Why educating women is more important than we realize

The Times of India
The Stri or the Female Energy is the creatrix, mother of all gods, conqueror of all evil, dispenser of all boons in the Indian culture. She is considered the divine power of the universe from where all beings are born. This divine female energy is worshipped with intense adoration and devotion in India.
Yet, it is in India itself that we find the most intense contradiction towards the female shakti.
On one hand we surrender to the divine Durga to protect us and on the other hand we look down upon the feminine principle with condemnation, contempt, cause of all failures, source of lust and miseries.
An Indian woman suffers this wrath both in her mind and heart right from her birth. She struggles to understand her true role, position, and identity in human society. She lives in a dilemma, wondering whether to relate to the feminine deities being erected all around her or to an unborn female avatar which was never allowed to be born.
Since ancient times women have not been denied legal, social, and educational rights in India but certainly in practise they have been more preoccupied and confined to domestic affairs and that is where their social subordination began.
Despite such subjugation, women have survived important roles such as bold householders, strong mothers, queens, administrators, warriors, elected representatives and leaders. Therefore, despite oppression and denial, India has, time and again, truly experienced the shakti of this female creative force.
The way forward for India and humans in general is to treat the Female Shakti (The Feminine Powerhouse) with respect, deep regard, equal access to experiences, learning and opportunities. All sexes should be allowed to find, above all sexual differences, their full inner potential.
India, the land of diversity and contrast, India the ardent worshipper of the Shakti-The Durga can perhaps lead mankind into human success based in deep regard for the deep inner potential, intellectual prowess and ingenuity of women. Denying women their due place is denying mankind its due success.

Women Across the Globe
The battle for legal, civil, social, and educational equality is a central element of woman’s rights globally. However, a deeper understanding of the women’s needs has revealed that in daily life they struggle to voice their objections and opinions, struggle to agree or disagree, condemn, or promote, speak, share, discuss, and struggle to manage, participate and lead.
Therefore, it would not be incorrect to state that the battle is only half won if the women get access to education and opportunities but no access to exercise their will.
Women across the globe may be characterized by diversity in feminine energy and feminine approach to life, work, family, and society yet their basic emotional, psychological, physical, mental, intellectual, social, professional, and creative needs tie them together to a common cause. The common cause being-women across the globe want to be active participants and decision makers in their own lives and refuse the passivity that is expected of them.
A modern progressive woman prides herself with all her feminine virtues. She wishes to embrace her own self in entirety not to put men down but only to break out of an oppressed state so that she can realize her own untapped full potential.
Women today are capable of and want to accumulate the advantages of both the sexes, but she is not willing to pay an unfair price for achieving this. For instance, a young mother wants the right to work or not to work to lie within the realms of her decision-making powers.
She wishes to be able to make a choice between scenarios where in one she wishes to fully involve herself in her motherhood and suspend her professional aspirations without being made to feel undeserving or financially dependent. Or in another scenario where she wishes to strike a balance between her motherhood and professional duties and yet not labelled as irresponsible and selfish. Such a state of choice with dignity would be true liberation for a young mother.
Equal Education is a Steppingstone Towards Gender Equality, Quality Socialization and Economic Growth
Denying women access to equal and quality education opportunities encourages gender segregation and stereotypical behaviour in society. Perceptions towards gender roles are sowed by members of family and society very early on in the lives of men and women which adversely impacts the quality of the socialization process.
Creating gender neutral learning environments can serve as a steppingstone to quality socialization. This in turn can help in creating favourable position for women in creative, scientific, technological, professional endeavours and lessen their personal and social struggles.
Any society that denies and discourages women from boldly participating in the learning process is only encouraging biased patterns that are deeply rooted in promoting the influential masculine identity.
Quality education can help both men and women understand these deep-seated issues in our society, raise their collective and individual levels of awareness, understand the importance of all people, irrespective of sex, in building a healthy and conscious society. In order to ensure sustainable development, it has become imperative to recognize the importance of all the sexes.
When a girl is educated, she is empowered. She can make her own decisions, raise the standard of living for her family and children, create more job opportunities, and reform society as a whole. As a result, a shift in attitudes toward girl child education in India is urgently needed. Every girl child deserves to be treated with love and respect. If all girls complete their education and participate in the workforce, India could add a whopping $770 billion to the country’s GDP by 2025!
Some Important Statistics
As per statistics presented by UNICEF, 129 million girls are out of school around the world, including 32 million of primary school age, 30 million of lower-secondary school age, and 67 million of upper-secondary school age.
Borgen Project, a US based not for profit, study has revealed that every year, 23 million girls in India drop out of school after they begin menstruating due to lack of sanitary napkin dispensers and overall hygiene awareness in schools.
As per National Survey of India, Literacy Rate in India has increased from 73% in 2011 to 77.7% in 2022, however it still stands behind the global literacy rate which stands at 86.5% (as per UNESCO). Of the 77.7% Indian literacy rate in 2022, male literacy rate stands at 84.7% and female literacy rate stands at 70.3% as compared to global average female literacy rate of 79% (as per UNESCO).
There are several factors that influence poorer literacy rates in women as compared to men, the biggest and most crucial factors being inequality and sex-based discrimination. This discrimination pushes the girl child to either never be born (female infanticide) or the woman to be predominantly pushed into household affairs.
Low enrolment rates, high dropout rates, social discrimination, unsafe public spaces, prioritizing boy child education are some other important factors that negatively influence female education.
Related items
- Gender equality
Other recent articles
Article Forum on AI in Africa: Ai Movement, the new category II center for artificial intelligence in Africa, organizes a Forum on Artificial Intelligence in Rabat, in partnership with UNESCO. 20 June 2024
Article Supporting Education for Refugees: Teacher Professional Development in Emergency Contexts 20 June 2024

- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Advanced Cutoff
- JEE Main Cutoff
- MHT CET Result 2024
- JEE Advanced Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- AP EAMCET Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2024
- CAT 2024 College Predictor
- Top MBA Entrance Exams 2024
- AP ICET Counselling 2024
- GD Topics for MBA
- CAT Exam Date 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Asnwer Key 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET DU CSAS Portal 2024
- CUET Response Sheet 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET PG Counselling 2024
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Women's Education Essay
Essay on women's education -.
Education for women has been a global concern for many decades, with organisations and governments working towards providing equal opportunities and education for all genders. According to UNESCO, there are still significant disparities in education attainment between men and women, particularly in low-income countries.
100 Words Essay On Women's Education
Women's education is critical to empowering women and promoting gender equality. Education helps women break the cycle of poverty and provides them with opportunities for personal and professional growth. It also leads to better health outcomes and reduced population growth rates.
Women who are highly educated are more likely to be active participants in the political and social process and are better equipped to advocate for their rights and those of their families. Educated women are also more likely to prioritise their children's education, perpetuating a positive cycle of education and empowerment. The government has implemented several programs and policies to promote girls’ education, including the Right to Education Act, which ensures that all children between the ages of 6 and 14 have access to free and compulsory education.
200 Words Essay On Women's Education
Education is one of the most fundamental human rights essential for individuals and society's overall development and progress. Women's education is significant in this regard, as it has already been proven to be one of the most effective ways to empower our women and promote gender equality.
Why Women Education Is Necessary
Studies show that educating women leads to improved health, well-being for themselves and their families, and greater economic growth and stability. Women who are educated are more likely to participate in the workforce and have higher-paying jobs, which contributes to the overall prosperity of communities. In addition, educated women are more likely to make informed decisions for themselves and their families, leading to better health outcomes.
Challenges Faced
However, despite the numerous benefits, many girls and women worldwide still face significant educational barriers. Poverty, cultural norms, and lack of access to resources are just some challenges preventing girls from attending school. Governments, civil society organizations, and international bodies must work together to provide equal educational opportunities for all, regardless of gender.
In India, education for women has improved over the years. However, there are still challenges, such as socio-cultural barriers, poverty, and lack of access to education facilities that hinder the education of many girls. However, despite the numerous benefits of women's education, there are still many barriers to its attainment, including poverty, cultural norms, and limited access to educational resources. Despite the efforts, the literacy rate among women in India remains lower than that of men, and there is still much progress.
In conclusion, educating women is a basic human right and crucial for promoting gender equality, reducing poverty, and advancing economic development. We must work towards creating a world where every girl and woman has access to quality education and is empowered to reach their full potential.
500 Words Essay On Women's Education
Women's education is crucial to a society's development and growth. It is widely recognised that educating women can have many positive impacts not just on the women themselves but also on their families, communities, and even entire countries.
The Importance Of Women's Education
The importance of women's education cannot be overstated.
Education empowers women to make informed decisions, increases their employment opportunities, and improves their economic status.
Education also leads to better health outcomes for women and their families.
Women educated are more likely to seek medical care, use contraception, and vaccinate their children, resulting in improved health outcomes for both mothers and children.
Additionally, educated women are more likely to participate in the political process and advocate for their rights, leading to a more equitable and just society.
Challenges To Women Education
Despite the many benefits of women's education, numerous challenges still prevent women from accessing education. These challenges vary from country to country, but some of the most common obstacles include poverty, cultural attitudes, lack of infrastructure, and conflict. In many developing countries, families cannot afford to send their daughters to school, and girls are often forced to work instead of attending school. In addition, cultural attitudes that view women as inferior to men and discourage their education also significantly limit women's access to education.
Another major challenge is the need for more infrastructure in many rural and underdeveloped areas. Schools in these areas are often of poor quality and need more basic facilities like clean water, toilets, and electricity. This makes it difficult for girls to attend school, especially during their menstrual periods.
Initiatives
Several strategies can be implemented to overcome these challenges and ensure that women have access to education.
Firstly, governments and organisations can provide financial assistance to families so that they can afford to send their daughters to school. This can be done through scholarships, school fee subsidies, and other forms of financial support.
Secondly, efforts must be made to change cultural attitudes and challenge gender-based discrimination. This can be done through education campaigns, media, and community engagement.
Real-Life Examples On Women’s Education
These are some examples of organisations working towards promoting women's education in India.
Kasturba Gandhi National Memorial Trust | This was founded by Mahatma Gandhi. This organisation provides education and training programs for women in rural areas of India.
SABLA | The Rajiv Gandhi Scheme for Empowerment of Adolescent Girls provides education and nutrition support to young girls in India.
Pratham Education Foundation | This non-profit organisation works to improve the educational quality for underprivileged children, with a special focus on girls.
Akshaya Patra Foundation | This organisation provides mid-day meals to school-going children, including girls, to improve their attendance and retention.
Room to Read | This global organisation focuses on girls' education in India and other developing countries, providing support for literacy and gender equality programs.
Women's education is crucial for promoting gender equality and ensuring the overall development of society. Despite significant progress made in the past few decades, there still exists a significant gender gap in education worldwide, particularly in developing countries. It is important to address the cultural, social, and economic barriers that prevent women from accessing education.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Accepted by more than 11,000 universities in over 150 countries worldwide
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

- High contrast
- Press Centre
Search UNICEF
Girls' education, gender equality in education benefits every child..

- Girls' education
- Available in:
Investing in girls’ education transforms communities, countries and the entire world. Girls who receive an education are less likely to marry young and more likely to lead healthy, productive lives. They earn higher incomes, participate in the decisions that most affect them, and build better futures for themselves and their families.
Girls’ education strengthens economies and reduces inequality. It contributes to more stable, resilient societies that give all individuals – including boys and men – the opportunity to fulfil their potential.
But education for girls is about more than access to school. It’s also about girls feeling safe in classrooms and supported in the subjects and careers they choose to pursue – including those in which they are often under-represented.
When we invest in girls’ secondary education
- The lifetime earnings of girls dramatically increase
- National growth rates rise
- Child marriage rates decline
- Child mortality rates fall
- Maternal mortality rates fall
- Child stunting drops
Why are girls out of school?
Despite evidence demonstrating how central girls’ education is to development, gender disparities in education persist.
Around the world, 129 million girls are out of school, including 32 million of primary school age, 30 million of lower-secondary school age, and 67 million of upper-secondary school age. In countries affected by conflict, girls are more than twice as likely to be out of school than girls living in non-affected countries.
Worldwide, 129 million girls are out of school.
Only 49 per cent of countries have achieved gender parity in primary education. At the secondary level, the gap widens: 42 per cent of countries have achieved gender parity in lower secondary education, and 24 per cent in upper secondary education.
The reasons are many. Barriers to girls’ education – like poverty, child marriage and gender-based violence – vary among countries and communities. Poor families often favour boys when investing in education.
In some places, schools do not meet the safety, hygiene or sanitation needs of girls. In others, teaching practices are not gender-responsive and result in gender gaps in learning and skills development.

Gender equality in education
Gender-equitable education systems empower girls and boys and promote the development of life skills – like self-management, communication, negotiation and critical thinking – that young people need to succeed. They close skills gaps that perpetuate pay gaps, and build prosperity for entire countries.
Gender-equitable education systems can contribute to reductions in school-related gender-based violence and harmful practices, including child marriage and female genital mutilation .
Gender-equitable education systems help keep both girls and boys in school, building prosperity for entire countries.
An education free of negative gender norms has direct benefits for boys, too. In many countries, norms around masculinity can fuel disengagement from school, child labour, gang violence and recruitment into armed groups. The need or desire to earn an income also causes boys to drop out of secondary school, as many of them believe the curriculum is not relevant to work opportunities.
UNICEF’s work to promote girls’ education
UNICEF works with communities, Governments and partners to remove barriers to girls’ education and promote gender equality in education – even in the most challenging settings.
Because investing in girls’ secondary education is one of the most transformative development strategies, we prioritize efforts that enable all girls to complete secondary education and develop the knowledge and skills they need for life and work.
This will only be achieved when the most disadvantaged girls are supported to enter and complete pre-primary and primary education. Our work:
- Tackles discriminatory gender norms and harmful practices that deny girls access to school and quality learning.
- Supports Governments to ensure that budgets are gender-responsive and that national education plans and policies prioritize gender equality.
- Helps schools and Governments use assessment data to eliminate gender gaps in learning.
- Promotes social protection measures, including cash transfers, to improve girls’ transition to and retention in secondary school.
- Focuses teacher training and professional development on gender-responsive pedagogies.
- Removes gender stereotypes from learning materials.
- Addresses other obstacles, like distance-related barriers to education, re-entry policies for young mothers, and menstrual hygiene management in schools.
More from UNICEF

1 in 3 adolescent girls from the poorest households has never been to school

Let’s shape tech to be transformative
Gender-responsive digital pedagogies: A guide for educators

Stories of suffering and hope: Afghanistan and Pakistan
Catherine Russell reflects on her first field visit as UNICEF's Executive Director

Where are the girls and why it matters as schools reopen?
School closures due to the COVID-19 pandemic risk reversing the massive gains to girls’ education
Advancing Girls' Education and Gender Equality through Digital Learning
This brief note highlights how UNICEF will advance inclusive and transformative digital technology to enhance girls’ learning and skills development for work and life.
Reimagining Girls' Education: Solutions to Keep Girls Learning in Emergencies
This resource presents an empirical overview of what works to support learning outcomes for girls in emergencies.
e-Toolkit on Gender Equality in Education
This course aims to strengthen the capacity of UNICEF's education staff globally in gender equality applied to education programming.
Fixing the Broken Promise of Education for All
This report draws on national studies to examine why millions of children continue to be denied the fundamental right to primary education.
GirlForce: Skills, Education and Training for Girls Now
This report discusses persistent barriers girls face in the transition from education to the workforce, and how gender gaps in employment outcomes persist despite girls’ gains in education.
UNICEF Gender Action Plan (2022-2025)
This plan specifies how UNICEF will promote gender equality across the organization’s work, in alignment with the UNICEF Strategic Plan.
Global Partnership for Education
This partnership site provides data and programming results for the only global fund solely dedicated to education in developing countries.
United Nations Girls’ Education Initiative
UNGEI promotes girls’ education and gender equality through policy advocacy and support to Governments and other development actors.
The US role in advancing gender equality globally through girls’ education
In 1995, just after the 75th anniversary of the 19th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, then-First Lady Hillary Rodham Clinton gave a historic speech in Beijing at the United Nations Fourth World Conference on Women. There, she famously declared that “human rights are women’s rights, and women’s rights are human rights,” discursively weaving the struggle for gender equality in the U.S. to the struggle for gender equality around the world.
As the U.S. commemorates the centenary of the 19th Amendment and the world celebrates 25 years since the Beijing Platform for Action —which set a global agenda to remove systemic barriers holding back women’s full participation in public and private life—there is much stocktaking that the U.S. needs to do with regard to its role in advancing gender equality beyond our borders. In particular, the U.S. government’s role in promoting girls’ education, a key pathway to achieving gender equality, must be stepped up significantly.
Why girls’ education?
Girls’ education, alongside improved sexual and reproductive health and rights, has often been cited as the world’s best investment , the key to enabling girls and women more agency in their homes, communities, and countries. Educating girls contributes later to their increased formal economic opportunity and wages , decreases in pregnancy and early marriage , reduction in child and maternal mortality , better educated children when they do bear children, increased participation in politics , and decreased climate risk vulnerability . The list of spillover effects from an investment in girls’ education runs long as a result of empowered women; healthier families; and more resilient economies.
In the United States, progress in the education of women and girls has been an important step to (and byproduct of) advancing gender equality in all facets of domestic and work life. The story of female education and progress toward gender equality has been similar in many other high-income and upper-middle income countries around the world. But it has been patchwork or stalled in many low-income countries due to geopolitical, economic, and social barriers, as well as a lack of funding targeting countries with the greatest gender gaps in education.
An uneven story of progress, threatened by COVID-19
While women in the U.S. were surpassing men in earning doctoral degrees in the early 2000s , the number of illiterate women in low-income countries was actually increasing by 20 million between 2000 and 2016 )—although this trend was primarily the result of decades of exclusion from education as girls aged into adulthood. During this same period, access to education for successive cohorts of girls began to increase as the era of the Millennium Development Goals ushered political attention to address gender gaps in education. Indeed, in just under two decades, gender gaps in education closed tremendously. Between 2000 and 2018, the number of primary school aged girls out of school fell by 44% , and by 2019 nearly two-thirds of countries had achieved gender parity in primary education. However, progress has plateaued over the last decade. Conflict in Northern Africa and Western Asia have made the region furthest from parity in primary education, and gender gaps in secondary education persist in sub-Saharan Africa.
Some of the barriers obstructing progress in low-income countries include gender discriminatory policies like prohibiting pregnant schoolgirls and adolescent mothers from attending school; gender-blind education budgets that may disproportionately benefit boys; gender-insensitive school facilities that may discourage girls and female teachers from attending school especially during their menstrual cycles; gender biased curriculum and teaching that may teach girls their future is in the marriage market rather than the labor market; and harmful gender practices like child marriage and female genital mutilation that may lead to girls dropping out of school prematurely.
Analysis at the Brookings Institution estimates that education gaps between rich and poor girls will take a long time to close; universal secondary education for the poorest girls in sub-Saharan Africa is estimated to be achieved by 2111. When it comes to individual countries, these gaps may take even longer to close .
The COVID-19 pandemic is worsening this timeline. Girls’ increased burden on domestic work and unpaid care during stay-at-home orders, their increased vulnerability to gender-based violence due to limited mobility during lockdown, and their lower access to technology and the internet means girls have less time and fewer resources to engage in remote learning , are at risk of unwanted and unplanned pregnancies , and are more likely to remain out of school when they eventually reopen. We don’t yet have a full understanding of what the long-term effects of COVID-19 school closures will be on girls, but research from previous protracted school closures suggests that learning loss combined with girls’ unique vulnerabilities can have long-term consequences for girls and the road to gender equality.
Prior to the pandemic, estimates suggest that 130 million girls were out of school around the world. If countries like the U.S. do not actively work to ensure special attention is paid to girls in the COVID-19 recovery plans of countries where girls face increased vulnerabilities, there could be an additional 20 million girls globally who do not return to school.
A troubling trend toward realizing gender equality through education
Since First Lady Clinton’s speech, girls’ education has become a political priority among many governments and high-level political fora promoting gender equality. The money appeared to have followed, most notably in the last decade as corporate engagement in girls’ education increased and as special funds, like the UK Department for International Development’s Girls’ Education Challenge , were dedicated. In 2010, 20% of overseas development assistance (ODA) targeted at gender equality went to the education sector, making the education sector the largest recipient of ODA targeting gender equality . But in 2018, while the overall ODA bucket to gender equality nearly doubled (from US$25.3 billion in 2010 to US$48.7 billion ), the education sector’s share has been halved .
Moreover, globally, investment decisions have not always appeared to be made on the assessment of need alone. For example, a Brookings analysis of multilateral, bilateral, foundation, and corporation financing of girls’ education found that countries with some of the largest gender gaps in education were not receiving any ODA or philanthropic donor funding targeting gender equality in education.
So, while investments toward promoting gender equality are on an upward trend, countries may be losing sight of the importance of investing in girls’ education as a critical entry point. And, those funds that have been allocated may not be targeting geographies where the road to gender equality is the longest and hardest.
A troubling trend in U.S. leadership
Amidst this global trend in girls’ education leadership and financing, it appears that the United States may be moving in the wrong direction for girls as well. Indeed, the U.S. record on advancing gender equality overseas has been inconsistent and highly dependent on the incumbent administration’s priorities. The last few years suggest a troubling trend.
Under the Obama administration, bilateral, allocable aid targeting gender equality grew from 0.05% to 7.91% of total aid between 2009 and 2016 . Within his first week in office, President Obama signed into law legislation that would strengthen women’s ability to challenge pay discrimination in the U.S., setting in motion a host of government initiatives and programs that would signal his feminist presidency at home and to the world. During this time, too, the U.S. adopted a whole of government approach to empower adolescent girls, which focused attention on enhancing girls’ access to quality education among other strategies to enhance the status of girls, improve girls’ health, and build girls’ leadership.
However, the Trump administration brought quick rollbacks. Notwithstanding his unabashed parading of misogyny and sexism, within his first 100 days in office President Trump reinstated and expanded President Reagan’s Global Gag Rule , which cut all federal aid associated with efforts to provide girls and women access to safe family planning, and derailed Let Girls Learn , First Lady Michelle Obama’s initiative targeting educational opportunities for adolescent girls. Such signaling was followed by a host of setbacks for gender equality in the U.S. and a sharp fall in the percentage of U.S. aid (to 2.6% by 2018) aimed at principally advancing gender equality overseas.
Although Ivanka Trump, an advisor to the president, spearheaded the Women’s Global Development and Prosperity Initiative in 2019 as a means of maintaining U.S. foreign policy objectives in women’s economic empowerment, there is a notable absence of attention to girls’ education and family planning—two important factors to ensuring women’s economic inclusion. And while attention to girls’ education is present in USAID’s 2020 draft, Gender Equality and Women’s Empowerment Policy , the absence of attention to “gender-related power imbalances” (which was referenced in the 2012 policy), sexual and reproductive health and rights, and girls’ and women’s access to comprehensive family planning, means that efforts to advance gender equality through education will ultimately fall short.
As things currently stand, the U.S. has gone from an intersectional approach to gender equality that sought to combat discrimination on multiple, simultaneous, and intersecting fronts, to one that is piecemeal, incoherent, and takes several steps backward .
Three actions to reverse course
As we mark 100 years since the 19th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution and 25 years since the Beijing Declaration, we must consider that girls today in developing countries do not have another 100 years to wait for gender equality. If humanity is to realize Generation Equality by 2030, the U.S. has an important role to play in helping other countries “ build back equal ” for girls, especially in the wake of COVID-19. It can start in three ways:
1. Adopt a feminist foreign policy . A feminist foreign policy can be defined as: “the policy of a state that defines its interactions with other states … in a manner that prioritizes peace, gender equality and environmental integrity [and] seeks to disrupt colonial, racist, patriarchal and male-dominated power structures.” To date, only five countries (Sweden, Canada, France, Luxembourg, and Mexico) have adopted a feminist foreign policy—although many more countries have declared being a feminist government.
The U.S. should lead the charge in the second wave of countries adopting a feminist foreign policy. It can do so by centering girls’ education (as well as girls’ sexual and reproductive health and rights) into U.S. foreign policy, national security, international development, and humanitarian assistance. With such strong returns on investments in girls’ education and the current lack of such funding in the regions that need it most, girls’ education is low-hanging fruit when it comes to advancing progress in gender equality and promoting girls’ and women’s full participation in public and private life.
This idea already has momentum on Capitol Hill. In September, Congresswomen Jackie Speier (CA-14), Lois Frankel (FL-21), and Barbara Lee (CA-13) introduced legislation to support the goals of a feminist foreign policy. Their legislation calls for a U.S. foreign assistance policy among others that will “promote gender equality and focus on the experience of women and people who experience multiple and intersecting forms of discrimination, such as gender-based violence, lack of access to sexual and reproductive health, lack of access to education, and the burden of unpaid care responsibilities.”
2. Increase ODA toward gender equality as a principal goal . Feminist advocates recommend that countries should allocate at least 20 percent of their total aid to investments with gender equality as a principal objective, and at least 85 percent as a significant objective. Presently, the U.S. is far below the OECD average and trails behind Sweden and Canada, two governments that have adopted a feminist foreign policy. Although the U.S. is the fourth largest net funder of gender equality ODA, this amount reflects only 21% of its overall aid (compared to 90% in Canada and 87% in Sweden). The U.S. needs to dramatically increase its gender equality ODA if it wants to walk its talk.
3. Give way to gender transformative leadership . Research has pointed to the important role of transformative leadership to promote progress in girls’ education specifically and gender equality broadly. Such leadership is needed not only at the level of individual political leadership (e.g., President and First Lady Obama, Congresswoman Nita Lowey, former Executive Director of the White House Council on Women and Girls Tina Tchen, etc.), but also through collective political leadership (e.g., through whole of government approaches, bipartisan working groups, cross-agency partnerships, and the members of the Democratic Women’s Caucus pushing for a feminist foreign policy today). Luckily, the U.S. isn’t short on transformative feminist leaders whose leadership on issues of gender equality should be amplified throughout U.S. international development programs, including education.
Congress doesn’t have to start from scratch when it comes to enabling policy frameworks for greater feminist action. For example, Congress passed the bipartisan Reinforcing Education Accountability in Development (READ) Act in September 2017, making it easier for the U.S. to partner with other countries and organizations to promote basic education in developing countries. Congress should use this groundwork to further advance legislative efforts that identify and address the specific barriers girls face in accessing and completing quality, gender transformative education around the world. Requiring outward facing departments such as the Department of State and USAID to develop strategies that bolster adolescent girls’ participation in democracy, human rights, and governance would help cement women’s and girls’ rights in the center of foreign policy decisions instead of being tacked on to programs with other aims.
There never was a better moment to take stock of the United States’ role in advancing gender equality at home and overseas. As the world is still trying to land on its feet from the COVID-19 shock, a fuller commitment to girls’ education through a U.S. feminist foreign policy could help reinvigorate global progress toward gender equality. In another 100 years, we should hopefully be able to look back and say that universal education for girls did for women and girls in the world what the enactment of the 19th Amendment did for gender equality in the U.S.
I would like to thank Katie Poteet for providing valuable research assistance.
This piece is part of 19A: The Brookings Gender Equality Series. Learn more about the series and read published work »
About the Author
Christina kwauk, fellow – global economy and development, center for universal education, more from christina kwuak, congress may now have historic female representation, but women in leadership still have a long way to go.
Last week, the 116th U.S. Congress was sworn in. Regardless of where you sit on the political spectrum, the country has much to celebrate in its historic increase in representation by women, from 19 percent in 2017 to 24 percent in 2019, lifting us—finally—to the world average (24 percent) of women in national parliaments or congressional […]

Education’s role in building back better for the planet
The COVID-19 pandemic is a stark reminder that we live in a socio-ecological system in which our human systems are deeply interconnected with our natural systems. Yet our education systems do not educate us to recognize, respect, or nurture this interdependency. The zoonotic nature of the coronavirus has exposed how human-caused environmental degradation and destruction […]

National climate strategies are forgetting about girls, children, and youth
In Madrid this week, the 25th session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP25) meets to finalize key decisions of the Paris Agreement before implementation next year. With countries set to submit revised Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs—or, a country’s plan to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions […]
MOre from 19a Series

A global story: Women’s suffrage, forgotten history, and a way forward
“Julia Gillard, the first woman to serve as Australia’s prime minister, outlines policies to break down the structures that prevent women from being elected to office or becoming leaders.”

The fate of women’s rights in Afghanistan
John R. Allen and Vanda Felbab-Brown write that as peace negotiations between the Afghan government and the Taliban commence, uncertainty hangs over the fate of Afghan women and their rights.
- Media Relations
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 2: Women and Education
Chapter summary.
- Why Educating Girls Matters
- How Girls and Women Have Fared since Beijing
- What We Can Learn from Successful Efforts?
- Profile: Rita Conceição
- Project: Educating Women about Technology
Additional Resources
This chapter discusses the right to education and provides several examples of non-profit organizations that are working towards enhancing education among women. Education escalated as a global priority during the 1990s, featured at the 1994 International Conference on Population and Development, the 1995 Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing, and the 2000 Millennium Summit. Prior to the adoption of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), evidence of the economic and social benefits resulting from educating women and girls began to accumulate. The links were clear: educated women are more likely to have fewer, healthier, and better-educated children that will survive into adulthood and ultimately contribute to economic growth. According to UNESCO, in 2008 there were 96 and 95 girls per 100 boys in primary and secondary school, respectively. While the chapter does not discuss tertiary education, additional resources below will fill in statistics on gender gaps in post-secondary, which continue to vary at national and regional levels; women outnumber men in the post-secondary environment of developed countries by a significant margin, yet are still underrepresented in high-paying disciplines such as science and engineering and constitute only 30 percent of researchers.
The chapter examines several organizations working to improve women’s education from the standpoints of both community organizing and technology education. Bahia Street was founded by Rita Conceição in the informal communities of Salvador, Brazil. It began as a lunch program and evolved into a community centre conducting social-justice education among black women and girls on racism, gender-based violence, and reproductive rights. In rural Senegal, the international organization Tostan formed the Community Empowerment Program (CEP) to integrate mobile technology into writing and literacy programs. This initiative was developed in Wolof, the local language, and the program’s exercises in learning to use mobile phones are carried out using culturally appropriate and recognizable symbols. Tostan also initiated the Rural Energy Foundation, a community-based project to provide solar-powered charging stations for mobile phones.
- Bahia Street
- Community Empowerment Program (CEP)
- Gender-based violence
- International non-governmental organization (INGO)
- Jokko Initiative
- Non-formal education
- Non-governmental organization (NGO)
- Non-profit organization
- Reproduction
- Sexual violence
- Rita Conceição
- Rural Energy Foundation
- United Nations Children’s Rights and Emergency Relief Organization (UNICEF)
- United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
- United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Millennium Summit
- United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
- 1994 International Conference on Population and Development
- 1995 Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing
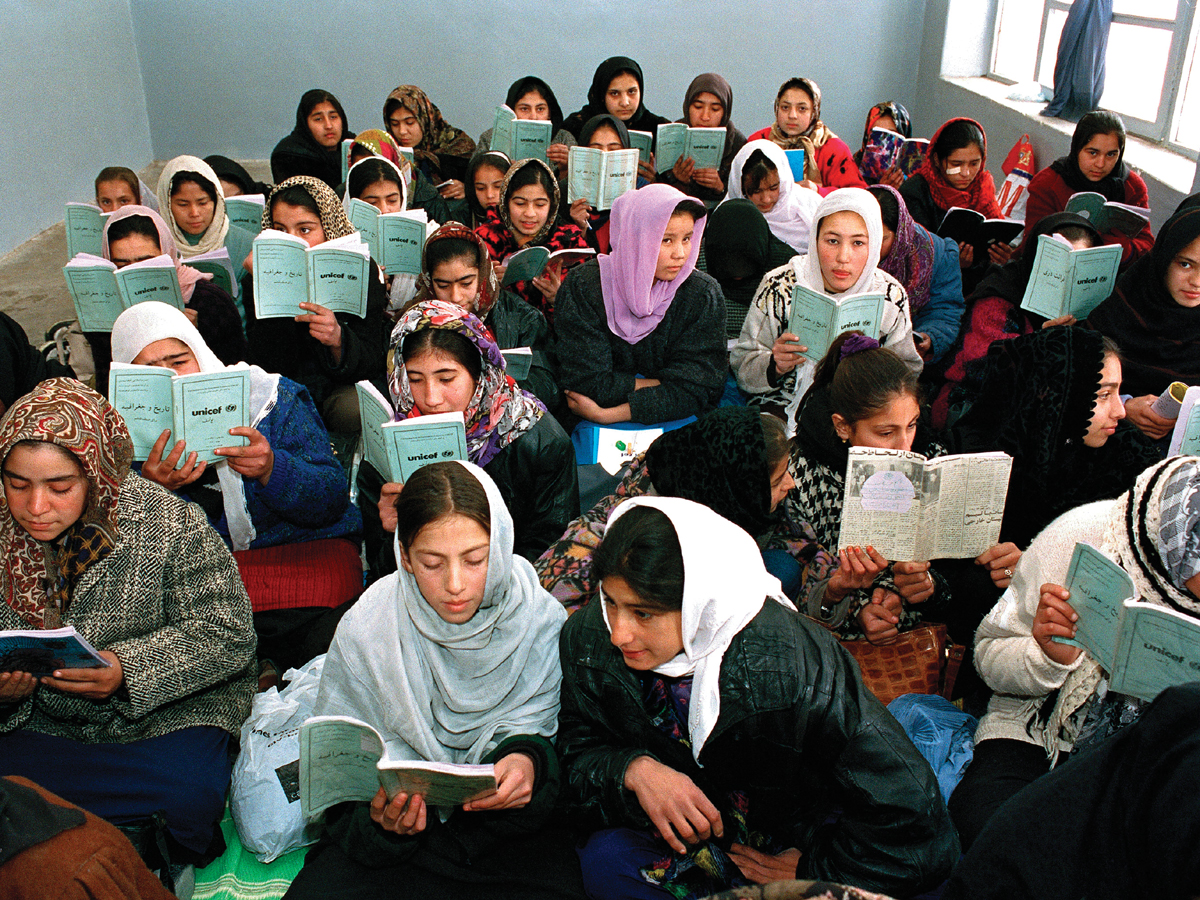

By Lori S. Ashford
T he right to education for all has been an international goal for decades, but since the 1990s, women’s education and empowerment have come into sharp focus. Several landmark conferences, including the 1994 International Conference on Population and Development, held in Cairo, and the 1995 Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing, placed these issues at the center of development efforts.
The Millennium Development Goals — agreed to by world leaders at the U.N. Millennium Summit in 2000 — call for universal primary education and for closing the gender gap in secondary and higher education. These high-level agreements spawned initiatives around the world to increase girls’ school enrollments. Changes since 1990 have been remarkable, considering the barriers that had to be overcome in developing countries.
In many traditional societies, girls are prevented from attaining their full potential because of lower priority placed on educating daughters (who marry and leave the family) and the lower status of girls and women in general. Families may also have concerns about the school fees, girls being taught by male teachers and girls’ safety away from home. Governments and communities have begun to break down these barriers, however, because of overwhelming evidence of the benefits of educating girls.
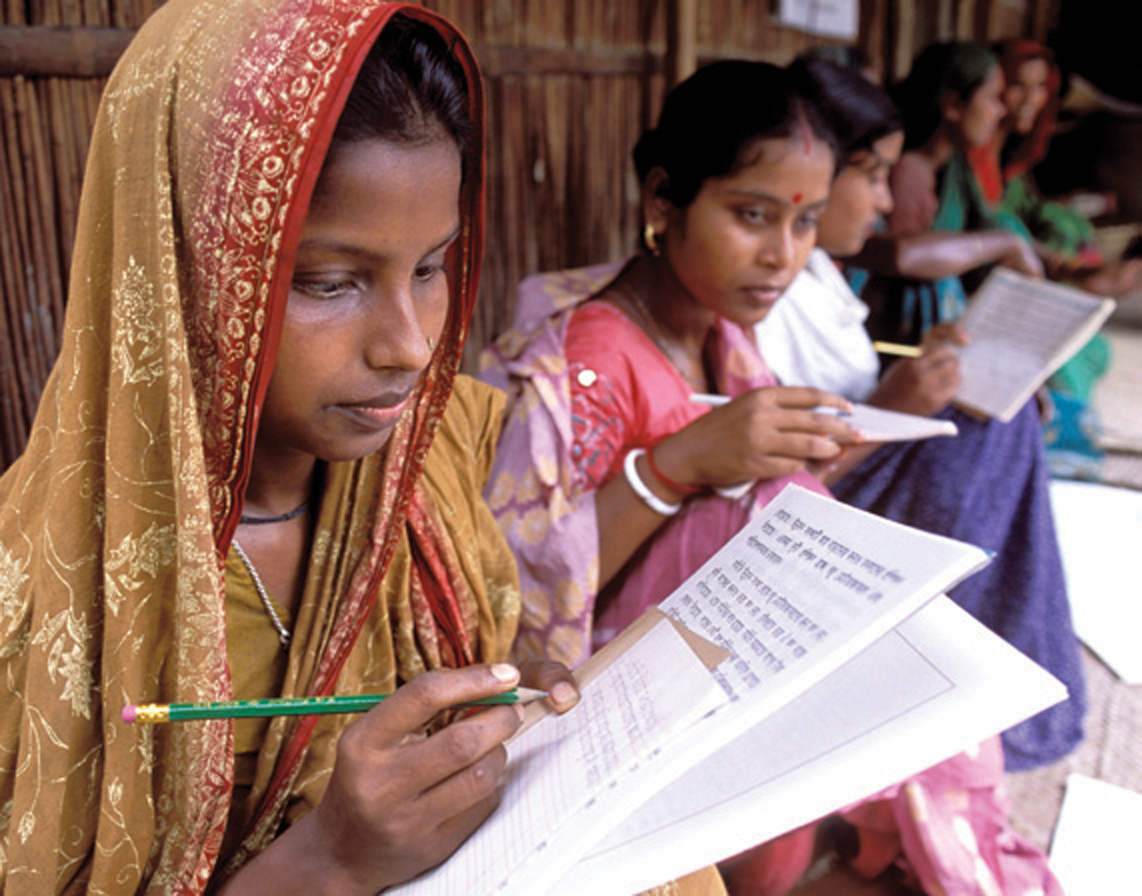

Why educating girls matters
Few investments have as large a payoff as girls’ education. Household surveys in developing countries have consistently shown that women with more education have smaller, healthier and better-educated families. The linkages are clear: Educated women are more likely to take care of their health, desire fewer children and educate them well, which, in turn, makes it more likely their children will survive and thrive into adulthood.
Research by the World Bank and other organizations has shown that increasing girls’ schooling boosts women’s wages and leads to faster economic growth than educating only boys. Moreover, when women earn more money, they are more likely to invest it in their children and households, enhancing family wealth and well-being. Other benefits of women’s education captured in studies include lower levels of HIV infection, domestic violence and harmful practices toward women, such as female genital cutting and bride burning.

How girls and women have fared since Beijing
Advances in girls’ education worldwide have been a success story in development. According to UNESCO, 96 girls were enrolled in primary school for every 100 boys in 2008, up from 84 girls per 100 boys in 1995. The ratio for secondary school is close behind, at 95 girls to 100 boys in 2008. By 2005, nearly two-thirds of countries had closed the gap between girls’ and boys’ school enrollments. Girls still lag behind boys in university-level education worldwide, but the gap is closing over time.
Girls lag farthest behind in the poorest countries, such as Afghanistan, Chad, Central African Republic and Mali, where overall school enrollments are low. In Somalia, only half as many girls are enrolled in school as boys: 23 percent of girls compared to 42 percent of boys in 2008, according to UNESCO. Girls’ schooling and literacy lag well behind boys in much of sub-Saharan Africa and Western and Southern Asia, where much work remains to be done.
At the other end of the spectrum, in countries with high levels of school enrollment, girls often fare better than boys. In much of Latin America, Europe, East Asia and in the United States, girls’ enrollments in secondary and higher education have surpassed those of their male peers, demonstrating what girls and women can achieve once the barriers to education have been overcome.
Still, women account for two-thirds of the world’s illiterate adults, because older women are less likely to have attended school than their younger counterparts. They are also much more likely to be illiterate if they are poor and live in rural areas. Literacy programs and continuing education exist, but the efforts are not systematically reported across countries. In addition, girls and women are disadvantaged when it comes to technical and vocational education, in fields such as science and technology that have long been dominated by men.
What can we learn from successful efforts?
Many gains in women’s education can be attributed to special interventions such as the elimination of school fees, scholarships, community schools for girls and the training of women teachers. Such targeted efforts have translated into higher girls’ school enrollments in countries as diverse as Bangladesh, Yemen, Morocco, Uganda and Brazil. Political commitment is essential for raising the profile of the issue and increasing girls’ access to schooling. Mexico pioneered a major social program — now replicated in impoverished communities in the United States and other countries — that pays families to keep their children, particularly girls, in school.
Because the gender gap is wider at higher levels of education, it will not be enough for girls to merely sign up for school; they need to stay in school. Governments, educators and communities must address issues such as gender stereotypes that reinforce women’s lower status, poor school quality, and early marriage and childbearing, which often cut short women’s education. Also, the mismatch between education and the skills needed for today’s workforce must be corrected. These steps may ensure that girls reap the greatest benefits from education. Countries that are committed to gender equality will not only see better report cards in education, they’ll be healthier and wealthier as well.
Lori S. Ashford, a freelance consultant, has written about global population, health and women’s issues for 20 years. Formerly with the Population Reference Bureau (PRB), she authored the widely disseminated PRB “Women of Our World” data sheets and “New Population Policies: Advancing Women’s Health and Rights” for the Population Bulletin, among other publications.
PROFILE: Rita Conceição – Bahia Street
By Margaret Willson
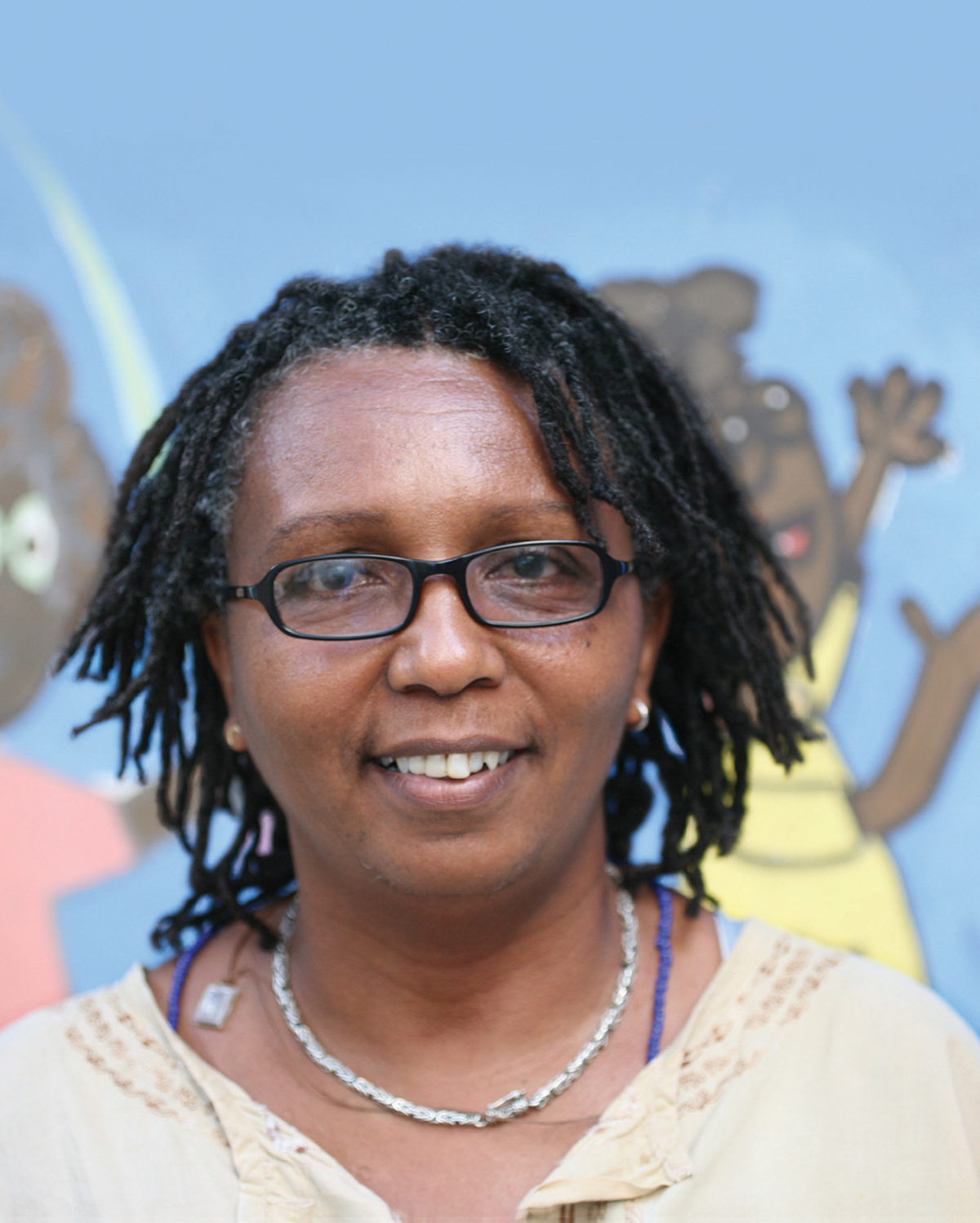

B orn in one of the vast shantytowns of Salvador, Brazil, Rita Conceição knew at an early age the realities of violence, poverty and death. She also knew she wanted something different.
“My mother had lots of children and a hard life. She died young, so I brought up my brothers and sisters. I knew I didn’t want that life.”
With great determination, Rita traveled more than an hour each way by public bus to a school where she could learn to read and write. She loved the arts and took up photography. While still a teenager, Rita took courageous photos of protests against the then-ruling Brazilian military dictatorship.
“I didn’t think of a black or gender consciousness,” she says. “People never talked about racism then.” But all around her she saw women like herself working as maids for slave wages, the only job (except prostitution) open to them.
Rita decided she wanted to go to university, an almost impossible dream for someone from the shantytowns. While working a full-time job, she tried the difficult university entrance exam three times and failed. Refusing to give up, she took it a fourth time and passed, gaining entrance into the Federal University of Bahia, the best in her state.
When I first met Rita in 1991, she had earned her university degree in sociology. Once she had a chance to leave the shantytown where she was born, Rita, unlike any other person I ever met there, decided instead to stay and fight the inequality she knew so well. So in 1996, when she invited me to join her in working for equality for the people of her communities, I committed to help in any way I could. From this partnership the nonprofit Bahia Street was born.
Listening to what the people in her community told her answered their dire need for expression and opened a strong avenue for change. Rita initiated a quality education program for girls that would allow them to enter university and change their futures. Rita drew on her own struggles, using the strengths that propelled her from a shantytown to university. She incorporated race and gender consciousness into the Bahia Street classes. Seeing that the girls could not study because they were half starving, she began a lunch program, cooking and buying the food herself until she could find someone to help her. She knew that most girls from these shantytowns get pregnant by age 14, so she began teaching the girls about reproduction, sexual violence and self-esteem.
“As I was growing up,” she says, “the girls in my family were never valued as much as the boys. This still exists in our society, but I say to the girls that their roots are their reality. I pass on to them the importance of ethics, self-respect and the solidarity of women. They see in me the difference it makes — what choices you make in your life — and also the strength it takes. If women are to become equal, these qualities and knowledge are vital.”
After years of renting or borrowing tiny rooms for its classes, Bahia Street was finally able to buy a building. The only problem was that the building was falling down. Rita saw this as no problem at all. She employed local men and oversaw its complete reconstruction. To save money, the men mixed the cement in wheelbarrows and poured it by hand. Rita roamed the city, looking for sales; she negotiated with merchants to donate materials that she then brought back on public bus, since she had no car. Slowly, the building took shape. When the first floor was mostly finished, Rita, her staff and the girls moved in.
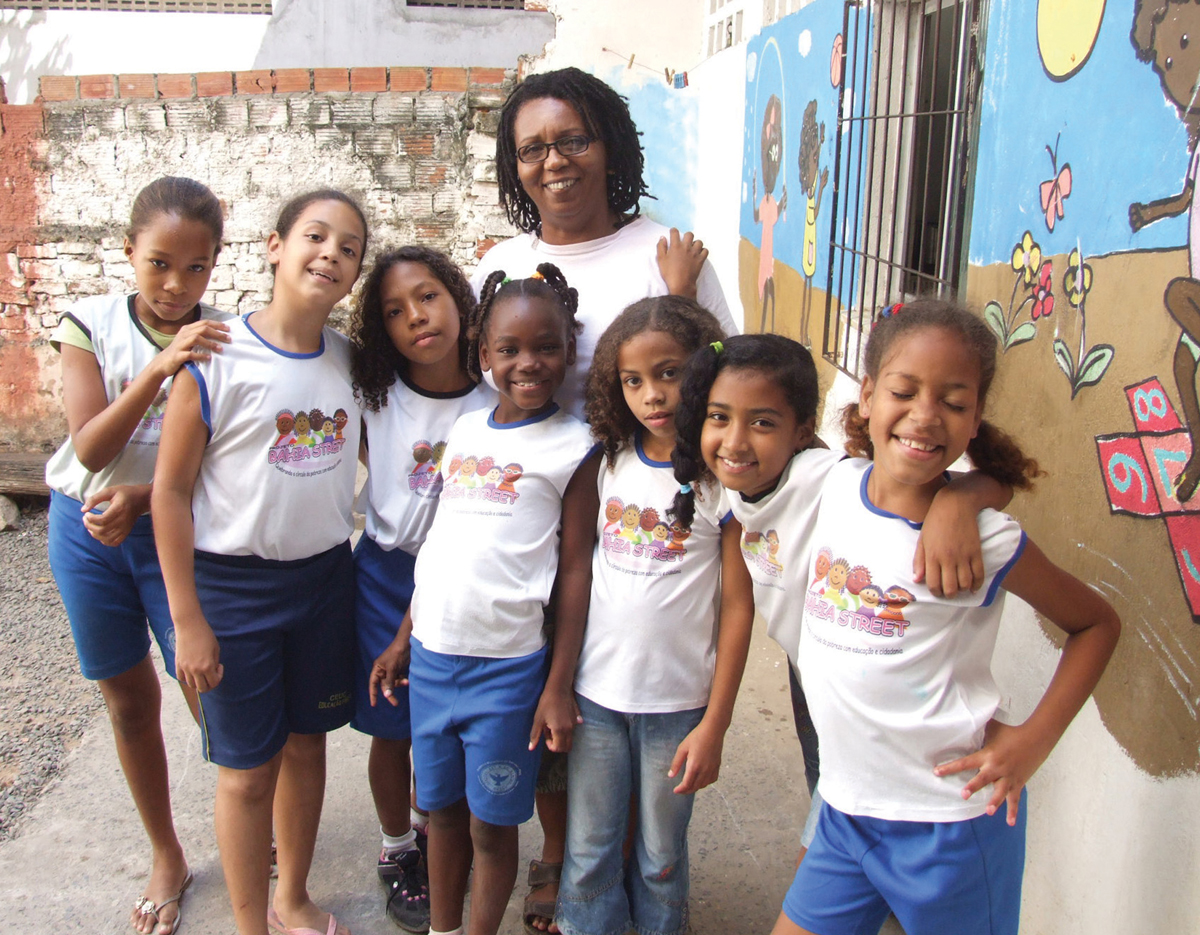

The five-story Bahia Street Center is now complete, with classrooms, kitchen, library, computer lab and much more. In addition to education and support programs for the girls, Bahia Street now offers classes for the girls’ caregivers and other community members. It has become a haven for the girls and a community gathering place.
“We teach the girls to take care of others in their lives as well. Women take care of the children, and in that is the future of our society. The work we do is a form of black resistance. We are working for the survival of the black people in Bahia, showing that as black women, we can have equality and shape the future. In Bahia Street, we are giving girls the chance my mother never had.”
When people talk with her about her remarkable achievements, Rita is humble and realistic. “In Bahia Street,” she says, “I really found my identity. Managing to create Bahia Street continues to be an amazing process, and I have learned a consciousness myself through this process.”
Recently, Bahia Street graduate Daza completed university with a journalism degree. In Daza, shantytown residents have a voice they never had before. And the long-term Bahia Street vision of fostering equality for shantytown women is becoming a reality.
Rita laughs with a smile that, in its brightness, knows suffering, love and strength. “And the work continues. That is the way for all of us. If we are to make a better world, the work is what we do.”
Margaret Willson is co-founder and international director of Bahia Street. She is affiliate assistant professor in anthropology at the University of Washington. Her most recent book is Dance Lest We All Fall Down: Breaking Cycles of Poverty in Brazil and Beyond (University of Washington Press, 2010).
PROJECT: Educating Women About Technology
By Renee Ho
Mobile technology is improving the lives of illiterate women and girls in rural Senegal, and educating them in the process, thanks to an organization that teaches them to use mobile phones.
A stou watches as the photographer raises his camera to capture the crowded village classroom. She adjusts her nursing infant and turns her own camera on him — only hers is a mobile phone. For the past few weeks, Astou has been participating in a community-led mobile technology course taught in her local language of Wolof. She and hundreds of other women and girls throughout rural Senegal have learned how to make and receive calls, compose and send SMS messages and use phone functions such as calculators, alarms and, yes, sometimes even cameras.
Astou is a bright 24-year-old mother of four children. She had seen her husband use a mobile phone, but prior to this class she had never touched one herself. “Before, he would not let me use the phone because he feared I would waste the credit,” she laughs, “but now he asks me to teach him and we are saving to buy another for me.”
Two years ago, Astou was not only unfamiliar with how to use a mobile phone, but she was illiterate. Composing or reading an SMS text message would have been impossible for her. Like most of the women and girls in her village in the region of Vélingara, Senegal, Astou never attended school. Household responsibilities and the cost of schooling prevented her from receiving a formal education. She married at 16 years of age — the average age for girls in rural Senegal.
In a country with a 41.9 percent literacy rate, Astou is breaking norms and the cyclical trap of poverty. In 2008, Tostan, an international nongovernmental development organization, started the Community Empowerment Program (CEP) — a 30-month human rights-based, nonformal education program — in her village. More than 80 percent of CEP participants are women and girls. They begin the program with sessions on human rights, democracy, health and hygiene and problem-solving. Later, they continue with lessons on literacy, numeracy and project management.
Once participants have achieved basic literacy, however, they often lack a practical means of maintaining it. As a solution, Tostan partnered with UNICEF to launch the Jokko Initiative in 2009 (jokko means “communication” in Wolof). The initiative incorporates mobile technology into CEP as way to reinforce reading and writing skills. The Jokko module teaches participants how to use basic mobile phone functions and SMS texting. It uses interactive visuals and skits that focus on relevant applications and the relative affordability of texting. “I text messages better [than my husband] and that saves us money on expensive calls,” explains Astou.
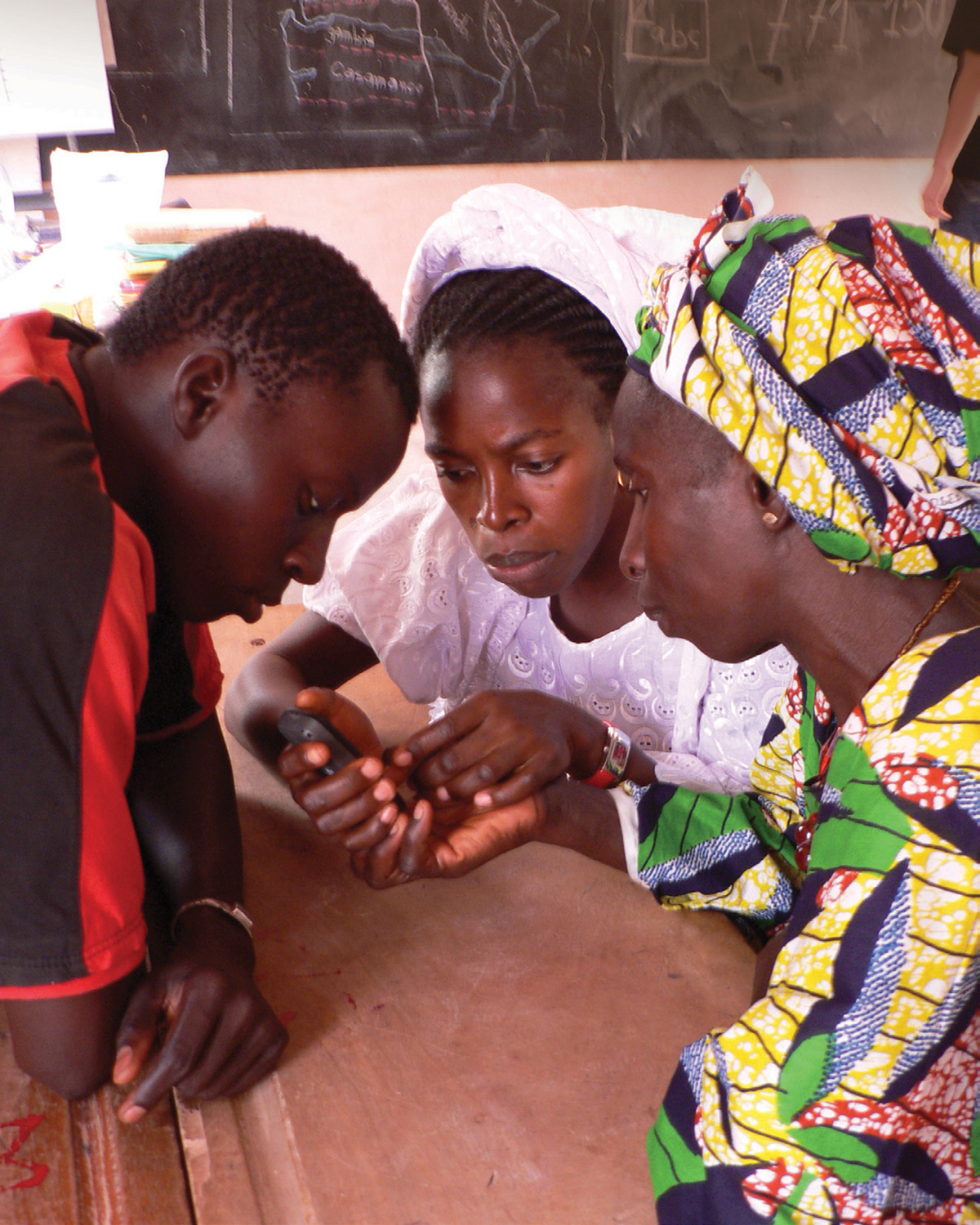

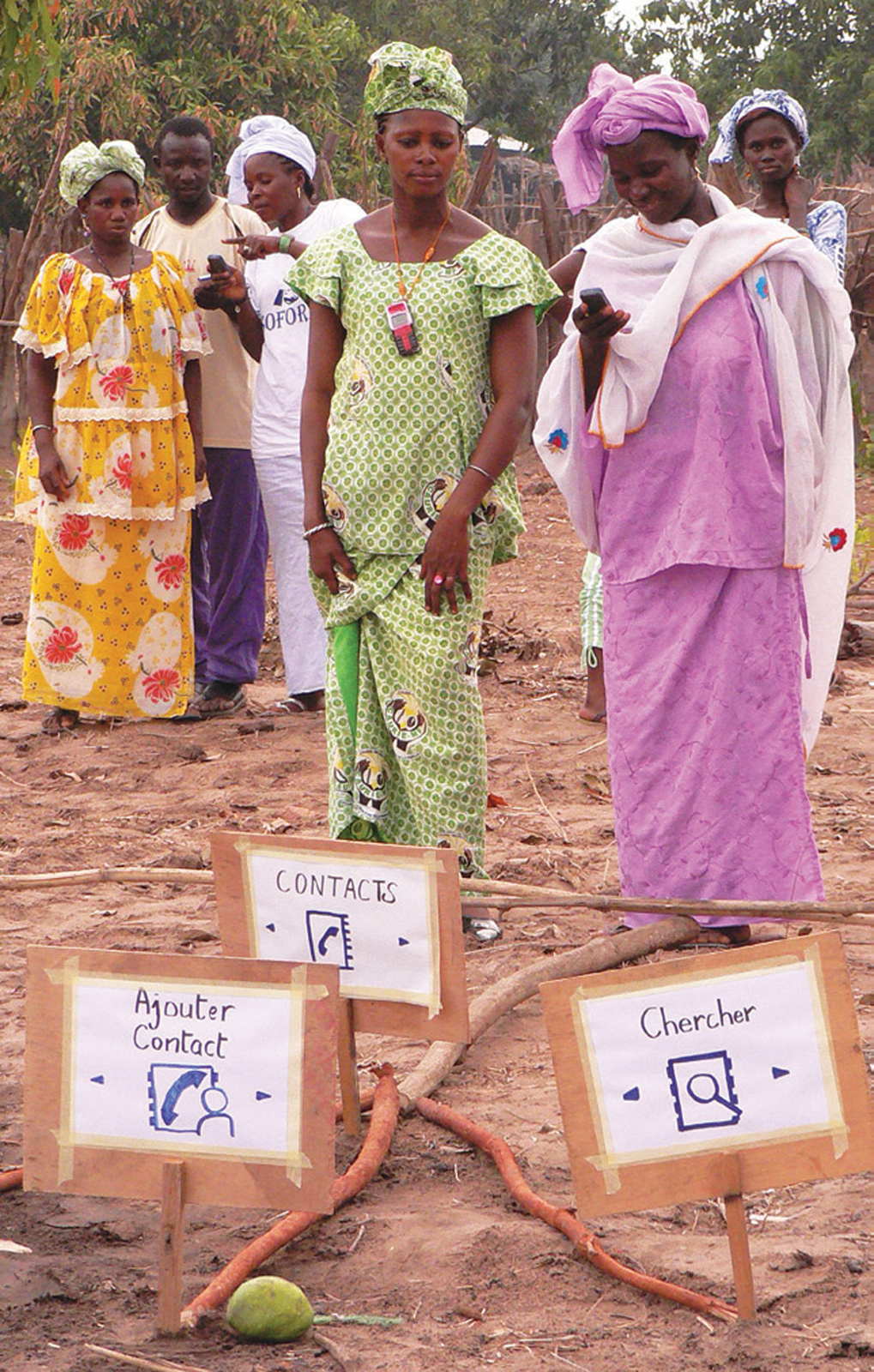
Outside of the classroom, students circle around a strange arrangement of sticks. With a little explanation, the sticks come to represent a mango tree. Khady, age 52, walks along the “tree branches” and stops at each fork where signs are placed: Contacts, Search, Add Contact. This activity teaches participants how to navigate the phone’s main menu. It is just one example of what makes Tostan’s educational model work: adapting lessons to cultural contexts and using appropriate local references.
“Before, if I wanted to send a text message, I had to ask for help,” Khady says, “but now I am much more independent. Now people come to me and I’m happy to teach them.” When mobile phone technology reaches women and girls, it amplifies their voices and influence in community decisionmaking. They become agents of their own change. Khady continues to explain how the CEP provided her with basic math and management skills. With several boys and girls huddled around, she demonstrates how the phone’s calculator helps her manage her peanut-selling business.
Mobile phone technology has connected women and girls to market information and opportunities, family in the diaspora and, perhaps most fundamentally, to each other. The phones have been critical for community organization and social mobilization. Tostan’s Jokko Initiative has developed a unique social networking platform that allows participants to send an SMS message to a central server, where it is then sent out to an entire community of other users. One participant explains, “It’s when you send multiple messages at once — a cheaper method of communication.” The platform is used for community advocacy campaigns. Women send, for example, reminders of vaccination and school enrollment dates.
The Jokko Initiative has reached 350 villages and continues to grow. Tostan has directly trained about 23,585 people, but the high demand for knowledge and the eagerness of participants to share information suggests that thousands more have benefited.
In the project’s next phase, Tostan will partner with the Rural Energy Foundation ( http://ruralenergy.nl/ ), a nonprofit organization that helps rural communities gain access to renewable energy. Currently, about 80 percent of rural Senegal lacks electricity, so charging phones often involves risky and inconvenient trips into the nearest small town. To alleviate this, Tostan will pilot community-led, solar-powered charging stations. These telecenters will provide electricity for mobile phones, and the income generated by these microenterprises will be reinvested in other community-led development projects.

Mobile phone use in Africa is growing twice as fast as in any other region in the world. In Senegal, the number of SIM card purchases nearly doubled from 2007 to 2009, up to 6.9 million. But as Tostan has found, absolute numbers alone do not empower communities. Success in low-income countries requires bridging the gender gap. Putting knowledge and technology in the hands of women — literally— is critical to achieving lasting development.
Renee Ho is a volunteer at Tostan International in Dakar, Senegal. Her interests include women and the technology divide in lower-income countries. More information is online at http://www.tostan.org .
Multiple Choice Questions
- 2000 Millennium Development Summit
- None of the above
- Take care of their health
- Desire fewer children
- Educate their children well
- All of the above
- Afghanistan
- Older women are less likely to have attended school than their younger counterparts
- High-paying majors such as science and technology remain dominated by men
- Women living in rural areas have less access to educational services
- Engages in community building, gender and race consciousness work.
- Provides small-interest loans to allow women in the shantytowns of Salvador to become entrepreneurs
- Teaches women to use Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) more efficiently
- Helps rural communities gain access to renewable energy
- Margaret Wilson
- Sheryl Sandberg
- The importance of domestic and household responsibilities
- Project management
- The Community Empowerment Program (CEP)
- Free the Children
- The Jokko Initiative
- Incorporates mobile technology into CEP as a way to reinforce reading and writing skills
- Teaches participants how to use SMS functions
- Connects women and girls to market information opportunities
- All the above
- Was developed in partnership with the UNICEF
- Focuses on rights-based empowerment rather than economic and entrepreneurial capacity building
- Adapts lessons to cultural contexts and uses appropriate cultural references
- Held focus groups with local government officials instead of community stakeholders
- Fund an increase in the amount of mobile phones in sub-Saharan Africa
- Pilot community-led solar-power charging stations for mobile phones
- Fund a the construction and operation of a solar-energy plant in Vélingara, Senegal
- Construct several powerlines to provide energy to rural Senegalese communities
- Putting knowledge and technology in the hands of women
- More efficient mechanisms to send text messages
- More affordable mobile phones for women and children
- The correct answer is C. The 1994 International Conference on Population and Development (answer A) and the 1995 Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing (answer B) were both milestones in placing women’s empowerment on the global agenda. However, it was the 2000 Millennium Development Summit (answer C) where world leaders agreed on the target of universal primary education as part of the MDGs.
- The correct answer is D (all of the above).
- Answers A and D are correct. Morocco (answer B) and Bangladesh (answer C) are both countries where governments have committed to action and have seen higher enrollment among women and girls in education.
- Answer C is correct. The gender ratio is the most equal for primary school enrollment (answer A) with 96 girls for every 100 boys, and the ratio for secondary school (answer B) is similar, at 95 girls per 100 boys. The education gap is the widest at the post-secondary, or tertiary, level (answer C).
- Answer D (all of the above) is correct.
- Answer A is correct. Bahia Street works to builds solidarity and facilitates consciousness around gender and race among black communities in Salvador, Brazil. The organization is not a microfinance institution (answer B). The Community Empowerment Program (CEP) in Velingara, Senegal, provides capacity building for women to use ICTs (answer C), and the Rural Energy Foundation (answer D) is a non-profit that helps rural communities gain access to renewable energy.
- The correct answer is D. Bahia Street was founded by Rita Conceição, who grew up in the shantytowns of Salvador and wanted to build community and raise political consciousness among young black girls living in the community. Renee Ho (answer B) was the writer of the chapter on the Community Empowerment Program. Margaret Wilson (answer A) is the co-founder of Bahia Street. Sheryl Sandberg (answer C) is the Chief Operating Officer (COO) of Facebook and the author of the book Lean In.
- The correct answer is A. The CEP does NOT teach girls about the importance of domestic responsibilities. The program recognizes that unpaid domestic labour among women can prevent them from progressing in formal education and instead teaches skills in literacy (answer B), numeracy (answer C), and project management (answer D).
- The correct answer is D (the Jokko Initiative). UNICEF (answer A) is a partner in the Jokko project. The CEP (answer B) is also implemented by Tostan but is a rights-based education program.
- The correct answer is D. (all the above).
- The correct answer is C. Tostan’s educational model works because it adapts lessons to cultural contexts and uses appropriate cultural references. The CEP focuses on rights-based empowerment (answer B). The Jokko Initiative was developed in partnership with UNICEF (answer A) but was not emphasized by the textbook as the primary reason for the project’s success. Tostan’s model was developed in close consultation with the community, so answer D is incorrect.
- Answer B is correct. The Rural Energy Foundation will pilot the development of community-led solar-power charging stations for mobile phones in Senegal. Mobile phone ownership rates are rapidly increasing across Africa, but the Foundation will be making this trend more sustainable, rather than simply contributing to the volume of phones (answer A). The Foundation is not supporting the construction of a solar energy plant (answer C) or powerlines (answer D).
- Answer A is correct. The Rural Energy Foundation will put knowledge and technology in the hands of women as means to achieve long-lasting development. More efficient and affordable text messages (answers B and C) are a product of the Jokko Foundation.
Discussion Questions
- Rita Conceição names a number of values she incorporates into advice she gives to girls who are a part of Bahia Street. What are some of these values and why do you think they are important to her?
- Describe some methods Jokko Initiative uses to educate women about technology. Compare and contrast Bahia Street with the Jokko Initiative.
- Use external research to find the most recent gender ratio for tertiary education. How does this ratio change at national, regional, and global levels?
- What are the risks of grouping different countries into categories of most and least educated? What trends are included and overlooked when using this approach?
- How did the emphasis on education from the Millennial Development Goals transfer over to the Sustainable Development Goals? What kind of presence do education, gender, and technology have in the Sustainable Development Goals?
- What are some examples of the role of technology in political change? Is there a connection between the use of technology for education and its use for broader social movements?
- What are some examples of how social media has influenced women’s political, social, or economic empowerment?
Essay Questions
- The textbook notes that “mobile phone use is increasing twice as fast in Africa as in any other region in the world” (p. 37). What are the benefits of having a mobile phone on an individual, organizational, or community level? Are mobile phones or other pieces of information and communication technology simply neutral devices or tools of political influence?
- What does the Jokko Initiative demonstrate about the benefits of incorporating local knowledge into development programs? What are some ways of ensuring that local symbols, values, and perspectives are integrated into education and capacity-building projects?
- Rita Conceição, founder of Bahia Street, was quoted saying “we teach the girls to take care of others in their lives as well. Women take care of the children, and that is the future of our society.” What are the implications of this statement in the context of gender norms, care, and domestic labour?
EdTechWomen. “About ETW.” (2016). New York, NY. A New York-based organization that supports the leadership and capacity of women in education technology.
http://edtechwomen.com/
Cornwall, A. “Women’s Empowerment: What Works?” Journal of International Development 28 (3), 342 – 359. (2016). Draws on a multi-country research study to examine women’s individual journeys towards empowerment.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jid.3210/full
Foster, D. & Fitzgerald, M. “Is Capitalism Destroying Feminism? An Interview with Dawn Foster.” OpenDemocracy. (2016). An interview with Dawn Foster, a journalist who writes on gender, politics and social affairs. Her book Lean Out is a response to Sandberg’s Lean In , and takes a more institutional approach to discussing women in the workplace through a lens of not only gender, but also class, race, and empire.
https://www.opendemocracy.net/dawn-foster-mary-fitzgerald/is-capitalism-destroying-feminism-interview-with-dawn-foster
Perryman, L. & de los Artocs, B . “Women’s Empowerment Through Openness: OER, OEP and the Sustainable Development Goals.” Open Praxis 8 (2), April – June 2016, 163 – 180. (2016). Based on survey responses from 7,700 educators from 175 countries, this paper explores the ability of Open Education Resources (OERs) to increase women’s voices in education.
http://openpraxis.org/index.php/OpenPraxis/article/view/289/206
Rice, C. et al. “Pedagogical Possibilities for Unruly Bodies.” Gender and Education . 1 – 20. (2016). Paper on the use of digital art to tell untold narratives of activism by people with disabilities.
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09540253.2016.1247947
Sandberg, S. “Why We Have Too Few Women Leaders.” TED. (2010). TEDTalk by Sheryl Sandberg based on her widely acclaimed book Lean In , on navigating the male-dominated business world as a woman.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=18uDutylDa4
Rossatto, C. “Global Activism and Social Transformation vis-à-vis Dominant Forms of Economic Organization: Critical Education within Afro-Brazilian and Transnational Pedagogical Praxis.” Journal for Critical Education Policy Studies 2 (3), 228 – 260. (2015). Discusses grassroots social movements across race and gender divisions and national borders to challenge notions of market competition within education.
http://www.jceps.com/archives/2347
The World’s Women 2015 . “Education.” (2015). Annually updated global data and analysis on gender disparities in educational access with indicators including primary and secondary school enrollment rates as well as illiteracy.
http://unstats.un.org/unsd/gender/chapter3/chapter3.html
UN Statistics . “Millennium Development Goal Indicators.” (2016). Updated statistics and baseline indicators on the progress made in achieving the Millennium Development Goals, with data available in national, regional and global contexts.
http://mdgs.un.org/unsd/mdg/default.aspx
This work ( Global Women's Issues: Women in the World Today, extended version by Bureau of International Information Programs, United States Department of State) is free of known copyright restrictions.
Share This Book

- Chronicle Conversations
- Article archives
- Issue archives
- Join our mailing list

Education as the Pathway towards Gender Equality
About the author.
Amartya Sen, often referred to as the father of the concept of ‘human development’, reminds us of a quote by H.G. Wells, where he said that “human history becomes more and more a race between education and catastrophe”. Sen maintains that “if we continue to leave vast sections of the people of the world outside the orbit of education, we make the world not only less just, but also less secure”. To Sen, the gender aspect of education is a direct link between illiteracy and women’s security.
Not being able to read or write is a significant barrier for underprivileged women, since this can lead to their failure to make use of even the rather limited rights they may legally have (to own land or other property, or to appeal against unfair judgment and unjust treatment). There are often legal rights in rule books that are not used because the aggrieved parties cannot read those rule books. Gaps in schooling can, therefore, directly lead to insecurity by distancing the deprived from the ways and means of fighting against that deprivation. 1
For Sen, illiteracy and innumeracy are forms of insecurity in themselves, “not to be able to read or write or count or communicate is a tremendous deprivation. The extreme case of insecurity is the certainty of deprivation, and the absence of any chance of avoiding that fate”. 2 The link between education and security underlines the importance of education as akin to a basic need in the twenty-first century of human development.
GENDERED EDUCATION GAPS: SOME CRITICAL FACTS
While a moral and political argument can continue to be made for the education of girls and women, some facts speak powerfully to the issue at hand. Girls accounted for 53 per cent of the 61 million children of primary school age who were out of school in 2010. Girls accounted for 49 per cent of the 57 million children out of school in 2013. In surveys of 30 countries with more than 100,000 out-of-school children, 28 per cent of girls were out of school on average compared to 25 per cent of boys. Completion of primary school is a particular problem for girls in sub-Saharan Africa and Western Asia. 3
Surveys in 55 developing countries reveal that girls are more likely to be out of school at a lower secondary age than boys, regardless of the wealth or location of the household. Almost two thirds of the world’s 775 million illiterate adults are women. In developing regions, there are 98 women per 100 men in tertiary education. There are significant inequalities in tertiary education in general, as well as in relation to areas of study, with women being over-represented in the humanities and social sciences and significantly under-represented in engineering, science and technology.
Gender-based violence in schools undermines the right to education and presents a major challenge to achieving gender equality in education because it negatively impacts girls’ participation and their retention in school. In addition, ineffective sexual and reproductive health education inhibits adolescents’ access to information and contributes to school dropouts, especially among girls who have reached puberty.
The education of girls and women can lead to a wide range of benefits from improved maternal health, reduced infant mortality and fertility rates to increased prevention against HIV and AIDS. 4 Educated mothers are more likely to know that HIV can be transmitted by breastfeeding, and that the risk of mother-to-child transmission can be reduced by taking drugs during pregnancy.
Each extra year of a mother’s schooling reduces the probability of infant mortality by 5-10 per cent. Children of mothers with secondary education or higher are twice as likely to survive beyond age 5 compared to those whose mothers have no education. Improvements in women’s education explained half of the reduction in child deaths between 1990 and 2009. A child born to a mother who can read is 50 per cent more likely to survive past age 5. In sub-Saharan Africa, an estimated 1.8 million children’s lives could have been saved in 2008 if their mothers had at least a secondary education. In Indonesia, 68 per cent of children with mothers who have attended secondary school are immunized, compared with 19 per cent of children whose mothers have no primary schooling. Wages, agricultural income and productivity—all critical for reducing poverty— are higher where women involved in agriculture receive a better education. Each additional year of schooling beyond primary offers greater payoffs for improved opportunities, options and outcomes for girls and women.
In the varied discussions on the post-2015 education related agendas, there was strong consensus that gender equality in education remains a priority. Various inputs noted that inequalities in general, and particularly gender equality, need to be addressed simultaneously on multiple levels—economic, social, political and cultural. A response on behalf of the International Women’s Health Coalition maintained that “all girls, no matter how poor, isolated or disadvantaged, should be able to attend school regularly and without the interruption of early pregnancy, forced marriage, maternal injuries and death, and unequal domestic and childcare burdens”.
Other inputs highlighted the importance of ensuring access to post-basic and post-secondary education for girls and women. Referring to secondary education, the German Foundation for World Population noted that the “completion of secondary education has a strong correlation with girls marrying later and delaying first pregnancy.” While access to good quality education is important for girls and women, preventing gender-based violence and equality through education clearly also remains a priority.
Gender-based discrimination in education is, in effect, both a cause and a consequence of deep-rooted differences in society. Disparities, whether in terms of poverty, ethnic background, disability, or traditional attitudes about their status and role all undermine the ability of women and girls to exercise their rights. Moreover, harmful practices such as early marriage, gender-based violence, as well as discriminatory education laws and policies still prevent millions of girls from enrolling and completing their respective education. 5
Additionally, given the extensive and growing participation of women in income generating activities, education for girls and women is particularly important, especially in attempting to reverse gendered patterns of discrimination. Not only is it impossible to achieve gender equality without education, but expanding education opportunities for all can help stimulate productivity and thereby also reduce the economic vulnerability of poor households.
GENDER EQUALITY, EQUITY AND HUMAN RIGHTS
Equity is the strongest framing principle of a post-2015 rights-based agenda, and underlines the need to redress historical and structural inequalities in order to provide access to quality education at all levels. This heralds what was effectively one of the strongest themes that emerged in the post-2015 education consultations, i.e., a rights-based approach in which rights are indivisible. This implies that all aspects of education should be considered from a rights perspective, including structural features of education systems, methods of education, as well as the contents of the education curricula. Indeed, overcoming structural barriers to accessing good quality education is vital for realizing education rights for all.
In related post-2015 consultations, equity is affirmed as a fundamental value in education. Several inputs noted that inequality in education remains a persistent challenge. This is connected to a focus in the Millennium Development Goals on averages without an accompanying consideration of trends beneath the averages. Many contributions in the education consultation, as well as in the other thematic consultations, highlighted the lack of attention to marginalized and vulnerable groups.
Equal access to good quality education requires addressing wide-ranging and persistent inequalities in society and should include a stronger focus on how different forms of inequality intersect to produce unequal outcomes for marginalized and vulnerable groups. Post-2015 consultations suggest that overcoming inequality requires a goal that makes national governments accountable for providing minimum standards and implementing country specific plans for basic services, including education. Equity in education also implies various proactive and targeted measures to offer progressive support to disadvantaged groups.
Amartya Sen notes empirical work which has brought out very clearly how the relative respect and regard for women’s well-being is strongly influenced by their literacy and educated participation in decisions within and outside the family. Even the survival disadvantage of women compared with men in many developing countries (which leads to “such terrible phenomenon as a hundred million of ‘missing women’) seems to go down sharply, and may even get eliminated, with progress in women’s empowerment, for which literacy is a basic ingredient”.
In the summer of 2009, the International Labour Organization (ILO) issued a report entitled “Give Girls a Chance: Tackling child labour, a key to the future”, which makes a disturbing link between increasing child labour and the preference being given to boys when making decisions on education of children. The report states that in cultures in which a higher value is placed on education of male children, girls risk being taken out of school and are then likely to enter the workforce at an early age. The ILO report noted global estimates where more than 100 million girls were involved in child labour, and many were exposed to some of its worst forms.
Much of the research around women and education highlights the importance of investing in the education of girls as an effective way of tackling the gamut of poverty. This is in line with assertions made in numerous other references, which also point to a strong link between education, increased women’s (as opposed to girls’) labour force participation, the wages they earn and overall productivity, all of which ultimately yields higher benefits for communities and nations. In other words, it pays to invest in girls’ and women’s education.
GENDER SOCIALIZATION
In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Western feminist stalwarts, such as Simone de Beauvoir, were elaborating the difference between biological ‘sex’ and social gender. Anne Oakley in particular, is known for coining the term gender socialization (1979), which indicates that gender is socially constructed. According to Oakley, parents are engaged in gender socialization but society holds the largest influence in constructing gender. She identified three social mechanisms of gender socialization: manipulation, canalization, and verbalization (Oakley, 1972). Oakley noted that gender is not a fixed concept but is determined by culture through the use of verbal and nonverbal signifiers and the creation of social norms and stereotypes, which identify proper and acceptable behavior. The signifiers are then perpetuated on a macro level, reinforced by the use of the media, as well as at the micro level, through individual relationships.
The concept entered mainstream lexicon on gender relations and development dynamics, and through criticism and counter criticism, ‘gender socialization’ itself became an important signifier. As a tool to highlight discriminatory practices, laws and perceptions (including stereotypes), gender socialization is often identified as the ‘root cause’ which explains various aspects of gender identities, and what underlies many gender dynamics.
In 2007, the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) defined gender socialization as “[T]he process by which people learn to behave in a certain way, as dictated by societal beliefs, values, attitudes and examples. Gender socialization begins as early as when a woman becomes pregnant and people start making judgments about the value of males over females. These stereotypes are perpetuated by family members, teachers and others by having different expectations for males and females.”
There is, therefore, a clear interaction between socio-cultural values (and praxis) with gender socialization. This only partly explains why it is that in many developing societies there is a persistent prioritization of women’s ‘domestic’ roles and responsibilities over public ones. Most young girls are socialized into the ‘biological inevitability’ of their socially determined future roles as mothers. This is closely connected, in many relatively socially conservative contexts, with the need to ensure (the prerequisite of) marriage.
Most related studies maintain that women with formal education are much more likely to use reliable family planning methods, delay marriage and childbearing, and have fewer and healthier babies than women with no formal education. The World Bank estimates that one year of female schooling reduces fertility by 10 per cent, particularly where secondary schooling is undertaken.
In fact, because women with some formal education are more likely to seek medical care and be better informed about health care practices for themselves and their children, their offspring have higher survival rates and are better nourished. Not only that, but as indicated earlier, these women are less likely to undergo early pregnancy. Being better informed increases the chances of women knowing how to space their pregnancies better, how to access pre and post-natal care, including prevention of HIV/AIDS, sexually transmitted diseases and family planning in general. The World Bank estimates that an additional year of schooling for 1,000 women helps prevent two maternal deaths.
The World Bank, along with UNICEF and the United Nations Population Fund highlight in several of their reports the intergenerational benefits of women’s education. An educated mother is more likely, it is maintained, to attempt to ensure educational opportunities for her children. Indeed, the World Bank specifically notes that “ in many countries each additional year of formal education completed by a mother translates into her children remaining in school for an additional one- third to one-half year”. 6
In short, girls’ education and the promotion of gender equality in education are critical to development, thus underlining the need to broadly address gender disparities in education.
The rhetorical question that needs to be raised here is whether the consistent elements of gender socialization in the region, and the confusing messages for both sexes, can only lead to entrenching processes of gender inequality. At the very least, it is safe to argue that gender socialization, combined with the continuing discrepancies in education opportunities and outcomes not only provide a negative feedback loop, but effectively contribute to entrenching patriarchal norms.
Political events and the endorsement of political leadership are often catalytic, if not necessary determinants, of policy change. In fact, most education reform programmes are often linked to political dynamics. To date, such reforms are typically launched through a political or legal act. In most cases, countries prioritize aspects such as forging a common heritage and understanding of citizenship, instruction in particular language(s), and other means of building capacities as well as popular support for party programmes. All developing country governments have, at one time or another, put special effort into including girls in the education system. While there is a continuous role for policy makers and governments, it is increasingly clear that the socio-cultural terrain is where the real battles need to be waged in a studied, deliberate and targeted fashion.
Influencing the way people think, believe and behave; i.e., culture is the single most complicated task of human development. And yet, in policy and advocacy circles globally, this particular challenge still remains largely considered as ‘soft’ and, at best, secondary in most considerations. What is maintained here is that within the current global geopolitical climate, particularly where an increasing number of young men—and now also young women—are reverting to extremes such as inflicting violence, and where this is often exacerbated by socialization processes which often enforce certain harmful practices (e.g., early marriage) and outdated forms of gender identity and roles, then culture needs to be a high priority.
Needed cultural shifts require several key conditions. One of these is the importance of bridging the activism around gender equality and doing so by involving both men and women. While this still remains anathema to many women’s rights activists, it is nevertheless necessary that men become more engaged in gender equality work, and that women realize that their rights are incumbent on the systematic partnership with men and on appreciating the specific needs and challenges that young boys and men themselves are struggling with.
Another critical determinant of cultural change is that it has to be from within. Those who have worked with human rights issues more broadly have had to learn the hard way that any change that appears to be induced ‘from outside’, even if responding to a dire need and with perfectly sound reason, is destined for failure in many cases. Sustainable change has to be owned and operated locally. This points to the importance of identifying the ‘cultural agents of change’ in any given society, which include both its men and women activists, religious leaders, traditional and community leaders (in some cases these categories converge), media figures, charismatic community mobilizers, and especially youth themselves, who are the most critical agents of change.
At the same time, it is a fallacy to think that there can be no linkages whatsoever between local ownership and external dynamics. International, especially multilateral, development partners have an important role to play in facilitating the bridge building between and among the cultural agents of change themselves on the one hand, and between them and their respective policymakers on the other. But in this day and age of technology and increasing speed of technology, international development actors, as well as transnational academic actors, are already facilitating the building of bridges between youth. Some of this is already happening through a plethora of fora (including social websites), and the impact remains difficult to gauge.
All this points to the fact that education in the traditional sense of school enrolment, drop-out rates, curricula development, and structural dynamics thereof are in multiple stages of transition. It remains to be seen how, and in what way, new forms of education, knowledge acquisition, and information sharing will significantly change patterns of gender socialization itself. It is too soon to definitely assess the shifting sands we are standing on. Nevertheless, it would be a mistake to either overestimate the power of entrenched patriarchy, or to underestimate the capacity of women and men to significantly refashion their realities. At the same time, the changes in the culture of international development goal setting are already producing critical insights and inputs which are shaping the agenda of global, regional and national dynamics for upcoming decades.
The opinions expressed in this article belong to the author only and do not necessarily reflect the opinions or positions of any institution, Board or staff member.
1 UNICEF and UNESCO: The World We Want— Making Education a Priority in the Post-2015 Development Agenda: Report of the Global Thematic Consultation on Education in the Post-2015 Development Agenda, 2013 . Available at http://www.unicef.org/education/files/ Making_education_a_Priority_in_the_Post-2015_Development_ Agenda.pdf.
3 “Making education a Priority in the Post-2015 Development Agenda: report of the Global Thematic Consultation on education in the Post-2015 Development Agenda”.
4 All the figures and data herein presented from UNESCO. 2011b. EFA Global Monitoring Report 2011. The Hidden Crisis: Armed Conflict and Education, Paris and UNESCO . World Atlas of Gender equality in education. Paris, 2012.
5 UNESCO— http://www.unesco.org/new/en/education/themes/leading-the-international-...
Alger, Chadwick. “Religion as a Peace Tool”, The Global Review of Ethnopolitics , vol.1,4: 94 -109. (June 2002).
Diamond, Larry (ed.). Political Culture and Democracy in Developing Countries (Boulder and London, Lynne Rienner, 1994). Huntington, Samuel. ‘The Clash of Civilizations?’, Foreign Affairs , vol.72, No.3, Summer 1993, pp. 19 -23.
Johnson, Chalmers. Blowback: The Costs and Consequences of American Empire (New York , Henry Holt and Company, 2000).
Karam, Azza. Transnational Political Islam: Religion, Ideology and Power (London, Pluto Press, 2004).
Leftwich, Adrian (ed.). Democracy and Development: Theory and Practice (London, Polity Press, 1996).
Macrae, Joanna. Aiding Recovery? The Crisis of AID in Chronic Political Emergencies (London and New York, Zed Books in Association with ODI, 2001).
Pilch, John J. “Beat His ribs While He is young” (Sir 30:12): A Window on the Mediterranean World”, Biblical Theology Bulletin: A Journal of Bible and Theology, vol. 23, 3 (1993) pp 101-113.
Tynedale, Wendy. (ed.). Visions of Development: Faith-based Initiatives (UK: Ashgate, 2006).
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)’s Arab Human Development Report (New York, 2002, 2004, and 2005).
UNESCO, “Key Messages and Data on Girls’ and Women’s education and literacy” (Paris, April 2012).
UNICEF and UNESCO, The World We Want—Making Education a Priority in the Post-2015 Development Agenda: Report of the Global Thematic Consultation on Education in the Post-2015 Development Agenda, 2013 . Available at http://www.unicef.org/education/files/Making_education_a_Priority_in_the... . United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) State of World Population Report: Reaching Common Ground—Culture, Gender and Human Rights (2008).
Williams, Brett (ed.). The Politics of Culture (Washington D.C., The Smithsonian Institution, 1991).
World Bank MENA report: The Road Not Travelled: Education Reform in the Middle East and North Africa , (Washington D.C. The World Bank, 2008).
The UN Chronicle is not an official record. It is privileged to host senior United Nations officials as well as distinguished contributors from outside the United Nations system whose views are not necessarily those of the United Nations. Similarly, the boundaries and names shown, and the designations used, in maps or articles do not necessarily imply endorsement or acceptance by the United Nations.

A Chronicle Conversation with Pradeep Kurukulasuriya (Part 2)
In April 2024, Pradeep Kurukulasuriya was appointed Executive Secretary of the United Nations Capital Development Fund (UNCDF). The UN Chronicle took the opportunity to ask Mr. Kurukulasuriya about the Fund and its unique role in implementing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. This is Part 2 of our two-part interview.

A Closer Look at Child Labour in Timor-Leste—Challenges and Progress Towards Ending the Practice
Thankfully, the Government of Timor-Leste, United Nations agencies and civil society organizations all acknowledge the scope of child labour and its deep-rooted causes. This means that there is a great opportunity for different institutions in Timor-Leste to work together towards change.

Keeping Food Safe, Even in Unexpected Situations
Food safety is everyone’s business and all of the players along the production chain can do their part.
Documents and publications
- Yearbook of the United Nations
- Basic Facts About the United Nations
- Journal of the United Nations
- Meetings Coverage and Press Releases
- United Nations Official Document System (ODS)
- Africa Renewal
Libraries and Archives
- Dag Hammarskjöld Library
- UN Audiovisual Library
- UN Archives and Records Management
- Audiovisual Library of International Law
- UN iLibrary
News and media
- UN News Centre
- UN Chronicle on Twitter
- UN Chronicle on Facebook
The UN at Work
- 17 Goals to Transform Our World
- Official observances
- United Nations Academic Impact (UNAI)
- Protecting Human Rights
- Maintaining International Peace and Security
- The Office of the Secretary-General’s Envoy on Youth
- United Nations Careers
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Editorial article, editorial: ways of seeing women’s leadership in education—stories, images, metaphors, methods and theories.

- 1 School of Education, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom
- 2 Centre for Education Studies, University of Warwick, Coventry, United Kingdom
- 3 UCL Institute of Education, University College London, London, United Kingdom
- 4 School of Education, University of Leicester, Leicester, United Kingdom
Editorial on the Research Topic Ways of Seeing Women’s Leadership in Education–Stories, Images, Metaphors, Methods and Theories
Introduction
Gender and educational leadership remains a focus for scholarly interest precisely because gender inequalities remain. That is the case 30 years on from the publication of seminal works that established gender and women in educational leadership as a focus for research ( Shakeshaft 1987 ; Blackmore 1989 ; Dillard 1995 ). Scholars continue to document women’s under-representation in leadership ( Alston, 2005 ). This Research Topic focuses on accounts of doing leadership (e.g. Cook ), as well as showing how their inclusion transforms leadership theory e.g. by incorporating gender, feminist, intersectionality and Afrocentric theories (e.g. Gullo and Sperandio , Tripses and Lazaridou , Malachias et al. , Williams ). Feminist epistemology ensures women’s experiences and ways of seeing are central to the research purpose and process; that women as leaders are not solely the object of the researcher’s gaze. In particular, feminist standpoint theory recognises there is epistemic privilege so that situated knowledge, what is known and the ways it can be known, is shaped by the positionality of knowledge producers. A reflexive approach prompts feminist researchers to reflect deeply on context, as well as their positionality, in relation to the focus of research. The theme of this Research Topic—“Ways of seeing women’s leadership in education: stories, images, metaphors, methods and theories”—reflects collective experiences from diverse perspectives. Earlier versions of these eighteen papers were first presented at the seventh Women Leading Education across Continents conference at the University of Nottingham, UK in the summer of 2019.
Papers draw on individual narratives, as autoethnographies (e.g. Fuller , Kappert , Williams ) and narrative inquiries (e.g. Cook , Reilly , Showunmi ). Annette Kappert complements her presentation of critical cultural autoethnographical stories of leadership with fictionalised stories and poetry using a historical lens to illustrate the value of conducting research into a female Black and Minority Ethnic educator’s personal and professional experiences; she “gives voice to previously silenced and marginalized experiences” ( Boylorn and Orbe 2014 p. 15).
Victoria Showunmi offers a view on narrative inquiries based upon leadership through a lens of gender, race and class. The paper takes the reader through a journey of difference as it navigates with the voices of women leaders across three countries. Elizabeth Reilly ’s work in the context of Rwanda explores and gives voice to Rwandan women leaders. The research draws on African feminist theories that explicitly challenge Western theories of gender and focus on “mov[ing] gender research towards post-colonial and indigenous approaches and the construction of knowledge derived from the experiences of girls/women in their specific locations and histories” that emphasize agency, resilience, and persistence ( Chilisa and Ntseane, 2010 p. 620).
Pontso Moorosi uses narratives to portray the construction of leadership identity by three women leaders in African schools. These women’s stories demonstrate how a leadership self-perception instils a sense of agency that facilitates leaderful actions to strengthen leadership identity. Women’s stories of leadership identity development are gendered and shaped by values instilled from childhood that shape their leadership dispositions. The paper highlights the intricate nature of self-perception, gender and leadership identity, arguing that these aspects cannot be left to chance if we are serious about leadership development and increasing the pool of women in leadership.
Sheralyn Cook explores the stories of two women’s professional and personal struggles turning around the New Zealand schools they led during turbulent times.
Images and Metaphors
Sharon Curtis’s paper positions the experiences of Black women leaders as a metaphorical visualisation of a single thread. A thread that manoeuvers and meanders apparently aimlessly, not through choice, but enforced by navigating a way through institutions and systems, fuelled with micro aggressions, convoluted racial barriers and obstacles placed in their paths and journeys as Black women reach for and sustain leadership positions.
Innovative work, exploring the metaphors and images used to describe leadership in a range of cultural contexts, reveals how differently we conceptualise women’s leadership across continents (e.g. Randell and Yerbury , Burkinshaw and White ). Shirley Randell and Hilary Yerbury attempt to break the mould, through the use of metaphors as a way to understand women’s leadership across two different continents. The paper draws on the notion that leadership is generally thought of as “a good thing”, as something important carried out by people with desirable attributes, such as courage and insight, or with attractive personalities and communication skills. However, using metaphors that highlight the obstacles women face, for example, the glass ceiling, glass cliff, sticky floors and the labyrinth is ubiquitous in educational leadership. Instead, they demonstrate women’s alternative use of metaphors from the natural world.
Paula Burkinshaw and Kate White explore the use of images and metaphors to describe doing leadership across two generations of women leaders in higher education in two different country contexts. This innovative approach draws from experiences of an older generation of women in top leadership in the UK and a younger generation in middle leadership in Australia. They established that the older generation of women leaders conforms to metaphors and images of masculinist leadership thereby maintaining the status quo, while the younger generation use more positive images of leadership to disrupt the status quo. They portray an alternative model of leadership constructed on re-negotiated terms that bear more prospects for equality.
Rosangela Malachias et al. innovative use of film narratives reveals women’s activist leadership as community educators and film-makers in the Baixada Fluminense region near Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. These stories: of a Black deaf woman teaching the history and culture of black deaf people; and “a young black woman, graffiti artist, filmmaker, actress, and pedagogical specialist with a master’s degree in Education” demonstrate that educational leadership can be found in communities even when there is limited recognition of it in the academy.
Pen Mendonça demonstrates the power of graphic illustration in articulating and exploring women’s leadership through values-based cartooning. She provides a powerful personal account of her work with women leaders working in higher education and with grassroots movements. Her use of visual methods is innovative in the field of women, gender and feminism in educational leadership. Both papers expand the field to consider the leadership of women’s leadership activism in education.
Kay Fuller has developed an intersectional life grid at 7 year intervals in her critical autoethnography to reveal reflexivities of complacency, reflexivities that discomfort and reflexivities that transform in a scholarly and professional career in educational leadership.
Historical research by Jenny Tripses and Angeliki Lazaridou make certain that women are written into the field to ensure we know “where we have come from, and where we are going”. In particular, they focus on the lives of two women with long-lasting and powerful legacies—one Greek, the other American—Aikaterini Laskaridou and Lydia Moss Bradley lived and worked in the 19th century.
Qualitative methods such as narrative inquiry (e.g. Cook , Moorosi ) and life story (e.g. Cunneen ) bring out the depth of emotions, feelings and images attached to the gendered stories of women’s lives. Analyses of quantitative data enable analysis of larger datasets about women’s ways of doing leadership (e.g. Calderone et al. , Reed and Reedman ).
Diane Reed and Ashley Reedman use quantitative methods to compare leader resilience by gender and age. Based on an on-going study that involves women and men, this innovative work shows that resilience increases with age for both genders. This work centres important life aspects such as well-being, resilient aging and quality of life. Increasingly, wellbeing is receiving attention as an important element to work-life balance for women in leadership and Reed and Reedman’s work is on point.
Gina Gullo and Jill Sperandio ’s paper investigates the career paths and perspectives of current and aspirant superintendents in Pennsylvania. The research uses a mixed method approach which includes both quantitative and qualitative tools. Initial findings suggest, that there are similarities and differences in career planning preferences by men and women aspirant superintendents indicates an understanding by women of the insider pathway potential to overcome bias regarding women in leadership roles. As this career path is frequently not an option, women must choose not to aspire or to prepare themselves for possible gender bias in hiring when applying as outsiders.
To illustrate how structural inequalities operate at multiple levels, scholars show how the use of gender (e.g. Gullo and Sperandio ), feminist (e.g. Calderone et al. , Tripses and Lazaridou ), critical race (e.g. Curtis ), intersectionality (e.g. Fuller, Showunmi ) and other social theories (e.g. Kappert ) enables us to think about and articulate our ways of seeing women’s leadership in formal and informal educational settings for learners of all ages.
Laura Burton’s et al. paper examines how ten Black female school leaders coped with gendered racism and the costs associated with doing so. Their use of adaptive and maladaptive strategies, more or less affirming, highlighted the ways both types of strategies were effective and enabled participants to persist and succeed in their leadership roles.
Calderone et al. draw on feminist life course theory to understand how women’s perspectives on the accessibility of the (United States) superintendency have shifted in recent times to become a largely contingent decision—a strategic, individual-level assessment focusing on the favourability of district work conditions to their success as leaders.
Patricia Williams draws on African-centred pedagogy, African womanism, and transformational leadership to explore her leadership practice in a Charter School in an autoethnographical account that locates her experience in a neoliberal context.
Collective Experience
Importantly, these papers document the collective experiences of women leading education across continents. Of course, there are accounts of similarities and differences among the women whose leadership stories are told. Collectively, the papers present women leaders in their heterogeneity. There are accounts of challenges faced and overcome; of resistance enacted and agency exercised against the backdrop of institutional, systemic and societal misogyny and racism. Importantly there are accounts of abundance in their cultural and leadership capital.
In this collection of papers, intercontinental perspectives are presented from South America ( Malachias et al. ), North America ( Burton et al. , Calderone et al. , Gullo and Sperandio , Reed and Reedman , Williams ), Europe ( Cunneen , Curtis , Fuller , Mendonça ), Africa ( Moorosi , Reilly ), Asia (see comparative scholarship) and Australasia ( Cook ). Cross-continental perspectives are found in comparative scholarship ( Burkinshaw and White , Randell and Yerbury , Showunmi , Tripses and Lazaridou ) and the transcontinental life histories of educational leaders ( Kappert ).
However, the underrepresentation of papers in this collection from South American, African, Middle Eastern and Asian countries, when scholars from those continents presented their research at the conference in 2019 reveals the persistence of coloniality in knowledge production and dissemination in the field of women, gender and feminism in educational leadership. It persists despite best efforts to decolonise the conference ( Fuller et al., 2020 ).
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The handling editor declared a shared committee (Women Leading Education Across Continents) with the authors at time of review.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alston, J. A. (2005). Tempered Radicals and Servant Leaders: Black Females Persevering in the Superintendency. Educ. Adm. Q. 41 (4), 675–688.
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Blackmore, J. (1989) “Educational Leadership: A Feminist Critique and Reconstruction,” in Critical Perspectives on Educational Leadership . Editors J. Smyth (London: Falmer ).
Google Scholar
Boylorn, R. M., and Orbe, M. P. (Editors) (2014) Critical Autoethnography: Intersecting Cultural Identities in Everyday Life . Walnut Creek, CA: Left Coast Press .
Chilisa, B., and Ntseane, G. (2010) Resisting Dominant Discourses: Implications of Indigenous, African Feminist Theory and Methods for Gender and Education Research, Gender and Education . 22 (6), 617–632.
Dillard, C. (1995). Leading with her Life: An African American Feminist (re)interpretation of Leadership for an Urban High School Principal. Educ. Adm. Q. 31 (4), 539–563.
Fuller, K., Moorosi, P., Shah, S., and Showunmi, V. (2020). Coming Full Circle: The Gender and Leadership Research Interest Group. Manag. Educ. 34 (3), 115–116.
Shakeshaft, C. (1987) Women in Educational Administration . Newbury Park, CA: Sage .
Keywords: women, gender, feminism, educational leadership, images and metaphors, methods, theories
Citation: Fuller K, Moorosi P, Showunmi V and Shah S (2021) Editorial: Ways of Seeing Women’s Leadership in Education—Stories, Images, Metaphors, Methods and Theories. Front. Educ. 6:781049. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.781049
Received: 22 September 2021; Accepted: 28 September 2021; Published: 05 November 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Fuller, Moorosi, Showunmi and Shah. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kay Fuller, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Ways of Seeing Women’s Leadership in Education: Stories, Images, Metaphors, Methods and Theories
Essay Service Examples Education Importance of Education
Essay about the Importance of Women's Education
- Proper editing and formatting
- Free revision, title page, and bibliography
- Flexible prices and money-back guarantee

Our writers will provide you with an essay sample written from scratch: any topic, any deadline, any instructions.
Cite this paper
Related essay topics.
Get your paper done in as fast as 3 hours, 24/7.
Related articles

Most popular essays
- African American History
- Importance of Education
Monique Rizer wrote, “in my experience, there is no better motivation to finish college and to...
Information is the oil of the 21st century, and analytics is the combustion engine” By Peter...
- Frederick Douglass
In the excerpt of learning to read and write, Frederick Douglass describes the struggles he faced...
- College Education
It is very true that education is one of main factor to succeed in life in our society. Everyone...
- Personal Life
- Perspective
The term education is derived from the two Latin words Educare and Educere. Educare means to...
A non-equivalent control group study was conducted by Chan, et al (2012) exploring the effects of...
- Animal Farm
Only some animals can read and this can be taken advantage of. The pigs change the commandments...
- Study Skills
Modern society is moving from an information society to a knowledge society. This research has...
Throughout our United State history, there were many people that were significant in the rise of...

Join our 150k of happy users
- Get original paper written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Fair Use Policy
EduBirdie considers academic integrity to be the essential part of the learning process and does not support any violation of the academic standards. Should you have any questions regarding our Fair Use Policy or become aware of any violations, please do not hesitate to contact us via [email protected].
We are here 24/7 to write your paper in as fast as 3 hours.
Provide your email, and we'll send you this sample!
By providing your email, you agree to our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
Say goodbye to copy-pasting!
Get custom-crafted papers for you.
Enter your email, and we'll promptly send you the full essay. No need to copy piece by piece. It's in your inbox!

Essay on Women Education 500+ Words
Education is a powerful tool that opens doors to opportunities, growth, and progress. One crucial aspect of education is ensuring that women have equal access to it. In this essay, we will explore the significance of women’s education, its impact on individuals and societies, and why it is essential to promote and support women’s educational rights.
Defining Women’s Education
Women’s education refers to the provision of learning opportunities and resources to girls and women. It encompasses formal education in schools, colleges, and universities, as well as informal education through workshops, community programs, and self-directed learning. Women’s education is a fundamental human right and a key driver of gender equality.
The Historical Perspective
Throughout history, access to education for women has been limited in many parts of the world. Women were often denied the opportunity to learn, and their potential remained untapped. However, brave individuals and movements fought for women’s right to education, paving the way for progress.
For instance, pioneers like Malala Yousafzai, the youngest Nobel Prize laureate, championed girls’ education in Pakistan and worldwide. Her advocacy highlights the importance of education for girls and women and the need to break down barriers that prevent them from learning.
The Benefits of Women’s Education
Women’s education offers numerous benefits, both on an individual and societal level. When women are educated, they have better opportunities for employment and career advancement. This economic independence can lead to improved living standards and reduced poverty.
According to UNESCO, educating women can have a profound impact on child health and nutrition. Educated mothers are more likely to make informed decisions about their children’s health and well-being, leading to healthier families.
Empowerment and Gender Equality
Education empowers women by providing them with knowledge, skills, and confidence. It enables them to participate in decision-making processes, advocate for their rights, and challenge gender stereotypes and discrimination. Women who are educated are more likely to become leaders in their communities and contribute to positive societal change.
For example, women like Ruth Bader Ginsburg, the former Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, used their education and legal expertise to advance gender equality and women’s rights through their work.
Breaking the Cycle of Poverty
Women’s education is a powerful tool for breaking the cycle of poverty. When women have access to education, they can secure better-paying jobs and provide for their families. This economic stability has a ripple effect on future generations, as educated mothers are more likely to invest in their children’s education and well-being.
A study by the World Bank found that increasing girls’ education by one year can lead to an 18% increase in a country’s GDP. This demonstrates the significant economic impact of women’s education.
Women as Agents of Change
Educated women are not only beneficiaries of change but also agents of change in their communities and nations. They play a vital role in addressing social and environmental issues, promoting peace, and advocating for human rights. Women’s education equips them with the tools to be leaders and catalysts for positive transformation.
Conclusion of Essay on Women Education
In conclusion, women’s education is a fundamental right that has far-reaching positive effects on individuals, families, and societies. It empowers women, promotes gender equality, and contributes to economic growth and poverty reduction. Moreover, educated women become advocates for change and leaders in their communities, making the world a better place for all.
As we continue to champion women’s education, let us remember the words of Malala Yousafzai: “One child, one teacher, one book, one pen can change the world.” By ensuring that girls and women have access to education, we are not only changing their lives but also shaping a brighter future for everyone.
Also Check: List of 500+ Topics for Writing Essay
Essay on Girl Education for Students and Children
500+ words essay on girl education.
If we look at the demographics, India is one of the most populated countries. However, the rate of girl education is quite low in the country. It is quite troubling to see the figures in a country where women are given the status of goddesses. The figures have significantly improved to an extent but there’s still a long way to go.

Women were not allowed to even step out of their houses in ancient India , but times are changing. Along with changing times, people’s thinking is also changing. They wish to educate their girls and see them succeed in life. However, this is not the case in rural India which makes for more than 60% of the population. We need to identify the factors responsible for such low rates of girl education to find some solutions.
Factors Contributing to Low Rate of Girl Education
There are various factors that make it impossible for girls to get an education in our country. Firstly, the poverty rate is alarming. Even though education is being made free, it still involves a substantial cost to send girls to school. Therefore, families who are struggling to make ends meet fail to pay the educational expenses of their children.
Secondly, in rural areas, there aren’t many schools. This creates a distance problem as they are located far from the villages. In some areas, students have to walk for three to four hours to reach their school. This is where the safety of the girls gets compromised so parents don’t see it fit to send them off so far.
Furthermore, the regressive thinking of the people makes it tougher for girls to get an education. Some people still believe girls are meant to stay in their houses and look after the kitchen. They do not like women to do any other tasks expect for household ones.
Other than that, social issues like child marriage and child labor also stop the girl from getting an education. Parents pull daughters out of school to marry them off at an early age. Also, when girls indulge in child labor, they do not get time to study.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Benefits of Girl Education
If we wish to see India progress and develop, we need to educate our girl child. They are indeed the future of our nation. Moreover, when they become educated, they will not have to be dependent on others for their livelihood.
One of the most important benefits of girl education is that the country’s future will be brighter and better. Similarly, our economy can grow faster if more and more women become financially strong thereby reducing poverty.
Furthermore, women who are educated can take proper care of their children. This will strengthen the future as lesser kids will die due to a lack of vaccination or a similar reason. Even for women, they will be less likely to become a patient of HIV/AIDS as they will be aware of the consequences.
Most importantly, educated women can result in a decrease in social issues like corruption, child marriage , domestic abuse and more. They will become more confident and handle their families better in all spheres. Thus we see how one educated woman can bring so much change in her life along with the others as well.
Some FAQs on Girl Education
Q.1 Why is girl education not encouraged in India?
A.1 India is still a developing country. It has too much poverty and regressive thinking. It is one of the main reasons why people don’t encourage girls to get an education.
Q.2 What are the advantages of educating girls?
A.2 When we educate girls, we educate a whole nation. As she teaches everyone around her. The education of girls will result in a better economy and a brighter future along with enhanced confidence of the girl.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Essay on Female Education: For All Students
Female education is a very important topic to talk about in our country. That’s why we are sharing a few short and long essays on Female Education. Any students can learn these easy and simple essays.
In This Blog We Will Discuss
Female Education: Short Essay (200 Words)
In a country like India , female education is being appreciated day by day. But a few years ago, the situation was not like now. People are changing and they are being smart and educated. Educated people can realize the importance of girl’s education.
But there are still a large number of girls are illiterate and they are not able to get an education. We need to stand for them and make education easy for every single girl in the world. An educated girl or women could do so many things that others can’t.
We can see that they are smarter than others. They raise their kids better and in a proper way. They study and learn things that help them to lead a better life. We all need to realize that and let our girls be educated.
Our country is growing according to a better economy. And females have a big share of this economy. Educated females are participating in everywhere. And that will help us to change our country soon.
Female Education: Essay (300 Words)
Introduction: Female education is a really important term right now for the entire world. From the very beginning, people used to neglect female education, as a result, women are so much behind according to research. Few first world countries are done really amazing in this, but still, now there are problems. Here, in this essay, we will take look at ‘female education in Bangladesh and others’.
Napoleon said, ‘give me an educated mother, I will give you an educated nation’. Can you realize the quote? An educated mother can create an educated nation. If our wives and our sisters won’t get proper education then how can we expect that our next generation will be educated? That’s why we need to put some extra effort into ‘Female Education’.
Female Education in Bangladesh: Bangladesh is a growing country with a fair amount of female education ratio. But a few years earlier, girls were really rare in school and colleges. But right now, in some boards, girls are doing far better than boys. So we can realize the evolution of education among female in Bangladesh.
Economically Bangladesh is a growing country. Females also have a great share of that. Due to the increase in their education ration, they are participating everywhere. They are doing a corporate job and also starting their own businesses. That is really good news for any country. They are working in every sector.
Importance of Female Education: There is a huge importance of female education. We need to emphasize that. Women are a vital part of us. We can’t arrange a better society or a better nation without them. They should be our partner in the journey. And we, of course, appreciate educated and well-learned partner with us. Whatever we do, they are helping us to complete that.
Conclusion: Female education is really necessary for every woman in this world. We should focus on that.
Female Education: Essay (500 Words)
Introduction: The world is growing and being special day by day. But in every sector, girls are not participating equally with boys. What’s the main reason behind this? I think of female education. Our life starts with education and if we can pursue education properly we can go really long in our life.
And if we can’t, we may not be able to go long. But in this world, lots of females are still away from education. Sometimes they leave study after a certain age. We need to work on that and make awareness among people. That will help us to understand the importance of female education.
Controversy: There are huge controversies about education for a girl. Some people present really funny and weak logic to prevent a girl’s education. But we should stand against them and let our girls to be educated. We can’t imagine a good nation without educated girls.
If we look at history, there are lots of female scholars who have done really well for their country. We have ‘Begum Rokeya’, she has started a revolution in India and Bangladesh which let girls start studying. We always need to stay away from the controversies and try to make our girl’s educated.
Female Education Advantages: There are lots of advantages of female education. Our whole society can be benefited from the process. Girls are working with boys outside nowadays; if they don’t get the proper education they won’t get a better job.
That’s why they need to pay attention to education. We also need to ensure their study. An educated mother can build an educated family. People won’t get proper good behaviour and manners without a good education.
Importance of an Educated Wife: In your family, of course, you don’t want an illiterate wife. You want an educated girl as your wife. But why, because the future of your kids depends on that. If she is educated, there is a high chance for your kids to be educated. So there is really high importance of educated wife in a family.
Equality in Education: We should bring equality in the education system all across the world. In this world, there are still lots of people don’t believe in equality among boys and girls. But being honest, they are the same. We need to treat the same and make them perfect for each other. If we don’t keep the equality, that will hurt them and don’t let them grow properly.
Conclusion: Female education essay is a really important one. We all can make awareness to our area and let people realize the importance of education for their girls. If we all start trying, then there will be a change and this change will change the world. We all can change the world together.
Related Essays and Paragraphs
- Environment Pollution Essay Writing for Students
- Essay on Aim in Life | 100, 150, 300, 500 Words Paragraphs and Essays
- Essay on Railway Station | Short and Long Essays for Students
- Essay on My Mother: 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 Words Essays
- Rainy Season Essay and Paragraph for School Students
- Essay on Winter Vacation for All Class Students
- My Grandmother Essay in 100, 150, 250, 300, 400 Words for Students
- Essay on Social Media for School and College Students
- Essay on Myself: For All Classes Students and Children
- Essay on Travelling in English for All Class
- Essay on Save Water in 200, 300, 400, 500 and 600 Words for All Classes
- Essay on My Best Friend in 200, 300, 400, 500 and 600 Words
- Essay on My Parents: 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 Words
- My Sister Essay in 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 Words for All Students
- Visit to a Historical Place Essay for All Class
- Essay on How I Spent My Holidays at Home
- Essay on My Dad My Hero for All Classes
- Essay on My School for All Class Students
Related posts:
- A Rainy Day Essay: 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 Words
- Essay on My Father in 300, 400, 500, 600, 700 Words for Class 1-10
- Essay on Childhood Memories in 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 Words
- Essay on Advantages and Disadvantages of Mobile Phone for Class 1-12
- Essay on Early Rising in 300, 400, 500, 600 Words for Class 1-10


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.2: Women and Education
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 150079
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Chapter 2: Women and Education
Chapter summary.
- Why Educating Girls Matters
- How Girls and Women Have Fared since Beijing
- What We Can Learn from Successful Efforts?
- Profile: Rita Conceição
- Project: Educating Women about Technology
Additional Resources
This chapter discusses the right to education and provides several examples of non-profit organizations that are working towards enhancing education among women. Education escalated as a global priority during the 1990s, featured at the 1994 International Conference on Population and Development, the 1995 Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing, and the 2000 Millennium Summit. Prior to the adoption of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), evidence of the economic and social benefits resulting from educating women and girls began to accumulate. The links were clear: educated women are more likely to have fewer, healthier, and better-educated children that will survive into adulthood and ultimately contribute to economic growth. According to UNESCO, in 2008 there were 96 and 95 girls per 100 boys in primary and secondary school, respectively. While the chapter does not discuss tertiary education, additional resources below will fill in statistics on gender gaps in post-secondary, which continue to vary at national and regional levels; women outnumber men in the post-secondary environment of developed countries by a significant margin, yet are still underrepresented in high-paying disciplines such as science and engineering and constitute only 30 percent of researchers.
The chapter examines several organizations working to improve women’s education from the standpoints of both community organizing and technology education. Bahia Street was founded by Rita Conceição in the informal communities of Salvador, Brazil. It began as a lunch program and evolved into a community centre conducting social-justice education among black women and girls on racism, gender-based violence, and reproductive rights. In rural Senegal, the international organization Tostan formed the Community Empowerment Program (CEP) to integrate mobile technology into writing and literacy programs. This initiative was developed in Wolof, the local language, and the program’s exercises in learning to use mobile phones are carried out using culturally appropriate and recognizable symbols. Tostan also initiated the Rural Energy Foundation, a community-based project to provide solar-powered charging stations for mobile phones.
- Bahia Street
- Community Empowerment Program (CEP)
- Gender-based violence
- International non-governmental organization (INGO)
- Jokko Initiative
- Non-formal education
- Non-governmental organization (NGO)
- Non-profit organization
- Reproduction
- Sexual violence
- Rita Conceição
- Rural Energy Foundation
- United Nations Children’s Rights and Emergency Relief Organization (UNICEF)
- United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
- United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Millennium Summit
- United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
- 1994 International Conference on Population and Development
- 1995 Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing
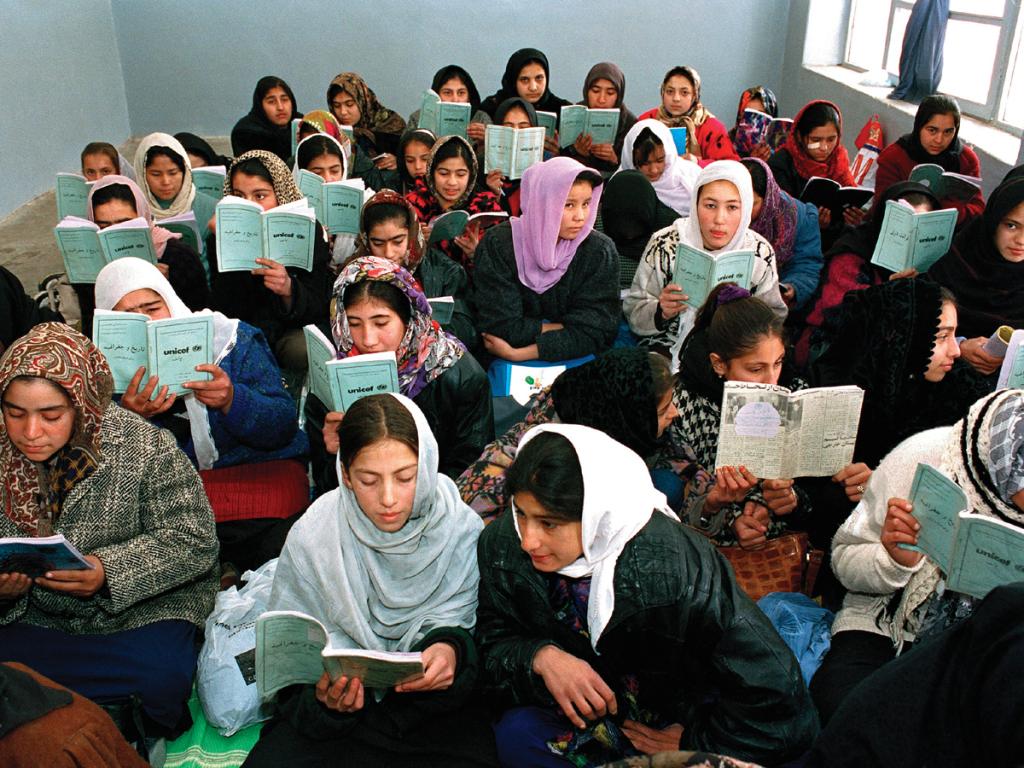

Figure 2.1: Few investments have as large a payoff as girls’ education. Educated women are more likely to ensure health care for their families, educate their children and become income earners. The Zarghuna Girls School in Kabul, Afghanistan, depicted here, is supported by the United Nations Children’s’ Fund (UNICEF).
By Lori S. Ashford
T he right to education for all has been an international goal for decades, but since the 1990s, women’s education and empowerment have come into sharp focus. Several landmark conferences, including the 1994 International Conference on Population and Development, held in Cairo, and the 1995 Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing, placed these issues at the center of development efforts.
The Millennium Development Goals — agreed to by world leaders at the U.N. Millennium Summit in 2000 — call for universal primary education and for closing the gender gap in secondary and higher education. These high-level agreements spawned initiatives around the world to increase girls’ school enrollments. Changes since 1990 have been remarkable, considering the barriers that had to be overcome in developing countries.
In many traditional societies, girls are prevented from attaining their full potential because of lower priority placed on educating daughters (who marry and leave the family) and the lower status of girls and women in general. Families may also have concerns about the school fees, girls being taught by male teachers and girls’ safety away from home. Governments and communities have begun to break down these barriers, however, because of overwhelming evidence of the benefits of educating girls.
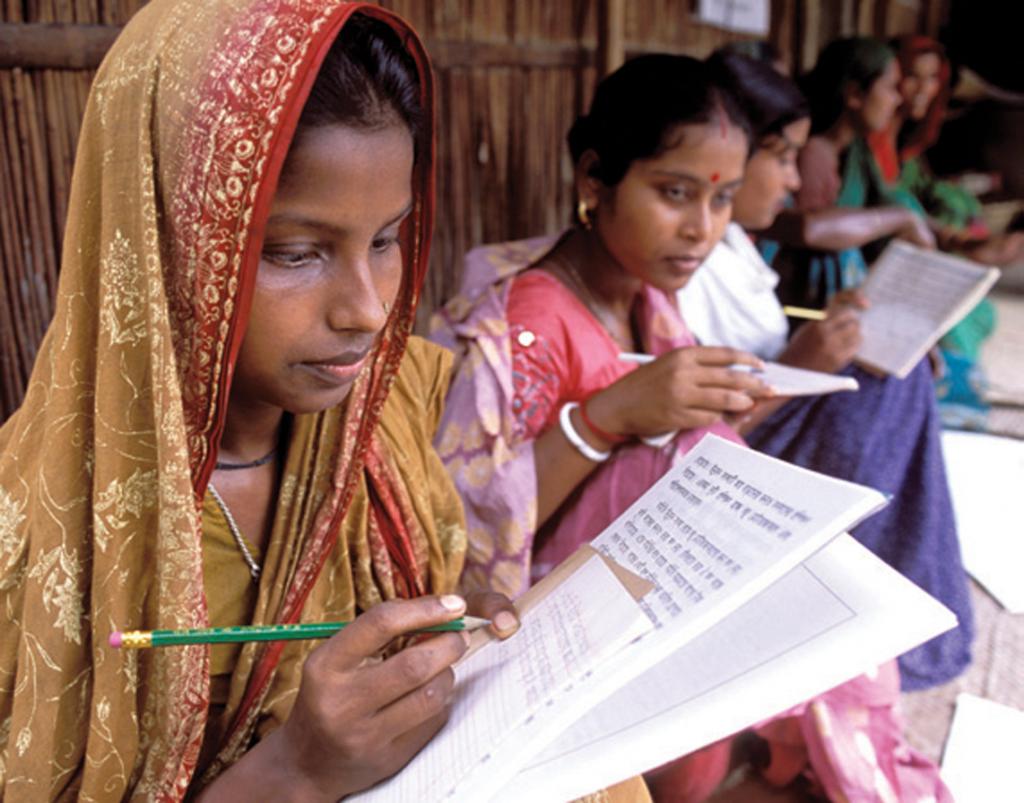

Figure 2.2: A woman in Bangladesh studies in an adult literacy class in a rural village. The teacher is from the village and trained at a college nearby.
Why educating girls matters
Few investments have as large a payoff as girls’ education. Household surveys in developing countries have consistently shown that women with more education have smaller, healthier and better-educated families. The linkages are clear: Educated women are more likely to take care of their health, desire fewer children and educate them well, which, in turn, makes it more likely their children will survive and thrive into adulthood.
Research by the World Bank and other organizations has shown that increasing girls’ schooling boosts women’s wages and leads to faster economic growth than educating only boys. Moreover, when women earn more money, they are more likely to invest it in their children and households, enhancing family wealth and well-being. Other benefits of women’s education captured in studies include lower levels of HIV infection, domestic violence and harmful practices toward women, such as female genital cutting and bride burning.

Figure 2.3: Corporate support of girls’ education is exemplified by Motorola’s “Introduce a Girl to Engineering” event, part of the company’s initiative to attract U.S. children to science and foster innovation early. Here Motorola engineer Deb Matteo conducts a light and color experiment with two young participants.
How girls and women have fared since Beijing
Advances in girls’ education worldwide have been a success story in development. According to UNESCO, 96 girls were enrolled in primary school for every 100 boys in 2008, up from 84 girls per 100 boys in 1995. The ratio for secondary school is close behind, at 95 girls to 100 boys in 2008. By 2005, nearly two-thirds of countries had closed the gap between girls’ and boys’ school enrollments. Girls still lag behind boys in university-level education worldwide, but the gap is closing over time.
Girls lag farthest behind in the poorest countries, such as Afghanistan, Chad, Central African Republic and Mali, where overall school enrollments are low. In Somalia, only half as many girls are enrolled in school as boys: 23 percent of girls compared to 42 percent of boys in 2008, according to UNESCO. Girls’ schooling and literacy lag well behind boys in much of sub-Saharan Africa and Western and Southern Asia, where much work remains to be done.
At the other end of the spectrum, in countries with high levels of school enrollment, girls often fare better than boys. In much of Latin America, Europe, East Asia and in the United States, girls’ enrollments in secondary and higher education have surpassed those of their male peers, demonstrating what girls and women can achieve once the barriers to education have been overcome.
Still, women account for two-thirds of the world’s illiterate adults, because older women are less likely to have attended school than their younger counterparts. They are also much more likely to be illiterate if they are poor and live in rural areas. Literacy programs and continuing education exist, but the efforts are not systematically reported across countries. In addition, girls and women are disadvantaged when it comes to technical and vocational education, in fields such as science and technology that have long been dominated by men.
What can we learn from successful efforts?
Many gains in women’s education can be attributed to special interventions such as the elimination of school fees, scholarships, community schools for girls and the training of women teachers. Such targeted efforts have translated into higher girls’ school enrollments in countries as diverse as Bangladesh, Yemen, Morocco, Uganda and Brazil. Political commitment is essential for raising the profile of the issue and increasing girls’ access to schooling. Mexico pioneered a major social program — now replicated in impoverished communities in the United States and other countries — that pays families to keep their children, particularly girls, in school.
Because the gender gap is wider at higher levels of education, it will not be enough for girls to merely sign up for school; they need to stay in school. Governments, educators and communities must address issues such as gender stereotypes that reinforce women’s lower status, poor school quality, and early marriage and childbearing, which often cut short women’s education. Also, the mismatch between education and the skills needed for today’s workforce must be corrected. These steps may ensure that girls reap the greatest benefits from education. Countries that are committed to gender equality will not only see better report cards in education, they’ll be healthier and wealthier as well.
Lori S. Ashford, a freelance consultant, has written about global population, health and women’s issues for 20 years. Formerly with the Population Reference Bureau (PRB), she authored the widely disseminated PRB “Women of Our World” data sheets and “New Population Policies: Advancing Women’s Health and Rights” for the Population Bulletin, among other publications.
PROFILE: Rita Conceição – Bahia Street
By Margaret Willson

Figure 2.4: After growing up poor in Brazil, Rita Conceição saw education as the path out of poverty. Her determination got her to university, and her desire to help other women led her to found Bahia Street.
B orn in one of the vast shantytowns of Salvador, Brazil, Rita Conceição knew at an early age the realities of violence, poverty and death. She also knew she wanted something different.
“My mother had lots of children and a hard life. She died young, so I brought up my brothers and sisters. I knew I didn’t want that life.”
With great determination, Rita traveled more than an hour each way by public bus to a school where she could learn to read and write. She loved the arts and took up photography. While still a teenager, Rita took courageous photos of protests against the then-ruling Brazilian military dictatorship.
“I didn’t think of a black or gender consciousness,” she says. “People never talked about racism then.” But all around her she saw women like herself working as maids for slave wages, the only job (except prostitution) open to them.
Rita decided she wanted to go to university, an almost impossible dream for someone from the shantytowns. While working a full-time job, she tried the difficult university entrance exam three times and failed. Refusing to give up, she took it a fourth time and passed, gaining entrance into the Federal University of Bahia, the best in her state.
When I first met Rita in 1991, she had earned her university degree in sociology. Once she had a chance to leave the shantytown where she was born, Rita, unlike any other person I ever met there, decided instead to stay and fight the inequality she knew so well. So in 1996, when she invited me to join her in working for equality for the people of her communities, I committed to help in any way I could. From this partnership the nonprofit Bahia Street was born.
Listening to what the people in her community told her answered their dire need for expression and opened a strong avenue for change. Rita initiated a quality education program for girls that would allow them to enter university and change their futures. Rita drew on her own struggles, using the strengths that propelled her from a shantytown to university. She incorporated race and gender consciousness into the Bahia Street classes. Seeing that the girls could not study because they were half starving, she began a lunch program, cooking and buying the food herself until she could find someone to help her. She knew that most girls from these shantytowns get pregnant by age 14, so she began teaching the girls about reproduction, sexual violence and self-esteem.
“As I was growing up,” she says, “the girls in my family were never valued as much as the boys. This still exists in our society, but I say to the girls that their roots are their reality. I pass on to them the importance of ethics, self-respect and the solidarity of women. They see in me the difference it makes — what choices you make in your life — and also the strength it takes. If women are to become equal, these qualities and knowledge are vital.”
After years of renting or borrowing tiny rooms for its classes, Bahia Street was finally able to buy a building. The only problem was that the building was falling down. Rita saw this as no problem at all. She employed local men and oversaw its complete reconstruction. To save money, the men mixed the cement in wheelbarrows and poured it by hand. Rita roamed the city, looking for sales; she negotiated with merchants to donate materials that she then brought back on public bus, since she had no car. Slowly, the building took shape. When the first floor was mostly finished, Rita, her staff and the girls moved in.
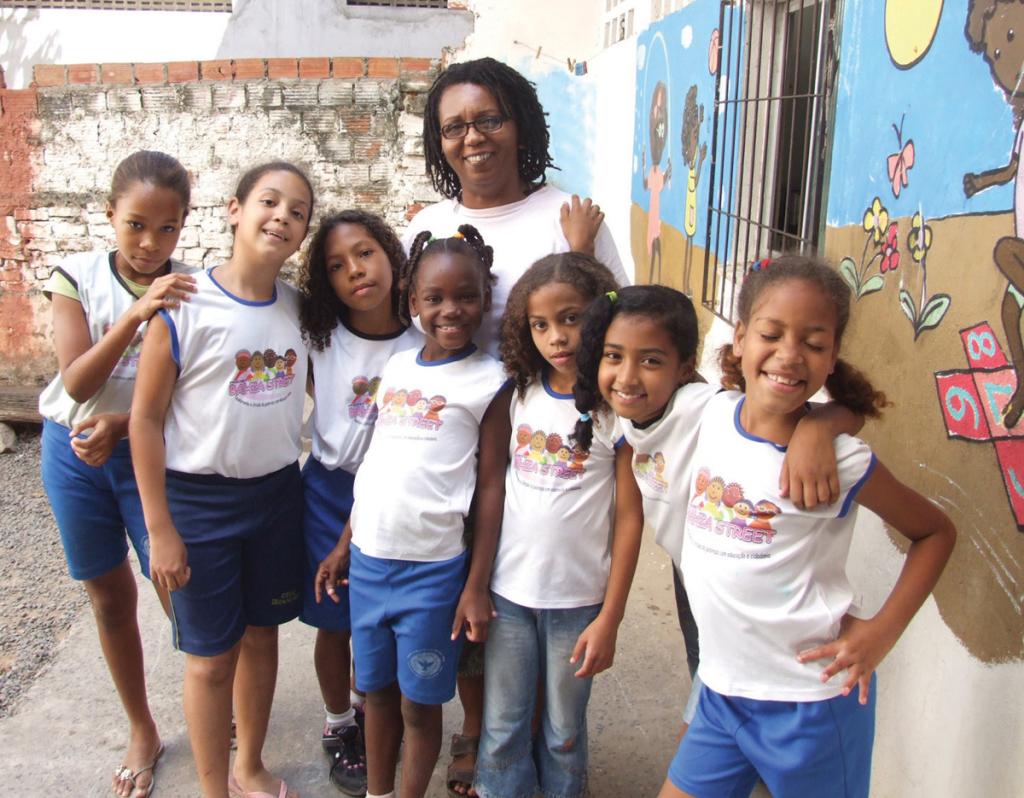

Figure 2.5: Conceição poses with some of the students at Bahia Street.
The five-story Bahia Street Center is now complete, with classrooms, kitchen, library, computer lab and much more. In addition to education and support programs for the girls, Bahia Street now offers classes for the girls’ caregivers and other community members. It has become a haven for the girls and a community gathering place.
“We teach the girls to take care of others in their lives as well. Women take care of the children, and in that is the future of our society. The work we do is a form of black resistance. We are working for the survival of the black people in Bahia, showing that as black women, we can have equality and shape the future. In Bahia Street, we are giving girls the chance my mother never had.”
When people talk with her about her remarkable achievements, Rita is humble and realistic. “In Bahia Street,” she says, “I really found my identity. Managing to create Bahia Street continues to be an amazing process, and I have learned a consciousness myself through this process.”
Recently, Bahia Street graduate Daza completed university with a journalism degree. In Daza, shantytown residents have a voice they never had before. And the long-term Bahia Street vision of fostering equality for shantytown women is becoming a reality.
Rita laughs with a smile that, in its brightness, knows suffering, love and strength. “And the work continues. That is the way for all of us. If we are to make a better world, the work is what we do.”
Margaret Willson is co-founder and international director of Bahia Street. She is affiliate assistant professor in anthropology at the University of Washington. Her most recent book is Dance Lest We All Fall Down: Breaking Cycles of Poverty in Brazil and Beyond (University of Washington Press, 2010).
PROJECT: Educating Women About Technology
By Renee Ho
Mobile technology is improving the lives of illiterate women and girls in rural Senegal, and educating them in the process, thanks to an organization that teaches them to use mobile phones.
A stou watches as the photographer raises his camera to capture the crowded village classroom. She adjusts her nursing infant and turns her own camera on him — only hers is a mobile phone. For the past few weeks, Astou has been participating in a community-led mobile technology course taught in her local language of Wolof. She and hundreds of other women and girls throughout rural Senegal have learned how to make and receive calls, compose and send SMS messages and use phone functions such as calculators, alarms and, yes, sometimes even cameras.
Astou is a bright 24-year-old mother of four children. She had seen her husband use a mobile phone, but prior to this class she had never touched one herself. “Before, he would not let me use the phone because he feared I would waste the credit,” she laughs, “but now he asks me to teach him and we are saving to buy another for me.”
Two years ago, Astou was not only unfamiliar with how to use a mobile phone, but she was illiterate. Composing or reading an SMS text message would have been impossible for her. Like most of the women and girls in her village in the region of Vélingara, Senegal, Astou never attended school. Household responsibilities and the cost of schooling prevented her from receiving a formal education. She married at 16 years of age — the average age for girls in rural Senegal.
In a country with a 41.9 percent literacy rate, Astou is breaking norms and the cyclical trap of poverty. In 2008, Tostan, an international nongovernmental development organization, started the Community Empowerment Program (CEP) — a 30-month human rights-based, nonformal education program — in her village. More than 80 percent of CEP participants are women and girls. They begin the program with sessions on human rights, democracy, health and hygiene and problem-solving. Later, they continue with lessons on literacy, numeracy and project management.
Once participants have achieved basic literacy, however, they often lack a practical means of maintaining it. As a solution, Tostan partnered with UNICEF to launch the Jokko Initiative in 2009 (jokko means “communication” in Wolof). The initiative incorporates mobile technology into CEP as way to reinforce reading and writing skills. The Jokko module teaches participants how to use basic mobile phone functions and SMS texting. It uses interactive visuals and skits that focus on relevant applications and the relative affordability of texting. “I text messages better [than my husband] and that saves us money on expensive calls,” explains Astou.
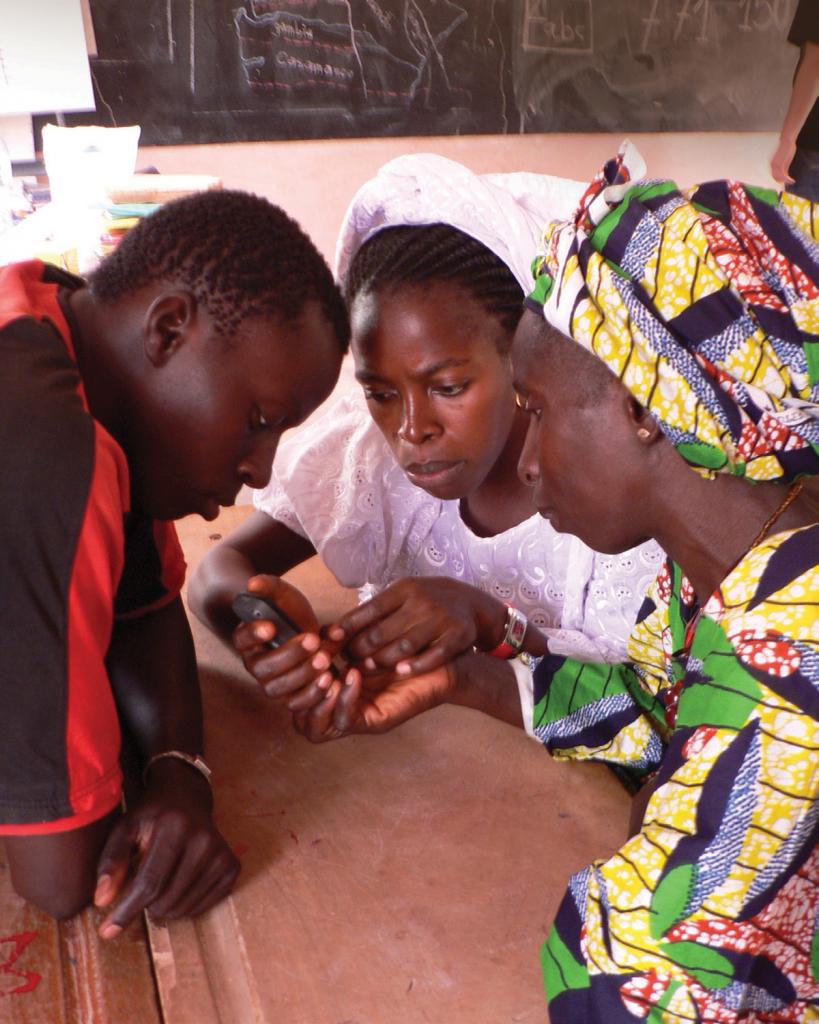

Figure 2.6: The Tostan Jokko community empowerment program teaches women to use mobile phones.
Outside of the classroom, students circle around a strange arrangement of sticks. With a little explanation, the sticks come to represent a mango tree. Khady, age 52, walks along the “tree branches” and stops at each fork where signs are placed: Contacts, Search, Add Contact. This activity teaches participants how to navigate the phone’s main menu. It is just one example of what makes Tostan’s educational model work: adapting lessons to cultural contexts and using appropriate local references.
“Before, if I wanted to send a text message, I had to ask for help,” Khady says, “but now I am much more independent. Now people come to me and I’m happy to teach them.” When mobile phone technology reaches women and girls, it amplifies their voices and influence in community decisionmaking. They become agents of their own change. Khady continues to explain how the CEP provided her with basic math and management skills. With several boys and girls huddled around, she demonstrates how the phone’s calculator helps her manage her peanut-selling business.
Mobile phone technology has connected women and girls to market information and opportunities, family in the diaspora and, perhaps most fundamentally, to each other. The phones have been critical for community organization and social mobilization. Tostan’s Jokko Initiative has developed a unique social networking platform that allows participants to send an SMS message to a central server, where it is then sent out to an entire community of other users. One participant explains, “It’s when you send multiple messages at once — a cheaper method of communication.” The platform is used for community advocacy campaigns. Women send, for example, reminders of vaccination and school enrollment dates.
The Jokko Initiative has reached 350 villages and continues to grow. Tostan has directly trained about 23,585 people, but the high demand for knowledge and the eagerness of participants to share information suggests that thousands more have benefited.
In the project’s next phase, Tostan will partner with the Rural Energy Foundation (ruralenergy.nl/), a nonprofit organization that helps rural communities gain access to renewable energy. Currently, about 80 percent of rural Senegal lacks electricity, so charging phones often involves risky and inconvenient trips into the nearest small town. To alleviate this, Tostan will pilot community-led, solar-powered charging stations. These telecenters will provide electricity for mobile phones, and the income generated by these microenterprises will be reinvested in other community-led development projects.
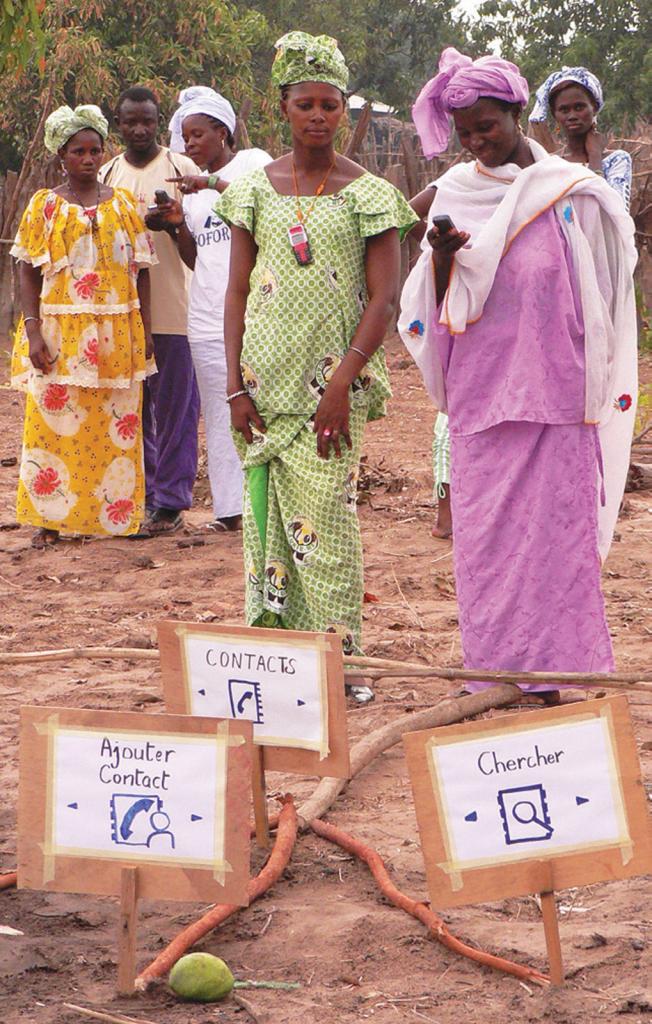

Figure 2.7: Women, some of them illiterate, learn to navigate the main menu of a mobile phone through an arrangement of branches on the ground.
Mobile phone use in Africa is growing twice as fast as in any other region in the world. In Senegal, the number of SIM card purchases nearly doubled from 2007 to 2009, up to 6.9 million. But as Tostan has found, absolute numbers alone do not empower communities. Success in low-income countries requires bridging the gender gap. Putting knowledge and technology in the hands of women — literally— is critical to achieving lasting development.
Renee Ho is a volunteer at Tostan International in Dakar, Senegal. Her interests include women and the technology divide in lower-income countries. More information is online at http://www.tostan.org .
Multiple Choice Questions
- 2000 Millennium Development Summit
- None of the above
- Take care of their health
- Desire fewer children
- Educate their children well
- All of the above
- Afghanistan
- Older women are less likely to have attended school than their younger counterparts
- High-paying majors such as science and technology remain dominated by men
- Women living in rural areas have less access to educational services
- Engages in community building, gender and race consciousness work.
- Provides small-interest loans to allow women in the shantytowns of Salvador to become entrepreneurs
- Teaches women to use Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) more efficiently
- Helps rural communities gain access to renewable energy
- Margaret Wilson
- Sheryl Sandberg
- The importance of domestic and household responsibilities
- Project management
- The Community Empowerment Program (CEP)
- Free the Children
- The Jokko Initiative
- Incorporates mobile technology into CEP as a way to reinforce reading and writing skills
- Teaches participants how to use SMS functions
- Connects women and girls to market information opportunities
- All the above
- Was developed in partnership with the UNICEF
- Focuses on rights-based empowerment rather than economic and entrepreneurial capacity building
- Adapts lessons to cultural contexts and uses appropriate cultural references
- Held focus groups with local government officials instead of community stakeholders
- Fund an increase in the amount of mobile phones in sub-Saharan Africa
- Pilot community-led solar-power charging stations for mobile phones
- Fund a the construction and operation of a solar-energy plant in Vélingara, Senegal
- Construct several powerlines to provide energy to rural Senegalese communities
- Putting knowledge and technology in the hands of women
- More efficient mechanisms to send text messages
- More affordable mobile phones for women and children
- The correct answer is C. The 1994 International Conference on Population and Development (answer A) and the 1995 Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing (answer B) were both milestones in placing women’s empowerment on the global agenda. However, it was the 2000 Millennium Development Summit (answer C) where world leaders agreed on the target of universal primary education as part of the MDGs.
- The correct answer is D (all of the above).
- Answers A and D are correct. Morocco (answer B) and Bangladesh (answer C) are both countries where governments have committed to action and have seen higher enrollment among women and girls in education.
- Answer C is correct. The gender ratio is the most equal for primary school enrollment (answer A) with 96 girls for every 100 boys, and the ratio for secondary school (answer B) is similar, at 95 girls per 100 boys. The education gap is the widest at the post-secondary, or tertiary, level (answer C).
- Answer D (all of the above) is correct.
- Answer A is correct. Bahia Street works to builds solidarity and facilitates consciousness around gender and race among black communities in Salvador, Brazil. The organization is not a microfinance institution (answer B). The Community Empowerment Program (CEP) in Velingara, Senegal, provides capacity building for women to use ICTs (answer C), and the Rural Energy Foundation (answer D) is a non-profit that helps rural communities gain access to renewable energy.
- The correct answer is D. Bahia Street was founded by Rita Conceição, who grew up in the shantytowns of Salvador and wanted to build community and raise political consciousness among young black girls living in the community. Renee Ho (answer B) was the writer of the chapter on the Community Empowerment Program. Margaret Wilson (answer A) is the co-founder of Bahia Street. Sheryl Sandberg (answer C) is the Chief Operating Officer (COO) of Facebook and the author of the book Lean In.
- The correct answer is A. The CEP does NOT teach girls about the importance of domestic responsibilities. The program recognizes that unpaid domestic labour among women can prevent them from progressing in formal education and instead teaches skills in literacy (answer B), numeracy (answer C), and project management (answer D).
- The correct answer is D (the Jokko Initiative). UNICEF (answer A) is a partner in the Jokko project. The CEP (answer B) is also implemented by Tostan but is a rights-based education program.
- The correct answer is D. (all the above).
- The correct answer is C. Tostan’s educational model works because it adapts lessons to cultural contexts and uses appropriate cultural references. The CEP focuses on rights-based empowerment (answer B). The Jokko Initiative was developed in partnership with UNICEF (answer A) but was not emphasized by the textbook as the primary reason for the project’s success. Tostan’s model was developed in close consultation with the community, so answer D is incorrect.
- Answer B is correct. The Rural Energy Foundation will pilot the development of community-led solar-power charging stations for mobile phones in Senegal. Mobile phone ownership rates are rapidly increasing across Africa, but the Foundation will be making this trend more sustainable, rather than simply contributing to the volume of phones (answer A). The Foundation is not supporting the construction of a solar energy plant (answer C) or powerlines (answer D).
- Answer A is correct. The Rural Energy Foundation will put knowledge and technology in the hands of women as means to achieve long-lasting development. More efficient and affordable text messages (answers B and C) are a product of the Jokko Foundation.
Discussion Questions
- Rita Conceição names a number of values she incorporates into advice she gives to girls who are a part of Bahia Street. What are some of these values and why do you think they are important to her?
- Describe some methods Jokko Initiative uses to educate women about technology. Compare and contrast Bahia Street with the Jokko Initiative.
- Use external research to find the most recent gender ratio for tertiary education. How does this ratio change at national, regional, and global levels?
- What are the risks of grouping different countries into categories of most and least educated? What trends are included and overlooked when using this approach?
- How did the emphasis on education from the Millennial Development Goals transfer over to the Sustainable Development Goals? What kind of presence do education, gender, and technology have in the Sustainable Development Goals?
- What are some examples of the role of technology in political change? Is there a connection between the use of technology for education and its use for broader social movements?
- What are some examples of how social media has influenced women’s political, social, or economic empowerment?
Essay Questions
- The textbook notes that “mobile phone use is increasing twice as fast in Africa as in any other region in the world” (p. 37). What are the benefits of having a mobile phone on an individual, organizational, or community level? Are mobile phones or other pieces of information and communication technology simply neutral devices or tools of political influence?
- What does the Jokko Initiative demonstrate about the benefits of incorporating local knowledge into development programs? What are some ways of ensuring that local symbols, values, and perspectives are integrated into education and capacity-building projects?
- Rita Conceição, founder of Bahia Street, was quoted saying “we teach the girls to take care of others in their lives as well. Women take care of the children, and that is the future of our society.” What are the implications of this statement in the context of gender norms, care, and domestic labour?
EdTechWomen. “About ETW.” (2016). New York, NY. A New York-based organization that supports the leadership and capacity of women in education technology.
http://edtechwomen.com/
Cornwall, A. “Women’s Empowerment: What Works?” Journal of International Development 28 (3), 342 – 359. (2016). Draws on a multi-country research study to examine women’s individual journeys towards empowerment.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jid.3210/full
Foster, D. & Fitzgerald, M. “Is Capitalism Destroying Feminism? An Interview with Dawn Foster.” OpenDemocracy. (2016). An interview with Dawn Foster, a journalist who writes on gender, politics and social affairs. Her book Lean Out is a response to Sandberg’s Lean In , and takes a more institutional approach to discussing women in the workplace through a lens of not only gender, but also class, race, and empire.
https://www.opendemocracy.net/dawn-foster-mary-fitzgerald/is-capitalism-destroying-feminism-interview-with-dawn-foster
Perryman, L. & de los Artocs, B . “Women’s Empowerment Through Openness: OER, OEP and the Sustainable Development Goals.” Open Praxis 8 (2), April – June 2016, 163 – 180. (2016). Based on survey responses from 7,700 educators from 175 countries, this paper explores the ability of Open Education Resources (OERs) to increase women’s voices in education.
http://openpraxis.org/index.php/OpenPraxis/article/view/289/206
Rice, C. et al. “Pedagogical Possibilities for Unruly Bodies.” Gender and Education . 1 – 20. (2016). Paper on the use of digital art to tell untold narratives of activism by people with disabilities.
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09540253.2016.1247947
Sandberg, S. “Why We Have Too Few Women Leaders.” TED. (2010). TEDTalk by Sheryl Sandberg based on her widely acclaimed book Lean In , on navigating the male-dominated business world as a woman.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=18uDutylDa4
Rossatto, C. “Global Activism and Social Transformation vis-à-vis Dominant Forms of Economic Organization: Critical Education within Afro-Brazilian and Transnational Pedagogical Praxis.” Journal for Critical Education Policy Studies 2 (3), 228 – 260. (2015). Discusses grassroots social movements across race and gender divisions and national borders to challenge notions of market competition within education.
http://www.jceps.com/archives/2347
The World’s Women 2015 . “Education.” (2015). Annually updated global data and analysis on gender disparities in educational access with indicators including primary and secondary school enrollment rates as well as illiteracy.
http://unstats.un.org/unsd/gender/chapter3/chapter3.html
UN Statistics . “Millennium Development Goal Indicators.” (2016). Updated statistics and baseline indicators on the progress made in achieving the Millennium Development Goals, with data available in national, regional and global contexts.
http://mdgs.un.org/unsd/mdg/default.aspx

Why reporting sexual violence against men or women is important
- By Mr. Digital Fingers
- Jun 22, 2024

Sexual violence is a deeply traumatic experience that affects both men and women, yet reporting these crimes is crucial for several reasons. Understanding the importance of reporting sexual violence can help victims find the strength to come forward, ensuring justice and healing. This article will explore the significance of reporting sexual violence, the barriers victims face, and the support systems available to those who decide to report.
The significance of reporting sexual violence
When victims come forward, the justice system can hold perpetrators accountable, potentially preventing future assaults. Each report contributes to a larger picture, helping authorities identify patterns and address systemic issues. Additionally, reporting can give victims a sense of empowerment and control over their situation.
Justice and accountability
When victims report sexual violence, it triggers an investigation that can lead to the arrest and prosecution of the perpetrator. This process is essential for ensuring that justice is served. Holding offenders accountable not only punishes the crime but also acts as a deterrent to others who might commit similar offenses. The legal repercussions can vary, including imprisonment, fines, or mandated therapy, all aimed at reducing recidivism.
Empowerment and healing
For many victims, reporting the violence is a crucial step in the healing process. It allows them to reclaim their narrative and assert their right to safety and respect. Reporting can be empowering, providing a sense of closure and a way to move forward. Moreover, it can inspire other victims to come forward, creating a supportive community that fosters collective healing.
Barriers to reporting sexual violence
Despite the importance of reporting, many victims face significant barriers that prevent them from coming forward. These barriers can be psychological, social, or systemic, making understanding and addressing them essential to support victims better.
Psychological barriers
Fear, shame, and guilt are powerful emotions that can prevent victims from reporting sexual violence. Many victims worry about not being believed or being blamed for the assault. These feelings are often compounded by the trauma of the assault itself, making it difficult for victims to take the step of reporting.
Social barriers
The societal stigma surrounding sexual violence can be a significant deterrent for victims. Victims may fear judgment from family, friends, or the community. Men, in particular, may face additional stigma due to societal expectations of masculinity, which can make it harder for them to come forward. The fear of retaliation from the perpetrator or their associates also significantly discourages victims from reporting.
Systemic barriers
The legal and medical systems themselves can sometimes be barriers to reporting. Victims might be discouraged by the lengthy and invasive nature of investigations and court proceedings. Additionally, a lack of training and sensitivity among law enforcement and medical professionals can result in the re-traumatization of victims, further deterring them from coming forward.
Support systems for victims of sexual violence
Robust support systems are crucial to encouraging reporting and supporting victims. These systems can provide the necessary resources and emotional support to help victims navigate the reporting process and begin their healing journey.
Legal and medical support
Many organizations offer legal assistance to victims of sexual assault, helping them understand their rights and the legal process. Medical support is also vital, as timely medical examinations can collect crucial evidence and provide necessary healthcare. Hospitals and clinics often have specially trained staff to handle sexual assault cases with the sensitivity and care required.
Counseling and therapy
Counseling and therapy are essential for helping victims deal with the emotional aftermath of sexual assault. Many victims benefit from speaking with a therapist who specializes in trauma, providing a safe space to process their feelings and develop coping strategies. Support groups can also be beneficial, allowing victims to connect with others who have similar experiences.
Advocacy and community resources
Numerous advocacy organizations work to support victims of sexual assault, providing a range of services from hotlines to legal advocacy. These organizations often offer resources such as emergency shelter, financial assistance, and guidance through the reporting process. Community education programs can also help reduce stigma and create a more supportive environment for victims.
The role of education and awareness
Education and awareness are crucial components in the fight against sexual violence. By raising awareness about the importance of reporting sexual assault, we can encourage more victims to come forward and seek justice. Education programs in schools, workplaces, and communities can help change societal attitudes and reduce the stigma associated with being a victim of sexual assault.
Preventative education
Preventative education programs aim to reduce the incidence of sexual assault by teaching individuals about consent, respect, and healthy relationships. These programs often target young people, equipping them with the knowledge and skills to prevent sexual violence. By fostering a culture of respect and consent, we can reduce the number of sexual assaults and encourage reporting when they do occur.
Public awareness campaigns
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in changing societal attitudes towards sexual assault. These campaigns can help dispel myths and misconceptions about sexual assault, promote supportive responses, and highlight the importance of reporting. By creating a more informed and empathetic society, we can support victims’ decision to come forward.
Reporting sexual assault on men and women is vital for ensuring justice, supporting healing, and preventing future assaults. While many barriers exist, robust support systems and increased education and awareness can help victims overcome these obstacles. By fostering a more supportive and informed society, we can encourage more victims to report their assaults, ensuring that justice is served and healing can begin .
This story was created using AI technology.
Sign up for Rolling Out news straight to your inbox.
- accountability , education and awareness , empowerment , Healing , justice , News2 , psychological barriers , sexual assault reporting , social stigma , support systems , systemic barriers

Why good people tolerate bad treatment from partners

Boxer Ryan Garcia suspended for 1 year after positive drug test

Why lovers like to renegotiate their love and sex arrangements

Jennifer Hudson reveals her father had 27 children
How party host Boss Lady Ace controls a room, studio or pool

Travis Scott breaks silence after his arrest in Miami
- More in Crime

How decoys are starting to catch package thieves

Remy Ma’s son charged with murder; she responds

This request in the YSL RICO trial can change the entire outcome
- Community News
- Justice For All
- All Entertainment
- Reality Check
- All Culture
- Relationships
- Cocktail & Beer
- Creative Lens
- All Business
- Black Intellectuals
- Diversity Equity & Focus
- Sisters with Superpowers
- Home Ownership & Real Estate
- Entrepreneurs & Business Leaders
- Executive Suite
- Finance & Wealth
- Marketing & Branding
- Be the Match Atlanta
- Food & Nutrition
- Browse Places & Events
- HBCU Culture
- Privacy Policy
Change Location
Find awesome listings near you.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Reading Day: A Celebration of Literacy and Learning

- Updated on
- Jun 19, 2024

Are you familiar with Puthuvayil Narayana Panicker? He is regarded as the Father of India’s Library Movement because of his efforts to promote education and literacy in India. His dream was to make India an educational society by reading books and other academic sources. Today, we observe National Reading Day on 19 June every year to honour his determination and hard work. We will discuss a 500-word essay on Reading Day to help students understand the importance of reading and what doors of opportunities this simple habit can open.

Table of Contents
- 1.1 History
- 1.2 Importance of Reading
- 1.3 Promoting Literacy and Education
- 1.4 Celebrating Reading Day
- 1.5 The Power of Reading
- 1.6 Conclusion
Essay on Reading Day in 500 words
Reading Day is marked annually on June 19th, a day dedicated to the importance of reading. Reading Day serves as a reminder of the power that books and literature have in people’s lives. This day not only honours the act of reading but also promotes literacy and education worldwide. By recognising a day to read, we highlight the importance of literature for our personal growth and societal development.
This day is celebrated in honour of P.N. Panicker, a Keralite teacher renowned as the ‘father of the Library Movement’. Puthuvayil Narayana Panicker, also known as P.N. Panicker, worked towards the betterment of society through his literacy movements in India. Even Though the day was first observed in the 1990s, Prime Minister Narendra Modi officially declared June 19 as National Reading Day. Since then, the day has been honoured on June 19 every year.
Importance of Reading
Reading is a fundamental skill that is necessary for education and personal growth. Reading helps us gain information, critical thinking skills, and problem-solving skills. Reading is vital for typing children to learn the language, improve comprehension, and enhance vocabulary. Books provide a glimpse into many worlds and broaden one’s understanding of various perspectives and ideas.
For adults, reading is a tool that allows them to learn and improve themselves continuously. Fictional books inspire our imagination and creativity, whereas non-fictional books teach us about the realities of life. In a constantly changing world, understanding complicated information and being able to read are critical skills. It enables people to stay informed, make sound decisions, and fully engage in society.
Promoting Literacy and Education
One of the main objectives of Reading Day is to encourage literacy and address challenges associated with it worldwide. Despite significant educational advancements, the world continues to face challenges with literacy. According to UNESCO, around 773 million individuals globally lack basic literacy abilities, while millions of youngsters do not receive an education. Reading Day emphasises the need for successful literacy programmes and equal access to reading resources for all. Community initiatives, such as book distribution or library expansions, can have a huge impact. Working together, we can ensure that everyone has the opportunity to study and benefit from the knowledge that books offer.
Celebrating Reading Day
Reading Day can be celebrated in a variety of ways. Schools frequently play an important part in the celebration of reading. By organising book fairs, creative writing workshops, and storytelling sessions, we can instill a love of reading in the next generation. Libraries are also an important element of this event. Public libraries can reach out to the community by organising mobile libraries and establishing reading areas in public places. Parents can also help their children develop the habit of reading.
The Power of Reading
The impact of reading extends far beyond the individual. It can transform societies. Reading promotes empathy and cultural awareness. Through literature, an individual can learn about diverse ideas and cultures, allowing them to be a more active participant in the democratic process. Furthermore, reading can inspire and stimulate creativity. Many stories inspire us to pursue our dreams and fight social norms.
Reading Day celebrates written words and their importance in our lives. This occasion is an opportunity to promote literacy, instil a love of books, and acknowledge the significant impact reading has on individuals and societies. Let us celebrate this day as a chance to instill a lifelong appreciation of reading in individuals and work towards an educated and progressive society.
Also Read: Importance of Reading for Students
Ans: Reading Day is marked annually on June 19th, a day dedicated to the importance of reading. The first reading was celebrated on 19th June 1996 in honor of P.N. Panicker, a Kerala teacher.
Ans: This day is celebrated in honour of P.N. Panicker, a Keralite teacher renowned as the ‘father of the Library Movement’. Puthuvayil Narayana Panicker, also known as P.N. Panicker, worked towards the betterment of society through his literacy movements in India. Reading Day serves as a reminder of the power that books and literature have in people’s lives. This day not only honours the act of reading but also promotes literacy and education worldwide.
Ans: Reading is a tool that allows them to learn and improve themselves continuously. Fictional books inspire our imagination and creativity, whereas non-fictional books teach us about the realities of life. In a constantly changing world, understanding complicated information and being able to read are critical skills. It enables people to stay informed, make sound decisions, and fully engage in society.
Popular Essay Topics
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Bhumika Sharma
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies and similar tracking technologies described in our privacy policy .
Supporting Educators & Students
Teaching & learning.
As part of its broad-based teaching mission, the AHA develops and shares resources for educators and students. From regional teaching conferences and online programs to pathbreaking research projects, AHA initiatives foster a community grounded in our shared commitment to understanding the past. We support and convene people who share a love of history and historical thinking.
Resources for Educators & Students

K–12 Education
The AHA strives to ensure that every K–12 student has access to high quality history instruction. We create resources for the classroom, advise on state and federal policy, and advocate for the vital importance of history in public education.

Undergraduate Education
Teaching and learning are at the foundation of the AHA’s mission to promote historical thinking in public life. What do students learn in undergraduate history courses? How and why are history majors so successful in a variety of careers?

Graduate Education
Many historians will pursue graduate training at some stage in their career. To meet the needs of both students and graduate programs, the AHA creates resources, provides platforms, and convenes conversations about student success from application to completion.
For Academic Departments
History department chairs are on the front lines of the discipline, defending historians’ work and supporting their professional lives at all stages of their academic careers. The AHA strives to strengthen this work and provide resources and opportunities that make chairs’ work easier and valued. The AHA provides resources and hosts a variety of events and opportunities to benefit department chairs and build community, including webinars, sessions at the annual meeting, and an in-person workshop.
Current Events in Historical Context
Essential, carefully researched resources by historians providing context for conversations about current events.
Regional Conferences on Introductory History Courses
What do students learn in introductory history courses? How can historical thinking support student learning and success across the curriculum? Our regional conferences endeavor to strengthen the community of practice focused on introductory history courses, both in secondary and higher education.
Standards & Guidelines

June 10, 2024
Guidelines for Academic Tenure-Track Job Offers in History
June 9, 2024
Statement on Age Discrimination
Aha historical collections.
The AHA has made primary sources available for research purposes, along with AHA archival reports and documents.
Vetted Resources
Vetted Resources compiles in a central location materials and tools that have been professionally vetted by historians, offering instructors access to high-quality materials that meet professional standards
AHA Resource Library

June 20, 2024
16 Months to Sumter: Newspaper Editorials on the Path to Secession

June 16, 2024
The History of Racism and Racist Violence: International Contexts and Comparisons
The history of racism and racist violence: monuments and museums, join the aha.
The AHA brings together historians from all specializations and all work contexts, embracing the breadth and variety of activity in history today.
What is STEM Education?
STEM education, now also know as STEAM, is a multi-discipline approach to teaching.

- Importance of STEAM education
STEAM blended learning
- Inequalities in STEAM
Additional resources
Bibliography.
STEM education is a teaching approach that combines science, technology, engineering and math . Its recent successor, STEAM, also incorporates the arts, which have the "ability to expand the limits of STEM education and application," according to Stem Education Guide . STEAM is designed to encourage discussions and problem-solving among students, developing both practical skills and appreciation for collaborations, according to the Institution for Art Integration and STEAM .
Rather than teach the five disciplines as separate and discrete subjects, STEAM integrates them into a cohesive learning paradigm based on real-world applications.
According to the U.S. Department of Education "In an ever-changing, increasingly complex world, it's more important than ever that our nation's youth are prepared to bring knowledge and skills to solve problems, make sense of information, and know how to gather and evaluate evidence to make decisions."
In 2009, the Obama administration announced the " Educate to Innovate " campaign to motivate and inspire students to excel in STEAM subjects. This campaign also addresses the inadequate number of teachers skilled to educate in these subjects.
The Department of Education now offers a number of STEM-based programs , including research programs with a STEAM emphasis, STEAM grant selection programs and general programs that support STEAM education.
In 2020, the U.S. Department of Education awarded $141 million in new grants and $437 million to continue existing STEAM projects a breakdown of grants can be seen in their investment report .
The importance of STEM and STEAM education

STEAM education is crucial to meet the needs of a changing world. According to an article from iD Tech , millions of STEAM jobs remain unfilled in the U.S., therefore efforts to fill this skill gap are of great importance. According to a report from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics there is a projected growth of STEAM-related occupations of 10.5% between 2020 and 2030 compared to 7.5% in non-STEAM-related occupations. The median wage in 2020 was also higher in STEAM occupations ($89,780) compared to non-STEAM occupations ($40,020).
Between 2014 and 2024, employment in computer occupations is projected to increase by 12.5 percent between 2014 and 2024, according to a STEAM occupation report . With projected increases in STEAM-related occupations, there needs to be an equal increase in STEAM education efforts to encourage students into these fields otherwise the skill gap will continue to grow.
STEAM jobs do not all require higher education or even a college degree. Less than half of entry-level STEAM jobs require a bachelor's degree or higher, according to skills gap website Burning Glass Technologies . However, a four-year degree is incredibly helpful with salary — the average advertised starting salary for entry-level STEAM jobs with a bachelor's requirement was 26 percent higher than jobs in the non-STEAM fields.. For every job posting for a bachelor's degree recipient in a non-STEAM field, there were 2.5 entry-level job postings for a bachelor's degree recipient in a STEAM field.
What separates STEAM from traditional science and math education is the blended learning environment and showing students how the scientific method can be applied to everyday life. It teaches students computational thinking and focuses on the real-world applications of problem-solving. As mentioned before, STEAM education begins while students are very young:
Elementary school — STEAM education focuses on the introductory level STEAM courses, as well as awareness of the STEAM fields and occupations. This initial step provides standards-based structured inquiry-based and real-world problem-based learning, connecting all four of the STEAM subjects. The goal is to pique students' interest into them wanting to pursue the courses, not because they have to. There is also an emphasis placed on bridging in-school and out-of-school STEAM learning opportunities.
– Best microscopes for kids
– What is a scientific theory?
– Science experiments for kids
Middle school — At this stage, the courses become more rigorous and challenging. Student awareness of STEAM fields and occupations is still pursued, as well as the academic requirements of such fields. Student exploration of STEAM-related careers begins at this level, particularly for underrepresented populations.
High school — The program of study focuses on the application of the subjects in a challenging and rigorous manner. Courses and pathways are now available in STEAM fields and occupations, as well as preparation for post-secondary education and employment. More emphasis is placed on bridging in-school and out-of-school STEAM opportunities.
Much of the STEAM curriculum is aimed toward attracting underrepresented populations. There is a significant disparity in the female to male ratio when it comes to those employed in STEAM fields, according to Stem Women . Approximately 1 in 4 STEAM graduates is female.

Inequalities in STEAM education
Ethnically, people from Black backgrounds in STEAM education in the UK have poorer degree outcomes and lower rates of academic career progression compared to other ethnic groups, according to a report from The Royal Society . Although the proportion of Black students in STEAM higher education has increased over the last decade, they are leaving STEAM careers at a higher rate compared to other ethnic groups.
"These reports highlight the challenges faced by Black researchers, but we also need to tackle the wider inequalities which exist across our society and prevent talented people from pursuing careers in science." President of the Royal Society, Sir Adrian Smith said.
Asian students typically have the highest level of interest in STEAM. According to the Royal Society report in 2018/19 18.7% of academic staff in STEAM were from ethnic minority groups, of these groups 13.2% were Asian compared to 1.7% who were Black.
If you want to learn more about why STEAM is so important check out this informative article from the University of San Diego . Explore some handy STEAM education teaching resources courtesy of the Resilient Educator . Looking for tips to help get children into STEAM? Forbes has got you covered.
- Lee, Meggan J., et al. ' If you aren't White, Asian or Indian, you aren't an engineer': racial microaggressions in STEM education. " International Journal of STEM Education 7.1 (2020): 1-16.
- STEM Occupations: Past, Present, And Future . Stella Fayer, Alan Lacey, and Audrey Watson. A report. 2017.
- Institution for Art Integration and STEAM What is STEAM education?
- Barone, Ryan, ' The state of STEM education told through 18 stats ', iD Tech.
- U.S. Department of Education , Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math, including Computer Science.
- ' STEM sector must step up and end unacceptable disparities in Black staff ', The Royal Society. A report, March 25, 2021.
- 'Percentages of Women in STEM Statistics' Stemwomen.com
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Newfound dinosaur with giant, horned headpiece named after iconic Norse god
This AI-powered robot has worked out how to solve a Rubik's Cube in just 0.305 seconds
Supermassive black hole roars to life before astronomers' eyes in world-1st observations
Most Popular
- 2 Y chromosome is evolving faster than the X, primate study reveals
- 3 Ming dynasty shipwrecks hide a treasure trove of artifacts in the South China Sea, excavation reveals
- 4 Gulf Stream's fate to be decided by climate 'tug-of-war'
- 5 Astronomers discover the 1st-ever merging galaxy cores at cosmic dawn
- 2 '1st of its kind': NASA spots unusually light-colored boulder on Mars that may reveal clues of the planet's past
- 3 Newly deciphered papyrus describes 'miracle' performed by 5-year-old Jesus
- 4 Long-lost Assyrian military camp devastated by 'the angel of the Lord' finally found, scientist claims
- 5 Tuberculosis triggered giant, crusty wart to sprout on man's hand
- DOI: 10.2196/54987
- Corpus ID: 269977987
Evolution of Chatbots in Nursing Education: Narrative Review
- Fang Zhang , Xiaoliu Liu , +1 author Shiben Zhu
- Published in JMIR Medical Education 29 November 2023
- Education, Medicine
Figures and Tables from this paper

69 References
Challenges for future directions for artificial intelligence integrated nursing simulation education.
- Highly Influential
How artificial intelligence (AI) supports nursing education: profiling the roles, applications, and trends of AI in nursing education research (1993–2020)
Role of ai chatbots in education: systematic literature review, the application of chat generative pre-trained transformer in nursing education., awareness of using chatbots and factors influencing usage intention among nursing students in south korea: a descriptive study, personalized medical terminology learning game: guess the term., mastering medical terminology with chatgpt and termbot, ai chatbots in clinical laboratory medicine: foundations and trends., enhancing kidney transplant care through the integration of chatbot, a holistic approach to remote patient monitoring, fueled by chatgpt and metaverse technology: the future of nursing education., related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
200 Words Essay On Importance Of Women's Education. Women's education is crucial for the development and progress of any society. Education is a fundamental human right and women have the same right to education as men. Educated women have the potential to become strong leaders, role models, and agents of change in their communities.
Quality education can help both men and women understand these deep-seated issues in our society, raise their collective and individual levels of awareness, understand the importance of all people, irrespective of sex, in building a healthy and conscious society. In order to ensure sustainable development, it has become imperative to recognize ...
500 Words Essay On Women's Education. Women's education is crucial to a society's development and growth. It is widely recognised that educating women can have many positive impacts not just on the women themselves but also on their families, communities, and even entire countries. The Importance Of Women's Education. The importance of women's ...
wisdom of investing in women's education and acknowledged the importance of the advancement of women as a global issue. He then recognized that women's rights are a central part of the foreign policy of his administration. ―And it is no coincidence that countries where women are well educated are far more likely to be prosperous…
Around the world, 129 million girls are out of school, including 32 million of primary school age, 30 million of lower-secondary school age, and 67 million of upper-secondary school age. In countries affected by conflict, girls are more than twice as likely to be out of school than girls living in non-affected countries.
Female education is a catch-all term for a complex set of issues and debates surrounding education ( primary education, secondary education, tertiary education, and health education in particular) for girls and women. [1] [2] It is frequently called girls' education or women's education. It includes areas of gender equality and access to education.
In the United States, progress in the education of women and girls has been an important step to (and byproduct of) advancing gender equality in all facets of domestic and work life. The story of ...
Educated girls tend to become role models and inspire others to pursue education. Education gives them the ability to positively influence their lives and the lives of their families and wider communities. Educated women tend to take leadership roles, especially within the community and focus on societal development.
Findings of the study shown that more female pupils are enrolled in the 107 primary school which implies high level of female education, women engage in various programmes like educational ...
J.C. Bose University of Science and Technology, YMCA, Faridabad, Haryana, India. This review paper critically examines the role of education in empowering women and promoting. gender inequality ...
How girls and women have fared since Beijing. Advances in girls' education worldwide have been a success story in development. According to UNESCO, 96 girls were enrolled in primary school for every 100 boys in 2008, up from 84 girls per 100 boys in 1995. The ratio for secondary school is close behind, at 95 girls to 100 boys in 2008.
In many countries around the world, there are multiple barriers standing in the way of girls getting an education, ranging from insufficient or unsafe transportation, to the high cost of books and other necessary learning materials to gender norms at a community level.. An important part of UNICEF's global mission in education is to work with governments to strengthen social protection ...
While access to good quality education is important for girls and women, preventing gender-based violence and equality through education clearly also remains a priority. Gender-based ...
Gender and educational leadership remains a focus for scholarly interest precisely because gender inequalities remain. That is the case thirty years on from the publication of seminal works that established gender and women in educational leadership as a focus for research (Shakeshaft 1987;Blackmore 1989;Dillard 1995). Scholars continue to document women's under-representation in leadership ...
Education is considered the most important tool for empowering women in society. It is not only limited to developing the personality of an individual but also plays an important role in economic, social, and cultural development. UNESCO put its effort to achieve equal opportunity in education regardless of age, gender, race, or any other ...
Defining Women's Education. Women's education refers to the provision of learning opportunities and resources to girls and women. It encompasses formal education in schools, colleges, and universities, as well as informal education through workshops, community programs, and self-directed learning. Women's education is a fundamental human ...
The oft-cited African proverb—"If you educate a man, you educate an individual, but if you educate a woman, you educate a nation"—has always left me cold. It implies that the only value of a woman's education is to make her a better mother, especially to her sons, traditionally viewed as the nation's future leaders.
ROLE OF EDUCATION IN EMPOWERMENT OF WOMEN. 1] Education Manumit- Education manumit the thinking, mind, thoughts, imagination, power, principle in various field for easy to survive and achieve ...
Women's education is critical to the country's entire development. It's similar to an effective medicine that may know how to cure a patient and recover their health. A well-educated lady is capable of managing both her personal and professional lives. The physical and intellectual growth of the child is the moral goal of education.
500+ Words Essay on Girl Education. If we look at the demographics, India is one of the most populated countries. However, the rate of girl education is quite low in the country. It is quite troubling to see the figures in a country where women are given the status of goddesses.
Therefore, women's empowerment can't be effected unless we persuade the importance of women's education. 6 Importance of Women participation Women's participation may be used both for support by an agency and as a control device by the law-makers. Participation may be direct or indirect, formal or informal; it may be political, social or ...
Female Education: Essay (300 Words) Introduction: Female education is a really important term right now for the entire world. From the very beginning, people used to neglect female education, as a result, women are so much behind according to research. Few first world countries are done really amazing in this, but still, now there are problems.
Awards & Grants The AHA offers annual prizes honoring exceptional books, distinguished teaching and mentoring in the classroom, public history, digital projects, and other historical work. We also offer grants and fellowships supporting the research of historians. Upcoming Opportunities Professional and Career Resources View More Resources Standards & Guidelines for…
21 June 2024 marks the 10th International Yoga Day. The theme for this year is "Yoga for Women's Empowerment" intending to transform yoga into a widespread movement. It will emphasise the well-being of women and promote global health and peace. It will help women cultivate a sense of determination, resilience, etc.
How girls and women have fared since Beijing. Advances in girls' education worldwide have been a success story in development. According to UNESCO, 96 girls were enrolled in primary school for every 100 boys in 2008, up from 84 girls per 100 boys in 1995. The ratio for secondary school is close behind, at 95 girls to 100 boys in 2008.
Education and awareness are crucial components in the fight against sexual violence. By raising awareness about the importance of reporting sexual assault, we can encourage more victims to come ...
Essay on Reading Day in 500 words. Reading Day is marked annually on June 19th, a day dedicated to the importance of reading. Reading Day serves as a reminder of the power that books and literature have in people's lives. This day not only honours the act of reading but also promotes literacy and education worldwide.
Resources for Educators & Students K-12 Education The AHA strives to ensure that every K-12 student has access to high quality history instruction. We create resources for the classroom, advise on state and federal policy, and advocate for the vital importance of history in public education. Learn More Undergraduate Education…
The importance of STEM and STEAM education. ... There is a significant disparity in the female to male ratio when it comes to those employed in STEAM fields, according to Stem Women. Approximately ...
This narrative review aims to synthesize and analyze the existing literature on chatbots in nursing education, highlighting the urgent need for original research and the importance of ethical considerations. Abstract Background The integration of chatbots in nursing education is a rapidly evolving area with potential transformative impacts. This narrative review aims to synthesize and analyze ...