How to Write a Business Proposal [Examples + Template]
Published: December 05, 2023
Here's what every new business owner needs: an extra 8 hours in the day, an endless supply of coffee, and, most importantly, a really strong business proposal.

A business proposal can bridge the gap between you and potential clients. Done correctly, and it will outline your value proposition and persuade a company or organization to do business with you.
Here, we'll take a look at the various kinds of business proposals and go over how to write one. We’ll also see some ideas and examples to help guide yours.
Know exactly what you need? Jump to one of the following sections:

What is a business proposal?
Types of business proposals, how to write a business proposal, business proposal templates, business proposal example, tips for writing a business proposal, business proposal ideas.
A business proposal is a formal document that’s created by a company and given to a prospect to secure a business agreement.
It's a common misconception that business proposals and business plans are the same. However, a proposal helps you sell your product or service — not your business itself.
Think of it this way: instead of assisting your search for investors to fund your business, a proposal helps you seek new customers.
Follow Along With HubSpot's Business Proposal Template

Download the Template for Free
There are two types of business proposals: unsolicited and solicited.
- Unsolicited Business Proposals : With unsolicited business proposals, you approach a potential customer with a proposal, even if they don't request one, to gain their business.
- Solicited Business Proposals : Solicited business proposals are requested by prospective clients so that they can decide whether to do business with your company.
In a solicited business proposal, the other organization asks for a request for proposal (RFP). When a company needs a problem solved, they invite other businesses to submit a proposal that details how they'd solve it.

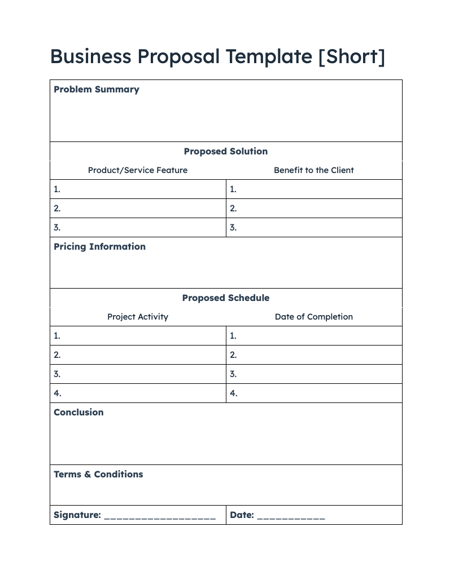
Free Business Proposal Template
Propose your business as the ideal solution using our Free Business Proposal Templates
- Problem summary
- Proposed solution
- Pricing information
- Project timeline
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out the form to get your template.
Whether the proposal is solicited or unsolicited, the steps to create your proposal are similar. Make sure it includes three main points:
- A statement of the organization's problem
- Begin with a title page.
- Explain your why with an executive summary.
- State the problem or need.
- Propose a solution.
- Share your qualifications.
- Include pricing options.
- Summarize with a conclusion.
Before writing your business proposal, it's crucial you understand the company. If they've sent you an RFP, make sure you read it carefully, so you know exactly what they want.
I recommend having an initial call or meeting with any new clients to ensure you fully understand their objectives. Ask open-ended questions to understand not just what they want, but why they want it.
Once you've done your research, it's time to begin writing your business proposal. While there's no one-size-fits-all approach to writing a business proposal, there's several elements most proposals include. (I designed this example business proposal using Canva .)
1. Begin with a title page.
You have to convey some basic information here. Introduce yourself and your business. Be sure to include:
- Your company's name
- The date you submitted the proposal
- The name of the client or individual you're submitting the proposal to
Your title page should reconcile engagement with professionalism. I think of it as your first tone-setter, so you need to make sure yours is sleek, aesthetically appealing, and not too "out there."
Here's an example of what a business proposal template looks like when done right:

The executive summary details exactly why you're sending the proposal and why your solution is the best for the prospective client.
Specificity is key here. Why are you the best choice for them?
Like a value proposition, your executive summary outlines the benefits of your company's products or services and how they can solve your potential client's problem.
After reading your executive summary, the prospect should offer a clear idea of how you can help them, even if they don't read the entire proposal. Here's what one should look like:

3. State the problem or need.
This is where you share a summary of the issue impacting the potential client. This is your opportunity to show them you understand their needs and the problem they need help solving.

In the example above, I included several signals to showcase my expertise – that I've been in the photography biz for 10 years, that I've worked with over 500 clients, and that I've been featured a number of publications.
As you approach this section, focus on presenting yourself as an authority. Consider leveraging tools like:
- Case studies
- Client testimonials
- Relevant awards
- Industry accreditations
6. Include pricing options.
Pricing is where things can get a bit tricky, as you don't want to under or over-price your product.
The pricing section of your proposal could include:
- A detailed pricing breakdown, including packages, tiers, and add-ons or optional services
- How product features and benefits align with pricing choices
- Pricing for different needs and budgets
- How your pricing compares with competitors
- An FAQ section to respond to anticipated objections and explain your pricing strategy
7. Summarize with a conclusion.
After sharing the above information, simplify it all into one final section.
- First, briefly summarize the proposal. Be sure to share your qualifications and why you’d serve as the best choice.
- Then, to prompt further conversation, confirm your availability to go over the next steps.
- At the end of the proposal, the goal is to have the client ready to work with you. So, be sure to offer your contact information for easy follow-up.
In need of some inspiration before you begin writing? Here are example business proposal templates from popular business proposal software companies you can use to help create your proposal.
1. HubSpot's Free Business Plan Templates
Download these Templates
We know how crucial a great business proposal is to your and your client’s success. That's why we've compiled 2 Free Business Proposal Templates for you to use and customize for any of your projects.
You'll gain access to a concise, one-page template (pictured above), as well as a longer template for you to refine your plan and proposal.
Download the templates now to get started on building your proposal.
What We Like
The one-page template is clear, straightforward, and easy to read — without skipping on the key elements of a business proposal. This format is especially useful for busy clients who appreciate brevity and clarity.
2. Web Design Proposal

With advertising on social networks projected to reach $82.23 billion dollars in 2025 , it's in your business's best interest to have a plan for growing your client's social media presence.
To help you in that effort, the information in this social media marketing proposal includes an executive summary to help introduce your high-level ideas, an assessment of the client’s company to show your diligence, and a breakdown of billing to show how your company charges for posting, content creation, and analytics.
This template includes all the bells and whistles of a social media proposal packaged in a fun yet professional design. It also includes helpful writing instructions under each section.
8. Content Marketing Proposal

Business proposal templates are helpful places to get started, but what should your business proposal look like when it's complete? This template should inspire you.
When pitching your content marketing services to clients, this template can help you organize your ideas. While it walks you through initial objectives and how to communicate your prospected results, one of the most helpful parts of this template is the pricing ideas it gives you when charging for your services.
In the business template example below, Social Portal Consulting (SPC) pitches a marketing proposal to Graphic Bean. At first sight, this proposal appeals to the creative. I recommend going a step forward and designing the layout in your or your client’s brand colors.
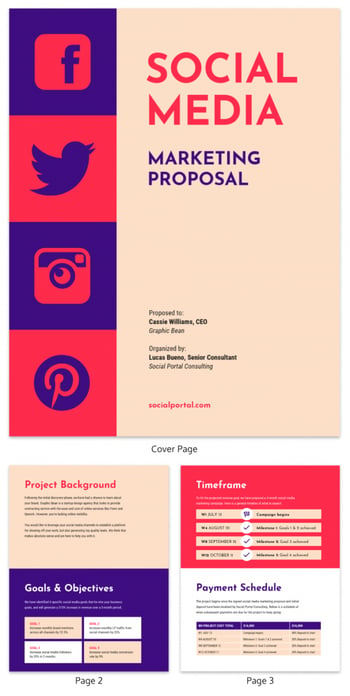
Besides the design, the social media icons quickly tell the prospect what platforms Social Portal is pitching. Because we see Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Pinterest icons, the client instantly knows that this proposal doesn’t include LinkedIn, YouTube, or other platforms.
While maintaining its design, this example outlines Social Portal Consulting’s plans efficiently. It begins by providing insight into Graphic Bean and its goals before elaborating on how SPC can leverage its expertise to help them achieve them.
This business proposal template includes an easy-to-follow timeframe for goals and objectives while keeping the client abreast of how payment will happen across the project.
Overall, this is an excellent example of how to combine the elements of social media marketing into a creative and concise business proposal. Finally, we'll leave you with some business proposal ideas to get you started on your own.
- Start with an outline.
- Keep it simple.
- Stay on brand.
- Quality control.
- Include data and visuals.
- Add social proof.
- Use a call-to-action.
- Create a sense of urgency.
- Make the decision for them.
- Incorporate video into your proposal.
- Include up-sell and add-on opportunities.
- Clarify your terms and conditions.
- Include a space for signatures to document agreement.
- Create a table of contents.
1. Start with an outline.
If you want to produce a thoughtful, effective business proposal, you need to have some idea of what you're hoping to achieve with it.
Before I dive into writing a proposal, I always outline the major sections of the proposal that I want to include. That way, I can stay focused and make sure my message stays intact as I write.
Use these free business proposal templates to make sure that your outline includes everything you need.
2. Keep it simple.
Ultimately, there's no definitive blueprint for how long a business proposal has to be. Yours should be however long it takes to convey the information you want to get across.
That said, I'm a firm believer in quality over quantity, especially when it comes to business proposals. Keep your sentences short and simple, and avoid including too much business jargon.
You want anyone who picks up your proposal to make sense of it. So, be straightforward and don't get too fancy. Aim for substance over flash.
3. Stay on brand.
Don't be afraid to let your company's personality shine through in your proposal. Stay true to your brand and show the client what sets you apart from your competitors.
4. Quality control.
I've made it a habit to add an editing/QA step in my writing process. During this step, I do a quick spelling and grammar check before hitting send.
So, as you draft your proposal, and after checking for the basics, keep scanning this document until it's just right.
Check to make sure your proposal:
- Meets client needs and expectations
- Highlights your value proposition
- Is well-structured and easy to read or skim
- Complies with legal, ethical, and regulatory requirements
- Looks professional and engaging
5. Include data and visuals.
You want your business proposal to capture your prospect's attention and help set you apart from any other ones they might have received. One of the best ways to do that is to include hard, quantitative data that helps stress the value of your business.
Use relevant, compelling figures that highlight what you have to offer. This can establish authority and make your proposal more convincing. It also helps to include visuals such as charts and graphs to enhance your proposal.
6. Add social proof.
From my experience, you can only be so convincing when you're personally talking up how great your business is — which is why adding social proof is key to establishing credibility.
At the end of the day, prospects are skeptical. They may not take you at your word. But they'll likely trust peers and fellow customers. That's why including elements like customer quotes and testimonials can go a long way.
7. Use a call-to-action.
I've learned that the best proposal in the world can only take you so far if you don't clearly define the next steps. That's why you have to make sure the reader knows what to do after reading your proposal.
A clear call-to-action is the best way to get there.
Define and highlight exactly what they should do to act on the interest your proposal has generated. Without that guidance, you might leave your reader in limbo.
HubSpot customers : Use this CTA builder to create powerful customized CTAs.
8. Create a sense of urgency.
No one wants to feel as if they missed out on a great opportunity. From my experience, prospect tend to drag their feet and put off making a decision if there isn't a sense of urgency.
So, as you create your business proposal, your goal should be to add a degree of urgency. When prospective clients read your business proposal they should feel that the best time to sign up for your service is now .
One way I accomplish this is by stating short and long-term goals for their business. They'll have to wait for the long-term goals, but I make the short-term goals so enticing that they'll be ready to begin a collaboration.
9. Make the decision for them.
Craft your copy in a way that seems like saying "no" to the proposal would be stepping over dollars to pick up pennies. Your offer should go above and beyond their expectations. Do everything in your power to remove friction and objections along the way.
10. Incorporate video into your proposal.
If you're creating an online proposal using document file formats like PDF, add multimedia elements. This will enhance the proposal experience, make your document richer, and keep them engaged.
Try adding a video at the beginning as an intro to your proposal. Or, put a video in the project breakdown to verbally discuss some of the more confusing parts.
Extras like this can make an impression. This tip works especially well with prospects who are visual or auditory communicators.
Pro tip : HubSpot Video makes it easy to record and embed video into a website or email for a big proposal boost.
11. Include up-sell and add-on opportunities.
They say you won't receive unless you ask. And readers won't explore the upper tiers of your solutions if you don't give them the opportunity.
So, share some upsells and add-ons about your business that they can act on. Call out a specific pain point and how this extra can add value.
With this step, balance is important. Show them everything your business has to offer without overwhelming your recipient.
12. Clarify your terms and conditions.
Your business proposal should include details on your project timeline and payment schedule. This summary is basically what you and the client agree to if they accept your proposal.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

70 Small Business Ideas for Anyone Who Wants to Run Their Own Business
![proposed a business plan How to Start a Business: A Startup Guide for Entrepreneurs [Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/How-to-Start-a-Business-Aug-11-2023-10-39-02-4844-PM.jpg)
How to Start a Business: A Startup Guide for Entrepreneurs [Template]

Door-to-Door Sales: The Complete Guide

Amazon Affiliate Program: How to Become an Amazon Associate to Boost Income

Product Differentiation and What it Means for Your Brand
![proposed a business plan How to Write a Business Proposal [Examples + Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-to-write-business-proposal%20%281%29.webp)
The 25 Best PayPal Alternatives of 2023

The First-Mover Advantage, Explained

Intrapreneurship vs. Entrepreneurship: What's the Difference?

What Are Current Assets? Definition + Examples
Propose your business as the ideal solution using this free template.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-14343635291-33bf053f368c43f6a792e94775285bbd.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily, just like you can leverage an example business plan template to write your plan, we also have a gallery of over 50 pitch decks for you to reference.
With this gallery, you have the option to view specific industry pitches or get inspired by real-world pitch deck examples.
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Transform Tax Season into Growth Season
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

How to Write a Business Proposal [Steps, Tips, & Templates]
You need to send a business proposal, and you want it to close. But how can you improve your chances?
Every year, we analyze the proposals sent with our software to discover what makes closing more likely. We used this research to craft this very guide .
To help you write better business proposals, we’ve curated the essential proposal format, a step-by-step process, plenty of templates to help you get started, and strategies for following up.
From images to esignatures, keep reading for data-backed insights into the most successful proposals.

What’s in this guide:
What is a business proposal?
Basic proposal format, what to prepare before writing a business proposal, how to write a business proposal in 7 steps, 8 business proposal templates, 5 ideas to take your business proposal to the next level, what to do after you send a business proposal, using analytics for business proposal insights.
A business proposal is sent by a salesperson or account manager to a prospective client in order to pitch a product or service. A great proposal should include an executive summary or cover letter, details on the project timelines and deliverables, what makes the company the right choice for the job, and pricing and payment details.
Business proposals are typically sent from one business to another for all sorts of different services, such as enterprise software subscriptions, interior design, accounting, marketing, event catering, etc.
The purpose of a business proposal is to:
Sell your product or service with details, client results, testimonials, etc.
Clarify what is and isn’t included in the proposal to accurately manage expectations
Layout terms and conditions to protect both parties
Lock in the deal right away with esignatures built into the proposal
Large corporations and government agencies will typically send out a request for proposal to competing companies and then choose the best (or cheapest) one.
A business proposal is very different from a business plan, because it is typically written to clarify a paid engagement between two companies. This might be a short project or a long contract. A business plan, on the other hand, is typically an internal document crafted to chart a businesses path forward towards goals, such as market expansion, revenue growth, new product lines, etc.
Types of business proposals
There are many different types of business proposals. They are typically broken down by industry.
Here are some common types of business proposals, by industry :
Real estate and construction
Professional services
Proposals can also be categorized based on the type of offering :
One-off projects
Recurring subscription
Ongoing service
Package options
Later on in this guide, we include a variety of proposal templates. Depending on what you selling, you might find it easier to begin with a template designed for your industry or for the type of offer you’re selling (such as a one-off project). So be sure to peruse through the previews of each proposal so that you can see which template will save you the most time.
Business proposal example
An excellent business proposal addresses the client’s pain points and showcases the proposed solution.
Here’s an example business proposal to inspire you. The accounting proposal kicks things off with an attractive cover page.

All in all, it includes the cover page, an executive summary letter, an about us section, team photos and bios, a project summary, a breakdown of the proposed services, a pricing section, onboarding steps, and a contract with esignatures.
The services breakdown offers a great example of how to categorize your services and provide hourly estimates.

After researching over 1 million proposals, we found that winning proposals are most likely to include all of the following.
Here’s the idea proposal structure :

1. Cover page
The cover page, also called a title page, should be kept simple. It prominently features a photograph or graphic design that is on-brand, you can use graphic design templates as a starting point. It also usually includes the project name, or the client name, as well as your company name. Some companies might include contact information on the cover page, while others will save that for a separate page.
Check out this cover page , which is bright, bold, and on-brand.

2. Executive summary
The executive summary is essentially your pitch.
It’s your shot at capturing the client’s attention and showing them that you have an approach that will exceed their expectations.
It’s typically written in paragraph form (1 to 3 paragraphs) but can also include a bulleted list for a more skimmable style.
Make sure that your executive summary includes:
A quick description of the client’s problem or starting point
How your company will serve the client and why you’re suggesting this unique approach
Why your company is the best choice (average results, unique selling propositions, differentiators, awards, etc.)
This content marketing proposal offers an excellent example of an executive summary. Though in this proposal, the section is instead titled “Focus and Objectives.” What makes it great is that it’s on brand, goal-oriented, personable, and skimmable.

3. Approach or solution
In this section, you write about your process and why you approach things the way you do. For example, a Facebook marketing agency might say that they believe that creative work is essential to advertising success, and that’s why they devote 90% of their time to developing videos, images, and copy.
Some companies will craft a custom approach section for each client, while others will re-use the section again and again. It all comes down to the number of services you offer and how much or how little you customize your work.
In corporate training, it’s essential to clarify your approach so the client knows why your system will be effective. In this training template example , their process shows the essential steps in their proprietary approach.

4. About the company
This is your chance to brag. In your company bio, be sure to mention all of the important things that set your company apart. That might include your management style, the talent you have on your team, your average client retention rate or contract length, and any accolades.
With their location, awards, and team structure, this About Us page is an excellent example of how to sell yourself with authority.

5. Deliverables
Use the deliverables section to summarize exactly what the client will receive from the engagement.
A TikTok ads management firm might include 15 ad creatives per month in their deliverables, for example. While an accounting firm might list the reports that will be sent weekly or monthly, along with the bookkeeping service.
In a construction project, on the other hand, the company might showcase the different milestones that the project will hit, and when these milestones are expected to be completed.
In this proposal , the Deliverables section is titled “Scope of Services,” and it includes a list of all of the services that the prospective client will receive. Deliverables are mentioned within the scope, including a logo, brand colors, business cards, and brand guidelines.

6. Social proof or work samples
No matter what you sell, prospective clients will want to know that you have the right experience for the job.
Social proof can come in the form of written testimonials and case studies, video testimonials and case studies, portfolio photographs, G2 and Capterra badges, and rating averages from Google, Trustpilot, or other review sites.
For an architecture firm, construction company, or website designer, work examples can prove more powerful than testimonials. Prospects want to see what you can do. This architecture proposal showcases the company’s work on a rehabilitation project.

The pricing section is of course the one that your clients will read again and again and deliberate over. That’s why it’s so important to make it clear, simple, and well-formatted.
Tables are a great way to showcase what’s included in the total project cost or to provide package options.
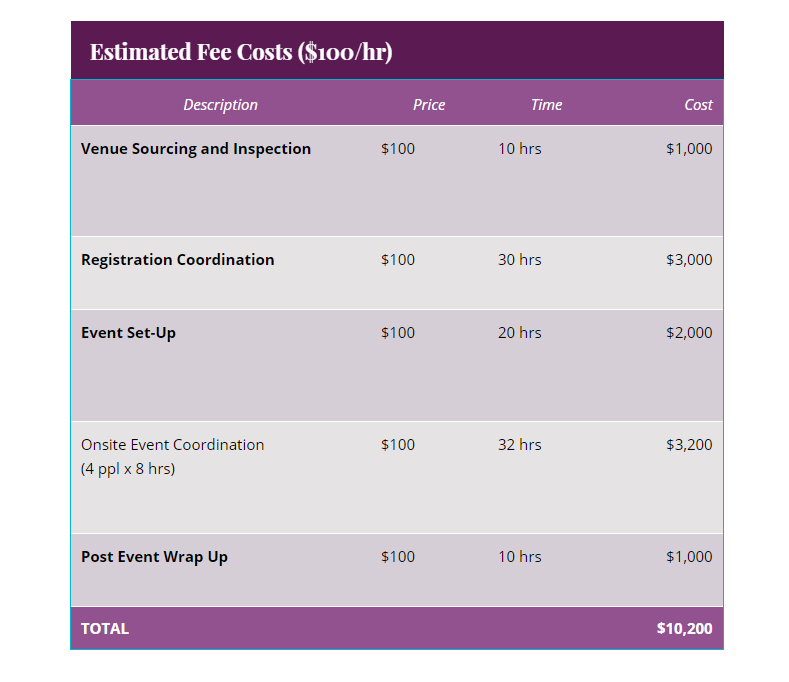
Similar to interior design and construction services, event planning typically includes both hourly costs and hard costs (for products and venues). Here’s an example of an event management proposal that includes a breakdown of the hourly work and the hard costs.
8. Terms and conditions
When you use modern proposal software , you can build a contract right into your proposal, eliminating the need for separate contract software.
Your proposal should include legal jargon that can protect both you and your client. You might have a statement of work and a master service agreement or terms and conditions.
In this website design proposal , there are 6 pages in total for the contract section. The potential client can easily click around to view all of these pages and share the proposal with their legal team if needed.

For proposals that are longer than 8 pages, it’s wise to include a table of contents. If you use Proposify as your proposal software, then every proposal will automatically have the table of contents on the left-hand side, making it easier for the potential client to click around and review important sections multiple times.
A lot goes into writing a proposal. Before you can get to the writing part, you need to prepare.
This means talking with the client to figure out their needs, using your experience to pitch the best project, and talking with colleagues who will be involved in the project to see if they agree on the services you plan to propose.
You might also need to talk with your legal department and ask them for a contract template that you can include at the end of the proposal so that when the client signs off, it's legally binding.
Everything you need to prepare to write a business proposal:
An understanding of the client's needs
Your determination of the best approach
Details that will get the client to say yes
Agreement with internal colleagues
The pricing options you want to offer
Knowledge of who needs to sign off
Legal contract language or templates
To be a good writer , you must be concise, specific, and detailed. It really is that simple. The more examples and details you provide, the better.
That said, it does help to follow a process so that you can be sure you’re providing everything that the decision-makers expect and more.
Here are the 7 essential steps for writing a business proposal:
Step 1. Determine the client’s needs
The first step is to figure out what your client needs.
As mentioned in our section on preparation above, you’ll need to speak with your client. If this is a new client, it might take two to five sales calls to collect all of the information you need. For an existing client, you can probably figure out what to include in their renewal proposal with just one call.
But of course, asking your client what they need isn’t enough. You need to use your expertise to choose the best solution for them, even if it’s not what they want or expect.
Step 2. Kick off your proposal with a template
Once you’ve done your due diligence, the next step is to choose a proposal template so you’ll save time on both writing and designing.
You can use a template that matches your specific business or click around to find one with all the sections and a design style you like. Even if it’s not created for your specific industry, it’ll be easy to update the content to match your service or product.
Check out our full library of proposal templates.

Step 3. Write the evergreen messaging about your company
It’s always smart to tackle writing section by section. This way, you don’t get overwhelmed.
We recommend starting with the sections that are relevant to your business and that can be reused again and again. Your value propositions should guide the content.
Tackle these sections:
The cover page
The approach section
The about us page and team bios
The social proof or portfolio pieces
By starting off with what makes your company special, you’ll break the ice during your writing process and also create your own custom template that you can use for further proposal writing.

Step 4. Craft the meat of the proposal (executive summary, approach, deliverables, etc.)
By now, you should have chosen a template and written your core company messaging.
Now it’s time to write the meat of the proposal.
In this step, you’ll be catering your proposal to the new client. A startup will require a different proposal than a small business, and the same goes for an enterprise.
Here are some of the things you might need to write:
The unique methodology or approach you’ll offer this client (if it changes per client)
The problem statement or executive summary
The client’s goals
The scope of work
The project process and timelines
The deliverables

You can fill in your template’s sections and take a peek at other templates to get inspiration and see if there are any additional sections or details you should add.
Step 5. Add in the project total or pricing options
Next, you should calculate your fees.
Depending on your business, you might add up flat rates, product costs, or hourly estimates to come up with a fixed project total. Or, you might present a price range that the project will likely fall between (making it clear that additional hourly costs could arise. Or perhaps, you’ll offer a pricing table with different options to choose from.

Step 6. Add legal terms and conditions and esignatures
When you use proposal software (instead of just a PDF or Google slides), you can add a contract directly to your proposal.
If you already have approved contract language from your legal department, you can simply add it to the contract section of your proposal in Proposify. If not, you’ll need to chat with your legal team or business lawyer to ensure you’re adding all the right stipulations.
Proposals with esignatures close 35% faster and are 426% more likely to be accepted. So be sure to assign an esignature both to yourself and your client.

Step 7. Finalize the design and review all of the content before sending
Now it’s time to review and finalize your proposal. Check for errors, places in the template you forgot to fill out, and wording that can be improved.
Make sure the graphic design is on point too. Switch out the template with your own brand colors and fonts. You can have a designer on your team handle this, or handle style customization yourself (with no design experience necessary).
The best way to write a business proposal? With a template of course.
We’ve rounded up 10 of the best templates for different types of businesses. And for each, we show you the proposal sections included to help you pick the right one for you.
Keep in mind that with any of these proposals, you can add and remove sections and also customize any page with text, headlines, images, videos, fee tables, and more.
1. Business consulting proposal template

This consulting proposal template can be used by any type of consulting firm.
Proposal sections :
Project Summary
Project Activities
Your Investment
2. Advertising Proposal Template
With this advertising proposal template, you can showcase your digital or traditional advertising services. The template includes TV, web, radio, and magazine, but you can update it to reflect your pitch.
Cover Letter
Who Are We?
Testimonials
Your Advertising Media Mix
3. Branding Proposal Template
Perfect for branding consultants, logo designers, and messaging strategists, this branding proposal template includes the project scope and timeline to help you clarify your process to potential clients.
Overview & Goals
Scope of Services
Sample Case Study
4. Commercial Lease Proposal Template
This commercial lease proposal template can be used for leasing office buildings, manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and event spaces.
Our Process
Meet Our Team
Terms and Conditions
5. Construction Bid Template
Use this construction bid template for new construction projects or renovations. It includes a detailed cost estimate table and a required deposit.
Cost Estimate
6. Catering Proposal Template
This catering proposal template is perfect for corporate projects but can work for weddings or personal events as well. You can use it for conferences, luncheons, retreats, or any other type of event.
Introduction
Event Details
7. Corporate Photography Proposal Template
With a beautifully designed portfolio section and a very detailed pricing table and print options, this is the perfect template for corporate photography . It also includes tips for success, so clients know how to make the most of their photoshoot time.
What We Offer
Photography Packages
Tips for Success
8. Financial Services Proposal Template
You can use this financial services proposal template to pitch financial services like risk management, budgeting, and investment management.
Services and Fees
Looking to kick up your proposals a notch?
Try one of these smart ideas:
1. Make your pricing dynamic
Dynamic pricing means that clients can choose what they want and that will automatically change the project total that they sign off on.
Proposals with options and add-ons have a 35.8% higher closing rate . Try giving package options and including add-ons such as ancillary services or maintenance work.
2. Create graphic designs for timelines and processes
Winning business proposals often include informative visuals to help clients understand your process at a glance.
You could create a graphic for project phases, milestones, or big deliverables.

3. Get creative with your social proof
Client testimonials are an easy starting point when it comes to social proof.
But can you do better? Can you get more creative and stand out from other consulting firms?
Here are some ways to improve your social proof game:
Include visuals for your average ratings (for example 4 and a half stars filled in).
Add any badges or graphics available from review sites like G2 and Trustpilot.
Film professional case study videos and embed them in your proposal.
Create a screenshare video where you talk through your digital portfolio samples.
Include an informal video testimonial from your client.
Add a video showing your team at work (ie, on the job site, running a workshop, speaking, etc.)
Write mini case studies with before and after transformations, result data, etc.
4. Have an “excludes” section
Is there something that is definitely not included in your proposal? Do clients often assume it’s included or do they get confused?
If so, try adding a section that describes everything that isn’t included in the proposal. You could mention that you don’t offer these services, or state that they’re available at an additional fee (if you want to upsell them).

5. Include videos for introductions or complex concepts
When you add a video to your proposal, you increase its chances of closing by 41% .
Here are some video ideas to try:
Informal intros filmed with Loom
Professional videos of your team at work
Case study videos
Quick descriptions of complex deliverables, methodologies, etc.

You sent the proposal. Now what?
Here’s what to do next.
Sign it yourself
Make sure you sign the proposal right away (before your client opens it). This offers a more professional presentation and makes it more likely that your new client will add their signature too.

Be prepared to follow up
Project proposals don’t always close all by themselves. As any good salesperson knows, follow-up is essential.
With Proposify, you can set up automated reminders. When we analyzed over 1 million proposals sent with our software, we found that proposals with pre-scheduled reminders have a 35% higher closing rate than those without.
Make adjustments to the proposal to close the deal
It’s okay to make changes. In fact, proposals that get revised are actually more likely to close than ones that don’t. When a client asks for revisions, it means they’re interested.
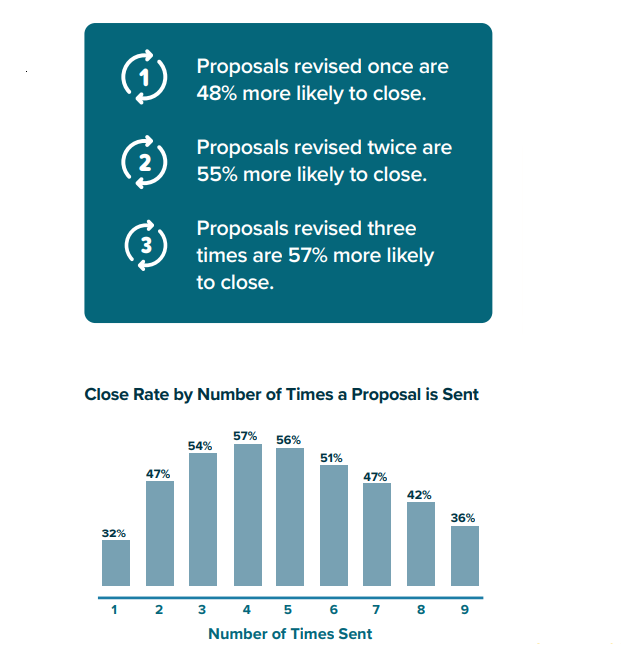
You might need to adjust your proposal document for its scope, deliverables, timeframe, or payment schedules.
Save different proposal templates
After you’ve created one proposal, you should save it as a template and give it a name. You might also want to duplicate it and adjust it to create a new proposal template. For example, if you offer SEO services , you might want to have one proposal for an SEO audit and another one for your monthly SEO retainer.
Create email templates
You can also create and store email templates that will save you time in the long run.
Try creating different templates for sending, reminders, and thank yous. If you offer different types of services, you can craft a unique sending template for each one.

Get feedback from clients on both won and lost proposals
One of the best ways to improve is to take feedback. Whether you win or lose the proposal, find out why.
Here are some tips on how to do this:
Won - When you win a proposal, you might ask the client why they decided to move forward with you on their first strategy call. Or, have their account manager ask the same question and pass the info to you.
Lost - If a client doesn’t sign the proposal after 3 weeks, you can send a quick email with something like, “Just looking for some feedback. Can you let me know why you decided not to move forward? Thanks.”
In today’s digital world, a business proposal should be more than a formal document.
When you use the right tool to create and send your proposal, you should be able to gather important insights and trends.
Viewing metrics for a specific client
With Proposify, you can see the activity for every proposal. Know when clients are opening and viewing proposals so you can follow up in a way that matches their activity.

Average viewing metrics
Proposify also offers average viewing metrics that help you benchmark your views:
Total viewed
Average time to view
Average length of viewing
Average views per proposal
This is great for gauging how a new client compares with past activity.

Average closing metrics
You can also check your average closing rate and track it over time.
Check these closing metrics:
Closing rate
Try setting goals for improving your closing rate and then check your progress each month.
Insights by proposal type
Segment viewing and closing metrics by workspace, client name, or stream. A stream is a custom category that you can use for different service types, client industries, etc.
Growth trends
And lastly, you can check your growth trends to find out how much you’re earning in new contracts and existing contracts. This is great for seeing your past revenue growth and for forecasting.
Trends include:
New won proposals (chart)
Active income (chart)
Start with a solid understanding of your client’s goals and needs. Use a template to save time creating messaging and tables that will seal the deal. Then, try advanced techniques like dynamic pricing and videos to improve your closing rates even further.
Sign up for Proposify free for 14 days or get started with one of our templates .

How to Create a Business Proposal That Closes Deals
June 28, 2022

Winning Proposal Structure Tips (What The Research Says)
June 21, 2022
Business Plan and Proposal: Everything You Need to Know
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. A business plan is a document that clearly spells out how a business intends to realize its objectives and goals, while a business proposal is a sales document that a business entity uses to request a contract from a client.
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
A business plan and a business proposal are different from each other by content, goals, writing style, and structure. The major difference between both is that a business plan is a document that presents facts, while a business proposal is a request for a deal and a quotation of prices.
A Business Plan
You can think of a business plan as the documentation of a company's grand vision. Business plans are naturally tactical. It's like stating where and when you want to start, when you want to get to the next point in view, and how you intend to accomplish that progress. A business plan includes descriptions of how the business is intended to run, the details of financial goals, possible business rivalry, marketing strategy, executive summary, and other factors that affect a company's planned business growth.
A business plan is particularly effective in making potential investors interested in a company (especially a startup company that's yet to make a name in its industry). Additionally, a business plan can provide an idea of what a company requires for professionals such as attorneys, accountants, and potential employees. A business plan distinctly describes the scope of the business, and in so doing, clears your thoughts as a business owner.
The business plan should be honestly made because it's the outline of the company's vision. It indicates whether or not the business goals of the company are realistically achievable. Experts say an effective business plan would take approximately six weeks of thorough research and groundwork to create. In other words, you typically can't create an effective business plan in one day, present it to potential investors the next day, and achieve desired results.
A Business Proposal
A business proposal goes to a prospective client directly from an established business. It's an attempt to sell a business entity's service or product to a client, and not an attempt to sell the business itself. Also, a business proposal isn't an estimate. Though costs and certain other details will be provided in the business proposal, an estimate is a lot more unofficial and simply a provision to skim over the costs. It doesn't present the entire picture.
Basically, business proposals show a particular idea, such as a new, profitable undertaking. The proposal is intended to get investors to support the particular business endeavor being suggested. For instance, a well-known eatery chain may wish to extend its business to a nearby state. Such an eatery would have to compose a business proposal in order to get the financial support of its target investors.
Though the business proposal provides an overview of what the company does (similar to a business plan), its major objective is to provide the details of the suggested business idea, including providing answers in advance for any concerns that could be raised by potential investors.
Components of a Business Plan
Basically, a business plan has three components: business model description, sales tactics, and financial goals. However, more elaborately, it has the following sections of information:
- Executive summary
- Description of products and services
- Industry analysis (analysis of possible business rivalry)
- Marketing strategy
- Operating plan
- Structure of leadership
- Internal analysis
- Built-out plan
- Introduction of management
- Financial goals (deliberations on monetary concerns, and how to address them and achieve expected results).
Solicited vs. Unsolicited Business Proposals
A solicited business proposal, when presented in response to a request for proposal (RFP), should be in the format requested by the client in their RFP. The same format may or may not be used for an unsolicited business proposal. Its purpose is to suggest and develop a business idea. Therefore, it's recommended to use the same format or some other format that's well-known in the field of endeavor.
An unsolicited business proposal offers a business entity the flexibility to choose what structure they deem appropriate. However, the proposal is expected to meet industry standards, no matter what format is used. For instance, it should emphasize major areas of interest, be thoroughly researched, offer a proposition of value, and feature a call to action.
If you need help with a business plan and proposal, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Business Proposal Ideas
- Comparison Between Business Proposal and Business Plan
- Business Contract Proposal
- Business Proposal Introduction
- How To Write A Business Proposal
- Writing A Contract Proposal
- LLC Business Plan Template
- Sample of a Good Business Plan
- Service Business Plan
- How to Contact Companies for Business

Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
The terms “business plan” and “business proposal” are sometimes used interchangeably, however, they are very different. The main difference between a business plan and a business proposal is that a business plan documents your growth strategy while a business proposal is a specific ask for someone to take an action you desire (e.g., buy your product/service, invest in your company, partner with you, etc.).
In this article, we will define a business plan and a business proposal and give you examples of when each is appropriate for you to use.
What is a Business Plan?

Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
Business Plan Structure
Typically, the business plan structure contains the following 10 components:
- Executive Summary
- Business Description & Overview
- Market Research & Analysis
- Customer Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Strategy & Plan
- Operations Plan
- Management Team
- Financial Projections & Plan
It is recommended that a business plan is updated annually to adjust for changes in the industry trends and the business itself.
What is a Business Proposal?

In terms of what you are asking from them, it can be anything that involves funds and time on their end including cash investment, product development assistance, and even employees if they have applicable skill sets.
Business Proposal Structure
An invited business proposal is written in response to an RFP. A request for proposal (RFP) is a document that invites potential suppliers to submit business proposals. How to write a business proposal depends on the format requested and the questions included in the RFP.
The following are the components that usually make up a business proposal:
- Brief description of your company’s services/products as the proposed solution to the goals of the RFP
- Reiteration of the scope of the particular project
- Responses to questions asked in the RFP
- Cost of the project, including drafting services, materials, tools, labor, delivery and other expenses
An unsolicited business proposal is essentially the same format, but it will solicit the client’s business while anticipating the clients’ concerns and issues. A business proposal is more of a marketing document than an offer because it attempts to persuade the potential client to do business by demonstrating your value proposition and a call to action.
So, What’s the Difference Between a Business Proposal vs. a Business Plan?
In a business proposal, company representatives typically work with the customer to tailor a business proposition that is attractive to both parties. This usually comes in the form of a written document detailing the services and cost associated with fulfilling an offer or request but can also include electronic contracts.
In contrast, a business plan is a description of your company on the executive and operational levels aimed at investors for raising financial support or other stakeholders in order to facilitate long-term growth. For example, an investor will want to know about how different departments within your business interact with one another, while somebody who will be implementing your product probably only needs more limited information such as design specs because they are not going into production themselves.
A business proposal may provide you with more details of the project, but it does not include information about your company’s operations or future plans.
Examples of Business Plans vs. Business Proposals
- When you give a potential investor your business plan which includes all sorts of information about how we will achieve your goals together as well as the amount of money it’s going to take. The business proposal is for them to write you a check in return for interest/principal payments or a percentage of your company.
- You might be getting partners involved in your business who will help with product development and distribution. You are offering them a business proposal to work together. However, they may request to see your business plan to better understand your goals, potential profitability, and how you plan to reach these goals before deciding to work with you.
- Your existing business has been so successful that you decide to outsource the social media marketing efforts to a freelancer to free up more of your time. The freelancer would provide a business proposal stating their terms and conditions along with the agreed-upon pay arrangement for their services. This change in organizational structure may be noted in your business plan to demonstrate expansion and financial stability to continue growth.
- In your business plan , one of your goals is to grow your client base by 5% each month. You identify potential clients in need of your services or products and send an unsolicited business proposal to demonstrate how your products or services can benefit them in order to develop a new prospective client list.
The business plan is a roadmap for your company’s present and future, while the business proposal has to do with what you are asking someone else for money. Applying this difference into practice can be difficult at times because business plans are often marketed as business proposals. However, it is important to be able to identify the difference between a business plan and business proposal in order to maximize their effectiveness and importance with potential investors or partners.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 21274

- Lee A. Swanson
- University of Saskatchewan
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the purposes for business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- Explain common business plan development guidelines and tools
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process
- Explain the purposes of each element of the business plan development process
- Explain how applying the business plan development process can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan.
Purposes for Developing Business Plans
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. Externally, the most common purpose is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
As the road map for a business’s development, the business plan
- Defines the vision for the company
- Establishes the company’s strategy
- Describes how the strategy will be implemented
- Provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- Provides a plan for the development of the business
- Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical success factors
- Helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and test theories
External Purposes
The business plan provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business. Thus, it is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel.
Business Plan Development Principles
Hindle and Mainprize (2006) suggested that business plan writers must strive to effectively communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future and to project credibility. The liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures much more difficult than for existing businesses. Consequently, business plan writers should adhere to five specific communication principles .
First, business plans must be written to meet the expectations of targeted readers in terms of what they need to know to support the proposed business. They should also lay out the milestones that investors or other targeted readers need to know. Finally, writers must clearly outline the opportunity , the context within the proposed venture will operate (internal and external environment), and the business model (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
There are also five business plan credibility principles that writers should consider. Business plan writers should build and establish their credibility by highlighting important and relevant information about the venture team . Writers need to elaborate on the plans they outline in their document so that targeted readers have the information they need to assess the plan’s credibility. To build and establish credibility, they must integrate scenarios to show that the entrepreneur has made realistic assumptions and has effectively anticipated what the future holds for their proposed venture. Writers need to provide comprehensive and realistic financial links between all relevant components of the plan. Finally, they must outline the deal , or the value that targeted readers should expect to derive from their involvement with the venture (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
General Guidelines for Developing Business Plans
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. Using a standard format helps the reader understand that the you have thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
As You Write Your Business Plan
1. If appropriate, include nice, catchy, professional graphics on your title page to make it appealing to targeted readers, but don’t go overboard.
2. Bind your document so readers can go through it easily without it falling apart. You might use a three-ring binder, coil binding, or a similar method. Make sure the binding method you use does not obscure the information next to where it is bound.
3. Make certain all of your pages are ordered and numbered correctly.
4. The usual business plan convention is to number all major sections and subsections within your plan using the format as follows:
1. First main heading
1.1 First subheading under the first main heading
1.1.1. First sub-subheading under the first subheading
2. Second main heading
2.1 First subheading under the second main heading
Use the styles and references features in Word to automatically number and format your section titles and to generate your table of contents. Be sure that the last thing you do before printing your document is update your automatic numbering and automatically generated tables. If you fail to do this, your numbering may be incorrect.
5. Prior to submitting your plan, be 100% certain each of the following requirements are met:
- Everything must be completely integrated. The written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part.
- All financial statements must be completely linked and valid. Make sure all of your balance sheets balance.
- Everything must be correct. There should be NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors.
- Your document must be well organized and formatted. The layout you choose should make the document easy to read and comprehend. All of your diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions should be easy to find and be located in the parts of the plan best suited to them.
- In some cases it can strengthen your business plan to show some information in both text and table or figure formats. You should avoid unnecessary repetition , however, as it is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once.
- You should include all the information necessary for readers to understand everything in your document.
- The terms you use in your plan should be clear and consistent. For example, the following statement in a business plan would leave a reader completely confused: “There is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units.”
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Developing a Business Plan

An important task in starting a new venture is to develop a business plan. As the phrase suggests, a business plan is a "road map" to guide the future of the business or venture. The elements of the business plan will impact the daily decisions of the business and provide direction for expansion, diversification, and future evaluation of the business.
This publication will assist in drafting your own business plan. It includes a discussion of the makeup of the plan and the information needed to develop a business plan. Business plans are traditionally developed and written by the owner with input from family members and the members of the business team. Business plans are "living" documents that should be reviewed and updated every year or if an opportunity for change presents itself. Reviews reinforce the thoughts and plans of the owner and the business and are a key item in the evaluation process. For an established venture, evaluation determines if the business is in need of change or if it is meeting the expectations of the owners.
Using the Proper Format
The format and appearance of the plan should be as professional as possible to portray your business in a positive manner. When dealing with a lender or possible investor, the plan will be reviewed for accuracy and suggestions for changes to the plan may be offered. The decision to recommend a loan for approval will be largely based on your business plan. Often loan officers will not know a great deal about the proposed venture, but they will know the correct structure of a business plan.
Investors will make their decision based on the plan and the integrity of the owner. For this reason, it is necessary to use a professional format. After loan officers complete their evaluations, the loan committee will further review the business plan and make a decision. The committee members often spend limited time reviewing the document, focusing on the message of the executive summary and financial statements to make their determination. They will refer to other sections of the plan for details and clarification. Because of this, these portions need to be the strongest parts of the plan and based on sound in-depth research and analysis.
Sections of the Business Plan
A business plan should be structured like a book with the title or cover page, followed by a table of contents. Following these two pages, the body of the plan normally appears in this order: executive summary, business mission statement, goals and objectives, background information, organizational matters, marketing plan, and financial plan.
Executive Summary
The executive summary is placed at the front of the business plan, but it should be the last part written. The summary should identify the type of business and describe the proposed business, or changes to the existing business. Research findings and recommendations should be summarized concisely to provide the reader with the information required to make any decisions. The summary outlines the direction and future plans or goals of the business, as well as the methods that will be used to achieve these goals. The summary should include adequate background information to support these recommendations.
The final financial analysis and the assumptions used are also a part of the executive summary. The analysis should show how proposed changes will ensure the sustainability of the current or proposed business. All challenges facing the existing business or proposed venture should be discussed in this section. Identifying such challenges shows the reader that all possibilities have been explored and taken into account during the research process.
Overview, Mission, and Goals and Objectives
This section has three separate portions. It begins with a brief overview that includes a general description of the existing or planned business. The overview is followed by the mission statement of the business. You should try to limit the mission statement to three sentences if possible and include only the key ideas about why the business exists. An example of a mission statement for a produce farm might be: The mission of XYZ Produce is to provide fresh, healthy produce to our customers, and to provide a safe, friendly working environment for our employees. If you have more than three sentences, you should be as concise as possible.
The final portion sets the business's goals and objectives. There are at least two schools of thought about goals and objectives. Goals and objectives should show the reader what the business wishes to accomplish, and the steps needed to obtain the desired results. Conducting a SWOT analysis will assist your team when developing goals and objectives. SWOT in an acronym for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats and is covered more in-depth later in the publication. You may want to include marketing topics in the SWOT or conduct two SWOT analyses, one for the entire business and one for the marketing plan.
Goals should follow the acronym DRIVE, which stands for D irectional, R easonable, I nspiring, V isible, and E ventual. The definitions of DRIVE are:
- Directional: It should guide you to follow your vision.
- Reasonable: You should be able to reach the goal, and it should be related to your business.
- Inspiring: Make sure the goal is positive but should challenge the business to grow into the goal.
- Visible: You and your employees should be able to easily recognize the goal. Goals should be posted where everyone sees them every day.
- Eventual: The goals should focus on the future and be structured to provide motivation to all to strive towards the goals.
Objectives should follow the acronym SMART, which stands for S pecific, M easurable, A ttainable, R ewarding, and T imed. Objectives are the building blocks to achieve the goals and stand for:
- Specific: Each objective should focus on one building block to reach the goal.
- Measurable: You should be able to determine if your progress is going in the right direction.
- Attainable: You should be able to complete the objective with an appropriate amount of work.
- Rewarding: Reaching the objective should be something to celebrate and provide positive reinforcement to the business.
- Timed: You must have a deadline for the objective to be achieved. You do not want to have the objectives linger for too long. Not reaching the objectives delays reaching the goals. Not achieving goals is detrimental to the morale of the business.
Goals and objectives should follow these formats to allow for evaluation of the entire process and provide valuable feedback along the way. The business owner should continually evaluate the outcomes of decisions and practices to determine if the goals or objectives are being met and make modifications when needed.
Background Information
Background information should come from the research conducted during the writing process. This portion should include information regarding the history of the industry, the current state of the industry, and information from reputable sources concerning the future of the industry.
This portion of the business plan requires the most investment of time by the writer, with information gathered from multiple sources to prevent bias or undue optimism. The writer should take all aspects of the industry (past, present, and future) and business into account. If there are concerns or questions about the viability of the industry or business, these must be addressed. In writing this portion of the plan, information may be obtained from your local public library, periodicals, industry personnel, trusted sources on the Internet, and publications such as the Penn State Extension Agricultural Alternatives series . Industry periodicals are another excellent source of up-to-date information. The more varied the sources, the better the evaluation of the industry and the business, and the greater the opportunity to have a viable plan.
The business owner must first choose an appropriate legal structure for the business. The business structure will have an impact on the future, including potential expansion and exit from the business. If the proper legal structure is not chosen, the business may be negatively impacted down the road. Only after the decision is made about the type of business can the detailed planning begin.
Organizational Matters
This section of the plan describes the current or planned business structure, the management team, and risk-management strategies. There are several forms of business structure to choose from, including sole proprietorship, partnership, corporations (subchapter S or subchapter C), cooperative, and limited liability corporation or partnership (LLC or LLP). These business structures are discussed in Agricultural Alternatives: Starting or Diversifying an Agricultural Business .
The type of business structure is an important decision and often requires the advice of an attorney (and an accountant). The business structure should fit the management skills and style(s) of the owner(s) and take into account the risk management needs (both liability and financial) of the business. For example, if there is more than one owner (or multiple investors), a sole proprietorship is not an option because more than one person has invested time and/or money into the business. In this case a partnership, cooperative, corporation, LLC, or LLP would be the proper choice.
Another consideration for the type of business structure is the transfer of the business to the next generation or the dissolution of the business. There are benefits and drawbacks for each type of structure covering the transition of ownership. If the business has a high exposure to risk or liability, then an LLC might be preferred over a partnership or sole proprietorship.
If the business is not a sole proprietorship, the management team should be described in the business plan. The management team should consist of all parties involved in the decisions and activities of the business. The strengths and backgrounds of the management team members should be discussed to highlight the positive aspects of the team. Even if the business is a sole proprietorship, usually more than one person (often a spouse, child, relative, or other trusted person) will have input into the decisions, and so should be included as team members.
Regardless of the business structure, all businesses should also have an external management support team. This external management support team should consist of the business's lawyer, accountant, insurance agent or broker, and possibly a mentor. These external members are an integral part of the management team. Many large businesses have these experts on staff or on retainer. For small businesses, the external management team replaces full-time experts; the business owner(s) should consult with this external team on a regular basis (at least once a year) to determine if the business is complying with all rules and regulations. Listing the management team in the business plan allows the reader to know that the business owner has developed a network of experts to provide advice.
The risk-management portion of the business plan provides a description of how the business will handle unexpected or unusual events. For example, if the business engages in agricultural production, will the business purchase crop insurance? Does the business have adequate liability insurance? Is the business diversified to protect against the unexpected, rather than "putting all its eggs in one basket"? If the business has employees, does the business carry adequate workers' compensation insurance? All of these questions should be answered in the risk-management portion of the business plan. More information on how liability can affect your business and on the use of insurance as a risk-management tool can be found in Agricultural Alternatives: Agricultural Business Insurance and Agricultural Alternatives: Understanding Agricultural Liability . The business structure will also determine a portion of the risk-management strategy because the way that a business is structured carries varying levels of risk to the owner and/or owners. All opportunities carry a degree of risk that must be evaluated, and mitigation strategies should be included in this portion of the plan.
Marketing Plan
Every purchase decision that a consumer makes is influenced by the marketing strategy or plan of the company selling the product or service. Products are usually purchased based on consumer preferences, including brand name, price, and perceived quality attributes. Consumer preferences develop (and change) over time and an effective marketing plan takes these preferences into account. This makes the marketing plan an important part of the overall business plan.
In order to be viable, the marketing plan must coincide with the production activities. The marketing plan must address consumer desires and needs. For example, if a perishable or seasonal crop (such as strawberries) will be produced, the marketing plan should not include sales of locally grown berries in January if the business is in northeastern United States. If the business plans to purchase berries in the off-season from other sources to market, this information needs to be included. In this way, the marketing plan must fit the production capabilities (or the capability to obtain products from other sources).
A complete marketing plan should identify target customers, including where they live, work, and purchase the product or service you are providing. This portion of the plan contains a description of the characteristics and advantages of your product or service. Identifying a "niche" market will be of great value to your business.
Products may be sold directly to the consumer (retail) or through another business (wholesale) or a combination of both. Whichever marketing avenue you choose, if you are starting a new enterprise or expanding an existing one, you will need to decide if the market can bear more of what you plan to produce. Your industry research will assist in this determination. The plan must also address the challenges of the proposed marketing strategy.
Other variables to consider are sales location, market location, promotion, advertising, pricing, staffing, and the costs associated with all of these. All of these aspects of the marketing plan will take time to develop and should not be taken lightly. Further discussion on marketing fruits and vegetables can be found in Agricultural Alternatives: Fruit and Vegetable Marketing for Small-Scale and Part-Time Growers .
SWOT Analysis
An adequate way of determining the answers to business and marketing issues is to conduct a SWOT analysis. The acronym SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Strengths represent internal attributes and may include aspects like previous experience in the business. Experience in sales or marketing would be an area of strength for a retail farm market. Weaknesses are also internal and may include aspects such as the time, cost, and effort needed to introduce a new product or service to the marketplace.
Opportunities are external aspects that will help your business to take off and be sustained. If no one is offering identical products or services in your immediate area, you may have the opportunity to capture the market. Threats are external and may include aspects like other businesses offering the same product in close proximity to your business or government regulations impacting business practices and cost.
Financial Plan
The financial plan and assumptions are crucial to the success of the business and should be included in the business plan. One of the foremost reasons new businesses fail is because they do not have enough start-up capital to cover all expenses to make a profit. The scope of your business will be determined by the financial resources you can acquire. Because of this, you will need to develop a financial plan and create the supporting documents to substantiate it.
The financial plan has its basis in historical data (if you are an existing business) or from projections (for a proposed business). The first issue to address is recordkeeping. You should indicate who will keep the necessary records and how these records will be used. Internal controls, such as who will sign checks and handle any funds, should also be addressed. A good rule to follow for businesses that are not sole proprietorships is having at least two people sign all checks.
The next portion of the financial plan should detail where funding will come from. This includes if (and when) the business will need additional capital, how much capital will be needed, and how these funds will be obtained. If start-up capital is needed, this information should be included in this portion. Personal contributions should be included, along with other funding sources. The amount of money and repayment terms should be listed. One common mistake affecting many new businesses is under-funding at start-up. Many start-up businesses do not evaluate all areas of expense and underestimate the amount of capital needed to see a new business through the development stages (including personal living expenses, if off-farm income is not available).
Typically, a balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and partial budget or enterprise budgets are included in a business plan. More information on agricultural budgets can be found in Agricultural Alternatives: Budgeting for Agricultural Decision Making . These documents will display the financial information in a form that lending institutions are used to seeing. If these are not prepared by an accountant, having one review them will ensure that the proper format has been used.
Financial projections should be completed for at least two years and, ideally, for five years. In agricultural businesses, five-year projections are sometimes difficult to make because of variability in prices, weather, and other aspects affecting production. One way to illustrate these risks is to develop several projection scenarios covering a range of production assumptions. This attention to detail will often result in a positive experience with lenders because they realize that the plan covers several possible circumstances and provides insight into how the business plans to manage risk. More information on financing agricultural businesses can be found in the publication Agricultural Alternatives: Financing Small-Scale and Part-Time Farms .
Financial Statements
To keep personal assets and liabilities separate from business assets and liabilities, it is beneficial to create both business and personal financial statements. A lender will need to see both, but the separation will show how the business will support the family or how the off-farm income will support the business.
Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement is the predicted flow of cash into and out of a business over a year. Cash flow statements are prepared by showing the total amounts predicted for each item of income or expense. This total is then broken down by month to show when surpluses and shortfalls in cash will occur. In this way, the cash flow statement can be used to predict when additional cash is needed and when the business will have a surplus to pay back any debt. This monthly prediction allows the owner(s) to better evaluate the cash needs of the business, taking out applicable loans and repaying outstanding debts. The cash flow statement often uses the same categories as the income statement plus additional categories to cover debt payments and borrowing.
After these financial statements are completed, the business plan writer will have an accurate picture of how the business has performed and can project how the business will perform in the coming year(s). With such information, the owner—and any readers of the business plan—will be able to evaluate the viability of the business and will have an accurate understanding of actions and activities that will contribute to its sustainability. This understanding will enable them to make better informed decisions regarding loans or investments in the business.
Income Statement
The income statement is a summary of the income (revenue) and expenses for a given accounting cycle. If the balance sheet is a "snapshot" of the financial health of the business, the income statement is a "motion picture" of the financial health of the business over a specific time period. An income statement is constructed by listing the income (or revenue) at the top of the page and the expenses (and the resulting profit or loss) at the bottom of the page.
Revenue is any income realized by the sale of crops or livestock, government payments, and any other income the business may have (including such items as fuel tax refunds, patronage dividends, and custom work). Other items impacting revenues are changes in inventory and accounts receivable between the start of the time period and the end—even if these changes are negative.
Expenses include any expense the business has incurred from the production of the products sold. Examples of expenses include feed, fertilizer, pesticides, fuel, labor, maintenance, repairs, insurance, taxes, utilities, and any changes in accounts payable. Depreciation, which is the calculated wear and tear on assets (excluding land), is included as an expense for accounting purposes. Interest is considered an expense, but any principal payments related to loans are not an expense. Repayment of principal is recorded on the balance sheet under "Loans Payable."
As the income statement is created, the desired outcome is to have more income than expenses, so the income statement shows a profit. If not, the final number is shown in parentheses (signifying a negative number). Another name for this financial record is a Profit and Loss Statement. Income statements are one way to clearly show how the farm is making progress from one year to the next and may show a much more optimistic view of sustainability than can be seen by looking at a single year's balance sheet.
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a snapshot of a business’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity at a specific point in time. A balance sheet can be prepared at any time, but is usually done at the end of the fiscal year (for many businesses, this is the end of the calendar year). Evaluating the business by using the balance sheet requires several years of balance sheets to tell the true story of the business’s progress over time. A balance sheet is typically constructed by listing assets on the left and liabilities and owner’s equity on the right. The difference between the assets and liabilities of the business is called the "owner's equity" and provides an estimate of how much of the business is owned outright.
Assets are anything owned by, or owed to, the business. These include cash (and checking account balances), accounts receivable (money owed to the business), inventory (any crops or supplies that the business has stored on farm), land, equipment, and buildings. This may also include machinery, breeding stock, small-fruit bushes or canes, and fruit trees. Sometimes assets are listed as current (those easily converted to cash) and fixed (those that are required for the business to continue). Assets are basically anything of value to the business. Some valuations of assets are not easily determined for items such as breeding stock, small-fruit bushes or canes, and fruit trees and may require the use of a certified appraiser familiar with the items.
Balance sheets may use a market-basis or a cost-basis to calculate the value of assets. A market-basis balance sheet better reflects the current economic conditions because it relies on current or market value for the assets, rather than what those assets originally cost. Market values are more difficult to obtain because of the difficulty in finding accurate current prices of assets and often results in the inflation of the value of assets. Cost-basis balance sheets are more conservative because the values are often from prior years. For example, a cost-basis balance sheet would use the original purchase price of land, rather than what selling that land would bring today. Because purchase records are easily obtained, constructing a cost-basis balance sheet is easier. Depreciable assets such as buildings, tractors, and equipment are listed on the cost-basis balance sheet at purchase price less accumulated depreciation. Most accountants use the cost-basis balance sheet method. Whether you choose to use market-basis or cost-basis, it is critical that you remain consistent over the years to allow for accurate comparison.
Liabilities are what the business owes on the date the balance sheet is prepared. Liabilities include both current liabilities (accounts payable, any account the business has with a supplier, short-term notes, operating loans, and the current portion of long-term debt), which are payable within the current year, and noncurrent liabilities (mortgages and loans with a term that extends over one year).
Owner's equity is what remains after all liabilities have been subtracted from all assets. It represents money that the owner(s) have invested in the business, profits that are retained in the business, and changes caused by fluctuating market values (on a market-basis balance sheet). Owner’s equity will be affected whenever there are changes in capital contributed to the business or retained earnings, so if your practice is to use all earnings as your "paycheck," rather than reinvesting them in the business, your owner's equity will be impacted. On the balance sheet, owner’s equity plus liabilities equals assets. Or stated another way, all of the assets less the amount owed (liabilities) equals the owner’s equity (sometimes referred to as "net worth"). Owner's equity provides the "balance" in a balance sheet.
Putting It All Together
After the mission, background information, organization, and marketing and financial plans are complete, an executive summary can then be prepared. Armed with the research results and information in the other sections, the business will come alive through this section. Research results can be included in an appendix if desired. The next step is to share this plan with others whose opinions you respect. Have them ask you the hard questions—make you defend an opinion you have expressed or challenge you to describe what you plan to do in more detail. Often, people are hesitant to share what they have written with their families or friends because they fear the plan will not be taken seriously. However, it is much better to receive constructive criticism from family and friends (and gain the opportunity to strengthen your plan) than it is to take it immediately to the lender, only to have any problems pointed out and receive a rejection.
Once all parts of the business plan have been written, you will have a document that will enable you to analyze your business and determine which, if any, changes need to be made. Changes on paper take time and effort but are not as expensive as changing a business practice only to find that the chosen method is not viable. For a proposed venture, if the written plan points to the business not being viable, large sums of money have not been invested and possibly lost. In short, challenges are better faced on paper than with investment capital.
Remember, a business plan is a "road map" that will guide the future of the business. The best business plan is a document in continual change, reacting to the influence of the outside world on the business. Having the basis of a written plan will give you the confidence to consider changes in the business to remain competitive. Once the plan is in place, the business will have a better chance of future success.
For More Information
Publications.
Abrams, R. The Successful Business Plan: Secrets and Strategies (Successful Business Plan Secrets and Strategies) . Palo Alto, Calif.: Planning Shop, 2014.
Becker, J. C., L. F. Kime, J. K. Harper, and R. Pifer. Agricultural Alternatives: Understanding Agricultural Liability . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2011.
Dethomas, A., and L. and S. Derammelaere. Writing a Convincing Business Plan (Barron's Business Library) . Hauppauge, N.Y.: Barron's Educational Series. 2015.
Dunn, J., J. K. Harper, and L. F. Kime. Agricultural Alternatives: Fruit and Vegetable Marketing for Small-scale and Part-time Growers . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2009.
Grant, W. How to Write a Winning Business Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide for Startup Entrepreneurs to Build a Solid Foundation, Attract Investors and Achieve Success with a Bulletproof Business Plan (Business 101). Independently published. 2020.
Harper, J. K., S. Cornelisse, L. F. Kime, and J. Hyde. Agricultural Alternatives: Budgeting for Agricultural Decision Making . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2019.
Kime, L. F., J. A. Adamik, E. E. Gantz, and J. K. Harper. Agricultural Alternatives: Agricultural Business Insurance . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2019.
Kime, L. F., S. Cornelisse, and J. K. Harper. Agricultural Alternatives: Starting or Diversifying an Agricultural Business . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2018.
Lesonsky, R. Start Your Own Business Fifth Edition: The Only Start-Up Book You'll Ever Need. Irvine, Calif.: Entrepreneur Media Inc., 2010.
Shelton, H. The Secrets to Writing a Successful Business Plan: A Pro Shares a Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Plan That Gets Results. Rockville, Md.: Summit Valley Press, 2017.
Stokes, J. S., G. D. Hanson, J. K. Harper, and L. F. Kime. Agricultural Alternatives: Financing Small-scale and Part-time Farms . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2005.
Online Course
Starting a Farm: Business Planning
Periodicals
- American Agriculturist Magazine Farm Progress Companies Inc. 5482 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 260 Los Angeles, CA 90036
- Businessweek Magazine
- Fortune Magazine
- Kiplinger's Personal Finance
- Money Magazine
- BizPlanit - Virtual Business Plan
- PA Business One-Stop Shop
- Small Business Administration
- SCORE—volunteer business assistance
- The Pennsylvania Department of Revenue Starting a Business in Pennsylvania—A Guide to Pennsylvania Taxes
- The Pennsylvania State University Agricultural Alternative Tools
- The Pennsylvania State University Conducting a SWOT Analysis
- The Pennsylvania State University Happy Valley Launch Box
Prepared by Lynn F. Kime, senior extension associate; Linda Falcone, extension educator in Wyoming County, Jayson K. Harper, professor of agricultural economics; and Winifred W. McGee, retired extension educator in Dauphin County
Additional financial support for this publication was provided by the Risk Management Agency of the United States Department of Agriculture and the Pennsylvania Department of Agriculture.
This publication was developed by the Small-scale and Part-time Farming Project at Penn State with support from the U.S. Department of Agriculture-Extension Service.
You may also be interested in ...

A Guide to Farming in Pennsylvania: Planning

Starting a New Agricultural Business

Starting or Diversifying an Agricultural Business

Conducting a SWOT Analysis

Choosing a Legal Structure for Your Agriculture Business

Cooperatives

Example Business Plan

Obtaining a Loan - The C's of Credit

Opportunities for Veterans in Pennsylvania Agriculture

Milk Production Records for Management Control
Personalize your experience with penn state extension and stay informed of the latest in agriculture..
Select Region or Brand
- New Orleans, LA
- Long Island, NY
- Oklahoma City, OK
- Rochester, NY
- Lehigh Valley, PA
- Mecklenburg, NC
- South Carolina
- Columbia, SC
- Charleston, SC
- Greenville, SC
- Color Magazine
- Massachusetts
- North Carolina
- Rhode Island
- Milwaukee, WI
- Designers Today
- Furniture Today
- Gifts & Decorative Accessories
- Home Accents Today
- Home Furnishings News
- Home Textiles Today
- Manage Print or Online Subscription
- Manage Email Subscription
Upcoming Event
- Executive Circle Awards
- Leads & Data Center
- About Leads & Data Center
- Add My Business
- Contact Leads & Data Center
- Classifieds
- Public Notice
- Reader Rankings
- Influencers
- Marketing Tips
- Free eGuide
- Editorial and Special Products Calendar
- Advertising in Economic Uncertainty – A Marketing Guide
- Food Business
- Law & Government
Real Estate
- Priciest Home Sales
- Small Business
- Editors Picks
- Movers & Shakers
- Influencer Lists
- Influencer Recommendation Form
- Special Publications
- Digital Edition
- Diversity in Business Awards
- Healthcare Forum
- Real Estate, Architecture & Engineering
- Empowering Women
- 30 Under Thirty
- Corporate Citizenship
- Top 50 Women in Business
- Hall of Fame
- Business and Finance Awards
- Leadership in Law
- 40 Under Forty
- Best Places to Work
- Advertise With LIBN
- Print Advertising
- Event Advertising
- Classified Advertising
- Plaques & Permissions
- Event Calendar
- Networking Events
- Editorial Calendar
- Digital Edition Archives
- Special Pub Archives
- Leads & Data
- Back Issues
Proposed $35M Hauppauge project adds community sports facility
David Winzelberg // April 2, 2024 //

Rendering of the proposed warehouse/sports facility in Hauppauge. / Courtesy of Barone Management
Share this!
Related Content

Long Island hotel property trades for $14M
The three-story, 48,000-square-foot hotel has 82 guest rooms.
April 2, 2024

Complete Streets Summit advocates for pedestrian safety
The 16th annual summit will focus on improving safety for pedestrians and cyclists along some of the area’s [...]
April 1, 2024

Backyard Masters expanding with new Roosevelt Field showroom
The company leased a 12,816-square-foot space at the Garden City mall.

Foodservice firm expands with $8.35M Edgewood deal
The company will be relocating from Hauppauge with the help of a creative real estate transaction.
March 29, 2024

Inked: Recent LI real estate deals
The latest transactions in Long Island commercial real estate...
March 28, 2024

Former Huntington Station bank property trades for $2.115M
The 4,435-square-foot building is on .77 acres.
Sponsored Content

A CFO Explains Why Every Business Needs 1Password
As the Chief Financial Officer of 1Password, I’d love to share how 1Password t[...]
Uncategorized

Unforgettable Experiences Await at UBS Arena
Boutique hospitality has found a home for live entertainment in New York. The me[...]

How to plan for Anticipated Economic Growth in 2024
With the anticipation of reduced interest rates and lower inflation, businesses [...]
LIBN Daily Newsletter
Sign up for your daily digest of Long Island Business News.
- By signing up you agree to our
- Privacy Policy
Editor’s Picks

Long Island Business News announces 2024 Executive Circle Awards
Listen to this article Long Island Business News announced that it has selected this year’s winner[...]

Church of Scientology buys Long Island office property for $15.2M
The 62,500-square-foot office building is on 5.5 acres.

Women Who Lead 2024
March 8, 2024, marks a global celebration of women’s achievements. This special section honors out[...]

Long Island Business News announces 2024 Diversity in Business Awards
Long Island Business News announced this morning it has selected this year’s winners of the 2024 D[...]

Bingo Wholesale opening its first Long Island store
The bulk grocery concept that’s been called the “kosher Costco” is expected to open in the sec[...]

Developers plan to donate the sports facility to local youth sports groups.

The 16th annual summit will focus on improving safety for pedestrians and cyclists along some of the[...]

Weekly Edition
On Our Island 3/29/2024
Helpful hires: recruiting and retaining staff at nonprofits
On Our Island 3/22/2024
Privacy Overview
Steward Health Care has deal to sell doctor network to UnitedHealth
Insurance giant’s optum unit is already a major player in physicians’ offices.

Troubled hospital operator Steward Health Care, grappling with a financial crisis that’s engulfed its eight Massachusetts hospitals, has struck a deal to sell its nationwide physician network to insurance giant UnitedHealth’s Optum unit.
The proposed sale of the doctors group, called Stewardship Health, is part of Steward’s plan to shore up its finances and bolster its nationwide network of 33 hospitals after the Dallas-based company last year fell behind in paying bills and rents.
The sale will be reviewed closely in Massachusetts, where policy makers are looking for a potential leverage point to force Steward to plow the proceeds into its struggling hospitals and to prevent closure of crucial facilities. Already, some elected officials who have repeatedly accused for-profit Steward of prioritizing shareholders over public health are sounding warnings about the sale of the physicians practice.
Advertisement
“After years of gross profiteering and mismanagement, Steward’s latest plan raises more serious questions about the future of the Massachusetts health care system,” Senator Elizabeth Warren said in a statement. “My top priority is ensuring Steward’s Massachusetts hospitals remain open. But Steward executives have no credibility, and I am concerned that this sale will not benefit patients or health care workers, or guarantee the survival of these facilities.”
On Tuesday, a subsidiary of Optum, called Collaborative Care Holdings, filed notice with the Massachusetts Health Policy Commission over the sale. A price tag was not included in documents filed with the state, and Optum officials did not immediately respond to comment.
Steward did not respond to requests for comment.
The commission’s executive director, David Seltz, said the agency would examine the impact of the deal on health care costs, quality, access, and equity before the sale can be completed. The commission will have 30 days after receiving the required information to assess the impacts of the transaction, but could conduct a more extensive review. If it finds the sale would worsen quality or drive up health care costs, the commission can refer its findings to the Massachusetts attorney general.
The deal may also be scrutinized by other state regulators or federal antitrust authorities.
“This is a significant proposed change involving two large medical providers, both in Massachusetts and nationally, with important implications for the delivery and cost of health care across Massachusetts,” Seltz said.
But Julie Pinkham, executive director for the Massachusetts Nurses Association, said state officials might not have enough authority to stop or influence the deal.
”While it is essential that the Health Policy Commission conduct a thorough review of this sale and its impact on the Commonwealth, the key question is if the HPC or other agencies of the state have the requisite authority to reject the proposal or assign any obligations to the proposal to protect the public,” Pinkham said in a statement.
Under the proposed deal, Optum would acquire Stewardship Health, a Steward affiliate that includes the company’s primary care doctors and other clinicians in nine states, as well as its contracting network for physicians. It was unclear whether the sale might alter the value of the hospitals, which Steward has also been trying to sell.
Massachusetts political and community leaders said they worried about whether the deal would further weaken Steward hospitals in the state because its former physicians could soon refer patients to other hospitals.
Boston City Councilor Liz Breadon, who represents the Brighton neighborhood of Steward’s flagship Massachusetts hospital, St. Elizabeth’s, said she wants to study the Optum deal but is worried that UnitedHealth may be “cherrypicking” Steward’s more profitable assets at the expense of vital community hospitals.
”We need quality hospitals that deliver comprehensive care,” Breadon said. “But I’m not sure they want to take hospitals.”
Noting that the hospital buildings are saddled with rent obligations to an out-of-state landlord, Medical Properties Trust, she said, “When you don’t own the buildings and you’re going to be liable for a lot of rent,” the hospitals become less attractive to another prospective operator.
Others worried about the growing market power of Optum.
“Optum is particularly aggressive, and they’re growing their footprint in Massachusetts in a significant way,” said John McDonough, professor at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. “It’s not a good sign with where we’re headed with Steward, and we need to hear from state government about what their strategy is, what are they trying to achieve.”
David E. Williams, president of Health Business Group, a Boston management consulting firm, said Optum is focused on buying more profitable physicians practices rather than brick-and-mortar hospitals.
“They don’t want the facilities,” Williams said. “They want to control more primary care, control the patient flow.”
The purchase of Stewardship Health could potentially be challenged on antitrust grounds, since Optum’s doctor network — the largest employer of physicians nationally — is also one of the largest in Massachusetts.
The Justice Department is investigating the relationship between UnitedHealth’s insurance unit and its doctor networks for potentially anticompetitive practices, the Wall Street Journal reported last month.
Optum has already expanded its Massachusetts presence through two major acquisitions. In 2018, Optum bought Reliant Medical Group, a nonprofit network with more than 500 care providers, for $28 million plus agreements to pour more resources into the network. And in 2022, Optum paid $236 million for nonprofit Atrius Health and its network of close to 1,000 doctors and providers.
Nationwide, the unit includes 90,000 doctors, a major pharmacy benefits manager, surgery centers, and a health data business.
Optum’s Change Healthcare unit, which processes insurance payments at pharmacies and other providers has also caused headaches in Massachusetts. Due to a cyberattack last month, Change was unable to process payments , forcing doctors and patients to scramble for coverage of prescriptions.
Steward Health was formed in 2010 when chief executive Ralph de la Torre led an effort to convert what was then a chain of financially shaky Catholic hospitals to a for-profit system backed by a private equity firm. In the years since, the company, with de la Torre at the helm, sold Steward’s hospital buildings to Medical Properties Trust, freeing capital to expand nationally but saddling its hospitals with large rent payments.
He also moved Steward’s headquarters from Boston to Dallas, bought out its private equity investor, and went on a personal spending spree , buying a Dallas mansion, a super yacht, and a high-end sports fishing boat.
Steward’s financial crisis has prompted lawsuits from suppliers and the loss of leased medical equipment. In October, a woman died after giving birth at St. Elizabeth’s , where a vital device called an embolism coil had been repossessed by creditors.
Last month, Steward obtained new loans from its landlord, MPT, and other creditors as part of a plan that depended on selling assets such as its physician network. Other hospital operators in Massachusetts are also in the running to take over Steward facilities . Governor Maura Healey and other politicians have called for Steward to leave the state.
Aaron Pressman can be reached at [email protected] . Follow him @ampressman . Jessica Bartlett can be reached at [email protected] . Follow her @ByJessBartlett . Robert Weisman can be reached at [email protected] .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
How a New Rule Could Change the Way Advisers Handle Your Retirement Money
The Labor Department’s latest push for a new fiduciary rule would protect investors’ retirement savings and require financial services providers to change.

By Tara Siegel Bernard
It seems like an issue everyone can agree on: Financial professionals should be required to handle our retirement money with the utmost care, putting investors’ interests first.
But that type of care comes in degrees, and deciding exactly how far advisers should go has been the center of heated debate for nearly 15 years, pitting financial industry stakeholders, who argue their existing regulatory framework is enough, against the U.S. Labor Department, the retirement plan regulator, which says there are gaping holes.
The issue has re-emerged as the department prepares to release a final rule that would require more financial professionals to act as fiduciaries — that is, they’d be held to the highest standard, across the investment landscape, when providing advice on retirement money held or destined for tax-advantaged accounts, like individual retirement accounts.
Most retirement plan administrators who oversee the trillions of dollars held in 401(k) plans are already held to this standard, part of a 1974 law known as ERISA, which was established to oversee private pension plans before 401(k)s existed. But it doesn’t generally apply, for example, when workers roll over their pile of money into an I.R.A. when they leave a job or retire from the work force. Nearly 5.7 million people rolled $620 billion into I.R.A.s in 2020, according to the latest Internal Revenue Service data.
The Biden administration’s final regulation, which will be released this spring, is expected to change that and patch other gaps: Investment professionals selling retirement plans and recommending investment menus to businesses would also be held to its fiduciary standard, as would professionals selling annuities inside retirement accounts.
“It shouldn’t matter whether you’re getting advice on an annuity, any kind of annuity, a security — if it’s advice about your retirement, that should have a high standard that applies across the board,” said Ali Khawar, the Labor Department’s principal deputy assistant secretary of the Employee Benefits Security Administration.
The evolution of brokers’ and advisers’ duties to American investors stretches back decades. But the journey to extend more stringent protections over investors’ retirement money began during the Obama administration, which issued a rule in 2016 that was halted shortly after President Donald J. Trump took office and was never fully enacted : It was struck down in 2018 by an appeals court in the Fifth Circuit. That rule went further than the current one — it required financial firms to enter contracts with customers, which allowed them to sue, something the court argued went too far.
The Biden administration’s plan — and the final rule could differ from the initial October proposal — would require more financial professionals to act as gold-standard fiduciaries when they’re making an investment recommendation or providing advice for compensation, at least when holding themselves out as trusted professionals.
The standard also kicks into play when advisers call themselves fiduciaries, or if they control or manage someone else’s money.
As it stands, it is much easier to avoid fiduciary status under the ERISA retirement law. Investment professionals must meet a five-part test before they are held to that standard, and one component states that professionals must provide advice on a regular basis. This means that if an investment professional makes a one-time recommendation, that person is off the hook — even if the advice was to roll over someone’s lifetime savings.
Though investor protections have improved in recent years, there isn’t a universal standard for all advisers, investment products and accounts.
The varying “best interest” standards can be dizzying: Registered investment advisers are fiduciaries under the 1940 law that regulates them, but even their duty isn’t viewed as quite as stringent as an ERISA fiduciary. Professionals at brokerage firms may be registered investment advisers, to whom the 1940 fiduciary standard applies — or registered representatives , to whom it does not. In that case, they’re generally held to the Securities and Exchange Commission’s best interest standard. Confused? There’s more.
Annuity sellers are largely regulated by the state insurance commissioners, but legal experts say their best interest code of conduct, adopted in 45 states , is a weaker version than the one for investment brokers. Variable annuity and other products, however, fall within the domains of both the S.E.C. and the states.
Stakeholders in the financial services and annuities industries say the current standards that apply are enough. This includes Regulation Best Interest , enacted by the S.E.C. in 2019, which requires brokers to act in their customers’ best interests when making securities recommendations to retail customers. They argue that the more stringent ERISA standard would cause customers to lose access to advice (though comprehensive lower-cost advice from fiduciaries has become more accessible in recent years).
The S.E.C.’s adoption of Regulation Best Interest “requires all financial professionals subject to the S.E.C.’s jurisdiction to put their clients’ interest first — to not make recommendations that line their own pockets at the expense of their client,” said Jason Berkowitz, chief legal and regulatory affairs officer at the Insured Retirement Institute, an industry group , during a House hearing about the rule in January.
But there is enough of a difference between the different best interest standards and ERISA fiduciary status that firms take pains to make disclosures on their websites that they aren’t that kind of fiduciary.
On its website, Janney Montgomery Scott, a financial services firm in Philadelphia, said fiduciary status was “highly technical” when it came to retirement and other qualified accounts and depended on the services chosen. “Unless we agree in writing, we do not act as a ‘fiduciary’ under the retirement laws,” the firm said, referring to ERISA, “including when we have a ‘best interest’ or ‘fiduciary’ obligation under other federal or state laws.”
“It would be unreasonable to expect ordinary retirement investors to understand the implications of these disclosures,” said Micah Hauptman, director of the Consumer Federation of America, a nonprofit consumer association.
Under the latest proposal, fiduciaries must avoid conflicts of interest. That means they can’t provide advice that affects their compensation, unless they meet certain conditions to ensure investors are protected — that includes putting policies in place to mitigate those conflicts. Disclosing conflicts alone isn’t enough, department officials said.
“Our statute is very anti-conflict in its DNA,” Mr. Khawar of the Labor Department said. “There are ways that we’re going to expect you to behave to ensure that the conflict doesn’t drive the decision that you make.”
Kamila Elliott, the founder and chief executive of Collective Wealth Partners , a financial planning firm in Atlanta whose clients include middle-income to high-earning Black households, testified at a congressional hearing in favor of the so-called retirement security rule. Ms. Elliott, who is also a certified financial planner, said she had seen the effects of inappropriate advice through her clients, who came to her after working with annuity and insurance brokers.
One client was sold a fixed annuity in a one-time transaction when she was 48. She invested most of her retirement money into the product, which had an interest rate of less than 2.5 percent and a surrender period of seven years. If she wanted to allocate any of that money in the market, which Ms. Elliott felt was more appropriate for her age and circumstances, she would owe a penalty of more than 60 percent of her retirement assets.
“A one-time and irrevocable decision as to whether and how to roll over employer-sponsored retirement assets may be the single most important decision a retirement investor will ever make,” she said before a House committee in January.
Another client who had just $10,000 in an individual retirement account was sold a whole life insurance policy with an annual premium of $20,000 — something most average investors cannot keep up with, causing them to lose the policies before they can benefit from them.
“For many investors, it would not be wise to put your entire retirement portfolio in an insurance product,” she said.
Jason C. Roberts, chief executive of the Pension Resource Institute, a consulting firm for banks, brokerage and advisory firms, said he expected that financial services providers would need to change certain policies to adhere to the new rule, such as making the compensation more level across products, so advisers would not be paid more for making certain recommendations, and curb certain sales incentives and contests.
“It’s really going to hit the broker-dealers,” he said, adding that parts of the annuity industry may be more affected.
Labor Department officials said they took industry stakeholder and other comments into consideration when drafting the final rule, though they declined to provide details.
After the White House’ s Office of Management and Budget completes its review of the final rule, it could be published as soon as next month.
Given the rule’s history, that may not be the end of the road. Legal challenges are expected, but fiduciary experts say regulators devised the rule with that in mind.
Arthur B. Laby, vice dean and professor at Rutgers Law School, said the court that voided the Obama-era rule did not recognize the societal changes that had affected the market for retirement advice.
In her opinion on behalf of the majority, the judge argued that when Congress enacted ERISA — in 1974 — it was well aware of the differences between investment advisers, who are fiduciaries, and stockbrokers and insurance agents, who “generally assumed no such status in selling products to clients.” That’s why, in part, the court argued fiduciary status shouldn’t apply to brokers now.
But times have changed. “Today,” Mr. Laby said, “many brokers function as advisers through and through.”
The latest proposal acknowledges that: If a professional making a recommendation can be viewed as someone with whom an investor has a relationship of trust and confidence — whether a broker or an insurance agent — that person would be considered a fiduciary.
“A relationship of trust, vulnerability and reliance,” Mr. Laby said, “calls for the protections afforded by a fiduciary duty. ”
Tara Siegel Bernard writes about personal finance, from saving for college to paying for retirement and everything in between. More about Tara Siegel Bernard
Let Us Help You Plan for Retirement
The good news is that we’re living longer. the bad news is you need to save for all those future retirement years. we’re here to help..
For a growing number of older Americans, signing up for a mortgage that is most likely to outlive them makes good economic sense. But there are risks to consider .
If you’re on Medicare, you could save money on prescription drugs this year — in many cases, by thousands of dollars. Here’s why .
Entering your 40s can throw you into an emotional tailspin — one that may lead you to spend more and jeopardize your nest egg. Here is how to avoid that .
It’s difficult to know when to get help managing finances after you retire . Communicating with loved ones, even when you don’t want to, is the first step.
These days, many Americans thinking about retiring feel the stakes are higher than ever. We sought the advice of financial planners on some of the most pressing questions.
Retirement plan administrators are noting an uptick in 401(k) hardship withdrawals . But taking that money out can harm your future financial security.
Canberra Liberals' proposed public transport plan would see a busway replace light rail with locally built electric buses
Dedicated bus lanes instead of light rail to Woden, extra rapid routes and hundreds of additional, locally-built electric buses are all part of the Canberra Liberals' proposed public transport plan.
The party's leader Elizabeth Lee has long vowed to axe Stage 2B of the light rail project from Commonwealth Park to Woden , which they now claim could cost more than $5 billion to build.
The ACT government hasn't revealed the cost of the project — which they expect will be built over about five years from 2028 — arguing it can't be confirmed while planning, contract negotiations and approval processes are underway.
Ms Lee said, that if her party wins government in the coming ACT election, it'll still honour the contract signed for Stage 2A of light rail from Alinga Street in the city to Commonwealth Park.
But instead of extending the line further south, she argues new and reinstated bus lanes to Woden – to be completed by late 2027 – along with additional rapid routes, would be a quicker way to deliver public transport improvements across the city.
"Through a number of major capital works projects such as the City to Woden transport corridor, a new Civic transport interchange and a northside bus depot, we will prioritise a bus system that will adapt to Canberra's growing population," the policy states.
"The Canberra Liberals will implement a range of transport improvements across the ACT with more reliable, frequent, and direct bus routes on rapid, local, school and Xpresso services seven days a week, backed by a legislated service guarantee."
That guarantee, to be legislated within 12 months of the report from a review of the ACT transport network, would include rapid services at least every 15 minutes from 7am to 7pm, seven days a week and local services at least every 30 minutes — with increased frequency during peak times.
The policy also commits to extending the dedicated busway to Mawson by 2028 and trialling on-demand local area services.
"The busway will also link key employment and recreation precincts in the City, Acton Waterfront, Commonwealth Park, Adelaide Avenue corridor and the Woden Town Centre," the policy states.
"Priority works will speed up travel times for people travelling to the City from Woden, Weston Creek, Molonglo and Tuggeranong. Commuters will no longer need to change buses to complete their journey.
"We will reduce the number of stop-starts at traffic lights with bus priority along dedicated bus lanes and roadways."
Under the plan, a "free travel zone" would be established around the city, while fares would be capped weekly at $25 for adults for an estimated saving of between $5.50 and $19.70 weekly for a regular commuter.
"The weekly cap would also encourage people to change from driving their car and save on car parking," the policy says.
"This policy will encourage use of public transport off-peak and on the weekends, as weekend usage would essentially become free for weekday commuters."
The ACT already has about a dozen electric buses operating in its fleet and has signed a contract to take delivery of 90 additional vehicles by 2026 .
Work is also underway to upgrade the grid infrastructure for the new Woden and existing Tuggeranong bus depots to charge up to 300 vehicles .
But the Canberra Liberals argue 500 new buses will be needed over the next decade to modernise the fleet and account for population growth.
Ms Lee said those buses could be assembled locally.
"Our plan is to assemble our electric buses for Canberrans, by Canberrans, which will create local jobs," Ms Lee said.
"I know a lot of people have always looked at Canberra and said it's too small for this kind of thinking but, you know, Tasmania is doing it and I don't see any other reason why we couldn't give it a go as well."
The Liberals also propose investigating the use of "high-capacity electric buses".
A new bus timetable
A new Saturday bus timetable will begin this week after Transport Canberra staff locked in a new enterprise bargaining agreement with the ACT government last month, which includes incentives for permanent drivers and transport officers to work weekend shifts .
Transport Canberra says the new timetable will increase local bus frequency on Saturdays , extending hourly services from first service in the morning until 6pm, while rapid bus services will continue to run every 15 to 30 minutes across the entire weekend.
The government has previously argued its focus has been on the reliability of services over frequency on weekends, amid longstanding issues with weekend rostering.
But the opposition leader said services have been unsatisfactory, vowing to focus on attracting and retaining bus and light rail vehicle drivers.
"We're going to make sure we provide the best work experience that we can attract and retain — importantly — bus drivers and other Transport Canberra workers," Ms Lee said.
"It is about making sure that we provide a valuable service for the Canberra community, and making sure that we have an incredibly dedicated team within Transport Canberra is a key aspect of that."
Ms Lee said the proposal will go through the ACT Treasury costings process in the lead-up to the election.
She also pointed out Chief Minister Andrew Barr will deliver another territory budget before the October poll.
"We have done the legwork in terms of costing for this policy and what we have is a $450 million package – but that will of course be dependent on those factors," Ms Lee said.
'Cities are not built on bus networks': Barr
Mr Barr was scathing of the Liberals' plan.
"This is the sort of public transport announcement you make when you are not really committed to public transport," Mr Barr said in a statement.
"The Liberal policy will not deliver the public transport network Canberra will need as we grow beyond half a million people in the next few years."
He said the ACT already had buses running on transit lanes from Woden to Civic.
"Canberrans would see no housing benefits, job opportunities or economic gains that light rail has delivered for our city," he said.
"The world's greatest cities are not built on bus networks. They all have mass transit."
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
'the economics do not add up': why the canberra liberals plan to dump light rail to woden if elected.
- Electric Vehicles
- Public Transport
- State and Territory Government
Joint venture of Venezuela's PDVSA, Chevron launches new drilling plan

- Chevron Corp Follow
- Petroleos de Venezuela SA Follow
- PetroIndependencia, S.A. Follow
The Reuters Power Up newsletter provides everything you need to know about the global energy industry. Sign up here.
Reporting by Deisy Buitrago; Editing by Christian Schmollinger
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

US senator urges Biden to review alleged Nippon Steel ties to China
The head of the U.S. Senate Banking Committee on Tuesday urged the White House to scrutinize the relationship between Nippon Steel and the Chinese steel industry, citing national security concerns amid bipartisan opposition in Congress to the Japanese company's $14.9 billion deal to acquire U.S. Steel Corp .

Trump's proposed tariff would cost the average American household an extra $1,500 a year, left-leaning think tank says
- Trump's proposed import tariff would cost an extra $1,500 annually for Americans, according to a left-leaning think tank.
- The Center for American Progress Action Fund says this will fail to boost US manufacturing and jobs.
- Trump has championed his tax plan as favoring US interests over China, but the think tank argues he misunderstands tariffs.

Trump's proposed import tariff would tack on an extra $1,500 per year for Americans, says a left-leaning Washington think tank.
The former president floated his plan to impose a 10% tariff on every imported foreign item if he were to move back to the White House, but a recent Center for American Progress analysis shows that his plan would burden households with extra annual costs.
Broken down by sectors, Trump's tax package includes a $90 increase on food, a $90 boost on prescription drugs, and a $120 spike on oil and petroleum products.
Related stories
"This tax increase would drive up the price of goods while failing to significantly boost U.S. manufacturing and jobs," analysts Brendan Duke and Ryan Mulholland wrote in a note.
The think tank estimated Americans will face a whopping $3.2 trillion influx of foreign goods. With a 10% tariff, that'd be an extra $300 billion in taxes on goods, roughly translating into $1,700 per household in the tariff's debut year.
"Middle-income U.S. households — those in the 40th to 60th percentile of the income distribution — consume about 85 percent as much as the average household according to the Consumer Expenditure Surveys, which suggests a roughly $1,500 tax increase for the typical household," analysts wrote, adding that these households would keep footing the bill for the tax as long as the tariff stays put.
The Republican presidential candidate championed his tax plan as prioritizing US interests over foreign nations , particularly China, but the think tank weighed that his rationale "shows a complete misunderstanding of how tariffs actually work."
"Tariffs are a tax levied on U.S. importers when their purchased product crosses into the US market. These importers are usually domestic companies that import products for distribution to US consumers, and no Chinese company falls within the top 10 importers," the note added.
On top of that, the analysis said the tariff would raise taxes by $610 per average American household, impacting crucial industrial supplies and capital goods vital for domestic production and exports. Furthermore, it would undermine US exporters' competitiveness against foreign counterparts, reliant as they are on imports for domestic production.
Watch: The biggest revelations from Trump's tax returns
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the overall vision, strategy and goals of your business. In contrast, a business proposal is a targeted pitch to a specific client or ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
A business proposal is a document designed to outline a business plan to convince potential client, investor or partner to engage in a business agreement with you or your company. It's basically a sales pitch in writing to persuade potential clients to show them benefits of working with you or your company for their business success.
Differences between a business proposal and a business plan. A business proposal is not the same as a business plan.This is the most common misconception, but while there are areas of overlap (like your executive summary) the two are different.. That being said, you can certainly pull information from your business plan while writing your business proposal—in fact, that's a great way to start.
Here's an example of what a business proposal template looks like when done right: 2. Explain your "why" with an executive summary. The executive summary details exactly why you're sending the proposal and why your solution is the best for the prospective client. Specificity is key here.
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
1. Create a cover page. This section of a business proposal includes basic information like your company's name and contact information, your company logo, your client's name, and contact information, the date, and a title. A strong title page makes the project proposal look neat, organized, and well put together.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Business Proposal FAQs Q. What Is the Difference Between a Business Proposal and a Business Plan? A business proposal is a document crafted to persuade a prospective client to choose a company for a particular task or project. It outlines the specific project or service, pricing, deliverables and the value the company can provide.
A business proposal is a document that aims to secure a business agreement. Whether printed or digital, a business proposal is written by a business and offered to a prospective customer. In many cases, the prospective customer is also a business that's looking for the best B2B solution. The purpose of a business proposal varies.
If you need to showcase more extensive data sets, try Visme's 20+ types of charts and graphs, including pie charts, bar graphs, line graphs, scatter plot and more. 17. SaaS Startup One Pager Business Proposal Example. Customize this template and make it your own! Edit and Download.
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
A business proposal is very different from a business plan, because it is typically written to clarify a paid engagement between two companies. This might be a short project or a long contract. A business plan, on the other hand, is typically an internal document crafted to chart a businesses path forward towards goals, such as market expansion ...
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. A business plan is a document that clearly spells out how a business intends to realize its objectives and goals, while a business proposal is a sales document that a business entity uses to request a contract from a client.
The terms "business plan" and "business proposal" are sometimes used interchangeably, however, they are very different. The main difference between a business plan and a business proposal is that a business plan documents your growth strategy while a business proposal is a specific ask for someone to take an action you desire (e.g., buy your product/service, invest in your company ...
Create a Brief Business Plan. Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business.
As the road map for a business's development, the business plan. Defines the vision for the company. Establishes the company's strategy. Describes how the strategy will be implemented. Provides a framework for analysis of key issues. Provides a plan for the development of the business. Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical ...
Developing a Business Plan. An important task in starting a new venture is to develop a business plan. As the phrase suggests, a business plan is a "road map" to guide the future of the business or venture. The elements of the business plan will impact the daily decisions of the business and provide direction for expansion, diversification, and ...
A plan to build a new $35 million warehouse in Hauppauge has added a youth sports component to be donated to the community. Rob Mannino, Scott Barone and Devin Kulka. / Photo by Judy Walker The ...
Under the proposal, the flat rate would be $24.15 per month, which would reduce the price of a unit of electricity for all customers by 5 to 7 cents per kilowatt-hour. $24.15 is the same amount as the flat rate for Sacramento Municipal Utility District (SMUD) customers, and significantly less than some stakeholder proposals that ranged up to ...
The proposed sale of the doctors group, called Stewardship Health, is part of Steward's plan to shore up its finances and bolster its nationwide network of 33 hospitals after the Dallas-based ...
"Undercooked": The city's latest review of the 76ers' Center City arena proposal ended with officials pushing the development team to make the project more of a year-round destination.
Retirement plan administrators are noting an uptick in 401 (k) hardship withdrawals. But taking that money out can harm your future financial security. The Labor Department's latest push for a ...
The Canberra Liberals proposed public transport plan includes busways instead of light rail to Woden, extra rapid routes, and hundreds of additional, locally built electric buses if the party is ...
Chevron , opens new tab has proposed adding 65,000 barrels per day (bpd) to its ... "The CMI14 well, the first of 17 planned in the business plan this year, represents an important advance for the ...
Trump's proposed import tariff would tack on an extra $1,500 per year for Americans, says a left-leaning Washington think tank. The former president floated his plan to impose a 10% tariff on ...