
26 Expert-Backed Problem Solving Examples – Interview Answers
Published: February 13, 2023
Interview Questions and Answers
Actionable advice from real experts:

Biron Clark
Former Recruiter

Contributor
Dr. Kyle Elliott
Career Coach

Hayley Jukes
Editor-in-Chief

Biron Clark , Former Recruiter
Kyle Elliott , Career Coach

Hayley Jukes , Editor
As a recruiter , I know employers like to hire people who can solve problems and work well under pressure.
A job rarely goes 100% according to plan, so hiring managers are more likely to hire you if you seem like you can handle unexpected challenges while staying calm and logical.
But how do they measure this?
Hiring managers will ask you interview questions about your problem-solving skills, and they might also look for examples of problem-solving on your resume and cover letter.
In this article, I’m going to share a list of problem-solving examples and sample interview answers to questions like, “Give an example of a time you used logic to solve a problem?” and “Describe a time when you had to solve a problem without managerial input. How did you handle it, and what was the result?”
- Problem-solving involves identifying, prioritizing, analyzing, and solving problems using a variety of skills like critical thinking, creativity, decision making, and communication.
- Describe the Situation, Task, Action, and Result ( STAR method ) when discussing your problem-solving experiences.
- Tailor your interview answer with the specific skills and qualifications outlined in the job description.
- Provide numerical data or metrics to demonstrate the tangible impact of your problem-solving efforts.
What are Problem Solving Skills?
Problem-solving is the ability to identify a problem, prioritize based on gravity and urgency, analyze the root cause, gather relevant information, develop and evaluate viable solutions, decide on the most effective and logical solution, and plan and execute implementation.
Problem-solving encompasses other skills that can be showcased in an interview response and your resume. Problem-solving skills examples include:
- Critical thinking
- Analytical skills
- Decision making
- Research skills
- Technical skills
- Communication skills
- Adaptability and flexibility
Why is Problem Solving Important in the Workplace?
Problem-solving is essential in the workplace because it directly impacts productivity and efficiency. Whenever you encounter a problem, tackling it head-on prevents minor issues from escalating into bigger ones that could disrupt the entire workflow.
Beyond maintaining smooth operations, your ability to solve problems fosters innovation. It encourages you to think creatively, finding better ways to achieve goals, which keeps the business competitive and pushes the boundaries of what you can achieve.
Effective problem-solving also contributes to a healthier work environment; it reduces stress by providing clear strategies for overcoming obstacles and builds confidence within teams.
Examples of Problem-Solving in the Workplace
- Correcting a mistake at work, whether it was made by you or someone else
- Overcoming a delay at work through problem solving and communication
- Resolving an issue with a difficult or upset customer
- Overcoming issues related to a limited budget, and still delivering good work through the use of creative problem solving
- Overcoming a scheduling/staffing shortage in the department to still deliver excellent work
- Troubleshooting and resolving technical issues
- Handling and resolving a conflict with a coworker
- Solving any problems related to money, customer billing, accounting and bookkeeping, etc.
- Taking initiative when another team member overlooked or missed something important
- Taking initiative to meet with your superior to discuss a problem before it became potentially worse
- Solving a safety issue at work or reporting the issue to those who could solve it
- Using problem solving abilities to reduce/eliminate a company expense
- Finding a way to make the company more profitable through new service or product offerings, new pricing ideas, promotion and sale ideas, etc.
- Changing how a process, team, or task is organized to make it more efficient
- Using creative thinking to come up with a solution that the company hasn’t used before
- Performing research to collect data and information to find a new solution to a problem
- Boosting a company or team’s performance by improving some aspect of communication among employees
- Finding a new piece of data that can guide a company’s decisions or strategy better in a certain area
Problem-Solving Examples for Recent Grads/Entry-Level Job Seekers
- Coordinating work between team members in a class project
- Reassigning a missing team member’s work to other group members in a class project
- Adjusting your workflow on a project to accommodate a tight deadline
- Speaking to your professor to get help when you were struggling or unsure about a project
- Asking classmates, peers, or professors for help in an area of struggle
- Talking to your academic advisor to brainstorm solutions to a problem you were facing
- Researching solutions to an academic problem online, via Google or other methods
- Using problem solving and creative thinking to obtain an internship or other work opportunity during school after struggling at first
How To Answer “Tell Us About a Problem You Solved”
When you answer interview questions about problem-solving scenarios, or if you decide to demonstrate your problem-solving skills in a cover letter (which is a good idea any time the job description mentions problem-solving as a necessary skill), I recommend using the STAR method.
STAR stands for:
It’s a simple way of walking the listener or reader through the story in a way that will make sense to them.
Start by briefly describing the general situation and the task at hand. After this, describe the course of action you chose and why. Ideally, show that you evaluated all the information you could given the time you had, and made a decision based on logic and fact. Finally, describe the positive result you achieved.
Note: Our sample answers below are structured following the STAR formula. Be sure to check them out!
EXPERT ADVICE

Dr. Kyle Elliott , MPA, CHES Tech & Interview Career Coach caffeinatedkyle.com
How can I communicate complex problem-solving experiences clearly and succinctly?
Before answering any interview question, it’s important to understand why the interviewer is asking the question in the first place.
When it comes to questions about your complex problem-solving experiences, for example, the interviewer likely wants to know about your leadership acumen, collaboration abilities, and communication skills, not the problem itself.
Therefore, your answer should be focused on highlighting how you excelled in each of these areas, not diving into the weeds of the problem itself, which is a common mistake less-experienced interviewees often make.
Tailoring Your Answer Based on the Skills Mentioned in the Job Description
As a recruiter, one of the top tips I can give you when responding to the prompt “Tell us about a problem you solved,” is to tailor your answer to the specific skills and qualifications outlined in the job description.
Once you’ve pinpointed the skills and key competencies the employer is seeking, craft your response to highlight experiences where you successfully utilized or developed those particular abilities.
For instance, if the job requires strong leadership skills, focus on a problem-solving scenario where you took charge and effectively guided a team toward resolution.
By aligning your answer with the desired skills outlined in the job description, you demonstrate your suitability for the role and show the employer that you understand their needs.
Amanda Augustine expands on this by saying:
“Showcase the specific skills you used to solve the problem. Did it require critical thinking, analytical abilities, or strong collaboration? Highlight the relevant skills the employer is seeking.”
Interview Answers to “Tell Me About a Time You Solved a Problem”
Now, let’s look at some sample interview answers to, “Give me an example of a time you used logic to solve a problem,” or “Tell me about a time you solved a problem,” since you’re likely to hear different versions of this interview question in all sorts of industries.
The example interview responses are structured using the STAR method and are categorized into the top 5 key problem-solving skills recruiters look for in a candidate.
1. Analytical Thinking

Situation: In my previous role as a data analyst , our team encountered a significant drop in website traffic.
Task: I was tasked with identifying the root cause of the decrease.
Action: I conducted a thorough analysis of website metrics, including traffic sources, user demographics, and page performance. Through my analysis, I discovered a technical issue with our website’s loading speed, causing users to bounce.
Result: By optimizing server response time, compressing images, and minimizing redirects, we saw a 20% increase in traffic within two weeks.
2. Critical Thinking

Situation: During a project deadline crunch, our team encountered a major technical issue that threatened to derail our progress.
Task: My task was to assess the situation and devise a solution quickly.
Action: I immediately convened a meeting with the team to brainstorm potential solutions. Instead of panicking, I encouraged everyone to think outside the box and consider unconventional approaches. We analyzed the problem from different angles and weighed the pros and cons of each solution.
Result: By devising a workaround solution, we were able to meet the project deadline, avoiding potential delays that could have cost the company $100,000 in penalties for missing contractual obligations.
3. Decision Making

Situation: As a project manager , I was faced with a dilemma when two key team members had conflicting opinions on the project direction.
Task: My task was to make a decisive choice that would align with the project goals and maintain team cohesion.
Action: I scheduled a meeting with both team members to understand their perspectives in detail. I listened actively, asked probing questions, and encouraged open dialogue. After carefully weighing the pros and cons of each approach, I made a decision that incorporated elements from both viewpoints.
Result: The decision I made not only resolved the immediate conflict but also led to a stronger sense of collaboration within the team. By valuing input from all team members and making a well-informed decision, we were able to achieve our project objectives efficiently.
4. Communication (Teamwork)

Situation: During a cross-functional project, miscommunication between departments was causing delays and misunderstandings.
Task: My task was to improve communication channels and foster better teamwork among team members.
Action: I initiated regular cross-departmental meetings to ensure that everyone was on the same page regarding project goals and timelines. I also implemented a centralized communication platform where team members could share updates, ask questions, and collaborate more effectively.
Result: Streamlining workflows and improving communication channels led to a 30% reduction in project completion time, saving the company $25,000 in operational costs.
5. Persistence
Situation: During a challenging sales quarter, I encountered numerous rejections and setbacks while trying to close a major client deal.
Task: My task was to persistently pursue the client and overcome obstacles to secure the deal.
Action: I maintained regular communication with the client, addressing their concerns and demonstrating the value proposition of our product. Despite facing multiple rejections, I remained persistent and resilient, adjusting my approach based on feedback and market dynamics.
Result: After months of perseverance, I successfully closed the deal with the client. By closing the major client deal, I exceeded quarterly sales targets by 25%, resulting in a revenue increase of $250,000 for the company.
Tips to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
Throughout your career, being able to showcase and effectively communicate your problem-solving skills gives you more leverage in achieving better jobs and earning more money .
So to improve your problem-solving skills, I recommend always analyzing a problem and situation before acting.
When discussing problem-solving with employers, you never want to sound like you rush or make impulsive decisions. They want to see fact-based or data-based decisions when you solve problems.
Don’t just say you’re good at solving problems. Show it with specifics. How much did you boost efficiency? Did you save the company money? Adding numbers can really make your achievements stand out.
To get better at solving problems, analyze the outcomes of past solutions you came up with. You can recognize what works and what doesn’t.
Think about how you can improve researching and analyzing a situation, how you can get better at communicating, and deciding on the right people in the organization to talk to and “pull in” to help you if needed, etc.
Finally, practice staying calm even in stressful situations. Take a few minutes to walk outside if needed. Step away from your phone and computer to clear your head. A work problem is rarely so urgent that you cannot take five minutes to think (with the possible exception of safety problems), and you’ll get better outcomes if you solve problems by acting logically instead of rushing to react in a panic.
You can use all of the ideas above to describe your problem-solving skills when asked interview questions about the topic. If you say that you do the things above, employers will be impressed when they assess your problem-solving ability.
More Interview Resources
- 3 Answers to “How Do You Handle Stress?”
- How to Answer “How Do You Handle Conflict?” (Interview Question)
- Sample Answers to “Tell Me About a Time You Failed”

About the Author
Biron Clark is a former executive recruiter who has worked individually with hundreds of job seekers, reviewed thousands of resumes and LinkedIn profiles, and recruited for top venture-backed startups and Fortune 500 companies. He has been advising job seekers since 2012 to think differently in their job search and land high-paying, competitive positions. Follow on Twitter and LinkedIn .
Read more articles by Biron Clark
About the Contributor
Kyle Elliott , career coach and mental health advocate, transforms his side hustle into a notable practice, aiding Silicon Valley professionals in maximizing potential. Follow Kyle on LinkedIn .

About the Editor
Hayley Jukes is the Editor-in-Chief at CareerSidekick with five years of experience creating engaging articles, books, and transcripts for diverse platforms and audiences.
Continue Reading
12 Expert-Approved Responses to ‘What Makes You Unique?’ in Job Interviews
15 most common pharmacist interview questions and answers, 15 most common paralegal interview questions and answers, top 30+ funny interview questions and answers, 60 hardest interview questions and answers, 100+ best ice breaker questions to ask candidates, top 20 situational interview questions (& sample answers), 15 most common physical therapist interview questions and answers.

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
What Are Problem-Solving Skills? Definition and Examples
- Share on Twitter Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn

Forage puts students first. Our blog articles are written independently by our editorial team. They have not been paid for or sponsored by our partners. See our full editorial guidelines .
Why do employers hire employees? To help them solve problems. Whether you’re a financial analyst deciding where to invest your firm’s money, or a marketer trying to figure out which channel to direct your efforts, companies hire people to help them find solutions. Problem-solving is an essential and marketable soft skill in the workplace.
So, how can you improve your problem-solving and show employers you have this valuable skill? In this guide, we’ll cover:
Problem-Solving Skills Definition
Why are problem-solving skills important, problem-solving skills examples, how to include problem-solving skills in a job application, how to improve problem-solving skills, problem-solving: the bottom line.
Problem-solving skills are the ability to identify problems, brainstorm and analyze answers, and implement the best solutions. An employee with good problem-solving skills is both a self-starter and a collaborative teammate; they are proactive in understanding the root of a problem and work with others to consider a wide range of solutions before deciding how to move forward.
Examples of using problem-solving skills in the workplace include:
- Researching patterns to understand why revenue decreased last quarter
- Experimenting with a new marketing channel to increase website sign-ups
- Brainstorming content types to share with potential customers
- Testing calls to action to see which ones drive the most product sales
- Implementing a new workflow to automate a team process and increase productivity
Problem-solving skills are the most sought-after soft skill of 2022. In fact, 86% of employers look for problem-solving skills on student resumes, according to the National Association of Colleges and Employers Job Outlook 2022 survey .
It’s unsurprising why employers are looking for this skill: companies will always need people to help them find solutions to their problems. Someone proactive and successful at problem-solving is valuable to any team.
“Employers are looking for employees who can make decisions independently, especially with the prevalence of remote/hybrid work and the need to communicate asynchronously,” Eric Mochnacz, senior HR consultant at Red Clover, says. “Employers want to see individuals who can make well-informed decisions that mitigate risk, and they can do so without suffering from analysis paralysis.”
Showcase new skills
Build the confidence and practical skills that employers are looking for with Forage’s free job simulations.
Problem-solving includes three main parts: identifying the problem, analyzing possible solutions, and deciding on the best course of action.
>>MORE: Discover the right career for you based on your skills with a career aptitude test .
Research is the first step of problem-solving because it helps you understand the context of a problem. Researching a problem enables you to learn why the problem is happening. For example, is revenue down because of a new sales tactic? Or because of seasonality? Is there a problem with who the sales team is reaching out to?
Research broadens your scope to all possible reasons why the problem could be happening. Then once you figure it out, it helps you narrow your scope to start solving it.
Analysis is the next step of problem-solving. Now that you’ve identified the problem, analytical skills help you look at what potential solutions there might be.
“The goal of analysis isn’t to solve a problem, actually — it’s to better understand it because that’s where the real solution will be found,” Gretchen Skalka, owner of Career Insights Consulting, says. “Looking at a problem through the lens of impartiality is the only way to get a true understanding of it from all angles.”
Decision-Making
Once you’ve figured out where the problem is coming from and what solutions are, it’s time to decide on the best way to go forth. Decision-making skills help you determine what resources are available, what a feasible action plan entails, and what solution is likely to lead to success.
On a Resume
Employers looking for problem-solving skills might include the word “problem-solving” or other synonyms like “ critical thinking ” or “analytical skills” in the job description.
“I would add ‘buzzwords’ you can find from the job descriptions or LinkedIn endorsements section to filter into your resume to comply with the ATS,” Matthew Warzel, CPRW resume writer, advises. Warzel recommends including these skills on your resume but warns to “leave the soft skills as adjectives in the summary section. That is the only place soft skills should be mentioned.”
On the other hand, you can list hard skills separately in a skills section on your resume .

Forage Resume Writing Masterclass
Learn how to showcase your skills and craft an award-winning resume with this free masterclass from Forage.
Avg. Time: 5 to 6 hours
Skills you’ll build: Resume writing, professional brand, professional summary, narrative, transferable skills, industry keywords, illustrating your impact, standing out
In a Cover Letter or an Interview
Explaining your problem-solving skills in an interview can seem daunting. You’re required to expand on your process — how you identified a problem, analyzed potential solutions, and made a choice. As long as you can explain your approach, it’s okay if that solution didn’t come from a professional work experience.
“Young professionals shortchange themselves by thinking only paid-for solutions matter to employers,” Skalka says. “People at the genesis of their careers don’t have a wealth of professional experience to pull from, but they do have relevant experience to share.”
Aaron Case, career counselor and CPRW at Resume Genius, agrees and encourages early professionals to share this skill. “If you don’t have any relevant work experience yet, you can still highlight your problem-solving skills in your cover letter,” he says. “Just showcase examples of problems you solved while completing your degree, working at internships, or volunteering. You can even pull examples from completely unrelated part-time jobs, as long as you make it clear how your problem-solving ability transfers to your new line of work.”
Learn How to Identify Problems
Problem-solving doesn’t just require finding solutions to problems that are already there. It’s also about being proactive when something isn’t working as you hoped it would. Practice questioning and getting curious about processes and activities in your everyday life. What could you improve? What would you do if you had more resources for this process? If you had fewer? Challenge yourself to challenge the world around you.
Think Digitally
“Employers in the modern workplace value digital problem-solving skills, like being able to find a technology solution to a traditional issue,” Case says. “For example, when I first started working as a marketing writer, my department didn’t have the budget to hire a professional voice actor for marketing video voiceovers. But I found a perfect solution to the problem with an AI voiceover service that cost a fraction of the price of an actor.”
Being comfortable with new technology — even ones you haven’t used before — is a valuable skill in an increasingly hybrid and remote world. Don’t be afraid to research new and innovative technologies to help automate processes or find a more efficient technological solution.
Collaborate
Problem-solving isn’t done in a silo, and it shouldn’t be. Use your collaboration skills to gather multiple perspectives, help eliminate bias, and listen to alternative solutions. Ask others where they think the problem is coming from and what solutions would help them with your workflow. From there, try to compromise on a solution that can benefit everyone.
If we’ve learned anything from the past few years, it’s that the world of work is constantly changing — which means it’s crucial to know how to adapt . Be comfortable narrowing down a solution, then changing your direction when a colleague provides a new piece of information. Challenge yourself to get out of your comfort zone, whether with your personal routine or trying a new system at work.
Put Yourself in the Middle of Tough Moments
Just like adapting requires you to challenge your routine and tradition, good problem-solving requires you to put yourself in challenging situations — especially ones where you don’t have relevant experience or expertise to find a solution. Because you won’t know how to tackle the problem, you’ll learn new problem-solving skills and how to navigate new challenges. Ask your manager or a peer if you can help them work on a complicated problem, and be proactive about asking them questions along the way.
Career Aptitude Test
What careers are right for you based on your skills? Take this quiz to find out. It’s completely free — you’ll just need to sign up to get your results!
Step 1 of 3
Companies always need people to help them find solutions — especially proactive employees who have practical analytical skills and can collaborate to decide the best way to move forward. Whether or not you have experience solving problems in a professional workplace, illustrate your problem-solving skills by describing your research, analysis, and decision-making process — and make it clear that you’re the solution to the employer’s current problems.
Looking to learn more workplace professional skills? Check out Two Sigma’s Professional Skills Development Virtual Experience Program .
Image Credit: Christina Morillo / Pexels

Related Posts
6 negotiation skills to level up your work life, how to build conflict resolution skills: case studies and examples, what is github uses and getting started, upskill with forage.

Build career skills recruiters are looking for.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills? (Examples Included)
Mike Simpson 0 Comments

By Mike Simpson
Problem-solving skills are important not just for work. In the words of Karl Popper , “All life is problem-solving.”
What on earth does that mean? Simply that being alive means facing challenges. With problem-solving skills, you can navigate issues with greater ease, making hard times, well, less hard.
But what are problem-solving skills? How do you know if you have them or not? Why do they matter to your job search? And what should you do if you don’t feel yours are up to snuff? Luckily, we’re about to get into all of that.
If you’re curious about the world of problem-solving skills, here’s what you need to know.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Before we dig into any examples, let’s focus first on an important question: what are problem-solving skills.
To answer that question, let’s start with the barebones basics. According to Merriam-Webster , problem-solving is “the process or act of finding a solution to a problem.” Why does that matter? Well, because it gives you insight into what problem-solving skills are.
Any skill that helps you find solutions to problems can qualify. And that means problem-solving skills aren’t just one capability, but a toolbox filled with soft skills and hard skills that come together during your time of need.
The ability to solve problems is relevant to any part of your life. Whether your writing a grocery list or dealing with a car that won’t start, you’re actually problem-solving.
The same is true at work, too. Most tasks actually involve a degree of problem-solving. Really? Really.
Think about it this way; when you’re given an assignment, you’re being asked, “Can you do this thing?” Doing that thing is the problem.
Then, you have to find a path that lets you accomplish what you need to do. That is problem-solving.
Yes, sometimes what you need to handle isn’t “challenging” in the difficulty sense. But that doesn’t mean it doesn’t count.
Besides, some of what you need to do will legitimately be hard. Maybe you’re given a new responsibility, or something goes wrong during a project. When that happens, you’ll have to navigate unfamiliar territory, gather new information, and think outside of the box. That’s problem-solving, too.
That’s why hiring managers favor candidates with problem-solving skills. They make you more effective in your role, increasing the odds that you can find solutions whenever the need arises.
How Are Problem-Solving Skills Relevant to a Job Search?
Alright, you probably have a good idea of what problem-solving skills are. Now, it’s time to talk about why they matter to your job search.
We’ve already touched on one major point: hiring managers prefer candidates with strong problem-solving skills. That alone makes these capabilities a relevant part of the equation. If you don’t show the hiring manager you’ve got what it takes to excel, you may struggle to land a position.
But that isn’t the only reason these skills matter. Problem-solving skills can help you during the entire job search process. After all, what’s a job search but a problem – or a series of problems – that needs an answer.
You need a new job; that’s the core problem you’re solving. But every step is its own unique challenge. Finding an opening that matches your skills, creating a resume that resonates with the hiring manager, nailing the interview, and negotiating a salary … those are all smaller problems that are part of the bigger one.
So, problem-solving skills really are at the core of the job search experience. By having strong capabilities in this area, you may find a new position faster than you’d expect.
Okay, you may be thinking, “If hiring managers prefer candidates with problem-solving skills, which ones are they after? Are certain problem-solving capabilities more important today? Is there something I should be going out of my way to showcase?”
While any related skills are worth highlighting, some may get you further than others. Analysis, research, creativity, collaboration , organization, and decision-making are all biggies. With those skills, you can work through the entire problem-solving process, making them worthwhile additions to your resume.
But that doesn’t mean you have to focus there solely. Don’t shy away from showcasing everything you bring to the table. That way, if a particular hiring manager is looking for a certain capability, you’re more likely to tap on what they’re after.
How to Highlight Problem-Solving Skills for Job Search
At this point, it’s ridiculously clear that problem-solving skills are valuable in the eyes of hiring managers. So, how do you show them that you’ve got all of the capabilities they are after? By using the right approach.
When you’re writing your resume or cover letter , your best bet is to highlight achievements that let you put your problem-solving skills to work. That way, you can “show” the hiring manager you have what it takes.
Showing is always better than telling. Anyone can write down, “I have awesome problem-solving skills.” The thing is, that doesn’t really prove that you do. With a great example, you offer up some context, and that makes a difference.
How do you decide on which skills to highlight on your resume or cover letter? By having a great strategy. With the Tailoring Method , it’s all about relevancy. The technique helps you identify skills that matter to that particular hiring manager, allowing you to speak directly to their needs.
Plus, you can use the Tailoring Method when you answer job interview questions . With that approach, you’re making sure those responses are on-point, too.
But when do you talk about your problem-solving capabilities during an interview? Well, there’s a good chance you’ll get asked problem-solving interview questions during your meeting. Take a look at those to see the kinds of questions that are perfect for mentioning these skills.
However, you don’t have to stop there. If you’re asked about your greatest achievement or your strengths, those could be opportunities, too. Nearly any open-ended question could be the right time to discuss those skills, so keep that in mind as you practice for your interview.
How to Develop Problem-Solving Skills If You Don’t Have Them
Developing problem-solving skills may seem a bit tricky on the surface, especially if you think you don’t have them. The thing is, it doesn’t actually have to be hard. You simply need to use the right strategy.
First, understand that you probably do have problem-solving skills; you simply may not have realized it. After all, life is full of challenges that you have to tackle, so there’s a good chance you’ve developed some abilities along the way.
Now, let’s reframe the question and focus on how to improve your problem-solving skills. Here’s how to go about it.
Understand the Problem-Solving Process
In many cases, problem-solving is all about the process. You:
- Identify the problem
- Analyze the key elements
- Look for potential solutions
- Examine the options for viability and risk
- Decide on an approach
- Review the outcome for lessons
By understanding the core process, you can apply it more effectively. That way, when you encounter an issue, you’ll know how to approach it, increasing the odds you’ll handle the situation effectively.
Try Puzzles and Games
Any activity that lets you take the steps listed above could help you hone your problem-solving skills. For example, brainteasers, puzzles, and logic-based games can be great places to start.
Whether it’s something as straightforward – but nonetheless challenging – as Sudoku or a Rubik’s Cube, or something as complex as Settlers of Catan, it puts your problem-solving skills to work. Plus, if you enjoy the activity, it makes skill-building fun, making it a win-win.
Look for Daily Opportunities
If you’re looking for a practical approach, you’re in luck. You can also look at the various challenges you face during the day and think about how to overcome them.
For example, if you always experience a mid-day energy slump that hurts your productivity, take a deep dive into that problem. Define what’s happening, think about why it occurs, consider various solutions, pick one to try, and analyze the results.
By using the problem-solving approach more often in your life, you’ll develop those skills further and make using these capabilities a habit. Plus, you may find ways to improve your day-to-day living, which is a nice bonus.
Volunteer for “Stretch” Projects
If you’re currently employed, volunteering for projects that push you slightly outside of your comfort zone can help you develop problem-solving skills, too. You’ll encounter the unknown and have to think outside of the box, both of which can boost critical problem-solving-related skills.
Plus, you may gain other capabilities along the way, like experience with new technologies or tools. That makes the project an even bigger career booster, which is pretty awesome.
List of Problem-Solving Skills
Alright, we’ve taken a pretty deep dive into what problem-solving skills are. Now, it’s time for some problem-solving skills examples.
As we mentioned above, there are a ton of capabilities and traits that can support better problem-solving. By understanding what they are, you can showcase the right abilities during your job search.
So, without further ado, here is a quick list of problem-solving skill examples:
- Collaboration
- Organization
- Decision-Making
- Troubleshooting
- Self-Reliance
- Self-Motivation
- Communication
- Attention to Detail
- Brainstorming
- Forecasting
- Active Listening
- Accountability
- Open-Mindedness
- Critical Thinking
- Flexibility
Do you have to showcase all of those skills during your job search individually? No, not necessarily. Instead, you want to highlight a range of capabilities based on what the hiring manager is after. If you’re using the Tailoring Method, you’ll know which ones need to make their way into your resume, cover letter, and interview answers.
Now, are there other skills that support problem-solving? Yes, there certainly can be.
Essentially any skill that helps you go from the problem to the solution can, in its own right, be a problem-solving skill.
All of the skills above can be part of the equation. But, if you have another capability that helps you flourish when you encounter an obstacle, it can count, too.
Reflect on your past experience and consider how you’ve navigated challenges in the past. If a particular skill helped you do that, then it’s worth highlighting during a job search.
If you would like to find out more about skills to put on a resume , we’ve taken a close look at the topic before. Along with problem-solving skills, we dig into a variety of other areas, helping you choose what to highlight so that you can increase your odds of landing your perfect job.
Putting It All Together
Ultimately, problem-solving skills are essential for professionals in any kind of field. By honing your capabilities and showcasing them during your job search, you can become a stronger candidate and employee. In the end, that’s all good stuff, making it easier for you to keep your career on track today, tomorrow, and well into the future.

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com.
His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others.
Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
About The Author
Mike simpson.

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com. His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others. Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
Copyright © 2024 · TheInterviewguys.com · All Rights Reserved
- Our Products
- Case Studies
- Interview Questions
- Jobs Articles
- Members Login
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Career Blog
50 Problem Solving Examples for Interview Success in 2024

Problem-solving interview questions are a common tool used by employers to assess a candidate’s problem-solving skills. These questions are designed to evaluate a candidate’s ability to think critically, analyze information, and propose effective solutions to complex problems.
Importance of Problem-Solving Skills in the Workplace
Problem-solving skills are essential in the workplace as they help individuals to overcome challenges, make informed decisions, and improve productivity. With the rise of automation and artificial intelligence, problem-solving skills are becoming increasingly important, as they are one of the few skills that cannot be easily automated. Employers value individuals with strong problem-solving skills as they believe that these individuals can lead to better decision-making and improved organizational performance.
Understanding the Problem-Solving Process
When it comes to problem-solving, there is a well-established process that can guide individuals in reaching the best possible solutions. This process is composed of seven steps that can be applied to any problem or challenge one might encounter.
A. Define the Problem
The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step involves identifying and understanding what the problem is, why it is occurring, and what its impact is on the situation or environment. A well-defined problem allows for a better understanding of the issue and helps in finding an appropriate solution.
B. Gather Information
The second step of the process is to gather information. In order to find the best solution, one must have complete and accurate information about the problem. Gathering information can be done through research, surveys, interviews, or any other means of collecting data relevant to the problem at hand.
C. Analyze Information
Once enough information has been collected, it is time to analyze it. This step involves the process of examining the data, identifying patterns, and looking for any underlying causes that might be contributing to the problem.

D. Develop Solutions
After analyzing the data, it is time to develop solutions. This step involves brainstorming potential solutions, evaluating their feasibility, and assessing their effectiveness. It is important to keep an open mind and to consider multiple approaches when developing solutions.
E. Select the Best Solution
Once potential solutions have been identified, it is time to select the best one. This involves weighing the pros and cons of each solution and selecting the one that is most likely to be effective in resolving the problem.
F. Implement the Solution
With the best solution selected, it is time to put it into action. This step involves developing an implementation plan, allocating resources, and taking the necessary steps to put the chosen solution into practice.
G. Monitor and Evaluate the Solution
The final step in the problem-solving process is to monitor and evaluate the chosen solution. It is important to assess its effectiveness and to make adjustments as necessary. This step involves monitoring the situation over time, collecting feedback, and identifying areas for improvement.
Understanding the problem-solving process is critical for success in interviews and in life. By following the seven steps outlined above, individuals can improve their ability to identify, analyze, and solve problems in a systematic and effective manner.
Behavioral Interview Questions
One of the most common interview techniques used by employers is the behavioral interview. This type of interview focuses on asking questions about past experiences to better understand how a candidate might behave in certain situations.
A. Explanation of Behavioral Interview Questions
Behavioral interview questions are designed to help the employer get a sense of how the candidate has handled specific situations in the past. For example, a question might ask the candidate to describe a time when they had to deal with a difficult customer or how they handle conflicts in the workplace. By asking these types of questions, the interviewer can get a better sense of the candidate’s skills and abilities.
B. How to Answer Behavioral Interview Questions with Problem-Solving Examples
When answering behavioral interview questions, it is important to provide specific examples of how you handled similar situations in the past. One effective strategy is to use the STAR method, which stands for Situation, Task, Action, and Result. Here’s how it works:
- Situation: Describe the situation or problem you faced.
- Task: Explain what your role was in the situation.
- Action: Describe the steps you took to solve the problem.
- Result: Explain the outcome of your actions.
By using the STAR method, you can provide a clear and structured response that demonstrates your problem-solving abilities.
C. Tips and Tricks for Mastering Behavioral Interview Questions
Here are some additional tips to help you master behavioral interview questions:
- Research common behavioral interview questions beforehand so that you can prepare your answers in advance.
- Use specific examples from your past experience to illustrate your skills and abilities.
- Be honest. Don’t try to misrepresent your past experiences to make yourself look better.
- Avoid using generic or clichéd responses. Instead, be creative and try to showcase your unique strengths.
- Practice your responses with a friend or mentor to gain confidence and improve your delivery.
With these tips in mind, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle any behavioral interview questions that come your way. Remember that the key is to demonstrate your problem-solving abilities by providing specific and relevant examples from your past experiences. Good luck!
Situational Interview Questions
Situational interview questions are a popular interviewing technique that is commonly used by recruiters to measure how well a candidate can handle real-life work scenarios. It’s a highly effective way to determine whether the individual has the necessary skills and knowledge to handle the demands of a particular job role.

A. Explanation of Situational Interview Questions
In situational interview questions, the recruiter will develop a hypothetical scenario about a specific work challenge or issue, which the candidate would typically experience in the role they are being interviewed for. The goal is to evaluate not only the candidate’s knowledge and skills but also to assess their critical thinking skills, decision-making skills, and problem-solving abilities.
B. How to Answer Situational Interview Questions with Problem-Solving Examples
The best way to answer situational interview questions is to use a structured problem-solving approach. This approach involves analyzing and breaking down the situation into smaller components, identifying the root cause of the problem, and devising a solution that is not only practical but also effective.
For instance, if you were asked to describe how you would handle a difficult customer in a sales role, you would first identify the source of the customer’s frustration, listen to their concerns, and develop a tailored resolution plan using the company’s policies as guidelines.
C. Tips and Tricks for Mastering Situational Interview Questions
To master situational interview questions, candidates need to prepare in advance by researching the company’s values, culture and analyzing the job description’s requirements. Candidates should also practice solving hypothetical scenarios with friends or family to become more comfortable in their approach.
It is also essential to remain calm throughout the interview, as situational interview questions can be stressful. Candidates should take their time to carefully listen to each question and ensure that they understand the question before attempting to answer.
Lastly, when answering situational interview questions, it is always best to provide specific examples of past experiences, such as a time where a problem was successfully solved, highlighting relevant skills to the role being interviewed.
By following these tips and using a structured problem-solving approach, candidates can conquer the situational interview and demonstrate their ability to handle real-world challenges effectively.
Communication Skills
Effective communication is indispensable in problem-solving. The ability to communicate effectively in a team environment is essential to achieving success. It allows each team member to synthesize their ideas, express their opinions, and share their knowledge.
A. Importance of Communication Skills in Problem-Solving
In problem-solving, communication plays a vital role in ensuring that everyone is on the same page. Without effective communication, the team may misunderstand the problem, the solution, or the approach, which may lead to delays, inefficiencies, or potential failure.
Communication skills are crucial in problem-solving for several reasons, including:
- Fostering a collaborative environment where ideas can be shared and discussed openly
- Ensuring that each team member understands their role and responsibilities
- Clarifying expectations and goals
- Encouraging feedback and constructive criticism
- Delineating potential risks and challenges
- Building rapport and trust among team members
B. Examples of Problem-Solving Scenarios That Highlight Communication Skills
Effective communication skills are essential in all problem-solving scenarios, but some scenarios require stronger communication skills than others. A few examples of problem-solving scenarios that highlight the importance of communication skills include:
- Dealing with a difficult client: A team may face a client who is dissatisfied with the project’s progress or outcome. The team must use effective communication skills to understand the client’s concerns, address their issues, and find a solution that satisfies both the client and the team.
- Handling a conflict within the team: Conflict is a natural occurrence when working in a team. The team must use effective communication skills to identify the root cause of the conflict, discuss potential solutions, and reach a resolution that all team members agree on.
- Brainstorming new ideas: Effective communication skills are crucial when brainstorming new ideas. Team members must use active listening skills to understand each other’s ideas, communicate their thoughts clearly, and provide feedback constructively.
C. Tips for Improving Communication Skills in Problem-Solving
Communication skills are not inherent but can be learned and improved. Here are a few tips for improving communication skills in problem-solving.
- Practice active listening: Active listening entails being completely present in the conversation, focusing your attention on what the speaker is saying, asking questions to clarify your understanding, and providing feedback.
- Be clear and concise: Clarity is critical in communication. Be sure to articulate your ideas clearly and concisely to avoid miscommunication.
- Use open-ended questions: Open-ended questions encourage discussion and provide more in-depth insights than closed-ended questions.
- Provide feedback constructively: Feedback must be constructive, objective, and sensitive to the recipient’s feelings. Focus on specific actions rather than personal traits, offer suggestions, and seek feedback in return.
- Use visual aids: Visuals can help explain complex topics and ideas, making them easier to understand for everyone.
Effective communication skills are essential in problem-solving scenarios.
Analytical Skills
In any problem-solving scenario, analytical skills are crucial to successful outcomes. Employers seek candidates who can evaluate information, identify patterns, and develop solutions based on data-driven insights. Here are the key elements to understand:
A. Importance of Analytical Skills in Problem-Solving
Analytical skills are essential in problem-solving because they enable one to identify the root cause of a problem and develop solutions that directly address it. This approach ensures that solutions are efficient, effective, and sustainable for the long-term. Employers value analytical skills as they are essential in any competitive business environment, helping organizations stay ahead of the curve and outperform their competitors.
B. Examples of Problem-Solving Scenarios That Highlight Analytical Skills
One scenario that highlights the importance of analytical skills is when a company aims to expand its operations to a new market. To achieve this goal, the organization must first conduct market research and analyze data regarding the new market’s economic, cultural, and geopolitical landscape. With this information, the company can identify potential barriers to entry, risks and rewards, and develop a successful entry strategy.
Another example is when a manufacturing company experiences consistent product failures. Instead of implementing a quick fix, the organization could conduct a root cause analysis to identify the underlying problem. This process involves analyzing production data and investigating distinct variables such as raw materials, production methodology, and machine maintenance. By identifying the root cause, the company can then develop an effective solution to prevent future product failures.
C. Tips for Improving Analytical Skills in Problem-Solving
There are several ways to improve your analytical skills in problem-solving. The first is to improve your ability to gather and analyze data effectively. This can be achieved by becoming more proficient in data analysis tools, such as Excel, or attending training sessions on data analysis.
Secondly, it is essential to cultivate critical thinking skills. This involves analyzing information objectively, considering various perspectives, and questioning assumptions. By doing so, you may arrive at a solution that is more efficient, effective, and innovative.
Finally, it is crucial to take advantage of opportunities to develop problem-solving skills. This includes taking on challenging projects, participating in cross-functional teams, and seeking feedback from colleagues. By continually practicing problem-solving skills, you can improve your ability to evaluate information, identify patterns, and develop innovative solutions.
Analytical skills are essential in problem-solving scenarios, and applicants demonstrating these skills have a higher chance of success in job interviews. By understanding the importance of analytical skills, highlighting examples of their implementation in various contexts, and cultivating strategies to enhance these skills, you can become a more adept problem-solver and stand out to potential employers.
Creative Problem-Solving
A. importance of creative problem-solving in the workplace.
Creative problem-solving is a vital skill that is highly sought after in most workplaces. It involves applying innovative and out-of-the-box thinking to identify and fix complex problems. In today’s fast-paced business world, where competition is fierce, companies require employees who can anticipate and solve problems quickly and efficiently. As such, creative problem-solving skills have become indispensable in almost all industries, from IT to healthcare and finance.
Those who possess strong creative problem-solving skills are assets to their organizations. They are likely to be better at tackling difficult tasks and sorting out problems that other employees may have difficulty resolving. Additionally, these individuals bring new ideas and approaches to the table, improve productivity, and increase overall efficiency.
B. Examples of Creative Problem-Solving Techniques
There are numerous creative problem-solving techniques that organizations and individuals can use to enhance their ability to solve problems effectively. Some examples include:
Mind Mapping: This technique fosters creative thinking by allowing individuals to document their ideas visually. It is a great way to organize complex information and identify new connections between concepts.
Brainstorming: Brainstorming involves generating a large amount of ideas without criticizing or evaluating any of them initially. It is often used to come up with creative solutions to a particular problem.
Reverse Thinking: This technique involves considering the opposite of the problem and then brainstorming ways to achieve it. It challenges individuals to think in a different way and can produce unique solutions.
SCAMPER: An acronym for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify or Magnify, Put to another use, Eliminate or Reverse, SCAMPER is a creative problem-solving technique that utilizes various ways to manipulate an idea or item to generate new solutions.
C. Tips for Developing Creative Problem-Solving Skills
Creative problem-solving is a skill that can be developed and honed through consistent practice. Some useful tips in developing creative problem-solving skills include:
Keep an open mind: Try to be open to new ideas and ways of thinking, even if they seem unconventional or unusual.
Take calculated risks: Do not be afraid to take calculated risks and try new approaches. Even if you fail, you will have learned something valuable.
Collaborate with others: Working with others allows for a broader range of perspectives and ideas. It can lead to more innovative solutions.
Experiment: Experiment with different creative problem-solving techniques until you find the ones that work best for you.
Keep learning: Keep up-to-date with the latest problem-solving techniques and strategies by reading books or attending workshops and seminars.
Mastering creative problem-solving is essential for career success in most industries. It enhances overall productivity, improves efficiency, and encourages innovation. By practicing various techniques and adopting several strategies, individuals can develop their creative problem-solving skills and set themselves apart in the job market.
Decision-Making Skills
Effective problem-solving requires strong decision-making skills. Decision-making is the process of choosing a course of action to address a particular situation or problem. It involves analyzing, evaluating, and selecting the most appropriate solution.
A. Importance of Decision-Making Skills in Problem-Solving
Decision-making skills are essential for effective problem-solving. Without good decision-making skills, one may struggle to make the right choices and solve problems efficiently. The ability to make informed decisions helps individuals to identify problems, explore possible solutions, and select the most suitable option.
In addition, decision-making skills enable individuals to evaluate the impact of their decisions and consider potential risks and benefits. They also allow individuals to weigh the consequences of inaction against those of action and make timely decisions.
B. Examples of Decision-Making Scenarios in Problem-Solving
There are several decision-making scenarios that individuals may encounter when solving problems. Examples include:
- Deciding on the best course of action to take when a project is behind schedule
- Choosing the most appropriate supplier for a particular product
- Deciding whether to invest in a new technology or stick with the status quo
- Prioritizing tasks when workload is overwhelming
- Evaluating competing job offers and selecting the best one.
C. Tips for Improving Decision-Making Skills in Problem-Solving
Improving decision-making skills requires effort and practice. Here are some tips to help you improve your decision-making skills:
Gather relevant information: Before making a decision, ensure that you have access to the relevant information. This may include data, reports, and expert opinions.
Analyze and evaluate options: Consider all possible solutions and evaluate them based on their effectiveness, feasibility, and potential risks and benefits.
Seek advice: When making an important decision, seek advice from colleagues or experts in the field. This can help you gain a different perspective and identify potential blind spots.
Consider the consequences: Anticipate the consequences of your decision and evaluate the impact it may have on stakeholders, resources, and goals.
Learn from experience: Reflect on past decisions and their outcomes to improve future decision-making skills. Consider what worked well and what could have been done differently.
Decision-making skills are critical in problem-solving. The ability to make informed decisions can help individuals to identify problems, explore possible solutions, and select the most appropriate option. By following the tips outlined in this section, you can improve your decision-making skills and enhance your problem-solving abilities.
Leadership Skills
Effective leadership skills play a crucial role in problem-solving, making it an indispensable part of any job interview. Employers look for candidates who possess leadership traits and can lead a team to success. In this section, we’ll discuss the importance of leadership skills in problem-solving, give examples of how leaders approach problem-solving scenarios, and provide tips on how to develop leadership skills in problem-solving.
A. Importance of Leadership Skills in Problem-Solving
When faced with a problem, a good leader takes charge and motivates their team to find a solution. They inspire confidence and provide direction, leading the team in the right direction. A leader who can effectively resolve problems creates a sense of trust and respect among their team members.
Effective leadership skills in problem-solving lead to better collaboration, communication, and decision-making. They foster creativity and innovation, empower team members, and build a resilient team equipped to tackle any challenge.
B. Examples of Leadership in Problem-Solving Scenarios
Leadership skills are particularly crucial in problem-solving scenarios, where creative, out-of-the-box thinking is required. Leaders must be able to approach problems with a clear mind, analyze the situation, and provide a solution that works for all stakeholders involved.
A good example of leadership in problem-solving is how NASA responded to the Apollo 13 crisis. When the spacecraft experienced an oxygen tank explosion, the crew needed to maneuver their way back to Earth safely. The NASA team worked tirelessly through numerous challenges, ultimately developing a solution that saved the crew’s lives.
Another example is how Airbnb’s leadership dealt with a growing concern over discrimination on their platform. They took immediate action, appointing a team of experts to address the issue and implementing policies to address the underlying problem.
C. Tips for Developing Leadership Skills in Problem-Solving
Leadership skills can be developed through practice, self-reflection, and learning from others. Here are some tips for developing leadership skills in problem-solving:
Practice active listening: Listening to different perspectives is critical in problem-solving. Actively listening to team members and stakeholders helps to gather valuable insights and build a shared understanding of the problem.
Encourage creativity: Leaders must foster an environment that promotes creativity and brainstorming. Encourage team members to approach problems from different angles, generating innovative solutions.
Focus on solutions: Rather than dwelling on the problem, leaders must remain focused on solutions. They should use their problem-solving skills to identify root causes and develop strategies that provide long-term solutions.
Lead by example: Effective leadership in problem-solving is not just about delegating tasks but leading by example. Leaders should participate in problem-solving alongside their team members, demonstrating their commitment to finding a solution.
Learn from failure: Failure is often an essential component of the problem-solving process. Leaders should focus on learning from failures, analyzing what worked and what didn’t, and adapting their approach moving forward.
Leadership skills are a cornerstone of effective problem-solving.
Time Management Skills
Effective time management skills play a critical role in successful problem-solving. Proper use of time ensures that problems are tackled comprehensively without inconveniencing other essential activities. Time management skills aid in the optimization of time usage, thereby improving productivity and bolstering overall performance.
A. Importance of Time Management Skills in Problem-Solving
In problem-solving, time is a precious commodity that cannot be wasted. Time management skills allow individuals to allocate sufficient time to different stages of the problem-solving process. Proper time allocation ensures that each stage of the problem-solving process is fully addressed, and no critical task is left incomplete. Time management helps maintain momentum in the problem-solving process, ensuring that hiccups, obstacles, or delays that may arise during the process are effectively handled. Effective time management skills also aid in decision-making, where required data and information are gathered promptly and analysed, leading to sound conclusions.
B. Examples of Problem-Solving Situations That Require Time Management Skills
Problem-solving situations requiring good time management skills are common in various industries. For instance, in tech industries, software troubleshooting and bug fixing require quick and efficient problem-solving abilities. Time management skills are crucial in such situations, where the capacity to swiftly and accurately identify a problem, evaluate potential solutions, and implement fixes directly affects the quality and performance of the software. In healthcare, emergency response situations require excellent time management abilities. In such situations, healthcare personnel must quickly and accurately assess a patient’s condition, gather their medical history, and provide proper treatment within the shortest time possible.
C. Tips for Improving Time Management Skills in Problem-Solving
To improve time management skills in problem-solving, individuals should:
i. Set Clear Priorities
Effective time management skills require individuals to set priorities based on the importance and urgency of each task. Create a to-do list and assign priorities to each task in line with the importance and urgency of each.
Eliminate Distractions
In problem-solving, distractions may hamper productivity, causing a delay in the problem-solving process. Ensure that any distractions are eliminated, and a conducive environment is set up to encourage focus and concentration.
Delegate Tasks
When possible, delegate tasks to other individuals to ensure a balanced workload. Delegation helps free up time, allowing individuals to focus on critical aspects of the problem-solving process.
Take Breaks
Taking regular breaks allows individuals to recharge and refocus, leading to better productivity. Ensure that breaks are taken at appropriate intervals to avoid prolonged distractions.
Leverage Technology
Technology has numerous tools and resources that aid in time management. Take advantage of these resources to optimize and streamline the problem-solving process.
Relevant Work Experience
A. explanation of the importance of relevant work experience in problem-solving.
When it comes to problem-solving, relevant work experience can make a significant difference. Employers are always looking for candidates who have the skills and experience necessary to tackle the challenges of the job. The ability to solve problems is a key skill that employers are constantly seeking, and relevant work experience is a great way to demonstrate your ability.
Relevant work experience helps you to develop problem-solving skills that are specific to your industry or field. For example, an IT professional who has worked on complex projects will have developed skills in problem-solving that are unique to the field of technology. Similarly, a lawyer who has worked on a high-profile case will have gained experience in problem-solving that is specific to the legal profession.
In addition to developing industry-specific skills, relevant work experience can also help you to develop transferable skills that can be applied in any profession. These skills include communication, critical thinking, creativity, and strategic thinking. Employers are looking for candidates who can demonstrate these skills, and relevant work experience is a great way to showcase them.
Relevant work experience also shows employers that you can handle challenges and overcome obstacles. Interviewers want to know that you have the ability to think on your feet and find solutions to problems that may arise in the workplace. By highlighting your relevant work experience, you can demonstrate to employers that you have a track record of success.
Relevant work experience is an essential component of problem-solving. It not only demonstrates your ability to solve problems in your industry or field, but it also highlights your transferable skills and ability to handle challenges. By showcasing your relevant work experience, you can increase your chances of landing your dream job and showcasing your problem-solving skills.
Related Articles
- Route Driver Job Description: A Complete Guide for 2023
- Crafting a Strong Reference Letter for a Friend in 2023
- The Best Resume Layout for 2023: Free Template and Tips
- Top Ecommerce Manager Resume Examples for 2023
- Utility Worker Job Description: A Complete Guide for 2023
Rate this article
0 / 5. Reviews: 0

More from ResumeHead


39 Best Problem-Solving Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Problem-solving is a process where you’re tasked with identifying an issue and coming up with the most practical and effective solution.
This indispensable skill is necessary in several aspects of life, from personal relationships to education to business decisions.
Problem-solving aptitude boosts rational thinking, creativity, and the ability to cooperate with others. It’s also considered essential in 21st Century workplaces.
If explaining your problem-solving skills in an interview, remember that the employer is trying to determine your ability to handle difficulties. Focus on explaining exactly how you solve problems, including by introducing your thoughts on some of the following frameworks and how you’ve applied them in the past.
Problem-Solving Examples
1. divergent thinking.
Divergent thinking refers to the process of coming up with multiple different answers to a single problem. It’s the opposite of convergent thinking, which would involve coming up with a singular answer .
The benefit of a divergent thinking approach is that it can help us achieve blue skies thinking – it lets us generate several possible solutions that we can then critique and analyze .
In the realm of problem-solving, divergent thinking acts as the initial spark. You’re working to create an array of potential solutions, even those that seem outwardly unrelated or unconventional, to get your brain turning and unlock out-of-the-box ideas.
This process paves the way for the decision-making stage, where the most promising ideas are selected and refined.
Go Deeper: Divervent Thinking Examples
2. Convergent Thinking
Next comes convergent thinking, the process of narrowing down multiple possibilities to arrive at a single solution.
This involves using your analytical skills to identify the best, most practical, or most economical solution from the pool of ideas that you generated in the divergent thinking stage.
In a way, convergent thinking shapes the “roadmap” to solve a problem after divergent thinking has supplied the “destinations.”
Have a think about which of these problem-solving skills you’re more adept at: divergent or convergent thinking?
Go Deeper: Convergent Thinking Examples
3. Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a group activity designed to generate a multitude of ideas regarding a specific problem. It’s divergent thinking as a group , which helps unlock even more possibilities.
A typical brainstorming session involves uninhibited and spontaneous ideation, encouraging participants to voice any possible solutions, no matter how unconventional they might appear.
It’s important in a brainstorming session to suspend judgment and be as inclusive as possible, allowing all participants to get involved.
By widening the scope of potential solutions, brainstorming allows better problem definition, more creative solutions, and helps to avoid thinking “traps” that might limit your perspective.
Go Deeper: Brainstorming Examples
4. Thinking Outside the Box
The concept of “thinking outside the box” encourages a shift in perspective, urging you to approach problems from an entirely new angle.
Rather than sticking to traditional methods and processes, it involves breaking away from conventional norms to cultivate unique solutions.
In problem-solving, this mindset can bypass established hurdles and bring you to fresh ideas that might otherwise remain undiscovered.
Think of it as going off the beaten track when regular routes present roadblocks to effective resolution.
5. Case Study Analysis
Analyzing case studies involves a detailed examination of real-life situations that bear relevance to the current problem at hand.
For example, if you’re facing a problem, you could go to another environment that has faced a similar problem and examine how they solved it. You’d then bring the insights from that case study back to your own problem.
This approach provides a practical backdrop against which theories and assumptions can be tested, offering valuable insights into how similar problems have been approached and resolved in the past.
See a Broader Range of Analysis Examples Here
6. Action Research
Action research involves a repetitive process of identifying a problem, formulating a plan to address it, implementing the plan, and then analyzing the results. It’s common in educational research contexts.
The objective is to promote continuous learning and improvement through reflection and action. You conduct research into your problem, attempt to apply a solution, then assess how well the solution worked. This becomes an iterative process of continual improvement over time.
For problem-solving, this method offers a way to test solutions in real-time and allows for changes and refinements along the way, based on feedback or observed outcomes. It’s a form of active problem-solving that integrates lessons learned into the next cycle of action.
Go Deeper: Action Research Examples
7. Information Gathering
Fundamental to solving any problem is the process of information gathering.
This involves collecting relevant data , facts, and details about the issue at hand, significantly aiding in the understanding and conceptualization of the problem.
In problem-solving, information gathering underpins every decision you make.
This process ensures your actions are based on concrete information and evidence, allowing for an informed approach to tackle the problem effectively.
8. Seeking Advice
Seeking advice implies turning to knowledgeable and experienced individuals or entities to gain insights on problem-solving.
It could include mentors, industry experts, peers, or even specialized literature.
The value in this process lies in leveraging different perspectives and proven strategies when dealing with a problem. Moreover, it aids you in avoiding pitfalls, saving time, and learning from others’ experiences.
9. Creative Thinking
Creative thinking refers to the ability to perceive a problem in a new way, identify unconventional patterns, or produce original solutions.
It encourages innovation and uniqueness, often leading to the most effective results.
When applied to problem-solving, creative thinking can help you break free from traditional constraints, ideal for potentially complex or unusual problems.
Go Deeper: Creative Thinking Examples
10. Conflict Resolution
Conflict resolution is a strategy developed to resolve disagreements and arguments, often involving communication, negotiation, and compromise.
When employed as a problem-solving technique, it can diffuse tension, clear bottlenecks, and create a collaborative environment.
Effective conflict resolution ensures that differing views or disagreements do not become roadblocks in the process of problem-solving.
Go Deeper: Conflict Resolution Examples
11. Addressing Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks refer to obstacles or hindrances that slow down or even halt a process.
In problem-solving, addressing bottlenecks involves identifying these impediments and finding ways to eliminate them.
This effort not only smooths the path to resolution but also enhances the overall efficiency of the problem-solving process.
For example, if your workflow is not working well, you’d go to the bottleneck – that one point that is most time consuming – and focus on that. Once you ‘break’ this bottleneck, the entire process will run more smoothly.
12. Market Research
Market research involves gathering and analyzing information about target markets, consumers, and competitors.
In sales and marketing, this is one of the most effective problem-solving methods. The research collected from your market (e.g. from consumer surveys) generates data that can help identify market trends, customer preferences, and competitor strategies.
In this sense, it allows a company to make informed decisions, solve existing problems, and even predict and prevent future ones.
13. Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a method used to identify the origin or the fundamental reason for a problem.
Once the root cause is determined, you can implement corrective actions to prevent the problem from recurring.
As a problem-solving procedure, root cause analysis helps you to tackle the problem at its source, rather than dealing with its surface symptoms.
Go Deeper: Root Cause Analysis Examples
14. Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual tool used to structure information, helping you better analyze, comprehend and generate new ideas.
By laying out your thoughts visually, it can lead you to solutions that might not have been apparent with linear thinking.
In problem-solving, mind mapping helps in organizing ideas and identifying connections between them, providing a holistic view of the situation and potential solutions.
15. Trial and Error
The trial and error method involves attempting various solutions until you find one that resolves the problem.
It’s an empirical technique that relies on practical actions instead of theories or rules.
In the context of problem-solving, trial and error allows you the flexibility to test different strategies in real situations, gaining insights about what works and what doesn’t.
16. SWOT Analysis
SWOT is an acronym standing for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
It’s an analytic framework used to evaluate these aspects in relation to a particular objective or problem.
In problem-solving, SWOT Analysis helps you to identify favorable and unfavorable internal and external factors. It helps to craft strategies that make best use of your strengths and opportunities, whilst addressing weaknesses and threats.
Go Deeper: SWOT Analysis Examples
17. Scenario Planning
Scenario planning is a strategic planning method used to make flexible long-term plans.
It involves imagining, and then planning for, multiple likely future scenarios.
By forecasting various directions a problem could take, scenario planning helps manage uncertainty and is an effective tool for problem-solving in volatile conditions.
18. Six Thinking Hats
The Six Thinking Hats is a concept devised by Edward de Bono that proposes six different directions or modes of thinking, symbolized by six different hat colors.
Each hat signifies a different perspective, encouraging you to switch ‘thinking modes’ as you switch hats. This method can help remove bias and broaden perspectives when dealing with a problem.
19. Decision Matrix Analysis
Decision Matrix Analysis is a technique that allows you to weigh different factors when faced with several possible solutions.
After listing down the options and determining the factors of importance, each option is scored based on each factor.
Revealing a clear winner that both serves your objectives and reflects your values, Decision Matrix Analysis grounds your problem-solving process in objectivity and comprehensiveness.
20. Pareto Analysis
Also known as the 80/20 rule, Pareto Analysis is a decision-making technique.
It’s based on the principle that 80% of problems are typically caused by 20% of the causes, making it a handy tool for identifying the most significant issues in a situation.
Using this analysis, you’re likely to direct your problem-solving efforts more effectively, tackling the root causes producing most of the problem’s impact.
21. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze facts to form a judgment objectively.
It involves logical, disciplined thinking that is clear, rational, open-minded, and informed by evidence.
For problem-solving, critical thinking helps evaluate options and decide the most effective solution. It ensures your decisions are grounded in reason and facts, and not biased or irrational assumptions.
Go Deeper: Critical Thinking Examples
22. Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing usually involves formulating a claim, testing it against actual data, and deciding whether to accept or reject the claim based on the results.
In problem-solving, hypotheses often represent potential solutions. Hypothesis testing provides verification, giving a statistical basis for decision-making and problem resolution.
Usually, this will require research methods and a scientific approach to see whether the hypothesis stands up or not.
Go Deeper: Types of Hypothesis Testing
23. Cost-Benefit Analysis
A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is a systematic process of weighing the pros and cons of different solutions in terms of their potential costs and benefits.
It allows you to measure the positive effects against the negatives and informs your problem-solving strategy.
By using CBA, you can identify which solution offers the greatest benefit for the least cost, significantly improving efficacy and efficiency in your problem-solving process.
Go Deeper: Cost-Benefit Analysis Examples
24. Simulation and Modeling
Simulations and models allow you to create a simplified replica of real-world systems to test outcomes under controlled conditions.
In problem-solving, you can broadly understand potential repercussions of different solutions before implementation.
It offers a cost-effective way to predict the impacts of your decisions, minimizing potential risks associated with various solutions.
25. Delphi Method
The Delphi Method is a structured communication technique used to gather expert opinions.
The method involves a group of experts who respond to questionnaires about a problem. The responses are aggregated and shared with the group, and the process repeats until a consensus is reached.
This method of problem solving can provide a diverse range of insights and solutions, shaped by the wisdom of a collective expert group.
26. Cross-functional Team Collaboration
Cross-functional team collaboration involves individuals from different departments or areas of expertise coming together to solve a common problem or achieve a shared goal.
When you bring diverse skills, knowledge, and perspectives to a problem, it can lead to a more comprehensive and innovative solution.
In problem-solving, this promotes communal thinking and ensures that solutions are inclusive and holistic, with various aspects of the problem being addressed.
27. Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing one’s business processes and performance metrics to the best practices from other companies or industries.
In problem-solving, it allows you to identify gaps in your own processes, determine how others have solved similar problems, and apply those solutions that have proven to be successful.
It also allows you to compare yourself to the best (the benchmark) and assess where you’re not as good.
28. Pros-Cons Lists
A pro-con analysis aids in problem-solving by weighing the advantages (pros) and disadvantages (cons) of various possible solutions.
This simple but powerful tool helps in making a balanced, informed decision.
When confronted with a problem, a pro-con analysis can guide you through the decision-making process, ensuring all possible outcomes and implications are scrutinized before arriving at the optimal solution. Thus, it helps to make the problem-solving process both methodical and comprehensive.
29. 5 Whys Analysis
The 5 Whys Analysis involves repeatedly asking the question ‘why’ (around five times) to peel away the layers of an issue and discover the root cause of a problem.
As a problem-solving technique, it enables you to delve into details that you might otherwise overlook and offers a simple, yet powerful, approach to uncover the origin of a problem.
For example, if your task is to find out why a product isn’t selling your first answer might be: “because customers don’t want it”, then you ask why again – “they don’t want it because it doesn’t solve their problem”, then why again – “because the product is missing a certain feature” … and so on, until you get to the root “why”.
30. Gap Analysis
Gap analysis entails comparing current performance with potential or desired performance.
You’re identifying the ‘gaps’, or the differences, between where you are and where you want to be.
In terms of problem-solving, a Gap Analysis can help identify key areas for improvement and design a roadmap of how to get from the current state to the desired one.
31. Design Thinking
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that involves empathy, experimentation, and iteration.
The process focuses on understanding user needs, challenging assumptions , and redefining problems from a user-centric perspective.
In problem-solving, design thinking uncovers innovative solutions that may not have been initially apparent and ensures the solution is tailored to the needs of those affected by the issue.
32. Analogical Thinking
Analogical thinking involves the transfer of information from a particular subject (the analogue or source) to another particular subject (the target).
In problem-solving, you’re drawing parallels between similar situations and applying the problem-solving techniques used in one situation to the other.
Thus, it allows you to apply proven strategies to new, but related problems.
33. Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking requires looking at a situation or problem from a unique, sometimes abstract, often non-sequential viewpoint.
Unlike traditional logical thinking methods, lateral thinking encourages you to employ creative and out-of-the-box techniques.
In solving problems, this type of thinking boosts ingenuity and drives innovation, often leading to novel and effective solutions.
Go Deeper: Lateral Thinking Examples
34. Flowcharting
Flowcharting is the process of visually mapping a process or procedure.
This form of diagram can show every step of a system, process, or workflow, enabling an easy tracking of the progress.
As a problem-solving tool, flowcharts help identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in a process, guiding improved strategies and providing clarity on task ownership and process outcomes.
35. Multivoting
Multivoting, or N/3 voting, is a method where participants reduce a large list of ideas to a prioritized shortlist by casting multiple votes.
This voting system elevates the most preferred options for further consideration and decision-making.
As a problem-solving technique, multivoting allows a group to narrow options and focus on the most promising solutions, ensuring more effective and democratic decision-making.
36. Force Field Analysis
Force Field Analysis is a decision-making technique that identifies the forces for and against change when contemplating a decision.
The ‘forces’ represent the differing factors that can drive or hinder change.
In problem-solving, Force Field Analysis allows you to understand the entirety of the context, favoring a balanced view over a one-sided perspective. A comprehensive view of all the forces at play can lead to better-informed problem-solving decisions.
TRIZ, which stands for “The Theory of Inventive Problem Solving,” is a problem-solving, analysis, and forecasting methodology.
It focuses on finding contradictions inherent in a scenario. Then, you work toward eliminating the contraditions through finding innovative solutions.
So, when you’re tackling a problem, TRIZ provides a disciplined, systematic approach that aims for ideal solutions and not just acceptable ones. Using TRIZ, you can leverage patterns of problem-solving that have proven effective in different cases, pivoting them to solve the problem at hand.
38. A3 Problem Solving
A3 Problem Solving, derived from Lean Management, is a structured method that uses a single sheet of A3-sized paper to document knowledge from a problem-solving process.
Named after the international paper size standard of A3 (or 11-inch by 17-inch paper), it succinctly records all key details of the problem-solving process from problem description to the root cause and corrective actions.
Used in problem-solving, this provides a straightforward and logical structure for addressing the problem, facilitating communication between team members, ensuring all critical details are included, and providing a record of decisions made.
39. Scenario Analysis
Scenario Analysis is all about predicting different possible future events depending upon your decision.
To do this, you look at each course of action and try to identify the most likely outcomes or scenarios down the track if you take that course of action.
This technique helps forecast the impacts of various strategies, playing each out to their (logical or potential) end. It’s a good strategy for project managers who need to keep a firm eye on the horizon at all times.
When solving problems, Scenario Analysis assists in preparing for uncertainties, making sure your solution remains viable, regardless of changes in circumstances.
How to Answer “Demonstrate Problem-Solving Skills” in an Interview
When asked to demonstrate your problem-solving skills in an interview, the STAR method often proves useful. STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action, and Result.
Situation: Begin by describing a specific circumstance or challenge you encountered. Make sure to provide enough detail to allow the interviewer a clear understanding. You should select an event that adequately showcases your problem-solving abilities.
For instance, “In my previous role as a project manager, we faced a significant issue when our key supplier abruptly went out of business.”
Task: Explain what your responsibilities were in that situation. This serves to provide context, allowing the interviewer to understand your role and the expectations placed upon you.
For instance, “It was my task to ensure the project remained on track despite this setback. Alternative suppliers needed to be found without sacrificing quality or significantly increasing costs.”
Action: Describe the steps you took to manage the problem. Highlight your problem-solving process. Mention any creative approaches or techniques that you used.
For instance, “I conducted thorough research to identify potential new suppliers. After creating a shortlist, I initiated contact, negotiated terms, assessed samples for quality and made a selection. I also worked closely with the team to re-adjust the project timeline.”
Result: Share the outcomes of your actions. How did the situation end? Did your actions lead to success? It’s particularly effective if you can quantify these results.
For instance, “As a result of my active problem solving, we were able to secure a new supplier whose costs were actually 10% cheaper and whose quality was comparable. We adjusted the project plan and managed to complete the project just two weeks later than originally planned, despite the major vendor setback.”
Remember, when you’re explaining your problem-solving skills to an interviewer, what they’re really interested in is your approach to handling difficulties, your creativity and persistence in seeking a resolution, and your ability to carry your solution through to fruition. Tailoring your story to highlight these aspects will help exemplify your problem-solving prowess.
Go Deeper: STAR Interview Method Examples
Benefits of Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is beneficial for the following reasons (among others):
- It can help you to overcome challenges, roadblocks, and bottlenecks in your life.
- It can save a company money.
- It can help you to achieve clarity in your thinking.
- It can make procedures more efficient and save time.
- It can strengthen your decision-making capacities.
- It can lead to better risk management.
Whether for a job interview or school, problem-solving helps you to become a better thinking, solve your problems more effectively, and achieve your goals. Build up your problem-solving frameworks (I presented over 40 in this piece for you!) and work on applying them in real-life situations.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Classroom Wall Decoration Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 31 Cute & Cozy Play Corner Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 24 Steiner-Waldorf Classroom Design Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Kindergarten Decoration Ideas
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

The Art of Effective Problem Solving: A Step-by-Step Guide
Author: Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
Whether we realise it or not, problem solving skills are an important part of our daily lives. From resolving a minor annoyance at home to tackling complex business challenges at work, our ability to solve problems has a significant impact on our success and happiness. However, not everyone is naturally gifted at problem-solving, and even those who are can always improve their skills. In this blog post, we will go over the art of effective problem-solving step by step.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let’s get started!
Problem Solving Methodologies
Individuals and organisations can use a variety of problem-solving methodologies to address complex challenges. 8D and A3 problem solving techniques are two popular methodologies in the Lean Six Sigma framework.
Methodology of 8D (Eight Discipline) Problem Solving:
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
The 8D process consists of the following steps:

- Form a team: Assemble a group of people who have the necessary expertise to work on the problem.
- Define the issue: Clearly identify and define the problem, including the root cause and the customer impact.
- Create a temporary containment plan: Put in place a plan to lessen the impact of the problem until a permanent solution can be found.
- Identify the root cause: To identify the underlying causes of the problem, use root cause analysis techniques such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts.
- Create and test long-term corrective actions: Create and test a long-term solution to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
- Implement and validate the permanent solution: Implement and validate the permanent solution’s effectiveness.
- Prevent recurrence: Put in place measures to keep the problem from recurring.
- Recognize and reward the team: Recognize and reward the team for its efforts.
Download the 8D Problem Solving Template
A3 Problem Solving Method:
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
The A3 problem-solving procedure consists of the following steps:
- Determine the issue: Define the issue clearly, including its impact on the customer.
- Perform root cause analysis: Identify the underlying causes of the problem using root cause analysis techniques.
- Create and implement a solution: Create and implement a solution that addresses the problem’s root cause.
- Monitor and improve the solution: Keep an eye on the solution’s effectiveness and make any necessary changes.
Subsequently, in the Lean Six Sigma framework, the 8D and A3 problem solving methodologies are two popular approaches to problem solving. Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Step 1 – Define the Problem
The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause. To avoid this pitfall, it is critical to thoroughly understand the problem.
To begin, ask yourself some clarifying questions:
- What exactly is the issue?
- What are the problem’s symptoms or consequences?
- Who or what is impacted by the issue?
- When and where does the issue arise?
Answering these questions will assist you in determining the scope of the problem. However, simply describing the problem is not always sufficient; you must also identify the root cause. The root cause is the underlying cause of the problem and is usually the key to resolving it permanently.
Try asking “why” questions to find the root cause:
- What causes the problem?
- Why does it continue?
- Why does it have the effects that it does?
By repeatedly asking “ why ,” you’ll eventually get to the bottom of the problem. This is an important step in the problem-solving process because it ensures that you’re dealing with the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
Once you have a firm grasp on the issue, it is time to divide it into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes tackling the problem easier and reduces the risk of becoming overwhelmed. For example, if you’re attempting to solve a complex business problem, you might divide it into smaller components like market research, product development, and sales strategies.
To summarise step 1, defining the problem is an important first step in effective problem-solving. You will be able to identify the root cause and break it down into manageable parts if you take the time to thoroughly understand the problem. This will prepare you for the next step in the problem-solving process, which is gathering information and brainstorming ideas.
Step 2 – Gather Information and Brainstorm Ideas

Gathering information and brainstorming ideas is the next step in effective problem solving. This entails researching the problem and relevant information, collaborating with others, and coming up with a variety of potential solutions. This increases your chances of finding the best solution to the problem.
Begin by researching the problem and relevant information. This could include reading articles, conducting surveys, or consulting with experts. The goal is to collect as much information as possible in order to better understand the problem and possible solutions.
Next, work with others to gather a variety of perspectives. Brainstorming with others can be an excellent way to come up with new and creative ideas. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas when working in a group, and make an effort to actively listen to what others have to say. Be open to new and unconventional ideas and resist the urge to dismiss them too quickly.
Finally, use brainstorming to generate a wide range of potential solutions. This is the place where you can let your imagination run wild. At this stage, don’t worry about the feasibility or practicality of the solutions; instead, focus on generating as many ideas as possible. Write down everything that comes to mind, no matter how ridiculous or unusual it may appear. This can be done individually or in groups.
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the next step in the problem-solving process, which we’ll go over in greater detail in the following section.
Step 3 – Evaluate Options and Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the third step in effective problem solving, and it entails weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, considering their feasibility and practicability, and selecting the solution that is most likely to solve the problem effectively.
To begin, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. This will assist you in determining the potential outcomes of each solution and deciding which is the best option. For example, a quick and easy solution may not be the most effective in the long run, whereas a more complex and time-consuming solution may be more effective in solving the problem in the long run.
Consider each solution’s feasibility and practicability. Consider the following:
- Can the solution be implemented within the available resources, time, and budget?
- What are the possible barriers to implementing the solution?
- Is the solution feasible in today’s political, economic, and social environment?
You’ll be able to tell which solutions are likely to succeed and which aren’t by assessing their feasibility and practicability.
Finally, choose the solution that is most likely to effectively solve the problem. This solution should be based on the criteria you’ve established, such as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and your overall goals.
It is critical to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to problems. What is effective for one person or situation may not be effective for another. This is why it is critical to consider a wide range of solutions and evaluate each one based on its ability to effectively solve the problem.

Step 4 – Implement and Monitor the Solution

When you’ve decided on the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. The fourth and final step in effective problem solving is to put the solution into action, monitor its progress, and make any necessary adjustments.
To begin, implement the solution. This may entail delegating tasks, developing a strategy, and allocating resources. Ascertain that everyone involved understands their role and responsibilities in the solution’s implementation.
Next, keep an eye on the solution’s progress. This may entail scheduling regular check-ins, tracking metrics, and soliciting feedback from others. You will be able to identify any potential roadblocks and make any necessary adjustments in a timely manner if you monitor the progress of the solution.
Finally, make any necessary modifications to the solution. This could entail changing the solution, altering the plan of action, or delegating different tasks. Be willing to make changes if they will improve the solution or help it solve the problem more effectively.
It’s important to remember that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to start from scratch. This is especially true if the initial solution does not effectively solve the problem. In these situations, it’s critical to be adaptable and flexible and to keep trying new solutions until you find the one that works best.
To summarise, effective problem solving is a critical skill that can assist individuals and organisations in overcoming challenges and achieving their objectives. Effective problem solving consists of four key steps: defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives and selecting the best solution, and implementing the solution.
You can increase your chances of success in problem solving by following these steps and considering factors such as the pros and cons of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and making any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, keep in mind that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to go back to the beginning and restart. Maintain your adaptability and try new solutions until you find the one that works best for you.
- Novick, L.R. and Bassok, M., 2005. Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press.
Was this helpful?

Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website www.learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.

Improvement Methodology: Selecting The Right 1

The 12 Principles of Agile Development: Understanding the Basics
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…
How to Nail your next Technical Interview
You may be missing out on a 66.5% salary hike*, nick camilleri, how many years of coding experience do you have, free course on 'sorting algorithms' by omkar deshpande (stanford phd, head of curriculum, ik).

What are problem-solving skills? (Examples included!)
Last updated by Swaminathan Iyer on Apr 01, 2024 at 01:09 PM | Reading time: 13 minutes
Life in the 21st century is all about efficiency and development. The unending quench of discovering the unknown, materializing one dream after another, has helped push the limits through the sky. But have you ever thought what the key to all of these astronomical successes is?
It is the zeal to solve a problem with the resources available to generate the best possible results.
Here's what this article will cover:
What are problem-solving skills , how do problem-solving skills help or act as your pillars of success, how do employers assess your problem-solving skills , steps to execute problem-solving skills, skills to hone for an apt solution-finder, examples of problem-solving techniques.
Dos and Don'ts in interviews
How to improve your problem-solving skills ?
How to highlight problem-solving skills .
Problem-solving is hunting; it is a savage pleasure, and we are born to it." –Thomas Harris .
The truth is, problem-solving skills are acquirable for some people while others adapt to it like fish in the water. Working in IT, web development, coding, machine learning, and the likes demand the ability to make decisions at a moment's notice.
So, do you want to back off when the time comes or take it up as a challenge?
Brush up your problem-solving skills or better, enhance them, and make them your forte by reading this article. No technical interview preparation guide is complete without tips to improve such problem-solving skills.
Also read: Why do FAANG companies test for problem-solving skills in their interviews.
Larry and his team suddenly face a major crisis. Not a single developer in his team who is good with String is coming to the office, but there is an urgent client requirement. Larry asks his team if anybody is confident enough to pull it through, and surprisingly, he sees one solitary hand of Jim in the mix. But it is a 4-men job, at least. Realizing that there is no way out other than working with another team(s), he wastes no time. He sends out emails to other teams asking for at least two more developers, counting himself and Jim. 4 more fellow coders came to the rescue and delivered the project before the deadline!
Problem-solving skills enable you to observe the situation and determine the contributing factors of the issue. Identifying the root cause and the ability to take necessary steps with available resources are integral in finessing your problem-solving ability.
All technical interview preparation courses , therefore, cover this crucial aspect.
Employers seek problem-solving skills in their employees . And why not?
Who wouldn't want to have an efficient employee like Larry? The knack of not backing down from a challenge is the perfect catalyst for business expansion.
Problem-solving skills help you attain insight into the source of the problem and figuring out an ideal solution. However, several skills and their correct implementation are essential, which are listed below.
- Patient listener : To identify a problem, you must first be all ears to gain information about the situation.
- Eye for detail : Once you start listening minutely, you now need to identify the data's discrepancies and have an intuitive eye for detail.
- Thorough research : Background research and data verification is bread and butter for efficient problem-solvers.
- Innovative approach : It is not just about getting it done. It's about taking a challenging approach in a mission to maximize results.
- Communication skills: Flawless communication skills are necessary to negate any misunderstanding and ensure conveying the message with clarity. You can indeed consider this as a great time saver!
- Composure : Your ability to remain calm even in a demanding situation will always earn you dividends in the path to success. It is not a quality that you can imbibe easily, but rigorous practice can do the trick for you.
- Decision-making ability : Having a knack for making the right decisions under pressure is a highly sought-after attribute by employers when hiring people. Taking quick decisions in dire straits is the reason why the company is paying you the big bucks.
- Team player : Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of your team is instrumental in maintaining team spirit. Higher the team spirit, the better the performance!
Employers today prioritize hiring people with soft skills like problem-solving abilities to maximize business output even when the going gets tough. Your problem-solving ability is judged based on:
- If you have accomplished any remarkable feat in a taxing situation. This gives an insight into the upper benchmark of your performance.
- Presenting hypothetical problems for the interviewee to solve is another commonly used trick to ascertain your productivity metrics and creative problem-solving techniques in tough conditions.
- Some organizations may even line up some challenging tests and exercises to have a firsthand look at the execution and effectiveness of your technical skills in the approach to problem-solving.
"We cannot solve a problem with the same level of thinking that created them." – Albert Einstein
- Analyze contributing factors
James was getting an error code during the execution of specific UI updates. He started analyzing the code and rechecking the repository for any possible mistake. To his delight, his hunch turned out to be accurate. He immediately made the necessary changes, and the updates were successfully executed.
Analysis of contributing factors and its repercussions in the ebb and flow of the task is a preliminary attribute of an able problem-solver. To acquire perfection in analysis and problem-solving skills, you must ensure a thorough:
- Gathering of data
- Diligent study of the collected data
- Scrutiny to filter relevant data
- Historical analysis
- Generate interventions
Working at a software development firm, Donald is perturbed by the lack of advancement in the deep learning project. Lack of idea and innovation is leading to nowhere. He decided that enough is enough. He asked for a group session to brainstorm in the hope of generating some leads. The session was a huge success, and Donald was finally able to catch a breather.
It is not an unknown fact that 'we' is always more productive than 'I' under any circumstance.
Utilizing the versatility of your available resources with the help of various sessions can work miracles. Such sessions can be for:
- Creative thinking
- Brainstorming
- Planning a project
- Forecasting future trends
- Prediction of possible outcomes
- Designing your project with originality, etc.
- Evaluate solutions
This is more up the alley for managers and team leads. To become adept at evaluating solutions, one must gain prolonged experience in corporate decision-making. The evaluation process needs to consider potential costs, available resources, and possible hurdles of project completion.
Remember Donald?
Yes, he is a team lead, and therefore, he had the authority to initiate a brainstorming session with multiple teams to bring in new ideas.
The secret to evaluating solutions?
- Corroboration
- Identifying change in trends
- Prioritization
- Implement a plan
Choosing the right course of action is the preliminary step to solve the problems. The success of the execution is streamlined with the help of quality benchmarks to indicate its effectiveness.
"A problem is a chance for you to do the best!" – Duke Ellington .
Knowing the right people to do it for you is essential for successful implementation. It is also crucial that you are accustomed to your organization's operating procedures before you formulate the best possible strategy.
Skills you need are:
- Project management
- Implementation of project strategy
- Collaboration
- Time management
- Developing appropriate quality benchmark
- Assess the solution's effectiveness
An ideal way to detect whether a solution is effective or not is to check if the problem still exists after applying the solution. Benchmarks need to be set as per organizational standards to help them assess the situation and if any further changes are required in the interim.
- Data analysis
- Communication
- Close follow-ups
- Troubleshooting
"A problem well stated is a problem half solved." –John Dewey
- Research: Problem-solving is not complete without extensive research. It is otherwise impossible to identify the problem without gathering enough data on the errors and their analysis. Consulting with your team gives you an edge to find the solution quicker.
- Analysis: Analysis of the situation is a must. Analytical skills further assist you in identifying the discrepancies and the possible actions which can resolve the issue.
- Decision-making: The ability to make decisions in hours of need defines your mettle. The onus is on you to be proactive and choose the right course of action.
- Communication: Are you great at conversations? If so, communication skills can help you garner much-required assistance for the project. Communication of the issues and how you want the project done are critical for the problem-solving process's smooth flow.
- Dependability: Having dependable members boosts the morale of the team. If you are a problem-solver, taking responsibility and taking it on the chin to solve the issues needs to be your forte.
- Select an example or situation that you can handle without any issue.
- Do not stray off topic and stay on track.
- Do not use jargon in your interview. So, choose your example and words wisely.
- Do not choose a redundant issue.
Sam has come to an interview for a team-lead profile. The recruiter asks a situation-based problem in regards to machine learning software. Though tricky, Sam knew the exact way around for the problem and answered it precisely to the point. The recruiter is delighted and hires Sam for the position.
- Thirst for knowledge : An insatiable thirst for knowledge is the secret door to success in problem-solving skills. If Sam was unaware of the tweaks needed to solve the problem, do you think the manager would have been impressed? No, managers at companies like Google and Facebook are looking for people who can act independently with their available resources. The question is, are you the problem solver who can be a catch to any company?
- An intuition for challenge : You need to be intuitive and have a sharp nose for challenges. The more you take up difficult situations and handle them with panache and ease, the more you can hone your problem-solving skills .
- Practice and more practice: Practice makes a man perfect – truer words have never been said. Effective problem solving is achieved not by slacking off but by acquainting yourself with various situations and applying your skills to resolve them. Remember, experience can never be substituted, and you have to take the long route to success!
- Keen and observant eyes : Do you have an eye for detail, and are you quick to point out discrepancies in data analysis? If yes, you are already one step towards becoming a valued problem solver in your company. Also, if you are a person who observes closely what is being done and why others do it, it helps develop your decision-making skills in future. Don't forget to mention this in your resume.
Tom has been applying frantically for a job since he moved to Arizona but seemed unable to find just the right one. When he sees his attempts are futile, he decides to add some of his previous company's achievements, thinking it might help. Oh, boy, did it help! Tom writes about when he was asked to handle a team of 12 single-handedly while his manager suddenly went on a sabbatical. Tom had no prior experience of leading a team but appeared to come out of this fix with flying colors.
Megan is currently looking for a step up in her career. She carefully drafts a cover letter that entails her achievements with clarity. The cover letter explained her contributions in reviving team spirit in the office after her predecessor, with his poor man-management, had successfully built a wall of distrust among the employees.
- Problem-solving skills for resume : You can convey your achievements or even your hobbies to the person sitting in front of you, or not, depending on his/her nature. But you cannot afford to miss the chance to showcase your best achievement. It is in your best interest to build your CV around the achievements to give it maximum traction and attention. Mention the problem you faced and jot down the course of action you took to nullify the situation. Nobody can stop you if this is done right!
- Problem-solving skills for cover letter : Use it as an opportunity to let the company delve into your success story so far and the factors leading to it. If you have done your research on the organization you're applying for, it will not hurt your chances of identifying some challenges of the company and suggesting some solutions. It goes down a long way if you indeed join forces!
If you are adequately seasoned with problem-solving skills with dedication and practice, you're already almost there. Proper interview preparation tips can further help you in this regard.

Swaminathan Iyer
Attend our free webinar on how to nail your next technical interview.

What is Diffing? How Does it Impact Code Management?
The role of a technical program manager, arraylist vs. linkedlist in java: choosing the right data structure, extend vs. append in python: list operations explained, nailing amazon's behavioral interview questions, git flow vs. github flow: a comparative guide to workflow strategies, top python scripting interview questions and answers you should practice, complex sql interview questions for interview preparation, zoox software engineer interview questions to crack your tech interview, rubrik interview questions for software engineers, top advanced sql interview questions and answers, twilio interview questions, ready to enroll, next webinar starts in.

Get tech interview-ready to navigate a tough job market
- Designed by 500 FAANG+ experts
- Live training and mock interviews
- 17000+ tech professionals trained
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

The 5 steps of the solving problem process
August 17, 2023 by MindManager Blog
Whether you run a business, manage a team, or work in an industry where change is the norm, it may feel like something is always going wrong. Thankfully, becoming proficient in the problem solving process can alleviate a great deal of the stress that business issues can create.
Understanding the right way to solve problems not only takes the guesswork out of how to deal with difficult, unexpected, or complex situations, it can lead to more effective long-term solutions.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the 5 steps of problem solving, and help you explore a few examples of problem solving scenarios where you can see the problem solving process in action before putting it to work.
Understanding the problem solving process
When something isn’t working, it’s important to understand what’s at the root of the problem so you can fix it and prevent it from happening again. That’s why resolving difficult or complex issues works best when you apply proven business problem solving tools and techniques – from soft skills, to software.
The problem solving process typically includes:
- Pinpointing what’s broken by gathering data and consulting with team members.
- Figuring out why it’s not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem.
- Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution.
While skills like active listening, collaboration, and leadership play an important role in problem solving, tools like visual mapping software make it easier to define and share problem solving objectives, play out various solutions, and even put the best fit to work.
Before you can take your first step toward solving a problem, you need to have a clear idea of what the issue is and the outcome you want to achieve by resolving it.
For example, if your company currently manufactures 50 widgets a day, but you’ve started processing orders for 75 widgets a day, you could simply say you have a production deficit.
However, the problem solving process will prove far more valuable if you define the start and end point by clarifying that production is running short by 25 widgets a day, and you need to increase daily production by 50%.
Once you know where you’re at and where you need to end up, these five steps will take you from Point A to Point B:
- Figure out what’s causing the problem . You may need to gather knowledge and evaluate input from different documents, departments, and personnel to isolate the factors that are contributing to your problem. Knowledge visualization software like MindManager can help.
- Come up with a few viable solutions . Since hitting on exactly the right solution – right away – can be tough, brainstorming with your team and mapping out various scenarios is the best way to move forward. If your first strategy doesn’t pan out, you’ll have others on tap you can turn to.
- Choose the best option . Decision-making skills, and software that lets you lay out process relationships, priorities, and criteria, are invaluable for selecting the most promising solution. Whether it’s you or someone higher up making that choice, it should include weighing costs, time commitments, and any implementation hurdles.
- Put your chosen solution to work . Before implementing your fix of choice, you should make key personnel aware of changes that might affect their daily workflow, and set up benchmarks that will make it easy to see if your solution is working.
- Evaluate your outcome . Now comes the moment of truth: did the solution you implemented solve your problem? Do your benchmarks show you achieved the outcome you wanted? If so, congratulations! If not, you’ll need to tweak your solution to meet your problem solving goal.
In practice, you might not hit a home-run with every solution you execute. But the beauty of a repeatable process like problem solving is that you can carry out steps 4 and 5 again by drawing from the brainstorm options you documented during step 2.
Examples of problem solving scenarios
The best way to get a sense of how the problem solving process works before you try it for yourself is to work through some simple scenarios.
Here are three examples of how you can apply business problem solving techniques to common workplace challenges.
Scenario #1: Manufacturing
Building on our original manufacturing example, you determine that your company is consistently short producing 25 widgets a day and needs to increase daily production by 50%.
Since you’d like to gather data and input from both your manufacturing and sales order departments, you schedule a brainstorming session to discover the root cause of the shortage.
After examining four key production areas – machines, materials, methods, and management – you determine the cause of the problem: the material used to manufacture your widgets can only be fed into your equipment once the machinery warms up to a specific temperature for the day.
Your team comes up with three possible solutions.
- Leave your machinery running 24 hours so it’s always at temperature.
- Invest in equipment that heats up faster.
- Find an alternate material for your widgets.
After weighing the expense of the first two solutions, and conducting some online research, you decide that switching to a comparable but less expensive material that can be worked at a lower temperature is your best option.
You implement your plan, monitor your widget quality and output over the following week, and declare your solution a success when daily production increases by 100%.
Scenario #2: Service Delivery
Business training is booming and you’ve had to onboard new staff over the past month. Now you learn that several clients have expressed concern about the quality of your recent training sessions.
After speaking with both clients and staff, you discover there are actually two distinct factors contributing to your quality problem:
- The additional conference room you’ve leased to accommodate your expanding training sessions has terrible acoustics
- The AV equipment you’ve purchased to accommodate your expanding workforce is on back-order – and your new hires have been making do without
You could look for a new conference room or re-schedule upcoming training sessions until after your new equipment arrives. But your team collaboratively determines that the best way to mitigate both issues at once is by temporarily renting the high-quality sound and visual system they need.
Using benchmarks that include several weeks of feedback from session attendees, and random session spot-checks you conduct personally, you conclude the solution has worked.
Scenario #3: Marketing
You’ve invested heavily in product marketing, but still can’t meet your sales goals. Specifically, you missed your revenue target by 30% last year and would like to meet that same target this year.
After collecting and examining reams of information from your sales and accounting departments, you sit down with your marketing team to figure out what’s hindering your success in the marketplace.
Determining that your product isn’t competitively priced, you map out two viable solutions.
- Hire a third-party specialist to conduct a detailed market analysis.
- Drop the price of your product to undercut competitors.
Since you’re in a hurry for results, you decide to immediately reduce the price of your product and market it accordingly.
When revenue figures for the following quarter show sales have declined even further – and marketing surveys show potential customers are doubting the quality of your product – you revert back to your original pricing, revisit your problem solving process, and implement the market analysis solution instead.
With the valuable information you gain, you finally arrive at just the right product price for your target market and sales begin to pick up. Although you miss your revenue target again this year, you meet it by the second quarter of the following year.
Kickstart your collaborative brainstorming sessions and try MindManager for free today !
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager

Culture Development
Workplace problem-solving examples: real scenarios, practical solutions.
- March 11, 2024
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing work environment, problems are inevitable. From conflicts among employees to high levels of stress, workplace problems can significantly impact productivity and overall well-being. However, by developing the art of problem-solving and implementing practical solutions, organizations can effectively tackle these challenges and foster a positive work culture. In this article, we will delve into various workplace problem scenarios and explore strategies for resolution. By understanding common workplace problems and acquiring essential problem-solving skills, individuals and organizations can navigate these challenges with confidence and success.

Understanding Workplace Problems
Before we can effectively solve workplace problems , it is essential to gain a clear understanding of the issues at hand. Identifying common workplace problems is the first step toward finding practical solutions. By recognizing these challenges, organizations can develop targeted strategies and initiatives to address them.
Identifying Common Workplace Problems
One of the most common workplace problems is conflict. Whether it stems from differences in opinions, miscommunication, or personality clashes, conflict can disrupt collaboration and hinder productivity. It is important to note that conflict is a natural part of any workplace, as individuals with different backgrounds and perspectives come together to work towards a common goal. However, when conflict is not managed effectively, it can escalate and create a toxic work environment.
In addition to conflict, workplace stress and burnout pose significant challenges. High workloads, tight deadlines, and a lack of work-life balance can all contribute to employee stress and dissatisfaction. When employees are overwhelmed and exhausted, their performance and overall well-being are compromised. This not only affects the individuals directly, but it also has a ripple effect on the entire organization.
Another common workplace problem is poor communication. Ineffective communication can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and errors. It can also create a sense of confusion and frustration among employees. Clear and open communication is vital for successful collaboration and the smooth functioning of any organization.
The Impact of Workplace Problems on Productivity
Workplace problems can have a detrimental effect on productivity levels. When conflicts are left unresolved, they can create a tense work environment, leading to decreased employee motivation and engagement. The negative energy generated by unresolved conflicts can spread throughout the organization, affecting team dynamics and overall performance.
Similarly, high levels of stress and burnout can result in decreased productivity, as individuals may struggle to focus and perform optimally. When employees are constantly under pressure and overwhelmed, their ability to think creatively and problem-solve diminishes. This can lead to a decline in the quality of work produced and an increase in errors and inefficiencies.
Poor communication also hampers productivity. When information is not effectively shared or understood, it can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and rework. This not only wastes time and resources but also creates frustration and demotivation among employees.
Furthermore, workplace problems can negatively impact employee morale and job satisfaction. When individuals are constantly dealing with conflicts, stress, and poor communication, their overall job satisfaction and engagement suffer. This can result in higher turnover rates, as employees seek a healthier and more supportive work environment.
In conclusion, workplace problems such as conflict, stress, burnout, and poor communication can significantly hinder productivity and employee well-being. Organizations must address these issues promptly and proactively to create a positive and productive work atmosphere. By fostering open communication, providing support for stress management, and promoting conflict resolution strategies, organizations can create a work environment that encourages collaboration, innovation, and employee satisfaction.

The Art of Problem Solving in the Workplace
Now that we have a clear understanding of workplace problems, let’s explore the essential skills necessary for effective problem-solving in the workplace. By developing these skills and adopting a proactive approach, individuals can tackle problems head-on and find practical solutions.
Problem-solving in the workplace is a complex and multifaceted skill that requires a combination of analytical thinking, creativity, and effective communication. It goes beyond simply identifying problems and extends to finding innovative solutions that address the root causes.
Essential Problem-Solving Skills for the Workplace
To effectively solve workplace problems, individuals should possess a range of skills. These include strong analytical and critical thinking abilities, excellent communication and interpersonal skills, the ability to collaborate and work well in a team, and the capacity to adapt to change. By honing these skills, individuals can approach workplace problems with confidence and creativity.
Analytical and critical thinking skills are essential for problem-solving in the workplace. They involve the ability to gather and analyze relevant information, identify patterns and trends, and make logical connections. These skills enable individuals to break down complex problems into manageable components and develop effective strategies to solve them.
Effective communication and interpersonal skills are also crucial for problem-solving in the workplace. These skills enable individuals to clearly articulate their thoughts and ideas, actively listen to others, and collaborate effectively with colleagues. By fostering open and honest communication channels, individuals can better understand the root causes of problems and work towards finding practical solutions.
Collaboration and teamwork are essential for problem-solving in the workplace. By working together, individuals can leverage their diverse skills, knowledge, and perspectives to generate innovative solutions. Collaboration fosters a supportive and inclusive environment where everyone’s ideas are valued, leading to more effective problem-solving outcomes.
The ability to adapt to change is another important skill for problem-solving in the workplace. In today’s fast-paced and dynamic work environment, problems often arise due to changes in technology, processes, or market conditions. Individuals who can embrace change and adapt quickly are better equipped to find solutions that address the evolving needs of the organization.
The Role of Communication in Problem Solving
Communication is a key component of effective problem-solving in the workplace. By fostering open and honest communication channels, individuals can better understand the root causes of problems and work towards finding practical solutions. Active listening, clear and concise articulation of thoughts and ideas, and the ability to empathize are all valuable communication skills that facilitate problem-solving.
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker, paying attention to both verbal and non-verbal cues, and seeking clarification when necessary. By actively listening, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the problem at hand and the perspectives of others involved. This understanding is crucial for developing comprehensive and effective solutions.
Clear and concise articulation of thoughts and ideas is essential for effective problem-solving communication. By expressing oneself clearly, individuals can ensure that their ideas are understood by others. This clarity helps to avoid misunderstandings and promotes effective collaboration.
Empathy is a valuable communication skill that plays a significant role in problem-solving. By putting oneself in the shoes of others and understanding their emotions and perspectives, individuals can build trust and rapport. This empathetic connection fosters a supportive and collaborative environment where everyone feels valued and motivated to contribute to finding solutions.
In conclusion, problem-solving in the workplace requires a combination of essential skills such as analytical thinking, effective communication, collaboration, and adaptability. By honing these skills and fostering open communication channels, individuals can approach workplace problems with confidence and creativity, leading to practical and innovative solutions.
Real Scenarios of Workplace Problems
Now, let’s explore some real scenarios of workplace problems and delve into strategies for resolution. By examining these practical examples, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of how to approach and solve workplace problems.
Conflict Resolution in the Workplace
Imagine a scenario where two team members have conflicting ideas on how to approach a project. The disagreement becomes heated, leading to a tense work environment. To resolve this conflict, it is crucial to encourage open dialogue between the team members. Facilitating a calm and respectful conversation can help uncover underlying concerns and find common ground. Collaboration and compromise are key in reaching a resolution that satisfies all parties involved.
In this particular scenario, let’s dive deeper into the dynamics between the team members. One team member, let’s call her Sarah, strongly believes that a more conservative and traditional approach is necessary for the project’s success. On the other hand, her colleague, John, advocates for a more innovative and out-of-the-box strategy. The clash between their perspectives arises from their different backgrounds and experiences.
As the conflict escalates, it is essential for a neutral party, such as a team leader or a mediator, to step in and facilitate the conversation. This person should create a safe space for both Sarah and John to express their ideas and concerns without fear of judgment or retribution. By actively listening to each other, they can gain a better understanding of the underlying motivations behind their respective approaches.
During the conversation, it may become apparent that Sarah’s conservative approach stems from a fear of taking risks and a desire for stability. On the other hand, John’s innovative mindset is driven by a passion for pushing boundaries and finding creative solutions. Recognizing these underlying motivations can help foster empathy and create a foundation for collaboration.
As the dialogue progresses, Sarah and John can begin to identify areas of overlap and potential compromise. They may realize that while Sarah’s conservative approach provides stability, John’s innovative ideas can inject fresh perspectives into the project. By combining their strengths and finding a middle ground, they can develop a hybrid strategy that incorporates both stability and innovation.
Ultimately, conflict resolution in the workplace requires effective communication, active listening, empathy, and a willingness to find common ground. By addressing conflicts head-on and fostering a collaborative environment, teams can overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
Dealing with Workplace Stress and Burnout
Workplace stress and burnout can be debilitating for individuals and organizations alike. In this scenario, an employee is consistently overwhelmed by their workload and experiencing signs of burnout. To address this issue, organizations should promote a healthy work-life balance and provide resources to manage stress effectively. Encouraging employees to take breaks, providing access to mental health support, and fostering a supportive work culture are all practical solutions to alleviate workplace stress.
In this particular scenario, let’s imagine that the employee facing stress and burnout is named Alex. Alex has been working long hours, often sacrificing personal time and rest to meet tight deadlines and demanding expectations. As a result, Alex is experiencing physical and mental exhaustion, reduced productivity, and a sense of detachment from work.
Recognizing the signs of burnout, Alex’s organization takes proactive measures to address the issue. They understand that employee well-being is crucial for maintaining a healthy and productive workforce. To promote a healthy work-life balance, the organization encourages employees to take regular breaks and prioritize self-care. They emphasize the importance of disconnecting from work during non-working hours and encourage employees to engage in activities that promote relaxation and rejuvenation.
Additionally, the organization provides access to mental health support services, such as counseling or therapy sessions. They recognize that stress and burnout can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental well-being and offer resources to help employees manage their stress effectively. By destigmatizing mental health and providing confidential support, the organization creates an environment where employees feel comfortable seeking help when needed.
Furthermore, the organization fosters a supportive work culture by promoting open communication and empathy. They encourage managers and colleagues to check in with each other regularly, offering support and understanding. Team members are encouraged to collaborate and share the workload, ensuring that no one person is overwhelmed with excessive responsibilities.
By implementing these strategies, Alex’s organization aims to alleviate workplace stress and prevent burnout. They understand that a healthy and balanced workforce is more likely to be engaged, productive, and satisfied. Through a combination of promoting work-life balance, providing mental health support, and fostering a supportive work culture, organizations can effectively address workplace stress and create an environment conducive to employee well-being.
Practical Solutions to Workplace Problems
Now that we have explored real scenarios, let’s discuss practical solutions that organizations can implement to address workplace problems. By adopting proactive strategies and establishing effective policies, organizations can create a positive work environment conducive to problem-solving and productivity.
Implementing Effective Policies for Problem Resolution
Organizations should have clear and well-defined policies in place to address workplace problems. These policies should outline procedures for conflict resolution, channels for reporting problems, and accountability measures. By ensuring that employees are aware of these policies and have easy access to them, organizations can facilitate problem-solving and prevent issues from escalating.
Promoting a Positive Workplace Culture
A positive workplace culture is vital for problem-solving. By fostering an environment of respect, collaboration, and open communication, organizations can create a space where individuals feel empowered to address and solve problems. Encouraging teamwork, recognizing and appreciating employees’ contributions, and promoting a healthy work-life balance are all ways to cultivate a positive workplace culture.
The Role of Leadership in Problem Solving
Leadership plays a crucial role in facilitating effective problem-solving within organizations. Different leadership styles can impact how problems are approached and resolved.
Leadership Styles and Their Impact on Problem-Solving
Leaders who adopt an autocratic leadership style may make decisions independently, potentially leaving their team members feeling excluded and undervalued. On the other hand, leaders who adopt a democratic leadership style involve their team members in the problem-solving process, fostering a sense of ownership and empowerment. By encouraging employee participation, organizations can leverage the diverse perspectives and expertise of their workforce to find innovative solutions to workplace problems.
Encouraging Employee Participation in Problem Solving
To harness the collective problem-solving abilities of an organization, it is crucial to encourage employee participation. Leaders can create opportunities for employees to contribute their ideas and perspectives through brainstorming sessions, team meetings, and collaborative projects. By valuing employee input and involving them in decision-making processes, organizations can foster a culture of inclusivity and drive innovative problem-solving efforts.
In today’s dynamic work environment, workplace problems are unavoidable. However, by understanding common workplace problems, developing essential problem-solving skills, and implementing practical solutions, individuals and organizations can navigate these challenges effectively. By fostering a positive work culture, implementing effective policies, and encouraging employee participation, organizations can create an environment conducive to problem-solving and productivity. With proactive problem-solving strategies in place, organizations can thrive and overcome obstacles, ensuring long-term success and growth.
Related Stories
- June 17, 2024
What is Team Morale and How to Boost It
Navigating through the maze: understanding types of organizational change, transform your business with a top change management consultant, what can we help you find.
- Resume Writing
- Resume Examples
- Cover Letter
- Remote Work
- Famous Resumes
- Try Kickresume
7 Problem Solving Skills That Aren’t Just Buzzwords (+ Resume Example)
- Julia Mlcuchova ,
- Updated April 8, 2024 9 min read
Problem-solving skills are something everybody should include on their resume, yet only a few seem to understand what these skills actually are. If you've always felt that the term "problem-solving skills" is rather vague and wanted to know more, you've come to the right place.
In this article, we're going to explain what problem-solving skills really mean. We'll talk about what makes up good problem-solving skills and give you tips on how to get better at them. You'll also find out how to make your problem-solving abilities look more impressive to those who might want to hire you.
Sounds good, right? Curious to learn more?
In this article we’ll show you:
- What are problem solving skills;
- Why are they important;
- Specific problem solving skills examples;
- How to develop your problem solving skills;
- And, how to showcase them on your resume.
Table of Contents
Click on a section to skip
What are problem solving skills?
Why are problem solving skills important, the best 7 problem solving skills examples, how to develop problem solving skills, problem solving skills resume example, key takeaways: problem solving skills.
First of all, they're more than just a buzzword!
Problem-solving skills are a set of specific abilities that allow you to deal with unexpected situations in the workplace, whether it be job related or team related.
It's a complex process that involves several “sub skills” or “sub steps,” namely:
- Recognizing and identifying the issue at hand.
- Breaking the problem down into smaller parts and analyzing how they relate to one another.
- Creating potential solutions to the problem, evaluating them and picking the best one.
- Applying the chosen solution and assessing its outcome.
- Learning from the whole process to deal with future problems more effectively.
As you can see, it's not just about solving problems that are right in front of us, but also about predicting potential issues and being prepared to deal with them before they arise.
Despite what you may believe, problem-solving skills aren't just for managers .
Think about it this way: Why do employers hire employees in the first place? To solve problems for them!
And, as we all know, problems don't discriminate. In other words, it doesn't matter whether you're just an intern, an entry-level professional, or a seasoned veteran, you'll constantly face some kind of challenges. And the only difference is in how complex they will get.
This is also reflected in the way employers assess suitability of potential job candidates.
In fact, research shows that the ability to deal with unexpected complications is prioritized by an overwhelming 60% of employers across all industries, making it one of the most compelling skills on your resume.
So, regardless of your job description or your career level, you're always expected to find solutions for problems, either independently or as a part of a team.
And that's precisely what makes problem-solving skills so invaluable and universal !
Wondering how good is your resume?
Find out with our AI Resume Checker! Just upload your resume and see what can be improved.
As we've said before, problem-solving isn't really just one single skill.
Instead, your ability to handle workplace issues with composure depends on several different “sub-skills”.
So, which specific skills make an employee desirable even for the most demanding of recruiters?
In no particular order, you should focus on these 7 skills :
- Analytical skills
- Research skills
- Critical thinking
- Decision-making
- Collaboration
- Having a growth mindset
Let's have a look at each of them in greater detail!
#1 Analytical skills
Firstly, to truly understand complex problems, you need to break them down into more manageable parts . Then, you observe them closely and ask yourself: “ Which parts work and which don't,” How do these parts contribute to the problem as a whole,” and "What exactly needs to be fixed?” In other words, you gather data , you study it, and compare it - all to pinpoint the cause of the issue as closely as possible.
#2 Research skills
Another priceless tool is your research skills (sometimes relying on just one source of information isn't enough). Besides, to make a truly informed decision , you'll have to dig a little deeper. Being a good researcher means looking for potential solutions to a problem in a wider context. For example: going through team reports, customer feedback, quarterly sales or current market trends.
#3 Critical thinking
Every employer wants to hire people who can think critically. Yet, the ability to evaluate situations objectively and from different perspectives , is actually pretty hard to come by. But as long as you stay open-minded, inquisitive, and with a healthy dose of skepticism, you'll be able to assess situations based on facts and evidence more successfully. Plus, critical thinking comes in especially handy when you need to examine your own actions and processes.
#4 Creativity
Instead of following the old established processes that don't work anymore, you should feel comfortable thinking outside the box. The thing is, problems have a nasty habit of popping up unexpectedly and rapidly. And sometimes, you have to get creative in order to solve them fast. Especially those that have no precedence. But this requires a blend of intuition, industry knowledge, and quick thinking - a truly rare combination.
#5 Decision-making
The analysis, research, and brainstorming are done. Now, you need to look at the possible solutions, and make the final decision (informed, of course). And not only that, you also have to stand by it ! Because once the train gets moving, there's no room for second guessing. Also, keep in mind that you need to be prepared to take responsibility for all decisions you make. That's no small feat!
#6 Collaboration
Not every problem you encounter can be solved by yourself alone. And this is especially true when it comes to complex projects. So, being able to actively listen to your colleagues, take their ideas into account, and being respectful of their opinions enables you to solve problems together. Because every individual can offer a unique perspective and skill set. Yes, democracy is hard, but at the end of the day, it's teamwork that makes the corporate world go round.
#7 Having a growth mindset
Let's be honest, no one wants their work to be riddled with problems. But facing constant challenges and changes is inevitable. And that can be scary! However, when you're able to see these situations as opportunities to grow instead of issues that hold you back, your problem solving skills reach new heights. And the employers know that too!
Now that we've shown you the value problem-solving skills can add to your resume, let's ask the all-important question: “How can I learn them?”
Well…you can't. At least not in the traditional sense of the word.
Let us explain: Since problem-solving skills fall under the umbrella of soft skills , they can't be taught through formal education, unlike computer skills for example. There's no university course that you can take and graduate as a professional problem solver.
But, just like other interpersonal skills, they can be nurtured and refined over time through practice and experience.
Unfortunately, there's no one-size-fits-all approach, but the following tips can offer you inspiration on how to improve your problem solving skills:
- Cultivate a growth mindset. Remember what we've said before? Your attitude towards obstacles is the first step to unlocking your problem-solving potential.
- Gain further knowledge in your specialized field. Secondly, it's a good idea to delve a little deeper into your chosen profession. Because the more you read on a subject, the easier it becomes to spot certain patterns and relations.
- Start with small steps. Don't attack the big questions straight away — you'll only set yourself up for failure. Instead, start with more straightforward tasks and work your way up to more complex problems.
- Break problems down into more digestible pieces. Complex issues are made up of smaller problems. And those can be further divided into even smaller problems, and so on. Until you're left with only the basics.
- Don't settle for a single solution. Instead, keep on exploring other possible answers.
- Accept failure as a part of the learning process. Finally, don't let your failures discourage you. After all, you're bound to misstep a couple of times before you find your footing. Just keep on practicing.
How to improve problem solving skills with online courses
While it’s true that formal education won’t turn you into a master problem solver, you can still hone your skills with courses and certifications offered by online learning platforms :
- Analytical skills. You can sharpen your analytical skills with Data Analytics Basics for Everyone from IBM provided by edX (Free); or Decision Making and Analytical Thinking: Fortune 500 provided by Udemy ($21,74).
- Creativity. And, to unlock your inner creative mind, you can try Creative Thinking: Techniques and Tools for Success from the Imperial College London provided by Coursera (Free).
- Critical thinking. Try Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking Specialization from Duke University provided by Coursera (Free); or Logical and Critical Thinking offered by The University of Auckland via FutureLearn.
- Decision-making. Or, you can learn how to become more confident when it's time to make a decision with Decision-Making Strategies and Executive Decision-Making both offered by LinkedIn Learning (1 month free trial).
- Communication skills . Lastly, to improve your collaborative skills, check out Communicating for Influence and Impact online at University of Cambridge.
The fact that everybody and their grandmothers put “ problem-solving skills ” on their CVs has turned the phrase into a cliche.
But there's a way to incorporate these skills into your resume without sounding pretentious and empty. Below, we've prepared a mock-up resume that manages to do just that.
FYI, if you like this design, you can use the template to create your very own resume. Just click the red button and fill in your information (or let the AI do it for you).
Problem solving skills on resume example
This resume was written by our experienced resume writers specifically for this profession.
Why this example works?
- Firstly, the job description itself is neatly organized into bullet points .
- Instead of simply listing soft skills in a skills section , you can incorporate them into the description of your work experience entry.
- Also, the language here isn't vague . This resume puts each problem-solving skill into a real-life context by detailing specific situations and obstacles.
- And, to highlight the impact of each skill on your previous job position, we recommend quantifying your results whenever possible.
- Finally, starting each bullet point with an action verb (in bold) makes you look more dynamic and proactive.
To sum it all up, problem-solving skills continue gaining popularity among employers and employees alike. And for a good reason!
Because of them, you can overcome any obstacles that stand in the way of your professional life more efficiently and systematically.
In essence, problem-solving skills refer to the ability to recognize a challenge, identify its root cause, think of possible solutions , and then implement the most effective one.
Believing that these skills are all the same would be a serious misconception. In reality, this term encompasses a variety of different abilities , including:
In short, understanding, developing, and showcasing these skills, can greatly boost your chances at getting noticed by the hiring managers. So, don't hesitate and start working on your problem-solving skills right now!
Julia has recently joined Kickresume as a career writer. From helping people with their English to get admitted to the uni of their dreams to advising them on how to succeed in the job market. It would seem that her career is on a steadfast trajectory. Julia holds a degree in Anglophone studies from Metropolitan University in Prague, where she also resides. Apart from creative writing and languages, she takes a keen interest in literature and theatre.
Related Posts
These resume mistakes are sabotaging your job search — how to avoid them, how to create an automotive resume that wins the job race (+resume examples), share this article, join our newsletter.
Every month, we’ll send you resume advice, job search tips, career hacks and more in pithy, bite-sized chunks. Sounds good?
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Career Planning
- Skills Development
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Definition & Examples of Problem-Solving Skills
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
- Problem-solving skills help you determine why an issue is happening and how to resolve that issue.
Learn more about problem-solving skills and how they work.
Problem-solving skills help you solve issues quickly and effectively. It's one of the key skills that employers seek in job applicants, as employees with these skills tend to be self-reliant. Problem-solving skills require quickly identifying the underlying issue and implementing a solution.
Problem-solving is considered a soft skill (a personal strength) rather than a hard skill that's learned through education or training. You can improve your problem-solving skills by familiarizing yourself with common issues in your industry and learning from more experienced employees.
How Problem-Solving Skills Work
Problem-solving starts with identifying the issue. For example, a teacher might need to figure out how to improve student performance on a writing proficiency test. To do that, the teacher will review the writing tests looking for areas of improvement. They might see that students can construct simple sentences, but they're struggling with writing paragraphs and organizing those paragraphs into an essay.
To solve the problem, the teacher would work with students on how and when to write compound sentences, how to write paragraphs, and ways to organize an essay.
Theresa Chiechi / The Balance
There are five steps typically used in problem-solving.
1. Analyze Contributing Factors
To solve a problem, you must find out what caused it. This requires you to gather and evaluate data, isolate possible contributing circumstances, and pinpoint what needs to be addressed for a resolution.
To do this, you'll use skills like :
- Data gathering
- Data analysis
- Fact-finding
- Historical analysis
2. Generate Interventions
Once you’ve determined the cause, brainstorm possible solutions. Sometimes this involves teamwork since two (or more) minds are often better than one. A single strategy is rarely the obvious route to solving a complex problem; devising a set of alternatives helps you cover your bases and reduces your risk of exposure should the first strategy you implement fail.
This involves skills like :
- Brainstorming
- Creative thinking
- Forecasting
- Project design
- Project planning
3. Evaluate Solutions
Depending on the nature of the problem and your chain of command, evaluating best solutions may be performed by assigned teams, team leads, or forwarded to corporate decision-makers. Whoever makes the decision must evaluate potential costs, required resources, and possible barriers to successful solution implementation.
This requires several skills, including:
- Corroboration
- Test development
- Prioritizing
4. Implement a Plan
Once a course of action has been decided, it must be implemented along with benchmarks that can quickly and accurately determine whether it’s working. Plan implementation also involves letting personnel know about changes in standard operating procedures.
This requires skills like:
- Project management
- Project implementation
- Collaboration
- Time management
- Benchmark development
5. Assess the Solution's Effectiveness
Once a solution is implemented, the best problem-solvers have systems in place to evaluate if and how quickly it's working. This way, they know as soon as possible whether the issue has been resolved or whether they’ll have to change their response to the problem mid-stream.
This requires:
- Communication
- Customer feedback
- Follow-through
- Troubleshooting
Here's an example of showing your problem-solving skills in a cover letter.
When I was first hired as a paralegal, I inherited a backlog of 25 sets of medical records that needed to be summarized, each of which was hundreds of pages long. At the same time, I had to help prepare for three major cases, and there weren’t enough hours in the day. After I explained the problem to my supervisor, she agreed to pay me to come in on Saturday mornings to focus on the backlog. I was able to eliminate the backlog in a month.
Here's another example of how to show your problem-solving skills in a cover letter:
When I joined the team at Great Graphics as Artistic Director, the designers had become uninspired because of a former director who attempted to micro-manage every step in the design process. I used weekly round-table discussions to solicit creative input and ensured that each designer was given full autonomy to do their best work. I also introduced monthly team-based competitions that helped build morale, spark new ideas, and improve collaboration.
Highlighting Problem-Solving Skills
- Since this is a skill that's important to most employers, put them front and center on your resume, cover letter, and in interviews.
If you're not sure what to include, look to previous roles—whether in academic, work, or volunteer settings—for examples of challenges you met and problems you solved. Highlight relevant examples in your cover letter and use bullet points in your resume to show how you solved a problem.
During interviews, be ready to describe situations you've encountered in previous roles, the processes you followed to address problems, the skills you applied, and the results of your actions. Potential employers are eager to hear a coherent narrative of the ways you've used problem-solving skills .
Interviewers may pose hypothetical problems for you to solve. Base your answers on the five steps and refer to similar problems you've resolved, if possible. Here are tips for answering problem-solving interview questions , with examples of the best answers.
Key Takeaways
- It's one of the key skills that employers seek in job applicants.
- Problem-solving starts with identifying the issue, coming up with solutions, implementing those solutions, and evaluating their effectiveness.
- For Individuals
- For Businesses
- For Universities
- For Governments
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
7 Problem-Solving Skills That Can Help You Be a More Successful Manager
Discover what problem-solving is, and why it's important for managers. Understand the steps of the process and learn about seven problem-solving skills.
![what is a example for problem solving [Featured Image]: A manager wearing a black suit is talking to a team member, handling an issue utilizing the process of problem-solving](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/6uiffmHlG1nCAhji06VPaV/06ef7be91702ee158c66d2caeae98607/iStock-1176251115__2_.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
1Managers oversee the day-to-day operations of a particular department, and sometimes a whole company, using their problem-solving skills regularly. Managers with good problem-solving skills can help ensure companies run smoothly and prosper.
If you're a current manager or are striving to become one, read this guide to discover what problem-solving skills are and why it's important for managers to have them. Learn the steps of the problem-solving process, and explore seven skills that can help make problem-solving easier and more effective.
What is problem-solving?
Problem-solving is both an ability and a process. As an ability, problem-solving can aid in resolving issues faced in different environments like home, school, abroad, and social situations, among others. As a process, problem-solving involves a series of steps for finding solutions to questions or concerns that arise throughout life.
The importance of problem-solving for managers
Managers deal with problems regularly, whether supervising a staff of two or 100. When people solve problems quickly and effectively, workplaces can benefit in a number of ways. These include:
Greater creativity
Higher productivity
Increased job fulfillment
Satisfied clients or customers
Better cooperation and cohesion
Improved environments for employees and customers
7 skills that make problem-solving easier
Companies depend on managers who can solve problems adeptly. Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork.
1. Analysis
As a manager , you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first. Then, you’ll use analytical skills to distinguish between ineffective and effective solutions.
2. Communication
Effective communication plays a significant role in problem-solving, particularly when others are involved. Some skills that can help enhance communication at work include active listening, speaking with an even tone and volume, and supporting verbal information with written communication.
3. Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is the ability to recognize and manage emotions in any situation. People with emotional intelligence usually solve problems calmly and systematically, which often yields better results.
4. Resilience
Emotional intelligence and resilience are closely related traits. Resiliency is the ability to cope with and bounce back quickly from difficult situations. Those who possess resilience are often capable of accurately interpreting people and situations, which can be incredibly advantageous when difficulties arise.
5. Creativity
When brainstorming solutions to problems, creativity can help you to think outside the box. Problem-solving strategies can be enhanced with the application of creative techniques. You can use creativity to:
Approach problems from different angles
Improve your problem-solving process
Spark creativity in your employees and peers
6. Adaptability
Adaptability is the capacity to adjust to change. When a particular solution to an issue doesn't work, an adaptable person can revisit the concern to think up another one without getting frustrated.
7. Teamwork
Finding a solution to a problem regularly involves working in a team. Good teamwork requires being comfortable working with others and collaborating with them, which can result in better problem-solving overall.
Steps of the problem-solving process
Effective problem-solving involves five essential steps. One way to remember them is through the IDEAL model created in 1984 by psychology professors John D. Bransford and Barry S. Stein [ 1 ]. The steps to solving problems in this model include: identifying that there is a problem, defining the goals you hope to achieve, exploring potential solutions, choosing a solution and acting on it, and looking at (or evaluating) the outcome.
1. Identify that there is a problem and root out its cause.
To solve a problem, you must first admit that one exists to then find its root cause. Finding the cause of the problem may involve asking questions like:
Can the problem be solved?
How big of a problem is it?
Why do I think the problem is occurring?
What are some things I know about the situation?
What are some things I don't know about the situation?
Are there any people who contributed to the problem?
Are there materials or processes that contributed to the problem?
Are there any patterns I can identify?
2. Define the goals you hope to achieve.
Every problem is different. The goals you hope to achieve when problem-solving depend on the scope of the problem. Some examples of goals you might set include:
Gather as much factual information as possible.
Brainstorm many different strategies to come up with the best one.
Be flexible when considering other viewpoints.
Articulate clearly and encourage questions, so everyone involved is on the same page.
Be open to other strategies if the chosen strategy doesn't work.
Stay positive throughout the process.
3. Explore potential solutions.
Once you've defined the goals you hope to achieve when problem-solving , it's time to start the process. This involves steps that often include fact-finding, brainstorming, prioritizing solutions, and assessing the cost of top solutions in terms of time, labor, and money.
4. Choose a solution and act on it.
Evaluate the pros and cons of each potential solution, and choose the one most likely to solve the problem within your given budget, abilities, and resources. Once you choose a solution, it's important to make a commitment and see it through. Draw up a plan of action for implementation, and share it with all involved parties clearly and effectively, both verbally and in writing. Make sure everyone understands their role for a successful conclusion.
5. Look at (or evaluate) the outcome.
Evaluation offers insights into your current situation and future problem-solving. When evaluating the outcome, ask yourself questions like:
Did the solution work?
Will this solution work for other problems?
Were there any changes you would have made?
Would another solution have worked better?
As a current or future manager looking to build your problem-solving skills, it is often helpful to take a professional course. Consider Improving Communication Skills offered by the University of Pennsylvania on Coursera. You'll learn how to boost your ability to persuade, ask questions, negotiate, apologize, and more.
You might also consider taking Emotional Intelligence: Cultivating Immensely Human Interactions , offered by the University of Michigan on Coursera. You'll explore the interpersonal and intrapersonal skills common to people with emotional intelligence, and you'll learn how emotional intelligence is connected to team success and leadership.
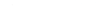
Build job-ready skills with a Coursera Plus subscription
- Get access to 7,000+ learning programs from world-class universities and companies, including Google, Yale, Salesforce, and more
- Try different courses and find your best fit at no additional cost
- Earn certificates for learning programs you complete
- A subscription price of $59/month, cancel anytime
Article sources
Tennessee Tech. “ The Ideal Problem Solver (2nd ed.) , https://www.tntech.edu/cat/pdf/useful_links/idealproblemsolver.pdf.” Accessed December 6, 2022.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

10 Examples of Problem Solving for Job Candidates

- Early Career

What is one good example of problem-solving that a candidate can reference in a job interview?
It’s common interview advice you’ve likely heard before: provide specific examples of your past accomplishments. Need some help narrowing down just which accomplishment you should share during an interview? Try referencing a time when you provided a solution to a tricky business-oriented problem.
This is sure to impress any interviewer, but don’t take our word for it. Here are 10 recruiters weighing in with examples they’d love to hear when interviewing candidates.
Sold reluctant team members on a new process, rescued the team from a website crash, got creative with a limited, tight budget, discovered & corrected their own mistake, delivered on a time-crunch deadline with limited resources, a comeback from a lagging project to on-time delivery, didn’t let conflict indefinitely stall a project, thought outside of the box for an innovative solution, used a competitor’s mistake as a learning opportunity, sought external partnership to address a budget crunch.
A good example of problem-solving is when a candidate I was interviewing for a position told me about the situation in which he was working with a team, and he wanted to implement a new process, but the whole team was against it. The candidate was able to go around and talk to each person on the team individually, work out their concerns and then present that information in a way that everyone could understand and agree with. This allowed the team to progress on the project, which helped them meet deadlines and ultimately implement the new process.
This is a great example, and especially so with how he described it in an engaging and convincing storytelling fashion. It shows that the candidate can work with people from all different backgrounds and personalities. It also shows that he has the ability to listen, understand, and communicate effectively in order to get a problem solved while working in a team.
Shaun Connell, Connell Media

Discuss an unexpected challenge that you handled without managerial input. For example, maybe the website crashed or some site assets were delayed for a new product launch. How did you come to the rescue for your team and use your problem-solving skills to find a resolution? This shows that you can take initiative and don’t panic at the sight of conflict.
Natália Sadowski, Nourishing Biologicals
One great example of problem-solving a candidate can reference in a job interview is a time they worked through a limited budget. Finding creative solutions to money problems is always a desired characteristic, even outside accounting. It shows a candidate knows how to make use of what they have. Specific examples of resourcefulness will also go a long way in an interview.
Sasha Ramani, MPOWER Financing
Problem-solving requires multiple reasoning stages—from recognizing the problem, analyzing it, looking for a solution, and finding the winning one. Sharing how you fixed your own mistake is probably the best way to include all of those elements. If you talk about your own experience, you can describe how you discovered your error and your step-by-step journey to finding the appropriate solution. This story is double-beneficial. Besides showing your problem-solving skills, it shows that you are an ambitious, independent employee.
Karolina Zajac, PhotoAiD
A job candidate can reference an instance where they resolved a time-management problem. While this is specific to each applicant, it can be a situation where a deadline was crucial and resources were lacking. Describe how you resolved the resource issue to meet the product or service deadline along with the results afterward. Your answer should describe the steps you took to resolve the problem as well as how you came up with the solution to meet the need.
Tanya Klien, Anta Plumbing
The interviewer likes to hear a story that demonstrates you can face obstacles under pressure while working well with others. Speak briefly to a project and what proved challenging. For example, you can talk about a specific social media campaign that required involvement from many different departments. You realized that some of the departments were behind the deadline, so you arranged one-on-one meetings with them. You heard these workers out on how you can help them get the job done on time and scheduled follow-up meetings to check their progress. The project was delivered on time.
Monte Deere, Kizik

A fantastic problem-solving example to use in a job interview is conflict resolution. Tackling disagreements between others whether they include you or not can show off valuable skills that an employer would be interested in. It shows that you are adaptable and have excellent negotiation skills, making yourself that much more attractive as a candidate. Think of any kind of disagreement that could have stalled the progress of work and explain how you went about efficiently addressing everyone’s grievances and how the conflict was ultimately resolved.
Adrien Dissous, Babo Botanicals
Refer to a situation where, thanks to thinking out of the box, you were able to come up with a new, innovative solution never used before. Be specific about the problem in question and explain why solving it mattered. Don’t forget to mention how proud you felt once your idea turned out to be successful. The given example covers a wide range of aspects worth noting by potential employers.
Actually, you indirectly show that you are determined, creative, and willing to improve your work environment. An action-driven approach, not standing still, and willingness to find the “ways out” are precious. Therefore, they should be valued and appreciated in all workplaces as the benefits they may bring are universal.
Agata Szczepanek, Resume Now
You don’t have to be an expert to give a generic problem-solving example. Such as, you might explain your approach to a problem by pointing out a mistake made by a competitor and how you would have handled the situation differently. If the same situation occurs at your new company, mention what you learned from the mistake and how you plan to handle it.
Jon Torres, Jon Torres

To showcase your problem-solving skills, the best example is about saving money for the organization. You can think of a situation where the lack of funds could drop or decrease the company’s profits. You can start by giving the background about how the lack of funds occurred and how you solved the issue. A typical example can be as simple as a department facing a money crunch due to previous delayed payments.
This is an especially difficult time as new projects often need new and costly pieces of equipment. But the lack of funds resulted in you digging up and finding a collaborative partner for an organization that helped complete the work with minimum investments. A situation like this will make the current recruiter aware of your management skills and dedication to saving money, allowing the organization to prosper.
Nathan Hughes, Art Ignition
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
About the author: featured.
Related Articles

What to Do If You Don’t Know the Answer to an Interview Question
54392 Jul 9th, 2024 / 3 mins for reading / 39
What to Do If You Don’t Know the Answer to an Interview Question Navigating the tricky waters of an interview can be daunting, especially when ...

Conquering Imposter Syndrome: 14 Strategies for Early Career Confidence
54025 Jul 2nd, 2024 / 3 mins for reading / 114
Conquering Imposter Syndrome: 14 Strategies for Early Career Confidence Battling imposter syndrome can be a pivotal challenge in fourteen's career, so we've gathered firsthand insights ...

14 Essential Sections to Include in Your Resume
53670 Jun 25th, 2024 / 3 mins for reading / 149
14 Essential Sections to Include in Your Resume When crafting a comprehensive resume, CEOs and recruitment experts know that it goes beyond just experience and ...
FILL OUT THE FORM BELOW AND WE WILL EMAIL YOU OUR EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW TIPS CHECKLIST
Questions or Comments
More From Forbes
Stumped five ways to hone your problem-solving skills.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Respect the worth of other people's insights
Problems continuously arise in organizational life, making problem-solving an essential skill for leaders. Leaders who are good at tackling conundrums are likely to be more effective at overcoming obstacles and guiding their teams to achieve their goals. So, what’s the secret to better problem-solving skills?
1. Understand the root cause of the problem
“Too often, people fail because they haven’t correctly defined what the problem is,” says David Ross, an international strategist, founder of consultancy Phoenix Strategic Management and author of Confronting the Storm: Regenerating Leadership and Hope in the Age of Uncertainty .
Ross explains that as teams grapple with “wicked” problems – those where there can be several root causes for why a problem exists – there can often be disagreement on the initial assumptions made. As a result, their chances of successfully solving the problem are low.
“Before commencing the process of solving the problem, it is worthwhile identifying who your key stakeholders are and talking to them about the issue,” Ross recommends. “Who could be affected by the issue? What is the problem – and why? How are people affected?”
He argues that if leaders treat people with dignity, respecting the worth of their insights, they are more likely to successfully solve problems.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, 2. unfocus the mind.
“To solve problems, we need to commit to making time to face a problem in its full complexity, which also requires that we take back control of our thinking,” says Chris Griffiths, an expert on creativity and innovative thinking skills, founder and CEO of software provider OpenGenius, and co-author of The Focus Fix: Finding Clarity, Creativity and Resilience in an Overwhelming World .
To do this, it’s necessary to harness the power of the unfocused mind, according to Griffiths. “It might sound oxymoronic, but just like our devices, our brain needs time to recharge,” he says. “ A plethora of research has shown that daydreaming allows us to make creative connections and see abstract solutions that are not obvious when we’re engaged in direct work.”
To make use of the unfocused mind in problem solving, you must begin by getting to know the problem from all angles. “At this stage, don’t worry about actually solving the problem,” says Griffiths. “You’re simply giving your subconscious mind the information it needs to get creative with when you zone out. From here, pick a monotonous or rhythmic activity that will help you to activate the daydreaming state – that might be a walk, some doodling, or even some chores.”
Do this regularly, argues Griffiths, and you’ll soon find that flashes of inspiration and novel solutions naturally present themselves while you’re ostensibly thinking of other things. He says: “By allowing you to access the fullest creative potential of your own brain, daydreaming acts as a skeleton key for a wide range of problems.”
3. Be comfortable making judgment calls
“Admitting to not knowing the future takes courage,” says Professor Stephen Wyatt, founder and lead consultant at consultancy Corporate Rebirth and author of Antidote to the Crisis of Leadership: Opportunity in Complexity . “Leaders are worried our teams won’t respect us and our boards will lose faith in us, but what doesn’t work is drawing up plans and forecasts and holding yourself or others rigidly to them.”
Wyatt advises leaders to heighten their situational awareness – to look broadly, integrate more perspectives and be able to connect the dots. “We need to be comfortable in making judgment calls as the future is unknown,” he says. “There is no data on it. But equally, very few initiatives cannot be adjusted, refined or reviewed while in motion.”
Leaders need to stay vigilant, according to Wyatt, create the capacity of the enterprise to adapt and maintain the support of stakeholders. “The concept of the infallible leader needs to be updated,” he concludes.
4. Be prepared to fail and learn
“Organisations, and arguably society more widely, are obsessed with problems and the notion of problems,” says Steve Hearsum, founder of organizational change consultancy Edge + Stretch and author of No Silver Bullet: Bursting the Bubble of the Organisational Quick Fix .
Hearsum argues that this tendency is complicated by the myth of fixability, namely the idea that all problems, however complex, have a solution. “Our need for certainty, to minimize and dampen the anxiety of ‘not knowing,’ leads us to oversimplify and ignore or filter out anything that challenges the idea that there is a solution,” he says.
Leaders need to shift their mindset to cultivate their comfort with not knowing and couple that with being OK with being wrong, sometimes, notes Hearsum. He adds: “That means developing reflexivity to understand your own beliefs and judgments, and what influences these, asking questions and experimenting.”
5. Unleash the power of empathy
Leaders must be able to communicate problems in order to find solutions to them. But they should avoid bombarding their teams with complex, technical details since these can overwhelm their people’s cognitive load, says Dr Jessica Barker MBE , author of Hacked: The Secrets Behind Cyber Attacks .
Instead, she recommends that leaders frame their messages in ways that cut through jargon and ensure that their advice is relevant, accessible and actionable. “An essential leadership skill for this is empathy,” Barker explains. “When you’re trying to build a positive culture, it is crucial to understand why people are not practicing the behaviors you want rather than trying to force that behavioral change with fear, uncertainty and doubt.”

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

Empowering Teams: Equipping for Independent Problem Solving
Like a conductor guiding an orchestra, effective managers play a crucial role in empowering teams to independently tackle and solve problems. However, the practice of ‘umbrella management,’ where managers shield their teams from challenges, has been found to have negative consequences. This article explores the drawbacks of such an approach and offers strategies for managers to shift from protection to support, equipping their teams with problem-solving skills. By delegating tasks, providing training and resources, fostering collaboration, and recognizing team efforts, managers can empower their teams to excel independently, leading to increased autonomy, engagement, and overall performance.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Umbrella managers should shift from protecting to supporting their employees.
- Managers should focus on developing their team’s problem-solving skills.
- Managers should delegate tasks and empower their team members.
- Equipping teams to problem solve without the manager leads to increased employee engagement, job satisfaction, team performance, productivity, creativity, and innovation.
The Drawbacks of Umbrella Management
The drawbacks of umbrella management are evident as it can have negative consequences for the manager, team, and organization, necessitating the need for managers to find a balance between support and delegation. Umbrella managers, who adopt this leadership style to protect their teams from challenges, inadvertently intercept and shield their teams from important growth opportunities and learning experiences. This overprotection can hinder the development of essential skills, problem-solving abilities, and independence within the team. Moreover, it can lead to a lack of accountability and motivation among team members, as they rely heavily on the manager for guidance and decision-making. Overcoming the challenges of umbrella management requires a mental shift from protecting to supporting employees, encouraging them to take on challenges, and building resilience and problem-solving skills. Managers must trust the capabilities of their team members and empower them through delegation and the provision of resources and training.
Shifting From Protection to Support: Mental Shifts for Managers
One important aspect for managers to consider is shifting their mindset from a protective role to a supportive one. This shift in perspective is crucial for developing resilient teams and fostering a supportive leadership style.
To evoke an emotional response in the audience, here are four items to consider:
Empowering employees: By shifting from protection to support, managers can empower their employees to take on challenges and responsibilities. This not only builds their confidence but also enhances their problem-solving skills.
Developing resilience: Supportive leadership encourages the development of resilience within the team. It enables team members to bounce back from setbacks, adapt to change, and persevere in the face of challenges.
Trust and delegation: Managers need to trust their team’s abilities and delegate tasks effectively. This allows team members to take ownership of their work and develop their problem-solving capabilities.
Collaboration and teamwork: Supportive managers foster a culture of collaboration and teamwork within the team. By encouraging open communication and collaboration, managers can enhance problem-solving efforts and tap into the collective intelligence of the team.
Overall, shifting from a protective to a supportive role as a manager is essential for developing resilient teams and promoting a supportive leadership style.
Strategies for Delegating and Empowering Teams
Strategies for delegating and empowering teams include assigning tasks and responsibilities, providing necessary resources and training, fostering collaboration and teamwork, promoting a culture of experimentation and learning, and recognizing and rewarding team members’ efforts and successes. Delegation techniques involve distributing tasks and responsibilities among team members based on their skills and capabilities. This not only enhances individual growth but also promotes a sense of ownership and accountability within the team. Additionally, providing necessary resources and training equips team members with the knowledge and tools required to successfully complete their assigned tasks. Fostering collaboration and teamwork encourages the sharing of ideas and skills, leading to more effective problem-solving. Promoting a culture of experimentation and learning allows team members to explore new approaches and learn from failures, fostering innovation and continuous improvement. Recognizing and rewarding team members’ efforts and successes not only boosts morale but also reinforces the importance of independent problem-solving within the team. These empowerment strategies contribute to the development of autonomous and self-sufficient teams, resulting in increased employee engagement, improved performance, and enhanced creativity and innovation.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills Through Training and Resources
Enhancing problem-solving skills through training and resources requires providing team members with the necessary knowledge, tools, and support to effectively analyze and address challenges. To evoke an emotional response in the audience, consider the following:
Training effectiveness: By investing in high-quality training programs, team members can develop the skills and competencies needed to tackle complex problems. This not only boosts their confidence but also enhances their sense of achievement and personal growth.
Resource allocation: Providing adequate resources, such as access to relevant information, technology, and experts, can empower team members to overcome obstacles and find innovative solutions. This fosters a sense of empowerment and ownership over their work, leading to increased motivation and job satisfaction.
Skill development: Equipping team members with problem-solving techniques and strategies can enhance their problem-solving abilities. This not only improves their performance but also cultivates a sense of self-efficacy and resilience, enabling them to navigate challenges more effectively.
Supportive environment: Creating a supportive and collaborative work environment where team members feel safe to take risks and make mistakes fosters a culture of continuous learning and improvement. This instills a sense of belonging and trust among team members, enhancing their problem-solving effectiveness.
Fostering Collaboration and a Culture of Experimentation
Fostering collaboration and a culture of experimentation within the organization encourages collective problem-solving and promotes innovation. Collaboration allows individuals to bring their diverse perspectives and expertise to the table, leading to more comprehensive and effective solutions. By embracing experimentation, organizations create an environment where individuals feel empowered to take risks and try new approaches. This encourages creativity and allows for the exploration of innovative ideas. Through collaboration, team members can leverage each other’s strengths and knowledge, enhancing problem-solving capabilities. Additionally, embracing experimentation allows for the identification of new and improved solutions, as well as the ability to learn from failures. Overall, fostering collaboration and embracing experimentation within the organization cultivates an environment that supports and encourages collective problem-solving and innovation.
Recognizing and Rewarding Team Problem-Solving Efforts
Teams that are empowered and equipped to problem solve independently can greatly benefit from recognition and rewards for their efforts. Recognizing team contributions and incentivizing problem solving not only acknowledges the hard work and dedication of the team members but also motivates them to continue their problem-solving efforts. This can be achieved through various strategies such as:
- Publicly acknowledging and appreciating the team’s problem-solving efforts in team meetings or company-wide communications.
- Providing tangible rewards or incentives, such as bonuses or promotions, to team members who consistently demonstrate exceptional problem-solving skills.
- Creating a culture of peer recognition, where team members can nominate and recognize their colleagues for their problem-solving contributions.
- Offering opportunities for professional development and growth, such as additional training or mentorship programs, to team members who excel in problem-solving.
Benefits of Empowering Teams for Independent Problem Solving
Increased autonomy in decision-making and improved problem-solving capabilities contribute to a more efficient and adaptable workforce. When teams are empowered to solve problems independently, they are able to take ownership of their work and make decisions that align with the organization’s goals. This increased autonomy not only enhances the team’s engagement, but also fosters a sense of responsibility and accountability. By trusting their team members’ abilities, managers create an environment that encourages creativity and innovation. Furthermore, empowering teams to problem solve without constant managerial intervention leads to improved team performance and productivity. As team members gain confidence in their problem-solving skills, they become more autonomous and self-sufficient, allowing managers to focus on strategic initiatives and higher-level tasks. In conclusion, equipping teams for independent problem solving not only benefits the team itself, but also has a positive impact on the overall efficiency and adaptability of the workforce.
Examples of Successful Team Problem-Solving Cases
Successful team problem-solving cases demonstrate the effectiveness of strategies employed by teams to overcome challenges and achieve desired outcomes. These case studies provide valuable insights into the impact of team problem-solving on overall performance. By analyzing these cases, managers can gain a deeper understanding of the strategies and approaches used by successful teams. This knowledge can inspire managers to empower their teams and trust their problem-solving abilities. The impact analysis of these cases reveals several emotional responses that can resonate with the audience:
- A sense of admiration for the teams’ resilience and determination to overcome challenges.
- Inspiration to foster a culture of collaboration and experimentation within their own teams.
- Excitement about the enhanced creativity and innovation that can result from empowering teams to problem solve independently.
- Satisfaction in witnessing the improved performance and productivity of teams that are equipped to solve problems without constant manager intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can umbrella managers find the balance between support and delegation for their teams.
Supportive leadership involves finding the balance between support and delegation for teams. By empowering teams and fostering autonomy, umbrella managers can enhance problem-solving abilities and promote team self-sufficiency.
What Are Some Effective Ways for Managers to Build Resilience Within Their Teams?
Effective ways for managers to build resilience within teams include encouraging problem-solving skills, fostering a culture of experimentation and learning from failures, providing training and resources, and recognizing and rewarding problem-solving efforts.
How Can Managers Foster a Culture of Experimentation and Learning From Failures Within Their Teams?
To foster a culture of experimentation and learning from failures, managers can cultivate curiosity and promote psychological safety within their teams. This encourages risk-taking, open communication, and a willingness to learn from mistakes, leading to innovation and continuous improvement.
What Strategies Can Managers Use to Enhance Their Team’s Problem-Solving Skills?
Strategies for enhancing team problem-solving skills include fostering collaboration, developing critical thinking skills, providing training and resources, promoting experimentation and learning from failures, and recognizing and rewarding problem-solving efforts and successes.
How Can Managers Effectively Recognize and Reward Their Team Members’ Problem-Solving Efforts and Successes?
Recognition and motivation are key factors in effectively acknowledging and rewarding team members’ problem-solving efforts and successes. Managers can utilize various strategies, such as verbal praise, monetary incentives, and public recognition, to foster a culture of appreciation and encourage continued excellence.
The foundation of effective problem solving
View or edit this activity in your CPD log.

The problem identification process is really about asking the question; what problem are we trying to solve and what are we trying to answer.
But before we can identify the problem and really understand it, we first need to understand how does a situation evolve into a problem? How does the problem identification task get started? What causes us to start looking into this? In this blog I try to answer these questions and create a guide to successful problem identification.
Below you’ll find four tips for the most effective problem identification:
1. Don’t start with the solution
It's very important to only focus on the problem and the structure of the problem at the initial steps of problem identification. Naturally, as we encounter an issue, we start brainstorming and thinking of the solution, however, if you focus on the problem first, you’ll fail to identify the core of the issue.
2. Find the root cause
It's not only about identifying the problem, but it's also about identifying the right issue and really getting to the root of it. What I mean by this is that one problem may actually be because of another lower-level root problem. A common technique for finding the core of a problem is the 5 Whys. The method is remarkably simple: when a problem occurs, you drill down to its root cause by asking "Why?" five times.
For example:
Why does the client not like this feature? Because the users cannot easily navigate it.
Why can’t the users easily navigate it? Because the landing page is not helpful.
Why is the landing page not helpful? Because the menu is too complex and there are too many options.
Why is the menu so complicated and there are too many options? Because no UX considerations were made in the design process.
Why was there no UX considerations made in the design process? Because the team members have no experience in UX design.
Using the Why method, we have found the root cause of the problem which is that the team lacks members that are experienced and knowledgeable in UX design.
3. Keep it simple
Simplicity doesn’t mean a lack of understanding — it may mean a good solid understanding of the project but something in the plan didn’t quite work. Try to approach any complex situation by breaking it down into more simple elements.
4. Exploit the collective wisdom and synergies
We need the collective wisdom of the people around us and to accept different perspectives. It’s the only way a complete understanding of the problem will be achieved. Don’t forget to leave yourself open to different ideas and perspectives that may be contrary to your established beliefs and thinking patterns.
Identifying the real problem and solving it in the most effective way is the fundamental step for finding an ideal solution and problem identification is the first step to finding the perfect result. Correctly defining the problem or asking the right question is the most critical stage of the decision-making process if we want to have the best choices and adopt the best solutions.
You may also be interested in:
- What is project planning?
- developing effective approaches and solutions to problem identification
- project leadership

George Sioutzos is an experienced Sr. Business Analyst at Netcompany, working on a large-scale social security project. He has authored numerous articles on business analysis, engaged in voluntary activities with the International Institute of Business Analysis, and conducted trainings.
LinkedIn Profile: www.linkedin.com/in/gsioutzos
Log in to post a comment, or create an account if you don't have one already.
- Certainities, Suppositions & Doubts
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- Cynefin Framework
- DACI Framework
- Decision Making Framework
- Decision Making Model
- Decision Making Techniques
- Decision Matrix
- Digital Customer Journey
- Hedgehog Concept
- Macro Environmental Analysis
- NOISE Analysis
- Product Portfolio
- Profit & Loss Templates
- RAPID Framework
- Scenario Planning
- Second Order Thinking
- SPACE Analysis
- Stakeholder Communication Plan
- Strategic Vs Tactical Planning
- Strategy vs Plan
- What are Tree Diagrams
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Balanced Scorecard
- Developing Action Plans
- Guide to setting OKRS
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Analysis
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Program Planning
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Cash Cow Matrix
- Decision Tree Guide
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- Strategy vs Tactics
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Experience Mapping Guide
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Perceptual Maps
- Position Maps
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Value-Proposition-Canvas
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Visual Note Taking
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- Conceptual Framework
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Phylogenetic Trees
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Using Creately VIZ
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
CATWOE Analysis: Your Guide to Developing a Problem-Solving Framework
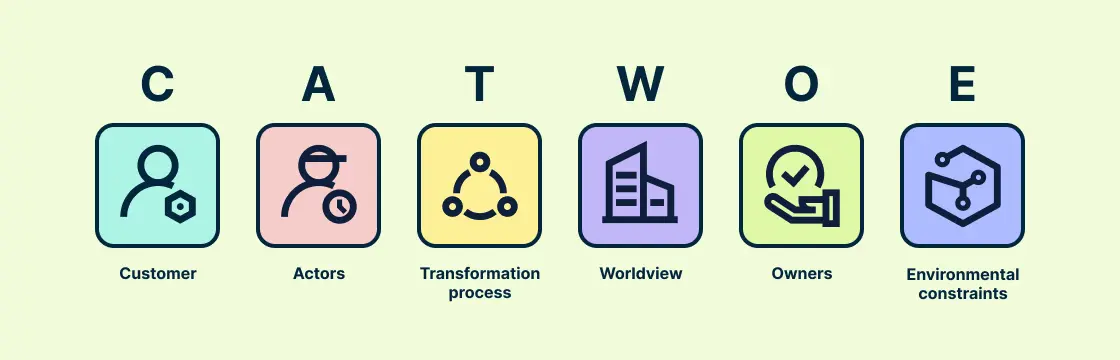
When businesses encounter complex challenges, such as low staff retention with unclear causes, the initial reaction might be to brainstorm solutions and apply various problem-solving techniques. However, this approach often risks addressing only surface symptoms rather than the underlying issues. Focusing too narrowly on one aspect can lead to overlooking broader, more critical problems. This is where CATWOE Analysis becomes invaluable. By examining the problem from multiple perspectives ensures no critical factor is missed, enabling businesses to tackle intricate problems with confidence and clarity.
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

What is CATWOE Analysis?
CATWOE Analysis is a structured problem-solving tool that offers businesses a comprehensive framework to address complex issues comprehensively. The acronym CATWOE stands for Customers, Actors, Transformation process, Worldview, Owners, and Environmental constraints. By exploring these six facets, organizations can gain a holistic understanding of the factors influencing their processes and the input of various stakeholders. This detailed scrutiny aids in identifying problems, conceptualizing actionable solutions, and mitigating potential conflicts, thereby streamlining business transformation and decision-making processes.
The method was developed as part of the Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) by David Smyth, with significant contributions from Peter Checkland. The technique emerged in the 1970s, aiming to provide a structured approach to understanding and addressing business challenges from multiple perspectives. Its roots in systems thinking enable it to unfold the intricate layers of business processes, ensuring that every stakeholder’s viewpoint is considered and aligned towards a common goal. This historical development underscores its robustness and relevance across different eras and business environments.
| Customers | Stakeholders and users who benefit from changes in the system or process. |
| Actors | Employees within an organization responsible for carrying out the transformation processes. |
| Transformation process | The evolution of input into output through the organization’s activities. |
| Worldview | A comprehensive perspective that considers various stakeholders and their perspectives to appreciate the bigger picture. |
| Owners | Decision-makers like entrepreneurs or investors who have the authority to make critical changes. |
| Environmental constraints | External factors such as regulations, ethical boundaries, and financial constraints that can limit or restrict the system’s changes. |
The Elements of a Catwoe Analysis
Customers: who they are and their interests.
The first element in CATWOE Analysis is customers. Customers are the stakeholders and end-users who directly benefit from changes in a business system or process. Identifying who your customers are and understanding their needs is crucial. For example, in the catwoe analysis example of Coca-Cola, the customers range from children to adults worldwide. By understanding the different demographics and their unique needs, businesses can tailor their solutions effectively.
Actors: Roles and responsibilities
Actors are the individuals or groups responsible for carrying out the transformation process within an organization. These are often employees or team members involved in various business activities. Understanding the roles and responsibilities of actors helps in identifying who will implement necessary changes and how they will do it. For instance, in a catwoe analysis example of Amazon, the actors might include supply chain managers, IT support staff, and customer service representatives, all playing pivotal roles in ensuring smooth operations and customer satisfaction.
Transformation Process: Turning inputs into outputs
The transformation process is central to CATWOE Analysis. This component examines how inputs are converted into desired outputs within a business system. The transformation process involves recognizing what changes need to be made and how these changes will be executed. For example, Amazon’s transformation process involves converting user demands into delivered products efficiently and promptly. By focusing on optimizing this process, businesses can improve their overall performance and customer experience.
Worldview: The bigger picture
Worldview, or Weltanschauung, considers the broader perspective, including varying stakeholder viewpoints and the larger impact on the organization. It helps in understanding how different stakeholders perceive the situation and the implications of potential changes. In the case of the Hyperloop project, the worldview envisions rapid, accessible travel for individuals across different regions. This component ensures that the proposed solution aligns with the overarching goals and values of the business.
Owners: Authority and decision-making
Owners in CATWOE Analysis refer to individuals or groups with the power to approve or halt changes. They are typically entrepreneurs, investors, or senior management with decision-making authority. Understanding the owners' motivations and concerns is essential for gaining support for any changes. In the context of Coca-Cola, major stakeholders like Berkshire Hathaway would be considered owners, with significant influence over business decisions.
Environmental Constraints: External limitations
Environmental constraints involve external factors that can limit or restrict business operations. These may include legal regulations, ethical considerations, financial limitations, and physical constraints. Recognizing these constraints is vital for realistic and feasible planning. For example, environmental sustainability is a significant constraint for Coca-Cola, influencing its production methods and corporate policies. Addressing these constraints ensures that proposed changes are not only effective but also compliant and sustainable.
Utilizing a visual collaboration platform like Creately can significantly enhance the understanding and implementation of each CATWOE component. With Creately’s infinite canvas for diagramming and seamless collaboration tools, teams can brainstorm, plan, and document each element of CATWOE Analysis effectively, ensuring comprehensive and coordinated problem-solving efforts.
Benefits of CATWOE Analysis in Modern Businesses
Solving complex problems.
CATWOE Analysis excels in addressing complex business challenges by offering a structured framework for problem-solving. By analyzing problems through multiple lenses—Customers, Actors, Transformation Process, Worldview, Owners, and Environmental Constraints—businesses can pinpoint issues more accurately and develop effective solutions. The method’s holistic approach ensures that no aspect is overlooked, making it ideal for tackling intricate problems with varied stakeholder interests.
CATWOE for Stakeholder Management
Managing stakeholders effectively is crucial for the success of any business transformation. CATWOE Analysis aids in identifying and prioritizing stakeholder perspectives, helping to mitigate conflicts and align goals. For instance, the ‘Worldview’ component allows businesses to understand and harmonize different viewpoints, resulting in smoother project execution. Implementing this with visual collaboration tools, like those provided by Creately, enhances stakeholder engagement by making complex relationships and impacts more transparent.
Enhanced Decision-Making
CATWOE Analysis facilitates better decision-making by ensuring all critical factors are considered. By systematically evaluating each element, businesses can make more informed choices that align with their strategic objectives. This comprehensive assessment helps in identifying potential risks and opportunities, leading to more robust and resilient business strategies.
Improved Communication
Using CATWOE Analysis promotes clearer communication among team members and stakeholders. The structured approach ensures that everyone involved has a shared understanding of the problem and the proposed solutions. This common framework reduces misunderstandings and fosters more effective collaboration, essential for successful project outcomes.
Increased Adaptability
In today’s fast-paced business environment, adaptability is key. CATWOE Analysis helps businesses remain agile by providing a clear understanding of the various elements impacting a problem. This insight allows for quicker adjustments and realignment of strategies in response to changing conditions, ensuring sustained competitive advantage.
Comprehensive Problem Understanding
CATWOE Analysis encourages a deep dive into each problem component, fostering a thorough understanding of the issue at hand. This in-depth analysis ensures that solutions are not just superficial but address the root causes of problems, leading to more sustainable and impactful outcomes.
How to Implement CATWOE Analysis
Implementing CATWOE Analysis involves a structured approach to ensure all perspectives and components are adequately addressed. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Describe the Situation
Begin by detailing the problem or situation at hand. This involves gathering all relevant data and understanding the context in which the issue exists. Use Creately’s infinite canvas to map out the key points, enabling your team to visualize the problem comprehensively.
Step 2: Brainstorm Ideas
Engage in a collaborative brainstorming session to explore different angles and possible solutions. Creately’s visual collaboration tools facilitate seamless idea exchange, allowing team members to contribute and develop concepts in real-time. Utilize Creately’s mind mapping software to create diagrams and flowcharts that represent various ideas surrounding the problem.
Step 3: Zero in on the Problem
Narrow down to the core issue by analyzing the components of CATWOE Analysis – Customers, Actors, Transformation process, Worldview, Owners, and Environmental constraints. Creately’s capabilities allow you to create detailed maps and charts that encapsulate the insights gathered during this phase. Here’s a brief overview:
Customers: Identify who benefits from the change and their interests.
Actors: Recognize the roles responsible for implementing the changes within the organization.
Transformation Process: Understand the process through which inputs are converted to outputs.
Worldview: Consider the bigger picture, including different stakeholders’ perspectives.
Owners: Identify the key decision-makers who have the authority to approve changes.
Environmental Constraints: Account for external factors such as regulations and financial restrictions that might impact the change.
Step 4: Start to Solve the Problem
With a deep understanding of the problem and its components, proceed to develop a solution strategy. Utilize Creately to create a collaborative action plan, ensuring all team members are on the same page. The platform’s diagramming and visualization tools help in outlining a clear, actionable path forward.
By following these steps within the Creately platform, you streamline the CATWOE Analysis process, making it more efficient and effective for your business.
Note: Placeholder for any relevant images or diagrams created using Creately’s tools to further illustrate the implementation steps.
CATWOE Analysis Template and Example
Understanding the intricate details of CATWOE Analysis can be greatly streamlined with a structured template. By utilizing a CATWOE Analysis template, teams can systematically evaluate each component, ensuring no critical elements are overlooked. Download our comprehensive CATWOE Analysis template to kickstart your problem-solving framework effectively. This template includes sections for all six elements—Customers, Actors, Transformation Process, Worldview, Owners, and Environmental Constraints—offering a structured approach to dissect and address business challenges.
Amazon Case Study
Let’s illustrate the power of CATWOE Analysis with a real-world example. Consider Amazon, a global e-commerce giant that constantly navigates complex business environments:
Customers: A diverse range of consumers worldwide, including individual buyers, businesses, and sellers on the platform.
Actors: Employees ranging from logistics staff to IT professionals and customer service representatives.
Transformation Process: The seamless conversion of website visits into sales transactions, supported by a robust logistics network that ensures timely delivery.
Worldview: To be the most customer-focused company on Earth, enriching the shopping experience and offering unparalleled convenience.
Owners: Key decision-makers include Jeff Bezos, the board of directors, and major shareholders who steer strategic directions.
Environmental Constraints: Regulations from different countries, sustainability commitments, and societal shifts towards ethical shopping practices.
Using these steps, you can create a powerful and bespoke CATWOE Analysis that addresses your unique business challenges. With tools like Creately’s visual collaboration platform, you can enhance this process, enabling seamless brainstorming, planning, and diagramming on an infinite canvas.
- Decision Making Models
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Chiraag George is a communication specialist here at Creately. He is a marketing junkie that is fascinated by how brands occupy consumer mind space. A lover of all things tech, he writes a lot about the intersection of technology, branding and culture at large.
There Are Exceptionally Sharp Octogenarians. Biden Isn’t One.
The president’s age isn’t his problem.

Listen to this article
Produced by ElevenLabs and News Over Audio (NOA) using AI narration.
Joe Biden’s problem isn’t his age. It’s his ability to function.
America has known a number of exceptional octogenarians who have demonstrated the cognitive and physical stamina to serve in demanding leadership roles. In 1787, at age 81, Benjamin Franklin, who a few years earlier had negotiated a highly advantageous treaty to end the Revolutionary War and had recently invented bifocals, played a pivotal role at the Constitutional Convention, persuading the delegates to allow citizens of the brand-new United States to vote without any property qualification. At the convention’s closing, Franklin wrote one of the finest speeches of the early American experiment, urging compromise and a unanimous vote to support the Constitution.
That September, the Philadelphia socialite Elizabeth Willing Powel asked Franklin, “What have we got, a republic or a monarchy?” In response, Franklin spontaneously delivered an immortal description of the United States: “A republic, if you can keep it.” Until his death at age 84, Franklin continued to invent new gadgets and write lucidly, humorously, and perceptively, including a petition for Congress to end the slave trade and a satiric takedown of southerners’ justification for slavery, published just weeks before he died.
Franklin was an outlier. At an age when cognitive decline is common—when people tend to face challenges performing everyday activities such as managing money and organizing medications—he retained his capacity for mental focus, creativity, and sustained intellectual engagement. The same cannot be said of President Joe Biden. His disastrous debate performance last week indicated possible cognitive problems that interfere with his ability to function. Since then, his public speech has vacillated between energetic clarity and outright confusion . Some 80-year-olds are still sharp enough to be president. Biden has shown that he is not one of them.
Biden, following in Franklin’s footsteps, is a remarkably active octogenarian. At age 79, he negotiated the landmark Inflation Reduction Act. Now, at age 81, he is supporting U.S. allies through wars in Ukraine and Gaza. In the months leading up to the debate, he has flown around the country to campaign for reelection, and around the world to meet with other heads of state. But the debate featured telltale signs that his age is catching up with him.
As people age, they tend to retain what is called crystallized intelligence , the knowledge and skills that accumulate over a lifetime. Barring any brain injury or neurodegenerative disease (Alzheimer’s and its ilk), one’s vocabulary, general storehouse of facts, and recall of how to do things, such as knitting and skiing, remain robust—and may even improve—into old age. Conversely, even in the absence of disease, a different set of cognitive skills—fluid intelligence—tends to peak in a person’s middle years and then progressively decline with age.
Read: The kind of smarts you don’t find in young people
Fluid intelligence describes our ability to pay attention, exercise mental flexibility, and solve problems. People use fluid intelligence when faced with unfamiliar information that must be organized, and when they have to solve a new problem or navigate a familiar one in unusual circumstances. It’s what allows us to focus on important information or tasks while ignoring extraneous factors, and to hold one thing in mind while manipulating it, as we do when, say, calculating a tip.
In the debate, Biden displayed a striking deficit of fluid intelligence. He showed problems concentrating, difficulty with verbal fluency at the end of almost every response, an inability to spontaneously recall information, poor reasoning concerning issues that he was asked about, and a failure to respond to unexpected challenges by Donald Trump. Crucially, the debate was not unique. Biden has had good and bad days throughout his presidency, but diplomats , journalists , and even Democratic lawmakers have noticed and commented on his growing cognitive problems for many months.
Trump also displays many of these mental weaknesses—and others. His recall of names and events is poor, as is his capacity to concentrate, maintain his attention, and reason about new situations. Just consider his recent assertion that electric batteries could sink boats (and enable shark attacks ), or that battery-powered airplanes would be grounded by the mere presence of clouds . But Trump’s displays of cognitive lapses have in many cases been eclipsed by his shameless, chronic lying. He appeared more energetic and lucid than Biden at the debate, but his answers were stuffed with factually false claims —thrice as many as Biden made.
Read: Trump rants about sharks, and everyone just pretends it’s normal
The different components of fluid intelligence begin to decline at different ages—mental-processing speed, for example, appears to peak in your 30s —and the exact timing and speed of that decay is highly variable from person to person. Some people’s mental slowdown becomes more pronounced in their 60s. For others, fluid intelligence remains strong well into their 80s. The rate of decline depends on many factors, including genes, physical activity, and education. Brain diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Lewy body dementia will accelerate the decline. Biden’s cognitive changes do not necessarily indicate dementia or neurological disease. (The White House has denied that the president has Alzheimer’s or any other form of dementia.) His performance is perfectly consistent with normal aging. And that is just as worrisome.
We need not go back 250 years to find examples of prominent older Americans with strong fluid intelligence. Warren Buffett is 93 and continues to be a successful investor, perceptive commentator, and masterful speaker at his shareholder conclaves. Nancy Pelosi is 84 and remarkably sharp. In her most recent term as speaker of the House, which ended when she was 82, she managed the passage of the American Rescue Plan and shepherded the bipartisan CHIPS and Science Act. She often went toe-to-toe with a younger President Trump and outshone him in wit . And the late Supreme Court Chief Justice William Rehnquist served capably in that role until his death at 80.
Early in his presidency, Biden asked perceptive questions, concentrated fully, and was engaged and lucid in his comments. I spoke with him in small groups on Zoom several times during the 2020 campaign, and was honored to serve on his COVID advisory board in 2020 and 2021. I did not notice any of the problems that have become so apparent in the past week. But now he has clearly deteriorated. His recent declaration that he will avoid events after 8 p.m. suggests that, somewhere inside, he recognizes the decline too.
Adam Serwer: Biden must resign
As a politician, Biden has been engaging in debates and Q&A sessions for some 50 years. His responses on expected topics such as abortion should come easily. Yet a slight change in setting—a silent stage with only Trump and CNN moderators for company—was enough to make his comments on the subject display a staggering failure of fluid intelligence: “Look, there are so many young women who have been, including a young woman who just was murdered, and he went to the funeral. And the idea that she was murdered by an immigrant coming in, to talk about that. But here’s the deal. There’s a lot of young women are being raped by their in-laws, by their, by their spouses. Brothers and sisters, by—it’s just ridiculous. And they can do nothing about it. And they try to arrest them and they cross state lines.” Such incoherence points to the kind of deterioration that was not known to have plagued Franklin or Rehnquist at Biden’s age.
In the days since the debate, people close to Biden have insisted that he is as sharp as ever, if not at every hour of every day. Regardless of the cause—normal aging, disease, or both—people with declining fluid intelligence can experience fluctuations in their day-to-day functioning . But an elderly person’s loved ones, and especially their family, tend not to recognize their deterioration until it is advanced. They see the person daily, so small changes often go unnoticed. They also accommodate their expectations to the decline. They tend to not be good diagnosticians unless asked very specific questions about daily habits and symptoms. But the rest of us, the American public, were shocked and shaken by what we saw, especially in contrast to Biden’s relatively strong State of the Union performance just a few months ago.
Read: Joe Biden’s ‘cognitive fluctuations’
The White House and the Biden campaign have suggested that the president’s problems at the debate stemmed from an exhausting travel schedule and a cold. Such explanations do not inspire confidence. Yes, it’s common for elderly people to bounce back more slowly from stressors. But even if jet lag and illness exacerbated normal cognitive limitations, said limitations remain, ready to surface again. And who knows when the next life-and-death decision will need to be made? Crises don’t wait patiently for presidents to be fully prepared. Someone whose cognitive competencies can be compromised as badly as Biden’s were by routine travel and a mere cold may be able to live a normal life, but they’d be hard-pressed to endure the rigors of negotiating with Congress or a foreign leader, much less making multiple rapid decisions when some future domestic or global disaster emerges.
In 1796, at the end of George Washington’s second term, he knew that the public would have elected him again and again, as many times as he wished. But he shocked the world by voluntarily relinquishing his executive authority. It made him a hero for all time.
Biden should take Washington’s example and withdraw from the 2024 race. In so doing, he can teach the world how to rise above politics, to sacrifice for the greater good. He, too, could become a hero . This election will determine the fate of the democracy in this nation. Many talented Democratic leaders from swing states could beat Trump . One of them should take the baton from Biden. That would truly solidify Biden’s legacy as a public servant and a successful president.
- {{subColumn.name}}
STEM Education
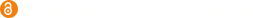
- {{newsColumn.name}}
- Share facebook twitter google linkedin

Solving word problems involving triangles and implications on training pre-service mathematics teachers
- William Guo ,
- School of Engineering and Technology, Central Queensland University, North Rockhampton, QLD 4702, Australia
- Academic Editor: Zlatko Jovanoski
- Received: 18 June 2024 Revised: 02 July 2024 Accepted: 05 July 2024 Published: 09 July 2024
- Full Text(HTML)
- Download PDF
Triangles and trigonometry are always difficult topics for both mathematics students and teachers. Hence, students' performance in solving mathematical word problems in these topics is not only a reflection of their learning outcomes but also an indication of teaching effectiveness. This case study drew from two examples of solving word problems involving triangles by pre-service mathematics teachers in a foundation mathematics course delivered by the author. The focus of this case study was on reasoning implications of students' performances on the effective training of pre-service mathematics teachers, from which a three-step interactive explicit teaching-learning approach, comprising teacher-led precise and inspiring teaching (or explicit teaching), student-driven engaged learning (or imitative learning), and student-led and teacher-guided problem-solving for real-world problems or projects (or active application), was summarized. Explicit teaching establishes a solid foundation for students to further their understanding of new mathematical concepts and to conceptualize the technical processes associated with these new concepts. Imitative learning helps students build technical abilities and enhance technical efficacy by engaging in learning activities. Once these first two steps have been completed, students should have a decent understanding of new mathematical concepts and technical efficacy to analyze, formulate, and finally solve real-world applications with assistance from teachers whenever required. Specially crafted professional development should also be considered for some in-service mathematics teachers to adopt this three-step interactive teaching-learning process.
- pre-service mathematics teacher ,
- word problem ,
- triangles ,
- problem-solving ,
- explicit teaching ,
- imitated learning ,
- active applications ,
- professional development
Citation: William Guo. Solving word problems involving triangles and implications on training pre-service mathematics teachers[J]. STEM Education, 2024, 4(3): 263-281. doi: 10.3934/steme.2024016
Related Papers:
| [1] | , 2016, 47(7): 1028-1047. http://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2016.1155774 --> Koyunkaya, M.Y., Mathematics education graduate students' understanding of trigonometric ratios. , 2016, 47(7): 1028-1047. http://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2016.1155774 doi: |
| [2] | , 2018, 6(1): 58-78. http://doi.org/10.18404/ijemst.328344 --> Koyunkaya, M.Y., An examination of a pre-service mathematics teacher's mental constructions of relationships in a right triangle. , 2018, 6(1): 58-78. http://doi.org/10.18404/ijemst.328344 doi: |
| [3] | , 2019, 14(2): 72-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teln.2018.11.004 --> Ngcobo, A.Z., Madonsela, S.P. and Brijlall, D., The teaching and learning of trigonometry. , 2019, 14(2): 72-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teln.2018.11.004 doi: |
| [4] | , 2022, 10(2): 208-224. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/11716 --> Durmaz, A.B. and Bostan, I.M., Pre-service teachers' knowledge regarding the area of triangle. , 2022, 10(2): 208-224. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/11716 doi: |
| [5] | , 2018, 39: 171–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13138-017-0123-y --> Rellensmann, J. and Schukajlow, S., Do students enjoy computing a triangle's side? Enjoyment and boredom while solving problems with and without a connection to reality from students' and pre-service teachers' perspectives. , 2018, 39: 171–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13138-017-0123-y doi: |
| [6] | , 2017, 5(1): 28-42. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/9495 --> Fyhn, A.B., What happens when a climber falls? Young climbers mathematise a climbing situation. , 2017, 5(1): 28-42. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/9495 doi: |
| [7] | , 2023, 11(2): 249-258. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/12582 --> Guo, W., Solving word problems involving triangles by transitional engineering students: Learning outcomes and implications. , 2023, 11(2): 249-258. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/12582 doi: |
| [8] | , 2015, 11(6): 1379-1397. https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2015.1396a --> Dündar, S., Mathematics teacher-candidates' performance in solving problems with different representation styles: The trigonometry example. , 2015, 11(6): 1379-1397. https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2015.1396a doi: |
| [9] | , 2017, 36(3): 273-306. https://doi.org/10.1080/03323315.2017.1327361 --> Walsh, R., Fitzmaurice, O. and O'Donoghue, J., What subject matter knowledge do second-level teachers need to know to teach trigonometry? An exploration and case study. , 2017, 36(3): 273-306. https://doi.org/10.1080/03323315.2017.1327361 doi: |
| [10] | , 2018, 9(1): 169-182. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.2.5261.169-182 --> Nabie, M. J., Akayuure, P., Ibrahim-Bariham, U.A. and Sofo, S., Trigonometric concepts: Pre-service teachers' perceptions and knowledge. , 2018, 9(1): 169-182. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.2.5261.169-182 doi: |
| [11] | , 2021, 53(8): 2004–2025. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2020.1857858 --> Ubah, I., Pre-service mathematics teachers' semiotic transformation of similar triangles: Euclidean geometry. , 2021, 53(8): 2004–2025. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2020.1857858 doi: |
| [12] | , 2022, 10(20): 3786. http://doi.org/10.3390/math10203786 --> Guo, W., Exploratory case study on solving word problems involving triangles by pre-service mathematics teachers in a regional university in Australia. , 2022, 10(20): 3786. http://doi.org/10.3390/math10203786 |
| [13] | , 2024, 16(1): 58-68. https://doi.org/10.69721/TPS.J.2024.16.1.07 --> Pentang J.T., Andrade, L.J.T., Golben, J.C., Talua, J.P., Bautista, R.M., Sercenia, J.C., et al., Problem-solving difficulties, performance, and differences among preservice teachers in Western Philippines University. , 2024, 16(1): 58-68. https://doi.org/10.69721/TPS.J.2024.16.1.07 doi: |
| [14] | , 2020, Pearson. --> Christensen, L.B., Johnson, R.B., Turner, L.A. and Christensen, L.B., , 2020, Pearson. |
| [15] | , 2 ed. 2020, Melbourne, Australia: Pearson. --> Guo, W.W., , 2 ed. 2020, Melbourne, Australia: Pearson. |
| [16] | , 2022, 10(16): 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162862 --> Rézio, S., Andrade, M.P. and Teodoro, M.F., Problem-based learning and applied mathematics. , 2022, 10(16): 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162862 doi: |
| [17] | , 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-023-00468-8 --> Gómez-Chacón, I.M., Bacelo, A., Marbán, J.M. and Palacios, A., Inquiry-based mathematics education and attitudes towards mathematics: tracking profiles for teaching. , 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-023-00468-8 doi: |
| [18] | , 1984, 77(6): 351-359. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.1984.10885555 --> Darch, C., Carnine D. and Gersten, R., Explicit instruction in mathematics problem solving. , 1984, 77(6): 351-359. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.1984.10885555 doi: |
| [19] | , 2004,104(3): 233–251. https://doi.org/10.1086/499751 --> Kroesbergen, E.H., Van Luit, J.E.H. and Maas, C.J.M., Effectiveness of explicit and constructivist mathematics instruction for low-achieving students in The Netherlands. , 2004,104(3): 233–251. https://doi.org/10.1086/499751 doi: |
| [20] | , 2015,115: 303–333. https://doi.org/10.1086/679969 --> Doabler, C.T., Baker, S.K., Kosty, D.B., Smolkowski, K., Clarke, B., Miller, S.J., et al., Examining the association between explicit mathematics instruction and student mathematics achievement. , 2015,115: 303–333. https://doi.org/10.1086/679969 doi: |
| [21] | , 2021, 44(2-3): 267-283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-021-00291-1 --> Gunn, B., Smolkowski, K., Strycker, L.A. and Dennis, C., Measuring Explicit Instruction Using Classroom Observations of Student-Teacher Interactions (COSTI). , 2021, 44(2-3): 267-283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-021-00291-1 doi: |
| [22] | , April 2024. Available from: . --> Evans, T., We need to go back to teacher-led explicit instruction: maths expert. , April 2024. Available from: . |
| [23] | , 2018, 5(6): 2349–5219. --> Magbanua, M.U., Explicit instruction in problem-solving skills, creative and critical thinking skills of the elementary education students. , 2018, 5(6): 2349–5219. |
| [24] | , 2022, 6(5): 7781–7787. --> Joaquin, C.J.A., A guided-discovery approach to problem solving: An explicit instruction. , 2022, 6(5): 7781–7787. |
| [25] | , 2021, 9(14): 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9141623 --> Guo, W., Li, W. and Tisdell, C.C., Effective pedagogy of guiding undergraduate engineering students solving first-order ordinary differential equations. , 2021, 9(14): 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9141623 doi: |
| [26] | , 2024, 12(1): 71-84. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/13831 --> Guo, W., Special tutorials to support pre-service mathematics teachers learning differential equations and mathematical modelling. , 2024, 12(1): 71-84. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/13831 doi: |
| [27] | , 2022, 2(3): 221-244. https://doi.org/10.3934/steme.2022014 --> Evans, T. and Dietrich, H., Inquiry-based mathematics education: a call for reform in tertiary education seems unjustified. , 2022, 2(3): 221-244. https://doi.org/10.3934/steme.2022014 doi: |
- This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 4.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/ -->
Supplements
Access History
- Corresponding author: Email: [email protected]
Reader Comments
- © 2024 the Author(s), licensee AIMS Press. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0 )
通讯作者: 陈斌, [email protected]
沈阳化工大学材料科学与工程学院 沈阳 110142

Article views( 66 ) PDF downloads( 5 ) Cited by( 0 )
Figures and Tables
Figures( 5 ) / Tables( 3 )
Associated material
Other articles by authors.
- William Guo
Related pages
- on Google Scholar
- Email to a friend
- Order reprints
Export File

- Figure 1. A sketch of isosceles triangle for the first word problem
- Figure 2. A reworked sketch for the second problem with derived angles (in red)
- Figure 3. The first reworked sketch for solving the second problem through right triangles
- Figure 4. The second reworked sketch for solving the second problem through right triangles
- Figure 5. The third reworked sketch for solving the second problem through right triangles
- Data Science
- Trending Now
- Data Structures
- System Design
- Foundational Courses
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- Data Science Using Python
- Web Development
- Web Browser
- Design Patterns
- Software Development
- Product Management
- Programming
Welcome to the daily solving of our PROBLEM OF THE DAY with Jay Dalsaniya We will discuss the entire problem step-by-step and work towards developing an optimized solution. This will not only help you brush up on your concepts of Tree but also build up problem-solving skills. Given a binary tree and an integer target , check whether there is a root-to-leaf path with its sum as target .
Input: tree = 1, target = 2 / \ 2 3 Output: false Explanation: There is no root to leaf path with sum 2.
Give the problem a try before going through the video. All the best!!! Problem Link: https://practice.geeksforgeeks.org/problems/root-to-leaf-path-sum/1


COMMENTS
Our career experts provide insights into problem-solving examples that you can use in job interviews, complete with sample answers and expert tips.
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Problem solving is the process of overcoming issues, mistakes, errors, failures and risks to move forward. This includes approaches such as troubleshooting, analysis, experimenting, rational thought, intuition and creativity designed to find solutions. The following are examples of problem solving followed by a list of problem solving techniques. An overview of problem solving with examples.
Problem-solving skills are valuable soft skills that help you identify the root of a problem, analyze potential solutions, and decide what to do.
Our complete guide to using and honing problem solving skills in your job search. Also includes a list of problem solving skills examples...
Got a problem to solve? From school to relationships, we look at examples of problem-solving strategies and how to use them.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
Problem-solving interview questions are a common tool used by employers to assess a candidate's problem-solving skills. These questions are designed to evaluate a candidate's ability to think critically, analyze information, and propose effective solutions to complex problems. Importance of Problem-Solving Skills in the Workplace Problem-solving skills are essential in the workplace as they ...
Diagnose the situation so that your focus is on the problem, not just its symptoms. Helpful problem-solving techniques include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect diagrams to define and analyze root causes.
The first step in solving a problem is understanding what that problem actually is. You need to be sure that you're dealing with the real problem - not its symptoms. For example, if performance in your department is substandard, you might think that the problem lies with the individuals submitting work. However, if you look a bit deeper, the ...
Problem-solving is a process where you're tasked with identifying an issue and coming up with the most practical and effective solution.
Problem-solving skills are skills that enable people to handle unexpected situations or difficult challenges at work. Organisations need people who can accurately assess problems and come up with effective solutions. In this article, we explain what problem-solving skills are, provide some examples of these skills and outline how to improve them.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you're a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let's get started!
Problem-solving skills help you attain insight into the source of the problem and figuring out an ideal solution. However, several skills and their correct implementation are essential, which are listed below. Patient listener: To identify a problem, you must first be all ears to gain information about the situation.
In this article, we'll walk you through the 5 steps of problem solving, and help you explore a few examples of problem solving scenarios where you can see the problem solving process in action before putting it to work.
Learn what problem-solving strategies are, explore why they are important, and discover 14 examples of effective problem-solving strategies you can try.
Problem-solving in the workplace is a complex and multifaceted skill that requires a combination of analytical thinking, creativity, and effective communication. It goes beyond simply identifying problems and extends to finding innovative solutions that address the root causes.
In this article, we're going to explain what problem-solving skills really mean. We'll talk about what makes up good problem-solving skills and give you tips on how to get better at them. You'll also find out how to make your problem-solving abilities look more impressive to those who might want to hire you.
Problem-solving skills help you determine why an issue is happening and how to resolve that issue. It's one of the key skills that employers seek in job applicants. Problem-solving starts with identifying the issue, coming up with solutions, implementing those solutions, and evaluating their effectiveness. Since this is a skill that's important ...
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Problem-solving skills help you to resolve obstacles in a situation. Problem-solving is made up of several skills that can improve how well you solve problems on the job.
Problem-solving is an important skill to develop because life will always throw you curveballs. Being able to respond to these problems with flexibility and calmness will generate much better results than if you respond to the problem with resistance or avoidance. Also, research has shown that increasing problem-solving skills through problem-solving therapy is beneficial for several physical ...
Problem-solving requires multiple reasoning stages—from recognizing the problem, analyzing it, looking for a solution, and finding the winning one. Sharing how you fixed your own mistake is probably the best way to include all of those elements.
Problems often arise in organizational life. From understanding the root cause of a problem to using the power of empathy, here are five strategies for solving problems.
Examples of Successful Team Problem-Solving Cases. Successful team problem-solving cases demonstrate the effectiveness of strategies employed by teams to overcome challenges and achieve desired outcomes. These case studies provide valuable insights into the impact of team problem-solving on overall performance.
Identifying the real problem and solving it in the most effective way is the fundamental step for finding an ideal solution and problem identification is the first step to finding the perfect result. Correctly defining the problem or asking the right question is the most critical stage of the decision-making process if we want to have the best ...
CATWOE Analysis is a structured problem-solving tool that offers businesses a comprehensive framework to address complex issues comprehensively. The acronym CATWOE stands for Customers, Actors, Transformation process, Worldview, Owners, and Environmental constraints. ... For example, environmental sustainability is a significant constraint for ...
Produced by ElevenLabs and News Over Audio (NOA) using AI narration. Joe Biden's problem isn't his age. It's his ability to function. America has known a number of exceptional octogenarians ...
Triangles and trigonometry are always difficult topics for both mathematics students and teachers. Hence, students' performance in solving mathematical word problems in these topics is not only a reflection of their learning outcomes but also an indication of teaching effectiveness. This case study drew from two examples of solving word problems involving triangles by pre-service mathematics ...
Welcome to the daily solving of our PROBLEM OF THE DAY with Jay Dalsaniya We will discuss the entire problem step-by-step and work towards developing an optimized solution. This will not only help you brush up on your concepts of Tree but also build up problem-solving skills. Given a binary tree and an integer target, check whether there is a root-to-leaf path with its sum as target.