- Bihar Board

SRM University
- AP SSC Results 2024
UP Board Result 2024
- UP Board 10th Result 2024
- UP Board 12th Result 2024
- AP Board Result 2024
- JAC Board Result 2024
- Assam Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations (Published by CBSE)
Cbse class 10 maths case study questions for chapter 4 - quadratic equations are released by the board. solve all these questions to perform well in your cbse class 10 maths exam 2021-22..

Check here the case study questions for CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations. The board has published these questions to help class 10 students to understand the new format of questions. All the questions are provided with answers. Students must practice all the case study questions to prepare well for their Maths exam 2021-2022.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations
CASE STUDY 1:
Raj and Ajay are very close friends. Both the families decide to go to Ranikhet by their own cars. Raj’s car travels at a speed of x km/h while Ajay’s car travels 5 km/h faster than Raj’s car. Raj took 4 hours more than Ajay to complete the journey of 400 km.

1. What will be the distance covered by Ajay’s car in two hours?
a) 2(x + 5)km
b) (x – 5)km
c) 2(x + 10)km
d) (2x + 5)km
Answer: a) 2(x + 5)km
2. Which of the following quadratic equation describe the speed of Raj’s car?
a) x 2 – 5x – 500 = 0
b) x 2 + 4x – 400 = 0
c) x 2 + 5x – 500 = 0
d) x 2 – 4x + 400 = 0
Answer: c) x 2 + 5x – 500 = 0
3. What is the speed of Raj’s car?
a) 20 km/hour
b) 15 km/hour
c) 25 km/hour
d) 10 km/hour
Answer: a) 20 km/hour
4. How much time took Ajay to travel 400 km?
Answer: d) 16 hour
CASE STUDY 2:
The speed of a motor boat is 20 km/hr. For covering the distance of 15 km the boat took 1 hour more for upstream than downstream.

1. Let speed of the stream be x km/hr. then speed of the motorboat in upstream will be
a) 20 km/hr
b) (20 + x) km/hr
c) (20 – x) km/hr
Answer: c) (20 – x)km/hr
2. What is the relation between speed ,distance and time?
a) speed = (distance )/time
b) distance = (speed )/time
c) time = speed x distance
d) speed = distance x time
Answer: b) distance = (speed )/time
3. Which is the correct quadratic equation for the speed of the current?
a) x 2 + 30x − 200 = 0
b) x 2 + 20x − 400 = 0
c) x 2 + 30x − 400 = 0
d) x 2 − 20x − 400 = 0
Answer: c) x 2 + 30x − 400 = 0
4. What is the speed of current ?
b) 10 km/hour
c) 15 km/hour
d) 25 km/hour
Answer: b) 10 km/hour
5. How much time boat took in downstream?
a) 90 minute
b) 15 minute
c) 30 minute
d) 45 minute
Answer: d) 45 minute
Also Check:
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths - All Chapters
Tips to Solve Case Study Based Questions Accurately
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- AP Board Results 2024
- MP Board 5th, 8th Result 2024
- 10th Class Results 2024 AP
- AP 10th Class Results 2024
- bse.ap.gov.in Manabadi 10th Results 2024 AP
- Manabadi 10th Public Exam Results 2024
- BSEAP AP SSC Results 2024
- AP SSC Results 2024 Manabadi by Jagran Josh
- AP SSC Topper List 2024
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
LIVE MP Board 5th, 8th Result 2024: थोड़ी देर में एमपी बोर्ड कक्षा 5वीं, 8वीं के नतीजे rskmp.in पर, इस Direct Link से कर सकेंगे चेक
RSKMP Result 2024 Class 5th, 8th: QR कोड से rskmp.in पर कैसे चेक करें एमपी बोर्ड के नतीजे?
NVS Teacher Recruitment 2024: Apply Online for 500 TGT and PGT posts, check eligibility, salary and others
MP Board 5th, 8th Result 2024 LIVE: आज 12:30 बजे से यहाँ देखें एमपी बोर्ड 5वीं और 8वीं के नतीजे सबसे तेज, ये रहा डायरेक्ट डाउनलोड लिंक
[Official] MP Board Result 2024 Class 5th 8th Date and Time Announced: Check Notice for RSKMP Classes Results Here
TS Inter 2nd Year VOC Results 2024 Result Date And Time at tsbie.cgg.gov.in
TS Inter 2nd Year Results 2024: Telangana Board Inter 2nd Year Result Date And Time at tsbie.cgg.gov.in
TS Inter 1st Year VOC Results 2024: Telangana 1st Year Vocational Result Date And Time at tsbie.cgg.gov.in
TS Inter 1st Year Results 2024: Telangana Intermediate 1st Year Results Date and Time at bie.telangana.gov.in
TS Result 2024: Telangana Board SSC, Intermediate Result Date And Time at bse.telangana.gov.in
Purple Cap in IPL 2024: Top Players List with Most Wickets in TATA IPL
Orange Cap in IPL 2024: Top Players List with Most Runs in TATA IPL
[Current] Orange Cap and Purple Cap Holders in IPL 2024
[Today] IPL 2024 Points Table: Team Rankings and Net Run Rate
(Updated) LSG vs CSK Head to Head in IPL: Check Stats, Records and Results
Who Won Yesterday IPL Match: MI vs RR, Match 38, Check All Details and Latest Points Table
Today’s IPL Match (23 April) - CSK vs LSG: Team Squad, Match Time, Where to Watch Live and Stadium
Even The Smartest Of All Failed To Find The Mistake In This Picture Puzzle For IQ Test. Try Your Skills!
IPL Points Table 2024: आईपीएल 2024 अपडेटेड पॉइंट टेबल यहां देखें, राजस्थान ऑन टॉप
Lok Sabha election 2024: केंद्रीय गृह मंत्री Amit Shah कितनी संपत्ति के मालिक है? देखें पूरी Net Worth

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
- Last modified on: 9 months ago
- Reading Time: 4 Minutes
Question 1:
Raj and Ajay are very close friends. Both the families decide to go to Ranikhet by their own cars. Raj’s car travels at a speed of x km/h while Ajay’s car travels 5 km/h faster than Raj’s car. Raj took 4 h more than Ajay to complete the journey of 400 km.

(i) What will be the distance covered by Ajay’s car in two hours? (a) 2 (x + 5) km (b) (x – 5) km (c) 2 (x + 10) km (d) (2x + 5) km
(ii) Which of the following quadratic equation describe the speed of Raj’s car? (a) x 2 − 5x − 500 = 0 (b) x 2 + 4x − 400 = 0 (c) x 2 + 5x − 500 = 0 (d) x 2 − 4x + 400 = 0
(iii) What is the speed of Raj’s car? (a) 20 km/h (b) 15 km/h (c) 25 km/h (d) 10 km/h
(iv) How much time took Ajay to travel 400 km? (a) 20 h (b) 40 h (c) 25 h (d) 16 h
(v) How much time took Raj to travel 400 km? (a) 15 h (b) 20 h (c) 18 h (d) 22 h
✨ Free Quizzes, Test Series and Learning Videos for CBSE Class 10 Maths
You may also like:
Chapter 1 Real Numbers Chapter 2 Polynomials Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables C hapter 4 Quadratic Equations Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Chapter 6 Triangles Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry Chapter 10 Circles Chapter 11 Constructions Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Chapter 14 Statistics Chapter 15 Probability
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions PDF
Download Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 10 Final Exam. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 10 so that they can score 100% on Boards.

CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Exam 2024 will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
Table of Contents
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
The above Case studies for Class 10 Maths will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of cbseexpert.com for the benefit of Class 10 students.
- Class 10th Science Case Study Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions of Class 10th Science
- Assertion and Reason Questions of Class 10th Social Science
Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2024
Chapter-1 real numbers.
Starting with an introduction to real numbers, properties of real numbers, Euclid’s division lemma, fundamentals of arithmetic, Euclid’s division algorithm, revisiting irrational numbers, revisiting rational numbers and their decimal expansions followed by a bunch of problems for a thorough and better understanding.
Chapter-2 Polynomials
This chapter is quite important and marks securing topics in the syllabus. As this chapter is repeated almost every year, students find this a very easy and simple subject to understand. Topics like the geometrical meaning of the zeroes of a polynomial, the relationship between zeroes and coefficients of a polynomial, division algorithm for polynomials followed with exercises and solved examples for thorough understanding.
Chapter-3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
This chapter is very intriguing and the topics covered here are explained very clearly and perfectly using examples and exercises for each topic. Starting with the introduction, pair of linear equations in two variables, graphical method of solution of a pair of linear equations, algebraic methods of solving a pair of linear equations, substitution method, elimination method, cross-multiplication method, equations reducible to a pair of linear equations in two variables, etc are a few topics that are discussed in this chapter.
Chapter-4 Quadratic Equations
The Quadratic Equations chapter is a very important and high priority subject in terms of examination, and securing as well as the problems are very simple and easy. Problems like finding the value of X from a given equation, comparing and solving two equations to find X, Y values, proving the given equation is quadratic or not by knowing the highest power, from the given statement deriving the required quadratic equation, etc are few topics covered in this chapter and also an ample set of problems are provided for better practice purposes.
Chapter-5 Arithmetic Progressions
This chapter is another interesting and simpler topic where the problems here are mostly based on a single formula and the rest are derivations of the original one. Beginning with a basic brief introduction, definitions of arithmetic progressions, nth term of an AP, the sum of first n terms of an AP are a few important and priority topics covered under this chapter. Apart from that, there are many problems and exercises followed with each topic for good understanding.
Chapter-6 Triangles
This chapter Triangle is an interesting and easy chapter and students often like this very much and a securing unit as well. Here beginning with the introduction to triangles followed by other topics like similar figures, the similarity of triangles, criteria for similarity of triangles, areas of similar triangles, Pythagoras theorem, along with a page summary for revision purposes are discussed in this chapter with examples and exercises for practice purposes.
Chapter-7 Coordinate Geometry
Here starting with a general introduction, distance formula, section formula, area of the triangle are a few topics covered in this chapter followed with examples and exercises for better and thorough practice purposes.
Chapter-8 Introduction to Trigonometry
As trigonometry is a very important and vast subject, this topic is divided into two parts where one chapter is Introduction to Trigonometry and another part is Applications of Trigonometry. This Introduction to Trigonometry chapter is started with a general introduction, trigonometric ratios, trigonometric ratios of some specific angles, trigonometric ratios of complementary angles, trigonometric identities, etc are a few important topics covered in this chapter.
Chapter-9 Applications of Trigonometry
This chapter is the continuation of the previous chapter, where the various modeled applications are discussed here with examples and exercises for better understanding. Topics like heights and distances are covered here and at the end, a summary is provided with all the important and frequently used formulas used in this chapter for solving the problems.
Chapter-10 Circle
Beginning with the introduction to circles, tangent to a circle, several tangents from a point on a circle are some of the important topics covered in this chapter. This chapter being practical, there are an ample number of problems and solved examples for better understanding and practice purposes.
Chapter-11 Constructions
This chapter has more practical problems than theory-based definitions. Beginning with a general introduction to constructions, tools used, etc, the topics like division of a line segment, construction of tangents to a circle, and followed with few solved examples that help in solving the exercises provided after each topic.
Chapter-12 Areas related to Circles
This chapter problem is exclusively formula based wherein topics like perimeter and area of a circle- A Review, areas of sector and segment of a circle, areas of combinations of plane figures, and a page summary is provided just as a revision of the topics and formulas covered in the entire chapter and also there are many exercises and solved examples for practice purposes.
Chapter-13 Surface Areas and Volumes
Starting with the introduction, the surface area of a combination of solids, the volume of a combination of solids, conversion of solid from one shape to another, frustum of a cone, etc are to name a few topics explained in detail provided with a set of examples for a better comprehension of the concepts.
Chapter-14 Statistics
In this chapter starting with an introduction, topics like mean of grouped data, mode of grouped data, a median of grouped, graphical representation of cumulative frequency distribution are explained in detail with exercises for practice purposes. This chapter being a simple and easy subject, securing the marks is not difficult for students.
Chapter-15 Probability
Probability is another simple and important chapter in examination point of view and as seeking knowledge purposes as well. Beginning with an introduction to probability, an important topic called A theoretical approach is explained here. Since this chapter is one of the smallest in the syllabus and problems are also quite easy, students often like this chapter
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Case Based Questions - Quadratic Equations
Case study - 1.

Q1: Let speed of the stream be x km/hr. then speed of the motorboat in upstream will be (a) 20 km/hr (b) (20 + x) km/hr (c) (20 – x) km/hr (d) 2 km/hr Ans: (c) Explanation: The speed of the motorboat in still water is given as 20 km/hr. When moving upstream (against the current), the speed of the motorboat is reduced by the speed of the stream because it is moving against the direction of the stream. Let's denote the speed of the stream as 'x' km/hr. Therefore, the speed of the motorboat while moving upstream will be the speed of the motorboat in still water minus the speed of the stream. In mathematical terms, this can be represented as (20 - x) km/hr. Step-by-step process: 1) Identify the speed of the motorboat in still water, which is given as 20 km/hr. 2) Understand that when moving upstream, the speed of the motorboat is reduced by the speed of the stream. 3) Denote the speed of the stream as 'x' km/hr. 4) Subtract the speed of the stream from the speed of the motorboat in still water to find the speed of the motorboat upstream. 5) Represent this as (20 - x) km/hr. Therefore, the answer is (c) (20 – x) km/hr. Q2: What is the relation between speed, distance and time? (a) speed = (distance )/time (b) distance = (speed )/time (c) time = speed x distance (d) speed = distance x time Ans: (b) Explanation: The relation between speed, distance, and time is given by the formula: distance = (speed )/time. Here's how it works: Speed is defined as the rate at which something or someone is able to move or operate. In simpler terms, it is how fast an object is moving. Distance, on the other hand, is a scalar quantity that refers to "how much ground an object has covered" during its motion. Time is simply the duration during which an event occurs. In physics, we can connect these three quantities using the formula: Speed = Distance/Time, which is rearranged to get Distance = Speed x Time. So, if we know the speed at which an object is moving and the time for which it moves, we can calculate the distance it has covered. Therefore, option (b) is correct - distance = (speed )/time. To illustrate, let's take the given case. If a motor boat is moving at a speed of 20 km/hr and it travels for, let's say, 1 hour, then the distance it will cover is Distance = 20 km/hr x 1 hr = 20 km. Q 3: Which is the correct quadratic equation for the speed of the current? ( a) x 2 + 30x − 200 = 0 (b) x 2 + 20x − 400 = 0 (c) x 2 + 30x − 400 = 0 (d) x 2 − 20x − 400 = 0 Ans: ( c) Explanation: The speed of the motor boat in still water is given as 20 km/hr. Let's denote the speed of the current as 'x' km/hr. When the boat is moving downstream (i.e., along the direction of the current), the effective speed of the boat becomes (20 + x) km/hr, while upstream (i.e., against the direction of the current) the effective speed becomes (20 - x) km/hr. Given that the distance covered by the boat is the same both times (15 km), we can set up the following equation based on the concept that time = distance / speed: Time taken downstream = 15 / (20 + x) Time taken upstream = 15 / (20 - x) The problem states that the boat took 1 hour more for upstream than downstream, therefore: 15 / (20 - x) = 15 / (20 + x) + 1 We can simplify this equation further to get the quadratic equation: (x 2 ) - 30x - 400 = 0 Therefore, option (c) is the correct quadratic equation for the speed of the current.
Q4: What is the speed of current? ( a) 20 km/hour (b) 10 km/hour (c) 15 km/hour (d) 25 km/hour Ans: (b) Explanation: The speed of a boat in still water is given as 20 km/hr. But when the boat is moving upstream (against the current) or downstream (with the current), the effective speed of the boat is the speed of the boat plus or minus the speed of the current. Let's denote the speed of the current as 'x' km/hr. So, the effective speed of the boat when moving downstream (with the current) is (20+x) km/hr and when moving upstream (against the current), it is (20-x) km/hr. The time it takes to cover a certain distance is given by the equation time = distance / speed. Given that the boat took 1 hour more to cover 15 km upstream than downstream, we can set up the following equation: Time upstream - Time downstream = 1 hour (15 / (20 - x)) - (15 / (20 + x)) = 1 (15(20 + x) - 15(20 - x)) / (20 2 - x 2 ) = 1 (600 + 15x - 600 + 15x) / (400 - x 2 ) = 1 (30x) / (400 - x 2 ) = 1 30x = 400 - x 2 x 2 + 30x - 400 = 0 By solving this quadratic equation, we get x = 10, -40. Since speed cannot be negative, we discard -40. So, the speed of the current is 10 km/hr. Hence, the answer is (b) 10 km/hr. Q5: How much time boat took in downstream? (a) 90 minute (b) 15 minute (c) 30 minute (d) 45 minute Ans: (d) Explanation: The speed of the boat in still water is given as 20 km/hr. Let's denote the speed of the current as 'c' km/hr. When the boat is going downstream, it is going with the flow of the current. So, the effective speed of the boat is (20+c) km/hr. When the boat is going upstream, it is going against the current. So, the effective speed of the boat is (20-c) km/hr. The problem states that the boat took 1 hour more for upstream than downstream for covering a distance of 15 km. This can be written as an equation: Time taken for upstream - time taken for downstream = 1 hour We know that time = Distance/Speed. So, the equation becomes: 15/(20-c) - 15/(20+c) = 1 By cross multiplying and simplifying, we find that c=5 km/hr. Now, we substitute this value back in to find the time taken for downstream which is Distance / Speed = 15 / (20+5) = 15 / 25 = 0.6 hours. Converting 0.6 hours into minutes (since 1 hour = 60 minutes), we get 0.6 * 60 = 36 minutes. The closest answer to 36 minutes is 45 minutes. Therefore, the answer is (d) 45 minutes.
Case Study - 2
Raj and Ajay are very close friends. Both the families decide to go to Ranikhet by their own cars. Raj’s car travels at a speed of x km/h while Ajay’s car travels 5 km/h faster than Raj’s car. Raj took 4 hours more than Ajay to complete the journey of 400 km.

Q1: What will be the distance covered by Ajay’s car in two hours? (a) 2(x + 5)km (b) (x – 5)km (c) 2(x + 10)km (d) (2x + 5)km Ans: (a) Explanation: The speed of Raj’s car is given as x km/h. Ajay’s car travels at a speed that is 5 km/h faster than Raj's car. Therefore, the speed of Ajay’s car is (x+5) km/h. Distance is calculated by multiplying speed by time. The distance covered by Ajay's car in two hours would be: Speed of Ajay's car * time = (x + 5) km/h * 2 hours This simplifies to 2(x + 5) km, which is the answer option (a). Q2: Which of the following quadratic equation describe the speed of Raj’s car? (a) x 2 – 5x – 500 = 0 (b) x 2 + 4x – 400 = 0 (c) x 2 + 5x – 500 = 0 (d) x 2 – 4x + 400 = 0 Ans: (c) Q3: What is the speed of Raj’s car? (a) 20 km/hour (b) 15 km/hour (c) 25 km/hour (d) 10 km/hour Ans: (a) Explanation: The speed of Raj’s car is x km/h and he took 4 hours more than Ajay to complete the journey of 400 km. Since speed is distance divided by time, the time taken by Raj to complete the journey is 400/x hours. Ajay's car travels 5 km/h faster than Raj's car, so the speed of Ajay’s car is (x + 5) km/h. The time taken by Ajay to complete the journey is 400/(x + 5) hours. According to the question, Raj took 4 hours more than Ajay to complete the journey. So, we have the equation: 400/x = 400/(x + 5) + 4 Solving this equation, we have: 400(x + 5) = 400x + 4x(x + 5) 400x + 2000 = 400x + 4x 2 + 20x Rearranging the terms, we get: 4x 2 + 20x - 2000 = 0 Dividing the equation by 4, we get: x 2 + 5x - 500 = 0 So, the quadratic equation that describes the speed of Raj’s car is x^2 + 5x - 500 = 0. Hence, the correct answer is (c). Q4: How much time took Ajay to travel 400 km? (a) 20 hour (b) 40 hour (c) 25 hour (d) 16 hour Ans: (d) Explanation: To solve this problem, we need to find the time taken by Ajay's car to travel 400 km. Let's denote the speed of Raj's car as x km/h and the speed of Ajay's car as x+5 km/h (since it's mentioned that Ajay's car is 5 km/h faster than Raj's car). The formula for time is distance divided by speed. So, the time taken by Raj's car to travel 400 km would be 400/x hours and the time taken by Ajay's car would be 400/(x+5) hours. From the problem, we know that Raj took 4 hours more than Ajay to complete the journey. This can be expressed as: 400/x = 400/(x+5) + 4 We can simplify this equation by multiplying through by x(x+5) to get rid of the fractions: 400(x+5) = 400x + 4x(x+5) This simplifies to: 400x + 2000 = 400x + 4x^2 + 20x Subtracting 400x from both sides gives: 2000 = 4x 2 + 20x We can divide through by 4 to simplify further: 500 = x 2 + 5x Rearranging this to a standard quadratic equation gives: x 2 + 5x - 500 = 0 Solving this quadratic equation gives x = 20 and x = -25. Since a speed can't be negative, we discard the -25 solution. So, the speed of Raj's car is 20 km/h and the speed of Ajay's car is 25 km/h. Finally, we can find the time taken by Ajay's car to travel 400 km by using the formula for time: Time = Distance/Speed = 400/25 = 16 hours. Therefore, the answer is (d) 16 hours.
Top Courses for Class 10
Practice quizzes, semester notes, video lectures, sample paper, extra questions, important questions, study material, past year papers, mock tests for examination, viva questions, shortcuts and tricks, previous year questions with solutions, objective type questions.

Case Based Questions: Quadratic Equations Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: quadratic equations, case based questions: quadratic equations notes, case based questions: quadratic equations class 10, study case based questions: quadratic equations on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations
- NCERT Solutions

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations - Free PDF
Maths is a subject that deals with lots of formulas and tricks. It requires a good understanding and lots of practice. Quadratic Equation is a chapter in class 10, which is quite tricky and difficult. But, it has good weightage from the board examination’s point of view. This is the reason why Vedantu has prepared NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Solutions. NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 available at Vedantu’s website and app is very simple and easy to understand. Students acquire a complete knowledge about the basic concepts in detail step by step first and then go through the solved examples. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science is also available on Vedantu.
Also, students can download Quadratic Equations Class 10 Solutions in PDF form to use offline. Those who want to secure the highest marks in their board examinations should not miss this Maths Chapter 4 Class 10. It has been recorded that every year, at least two or three questions are asked from this chapter. Therefore, it is advised to every student to start practice for Class 10 Maths Ch 4 with NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Ch 4 offered by Vedantu.
All Topics of NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations
The topics covered under Chapter 4 Maths Class 10 are given below.
Important Points
A quadratic equation can be represented as:
ax 2 + bx + c = 0
Where x is the variable of the equation and a, b and c are the real numbers. Also, a≠0.
The nature of roots of a quadratic equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0 can be find as:
A real number α be root of quadratic equations ax 2 + bx + c = 0 if and only if
aα 2 + bα + c = 0.
Quadratic equations are very important in real-life situations. Learn all the concepts deeply and understand each topic conceptually. And, now let us solve questions related to quadratic equations.

Related Chapters
Exercises under NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Chapter 4 of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths is titled "Quadratic Equations". In this chapter, students will learn about the standard form of a quadratic equation, methods for solving quadratic equations, and the nature of the roots of quadratic equations.
The chapter includes four exercises, each of which covers different aspects of quadratic equations.
Exercise 4.1:
This exercise covers the introduction to quadratic equations and the standard form of a quadratic equation. It also includes methods for solving quadratic equations by factorisation. In this exercise, students will learn how to identify a quadratic equation, how to convert a quadratic equation into standard form, and how to factorise quadratic equations using different methods. The exercise includes a set of questions that range from easy to difficult, allowing students to gradually build their understanding of the concepts.
Exercise 4.2:
This exercise covers more advanced methods for solving quadratic equations, such as completing the square and using the quadratic formula. It includes the derivation of the quadratic formula and shows how to apply it to solve quadratic equations. In this exercise, students will learn how to complete the square of a quadratic equation to convert it into standard form, and how to use the quadratic formula to solve quadratic equations. The exercise includes questions that require students to use both methods to solve quadratic equations.
Exercise 4.3:
This exercise focuses on the nature of the roots of quadratic equations and the discriminant of a quadratic equation. Students will learn how to determine the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation based on the value of its discriminant. The exercise covers the relationship between the coefficients and roots of a quadratic equation, and how to find the sum and product of the roots. The exercise includes a set of questions that require students to apply their knowledge of discriminant and the nature of roots to solve quadratic equations.
Exercise 4.4:
This exercise covers real-life applications of quadratic equations and includes word problems that require students to apply their knowledge of quadratic equations to solve practical problems. The exercise includes problems related to the trajectory of a projectile, finding the distance between two ships, and the dimensions of a garden. Students will learn how to formulate and solve quadratic equations to solve real-life problems. The exercise includes a set of word problems that gradually increase in difficulty, allowing students to develop their problem-solving skills.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class - 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations
Exercise 4.1
1. Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
i. ${{\left( \text{x+1} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=2}\left( \text{x-3} \right)$
Ans : ${{\left( \text{x+1} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=2}\left( \text{x-3} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+2x+1=2x-6}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+7=0}$
Since, it is in the form of $\text{a}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+bx+c=0}$.
Therefore, the given equation is a quadratic equation.
ii. ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-2x=}\left( \text{-2} \right)\left( \text{3-x} \right)$
Ans : ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-2x=}\left( \text{-2} \right)\left( \text{3-x} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-2x=-6+2x}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4x+6=0}$
iii. $\left( \text{x-2} \right)\left( \text{x+1} \right)\text{=}\left( \text{x-1} \right)\left( \text{x+3} \right)$
Ans : $\left( \text{x-2} \right)\left( \text{x+1} \right)\text{=}\left( \text{x-1} \right)\left( \text{x+3} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-x-2=}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+2x-3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{3x-1=0}$
Since, it is not in the form of $\text{a}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+bx+c=0}$.
Therefore, the given equation is not a quadratic equation.
iv. $\left( \text{x-3} \right)\left( \text{2x+1} \right)\text{=x}\left( \text{x+5} \right)$
Ans : $\left( \text{x-3} \right)\left( \text{2x+1} \right)\text{=x}\left( \text{x+5} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-5x-3=}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+5x}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-10x-3=0}$
v. $\left( \text{2x-1} \right)\left( \text{x-3} \right)\text{=}\left( \text{x+5} \right)\left( \text{x-1} \right)$
Ans : $\left( \text{2x-1} \right)\left( \text{x-3} \right)\text{=}\left( \text{x+5} \right)\left( \text{x-1} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-7x+3=}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+4x-5}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-11x+8=0}$
vi. ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+3x+1=}{{\left( \text{x-2} \right)}^{\text{2}}}$
Ans : ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+3x+1=}{{\left( \text{x-2} \right)}^{\text{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+3x+1=}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+4-4x}$
$\Rightarrow \text{7x-3=0}$
vii. ${{\left( \text{x+2} \right)}^{\text{3}}}\text{=2x}\left( {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1} \right)$
Ans : ${{\left( \text{x+2} \right)}^{\text{3}}}\text{=2x}\left( {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}\text{+8+6}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+12x=2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}\text{-2x}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}\text{-14x-6}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-8=0}$
viii. ${{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}\text{-4}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-x+1=}{{\left( \text{x-2} \right)}^{\text{3}}}$
Ans : ${{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}\text{-4}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-x+1=}{{\left( \text{x-2} \right)}^{\text{3}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}\text{-4}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-x+1=}{{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}\text{-8-6}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+12x}$
$\Rightarrow \text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-13x+9=0}$
2. Represent the following situations in the form of quadratic equations.
i. The area of a rectangular plot is $\text{528 }{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$. The length of the plot (in metres) is one more than twice its breadth. We need to find the length and breadth of the plot.
Ans : Let the breath of the plot be $\text{x m}$.
Thus, length would be-
$\text{Length=}\left( \text{2x+1} \right)\text{m}$
Hence, Area of rectangle $=$$\text{Length }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ breadth}$
So, $\text{528=x}\left( \text{2x+1} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+x-528=0}$
ii. The product of two consecutive positive integers is $\text{306}$. We need to find the integers.
Ans : Let the consecutive integers be $\text{x}$ and $\text{x+1}$.
Thus, according to question-
$\text{x}\left( \text{x+1} \right)\text{=306}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+x-306=0}$
iii. Rohan’s mother is $\text{26}$ years older than him. The product of their ages (in years) $\text{3}$ years from now will be $\text{360}$. We would like to find Rohan’s present age.
Ans : Let Rohan’s age be $\text{x}$.
Hence, his mother’s age is $\text{x+26}$ .
Now, after $\text{3 years}$.
Rohan’s age will be $\text{x+3}$.
His mother’s age will be $\text{x+29}$ .
So, according to question-
$\left( \text{x+3} \right)\left( \text{x+29} \right)\text{=360}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+3x+29x+87=360}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+32x-273=0}$
iv. A train travels a distance of $\text{480 km}$ at a uniform speed. If the speed had been $\text{8km/h}$ less, then it would have taken $\text{3}$ hours more to cover the same distance. We need to find the speed of the train.
Ans : Let the speed of train be $\text{x km/h}$.
Thus, time taken to travel $\text{482 km}$ is $\dfrac{\text{480}}{\text{x}}\text{hrs}$.
Now, let the speed of train $\text{=}\left( \text{x-8} \right)\text{km/h}$.
Therefore, time taken to travel $\text{480 km}$ is $\left( \dfrac{\text{480}}{\text{x}}+3 \right)\text{hrs}$.
Hence, $\text{speed }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ time=distance}$
i.e $\left( \text{x-8} \right)\left( \dfrac{\text{480}}{\text{x}}\text{+3} \right)\text{=480}$
$\Rightarrow \text{480+3x-}\dfrac{\text{3840}}{\text{x}}\text{-24=480}$
$\Rightarrow \text{3x-}\dfrac{\text{3840}}{\text{x}}\text{=24}$
$\Rightarrow \text{3}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-24x-3840=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-8x-1280=0}$
Exercise 4.2
1. Find the roots of the following quadratic equations by factorisation:
i. ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-3x-10=0}$
Ans : ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-3x-10=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-5x+2x-10}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-5} \right)\text{+2}\left( \text{x-5} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-5} \right)\left( \text{x+2} \right)$
Therefore, roots of this equation are –
$\text{x-5=0}$ or $\text{x+2=0}$
i.e $\text{x=5}$ or $\text{x=-2}$
ii. $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+x-6=0}$
Ans : $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+x-6=0}$
$\Rightarrow 2{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+4x-3x-6}$
$\Rightarrow 2\text{x}\left( \text{x+2} \right)-3\left( \text{x+2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x+2} \right)\left( \text{2x-3} \right)$
$\text{x+2=0}$ or $\text{2x-3=0}$
i.e $\text{x=-2}$ or $\text{x=}\dfrac{3}{2}$
iii. $\sqrt{\text{2}}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+7x+5}\sqrt{\text{2}}\text{=0}$
Ans : $\sqrt{\text{2}}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+7x+5}\sqrt{\text{2}}\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{\text{2}}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+5x+2x+5}\sqrt{\text{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \sqrt{\text{2}}\text{x+5} \right)+\sqrt{\text{2}}\left( \sqrt{\text{2}}\text{x+5} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{\text{2}}\text{x+5} \right)\left( \text{x+}\sqrt{\text{2}} \right)$
$\sqrt{\text{2}}\text{x+5=0}$ or $\text{x+}\sqrt{\text{2}}\text{=0}$
i.e $\text{x=}\dfrac{-5}{\sqrt{\text{2}}}$ or $\text{x=-}\sqrt{\text{2}}$
iv. $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-x+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{8}}\text{=0}$
Ans : $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-x+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{8}}\text{=0}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{8}}\left( 16{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}-8x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{8}}\left( 4x\left( 4x-1 \right)-1\left( 4x-1 \right) \right)\]
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{8}} {{\left( \text{4x-1} \right)}^{2}}$
$\text{4x-1=0}$ or $\text{4x-1=0}$
i.e $\text{x=}\dfrac{1}{4}$ or $\text{x=}\dfrac{1}{4}$
v. $\text{100}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-20x+1=0}$
Ans : $\text{100}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-20x+1=0}$
$\Rightarrow 100{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-10x-10x+1}$
$\Rightarrow 10\text{x}\left( \text{10x-1} \right)-1\left( \text{10x-1} \right)$
\[\Rightarrow \left( \text{10x-1} \right)\left( \text{10x-1} \right)\]
\[\left( \text{10x-1} \right)=0\]or \[\left( \text{10x-1} \right)=0\]
i.e $\text{x=}\dfrac{1}{10}$ or $\text{x=}\dfrac{1}{10}$
2. i. John and Jivanti together have $\text{45}$ marbles. Both of them lost $\text{5}$ marbles each, and the product of the number of marbles they now have is $\text{124}$. Find out how many marbles they had to start with.
Ans : Let the number of john’s marbles be $\text{x}$.
Thus, number of Jivanti’s marble be $\text{45-x}$.
According to question i.e,
After losing $\text{5}$ marbles.
Number of john’s marbles be $\text{x-5}$
And number of Jivanti’s marble be $\text{40-x}$.
Therefore, $\left( \text{x-5} \right)\left( \text{40-x} \right)\text{=124}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-45x+324=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-36x-9x+324=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-36} \right)\text{-9}\left( \text{x-36} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-36} \right)\left( \text{x-9} \right)\text{=0}$
Case 1 - If $\text{x-36=0}$ i.e $\text{x=36}$
So, the number of john’s marbles be $\text{36}$.
Thus, number of Jivanti’s marble be $\text{9}$.
Case 2 - If $\text{x-9=0}$ i.e $\text{x=9}$
So, the number of john’s marbles be $9$.
Thus, number of Jivanti’s marble be $36$.
ii. A cottage industry produces a certain number of toys in a day. The cost of production of each toy (in rupees) was found to be $\text{55}$ minus the number of toys produced in a day. On a particular day, the total cost of production was Rs $\text{750}$. Find out the number of toys produced on that day.
Ans: Let the number of toys produced be $\text{x}$.
Therefore, Cost of production of each toy be $\text{Rs}\left( \text{55-x} \right)$.
Thus, $\left( \text{55-x} \right)\text{x=750}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-55x+750=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-25x-30x+750=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-25} \right)-30\left( \text{x-25} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-25} \right)\left( \text{x-30} \right)\text{=0}$
Case 1 - If $\text{x-25=0}$ i.e $\text{x=25}$
So, the number of toys be $25$.
Case 2 - If $\text{x-30=0}$ i.e $\text{x=30}$
So, the number of toys be $30$.
3. Find two numbers whose sum is $\text{27}$ and product is $\text{182}$ .
Ans: Let the first number be $\text{x}$ ,
Thus, the second number be $\text{27-x}$.
$\text{x}\left( \text{27-x} \right)\text{=182}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-27x+182=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-13x-14x+182=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-13} \right)-14\left( \text{x-13} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-13} \right)\left( \text{x-14} \right)\text{=0}$
Case 1 - If $\text{x-13=0}$ i.e $\text{x=13}$
So, the first number be $13$ ,
Thus, the second number be $\text{14}$.
Case 2 - If $\text{x-14=0}$ i.e $\text{x=14}$
So, the first number be $\text{14}$.
Thus, the second number be$13$.
4. Find two consecutive positive integers, sum of whose squares is $\text{365}$.
Ans: Let the consecutive positive integers be $\text{x}$ and $\text{x+1}$.
Thus, ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\left( \text{x+1} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=365}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}+1+2\text{x=365}$
$\Rightarrow 2{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+2x-364=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+x-182=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+14x-13x-182=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x+14} \right)-13\left( \text{x+14} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x+14} \right)\left( \text{x-13} \right)\text{=0}$
Case 1 - If $\text{x+14=0}$ i.e $\text{x=-14}$.
This case is rejected because number is positive.
Case 2 - If $\text{x-13=0}$ i.e $\text{x=13}$
So, the first number be $\text{13}$.
Thus, the second number be $14$.
Hence, the two consecutive positive integers are $\text{13}$ and $14$.
5. The altitude of a right triangle is $\text{7 cm}$ less than its base. If the hypotenuse is $\text{13 cm}$, find the other two sides.
Ans: Let the base of the right-angled triangle be $\text{x cm}$.
Its altitude be $\left( \text{x-7} \right)\text{cm}$.
Thus, by pythagores theorem-
$\text{bas}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+altitud}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=hypotenus}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}}$
\[\therefore {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\left( \text{x-7} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=1}{{\text{3}}^{\text{2}}}\]
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}+49-14\text{x=169}$
$\Rightarrow 2{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-14x-120=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-7x-60=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+12x+5x-60=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-12} \right)+5\left( \text{x-12} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-12} \right)\left( \text{x+5} \right)\text{=0}$
Case 1 - If $\text{x-12=0}$ i.e $\text{x=12}$.
So, the base of the right-angled triangle be $\text{12 cm}$ and Its altitude be $\text{5cm}$
Case 2 - If $\text{x+5=0}$ i.e $\text{x=-5}$
This case is rejected because side is always positive.
Hence, the base of the right-angled triangle be $\text{12 cm}$ and Its altitude be $\text{5cm}$.
6. A cottage industry produces a certain number of pottery articles in a day. It was observed on a particular day that the cost of production of each article (in rupees) was $\text{3}$ more than twice the number of articles produced on that day. If the total cost of production on that day was Rs $\text{90}$, find the number of articles produced and the cost of each article.
Ans: Let the number of articles produced be $\text{x}$.
Therefore, cost of production of each article be $\text{Rs}\left( \text{2x+3} \right)$.
Thus, $\text{x}\left( \text{2x+3} \right)\text{=90}$
$\Rightarrow 2{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+3x-90=0}$
$\Rightarrow 2{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+15x-12x-90=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{2x+15} \right)-6\left( \text{2x+15} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{2x+15} \right)\left( \text{x-6} \right)\text{=0}$
Case 1 - If $\text{2x-15=0}$ i.e $\text{x=}\dfrac{-15}{2}$.
This case is rejected because number of articles is always positive.
Case 2 - If $\text{x-6=0}$ i.e $\text{x=6}$
Hence, the number of articles produced be $6$.
Therefore, cost of production of each article be $\text{Rs15}$.
Exercise 4.3
1. Find the roots of the following quadratic equations, if they exist, by the method of completing the square:
i. $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-7x+3=0}$
Ans: $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-7x+3=0}$
On dividing both sides of the equation by $\text{2}$.
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-}\dfrac{\text{7}}{\text{2}}\text{x=-}\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-2}\left( \dfrac{\text{7}}{\text{4}} \right)\text{x=-}\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{2}}$
On adding ${{\left( \dfrac{7}{4} \right)}^{2}}$ both sides of equation.
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-2}\left( \dfrac{\text{7}}{\text{4}} \right)\text{x+}{{\left( \dfrac{7}{4} \right)}^{2}}\text{=-}\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{7}{4} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \text{x-}\dfrac{\text{7}}{\text{4}} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{49}}{\text{16}}\text{-}\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \text{x-}\dfrac{\text{7}}{\text{4}} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{25}}{\text{16}}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-}\dfrac{\text{7}}{\text{4}} \right)\text{=}\pm \dfrac{5}{4}$
$\Rightarrow x\text{=}\dfrac{\text{7}}{\text{4}}\pm \dfrac{5}{4}$
$\Rightarrow x\text{=}\dfrac{\text{7}}{\text{4}}+\dfrac{5}{4}$ or $x\text{=}\dfrac{\text{7}}{\text{4}}-\dfrac{5}{4}$
$\Rightarrow x\text{=}\dfrac{12}{\text{4}}$ or $x\text{=}\dfrac{2}{\text{4}}$
$\Rightarrow x\text{=}3$ or $x\text{=}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$
ii. $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+x-4=0}$
Ans: $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+x-4=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}\dfrac{1}{2}\text{x=2}$
On adding ${{\left( \dfrac{1}{4} \right)}^{2}}$ both sides of equation.
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+2}\left( \dfrac{1}{4} \right)\text{x+}{{\left( \dfrac{1}{4} \right)}^{2}}\text{=2+}{{\left( \dfrac{1}{4} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \text{x+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{4}} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{33}}{\text{16}}$
\[\Rightarrow \left( \text{x+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{4}} \right)\text{=}\pm \dfrac{\sqrt{\text{33}}}{4}\]
\[\Rightarrow \text{x= }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\sqrt{\text{33}}}{\text{4}}\text{-}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \text{x= }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\sqrt{\text{33}}-1}{\text{4}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\sqrt{\text{33}}-1}{\text{4}}\] or \[\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\sqrt{\text{-33}}-1}{\text{4}}\]
iii. $\text{4}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+4}\sqrt{3}\text{x+3=0}$
Ans: $\text{4}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+4}\sqrt{3}\text{x+3=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( 2\text{x} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{+2}\left( 2\sqrt{3} \right)\text{x+}{{\left( \sqrt{\text{3}} \right)}^{2}}\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \text{2x+}\sqrt{\text{3}} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{2x+}\sqrt{\text{3}} \right)\text{=0}$ and $\Rightarrow \left( \text{2x+}\sqrt{\text{3}} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-}\sqrt{\text{3}}}{\text{2}}$ and $\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-}\sqrt{\text{3}}}{\text{2}}$
iv. $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+x+4=0}$
Ans: $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+x+4=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{x+2=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+2}\left( \dfrac{\text{1}}{4} \right)\text{x=-2}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+2}\left( \dfrac{\text{1}}{4} \right)\text{x+}{{\left( \dfrac{1}{4} \right)}^{2}}\text{=-2+}{{\left( \dfrac{1}{4} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \text{x+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{4}} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{16}}\text{-2}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \text{x+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{4}} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=-}\dfrac{\text{31}}{\text{16}}$
Since, the square of a number cannot be negative.
Therefore, there is no real root for the given equation.
2. Find the roots of the quadratic equations given in Q.1 above by applying the quadratic formula.
Ans : $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-7x+3=0}$
On comparing this equation with $\text{a}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+bx+c=}0$.
So, $\text{a=2}$, $\text{b=-7}$, $\text{c=3}$.
Therefore, by using quadratic formula-
$\text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-b }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{{{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac}}}{\text{2a}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{7 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{49-24}}}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{7 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ 5}}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{7+5}}{4}$ or $\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{7-5}}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{12}{4}$ or $\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{2}}{4}$
$\therefore \text{x=3 or }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$.
So, $\text{a=2}$, $\text{b=1}$, $\text{c=-4}$.
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-1 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{1-32}}}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-1 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{33}}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-1+}\sqrt{33}}{4}$ or $\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-1-}\sqrt{33}}{4}$
$\therefore \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-1+}\sqrt{33}}{4}\text{ or }\dfrac{\text{-1-}\sqrt{33}}{4}$.
So, $\text{a=4}$, $\text{b=4}\sqrt{3}$, $\text{c=3}$.
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-4}\sqrt{3}\text{ }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{48-48}}}{8}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-4}\sqrt{3}}{8}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-}\sqrt{3}}{2}$ or $\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-}\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\therefore \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-}\sqrt{3}}{2}\text{ or }\dfrac{\text{-}\sqrt{3}}{2}$.
So, $\text{a=2}$, $\text{b=1}$, $\text{c=4}$.
\[\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-1 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{1-32}}}{4}\]
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-1 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{-31}}}{4}$
Since, there can not be any negative number inside square root for any real root to exist.
3. Find the roots of the following equations:
i. $\text{x-}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x}}\text{=3,x}\ne \text{0}$
Ans: $\text{x-}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x}}\text{=3,x}\ne \text{0}$
$\Rightarrow\text{1}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-3x-1=}0$.
So, $\text{a=1}$, $\text{b=-3}$, $\text{c=-1}$.
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{3 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{9+4}}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{3 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{13}}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{3+}\sqrt{\text{13}}}{2}$ or $\Rightarrow \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{3-}\sqrt{\text{13}}}{2}$
$\therefore \text{x=}\dfrac{\text{3+}\sqrt{\text{13}}}{2}\text{ or }\dfrac{\text{3-}\sqrt{\text{13}}}{2}$.
ii. $\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x+4}}\text{-}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x-7}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{11}}{\text{30}}\text{,x}\ne \text{-4,7}$
Ans: $\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x+4}}\text{-}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x-7}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{11}}{\text{30}}\text{,x}\ne \text{-4,7}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{x-7-x-4}}{\left( \text{x+4} \right)\left( \text{x-7} \right)}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{11}}{\text{30}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{-11}}{\left( \text{x+4} \right)\left( \text{x-7} \right)}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{11}}{\text{30}}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x+4} \right)\left( \text{x-7} \right)=-30$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-3x-28=-3}0$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-3x+2=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-2x-x+2=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-2} \right)\text{-1}\left( \text{x-2} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-2} \right)\left( \text{x-1} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow x\text{=1 or 2}$
4. The sum of the reciprocals of Rehman’s ages, (in years) $\text{3}$ years ago
and $\text{5}$ years from now is \[\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\]. Find his present age.
Ans: Let the present age of Rehman be $\text{x}$ years.
Three years ago, his age was $\left( \text{x-3} \right)\text{years}$.
Five years hence, his age will be $\left( \text{x+5} \right)\text{years}$.
Therefore,$\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x-3}}\text{+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x+5}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{x+5+x-3}}{\left( \text{x-3} \right)\left( \text{x+5} \right)}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{2x+2}}{\left( \text{x-3} \right)\left( \text{x+5} \right)}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\]
$\Rightarrow 3\left( \text{2x+2} \right)=\left( \text{x-3} \right)\left( \text{x+5} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{6x+6=}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+2x-15}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4x-21=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-7x+3x-21=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-7} \right)\text{+3}\left( \text{x-7} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-7} \right)\left( \text{x+3} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow x\text{=7 or -3}$
Therefore, Rehman’s age is $\text{7 years}$.
5. In a class test, the sum of Shefali’s marks in Mathematics and English is $\text{30}$. Had she got $\text{2}$ marks more in Mathematics and $\text{3}$ marks less in English, the product of their marks would have been $\text{210}$. Find her marks in the two subjects.
Ans: Let the marks in maths be $\text{x}$.
Thus, marks in English will be $\text{30-x}$.
Hence, according to question –
$\left( \text{x+2} \right)\left( \text{30-x-3} \right)\text{=210}$
$\left( \text{x+2} \right)\left( \text{27-x} \right)\text{=210}$
$\Rightarrow \text{-}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+25x+54=210}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-25x+156=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-12x-13x+156=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-12} \right)\text{-13}\left( \text{x-12} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-12} \right)\left( \text{x-13} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=12,13}$
Case 1 - If the marks in mathematics are $\text{12}$ , then marks in English will be $18$.
Case 2 - If the marks in mathematics are $\text{13}$ , then marks in English will be $17$.
6. The diagonal of a rectangular field is $\text{60}$ metres more than the shorter side. If the longer side is $\text{30}$ metres more than the shorter side, find the sides of the field.
Ans: Let the shorter side of the rectangle be $\text{x m}$.
Thus, Larger side of the rectangle will be $\left( \text{x+30} \right)\text{m}$.
Diagonal of the rectangle be $\sqrt{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\left( \text{x+30} \right)}^{\text{2}}}}$
Hence, according to question-
$\sqrt{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\left( \text{x+30} \right)}^{\text{2}}}}\text{=x+60}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\left( \text{x+30} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}{{\left( \text{x+60} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+900+60x=}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+3600+120x}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-60x-2700=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-90x+30x-2700=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-90} \right)+30\left( \text{x-90} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-90} \right)\left( \text{x+30} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=90,-30}$
Since, side cannot be negative.
Therefore, the length of the shorter side of rectangle is $\text{90 m}$.
Hence, length of the larger side of the rectangle be $\text{120 m}$.
7. The difference of squares of two numbers is $\text{180}$. The square of the smaller number is $\text{8}$ times the larger number. Find the two numbers.
Ans: Let the larger number be $\text{x}$ and smaller number be $\text{y}$.
According to question-
${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=180}$ and ${{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=8x}$
\[\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-8x=180}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-8x-180=0}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-18x+10x-180=0}\]
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x-18} \right)+10\left( \text{x-18} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-18} \right)\left( \text{x+10} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=18,-10}$
Since, larger cannot be negative as $8$ times of the larger number will be negative and hence, the square of the smaller number will be negative which is not possible.
Therefore, the larger number will be $18$.
$\therefore {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=8}\left( \text{18} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=144}$
$\Rightarrow \text{y= }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ 12}$
Hence, smaller number be $\pm 12$.
Therefore, the numbers are $18$ and $12$ or $18$ and $-12$ .
8. A train travels $\text{360 km}$km at a uniform speed. If the speed had been $\text{5km/h}$ more, it would have taken $\text{1}$hour less for the same journey. Find the speed of the train.
Ans: Let the speed of the train be $\text{x km/h}$.
Time taken to cover $\text{360 km/h}$ be $\dfrac{\text{360}}{\text{x}}$.
$\left( \text{x+5} \right)\left( \dfrac{\text{360}}{\text{x}}\text{-1} \right)\text{=360}$
$\Rightarrow \text{360-x+}\dfrac{\text{1800}}{\text{x}}\text{-5=360}$
\[\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+5x-1800=0}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+45x-40x-1800=0}\]
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x+45} \right)-40\left( \text{x+45} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x+45} \right)\left( \text{x-40} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=40,-45}$
Since, the speed cannot be negative.
Therefore, the speed of the train is $\text{40 km/h}$.
9. Two water taps together can fill a tank in $\text{9}\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{8}}$ hours. The tap of larger diameter takes $\text{10}$ hours less than the smaller one to fill the tank separately. Find the time in which each tap can separately fill the tank.
Ans: Let the time taken by the smaller pipe to fill the tank be $\text{x hr}$.
So, time taken by larger pipe be $\left( \text{x-10} \right)\text{hr}$.
Part of the tank filled by smaller pipe in $1$ hour is $\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x}}$.
Part of the tank filled by larger pipe in $1$ hour is $\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x-10}}$.
So, according to the question-
$\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x}}\text{+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x-10}}\text{=9}\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{8}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x}}\text{+}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{x-10}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{75}}{\text{8}}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{x-10+x}}{\text{x}\left( \text{x-10} \right)}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{8}}{\text{75}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{2x-10}}{\text{x}\left( \text{x-10} \right)}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{8}}{\text{75}}\]
$\Rightarrow \text{75}\left( \text{2x-10} \right)\text{=8}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-80x}$
$\Rightarrow \text{150x-750=8}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-80x}$
$\Rightarrow \text{8}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-230x+750=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{8}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-200x-30x+750=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{8x}\left( \text{x-25} \right)\text{-30}\left( \text{x-25} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x-25} \right)\left( \text{8x-30} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow x\text{=25 or }\dfrac{\text{30}}{\text{8}}$
Case 1- If time taken by smaller pipe be $\dfrac{\text{30}}{\text{8}}$ i.e $\text{3}\text{.75 hours}$.
So, Time taken by larger pipe will be negative which is not possible.
Hence, this case is rejected.
Case 2- If the time taken by smaller pipe be $\text{25}$.Then, time taken by larger pipe will be $\text{15 hours}$.
Therefore, time taken by smaller pipe be $\text{25 hours}$ and time taken by larger pipe will be $\text{15 hours}$.
10. An express train takes $\text{1}$ hour less than a passenger train to travel $\text{132 km}$ between Mysore and Bangalore (without taking into consideration the time they stop at intermediate stations). If the average speeds of the express train is $\text{11 km/h}$ more than that of the passenger train, find the average speed of the two trains.
Ans: Let the average speed of passenger train be $\text{x km/h}$.
So, Average speed of express train be $\left( \text{x+11} \right)\text{km/h}$.
Thus, according to question.
$\therefore \dfrac{\text{132}}{\text{x}}\text{-}\dfrac{\text{132}}{\text{x+11}}\text{=1}$
$\Rightarrow \text{132}\left[ \dfrac{\text{x+11-x}}{\text{x}\left( \text{x+11} \right)} \right]\text{=1}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{132 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 11}}{\text{x}\left( \text{x+11} \right)}\text{=1}$
$\Rightarrow \text{132 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 11=x}\left( \text{x+11} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+11x-1452=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+44x-33x-1452=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}\left( \text{x+44} \right)\text{-33}\left( \text{x+44} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{x+44} \right)\left( \text{x-33} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow x\text{=-44 or 33}$
Since, speed cannot be negative.
Therefore, the speed of the passenger train will be $\text{33 km/h}$ and thus, the speed of the express train will be $\text{44 km/h}$ .
11. Sum of the areas of two squares is $\text{468 }{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$. If the difference of their perimeters are $\text{24 m}$, find the sides of the two squares .
Ans: Let the sides of the two squares be $\text{x m}$ and $\text{y m}$.
Thus, their perimeters will be $\text{4x}$ and $\text{4y}$ and areas will be ${{\text{x}}^{2}}$ and ${{\text{y}}^{2}}$.
$\text{4x-4y=24}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x-y=6}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x=y+6}$
And ${{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=468}$
Substituting value of x-
${{\left( \text{y+6} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=468}$
$\Rightarrow \text{36+}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+12y+}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=468}$
$\Rightarrow \text{2}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+12y-432=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+6y-216=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+18y-12y-216=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{y}\left( \text{y+18} \right)\text{-12}\left( \text{y+18} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{y+18} \right)\left( \text{y-12} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{y=-18 or 12}$
Since, side cannot be negative.
Therefore, the sides of the square are $\text{12 m}$ and $\left( \text{12+6} \right)\text{m}$ i.e $\text{18 m}$.
Exercise 4.4
1. Find the nature of the roots of the following quadratic equations.
If the real roots exist, find them-
i. $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-3x+5=0}$
Ans: For a quadratic equation $\text{a}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+bx+c=0}$.
Where Discriminant $\text{=}{{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac}$
Case 1- If ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac>0}$ then there will be two distinct real roots.
Case 2- If ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac=0}$ then there will be two equal real roots.
Case 3- If ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac<0}$ then there will be no real roots.
Thus, for $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-3x+5=0}$ .
So, $\text{a=2}$, $\text{b=-3}$, $\text{c=5}$.
Discriminant $\text{=}{{\left( \text{-3} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( \text{2} \right)\left( \text{5} \right)$
$\text{=9-40}$
$\text{=-31}$
Since, Discriminant: ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac < 0}$.
ii. $\text{3}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\sqrt{\text{3}}\text{x+4=0}$
Case 1- If ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac > 0}$ then there will be two distinct real roots.
Case 3- If ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac < 0}$ then there will be no real roots.
Thus, for $\text{3}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\sqrt{\text{3}}\text{x+4=0}$ .
So, $\text{a=3}$, $\text{b=-4}\sqrt{\text{3}}$, $\text{c=4}$.
Discriminant $\text{=}{{\left( \text{-4}\sqrt{\text{3}} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( \text{3} \right)\left( \text{4} \right)$
$\text{=48-48}$
$\text{=0}$
Since, Discriminant: ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac=0}$.
Therefore, there is equal real root for the given equation and the roots are-
$\dfrac{\text{-b}}{\text{2a}}$ and $\dfrac{\text{-b}}{\text{2a}}$.
Hence, roots are-
$\dfrac{\text{-b}}{\text{2a}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{-}\left( \text{-4}\sqrt{\text{3}} \right)}{\text{6}}$
$\text{=}\dfrac{\text{4}\sqrt{\text{3}}}{\text{6}}$
\[\text{=}\dfrac{\text{2}\sqrt{\text{3}}}{3}\]
Therefore, roots are \[\dfrac{\text{2}\sqrt{\text{3}}}{3}\] and \[\dfrac{\text{2}\sqrt{\text{3}}}{3}\].
iii. $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-6x+3=0}$
Thus, for $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-6x+3=0}$ .
So, $\text{a=2}$, $\text{b=-6}$, $\text{c=3}$.
Discriminant $\text{=}{{\left( \text{-6} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( \text{2} \right)\left( \text{3} \right)$
$\text{=36-24}$
$\text{=12}$
Since, Discriminant: ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac>0}$.
Therefore, distinct real roots exists for the given equation and the roots are-
$\text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-}\left( \text{-6} \right)\text{ }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{{{\left( \text{-6} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( \text{2} \right)\left( \text{3} \right)}}{\text{4}}$
$\text{=}\dfrac{\text{6 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{36-24}}}{\text{4}}$
$\text{=}\dfrac{\text{6 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{12}}}{\text{4}}$
$\text{=}\dfrac{\text{6 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ 2}\sqrt{\text{3}}}{\text{4}}$
$\text{=}\dfrac{\text{3 }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{\text{3}}}{\text{2}}$
Therefore, roots are $\dfrac{\text{3+}\sqrt{\text{3}}}{\text{2}}$ and $\dfrac{\text{3-}\sqrt{\text{3}}}{\text{2}}$.
2. Find the values of $\text{k}$ for each of the following quadratic equations, so
that they have two equal roots.
i. $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+kx+3=0}$
Ans: If a quadratic equation $\text{a}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+bx+c=0}$ has two equal roots, then its discriminant will be $\text{0}$ i.e., ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac=0}$
So, for $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+kx+3=0}$ .
So, $\text{a=2}$, $\text{b=k}$, $\text{c=3}$.
Discriminant $\text{=}{{\left( \text{k} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( \text{2} \right)\left( \text{3} \right)$
$\text{=}{{\text{k}}^{2}}-24$
For equal roots-
${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac=0}$
$\therefore {{\text{k}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-24=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{k}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=24}$
$\Rightarrow \text{k=}\sqrt{\text{24}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{k=}\pm \text{2}\sqrt{\text{6}}$
ii. $\text{kx}\left( \text{x-2} \right)\text{+6=0}$
So, for $\text{kx}\left( \text{x-2} \right)\text{+6=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{k}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-2kx+6=0}$
So, $\text{a=k}$, $\text{b=-2k}$, $\text{c=6}$.
Discriminant $\text{=}{{\left( \text{-2k} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( \text{k} \right)\left( \text{6} \right)$
$\text{=4}{{\text{k}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-24k}$
$\therefore \text{4}{{\text{k}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-24k=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{4k}\left( \text{k-6} \right)\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{k=0 or k=6}$
But $\text{k}$ cannot be zero. Thus, this equation has two equal roots when $\text{k}$ should be $\text{6}$ .
3. Is it possible to design a rectangular mango grove whose length is
twice its breadth, and the area is $\text{800}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ ? If so, find its length and breadth.
Ans: Let the breadth of mango grove be $\text{x}$.
So, length of mango grove will be $\text{2x}$.
Hence, Area of mango grove is $=\left( \text{2x} \right)\text{x}$
$\text{=2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}$.
So, $\text{2}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=800}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=400}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-400=0}$
So, $\text{a=1}$, $\text{b=0}$, $\text{c=400}$.
Discriminant $\text{=}{{\left( \text{0} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( \text{1} \right)\left( \text{-400} \right)$
$\text{=1600}$
Therefore, distinct real roots exist for the given equation and the roots are-
$\text{x=}\dfrac{\text{-}\left( 0 \right)\text{ }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\sqrt{{{\left( 0 \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( 1 \right)\left( -400 \right)}}{2}$
$\text{=}\dfrac{\pm \sqrt{\text{1600}}}{2}$
$\text{=}\dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ 40}}{2}$
$\text{=}\pm \text{20}$
Since, length cannot be negative.
Therefore, breadth of the mango grove is $\text{20m}$.
And length of the mango grove be $\text{2}\left( \text{20} \right)\text{m}$ i.e., $\text{40m}$.
4. Is the following situation possible? If so, determine their present ages. The sum of the ages of two friends is $\text{20}$ years. Four years ago, the product of their ages in years was $\text{48}$.
Ans: Let the age of one friend be $\text{x years}$.
So, age of the other friend will be $\left( \text{20-x} \right)\text{years}$.
Thus, four years ago, the age of one friend be $\left( \text{x-4} \right)\text{years}$.
And age of the other friend will be $\left( \text{16-x} \right)\text{years}$.
$\left( \text{x-4} \right)\left( \text{16-x} \right)\text{=48}$
$\Rightarrow \text{16x-64-}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+4x=48}$
$\Rightarrow 20\text{x-112-}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=0}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-20x+112-=0}$
So, $\text{a=1}$, $\text{b=-20}$, $\text{c=112}$.
Discriminant $\text{=}{{\left( \text{-20} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( \text{1} \right)\left( \text{112} \right)$
$\text{=400-448}$
$\text{=-48}$
Since, Discriminant: ${{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4ac <0}$.
Therefore, there is no real root for the given equation and hence, this situation is not possible.
5. Is it possible to design a rectangular park of perimeter $\text{80 m}$ and area $\text{400}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$? If so find its length and breadth.
Ans: Let the length of the park be $\text{x m}$ and breadth of the park be $\text{x m}$.
Thus, $\text{Perimeter=2}\left( \text{x+y} \right)$.
$\text{2}\left( \text{x+y} \right)\text{=80}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x+y=40}$
$\Rightarrow \text{y=40-x}$.
Now, $\text{Area=x }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ y}$.
Substituting value of y.
$\text{Area=x}\left( \text{40-x} \right)$
$\text{x}\left( \text{40-x} \right)\text{=400}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-40x+400=0}$
So, $\text{a=1}$, $\text{b=-40}$, $\text{c=400}$.
Discriminant $\text{=}{{\left( \text{-40} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-4}\left( \text{1} \right)\left( 400 \right)$
$\text{=1600-1600}$
Therefore, there is equal real roots for the given equation and hence, this situation is possible.
$\dfrac{\text{-b}}{\text{2a}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{-}\left( -40 \right)}{2}$
$\text{=}\dfrac{\text{40}}{2}$
\[\text{=20}\]
Therefore, length of park is $\text{x=20m}$ .
And breadth of park be $\text{y=}\left( \text{40-20} \right)\text{m}$ i.e., $\text{y=20m}$.
Overview of the Exercises Covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Ex 4.1: There are 2 sums with a total of 12 sub-parts in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Ch-4 Exercise 4.1. Students will have to verify if the given equations are quadratic equations or not, for the first few sums. For the sums covered in the latter part of the exercise, students will have to form quadratic equations from the given word problems. These sums will familiarize them with the standard quadratic equation formula ax 2 +bx+c=0 .
Ex 4.2: There are a total of 6 sums covered in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Ch-4 Exercise 4.2. These sums are based on the application of the concept of factorisation in quadratic equations. Students will have to form the quadratic equation from the given word problems and find the roots of the quadratic equations by the middle term factor method.
Ex 4.3: There are a total of 11 sums in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Ch-4 Exercise 4.3. Students need to have a good understanding of the concepts of speed, time, and distance, time and work, average speed, perimeter and area, etc. to solve the sums covered in this exercise. The first few sums of this exercise require students to apply the method of completing the perfect square terms in quadratic equations. Also, the some of the sums covered in this exercise have the application of the quadratic formula,
\[ x = \frac{-b\pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4ac}}{2a} \]
Ex.4.4: There are a total of 5 sums in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Ch-4 Exercise 4.4. The sums covered in this exercise will familiarize themselves with the nature of roots i.e., real, imaginary, equal, and unequal roots. The sums will help them to identify and deduce the discriminants of quadratic equations and solve the sums to find the nature of roots.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations - PDF Download
You can opt for Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equation NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths PDF for Upcoming Exams and also You can Find the Solutions of All the Maths Chapters below.
Chapter 1 - Real Numbers
Chapter 2 - Polynomials
Chapter 3 - Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variable
Chapter 5 - Arithmetic Progressions
Chapter 6 - Triangles
Chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry
Chapter 8 - Introduction to Trigonometry
Chapter 9 - Some Applications of Trigonometry
Chapter 10 - Circles
Chapter 11 - Constructions
Chapter 12 - Areas Related to Circles
Chapter 13 - Surface Areas and Volumes
Chapter 14 - Statistics
Chapter 15 - Probability
Quadratic Equations Class 10 NCERT Solutions have composed in such a way that every student can understand all concepts easily. The expert team of Vedantu has put all their possible efforts in Class 10 CBSE Maths Chapter 4 Solutions to make it exciting and fun-loving. No doubt that Maths is a subject which is not easy to learn. The formulas are not easy to learn, and students don't catch tricks easily where they should apply.
Chapter 4 Maths Class 10 contains quadratic equations to find the value of x. Apart from this, there are approximately three methods given in Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 for this. But, not all three methods are easy to understand to an individual. But in Chapter 4 Maths Class 10 NCERT Solutions, the experts of Vedantu have explained all three methods in very interesting ways that any student can learn quickly. All concepts of quadratic equations and formulas have been explained well. From where the formula comes, how it is discovered, by whom it is discovered, and many other things are mentioned first for the basic knowledge.
After that, many solved examples have been given in NCERT Solution Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 to teach students how to apply formulas and solve numerical problems. All NCERT exercises have been solved by the experts of Vedantu for the students. Some unsolved questions are also included in Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 NCERT Solutions for the practice of the students. Along with this, previous year's questions have also been stated in between the NCERT Solutions. For the ease of the students, it is also mentioned which question came in which year. Some of the mock test papers are also available at the end of pdf for the students' better preparation. Aspirants who don't want to miss any single question in the board exam should practice regularly with Class 10 NCERT Maths Chapter 4 Solutions.
We can say with full confidence that Vedantu’s NCERT Maths Solution Class 10 Chapter 4 is the single key to get success in board examinations. Students can download the free PDF by a single click on the link available in the website of Vedantu.
Key Features for NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 on Vedantu are highly recommended by the CBSE 10th Board teachers. These solutions are among the best guides for self-study purposes for the students of Class 10. The key features of these solutions for Quadratic Equations given below explain how these solutions are a must-have for CBSE Term 2 Class 10 Maths exam.
These NCERT Solutions PDFs for Class 10 Quadratic Equations are easy to access online and free to download for offline practice purposes.
Since these NCERT Solution PDFs are available on the Vedantu mobile app, students can download them on their mobile phones and study at any time.
Each sum covered in the four exercises of Class 10 Ch-4 Quadratic Equations is solved in a step-by-step manner for a thorough understanding of all students.
Students can refer to these NCERT Solutions for their exam preparation as our highly experienced Maths teachers have prepared these solutions as per the latest CBSE guidelines for Class 10.
Students can refer to these NCERT Solutions whenever they are stuck with any sum. Thus, they can address their doubts in Quadratic Equations during the last-minute revisions without wasting any time or having to wait to consult any friend.
Along with this, students can also download additional study materials provided by Vedantu, for Chapter 4 of CBSE Class 10 Maths Solutions –
Chapter 4: Important Questions
Chapter 4: Important Formulas
Chapter 4: Revision Notes
Chapter 4: NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 4: RD Sharma Solutions
What is the Advantage of Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 4 Provided by Vedantu?
Maths NCERT Solutions Class 10 Chapter 4 includes all solutions for the numerical problem given in the NCERT book. It follows the latest instructions and guidelines announced by the NCERT. Vedantu doesn’t leave any question or concept that is important for the exams. All numerical problems are framed well and solved accurately in NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 solution. It would not be wrong if we say that the study materials provided by Vedantu is the bible for all those students who want to score good marks.
The subject experts at Vedantu have prepared the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations for the Term 2 exam preparation and revision purposes for students. To solve the sums covered in this chapter, students should have a sound understanding of other concepts of Maths, like perimeter and area, time and work, linear equations, etc. Therefore, downloading and referring to the Maths NCERT Solutions Class 10 Ch-4 will help students to prepare very well for their exams.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations
The subject’s experts take online classes available at Vedantu. They have lots of experience in their respective subjects. Along with this, they are working in their field with consistency. So, they have been faced with all kinds of problems and learned the tricks on how to come out from it.
In online classes, teachers share all their experiences with the students and teach some essential tricks. These tricks will be useful at the time of solving questions in the examination hall. Apart from the teaching concepts and formulas, they also motivate students and remove the fear of examinations from the student’s mind that is built up somewhere due to some kind of society’s pressure and other things.
2. Instead of Class 10th Maths Chapter 4, What is the Maths Syllabus for Class 10 for 202 4-25 ?
Here is the complete syllabus for Class 10 Mathematics Revised Syllabus 2024-25:-
Unit- I: Number Systems
Real Numbers
Unit II: Algebra
Polynomials
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Quadratic Equations
Arithmetic Progressions
Unit III: Coordinate Geometry
Lines (In two-dimensions)
Unit IV: Geomtry
Constructions
Unit V: Trigonometry
Introduction to Trigonometry
Trigonometric Identities
Heights and Distances: Angle of elevation, Angle of Depression
Unit VI: Mensuration
Areas Related to Circles
Surface Areas and Volumes
Unit VII: Statistics and Probability
Statistics
Probability
3. What is the Weightage for Class 10 Mathematics Unit-Wise?
Students who don’t know the weightage then they should go through the table given below. Here, we have mentioned the entire Class 10 Mathematics Unit-Wise Weightage for the knowledge of the students.
4. Mention the important concepts that you learn in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations.
If you want to score 100 per cent marks in Class 10 Maths, you have to practice daily. Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations is an important chapter. Students can find NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations on Vedantu. There are five exercises in Chapter 4. Students can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations to learn the important concepts that will help them understand the topic.
5. How to download Class 10 Maths Quadratic Equations NCERT Textbooks PDF?
Students can easily download Class 10 Maths Quadratic Equations NCERT textbooks PDF online. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Quadratic Equations are explained in an easy and simple language. Follow the given steps:
Click NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations.
Click on “Download PDF”.
Download and save it.
Students can use the PDF document without having an internet connection and can study Maths Quadratic Equations anytime. The NCERT Solutions give a clear understanding to them.
6. What is the Quadratic formula Class 10th?
When a quadratic polynomial is equated to a constant, it forms a quadratic equation. An equation such as Ax = D, where Ax is a polynomial of degree two and D is a constant, forms a quadratic equation. The standard quadratic equation is a x 2 +bx+c=0 where a, b, and c are not equal to zero. You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations to understand more about the topic. You can also download Vedantu’s app. All the resources are available free of cost.
7. What are the important topics covered in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 4?
Chapter 4 Class 10 Maths is based on Quadratic Equations. The chapter includes important concepts about quadratic equations. This chapter includes five exercises that explain the different concepts of quadratic equations. The following topics are covered:
Exercise 4.1- Introduction
Exercise 4.2- Quadratic Equations
Exercise 4.3- Solution of a Quadratic Equation by Factorisation
Exercise 4.4- Solution of a Quadratic Equation by Completing the Square
Exercise 4.5- Nature of Roots
8. How do you solve Quadratic Equations in Class 10?
If you want to learn how to solve quadratic equations in Class 10, you can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations. All the solutions are prepared by experts in an easy language. Students can understand the equations clearly. Students have to find the roots by using the quadratic formula. They can find the sum and product of both the roots. The method is simple and explained properly for easier understanding.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
Ncert solutions for class 10.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Revised NCERT Solutions for class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations in Hindi and English Medium updated for board exams 2024. The question answers and explanation of chapter 4 of 10th Maths are based on NCERT textbooks published for 2024-25. Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Solutions for CBSE Board Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1 Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Exercise 4.2 Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Exercise 4.3 Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Important Questions
Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Solutions for State Boards Class 10 Maths Exercise 4.1 Class 10 Maths Exercise 4.2 Class 10 Maths Exercise 4.3 Class 10 Maths Exercise 4.4

Get the free Hindi Medium solutions for the academic session 2024-25. Download here UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 all exercises. 10th Maths Chapter 4 solutions are online or download in PDF format. Download Assignments for practice with Solutions 10th Maths Chapter 4 Assignment 1 10th Maths Chapter 4 Assignment 2 10th Maths Chapter 4 Assignment 3 10th Maths Chapter 4 Assignment 4
10th Maths Chapter 4 NCERT Solutions follows the latest CBSE syllabus. Students of MP, UP, Gujarat board and CBSE can use it for Board exams. Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Offline Apps in Hindi or English for offline use. For any scholarly help, you may contact us. We will try to help you in the best possible ways.
NCERT Solutions for class 10 Maths Chapter 4 are given below in PDF format or view online. Solutions are in Hindi and English Medium. Uttar Pradesh students also can download UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 here in Hindi Medium.
It is very essential to learn quadratic equations, because it have wide applications in other branches of mathematics, physics, in other subjects and also in real life situations. Download NCERT books 2024-25, revision books and solutions from the links given below.
Previous Year’s CBSE Questions
1. Two marks questions Find the roots of the quadratic equation √2 x² + 7x + 5√2 = 0. [CBSE 2017] 2. Find the value of k for which the equation x²+k(2x + k – 1) + 2 = 0 has real and equal roots. [CBSE 2017] 2. Three marks questions If the equation (1 + m² ) x² +2mcx + c² – a² = 0 has equal roots then show that c² = a² (1 + m²). 3. Four marks questions Speed of a boat in still water is 15 km/h. It goes 30 km upstream and returns back at the same point in 4 hours 30 minutes. Find the speed of the stream. [CBSE 2017]
The word quadratic is derived from the Latin word “Quadratum” which means “A square figure”. Brahmagupta (an ancient Indian Mathematician )(A.D. 598-665) gave an explicit formula to solve a quadratic equation. Later Sridharacharya (A.D. 1025) derived a formula, now known as the quadratic formula, for solving a quadratic equation by the method of completing the square. An Arab mathematician Al-khwarizni(about A.D. 800) also studied quadratic equations of different types. It is believed that Babylonians were the first to solve quadratic equations. Greek mathematician Euclid developed a geometrical approach for finding lengths, which are nothing but solutions of quadratic equations.
Important Questions on Class 10 Maths Chapter 4
Check whether the following is quadratic equation: (x + 1)² = 2(x – 3).
(x + 1)² = 2(x – 3) Simplifying the given equation, we get (x + 1)² = 2(x – 3) ⇒ x² + 2x + 1 = 2x – 6 ⇒ x² + 7 = 0 or x² + 0x + 7 = 0 This is an equation of type ax² + bx + c = 0. Hence, the given equation is a quadratic equation.
Represent the following situation in the form of quadratic equation: The product of two consecutive positive integers is 306. We need to find the integers.
Let the first integer = x Therefore, the second integer = x + 1 Hence, the product = x(x + 1) According to questions, x(x + 1) = 306 ⇒ x² + x = 306 ⇒ x² + x – 306 = 0 Hence, the two consecutive integers satisfies the quadratic equation x² + x – 306 = 0.
In a class test, the sum of Shefali’s marks in Mathematics and English is 30. Had she got 2 marks more in Mathematics and 3 marks less in English, the product of their marks would have been 210. Find her marks in the two subjects.
Let, Shefali’s marks in Mathematics = x Therefore, Shefali’s marks in English = 30 – x If she got 2 marks more in Mathematics and 3 marks less in English, Marks in Mathematics = x + 2 Marks in English = 30 – x – 3 According to questions, Product = (x + 2)(27 – x) = 210 ⇒ 27x – x² + 54 – 2x = 210 ⇒(-x)² + 25x – 156 = 0 ⇒ x² – 25x + 156 = 0 ⇒ x² – 12x – 13x + 156 = 0 ⇒ x(x – 12) – 13(x – 12) = 0 ⇒ (x – 12)(x – 13) = 0 ⇒ (x – 12) = 0 or (x – 13) = 0 Either x = 12 or x = 13 If x = 12 then, marks in Maths = 12 and marks in English = 30 – 12 = 18 If x = 13 then, marks in Maths = 13 and marks in English = 30 – 13 = 1
The difference of squares of two numbers is 180. The square of the smaller number is 8 times the larger number. Find the two numbers.
Let the larger number = x Let the smaller number = y Therefore, y² = 8x According to question, x² – y² = 180 ⇒ x² – 8x = 180 [As y² = 8x] ⇒ x² – 8x – 180 = 0 ⇒ x² – 18x + 10x – 180 = 0 ⇒ x(x – 18) + 10(x – 18) = 0 ⇒ (x – 18)(x + 10) = 0 ⇒ (x – 18) = 0 or (x + 10) = 0 Either x = 18 or x = -10 But x ≠ -10 , as x is the larger of two numbers. So, x = 18 Therefore, the larger number = 18 Hence, the smaller number = y = √144 = 12
Sum of the areas of two squares is 468 m². If the difference of their perimeters is 24 m, find the sides of the two squares.
Let the side of larger square = x m Let the side of smaller square = y m According to question, x² + y² = 468 …(i) Difference between perimeters, 4x – 4y = 24 ⇒ x – y = 6 ⇒ x = 6 + y … (ii) Putting the value of x in equation (i), we get (y + 6)² + y² = 468 ⇒ y² + 12y + 36 + y² = 468 ⇒ (2y)² +12y – 432 = 0 ⇒ y² + 6y – 216 = 0 ⇒ y² + 18y – 12y – 216 = 0 ⇒ y(y + 18) – 12(y + 18) = 0 ⇒ (y + 18)(y – 12) = 0 ⇒ (y + 18) = 0 or (y – 12) = 0 Either y = -18 or y = 12 But, y ≠ -18 , as x is the side of square, which can’t be negative. So, y = 12 Hence, the side of smaller square = 12 m Putting the value of y in equation (ii), we get Side of larger square = x = y + 6 = 12 + 6 = 18 m
How to Revise 10th Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations for Exams
Schools and institutions across the world promptly acted according to a pandemic, by moving online. Tech advancement helped institutions transition physical classrooms to virtual ones in record time. For as long as I can remember, I have liked everything about mathematics – especially teaching young schoolers, I have seen some of the brilliant minds grapple to comprehend the concepts. I have seen hard-working bright-eyed students losing to perform better than average in the classroom. In this article, you will read some of the effective practices that helped many students score 100% in math of 10th standard chapter Quadratic equations.
Step 1: NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 helps to practice real life based Problems in Exercise 4.3.
Step 2: class 10 maths chapter 4 solutions provides the fundamental facts of quadratic equations., step 3: ncert solutions class 10 maths chapter 4 by applying the perfect formula for answers., step 4: class 10 maths chapter 4 needs regular practice session after short intervals., step 5: practice class 10 maths chapter 4 from ncert textbook for exams..

How can I get good marks in Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations?
Student should know the methods of factorization to a quadratic equation. It will help a lot during the solution of questions in 10th Maths chapter 4. Quadratic formula is the ultimate trick to find the roots of difficult or easy format of any quadratic equation. So if someone has practiced well the factorization method and quadratic formula method, he will score better then ever in chapter 4 of class 10 mathematics.
How a quadratic polynomial is different from a quadratic equation in 10th Maths Chapter 4?
A polynomial of degree two is called a quadratic polynomial. When a quadratic polynomial is equated to zero, it is called a quadratic equation. A quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0, a > 0, where a, b, c are constants and x is a variable is called a quadratic equation in the standard format.
In Class 10 Maths Chapter 4, which exercise is considered as the most difficult to solve?
Class 10 Maths, exercise 4.1, and 4.2 are easy to solve and having less number of questions. Exercise 4.3 is tricky to find the solutions and answers also. In this exercise most of the questions are based on application of quadratic equations.
What is meant by zeros of a quadratic equation in Chapter 4 of 10th Maths?
A zero of a polynomial is that real number, which when substituted for the variable makes the value of the polynomial zero. In case of a quadratic equation, the value of the variable for which LHS and RHS of the equation become equal is called a root or solution of the quadratic equation. There are three algebraic methods for finding the solution of a quadratic equation. These are (i) Factor Method (ii) Completing the square method and (iii) Using the Quadratic Formula.

What are the main topics to study in Class 10 Maths chapter 4?
In chapter 4 (Quadratic equations) of class 10th mathematics, Students will study
- 1) Meaning of Quadratic equations
- 2) Solution of a quadratic equation by factorization.
- 3) Solution of a quadratic equation by completing the square.
- 4) Solution of a quadratic equation using quadratic formula.
- 5) Nature of roots.
How many exercises are there in chapter 4 of Class 10th Maths?
There are in all 4 exercises in class 10 mathematics chapter 4 (Quadratic equations). In first exercise (Ex 4.1), there are only 2 questions (Q1 having 8 parts and Q2 having 4 parts). In second exercise (Ex 4.2), there are in all 6 questions. In fourth exercise (Ex 4.3), there are in all 5 questions. So, there are total 13 questions in class 10 mathematics chapter 4 (Quadratic equations). In this chapter there are in all 18 examples. Examples 1, 2 are based on Ex 4.1, Examples 3, 4, 5, 6 are based on Ex 4.2, Examples 16, 17, 18 are based on Ex 4.3.
Does chapter 4 of class 10th mathematics contain optional exercise?
No, chapter 4 (Quadratic equations) of class 10th mathematics doesn’t contain any optional exercise. All the four exercises are compulsory for the exams.
How much time required to complete chapter 4 of 10th Maths?
Students need maximum 3-4 days to complete chapter 4 (Quadratic equations) of class 10th mathematics. But even after this time, revision is compulsory to retain the way to solving questions.
« Chapter 3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Chapter 5: arithmetic progression ».
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 4 Class 10 Quadratic Equations
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for Latest NCERT for 2023-2024 Boards.
Get NCERT Solutions for all exercise questions and examples of Chapter 4 Class 10 Quadratic Equations free at Teachoo. Answers to each and every question is provided video solutions.
In this chapter, we will learn
- What is a Quadratic Equation
- What is the Standard Form of a Quadratic Equation
- Solution of a Quadratic Equation by Factorisation ( Splitting the Middle Term method)
- Solving a Quadratic Equation by Completing the Square
- Solving a Quadratic Equation using D Formula (x = -b ± √b 2 - 4ac / 2a)
- Checking if roots are real, equal or no real roots (By Checking the value of D = b 2 - 4ac)
This chapter is divided into two parts - Serial Order Wise, Concept Wise
In Serial Order Wise, the chapter is divided into exercise questions and examples.
In Concept Wise, the chapter is divided into concepts. First the concepts are explained, and then the questions of the topic are solved - from easy to difficult.
We suggest you do the Chapter from Concept Wise - it is the Teachoo (टीचू) way of learning.
Note: When you click on a link, the first question of the exercise will open. To open other question of the exercise, go to bottom of the page. There is a list with arrows. It has all the questions with Important Questions also marked.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations are provided here to help the students of CBSE class 10. Our expert teachers prepared all these solutions as per the latest CBSE syllabus and guidelines. In this chapter, we have discussed how to find the solution of a quadratic equation by – factorisation, completing the square method in details. CBSE Class 10 Maths solutions provide a detailed and step-wise explanation of each answer to the questions given in the exercises of NCERT books.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Solutions
Below we have given the answers to all the questions present in Quadratic Equations in our NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths chapter 4. In this lesson, students are introduced to a lot of important concepts that will be useful for those who wish to pursue mathematics as a subject in their future classes. Based on these solutions, students can prepare for their upcoming Board Exams. These solutions are helpful as the syllabus covered here follows NCERT guidelines.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Exercise 4.1

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Exercise 4.2

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Exercise 4.3

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Exercise 4.4

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Case Study Class 10 Maths Questions and Answers (Download PDF)
Free pdf download.
SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
Case Study Class 10 Maths
If you are looking for the CBSE Case Study class 10 Maths in PDF, then you are in the right place. CBSE 10th Class Case Study for the Maths Subject is available here on this website. These Case studies can help the students to solve the different types of questions that are based on the case study or passage.
CBSE Board will be asking case study questions based on Maths subjects in the upcoming board exams. Thus, it becomes an essential resource to study.
The Case Study Class 10 Maths Questions cover a wide range of chapters from the subject. Students willing to score good marks in their board exams can use it to practice questions during the exam preparation. The questions are highly interactive and it allows students to use their thoughts and skills to solve the given Case study questions.
Download Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions and Answers PDF (Passage Based)
Download links of class 10 Maths Case Study questions and answers pdf is given on this website. Students can download them for free of cost because it is going to help them to practice a variety of questions from the exam perspective.
Case Study questions class 10 Maths include all chapters wise questions. A few passages are given in the case study PDF of Maths. Students can download them to read and solve the relevant questions that are given in the passage.
Students are advised to access Case Study questions class 10 Maths CBSE chapter wise PDF and learn how to easily solve questions. For gaining the basic knowledge students can refer to the NCERT Class 10th Textbooks. After gaining the basic information students can easily solve the Case Study class 10 Maths questions.
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Equations in Two Variables
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8. Introduction to Trigonometry
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas & Volumes
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics
Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
How to Solve Case Study Based Questions Class 10 Maths?
In order to solve the Case Study Based Questions Class 10 Maths students are needed to observe or analyse the given information or data. Students willing to solve Case Study Based Questions are required to read the passage carefully and then solve them.
While solving the class 10 Maths Case Study questions, the ideal way is to highlight the key information or given data. Because, later it will ease them to write the final answers.
Case Study class 10 Maths consists of 4 to 5 questions that should be answered in MCQ manner. While answering the MCQs of Case Study, students are required to read the paragraph as they can get some clue in between related to the topics discussed.
Also, before solving the Case study type questions it is ideal to use the CBSE Syllabus to brush up the previous learnings.
Features Of Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions And Answers Pdf
Students referring to the Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions And Answers Pdf from Selfstudys will find these features:-
- Accurate answers of all the Case-based questions given in the PDF.
- Case Study class 10 Maths solutions are prepared by subject experts referring to the CBSE Syllabus of class 10.
- Free to download in Portable Document Format (PDF) so that students can study without having access to the internet.
Benefits of Using CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions and Answers
Since, CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions and Answers are prepared by our maths experts referring to the CBSE Class 10 Syllabus, it provided benefits in various way:-
- Case study class 10 maths helps in exam preparation since, CBSE Class 10 Question Papers contain case-based questions.
- It allows students to utilise their learning to solve real life problems.
- Solving case study questions class 10 maths helps students in developing their observation skills.
- Those students who solve Case Study Class 10 Maths on a regular basis become extremely good at answering normal formula based maths questions.
- By using class 10 Maths Case Study questions and answers pdf, students focus more on Selfstudys instead of wasting their valuable time.
- With the help of given solutions students learn to solve all Case Study questions class 10 Maths CBSE chapter wise pdf regardless of its difficulty level.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Chapter 4: Quadratic Equations
- Exercise 4.4
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.4
NCERT Solutions is the best guide for students with detailed study material, including important topics. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations is an important chapter, and the students are advised to study it carefully. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.4 contains solutions to all the questions mentioned on page number 91 in the textbook.
Mathematics is one subject that requires a lot of practice. Stepwise solutions to the questions are provided on this page for better practice. The solutions are provided by the subject experts and are beneficial in scoring good marks in the examinations. Students should go through the questions provided in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths after completing each chapter. This helps to analyse their shortcomings and study accordingly.
NCERT Solutions are very helpful from the examination perspective. The subject experts have tried to include all topics and concepts that are important. Students can refer to the NCERT Class 10 solutions for a better understanding of the topics. Students appearing for the board examinations will find it helpful to prepare for the examinations.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.4
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access Other Exercise Solutions of Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations
Exercise 4.1 Solutions – 2 Questions
Exercise 4.2 Solutions – 6 Questions
Exercise 4.3 Solutions – 11 Questions
Access Answers of Maths NCERT Class 10 Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.4
1. Find the nature of the roots of the following quadratic equations. If the real roots exist, find them: (i) 2 x 2 – 3 x + 5 = 0 (ii) 3 x 2 – 4√3 x + 4 = 0 (iii) 2 x 2 – 6 x + 3 = 0
2x 2 – 3 x + 5 = 0
Comparing the equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 2, b = -3 and c = 5
We know, discriminant = b 2 – 4 ac
= ( – 3) 2 – 4 (2) (5) = 9 – 40
As you can see, b 2 – 4ac < 0
Therefore, no real root is possible for the given equation, 2x 2 – 3 x + 5 = 0.
(ii) 3 x 2 – 4√3 x + 4 = 0
a = 3, b = -4√3 and c = 4
We know, Discriminant = b 2 – 4 ac
= (-4√3) 2 – 4(3)(4)
= 48 – 48 = 0
As b 2 – 4 ac = 0,
Real roots exist for the given equation, and they are equal to each other.
Hence, the roots will be – b /2 a and – b /2 a .
– b /2 a = -(-4√3)/2×3 = 4√3/6 = 2√3/3 = 2/√3
Therefore, the roots are 2/√3 and 2/√3.
(iii) 2 x 2 – 6 x + 3 = 0
a = 2, b = -6, c = 3
As we know, discriminant = b 2 – 4 ac
= (-6) 2 – 4 (2) (3)
= 36 – 24 = 12
As b 2 – 4 ac > 0,
Therefore, there are distinct real roots that exist for this equation, 2 x 2 – 6 x + 3 = 0.
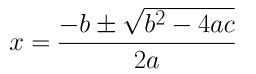
= (-(-6) ± √(-6 2 -4(2)(3)) )/ 2(2)
= (6±2√3 )/4
Therefore, the roots for the given equation are (3+√3)/2 and (3-√3)/2.
2. Find the values of k for each of the following quadratic equations so that they have two equal roots. (i) 2 x 2 + kx + 3 = 0 (ii) kx ( x – 2) + 6 = 0
(i) 2 x 2 + kx + 3 = 0
Comparing the given equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 2, b = k and c = 3
= ( k ) 2 – 4(2) (3)
= k 2 – 24
For equal roots, we know,
Discriminant = 0
k 2 – 24 = 0
k = ±√24 = ±2√6
(ii) kx ( x – 2) + 6 = 0
or kx 2 – 2 kx + 6 = 0
Comparing the given equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = k , b = – 2 k and c = 6
= ( – 2 k ) 2 – 4 ( k ) (6)
= 4 k 2 – 24 k
b 2 – 4 ac = 0
4 k 2 – 24 k = 0
4 k ( k – 6) = 0
Either 4 k = 0 or k = 6 = 0
k = 0 or k = 6
However, if k = 0, then the equation will not have the terms ‘ x 2 ‘ and ‘ x ‘.
Therefore, if this equation has two equal roots, k should be 6 only.
3. Is it possible to design a rectangular mango grove whose length is twice its breadth and the area is 800 m 2 ? If so, find its length and breadth.
Let the breadth of the mango grove be l .
The length of the mango grove will be 2 l .
Area of the mango grove = (2 l ) ( l )= 2 l 2
2 l 2 = 800
l 2 = 800/2 = 400
l 2 – 400 =0
a = 1, b = 0, c = 400
=> (0) 2 – 4 × (1) × ( – 400) = 1600
Here, b 2 – 4 ac > 0
Thus, the equation will have real roots. And hence, the desired rectangular mango grove can be designed.
As we know, the value of length cannot be negative.
Therefore, the breadth of the mango grove = 20 m.
Length of the mango grove = 2 × 20 = 40 m.
4. Is the following situation possible? If so, determine their present ages. The sum of the ages of the two friends is 20 years. Four years ago, the product of their age in years was 48.
Let’s say the age of one friend is x years.
Then, the age of the other friend will be (20 – x) years.
Four years ago,
Age of first friend = ( x – 4) years
Age of second friend = (20 – x – 4) = (16 – x ) years
As per the given question, we can write,
( x – 4) (16 – x ) = 48
16 x – x 2 – 64 + 4 x = 48
– x 2 + 20 x – 112 = 0
x 2 – 20 x + 112 = 0
a = 1 , b = -2 0 and c = 112
Discriminant = b 2 – 4 ac
= (- 20 ) 2 – 4 × 112
= 400 – 448 = -48
b 2 – 4 ac < 0
Therefore, there will be no real solution possible for the equations. Hence, the condition doesn’t exist.
5. Is it possible to design a rectangular park with a perimeter of 80 and an area of 400 m2? If so, find its length and breadth.
Let the length and breadth of the park be l and b.
Perimeter of the rectangular park = 2 ( l + b ) = 80
So, l + b = 40
Or, b = 40 – l
Area of the rectangular park = l×b = l(40 – l) = 40 l – l 2 = 400
l 2 – 40 l + 400 = 0, which is a quadratic equation.
a = 1, b = -40, c = 400
Since discriminant = b 2 – 4 ac
=(- 40 ) 2 – 4 × 400
= 1600 – 1600 = 0
Thus, b 2 – 4 ac = 0
Therefore, this equation has equal real roots. Hence, the situation is possible.
The root of the equation,
l = – b /2 a
l = -(-40)/2(1) = 40/2 = 20
Therefore, the length of the rectangular park, l = 20 m
And the breadth of the park, b = 40 – l = 40 – 20 = 20 m.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.4
- Subject experts have provided the solutions after a lot of brainstorming.
- The answers are accurate.
- Each question in the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.4 is explained in a stepwise manner.
- The solutions will help students score well in the board examinations.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Nice I love byjus….. Thanks
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- Case Study Class 10...
Case Study Class 10 Maths Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Now, CBSE will ask only subjective questions in class 10 Maths case studies. But if you search over the internet or even check many books, you will get only MCQs in the class 10 Maths case study in the session 2022-23. It is not the correct pattern. Just beware of such misleading websites and books.
We advise you to visit CBSE official website ( cbseacademic.nic.in ) and go through class 10 model question papers . You will find that CBSE is asking only subjective questions under case study in class 10 Maths. We at myCBSEguide helping CBSE students for the past 15 years and are committed to providing the most authentic study material to our students.
Here, myCBSEguide is the only application that has the most relevant and updated study material for CBSE students as per the official curriculum document 2022 – 2023. You can download updated sample papers for class 10 maths .
First of all, we would like to clarify that class 10 maths case study questions are subjective and CBSE will not ask multiple-choice questions in case studies. So, you must download the myCBSEguide app to get updated model question papers having new pattern subjective case study questions for class 10 the mathematics year 2022-23.
Class 10 Maths has the following chapters.
- Real Numbers Case Study Question
- Polynomials Case Study Question
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Case Study Question
- Quadratic Equations Case Study Question
- Arithmetic Progressions Case Study Question
- Triangles Case Study Question
- Coordinate Geometry Case Study Question
- Introduction to Trigonometry Case Study Question
- Some Applications of Trigonometry Case Study Question
- Circles Case Study Question
- Area Related to Circles Case Study Question
- Surface Areas and Volumes Case Study Question
- Statistics Case Study Question
- Probability Case Study Question
Format of Maths Case-Based Questions
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions will have one passage and four questions. As you know, CBSE has introduced Case Study Questions in class 10 and class 12 this year, the annual examination will have case-based questions in almost all major subjects. This article will help you to find sample questions based on case studies and model question papers for CBSE class 10 Board Exams.
Maths Case Study Question Paper 2023
Here is the marks distribution of the CBSE class 10 maths board exam question paper. CBSE may ask case study questions from any of the following chapters. However, Mensuration, statistics, probability and Algebra are some important chapters in this regard.
Case Study Question in Mathematics
Here are some examples of case study-based questions for class 10 Mathematics. To get more questions and model question papers for the 2021 examination, download myCBSEguide Mobile App .
Case Study Question – 1
In the month of April to June 2022, the exports of passenger cars from India increased by 26% in the corresponding quarter of 2021–22, as per a report. A car manufacturing company planned to produce 1800 cars in 4th year and 2600 cars in 8th year. Assuming that the production increases uniformly by a fixed number every year.
- Find the production in the 1 st year.
- Find the production in the 12 th year.
- Find the total production in first 10 years. OR In which year the total production will reach to 15000 cars?
Case Study Question – 2
In a GPS, The lines that run east-west are known as lines of latitude, and the lines running north-south are known as lines of longitude. The latitude and the longitude of a place are its coordinates and the distance formula is used to find the distance between two places. The distance between two parallel lines is approximately 150 km. A family from Uttar Pradesh planned a round trip from Lucknow (L) to Puri (P) via Bhuj (B) and Nashik (N) as shown in the given figure below.
- Find the distance between Lucknow (L) to Bhuj(B).
- If Kota (K), internally divide the line segment joining Lucknow (L) to Bhuj (B) into 3 : 2 then find the coordinate of Kota (K).
- Name the type of triangle formed by the places Lucknow (L), Nashik (N) and Puri (P) OR Find a place (point) on the longitude (y-axis) which is equidistant from the points Lucknow (L) and Puri (P).
Case Study Question – 3
- Find the distance PA.
- Find the distance PB
- Find the width AB of the river. OR Find the height BQ if the angle of the elevation from P to Q be 30 o .
Case Study Question – 4
- What is the length of the line segment joining points B and F?
- The centre ‘Z’ of the figure will be the point of intersection of the diagonals of quadrilateral WXOP. Then what are the coordinates of Z?
- What are the coordinates of the point on y axis equidistant from A and G? OR What is the area of area of Trapezium AFGH?
Case Study Question – 5
The school auditorium was to be constructed to accommodate at least 1500 people. The chairs are to be placed in concentric circular arrangement in such a way that each succeeding circular row has 10 seats more than the previous one.
- If the first circular row has 30 seats, how many seats will be there in the 10th row?
- For 1500 seats in the auditorium, how many rows need to be there? OR If 1500 seats are to be arranged in the auditorium, how many seats are still left to be put after 10 th row?
- If there were 17 rows in the auditorium, how many seats will be there in the middle row?
Case Study Question – 6
- Draw a neat labelled figure to show the above situation diagrammatically.
- What is the speed of the plane in km/hr.
More Case Study Questions
We have class 10 maths case study questions in every chapter. You can download them as PDFs from the myCBSEguide App or from our free student dashboard .
As you know CBSE has reduced the syllabus this year, you should be careful while downloading these case study questions from the internet. You may get outdated or irrelevant questions there. It will not only be a waste of time but also lead to confusion.
Here, myCBSEguide is the most authentic learning app for CBSE students that is providing you up to date study material. You can download the myCBSEguide app and get access to 100+ case study questions for class 10 Maths.
How to Solve Case-Based Questions?
Questions based on a given case study are normally taken from real-life situations. These are certainly related to the concepts provided in the textbook but the plot of the question is always based on a day-to-day life problem. There will be all subjective-type questions in the case study. You should answer the case-based questions to the point.
What are Class 10 competency-based questions?
Competency-based questions are questions that are based on real-life situations. Case study questions are a type of competency-based questions. There may be multiple ways to assess the competencies. The case study is assumed to be one of the best methods to evaluate competencies. In class 10 maths, you will find 1-2 case study questions. We advise you to read the passage carefully before answering the questions.
Case Study Questions in Maths Question Paper
CBSE has released new model question papers for annual examinations. myCBSEguide App has also created many model papers based on the new format (reduced syllabus) for the current session and uploaded them to myCBSEguide App. We advise all the students to download the myCBSEguide app and practice case study questions for class 10 maths as much as possible.
Case Studies on CBSE’s Official Website
CBSE has uploaded many case study questions on class 10 maths. You can download them from CBSE Official Website for free. Here you will find around 40-50 case study questions in PDF format for CBSE 10th class.
10 Maths Case Studies in myCBSEguide App
You can also download chapter-wise case study questions for class 10 maths from the myCBSEguide app. These class 10 case-based questions are prepared by our team of expert teachers. We have kept the new reduced syllabus in mind while creating these case-based questions. So, you will get the updated questions only.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2020-21
- Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions
- CBSE Reduced Syllabus Class 10 (2020-21)
- Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper 2024
- How to Revise CBSE Class 10 Maths in 3 Days
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Maths Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Maths Subject Real Number Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Case Study Questions
Srikanth has made a project on real numbers, where he finely explained the applicability of exponential laws and divisibility conditions on real numbers. He also included some assessment questions at the end of his project as listed below. Answer them. (i) For what value of n, 4 n ends in 0?
(ii) If a is a positive rational number and n is a positive integer greater than 1, then for what value of n, a n is a rational number?
(iii) If x and yare two odd positive integers, then which of the following is true?
(iv) The statement 'One of every three consecutive positive integers is divisible by 3' is
(v) If n is any odd integer, then n2 - 1 is divisible by
Real numbers are extremely useful in everyday life. That is probably one of the main reasons we all learn how to count and add and subtract from a very young age. Real numbers help us to count and to measure out quantities of different items in various fields like retail, buying, catering, publishing etc. Every normal person uses real numbers in his daily life. After knowing the importance of real numbers, try and improve your knowledge about them by answering the following questions on real life based situations. (i) Three people go for a morning walk together from the same place. Their steps measure 80 cm, 85 cm, and 90 cm respectively. What is the minimum distance travelled when they meet at first time after starting the walk assuming that their walking speed is same?
(ii) In a school Independence Day parade, a group of 594 students need to march behind a band of 189 members. The two groups have to march in the same number of columns. What is the maximum number of columns in which they can march?
(iii) Two tankers contain 768litres and 420 litres of fuel respectively. Find the maximum capacity of the container which can measure the fuel of either tanker exactly.
(iv) The dimensions of a room are 8 m 25 cm, 6 m 75 crn and 4 m 50 cm. Find the length of the largest measuring rod which can measure the dimensions of room exactly.
(v) Pens are sold in pack of 8 and notepads are sold in pack of 12. Find the least number of pack of each type that one should buy so that there are equal number of pens and notepads
In a classroom activity on real numbers, the students have to pick a number card from a pile and frame question on it if it is not a rational number for the rest of the class. The number cards picked up by first 5 students and their questions on the numbers for the rest of the class are as shown below. Answer them. (i) Suraj picked up \(\sqrt{8}\) and his question was - Which of the following is true about \(\sqrt{8}\) ?
(ii) Shreya picked up 'BONUS' and her question was - Which of the following is not irrational?
(iii) Ananya picked up \(\sqrt{5}\) -. \(\sqrt{10}\) and her question was - \(\sqrt{5}\) -. \(\sqrt{10}\) _________is number.
(iv) Suman picked up \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\) and her question was - \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\) is __________ number.
(v) Preethi picked up \(\sqrt{6}\) and her question was - Which of the following is not irrational?
Decimal form of rational numbers can be classified into two types. (i) Let x be a rational number whose decimal expansion terminates. Then x can be expressed in the form \(\frac{p}{\sqrt{q}}\) where p and q are co-prime and the prime faetorisation of q is of the form 2 n ·5 m , where n, mare non-negative integers and vice-versa. (ii) Let x = \(\frac{p}{\sqrt{q}}\) be a rational number, such that the prime faetorisation of q is not of the form 2 n 5 m , where n and m are non-negative integers. Then x has a non-terminating repeating decimal expansion. (i) Which of the following rational numbers have a terminating decimal expansion?
(ii) 23/(2 3 x 5 2 ) =
(iii) 441/(2 2 x 5 7 x 7 2 ) is a_________decimal.
(iv) For which of the following value(s) of p, 251/(2 3 x p 2 ) is a non-terminating recurring decimal?
(v) 241/(2 5 x 5 3 ) is a _________decimal.
HCF and LCM are widely used in number system especially in real numbers in finding relationship between different numbers and their general forms. Also, product of two positive integers is equal to the product of their HCF and LCM. Based on the above information answer the following questions. (i) If two positive integers x and yare expressible in terms of primes as x = p2q3 and y = p3 q, then which of the following is true?
(ii) A boy with collection of marbles realizes that if he makes a group of 5 or 6 marbles, there are always two marbles left, then which of the following is correct if the number of marbles is p?
(iii) Find the largest possible positive integer that will divide 398, 436 and 542 leaving remainder 7, 11, 15 respectively.
(iv) Find the least positive integer which on adding 1 is exactly divisible by 126 and 600.
(v) If A, Band C are three rational numbers such that 85C - 340A :::109, 425A + 85B = 146, then the sum of A, B and C is divisible by
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard maths subject real number case study questions with solution 2021 answer keys.
(i) (d) : For a number to end in zero it must be divisible by 5, but 4 n = 22 n is never divisible by 5. So, 4 n never ends in zero for any value of n. (ii) (c) : We know that product of two rational numbers is also a rational number. So, a 2 = a x a = rational number a 3 = a 2 x a = rational number a 4 = a 3 x a = rational number ................................................ ............................................... a n = a n-1 x a = rational number. (iii) (d): Let x = 2m + 1 and y = 2k + 1 Then x 2 + y 2 = (2m + 1) 2 + (2k + 1) 2 = 4m 2 + 4m + 1 + 4k 2 + 4k + 1 = 4(m 2 + k 2 + m + k) + 2 So, it is even but not divisible by 4. (iv) (a): Let three consecutive positive integers be n, n + 1 and n + 2. We know that when a number is divided by 3, the remainder obtained is either 0 or 1 or 2. So, n = 3p or 3p + lor 3p + 2, where p is some integer. If n = 3p, then n is divisible by 3. If n = 3p + 1, then n + 2 = 3p + 1 + 2 = 3p + 3 = 3(p + 1) is divisible by 3. If n = 3p + 2, then n + 1 = 3p + 2 + 1 = 3p + 3 = 3(p + 1) is divisible by 3. So, we can say that one of the numbers among n, n + 1 and n + 2 Wi always divisible by 3. (v) (d): Any odd number is of the form of (2k +1), where k is any integer. So, n 2 - 1 = (2k + 1)2 -1 = 4k 2 + 4k For k = 1, 4k 2 + 4k = 8, which is divisible by 8. Similarly, for k = 2, 4k 2 + 4k = 24, which is divisible by 8. And for k = 3, 4k 2 + 4k = 48, which is also divisible by 8. So, 4k 2 + 4k is divisible by 8 for all integers k, i.e., n 2 - 1 is divisible by 8 for all odd values of n.
(i) (b): Here 80 = 2 4 x 5, 85 = 17 x 5 and 90 = 2 x 3 2 x 5 L.C.M of 80, 85 and 90 = 2 4 x 3 x 3 x 5 x 17 = 12240 Hence, the minimum distance each should walk when they at first time is 12240 cm. (ii) (c): Here 594 = 2 x 3 3 x 11 and 189 = 3 3 x 7 HCF of 594 and 189 = 3 3 = 27 Hence, the maximum number of columns in which they can march is 27. (iii) (c) : Here 768 = 2 8 x 3 and 420 = 2 2 x 3 x 5 x 7 HCF of 768 and 420 = 2 2 x 3 = 12 So, the container which can measure fuel of either tanker exactly must be of 12litres. (iv) (b): Here, Length = 825 ern, Breadth = 675 cm and Height = 450 cm Also, 825 = 5 x 5 x 3 x 11 , 675 = 5 x 5 x 3 x 3 x 3 and 450 = 2 x 3 x 3 x 5 x 5 HCF = 5 x 5 x 3 = 75 Therefore, the length of the longest rod which can measure the three dimensions of the room exactly is 75cm. (v) (a): LCM of 8 and 12 is 24. \(\therefore \) The least number of pack of pens = 24/8 = 3 \(\therefore \) The least number of pack of note pads = 24/12 = 2
(i) (b): Here \(\sqrt{8}\) = 2 \(\sqrt{2}\) = product of rational and irrational numbers = irrational number (ii) (c): Here, \(\sqrt{9}\) = 3 So, 2 + 2 \(\sqrt{9}\) = 2 + 6 = 8 , which is not irrational. (iii) (b): Here. \(\sqrt{15}\) and \(\sqrt{10}\) are both irrational and difference of two irrational numbers is also irrational. (iv) (c): As \(\sqrt{5}\) is irrational, so its reciprocal is also irrational. (v) (d): We know that \(\sqrt{6}\) is irrational. So, 15 + 3. \(\sqrt{6}\) is irrational. Similarly, \(\sqrt{24}\) - 9 = 2. \(\sqrt{6}\) - 9 is irrational. And 5 \(\sqrt{150}\) = 5 x 5. \(\sqrt{6}\) = 25 \(\sqrt{6}\) is irrational.
(i) (c): Here, the simplest form of given options are 125/441 = 5 3 /(3 2 x 7 2 ), 77/210 = 11/(2 x 3 x 5), 15/1600 = 3/(2 6 x 5) Out of all the given options, the denominator of option (c) alone has only 2 and 5 as factors. So, it is a terminating decimal. (ii) (b): 23/(2 3 x 5 2 ) = 23/200 = 0.115 (iii) (a): 441/(2 2 x 5 7 x 7 2 ) = 9/(2 2 x 5 7 ), which is a terminating decimal. (iv) (d): The fraction form of a non-terminating recurring decimal will have at least one prime number other than 2 and 5 as its factors in denominator. So, p can take either of 3, 7 or 15. (v) (a): Here denominator has only two prime factors i.e., 2 and 5 and hence it is a terminating decimal.
(i) (b): LCM of x and y = p 3 q 3 and HCF of x and y = p 2 q Also, LCM = pq 2 x HCF. (ii) (d): Number of marbles = 5m + 2 or 6n + 2. Thus, number of marbles, p = (multiple of 5 x 6) + 2 = 30k + 2 = 2(15k + 1) = which is an even number but not prime (iii) (d): Here, required numbers = HCF (398 - 7, 436 - 11,542 -15) = HCF (391,425,527) = 17 (iv) (b): LCMof126and600 = 2 x 3 x 21 x 100= 12600 The least positive integer which on adding 1 is exactly divisible by 126 and 600 = 12600 - 1 = 12599 (v) (a): Here 8SC - 340A = 109 and 425A + 85B = 146 On adding them, we get 85A + 85B + 85C = 255 ~ A + B + C = 3, which is divisible by 3.
Related 10th Standard CBSE Maths Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th science metals and non metals chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th science acids, bases and salts chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th science chemical reactions and equations chapter case study question with answers, class 10th science - our environment case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - magnetic effects of electric current case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - human eye and the colourful world case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - light reflection and refraction case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - heredity and evolution case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - how do organisms reproduce case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - life processes case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - periodic classification of elements case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Real Numbers Free PDF

Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Real Numbers in order to fully complete your preparation . They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!
I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams. To download the latest CBSE Case Study Questions , just click ‘ Download PDF ’.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Real Numbers PDF
Mcq set 1 -, mcq set 2 -, checkout our case study questions for other chapters.
- Chapter 2: Polynomials Case Study Questions
- Chapter 3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Case Study Questions
- Chapter 4: Quadratic Equation Case Study Questions
- Chapter 5: Arithmetic Progressions Case Study Questions
How should I study for my upcoming exams?
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch
Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution.
Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available)
Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS
Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)
Practice Assertion Reason & Case Study Based Questions
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions
After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS.
Contact Form
Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations are released by the board. Solve all these questions to perform well in your CBSE Class 10 Maths Exam 2021-22. By ...
Case study Questions on the Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 4 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
Furthermore, we have provided the PDF File of CBSE Class 10 maths case study 2021-2022. CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter Wise Case Study. Maths Chapter 1 Real Number Case Study. Maths Chapter 2 Polynomial Case Study. Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Case Study. Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Case Study.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Question 1: Raj and Ajay are very close friends. Both the families decide to go to Ranikhet by their own cars. Raj's car travels at a speed of x km/h while Ajay's car travels 5 km/h faster than Raj's car. Raj took 4 h … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams ... ,10th maths Quadratic Equations case study questions with answer key,chapter wise ...
Download Case Study Questions for Class 10 Mathematics to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 10 Final Exam of 2022-23. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 10 so that they can score 100% on Boards. ... Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2024 Chapter-1 Real Numbers ...
Full syllabus notes, lecture and questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Case Based Questions - Quadratic Equations ... Case Study - 1. The speed of a motor boat is 20 km/hr. For covering the distance of 15 km the boat took 1 hour more for upstream than downstream. Q1: Let speed of the stream be x km/hr. then speed of the motorboat in upstream ...
Students looking for Case Study on Quadratic Equations Class 10 Maths can use this page to download the PDF file. The case study questions on Quadratic Equations are based on the CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus, and therefore, referring to the Quadratic Equations case study questions enable students to gain the appropriate knowledge and prepare ...
An equation such as Ax = D, where Ax is a polynomial of degree two and D is a constant, forms a quadratic equation. The standard quadratic equation is ax2+bx+c=0 where a, b, and c are not equal to zero. You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations to understand more about the topic.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 - CBSE Free PDF Download. NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations contain all the solutions to the problems provided in the Class 10 Maths NCERT textbook for CBSE exam preparations.The questions from every section are framed and solved accurately by the subject experts.
There are in all 4 exercises in class 10 mathematics chapter 4 (Quadratic equations). In first exercise (Ex 4.1), there are only 2 questions (Q1 having 8 parts and Q2 having 4 parts). In second exercise (Ex 4.2), there are in all 6 questions. In fourth exercise (Ex 4.3), there are in all 5 questions.
Updated for Latest NCERT for 2023-2024 Boards. Get NCERT Solutions for all exercise questions and examples of Chapter 4 Class 10 Quadratic Equations free at Teachoo. Answers to each and every question is provided video solutions. In this chapter, we will learn. This chapter is divided into two parts - Serial Order Wise, Concept Wise.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Solutions. Below we have given the answers to all the questions present in Quadratic Equations in our NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths chapter 4. In this lesson, students are introduced to a lot of important concepts that will be useful for those who wish to pursue mathematics as a subject in their future classes.
Case Study Based Question - Quadratic Equations Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 | CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4. In T...
You can also watch the video solutions of NCERT Class10 Maths chapter 4 Quadratic Equations here. Ex 4.1 Class 10 Maths Question 2. Represent the following situations in the form of quadratic equations: (i) The area of a rectangular plot is 528 m 2. The length of the plot (in metres) is one more than twice its breadth.
Welcome to CBSE Worldz. In this video we will be discussing CBSE class 10 Case Study Based Questions of maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations for Term 2CASE ST...
Students referring to the Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions And Answers Pdf from Selfstudys will find these features:-. Accurate answers of all the Case-based questions given in the PDF. Case Study class 10 Maths solutions are prepared by subject experts referring to the CBSE Syllabus of class 10. Free to download in Portable Document Format ...
Access Answers of Maths NCERT Class 10 Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.4. 1. Find the nature of the roots of the following quadratic equations. If the real roots exist, find them: Solutions: (i) Given, 2x2 - 3 x + 5 = 0. Comparing the equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get. a = 2, b = -3 and c = 5.
First of all, we would like to clarify that class 10 maths case study questions are subjective and CBSE will not ask multiple-choice questions in case studies. So, you must download the myCBSEguide app to get updated model question papers having new pattern subjective case study questions for class 10 the mathematics year 2022-23.
REAL NUMBERS- CASE STUDY CASE STUDY 1. To enhance the reading skills of grade X students, the school nominates you and two of your friends to set up a class library. There are two sections- section A and section B of grade X. There are 32 students in section A and 36 students in section B. 1. What is the minimum number of books you will acquire ...
CBSE 10th Standard Maths Subject Real Number Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys. Case Study Questions. (i) (d) : For a number to end in zero it must be divisible by 5, but 4 n = 22 n is never divisible by 5. So, 4 n never ends in zero for any value of n. (ii) (c) : We know that product of two rational numbers is also a rational ...
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch. Level 2. Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution. Level 3. Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available) Level 4. Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS. Level 5. Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)