Department of

Department of Education
Research projects, the role of research in higher education and research assessment.
Theme: Centre for Global Higher Education (CGHE) Higher Education
This project aims to study the importance of the research function in understanding the wider dynamics of higher education.
This strand of research is a new project, part of the ESRC CGHE Transition Centre. It draws together multi-disciplinary scholarship and a strong comparative dimension, internationally and institutionally, in order to study the importance of the research function in understanding the wider dynamics of higher education.
Over three years, the team, led by Professor Alis Oancea and involving Dr James Robson and Dr Xin Xu (Oxford) and Dr Gemma Derrick (Lancaster), will conduct a comparative study of the weight given to research in academic life and evaluations, in relation to: individual careers, organisational environments, teaching and learning, sectoral policy, and relationships with other sectors, including publishing and industry. This will be complemented by a comparative international review of assessment systems for higher education-based research, considering critically their role in framing arguments about the public contributions and value of research in higher education.

Funder : Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC)
Funder : Centre for Global Higher Education (ES/T014768/1)
Start Date : 2020
End Date : 2023
Research Team

Alis Oancea
Professor of Philosophy of Education and Research Policy

James Robson
Associate Professor of Tertiary Education Systems and Director of SKOPE

Departmental Lecturer in Higher/Tertiary Education
Publications
- Journal Articles
- Books: Books, Chapters, Reviews
- Working Papers
- The role of research in educational improvement
John D. Bransford
Deborah Stipek
Nancy J. Vye
Louis M. Gomez

Primary Research Area:
Topic areas:, apa citation, you are here.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 13 October 2017
Rethinking higher education and its relationship with social inequalities: past knowledge, present state and future potential
- Theocharis Kromydas 1
Palgrave Communications volume 3 , Article number: 1 ( 2017 ) Cite this article
127k Accesses
147 Citations
77 Altmetric
Metrics details
The purposes and impact of higher education on the economy and the broader society have been transformed through time in various ways. Higher education institutional and policy dynamics differ across time, but also between countries and political regimes and therefore context cannot be neglected. This article reviews the purpose of higher education and its institutional characteristics juxtaposing two, allegedly rival, conceptual frameworks; the instrumental and the intrinsic one. Various pedagogical traditions are critically reviewed and used as examples, which can potentially inform today’s policy making. Since, higher education cannot be seen as detached from all other lower levels of education appropriate conceptual links are offered throughout this article. Its significance lies on the organic synthesis of literature across social science, suggesting ways of going forward based on the traditions that already exist but seem underutilized so far because of overdependence in market-driven practices. This offers a new insight on how theories can inform policy making, through conceptual “bridging” and reconciliation. The debate on the purpose of higher education is placed under the context of the most recent developments of increasing social inequalities in the western world and its relation to the mass model of higher education and the relevant policy decisions for a continuous increase in participation. This article suggests that the current policy focus on labor market driven policies in higher education have led to an ever growing competition transforming this social institution to an ordinary market-place, where attainment and degrees are seen as a currency that can be converted to a labour market value. Education has become an instrument for economic progress moving away from its original role to provide context for human development. As a result, higher education becomes very expensive and even if policies are directed towards openness, in practice, just a few have the money to afford it. A shift toward a hybrid model, where the intrinsic purpose of higher education is equally acknowledged along with its instrumental purpose should be seen by policy makers as the way forward to create educational systems that are more inclusive and societies that are more knowledgeable and just.
Similar content being viewed by others
How popularising higher education affects economic growth and poverty alleviation: empirical evidence from 38 countries

Dreams and realities of school tracking and vocational education
Dynamics of returns to vocational education in China: 2010–2017
Introduction.
The mainstream view in the western world, as informed by the human capital theory sees education, as an ordinary investment and the main reason why someone consumes time and money to undertake higher levels of education, is the high returns expected from the corresponding wage premium, when enters the labour market (Becker, 1964 , 1993 ). Nevertheless, things in practice are more complicated and this sequence of events is unlikely to be sustained, especially in recession periods like the one we currently live in. On the contrary, one notion of education, related somewhat to the American liberal arts tradition, is the intrinsic notion, which interprets that the purpose of education is to ‘equip people to make their own free, autonomous choices about the life they will lead’ (Bridges, 1992 : 92). There might be an economic basis underpinning this individual choice, but the intrinsic notion permits more subjective motivations, which are not necessarily affected by economic circumstances.
Robinson and Aronica ( 2009 ) argue that education, have become an impersonal linear process, a type of assembly line, similar to a factory production. They challenge this view and call for a less standardised pedagogy; more personalised to students needs as well as talents. Education is not similar to a manufacturing production-line, since students are highly concerned about the quality of education they receive as opposed to motor cars, which are indifferent to the process by which they are manufactured. Along these lines, Waters ( 2012 ), following Weber’s ( 1947 , 1968 ) rationale on the role of bureaucracy in modern societies, adds that this manufacturing process is achieved through rigid, rationalised and productively efficient but totally impersonal bureaucracy, operated in a way that sees children as raw materials for the creation of adults, which is the final product properly equipped to reproduce “itself” by being a parent to a new born “raw material” and so forth. Durkheim ( 1956 , 2006 ) sees this as a mechanism where adults exercise their influence over the younger in order to maintain the status quo they desire. However, since education entails ontological as well as epistemological implications, primary focus should be given to learning in such a way that educative and social functions could be amalgamated, rather than solely focusing on the delivery of existing knowledge per se, which becomes a reiterated process and an unchallenged absolute truth (Freire, 1970 ; Heidegger, 1988 ; Dall’ Alba and Barnacle, 2007 ).
This article focus on higher education; since it is the last stage before somebody enters the labour market and thus the instrumental view becomes more dominant over the intrinsic view, compared to the lower levels of education. Higher education, is being traditionally offered by universities. The first established university in Europe is the University of Bologna, where the term “academic freedom” was introduced as the kernel of its culture (Newman, 1996 ). Graham ( 2013 ) distinguishes between three different models of higher education. These are: the university college, the research and the technical university. He provides a historical review of the origins of these three models. The university college is the oldest one, where Christian values were the core values. Later on, when scientific knowledge questioned the universal theological truth, another type of university has been established, where research was the ultimate goal of the scholarship. This type of university has subsequently transformed by the introduction of the liberal arts tradition, flourished in the US. The research university model, originated circa 16 th century in Cambridge and established in Berlin by the introduction of the Humboldian University, shared a common aim: the pursuit of knowledge and its dissemination to the greater society. The third model of university is the technical one. It has been established in an industrial revolution context in Scotland and particularly in Glasgow in the premises of what is currently known as the University of Strathclyde. While the introduction of capitalism changed radically the structure and the format of labour relations, the technical model was based on the idea that industrial skills had to be acquired by formal education and somehow verified institutionally in order to be applied to the broader society. This is the first time where the up to then distinct fields of education and industry, started to be conceived as inextricably tight in a rather linear way.
These different models of higher education cultures and traditions still exist, but in reality, Universities worldwide follow a hybrid approach, where all traditions collaborate with each other. However, there are some universities that still carry the reputation and tradition of a specific model and to some extent this tradition differentiates them from all others. It is not the scope of this research to analyse this in detail, as the main aim is to offer an institutional and policy narrative, exploring the purpose of higher education and its relationship with social inequalities, focusing primarily on the western world.
Nowadays, in a rapidly changing word, the major debate is placed under the forms of institutional transformation of higher education. Brennan ( 2004 ), based on Trow ( 1979 , 2000 ), allocates three forms of higher education. The first one is the elite form, which main aim is to prepare and shape the mind-set of students originated from the most dominant class. The second is the mass form of higher education, which transmits the knowledge and skills acquired in higher education into the technical and economic roles students subsequently perform in the labour market. Lastly, the third is the universal form, which main purpose is to adapt students and the general population to the rapid social and technological changes.
This article reviews the contemporary trends in higher education and its widespread diffusion as interacted with the evolutions in western economies and societies, where social inequalities persist and even become wider (Dorling and Dorling, 2015 ). The narrative used in this article is more suitable to conceptualise higher education in a western world context, though we acknowledge that via globalisation, the way education and particularly higher education is delivered in the rest of the world seems to follow similar to the Western worlds paths, despite the apparent differences in culture, social and economic systems as well as writing systems. Footnote 1
An interdisciplinary and critical synthesis of the relevant literature is conducted, presenting two stances that are largely considered as rival: The instrumental one that treats higher education as an ordinary investment with particular financial yields in the labour market and the more intrinsic one which sees higher education as mainly detached from the logic of economic costs and benefits. The theoretical rivalry is apparent since in the former approach higher education is an inevitable property of labour market and thus an indispensable part of the mainstream economic neoliberal regime, whereas the latter sees no logical link between higher education and labour market purposes and therefore the content and substance of learning and knowledge acquisition in education and specifically in higher education should not be market-driven or aligned to the functions of specific economic regimes. However, this article argues that educational systems, and particularly their higher levels, are amalgamated parts of contemporary societies and therefore theories and practices need to move away from rather futile binary rationales.
The remainder of this paper explains why both the intrinsic and instrumental approaches are doomed to fail in practice when used in isolation. In a rapidly diverging and polarised world, where social inequalities rise within as well as between countries, common sense dictates social theories and practices to move towards reconciliation rather than stubborn rivalry. In that spirit, this paper argues that the intrinsic and instrumental approach are in fact complementary to each other. Such view can inform policy making towards building more inclusive educational systems; organically tight with the broader society. The narrative this article uses departs and expands on the rationale of eminent critical pedagogists such as Freire, Bronfenbrenner, Bourdieu and Kozol in order to challenge the current instrumental world-view of education, at least as this is apparent in the western world. Then the article moves into offering a reasoning for an organic synthesis of existing knowledge in order the two rival theories to be actualised in practice as a unified and reconciled pedagogical strategy. This reasoning builds on the research conducted by Durst’s ( 1999 ), Payne ( 1999 ) and Lu and Horner ( 2009 ). Durst ( 1999 ) suggests a “reflective instrumentalism”, where student’s pragmatic view that education is just a way of finding a well-paid job, operated in tandem with critical pedagogical canons, is indeed possible. Payne ( 1999 ) proposes a similar approach, where students are equipped with the necessary tools to find a job in the labour market; however educators should engage students with this knowledge in a critical way in order to be able to produce something new. Likewise Lu and Horner ( 2009 ) note that educators and students need to work together in such a way that perceptions of both are amenable to change and career choices are critically discussed in a constantly changing social context.
The purpose of higher education in western societies
Mokyr ( 2002 ) suggests that education should be integrated by both inculcation and emancipation in order to serve individual intellectual development as well as social progression. Shapiro ( 2005 ) emphasizes the need for the higher education institutions to serve a public purpose moving beyond narrow self-serving concerns, as well as to enforce social change in order to reflect the nature of a society that its members desire. More recently, in philosophical terms Barnett ( 2017 , p 10) calls for a wider conceptual landscape in higher education where “The task of an adequate philosophy of higher education…is not merely to understand the university or even to defend it but to change it”. )
The purpose of education and its meaning in the contemporary western societies has been also criticised by Bo ( 2009 ), suggesting that education has become a contradictory notion that leaves no space for emancipation since it gives no opportunity for improvisation to students. Thus, the students feel encaged within the system instead of being liberated. Bo agrees with Mokyr, who highlighted the need for recalling the basic notions of education from ancient philosophies: that education should be integrated by both inculcation and emancipation in order to serve individual intellectual development as well as social progression (Mokyr, 2002 ; Bo, 2009 ).
Not all individuals and societies agree on the purposes and roles of higher education in the modern world. However, in any case, it is a place where teaching and research can be accommodated in an organised fashion for the promotion of various types of knowledge, applied and non-applied. It is a place where money and moral values compete and collaborate simultaneously, where the development of labour market skills and competences coexist with the identification and utilisations of people’s skills and talents as well as the pursuit of employment, morality and citizenship.
The post-WWII era has been characterised by the mass model of higher education. Before this, higher education was for those belonging to higher social classes (Brennan, 2004 ). This model became the kernel of educational policies in Europe and generally, in the western world (Shapiro, 2005 ). Such policies have been boosted by the advent of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT), which enhance commercial and non-commercial bonds between countries and higher education institutions, transforming the role of higher education even further, making it rather universal (Jongbloed et al., 2008 ). Higher education’s boundaries have become vague and the predefined “social contract” between its institutions and those participated in them, is more complicated to be defined in absolute terms. Higher education institutions are now characterised by economic competition in a strict global market environment, where governments are not the key players anymore (Brennan, 2004 ).
Moreover, student demographics in higher education are constantly changing. Higher education is now an industry operating in a global market. Competition to attract talents from around the world is growing rapidly as an increasing number of countries offer additional graduate and post graduate positions to non-nationals, usually at a higher cost compared to nationals (Barber et al., 2013 ). Countries such as China or Singapore that are growing economically very rapidly are investing huge amounts of money to develop their higher education system and make it more friendly to talented people from around the world. The advent of new technologies have changed the traditional model of higher education, where physical presence is not a necessary requirement anymore (Yuan et al., 2013 ). Studying while working is much easier and therefore more mature students have now the opportunity to study towards a graduate or post-graduate degree. All these developments have increased the potential for profit; however it also requires huge amount of money to be invested in new technologies and all kinds of infrastructures and resources. The need for diversification in funding sources is simply essential and therefore all other industries become inevitably more engaged (Kaiser et al., 2014 ). On top of all these, climate change, the rise of terrorism, the prolonged economic uncertainty and the automazation of labour will likely increase cross-national and intraoccupational mobility and therefore the demand for higher education, especially in the recipient countries of the economically developed western world will inevitably rise. Summing up, higher education institutions operate under a very fluid and unpredictable environment and therefore approaches that are informed by adaptability and flexibility are absolutely crucial. The hybrid approach we propose where instrumental and intrinsic values are reconciled is along these lines.
Modern views of higher education place its function under a digital knowledge-based society, where economy dominates. Labour markets demand for skills such as technological competence and complex problem-solving by critical thinking and multitasking, which increases competition and in turn, accelerates the pace of the working day (Westerheijden et al., 2007 ). Haigh and Clifford ( 2011 ) argue that high competency, in both hard and soft skills, is not enough, as higher education needs to go deeper into changing attitudes and behaviours becoming the core of a globalised knowledge-based-economy. However, the trends of transferring knowledge and skills by universities, which “increasingly instrumentalize, professionalize, vocationalize, corporatize, and ultimately technologize education” (Thomson, 2001 : 244), have been extensively criticised in epistemological as well as in ontological terms (Bourdieu, 1998 ; Dall’ Alba and Barnacle, 2007 ). Livingstone ( 2009 ) argues that education and labour market have different philosophical departures and institutional principles to fulfill and therefore conceptualising them as concomitant economic events, with strong causal conjunctions, leads to logical fallacies. Livingstone sees the intrinsic purposes of education and contemporary labour market as rather contradictory than complimentary and any attempt to see them as the latter, leads to arbitrary and ambiguous outcomes, which in turn mislead rather than inform policy making. The current article, building on the arguments of Durst’s ( 1999 ), Payne ( 1999 ) and Lu and Horner ( 2009 ) challenges this view introducing a “bridging” rationale between the two theories, which can be also actualized in practice and inform policy making.
When education, and especially higher education, is considered as a public social right that everyone should have access to, human capital, as solely informed by the investment approach, cannot be seen as the most appropriate tool to explain the benefits an individual and society can gain from education. Citizenship can be regarded as one of these tools and perhaps concepts, such as the social and c ultural capital or habitus , which contrary to human capital acknowledge that students are not engaged with education just to succeed high returns in the labour market but apart from the economic capital, should be of equal importance when we try to offer a better explanation of the individuals’ drivers to undertake higher education. (Bourdieu, 1986 ; Coleman, 1988 ). Footnote 2 For example, Bourdieu ( 1984 ) thinks that certificates and diplomas are neither indications of academic or applied to the labour market knowledge, nor signals of competences but rather take the form of tacit criteria set by the ruling class to identify people from a particular social origin. Yet, Bourdieu does not disregard the human capital theory as invalid; however he remains very sceptical on its narrow social meaning as it becomes a property of ruling class and used as a mechanism to maintain their power and tacitly reproduce social inequalities.
Higher education attainment cannot be examined irrespectively of someone’s capabilities, as its conceptual framework presupposes a social construction of interacting and competing individuals, fulfilling a certain and, sometimes common to all, task each time. Capabilities, certainly, exist in and out of this context, as it includes both innate traits and acquired skills in a dynamic social environment. Sen ( 1993 : 30) defines capability as “a person’s ability to do valuable acts or reach valuable states of being; [it] represents the alternative combinations of things a person is able to do or be”. Moreover, Sen argues that capabilities should not be seen only as a means for succeeding a certain goal, but rather as an end itself (Sen, 1985 ; Saito, 2003 ; Walker and Unterhalter, 2007 ).
Capabilities are a prerequisite of well-being and therefore, social institutions should direct people into fulfilling this aim in order to feel satisfied with their lives. However, since satisfaction is commonly understood as a subjective concept, it cannot be implied that equal levels of life satisfaction, as these perceived by people of different demographic and socio-economic characteristics, mean social and economic equality. Usually, the sense of life satisfaction is relative to future expectations, aspirations and past empirical experiences, informed by the socio-economic circumstances people live in (Saito, 2003 ).
According to the capability approach, assessing the educational attainment of individuals or the quality of teachers and curriculum are not such useful tasks, if not complemented by the capacity of a learner to convert resources into capabilities. Sen’s ( 1985 , 1993 ) capability approach, challenges the human capital theory, which sees education as an ordinary investment undertaken by individuals. It also remains sceptical towards structuralist and post-structruralist approaches, which support the dominance of institutional settings and power over the individual acts. According to Sen ( 1985 , 1993 ), educational outcomes, as these are measured by student enrolments, their performance on tests or their expected future income, are very poor indicators for evaluating the overall purpose of education, related to human well-being. Moreover, the capability approach does not imply that education can only enhance peoples’ capabilities. It also implies that education, can be detrimental, imposing severe life-long disadvantages to individuals and societies, if delivered poorly (Unterhalter, 2003 , 2005 ).
From Sen’s writings, it is not clear whether the capability approach imply a distinction between instrumental and intrinsic values. Even if someone attempts an interpretation of the capability approach by arguing that it is only means that have an instrumental value, whereas ends only an intrinsic one, it is still unclear how can we draw a line between means and ends in a rather objective way. Escaping from this rather dualistic interpretation, a common-sense argument seems apparent: Capabilities have both intrinsic and instrumental value. Material resources can be obtained through people’s innate talents and acquired skills; however through the same resources transformed into capabilities a person who does not see this as an end but rather as a means, can also become a trusted member of the community and a good citizen, given that some kind of freedom of choice exists. Thus, resources apart from their instrumental value can also have an intrinsic one, with the caveat that the person chooses to conceive them as means towards a socially responsible end.
The American tradition in student development goes back to the liberal arts tradition, which main aim is to build a free person as an active member of a civic society. The essence of this tradition can be found in Nussbaum ( 1998 : 8)
“When we ask about the relationship of a liberal education to citizenship, we are asking a question with a long history in the Western philosophical tradition. We are drawing on Socrates’ concept of ‘the examined life,’ on Aristotle’s notions of reflective citizenship, and above all on Greek and Roman Stoic notions of an education that is ‘liberal’ in that it liberates the mind from bondage of habit and custom, producing people who can function with sensitivity and alertness as citizens of the whole world.”
Nowadays, liberal arts tradition is regarded as the delivery of interdisciplinary education across the social sciences but also beyond that, aiming to prepare students for the challenges they are facing both as professionals and as members of civic society. However, as Kozol notes in reality things are quite different (Kozol, 2005 , 2012 ). Kozol devoted much of his work examining the social context of schools in the US by focusing on the interrelationships that exist, maintained or transformed between students, teachers and parents. He points out that segregation and local disparities in the US schools are continuously increasing. The US schools and especially urban schools are seen as distinctive examples of institutions where social discrimination propagates while the US educational system currently functions as a mechanism of reproducing social inequality. Kozol is very critical on the instrumental purpose of market-driven education as this places businesses and commerce as the “key players”, since they shape the purpose, content and curriculum of education. At the same time, students, their parents as well as teachers, whose roles should have been essential, are displaced into some kind of token participants.
Hess ( 2004 ) might agree that US schools have become vehicles of increasing social inequalities but he suggest a very different to Kozol’s approach. Since schools are social institutions that operate and constantly interact with the rest of economy they have to become accountable in the way that ordinary business are, at least when it comes to basic knowledge delivery. Hess insists that all schools across the US should be able to deliver high quality basic knowledge and literacy. Such knowledge can be easily standardised and a national curriculum, equal and identical to all US school can be designed. By this, all schools are able to deliver high quality basic knowledge and all pupils, irrespective of their social background, would be able to receive it. Then, each school, teacher and pupil are held accountable for their performance and failure to meet the national standards should result in schools closed down, teachers laid off and pupils change school environment or even lose their chance to graduate. Hess distinguishes between two types of reformers; the status quo reformers who do not challenge the state control education and the common-sense reformers who are in favour of a non-bureaucratic educational system, governed by market competition, subjected to accountability measures similar to those used in the ordinary business world.
While Hess presents evidence that the problem in higher education is not underfunding but efficiency in spending, the argument he makes that schools can only reformed and flourish through the laws of market competition is not adequately backed up as there are plenty of examples in many industrial sectors, where the actual implementation of market competition instead of opening up opportunities for the more disadvantaged, has finally generated huge multinationals corporations, which operate in a rather monopolistic or at best oligopolistic environment, satisfying their own interests on the expense of the most deprived and disadvantaged members of the society. The ever growing increasing competition in the financial, pharmaceutical or IT software and hardware (Apple Microsoft, IOS and Android software etc.) sectors have not really helped the disadvantaged or the sector itself but rather created powerful “too big to fail” corporations that dominate the market if not own it.
Hess indeed believes that the US educational system apart from preparing students for the labour market has a social role to fulfil. When the purpose of higher education is solely labour market-oriented teaching and learning become inadequate to respond to the social needs of a well-functioned civic democracy, which requires active learners and critical thinkers who, apart from having a job and a profession, are able “ to frame and express their thoughts and participate in their local and national communities”(p. 4) . Creating rigorous standards for basic knowledge in all US schools is a goal that is sound and rather achievable. However, when such goals are based on a Darwinian like competition and coercion where only the fittest can survive they become rather inapplicable for satisfying the needs of human development, equity and sustainable social progress.
Bronfenbrenner’s ecological systems theory ( 1979 , 2005 , 2009 ) (subsequently named from Bronfenbrenner himself as bioecological systems theory) is also an example of schools as organic ingredients of a single concentric system that includes four sub systems; the micro, the meso, the exo and the macro as well as the chronosystem that refers to the change of the other four through time. The Micro system involves activities and roles that are experienced through interpersonal relationships such as the family, schools, religious or social institutions or any interactions with peers. The meso system includes the relationships developed between the various microsystem components, such as the relationship between school and workplace or family and schools. The exosystem comprises various interactions between systems that the person who is in the process of development does not directly participates but influence the way microsystems function and impact on the person. Some examples of exosystems are the relationships between family and peers of the developing person, family and schools, etc. The macrosystem incorporates all these things that can be considered as cultural environment and social context in which the developing person lives. Finally, the chronosystem introduces a time dimension, which encompasses all other sub-systems, subjecting them to the changes occurred through time. All these systems constantly interact, shaping a dynamic, complex but also natural ecological environment, in which a person develops its understanding of the world. In practical terms, this theory has found application in Finland, gradually transforming the Finish educational system to such a degree that is now considered the best all over the world (Määttä and Uusiautti, 2014 ; Takala et al., 2015 ). Finally, Bronfenbrenner is also an advocate that poverty and social inequalities are developed not because of differences in individual characteristics and capabilities but because of institutional constraints that are insurmountable to those from a lower socio-economic background.
Freire ( 1970 , 2009 ) criticizes the way schooling is delivered in contemporary societies. The term he uses to describe the current state of education is “banking education”, where teachers and students have very discrete roles with the former to be perceived as depositors of knowledge and the latter as depositories. This approach sees the knowledge acquired within the institutional premises of formal education as an absolute truth, where reality is perceived as something static aiming to preserve the status quo in education and in turn in society and satisfy the interests of the elite. This actual power play means that those who hold knowledge and accept its acquiring procedure as static, become the oppressors whereas those who either lack knowledge or even hold it but challenge it in order to transform it, the oppressed. From the one side the oppressors achieve to maintain their dominance over the oppressed and on the other side the oppressed accept their inferior role as an unchallenged normality where their destiny is predetermined and can never be transformed. Therefore, through this distinction of social roles, social inequalities are maintained and even intensified through time. Freire sees the “banking education” approach as a historical hubris since social reality is a process of constant transformation and hence, it is by definition dynamic and non-static. What we actually know today cannot determine our future social roles, neither can prohibit individuals from challenging and transforming it into something new (Freire, 1970 ; Giroux, 1983 ; Darder, 2003 ).
The banking education approach resembles very much the ethos of the human capital theory, where individuals utilise educational attainment as an investment instrument for succeeding higher wages in the future and also climb the levels of social hierarchy. The assumption of linearity between past individual actions and future economic and social outcomes is at the core of banking education and thus human capital theory. However, this assumption introduces a serious logical fallacy that surprisingly policy makers seem to value very little nowadays, at least in the Western societies. Freire ( 2009 ) apart from criticizing the current state of education argues that a pedagogical approach that “demythologize” and unveils reality by promoting dialogue between teachers and students create critical thinkers, who are engaged in inquiry in order to create social reality by constantly transforming it. This is the process of problem-posing education , which aligns its meaning with the intrinsic view of education that regards human development as mainly detached from the acquisition of material objects and accumulation of wealth through increased levels of educational attainment.
Originated in Germany, the term Bildung —at least as this was interpreted from 18 th century onwards, after Middle Ages era where everything was explained in the prism of a strict and theocratic society- shaped the philosophy by which the German educational system has been functioning even until nowadays (Waters, 2016 ). Bildung aims to provide the individual education with the appropriate context, through which can reach high levels of professional development as well as citizenship. It is a term strongly associated with the liberation of mind from superstition and social stereotypes. Education is assumed to have philosophical underpinnings but it needs, as philosophy itself as a whole does too, to be of some practical use and therefore some context needs to be provided Footnote 3 (Herder, 2002 ).
For Goethe ( 2006 ) Bildung , is a self-realisation process that the individual undertakes under a specific context, which aims to inculcate altruism where individual actions are consider benevolent only if they are able to serve the general society. Although Bildung tradition, from the one hand, assumes that educational process should be contextualised, it approach context as something fluid that is constantly changing. Therefore, it sees education as an interactive and dynamic process, where roles are predetermined; however at the same time they are also amenable to constant transformation (Hegel, 1977 ). Consequently, this means that Bildung tradition is more closely to what Freire calls problem-posing education and therefore to the intrinsic notion of education. Weber ( 1968 ), looked on the Bildung tradition as a means to educate scientists to be involved in policy making and overcome the problems of ineffective bureaucracy. Waters ( 2016 ) based on his experiences with teaching in German higher education argue that the Bildung tradition is still apparent today in the educational system in Germany.
However, higher education, as an institution, involves students, teachers, administrators, policy makers, workers, businessmen, marketers and generally, individuals with various social roles, different demographic characteristics and even different socio-economic backgrounds. It comes natural that their interests can be conflicting and thus, they perceive the purpose of higher education differently.
Higher education expansion and social inequalities: contemporary trends
Higher education enrolment rates have been continuously rising for the last 30 years. In Europe, and especially in the Anglo-Saxon world, policies are directed towards widening the access to higher education to a broader population (Bowl, 2012 ). However, it is very difficult for policy-makers to design a framework towards openness in higher education, mainly due to the heterogeneity of the population the policies are targeted upon. Such population includes individuals from various socio-economic, demographic, ethnic, innate ability, talent orientation or disability groups, as well as people with very different social commitments and therefore the vested interests of each group contradict each other, rendering policy-making an extremely complicated task (CFE and Edge Hill University, 2013 ).
A collection of essays, edited by Giroux and Myrsiades ( 2001 ), provided valuable insights to the humanities and social sciences literature regarding the notion of corporate university and its implications to society’s structure. As Williams ( 2001 : 18) notes in one of this essays:
“Universities are now being conscripted directly as training grounds for the corporate workforce…university work has been more directly construed to serve not only corporate-profit agendas via its grant-supplicant status, but universities have become franchises in their own right, reconfigured to corporate management, labor, and consumer models and delivering a name-brand product”.
Chang et al. ( 2013 ) argues that institutional purposes do not always coincide with the expectations students have from their studies. In most cases, students hold a more pragmatic and instrumental understanding towards the purpose of higher education, primarily aiming for a better-paid and high quality jobs.
Arum and Roksa ( 2011 ) claim that students during their studies in higher education make no real progress in critical thinking and complex problem-solving. Nonetheless, it is notable that those who state that they seek some “deeper meaning” in higher education, looking at a broader picture of things, tend to perform better than those who see university through instrumental lenses (Entwistle and Peterson, 2004 ). These findings question the validity of the instrumental view in higher education as it seems that those that are intrinsically motivated to attend higher education, end up performing much better in higher education and also later on in the labour market. Therefore, in practice, the theoretical rivalry between the intrinsic and instrumental approach operate in a rather dialectic manner, where interactions between social actors move towards a convergence, despite the focus given by policy makers on the instrumental view.
Bourdieu ( 1984 , 1986 , 1998 , 2000 ) based on his radical democratic politics, argued that education inequalities are just a transformation of social inequalities and a way of reproduction of social status quo. Aronowitz ( 2004 ) acknowledged that the main function of public education in the US is to prepare students to meet the changes, occurred in contemporary workplaces. Even if this instrumental model involves the broad expansion of educational attainment, it also fails to alleviate class-based inequalities. He is in line with Bourdieu’s argument that social class relations are reproduced through schooling, as schools reinforce, rather than reduce, class-based inequalities. More recently, similar findings from various countries are very common in the literature (Chapman et al., 2011 ; Stephens et al., 2015 )
Apple ( 2001 ) argues that despite neoliberalism’s claims that privatisation, marketization, harmonisation and generally the globalisation of educational systems increase the quality of education, there are considerable findings in numerous studies that show that the expansion of higher education happens in tandem with the increase of income inequality and the aggravation of racial, gender and class differences. Gouthro ( 2002 ) argues that there has been a misrepresentation of the basic notions that characterise the purpose of education, such as critical thinking, justice and equity. Ganding and Apple ( 2002 ) went one step further by suggesting an alternative solution, which lies on the decentralisation of educational systems, using the “Citizen School” as an example of an educational institution, which prioritises quality in education and its provision to impoverished people. Finally, they call for a radical structural reform on educational systems worldwide, where the relationship between various social communities and the state is based on social justice and not on power.
Brown and Lauder ( 2006 ) investigated the impact of the fundamental changes on education, as related to the influence that various socio-economic and cultural factors have on policy making. Remaining sceptical against the empirical validity of human capital theory, they conclude that it cannot be guaranteed that graduates will secure employment and higher wages. Contrary to Card and Lemieux’s ( 2001 ) findings, the authors argue that when the wage-premium is not measured by averages, but is split in deciles within graduates, it is only the high-earning graduates that have experienced an increasing wage-gap during this period. Increasing incidences of over-education, due to an ever-increasing supply of graduates compared to the relatively modest growth rates of high-skilled jobs, have also been observed. Any differences in pay, between graduates and non-graduates, can be ascribed more to the stagnation of non-graduates' pay, rather than to graduates’ additional pay, because of their higher educational attainment. More recently, Mettler ( 2014 ) argues that the focus on corporate interests in policy making in the US has transformed higher education into a caste system that reproduces and also intensifies social inequalities.
There are evidence, which illustrate that families play a distinctive role in encouraging children’s abilities and traits through a warm and friendly family environment. As higher education requires a significant amount of money to be invested, families with high-income have more chances and means to promote their children’s abilities and traits as well as their career prospects, when compared with the low-income ones. Certainly, there are other factors, which can affect children’s prospects, but the advantage in favour of high-income families is relatively apparent in the empirical literature (Solon, 1999 ).
Livingstone and Stowe ( 2007 ), based on the General Social Survey (GSS), conducted an empirical study on the school completion rates partitioning individuals into family and class origin, residential area as well as race and gender. They focused on the relatively low completion rates of low-class individuals, from the inner city and rural areas of the US. Their findings reveal that working-class children are being discriminated on their school completion rates, compared with the mid- and high-class children. Race and gender discrimination has been detected in rural areas but not in inner cities and suburb areas, where the completion rates are more balanced.
Stone ( 2013 ), finally sees things from a very different perspective, where inequalities exist mainly because of simply bad luck. He argues in favour of lots, when a university has to decide whether to accept an applicant or not. Even if, an argument like this seems highly controversial, it consists of something that has been implemented in many countries, several times in the past (Hyland, 2011 ). The argument that an individual deserves a place in university just because he/she scored higher marks in a standardised sorting examination test does not prove that he/she will perform better in his/her subsequent academic tasks. Likewise, if an individual, who failed to secure a place in university due to low marks, was given a chance to enter university through a different procedure, he/she might have performed exceptionally well. Yet, human society cannot solely depend on lotteries and computer random algorithms, but sometimes, up to a certain point and in the name of fairness and transparency, there is a strong case for also looking on the merits for using one (Stone, 2013 ).
Furthermore, Lowe ( 2000 ) argued that the widening of higher education participation can create a hyper-inflation of credentials, causing their serious devaluation in the labour market. This relates to the concept of diploma disease, where labour markets create a false impression that a higher degree is a prerequisite for a job and therefore, induce individuals to undertake them only for the sake of getting a job (Dore, 1976 ; Collins, 1979 ). This situation can create a highly competitive credential market, and even if there are indications of higher education expansion, individuals from lower social class do not have equal opportunities to get a degree, which can lead them to a more prestigious occupational category. This is, in turn, very similar to the Weberian theory of educational credentialism, where credentials determine social stratum (Brown, 2003 ; Karabel, 2006 ; Douthat, 2005 ; Waters, 2012 ).
The concept of credential inflation has been extensively debated from many scholars, who question the role of formal education and the usefulness of the acquisition of skills within universities (Dore 1997 ; Collins, 1979 ; Walters, 2004 ; Hayes and Wynard, 2006 ). Evans et al. ( 2004 ) focuses on the tacit skills, which cannot be acquired by formal learning, mainly obtained by work and life experience as well as informal learning. These skills are competences related to the way a complex situation could be best approached or resemble to personal traits, which can be used for handling unforeseen situations.
Policy implications
Higher educational attainment that leads to a specific academic degree is a dynamic procedure, but with a pre-defined end. This renders the knowledge acquired there, as obsolete. Policies, such as Bologna Declaration supports an agenda, where graduates should be further encouraged to engage with on-the-job training and life-long education programmes (Coffield, 1999 ). Other scholars argue that institutions should have a broader role, acknowledging the benefits that higher educational attainment bring to societies as a whole by the simultaneous promotion of productivity, innovation and democratisation as well as the mitigation of social inequalities (Harvey, 2000 ; Hayward and James, 2004 ). Boosting employability for graduates is crucial and many international organisations are working towards the establishment of a framework, which can ensure that higher education satisfies this aim (Diamond et al., 2011 ). Yet, this can have negative side-effects making the employability gap between high- and low-skilled even wider, since there is no any policy framework specifically designed for low-skilled non-graduates on a similar to Bologna Declaration, supranational context. Heinze and Knill ( 2008 ) argue that convergence in higher education policy-making, as a result of the Bologna Process, depends on a combination of cultural, institutional and socio-economic national characteristics. Even if, it can be assumed that more equal countries, in terms of these characteristics, can converge much easier, it is still questionable if and how much national policy developments have been affected by the Bologna Declaration.
However, the political narrative of equal opportunities in terms of higher education participation rates does not seem very convincing (Brown and Hesketh, 2004 ; The Milburn Commission, 2009 ). It appears that a consensus has been reached in the relevant literature that there is a bias towards graduates from the higher social classes, but it has been gradually decreasing since 1960 (Bekhradnia, 2003 ; Tight, 2012 ). Nonetheless, despite the fact that, during the last few decades, there has been an improvement in the participation rates for the most vulnerable groups, such as women and ethnic minorities, the inequality is still obvious in some occasions (Greenbank and Hepworth, 2008 ). Machin and Van Reenen ( 1998 ) trace the causes of the under-participation in an intergenerational context, arguing that the positive relationship between parental income and participation rates is apparent even from the secondary school. Likewise, Gorard ( 2008 ) identifies underrepresentation on the previous poor school performance, which leads to early drop-outs in the secondary education, or into poor grades, which do not allow for a place in higher education. Other researchers argue that paradoxically, educational inequality persists even nowadays, albeit the policy orientation worldwide towards the widening of higher education participation across all social classes (Burke, 2012 ; Bathmaker et al., 2013 ).
There are different aspects on the purpose of higher education, which particularly, under the context of the ongoing economic uncertainty, gain some recognition and greater respect from academics and policy-makers. Lorenz ( 2006 ) notes that the employability agenda, which is constantly promoted within higher education institutions lately, cannot stand as a sustainable rationale in a diverse global environment. This harmonisation and standardisation of higher education creates permanent winners and losers, centralising all the gains, monetary and non-monetary, towards the most dominant countries, particularly towards Anglo-phone countries and specific industries and therefore social inequalities increase between as well as within countries. Some scholars call this phenomenon as Englishization (Coleman, 2006 ; Phillipson, 2009 ).
Tomusk ( 2002 , 2004 ) positioned education within the general framework of the recent institutional changes and the rapid rise of the short-term profits of the financial global capital. Specifically, the author sees World Bank as a transnational organisation. Given this, any loan agreement planned from the World Bank regarding higher education reforms in developing countries, has the same ultimate, but tacit, goal, which is the continuous rise of the national debt and in turn, the vitiation of national fiscal and monetary policies, in order the human resources of the so called “recipient countries”, to be redistributed in favour of a transnational dominant class.
Hunter ( 2013 ) places the debate under a broader political framework, juxtaposing neo-liberalism with the trends formulated by the OECD. She concludes that OECD is a very complex and multi-vocal organisation and when it comes to higher education policy suggestions, there is not any clear trend, especially towards neo-liberalism. This does not mean that economic thinking is not dominant within the OECD. This is, in fact, OECD’s main concern and it is clear to all. Hunter ( 2013 : 15–16) accordingly states that:
“Some may feel offended by the vocational and economic foci in OECD discourse. Many would like to see HE held up for “higher” ideals. However, it is fair for OECD to be concerned with economics. They do not deny that they are primarily an organization concerned with economics. It is up to us, the readers, politicians, scholars, voters, teachers, administrators, and policy makers, to be aware that this is an economic organization and be careful of from whom we get our assumptions”.
Hyslop-Margison ( 2000 ) investigated how the market economy affects higher education in Canada, when international organisations and Canadian business interfere in higher education policy making, under the support of government agencies. He argues that such economy-oriented policies deteriorate curriculum theory and development.
Letizia ( 2013 ) criticises market-oriented reforms, enacted by The Virginia Higher Education Opportunity Act of 2011, placing them within the context of market-driven policies informed by neoliberalism, where social institutions, such as higher education, should be governed by the law of free market. According to Letizia, this will have very negative implications to the humanistic character of education, affecting people’s intellectual and critical thinking, while perpetuating social inequalities.
The term Mcdonaldisation has been also used recently to capture functional similarities and trends in common, between higher education and ordinary commercial businesses. Thus, efficiency, calculability, predictability and maximisation are high priorities in the American and British educational systems and because of their global influence, these characteristics are being expanding worldwide (Hayes and Wynard, 2006 ; Garland, 2008 ; Ritzer, 2010 ).
The notion of Mcdonaldisation is very well explained by Garland ( 2008 , no pagination):
“Mcdonaldisation can be seen as the tendency toward hyper-rationalisation of these same processes, in which each and every task is broken down into its most finite part, and over which the individual performing it has little or no control becoming all by interchangeable. It may be argued that the labour processes involved in advanced technological capitalism increasingly depend on either the handling and processing of information, or provision of services requiring instrumentalised forms of communication and interaction, just as the same “professional” roles frequently consist of largely mechanized, functional tasks requiring a minimum of individual input or initiative, let alone creative or critical thought, a process illustrated in blackly comic by the 1999 film Office Space”.
Realistically, higher education cannot be solely conceptualised by the human capital approach and similar quantitative interpretations, as it has cultural, psychological, idiosyncratic and social implications. Additionally, Hoxby ( 1996 ) argued that policy environment and systems of governance in higher education play a significant role to an individuals’ decision-making process to obtain further education and unfortunately, policy makers regard this aspect as static that can never be transformed.
Lepori and Bonaccorsi ( 2013 ), following Latour and Woolgar’s ( 1979 ) rationale of the high importance of vested interest in scientific endeavours, argue that higher education trends are too complex to be reduced and captured adequately, by the use of economic indicators as related to the labour market. However, the market and money value of higher education should not be neglected, especially in developing countries, as there is evidence that it can help people escape the vicious cycle of poverty and therefore it has a practical and more pragmatic purpose to fulfil (Psacharopoulos and Patrinos, 2004 ). According to World Bank ( 2013 ), education can contribute to a significant decrease of the number of poor people globally and increase social mobility when it manages to provides greater opportunities for children coming from poor families. There are also other studies that do not only focus to strict economic factors, but also to the contribution of educational attainment to fertility and mortality rates as well as to the level of health and the creation of more responsible and participative citizens, bolstering democracy and social justice (Council of Europe, 2004 ; Osler and Starkey, 2006 ; Cogan and Derricott, 2014 ).
Mountford-Zimdars and Sabbagh ( 2013 ), analysing the British Social Attitudes (BSA) survey, offer a plausible explanation on why the widening of participation in higher education is not that easy to be implemented politically, in the contemporary western democracies. The majority of the people, who have benefited from higher educational attainment in monetary and non-monetary terms, are reluctant to support the openness of higher education to a broader population. On the contrary, those that did not succeed or never tried to secure a place in a higher education institute, are very supportive of this idea. This clash of interests creates a political perplexity, making the process of policy-making rather dubious. Therefore, the apparent paradox of the increase in higher educational attainment, along with a stable rate in educational inequalities, does not seem that strange when vested interests of certain groups are taken into account.
Moreover, the decision for someone to undertake higher education is not solely influenced by its added value in the labour market. Since an individual is exposed to different experiences and influences, strategic decisions can easily change, especially when these are taken from adolescents or individuals in their early stages of their adulthood. Given this, perceptions and preferences do change with ageing and this is why there are some individuals who drop out from university, others who choose radical shifts in their career or others who return to education after having worked in the labour market for many years and in different types of jobs.
Higher education has expanded rapidly after WWII. The advent of new technologies dictates the enhancement of people’s talents and skills and the creation of a knowledge-based-economy, which in turn, demands for even more high-skilled workers. Policy aims for higher education in the western world is undoubtedly focusing on its diffusion to a broader population. This expansion is seen as a policy instrument to alleviate social and income inequalities. However, the implementation of such policies has been proved extremely difficult in practise, mainly because of existent conflicted interests between groups of people, but also because of its institutional incapacity to target the most vulnerable. Nonetheless, it has been observed a constant marketization process in higher education, making it less accessible to people from poor economic background. Concerns on the persistence of policy-makers to focus primarily on the economic values of higher education have been increasingly expressed, as strict economic reasoning in higher education contradicts with political claims for its continuing expansion.
On the other hand, there are studies arguing that the instrumental model can make the transition of graduates into the labour market smoother. Such studies are placed under the mainstream economics framework and are also informed by policy decisions implemented by the Bologna Process, where competitiveness, harmonisation and employability are the main policy axes. The Bologna Process and various other institutions (e.g., the EU, World Bank, OECD) have provided a framework under which higher education can be seen as inextricably linked with labour market dynamics; however, the intrinsic notion of higher education is treated more as a nuisance and less as a vital component on this framework. Nevertheless, this makes the job competition between graduates much more intense and also creates very negative implications for those that remain with low qualifications as they effectively become socially and economically marginalised.
The purpose of higher education and its role in modern societies remains a heated philosophical debate, with strong practical and policy implications. This article sheds more light to this debate by presenting a synthetic narrative of the relevant literature, which can be used as a basis for future theoretical and empirical research in understanding contemporary trends in higher education as interwoven with the evolutions in the broader socio-economic sphere. Specifically, two conflicting theoretical stances have been discussed. The mainstream view primarily aims to assist individuals to increase their income and their relative position in the labour market. On the other hand, the intrinsic notion focus on understanding its purpose under ontological and epistemological considerations. Under this conceptual framework, the enhancement of individual creativity and emancipation are in conflict with the contemporary institutional settings related to power, dominance and economic reasoning. This conflict can influence people’s perceptions on the purpose of higher education, which can in turn perpetuate or otherwise revolutionise social relations and roles.
However, even if the two theoretical stances presented are regarded as contradictory, this article argues that, in practical terms, they can be better seen as complementing each other. From one hand, using an instrumental perspective, an increase in higher education participation, focusing particularly on the most vulnerable and deprived members of society, can alleviate problems of income and social inequalities. The instrumental view of education has a very important role to play if focused on lower-income social classes, as it can become the mechanism towards the alleviation of income inequalities. On the other hand, apart from the pecuniary, there are also other non-pecuniary benefits associated with this, such as the improvement in the fertility and mortality and general health level rates or the boost of active democracy and citizenship even within workplaces and therefore a shift of higher education towards its intrinsic purposes is also needed. (Bowles and Gintis, 2002 ; Council of Europe, 2004 ; Brennan, 2004 ; Brown and Lauder, 2006 ; Wolff and Barsamian, 2012 ).
Summing up, education is not a simply just another market process. It is not just an institution that supply graduates as products that have some predetermined value in the labour market. Consequently, acquired knowledge in education verified by college degrees is neither a necessary nor a sufficient condition for the labour market to create appropriate jobs, where graduates utilise and expand this knowledge. In fact, the increasing costs of higher education, mostly due to its internationalisation, and the rising levels of job mismatch create a rather gloomy picture of the current economic environment, which seems to preserve the well-paid jobs mostly to those from a certain socio-economic class background. At the same time, poor students are vastly disadvantaged to more wealthy ones, considering the huge differences in terms of higher as well as their past education, their parent’s education and also certain elitist traditions that work towards perpetuating power relations in favour of the dominant class.
As Castoriadis ( 1997 ) notes, it is impossible to separate education from its social context. We, as human beings, acquire knowledge, in the sense of what Castoriadis calls paideia , from the day we born until the day we die. We are being constantly developed and transformed along with the social transformations that happen around us. The transformation on the individual is in constant interaction with social transformations, where no cause and effect exists. Formal schooling has become nowadays an apathetic task where no real engagement with learning happens, while its major components such as educators, families and students are largely disconnected with each other. Educators, cynically execute the teaching task that a curriculum dictates each time, families’ main concern is to attach a market value to their children educational attainment, “labelling” them with a credential that the labour market allegedly desires, while students pay attention to anything else apart from the knowledge they get per se and therefore they care too little for its quality and also its practical use.
To tackle the ever-growing social inequalities due to the narrow economic policy making in education, we need a radical shift towards policies that are informed from Freire’s problem-posing education and Sen’s capabilities approach, get insights in terms of structure from Bronfenbrenner’s bioecological systems theory, while giving context according to the Bildung tradition also acknowledging that education, apart from instrument, is a vehicle towards liberation, cultural realisation as well as social transformation. In practical terms, real-world examples from Finland or Germany can be used, which policy makers from around the world should start paying more attention to, moving away from narrow and sterile instrumentalism that has spectacularly failed to tackle social inequalities.
In the context of a modern world where monetary costs and benefits are the basis of policy arguments, a massification and broader diffusion of higher education to a much broader population implies marketisation and commercialisation of its purpose and in turn its inclusion on an economy-oriented model where knowledge, skills, curriculum and academic credentials inevitably presuppose a money-value and have a financial purpose to fulfil. The policy trends towards an economy-based-knowledge, through a strict instrumental reasoning, rather than the alleged knowledge-based-economy seems to persist and prevail, albeit its poor performance on alleviating income and social inequalities. Yet, in a global context of a prolonged economic stagnation and a continuous deterioration of society’s democratic reflexes, a shift towards a model, where knowledge is not subdued to economic reasoning, can inform a new societal paradigm of a genuine knowledge-based-economy, where economy would become a means rather than an ultimate goal for human development and social progress.
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
For example, Confucian tradition is very rich, when it comes to education and human development. It is indeed very interesting to see how the basic principles of Confucian education, such as humanism, harmony and hierarchy, has been transformed through time and especially after the change in China’s economic model by Den Xiaoping’s reforms towards a more open economic system and along this a more business-oriented and globalised educational system. Perhaps the Chinese tradition in education, which mainly regards education as a route to social status and material success based on merit and constant examination can explain why the human capital theory is more applicable. On the other hand, additional notions in the Confucian tradition that education should be open to all, irrespective of the social class each person belongs to (apart perhaps from women and servants that were rather considered as human beings with limited social rights), its focus on ethics and its purpose to prepare efficient and loyal practitioners for the government introduces an apparent paradox with human capital theory but not necessarily with the instrumental view of education. This contradiction deserves to be appropriately and thoroughly examined in a separate analysis before it is contrasted to the Western tradition. For this reason the current research focuses only on the Western world leaving the comparison analysis with educational traditions found around the world, among them the Confucian tradition, as a task that will be conducted in the near future.
The use of capital in Bourdieu is criticised by a stream of social science scholars as rather promiscuous and unfortunate (Goldthorpe, 2007 ). They argue that a paradox here is apparent as in English linguistic etymological terms, the word capital implies, if not presupposes market activity. The same time Bourdieu criticises Becker’s human capital tradition as solely market-driven and a tacit way where the ruling class maintain their power through universities and other institutions. Waters ( 2012 ) argue that the use of the term “capital” in both Becker’s and Bourdieu’s writings is unfortunate, while both use the term to mean different things. Bourdieu’s understanding on the nature of “habitus” is a much more applicable term to explain the social role of education systems. Habitus is not capital, even if there is constant interaction between the two. Becker on the other hand, seem to neglect social and cultural capital as well as Bourdieu’s notion of habitus, which in turn is about the reproduction of society and power relations by universities and other institutions.
Some might have valid ontological objections on this, in terms of the purpose of philosophy as a whole; however the concept of Bildung has given education a role within society that moves away from individualism and the constant pursuit of material objects as ultimate means of well-being.
Apple M (2001) Comparing neo-liberal projects and inequality in education. Comp Educ 37(4):409–423
Article Google Scholar
Aronowitz S (2004) Against schooling: Education and social class. Soc Text 22(2):13–35
Arum R, Roksa J (2011) Academically adrift: Limited learning on college campuses. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL
Google Scholar
Barber M, Donnelly K, Rizvi S, Summers L (2013) An avalanche is coming: Higher education and the revolution ahead. Institute for Public Policy Research, London, p 78
Barnett R (2017) Constructing the university: Towards a social philosophy of higher education. Educ Philos Theory 49(1):78–88
Bathmaker AM, Ingram N, Waller R (2013) Higher education, social class and the mobilisation of capitals: Recognising and playing the game. Br J Sociol Educ 34(5-6):723–743
Becker GS (1964) Human capital: A theoretical and empirical analysis with special reference to education. National Bureau of Economic Research, New York
Becker GS (1993) Human capital: A theoretical and empirical analysis with special reference to education, 3rd edn.. National Bureau of Economic Research, Chicago
Book Google Scholar
Bekhradnia B (2003) Widening participation and fair access: An overview of the evidence. Higher Education Policy Institute, London
Bo W (2009) Education as both Inculcation and emancipation [Online] Institute of Social Economy and Culture 1-6, Peking University Education Review. Available at http://www2.hawaii.edu/~pesaconf/zpdfs/30bo.pdf
Bourdieu P (1984) Distinction: A social critique of the judgement of taste. Cambridge, MA: Harvard university press.
Bourdieu P (1986) The forms of capital. In: Richardson J (ed) Handbook of Theory and Research for the Sociology of Education. Greenwood, Westport, CT, p 241–258
Bourdieu P (1998) Practical reason: On the theory of action. Stanford University Press, Stanford, CA.
Bourdieu P (2000) Participant objectivation: Breaching the boundary between anthropology and sociology- How? Lecture on the occasion of the presentation of the Huxley Memorial Medal for 2000. Royal Anthropological Institute, London, 6 Dec
Bowl M (2012) The contribution of further education and sixth-form colleges to widening participation [Online] York: Higher Education Academy. Available at: http://www.heacademy.ac.uk/resources/detail/WP_syntheses/Bowl
Bowles S, Gintis H (2002) Schooling in capitalist America revisited. Sociol Educ 75(1):1–18
Brennan J (ed) (2004) The social role of the contemporary university: contradictions, boundaries and change. In: TenYears on: changing education in a changing world. Center for Higher Education Research and Information, Open University Press, Maidenhead, UK, p 23–54
Bridges D (1992) Enterprise and liberal education. J Philos Educ 26(1):91–98
Bronfenbrenner U (1979) The ecology of human development: experiments by nature and design. Am Psychol 32:513–531
Bronfenbrenner, U (2005). Making human beings human: bioecological perspectives on human development. Sage.
Bronfenbrenner U (2009) The ecology of human development . Harvard university press.
Brown P (2003) The opportunity trap: Education and employment in a global economy. Eur Educ Res J 2(1):141–179
Brown P, Hesketh A (2004) The mismanagement of talent: Employability and jobs in the knowledge economy. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Brown P, Lauder H (2006) “Globalisation, knowledge and the myth of the magnet economy”. Globalisation, Societies and Education 4(1):25–57
Burke PJ (2012) The right to higher education: Beyond widening participation. Routledge, Oxon
Card D, Lemieux T (2001) Can falling supply explain the rising return to college for younger men? A cohort-based analysis”. Q J Econ 116(2):705–746
Article MATH Google Scholar
Castoriadis C (1997) The Castoriadis reader. Blackwell, Oxford
CFE and Edge Hill University (2013) The uses and impact of HEFCE funding for widening participation. HEFCE, Bristol, http://www.hefce.ac.uk/media/hefce/content/pubs/indirreports/2013/usesandimpactofwpfunding/The%20uses%20and%20impact%20of%20HEFCE%20funding%20for%20widening%20participation.pdf
Chang SS, Stuckler D, Yip P, Gunnell D (2013) Impact of 2008 global economic crisis on suicide: Time trend study in 54 countries. Br Med J 347:1–15
Chapman C, Laird J, Ifill N, KewalRamani A (2011) Trends in High School Dropout and Completion Rates in the United States: 1972-2009 . Compendium Report. NCES 2012-006. National Center for Education Statistics
Coffield F (1999) Breaking the consensus: Lifelong learning and social control. Br Educ Res J 25(4):479–499
Cogan J, Derricott R (eds) (2014) Citizenship for the 21st century: An international perspective on education. Routledge, London
Coleman JA (2006) English-medium teaching in European higher education. Lang Teach 39(1):1–14
Coleman JS (1988) Social capital in the creation of human capital. Am J Sociol 94(Supplement):S95–S120
Collins R (1979) Credential society: Historical sociology of education and stratification. Academic Press, New York
Council of Europe (Ed.) (2004) All European study on education for democratic citizenship policies. Council of Europe Publishing, Strasbourg, http://www.coe.int/t/dg4/education/edc/Source/Resources/Pack/AllEuropeanStudyEDCPolicies_En.pdf
Dall’ Alba G, Barnacle R (2007) An ontological turn for higher education. Stud High Educ 32(6):679–691
Darder A (2003) The critical pedagogy reader. Psychology Press, New York
Diamond A, Walkley L, Scott-Davies S (2011) Global graduates into global leaders. CIHE, London
Dore R (1976) The diploma disease: Education, qualification and development. Allen & Unwin, London
Dore R (1997) Reflections on the diploma disease twenty years later. Assessment in Education 4(1):189–205
Dorling D, Dorling D (2015) Injustice: Why social inequality still persists. Policy Press, Bristol
Douthat RG (ed) (2005) Privilege: Harvard and the education of the ruling class. Hyperion, New York
Durkheim E (1956) Education and Sociology. Free Press, Glencoe, IL
Durkheim E (2006) Education: Its nature and its role. In: Lauder, et al. (Eds) Education, globalisation & social change. Taylor and Francis Ltd, San Francisco, p 76–88
Durst RK (1999) Collision Course: Conflict, Negotiation, and Learning in College Composition. National Council of Teachers of English, Urbana, IL
Entwistle NJ, Peterson ER (2004) Conceptions of learning and knowledge in higher education: Relationships with study behaviour and influences of learning environments. Int J Educ Res 41(6):407–428
Evans K, Hodkinson P, Unwin L (eds) (2004) Working to learn: Transforming learning in the workplace. Routledge, London
Freire P (1970) Pedagogy of the Oppressed. Herder& Herder, New York
Freire P (2009) Pedagogy of the Oppressed 30th Anniversary Eds. Continuum, New York
Ganding LA, Apple M (2002) Can education challenge neoliberalism? The citizen school and the struggle for democracy in Porto Alegre, Brazil. Social Justice 29(4):26–40
Garland C (2008) The McDonaldization of higher education: Notes on the UK experience. Fast Capitalism 4(1). Available at: http://www.uta.edu/huma/agger/fastcapitalism/4_1/garland.html
Giroux H, Myrsiades K (eds) (2001) Beyond the corporate university: Culture and pedagogy in the new millennium. Rowan and Littlefield Publishers, Lanham
Giroux HA (1983) Theory and resistance in education: A pedagogy for the opposition. Bergin & Garvey, South Hadley, MA
Goethe J (2006) The Sorrows of Young Werther. Penguin, UK, (Vol. 10)
Goldthorpe JH (2007) “Cultural Capital”: some critical observation. In: Scherer S, Pollak R, Otte G, Gangl M (eds) From Origin to Destination. Campus, Frankfurt am Main, p 78–101
Gorard S (2008) Who is missing from higher education? Camb J Educ 38(3):421–437
Gouthro PA (2002) Education for sale: At what cost? Lifelong learning and the marketplace. Int J Lifelong Educ 21(4):334–346
Graham G (2013) The university: A critical comparison of three ideal types. In: Sugden R, Valania M, Wilson JR (eds) Leadership and cooperation in academia reflecting on the roles and responsibilities of university faculty and management. Edward Elgar Publishing Limited, Cheltenham, UK, p 1–16
Greenbank P, Hepworth S (2008) Working class students, the career decision-making process: a qualitatitive study. Higher Education Careers Service Unit, Manchester
Haigh M, Clifford VA (2011) Integral vision: A multi-perspective approach to the recognition of graduate attributes. High Educ Res Dev 30(5):573–584
Harvey L (2000) New realities: The relationship between higher education and employment. Tert Educ Manag 6(1):3–17
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Hayes D, Wynard R (eds) (2006) The McDonaldization of higher education, 2nd edn. Bergin and Harvey, Westport, CT
Hayward G, James S (eds) (2004) Balancing the skills equation: Key issues for policy and practice. Policy Press, Bristol
Hegel GWF (1977) The Phenomenology of Spirit. Translated by A. V. Miller. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Heinze T, Knill C (2008) Analysing the differential impact of the Bologna Process: Theoretical considerations on national conditions for international policy convergence. High Educ 56(4):493–510
Heidegger M (1998) Plato’s doctrine of truth. In: McNeill W (ed) Pathmarks. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 155–182
Chapter Google Scholar
Herder JG (2002) Herder: Philosophical Writings. Translated and Edited by M. Foster. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hess FM (2004) Common sense school reform. Palgrave MacMillan, New York
Hoxby CM (1996) How teachers’ unions affect education production. Q J Econ 111(3):671–718
Hunter CP (2013) Shifting themes in OECD country reviews of higher education. High Educ 66(6):707–723
Hyland A ( 2011) Entry to higher education in Ireland in the 21st century. National Council for Curriculum and Assessment/Higher Education Authority (NCCA/HEA) Seminar, Discussion Paper, Cork, Ireland. 21 September 2011. Available at: http://hea.ie/assets/uploads/2017/04/Aine-Hyland_Entry-to-Higher-Education-in-Ireland-in-21st-Century-2011.pdf
Hyslop-Margison EJ (2000) The market economy discourse on education: Interpretation, impact, and resistance. Alta J Educ Res 46(3):203–213
Jongbloed B, Enders J, Salerno C (2008) Higher education and its communities: interconnections, interdependencies and a research agenda. Higher Education 56(3):303–324
Kaiser F, Maassen P, Meek L, van Vught F, de Weert E, Goedegebuure L (eds) (2014) Higher education policy: An international comparative perspective . Pergamont Press, Oxford.
Karabel J (2006) The chosen: The hidden history of admission and exclusion at Harvard, Yale, and Princeton. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Boston, MA
Kozol J (2005) The shame of the nation: The restoration of apartheid schooling in America. Crown Publishing, New York
Kozol J (2012) Savage inequalities: Children in America’s schools. Broadway Books, New York
Latour B, Woolgar S (1979) Laboratory life: The social construction of scientific facts. Sage, Beverly Hills
Lepori B, Bonaccorsi A (2013) The socio-political construction of a European Census of higher education institutions: Design, methodological and comparability Issues. Minerva 51(3):271–293
Letizia A (2013) Dialectical constellations of progress: New visions of public higher education for the twenty-first century. J Crit Thought Prax 2(1):55–82
Livingstone (2009) Education & jobs: Exploring the gaps. University of Toronto Press, Toronto
Livingstone DW, Stowe S (2007) Class, race, space, and unequal educational outcomes in the United States: Beyond dichotomies. In: Kincheloe J, Steinberg S (eds.) Cutting class: Socioeconomic status and education. Rowman and Littlefield Publishers, Plymouth, p 97–119
Lorenz C (2006) Will the universities survive the European Integration? Higher education policies in the EU and in the Netherlands before and after the Bologna Declaration. Sociologia Internationalis 44(1):1–28
Lowe J (2000) International examinations: The new credentialism and reproduction of advantage in a globalising world. Assessment in Education 7(3):363–377
Lu MZ, Horner B (2009) Composing in a global-local context: Careers, mobility, skills. Coll Eng 72(2):113–133
Määttä K, Uusiautti S (eds) (2014) Early child care and education in Finland . Routledge, Abingdon
Machin S, Van Reenen J (1998) Technology and changes in skill structure: evidence from seven OECD countries. Q J Econ 113(4):1215–1244
Mettler S (2014) Degrees of inequality: How the politics of higher education sabotaged the American dream. Basic Books, New York
Milburn AC (2009) Unleashing aspiration: the final report of the panel on fair access to the professions. Cabinet office, London
Mokyr J (2002) The gifts of Athena: Historical origins of the knowledge economy. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Mountford-Zimdars A, Sabbagh D (2013) Fair access to higher education: A comparative perspective. Comp Educ Rev 57(3):359–368
Newman JH (1996) The idea of a university. University Press, Yale
Nussbaum MC (1998) Cultivating humanity. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Osler A, Starkey H (2006) Education for democratic citizenship: A review of research, policy and practice 1995–2005. Research Papers in Education 21(4):433–466
Payne D (1999) Composition, interdisciplinary collaboration, and the postindustrial concern. JAC 19(4):607–632
Phillipson R (2009) Linguistic imperialism continued. Routledge, London and New York
Psacharopoulos G, Patrinos HA (2004) Human capital and rates of return. In: Johnes G, Johnes J (eds) International handbook on the economics of education. Elgar, Cheltenham, p 1–57
Ritzer G (2010) McDonaldization: The Reader, 3rd edn. Pine Forge Press, Thousand Oaks
Robinson K, Aronica L (2009) The element: How finding your passion changes everything. Viking, New Work
Saito M (2003) Amartya Sen’s Capability approach to education: A critical exploration. J Philos Educ 37(1):17–33
Sen A (1985) Commodities and capabilities. Oxford University Press, Amsterdam, North Holland, reprinted by Delhi
Sen A (1993) Capability and well-being. In: Nussbaum M, Sen A (eds) The Quality of Life. Clarendon Press, Oxford, p 30–53
Shapiro HT (2005) A larger sense of purpose: Higher education and society. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Solon G (1999) Intergenerational mobility in the labor market. Handbook of labor economics 3(Part A):1761–1800
Stephens NM, Brannon TN, Markus HR, Nelson JE (2015) Feeling at home in college: Fortifying school‐relevant selves to reduce social class disparities in higher education. Soc Issue Policy Rev 9(1):1–24
Stone P (2013) Access to higher education by the luck of the draw. Comp Educ Rev 57(3):577–599
Takala M, Wickman K, Uusitalo-Malmivaara L, Lundström A (2015) Becoming a special educator–Finnish and Swedish students’ views on their future professions. Educ Inq 6(1):25–51
Tight M (2012) Researching higher education. Open University Press, Maidenhead, UK
Thomson I (2001) Heidegger on ontological education, or: how we become what we are. Inquiry 44(3):243–268
Tomusk V (2002) The rise of the transnational capitalist class and World Bank “aid” for higher education. International Studies in Sociology of Education 12(3):335–352
Tomusk V (2004) Three Bolognas and a pizza pie: notes on institutionalization of the European higher education system. Int Stud Sociol Educ 14(1):75–96
Trow M (1979) Elite and mass higher education: American models and European realities. National Board of Universities, Stockholm
Trow M (2000) From mass higher education to universal access: The American advantage. Minerva 37(4):303–328
Unterhalter E (2003) The Capabilities approach and gendered education: An examination of south African complexities. Theory Res Educ 1(1):7–22
Unterhalter E (2005) Global inequality, capabilities, social justice: The millennium development goal for gender equality in education. Int J Educ Dev 25(2):111–122
Walker M, Unterhalter E (eds) (2007) Amartya Sen’s capability approach and social justice in education. Palgrave Macmillan, New York
Walters D (2004) A comparison of the labour market outcomes of postsecondary graduates of various levels and fields over a four-cohort period. Can J Sociol 29(1):1–27
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Waters T (2012) Schooling, childhood, and bureaucracy: Bureaucratizing the child. Palgrave Macmillan, New York
Waters T (2016) “Teaching like you do in America” –personal reflections from teaching across borders in Tanzania and Germany. Palgrave Communications. 1 (2015) (on-line) Available at: https://doi.org/10.1057/palcomms.2015.26
Weber M (1947) The Theory of Social and Economic Organization. Free Press, Glencoe, III
Weber M (1968) Economy and Society (2 volumes). University of California, Berkeley, CA
Westerheijden DF, Stensaker B, Rosa MJ (eds) (2007) Quality assurance in higher education: Trends in regulation, translation and transformation. Springer, Dordrecht, NL
Williams JJ (2001) Franchising the University. In: I Giroux H, Myrsiades K (eds) Beyond the corporate university: Culture and pedagogy in the new millennium. Rowan and Littlefield, Lanham, p 15–28
Wolff R, Barsamian D (2012) Occupy the economy: Challenging capitalism. City Lights Books, San Francisco
World Bank (2013) The Human Capital report. World Bank, Washington DC
Yuan L, Powell S, CETIS J (2013) MOOCs and open education: Implications for higher education. JISC CETIS (White Paper)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK
Theocharis Kromydas
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Theocharis Kromydas .
Additional information
Competing interests: The author declares that there are no competing financial interests.
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kromydas, T. Rethinking higher education and its relationship with social inequalities: past knowledge, present state and future potential. Palgrave Commun 3 , 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-017-0001-8
Download citation
Received : 14 February 2017
Accepted : 30 August 2017
Published : 13 October 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-017-0001-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Hyper-ambition and the replication crisis: why measures to promote research integrity can falter.
- Yasemin J. Erden
Journal of Academic Ethics (2024)
Differentiated socio-ecological system approach for vulnerability and adaptation assessment in the Central Himalaya
- Praveen Kumar
- Christine Fürst
- P. K. Joshi
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change (2024)
Democracy and Lifelong Learning in Africa
- Chimere O. Iheonu
- Simplice A. Asongu
Journal of the Knowledge Economy (2024)
Research- vs. government-driven physical activity policy monitoring: a systematic review across different levels of government
- Sven Messing
- Antonina Tcymbal
- Peter Gelius
Health Research Policy and Systems (2023)
The neglect of researchers during the first COVID-19 pandemic induced national lockdown in India: inside the lives of JNU’s research scholars
- Yangchen Roy
- Somashree Das
Higher Education (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

What you need to know about higher education
UNESCO, as the only United Nations agency with a mandate in higher education, works with countries to ensure all students have equal opportunities to access and complete good quality higher education with internationally recognized qualifications. It places special focus on developing countries, notably Africa.
Why does higher education matter?
Higher education is a rich cultural and scientific asset which enables personal development and promotes economic, technological and social change. It promotes the exchange of knowledge, research and innovation and equips students with the skills needed to meet ever changing labour markets. For students in vulnerable circumstances, it is a passport to economic security and a stable future.
What is the current situation?
Higher education has changed dramatically over the past decades with increasing enrolment, student mobility, diversity of provision, research dynamics and technology. Some 254 million students are enrolled in universities around the world – a number that has more than doubled in the last 20 years and is set to expand. Yet despite the boom in demand, the overall enrolment ratio is 42% with large differences between countries and regions. More than 6.4 million students are pursuing their further education abroad. And among the world’s more than 82 million refugees, only 7% of eligible youth are enrolled in higher education, whereas comparative figures for primary and secondary education are 68% and 34%, respectively ( UNHCR) . The COVID-19 pandemic further disrupted the way higher education was provided.
What does UNESCO do to ensure access for everyone to higher education?
UNESCO's work is aligned with Target 4.3 of SDG 4 which aims, by 2030, “to ensure equal access for all women and men to affordable quality technical, vocational and tertiary education, including university”. To achieve this, UNESCO supports countries by providing knowledge, evidence-based information and technical assistance in the development of higher education systems and policies based on the equal distribution of opportunities for all students.
UNESCO supports countries to enhance recognition, mobility and inter-university cooperation through the ratification and implementation of the Global Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications concerning Higher Education and regional recognition conventions . To tackle the low rate of refugee youth in higher education UNESCO has developed the UNESCO Qualifications Passport for Refugees and Vulnerable Migrants , a tool which makes it easier for those groups with qualifications to move between countries. The passport brings together information on educational and other qualifications, language, work history. UNESCO places a special focus on Africa with projects such as the Higher Technical Education in Africa for a technical and innovative workforce supported by China Funds-in-Trust.
How does UNESCO ensure the quality of higher education?
The explosion in demand for higher education and increasing internationalization means UNESCO is expanding its work on quality assurance, helping Member States countries to establish their own agencies and mechanisms to enhance quality and develop policies particularly in developing countries and based on the Conventions. Such bodies are absent in many countries, making learners more vulnerable to exploitative providers.
It also facilitates the sharing of good practices and innovative approaches to widen inclusion in higher education. As part of this work, it collaborates with the International Association of Universities to produce the World Higher Education Database which provides information on higher education systems, credentials and institutions worldwide.
How does UNESCO keep pace with digital change?
The expansion of connectivity worldwide has boosted the growth of online and blended learning, and revealed the importance of digital services, such as Artificial Intelligence, Big Data and Higher Education Management Information Systems in helping higher education institutions utilize data for better planning, financing and quality.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this transformation and increased the number of providers and the range of degree offerings from cross-border to offshore education. The Organization provides technical support and policy advice on innovative approaches to widening access and inclusion including through the use of ICTs and by developing new types of learning opportunities both on-campus and online.
How does UNESCO address the needs of a changing job market?
Labour markets are experiencing rapid changes, with increased digitization and greening of economies, but also the rising internationalization of higher education. UNESCO places a strong emphasis on developing science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) education, indispensable to sustainable development and innovation. It aims to strengthen skills development for youth and adults, particularly literacy, TVET, STEM and higher education to meet individual, labour market and societal demands.
Related items
- Higher education
Reimagining higher education in the United States
Higher education in the United States is at an inflection point. The core mission of the university—instruction, research, and service—has not changed. Nor has the need for advanced education to prepare individuals for a fulfilling life and to drive the knowledge economy. For individuals, the economic benefit of earning a college degree remains clear. College graduates are on average wealthier, healthier, and happier over a lifetime. 1 William R. Emmons, Ana H. Kent, and Lowell R. Ricketts, “Is college still worth it? The new calculus of falling returns,” Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Review, 2019, Volume 101, Number 4, pp. 297–329, stlouisfed.org.
Even before the COVID-19 crisis, however, the higher-education sector faced significant challenges. Consider student completion: only 60 percent of all those who started college actually earned a degree within six years in 2017 (the latest year for which data is available). The figures are even worse for Black (39.9 percent) and Hispanic (54.4 percent) students. Other troubling disparities persist. In student enrollment, for example, 69 percent of white high-school graduates enroll in college, compared with 59 percent of Black high-schoolers and 61 percent of Hispanics. Furthermore, the level of student debt is rising, while repayment rates plummet, creating a potentially unsustainable burden for many students.
The pandemic is intensifying these challenges and creating new ones. Students and their families are struggling with the impact of campus shutdowns and questioning whether it is worth it to pay for an on-campus experience when much of the instruction is being done remotely. Under these circumstances, the risk of outcome inequities—from completion to employment to lifetime earnings—could worsen. For example, evidence suggests that lower-income students are 55 percent more likely than their higher-income peers to delay graduation 2 Esteban Aucejo et al.,“The impact of COVID-19 on student experiences and expectations: Evidence from a survey,” Journal of Public Economics , August 2020, sciencedirect.com. due to the COVID-19 crisis. Underpinning all of these challenges is a business model at its breaking point, as institutions face falling revenues and rising health-and-safety costs.
In short, the coronavirus has confirmed the case for fast and fundamental change. It has also demonstrated that change is possible. When the pandemic hit, many US colleges and universities moved quickly to remote learning and other delivery models, launched affordability initiatives, and found creative ways to support their students. Now is the time to build on these lessons to reimagine the next five to ten years and beyond.
With that in mind, we pose five questions for US higher-education leaders to address as they look to the future. For each question, we describe the current conventional wisdom and then make the case for challenging it—to the benefit of students, faculty, staff, institutions, and society.
What makes our university distinctive?
The conventional wisdom: To successfully attract students and maintain competitive national rankings, colleges and universities must be well rounded.
National-ranking systems emphasize admissions selectivity, small class sizes, per-student spending, and standardized test scores. Focusing on this narrow set of variables can incentivize institutions to make strategic and operational choices that may boost their rankings without necessarily improving their core educational missions. It may also lead to greater homogenization in the higher-education landscape.
Instead, there may be more benefit to creating thoughtful differentiation, building on the institution’s existing strengths, resources, and local context. The question to ask is: “What should my institution be known for?” There are many ways to differentiate, including student mix and outcomes, faculty development, research capabilities, facilities, and community impact. Doing so may serve institutions and their students better than the conventional wisdom for three reasons.
First, identifying and prioritizing what makes an institution distinctive can be a competitive advantage that attracts committed students and faculty. Second, specializing—doing fewer things better—could improve outcomes. And third, creating a distinctive profile can be a source of resilience, enabling institutions to survive after a crisis.
Such differentiation will be critical given the trends that are challenging the higher-education sector. One trend is the coming “demographic cliff”—the number of high-school graduates in the United States will peak at around 3.6 million students in 2026 and then decline to 3.3 million students by 2030. Another is the drop, since 2016, in international-student enrollment, an important source of revenues for many colleges. The COVID-19 crisis could well accelerate this decline. A third trend is the competition for research funding. In terms of the percentage of GDP and of budget allocation, federal investment in R&D has fallen steadily since the 1960s (although it has risen in absolute terms, and in the past two decades, nonfederal investment has grown, too). Moreover, about 35 percent of federal funding went to just 22 schools in 2018. Given these constraints, leaders need to ask how research can serve their institutions and identify where they stand the best chance of attracting faculty and funding.
By defining their areas of distinction and then directing resources to support them, higher-education institutions can set themselves apart—making them stronger and enabling them to deliver high-quality programs and outcomes.
How can we build a diverse and inclusive institution?
The conventional wisdom: Current efforts are likely to fulfill diversity and inclusion (D&I) goals in a reasonable time frame.
Higher-education institutions have been at the forefront of recognizing, and taking steps to foster, D&I. Many feature chief diversity officers, D&I curriculum requirements, and training sessions on implicit bias, as part of the growing diversity infrastructure. Even so, there are sizeable gaps. College enrollment and completion rates for Black and Hispanic students are much lower than for their white or Asian counterparts. Another area to address is the student experience itself. According to a 2019 study, Black, Hispanic, and first-generation students report a lower sense of belonging at four-year schools (but not at two-year schools). 3 Shannon T. Brady et al., “College students’ sense of belonging: A national perspective,” Educational Researcher , 2020, Volume 49, Number 2, pp. 134–37, sagepub.com.
Faculty composition is even less representative. In 2017, only 6 percent of full-time faculty in degree-granting postsecondary institutions were Black and 6 percent were Hispanic, compared with 14 percent and 18 percent of the US population, respectively. Women make up only 33 percent of full-time professors.
Doing more of the same, then, is not enough, and time is of the essence because of changing student demographics. Between the 2012–13 and the 2031–32 academic years, the proportion of high-school graduates who identify as Asian and Hispanic will grow to 31 percent, from 24 percent, of all students.
There is evidence from the business sector that prioritizing D&I as a core value is sound management. McKinsey research has consistently found that businesses with top-quartile diversity on executive teams were likelier to have superior results; in the latest results from the 2019 study, companies with top-quartile ethnic and gender diversity were 36 percent and 25 percent, respectively, more likely to have above-average profitability. While the analogy between executive teams and higher education administrations is not precise, it is likely that campuses, like the C-suite, would benefit from a more diverse leadership composition.
Current higher-education D&I efforts are necessary yet insufficient, particularly given how the COVID-19 crisis is disproportionately impacting the lives, livelihoods, and education of Black and Hispanic Americans. Leaders must, therefore, act with a sense of urgency, seeking opportunities to strengthen D&I across their institutions—from redesigning student recruitment to updating faculty-performance measurement to account for the significant roles that under-represented faculty often play in mentoring to the social and academic experiences to postgraduate success. To do so may require new strategic initiatives and accountability measures, such as sharing the breakdown of tenure appointments by ethnicity and creating programs to encourage opportunities for intergroup dialogue and promote cross-race understanding. 4 This constitutes McKinsey’s view on best practices and optimized environments. Legal restrictions, however, could affect universities’ ability to adopt them; they should consult their legal counsel to understand any implications created by the recent “Executive Order on Combating Race and Sex Stereotyping,” September 22, 2020, whitehouse.gov.
What services are necessary to create a high-quality student experience? And what aren’t?
The conventional wisdom: In addition to learning, higher-education institutions must be responsive to a wide range of student wants and needs.
The core mission of colleges and universities is instruction, research, and service. In recent decades, though, many have engaged in the so-called student-amenities arms race, with expansive offerings in areas such as entertainment, gourmet dining, and wellness. Higher-education institutions want to deliver an enjoyable experience, and of course some student services are essential, especially those related to physical and mental health. But it is notable that since at least 2010, the costs for student services have risen much faster than costs for instruction and research (Exhibit 1). While this spending does include some core services, this trend may no longer be sustainable for many institutions.
Spending on student services has been growing four times as fast as spending on instruction.
Chart summary.
Although more than half of total spending at four-year universities was invested in research and instruction, growth over ten years since 2007 showed 0.3% less was spent on research and only 0.5% more on instruction. Meanwhile, 8.5% of the total was invested in student services 4 , the largest area of growth in spending per student (2.1%) over ten years.
1 Adjusted for inflation.
2 Includes expenses for the day-to-day operational support of the institution. Includes expenses for general administrative services, central executive-level activities concerned with management and long-range planning, legal and fiscal operations, space management, employee personnel and records, logistical services such as purchasing and printing, and public relations and development.
3 Includes expenses for activities and services that support the institution's primary missions of instruction, research, and public service.
4 Includes expenses for admissions, registrar activities, and activities whose primary purpose is to contribute to students' emotional and physical well-being and to their intellectual, cultural, and social development outside the context of the formal instructional program. Examples include student activities, cultural events, student newspapers, intramural athletics, student organizations, supplemental instruction outside the normal administration, and student records.
Source: College Scorecard; Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis (CPI); National Center for Education Statistics Trend Generator
McKinsey & Company
One of the most difficult things to do on a college campus is to stop doing something. That said, some institutions have shown how to make such tradeoffs. Spelman College, for example, announced in 2012 that it would drop competitive intercollegiate sports in favor of expanding campus-wide health and fitness programs. This exact tradeoff is being faced again, and some institutions are making the difficult choice to trim athletics; most notably, in July 2020, Stanford announced it will permanently cut 11 athletics programs.
While students surely appreciate things like luxury gyms and other services, there is a need to distinguish between what students like and what is necessary to serve the core education mission. Given the budget stresses of the COVID-19 crisis, higher-education institutions may want to consider providing fewer, better ancillary services, while keeping the broader well being of their students in mind.
What delivery channels and models should we use to fulfill our core educational mission?
The conventional wisdom: The best college experiences and educational outcomes are delivered in person, on a residential campus.
The quad, the ivy, the lecture hall, the dorm, the tailgate parties: these are some of the well-known totems of the quintessential college experience. These images are ingrained; they are also part of the reason why many (and maybe most) traditional four-year, higher-education institutions were slow to adopt new methods and technologies, such as remote instruction and competency-based learning that have the potential to advance student success while also lowering costs.
Global private investment in learning-technology companies has been growing fast, from $2 billion in 2012 to $19 billion in 2019. Areas such as online-learning management systems and innovations such as virtual-lab applications and immersive story learning are beginning to spread. And the COVID-19 crisis hustled even reluctant students and institutions into action. In 2018, only about 35 percent of undergraduates took a distance-education course. This year, that figure is close to 100 percent, as the pandemic forced the adoption of remote learning.
In 2018, only about 35 percent of undergraduates took a distance-education course. This year, that figure is close to 100 percent.
Institutional acceptance of the online delivery model also may be increasing. According to a poll of 2,000 US faculty members by Inside Higher Ed and Gallup in October 2019 5 Doug Lederman, “Professors’ slow, steady acceptance of online learning: A survey,” Inside Higher Education, October 30, 2019, insidehighered.com. —that is, well before the COVID-19 crisis—39 percent fully supported the increased use of education technologies, up from 29 percent in 2017. And a national survey of more than 4,000 faculty members earlier this year 6 “Time for class: COVID-19 edition,” Tyton Partners, July 2020, everylearnereverywhere.org. found that 45 percent had a better opinion of remote learning since the pandemic began; fewer than one in five (17 percent) had a more negative perception.
Remote and online learning are here to stay. The need is to determine what combination of remote and in-person learning delivers the highest educational quality and equity. As institutions refine this hybrid model, they have a once-in-a-generation chance to reconfigure their use of physical and virtual space. They may be able to reduce the number of large lecture halls, for example, and convert them into flexible working pods or performance spaces. Or they could reimagine the academic calendar, offering instruction into the summer months.
What is our business model?
The conventional wisdom: The current higher-education business model, which relies heavily on ongoing tuition increases, can be sustained.
For decades, the financial model of US colleges and universities rested on two revenue streams. Student tuition and fees were the most important; the rest came from a mix of different sources, such as athletics, research grants, endowments, and government appropriations, that varied greatly. Both revenue streams are now under stress. These unprecedented times require a reimagined business model that protects the core educational mission and financial viability of the institution, while limiting economic burdens on students.
As mentioned, athletics, research grants, and other revenue sources are sputtering in the pandemic. But the bigger stress is on tuition and fees, which comprise at least half of revenues for about 55 percent of four-year private nonprofit institutions in the United States; meanwhile they account for more than a third of revenues for about 30 percent of public institutions. Even before the COVID-19 crisis, administrators realized that they had limited scope to increase tuition; now it has become even more difficult to do so.
Two issues threaten the traditional tuition-reliant financial model. First, there is affordability. To offer financial aid, institutions manage a complicated pricing system in which higher-income and international students effectively subsidize needier ones. This lack of price transparency feeds into the perception of the increasing costs—and unaffordability—of college. In fact, from 2007–17, net costs rose only 4 percent , reversing the trend of previous decades. Yet the perception of unaffordability means that some young people might be discouraged from trying to attend: they see the high sticker prices and assume that they are priced out.
Second, there are also questions around the value of higher education when debt levels and repayment rates are considered. Median student debt levels have climbed by 45 percent since 2006, while repayment rates have dropped by 24 percent since 2009 (Exhibit 2). The situation appears to be worsening; in 2016, only 6 percent of students were at colleges where students left with moderate debt and managed high repayment rates, compared with 54 percent in 2009. The situation is even worse for students who incur debt but don’t graduate and, therefore, don’t benefit from the income-raising advantage of a degree.
The COVID-19 crisis could accelerate these trends. In our April 2020 student survey , 45 percent of prospective students cited cost as extremely important in selecting a college, 44 percent of students who switched schools between January and April did so to save money, and 30 percent reported that the COVID-19 crisis was likely to have a strong or extremely strong impact on their ability to afford college.
Another important factor is to ensure students realize an economic return on their investment in higher education; without that assurance, young people will not be willing to enroll in the first place, or finish. Colleges are under pressure to ensure that students don’t just graduate with a degree, but with a pathway to sustainable employment that secures a reasonable standard of living.
Given these financial constraints, it is not surprising to see consolidation. Since 2000, there have been about 100 higher-education mergers in the United States, 7 John Hanc, “For some colleges, the best move is to merge,” October 10, 2019, New York Times , nytimes.com. and more are likely. The Pennsylvania State University system, 8 Jan Murphy, “Pa. state system of higher education exploring costs of combining some universities,” July 16, 2020, Patriot-News , pennlive.com. for example, is considering restructuring the different institutions in the system. Properties, buildings, and talent from less-affluent campuses may well become available. An interesting example comes from Connecticut, where three schools are buying the assets of the University of Bridgeport 9 Goldie Blumenstyk, “The edge: As colleges’ finances get shakier, what lessons does this ‘sorta’ merger offer?”, July 8, 2020, Chronicle of Higher Education , chronicle.com. ; the latter’s academic programs will continue for the time being, while other operations, such as the library and security, are shared.
The opportunity—indeed, the necessity—is to reimagine higher education financials so that students do not find themselves mired in debt. There is little room to increase tuition, and there are also challenges to other revenue sources, such as athletics and research funding; education leaders must therefore ask how they can reevaluate their spending and/or reallocate existing resources.
Colleges and universities must reimagine their business models and consider new ways to operate—either on a standalone basis or through partnerships that accomplish the same goals, at lower cost.
How do we challenge the conventional wisdom?
Higher-education leaders face a complex situation, negotiating how to manage the COVID-19 crisis in a context of economic, demographic, and technological challenges. At the same time, universities have a reputation for making decisions slowly. “It’s easier to change the course of history,” the saying goes, “than it is to change the history course.” The deliberate, and deliberative, nature of university governance has many benefits, but it can also be a hindrance to decisive action. That said, many university leaders have reacted creatively and swiftly to meet the challenge of protecting their communities’ health while delivering on their educational mission.
Three mechanisms can help universities to sustain this momentum: planning, stakeholder engagement, and board governance:
- Plan ahead. Responding to a crisis like the COVID-19 pandemic requires leaders to take decisive short-term actions. But they also need to dedicate time to develop longer-term strategic thinking. One way to do so is to create plan-ahead teams that include people identified as future leaders. The team should be tasked with developing scenarios, recommending actions, and identifying trigger points for escalation to the university’s board and administrative leadership.
- Stakeholder engagement. Universities should engage early and often with important stakeholder groups—including faculty, staff, students, and parents—when making critical strategic decisions. Leaders must be transparent about decision-making processes, establish clear timelines, and meet them. By embedding engagement into decision making, rather than as an afterthought, the shared governance culture of higher education can be respected, while still allowing universities to act quickly.
- Board governance. In moments of crisis, boards can play a critical role. But that role must not slip into micro-management. Board members should evaluate their operating model—the board’s size, structure, and decision rights—to ensure they provide the necessary governance without interfering with administrators.
This is not the first time, nor will it be the last, that universities will need to adapt. “The inertia of a massive university is formidable,” noted Harvard President Charles W. Eliot in his inaugural address. “A good past is positively dangerous, if it makes us content with the present, and so unprepared for the future.”
President Eliot made those remarks in 1869. The time to prepare for a new future is now.
André Dua is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Miami office; Jonathan Law is a senior partner in the New York office; Ted Rounsaville is a senior expert in the Washington, DC, office; and Nadia Viswanath is a consultant in the San Francisco office.
The authors wish to thank Arthur Bianchi and Kathleen Zhu for their contributions to this article, as well as the hundreds of university leaders who shared their experiences and perspectives with us.
Explore a career with us

Search the United Nations
- UNAI Principles
- Map of UNAI Members
- List of UNAI Members
- Special Series
- Select UN Events
- UNAI Events
- SDGs Best Practices
- SDGs Guidelines
- SDGs Training Sessions
- SDGs Workshops
- The Why Join Guide
- Tools for Researchers
- Bulletin Board
- Submit the 2024 Activity Report
- Become a Millennium Fellow
- UNAI Voices
- Sustainable Development Goals
- UN Agencies
- UN Information Centres
- Dag Hammarskjöld Library
- UN Stories Archive
- UN Publications
- Internships

The Role of Higher Education Institutions in the Transformation of Future-Fit Education
Education is a critical driver of the 2030 Agenda . Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) including universities and colleges worldwide are preparing future professionals, conducting meaningful research, and engaging with the community and stakeholders to tackle local, national, regional, and global challenges. These HEIs are at the forefront of the solutions required to advance the Sustainable Development Goals, which underscores the fundamental role of education in creating healthy and inclusive societies as envisioned in the 2030 Agenda.
The role of HEIs is not confined to that exclusively of higher education per se. In practice, the contribution of HEIs is quite significant to creating a continuum between all levels of education while training future and current teachers, making curricula adjustments and developing new curricula, nurturing ideas and new pedagogical approaches, instilling fundamental values through various learning methods and platforms, and cultivating innovations -including technological ones- to improve the educational experience and educational outcomes.
The debate about the education we need for the future largely depends on the complexities we face and the several conflicting crises and emergencies around us. In this sense, universities and colleges are very well placed to assess such challenges and how they can be addressed. To analyze this, the United Nations Academic Impact (UNAI) within the context of the Transforming Education Summit convened by the United Nations, co-organized this event to be hosted by the Center for Global Affairs of New York University , a UNAI member institution in the United States:
Topic: THE ROLE OF HIGHER EDUCATION INSTITUTIONS IN THE TRANSFORMATION OF FUTURE-FIT EDUCATION
Date: Thursday, 22 September 2022
Time: 10am - 12:30pm (EDT/New York time)
Venue: New York University (United States), with broadcast (further details to be announced prior to the event)
RSVP/Registration form: Click here
Those who would like to attend this event in-person will need to upload proof of vaccination and booster if eligible to the New York University (NYU) portal and show a "Green" Daily Screener pass upon entry to the campus. Attendees will also be required to follow any mask requirements or COVID-19-related protocols in place. Attendees will receive more information via e-mail about accessing the campus 1-2 weeks before the event.
As of now, registrations for attending in-person are no longer possible.
Please note that UNAI cannot cover travel-related expenses to attend this event, if you decide to do so in-person.
No certificate of attendance or participation will be provided.
**************************************************************************************************************************************
First panel: The role of higher education in the transformation of education for the realization of the SDGs
- Mr. Robert Skinner , Deputy Director and Chief of Partnerships and Global Engagement at the Outreach Division of the United Nations Department for Global Communications
Presenters:
- Dr. Carolyn Kissane , Clinical Professor, Academic Director of the graduate programs in Global Affairs and Global Security, Conflict and Cybercrime at the Center for Global Affairs, and Director of the SPS Energy, Climate Justice and Sustainability Lab of New York University (United States)
- Mr. Sarmad Khan , Board Director of the Academic Council on the United Nations System. Co-author of the upcoming book The Sustainable University of the Future: Reimagining Higher Education and Research . Former Head and Senior Policy Adviser of the Resident Coordinator System Leadership Branch at the United Nations Development Operations Coordination Office.
- Dr. Patrick Paul Walsh , Vice President of Education and Director of the SDG Academy at the Sustainable Development Solutions Network. Professor of International Development Studies and Director of the Centre for Sustainable Development Studies at the University College Dublin (Ireland)
- Dr. Mette Morsing , Head of Principles for Responsible Management Education - PRME) at the United Nations Global Compact. Previous Professor, Misum Chair and Executive Director of the Misum Center for Sustainable Markets, Stockholm School of Economics (Sweden)
- Dr. Priyadarshani Joshi , Senior Research Officer at the Global Education Monitoring Report of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization – UNESCO. Specialist on Non-State Actors in Education and Education’s Role in the Sustainable Development Goals
Second panel: Best practices and case studies from the UNAI SDG Hubs
- Dr. Waheguru Pal Singh , Clinical Professor and Director of the United Nations Specialization at the Center for Global Affairs of New York University (United States). Co-Author of the book The Future of Global Affairs Managing Discontinuity, Disruption and Destruction [2021]
- Prof. Juan José Vásquez , Legal Advisor and Professor of Conflict Resolution, Peace and Mediation at the University for Peace (Costa Rica) / SDG Hub for Goal 12
- Prof. Katja Enberg , Professor at the Department of Biological Sciences of the University of Bergen (Norway) / SDG Hub for Goal 14
- Prof. Sheryl Hendriks , Professor and Head of the Department of Agricultural Economics, Extension and Rural Development at the University of Pretoria (South Africa) / SDG Hub for Goal 2
- Dr. Jonas Richard , Professor and Head of the Department of Social Work at Kristu Jayanti College (India) / SDG Hub for Goal 1

Goal of the Month | May 2024: Goal 15 - Life on Land

How UNAI SDG Hub 7 is setting a tree planting initiative against climate change
Since 2020, the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Energy Policy and Development Centre (KEPA) has led a tree planting initiative to celebrate the anniversary of the United Nations. In its first phase includes the planting of 4,984 trees that correspond to more than 105 tons of sequestrated CO2 per year, showcasing that trees are the silent allies for facing climate change. KEPA continues to serve as UNAI SDG Hub 7, to participate in the efforts to ensure access to clean and affordable energy for all.

Panel discussion on "Strengthening Gender Equality in Generative AI"
This event aimed to facilitate a discourse on academic research related to generative AI with a specific focus on advancing, promoting, and safeguarding gender equality. It will delve into the incorporation of human flaws, such as gender bias, into generative AI systems and emphasize the responsibility of academia and users in ensuring gender equality within these applications.
UNITED NATIONS
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights
TAKE ACTION
- Lazy Person's Guide
- UN Volunteers
- Youth Engagement
- Past Contests and Scholarships
- Request a Speaker
- Visit the UN
NEWS AND MEDIA
- UN News Centre
- Press Releases
- Office of the Spokesperson
- UN in Action
- UN Social Media
- The Essential UN
ISSUES AND CAMPAIGNS
- SDG of the Month
- Observances and Commemorations
- Celebrity Advocates for the UN
The following navigation utilizes arrow, enter, escape, and space bar key commands. Left and right arrows move through main tier links and expand / close menus in sub tiers. Up and Down arrows will open main tier menus and toggle through sub tier links. Enter and space open menus and escape closes them as well. Tab will move on to the next part of the site rather than go through menu items.
Due to system maintenance, users will be unable to log into airweb.org December 12–14, 2022. If you need assistance, please email [email protected].
- Duties and Functions of Institutional Research
Introduction
The professionalization of the field of institutional research (IR) has expanded rapidly since 1966 when AIR was incorporated as the professional association for institutional researchers. In today’s economy, where data and information are valued and those who assist organizations in utilizing these data and information to make informed decisions are seen as assets, the field of IR looks to continue its importance in higher education institutions, systems, and organizations. The following list of Duties & Functions of Institutional Research was developed by AIR, with input from members, to continue the process of defining the function of IR to explain and assess our work. While not all offices of IR, or all institutional researchers, will necessarily be tasked with all the duties and functions listed, and some may be tasked with duties and functions not listed, an effective institutional research function at an institution, system, or organization will include all of these aspects. We invite you to consider, discuss, and utilize this list to reflect on your work. As the project progresses, this webpage will act as a repository of resources and companion materials to the list.
Download the Duties and Functions List
Download the Duties and Functions list as a a (pdf) PDF , or use the Word version as a handout and add your own IR information to the back (Use the Save As feature to download the document).
For more information on how the list was developed, view the Development of the Duties and Functions of IR PDF.
Duties and Functions
Identify information needs.


Collect, analyze, interpret, and report data and information

Plan and evaluate

Serve as stewards of data and information

Educate information producers, users, and consumers

- Professional Overview
- Submit A Post
- EdTech Trainers and Consultants
- Your Campus EdTech
- Your EdTech Product
- Your Feedback
- Your Love for Us
- EdTech Product Reviews
ETR Resources
- Mission/Vision
- Testimonials
- Our Clients
- Press Release
Role and Need of Research in Higher Education
On hear of the term higher education one thing that makes a lot of significance is the outcome from the learning that has been done in those crucial years.
Students investing in higher education must be given exposure and opportunities to be able to use all that knowledge to evolve themselves as well as be able to contribute in the discipline with better research, studies and other discoveries made.
The pointers mentioned below implies the role and need of research in higher education and why research must be a part of every higher education institution.
1. Teaching will improve if the staff engages in research (research-based teaching):
The first argument emphasizes on the necessity of research oriented teaching. Educators engaged in research are updated with latest information and updated facts instead of all that is mentioned in a book years old. It is essential that teachers engage in research to come out with latest and original information but also when they expect students to be research oriented they must have familiarity with various aspects to the concept. Also, educators familiar with research based teaching can help students with the following things:
– Teaching research results
– Making research known
– Showing what it means to be a researcher
– Helping to conduct research
– Providing research experience
2. Students will learn more if they come into contact with research (research-based learning):
Students when involved in research based learning are bound to learn more and better than they would without the integration of research. Students start as consumers of knowledge and move toward knowledge producers in the following eight steps.
– Students are provided with an overview of the basic facts, terms, and ideas related to the discipline.
– Students learn about research findings in the (sub) field through lectures and readings dedicated to current research.
– Students discuss and critique research findings and approaches in the discipline or (sub) field; assignments include literature reviews or summaries.
– Students learn some research methodologies; engage in limited applications of those approaches in course assignments, such as statistical analyses.
– Students learn in a course dedicated to the research methodologies, engage in extensive applications of a variety of approaches.
– Students engage in faculty designed and led original (to the student) research such as replications of existing studies.
– Students engage in faculty designed and led original research such as research related to faculty projects and/or conducted in faculty labs.
– Students engage in student designed and led original (to the discipline) research such as a senior thesis or capstone project
3. Professional practice will improve if professional workers in their training learn how to base their work on research-based knowledge (research-based practice):
This highlights the importance of hiring professionals who are familiar with research based practice. Having trainers who can help the current staff to make research based modules is also essential. To integrate the practice of research it is important to learn how to base curriculum aligned to the practice of research.
4. Professional programs have an obligation to improve the knowledge basis of professional work through research (research-based knowledge production):
The main concern of this point is the importance of doing research to enhance ‘evidence-based’ knowledge. The need of this practice is to help students learn with hands-on experience and not just what’s said and done but speak and do!
What to do for more research based teaching –learning
– Deciding that education and research are equally important.
– Appointing at least one university professor of research education.
– Establishing a university Centre for Teaching and Learning.
– Building a university Teaching and Learning House.
– Linking research and teaching committees.
– Bridging any divides between research staff and teaching staff.
– Appointing only academics who excel in both research and teaching.
– Strengthening positive attitudes towards research by students among staff and students.
– Making resources available for students to do research.
– Making it possible that libraries give information literacy instruction to students.
– Offering opportunities and incentives for teachers for further development of their ‘research based’ teaching competence and excellence.
– Creating and stimulating opportunities for dissemination of successful practices.
– Recognizing teaching excellence.
– Introducing an undergraduate student research award.
– Monitoring the growth of ‘research-based’ teaching.
– Ordering and financing more research of the teaching-research nexus and of research-based teaching and learning in particular.
Universities can improve the relevance of the education and can better prepare the students for follow-up studies and to the new and emerging demands of the labor market in the twenty-first century. Moreover, a close intertwining of teaching and research strengthens their identity. Academics can help students by engaging them in research to better develop highly valued competencies. More research-based teaching can also make teaching more attractive for academics and can make teaching instrumental to the academics’ own research.
“Re-inventing Research-Based Teaching and Learning by Henk Dekker and Sylvia Walsarie Wolff” is a paper prepared for presentation at the meeting of the European Forum for Enhanced Collaboration in Teaching of the European University Association from December 2016. This is a must read to get to the depths of understanding about the need and importance of research in higher education.
Don’t forget to share your views on the importance of research in higher education. Make a mention in the comment section below!
Latest EdTech News To Your Inbox
Stay connected.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
- Open access
- Published: 08 May 2024
Measurement and analysis of change in research scholars’ knowledge and attitudes toward statistics after PhD coursework
- Mariyamma Philip 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 512 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
134 Accesses
Metrics details
Knowledge of statistics is highly important for research scholars, as they are expected to submit a thesis based on original research as part of a PhD program. As statistics play a major role in the analysis and interpretation of scientific data, intensive training at the beginning of a PhD programme is essential. PhD coursework is mandatory in universities and higher education institutes in India. This study aimed to compare the scores of knowledge in statistics and attitudes towards statistics among the research scholars of an institute of medical higher education in South India at different time points of their PhD (i.e., before, soon after and 2–3 years after the coursework) to determine whether intensive training programs such as PhD coursework can change their knowledge or attitudes toward statistics.
One hundred and thirty research scholars who had completed PhD coursework in the last three years were invited by e-mail to be part of the study. Knowledge and attitudes toward statistics before and soon after the coursework were already assessed as part of the coursework module. Knowledge and attitudes towards statistics 2–3 years after the coursework were assessed using Google forms. Participation was voluntary, and informed consent was also sought.
Knowledge and attitude scores improved significantly subsequent to the coursework (i.e., soon after, percentage of change: 77%, 43% respectively). However, there was significant reduction in knowledge and attitude scores 2–3 years after coursework compared to the scores soon after coursework; knowledge and attitude scores have decreased by 10%, 37% respectively.
The study concluded that the coursework program was beneficial for improving research scholars’ knowledge and attitudes toward statistics. A refresher program 2–3 years after the coursework would greatly benefit the research scholars. Statistics educators must be empathetic to understanding scholars’ anxiety and attitudes toward statistics and its influence on learning outcomes.
Peer Review reports
A PhD degree is a research degree, and research scholars submit a thesis based on original research in their chosen field. Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degrees are awarded in a wide range of academic disciplines, and the PhD students are usually referred as research scholars. A comprehensive understanding of statistics allows research scholars to add rigour to their research. This approach helps them evaluate the current practices and draw informed conclusions from studies that were undertaken to generate their own hypotheses and to design, analyse and interpret complex clinical decisions. Therefore, intensive training at the beginning of the PhD journey is essential, as intensive training in research methodology and statistics in the early stages of research helps scholars design and plan their studies efficiently.
The University Grants Commission of India has taken various initiatives to introduce academic reforms to higher education institutions in India and mandated in 2009 that coursework be treated as a prerequisite for PhD preparation and that a minimum of four credits be assigned to one or more courses on research methodology, which could cover areas such as quantitative methods, computer applications, and research ethics. UGC also clearly states that all candidates admitted to PhD programmes shall be required to complete the prescribed coursework during the initial two semesters [ 1 ]. National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS) at Bangalore, a tertiary care hospital and medical higher education institute in South India, that trains students in higher education in clinical fields, also introduced coursework in the PhD program for research scholars from various backgrounds, such as basic, behavioral and neurosciences, as per the UGC mandate. Research scholars undertake coursework programs soon after admission, which consist of several modules that include research methodology and statistical software training, among others.
Most scholars approach a course in statistics with the prejudice that statistics is uninteresting, demanding, complex or involve much mathematics and, most importantly, it is not relevant to their career goals. They approach statistics with considerable apprehension and negative attitudes, probably because of their inability to grasp the relevance of the application of the methods in their fields of study. This could be resolved by providing sufficient and relevant examples of the application of statistical techniques from various fields of medical research and by providing hands-on experience to learn how these techniques are applied and interpreted on real data. Hence, research methodology and statistical methods and the application of statistical methods using software have been given much importance and are taught as two modules, named Research Methodology and Statistics and Statistical Software Training, at this institute of medical higher education that trains research scholars in fields as diverse as basic, behavioural and neurosciences. Approximately 50% of the coursework curriculum focused on these two modules. Research scholars were thus given an opportunity to understand the theoretical aspects of the research methodology and statistical methods. They were also given hands-on training on statistical software to analyse the data using these methods and to interpret the findings. The coursework program was designed in this specific manner, as this intensive training would enable the research scholars to design their research studies more effectively and analyse their data in a better manner.
It is important to study attitudes toward statistics because attitudes are known to impact the learning process. Also, most importantly, these scholars are expected to utilize the skills in statistics and research methods to design research projects or guide postgraduate students and research scholars in the near future. Several authors have assessed attitudes toward statistics among various students and examined how attitudes affect academic achievement, how attitudes are correlated with knowledge in statistics and how attitudes change after a training program. There are studies on attitudes toward statistics among graduate [ 2 , 3 , 4 ] and postgraduate [ 5 ] medical students, politics, sociology, ( 6 – 7 ) psychology [ 8 , 9 , 10 ], social work [ 11 ], and management students [ 12 ]. However, there is a dearth of related literature on research scholars, and there are only two studies on the attitudes of research scholars. In their study of doctoral students in education-related fields, Cook & Catanzaro (2022) investigated the factors that contribute to statistics anxiety and attitudes toward statistics and how anxiety, attitudes and plans for future research use are connected among doctoral students [ 13 ]. Another study by Sohrabi et al. (2018) on research scholars assessed the change in knowledge and attitude towards teaching and educational design of basic science PhD students at a Medical University after a two-day workshop on empowerment and familiarity with the teaching and learning principles [ 14 ]. There were no studies that assessed changes in the attitudes or knowledge of research scholars across the PhD training period or after intensive training programmes such as PhD coursework. Even though PhD coursework has been established in institutes of higher education in India for more than a decade, there are no published research on the effectiveness of coursework from Indian universities or institutes of higher education.
This study aimed to determine the effectiveness of PhD coursework and whether intensive training programs such as PhD coursework can influence the knowledge and attitudes toward statistics of research scholars. Additionally, it would be interesting to know if the acquired knowledge could be retained longer, especially 2–3 years after the coursework, the crucial time of PhD data analysis. Hence, this study compares the scores of knowledge in statistics and attitude toward statistics of the research scholars at different time points of their PhD training, i.e., before, soon after and 2–3 years after the coursework.
Participants
This is an observational study of single group with repeated assessments. The institute offers a three-month coursework program consisting of seven modules, the first module is ethics; the fifth is research methodology and statistics; and the last is neurosciences. The study was conducted in January 2020. All research scholars of the institute who had completed PhD coursework in the last three years were considered for this study ( n = 130). Knowledge and attitudes toward statistics before and soon after the coursework module were assessed as part of the coursework program. They were collected on the first and last day of the program respectively. The author who was also the coordinator of the research methodology and statistics module of the coursework have obtained the necessary permission to use the data for this study. The scholars invited to be part of the study by e-mail. Knowledge and attitude towards statistics 2–3 years after the coursework were assessed online using Google forms. They were also administered a semi structured questionnaire to elicit details about the usefulness of coursework. Participation was voluntary, and consent was also sought online. The confidentiality of the data was assured. Data were not collected from research scholars of Biostatistics or from research scholars who had more than a decade of experience or who had been working in the institute as faculty, assuming that their scores could be higher and could bias the findings. This non funded study was reviewed and approved by the Institute Ethics Committee.
Instruments
Knowledge in Statistics was assessed by a questionnaire prepared by the author and was used as part of the coursework evaluation. The survey included 25 questions that assessed the knowledge of statistics on areas such as descriptive statistics, sampling methods, study design, parametric and nonparametric tests and multivariate analyses. Right answers were assigned a score of 1, and wrong answers were assigned a score of 0. Total scores ranged from 0 to 25. Statistics attitudes were assessed by the Survey of Attitudes toward Statistics (SATS) scale. The SATS is a 36-item scale that measures 6 domains of attitudes towards statistics. The possible range of scores for each item is between 1 and 7. The total score was calculated by dividing the summed score by the number of items. Higher scores indicate more positive attitudes. The SAT-36 is a copyrighted scale, and researchers are allowed to use it only with prior permission. ( 15 – 16 ) The author obtained permission for use in the coursework evaluation and this study. A semi structured questionnaire was also used to elicit details about the usefulness of coursework.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics such as mean, standard deviation, number and percentages were used to describe the socio-demographic data. General Linear Model Repeated Measures of Analysis of variance was used to compare knowledge and attitude scores across assessments. Categorical data from the semi structured questionnaire are presented as percentages. All the statistical tests were two-tailed, and a p value < 0.05 was set a priori as the threshold for statistical significance. IBM SPSS (28.0) was used to analyse the data.
One hundred and thirty research scholars who had completed coursework (CW) in the last 2–3 years were considered for the study. These scholars were sent Google forms to assess their knowledge and attitudes 2–3 years after coursework. 81 scholars responded (62%), and 4 scholars did not consent to participate in the study. The data of 77 scholars were merged with the data obtained during the coursework program (before and soon after CW). Socio-demographic characteristics of the scholars are presented in Table 1 .
The age of the respondents ranged from 23 to 36 years, with an average of 28.7 years (3.01), and the majority of the respondents were females (65%). Years of experience (i.e., after masters) before joining a PhD programme ranged from 0.5 to 9 years, and half of them had less than three years of experience before joining the PhD programme (median-3). More than half of those who responded were research scholars from the behavioural sciences (55%), while approximately 30% were from the basic sciences (29%).
General Linear Model Repeated Measures of Analysis of variance was used to compare the knowledge and attitude scores of scholars before, soon after and 2–3 after the coursework (will now be referred as “later the CW”), and the results are presented below (Table 2 ; Fig. 1 ).
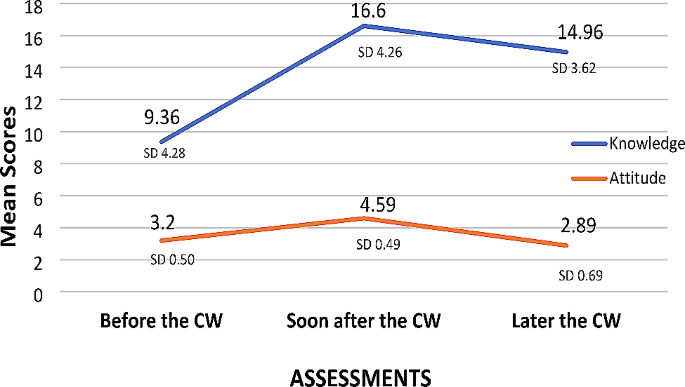
Comparison of knowledge and attitude scores across the assessments. Later the CW – 2–3 years after the coursework
The scores for knowledge and attitude differed significantly across time. Scores of knowledge and attitude increased soon after the coursework; the percentage of change was 77% and 43% respectively. However, significant reductions in knowledge and attitude scores were observed 2–3 years after the coursework compared to scores soon after the coursework. The reduction was higher for attitude scores; knowledge and attitude scores have decreased by 10% and 37% respectively. The change in scores across assessments is evident from the graph, and clearly the effect size is higher for attitude than knowledge.
The scores of knowledge or attitude before the coursework did not significantly differ with respect to gender or age or were not correlated with years of experience. Hence, they were not considered as covariates in the above analysis.
A semi structured questionnaire with open ended questions was also administered to elicit in-depth information about the usefulness of the coursework programme, in which they were also asked to self- rate their knowledge. The data were mostly categorical or narratives. Research scholars’ self-rated knowledge scores (on a scale of 0–10) also showed similar changes; knowledge improved significantly and was retained even after the training (Fig. 2 ).
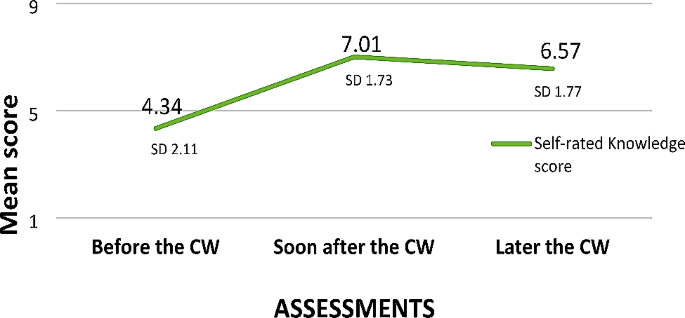
Self-rated knowledge scores of research scholars over time. Later the CW – 2–3 years after the coursework
The response to the question “ How has coursework changed your attitude toward statistics?”, is presented in Fig. 3 . The responses were Yes, positively, Yes - Negatively, No change – still apprehensive, No change – still appreciate, No change – still hate statistics. The majority of the scholars (70%) reported a positive change in their attitude toward statistics. Moreover, none of the scholars reported negative changes. Approximately 9% of the scholars reported that they were still apprehensive about statistics or hate statistics after the coursework.
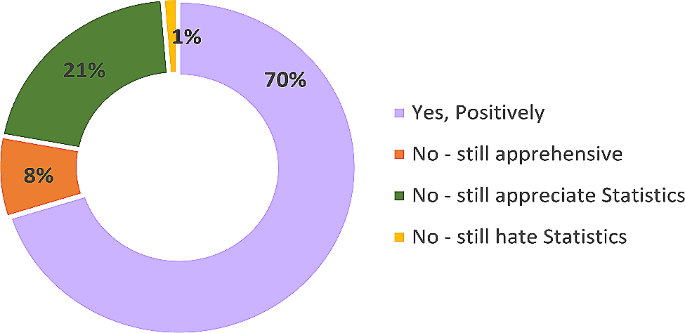
How has coursework changed your attitude toward statistics?
Those scholars who reported that they were apprehensive about statistics or hate statistics noted the complexity of the subject, lack of clarity, improper instructions and fear of mathematics as major reasons for their attitude. Some responses are listed below.
“The statistical concepts were not taught in an understandable manner from the UG level” , “I am weak in mathematical concepts. The equations and formulae in statistics scare me”. “Lack of knowledge about the importance of statistics and fear of mathematical equations”. “The preconceived notion that Statistics is difficult to learn” . “In most of the places, it is not taught properly and conceptual clarity is not focused on, and because of this an avoidance builds up, which might be a reason for the negative attitude”.
Majority of the scholars (92%) felt that coursework has helped them in their PhD, and they were happy to recommend it for other research scholars (97%). The responses of the scholars to the question “ How was coursework helpful in your PhD journey ?”, are listed below.
“Course work gave a fair idea on various things related to research as well as statistics” . “Creating the best design while planning methodology, which is learnt form course work, will increase efficiency in completing the thesis, thereby making it faster”. “Course work give better idea of how to proceed in many areas like literature search, referencing, choosing statistical methods, and learning about research procedures”. “Course work gave a good idea of research methodology, biostatistics and ethics. This would help in writing a better protocol and a better thesis”. “It helps us to plan our research well and to formulate, collect and plan for analysis”. “It makes people to plan their statistical analysis well in advance” .
This study evaluated the effectiveness of the existing coursework programme in an institution of higher medical education, and investigated whether the coursework programme benefits research scholars by improving their knowledge of statistics and attitudes towards statistics. The study concluded that the coursework program was beneficial for improving scholars’ knowledge about statistics and attitudes toward statistics.
Unlike other studies that have assessed attitudes toward statistics, the study participants in this study were research scholars. Research scholars need extensive training in statistics, as they need to apply statistical tests and use statistical reasoning in their research thesis, and in their profession to design research projects or their future student dissertations. Notably, no studies have assessed the attitudes or knowledge of research scholars in statistics either across the PhD training period or after intensive statistics training programs. However, the findings of this study are consistent with the findings of a study that compared the knowledge and attitudes toward teaching and education design of PhD students after a two-day educational course and instructional design workshop [ 14 ].
Statistics educators need not only impart knowledge but they should also motivate the learners to appreciate the role of statistics and to continue to learn the quantitative skills that is needed in their professional lives. Therefore, the role of learners’ attitudes toward statistics requires special attention. Since PhD coursework is possibly a major contributor to creating a statistically literate research community, scholars’ attitudes toward statistics need to be considered important and given special attention. Passionate and engaging statistics educators who have adequate experience in illustrating relatable examples could help scholars feel less anxious and build competence and better attitudes toward statistics. Statistics educators should be aware of scholars’ anxiety, fears and attitudes toward statistics and about its influence on learning outcomes and further interest in the subject.
Strengths and limitations
Analysis of changes in knowledge and attitudes scores across various time points of PhD training is the major strength of the study. Additionally, this study evaluates the effectiveness of intensive statistical courses for research scholars in terms of changes in knowledge and attitudes. This study has its own limitations: the data were collected through online platforms, and the nonresponse rate was about 38%. Ability in mathematics or prior learning experience in statistics, interest in the subject, statistics anxiety or performance in coursework were not assessed; hence, their influence could not be studied. The reliability and validity of the knowledge questionnaire have not been established at the time of this study. However, author who had prepared the questionnaire had ensured questions from different areas of statistics that were covered during the coursework, it has also been used as part of the coursework evaluation. Despite these limitations, this study highlights the changes in attitudes and knowledge following an intensive training program. Future research could investigate the roles of age, sex, mathematical ability, achievement or performance outcomes and statistics anxiety.
The study concluded that a rigorous and intensive training program such as PhD coursework was beneficial for improving knowledge about statistics and attitudes toward statistics. However, the significant reduction in attitude and knowledge scores after 2–3 years of coursework indicates that a refresher program might be helpful for research scholars as they approach the analysis stage of their thesis. Statistics educators must develop innovative methods to teach research scholars from nonstatistical backgrounds. They also must be empathetic to understanding scholars’ anxiety, fears and attitudes toward statistics and to understand its influence on learning outcomes and further interest in the subject.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
UGC Regulations on Minimum Standards and Procedure for the award of, M.Phil/Ph D, Degree R. 2009. Ugc.ac.in. [cited 2023 Oct 26]. https://www.ugc.ac.in/oldpdf/regulations/mphilphdclarification.pdf .
Althubaiti A. Attitudes of medical students toward statistics in medical research: Evidence from Saudi Arabia. J Stat Data Sci Educ [Internet]. 2021;29(1):115–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/10691898.2020.1850220 .
Hannigan A, Hegarty AC, McGrath D. Attitudes towards statistics of graduate entry medical students: the role of prior learning experiences. BMC Med Educ [Internet]. 2014;14(1):70. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-14-70 .
Hasabo EA, Ahmed GEM, Alkhalifa RM, Mahmoud MD, Emad S, Albashir RB et al. Statistics for undergraduate medical students in Sudan: associated factors for using statistical analysis software and attitude toward statistics among undergraduate medical students in Sudan. BMC Med Educ [Internet]. 2022;22(1):889. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-022-03960-0 .
Zhang Y, Shang L, Wang R, Zhao Q, Li C, Xu Y et al. Attitudes toward statistics in medical postgraduates: measuring, evaluating and monitoring. BMC Med Educ [Internet]. 2012;12(1):117. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-12-117 .
Bechrakis T, Gialamas V, Barkatsas A. Survey of attitudes towards statistics (SATS): an investigation of its construct validity and its factor structure invariance by gender. Int J Theoretical Educational Pract. 2011;1(1):1–15.
Google Scholar
Khavenson T, Orel E, Tryakshina M. Adaptation of survey of attitudes towards statistics (SATS 36) for Russian sample. Procedia Soc Behav Sci [Internet]. 2012; 46:2126–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.05.440 .
Coetzee S, Van Der Merwe P. Industrial psychology students’ attitudes towards statistics. J Industrial Psychol. 2010;36(1):843–51.
Francesca C, Primi C. Assessing statistics attitudes among College Students: Psychometric properties of the Italian version of the Survey of attitudes toward statistics (SATS). Learn Individual Differences. 2009;2:309–13.
Counsell A, Cribbie RA. Students’ attitudes toward learning statistics with R. Psychol Teach Rev [Internet]. 2020;26(2):36–56. https://doi.org/10.53841/bpsptr.2020.26.2.36 .
Yoon E, Lee J. Attitudes toward learning statistics among social work students: Predictors for future professional use of statistics. J Teach Soc Work [Internet]. 2022;42(1):65–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/08841233.2021.2014018 .
Melad AF. Students’ attitude and academic achievement in statistics: a Correlational Study. J Posit School Psychol. 2022;6(2):4640–6.
Cook KD, Catanzaro BA. Constantly Working on My Attitude Towards Statistics! Education Doctoral Students’ Experiences with and Motivations for Learning Statistics. Innov High Educ. 2023; 48:257–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10755-022-09621-w .
Sohrabi Z, Koohestani HR, Nahardani SZ, Keshavarzi MH. Data on the knowledge, attitude, and performance of Ph.D. students attending an educational course (Tehran, Iran). Data Brief [Internet]. 2018; 21:1325–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.08.081 .
Chau C, Stevens J, Dauphine T. Del V. A: The development and validation of the survey of attitudes toward statistics. Educ Psychol Meas. 1995;(5):868–75.
Student attitude surveys. and online educational consulting [Internet]. Evaluationandstatistics.com. [cited 2023 Oct 26]. https://www.evaluationandstatistics.com/ .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the participants of the study and peers and experts who examined the content of the questionnaire for their time and effort.
This research did not receive any grants from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Biostatistics, Dr. M.V. Govindaswamy Centre, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore, 560 029, India
Mariyamma Philip
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Mariyamma Philip: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Writing- Original draft, Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mariyamma Philip .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study used data already collected data (before and soon after coursework). The data pertaining to knowledge and attitude towards statistics 2–3 years after coursework were collected from research scholars through the online survey platform Google forms. The participants were invited to participate in the survey through e-mail. The study was explained in detail, and participation in the study was completely voluntary. Informed consent was obtained online in the form of a statement of consent. The confidentiality of the data was assured, even though identifiable personal information was not collected. This non-funded study was reviewed and approved by NIMHANS Institute Ethics Committee (No. NIMHANS/21st IEC (BS&NS Div.)
Consent for publication
Not applicable because there is no personal information or images that could lead to the identification of a study participant.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Philip, M. Measurement and analysis of change in research scholars’ knowledge and attitudes toward statistics after PhD coursework. BMC Med Educ 24 , 512 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05487-y
Download citation
Received : 27 October 2023
Accepted : 29 April 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05487-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Knowledge of statistics
- Attitude towards statistics
- PhD coursework
- Research scholars
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
ChatGPT in higher education - a synthesis of the literature and a future research agenda
- Open access
- Published: 02 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Pritpal Singh Bhullar 1 ,
- Mahesh Joshi 2 &
- Ritesh Chugh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0061-7206 3
1571 Accesses
33 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
ChatGPT has emerged as a significant subject of research and exploration, casting a critical spotlight on teaching and learning practices in the higher education domain. This study examines the most influential articles, leading journals, and productive countries concerning citations and publications related to ChatGPT in higher education, while also shedding light on emerging thematic and geographic clusters within research on ChatGPT’s role and challenges in teaching and learning at higher education institutions. Forty-seven research papers from the Scopus database were shortlisted for bibliometric analysis. The findings indicate that the use of ChatGPT in higher education, particularly issues of academic integrity and research, has been studied extensively by scholars in the United States, who have produced the largest volume of publications, alongside the highest number of citations. This study uncovers four distinct thematic clusters (academic integrity, learning environment, student engagement, and scholarly research) and highlights the predominant areas of focus in research related to ChatGPT in higher education, including student examinations, academic integrity, student learning, and field-specific research, through a country-based bibliographic analysis. Plagiarism is a significant concern in the use of ChatGPT, which may reduce students’ ability to produce imaginative, inventive, and original material. This study offers valuable insights into the current state of ChatGPT in higher education literature, providing essential guidance for scholars, researchers, and policymakers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Mapping the global evidence around the use of ChatGPT in higher education: A systematic scoping review

ChatGPT and the digitisation of writing
The Educational Affordances and Challenges of ChatGPT: State of the Field
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
ChatGPT, or Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer, is a popular generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) chatbot developed by OpenAI, employing natural language processing to deliver interactive human-like conversational experiences (Jeon et al., 2023 ; Angelis et al., 2023 ). ChatGPT utilises a pre-trained language learning model, derived from an extensive big-data corpus, to predict outcomes based on a given prompt (Crawford et al., 2023 ; Geerling et al., 2023 ; Li et al., 2023 ). Since its inception, ChatGPT has attracted widespread attention and popularity and has the potential to disrupt the education sector (Rana, 2023 ). According to a research survey of adults conducted by the Pew Research Centre, approximately 60% of adults in the United States and 78% of adults in Asia possess knowledge of ChatGPT; furthermore, men are more familiar with ChatGPT than women (Vogels, 2023 ). The study also found that among ethnic groups globally, individuals of Asian descent have the highest level of familiarity with AI-based large language models (LLMs).
People have found value in using ChatGPT for a wide range of purposes, including generating creative content, answering questions, providing explanations, offering suggestions, and even having casual conversations (Crawford et al., 2023 ; Throp, 2023 ; Wu et al., 2023 ). Furthermore, ChatGPT is an effective digital assistant for facilitating a thorough understanding of diverse and intricate subjects using simple and accessible language. Given these features, ChatGPT has the potential to bring about a paradigm shift in traditional methods of delivering instruction and revolutionise the future of education (Tlili et al., 2023 ). ChatGPT stands out as a promising tool for open education, enhancing the independence and autonomy of autodidactic learners through personalised support, guidance, and feedback, potentially fostering increased motivation and engagement (Firat, 2023 ). Its capabilities encompass facilitating complex learning, asynchronous communication, feedback provision, and cognitive offloading (Memarian & Doleck, 2023 ).
However, the rapid expansion of ChatGPT has also aroused apprehensions in the academic world, particularly after reports surfaced that the New York Department of Education had unexpectedly imposed a ban on access to the tool due to concerns about academic integrity violations (Sun et al., 2023 ; Neumann et al., 2023 ; Crawford et al., 2023 ). Students who use ChatGPT to produce superior written assignments may have an unfair advantage over peers who lack access (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Cotton et al., 2023 ). Ethical concerns about the deployment of LLMs include the potential for bias, effects on employment, misuse and unethical deployment, and loss of integrity. However, there has been little research on the potential dangers that a sophisticated chatbot such as ChatGPT poses in the realm of higher education, particularly through the lens of a systematic literature review and bibliometric techniques.
In this light, this paper explores the literature on the application of ChatGPT in higher education institutions and the obstacles encountered in various disciplines from the perspectives of both faculty and students. The paper aims to analyse the current state of the field by addressing the following overarching research questions using bibliographic coupling, co-occurrence analysis, citation analysis, and co-authorship analysis:
What are the most influential articles in terms of citations in research related to ChatGPT in education?
What are the top journals and countries in terms of publication productivity related to the implications of ChatGPT in higher education institutions?
What are the emerging thematic clusters in research on the role and challenges of ChatGPT in teaching and learning in higher education institutions?
What are the geographic clusters in research on the role and challenges of ChatGPT in teaching and learning in higher education institutions?
2 Methodology
In conducting this study, publications on the impact of ChatGPT on various aspects of higher education institutions were systematically identified through an extensive search using Elsevier’s Scopus database, a comprehensive repository hosting over 20,000 globally ranked, peer-reviewed journals (Mishra et al., 2017 ; Palomo et al., 2017 ; Vijaya & Mathur, 2023 ). Scopus is a widely used database for bibliometric analyses and is considered one of the “largest curated databases covering scientific journals” (pg. 5116) in different subject areas (Singh et al., 2021 ). Widely acclaimed for its comprehensive coverage, Scopus has been extensively employed in bibliometric analyses across diverse disciplines, as evidenced by studies in capital structure theories, business research, entrepreneurial orientation and blockchain security (Bajaj et al., 2020 ; Donthu et al., 2020 ; Gupta et al., 2021 ; Patrício & Ferreira, 2020 ). Notably, despite the “extremely high” correlation between the Web of Science and Scopus databases, Scopus’s status as a superior and versatile data source for literature extraction is reinforced by its broader coverage of subject areas and categories compared to the narrower journal scope of Web of Science, facilitating scholars in locating literature most pertinent to the review area (Archambault et al., 2009 ; Paul et al., 2021 ). To ensure a systematic literature review, we adhered to the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) guidelines (Page et al., 2021 ) for the search, identification, selection, reading, and data extraction from the articles retrieved through the Scopus database (Fig. 1 ). Reliance on a single database is acceptable within the PRISMA framework (Moher et al., 2009 ).
Employing Boolean-assisted search queries, we aimed to capture a comprehensive range of topics related to ChatGPT’s impact on higher education institutions. Specific search queries were carefully selected to ensure a broad yet relevant search scope and included the following:
“ChatGPT and Teaching learning in universities” OR “Effect of ChatGPT in higher education institution” OR “ChatGPT and student assessment in higher education” OR “ChatGPT and academic integrity” OR “ChatGPT and teaching pedagogy in higher education institution” OR “ChatGPT and cheating student course assignment” OR “ChatGPT and teaching in higher education” OR “Implications of ChatGPT in higher education institutions” OR “ChatGPT and evaluation criteria in higher education institution” OR “ChatGPT in universities” OR “ChatGPT and student learnings. ”
The study includes papers published and included in the Scopus database on or before May 26, 2023 on the theme of ChatGPT and higher education. This timeframe was chosen to encompass the most recent and relevant literature available up to the point of data retrieval. Papers identified through the search queries underwent inclusion or exclusion based on predetermined criteria. Specifically, only papers published in journals were considered for this study, as these undergo a peer-review process and are subject to stringent selection criteria set by the journals, ensuring their quality and reliability. Papers in conference proceedings were excluded from the start of the search. Only papers written in English were included to maintain consistency and clarity, whereas others were excluded. Of the 48 research papers that were initially identified, 47 were ultimately selected for the bibliometric analysis, which was conducted using VOSviewer, a bibliometric analysis tool.
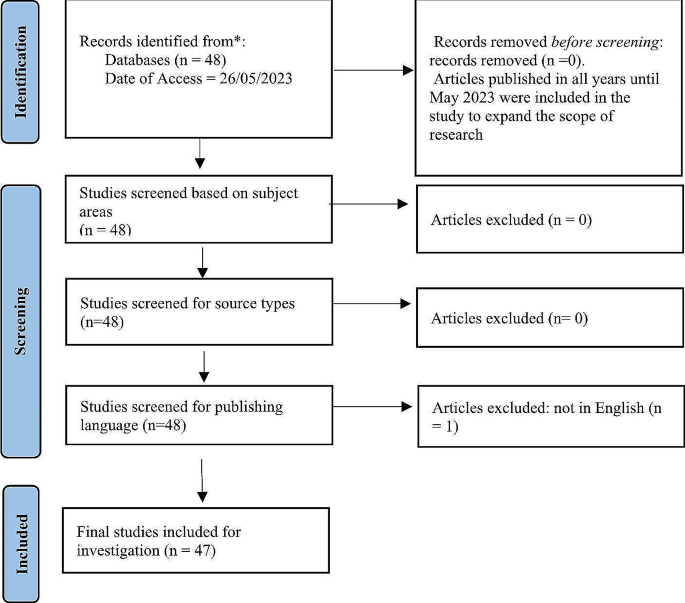
PRISMA Flowchart
From the identified pool of 47 articles, the analysis uncovered a nuanced distribution of research methodologies. Specifically, 11 studies were grounded in quantitative research methodologies, underscoring a quantitative focus within the literature. In contrast, a substantial majority of 31 articles embraced a qualitative framework, showcasing a diverse spectrum that included pure qualitative research, editorials, letters to the editor, and opinion pieces. Furthermore, the review brought to light four literature reviews, signifying a synthesis of existing knowledge, and identified one study that strategically employed a mixed-methods approach, blending both qualitative and quantitative research techniques.
To address the research questions, the selected publications underwent analysis using various bibliometric techniques. For the first and second research questions, citation analysis was employed. For the third and fourth research questions, bibliographic analysis was performed in VOSviewer software to generate clusters.
3 Findings and discussion
3.1 publication trend.
Information from the Scopus database indicates that academics began focusing on investigating various aspects of ChatGPT’s potential in higher education in 2022, as they published their findings in 2023. All academic articles in reputable publications in the Scopus database were published in 2023.
3.2 Citation analysis
Table 1 presents the top ten articles according to the number of citations. The number of articles increased significantly in 2023, consistent with the emerging nature and growing relevance of the topic. Exploring the ramifications of ChatGPT in higher education is a recent focal point for scholars, with numerous aspects warranting deeper investigation. The limited citation count, as anticipated, underscores that publications from 2023 are in the early stages of gaining visibility and recognition within the academic community.
The article by Thorp ( 2023 ), entitled “ChatGPT is fun, but not an author”, has received the highest number of citations (79). Thorp stresses the risks associated with implementing ChatGPT in the classroom. Although ChatGPT is an innovative AI tool, significant barriers remain to its implementation in the field of education. According to Thorp, using ChatGPT in academic writing is still inefficient. Thorp also expresses concerns about the rising prevalence of ChatGPT in the fabrication of scientific publications. The second most-cited work, “How Does ChatGPT Perform on the United States Medical Licensing Examination?” by Gilson and colleagues, has received 27 citations. Gilson et al. ( 2023 ) evaluated the accuracy, speed and clarity of ChatGPT’s responses to questions on the United States Medical Licensing Examination’s Step 1 and Step 2 tests. The text responses generated by ChatGPT were evaluated using three qualitative metrics: the logical justification of the chosen answer, the inclusion of information relevant to the question, and the inclusion of information extraneous to the question. The model attained a level of proficiency comparable to that of a third-year medical student. The study demonstrates the potential utility of ChatGPT as an interactive educational resource in the field of medicine to facilitate the acquisition of knowledge and skills. Third is Kasneci et al.’s article “ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education”, with 13 citations. This paper examines the benefits and drawbacks of using language models in the classroom from the perspectives of both teachers and students. The authors find that these comprehensive language models can serve as a supplement rather than a replacement for classroom instruction. Each of the remaining top-ten articles mentioned the impact of ChatGPT on academic integrity in education and had received fewer than ten citations at the time of analysis.
Table 2 presents the top 10 journals in terms of the number of citations of publications related to the topic of ChatGPT in higher education. The journal Science , which published “ChatGPT is fun, but not an author,” was deemed most influential because it received the highest number of citations (79). JMIR Medical Education has published two articles that have been cited by 30 other research articles on the same topic. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practise has published the most articles: three. Innovations in Education and Teaching International has published two articles on this topic, which together have been cited by six articles.
As shown in Table 3 , the majority of research articles pertaining to ChatGPT and higher education have originated from countries in Asia. Six of the top 10 countries for publishing articles on this topic are located in the Asian continent. However, the most influential studies in terms of citations have been produced by the United States, Germany, Australia, and the United Kingdom. Combined, these countries have received a total of 63 citations, with individual counts of 36, 17, 7, and 7, respectively. These four countries have 90% of the total citations of the top 10 most productive countries in the field of research on higher education perspectives on ChatGPT.
3.3 Bibliographic coupling
3.3.1 thematic clusters.
Four thematic clusters (TCs) were identified from the included research articles, as shown in Table 4 . VOSviewer was used to perform clustering based on bibliographic coupling. This method identifies relations between documents by examining publications that cite the same sources (Boyack & Klavans, 2010 ). VOSviewer clusters articles with a common knowledge base, assigning each publication to exactly one cluster. To implement this clustering technique, we assessed the co-occurrence of bibliographic references among articles within our dataset. Co-occurrence was determined by identifying shared references between articles, indicating a thematic connection (Boyack & Klavans, 2010 ). Articles sharing common references were considered to co-occur, enabling us to quantify the extent of thematic relationships based on the frequency of shared references. We identified and categorised thematic clusters within our dataset through the combined approach of VOSviewer clustering and co-occurrence analysis. This method typically results in a distribution of clusters, with a limited number of larger clusters and a more substantial number of smaller clusters.
The clusters were derived through an analysis of subordinate articles extracted from the Scopus database. VOSviewer systematically organised similar articles into distinct clusters based on the shared patterns of bibliographic references (Van Eck & Waltman, 2010 ). To ensure methodological transparency and robustness, we established clear criteria and parameters for clustering. Specifically, keywords with a minimum frequency ( n = 5) were included in the analysis, and co-occurrence was calculated based on a pairwise comparison method. This systematic approach ensured the meaningful representation of thematic relationships within the dataset, guided by insights from previous literature (Jarneving, 2007 ). Using cluster analysis techniques, the articles were organised into cohesive groups characterised by the degree of thematic homogeneity guided by the nature of the research findings. This approach ensured a robust representation of the underlying thematic structure (Jarneving, 2007 ).
Furthermore, to mitigate the risk of subjective bias in thematic categorisation, a counter-coding approach was employed. A second researcher independently categorised thematic clusters identified by VOSviewer to assess inter-rater agreement. The level of agreement between the two researchers was assessed using Cohen’s kappa coefficient, ensuring the reliability and validity of the thematic classification process. The resulting kappa coefficient (0.69) indicated substantial agreement, suggesting a high level of agreement beyond what would be expected by chance alone (Gisev et al., 2013 ). Furthermore, the nomenclature assigned to each cluster was finalised based on the predominant research theme emerging from the analysis, providing a concise and informative label for each group.
TC1: ChatGPT and Academic Integrity: Cotton et al. ( 2023 ) describe ChatGPT as a double-edged sword that potentially threatens academic integrity. AI essay writing systems are programmed to churn out essays based on specific guidelines or prompts, and it can be difficult to distinguish between human and machine-generated writing. Thus, students could potentially use these systems to cheat by submitting essays that are not their original work (Dehouche, 2021 ). Kasneci et al. ( 2023 ) argue that effective pedagogical practices must be developed in order to implement large language models in classrooms. These skills include not only a deep understanding of the technology but also an appreciation of its constraints and the vulnerability of complex systems in general. In addition, educational institutions need to develop a clearly articulated plan for the successful integration and optimal use of big language models in educational contexts and teaching curricula. In addition, students need to be taught how to verify information through a teaching strategy emphasising critical thinking effectively. Possible bias in the generated output, the need for continuous human supervision, and the likelihood of unforeseen effects are just a few of the challenges that come with the employment of AI systems. Continuous monitoring and transparency are necessary to ensure academic integrity while using ChatGPT. Lim et al. ( 2023 ) report that ChatGPT poses academic integrity challenges for the faculty of higher education institutions, who must verify whether academic work (assignments, research reports, etc.) submitted by students is derived from the fresh perspective of data analysis or plagiarised and recycled (copying and pasting original work) by ChatGPT. ChatGPT may threaten student learning and classroom engagement if students have access to information and course assignments without assessing their integrity. Perkins ( 2023 ) also expresses concerns regarding academic integrity in the use of ChatGPT. Students are utilising ChatGPT to complete their course assignments without attribution rather than producing original work. Higher education institutions must establish clear boundaries regarding academic integrity and plagiarism in light of the growing utilisation of AI tools in academic and research settings. In addition, the challenges posed by AI essay writing systems like ChatGPT necessitate a multifaceted approach to safeguard academic integrity. Educational institutions should invest in comprehensive educational programs that not only teach students the ethical use of technology but also incorporate rigorous assessments of critical thinking skills. Additionally, integrating AI literacy into the curriculum, with a focus on understanding the limitations and potential biases of big language models, can empower students to discern between human and machine-generated content.
TC2: ChatGPT and Learning Environment: According to Crawford et al. ( 2023 ), increased stress levels and peer pressure among university students have created a favourable environment for the use of AI tools. ChatGPT provides enhanced educational opportunities for college-level students. It can help students identify areas they may have overlooked, offer guidance on additional reading materials, and enhance existing peer and teacher connections. In addition, ChatGPT can propose alternative methods of evaluating students beyond conventional assignments. Crawford et al. ( 2023 ) recommend providing practical assignments incorporating ChatGPT as a supplementary tool to reduce plagiarism. Su ( 2023 ) documents that ChatGPT can provide students with a personalised learning experience based on their specific needs. In addition, the ChatGPT platform can be used to create a virtual coaching system that offers prompt feedback to educators during their classroom evaluations. This approach fosters critical thinking and supports early childhood educators in refining their teaching methodologies to optimise interactive learning outcomes for students. Tang ( 2023b ) proposes that bolstering research integrity can be achieved by imposing restrictions on the utilisation of NLP-generated content in research papers. Additionally, the author advocates for transparency from researchers, emphasising the importance of explicitly stating the proportion of NLP-generated content incorporated in their papers. This recommendation prompts a critical examination of the role of AI-generated content in scholarly work, emphasising the importance of nurturing independent research and writing skills for both students and researchers.
TC3: ChatGPT and Student Engagement: Lee ( 2023 ) examines the ability of ChatGPT to provide an interactive learning experience and boost student engagement beyond textbook pedagogy. Iskender ( 2023 ) explains that ChatGPT provides a mechanism for students to generate and investigate diverse concepts expeditiously, thereby helping them engage in imaginative and evaluative thinking on specific subject matter. This approach has the potential to optimise time management for students and allow them to concentrate on more advanced cognitive activities. AI tools such as ChatGPT can potentially enhance the personalisation of learning materials by providing visual aids and summaries that can aid the learning process and significantly improve students’ competencies. Hence, leveraging ChatGPT in education can revolutionise learning by facilitating interactive experiences, nurturing imaginative thinking, and optimising time management for students.
TC4: ChatGPT and Scholarly Research: Ivanov and Soliman ( 2023 ) and Yan ( 2023 ) focus on the practical applications and implications of LLMs like ChatGPT in educational settings and scholarly research within the context of language learning, writing, and tourism. Yan’s investigation into ChatGPT’s application in second-language writing examines its effectiveness in addressing specific writing tasks at the undergraduate level. The findings underscore the nuanced balance between the strengths of ChatGPT and the inherent limitations in handling demanding academic writing tasks. Nevertheless, ChatGPT is also labelled as an ‘all-in-one’ solution for scholarly research and writing (Yan, 2023 ). In parallel, Ivanov and Soliman ( 2023 ) highlight that ChatGPT can assist scholars in the field of tourism research by composing preliminary literature reviews, substantiating their chosen methodologies, and creating visual aids such as tables and charts. Furthermore, the researchers outline that ChatGPT could provide valuable methodological ideas and insights by helping researchers generate questions and corresponding scales for inclusion in questionnaires. Hence, ChatGPT has the potential to become a valuable ally as a facilitator in academic writing processes and has the potential to transform the research workflow.
3.3.2 Geographic clusters
The results of the country-based bibliographic analysis are summarised in Table 5 . The present study utilised the prevailing research theme in the existing literature as a framework for categorising the countries into four distinct clusters on the basis of the number of documents published from different countries.
Cluster 1: Implications of ChatGPT for Student Examinations and Education : Cluster 1 is composed of five countries: Germany, Ireland, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United States. Researchers in these countries have emphasised the potential role of ChatGPT in higher education within the context of AI language models. Eleven research articles related to this theme were published by researchers based in the United States, the most in this cluster. The top three articles in Table 1 are from the United States. The study entitled “Opportunities and Challenges of Large Language Models for Education,” was authored by German researchers (Kasneci et al., 2023 ) and has been widely cited in the academic community (13 citations). The remaining studies were conducted by researchers from South Korea and Taiwan and focused on the impact of ChatGPT on the education sector and its associated opportunities and challenges. This cluster demonstrates that students could benefit greatly from using ChatGPT in performing various academic tasks, such as reviewing and revising their work, verifying the accuracy of homework answers, and improving the quality of their essays. It has also aided postgraduates whose first language is not English improve their writing, as ChatGPT can be instructed to rewrite a paragraph in a scholarly tone from scratch. The outcomes have demonstrated significant efficacy, thereby alleviating the cognitive load associated with translation for these students, enabling them to concentrate on the substance of their writing rather than the intricacies of composing in an unfamiliar language. To harness the potential benefits, future research could focus on developing targeted training programs for students and educators that emphasise the effective utilisation of ChatGPT to enhance not only academic tasks but also language proficiency for non-native English speakers, addressing both cognitive load and language intricacies.
Cluster 2: ChatGPT and Academic Integrity : Cluster 2 comprises research studies conducted by authors from Japan, Bangladesh, Hong Kong, Nigeria, Pakistan, UAE, the UK, Vietnam and the Netherlands. The most influential study in this cluster, “Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: A framework for applying Generative AI in education”, was authored by researchers from Hong Kong (Su & Yang, 2023 ). They document that ChatGPT can be used to respond to student inquiries, reducing the time and effort required of educators and allowing them to focus their resources on other activities, such as scholarly investigations. Farrokhnia et al. ( 2023 ) and Yeadon et al. ( 2023 ) state that ChatGPT can write scientific abstracts with fabricated data and essays that can evade detection by reviewers. According to Liebrenz et al. ( 2023 ), ChatGPT tends to produce erroneous and incoherent responses, thereby raising the potential for disseminating inaccurate information in scholarly literature. The higher-order cognitive abilities of ChatGPT are relatively low, especially in areas related to creativity, critical thinking, reasoning, and problem-solving. ChatGPT could reduce students’ motivation to explore topics independently, draw their own conclusions, and solve problems independently (Kasneci et al., 2023 ). Ibrahim et al. ( 2023 ) find that ChatGPT can engage students in their academic pursuits. ChatGPT can enhance the writing abilities of non-native English speakers to allow them to concentrate on higher-order cognitive processes. This technological development allows faculty members to allocate more attention to conceptualisation and writing rather than focusing on the mechanics of grammar and spelling. However, there is a debate among intellectuals regarding the implications of AI for content creation, with some asserting that it detracts from innovative content development. The possibility that ChatGPT threatens academic honesty by facilitating essay plagiarism is being acknowledged. In addition, in the absence of appropriate citations, this textual content may violate copyright regulations. Cotton et al. ( 2023 ) express concerns about the potential impact of ChatGPT on academic integrity and plagiarism. Their work corroborates Dehouche’s ( 2021 ) assertion that students may use ChatGPT to engage in academic dishonesty by submitting essays that are not their original work. According to Cotton et al. ( 2023 ), ChatGPT users have a competitive advantage over non-users and can achieve higher grades on their coursework assignments by utilising the AI-based language tool. They classify ChatGPT as a versatile instrument with the potential to pose a threat to academic integrity, noting that AI essay writing systems are specifically programmed to generate content based on specific parameters or prompts, thereby challenging the discernment between human-authored and machine-generated content. Distinguishing between the academic work produced by students and the content of ChatGPT when evaluating assignments is a significant challenge for faculty. It is recommended that academic staff continually monitor student assignments for academic misconduct infractions, coupled with transparent communication about the potential risks associated with AI-generated content.
Cluster 3: ChatGPT and Students’ Learning : Cluster 3 comprises Malaysia, China and Australia. This cluster mainly includes studies of the role of AI-based models in student learning. Researchers from Australia (Crawford et al., 2023 ; Lim et al., 2023 ; Lawrie, 2023 ; Li et al., 2023 ; Seth et al., 2023 ; Cingillioglu, 2023 ; Skavronskaya, 2023 ; and Johinke, 2023 ) have contributed the most (8 studies) to this cluster and put their weight behind the role of AI and student learning in various disciplines. One of the most influential papers, “Generative AI and the future of education: Ragnarök or reformation? A paradoxical perspective from management educators”, was authored by researchers from both Australia and Malaysia (Lim et al., 2023 ) and reflected on the role of AI in classroom learning and teaching. Rather than banning AI tools, the authors advocate for the productive use of these tools in classrooms to facilitate more engaging student learning. Another Australian study titled, “Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI)” (Crawford et al., 2023 ) highlights AI as an alternative path of learning for students. ChatGPT can promptly evaluate students’ assignments and help them identify areas of weakness. Educators have the option to provide innovative assessments to their students instead of adhering solely to conventional assessments. ChatGPT can augment pedagogical approaches, evaluation structures, and the comprehensive educational milieu by reinforcing the trilateral association among instructors, learners, and technology. The implementation of ChatGPT can provide students with a personalised and interactive learning and research experience facilitated by virtual tutors and customised recommendations. In light of the research in this cluster, the integration of ChatGPT into education should inspire a paradigm shift towards a more dynamic and personalised learning environment. Institutions can explore strategic partnerships with AI researchers to develop context-specific applications of ChatGPT that cater to diverse educational needs, promoting a symbiotic relationship between human instructors, students, and technology for an enriched learning experience.
Cluster 4: ChatGPT and Field-specific Research : This cluster includes research by authors in Asian and European countries (India, Oman, Bulgaria and New Zealand) that has emphasised the potential role of ChatGPT in the medical and tourism industries. Authors from India explored the role of ChatGPT in the medical field (Seetharaman, 2023 ; Subramani et al., 2023 ). Seetharaman ( 2023 ) reports that ChatGPT offers supplementary language assistance to students who are not proficient in English, enabling them to enhance their language proficiency and effectively communicate in English, the principal language of instruction in medical establishments. The ChatGPT platform has the potential to serve as a tool for medical students to replicate patient interactions in a simulated environment, such as accurately obtaining medical histories and documenting symptoms. According to Subramani et al. ( 2023 ), ChatGPT is a highly efficient and user-friendly AI technology that can aid healthcare professionals in various aspects, such as diagnosis, critical decision-making, and devising appropriate treatment plans. ChatGPT has demonstrated impressive performance on medical exams, indicating its potential as a valuable resource for enhancing medical education and assessment (Subramani et al., 2023 ) and can support interdisciplinarity in tourism research (Nautiyal et al., 2023 ). Ivanov and Soliman ( 2023 ) note the potential of ChatGPT to serve as a digital instructor to provide students with enhanced and effective learning experiences and outcomes. Digital instructors can impart knowledge in diverse languages and thus can be used to educate individuals of varying nationalities and backgrounds in the field of tourism. Furthermore, LLM-based chatbots, including ChatGPT, can assess written assignments and provide direction on linguistic proficiency, syntax, and composition, ultimately enhancing students’ scholarly writing proficiency. In exploring the intersection of ChatGPT with medical education, institutions can pioneer innovative approaches by using the platform to create immersive, simulated patient interactions that go beyond language assistance, allowing medical students to practice nuanced skills such as medical history gathering and symptom documentation. Simultaneously, leveraging ChatGPT as a versatile digital instructor offers a unique opportunity to provide cross-cultural and multilingual education, contributing to a more inclusive and globally competent workforce within the tourism industry.
3.4 Challenges of ChatGPT in higher education
In addition to some previously mentioned challenges, such as the potential for plagiarism, the investigation also identified other key challenges in implementing ChatGPT within the context of higher education’s teaching and learning environment. Wu and Yu ( 2023 ) found that the benefits of AI-based ChatGPT are more in higher education as compared to primary and secondary education. The study also reported that the novelty effects of AI chatbots may enhance learning outcomes in brief interventions, but their efficacy diminishes in longer interventions.
First, the implementation of ChatGPT within the educational context engenders learning impediments. In the absence of adequate monitoring and regulation, the technology could lead to human unintelligence and unlearning, but teachers will become more adaptive and create authentic assessments to enhance student learning (Alafnan et al., 2023 ; Lawrie, 2023 ). Second, the technology could be used in a manner that violates students’ privacy. If the model is not adequately secured, it could surreptitiously gather confidential data from students without their explicit awareness or authorisation (Kanseci, 2023). Third, the technology could facilitate discrimination against particular students. If the model is not trained on a dataset that accurately represents the entire student population, it has the potential to create disparities in educational access (Cingillioglu, 2023 ; Lin et al., 2023 ). Fourth, according to Ivanov and Soloman (2023), ChatGPT lacks access to real-time data. Therefore, its responses may be inconsequential, inaccurate, or outdated. The information provided in response to a specific query may also be insufficient. Gao et al. (2022) highlight the need for further investigation of the precision and scholarly authenticity of ChatGPT. Fifth, it may be difficult for ChatGPT to comprehend the context and subtleties of complex academic subjects and answer complex questions (Adetayo, 2023 ; Eysenbach, 2023 ; Neumann et al., 2023 ). The system can misinterpret inquiries, offer inadequate or inaccurate responses, or struggle to comprehend the fundamental purpose behind questions (Clark, 2023 ). In particular, ChatGPT may not have the requisite expertise in highly specialised or advanced subjects such as advanced mathematics or specific sciences. Hence, it may not deliver precise and accurate answers (Neumann et al., 2023 ; Fergus et al., 2023 ). Karaali ( 2023 ) claimed that the primary emphasis in the field of AI is currently directed towards the enhancement of advanced cognitive abilities and mental processes associated with quantitative literacy and quantitative reasoning. However, it is important to acknowledge that fundamental skills such as writing, critical thinking, and numeracy continue to serve as essential foundational components among students. Although AI is making significant progress in fundamental domains, it appears that students are experiencing a decline in performance in the context of fundamental skills. Consequently, NLP-based adaptive learner support and education require further investigation (Bauer et al., 2023 ).
In addressing the challenges of ChatGPT in education, educators need to adapt and develop authentic assessments that mitigate the risk of human unlearning, ensuring that technology enhances, rather than hinders, student learning experiences. Simultaneously, recognising the limitations of ChatGPT in comprehending the nuances of highly specialised subjects underscores the importance of balancing advancements in AI’s cognitive abilities with continued emphasis on fundamental skills like critical thinking, writing, and numeracy, urging a reevaluation of priorities in AI-driven educational research towards comprehensive learner support.
4 Conclusion, implications and agenda for future research
This study identified the most influential articles and top journals and countries in terms of citations and publication productivity related to ChatGPT in higher education, as well as highlighted emerging thematic clusters and geographic clusters in research on the role and challenges of ChatGPT in teaching and learning in higher education institutions. Articles on the topic of ChatGPT in higher education published up to May 2023 were identified by searching the Scopus database. Given the emergent nature of ChatGPT starting in late 2022, all the included articles were published in 2023. Thus, this specific research domain remains relatively unexplored. The findings of this analysis reveal that the United States is the most productive country in terms of research on the role of ChatGPT in higher education, especially relating to academic integrity and research. US researchers also emerged as the most influential in terms of number of citations in the literature. Our findings corroborate those of previous research (Crompton & Burke, 2023 ). However, 60% of the articles in our shortlisted literature emanated from Asian countries.
Four thematic clusters (academic integrity, student engagement, learning environment and research) were identified. Furthermore, the country-based bibliographic analysis revealed that research has focused on student examinations, academic integrity, student learning and field-specific research in medical and tourism education (Nautiyal et al., 2023 ; Subramani et al., 2023 ). Plagiarism is recognised as a major challenge that hinders students’ creativity, innovativeness and originality when using ChatGPT in their academic pursuits. To mitigate the potential drawbacks of using ChatGPT in educational and research settings, proactive measures should be taken to educate students and researchers alike on the nature of plagiarism, its negative impacts and academic integrity (Shoufan, 2023 ; Teixeira, 2023 ) Educators may ask students to provide a written acknowledgement of the authenticity of their assignments and their non-reliance on ChatGPT. Such an acknowledgement would discourage students from utilising ChatGPT in their academic and research endeavours and establish accountability for their academic pursuits. In addition, educators should develop authentic assessments that are ChatGPT-proof.
ChatGPT lacks emotional intelligence and empathy, both of which are crucial in effectively addressing the emotional and psychological dimensions of the learning process (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Neumann et al., 2023 ). Higher education institutions may encounter challenges in using ChatGPT to deliver suitable assistance, comprehension, or direction to students needing emotional or mental health support. The significance of human interaction in learning cannot be overstated. Achieving a balance between using AI and the advantages of human guidance and mentorship is a persistent challenge that requires attention (Neumann et al., 2023 ; Rahman et al., 2023 ). Strzelecki ( 2023 ) observed in his research that behavioural intention and personal innovativeness are the two major determinants behind the adoption of ChatGPT among students.
4.1 Implications
The findings of the present study have numerous important implications. This study provides insight into the current state of ChatGPT in higher education and thus can serve as valuable guidance for academics, practitioners, and policymakers. The study’s findings contribute to the literature by providing new insights into the role of ChatGPT and strategies for mitigating its negative aspects and emphasising its positive attributes.
First, the implementation of AI in education can improve academic performance and student motivation, particularly by facilitating personalised learning. Educational institutions should monitor and regulate students’ use of such technologies proactively. Higher education institutions also ought to prioritise the training of their educators in effectively utilising AI technologies, including ChatGPT. Concurrently, it is imperative for these institutions to equip students with comprehensive academic integrity training, shedding light on the appropriate and inappropriate applications of AI tools like ChatGPT. This includes creating awareness about the potential consequences of utilising these technologies for dishonest practices. Furthermore, educational establishments need to urgently revisit and refine their academic integrity policies to address the evolving landscape shaped by the integration of artificial intelligence tools in various academic facets. This proactive approach will foster a learning environment that embraces technological advancements and upholds the principles of honesty and responsible use. Institutional regulations on accountability and transparency should guide the frameworks that govern the use of AI in the campus environment (Pechenkina, 2023 ; Sun & Hoelscher, 2023 ; Dencik & Sanchez-Monedero, 2022 ).
Second, faculty members must proactively replace traditional coursework with modern alternatives that foster elevated levels of critical thinking among students, as suggested by Zhai ( 2022 ). Educators and learners can augment the academic material produced by ChatGPT with their own insights and information obtained from credible scholarly resources (Emenike & Emenike, 2023 ).
Third, ChatGPT should not be considered a threat to the education sector but a supplementary tool for human instruction that can enhance teaching and learning. It is imperative to acknowledge that the vital role of human educators cannot be replaced (Karaali, 2023 ) Moreover, ChatGPT can potentially enhance the accessibility and inclusivity of higher education. Alternative formats, linguistic support, and individualised explanations can help students who are studying English as a second language, are not native English speakers, or have other unique learning needs. Furthermore, Alnaqbi and Fouda ( 2023 ) highlight the implications of AI in evaluating the teaching style of faculty in higher education by collecting the feedback of students through social media and ChatGPT.
Fourth, the faculty in higher education institutions could address ethical concerns by providing students with explicit and comprehensive guidelines about the prescribed structure of academic assignments (Cotton et al., 2023 ; Gardner & Giordano, 2023 ). This practice can facilitate the production of more cohesive assignments. In addition, teachers can use rubrics to assess assignments and blend automated and manual assessment methodologies to evaluate students’ comprehension of the subject matter (Cotton et al., 2023 ; Shoufan, 2023 ).
In summary, using ChatGPT is recommended for enhancing creativity, refining writing proficiency, and improving research abilities. Nonetheless, it is crucial to emphasise that ChatGPT should not be employed as a substitute for critical thinking and producing original work. While it serves as a valuable tool for augmentation, upholding the integrity of independent thought and authentic content creation in academic endeavours is essential.
4.2 Limitations
The present study acknowledges several limitations. Firstly, the reliance on Scopus as the primary data source for bibliometric analysis may have limitations in capturing the full landscape of relevant literature. Future research may consider incorporating additional databases like Web of Science to ensure a comprehensive assessment. Secondly, due to the English language restriction in the review, potentially relevant studies may have been omitted. Future research could enhance inclusivity by extending its scope to encompass papers written in languages other than English. Thirdly, the current study exclusively focused on journal articles. Expanding the scope to include diverse sources, such as conference proceedings or book chapters, could offer a more comprehensive overview.
Additionally, as a rapidly evolving field, literature published after our inclusion dates need capturing, and future studies should consider adjusting their inclusion criteria to accommodate the dynamic nature of the subject matter. Lastly, the specificity of the bibliometric data search, centred around terms like ChatGPT, AI, higher education, and academic integrity, may have excluded certain relevant articles. Future studies should consider employing more generalised search parameters to encompass synonyms associated with these terms.
4.3 Future scope
The findings of the study suggest new avenues for future research. The effectiveness of evaluation criteria for assessments incorporating ChatGPT-generated text needs to be investigated. Specifically, the appropriate level of ChatGPT-produced text that students may use in academic tasks or assessments has not been established. Research on the ethical implications of using AI tools such as ChatGPT in higher education is also needed. Issues pertaining to data confidentiality, bias, and transparency in algorithms used for decision-making remain to be addressed. Feasible approaches for mitigating the excessive reliance of scholars and learners on ChatGPT or similar AI models are needed. Researchers could also explore the implementation of verification processes that go beyond traditional plagiarism detection methods, accounting for the unique challenges posed by AI systems. Future research in this domain could focus on establishing guidelines and best practices for the integration of AI tools like ChatGPT in academic settings, ensuring a balance between technological innovation and the preservation of academic rigour. Finally, the literature on ChatGPT in higher education has largely focused on the medical and tourism sectors. Future researchers must explore applications of ChatGPT in other disciplines.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Adetayo, A. J. (2023). ChatGPT and librarians for reference consultations. Internet Reference Services Quarterly , 27 (3), 131–147.
Article Google Scholar
AlAfnan, M. A., Dishari, S., Jovic, M., & Lomidze, K. (2023). ChatGPT as an educational tool: Opportunities, challenges, and recommendations for communication, business writing, and composition courses. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Technology , 3 (2), 60–68. https://doi.org/10.37965/jait.2023.0184 .
Alnaqbi, N. M., & Fouda, W. (2023). Exploring the role of ChatGPT and social media in enhancing student evaluation of teaching style in higher education using Neutrosophic sets. International Journal of Neutrosophic Science , 20 (4), 181–190.
Angelis, L. D., Baglivo, F., Arzilli, G., Privitera, G. P., Ferragina, P., Tozzi, A. E., & Rizzo, C. (2023). ChatGPT and the rise of large language models: The new AI-driven infodemic threat in public health. Frontiers in Public Health , 11 , 1–8.
Archambault, E., Campbell, D., Gingras, Y., & Larivière, V. (2009). Comparing bibliometric statistics obtained from the web of Science and Scopus. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology , 60 (7), 1320–1326.
Bajaj, Y., Kashiramka, S., & Singh, S. (2020). Application of capital structure theories: A systematic review. Journal of Advances in Management Research , 18 (2), 173–199. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAMR-01-2020-001 .
Bauer, E., Greisel, M., Kuznetsov, I., Berndt, M., Kollar, I., Dresel, M., Fischer, M. R., & Fischer, F. (2023). Using natural language processing to support peer-feedback in the age of artificial intelligence: A cross-disciplinary framework and a research agenda. British Journal of Educational Technology , 54 (5), 1222–1245.
Boyack, K. W., & Klavans, R. (2010). Co-citation analysis, bibliographic coupling, and direct citation: Which citation approach represents the research front most accurately? Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology , 61 (12), 2389–2404.
Cingillioglu, I. (2023). Detecting AI-generated essays: The ChatGPT challenge. International Journal of Information and Learning Technology , 40 (3), 259–268. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJILT-03-2023-0043 .
Clark, T. M. (2023). Investigating the Use of an Artificial Intelligence Chatbot with General Chemistry exam questions. Journal of Chemical Education , 100 (5), 1905–1916.
Cotton, D. R. E., Cotton, P. A., & Shipway, J. R. (2023). Chatting and cheating: Ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innovations in Education and Teaching International , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2190148 .
Crawford, J., Cowling, M., & Allen, K. (2023). Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice , 20 (3), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.3.02 .
Crompton, H., & Burke, D. (2023). Artificial intelligence and higher education: The state of the field. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education , 20 , 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00392-8 .
Dehouche, N. (2021). Plagiarism in the age of massive generative pre-trained transformers (GPT-3). Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics , 2 , 17–23. https://doi.org/10.3354/esep00195 .
Dencik, L., & Sanchez-Monedero, J. (2022). Data justice. Internet Policy Review , 11 (1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.14763/2022.1.1615 .
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., & Pattnaik, D. (2020). Forty-five years of Journal of Business Research : A bibliometric analysis. Journal of Business Research , 109 , 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.10.039 .
Emenike, M., & Emenike, B. (2023). Was this title generated by ChatGPT? Considerations for artificial intelligence text-generation software programs for chemists and chemistry educators. Journal of Chemical Education , 100 (4), 1413–1418. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00063 .
Eysenbach, G. (2023). The role of ChatGPT, generative language models, and artificial intelligence in medical education: A conversation with ChatGPT and a call for papers. JMIR Medical Education , 6 (9), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.2196/46885 .
Farrokhnia, M., Banihashem, K. S., Noroozi, O., & Wals, A. (2023). A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: Implications for educational practice and research. Innovations in Education and Teaching International , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 .
Fergus, S., Botha, M., & Ostovar, M. (2023). Evaluating academic answers generated using ChatGPT. Journal of Chemical Education , 100 (4), 1672–1675. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00087 .
Firat, M. (2023). How chat GPT can transform autodidactic experiences and open education. Department of Distance Education, Open Education Faculty , Anadolu University, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/9ge8m .
Gardner, D. E., & Giordano, A. E. (2023). The challenges and value of undergraduate oral exams in the physical chemistry classrooms: A useful tool in the assessment toolbox. Journal of Chemical Education , 100 (5), 1705–1709.
Geerling, W., Mateer, G. D., Wooten, J., & Damodaran, N. (2023). ChatGPT has aced the test of understanding in college economics: Now what? The American Economist , 68 (2), 233–245.
Gilson, A., Safranek, C. W., Huang, T., Socrates, V., Chi, L., Taylor, R. A., & Chartash, D. (2023). How does ChatGPT perform on the United States medical licensing examination? The implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Medical Education , 9 , 1–9. https://doi.org/10.2196/45312 .
Gisev, N., Bell, J. S., & Chen, T. F. (2013). Interrater agreement and interrater reliability: Key concepts, approaches, and applications. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy , 9 (3), 330–338.
Gupta, R., Pandey, R., & Sebastian, V. J. (2021). International entrepreneurial orientation (IEO): A bibliometric overview of scholarly research. Journal of Business Research , 125 , 74–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.12.00 .
Ibrahim, H., Asim, R., & Zaffar, F. (2023). Rethinking homework in the age of artificial intelligence. Intelligent Systems , 38 (2), 24–27.
Google Scholar
Iskender, A. (2023). Holy or Unholy? Interview with Open AI’s ChatGPT. European Journal of Tourism Research , 34 , 3414. https://doi.org/10.54055/ejtr.v34i.3169 .
Ivanov, S., & Soliman, M. (2023). Game of algorithms: ChatGPT implications for the future of tourism education and research. Journal of Tourism Futures , 9 (2), 214–221.
Jarneving, B. (2007). Bibliographic coupling and its application to research-front and other core documents. Journal of Informetrics , 1 (4), 287–307.
Jeon, J., Lee, S., & Cho, S. (2023). A systematic review of research on speech-recognition chatbots for language learning: Implications for future directions in the era of large language models. Interactive Learning Environment , 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2204343 .
Johinke, R., Cummings, R., & Di Lauro, F. (2023). Reclaiming the technology of higher education for teaching digital writing in a post-pandemic world. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice , 20 (2), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.02.01 .
Karaali, G. (2023). Artificial Intelligence, Basic skills, and quantitative literacy. Numeracy , 16 (1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.5038/1936-4660.16.1.1438 .
Kasneci, E., Seßler, K., Küchemann, S., Bannert, M., Dementieva, D., Fischer, F., & Kasneci, G. (2023). ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learning and Individual Differences , 103 (2023), 102274–102271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2023.102274 .
Lawrie, G. (2023). Establishing a delicate balance in the relationship between artificial intelligence and authenticate assessment in student learning. Chemistry Education Research and Practice , 24 (2), 392–393.
Lee, H. (2023). The rise of ChatGPT: Exploring its potential in medical education. Anatomical Science Education , 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2270 .
Li, Y., Sha, L., Yan, L., Lin, J., Raković, M., Galbraith, K., Lyons, K., Gašević, D., & Chen, G. (2023). Can large language models write reflectively. Computer and Education: Artificial Intelligence , 4 (2023), 100140–100141.
Liebrenz, M., Schleifer, R., Buadze, A., Bhugra, D., & Smith, A. (2023). Generating scholarly content with ChatGPT: Ethical challenges for medical publishing. Lancet Digital Health , 5 (3), e105–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00019-5 .
Lim, W. M., Gunasekara, A., Pallant, J. L., Pallant, J. I., & Pechenkina, E. (2023). Generative AI and the future of education: Ragnarök or reformation? A paradoxical perspective from management educators. The International Journal of Management Education , 21 (2), 1–13.
Lin, C. C., Huang, A. Y. Q., Stephen, J. H., & Yang (2023). A review of AI-Driven conversational chatbots implementation methodologies and challenges (1999–2022). Sustainability , 15 (5), 4012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054012 .
Memarian, B., & Doleck, T. (2023). ChatGPT in education: Methods, potentials and limitations. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans , 100022 , 1–11.
Mishra, D., Gunasekaran, A., Papadopoulos, T., & Hazen, B. (2017). Green supply chain performance measures: A review and bibliometric analysis. Sustainable Production and Consumption , 10 , 85–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2017.01.003
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & The PRISMA Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Annals of Internal Medicine , 151 (4), 264–269.
Nautiyal, R., Albrecht, J. N., & Nautiyal, A. (2023). ChatGPT and tourism academia. Annals of Tourism Research , 99 , 1–3.
Neumann, M., Rauschenberger, M., & Schon, E-M. (2023). 2023 IEEE/ACM 5th International Workshop on Software Engineering Education for the Next Generation (SEENG), Melbourne, Australia, 2023, pp. 29–32, https://doi.org/10.1109/SEENG59157.2023.00010 .
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., … & Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ , 372 (71), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Palomo, J., Figueroa-Domecq, C., & Laguna, P. (2017). Women, peace and security state-of-art: A bibliometric analysis in social sciences based on SCOPUS database. Scientometrics , 113 (1), 123–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2484-x .
Patrício, L. D., & Ferreira, J. J. (2020). Blockchain security research: Theorizing through bibliographic-coupling analysis. Journal of Advances in Management Research , 18 (1), 1–35. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAMR-04-2020-0051 .
Paul, J., Lim, W. M., O’Cass, A., Hao, A. W., & Bresciani, S. (2021). Scientific procedures and rationales for systematic literature reviews (SPAR-4-SLR). International Journal of Consumer Studies . https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12695 .
Pechenkina, K. (2023). Artificial intelligence for good? Challenges and possibilities of AI in higher education from a data justice perspective. In L. Czerniewicz, & C. Cronin (Eds.), Higher education for good: Teaching and learning futures (#HE4Good) . Open Book.
Perkins, M. (2023). Academic integrity considerations of AI large Language models in the post-pandemic era: ChatGPT and beyond. Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice , 20 (2), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.02.07 .
Rahman, M., Mostafizer, & Yutaka Watanobe. (2023). ChatGPT for Education and Research: Opportunities, threats, and strategies. Applied Sciences , 13 (9), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095783 .
Rana, S. (2023). AI and GPT for Management scholars and practitioners: Guidelines and implications. FIIB Business Review , 12 (1), 7–9.
Seetharaman, R. (2023). Revolutionising medical education: Can ChatGPT boost subjective learning and expression? Journal of Medical System , 47 (61), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-023-01957-w .
Seth, I., Bulloch, G., & Lee, C. H. A. (2023). Redefining academic integrity, authorship, and innovation: The impact of ChatGPT on surgical research. Annals of Surgical Oncology , 30 , 5284–5285. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-023-13642-w .
Shoufan, A. (2023). Exploring students’ perceptions of ChatGPT: Thematic analysis and follow-up survey. IEEE Access , 11, 38805–38818, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3268224 .
Singh, V. K., Singh, P., Karmakar, M., Leta, J., & Mayr, P. (2021). The journal coverage of web of Science, Scopus and dimensions: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics , 126 , 5113–5142.
Skavronskaya, L., Hadinejad, A., & Cotterell, D. (2023). Reversing the threat of artificial intelligence to opportunity: A discussion of ChatGPT in tourism education. Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism , 23 , 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/15313220.2023.2196658 .
Strzelecki, A. (2023). To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2209881 .
Su, J., & Yang, W. (2023). Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: A framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Review of Education , 6 (3), 355–366.
Subramani, M., Jallel, I., & Mohan, S. K. (2023). Evaluating the performance of ChatGPT in medical physiology university examination of phase I MBBS. Advances in Physical Education , 47 , 270–271.
Sun, G. H., & Hoelscher, S. H. (2023). The ChatGPT Storm and what Faculty can do. Nurse Educator , 48 , 119–124.
Tang, G. (2023a). Academic journals cannot simply require authors to declare that they used ChatGPT. Irish Journal of Medical Science , 192 (6), 3195–3196.
Tang, G. (2023b). Letter to editor: Academic journals should clarify the proportion of NLP-generated content in papers. Accountability in Research , 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989621.2023.2180359 .
Teixeira da Silva, J. A. (2023). How are authors’ contributions verified in the ICMJE model? Plant Cell Reports , 42 , 1529–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03022-9 .
Thorp, H. H. (2023). ChatGPT is fun, but not an author. Science , 379 (6630), 313–313.
Tlili, A., Shehata, B., Adarkwah, M., Bozkurt, A., Hickey, D. T., Huang, R., & Agyemang, B. (2023). What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learning Environments , 10 (15), 1–24.
Van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics , 84 (2), 523–538.
Vijaya, V., & Mathur, H. P. (2023). A decade of donation-based crowdfunding: A bibliometric analysis using the SCOPUS Database. Purushartha , 15 (2), 32–51.
Vogels, E. A. (2023). A majority of Americans have heard of ChatGPT, but few have tried it themselves, https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/05/24/a-majority-of-americans-have-heard-of-chatgpt-but-few-have-tried-it-themselves/ .
Wu, R., & Yu, Z. (2023). Do AI Chatbots improve students learning outcome? Evidence from a meta analysis. British Journal of Educational Technology . https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.13334 .
Wu, T. Y., He, S. Z., Liu, J. P., Sun, S. Q., Liu, K., Han, Q. L., & Tang, Y. (2023). A brief overview of ChatGPT: The history, status quo and potential future development. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica , 10 (5), 1122–1136. https://doi.org/10.1109/JAS.2023.123618 .
Yan, D. (2023). Impact of ChatGPT on learners in a L2 writing practicum: An exploratory investigation. Education and Information Technologies , 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11742-4 .
Yeadon, W., Inyang, O-O., Mizouri, A., Peach, A., & Testrow, C. P. (May 2023). The death of the short-term physics essay in the coming AI revolution. Physics Education , 58 , 1–13.
Zhai, X. (2022). ChatGPT user experience: Implications for education. SSRN , 4312418 , 1–18.
Download references
Open Access funding enabled and organized by CAUL and its Member Institutions
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University Business School, Maharaja Ranjit Singh Punjab Technical University, Punjab, India
Pritpal Singh Bhullar
Department of Financial Planning and Tax, School of Accounting, Information Systems and Supply Chain, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia
Mahesh Joshi
School of Engineering and Technology, CML‑NET & CREATE Research Centres, Central Queensland University, Queensland, Australia
Ritesh Chugh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ritesh Chugh .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
No Conflict of Interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bhullar, P.S., Joshi, M. & Chugh, R. ChatGPT in higher education - a synthesis of the literature and a future research agenda. Educ Inf Technol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12723-x
Download citation
Received : 04 October 2023
Accepted : 16 April 2024
Published : 02 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12723-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Higher education
- Academic integrity
- Systematic review
- Bibliometric analysis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research in Higher Education publishes empirical studies that enhance our understanding of an educational institution or allow comparison among institutions. It focuses on post-secondary education, including two-year and four-year colleges, universities, and graduate and professional schools. Papers in the journal assist faculty and ...
Overview. Research in Higher Education is a journal that publishes empirical research on postsecondary education. Open to studies using a wide range of methods, with a special interest in advanced quantitative research methods. Covers topics such as student access, retention, success, faculty issues, institutional assessment, and higher ...
Research projects. The role of research in Higher Education and research assessment. This project aims to study the importance of the research function in understanding the wider dynamics of higher education. This strand of research is a new project, part of the ESRC CGHE Transition Centre. It draws together multi-disciplinary scholarship and a ...
The majority of the respondents viewed the research role of higher education in addressing the biggest development challenges in applied terms. Applied research is underpinned by human capital and modernisation theories and assumes that the value of research is that it is 'scientific' (vs. 'political' or 'moral') and aims to reveal ...
Other. The role of research in educational improvement. Critics within and outside the field of education often point out the absence of a strong reciprocal connection between research and practice. The emergence of standards-based reform and the passage of NCLB have generated increasing pressure for evidence-based decision making at all levels.
Higher education pedagogical research issues and concerns. The role of pedagogical research in relation to 'excellence' in teaching has historically been contested (Gordon et al. Citation 2003).The field has been perceived as lacking respect across universities (Yorke Citation 2000; Tierney Citation 2020), offering 'little intellectual value' (Macfarlane Citation 2011), being only of ...
The present research consists of a case study developed in the UK context and intends to bring some insights about the experiences of researchers from the educational field involved in the UK’s Research Assessment Exercise (RAE) regarding the influence and impact of such a system on teaching and student learning.
This article distinguishes between six tasks related to the academic researcher role: (1) networking; (2) collaboration; (3) managing research; (4) doing research; (5) publishing research; and (6) evaluation of research. Data drawn from surveys of academic staff, conducted in Norwegian universities over three decades, provide evidence that the researcher role has become more demanding with ...
1.1. Research on the roles of assessment, teaching and student learning. In re cent times, many distinc t i nfluences and force s ha ve c ontribute d to signi ficant changes in ho w re search and ...
The purpose of higher education and its role in modern societies remains a heated philosophical debate, with strong practical and policy implications. ... Center for Higher Education Research and ...
Higher education is a rich cultural and scientific asset which enables personal development and promotes economic, technological and social change. It promotes the exchange of knowledge, research and innovation and equips students with the skills needed to meet ever changing labour markets. For students in vulnerable circumstances, it is a ...
What is the Role of Research in Higher Education? Peter Scott Professor of Higher Education Studies [email protected]. Two views of university research • John Henry Newman (Dublin, 1852) The Idea of a University • Clark Kerr (Harvard, 1963) The Uses of the University. Plan of presentation 1. Research in universities in historical context
Research as a Function in Higher Education: Focus on Colleges of Education. Peseau, Bruce A. This paper explores the research function in higher education. It specifically addresses the following questions: (a) What is the complex role of research as a function in higher education?; (b) How do research results contribute to the resolution of ...
"Research and inquiry is not just for those who choose to pursue an academic career. It is central to professional life in the twenty-first century." (Brew 2007, p.7) This monograph is aimed at academic staff in higher education institutions interested in developing or enhancing learning through a 'students as researchers' pedagogy.
One trend is the coming "demographic cliff"—the number of high-school graduates in the United States will peak at around 3.6 million students in 2026 and then decline to 3.3 million students by 2030. Another is the drop, since 2016, in international-student enrollment, an important source of revenues for many colleges.
Research in higher education institutions: its organization and role in upgrading specialist training
Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) including universities and colleges worldwide are preparing future professionals, conducting meaningful research, and engaging with the community and ...
It is. now realized that research is necessary in order to provide a basis for. educational planning and to assess the effects of such planning. Examples. of research concerning social aspects of education, the development of children and teaching methods are considered.
Education can be focused on ensuring the ability to collect, access, analyze, and interpret information independently and in collaboration with other stakeholders. The function also includes a collaborative role in convening discussions related to information needs and connecting internal and external producers and users of data with one ...
ABSTRACT. This article weighs in on the developing discourse on AI's role in higher education research through a structured dialogue between two diametrically opposed academics. Utilising a dialectical framework, the discourse transcends surface-level debates to grapple with ethical, methodological, and epistemological questions that are often ...
The pointers mentioned below implies the role and need of research in higher education and why research must be a part of every higher education institution. 1. Teaching will improve if the staff engages in research (research-based teaching): The first argument emphasizes on the necessity of research oriented teaching.
Furthermore, current research suggests that higher education is not just about . ... Dewey in the 19 th century emphasized higher education's role in sustaining our way of life when .
Knowledge of statistics is highly important for research scholars, as they are expected to submit a thesis based on original research as part of a PhD program. As statistics play a major role in the analysis and interpretation of scientific data, intensive training at the beginning of a PhD programme is essential. PhD coursework is mandatory in universities and higher education institutes in ...
The role of the teacher in such curricula is to adopt mentoring or coaching behaviors to facilitate the students' learning process. ... However, it appears that most empirical research on mentoring in higher education lacks a theoretical foundation (Crisp & Cruz, 2009).
This research focuses on including people with disabilities in higher education. It proposes that reflective teaching is a tool to move from an integrative to an inclusive approach. Using a qualitative methodology, it analyzes teachers' positions on integration and inclusion, using focus groups to collect information.
However, it also raises concerns about the broader purpose of higher education. There is a risk that in focusing heavily on specialization and practical skills, a college education overlooks its essential role in developing critical thinkers, informed citizens and mature adults. Such an education also undervalues the humanities, resulting in ...
On the basis of document analysis of the governmental and university websites, in-person consultations with the experts on the Catalan higher education system and insider knowledge of higher education sector employees, we identified four main intermediary actors in Catalan higher education (Table 3). During the exploratory phase of our research ...
Thus, this specific research domain remains relatively unexplored. The findings of this analysis reveal that the United States is the most productive country in terms of research on the role of ChatGPT in higher education, especially relating to academic integrity and research.
The study explored how students at higher education institutes (HEIs) engaged in Recreational Sports during the lockdown and its role in increasing social bonds, experiencing a feeling of ...