Carrefour Supermarket’s Supply Chain Management Research Paper
Introduction.
Considered the second largest retailer in the world, Carrefour’s supply chain management is vast and contains thousands of suppliers (Basu & Wright 2016). Founded in 1958, Carrefour operates more than 1,200 supermarkets and 3,245 convenience stores (Basu & Wright 2016). Its global operations span several continents, including Africa, Europe, Asia, and South America. Currently, the company employs more than 500,000 people and has annual sales in excess of €86.3 million (Basu & Wright 2016). Based on the extent of its operations and changing market dynamics, Carrefour needs to review the efficiency of its supply chain management process to make sure it responds to the needs of the organization, market, customers, and suppliers.
This paper seeks to review the operations of the French-based multinational and the role that supply chain management plays in making its operations successful. This research paper is divided into two tasks. The first one highlights the role of supply chain management and logistics, the link between the company’s structure and its supply chain functions, as well as ways to provide supply chain intelligence. The second task explores the role of supply chain relationships in the management of procurement functions and the role of technology in influencing this relationship.

Why Carrefour Needs Supply Chain Management and Logistics
As Basu and Wright (2016) observe, the supply chain functions of large multinationals, such as Carrefour, are often complex and sensitive to changing market dynamics. Therefore, the need for an efficient supply chain management is paramount. Carrefour Supermarket needs an efficient supply chain and logistics management to satisfy the demand for its goods and services. Implementing seamless logistics in the company’s operations could benefit the organization by increasing its response to its customers’ needs (Xu, Xu & Liu 2014). It could also reduce the time spent by the supermarket chain to move goods from one point to another. These advantages could increase the competitive advantage of Carrefour supermarket.
Effective supply chain management and logistics could also improve the quality standards of Carrefour because it gives managers an opportunity to determine what products they sell to their customers and the quality specifications they should have (Xu, Xu & Liu 2014). For example, the supermarket has a product line of Carrefour-branded products (Xu, Xu & Liu 2014). To safeguard its quality standards, the company makes sure that all suppliers who were approved to provide products within this business segment meet high-quality standards (Xu, Xu & Liu 2014).
Supply chain management and logistics operations are also vital to the operations of Carrefour because they could improve the company’s ability to coordinate different departmental functions (Basu & Wright 2016). For example, they could help managers to coordinate the functions of the procurement, sales, transportation, and warehousing departments. Overall, effective supply chain management creates an opportunity for management to develop a holistic understanding of the organization’s processes. This way, it is easier for the company to maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of its retail functions.
Organizational Structure of Carrefour Supermarket and its Relation with Supply Chain Functions
Carrefour’s organizational structure.
At the helm of Carrefour’s organizational structure is the executive director in charge of merchandise and supply (Carrefour Group 2018). Under his office, five board of directors oversee the functions of five specialized departments – audit, remuneration, appointments, corporate social responsibility (CSR), and strategic (Carrefour Group 2018). The third level of organizational structure is the group executive committee, which comprises of 14 members (Carrefour Group 2018). The chairperson and group chief executive officer are among the members. Their key responsibilities include managing the company’s operations in different geographic zones, managing its group functions, and directing corporate responsibilities (Carrefour Group 2018). Figure 1 below presents the company’s organizational structure.
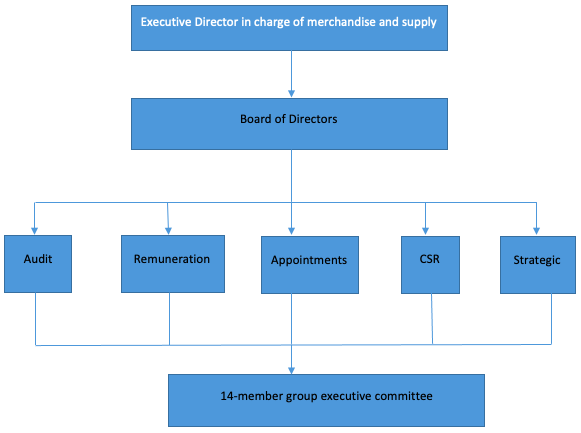
How the Organization Structure Works With the Supply Chain
The aforementioned organizational structure complements Carrefour’s supply chain functions by developing a centrally led supply chain system that aligns with the supermarket’s corporate goals. The centralized nature of the organizational structure makes sure that the entire supply chain is not fragmented, thereby increasing the level of collaboration among its key partners. It also facilitates the behavioral and cultural changes required in different operating regions to make supply chain management more effective and efficient.
Carrefour’s organizational structure is also instrumental to the proper functioning of the company’s supply chain plan because it provides room to leverage its corporate spend. Stated differently, it provides an opportunity for management to influence how the organization allocates its resources to support key supply chain functions. Basu and Wright (2016) explain this strategy by saying it is an innovative way for companies to manage new challenges in their supply chain functions and remain competitive in the end.
In the context of Carrefour’s operations, the organization’s management structure ensures that efforts to leverage corporate spend are primarily directed at improving the performance of strategic supply chain functions (Xu, Xu & Liu 2014). In other words, only those operations that are considered to have a high risk of supply loss are deemed the primary beneficiaries of the corporate spend strategy (Xu, Xu & Liu 2014).
Improvements through Sales Forecasting
The supply chain functions of Carrefour could be improved by following four sales forecasting steps, which are defined by Saracene (2014) as the definition of terms, clarification of sales stages, elevation of CRM as the only source of forecasting, and going beyond pipeline and bookings. The first step (definition of terms) could make all parties in the supply chain process understand key terms that define supply chain communications at Carrefour. This step is closely connected with the second part of sales forecasting, which is the clarification and communication of sales processes.
The connection comes from the fact that after defining the terms to be used in the supply chain management process, all concerned parties need to be made aware of what it would take to move from one step of the supply chain management process to another. The third step of forecasting identifies the need to model the behaviors of suppliers and third parties who are involved the company’s supply chain. This strategy could improve supplier relationships at Carrefour. After implementing this step, it would be possible for the supply chain manager of Carrefour to make accurate bookings and projections in the supply chain management.
Ways to Provide Supply Chain Intelligence
Supply chain intelligence is an important part of Carrefour’s business because it provides real-time insights regarding the performance of different aspects of the company’s supply chain. Collecting intelligence allows executives to understand which aspects of the company’s overall supply chain processes are weak or strong, thereby providing them with adequate information for making strategic decisions. Carrefour could use three ways to gather intelligence. They are outlined below.
Advanced Information Technology Management
One way to provide supply chain intelligence for Carrefour Supermarket is to embrace advanced information technology management. Such a system should engage multipurpose shops, supermarkets, and convenience shops that are within the company’s supply network (Basu & Wright 2016). At the same time, it should include the thousands of suppliers who are integrated in the company’s distribution network because it should be designed in such a manner that the company’s employees could log into the system, get goods from dispatch centers, settle outstanding accounts, and send orders to suppliers through virtual platforms (Basu & Wright 2016).
The logistics dispatch system could also be used to support long-distance communication between the company’s headquarters and its different regional branches, thereby providing real-time supply chain management support (Jue 2014).
Cooperating with Partners
For a long time, many companies have not embraced information sharing because of its perceived risk to intellectual property rights (Lotfi et al. 2013). However, as a coordinator of Carrefour’s supply chain management, I would embrace this strategy as an intelligence-gathering tool. Intelligence will be gathered through partnerships that will be fostered by seeking collaboration with different entities who are involved in Carrefour’s horizontal and vertical integration strategies. This strategy will involve distributing useful information relating to suppliers, logistics, market demand and any other issue that may affect the company’s supply chain plan.
Customer Feedback
Most supply chain management functions are intended to satisfy customer needs. Today, companies have different methods they can use to get instant feedback from customers. As a supply chain coordinator at Carrefour supermarket, I would rely on customer feedback as a source of supply chain intelligence. Negative feedback from customers would typically mean that the supply chain process needs improvement, but positive feedback would imply that the supply chain function is effective.
However, attempts have to be made to evaluate the kind of information provided by customers because some negative feedback could be related to the operations of specific stores and not necessarily the broader supply chain process that supports Carrefour’s operations. Customer feedback could be sourced from multiple sources, including social media sites, the company website, or even electronic mails sent to the company (Basu & Wright 2016).
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
The success of supply chain management partly depends on the creation of effective supplier relationship management (SRM) (Basu & Wright 2016). The field of SRM is primarily concerned with managing supplier relationships as a key aspect of supply chain management. Relationships built within this type of structure usually create a positive and financially productive engagement between companies and suppliers. According to Monczka et al. (2015), five kinds of relationships can be pursued with the larger SRM structure. They are transactional, contractual, value-additional, collaborative, and partnership arrangements.
As a supply chain coordinator at Carrefour Supermarket, I would pursue the transactional relationship as the main model of interaction with suppliers. This type of relationship simply refers to the exchange of goods and services within a specific time and at a certain price (Monczka et al. 2015). This type of relationship should be pursued at Carrefour because the supermarket sells many perishable products.
The transactional relationship recognizes the time-sensitive nature of the products delivered. Indeed, by agreeing on a specific price and time for delivering goods, Carrefour would reduce the risk of product write-offs. My model for a transaction relationship with the suppliers would be based on long-term relationships because my goal would be to develop trust with the suppliers. Trust could later be leveraged to improve the quality of goods and services delivered to the supermarket.
As a supply chain coordinator of Carrefour Supermarket, I would also consider a collaborative relationship with suppliers to manage the company’s expectations of service delivery and to create value in the supply chain management. Basu and Wright (2016) define a collaborative relationship as that which is premised on the need to add value to products and to mutually benefit suppliers and companies.
This kind of relationship could be pursued because the products provided by Carrefour’s suppliers are not products of one-off transactions. A collaborative relationship would make sure that Carrefour continues to get value from the systems and processes it buys from technology vendors. Such relationships should be mutually beneficial to both parties because most of the company’s operations are automated (Carrefour Group 2018). Therefore, if there is no proper mutually beneficial relationship with third party service providers, the company’s operations could be severely affected.
As a supply chain coordinator, I would also complete order fulfillment processes by delegating the same responsibility to store managers. Stated differently, instead of centralizing the supply chain management at the headquarters, I would allow the store managers to have some control in the supply chain process by giving their input regarding order fulfillment initiatives. This strategy has been associated with an increased enthusiasm for store managers and departmental heads to participate in supply chain management. As highlighted by Xu, Xu, and Liu (2014), Carrefour’s Chinese operations have successfully utilized the strategy.
Information Technology Needed to Enhance Supplier Relationships
Information technology is an important tool in supply chain management. Its relevance in improving supplier relationships has been highlighted by researchers, such as Basu and Wright (2016). In the context of Carrefour’s operations, information technology tools could be used to enhance supplier relationships by attracting the support of senior managers (Donati 2018). In the same manner, it could be used to source funds or resources for meeting the terms of suppliers, thereby improving their relationship in the end.
The role of information technology in improving supplier relationships has been highlighted by researchers, such as Basu and Wright (2016), who have pointed out that supplier segmentation, supplier governance and the development of supplier relationships are among key areas of supply chain management that have benefitted from the adoption of information technology. For example, the process of identifying suppliers and segmenting them is often a difficult one if done manually.
However, when automated, the process is simplified. At the same time, information technology tools could be used to identify the right type of fit for suppliers, thereby improving the efficiency of the supply chain management process (Basu & Wright 2016). The role of information technology does not stop here because it spreads into the establishment of convenient communication channels that Carrefour could use to keep in touch with its suppliers and establish reliable payment procedures that are trusted by both parties.
The use of information technology tools in the management of supplier relationships is also supported by the fact that it could increase transparency in the contractual relationship that Carrefour would have with its suppliers (Basu & Wright 2016). This benefit is crucial to the development of a sound relationship between Carrefour and its suppliers because transparency helps to nurture trust, which is the foundation of positive supplier relationships (Donati 2018).
Although information technology could be used to improve supplier relationships at Carrefour, Basu and Wright (2016) posit that the biggest problem associated with its adoption is its underutilization in supporting internal and external organizational functions of a company. The benefits accrued from the use of technology in improving supplier relationships stem from the view that supplier relationships are often undervalued because most companies fail to understand how maintaining a good relationship with suppliers could be beneficial to both parties (Donati 2018). However, their views could change if a system for managing supplier relationships is developed.
System for Managing Supplier Relationships
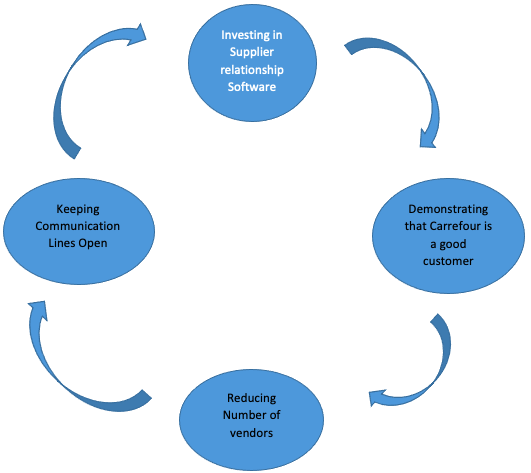
As identified by Basu and Wright (2016), supplier relationships refer to the development of sound engagements with suppliers. Indeed, when there are good lines of communication between suppliers and managers, the entire supply chain process becomes smoother and more effective. As a supply chain coordinator of Carrefour Supermarket, I would develop a system for managing supplier relationships by integrating four key pillars: investing in a supplier management software, demonstrating to the suppliers that Carrefour is a good customer, reducing the number of vendors, and keeping the lines of communication open. Tolhurst (2013) highlights these four key aspects of supplier relationships as the main steps in effective supply chain management.
A software with relationship-building features could be instrumental in improving supplier relationships at Carrefour because the company’s operations are vast and include thousands of suppliers (Carrefour Group 2018).
Therefore, it may be difficult to keep track or maintain a good relationship with all these vendors. However, investing in a good supplier relationship software could help to develop a good relationship with suppliers by monitoring their performance and creating opportunities to accommodate new vendors (Tolhurst 2013). The software would also be instrumental in gathering suppliers’ information and manipulating it from one central location. Overall, the software could help to standardize supplier relationships and identify new areas of engagement that may require further attention (Tolhurst 2013).
As highlighted in earlier sections of this research paper, the second step I would pursue as a supply chain coordinator of Carrefour supermarket would be to demonstrate to the vendors that Carrefour is a good customer. This strategy stems from the recommendations of Tolhurst (2013), which encourage companies to maintain a positive working relationship with their vendors because suppliers also evaluate their performance in the same manner as companies review the performance of third-party players. One way I would demonstrate that Carrefour is a good customer is to make sure the vendors get their pay on time.
If it is impossible to do so, attempts should be made to notify them of the issue and to give them an estimate of when they should be expecting the payments. Lastly, the vendors should be provided with adequate lead-time to supply their products or services. All engagements will be done transparently.
Another step in the design of the supplier relationship system is to reduce the number of vendors to a minimum. This strategy also stems from the recommendations of Tolhurst (2013), which suggest that good supplier relationships are best achieved when the number of suppliers is low. Stated differently, it may be difficult to manage many vendors because of the overwhelming responsibility of maintaining a positive relationship with each one of them. Therefore, having a small number of vendors would improve the quality of the relationship between Carrefour and its vendors because it would make it easier to manage costs and eliminate unreliable suppliers. The criteria for eliminating vendors will be based on performance indicators.
Lastly, the process of developing positive supplier relationships will be premised on keeping communication lines open. For example, attempts could be made to include some vendors in company parties or meetings to make them feel welcomed and appreciated. Similarly, attempts could be made by Carrefour to visit the premises of some of the suppliers and be acquainted with their businesses. Basu and Wright (2016) agree that pursuing such a plan provides a “personal touch” to the relationship between suppliers and companies. At the same time, it creates the foundation for a solid partnership with the parties involved. Overall, this four-stage system for building an effective supplier relationship is intended to ensure optimal supplier performance. Broadly, figure 2 below explains the system’s design.
Order Fulfillment Activities and Inventory Control
Order fulfillment activities refer to processes Carrefour undertakes, from the point of ordering to end-user receipt of products or services (Lotfi et al. 2013). The smooth running of these activities requires proper inventory control. However, the process of fulfilling a company’s inventory needs is often a difficult one because each organization has its own customized needs (Lotfi et al. 2013). As the supply chain coordinator of Carrefour, I would embrace quality management and set par levels as the major activities of inventory control.
The goal of setting par levels would be premised on the need to make sure that inventory quantities do not fall below a specific predetermined level. Therefore, when the quantity of product falls below the set standards, new purchase orders will be placed. As a supply chain coordinator of Carrefour, I would also adopt the first-in-first-out system (FIFO), which ensures that the first products ordered are the ones to be sold (Basu & Wright 2016).
This system has a high efficacy level in retail chain management (particularly in the sale of perishables) because it ensures that the oldest stocks are sold out first and new ones preserved for a later sale date. This type of system ensures that orders are effectively fulfilled and the inventory tactfully controlled.
This report has covered the key tenets of supply chain management and their relation with the operations of Carrefour Supermarket. This case study gives insight into how companies, such as Carrefour, which have widespread operations, could use the competencies available in global supply chain management to improve their supply chain management functions. The importance of developing good supplier relationships has also been highlighted as an anchor to the realization of an effective and efficient supply chain management plan.
This research paper has also emphasized the role of technology in the development of such relationships and its efficacy in the development of efficient supply chain software and techniques, as witnessed in the development of Carrefour’s system for managing supplier relationships. Overall, to improve its supply chain functions, Carrefour needs to understand the effectiveness of its current supply chain management process because doing so would make sure the company’s products and services are provided in a timely manner. Setting par limits and FIFO are examples of techniques that could be adopted by the organization to improve its supply chain management plan.
Reference List
Basu, R & Wright, NJ 2016, Managing global supply chains , Taylor & Francis, London.
Carrefour Group 2018, Governance structure . Web.
Donati, M 2018, Use IT to attract top-level SRM support . Web.
Jue, G 2014, The use of business intelligence techniques in supply chain performance. Web.
Lotfi, Z, Mukhtar, M, Sahran, S & Zadeh, AT 2013, ‘Information sharing in supply chain management,’ Procedia Technology , vol. 11, no. 2013, pp. 298-304.
Monczka, RM, Handfield, RB, Giunipero, LC & Patterson, JL 2015, Purchasing and supply chain management , 6th edn, Cengage Learning, New York, NY.
Saracene, T 2014, 4 steps to accurate sales forecasts . Web.
Tolhurst, C 2013, 4 steps to effective supplier relationship management . Web.
Xu, L, Xu, Q & Liu, X 2014, ‘Wal-Mart and Carrefour’s supply chain management strategies in China’, International Journal of Business and Management , vol. 9, no. 7, pp. 155-161.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, December 2). Carrefour Supermarket's Supply Chain Management. https://ivypanda.com/essays/carrefour-supermarkets-supply-chain-management/
"Carrefour Supermarket's Supply Chain Management." IvyPanda , 2 Dec. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/carrefour-supermarkets-supply-chain-management/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Carrefour Supermarket's Supply Chain Management'. 2 December.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Carrefour Supermarket's Supply Chain Management." December 2, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/carrefour-supermarkets-supply-chain-management/.
1. IvyPanda . "Carrefour Supermarket's Supply Chain Management." December 2, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/carrefour-supermarkets-supply-chain-management/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Carrefour Supermarket's Supply Chain Management." December 2, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/carrefour-supermarkets-supply-chain-management/.
- Carrefour Company Problems and Solutions
- Analysis of Walmart and Carrefour
- Carrefour Hypermarket: Company Analysis
- Carrefour Business Failure in the Japanese Market
- Carrefour Management Strategies
- Carrefour's "Art for Food" Initiative: Creative Brief
- Carrefour and Emirates Islamic Bank Analysis
- Carrefour: Healthcare Plans and Programs
- Human Resources Management: The Case of Carrefour in UAE
- Carrefour Company: Corporate Operations Strategy
- Logistics Improvement for Timely Food Delivery
- Alpine Beverages Company's Third-Party Logistics
- Energy and Utility Firms and Their Final Consumers
- EnGlobal Logistics Firm's Supply Chain Operations
- Transportation and Logistics in the Middle East
SCM Insight
Carrefour supply chain management .
Carrefour has a very advanced supply chain management system and it allows the company to manage its global operations. The company has successfully differentiated its brand name and it helped the company to increase its revenue and establish a strong database of loyal customers. Today, we’ll discuss Carrefour supply chain management; its supplier relationship management, and how it is using technology to improve relationships.
Some of the key statistical facts and figures about Carrefour Supply Chain Management;
- Carrefour started operating its business in 1958
- Has a network of 1200 supermarkets and 3245 convenience store
- Approximately 500,000 employees are working for the company
What is Carrefour Supply Chain Management?
Carrefour employs the latest technological tools and software to deal with its supply chain processes and operations like warehouse management, logistics, and procurement. The supermarket brand employs radio frequency and cross-docking technology to move and transport goods and products from the warehouse to the retail stores. Usually, Carrefour employs 3PLs (third-party logistics service providers) to deal with its global SC operations.
In order to satisfy the needs and wishes of customers with products and services, Carrefour requires an efficient and effective SCM system. Launching SCM and a logistic system would help the company to amplify the response rate relevant to the needs and wishes of customers.
Benefits of Carrefour SCM
Effective implementation of SCM benefits the supermarket Carrefour in the following ways;
- Amplifying the quality standards
- Knowing what products to sell to the customers
- The specific product line for the branded product line
- Providing products that meet quality standards
- Improving coordination among various departments like warehousing, transportation, sales, and procurement
- Maximizing efficiency and effectiveness of the retail functions
- Developing comprehension of various processes
Carrefour Supplier Relationship Management
The growth and success of SCM rely on developing stronger supplier relationship management. Some of the main elements of Carrefour supplier relationship management are as follows;
Transactional Relationship
Transactional connection is the main element of developing a relationship with the supplier. It is a type of relationship that focuses on sharing goods and products within a certain time at a specific price. Carrefour should establish such relationships for the sale of perishable goods and products.
The transactional relationship helps you to identify the time-sensitive products, and deliver them at the specific time at the right time. However, managing the long-term relationship with the suppliers would require you to establish a trusting bond with them.
Collaborative Relationship
Carrefour establishes collaborative relationships with its suppliers to meet the expectations of the delivery service and develop value with SCM. The collaborative relationship focuses on adding value to the products and developing beneficial relationships between companies and suppliers.
However, it makes sure that the company receives value from processes and systems from the tech vendors. Such relationships are highly relationship because it automates the company’s operations.
Order Fulfillment
The company shifts the responsibility by completing the order fulfillment. Instead of centralizing SCM processes, the company gives the SCM control to the managers by giving order fulfillment input. However, it is a successful SCM strategy for the company’s stores and supermarkets.
Carrefour Employing Technology to Improve Relationship
Carrefour employs various IT tools and applications to improve the supplier relationship in the SCM. Many researchers and experts have pointed out the role of IT (information technology) in amplifying the supplier relationship. Some of the key areas supply chain areas of Carrefour that have taken advantage of the usage of technology are as follows;
- Supplier relationship
- Supplier governance and management
- Supplier segmentation
Automation technology simplifies various processes and operations. You can employ IT tools and applications to recognize the right suppliers at the same time. It allows you to amplify the efficiency and effectiveness of SCM processes. The role of IT doesn’t stop here; rather it focuses on developing a simple communication channel that allows Carrefour to remain in touch with suppliers. However, it develops such a payment method that is acceptable for both parties.
Transparency & Visibility
The reason various IT tools and applications support supplier relationship management is that it amplifies visibility and transparency in the contractual relationships of suppliers. It is highly beneficial for developing a strong relationship between Carrefour and its suppliers. However, transparency promotes trust and confidence, and it is the foundation of strong supplier relationships.
The benefits derived from the usage of technology amplify the supplier relationship. The reason supplier relationship doesn’t receive a lot of emphases is because companies don’t fully comprehend the significance of supplier relationship and how it is beneficial for both parties.
Conclusion: Carrefour Supply Chain Management
After an in-depth study of Carrefour supply chain management; we have realized that Carrefour is the world’s leading organization that develops better supplier relationships. If you are learning about Carrefour supplier relationships and SCM processes, then you should keep in mind the abovementioned factors.
Ahsan is an accomplished researcher and has a deep insight in worldly life affairs. He goes Live 3 days a week on various social media platforms. Other than research writing, he’s a very interesting person.
Related Posts

Efficient Supply Chain Management

Woolworths Supply Chain Management

Inventory Optimization in Supply Chain

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
Carrefour: Business Model, SWOT Analysis, and Competitors 2023
Inside This Article
In this blog article, we will delve into the business model, SWOT analysis, and competitors of Carrefour, one of the leading retail giants in the world. Carrefour has established itself as a dominant player in the industry with its innovative strategies and customer-centric approach. Through a detailed examination of its business model, we will explore the key factors contributing to Carrefour's success. Additionally, a comprehensive SWOT analysis will shed light on the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Furthermore, we will identify and analyze Carrefour's major competitors in the market, providing valuable insights into the company's positioning in the industry.
What You Will Learn:
- Who owns Carrefour and the significance of its ownership structure in the company's decision-making and operations.
- The mission statement of Carrefour and how it reflects the company's goals, values, and commitment to its stakeholders.
- Understanding how Carrefour makes money through its diverse revenue streams and business strategies.
- An in-depth explanation of Carrefour's Business Model Canvas, highlighting the key components that contribute to its success and profitability.
- Identification of Carrefour's main competitors in the retail industry and an analysis of their market position and strategies.
- A comprehensive SWOT analysis of Carrefour, examining its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the competitive market landscape.
Who owns Carrefour?
Introduction.
Carrefour, a multinational retail corporation, is one of the largest supermarket chains in the world. With its headquarters in France, Carrefour operates thousands of stores across various countries. This section will explore the ownership structure of Carrefour and shed light on the key stakeholders involved.
Major Shareholders
Carrefour has a diverse ownership structure, with both institutional and individual investors holding significant stakes in the company. Here are some of the major shareholders of Carrefour:
Groupe Arnault: Groupe Arnault, led by Bernard Arnault, is a prominent French business conglomerate and luxury goods company. As of the latest available data, Groupe Arnault owns a substantial stake in Carrefour, making it one of the largest shareholders.
Norges Bank Investment Management: Norges Bank Investment Management, also known as NBIM, is the investment arm of the Norwegian central bank. It manages the Government Pension Fund Global, which owns a notable stake in Carrefour.
Qatar Investment Authority: The Qatar Investment Authority (QIA) is the sovereign wealth fund of the State of Qatar. QIA has made significant investments in various sectors globally, including retail. It holds a considerable stake in Carrefour.
BlackRock: As one of the world's largest investment management firms, BlackRock has a diversified portfolio of investments. It also holds a significant stake in Carrefour, reflecting its confidence in the company's long-term prospects.
Employee Ownership
Apart from institutional investors, Carrefour also encourages employee ownership. The company has implemented various employee share ownership plans, enabling its workforce to become shareholders. This approach fosters a sense of ownership, aligning the interests of employees with the company's success.
Publicly Traded Shares
Carrefour's shares are publicly traded on several stock exchanges, including Euronext Paris. This listing allows individual investors to purchase and trade Carrefour shares on the open market. The liquidity provided by the public trading of shares contributes to the overall ownership dynamics of Carrefour.
The ownership of Carrefour is spread across a range of stakeholders, including institutional investors, individual shareholders, and employee shareholders. Notable entities such as Groupe Arnault, Norges Bank Investment Management, Qatar Investment Authority, and BlackRock hold significant stakes in the company. Additionally, Carrefour's emphasis on employee ownership underscores its commitment to fostering a shared sense of responsibility and alignment among its workforce. With its publicly traded shares, Carrefour provides opportunities for individual investors to participate in its ownership structure.
What is the mission statement of Carrefour?
Carrefour, one of the largest retail chains in the world, has a clear and concise mission statement that guides its operations and strategy. Their mission statement can be summarized as follows:
Enhancing the daily lives of customers with quality and affordable products
Carrefour's primary goal is to provide customers with a wide range of quality products at affordable prices, ensuring that their daily needs are met conveniently. By offering a diverse selection of goods, including food, household items, electronics, and more, Carrefour aims to enhance the lives of its customers by making their shopping experience easier and more enjoyable.
Promoting sustainability and social responsibility
In addition to meeting customer needs, Carrefour is committed to promoting sustainability and social responsibility in its operations. They prioritize initiatives that reduce their environmental impact, such as energy-efficient stores, waste management, and promoting sustainable sourcing and production. Carrefour also strives to contribute positively to the communities they operate in, supporting local initiatives, and engaging in philanthropic activities.
Fostering innovation and technological advancements
Carrefour recognizes the importance of staying at the forefront of technological advancements and embracing innovation in the retail industry. Their mission statement reflects their commitment to leveraging technology to improve the customer experience, enhance operational efficiency, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market. By embracing digital transformation and investing in innovative solutions, Carrefour aims to provide customers with a seamless and personalized shopping experience.
Empowering employees and promoting diversity
Carrefour acknowledges the crucial role of its employees in delivering on its mission. Their mission statement emphasizes the importance of empowering employees, fostering a collaborative and inclusive work environment, and providing opportunities for growth and development. Carrefour values diversity and strives to create an inclusive workforce that reflects the diversity of the communities they serve.
In summary, Carrefour's mission statement focuses on enhancing the daily lives of customers through the provision of quality and affordable products, while also promoting sustainability, innovation, and employee empowerment. By adhering to this mission, Carrefour aims to be a trusted and preferred retail destination for customers worldwide.
How does Carrefour make money?
Retail sales.
Carrefour primarily generates revenue through its retail sales. As one of the largest retail chains in the world, Carrefour operates a vast network of hypermarkets, supermarkets, convenience stores, and e-commerce platforms. These retail outlets offer a wide range of products including groceries, household goods, electronics, clothing, and more.
Carrefour's retail sales are driven by consumer demand for everyday essentials and discretionary items. The company strategically positions its stores in high-traffic areas and tailors its product offerings to meet the specific needs and preferences of local customers. By effectively managing its supply chain, Carrefour ensures a constant flow of products to its stores, enabling it to meet customer demand and drive sales.
Private label brands
Another significant source of revenue for Carrefour comes from its private label brands. These are products manufactured by Carrefour and sold exclusively in its stores. Private label brands allow Carrefour to offer quality products at competitive prices, creating a unique selling proposition for its customers.
Carrefour's private label brands span various categories, including food, beverages, household items, and personal care products. By leveraging its extensive global supply chain and partnering with trusted manufacturers, Carrefour can maintain control over the production process and deliver products that meet its quality standards. The higher profit margins associated with private label brands contribute to Carrefour's overall revenue.
Services and partnerships
Carrefour also generates revenue through the provision of services and partnerships. For instance, the company offers financial services such as consumer credit, insurance, and loyalty programs. These services not only generate additional income but also strengthen customer loyalty and engagement.
Furthermore, Carrefour forms strategic partnerships with other companies to enhance its product offerings and customer experience. By collaborating with renowned brands, Carrefour can introduce exclusive products, promotions, and events that attract customers and drive sales. These partnerships often involve revenue-sharing arrangements, providing Carrefour with a percentage of the profits generated through the joint initiatives.
Real estate
Additionally, Carrefour benefits from its extensive real estate portfolio. The company owns or leases numerous properties worldwide, including its retail locations and distribution centers. By strategically managing its real estate assets, Carrefour can optimize space utilization, reduce costs, and potentially generate rental income through subleasing.
Moreover, Carrefour occasionally sells or divests underperforming properties, allowing it to unlock capital and reinvest in more promising locations or strategic initiatives. This real estate strategy serves as an additional revenue stream for Carrefour.
In conclusion, Carrefour generates revenue through various channels, including retail sales, private label brands, services and partnerships, and real estate. These revenue streams contribute to Carrefour's financial success and enable the company to maintain its position as a leading global retailer.
Carrefour Business Model Canvas Explained
The Carrefour business model canvas is a strategic management tool that provides a comprehensive overview of the key elements involved in Carrefour's business operations. It helps to identify and understand the various components of Carrefour's business model, including its value proposition, customer segments, key activities, resources, partnerships, and revenue streams. In this section, we will delve deeper into each of these elements to gain a better understanding of Carrefour's business model.
Value Proposition
Carrefour's value proposition lies in its ability to offer customers a wide range of high-quality products at competitive prices. With a focus on convenience and affordability, Carrefour aims to meet the diverse needs of its customer segments, which include individuals, families, and businesses. By providing an extensive selection of products, including groceries, household items, electronics, and clothing, Carrefour creates value by offering customers a one-stop shopping experience.
Customer Segments
Carrefour caters to a wide range of customer segments, including individuals, families, and businesses. The company has tailored its offerings to meet the unique needs and preferences of each segment. For instance, it offers a variety of fresh produce and groceries for individuals and families, while also providing bulk purchasing options for businesses. By understanding the distinct requirements of its customer segments, Carrefour is able to deliver personalized and targeted solutions.
Key Activities
Carrefour's key activities revolve around its retail operations, which include sourcing, purchasing, and merchandising a diverse range of products. The company invests heavily in supply chain management to ensure the availability of products and efficient logistics. Additionally, Carrefour focuses on store management, customer service, and marketing activities to enhance the overall shopping experience and build customer loyalty.
Key Resources
Carrefour's key resources include its physical stores, distribution centers, and technology infrastructure. The company operates a large network of stores across different regions, which serve as the primary touchpoints for customers. Furthermore, Carrefour relies on its robust supply chain and logistics capabilities to ensure a steady flow of products. The integration of technology, such as online platforms and mobile apps, also plays a crucial role in enhancing customer engagement and driving sales.

Partnerships
Carrefour has formed strategic partnerships with various suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to ensure a reliable and diverse product offering. By collaborating with trusted partners, Carrefour can source products at competitive prices and maintain a consistent supply chain. Additionally, the company has established partnerships with financial institutions, enabling it to offer payment solutions and credit services to customers.
Revenue Streams
Carrefour generates revenue primarily through the sale of products across its retail outlets. The company earns income from the margins between the purchase price and the sale price of the products. Furthermore, Carrefour also offers additional services, such as home delivery and click-and-collect, which contribute to its revenue streams. The company may also generate revenue through strategic partnerships and collaborations, where it earns commissions or licensing fees.
The Carrefour business model canvas provides a holistic view of how the company delivers value to its customers and generates revenue. By understanding each element of the canvas, we can appreciate the strategic decisions and activities that Carrefour undertakes to maintain its position as a leading retail player. From its value proposition and customer segments to its key activities, resources, partnerships, and revenue streams, Carrefour's business model demonstrates the intricacies of its operations and its commitment to customer satisfaction.
Which companies are the competitors of Carrefour?
Major competitors.
Carrefour, being one of the largest retail chains in the world, faces stiff competition from several major players in the industry. These competitors not only challenge Carrefour's market share but also constantly strive to attract the same consumer base. Here are some of the notable competitors of Carrefour:
Walmart: As the world's largest retailer, Walmart poses a significant threat to Carrefour. With its extensive network of stores and aggressive pricing strategies, Walmart competes fiercely with Carrefour in various global markets.
Tesco: Another major competitor of Carrefour is Tesco, the largest retailer in the United Kingdom. Tesco's strong presence in Europe, Asia, and other parts of the world puts them in direct competition with Carrefour, especially in the grocery sector.
Amazon: The e-commerce giant, Amazon, has been making significant strides in the retail industry through its online marketplace and acquisition of Whole Foods Market. With its convenience, vast product selection, and fast delivery options, Amazon competes with Carrefour both online and offline.
Aldi: As a leading discount supermarket chain, Aldi poses a strong competition to Carrefour in terms of price and affordability. Aldi's no-frills approach and emphasis on private-label products attract price-conscious consumers and directly challenge Carrefour's market position.
Regional Competitors
Apart from the major global competitors, Carrefour also faces competition from regional players in different countries and markets. Some of the prominent regional competitors include:
Auchan: Headquartered in France, Auchan is a multinational retail group that competes directly with Carrefour, particularly in Europe. Auchan operates hypermarkets, supermarkets, and convenience stores, offering a wide range of products across various price segments.
Metro AG: Based in Germany, Metro AG is a leading international wholesale company that competes with Carrefour in the wholesale and cash-and-carry sector. It serves professional customers such as hotels, restaurants, and independent retailers, providing them with a wide range of products at competitive prices.
E.Leclerc: E.Leclerc, a French cooperative society, operates a network of hypermarkets, supermarkets, and specialty stores. It competes with Carrefour in France and other European countries, focusing on competitive pricing, promotions, and customer loyalty programs.
Lidl: Lidl, a German discount supermarket chain, has rapidly expanded its presence across Europe, including countries where Carrefour operates. Lidl's focus on low prices, quality products, and efficiency makes it a formidable competitor for Carrefour in the discount grocery sector.
These are just a few examples of the major global and regional competitors that Carrefour faces in the retail industry. The intense competition among these players pushes Carrefour to continuously innovate, improve its offerings, and adapt to changing consumer demands in order to maintain its market position.
Carrefour SWOT Analysis
Carrefour, one of the largest retail chains in the world, possesses several key strengths that have contributed to its success. Firstly, the company benefits from a strong brand image and recognition globally. With over 12,000 stores in more than 30 countries, Carrefour has established a trusted reputation among consumers.
Another strength of Carrefour is its extensive product range. The company offers a wide variety of products, ranging from groceries and household goods to electronics and clothing. This diversity allows Carrefour to appeal to a broad customer base and cater to different consumer needs.
Carrefour's strong supply chain management is also a significant strength. The company has developed efficient logistics systems, enabling it to maintain adequate product availability and deliver products to stores promptly. This ensures that customers can find the desired products in-stock, enhancing their shopping experience.
Furthermore, Carrefour has successfully implemented a multi-channel retail strategy. The company operates both physical stores and an online platform, providing customers with convenience and flexibility in their shopping choices. This omni-channel approach has helped Carrefour remain competitive in an increasingly digital retail landscape.
Despite its strengths, Carrefour also faces certain weaknesses that it needs to address. One of the weaknesses is the company's limited presence in some key markets. While Carrefour has a strong global presence, it still lacks significant market share in certain regions, such as North America. This limits its potential for growth and exposes the company to the risk of missing out on opportunities in these markets.
Another weakness of Carrefour is its relatively high operating costs. The company's extensive store network and complex supply chain contribute to increased expenses. This can impact Carrefour's profitability and make it challenging to compete with low-cost retailers.
Additionally, Carrefour has faced criticism for its slow adaptation to e-commerce. Although the company has made efforts to expand its online presence, it still lags behind some competitors in terms of digital innovation. This weakness could hinder Carrefour's ability to attract tech-savvy consumers and could result in a loss of market share in the long run.
Opportunities
Carrefour has several opportunities to capitalize on in the retail industry. One significant opportunity is the growing demand for organic and sustainable products. As consumers become more conscious of their environmental impact and health, there is an increasing preference for organic and sustainable options. By expanding its range of such products and promoting them, Carrefour can tap into this emerging market segment and attract environmentally and health-conscious customers.
Another opportunity lies in the expansion of e-commerce. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift towards online shopping, and this trend is expected to continue. Carrefour can leverage its existing online platform and invest in enhancing its digital capabilities to capture a larger share of the e-commerce market. This could include initiatives such as improving website functionality, offering personalized recommendations, and providing seamless online-to-offline shopping experiences.
Furthermore, Carrefour can explore partnerships and collaborations to expand its offerings and reach new customer segments. For instance, partnering with local farmers or specialty stores can help Carrefour enhance its product range and cater to specific regional preferences. Collaborating with technology companies can also enable Carrefour to leverage innovative solutions such as artificial intelligence and data analytics to improve customer experiences and operational efficiency.
In addition to opportunities, Carrefour faces certain threats that could impact its performance and market position. One significant threat is intense competition from both traditional and online retailers. The retail industry is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share. Carrefour must continuously innovate and differentiate itself to stay ahead of competitors and retain its customer base.
Another threat is the potential for economic downturns and fluctuations in consumer spending. During periods of economic uncertainty, consumers tend to reduce discretionary spending, which can impact Carrefour's sales and revenue. The company needs to be prepared to adapt its strategies and offerings during such times to maintain customer loyalty and mitigate the impact of economic downturns.
Additionally, changing consumer preferences and shopping habits pose a threat to Carrefour. As consumers increasingly prioritize convenience and value, retailers must adapt to meet these evolving needs. Failure to anticipate and address these changing preferences can result in a loss of market share to competitors that better align with customer demands.
In conclusion, Carrefour's SWOT analysis highlights its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the retail industry. By leveraging its strengths, addressing weaknesses, capitalizing on opportunities, and mitigating threats, Carrefour can maintain its position as a leading global retailer and continue to thrive in an ever-changing market.
Key Takeaways
- Carrefour is a multinational retail corporation, owned by various shareholders including institutional investors and individual shareholders.
- The mission statement of Carrefour is to be the preferred retailer wherever it operates, by meeting the evolving needs and desires of its customers.
- Carrefour generates revenue primarily through the sale of groceries, consumer electronics, clothing, and other household products in its stores worldwide.
- The Carrefour Business Model Canvas highlights the key elements of the company's operations, including its value proposition, customer segments, channels, revenue streams, and key activities.
- Carrefour faces competition from other major retail corporations such as Walmart, Tesco, and Costco. However, it also competes with local supermarkets and online retailers in each country it operates.
- In terms of SWOT analysis, Carrefour's strengths include its global presence and diverse product offerings, while its weaknesses may include intense competition and challenges in adapting to changing consumer preferences. Opportunities for growth include expanding into emerging markets, while threats include economic downturns and increasing competition from e-commerce giants.
In conclusion, Carrefour is a global retail giant, and it is owned by a combination of shareholders, including institutional investors and individual shareholders.
The mission statement of Carrefour is to be the leader in the retail industry by offering quality products at competitive prices, while also promoting sustainability and social responsibility.
Carrefour generates revenue through various channels, such as the sale of groceries, household items, electronics, and clothing. Additionally, it operates various formats, including hypermarkets, supermarkets, convenience stores, and e-commerce platforms.
The Carrefour Business Model Canvas explains how the company creates value by focusing on key activities such as procurement, logistics, and store operations. It also highlights the importance of customer relationships, marketing, and the use of technology to enhance efficiency and customer experience.
Some of the main competitors of Carrefour include Walmart, Tesco, Aldi, and Amazon. These companies compete for market share and strive to offer customers similar products and services.
Lastly, a SWOT analysis of Carrefour reveals its strengths, such as its global presence and strong brand recognition, as well as weaknesses, such as high competition and limited online presence. It also identifies opportunities for growth, such as expanding into emerging markets, and threats, such as changing consumer preferences and economic fluctuations.
Overall, Carrefour continues to be a major player in the retail industry, constantly adapting to market dynamics and striving to meet customer demands while staying true to its mission of providing quality products in a sustainable manner.
What are the weaknesses of Carrefour?
Some of the weaknesses of Carrefour include:
Intense competition: Carrefour faces strong competition from both local and international retailers. This can limit their market share and affect their profitability.
Dependence on mature markets: Carrefour heavily relies on mature markets in Europe, where economic conditions can be unpredictable. This makes them vulnerable to economic downturns and reduces their growth opportunities.
Large store format: Carrefour's hypermarket format requires a significant amount of floor space, which can be expensive to maintain. It also limits their ability to enter smaller markets or urban areas where space is limited.
Limited online presence: Carrefour has been relatively slow in adapting to the e-commerce boom. Although they have made efforts to expand their online presence, they still lag behind some competitors, which can be a disadvantage in the digital age.
Complexity in operations: Carrefour operates in multiple countries, each with its own regulations, cultural differences, and consumer preferences. This complexity can make it challenging to maintain consistency and efficiency across all their operations.
Lack of specialization: Carrefour offers a wide range of products, including groceries, clothing, electronics, and household items. While this diversification can attract a broad customer base, it may also lead to a lack of specialization and expertise in any particular product category.
Brand perception: In some markets, Carrefour may face negative brand perception due to issues related to labor practices, sustainability, or other controversies. This can impact customer loyalty and affect their reputation.
High debt levels: Carrefour has a significant amount of debt, which can limit their financial flexibility and increase their vulnerability to economic downturns or fluctuations in interest rates.
Inconsistency in customer experience: Carrefour operates in various countries, and the customer experience can vary across different locations. Inconsistent service quality or product availability may lead to dissatisfaction among customers.
Dependence on private label products: Carrefour relies heavily on private label products, which can be perceived as lower quality compared to well-known brands. This may limit their ability to compete with retailers that offer a larger selection of branded products.
What is the competitive advantage of Carrefour?
Carrefour, one of the largest retail chains in the world, has several competitive advantages that contribute to its success. Some of the key competitive advantages of Carrefour include:
Global presence: Carrefour operates in over 30 countries and has a strong international presence, allowing it to benefit from economies of scale, global sourcing, and brand recognition. This global reach provides the company with a competitive edge over local or regional retailers.
Diverse store formats: Carrefour offers a variety of store formats, including hypermarkets, supermarkets, convenience stores, and e-commerce platforms. This diverse range of store formats allows Carrefour to cater to different customer needs and preferences in various locations, giving it a competitive advantage over retailers with a limited store format offering.
Strong supply chain management: Carrefour has a well-established and efficient supply chain management system. The company works closely with suppliers, using advanced technology and data analytics to optimize inventory management, reduce costs, and ensure product availability. This robust supply chain contributes to Carrefour's ability to offer competitive prices and a wide range of products to customers.
Private label brands: Carrefour has a strong portfolio of private label brands, which are products manufactured and sold under the company's own brand. These private label brands offer customers quality products at lower prices compared to national brands, helping Carrefour differentiate itself and attract price-conscious consumers.
Customer loyalty programs: Carrefour has implemented customer loyalty programs, such as the Carrefour Club Card, which offer various benefits and discounts to members. These programs help Carrefour build customer loyalty and incentivize repeat purchases, giving the company a competitive advantage in customer retention.
Embracing digital transformation: Carrefour has been proactive in adopting digital technologies and integrating e-commerce into its operations. The company has invested in online platforms, mobile apps, and omnichannel strategies, allowing customers to shop conveniently online or in-store. This digital transformation gives Carrefour an advantage in capturing the growing online retail market and meeting evolving customer expectations.
Overall, Carrefour's competitive advantages stem from its global presence, diverse store formats, efficient supply chain management, private label brands, customer loyalty programs, and commitment to digital transformation.
What is the target audience of Carrefour?
The target audience of Carrefour can vary depending on the location and format of its stores. However, in general, Carrefour's target audience consists of middle to upper-middle-class individuals and families who are looking for a wide range of products at affordable prices. Carrefour aims to cater to the diverse needs of its customers, offering a variety of products including groceries, household items, electronics, clothing, and more.
What strategy does Carrefour use?
Carrefour uses various strategies to maintain its competitive position in the retail industry. Some of the key strategies employed by Carrefour include:
Multiformat Retailing: Carrefour operates a wide range of store formats, including hypermarkets, supermarkets, convenience stores, and online platforms. This strategy allows the company to cater to different customer segments and maximize market coverage.
Private Label Products: Carrefour emphasizes the sale of its own private label products alongside national and international brands. This strategy helps the company achieve higher profit margins and build customer loyalty by offering quality products at competitive prices.
International Expansion: Carrefour has a strong presence in numerous countries, with operations in Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America. The company focuses on expanding its footprint in emerging markets to tap into the growing consumer base and capture new market opportunities.
Digital Transformation: Carrefour has been investing heavily in digital technologies to enhance its online and offline shopping experiences. This includes initiatives such as e-commerce platforms, mobile apps, digital loyalty programs, and data analytics to personalize customer offerings and improve operational efficiency.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility: Carrefour places a strong emphasis on sustainable practices and social responsibility. The company focuses on reducing its environmental footprint, promoting responsible sourcing, and supporting local communities. This strategy aligns with the evolving consumer preferences for ethical and environmentally friendly products.
Cost Efficiency: Carrefour continuously works on optimizing its supply chain, improving operational efficiency, and reducing costs. This allows the company to offer competitive prices to customers while maintaining profitability.
Overall, Carrefour's strategy revolves around offering a diverse range of products, expanding its global presence, embracing digital transformation, and prioritizing sustainability and social responsibility.
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

How Carrefour Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management: Case From the United Arab Emirates

2019, International Journal of Afro-Eurasian Research (IJAR)
Carrefour stands out as one of the largest and most successful hypermarket chains. It provides the customers with the great variety of the household goods, high-quality products, and food brands. Eventually, the hypermarket attracts the customers with the help of special offers and product promotions which customers are interested in. Nowadays, Carrefour in the United Arab Emirates serves over 200,000 customers a day operating 28 hypermarkets and 43 supermarkets (Carrefour Annual Report, 2016). Considering the high dynamics of UAE’s economy development, it is possible to emphasize the role of Carrefour’s power. In fact, it provides all necessary aspects for the cultivation of the effective supply chain, logistics, sourcing, supply management, customer service, demand management, inventory and transportation management, distribution, supply chain outsourcing and other aspects. The current paper is aimed to analyze the advantages and fallbacks of Carrefour within the mentioned area in order to explain the factors contributing to its success and competitiveness to better understand the uniqueness of supply chain in the UAE.
Related Papers
Harun Biçakcı
ÖZ Dünyanın en az kentleşme oranına sahip olan Afrika kıtasında son yıllarda kentleşme hızı artış göstermektedir. Özellikle Batı Afrika, Doğu Afrika'dan sonra kıtanın en hızlı kentleşen alt bölgesidir. Bu noktada, kıtanın bu alt bölgesindeki ülkeler ve kentler artan nüfus ve kentleşme oranı nedeniyle çok çeşitli sorunlarla karşı karşıyadır. Ayrıca, Afrika genelinde kentsel gelişim modelleri ve bunların nasıl tanımlandığına ve yorumlandığına ilişkin çok önemli farklılıklar da vardır. Bu bağlamda, çalışmanın amacı Batı Afrika'daki kentleri ve kentleşme hareketlerini Lagos kenti özelinde geçmişten bugüne incelemektir. Çalışma, literatür taramasına dayalıdır. Üç bölümden oluşmaktadır. Birinci bölümde Batı Afrika'daki kentlerin durumu irdelenmiştir. Bölgedeki ekonomik büyüme ve kalkınma ile altyapı ve hizmetlerin durumu incelenmiştir. İkinci bölümde ise Nijerya özelinde analizler söz konusudur. Üçüncü bölümde de Nijerya'nın önemli bir kenti olan Lagos seçilmiş ve kentin karşı karşıya olduğu kentsel gelişim süreci ve yaşadığı sorunlar irdelenmiştir. Ayrıca, kentbilim literatüründe Lagos kentini kentsel gelişim bağlamında geçmişten bugüne inceleyen ilk çalışmadır. ABSTRACT In recent years, the rate of urbanization has been increasing on the African continent, which has the least urbanization rate in the world. Especially, West Africa is the fastest urbanizing sub-region of the continent after East Africa. At this point, the countries and cities in this sub-region of the continent face a wide range of problems due to the increasing population and urbanization rate. In addition, there are significant differences in the patterns of urban development across Africa and in terms of how they are defined and interpreted. In this context, the aim of the study is to examine the cities and urbanization movements in West Africa from the past to the present in the case of Lagos. The study is based on literature review. It consists of three parts. At first, the situation of the cities in West Africa is examined. Economic growth and development in the region and the status of infrastructure and services are examined. Secondly, the general condition in Nigeria was analyzed. Finally, Lagos, an important city in Nigeria, was selected and the urban development process and problems faced by the city were examined. Moreover, this is the first study to examine the city of Lagos from the past to the present in the urban science literature in Turkey.
Nesrin Duman
ÖZ Travma sonrası büyüme, son derece zorlu yaşam krizleriyle mücadelenin sonucu olarak ortaya çıkan olumlu değişim deneyimidir. Travmanın akabinde hayatta kalan kişide gözlemlenen büyüme ve gelişim tek bir alanda olmayıp, birçok farklı alandaki değişimler ile kendini göstermektedir. Bu olumlu değişim; yaşamın daha fazla kıymetinin bilinmesi, daha anlamlı kişilerarası ilişkiler, artan kişisel güç duygusu, değişen öncelikler ve daha zengin varoluşsal ve manevi hayat da dâhil olmak üzere çeşitli şekillerde ortaya çıkabilmektedir. Travma sonrası büyüme terimi literatürde yeni olmasına rağmen, büyük iyiliğin büyük çileden gelebileceği fikri çok eski dönemlere dayanmaktadır. Travma sonrası büyüme ve gelişim konusunda son dönemlerde yapılan çalışmalar bu olgunun sistematik çalışılmasından ibarettir. Bu çalışma da travma sonrası büyüme konusunun daha iyi anlaşılmasına yönelik alanda yapılan çalışmalardan bir tanesidir. Bu amaçla alanyazın taranarak travma sonrası büyüme ve gelişim olgusu değerlendirilmiş, travma sonrası büyüme alanları ve bu alanlara etki eden faktörler anlatılmıştır. Anahtar Kelimeler: Travma, büyüme, gelişim, travma sonrası, gelişme. ABSTRACT Posttraumatic growth is an experience of positive change as a result of the struggle against extremely difficult life crises. Observed growth and development in the trauma survivor is not limited by a single area, but changes might appear in many different areas. These positive changes can be revealed in different aspects including knowledge of the greater value of life, more meaningful interpersonal relationships, increased sense of personal power, changing priorities, and richer existential and spiritual life. Although the term post-traumatic growth is new in the literature, the idea that great benevolence can be a great ordeal is based on very ancient times of history. Recent studies on post-traumatic growth and development consist of the systematic study of this phenomenon. This study is one of the studies conducted in the field for a better understanding of post-traumatic growth. For this purpose, the phenomen of posttraumatic growth and development was evaluated and development areas after traumatic experience and the factors affecting these areas were explained
Gizem Özgürel
ULUSLARARASI AFRO-AVRASYA ARAŞTIRMALARI DERGİSİ
Soğuk savaşın galibi olarak uluslararası düzende ABD hegemonyası ile tek kutupluluğun oluşması ve tarih boyunca ötekileştirilmiş, uluslararası sistemde dışarıda bırakılmış üçüncü dünya ülkelerinin bu düzende kendilerinde yer arayışı 2008 krizi ile hız kazanarak güç dengesinin gidişatını tekrar sorgulatmıştır. 2008 krizi aynı zamanda uluslararası ekonomik yönetişimin sadece lider sanayi ülkeleri ile devam edemediğini yeni pazarlara, yükselen ekonomiler ile işbirliğine ihtiyaç duyulduğunu tüm yıkıcı etkisi ile açıkça gözler önüne sermiştir. Tek kutuplu dünya düzeni değişirken küresel yönetişimde ortaya çıkan yeni aktörlerin yarattığı uluslararası hiyerarşi BRICS ile daha da belirginlik kazanmaktadır. 2000’li yıllardan itibaren yükselen güçler olarak karşımıza çıkan BRICS ülkeleri bugün küresel yönetişimde büyük oranda söz sahibi olmaktayken, BRICS yapılanması içinde Güney Afrika’nın ‘yükselen güç’ kimliği ile uyuşmadığı iddia edilmektedir. Bu iddiaların temel sebebi ise Güney Afrika’nın, uluslararası ekonomik ve siyasi entegrasyon anlamında diğer BRIC ülkeleri ile arasında belirgin farklılıklar bulunuyor olmasıdır. Bu farklıları anlayabilmek için öncelikle ‘yükselen güç’ ve ‘orta ölçekli güç’ kimliklerinin tanımlamasını iyi anlamlandırmak gerekir. Güney Afrika’nın 2013 yılı itibari ile BRIC’lere katılmış olması Güney Afrika ve dolayısıyla bahsi geçen iki önemli kavram üzerine düşünülmesini literatürde zorunlu hale getirmektedir. Bu çalışmanın amacı da literatürdeki ‘yükselen güç’ ve ‘orta ölçekli güç’ kavramlarının anlamsal kargaşasını açıklayabilmek adına kavramların yapısal ve davranışsal gerekliliklerini analiz ederek Güney Afrika’nın BRICS yapılanmasındaki kimliğini ortaya koyabilmektir
Supply chain management is a key of retail enterprises survival and development. For a better understanding, we intended to illustrate this concept with the case of Wal-Mart and Carrefour in China. In this article, we focused on the Wal-Mart and Carrefour's supply chain management strategies in China, introduced the supply chain management from four parts. " Customer is the first consideration! " and " Thinking global and acting local " are also pertinent to application in the management of supply chains. Managers may identify key processes and consider the possible contributions of each to the efficiency of their own chains. Through comparisons of supply chain management between Wal-Mart and Carrefour's strategies in China to give Chinese local retail enterprises enlightenment, and should help those wishing to explore the uniqueness of the Chinese market and the challenges that will be encountered when expanding their businesses in China.
Interal Res journa Managt Sci Tech
Supply Chain Management is a methodology of improving the business processes, making them more resilient, more agile and as a result, more competitive. The main function of SCM is to improve the product or service competitiveness (Machowiak, W. (2012). This paper is an endeavour to study, understand and interpret the evolution of supply chain management. On the basis of systematic literature review, we have attempted to explore the future of Supply Chain. We have captured various definitions of SCM provided by experts from the initial to recent period along with major classical definitions. Various dimensions of Supply chain are an integral part of this study. The paper discusses SCM and its dimensions; and tries to delineate SCM from related areas like Logistics Management, Value Chain Management and Operations Management. The paper also elaborates various theories of SCM. On completion of thorough literature review, the paper ends with a conclusion and future scope of work.
Regina Vina
Pak. J. Biological Sci
Md.Nahid Hasan
Abstract: Sixty-five bacterial strains were isolated from urine samples of patients suffering from urinary tract infection and identified by conventional methods. Eighty percent of total isolated organisms were found to be gram negative while remaining 20% were gram ...
Mathematical Problems in Engineering
Fabiana Rodrigues Leta
We used a Hierarchical Neuro-Fuzzy Class Method based on binary space partitioning (NFHB-Class Method) for macroscopic rock texture classification. The relevance of this study is in helping Geologists in the diagnosis and planning of oil reservoir exploration. The proposed method is capable of generating its own decision structure, with automatic extraction of fuzzy rules. These rules are linguistically interpretable, thus explaining the obtained data structure. The presented image classification for macroscopic rocks is based on texture descriptors, such as spatial variation coefficient, Hurst coefficient, entropy, and cooccurrence matrix. Four rock classes have been evaluated by the NFHB-Class Method: gneiss (two subclasses), basalt (four subclasses), diabase (five subclasses), and rhyolite (five subclasses). These four rock classes are of great interest in the evaluation of oil boreholes, which is considered a complex task by geologists. We present a computer method to solve this...
Physics Letters B
The first measurement of the cross section for top-quark pair production in pp collisions at the Large Hadron Collider at center-of-mass energy s= 7 TeV has been performed using a data sample corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 3.1±0.3 pb− 1 recorded by the CMS detector. This result utilizes the final state with two isolated, highly energetic charged leptons, large missing transverse energy, and two or more jets. Backgrounds from Drell–Yan and non-W/Z boson production are estimated from data. Eleven events are observed in ...
RELATED PAPERS
Bulletin de l' …
Jean-loup Lemesre
Riccardo Ursi
Zulfikri S Pou
Cancer research
Annie Leszkowicz
Physical Therapy
Robert Jarski
ROSALVO SILVA
Philosophical Studies
Justin Capes
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery
Vinka Petrovic
American journal of obstetrics and gynecology
Daniel Rolnik
International Journal of Scientific Research in Science and Technology
International Journal of Scientific Research in Science and Technology IJSRST
Sylvain SIMON
Ibrahim Amadou
Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders
hakimeh akbari
Physical Review D
Thomas Bock & Stefan Mitzlaff (Hg.): Von Langzeitpatienten für Akutpsychiatrie lernen – ›Die Entdeckung der Langsamkeit‹
Peter Lehmann
The Science of The Total Environment
edinaldo castro e Silva
Biomacromolecules
Eibhilin McGleenan
Mundher Alsamarraie
Molecular Pharmacology
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Uluslararası Afro-Avrasya Araştırmaları Dergisi
Kütüphaneme ekle.

HOW CARREFOUR REVOLUTIONIZING SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT: CASE FROM THE UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
Almaz Sandybayev
Carrefour stands out as one of the largest and most successful hypermarket chains. It provides the customers with the great variety of the household goods, high-quality products, and food brands.
Eventually, the hypermarket attracts the customers with the help of special offers and product promotions which customers are interested in. Nowadays, Carrefour in the United Arab Emirates serves over 200,000 customers a day operating 28 hypermarkets and 43 supermarkets (Carrefour Annual Report, 2016). Considering the high dynamics of UAE’s economy development, it is possible to emphasize the role of Carrefour’s power. In fact, it provides all necessary aspects for the cultivation of the effective supply chain, logistics, sourcing, supply management, customer service, demand management, inventory and transportation management, distribution, supply chain outsourcing and other aspects. The current paper is aimed to analyze the advantages and fallbacks of Carrefour within the mentioned area in order to explain the factors contributing to its success and competitiveness to better understand the uniqueness of supply chain in the UAE.
Anahtar Kelimeler
UAE , Supply Chain Management , Carrefour , UAE
- 1. Baofeng, H., Flynn, B., Xiande, Z. (2017). Supply chain power configurations and their relationship with performance. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 53(2), 4-52.
- 2. Blackburn, J.D. (1991). Time-based competition: The next battleground in American manufacturing, The Business One/APICS Series in Production Management, ILL, 160-269.
- 3. Brooks, A. D and Pawar, K. (2000) Dynamics of user/contractor interface in the public sector disentangled. Proceedings of the 9th International annual IPSERA conference & worldwide symposium on purchasing & supply chain management, 24-27 May, 99-109, University of Western Ontario.
- 4. Cooper, M.C., Lambert, D.M. and Pagh, J.D. (1997) Supply chain management: More than a new name for logistics. The International Journal of Logistics Management 8(1), 1-14.
- 5. Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & supply chain management. Pearson UK.
- 6. Douglas A. Smock and Stephen C. Rogers, Sourcing Strategy: The Brains behind the Game, Supply Chain Management Review, May/June 2007.
- 7. Gbadamosi, K. T. (2010). An Evaluation of the impact of bus rapid transit in urban intracity passenger movement in Lagos state. A paper to be presented at WCTR 2010, Lisbon. Nigeria: Centre for Transport Studies.
- 8. Hunter, N.A (1994). Quick Response in Apparel Manufacturing, the Textile Institute, Manchester, 1994, 1-271.
- 9. Handfield, R. B., Cousins, P. D., Lawson, B., & Petersen, K. J. (2015). How can supply management really improve performance? A knowledge‐based model of alignment capabilities. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 51(3), 3-17.
- 10. Hemalatha, M. and Sivakumar, V. J. (2009). Hyper market industry in Dubai–An evaluation using AHP technique. International Journal of Applied Management and Technology, 7(1), 6-9.
- 11. Hsu, P. K., and Chou, E. Y. (2015). Exploring the relationship among service quality, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty: A case study of Carrefour hypermarket. In LISS 2014, 1565-1571. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
- 12. Notteboom, T., and Yang, Z. (2016). Research in transportation business and management.
- 13. Ptak, C. A., and Schragenheim, E. (2016). ERP: tools, techniques, and applications for integrating the supply chain. Crc Press.
- 14. Sterling, J. U., and Lambert, D. (1989). Customer service research: Past, present, and future. International Journal of Physical Distribution and Material Management, 19(2), 17-27.
- 15. Turner, R. (2011). Supply management and procurement. Ft. Lauderdale, Fia: J. Ross Publication.
- 16. Reardon, T., Timmer, P., and Minten, B. (2012). Supermarket revolution in Asia and emerging development strategies to include small farmers. PNAS, 109(31), 1-6.
- 17. Reardon, T., Henson, S. and Berdegue, J. (2008). Proactive fast-tracking diffusion of supermarkets in developing countries: implications for market institutions and trade. Journal of Economic Geography, 7(4), 399-431.
- 18. Williamson, K. C., & Bloomberg, D. J. (1990). Modern logistics systems: Theory and practice. Journal of Business Logistics, 11(2), 65-86.
- 19. Wild, T. (2017). Best practice in inventory management. London: Routledge.
- 20. Yue, L. (2008). A comparative study of strategies adopted by Wal-Mart and Carrefour. A resource-based perspective acknowledgement. Fu Jen Catholic University, China, 59-80.
- 21. Carrefour UAE - Online Shopping in Dubai, UAE, Best Deals and Offers. (2018). Carrefour: Official website. Retrieved from https://www.carrefouruae.com/
TEDARİK ZİNCİRİ YÖNETİMİNİ CARREFOUR NASIL GERİ DÖNÜŞTÜRDÜ:BİRLEŞİK ARAP EMİRLİKLERİNDEN BİR VAKA
Carrefour, en büyük ve en başarılı hipermarket zincirlerinden biri olarak öne
çıkıyor. Müşterilere çok çeşitli ev eşyaları, yüksek kaliteli ürünler ve gıda markaları sunar.
Sonunda, hipermarket, müşterilerin ilgisini çeken özel teklifler ve ürün promosyonları
sayesinde müşterileri kendine çekiyor. Günümüzde Birleşik Arap Emirlikleri'ndeki
Carrefour, 28 hipermarket ve 43 süpermarket işleten günde 200.000'den fazla müşteriye
hizmet veriyor (Carrefour Faaliyet Raporu, 2016). BAE’nin ekonomi gelişiminin yüksek
dinamiklerini dikkate alarak, Carrefour’un gücünün rolünü vurgulamak mümkündür.
Aslında, etkin tedarik zinciri, lojistik, tedarik, tedarik yönetimi, müşteri hizmetleri, talep
yönetimi, envanter ve taşımacılık yönetimi, dağıtım, tedarik zinciri dış kaynak kullanımı
ve diğer hususların geliştirilmesi için gerekli tüm unsurları sağlar. Bu makalede, BAE'deki
tedarik zincirinin benzersizliğini daha iyi anlamak için başarısı ve rekabet edebilirliğine
katkıda bulunan faktörleri açıklamak için Carrefour'un bu alandaki avantajlarını ve geri
dönüşlerini analiz etmeyi amaçlamaktadır.
Carrefour , TEDARİK ZİNCİRİ YÖNETİMİ , BİRLEŞİK ARAP EMİRLİKLERİ
Kaynak Göster

- Makale Dosyaları
- Dergi Ana Sayfası
- Cilt: 3 Sayı: 5
- Cilt: 3 Sayı: 6
- Cilt: 4 Sayı: 7
- Cilt: 4 Sayı: 8
- Cilt: 5 Sayı: 9
All rights reserved. International Journal of Afro-Eurasian Research (IJAR ) is an International refereed journal and published biannually. Authors are responsible for the content and linguistic of their articles. Articles published here could not be used without referring to the Journal. The opinions in the articles published belong to the authors only and do not reflect those of International Journal of Afro-Eurasian Research .

Carrefour becomes first French retailer to utilise AI in supply chain optimisation

One of the world’s leading food retailers has become the first French retailer to use artificial intelligence to optimise its supply chain process.
Carrefour Group announced in a statement this week that, as part of a €2bn annual investment budget included in the "Carrefour 2022" transformation plan, the company’s supply chain has selected Viya’s AI solution developed by SAS. Carrefour will complete an 18-month trial period and utilise the SAS solution to collect and process data from its stores, warehouses and e-commerce websites. It will allow the company to predict demand and refine supplier orders.
"The deployment of the SAS platform will help us turn the corner in optimising our supply chain," says Franck Noël-Fontana, Forecast Director at Carrefour France. “By freeing up time for teams, artificial intelligence will allow them to focus on developing differentiated forecasting strategies and better meeting customer expectations while reducing waste."
Related stories:
HighJump to redefine retail supply chain through cloud technology
Technology, governance and recruitment: could 2019 be the tipping point for procurement?
Accenture granted US patent for quantum computing technology
The implementation of AI represents an industry first in the French retail sector. Carrefour will take advantage of SAS Viya’s multi-channel distribution and inventory optimisation to reduce waste and create value.
“AI will also enable people in new occupations - such as data scientists for data processing and demand planners for business expertise - to work in parallel on forward planning tasks,” says Carrefour. “Optimising the work of the supply and planning teams, the SAS platform can process a variety of data from the Carrefour Supply Chain information system. It will also make teams more agile by allowing them to integrate new working methods and continuously improve their forecasting processes. The SAS open AI solution will also offer Carrefour experts an opportunity to develop their own bespoke algorithms to meet their specific needs.”
- Hyve Co-Founder on Cloud's Potential to Transform Logistics Logistics
- Why Accenture is Investing in AI-Powered Humanoid Robots Technology
- Elevate Your Sustainability Transparency Sustainability
- Peter Sharoff Procurement Specialist: P&SC LIVE New York Technology
Featured Articles

Top 100 Women 2024: Carol B. Tomé, UPS – No. 7
Supply Chain Digital’s Top 100 Women in Supply Chain honours UPS’s Carol B. Tomé at Number 7 for 2024 …

The Global P&SC Awards: One Month Until Submissions Close
Just one more month until submissions close for The Global Procurement & Supply Chain Awards in 2024 …

Top 100 Women 2024: Susan Johnson, AT&T – No. 6
Supply Chain Digital’s Top 100 Women in Supply Chain honours AT&T’s Susan Johnson at Number 6 for 2024 …

WATCH: Ivalua and PwC Navigate the Future of Procurement

Top 100 Women 2024: Karen Jordan, PepsiCo – No. 5

P&SC LIVE New York: Patricia Mendoza Rodriguez – VP
- One More Month to Go: Procurement & Supply Chain LIVE Dubai
- Top 100 Women 2024: Taryn Thompson, Bank of America – No. 4
- EU Supply Chain Law: Key Supply Chain Consulting Firms
- The Categories – Part 3: Procurement & Supply Chain Awards
- Meet our Sponsors: Procurement & Supply Chain LIVE New York
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, walmart and carrefour experiences in china: resolving the structural paradox.
Cross Cultural Management: An International Journal
ISSN : 1352-7606
Article publication date: 25 October 2011
The purpose of this paper is to combine secondary sources and interviews with Chinese suppliers to explore the structural paradox faced by retail multinational firms in China as they balance the competing demands of standardization and localization. The authors describe the challenges faced by two retail giants, Walmart and Carrefour, as they attempt to replicate in China their lean retailing successes elsewhere in the world.
Design/methodology/approach
This is a comparative study of Walmart's and Carrefour's ventures into the Chinese market, largely based on publicly available secondary sources, but also incorporating interviews with three Chinese nationals engaged in supplying these firms.
Walmart and Carrefour have so far failed to extend their oligopolistic dominance to the Chinese market. Walmart has stressed its well‐known standardization of operations, whereas Carrefour has better adapted to the Chinese economic culture. Issues identified are: the formation of partnership alliances and their impact on store location choice; the effect of under‐developed infrastructure on distribution and logistics; the unique Chinese business culture – guanxi (using social capital to build business relationships) and its influence on supplier relationships; the variety of consumer behavior and its effect on procurement and sourcing; and an immature information technology environment which impedes information sharing between supply chain partners. While both firms have had some degree of success, neither has been able to match the combined growth of their larger Chinese competitors.
Research limitations/implications
The authors are cautious in drawing normative conclusions or making predictions about the future. Both firms face significant obstacles as they challenge China's largest domestic retailers.
Originality/value
Many multinational corporations are aware of the topology of the Chinese market, what they lack is an in‐depth understanding and the skills needed for effective operations. This paper discusses the effectiveness of the strategies adopted by two leading global retailers as they attempt to resolve the paradox presented by the competing demands for standardization and localization and includes information provided by three of Walmart's and Carrefour's local Chinese suppliers.
- Multinational companies
- Globalization
- Standardization
- Localization
- Chinese business culture
- Structural paradox
- Retail multinational corporations
Chuang, M. , Donegan, J.J. , Ganon, M.W. and Wei, K. (2011), "Walmart and Carrefour experiences in China: resolving the structural paradox", Cross Cultural Management: An International Journal , Vol. 18 No. 4, pp. 443-463. https://doi.org/10.1108/13527601111179519
Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2011, Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services Editing Proofreading Rewriting
- Extra Tools Essay Topic Generator Thesis Generator Citation Generator GPA Calculator Study Guides Donate Paper
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us About Us Testimonials FAQ
- Studentshare
- Supply Chain Management of Carrefour
Supply Chain Management of Carrefour - Case Study Example

- Subject: Management
- Type: Case Study
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 17 (4250 words)
- Downloads: 6
- Author: mdietrich
Extract of sample "Supply Chain Management of Carrefour"
- Procurement
- Cited: 3 times
- Copy Citation Citation is copied Copy Citation Citation is copied Copy Citation Citation is copied
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Supply Chain Management of Carrefour
Carrefour china - french hypermarket retail chain, implementing business strategy by ikea, strategic assessment of wal-mart for an itm class, carrefour company analysis, sustainable operations of carrefour, value chain for carrefour company, carrefour's misadventure in russia.

- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY

Product details

Teaching delivery modes

- Español – América Latina
- Português – Brasil
Carrefour: Providing great retail experiences, on- and offline, powered by Google Cloud
About Carrefour
Originating in France, the Carrefour Group now has stores in more than 30 countries reaching 104 million households across the world each year. Carrefour has been a pioneer in food retail for more than 60 years, continuously striving to make its products both affordable and accessible to everyone.
Tell us your challenge. We're here to help.
Carrefour runs sap on google cloud with full data centralization for the best possible customer service, both on- and offline., google cloud results.
- Adopts industry best practices for back office management with SAP on Google Cloud
- Deploys a new ecommerce solution over Google Kubernetes Engine to provide scalability, flexibility, and stability to the platform
- Scales on demand with the speed of the business without the delays of hardware procurement, configuration, and maintenance
Google Cloud collates 2,000+ data streams in one place
In 1963, Carrefour was the first chain to bring the hypermarket model to France, opening a 2,500 m2 store that offered its customers the previously unseen combination of self-service shelves, a vast range of products, and free parking spaces. Since its foundation, the group has grown into one of the world's largest food retailers and has continued to innovate. It now aims to transform the future of retail by offering the best retail experience and the best products at the best price to customers around the world, pursuing an omnichannel strategy that encompasses ecommerce alongside brick-and-mortar stores.
For Carrefour Spain , the Spanish subsidiary of the group, this is a logical step. “Our focus is on our customers,” says Jose Antonio Santana, CIO at Carrefour Spain. “We want to meet them wherever they are, whether that’s in our hypermarkets, supermarkets, gas stations, or online.” Today, Carrefour thrives on- and offline with more than 1,000 physical stores across the country and 1.4 million online transactions a year.
In 2018, Carrefour Spain decided to overhaul its aging IT infrastructure and build a technological foundation designed to provide its customers with even better service. But making that change is a big decision for a company as big as Carrefour Spain, with so many different stores spread out across the country. The solution had to be powerful enough to handle large data processing tasks and designed to scale rapidly during peak shopping times such as the holidays or Black Friday.
“The goal was to build a data-centric technology infrastructure, so that we could serve our customers better and improve their experience. We needed to reconfigure our core infrastructure from the ground up, transforming our back office with Google Cloud and SAP.”
A cloud-based solution was the only way to handle the scale needed. However, the company could not afford to put its operations on hold during the migration, so it also needed a hybrid platform that could work with the existing on-premises infrastructure in the short term. To make that foundation a reality, the company turned to Google Cloud .
“The goal was to build a data-centric technology infrastructure, so that we could serve our customers better and improve their experience,” says Jose Antonio. “We needed to reconfigure our core infrastructure from the ground up, transforming our back office with Google Cloud and SAP.”
Accessing the right expertise for a successful migration
Combining on- and offline retail is a simple concept, but it involves managing complex factors. As ecommerce has become a much bigger part of customers' lives, their behavior has changed, even when they are shopping in physical stores. “Our customers today are much more sophisticated than before, with higher expectations,” says Jose Antonio. “Often, they want to have all the information about a product, even before they walk into the store.” Customers don’t exclusively shop on- or offline, either. For example, they might want to buy bread in-store, but prefer to buy other products in bulk online.
To ensure that Carrefour delivers the same high quality service whichever channel the customer uses, the company has to collate multiple strands of data, relating to products, prices, stock levels, and local availability. The existing on-premises IT infrastructure was not designed for the amount of data processing such services require and had reached its technological limits. In order to scale up and meet demand, the company would have had to carefully plan its capacity in advance, sinking costs into hardware that had to be ordered, installed, configured, and maintained. By 2018, Carrefour Spain needed not just new equipment, but a new kind of infrastructure.
With so many unique aspects to consider, Carrefour Spain worked closely with Google Cloud consulting services to ensure an orderly, phased migration with minimal disruption to the business. “We pride ourselves on our innovation, but our business isn’t to specialize in cloud technology,” says Esther Vázquez Hevia, Director of Digital Transformation and Production and CISO at Carrefour Spain. “We wanted access to experts with the best knowledge and expertise, who could guide us through a successful migration. The best way for us to do that was with Google Cloud Consulting services.”
Updating ERP infrastructure for complete data consolidation
Large retail organizations such as Carrefour depend on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) tools for back-office operations such as inventory management, payroll, or supply processing. Over the years, the company had built up an assortment of applications to deal with its ERP needs, which resulted in data silos that took time to collate and analyze.
Moving to Google Cloud provided Carrefour with the perfect opportunity to update and standardize its back-office procedures and consolidate its data streams. It runs SAP on Google Cloud , which gives retailers access to the world’s leading ERP application vendor combined with the advantages of a cloud-based infrastructure.
With help from Google Cloud consulting services, Carrefour Spain began implementing SAP HANA on Compute Engine virtual machines in September. Within four months, the company had deployed the first phase of its new hybrid infrastructure, made up of 150 virtual machines. Around 40 of these are dedicated just to SAP HANA, while the others are given over other major services such as data processing.
With SAP on Google Cloud, Carrefour Spain has built an infrastructure optimized for customer service. The company has consolidated more than 2,000 data streams into a single place, and it now has the capacity and power to collate, analyze, and act on that information in real time.
“With Google Kubernetes Engine on Google Cloud, we can deploy and deliver new environments very quickly. We can grow and resize our environments at the same speed that we roll out our projects.”
Getting ready for annual peaks with automatic scaling
As well as transforming its data processing, Carrefour Spain also had its eye on boosting its ecommerce infrastructure ahead of the holiday season. Just a month before Black Friday, the company began migrating its ecommerce solution to Google Kubernetes Engine clusters. By using Kubernetes, the open-source container technology developed at Google, Carrefour Spain does not have to worry about provisioning new servers when it scales up.
When Black Friday came, the new ecommerce platform built on Google Cloud passed the test with flying colors, able to scale up and down automatically without compromising performance.
“With Google Kubernetes Engine on Google Cloud, we can deploy and deliver new environments very quickly,” says Esther. “We can grow and resize our environments at the same speed that we roll out our projects.”
“Google Cloud has given us the flexibility to adapt our infrastructure and the agility to make changes very quickly. We’ve been able to adopt and standardize industry best practices across the whole company and provide the highest possible service to our customers.”
A solution for the present, a foundation for the future
The migration to Google Cloud has also made an impact on Carrefour’s developers and engineers, changing how they work. The operations team has adopted an “infrastructure as code” methodology, which allows it to make quick and easy changes to environments in minutes, without having to manage or maintain hardware. The team can build and iterate through different updates much more efficiently than before, resulting in higher quality services.
“Google Cloud has given us the flexibility to adapt our infrastructure and the agility to make changes very quickly,” says Jose Antonio. “We’ve been able to adopt and standardize industry best practices across the whole company and provide the highest possible service to our customers.”
Carrefour Spain has also reduced infrastructure costs with pay-per-use pricing on Google Cloud. With only one of its seven Google Cloud environments designated as a production environment, the company can shut the others down at night or on weekends when developers aren't working on them, saving resources for where they are really needed.
After the success of the 2018 holiday season, Carrefour Spain has focused on migrating its legacy on-premises architecture to Google Cloud and completing its digital transformation. With Google Cloud in place, the company can look forward to accessing new technology such as machine learning capabilities for enhanced data analysis, or SAP Leonardo, which can integrate Internet of Things functionality to its existing ERP capabilities.
“Together, Google Cloud and Carrefour are developing solutions for the retail experience of the future,” says Jose Antonio. “We want to provide our customers with the best service, wherever they are, whenever they need it.”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
INTRODUC TION. The article tries to examine Carrefour in the UAE through implementation of the management of supply. chain in order to analyze and de termine the success of a company. Carrefour is ...
This report has covered the key tenets of supply chain management and their relation with the operations of Carrefour Supermarket. This case study gives insight into how companies, such as Carrefour, which have widespread operations, could use the competencies available in global supply chain management to improve their supply chain management ...
social audits performed throughout the world in Carrefour's supply chain. An alert is a critical point of non-compliance identified during an audit. In 2019, 19% of potential production site audits generated one or more alerts. In the case of a listed supplier, immediate action is required.
Today, we'll discuss Carrefour supply chain management; its supplier relationship management, and how it is using technology to improve relationships. Some of the key statistical facts and figures about Carrefour Supply Chain Management; Carrefour started operating its business in 1958. Has a network of 1200 supermarkets and 3245 convenience ...
Carrefour is tapping the power of AI to optimize its supply chain including inventory management, and reduce waste. ... Carrefour has partnered with Capgemini and SAP to deploy SAP S/4HANA ...
The case examines the supply chain management practices of Carrefour and describes how it managed its supply chain including procurement, logistics and warehouse management, globally. It explains how the company customised its supply chain operations according to the countries in which it operated. The case also discusses the use of information ...
Carrefour's strong supply chain management is also a significant strength. The company has developed efficient logistics systems, enabling it to maintain adequate product availability and deliver products to stores promptly. This ensures that customers can find the desired products in-stock, enhancing their shopping experience. ...
Carrefour has become the first French retailer to use artificial intelligence to optimise inventory management and reduce waste by integrating software developed by advanced analytics leader SAS into its supply chain. Drawing on the €2 billion annual investment budget included in the "Carrefour 2022" transformation plan, mainly for IT and ...
Proceedings of the 9th International annual IPSERA conference & worldwide symposium on purchasing & supply chain management, 24-27 May, 99-109, University of Western Ontario. Cooper, M.C., Lambert, D.M. and Pagh, J.D. (1997) Supply chain management: More than a new name for logistics. The International Journal of Logistics Management 8(1), 1-14.
The French retail giant looks back on its supply chain evolutions 15 years after implementation of GS1 GDSN. GS1 and Carrefour have collaborated on a new case study to explore how the organisation has leveraged the GS1 Global Data Synchronisation Network (GS1 GDSN) to improve global communication with its trading partners. The impact of GS1 GDSN implementation can be seen across nearly every ...
Settings. Abstract. France based Carrefour (the second largest retailer in the world) is believed to be the most global retailer with its operations spread out all over the world. Managing a global supply chain is a very difficult and complex task. The case examines the supply chain management practices of Carrefour and describes how it managed ...
Carrefour's automatic distribution centers, which keep functioning 24/7 and are supplied by Carrefour's truck fleet, are the base of its development strategy and supply-chain management. In the ...
France based Carrefour (the second largest retailer in the world) is believed to be the most global retailer with its operations spread out all over the world. Managing a global supply chain is a very difficult and complex task. The case examines the supply chain management practices of Carrefour and describes how it managed its supply chain including procurement, logistics and warehouse ...
HOW CARREFOUR REVOLUTIONIZING SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT: CASE FROM THE UNITED ARAB EMIRATES ... and Chou, E. Y. (2015). Exploring the relationship among service quality, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty: A case study of Carrefour hypermarket. In LISS 2014, 1565-1571. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. 12. Notteboom, T., and Yang, Z. (2016 ...
and equitable supply chains for all market and non-market purchases. In accordance with Carrefour's procurement rules, all supply plants located in high-risk or at-risk countries must undergo a social audit. The audits are conducted under Initiative for Compliance and Sustainability (ICS) and Business Social Compliance Programme (BSCI) standards.
One of the world's leading food retailers has become the first French retailer to use artificial intelligence to optimise its supply chain process. Carrefour Group announced in a statement this week that, as part of a €2bn annual investment budget included in the "Carrefour 2022" transformation plan, the company's supply chain has ...
The purpose of this paper is to combine secondary sources and interviews with Chinese suppliers to explore the structural paradox faced by retail multinational firms in China as they balance the competing demands of standardization and localization. The authors describe the challenges faced by two retail giants, Walmart and Carrefour, as they ...
Stream 1: Front-end customer experience, creating a unified Carrefour shopping website and a single ecommerce app (The ultimate goal was to create a "One Carrefour" omni-channel experience for customers.) Stream 2: Logistics and supply chain, covering everything from order management systems,
This case study looks at the practices of Carrefour supply chain management in respect to practices, procurement, warehouse management, logistics, as well as operational strategies in the global market (Carrefour 2009). Further, the paper will consider the customization process of Carrefour supply chain management in respect to the laws of the ...
Carrefour: Managing the Global Supply Chain. Case -Reference no. 604-022-1 Subject category: ... Logistics management; Warehouse management; Evaluation of global suppliers; Cross docking; Information technology in supply chain management; Customising the supply chain; Global sourcing. ... The Case Centre is a not-for-profit company limited by ...
Google Cloud collates 2,000+ data streams in one place. In 1963, Carrefour was the first chain to bring the hypermarket model to France, opening a 2,500 m2 store that offered its customers the previously unseen combination of self-service shelves, a vast range of products, and free parking spaces. Since its foundation, the group has grown into ...
This study aims at analysing the collaboration process between Coca-Cola and Carrefour. Graph model for conflict resolution (GMCR) and drama theory are employed as complementary methods in ...
This case Carrefour in China, Savoring the Success focus on Carrefour, the world's second biggest retailer from France, initiated the idea of hyper-market in 1959, stressing the need for mass-sales, low delivery cost and everyday discount to achieve high sales turnover. The reasons for its phenomenal success throughout the world were the facilities it offered at its hypermarkets such as one ...