How to Write a Psychology Essay
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Before you write your essay, it’s important to analyse the task and understand exactly what the essay question is asking. Your lecturer may give you some advice – pay attention to this as it will help you plan your answer.
Next conduct preliminary reading based on your lecture notes. At this stage, it’s not crucial to have a robust understanding of key theories or studies, but you should at least have a general “gist” of the literature.
After reading, plan a response to the task. This plan could be in the form of a mind map, a summary table, or by writing a core statement (which encompasses the entire argument of your essay in just a few sentences).
After writing your plan, conduct supplementary reading, refine your plan, and make it more detailed.
It is tempting to skip these preliminary steps and write the first draft while reading at the same time. However, reading and planning will make the essay writing process easier, quicker, and ensure a higher quality essay is produced.

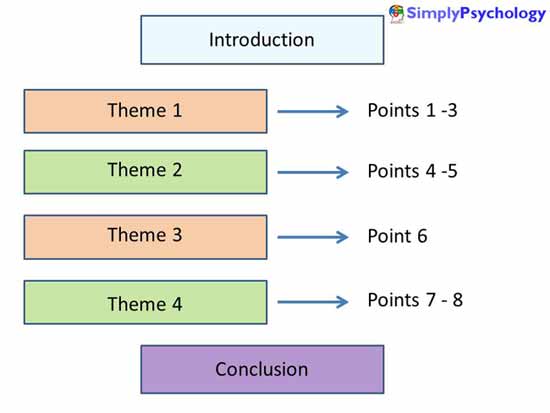
Components of a Good Essay
Now, let us look at what constitutes a good essay in psychology. There are a number of important features.
- Global Structure – structure the material to allow for a logical sequence of ideas. Each paragraph / statement should follow sensibly from its predecessor. The essay should “flow”. The introduction, main body and conclusion should all be linked.
- Each paragraph should comprise a main theme, which is illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
- Knowledge and Understanding – recognize, recall, and show understanding of a range of scientific material that accurately reflects the main theoretical perspectives.
- Critical Evaluation – arguments should be supported by appropriate evidence and/or theory from the literature. Evidence of independent thinking, insight, and evaluation of the evidence.
- Quality of Written Communication – writing clearly and succinctly with appropriate use of paragraphs, spelling, and grammar. All sources are referenced accurately and in line with APA guidelines.
In the main body of the essay, every paragraph should demonstrate both knowledge and critical evaluation.
There should also be an appropriate balance between these two essay components. Try to aim for about a 60/40 split if possible.
Most students make the mistake of writing too much knowledge and not enough evaluation (which is the difficult bit).
It is best to structure your essay according to key themes. Themes are illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
Choose relevant points only, ones that most reveal the theme or help to make a convincing and interesting argument.
Knowledge and Understanding
Remember that an essay is simply a discussion / argument on paper. Don’t make the mistake of writing all the information you know regarding a particular topic.
You need to be concise, and clearly articulate your argument. A sentence should contain no unnecessary words, a paragraph no unnecessary sentences.
Each paragraph should have a purpose / theme, and make a number of points – which need to be support by high quality evidence. Be clear why each point is is relevant to the argument. It would be useful at the beginning of each paragraph if you explicitly outlined the theme being discussed (.e.g. cognitive development, social development etc.).
Try not to overuse quotations in your essays. It is more appropriate to use original content to demonstrate your understanding.
Psychology is a science so you must support your ideas with evidence (not your own personal opinion). If you are discussing a theory or research study make sure you cite the source of the information.
Note this is not the author of a textbook you have read – but the original source / author(s) of the theory or research study.
For example:
Bowlby (1951) claimed that mothering is almost useless if delayed until after two and a half to three years and, for most children, if delayed till after 12 months, i.e. there is a critical period.
Maslow (1943) stated that people are motivated to achieve certain needs. When one need is fulfilled a person seeks to fullfil the next one, and so on.
As a general rule, make sure there is at least one citation (i.e. name of psychologist and date of publication) in each paragraph.
Remember to answer the essay question. Underline the keywords in the essay title. Don’t make the mistake of simply writing everything you know of a particular topic, be selective. Each paragraph in your essay should contribute to answering the essay question.
Critical Evaluation
In simple terms, this means outlining the strengths and limitations of a theory or research study.
There are many ways you can critically evaluate:
Methodological evaluation of research
Is the study valid / reliable ? Is the sample biased, or can we generalize the findings to other populations? What are the strengths and limitations of the method used and data obtained?
Be careful to ensure that any methodological criticisms are justified and not trite.
Rather than hunting for weaknesses in every study; only highlight limitations that make you doubt the conclusions that the authors have drawn – e.g., where an alternative explanation might be equally likely because something hasn’t been adequately controlled.
Compare or contrast different theories
Outline how the theories are similar and how they differ. This could be two (or more) theories of personality / memory / child development etc. Also try to communicate the value of the theory / study.
Debates or perspectives
Refer to debates such as nature or nurture, reductionism vs. holism, or the perspectives in psychology . For example, would they agree or disagree with a theory or the findings of the study?
What are the ethical issues of the research?
Does a study involve ethical issues such as deception, privacy, psychological or physical harm?
Gender bias
If research is biased towards men or women it does not provide a clear view of the behavior that has been studied. A dominantly male perspective is known as an androcentric bias.
Cultural bias
Is the theory / study ethnocentric? Psychology is predominantly a white, Euro-American enterprise. In some texts, over 90% of studies have US participants, who are predominantly white and middle class.
Does the theory or study being discussed judge other cultures by Western standards?
Animal Research
This raises the issue of whether it’s morally and/or scientifically right to use animals. The main criterion is that benefits must outweigh costs. But benefits are almost always to humans and costs to animals.
Animal research also raises the issue of extrapolation. Can we generalize from studies on animals to humans as their anatomy & physiology is different from humans?
The PEC System
It is very important to elaborate on your evaluation. Don’t just write a shopping list of brief (one or two sentence) evaluation points.
Instead, make sure you expand on your points, remember, quality of evaluation is most important than quantity.
When you are writing an evaluation paragraph, use the PEC system.
- Make your P oint.
- E xplain how and why the point is relevant.
- Discuss the C onsequences / implications of the theory or study. Are they positive or negative?
For Example
- Point: It is argued that psychoanalytic therapy is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority.
- Explain: Because psychoanalytic therapy involves talking and gaining insight, and is costly and time-consuming, it is argued that it is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority. Evidence suggests psychoanalytic therapy works best if the client is motivated and has a positive attitude.
- Consequences: A depressed client’s apathy, flat emotional state, and lack of motivation limit the appropriateness of psychoanalytic therapy for depression.
Furthermore, the levels of dependency of depressed clients mean that transference is more likely to develop.
Using Research Studies in your Essays
Research studies can either be knowledge or evaluation.
- If you refer to the procedures and findings of a study, this shows knowledge and understanding.
- If you comment on what the studies shows, and what it supports and challenges about the theory in question, this shows evaluation.
Writing an Introduction
It is often best to write your introduction when you have finished the main body of the essay, so that you have a good understanding of the topic area.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your introduction.
Ideally, the introduction should;
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which “lie behind” the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. “Signpost” the essay’s key argument, (and, if possible, how this argument is structured).
Introductions are very important as first impressions count and they can create a h alo effect in the mind of the lecturer grading your essay. If you start off well then you are more likely to be forgiven for the odd mistake later one.
Writing a Conclusion
So many students either forget to write a conclusion or fail to give it the attention it deserves.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your conclusion.
Ideally the conclusion should summarize the key themes / arguments of your essay. State the take home message – don’t sit on the fence, instead weigh up the evidence presented in the essay and make a decision which side of the argument has more support.
Also, you might like to suggest what future research may need to be conducted and why (read the discussion section of journal articles for this).
Don”t include new information / arguments (only information discussed in the main body of the essay).
If you are unsure of what to write read the essay question and answer it in one paragraph.
Points that unite or embrace several themes can be used to great effect as part of your conclusion.
The Importance of Flow
Obviously, what you write is important, but how you communicate your ideas / arguments has a significant influence on your overall grade. Most students may have similar information / content in their essays, but the better students communicate this information concisely and articulately.
When you have finished the first draft of your essay you must check if it “flows”. This is an important feature of quality of communication (along with spelling and grammar).
This means that the paragraphs follow a logical order (like the chapters in a novel). Have a global structure with themes arranged in a way that allows for a logical sequence of ideas. You might want to rearrange (cut and paste) paragraphs to a different position in your essay if they don”t appear to fit in with the essay structure.
To improve the flow of your essay make sure the last sentence of one paragraph links to first sentence of the next paragraph. This will help the essay flow and make it easier to read.
Finally, only repeat citations when it is unclear which study / theory you are discussing. Repeating citations unnecessarily disrupts the flow of an essay.
Referencing
The reference section is the list of all the sources cited in the essay (in alphabetical order). It is not a bibliography (a list of the books you used).
In simple terms every time you cite/refer to a name (and date) of a psychologist you need to reference the original source of the information.
If you have been using textbooks this is easy as the references are usually at the back of the book and you can just copy them down. If you have been using websites, then you may have a problem as they might not provide a reference section for you to copy.
References need to be set out APA style :
Author, A. A. (year). Title of work . Location: Publisher.
Journal Articles
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (year). Article title. Journal Title, volume number (issue number), page numbers
A simple way to write your reference section is use Google scholar . Just type the name and date of the psychologist in the search box and click on the “cite” link.
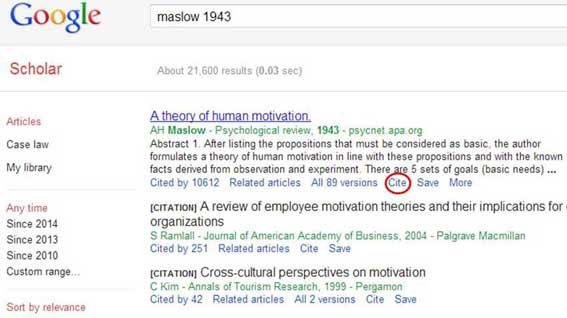
Next, copy and paste the APA reference into the reference section of your essay.

Once again, remember that references need to be in alphabetical order according to surname.
Related Articles

Student Resources
How To Cite A YouTube Video In APA Style – With Examples

How to Write an Abstract APA Format

APA References Page Formatting and Example

APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates

How do I Cite a Source with Multiple Authors in APA Style?

Lab Report Format: Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Your Introduction
Introductions [1].
There is no doubt about it: the introduction is important for any kind of writing. Not only does a good introduction capture your reader’s attention and make him or her want to read on, it’s how you put the topic of your paper into context for the reader.
But just because the introduction comes at the beginning, it doesn’t have to be written first. Many writers compose their introductions last, once they are sure of the main points of their paper and have had time to construct a thought provoking beginning, and a clear, cogent research statement.
Introductions Purpose
The introduction has work to do, besides grabbing the reader’s attention. Below are some things to consider about the purposes or the tasks for your introduction and some examples of how you might approach those tasks.
The introduction needs to alert the reader to what the central issue of the paper is.
The introduction is where you provide any important background information the reader should have before getting to the thesis.
The introduction tells why you have written the paper and what the reader should understand about your topic and your perspective.
The introduction tells the reader what to expect and what to look for in your essay.
The research question or statement (typically at the end of the introduction) should clearly state the claim, question, or point of view the writer is putting forth in the paper.
Introductions Strategies
Although there is no one “right” way to write your introduction, there are some common introductory strategies that work well. The strategies below are ones you should consider, especially when you are feeling stuck and having a hard time getting started.
Consider opening with an anecdote, a pithy quotation, a question, or a startling fact to provoke your reader’s interest. Just make sure that the opening helps put your topic in some useful context for the reader.
Of course, these are just some examples of how you might get your introduction started , but there should be more to your introduction. Once you have your readers’ attention, you want to provide context for your topic and begin to transition to your research question, and don’t forget to include that research question (usually at or near the end of your introduction).
- Adapted from Excelsior Online Writing Lab (OWL). (n.d.). Introductions & conclusions. Retrieved from https://owl.excelsior.edu/writing-process/introductions-and-conclusions/. Licensed under CC-BY-4.0. ↵
PSY-250 Research Paper Guidelines and Resources Copyright © by David Adams. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Tips for Writing Psychology Papers
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Hero Images / Getty Images
Writing in psychology is formal, concise, and straightforward. When writing a psychology paper, avoid using metaphors, anecdotes, or narrative. Your paper should be well-cited and the point should be clear. In almost all cases, you will need to structure your paper in a specific way and follow the rules of APA format.
Learn more about writing in psychology and how to write a psychology paper.
The Importance of Writing in Psychology
Writing is important in psychology because the study and practice of psychology involves complex concepts. Writing is an important way to note observations, communicate new ideas, and support theories.
Most psychology courses require a significant amount of writing, including essays, case studies, research reports, and other papers . Start by viewing each class assignment as an opportunity to learn and practice. Check out resources offered by your school, such as tutors or writing labs, and learn more about the different types of psychology writing.
The following resources offer tips, guidelines, and advice on how to write psychology papers. If you are struggling with writing a psychology paper, following some of the guidelines below may help.
Basic Tips for Writing a Psychology Paper
If you have never written a psychology paper before, you need to start with the basics. Psychology writing is much like other types of writing, but most instructors will have special requirements for each assignment.
When writing a psychology paper, you will be expected to follow a few specific style guidelines. Some important tips to keep in mind include:
- Back up your words and ideas with evidence. Your work should be well-cited using evidence from the scientific literature. Avoid expressing your opinion or using examples from your own life.
- Use clear, concise language. Get directly to the point and make sure you are making logical connections between your arguments and conclusions and the evidence you cite.
- Avoid literary devices. Metaphors, anecdotes, and other literary devices you may have used in other types of writing aren't appropriate when you are writing a psychology paper.
- Use the correct format. Most psychology writing uses APA style, but your instructor may have additional formatting requirements.
- Check the rubric. Before you start a psychology paper, you'll need to learn more about what you should write about, how you should structure your paper, and what type of sources you should use. Always check the grading rubric for an assignment before you begin writing and brush up on the basics.
Types of Psychology Writing
There are a few different types of psychology papers you may be asked to write. Some examples and how to write them are listed below.
How to Write a Psychology Case Study
Students taking courses in abnormal psychology , child development , or psychotherapy will often be expected to write a case study on an individual—either real or imagined. Case studies vary somewhat, but most include a detailed history of the client, a description of the presenting problem, a diagnosis, and a discussion of possible treatments.
This type of paper can be both challenging and interesting. You will get a chance to explore an individual in great depth and find insights into their behaviors and motivations. Before you begin your assignment, learn more about how to write a psychology case study .
How to Write a Psychology Lab Report
Lab reports are commonly assigned in experimental or research-based psychology courses. The structure of a lab report is very similar to that of a professional journal article, so reading a few research articles is a good way to start learning more about the basic format of a lab report.
There are some basic rules to follow when writing a psychology lab report. Your report should provide a clear and concise overview of the experiment, research, or study you conducted. Before you begin working on your paper, read more about how to write a psychology lab report .
How to Write a Psychology Critique Paper
Psychology critique papers are often required in psychology courses, so you should expect to write one at some point in your studies. Your professor may expect you to provide a critique on a book, journal article , or psychological theory .
Students sometimes find that writing a critique can actually be quite challenging. How can you prepare for this type of assignment? Start by reading these tips and guidelines on how to write a psychology critique paper .
Remember to Edit Your Psychology Paper
Before you turn in any type of psychology writing, it is vital to proofread and edit your work for errors, typos, and grammar. Do not just rely on your computer's spellchecker to do the job! Always read thoroughly through your paper to remove mistakes and ensure that your writing flows well and is structured logically.
Finally, always have another person read your work to spot any mistakes you may have missed. After you have read something so many times, it can become difficult to spot your own errors. Getting a fresh set of eyes to read through it can be very helpful. Plus, your proofreader can ask questions and point out areas that might not be clear to the reader.
Know the Rules of APA Format
Not learning APA format is a mistake that costs points for many students. APA format is the official style of the American Psychological Association and is used in many different types of science writing, especially the social sciences. Before you hand in any writing assignment, always double-check your page format, in-text citations, and references for correct APA format. If you need directions or examples, check out this guide to APA format .
A Word From Verywell
Writing psychology papers is an important part of earning a degree in psychology. Even non-majors often find themselves writing such papers when taking general education psychology classes. Fortunately, paying attention to the directions provided by your instructor, familiarizing yourself with APA style, and following some basic guidelines for different types of psychology papers can make the process much easier.
Levitt HM. Reporting qualitative research in psychology: How to meet APA style journal article reporting standards . American Psychological Association; 2020. doi:10.1037/0000179-000
Willemsen J, Della Rosa E, Kegerreis S. Clinical case studies in psychoanalytic and psychodynamic treatment . Front Psychol . 2017;8:108. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00108
Klein RM, Saint-Aubin J. What a simple letter-detection task can tell us about cognitive processes in reading . Curr Dir Psychol Sci . 2016;25(6):417-424. doi:10.1177/0963721416661173
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Educational and developmental psychology
How to Write a Psychology Paper: An Expert Guide


5. Find a sample
This is often the trickiest part, even for a professional researcher. If your paper requires an empirical section and implies a study, you’ll need participants. There are many sampling techniques out there (simple random, stratified, systematic, to name a few), and it’s a smart idea to read up on them. However, what matters the most, at least for a student paper, is how you intend to find participants and convince them to take part in your research. Perhaps, you’ll connect with them online, on social media. Alternatively, you might ask your classmates. Consider the options available to you and find the most realistic yet appropriate one.
6. Do the research
Once you have a research question, a well-thought-out research design , and a sample ready, it’s time to do the research. This is the second part of the paper-writing process, the empirical data collecting stage. The first part was purely theoretical when you researched your topic and prepared a literature review. To make sure that everything runs smoothly, follow your research design. It might help you to write down the process in the form of custom step-by-step guidelines to have close at hand.
7. Analyze the results
This stage is when you take the data you’ve collected and try to make sense of it. The ‘Results’ sections of academic articles often look terrifying, but this is rarely the case with student papers. In fact, all you have to do is systematize the data and identify the patterns that are relevant to your research question. For example, if you’re investigating the relationship between goal-setting and self-assurance, you’ll have to compare participants’ self-assurance levels (which you measured using a questionnaire) before and after the intervention.

How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays
- Paul Dickerson - University of Roehampton, UK
- Description
“This book is one I wish I had bought at the start of my Psychology degree.” – Five-star review Essay writing is a key part of the Psychology degree and knowing how to write effective and compelling academic essays is key to success. Whether it's understanding how to implement feedback you receive on essays, how to stop procrastinating or what makes an effective introduction, this book covers it all. Drawing on insights derived from teaching thousands of students over a 25-year period How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays provides the keys that will unlock your writing potential.
Ace your Assignment provide practical tips to help succeed
Exercises help try the theory out in practice
Take away points highlight the key learnings from each chapter
Online resources provide even more help and guidance.
Supplements
Paul Dickerson, Emma McDonald and Christian van Nieuwerburgh discuss study skills, wellbeing and employability and explore how university lecturers and student welfare teams can better support Psychology students through their university journey.
Students enjoyed this text - they found it easy to read and the author's dry sense of humour appealed to many. Not just for psychologists!
A really useful guide for students, breaking down the components of what constitutes a good essay and written from a subject-specific view - highly recommend
I have recommended this to my first year tutorial groups as it provides them with everything they need to know about producing an excellent psychology essay.
Preview this book
For instructors.
Please select a format:
Select a Purchasing Option
Order from:.
- VitalSource
- Amazon Kindle
- Google Play
Related Products


How to Really Write a Psychology Paper
Remember that every research paper is a story..
Posted April 1, 2017 | Reviewed by Matt Huston
I taught my first psychology class in 1994—and I almost always include some kind of paper assignment in each of my classes. Quick math says that I have probably read nearly 2,000 student papers. I think I’m qualified to give advice on this topic.
With a large batch of student papers set to hit my desk on Monday upcoming, it occurred to me that it might be nice to write a formal statement to help guide this process. Here it is.

Tell a Story
If you are writing a research paper, or any paper, you are telling a story. It should have a beginning, middle, and end. Further, it should read how you speak. Some students think that when they are writing for a college professor, they have to up their language and start using all kinds of fancy words and such. Please! We are training you to communicate effectively—not to show others how smart you are. We know you are smart—that is how you got into college in the first place!
While there are certain standards of formality that should be followed in your paper, at the end of the day, always remember that you are primarily trying to communicate some set of ideas to an audience. Thus, you should be keen to attend to the following:
- Create an outline and use it as a roadmap.
- Start from the top. That is, think about your actual question of interest—and start there—clearly and explicitly.
- Make sure that every single sentence points to the next sentence. And every paragraph points to the next paragraph. And every section points to the next section.
- Write how you speak—imagine that you are telling these ideas to someone—and always assume that someone is a layperson (just a regular old person, not an expert in the field).
- Make the paper as long as it needs to be to tell your story fully and effectively—don’t let page limits drive your process (to the extent that this is possible).
- All things equal, note that writing a high number of relatively brief sentences is a better approach than is writing a lower number of relatively long sentences. Often when students write long sentences, the main points get confused.
Use APA Style for Good
Psychology students have to master APA format. This means using the formal writing style of the American Psychological Association . At first, APA style may well seem like a huge pain, but all of the details of APA style actually exist for a reason. This style was designed so that journal editors are able to see a bunch of different papers (manuscripts) that are in the same standardized format. In this context, the editor is then able to make judgments of the differential quality of the different papers based on content and quality. So APA style exists for a reason!
Once you get the basics down, APA style can actually be a tool to help facilitate great writing.
Write a Good Outline and Flesh it Out
For me, the best thing about APA Style is that it gets you to think in terms of an outline. APA style requires you to create headings and subheadings. Every paper I ever write starts with just an outline of APA-inspired headings and subheadings. I make sure that these follow a linear progression—so I can see the big, basic idea at the start—and follow the headings all the way to the end. The headings should be like the Cliff Notes of your story. Someone should be able to read your headings (just like the headings for this post) and get a basic understanding of the story that you are trying to communicate.
Another great thing about starting with an APA-inspired outline is that it affords you a very clear way to compartmentalize your work on the paper. If you are supposed to write a “big” college paper (maybe 20 or so pages), you may dread thinking about it—and you may put it off because you see the task as too daunting.
However, suppose you have an outline with 10 headings and subheadings. Now suppose that you pretty much have about two pages worth of content to say for each such heading. Well you can probably write two pages in about an hour or maybe less. So maybe you flesh out the first heading or two—then watch an episode of The Office or go for a run. Maybe you flesh out another section later in the day. And then tomorrow you wake up and you’ve completed 30% of your paper already. That doesn’t sound so dreadful, now, does it?
No One Wants to Hear Minutia about Other Studies in Your Research Paper!
I’m usually pretty tolerant of the work that my students submit to me. I know that college is all about learning and developing—and I always remind my students that the reason they are in school is to develop skills such as writing—so I don’t expect any 19-year-old to be Walt Whitman.
This said, there are some rookie mistakes that make me shake my head. A very common thing that students tend to do is to describe the research of others in unnecessary detail. For your introduction, you often have to provide evidence to support the points that you raise. So if you are writing a paper about the importance of, say, familial relatedness in affecting altruistic behavior, you probably need to cite some of the classic scientific literature in this area (e.g., Hamilton, 1964).

This said, please, I urge you , don’t describe more about these past studies that you cite than is necessary to tell your story! If your point is that there past work has found that individuals across various species are more likely to help kin than non-kin, maybe just say that! There is a time and a place for describing the details of the studies of others in your own research paper. On occasion, it is actually helpful to elaborate a bit on past studies. But from where I sit, it’s much more common to see students describe others’ studies in painstaking detail in what looks like an attempt to fill up pages.
As a guide on this issue, here are some things that I suggest you NEVER include in your paper:
- The number of participants that were in someone else’s study.
- Information from statistical tests from someone else’s study (e.g., The researchers found a significant F ratio (F(2,199) = 4.32, p = 0.008) ).
- The various conditions or variables that were included in some other study (e.g., These researchers used a mixed-ANOVA model with three between-subject factors and two within-subject factors ).
When you mention the work of others, you are doing so for a purpose. You are citing just enough of their work to substantiate some point that you are making as you work toward creating a coherent story. Don’t ever lose sight of this!
Bottom Line
I’ve read nearly 2,000 student papers to this point in my life. And I hope I am lucky enough to read another 4,000+ before I am pushing up daisies. As I tell my students, if you are going to develop a single skill in college, let it be your ability to write in a clear, effective, and engaging manner.
Students who write psychology papers often find it difficult. That’s OK—that’s expected. If you are a college student, then don’t forget the fact that college is primarily about developing your skills.
Everything you write has the ultimate purpose of communicating to an audience. Clear, straightforward, and narrative approaches to any writing assignment, then, are most likely to hit the mark.
Hamilton W.D. (1964). The genetical evolution of social behaviour. International Journal of Theoretical Biology, 7 , 1–16.

Glenn Geher, Ph.D. , is professor of psychology at the State University of New York at New Paltz. He is founding director of the campus’ Evolutionary Studies (EvoS) program.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
How to Write a Psychology Essay
Writing a psychology essay can be daunting, because of the constant changes in understanding and differing perspectives that exist in the field. However, if you follow our tips and guidelines you are guaranteed to produce a first-class, high quality psychology essay.
Types of Psychology essay
Psychology essays can come in a range of formats:
- Compare and contrast.
For example:
- Compare the benefits of cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) with psychoanalysis on patients with schizophrenia.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of family therapy for children of drug addicts.
- CBT is the most effective form of treatment for those struggling with mental illness. Discuss
Once you understand what is being asked of you, and thus the focus of your essay, you can move on to identifying how to structure your work. In all cases the broad structure is similar – an introduction – body section and conclusion. Furthermore, in all cases, your work, and any statements you make should be made using only verifiable, credible sources that should be referenced clearly at the end of your work. To support you in delivering a premium psychology essay, we have indicated a general structure for you to follow.
Introduction
The most important thing about your introduction is it just that. An introduction. It should be short, captivating and hook your reader into wanting to carry on. A good introduction introduces a few key points about the topic so that the reader knows the subject of your paper and its background.
You should also include a thesis statement which describes your intent and perspective on the matter. The statement comes from first identifying a question you wish to ask, for example, “how does CBT differ from psychoanalysis in treating schizophrenics”. This will then enable you to identify a clear statement such as “CBT is more effective in treating schizophrenics than psychoanalysis”. In effect, a captivating introduction sets out what you will be saying in your essay, clearly, concisely, and objectively.
Body of the Essay
The body of the essay is where you make all your relevant points and undertake a dissection of the central themes of your work in the topic area. Note when undertaking a compare and contrast essay it is a good practice to indicate all the similarities and then the differences to ensure a smooth coherent flow.
For each point you make, use a separate paragraph, and ensure that any statements you make are backed up by credible evidence and properly referenced sources. In an evaluation essay, you should indicate the analysis undertaken to make the judgement you have, again backed by credible sources. Discussive psychology essays require you to state your point and then debate it with pros and cons for each side.
Overall, in the body section, you body text should be focused on providing valuable insights and evaluation of the topic and enable you to demonstrate deductive reasoning (“as a result of x… it can be indicated that”) and evidence based analysis (“although x indicates that y, a suggests an alternative view based on…”). Following a logical flow with one point per paragraph ensures the reader is able to follow your thinking process and eventually draw the same conclusions.
Furthermore, it is important when writing a psychology essay to examine a wide range of sources, that cover both sides of a topic or phenomenon. Without demonstrating a wide-ranging knowledge of the diversity of perspectives, you cannot be objective in evaluating a subject area.
In addition, you should recognise that not all your readers may be familiar with psychological terms or acronyms so these need to be explained briefly and concisely the first time they are used. Furthermore, you should avoid definitive statements, because psychology is constantly evolving so do not use phrases such as “this proves…”, instead use terms such as “this is consistent with work by…” or “this supports x’s view that…”. It is also not appropriate to use the first person (“I”), even when expressing opinions, always use the third person and where possible the past tense.
As with the introduction, the conclusion should hold the reader, and crystallise all the arguments and points made into an overall summation of your views. This summation should be in line with your thesis statement which has to be restated here and leave no room for unanswered questions. Your aim is to reaffirm that the points you have made in your body text sum up and provide a clear answer to the task of the psychology essay – whether this compare and contrast, discussion, or evaluation.
Key Phrases for a Psychology Essay
- Previous work in the area has suggested that…
- However, prior studies did not consider…
- In this paper it is therefore argued that…
- The significance of this view is that…
- In light of this indication, there is a potential that…
- In order to understand x, it is necessary to also recognise that…
- Similarly, it has been suggested that…
- Furthermore, additional evidence from x indicates that…
- Conversely, x suggests that…
- Similarly, the indications from … are that…
- That being said, it is also evident that…
You may also like

- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Argumentative Essays
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- +1 (888) 398 0091
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Writing Tips
How to Write Psychology Essay: Comprehensive Guide
September 1, 2022
Choosing a Good Topic for Your Psychology Essay
The process of writing a psychology essay begins with selecting a compelling and appropriate topic. A good topic sets the stage for a well-crafted and engaging essay. When choosing a topic, it is essential to consider your interests, the guidelines provided by your instructor, and the scope of your assignment. Aim for a topic that is specific enough to allow for in-depth analysis, yet broad enough to provide ample research material. It is also helpful to consider current trends, controversies, or unanswered questions in the field of psychology. Your topic should be thought-provoking, relevant, and capable of generating insightful discussions. By carefully selecting a strong topic, you lay the foundation for a successful and impactful psychology essay.
Possible Psychology Essay Topics:
- The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- The Role of Parenting Styles in Child Development
- The Influence of Cognitive Biases on Decision Making
- The Effects of Stress on Psychological Well-being
- The Relationship between Sleep and Memory Consolidation
- The Role of Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Development
- The Impact of Trauma on Psychological Functioning
- The Psychology of Social Influence and Conformity
- The Influence of Technology on Human Behavior and Communication
- The Psychological Factors behind Addiction and Recovery
Writing a Thesis Statement for Your Psychology Essay
Crafting a strong and clear thesis statement is essential for delivering a focused and well-structured psychology essay. The thesis statement serves as the central argument or claim that guides and organizes your entire essay. It is essential to carefully construct a thesis statement that is specific, concise, and reflective of your main argument. Here are some tips to consider when writing your thesis statement:
- Identify the main purpose: Determine the main objective of your essay. Are you attempting to explain a concept, analyze a theory, or argue a particular viewpoint?
- Summarize your main argument: Clearly state the position or argument you will be defending in your essay. Make sure it is clear and concise, providing a roadmap for your reader.
- Be specific: Avoid vague or general statements. Instead, focus on a specific aspect of the topic you will be addressing in your essay.
- Consider the significance: Highlight why your topic and argument are important within the field of psychology. What is the broader implication or relevance of your argument?
Remember, your thesis statement should be debatable and open to discussion. It should provide a clear direction for your essay while capturing the essence of your overall argument. By creating a strong and focused thesis statement, you lay the foundation for a coherent and persuasive psychology essay.
Example: “The increasing use of social media among adolescents has significant implications for their mental health, as it contributes to feelings of loneliness, low self-esteem, and increased risk of developing anxiety and depression.”
Structuring the Essay
A well-structured psychology essay is crucial for conveying your arguments clearly and effectively. Here are a few tips on how to structure your essay:
- Develop an outline: Before starting to write, it is essential to develop an outline that lists the key points you will be addressing in your essay. This outline will serve as a roadmap for your writing and ensure that you maintain a focused and coherent flow throughout the essay.
- Introduction: Begin your essay with an introduction that captures the reader’s attention and provides context for the topic you will be addressing. The introduction should end with a clear and concise thesis statement that identifies the main argument of your essay.
- Body: The body of your essay should be structured around the main points you identified in your outline. Each paragraph should focus on a single point and provide evidence and examples to support your argument.
- Conclusion: Conclude your essay with a summary of the main points and restate your thesis statement in a new way. Finally, leave the reader with a thought-provoking statement or question that encourages them to consider the broader implications of your argument.
- Edit and proofread: Once you have finished writing your essay, take some time to edit and proofread it. Check for any grammar or spelling errors, ensure that your arguments are coherent and well-supported by evidence, and that the overall structure flows smoothly.
By following these tips, you can create a well-structured psychology essay that communicates your arguments clearly and effectively.
Sample Outline for a Psychology Essay
I. Introduction A. Hook or attention grabber B. Background information on the topic C. Thesis statement
II. Body Paragraph 1: Impact of Social Media on Mental Health A. Explanation of the link between social media and mental health B. Discussion of the negative effects, such as increased anxiety and depression C. Supporting evidence or examples from research studies
III. Body Paragraph 2: Effects of Parenting Styles on Child Development A. Explanation of different parenting styles (authoritative, permissive, authoritarian) B. Discussion of how each style impacts a child’s psychological development C. Supporting evidence or examples from studies on parenting styles
IV. Body Paragraph 3: Cognitive Biases and Decision Making A. Explanation of common cognitive biases (confirmation bias, availability heuristic, etc.) B. Discussion of how these biases influence decision making C. Supporting evidence or examples from psychological research
V. Conclusion A. Summary of the main points discussed B. Restatement of the thesis statement C. Final thoughts or call to action for further research or consideration
Note: This is just a sample outline and can be modified based on the specific requirements or focus of your psychology essay. Ensure that each paragraph has a clear topic sentence and provides supporting evidence or examples to back up your claims.
Writing Style and Tone
When writing a psychology essay, it is important to pay attention to your writing style and tone to effectively communicate your ideas and engage your readers. Here are some key considerations for your writing style and tone:
- Clarity and Conciseness: Use clear and concise language to convey your ideas. Avoid unnecessary jargon or technical terms that may confuse your readers. Clearly define and explain any specialized terminology you do use.
- Formality: Maintain a formal and professional tone throughout your essay. Avoid using slang or informal language. Aim for an objective tone that focuses on presenting evidence and arguments in a logical manner.
- Precision and Accuracy: Be precise and accurate in your language and statements. Use specific terms and examples to support your arguments. Avoid generalizations or sweeping statements without proper evidence.
- Objectivity: While it is important to present and support your own arguments, maintain objectivity in your writing. Avoid personal opinions or biases that may weaken the credibility of your essay. Back up your claims with evidence from reputable sources.
- Cohesion and Coherence: Ensure that your essay flows smoothly between paragraphs and sections. Use clear transitions to connect ideas and maintain a logical progression throughout your essay.
- Proper Citations: When referencing research or sources, use proper citation styles such as APA or MLA. Follow the guidelines for in-text citations and include a comprehensive list of references at the end of your essay.
By embracing these writing style and tone guidelines, you can effectively convey your ideas, maintain credibility, and engage your readers in your psychology essay.
Writing an Introduction
The introduction of your psychology essay sets the stage for your entire paper and captures the reader’s attention. It should provide crucial background information and present your thesis statement. Here are some tips for writing an effective introduction:
- Grab the reader’s attention: Start with an attention-grabbing hook or opening sentence that piques the reader’s curiosity. This could be a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a compelling anecdote.
- Provide context: Give a brief overview of the topic and its significance in the field of psychology. Explain why it is important to study or discuss this particular topic and how it relates to broader psychological concepts or theories.
- Background information: Provide relevant background information to give the reader a foundation for understanding your essay. This could include a historical overview, a summary of previous research findings, or a discussion of current debates or controversies.
- Thesis statement: Clearly state your thesis statement – the main argument or claim you will be making in your essay. Make sure it is concise, specific, and provides a clear focus for your essay.
- Preview the main points: Briefly outline the main points or arguments that you will be discussing in the body paragraphs. This helps the reader anticipate the structure of your essay and understand the key aspects you will be addressing.
By following these tips, you can craft an engaging and informative introduction that sets the tone for your psychology essay and captures the reader’s attention from the start. Remember to keep it concise and focused on the main objective of your paper.
Incorporating Theories and Concepts
When writing a psychology essay, it is essential to incorporate relevant theories and concepts to support your arguments and convey a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Here are some guidelines for effectively incorporating theories and concepts into your essay:
- Choose relevant theories: Identify the theories or concepts that are most applicable to your topic. Select those that are widely recognized and have empirical evidence supporting their validity.
- Explain the theories: Provide a clear and concise explanation of the chosen theories or concepts. Define key terms and outline the fundamental principles underlying the theories.
- Connect theories to your arguments: Demonstrate how the theories or concepts align with your arguments or claims. Explain how they provide a framework for understanding the phenomenon you are discussing.
- Provide examples and evidence: Support your discussion of theories with relevant examples or empirical evidence. These could come from research studies, case studies, or real-life examples that illustrate the application or relevance of the theories.
- Compare and contrast theories: If applicable, explore different theories or perspectives related to your topic. Highlight similarities and differences between theories and discuss their implications for understanding the topic.
- Critically analyze theories: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the theories you are incorporating. Discuss any controversies or alternative viewpoints within the field.
By incorporating relevant theories and concepts into your psychology essay, you strengthen the foundation of your arguments and demonstrate a well-rounded understanding of the topic. Remember to cite your sources properly and use specific examples to enhance the clarity and persuasiveness of your essay.
Presenting and Analyzing Data
Data analysis is a critical component of a psychology essay, showcasing your ability to draw meaningful conclusions from research findings. Here are some guidelines for presenting and analyzing data effectively:
- Choose appropriate data: Select data that directly supports your arguments or research question. Ensure it is reliable, relevant, and from reputable sources.
- Data presentation: Organize and present your data in a clear and concise manner. Visual aids like graphs, charts, or tables can enhance understanding. Use proper labeling and titles to provide context.
- Interpret the data: Analyze the patterns, trends, or relationships within the data. Explain what the data implies or reveals about the topic being discussed.
- Use statistical analysis: If applicable, employ appropriate statistical analysis techniques to derive meaningful conclusions from the data. This may include calculating means, standard deviations, correlations, or performing inferential tests.
- Link data to your arguments: Connect the data to your main arguments or research question. Explain how the data either supports or challenges existing theories or concepts.
- Discuss limitations: Acknowledge any limitations or constraints of the data analysis. Address potential biases, sample size issues, or methodological limitations that may affect the interpretation of the data.
- Incorporate citations: Properly cite the sources of your data and any statistical analysis methods used. Ensure you adhere to the appropriate citation style, such as APA or MLA.
By effectively presenting and analyzing data, you can demonstrate your ability to interpret research findings and draw valid conclusions in your psychology essay. Remember to provide clear explanations, relate the data to your arguments, and critically evaluate any limitations of the data analysis.
Writing the Body of a Psychology Essay
The body paragraphs of your psychology essay provide an opportunity to delve deeper into your arguments and present supporting evidence or research. Here are some guidelines for effectively writing the body of your essay:
- Develop a clear structure: Organize your body paragraphs in a logical and coherent manner. Each paragraph should focus on a specific idea or argument related to your thesis statement.
- Present supporting evidence: Support your arguments with relevant evidence, such as research studies, experiments, or case examples. Use reputable sources and cite them appropriately.
- Discuss research findings: Summarize and critically analyze the research findings that support your arguments. Explain how these findings contribute to the understanding of the topic.
- Provide examples: Use real-world examples or case studies to illustrate your points. These examples help to make your arguments more concrete and relatable to the reader.
- Address counterarguments: Acknowledge and address counterarguments or alternative perspectives on the topic. Assess the validity of opposing viewpoints and explain why your arguments are more persuasive or credible.
- Use clear and concise language: Write in clear and concise language to effectively convey your ideas. Use appropriate terminology and define any specialized terms you introduce.
- Use transitional words and phrases: Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs by using transitional words and phrases. These help to maintain coherence and guide the reader through your arguments.
Remember to focus on one main idea per paragraph, provide sufficient evidence and analysis, and maintain a logical flow throughout the body of your psychology essay. With a well-structured and well-supported body, you can effectively present and substantiate your arguments.
Writing a Conclusion
The conclusion of your psychology essay is your final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on the reader. It should effectively summarize your main points, restate your thesis statement, and leave the reader with a clear understanding of your argument. Here are some guidelines for writing a strong conclusion:
- Summarize your main points: Briefly recap the main arguments or findings presented in the body of your essay. Ensure that the summary is concise and reflects the key aspects of your paper.
- Restate your thesis: Reinstate your thesis statement in a slightly different way, emphasizing the main points you have made throughout the essay. Avoid simply copying and pasting your original thesis statement.
- Provide a final thought or reflection: End your conclusion with a thought-provoking statement, reflection, or possible implication of your argument. This can encourage the reader to consider the broader implications of the topic you have discussed.
- Address the significance: Highlight the significance of your research or argument in the broader context of psychology. Explain how your findings contribute to the existing knowledge or understanding of the topic.
- Avoid introducing new information: The conclusion is not the place to introduce new arguments or evidence. It should only summarize and synthesize the information already presented.
- End with a strong closing sentence: Finish your conclusion with a memorable and impactful closing sentence. This can leave a lasting impression on the reader and provide a sense of closure to your essay.
By following these guidelines, you can write a strong conclusion that effectively wraps up your psychology essay and leaves the reader with a sense of satisfaction and understanding.
Psychology Essay Example: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
Introduction:.
Social media has become an integral part of our daily lives, with millions of people spending a significant amount of time on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. While social media offers numerous benefits, there is growing concern about its impact on mental health. This essay will explore the influence of social media on mental well-being, examining both the positive and negative effects.
One significant positive aspect of social media is its ability to foster social connections and support networks. Platforms like Facebook enable individuals to stay connected with friends and family, irrespective of geographical distance. Research has shown that maintaining strong social ties has a positive impact on mental health, reducing feelings of loneliness and improving overall well-being (Grieve et al., 2013). Moreover, social media platforms can serve as spaces for individuals to seek emotional support and find communities with shared interests or experiences.
However, the excessive use of social media can have detrimental effects on mental health. One prominent negative impact is the increased risk of developing symptoms of depression and anxiety. Studies have found a correlation between heavy social media usage and higher levels of depression and anxiety symptoms (Primack et al., 2017). The constant exposure to carefully curated, highlight-reel versions of others’ lives can lead to social comparison and feelings of inadequacy or low self-esteem. Moreover, cyberbullying and online harassment on social media platforms can contribute significantly to psychological distress and adversely affect mental well-being.
Furthermore, the addictive nature of social media poses another concern. Studies have shown that the reward mechanisms triggered by social media use can lead to compulsive behaviors and online addiction (Kuss & Griffiths, 2017). Excessive use of social media can result in neglecting real-world relationships, declining academic or occupational performance, and experiencing symptoms of withdrawal when unable to access social media platforms.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, social media has both positive and negative effects on mental health. While it can enhance social connections and support networks, excessive and addictive use can lead to increased levels of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. It is crucial to strike a balance between the benefits and drawbacks of social media usage. Individuals should be mindful of their social media consumption, manage their online interactions, and seek support offline when needed. Additionally, future research should focus on developing strategies to mitigate the negative impact of social media and promote mental well-being in the digital age.
References:
Grieve, R., Indian, M., Witteveen, K., Tolan, G. A., & Marrington, J. (2013). Face-to-face or Facebook: Can social connectedness be derived online? Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 604-609.
Kuss, D. J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2017). Social networking sites and addiction: Ten lessons learned. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(3), 311.
Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Sidani, J. E., Whaite, E. O., Lin, L. Y., Rosen, D., … & Colditz, J. B. (2017). Social media use and depression and anxiety symptoms: A cluster analysis. American Journal of Health Behavior, 41(6), 670-678.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
In today’s digital era, the fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) with academic writing has revolutionized how students approach essay composition....
Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in education is changing how things are taught and learned in standard ways. With its ability...
The advancement of artificial intelligence has made it increasingly common for essays and articles to be written by AI. But...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. Introducing Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior . The word “psychology” comes from the Greek words “psyche,” meaning life , and “logos,” meaning explanation . Psychology is a popular major for students, a popular topic in the public media, and a part of our everyday lives. Television shows such as Dr. Phil feature psychologists who provide personal advice to those with personal or family difficulties. Crime dramas such as CSI , Lie to Me , and others feature the work of forensic psychologists who use psychological principles to help solve crimes. And many people have direct knowledge about psychology because they have visited psychologists, for instance, school counselors, family therapists, and religious, marriage, or bereavement counselors.
Because we are frequently exposed to the work of psychologists in our everyday lives, we all have an idea about what psychology is and what psychologists do. In many ways I am sure that your conceptions are correct. Psychologists do work in forensic fields, and they do provide counseling and therapy for people in distress. But there are hundreds of thousands of psychologists in the world, and most of them work in other places, doing work that you are probably not aware of.
Most psychologists work in research laboratories, hospitals, and other field settings where they study the behavior of humans and animals. For instance, my colleagues in the Psychology Department at the University of Maryland study such diverse topics as anxiety in children, the interpretation of dreams, the effects of caffeine on thinking, how birds recognize each other, how praying mantises hear, how people from different cultures react differently in negotiation, and the factors that lead people to engage in terrorism. Other psychologists study such topics as alcohol and drug addiction, memory, emotion, hypnosis, love, what makes people aggressive or helpful, and the psychologies of politics, prejudice, culture, and religion. Psychologists also work in schools and businesses, and they use a variety of methods, including observation, questionnaires, interviews, and laboratory studies, to help them understand behavior.
This chapter provides an introduction to the broad field of psychology and the many approaches that psychologists take to understanding human behavior. We will consider how psychologists conduct scientific research, with an overview of some of the most important approaches used and topics studied by psychologists, and also consider the variety of fields in which psychologists work and the careers that are available to people with psychology degrees. I expect that you may find that at least some of your preconceptions about psychology will be challenged and changed, and you will learn that psychology is a field that will provide you with new ways of thinking about your own thoughts, feelings, and actions.

Psychology is in part the study of behavior. Why do you think these people are behaving the way they are?
- Dominic Alves - Café Smokers - CC BY 2.0; Daniela Vladimirova - Reservoir Dogs debate, 3 in the morning - CC BY 2.0; Kim Scarborough - Old Ladies - CC BY-SA 2.0; Pedro Ribeiro Simões - Playing Chess - CC BY 2.0; epSos .de - Young Teenagers Playing Guitar Band of Youth - CC BY 2.0; Marco Zanferrari - 1... - CC BY-SA 2.0; CC BY 2.0 Pedro Ribeiro Simões - Relaxing - CC BY 2.0. ↵
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
At a Glance. Writing a great introduction can be a great foundation for the rest of your psychology paper. To create a strong intro: Research your topic. Outline your paper. Introduce your topic. Summarize the previous research. Present your hypothesis or main argument.
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which "lie behind" the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. "Signpost" the essay's key argument, (and, if possible, how. this argument is structured).
lines to help you read critically. In Writing a Conceptually Coherent Paper, we will go through, step by step, the process of writing an essay or term paper in psychology. The section on Academic Honesty in Writing reinforces information you have previously received about using sources responsibly (and avoiding plagiarism). The Do's and Don'ts
When you write a psychology paper, you are, above all, writing to convey factual knowledge that is supported by research. You are striving to be precise, and thus you should expect every word you write to be read literally. Psychology writing can be very dense, with many references to previous research. Writers of psychology almost never ...
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
In this video, Dr. Sam Fairlamb provides some key tips to how to write a first class introduction to a psychological essay.Producer & Editors: Eloise Giddens...
THE STRUCTURE. The most common way of structuring an essay is to base it around three parts — an introduction, main body, and conclusion. I suggest that you stick that structure! It works well, and is also what a marker will be expecting to see. At the same time, you should remember that this structure is only a foundation.
Consider opening with an anecdote, a pithy quotation, a question, or a startling fact to provoke your reader's interest. Just make sure that the opening helps put your topic in some useful context for the reader. Overall, your focus in an introduction should be on orienting your reader. Keep in mind the following five Ws: who, what, when ...
Hero Images / Getty Images. Writing in psychology is formal, concise, and straightforward. When writing a psychology paper, avoid using metaphors, anecdotes, or narrative. Your paper should be well-cited and the point should be clear. In almost all cases, you will need to structure your paper in a specific way and follow the rules of APA format.
Point: Make a clear point or argument. Evidence: Provide evidence such as research findings, studies, or theories. Explanation: Explain the significance of the evidence and how it supports your point. Link: Connect your point to the essay question and the next point you will discuss. Use clear and concise language.
In fact, if you follow these nine steps to get things under control, you'll end up with an excellent psychology paper. 1. Choose a topic you're actually excited about. Psychology is one of those disciplines where choice overload is inevitable when you're selecting a topic to write about.
Essay writing is a key part of the Psychology degree and knowing how to write effective and compelling academic essays is key to success. Whether it's understanding how to implement feedback you receive on essays, how to stop procrastinating or what makes an effective introduction, this book covers it all.
Component 1: The Title Page. • On the right side of the header, type the first 2-3 words of your full title followed by the page number. This header will appear on every page of you report. • At the top of the page, type flush left the words "Running head:" followed by an abbreviation of your title in all caps.
Create an outline and use it as a roadmap. Start from the top. That is, think about your actual question of interest—and start there—clearly and explicitly. Make sure that every single ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
How to Write Psychology Research Reports and Assignments. 3.3 References 47. 3.3.1 Books 48. 3.3.2 Journal Articles 50. 3.3.3 Internet Sources 53.
2 Writing Argumentative Essays Once you have chosen a topic, you should produce an argumentative essay of 3,000 words. This section contains basic advice on writing argumentative essays, which may be of use if you come from a more technical background. Organisation Essays should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. The introduction should ...
It should be short, captivating and hook your reader into wanting to carry on. A good introduction introduces a few key points about the topic so that the reader knows the subject of your paper and its background. You should also include a thesis statement which describes your intent and perspective on the matter.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Describe the purpose of writing and presenting in the context of a psychology degree. Describe some of the diferent types of psychology assignment formats including laboratory reports, essay, reviews, and presentations. Identify the sections of this book that will help you to complete diferent types of psychology assignments.
By embracing these writing style and tone guidelines, you can effectively convey your ideas, maintain credibility, and engage your readers in your psychology essay. Writing an Introduction. The introduction of your psychology essay sets the stage for your entire paper and captures the reader's attention.
Chapter 1. Introducing Psychology. Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. The word "psychology" comes from the Greek words "psyche," meaning life, and "logos," meaning explanation. Psychology is a popular major for students, a popular topic in the public media, and a part of our everyday lives.
You need to get your reader's attention and drawn them into the topic you're writing about. Use of statistics related to a problem, such as the number of people with learning disabilities, the number of people diagnosed with schizophrenia, etc. can help focus the reader and add a sense of urgency. 1. Plan your strategy.
to your argument / essay topic Example conclusion NOTE: Sometimes in the discipline of Psychology you may be asked to use headings and sub-headings in your essay. Check the task requirements and ask your tutor before doing so. In conclusion, the theories related to personality development include Psychodynamic
Misinformation is false or inaccurate information—getting the facts wrong. Disinformation is false information which is deliberately intended to mislead—intentionally misstating the facts. The spread of misinformation and disinformation has affected our ability to improve public health, address climate change, maintain a stable democracy ...