

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
Join our FREE training and learn the 5 things you can do to become a top 1% facilitator
What is problem-solving and how to do it right steps, processes, exercises.
The better your problem-solving skills are, the better (and easier!) your life will be. Organized problem-solving is a killer career skill - learn all about it here.
Whether we’re trying to solve a technical problem at work, or trying to navigate around a roadblock that Google Maps doesn’t see – most people are problem-solving every single day .
But how effective are you at tackling the challenges in your life? Do you have a bullet-proof process you follow that ensures solid outcomes, or... Do you act on a whim of inspiration (or lack thereof) to resolve your pressing problems?
Here’s the thing: the better your problem-solving skills are - the better (and easier!) your life will be (both professionally and personally). Organized problem-solving is a killer career (and life!) skill, so if you want to learn how to do it in the most efficient way possible, you’ve come to the right place.
Read along to learn more about the steps, techniques and exercises of the problem-solving process.
- 1. Do you want a Career in UX?
- Learn the Principles of UX Design
- Master a UX Design Tool
What is Problem-Solving?
We’re faced with the reality of having to solve problems every day, both in our private and professional lives. So why do we even need to learn about problem-solving? Aren’t we versed in it well enough already?
Well, what separates problem-solving from dealing with the usual day-to-day issues is that it’s a distinct process that allows you to go beyond the standard approaches to solving a problem and allows you to come up with more effective and efficient solutions. Or in other words, problem-solving allows you to knock out those problems with less effort.
Just like with any other skill, there’s an efficient way to solve problems, and a non-efficient one. While it might be tempting to go for the quickest fix for your challenge without giving it much thought, it will only end up costing you more time down the road. Quick fixes are rarely (if ever!) effective and end up being massive time wasters.
What separates problem-solving from dealing with the usual day-to-day issues is that it’s a distinct process that allows you to go beyond the standard approaches to solving a problem and allows you to come up with more effective and efficient solutions.
On the other hand, following a systemized clear process for problem-solving allows you to shortcut inefficiencies and time-wasters, turn your challenges into opportunities, and tackle problems of any scope without the usual stress and hassle.
What is the process that you need to follow, then? We’re glad you asked...
The Five Stages of Problem-Solving
So what’s the best way to move through the problem-solving process? There’s a 5-step process that you can follow that will allow you to solve your challenges more efficiently and effectively. In short, you need to move through these 5 steps:
- Defining a problem
- Ideating on a solution
- Committing to a course of action
- Implementing your solution
- And finally – analyzing the results.

Let’s look at each of those stages in detail.
Step 1: Defining The Problem
The first step might sound obvious, but trust us, you don’t want to skip it! Clearly defining and framing your challenge will help you guide your efforts and make sure you’re focussing on the things that matter, instead of being distracted by a myriad of other options, problems and issues that come up.
For once, you have to make sure you’re trying to solve the root cause, and not trying to mend the symptoms of it. For instance, if you keep losing users during your app onboarding process, you might jump to the conclusion that you need to tweak the process itself: change the copy, the screens, or the sequence of steps.
But unless you have clear evidence that confirms your hypothesis, your challenge might have an entirely different root cause, e.g. in confusing marketing communication prior to the app download.
Clearly defining and framing your challenge will help you guide your efforts and make sure you’re focussing on the things that matter, all the while ensuring that you’re trying to solve the root cause, and not trying to mend the symptoms of it
That’s why it’s essential you take a close look at the entire problem, not just at a fraction of it.
There are several exercises that can help you get a broader, more holistic view of the problem, some of our all-time favorites include Expert Interviews, How Might We, or The Map. Check out the step-by-step instructions on how to run them (along with 5 more exercises for framing your challenge!) here.
When in doubt, map out your challenge, and always try to tackle the bottlenecks that are more upstream - it’s likely that solving them will solve a couple of other challenges down the flow.
You also have to be mindful of how you frame the challenge: resist the urge to include a pre-defined solution into your problem statement. Priming your solutions to a predestined outcome destroys the purpose of following a step-by-step process in the first place!
Steer clear of formulations like:
We need to change the onboarding process... or We need to improve ad copy to increase conversions.
Instead, opt for more neutral, problem-oriented statements that don’t include a solution suggestion in them:
The drop off rate during the onboarding process is too high or Our ad conversion rates are below the norm.
Pro tip: Reframing your challenge as a ‘How Might We’ statement is a great way to spark up new ideas, opening your problem to a broader set of solutions, and is just a great way to reframe your problem into a more positive statement (without implying the possible solution!)
For example, following the onboarding drop-off rate problem we mentioned earlier, instead of framing it as a problem, you could opt for:
How Might We decrease the drop-off rate during the onboarding process?
Find out more about the best exercises for problem framing here!
Now that you have a clear idea of what you’re trying to solve, it’s move on to the next phase of the problem-solving process.
Learn more about facilitation and workshopping in our FREE FACILITATION COMMUNITY
Step 2: ideating a solution.
Get ready to roll up your sleeves and challenge the status quo! This step of the problem-solving process is all about thinking outside of the box, challenging old assumptions, and thinking laterally.
This stage is the one that tends to cause the most overwhelm in teams because it requires just the right balance of creativity and critical thinking, which tends to cause a lot of friction.
Our best advice?
Let go of the pressure to produce a polished, thought-through solution at this stage. You can hash out the details at a later point. Our goal right now is to come up with a direction, a prototype if you may, of where we want to move towards.
Embrace the “quantity over quality” motto, and let your creative juices flow! Now, we’re not saying you should roll with sub-par ideas. But you shouldn’t get too fixated on feasibility and viability just yet .
Your main goal during this step is to spark ideas, kick off your thinking process in the right direction, venture out of the familiar territories and think outside the box.
For the ideation to be the most effective your team will have to feel safe to challenge the norm and wide-spread assumptions. So lay judgment by side, there is no space for “that’s the way it’s always been done” in this step.
For your ideation sessions to be as efficient as possible, we highly recommend to run them in a workshop setting: this helps reduce the usual drawbacks of open discussions in teams (i.e. groupthink & team politics!)
Our favorite exercises to run during this phase include Lightning Demos, Sketching, and variations of Brainstorming. We crafted an entire article on how to run and facilitate these exercises in a separate article, so check it out of you’re going to be running an ideation session anytime soon!
Step 3: Choosing the Best Strategy & Committing
It’s time to decide which of the ideas that you generated in the last step will be the one you’ll implement.
This step is arguably the hardest one to complete smoothly: groupthink, team politics, differences in opinions and communication styles all make it very hard to align a team on a common course of action.
If you want to avoid the usual pitfalls of team decision-making, we recommend you steer clear of open unstructured discussion. While it’s useful in some scenarios, it’s a poor choice for when you need to make a decision, because it tends to reward the loudest people in the room, rather than give way to the best ideas.
It’s crucial you not only commit to a course of action but get full buy-in from the team. If your team members don’t understand the reasons for a decision, or are not fully onboard, the implementation of your decision will be half-hearted, and that’s definitely not what you want!
To achieve that, opt for anonymized, multi-layered voting, and include guided exercises like Storyboarding to prioritize your ideas.
We’ve gathered the list of our top-rated decision-making exercises, along with step-by-step instructions on how to run them in this article!
As a bonus tip, we recommend you involve a facilitator throughout the entire process. They will help align the team, and guide them through prioritizing and de-prioritizing solutions, as well as defining the next steps.
Pro tip : If you’re not the ultimate decision maker on the issue you’re trying to solve, make sure they’re in the room when the call is being made! Having a Decider in the room ensures that the decisions you come to will actually get executed on after, instead of getting shut down by your superiors after.
Join our FREE community and connect with other Facilitators and Workshoppers
Step 4: implementing your solution.
Here’s a truth that might be hard to swallow: it doesn’t matter how innovative, creative, or original your idea is, if your execution is weak.
One of our favourite illustrations of how this works in practice comes from the book “ Anything you want ” by Derek Sivers. He reveals that ideas should be treated as multipliers of execution. What this means is that a mediocre, “so-so” idea could be worth millions if executed well, while a “brilliant” idea can completely flop with bad execution.
That’s why this step is crucial if you want to really master the problem-solving process.
What do we mean by execution? Everything that happens after the whiteboards are wiped clean and your team starts to action the outcomes of your sessions, be it prototyping, development, or promotion.
But don’t just take our word for it, look at the example of how execution affected Nintendo’s sales:
In the past few years, Nintendo has come up with 3 products: the Wii, the Wii U and the Switch. Check out their sales figures on the graph below - Wii is the clear-cut leader, followed by Switch, and finally Wii U lagging behind.

The Wii was unbelievably successful - it was a genuinely unique, “brilliant”-level idea and it had a “brilliant” execution (20x $10 million = $200 million). It is one of the fastest selling game consoles of all time and it completely took over the market.
The next product was called Wii U and it was a “great” concept but the execution was absolutely terrible. So even though this product was very interesting and innovative, the end result was 15x $1,000 = $15,000.
Finally, Nintendo took the Wii U concept and tried it again with the Switch. The idea was “so so” as it was already done before, but the execution was “brilliant”. So, 5x $10 million = $50 million! Much better.

Bottom line?
The same idea can either make no dent in the market and damage your share price OR become a market hit and increase your share price dramatically. The only difference between the two scenarios – execution.
So shift your focus from coming up with crazy, innovative, outlandish ideas that will disrupt the market, and concentrate on really nailing down your execution instead.
This is likely the least “workshoppy” step out of the entire problem-solving process because it requires less alignment and decision-making and more..well.. Execution!
But hey, we wouldn’t be called “Workshopper” if we didn't offer you at least one way to optimize and workshopify (yup, we’re making it a thing) your execution process.
Cue in….prototyping.
We’re huge fans of prototyping all big solutions (and testing them!) The main reason?
This saves us time AND money! Prototyping and testing your solutions (especially if they’re time and investment-demanding) is a great way to make sure you’re creating something that is actually needed.
The key with prototyping the right way is to keep it simple. Don’t invest too much time, or resources into it. The goal is to gather data for your future decisions, not to create a near-to-perfect mockup of your solution.
There are LOADS of prototyping forms and techniques, and if you’d like to learn more on the subject you should definitely check out our extensive prototyping guide.
Step 5: Analyzing the Results
You’re nearly done, woo! Now that you have defined the right problem to tackle, brainstormed the solutions, aligned your team on the course of action, and put your plan into action it’s time to take stock of your efforts.
Seek feedback from all involved parties, analyze the data you’ve gathered, look at the bottom line of your efforts, and take a hard look at your problem: did it get solved? And even more than that, did the process feel smoother, easier, and more efficient than it normally is?
Running a retrospective is a great way to highlight things that went well and that you should keep for your next round of problem.solving, as well as pinpoint inefficiencies that you can eliminate.
But which kind of retrospective should you run? There are loads of options, and it’s easy to feel overwhelmed by them all, so we gathered our favorite retrospective variations in this article.
And there you have it, you just completed the cycle of problem-solving. We highly recommend you follow through with all the steps, without leaving any out. They all complement and build on each other, and it’s the combination of all 5 of them that makes the process effective.
Now that you have the problem solving process down, you might be wondering…
Do I need any special skills in order to be able to move through that process?
And the answer is… sort of! More in this in the next section.
Problem-Solving Skills
While your skill set will need to adapt and change based on the challenges you’ll be working on, most efficient problem-solvers have a solid foundation of these key skills:
- Active listening. While you might be the expert in the area of your challenge, there’s not a single person on Earth that knows it all! Being open to others’ perspectives and practicing active listening will come in very handy during step 1 of the process, as you’re trying to define the scope and the exact angle of the problem you’re working on.
- Analytical approach. Your analytical skills will help you understand problems and effectively develop solutions. You will also need analytical skills during research to help distinguish between effective and ineffective solutions.
- Communication. Is there a single area of expertise that DOESN’T require strong communication skills? We honestly don’t think so! Just like with any other life area, clear communication can make or break your problem-solving process. Being able to clearly communicate why you need to solve this challenge to your team, as well as align your team on the course of action are crucial for the success of the process.
- Decision-making. Ultimately, you will need to make a decision about how to solve problems that arise. A process without outcomes–regardless of how well thought-out and elaborate–is useless! If you want your problem-solving huddles to be effective, you have to come to grips with prioritization techniques and decision-making frameworks.
- Facilitation. Problem-solving revolves around being able to guide a group or a team to a common decision, and facilitation skills are essential in making that happen. Knowing how to facilitate will make it easy to keep the group focussed on the challenge, shortcut circular discussions, and make sure you’re moving along to solving the problem instead of just treading waters with fruitless discussions.
Not checking every single skill of your list just yet? Not to worry, the next section will give you practical tools on how to level up and improve your problem-solving skills.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
Just like with any other skill, problem-solving is not an innate talent that you either have or you don’t. There are concrete steps you can take to improve your skills.
Here are some things that will get you closer to mastering the problem-solving process:
- Practice, Practice, Practice
Practice makes perfect, and problem-solving skills are no exception! Seek opportunities to utilize and develop these skills any time you can.
If you don’t know where or how to start just yet, here’s a suggestion that will get you up and running in no time: run a quick problem-solving session on a challenge that has been bothering your team for a while now.
It doesn’t need to be the big strategic decision or the issue defining the future of the company. Something easy and manageable (like optimizing office space or improving team communication) will do.
As you start feeling more comfortable with the problem-solving techniques, you can start tackling bigger challenges. Before you know it, you’ll master the art of creative problem-solving!
- Use a tried and tested problem-solving workshop
Facilitation is one of the essential skills for problem-solving. But here’s the thing… Facilitation skills on their own won’t lead you to a solved challenge.
While being able to shortcut aimless discussions is a great skill, you have to make sure your problem-solving session has tangible outcomes. Using a tried and tested method, a workshop, is one of the easiest ways to do that.
Our best advice is to get started with a tried and tested problem-solving workshop like the Lightning Decision Jam . The LDJ has all the right ingredients for quick, effective problem solving that leads to tangible outcomes. Give it a go!
- Learn from your peers
You may have colleagues who are skilled problem solvers. Observing how those colleagues solve problems can help you improve your own skills.
If possible, ask one of your more experienced colleagues if you can observe their techniques. Ask them relevant questions and try to apply as many of the new found skills i your career as possible.
- Learn & Practice the best problem-solving exercises
Having a toolbox of problem-solving exercises to pull from that can fit any type of challenge will make you a more versatile problem-solver and will make solving challenges that much easier for you!
Once you get used to the groove of learning how to combine them into effective sessions or workshops, there’ll be no stopping you. What are some of the most effective problem-solving exercises? Glad you asked! We’ve gathered our favorite ones here, check it out!
And there you have it, you’re now fully equipped for running creative problem-sessions with confidence and ease! Whichever method or exercise you choose, remember to keep track of your wins, and learn as much as you can from your losses!
Anastasia Ushakova
Brand Strategist, Digital Marketer, and a Workshopper.

When Do You Need a Facilitator?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Suspendisse varius enim in eros elementum tristique. Duis cursus.

The Ultimate Facilitation Glossary: 50 Facilitation Terms You Should Know (From A-Z)

How To Improve Team Collaboration
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
In this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , Simon London speaks with Charles Conn, CEO of venture-capital firm Oxford Sciences Innovation, and McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin about the complexities of different problem-solving strategies.
Podcast transcript
Simon London: Hello, and welcome to this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , with me, Simon London. What’s the number-one skill you need to succeed professionally? Salesmanship, perhaps? Or a facility with statistics? Or maybe the ability to communicate crisply and clearly? Many would argue that at the very top of the list comes problem solving: that is, the ability to think through and come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Looked at this way, it’s no surprise that McKinsey takes problem solving very seriously, testing for it during the recruiting process and then honing it, in McKinsey consultants, through immersion in a structured seven-step method. To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
Charles and Hugo, welcome to the podcast. Thank you for being here.
Hugo Sarrazin: Our pleasure.
Charles Conn: It’s terrific to be here.
Simon London: Problem solving is a really interesting piece of terminology. It could mean so many different things. I have a son who’s a teenage climber. They talk about solving problems. Climbing is problem solving. Charles, when you talk about problem solving, what are you talking about?
Charles Conn: For me, problem solving is the answer to the question “What should I do?” It’s interesting when there’s uncertainty and complexity, and when it’s meaningful because there are consequences. Your son’s climbing is a perfect example. There are consequences, and it’s complicated, and there’s uncertainty—can he make that grab? I think we can apply that same frame almost at any level. You can think about questions like “What town would I like to live in?” or “Should I put solar panels on my roof?”
You might think that’s a funny thing to apply problem solving to, but in my mind it’s not fundamentally different from business problem solving, which answers the question “What should my strategy be?” Or problem solving at the policy level: “How do we combat climate change?” “Should I support the local school bond?” I think these are all part and parcel of the same type of question, “What should I do?”
I’m a big fan of structured problem solving. By following steps, we can more clearly understand what problem it is we’re solving, what are the components of the problem that we’re solving, which components are the most important ones for us to pay attention to, which analytic techniques we should apply to those, and how we can synthesize what we’ve learned back into a compelling story. That’s all it is, at its heart.
I think sometimes when people think about seven steps, they assume that there’s a rigidity to this. That’s not it at all. It’s actually to give you the scope for creativity, which often doesn’t exist when your problem solving is muddled.
Simon London: You were just talking about the seven-step process. That’s what’s written down in the book, but it’s a very McKinsey process as well. Without getting too deep into the weeds, let’s go through the steps, one by one. You were just talking about problem definition as being a particularly important thing to get right first. That’s the first step. Hugo, tell us about that.
Hugo Sarrazin: It is surprising how often people jump past this step and make a bunch of assumptions. The most powerful thing is to step back and ask the basic questions—“What are we trying to solve? What are the constraints that exist? What are the dependencies?” Let’s make those explicit and really push the thinking and defining. At McKinsey, we spend an enormous amount of time in writing that little statement, and the statement, if you’re a logic purist, is great. You debate. “Is it an ‘or’? Is it an ‘and’? What’s the action verb?” Because all these specific words help you get to the heart of what matters.
Want to subscribe to The McKinsey Podcast ?
Simon London: So this is a concise problem statement.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah. It’s not like “Can we grow in Japan?” That’s interesting, but it is “What, specifically, are we trying to uncover in the growth of a product in Japan? Or a segment in Japan? Or a channel in Japan?” When you spend an enormous amount of time, in the first meeting of the different stakeholders, debating this and having different people put forward what they think the problem definition is, you realize that people have completely different views of why they’re here. That, to me, is the most important step.
Charles Conn: I would agree with that. For me, the problem context is critical. When we understand “What are the forces acting upon your decision maker? How quickly is the answer needed? With what precision is the answer needed? Are there areas that are off limits or areas where we would particularly like to find our solution? Is the decision maker open to exploring other areas?” then you not only become more efficient, and move toward what we call the critical path in problem solving, but you also make it so much more likely that you’re not going to waste your time or your decision maker’s time.
How often do especially bright young people run off with half of the idea about what the problem is and start collecting data and start building models—only to discover that they’ve really gone off half-cocked.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah.
Charles Conn: And in the wrong direction.
Simon London: OK. So step one—and there is a real art and a structure to it—is define the problem. Step two, Charles?
Charles Conn: My favorite step is step two, which is to use logic trees to disaggregate the problem. Every problem we’re solving has some complexity and some uncertainty in it. The only way that we can really get our team working on the problem is to take the problem apart into logical pieces.
What we find, of course, is that the way to disaggregate the problem often gives you an insight into the answer to the problem quite quickly. I love to do two or three different cuts at it, each one giving a bit of a different insight into what might be going wrong. By doing sensible disaggregations, using logic trees, we can figure out which parts of the problem we should be looking at, and we can assign those different parts to team members.
Simon London: What’s a good example of a logic tree on a sort of ratable problem?
Charles Conn: Maybe the easiest one is the classic profit tree. Almost in every business that I would take a look at, I would start with a profit or return-on-assets tree. In its simplest form, you have the components of revenue, which are price and quantity, and the components of cost, which are cost and quantity. Each of those can be broken out. Cost can be broken into variable cost and fixed cost. The components of price can be broken into what your pricing scheme is. That simple tree often provides insight into what’s going on in a business or what the difference is between that business and the competitors.
If we add the leg, which is “What’s the asset base or investment element?”—so profit divided by assets—then we can ask the question “Is the business using its investments sensibly?” whether that’s in stores or in manufacturing or in transportation assets. I hope we can see just how simple this is, even though we’re describing it in words.
When I went to work with Gordon Moore at the Moore Foundation, the problem that he asked us to look at was “How can we save Pacific salmon?” Now, that sounds like an impossible question, but it was amenable to precisely the same type of disaggregation and allowed us to organize what became a 15-year effort to improve the likelihood of good outcomes for Pacific salmon.
Simon London: Now, is there a danger that your logic tree can be impossibly large? This, I think, brings us onto the third step in the process, which is that you have to prioritize.
Charles Conn: Absolutely. The third step, which we also emphasize, along with good problem definition, is rigorous prioritization—we ask the questions “How important is this lever or this branch of the tree in the overall outcome that we seek to achieve? How much can I move that lever?” Obviously, we try and focus our efforts on ones that have a big impact on the problem and the ones that we have the ability to change. With salmon, ocean conditions turned out to be a big lever, but not one that we could adjust. We focused our attention on fish habitats and fish-harvesting practices, which were big levers that we could affect.
People spend a lot of time arguing about branches that are either not important or that none of us can change. We see it in the public square. When we deal with questions at the policy level—“Should you support the death penalty?” “How do we affect climate change?” “How can we uncover the causes and address homelessness?”—it’s even more important that we’re focusing on levers that are big and movable.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
Simon London: Let’s move swiftly on to step four. You’ve defined your problem, you disaggregate it, you prioritize where you want to analyze—what you want to really look at hard. Then you got to the work plan. Now, what does that mean in practice?
Hugo Sarrazin: Depending on what you’ve prioritized, there are many things you could do. It could be breaking the work among the team members so that people have a clear piece of the work to do. It could be defining the specific analyses that need to get done and executed, and being clear on time lines. There’s always a level-one answer, there’s a level-two answer, there’s a level-three answer. Without being too flippant, I can solve any problem during a good dinner with wine. It won’t have a whole lot of backing.
Simon London: Not going to have a lot of depth to it.
Hugo Sarrazin: No, but it may be useful as a starting point. If the stakes are not that high, that could be OK. If it’s really high stakes, you may need level three and have the whole model validated in three different ways. You need to find a work plan that reflects the level of precision, the time frame you have, and the stakeholders you need to bring along in the exercise.
Charles Conn: I love the way you’ve described that, because, again, some people think of problem solving as a linear thing, but of course what’s critical is that it’s iterative. As you say, you can solve the problem in one day or even one hour.
Charles Conn: We encourage our teams everywhere to do that. We call it the one-day answer or the one-hour answer. In work planning, we’re always iterating. Every time you see a 50-page work plan that stretches out to three months, you know it’s wrong. It will be outmoded very quickly by that learning process that you described. Iterative problem solving is a critical part of this. Sometimes, people think work planning sounds dull, but it isn’t. It’s how we know what’s expected of us and when we need to deliver it and how we’re progressing toward the answer. It’s also the place where we can deal with biases. Bias is a feature of every human decision-making process. If we design our team interactions intelligently, we can avoid the worst sort of biases.
Simon London: Here we’re talking about cognitive biases primarily, right? It’s not that I’m biased against you because of your accent or something. These are the cognitive biases that behavioral sciences have shown we all carry around, things like anchoring, overoptimism—these kinds of things.
Both: Yeah.
Charles Conn: Availability bias is the one that I’m always alert to. You think you’ve seen the problem before, and therefore what’s available is your previous conception of it—and we have to be most careful about that. In any human setting, we also have to be careful about biases that are based on hierarchies, sometimes called sunflower bias. I’m sure, Hugo, with your teams, you make sure that the youngest team members speak first. Not the oldest team members, because it’s easy for people to look at who’s senior and alter their own creative approaches.
Hugo Sarrazin: It’s helpful, at that moment—if someone is asserting a point of view—to ask the question “This was true in what context?” You’re trying to apply something that worked in one context to a different one. That can be deadly if the context has changed, and that’s why organizations struggle to change. You promote all these people because they did something that worked well in the past, and then there’s a disruption in the industry, and they keep doing what got them promoted even though the context has changed.
Simon London: Right. Right.
Hugo Sarrazin: So it’s the same thing in problem solving.
Charles Conn: And it’s why diversity in our teams is so important. It’s one of the best things about the world that we’re in now. We’re likely to have people from different socioeconomic, ethnic, and national backgrounds, each of whom sees problems from a slightly different perspective. It is therefore much more likely that the team will uncover a truly creative and clever approach to problem solving.
Simon London: Let’s move on to step five. You’ve done your work plan. Now you’ve actually got to do the analysis. The thing that strikes me here is that the range of tools that we have at our disposal now, of course, is just huge, particularly with advances in computation, advanced analytics. There’s so many things that you can apply here. Just talk about the analysis stage. How do you pick the right tools?
Charles Conn: For me, the most important thing is that we start with simple heuristics and explanatory statistics before we go off and use the big-gun tools. We need to understand the shape and scope of our problem before we start applying these massive and complex analytical approaches.
Simon London: Would you agree with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: I agree. I think there are so many wonderful heuristics. You need to start there before you go deep into the modeling exercise. There’s an interesting dynamic that’s happening, though. In some cases, for some types of problems, it is even better to set yourself up to maximize your learning. Your problem-solving methodology is test and learn, test and learn, test and learn, and iterate. That is a heuristic in itself, the A/B testing that is used in many parts of the world. So that’s a problem-solving methodology. It’s nothing different. It just uses technology and feedback loops in a fast way. The other one is exploratory data analysis. When you’re dealing with a large-scale problem, and there’s so much data, I can get to the heuristics that Charles was talking about through very clever visualization of data.
You test with your data. You need to set up an environment to do so, but don’t get caught up in neural-network modeling immediately. You’re testing, you’re checking—“Is the data right? Is it sound? Does it make sense?”—before you launch too far.
Simon London: You do hear these ideas—that if you have a big enough data set and enough algorithms, they’re going to find things that you just wouldn’t have spotted, find solutions that maybe you wouldn’t have thought of. Does machine learning sort of revolutionize the problem-solving process? Or are these actually just other tools in the toolbox for structured problem solving?
Charles Conn: It can be revolutionary. There are some areas in which the pattern recognition of large data sets and good algorithms can help us see things that we otherwise couldn’t see. But I do think it’s terribly important we don’t think that this particular technique is a substitute for superb problem solving, starting with good problem definition. Many people use machine learning without understanding algorithms that themselves can have biases built into them. Just as 20 years ago, when we were doing statistical analysis, we knew that we needed good model definition, we still need a good understanding of our algorithms and really good problem definition before we launch off into big data sets and unknown algorithms.
Simon London: Step six. You’ve done your analysis.
Charles Conn: I take six and seven together, and this is the place where young problem solvers often make a mistake. They’ve got their analysis, and they assume that’s the answer, and of course it isn’t the answer. The ability to synthesize the pieces that came out of the analysis and begin to weave those into a story that helps people answer the question “What should I do?” This is back to where we started. If we can’t synthesize, and we can’t tell a story, then our decision maker can’t find the answer to “What should I do?”
Simon London: But, again, these final steps are about motivating people to action, right?
Charles Conn: Yeah.
Simon London: I am slightly torn about the nomenclature of problem solving because it’s on paper, right? Until you motivate people to action, you actually haven’t solved anything.
Charles Conn: I love this question because I think decision-making theory, without a bias to action, is a waste of time. Everything in how I approach this is to help people take action that makes the world better.
Simon London: Hence, these are absolutely critical steps. If you don’t do this well, you’ve just got a bunch of analysis.
Charles Conn: We end up in exactly the same place where we started, which is people speaking across each other, past each other in the public square, rather than actually working together, shoulder to shoulder, to crack these important problems.
Simon London: In the real world, we have a lot of uncertainty—arguably, increasing uncertainty. How do good problem solvers deal with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: At every step of the process. In the problem definition, when you’re defining the context, you need to understand those sources of uncertainty and whether they’re important or not important. It becomes important in the definition of the tree.
You need to think carefully about the branches of the tree that are more certain and less certain as you define them. They don’t have equal weight just because they’ve got equal space on the page. Then, when you’re prioritizing, your prioritization approach may put more emphasis on things that have low probability but huge impact—or, vice versa, may put a lot of priority on things that are very likely and, hopefully, have a reasonable impact. You can introduce that along the way. When you come back to the synthesis, you just need to be nuanced about what you’re understanding, the likelihood.
Often, people lack humility in the way they make their recommendations: “This is the answer.” They’re very precise, and I think we would all be well-served to say, “This is a likely answer under the following sets of conditions” and then make the level of uncertainty clearer, if that is appropriate. It doesn’t mean you’re always in the gray zone; it doesn’t mean you don’t have a point of view. It just means that you can be explicit about the certainty of your answer when you make that recommendation.
Simon London: So it sounds like there is an underlying principle: “Acknowledge and embrace the uncertainty. Don’t pretend that it isn’t there. Be very clear about what the uncertainties are up front, and then build that into every step of the process.”
Hugo Sarrazin: Every step of the process.
Simon London: Yeah. We have just walked through a particular structured methodology for problem solving. But, of course, this is not the only structured methodology for problem solving. One that is also very well-known is design thinking, which comes at things very differently. So, Hugo, I know you have worked with a lot of designers. Just give us a very quick summary. Design thinking—what is it, and how does it relate?
Hugo Sarrazin: It starts with an incredible amount of empathy for the user and uses that to define the problem. It does pause and go out in the wild and spend an enormous amount of time seeing how people interact with objects, seeing the experience they’re getting, seeing the pain points or joy—and uses that to infer and define the problem.
Simon London: Problem definition, but out in the world.
Hugo Sarrazin: With an enormous amount of empathy. There’s a huge emphasis on empathy. Traditional, more classic problem solving is you define the problem based on an understanding of the situation. This one almost presupposes that we don’t know the problem until we go see it. The second thing is you need to come up with multiple scenarios or answers or ideas or concepts, and there’s a lot of divergent thinking initially. That’s slightly different, versus the prioritization, but not for long. Eventually, you need to kind of say, “OK, I’m going to converge again.” Then you go and you bring things back to the customer and get feedback and iterate. Then you rinse and repeat, rinse and repeat. There’s a lot of tactile building, along the way, of prototypes and things like that. It’s very iterative.
Simon London: So, Charles, are these complements or are these alternatives?
Charles Conn: I think they’re entirely complementary, and I think Hugo’s description is perfect. When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that’s very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use contrasting teams, so that we do have divergent thinking. The best teams allow divergent thinking to bump them off whatever their initial biases in problem solving are. For me, design thinking gives us a constant reminder of creativity, empathy, and the tactile nature of problem solving, but it’s absolutely complementary, not alternative.
Simon London: I think, in a world of cross-functional teams, an interesting question is do people with design-thinking backgrounds really work well together with classical problem solvers? How do you make that chemistry happen?
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah, it is not easy when people have spent an enormous amount of time seeped in design thinking or user-centric design, whichever word you want to use. If the person who’s applying classic problem-solving methodology is very rigid and mechanical in the way they’re doing it, there could be an enormous amount of tension. If there’s not clarity in the role and not clarity in the process, I think having the two together can be, sometimes, problematic.
The second thing that happens often is that the artifacts the two methodologies try to gravitate toward can be different. Classic problem solving often gravitates toward a model; design thinking migrates toward a prototype. Rather than writing a big deck with all my supporting evidence, they’ll bring an example, a thing, and that feels different. Then you spend your time differently to achieve those two end products, so that’s another source of friction.
Now, I still think it can be an incredibly powerful thing to have the two—if there are the right people with the right mind-set, if there is a team that is explicit about the roles, if we’re clear about the kind of outcomes we are attempting to bring forward. There’s an enormous amount of collaborativeness and respect.
Simon London: But they have to respect each other’s methodology and be prepared to flex, maybe, a little bit, in how this process is going to work.
Hugo Sarrazin: Absolutely.
Simon London: The other area where, it strikes me, there could be a little bit of a different sort of friction is this whole concept of the day-one answer, which is what we were just talking about in classical problem solving. Now, you know that this is probably not going to be your final answer, but that’s how you begin to structure the problem. Whereas I would imagine your design thinkers—no, they’re going off to do their ethnographic research and get out into the field, potentially for a long time, before they come back with at least an initial hypothesis.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Hugo Sarrazin: That is a great callout, and that’s another difference. Designers typically will like to soak into the situation and avoid converging too quickly. There’s optionality and exploring different options. There’s a strong belief that keeps the solution space wide enough that you can come up with more radical ideas. If there’s a large design team or many designers on the team, and you come on Friday and say, “What’s our week-one answer?” they’re going to struggle. They’re not going to be comfortable, naturally, to give that answer. It doesn’t mean they don’t have an answer; it’s just not where they are in their thinking process.
Simon London: I think we are, sadly, out of time for today. But Charles and Hugo, thank you so much.
Charles Conn: It was a pleasure to be here, Simon.
Hugo Sarrazin: It was a pleasure. Thank you.
Simon London: And thanks, as always, to you, our listeners, for tuning into this episode of the McKinsey Podcast . If you want to learn more about problem solving, you can find the book, Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything , online or order it through your local bookstore. To learn more about McKinsey, you can of course find us at McKinsey.com.
Charles Conn is CEO of Oxford Sciences Innovation and an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office. Hugo Sarrazin is a senior partner in the Silicon Valley office, where Simon London, a member of McKinsey Publishing, is also based.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Five routes to more innovative problem solving
- The Art of Effective Problem Solving: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Learn Lean Sigma
- Problem Solving
Whether we realise it or not, problem solving skills are an important part of our daily lives. From resolving a minor annoyance at home to tackling complex business challenges at work, our ability to solve problems has a significant impact on our success and happiness. However, not everyone is naturally gifted at problem-solving, and even those who are can always improve their skills. In this blog post, we will go over the art of effective problem-solving step by step.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Problem solving methodologies.
Individuals and organisations can use a variety of problem-solving methodologies to address complex challenges. 8D and A3 problem solving techniques are two popular methodologies in the Lean Six Sigma framework.
Methodology of 8D (Eight Discipline) Problem Solving:
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
The 8D process consists of the following steps:
- Form a team: Assemble a group of people who have the necessary expertise to work on the problem.
- Define the issue: Clearly identify and define the problem, including the root cause and the customer impact.
- Create a temporary containment plan: Put in place a plan to lessen the impact of the problem until a permanent solution can be found.
- Identify the root cause: To identify the underlying causes of the problem, use root cause analysis techniques such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts.
- Create and test long-term corrective actions: Create and test a long-term solution to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
- Implement and validate the permanent solution: Implement and validate the permanent solution’s effectiveness.
- Prevent recurrence: Put in place measures to keep the problem from recurring.
- Recognize and reward the team: Recognize and reward the team for its efforts.
Download the 8D Problem Solving Template
A3 Problem Solving Method:
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
The A3 problem-solving procedure consists of the following steps:
- Determine the issue: Define the issue clearly, including its impact on the customer.
- Perform root cause analysis: Identify the underlying causes of the problem using root cause analysis techniques.
- Create and implement a solution: Create and implement a solution that addresses the problem’s root cause.
- Monitor and improve the solution: Keep an eye on the solution’s effectiveness and make any necessary changes.
Subsequently, in the Lean Six Sigma framework, the 8D and A3 problem solving methodologies are two popular approaches to problem solving. Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Step 1 – Define the Problem
The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause. To avoid this pitfall, it is critical to thoroughly understand the problem.
To begin, ask yourself some clarifying questions:
- What exactly is the issue?
- What are the problem’s symptoms or consequences?
- Who or what is impacted by the issue?
- When and where does the issue arise?
Answering these questions will assist you in determining the scope of the problem. However, simply describing the problem is not always sufficient; you must also identify the root cause. The root cause is the underlying cause of the problem and is usually the key to resolving it permanently.
Try asking “why” questions to find the root cause:
- What causes the problem?
- Why does it continue?
- Why does it have the effects that it does?
By repeatedly asking “ why ,” you’ll eventually get to the bottom of the problem. This is an important step in the problem-solving process because it ensures that you’re dealing with the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
Once you have a firm grasp on the issue, it is time to divide it into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes tackling the problem easier and reduces the risk of becoming overwhelmed. For example, if you’re attempting to solve a complex business problem, you might divide it into smaller components like market research, product development, and sales strategies.
To summarise step 1, defining the problem is an important first step in effective problem-solving. You will be able to identify the root cause and break it down into manageable parts if you take the time to thoroughly understand the problem. This will prepare you for the next step in the problem-solving process, which is gathering information and brainstorming ideas.
Step 2 – Gather Information and Brainstorm Ideas
Gathering information and brainstorming ideas is the next step in effective problem solving. This entails researching the problem and relevant information, collaborating with others, and coming up with a variety of potential solutions. This increases your chances of finding the best solution to the problem.
Begin by researching the problem and relevant information. This could include reading articles, conducting surveys, or consulting with experts. The goal is to collect as much information as possible in order to better understand the problem and possible solutions.
Next, work with others to gather a variety of perspectives. Brainstorming with others can be an excellent way to come up with new and creative ideas. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas when working in a group, and make an effort to actively listen to what others have to say. Be open to new and unconventional ideas and resist the urge to dismiss them too quickly.
Finally, use brainstorming to generate a wide range of potential solutions. This is the place where you can let your imagination run wild. At this stage, don’t worry about the feasibility or practicality of the solutions; instead, focus on generating as many ideas as possible. Write down everything that comes to mind, no matter how ridiculous or unusual it may appear. This can be done individually or in groups.
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the next step in the problem-solving process, which we’ll go over in greater detail in the following section.
Step 3 – Evaluate Options and Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the third step in effective problem solving, and it entails weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, considering their feasibility and practicability, and selecting the solution that is most likely to solve the problem effectively.
To begin, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. This will assist you in determining the potential outcomes of each solution and deciding which is the best option. For example, a quick and easy solution may not be the most effective in the long run, whereas a more complex and time-consuming solution may be more effective in solving the problem in the long run.
Consider each solution’s feasibility and practicability. Consider the following:
- Can the solution be implemented within the available resources, time, and budget?
- What are the possible barriers to implementing the solution?
- Is the solution feasible in today’s political, economic, and social environment?
You’ll be able to tell which solutions are likely to succeed and which aren’t by assessing their feasibility and practicability.
Finally, choose the solution that is most likely to effectively solve the problem. This solution should be based on the criteria you’ve established, such as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and your overall goals.
It is critical to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to problems. What is effective for one person or situation may not be effective for another. This is why it is critical to consider a wide range of solutions and evaluate each one based on its ability to effectively solve the problem.
Step 4 – Implement and Monitor the Solution
When you’ve decided on the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. The fourth and final step in effective problem solving is to put the solution into action, monitor its progress, and make any necessary adjustments.
To begin, implement the solution. This may entail delegating tasks, developing a strategy, and allocating resources. Ascertain that everyone involved understands their role and responsibilities in the solution’s implementation.
Next, keep an eye on the solution’s progress. This may entail scheduling regular check-ins, tracking metrics, and soliciting feedback from others. You will be able to identify any potential roadblocks and make any necessary adjustments in a timely manner if you monitor the progress of the solution.
Finally, make any necessary modifications to the solution. This could entail changing the solution, altering the plan of action, or delegating different tasks. Be willing to make changes if they will improve the solution or help it solve the problem more effectively.
It’s important to remember that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to start from scratch. This is especially true if the initial solution does not effectively solve the problem. In these situations, it’s critical to be adaptable and flexible and to keep trying new solutions until you find the one that works best.
To summarise, effective problem solving is a critical skill that can assist individuals and organisations in overcoming challenges and achieving their objectives. Effective problem solving consists of four key steps: defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives and selecting the best solution, and implementing the solution.
You can increase your chances of success in problem solving by following these steps and considering factors such as the pros and cons of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and making any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, keep in mind that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to go back to the beginning and restart. Maintain your adaptability and try new solutions until you find the one that works best for you.
- Novick, L.R. and Bassok, M., 2005. Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press.
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…


Search form

- Table of Contents
- Troubleshooting Guide
- A Model for Getting Started
- Justice Action Toolkit
- Best Change Processes
- Databases of Best Practices
- Online Courses
- Ask an Advisor
- Subscribe to eNewsletter
- Community Stories
- YouTube Channel
- About the Tool Box
- How to Use the Tool Box
- Privacy Statement
- Workstation/Check Box Sign-In
- Online Training Courses
- Capacity Building Training
- Training Curriculum - Order Now
- Community Check Box Evaluation System
- Build Your Toolbox
- Facilitation of Community Processes
- Community Health Assessment and Planning
- Section 1. An Introduction to the Problem-Solving Process
Chapter 17 Sections
- Section 2. Thinking Critically
- Section 3. Defining and Analyzing the Problem
- Section 4. Analyzing Root Causes of Problems: The "But Why?" Technique
- Section 5. Addressing Social Determinants of Health and Development
- Section 6. Generating and Choosing Solutions
- Section 7. Putting Your Solution into Practice
- Main Section
What is a problem?
Why is a group process particularly important, what is the problem-solving process.
"We must try to trust one another. Stay and cooperate." - Jomo Kenyatta, (1891 - 1978), former president of the Republic of Kenya
Imagine for a moment that your coalition's mission is to encourage development in a traditionally poor downtown neighborhood. Your first goal is to recruit members, but you find a lack of interest among area residents. So you work for months to convince people to join, and meet with some modest success. Then, at your first all-coalition meeting, you find that members don't want to work together. The students you have recruited don't trust the police officers who have shown up; the police officers, in turn, pay no attention to the students; and an argument has broken out in one corner of the room between a few fundamentalist Christians and gay rights activists. Your head is in your hands. You are halfway through your grant, and it seems that you haven't made any headway whatsoever towards your stated goal. What are you going to do now?
Problems are a fact of life at home, at play, and at work. Unfortunately, problems aren't always isolated cases. They tend to be like onions - you peel away one problem only to find another, and then another, and you can't solve the problem you were first interested in until you solve a variety of related problems. For example, you can't increase safety at a crosswalk until you hire more crossing guards. And nobody will apply for the job until you can increase the salary.
In short, we will always be confronted with problems, so the importance of problem solving can't be overstated. That's why this chapter of the Tool Box is focused wholly on the subject. Because most of us labor in groups or coalitions that are working together on an issue, we will focus primarily on the group problem-solving process.
So, what's a problem? How would you define one? We usually define a problem fairly negatively: a problem is a hassle, it's a pain in the neck. This is often true, but more generally, a problem can be considered the difference between what is , and what might or should be. And believe it or not, problems have their advantages, too. What are some of the good things about problems?
- Most problems are solvable (or partially solvable, or at least improvable). We can do something about them. The task may seem overwhelming (it surely did when David fought Goliath, or when suffragettes worked to give women the right to vote), but it's not hopeless. Our optimistic assumption is that we can change the world.
- Problems are opportunities to make some good things happen. If it weren't for problems, what would be our motivation to create change?
- Problems are also challenges . They call upon the best of our abilities, and ask us to go beyond what we thought we could do. They make life interesting, and, at least sometimes, fun. Without problems, life could be pretty boring.
You don't agree? Think of all of the games based on problem solving. Chess is thousands of years old and is still as popular as ever, based on the number of books you might find on it at your local bookstore. The Rubik's Cube was a national rage some years back. True, the stakes may be very different between a chess game and finding a way to connect with local young people. But both can present a challenge that stretches us in the same ways.
With all this in mind, what is "problem solving?" A good definition can be found in Lead on! The complete handbook for group leaders. The authors define problem solving as "an individual or collaborative process composed of two different skills: (1) to analyze a situation accurately, and (2) to make a good decision based on that analysis."
Why are we focusing on a collaborative process in this chapter? Well, for several reasons. You probably already do a lot of individual problem solving , and there's a good deal of merit in that. But many of the problems and challenges we face as members of our organizations affect everyone in the group. It makes sense then, that everyone is part of the solution. And, as the saying goes, two heads are better than one - so just imagine what can be accomplished with a room full of dedicated people!
Now, let's change the emphasis for a moment. Why are we focusing on a collaborative process in this chapter? Maybe your group is used to doing things haphazardly on an as-absolutely-necessary basis. Why should you take more time (already a precious commodity among most groups) to go through a lengthy process?
- Effective group processes enhance a group's ability to solve problems and make decisions. When working with more than just a couple of people, solving a problem with a set process becomes more manageable.
- It increases the group's efficiency and productivity.
- It increases the group's participation - more people tend to be involved, and, as a result,
- It increases group satisfaction. This means, among other things, that the group is more likely to want to take on other problems. And when they do so, they'll be better placed to solve them.
Like any other process, there are many different tasks that need to be done to properly solve problems. And again, like any other process, skipping some of the steps will make the job more difficult in the long run. Here is a brief explanation of each of the steps, to be discussed in more detail in the following sections:
- Running effective meetings - Since your work will be in a group, the first thing you need to understand is how to hold a good meeting. You may have the problem-solving process down pat, but that won't make any difference if nobody shows up at your meeting, or if no one pays attention to what goes on.
- Developing facilitation skills - Strong facilitation skills go hand in hand with running an effective meeting. A good facilitator helps diffuse explosive emotions, makes sure everyone's voice is heard, and steers the group towards the best decisions.
- Developing recorder skills - Again, these skills are part of running an effective meeting. A good recorder works hand in hand with the facilitator, and together, they make sure that not only are everyone's opinions heard, they are also seen, remembered, and followed up on. Having a good recorder is one of the most important parts of setting up an effective meeting.
- Defining and analyzing the problem - This is the core of the problem solving process. Sometimes, the real problem isn't originally apparent.
- Generating and choosing solutions
- Putting your solution into practice - If you have followed the process carefully, you'll be surprised at how easy implementing it actually is!
In Summary:
As we said before, the world is full of problems, and some of them look pretty challenging, to say the least. But the rewards are great. Solutions that are well thought out and carefully implemented can work. How much can you do?
Print Resources
Avery, M., Auvine, B., Streibel, B., & Weiss, L. (1981). A handbook for consensus decision making: Building united judgement . Madison, WI: Center for Conflict Resolution.
Dale, D., & Mitiguy, N. Planning, for a change: A citizen's guide to creative planning and program development .
Dashiell, K.A. (1990). Managing meetings for collaboration and consensus Honolulu, HI: Neighborhood Justice Center of Honolulu, Inc.
Interaction Associates, Inc. (1987). Facilitator institute handbook . San Francisco, CA: Author.
Lawson, L., Donant, F., & Lawson, J. (1982). Lead on! The complete handbook for group leaders . San Luis Obispo, CA: Impact Publishers.
Meacham, W. (1980). Human development training manual . Austin, TX: Human Development Training.
Morrison, E.(1994). Leadership skills: Developing volunteers for organizational success . Tucson, AZ: Fisher Books.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Sean is a fact-checker and researcher with experience in sociology, field research, and data analytics.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Sean-Blackburn-1000-a8b2229366944421bc4b2f2ba26a1003.jpg)
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Application
- Improvement
From deciding what to eat for dinner to considering whether it's the right time to buy a house, problem-solving is a large part of our daily lives. Learn some of the problem-solving strategies that exist and how to use them in real life, along with ways to overcome obstacles that are making it harder to resolve the issues you face.
What Is Problem-Solving?
In cognitive psychology , the term 'problem-solving' refers to the mental process that people go through to discover, analyze, and solve problems.
A problem exists when there is a goal that we want to achieve but the process by which we will achieve it is not obvious to us. Put another way, there is something that we want to occur in our life, yet we are not immediately certain how to make it happen.
Maybe you want a better relationship with your spouse or another family member but you're not sure how to improve it. Or you want to start a business but are unsure what steps to take. Problem-solving helps you figure out how to achieve these desires.
The problem-solving process involves:
- Discovery of the problem
- Deciding to tackle the issue
- Seeking to understand the problem more fully
- Researching available options or solutions
- Taking action to resolve the issue
Before problem-solving can occur, it is important to first understand the exact nature of the problem itself. If your understanding of the issue is faulty, your attempts to resolve it will also be incorrect or flawed.
Problem-Solving Mental Processes
Several mental processes are at work during problem-solving. Among them are:
- Perceptually recognizing the problem
- Representing the problem in memory
- Considering relevant information that applies to the problem
- Identifying different aspects of the problem
- Labeling and describing the problem
Problem-Solving Strategies
There are many ways to go about solving a problem. Some of these strategies might be used on their own, or you may decide to employ multiple approaches when working to figure out and fix a problem.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that, by following certain "rules" produces a solution. Algorithms are commonly used in mathematics to solve division or multiplication problems. But they can be used in other fields as well.
In psychology, algorithms can be used to help identify individuals with a greater risk of mental health issues. For instance, research suggests that certain algorithms might help us recognize children with an elevated risk of suicide or self-harm.
One benefit of algorithms is that they guarantee an accurate answer. However, they aren't always the best approach to problem-solving, in part because detecting patterns can be incredibly time-consuming.
There are also concerns when machine learning is involved—also known as artificial intelligence (AI)—such as whether they can accurately predict human behaviors.
Heuristics are shortcut strategies that people can use to solve a problem at hand. These "rule of thumb" approaches allow you to simplify complex problems, reducing the total number of possible solutions to a more manageable set.
If you find yourself sitting in a traffic jam, for example, you may quickly consider other routes, taking one to get moving once again. When shopping for a new car, you might think back to a prior experience when negotiating got you a lower price, then employ the same tactics.
While heuristics may be helpful when facing smaller issues, major decisions shouldn't necessarily be made using a shortcut approach. Heuristics also don't guarantee an effective solution, such as when trying to drive around a traffic jam only to find yourself on an equally crowded route.
Trial and Error
A trial-and-error approach to problem-solving involves trying a number of potential solutions to a particular issue, then ruling out those that do not work. If you're not sure whether to buy a shirt in blue or green, for instance, you may try on each before deciding which one to purchase.
This can be a good strategy to use if you have a limited number of solutions available. But if there are many different choices available, narrowing down the possible options using another problem-solving technique can be helpful before attempting trial and error.
In some cases, the solution to a problem can appear as a sudden insight. You are facing an issue in a relationship or your career when, out of nowhere, the solution appears in your mind and you know exactly what to do.
Insight can occur when the problem in front of you is similar to an issue that you've dealt with in the past. Although, you may not recognize what is occurring since the underlying mental processes that lead to insight often happen outside of conscious awareness .
Research indicates that insight is most likely to occur during times when you are alone—such as when going on a walk by yourself, when you're in the shower, or when lying in bed after waking up.
How to Apply Problem-Solving Strategies in Real Life
If you're facing a problem, you can implement one or more of these strategies to find a potential solution. Here's how to use them in real life:
- Create a flow chart . If you have time, you can take advantage of the algorithm approach to problem-solving by sitting down and making a flow chart of each potential solution, its consequences, and what happens next.
- Recall your past experiences . When a problem needs to be solved fairly quickly, heuristics may be a better approach. Think back to when you faced a similar issue, then use your knowledge and experience to choose the best option possible.
- Start trying potential solutions . If your options are limited, start trying them one by one to see which solution is best for achieving your desired goal. If a particular solution doesn't work, move on to the next.
- Take some time alone . Since insight is often achieved when you're alone, carve out time to be by yourself for a while. The answer to your problem may come to you, seemingly out of the blue, if you spend some time away from others.
Obstacles to Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include:
- Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions. Thus, they may not even try some potential options.
- Functional fixedness : This term refers to the tendency to view problems only in their customary manner. Functional fixedness prevents people from fully seeing all of the different options that might be available to find a solution.
- Irrelevant or misleading information: When trying to solve a problem, it's important to distinguish between information that is relevant to the issue and irrelevant data that can lead to faulty solutions. The more complex the problem, the easier it is to focus on misleading or irrelevant information.
- Mental set: A mental set is a tendency to only use solutions that have worked in the past rather than looking for alternative ideas. A mental set can work as a heuristic, making it a useful problem-solving tool. However, mental sets can also lead to inflexibility, making it more difficult to find effective solutions.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
In the end, if your goal is to become a better problem-solver, it's helpful to remember that this is a process. Thus, if you want to improve your problem-solving skills, following these steps can help lead you to your solution:
- Recognize that a problem exists . If you are facing a problem, there are generally signs. For instance, if you have a mental illness , you may experience excessive fear or sadness, mood changes, and changes in sleeping or eating habits. Recognizing these signs can help you realize that an issue exists.
- Decide to solve the problem . Make a conscious decision to solve the issue at hand. Commit to yourself that you will go through the steps necessary to find a solution.
- Seek to fully understand the issue . Analyze the problem you face, looking at it from all sides. If your problem is relationship-related, for instance, ask yourself how the other person may be interpreting the issue. You might also consider how your actions might be contributing to the situation.
- Research potential options . Using the problem-solving strategies mentioned, research potential solutions. Make a list of options, then consider each one individually. What are some pros and cons of taking the available routes? What would you need to do to make them happen?
- Take action . Select the best solution possible and take action. Action is one of the steps required for change . So, go through the motions needed to resolve the issue.
- Try another option, if needed . If the solution you chose didn't work, don't give up. Either go through the problem-solving process again or simply try another option.
You can find a way to solve your problems as long as you keep working toward this goal—even if the best solution is simply to let go because no other good solution exists.
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
Dunbar K. Problem solving . A Companion to Cognitive Science . 2017. doi:10.1002/9781405164535.ch20
Stewart SL, Celebre A, Hirdes JP, Poss JW. Risk of suicide and self-harm in kids: The development of an algorithm to identify high-risk individuals within the children's mental health system . Child Psychiat Human Develop . 2020;51:913-924. doi:10.1007/s10578-020-00968-9
Rosenbusch H, Soldner F, Evans AM, Zeelenberg M. Supervised machine learning methods in psychology: A practical introduction with annotated R code . Soc Personal Psychol Compass . 2021;15(2):e12579. doi:10.1111/spc3.12579
Mishra S. Decision-making under risk: Integrating perspectives from biology, economics, and psychology . Personal Soc Psychol Rev . 2014;18(3):280-307. doi:10.1177/1088868314530517
Csikszentmihalyi M, Sawyer K. Creative insight: The social dimension of a solitary moment . In: The Systems Model of Creativity . 2015:73-98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9085-7_7
Chrysikou EG, Motyka K, Nigro C, Yang SI, Thompson-Schill SL. Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality . Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts . 2016;10(4):425‐435. doi:10.1037/aca0000050
Huang F, Tang S, Hu Z. Unconditional perseveration of the short-term mental set in chunk decomposition . Front Psychol . 2018;9:2568. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02568
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Warning signs and symptoms .
Mayer RE. Thinking, problem solving, cognition, 2nd ed .
Schooler JW, Ohlsson S, Brooks K. Thoughts beyond words: When language overshadows insight. J Experiment Psychol: General . 1993;122:166-183. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.2.166
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Master the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process for Better Decision-Making
Discover the powerful 7-Step Problem-Solving Process to make better decisions and achieve better outcomes. Master the art of problem-solving in this comprehensive guide. Download the Free PowerPoint and PDF Template.

StrategyPunk
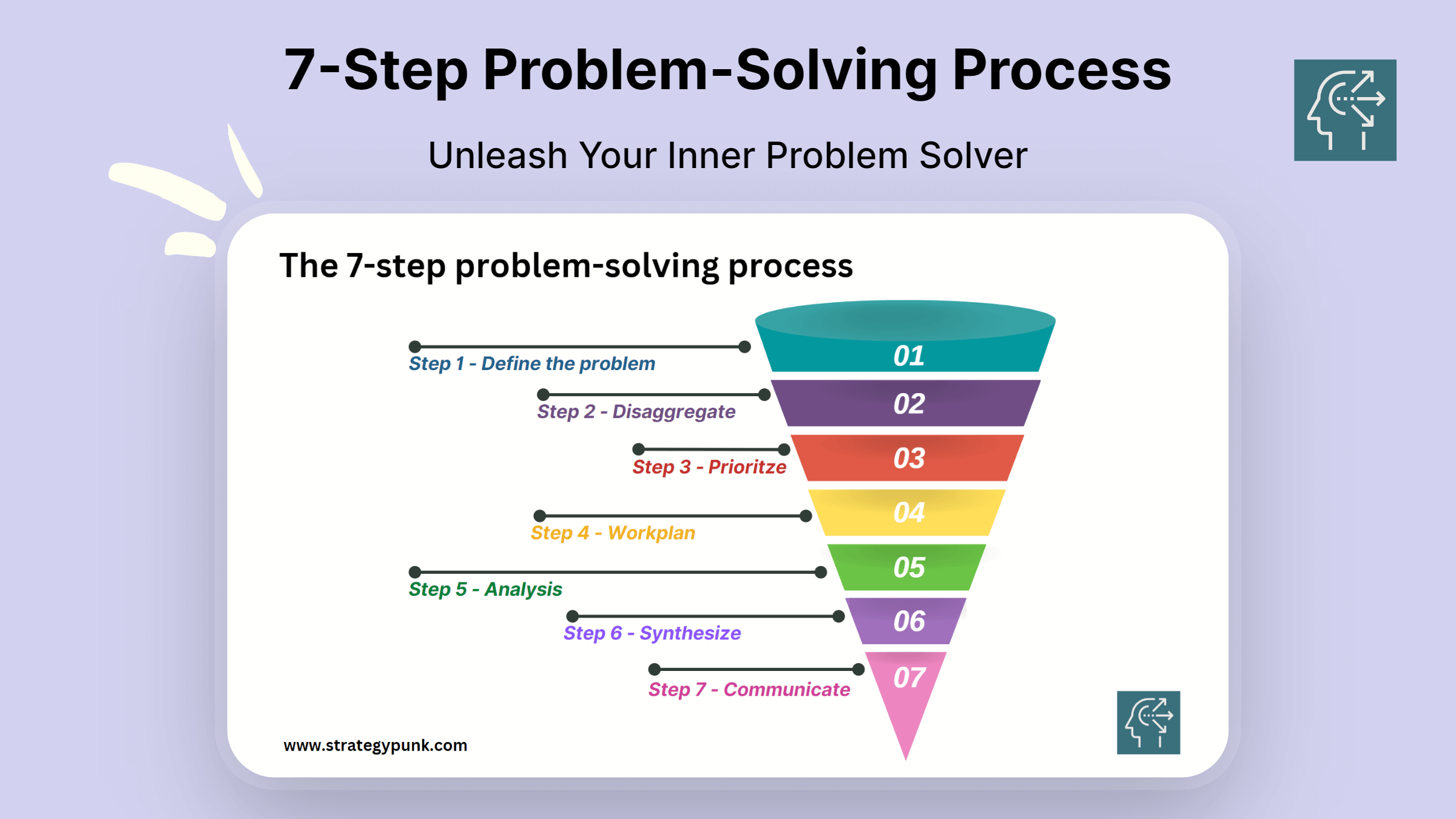
Introduction
Mastering the art of problem-solving is crucial for making better decisions. Whether you're a student, a business owner, or an employee, problem-solving skills can help you tackle complex issues and find practical solutions. The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a proven method that can help you approach problems systematically and efficiently.
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the information, and communicate your findings to others.
By following this process, you can avoid jumping to conclusions, overlooking important details, or making hasty decisions. Instead, you can approach problems with a clear and structured mindset, which can help you make better decisions and achieve better outcomes.
In this article, we'll explore each step of the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process in detail so you can start mastering this valuable skill. At the end of the blog post, you can download the process's free PowerPoint and PDF templates .
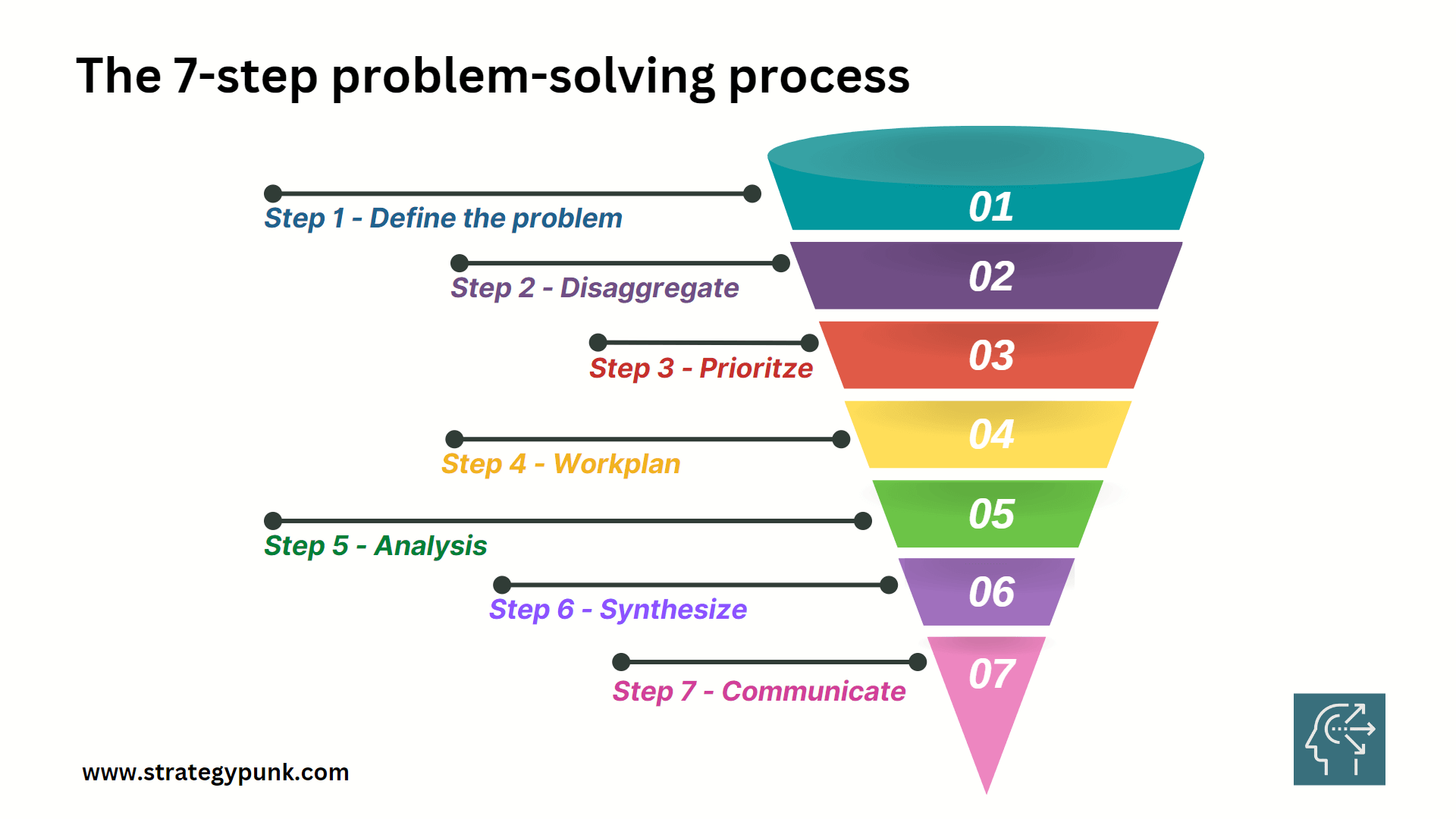
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step is crucial because finding a solution is only accessible if the problem is clearly defined. The problem must be specific, measurable, and achievable.
One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions. Questions like "What is the problem?" and "What are the causes of the problem?" can help. Gathering data and information about the issue to assist in the definition process is also essential.
Another critical aspect of defining the problem is identifying the stakeholders. Who is affected by it? Who has a stake in finding a solution? Identifying the stakeholders can help ensure that the problem is defined in a way that considers the needs and concerns of all those affected.
Once the problem is defined, it is essential to communicate the definition to all stakeholders. This helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that there is a shared understanding of the problem.
Step 2: Disaggregate
After defining the problem, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to disaggregate the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Disaggregation helps break down the problem into smaller pieces that can be analyzed individually. This step is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problem and identifying the most effective solutions.
Disaggregation can be achieved by breaking down the problem into sub-problems, identifying the contributing factors, and analyzing the relationships between these factors. This step helps identify the most critical factors that must be addressed to solve the problem.
A tree or fishbone diagram is one effective way to disaggregate a problem. These diagrams help identify the different factors contributing to the problem and how they are related. Another way is to use a table to list the other factors contributing to the situation and their corresponding impact on the issue.
Disaggregation helps in breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It helps understand the relationships between different factors contributing to the problem and identify the most critical factors that must be addressed. By disaggregating the problem, decision-makers can focus on the most vital areas, leading to more effective solutions.
Step 3: Prioritize
After defining the problem and disaggregating it into smaller parts, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is prioritizing the issues that need addressing. Prioritizing helps to focus on the most pressing issues and allocate resources more effectively.
There are several ways to prioritize issues, including:
- Urgency: Prioritize issues based on their urgency. Problems that require immediate attention should be addressed first.
- Impact: Prioritize issues based on their impact on the organization or stakeholders. Problems with a high impact should be given priority.
- Resources: Prioritize issues based on the resources required to address them. Problems that require fewer resources should be dealt with first.
It is important to involve stakeholders in the prioritization process, considering their concerns and needs. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of engagement.
Once the issues have been prioritized, developing a plan of action to address them is essential. This involves identifying the resources required, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities.
Prioritizing issues is a critical step in problem-solving. By focusing on the most pressing problems, organizations can allocate resources more effectively and make better decisions.
Step 4: Workplan
After defining the problem, disaggregating, and prioritizing the issues, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to develop a work plan. This step involves creating a roadmap that outlines the steps needed to solve the problem.
The work plan should include a list of tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities for each team member involved in the problem-solving process. Assigning tasks based on each team member's strengths and expertise ensures the work is completed efficiently and effectively.
Creating a work plan can help keep the team on track and ensure everyone is working towards the same goal. It can also help to identify potential roadblocks or challenges that may arise during the problem-solving process and develop contingency plans to address them.
Several tools and techniques can be used to develop a work plan, including Gantt charts, flowcharts, and mind maps. These tools can help to visualize the steps needed to solve the problem and identify dependencies between tasks.
Developing a work plan is a critical step in the problem-solving process. It provides a clear roadmap for solving the problem and ensures everyone involved is aligned and working towards the same goal.
Step 5: Analysis
Once the problem has been defined and disaggregated, the next step is to analyze the information gathered. This step involves examining the data, identifying patterns, and determining the root cause of the problem.
Several methods can be used during the analysis phase, including:
- Root cause analysis
- Pareto analysis
- SWOT analysis
Root cause analysis is a popular method used to identify the underlying cause of a problem. This method involves asking a series of "why" questions to get to the root cause of the issue.
Pareto analysis is another method that can be used during the analysis phase. This method involves identifying the 20% of causes responsible for 80% of the problems. By focusing on these critical causes, organizations can make significant improvements.
Finally, SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for analyzing the internal and external factors that may impact the problem. This method involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the issue.
Overall, the analysis phase is critical for identifying the root cause of the problem and developing practical solutions. By using a combination of methods, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the issue and make informed decisions.
Step 6: Synthesize
Once the analysis phase is complete, it is time to synthesize the information gathered to arrive at a solution. During this step, the focus is on identifying the most viable solution that addresses the problem. This involves examining and combining the analysis results for a clear and concise conclusion.
One way to synthesize the information is to use a decision matrix. This involves creating a table that lists the potential solutions and the essential criteria for making a decision. Each answer is then rated against each standard, and the scores are tallied to arrive at a final decision.
Another approach to synthesizing the information is to use a mind map. This involves creating a visual representation of the problem and the potential solutions. The mind map can identify the relationships between the different pieces of information and help prioritize the solutions.
During the synthesis phase, it is vital to remain open-minded and consider all potential solutions. Involving all stakeholders in the decision-making process is essential to ensure everyone's perspectives are considered.
Step 7: Communicate
After synthesizing the information, the next step is communicating the findings to the relevant stakeholders. This is a crucial step because it helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the decision-making process is transparent.
One effective way to communicate the findings is through a well-organized report. The report should include the problem statement, the analysis, the synthesis, and the recommended solution. It should be clear, concise, and easy to understand.
In addition to the report, a presentation explaining the findings is essential. The presentation should be tailored to the audience and highlight the report's key points. Visual aids such as tables, graphs, and charts can make the presentation more engaging.
During the presentation, it is essential to be open to feedback and questions from the audience. This helps ensure everyone agrees with the recommended solution and addresses concerns or objections.
Effective communication is vital to ensuring the decision-making process is successful. Stakeholders can make informed decisions and work towards a common goal by communicating the findings clearly and concisely.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to complex business problems.
Through disaggregation, individuals can break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. By prioritizing potential solutions, individuals can focus their efforts on the most impactful actions. The work step allows individuals to develop a clear action plan, while the analysis step provides a framework for evaluating possible solutions.
The synthesis step combines all the information gathered to develop a comprehensive solution. Finally, the communication step allows individuals to share their answers with others and gather feedback.
By mastering the 7-step problem-solving process, individuals can become more effective decision-makers and problem-solvers. This process can help individuals and organizations save time and resources while improving outcomes. With practice, individuals can develop the skills to apply this process to a wide range of scenarios and make better decisions in all areas of life.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PPT Template
Free powerpoint and pdf template, executive summary: the 7-step problem-solving process.
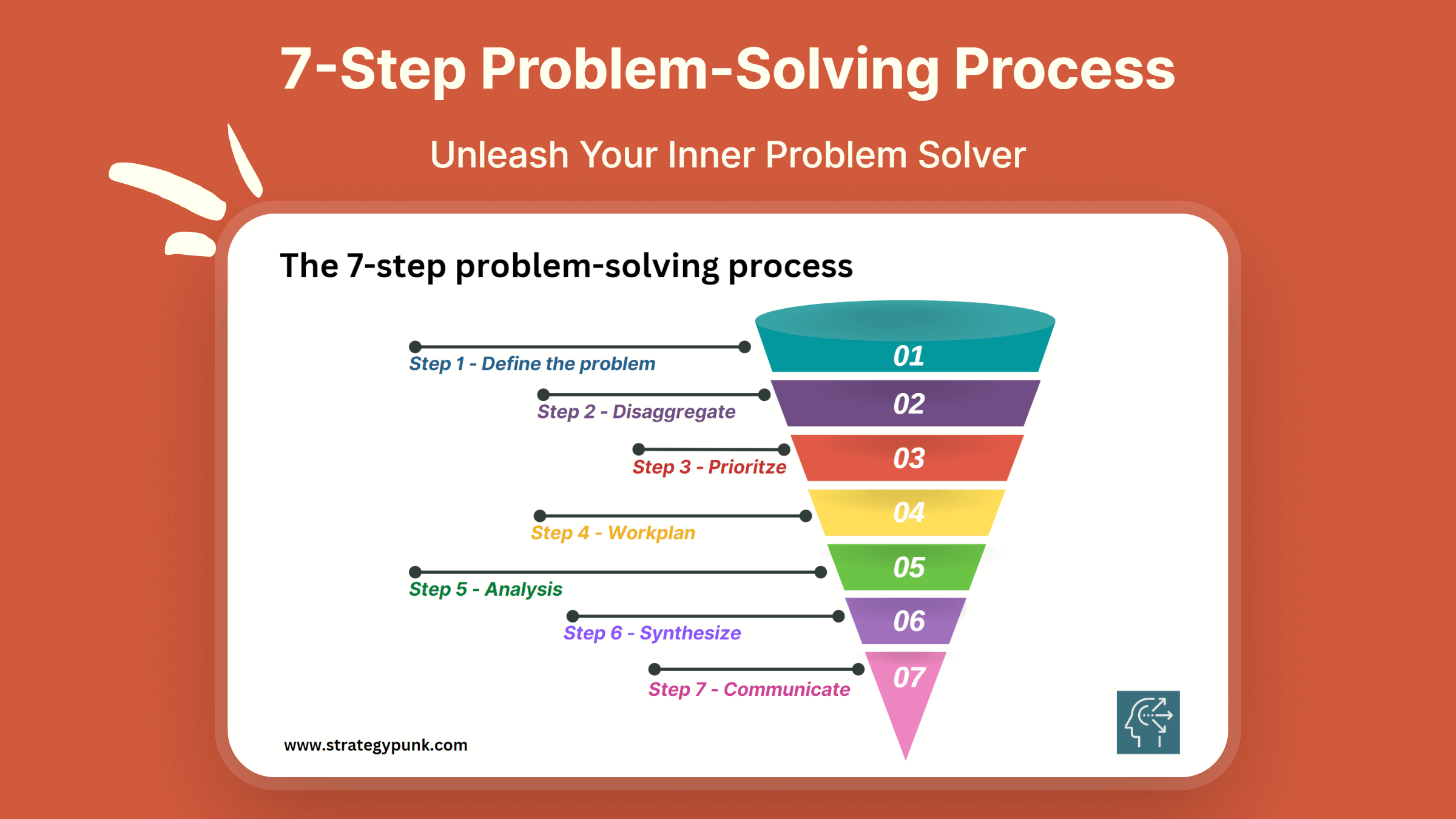
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a robust and systematic method to help individuals and organizations make better decisions by tackling complex issues and finding practical solutions. This process comprises defining the problem, disaggregating it into smaller parts, prioritizing the issues, creating a work plan, analyzing the data, synthesizing the information, and communicating the findings.
By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, break it down into manageable components, and prioritize the most impactful actions. The work plan, analysis, and synthesis steps provide a framework for developing comprehensive solutions, while the communication step ensures transparency and stakeholder engagement.
Mastering this process can improve decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, save time and resources, and improve outcomes in personal and professional contexts.
Please buy me a coffee.
I'd appreciate your support if my templates have saved you time or helped you start a project. Buy Me a Coffee is a simple way to show your appreciation and help me continue creating high-quality templates that meet your needs.

7-Step Problem-Solving Process PDF Template
7-step problem-solving process powerpoint template.

Global Bites: PESTLE Insights into Nestlé (Free PPT)
Download our free PPT template for in-depth PESTLE insights into Nestlé's global strategy. Learn more today!

PESTLE Analysis: Decoding Reddit's Landscape (Free PPT)
Decode Reddit's global influence with our free PowerPoint PESTLE Analysis. Explore the hub of vibrant discussions and ideas.

Navigating the Terrain: A PESTLE Analysis of Lululemon (Free PowerPoint)
Explore Lululemon's business terrain with our free PESTLE analysis PowerPoint. Instant access!

The Art of Strategic Leadership: 5 Keys to Success by Willie Peterson
Explore Willie Peterson's 5 crucial strategies for strategic leadership. Master learning, customer focus, and effective storytelling.


How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
The Problem-Definition Process
Developing the right solution.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

When we try to solve business problems, we can often pressurize ourselves to find solutions quickly.
The problem with this is that we can end up only partially solving the problem, or we can solve the wrong problem altogether, with all of the delay, expense, and lost business opportunity that goes with this.
The Problem-Definition Process helps you avoid this. In this article, we'll look at this process and we'll see how to apply it.
Dwayne Spradlin published the Problem-Definition Process in September 2012's Harvard Business Review . (We refer to this with permission.)
Spradlin was the President and CEO of Innocentive, an organization that connected organizations with freelance problem solvers. He developed the process over 10 years, while working with a community of more than 25,000 "problem solvers" such as engineers, scientists, and industry experts.
The process gives you four steps that help you better understand complex problems. These steps are:
- Establish the need.
- Justify the need.
- Understand the problem and its wider context.
- Write a problem statement.
The Problem-Definition Process encourages you to define and understand the problem that you're trying to solve, in detail. It also helps you confirm that solving the problem contributes towards your organization's objectives.
This stops you spending time, energy, and resources on unimportant problems, or on initiatives that don't align with your organization's overall strategy.
It also encourages you to fully define the problem and its boundaries. You can then use this information to justify the need for change, brief designers and contractors, and kick-off new projects successfully.
Use the Problem-Definition Process alongside tools such as Simplex and Hurson's Productive Thinking Model . These will guide you through the full problem-solving process .
Using the Problem-Definition Process
The four main steps in the Problem-Definition Process contain several smaller questions that, once answered, help you define and clarify the problem thoroughly.
Let's look at each step in more detail.
The process we present below is an adaptation of Spradlin's original model. We’ve included additional questions and sub-steps where appropriate.
1. Establish the Need
The first step is to identify why you need a solution to the problem. To do this, answer these questions:
a. What is the basic need? First, write your problem down in simple terms. Then, identify the basic need that you'll fulfill once you've solved the problem.
For example:
b. What is the ideal outcome? Next, identify the outcome that you want to see once you've implemented a solution.
Don't think of any particular solutions at this point – your aim is to visualize the result of a successful solution, not the solution itself.
It helps to be specific here: "Increase weekly sign-ups by 20 percent" is more useful than "Increase weekly sign-ups."
c. Who will (and won't) benefit? Finally in this step, identify all of the stakeholders who will benefit, both directly and indirectly, once you've solved the problem and reached your desired outcome. Write down who these people or groups are, and the advantages that they'll see.
Also consider who may be at a disadvantage if you solve the problem.
Tools like Impact Analysis and the Futures Wheel are useful here, as they help identify the possible consequences of a change.
As you work through the next steps of this process and get more of an understanding of your problem, you may find it useful to go back and refine your answers to previous questions.
2. Justify the Need
Once you understand the need for solving the problem, you must then justify why you should solve it. To do this, answer these questions:
a. Is effort aligned with your overall strategy? This problem, and the effort that you'll be putting into solving it, must align with your organization's strategic priorities , as well as its mission and values .
b. What benefits do we want, and how can we measure these? Identify what benefits your organization, as a whole, will see when you solve this problem, and think about how you can measure these in relation to its overall strategy and objectives. Be as specific as possible.
c. Are we likely to be able to implement a solution? Think about factors such as how you'll get support from stakeholders and decision-makers, and how you'll access the required resources and expertise. This may involve speaking with senior managers in your organization to understand what resources may be available.
3. Understand the Problem and Its Wider Context
In steps 1 and 2, you identified why you need a solution, and why it's important to your strategy and mission.
The three questions in this third step encourage you to look at the problem in more depth, and to look back into the past to see what you can learn from past efforts.
a. What's the cause? First in this step, make sure that you've identified all of the causes of your problem, using tools like CATWOE , Root Cause Analysis , Cause and Effect Analysis , Systems Diagrams , and Interrelationship Diagrams .
b. What solutions already exist? Have other people in your organization tried to solve this or a similar problem in the past? If so, what did they do? What worked and what didn't work?
Next you need to find out if people outside of your organization have already tried to do something about this problem. Widen your search to include trade journals, field studies, past research, competitors, industry experts, and your personal network.
Your goal is to look at what's been done already, and what hasn't worked, so that you don't waste time working on a solution that already exists, or working on a solution that's likely to fail.
c. What are the constraints? By now, you're starting to have a deeper understanding of the problem and how it relates to your organization. Now you can brainstorm factors that might prevent you from implementing a solution. (Use your answers from question c in step 2 to help with this.)
First, look at internal constraints. Will you have access to enough people, money, and other resources to solve this problem? Are there any stakeholders who might try to block your efforts? Are there any rules or procedures that you must follow? (For instance, a new website would need to align with your organization's brand guidelines.)
Next, look externally. Are there any government regulations or laws that might stall or block your solutions? Is the technology available?
d. What requirements must a solution meet? Write down the requirements that the solution must meet in order to solve the problem successfully. As part of this, also identify other factors that, while not essential for solving the problem successfully, would add value to the final solution. For example, you might want "quiet machinery," or a "database that you can access from anywhere with an Internet connection."
e. How will we define success? Identify how you'll define success once you've implemented a solution.
4. Write a Problem Statement
The final step is to pull together all of the information that you've gathered into a clear, comprehensive problem statement. This should provide a thorough overview of the problem, and outline a plan for how you will go about solving it.
If someone else (for example, a contractor, outside organization, or other department) will be tasked with solving the problem, also work through the following questions, and include the answers to these in your problem statement:
a. Which problem solvers should we use? Identify who, specifically, is best placed to help solve this problem. This could be a person, a team, or an outside firm.
b. What information and language should the problem statement include? The problem statement needs to be clear, specific, and understood by the people who should solve it. Avoid industry jargon , and make sure that it relates to its intended audience.
c. What do problem solvers need to produce? What will you or your organization need from them? For instance, will you need a comprehensive report, or a presentation on the proposed solution? Do you want a prototype? Is there a deadline? Spell the details out here.
d. What incentives do solvers need? This question addresses motivation. If an internal team will be working on the solution, how will they be rewarded? If an external team or firm will be addressing this problem, what incentives are you offering?
e. How will we evaluate the solutions? Who will be responsible for analyzing proposals, and what evaluation method will you use?
Dwayne Spradlin published the Problem-Definition Process in the September 2012 Harvard Business Review.
The process presents four steps that help you better understand complex problems. These four steps are:
The main advantage of using the process is that it helps you to define and understand the problem in detail, and helps you understand how important a problem is in relation to your organization's mission and strategy. From this, you can determine whether or not it's worth developing a solution.
Spradlin, D. (2012) 'Are You Solving the Right Problem?' Harvard Business Review . Available here . [Accessed November 8, 2018.]
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
The problem-solving process.
Looking at the Basic Problem-Solving Process to Help Keep You on the Right Track
Creative Problem-Solving Technique
Using Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Tips for Dealing with Customers Effectively

Tips for Creating an Inclusive Culture
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
New meaningful conversations.
Making real connections in hybrid teams
Pain Points - Managing New Hires
Getting onboarding right
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
How to be patient.
Identify Your Triggers and Control Your Reactions
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

- Miles Anthony Smith
- Sep 12, 2022
- 12 min read
The Ultimate Problem-Solving Process Guide: 31 Steps and Resources
Updated: Jan 24, 2023
GOT CHALLENGES WITH YOUR PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS? ARE YOU FRUSTRATED?
prob·lem-solv·ing noun -the process of finding solutions to difficult or complex issues. It sounds so simple, doesn’t it? But in reality problem-solving is hard. It's almost always more complex than it seems. That's why problem-solving can be so frustrating sometimes. You can feel like you’re spinning your wheels, arguing in circles, or just failing to find answers that actually work. And when you've got a group working on a problem, it can get even muddier …differences of opinions, viewpoints colored by different backgrounds, history, life experiences, you name it. We’re all looking at life and work from different angles, and that often means disagreement. Sometimes sharp disagreement. That human element, figuring out how to take ourselves out of the equation and make solid, fact-based decisions , is precisely why there’s been so much written on problem-solving. Which creates its own set of problems. Whose method is best? How can you possibly sift through them all? Are we to have one person complete the entire problem-solving process by themselves or rely on a larger team to find answers to our most vexing challenges in the workplace ? Today, we’re going to make sense of it all. We’ll take a close look at nine top problem-solving methods. Then we’ll grab the best elements of all of them to give you a process that will have your team solving problems faster, with better results , and maybe with less sharp disagreement. Ready to dive in? Let’s go!
9 PROFITABLE PROBLEM-SOLVING TECHNIQUES AND METHODS
While there are loads of methods to choose from, we are going to focus on nine of the more common ones. You can use some of these problem-solving techniques reactively to solve a known issue or proactively to find more efficient or effective ways of performing tasks. If you want to explore other methods, check out this resource here . A helpful bit of advice here is to reassure people that you aren’t here to identify the person that caused the problem . You’re working to surface the issue, solve it and make sure it doesn’t happen again, regardless of the person working on the process. It can’t be understated how important it is to continually reassure people of this so that you get unfiltered access to information. Without this, people will often hide things to protect themselves . After all, nobody wants to look bad, do they? With that said, let’s get started...
1. CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING (CPS)
Alex Osborn coined the term “Creative Problem Solving” in the 1940s with this simple four-step process:
Clarify : Explore the vision, gather data, and formulate questions.
Ideate : This stage should use brainstorming to generate divergent thinking and ideas rather than the random ideas normally associated with brainstorming.
Develop : Formulate solutions as part of an overall plan.
Implement : Put the plan into practice and communicate it to all parties.
2. APPRECIATIVE INQUIRY

Source: http://www.davidcooperrider.com/ai-process/ This method seeks, first and foremost, to identify the strengths in people and organizations and play to that “positive core” rather than focus our energies on improving weaknesses . It starts with an “affirmative topic,” followed by the “positive core (strengths).” Then this method delves into the following stages:
Discovery (fact-finding)
Dream (visioning the future)
Design (strategic purpose)
Destiny (continuous improvement)
3. “FIVE WHYS” METHOD
This method simply suggests that we ask “Why” at least five times during our review of the problem and in search of a fix. This helps us dig deeper to find the the true reason for the problem, or the root cause. Now, this doesn’t mean we just keeping asking the same question five times. Once we get an answer to our first “why”, we ask why to that answer until we get to five “whys”.
Using the “five whys” is part of the “Analyze” phase of Six Sigma but can be used with or without the full Six Sigma process.
Review this simple Wikipedia example of the 5 Whys in action:
The vehicle will not start. (the problem)
Why? - The battery is dead. (First why)
Why? - The alternator is not functioning. (Second why)
Why? - The alternator belt has broken. (Third why)
Why? - The alternator belt was well beyond its useful service life and not replaced. (Fourth why)
Why? - The vehicle was not maintained according to the recommended service schedule. (Fifth why, a root cause)
4. LEAN SIX SIGMA (DMAIC METHOD)

While many people have at least heard of Lean or Six Sigma, do we know what it is? Like many problem-solving processes, it has five main steps to follow.
Define : Clearly laying out the problem and soliciting feedback from those who are customers of the process is necessary to starting off on the right foot.
Measure : Quantifying the current state of the problem is a key to measuring how well the fix performed once it was implemented.
Analyze : Finding out the root cause of the problem (see number 5 “Root Cause Analysis” below) is one of the hardest and least explored steps of Six Sigma.
Improve : Crafting, executing, and testing the solution for measureable improvement is key. What doesn’t get implemented and measured really won’t make a difference.
Control : Sustaining the fix through a monitoring plan will ensure things continue to stay on track rather than being a short-lived solution.
5. ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS
Compared to other methods, you’ll more often find this technique in a reactive problem-solving mode, but it is helpful nonetheless. Put simply, it requires a persistent approach to finding the highest-level cause, since most reasons you’ll uncover for a problem don’t tell the whole story.
Most of the time, there are many factors that contributed to an issue. The main reason is often shrouded in either intentional or unintentional secrecy. Taking the time to drill down to the root of the issue is key to truly solving the problem.
6. DEMING-SHEWHART CYCLE: PLAN-DO-CHECK-ACT (PDCA)
Named for W. Edwards Deming and Walter A. Shewhart, this model follows a four-step process:
Plan: Establish goals and objectives at the outset to gain agreement. It’s best to start on a small scale in order to test results and get a quick win.
Do: This step is all about the implementation and execution of the solution.
Check: Study and compare actual to expected results. Chart this data to identify trends.
Act/Adjust: If the check phase showed different results, then adjust accordingly. If worse than expected, then try another fix. If the same or better than expected, then use that as the new baseline for future improvements.
7. 8D PROBLEM-SOLVING

While this is named “8D” for eight disciplines, there are actually nine , because the first is listed as step zero. Each of the disciplines represents a phase of this process. Its aim is to implement a quick fix in the short term while working on a more permanent solution with no recurring issues.
Prepare and Plan : Collecting initial information from the team and preparing your approach to the process is a necessary first step.
Form a Team : Select a cross-functional team of people, one leader to run meetings and the process, and one champion/sponsor who will be the final decision-maker.
Describe the Problem : Using inductive and deductive reasoning approaches, lay out the precise issue to be corrected.
Interim Containment Action : Determine if an interim solution needs to be implemented or if it can wait until the final fix is firmed up. If necessary, the interim action is usually removed once the permanent solution is ready for implementation.
Root Cause Analysis and Escape Point : Finding the root of the issue and where in the process it could’ve been found but was not will help identify where and why the issue happened.
Permanent Corrective Action : Incorporating key criteria into the solution, including requirements and wants, will help ensure buy-in from the team and your champion.
Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action : Measuring results from the fix implemented validates it or sends the team back to the drawing board to identity a more robust solution.
Prevent Recurrence : Updating work procedure documents and regular communication about the changes are important to keep old habits in check.
Closure and Team Celebration : Taking time to praise the team for their efforts in resolving the problem acknowledges the part each person played and offers a way to move forward.
8. ARMY PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS
The US Army has been solving problems for more than a couple of centuries , so why not take a look at the problem-solving process they’ve refined over many years? They recommend this five step process:
Identify the Problem : Take time to understand the situation and define a scope and limitations before moving forward.
Gather Information : Uncover facts, assumptions, and opinions about the problem, and challenge them to get to the truth.
Develop Screening and Evaluation Criteria :
Five screening items should be questioned. Is it feasible, acceptable, distinguishable, and complete?
Evaluation criteria should have these 5 elements: short title, definition, unit of measure, benchmark, and formula.
Generate, Analyze, and Compare Possible Solutions : Most fixes are analyzed, but do you compare yours to one another as a final vetting method?
Choose a Solution and Implement : Put the fix into practice and follow up to ensure it is being followed consistently and having the desired effect.
9. HURSON'S PRODUCTIVE THINKING MODEL

Tim Hurson introduced this model in 2007 with his book, Think Better. It consists of the following six actions.
Ask "What is going on?" : Define the impact of the problem and the aim of its solution.
Ask "What is success?" : Spell out the expected outcome, what should not be in fix, values to be considered, and how things will be evaluated.
Ask "What is the question?" : Tailor questions to the problem type. Valuable resources can be wasted asking questions that aren’t truly relevant to the issue.
Generate answers : Prioritize answers that are the most relevant to solutions, without excluding any suggestion to present to the decision-makers.
Forge the solution : Refine the raw list of prioritized fixes, looking for ways to combine them for a more powerful solution or eliminate fixes that don’t fit the evaluation criteria.
Align resources: Identify resources, team, and stakeholders needed to implement and maintain the solution.
STEAL THIS THOROUGH 8-STEP PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS

Now that we’ve reviewed a number of problem-solving methods, we’ve compiled the various steps into a straightforward, yet in-depth, s tep-by-step process to use the best of all methods.
1. DIG DEEP: IDENTIFY, DEFINE, AND CLARIFY THE ISSUE
“Elementary, my dear Watson,” you might say.
This is true, but we often forget the fundamentals before trying to solve a problem. So take some time to gain understanding of critical stakeholder’s viewpoints to clarify the problem and cement consensus behind what the issue really is.
Sometimes it feels like you’re on the same page, but minor misunderstandings mean you’re not really in full agreement.. It’s better to take the time to drill down on an issue before you get too far into solving a problem that may not be the exact problem . Which leads us to…
2. DIG DEEPER: ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS

This part of the process involves identifying these three items :
What happened?
Why did it happen?
What process do we need to employ to significantly reduce the chances of it happening again ?
You’ll usually need to sort through a series of situations to find the primary cause. So be careful not to stop at the first cause you uncover . Dig further into the situation to expose the root of the issue. We don’t want to install a solution that only fixes a surface-level issue and not the root. T here are typically three types of causes :
Physical: Perhaps a part failed due to poor design or manufacturing.
Human error: A person either did something wrong or didn’t do what needed to be done.
Organizational: This one is mostly about a system, process, or policy that contributed to the error .
When searching for the root cause, it is important to ensure people that you aren’t there to assign blame to a person but rather identify the problem so a fix can prevent future issues.
3. PRODUCE A VARIETY OF SOLUTION OPTIONS
So far, you’ve approached the problem as a data scientist, searching for clues to the real issue. Now, it’s important to keep your eyes and ears open, in case you run across a fix suggested by one of those involved in the process failure. Because they are closest to the problem, they will often have an idea of how to fix things. In other cases, they may be too close, and unable to see how the process could change.
The bottom line is to solicit solution ideas from a variety of sources , both close to and far away from the process you’re trying to improve.
You just never know where the top fix might come from!
4. FULLY EVALUATE AND SELECT PLANNED FIX(ES)

Evaluating solutions to a defined problem can be tricky since each one will have cost, political, or other factors associated with it. Running each fix through a filter of cost and impact is a vital step toward identifying a solid solution and hopefully settling on the one with the highest impact and low or acceptable cost.
Categorizing each solution in one of these four categoriescan help teams sift through them:
High Cost/Low Impact: Implement these last, if at all, since t hey are expensive and won’t move the needle much .
Low Cost/Low Impact: These are cheap, but you won’t get much impact.
High Cost/High Impact: These can be used but should be second to the next category.
Low Cost/High Impact: Getting a solid “bang for your buck” is what these fixes are all about. Start with these first .
5. DOCUMENT THE FINAL SOLUTION AND WHAT SUCCESS LOOKS LIKE
Formalize a document that all interested parties (front-line staff, supervisors, leadership, etc.) agree to follow. This will go a long way towards making sure everyone fully understands what the new process looks like, as well as what success will look like .
While it might seem tedious, try to be overly descriptive in the explanation of the solution and how success will be achieved. This is usually necessary to gain full buy-in and commitment to continually following the solution. We often assume certain things that others may not know unless we are more explicit with our communications.
6. SUCCESSFULLY SELL AND EXECUTE THE FIX

Arriving at this stage in the process only to forget to consistently apply the solution would be a waste of time, yet many organizations fall down in the execution phase . Part of making sure that doesn’t happen is to communicate the fix and ask for questions multiple times until all parties have a solid grasp on what is now required of them.
One often-overlooked element of this is the politics involved in gaining approval for your solution. Knowing and anticipating objections of those in senior or key leadership positions is central to gaining buy-in before fix implementation.
7. RINSE AND REPEAT: EVALUATE, MONITOR, AND FOLLOW UP
Next, doing check-ins with the new process will ensure that the solution is working (or identity if further reforms are necessary) . You’ll also see if the measure of predefined success has been attained (or is making progress in that regard).
Without regularly monitoring the fix, you can only gauge the success or failure of the solution by speculation and hearsay. And without hard data to review, most people will tell their own version of the story.
8. COLLABORATIVE CONTINGENCIES, ITERATION, AND COURSE CORRECTION

Going into any problem-solving process, we should take note that we will not be done once the solution is implemented (or even if it seems to be working better at the moment). Any part of any process will always be subject to the need for future iterations and course corrections . To think otherwise would be either foolish or naive.
There might need to be slight, moderate, or wholesale changes to the solution previously implemented as new information is gained, new technologies are discovered, etc.
14 FRUITFUL RESOURCES AND EXERCISES FOR YOUR PROBLEM-SOLVING JOURNEY

Want to test your problem-solving skills?
Take a look at these twenty case study scenario exercises to see how well you can come up with solutions to these problems.
Still have a desire to discover more about solving problems?
Check out these 14 articles and books...
1. THE LEAN SIX SIGMA POCKET TOOLBOOK: A QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO NEARLY 100 TOOLS FOR IMPROVING QUALITY AND SPEED
This book is like a Bible for Lean Six Sigma , all in a pocket-sized package.
2. SOME SAGE PROBLEM SOLVING ADVICE

The American Society for Quality has a short article on how it’s important to focus on the problem before searching for a solution.
3. THE SECRET TO BETTER PROBLEM SOLVING: HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW
Wondering if you are solving the right problems? Check out this Harvard Business Review article.
4. PROBLEM SOLVING 101 : A SIMPLE BOOK FOR SMART PEOPLE
Looking for a fun and easy problem-solving book that was written by a McKinsey consultant? Take a look!
5. THE BASICS OF CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING – CPS

If you want a deeper dive into the seven steps of Creative Problem Solving , see this article.
6. APPRECIATIVE INQUIRY : A POSITIVE REVOLUTION IN CHANGE
Appreciative Inquiry has been proven effective in organizations ranging from Roadway Express and British Airways to the United Nations and the United States Navy. Review this book to join the positive revolution.
7. PROBLEM SOLVING: NINE CASE STUDIES AND LESSONS LEARNED
The Seattle Police Department has put together nine case studies that you can practice solving . While they are about police work, they have practical application in the sleuthing of work-related problems.
8. ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS : THE CORE OF PROBLEM SOLVING AND CORRECTIVE ACTION
Need a resource to delve further into Root Cause Analysis? Look no further than this book for answers to your most vexing questions .
9. SOLVING BUSINESS PROBLEMS : THE CASE OF POOR FRANK

This solid case study illustrates the complexities of solving problems in business.
10. THE 8-DISCIPLINES PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY
Learn all about the “8Ds” with this concise primer.
11. THE PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS THAT PREVENTS GROUPTHINK HBR
Need to reduce groupthink in your organization’s problem-solving process ? Check out this article from the Harvard Business Review.
12. THINK BETTER : AN INNOVATOR'S GUIDE TO PRODUCTIVE THINKING

Tim Hurson details his own Productive Thinking Model at great length in this book from the author.
13. 5 STEPS TO SOLVING THE PROBLEMS WITH YOUR PROBLEM SOLVING INC MAGAZINE
This simple five-step process will help you break down the problem, analyze it, prioritize solutions, and sell them internally.
14. CRITICAL THINKING : A BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO CRITICAL THINKING, BETTER DECISION MAKING, AND PROBLEM SOLVING!
LOOKING FOR ASSISTANCE WITH YOUR PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS?
There's a lot to take in here, but following some of these methods are sure to improve your problem-solving process. However, if you really want to take problem-solving to the next level, InitiativeOne can come alongside your team to help you solve problems much faster than you ever have before.
There are several parts to this leadership transformation process provided by InitiativeOne, including a personal profile assessment, cognitive learning, group sessions with real-world challenges, personal discovery, and a toolkit to empower leaders to perform at their best.
There are really only two things stopping good teams from being great. One is how they make decisions and two is how they solve problems. Contact us today to grow your team’s leadership performance by making decisions and solving problems more swiftly than ever before!
- Featured Post
Recent Posts
Does Your Leadership Deserve Two Thumbs Up?
3 Ways to Harness the Power of Inspiration
Leadership Self-Check
Comentários
Table of Contents
The problem-solving process, how to solve problems: 5 steps, train to solve problems with lean today, what is problem solving steps, techniques, & best practices explained.

Problem solving is the art of identifying problems and implementing the best possible solutions. Revisiting your problem-solving skills may be the missing piece to leveraging the performance of your business, achieving Lean success, or unlocking your professional potential.
Ask any colleague if they’re an effective problem-solver and their likely answer will be, “Of course! I solve problems every day.”
Problem solving is part of most job descriptions, sure. But not everyone can do it consistently.
Problem solving is the process of defining a problem, identifying its root cause, prioritizing and selecting potential solutions, and implementing the chosen solution.
There’s no one-size-fits-all problem-solving process. Often, it’s a unique methodology that aligns your short- and long-term objectives with the resources at your disposal. Nonetheless, many paradigms center problem solving as a pathway for achieving one’s goals faster and smarter.
One example is the Six Sigma framework , which emphasizes eliminating errors and refining the customer experience, thereby improving business outcomes. Developed originally by Motorola, the Six Sigma process identifies problems from the perspective of customer satisfaction and improving product delivery.
Lean management, a similar method, is about streamlining company processes over time so they become “leaner” while producing better outcomes.
Trendy business management lingo aside, both of these frameworks teach us that investing in your problem solving process for personal and professional arenas will bring better productivity.
1. Precisely Identify Problems
As obvious as it seems, identifying the problem is the first step in the problem-solving process. Pinpointing a problem at the beginning of the process will guide your research, collaboration, and solutions in the right direction.
At this stage, your task is to identify the scope and substance of the problem. Ask yourself a series of questions:
- What’s the problem?
- How many subsets of issues are underneath this problem?
- What subject areas, departments of work, or functions of business can best define this problem?
Although some problems are naturally large in scope, precision is key. Write out the problems as statements in planning sheets . Should information or feedback during a later step alter the scope of your problem, revise the statements.
Framing the problem at this stage will help you stay focused if distractions come up in later stages. Furthermore, how you frame a problem will aid your search for a solution. A strategy of building Lean success, for instance, will emphasize identifying and improving upon inefficient systems.
2. Collect Information and Plan
The second step is to collect information and plan the brainstorming process. This is another foundational step to road mapping your problem-solving process. Data, after all, is useful in identifying the scope and substance of your problems.
Collecting information on the exact details of the problem, however, is done to narrow the brainstorming portion to help you evaluate the outcomes later. Don’t overwhelm yourself with unnecessary information — use the problem statements that you identified in step one as a north star in your research process.
This stage should also include some planning. Ask yourself:
- What parties will ultimately decide a solution?
- Whose voices and ideas should be heard in the brainstorming process?
- What resources are at your disposal for implementing a solution?
Establish a plan and timeline for steps 3-5.
3. Brainstorm Solutions
Brainstorming solutions is the bread and butter of the problem-solving process. At this stage, focus on generating creative ideas. As long as the solution directly addresses the problem statements and achieves your goals, don’t immediately rule it out.
Moreover, solutions are rarely a one-step answer and are more like a roadmap with a set of actions. As you brainstorm ideas, map out these solutions visually and include any relevant factors such as costs involved, action steps, and involved parties.
With Lean success in mind, stay focused on solutions that minimize waste and improve the flow of business ecosystems.
Become a Quality Management Professional
- 10% Growth In Jobs Of Quality Managers Profiles By 2025
- 11% Revenue Growth For Organisations Improving Quality
Certified Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
- 4 hands-on projects to perfect the skills learnt
- 4 simulation test papers for self-assessment
Lean Six Sigma Expert
- IASSC® Lean Six Sigma Green Belt and Black Belt certification
- 13 Projects, 12 Simulation exams, 18 Case Studies & 114 PDUs
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Xueting Liu
Mechanical engineer student at sargents pty. ltd. ,.
A great training and proper exercise with step-by-step guide! I'll give a rating of 10 out of 10 for this training.
Abdus Salam
I have completed the Lean Six Sigma Expert Master’s Program from Simplilearn. And after the course, I could take up new projects and perform better. My average pay rate for a research position increased by 21%.
4. Decide and Implement
The most critical stage is selecting a solution. Easier said than done. Consider the criteria that has arisen in previous steps as you decide on a solution that meets your needs.
Once you select a course of action, implement it.
Practicing due diligence in earlier stages of the process will ensure that your chosen course of action has been evaluated from all angles. Often, efficient implementation requires us to act correctly and successfully the first time, rather than being hurried and sloppy. Further compilations will create more problems, bringing you back to step 1.
5. Evaluate
Exercise humility and evaluate your solution honestly. Did you achieve the results you hoped for? What would you do differently next time?
As some experts note, formulating feedback channels into your evaluation helps solidify future success. A framework like Lean success, for example, will use certain key performance indicators (KPIs) like quality, delivery success, reducing errors, and more. Establish metrics aligned with company goals to assess your solutions.
Master skills like measurement system analysis, lean principles, hypothesis testing, process analysis and DFSS tools with our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training Course . Sign-up today!
Become a quality expert with Simplilearn’s Lean Six Sigma Green Belt . This Lean Six Sigma certification program will help you gain key skills to excel in digital transformation projects while improving quality and ultimate business results.
In this course, you will learn about two critical operations management methodologies – Lean practices and Six Sigma to accelerate business improvement.
Our Quality Management Courses Duration And Fees
Explore our top Quality Management Courses and take the first step towards career success
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Quality Management
Lean Management
Project Management
Learn from industry experts with free masterclasses, digital marketing.
SEO vs. PPC: Which Digital Path Fits You Best in 2024?
The Top 10 AI Tools You Need to Master Marketing in 2024
Unlock Digital Marketing Career Success Secrets for 2024 with Purdue University
Recommended Reads
Introduction to Machine Learning: A Beginner's Guide
Webinar Wrap-up: Mastering Problem Solving: Career Tips for Digital Transformation Jobs
An Ultimate Guide That Helps You to Develop and Improve Problem Solving in Programming
Free eBook: 21 Resources to Find the Data You Need
ITIL Problem Workaround: A Leader’s Guide to Manage Problems
Your One-Stop Solution to Understand Coin Change Problem
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

The Five-Step Problem-Solving Process
Sometimes when you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s best to pause and take a step back. A break from…

Sometimes when you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s best to pause and take a step back. A break from routine will help you think creatively and objectively. Doing too much at the same time increases the chances of burnout.
Solving problems is easier when you align your thoughts with your actions. If you’re in multiple places at once mentally, you’re more likely to get overwhelmed under pressure. So, a problem-solving process follows specific steps to make it approachable and straightforward. This includes breaking down complex problems, understanding what you want to achieve, and allocating responsibilities to different people to ease some of the pressure.
The problem-solving process will help you measure your progress against factors like budget, timelines and deliverables. The point is to get the key stakeholders on the same page about the ‘what’, ‘why’ and ‘how’ of the process. ( Xanax ) Let’s discuss the five-step problem-solving process that you can adopt.
Problems at a workplace need not necessarily be situations that have a negative impact, such as a product failure or a change in government policy. Making a decision to alter the way your team works may also be a problem. Launching new products, technological upgrades, customer feedback collection exercises—all of these are also “problems” that need to be “solved”.
Here are the steps of a problem-solving process:
1. Defining the Problem
The first step in the process is often overlooked. To define the problem is to understand what it is that you’re solving for. This is also where you outline and write down your purpose—what you want to achieve and why. Making sure you know what the problem is can make it easier to follow up with the remaining steps. This will also help you identify which part of the problem needs more attention than others.
2. Analyzing the Problem
Analyze why the problem occurred and go deeper to understand the existing situation. If it’s a product that has malfunctioned, assess factors like raw material, assembly line, and people involved to identify the problem areas. This will help you figure out if the problem will persist or recur. You can measure the solution against existing factors to assess its future viability.
3. Weighing the Options
Once you’ve figured out what the problem is and why it occurred, you can move on to generating multiple options as solutions. You can combine your existing knowledge with research and data to come up with viable and effective solutions. Thinking objectively and getting inputs from those involved in the process will broaden your perspective of the problem. You’ll be able to come up with better options if you’re open to ideas other than your own.
4. Implementing The Best Solution
Implementation will depend on the type of data at hand and other variables. Consider the big picture when you’re selecting the best option. Look at factors like how the solution will impact your budget, how soon you can implement it, and whether it can withstand setbacks or failures. If you need to make any tweaks or upgrades, make them happen in this stage.
5. Monitoring Progress
The problem-solving process doesn’t end at implementation. It requires constant monitoring to watch out for recurrences and relapses. It’s possible that something doesn’t work out as expected on implementation. To ensure the process functions smoothly, you can make changes as soon as you catch a miscalculation. Always stay on top of things by monitoring how far you’ve come and how much farther you have to go.
You can learn to solve any problem—big or small—with experience and patience. Adopt an impartial and analytical approach that has room for multiple perspectives. In the workplace, you’re often faced with situations like an unexpected system failure or a key employee quitting in the middle of a crucial project.
Problem-solving skills will help you face these situations head-on. Harappa Education’s Structuring Problems course will show you how to classify and categorize problems to discover effective solutions. Equipping yourself with the right knowledge will help you navigate work-related problems in a calm and competent manner.
Explore topics such as Problem Solving , the PICK Chart , How to Solve Problems & the Barriers to Problem Solving from our Harappa Diaries blog section and develop your skills.


Problem Solving Process: The Ultimate Guide to the Process of Problem Solving
What is problem solving, the process for problem solving, be smart about problem solving.
Whether you manage a team or the entire organization, you need to apply excellent problem solving techniques to keep your organization going. Problems can occur between employees, which needs quick and effective problem solving tricks to continue with your business operations. That is why you need to learn about problem solving stages. Read on to learn more about problem solving.
Problem solving is the ability to offer solutions to difficult or complex issues and devising ways to avoid repetitive occurrences in the future.
Develop a positive approach
Before you handle any issue, the first thing is to have a positive mentality towards the problem. It could be a huge problem that may cause you to panic, but try as much as possible to remain composed and confident during the problem solving process. You want to give it the best outcome without involving emotions. So, stay positive as you figure out how to deal with the issue.
Understand the problem
The next problem solving method is to define the problem you are facing. The issue could be more profound than you think, and that is why you need to be intentional about diagnosing the root cause of the problem. This is the only way to solve the issue, because you can't solve what you cannot diagnose. Know the root cause and the effect of the issue. If possible, write down everything and use the notes as a guide on how to solve the problem.
Be creative about the problem
Creativity is a vital skill that a good problem solver should possess. It helps you think outside the box and approach the issue strategically. You need to address the issue from different angles to avoid leaning on one side.
Determine whether other issues could be a stumbling block to the current problem and devise ways to address it first before you proceed.
Looking for solutions
A single problem can have tens of practical solutions. This is why you need to think deeper and analyze all the possible solutions before making the final decision. Determine the problem solving model you're going to use to solve the issue.
You can brainstorm with your colleagues and take note of the possible solutions. Let it be an open platform where everyone can air out their views and ideas about the proposed solutions. But this doesn't mean that every solution is applicable.
Determine the effective solution
Once you highlight various scenarios, determine the problem solving techniques and approaches you will use. You do not have to apply every proposed solution. It is best to analyze what you have noted and settle for the best option.
Please choose an alternative that will solve the issue at hand without complicating it further. You only need to be smart and sensible when choosing the best problem solving strategies.
Solve the problem
Now, you already have a solution to the problem, and are ready to make the final decision. Go on and execute. Be patient at this moment as you weigh both sides to see how the involved parties react to the final decision. If you experience a drawback, you can quickly counter it by applying creative tips and remain persistent until you achieve your goals.
Be ready for the outcome
One thing you need to know is that not all decisions end up well with the involved parties. The solution could fail and cause more chaos in the long run. It is imperative to prepare for such outcomes to avoid dilemmas and confusion.
Remember, even if you do not get it right at first, this will be a learning lesson and you can be sure of doing better the next time. However, to avoid such scenarios, prepare adequately to handle the outcome, whether positive or negative.
Create a follow-up strategy
No matter the outcome, find creative problem solving steps to follow up until you're sure that the problem is entirely resolved. Do not assume that everything is okay, since this could be the beginning of new problems. You can involve your colleagues to offer support until you achieve your goals.
Today, there are more advanced ways of problem solving. Problem-solving software is a crucial tool that will help you solve your issues within a short time and without compromising quality. Check out MindManager to get all the tools you need for collaborative problem solving!
Need to Download MindManager?
Try the full version of mindmanager free for 30 days.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- Problem management: 8 steps to better p ...
Problem management: 8 steps to better problem solving

Problem management is an 8 step framework most commonly used by IT teams. You can use problem management to solve for repeating major incidents. By organizing and structuring your problem solving, you can more effectively get to the root cause of high-impact problems—and devise a solution. Solving the root cause prevents recurrence and creates a repeatable solution to use on similar errors in the future.
In an IT department, errors and mishaps are part of the job. You can't always control these problems, but you can control how you respond to them with problem management. Problem management helps you solve larger problems and reduce the risk that they’ll happen again by identifying all connected problems, solving them, and planning for the future.
What is problem management?
Problem management is an 8 step framework most commonly used by IT teams. Your team can use problem management to solve for repeating major incidents. By organizing and structuring your problem solving, you can more effectively get to the root cause of high-impact problems—and devise a solution. Problem management is a process—used mostly by IT teams—to identify, react, and respond to issues. It’s not for every problem, but it’s a useful response when multiple major incidents occur that cause large work interruptions. Unlike problem solving, problem management goes beyond the initial incident to discover and dissect the root causes, preventing future incidents with permanent solutions.
The goals of problem management are to:
Prevent problems before they start.
Solve for repetitive errors.
Lessen each incident’s impact.

Problem management vs. incident management
Example: Someone leaves their unprotected laptop in a coffee shop, causing a security breach. The security team can use incident management to solve for this one, isolated event. In this case, the team could manually shut down the accounts connected to that laptop. If this continues to happen, IT would use problem management to solve the root of this issue—perhaps installing more security features on each company laptop so that if employees lose them, no one else can access the information.
Problem management vs. problem solving
While similar in name, problem management differs slightly from problem-solving. Problem management focuses on every aspect of the incident—identifying the root cause of the problem, solving it, and prevention. Problem solving is, as the name implies, focused solely on the solution step.
Example: You’re launching a new password management system when it crashes—again. You don’t know if anything leaked, but you know it could contain confidential information. Plus, it’s happened before. You start the problem management process to ensure it doesn’t happen again. In that process, you’ll use problem solving as a step to fix the issue. In this case, perhaps securing confidential information before you try to launch a new software.
Problem management vs. change management
Change management targets large transitions within your workplace, good and bad. These inevitable changes aren’t always negative, so you can’t always apply problem management as a solution. That’s where change management comes in—a framework that helps you adjust to any new scenario.
Example: Your company is transitioning to a new cloud platform. The transition happens incident-free—meaning you won’t need problem management—but you can ease the transition by implementing some change management best practices. Preparing and training team members in the new software is a good place to start.
Problem management vs. project management
Project management is the framework for larger collections of work. It’s the overarching method for how you work on any project, hit goals, and get results. You can use project management to help you with problem management, but they are not the same thing. Problem management and project management work together to solve issues as part of your problem management process.
Example: During problem management, you uncover a backend security issue that needs to be addressed—employees are using storage software with outdated security measures. To solve this, you create a project and outline the tasks from start to finish. In this case, you might need to alert senior executives, get approval to remove the software, and alert employees. You create a project schedule with a defined timeline and assign the tasks to relevant teams. In this process, you identified a desired outcome—remove the unsafe software—and solved it. That’s project management.
The 8 steps of problem management
It’s easy to get upset when problems occur. In fact, it’s totally normal. But an emotional response is not always the best response when faced with new incidents. Having a reliable system—such as problem management—removes the temptation to respond emotionally. Proactive project management gives your team a framework for problem solving. It’s an iterative process —the more you use it, the more likely you are to have fewer problems, faster response times, and better outputs.
1. Identify the problem
During problem identification, you’re looking at the present—what’s happening right now? Here, you’ll define what the incident is and its scale. Is this a small, quick-fix, or a full overhaul? Consider using problem framing to define, prioritize, and understand the obstacles involved with these more complex problems.
2. Diagnose the cause
Use problem analysis or root cause analysis to strategically look at the cause of a problem. Follow the trail of issues all the way back to its beginnings.
To diagnose the underlying cause, you’ll want to answer:
What factors or conditions led to the incident?
Do you see related incidents? Could those be coming from the same source?
Did someone miss a step? Are processes responsible for this problem?
3. Organize and prioritize
Now it’s time to build out your framework. Use an IT project plan to organize information in a space where everyone can make and see updates in real time. The easiest way to do this is with a project management tool where you can input tasks, assign deadlines, and add dependencies to ensure nothing gets missed. To better organize your process, define:
What needs to be done?
Who’s responsible for each aspect? If no one is, can we assign someone?
When does each piece need to be completed?
What is the final number of incidents related to this problem?
Are any of these tasks dependent on another one? Do you need to set up dependencies ?
What are your highest priorities? How do they affect our larger business goals ?
How should you plan for this in the future?
4. Create a workaround
If the incident has stopped work or altered it, you might need to create a workaround. This is not always necessary, but temporary workarounds can keep work on track and avoid backlog while you go through the problem management steps. When these workarounds are especially effective, you can make them permanent processes.
5. Update your known error database
Every time an incident occurs, create a known error record and add it to your known error database (KEDB). Recording incidents helps you catch recurrences and logs the solution, so you know how to solve similar errors in the future.
![what is steps in the problem solving process [product ui] Incident log example (lists)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/4656a136-713e-4caf-8fa1-9556a8bb666e/inline-project-management-incident-management-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
6. Pause for change management (if necessary)
Larger, high-impact problems might require change management. For example, if you realize the problem’s root cause is a lack of staff, you might dedicate team members to help. You can use change management to help them transition their responsibilities, see how these new roles fit in with the entire team, and determine how they will collaborate moving forward.
7. Solve the problem
This is the fun part—you get to resolve problems. At this stage, you should know exactly what you’re dealing with and the steps you need to take. But remember—with problem management, it’s not enough to solve the current problem. You’ll want to take any steps to prevent this from happening again in the future. That could mean hiring a new role to cover gaps in workflows , investing in new softwares and tools, or training staff on best practices to prevent these types of incidents.
Read: Turn your team into skilled problem solvers with these problem-solving strategies
8. Reflect on the process
The problem management process has the added benefit of recording the process in its entirety, so you can review it in the future. Once you’ve solved the problem, take the time to review each step and reflect on the lessons learned during this process. Make note of who was involved, what you needed, and any opportunities to improve your response to the next incident. After you go through the problem management process a few times and understand the basic steps, stakeholders, workload, and resources you need, create a template to make the kickoff process easier in the future.
5 benefits of problem management
Problem management helps you discover every piece of the problem—from the current scenario down to its root cause. Not only does this have an immediate positive impact on the current issue at hand, it also promotes collaboration and helps to build a better product overall.
Here are five other ways problem management can benefit your team:
Avoids repeat incidents. When you manage the entire incident from start to finish, you will address the foundational problems that caused it. This leads to fewer repeat incidents.
Boosts cross-functional collaboration. Problem management is a collaborative process. One incident might require collaboration from IT, the security team, and legal. Depending on the level of the problem, it might trickle all the way back down to the product or service team, where core changes need to be made.
Creates a better user experience. It’s simple—the fewer incidents you have, the better your customer’s experience will be. Reducing incidents means fewer delays, downtime, and frustrations for your users, and a higher rate of customer satisfaction.
Improves response time. As you develop a flow and framework with a project management process, you’ll be better equipped to handle future incidents—even if they’re different scenarios.
Organizes problem solving. Problem management provides a structured, thoughtful approach to solving problems. This reduces impulsive responses and helps you keep a better problem record of incidents and solutions.
Problem management leads to better, faster solutions
IT teams will always have to deal with incidents, but they don’t have to be bogged down by them. That’s because problem management works. Whether you employ a full problem management team or choose to apply these practices to your current IT infrastructure, problem management—especially when combined with a project management tool—saves you time and effort down the road.
With IT project plans, we’ve made it easier than ever to track your problem management work in a shared tool. Try our free IT project template to see your work come together, effortlessly.
Related resources
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning

How Asana uses work management for organizational planning

Solve your tech overload with an intelligent transformation
What you need to know about the decision-making process
Last updated
30 April 2024
Reviewed by
Mary Mikhail
Decision-making is how we navigate the world and make choices, whether we’re looking for a new job or deciding on dinner. In business, it’s an adaptable project management tool that uses linear or non-linear procedures to overcome challenges.
Most organizations need to strengthen one of the core business fundamentals: The ability to analyze a problem and reach an adequate resolution.
Let’s get into everything you need to know about decision making, including best practices.
- What is a decision-making process?
A decision-making process is a strategy for analyzing a problem, comparing your options, and deciding on the best solution.
It's essential for everyone in business, from the C-suite to managers and their teams.
The most tried-and-true decision-making processes use seven steps. Let’s check them out.
- Seven fundamental steps for decision-making
While decision-making processes vary, almost all involve seven key principles.
Here’s a simple step-by-step process:
1. Define the decision
Clarify your goals. Ensure everyone understands the issue, your preferred outcome, and how to gauge success.
2. Info gathering
If not, you'll need to gather information to better understand the problem and what a good solution entails.
3. Identify your choices
Summon your creative problem-solving skills and compile a list of the likeliest solutions. What options are available based on the data?
4. Weigh your evidence
Next, thoroughly analyze the options you've compiled. Run each possibility through a cost-benefit analysis, calculate the odds of success, and estimate short- and long-term impacts.
A SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis can help you see the problem at a higher level.
5. Make your choice
Key decision-makers must decide once the critical data, analyses, and options are on the table.
6. Take action
Putting the final decision into action requires a plan for allocating tasks and organizing company resources. Ensure the plan also addresses how stakeholders will monitor progress.
7. Review your decision
The value of a good decision lives on, even after resolving the initial problem. Was the decision successful? Did the issue stay resolved? Will you need to make similar decisions in the future?
Consider these questions even after the pressure subsides. Use the success metrics from step one to adjust your implementation plan or the decision if necessary.
What are the advantages of involving others in the decision-making process?
Decision-making often requires hard work from separate parties, all wielding their skill sets and resources.
Though it's certainly possible to follow a decision-making process alone, working as a team carries tremendous benefits:
Combines a greater share of resources
Raises awareness of a problem
Shortens research time
Expands your range of options
Develops more ideas
Creates consensus and improves collaboration
Business is inherently social—even entrepreneurs must frequently defer to their customers.
- Tools to make better decisions for your customers
A comprehensive understanding of your customers’ wants, needs, and pain points is essential to frame almost any decision-making process.
Some of the most reliable and widely used customer analysis tools include:
Customer journey maps
All customers go through a unique personal decision-making process when making purchasing decisions. From initial awareness of a problem to final vendor comparison, customer journey maps help researchers adapt their decisions to the customer's process.
Empathy maps
An empathy map displays a team's knowledge of different end-users to reveal insights into their needs. It aids decision-making by clarifying what is most important to the customer base.
User personas
The user persona is useful for distilling research into one or several models representing your ideal customer. While purely fictional, a data-backed user persona can ensure you make the right decisions for your customers.
- What challenges arise during the decision-making process?
The decision-making process can create extra challenges, such as:
Disruption of normal business activities
Increased time pressures
Gaps in research or inconclusive data
Difficulty achieving buy-in
Disagreement and infighting
Ironically, the most difficult decision-making challenge can be determining the exact problem you need to solve.
That's partly because different problems evoke two distinct psychological patterns in response to problem-solving.
What are the two types of decisions?
A study from the January 2016 issue of the Journal of Experimental Psychology categorized decision-making into two broad categories:
Analytic problem-solving
Insight problem-solving
Analytical decision-making.
Analytical problem-solving entails a sequence of steps progressively leading to a resolution. It challenges participants to track various subtasks while keeping sight of the main goal.
This type of mental work often requires long stretches of undivided attention and high demands on working memory. It also relies heavily on data and incremental analysis.
Complex problems usually require analytical decision-making and can easily consume a team's attention. At its worst, a purely analytical mindset prevents novel, outside-the-box thinking.
Insight-based problem-solving occurs spontaneously, even arising in defiance of a step-by-step process.
Reflecting on a problem in a new way leads to outside-the-box thinking that can lead to novel solutions.
Still, any concerted attempt at decision-making requires structured effort. What differentiates analytical and insight-based approaches is whether the decision-makers’ efforts use an existing structure or modify it as the process unfolds.
The takeaway is to remain open to adapting your decision-making process, but don't throw it out if you reach an impasse. Friction may reveal flaws that help decision-makers see the issue in a different light.
- How a decision-making model can help
Most decision-making must work with limitations, which you can use to model an effective process.
Wh en to use decision-making models
A decision-making model is appropriate when generic decision-making efforts create more difficulty than solutions.
Times to use a decision-making model include:
Inability to clarify a problem or the type of decision required
Difficulty prioritizing options
Communication breakdowns
Process conflicts that inhibit action
Uncertainty over democratizing research functions
- Types of decision-making models
No decision-making model is best—until a novel, unexpected problem arises. Sometimes, you need confidence in how you’re making decisions to come to the most effective solution.
The following examples of decision-making models may be better for different types of problems, time constraints, and the team's capabilities:
Rational decision-making
The quintessential step-by-step approach to decision-making is best for analytical problem-solving. Rational decision-making involves a linear progression of tasks and is largely prescriptive.
It also depends on continuous logical reasoning and enough time for frequent meetings and thorough analysis.
Intuitive decision-making
Intuitive decision-making may be the best choice when you lack structure or time. It’s also ideal when decision-makers have a history of sound judgment. Some teams do well with a looser approach.
While formal structure may be lacking, an intuitive decision-making model usually reveals some hidden pattern below the surface.
Creative decision-making
What happens if a challenge is wholly novel? The answer is to tap into your creative reservoir because nothing but inventiveness will do.
This doesn't prevent you from researching other companies’ solutions to similar challenges, but it primarily hinges on creating a unique solution.
Creative decision-making requires flexible thinking and a blend of analytic and insight decision-making.
Recognition-primed decision-making
At its core, recognition-primed decision-making has two fundamentals: Assess your problem and compare it to similar challenges you've experienced. It's best for issues you have a wealth of knowledge in.
Like the intuitive decision-making model, the recognition-primed model is generally for fast-paced scenarios. However, its principles are useful for any issue you've effectively dealt with before.
With enough bandwidth and resources, you can even run parallel decision-making models and compare their findings.
- 10 best practices and techniques for improving decision-making
No one is born a great decision-maker. Depending on your experience and talents, any of the following may be just the right food for thought on your journey to becoming a master decision-maker.
Here are 10 tips to improve your decision making.
Understand your goals
Only you know what you truly want. What works for one company might not work for yours, so ensure your solution truly fits your problem. Choosing goals is key to ensuring you don’t settle for a decision that misses the mark.
Evaluate the impacts of your decisions
Continual improvement depends on routine self-evaluation and putting these efforts to the test. Are your solutions successful? Or do you need to tighten up your decision-making process?
Eliminate the downsides
While acknowledging disappointment is necessary, use setbacks for a better approach going forward. Once you’ve made a mistake, learn from it and use this knowledge to craft an improved decision-making process.
Compare timeframes
Each decision-making process or model unfolds along a timeline. If you need a fast decision, it might be better to work with intuitive decision-making rather than a drawn-out process.
Be open to new solutions
You probably won’t arrive at a solution with the same mindset as when the problem arose. Keeping an open mind can help you discover novel solutions.
Use data to evaluate opinions
The best business decisions come from data, especially when they involve customers. However, comparing a high volume of survey responses can be very time-consuming. That’s where a dedicated customer insights platform packed with analysis automation tools can help.
Make decisions
If you lack confidence in your decision-making ability, you’re unlikely to improve without stretching your capacities. Train your decision-making brain and learn from others by working with them.
Using decision trees
A decision tree is useful for plotting decisions on a flow chart and calculating the costs, benefits, and probable outcomes for each.
Leveraging SWOT analysis
Using a SWOT analysis to assess your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats makes you less likely to forget your advantages or overlook vulnerabilities.
Using cost-benefit analysis
Weighing the pros and cons of a decision helps you remember your priorities. It may also reveal biases and limitations by challenging your motives.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 8 April 2024
Last updated: 17 April 2024
Last updated: 12 April 2024
Last updated: 18 April 2024
Last updated: 27 March 2023
Last updated: 26 May 2023
Last updated: 12 April 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Free ready-to-use math resources
Hundreds of free math resources created by experienced math teachers to save time, build engagement and accelerate growth
20 Effective Math Strategies To Approach Problem-Solving
Katie Keeton
Math strategies for problem-solving help students use a range of approaches to solve many different types of problems. It involves identifying the problem and carrying out a plan of action to find the answer to mathematical problems.
Problem-solving skills are essential to math in the general classroom and real-life. They require logical reasoning and critical thinking skills. Students must be equipped with strategies to help them find solutions to problems.
This article explores mathematical problem solving strategies, logical reasoning and critical thinking skills to help learners with solving math word problems independently in real-life situations.
What are problem-solving strategies?
Problem-solving strategies in math are methods students can use to figure out solutions to math problems. Some problem-solving strategies:
- Draw a model
- Use different approaches
- Check the inverse to make sure the answer is correct
Students need to have a toolkit of math problem-solving strategies at their disposal to provide different ways to approach math problems. This makes it easier to find solutions and understand math better.
Strategies can help guide students to the solution when it is difficult ot know when to start.

The ultimate guide to problem solving techniques
Download these ready-to-go problem solving techniques that every student should know. Includes printable tasks for students including challenges, short explanations for teachers with questioning prompts.
20 Math Strategies For Problem-Solving
Different problem-solving math strategies are required for different parts of the problem. It is unlikely that students will use the same strategy to understand and solve the problem.
Here are 20 strategies to help students develop their problem-solving skills.
Strategies to understand the problem
Strategies that help students understand the problem before solving it helps ensure they understand:
- The context
- What the key information is
- How to form a plan to solve it
Following these steps leads students to the correct solution and makes the math word problem easier .
Here are five strategies to help students understand the content of the problem and identify key information.
1. Read the problem aloud
Read a word problem aloud to help understand it. Hearing the words engages auditory processing. This can make it easier to process and comprehend the context of the situation.
2. Highlight keywords
When keywords are highlighted in a word problem, it helps the student focus on the essential information needed to solve it. Some important keywords help determine which operation is needed. For example, if the word problem asks how many are left, the problem likely requires subtraction. Ensure students highlight the keywords carefully and do not highlight every number or keyword. There is likely irrelevant information in the word problem.
3. Summarize the information
Read the problem aloud, highlight the key information and then summarize the information. Students can do this in their heads or write down a quick summary. Summaries should include only the important information and be in simple terms that help contextualize the problem.
4. Determine the unknown
A common problem that students have when solving a word problem is misunderstanding what they are solving. Determine what the unknown information is before finding the answer. Often, a word problem contains a question where you can find the unknown information you need to solve. For example, in the question ‘How many apples are left?’ students need to find the number of apples left over.
5. Make a plan
Once students understand the context of the word problem, have dentified the important information and determined the unknown, they can make a plan to solve it. The plan will depend on the type of problem. Some problems involve more than one step to solve them as some require more than one answer. Encourage students to make a list of each step they need to take to solve the problem before getting started.
Strategies for solving the problem
1. draw a model or diagram.
Students may find it useful to draw a model, picture, diagram, or other visual aid to help with the problem solving process. It can help to visualize the problem to understand the relationships between the numbers in the problem. In turn, this helps students see the solution.
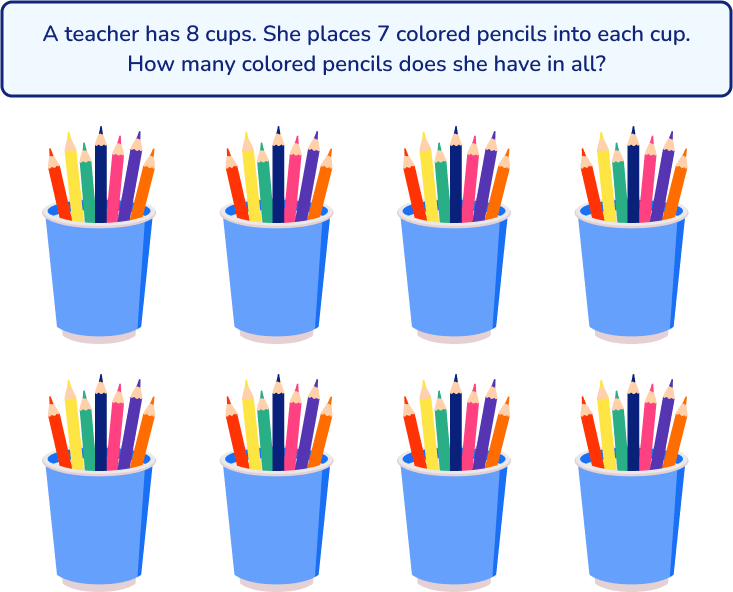
Similarly, you could draw a model to represent the objects in the problem:
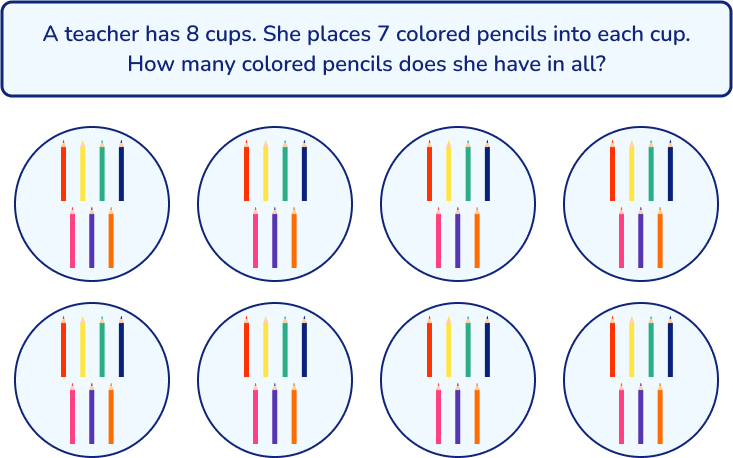
2. Act it out
This particular strategy is applicable at any grade level but is especially helpful in math investigation in elementary school . It involves a physical demonstration or students acting out the problem using movements, concrete resources and math manipulatives . When students act out a problem, they can visualize and contectualize the word problem in another way and secure an understanding of the math concepts. The examples below show how 1st-grade students could “act out” an addition and subtraction problem:
3. Work backwards
Working backwards is a popular problem-solving strategy. It involves starting with a possible solution and deciding what steps to take to arrive at that solution. This strategy can be particularly helpful when students solve math word problems involving multiple steps. They can start at the end and think carefully about each step taken as opposed to jumping to the end of the problem and missing steps in between.
For example,

To solve this problem working backwards, start with the final condition, which is Sam’s grandmother’s age (71) and work backwards to find Sam’s age. Subtract 20 from the grandmother’s age, which is 71. Then, divide the result by 3 to get Sam’s age. 71 – 20 = 51 51 ÷ 3 = 17 Sam is 17 years old.
4. Write a number sentence
When faced with a word problem, encourage students to write a number sentence based on the information. This helps translate the information in the word problem into a math equation or expression, which is more easily solved. It is important to fully understand the context of the word problem and what students need to solve before writing an equation to represent it.
5. Use a formula
Specific formulas help solve many math problems. For example, if a problem asks students to find the area of a rug, they would use the area formula (area = length × width) to solve. Make sure students know the important mathematical formulas they will need in tests and real-life. It can help to display these around the classroom or, for those who need more support, on students’ desks.
Strategies for checking the solution
Once the problem is solved using an appropriate strategy, it is equally important to check the solution to ensure it is correct and makes sense.
There are many strategies to check the solution. The strategy for a specific problem is dependent on the problem type and math content involved.
Here are five strategies to help students check their solutions.
1. Use the Inverse Operation
For simpler problems, a quick and easy problem solving strategy is to use the inverse operation. For example, if the operation to solve a word problem is 56 ÷ 8 = 7 students can check the answer is correct by multiplying 8 × 7. As good practice, encourage students to use the inverse operation routinely to check their work.
2. Estimate to check for reasonableness
Once students reach an answer, they can use estimation or rounding to see if the answer is reasonable. Round each number in the equation to a number that’s close and easy to work with, usually a multiple of ten. For example, if the question was 216 ÷ 18 and the quotient was 12, students might round 216 to 200 and round 18 to 20. Then use mental math to solve 200 ÷ 20, which is 10. When the estimate is clear the two numbers are close. This means your answer is reasonable.
3. Plug-In Method
This method is particularly useful for algebraic equations. Specifically when working with variables. To use the plug-in method, students solve the problem as asked and arrive at an answer. They can then plug the answer into the original equation to see if it works. If it does, the answer is correct.

If students use the equation 20m+80=300 to solve this problem and find that m = 11, they can plug that value back into the equation to see if it is correct. 20m + 80 = 300 20 (11) + 80 = 300 220 + 80 = 300 300 = 300 ✓
4. Peer Review
Peer review is a great tool to use at any grade level as it promotes critical thinking and collaboration between students. The reviewers can look at the problem from a different view as they check to see if the problem was solved correctly. Problem solvers receive immediate feedback and the opportunity to discuss their thinking with their peers. This strategy is effective with mixed-ability partners or similar-ability partners. In mixed-ability groups, the partner with stronger skills provides guidance and support to the partner with weaker skills, while reinforcing their own understanding of the content and communication skills. If partners have comparable ability levels and problem-solving skills, they may find that they approach problems differently or have unique insights to offer each other about the problem-solving process.
5. Use a Calculator
A calculator can be introduced at any grade level but may be best for older students who already have a foundational understanding of basic math operations. Provide students with a calculator to allow them to check their solutions independently, accurately, and quickly. Since calculators are so readily available on smartphones and tablets, they allow students to develop practical skills that apply to real-world situations.
Step-by-step problem-solving processes for your classroom
In his book, How to Solve It , published in 1945, mathematician George Polya introduced a 4-step process to solve problems.
Polya’s 4 steps include:
- Understand the problem
- Devise a plan
- Carry out the plan
Today, in the style of George Polya, many problem-solving strategies use various acronyms and steps to help students recall.
Many teachers create posters and anchor charts of their chosen process to display in their classrooms. They can be implemented in any elementary, middle school or high school classroom.
Here are 5 problem-solving strategies to introduce to students and use in the classroom.
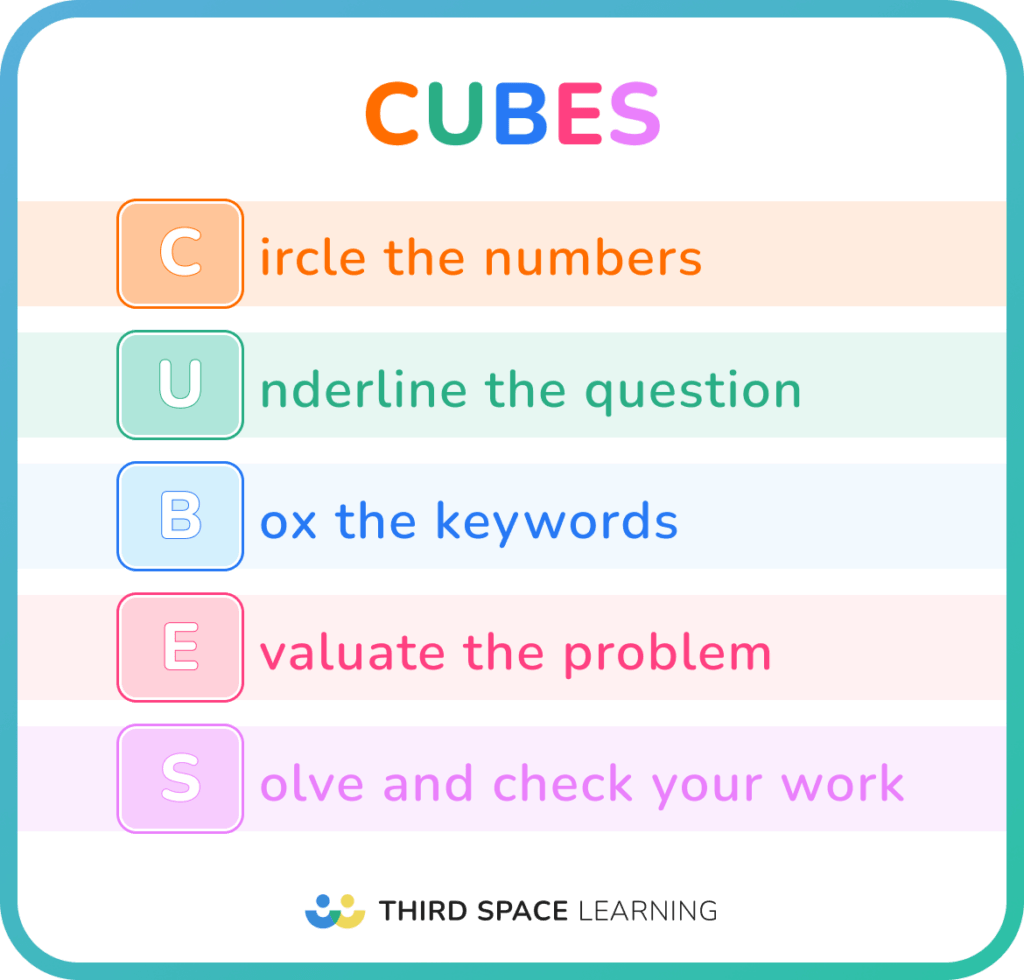
How Third Space Learning improves problem-solving
Resources .
Third Space Learning offers a free resource library is filled with hundreds of high-quality resources. A team of experienced math experts carefully created each resource to develop students mental arithmetic, problem solving and critical thinking.
Explore the range of problem solving resources for 2nd to 8th grade students.
One-on-one tutoring
Third Space Learning offers one-on-one math tutoring to help students improve their math skills. Highly qualified tutors deliver high-quality lessons aligned to state standards.
Former teachers and math experts write all of Third Space Learning’s tutoring lessons. Expertly designed lessons follow a “my turn, follow me, your turn” pedagogy to help students move from guided instruction and problem-solving to independent practice.
Throughout each lesson, tutors ask higher-level thinking questions to promote critical thinking and ensure students are developing a deep understanding of the content and problem-solving skills.
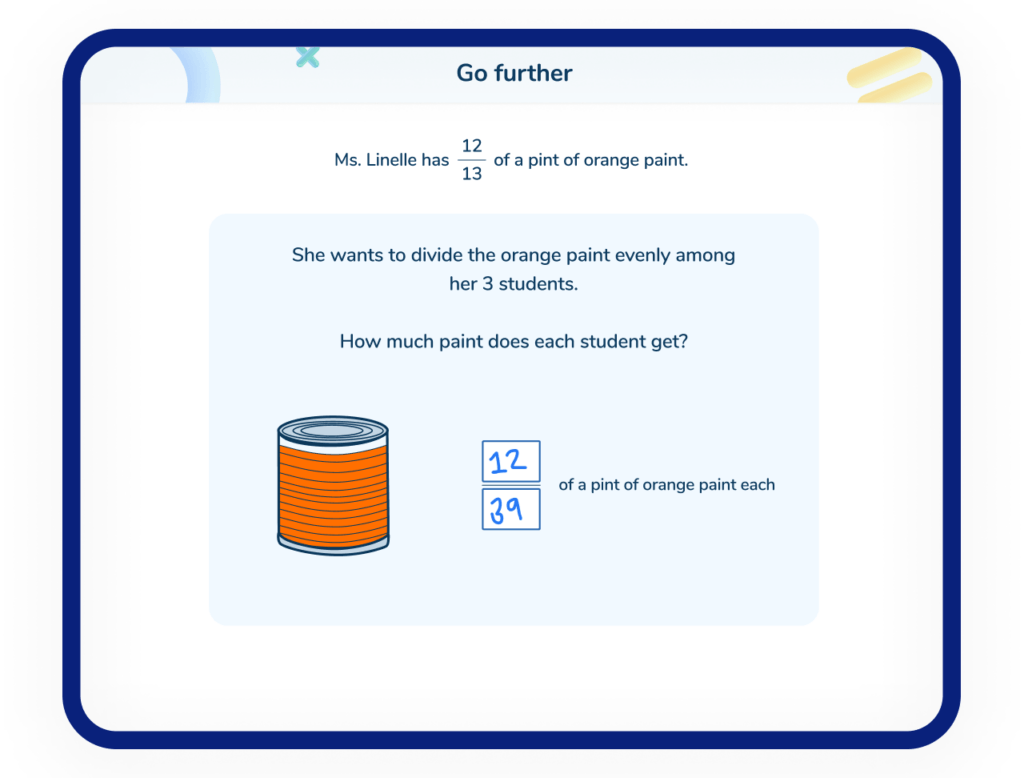
Problem-solving
Educators can use many different strategies to teach problem-solving and help students develop and carry out a plan when solving math problems. Incorporate these math strategies into any math program and use them with a variety of math concepts, from whole numbers and fractions to algebra.
Teaching students how to choose and implement problem-solving strategies helps them develop mathematical reasoning skills and critical thinking they can apply to real-life problem-solving.
READ MORE : 8 Common Core math examples
There are many different strategies for problem-solving; Here are 5 problem-solving strategies: • draw a model • act it out • work backwards • write a number sentence • use a formula
Here are 10 strategies of problem-solving: • Read the problem aloud • Highlight keywords • Summarize the information • Determine the unknown • Make a plan • Draw a model • Act it out • Work backwards • Write a number sentence • Use a formula
1. Understand the problem 2. Devise a plan 3. Carry out the plan 4. Look back
Some strategies you can use to solve challenging math problems are: breaking the problem into smaller parts, using diagrams or models, applying logical reasoning, and trying different approaches.
Related articles

Why Student Centered Learning Is Important: A Guide For Educators

13 Effective Learning Strategies: A Guide to Using them in your Math Classroom

Differentiated Instruction: 9 Differentiated Curriculum And Instruction Strategies For Teachers

5 Math Mastery Strategies To Incorporate Into Your 4th and 5th Grade Classrooms
Ultimate Guide to Metacognition [FREE]
Looking for a summary on metacognition in relation to math teaching and learning?
Check out this guide featuring practical examples, tips and strategies to successfully embed metacognition across your school to accelerate math growth.
Privacy Overview
- Leadership Development
- Operational Excellence
- Industry 4.0 – Management Digitalization
- Food & Bev
- Construction
- Manufacturing
- Heavy Industry
- The Manager's Journey
- Cross-platform tool
- Digital Gemba Walk
- Collaboration and Rituals
- Coaching and Improvement
- Knowledge Center - New
- All Features
- Industry 4.0 and 5.0
Case Studies
- Continuous Improvement
- Frontline Managers
- Key Behaviroral Indicators
- Management Skills
- Productivity
- Free Resources
TABLE OF CONTENT
Share this article, download a pdf version., subscribe to our newsletter, 10 effective tools and problem-solving methods for manufacturers.

Downloaded on: May 2, 2024

• April 30, 2024

Variability of demand, quality management, equipment maintenance, and integration of new technologies : problems are frequent and inevitable, and manufacturers face challenges very often. Acknowledging this reality enables teams to remain vigilant, quickly identify and resolve these difficulties, and constantly improve processes and products alike.
Why focus on problem-solving? In the Lean philosophy , a problem isn't just a problem; it's also, and above all, an opportunity to do better. Rather than hiding or ignoring what's not working, the idea is to face up to it, to find structured methods for optimizing efficiency and quality. For this, there are a number of possible solutions and tools available.
What are the different stages of problem-solving? Which methods and tools are most effective in production environments? And how do you use them?
This article provides all the answers and problem-solving tips.
Key takeways:
- By scrutinizing every action and aspect of processes, it is crucial to distinguish between activities that bring value and those that don't , in order to reduce or eliminate waste.
- Involving employees in identifying problems and suggesting solutions strengthens their sense of ownership, and improves team cohesion and efficiency.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA) helps to identify the underlying causes of problems to find more sustainable solutions and prevent problems from recurring.
- The use of tools such as the PDCA cycle and the 5S method, as well as techniques such as Six Sigma , is essential for optimizing processes and improving quality and efficiency.
- It is essential to monitor implemented changes and continuously improve them to maintain and increase Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
In a hurry? Save this article as a PDF.
Tired of scrolling? Download a PDF version for easier offline reading and sharing with coworkers.
Key steps of a problem-solving process in a factory
To better understand each of these steps, let's take the example of a factory manufacturing automotive components, faced with a sudden rise in the number of defective parts.

1. Identify the problem
The first step is to recognize that a problem exists. This involves observing the symptoms and identifying the gaps between the current state and the desired goal.
The QQOQCCP tool enables you to identify the problem by collecting factual information on incidents.
- Observation: Abnormal increase in the number of defective parts at the quality inspection station.
- Action: Collect data on the number of defective parts, the types of defects, and the times when they occur.
2. Define the problem
After identification, you need to precisely define the problem. This involves determining its scope (using the Four A’s method, for example), representing it clearly, and understanding its impact on operations.
- Analysis: 10% of parts produced have surface defects (higher than the acceptable standard of 2%).
- Action: Clearly define the problem as a significant increase in surface defects on automotive parts.
3. Find the root cause of the problem
This step aims to analyze the factors contributing to the problem in order to identify its root cause. This is a critical process requiring in-depth examination to avoid treating symptoms alone.
- Investigation: After using the 5 Whys method, the root cause turns out to be premature machine wear.
- Action: Examine maintenance records and machine operating parameters to confirm this cause.
4. Brainstorm solutions
Once the root cause has been identified, it's time to focus on finding solutions. This phase encourages creative problem-solving and innovation from the whole team. They have to explore existing ideas and generate new ones.
- Brainstorming: Several potential solutions are considered, such as replacing tools more frequently or modifying machine parameters.
- Action: Evaluate the advantages, disadvantages, and feasibility of each solution using the PDCA method.
5. Test your solutions
Before implementing a solution on a large scale, it is essential to test it in a controlled environment. This enables you to assess its effectiveness in real-life situations and adjust the action plan.
- Experimentation: Replace tools more frequently to see if this reduces the defect rate.
- Action: Implement the test plan over a set period using the "Do" phase of PDCA, then collect data on the impact of this change.
6. Standardize and document the chosen solution
Once you’ve found the best solution, it must be standardized and integrated into the organization's procedures. Documenting the process helps prevent the problem from recurring and facilitates employee training .
- Implementation: After confirmation that more frequent tool replacement reduces defects, this practice is standardized across the entire production line using the DMAIC method.
- Action: Document the new process using the 8Ds, train operators in the new practice, and integrate the change into standard operating procedures.

5 Useful problem-solving strategies for manufacturing
1. 8d (eight disciplines problem solving).
8D is a quality approach to solving complex problems requiring in-depth analysis and lasting corrective action.
The method comprises eight steps:
- Prepare the 8D process
- Describe the problem
- Identify and implement immediate actions
- Identify the real causes
- Identify and implement permanent corrective actions
- Validate permanent corrective actions
- Prevent recurrence
- Congratulate the team
Use case in the manufacturing industry
Problem: Recurrent failure of a major piece of equipment, leading to costly production stoppages.
8D would enable a multi-disciplinary team to systematically identify, analyze, and eliminate the root cause of the failure while implementing sustainable corrective actions.
2. PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act)
Also known as the Deming wheel, this systematic, iterative model comprises four stages or cycles: Plan, Do, Check, Act.
The PDCA method helps companies test changes under controlled conditions, evaluate the results, and then implement improvements progressively to optimize production and ensure consistent product quality.
Problem: Variation in the quality of the finished product, which does not always meet standards.
PDCA would address this problem by planning improvements, testing them, evaluating their effectiveness, and adjusting the production process to stabilize product quality.

3. DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control)
This Six Sigma method is highly effective in optimizing production processes, reducing variation, and eliminating defects by focusing on data and statistical analysis.
It involves clearly defining the problem (Define), measuring (Measure), and analyzing process data to identify root causes (Analyze), then implementing improvements (Improve) and controlling processes to ensure sustainable quality gains (Control).
Problem: High scrap and rework rates on an assembly line.
DMAIC would be used to specify the problem, measure performance, analyze data to find the cause, implement improvements, and control the process to reduce defects.
4. QRQC (Quick Response Quality Control)
This fast, effective method inspired by Lean Management, consists in identifying, analyzing and solving problems directly on the shop floor. It is particularly well suited to fast-paced production environments where immediate detection and resolution are necessary to maintain production continuity and efficiency.
Problem: Frequent safety incidents in the workplace.
QRQC would enable rapid reaction to identify and resolve the causes of such incidents immediately, thereby reducing their frequency and improving overall safety.
5. Four A’s
The Four A’s method is a structured approach that is designed to systematically address and solve problems within an organization.
- Assess: This step involves identifying and understanding the problem.
- Analyze: Once the problem is assessed, the next step is to analyze it to find the root causes.
- Address: With a clear understanding of the root causes, the third “A” involves developing and implementing solutions to address these causes.
- Act: The final “A” focuses on standardizing the correct solution and integrating it into the organization’s processes.
It is used where problems need to be solved quickly and efficiently while ensuring that lessons learned are integrated into standard practices.
Problem: Missed delivery deadlines due to production bottlenecks.
The Four A’s method would help to quickly detect bottlenecks, analyze their causes, find and implement effective solutions, and then integrate these changes into regular operations to improve on-time delivery.
How to choose the right problem-solving method
The choice of problem-solving method depends on several factors:
- The nature and complexity of the problem: Before choosing a problem-solving approach, you need to understand exactly what is wrong. If it's a complex and multifactorial problem, structured, in-depth methods such as 8D or DMAIC may be appropriate. For more immediate or quality-related problems, QRQC or Four A’s may be more appropriate.
- Company objectives: Look at the big picture; align the method with your strategic objectives, such as improving quality, reducing costs, or increasing customer satisfaction. For example, DMAIC is often chosen for defect reduction and process optimization objectives.
- Available resources: Think about the resources you can allocate to problem-solving processes (time, skills, budget). For example, PDCA can be implemented more quickly when resources are limited.
- Team expertise and problem-solving skills: Use a method that matches your team's qualifications. Training may be required for more complex approaches such as DMAIC or 8D.
- The need for standardization and documentation: If documentation and standardization of processes are essential, opt for methods that integrate these aspects, such as 8D or DMAIC.

5 Tools for structuring your problem-solving methods
Now it's time for the problem-solving tools! These will help structure the process and keep it moving in the right direction.
1. The 5 Whys
This problem-solving technique, created by Toyota founder Sakichi Toyoda, involves repeatedly asking the question "Why?" until the root cause of a given problem is revealed. It's a simple but powerful tool for finding root causes.
A factory has a problem with late delivery of finished products:
- Why is the plant experiencing delays in the delivery of finished products? Because the production of final units is often late.
- Why is the production of final units behind schedule? Because assembly takes longer than expected.
- Why does assembly take longer than expected? Because parts needed to complete assembly are often missing.
- Why are parts often missing? Because supplies regularly arrive late from the supplier.
- Why do supplies arrive late from the supplier? Because orders are placed too late, due to an inefficient procurement process.
2. The Ishikawa diagram (5M)
Also known as the "fishbone diagram" or "5M", this tool developed by Kaoru Ishikawa helps to systematically visualize all the potential causes of a specific problem, as well as the contributing factors.
Causes are divided into 5 main categories.
A factory encounters a problem with a drop in product quality:
- Problem or "Effect" (fish head): Decline in product quality
- Categories of causes (main branches):
- Manpower: Operator skills , training, motivation.
- Methods: Work procedures, quality standards, operating instructions.
- Materials: Raw material quality, batch variability, supplier specifications.
- Environment: Working conditions, temperature, humidity, dust.
- Equipment: Equipment wear, machine calibration, maintenance.
This evolution of the Ishikawa diagram focuses on not five, but seven major problem areas: Manpower, Method, Materials, Environment, Equipment, Management, Measurement.
A factory is experiencing machine failure problems:
- Manpower: Inadequate operator training, human error due to fatigue, or lack of experience.
- Methods: Obsolete production processes, and lack of standardized operating and maintenance procedures.
- Materials: Inconsistent quality of raw materials, premature wear of spare parts.
- Environment: Unsuitable working conditions, disturbances due to excessive noise or vibration.
- Equipment: Outdated equipment, neglected or inadequate preventive maintenance.
- Management: Inadequate decision-making, and insufficient communication between departments.
- Measurement: Uncalibrated or faulty measuring instruments, lack of regular quality controls.
4. The Pareto principe
The Pareto or 80/20 principle is very useful for focusing on the problems that will have the greatest impact once solved, and for making informed decisions.
In a factory producing electronic components, 80% of production defects stem from just 20% of the manufacturing processes.
By analyzing production data, the company could discover that the majority of defects are linked to errors in the soldering and PCB inspection stages. These two stages, although representing a small part of the total manufacturing process, are crucial and require special attention to reduce the overall number of defects.

5. The QQOQCCP
This tool helps gather comprehensive information on a problem by answering these key questions: Who, What, Where, When, How, How much, Why. Thus, it provides an in-depth understanding of the situation.
There is a delay in production at a furniture manufacturing plant:
- Who is affected by the problem? Assembly line operators and production managers are directly affected by the delay.
- What exactly is the problem? Deliveries of finished furniture to customers are several days behind schedule.
- Where exactly is the problem occurring? The problem occurs in the final assembly shop, where the furniture is prepared for shipment.
- When was the problem detected or when does it occur? The delay has been observed over the past two weeks, mainly during the third shift.
- How does the problem occur? The delay is due to a bottleneck in the finishing and packing stage, where there is a lack of personnel and problems with the packing equipment.
- How often has the problem occurred, or what is the scale of the problem? The problem caused a 30% delay in orders during this period.
- Why does the problem occur? The problem could be due to inadequate staff planning and recurring packaging equipment failures.
Other tools can also be useful for structuring problem-solving methods:
- Brainstorming
- Gemba Walks
- SWOT analysis
- Control charts
- Prioritization matrices
Tips for effective implementation of problem-solving techniques
Integrate problem-solving into daily routines.
Instead of seeing problem-solving as a separate activity, integrate it into daily routines. For example, set up SIM meetings to discuss ongoing problems as a group and monitor progress on solutions.
Use technology for your benefit
Adopt a Daily Management System (DMS) like UTrakk to quickly identify problems, track corrective actions, facilitate collaboration between teams, and document solutions in a centralized repository.
Develop specific key performance indicators for problem resolution
Define Lean KPIs that measure the effectiveness of the problem-solving process (average time to solve the problem, problem recurrence rate, and impact of solutions on business performance).
Practice problem-solving on the shop floor
To understand problems, you need to go where value is created. Encourage managers to go on the shop floor to directly observe processes, interact with operators, and identify possible improvements.
Create cross-functional problem-solving groups
Form teams with members from different departments to tackle complex problem-solving. Integrating different angles, perspectives, and expertise broadens the point of view on the subject, enriches the analysis, and generates more creative ideas.
Adopt a coaching approach to skills development
In addition to basic training, use mentoring and coaching to develop problem-solving skills . Experienced employees can guide less experienced ones, sharing their know-how.
Conduct post-mortem reviews
When a problem is solved, conduct a post-mortem to discuss what went well, what didn't, and how processes can be improved.
Tracking and evaluating each solution implemented allows you to adjust strategies as needed, learn from past experiences, and foster continuous improvement .

UTrakk: Your ally in structuring and optimizing problem-solving
Using organized methods and analytical tools to tackle challenges is essential for manufacturers seeking to improve operational efficiency and product quality. UTrakk DMS is the perfect solution for this structured approach to daily problem-solving. With its multiple functionalities – rituals, actions, dashboards, and more – this Daily Management System can adapt to any problem-solving method to optimize every step of the process. Once a solution is standardized, it can be documented in UTrakk’s Knowledge Center to ensure compliance and prevent recurrence.
Adopting these problem-solving techniques not only enables manufacturers to respond effectively to today's challenges, but it also lays the foundations for continuous improvement, ensuring their competitiveness in an ever-changing industrial environment .
FAQ on problem-solving methods
What are the key problem-solving methods for manufacturers.
The key problem-solving methods for manufacturers include Lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, and the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle. These methodologies focus on eliminating waste, optimizing processes, and implementing continuous improvement to enhance operational efficiency.
How can manufacturers effectively implement Lean principles?
Manufacturers can effectively implement Lean principles by identifying and eliminating waste, optimizing workflows, and improving overall efficiency through techniques like Kanban and 5S. Training employees and involving them in the continuous improvement process are also critical steps.
What is the importance of Six Sigma in manufacturing?
Six Sigma is important in manufacturing because it provides a data-driven approach for reducing defects and variability in processes. This methodology helps in improving product quality and operational efficiency by following the DMAIC (Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control) framework.
Can technology enhance problem-solving in manufacturing?
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing problem-solving in manufacturing. Digital twins, augmented reality, and collaborative robotics are technologies that help improve precision, efficiency, and safety, facilitating better decision-making and process optimization.
What benefits do continuous improvement practices offer to manufacturers?
Continuous improvement practices offer several benefits, including increased operational efficiency, reduced waste and costs, and improved employee engagement and customer satisfaction. These practices encourage a proactive approach to addressing inefficiencies and fostering innovation.
Turn your production challenges into opportunities for improvement!
In addition to providing the UTrakk solution, Proaction International supports you in implementing the best problem-solving methods and helps you achieve operational excellence.
Adeline de Oliveira
Writer and editorial manager for about 15 years, Adeline de Oliveira is passionate about human behavior and communication dynamics. At Proaction International, she covers topics ranging from Industry 5.0 to operational excellence, with a focus on leadership development. This expertise enables her to offer insights and advice on employee engagement and continuous improvement of managerial skills.

Déli-Porc Develops an Agile, Digitalized Culture Focused on Optimization
Kefor maximizes its performance by optimizing manager skills, le goupe maurice: motivate and retain talents by focusing on the leadership development of managers.
© 2023 Proaction International Inc. All rights reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Notice | Cookie Notice
May 1, 2024
How College Sets You Up With Entrepreneurial Skills for Career Success

As you’re gearing up to toss your caps in the air and say farewell to your college days, it’s the perfect time to reflect on the incredible journey you’ve invested in and the skills you’ve acquired along the way. Among them, entrepreneurship stands out as a beacon of opportunity, shaping not just your college experience, but also priming you for a remarkable career ahead. Let’s take a look at the entrepreneurial skills you’ve gained during your journey through college and how you can utilize them for career success.
1. Adaptability and Problem-Solving
As soon as you set foot on campus, you were challenged to adapt and navigate uncharted waters. Throughout your college journey, you were faced with challenges and forced to find solutions. Whether it’s securing your first job, launching a passion project, or charting a new career path, your ability to adapt and solve problems creatively will set you apart in the competitive post-graduation landscape.
Improve your problem-solving skills with design thinking
2. Creativity and Innovation
The ability to think outside the box will be your greatest asset and college has given you many opportunities to explore your ideas and interests. You’ve studied big ideas and been encouraged to look at them from new angles. Now is the time to unleash your creativity and innovation skills upon the world.
3. Risk-taking and Resilience
Whether it’s relocating to a new city, beginning your first job, or starting your own venture, don’t be afraid to take chances and pursue your passions. And when inevitable setbacks occur, as they often do, draw upon the resilience you’ve cultivated throughout college to bounce back stronger and more determined than ever before.
4. Networking and Collaboration
Graduation isn’t just about saying goodbye. It’s also about forging new connections and building bridges to your future. Your college community is a valuable resource that can support and guide you as you navigate the early stages of your career. So don’t be shy – reach out, collaborate, and build relationships that will propel you towards success in the years to come.

5. Entrepreneurial Mindset
Most importantly, in my opinion, carry with you the entrepreneurial mindset that has been instilled in you throughout your college journey. It’s a mindset that will help you embrace the ups and downs and always find ways to move forward and grow.
Explore more ways to cultivate your entrepreneurial mindset
Now that we’ve reflected on the entrepreneurial skills you’ve learned along the way and how they can propel you into your future career, I encourage you to think about how they can set you apart. A great first step is highlighting these skills on your resume. Here are a few tips to showcase these skills to potential employers.
- Adaptability and Problem-Solving: Highlight specific instances where you effectively navigated challenges or implemented innovative solutions, such as through projects, internships, or extracurricular activities.
- Creativity and Innovation: Showcase your creativity by mentioning projects, initiatives, or ideas you’ve developed that demonstrate your ability to think outside the box and bring fresh perspectives to the table.
- Risk-taking and Resilience: Describe situations where you took calculated risks or bounced back from setbacks, emphasizing your ability to embrace challenges and persevere in the face of adversity.
- Networking and Collaboration: Include experiences where you collaborated with others, built professional relationships, or contributed to team successes, showcasing your ability to work effectively in a team-oriented environment.
- Entrepreneurial Mindset: Express your entrepreneurial mindset through your resume’s overall tone and language, emphasizing traits such as ambition, initiative and a proactive approach to problem-solving and innovation.
As you set out on this exciting new chapter of your life, hold on to the entrepreneurial spirit within you and take that with you in everything you do. The journey ahead may be unpredictable, but with the skills, mindset and connections you’ve acquired along the way, you’re more than ready to conquer whatever challenges come your way.
If you feel like reconnecting with a diverse community of entrepreneurs, be sure to check our events from time to time for ongoing inspiration. Congratulations, graduates – the world is yours for the taking!
Bailey Johnson
Recent updates.

How These Student Creative Entrepreneurs Turned an Idea into a Business
April 11, 2024
How many of you have a passion or hobby that you truly can’t live without? And how many of you secretly daydream about turning your passion into an income-producing business?

How to Sell Value, Not Product, as a B2B Entrepreneur
March 14, 2024
B2B (Business-to-Business) entrepreneurs are always excited about their product. You can see it in their actions and hear it in their voices. And well they should be – after all

Making an Impact: A Community Leader's Journey on Campus and Beyond Graduation
February 05, 2024
Black History Month is not just a time to reflect on the lives and collective histories of the African diaspora. It is also a time to celebrate the diversity in
Check for Recalls Search vehicles, car seats, tires and other equipment for safety recalls, investigations, complaints and manufacturer communication.
Where’s my vin.
Every vehicle has a unique vehicle identification number , often referred to as a VIN. Look on the lower left of your car’s windshield for your 17-character VIN. Your VIN is also located on your car’s registration card, and it may be shown on your insurance card.
What information will display in the search results?
- When searching by license plate or VIN, you’ll learn if a specific vehicle needs to be repaired as part of a recall.
- When searching by a vehicle’s year, make and model, or for car seats, tires or equipment, you'll get general results for recalls, investigations, complaints and manufacturer communications.
What will the license plate and VIN search show?
- An unrepaired recall for a vehicle from certain manufacturers .
- If the vehicle has no unrepaired recalls, you will see the message: "0 unrepaired recalls associated with this VIN."
What won’t the license plate and VIN search show?
- A safety recall that has already been repaired.
- Some recently announced safety recalls for which not all VINs have been identified. VINs are added continuously so please check regularly.
- Safety recalls that are more than 15 years old (except where a manufacturer offers more coverage).
- Safety recalls conducted by small vehicle manufacturers, including some ultra-luxury brands and specialty applications.
- Manufacturer customer service or other non-safety recall campaigns.
- A recall involving an international vehicle.
Other search options, including by NHTSA ID
You can also search for recalls and safety issues information by NHTSA ID and complaints by keyword .
Get Recall Alerts
Download NHTSA's free SaferCar app. When SaferCar discovers a safety recall for the vehicle or equipment you entered, it will send you an alert on your phone.
You can also sign up for general recall alerts via email.
Report a Safety Problem by filing a complaint with NHTSA
Have you experienced a vehicle, tire, car seat, or equipment safety problem that could be a safety defect.
If so, you can file a complaint that we will carefully review — like we do with every safety problem submitted to NHTSA. Complaints like yours help us investigate possible defects, which could lead to a safety recall.
From complaints to recall
NHTSA issues vehicle safety standards and requires manufacturers to recall vehicles and equipment that have safety-related defects. Learn about NHTSA's recall process.
Reporting your problem is the important first step.
Your complaint will be added to a public NHTSA database after personally identifying information is removed.
If the agency receives similar reports from a number of people about the same product, this could indicate that a safety-related defect may exist that would warrant the opening of an investigation.
Investigations
Nhtsa conducts an investigation from reported complaints..
A. SCREENING
NHTSA reviews filed complaints from vehicle owners and other information related to alleged defects to decide whether to open an investigation.
B. ANALYSIS
NHTSA conducts an analysis of any petitions calling for defect investigations. If the petition is denied, the reasons for the denial are published in the Federal Register.
C. INVESTIGATION
NHTSA opens an investigation of alleged safety defects. It is closed when they notify the manufacturer of recall recommendations or they don’t identify a safety-related defect.
D. RECALL MANAGEMENT
NHTSA monitors the effectiveness and management of recalls, including the filing of recall notices with NHTSA, communicating with owners regarding the recalls and tracking the completion rate of each recall.
Initiated safety recalls require a manufacturer's action to announce and remedy the defects.
A recall is issued when a manufacturer or NHTSA determines that a vehicle, equipment, car seat, or tire creates an unreasonable safety risk or fails to meet minimum safety standards. Most decisions to conduct a recall and remedy a safety defect are made voluntarily by manufacturers prior to any involvement by NHTSA.
Manufacturers are required to fix the problem by repairing it, replacing it, offering a refund, or in rare cases repurchasing the vehicle.
Using our VIN lookup tool, you can access recall information provided by the manufacturer conducting the recall which may be not posted yet on NHTSA’s site.
Recall Spotlight
Recalls Spotlight monitors high-profile recalls and offers consumers resources to find and address vehicle recalls.
Defects Investigation and Recalls Resources
Quick links to databases, resources and reports related to defects investigations and recalls.
Roles in the Recall Process
Manufacturer
Manufacturers will notify registered owners by first class mail within 60 days of notifying NHTSA of a recall decision. Manufacturers should offer a proper remedy to the owner.
NHTSA will monitor each safety recall to make sure owners receive safe, free, and effective remedies from manufacturers according to the Safety Act and Federal regulations.
You (owner)
You’ll be notified via mail from the manufacturer. When you receive a notification, follow any interim safety guidance provided by the manufacturer and contact your local dealership to fix the recalled part for free.
Register your vehicle, tires, car seats & equipment and check recalls twice a year.
Motor Vehicle Safety Defects And Recalls - What Every Vehicle Owner Should Know
Download this brochure to get more information about how and why recall campaigns are initiated, and to know your rights and responsibilities when a vehicle or item of motor vehicle equipment is recalled.
Vehicle Comparison
Available manufacturers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Problem-Solving Process. In order to effectively manage and run a successful organization, leadership must guide their employees and develop problem-solving techniques. Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
The Problem-Solving Process. Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself. We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity.
This step of the problem-solving process is all about thinking outside of the box, challenging old assumptions, and thinking laterally. This stage is the one that tends to cause the most overwhelm in teams because it requires just the right balance of creativity and critical thinking, which tends to cause a lot of friction.
The Problem-Solving Process. The process of problem-solving is a methodical approach that involves several distinct stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in navigating from the initial recognition of a problem to its final resolution. Let's explore each of these stages in detail. Step 1: Identifying the Problem. This is the foundational ...
When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that's very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use ...
Step 1 - Define the Problem. The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause.
These steps build upon the basic, four-step process described above, and they create a cycle of problem finding and solving that will continually improve your organization. Appreciative Inquiry , which is a uniquely positive way of solving problems by examining what's working well in the areas surrounding them.
Defining and analyzing the problem - This is the core of the problem solving process. Sometimes, the real problem isn't originally apparent. Generating and choosing solutions; Putting your solution into practice - If you have followed the process carefully, you'll be surprised at how easy implementing it actually is! In Summary:
Problem-solving helps you figure out how to achieve these desires. The problem-solving process involves: Discovery of the problem. Deciding to tackle the issue. Seeking to understand the problem more fully. Researching available options or solutions. Taking action to resolve the issue.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to ...
The Problem-Definition Process encourages you to define and understand the problem that you're trying to solve, in detail. It also helps you confirm that solving the problem contributes towards your organization's objectives. This stops you spending time, energy, and resources on unimportant problems, or on initiatives that don't align with ...
It starts with an "affirmative topic," followed by the "positive core (strengths).". Then this method delves into the following stages: Discovery (fact-finding) Dream (visioning the future) Design (strategic purpose) Destiny (continuous improvement) 3. "FIVE WHYS" METHOD. The 5 Whys of Problem-Solving Method.
How to Solve Problems: 5 Steps. 1. Precisely Identify Problems. As obvious as it seems, identifying the problem is the first step in the problem-solving process. Pinpointing a problem at the beginning of the process will guide your research, collaboration, and solutions in the right direction. At this stage, your task is to identify the scope ...
In insight problem-solving, the cognitive processes that help you solve a problem happen outside your conscious awareness. 4. Working backward. Working backward is a problem-solving approach often ...
Making a decision to alter the way your team works may also be a problem. Launching new products, technological upgrades, customer feedback collection exercises—all of these are also "problems" that need to be "solved". Here are the steps of a problem-solving process: 1. Defining the Problem. The first step in the process is often ...
Understand the problem. The next problem solving method is to define the problem you are facing. The issue could be more profound than you think, and that is why you need to be intentional about diagnosing the root cause of the problem. This is the only way to solve the issue, because you can't solve what you cannot diagnose.
Here are six steps to an effective problem-solving process: Identify the issues. The first phase of problem-solving requires thought and analysis. Problem identification may sound clear, but it actually can be a difficult task. So you should spend some time to define the problem and know people's different views on the issue.
Related: 10 Ideation Techniques for Problem-Solving. 4. Ask for support and feedback. Another way to build your problem-solving strategy is by asking your team for feedback. You can get ideas from mentors or colleagues on how they solve problems, or you can ask for feedback on a draft of your problem-solving process.
Problem management is an 8 step framework most commonly used by IT teams. You can use problem management to solve for repeating major incidents. By organizing and structuring your problem solving, you can more effectively get to the root cause of high-impact problems—and devise a solution. Solving the root cause prevents recurrence and ...
The 8-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for tackling complex problems and driving organizational success. By following each step in a systematic and structured manner, you can define ...
Problem solving, and the techniques used to gain clarity, are most effective if the solution remains in place and is updated to respond to future changes. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Problem solving, The problem solving process, Step 1: Define the Problem and more.
Insight problem-solving. Insight-based problem-solving occurs spontaneously, even arising in defiance of a step-by-step process. Reflecting on a problem in a new way leads to outside-the-box thinking that can lead to novel solutions. Still, any concerted attempt at decision-making requires structured effort.
Students may find it useful to draw a model, picture, diagram, or other visual aid to help with the problem solving process. It can help to visualize the problem to understand the relationships between the numbers in the problem. ... published in 1945, mathematician George Polya introduced a 4-step process to solve problems. Polya's 4 steps ...
Key steps of a problem-solving process in a factory. To better understand each of these steps, let's take the example of a factory manufacturing automotive components, faced with a sudden rise in the number of defective parts. 1. Identify the problem. The first step is to recognize that a problem exists. This involves observing the symptoms and ...
A great first step is highlighting these skills on your resume. Here are a few tips to showcase these skills to potential employers. Adaptability and Problem-Solving: Highlight specific instances where you effectively navigated challenges or implemented innovative solutions, such as through projects, internships, or extracurricular activities.
Learn about NHTSA's recall process. 01 Complaints. Reporting your problem is the important first step. Your complaint will be added to a public NHTSA database after personally identifying information is removed. If the agency receives similar reports from a number of people about the same product, this could indicate that a safety-related ...