
39 Different Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay (Rated)

The phrase “In conclusion …” sounds reductive, simple and … well, just basic.
You can find better words to conclude an essay than that!
So below I’ve outlined a list of different ways to say in conclusion in an essay using a range of analysis verbs . Each one comes with an explanation of the best time to use each phrase and an example you could consider.
Read Also: How to Write a Conclusion using the 5C’s Method
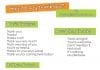
List of Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
The following are the best tips I have for to say in conclusion in an essay.
1. The Weight of the Evidence Suggests…
My Rating: 10/10
Overview: This is a good concluding phrase for an evaluative essay where you need to compare two different positions on a topic then conclude by saying which one has more evidence behind it than the other.
You could also use this phrase for argumentative essays where you’ve put forward all the evidence for your particular case.
Example: “The weight of the evidence suggests that climate change is a real phenomenon.”
2. A Thoughtful Analysis would Conclude…
My Rating: 9/10
Overview: I would use this phrase in either an argumentative essay or a comparison essay. As an argument, it highlights that you think your position is the most logical.
In a comparison essay, it shows that you have (or have intended to) thoughtfully explore the issue by looking at both sides.
Example: “A thoughtful analysis would conclude that there is substantial evidence highlighting that climate change is real.”
Related Article: 17+ Great Ideas For An Essay About Yourself
3. A Balanced Assessment of the Above Information…
Overview: This phrase can be used to show that you have made a thoughtful analysis of the information you found when researching the essay. You’re telling your teacher with this phrase that you have looked at all sides of the argument before coming to your conclusion.
Example: “A balanced assessment of the above information would be that climate change exists and will have a strong impact on the world for centuries to come.”
4. Across the Board…
My Rating: 5/10
Overview: I would use this phrase in a less formal context such as in a creative discussion but would leave it out of a formal third-person essay. To me, the phrase comes across as too colloquial.
Example: “Across the board, there are scientists around the world who consistently provide evidence for human-induced climate change.”
5. Logically…
My Rating: 7/10
Overview: This phrase can be used at the beginning of any paragraph that states out a series of facts that will be backed by clear step-by-step explanations that the reader should be able to follow to a conclusion.
Example: “Logically, the rise of the automobile would speed up economic expansion in the United States. Automobiles allowed goods to flow faster around the economy.
6. After all is Said and Done…
Overview: This is a colloquial term that is more useful in a speech than written text. If you feel that the phrase ‘In conclusion,’ is too basic, then I’d also avoid this term. However, use in speech is common, so if you’re giving a speech, it may be more acceptable.
Example: “After all is said and done, it’s clear that there is more evidence to suggest that climate change is real than a hoax.”
7. All in All…
Overview: ‘All in all’ is a colloquial term that I would use in speech but not in formal academic writing. Colloquialisms can show that you have poor command of the English language. However, I would consider using this phrase in the conclusion of a debate.
Example: “All in all, our debate team has shown that there is insurmountable evidence that our side of the argument is correct.”
8. All Things Considered…
My Rating: 6/10
Overview: This term is a good way of saying ‘I have considered everything above and now my conclusion is..’ However, it is another term that’s more commonly used in speech than writing. Use it in a high school debate, but when it comes to a formal essay, I would leave it out.
Example: “All things considered, there’s no doubt in my mind that climate change is man-made.”
9. As a Final Note…
My Rating: 3/10
Overview: This phrase gives me the impression that the student doesn’t understand the point of a conclusion. It’s not to simply make a ‘final note’, but to summarize and reiterate. So, I would personally avoid this one.
Example: “As a final note, I would say that I do think the automobile was one of the greatest inventions of the 20 th Century.”
10. As Already Stated…
My Rating: 2/10
Overview: I don’t like this phrase. It gives teachers the impression that you’re going around in circles and haven’t organized your essay properly. I would particularly avoid it in the body of an essay because I always think: “If you already stated it, why are you stating it again?” Of course, the conclusion does re-state things, but it also adds value because it also summarizes them. So, add value by using a phrase such as ‘summarizing’ or ‘weighing up’ in your conclusion instead.
Example: “As already stated, I’m going to repeat myself and annoy my teacher.”
11. At present, the Best Evidence Suggests…
My Rating: 8/10
Overview: In essays where the evidence may change in the future. Most fields of study do involve some evolution over time, so this phrase acknowledges that “right now” the best evidence is one thing, but it may change in the future. It also shows that you’ve looked at the latest information on the topic.
Example: “At present, the best evidence suggests that carbon dioxide emissions from power plants is the greatest influence on climate change.”
12. At the Core of the Issue…
Overview: I personally find this phrase to be useful for most essays. It highlights that you are able to identify the most important or central point from everything you have examined. It is slightly less formal than some other phrases on this list, but I also wouldn’t consider it too colloquial for an undergraduate essay.
Example: “At the core of the issue in this essay is the fact scientists have been unable to convince the broader public of the importance of action on climate change.”
13. Despite the shortcomings of…
Overview: This phrase can be useful in an argumentative essay. It shows that there are some limitations to your argument, but , on balance you still think your position is the best. This will allow you to show critical insight and knowledge while coming to your conclusion.
Often, my students make the mistake of thinking they can only take one side in an argumentative essay. On the contrary, you should be able to highlight the limitations of your point-of-view while also stating that it’s the best.
Example: “Despite the shortcomings of globalization, this essay has found that on balance it has been good for many areas in both the developed and developing world.”
14. Finally…
My Rating: 4/10
Overview: While the phrase ‘Finally,’ does indicate that you’re coming to the end of your discussion, it is usually used at the end of a list of ideas rather than in a conclusion. It also implies that you’re adding a point rather that summing up previous points you have made.
Example: “Finally, this essay has highlighted the importance of communication between policy makers and practitioners in order to ensure good policy is put into effect.”
15. Gathering the above points together…
Overview: While this is not a phrase I personally use very often, I do believe it has the effect of indicating that you are “summing up”, which is what you want out of a conclusion.
Example: “Gathering the above points together, it is clear that the weight of evidence highlights the importance of action on climate change.”
16. Given the above information…
Overview: This phrase shows that you are considering the information in the body of the piece when coming to your conclusion. Therefore, I believe it is appropriate for starting a conclusion.
Example: “Given the above information, it is reasonable to conclude that the World Health Organization is an appropriate vehicle for achieving improved health outcomes in the developing world.”
17. In a nutshell…
Overview: This phrase means to say everything in the fewest possible words. However, it is a colloquial phrase that is best used in speech rather than formal academic writing.
Example: “In a nutshell, there are valid arguments on both sides of the debate about socialism vs capitalism.”
18. In closing…
Overview: This phrase is an appropriate synonym for ‘In conclusion’ and I would be perfectly fine with a student using this phrase in their essay. Make sure you follow-up by explaining your position based upon the weight of evidence presented in the body of your piece
Example: “In closing, there is ample evidence to suggest that liberalism has been the greatest force for progress in the past 100 years.”
19. In essence…
Overview: While the phrase ‘In essence’ does suggest you are about to sum up the core findings of your discussion, it is somewhat colloquial and is best left for speech rather than formal academic writing.
Example: “In essence, this essay has shown that cattle farming is an industry that should be protected as an essential service for our country.”
20. In review…
Overview: We usually review someone else’s work, not our own. For example, you could review a book that you read or a film you watched. So, writing “In review” as a replacement for “In conclusion” comes across a little awkward.
Example: “In review, the above information has made a compelling case for compulsory military service in the United States.”
21. In short…
Overview: Personally, I find that this phrase is used more regularly by undergraduate student. As students get more confident with their writing, they tend to use higher-rated phrases from this list. Nevertheless, I would not take grades away from a student for using this phrase.
Example: “In short, this essay has shown the importance of sustainable agriculture for securing a healthy future for our nation.”
22. In Sum…
Overview: Short for “In summary”, the phrase “In sum” sufficiently shows that you are not coming to the moment where you will sum up the essay. It is an appropriate phrase to use instead of “In conclusion”.
But remember to not just summarize but also discuss the implications of your findings in your conclusion.
Example: “In sum, this essay has shown the importance of managers in ensuring efficient operation of medium-to-large enterprises.”
23. In Summary…
Overview: In summary and in sum are the same terms which can be supplemented for “In conclusion”. You will show that you are about to summarize the points you said in the body of the essay, which is what you want from an essay.
Example: “In summary, reflection is a very important metacognitive skill that all teachers need to master in order to improve their pedagogical skills.”
24. It cannot be conclusively stated that…
Overview: While this phrase is not always be a good fit for your essay, when it is, it does show knowledge and skill in writing. You would use this phrase if you are writing an expository essay where you have decided that there is not enough evidence currently to make a firm conclusion on the issue.
Example: “It cannot be conclusively stated that the Big Bang was when the universe began. However, it is the best theory so far, and none of the other theories explored in this essay have as much evidence behind them.”
25. It is apparent that…
Overview: The term ‘ apparent ’ means that something is ‘clear’ or even ‘obvious’. So, you would use this word in an argumentative essay where you think you have put forward a very compelling argument.
Example: “It is apparent that current migration patterns in the Americas are unsustainable and causing significant harm to the most vulnerable people in our society.”
26. Last but not least…
Overview: The phrase “last but not least” is a colloquial idiom that is best used in speech rather than formal academic writing. Furthermore, when you are saying ‘last’, you mean to say you’re making your last point rather than summing up all your points you already made. So, I’d avoid this one.
Example: “Last but not least, this essay has highlighted the importance of empowering patients to exercise choice over their own medical decisions.”
27. Overall…
My Rating: 7.5/10
Overview: This phrase means ‘taking everything into account’, which sounds a lot like what you would want to do in an essay. I don’t consider it to be a top-tier choice (which is why I rated it 7), but in my opinion it is perfectly acceptable to use in an undergraduate essay.
Example: “Overall, religious liberty continues to be threatened across the world, and faces significant threats in the 21 st Century.”
28. The above points illustrate…
Overview: This phrase is a good start to a conclusion paragraph that talks about the implications of the points you made in your essay. Follow it up with a statement that defends your thesis you are putting forward in the essay.
Example: “The above points illustrate that art has had an overwhelmingly positive impact on humanity since the renaissance.”
29. The evidence presented in this essay suggests that…
Overview: I like this phrase because it highlights that you are about to gather together the evidence from the body of the essay to put forward a final thesis statement .
Example: “The evidence presented in this essay suggests that the democratic system of government is the best for securing maximum individual liberty for citizens of a nation.”
30. This essay began by stating…
Overview: This phrase is one that I teach in my YouTube mini-course as an effective one to use in an essay conclusion. If you presented an interesting fact in your introduction , you can return to that point from the beginning of the essay to provide nice symmetry in your writing.
Example: “This essay began by stating that corruption has been growing in the Western world. However, the facts collected in the body of the essay show that institutional checks and balances can sufficiently minimize this corruption in the long-term.”
31. This essay has argued…
Overview: This term can be used effectively in an argumentative essay to provide a summary of your key points. Follow it up with an outline of all your key points, and then a sentence about the implications of the points you made. See the example below.
Example: “This essay has argued that standardized tests are damaging for students’ mental health. Tests like the SATs should therefore be replaced by project-based testing in schools.”
32. To close…
Overview: This is a very literal way of saying “In conclusion”. While it’s suitable and serves its purpose, it does come across as being a sophomoric term. Consider using one of the higher-rated phrases in this list.
Example: “To close, this essay has highlighted both the pros and cons of relational dialectics theory and argued that it is not the best communication theory for the 21 st Century.”
33. To Conclude…
Overview: Like ‘to close’ and ‘in summary’, the phrase ‘to conclude’ is very similar to ‘in conclusion’. It can therefore be used as a sufficient replacement for that term. However, as with the above terms, it’s just okay and you could probably find a better phrase to use.
Example: “To conclude, this essay has highlighted that there are multiple models of communication but there is no one perfect theory to explain each situation.”
34. To make a long story short…
My Rating: 1/10
Overview: This is not a good phrase to use in an academic essay. It is a colloquialism. It also implies that you have been rambling in your writing and you could have said everything more efficiently. I would personally not use this phrase.
Example: “To make a long story short, I don’t have very good command of academic language.”
35. To Sum up…
Overview: This phrase is the same as ‘In summary’. It shows that you have made all of your points and now you’re about to bring them all together in a ‘summary’. Just remember in your conclusion that you need to do more than summarize but also talk about the implications of your findings. So you’ll need to go beyond just a summary.
Example: “In summary, there is ample evidence that linear models of communication like Lasswell’s model are not as good at explaining 21 st Century communication as circular models like the Osgood-Schramm model .”
36. Ultimately…
Overview: While this phrase does say that you are coming to a final point – also known as a conclusion – it’s also a very strong statement that might not be best to use in all situations. I usually accept this phrase from my undergraduates, but for my postgraduates I’d probably suggest simply removing it.
Example: “Ultimately, new media has been bad for the world because it has led to the spread of mistruths around the internet.”
37. Undoubtedly…
Overview: If you are using it in a debate or argumentative essay, it can be helpful. However, in a regular academic essay, I would avoid it. We call this a ‘booster’, which is a term that emphasizes certainty. Unfortunately, certainty is a difficult thing to claim, so you’re better off ‘hedging’ with phrases like ‘It appears’ or ‘The best evidence suggests’.
Example: “Undoubtedly, I know everything about this topic and am one hundred percent certain even though I’m just an undergraduate student.”
38. Weighing up the facts, this essay finds…
Overview: This statement highlights that you are looking at all of the facts both for and against your points of view. It shows you’re not just blindly following one argument but being careful about seeing things from many perspectives.
Example: “Weighing up the facts, this essay finds that reading books is important for developing critical thinking skills in childhood.”
39. With that said…
Overview: This is another phrase that I would avoid. This is a colloquialism that’s best used in speech rather than writing. It is another term that feels sophomoric and is best to avoid. Instead, use a more formal term such as: ‘Weighing up the above points, this essay finds…’
Example: “With that said, this essay disagrees with the statement that you need to go to college to get a good job.”
Do you Need to Say Anything?
Something I often tell my students is: “Can you just remove that phrase?”
Consider this sentence:
- “In conclusion, the majority of scientists concur that climate change exists.”
Would it be possible to simply say:
- “ In conclusion, The majority of scientists concur that climate change exists.”
So, I’d recommend also just considering removing that phrase altogether! Sometimes the best writing is the shortest, simplest writing that gets to the point without any redundant language at all.
How to Write an Effective Conclusion
Before I go, I’d like to bring your attention to my video on ‘how to write an effective conclusion’. I think it would really help you out given that you’re looking for help on how to write a conclusion. It’s under 5 minutes long and has helped literally thousands of students write better conclusions for their essays:
You can also check out these conclusion examples for some copy-and-paste conclusions for your own essay.
In Conclusion…
Well, I had to begin this conclusion with ‘In conclusion…’ I liked the irony in it, and I couldn’t pass up that chance.
Overall, don’t forget that concluding an essay is a way to powerfully summarize what you’ve had to say and leave the reader with a strong impression that you’ve become an authority on the topic you’re researching.
So, whether you write it as a conclusion, summary, or any other synonym for conclusion, those other ways to say in conclusion are less important than making sure that the message in your conclusion is incredibly strong.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori's 4 Planes of Development, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori vs Reggio Emilia vs Steiner-Waldorf vs Froebel
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Learn English
- Infographics

- English Vocabulary
- English Vocabulary Dictionary
80 In Conclusion Examples! + Translation
Listen to audio.
List of ways to say in conclusion with Translation. Use these synonyms for in conclusion to be a better writer.
In Conclusion Synonyms
You can use the following expressions:
- All in all,
- In summary,
- To conclude,
- In closing,
- Finally, it may be concluded…
- To summarize,
- Overall, it may be said…
- Taking everything into account,
- On the whole,
- All things considered,
- Everything considered,
- By and large,
- In the end,
- In a nutshell,
- In general,
- As a conclusion,
- In the long run,
- On a final note,
- To finish with,
- As a matter of fact,
- Last but not least,
- Simply put,
- Generally speaking,
- Altogether,
- Principally,
- In a long term,
- Ultimately,
- To close up,
- Considering,
- In the final stages,
- For all intents and purposes
- After all, I’m done..
- All circumstances have been considered,…
- therefore,…
- As a final observation,
- At the end of the day
- To summarize briefly
- Lifting the back,
- Considering all this,
- simply put,
- In integration,…
- In essence,
- Under review,
- in the end,
- The bottom line is
- The conclusion is
- Obviously, through
- last but not least
- the last point
- on the whole,
- In general, it can be said that
- With this in mind,
- Main research paper says,
- Briefly explain
- Speaking of the point
- To end everything
- To make a long story short
- To put it bluntly…
- To summarize the above,
- To wrap it all up,…
In Conclusion Translation
In conclusion has over 600 possible synonyms , some complete synonyms and other very similar. Since in conclusion is used to conclude statements and show results , the synonyms do that as well. They are all often used to denote the final argument.
- in a nutshell,
- in general,
- to conclude,
- as a conclusion,
- in the long run,
- on a final note,
- to finish with,
- as a matter of fact,

image source
What does In Conclusion mean?
In conclusion means to provide a final argument . It is used to prepare the people listening or reading for your final statement . In conclusion is used at the end of essays, speeches, dissertations, books, etc.
In the most basic sense, it means exactly what is ways, that there is a conclusion coming.
Sentences with In Conclusion Examples
- In conclusion, it is safe to say that the results show how student motivation can be increased with the help of our new method.
- In conclusion, we have to direct our attention to the factors behind the rising crime rate, and not just the demographic it affects.
- In conclusion, the true goal of the poet’s expression will forever remain a mystery to us.
Please enable JavaScript

In Summary vs In Conclusion
In summary and in conclusion are considered close synonyms. They don’t have exactly the same meaning, but they are used in very similar fashion in writing and speaking. They both appear at the ends of various arguments in order to denote the final statement.
In summary is used when you want to announce your conclusion , but you present that conclusion as a summary of all the facts previously mentioned.
In conclusion is used when you want to make a final statement , and clarify your previous arguments. This is why in summary and in conclusion are different in meaning. In summary does not denote a final statement, only a summary of the facts.
To Conclude or In Conclusion
To conclude and in conclusion are complete synonyms , so they mean the same thing. You can use whichever you like more , or whichever best fits your needs.
In Conclusion Transition Words
In conclusion, is a transitional phrase in of itself. It denotes the final argument, so it is a transition between evidence and statement.
In conclusion, is also always divided by a comma . The phrase can only be used the start of a sentence , and cannot appear anywhere else. Therefore, it is a transitional phrase.
Learn English for free
- List of Sentence Connectors in English with Examples
- Essential Academic Writing Examples and Phrases!
- List of Sentence Connectors in English with Examples!
- Discover How to Be a Successful Negotiator in English
- Phrasal Verbs with HEAR
- Ultimate List of 50 INTERJECTIONS with Examples
- 👉IN OTHER WORDS Synonym 🤓 30 Other Ways to Say …
- 👉 Linking Words: List of Sentence Connectors in English with Examples! 😃
- Its vs. It’s
- Films and Novels ›› Vocabulary related to Films and Novels
- English for Sales People ›› English Sales Letter
- how to score band 8.0 in IELTS form the first time
Browse by Category
A Adjectives B Business English C D dictionary E English grammar English Idioms English language English Learning Tips English phrases English teacher English Vocabulary English Vocabulary English words F G H how to learn english I idioms Infographic K L Learn English M N new words noun O P phrasal verb Q R S T teach English Teaching English as a foreign language Text Abbreviations The Jungle Book U Verb W
- Abbreviations
- Advanced English Lesson
- Beginner English
- Business English
- Collocations
- Conjunctions
- Difference Between
- English Grammar
- English Idioms
- English Learning Tips
- English Questions and Answers
- English Speaking
- English Test
- English Videos
- English Writing
- For Teachers
- Intermediate English
- Listening Skills
- Phrasal Verbs
- Prepositions
- Teach English
- Uncategorized
- Understanding
- Useful English learning websites
Latest Comments
Hello. Thank you very much for the most detailed and clear explanation! Could you please comment on this sentence where…
“Hey there! Just wanted to send you a bunch of good luck vibes as you go for captain of the…
i need a good luck message for a teen trying out for captain of the drill team with the word…
Very useful for learning english language. Thank you!
thanks for post
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

Historic vs Historical

Nonverbal communication definition

Supposition Meaning

Understanding the Extroverted Introvert

Your Guide: List of 30 Helpful Synonyms with Explanation and Examples

50 Creative Ways to Say Happy Birthday: My Top Picks

Can you also use “with that being said”?

Yes, you can. Absolutely! Really good addition!

aye that just helped me out alot thank u

This was really helpful for my essay that was due today!! Thanks a lot ^^
I am so glad I could help!

Good I also want to help

Useful list 🙂 But it would have been great if you had given examples too. Still, it is worth sharing on twitter for me 🙂
this was rlly helpful to my essay tbh

This was pretty helpful and i was able to not just keep saying in conclusion for all of my school work. 🙂 But also, did anybody notice that it says 15 different ways to say in conclusion but it only gave 10?

Synonyms for opinion and secondly and I also need wow words
This was pretty helpful and i was able to not just keep saying in conclusion for all of my school work. 🙂 I am super proud you people are excellent!

This was an amazing list, came in useful so many times!!

MOST POPULAR

👉 A BIG List of Prefixes and Suffixes and Their Meanings
200 Phrases for saying THANK YOU in any situation!

Formal and Informal Email Phrases – from Greetings to Closing Phrases!

Linking Words: List of Sentence Connectors in English with Examples!

90 Names of Baby Animals and Their Parents
![Types of Adverb 🦠 Adverb Examples [All You Need] adverbs](https://www.myenglishteacher.eu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/adverbs-100x70.jpg)

Types of Adverb 🦠 Adverb Examples [All You Need]

Talk to Strangers / Free Chat Rooms
English Level Test

6 Ways to Immediately Improve Your English Communication Skills
What does TBH mean? (TBH full form) on Facebook, Instagram, Texting

25 Ways to Say “Keep Up The Good Work” 💪 &...

Subject and Predicate Exercises! – MyEnglishTeacher.eu
Stay connected, editor picks.

Difference between Alligator and Crocodile
Popular posts, popular category.
- Q&A 2437
- English Vocabulary 625
- English Vocabulary Dictionary 364
- English Grammar 200
- Synonyms 148
- Infographics 109
- Collocations 105
- Learn English 81
- English Idioms 69
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions

59 Ways to Say 'In Conclusion'

In this article, we’ll learn 59 alternative ways to say ‘in conclusion.’ In other words, you’re going to learn some synonyms of the common expression.
If you find yourself using the words ‘in conclusion’ a lot and wish you knew of other ways to say it, then you’ve come to the right place.
Other Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion'
So you want to learn new ways to say ‘in conclusion?’ Whether it’s for a formal or more casual setting, knowing alternative words for this popular expression can always come in handy.
So without further ado, let’s dive in.
‘In Conclusion’ Definition
First of all, what does ‘in conclusion’ mean? That’s an excellent place to start.
- It's an expression you use at the end of an idea to wrap up what you’ve said so far and to introduce your findings or thoughts on the matter.
- You’ll usually find these words at the end of a paragraph, a section, or at the very end of the piece itself.
Here are some examples of texts where you’ll often (if not always) find a conclusion:
- A blog article
- A research paper
For example, any well-structured blog deserves to be concluded. If you scroll to the end of any of our articles, you’ll always find that the very last section is a conclusion section where we summarize what was learned throughout the blog and any final thoughts on the topic.
Formal Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’
The expression ‘in conclusion’ is often used in formal writing, such as academic essays or research papers, because those are the kinds of writing that require one. But if there’s one crucial thing in a well-written paper, it’s avoiding repetition and showing that you have a wide and varied vocabulary.
Is that you? Are you currently writing an academic paper or other text you hope to impress with? If so, this section is for you.
Here are some alternative ways to say ‘in conclusion’ in a formal setting:
1. By way of conclusion 2. To conclude 3. On a final note 4. To summarize 5. In closing 6. All things considered 7. Finally 8. In brief 9. Ultimately 10. For all intents and purposes 11. In essence 12. The bottom line is 13. To bring things to a close 14. To wrap things up 15. The main takeaway 16. If you take anything from this, let it be that 17. As I've demonstrated 18. As has been shown 19. Lastly 20. To review 21. By way of final observation
Casual Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’
22. In a nutshell 23. Basically 24. Long story short 25. All in all 26. At the end of the day 27. So what I’m saying is 28. The gist of it is 29. On the whole 30. To sum up 31. To get to the point 32. After all is said and done
Different Ways to Conclude
There are a bunch of other ways you can conclude your argument, text, or speech. I'm going to list these below, and while they're not synonymous with 'in conclusion' like the phrases outlined above, they're still effective for rounding up or finalizing your argument.
33. By and large 34. Mostly 35. In general 36. Most importantly 37. Taking everything into account 38. In the end 39. As a result 40. As you can see 41. In the final analysis 42. For the most part 43. In the main 44. Chiefly 45. In short 46. Upon consideration 47. Upon further review 48. Overall 49. Predominantly 50. What I mean by that 51. In summary 52. What this means 53. Generally 54. With this in mind 55. Considering all this 56. Everything considered 57. All things considered 58. Considering all of the facts 59. In light of these facts
Examples in a Sentence
Okay, so now we’ve got some alternative ways of saying ‘in conclusion,’ how about we look at how to use some of these in context?
Let’s use some real-life sentence examples to illustrate.
Here are some formal setting examples:
To summarize our findings, it appears that when the rats were in a peaceful setting, they chose healthier food. For all intents and purposes, their hearts are in the right place. All things considered, the girls seemed just as likely as the boys to want to play team sports. I think the important thing here is to look at the bottom line. The bottom line is that it’s good for the soul to listen to music .
And now some examples of more casual conversations:
In a nutshell, I think you and I should be together. So what I'm saying is, what counts is what you do, not what you don't do. The gist of it is that it makes more sense to book in advance than to show up on the day. Long story short, I'm back in New York and looking for a job. At the end of the day, he just does whatever he wants to, regardless of the consequences.
Final Thoughts
And this is the moment where we begin our conclusion to this article. As I mentioned earlier, all good articles need a conclusion.
Let’s summarize what we’ve learned:
- Use a conclusion at the end of your text, speech, or argument.
- Choose the correct expression based on the context you’re in.
- Use the concluding section to make any final remarks about your findings or your thoughts on the topic.
And if you found this article helpful, head to our blog , where you’ll find lots more like this.
Learn More:
- 83 Ways to Say 'Goodbye'
- 'For Example' Synonyms: 41 Other Ways to Say 'For Example'
- 29 Ways to Say 'You're Welcome'
- 17 Ways to Say 'To Whom It May Concern'
- 41 Different Ways to Say 'I Love You'
- 21 Ways to Say 'Thank You'
- 51 Ways to Say 'Happy Birthday'
- 77 Ways to Say 'Have a Good Day'
- 81 Different Ways to Say 'Good Morning'
- 153 Ways to Say 'I Miss You'
- 109 Ways to Say 'Hello'
- 105 Different Ways to Say 'Yes'
- 131+ Ways to Say 'Hi' or 'Hello'
- 301 Ways to Say 'Beautiful'
- 110 Ways to Say 'Good Job'
We encourage you to share this article on Twitter and Facebook . Just click those two links - you'll see why.
It's important to share the news to spread the truth. Most people won't.
Add new comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment

- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Words to Use in an Essay: 300 Essay Words

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
Words to use in the essay introduction, words to use in the body of the essay, words to use in your essay conclusion, how to improve your essay writing vocabulary.
It’s not easy to write an academic essay .
Many students struggle to word their arguments in a logical and concise way.
To make matters worse, academic essays need to adhere to a certain level of formality, so we can’t always use the same word choices in essay writing that we would use in daily life.
If you’re struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don’t worry—you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay.
The introduction is one of the hardest parts of an essay to write.
You have only one chance to make a first impression, and you want to hook your reader. If the introduction isn’t effective, the reader might not even bother to read the rest of the essay.
That’s why it’s important to be thoughtful and deliberate with the words you choose at the beginning of your essay.
Many students use a quote in the introductory paragraph to establish credibility and set the tone for the rest of the essay.
When you’re referencing another author or speaker, try using some of these phrases:
To use the words of X
According to X
As X states
Example: To use the words of Hillary Clinton, “You cannot have maternal health without reproductive health.”
Near the end of the introduction, you should state the thesis to explain the central point of your paper.
If you’re not sure how to introduce your thesis, try using some of these phrases:
In this essay, I will…
The purpose of this essay…
This essay discusses…
In this paper, I put forward the claim that…
There are three main arguments for…

Example: In this essay, I will explain why dress codes in public schools are detrimental to students.
After you’ve stated your thesis, it’s time to start presenting the arguments you’ll use to back up that central idea.
When you’re introducing the first of a series of arguments, you can use the following words:
First and foremost
First of all
To begin with
Example: First , consider the effects that this new social security policy would have on low-income taxpayers.
All these words and phrases will help you create a more successful introduction and convince your audience to read on.
The body of your essay is where you’ll explain your core arguments and present your evidence.
It’s important to choose words and phrases for the body of your essay that will help the reader understand your position and convince them you’ve done your research.
Let’s look at some different types of words and phrases that you can use in the body of your essay, as well as some examples of what these words look like in a sentence.
Transition Words and Phrases
Transitioning from one argument to another is crucial for a good essay.
It’s important to guide your reader from one idea to the next so they don’t get lost or feel like you’re jumping around at random.
Transition phrases and linking words show your reader you’re about to move from one argument to the next, smoothing out their reading experience. They also make your writing look more professional.
The simplest transition involves moving from one idea to a separate one that supports the same overall argument. Try using these phrases when you want to introduce a second correlating idea:
Additionally
In addition
Furthermore
Another key thing to remember
In the same way
Correspondingly
Example: Additionally , public parks increase property value because home buyers prefer houses that are located close to green, open spaces.
Another type of transition involves restating. It’s often useful to restate complex ideas in simpler terms to help the reader digest them. When you’re restating an idea, you can use the following words:
In other words
To put it another way
That is to say
To put it more simply
Example: “The research showed that 53% of students surveyed expressed a mild or strong preference for more on-campus housing. In other words , over half the students wanted more dormitory options.”
Often, you’ll need to provide examples to illustrate your point more clearly for the reader. When you’re about to give an example of something you just said, you can use the following words:
For instance
To give an illustration of
To exemplify
To demonstrate
As evidence
Example: Humans have long tried to exert control over our natural environment. For instance , engineers reversed the Chicago River in 1900, causing it to permanently flow backward.
Sometimes, you’ll need to explain the impact or consequence of something you’ve just said.
When you’re drawing a conclusion from evidence you’ve presented, try using the following words:
As a result
Accordingly
As you can see
This suggests that
It follows that
It can be seen that
For this reason
For all of those reasons
Consequently
Example: “There wasn’t enough government funding to support the rest of the physics experiment. Thus , the team was forced to shut down their experiment in 1996.”

When introducing an idea that bolsters one you’ve already stated, or adds another important aspect to that same argument, you can use the following words:
What’s more
Not only…but also
Not to mention
To say nothing of
Another key point
Example: The volcanic eruption disrupted hundreds of thousands of people. Moreover , it impacted the local flora and fauna as well, causing nearly a hundred species to go extinct.
Often, you'll want to present two sides of the same argument. When you need to compare and contrast ideas, you can use the following words:
On the one hand / on the other hand
Alternatively
In contrast to
On the contrary
By contrast
In comparison
Example: On the one hand , the Black Death was undoubtedly a tragedy because it killed millions of Europeans. On the other hand , it created better living conditions for the peasants who survived.
Finally, when you’re introducing a new angle that contradicts your previous idea, you can use the following phrases:
Having said that
Differing from
In spite of
With this in mind
Provided that
Nevertheless
Nonetheless
Notwithstanding
Example: Shakespearean plays are classic works of literature that have stood the test of time. Having said that , I would argue that Shakespeare isn’t the most accessible form of literature to teach students in the twenty-first century.
Good essays include multiple types of logic. You can use a combination of the transitions above to create a strong, clear structure throughout the body of your essay.
Strong Verbs for Academic Writing
Verbs are especially important for writing clear essays. Often, you can convey a nuanced meaning simply by choosing the right verb.
You should use strong verbs that are precise and dynamic. Whenever possible, you should use an unambiguous verb, rather than a generic verb.
For example, alter and fluctuate are stronger verbs than change , because they give the reader more descriptive detail.
Here are some useful verbs that will help make your essay shine.
Verbs that show change:
Accommodate
Verbs that relate to causing or impacting something:
Verbs that show increase:
Verbs that show decrease:
Deteriorate
Verbs that relate to parts of a whole:
Comprises of
Is composed of
Constitutes
Encompasses
Incorporates
Verbs that show a negative stance:
Misconstrue

Verbs that show a positive stance:
Substantiate
Verbs that relate to drawing conclusions from evidence:
Corroborate
Demonstrate
Verbs that relate to thinking and analysis:
Contemplate
Hypothesize
Investigate
Verbs that relate to showing information in a visual format:
Useful Adjectives and Adverbs for Academic Essays
You should use adjectives and adverbs more sparingly than verbs when writing essays, since they sometimes add unnecessary fluff to sentences.
However, choosing the right adjectives and adverbs can help add detail and sophistication to your essay.
Sometimes you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is useful and should be taken seriously. Here are some adjectives that create positive emphasis:
Significant
Other times, you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is harmful or ineffective. Here are some adjectives that create a negative emphasis:
Controversial
Insignificant
Questionable
Unnecessary
Unrealistic
Finally, you might need to use an adverb to lend nuance to a sentence, or to express a specific degree of certainty. Here are some examples of adverbs that are often used in essays:
Comprehensively
Exhaustively
Extensively
Respectively
Surprisingly
Using these words will help you successfully convey the key points you want to express. Once you’ve nailed the body of your essay, it’s time to move on to the conclusion.
The conclusion of your paper is important for synthesizing the arguments you’ve laid out and restating your thesis.
In your concluding paragraph, try using some of these essay words:
In conclusion
To summarize
In a nutshell
Given the above
As described
All things considered
Example: In conclusion , it’s imperative that we take action to address climate change before we lose our coral reefs forever.
In addition to simply summarizing the key points from the body of your essay, you should also add some final takeaways. Give the reader your final opinion and a bit of a food for thought.
To place emphasis on a certain point or a key fact, use these essay words:
Unquestionably
Undoubtedly
Particularly
Importantly
Conclusively
It should be noted
On the whole
Example: Ada Lovelace is unquestionably a powerful role model for young girls around the world, and more of our public school curricula should include her as a historical figure.
These concluding phrases will help you finish writing your essay in a strong, confident way.
There are many useful essay words out there that we didn't include in this article, because they are specific to certain topics.
If you're writing about biology, for example, you will need to use different terminology than if you're writing about literature.
So how do you improve your vocabulary skills?
The vocabulary you use in your academic writing is a toolkit you can build up over time, as long as you take the time to learn new words.
One way to increase your vocabulary is by looking up words you don’t know when you’re reading.
Try reading more books and academic articles in the field you’re writing about and jotting down all the new words you find. You can use these words to bolster your own essays.
You can also consult a dictionary or a thesaurus. When you’re using a word you’re not confident about, researching its meaning and common synonyms can help you make sure it belongs in your essay.
Don't be afraid of using simpler words. Good essay writing boils down to choosing the best word to convey what you need to say, not the fanciest word possible.
Finally, you can use ProWritingAid’s synonym tool or essay checker to find more precise and sophisticated vocabulary. Click on weak words in your essay to find stronger alternatives.
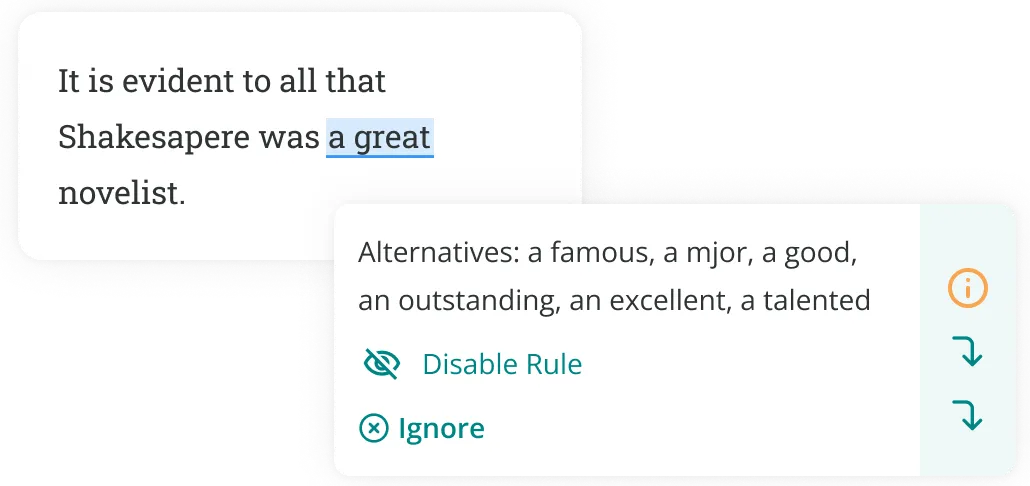
There you have it: our compilation of the best words and phrases to use in your next essay . Good luck!

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
- to conclude
adverb as in in conclusion
Weak matches
adverb as in lastly
Strong matches
- in conclusion
adverb as in lastly/last
- bringing up rear
- in the rear
Discover More
Related words.
Words related to to conclude are not direct synonyms, but are associated with the word to conclude . Browse related words to learn more about word associations.
adverb as in finally
- lastly/last
adverb as in in the end
On this page you'll find 27 synonyms, antonyms, and words related to to conclude, such as: last, and lastly.
From Roget's 21st Century Thesaurus, Third Edition Copyright © 2013 by the Philip Lief Group.
In a short paper—even a research paper—you don’t need to provide an exhaustive summary as part of your conclusion. But you do need to make some kind of transition between your final body paragraph and your concluding paragraph. This may come in the form of a few sentences of summary. Or it may come in the form of a sentence that brings your readers back to your thesis or main idea and reminds your readers where you began and how far you have traveled.
So, for example, in a paper about the relationship between ADHD and rejection sensitivity, Vanessa Roser begins by introducing readers to the fact that researchers have studied the relationship between the two conditions and then provides her explanation of that relationship. Here’s her thesis: “While socialization may indeed be an important factor in RS, I argue that individuals with ADHD may also possess a neurological predisposition to RS that is exacerbated by the differing executive and emotional regulation characteristic of ADHD.”
In her final paragraph, Roser reminds us of where she started by echoing her thesis: “This literature demonstrates that, as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Highlight the “so what”
At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what’s at stake—why they should care about the argument you’re making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put those stakes into a new or broader context.
In the conclusion to her paper about ADHD and RS, Roser echoes the stakes she established in her introduction—that research into connections between ADHD and RS has led to contradictory results, raising questions about the “behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
She writes, “as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Leave your readers with the “now what”
After the “what” and the “so what,” you should leave your reader with some final thoughts. If you have written a strong introduction, your readers will know why you have been arguing what you have been arguing—and why they should care. And if you’ve made a good case for your thesis, then your readers should be in a position to see things in a new way, understand new questions, or be ready for something that they weren’t ready for before they read your paper.
In her conclusion, Roser offers two “now what” statements. First, she explains that it is important to recognize that the flawed behavioral mediation hypothesis “seems to place a degree of fault on the individual. It implies that individuals with ADHD must have elicited such frequent or intense rejection by virtue of their inadequate social skills, erasing the possibility that they may simply possess a natural sensitivity to emotion.” She then highlights the broader implications for treatment of people with ADHD, noting that recognizing the actual connection between rejection sensitivity and ADHD “has profound implications for understanding how individuals with ADHD might best be treated in educational settings, by counselors, family, peers, or even society as a whole.”
To find your own “now what” for your essay’s conclusion, try asking yourself these questions:
- What can my readers now understand, see in a new light, or grapple with that they would not have understood in the same way before reading my paper? Are we a step closer to understanding a larger phenomenon or to understanding why what was at stake is so important?
- What questions can I now raise that would not have made sense at the beginning of my paper? Questions for further research? Other ways that this topic could be approached?
- Are there other applications for my research? Could my questions be asked about different data in a different context? Could I use my methods to answer a different question?
- What action should be taken in light of this argument? What action do I predict will be taken or could lead to a solution?
- What larger context might my argument be a part of?
What to avoid in your conclusion
- a complete restatement of all that you have said in your paper.
- a substantial counterargument that you do not have space to refute; you should introduce counterarguments before your conclusion.
- an apology for what you have not said. If you need to explain the scope of your paper, you should do this sooner—but don’t apologize for what you have not discussed in your paper.
- fake transitions like “in conclusion” that are followed by sentences that aren’t actually conclusions. (“In conclusion, I have now demonstrated that my thesis is correct.”)
- picture_as_pdf Conclusions
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Essay Conclusion

4-minute read
- 1st October 2022
Regardless of what you’re studying, writing essays is probably a significant part of your work as a student . Taking the time to understand how to write each section of an essay (i.e., introduction, body, and conclusion) can make the entire process easier and ensure that you’ll be successful.
Once you’ve put in the hard work of writing a coherent and compelling essay, it can be tempting to quickly throw together a conclusion without the same attention to detail. However, you won’t leave an impactful final impression on your readers without a strong conclusion.
We’ve compiled a few easy steps to help you write a great conclusion for your next essay . Watch our video, or check out our guide below to learn more!
1. Return to Your Thesis
Similar to how an introduction should capture your reader’s interest and present your argument, a conclusion should show why your argument matters and leave the reader with further curiosity about the topic.
To do this, you should begin by reminding the reader of your thesis statement. While you can use similar language and keywords when referring to your thesis, avoid copying it from the introduction and pasting it into your conclusion.
Try varying your vocabulary and sentence structure and presenting your thesis in a way that demonstrates how your argument has evolved throughout your essay.
2. Review Your Main Points
In addition to revisiting your thesis statement, you should review the main points you presented in your essay to support your argument.
However, a conclusion isn’t simply a summary of your essay . Rather, you should further examine your main points and demonstrate how each is connected.
Try to discuss these points concisely, in just a few sentences, in preparation for demonstrating how they fit in to the bigger picture of the topic.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Show the Significance of Your Essay
Next, it’s time to think about the topic of your essay beyond the scope of your argument. It’s helpful to keep the question “so what?” in mind when you’re doing this. The goal is to demonstrate why your argument matters.
If you need some ideas about what to discuss to show the significance of your essay, consider the following:
- What do your findings contribute to the current understanding of the topic?
- Did your findings raise new questions that would benefit from future research?
- Can you offer practical suggestions for future research or make predictions about the future of the field/topic?
- Are there other contexts, topics, or a broader debate that your ideas can be applied to?
While writing your essay, it can be helpful to keep a list of ideas or insights that you develop about the implications of your work so that you can refer back to it when you write the conclusion.
Making these kinds of connections will leave a memorable impression on the reader and inspire their interest in the topic you’ve written about.
4. Avoid Some Common Mistakes
To ensure you’ve written a strong conclusion that doesn’t leave your reader confused or lacking confidence in your work, avoid:
- Presenting new evidence: Don’t introduce new information or a new argument, as it can distract from your main topic, confuse your reader, and suggest that your essay isn’t organized.
- Undermining your argument: Don’t use statements such as “I’m not an expert,” “I feel,” or “I think,” as lacking confidence in your work will weaken your argument.
- Using generic statements: Don’t use generic concluding statements such as “In summary,” “To sum up,” or “In conclusion,” which are redundant since the reader will be able to see that they’ve reached the end of your essay.
Finally, don’t make the mistake of forgetting to proofread your essay ! Mistakes can be difficult to catch in your own writing, but they can detract from your writing.
Our expert editors can ensure that your essay is clear, concise, and free of spelling and grammar errors. Find out more by submitting a free trial document today!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Conclude an Essay (with Examples)
Last Updated: May 24, 2024 Fact Checked
Writing a Strong Conclusion
What to avoid, brainstorming tricks.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams and by wikiHow staff writer, Aly Rusciano . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,211,370 times.
So, you’ve written an outstanding essay and couldn’t be more proud. But now you have to write the final paragraph. The conclusion simply summarizes what you’ve already written, right? Well, not exactly. Your essay’s conclusion should be a bit more finessed than that. Luckily, you’ve come to the perfect place to learn how to write a conclusion. We’ve put together this guide to fill you in on everything you should and shouldn’t do when ending an essay. Follow our advice, and you’ll have a stellar conclusion worthy of an A+ in no time.
Tips for Ending an Essay
- Rephrase your thesis to include in your final paragraph to bring the essay full circle.
- End your essay with a call to action, warning, or image to make your argument meaningful.
- Keep your conclusion concise and to the point, so you don’t lose a reader’s attention.
- Do your best to avoid adding new information to your conclusion and only emphasize points you’ve already made in your essay.

- “All in all”
- “Ultimately”
- “Furthermore”
- “As a consequence”
- “As a result”

- Make sure to write your main points in a new and unique way to avoid repetition.

- Let’s say this is your original thesis statement: “Allowing students to visit the library during lunch improves campus life and supports academic achievement.”
- Restating your thesis for your conclusion could look like this: “Evidence shows students who have access to their school’s library during lunch check out more books and are more likely to complete their homework.”
- The restated thesis has the same sentiment as the original while also summarizing other points of the essay.

- “When you use plastic water bottles, you pollute the ocean. Switch to using a glass or metal water bottle instead. The planet and sea turtles will thank you.”
- “The average person spends roughly 7 hours on their phone a day, so there’s no wonder cybersickness is plaguing all generations.”
- “Imagine walking on the beach, except the soft sand is made up of cigarette butts. They burn your feet but keep washing in with the tide. If we don’t clean up the ocean, this will be our reality.”
- “ Lost is not only a show that changed the course of television, but it’s also a reflection of humanity as a whole.”
- “If action isn’t taken to end climate change today, the global temperature will dangerously rise from 4.5 to 8 °F (−15.3 to −13.3 °C) by 2100.”

- Focus on your essay's most prevalent or important parts. What key points do you want readers to take away or remember about your essay?

- For instance, instead of writing, “That’s why I think that Abraham Lincoln was the best American President,” write, “That’s why Abraham Lincoln was the best American President.”
- There’s no room for ifs, ands, or buts—your opinion matters and doesn’t need to be apologized for!

- For instance, words like “firstly,” “secondly,” and “thirdly” may be great transition statements for body paragraphs but are unnecessary in a conclusion.

- For instance, say you began your essay with the idea that humanity’s small sense of sense stems from space’s vast size. Try returning to this idea in the conclusion by emphasizing that as human knowledge grows, space becomes smaller.

- For example, you could extend an essay on the television show Orange is the New Black by bringing up the culture of imprisonment in America.
Community Q&A

- Always review your essay after writing it for proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation, and don’t be afraid to revise. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- Have somebody else proofread your essay before turning it in. The other person will often be able to see errors you may have missed!

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.uts.edu.au/current-students/support/helps/self-help-resources/grammar/transition-signals
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/argument_papers/conclusions.html
- ↑ http://writing2.richmond.edu/writing/wweb/conclude.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/ending-essay-conclusions
- ↑ https://www.pittsfordschools.org/site/handlers/filedownload.ashx?moduleinstanceid=542&dataid=4677&FileName=conclusions1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.cuyamaca.edu/student-support/tutoring-center/files/student-resources/how-to-write-a-good-conclusion.pdf
- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185935
About This Article

To end an essay, start your conclusion with a phrase that makes it clear your essay is coming to a close, like "In summary," or "All things considered." Then, use a few sentences to briefly summarize the main points of your essay by rephrasing the topic sentences of your body paragraphs. Finally, end your conclusion with a call to action that encourages your readers to do something or learn more about your topic. In general, try to keep your conclusion between 5 and 7 sentences long. For more tips from our English co-author, like how to avoid common pitfalls when writing an essay conclusion, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Eva Dettling
Jan 23, 2019
Did this article help you?

Mar 7, 2017
Jul 16, 2021
Gabby Suzuki
Oct 17, 2019
Nicole Murphy
Apr 26, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Synonyms of conclude
- as in to end
- as in to stop
- as in to arrange
- as in to decide
- as in to understand
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Thesaurus Definition of conclude
Synonyms & Similar Words
- round (off or out)
- ring down the curtain (on)
Antonyms & Near Antonyms
- discontinue
- bite the dust
- refrain (from)
- desist (from)
- lay off (of)
- pack (up or in)
- peter (out)
- settle (on or upon)
- renegotiate
- horse - trade
- hash (over)
- contemplate
- think (about or over)
- single (out)
- mull (over)
- shilly - shally
- extrapolate
- draw a conclusion
- rationalize
- philosophize
Synonym Chooser
How does the verb conclude differ from other similar words?
Some common synonyms of conclude are close , complete , end , finish , and terminate . While all these words mean "to bring or come to a stopping point or limit," conclude may imply a formal closing (as of a meeting).
Where would close be a reasonable alternative to conclude ?
While the synonyms close and conclude are close in meaning, close usually implies that something has been in some way open as well as unfinished.
When is it sensible to use complete instead of conclude ?
The meanings of complete and conclude largely overlap; however, complete implies the removal of all deficiencies or a successful finishing of what has been undertaken.
When might end be a better fit than conclude ?
The synonyms end and conclude are sometimes interchangeable, but end conveys a strong sense of finality.
In what contexts can finish take the place of conclude ?
The words finish and conclude can be used in similar contexts, but finish may stress completion of a final step in a process.
When could terminate be used to replace conclude ?
In some situations, the words terminate and conclude are roughly equivalent. However, terminate implies the setting of a limit in time or space.
Thesaurus Entries Near conclude
Cite this entry.
“Conclude.” Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/thesaurus/conclude. Accessed 7 Jun. 2024.
More from Merriam-Webster on conclude
Nglish: Translation of conclude for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of conclude for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
What's the difference between 'fascism' and 'socialism', more commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - june 7, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, 9 superb owl words, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, etymologies for every day of the week, games & quizzes.


Oscar Piastri’s four-word reaction and 2026 prediction as F1 scraps DRS
McLaren driver Oscar Piastri has proclaimed “goodbye old friend, DRS” after Formula 1 announced that DRS will be axed in 2026 in favour of a power boost.
Oscar Piastri has had a somewhat complicated relationship with the Drag Reduction System that’s been used in Formula 1 since 2011, and that’s also in Formula 3 and Formula 2.
The end of a complicated relationship
From declaring in 2020 that DRS was sending him “mixed signals” and that their relationship was “on a break”, he later reported they had “mended” their relationship.
However, a further breakdown in the relationship had the Aussie tweeting: “So I see DRS Told the rest of my car to stop working. Dick move DRS, dick move”. The messages were signed “old friend”.
While his relationship with DRS did improve as he climbed the ranks to join McLaren in Formula 1 in 2023, even then there were problems although the bulk of those were DRS trains.
Alas, the relationship is nearing its end after Formula 1 announced DRS would be dropped in 2026 in favour of a power boost.
Piastri responded to the F1 post on X: “Goodbye old friend, DRS.”
Driver reaction as F1 announced the new 2026 regulations
👉 More F1 2026 fears rise as Fernando Alonso questions ‘impossible’ weight target
👉 Lewis Hamilton claims F1 2026 regs weight saving falls short with cars looking ‘pretty slow’
As of 2026, Formula 1 will not only have new engines but also new cars on the grid with the sport introducing lighter and smaller cars.
Asked if he was concerned that the new regulations would create bigger gaps at a time when Red Bull’s rivals had closed in on them, the McLaren driver replied: “I think every time the regs have changed, it’s led to a pretty big spread, especially with engines, 2014 being the last time with that and kicking off a really long period of dominance.
“I think we’ve seen even with these regs, we’re only just starting to catch up to Red Bull, week in, week out, now.
“I think we have an important place in society to be at the forefront of technology and innovation, and I think that’s always what F1’s been about in some ways.
“And I guess you could argue that sometimes that does come at the cost of the racing, which is always a shame.
“I wouldn’t be surprised if the teams sort of separate a bit more in 2026, both with different aero regs and especially the engine regs. There’s a very big chance, I would say, that the teams are going to be more spread out than what they are now.
“But we’ll have to wait and see.”
Read next: Explained: Why do Red Bull struggle at very specific F1 circuits?

Trump called ‘Apprentice’ contestant a racist slur, former producer says
Bill Pruitt, who served as a producer on the reality show, said in an online essay that Trump used the slur when discussing who would win the show’s first season. “‘Yeah,’ he says to no one in particular, ‘but, I mean, would America buy a [n-word] winning?’” Pruitt wrote.

Former president Donald Trump used a racist slur while discussing a contestant on “The Apprentice” during a recorded conversation two decades ago, a former producer for the show wrote in a new essay .
The producer, Bill Pruitt, said Trump made the comment while deciding between a Black finalist, Kwame Jackson, and a White finalist, Bill Rancic, in the finale of the show’s first season, which aired in 2004. As Trump adviser Carolyn Kepcher, who served as a judge on the show, began advocating for Jackson, Trump winced multiple times and questioned Jackson’s performance on the show, Pruitt wrote.
“I mean, would America buy a [n-word] winning?” Trump asked, according to Pruitt in his essay that Slate published Thursday.
Trump ultimately picked Rancic and awarded him a job at the Trump Organization. The reality competition series ran for 15 seasons, helping make Trump a household name before his first presidential campaign in 2016. Trump is the presumptive Republican nominee in 2024, again running against President Biden after losing to him in 2020.
Trump’s campaign said Pruitt’s account was a “completely fabricated … story that was already peddled in 2016.”
“Nobody took it seriously then, and they won’t now, because it’s fake news,” Trump campaign spokesman Steven Cheung said in a statement to The Post. “Now that Crooked Joe Biden and the Democrats are losing the election and Black voters are rejecting their policies, they are bringing up old fake stories from the past because they are desperate.”
Trump has a long history of espousing antagonistic views toward African Americans. He declined to apologize in 2019 for taking out ads in 1989 that targeted the Central Park Five, a group of Black and Latino men who were wrongly convicted of raping a jogger in New York City. And Trump gained political notoriety during Barack Obama’s presidency by embracing the false claim that Obama — the nation’s first Black president — was ineligible to be president because he was not a natural-born citizen.
During the first year of his presidency, Trump drew widespread condemnation when he said there were “ very fine people on both sides ” of a 2017 white nationalist and supremacist rally in Charlottesville that turned violent.
Despite his history, Trump has been making increasing appeals to Black voters in his race against Biden, including during a South Bronx rally last week .
Pruitt, one of four producers who worked on the show in its first two seasons, said he was bound by an “expansive nondisclosure agreement” that expired this year. He would have faced a $5 million fine or possibly jail time if he violated the agreement, he said.
Pruitt said the conversation was recorded as part of the show’s efforts to ensure such off-air deliberations did not run afoul of federal regulations for game shows.
Jackson, the contestant Pruitt says Trump described using the slur, said in a 2016 interview with Salon that at the time he was on the show, he did not think race played a role in his loss to Rancic. But Jackson said he later came to believe race factored into the outcome.
Jackson spoke out against Trump’s 2016 candidacy in the interview , saying he has “no interest in supporting someone who I think is, at his core, racist.”
The essay also described multiple instances in which Trump made sexist remarks about the appearance of women working on the show. Trump once told a female camera operator to get off an elevator because she was “too heavy,” Pruitt recalled. Trump also told other people on the set that another female camera operator was a “beautiful woman” who is “all I want to look at,” according to the former producer.
There has been intrigue for years surrounding possible unreleased tapes from “The Apprentice,” especially after the 2016 campaign. Weeks before that election, a recording surfaced from a 2005 hot-mic conversation with “Access Hollywood” co-anchor Billy Bush in which Trump boasted about kissing, groping and trying to have sex with women.
The creator of “The Apprentice,” celebrity producer Mark Burnett, said at the time that he “does not have the ability nor the right to release footage or other material from ‘The Apprentice.’ ”
Trump said in a 2018 social media post that Burnett told him there were “NO TAPES of the Apprentice” where he used the same racist slur that Pruitt attributed to him. Trump called it a “terrible and disgusting word.” At the time, Trump was responding to claims by former White House aide Omarosa Manigault-Newman — once a contestant on the show — that there was a tape of him using the slur during the show’s filming.
Efforts to reach Burnett for comment Thursday through multiple publicly listed points of contact were unsuccessful.
Pruitt’s account comes as Biden is working to shore up his support among Black voters against Trump in their November election rematch. Biden and Vice President Harris, who is Black, visited Philadelphia on Wednesday to launch an initiative called “Black Voters for Biden-Harris.”
Responding to Pruitt’s essay, Biden’s campaign said it was more proof that Trump is a “textbook racist who disrespects and attacks the Black community every chance he gets, and the most ignorant man to ever run for president.”
“No one is surprised that Donald Trump, who entered public life by falsely accusing Black men of murder and entered political life spreading lies about the first Black president, reportedly used the N-word to casually denigrate a successful Black man,” Biden campaign spokesperson Jasmine Harris said in a statement. “Anyone notice a pattern?”
Election 2024
Get the latest news on the 2024 election from our reporters on the campaign trail and in Washington.
Who is running?: President Biden and Donald Trump secured their parties’ nominations for the presidency . Here’s how we ended up with a Trump-Biden rematch .
Presidential debates: Biden and Trump agreed to a June 27 debate on CNN and a Sept. 10 debate broadcast by ABC News.
Key dates and events: From January to June, voters in all states and U.S. territories will pick their party’s nominee for president ahead of the summer conventions. Here are key dates and events on the 2024 election calendar .
Abortion and the election: Voters in about a dozen states could decide the fate of abortion rights with constitutional amendments on the ballot in a pivotal election year. Biden supports legal access to abortion , and he has encouraged Congress to pass a law that would codify abortion rights nationwide. After months of mixed signals about his position, Trump said the issue should be left to states . Here’s how Biden’s and Trump’s abortion stances have shifted over the years.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
GuEST Essay
Mitch McConnell: We Cannot Repeat the Mistakes of the 1930s

By Mitch McConnell
Mr. McConnell is the Senate minority leader.
On this day in 1944, the liberation of Western Europe began with immense sacrifice. In a tribute delivered 40 years later from a Normandy cliff, President Ronald Reagan reminded us that “the boys of Pointe du Hoc” were “heroes who helped end a war.” That last detail is worth some reflection because we are in danger of forgetting why it matters.
American soldiers, sailors, airmen and Marines joined allies and took the fight to the Axis powers not as a first instinct, but as a last resort. They ended a war that the free world’s inaction had left them no choice but to fight.
Generations have taken pride in the triumph of the West’s wartime bravery and ingenuity, from the assembly lines to the front lines. We reflect less often on the fact that the world was plunged into war, and millions of innocents died, because European powers and the United States met the rise of a militant authoritarian with appeasement or naïve neglect in the first place.
We forget how influential isolationists persuaded millions of Americans that the fate of allies and partners mattered little to our own security and prosperity. We gloss over the powerful political forces that downplayed growing danger, resisted providing assistance to allies and partners, and tried to limit America’s ability to defend its national interests.
Of course, Americans heard much less from our disgraced isolationists after the attack on Pearl Harbor.
Today, America and our allies face some of the gravest threats to our security since Axis forces marched across Europe and the Pacific. And as these threats grow, some of the same forces that hampered our response in the 1930s have re-emerged.
Germany is now a close ally and trading partner. But it was caught flat-footed by the rise of a new axis of authoritarians made up of Russia, China, North Korea and Iran. So, too, were the advanced European powers who once united to defeat the Nazis.
Like the United States, they responded to Russia’s aggression in Ukraine in 2014 with wishful thinking. The disrepair of their militaries and defense industrial bases, and their overreliance on foreign energy and technology, were further exposed by Russia’s dramatic escalation in 2022.
By contrast, Japan needed fewer reminders about threats from aggressive neighbors or about the growing links between Russia and China. Increasingly, America’s allies and partners in the Indo-Pacific are taking seriously the urgent requirements of self-defense. Fortunately, in the past two years, some of our European allies have taken overdue steps in the same direction.
Here at home, we face problems of our own. Some vocal corners of the American right are trying to resurrect the discredited brand of prewar isolationism and deny the basic value of the alliance system that has kept the postwar peace. This dangerous proposition rivals the American left’s longstanding allergy to military spending in its potential to make America less safe.
It should not take another catastrophic attack like Pearl Harbor to wake today’s isolationists from the delusion that regional conflicts have no consequences for the world’s most powerful and prosperous nation. With global power comes global interests and global responsibilities.
Nor should President Biden or congressional Democrats require another major conflict to start investing seriously in American hard power.
The president began this year’s State of the Union with a reference to President Franklin Roosevelt’s 1941 effort to prepare the nation to meet the Axis threat. But until the commander in chief is willing to meaningfully invest in America’s deterrent power, this talk carries little weight.
In 1941, President Roosevelt justified a belated increase in military spending to 5.5 percent of gross domestic product. On the road to victory, that figure would reach 37 percent. Deterring conflict today costs less than fighting it tomorrow.
I was encouraged by the plan laid out last week by my friend, the ranking member of the Senate Armed Services Committee, Roger Wicker , which detailed specific actions the president and colleagues in Congress should take to prepare America for long-term strategic competition.
I hope my colleague’s work prompts overdue action to address shortcomings in shipbuilding and the production of long-range munitions and missile defenses. Rebuilding the arsenal of democracy would demonstrate to America’s allies and adversaries alike that our commitment to the stable order of international peace and prosperity is rock-solid.
Nothing else will suffice. Not a desperate pursuit of nuclear diplomacy with Iran, the world’s most active state sponsor of terrorism. Not cabinet junkets to Beijing in pursuit of common ground on climate policy. The way to prove that America means what it says is to show what we’re willing to fight for.
Eighty years ago, America and our allies fought because we had to. The forces assembled on the English Channel on June 6, 1944, represented the fruits of many months of feverish planning. And once victory was secure, the United States led the formation of the alliances that have underpinned Western peace and security ever since.
Today, the better part of valor is to build credible defenses before they are necessary and demonstrate American leadership before it is doubted any further.
Mr. McConnell, a Republican senator from Kentucky, is the Senate minority leader.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Example: "In a nutshell, there are valid arguments on both sides of the debate about socialism vs capitalism.". 18. In closing…. My Rating: 7/10. Overview: This phrase is an appropriate synonym for 'In conclusion' and I would be perfectly fine with a student using this phrase in their essay.
It's true: there are other ways to say "in conclusion" that don't feel as trite. Can't think of any? Find 57 different words and phrases right here.
Concluding your paper or presentation can feel redundant if you always say "in conclusion." These alternatives will help you end your project with style.
Other "In Conclusion" Synonyms for Informal Writing. You can use any of the synonyms in this article when writing informally, but these are particularly useful when you want your writing to sound conversational: All in all. By and large. On a final note. Last but not least. For all intents and purposes. In short. The bottom line is. To put it ...
Synonyms for "In Conclusion": Formal Phrases. Below, you'll find five synonyms for in conclusion that are best suited for formal settings, such as professional and academic writing.. 1) In summary. Like in conclusion, the phrase in summary serves as a transition phrase that signals you are starting the last paragraph of your writing. When using in summary, you should briefly review the ...
To Conclude or In Conclusion. To conclude and in conclusion are complete synonyms, so they mean the same thing. You can use whichever you like more, or whichever best fits your needs. In Conclusion Transition Words. In conclusion, is a transitional phrase in of itself. It denotes the final argument, so it is a transition between evidence and ...
Pin. In Conclusion Meaning "In conclusion" is a transitional phrase used to indicate that you are approaching the end of your writing.It serves to summarize the main points or indicate a final thought or opinion. Using synonyms for "in conclusion" can help maintain your reader's interest and offer a sense of variety and sophistication in your writing.
Here are some alternative ways to say 'in conclusion' in a formal setting: 1. By way of conclusion. 2. To conclude. 3. On a final note. 4. To summarize.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
If you're struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don't worry—you've come to the right place! In this article, we've compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay. Contents: Words to Use in the Essay Introduction. Words to Use in the Body of the Essay.
conclusion let me. concluding my remarks. in precis. forward to the conclusion. for you to finish. for the last part. for successful completion of. for its formal conclusion. for checkout.
Overall, It Can Be Said…. To recap an idea at the end of a critical or descriptive essay, you can use this phrase at the beginning of the concluding paragraph. "Overall" means "taking everything into account," and it sums up your essay in a formal way. You can use "overall" on its own as a transition signal, or you can use it as ...
Find 24 different ways to say TO CONCLUDE, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at Thesaurus.com.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
Highlight the "so what". At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what's at stake—why they should care about the argument you're making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put ...
1. Return to Your Thesis. Similar to how an introduction should capture your reader's interest and present your argument, a conclusion should show why your argument matters and leave the reader with further curiosity about the topic. To do this, you should begin by reminding the reader of your thesis statement.
End your essay with a call to action, warning, or image to make your argument meaningful. Keep your conclusion concise and to the point, so you don't lose a reader's attention. Do your best to avoid adding new information to your conclusion and only emphasize points you've already made in your essay. Method 1.
Synonyms for CONCLUDE: end, finish, complete, close, terminate, round (off or out), wind up, put paid to; Antonyms of CONCLUDE: begin, start, commence, open ...
Also read: How to Write a Thesis Statement. 2. Tying together the main points. Tying together all the main points of your essay does not mean simply summarizing them in an arbitrary manner. The key is to link each of your main essay points in a coherent structure. One point should follow the other in a logical format.
Whereas antisemitism in the literary world used to lurk in the shadows, according to the Jewish Book Council's chief executive, Naomi Firestone-Teeter, since Oct. 7, it has become increasingly ...
Oscar Piastri's four-word reaction and 2026 prediction as F1 scraps DRS. ... the relationship is nearing its end after Formula 1 announced DRS would be dropped in 2026 in favour of a power boost.
Bill Pruitt, who served as a producer on the reality show, said in an online essay that Trump used the slur when discussing who would win the show's first season. "'Yeah,' he says to no ...
My conclusions are based on the public record, my years of experience as a federal judge and a criminal defense lawyer and my decades teaching courses on sentencing at Yale and Harvard Law Schools.
1267. By Mitch McConnell. Mr. McConnell is the Senate minority leader. On this day in 1944, the liberation of Western Europe began with immense sacrifice. In a tribute delivered 40 years later ...