- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources

Effective Transition Words for Research Papers
What are transition words in academic writing?
A transition is a change from one idea to another idea in writing or speaking and can be achieved using transition terms or phrases. These transitions are usually placed at the beginning of sentences, independent clauses, and paragraphs and thus establish a specific relationship between ideas or groups of ideas. Transitions are used to enhance cohesion in your paper and make its logical development clearer to readers.
Types of Transition Words
Transitions accomplish many different objectives. We can divide all transitions into four basic categories:
- Additive transitions signal to the reader that you are adding or referencing information
- Adversative transitions indicate conflict or disagreement between pieces of information
- Causal transitions point to consequences and show cause-and-effect relationships
- Sequential transitions clarify the order and sequence of information and the overall structure of the paper
Additive Transitions
These terms signal that new information is being added (between both sentences and paragraphs), introduce or highlight information, refer to something that was just mentioned, add a similar situation, or identify certain information as important.
Adversative Transitions
These terms and phrases distinguish facts, arguments, and other information, whether by contrasting and showing differences; by conceding points or making counterarguments; by dismissing the importance of a fact or argument; or replacing and suggesting alternatives.
Causal Transitions
These terms and phrases signal the reasons, conditions, purposes, circumstances, and cause-and-effect relationships. These transitions often come after an important point in the research paper has been established or to explore hypothetical relationships or circumstances.
Sequential Transitions
These transition terms and phrases organize your paper by numerical sequence; by showing continuation in thought or action; by referring to previously-mentioned information; by indicating digressions; and, finally, by concluding and summing up your paper. Sequential transitions are essential to creating structure and helping the reader understand the logical development through your paper’s methods, results, and analysis.
How to Choose Transitions in Academic Writing
Transitions are commonplace elements in writing, but they are also powerful tools that can be abused or misapplied if one isn’t careful. Here are some ways to ensure you are using transitions effectively.
- Check for overused, awkward, or absent transitions during the paper editing process. Don’t spend too much time trying to find the “perfect” transition while writing the paper.
- When you find a suitable place where a transition could connect ideas, establish relationships, and make it easier for the reader to understand your point, use the list to find a suitable transition term or phrase.
- Similarly, if you have repeated some terms again and again, find a substitute transition from the list and use that instead. This will help vary your writing and enhance the communication of ideas.
- Read the beginning of each paragraph. Did you include a transition? If not, look at the information in that paragraph and the preceding paragraph and ask yourself: “How does this information connect?” Then locate the best transition from the list.
- Check the structure of your paper—are your ideas clearly laid out in order? You should be able to locate sequence terms such as “first,” “second,” “following this,” “another,” “in addition,” “finally,” “in conclusion,” etc. These terms will help outline your paper for the reader.
For more helpful information on academic writing and the journal publication process, visit Wordvice’s Academic Resources Page. And be sure to check out Wordvice’s professional English editing services if you are looking for paper editing and proofreading after composing your academic document.
Wordvice Tools
- Wordvice APA Citation Generator
- Wordvice MLA Citation Generator
- Wordvice Chicago Citation Generator
- Wordvice Vancouver Citation Generator
- Wordvice Plagiarism Checker
- Editing & Proofreading Guide
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write the Best Journal Submissions Cover Letter
- 100+ Strong Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- How to Write an Abstract
- Which Tense to Use in Your Abstract
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- Common Phrases Used in Academic Writing
Other Resources Around the Web
- MSU Writing Center. Transition Words.
- UW-Madison Writing Center. Transition Words and Phrases.
Transitional Words and Phrases
One of your primary goals as a writer is to present ideas in a clear and understandable way. To help readers move through your complex ideas, you want to be intentional about how you structure your paper as a whole as well as how you form the individual paragraphs that comprise it. In order to think through the challenges of presenting your ideas articulately, logically, and in ways that seem natural to your readers, check out some of these resources: Developing a Thesis Statement , Paragraphing , and Developing Strategic Transitions: Writing that Establishes Relationships and Connections Between Ideas.
While clear writing is mostly achieved through the deliberate sequencing of your ideas across your entire paper, you can guide readers through the connections you’re making by using transitional words in individual sentences. Transitional words and phrases can create powerful links between your ideas and can help your reader understand your paper’s logic.
In what follows, we’ve included a list of frequently used transitional words and phrases that can help you establish how your various ideas relate to each other. We’ve divided these words and phrases into categories based on the common kinds of relationships writers establish between ideas.
Two recommendations: Use these transitions strategically by making sure that the word or phrase you’re choosing matches the logic of the relationship you’re emphasizing or the connection you’re making. All of these words and phrases have different meanings, nuances, and connotations, so before using a particular transitional word in your paper, be sure you understand its meaning and usage completely, and be sure that it’s the right match for your paper’s logic. Use these transitional words and phrases sparingly because if you use too many of them, your readers might feel like you are overexplaining connections that are already clear.
Categories of Transition Words and Phrases
Causation Chronology Combinations Contrast Example
Importance Location Similarity Clarification Concession
Conclusion Intensification Purpose Summary
Transitions to help establish some of the most common kinds of relationships
Causation– Connecting instigator(s) to consequence(s).
accordingly as a result and so because
consequently for that reason hence on account of
since therefore thus
Chronology– Connecting what issues in regard to when they occur.
after afterwards always at length during earlier following immediately in the meantime
later never next now once simultaneously so far sometimes
soon subsequently then this time until now when whenever while
Combinations Lists– Connecting numerous events. Part/Whole– Connecting numerous elements that make up something bigger.
additionally again also and, or, not as a result besides even more
finally first, firstly further furthermore in addition in the first place in the second place
last, lastly moreover next second, secondly, etc. too
Contrast– Connecting two things by focusing on their differences.
after all although and yet at the same time but
despite however in contrast nevertheless nonetheless notwithstanding
on the contrary on the other hand otherwise though yet
Example– Connecting a general idea to a particular instance of this idea.
as an illustration e.g., (from a Latin abbreviation for “for example”)
for example for instance specifically that is
to demonstrate to illustrate
Importance– Connecting what is critical to what is more inconsequential.
chiefly critically
foundationally most importantly
of less importance primarily
Location– Connecting elements according to where they are placed in relationship to each other.
above adjacent to below beyond
centrally here nearby neighboring on
opposite to peripherally there wherever
Similarity– Connecting to things by suggesting that they are in some way alike.
by the same token in like manner
in similar fashion here in the same way
likewise wherever
Other kinds of transitional words and phrases Clarification
i.e., (from a Latin abbreviation for “that is”) in other words
that is that is to say to clarify to explain
to put it another way to rephrase it
granted it is true
naturally of course
finally lastly
in conclusion in the end
to conclude
Intensification
in fact indeed no
of course surely to repeat
undoubtedly without doubt yes
for this purpose in order that
so that to that end
to this end
in brief in sum
in summary in short
to sum up to summarize

Improving Your Writing Style
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Clear, Concise Sentences
Use the active voice
Put the action in the verb
Tidy up wordy phrases
Reduce wordy verbs
Reduce prepositional phrases
Reduce expletive constructions
Avoid using vague nouns
Avoid unneccessarily inflated words
Avoid noun strings
Connecting Ideas Through Transitions
Using Transitional Words and Phrases
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
Transition Sentences | Tips & Examples for Clear Writing
Published on June 9, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Clear transitions are crucial to clear writing: They show the reader how different parts of your essay, paper, or thesis are connected. Transition sentences can be used to structure your text and link together paragraphs or sections.
… In this case, the researchers concluded that the method was unreliable.
However , evidence from a more recent study points to a different conclusion . …
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Transitioning between paragraphs, transitioning to a new section, transitions within a paragraph, other interesting articles.
When you start a new paragraph , the first sentence should clearly express:
- What this paragraph will discuss
- How it relates to the previous paragraph
The examples below show some examples of transition sentences between paragraphs and what they express.
Placement of transition sentences
The beginning of a new paragraph is generally the right place for a transition sentence. Each paragraph should focus on one topic, so avoid spending time at the end of a paragraph explaining the theme of the next one.
The first dissenter to consider is …
However, several scholars dissent from this consensus. The first one to consider is …
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
While transitions between paragraphs are generally a single sentence, when you start a new section in a longer text, you may need an entire transition paragraph. Transitioning to a new section involves summarizing the content of the previous section and expressing how the new one will build upon or depart from it.
For example, the following sentences might be an effective transition for a new section in a literary analysis essay.
Having established that the subjective experience of time is one of Mann’s key concerns in The Magic Mountain , it is now possible to explore how this theme facilitates the novel’s connection with World War I. The war itself is not narrated in the book, but rather hinted at as something awaiting Castorp beyond the final pages. In this way, Mann links his protagonist’s subjective experience of time to more than just his illness; it is also used to explore the period leading up to the outbreak of war.
As in academic writing generally, aim to be as concise as you can while maintaining clarity: If you can transition to a new section clearly with a single sentence, do so, but use more when necessary.
It’s also important to use effective transitions within each paragraph you write, leading the reader through your arguments efficiently and avoiding ambiguity.
The known-new contract
The order of information within each of your sentences is important to the cohesion of your text. The known-new contract , a useful writing concept, states that a new sentence should generally begin with some reference to information from the previous sentence, and then go on to connect it to new information.
In the following example, the second sentence doesn’t follow very clearly from the first. The connection only becomes clear when we reach the end.
By reordering the information in the second sentence so that it begins with a reference to the first, we can help the reader follow our argument more smoothly.
Note that the known-new contract is just a general guideline. Not every sentence needs to be structured this way, but it’s a useful technique if you’re struggling to make your sentences cohere.
Transition words and phrases
Using appropriate transition words helps show your reader connections within and between sentences. Transition words and phrases come in four main types:
- Additive transitions, which introduce new information or examples
- Adversative transitions, which signal a contrast or departure from the previous text
- Causal transitions, which are used to describe cause and effect
- Sequential transitions, which indicate a sequence
The table below gives a few examples for each type:
Grouping similar information
While transition words and phrases are essential, and every essay will contain at least some of them, it’s also important to avoid overusing them. One way to do this is by grouping similar information together so that fewer transitions are needed.
For example, the following text uses three transition words and jumps back and forth between ideas. This makes it repetitive and difficult to follow.
Rewriting it to group similar information allows us to use just one transition, making the text more concise and readable.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Transition Sentences | Tips & Examples for Clear Writing. Scribbr. Retrieved March 20, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/transition-sentences/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, transition words & phrases | list & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Some experts argue that focusing on individual actions to combat climate change takes the focus away from the collective action required to keep carbon levels from rising. Change will not be effected, say some others, unless individual actions raise the necessary awareness.
While a reader can see the connection between the sentences above, it’s not immediately clear that the second sentence is providing a counterargument to the first. In the example below, key “old information” is repeated in the second sentence to help readers quickly see the connection. This makes the sequence of ideas easier to follow.
Sentence pair #2: Effective Transition
Some experts argue that focusing on individual actions to combat climate change takes the focus away from the collective action required to keep carbon levels from rising. Other experts argue that individual actions are key to raising the awareness necessary to effect change.
You can use this same technique to create clear transitions between paragraphs. Here’s an example:
Some experts argue that focusing on individual actions to combat climate change takes the focus away from the collective action required to keep carbon levels from rising. Other experts argue that individual actions are key to raising the awareness necessary to effect change. According to Annie Lowery, individual actions are important to making social change because when individuals take action, they can change values, which can lead to more people becoming invested in fighting climate change. She writes, “Researchers believe that these kinds of household-led trends can help avert climate catastrophe, even if government and corporate actions are far more important” (Lowery).
So, what’s an individual household supposed to do?
The repetition of the word “household” in the new paragraph helps readers see the connection between what has come before (a discussion of whether household actions matter) and what is about to come (a proposal for what types of actions households can take to combat climate change).
Sometimes, transitional words can help readers see how ideas are connected. But it’s not enough to just include a “therefore,” “moreover,” “also,” or “in addition.” You should choose these words carefully to show your readers what kind of connection you are making between your ideas.
To decide which transitional word to use, start by identifying the relationship between your ideas. For example, you might be
- making a comparison or showing a contrast Transitional words that compare and contrast include also, in the same way, similarly, in contrast, yet, on the one hand, on the other hand. But before you signal comparison, ask these questions: Do your readers need another example of the same thing? Is there a new nuance in this next point that distinguishes it from the previous example? For those relationships between ideas, you might try this type of transition: While x may appear the same, it actually raises a new question in a slightly different way.
- expressing agreement or disagreement When you are making an argument, you need to signal to readers where you stand in relation to other scholars and critics. You may agree with another person’s claim, you may want to concede some part of the argument even if you don’t agree with everything, or you may disagree. Transitional words that signal agreement, concession, and disagreement include however, nevertheless, actually, still, despite, admittedly, still, on the contrary, nonetheless .
- showing cause and effect Transitional phrases that show cause and effect include therefore, hence, consequently, thus, so. Before you choose one of these words, make sure that what you are about to illustrate is really a causal link. Novice writers tend to add therefore and hence when they aren’t sure how to transition; you should reserve these words for when they accurately signal the progression of your ideas.
- explaining or elaborating Transitions can signal to readers that you are going to expand on a point that you have just made or explain something further. Transitional words that signal explanation or elaboration include in other words, for example, for instance, in particular, that is, to illustrate, moreover .
- drawing conclusions You can use transitions to signal to readers that you are moving from the body of your argument to your conclusions. Before you use transitional words to signal conclusions, consider whether you can write a stronger conclusion by creating a transition that shows the relationship between your ideas rather than by flagging the paragraph simply as a conclusion. Transitional words that signal a conclusion include in conclusion , as a result, ultimately, overall— but strong conclusions do not necessarily have to include those phrases.
If you’re not sure which transitional words to use—or whether to use one at all—see if you can explain the connection between your paragraphs or sentence either out loud or in the margins of your draft.
For example, if you write a paragraph in which you summarize physician Atul Gawande’s argument about the value of incremental care, and then you move on to a paragraph that challenges those ideas, you might write down something like this next to the first paragraph: “In this paragraph I summarize Gawande’s main claim.” Then, next to the second paragraph, you might write, “In this paragraph I present a challenge to Gawande’s main claim.” Now that you have identified the relationship between those two paragraphs, you can choose the most effective transition between them. Since the second paragraph in this example challenges the ideas in the first, you might begin with something like “but,” or “however,” to signal that shift for your readers.
- picture_as_pdf Transitions
4 Types of Transition Words for Research Papers

Researchers often use transition words in academic writing to help guide the reader through text and communicate their ideas well. While these facilitate easy understanding and enhance the flow of the research paper, setting the wrong context with transition words in academic writing can disrupt tone and impact.
So how do you appropriately use transition words in research papers? This article explores the importance of using transitions in academic writing and explains the four types of transition words that can be used by students and researchers to improve their work.
Table of Contents
Why are transition words used in academic writing, additive transitions, adversative transitions, causal transitions, sequential transitions.
Transition words are the key language tools researchers use to communicate their ideas and concepts to readers. They not only reiterate the key arguments being made by the authors but are crucial to improving the structure and flow of the written language. Generally used at the beginning of sentences and paragraphs to form a bridge of communication, transition words can vary depending on your objective, placement, and structuring.
The four types of transition words in academic writing or research papers are additive transitions, adversative transitions, causal transitions, and sequential transitions. Let us look at each of these briefly below.
Types of Transition Words in Academic Writing
These types of transition words are used to inform or alert the reader that new or additional information is being introduced or added to something mentioned in the previous sentence or paragraph. Some examples of words in this category are – moreover, furthermore, additionally, and so on. Phrases like in fact, in addition to, considering this are examples of additive transition phrases that are commonly used.
Used to show contrast, offer alternative suggestions, or present counter arguments and differences, adversative transitions allow researchers to distinguish between different facts, or arguments by establishing or suggesting positions or alternatives opposing them. Examples of adversative transitions include, however, conversely, nevertheless, regardless, rather, and so on. Phrases like on the contrary, in any case, even though provide an adversative transition to arguments in a research paper.
By using causal transitions in their writing, authors can let readers know that there is a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more ideas or paragraphs. It is used to establish the key/important reasons, circumstances, or conditions of the argument being made or while studying hypothetical associations. Since, unless, consequently are some of the words in this type of transitions while in the event that, as a result are some of the causal phrases.
These transition words help to convey the continuation of a thought or action by a numerical sequence by alluding and referring to information or arguments that have been made earlier. Sequential transitions essentially bring order to the researcher’s main points or ideas in the research paper and help to create a logical outline to the arguments. These transition words and phrases essentially guide the reader through the research paper’s key methods, results, and analysis. Some examples of this type of transitions are initially, coincidentally, subsequently and so on. First of all, to conclude, by the way are a few examples of sequential transition phrases.
Researchers must carefully review their research paper, ensuring appropriate and effective use of transition words and phrases in academic writing. During the manuscript editing process, watch for transitions that may be out of context or misplaced. Remember, these words serve as tools to connect ideas and arguments, fostering logical and coherent flow in paragraphs. Double-check the necessity and accuracy of transitions at the beginning of sentences or paragraphs, ensuring they effectively bind and relate ideas and arguments. And finally, avoid repetition of the same transition words in your academic writing.
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- 3 Easy Ways for Researchers to Improve Their Academic Vocabulary
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
What is a Descriptive Essay? How to Write It (with Examples)
Gift $10, get $10: celebrate thanksgiving with paperpal, you may also like, how to write an essay introduction (with examples)..., similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and..., what is a master’s thesis: a guide for..., should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., what are the benefits of generative ai for..., how to avoid plagiarism tips and advice for..., plagiarism checkers vs. ai content detection: navigating the..., plagiarism prevention: why you need a plagiarism check..., how long should a chapter be, how to cite social media sources in academic writing .

Transitions
What this handout is about.
In this crazy, mixed-up world of ours, transitions glue our ideas and our essays together. This handout will introduce you to some useful transitional expressions and help you employ them effectively.
The function and importance of transitions
In both academic writing and professional writing, your goal is to convey information clearly and concisely, if not to convert the reader to your way of thinking. Transitions help you to achieve these goals by establishing logical connections between sentences, paragraphs, and sections of your papers. In other words, transitions tell readers what to do with the information you present to them. Whether single words, quick phrases, or full sentences, they function as signs that tell readers how to think about, organize, and react to old and new ideas as they read through what you have written.
Transitions signal relationships between ideas—relationships such as: “Another example coming up—stay alert!” or “Here’s an exception to my previous statement” or “Although this idea appears to be true, here’s the real story.” Basically, transitions provide the reader with directions for how to piece together your ideas into a logically coherent argument. Transitions are not just verbal decorations that embellish your paper by making it sound or read better. They are words with particular meanings that tell the reader to think and react in a particular way to your ideas. In providing the reader with these important cues, transitions help readers understand the logic of how your ideas fit together.
Signs that you might need to work on your transitions
How can you tell whether you need to work on your transitions? Here are some possible clues:
- Your instructor has written comments like “choppy,” “jumpy,” “abrupt,” “flow,” “need signposts,” or “how is this related?” on your papers.
- Your readers (instructors, friends, or classmates) tell you that they had trouble following your organization or train of thought.
- You tend to write the way you think—and your brain often jumps from one idea to another pretty quickly.
- You wrote your paper in several discrete “chunks” and then pasted them together.
- You are working on a group paper; the draft you are working on was created by pasting pieces of several people’s writing together.
Organization
Since the clarity and effectiveness of your transitions will depend greatly on how well you have organized your paper, you may want to evaluate your paper’s organization before you work on transitions. In the margins of your draft, summarize in a word or short phrase what each paragraph is about or how it fits into your analysis as a whole. This exercise should help you to see the order of and connection between your ideas more clearly.
If after doing this exercise you find that you still have difficulty linking your ideas together in a coherent fashion, your problem may not be with transitions but with organization. For help in this area (and a more thorough explanation of the “reverse outlining” technique described in the previous paragraph), please see the Writing Center’s handout on organization .
How transitions work
The organization of your written work includes two elements: (1) the order in which you have chosen to present the different parts of your discussion or argument, and (2) the relationships you construct between these parts. Transitions cannot substitute for good organization, but they can make your organization clearer and easier to follow. Take a look at the following example:
El Pais , a Latin American country, has a new democratic government after having been a dictatorship for many years. Assume that you want to argue that El Pais is not as democratic as the conventional view would have us believe.
One way to effectively organize your argument would be to present the conventional view and then to provide the reader with your critical response to this view. So, in Paragraph A you would enumerate all the reasons that someone might consider El Pais highly democratic, while in Paragraph B you would refute these points. The transition that would establish the logical connection between these two key elements of your argument would indicate to the reader that the information in paragraph B contradicts the information in paragraph A. As a result, you might organize your argument, including the transition that links paragraph A with paragraph B, in the following manner:
Paragraph A: points that support the view that El Pais’s new government is very democratic.
Transition: Despite the previous arguments, there are many reasons to think that El Pais’s new government is not as democratic as typically believed.
Paragraph B: points that contradict the view that El Pais’s new government is very democratic.
In this case, the transition words “Despite the previous arguments,” suggest that the reader should not believe paragraph A and instead should consider the writer’s reasons for viewing El Pais’s democracy as suspect.
As the example suggests, transitions can help reinforce the underlying logic of your paper’s organization by providing the reader with essential information regarding the relationship between your ideas. In this way, transitions act as the glue that binds the components of your argument or discussion into a unified, coherent, and persuasive whole.
Types of transitions
Now that you have a general idea of how to go about developing effective transitions in your writing, let us briefly discuss the types of transitions your writing will use.
The types of transitions available to you are as diverse as the circumstances in which you need to use them. A transition can be a single word, a phrase, a sentence, or an entire paragraph. In each case, it functions the same way: First, the transition either directly summarizes the content of a preceding sentence, paragraph, or section or implies such a summary (by reminding the reader of what has come before). Then, it helps the reader anticipate or comprehend the new information that you wish to present.
- Transitions between sections: Particularly in longer works, it may be necessary to include transitional paragraphs that summarize for the reader the information just covered and specify the relevance of this information to the discussion in the following section.
- Transitions between paragraphs: If you have done a good job of arranging paragraphs so that the content of one leads logically to the next, the transition will highlight a relationship that already exists by summarizing the previous paragraph and suggesting something of the content of the paragraph that follows. A transition between paragraphs can be a word or two (however, for example, similarly), a phrase, or a sentence. Transitions can be at the end of the first paragraph, at the beginning of the second paragraph, or in both places.
- Transitions within paragraphs: As with transitions between sections and paragraphs, transitions within paragraphs act as cues by helping readers to anticipate what is coming before they read it. Within paragraphs, transitions tend to be single words or short phrases.
Transitional expressions
Effectively constructing each transition often depends upon your ability to identify words or phrases that will indicate for the reader the kind of logical relationships you want to convey. The table below should make it easier for you to find these words or phrases. Whenever you have trouble finding a word, phrase, or sentence to serve as an effective transition, refer to the information in the table for assistance. Look in the left column of the table for the kind of logical relationship you are trying to express. Then look in the right column of the table for examples of words or phrases that express this logical relationship.
Keep in mind that each of these words or phrases may have a slightly different meaning. Consult a dictionary or writer’s handbook if you are unsure of the exact meaning of a word or phrase.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Writers' Center
Eastern Washington University
Writing Your Paper: Transitions
- Brainstorming
- Creating a Hook
- Revising, Editing, and Proofreading
Transitions
- Formal Writing
- Active vs. Passive Voice
- Peer Review
- Point of View
Transitions are words and/or phrases used to indicate movement or show change throughout a piece of writing. Transitions generally come at the beginning or end of a paragraph and can do the following:
- Alert readers of connections to, or further evidence for, the thesis
- Function as the topic sentence of paragraphs
- Guide readers through an argument
- Help writers stay on task
Transitions sentences often indicate or signal:
- Change to new topic
- Connection/flow from previous topic
- Continuity of overall argument/thesis
Transitions show connections between ideas. You must create these connections for the reader to move them along with your argument. Without transitions, you are building a house without nails. Things do not hold together.
Transition Words and Phrases
Transitions can signal change or relationship in these ways:
Time - order of events
Examples: while, immediately, never, after, later, earlier, always, soon, meanwhile, during, until now, next, following, once, then, simultaneously, so far
Contrast - show difference
Examples: yet, nevertheless, after all, but, however, though, otherwise, on the contrary, in contrast, on the other hand, at the same time
Compare - show similarity
Examples: in the same way, in like manner, similarly, likewise
Position - show spatial relationships
Examples: here, there, nearby, beyond, wherever, opposite to, above, below
Cause and effect
Examples: because, since, for that reason, therefore, consequently, accordingly, thus, as a result
Conclusion - wrap up/summarize the argument
Writing strong transitions often takes more than simply plugging in a transition word or phrase here and there. In a piece of academic writing, writers often need to use signposts, or transition sentences that signal the reader of connections to the thesis. To form a signpost, combine transition words, key terms from the thesis, and a mention of the previous topic and new topic.
Transition/signpost sentence structure:
[Transition word/phrase] + [previous topic] + [brief restatement of or reference to thesis/argument] + [new topic] = Signpost
- Do not think of this as a hard and fast template, but a general guide to what is included in a good transition.
- Transitions link the topic of the previous paragraph(s) to the topic of the present paragraph(s) and connect both to the overall goal/argument. You'll most often find signposts at the beginning of a paragraph, where they function as topic sentences .
Sample signpost using complimentary transition phrase:
According to [transition phrase] the same overall plan for first defeating Confederate forces in the field and then capturing major cities and rail hubs [overall thesis restated] that Grant followed by marching the Army of the Potomac into Virginia [previous topic] , Sherman likewise [transition word] advanced into Georgia to drive a dagger into the heart of the Confederacy [new topic] .
Contrasting ideas have the same essential format as complimentary but may use different transition words and phrases:
In contrast to [transition phrase] F.D.R., who maintained an ever-vigilant watchfulness over the Manhattan project [previous topic + reference to overall thesis] , Truman took over the presidency without any knowledge of the atomic bomb or its potential power [new topic] .
The overall structure of an essay with transitions may look something like this:

*Note how transitions may come at beginning or end of paragraphs, but either way they signal movement and change.
You can learn more about essay structure HERE .
[ Back to resource home ]

[email protected] 509.359.2779
Cheney Campus JFK Library Learning Commons
Spokane Campus Catalyst Building C451 and C452
Stay Connected! Instagram Facebook
Transition Resources
Here are a couple of good sites with extensive lists of transition words and phrases:
https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/Transitions.html
Academic Phrasebank http://www.phrasebank.manchester.ac.uk
- << Previous: Structure
- Next: Formal Writing >>
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2024 12:42 PM
- URL: https://research.ewu.edu/c.php?g=53658
Effective Transitions in Research Manuscripts
- Peer Review
- A transition is a word or phrase that connects consecutive sentences or paragraphs
- Transitions can strengthen your argument by joining ideas and clarifying parts of your manuscript
Updated on June 25, 2013

A transition is a word or phrase that connects consecutive sentences or paragraphs. Effective transitions can clarify the logical flow of your ideas and thus strengthen your argument or explanation. Here, two main transitional tools are discussed: demonstrative pronouns and introductory terms.
Demonstrative pronouns
The demonstrative pronouns this , that , these , and those can be used to emphasize the relationship between adjacent sentences. For example, “Western blotting is a widely used method. This [technique] is favored by protein biochemists.” The use of This or This technique rather than The technique helps to connect the two sentences, indicating that Western blotting is still being discussed in the second sentence. Note that the inclusion of a noun ( technique ) after the pronoun ( this ) decreases ambiguity .
Introductory words or phrases
These transitions are placed at the beginning of the second sentence and are often followed by a comma to improve readability. Introductory words and phrases are distinct from coordinating conjunctions ( and , but , for , nor , or , so , yet ), which are used to bridge two independent clauses within a single sentence rather than two separate sentences. These conjunctions should not be placed at the beginning of a sentence in formal writing. Below are several examples of transitional words and phrases that are frequently used in academic writing, including potential replacements for common informal terms:

To learn more about the special usage of the italicized terms in the table, please see our post on introductory phrases .
Keep in mind that transitions that are similar in meaning are not necessarily interchangeable (such as in conclusion and thus ). A few other transitional words may be particularly helpful when writing lists or describing sequential processes, such as in the methods section of a research paper: next , then , meanwhile , first , second , third , and finally .
In sum, transitions are small additions that can substantially improve the flow of your ideas. However, if your manuscript is not well organized, transitions will not be sufficient to ensure your reader's understanding, so be sure to outline the progression of your ideas before writing.
We hope that this editing tip will help you to integrate effective transitions into your writing. Keep in mind - AJE's English Editing Service specializes in word choice and grammar. Utilize our service for professional help. As always, please email us at [email protected] with any questions.

Michaela Panter, PhD
See our "Privacy Policy"

The Power of Transition Words: How they connect and clarify your academic writing
Academic writing demands clear communication of ideas to facilitate the exchange of knowledge, and to ensure that information is conveyed accurately and comprehensively. It serves as a vehicle for critical thinking, analysis, and synthesis, allowing scholars to contribute meaningfully to their fields of study. By employing suitable analogies and metaphors, writers can better understand the significance of their craft and strive to hone their skills in order to contribute meaningfully to the academic community. Let’s understand how we can achieve excellence in academic writing by using transition words.
What Are Transition Words?
Transition words are words or phrases that help establish connections between sentences, paragraphs, or ideas in a piece of writing. They act as bridges, guiding readers through the logical flow of information and signalling relationships between different parts of the text. Furthermore, they provide coherence and cohesion to your writing by clarifying the relationships between ideas, adding structure, and improving the overall readability.
Download this FREE infographic and make appropriate use of every transition word to enhance your academic writing.
Role of Transition Words in Effective Academic Writing
Transition words play a crucial role in enhancing clarity and coherence in academic writing. They act as linguistic signposts that guide readers through the text, helping them understand the relationships between ideas, and ensuring a smooth flow of information. The primary roles of these words in enhancing clarity and coherence can be summarized as follows:
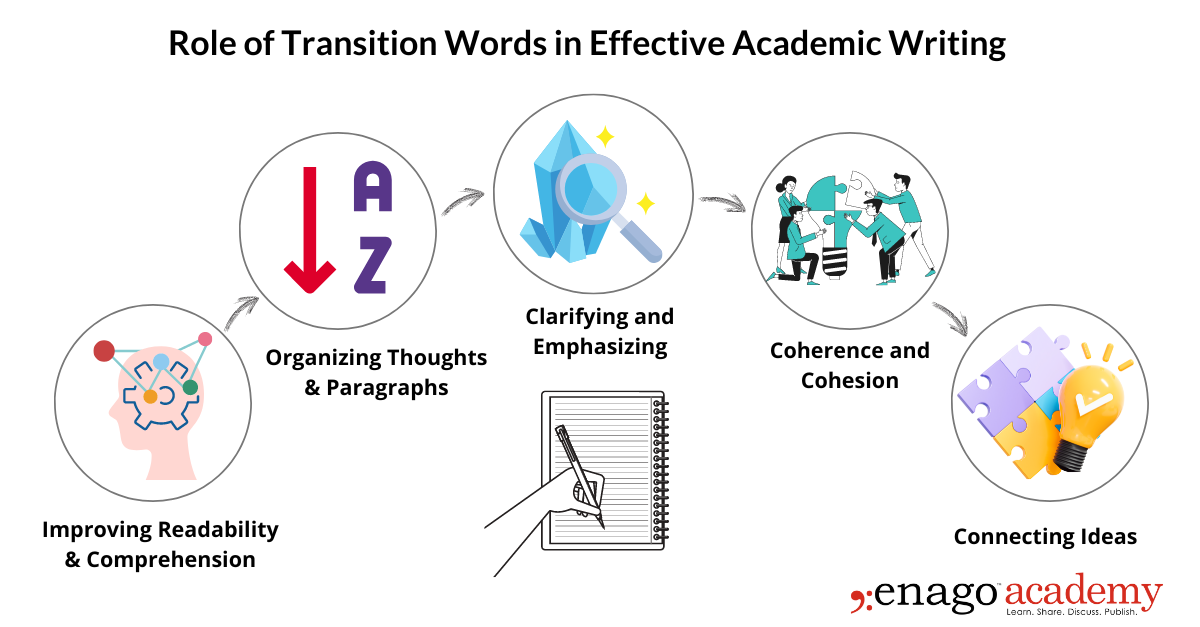
A. Improving Readability and Comprehension
By facilitating smooth transitions and organizing information effectively, these words enhance the readability and comprehension of academic writing. They help readers navigate through complex texts, understand complex ideas, and follow the structure of the argument. Transition words facilitate reader navigation and comprehension, enhancing the reading experience with increased engagement and accessibility.
B. Organizing Thoughts and Paragraphs
Transition words assist in organizing thoughts and structuring the content of an academic paper. They provide a framework for presenting ideas in a coherent and systematic manner. By indicating sequence, order, or cause and effect relationships, these words help writers create a logical flow that guides readers smoothly from one point to the next. They enable the construction of well-organized paragraphs and facilitate the development of cohesive arguments.
C. Clarifying and Emphasizing
Transition words contribute to the clarity and precision of academic writing. They help define terms, rephrase or restate ideas, and provide necessary explanations. Additionally, they aid in emphasizing key points and drawing attention to important information. By strategically utilizing these words, writers can guarantee clear understanding of their ideas and effective conveyance of the intended message to the reader.
D. Coherence and Cohesion
Transition words are instrumental in creating coherence and cohesion within an academic paper. Coherence refers to the logical and smooth progression of ideas, while cohesion refers to the interconnectedness and unity of the text. They act as cohesive devices, linking sentences and paragraphs together and establishing a cohesive flow of information. They strengthen the logical connections between ideas, prevent abrupt shifts, and enable readers to follow the writer’s argument effortlessly.
E. Connecting Ideas
Transition words bridge the gap between sentences, paragraphs, and sections of an academic paper. They establish logical connections, indicating how ideas are related and allowing readers to follow the author’s train of thought. Whether showing addition, similarity, contrast, or example, these words help readers navigate between concepts and comprehend the overall message more effectively.
Types of Transition Words in Academic Writing
The types of transition words vary based on the situations where you can use them to enhance the effectiveness of your academic writing.
1. Addition
“Addition” transition words are used to introduce additional information or ideas that support or supplement the main point being discussed. They serve to expand upon the topic, provide further evidence, or present examples that strengthen your claims.
Examples of Addition Transition Words:
- Furthermore, the study not only analyzed the effects of X but also examined the impact of Y.
- Moreover, the results not only confirmed the initial hypothesis but also revealed additional insights.
- Additionally, previous research has shown consistent findings, strengthening the validity of our study.
2. Comparison and Contrast
“Comparison and Contrast” transition words are used in academic writing when you want to highlight similarities, differences, or relationships between different concepts, ideas, or findings. They help to establish clear connections and facilitate the comparison and contrast of various elements within your research.
Examples of Comparison and Contrast Transition Words:
- Similarly, other researchers have reported comparable findings, corroborating the generalizability of our results.
- In contrast, previous studies have demonstrated consistent patterns, reinforcing the existing body of knowledge.
- In comparison, the current study offers a unique perspective by examining the relationship from a different angle.
3. Cause and Effect
“Cause and Effect” transition words are used when you want to demonstrate the relationship between a cause and its resulting effect or consequence. They help to clarify the cause-and-effect relationship, allowing readers to understand the connections between different variables, events, or phenomena.
Examples of Cause and Effect Transition Words:
- As a result, the data provides compelling evidence for a causal relationship between X and Y.
- Consequently, the hypothesis can be supported by the observed patterns in the collected data.
- Hence, the proposed model is validated, given the consistent and statistically significant results.
4. Example and Illustration
“Example and Illustration” transition words are used when you want to provide specific instances, evidence, or illustrations to support and clarify your main points or arguments. These words help to make your ideas more tangible and concrete by presenting real-life examples or specific cases.
Examples of “Example and Illustration” Transition Words:
- For example, one study conducted by Jackson et al. (2018) demonstrated a similar phenomenon in a different context.
- To illustrate this point, consider the case of Company X, which experienced similar challenges in implementing the proposed strategy.
- In particular, the data highlights the importance of considering demographic factors, such as age and gender, in the analysis.
5. Sequence and Chronology
“Sequence and Chronology” transition words are used in academic research papers when you want to indicate the order, progression, or sequence of events, ideas, or processes. These words help to organize information in a logical and coherent manner, ensuring that readers can follow the chronological flow of your research.
Examples of “Sequence and Chronology” Transition Words:
- First and foremost, the study aims to examine the long-term effects of intervention X on outcome Y.
- Subsequently, the participants were randomly assigned to either the control or experimental group.
- Finally, the data analysis revealed significant temporal trends that require further investigation.
6. Clarification and Restatement
“Clarification and Restatement” transition words are used in academic writing when you want to provide further explanation, clarify a point, or restate an idea in a different way. These words ensure that readers understand your arguments and ideas clearly, avoiding any ambiguity or confusion.
Examples of “Clarification and Restatement” Transition Words:
- In other words, the phenomenon can be explained by the interplay of various psychological and environmental factors.
- Specifically, the term “efficiency” refers to the ability to achieve maximum output with minimum resource utilization.
- To clarify, the concept of “sustainability” encompasses the ecological, economic, and social dimensions of development.
7. Emphasis
“Emphasis” transition words are used when you want to place special emphasis on certain points, ideas, or findings. These words help to draw attention to key information, highlight the significance of particular aspects, or underscore the importance of your arguments.
Examples of Emphasis Transition Words:
- Notably, this study addresses a significant gap in the existing literature.
- Importantly, the findings have implications for future policy decisions.
- In particular, the study examined the relationship between age and cognitive performance.
8. Summary and Conclusion
“Summary and Conclusion” transition words are employed in academic writing when you want to provide a concise summary of the main points discussed in your paper and draw a conclusion based on the findings or arguments presented. These help to signal the end of your paper and provide closure to your research.
Examples of “Summary and Conclusion” Transition Words
- In conclusion, the findings unequivocally support the initial hypothesis, emphasizing the significance of the proposed theory.
- Overall, the results indicate a consistent pattern, providing a foundation for future research in this area.
- In summary, this research makes a valuable contribution to the existing literature by extending our understanding of the topic.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Transition Words in Academic Writing
When using transition words in academic writing, it’s important to be mindful of common mistakes to ensure that your writing remains clear, cohesive, and effective.

1. Overusing Transition Words
Using too many transition words can make your writing appear cluttered and disrupt the flow of your ideas. Avoid overloading your sentences or paragraphs with excessive transitions. Instead, use them strategically to enhance clarity and coherence.
2. Using Inappropriate or Irrelevant Transitions
Choose transition words that are appropriate for the context and purpose of your writing. Avoid using them when they don’t align with the relationship between the ideas you are connecting. Ensure that the transitions you use are relevant and contribute to the overall coherence of your writing.
3. Neglecting Proofreading and Editing
As with any aspect of writing, proofreading and editing are crucial when using transition words. Carefully review your writing to ensure that you use transitions correctly and effectively. Look for any inconsistencies, redundancies, or errors in your use of transitions and make necessary revisions.
4. Failing to Understand the Meaning
It’s important to understand the precise meaning and usage of transition words before incorporating them into your writing. Using a transition word incorrectly or inappropriately can lead to confusion or misinterpretation. Therefore, it is important to consult reliable resources or style guides to familiarize yourself with the correct usage of each of these words.
5. Neglecting the Logical Flow
Transition words should help guide the reader through your writing and create a logical flow of ideas. Failing to use appropriate transitions can result in a disjointed or fragmented presentation. Ensure that your transitions establish clear connections and maintain the coherence of your writing.
6. Relying Only on Transition Words
While transition words are valuable tools, they should not replace effective writing and organization. Relying solely on transitions to connect your ideas can lead to weak or poorly structured writing. Focus on developing strong topic sentences, clear paragraph organization, and logical progression of ideas alongside the use of these words.
7. Ignoring Sentence Variety
Use transition words to enhance the variety and sophistication of your sentence structures. Avoid using the same words repeatedly, as this can make your writing monotonous. Instead, explore different transitions that convey the specific relationships between your ideas.
In essence, the strategic use of transition words is a powerful tool that connects and clarifies your academic writing. Furthermore, it elevates your work from a mere collection of ideas to a cohesive, well-structured, and thought-provoking piece of scholarship. By mastering the art of using these words effectively, you can enhance the impact of your academic writing and contribute meaningfully to your field of study.
What are your thoughts on other grammar nuances that can make academic writing more effective? Share your opinion in the comments below or write an article on our Open Platform !
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.


Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

Concept Papers in Research: Deciphering the blueprint of brilliance
Concept papers hold significant importance as a precursor to a full-fledged research proposal in academia…

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and…
Language as a Bridge, Not a Barrier: ESL researchers’ path to successful…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
- Editing Services
- Academic Editing Services
- Admissions Editing Services
- Admissions Essay Editing Services
- AI Content Editing Services
- APA Style Editing Services
- Application Essay Editing Services
- Book Editing Services
- Business Editing Services
- Capstone Paper Editing Services
- Children's Book Editing Services
- College Application Editing Services
- College Essay Editing Services
- Copy Editing Services
- Developmental Editing Services
- Dissertation Editing Services
- eBook Editing Services
- English Editing Services
- Horror Story Editing Services
- Legal Editing Services
- Line Editing Services
- Manuscript Editing Services
- MLA Style Editing Services
- Novel Editing Services
- Paper Editing Services
- Personal Statement Editing Services
- Research Paper Editing Services
- Résumé Editing Services
- Scientific Editing Services
- Short Story Editing Services
- Statement of Purpose Editing Services
- Substantive Editing Services
- Thesis Editing Services
Proofreading
- Proofreading Services
- Admissions Essay Proofreading Services
- Children's Book Proofreading Services
- Legal Proofreading Services
- Novel Proofreading Services
- Personal Statement Proofreading Services
- Research Proposal Proofreading Services
- Statement of Purpose Proofreading Services
Translation
- Translation Services
Graphic Design
- Graphic Design Services
- Dungeons & Dragons Design Services
- Sticker Design Services
- Writing Services
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
All the Transition Words You'll Ever Need for Academic Writing

In academic writing, transitions are the glue that holds your ideas together. Without them, your writing would be illogical and lack flow, making it difficult for your audience to understand or replicate your research.
In this article, we will discuss the types of transitions based on their purpose. Familiarizing yourself with these most-used and best transition terms for academic writing will help bring clarity to your essays and make the writing process much easier on you.

Types of transitions
There are four types of transitions: Causal, Sequential, Adversative and Additive. Below, we've listed the most commonly used transitions in each of these categories, as well as examples of how they might be used to begin a paragraph or sentence.
When you use causal transitions, you are letting your reader know that there is a cause-and-effect relationship between ideas or paragraphs or consequences.
- Accordingly ("Accordingly, the author states…")
- All else being equal ("All else being equal, these ideas correlate…")
- As a consequence ("As a consequence, all data were aggregated…")
- As a result (of this) ("As a result of this finding, scholars now agree…")
- Because (of the fact that) ("Because of the fact that these numbers show signs of declining,…")
- Because (of this) ("Because of this, scholars determined…")
- Consequently ("Consequently, the research was stalled…")
- Due to (the fact that) ("Due to the fact that all prior studies showed similar results,…")
- For the purpose(s) of ("For the purposes of our argument, we will…")
- For this reason ("For this reason, the researchers…")
- Granted (that) ("Granted that the numbers were significantly higher, the study…")
- Granting (that) ("Granting that the data was collected incorrectly, the researchers felt…")
- If…then ("If this data is significant, then it is obvious that…")
- If so ("If so, the data is not useable…")
- In the event ("In the event that it is not significant, we should consider that…")
- Inasmuch as ("Insomuch as the authors attempt to refute these findings, research suggests that…")
- In the hope that ("In the hope that new data will encourage more in-depth research, the author found that….")
- In that case ("In that case, we've found that…")
- Only if ("Only if data is insubstantial should findings be ignored, thus…")
- Otherwise ("Otherwise, the research would continue…")
- Owing to (the fact) ("Owing to the fact that the gathered data is incorrect, …")
- Provided (that) ("Provided that the same results occur, we can assume that…")
- Since ("Since it would seem futile to continue to study this topic, we posit that…")
- So as to ("So as to clarify past remarks, we initiated further research…")
- So long as ("So long as there is established credibility, this journal seeks….")
- So much (so) that ("The data is manipulated so much so that it can't be used to clarify…")
- Therefore ("Therefore, this result compromises the exploration into…")
- That being the case ("That being the case, we should look into alternatives…")
- Thus ("Thus, it would see that further research…")
- Unless ("Unless this calls to question the original hypothesis, the exploration of this topic would be…")
- With (this fact) in mind ("With this fact in mind, let's consider another alternative…")
- Under those circumstances ("Under those circumstances, fewer participants…")
Sequential transitions show a numerical sequence or the continuation of a thought or action. They are used to establish an order to your main points in an academic essay, and help create a logical outline for your writing.
- (Once) again ("Once again, this is not a reason for lack of rigor…")
- After (this) ("After this, it would seem most prudent to…")
- Afterwards ("Afterwards, it seemed a moot point to determine…")
- Altogether ("Altogether, these data suggest that…")
- Anyway ("Anyway, such loss would prove to be damaging..")
- As (was) mentioned earlier/above ("As was mentioned above, the lack of attention given to…")
- As (was) stated before ("As was stated before, there is little evidence show…")
- As a final point ("As a final point, consider the connection between…")
- At any rate ("At any rate, loss of significance was vital to…")
- By the way ("By the way, one can't assume that…")
- Coincidentally ("Coincidentally, this affected the nature of…")
- Consequently ("Consequently, Smith found that…")
- Eventually ("Eventually, more was needed to sustain…")
- Finally ("Finally, we now know that…"
- First ("First, it seems that even with the additional data…")
- First of all ("First of all, none of the respondents felt that…")
- Given these points ("Given these points, it's easy to see that…")
- Hence ("Hence, we see that the above details…")
- In conclusion ("In conclusion, since the data shows significant growth...")
- In summary ("In summary, there are not enough studies to show the correlation…")
- In the (first/second/third) place ("In the first place, we found that…")
- Incidentally ("Incidentally, no findings showed a positive outlook…")
- Initially ("Initially, we noticed that the authors….")
- Last ("Last, the most significant growth appeared to happen when…")
- Next ("Next, it's important to note that…")
- Overall ("Overall, we found that….")
- Previously ("Previously, it was shown that…")
- Returning to the subject ("Returning to the subject, careful observation of trends…")
- Second ("Second, it was impossible to know the…")
- Secondly ("Secondly, in looking at variable related to…")
- Subsequently ("Subsequently, we found that…")
- Summarizing (this) ("Summarizing this, the authors noted that…")
- Therefore ("Therefore, the connection is unknown between…")
- Third ("Third, when data were collected…")
- Thirdly ("Thirdly, we noticed that…")
- Thus ("Thus, there was no evidence that…)
- To conclude ("To conclude, the findings suggest that…")
- To repeat ("To repeat, no studies found evidence that…")
- To resume ("To resume the conversation, we began discussing…")
- To start with ("To start with, there is no evidence that…")
- To sum up ("To sum up, significant correlation was found…")
- Ultimately ("Ultimately, no studies found evidence of…")
Adversative Transitions
Adversative transitions show contrast, counter arguments or an alternative suggestion.
- Above all ("Above all, we found that…"
- Admittedly ("Admittedly, the findings suggest that…")
- All the same ("All the same, without knowing which direction the study would take…")
- Although ("Although much is to be learned from…")
- At any rate ("At any rate, we concluded that...")
- At least ("At least, with these results, we can…")
- Be that as it may ("Be that as it may, there was no significant correlation between…")
- Besides ("Besides, it is obvious that…")
- But ("But, the causal relationship between…")
- By way of contrast ("By the way of contrast, we note that…")
- Conversely ("Conversely, there was no correlation between…")
- Despite (this) ("Despite this, the findings are clear in that…")
- Either way ("Either way, studies fail to approach the topic from…")
- Even more ("Even more, we can conclude that…")
- Even so ("Even so, there is a lack of evidence showing…")
- Even though ("Even though the participants were unaware of which ….")
- However (However, it becomes clear that…")
- In any case ("In any case, there were enough reponses…")
- In any event ("In any event, we noted that…")
- In contrast ("In contrast, the new data suggests that…")
- In fact ("In fact, there is a loss of…")
- In spite of (this) ("In spite of this, we note that…")
- Indeed ("Indeed, it becomes clear that…")
- Instead (of) ("Instead of publishing our findings early, we chose to")
- More/Most importantly ("More importantly, there have not been any…")
- Nevertheless ("Nevertheless, it becomes clear that…")
- Nonetheless ("Nonetheless, we failed to note how…")
- Notwithstanding (this) ("Notwithstanding this, there was little evidence…")
- On the contrary ("On the contrary, no active users were…")
- On the other hand ("On the other hand, we cannot avoid…")
- Primarily ("Primarily, it becomes significant as…")
- Rather ("Rather, none of this is relevant…")
- Regardless (of) ("Regardless of previous results, the authors…")
- Significantly ("Significantly, there was little correlation between…")
- Still ("Still, nothing was noted in the diary…")
- Whereas ("Whereas little evidence has been given to…")
- While ("While causality is lacking…")
- Yet ("Yet, it becomes clear that…")
Additive Transitions
You'll use an additive transition to relate when new information is being added or highlighted to something that was just mentioned.
- Additionally ("Additionally, it can be noted that…")
- Also ("Also, there was no evidence that….")
- As a matter of fact ("As a matter of fact, the evidence fails to show…")
- As for (this) ("As for this, we can posit that…")
- By the same token ("By the same token, no studies have concluded…")
- Concerning (this) ("Concerning this, there is little evidence to…")
- Considering (this) ("Considering this, we must then return to…")
- Equally ("Equally, there was no correlation…")
- Especially ("Especially, the study reveals that…")
- For example ("For example, a loss of one's….")
- For instance ("For instance, there was little evidence showing…")
- Furthermore ("Furthermore, a lack of knowledge on…")
- In a similar way ("In a similar way, new findings show that…")
- In addition to ("In addition to this new evidence, we note that…")
- In fact ("In fact, none of the prior studies showed…")
- In other words ("In other words, there was a lack of…")
- In particular ("In particular, no relationship was revealed…")
- In the same way ("In the same way, new studies suggest that…")
- Likewise ("Likewise, we noted that…)
- Looking at (this information) ("Looking at this information, it's clear to see how…)
- Moreover ("Moreover, the loss of reputation of…")
- Namely ("Namely, the authors noted that…")
- Not only…but also ("Not only did the study reveal new findings, but also it demonstrated how….")
- Notably ("Notably, no other studies have been done…")
- On the subject of (this) ("On the subject of awareness, participants agreed that….")
- One example (of this is) ("One example of this is how the new data…")
- Particularly ("Particularly, there is little evidence showing…")
- Regarding (this) ("Regarding this, there were concerns that…")
- Similarly ("Similarly, we note that…")
- Specifically ("Specifically, there were responses that…")
- That is ("That is, little attention is given to…")
- The fact that ("The fact that the participants felt misinformed…")
- This means (that) ("This means that conclusive findings are…")
- To illustrate ("To illustrate, one participant wrote that….")
- To put it another way ("To put it another way, there is little reason to…")
- What this means is ("What this means is the authors failed to…")
- With regards to (this) ("With regards to this, we cannot assume that…")
Making the choice
When deciding which transition would best fit in each instance, keep in mind a few of these tips:
- Avoid using the same transition too much, as it could make your writing repetitive.
- Check at the beginning of each paragraph to ensure that a) you've included a transition, if one was needed, and b) it's the correct transition to accurately relate the type of logical connection you're forming between ideas.
- Be sure that if you are using sequential transitions, they match. For example, if you use "first" to highlight your first point, "second" should come next, then "third," etc. You wouldn't want to use "first", followed by "secondly."
Related Posts
Your Guide to Research Sampling Methods

415 Research Question Examples Across 15 Disciplines
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?
Research Paper Transition Examples

Searching for effective research paper transition examples? Learn how to make effective transitions between sections of a research paper. There are two distinct issues in making strong transitions:
- Does the upcoming section actually belong where you have placed it?
- Have you adequately signaled the reader why you are taking this next step?
The first is the most important: Does the upcoming section actually belong in the next spot? The sections in your research paper need to add up to your big point (or thesis statement) in a sensible progression. One way of putting that is, “Does the architecture of your paper correspond to the argument you are making?” Getting this architecture right is the goal of “large-scale editing,” which focuses on the order of the sections, their relationship to each other, and ultimately their correspondence to your thesis argument.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
It’s easy to craft graceful transitions when the sections are laid out in the right order. When they’re not, the transitions are bound to be rough. This difficulty, if you encounter it, is actually a valuable warning. It tells you that something is wrong and you need to change it. If the transitions are awkward and difficult to write, warning bells should ring. Something is wrong with the research paper’s overall structure.
After you’ve placed the sections in the right order, you still need to tell the reader when he is changing sections and briefly explain why. That’s an important part of line-by-line editing, which focuses on writing effective sentences and paragraphs.
Examples of Effective Transitions
Effective transition sentences and paragraphs often glance forward or backward, signaling that you are switching sections. Take this example from J. M. Roberts’s History of Europe . He is finishing a discussion of the Punic Wars between Rome and its great rival, Carthage. The last of these wars, he says, broke out in 149 B.C. and “ended with so complete a defeat for the Carthaginians that their city was destroyed . . . .” Now he turns to a new section on “Empire.” Here is the first sentence: “By then a Roman empire was in being in fact if not in name.”(J. M. Roberts, A History of Europe . London: Allen Lane, 1997, p. 48) Roberts signals the transition with just two words: “By then.” He is referring to the date (149 B.C.) given near the end of the previous section. Simple and smooth.
Michael Mandelbaum also accomplishes this transition between sections effortlessly, without bringing his narrative to a halt. In The Ideas That Conquered the World: Peace, Democracy, and Free Markets , one chapter shows how countries of the North Atlantic region invented the idea of peace and made it a reality among themselves. Here is his transition from one section of that chapter discussing “the idea of warlessness” to another section dealing with the history of that idea in Europe.
The widespread aversion to war within the countries of the Western core formed the foundation for common security, which in turn expressed the spirit of warlessness. To be sure, the rise of common security in Europe did not abolish war in other parts of the world and could not guarantee its permanent abolition even on the European continent. Neither, however, was it a flukish, transient product . . . . The European common security order did have historical precedents, and its principal features began to appear in other parts of the world. Precedents for Common Security The security arrangements in Europe at the dawn of the twenty-first century incorporated features of three different periods of the modern age: the nineteenth century, the interwar period, and the ColdWar. (Michael Mandelbaum, The Ideas That Conquered the World: Peace, Democracy, and Free Markets . New York: Public Affairs, 2002, p. 128)
It’s easier to make smooth transitions when neighboring sections deal with closely related subjects, as Mandelbaum’s do. Sometimes, however, you need to end one section with greater finality so you can switch to a different topic. The best way to do that is with a few summary comments at the end of the section. Your readers will understand you are drawing this topic to a close, and they won’t be blindsided by your shift to a new topic in the next section.
Here’s an example from economic historian Joel Mokyr’s book The Lever of Riches: Technological Creativity and Economic Progress . Mokyr is completing a section on social values in early industrial societies. The next section deals with a quite different aspect of technological progress: the role of property rights and institutions. So Mokyr needs to take the reader across a more abrupt change than Mandelbaum did. Mokyr does that in two ways. First, he summarizes his findings on social values, letting the reader know the section is ending. Then he says the impact of values is complicated, a point he illustrates in the final sentences, while the impact of property rights and institutions seems to be more straightforward. So he begins the new section with a nod to the old one, noting the contrast.
In commerce, war and politics, what was functional was often preferred [within Europe] to what was aesthetic or moral, and when it was not, natural selection saw to it that such pragmatism was never entirely absent in any society. . . . The contempt in which physical labor, commerce, and other economic activity were held did not disappear rapidly; much of European social history can be interpreted as a struggle between wealth and other values for a higher step in the hierarchy. The French concepts of bourgeois gentilhomme and nouveau riche still convey some contempt for people who joined the upper classes through economic success. Even in the nineteenth century, the accumulation of wealth was viewed as an admission ticket to social respectability to be abandoned as soon as a secure membership in the upper classes had been achieved. Institutions and Property Rights The institutional background of technological progress seems, on the surface, more straightforward. (Joel Mokyr, The Lever of Riches: Technological Creativity and Economic Progress . New York: Oxford University Press, 1990, p. 176)
Note the phrase, “on the surface.” Mokyr is hinting at his next point, that surface appearances are deceiving in this case. Good transitions between sections of your research paper depend on:
- Getting the sections in the right order
- Moving smoothly from one section to the next
- Signaling readers that they are taking the next step in your argument
- Explaining why this next step comes where it does
Return to writing a body of a research paper to see typical transition words and phrases.
Learn how to write a body of a research paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Complete List of Transition Words
100 Words and Phrases to Use Between Paragraphs
Viorika Prikhodko / E+ / Getty Images
- Writing Essays
- Writing Research Papers
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
Once you have completed the first draft of your paper, you will need to rewrite some of the introductory sentences at the beginning and the transition statements at the end of every paragraph . Transitions, which connect one idea to the next, may seem challenging at first, but they get easier once you consider the many possible methods for linking paragraphs together—even if they seem to be unrelated.
Transition words and phrases can help your paper move along, smoothly gliding from one topic to the next. If you have trouble thinking of a way to connect your paragraphs, consider a few of these 100 top transitions as inspiration. The type of transition words or phrases you use depends on the category of transition you need, as explained below.
Additive Transitions
Probably the most common type, additive transitions are those you use when you want to show that the current point is an addition to the previous one, notes Edusson , a website that provides students with essay-writing tips and advice . Put another way, additive transitions signal to the reader that you are adding to an idea and/or your ideas are similar, says Quizlet , an online teacher and student learning community. Some examples of additive transition words and phrases were compiled by Michigan State University writing lab. Follow each transition word or phrase with a comma:
- In the first place
- Furthermore
- Alternatively
- As well (as this)
- What is more
- In addition (to this)
- On the other hand
- Either (neither)
- As a matter of fact
- Besides (this)
- To say nothing of
- Additionally
- Not to mention (this)
- Not only (this) but also (that) as well
- In all honesty
- To tell the truth
An example of additive transitions used in a sentence would be:
" In the first place , no 'burning' in the sense of combustion, as in the burning of wood, occurs in a volcano; moreover , volcanoes are not necessarily mountains; furthermore , the activity takes place not always at the summit but more commonly on the sides or flanks..." – Fred Bullard, "Volcanoes in History, in Theory, in Eruption"
In this and the examples of transitions in subsequent sections, the transition words or phrases are printed in italics to make them easier to find as you peruse the passages.
Adversative Transitions
Adversative transitions are used to signal conflict, contradiction, concession, and dismissal, says Michigan State University. Examples include:
- In contrast
- But even so
- Nevertheless
- Nonetheless
- (And) still
- In either case
- (Or) at least
- Whichever happens
- Whatever happens
- In either event
An example of an adversative transition phrase used in a sentence would be:
" On the other hand, professor Smith completely disagreed with the author's argument."
Causal Transitions
Causal transitions—also called cause-and-effect transitions—show how certain circumstances or events were caused by other factors, says Academic Help . The website that offers assistance with academic writing adds: "They [causal transitions] make it easier for the reader to follow the logic of the arguments and clauses represented in paper." Examples include:
- Accordingly
- As a result
- Consequently
- For this reason
- Granting (that)
- On the condition (that)
- In the event that
- As a result (of this)
- Because (of this)
- As a consequence
- In consequence
- So much (so) that
- For the purpose of
- With this intention
- With this in mind
- Under those circumstances
- That being the case
An example of a causal transition used in a sentence would be:
"The study of human chromosomes is in its infancy, and so it has only recently become possible to study the effect of environmental factors upon them." –Rachel Carson, "Silent Spring"
Sequential Transitions
Sequential transitions express a numerical sequence, continuation, conclusion , digression , resumption, or summation, says Michigan State, which gives these examples:
- In the (first, second, third, etc.) place
- To begin with
- To start with
- Subsequently
- To conclude with
- As a final point
- Last but not least
- To change the topic
- Incidentally
- To get back to the point
- As was previously stated
An example of a sequential transition would be:
"We should teach that words are not the things to which they refer. We should teach that words are best understood as convenient tools for handling reality... Finally , we should teach widely that new words can and should be invented if the need arises." –Karol Janicki, "Language Misconceived"
In sum , use transition words and phrases judiciously to keep your paper moving, hold your readers' attention, and retain your audience until the final word.
- Definition and Examples of a Transition in Composition
- How to Teach Topic Sentences Using Models
- Cohesion Strategies: A List of Transitional Words and Phrases
- Make Your Paragraphs Flow to Improve Writing
- What You Need to Know About Conjunctive Adverbs
- Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in Spanish
- Conjugating the Verb 'To Be'
- Paragraph Transition: Definition and Examples
- Beef Up Critical Thinking and Writing Skills: Comparison Essays
- Persuasive Writing: For and Against
- How to Say "And" in Chinese
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Revising a Paper
- Definition and Examples of Paragraphing in Essays
- Paragraph Writing
- Objects in English Grammar

Using The Transition Words For a Research Paper
The function of the transition words.
Many things distinguish an average paper from a great one. Achieving greatness sounds like an impossible task. It’s actually simple. The key is knowing what to focus on. A single transition word can change the essay’s sound, making it more precise and concise. Changing the ideas or subjects from one to another gets easier when using transition words in a research paper.
When working on any writing task, it’s vital to make it understandable, easy to follow, and clear for those reading it. There’s nothing worse than an essay that’s confusing. Avoiding confusion is best achieved with research paper transition words. Transitions help establish the bond between groups of ideas.
Helpful Transition Words and Phrases for the Research Papers
If usage of transition words for a body paragraph in research paper or other parts you find unfamiliar, don’t worry. It’s all pretty easy to understand. Most students struggled with writing problem statement for the research paper , and still, they’ve become excellent at writing those over time. The same goes for transitional phrases. Learn the basics, and start implementing transitions.
Demonstrative pronouns — words including that, this, those, and these are often used to express the bond between adjacent sentences. Here’s an example:
“There’re many formulas of coordinate geometry. These (formulas) help calculate different things, including lengths and distances.”
Introductory phrases or words — These are mainly used at the start of the following sentence. They accomplish different things, including adding information, comparing, providing an alternative, giving an example, concluding, etc. Some words and phrases are also, besides, furthermore, moreover, yet, similarly, on the other hand, however, in particular, in fact, in conclusion, therefore, etc.
“The data showed many different factors. Furthermore, it pointed out that factor Y is the most important one.”
These are some general examples of transition words to use in a research paper. These can be used in different parts of it, including the results section of a research paper or other segments that you find more suitable. It all depends on the articles in question and your writing style. One thing is sure — just one transitional phrase can change the study flow and make it more professional. Over time, they’ll become part of all your papers and essays.
Depending on the article and subject, a transition word can be placed in other segments of the article. For example, if suitable, you can add them in the discussion section of your research paper , where you’ll be presenting different ideas and opinions on the topic. You can even use transition words to start a paragraph. Again, it’s up to you. Mix things up, try different options, and keep practicing.
Types of Transition Words
Using good transition words for a research paper is a game changer. The writing task becomes more serious, professional, on-point, and concise with just several phrases. With that said, it’s crucial to start using transitions. If you don’t have time or need assistance, you may consider a professional research paper writing service , as these are legit and extremely helpful. What’s more, they are available at affordable prices.
Now, let’s go back to transitions. They are used for different purposes. Below you’ll find transition words for conclusion, and you’ll figure out how to use transition words between paragraphs. All are very useful. Start with one word, and you’ll notice how the entire sentence sounds more professional and clearer. Now, let’s explore it all and start learning the basics.
Additive transitions
Let’s explore additives and when they’re used:
When adding more info — Moreover, furthermore, in addition
When pointing to similarities — Likewise, similarly, in a similar way
When specifying — Namely, specifically
Adding references — Regarding, concerning
Here’re some examples:
“Considering all the work that has been completed, we are satisfied.”
“Moreover, the data showed additional evidence.”
Adversative transitions
These are used in many situations, including:
Contrasting — In contrast, when in fact, however, yet, nevertheless
Emphasizing — Indeed, most importantly, primarily, significantly
Offering an alternative — Rather, on the other hand, alternatively
Disbanding the argument — In any case, regardless, either way
“However, the study requires more facts.”
“Most importantly, the results are excellent.”
“Either way, the study was effective.”
Causal transitions
These are often used in academic writing in different occasions, such as:
Signaling the reason — Because of, for the reason, due to, since
Showing the motive/purpose — In the hope that, for the purpose, in order to
Representing the effects — For the reason, thus, accordingly, therefore, for this reason
A few examples:
“Accordingly, the appropriate measures were included.”
“Since all the members are here, we can start.”
Sequential transitions
You’ll see these among helpful academic tips. They help build a structure in articles and essays.
Number organizing — Firstly, initially, secondly
Pointing something out again — as said before, as mentioned, again
Providing a conclusion — In summary, in sum, thus, hence, thus, therefore
“As said before, the results are amazing.”
“Thus, all is well.”
If you find all this too complicated to remember and implement, you may consider getting professional assistance. When you are struggling, are in a hurry, or have lots of work, you may beg your siblings or parents, please, write me a research paper , and you keep repeating the request hoping someone will agree to help you. But, you can always turn to professionals instead and focus on other things.
How to Avoid Plagiarism in Your Research Paper?
Providing 100 % authentic content is beyond important when working on papers and essays. Now, many in college keep wondering how plagiarism can be avoided. The easiest option of all is to explore a super simple and completely free plagiarism checker for students that will make your work easier and simpler in many ways. It’ll help you deliver articles that are original and plagiarism-free.
The checker is very easy to use, and it will ensure your paper is original and has no issues of this kind. Use it to check your essays, papers, and articles, focusing on authenticity and originality. Plus, original work will help you get better grades. If you find this task impossible, you can hire a professional. You can get research papers for sale online from a renowned website. Using their services, you can get a great essay.
You May Also Be Interested In
The research paper is a difficult work because it should contain a new look at…
The conclusion is a brief retelling of all your work. It’s something like the introduction,…
Before getting to the details, let’s know what a citation is. A citation mentions (usually published and derived from…
In just about every sphere of life, problems, big and small, can arise at any…
Always Ready to Help
Running out of time.
Type to search
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Transitional Devices

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A discussion of transition strategies and specific transitional devices.
Transitional devices are like bridges between parts of your paper. They are cues that help the reader to interpret ideas a paper develops. Transitional devices are words or phrases that help carry a thought from one sentence to another, from one idea to another, or from one paragraph to another. And finally, transitional devices link sentences and paragraphs together smoothly so that there are no abrupt jumps or breaks between ideas.
There are several types of transitional devices, and each category leads readers to make certain connections or assumptions. Some lead readers forward and imply the building of an idea or thought, while others make readers compare ideas or draw conclusions from the preceding thoughts.
Here is a list of some common transitional devices that can be used to cue readers in a given way.
and, again, and then, besides, equally important, finally, further, furthermore, nor, too, next, lastly, what's more, moreover, in addition, first (second, etc.)
To Compare:
whereas, but, yet, on the other hand, however, nevertheless, on the contrary, by comparison, where, compared to, up against, balanced against, vis a vis, but, although, conversely, meanwhile, after all, in contrast, although this may be true
because, for, since, for the same reason, obviously, evidently, furthermore, moreover, besides, indeed, in fact, in addition, in any case, that is
To Show Exception:
yet, still, however, nevertheless, in spite of, despite, of course, once in a while, sometimes
To Show Time:
immediately, thereafter, soon, after a few hours, finally, then, later, previously, formerly, first (second, etc.), next, and then
in brief, as I have said, as I have noted, as has been noted
To Emphasize:
definitely, extremely, obviously, in fact, indeed, in any case, absolutely, positively, naturally, surprisingly, always, forever, perennially, eternally, never, emphatically, unquestionably, without a doubt, certainly, undeniably, without reservation
To Show Sequence:
first, second, third, and so forth. A, B, C, and so forth. next, then, following this, at this time, now, at this point, after, afterward, subsequently, finally, consequently, previously, before this, simultaneously, concurrently, thus, therefore, hence, next, and then, soon
To Give an Example:
for example, for instance, in this case, in another case, on this occasion, in this situation, take the case of, to demonstrate, to illustrate, as an illustration, to illustrate
To Summarize or Conclude:
in brief, on the whole, summing up, to conclude, in conclusion, as I have shown, as I have said, hence, therefore, accordingly, thus, as a result, consequently
33 Transition Words and Phrases
Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one.
Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that “this follows logically from the preceding” include accordingly, therefore, and consequently . Words that mean “in addition to” include moreover, besides, and further . Words that mean “contrary to what was just stated” include however, nevertheless , and nonetheless .
as a result : THEREFORE : CONSEQUENTLY
The executive’s flight was delayed and they accordingly arrived late.
in or by way of addition : FURTHERMORE
The mountain has many marked hiking trails; additionally, there are several unmarked trails that lead to the summit.
at a later or succeeding time : SUBSEQUENTLY, THEREAFTER
Afterward, she got a promotion.
even though : ALTHOUGH
She appeared as a guest star on the show, albeit briefly.
in spite of the fact that : even though —used when making a statement that differs from or contrasts with a statement you have just made
They are good friends, although they don't see each other very often.
in addition to what has been said : MOREOVER, FURTHERMORE
I can't go, and besides, I wouldn't go if I could.
as a result : in view of the foregoing : ACCORDINGLY
The words are often confused and are consequently misused.
in a contrasting or opposite way —used to introduce a statement that contrasts with a previous statement or presents a differing interpretation or possibility
Large objects appear to be closer. Conversely, small objects seem farther away.
used to introduce a statement that is somehow different from what has just been said
These problems are not as bad as they were. Even so, there is much more work to be done.
used as a stronger way to say "though" or "although"
I'm planning to go even though it may rain.
in addition : MOREOVER
I had some money to invest, and, further, I realized that the risk was small.
in addition to what precedes : BESIDES —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
These findings seem plausible. Furthermore, several studies have confirmed them.
because of a preceding fact or premise : for this reason : THEREFORE
He was a newcomer and hence had no close friends here.
from this point on : starting now
She announced that henceforth she would be running the company.
in spite of that : on the other hand —used when you are saying something that is different from or contrasts with a previous statement
I'd like to go; however, I'd better not.
as something more : BESIDES —used for adding information to a statement
The city has the largest population in the country and in addition is a major shipping port.
all things considered : as a matter of fact —used when making a statement that adds to or strengthens a previous statement
He likes to have things his own way; indeed, he can be very stubborn.
for fear that —often used after an expression denoting fear or apprehension
He was concerned lest anyone think that he was guilty.
in addition : ALSO —often used to introduce a statement that adds to and is related to a previous statement
She is an acclaimed painter who is likewise a sculptor.
at or during the same time : in the meantime
You can set the table. Meanwhile, I'll start making dinner.
BESIDES, FURTHER : in addition to what has been said —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
It probably wouldn't work. Moreover, it would be very expensive to try it.
in spite of that : HOWEVER
It was a predictable, but nevertheless funny, story.
in spite of what has just been said : NEVERTHELESS
The hike was difficult, but fun nonetheless.
without being prevented by (something) : despite—used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
Notwithstanding their youth and inexperience, the team won the championship.
if not : or else
Finish your dinner. Otherwise, you won't get any dessert.
more correctly speaking —used to introduce a statement that corrects what you have just said
We can take the car, or rather, the van.
in spite of that —used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
I tried again and still I failed.
by that : by that means
He signed the contract, thereby forfeiting his right to the property.
for that reason : because of that
This tablet is thin and light and therefore very convenient to carry around.
immediately after that
The committee reviewed the documents and thereupon decided to accept the proposal.
because of this or that : HENCE, CONSEQUENTLY
This detergent is highly concentrated and thus you will need to dilute it.
while on the contrary —used to make a statement that describes how two people, groups, etc., are different
Some of these species have flourished, whereas others have struggled.
NEVERTHELESS, HOWEVER —used to introduce a statement that adds something to a previous statement and usually contrasts with it in some way
It was pouring rain out, yet his clothes didn’t seem very wet.
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Usage Notes
Prepositions, ending a sentence with, hypercorrections: are you making these 6 common mistakes, a comprehensive guide to forming compounds, can ‘criteria’ ever be singular, singular nonbinary ‘they’: is it ‘they are’ or ‘they is’, grammar & usage, words commonly mispronounced, more commonly misspelled words, is 'irregardless' a real word, 8 grammar terms you used to know, but forgot, homophones, homographs, and homonyms, great big list of beautiful and useless words, vol. 3, even more words that sound like insults but aren't, the words of the week - mar. 22, 12 words for signs of spring.
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, transitions – transition words – transitional phases.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida , Barbara McLain - The Out-of-Door Academy
Transitions are a lifeline for readers, listeners, users —a kind of conceptual superglue . Transition words and traditional phrases are crucial to helping audiences keep track of the author's reasoning and purposes for writing. Learn to identify when transitions are warranted in your work and the work of others. Distinguish between effective and ineffective transitions.

What are Transitions? Transition Words? Transition Phrases?
Transitions, Transition Words , Transitional Phases—these terms concern authors’ efforts to design the flow of information in a text in ways that promote clarity , brevity , simplicity , flow , unity for readers, listeners, users .
Accomplished writers understand interpretation is challenging. They understand readers can lose track of the big picture—the writer’s purpose , thesis , research question . Thus, when revising and editing , writers are careful to check the flow of information across words , sentences , paragraphs . They seek to identify and rewrite choppy spots in their writing when readers ask, “Why am I being given this information? So What? How does this relate to what’s been said thus far?”
Transitions refers to
- the act of shifting the focus in discourse from one idea, process, state, experience to something new
- the convention that writers address information literacy practices and perspectives when they cite textual evidence or empirical evidence
- efforts to clarify a text’s organizational schema,
Transition Words & Phrases are words and phrases (aka signs or signposts) that writers and speakers use to help their readers, listeners, or users understand the flow of information across a text .
Transitional Words refers to elements of spoken and written language (e.g., words, phrases, sentences, paragraphs, and sections) that authors use to help audiences understand the flow of information across a text .
- Transitions may be referred to as sticky points, wounds, seques, gaps
- Transition Words may also be referred to as transitional language , linking language, explanatory language, metalanguage, pivoting, signposting
Related Concepts: Communication ; Information Architecture ; Organization ; Organizational Schema; Rhetorical Analysis ; Rhetorical Reasoning ; Unity
Why Do Transitions Matter?
For readers, listeners, users , transitions are a lifeline —a kind of conceptual superglue . Transition words are crucial to helping audiences keep track of the author’s reasoning and purpose for writing.
At any given moment, people experience a tsunami of information coming at them at warp speed. When reading or listening, people may be distracted by any number of other things—an email, a plane flying overhead, a social media post, a poignant memory, a stock market crash. Their own personal concerns or a nudge from social media may get them off task in a jiffy.
Writers and speakers use transitions to keep the audience’s focus on their narrative , thesis , research question , hypothesis.
Function of Transition Words & Transitional Phrases
Transition words and transition phrases may be categorized by their rhetorical function —aim of discourse, as illustrated in Table 1 below.

Best Transition Words for Essays
The best transition words are the ones that best match your rhetorical situation .
In order to identify the best transition words for an essay you are writing, you should first engage in rhetorical analysis and rhetorical reasoning . Subsequently, you can then make rhetorically informed decisions regarding the appropriate persona , tone , and voice you should adopt when you begin your composition .
Sample Questions for Rhetorical Analysis of Transitions
In order to select appropriate transitions and transitional words for your texts , engage in rhetorical analysis . Ask yourself,
- What is my purpose (aka aim) ? What am I attempting to accomplish?
- If so, you may not even need transitions.
- Then you’ll need extensive transitional language to help your readers follow your reasoning.
- Are there any genre considerations or media considerations that inform your readers’ expectations regarding effective or ineffective uses of transitional language ?
Academic Writing Prose Conventions
Transition words in academic essays and academic writing in general tend
- to use formal diction .
- Academic essays often express transitions in paragraph form at the beginning of texts and interspersed between major sections
- to reflect the information literacy perspectives & practices of their intended audiences.
Template for Transitions in Academic Writing
Below are examples of common transitions in academic writing genres.
Professional Writing Prose Conventions
Transition words in professional writing (aka workplace writing ) are similar to those in academic writing . However, there are a few distinctions: workplace writing tends to rely more on headings and visual language than rely on paragraph-style transitions like those used in academic writing.
Transitions & Invention

For writers, transitions across topics can spark invention . Sometimes when revising, when looking in between sentences and paragraphs to check them for clarity , writers identify breakdowns in their reasoning or gaps in scholarly conversations or discover entirely new things to say.
How to Edit Transitions & Transition Words
Teachers and critic s write Transition? on texts when they
- They don’t understand why they are being told what they are being told.
- believe a t ransitional word or a transitional phrase is superfluous or used incorrectly (see Brevity )
You will find it helpful to examine your use of transition words if you have been told your organization needs work or that your writing is awkward or choppy .
Step 1: Rhetorical Analysis
First, make sure your transitions are appropriate for the rhetorical situation you are addressing. For example, if you are addressing a loved one in a personal note, you would want to use “also” instead of “moreover.”
Check, in particular, the tone and diction level of your transition words.
Step 2: Textual Analysis
When you revise , edit , or proofread your documents, you should consider whether or not you have provided sufficient transition s and transition words .
- between and within sentences : Transitional words or phrases are used to create connections between sentences, as well as within sentences; both uses enhance the progression of ideas at the sentence level .
- between paragraphs : Transitional sentences are used to create a bridge between paragraphs. These sentences should provide a summary of the main idea of one paragraph and give the reader a clue as to what is coming in the next paragraph (Internal link to: relate paragraphs logically to previous paragraph(s).
- between sections : Transitional paragraphs are used in longer works to summarize the discussion of one section and introduce the reader to the concept(s) presented in the next section.
Also, be sure to double check that you have avoided tedious repetition. Remember, when it comes to transition words, less is more. When possible, you want to vary your transition words.
Example of Unvaried transitional language that creates a primer-like style:
We went to the national mall. Then we visited the Air and Space Museum. Then we stopped for lunch at Jaleo.
Varied transitional language : To start the day, we went to the national mall. After a stroll around the reflecting pool, we visited the Air and Space Museum. When we couldn’t walk another step, we stopped at Jaleo for lunch.
Related Concepts
Transitions, Transition Words, Transitional Language — these concepts are intertwined with information architecture , organizational schema (aka organizational scaffolding), and recent research on cognitive development and learning science theory.
Transitions & Transition Words are a major textual attribute of a reader-based prose style , an academic prose style , and a professional writing prose style (aka workplace writing style).
In contrast, writer-based prose lacks needed transitions and transition words .

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are some of the most useful transition words for research papers. 1-888-627-6631; [email protected]; Jobs; FAQ; About Us About Us; Contact Us; Affiliate Program; My Account; English ... Types of Transition Words. Transitions accomplish many different objectives. We can divide all transitions into four basic categories:
Example sentence. Transition words and phrases. Addition. We found that the mixture was effective. Moreover, it appeared to have additional effects we had not predicted. indeed, furthermore, moreover, additionally, and, also, both x and y, not only x but also y, besides x, in fact. Introduction.
1. Make sure you are not overusing the same three or four transitions throughout your paper. 2. Even if you use a variety of transitions, it is possible to overdo it. If you have transitions at the beginning of every (or nearly every) sentence, look for places to remove some. This guide provides suggestions for possible words and phrases to use ...
Transitional words and phrases can create powerful links between ideas in your paper and can help your reader understand the logic of your paper. However, these words all have different meanings, nuances, and connotations. Before using a particular transitional word in your paper, be sure you understand its meaning and usage completely and be sure…
Transition sentence This paragraph… Further evidence in support of this hypothesis is provided by Smith (2019). …complements the previous one, providing more support for the same idea. However, Patel's arguments are not the final word on the matter. …contradicts the previous one by presenting new evidence related to the previous discussion. Having established the relationship between ...
Transitions can signal to readers that you are going to expand on a point that you have just made or explain something further. Transitional words that signal explanation or elaboration include in other words, for example, for instance, in particular, that is, to illustrate, moreover. drawing conclusions. You can use transitions to signal to ...
Generally used at the beginning of sentences and paragraphs to form a bridge of communication, transition words can vary depending on your objective, placement, and structuring. The four types of transition words in academic writing or research papers are additive transitions, adversative transitions, causal transitions, and sequential ...
A transition between paragraphs can be a word or two (however, for example, similarly), a phrase, or a sentence. Transitions can be at the end of the first paragraph, at the beginning of the second paragraph, or in both places. Transitions within paragraphs: As with transitions between sections and paragraphs, transitions within paragraphs act ...
Writing strong transitions often takes more than simply plugging in a transition word or phrase here and there. In a piece of academic writing, writers often need to use signposts, or transition sentences that signal the reader of connections to the thesis. To form a signpost, combine transition words, key terms from the thesis, and a mention of the previous topic and new topic.
A few other transitional words may be particularly helpful when writing lists or describing sequential processes, such as in the methods section of a research paper: next, then, meanwhile, first, second, third, and finally. In sum, transitions are small additions that can substantially improve the flow of your ideas.
Transitional Words & Phrases The word transition means change or passage. Transitions establish relationships between parts of your essay that a reader will need in order to fully understand the points you are making. Effective transitions are achieved in two ways: by using transitional words and expressions, and by carefully repeating words ...
These transitional words (like finally) have the function of limiting, restricting, and defining time. They can be used either alone or as part of adverbial expressions. at the present time. from time to time. sooner or later. at the same time. up to the present time. to begin with.
"Sequence and Chronology" transition words are used in academic research papers when you want to indicate the order, progression, or sequence of events, ideas, or processes. These words help to organize information in a logical and coherent manner, ensuring that readers can follow the chronological flow of your research.
Familiarizing yourself with these most-used and best transition terms for academic writing will help bring clarity to your essays and make the writing process much easier on you. Like the links on a chain, transition words hold an academic paper together and make ideas flow logically. Photo by Markus Spiske on Unsplash. Types of transitions
Return to writing a body of a research paper to see typical transition words and phrases. Learn how to write a body of a research paper. ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER. Always on-time. Plagiarism-Free . 100% Confidentiality. FREE INQUIRY. ORDER NOW. Special offer! Get 10% off with the 24START discount code!
These transition terms and phrases organize your paper by numerical sequence; by showing continuation in thought or action; by referring to previously-mentioned information; by indicating digressions; and, finally, by concluding and summing up your paper. "Initially, subjects were asked to write their names.".
Transition words and phrases can help your paper move along, smoothly gliding from one topic to the next. If you have trouble thinking of a way to connect your paragraphs, consider a few of these 100 top transitions as inspiration. The type of transition words or phrases you use depends on the category of transition you need, as explained below.
A single transition word can change the essay's sound, making it more precise and concise. Changing the ideas or subjects from one to another gets easier when using transition words in a research paper. When working on any writing task, it's vital to make it understandable, easy to follow, and clear for those reading it.
Transitional devices are like bridges between parts of your paper. They are cues that help the reader to interpret ideas a paper develops. Transitional devices are words or phrases that help carry a thought from one sentence to another, from one idea to another, or from one paragraph to another. And finally, transitional devices link sentences ...
33 Transition Words and Phrases. 'Besides,' 'furthermore,' 'although,' and other words to help you jump from one idea to the next. Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one. Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that ...
Transition Words & Phrases are words and phrases (aka signs or signposts) that writers and speakers use to help their readers, listeners, or users understand the flow of information across a text. Transitional Words refers to elements of spoken and written language (e.g., words, phrases, sentences, paragraphs, and sections) that authors use to ...