- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide

How to Write a Persuasive Essay: Tips and Tricks

Allison Bressmer

Most composition classes you’ll take will teach the art of persuasive writing. That’s a good thing.
Knowing where you stand on issues and knowing how to argue for or against something is a skill that will serve you well both inside and outside of the classroom.
Persuasion is the art of using logic to prompt audiences to change their mind or take action , and is generally seen as accomplishing that goal by appealing to emotions and feelings.
A persuasive essay is one that attempts to get a reader to agree with your perspective.

Ready for some tips on how to produce a well-written, well-rounded, well-structured persuasive essay? Just say yes. I don’t want to have to write another essay to convince you!
How Do I Write a Persuasive Essay?
What are some good topics for a persuasive essay, how do i identify an audience for my persuasive essay, how do you create an effective persuasive essay, how should i edit my persuasive essay.
Your persuasive essay needs to have the three components required of any essay: the introduction , body , and conclusion .
That is essay structure. However, there is flexibility in that structure.
There is no rule (unless the assignment has specific rules) for how many paragraphs any of those sections need.
Although the components should be proportional; the body paragraphs will comprise most of your persuasive essay.

How Do I Start a Persuasive Essay?
As with any essay introduction, this paragraph is where you grab your audience’s attention, provide context for the topic of discussion, and present your thesis statement.
TIP 1: Some writers find it easier to write their introductions last. As long as you have your working thesis, this is a perfectly acceptable approach. From that thesis, you can plan your body paragraphs and then go back and write your introduction.
TIP 2: Avoid “announcing” your thesis. Don’t include statements like this:
- “In my essay I will show why extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
- “The purpose of my essay is to argue that extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
Announcements take away from the originality, authority, and sophistication of your writing.
Instead, write a convincing thesis statement that answers the question "so what?" Why is the topic important, what do you think about it, and why do you think that? Be specific.
How Many Paragraphs Should a Persuasive Essay Have?
This body of your persuasive essay is the section in which you develop the arguments that support your thesis. Consider these questions as you plan this section of your essay:
- What arguments support your thesis?
- What is the best order for your arguments?
- What evidence do you have?
- Will you address the opposing argument to your own?
- How can you conclude convincingly?

TIP: Brainstorm and do your research before you decide which arguments you’ll focus on in your discussion. Make a list of possibilities and go with the ones that are strongest, that you can discuss with the most confidence, and that help you balance your rhetorical triangle .
What Should I Put in the Conclusion of a Persuasive Essay?
The conclusion is your “mic-drop” moment. Think about how you can leave your audience with a strong final comment.
And while a conclusion often re-emphasizes the main points of a discussion, it shouldn’t simply repeat them.
TIP 1: Be careful not to introduce a new argument in the conclusion—there’s no time to develop it now that you’ve reached the end of your discussion!
TIP 2 : As with your thesis, avoid announcing your conclusion. Don’t start your conclusion with “in conclusion” or “to conclude” or “to end my essay” type statements. Your audience should be able to see that you are bringing the discussion to a close without those overused, less sophisticated signals.

If your instructor has assigned you a topic, then you’ve already got your issue; you’ll just have to determine where you stand on the issue. Where you stand on your topic is your position on that topic.
Your position will ultimately become the thesis of your persuasive essay: the statement the rest of the essay argues for and supports, intending to convince your audience to consider your point of view.
If you have to choose your own topic, use these guidelines to help you make your selection:
- Choose an issue you truly care about
- Choose an issue that is actually debatable
Simple “tastes” (likes and dislikes) can’t really be argued. No matter how many ways someone tries to convince me that milk chocolate rules, I just won’t agree.
It’s dark chocolate or nothing as far as my tastes are concerned.
Similarly, you can’t convince a person to “like” one film more than another in an essay.
You could argue that one movie has superior qualities than another: cinematography, acting, directing, etc. but you can’t convince a person that the film really appeals to them.

Once you’ve selected your issue, determine your position just as you would for an assigned topic. That position will ultimately become your thesis.
Until you’ve finalized your work, consider your thesis a “working thesis.”
This means that your statement represents your position, but you might change its phrasing or structure for that final version.
When you’re writing an essay for a class, it can seem strange to identify an audience—isn’t the audience the instructor?
Your instructor will read and evaluate your essay, and may be part of your greater audience, but you shouldn’t just write for your teacher.
Think about who your intended audience is.
For an argument essay, think of your audience as the people who disagree with you—the people who need convincing.
That population could be quite broad, for example, if you’re arguing a political issue, or narrow, if you’re trying to convince your parents to extend your curfew.
Once you’ve got a sense of your audience, it’s time to consult with Aristotle. Aristotle’s teaching on persuasion has shaped communication since about 330 BC. Apparently, it works.

Aristotle taught that in order to convince an audience of something, the communicator needs to balance the three elements of the rhetorical triangle to achieve the best results.
Those three elements are ethos , logos , and pathos .
Ethos relates to credibility and trustworthiness. How can you, as the writer, demonstrate your credibility as a source of information to your audience?
How will you show them you are worthy of their trust?

- You show you’ve done your research: you understand the issue, both sides
- You show respect for the opposing side: if you disrespect your audience, they won’t respect you or your ideas
Logos relates to logic. How will you convince your audience that your arguments and ideas are reasonable?

You provide facts or other supporting evidence to support your claims.
That evidence may take the form of studies or expert input or reasonable examples or a combination of all of those things, depending on the specific requirements of your assignment.
Remember: if you use someone else’s ideas or words in your essay, you need to give them credit.
ProWritingAid's Plagiarism Checker checks your work against over a billion web-pages, published works, and academic papers so you can be sure of its originality.
Find out more about ProWritingAid’s Plagiarism checks.
Pathos relates to emotion. Audiences are people and people are emotional beings. We respond to emotional prompts. How will you engage your audience with your arguments on an emotional level?

- You make strategic word choices : words have denotations (dictionary meanings) and also connotations, or emotional values. Use words whose connotations will help prompt the feelings you want your audience to experience.
- You use emotionally engaging examples to support your claims or make a point, prompting your audience to be moved by your discussion.
Be mindful as you lean into elements of the triangle. Too much pathos and your audience might end up feeling manipulated, roll their eyes and move on.
An “all logos” approach will leave your essay dry and without a sense of voice; it will probably bore your audience rather than make them care.
Once you’ve got your essay planned, start writing! Don’t worry about perfection, just get your ideas out of your head and off your list and into a rough essay format.
After you’ve written your draft, evaluate your work. What works and what doesn’t? For help with evaluating and revising your work, check out this ProWritingAid post on manuscript revision .
After you’ve evaluated your draft, revise it. Repeat that process as many times as you need to make your work the best it can be.
When you’re satisfied with the content and structure of the essay, take it through the editing process .
Grammatical or sentence-level errors can distract your audience or even detract from the ethos—the authority—of your work.
You don’t have to edit alone! ProWritingAid’s Realtime Report will find errors and make suggestions for improvements.
You can even use it on emails to your professors:
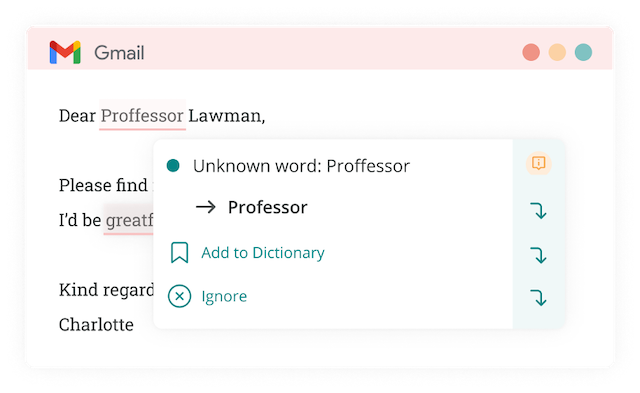
Try ProWritingAid with a free account.
How Can I Improve My Persuasion Skills?
You can develop your powers of persuasion every day just by observing what’s around you.
- How is that advertisement working to convince you to buy a product?
- How is a political candidate arguing for you to vote for them?
- How do you “argue” with friends about what to do over the weekend, or convince your boss to give you a raise?
- How are your parents working to convince you to follow a certain academic or career path?
As you observe these arguments in action, evaluate them. Why are they effective or why do they fail?
How could an argument be strengthened with more (or less) emphasis on ethos, logos, and pathos?
Every argument is an opportunity to learn! Observe them, evaluate them, and use them to perfect your own powers of persuasion.
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Allison Bressmer is a professor of freshman composition and critical reading at a community college and a freelance writer. If she isn’t writing or teaching, you’ll likely find her reading a book or listening to a podcast while happily sipping a semi-sweet iced tea or happy-houring with friends. She lives in New York with her family. Connect at linkedin.com/in/allisonbressmer.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Essay Papers Writing Online
10 effective techniques to master persuasive essay writing and convince any audience.

As a skilled communicator, your ability to persuade others is crucial in many areas of life. Whether you’re presenting an argument, advocating for a cause, or simply trying to convince someone of your point of view, your persuasive essay can be a powerful tool. However, crafting an essay that truly convinces your reader requires more than just strong opinions and eloquent language. It requires a strategic approach that combines logical reasoning, emotional appeal, and effective writing techniques.
1. Craft a Compelling Introduction: Your introduction is the first impression you make on your reader, so it’s essential to capture their attention right from the start. Consider using a captivating anecdote, a thought-provoking question, or a shocking statistic to engage your audience and set the tone for your essay. By immediately grabbing their interest, you increase the chances that they’ll continue reading and be open to your persuasive arguments.
2. Clearly Define Your Position: Before launching into the main body of your essay, make sure to clearly state your position on the topic. This will help your reader understand your stance and follow your line of reasoning throughout the essay. Use concise and assertive language to communicate your position, and consider reinforcing it with strong evidence or expert opinions that support your viewpoint.
3. Appeal to Emotions: While rational arguments are important, emotions often play a significant role in persuasive writing. Connect with your reader on an emotional level by using vivid descriptions, personal anecdotes, or powerful metaphors. By eliciting an emotional response, you can create a deeper connection with your audience and make your arguments more compelling.
Choose a compelling topic that ignites your passion

When crafting a persuasive essay, it is crucial to select a topic that not only captivates and engages your readers but also resonates strongly with you. By choosing a compelling topic that ignites your passion, you will be able to infuse enthusiasm and conviction into your writing, making it more convincing and persuasive.
While it may be tempting to select a popular or trending topic, it is essential to choose something that you deeply care about and have a genuine interest in. Your passion for the subject matter will shine through in your writing, capturing the attention and interest of your readers.
- Explore your hobbies and personal interests.
- Reflect on societal issues that deeply affect you.
- Consider topics that challenge conventional thinking.
- Analyze current events and their impact on your community or society as a whole.
- Look for subjects that inspire debate and differing opinions.
- Examine topics that align with your values and beliefs.
By choosing a topic that you are not only knowledgeable about but also passionate about, you will have a stronger emotional connection to your writing. This emotional connection will allow you to effectively convey your argument, influence your readers’ perspectives, and ultimately convince them to see things from your point of view.
Remember, the key to writing a persuasive essay lies in your ability to convey your ideas convincingly. By selecting a compelling topic that ignites your passion, you will have a solid foundation for crafting a persuasive essay that will resonate with readers and leave a lasting impact. So, take the time to explore your interests and choose a topic that truly captivates you.
Conduct thorough research to gather supporting evidence
Gathering strong evidence is a vital step in writing a persuasive essay. Convincing your readers requires you to present compelling facts, statistics, expert opinions, and examples that support your arguments. To achieve this, it is crucial to conduct thorough research to collect relevant and reliable information.
Begin by determining the main points you want to convey in your essay. These points should align with your thesis statement and support your overall argument. Once you have a clear idea of what you are trying to communicate, start gathering supporting evidence.
Research various credible sources such as academic journals, books, reputable websites, and expert interviews. Look for information that directly relates to your topic and can be used to reinforce your arguments. Be sure to verify the credibility and reliability of your sources to ensure the accuracy of the information.
Take notes as you conduct your research, highlighting key points, supporting evidence, and any quotes or statistics that you may want to include in your essay. It is essential to organize your findings in a way that makes sense and flows logically in your essay.
When using statistics or data, make sure to cite the sources properly to give credit to the original authors and establish your credibility as a writer. This will also allow your readers to verify the information themselves if they wish to do so.
By conducting thorough research and gathering strong supporting evidence, you will be able to present a persuasive and well-supported argument in your essay. This will not only convince your readers but also showcase your knowledge, understanding, and dedication to the topic at hand.
Develop a clear and concise thesis statement
One of the most important aspects of writing a persuasive essay is developing a thesis statement that is clear, concise, and compelling. A thesis statement serves as the main argument or central idea of your essay. It sets the tone for the entire piece and helps to guide your reader through your argument.
When developing your thesis statement, it’s essential to choose a strong and persuasive statement that clearly states your position on the topic. Avoid vague or ambiguous language that can confuse your reader and weaken your argument. Instead, use strong and specific language that clearly conveys your main point.
Your thesis statement should be concise, meaning it should be expressed in a clear and straightforward manner. Avoid unnecessary words or phrases that can dilute your message and make it less powerful. Instead, focus on getting your point across in as few words as possible while still maintaining clarity and impact.
Additionally, your thesis statement should be compelling and persuasive. It should motivate your reader to continue reading and consider your argument. Use persuasive language and strong evidence to support your thesis statement and convince your reader of its validity.
In summary, developing a clear and concise thesis statement is crucial for writing a persuasive essay. Choose a strong statement that clearly conveys your position, use concise language to express your point, and make your statement compelling and persuasive. By doing so, you will create a strong foundation for your entire essay and increase your chances of convincing your reader.
Use persuasive language and rhetorical devices

When it comes to crafting a compelling persuasive essay, one must master the art of persuasive language and employ various rhetorical devices. The way you choose your words and structure your sentences can make all the difference in captivating and convincing your readers.
One effective technique is to use strong and powerful language that evokes emotion and creates a sense of urgency. The use of vivid and descriptive words can paint a picture in the minds of your readers, making your arguments more relatable and engaging.
Additionally, employing rhetorical devices such as metaphors, similes, and analogies can effectively convey your message and help your readers understand complex ideas. By drawing comparisons and creating associations, you can make abstract concepts more tangible and easier to grasp.
Another valuable device is repetition. By repeating key phrases or ideas throughout your essay, you can emphasize your points and reinforce your arguments. This technique can help make your arguments more memorable and leave a lasting impact on your readers.
Furthermore, using rhetorical questions can encourage your readers to think critically about your topic and consider your perspective. By posing thought-provoking questions, you can guide your readers towards your desired conclusions and make them actively engage with your essay.
Lastly, employing the use of anecdotes and personal stories can make your essay more relatable and establish a connection with your readers. By sharing real-life examples or experiences, you can offer concrete evidence to support your arguments and establish credibility.
In conclusion, mastering persuasive language and employing rhetorical devices can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your persuasive essay. By choosing your words carefully, using powerful language, and incorporating various rhetorical techniques, you can captivate your readers and present your arguments in a compelling and convincing manner.
Address counterarguments and refute them with strong evidence
When writing a persuasive essay, it is crucial to anticipate and address potential counterarguments to strengthen your argument. By acknowledging opposing viewpoints and then refuting them with strong evidence, you can demonstrate the credibility and validity of your own position.
One effective way to address counterarguments is to acknowledge them upfront and present them in an objective and unbiased manner. By doing so, you show that you have considered different perspectives and are willing to engage in a fair and balanced discussion. This approach also helps you connect with readers who may initially hold opposing views, as it shows respect for their opinions and demonstrates your willingness to engage in thoughtful debate.
To effectively refute counterarguments, it is important to use strong evidence that supports your own position. This can include data, statistics, expert opinions, research findings, and real-life examples. By providing convincing evidence, you can demonstrate the superiority of your argument and weaken the credibility of counterarguments. Be sure to cite credible sources and use persuasive language to present your evidence in a convincing way.
In addition to providing strong evidence, it is also important to anticipate and address potential weaknesses in your own argument. By acknowledging and addressing these weaknesses, you can show that you have thoroughly considered your stance and are able to respond to potential criticisms. This helps to build trust and credibility with your readers, as they can see that you are aware of the limitations of your argument and have taken steps to address them.
In conclusion, addressing counterarguments and refuting them with strong evidence is a crucial component of persuasive writing. By acknowledging opposing viewpoints and providing solid evidence to support your own position, you can strengthen your argument and convince readers to adopt your point of view. Remember to always approach counterarguments objectively, use persuasive language, and address any potential weaknesses in your own argument. By doing so, you can create a compelling and persuasive essay that will resonate with your readers.
Edit and proofread your essay for grammar and clarity
Once you’ve completed your persuasive essay, the work isn’t quite finished. It’s essential to go back and review your writing with a critical eye, focusing on grammar and clarity. This final step is crucial in ensuring that your arguments are effectively communicated and that your reader can easily understand and follow your points.
First and foremost, pay attention to grammar. Look for any errors in your sentence structure, verb tense, subject-verb agreement, and punctuation. Make sure that your sentences are clear and concise, without any unnecessary or confusing phrases. Correct any spelling mistakes or typos that may have slipped through the cracks.
Next, consider the overall clarity of your essay. Read through each paragraph and ensure that your ideas flow logically and cohesively. Are your arguments supported by evidence and examples? Are your transitions smooth and seamless? If necessary, revise or rearrange your paragraphs to strengthen the overall structure of your essay.
It’s also important to check for any ambiguous or vague language. Make sure that your words and phrases have precise meanings and can be easily understood by your reader. Consider whether there are any areas where you could provide more clarification or add further details to strengthen your points.
When editing and proofreading, it can be helpful to read your essay out loud. This can help you identify any awkward or convoluted sentences, as well as any areas where you may have used repetitive or redundant language. Reading aloud also allows you to hear the natural rhythm and flow of your writing, giving you a better sense of how your words will be perceived by the reader.
Finally, consider seeking feedback from others. Share your essay with a trusted friend, family member, or teacher and ask for their input. They may be able to offer valuable suggestions or catch any errors that you may have missed. Sometimes, a fresh set of eyes can provide a new perspective and help you improve your essay even further.
By taking the time to edit and proofread your essay for grammar and clarity, you can ensure that your persuasive arguments are presented in the most effective and compelling way possible. This attention to detail will not only demonstrate your strong writing skills, but it will also increase the chances of convincing your reader to see things from your perspective.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Creative Ways to Use Graphic Novels in the Classroom! 🎥
40 Strong Persuasive Writing Examples (Essays, Speeches, Ads, and More)
Learn from the experts.

The more we read, the better writers we become. Teaching students to write strong persuasive essays should always start with reading some top-notch models. This round-up of persuasive writing examples includes famous speeches, influential ad campaigns, contemporary reviews of famous books, and more. Use them to inspire your students to write their own essays. (Need persuasive essay topics? Check out our list of interesting persuasive essay ideas here! )
- Persuasive Essays
- Persuasive Speeches
- Advertising Campaigns
Persuasive Essay Writing Examples

From the earliest days of print, authors have used persuasive essays to try to sway others to their own point of view. Check out these top persuasive essay writing examples.
Professions for Women by Virginia Woolf
Sample lines: “Outwardly, what is simpler than to write books? Outwardly, what obstacles are there for a woman rather than for a man? Inwardly, I think, the case is very different; she has still many ghosts to fight, many prejudices to overcome. Indeed it will be a long time still, I think, before a woman can sit down to write a book without finding a phantom to be slain, a rock to be dashed against. And if this is so in literature, the freest of all professions for women, how is it in the new professions which you are now for the first time entering?”
The Crisis by Thomas Paine
Sample lines: “These are the times that try men’s souls. The summer soldier and the sunshine patriot will, in this crisis, shrink from the service of their country; but he that stands by it now, deserves the love and thanks of man and woman. Tyranny, like hell, is not easily conquered; yet we have this consolation with us, that the harder the conflict, the more glorious the triumph. What we obtain too cheap, we esteem too lightly: it is dearness only that gives every thing its value.”
Politics and the English Language by George Orwell
Sample lines: “As I have tried to show, modern writing at its worst does not consist in picking out words for the sake of their meaning and inventing images in order to make the meaning clearer. It consists in gumming together long strips of words which have already been set in order by someone else, and making the results presentable by sheer humbug.”
Letter From a Birmingham Jail by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Sample lines: “We know through painful experience that freedom is never voluntarily given by the oppressor; it must be demanded by the oppressed. Frankly, I have yet to engage in a direct action campaign that was ‘well timed’ in the view of those who have not suffered unduly from the disease of segregation. For years now I have heard the word ‘Wait!’ It rings in the ear of every Negro with piercing familiarity. This ‘Wait’ has almost always meant ‘Never.’ We must come to see, with one of our distinguished jurists, that ‘justice too long delayed is justice denied.'”
Civil Disobedience by Henry David Thoreau
Sample lines: “Even voting for the right is doing nothing for it. It is only expressing to men feebly your desire that it should prevail. A wise man will not leave the right to the mercy of chance, nor wish it to prevail through the power of the majority. There is but little virtue in the action of masses of men.”
Go Gentle Into That Good Night by Roger Ebert
Sample lines: “‘Kindness’ covers all of my political beliefs. No need to spell them out. I believe that if, at the end of it all, according to our abilities, we have done something to make others a little happier, and something to make ourselves a little happier, that is about the best we can do. To make others less happy is a crime.”
The Way to Wealth by Benjamin Franklin
Sample lines: “Methinks I hear some of you say, must a man afford himself no leisure? I will tell thee, my friend, what Poor Richard says, employ thy time well if thou meanest to gain leisure; and, since thou art not sure of a minute, throw not away an hour. Leisure is time for doing something useful; this leisure the diligent man will obtain, but the lazy man never; so that, as Poor Richard says, a life of leisure and a life of laziness are two things.”
The Crack-Up by F. Scott Fitzgerald
Sample lines: “Of course all life is a process of breaking down, but the blows that do the dramatic side of the work—the big sudden blows that come, or seem to come, from outside—the ones you remember and blame things on and, in moments of weakness, tell your friends about, don’t show their effect all at once.”
Open Letter to the Kansas School Board by Bobby Henderson
Sample lines: “I am writing you with much concern after having read of your hearing to decide whether the alternative theory of Intelligent Design should be taught along with the theory of Evolution. … Let us remember that there are multiple theories of Intelligent Design. I and many others around the world are of the strong belief that the universe was created by a Flying Spaghetti Monster. … We feel strongly that the overwhelming scientific evidence pointing towards evolutionary processes is nothing but a coincidence, put in place by Him. It is for this reason that I’m writing you today, to formally request that this alternative theory be taught in your schools, along with the other two theories.”
Open Letter to the United Nations by Niels Bohr
Sample lines: “Humanity will, therefore, be confronted with dangers of unprecedented character unless, in due time, measures can be taken to forestall a disastrous competition in such formidable armaments and to establish an international control of the manufacture and use of the powerful materials.”
Persuasive Speech Writing Examples
Many persuasive speeches are political in nature, often addressing subjects like human rights. Here are some of history’s most well-known persuasive writing examples in the form of speeches.
I Have a Dream by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Sample lines: “And so even though we face the difficulties of today and tomorrow, I still have a dream. It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream. I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.”
Woodrow Wilson’s War Message to Congress, 1917
Sample lines: “There are, it may be, many months of fiery trial and sacrifice ahead of us. It is a fearful thing to lead this great peaceful people into war, into the most terrible and disastrous of all wars, civilization itself seeming to be in the balance. But the right is more precious than peace, and we shall fight for the things which we have always carried nearest our hearts—for democracy, for the right of those who submit to authority to have a voice in their own governments, for the rights and liberties of small nations, for a universal dominion of right by such a concert of free peoples as shall bring peace and safety to all nations and make the world itself at last free.”
Chief Seattle’s 1854 Oration
Sample lines: “I here and now make this condition that we will not be denied the privilege without molestation of visiting at any time the tombs of our ancestors, friends, and children. Every part of this soil is sacred in the estimation of my people. Every hillside, every valley, every plain and grove, has been hallowed by some sad or happy event in days long vanished. Even the rocks, which seem to be dumb and dead as they swelter in the sun along the silent shore, thrill with memories of stirring events connected with the lives of my people, and the very dust upon which you now stand responds more lovingly to their footsteps than yours, because it is rich with the blood of our ancestors, and our bare feet are conscious of the sympathetic touch.”
Women’s Rights Are Human Rights, Hillary Rodham Clinton
Sample lines: “What we are learning around the world is that if women are healthy and educated, their families will flourish. If women are free from violence, their families will flourish. If women have a chance to work and earn as full and equal partners in society, their families will flourish. And when families flourish, communities and nations do as well. … If there is one message that echoes forth from this conference, let it be that human rights are women’s rights and women’s rights are human rights once and for all.”
I Am Prepared to Die, Nelson Mandela
Sample lines: “Above all, My Lord, we want equal political rights, because without them our disabilities will be permanent. I know this sounds revolutionary to the whites in this country, because the majority of voters will be Africans. This makes the white man fear democracy. But this fear cannot be allowed to stand in the way of the only solution which will guarantee racial harmony and freedom for all. It is not true that the enfranchisement of all will result in racial domination. Political division, based on color, is entirely artificial and, when it disappears, so will the domination of one color group by another. … This then is what the ANC is fighting. Our struggle is a truly national one. It is a struggle of the African people, inspired by our own suffering and our own experience. It is a struggle for the right to live.”
The Struggle for Human Rights by Eleanor Roosevelt
Sample lines: “It is my belief, and I am sure it is also yours, that the struggle for democracy and freedom is a critical struggle, for their preservation is essential to the great objective of the United Nations to maintain international peace and security. Among free men the end cannot justify the means. We know the patterns of totalitarianism—the single political party, the control of schools, press, radio, the arts, the sciences, and the church to support autocratic authority; these are the age-old patterns against which men have struggled for 3,000 years. These are the signs of reaction, retreat, and retrogression. The United Nations must hold fast to the heritage of freedom won by the struggle of its people; it must help us to pass it on to generations to come.”
Freedom From Fear by Aung San Suu Kyi
Sample lines: “Saints, it has been said, are the sinners who go on trying. So free men are the oppressed who go on trying and who in the process make themselves fit to bear the responsibilities and to uphold the disciplines which will maintain a free society. Among the basic freedoms to which men aspire that their lives might be full and uncramped, freedom from fear stands out as both a means and an end. A people who would build a nation in which strong, democratic institutions are firmly established as a guarantee against state-induced power must first learn to liberate their own minds from apathy and fear.”
Harvey Milk’s “The Hope” Speech
Sample lines: “Some people are satisfied. And some people are not. You see there is a major difference—and it remains a vital difference—between a friend and a gay person, a friend in office and a gay person in office. Gay people have been slandered nationwide. We’ve been tarred and we’ve been brushed with the picture of pornography. In Dade County, we were accused of child molestation. It is not enough anymore just to have friends represent us, no matter how good that friend may be.”
The Union and the Strike, Cesar Chavez
Sample lines: “We are showing our unity in our strike. Our strike is stopping the work in the fields; our strike is stopping ships that would carry grapes; our strike is stopping the trucks that would carry the grapes. Our strike will stop every way the grower makes money until we have a union contract that guarantees us a fair share of the money he makes from our work! We are a union and we are strong and we are striking to force the growers to respect our strength!”
Nobel Lecture by Malala Yousafzai
Sample lines: “The world can no longer accept that basic education is enough. Why do leaders accept that for children in developing countries, only basic literacy is sufficient, when their own children do homework in algebra, mathematics, science, and physics? Leaders must seize this opportunity to guarantee a free, quality, primary and secondary education for every child. Some will say this is impractical, or too expensive, or too hard. Or maybe even impossible. But it is time the world thinks bigger.”
Persuasive Writing Examples in Advertising Campaigns
Ads are prime persuasive writing examples. You can flip open any magazine or watch TV for an hour or two to see sample after sample of persuasive language. Here are some of the most popular ad campaigns of all time, with links to articles explaining why they were so successful.
Nike: Just Do It

The iconic swoosh with the simple tagline has persuaded millions to buy their kicks from Nike and Nike alone. Teamed with pro sports-star endorsements, this campaign is one for the ages. Blinkist offers an opinion on what made it work.
Dove: Real Beauty
Beauty brand Dove changed the game by choosing “real” women to tell their stories instead of models. They used relatable images and language to make connections, and inspired other brands to try the same concept. Learn why Global Brands considers this one a true success story.
Wendy’s: Where’s the Beef?
Today’s kids are too young to remember the cranky old woman demanding to know where the beef was on her fast-food hamburger. But in the 1980s, it was a catchphrase that sold millions of Wendy’s burgers. Learn from Better Marketing how this ad campaign even found its way into the 1984 presidential debate.

De Beers: A Diamond Is Forever

A diamond engagement ring has become a standard these days, but the tradition isn’t as old as you might think. In fact, it was De Beers jewelry company’s 1948 campaign that created the modern engagement ring trend. The Drum has the whole story of this sparkling campaign.
Volkswagen: Think Small
Americans have always loved big cars. So in the 1960s, when Volkswagen wanted to introduce their small cars to a bigger market, they had a problem. The clever “Think Small” campaign gave buyers clever reasons to consider these models, like “If you run out of gas, it’s easy to push.” Learn how advertisers interested American buyers in little cars at Visual Rhetoric.
American Express: Don’t Leave Home Without It
AmEx was once better known for traveler’s checks than credit cards, and the original slogan was “Don’t leave home without them.” A simple word change convinced travelers that American Express was the credit card they needed when they headed out on adventures. Discover more about this persuasive campaign from Medium.
Skittles: Taste the Rainbow

These candy ads are weird and intriguing and probably not for everyone. But they definitely get you thinking, and that often leads to buying. Learn more about why these wacky ads are successful from The Drum.
Maybelline: Maybe She’s Born With It
Smart wordplay made this ad campaign slogan an instant hit. The ads teased, “Maybe she’s born with it. Maybe it’s Maybelline.” (So many literary devices all in one phrase!) Fashionista has more on this beauty campaign.
Coca-Cola: Share a Coke
Seeing their own name on a bottle made teens more likely to want to buy a Coke. What can that teach us about persuasive writing in general? It’s an interesting question to consider. Learn more about the “Share a Coke” campaign from Digital Vidya.
Always: #LikeaGirl

Talk about the power of words! This Always campaign turned the derogatory phrase “like a girl” on its head, and the world embraced it. Storytelling is an important part of persuasive writing, and these ads really do it well. Medium has more on this stereotype-bashing campaign.
Editorial Persuasive Writing Examples

Newspaper editors or publishers use editorials to share their personal opinions. Noted politicians, experts, or pundits may also offer their opinions on behalf of the editors or publishers. Here are a couple of older well-known editorials, along with a selection from current newspapers.
Yes, Virginia, There Is a Santa Claus (1897)
Sample lines: “Yes, Virginia, there is a Santa Claus. He exists as certainly as love and generosity and devotion exist, and you know that they abound and give to your life its highest beauty and joy. Alas! How dreary would be the world if there were no Santa Claus. It would be as dreary as if there were no Virginias.”
What’s the Matter With Kansas? (1896)
Sample lines: “Oh, this IS a state to be proud of! We are a people who can hold up our heads! What we need is not more money, but less capital, fewer white shirts and brains, fewer men with business judgment, and more of those fellows who boast that they are ‘just ordinary clodhoppers, but they know more in a minute about finance than John Sherman,’ we need more men … who hate prosperity, and who think, because a man believes in national honor, he is a tool of Wall Street.”
America Can Have Democracy or Political Violence. Not Both. (The New York Times)
Sample lines: “The nation is not powerless to stop a slide toward deadly chaos. If institutions and individuals do more to make it unacceptable in American public life, organized violence in the service of political objectives can still be pushed to the fringes. When a faction of one of the country’s two main political parties embraces extremism, that makes thwarting it both more difficult and more necessary. A well-functioning democracy demands it.”
The Booster Isn’t Perfect, But Still Can Help Against COVID (The Washington Post)
Sample lines: “The booster shots are still free, readily available and work better than the previous boosters even as the virus evolves. Much still needs to be done to build better vaccines that protect longer and against more variants, including those that might emerge in the future. But it is worth grabbing the booster that exists today, the jab being a small price for any measure that can help keep COVID at bay.”
If We Want Wildlife To Thrive in L.A., We Have To Share Our Neighborhoods With Them (Los Angeles Times)
Sample lines: “If there are no corridors for wildlife movement and if excessive excavation of dirt to build bigger, taller houses erodes the slope of a hillside, then we are slowly destroying wildlife habitat. For those people fretting about what this will do to their property values—isn’t open space, trees, and wildlife an amenity in these communities?”
Persuasive Review Writing Examples

Book or movie reviews are more great persuasive writing examples. Look for those written by professionals for the strongest arguments and writing styles. Here are reviews of some popular books and movies by well-known critics to use as samples.
The Great Gatsby (The Chicago Tribune, 1925)
Sample lines: “What ails it, fundamentally, is the plain fact that it is simply a story—that Fitzgerald seems to be far more interested in maintaining its suspense than in getting under the skins of its people. It is not that they are false: It is that they are taken too much for granted. Only Gatsby himself genuinely lives and breathes. The rest are mere marionettes—often astonishingly lifelike, but nevertheless not quite alive.”
Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone (The Washington Post, 1999)
Sample lines: “Obviously, Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone should make any modern 11-year-old a very happy reader. The novel moves quickly, packs in everything from a boa constrictor that winks to a melancholy Zen-spouting centaur to an owl postal system, and ends with a scary surprise. Yet it is, essentially, a light-hearted thriller, interrupted by occasional seriousness (the implications of Harry’s miserable childhood, a moral about the power of love).”
Twilight (The Telegraph, 2009)
Sample lines: “No secret, of course, at whom this book is aimed, and no doubt, either, that it has hit its mark. The four Twilight novels are not so much enjoyed, as devoured, by legions of young female fans worldwide. That’s not to say boys can’t enjoy these books; it’s just that the pages of heart-searching dialogue between Edward and Bella may prove too long on chat and too short on action for the average male reader.”
To Kill a Mockingbird (Time, 1960)
Sample lines: “Author Lee, 34, an Alabaman, has written her first novel with all of the tactile brilliance and none of the preciosity generally supposed to be standard swamp-warfare issue for Southern writers. The novel is an account of an awakening to good and evil, and a faint catechistic flavor may have been inevitable. But it is faint indeed; novelist Lee’s prose has an edge that cuts through cant, and she teaches the reader an astonishing number of useful truths about little girls and about Southern life.”
The Diary of Anne Frank (The New York Times, 1952)
Sample lines: “And this quality brings it home to any family in the world today. Just as the Franks lived in momentary fear of the Gestapo’s knock on their hidden door, so every family today lives in fear of the knock of war. Anne’s diary is a great affirmative answer to the life-question of today, for she shows how ordinary people, within this ordeal, consistently hold to the greater human values.”
What are your favorite persuasive writing examples to use with students? Come share your ideas in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, the big list of essay topics for high school (120+ ideas) ..

You Might Also Like
How I Use Kahoot! in Middle School Math
Linear expression, integers, and variables … oh my! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
How to Write a Persuasive Essay (This Convinced My Professor!)
.png)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
You can make your essay more persuasive by getting straight to the point.
In fact, that's exactly what we did here, and that's just the first tip of this guide. Throughout this guide, we share the steps needed to prove an argument and create a persuasive essay.
This AI tool helps you improve your essay > This AI tool helps you improve your essay >

Key takeaways: - Proven process to make any argument persuasive - 5-step process to structure arguments - How to use AI to formulate and optimize your essay
Why is being persuasive so difficult?
"Write an essay that persuades the reader of your opinion on a topic of your choice."
You might be staring at an assignment description just like this 👆from your professor. Your computer is open to a blank document, the cursor blinking impatiently. Do I even have opinions?
The persuasive essay can be one of the most intimidating academic papers to write: not only do you need to identify a narrow topic and research it, but you also have to come up with a position on that topic that you can back up with research while simultaneously addressing different viewpoints.
That’s a big ask. And let’s be real: most opinion pieces in major news publications don’t fulfill these requirements.
The upside? By researching and writing your own opinion, you can learn how to better formulate not only an argument but the actual positions you decide to hold.
Here, we break down exactly how to write a persuasive essay. We’ll start by taking a step that’s key for every piece of writing—defining the terms.
What Is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay is exactly what it sounds like: an essay that persuades . Over the course of several paragraphs or pages, you’ll use researched facts and logic to convince the reader of your opinion on a particular topic and discredit opposing opinions.
While you’ll spend some time explaining the topic or issue in question, most of your essay will flesh out your viewpoint and the evidence that supports it.
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay
If you’re intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place.
1. A topic or issue to argue
This is probably the hardest step. You need to identify a topic or issue that is narrow enough to cover in the length of your piece—and is also arguable from more than one position. Your topic must call for an opinion , and not be a simple fact .
It might be helpful to walk through this process:
- Identify a random topic
- Ask a question about the topic that involves a value claim or analysis to answer
- Answer the question
That answer is your opinion.
Let’s consider some examples, from silly to serious:
Topic: Dolphins and mermaids
Question: In a mythical match, who would win: a dolphin or a mermaid?
Answer/Opinion: The mermaid would win in a match against a dolphin.
Topic: Autumn
Question: Which has a better fall: New England or Colorado?
Answer/Opinion: Fall is better in New England than Colorado.
Topic: Electric transportation options
Question: Would it be better for an urban dweller to buy an electric bike or an electric car?
Answer/Opinion: An electric bike is a better investment than an electric car.
Your turn: Walk through the three-step process described above to identify your topic and your tentative opinion. You may want to start by brainstorming a list of topics you find interesting and then going use the three-step process to find the opinion that would make the best essay topic.
2. An unequivocal thesis statement
If you walked through our three-step process above, you already have some semblance of a thesis—but don’t get attached too soon!
A solid essay thesis is best developed through the research process. You shouldn’t land on an opinion before you know the facts. So press pause. Take a step back. And dive into your research.
You’ll want to learn:
- The basic facts of your topic. How long does fall last in New England vs. Colorado? What trees do they have? What colors do those trees turn?
- The facts specifically relevant to your question. Is there any science on how the varying colors of fall influence human brains and moods?
- What experts or other noteworthy and valid sources say about the question you’re considering. Has a well-known arborist waxed eloquent on the beauty of New England falls?
As you learn the different viewpoints people have on your topic, pay attention to the strengths and weaknesses of existing arguments. Is anyone arguing the perspective you’re leaning toward? Do you find their arguments convincing? What do you find unsatisfying about the various arguments?
Allow the research process to change your mind and/or refine your thinking on the topic. Your opinion may change entirely or become more specific based on what you learn.
Once you’ve done enough research to feel confident in your understanding of the topic and your opinion on it, craft your thesis.
Your thesis statement should be clear and concise. It should directly state your viewpoint on the topic, as well as the basic case for your thesis.
Thesis 1: In a mythical match, the mermaid would overcome the dolphin due to one distinct advantage: her ability to breathe underwater.
Thesis 2: The full spectrum of color displayed on New England hillsides is just one reason why fall in the northeast is better than in Colorado.
Thesis 3: In addition to not adding to vehicle traffic, electric bikes are a better investment than electric cars because they’re cheaper and require less energy to accomplish the same function of getting the rider from point A to point B.
Your turn: Dive into the research process with a radar up for the arguments your sources are making about your topic. What are the most convincing cases? Should you stick with your initial opinion or change it up? Write your fleshed-out thesis statement.
3. Evidence to back up your thesis
This is a typical place for everyone from undergrads to politicians to get stuck, but the good news is, if you developed your thesis from research, you already have a good bit of evidence to make your case.
Go back through your research notes and compile a list of every …
… or other piece of information that supports your thesis.
This info can come from research studies you found in scholarly journals, government publications, news sources, encyclopedias, or other credible sources (as long as they fit your professor’s standards).
As you put this list together, watch for any gaps or weak points. Are you missing information on how electric cars versus electric bicycles charge or how long their batteries last? Did you verify that dolphins are, in fact, mammals and can’t breathe underwater like totally-real-and-not-at-all-fake 😉mermaids can? Track down that information.
Next, organize your list. Group the entries so that similar or closely related information is together, and as you do that, start thinking through how to articulate the individual arguments to support your case.
Depending on the length of your essay, each argument may get only a paragraph or two of space. As you think through those specific arguments, consider what order to put them in. You’ll probably want to start with the simplest argument and work up to more complicated ones so that the arguments can build on each other.
Your turn: Organize your evidence and write a rough draft of your arguments. Play around with the order to find the most compelling way to argue your case.
4. Rebuttals to disprove opposing theses
You can’t just present the evidence to support your case and totally ignore other viewpoints. To persuade your readers, you’ll need to address any opposing ideas they may hold about your topic.
You probably found some holes in the opposing views during your research process. Now’s your chance to expose those holes.
Take some time (and space) to: describe the opposing views and show why those views don’t hold up. You can accomplish this using both logic and facts.
Is a perspective based on a faulty assumption or misconception of the truth? Shoot it down by providing the facts that disprove the opinion.
Is another opinion drawn from bad or unsound reasoning? Show how that argument falls apart.
Some cases may truly be only a matter of opinion, but you still need to articulate why you don’t find the opposing perspective convincing.
Yes, a dolphin might be stronger than a mermaid, but as a mammal, the dolphin must continually return to the surface for air. A mermaid can breathe both underwater and above water, which gives her a distinct advantage in this mythical battle.
While the Rocky Mountain views are stunning, their limited colors—yellow from aspen trees and green from various evergreens—leaves the autumn-lover less than thrilled. The rich reds and oranges and yellows of the New England fall are more satisfying and awe-inspiring.
But what about longer trips that go beyond the city center into the suburbs and beyond? An electric bike wouldn’t be great for those excursions. Wouldn’t an electric car be the better choice then?
Certainly, an electric car would be better in these cases than a gas-powered car, but if most of a person’s trips are in their hyper-local area, the electric bicycle is a more environmentally friendly option for those day-to-day outings. That person could then participate in a carshare or use public transit, a ride-sharing app, or even a gas-powered car for longer trips—and still use less energy overall than if they drove an electric car for hyper-local and longer area trips.
Your turn: Organize your rebuttal research and write a draft of each one.
5. A convincing conclusion
You have your arguments and rebuttals. You’ve proven your thesis is rock-solid. Now all you have to do is sum up your overall case and give your final word on the subject.
Don’t repeat everything you’ve already said. Instead, your conclusion should logically draw from the arguments you’ve made to show how they coherently prove your thesis. You’re pulling everything together and zooming back out with a better understanding of the what and why of your thesis.
A dolphin may never encounter a mermaid in the wild, but if it were to happen, we know how we’d place our bets. Long hair and fish tail, for the win.
For those of us who relish 50-degree days, sharp air, and the vibrant colors of fall, New England offers a season that’s cozier, longer-lasting, and more aesthetically pleasing than “colorful” Colorado. A leaf-peeper’s paradise.
When most of your trips from day to day are within five miles, the more energy-efficient—and yes, cost-efficient—choice is undoubtedly the electric bike. So strap on your helmet, fire up your pedals, and two-wheel away to your next destination with full confidence that you made the right decision for your wallet and the environment.
3 Quick Tips for Writing a Strong Argument
Once you have a draft to work with, use these tips to refine your argument and make sure you’re not losing readers for avoidable reasons.
1. Choose your words thoughtfully.
If you want to win people over to your side, don’t write in a way that shuts your opponents down. Avoid making abrasive or offensive statements. Instead, use a measured, reasonable tone. Appeal to shared values, and let your facts and logic do the hard work of changing people’s minds.
Choose words with AI

You can use AI to turn your general point into a readable argument. Then, you can paraphrase each sentence and choose between competing arguments generated by the AI, until your argument is well-articulated and concise.
2. Prioritize accuracy (and avoid fallacies).
Make sure the facts you use are actually factual. You don’t want to build your argument on false or disproven information. Use the most recent, respected research. Make sure you don’t misconstrue study findings. And when you’re building your case, avoid logical fallacies that undercut your argument.
A few common fallacies to watch out for:
- Strawman: Misrepresenting or oversimplifying an opposing argument to make it easier to refute.
- Appeal to ignorance: Arguing that a certain claim must be true because it hasn’t been proven false.
- Bandwagon: Assumes that if a group of people, experts, etc., agree with a claim, it must be true.
- Hasty generalization: Using a few examples, rather than substantial evidence, to make a sweeping claim.
- Appeal to authority: Overly relying on opinions of people who have authority of some kind.
The strongest arguments rely on trustworthy information and sound logic.
Research and add citations with AI

We recently wrote a three part piece on researching using AI, so be sure to check it out . Going through an organized process of researching and noting your sources correctly will make sure your written text is more accurate.
3. Persuasive essay structure

If you’re building a house, you start with the foundation and go from there. It’s the same with an argument. You want to build from the ground up: provide necessary background information, then your thesis. Then, start with the simplest part of your argument and build up in terms of complexity and the aspect of your thesis that the argument is tackling.
A consistent, internal logic will make it easier for the reader to follow your argument. Plus, you’ll avoid confusing your reader and you won’t be unnecessarily redundant.
The essay structure usually includes the following parts:
- Intro - Hook, Background information, Thesis statement
- Topic sentence #1 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence
- Topic sentence #2 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence Topic sentence #3 , with supporting facts or stats
- Conclusion - Thesis and main points restated, call to action, thought provoking ending
Are You Ready to Write?
Persuasive essays are a great way to hone your research, writing, and critical thinking skills. Approach this assignment well, and you’ll learn how to form opinions based on information (not just ideas) and make arguments that—if they don’t change minds—at least win readers’ respect.
Share This Article:

Grammarly Alternatives: Which Writing Assistant is the Best Choice for You?

The Dos and Don’ts of Using AI to Study
.webp)
How to Use Modal Verbs for Clear Communication
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A persuasive essay is one that attempts to get a reader to agree with your perspective. Ready for some tips on how to produce a well-written, well-rounded, well-structured persuasive essay? Just say yes.
Learn how to write a persuasive essay effectively and convince your audience with compelling arguments, thorough research, and persuasive language.
Teaching students to write strong persuasive essays should always start with reading some top-notch models. This round-up of persuasive writing examples includes famous speeches, influential ad campaigns, contemporary reviews of famous books, and more.
Persuasive writing is any written work that tries to convince the reader of the writer’s opinion. Aside from standard writing skills, a persuasive essay author can also draw on personal experience, logical arguments, an appeal to emotion, and compelling speech to influence readers.
Persuasive essays are a great way to hone your research, writing, and critical thinking skills. Approach this assignment well, and you’ll learn how to form opinions based on information (not just ideas) and make arguments that—if they don’t change minds—at least win readers’ respect.
The first step in writing a persuasive essay is choosing a topic and picking a side. If the topic is something you believe in, it will make the entire experience of researching, writing, and arguing your perspective more personal.