transfer devices
- Multi-physics modeling and simulation of thermoelastic damping in MEMS/NEMS devices
- Design and analysis of next-generation turbofan engines for aircraft propulsion
- Investigation of advanced cooling techniques for electronic devices in harsh environments
- Development of novel nanomaterials for efficient energy conversion and storage
- Optimization of piezoelectric energy harvesting systems for powering wireless sensor networks
- Investigation of microscale heat transfer phenomena in advanced cooling technologies
- Design and optimization of advanced composite materials for aerospace applications
- Development of bio-inspired materials for impact-resistant structures
- Exploration of advanced manufacturing techniques for producing complex geometries in aerospace components
- Integration of artificial intelligence algorithms for predictive maintenance in rotating machinery
- Design and optimization of advanced robotics systems for industrial automation
- Investigation of friction and wear behavior in advanced lubricants for high-speed applications
- Development of smart materials for adaptive structures and morphing aircraft wings
- Exploration of advanced control strategies for active vibration damping in mechanical systems
- Design and analysis of advanced wind turbine blade designs for improved energy capture
- Investigation of thermal management solutions for electric vehicle batteries
- Development of advanced sensors for real-time monitoring of structural health in civil infrastructure
- Optimization of additive manufacturing processes for producing high-performance metallic components
- Investigation of advanced corrosion-resistant coatings for marine applications
- Design and analysis of advanced hydraulic systems for heavy-duty machinery
- Exploration of advanced filtration technologies for water purification and wastewater treatment
- Development of advanced prosthetic limbs with biomimetic functionalities
- Investigation of microscale fluid flow phenomena in lab-on-a-chip devices for medical diagnostics
- Optimization of heat transfer in microscale heat exchangers for cooling electronics
- Development of advanced energy-efficient HVAC systems for buildings
- Exploration of advanced propulsion systems for space exploration missions
- Investigation of advanced control algorithms for autonomous vehicles in complex environments
- Development of advanced surgical robots for minimally invasive procedures
- Optimization of advanced suspension systems for improving vehicle ride comfort and handling
- Investigation of advanced materials for 3D printing in aerospace manufacturing
- Development of advanced thermal barrier coatings for gas turbine engines
- Exploration of advanced wear-resistant coatings for cutting tools in machining applications
- Investigation of advanced nanofluids for enhanced heat transfer in cooling applications
- Development of advanced biomaterials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
- Exploration of advanced actuators for soft robotics applications
- Investigation of advanced energy storage systems for grid-scale applications
- Development of advanced rehabilitation devices for individuals with mobility impairments
- Exploration of advanced materials for earthquake-resistant building structures
- Investigation of advanced aerodynamic concepts for reducing drag and improving fuel efficiency in vehicles
- Development of advanced microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) for biomedical applications
- Exploration of advanced control strategies for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
- Investigation of advanced materials for lightweight armor systems
- Development of advanced prosthetic interfaces for improving user comfort and functionality
- Exploration of advanced algorithms for autonomous navigation of underwater vehicles
- Investigation of advanced sensors for detecting and monitoring air pollution
- Development of advanced energy harvesting systems for powering wireless sensor networks
- Exploration of advanced concepts for next-generation space propulsion systems.
Mechanical engineering research encompasses a wide range of topics, from fundamental principles to cutting-edge technologies and interdisciplinary applications. By choosing the right mechanical engineering research topics and addressing key challenges, researchers can contribute to advancements in various industries and address pressing global issues. As we look to the future, the possibilities for innovation and discovery in mechanical engineering are endless, offering exciting opportunities to shape a better world for generations to come.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
Digital SAT Suite of Assessments
SAT Practice and Preparation
From free practice tests to a checklist of what to bring on test day, College Board provides everything you need to prepare for the digital SAT.
Step 1: Now
Download and install the Bluebook app.
Step 2: Two Weeks Before Test Day
Take a full-length practice test in Bluebook.
Step 3: Five Days Before Test Day
Complete exam setup in Bluebook and get your admission ticket.
Step 4: On Test Day
Arrive on time (check your admission ticket).
Studying and Practice Tests
Practice tests.
Find full-length practice tests on Bluebook™ as well as downloadable linear SAT practice tests.
Khan Academy
Official Digital SAT Prep on Khan Academy ® is free, comprehensive, and available to all students.
Assistive Technology
Get information on how to practice for the digital SAT if you're using assistive technology.

My Practice
Take full-length digital SAT practice exams by first downloading Bluebook and completing practice tests. Then sign into My Practice to view practice test results and review practice exam items, answers, and explanations.
What to Bring and Do on Test Day
Find out everything you need to bring and do for the digital SAT.
SAT Student Guide (U.S.)
This guide provides helpful information for students taking the SAT during a weekend administration in Spring 2024.
SAT International Student Guide
A guide to the SAT for international students to learn how to prepare for test day. It covers the structure of the digital test, how to download the app and practice, information about policies, and testing rules.
SAT School Day Student Guide
Information about SAT School Day, sample test materials, and test-taking advice and tips.
SAT Practice Quick Start Guide
Learn how to practice for the SAT with this step-by-step guide.
Guía de inicio rápido de la práctica
Aprende cómo practicar para el SAT con esta guía de inicio rápido.
Why Should I Practice for the SAT?
This resource informs students about the benefits of practicing for the SAT and provides links to free practice resources.
¿Por qué debería practicar para el SAT?
Este folleto ofrece información sobre los beneficios de practicar para el SAT e incluye enlaces hacia recursos de práctica.
A Parent/Guardian's Guide to Official SAT Practice: Getting Your Teen Ready for the SAT
This resource provides parents and guardians with a schedule outline to help their child prepare for the SAT and includes links to free official practice materials.
A Parent/Guardian's Guide to Official SAT Practice: Getting Your Teen Ready for the SAT (Spanish)
Sat suite question bank: overview.
Leading the Science of Reading Revolution
New RAND Study on Core5
Post-Pandemic Acceleration
Science of Reading
For Every Student and Educator
Introducing Aspire
Professional Learning for Grades 4-8 Based on the Science of Reading
Leader in Science of Reading Literacy Solutions
Through a singular focus on literacy and a full spectrum of professional learning, curriculum, and embedded assessment solutions to support it, Lexia® helps more learners read, write, and speak with confidence.
Together, we can make real literacy change
U.S. national reading scores have shown little improvement for decades, leaving people asking: Is real literacy change possible? We know when instruction is grounded in the science of reading, 95% of students can learn to read and Lexia’s solutions are helping school districts achieve meaningful literacy gains.
All for Literacy
A lifetime of support for multilingual learners.
Learn more about Lexia solutions
Proven by Research
RAND ESSA Moderate Study Finds that Core5 Helps Students Accelerate Learning
This RAND ESSA Moderate Study finds Lexia® Core5® Reading helps students accelerate learning.
Lexia for You
Lexia provides science of reading-based professional learning and curriculum solutions to 6.7 million K-12 students and their 360,000 educators at more than 23,000 schools nationwide.
Learn more about Lexia for your state.
Proven by Users
Recognition Matters: Virginia Middle School Empowers Adolescent Readers With Data-Driven Instruction and Celebrations of Success
When Nancy Sindle discovered Lexia® PowerUp Literacy®, she knew it was the program that would make a difference. With a resource hub and real-time data for teachers, and engaging, age-appropriate content for students, see how PowerUp made a difference at Shirley Heim Middle School.
“What’s so great about Lexia PowerUp is the teachers can see where the kids are working. They can see the progress. They can see the lack of progress. They can see where students are struggling. The ability for a teacher to click on a name, and drill into the data, and then address where a student needs help with specific resources, no other program is like it.” —Nancy Sindle, Reading Specialist
Our Literacy Suite
Our science of reading-based professional learning, curriculum, and embedded assessment literacy solutions can be used together or individually to meet the learning needs for any student as well as teachers who support them.
Literacy Acceleration for Students in Grades Pre-K–5
Literacy Acceleration for Students in Grades 6-12
English Language Development for Emergent Bilingual students in Grades K–6
Professional Learning
Professional Learning for Educators
Professional Learning for Literacy Instructional Leaders
Professional Learning for Early Childhood Educators
Science of Reading-Based Professional Learning for All Educators Grades 4–8
Online Professional Learning for Educators Grades K–12
A Cambium Learning® Group Brand
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
NEW: Classroom Clean-Up/Set-Up Email Course! 🧽
57 Tips, Tricks, and Ideas for Teaching 6th Grade
Brilliant ideas from brilliant teachers (like you).
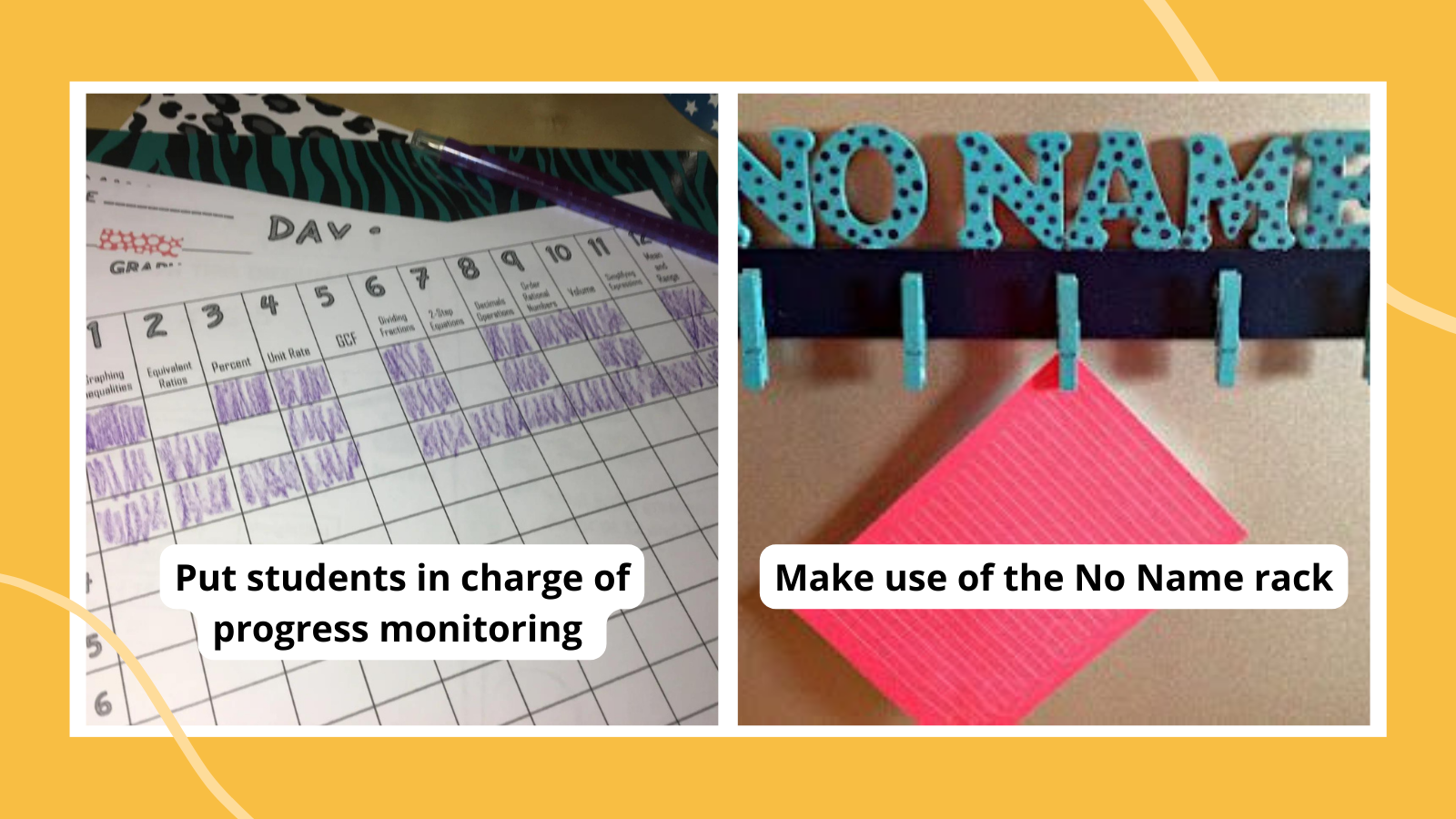
Ah, teaching sixth grade. Students fall into that sweet spot of demanding to be taken seriously but aren’t too cool to act out stories or play a group game. The wide range of sixth grade interests, abilities, and skills can be tricky to navigate, so we’ve gathered tips and ideas from our teacher community and around the web. You’ll love these ideas whether you’re a newbie to sixth grade or a longtime veteran.
Here are our favorite ideas for: The First Days of School, Classroom Management, Language Arts, Math, Social Studies, Science, and the Arts. Check it out!
The First Days of School
1. introduce yourself creatively.

There’s nothing quite like the very first moment of the first day of school when you’re teaching sixth grade. You stand at the front of the classroom looking at all those expectant faces for the very first time. Then you have your chance to introduce yourself to your students, to let them know who you are and what they can expect over the year to come. We love these creative ways to introduce yourself .
2. Start the year with an icebreaker
Get to know your students right away—they’re likely new to the school as well as your class. Check out our icebreakers for middle school students .
3. Ask thoughtful questions

Sixth graders (and most middle schoolers, for that matter) aren’t known for offering up their opinions or thoughts as readily as younger students. Come prepared with questions that are easy for kids to answer. Check out our favorite introduction questions for middle schoolers .
4. Ask silly questions too
You’d be surprised at the depth and complexity of your students’ answers to silly questions, like “Would you rather fight 100 duck-sized horses or one horse-sized duck?” Their responses will tell you so much about their personalities in the best ways. You may thank me later. Get a list of fun questions from our icebreaker question list .

5. Know how to handle student differences
Sixth graders often struggle to understand and deal with other kids’ behaviors. Here’s how one teacher handles it: “I often ask my sixth grade students, ‘Did he choose to be like that?’ If they are reasonable, they will say no, and then I say, ‘Well you have a choice about how you will respond to that, and that will show everyone what sort of person you are.’ End of matter.” — Amy K.
6. Establish a culture of kindness

Print these free downloadable posters to remind your students that kindness matters most of all.
7. Build your students’ social-emotional skills

Teaching sixth grade means building SEL skills. Use these read-alouds to talk about everything from kindness to courage to trying your best.
8. Give students jobs

Even big kids like jobs. And assigning jobs like keeping the classroom library organized or managing the day’s worksheets keeps your classroom operating smoothly. Check out this big list of classic and unique classroom jobs .
Tips for Classroom Management
Sixth graders are nothing if not squirrelly. But they will fall in line and will enjoy helping you manage the classroom. Here’s how to manage your gaggle of sixth graders.
9. Build routine
“It’s the nature of the middle school beast. You just have to get used to having to say the same thing day in and day out. We are two-thirds of the way through the school year and I still say, every day, ‘Turn around, look at the person behind you, take their paper, hand it up.’ Build routine and then stick to routine.” — Tracy S.
Also, check out these must-teach classroom procedures .
10. Be prepared for cyberbullying
Sixth graders seem young, but they’re no strangers to the internet—42% of kids have been bullied online. Make sure you know how to address cyberbullying. One of the best ways to do so is getting kids to report it and address it by being “upstanders.”
We also have a bunch of anti-bullying resources here .
11. Have a “No Name” rack

When you’re teaching sixth grade, you’re bound to get a few (read: a zillion) papers with no name on them. Here’s a place to put them!
Learn more: 3 rd Grade Thoughts
12. Include student photos in your sub folder
OK, this idea comes from a kindergarten blog, but we’ve known enough mischievous sixth graders who like to trade places when there’s a substitute. As part of your sub folder, include student photos along with their names so there’s no confusion about who’s who.
Also, check out these tips for preparing a tough class for a substitute teacher .
13. Remember that consequences don’t always need to be immediate
When I first started teaching middle school, I’d often get stuck feeling like I had to have the perfect response on the spot. What do you do when you turn around to see a student moving ceiling tiles with a wand he made from attaching 13 markers? (Note: I still don’t know. I think I would just laugh.)
Instead of putting pressure on yourself to respond perfectly in that moment, say something like, “I need to think about how to respond to this. I’ll let you know what I’ve decided at the beginning of class tomorrow.”
Also, check out these logical consequences for the classroom .
14. Laminate your checklists

“I gave my middle school art students a blank laminated flow chart titled ‘What do I do next?’ They used markers to fill in the instructions while I told them verbally and also filled out one on the board. When they asked what was next, I told them to check the chart. It worked great! They can erase the chart when moving to the next activity.” —Abbie B.
Check out our picks for the best laminators for teachers .
15. Help students make up for lost time
Put all the materials that an absent student will need upon return—homework assignments, worksheets, discussion notes—in one place. Then, when the student returns, they can quickly select the material they missed without disrupting class.
16. Use expert groups
Group students into four equal “Expert Groups” that are strategically organized into heterogeneous groups by ability. Then, give each group a topic to cover or a task to accomplish. After the experts have learned about their topic or completed their task, they move into new groups to share what they learned with one another. This idea comes from Go to Teach .
17. Get to know executive functioning
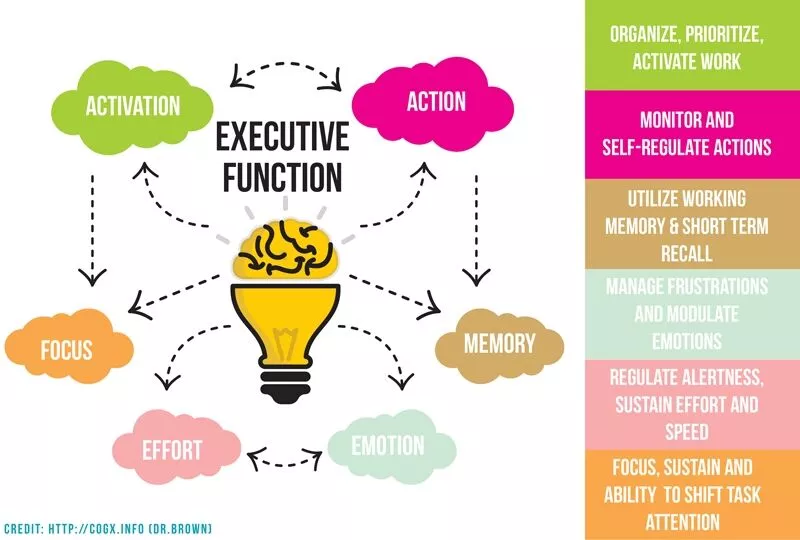
Waiting their turn, not acting on impulse, and handling setbacks are all important for navigating middle school. Here are the executive functioning skills students should have in each grade .
18. Have students monitor their goals
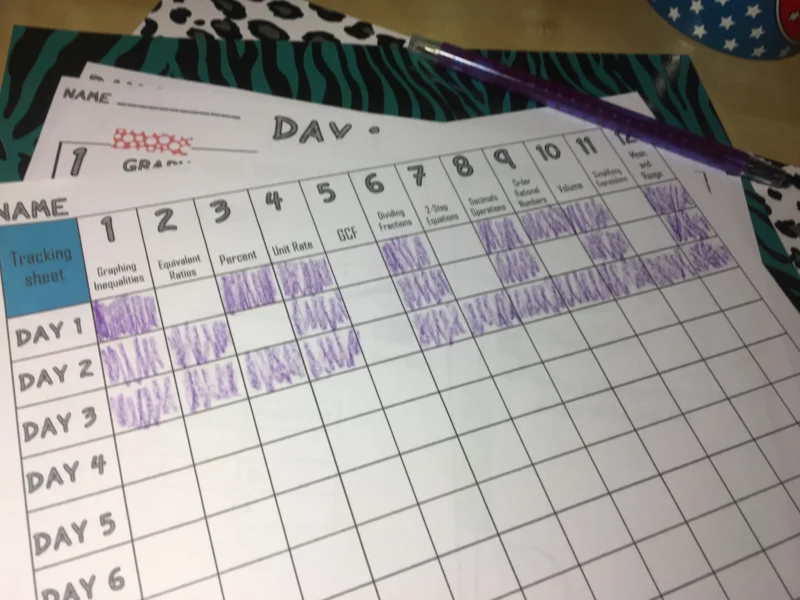
Speaking of executive functioning, when you’re teaching your sixth grade students a new topic or or having them review, have them practice goal setting and their own progress monitoring. Idea Galaxy Teacher shares one way to have students monitor their progress, not perfection, in math.
19. Plan to let kids move
If you don’t plan it into the lesson, sixth graders will fidget, squirm, or find an excuse to get out of their seats. Assigning them partners that require them to get up and move, passing out sticky notes that they can record answers on and post them on the wall, or having them stand during math fluency drills are all ways to keep them moving.
Also, here’s a tool kit of free printables to help get your students up and moving during the day.
20. Don’t shy away from a theme

“Kids will say silly things about a theme being childish, but if you watch them, they love it. Go with your gut if you choose a theme — your kids will love it.” —Laura K.
“My theme for teaching 6th grade was ‘Be More Awesome’ from Kid President . We watched his videos, set goals, and brainstormed ways to be more awesome as individuals, as a group, and in the community. We did service and writing projects, and the kids and parents loved it.” —Sharon R.
If you need inspiration, here are our favorite middle school classroom decorating ideas .
21. Celebrate more than meeting standards
“I make it a habit to celebrate everything. It is easy to become discouraged if your goals have to be ‘meet standards,’ ‘be proficient,’ ‘read at grade level,’ etc. In many classrooms, there are a few (or more!) kids who may not meet those goals during your year together. I tell my students that we celebrate moving forward. I try to recognize kindness and good character whenever possible, and I try to recognize those moments that matter in a different way. Whether it is having a pencil two days in a row, finishing a book, remembering 8 x 7 = 56, or using the word of the week in written or spoken language. In many ways, the encouragement buoys my spirits as much as the students’!” —Joy
22. Get ahead of the piles
Sixth-grade teacher blogger Joy in 6th uses a work basket to keep papers from piling up. Her rule: No double basketing! She makes sure she checks in each paper and takes care of it (grades it, returns it, etc.) so papers don’t get stashed or pile up. Set a consequence or reward for keeping that basket clean, because more papers are always on the way!
23. Bring your sense of humor

Teaching sixth grade will try your patience. Students will exercise their excuses, their lack of rationality, their insistence on fairness, and developing a sense of justice. The best way to deal with it is a healthy dose of humor. To start, find the funny in the things your students say (including the names they give you), and bring in comics and memes to reinforce your lessons and directions. Also, check out these cheesy teacher jokes , as well as math jokes , science jokes , and history jokes .
Tips for Language Arts
ELA is a sweet spot for sixth graders, who are young enough to enjoy read-alouds and old enough to have deep discussions.
24. Give students choice in literature circles

Sixth graders love literature circles, which encourage strong discussion and ownership over reading. Build choice into your literature circles by providing them with a few novel choices and a blank calendar to plan out their reading. Check out these life-changing books for middle school and classic middle-grade books .
25. Introduce short stories—we have over 50
When teaching sixth grade, it can be a challenge to get your students interested in reading. The thought of tackling a thick novel can be overwhelming, especially during distance learning. These short stories for middle school are always a great choice .
26. Blackout poetry is the best
Blackout or erasure poetry is not only fun for kids, it’s super easy to scaffold for students who need more of a challenge or a little more help. Check out this blackout poetry how-to guide with examples and ideas . (P.S. It’s also a great second life for your torn and battered books!)
27. Include other poetry too
It can be hard to know which poems will spur your sixth graders into deep, meaningful discussion and which will leave them yawning. So we asked experienced teachers to share their favorite poems that always get a reaction, even from tweens. Check out the list of poems for middle school here .
28. Build vocabulary
Sixth graders are exposed to more and more academic vocabulary, or words that are related to specific topics. Think: adjacent , metamorphize , isotope , Mesopotamia . Teach these words, then have students work with them using visuals and games, with ideas from MiddleWeb .
Learn more: EAP Foundation
29. Introduce students to Socratic seminar
Sixth graders are ready to start more formal discussions of open-ended questions. Socratic seminars require work on the front end to create the questions and prepare students, but they’re worth it when students really get into rich discussion. Here’s an easy way to do Socratic seminar .
30. Give students choice in how to present their work
Sometimes you’ll want a traditional writing assignment to build students’ analytical skills. Other times, you may want to give students options. “I let my students work in groups and read part of a chapter and then teach it to the class. They do various things such as present graphic organizers, skits, raps, acrostics, etc.” —Brittney R.
31. Do close readings of movies
Help students apply the same critical thinking and analysis they do during close reading to movies by using short movies and TV clips. Have students watch the movie clips with purpose and spend time analyzing the clips in depth. Here’s more on the idea from MiddleWeb .
32. Stock your library with graphic novels

Graphic novels are a great way for any sixth grader to get interested in a new story. They’re particularly helpful for students who struggle with reading and can use the pictures to do the high-level thinking required in middle school. “Graphic novels help struggling readers and also help with writing.” —Meaghan G.
Some great graphic novels to use with sixth graders are Bone: Out From Boneville by Jeff Smith, Drama by Raina Telgemeier, and Lewis & Clark by Nick Bertozzi. Also, check out our full list of middle school graphic novels .
33. Read aloud
Sixth graders still love to hear a read-aloud. Take advantage of this to read aloud a book that inspires your sixth graders to expand their world, and build empathy for characters similar to and different from themselves. Here’s a list of great read-alouds for 6th grade .
Tips for Math
Sixth graders need as much math connected to their actual lives as possible. Use these strategies to reactivate their math knowledge and keep them engaged.
34. Take up real-world math problems
Middle schoolers need to see math connected to the real world. Frame math lessons in actual scenarios with these lessons from PBS that will have students using ratios and proportions in a vending machine, or measuring variability with data from wildfires.
35. Post the essentials
Check out these sixth grade math essentials posters from Teachers Pay Teachers (free). To start, project the posters at the start of a lesson. Then have hand-outs ready for students who need reminders.
36. Get graphing dry-erase boards
Check out these graphing dry-erase boards to engage students in graphing work.
37. Build in writing time
Whether your school requires it or not, having your math students write not only builds interdisciplinary connections but helps sharpen literacy skills (which benefits everyone!). One teacher I know has students write children’s books using geometry concepts with accuracy, and then they actually read them to K-2 students.
38. Keep math centers moving
When teaching sixth grade, math centers are a great way to differentiate your classroom and engage sixth graders in math practice. For example, here’s how Middle School Math Man organizes math centers.
39. Assign an unforgettable math project
Every sixth grader is wondering what they’d do with a million dollars, so let them try it out with The Million Dollar Project .
40. Make math problems relevant
Ask your colleagues, staff, and administration how they’re using math in what they’re currently doing or planning. Then have your students help out! “Mr. Reynolds is making a sweet potato casserole for the English department Thanksgiving potluck and wants to make sure he can feed everyone. If he’s using a 9 x 13-inch pan, what size pieces should he cut to feed all 12 teachers in the English department?” Have them make a video with their answer to send to Mr. Reynolds. Word problems feel so different when they’re real .
41. Have math resources on hand
Sixth grade math covers a lot of ground, so you’ll want a lot of help at your fingertips. “We use Illustrated Math, the Georgia State resources, and EngageNY. Also brush up on ratios.” —Ingrid S.
Check out this list of our favorite math supplies for middle school .
Tips for Social Studies
From ancient Mesopotamia to government, sixth grade social studies covers a lot of ground.
42. Bring GRAPES to your ancient civilizations lesson
Mr. and Mrs. Social Studies help students understand the main elements of ancient civilizations with the acronym GRAPES:
- Achievements
Incorporate the GRAPES structure into your lessons to make sure students have all the essential info.
43. Teach the branches of government
More than ever, our country is examining the laws that were put in place to protect and guide us. It can be overwhelming, however, to explain exactly how that works. To help you give your lesson plans a boost, we’ve put together this list of resources that help teach kids about the branches of government.
44. Start the movie projector
Films are a great way to make history come alive or offer another representation of a favorite novel when you’re teaching sixth grade. Some middle school movie recommendations from our community: Remember the Titans , The Color of Freedom , Pay It Forward , Rudy , Mad Hot Ballroom , October Sky , Stand and Deliver , Wild Hearts Can’t Be Broken , and Mr. Holland’s Opus. All these films clearly present characters and themes that your students will remember long after middle school. Also, check out this big list of educational Netflix shows .
45. Get ready to go back in time
Here’s how one of our community members handled teaching ancient civilizations, a topic that can seem out of touch for sixth graders: “Students created cubes (made of poster board and cut and glued with hot glue) to create an informational cube about Egyptians. Then, students made commercials to get ‘tourists’ to visit their locations and they made brochures. For ancient Egypt, they make a sarcophagus. And for the Renaissance, they make a medieval feast.” —Brittney R.
46. Use online learning
There are some amazing websites out there for teaching sixth grade social studies lessons. Check out this big list of social studies website favorites .
47. Introduce debate
“We do a debate between the Patriots and the Loyalists (with costumes). The kids LOVED this activity.” —Sherrie R.
Check out this big list of debate topics for middle school .
Tips for Science
Sixth graders are budding scientists—curious about everything and just starting to work on more advanced experiments. Just keep a close eye on them when the Bunsen burners are out.
48. Bring SpongeBob into science class

Middle school is likely the first time that students are in a lab. Teach lab safety with some humor and a friendly sponge. Use this SpongeBob science safety lesson from Middle School Science and we’re sure students will refer back to it all year.
49. Conduct appropriate science experiments

Like kids of every age, sixth grade students love hands-on science! Teachers do, too, because when you’re teaching sixth grade, the learning is a lot more meaningful when students see concepts in action. This roundup of sixth grade science projects and activities has a little something for everyone — from biology and ecology to physics and chemistry.
50. Schedule labs first
“Try mixing up your teaching style by introducing topics with a lab first. Let the students get a hands-on feel for the material before any type of lecture is used.” —Christie E.
51. Pull up a science website
Science is exciting. Unfortunately, students may say they don’t like science because textbook lessons can be a little dry. Whether you’re in the classroom or teaching online, finding the right resources can bring these complex concepts to life! To help you get started, here’s a list of the best science websites for middle school .
52. Read the newspaper in science class
“Throw in current events as much as possible! My students love when a topic we cover relates to something happening now … for example, when we touched on viruses, we took a day to discuss the truths and myths of Ebola!” –Christie E.
Tips for the Arts
Sixth graders are all about self-expression. They’re at the start of that middle school journey. Use art to help them understand and express themselves.
53. Give them the stage
“I use a great company called Bad Wolf Press for plays. They sell short musicals (curriculum based). They are funny, and you can be as simple as you like with costumes and scenery.” —Rhona C.
Plus check out these steps to create your own readers theater scripts.
54. Incorporate classical music into art class
Have students chill out or merge art and music by having them draw along to a score. Spread out butcher paper or give each student their own piece of paper and let the music flow. Here’s our favorite classical music for the classroom .
55. Social media is your best friend for artsy ideas

Instagram in particular is a great resource for collecting ideas when you’re teaching sixth grade art classes. My favorite? Lambie_k on Instagram. I mean, just look at this backpack-wearing narwhal. The ocean swirls! The northern lights!
56. Get crafty
Even sixth graders like to make crafts like duct tape hearts for Valentine’s Day, flower pens for Mother’s Day, or 3D shaped flip-books in math. Also, it’s even better if crafts overlap with other concepts!
57. But don’t assume they can handle glitter
“My sixth graders cannot handle glue or glitter. Found that out the hard way this year.” —Sharon R.
Do you have any great tips for teaching sixth grade? Share them in the comments below!
For more articles like this, be sure to subscribe to our newsletters to find out when they’re posted.

You Might Also Like

8 FREE Kindness Posters to Help Spread the Love in Your Classroom
Because kindness matters most of all. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
- v.2013; 2013

Lavender and the Nervous System
Peir hossein koulivand.
1 Shefa Neuroscience Research Center, Tehran 1996835911, Iran
Maryam Khaleghi Ghadiri
2 Klinik und Poliklinik für Neurochirurgie, Universitätsklinikum Münster, 48149 Münster, Germany
3 Razavi Neuroscience Research Center, Mashhad 9198613636, Iran
4 Epilepsy Research Center, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, 48149 Münster, Germany
5 Institut für Physiologie I, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, 48149 Münster, Germany
6 Department of Neurology, 48149 Münster, Germany
Lavender is traditionally alleged to have a variety of therapeutic and curative properties, ranging from inducing relaxation to treating parasitic infections, burns, insect bites, and spasm. There is growing evidence suggesting that lavender oil may be an effective medicament in treatment of several neurological disorders. Several animal and human investigations suggest anxiolytic, mood stabilizer, sedative, analgesic, and anticonvulsive and neuroprotective properties for lavender. These studies raised the possibility of revival of lavender therapeutic efficacy in neurological disorders. In this paper, a survey on current experimental and clinical state of knowledge about the effect of lavender on the nervous system is given.
1. Introduction
The genus Lavandula is native to the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea and southern Europe through northern and eastern Africa and Middle Eastern countries to southwest Asia and southeast India. It includes more than 30 species, dozens of subspecies, and hundreds of hybrids and selected cultivars.
The different varieties of this plant range in height from 9 inches to 3 feet, although some may grow taller with age. Lavender are divided into four main categories: L. angustifolia , commonly known as English Lavender, is a frost hardy species that has many pretty cultivars, habit, and blossom color (formerly known as L. vera or L. officinalis ); L. stoechas is a large plant with greenish-grey foliage and late blooming with a very strong odor (sometimes known as French lavender); L. latifolia , a Mediterranean grass-like lavender; and L. intermedia , which is a sterile cross between L. latifolia and L. angustifolia . The various lavenders have similar ethnobotanical properties and major chemical constituents [ 1 ].
The main constituents of lavender are linalool, linalyl acetate, 1,8-cineole B -ocimene, terpinen-4-ol, and camphor. However, the relative level of each of these constituents varies in different species [ 1 , 2 ]. Lavender oil, obtained from the flowers of Lavandula angustifolia (Family: Lamiaceae) by steam distillation, is chiefly composed of linalyl acetate (3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3yl acetate), linalool (3,7-dimethylocta-1,6-dien-3-ol), lavandulol, 1,8-cineole, lavandulyl acetate, and camphor. Whole lavender oil and its major components linalool and linalyl acetate are used in aromatherapy. The major components of lavender oil were identified as 51% linalyl acetate and 35% linalool measured by gas chromatography and gas chromatography-linked Fourier Transform Infrared analysis [ 1 – 3 ].
Most commonly lavender is recommended for oral administration. However, it is also being employed in aromatherapy (inhalation of lavender; [ 4 , 5 ]), aromatherapy massage, dripping oil [ 6 ], and bathing [ 7 ]. Unlike many other essential oils used in aromatherapy, lavender oil is often applied undiluted to the skin. The study of Jager et al. [ 8 ] suggested that essential oils and their components are rapidly absorbed through the skin. Linalool and linalyl acetate were shown to be rapidly detected in plasma after topical application with massage, reaching peak levels after approximately 19 min [ 8 ]. At least since medieval periods, lavender has been a source of drugs as well as perfumes, soaps, flavorings, and crafts. Lavender has a long history of medicinal use and is suggested to possess anticonvulsant, antidepressive, anxiolytic, sedative, and calming properties [ 1 , 9 – 12 ]. Lavender also prescribed by some medieval physicians such as Ebn-e-sina and Razi for treatment of epilepsy and migraine attacks. Furthermore, lavender is considered beneficial in treatment of pain and tremor [ 9 – 12 ].
In recent years, several animal and human investigations have indeed evaluated traditional medical remedies of lavender using modern scientific methods. These studies raised the possibility of revival of lavender therapeutic efficacy in neurological disorders on the basis of evidence-based medicine [ 12 , 13 ].
2. Animal Studies
Several animal experiments suggest anxiolytic, sedative, analgesic, and anticonvulsive and neuroprotective properties for lavender [ 14 ]. It was shown that lavender possesses an anticonflict effect in mice [ 15 ]. Continuous exposures to lavender essential oils for 7 days significantly inhibited anxiety- and depression-like behaviors tested by elevated plus-maze and forced swimming tests in rats [ 16 ]. Lavender oil produced significant antianxiety effects in the Geller conflict and the Vogel conflict tests in mice. Linalool, a major constituent of lavender oil, produced significant anticonflict effects in the Geller and Vogel tests; findings that were similar to those of lavender oil [ 17 ]. Effects of lavender oil were compared with chlordiazepoxide, as a reference anxiolytic, on open-field behavior in rats. Lavender oil exhibited antianxiety properties similar to those of chlordiazepoxide [ 18 ]. Anxiolytic effect of lavender was also compared with diazepam in elevated plus-maze test in the Mongolian gerbil. Exposure to lavender odor showed an anxiolytic profile similar to diazepam in female gerbils [ 19 ]. Investigation of the effects of inhaled linalool on anxiety, aggressiveness, and social interaction in mice showed anxiolytic properties in the light/dark test, increased social interaction, and decreased aggressive behavior [ 20 ].
Local anesthetic effect of lavender and its constituents (linalool and linalyl acetate) is reported in both in vivo and in vitro animal experiments [ 21 ]. In the rabbit conjunctival reflex test, treatment with a solution of lavender essential oil as well as with linalyl acetate or linalool induced a dose-dependent enhancement in the number of stimuli necessary to provoke the reflex [ 21 ]. The methanolic extract of lavender (200–600 mg/kg) dose-dependently produced sedative effects in mice. This was indicated by the relatively longer time for the reestablishment and number of head dips during the traction and hole-board tests [ 22 ]. To evaluate the sedative effects of lavender, the immobility of overagitated mice induced by caffeine was ascertained after the inhalation of lavender. Lavender odor significantly increased the immobile state in mice treated with caffeine [ 23 ]. Exposure of mice to lavender odor in a dark cage resulted in depression of motor activity, whilst the plasma levels of linalool rose in proportion to the length of exposure [ 24 ]. The intraplantar injection of capsaicin produced an intense and short-lived licking/biting response in mice. The capsaicin-induced nociceptive response was reduced significantly by intraplantar injection of lavender and linalool [ 25 ]. Either oral administration or inhalation of lavender essential oil significantly reduced the chemical and thermal pain without evidence of central adverse effects in adult mice. Opioidergic neurotransmission seems to be involved in lavender-induced analgesia since only naloxone pretreatment prevents its effect in writhing test. Cholinergic neurotransmitter system also appears to play a role in lavender analgesia. The blockade of muscarinic and nicotinic receptors prevented analgesic effects of lavender [ 26 ].
Exposure to lavender effectively improved spatial memory deficits induced by dysfunction of the cholinergic system [ 27 ]. Administration of lavender in animal model of Alzheimer's disease (rat model established by intracerebroventricular injection of A β 1) effectively reversed spatial learning deficits [ 28 ]. Repeated application of lavender in mice demonstrated a more rapid sleep onset with longer duration of sleep [ 29 ]. Anticonvulsant effect for hydroalcoholic extract of lavender was reported against chemoconvulsant-induced seizures in male mice. Lavender inhibited the onset, shortened the duration, and reduced the intensity of seizure attacks [ 30 ]. Anticonvulsant effects of lavender together with diminution in spontaneous activity, when combined with other narcotics, have been reported [ 31 , 32 ]. Inhalation of lavender was also noted to inhibit convulsion induced by pentylenetetrazol, nicotine, or electroshock in mice [ 33 ]. Linalool, one of the major components of lavender oil, has been shown to inhibit the convulsion induced by pentylenetetrazol and transcorneal electroshock in different animal models [ 34 , 35 ], an effect that may induce via a direct interaction with the glutamatergic NMDA subreceptor as well as GABA A receptors [ 36 ]. The neuroprotective effect of lavender oil on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury was investigated in mice. Focal cerebral ischemia was induced by the intraluminal occlusion. An aqueous extract of lavender has been shown to diminish glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in rat pups cerebellar granular cell culture [ 37 ]. Lavender oil significantly decreased neurological deficit scores, infarct size, and the levels of mitochondria-generated reactive oxygen species and attenuated neuronal damage in focal cerebral ischemia induced by the intraluminal occlusion in mice [ 38 ].
3. Mechanisms of Action of Lavender in the Nervous System
Several investigations were performed to clarify the mechanism of action of lavender in neuronal tissues. Lavender inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory reaction in human monocyte THP-1 cells effect, which might be associated with the expression of HSP70 [ 39 ]. Antioxidant and relatively weak cholinergic inhibition was reported for lavender [ 38 , 40 ] and linalool [ 41 – 43 ]. Linalool inhibited acetylcholine release and alters ion channel function at the neuromuscular junction [ 44 ]. These findings indicate that several targets relevant to treatment of Alzheimer's disease; anticholinergic, neuroprotective, and antioxidant activities could be found in lavender. The neuroprotective effect of lavender oil against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury is suggested to be attributed to its antioxidant effects [ 38 ]. Evaluation of the effects of lavender oil on motor activity and its relationship to dopaminergic neurotransmission revealed that intraperitoneal application of lavender significantly increased rotarod activity and enhanced dopamine receptors subtype D 3 in the olfactory bulbs of mice [ 45 ]. Lavender oil is also suggested to modulate GABAergic neurotransmission, especially on GABA A receptors, and enhance inhibitory tone of the nervous system [ 29 , 36 , 46 ]. Cholinergic system is suggested to play a role in lavender analgesic, antianxiety, antidepression, and anticonvulsant effects of lavender [ 16 , 26 , 33 ].
Fos is a nuclear transcription factor protein encoded by an immediate early gene c-fos, and it is an early marker of neuronal activation. It serves as a transcriptional factor controlling the expression of genes expected to be involved in effective adaptation to certain situations. Lavender oil reduced c-fos expression in paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus [ 18 ]. Lavender oil inhibited dose-dependently the histamine release and anti-DNP IgE-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion from peritoneal mast cells in mice [ 47 ]. It has been shown that lavender oil inhibited the sympathetic nerves innervating the white and brown adipose tissues and adrenal gland and excites the parasympathetic gastric nerve [ 48 , 49 ]. Odor of lavender oil, and especially its component linalool, affects autonomic nerves probably through a histaminergic response, decreases lipolysis and heat production (energy consumption), and increases appetite and body weight in rats [ 50 ]. Lavender may inhibit the sympathetic nerve activity and lipolysis through activation of H 3 -receptors. The hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus and histamine neurons are involved in the lipolytic responses to the lavender oil, and tyrosine phosphorylation of BIT (a brain immunoglobulin-like molecule with tyrosine-based activation motifs, a member of the signal-regulator protein family) is implicated in the relevant signaling pathways [ 50 ].
4. Human Studies
Although there is considerable debate about whether lavender species have a significant clinical potential either alone or as additives to other substances, many human studies support its effectiveness in different neurological and psychological disorders. Lavender was used predominantly in oral administration, aromatherapy, or massage in several clinical studies, and many benefits were claimed for use in such a manner. In addition to psychological effects, aromatherapy is thought to be therapeutically effective due to physiological effects of the inhaled volatile compounds. It is believed that inhaled lavender act via the limbic system, particularly the amygdala and hippocampus [ 1 ]. Linalool and linalyl acetate are rapidly absorbed through the skin after topical application with massage and are thought to be able to cause central nervous system depression [ 8 ].
4.1. Anxiety, Depression, and Lavender
Lavender was used in the treatment of anxiety disorders and related conditions. Three clinical trials were identified which investigated the efficacy of oral lavender oil preparation (silexan; an essential oil produced from lavender flowers by steam distillation), administered once daily at a dose of 80 mg/day, in subsyndromal (mixed) anxiety disorder and generalized anxiety disorder as well as in restlessness and agitation. Anxiolytic effect of lavender was superior to placebo in 221 patients suffering from anxiety disorder. In addition, lavender improved associated symptoms such as restlessness, disturbed sleep, and somatic complaints and had a beneficial influence on general well-being and quality of life [ 51 , 52 ]. In line with this study, the efficacy of a 6-week-intake of oral lavender oil preparation (Silexan, 80 mg/day), compared to lorazepam, was investigated in adults with generalized anxiety disorder. This study indicates that lavender effectively ameliorates generalized anxiety comparable to 0.5 mg/daily lorazepam [ 53 ]. Alleviation of anxiety and mood improvement were reported in thirty-six patients admitted to an intensive care unit, who received lavender oil (diluted to 1% concentration) aromatherapy [ 54 ]. The same results were reported for fourteen female patients who were being treated with chronic hemodialysis [ 55 ]. A survey in a long-stay neurology in-patient department showed increased mood scores and reduced psychological distress following aromatherapy with lavender accompanied with tea tree and rosemary [ 56 ]. An investigation on the effect of lavender aromatherapy (diluted to 2% concentration) on anxiety and depression in the high risk postpartum woman showed a significant improvement of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale and Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale after four consecutive weeks of administration of lavender [ 57 ]. Lavender odor reduced anxiety in dental patients; however, it has no effect on dental anxiety surrounding thoughts of future dental visits [ 58 , 59 ]. Testing visual analog scales to assess anxiety, it is suggested that lavender is a simple, low-risk, cost-effective intervention with the potential to improve preoperative anxiety [ 60 ]. Orally administered lavender capsules contained 100 or 200 μ L of organic Lavandula angustifolia oil were tested on responses to anxiety-provoking film clips. In this study, evaluation of State Trait Anxiety Inventory, mood, positive and negative affect scale, heart rate, and galvanic skin response as well as heart rate variation after administration of lavender suggests that lavender has anxiolytic effects in humans suffering from low anxiety, but these effects may not extend to conditions of severe anxiety [ 61 ]. A clinical investigation points to antidepressive effect of lavender. Adjuvant therapy of lavender tincture (1 : 5 in 50% alcohol; 60 drops/day) and imipramine (100 mg/daily) in treatment of forty-eight adult outpatients suffering from mild-to-moderate depression led to a better and earlier improvement. Anticholinergic side effects of imipramine, such as dry mouth and urinary retention, were observed less often when lavender administered with impramine. These results suggest that lavender is an effective adjuvant therapy in combination with imipramine, resulting in a superior and quicker improvement in depressive symptoms [ 62 ].
4.2. Neuroimaging and Lavender
Evaluation of brain regional metabolic activity with positron emission tomography in ten healthy women after the lavender odor stimulus demonstrated neuronal enhancement in the orbitofrontal, posterior cingulate gyrus, brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum and reduction of activity in the pre/post-central gyrus and frontal eye field. These findings indicate that lavender aromatherapy in addition to relaxation effect may enhance arousal level in some subjects [ 63 ]. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), significant activation in major olfactory brain structures, including the primary olfactory cortex, entorhinal cortex, hippocampus and parahippocampal cortex, thalamus, hypothalamus, orbitofrontal cortex, and insular cortex and its extension into the inferior lateral frontal region was reported in nineteen healthy participants after application of 10% lavender diluted in dipropylene glycol [ 64 ]. Cortical perfusion increment after sensorial stimulation with lavender was evaluated by single photon emission computed tomography in ten healthy adults. A significant activation was observed in gyrus rectus, orbitofrontal cortex, and superior temporal cortical areas. A slight perfusion increase also existed in middle temporal and parieto-occipital regions [ 65 ]. Lavender odor was delivered via the orthonasal (odor perceived through the nose) and retronasal (odor perceived through the mouth) routes and brain response was measured with fMRI in 20 subjects. In addition to the activation at the base of the central sulcus by lavender, retronasal stimulation with odor resulted in a significant peak in the ventral insula compare to orthonasal application. In contrast, orthonasal application yielded a peak in the right caudate nucleus that approached significance in comparison to retronasal way [ 66 ].
4.3. Electroencephalography (EEG) and Lavender
It has been suggested that some neurological disorders with significant EEG changes, such as epilepsy, may be benefited by aromatherapy [ 10 , 11 ]. Lavender affects human EEG pattern accompanied with its anxiolytic effect. It is reported that inhalation of lavender (diluted to 10% concentration) for 3 minutes increases alpha power of EEG as decreases anxiety and brings the subject to a better mood in 40 healthy adults [ 67 ]. Increases in theta (4–8 Hz) and alpha (8–13 Hz) wave activity may cause a range of general relaxation effects and can be induced by chemical and nonchemical techniques [ 68 ]. It has been shown that during inhalation with lavender (diluted to 10% concentration) in 20 participants, the power of theta and alpha wave activities were significantly increased in all brain regions. This study found relaxing effects with increases of alpha wave activities after administering lavender; indicating the EEG evidence of relaxation by lavender aromatherapy [ 69 ]. Furthermore, lavender aromatherapy is reported to produces EEG patterns characteristics of subjects' feeling comfortable [ 70 ]. Lavender oil administered in an aroma stream shows modest efficacy in the treatment of agitated behavior in patients with severe dementia [ 71 ].
Resting frontal EEG asymmetry is suggested to be a predictor of symptom change and end-state functioning in patients with social anxiety disorder who undergo efficacious psychological treatment [ 72 ]. Evaluation of frontal EEG asymmetry shifting in thirty-nine adult participants and twenty-seven full-term newborns revealed greater relative left frontal EEG activation (associated with greater approach behavior and less depressed affect) after aromatherapy with lavender. Further studies in these volunteers indicate that lavender may induce left frontal EEG shifting in adults and infants, who show greater baselines relative to right frontal EEG activation. It is suggested that both infants and adults with greater relative right frontal EEG activation at baseline may be more affected by lavender application [ 73 ].
4.4. Sleep and Lavender
Lavender has been suggested as an excellent natural remedy to treat insomnia and improve the sleep quality. Single-blind randomized studies investigated the effectiveness of lavender odor on quality of sleep showed that lavender improved the mean scores of sleep quality in fifteen healthy students [ 74 ], in sixty-four ischemic heart disease patients [ 75 ], and in thirty-four midlife women with insomnia [ 76 ]. Ten individuals with insomnia, verified by a score of 5 or more on the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), were treated with lavender odor. Six to eight drops of lavender oil added each night to the cartridge improved the PSQI score by −2.5 points. More notable improvements were seen in females and younger participants. Milder insomnia also improved more than severe ones [ 77 ]. Oral lavender oil preparation (80 mg/day) showed a significant beneficial influence on quality and duration of sleep and improved general mental and physical health without causing any unwanted sedative or other drug specific effects in 221 patients suffering from subsyndromal (mixed) anxiety disorder [ 52 ]. A mixture of essential oils including lavender, basil, juniper, and sweet marjoram is shown to reduce sleep disturbance and improve overall well-being in older patients [ 78 ]. In a clinical study on four benzodiazepine dependent geriatric patients, there was a significant decrease in sleep duration by stopping benzodiazepine treatment, which was restored to previous levels by substitution of aromatherapy with lavender oil. This study suggested that ambient lavender oil might be used as a temporary relief from continued medication for insomnia and reduces the side-effects of these drugs [ 79 ]. In a study on thirty-one hospitalized patients, administration of lavender odor showed a trend towards an improved quality of daytime wakefulness and more sustained sleep at night [ 80 ]. In contrary to these data, it should be noted that the use of aromatherapy massage with lavender oil has no beneficial effect on the sleep patterns of children with autism attending a residential school. It was suggested that this therapy may show greater effects in the home environment or with longer-term interventions [ 81 ].
4.5. Pain and Lavender
Lavender reported to be useful in the treatment of acute as well as chronic or intractable pain [ 82 ]. It has been shown that foot massage using lavender essential oil in 100 ICU patients of whom 50% were receiving artificial ventilation was effective in lowering blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, wakefulness, and pain [ 83 ]. Treatment of recurrent aphthous ulceration with lavender oil in 115 patients revealed a significant pain relief mostly from the first dose, ulcer size reduction, increased rate of mucosal repair, and healing within three days of treatment compared to baseline and placebo groups [ 84 ]. Stress level, the bispectral index (a promising parameter for monitoring sedation), and pain intensity of needle insertion were significantly reduced after receiving oxygen with a face mask coated with lavender oil for five minutes compared with the control in thirty volunteers [ 85 ]. Aromatic oil massage with essential oils blended with lavender, clary sage, and marjoram in a 2 : 1 : 1 ratio in forty-eight outpatients with primary dysmenorrhea alleviated the pain and reduced the duration of dysmenorrhea [ 86 ]. Aromatherapy by using lavender essence was also reported as a successful and safe complementary therapy in reduction of pain after the cesarean section in 200 term pregnant women [ 87 ] and after episiotomy in 60 primiparous women [ 88 ] as well as in perineal discomfort following normal childbirth in 635 women [ 89 , 90 ]. It has been shown that lavender aromatherapy through an oxygen face mask with two drops of 2% lavender oil can be used to reduce the demand for opioids in twenty-five patients after immediate postoperative period of breast biopsy surgery [ 91 ] and for other analgesics in fifty-four patients undergoing laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding [ 92 ]. In contrast to these observations, the aroma of essential oil of lavender ease anxiety but not perception of pain during elective cosmetic facial injections of botulinum toxin for the correction of glabellar wrinkle [ 93 ]. A course of eight-session manual acupressure with lavender oil (3% lavender oil; used as the massage lubricant) over a three-week period in patients with nonspecific subacute neck pain (32 patients) or low back pain (61 patients) significantly alleviated the neck and back pain and improved movements of the cervical and lumbar spine [ 94 , 95 ]. Inhalation of lavender essential oil is suggested to be an effective and safe treatment modality in acute management of migraine headaches. Forty-seven patients suffering from migraine attacks reported significant reduction of pain severity and associated symptoms after fifteen minutes inhalation of lavender oil (2-3 drops of the lavender essential oil rubbed onto their upper lip) in the early stages of the attacks [ 5 ]. Aromatherapy massage with lavender accompanied with rose geranium, rose, and jasmine in almond and primrose oils once a week for 8 weeks is reported as an effective treatment of menopausal symptoms such as hot flushes, depression, and pain in climacteric women [ 96 ].
4.6. Cognition and Lavender
The use of aromas to modulate affect and mood has been reported by several ancient and medieval physicians [ 9 – 12 ]. The positive effects of different medicinal plants as cognition enhancers have been reported [ 97 ]. To assess the olfactory impact of the essential oils of lavender on cognitive performance and mood in healthy volunteers, the Cognitive Drug Research computerized cognitive assessment battery was performed in 144 participants. Analysis of performance revealed that lavender odor (four drops of oil were applied to a diffuser pad) produced a significant decrement in performance of working memory as well as impaired reaction times for both memory and attention. In addition, a significant effect was found for lavender compared to controls for degree of contentedness, indicating that lavender is capable of elevating mood, or at least maintaining good mood during the completion of a challenging test battery under laboratory conditions [ 98 ]. There is an improvement of emotional state in the work environment following the use of the lavender oil burners. Using lavender oil in burners for a 3-month period, nearly 90% of respondents (a total of 66 subjects) believed that there had been an improvement in the work environment following the use of lavender oil [ 99 ]. Aromatherapy consisted of the use of rosemary and lemon essential oils in the morning, and lavender and orange in the evening showed significant improvement in personal orientation related to cognitive function in 28 elderly patients suffering from different forms of dementia [ 100 ]. It has been shown that unconscious perception of lavender odor can significantly affect the rate of errors made in the mathematical and letter counting tests. In the presence of the odor of lavender, 108 subjects made fewer errors than in the presence of no odor or the odor of jasmine [ 101 ]. By comparison, it has been reported lavender to impair arithmetic reasoning, but not memory, when compared to cloves, with no concomitant effect on mood for either odor [ 102 ]. Application of oral lavender (80 mg/day) for six weeks in fifty patients suffering from neurasthenia or post-traumatic stress disorder showed significant improvements of their general mental health status and quality of life [ 103 ].
Although sufficient evidence exists to recommend lavender for short-term treatment of some neurological disorders, long-term trials and observational studies are needed to establish the safety of long-term use as well as overall efficacy in the context of treatment and management of these diseases. The available data suggests that short-term therapy with lavender is relatively safe. However, there are some reports of adverse effects after application of lavender. Gynecomastia coincided with the topical application of products, which contained lavender and tea tree oils was reported in three boys aged between 7 to 10 years. Gynecomastia resolved in all patients shortly after discontinuation of products containing these oils. Furthermore, studies in human cell lines indicated that the lavender oil had estrogenic and antiandrogenic activities [ 104 ]. Lavender should be also used cautiously or avoided in patients with known allergy to lavender [ 105 , 106 ]. In the oral lavender trials, Kasper et al. [ 52 ] reported slightly more adverse events in the lavender group than the placebo group; the most frequently reported adverse effects were related to infections and infestations, followed by gastrointestinal disorders and nervous system disorders. Woelk and Schläfke [ 107 ] reported slightly more adverse events in the lavender group than the lorazepam group but again none were described as serious. Gastrointestinal adverse events, such as nausea and dyspepsia, after receiving silexan were reported [ 107 ]. Ingestion should be avoided during pregnancy (due to emmenagogue effects) [ 108 ] and breastfeeding. Lavender oil has no potential for drug abuse [ 109 ].
6. Critical Overview and Conclusion
A recent increase in the popularity of alternative medicine and natural products has renewed interest in lavender and their essential oils as potential natural remedies [ 2 ]. This review may be useful to increase our knowledge of lavender pharmacological effects and improve our future experimental and clinical research plans. Although it is shown that lavender may have a significant clinical potential either in their own right or as adjuvant therapy in different disorders, however, due to some issues, such as methodological inadequacies, small sample sizes, short duration of lavender application, lack of information regarding dose rationale, variation between efficacy and effectiveness trials, variability of administration methods, the absence of a placebo comparator, or lack of control groups more standard experiments and researches are needed to confirm the beneficial effect of lavender in the neurological disorders [ 109 ]. Methodological and oil identification problems have also hampered the evaluation of the therapeutic significance of some of the research on lavender. The dried lavender flowers used in some trials were sourced from a local herb store (i.e., [ 62 ]). Although taxonomic identification was confirmed in these studies, without quantification of key constituents the quality of the herbal product may be questionable [ 110 ]. Although some studies defined the contents of lavender, it is essential that all future clinical studies specify the exact derivation of the oils used in the study and, preferably, include a profile of the liquid or the percentage composition of the major constituents. In addition, several factors, such as temperature, skin type and quality, and the size of area being treated, which may affect the level and rate of lavender absorption after massage or aromatherapy, were not considered in several investigations. Many discreet compounds in lavender oil have shown a myriad of potential therapeutic effects, and researchers continue to seek novel treatments to different ailments [ 2 ].
Only few clinical investigations on lavender are available using diverse administration methods (i.e., oral, aromatherapy, and as a massage oil). The evidence for oral lavender is promising; however, until independent studies emerge with long-term follow-up data, it remains inconclusive [ 109 ]. The use of more widely used forms of lavender administrations (aromatherapy, inhalation, massage, etc.) is not currently supported by good evidence of efficacy. Future clinical trials, well-reported and adopting rigorous standard methodology, in combination with experimental pharmacological research, would help to clarify the therapeutic value of lavender for neurological and psychological disorders [ 109 , 110 ].
The apparently low reporting of adverse reactions could imply tolerability and safety [ 110 ]. However, most studies failed to provide details which may have masked these and the studies only involved small numbers of participants. It is crucial to get good tolerability and safety data for all modes of lavender application. Thus longer-term follow ups would be required especially for oral lavender before it is recommended for treatment of neurological and/or psychological disorders.
Authors' Contribution
P. H. Koulivand and M. K. Ghadiri contributed equally to this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and Open Access Publication Fund of University of Muenster.
Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Characteristics of an Effective Health Education Curriculum
Today’s state-of-the-art health education curricula reflect the growing body of research that emphasizes:
- Teaching functional health information (essential knowledge).
- Shaping personal values and beliefs that support healthy behaviors.
- Shaping group norms that value a healthy lifestyle.
- Developing the essential health skills necessary to adopt, practice, and maintain health-enhancing behaviors.
Less effective curricula often overemphasize teaching scientific facts and increasing student knowledge. An effective health education curriculum has the following characteristics, according to reviews of effective programs and curricula and experts in the field of health education 1-14 :
An effective curriculum has clear health-related goals and behavioral outcomes that are directly related to these goals. Instructional strategies and learning experiences are directly related to the behavioral outcomes.
An effective curriculum has instructional strategies and learning experiences built on theoretical approaches (for example, social cognitive theory and social inoculation theory) that have effectively influenced health-related behaviors among youth. The most promising curriculum goes beyond the cognitive level and addresses health determinants, social factors, attitudes, values, norms, and skills that influence specific health-related behaviors.
An effective curriculum fosters attitudes, values, and beliefs that support positive health behaviors. It provides instructional strategies and learning experiences that motivate students to critically examine personal perspectives, thoughtfully consider new arguments that support health-promoting attitudes and values, and generate positive perceptions about protective behaviors and negative perceptions about risk behaviors.
An effective curriculum provides instructional strategies and learning experiences to help students accurately assess the level of risk-taking behavior among their peers (for example, how many of their peers use illegal drugs), correct misperceptions of peer and social norms, emphasizes the value of good health, and reinforces health-enhancing attitudes and beliefs.
An effective curriculum provides opportunities for students to validate positive health-promoting beliefs, intentions, and behaviors. It provides opportunities for students to assess their vulnerability to health problems, actual risk of engaging in harmful health behaviors, and exposure to unhealthy situations.
An effective curriculum provides opportunities for students to analyze personal and social pressures to engage in risky behaviors, such as media influence, peer pressure, and social barriers.
An effective curriculum builds essential skills — including communication, refusal, assessing accuracy of information, decision-making, planning and goal-setting, self-control, and self-management — that enable students to build their personal confidence, deal with social pressures, and avoid or reduce risk behaviors.
For each skill, students are guided through a series of developmental steps:
- Discussing the importance of the skill, its relevance, and relationship to other learned skills.
- Presenting steps for developing the skill.
- Modeling the skill.
- Practicing and rehearsing the skill using real–life scenarios.
- Providing feedback and reinforcement.
An effective curriculum provides accurate, reliable, and credible information for usable purposes so students can assess risk, clarify attitudes and beliefs, correct misperceptions about social norms, identify ways to avoid or minimize risky situations, examine internal and external influences, make behaviorally relevant decisions, and build personal and social competence. A curriculum that provides information for the sole purpose of improving knowledge of factual information will not change behavior.
An effective curriculum includes instructional strategies and learning experiences that are student-centered, interactive, and experiential (for example, group discussions, cooperative learning, problem solving, role playing, and peer-led activities). Learning experiences correspond with students’ cognitive and emotional development, help them personalize information, and maintain their interest and motivation while accommodating diverse capabilities and learning styles. Instructional strategies and learning experiences include methods for
- Addressing key health-related concepts.
- Encouraging creative expression.
- Sharing personal thoughts, feelings, and opinions.
- Thoughtfully considering new arguments.
- Developing critical thinking skills.
An effective curriculum addresses students’ needs, interests, concerns, developmental and emotional maturity levels, experiences, and current knowledge and skill levels. Learning is relevant and applicable to students’ daily lives. Concepts and skills are covered in a logical sequence.
An effective curriculum has materials that are free of culturally biased information but includes information, activities, and examples that are inclusive of diverse cultures and lifestyles (such as gender, race, ethnicity, religion, age, physical/mental ability, appearance, and sexual orientation). Strategies promote values, attitudes, and behaviors that acknowledge the cultural diversity of students; optimize relevance to students from multiple cultures in the school community; strengthen students’ skills necessary to engage in intercultural interactions; and build on the cultural resources of families and communities.
An effective curriculum provides enough time to promote understanding of key health concepts and practice skills. Behavior change requires an intensive and sustained effort. A short-term or “one shot” curriculum, delivered for a few hours at one grade level, is generally insufficient to support the adoption and maintenance of healthy behaviors.
An effective curriculum builds on previously learned concepts and skills and provides opportunities to reinforce health-promoting skills across health topics and grade levels. This can include incorporating more than one practice application of a skill, adding “skill booster” sessions at subsequent grade levels, or integrating skill application opportunities in other academic areas. A curriculum that addresses age-appropriate determinants of behavior across grade levels and reinforces and builds on learning is more likely to achieve longer-lasting results.
An effective curriculum links students to other influential persons who affirm and reinforce health–promoting norms, attitudes, values, beliefs, and behaviors. Instructional strategies build on protective factors that promote healthy behaviors and enable students to avoid or reduce health risk behaviors by engaging peers, parents, families, and other positive adult role models in student learning.
An effective curriculum is implemented by teachers who have a personal interest in promoting positive health behaviors, believe in what they are teaching, are knowledgeable about the curriculum content, and are comfortable and skilled in implementing expected instructional strategies. Ongoing professional development and training is critical for helping teachers implement a new curriculum or implement strategies that require new skills in teaching or assessment.
- Botvin GJ, Botvin EM, Ruchlin H. School-Based Approaches to Drug Abuse Prevention: Evidence for Effectiveness and Suggestions for Determining Cost-Effectiveness [pdf 85K] -->. In: Bukoski WJ, editor. Cost-Benefit/Cost-Effectiveness Research of Drug Abuse Prevention: Implications for Programming and Policy . NIDA Research Monograph, Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1998;176:59–82.
- Contento I, Balch GI, Bronner YL. Nutrition education for school-aged children. Journal of Nutrition Education 1995;27(6):298–311.
- Eisen M, Pallitto C, Bradner C, Bolshun N. Teen Risk-Taking: Promising Prevention Programs and Approaches --> . Washington, DC: Urban Institute; 2000.
- Gottfredson DC. School-Based Crime Prevention. In: Sherman LW, Gottfredson D, MacKenzie D, Eck J, Reuter P, Bushway S, editors. Preventing Crime: What Works, What Doesn’t, What’s Promising [pdf 100K] -->. National Institute of Justice; 1998.
- Kirby D. Emerging Answers: Research Findings on Programs to Reduce Teen Pregnancy . Washington, DC: National Campaign to Prevent Teen Pregnancy; 2001.
- Kirby D, Coyle K, Alton F, Rolleri L, Robin L. Reducing Adolescent Sexual Risk: A Theoretical Guide for Developing and Adapting Curriculum-Based Programs . Scotts Valley, CA: ETR Associates; 2011.
- Lohrmann DK, Wooley SF. Comprehensive School Health Education. In: Marx E, Wooley S, Northrop D, editors. Health Is Academic: A Guide to Coordinated School Health Programs . New York: Teachers College Press; 1998:43–45.
- Lytle L, Achterberg C. Changing the diet of America’s children: what works and why? Journal of Nutrition Education 1995;27(5):250–60.
- Nation M, Crusto C, Wandersman A, Kumpfer KL, Seybolt D, Morrissey-Kane, E, Davino K. What works: principles of effective prevention programs. American Psychologist 2003;58(6/7):449–456.
- Stone EJ, McKenzie TL, Welk GJ, Booth ML. Effects of physical activity interventions in youth. Review and synthesis. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 1998;15(4):298–315.
- Sussman, S. Risk factors for and prevention of tobacco use. Review. Pediatric Blood and Cancer 2005;44:614–619.
- Tobler NS, Stratton HH. Effectiveness of school-based drug prevention programs: a meta-analysis of the research. Journal of Primary Prevention 1997;18(1):71–128.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Preventing Tobacco Use Among Young People–An Update: A Report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta (GA): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health, 2011: 6-22–6-45.
- Weed SE, Ericksen I. A Model for Influencing Adolescent Sexual Behavior . Salt Lake City, UT: Institute for Research and Evaluation; 2005. Unpublished manuscript.

Healthy Youth
To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

SEBI Grade A Syllabus and Exam Pattern 2024 for Phase 1 and 2
Get the SEBI Grade A Syllabus and Exam Pattern for Phases I and II. Check out the latest SEBI Grade A Syllabus and Exam Pattern for Assistant Managers in various Streams here.

Table of Contents
SEBI Grade A Syllabus
Candidates who are going to prepare for the SEBI Grade A officer post must have a deep understanding of the SEBI Grade A syllabus and the latest exam pattern. SEBI Grade A Examination 2024 will be conducted in 3 stages such as Phase I, II, and Interview . To prepare for Phase 1 and Phase 3, the candidates need to go through the SEBI Grade A Syllabus 2024 for both stages. Here, we have provided the SEBI Grade A exam Pattern 2024 and a detailed subject-wise syllabus syllabus for all streams. Stay tuned with us.
SEBI Grade A Syllabus & Exam Pattern 2024
SEBI Grade A Officer Exam comprises three phases that are described in detail below.
- Phase I: On-line screening examination consisting of two papers of 100 marks each
- Phase II: On-line examination consisting of two papers of 100 marks each
- Phase III: Interview
Paper I and Paper II of the General Stream will be common to all the streams. All the questions in every phase will be Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) except the language subject. All question papers (in both Phases, except the test in English) will be set bilingually in Hindi as well as English. The detailed SEBI Grade A Syllabus and exam pattern has explained below.
The SEBI Grade A Syllabus and exam pattern have been released along with the Official notification PDF. Candidates can check the important information in the below article.
| SEBI Grade A Syllabus | |
|---|---|
| Organization | Securities And Exchange Board of India |
| Exam Name | SEBI Grade A Recruitment 2024 |
| Post | Officer Grade A (Assistant Manager) |
| Vacancy | 95 |
| Selection Process | Phase I, Phase II, and Interview |
| Exam Pattern | Paper 1 and Paper 2 (MCQ) |
| Exam Language | Hindi/English |
| Official Website | www.sebi.gov.in |
SEBI Grade A Notification 2024 Out – Click Here
SEBI Grade A Exam Pattern 2024
The SEBI Grade A Exam has two phases, Phase 1 and Phase 2. We have explained the phase-wise SEBI Grade A Exam Pattern below.
SEBI Grade A Exam Pattern For Phase I
SEBI Grade A Phase I Exam will have two papers: Paper I and Paper II. Both papers will have Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). Paper 1 will be common for all the streams whereas the exam pattern of Paper 2 will vary according to various disciplines. Both papers will be for 100 marks.
| All Streams: Multiple choice questions on the subjects viz. General Awareness (including some questions related to the Financial Sector of easy to moderate difficulty level), English Language, Quantitative Aptitude, and Test of Reasoning. | 100 | 60 minutes | 30% | |
| General Stream: Multiple choice questions on subjects Commerce, Accountancy, Management, Finance, Costing, Companies Act, and Economics | 100 | 40 minutes | 40% | |
| Legal, Information Technology, & Official Language stream: Multiple choice questions on Specialized subjects related to the stream | 100 | 40 minutes | 40% | |
| Research Stream:– Multiple choice questions on subjects of Economics, Econometrics, Statistics, Finance, and Commerce. | ||||
SEBI Grade A Phase I Marking Scheme
- There shall be a negative marking of 1/4th of the marks assigned to the question for every incorrect answer.
- There shall be a cut-off of a minimum of 30% for Paper 1 (no sectional cut-off shall be there)
- Candidates would need to secure a separate cut-off in each paper as mentioned above as well as an aggregate cut-off mark of 40% in the Phase I exam to be shortlisted for Phase II
- Candidates have to secure separate cut-offs in each paper as mentioned above as well as aggregate cut-off marks of 40% in the Phase I exam to be shortlisted for Phase II.
SEBI Grade A Exam Pattern For Phase II
Candidates who secure the cut-off will be eligible to appear for the SEBI Grade A Phase II Exam. SEBI Grade A Phase 2 will have two Papers: Paper I and Paper II of 100 marks each. Paper I and General Stream will be common to all. Candidates need to secure more marks in this phase as this would be taken into account for the final selection.
For candidates who have applied in multiple streams, Paper II will be conducted in various shifts, the timings of which will be intimated in the Hall Ticket.
| Paper I | All streams: English (Descriptive Test) to test the drafting skills | 100 | 60 minutes | 30% | 1/3rd |
| Paper-II | General Stream: Multiple choice questions on subjects of Commerce, Accountancy, Management, Finance, Costing, and Companies Act and Economics | 100 | 40 minutes | 40% | 2/3rd |
| Legal, and Official Language Stream: Multiple choice questions on Specialized subjects related to the stream. | 100 | 40 minutes | 40% | 2/3rd | |
| Research Stream: Multiple choice questions on subjects of Economics, Econometrics, Statistics, Finance, and Commerce. | |||||
| Information Technology Stream: Coding Test (Languages: C++/ JAVA/Python) | 100 | 180 minutes | 40% | 2/3rd | |
Marking Scheme For SEBI Grade A Phase II
- There shall be a negative marking of 1/4th of the marks assigned to the question for Paper 2 in Phase II (except IT stream for which details shall be informed in due course).
- There shall be a cut-off of a minimum of 30% for Paper 1 and a cut-off of a minimum of 40% for Paper 2 in Phase II.
- Candidates would need to secure separate cut-offs in each paper as mentioned above as well as aggregate cut-off marks of 40% in the Phase II exam (weightage of 1/3rd for Paper 1 and 2/3rd for Paper 2) to be shortlisted for Phase III.
SEBI Grade A Exam Pattern For Phase II for Legal Stream
The Exam Pattern for the SEBI Grade A Pase II Legal Stream is given below.
| Paper | Stream/Subjects | Max. Marks | Duration | Cut Off | Weightage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper I | All streams: English (Descriptive Test) to test drafting skills | 100 | 60 minutes | 30% | 1/3rd |
| Paper II | 70 Multiple choice questions on a Specialized subject | 100 | 60 minutes | 40% | 2/3rd |
| 3 Descriptive Questions (10 marks each) on a Specialized subject (Answers to be typed with the help of the keyboard) Candidates opting to type answers in Hindi may type with the help of: – Inscript keyboard layout – Remington (GAIL) keyboard layout | 60 minutes | ||||
| Aggregate Cut Off | 50% | ||||
SEBI Grade A Salary 2024 – Click Here
SEBI Grade A Syllabus- Subject Wise
As you have acquainted yourself with the SEBI Grade A Exam Pattern, Now we have the detailed SEBI Grade A Syllabus for both phases. Candidates can check the SEBI Grade A Syllabus for all the streams such as Legal, Management, General, IT, and Commerce streams. The marking scheme and subject-wise topics that are asked in the SEBI Grade A Exam are given here.
SEBI Grade A Syllabus Phase I, Paper I
SEBI Grade A Syllabus Phase 1 For Paper I will be common for all the candidates. This will have MCQs of 100 marks. Paper, I will have four sections:
English Language
Reasoning ability, quantitative aptitude.
- General Awareness (including Financial Awareness)
- Error Spotting
- Column-based Fillers and Sentence Connectors
- Paragraph Completion
- Sentence Rearrangement
- Comprehension
- Fill in the Blanks
- Synonyms and Antonyms
- Active and Passive Voice
- Direct and Indirect Speech
- Idioms & Phrases etc.
- Seating Arrangements
- Direction Sense
- Blood Relations
- Inequalities
- Order and Ranking
- Coding-Decoding
- Machine Input-Output
- Alpha-Numeric-Symbol Series
- Data Sufficiency
- Number System and Conversions
- Logical Reasoning etc.
- Data Interpretation
- Number Series
- Approximation and Simplification
- HCF and LCM
- Inequality (Quadratic & Quantity based)
- Profit and Loss
- Time and work & Pipe and cistern
- Permutation, Combination & Probability
- Problem on Ages
- Work and Time
- Speed Distance and Time
- Mensuration
- Average, Ratio, Proportion, etc.
General Awareness
The GA section will consist of contemporary events of national & international importance. The general awareness section of SEBI Grade A will revolve around the following aspects.
- Current Affairs
- Financial Awareness
- Current Affairs – National & International
- Awards and Honours
- Important Financial & Economic News
- Important Days
- International & National Organizations
- Books and Authors
- Science – Inventions & Discoveries
- Countries & Capitals etc
SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Phase I & Phase II Paper 2 – General Stream
SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Paper 2 will be common for Phase I & Phase II . The questions will be MCQ’s type of 100 marks for General Stream. The topics for the SEBI Grade A Paper II Syllabus for the General stream are given below.
A. SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Commerce & Accountancy
a) Accounting as a financial information system; b) Accounting Standards with specific reference to Accounting for Depreciation, Inventories, Revenue Recognition, Fixed Assets, Foreign Exchange Transactions, and Investments. c) Cash Flow Statement, Fund flow statement, Financial statement analysis; Ratio analysis; d) Accounting for Share Capital Transactions including Bonus Shares, Right Shares. e) Employees Stock Option and Buy-Back of Securities. f) Preparation and Presentation of Company Final Accounts.
B. SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Management
a) Management: its nature and scope; The Management Processes; Planning, Organization, Staffing, Directing, and Controlling; b) The Role of a Manager in an Organization. Leadership: The Tasks of a Leader; c) Leadership Styles; Leadership Theories; A successful Leader versus an effective Leader. d) Human Resource Development: Concept of HRD; Goals of HRD; e) Motivation, Morale, and Incentives: Theories of Motivation; How Managers Motivate; Concept of Morale; Factors determining Morale; Role of Incentives in Building up Morale. f) Communication: Steps in the Communication Process; Communication Channels; Oral versus Written Communication; Verbal versus non-verbal Communication; upward, downward and lateral communication; Barriers to Communication, Role of Information Technology.
C. SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Finance
1) financial system.
a) Role and Functions of Regulatory bodies in the Financial Sector.
2) Financial Markets
a) Primary and Secondary Markets (Forex, Money, Bond, Equity, etc.), functions, instruments, and recent developments.
3) General Topics
a) Basics of Derivatives: Forward, Futures and Swap b) Recent Developments in the Financial Sector c) Financial Inclusion- use of technology d) Alternate source of finance, private and social cost-benefit, Public-Private Partnership e) Direct and Indirect taxes; Non-tax sources of Revenue, GST, Finance Commission, Fiscal Policy, Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act (FRBM), f) Inflation: Definition, trends, estimates, consequences, and remedies (control): WPI, CPI – components and trends.
D. SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Costing
1. Overview of Cost and Management Accounting – Introduction to Cost and Management Accounting, Objectives and Scope of Cost and Management Accounting. 2. Methods of Costing – Single Output/ Unit Costing, Job Costing, Batch Costing, Contract Costing, Process/ Operation Costing, Costing of Service Sectors. 3. Basics of Cost Control and Analysis – (i) Standard Costing, (ii) Marginal Costing, (iii) Budget and Budgetary Control. 4. Lean System and Innovation:- a) Introduction to Lean System b) Just-in-Time (JIT) c) Kaizen Costing
d) 5 Ss e) Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) f) Cellular Manufacturing/ One-Piece Flow Production Systems g) Six Sigma (SS) h) Introduction to Process Innovation and Business Process Re-engineering (BPR).
E. S EBI Grade A Syllabus for Companies Act
The Companies Act, 2013 – Specific reference to Chapter III, Chapter IV, Chapter VIII, Chapter X, Chapter XI, Chapter XII and Chapter XXVII.
F. SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Economics
a) Demand and Supply, Market Structures, National Income: Concepts and Measurement, Classical & Keynesian Approach Determination of output and employment, Consumption Function, Investment Function, Multiplier and Accelerator, Demand, and Supply for Money, IS-LM, Inflation and Phillips Curve, Business Cycles b) Balance of Payments, Foreign Exchange Markets, Inflation, Monetary and Fiscal Policy, and Non-banking Financial Institutions.
SEBI Grade A Syllabus For Legal Stream Phase I & II
The syllabus for Phase I and Phase II for SEBI Grade A Officer will be common . This paper will be of 100 marks. There will be aggregate cut-off as well as paper-wise cut-off. The syllabus will be based on the Specialized Subject chosen by the candidate. The subjects for the specialization is given below. i.e.
- Information Technology
- Engineering: Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering
- Research Streams
- Official Language Stream
The syllabus for each of the specialized streams is given below.
SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Paper 2 – Legal Stream
SEBI Grade A Syllabus Legal: Candidates can check the topics mentioned below for the SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Legal posts. Questions will be asked from these topics only. Candidates can arrange and plan their study materials according to this list for both Phase 1 and Phase 2.
| Phase I | Phase II |
|---|---|
SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Information Technology Paper 2
Phase 1 it stream.
- Database Concepts
- SQL Queries
- Programming Concepts (Java/C C++ )
- Data Analytics Languages (Python / R)
- Algorithms for problem-solving
- Networking Concepts
- Information & Cyber Security Concepts
- Data warehousing
- Shell Programming
Phase 2 IT Stream
| 1 | Algorithms | Sorting, Searching, Greedy Algorithms, Dynamic Programming, Backtracking, Divide and Conquer, Pattern Searching | C++/JAVA/Python | 40 |
| 2 | Data Structure | Array, Linked List, Stack, Queue, Binary Tree, Indexing, Binary Search Tree, Heap, Hashing, Matrix | C++/JAVA/Python | 40 |
| 3 | String Manipulation | Length, Substring, Regex, Search | C++/JAVA/Python | 20 |
SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Research Stream
- Economics: Demand and Supply, Market Structures, National Income, Determination of output and employment, Investment Function, Multiplier and Accelerator, Demand and Supply for Money, IS-LM, Inflation and Phillips Curve, Business Cycles, Inflation, Monetary and Fiscal Policy, Non-banking Financial Institutions.
- Public Economics: Public Goods, Tax & Non-Tax Revenue, Direct & Indirect Taxes, Progressive and nonProgressive Taxation, Incidence and Effects of Taxation, Public expenditure, Public Debt, Public Budget and Budget Multiplier
- Statistics and Econometrics: Measures of Central tendency & dispersions, Correlation, Sampling methods, Sampling Distribution, Statistical Inferences, Hypothesis testing, Regression Analysis.
- International Economics: Balance of Payments, Foreign Exchange Markets, Role of International Financial Institutions: BIS, IOSCO, IMF & World Bank
- Financial Markets: Asymmetric Information, Market Model, Market Efficiency, Primary Market, Secondary Market, Commodity Markets, Mutual Funds, Stock Exchanges, Depositories, Clearing Corporations, Credit Rating Agencies, and Corporate Debt Market. Forwards, Futures, Options, Hedging, Speculation and Arbitrage.
SEBI Grade A Syllabus for Official Language
- भारत सरकार की राजभाषा नीति से सम्बंधित प्रश्न (Official Language Policy of the Govt. of India)
- हिन्दी से अंग्रेजी अनुवाद [शब्द / वाक्यांश/ वाक्य / Terms / Phrases / Sentences]
- अंग्रेजी से तिन्दी अनुवाद [शब्द / वाक्यांश / वाक्य / Terms / Phrases / Sentences]
- हिन्दी से अंग्रेजी – विधिक शब्दावली (Legal Terminology)
- अंग्रेजी से हिन्दी – विधिक शब्दावली (Legal Terminology)
- हिन्दी से अंग्रेजी – प्रशासनिक/ बैंकिंग/ पूंजी बाज़ार संबंधी शब्दावली (Administrative / Banking / Capital Market Terminology)
- अंग्रेजी से हिन्दी – प्रशासनिक/ बैंकिंग/ पूंजी बाज़ार संबंधी शब्दावली (Administrative / Banking / Capital Market Terminology)
SEBI Grade A Syllabus For Phase II – Paper I
This is common for all the candidates appearing for the SEBI Grade A Phase II Exam. This is the English Descriptive Test to test the drafting skills of the candidates. This test will be for 100 marks of 60 minutes.
English Writing Skill Syllabus
The paper on English shall be framed in a manner to assess the writing skills including expression and understanding of the topic including precis writing/ essay writing/ comprehension.
SEBI Grade A Interview
- The candidates who will be successful in Phase I and Phase II of SEBI Grade A Officer Recruitment will be called to appear for the Interview. Candidates equalling 3 times the number of vacancies shall be shortlisted, in order of merit, for Phase III i.e. the Interview.
- The shortlisted candidate may opt for the interview either in Hindi or English. The weightage of marks obtained in Phase II will be 85%, while marks obtained in the interview shall be given a weightage of 15%.
- Thus, the selection will be made on the marks secured in Phase II and Interview for the final selection of the candidates as SEBI Grade A Officer.
Tips to Prepare for SEBI Grade A 2024 Exam
Here, are some of the tips that the candidates can use to pass the SEBI Grade A Exam. Follow these tips to get through the examination process.
- Understand the SEBI Grade A exam pattern and marking scheme.
- Analyze the syllabus and create a study plan. Gather the best SEBI Grade A study material for each subject.
- Allocate time wisely based on subject weightage.
- Take regular mock tests and solve SEBI Grade A Previous Year Papers.
- Stay updated with current affairs related to finance.
- Focus on securities market topics in depth.
- Revise regularly and create concise notes.
- Join study groups or online forums for discussions.
Sharing is caring!
What is the process of selection into SEBI Grade A Officer Recruitment?
Phase I: On-line screening examination consisting of two papers of 100 marks each Phase II: On-line examination consisting of two papers of 100 marks each Phase III: Interview Marks of Phase II and III will be used for final selection.
What is the exam pattern of SEBI Grade A Officer Exam?
There will be two papers each for Phase I and Phase II. All the questions will be MCQ’s except that of language paper. The exam will be of 100 marks for each paper.
Which papers will be common for all the candidates?
Paper I of Phase I & Phase II, and General paper of Phase I & Phase II will be common to all the candidates.
Is there negative marking?
Yes, there is a negative marking of 1/4 for every incorrect answer in the objective questions.
What is the selection process for SEBI Grade A Officer Recruitment?
The selection will be made on the marks secured in Phase II and Interview for the final selection for the candidates as a SEBI Grade A Officer.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Recent Posts
State govt. jobs.
- Andhra Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- West Bengal
IMPORTANT EXAMS
- SSC CGL 2024
- SSC CHSL 2024
- SSC GD Constable 2024
- SSC Selection Post 202 4
- SSC Stenographer 2024
- SBI PO 2024
- SBI Clerk 2024
- RBI Grade B 2024
- LIC AAO 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
Our Other Websites
- Teachers Adda
- Defense Adda
- Engineers Adda
- Adda School
Exam Calendar 2024
- SSC Calendar 2024
- IBPS Calendar 2024
Jobs By Category
- State Govt Jobs
- Government Jobs
- 12th Pass Jobs
- Sarkari Result 2024
- States and Capitals Of INDIA

Adda247 Job portal has complete information about all Sarkari Jobs and Naukri Alerts, its latest recruitment notifications, from all state and national level jobs and their updates.
Download Adda247 App
Follow us on
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
- Biostatistics
- Environmental Health and Engineering
- Epidemiology
- Health Policy and Management
- Health, Behavior and Society
- International Health
- Mental Health
- Molecular Microbiology and Immunology
- Population, Family and Reproductive Health
- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
research@BSPH
The School’s research endeavors aim to improve the public’s health in the U.S. and throughout the world.
- Funding Opportunities and Support
- Faculty Innovation Award Winners
Conducting Research That Addresses Public Health Issues Worldwide
Systematic and rigorous inquiry allows us to discover the fundamental mechanisms and causes of disease and disparities. At our Office of Research ( research@BSPH), we translate that knowledge to develop, evaluate, and disseminate treatment and prevention strategies and inform public health practice. Research along this entire spectrum represents a fundamental mission of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
From laboratories at Baltimore’s Wolfe Street building, to Bangladesh maternity wards in densely packed neighborhoods, to field studies in rural Botswana, Bloomberg School faculty lead research that directly addresses the most critical public health issues worldwide. Research spans from molecules to societies and relies on methodologies as diverse as bench science and epidemiology. That research is translated into impact, from discovering ways to eliminate malaria, increase healthy behavior, reduce the toll of chronic disease, improve the health of mothers and infants, or change the biology of aging.
120+ countries
engaged in research activity by BSPH faculty and teams.
of all federal grants and contracts awarded to schools of public health are awarded to BSPH.
citations on publications where BSPH was listed in the authors' affiliation in 2019-2023.
publications where BSPH was listed in the authors' affiliation in 2019-2023.
Departments
Our 10 departments offer faculty and students the flexibility to focus on a variety of public health disciplines
Centers and Institutes Directory
Our 80+ Centers and Institutes provide a unique combination of breadth and depth, and rich opportunities for collaboration
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
The Institutional Review Board (IRB) oversees two IRBs registered with the U.S. Office of Human Research Protections, IRB X and IRB FC, which meet weekly to review human subjects research applications for Bloomberg School faculty and students
Generosity helps our community think outside the traditional boundaries of public health, working across disciplines and industries, to translate research into innovative health interventions and practices
Introducing the research@BSPH Ecosystem
The research@BSPH ecosystem aims to foster an interdependent sense of community among faculty researchers, their research teams, administration, and staff that leverages knowledge and develops shared responses to challenges. The ultimate goal is to work collectively to reduce administrative and bureaucratic barriers related to conducting experiments, recruiting participants, analyzing data, hiring staff, and more, so that faculty can focus on their core academic pursuits.

Research at the Bloomberg School is a team sport.
In order to provide extensive guidance, infrastructure, and support in pursuit of its research mission, research@BSPH employs three core areas: strategy and development, implementation and impact, and integrity and oversight. Our exceptional research teams comprised of faculty, postdoctoral fellows, students, and committed staff are united in our collaborative, collegial, and entrepreneurial approach to problem solving. T he Bloomberg School ensures that our research is accomplished according to the highest ethical standards and complies with all regulatory requirements. In addition to our institutional review board (IRB) which provides oversight for human subjects research, basic science studies employee techniques to ensure the reproducibility of research.
Research@BSPH in the News
Four bloomberg school faculty elected to national academy of medicine.
Considered one of the highest honors in the fields of health and medicine, NAM membership recognizes outstanding professional achievements and commitment to service.
The Maryland Maternal Health Innovation Program Grant Renewed with Johns Hopkins
Lerner center for public health advocacy announces inaugural sommer klag advocacy impact award winners.
Bloomberg School faculty Nadia Akseer and Cass Crifasi selected winners at Advocacy Impact Awards Pitch Competition
MLA Citation Generator
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
What is Cite This For Me’s Citation Generator?
Are you looking for an easy and reliable way to cite your sources in the MLA format? Look no further because Cite This For Me’s MLA citation generator is designed to remove the hassle of citing. You can use it to save valuable time by auto-generating all of your citations.
The Cite This For Me citation machine accesses information from across the web, assembling all of the relevant material into a fully-formatted works cited MLA format page that clearly maps out all of the sources that have contributed to your paper. Using a generator simplifies the frustrating citing process, allowing you to focus on what’s important: completing your assignment to the best of your ability.
Have you encountered an unusual source, such as a microfiche or a handwritten manuscript, and are unsure how to accurately cite this in the MLA format? Or are you struggling with the dozens of different ways to cite a book? If you need a helping hand with creating your citations, Cite This For Me’s accurate and powerful generator and handy MLA format template for each source type will help to get you one step closer to the finishing line.
Continue reading our handy style guide to learn how to cite like a pro. Find out exactly what a citation generator is, how to implement the MLA style in your writing, and how to organize and present your work according to the guidelines.
Popular MLA Citation Examples
- Archive material
- Book Chapter
- Dictionary entry
- E-book or PDF
- Image online or video
- Presentation or lecture
- Video, film, or DVD
Why Do I Need To Cite?
Whenever you use someone else’s ideas or words in your own work, even if you have paraphrased or completely reworded the information, you must give credit where credit is due to avoid charges of plagiarism. There are many reasons why.
First, using information from a credible source lends credibility to your own thesis or argument. Your writing will be more convincing if you can connect it to information that has been well-researched or written by a credible author. For example, you could argue that “dogs are smart“ based on your own experiences, but it would be more convincing if you could cite scientific research that tested the intelligence of dogs.
Second, you should cite sources because it demonstrates that you are capable of writing on an academic or professional level. Citations show that your writing was thoughtfully researched and composed, something that you would not find in more casual writing.
Lastly, and most importantly, citing is the ethical thing to do. Imagine that you spent months of your life on a paper: researching it, writing it, and revising it. It came out great and you received many compliments on your thesis and ideas. How would you feel if someone took those ideas (or even the whole paper) and turned them in as their own work without citations? You’d probably feel terrible.
All of the source material that has contributed to your work must be acknowledged with an MLA in-text citation (also known as a parenthetical citation ) and be featured in your works cited list as full references.
Create citations, whether manually or by using the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator, to maintain accuracy and consistency throughout your project.
Do I Have to Cite Everything?
When writing a research paper, any information used from another source needs to be cited. The only exceptions to this rule are everyday phrases (e.g., all the world’s a stage) and common knowledge (e.g., President Kennedy was killed in 1963).
Also, your own work does not need to be cited. That includes your opinions, ideas, and visuals (e.g., graphs, photos, etc.) you created. However, you do need to cite your own work if you have previously published it or used it in another assignment. Otherwise it’s considered self plagiarism . For example, submitting a paper that you wrote and already turned in for another class is still plagiarism, even though it is your own work.
If you have any doubts about whether or not something you’ve written requires a citation, it’s always better to cite the source. While it may be a tedious process without an MLA citation machine, attributing your research is essential in validating the statements and conclusions you make in your work. What’s more, drawing on numerous sources elevates your understanding of the topic, and accurately citing these sources reflects the impressive research journey that you have embarked on.
Consequences of Not Citing
The importance of crediting your sources goes far beyond ensuring that you don’t lose points on your assignment for citing incorrectly. Plagiarism, even when done unintentionally, can be a serious offense in both the academic and professional world.
If you’re a student, possible consequences include a failing assignment or class grade, loss of scholarship, academic probation, or even expulsion. If you plagiarize while writing professionally, you may suffer legal ramifications as well, such as fines, penalties, or lawsuits.
The consequences of plagiarism extend beyond just the person who plagiarized: it can result in the spread of misinformation. When work is copied and/or improperly cited, the facts and information presented can get misinterpreted, misconstrued, and mis-paraphrased. It can also be more difficult or impossible for readers and peers to check the information and original sources, making your work less credible.
What is the MLA Format?
The MLA format was developed by the Modern Language Association as a consistent way of documenting sources used in academic writing. It is a concise style predominantly used in the liberal arts and humanities, first and foremost in research focused on languages, literature, and culture. The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook has the most current format guidelines. It was updated to reflect the expanding digital world and how researchers and writers cite more online sources. You can find out more here .
It is important to present your work consistently, regardless of the style you are using. Accurately and coherently crediting your source material both demonstrates your attention to detail and enhances the credibility of your written work. The MLA format provides a uniform framework for consistency across a scholarly document, and caters to a large variety of sources. So, whether you are citing a website, an article, or even a podcast, the style guide outlines everything you need to know to correctly format all of your MLA citations.* The style also provides specific guidelines for formatting your research paper, and useful tips on the use of the English language in your writing.
Cite This For Me’s style guide is based on (but not associated with) the 9th edition of the Modern Language Association Handbook for Writers of Research Papers. Our MLA generator also uses the 9th edition – allowing you to shift focus from the formatting of your citations to what’s important – how each source contributes to your work.
MLA has been widely adopted by scholars, professors, journal publishers, and both academic and commercial presses across the world. However, many academic institutions and disciplines prefer a specific style of referencing (or have even developed their own unique format) so be sure to check which style you should be using with your professor. Cite This For Me supports citing in thousands of styles, so the odds are good that we have tools for the citation style you need. Whichever style you’re using, be consistent!
So, if you’re battling to get your citations finished in time, you’ve come to the right MLA citation website. The generator above will can cite any source in 7,000+ styles. So, whether your discipline uses the APA citation style, or your institution requires you to cite in the Chicago style citation , simply go to Cite This For Me’s website to find generators and style guides for ASA , IEEE , AMA and many more.
*You may need to cite a source type that is not covered by the format manual – for these instances we have developed additional guidance and MLA format examples, which we believe stick as closely as possible to the spirit of the style. It is clearly indicated where examples are not covered in the official handbook.
How Do I Create and Format MLA In-text Citations?
The MLA format is generally simpler than other referencing styles as it was developed to emphasize brevity and clarity. The style uses a straightforward two-part documentation system for citing sources: parenthetical citations in the author-page format that are keyed to an alphabetically ordered works cited page. This means that the author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text as a parenthetical citation, and a complete corresponding reference should appear in your works cited list.
Keep your MLA in-text citations brief, clear and accurate by only including the information needed to identify the sources. Furthermore, each parenthetical citation should be placed close to the idea or quote being cited, where a natural pause occurs – which is usually at the end of the sentence. Essentially you should be aiming to position your parenthetical citations where they minimize interruption to the reading flow, which is particularly important in an extensive piece of written work.
Check out the examples below…
Citation Examples
Parenthetical citation examples:
- Page specified, author mentioned in text:
If the author’s name already appears in the sentence itself then it does not need to appear in the parentheses. Only the page number appears in the citation. Here’s an MLA format example:
Sontag has theorized that collecting photographs is a way “to collect the world” (3).
- Page specified, author not mentioned in text:
Include the author’s last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken in a parenthetical citation after the quote. This way of citing foregrounds the information being cited.
“To collect photographs is to collect the world” (Sontag 3).
When the author is referred to more than once in the same paragraph, you may use a single MLA in-text citation at the end of the paragraph (as long as the work cannot be confused with others cited).
On Photography posits that “to collect photographs is to collect the world.” It intensifies that sentiment by saying photography “means putting oneself into a certain relation to the world that feels like knowledge—and, therefore, like power.” (Sontag 3, 4)
- Page specified, same author, different works:
If you are citing two works by the same author, you should put a comma after the author’s surname and add a shortened title to distinguish between them. Italicize book titles, put article titles within quotation marks. As with the above examples, if you mention the author in the text, they don’t need to be included in the parenthetical MLA citation.
In the line “Ask Benjy ef I did. I aint stud’in dat winder” ( The Sound 276), Faulkner employs spelling and diction to communicate the character background of Dilsey. He’s also seen doing this in other books. For example, “He kilt her.” ( As I Lay 54).
- Page specified, two authors, same last name:
In MLA citing, if there are two authors with the same surname, be sure to include their first initial in your citation to avoid confusion.
- Page specified, two authors, same work:
Each author’s name will be included in both the parenthetical and the full source reference in your MLA bibliography.
Crowley is in fact, the snake who convinced Eve to eat the apple in the Garden of Eden (Prattchett and Gaiman 4).
- Page specified, more than two authors, same work:
For any work with three authors or more, you’ll include the last name of the first author listed and the abbreviation “et al.” which is Latin for “and others.”
“The skills required to master high-stakes interactions are quite easy to spot and moderately easy to learn” (Patterson et al. 28).
- Websites and other online sources:
The MLA formatting examples below above are for information or quotes that have specified pages, usually from a book. If you are using information from a website or online source, the author rules below still apply but a page number is not needed. Instead, just include the first bit of identifiable information that will be shown in the source’s full reference (e.g., author name, video title, website name, etc.).
“Scientists speculate that this might be due to a large chunk of nickel and iron embedded beneath the crater – perhaps the remnants of the asteroid that created it” (Ravilious).
“There’s a flag on the flag; it’s bad design” (“In Defense of Bad Flags”)
Full citations/references MLA website citation:
One of the most common sources cited are websites, so it’s useful to know how to cite a website in MLA.
Ravilious, Kate. “Terrawatch: The Mysteries of the Moon’s Largest Crater.” The Guardian , 1 Oct 2019, www.theguardian.com/science/2019/oct/01/terrawatch-the-mysteries-of-the-moons-largest-crater.
Format for books:
Franke, Damon. Modernist Heresies: British Literary History, 1883-1924 . Ohio State UP, 2008.
Sontag, Susan. On Photography . Penguin, 2008.
MLA citation format for journal articles:
Stanton, Elizabeth Cady. “Progress of the American Woman.” The North American Review , vol. 171, no. 529, 1900, pp. 904–907. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/25105100.
Format for online videos:
“In Defense of Bad Flags.” YouTube , uploaded by Vlogbrothers, 4 Oct. 2019, www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkpAe3_qmq0.
Works cited / bibliography example:
Unlike an MLA in-text citation, you must include all of the publication information in your works cited entries.
Franke, Damon. Modernist Heresies: British Literary History, 1883-1924. Ohio State UP, 2008.
There’s a lot of formatting needed when you cite. Luckily for you, we know where the commas go, and our MLA citation maker will help you put them there.
If citing is giving you a headache, use Cite This For Me’s free, accurate and intuitive MLA citation generator to add all of your source material to your works cited page with just a click.
How Do I Format My MLA Works Cited Page?
A works cited page is a comprehensive list of all the sources that directly contributed to your work – each entry links to the brief parenthetical citations in the main body of your work. An in-text citation MLA only contains enough information to enable readers to find the source in the works cited list, so you’ll need to include the complete publication information for the source in your works cited entries.
Your works cited page in MLA should appear at the end of the main body of text on a separate page. Each entry should start at the left margin and be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name (note that if there is no author, you can alphabetize by title). For entries that run for more than one line, indent the subsequent line(s) – this format is called a ‘hanging indentation.’
The title of the page should be neither italicized nor bold – it is simply center-aligned. Like the rest of your MLA format paper the list should be double-spaced, both between and within entries.
Sometimes your professor will ask you to also list the works that you have read throughout your research process, but didn’t directly cite in your paper. This list should be called ‘Work Cited and Consulted,’ and is an excellent opportunity to demonstrate the full extent of the research you have carried out.
As long as you clearly indicate all of your sources via both parenthetical citations and an MLA format works cited list, it is very unlikely that you will lose points for citing incorrectly.
Works cited examples:
Anderson, Benedict. Imagined Communities. Verso, 1983.
Fox, Claire F. The Fence and the River: Culture and Politics at the U.S.-Mexico Border. U of Minnesota P, 1999.
Sontag, Susan. On Photography. Penguin, 2008.
MLA Style Research
When you are gathering sources in your research phase, be sure to make note of the following bibliographical items that will later make up your works cited MLA.
- Name of original source owner: author, editor, translator, illustrator, or director …
- Titles: article or newspaper title, title of publication, series title …
- Important dates: date of publication, date of composition, issue date, event date, date accessed …
- Publishing information: publisher name
- Identifying information: number of volumes, volume number, issue number, edition, chapter, pages, lines …
If you’re still in your research phase, why not try out Cite This For Me for Chrome? It’s an intuitive and easy-to-use browser extension that enables you to instantly create and edit a citation for any online source while you browse the web.
Racing against the clock? If your deadline has crept up on you and you’re running out of time, the Cite This For Me MLA citation maker will collect and add any source to your bibliography with just a click.
In today’s digital age, source material comes in all shapes and sizes. Thanks to the Cite This For Me citation generator, citing is no longer a chore. The citation generator will help you accurately and easily cite any type of source in a heartbeat, whether it be a musical score, a work of art, or even a comic strip. Cite This For Me helps to elevate a student’s research to the next level by enabling them to cite a wide range of sources.
MLA Citation Formatting Guidelines
Accurately citing sources for your assignment doesn’t just prevent the appearance of or accusations of plagiarism – presenting your source material in a clear and consistent way also ensures that your work is accessible to your reader. So, whether you’re following the MLA format citation guidelines or using the Cite This For Me citation generator, be sure to abide by the presentation rules on font type, margins, page headers, and line spacing.
For research papers, an MLA cover page or title page is not required. Still, some instructors request an MLA title page. In these cases, ask your instructor for an example of a title page so you know the format they want.
Instead of a cover page, headings are used on a paper’s first page to indicate details like the author’s name, instructor’s name, the class, and date written. Read on for more details.
General page and header formatting:
To format your research paper according to the MLA guidelines:
- Set the margins to 1 inch (or 2.5 cm) on all sides
- Choose an easily readable font, recommended Times New Roman
- Set font size to 12 point
- Set double space for your entire paper
- Indent every new paragraph by ½ inch – you can simply use your tab bar for this
- In the header section – on the top right corner of the pages – give your last name followed by the respective page number
For your headings (which replace the need for a cover page), do the following:
- On the first page, ensure that the text is left-aligned and then give your details: starting with your full name in line one, followed by the name of your teacher or professor, the course name and number, and the date in separate lines
- Center align your MLA format heading for the paper’s title – do not italicize, bold or underline, or use a period after the title
- The body of your text should start in the next line, left-aligned with an indentation

You’ll also need to include a running head on each page. It should include your last name and the page number. For example: Johnson 2. Place the running head in the upper right-hand corner of the paper, ½ inches from the top and 1 inch from the page’s right edge.

MLA Style 9th Edition - Changes From Previous Editions
It is worth bearing in mind that the MLA format is constantly evolving to meet the various challenges facing today’s researchers. Using the Cite This For Me citation generator will help you to stay ahead of the game without having to worry about the ways in which the style has changed.
Below is a list outlining the key ways in which MLA has developed since previous editions.
- Titles of independent works (such as books and periodicals) are now italicized rather than underlined .
- You are encouraged to include a source’s URL when citing a source from the internet, and you should no longer include “https://” at the beginning of the URL with the exception of DOIs.
- You are no longer required to include medium information at the end of your citation, i.e., Print, Web, etc.
- Including the city of publication is optional, and only encouraged if the version of the work changes based on location, or if it was published prior to 1900.
How Do I Cite My Sources With The Cite This For Me Citation Machine MLA?
If you’re frustrated by the time-consuming process of citing, the Cite This For Me multi-platform citation management tool will transform the way you conduct your research. Using this fast, accurate and accessible generator will give you more time to work on the content of your paper, so you can spend less time worrying about tedious references.
So if you’re having issues with accurately formatting your citations, sign up to Cite This For Me and let our MLA format generator do the grunt work for you.
To use the generator:
- Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g., website, book, journal & video)
- Enter the URL , DOI , ISBN , title, or other unique source information to locate your source
- Click the ‘Search’ button to begin looking for your source
- Look through the search results and click the ‘Cite’ button next to the correct source. Cite This For Me citation tool will automatically pull your sources data for you!
- Review the citation details and make sure that everything you need is included and accurate
- Click ‘Complete citation’
- Copy your fully-formatted citation into your MLA works cited list</li/>
- Repeat the same process for each source that has contributed to your work
As well as making use of the powerful generator, you can cite with our Chrome add-on or Word add-on.
Manage all your citations in one place
Create projects, add notes, cite directly from the browser.
Sign up to Cite This For Me – the ultimate citation management tool
Published October 1, 2015. Updated June 16, 2021.
There are many consequences for not providing a correct citation in MLA style. The biggest consequence is that without proper citations, your paper will lose marks for incorrect citations. In addition, your paper can also be considered plagiarism. The responsibility for using proper citations rests with the author of the paper. Failing to properly cite your sources implies that the information in the paper is solely yours when it is not.
While some instructors might be lenient about incorrect citations, others might not. Ultimately, this could land you in serious trouble with your school, organization, or institution. To avoid such issues, always ensure that you provide proper citations. If you are finding it difficult to provide proper citations, Chegg’s citation generator may help.
When citing multiple works by the same author, include the title (or a shortened version of the title) along with the author’s last name and page number in in-text citations.
You can include the author’s name and/or the title in the prose, or you can include all three pieces of information in the parenthetical citation.
(Last Name, Shortened Title page number)
(Sam, Notes to Live By 42)
(Sam, Pointers From a Friend 85)
If you’d like to shorten a title in parenthetical citations, the title can be condensed to the first noun phrase. In the examples above, the titles would be shortened to Notes and Pointers in the parenthetical citations.
When using MLA style to cite a source with two authors, the last names of both authors and the page number being referenced should be included in in-text citations. The names should be listed in the same order in which they appear on the works cited list and be separated by the word “and” in parenthetical citations. If mentioning the authors in the prose, be sure to use both authors’ first and last names on first reference.
Below are a template and example for how to create an in-text citation for a source with two authors in MLA style.
(Last Name 1 and Last Name 2 page number)
(Prusty and Patel 75)
When using MLA style to cite a source with more than two authors, include the last name of the first author listed on your works cited page along with “et. al” and the page number in your in-text citations.
You should only use “et. al” in your works cited list and parenthetical citations. If you include the authors’ names in your prose instead, you can list all the authors’ names or the name of the first author and a phrase like “and her co-authors,” “and others,” etc.
Below are a template and example for how to create an in-text citation for a source with more than two authors in MLA style.
(Author 1 Last Name et al. page number)
(Krishnaswamy et al. 75)
Sources may be cited for various reasons, including to provide credit to others’ ideas, to ensure that readers can find the right sources, and to improve a paper’s credibility. There are some situations when a citation might not be necessary. To avoid ambiguity, here are the situations in which you should include a citation in an MLA style paper:
- When you are directly quoting an expert or other source of information
- When you are paraphrasing a quotation, passage, or idea
- When you are summarizing another person’s ideas
- When you are specifically referencing a fact, phrase, or statistics found in another source
Things that may be considered common knowledge (like dates of historical events or widely known biographical facts) do not need to be cited. However, if you are unsure whether or not a source needs to be cited, it is always better to err on the side of caution and include a citation.
As per MLA standards, a title page is NOT required. In fact, MLA recommends using a header with all relevant information instead, including your name, instructor’s name, course name, date of submission, and title. However, when your instructor requires a title page or when you are authoring your paper as a group with other people, it is recommended to create a title page for your paper.
If you are creating a title page, you should include the below information:
- Name of the paper’s author(s)
- Names of the instructor(s)
- Course name and number
- Title of the paper
Since websites don’t usually have page numbers, include only the author’s last name within parentheses using the standard MLA format. If using a citation in prose, directly referring to the author’s name in the sentence, then there is no need to provide any additional parenthetical citation.
Plastics contribute to the single greatest pollutant source for oceans (Shimla).
Shimla states that plastics are the oceans’ greatest pollutant source. [No additional citation is needed since you include the author’s name in the citation in prose and there is no page number available.]
As per section 1.3 of the MLA 9 handbook, center the title of a paper and use double-spacing. Do NOT underline, italicize, bold, or use all capitals for the title. Instead, follow standard rules of capitalization. Any italicized words within the text (e.g., book titles or literary movements) would ALSO be italicized in the title. Don’t use a period after your paper’s title.
Usually, you nclude the paper title on your first page. Only when the instructor needs a specific title page or when the paper is a group paper necessitating a list of all authors should you provide a separate title page. Apart from these two situations, a title page is NOT required.
Below are some examples when you would need to italicize words in the title because they include names of books and/or literary movements.
Perspective Shift during the Baroque Period
Is Macbeth Relevant in 2022 and Beyond?
While the MLA handbook recommends using “an easily readable typeface” and a font size “between 11 and 13,” it also clarifies to follow a professor’s or instructor’s guidelines if they differ. The handbook advises using double-spacing and the same font and size throughout the paper.
Check with your instructor on their preferences, and in the absence of any such preference, use a decent and readable font, like Times New Roman, with font size 12, which is a good balance between readability and aesthetics. The most important thing is to use the same font and size consistently throughout your paper.
As per Sections 5 and 6 of the MLA 9 handbook, if you are referring multiple times to a single source in the same paragraph, you do not need to repeat the author’s name each time you make a reference. However, you must include the page number(s), or another applicable locator, if you are referring to different pages of the same source in the same paragraph. In the examples below, it is clear in the second sentence that you’re citing the same source, so you don’t need to include the author name again, only the page number you’re referring to.
However, if you quote or paraphrase a different source by a different author between mentions of a source by the same author in the same paragraph, you need to reintroduce the source and original author name to clarify who you’re citing.
Citation in Prose Example
According to Theodore Garner, “It is evident that Caucasian males have a proclivity toward thrift than their African counterparts” (352). This can be seen from the high saving levels over a decade (345).
Parenthetical Citation Example
“It is evident that Caucasian males have a proclivity toward thrift than their African counterparts” (Garner 352). This can be seen from the high saving levels over a decade (345).
If referring to different sources by the same author(s), include the source’s title in your in-text citation, so readers know which source you are referring to. You can style such citations in various ways, as shown below. The style remains the same for works with more than one author.
Example with the author’s name and the title in the citation in prose
Howitzer says it best when he talked about the Moonmakers in his poem (23). Howitzer does contradict himself at a later point in time in Sunchanters (46).
Example with the author’s name in prose and the title in a parenthetical citation
Shakespeare writes pessimistically about existence from Hamlet’s point of view (Hamlet 103) . In another work, Shakespeare writes, “Life is a tale told by an idiot, full of sound and fury, signifying nothing” ( Macbeth 55).
Example with the author’s name and the title in the parenthetical citation
A similar pessimism about existence is present in other works, for instance when Hamlet contemplates suicide (Shakespeare, Hamlet 103). Macbeth similarly claims, “Life is a tale told by an idiot, full of sound and fury, signifying nothing” (Shakespeare, Macbeth 55).
To format an MLA works-cited page, follow these fundamental steps:
Place the works-cited list at the end of the paper and after any endnotes, should they be used.
Set a one-inch margin all around (top, bottom, left, and right). Like the prose portion of the paper, use a left margin, not a justified margin.
Running head
Place a running head on the right side of the page in the one-inch header, one-half inch from the top of the page. The running head format includes Surname and page #. The page number continues from the last page of the prose portion of the paper.
Use an easily readable font in which the italics feature is clearly distinguishable. Use the same font as in the prose portion of the paper. Times New Roman and Helvetica are popular standard fonts. Use a font size between 11 and 13 points.
Title the heading “Works Cited”; do not use bold or italics. Align it to the center of the page. Then double-space to begin the first entry. Double-space throughout the page.
Begin the entries flush with the left margin. Indent the second and subsequent lines of each entry one-half inch from the left margin.
Arranging entries
Arrange the Works-cited-list entries alphabetically according to the name of the author, or title if there is no author. If there is more than one author, cite the author listed first on the title page of the work in the alphabetical entry.
A separate medium identification, such as “Print,” is no longer used; however, the medium usually can be identified by the information provided in the citation.
Gann, Ernest K. A Hostage to Fortune . Alfred A. Knopf, 1978.
Invest Answers [@InvestAnswers]. “Taking another run at $45,000.” Twitter , 2 Mar. 2022, twitter.com/invest_answers/status/1499033186734542850.
To include the URL in website citation in MLA style, copy the URL from the browser, but exclude the http:// or https:// unless it is used in a DOI. If the work has a DOI, it is used instead of the URL.
Woldermont, Slat. “Sharks Impacted by Great Atlantic Garbage.” The Atlantic Cleanup , 4 May 2020, www.theatlanticcleanup.com/updates/sharks-impacted-by-Great-Atlantic-Garbage.
Saunders, Judith P. “Philosophy and Fitness: Hemingway’s ‘A Clean, Well-Lighted Place’ and The Sun Also Rises .” American Classics: Evolutionary Perspectives , Academic Studies Press, 2018, pp. 204–25, https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctv4v3226.15.
The 6 th , 7 th , 8 th , and 9 th editions of MLA style are available on the Cite This For Me citation generator . The default MLA edition is the 9 th edition, the most current edition.
For a webpage/website, journal article, or book, you’ll need 1-2 pieces of basic publication information. For example:
- Website : URL, page title, etc.
- Journal article : Article title, DOI number, author(s), etc.
- Book : Book title, author, date published, etc.
Using those pieces of information, you can search for the source in the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator and it will help you to create a citation.
Other source types (newspaper article, video, government document, etc.) will provide a form on which you provide all source information. Using that information, the citation generator will create a properly formatted MLA citation for you.
Omitting or making up sources are unethical actions that can lead to plagiarism. An MLA citation generator can help a writer create citations for their sources, which is an ethical step needed to avoid plagiarism.
An MLA citation generator can make it easier (and sometimes faster) for a writer to create citations versus manually making each citation. We recommend trying the Cite This For Me MLA citation generator and deciding for yourself.
Course & Exam Pages
A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024
It’s time for a generative AI (gen AI) reset. The initial enthusiasm and flurry of activity in 2023 is giving way to second thoughts and recalibrations as companies realize that capturing gen AI’s enormous potential value is harder than expected .
With 2024 shaping up to be the year for gen AI to prove its value, companies should keep in mind the hard lessons learned with digital and AI transformations: competitive advantage comes from building organizational and technological capabilities to broadly innovate, deploy, and improve solutions at scale—in effect, rewiring the business for distributed digital and AI innovation.
About QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey
QuantumBlack, McKinsey’s AI arm, helps companies transform using the power of technology, technical expertise, and industry experts. With thousands of practitioners at QuantumBlack (data engineers, data scientists, product managers, designers, and software engineers) and McKinsey (industry and domain experts), we are working to solve the world’s most important AI challenges. QuantumBlack Labs is our center of technology development and client innovation, which has been driving cutting-edge advancements and developments in AI through locations across the globe.
Companies looking to score early wins with gen AI should move quickly. But those hoping that gen AI offers a shortcut past the tough—and necessary—organizational surgery are likely to meet with disappointing results. Launching pilots is (relatively) easy; getting pilots to scale and create meaningful value is hard because they require a broad set of changes to the way work actually gets done.
Let’s briefly look at what this has meant for one Pacific region telecommunications company. The company hired a chief data and AI officer with a mandate to “enable the organization to create value with data and AI.” The chief data and AI officer worked with the business to develop the strategic vision and implement the road map for the use cases. After a scan of domains (that is, customer journeys or functions) and use case opportunities across the enterprise, leadership prioritized the home-servicing/maintenance domain to pilot and then scale as part of a larger sequencing of initiatives. They targeted, in particular, the development of a gen AI tool to help dispatchers and service operators better predict the types of calls and parts needed when servicing homes.
Leadership put in place cross-functional product teams with shared objectives and incentives to build the gen AI tool. As part of an effort to upskill the entire enterprise to better work with data and gen AI tools, they also set up a data and AI academy, which the dispatchers and service operators enrolled in as part of their training. To provide the technology and data underpinnings for gen AI, the chief data and AI officer also selected a large language model (LLM) and cloud provider that could meet the needs of the domain as well as serve other parts of the enterprise. The chief data and AI officer also oversaw the implementation of a data architecture so that the clean and reliable data (including service histories and inventory databases) needed to build the gen AI tool could be delivered quickly and responsibly.

Creating value beyond the hype
Let’s deliver on the promise of technology from strategy to scale.
Our book Rewired: The McKinsey Guide to Outcompeting in the Age of Digital and AI (Wiley, June 2023) provides a detailed manual on the six capabilities needed to deliver the kind of broad change that harnesses digital and AI technology. In this article, we will explore how to extend each of those capabilities to implement a successful gen AI program at scale. While recognizing that these are still early days and that there is much more to learn, our experience has shown that breaking open the gen AI opportunity requires companies to rewire how they work in the following ways.
Figure out where gen AI copilots can give you a real competitive advantage
The broad excitement around gen AI and its relative ease of use has led to a burst of experimentation across organizations. Most of these initiatives, however, won’t generate a competitive advantage. One bank, for example, bought tens of thousands of GitHub Copilot licenses, but since it didn’t have a clear sense of how to work with the technology, progress was slow. Another unfocused effort we often see is when companies move to incorporate gen AI into their customer service capabilities. Customer service is a commodity capability, not part of the core business, for most companies. While gen AI might help with productivity in such cases, it won’t create a competitive advantage.
To create competitive advantage, companies should first understand the difference between being a “taker” (a user of available tools, often via APIs and subscription services), a “shaper” (an integrator of available models with proprietary data), and a “maker” (a builder of LLMs). For now, the maker approach is too expensive for most companies, so the sweet spot for businesses is implementing a taker model for productivity improvements while building shaper applications for competitive advantage.
Much of gen AI’s near-term value is closely tied to its ability to help people do their current jobs better. In this way, gen AI tools act as copilots that work side by side with an employee, creating an initial block of code that a developer can adapt, for example, or drafting a requisition order for a new part that a maintenance worker in the field can review and submit (see sidebar “Copilot examples across three generative AI archetypes”). This means companies should be focusing on where copilot technology can have the biggest impact on their priority programs.
Copilot examples across three generative AI archetypes
- “Taker” copilots help real estate customers sift through property options and find the most promising one, write code for a developer, and summarize investor transcripts.
- “Shaper” copilots provide recommendations to sales reps for upselling customers by connecting generative AI tools to customer relationship management systems, financial systems, and customer behavior histories; create virtual assistants to personalize treatments for patients; and recommend solutions for maintenance workers based on historical data.
- “Maker” copilots are foundation models that lab scientists at pharmaceutical companies can use to find and test new and better drugs more quickly.
Some industrial companies, for example, have identified maintenance as a critical domain for their business. Reviewing maintenance reports and spending time with workers on the front lines can help determine where a gen AI copilot could make a big difference, such as in identifying issues with equipment failures quickly and early on. A gen AI copilot can also help identify root causes of truck breakdowns and recommend resolutions much more quickly than usual, as well as act as an ongoing source for best practices or standard operating procedures.
The challenge with copilots is figuring out how to generate revenue from increased productivity. In the case of customer service centers, for example, companies can stop recruiting new agents and use attrition to potentially achieve real financial gains. Defining the plans for how to generate revenue from the increased productivity up front, therefore, is crucial to capturing the value.

McKinsey Live Event: Unlocking the full value of gen AI
Join our colleagues Jessica Lamb and Gayatri Shenai on April 8, as they discuss how companies can navigate the ever-changing world of gen AI.
Upskill the talent you have but be clear about the gen-AI-specific skills you need
By now, most companies have a decent understanding of the technical gen AI skills they need, such as model fine-tuning, vector database administration, prompt engineering, and context engineering. In many cases, these are skills that you can train your existing workforce to develop. Those with existing AI and machine learning (ML) capabilities have a strong head start. Data engineers, for example, can learn multimodal processing and vector database management, MLOps (ML operations) engineers can extend their skills to LLMOps (LLM operations), and data scientists can develop prompt engineering, bias detection, and fine-tuning skills.
A sample of new generative AI skills needed
The following are examples of new skills needed for the successful deployment of generative AI tools:
- data scientist:
- prompt engineering
- in-context learning
- bias detection
- pattern identification
- reinforcement learning from human feedback
- hyperparameter/large language model fine-tuning; transfer learning
- data engineer:
- data wrangling and data warehousing
- data pipeline construction
- multimodal processing
- vector database management
The learning process can take two to three months to get to a decent level of competence because of the complexities in learning what various LLMs can and can’t do and how best to use them. The coders need to gain experience building software, testing, and validating answers, for example. It took one financial-services company three months to train its best data scientists to a high level of competence. While courses and documentation are available—many LLM providers have boot camps for developers—we have found that the most effective way to build capabilities at scale is through apprenticeship, training people to then train others, and building communities of practitioners. Rotating experts through teams to train others, scheduling regular sessions for people to share learnings, and hosting biweekly documentation review sessions are practices that have proven successful in building communities of practitioners (see sidebar “A sample of new generative AI skills needed”).
It’s important to bear in mind that successful gen AI skills are about more than coding proficiency. Our experience in developing our own gen AI platform, Lilli , showed us that the best gen AI technical talent has design skills to uncover where to focus solutions, contextual understanding to ensure the most relevant and high-quality answers are generated, collaboration skills to work well with knowledge experts (to test and validate answers and develop an appropriate curation approach), strong forensic skills to figure out causes of breakdowns (is the issue the data, the interpretation of the user’s intent, the quality of metadata on embeddings, or something else?), and anticipation skills to conceive of and plan for possible outcomes and to put the right kind of tracking into their code. A pure coder who doesn’t intrinsically have these skills may not be as useful a team member.
While current upskilling is largely based on a “learn on the job” approach, we see a rapid market emerging for people who have learned these skills over the past year. That skill growth is moving quickly. GitHub reported that developers were working on gen AI projects “in big numbers,” and that 65,000 public gen AI projects were created on its platform in 2023—a jump of almost 250 percent over the previous year. If your company is just starting its gen AI journey, you could consider hiring two or three senior engineers who have built a gen AI shaper product for their companies. This could greatly accelerate your efforts.
Form a centralized team to establish standards that enable responsible scaling
To ensure that all parts of the business can scale gen AI capabilities, centralizing competencies is a natural first move. The critical focus for this central team will be to develop and put in place protocols and standards to support scale, ensuring that teams can access models while also minimizing risk and containing costs. The team’s work could include, for example, procuring models and prescribing ways to access them, developing standards for data readiness, setting up approved prompt libraries, and allocating resources.
While developing Lilli, our team had its mind on scale when it created an open plug-in architecture and setting standards for how APIs should function and be built. They developed standardized tooling and infrastructure where teams could securely experiment and access a GPT LLM , a gateway with preapproved APIs that teams could access, and a self-serve developer portal. Our goal is that this approach, over time, can help shift “Lilli as a product” (that a handful of teams use to build specific solutions) to “Lilli as a platform” (that teams across the enterprise can access to build other products).
For teams developing gen AI solutions, squad composition will be similar to AI teams but with data engineers and data scientists with gen AI experience and more contributors from risk management, compliance, and legal functions. The general idea of staffing squads with resources that are federated from the different expertise areas will not change, but the skill composition of a gen-AI-intensive squad will.
Set up the technology architecture to scale
Building a gen AI model is often relatively straightforward, but making it fully operational at scale is a different matter entirely. We’ve seen engineers build a basic chatbot in a week, but releasing a stable, accurate, and compliant version that scales can take four months. That’s why, our experience shows, the actual model costs may be less than 10 to 15 percent of the total costs of the solution.
Building for scale doesn’t mean building a new technology architecture. But it does mean focusing on a few core decisions that simplify and speed up processes without breaking the bank. Three such decisions stand out:
- Focus on reusing your technology. Reusing code can increase the development speed of gen AI use cases by 30 to 50 percent. One good approach is simply creating a source for approved tools, code, and components. A financial-services company, for example, created a library of production-grade tools, which had been approved by both the security and legal teams, and made them available in a library for teams to use. More important is taking the time to identify and build those capabilities that are common across the most priority use cases. The same financial-services company, for example, identified three components that could be reused for more than 100 identified use cases. By building those first, they were able to generate a significant portion of the code base for all the identified use cases—essentially giving every application a big head start.
- Focus the architecture on enabling efficient connections between gen AI models and internal systems. For gen AI models to work effectively in the shaper archetype, they need access to a business’s data and applications. Advances in integration and orchestration frameworks have significantly reduced the effort required to make those connections. But laying out what those integrations are and how to enable them is critical to ensure these models work efficiently and to avoid the complexity that creates technical debt (the “tax” a company pays in terms of time and resources needed to redress existing technology issues). Chief information officers and chief technology officers can define reference architectures and integration standards for their organizations. Key elements should include a model hub, which contains trained and approved models that can be provisioned on demand; standard APIs that act as bridges connecting gen AI models to applications or data; and context management and caching, which speed up processing by providing models with relevant information from enterprise data sources.
- Build up your testing and quality assurance capabilities. Our own experience building Lilli taught us to prioritize testing over development. Our team invested in not only developing testing protocols for each stage of development but also aligning the entire team so that, for example, it was clear who specifically needed to sign off on each stage of the process. This slowed down initial development but sped up the overall delivery pace and quality by cutting back on errors and the time needed to fix mistakes.
Ensure data quality and focus on unstructured data to fuel your models
The ability of a business to generate and scale value from gen AI models will depend on how well it takes advantage of its own data. As with technology, targeted upgrades to existing data architecture are needed to maximize the future strategic benefits of gen AI:
- Be targeted in ramping up your data quality and data augmentation efforts. While data quality has always been an important issue, the scale and scope of data that gen AI models can use—especially unstructured data—has made this issue much more consequential. For this reason, it’s critical to get the data foundations right, from clarifying decision rights to defining clear data processes to establishing taxonomies so models can access the data they need. The companies that do this well tie their data quality and augmentation efforts to the specific AI/gen AI application and use case—you don’t need this data foundation to extend to every corner of the enterprise. This could mean, for example, developing a new data repository for all equipment specifications and reported issues to better support maintenance copilot applications.
- Understand what value is locked into your unstructured data. Most organizations have traditionally focused their data efforts on structured data (values that can be organized in tables, such as prices and features). But the real value from LLMs comes from their ability to work with unstructured data (for example, PowerPoint slides, videos, and text). Companies can map out which unstructured data sources are most valuable and establish metadata tagging standards so models can process the data and teams can find what they need (tagging is particularly important to help companies remove data from models as well, if necessary). Be creative in thinking about data opportunities. Some companies, for example, are interviewing senior employees as they retire and feeding that captured institutional knowledge into an LLM to help improve their copilot performance.
- Optimize to lower costs at scale. There is often as much as a tenfold difference between what companies pay for data and what they could be paying if they optimized their data infrastructure and underlying costs. This issue often stems from companies scaling their proofs of concept without optimizing their data approach. Two costs generally stand out. One is storage costs arising from companies uploading terabytes of data into the cloud and wanting that data available 24/7. In practice, companies rarely need more than 10 percent of their data to have that level of availability, and accessing the rest over a 24- or 48-hour period is a much cheaper option. The other costs relate to computation with models that require on-call access to thousands of processors to run. This is especially the case when companies are building their own models (the maker archetype) but also when they are using pretrained models and running them with their own data and use cases (the shaper archetype). Companies could take a close look at how they can optimize computation costs on cloud platforms—for instance, putting some models in a queue to run when processors aren’t being used (such as when Americans go to bed and consumption of computing services like Netflix decreases) is a much cheaper option.
Build trust and reusability to drive adoption and scale
Because many people have concerns about gen AI, the bar on explaining how these tools work is much higher than for most solutions. People who use the tools want to know how they work, not just what they do. So it’s important to invest extra time and money to build trust by ensuring model accuracy and making it easy to check answers.
One insurance company, for example, created a gen AI tool to help manage claims. As part of the tool, it listed all the guardrails that had been put in place, and for each answer provided a link to the sentence or page of the relevant policy documents. The company also used an LLM to generate many variations of the same question to ensure answer consistency. These steps, among others, were critical to helping end users build trust in the tool.
Part of the training for maintenance teams using a gen AI tool should be to help them understand the limitations of models and how best to get the right answers. That includes teaching workers strategies to get to the best answer as fast as possible by starting with broad questions then narrowing them down. This provides the model with more context, and it also helps remove any bias of the people who might think they know the answer already. Having model interfaces that look and feel the same as existing tools also helps users feel less pressured to learn something new each time a new application is introduced.
Getting to scale means that businesses will need to stop building one-off solutions that are hard to use for other similar use cases. One global energy and materials company, for example, has established ease of reuse as a key requirement for all gen AI models, and has found in early iterations that 50 to 60 percent of its components can be reused. This means setting standards for developing gen AI assets (for example, prompts and context) that can be easily reused for other cases.
While many of the risk issues relating to gen AI are evolutions of discussions that were already brewing—for instance, data privacy, security, bias risk, job displacement, and intellectual property protection—gen AI has greatly expanded that risk landscape. Just 21 percent of companies reporting AI adoption say they have established policies governing employees’ use of gen AI technologies.
Similarly, a set of tests for AI/gen AI solutions should be established to demonstrate that data privacy, debiasing, and intellectual property protection are respected. Some organizations, in fact, are proposing to release models accompanied with documentation that details their performance characteristics. Documenting your decisions and rationales can be particularly helpful in conversations with regulators.
In some ways, this article is premature—so much is changing that we’ll likely have a profoundly different understanding of gen AI and its capabilities in a year’s time. But the core truths of finding value and driving change will still apply. How well companies have learned those lessons may largely determine how successful they’ll be in capturing that value.

The authors wish to thank Michael Chui, Juan Couto, Ben Ellencweig, Josh Gartner, Bryce Hall, Holger Harreis, Phil Hudelson, Suzana Iacob, Sid Kamath, Neerav Kingsland, Kitti Lakner, Robert Levin, Matej Macak, Lapo Mori, Alex Peluffo, Aldo Rosales, Erik Roth, Abdul Wahab Shaikh, and Stephen Xu for their contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Barr Seitz, an editorial director in the New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier

Rewired to outcompete

Meet Lilli, our generative AI tool that’s a researcher, a time saver, and an inspiration

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What is a research paper? A research paper is a type of academic writing that provides an in-depth analysis, evaluation, or interpretation of a single topic, based on empirical evidence. Research papers are similar to analytical essays, except that research papers emphasize the use of statistical data and preexisting research, along with a strict code for citations.
Familiarly known as Bloom's Taxonomy, this framework has been applied by generations of K-12 teachers and college instructors in their teaching. The framework elaborated by Bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.
The Publication Manual (7th ed.) has been thoroughly revised and updated to reflect best practices in scholarly writing and publishing. Resources for students on writing and formatting annotated bibliographies, response papers, and other paper types as well as guidelines on citing course materials.
Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper. However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style. Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples.
4. ( 1078) In this guide, students and researchers can learn the basics of creating a properly formatted research paper according to APA guidelines. It includes information on how to conceptualize, outline, and format the basic structure of your paper, as well as practical tips on spelling, abbreviation, punctuation, and more.
Duke University's Thompson Writing Program (n.d.) recommends that you organize the material within a paragraph according to the MEAL plan: Main Idea: Your topic sentence stating the concrete claim the paragraph is advancing. Evidence: Paraphrase or direct quotations from the source material you are using to support your topic sentence's claim.
The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated). The research aims, objectives and questions don't align. The research topic is not well justified. The study has a weak theoretical foundation. The research design is not well articulated well enough. Poor writing and sloppy presentation. Poor project planning and risk management.
Following the application of close reading strategies, the students' performance in Biology improved, with t-values of 3.95, 5.92, 12.31, 8.30, and 16.78, all exceeding the critical value of 2.080. Additionally, these strategies enhanced their reading comprehension skills, which are essential for understanding scientific concepts.
Directions: I designed these templates for an argumentative research paper on a controversial issue. Students choose a controversial issue in America and find reputable research to support their stance on it. The research paper consists of three main points: background (or history) of the controversial issue, argument, and counterargument, which the student addresses and refutes.
To avoid plagiarism, you need to correctly incorporate these sources into your text. You can avoid plagiarism by: Keeping track of the sources you consult in your research. Paraphrasing or quoting from your sources (by using a paraphrasing tool and adding your own ideas) Crediting the original author in an in-text citation and in your reference ...
Syllabus for Paper 2 in Phase I is available in the Annexure to this advertisement. b. Phase II On-Line Examination: An on-line examination consisting of two papers of 100 marks each will be held on August 31, 2024 (except Paper 2 of Information Technology Stream). Paper 2 of Information Technology Stream will be held on September 14, 2024.
Scientific paper publication (scientific proceedings) Eligibility of scientific paper publications. If you submit an abstract under the science and research track, your abstract may be selected for publication in a specific open access volume of the IOP Journal of Physics: Conference Serie. Selected abstracts will be invited to submit a paper ...
Recognizing this need, Keysight and Japan's National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to collaborate on quantum research and to drive the industrialization of quantum technologies. "We're in the early days of quantum, and while there is steady scientific progress, we ...
We then blindly graded these exams as part of our regular grading processes for each class. Over 95 multiple choice questions and 12 essay questions, ChatGPT performed on average at the level of a C+ student, achieving a low but passing grade in all four courses. ... University of Minnesota Law School Legal Studies Research Paper Series. Follow.
Look for emerging technologies, pressing industry challenges, and areas with significant research gaps. These trends can guide you towards relevant and timely research topics. Conduct Literature Review: Dive into existing literature and research papers within your field of interest. Identify gaps in knowledge, unanswered questions, or areas ...
My Practice. Take full-length digital SAT practice exams by first downloading Bluebook and completing practice tests. Then sign into My Practice to view practice test results and review practice exam items, answers, and explanations. Download Bluebook.
A lifetime of support for multilingual learners. Lexia® solutions are grounded in the science of reading, offering a robust portfolio of curriculum, professional learning, and implementation tools designed to enhance literacy education. With 40 years of experience, Lexia provides evidence-based programs that have been proven to accelerate ...
Set a consequence or reward for keeping that basket clean, because more papers are always on the way! 23. Bring your sense of humor. Teaching sixth grade will try your patience. Students will exercise their excuses, their lack of rationality, their insistence on fairness, and developing a sense of justice.
In this paper, a survey on current experimental and clinical state of knowledge about the effect of lavender on the nervous system is given. 1. Introduction. ... the Cognitive Drug Research computerized cognitive assessment battery was performed in 144 participants. Analysis of performance revealed that lavender odor (four drops of oil were ...
An effective health education curriculum has the following characteristics, according to reviews of effective programs and curricula and experts in the field of health education 1-14: Focuses on clear health goals and related behavioral outcomes. Is research-based and theory-driven. Addresses individual values, attitudes, and beliefs.
SEBI Grade A Exam Pattern For Phase I. SEBI Grade A Phase I Exam will have two papers: Paper I and Paper II. Both papers will have Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). Paper 1 will be common for all the streams whereas the exam pattern of Paper 2 will vary according to various disciplines. Both papers will be for 100 marks.
Research at the Bloomberg School is a team sport. In order to provide extensive guidance, infrastructure, and support in pursuit of its research mission, research@BSPH employs three core areas: strategy and development, implementation and impact, and integrity and oversight. Our exceptional research teams comprised of faculty, postdoctoral ...
Instead of a cover page, headings are used on a paper's first page to indicate details like the author's name, instructor's name, the class, and date written. Read on for more details. General page and header formatting: To format your research paper according to the MLA guidelines: Set the margins to 1 inch (or 2.5 cm) on all sides
We present the first systematic review of the scientific literature on smartphone use and academic success. We synthesise the theoretical mechanisms, empirical approaches, and empirical findings described in the multidisciplinary literature to date. Our analysis of the literature reveals a predominance of empirical results supporting a negative ...
AP French Language and Culture. AP German Language and Culture. AP Italian Language and Culture. AP Japanese Language and Culture. AP Latin. AP Spanish Language and Culture. AP Spanish Literature and Culture. A list of all current AP courses and exams by category.
A financial-services company, for example, created a library of production-grade tools, which had been approved by both the security and legal teams, and made them available in a library for teams to use. More important is taking the time to identify and build those capabilities that are common across the most priority use cases. The same ...